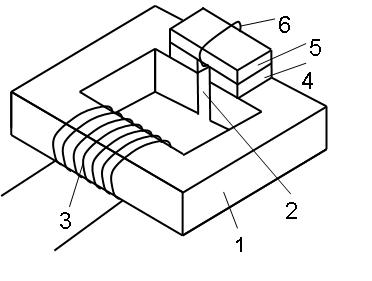
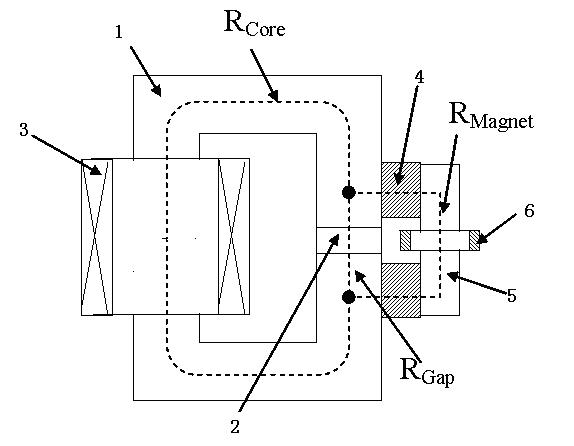
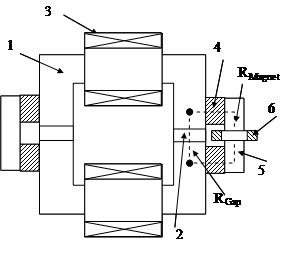
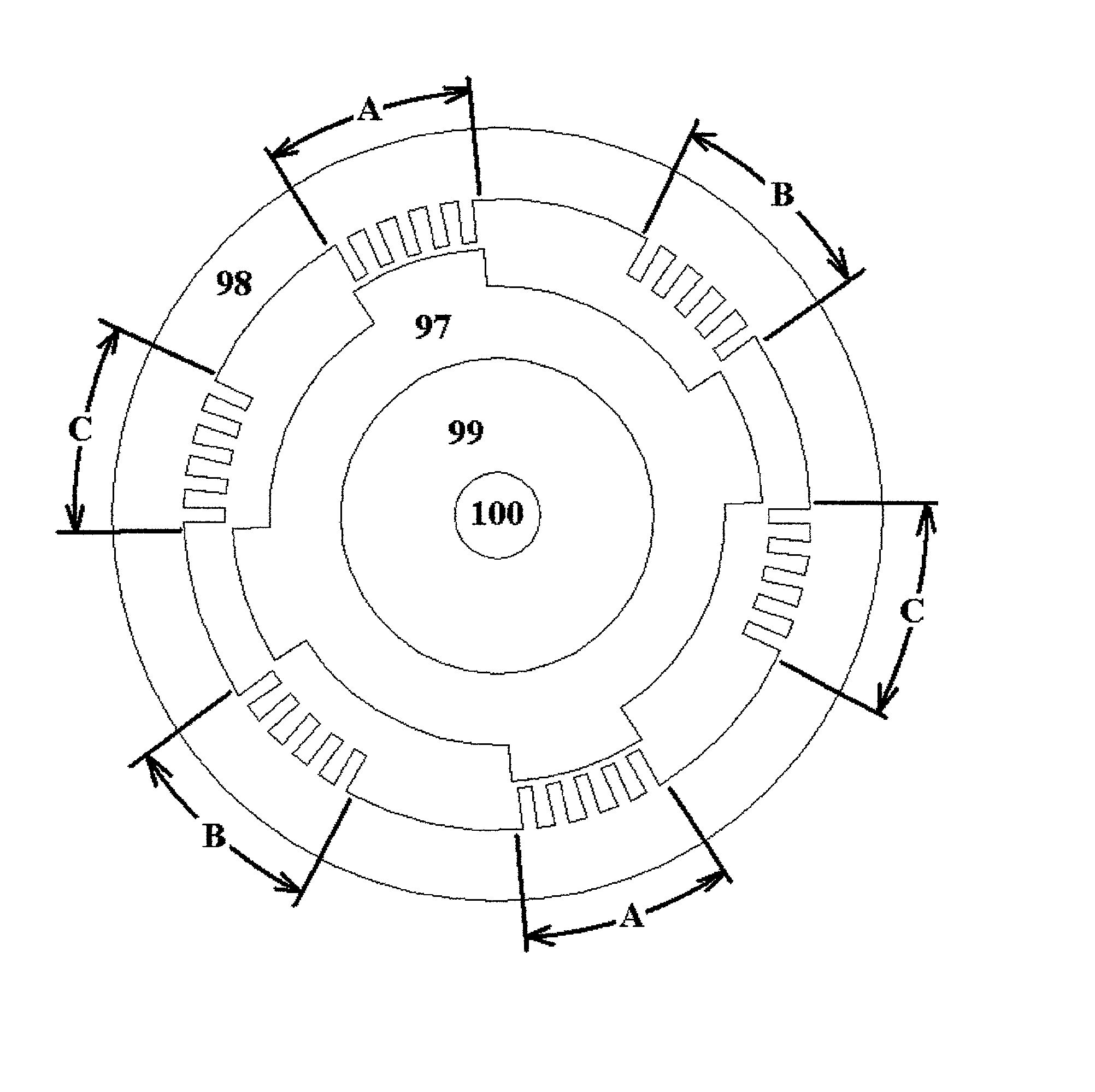
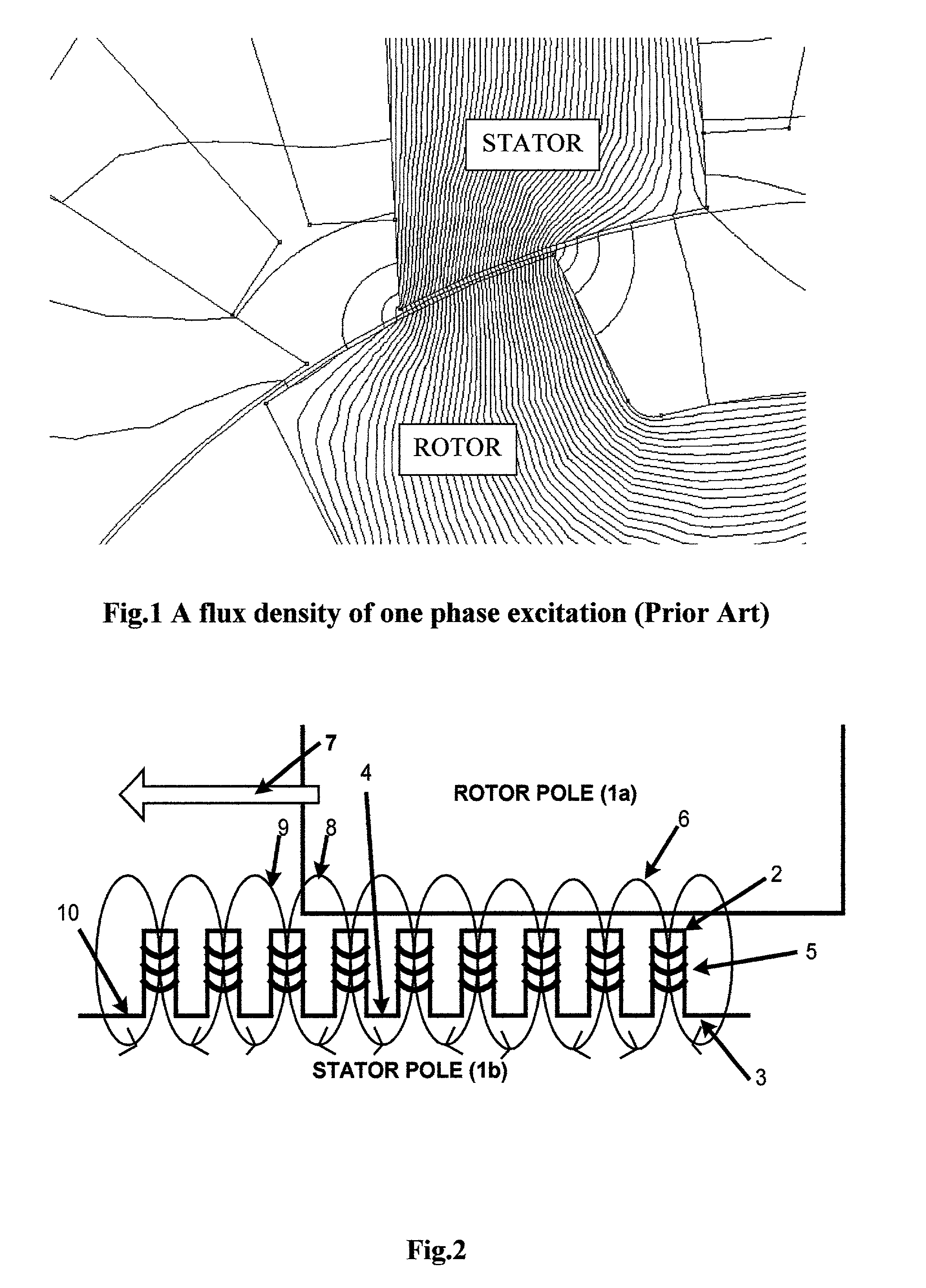
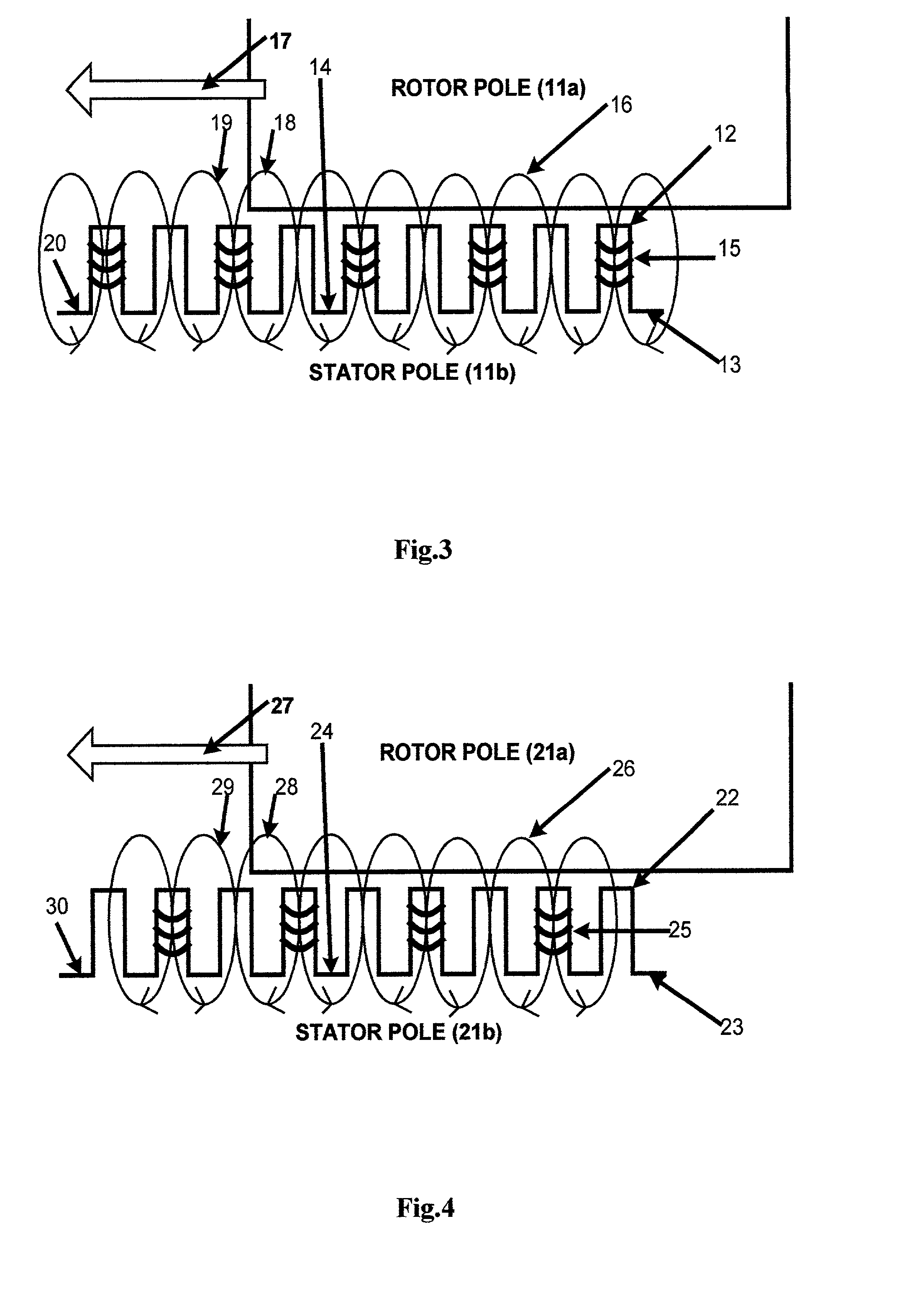
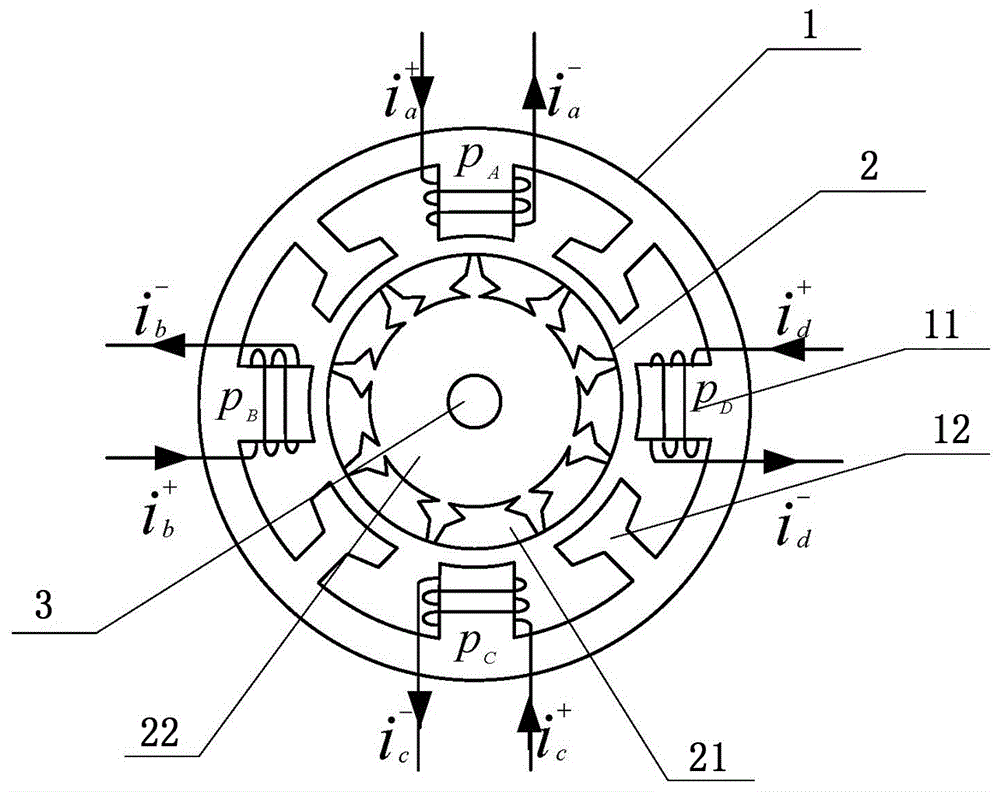
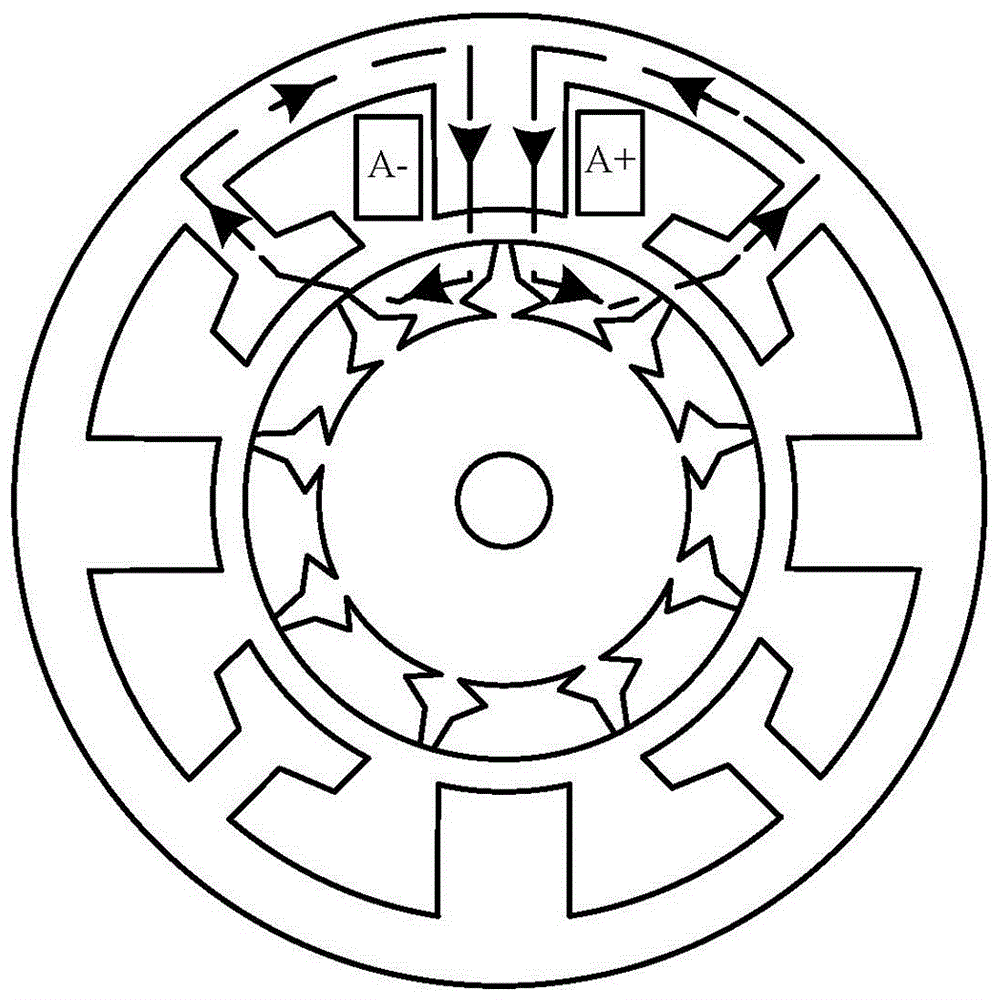
Patents
Literature
125 results about "Flux loop" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
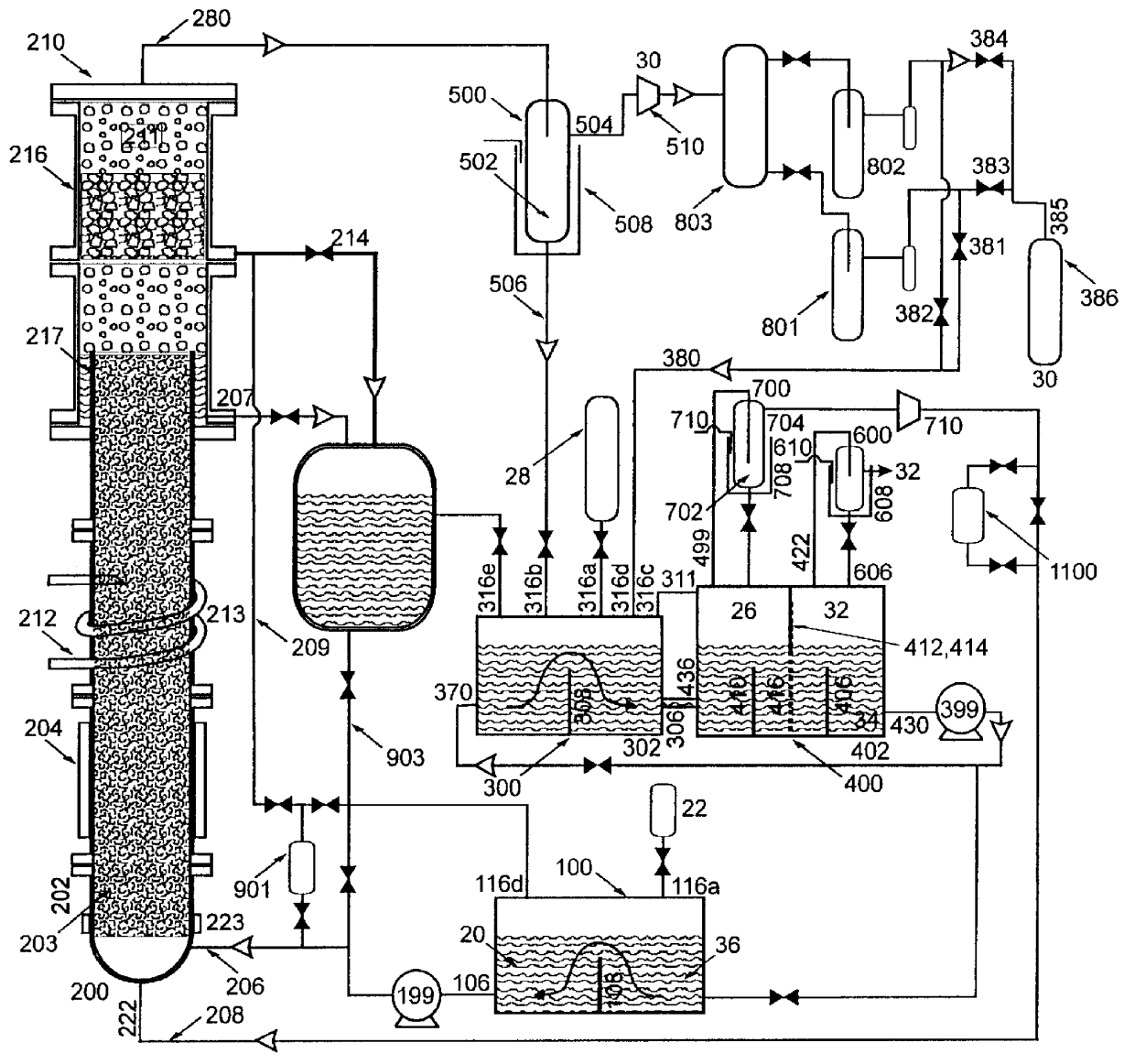
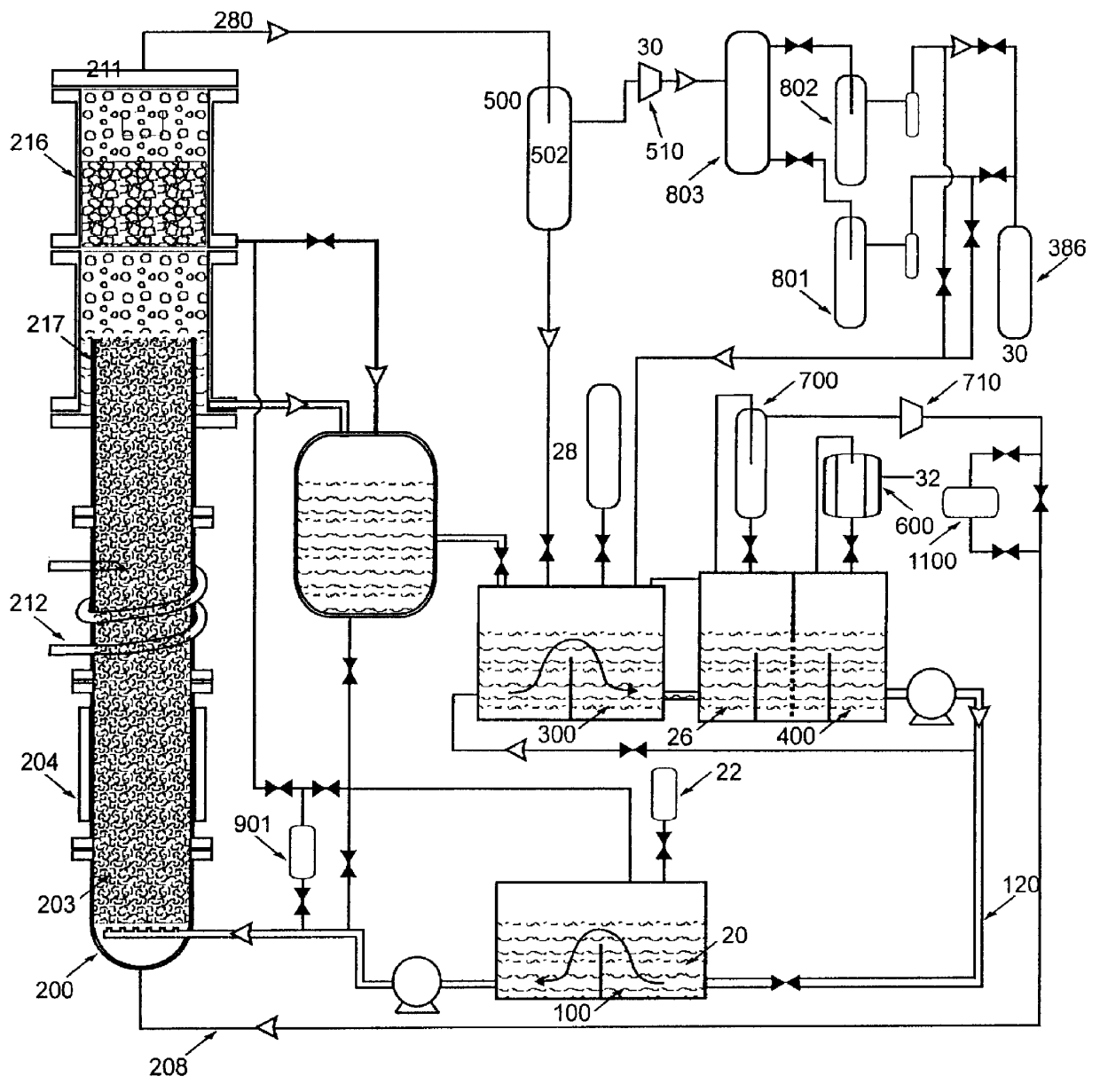
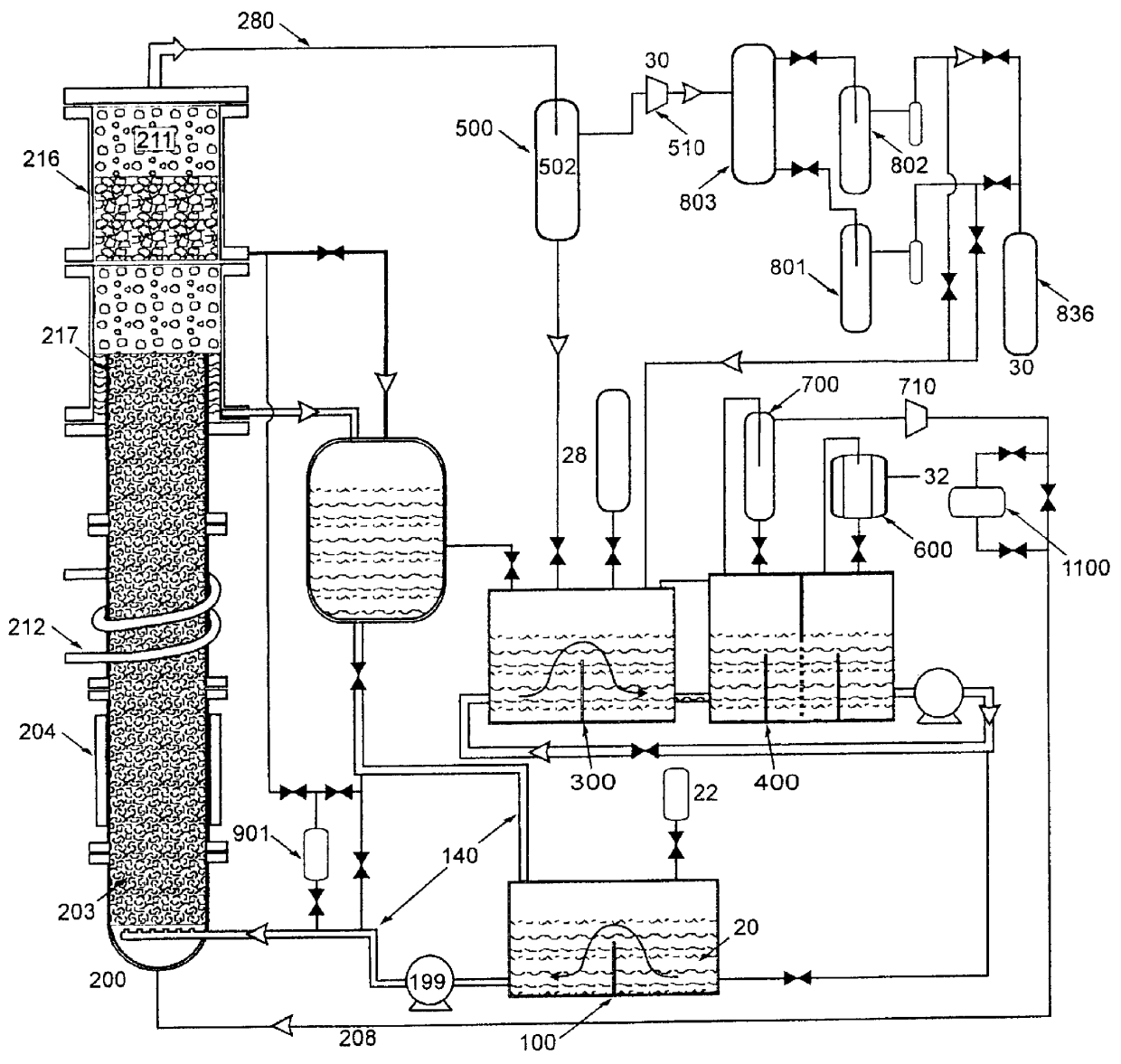
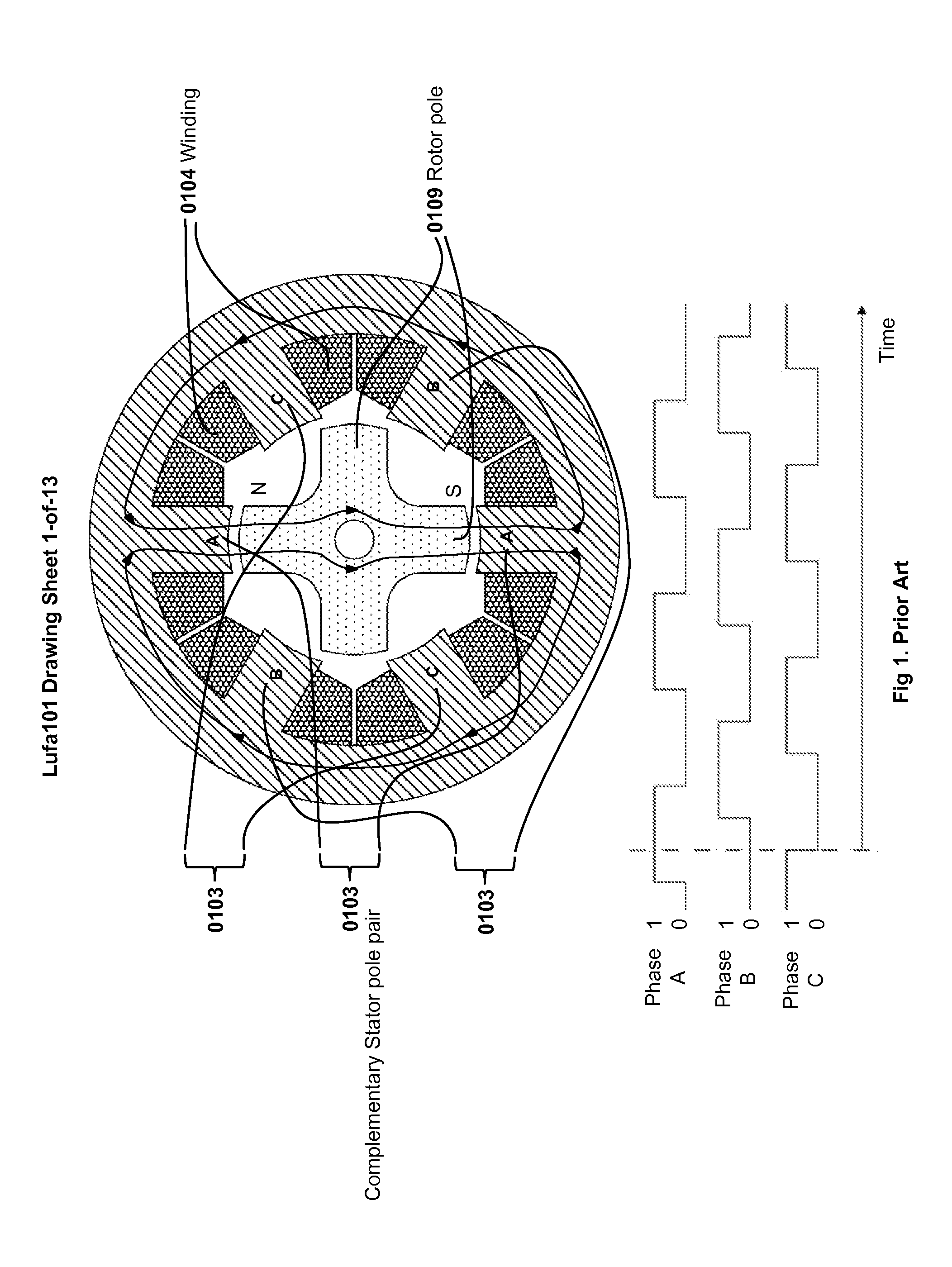
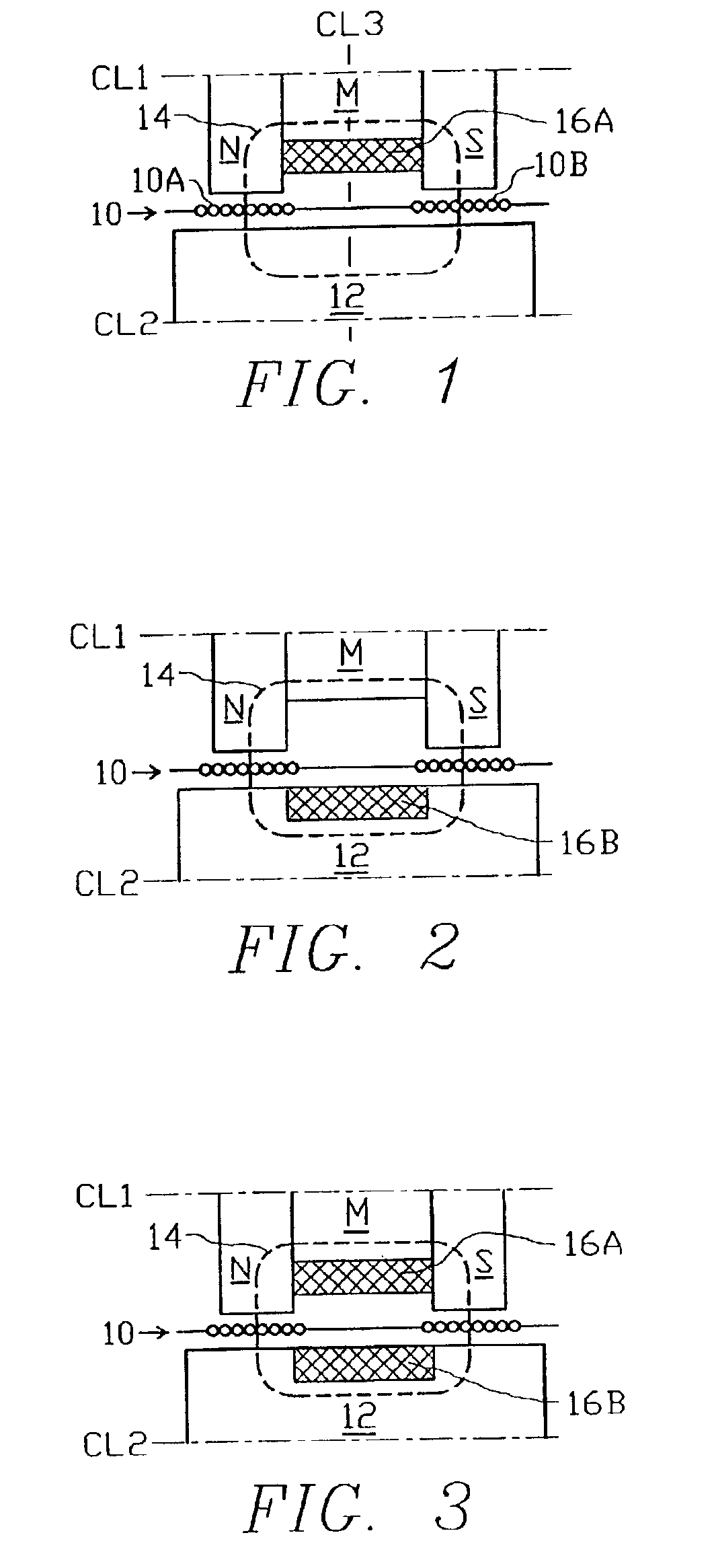
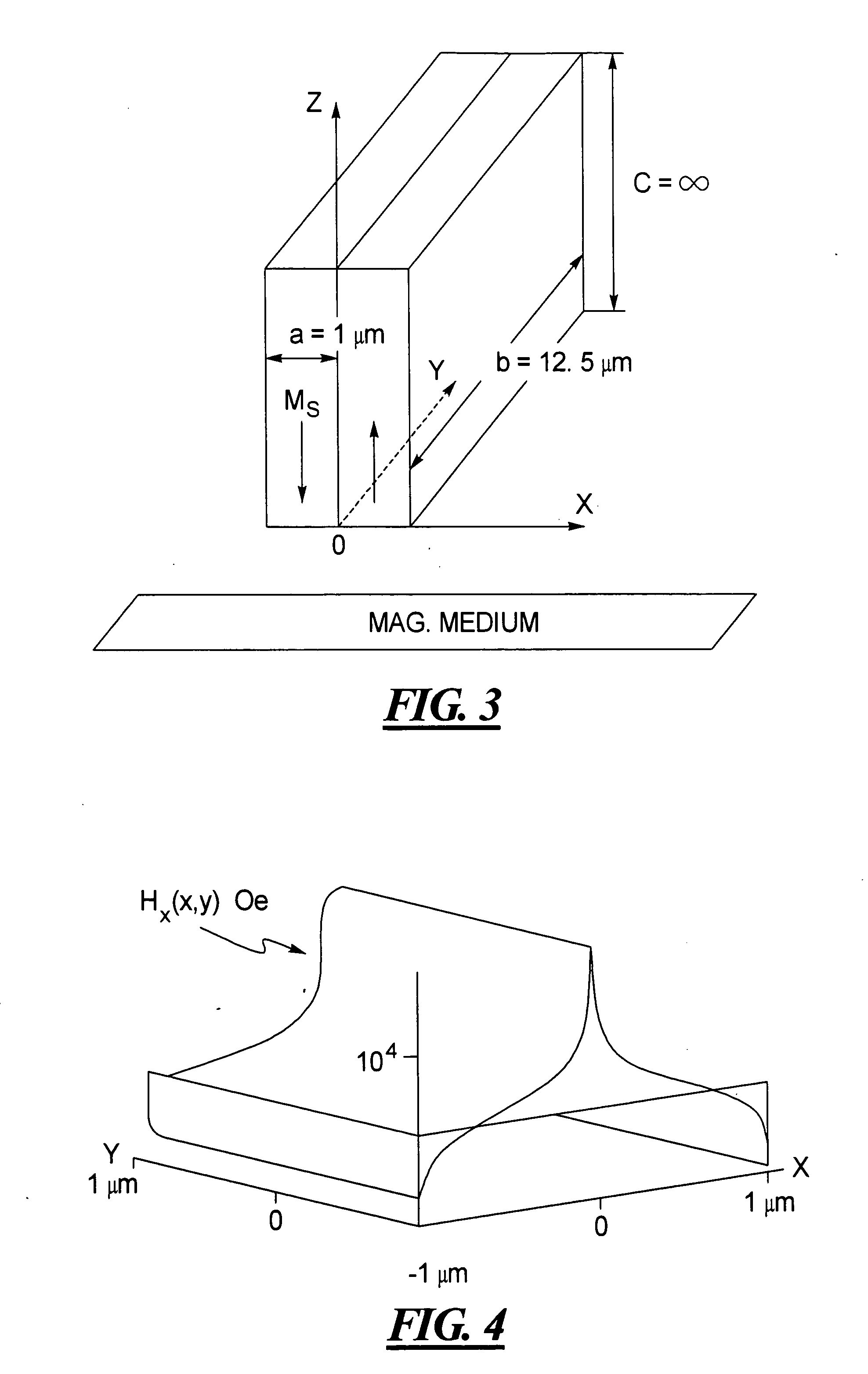
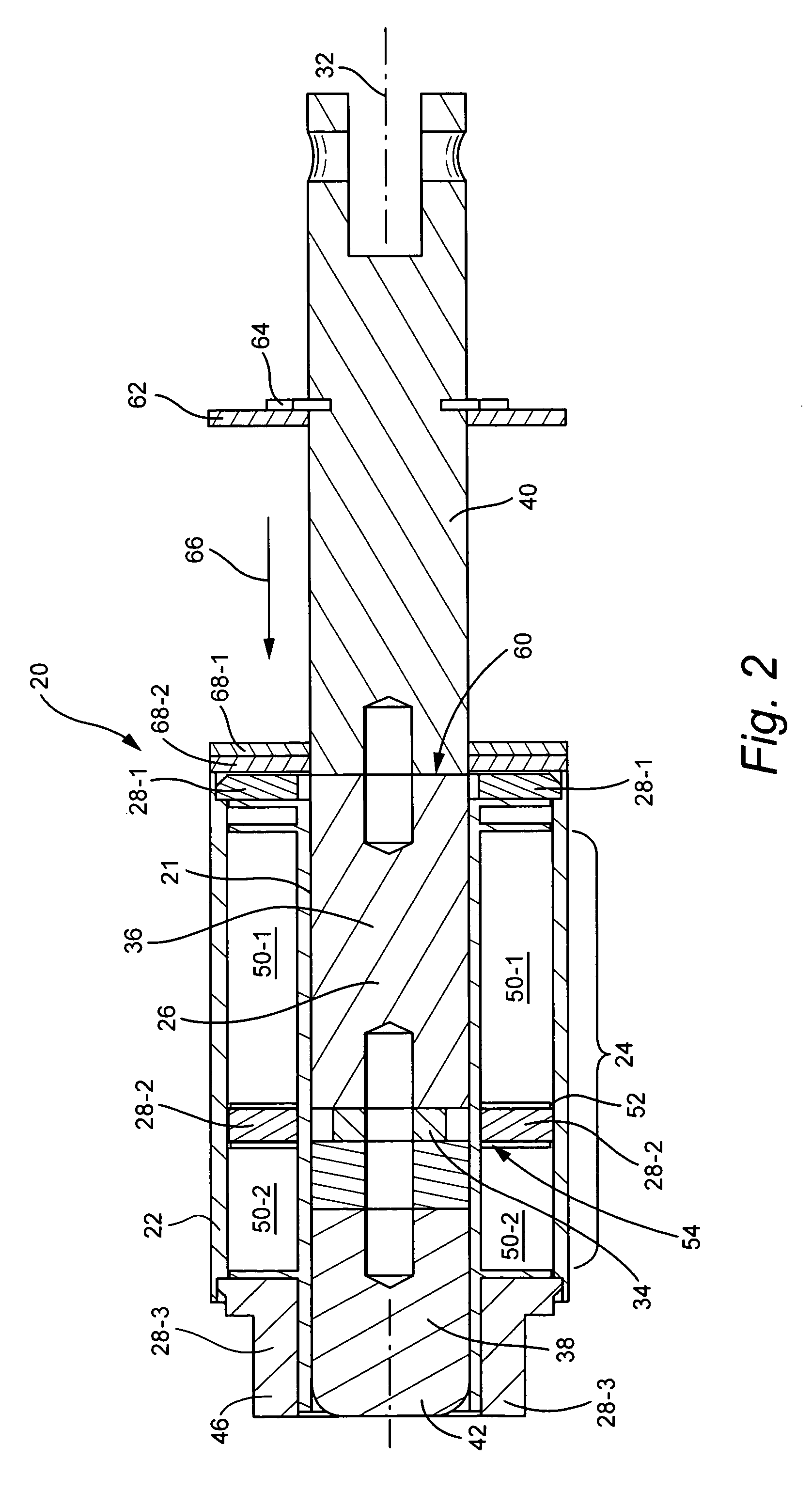
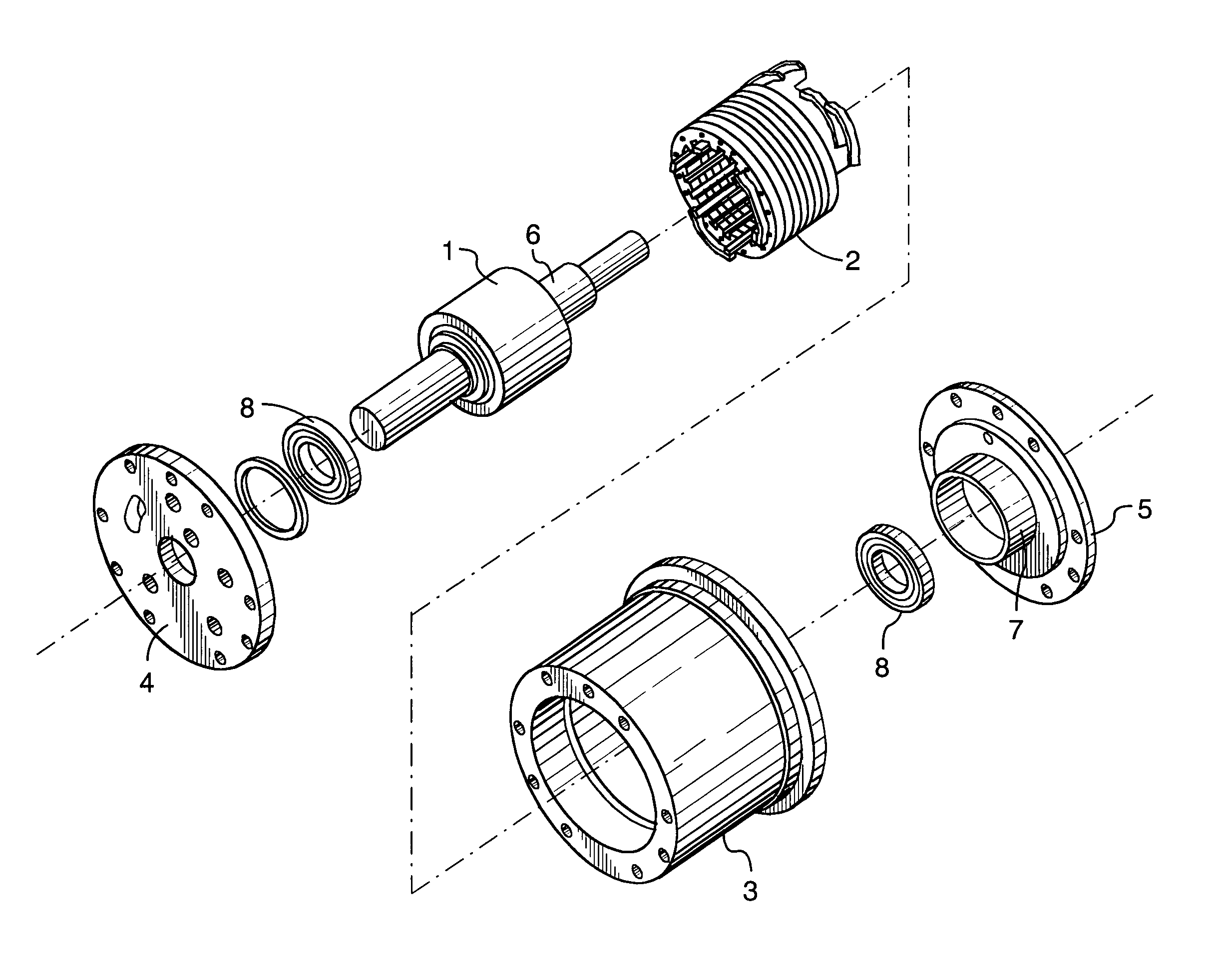
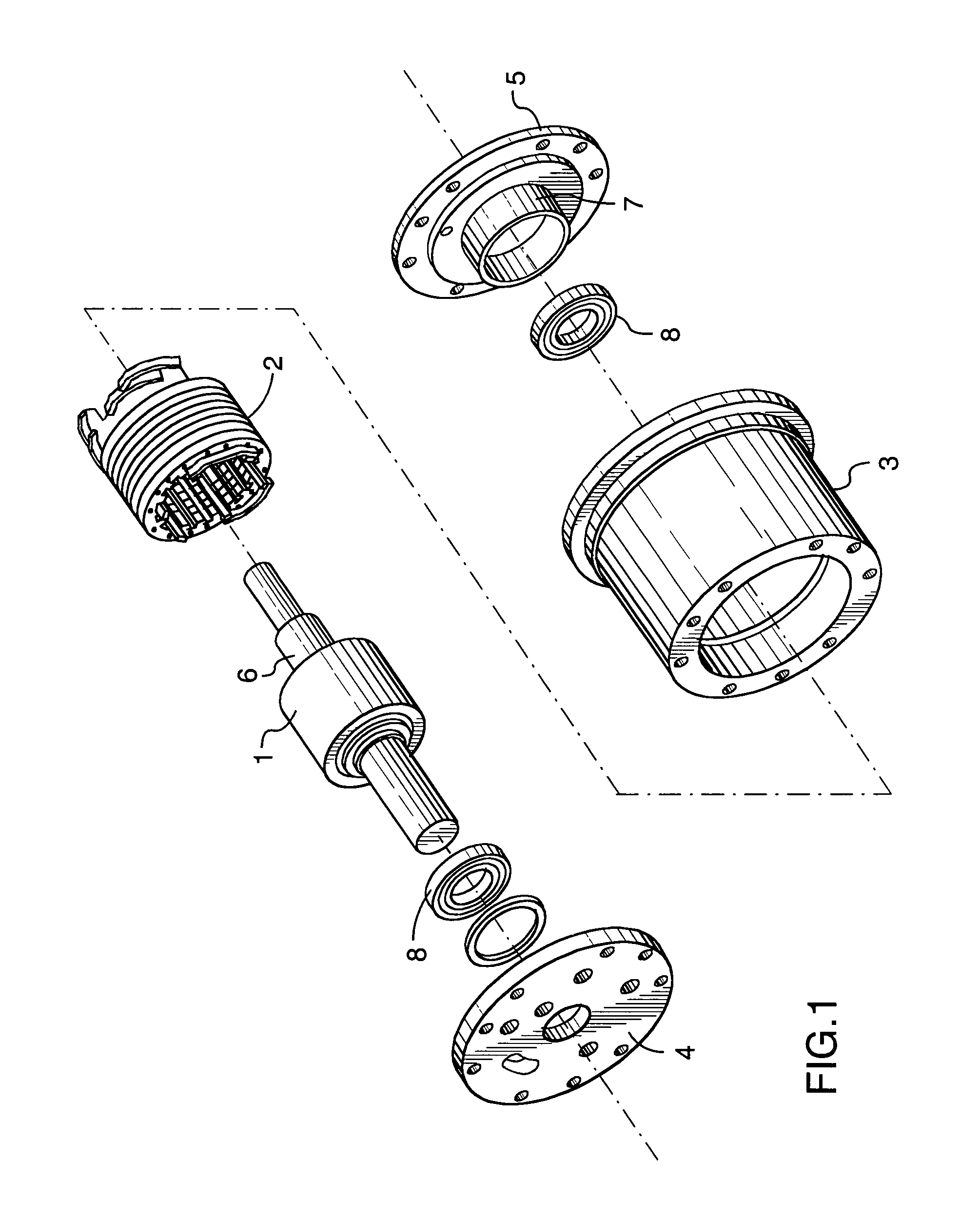
