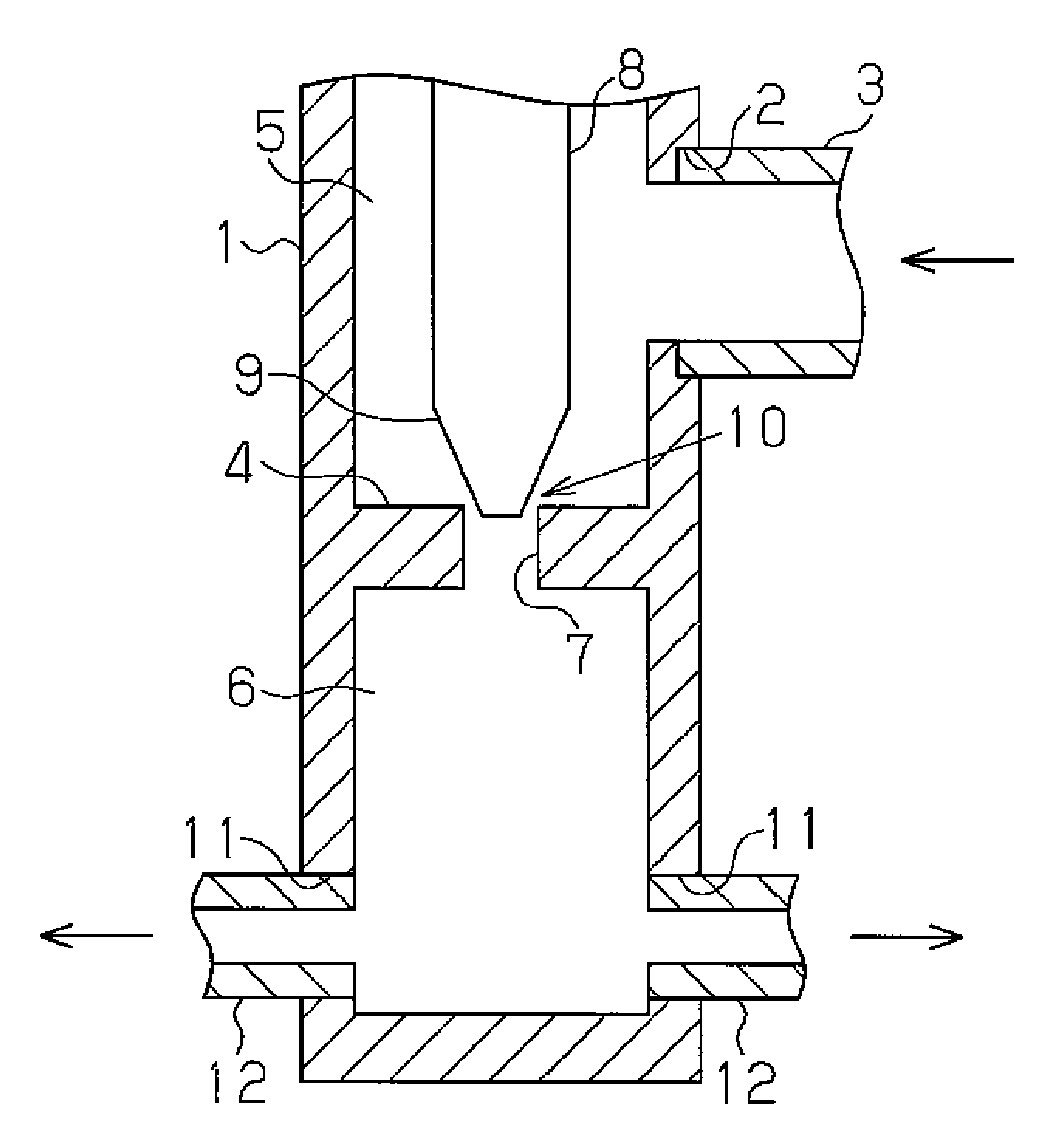
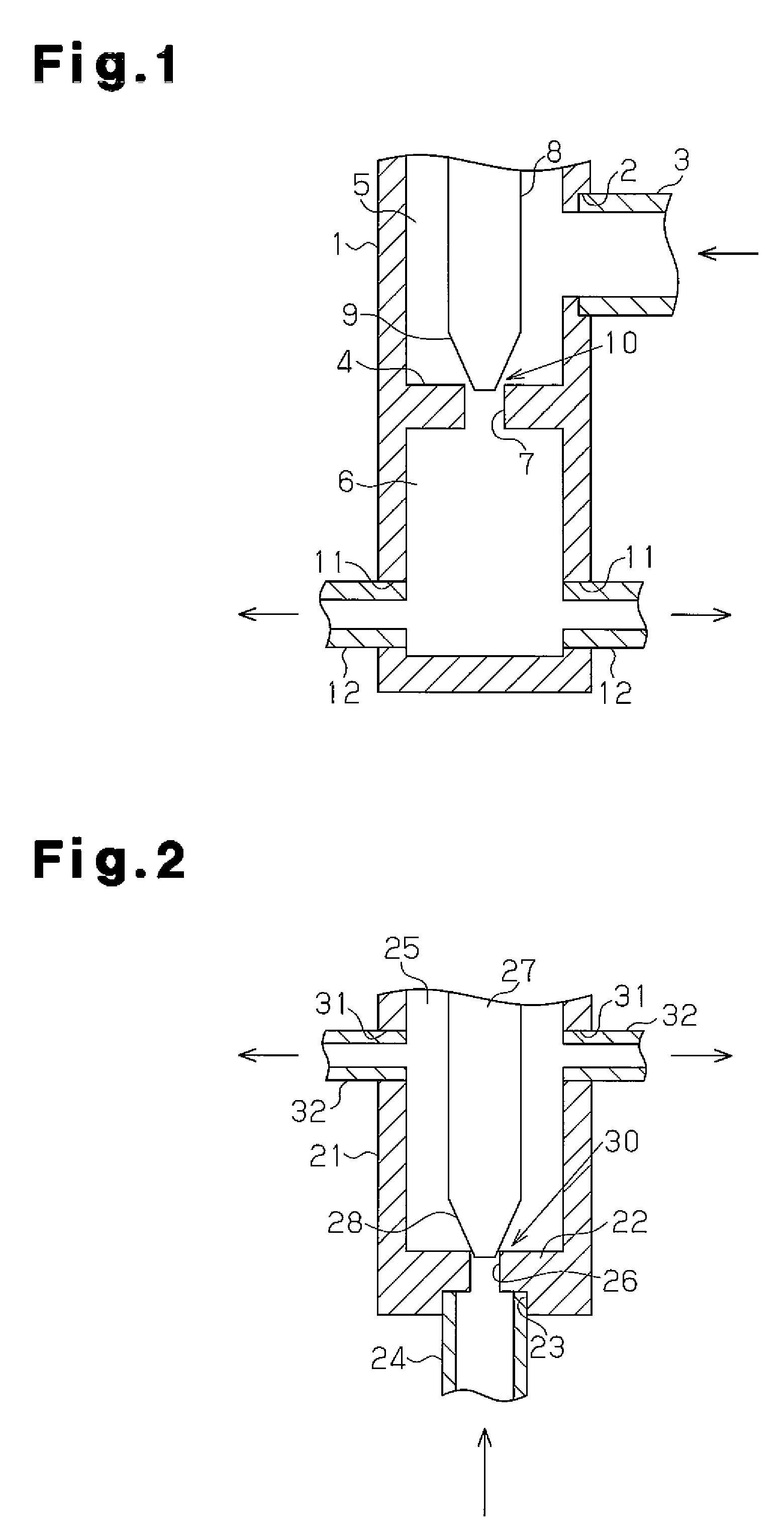
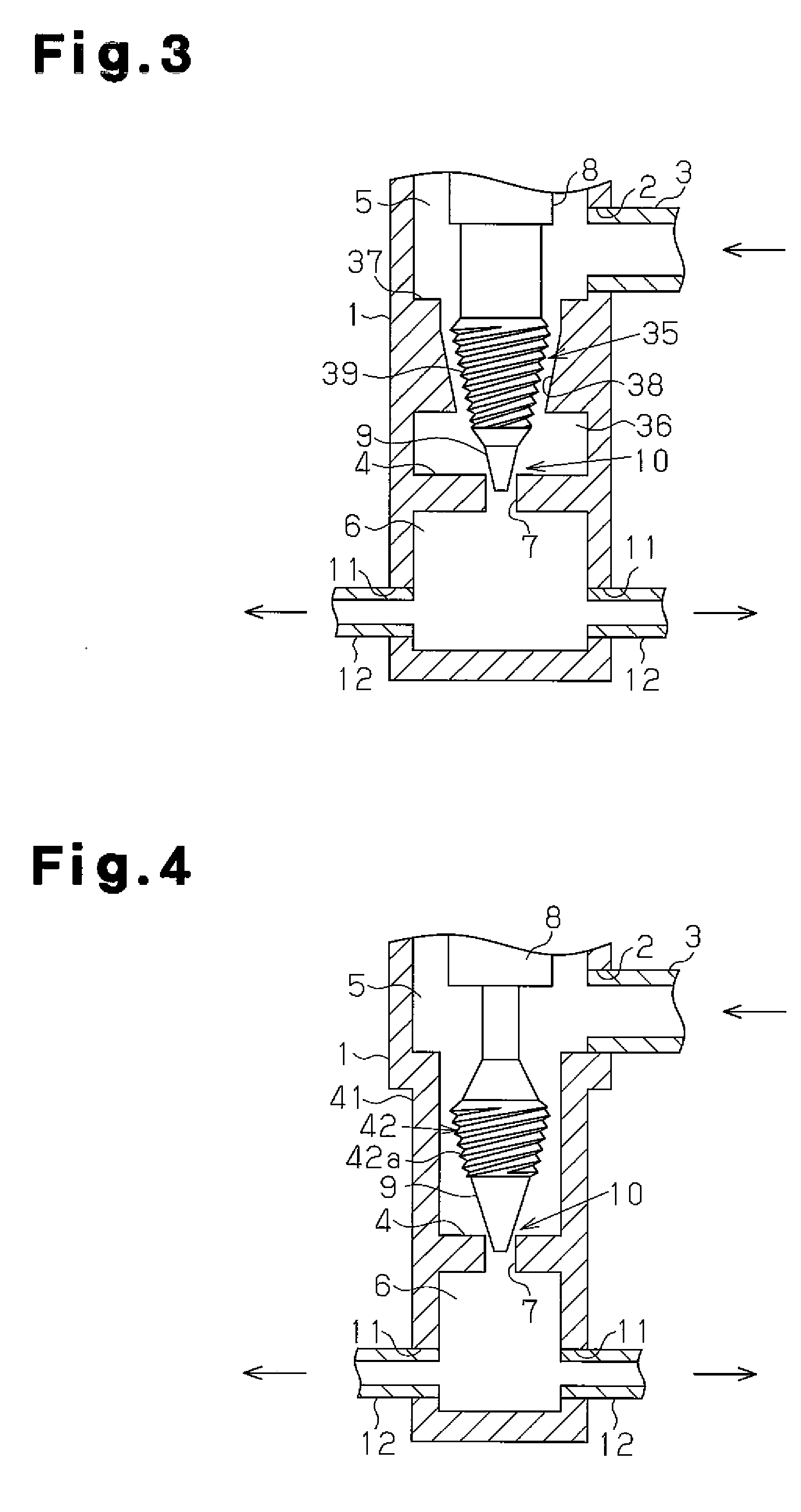
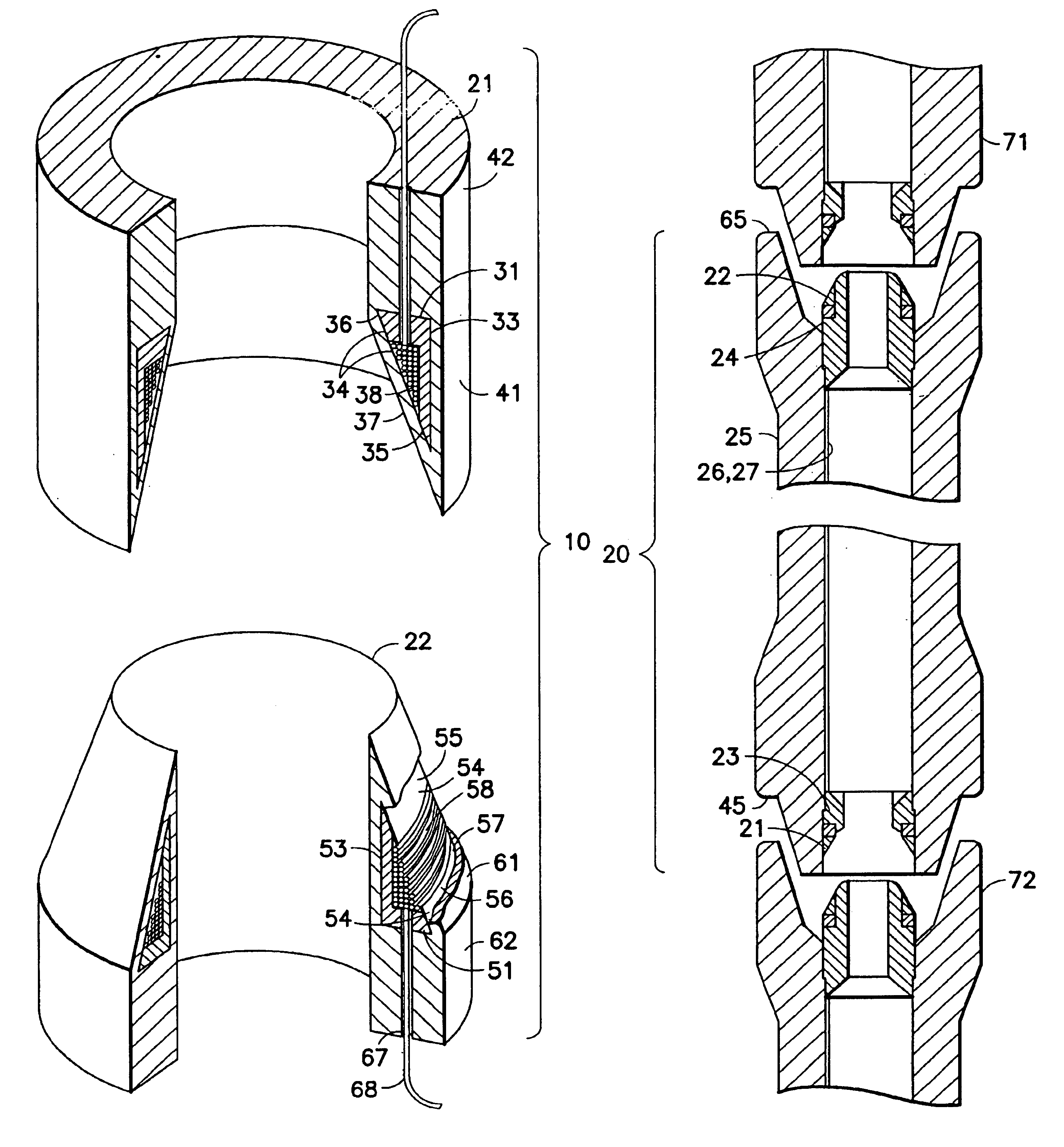
Patents
Literature
19202results about "Pipe elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
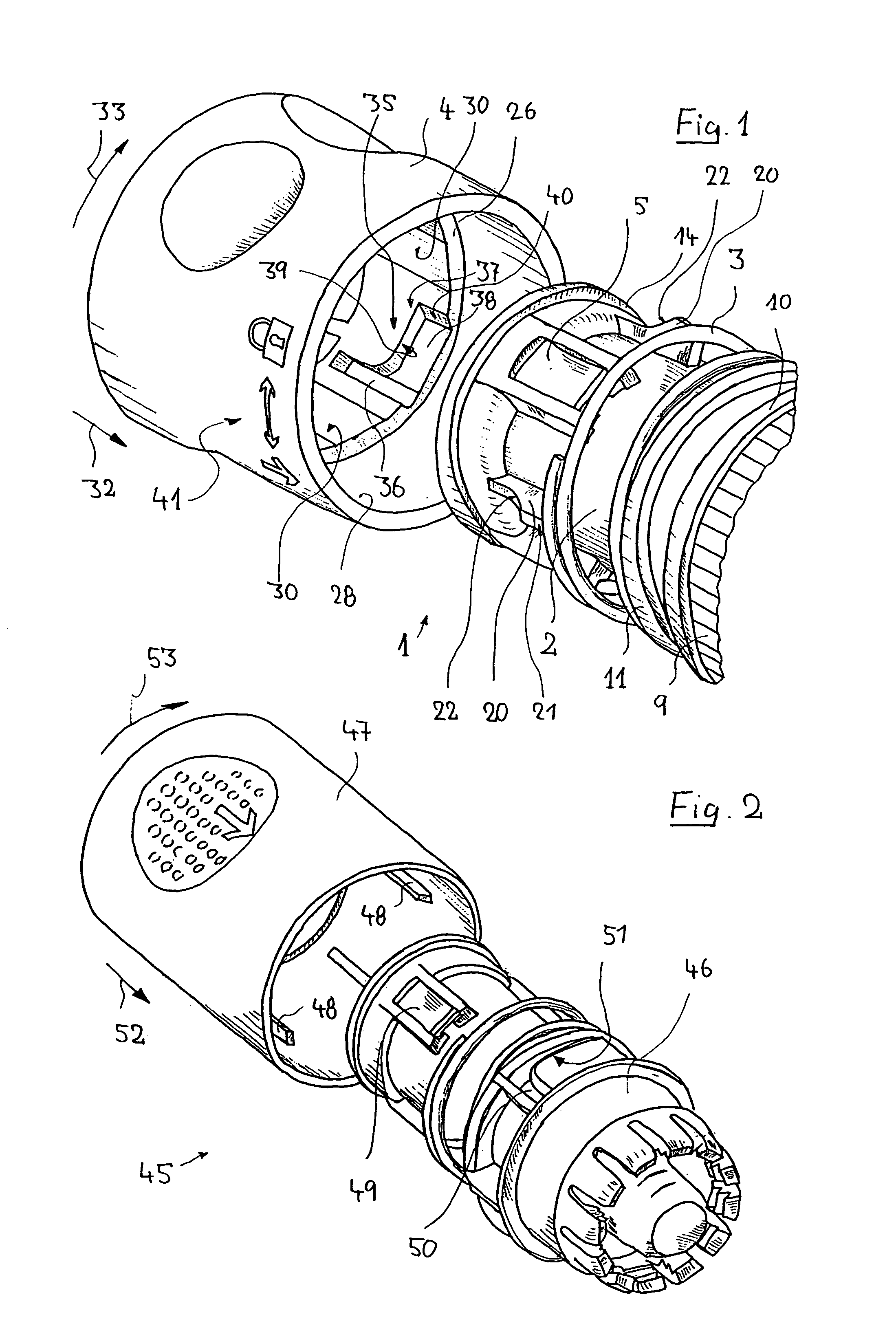
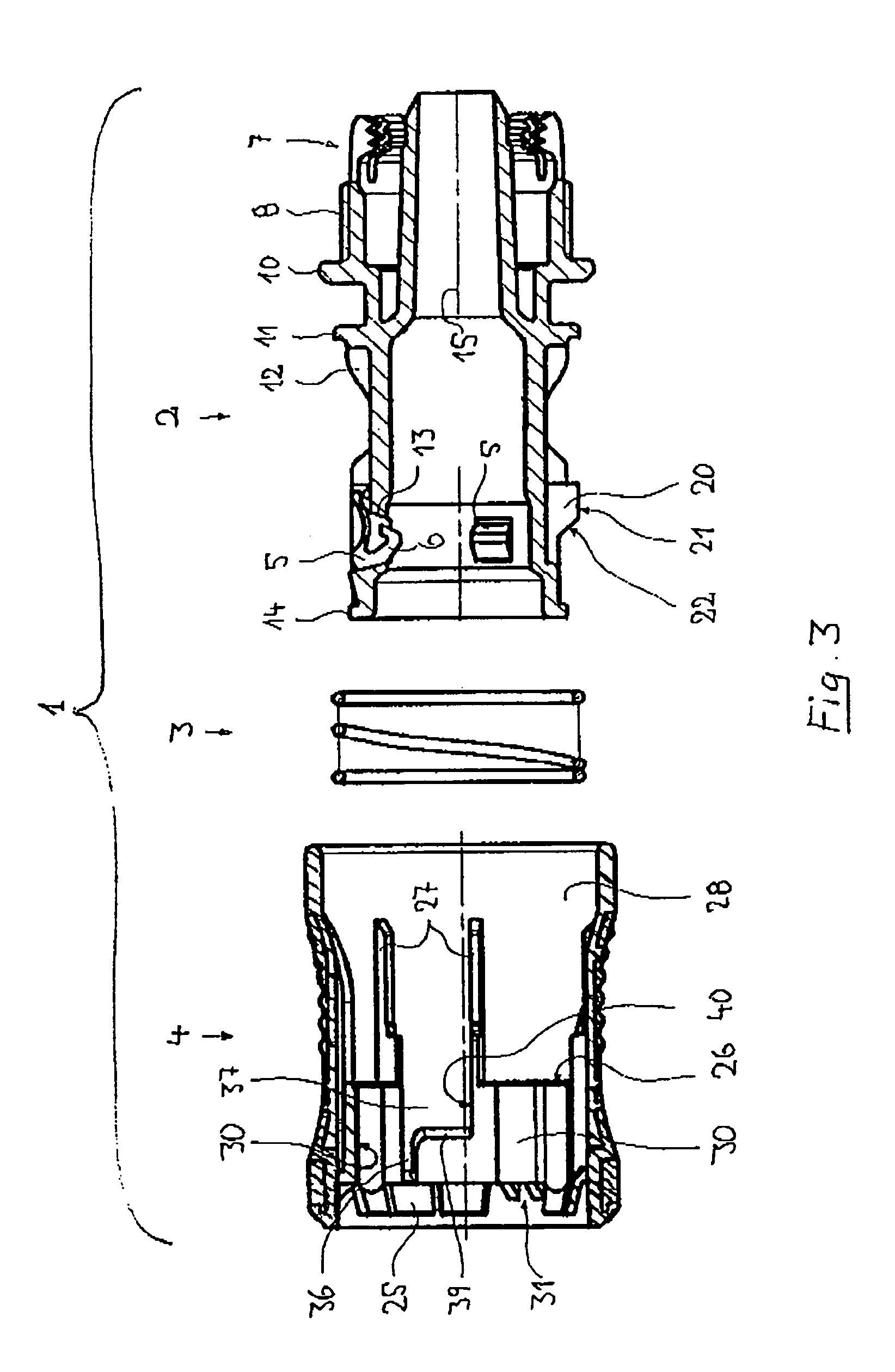
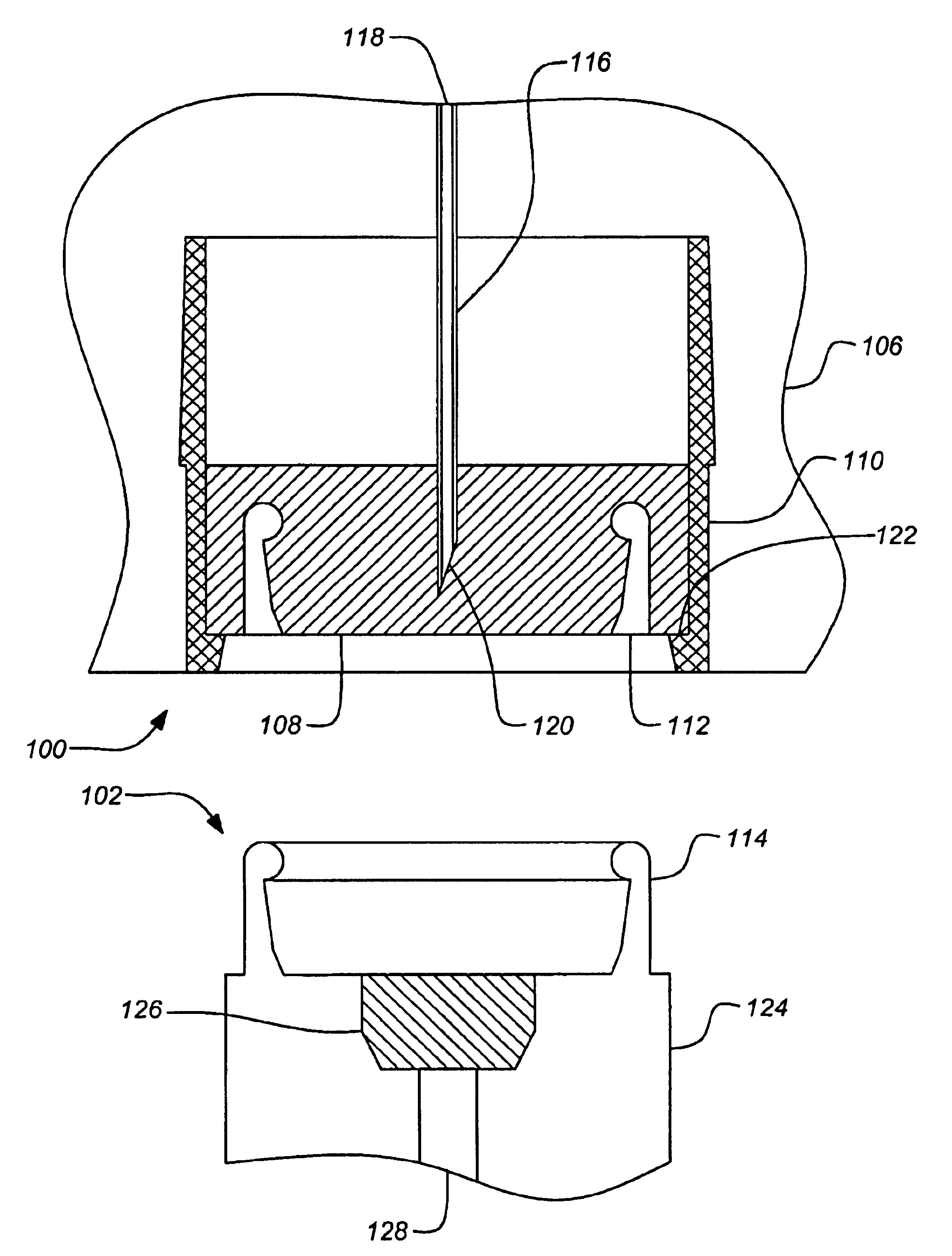
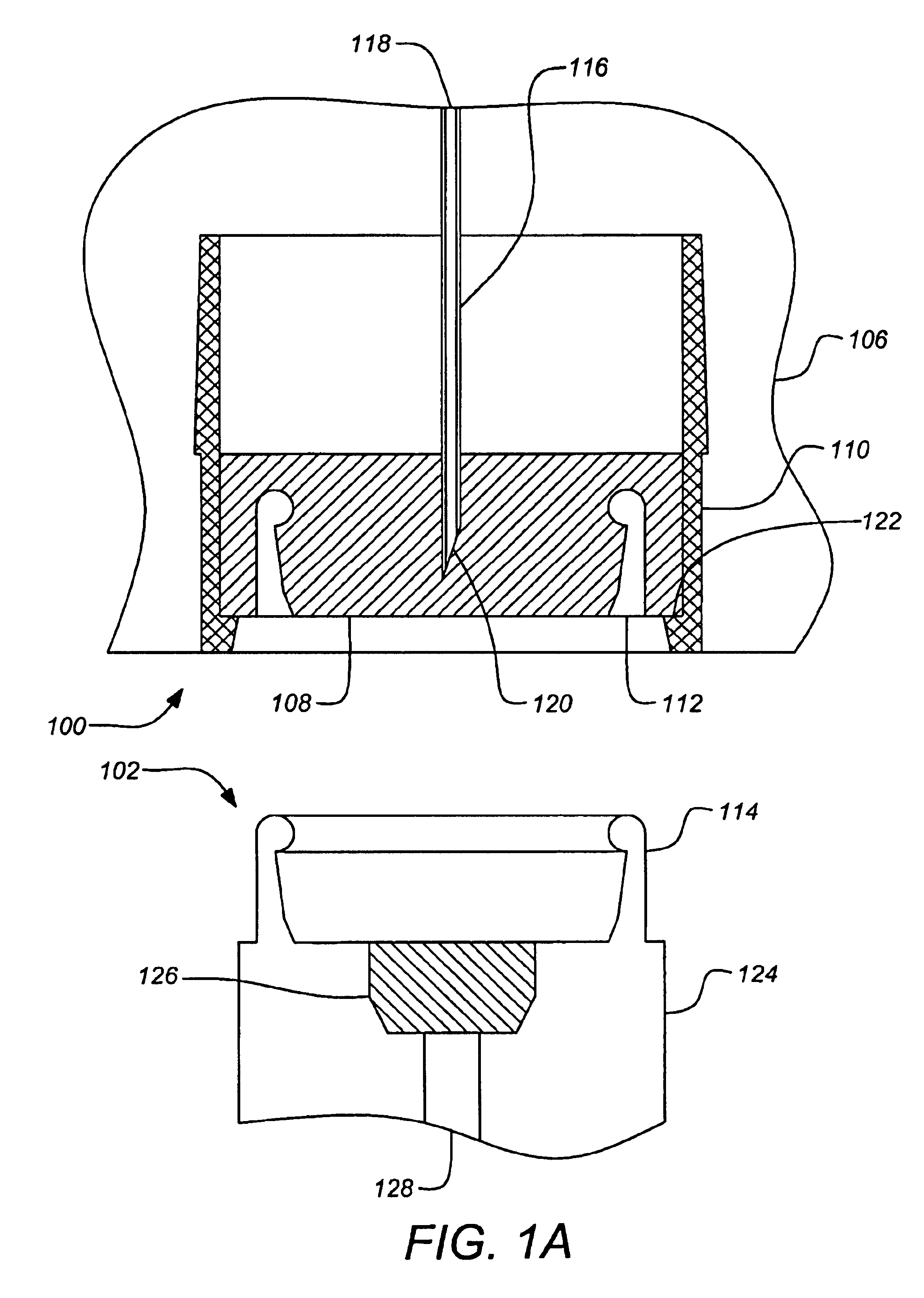
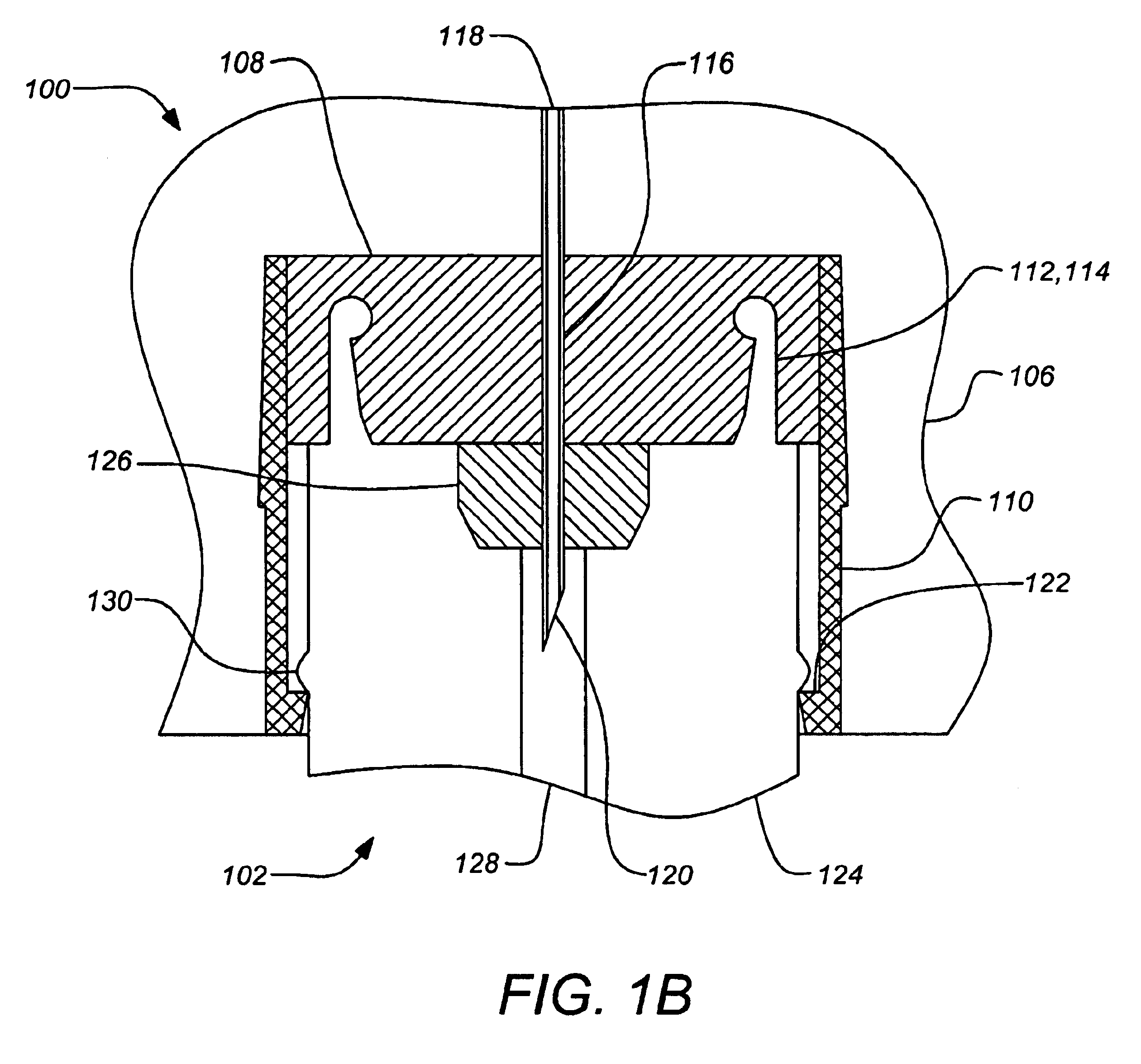
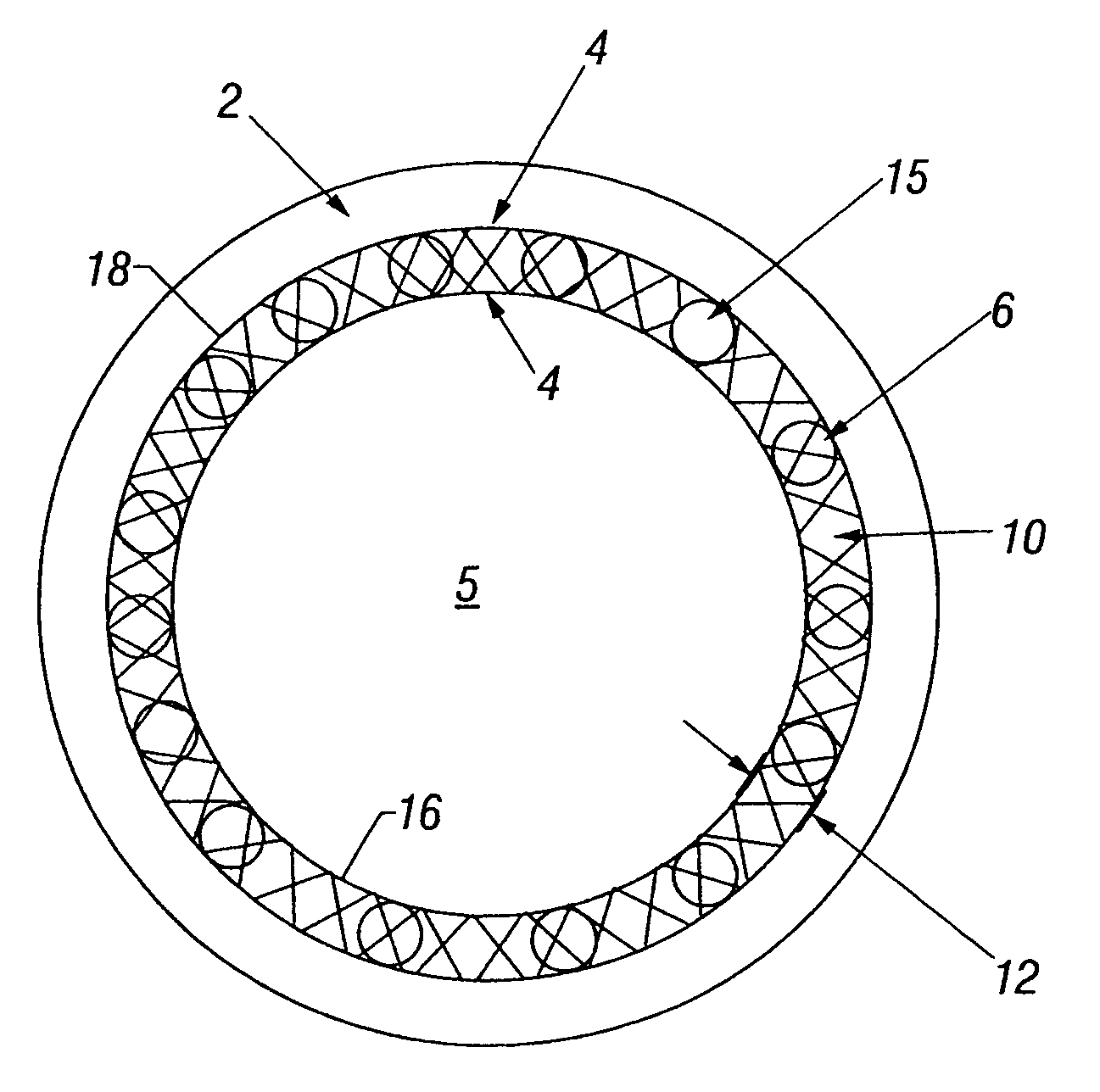
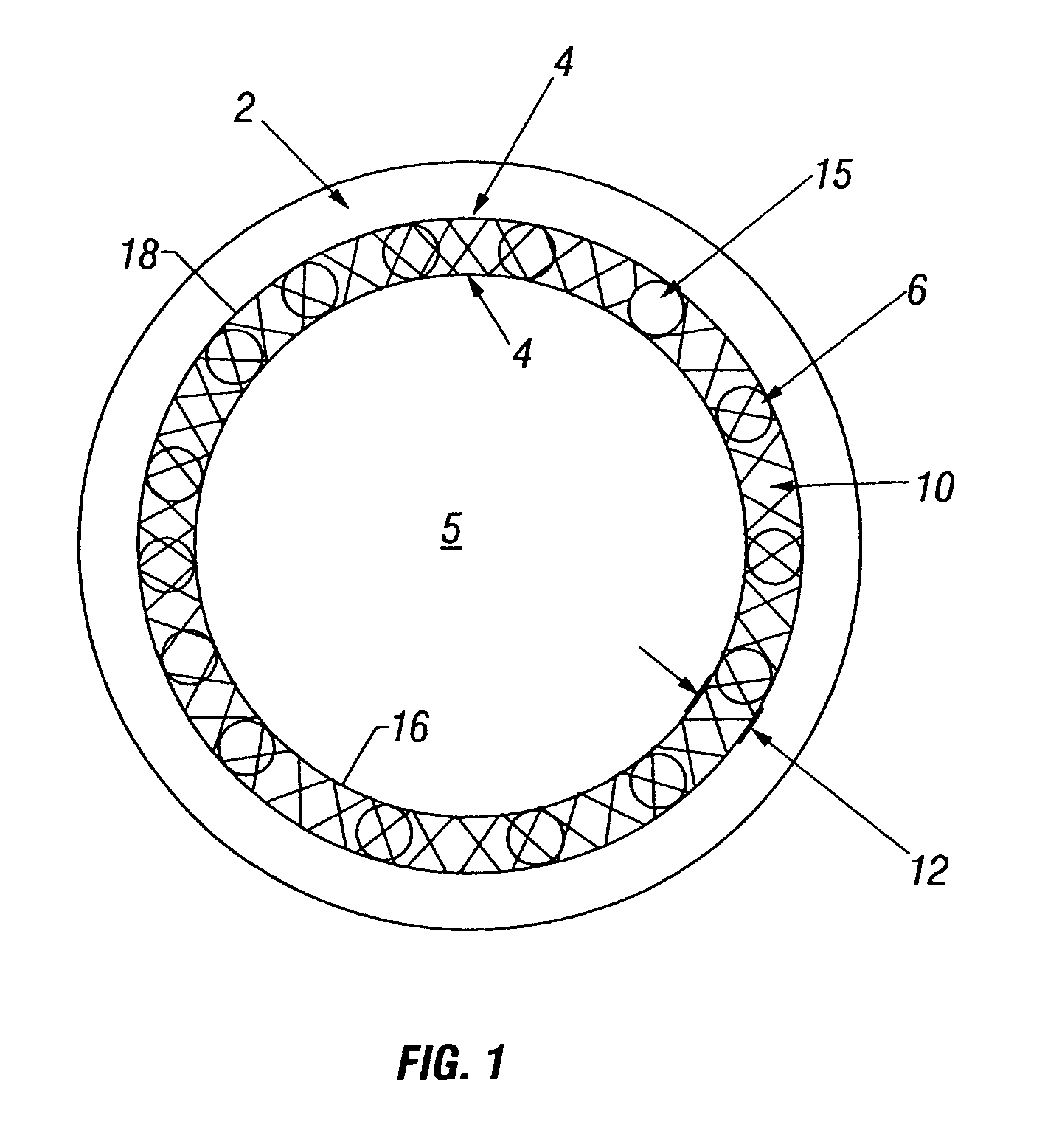
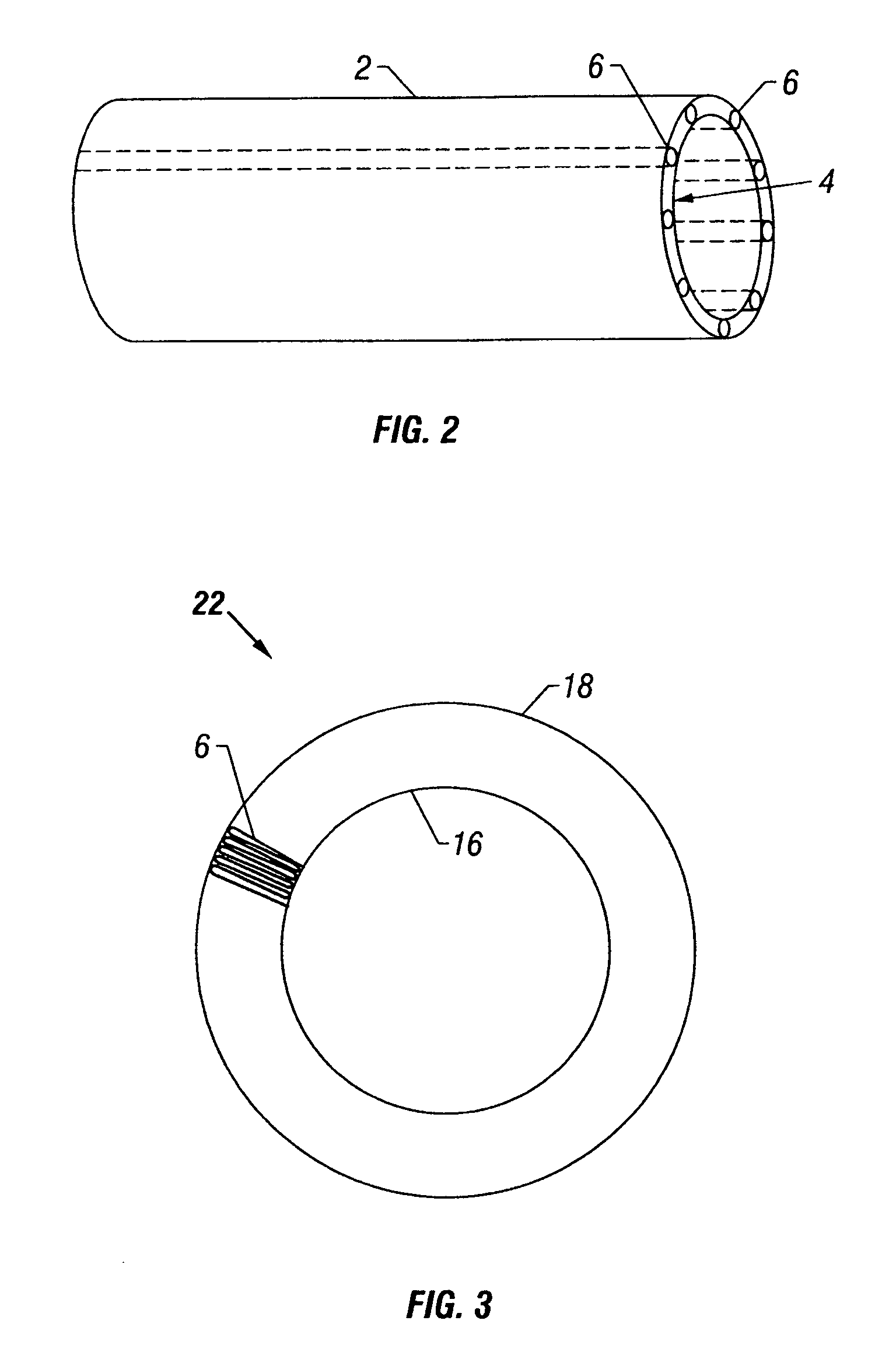
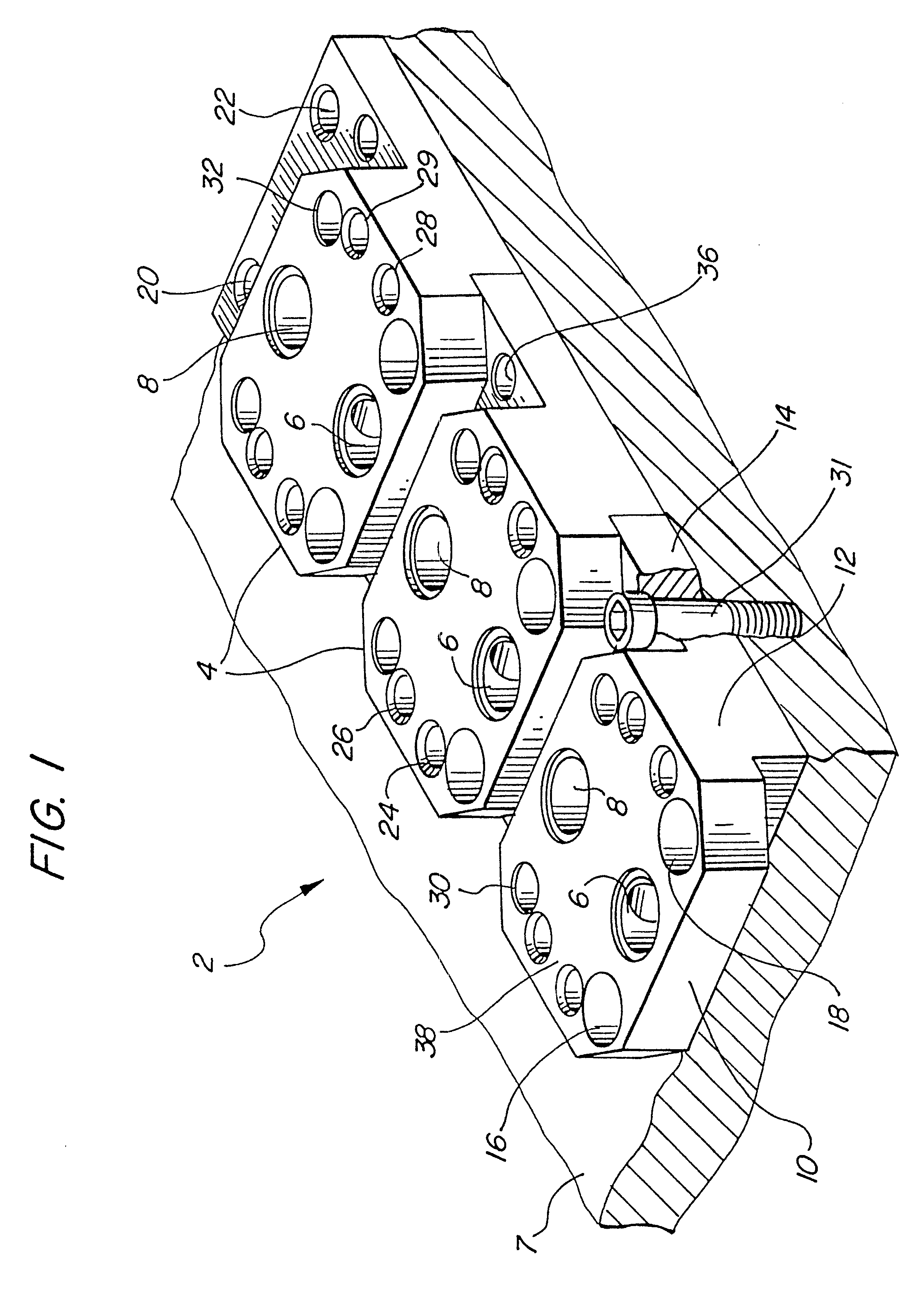
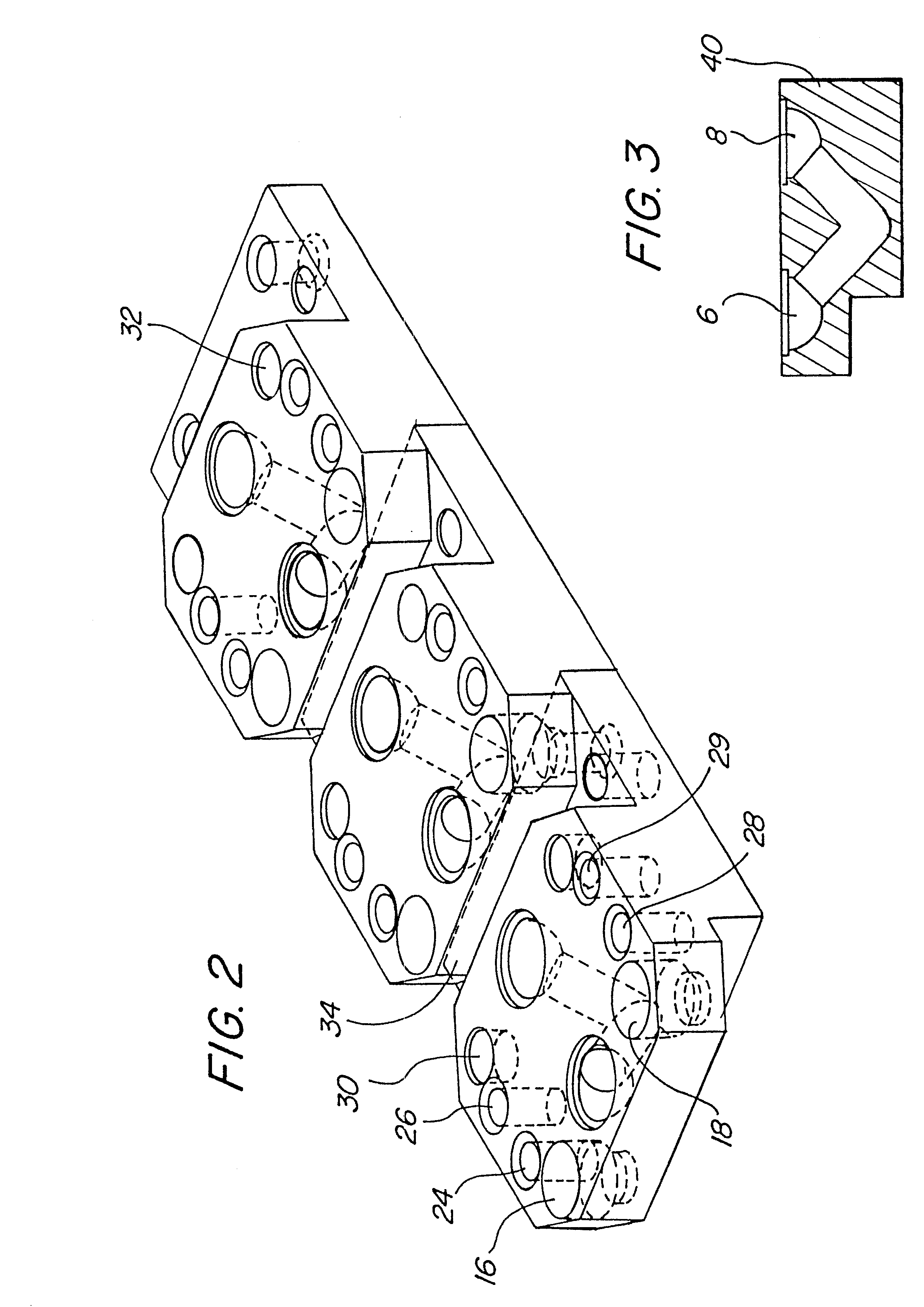
Plug-type connection arrangement for a hose and a pipe
InactiveUS7562910B2More compact constructionIncrease axial loadEngine sealsPipe elementsEngineeringFlange
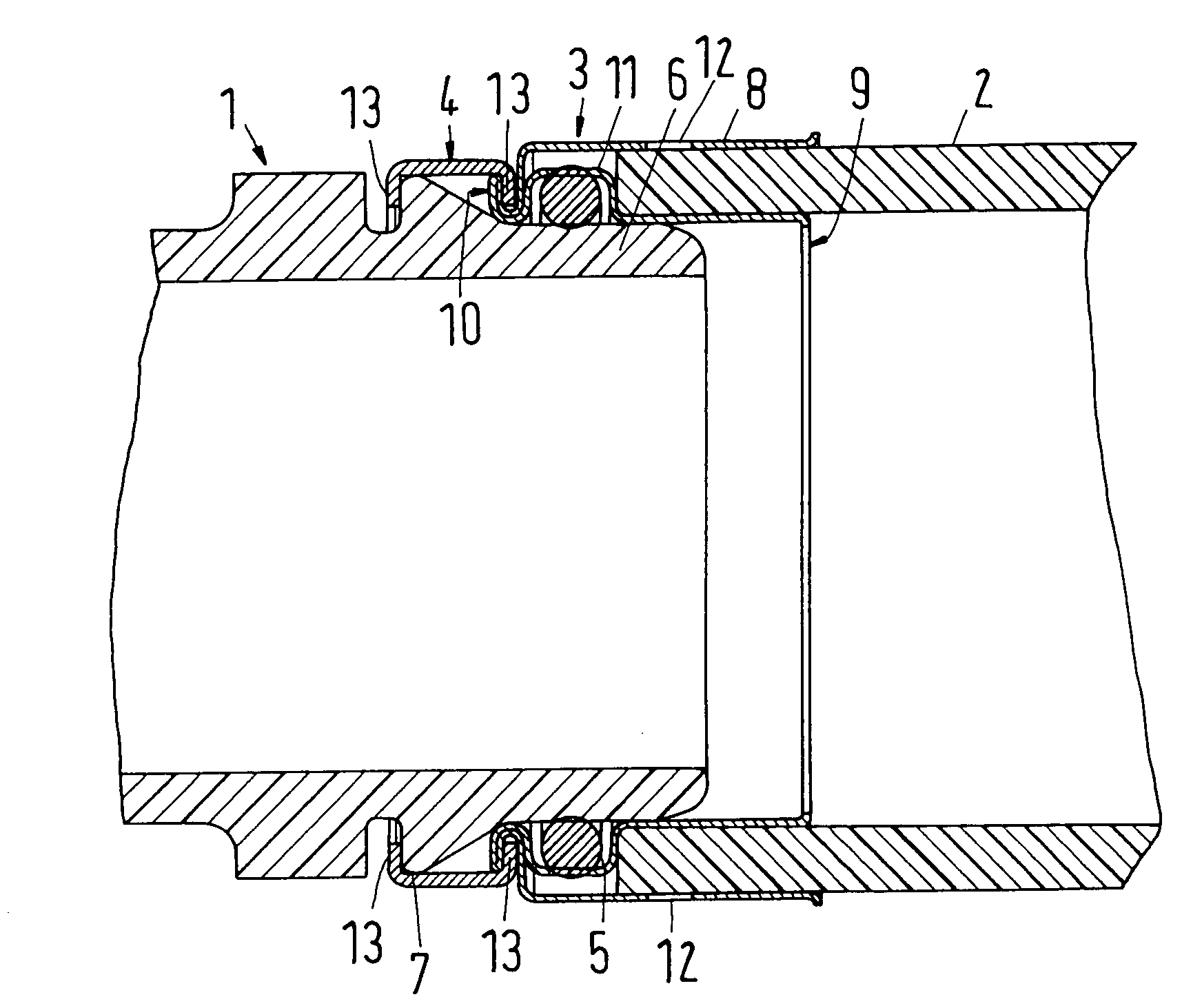
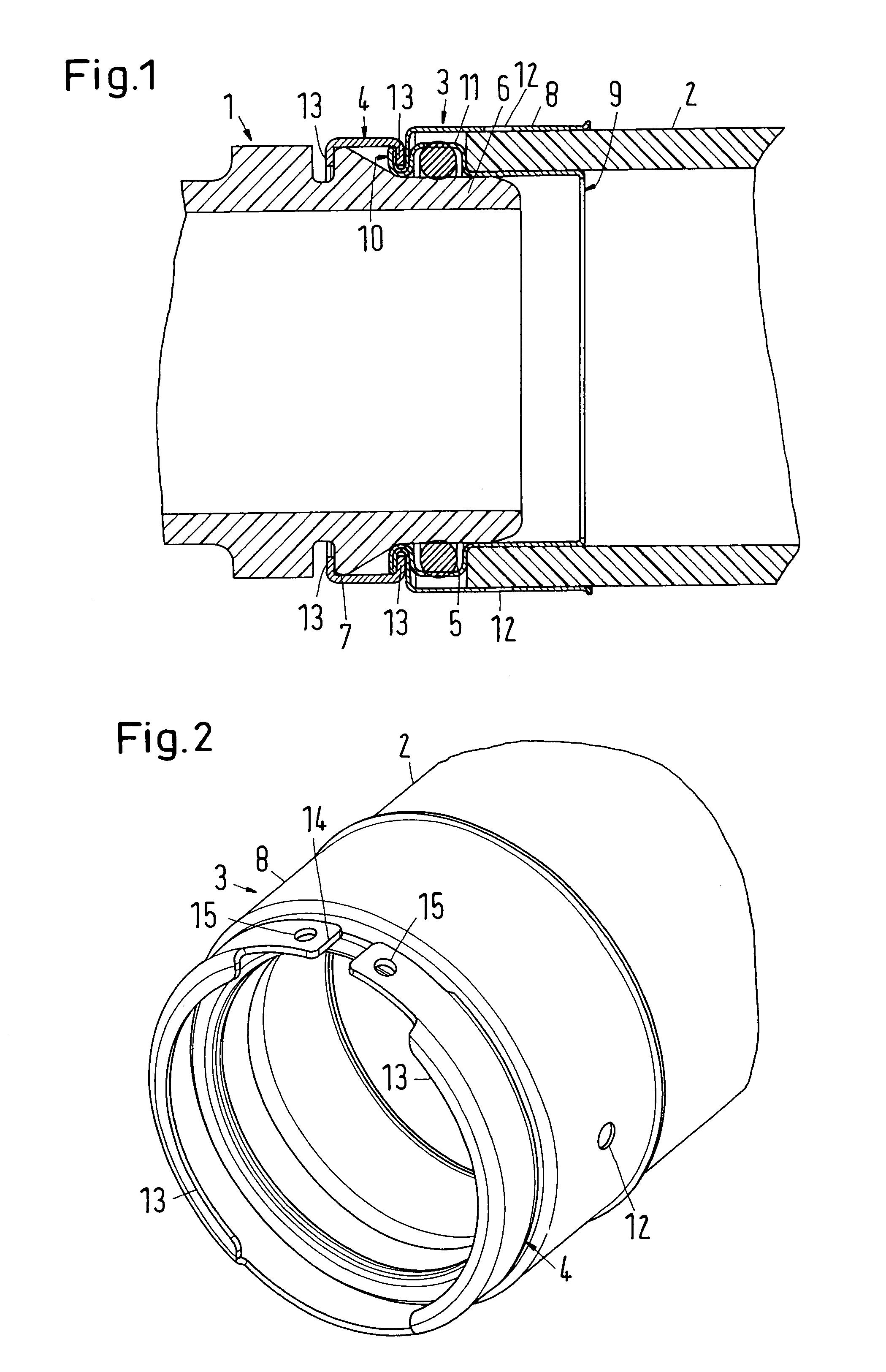
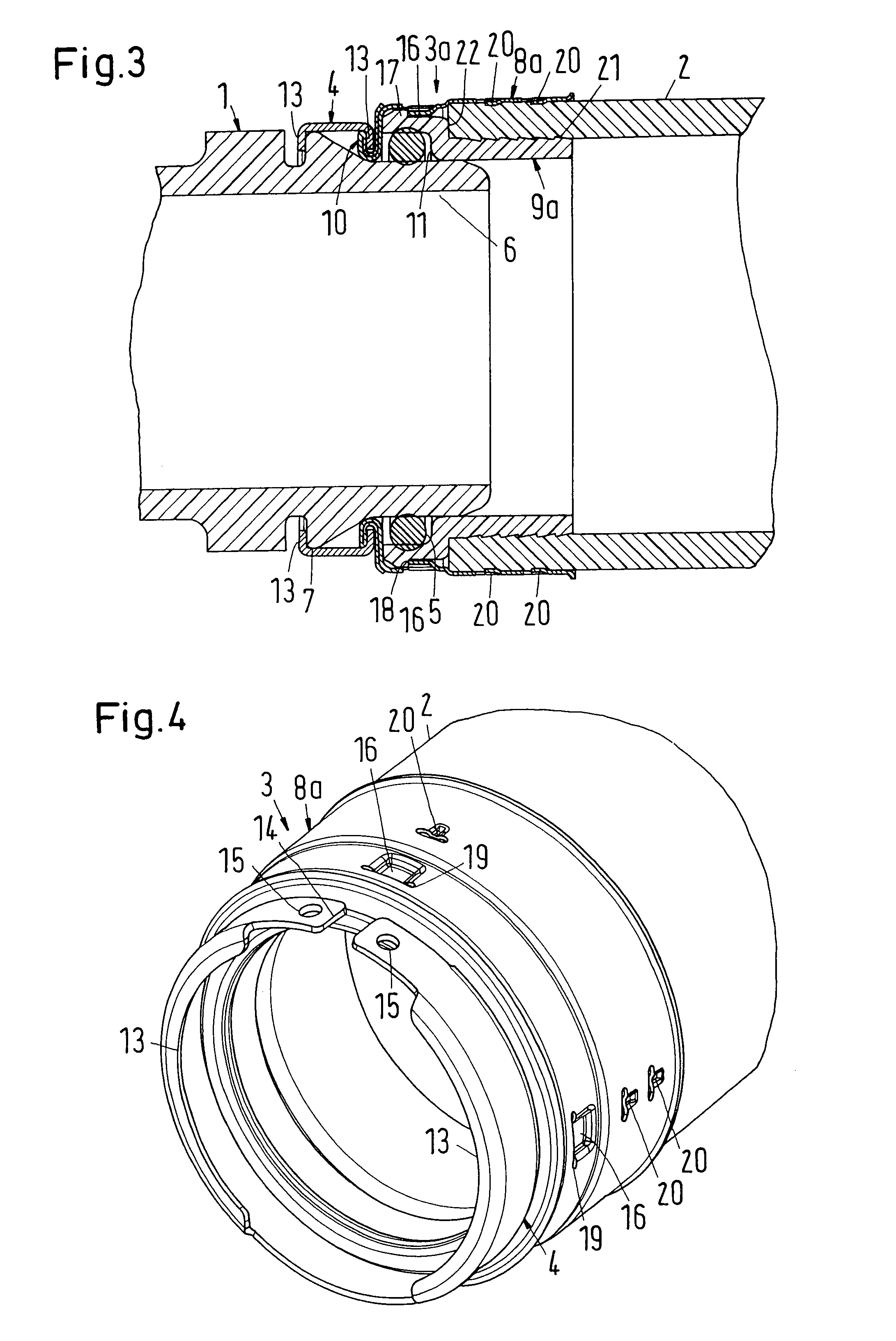
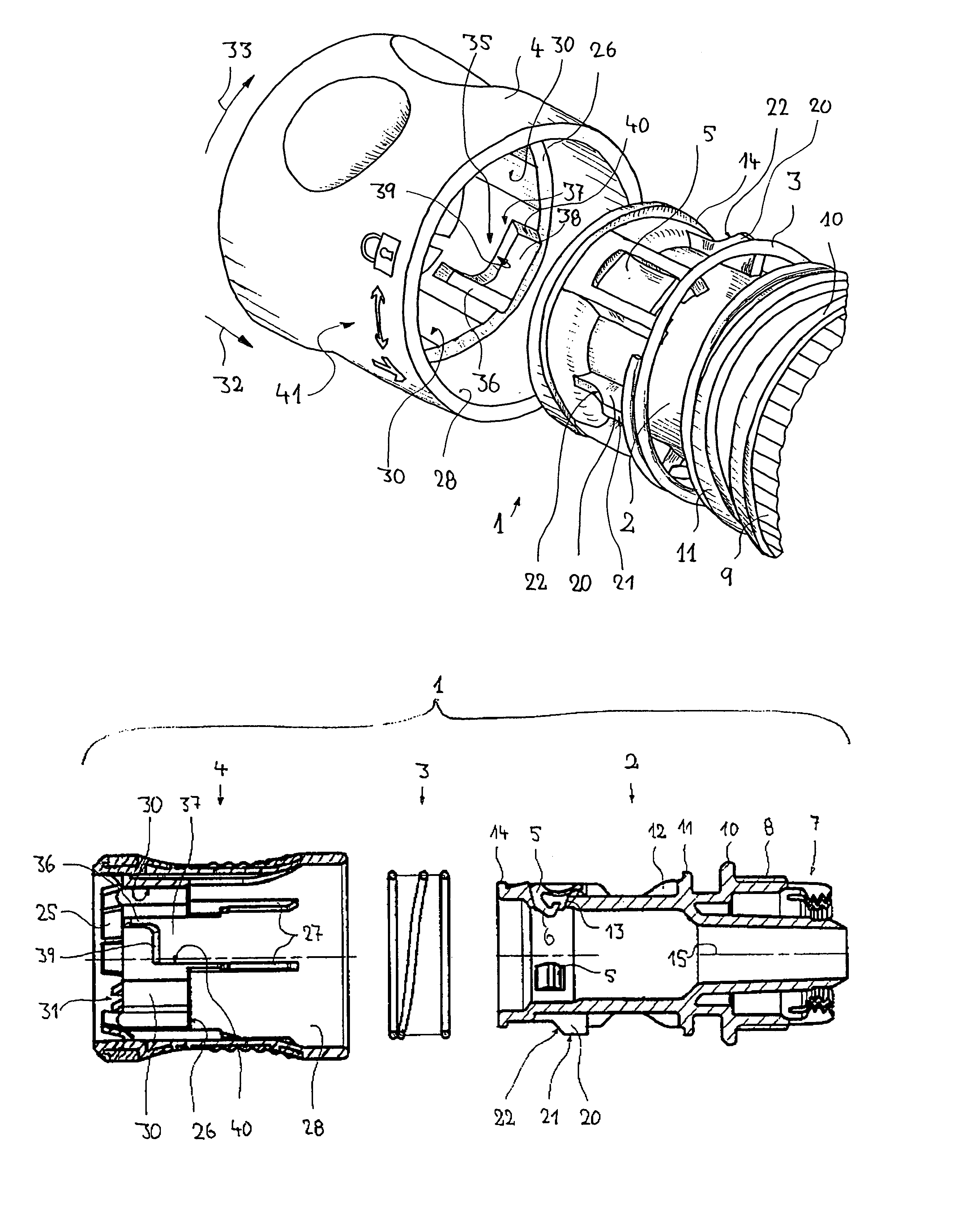
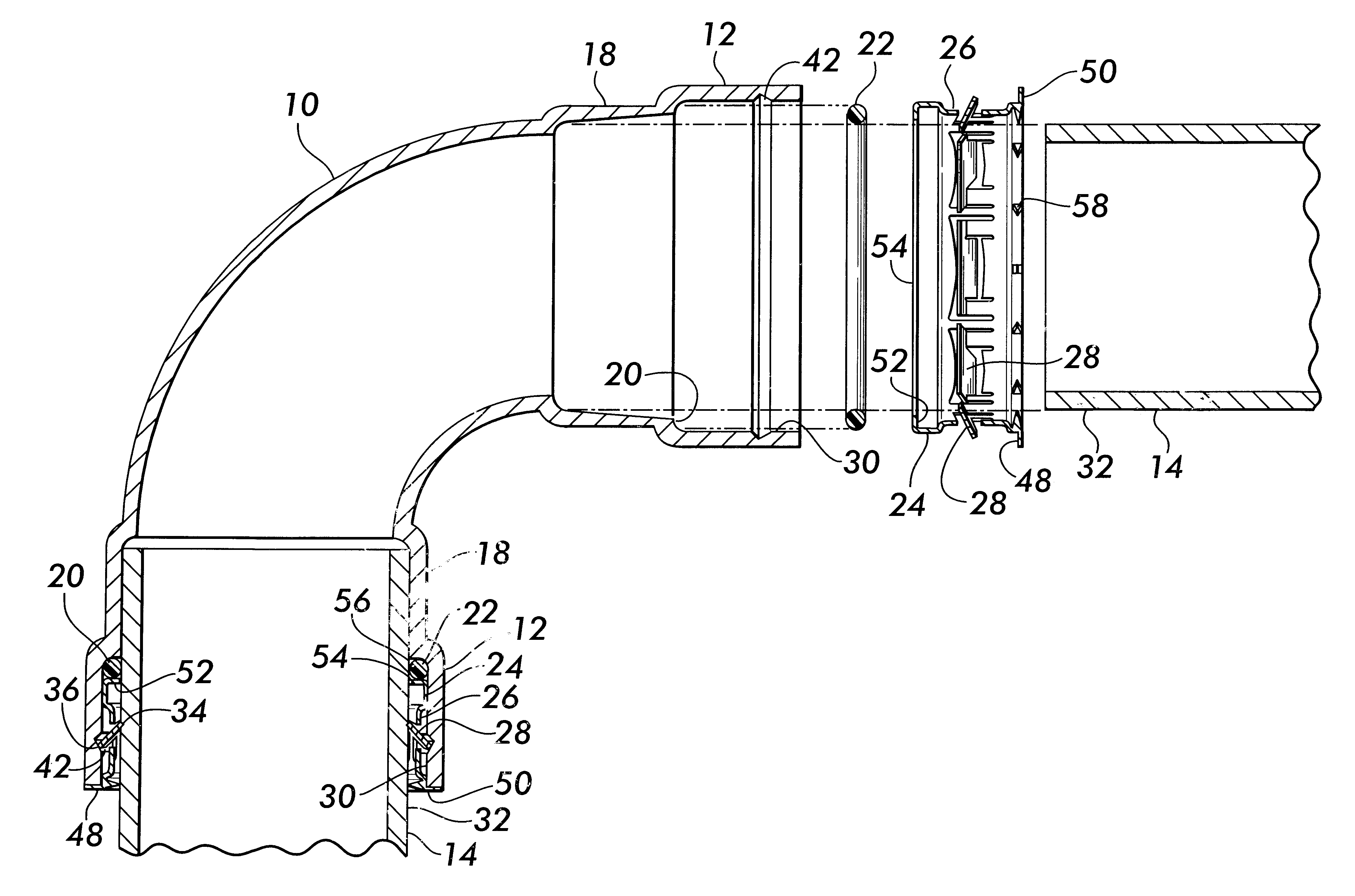
