Patents
Literature
707 results about "Rail pressure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
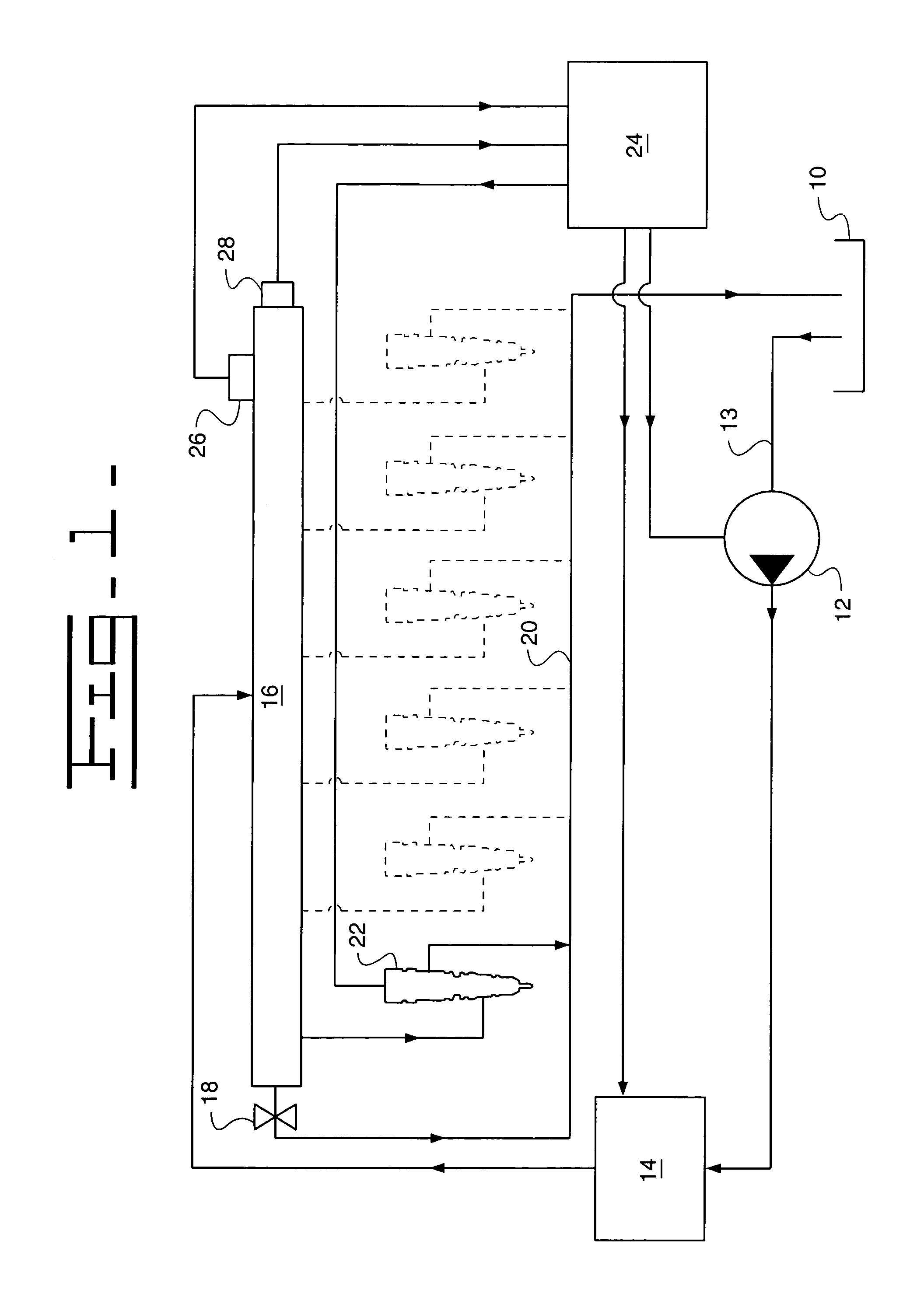
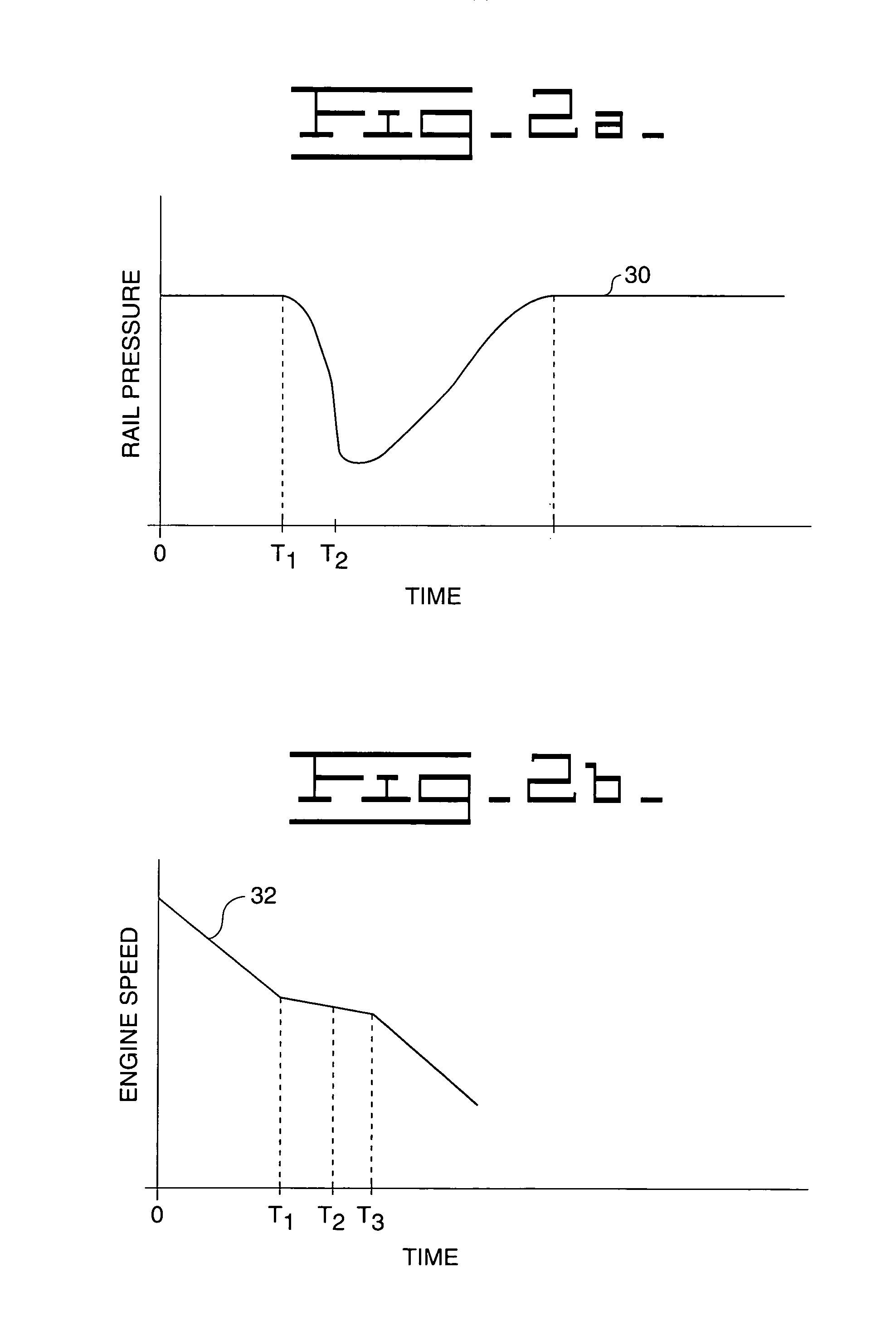
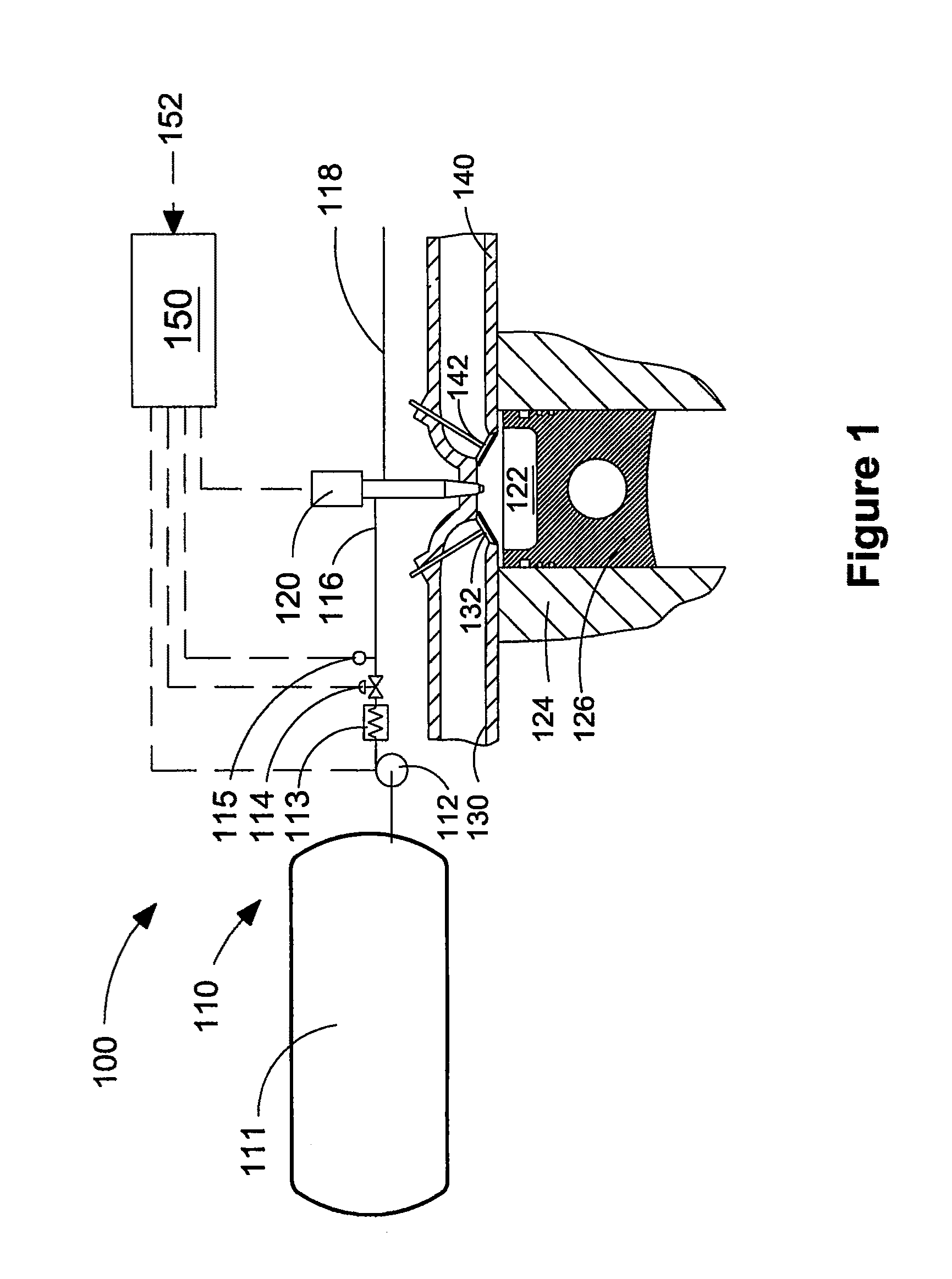
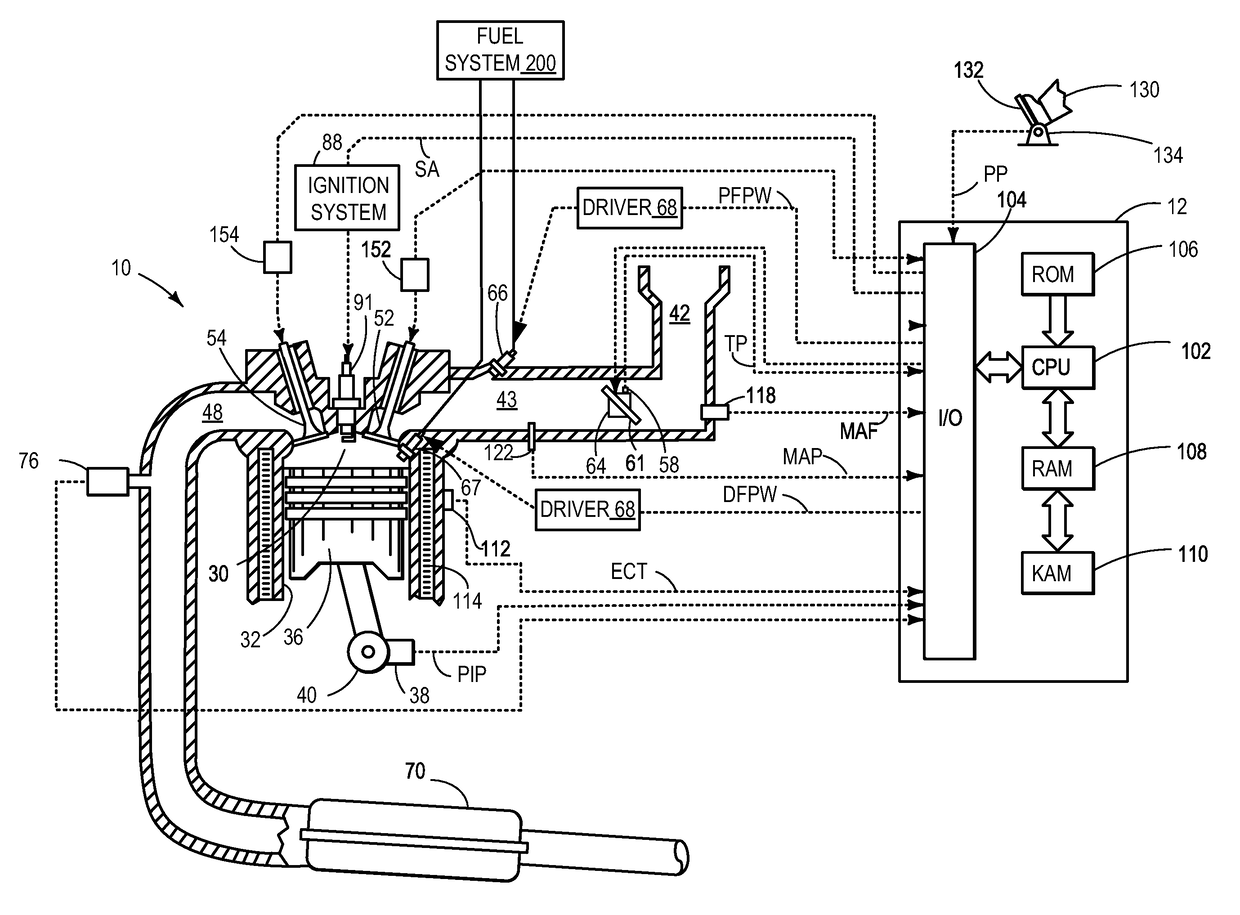
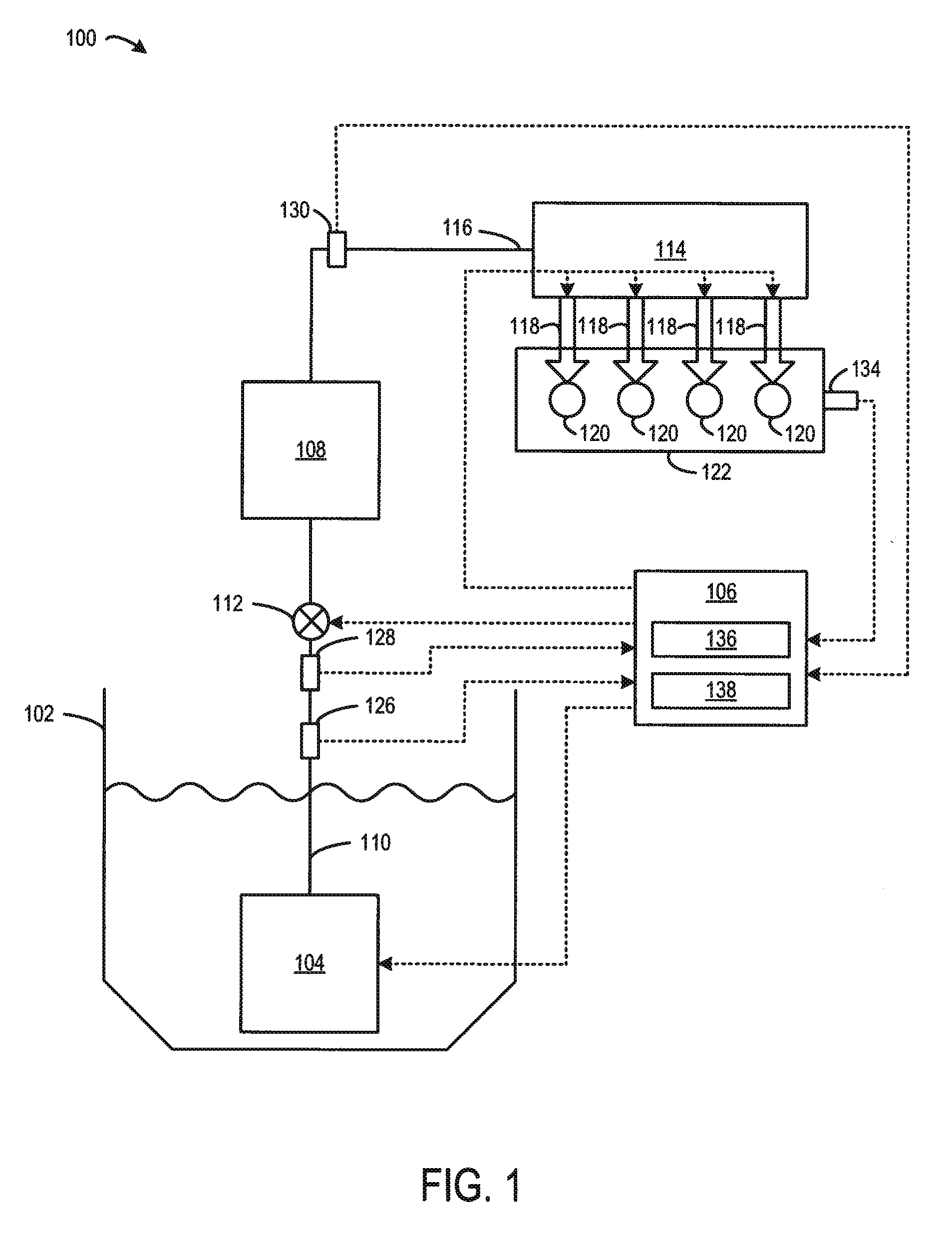
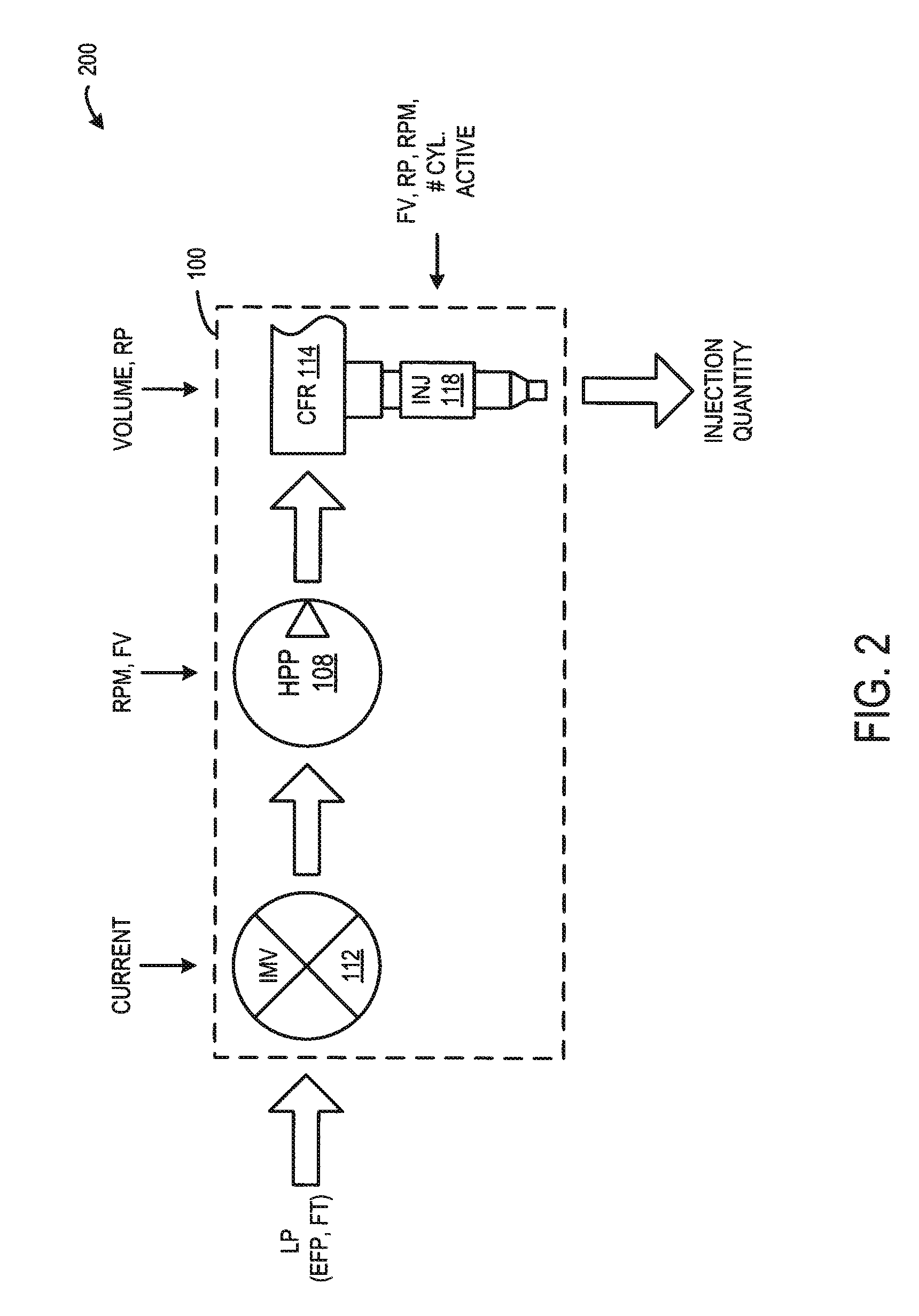
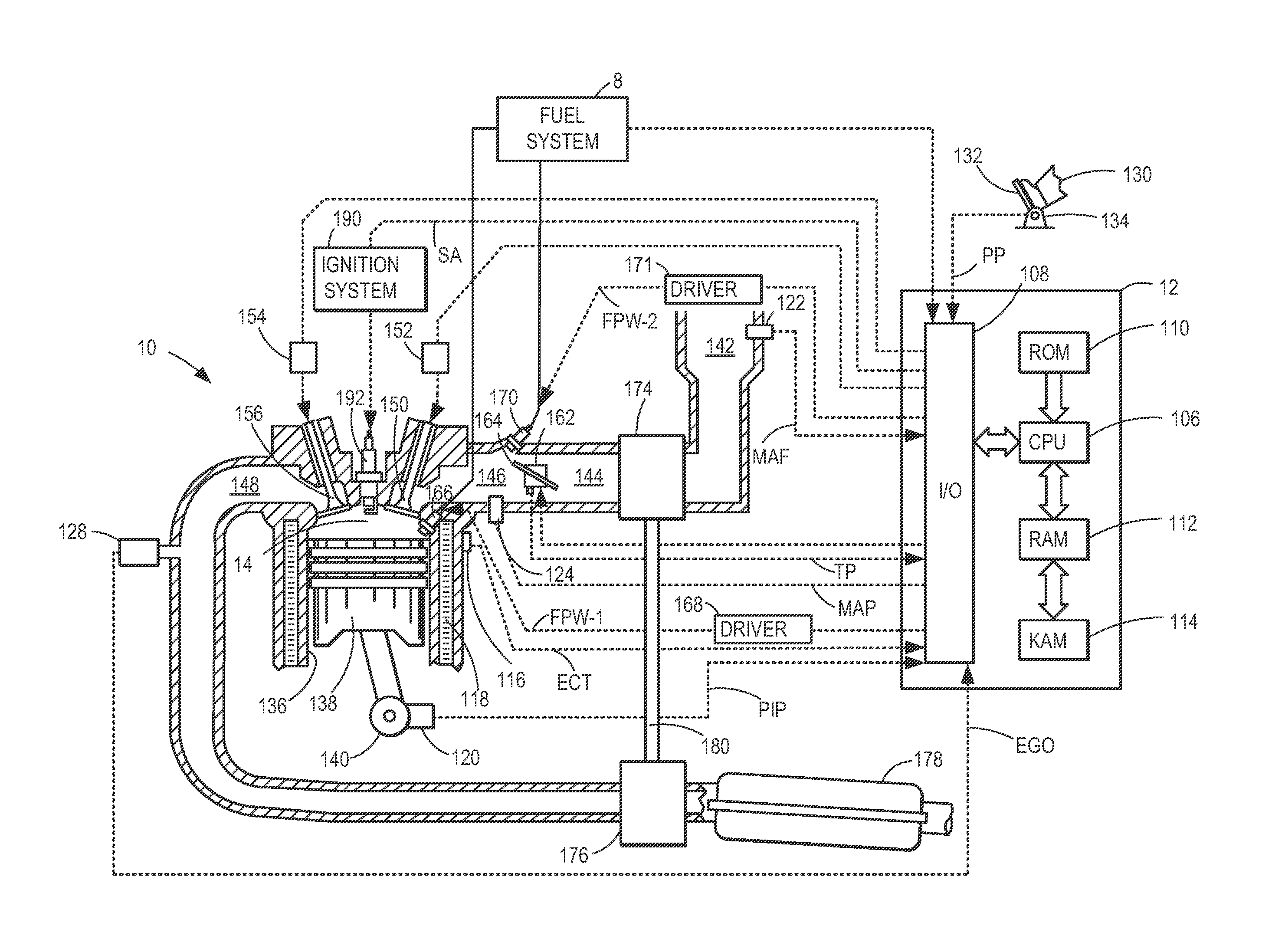
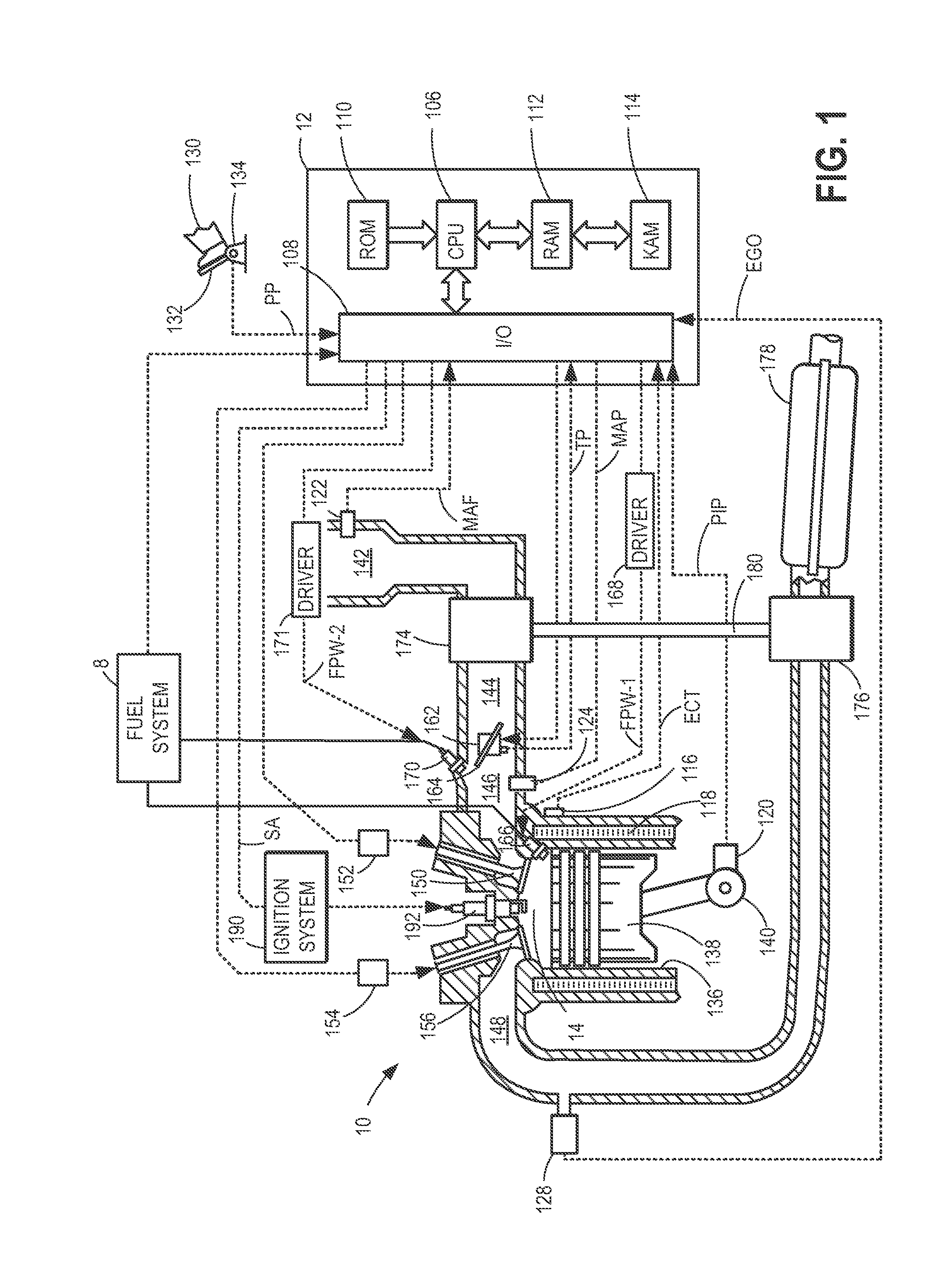
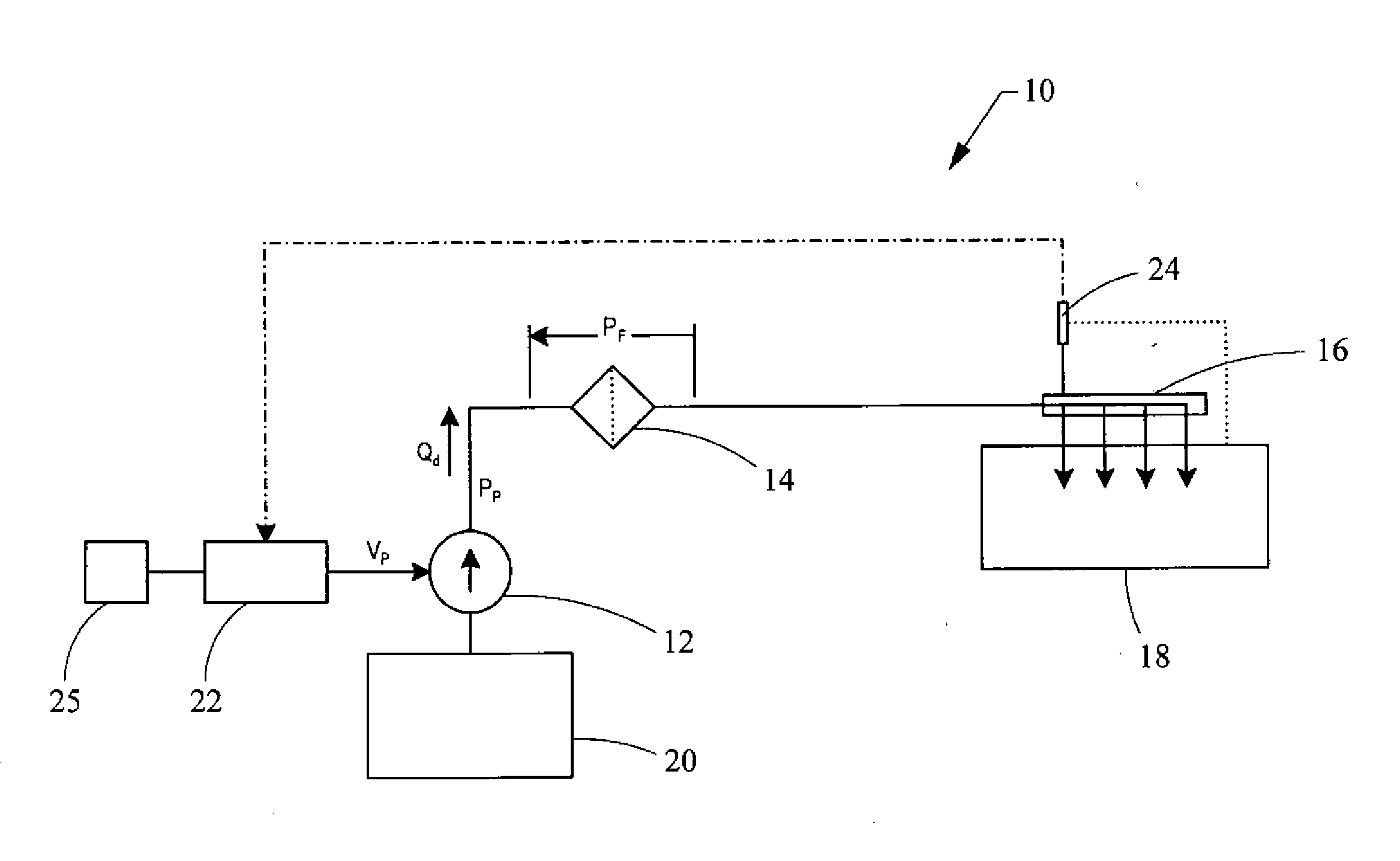
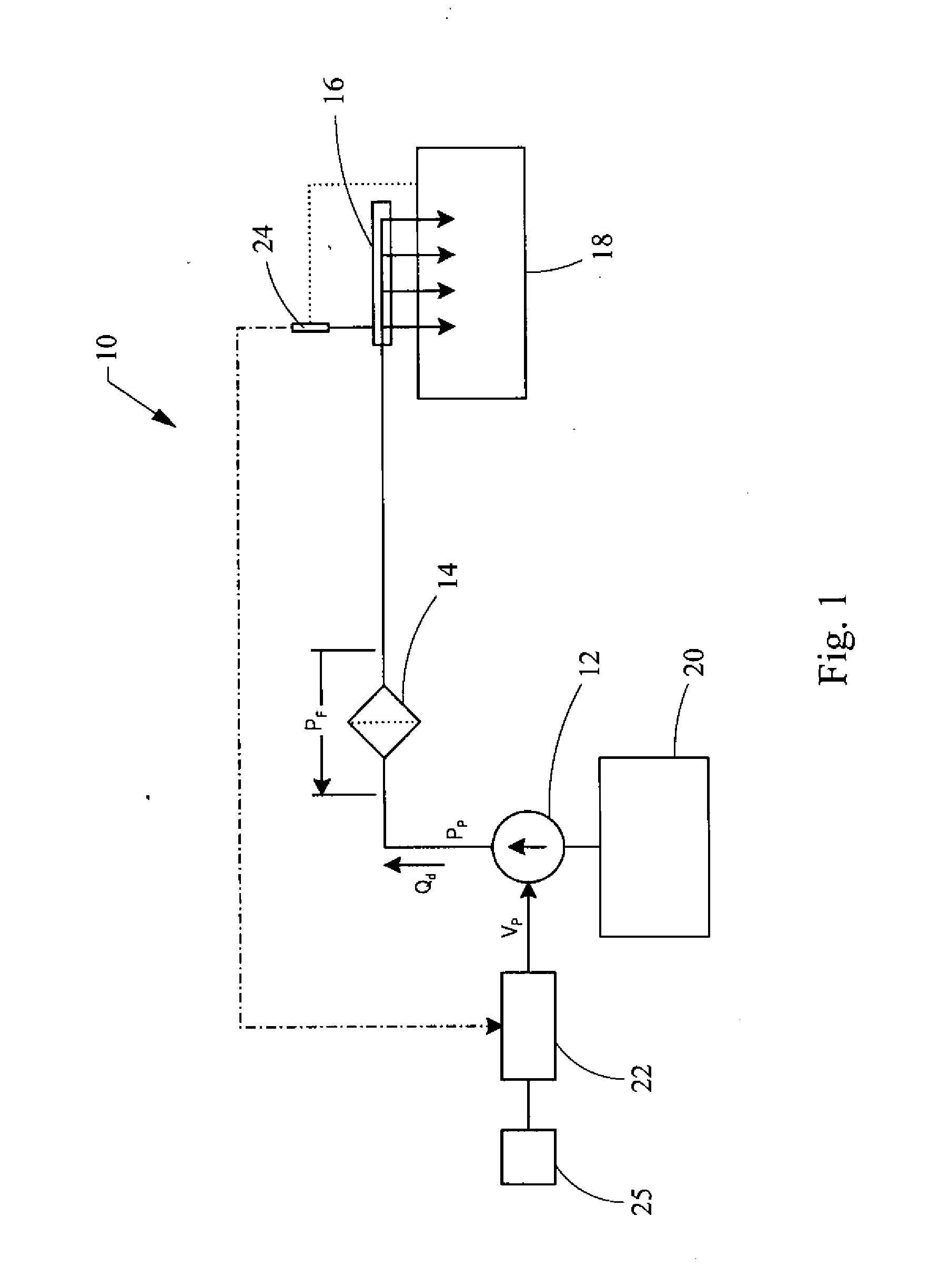
In control terminology, the rail pressure is the system output while the position of the actuator used to control the rail pressure is the system input. There are a number of approaches to control the pressure in the common rail.