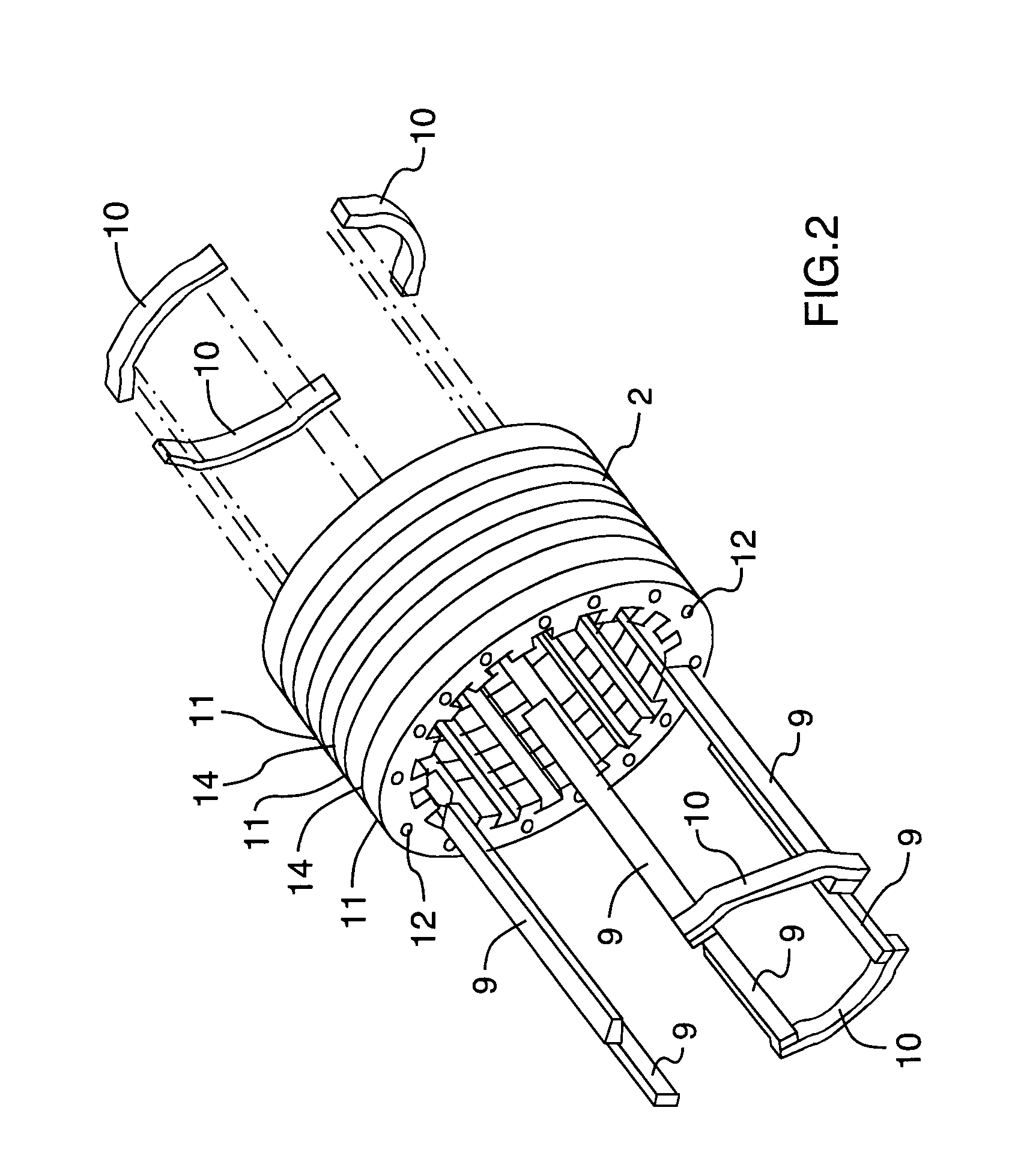
Low-loss inductive couplers for use in wired pipe strings
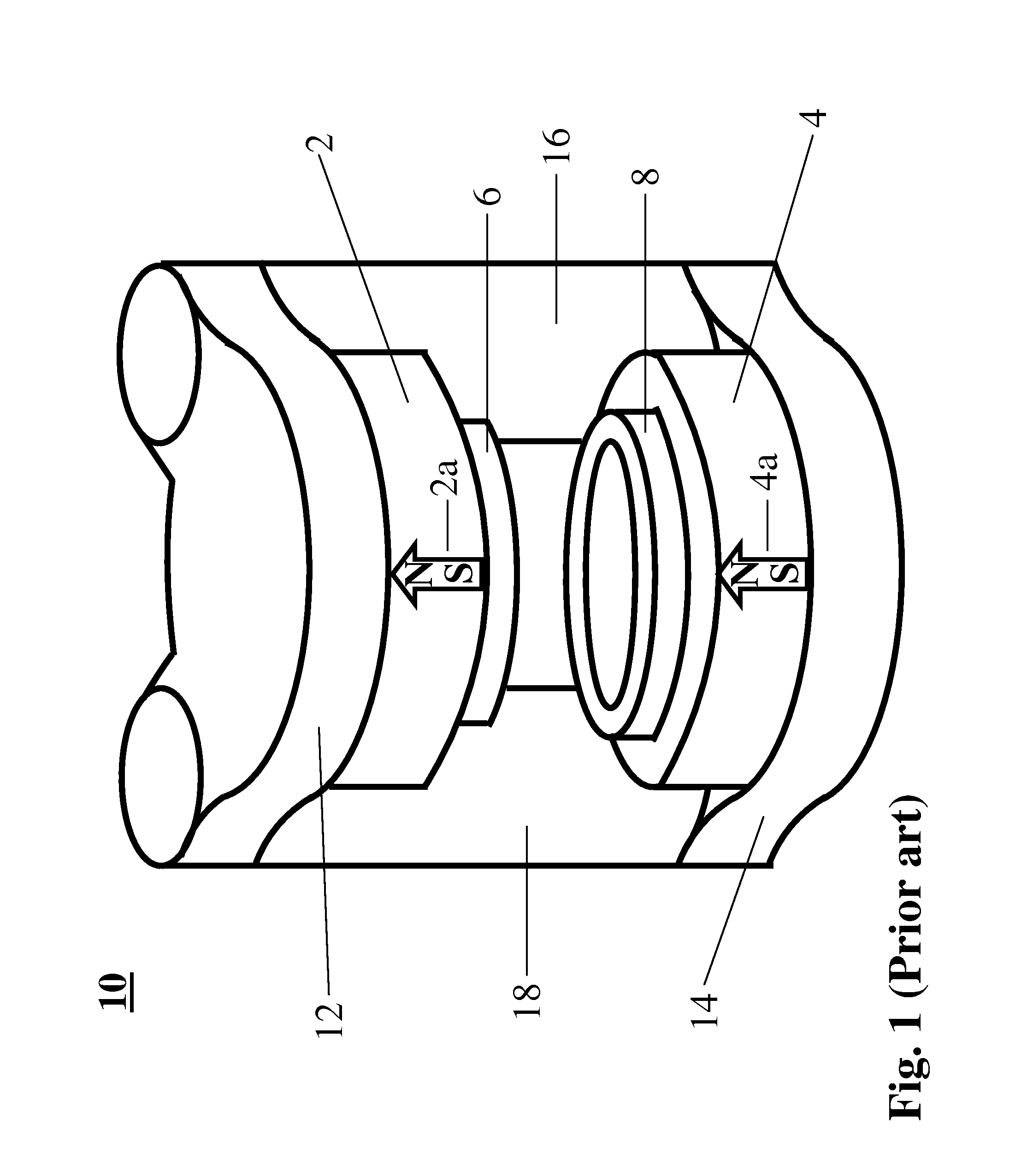
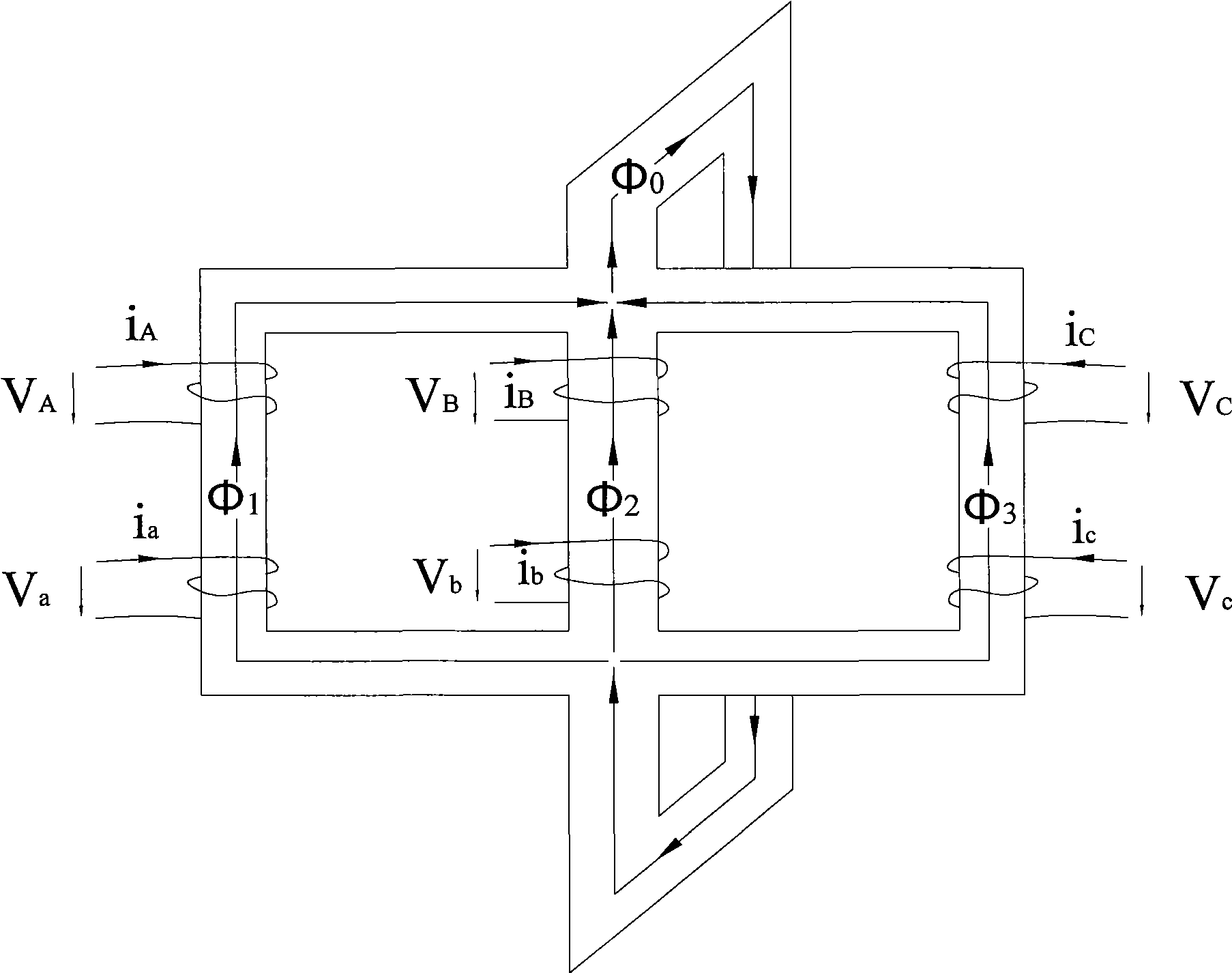
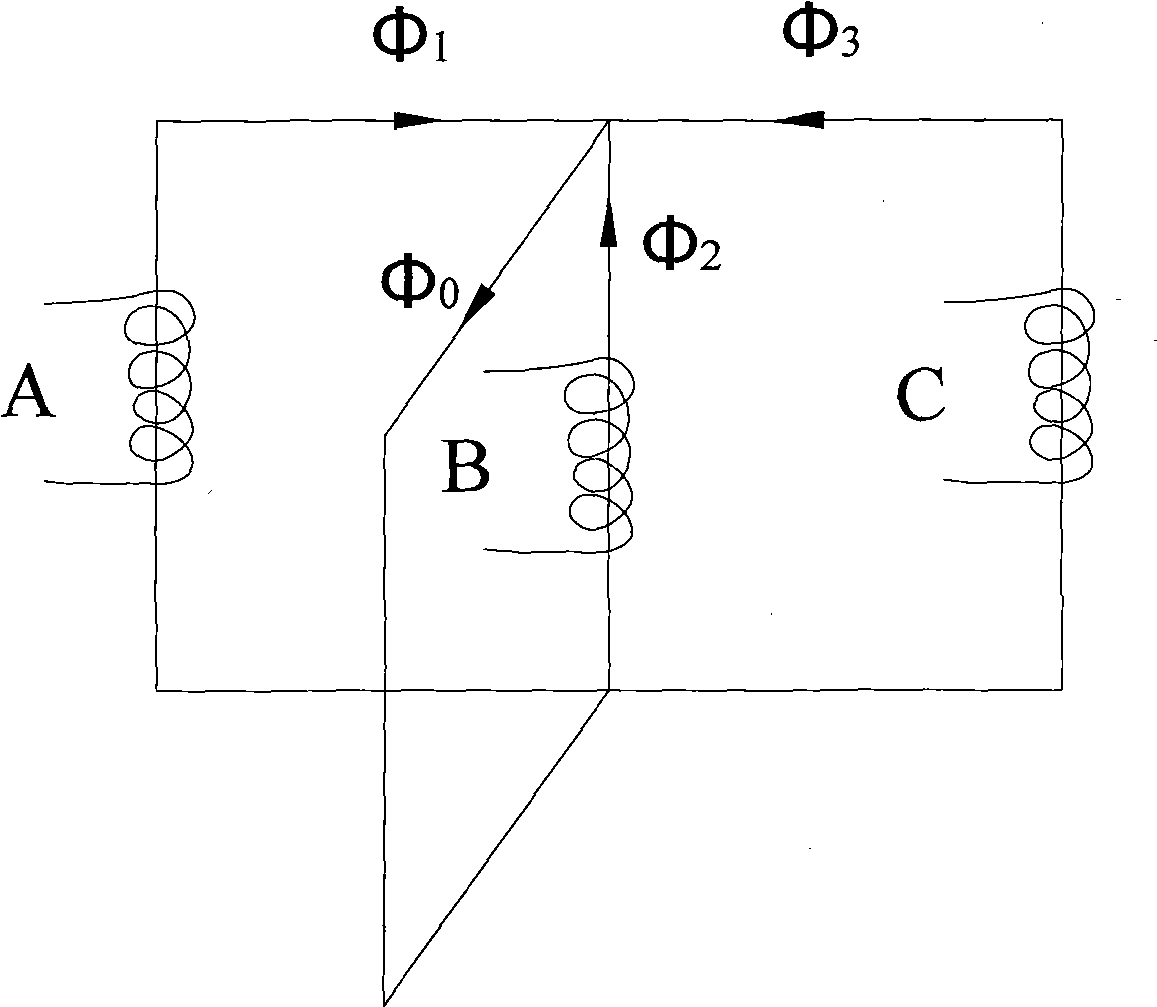
A first flux-loop inductive coupler element electrically couples with a second flux-loop inductive coupler element. The first flux-loop inductive coupler element comprises a first ring-like core having high magnetic permeability and a conical-section annular first face transverse to the plane of the first core. The first face has a first annular groove separating a first conical-section larger-diameter face and a first conical-section smaller-diameter face. A first coil is wound within the annular groove. The first and second cores form a