A plug-type connection arrangement for a hose and a pipe, the connection arrangement comprising a sleeve having an outer wall and an inner wall, wherein the hose is insertable from an end of the sleeve and is clampable in the sleeve, wherein the sleeve has at another end thereof a first annular groove with an open resilient connecting ring which extends over more than 180° and is lockable to the sleeve and the pipe, and a sealing ring for sealing the sleeve relative to the pipe in a connected state of the pipe and the hose, the connecting ring being comprised of a plate spring ring with inwardly directed flanges at both circumferential edges thereof, wherein the flanges of one circumferential edge are engageble in the first annular groove and the flanges of the other circumferential edge are engageable behind a holding rib on the pipe, wherein the sealing ring is mounted in a second annular groove formed by the inner wall of the sleeve and the axially inner wall of the first annular groove, and wherein an end portion of the pipe is insertable into the sleeve.
Owner:NORMA GERMANY GMBH
Coupling part for a fluid coupling device
InactiveUS7021669B1Avoid disconnectionGuaranteed uptimeSleeve/socket jointsEngine sealsFluid couplingEngineering
A coupling part for a fluid coupling device, especially a hose coupling, which has a looking device switchable between two positions. The locking device has locking elements mounted on a base body, and a socket-shaped actuating element that interacts with the locking elements. The coupling part is switchable between a retaining and releasing positions by an axial releasing movement of the actuating element. In the retaining position, the locking elements hold the counterpart of the coupling, e.g. a hose stem, to prevents it from being pulled out and, in the releasing position, the locking elements release the same in order to disengage the coupling. The actuating element can be moved from the retaining position into a locking position, prohibiting a releasing movement, by rotating the actuating element in a limited manner around the longitudinal axis of the coupling. As a result, the coupling is prevented from being unintentionally disengaged.
Owner:GARDENA KRESS KASTNER GMBH