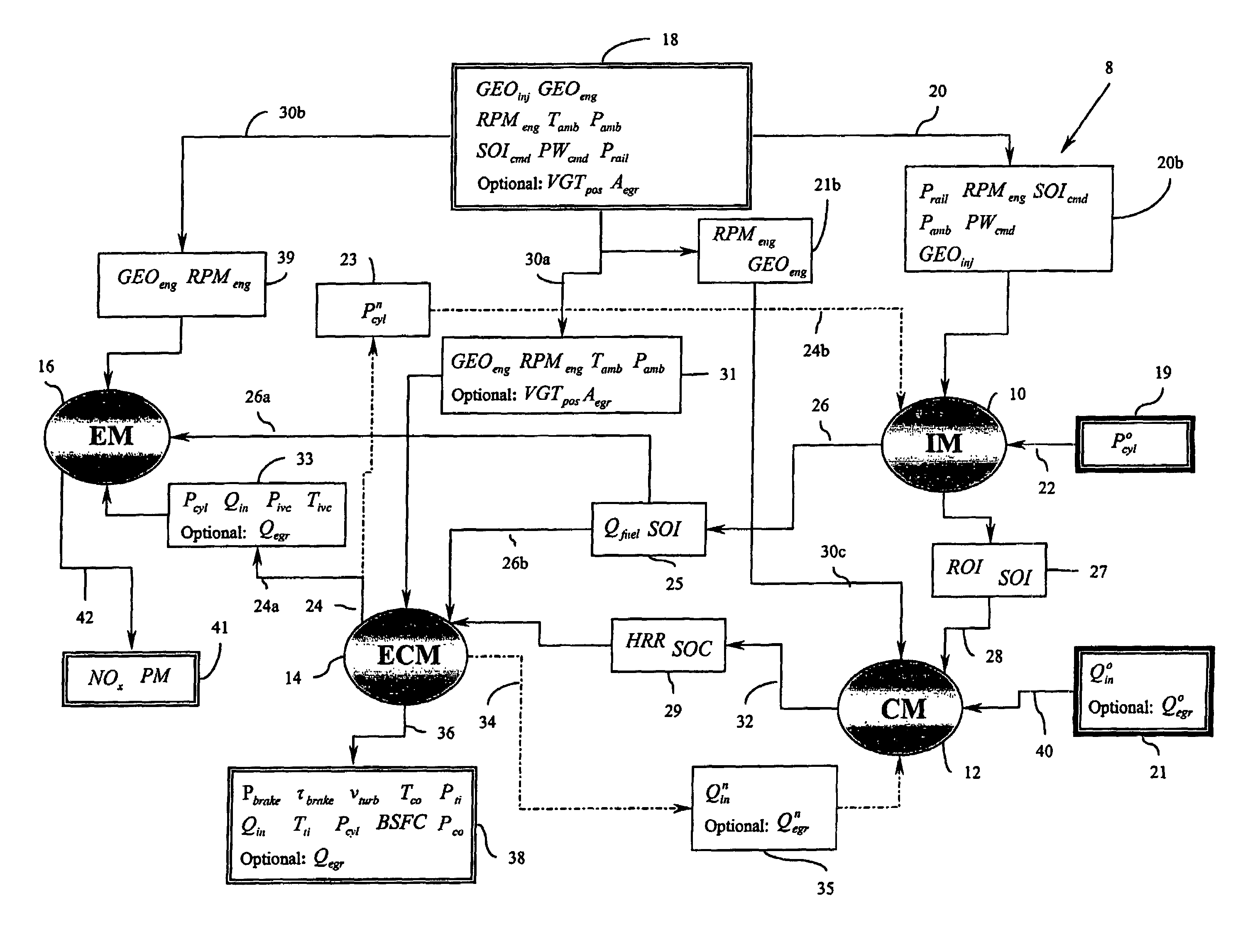
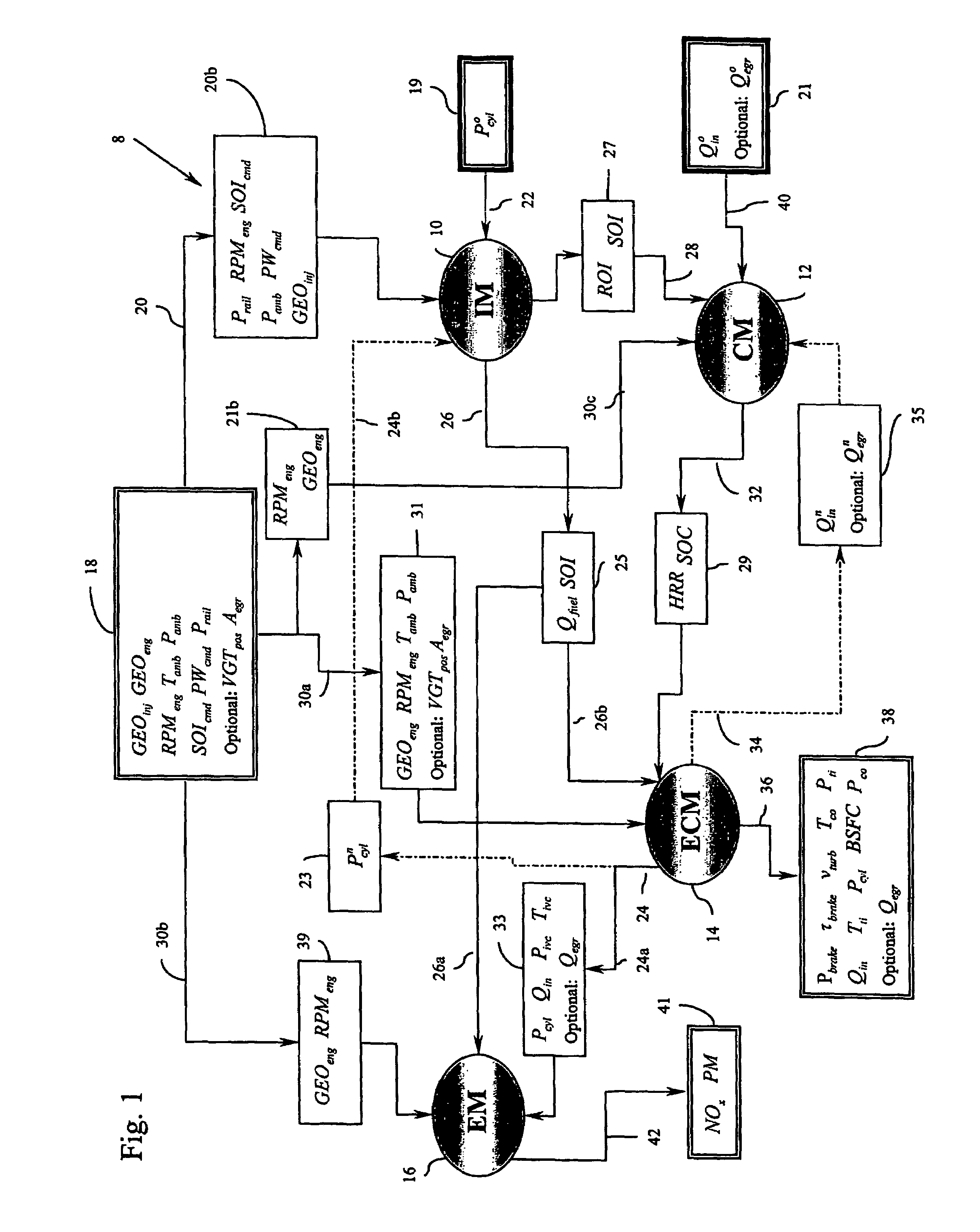
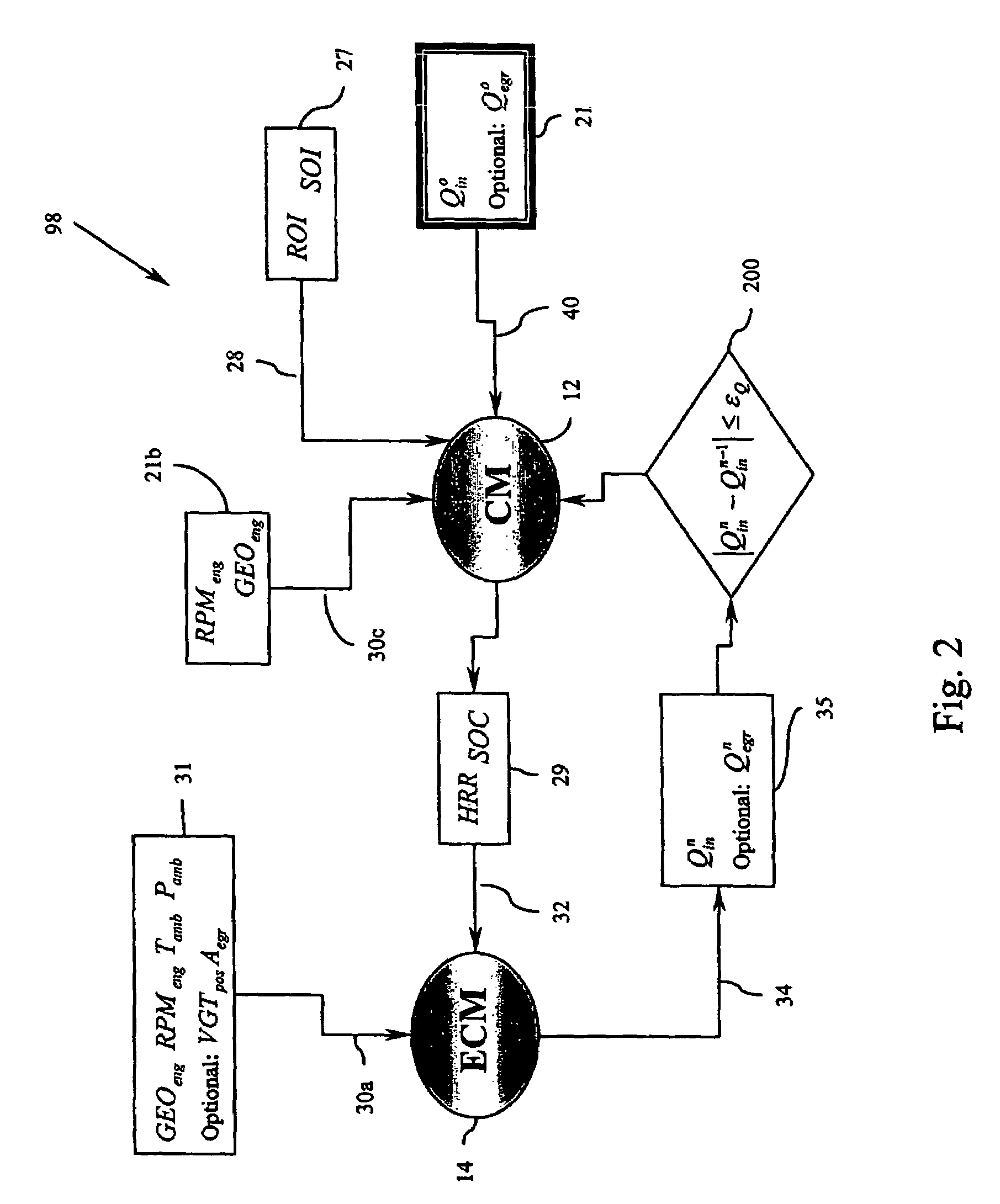
Method for controlling combustion in an internal combustion engine and predicting performance and emissions
InactiveUS7392129B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesBrake torqueBrake specific fuel consumption
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
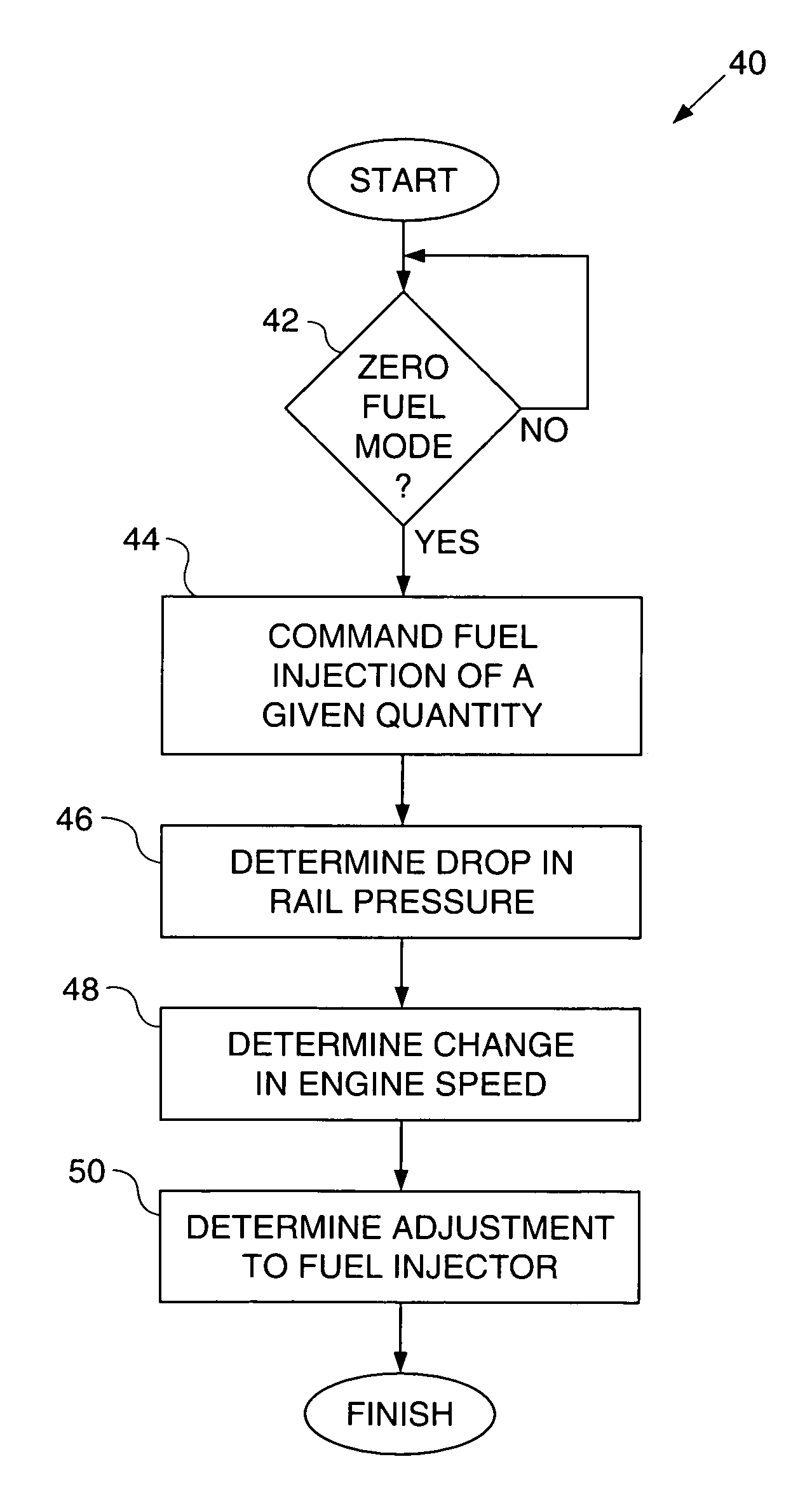
Adaptive fuel injector trimming during a zero fuel condition
Apparatuses and methods for controlling a fuel injector. A fuel shot is injected during a zero fuel condition. A rail pressure drop corresponding to the fuel shot is determined. A change in engine speed corresponding to the fuel shot is determined. An adjustment to the fuel injection as a function of the rail pressure drop and the corresponding change in engine speed is determined.
Owner:PERKINS ENGINES
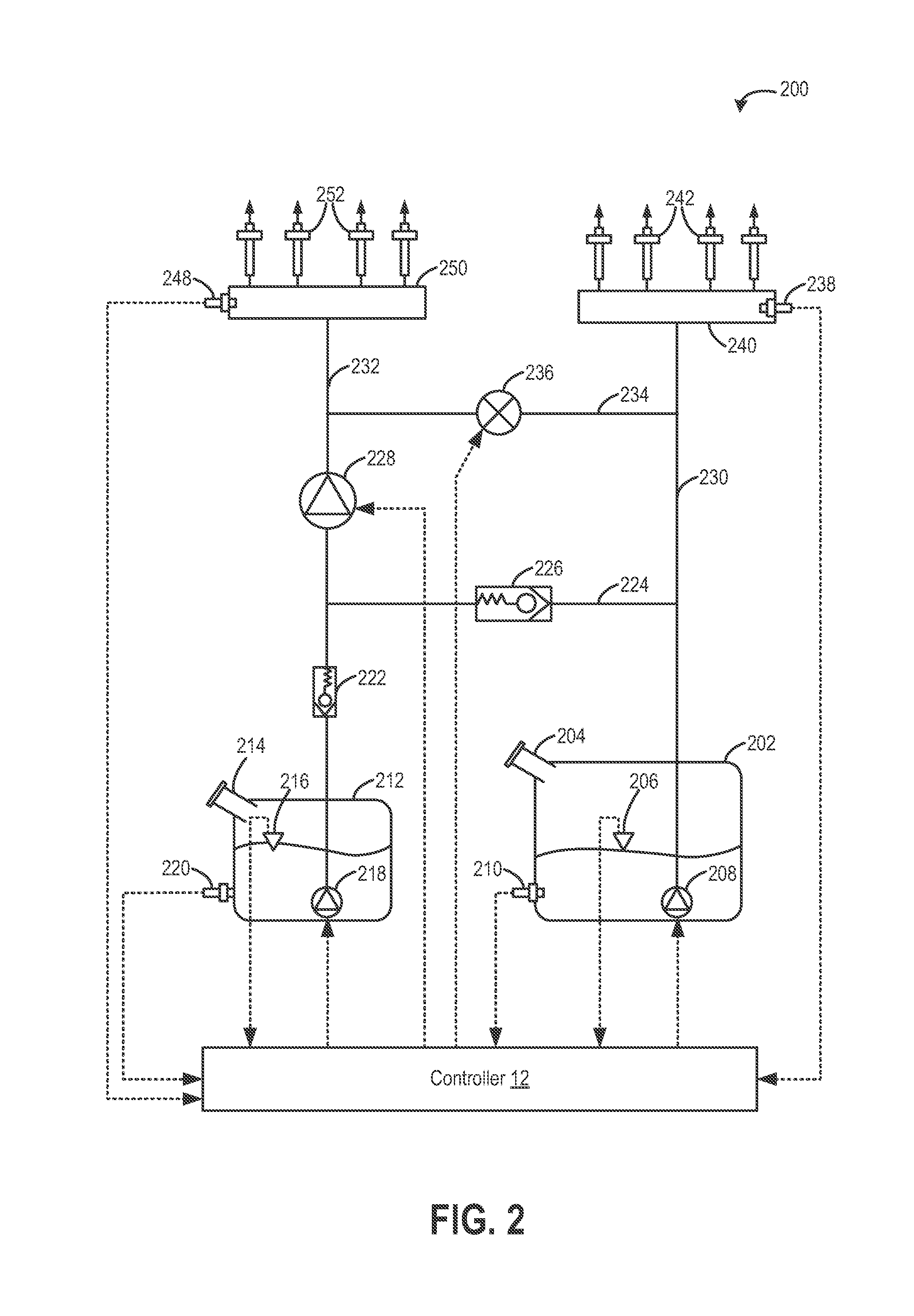
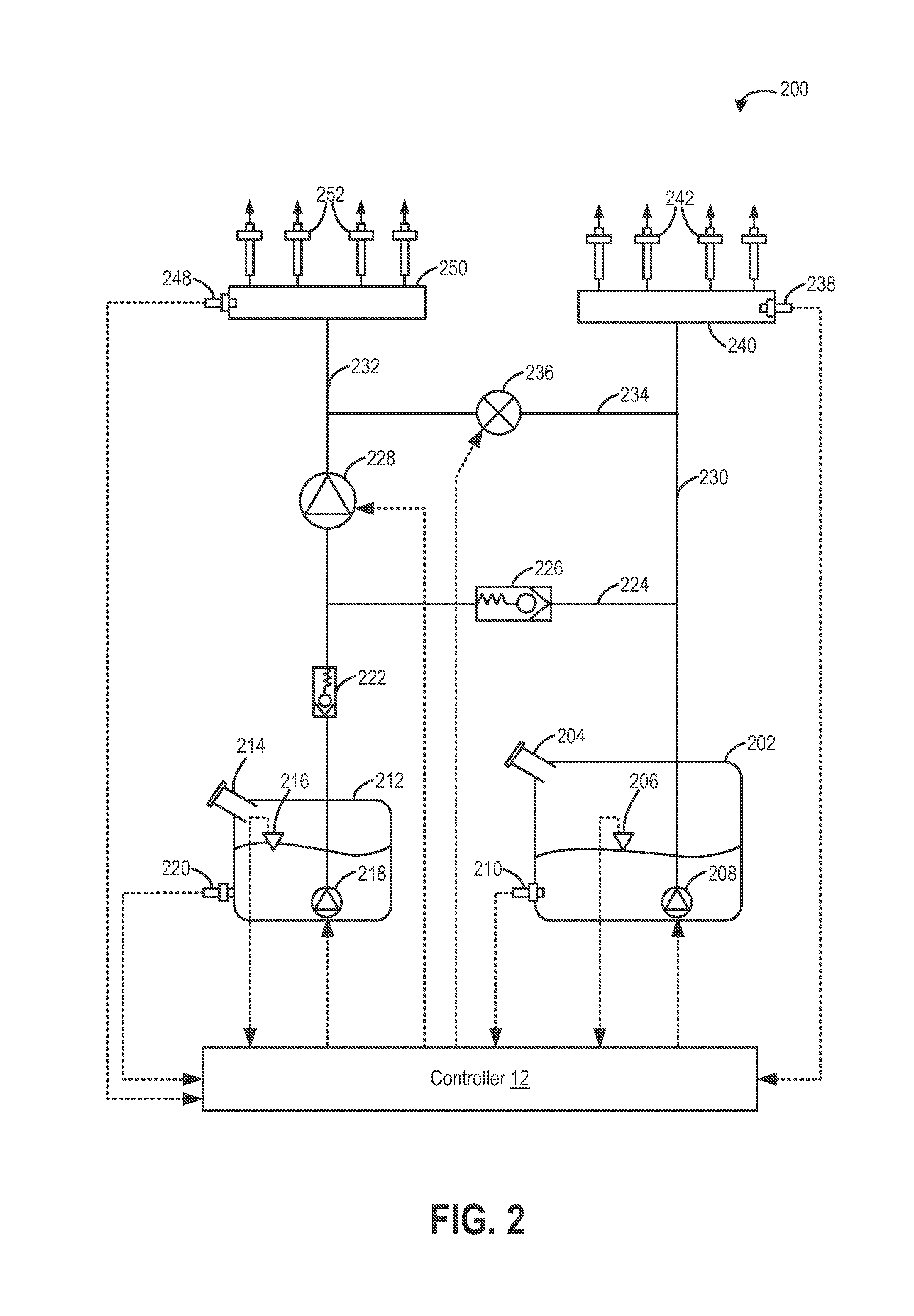
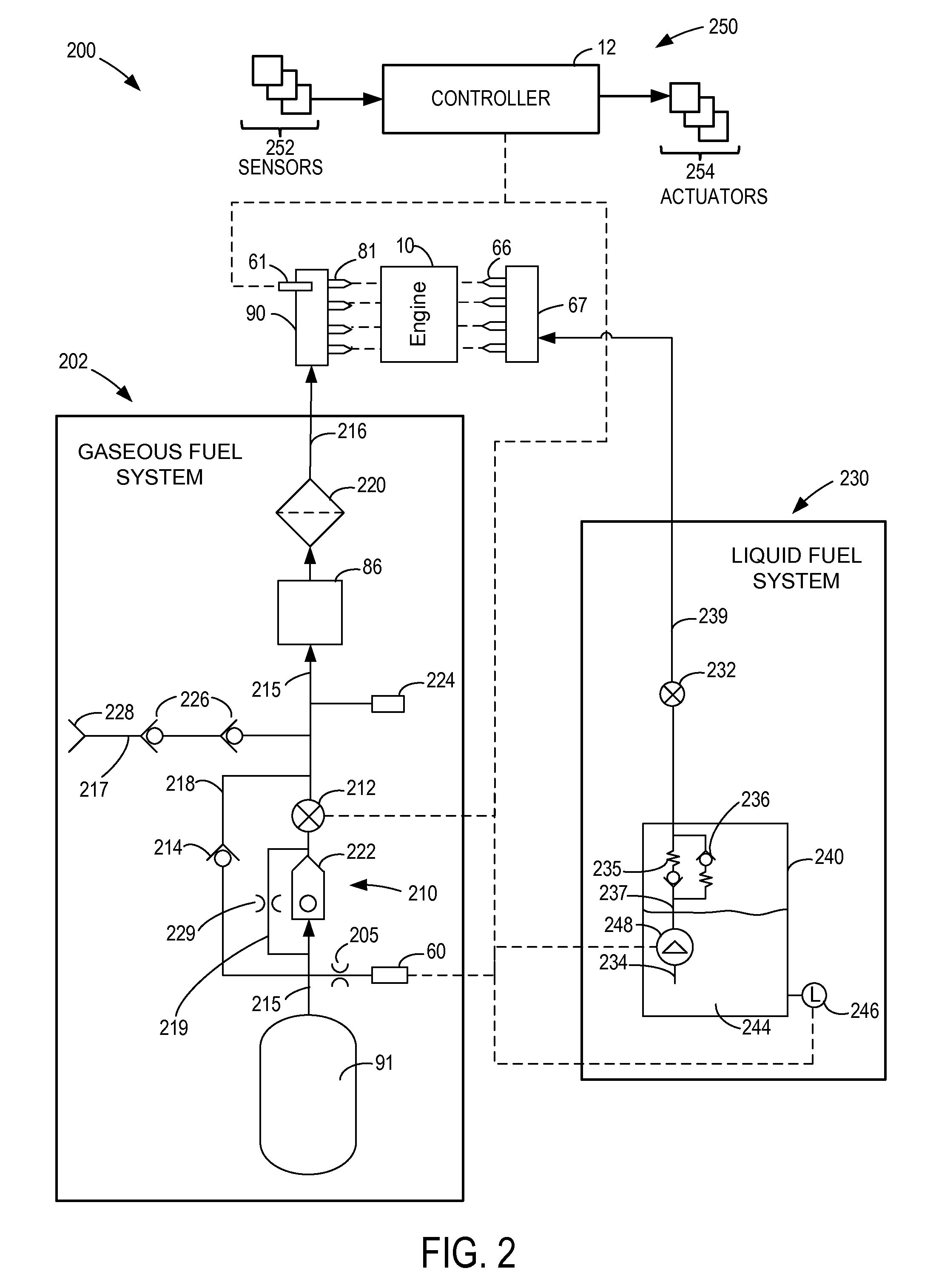
Fuel system for a multi-fuel engine
ActiveUS20120167859A1Reducing pump degradationFully filledInternal combustion piston enginesLow-pressure fuel injectionRail pressureFuel oil
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for determining fuel injection on-time in a gaseous-fuelled internal combustion engine
ActiveUS8095294B1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesRail pressureExternal combustion engine
A method and apparatus determine the fuel injection on-time to accurately meter fuel injected directly into the combustion chamber of a gaseous fuelled internal combustion engine. The fuel injection on-time is determined by interpolating between values retrieved from two of a plurality of predetermined look-up tables, which each define fuel injection on-time as a function of gaseous fuel rail pressure and fuelling amount. Each table corresponds to a fixed value of a third parameter that correlates to in-cylinder pressure.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
Method and apparatus of fuelling an internal combustion engine with hydrogen and methane
ActiveUS8091536B2Internal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelRail pressureElectronic controller
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
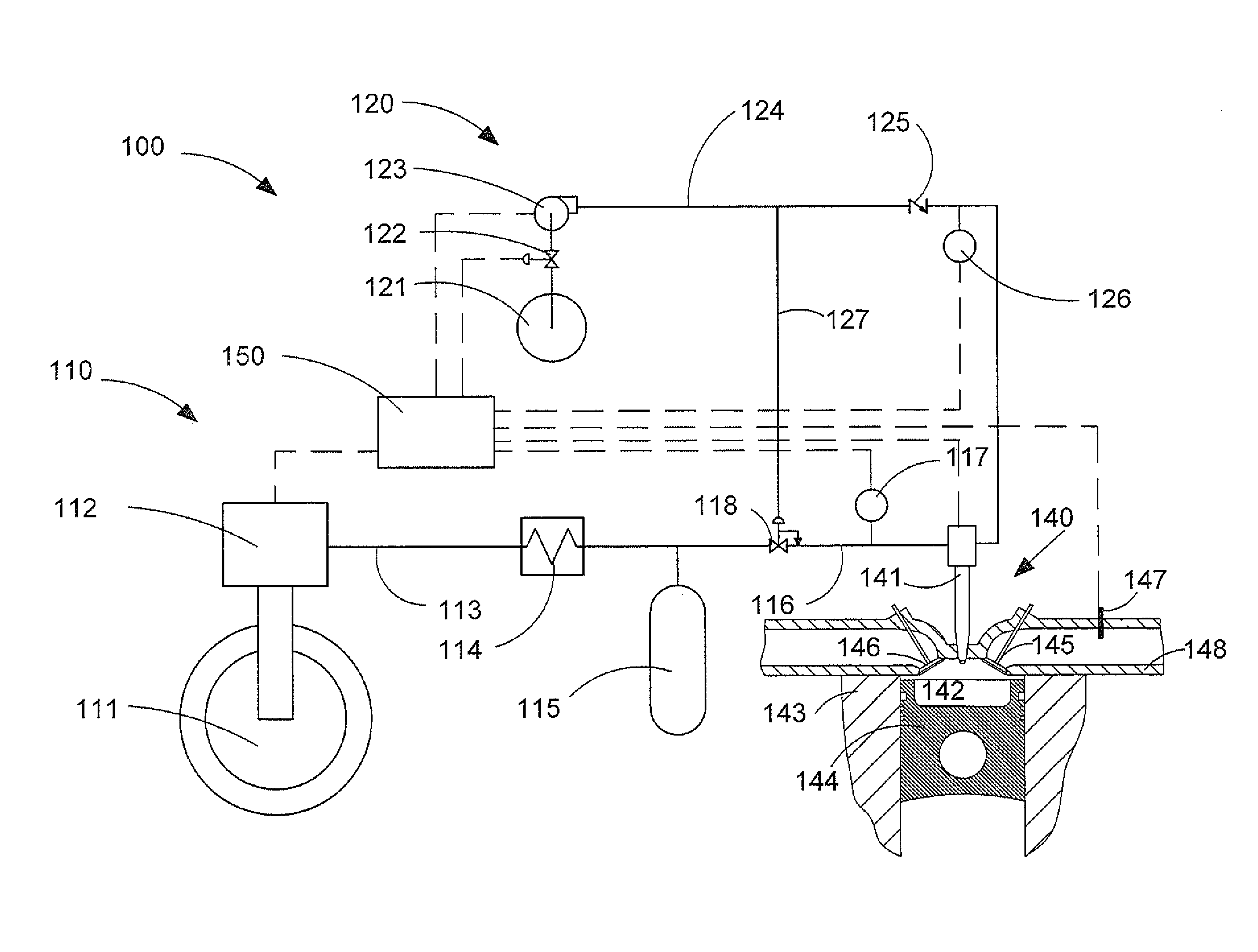
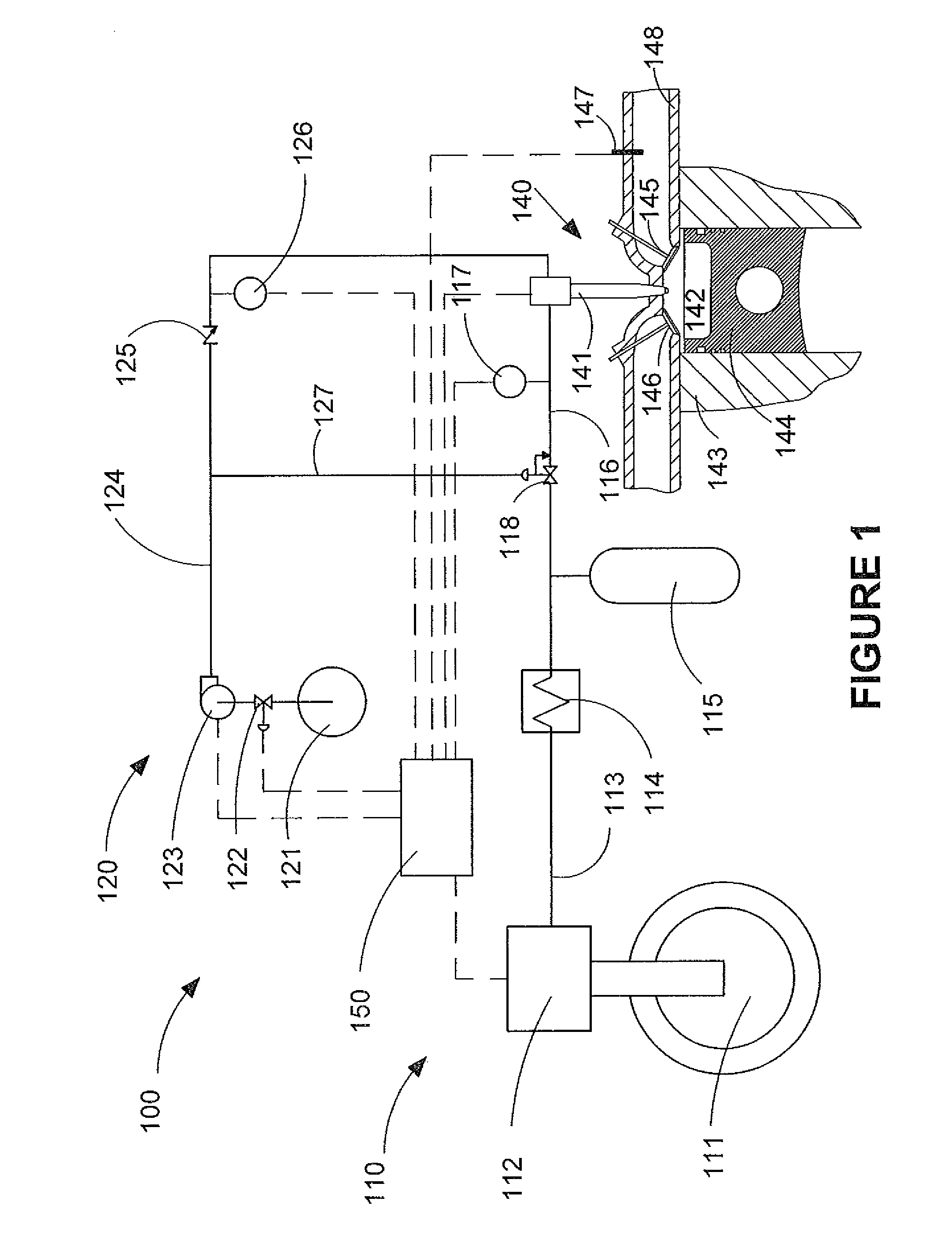
Fuel injection system ensuring operation in event of unusual condition
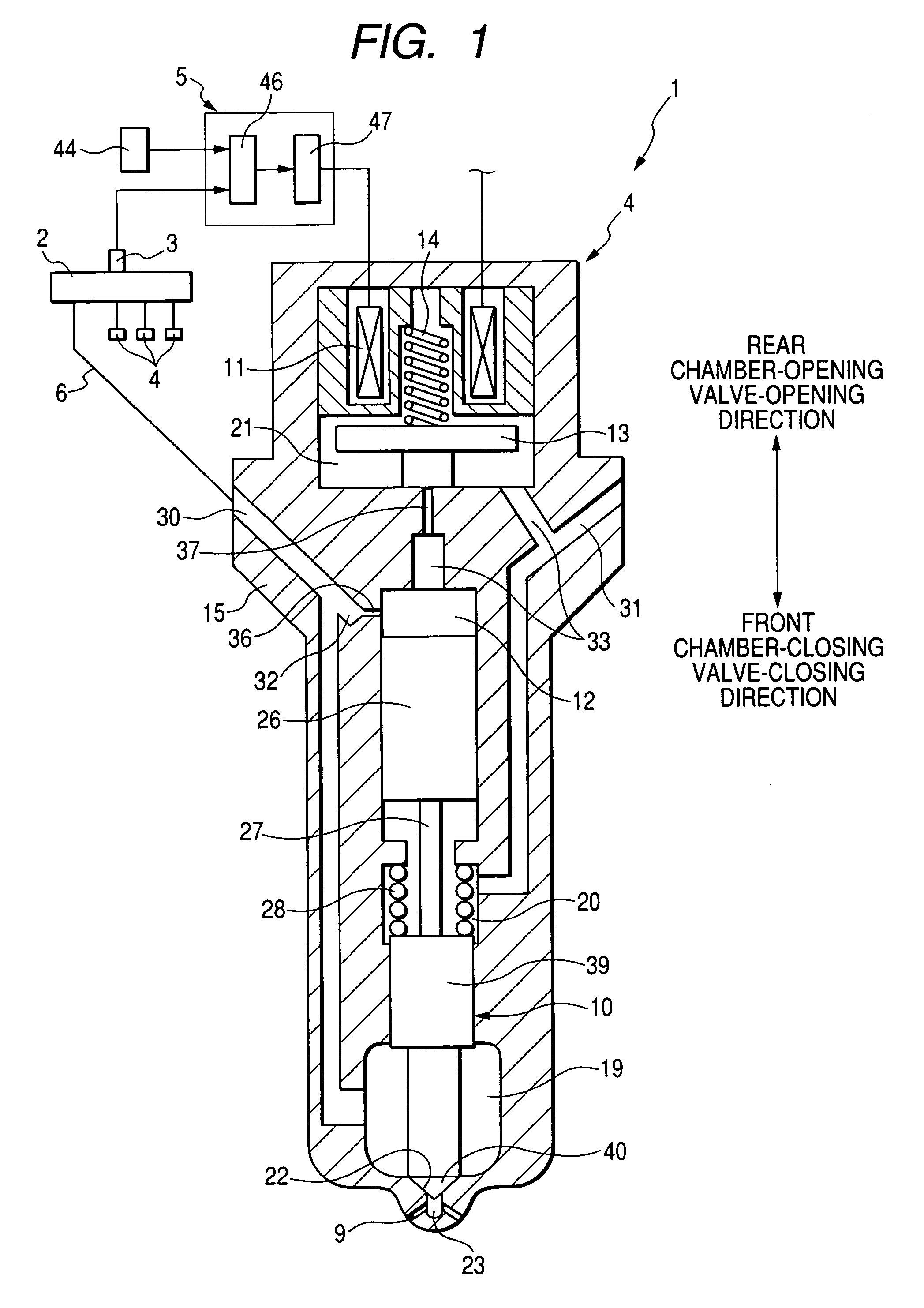
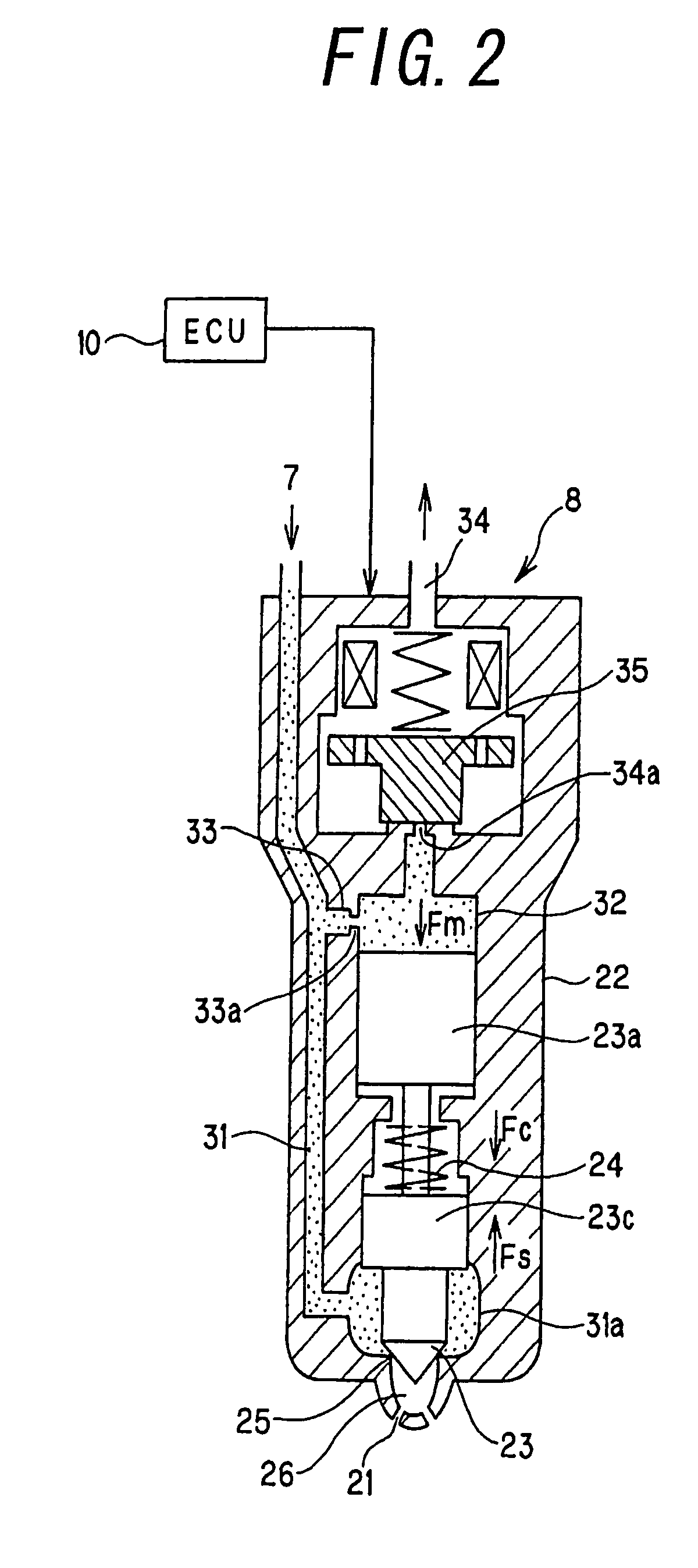
InactiveUS7305971B2Simple structureGuaranteed uptimeElectrical controlFuel injection apparatusRail pressureActuator
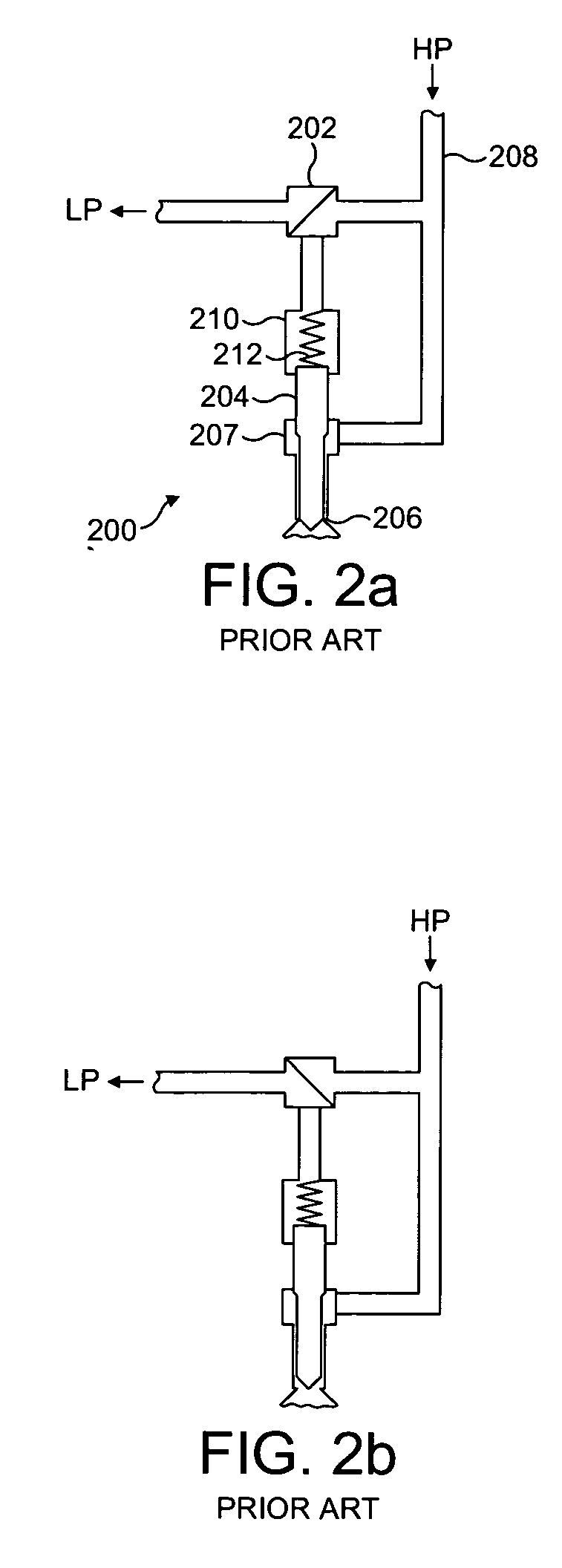
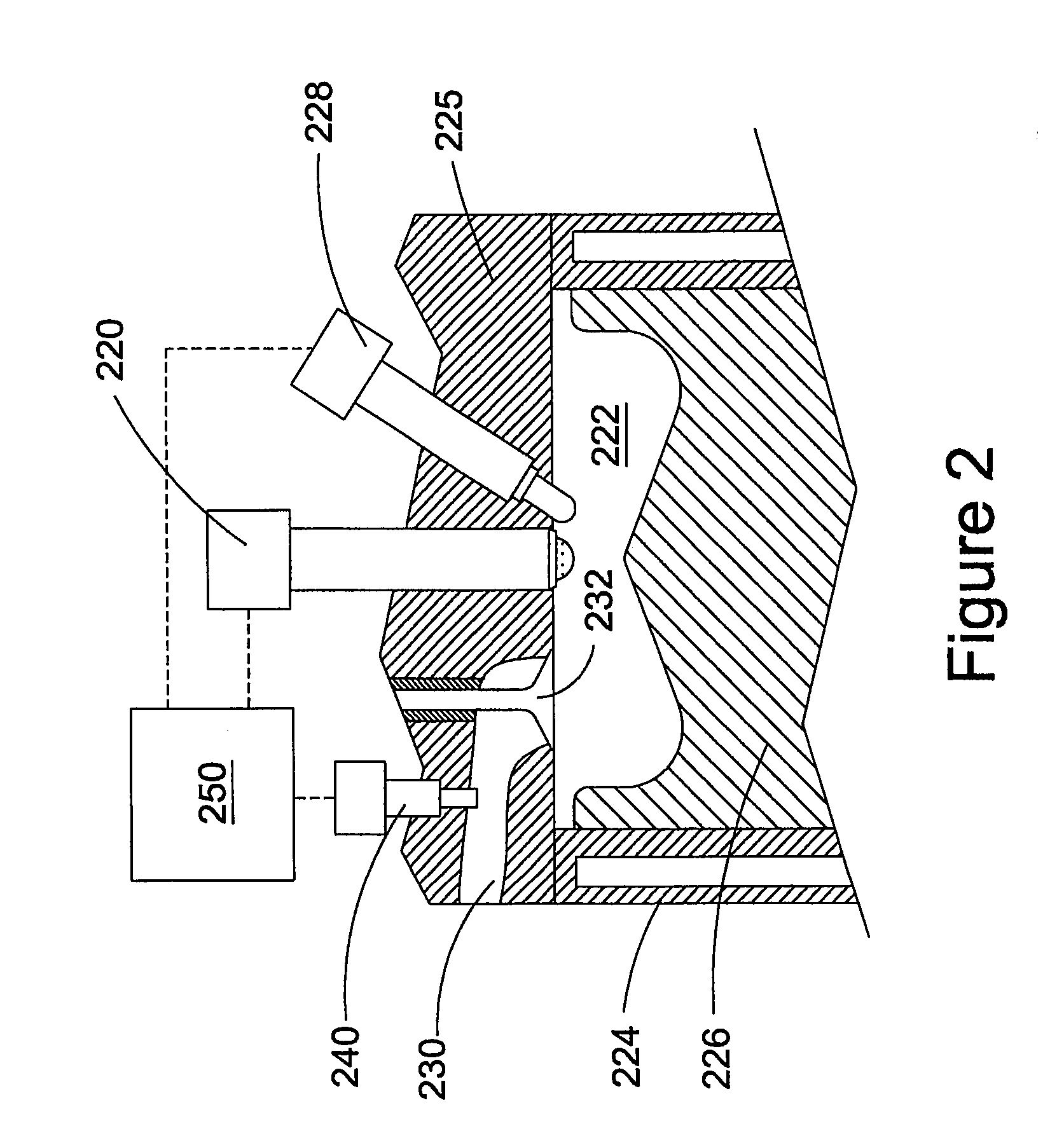
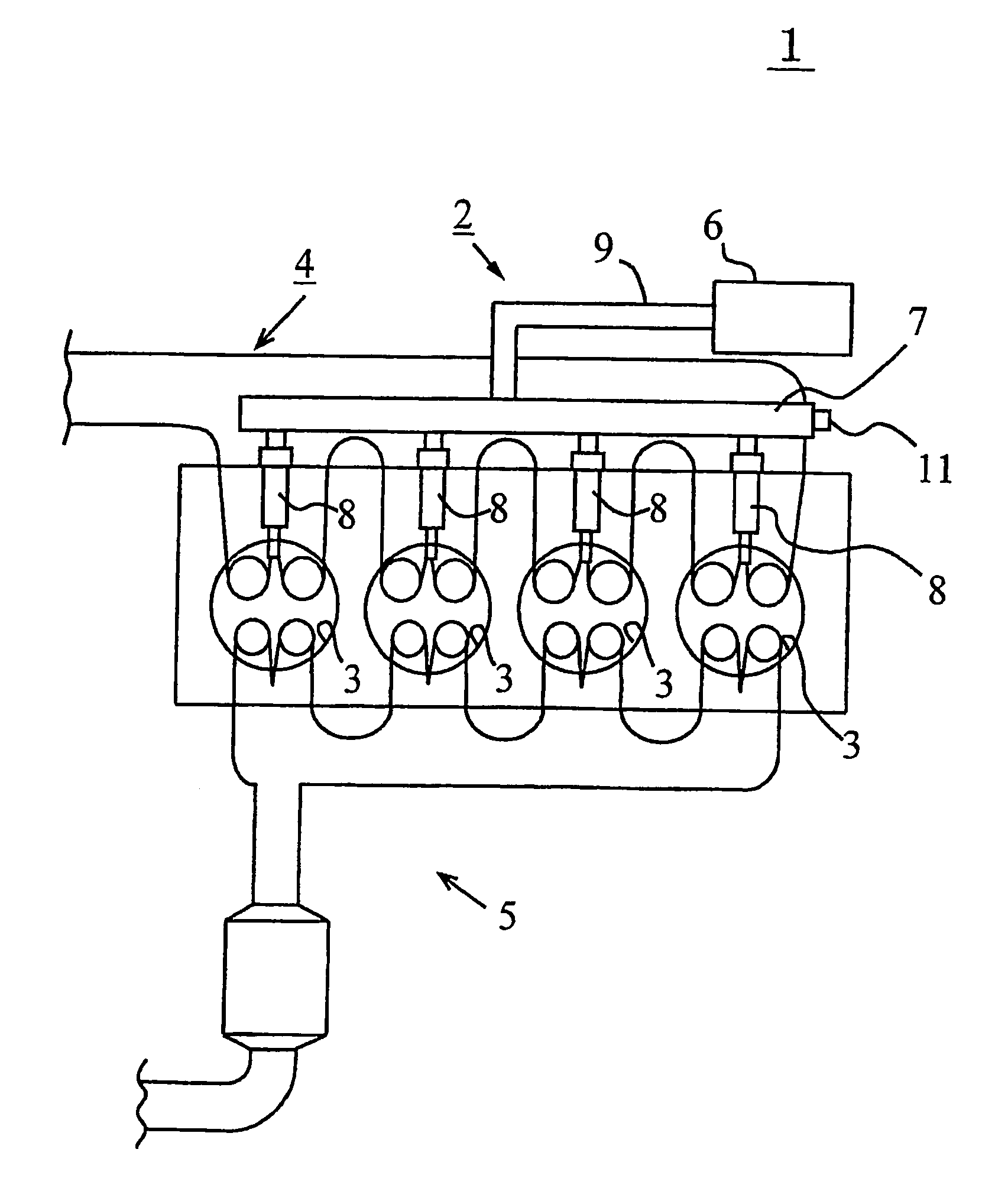
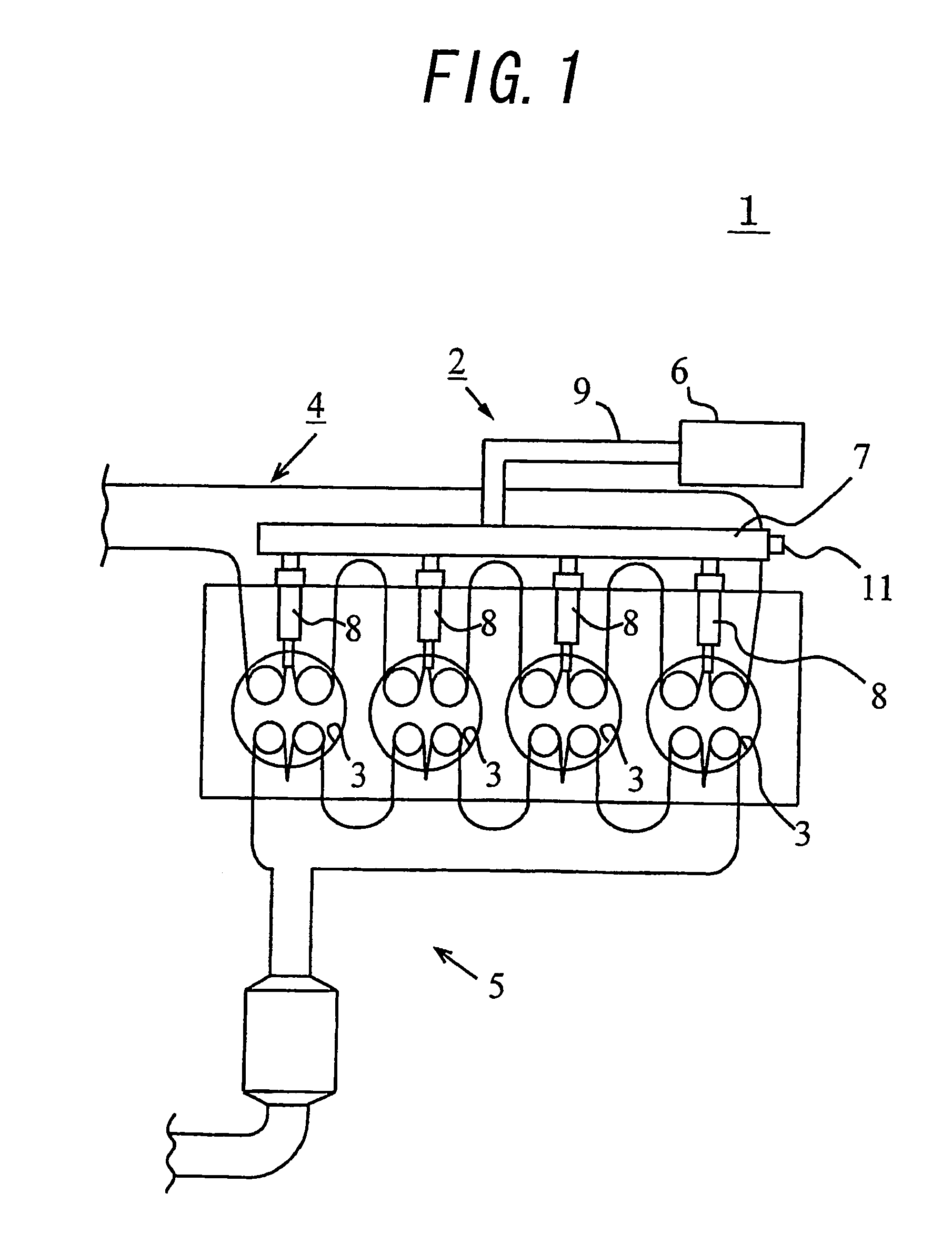
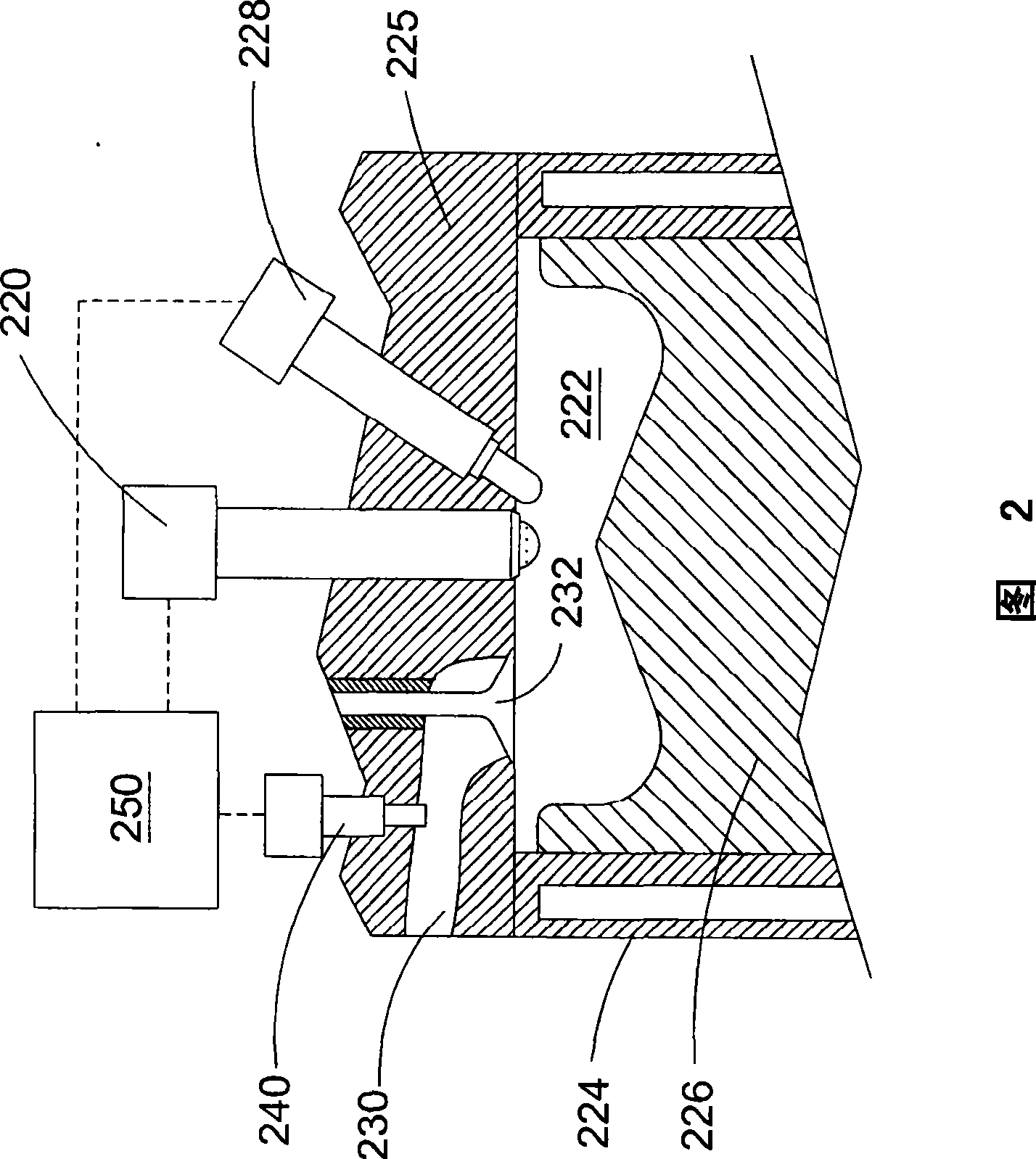
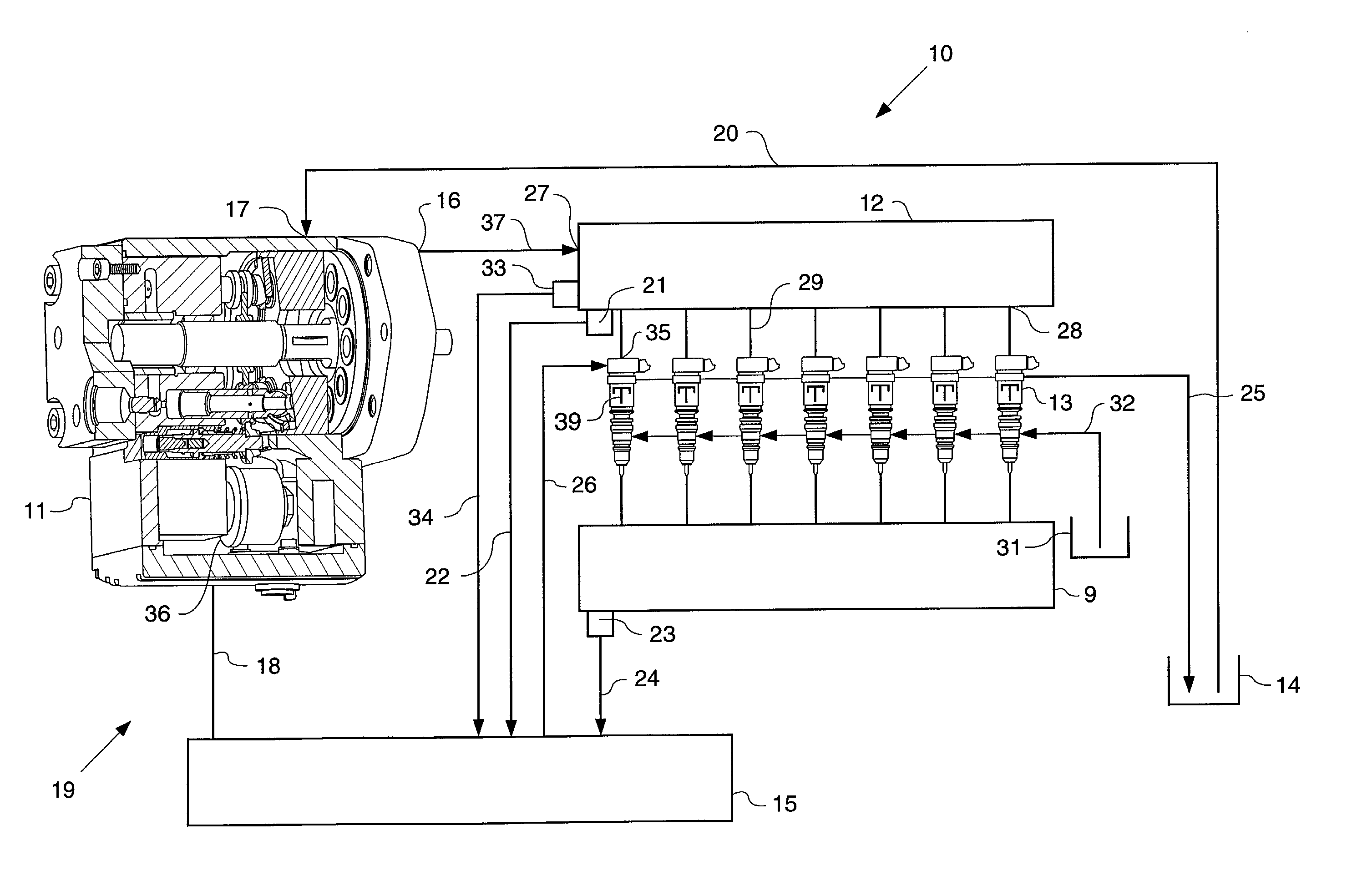
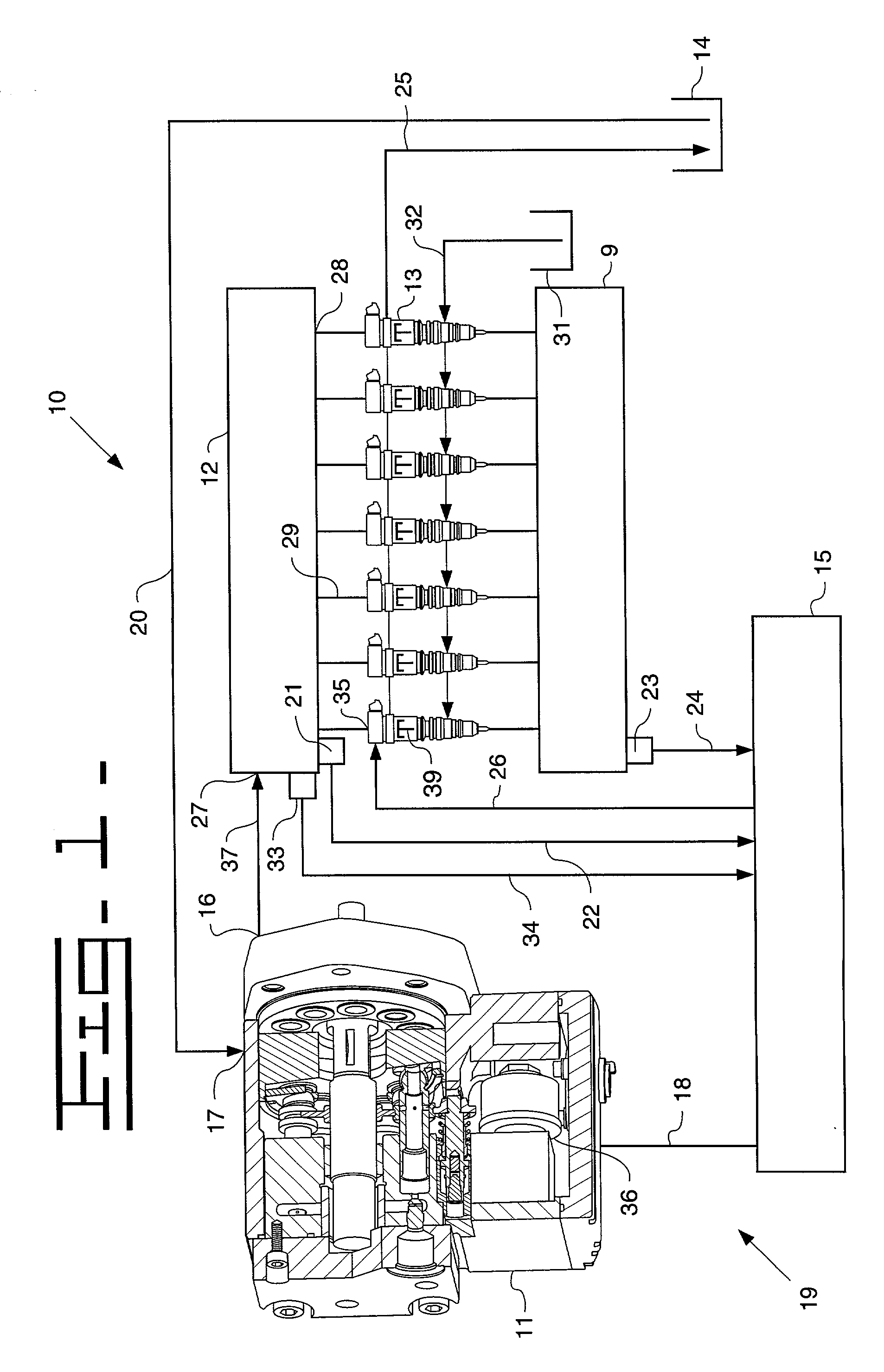
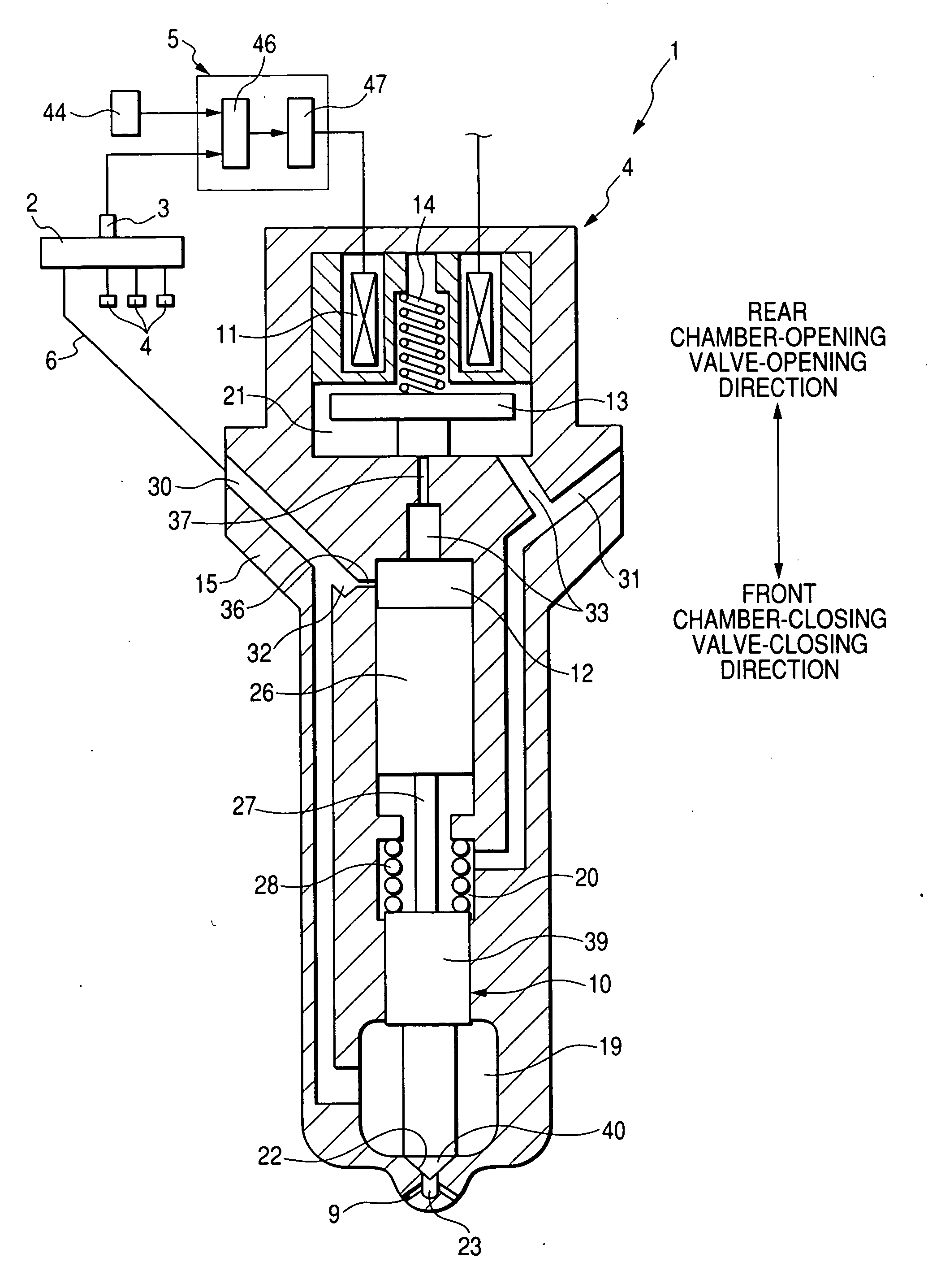
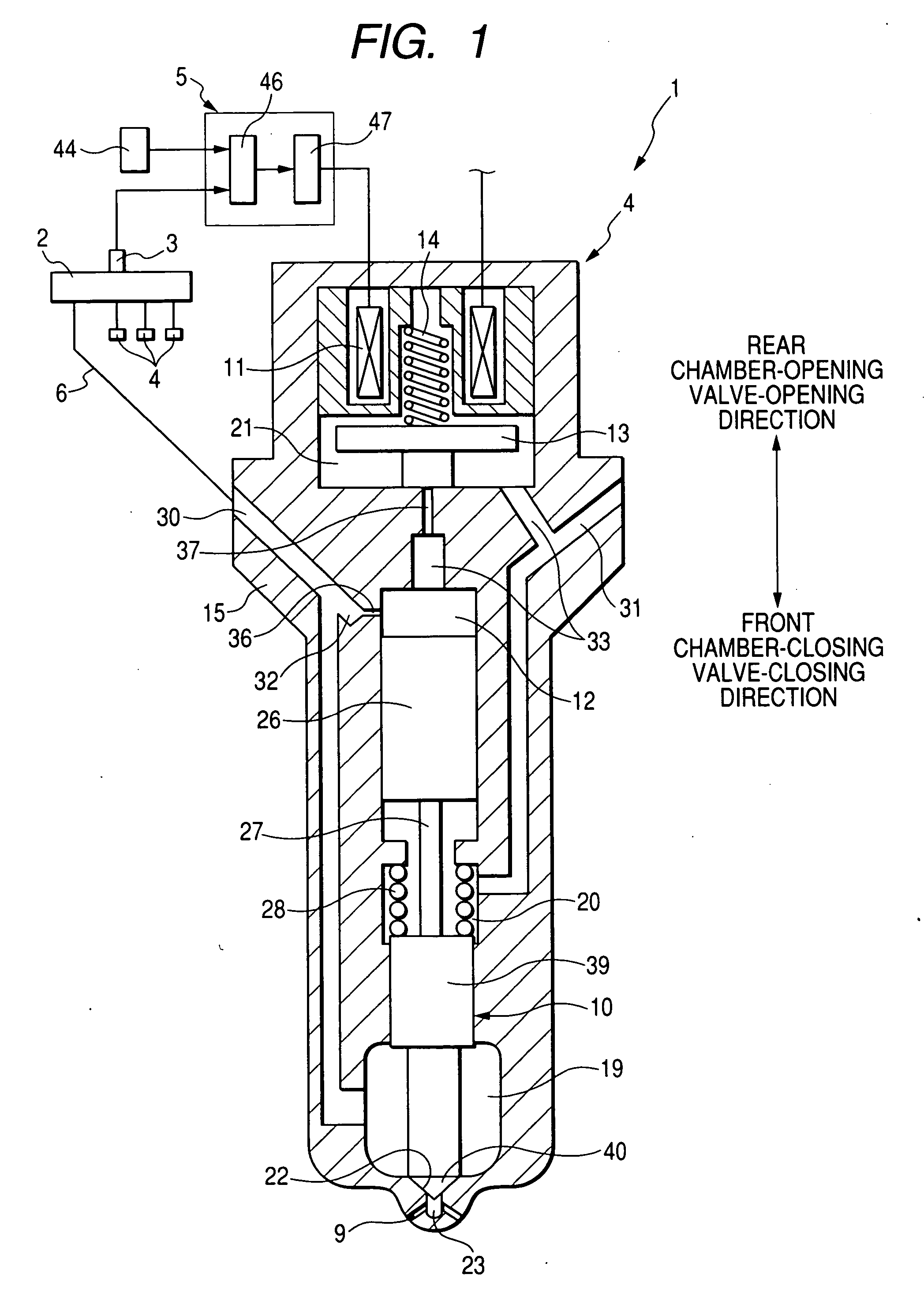
A common rail fuel injection apparatus for an engine is provided which is equipped with a rail pressure sensor working to measure the pressure of fuel in a common rail, fuel injectors, and a controller. When the operation state of the rail pressure sensor monitored to be unusual, the controller changes the value of electricity supplied to an actuator of one of the fuel injectors to induce a change in a preselected operation characteristic of the engine. Upon appearance of such a change, the controller estimates the value of the rail pressure using the changed value of the electricity and a physical property of balance among forces acting on a valve of one of the fuel injectors which has induced the change in operation characteristic of the engine. The estimated value of the rail pressure is used for subsequent injections of the fuel into the engine.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method And Apparatus Of Fuelling An Internal Combustion Engine With Hydrogen And Methane
ActiveUS20090120385A1Internal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelRail pressureElectronic controller