low-reluctance closed magnetic path around the first coil and a second coil of the second flux-loop inductive coupler element.A first current-loop inductive coupler element electrically couples with a second current-loop inductive coupler element. The first current-loop inductive coupler element has a first high-conductivity, low-permeability shaped belt of a first end of a first pipe joint, a first ring-like core located at the first end, and a first electrically conductive coil wound about the first ring-like core. The first high-conductivity, low-permeability shaped belt partially encloses the first coil. It is shaped to cooperate with the second high-conductivity, low-permeability shaped belt of an adjacent second pipe joint having a second electrically conductive coil and a second high-conductivity, low-permeability shaped belt to create a closed toroidal electrical conducting path. The closed toroidal electrical conducting path encloses the first coil and the second coil when the first and second pipe joints are mated.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
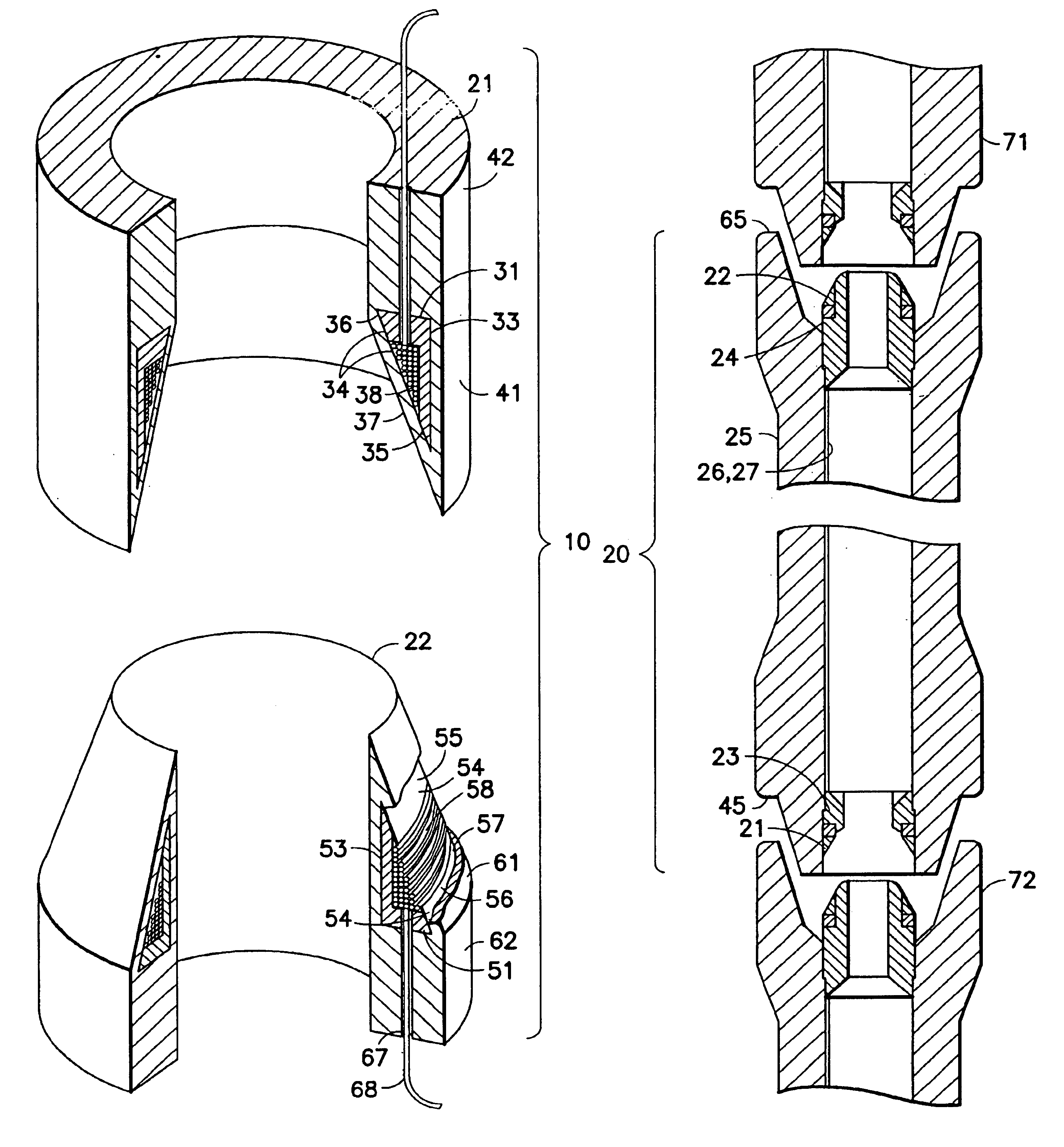
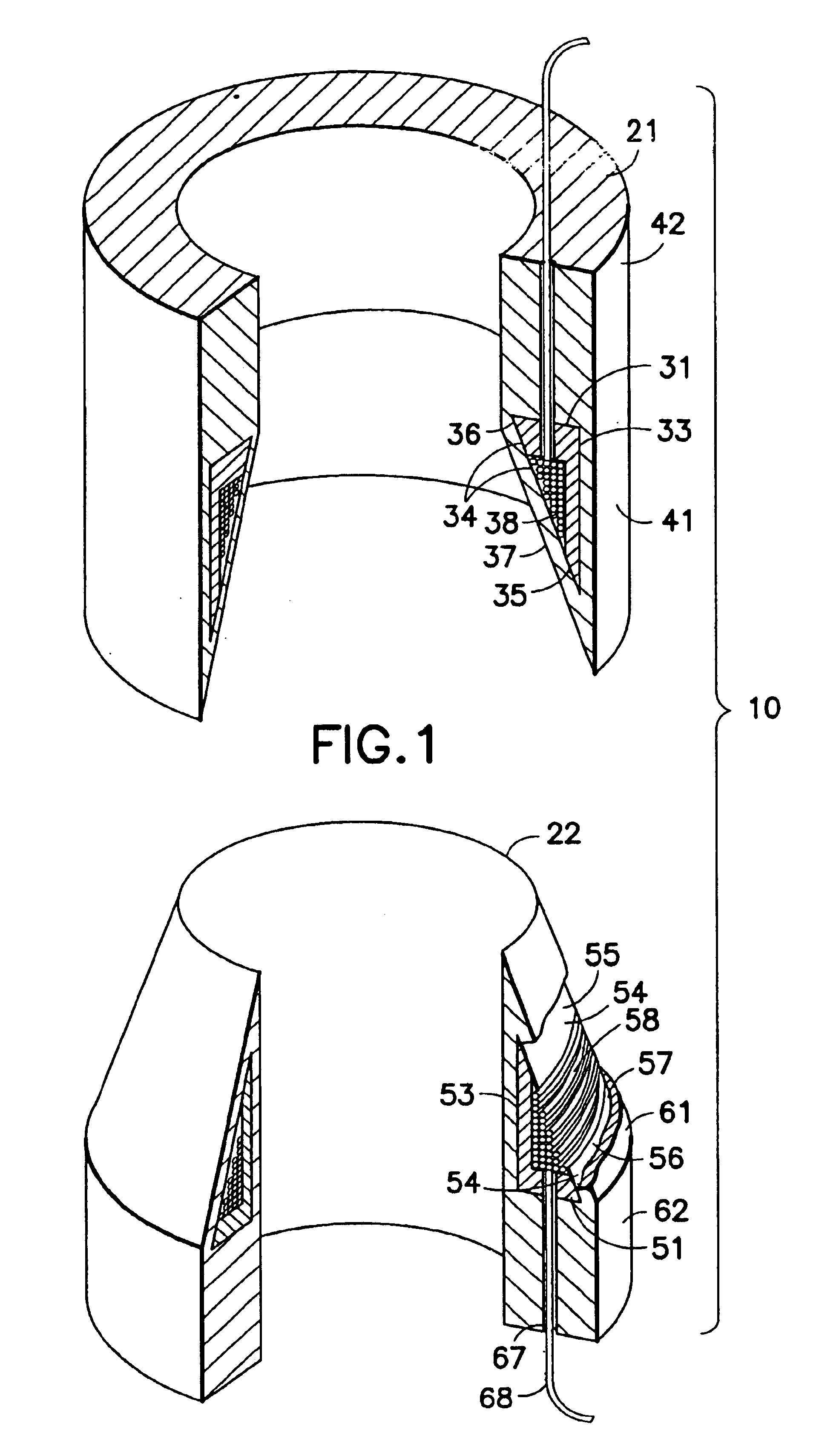
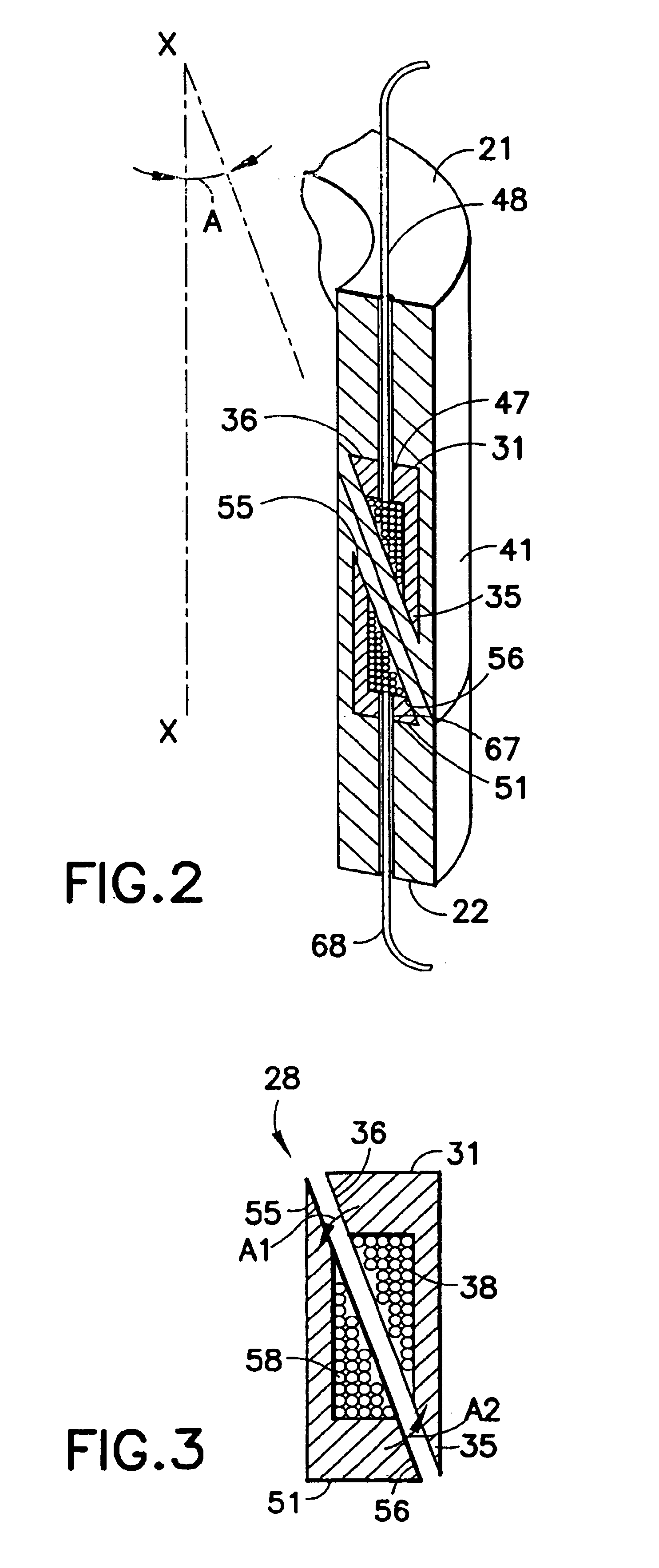
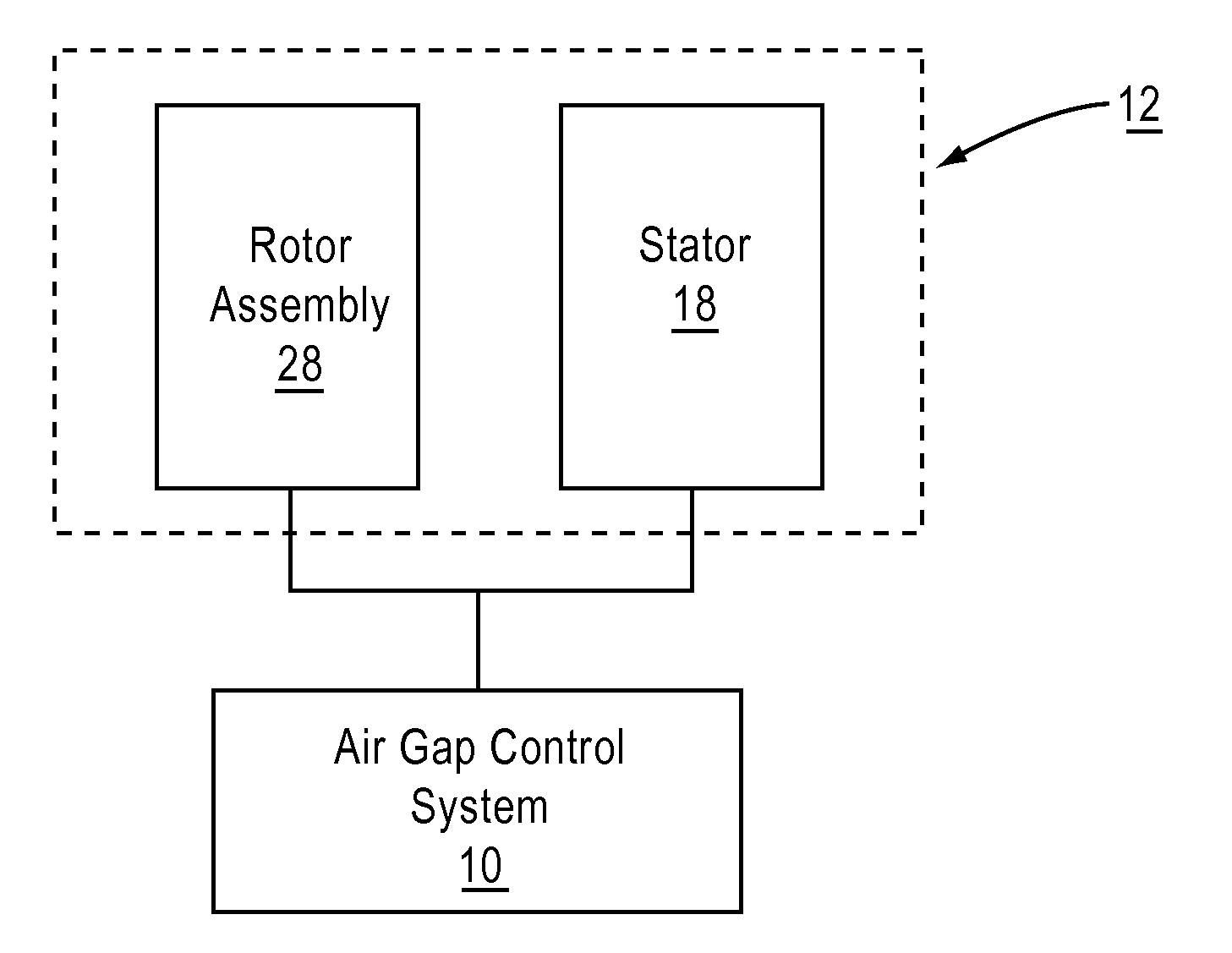
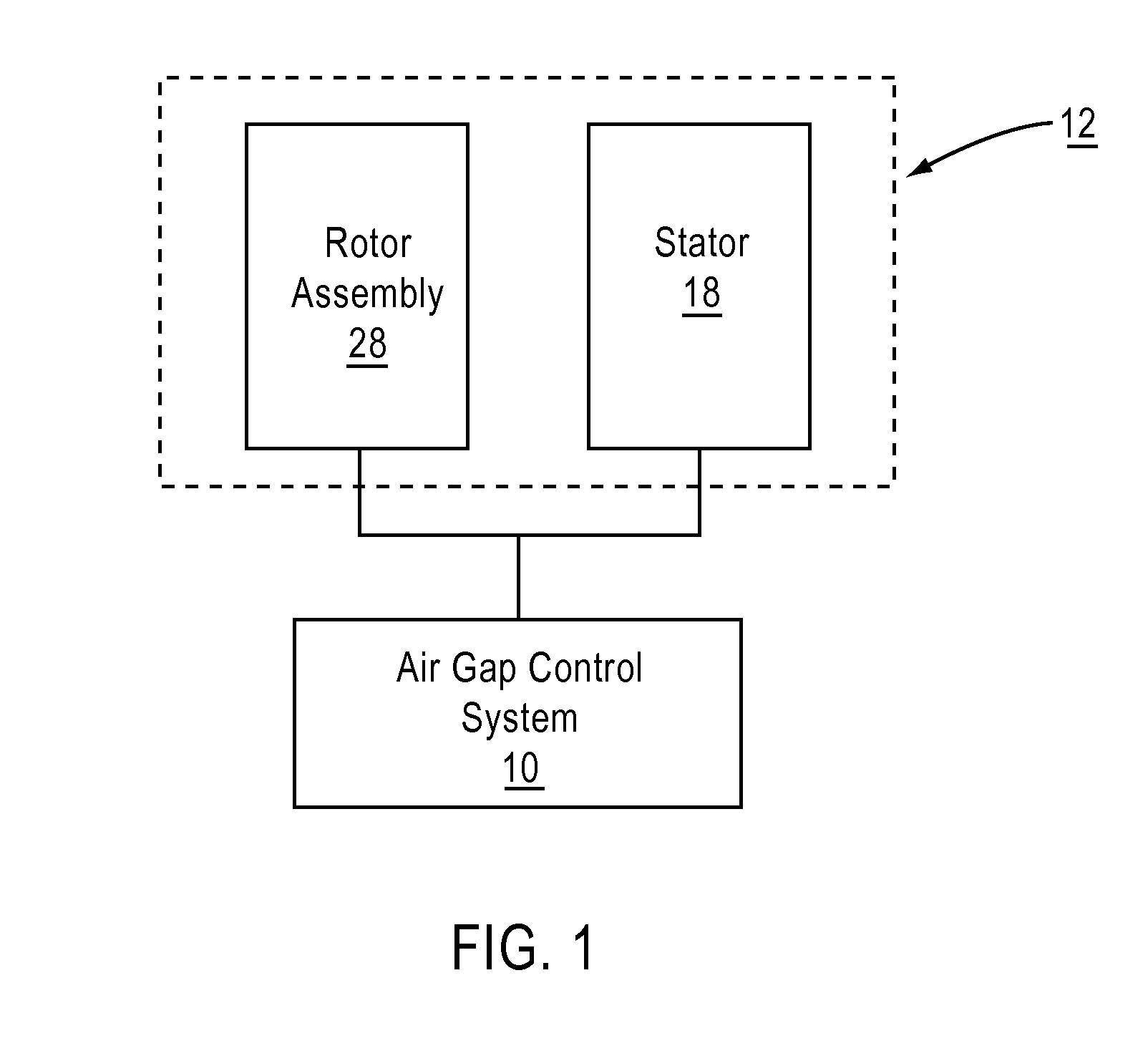
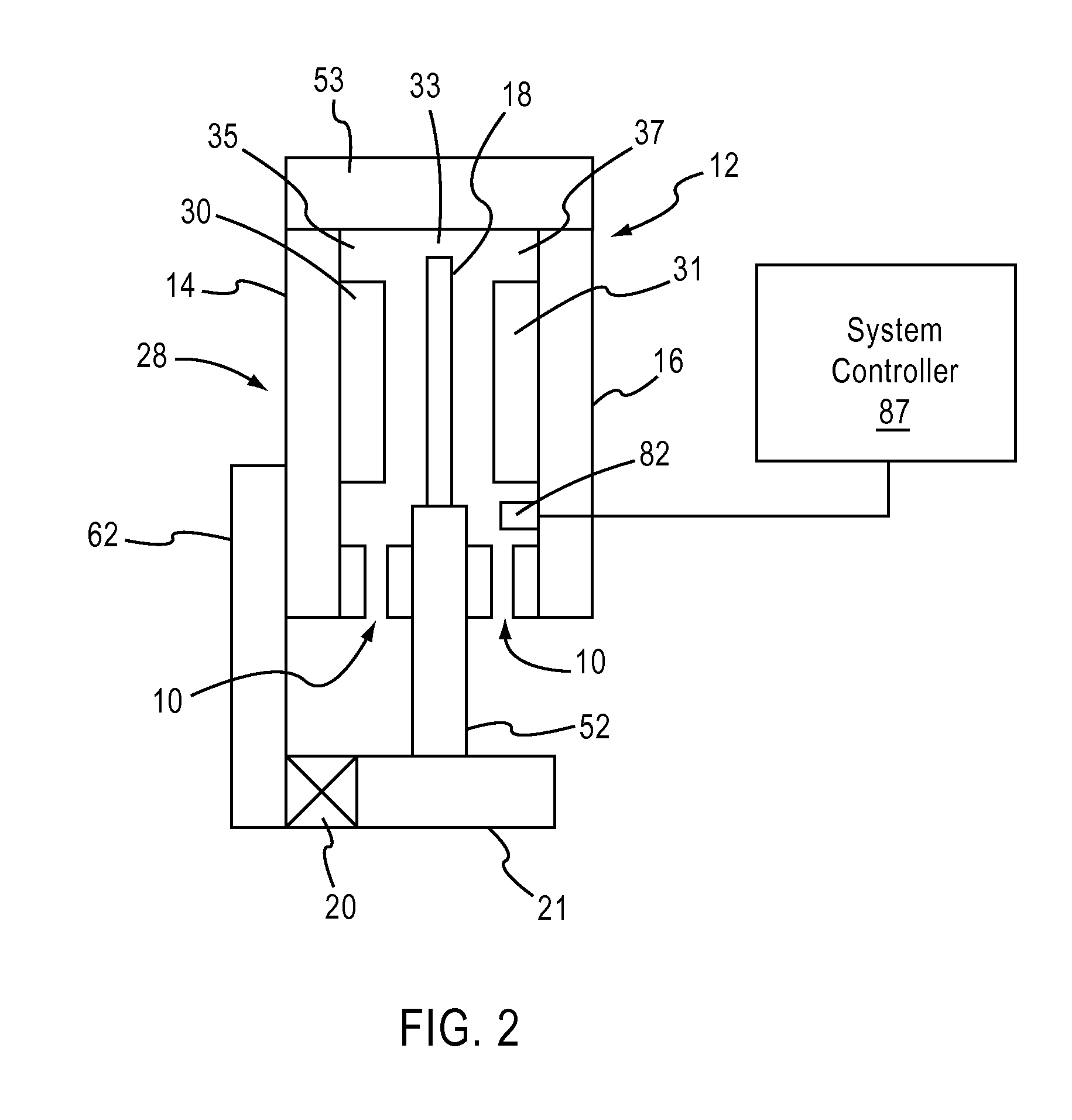
Air gap control systems and methods
ActiveUS20120262095A1Reduce distanceDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlControl systemFlux loop
In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a first member that supports a magnetic flux carrying member and a second member that supports a magnetic flux generating member disposed for movement relative to the first member. An air gap control system is coupled to at least one of the first member or the second member and includes an air gap control device that is separate from a primary magnetic flux circuit formed between the first member and the second member. The air gap control device is configured to exert a force on one of the first and second members in response to movement of the other of the first and second members in a direction that reduces a distance between the first and second members to maintain a minimum distance between the first and second members and / or substantially center the one of the first and second members within the other.