Exhaust apparatus, and substrate processing apparatus and thin film fabricating method using the same
ActiveUS20180057937A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Orientation independent canister for a negative pressure wound therapy device
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Downhole Coils
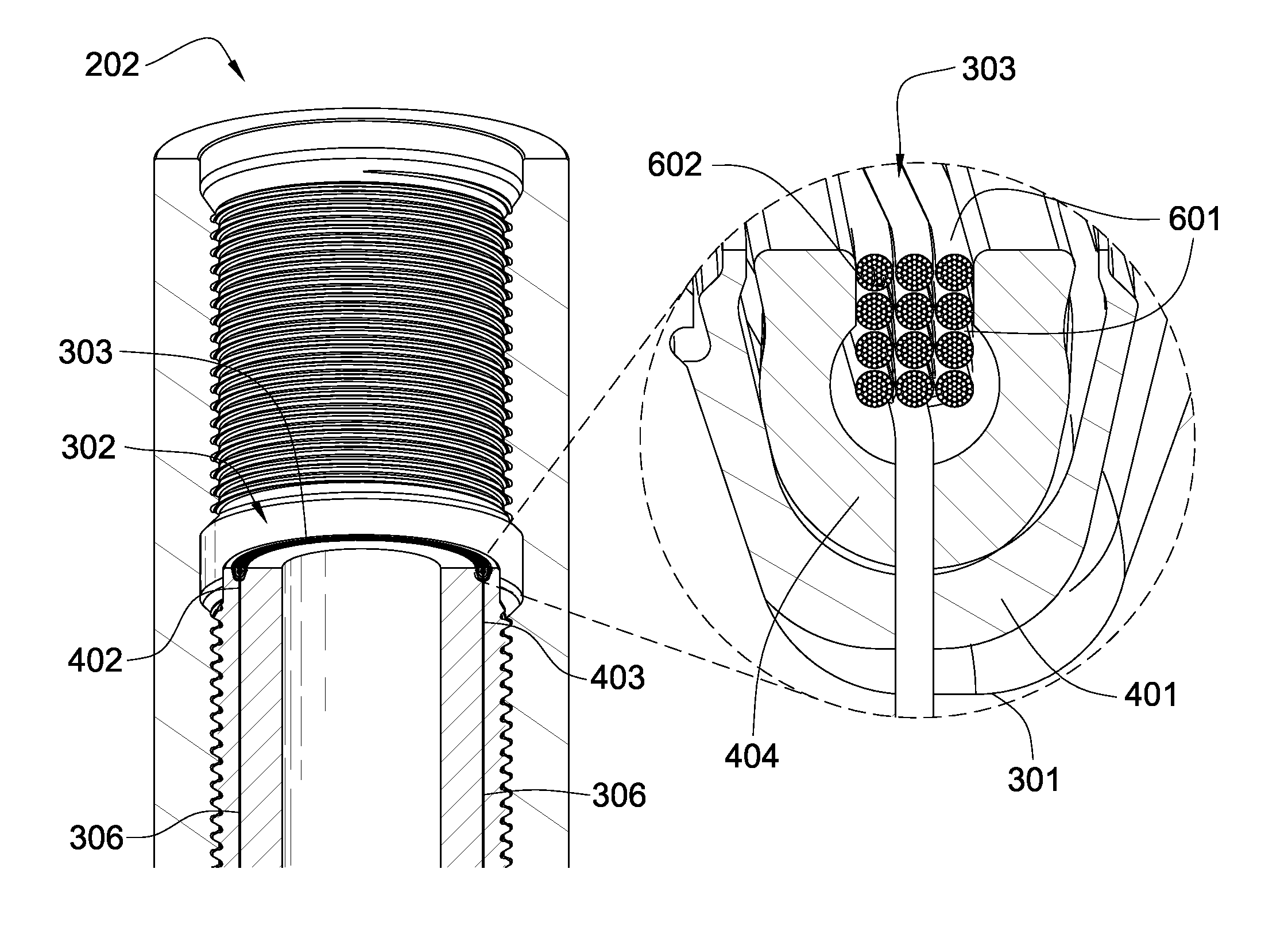
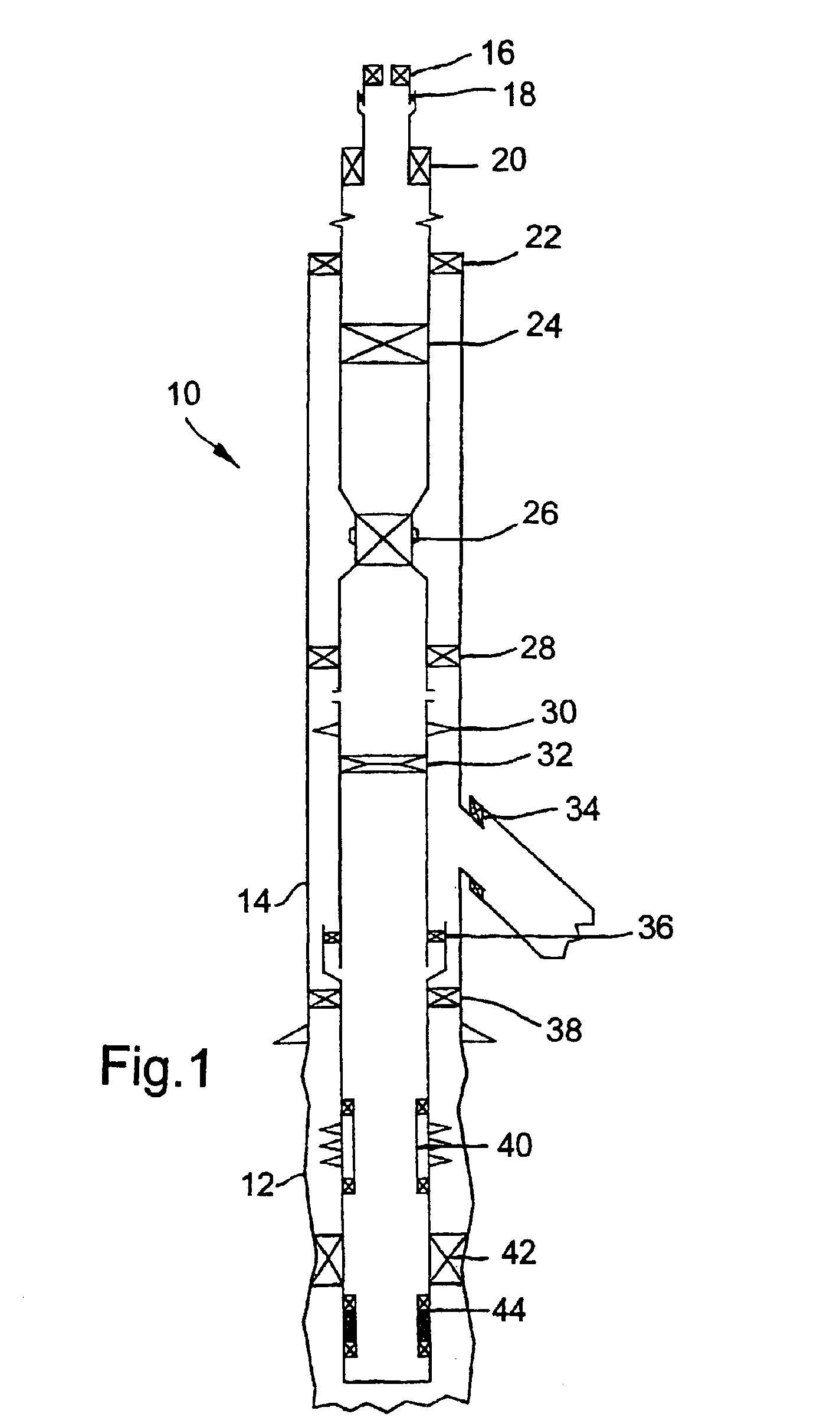
In one aspect of the invention, a downhole tool string component comprises a tubular body with at least one end adapted for threaded connection to an adjacent tool string component. The end comprises at least one shoulder adapted to abut an adjacent shoulder of an adjacent end of the adjacent tool string component. An annular magnetic coupler is disposed within an annular recess formed in the at least one shoulder, and the magnetic coupler comprises a coil in electrical communication with an electrical conductor that is in electrical communication with an electronic device secured to the tubular body. The coil comprises a plurality of windings of wire strands that are electrically isolated from one another and which are disposed in an annular trough of magnetic material secured within the annular recess.