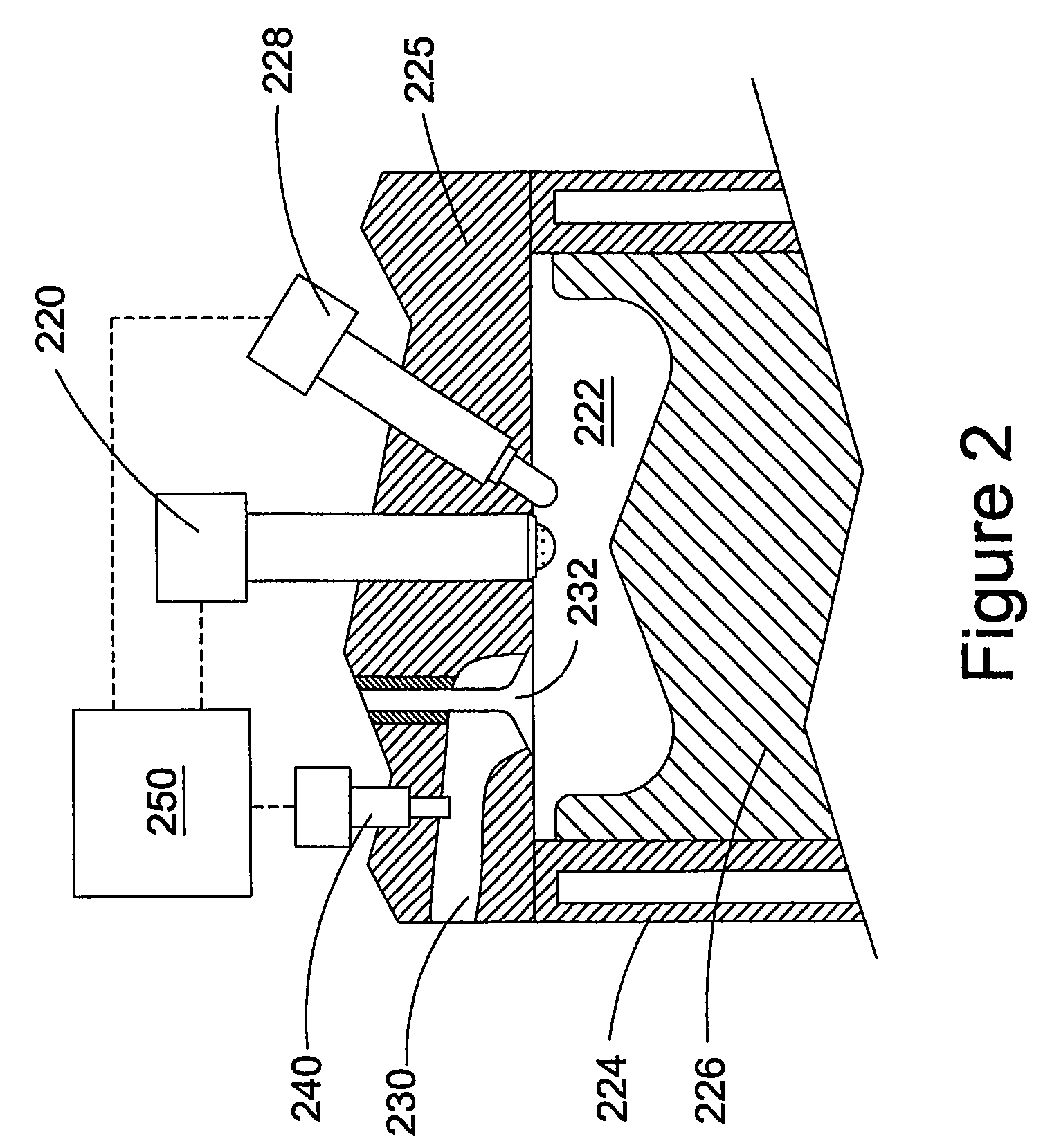
A gaseous-fuelled internal combustion engine and a method of engine operation improve combustion stability and reducing emissions of NOx, PM, and unburned hydrocarbons. The method comprises fuelling an internal combustion engine with hydrogen and natural gas, which can be directly injected into the combustion chamber together or introduced separately. Of the total gaseous fuel delivered to the engine, at least 5% by volume at standard temperature and pressure is hydrogen. For at least one engine operating condition, the ratio of fuel rail pressure to peak in-cylinder pressure is at least 1.5:1. A fuel injection valve introduces the gaseous fuel mixture directly into the combustion chamber. Two separate fuel injection valves could also introduce the methane and hydrogen separately. An electronic controller controls timing for operating the fuel injection valve(s). The engine has a preferred compression ratio of at least 14:1.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
Method and apparatus of fuelling an internal combustion engine with hydrogen and methane
ActiveUS8469009B2Reduce the amount of solutionInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelElectronic controllerRail pressure
A gaseous-fuelled internal combustion engine and a method of engine operation improve combustion stability and reducing emissions of NOx, PM, and unburned hydrocarbons. The method comprises fuelling an internal combustion engine with hydrogen and natural gas, which can be directly injected into the combustion chamber together or introduced separately. Of the total gaseous fuel delivered to the engine, at least 5% by volume at standard temperature and pressure is hydrogen. For at least one engine operating condition, the ratio of fuel rail pressure to peak in-cylinder pressure is at least 1.5:1. A fuel injection valve introduces the gaseous fuel mixture directly into the combustion chamber. Two separate fuel injection valves could also introduce the methane and hydrogen separately. An electronic controller controls timing for operating the fuel injection valve(s). The engine has a preferred compression ratio of at least 14:1.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
Method of diagnosing injector variability in a multiple injector system
ActiveUS9593637B2Accurate measurementEasy to adjustElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesRail pressureEngineering
Various systems and methods are described for diagnosing injector variability in a dual fuel, multi-injector system. In one example, a single injector in one cylinder is enabled while remaining cylinders are fueled with a first fuel and subsequently, a second fuel is injected via the enabled injector into the one cylinder in a predetermined sequence and fuel rail pressure drops are measured. Further, measured pressure drop after each injection event is corrected for an increase in injector closing delay.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
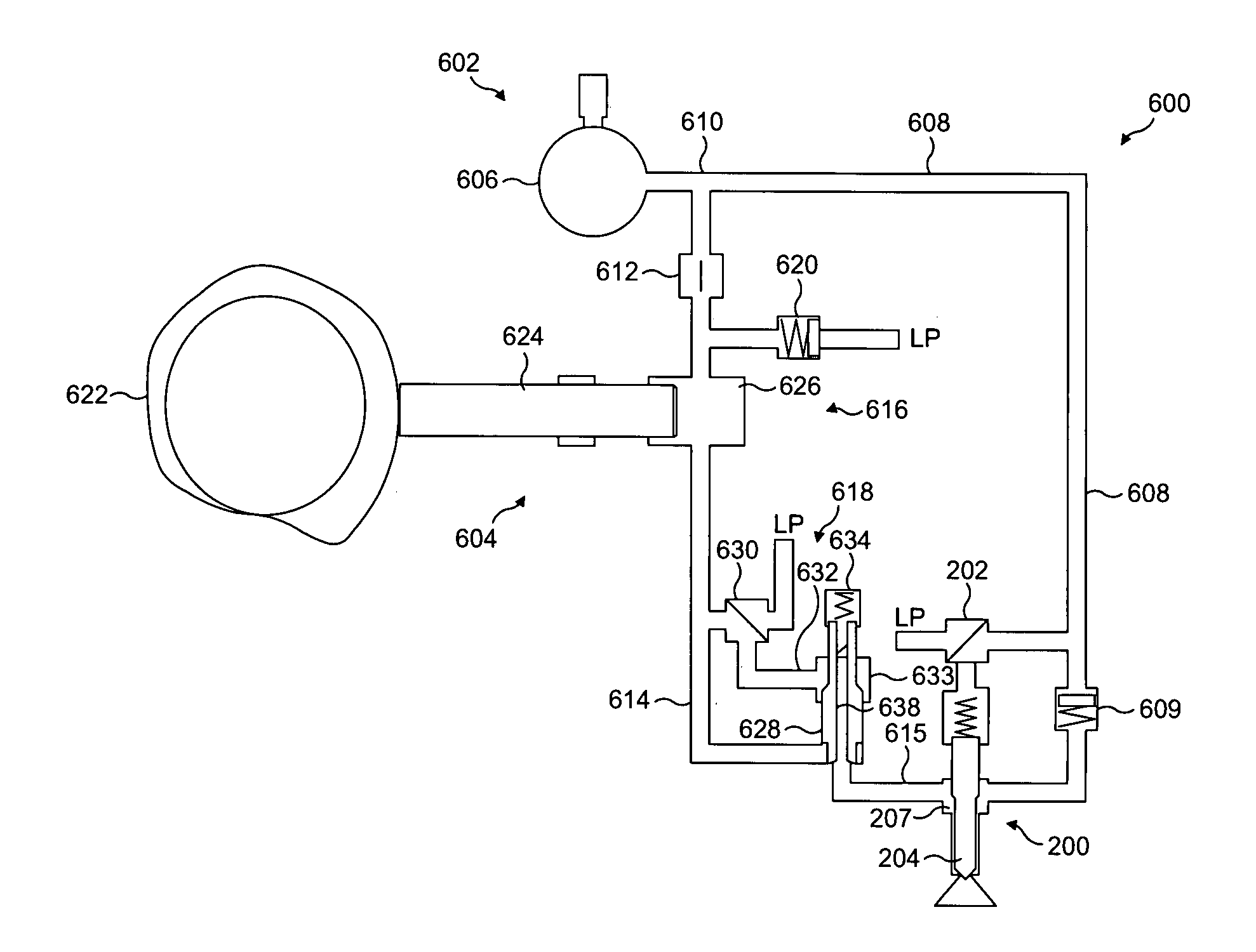
Relating to fuel injection systems
InactiveUS20060243253A1Increase pressurePrevent backflowLow-pressure fuel injectionMachines/enginesRail pressureFuel supply
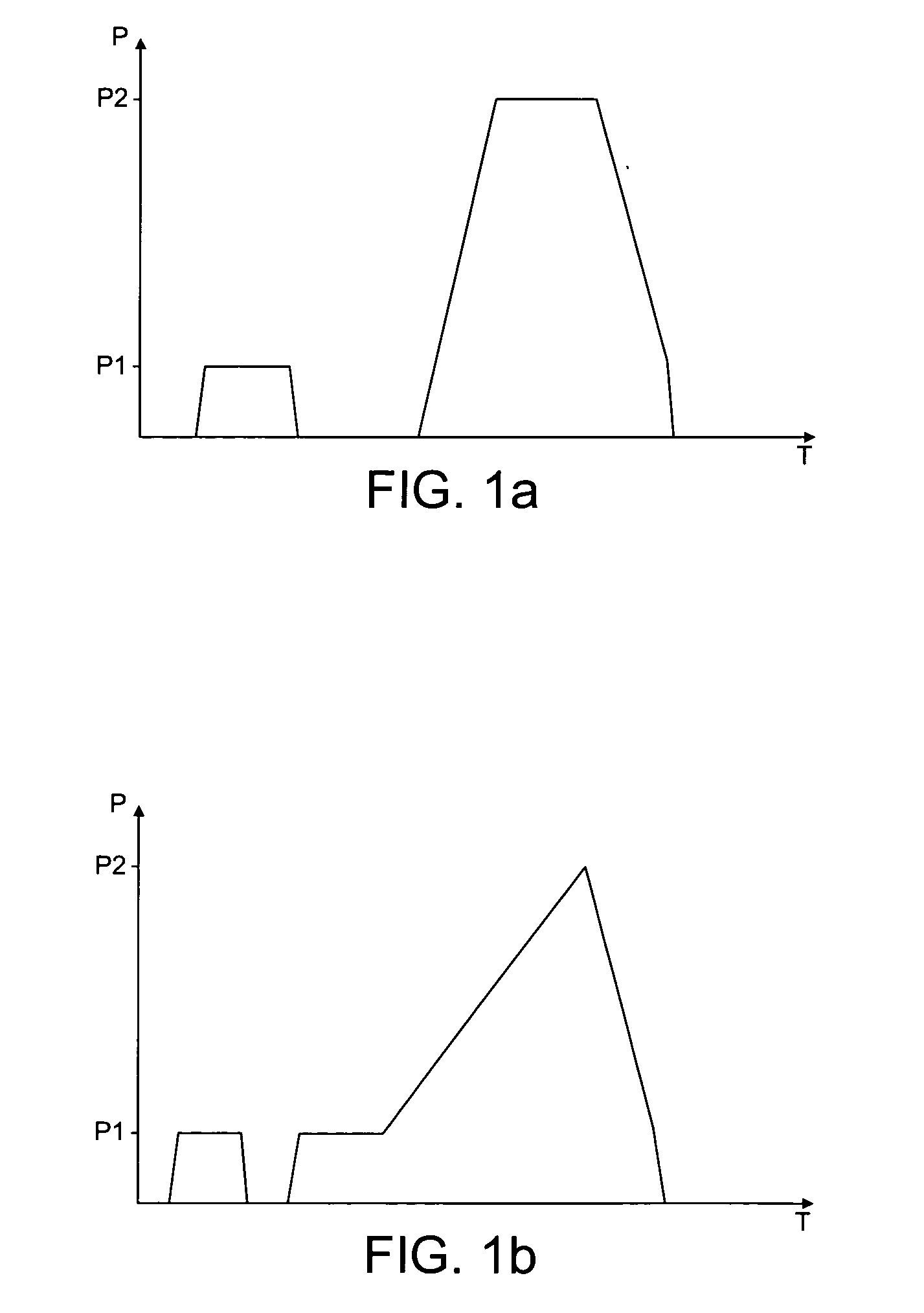
A fuel injection system for supplying pressurised fuel to a fuel injector (200) comprises an accumulator volume (606) for supplying fuel at rail pressure (P1) to the fuel injector (200) through a rail fuel supply passage (608) and a fuel pressurising arrangement (604) for supplying fuel at a selected pressure greater than rail pressure (P2) to the fuel injector (200) through a pressurised fuel supply passage (614). A fuel shut-off valve (618) is provided in the system which is operable between a closed position in which fuel is retained within the pressurising arrangement (604) and an open position in which pressurised fuel is supplied to the injector (200) from the pressurising arrangement (604) during an injection of fuel from the rail fuel supply passage (608). Operating the shut-off valve in this way provides a boost in the fuel pressure delivered during an injection event.