Owner:BWP GRP
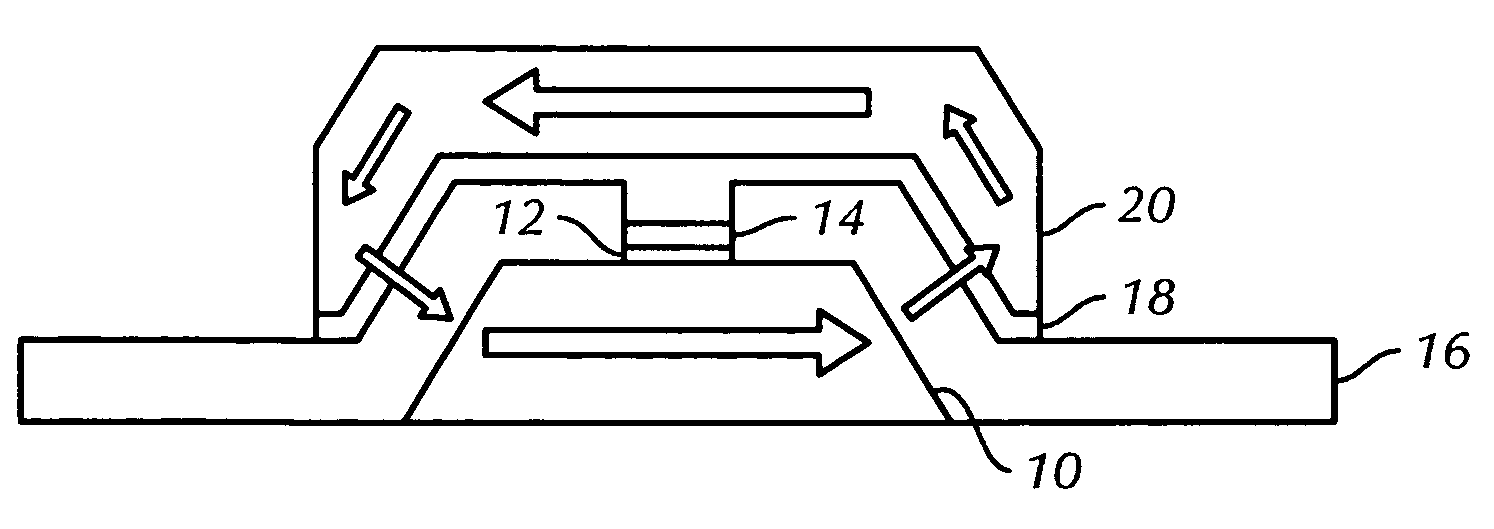
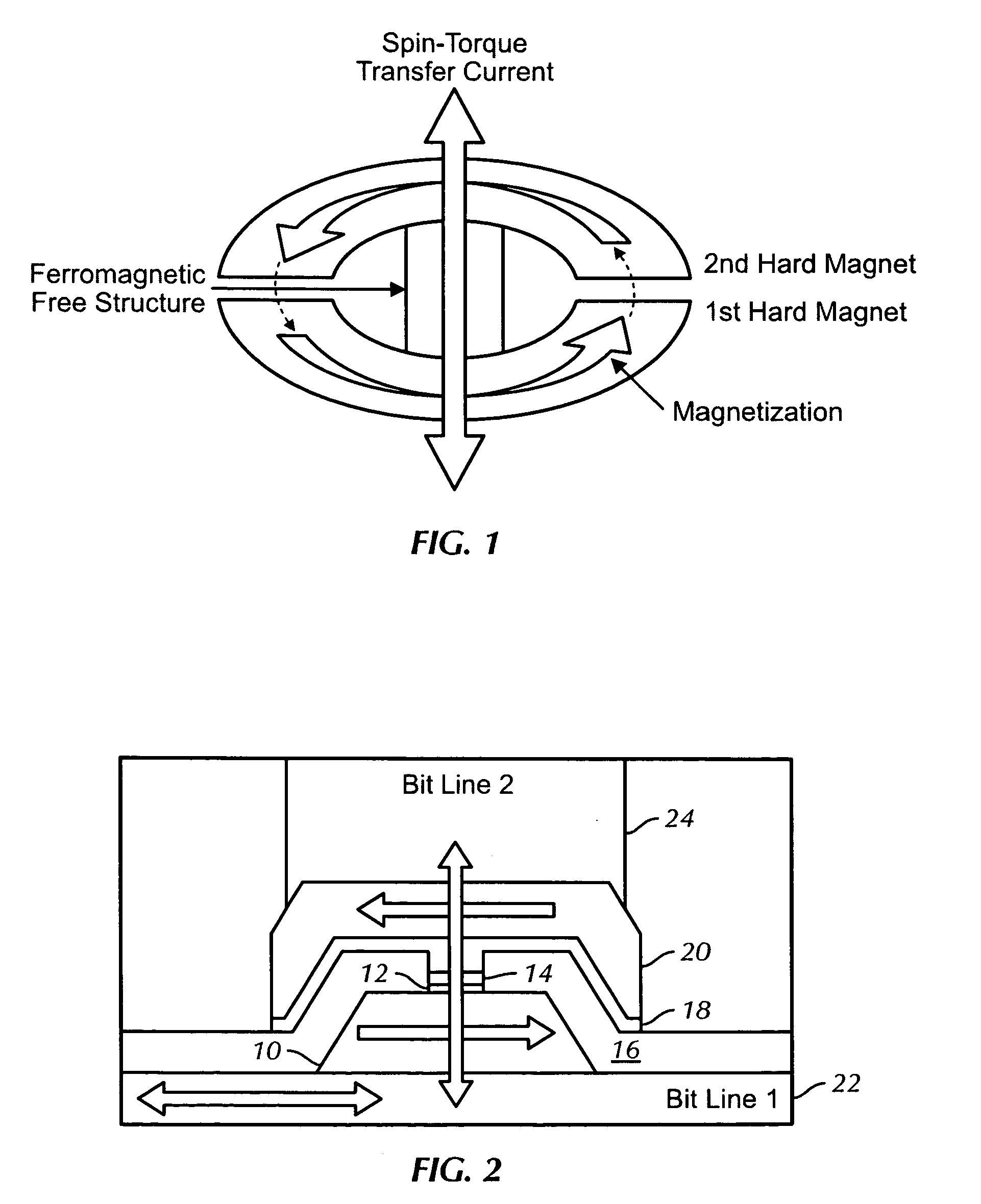
Structure of magnetic random access memory using spin-torque transfer writing and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20080130354A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityStatic random-access memory
A nano-magnetic device includes a first hard magnet having a first magnetization direction and having a central axis. The device also includes a second hard magnet separated from the first hard magnet by a dielectric liner. The second hard magnet has a second magnetization direction opposite to the first magnetization direction of the first hard magnet, and a central axis, such that when the first hard magnet and the second hard magnet are aligned a closed magnetic flux loop is formed through the first and second hard magnets. The device additionally includes a ferromagnetic free layer having a central axis. A spin-torque transfer current passes along the central axes of the first and second hard magnets and the ferromagnetic free layer, and affects the magnetization direction of the ferromagnetic free layer.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Open MRI Magnetic Field Generator
ActiveUS20090085700A1Reducing fringe field generationEfficient yokeMagnetic measurementsPermanent magnetsWhole bodyFlux loop
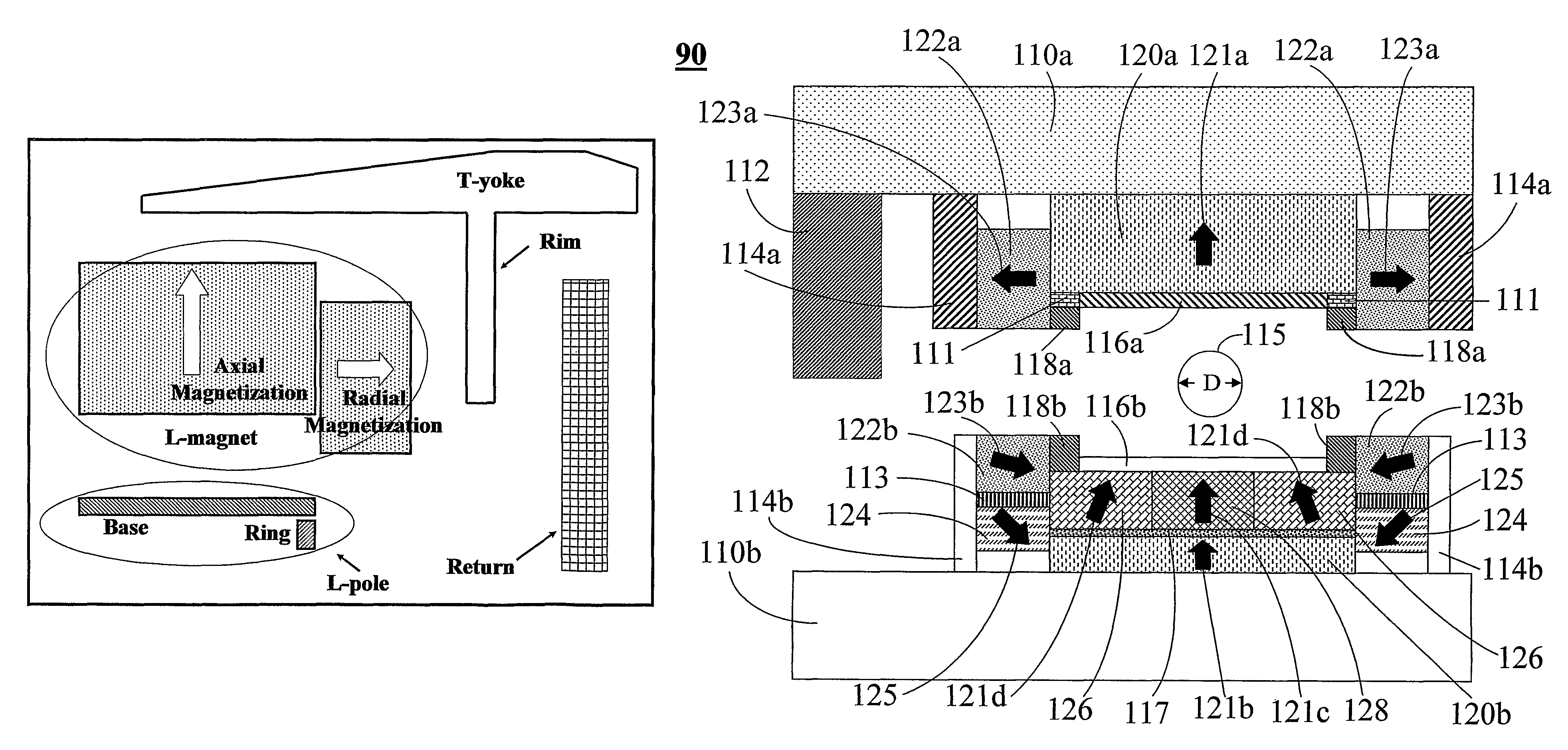
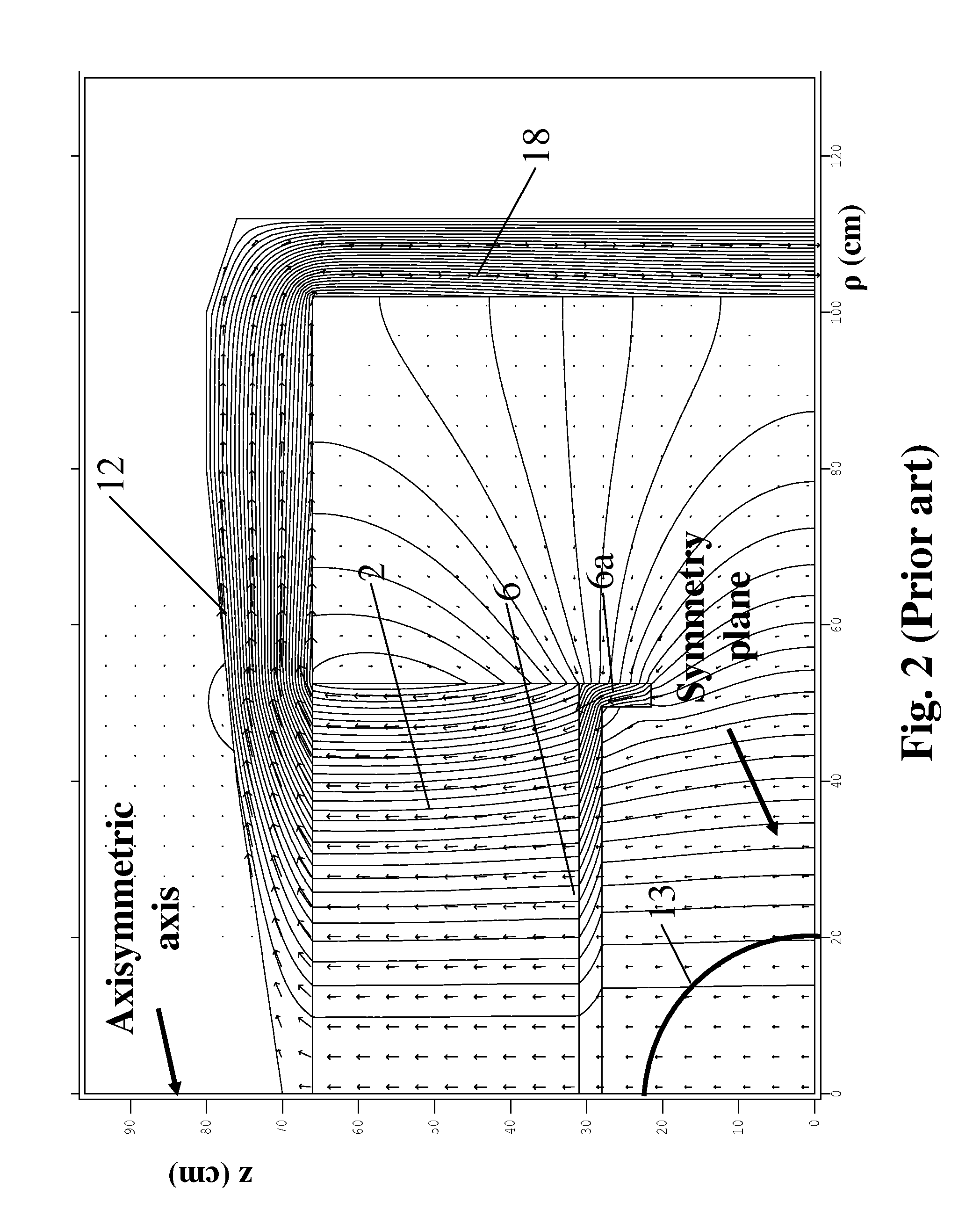
A magnet primarily for use in MRI applications comprises a pair of poles oriented about a plane of symmetry parallel to each therebetween defining an air gap region, magnetic field sources secured on the surfaces of the poles opposite the air gap that have yokes disposed on them, the yokes connected to each other by returns so that the entire magnet assembly can form a closed magnetic flux circuit to substantially confine the magnetic fields generated by the apparatus in the air gap where an imaging region is formed to place subjects for the purposes of examination. The main assembly being cylindrical in geometry has permanent magnets for magnetic field sources that are composed of two regions, a central disk-like portion magnetized substantially along the axial direction and an outer ring-like region magnetized substantially along the radial direction extending axially to form part of the pole together producing a very efficient and even flux distribution throughout the entire magnet assembly with minimal flux leakage. A further means of reducing flux leakage is incorporated in the yokes which have two sections, a disk-like region and an ring-like section to enclose the permanent magnets. The poles are made of multiple sections with a central disk-like region and an outer ring-like region that is a combination of permanent magnets and high permeability materials. This magnet assembly can achieve 1.0 Tesla or greater magnetic fields for whole-body scanning without saturating the magnet pole and other structures.
Owner:LIAN JIANYU +2
Nitrogen trifluoride production apparatus
InactiveUS6010605AHigh purityReduce impurityElectrolysis componentsNitrogen trifluorideHydrogen fluorideBoron trifluoride
Apparatus is disclosed for the production of nitrogen trifluoride (NF3), starting with an anhydrous molten flux including ammonia (NH3), a metal fluoride (MF), and hydrogen fluoride (HF). The apparatus includes an electrolyzer, an ammonia solubilizer, a hydrogen fluoride solubilizer, a nitrogen trifluoride reactor, two compressors, two pumps, three condensers a gas recycle loop, and, two flux loops of the same component ternary flux, but each loop with different concentration.