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Deformable member
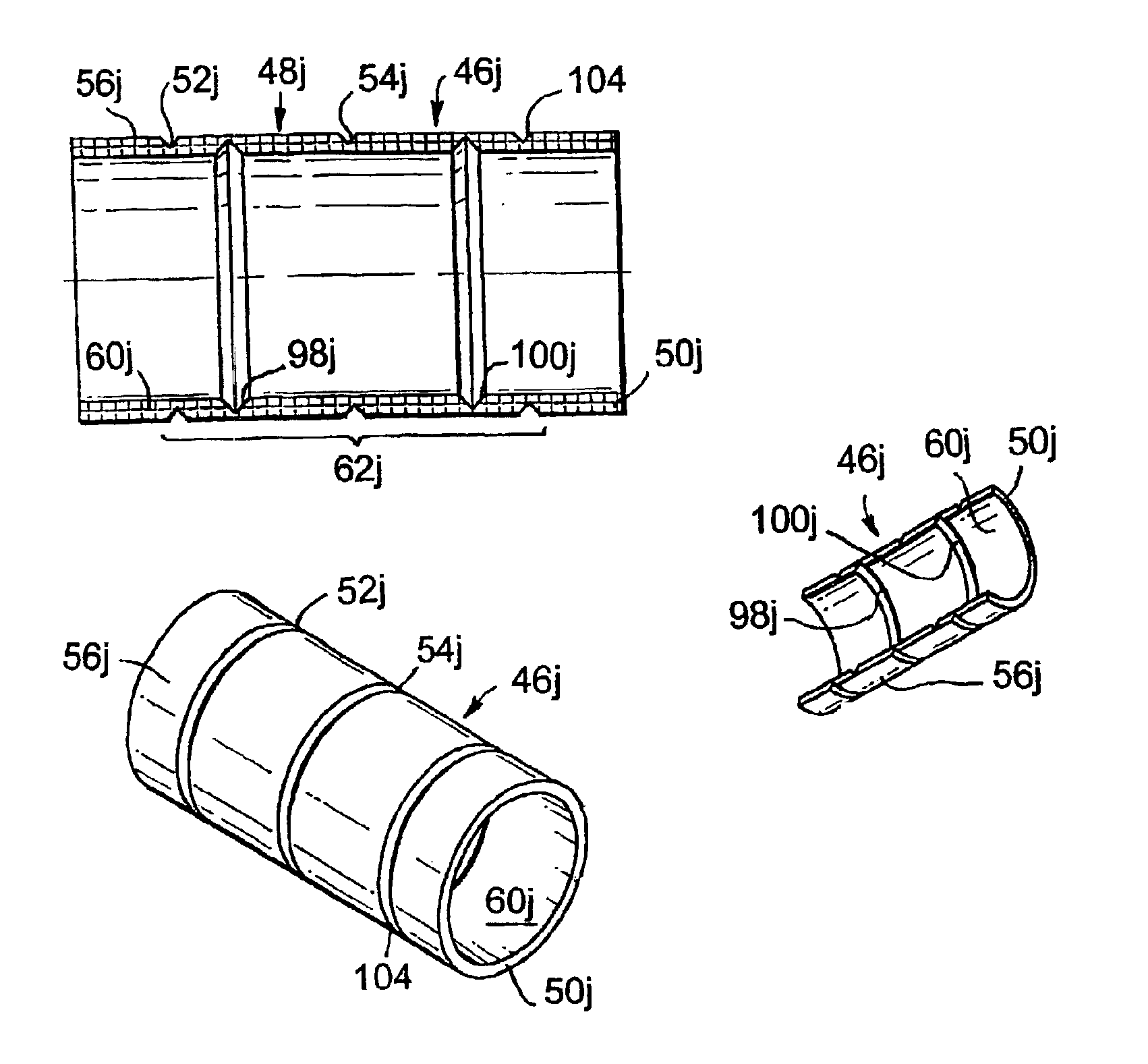
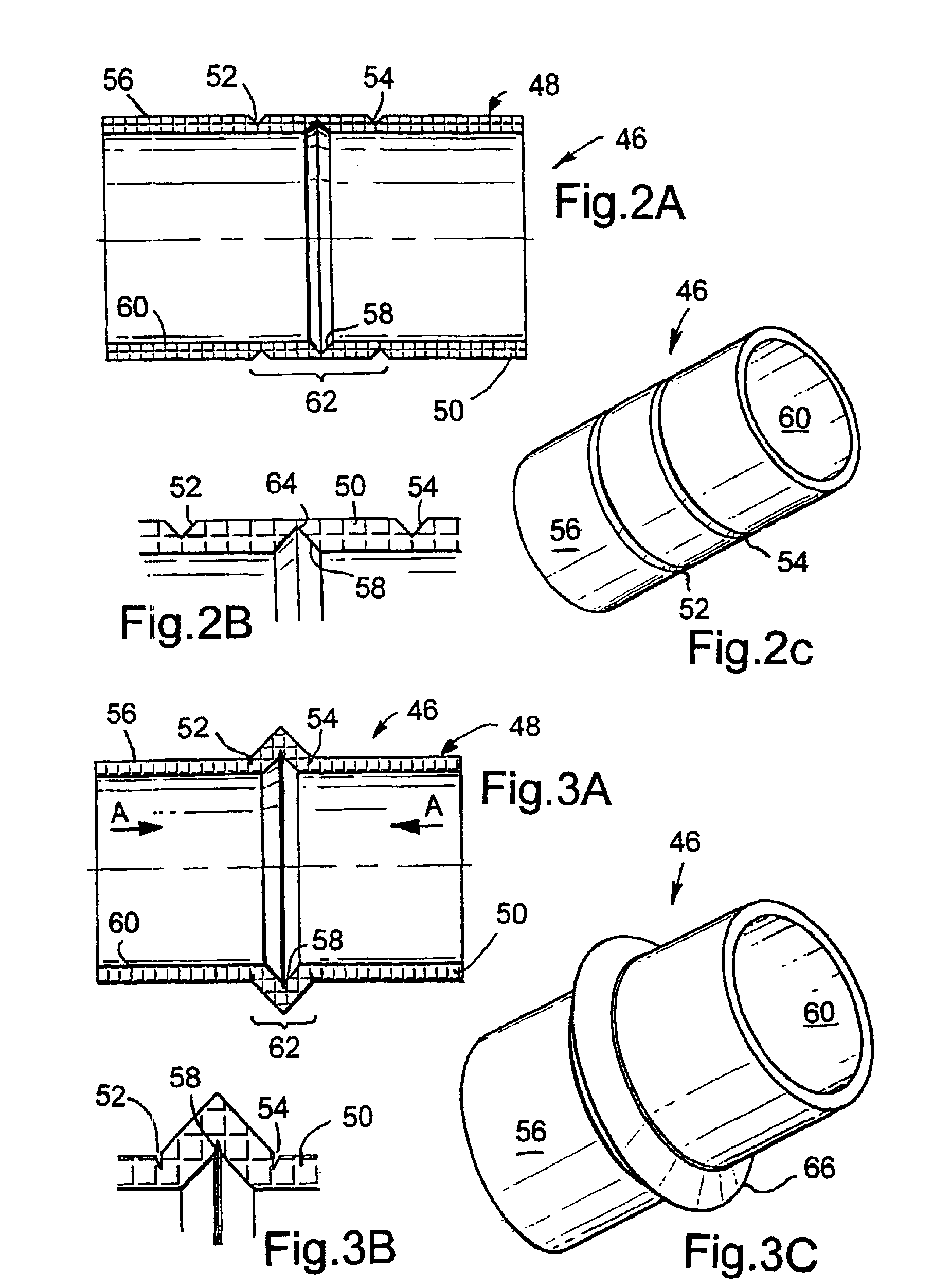
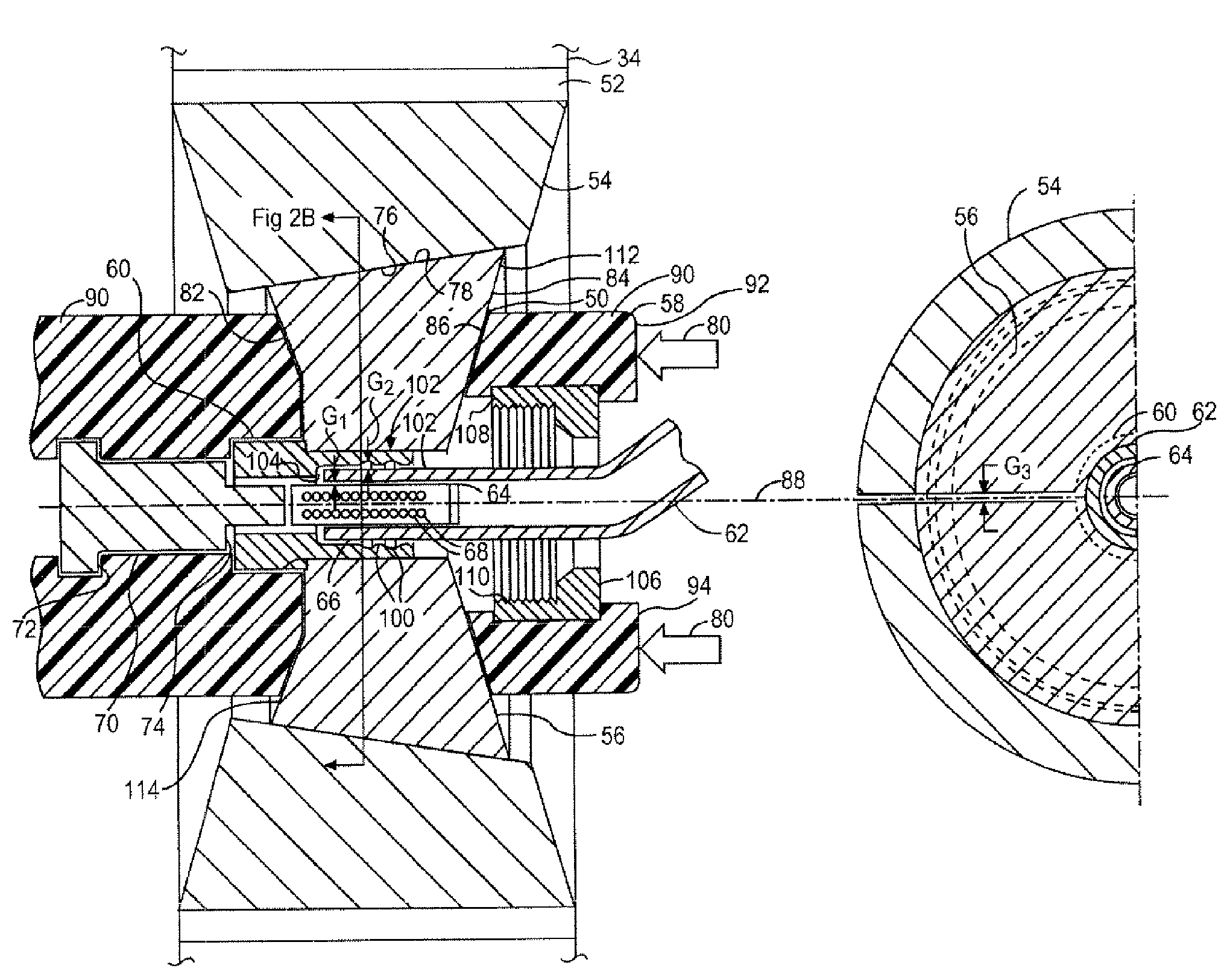
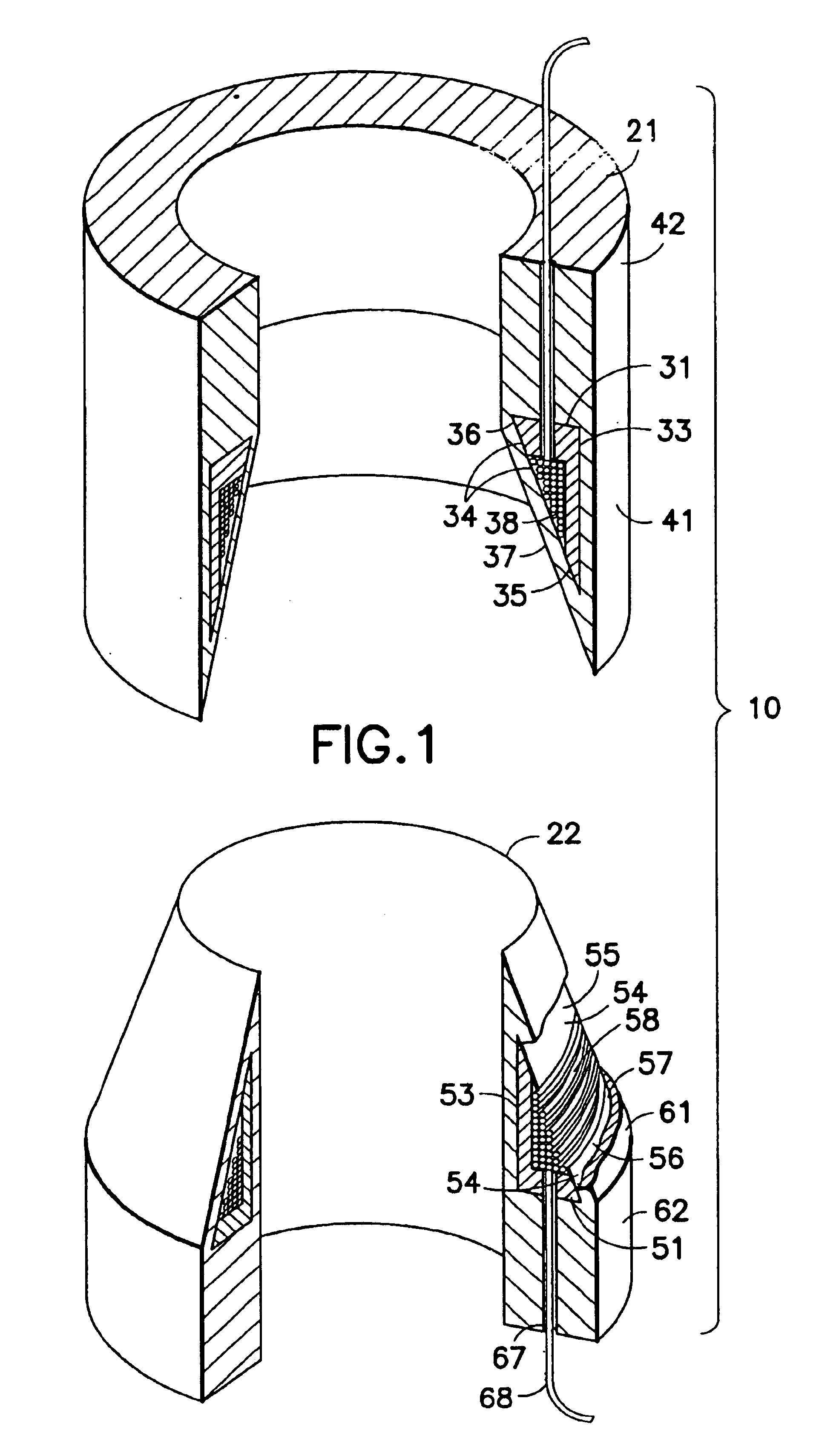
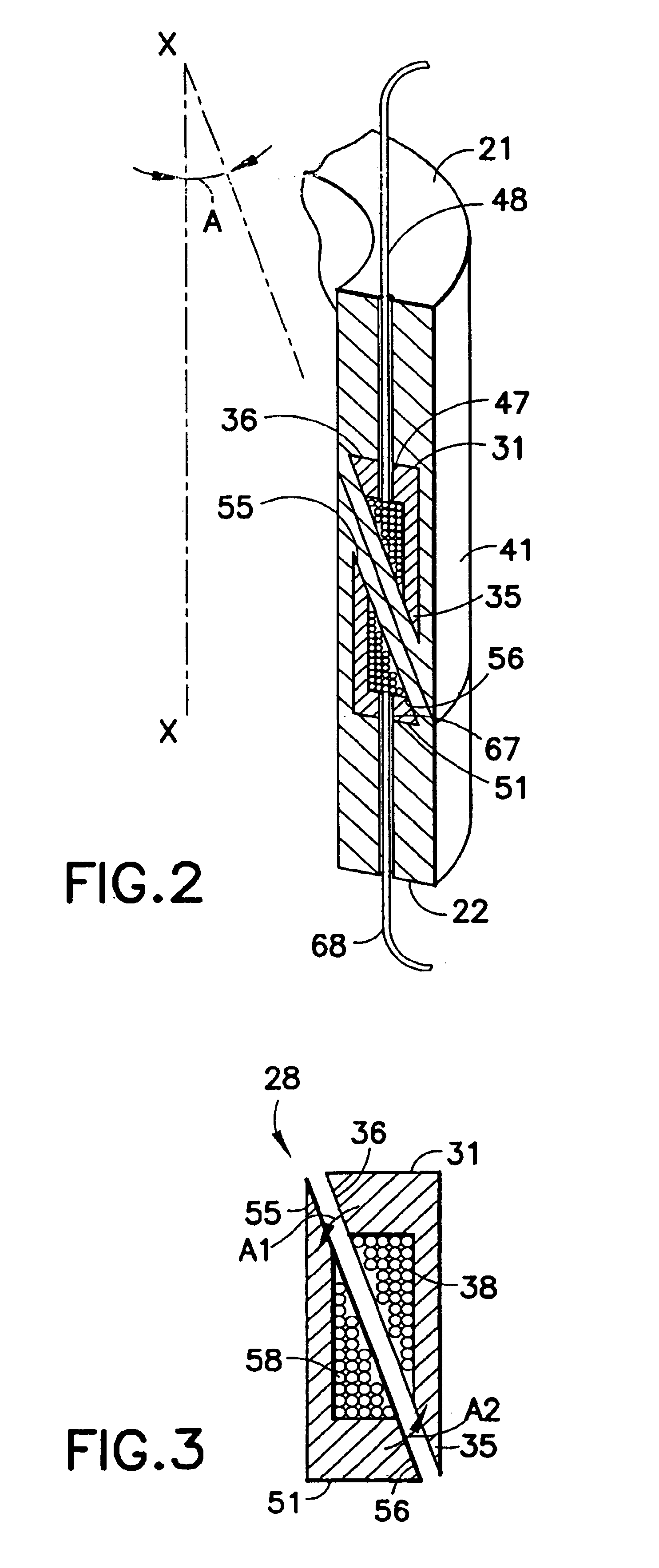
A deformable member can be used in a well tool for use in downhole oil / gas wells. In one embodiment, a deformable member (46) is described which is deformable between undeformed and deformed positions, and comprises a generally hollow cylindrical body (48) defining a wall (50). The wall (50) includes three circumferential lines of weakness in the form of grooves, with two grooves (52, 54) provided in an outer surface (56) of the member wall (50), and the other groove (58) provided in an inner surface (60). The member (46) is deformed outwardly by folding about the lines of weakness (52, 54, 56) and is used in particular to obtain sealing contact with a tube in which the member (46) is located.