Owner:DELPHI INT OPERATIONS LUXEMBOURG S A R L
Method And Apparatus Of Fuelling An Internal Combustion Engine With Hydrogen And Methane
ActiveUS20120160221A1Reduce the amount of solutionInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelRail pressureElectronic controller
A gaseous-fuelled internal combustion engine and a method of engine operation improve combustion stability and reducing emissions of NOx, PM, and unburned hydrocarbons. The method comprises fuelling an internal combustion engine with hydrogen and natural gas, which can be directly injected into the combustion chamber together or introduced separately. Of the total gaseous fuel delivered to the engine, at least 5% by volume at standard temperature and pressure is hydrogen. For at least one engine operating condition, the ratio of fuel rail pressure to peak in-cylinder pressure is at least 1.5:1. A fuel injection valve introduces the gaseous fuel mixture directly into the combustion chamber. Two separate fuel injection valves could also introduce the methane and hydrogen separately. An electronic controller controls timing for operating the fuel injection valve(s). The engine has a preferred compression ratio of at least 14:1.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
Injection control for a common rail fuel system
InactiveUS6848414B2Accurate injection controlEasy to controlElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesRail pressureFuel distribution
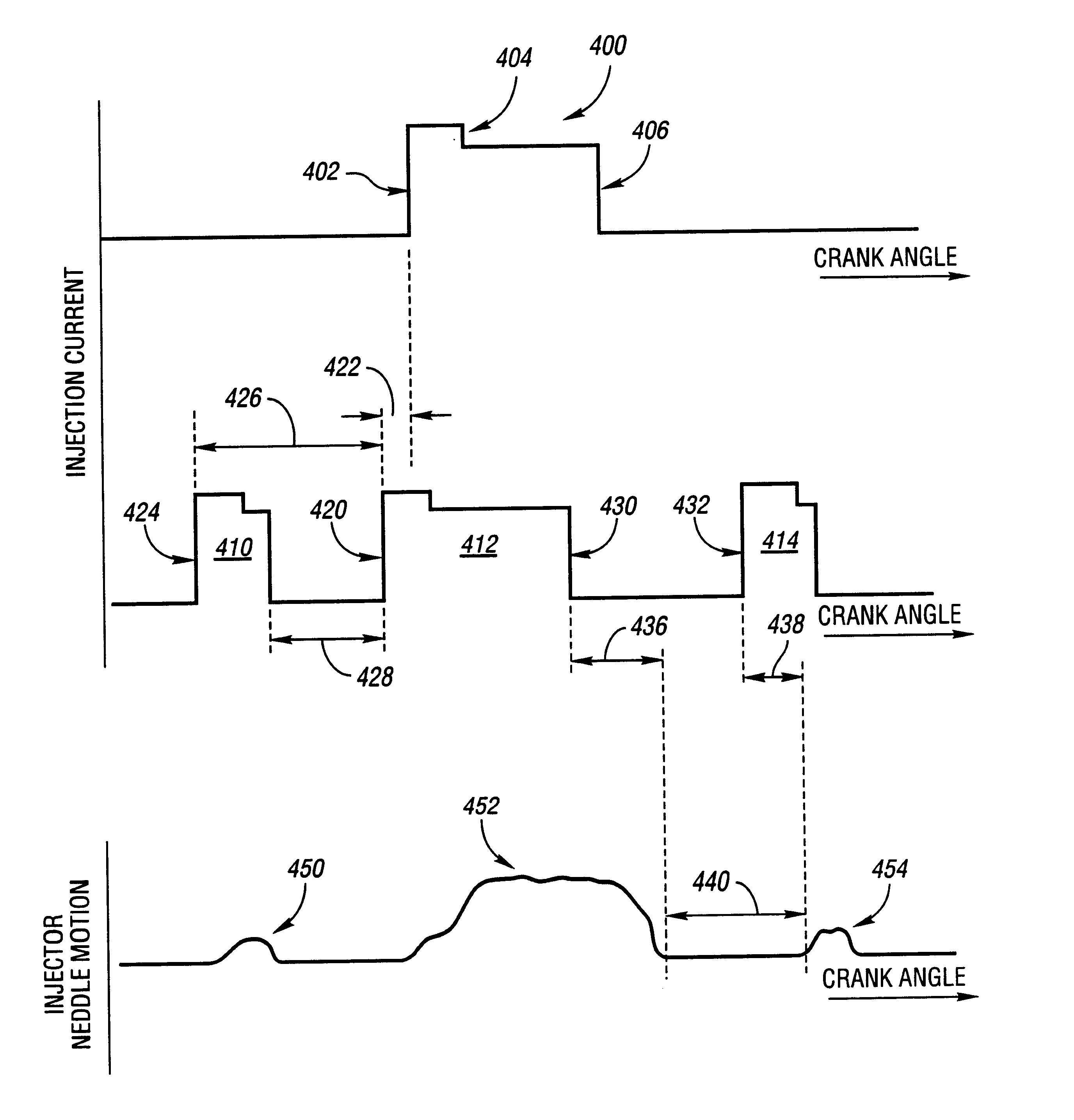
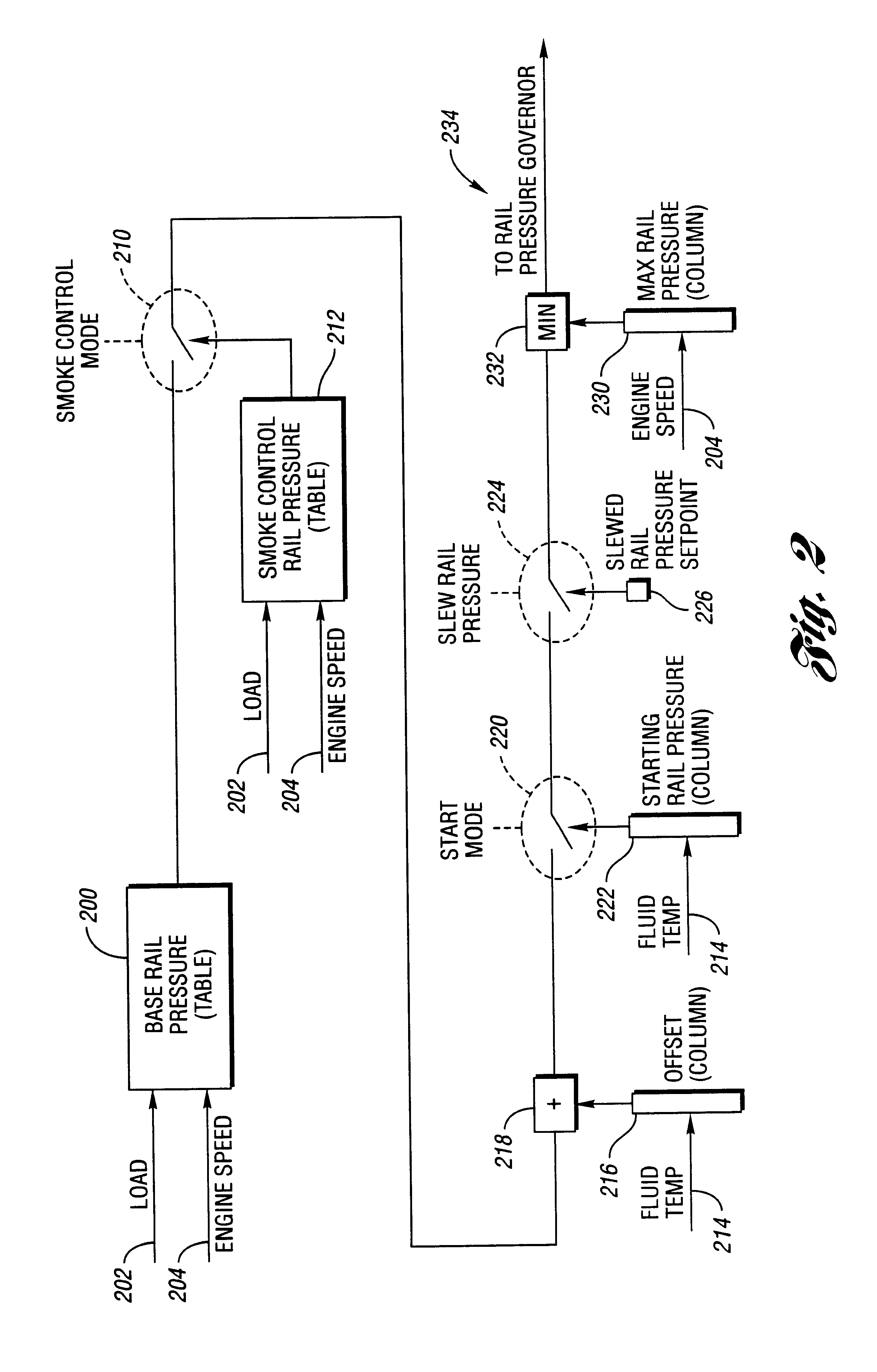
A system and method for controlling multiple fuel injections during a single combustion cycle for a multiple cylinder internal combustion engine having a common rail fuel distribution system determine the beginning of injection for the pilot and main injections based on crankshaft position while post injections are based on the main injection timing and an injector turn off delay determined using actual rail pressure. A rail pressure setpoint is determined based on current engine operating conditions including one or more fluid temperatures and current operating mode to provide more accurate injection control.
Owner:DETROIT DIESEL CORP
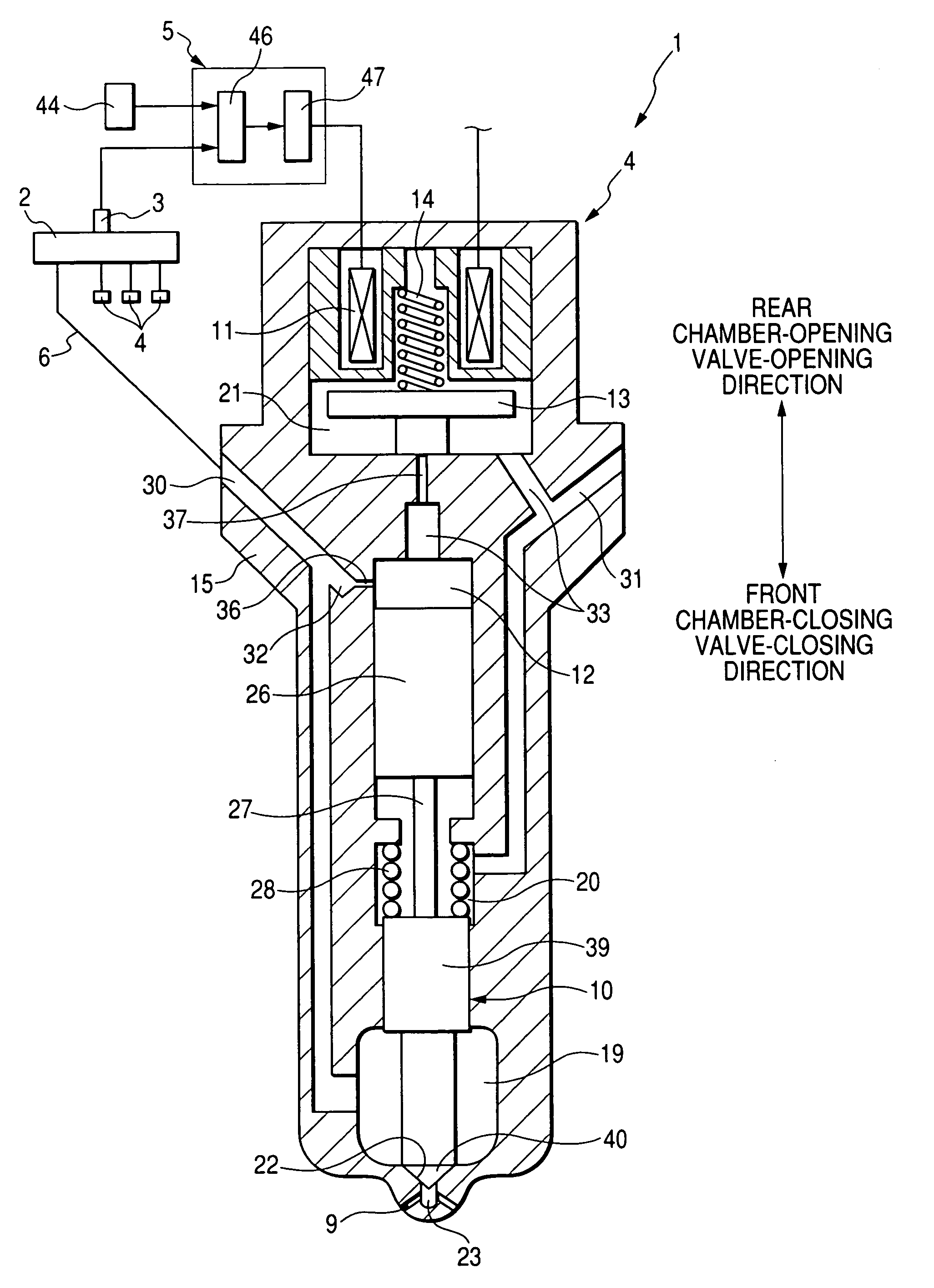
Pressure sensor failure diagnosis method and common rail type fuel injection control apparatus
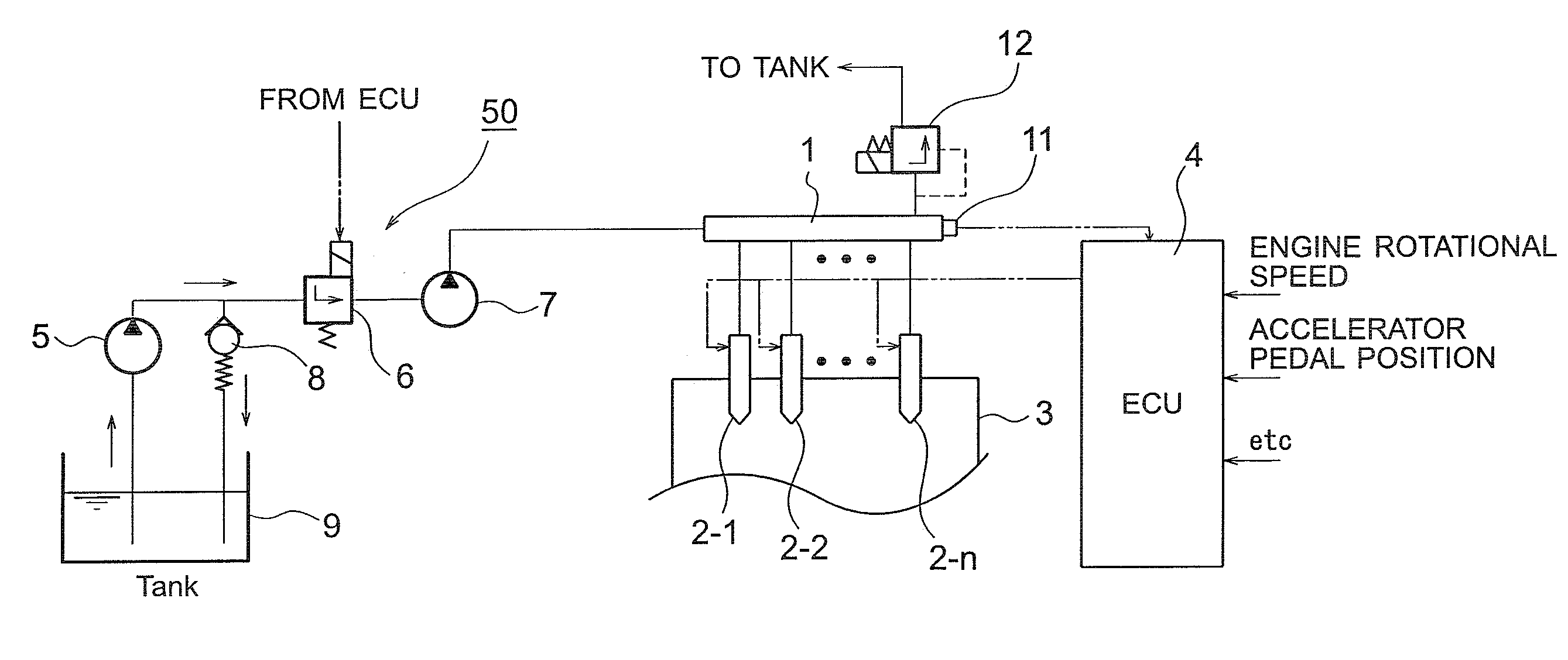
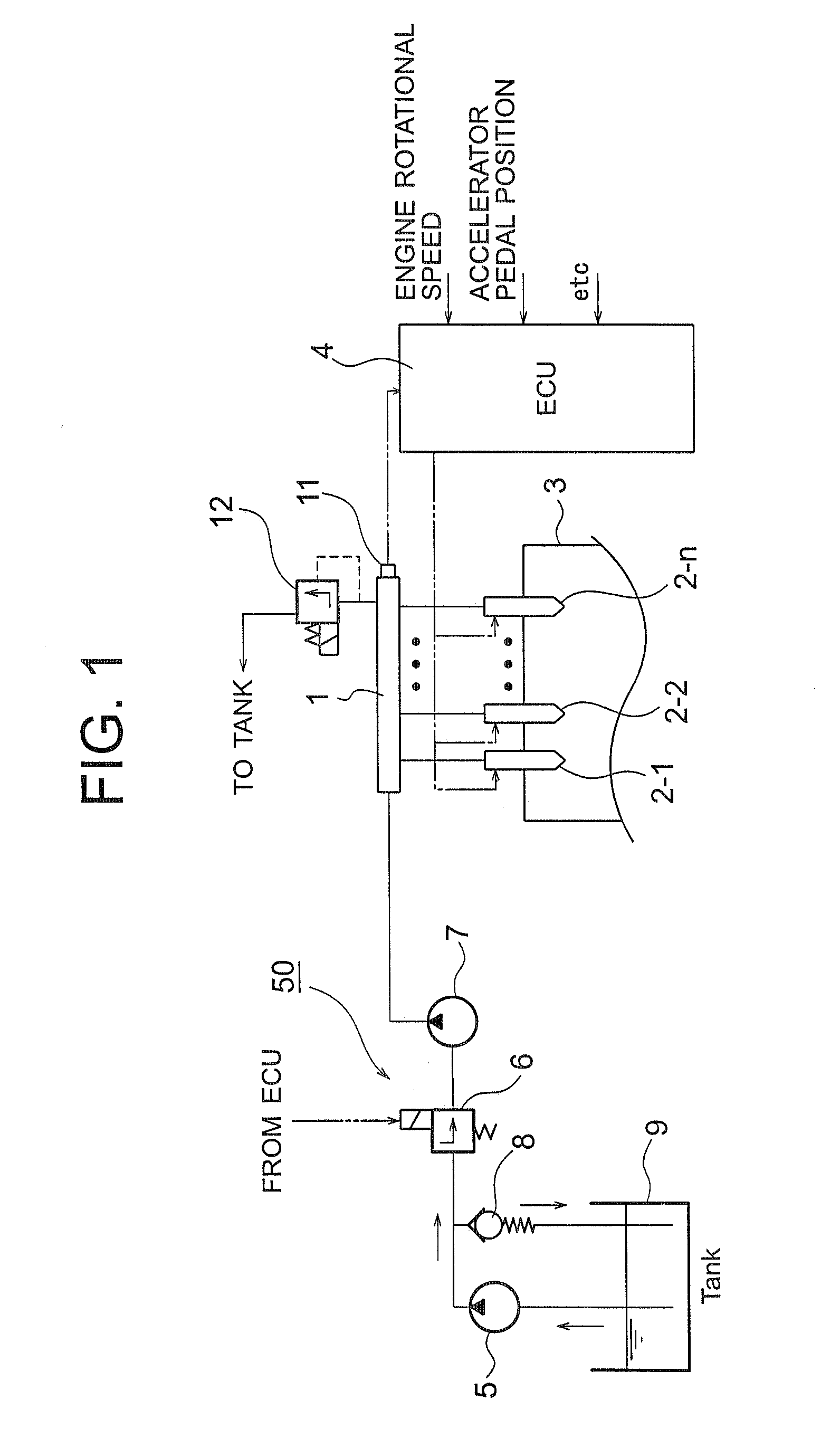
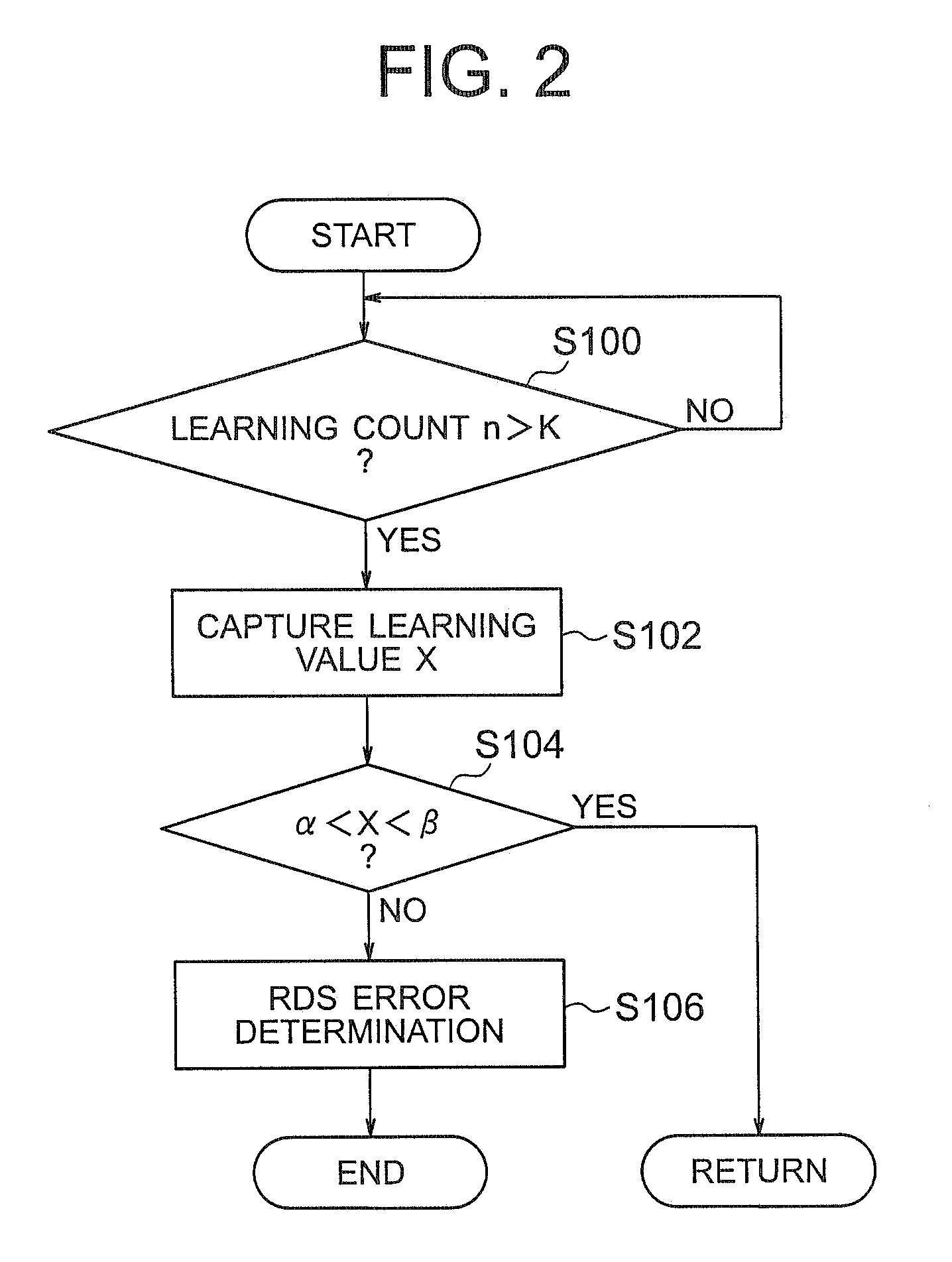
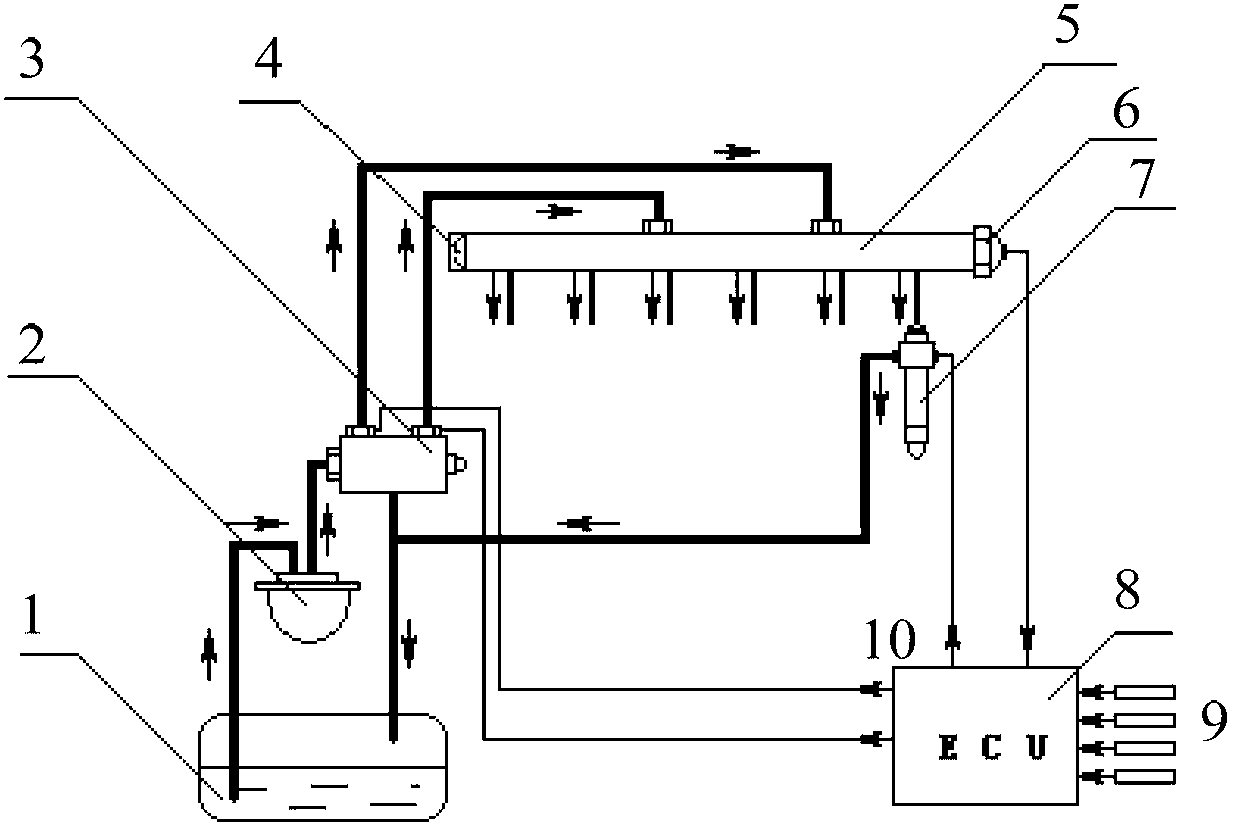
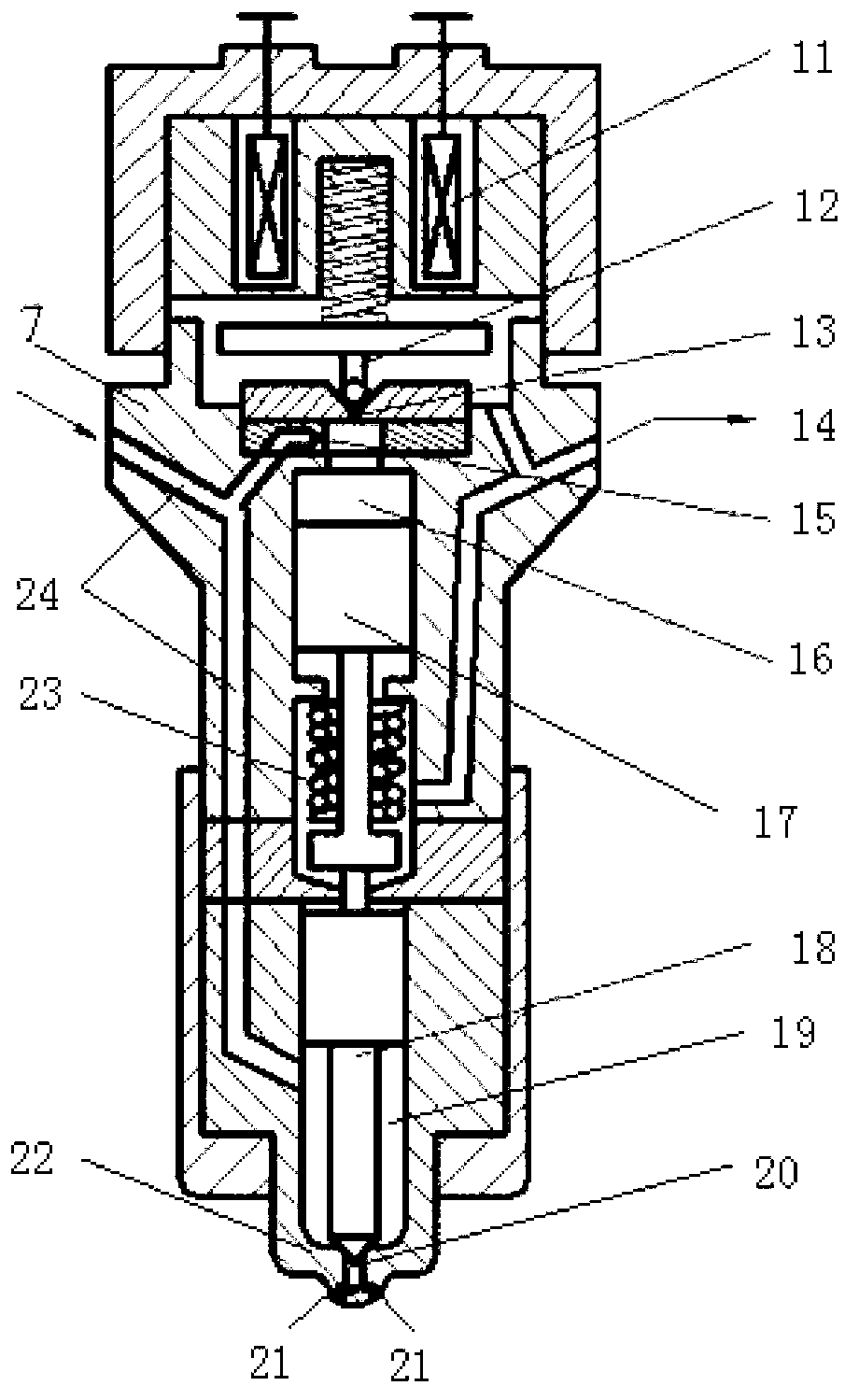
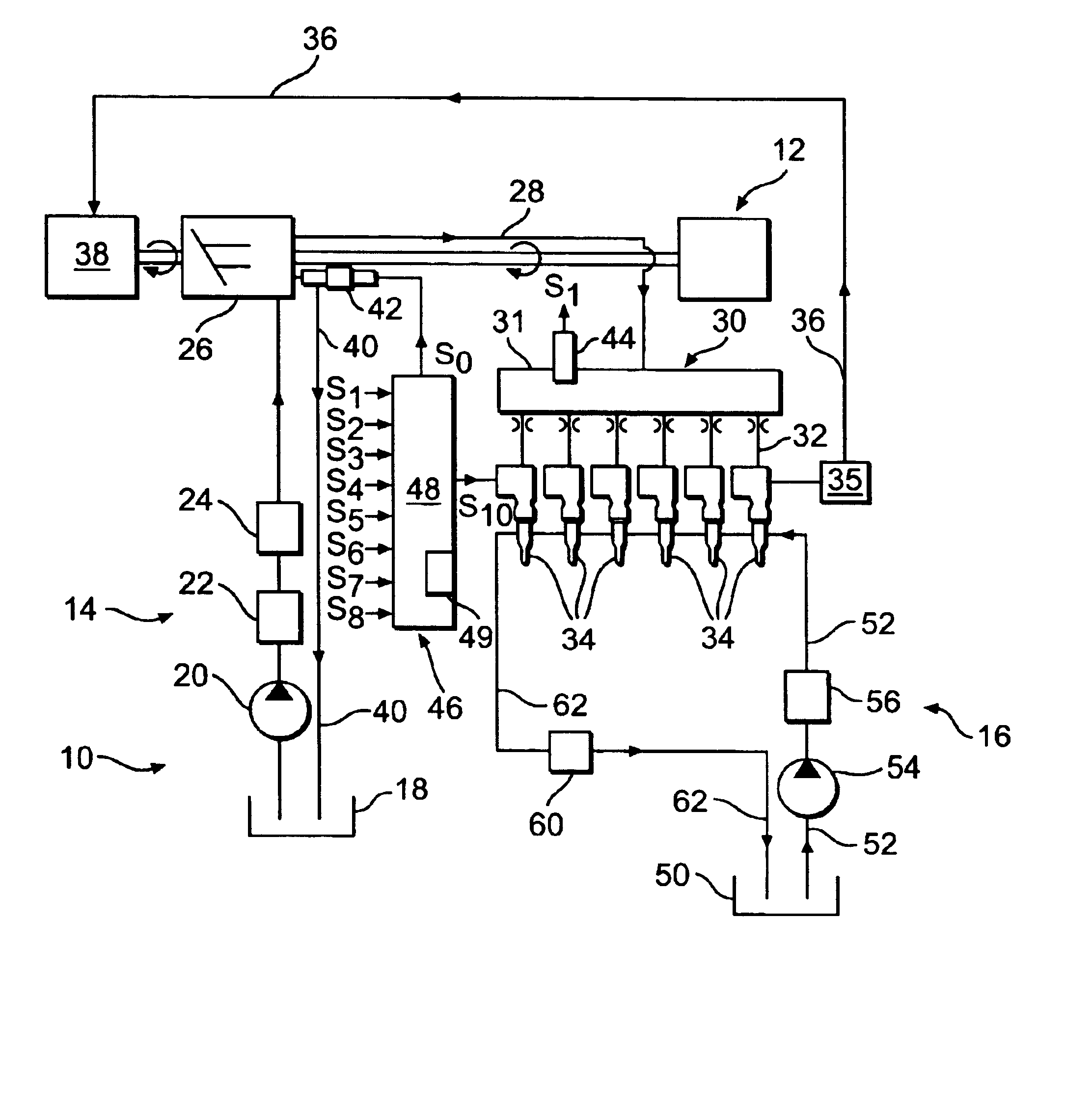
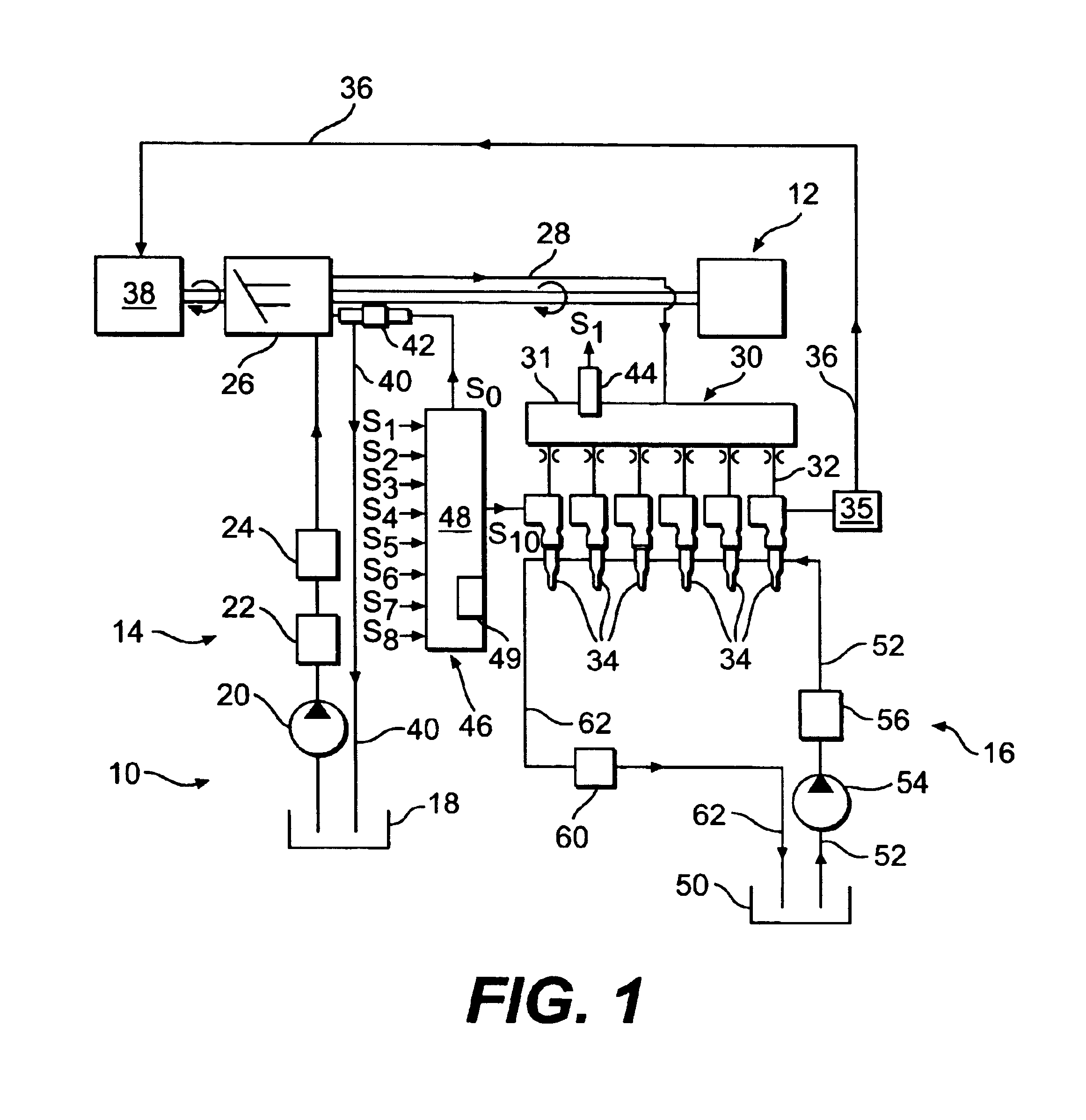
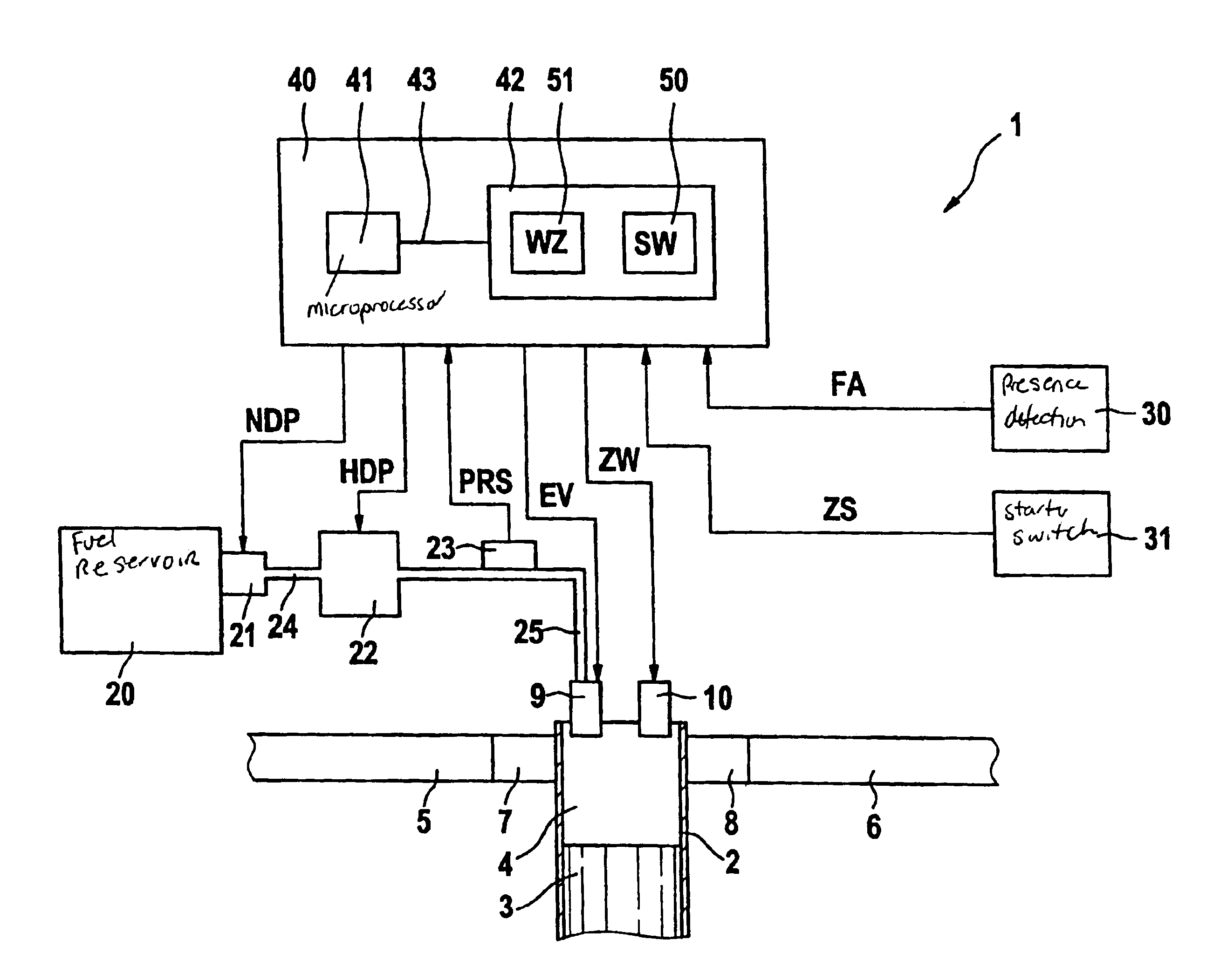
It is possible to perform a failure diagnosis of a pressure sensor with a simple structure without installing a dedicated circuit for the failure diagnosis.In a common rail type fuel injection control apparatus, a pressure control valve 12 is provided in a fuel return path from a common rail 1, and a rail pressure detected by a pressure sensor 11 can be controlled to match a target rail pressure through drive control of the pressure control valve 12 by an electronic control unit 4. The target rail pressure is calculated based on operational information of an engine 3. In the common rail type fuel injection control apparatus, learning processing is performed, in which a correction coefficient Cv is stored and updated as a learning value to correct energization characteristics of a median product of the pressure control valves 12 that are stored in the electronic control unit 4. At the same time, it is determined whether the learning value of the correction coefficient Cv is within a predetermined range. When it is determined that it is not within the predetermined range, the pressure sensor 11 is diagnosed as having a failure.