Owner:FLORIDA SCI LAB
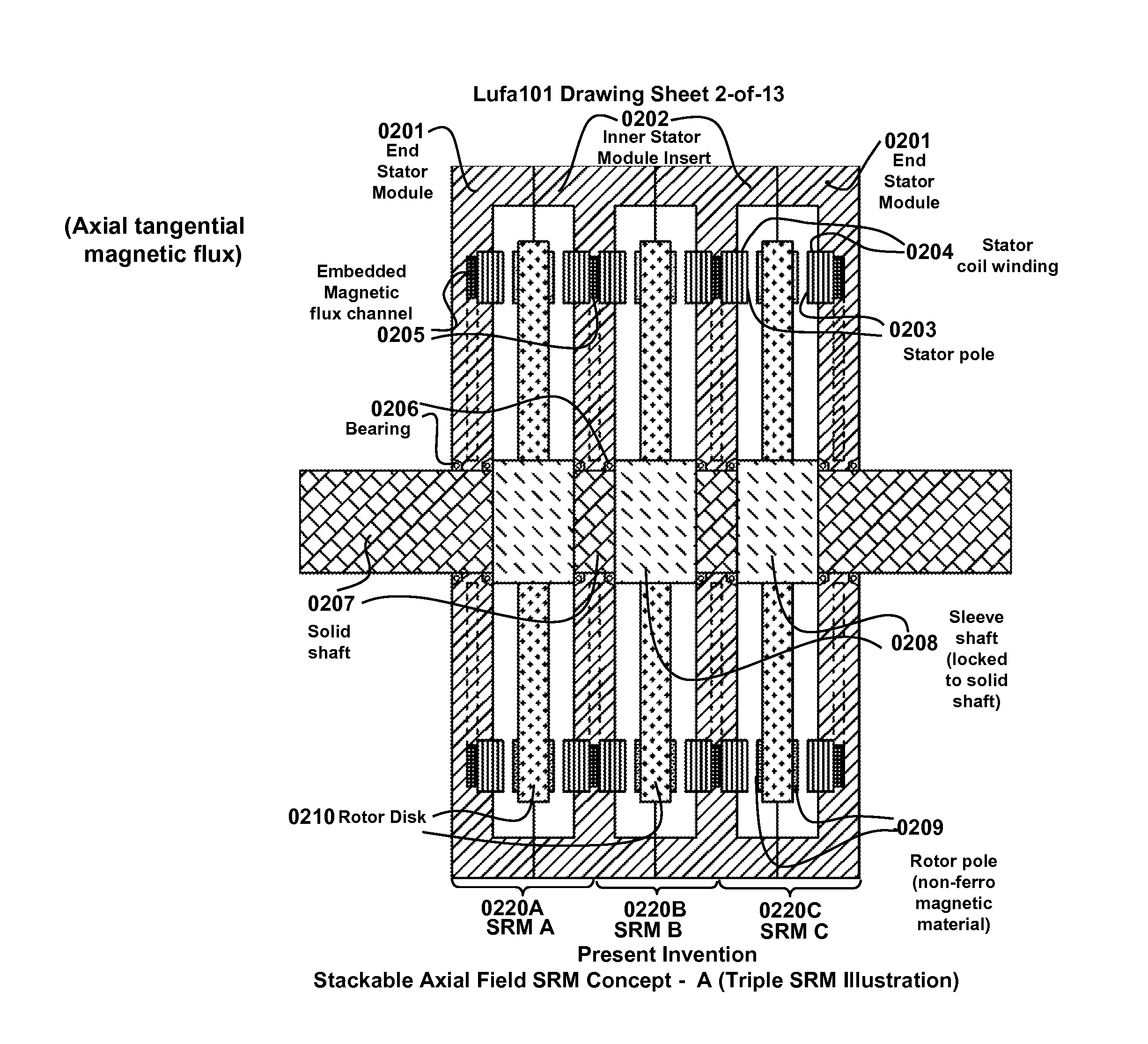
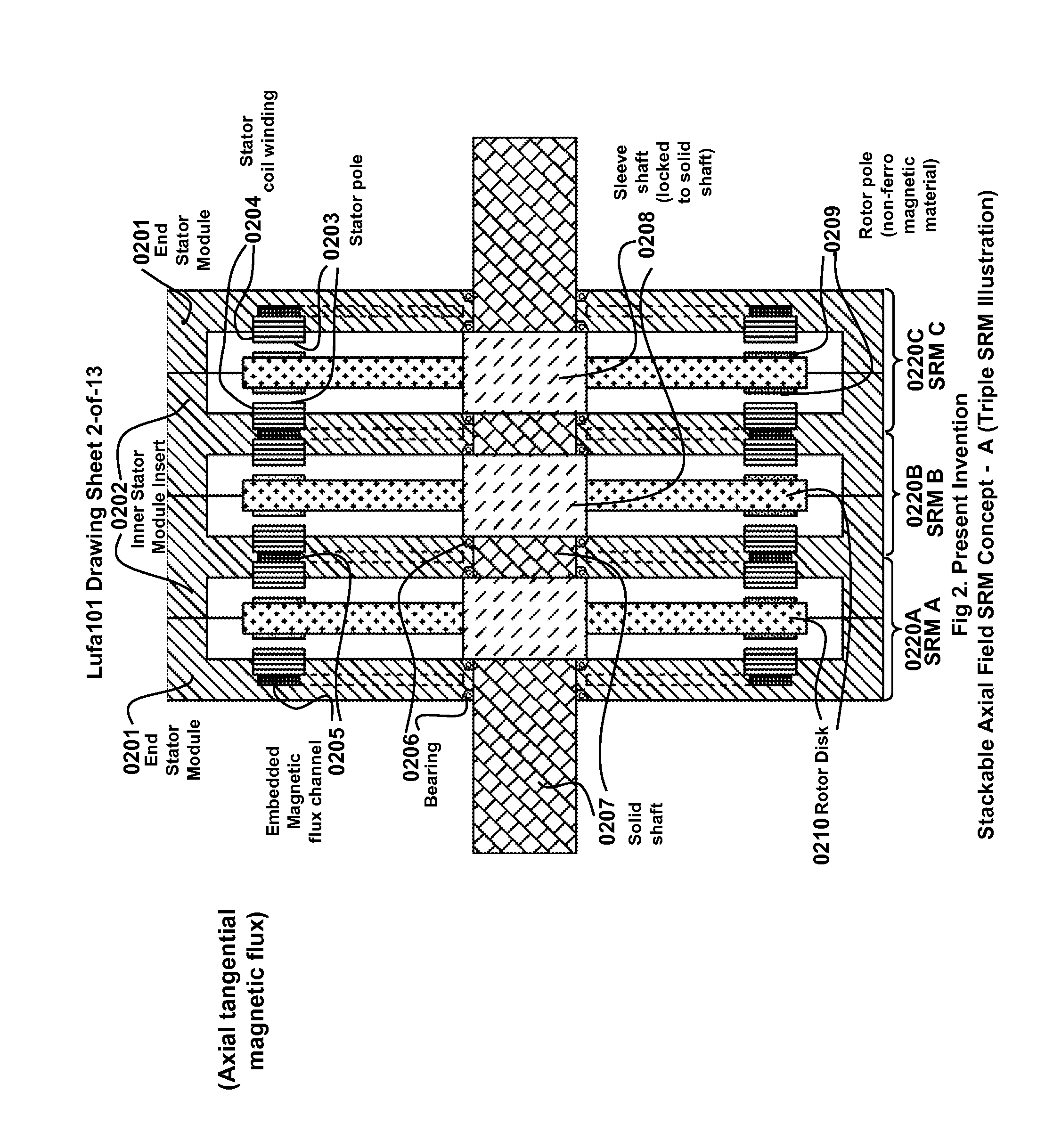
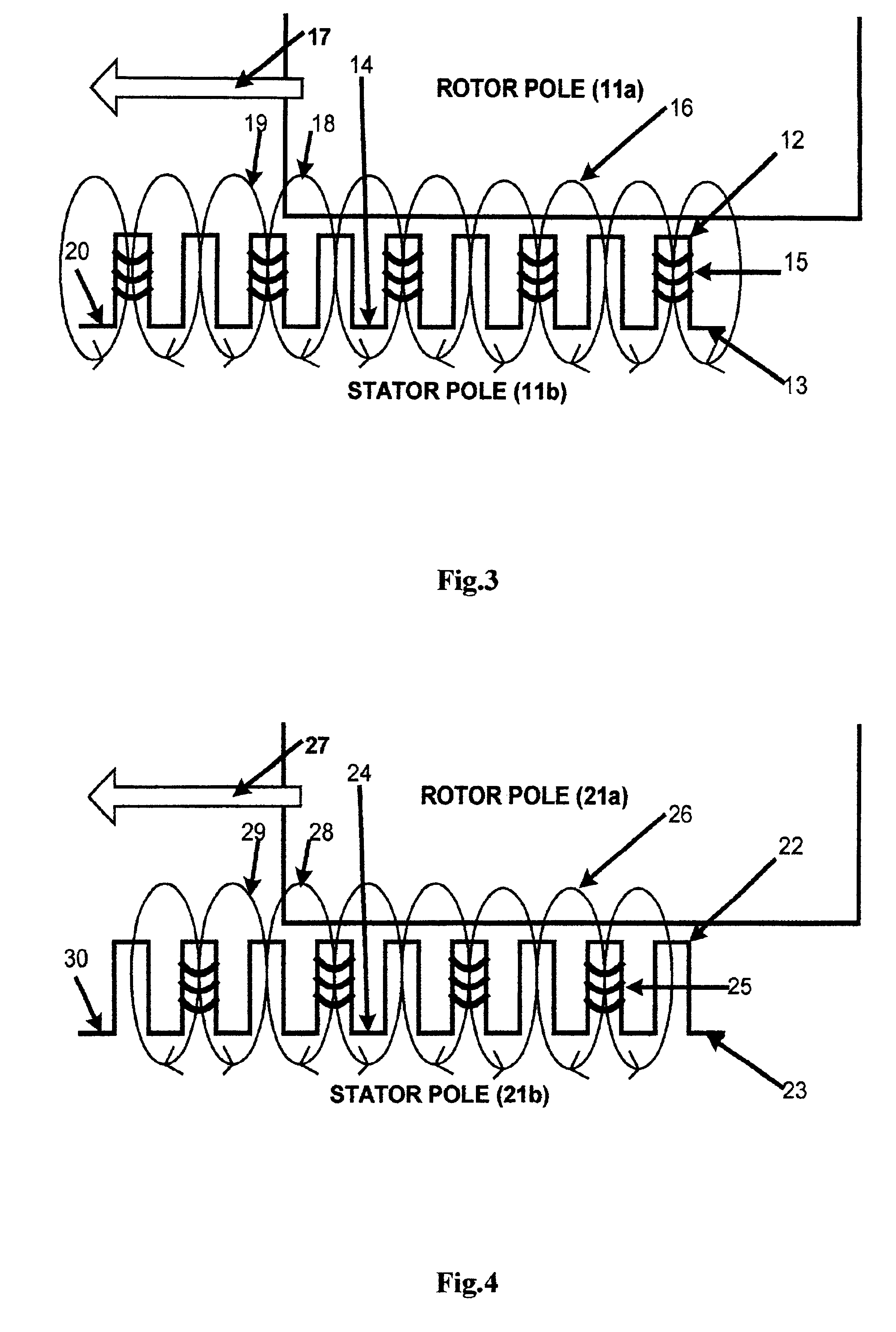
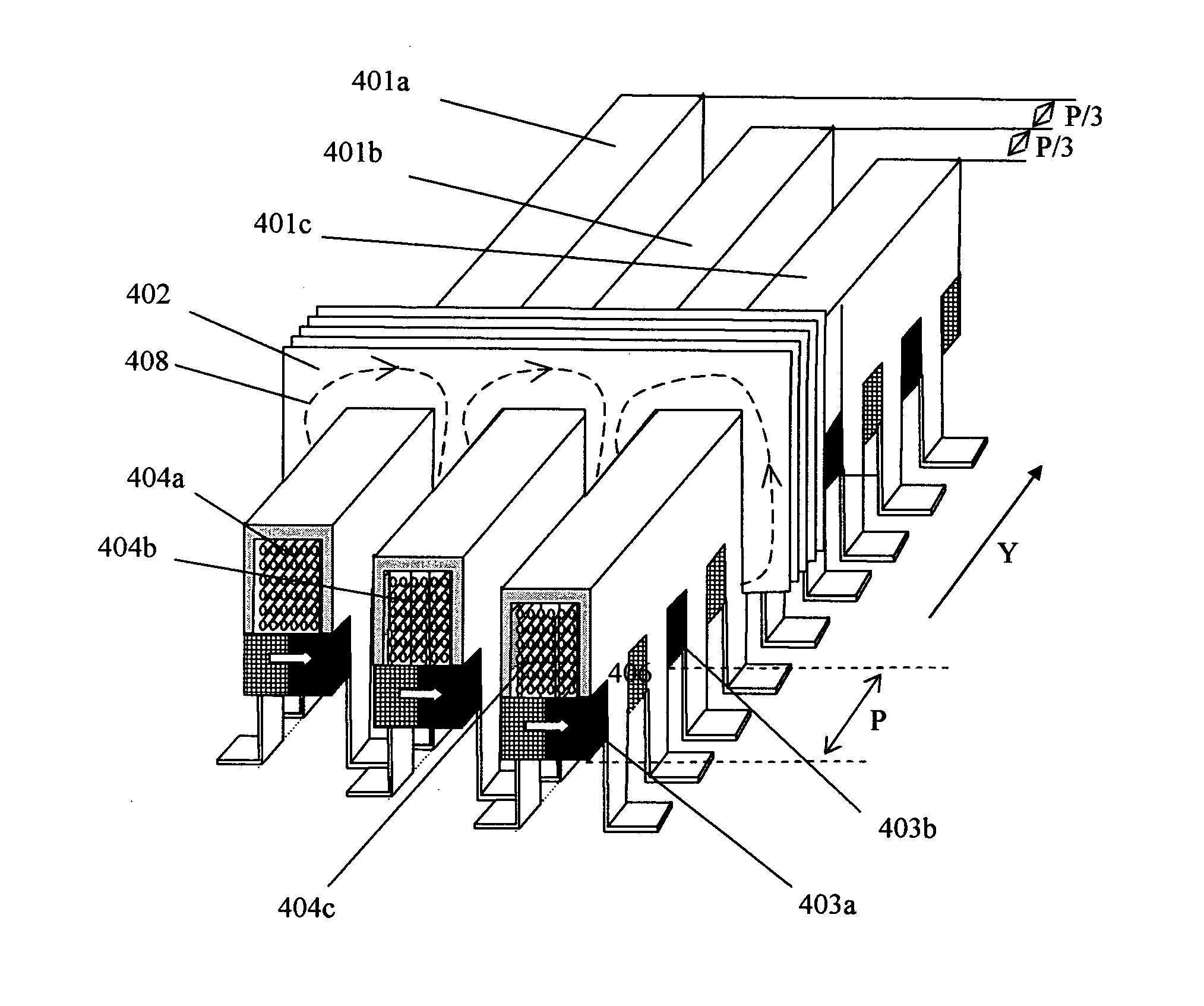
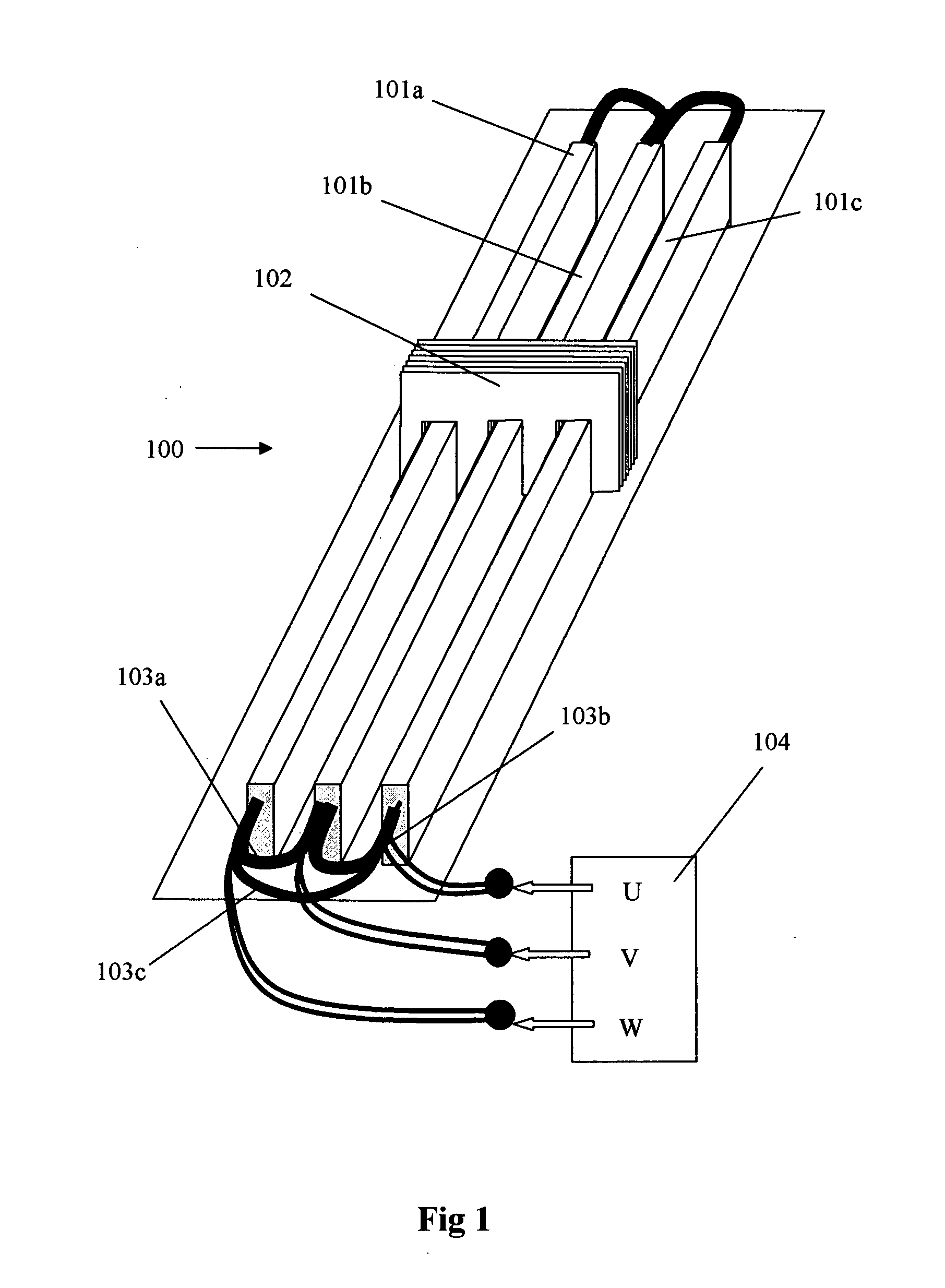
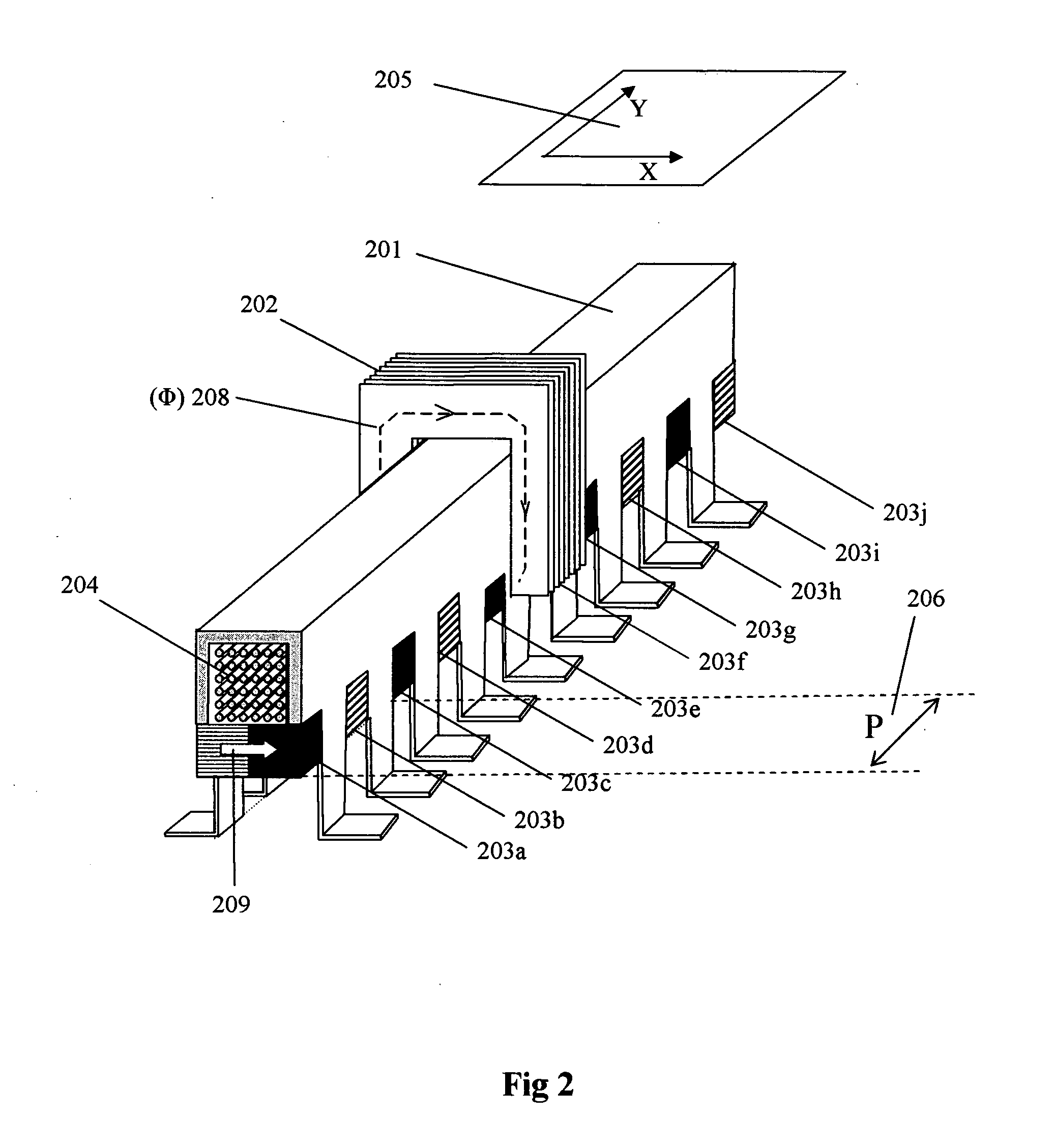
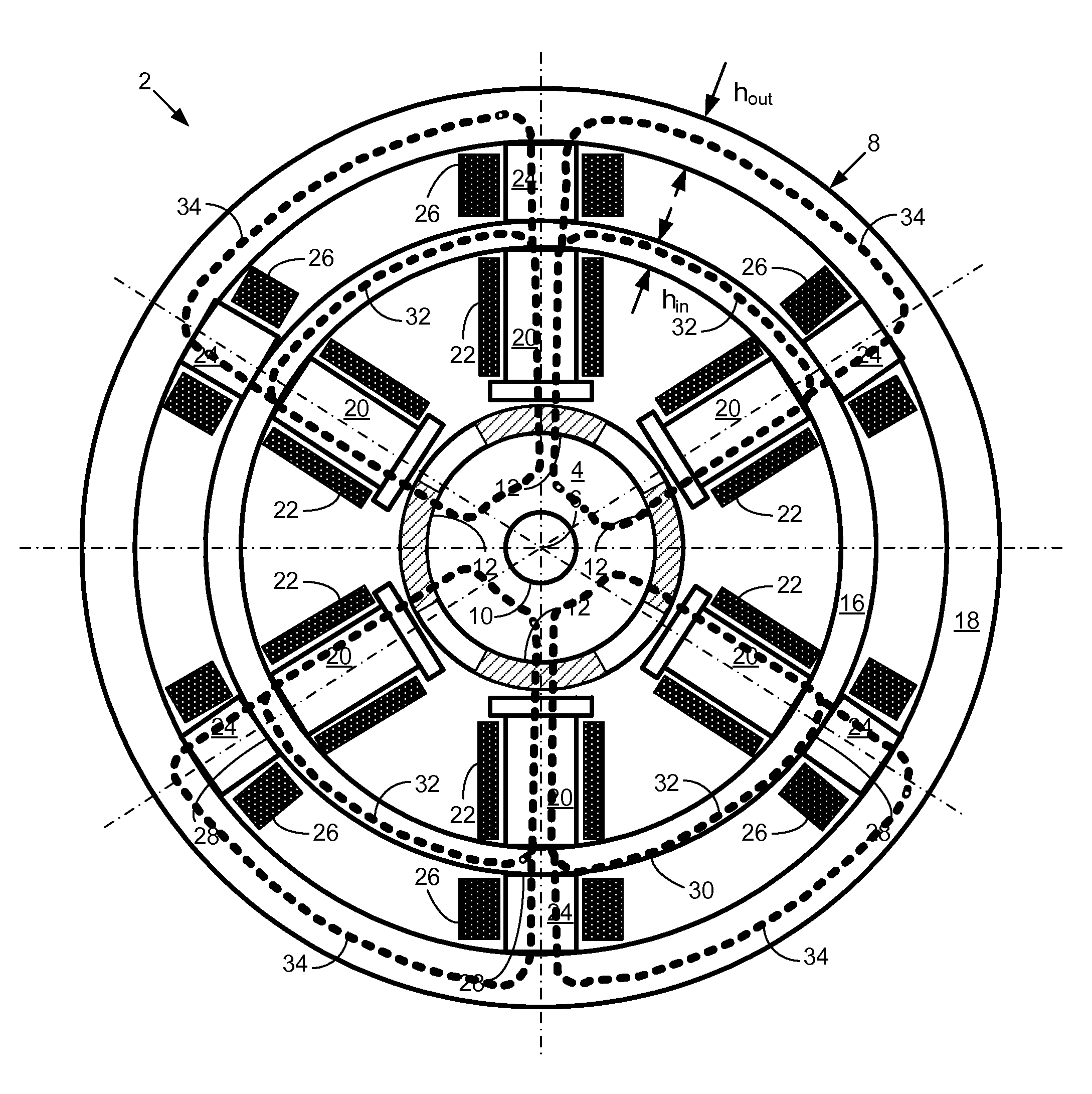
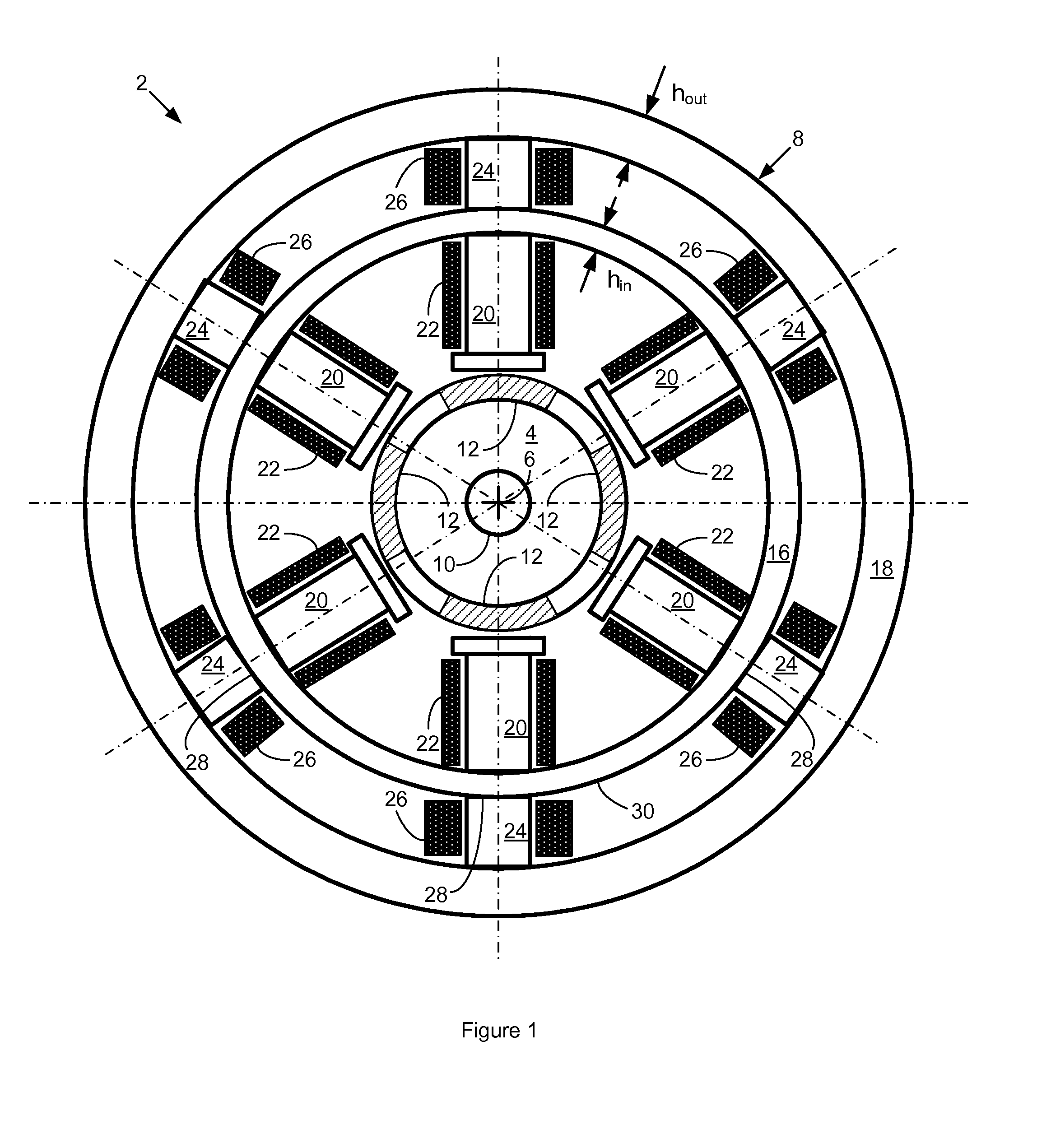
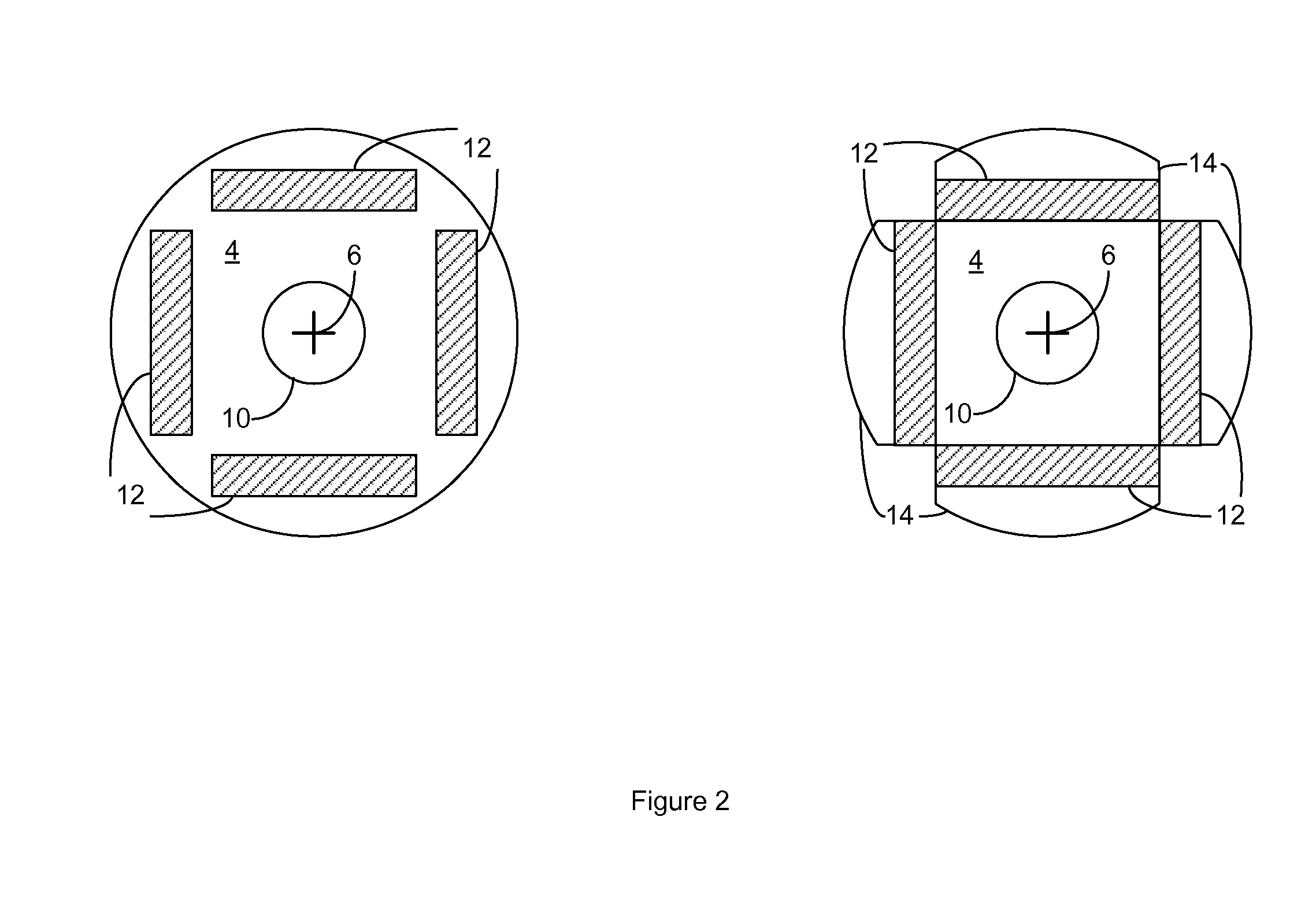
Multi-unit Modular Stackable Switched Reluctance Motor System with Parallely Excited Low Reluctance Circumferential Magnetic Flux loops for High Torque Density Generation
InactiveUS20120001502A1Increased torque densityLow costMagnetic circuitSynchronous machinesFlux loopTransformer
The present invention is a apparatus of multi-unit modular stackable switched reluctance motor system with parallely excited low reluctance circumferential magnetic flux loops for high torque density generation. For maximized benefits and advanced motor features, the present invention takes full combined advantages of both SRM architecture and “Axial Flux” architecture by applying “Axial Flux” architecture into SRM design without using any permanent magnet, by modularizing and stacking the “Axial Flux” SRM design for easy configuration and customization to satisfy various drive torque requirements and broad applications, and by incorporating