Owner:ZEROTH TECH
Magnetic field concentrator for electromagnetic forming
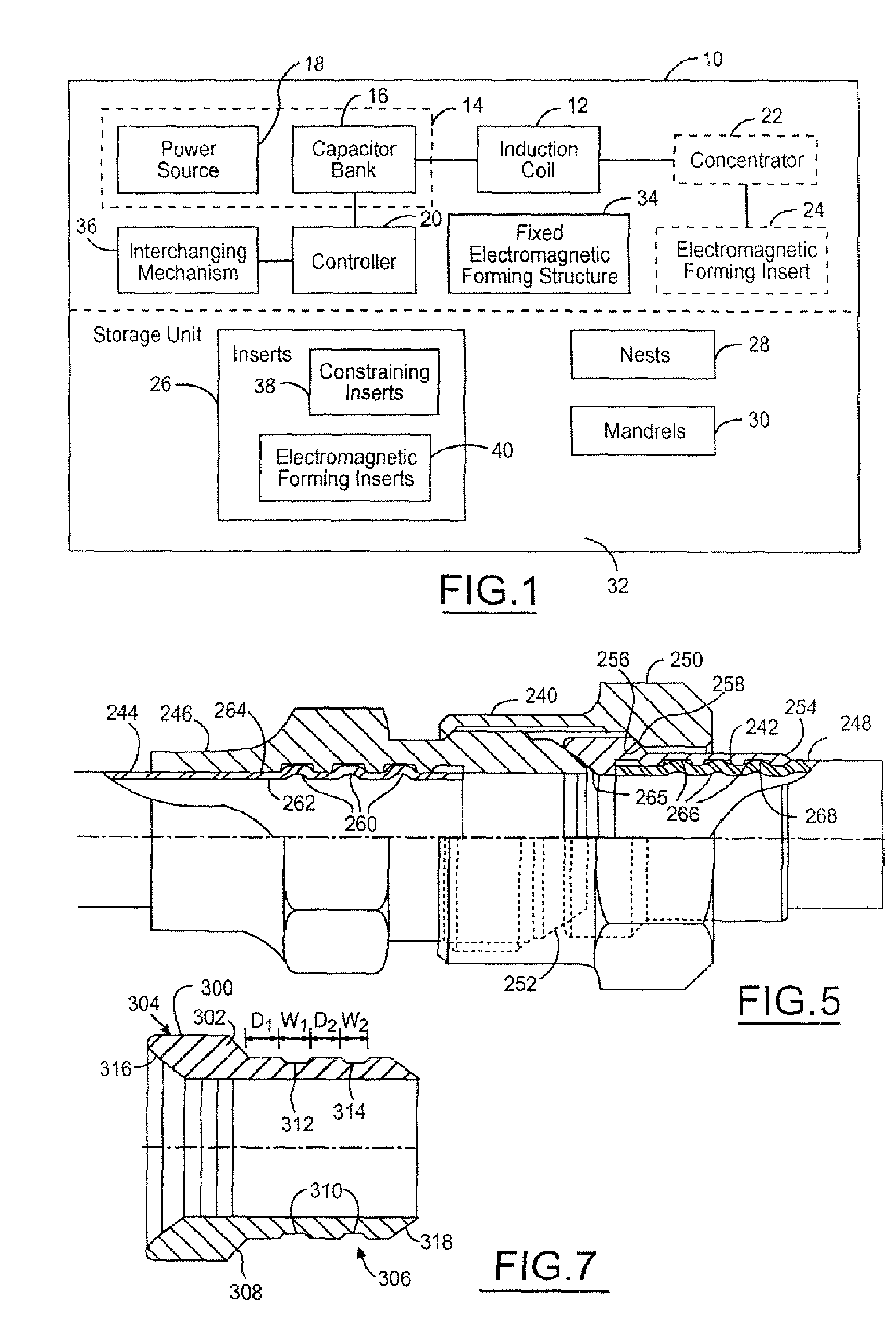
ActiveUS7513025B2Easily and quickly exchangedLow costJoints with sealing surfacesPipe elementsEngineeringElectromagnetic field
A magnetic forming system (10) for creating a fluid circuit joint between a tube and a fitting includes an induction coil (12). The induction coil (12) may form a first stage electromagnetic current. A field concentrator (132) may focus the first stage electromagnetic current to form a second stage electromagnetic current. An insert (136) may focus the second stage electromagnetic current to form an electromagnetic field. The electromagnetic field forms the fluid circuit joint. The induction coil (12) may be insertable within the tube, generate an electromagnetic field, and impose the electromagnetic field on and to expand a portion of the tube within the fitting to form the fluid circuit joint. The system (10) may include a receptacle (54) that is external to the tube and the fitting. An insert (56) may be mechanically coupled within the receptacle (54) and limit the outward expansion of the tube and the fitting.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Wellbore tubular patch system
A wellbore tubular patch for patching a hole in a wellbore has been invented, the tubular patch in certain aspects having an expandable top member having a hollow tubular body and a top end and a bottom end, an expandable bottom member having a hollow tubular body and a top end and a bottom end, an expandable outer sleeve in which is secured a portion of the bottom end of the expandable top member, and a portion of the top end of the expandable bottom member inserted into and held within expandable outer sleeve. A method for making a tubular patch for patching a hole in a tubular in an earth wellbore has been invented, the method in certain aspects including securing a portion of a bottom end of an expandable top member in an expandable outer sleeve, the expandable top member having a hollow tubular body and a top end, and securing a portion of a top end of an expandable bottom member within the expandable outer sleeve, the expandable bottom emmber having a hollow tubular body.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Expansion valve with refrigerant flow dividing structure and refrigeration unit utilizing the same
InactiveUS20090183520A1Reduce noiseShorten speedEvaporators/condensersValve members for absorbing fluid energyEngineeringRefrigeration
An expansion valve of the present invention has a structure which integrates a refrigerant flow divider. The expansion valve includes a refrigerant flow dividing chamber 6 on the downstream side of a first throttle 10. Flow dividing tubes 12 are connected to the refrigerant flow dividing chamber 6. In the expansion valve, refrigerant which has passed through the first throttle 10 is sprayed into the refrigerant flow dividing chamber 6, so that the flow dividing characteristic of the refrigerant is improved. Also, due to an enlargement of the passage in the refrigerant flow dividing chamber 6, the ejection energy of a flow of the refrigerant ejected from the first throttle 10 is dispersed, whereby a discontinuous refrigerant flow noise is reduced.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
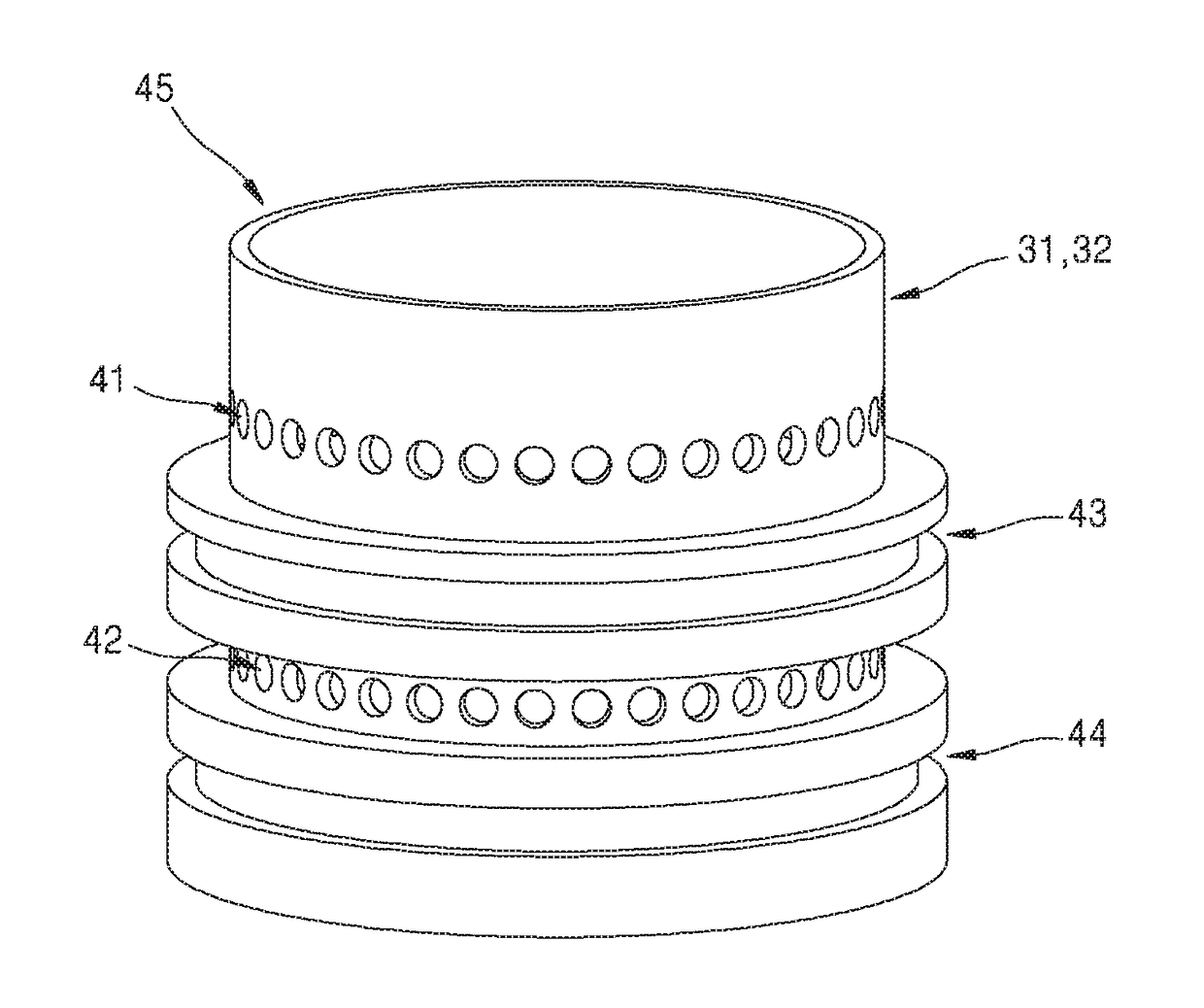
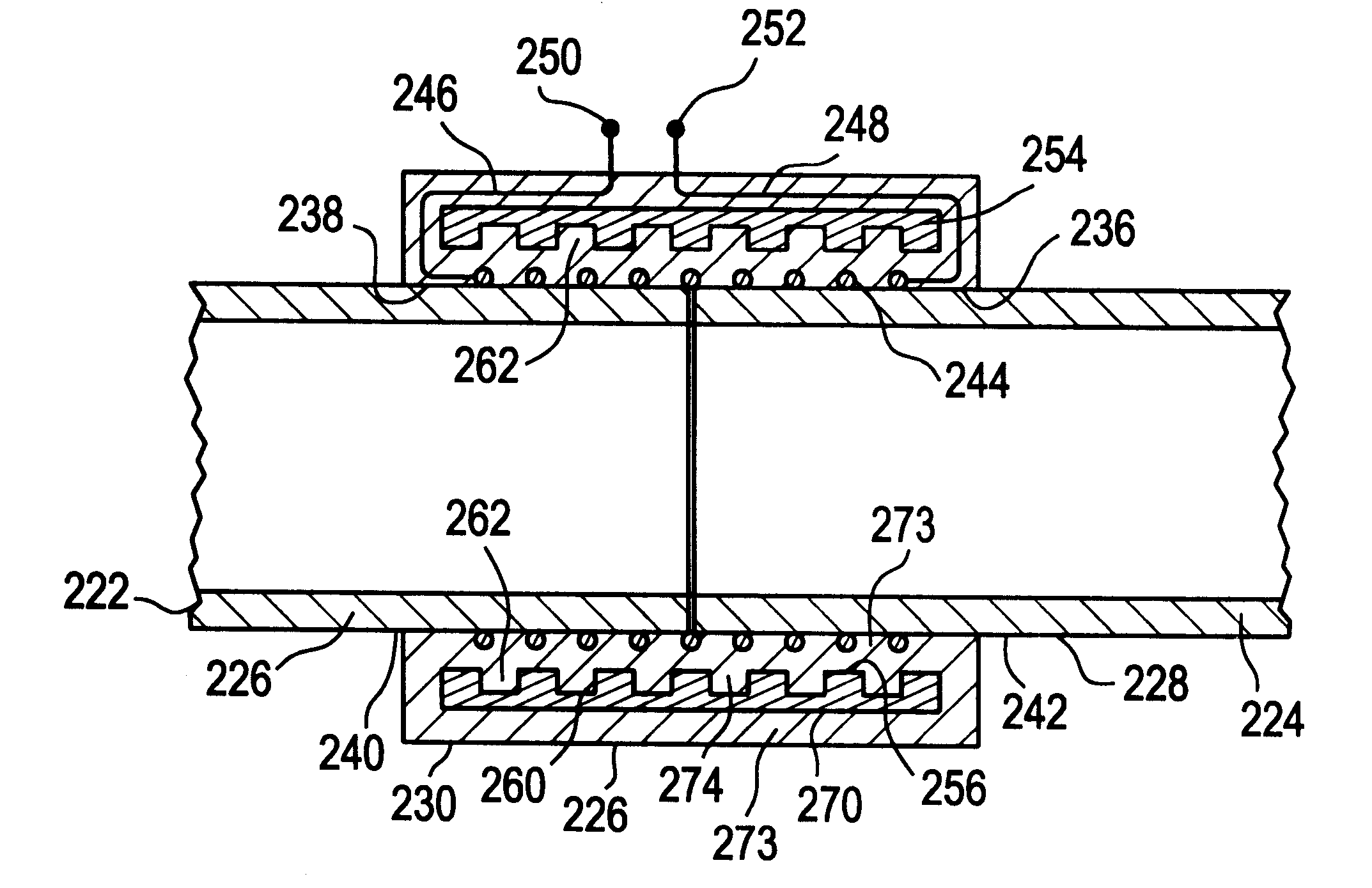
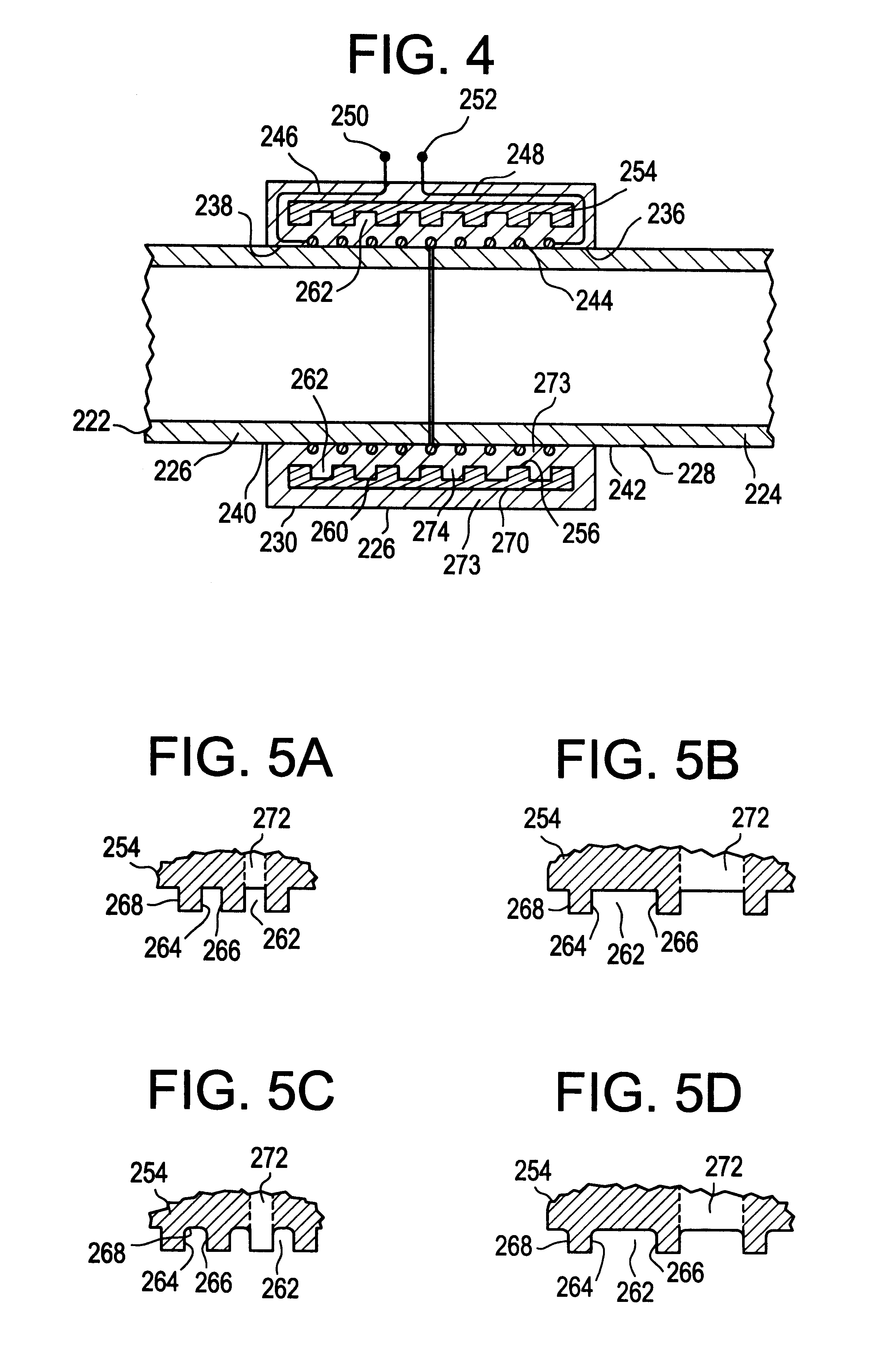
Low-loss inductive couplers for use in wired pipe strings
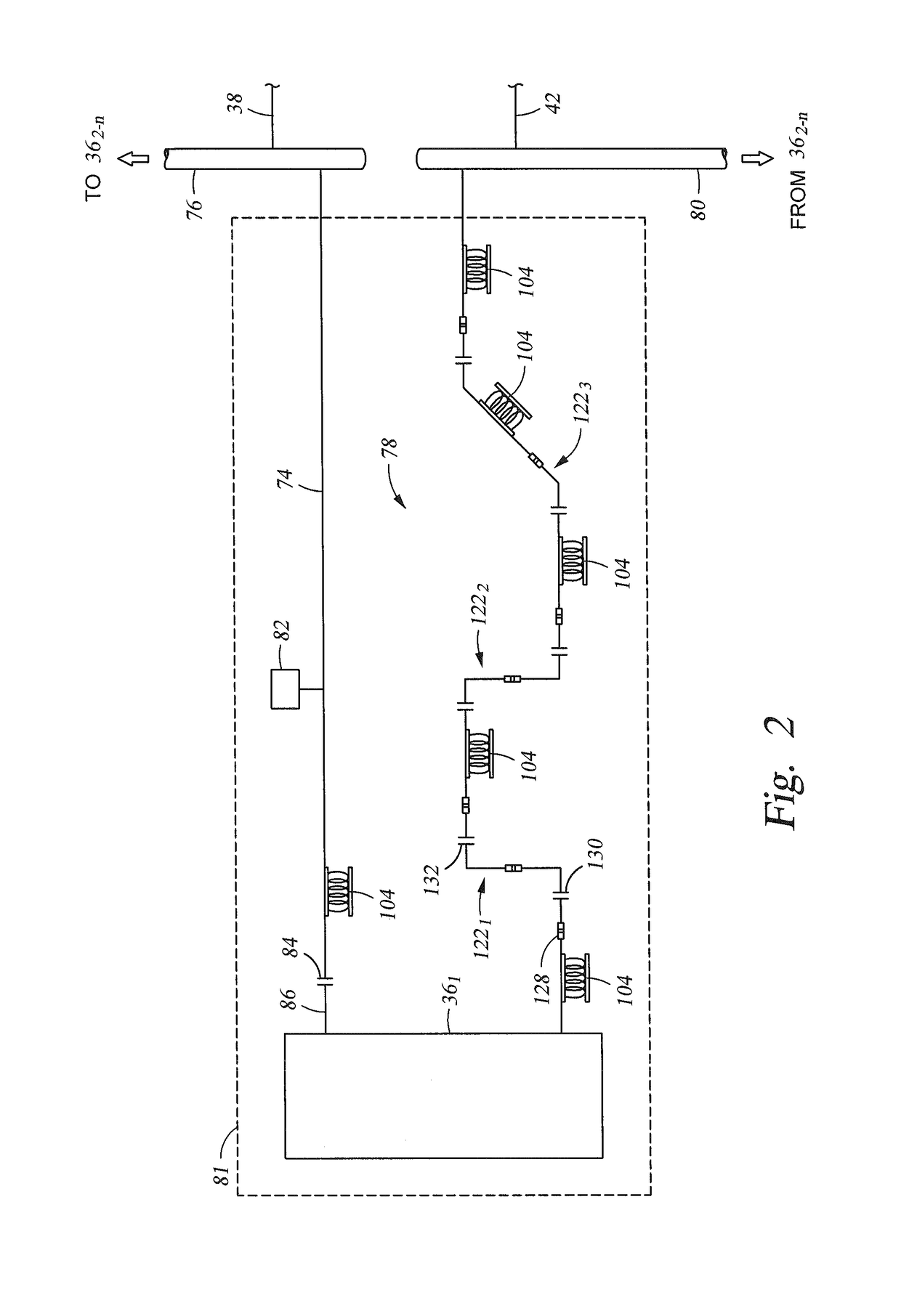
A first flux-loop inductive coupler element electrically couples with a second flux-loop inductive coupler element. The first flux-loop inductive coupler element comprises a first ring-like core having high magnetic permeability and a conical-section annular first face transverse to the plane of the first core. The first face has a first annular groove separating a first conical-section larger-diameter face and a first conical-section smaller-diameter face. A first coil is wound within the annular groove. The first and second cores form a low-reluctance closed magnetic path around the first coil and a second coil of the second flux-loop inductive coupler element.A first current-loop inductive coupler element electrically couples with a second current-loop inductive coupler element. The first current-loop inductive coupler element has a first high-conductivity, low-permeability shaped belt of a first end of a first pipe joint, a first ring-like core located at the first end, and a first electrically conductive coil wound about the first ring-like core. The first high-conductivity, low-permeability shaped belt partially encloses the first coil. It is shaped to cooperate with the second high-conductivity, low-permeability shaped belt of an adjacent second pipe joint having a second electrically conductive coil and a second high-conductivity, low-permeability shaped belt to create a closed toroidal electrical conducting path. The closed toroidal electrical conducting path encloses the first coil and the second coil when the first and second pipe joints are mated.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Network architecture for remote robot with interchangeable tools