Owner:BOSCH CORP
Method and apparatus for controlling the pressure in a common rail system
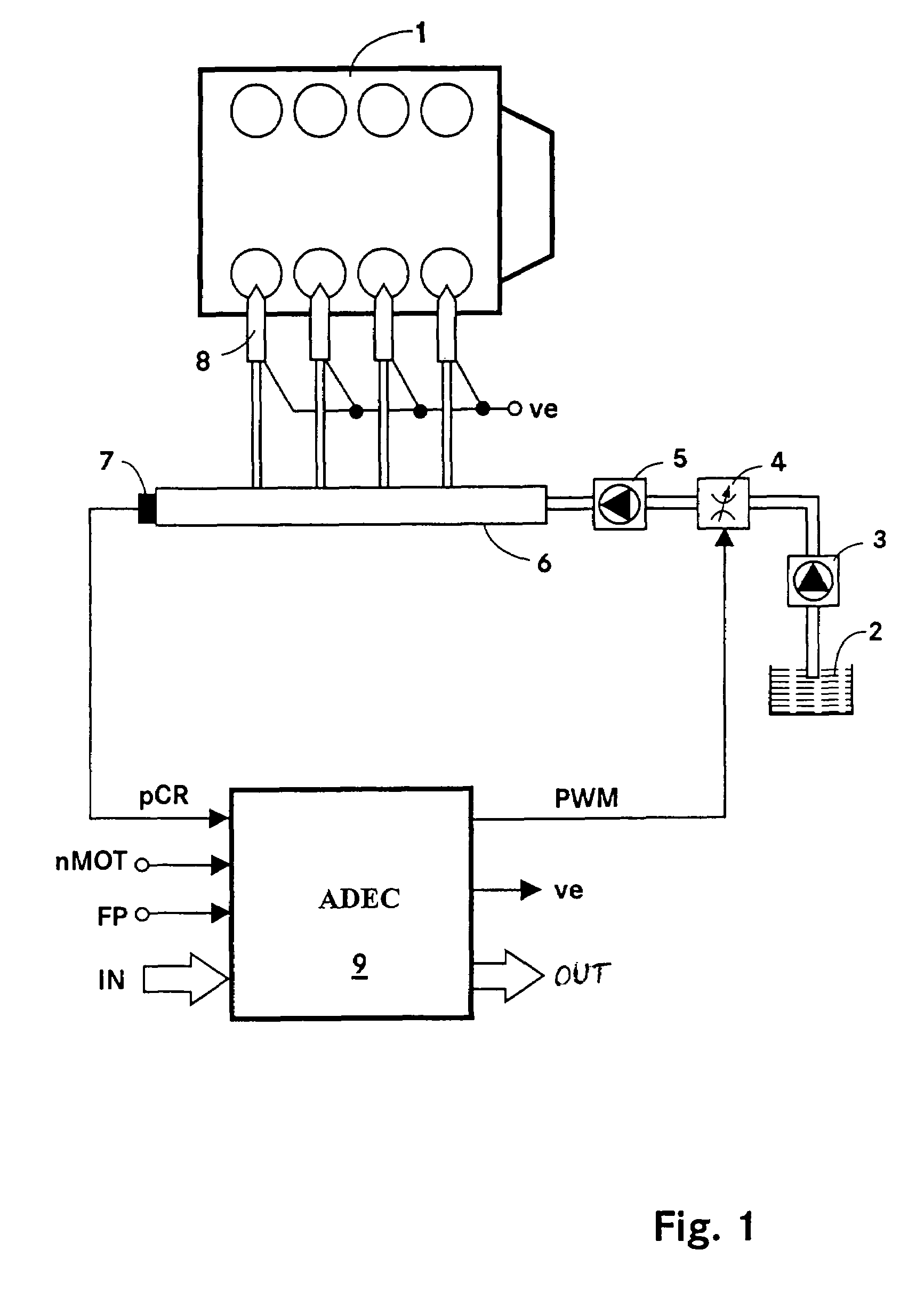
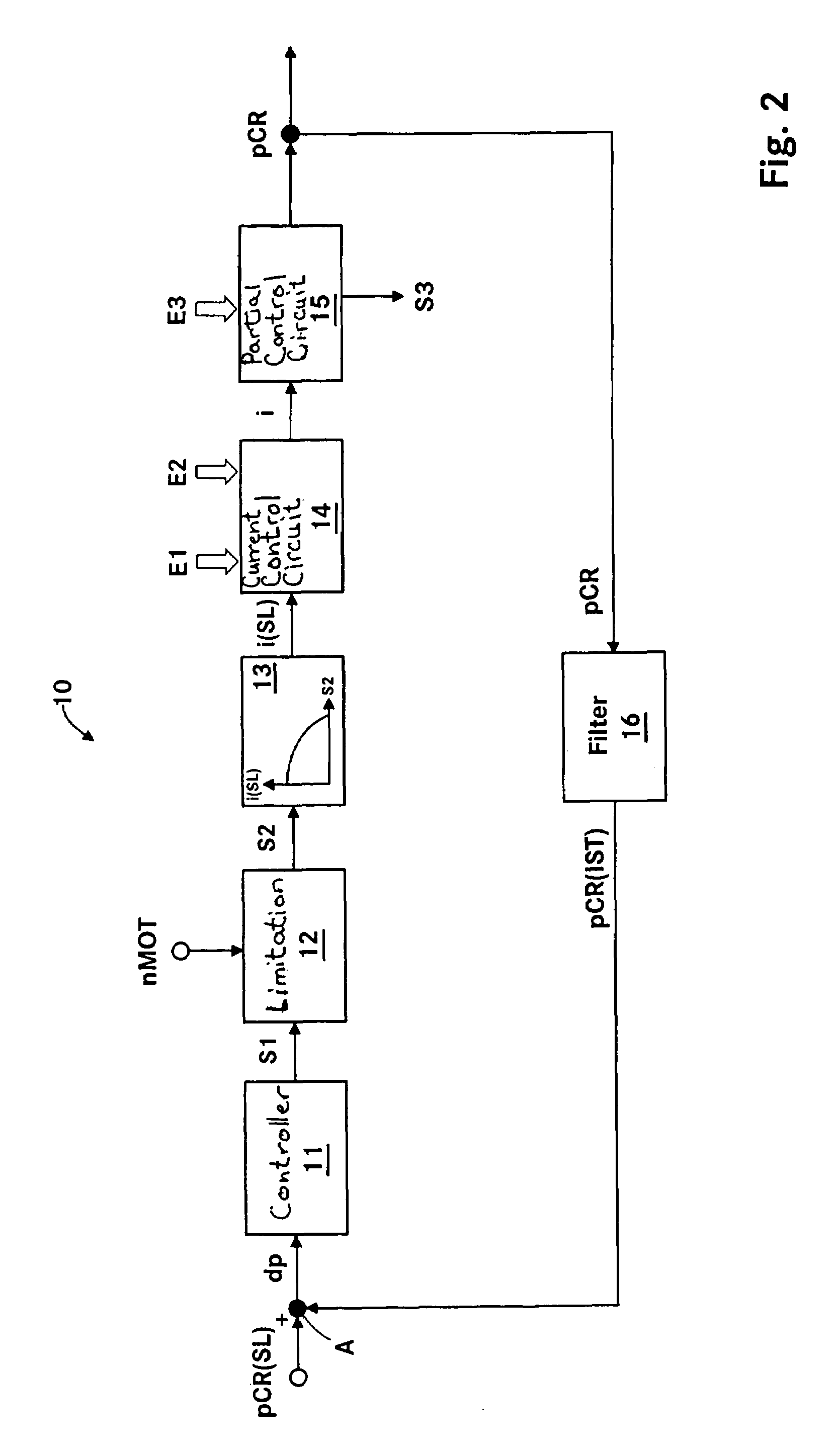
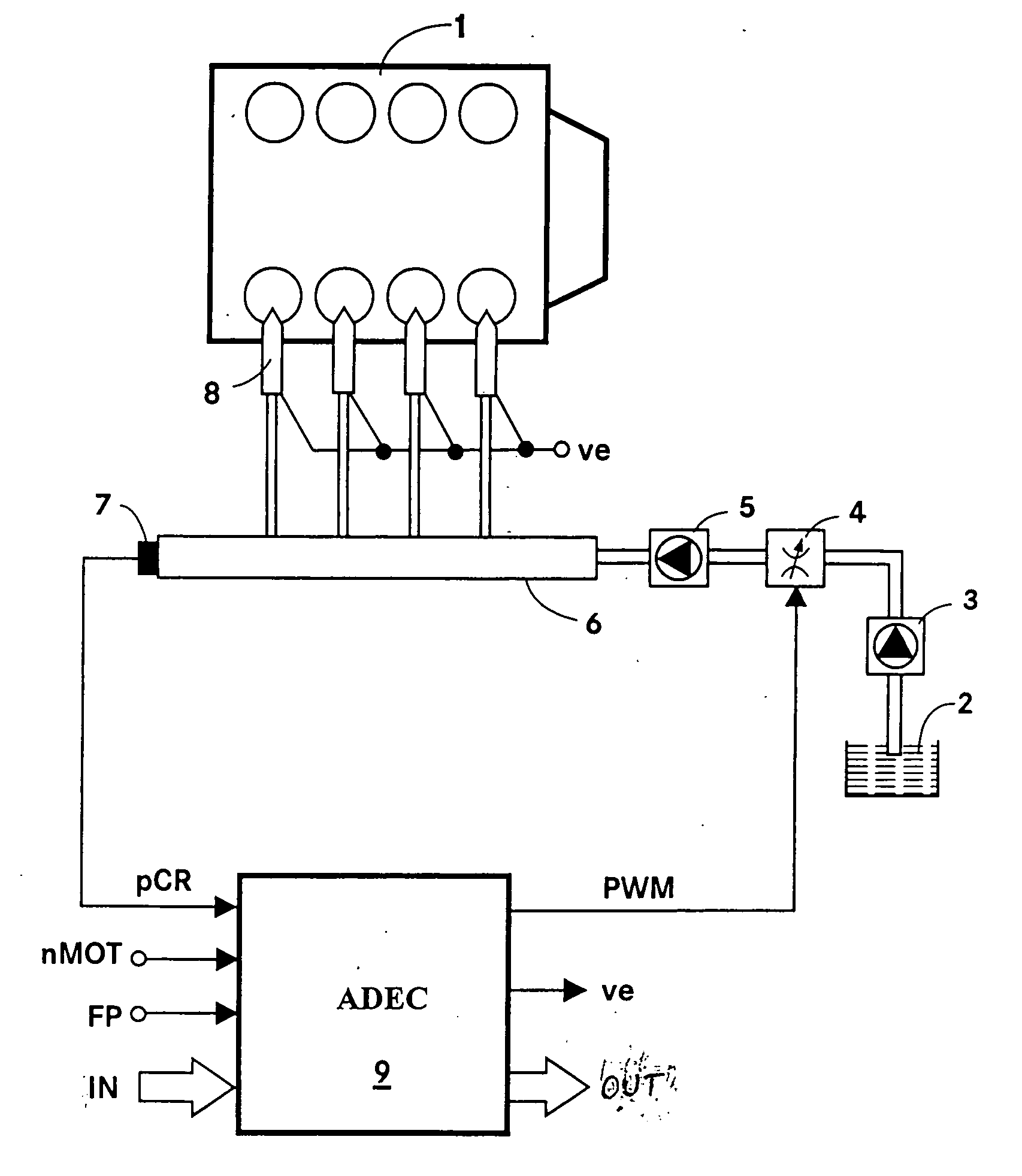
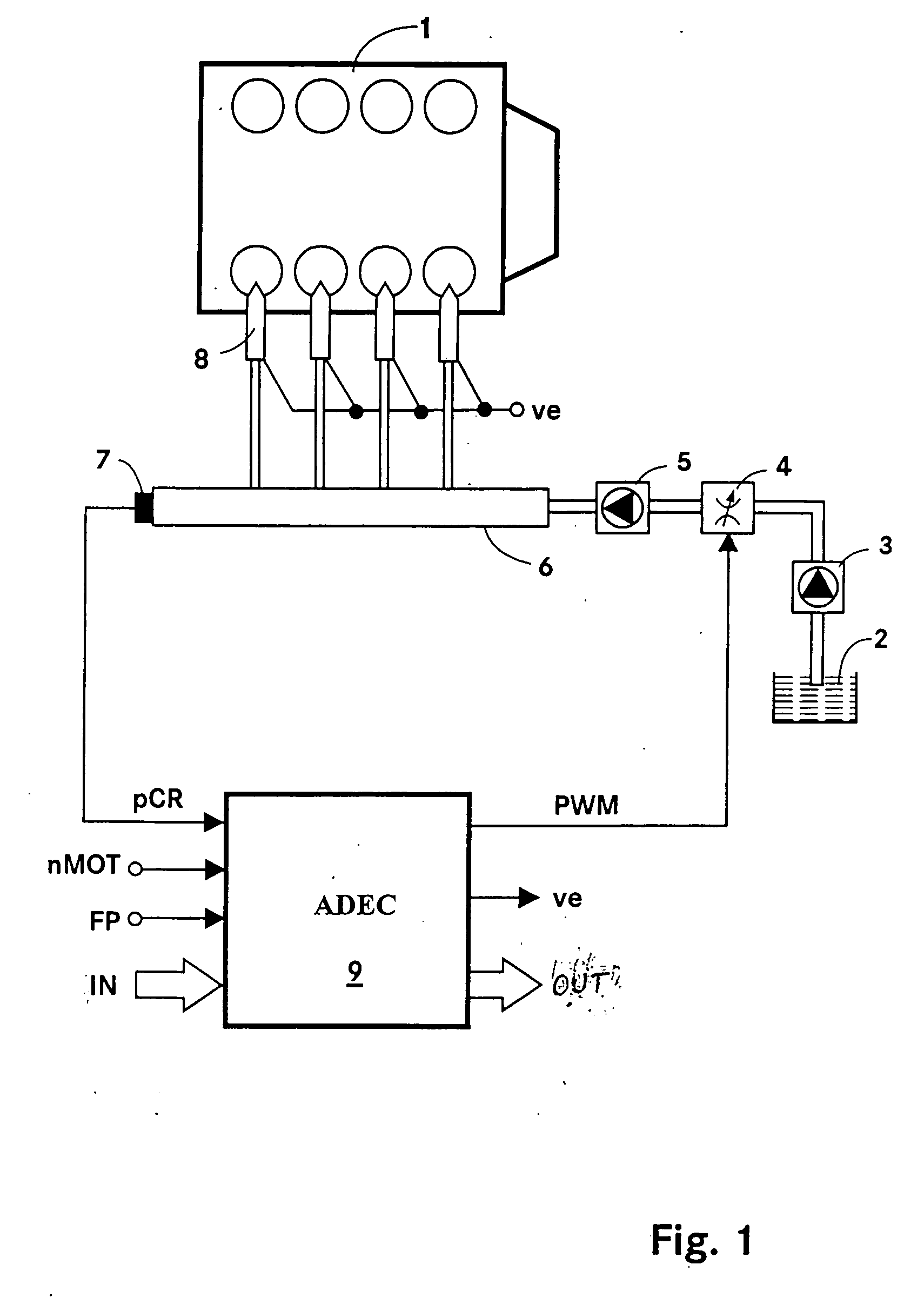
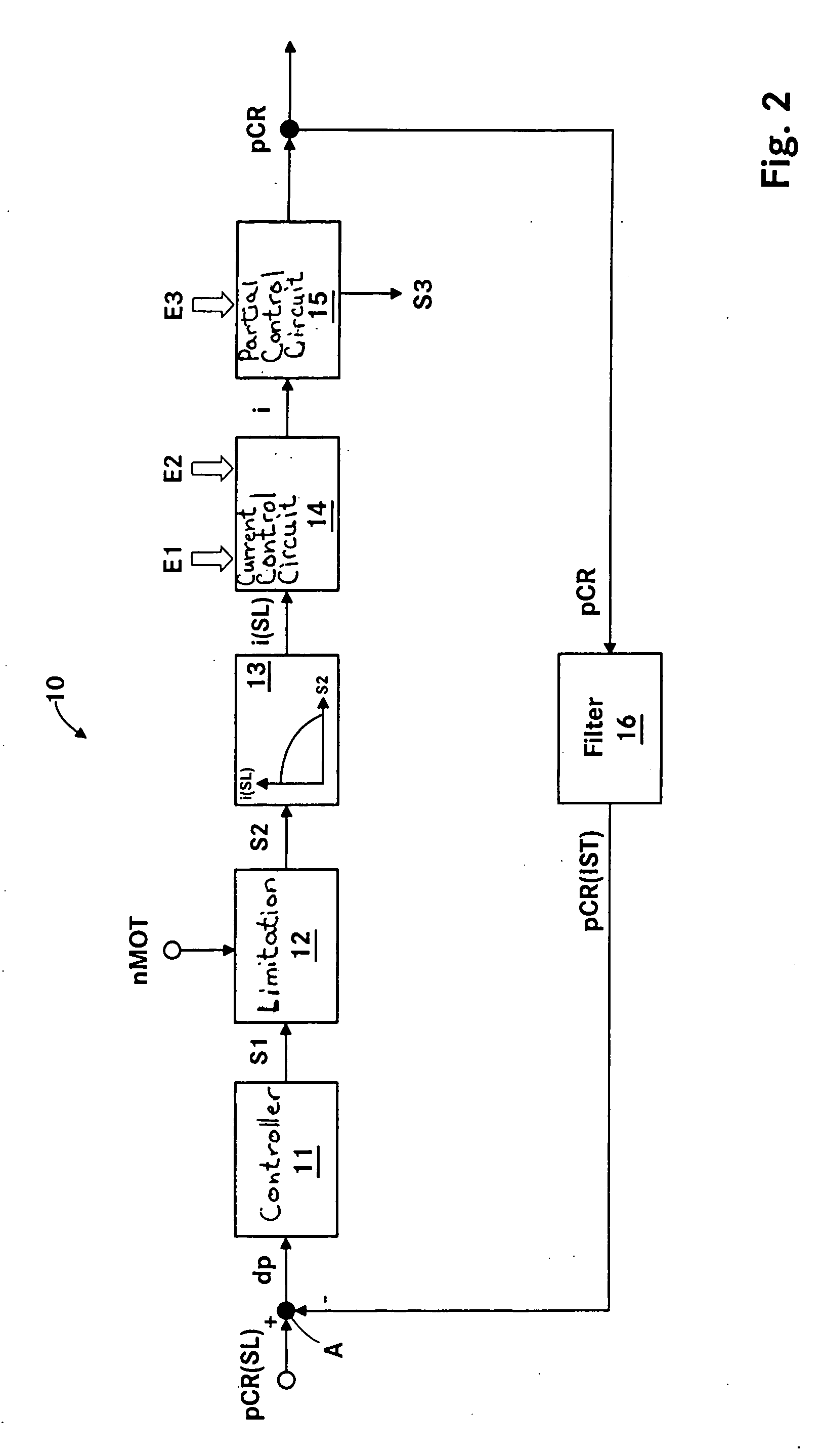
ActiveUS7240667B2Improve stabilityEliminates temperature dependenceElectrical controlLow pressure fuel injectionRail pressureSignal generator
In a common rail operating method and system, an arrangement for controlling the rail pressure is provided with a rail pressure controller including a current control circuit for controlling a suction throttle valve operating current (i) which valve is arranged in the fuel supply line to a high pressure pump supplying high pressure fuel to the common rail. The suction valve operating current control circuit includes a preliminary control value generator which serves also as an emergency control signal generator for the control of the suction valve if an error occurs in the system at least to permit an orderly engine shutdown procedure.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE SOLUTIONS GMBH
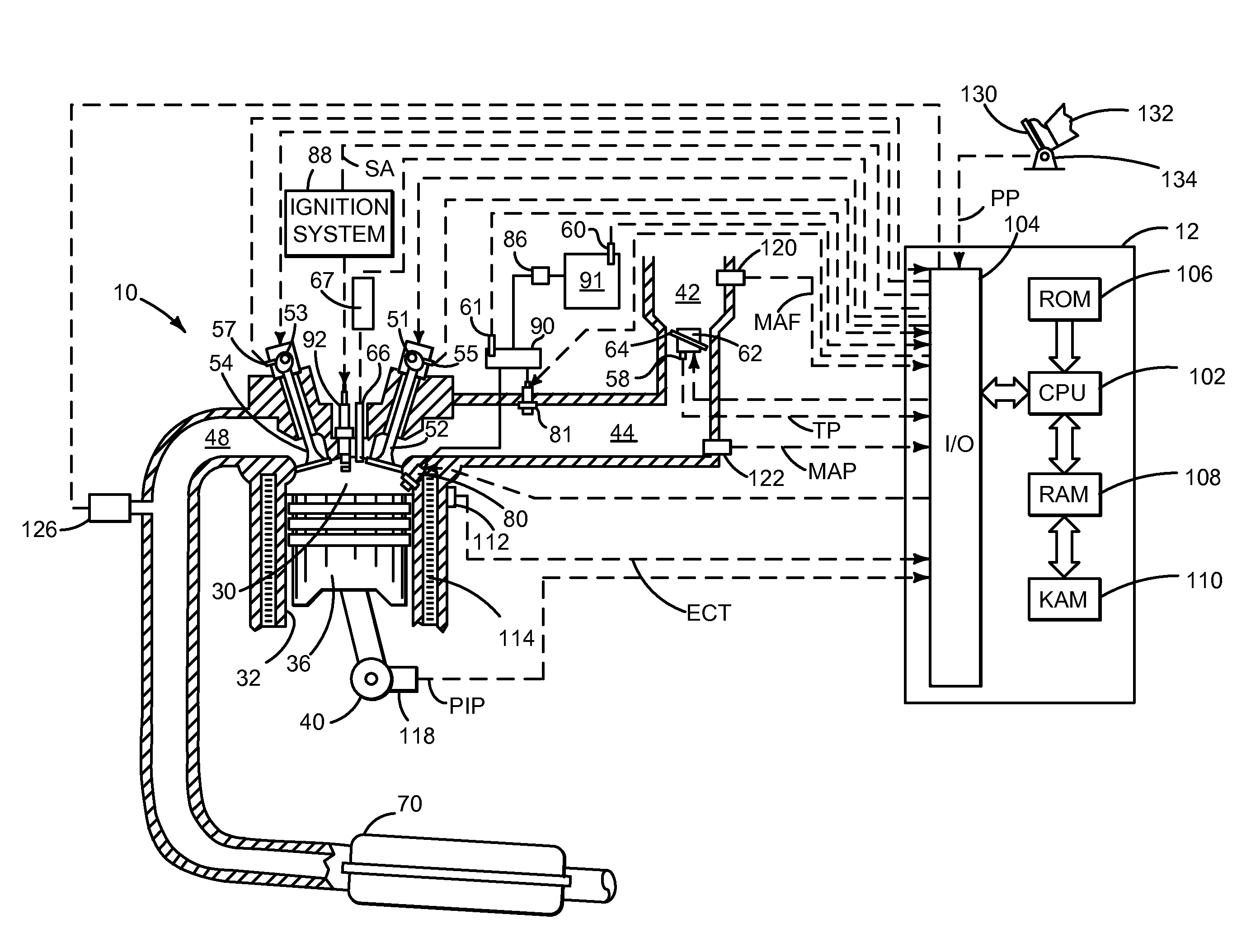
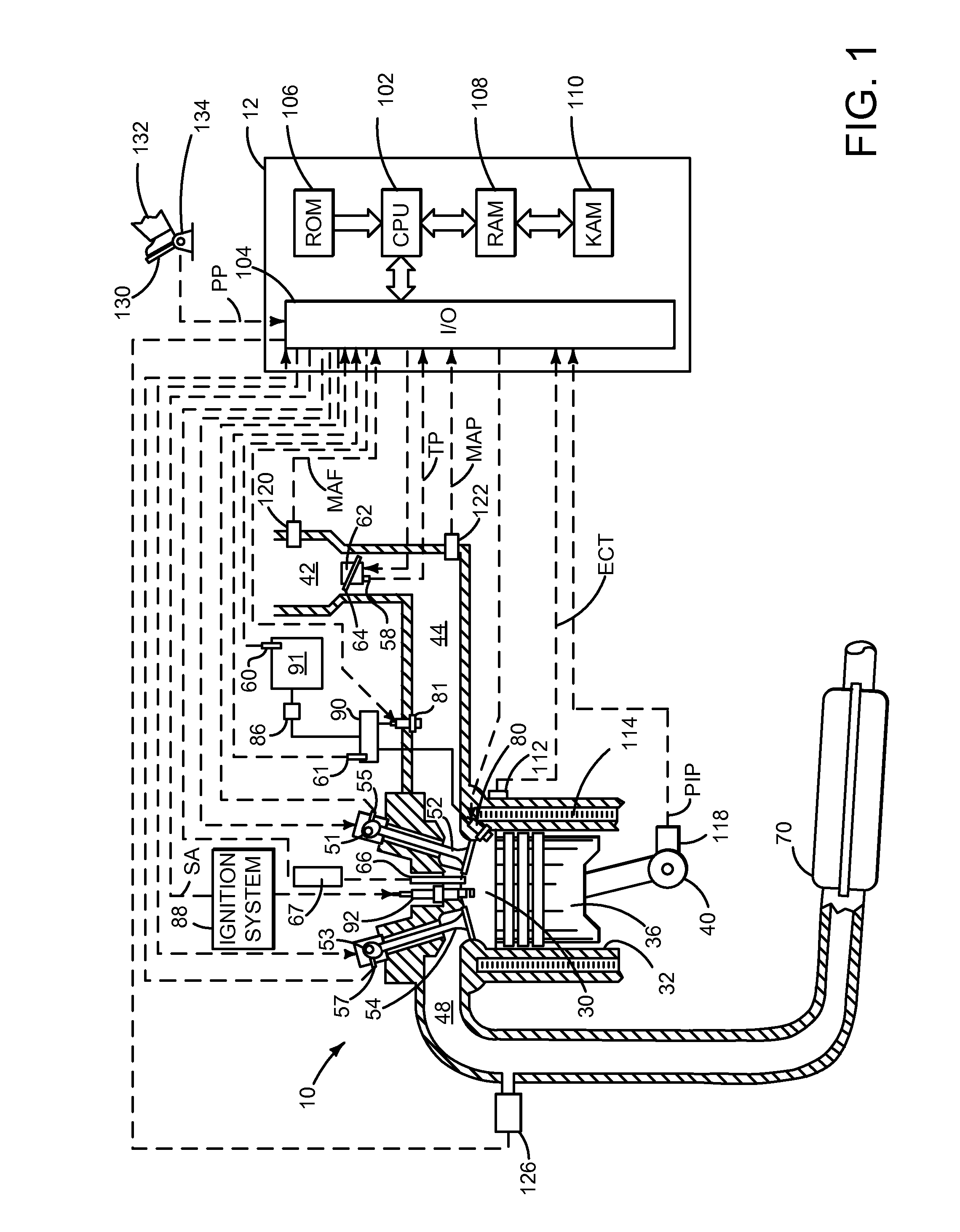
Fuel injection control apparatus for internal combustion engine
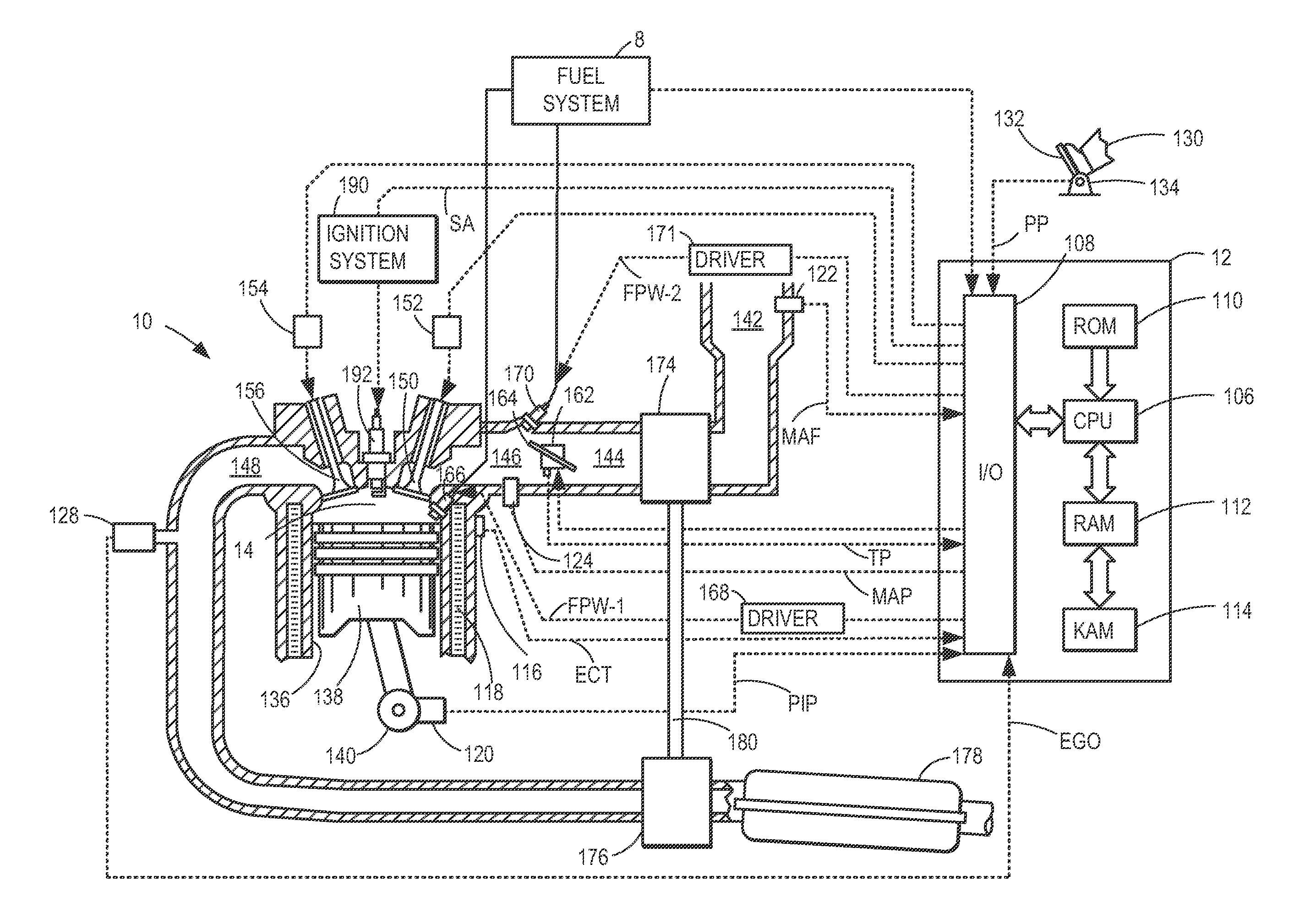
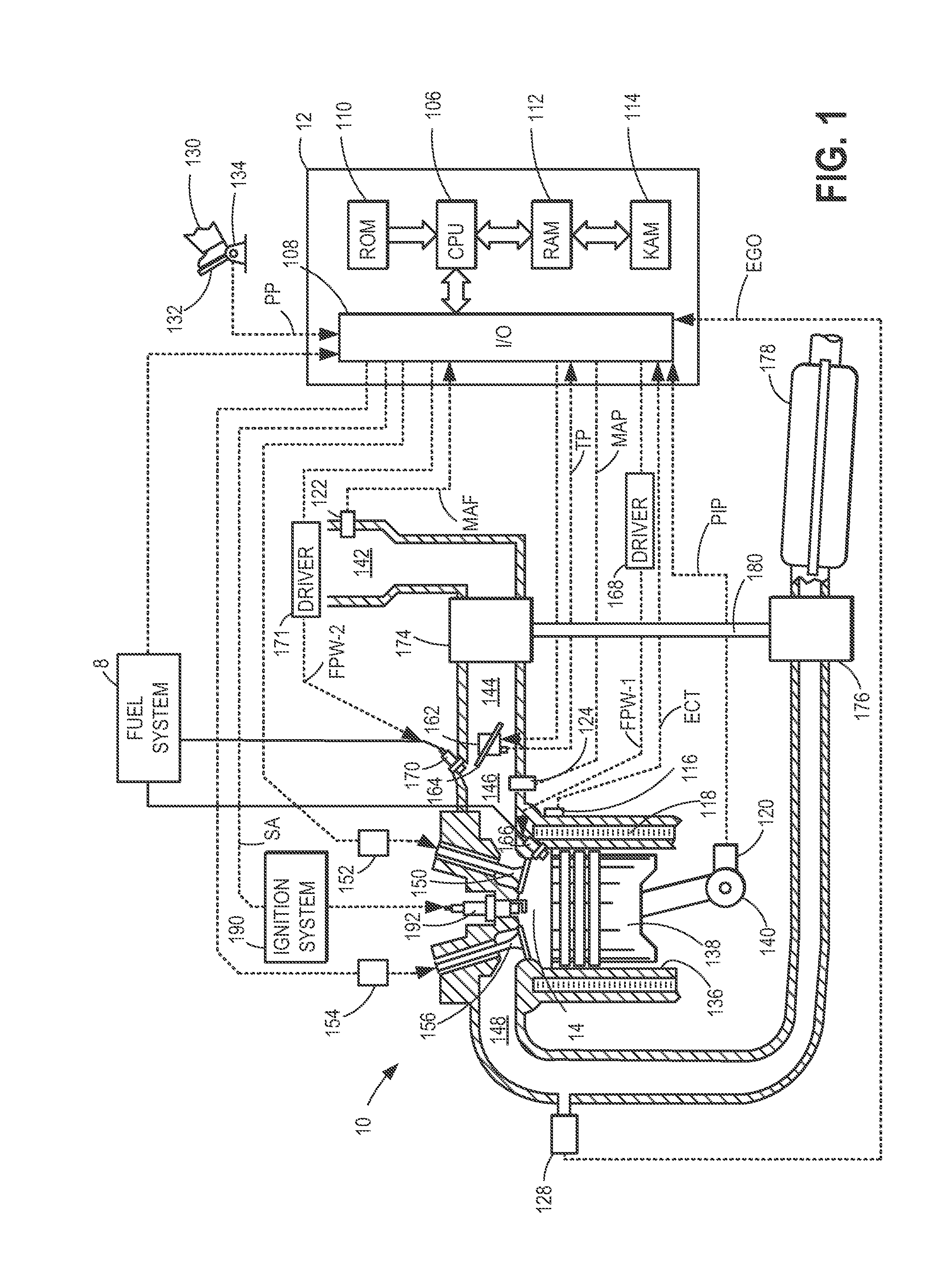
ActiveUS7000600B1Improve accuracyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesStart timeControl power
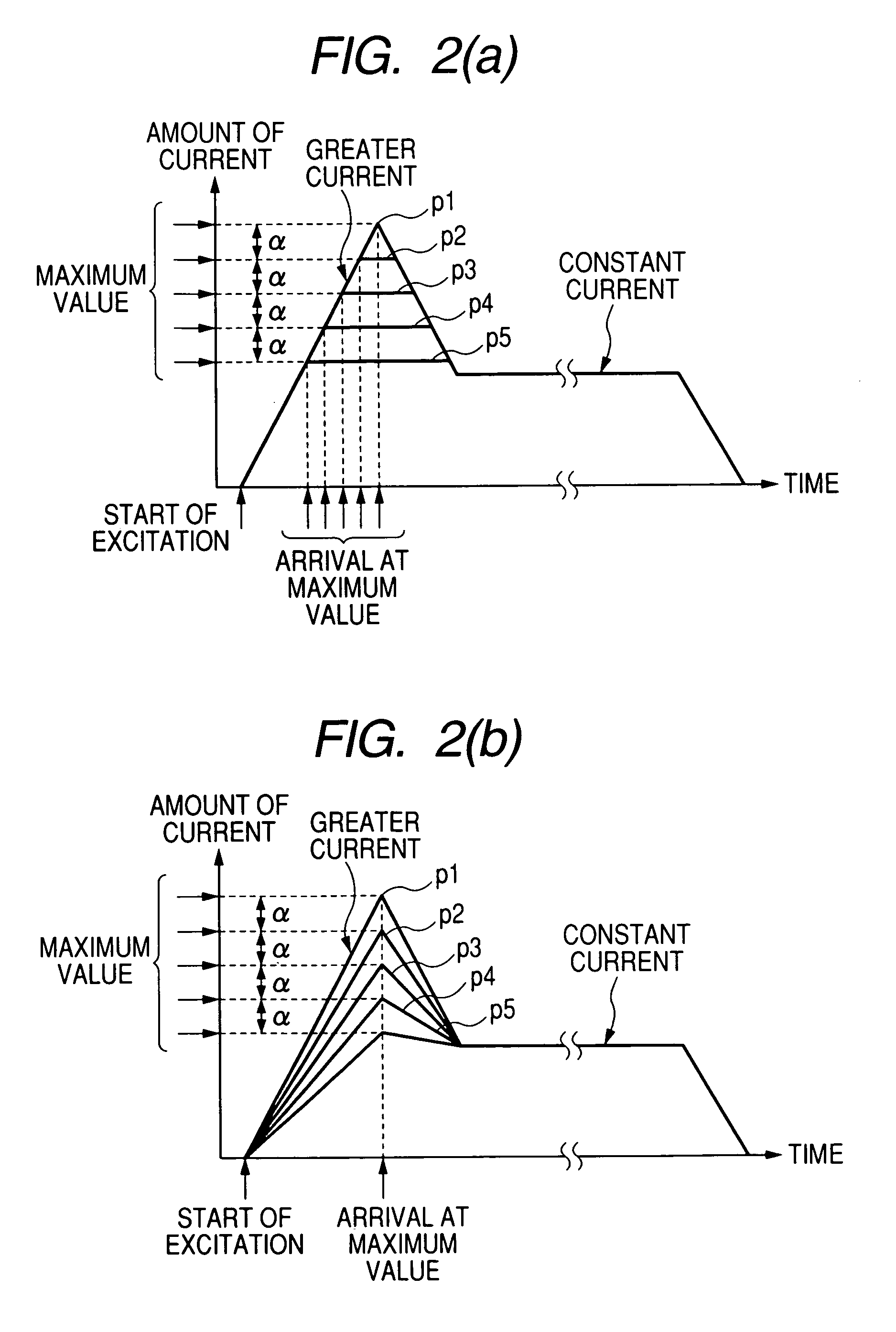
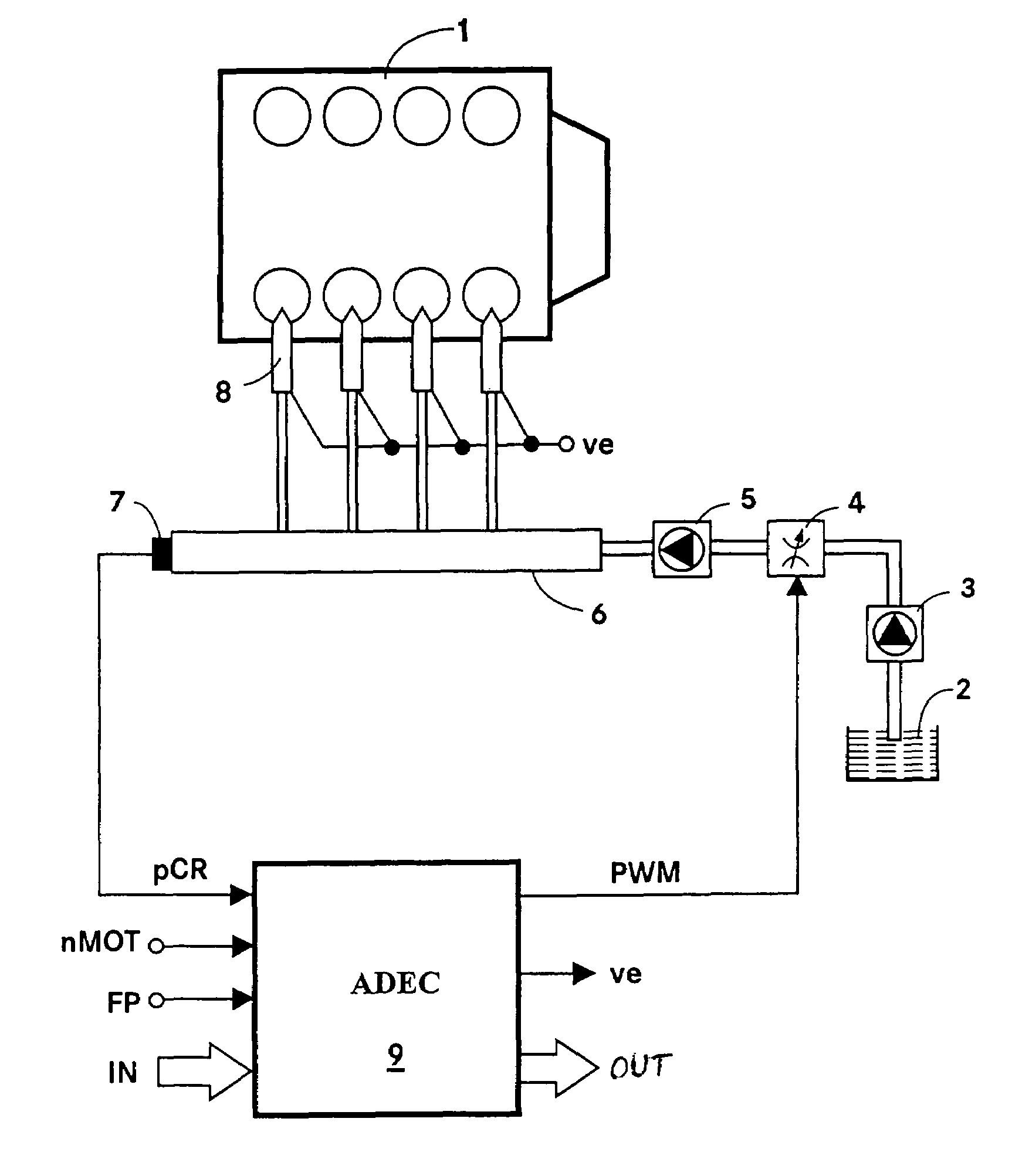
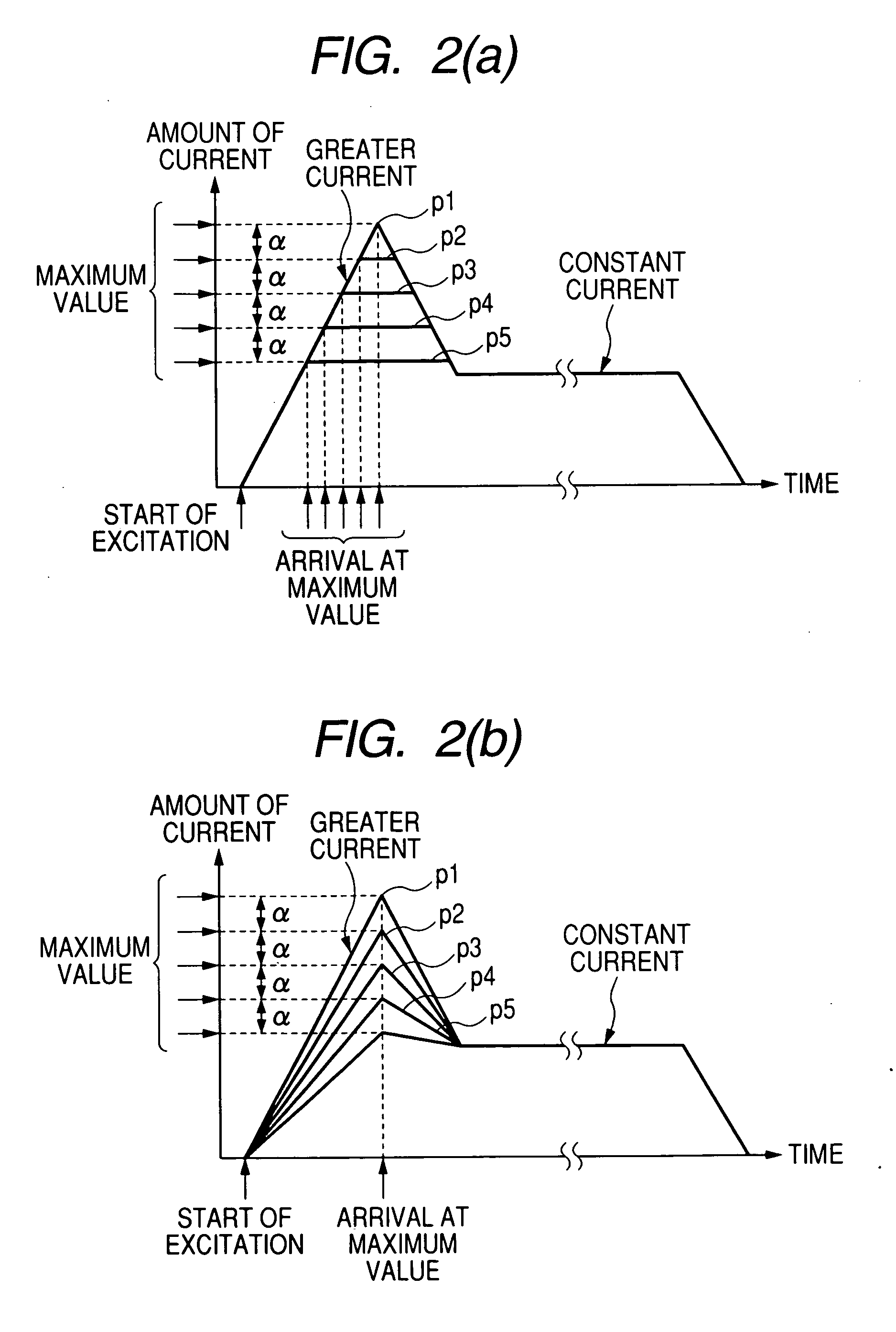
In controlling power supply time, a variation in the fuel injection quantity caused by a variation in the fuel injection rate at the in-cylinder pressure of the engine (detected or estimated value in the running state of the internal combustion engine) relative to the fuel injection rate at a reference in-cylinder pressure (under the condition of an injector characteristic measuring benchmark test), and in addition, a variation in the fuel injection start time is corrected. In the calculation of the variation in the fuel injection quantity, a fuel injection rate changing behavior model in which changing behavior of the fuel injection rate is modeled as a trapezoid is used to calculate the areas of Δq1 and Δq2. The variation in the fuel injection start time Δτd is calculated based on the rail pressure and the variation in the in-cylinder pressure. In this way, there is provided a technology for controlling the fuel injection quantity that changes with a change in the in-cylinder pressure with improved accuracy.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
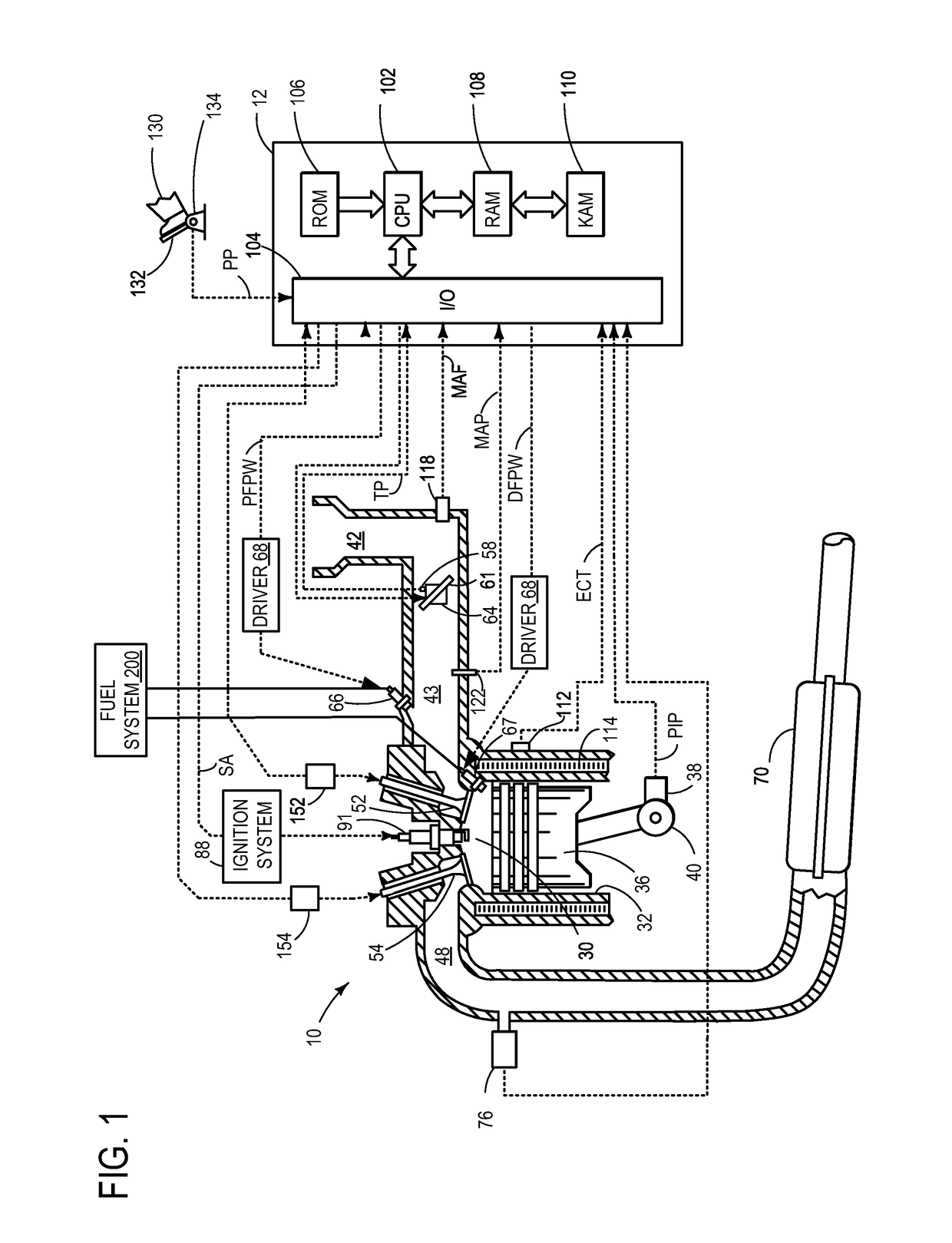
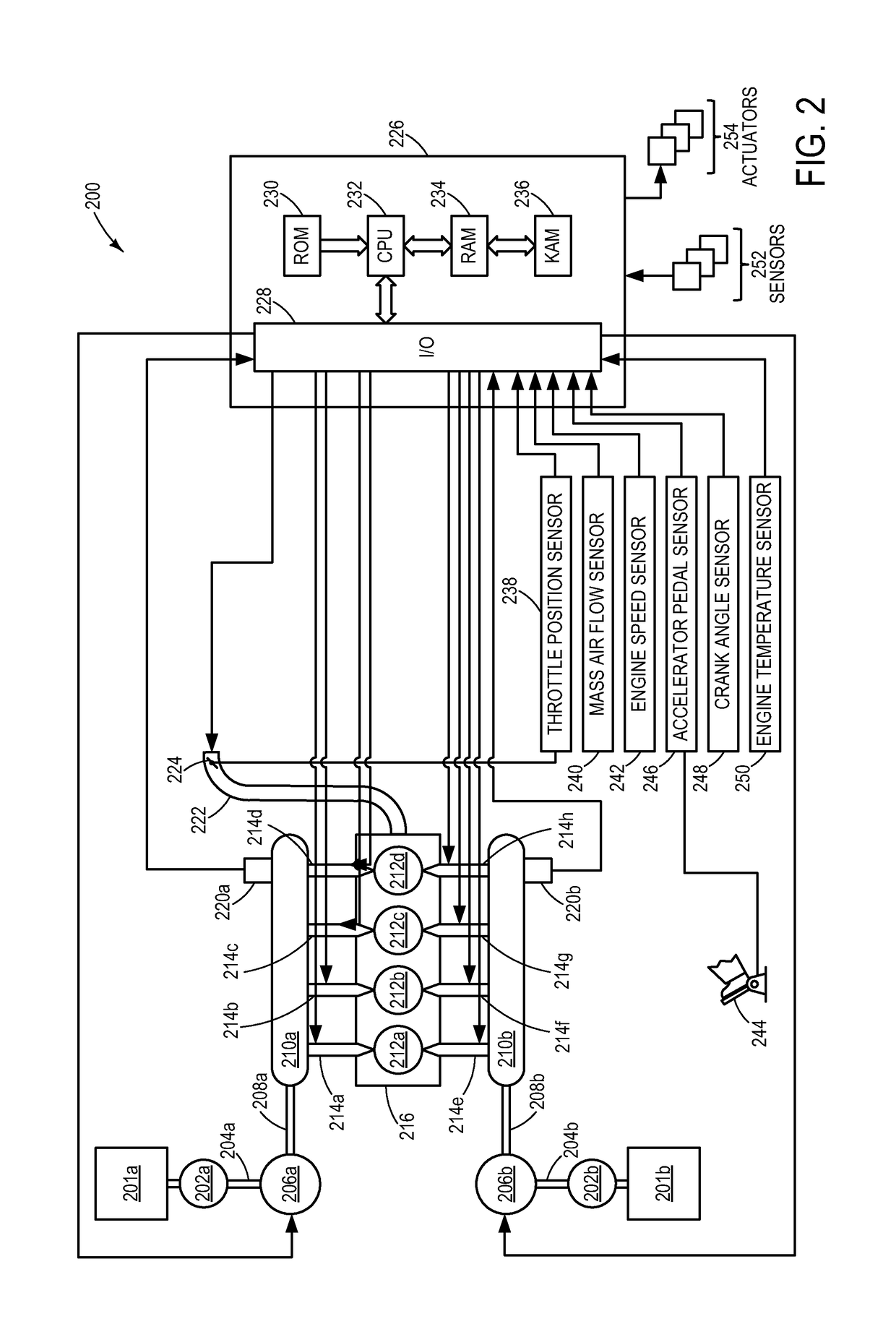
Multiple pressure mode operation for hydraulic hybrid vehicle powertrain
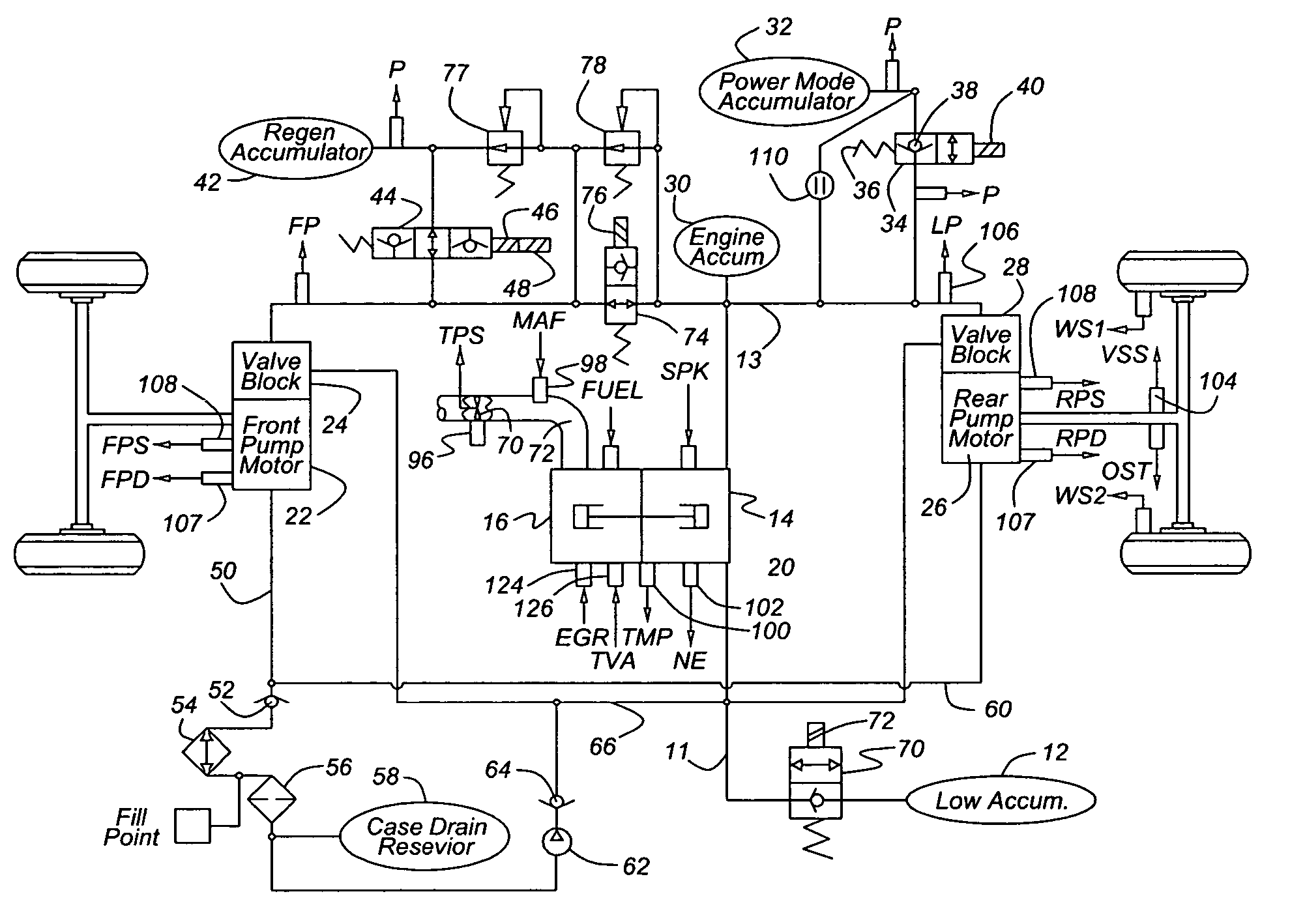
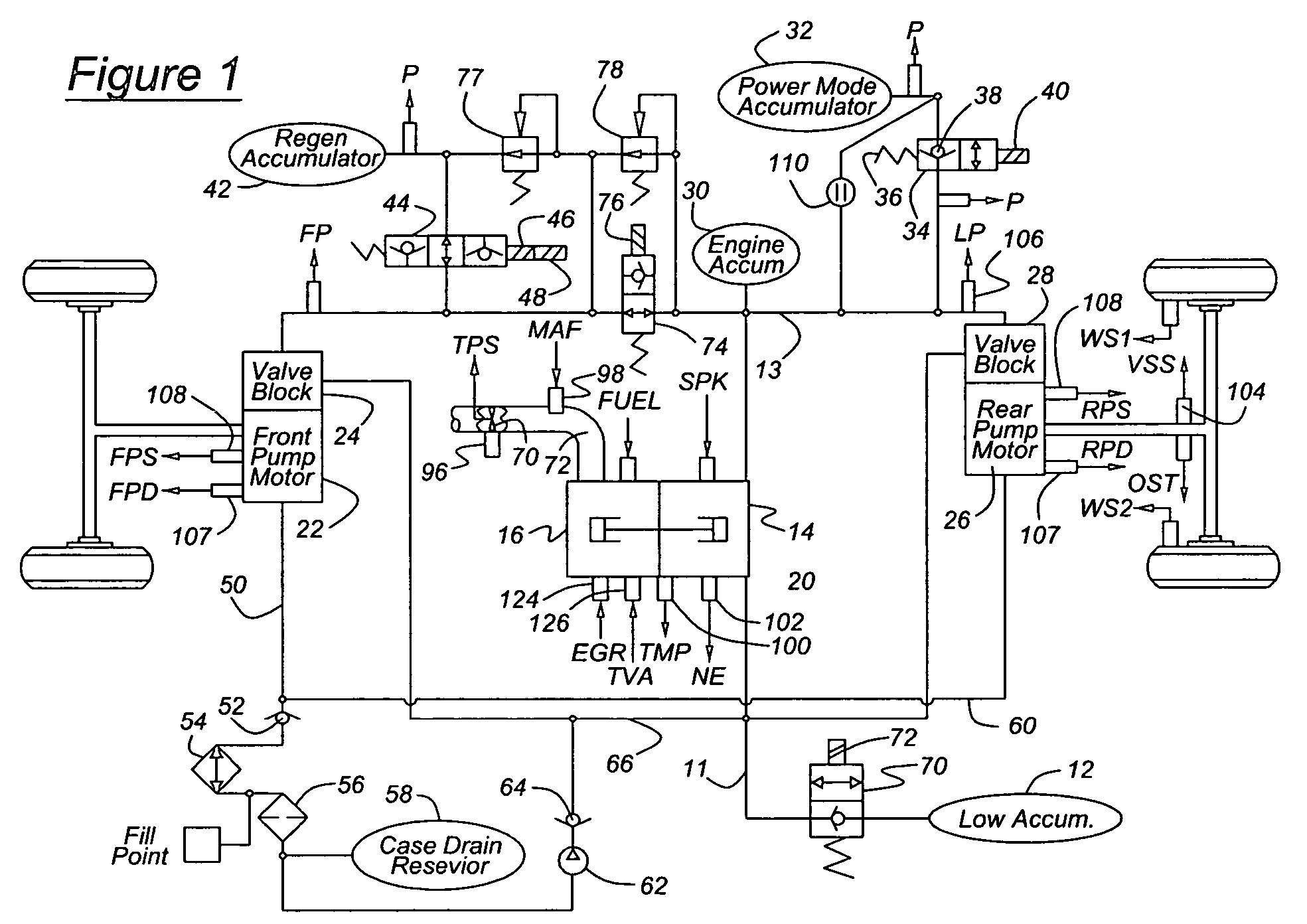
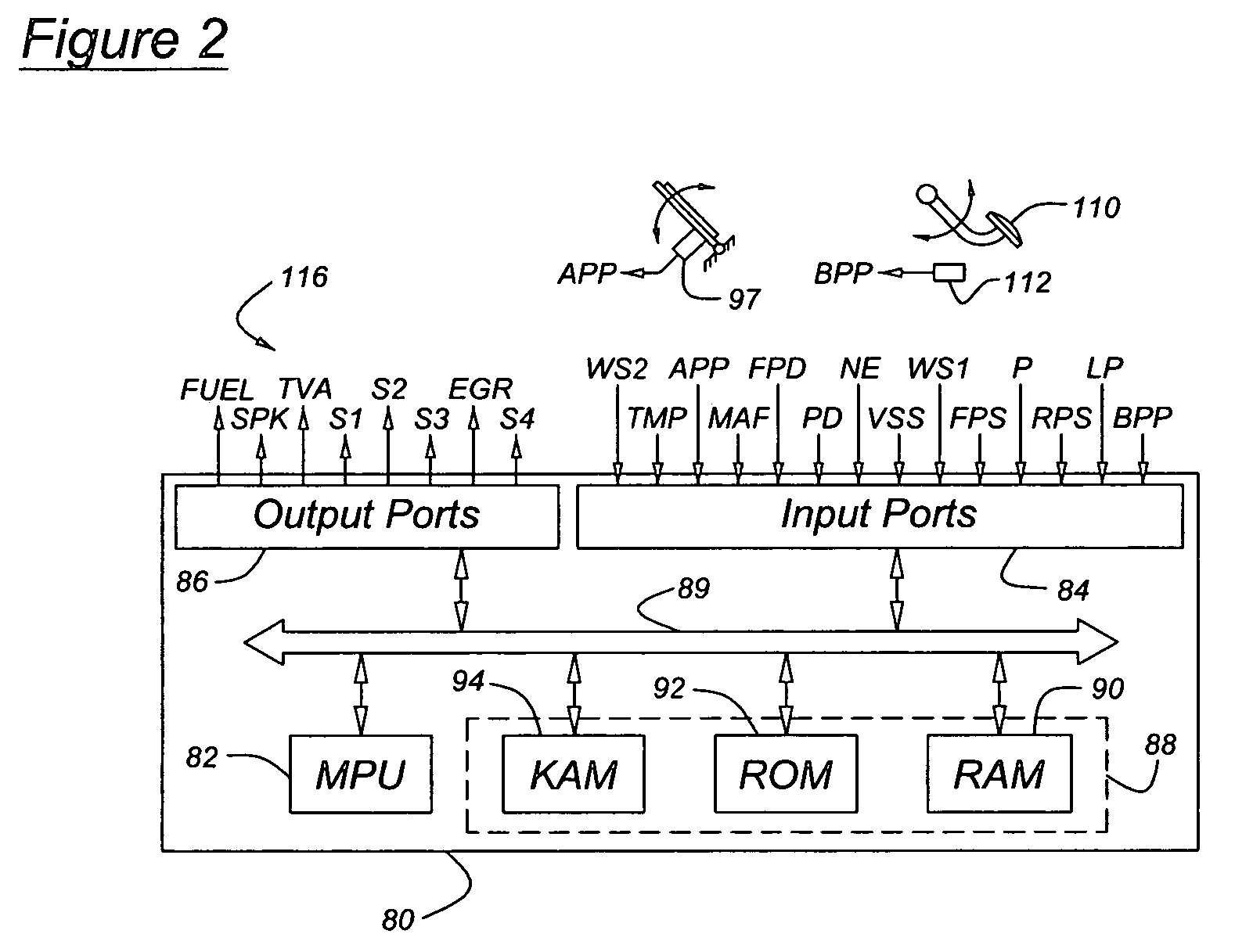
ActiveUS7100723B2Quick transitionWithout adverse performance effectAuxillary drivesGas pressure propulsion mountingMotor speedRail pressure
A system for a hydraulically driven vehicle includes a pump producing fluid flow at an outlet, pump-motors having variable flow rates for driving the wheels, a hydraulic rail having a pressure and connecting the pump and the pump-motors, sensors producing signals representing rail pressure, pump-motor speed, pump-motor displacement, and a controller for determining a target hydraulic system parameter, determining, based at least in part on the flow rate of the pump-motor, rail pressure, and a flow rate produced by the engine-pump, a flow rate produced by the engine-pump that is required to produce the target system parameter, and adjusting an engine operating parameter of a cylinder-pump bank such that the demanded magnitude of the system parameter is produced.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for controlling the pressure in a common rail system
ActiveUS20060130813A1Improve stabilityEliminates temperature dependenceElectrical controlLow-pressure fuel injectionRail pressureControl engineering
In a common rail operating method and system, an arrangement for controlling the rail pressure is provided with a rail pressure controller including a current control circuit for controlling a suction throttle valve operating current (i) which valve is arranged in the fuel supply line to a high pressure pump supplying high pressure fuel to the common rail. The suction valve operating current control circuit includes a preliminary control value generator which serves also as an emergency control signal generator for the control of the suction valve if an error occurs in the system at least to permit an orderly engine shutdown procedure.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE SOLUTIONS GMBH
Methods and systems for common rail fuel system maintenance health diagnostic
ActiveUS20130013174A1High resolutionLow maneuverabilityAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlRail pressureSystem maintenance
Dynamic health assessment systems and methods related to monitoring fuel flow control are provided. In one embodiment, a method for controlling a system having an engine is provided. The method includes during a no-load condition of the engine, stopping fuel injection by a plurality of fuel injectors of the engine, closing a valve that is operable to control fuel flow to a fuel pump that pumps fuel to a common fuel rail, and setting a degradation condition in response to a fuel rail pressure decay rate of a fuel pressure in the common fuel rail being greater than a decay threshold after a first designated duration.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
Method and system for diagnosing oil return failure of electronic control common rail oil sprayer
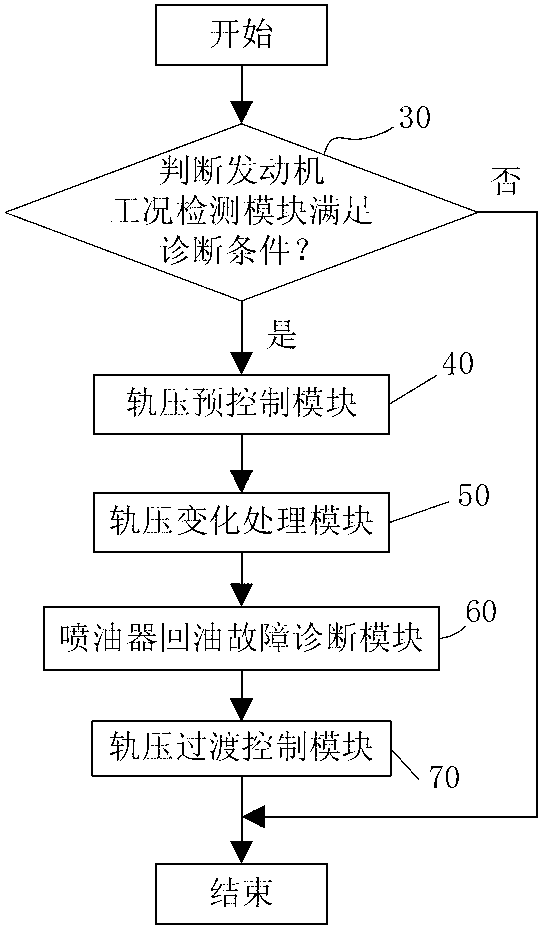
ActiveCN102996311ARealize online diagnosisReliable non-disintegration fault diagnosisEngine testingFuel injection apparatusRail pressureSprayer
The invention relates to a method and system for diagnosing an oil return failure of an electronic control common rail oil sprayer. The method comprises the following steps of: a, when the oil sprayer is in a non-spraying state and the rail pressure in a common rail pipe is more than a first preset threshold, diagnosing the oil return failure of the oil sprayer, otherwise, ending a diagnosis program; b, controlling a high-pressure oil pump to ensure that the rail pressure in the common rail pipe is a target pressure value PFin1, when the rail pressure in the common rail pipe is the target pressure value PFin1, stopping the working state of the high-pressure oil pump; c, calculating the variable required in the common rail pipe; d, comparing the variable with a preset reference value, judging whether the oil sprayer generates the oil return failure according to the relationship between the variable and the preset reference; and e, when the rail pressure in the common rail pipe is reduced to the preset pressure limit value, starting the high-pressure oil pump to ensure that the rail pressure in the common rail pipe is a target pressure value PFin2 under the current working condition. The method can be used for realizing online detection on the oil return failure of the oil sprayer and has the advantages of high automation degree and wide application range.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