ActiveUS20060074525A1Slow feedback loopLess time-critical decisionProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorDigital feedbackAuto-configuration
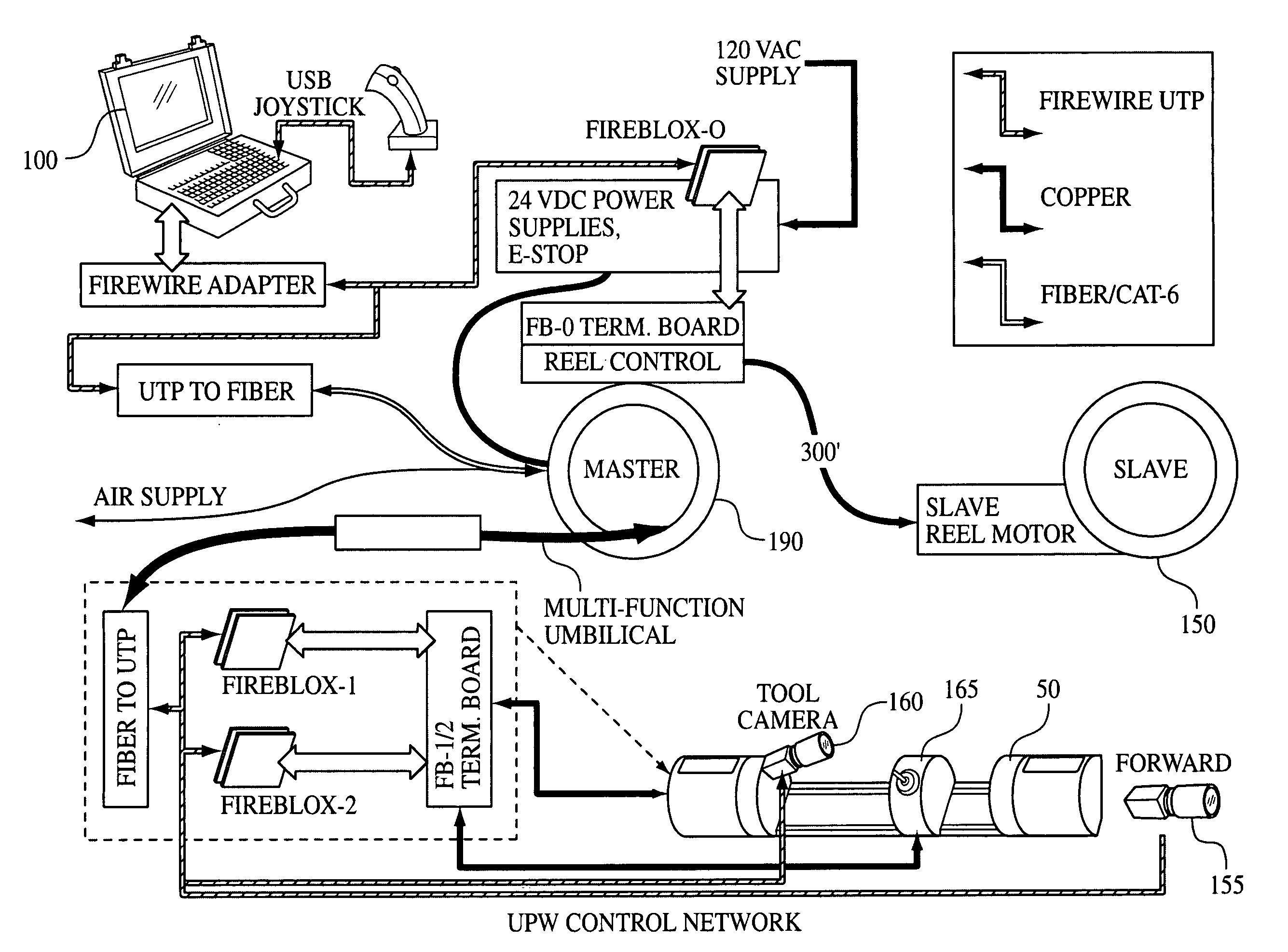
Systems, methods and devices for the remote control of a robot which incorporates interchangeable tool heads. Although applicable to many different industries, the core structure of the system includes a robot with a tool head interface for mechanically, electrically and operatively interconnecting a plurality of interchangeable tool heads to perform various work functions. The robot and tool head may include several levels of digital feedback (local, remote and wide area) depending on the application. The systems include a single umbilical cord to send power, air, and communications signals between the robot and a remote computer. Additionally, all communication (including video) is preferably sent in a digital format. Finally, a GUI running on the remote computer automatically queries and identifies all of the various devices on the network and automatically configures its user options to parallel the installed devices. Systems according to the preferred embodiments find particular application in the pipeline arts. For example, interchangeable tool heads may be designed to facilitate inspection, debris clearing, cleaning, relining, lateral cutting after relining, mapping, and various other common pipeline-related tasks.
Owner:REDZONE ROBOTICS
Actuator mounting assembly
InactiveUS20110114199A1Maintain positionOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPipe elementsEngineeringActuator
A mounting bracket for locating an actuator in a predetermined position relative to a valve at least partially controlled by the actuator. The mounting bracket includes a body element and three or more arms attached to the body element. Each arm extends between an inner end attached to the body element and an outer end distal to the body element, the outer ends of said at least three arms being positioned to define a plane on which the actuator is locatable, to maintain the actuator in the predetermined position.
Owner:GGOSCO ENG
Self sealing disconnect device
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Bracket for fluid transport tube
InactiveUS20050067548A1Reduce manufacturing costAttached with easePipe supportsStaplesFluid transportEngineering
The present invention is a bracket for a fluid transport tube including an elongated bracket body having a length in a longitudinal direction, a tube clamp for holding the fluid transport tube in a direction transverse to the longitudinal direction, a mounting component for securing the bracket body and tube clamp to the side of a car wherein the mounting component comprises a bolt passage hole for passing a bolt having a bolt head through the passage hole to secure the mounting component to the side of the car and a vibration-absorbing bushing 9 made of a rubber-like resilient material with an annular fitting groove 15 in the middle of its outer circumference in the thickness direction thereof fitted to the mounting component 5 in such a manner to clamp part of said bushing between the bolt head and said mounting component, and another part of said bushing between said mounting component and the car body.
Owner:SUMITOMO RIKO CO LTD
Method and Apparatus for Additive Mechanical Growth of Tubular Structures
InactiveUS20160031155A1High strengthEliminate needLiquid surface applicatorsManufacturing driving meansAdditive layer manufacturing3D printing
Owner:CONTINUOUS COMPOSITES INC
Apparatus and method for an autonomous robotic system for performing activities in a well
InactiveUS20050288819A1Achieve energy efficiencyBroad and effective collaboration and cooperationSurveyPipe elementsRobotic systemsControl system
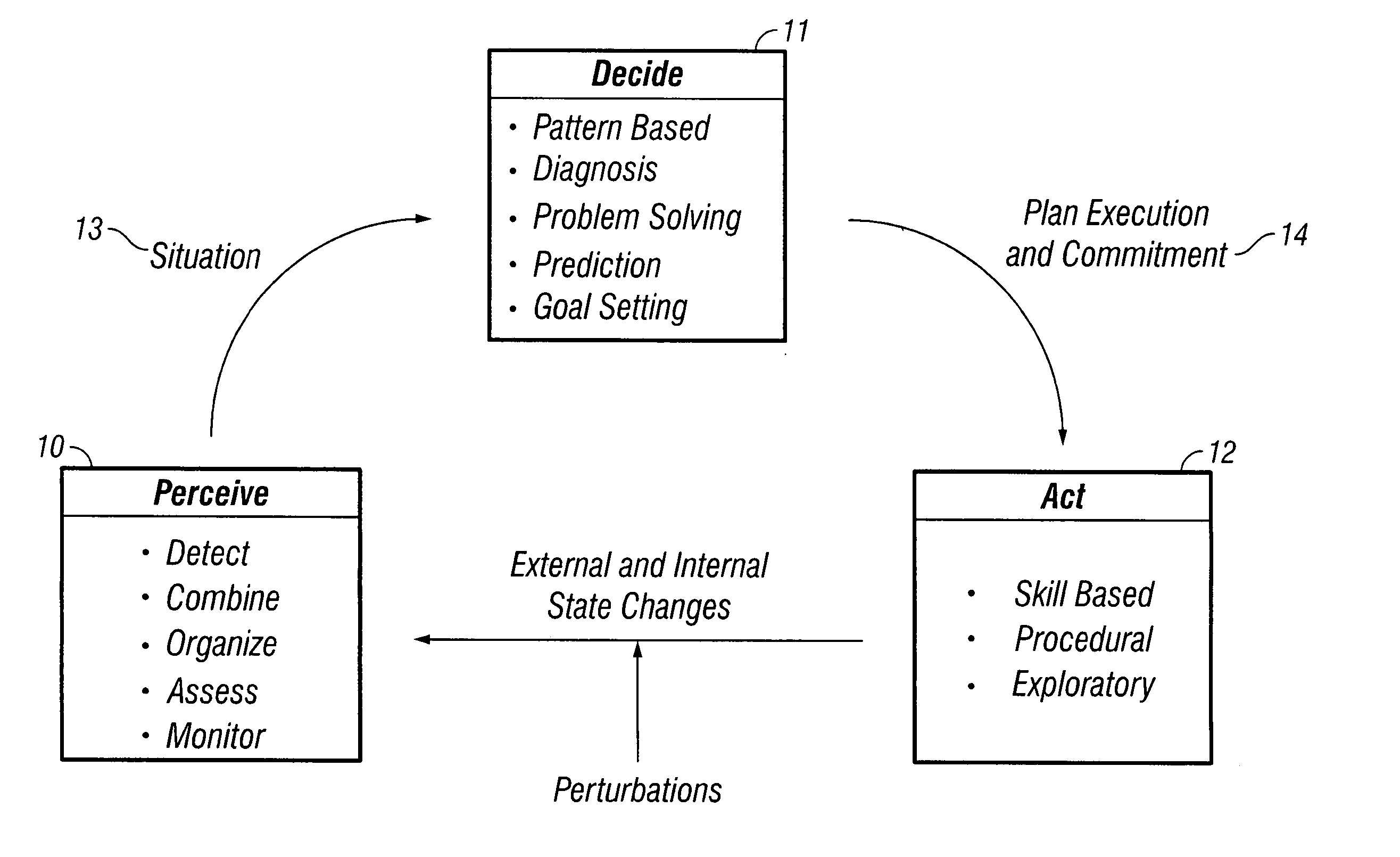
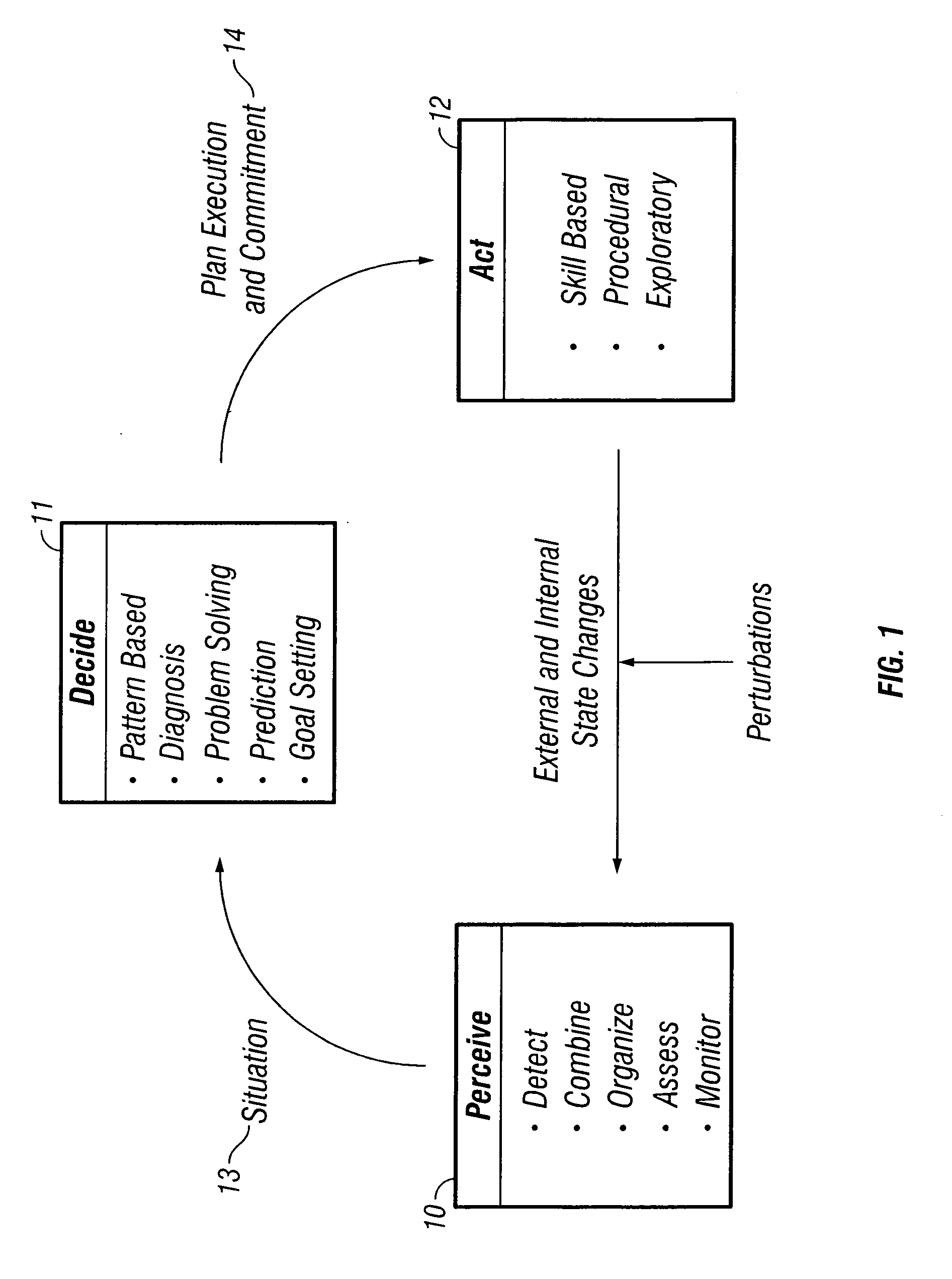
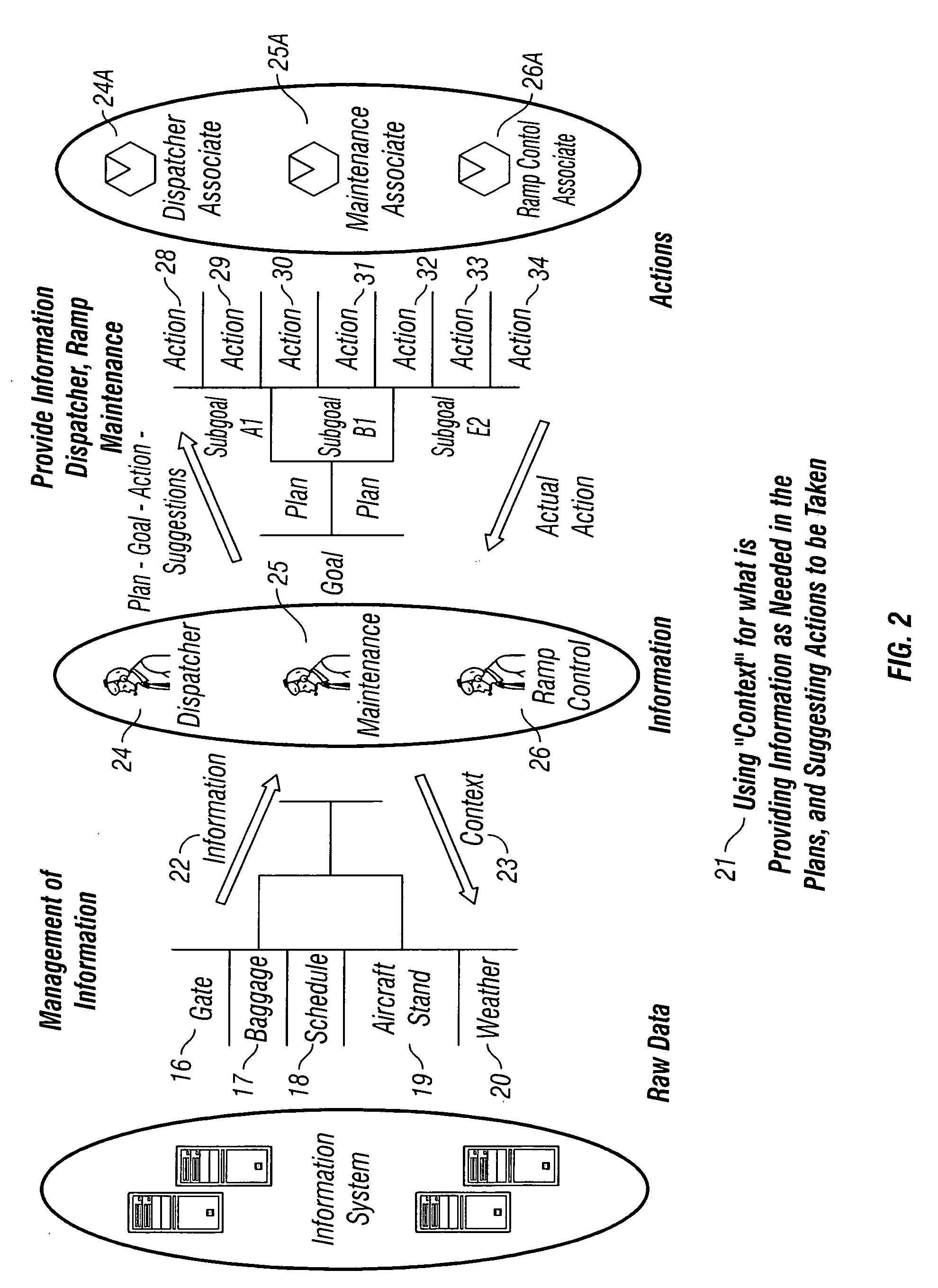
An autonomous robot performs maintenance and repair activities in oil and gas wells, and in pipelines. The robot uses the well and pipeline fluids to provide most of the energy required for the its mobility, and to charge a turbine from which it may recharge batteries or power a motor for additional propulsion. A control system of associated systems controls the robot, enabling the robot to share plans and goals, situations, and solution processes with wells, pipelines, and external control systems. The control system includes decision aids in a series of knowledge bases that contain the expertise in appropriate fields to provide intelligent behavior to the control system. The intelligent behavior of the control system enables real time maintenance management of wells and pipelines, through actively collecting information, goal-driven system, reasoning at multiple levels, context sensitive communication, activity performing, and estimation of the operators' intent.
Owner:INTELLIGENT ROBOTIC CORP
Method and apparatus for lining a conduit
Owner:HEAGY RICHARD T +3
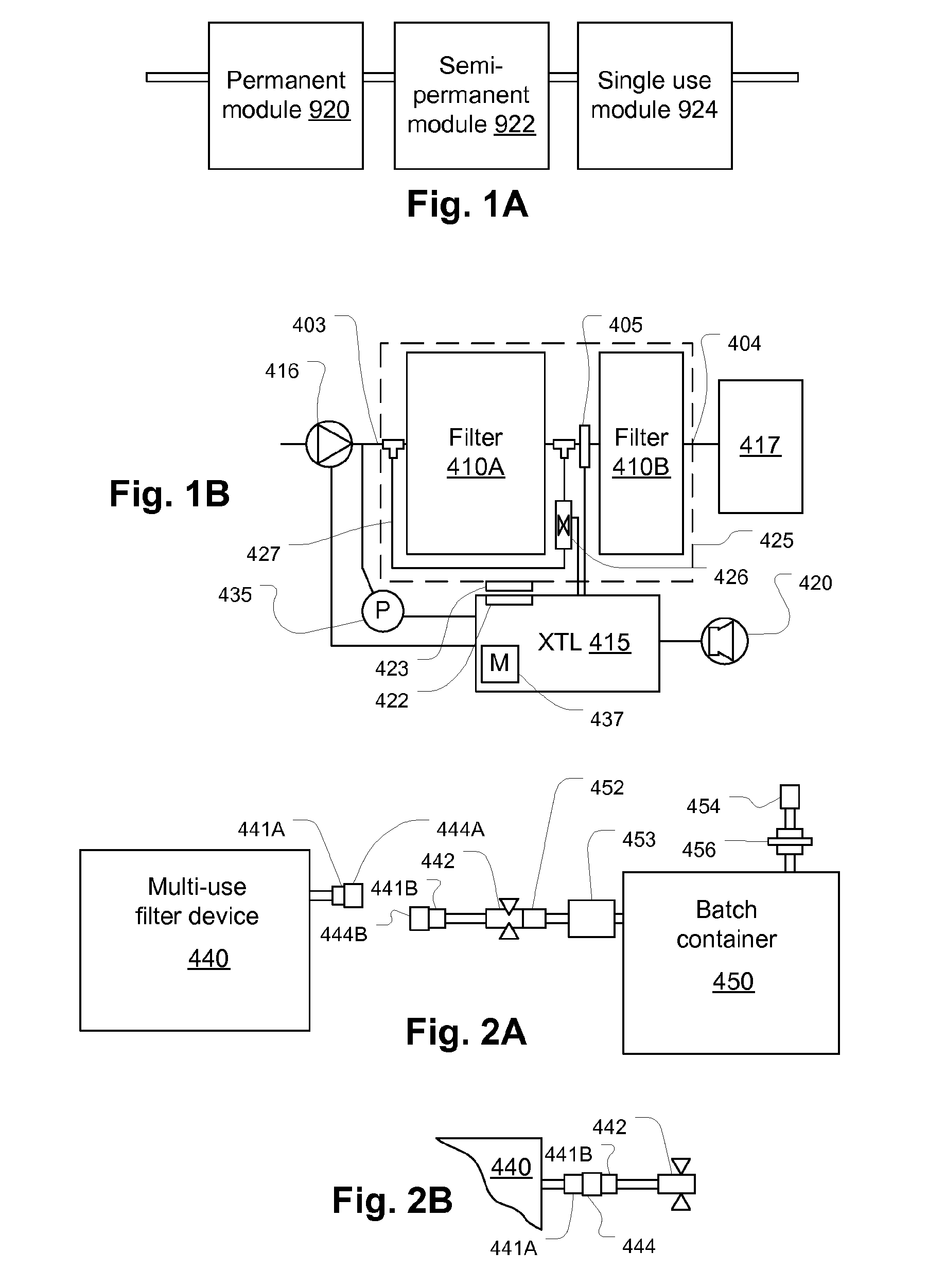
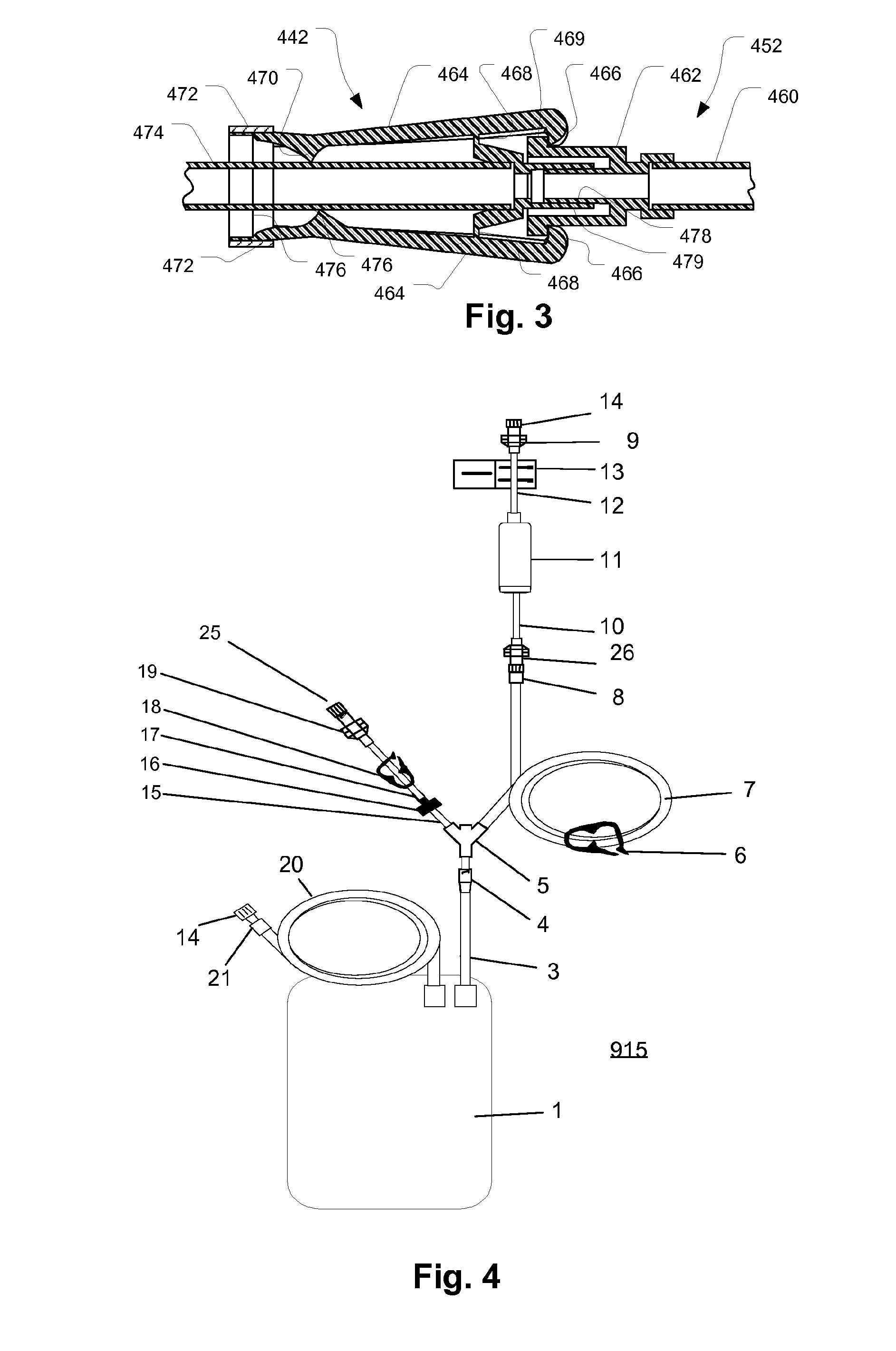
Filtration system for preparation of fluids for medical applications
ActiveUS20090182263A1Convenient and smoothIncrease the patency of the tubeEngine diaphragmsUltrafiltrationBlood treatmentsMedicine
Systems, methods, and devices for preparation of purified water and medicaments for various uses including blood treatment are described. Methods, devices, and systems for creating multiple-treatment batches are described.
Owner:NXSTAGE MEDICAL
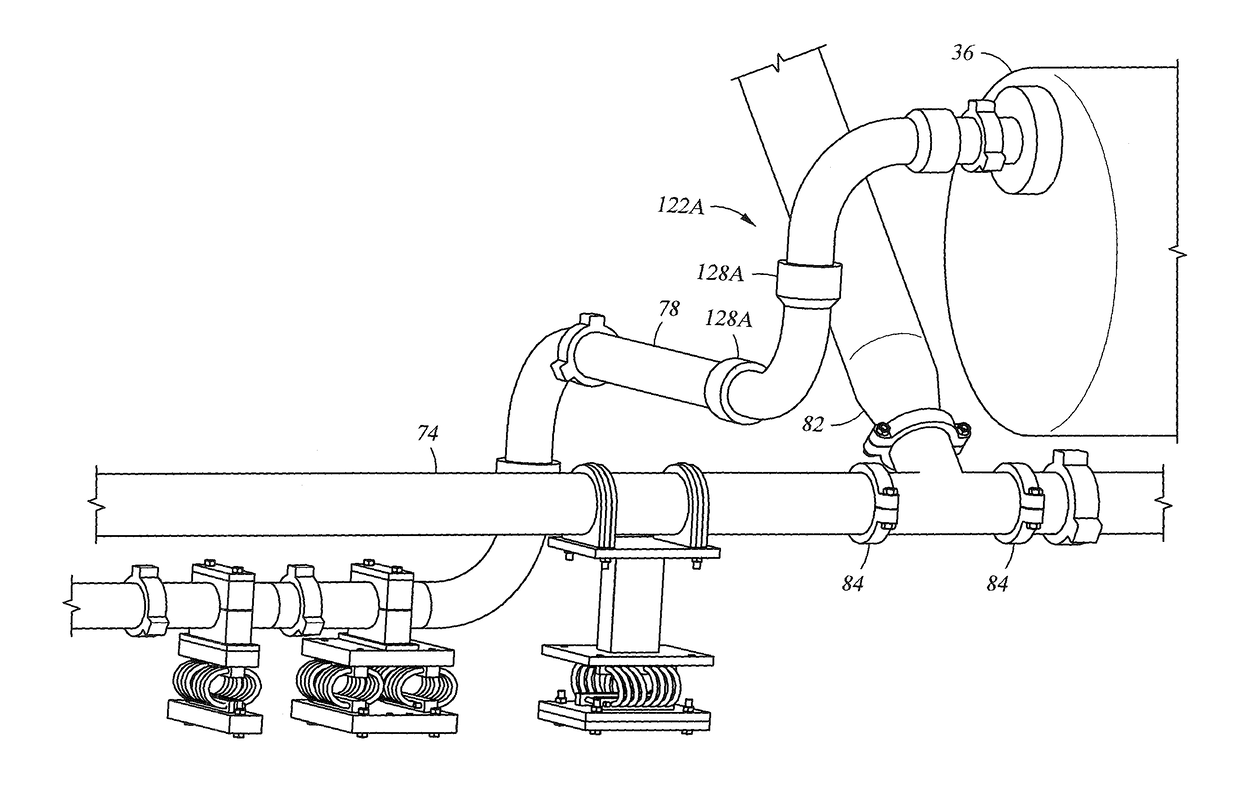
System for reducing vibrations in a pressure pumping fleet
ActiveUS10119381B2Vibration highReduce turbulenceAC motor controlPositive displacement pump componentsFracturing fluidHelical coil
An electrically powered hydraulic fracturing system having pumps for pressurizing fracturing fluid, piping for carrying fracturing fluid, and vibration reducing equipment for use with the piping. The vibration reducing equipment includes helical coils that support the piping. The coils are made of a wire rope made of strands of steel cable twisted together. Grooved fittings are provided on some piping connections, and which allow pivoting between adjacent fluid conveyance members. Swivel joints are strategically located in the piping which allow rotational flexing between adjacent sections of the piping; thereby attenuating vibration in the piping but without stressing the piping.
Owner:US WELL SERVICS LLC
Method and apparatus for autonomous downhole fluid selection with pathway dependent resistance system
An apparatus is described for controlling flow of fluid in a tubular positioned in a wellbore extending through a subterranean formation. A flow control system is placed in fluid communication with a main tubular. The flow control system has a flow ratio control system and a pathway dependent resistance system. The flow ratio control system has a first and second passageway, the production fluid flowing into the passageways with the ratio of fluid flow through the passageways related to the characteristic of the fluid flow. The pathway dependent resistance system includes a vortex chamber with a first and second inlet and an outlet, the first inlet of the pathway dependent resistance system in fluid communication with the first passageway of the fluid ratio control system and the second inlet in fluid communication with the second passageway of the fluid ratio control system. The first inlet is positioned to direct fluid into the vortex chamber such that it flows primarily tangentially into the vortex chamber, and the second inlet is positioned to direct fluid such that it flows primarily radially into the vortex chamber. Undesired fluids, such as natural gas or water, in an oil well, are directed, based on their relative characteristic, into the vortex primarily tangentially, thereby restricting fluid flow when the undesired fluid is present as a component of the production fluid.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Autonomous inspector mobile platform
ActiveUS20060290779A1Streamlined and low cost inspectionInexpensive and easily deployed/operatedPipe elementsColor television detailsCommunications systemMeasurement device
An autonomous inspector mobile platform robot that is used to inspect a pipe or network of pipes. The robot includes a locomotion device that enables the device to autonomously progress through the pipe and accurately track its pose and odometry during movement. At the same time, image data is autonomously captured to detail the interior portions of the pipe. Images are taken at periodic intervals using a wide angle lens, and additional video images may be captured at locations of interest. Either onboard or offboard the device, each captured image is unwarped (if necessary) and combined with images of adjacent pipe sections to create a complete image of the interior features of the inspected pipe. Optional features include additional sensors and measurement devices, various communications systems to communicate with an end node or the surface, and / or image compression software.
Owner:REDZONE ROBOTICS
Mechanical pipe coupling with toothed retainer
InactiveUS6499771B1Reduce energy lossPositive engagementSleeve/socket jointsFluid pressure sealed jointsPipe fitting
An open end of a standard pipe fitting is enlarged in diameter to coaxially receive an O-ring and a retainer having a cylindrical surface. A plurality of locking teeth project from the cylindrical surface and are engageable with both the inner surface of the fitting and an outer surface of a pipe end inserted coaxially into the fitting open end. Each of the locking teeth have oppositely disposed edges facing obliquely inwardly and outwardly to engage both the pipe end and the fitting and resisting motion of the pipe end relatively to the fitting. In an alternate embodiment, a first plurality of teeth each have an edge facing obliquely inwardly of the fitting to engage the pipe end and resist motion tending to withdraw the pipe end from the fitting. A second plurality of teeth each have an edge facing obliquely outwardly of the fitting and resist motion tending to withdraw the retainer from the fitting.
Owner:VICTAULIC
Medical tubing connector
A medical connector, usable to securely couple a first tubular medical device to a second tubular medical device, includes first and second fittings cooperating with the first and second medical devices, respectively. The first and second fittings may each include a nipple, a ferrule, or some other structure that is connected to the associated medical device and that is connectable to the other fitting. The second fitting may additionally include a tubular sleeve that slides over the second medical device and the ferrule or other component of the second fitting. The two components of the second fitting are sequentially connectable to the first fitting through distinctly different motions to provide a redundant, secure connection. For example, the first fitting may include a first set of left-handed threads and a second set of right-handed threads, and the components of the second fitting may have corresponding left-handed and right-handed threads.
Owner:A B KORKOR MEDICAL
Apparatus and method for sealing pipes and underground structures
ActiveUS20120267863A1Prevent water infiltrationReduce manufacturing costSleeve/socket jointsEngine sealsCompressible materialEngineering
An apparatus and method for sealing pipes or underground structures is provided. In one embodiment, the end of a pipe is sealed by the use of a pipe liner and a sealing member. The sealing member may be a hydrophilic material, a hydrophobic material, a compressible material, or a paste. The sealing member is held in place by a mechanical fastener and a liner is installed adjacent the sealing member and against the wall of the pipe or other structure to be sealed. In another embodiment, a manhole is sealed by the use of a sealing member, a mechanical fastener, and a manhole liner.
Owner:LMK TECH LLC
Pipe fittings
A pipe fitting for coupling together opposed ends of two plastics pipes by fusion welding, the pipe fitting comprising an annular body having an inner cylindrical surface of plastics material surrounding a cylindrical cavity for receiving opposed ends of two plastics pipes to be coupled together, an electrically conductive coil provided in said inner cylindrical surface and surrounding the cylindrical cavity, the coil having opposed ends, a pair of terminals each connected to a respective end of the coil and provided on the body for connection to a source of controlled electrical power, and an annular reinforcing member disposed in the body and surrounding the coil, the annular reinforcing member having a grooved surface which interfaces the annular body, the grooved surface defining a plurality of axially facing surfaces.
Owner:FINA RES SA
Anti-mismatch of near-sized coupling segments
A series of successively sized segmented arcuate pipe couplings in which anti-mismatch members are provided to prevent the inadvertent connection of two different, but closely sized coupling segments together. The anti-mismatch features are provided on the ends of the arcuate coupling segments which (a) will nest when the proper coupling segments are brought together, but (b) will be in an interference non-nested relationship when a mismatch is attempted. This will prevent the fully bolt tightened connection of the size mismatched coupling segments, as well as a visual indication to a user that a size mismatch is being attempted.
Owner:VICTAULIC
Pressure support system having a two-piece assembly
InactiveUS6837260B1Overcomes shortcomingAvoid the needRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSupporting systemEngineering
A pressure support system that includes a first housing member and a second housing member. The first housing member has a first plurality of cavities defined therein, and the second housing member has a second plurality of cavities defined therein. The first and second plurality of cavities cooperate to define (a) a first chamber adapted to receive a first component of the pressure support system, (b) a second chamber adapted to receive a second component of the pressure support system, and (c) a first conduit connecting the first component and the second in fluid communication when the first and second housing members are assembled. A fastening system secures the first and second housing members in an assembled relation.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Locking luer fitting
InactiveUS7347458B2Avoid disconnectionPrevent rotationEngine sealsFluid pressure sealed jointsEngineeringCam
A locking luer fitting for connecting fluid lines. In one variation the connection interface includes a male luer connector and a corresponding female luer connector. The female luer connector includes a rotatable collar which engages the male luer connector. In another variation the female luer connector includes a cam configured to prevent inadvertent disconnection of the male luer connector. The locking luer fittings described herein may be implemented in various medical and industrial applications where secured fluid line connection interfaces are desirable.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Autonomous robotic crawler for in-pipe inspection
The specification discloses a robot for inspection adapted to travel virtually unlimited distances through small-diameter enclosed spaces such as conduits or ducts, preferably using a fluid-driven screw-drive propulsion system. The robot preferably includes a drive module having a plurality of wheels inclined at an angle greater than zero degrees and less than ninety degrees to the longitudinal axis of the pipe, a driver module having a plurality of wheels aligned parallel to the longitudinal axis of the pipe, and a power module. The driver module is preferably connected to the drive module such that the drive and driver modules are capable of providing the locomotive motion of the robot. The power module preferably provides the power to the drive and driver modules.
Owner:RICE UNIV +1
Manifold system of removable components for distribution of fluids
InactiveUS6394138B1Improve sealingEasy to disassembleElectric discharge tubesServomotor componentsActive componentPort access
A manifold system for enabling a distribution of fluids includes a plurality of individual manifold blocks that can be joined together to form a gas stick. Each manifold block will have a fluid passage way with an entrance port and exit port accessing a common surface. An active component can be mounted to one manifold block, while extending across a port of an adjacent manifold block. An alignment system can be provided to ensure that the entrance and exit ports are positioned in a plane containing the common surface to facilitate sealing.
Owner:ICHOR SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com