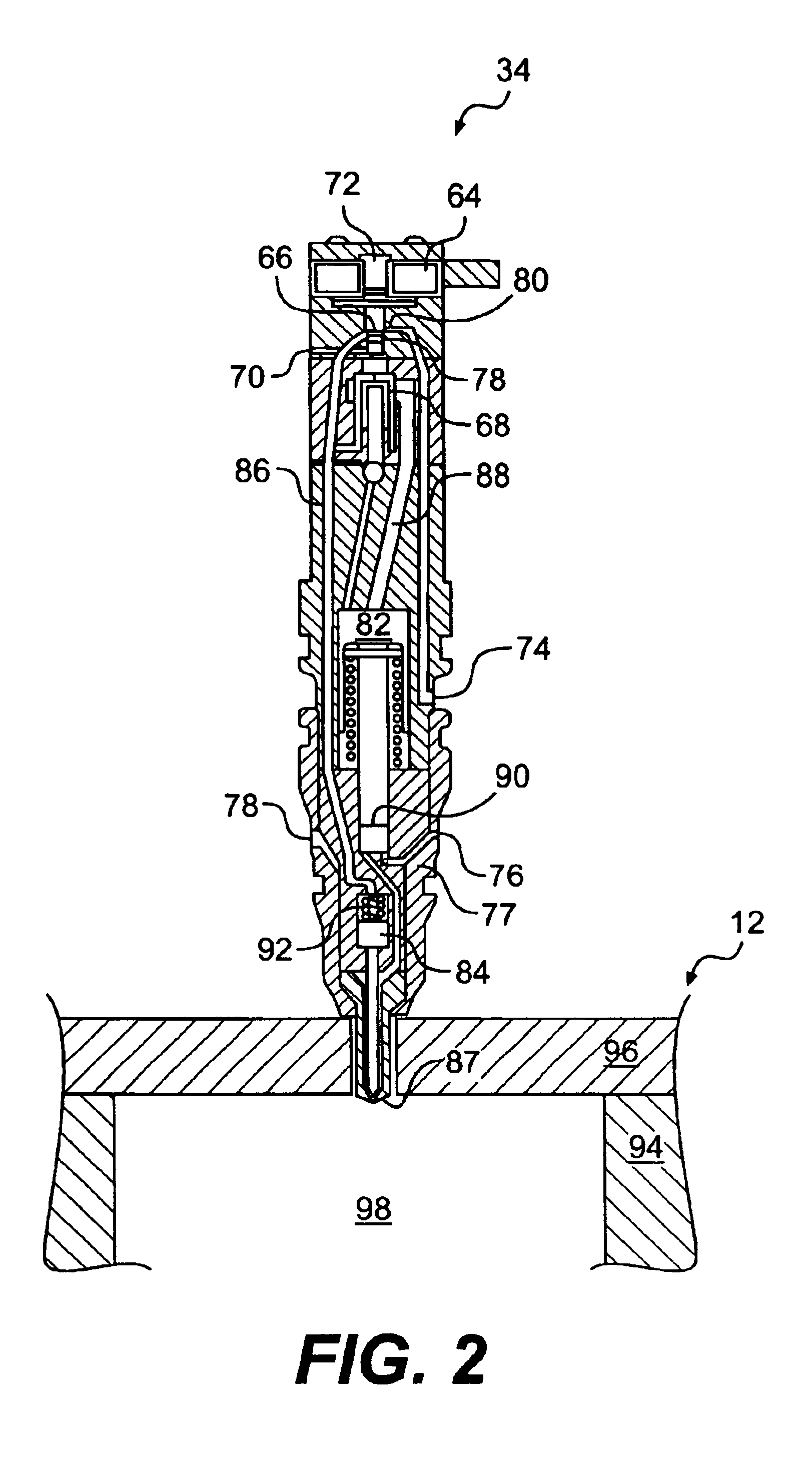
Method for controlling combustion in an internal combustion engine and predicting performance and emissions
InactiveUS20070073467A1Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesBrake torqueBrake specific fuel consumption
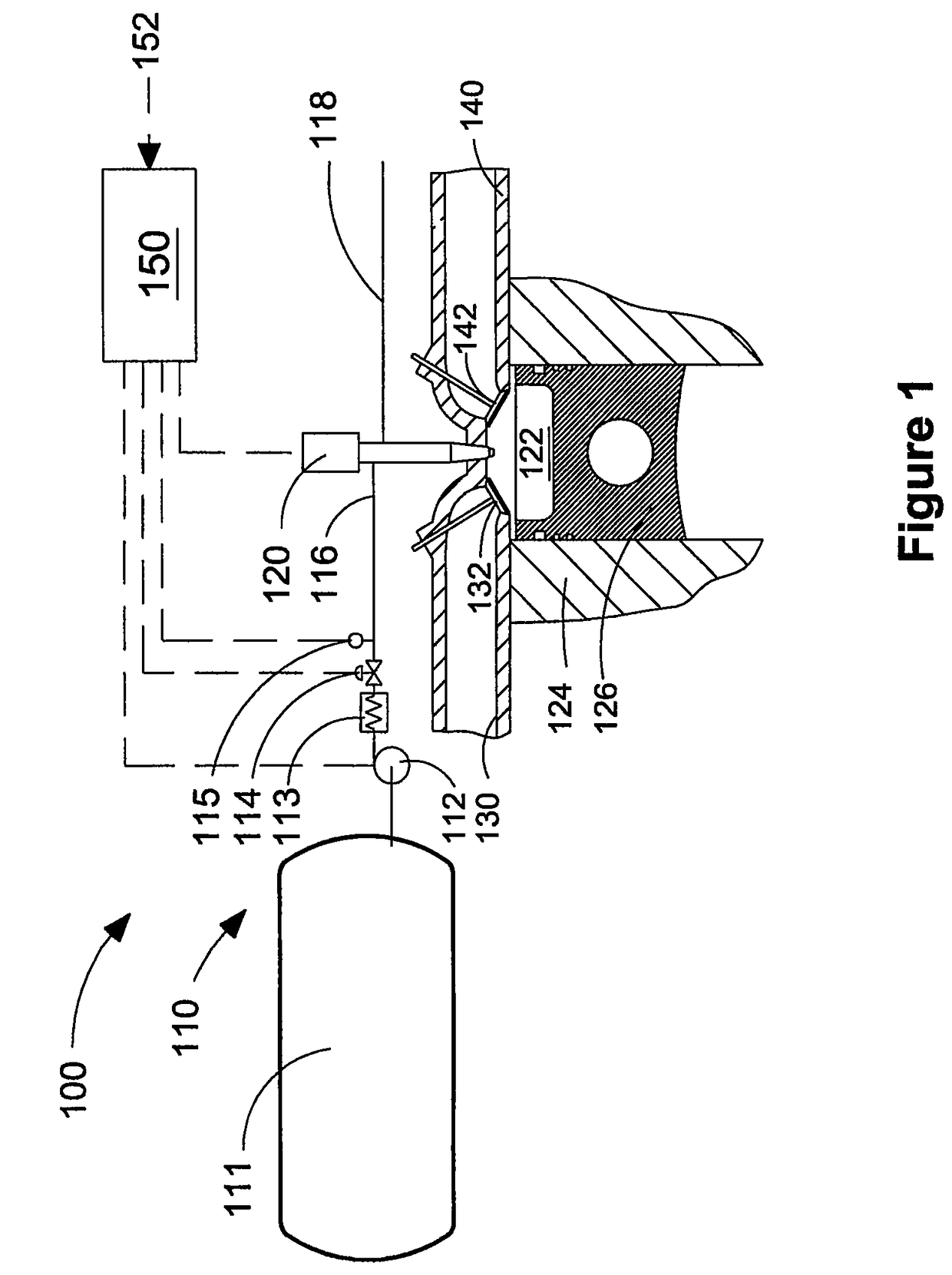
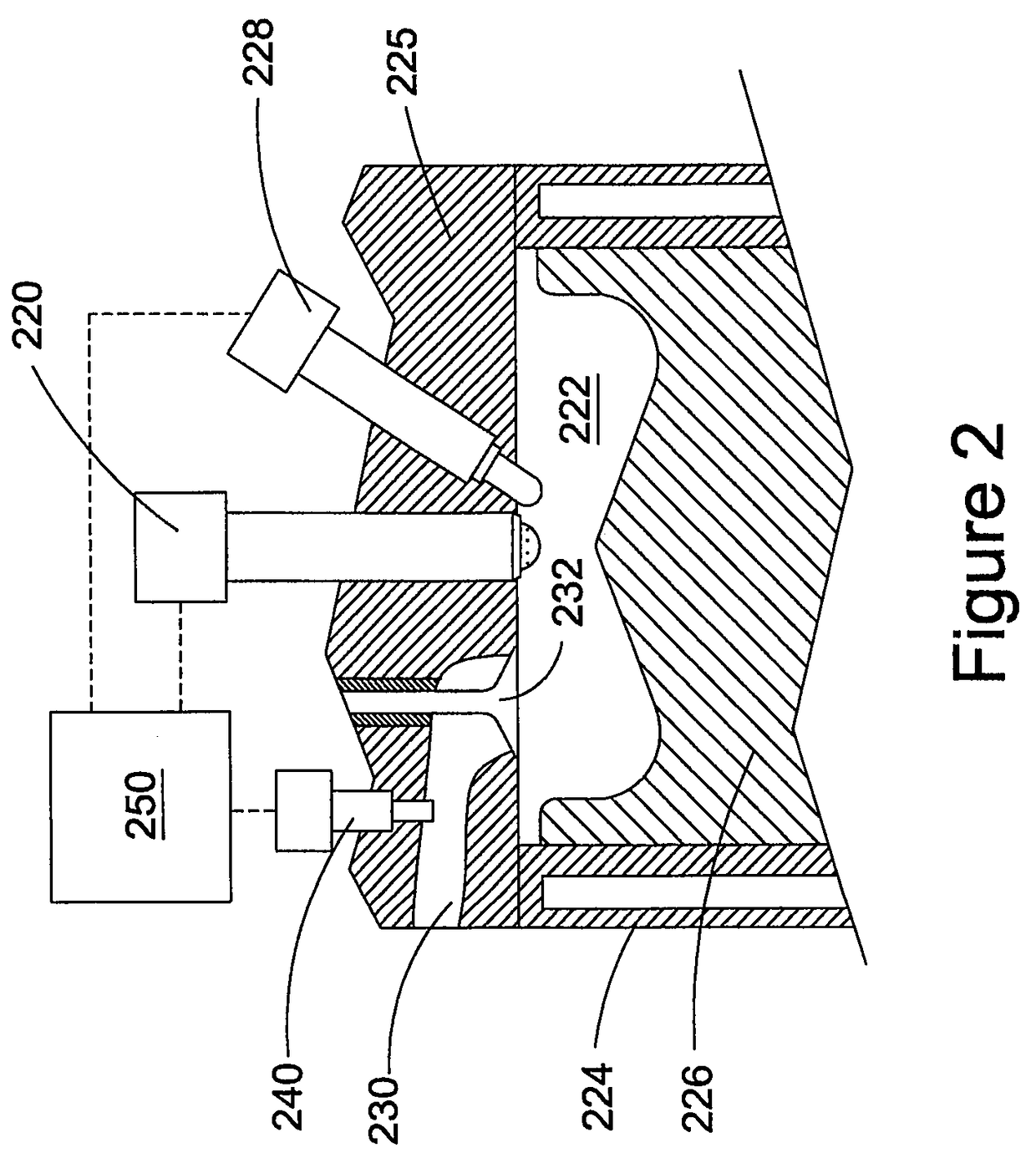
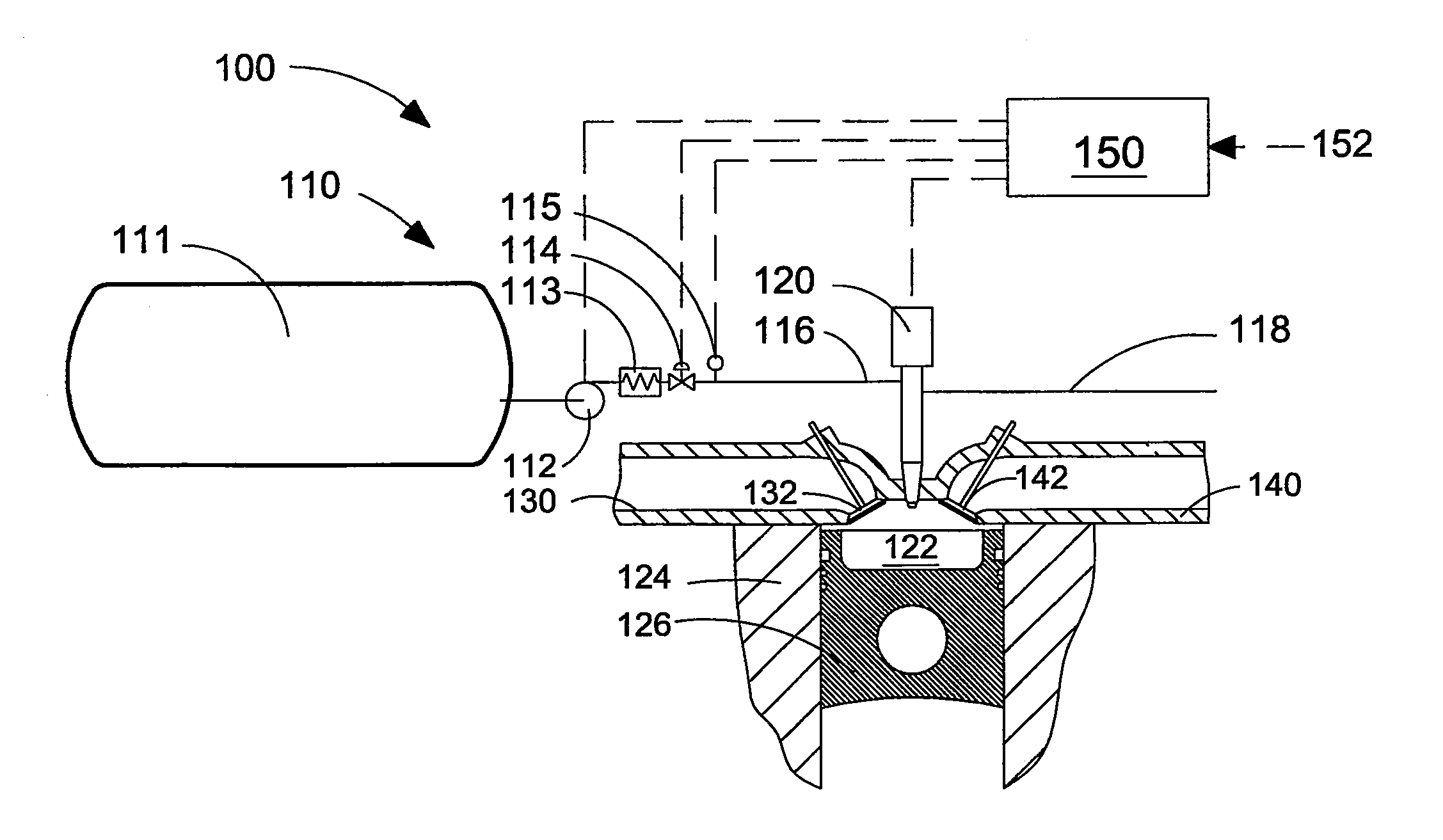
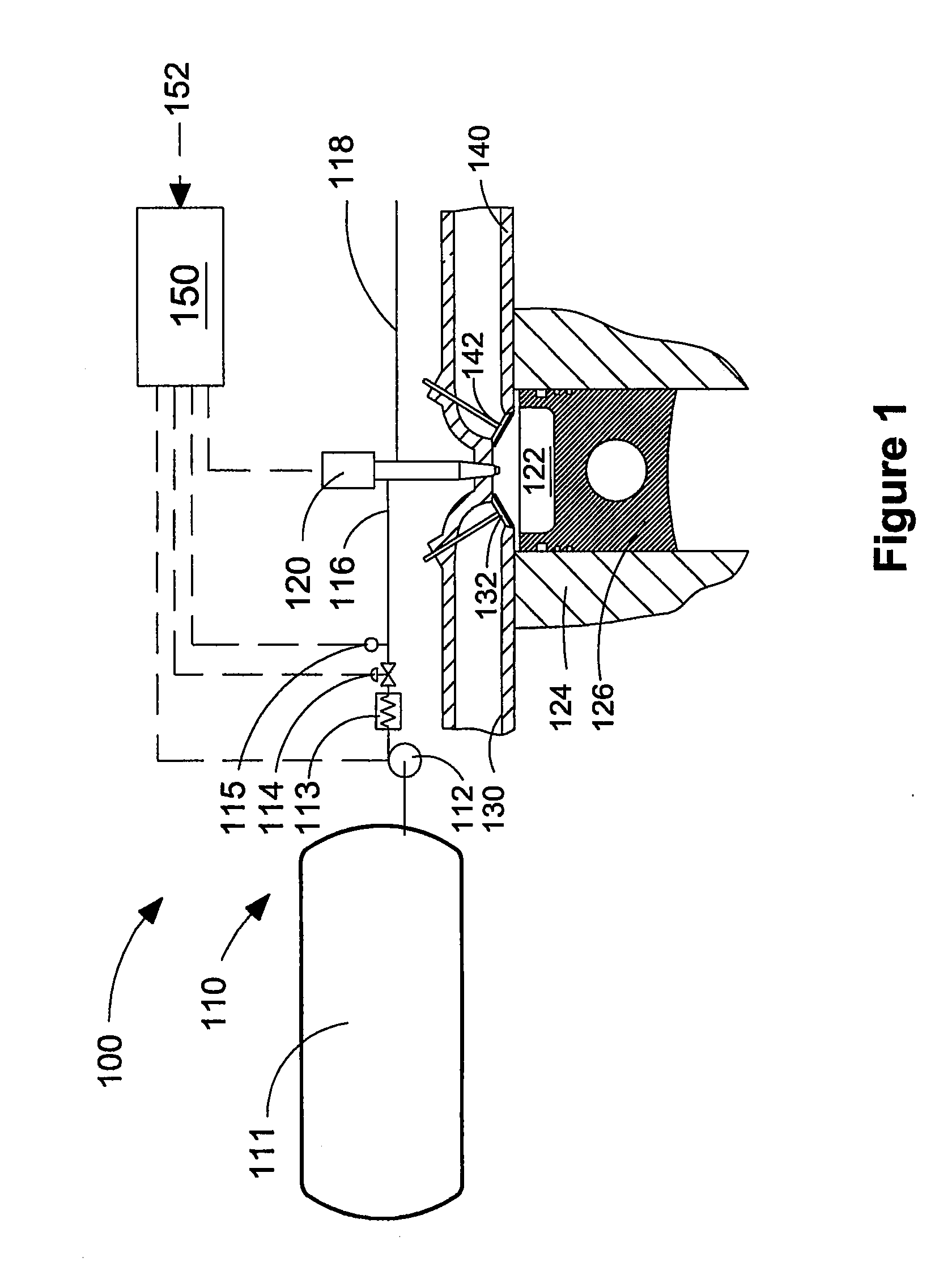
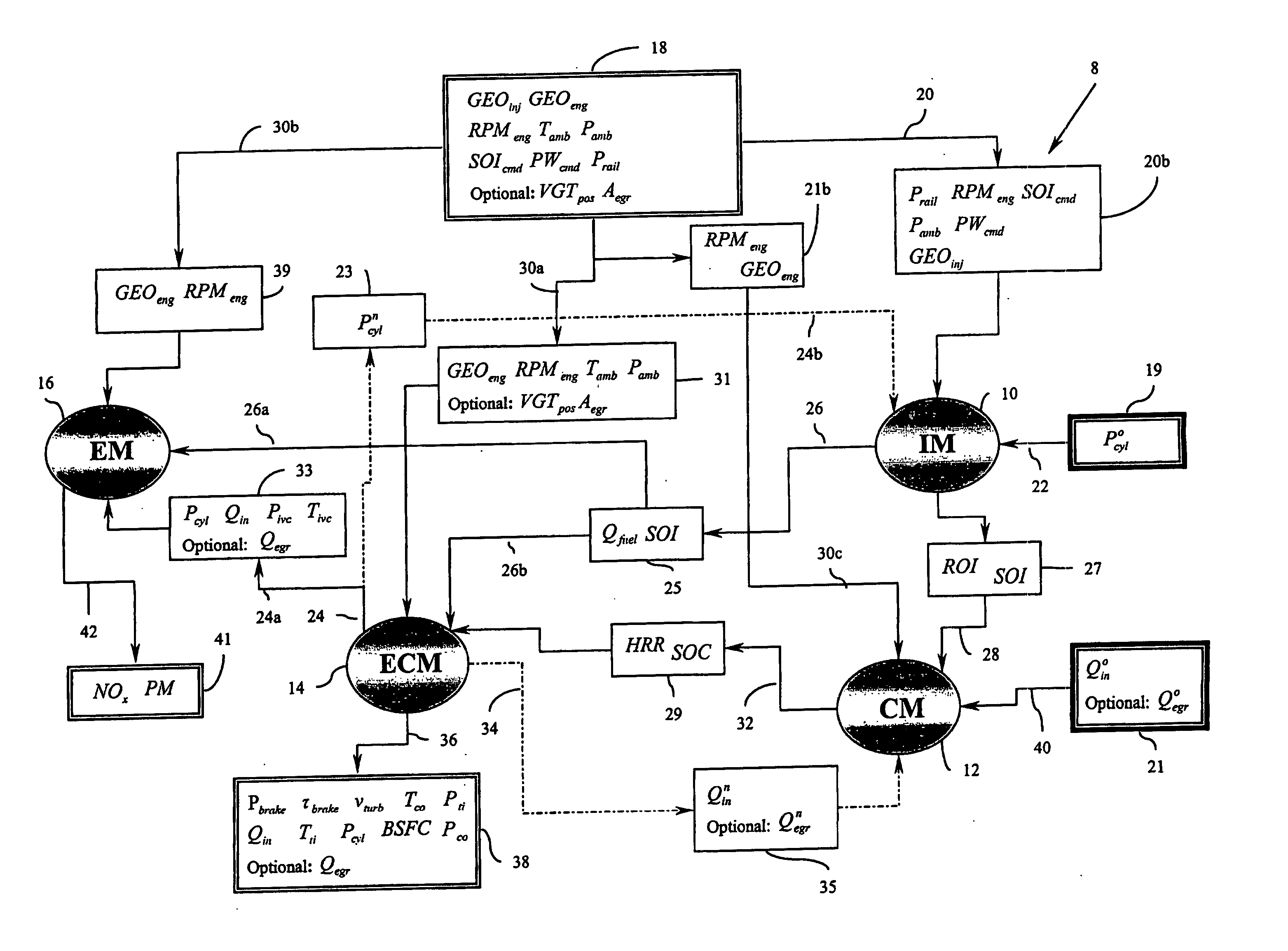
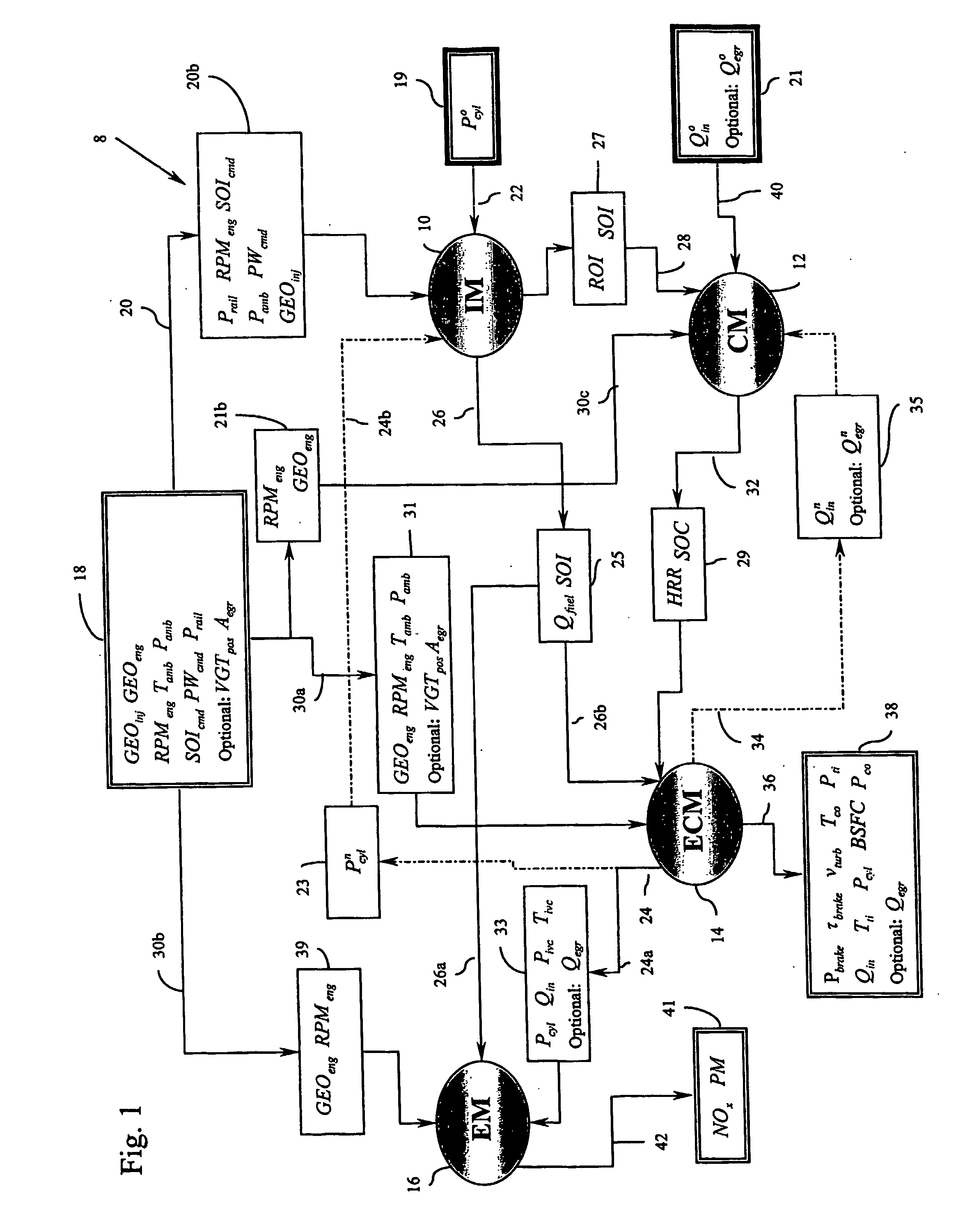
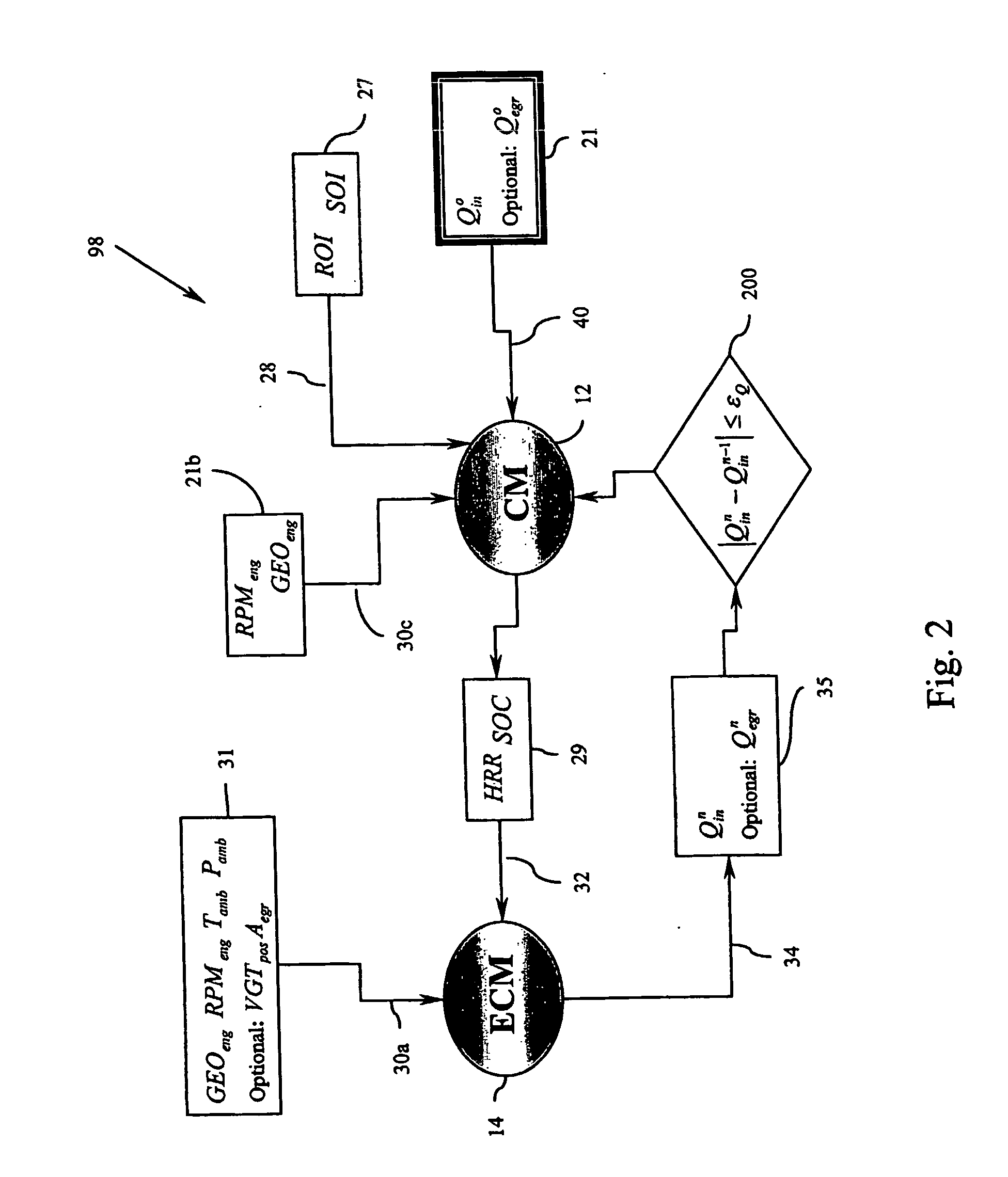
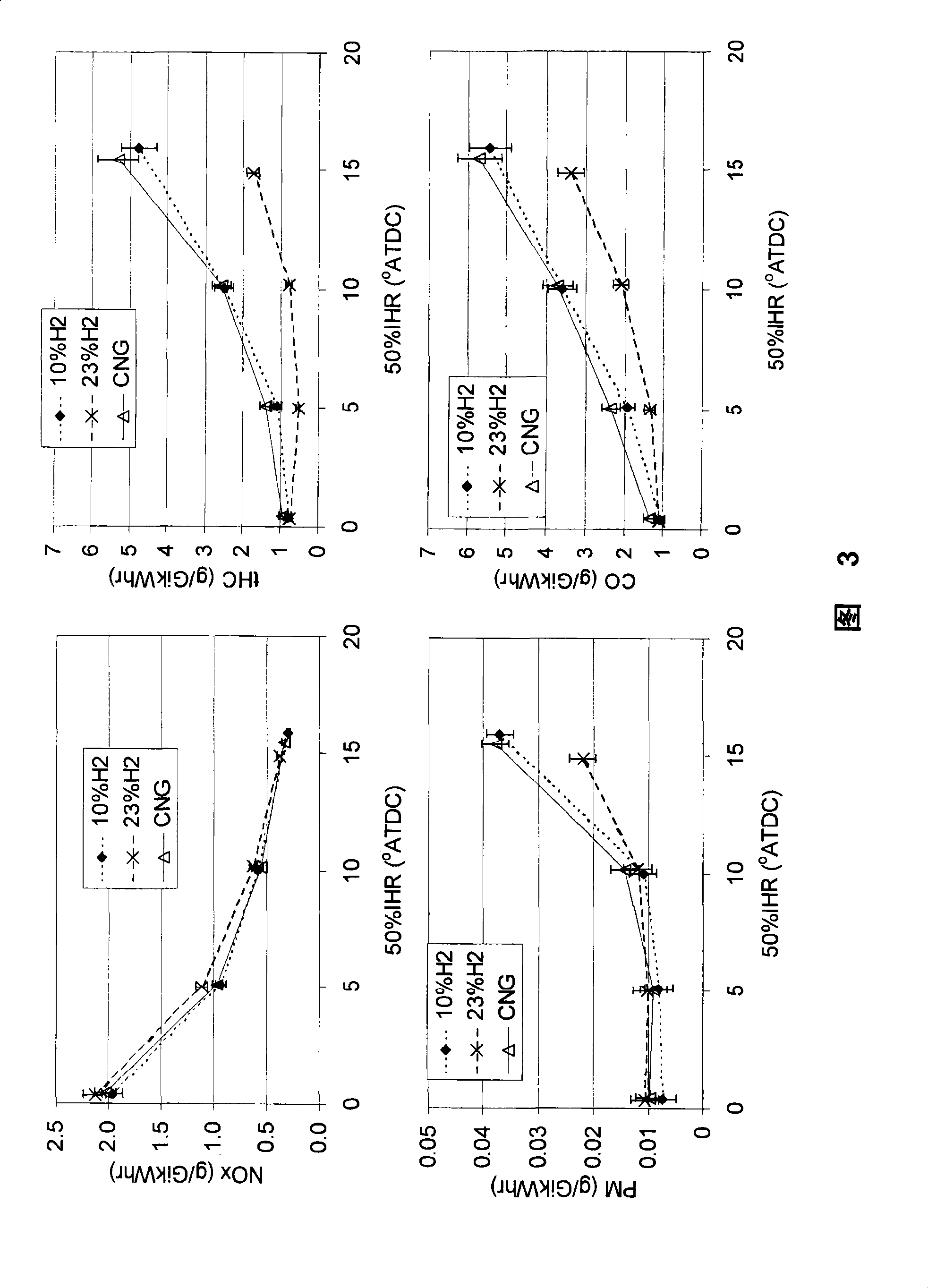
This disclosure teaches a method of controlling a direct injection internal combustion engine and predicting the behaviour of a direct injection internal combustion engine. An estimation of initial cylinder pressure, air flow and EGR flow (if applicable) is used to establish a system that provides engine behaviour by integrating an injection module, combustion module and engine control module to provide data indicative of engine behaviour such as brake torque and power, air flow, EGR flow, cylinder pressure, brake specific fuel consumption, start of combustion, heat release rate, turbo-charger speed and other variables. These values can then be used to adjust commanded variables such as start of injection, commanded pulse width, rail pressure to meet operator demand. Also the output data can be used as a tool to determine how a conceptualised engine design will behave. This is particularly useful for gaseous-fuelled internal combustion engines where cylinder pressure influences behaviour of injected gases in light of the fact that rail pressure and cylinder pressure are, generally, of a similar magnitude.
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
Fuel system for a multi-fuel engine
ActiveUS8776764B2Improve fuel vaporizationEmission reductionInternal combustion piston enginesLow pressure fuel injectionRail pressureFuel oil
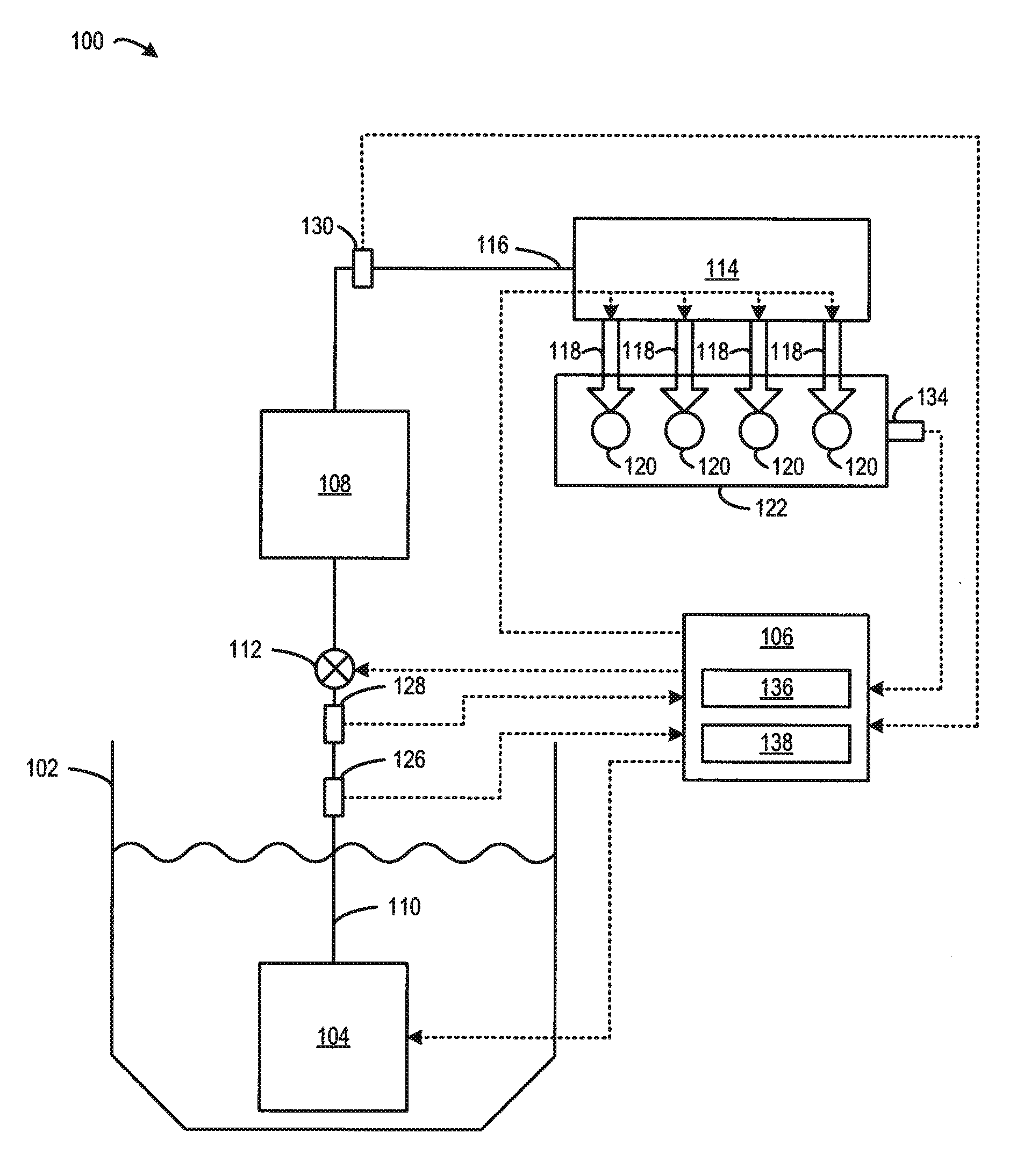
Methods and systems are provided for operating an engine fuel system including a low pressure pump and a high pressure pump. During conditions when direct injection is not requested, a fuel rail pressure is maintained by the low pressure pump and fuel is port injected. Further, a stroke amount of the high pressure pump is adjusted to maintain an outlet pressure of the high pressure pump just below the fuel rail pressure. By maintaining fuel flow within the high pressure pump when high pressure pump operation is not required, and without flowing fuel from the high pressure pump outlet into the fuel rail, the high pressure pump may be cooled and lubricated without affecting the fuel rail pressure.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Detection of fuel system problems
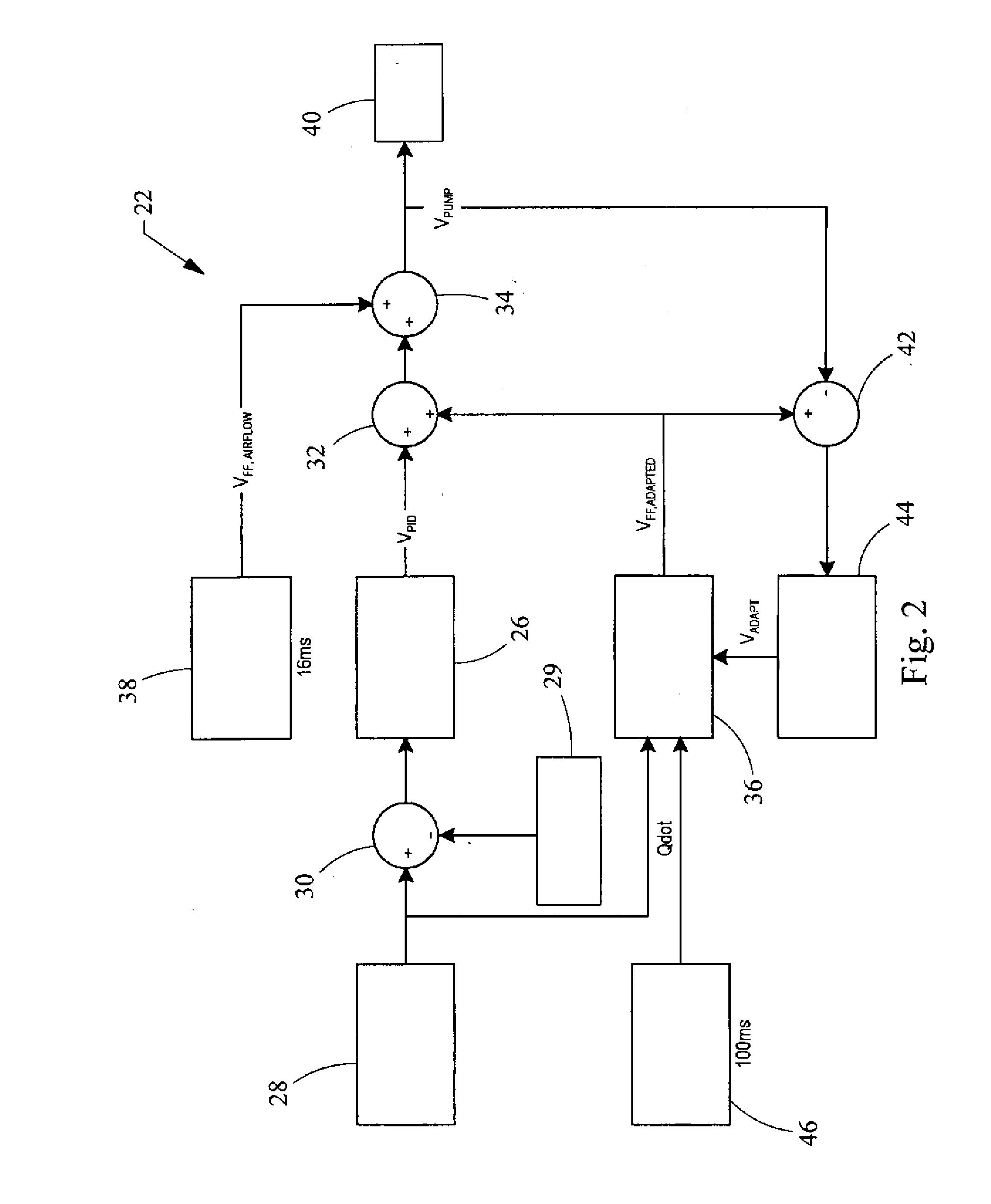
A method for detecting failures in a fuel system of a motor vehicle including monitoring a feed-forward table of a fuel pump controller that is electrically connected to a fuel pump of the fuel system. The fuel pump controller is electrically connected to a rail pressure sensor, which is coupled to the fuel injector rail. The actual fuel injector rail pressure measured by the rail pressure sensor is compared to a desired fuel injector rail pressure associated with the feed-forward table. The feed-forward table is adjusted if the actual fuel injector rail pressure is less than the desired fuel injector rail pressure. A fuel system error is signaled if an adjusted feed-forward table differs from an initial feed-forward table. A fuel system failure is signaled of the adjusted feed-forward table requires a saturation voltage of the controller.
Owner:MICHIGAN MOTOR TECH LLC
Method for estimating fuel injector performance
InactiveUS6879903B2Reduce determination errorAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlRail pressureInjector
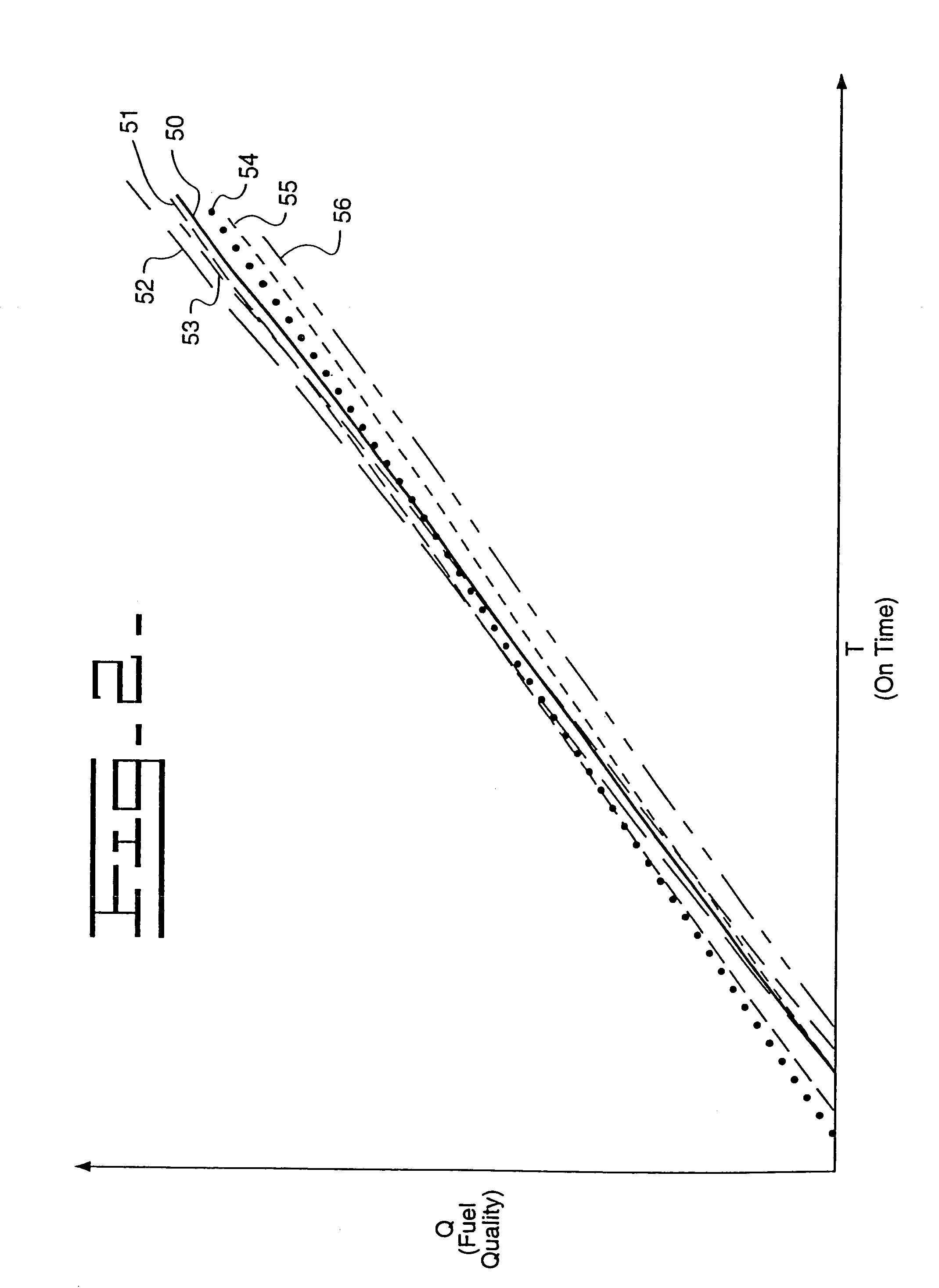
A method of estimating an injection delay of a fuel injector. A baseline injection delay curve representing an injection delay for a predetermined type of fuel injector is established for a range of rail pressures. At least one test rail pressure for the predetermined type of fuel injector is identified based on the baseline injection delay curve. An injection delay of a selected fuel injector of the predetermined type is measured at the at least one test rail pressure. The injection delay of the selected fuel injector is estimated based on the baseline injection delay curve and the measured injection delay of the selected fuel injector at the identified test rail pressure.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
System and method for closing a tank valve
ActiveUS20130255636A1Reduce lossesReduce the amount requiredElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesRail pressureSolenoid valve
A method for closing a storage tank valve in response to leaks in a fuel line or fuel rail and emptying the tank of a vehicle when no leaks are detected is described. The method includes comparing a tank pressure to a fuel line or fuel rail pressure in order to detect leaks therein and further includes using a dedicated tank pressure sensor to measure the gaseous pressure of the storage tank, and thereby the amount of fuel remaining. In response to leaks in the fuel system, a controller may close an electronic solenoid valve, which reinforces a mechanical excess flow valve, to block the flow of fuel and prevent fuel loss from the gaseous storage tank.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method and device for diagnosing faults of fuel injector
ActiveCN102748181AHigh precisionImprove accuracyInternal combustion piston enginesEngine testingRail pressureWork cycle
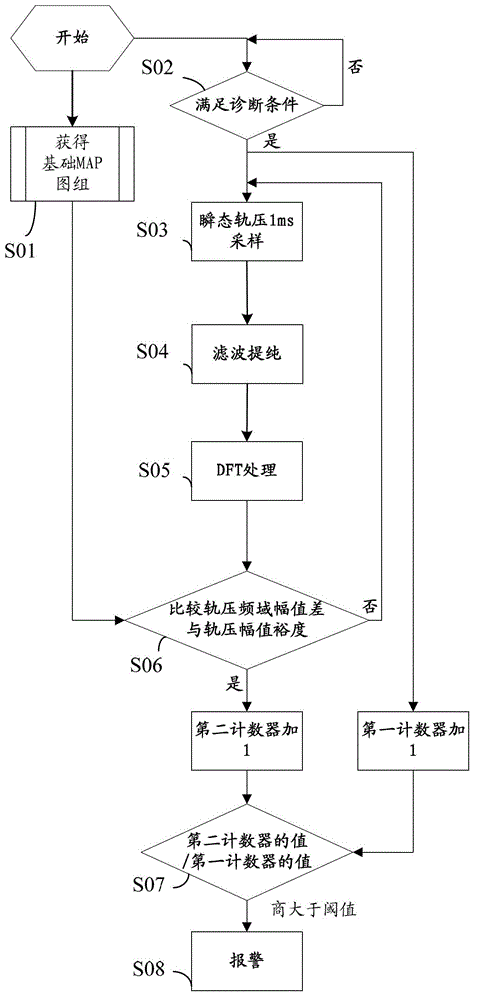
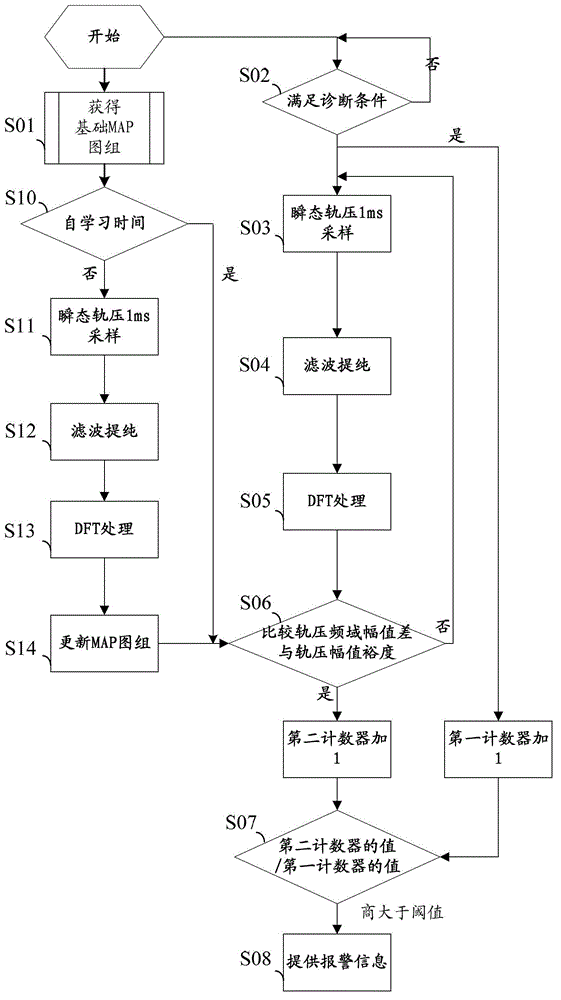
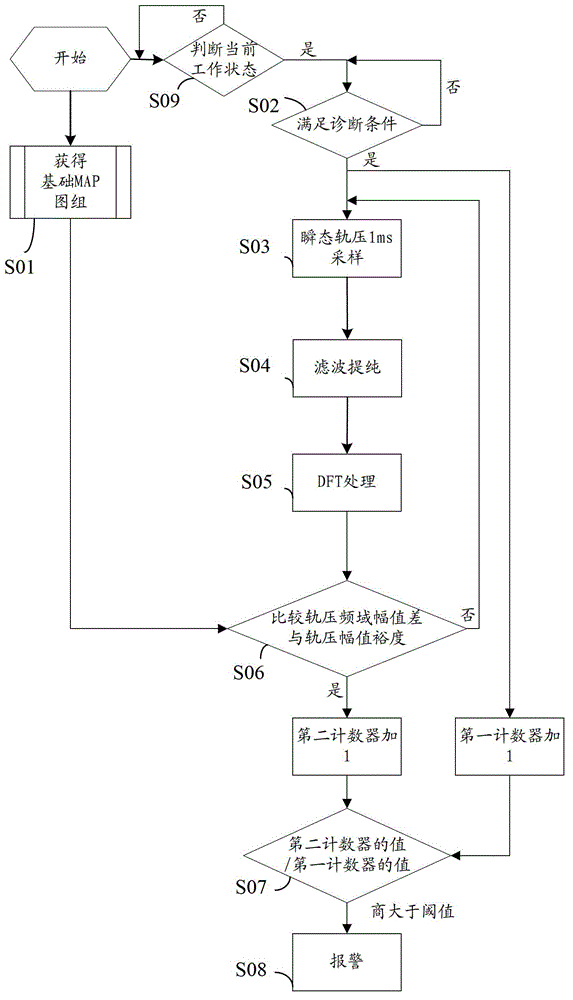
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for diagnosing faults of a fuel injector. Before the fuel injector leaves a factory, rail pressure signals of engines of each type are collected during work cycles in advance for one time when different working conditions are met, and discrete fourier transformation (DFT) processing is performed on the collected rail pressure signals to form a basic map group of rail pressure frequency domain amplitudes of the engines of each type based on different working conditions. After the fuel injector leaves the factory, rail pressure signals of diagnosed engines are collected for one time at set intervals when a preset external environment is met, the DFT processing is performed on the collected rail pressure signals, and the processed rail pressure frequency domain amplitudes are compared with the rail pressure frequency domain amplitudes based on the same working conditions in the basic map group of the rail pressure frequency domain amplitudes. Accordingly, due to the fact that the DFT processing is performed on the collected rail pressure signals, veracity and accuracy of fault judgement of the fuel injector are remarkably improved.
Owner:WEICHAI POWER CO LTD
Determination of fuel injector performance in chassis
InactiveUS7025047B2Electrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesRail pressureAcceleration Unit
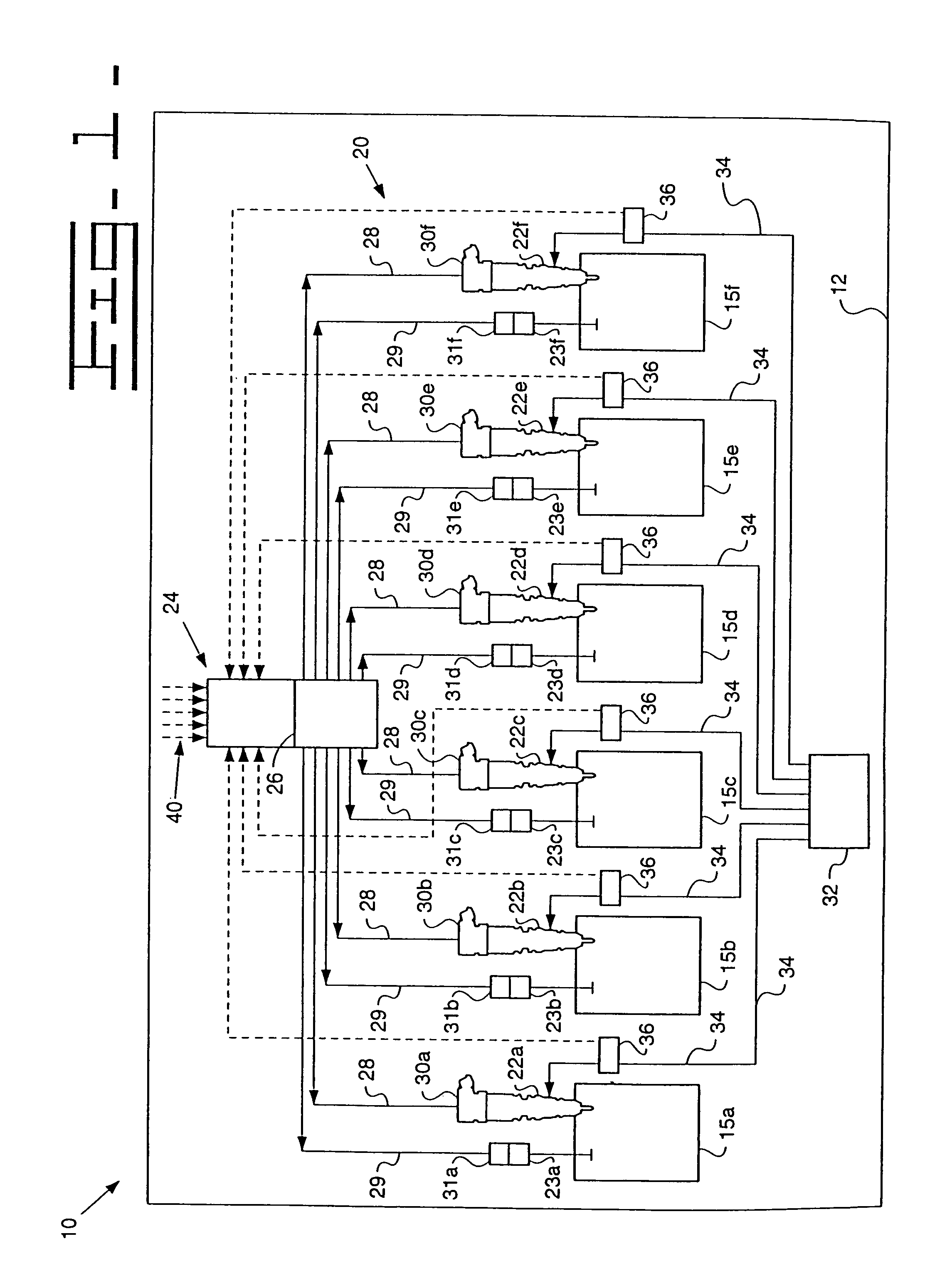
It is known that performance of actual fuel injectors tends to deviate from performance of a nominal injector as a function of rail pressure and on-time, due to such factors as machining tolerances of fuel injector components. In addition, performance characteristics of fuel injectors tend to change after they have been broken in. These changes can lead to unexpected inconsistencies with other engine components. For example, for those engines which utilize smoke limiting maps, when the injectors are not performing as expected, the injection adjustments that result from use of the smoke limiting maps can sometimes become fruitless. Therefore, the present invention includes two in-chassis strategies for evaluating fuel injector performance, including a bare acceleration test and a loaded fuel injector performance test.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Method and apparatus of fuelling an internal combustion engine with hydrogen and methane
ActiveCN101421500ANon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesElectronic controllerRail pressure
A gaseous-fuelled internal combustion engine and a method of operating same are provided for improving combustion stability and reducing emissions of NOx, PM, and unburned hydrocarbons. The method comprises fuelling an internal combustion engine with hydrogen and natural gas, which can be directly injected into the combustion chamber together or introduced separately. Of the total gaseous fuel delivered to the engine, at least 5% by volume at standard temperature and pressure is hydrogen. For at least one engine operating condition, the ratio of fuel rail pressure to peak in-cylinder pressure is at least 1.5: 1. The engine comprises a combustion chamber defined by a cylinder, a cylinder head, and a piston movable within the cylinder; and a fuel injection valve operable for introducing the gaseous fuel mixture directly into the combustion chamber, or two separate fuel injection valves for introducing the methane and hydrogen separately. An electronic controller is in communication with actuator(s) for the fuel injection valve(s) for controlling timing for operating the fuel injection valve(s). The engine has a compression ratio of at least 14:1.
Owner:WESTPORT POWER +1
Rail pressure sampling before fuel injection events
InactiveUS7188608B2Improve accuracyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesSufficient timeRail pressure
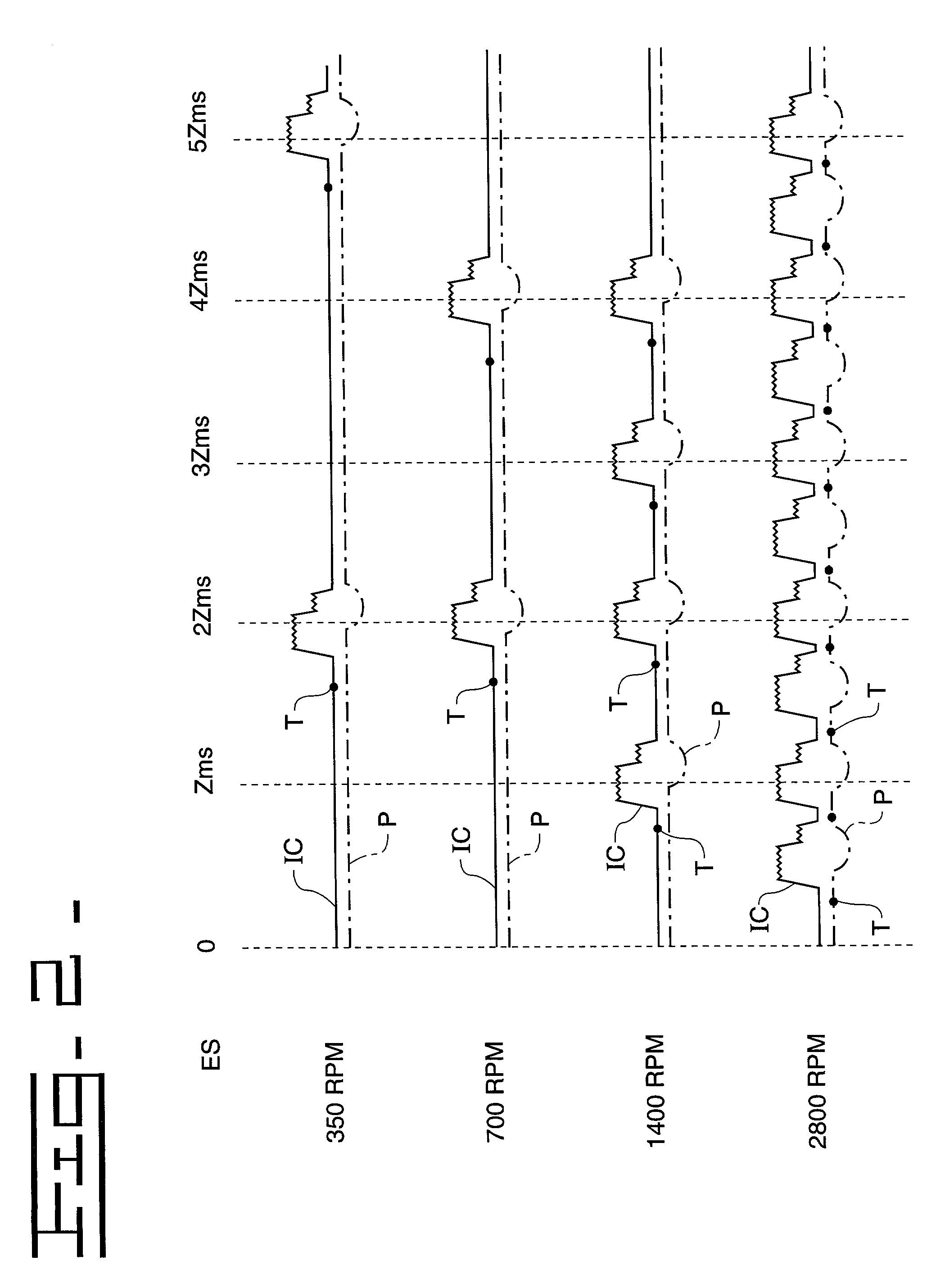
In common rail fuel injection systems, a sensed rail pressure is used to determine control signals to produce desired injection characteristics. Because rail pressure fluctuates, especially during cold start procedures, and because the rail pressure must be sensed before the injection event to be controlled, the accuracy of the timing and quantity of the injection event can be compromised if the rail pressure at the start of the injection event is different from the sensed rail pressure. In order to produce more accurate fuel injection characteristics, the rail pressure is sensed after the end of control signal for an immediately preceeding injection event but at least a predetermined time before the start of control signal for a succeeding injection event. Since the rail pressure is sensed close in time to the succeeding injection event but with adequate time to do control signal determination calculations, the accuracy in quantity and timing of the succeeding injection event can be improved because the quality of the sensed rail pressure is improved.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
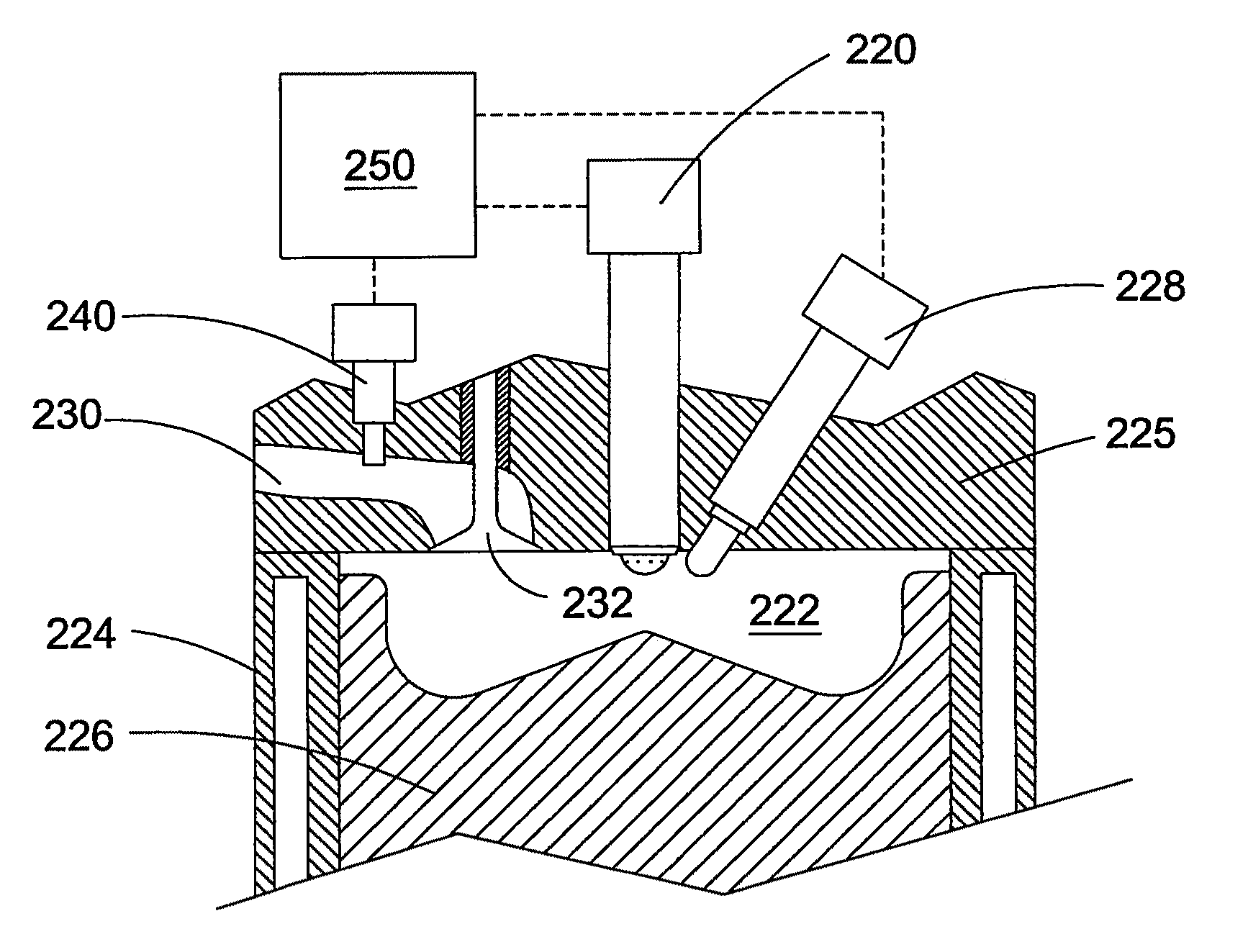
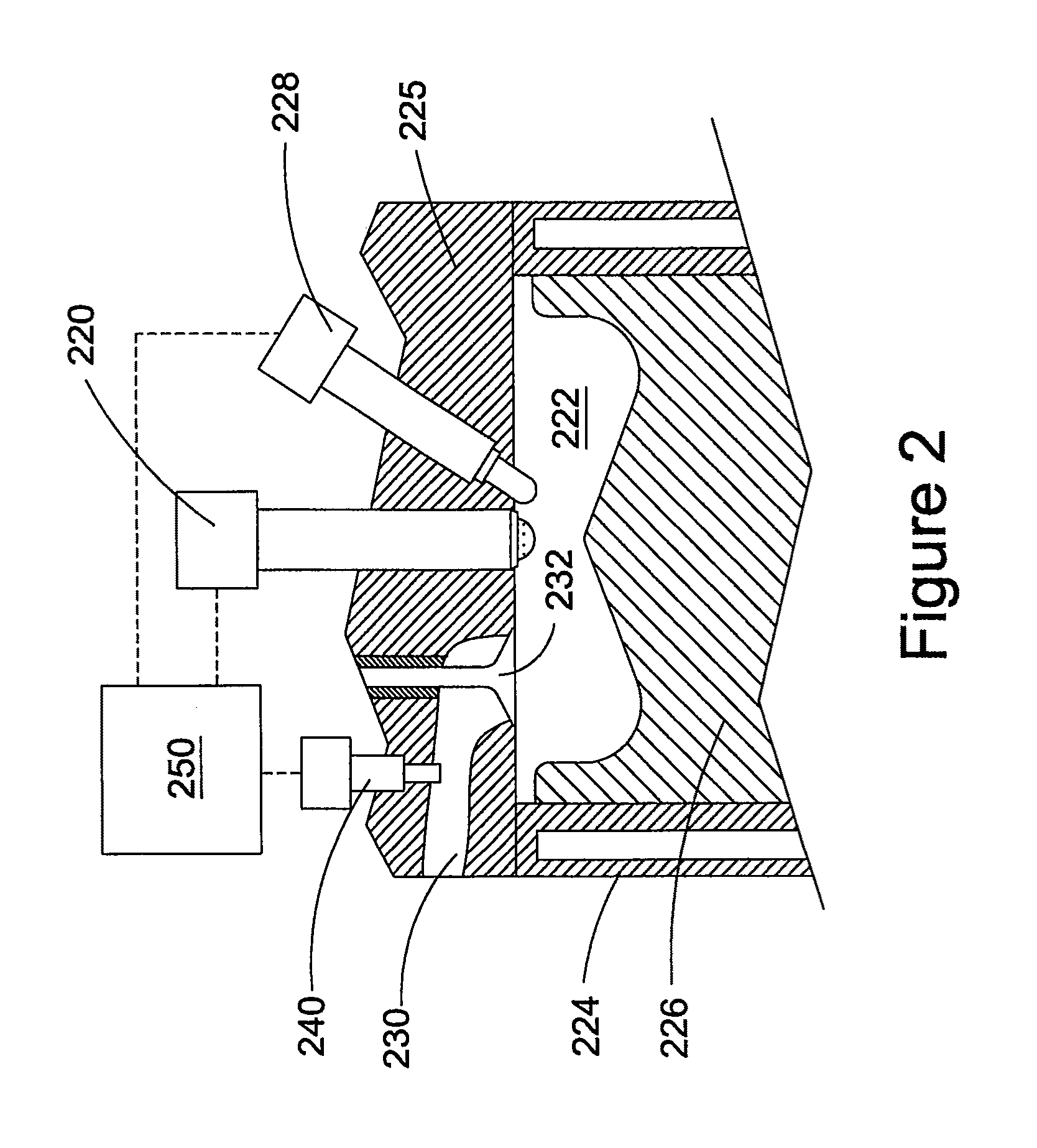
Fuel injection system ensuring operation in event of unusual condition
InactiveUS20070028895A1Simple structureGuaranteed uptimeElectrical controlFuel injection apparatusElectricityRail pressure
A common rail fuel injection apparatus for an engine is provided which is equipped with a rail pressure sensor working to measure the pressure of fuel in a common rail, fuel injectors, and a controller. When the operation state of the rail pressure sensor monitored to be unusual, the controller changes the value of electricity supplied to an actuator of one of the fuel injectors to induce a change in a preselected operation characteristic of the engine. Upon appearance of such a change, the controller estimates the value of the rail pressure using the changed value of the electricity and a physical property of balance among forces acting on a valve of one of the fuel injectors which has induced the change in operation characteristic of the engine. The estimated value of the rail pressure is used for subsequent injections of the fuel into the engine.
Owner:DENSO CORP
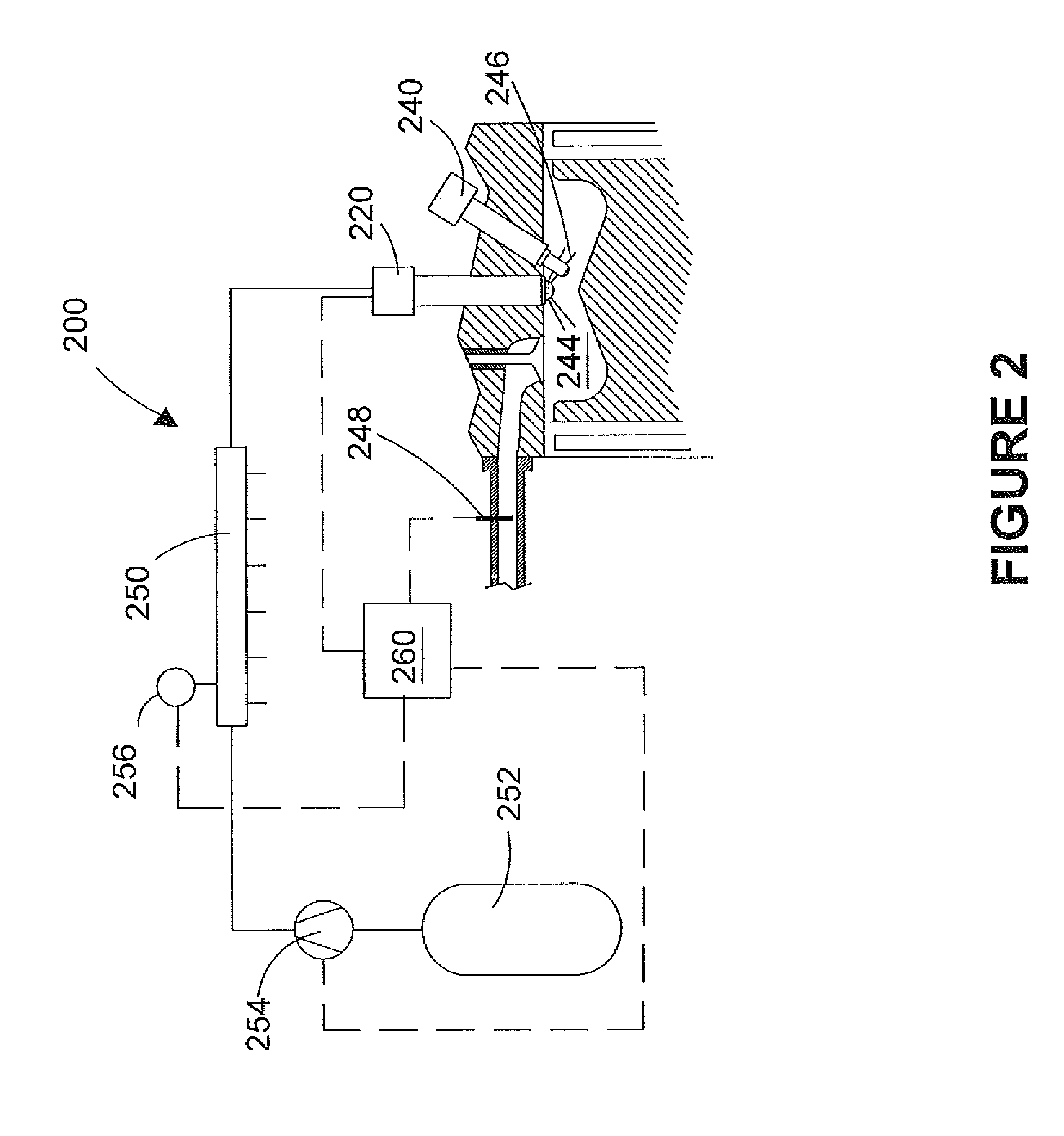
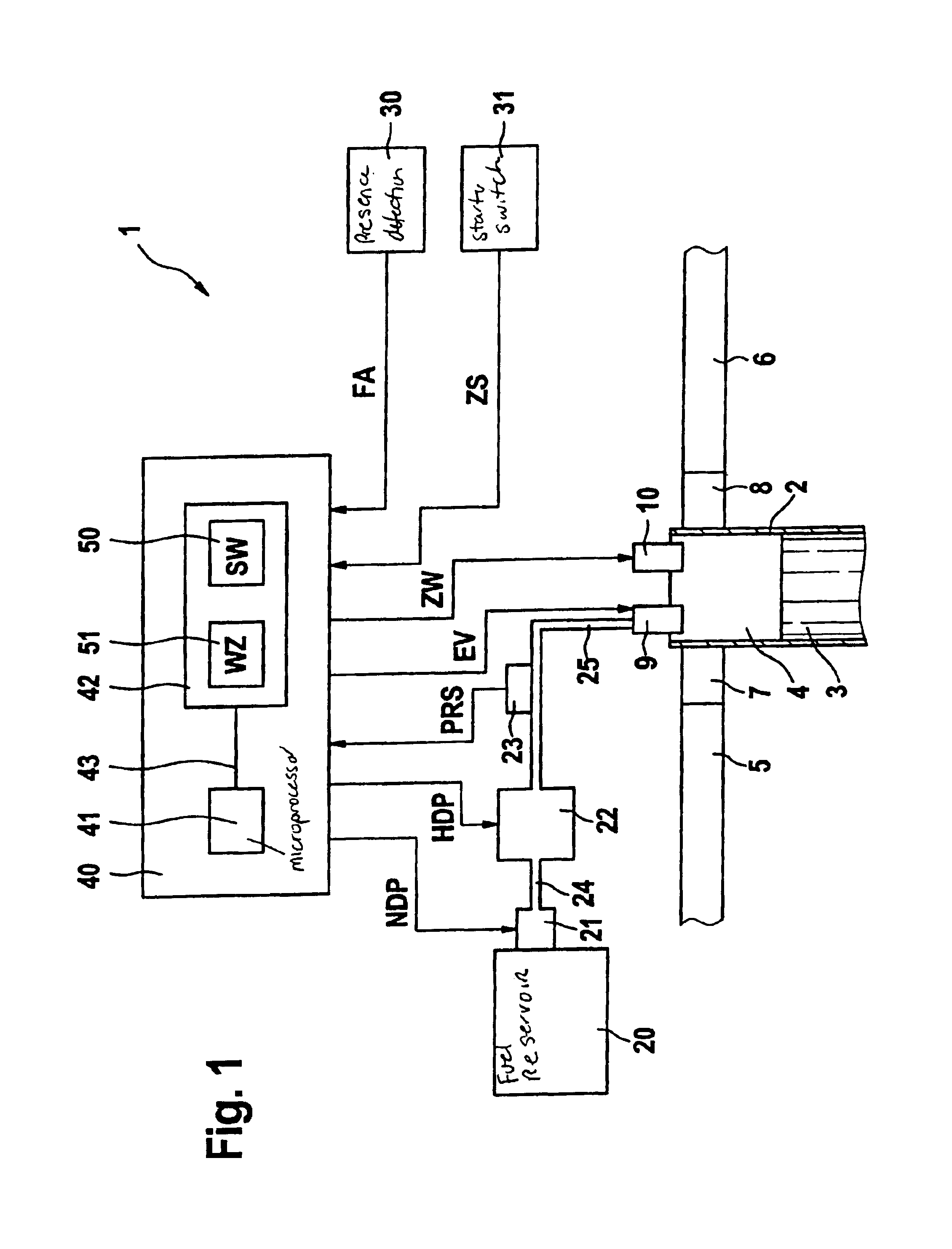
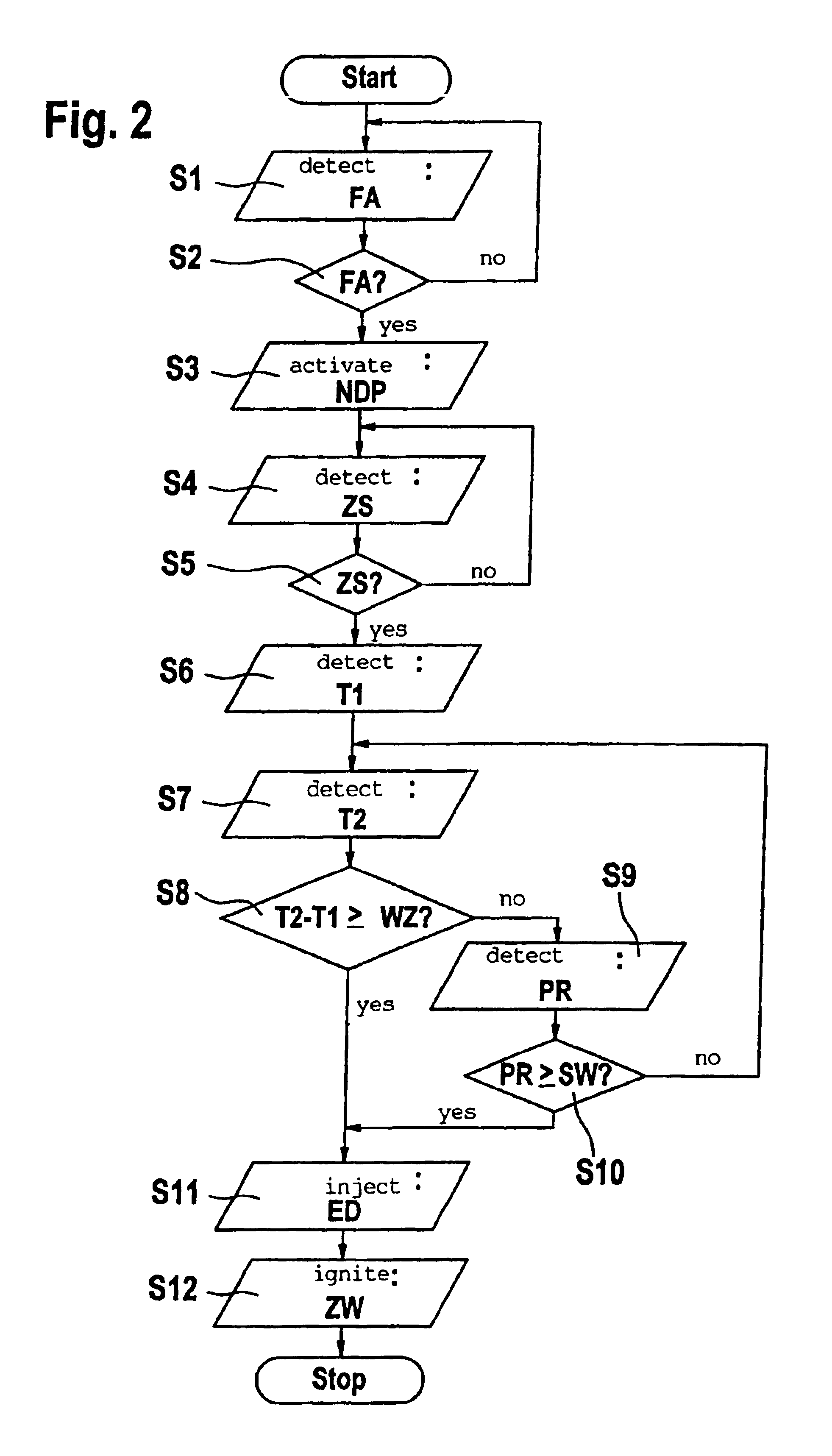
Method for starting an internal combustion engine, particularly an internal combustion engine having direct fuel injection
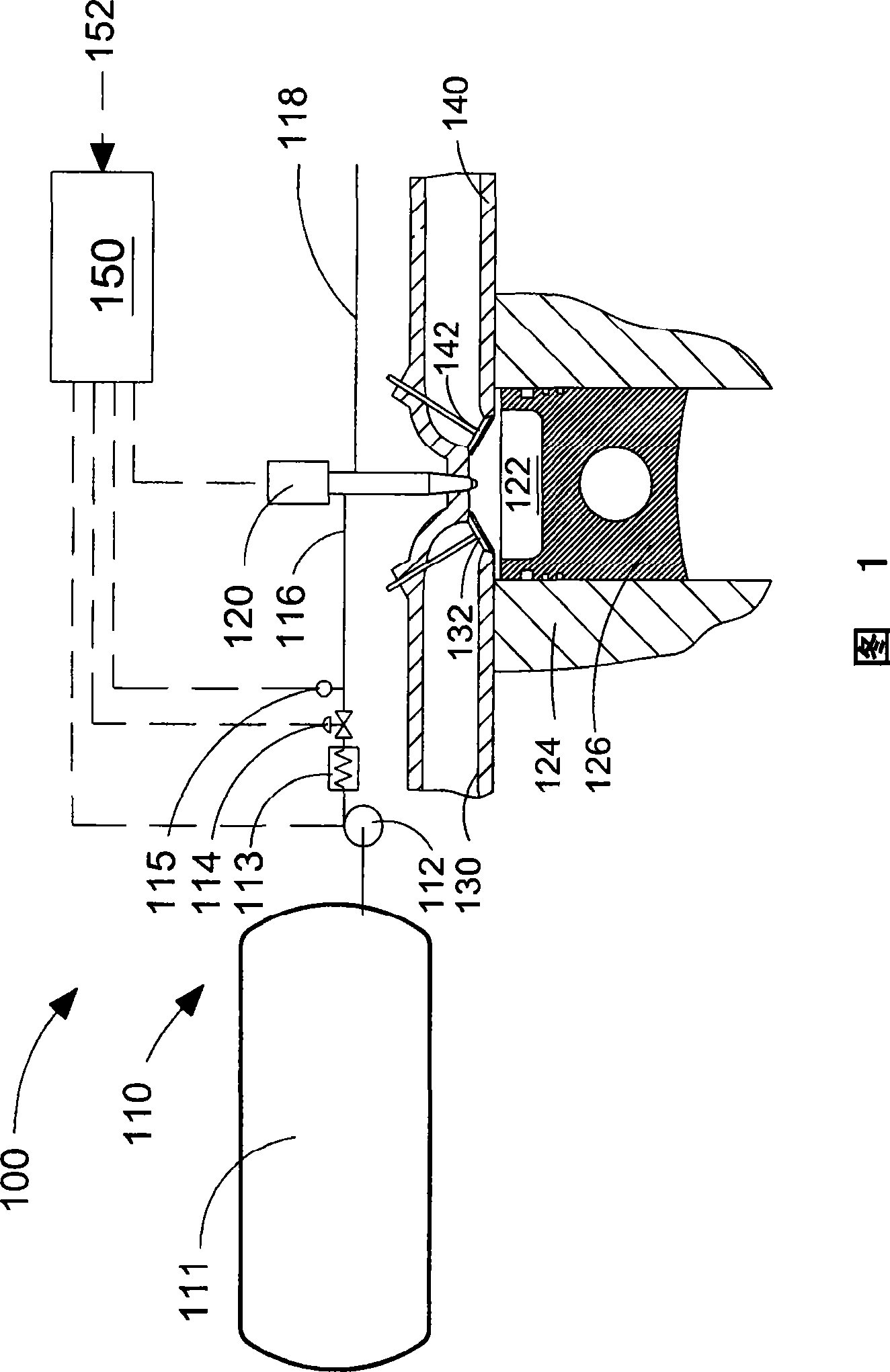
InactiveUS6918367B2Reliable judgmentElectrical controlCombustion enginesInjection pressureRail pressure
During a start, particularly during a cold start, of an internal combustion engine without additional auxiliary drive, a precisely metered fuel mass is introduced into a combustion chamber. In the case of an internal combustion engine having direct fuel injection, a rail pressure prevailing in a high-pressure accumulator is frequently only insufficiently built up during a start, which has an unfavorable effect on the mixture formation. To improve the start performance of the internal combustion engine, the injection pressure available in the high-pressure accumulator is monitored during the start, and fuel from the high-pressure accumulator is first injected into the at least one combustion chamber when the injection pressure has reached or exceeded a specifiable threshold value. This ensures that the rail pressure is high enough, in order to inject a sufficient quantity of fuel into the combustion chamber so that an ignitable air / fuel mixture is formed.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com