an en energy recovery transformer for minimizing switching circuitry thus further lowering the cost and further increasing the reliability and robustness. Unlike prior arts, the present invention does not use any permanent magnet and this “Axial Flux” SRM system is modularized and stackable with many benefits.
Owner:LUSTONE TECH
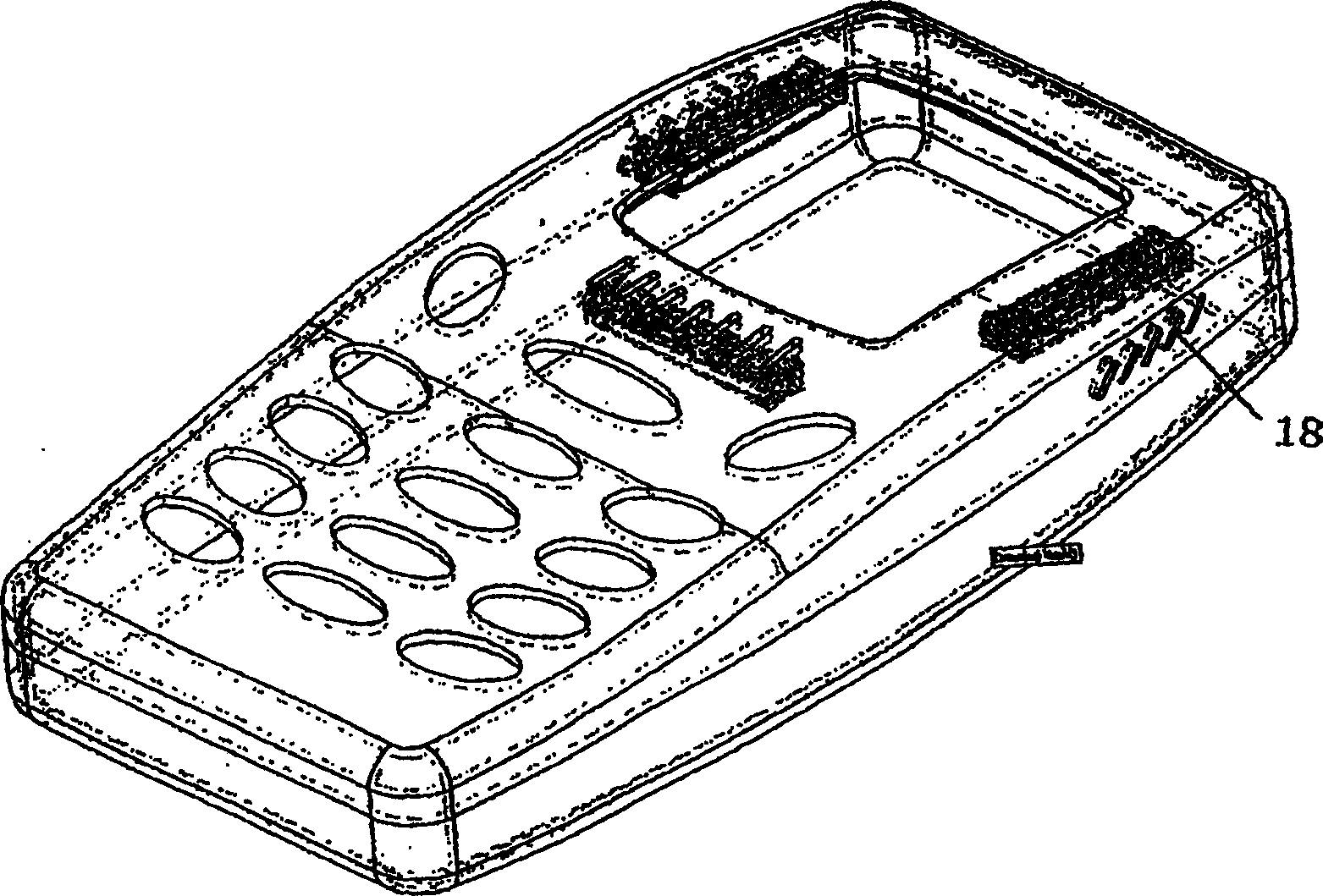
Mobile handset and assembly having multi-loudspeaker system
The present invention relates to a mobile handset comprising a handset housing comprising a front and a back cover, display means being visible from the front cover side of the handset housing, the display means being adapted to provide visual information to a user of the mobile handset. The mobile handset further comprises a plurality of loudspeakers being adapted to generate audio signals, wherein each of the plurality of loudspeakers comprises a magnetic circuit comprising a magnet, the magnetic circuit having at least one gap defined between two opposed and substantially parallel surfaces of the magnetic circuit. The magnet of the magnetic circuit causes a magnetic field to exist across the at least one gap. The magnetic circuit is so arranged that it defines magnetic return paths completely encircling the gap.
Owner:桑尼昂霍森斯公司
Soft latch bidirectional quiet solenoid
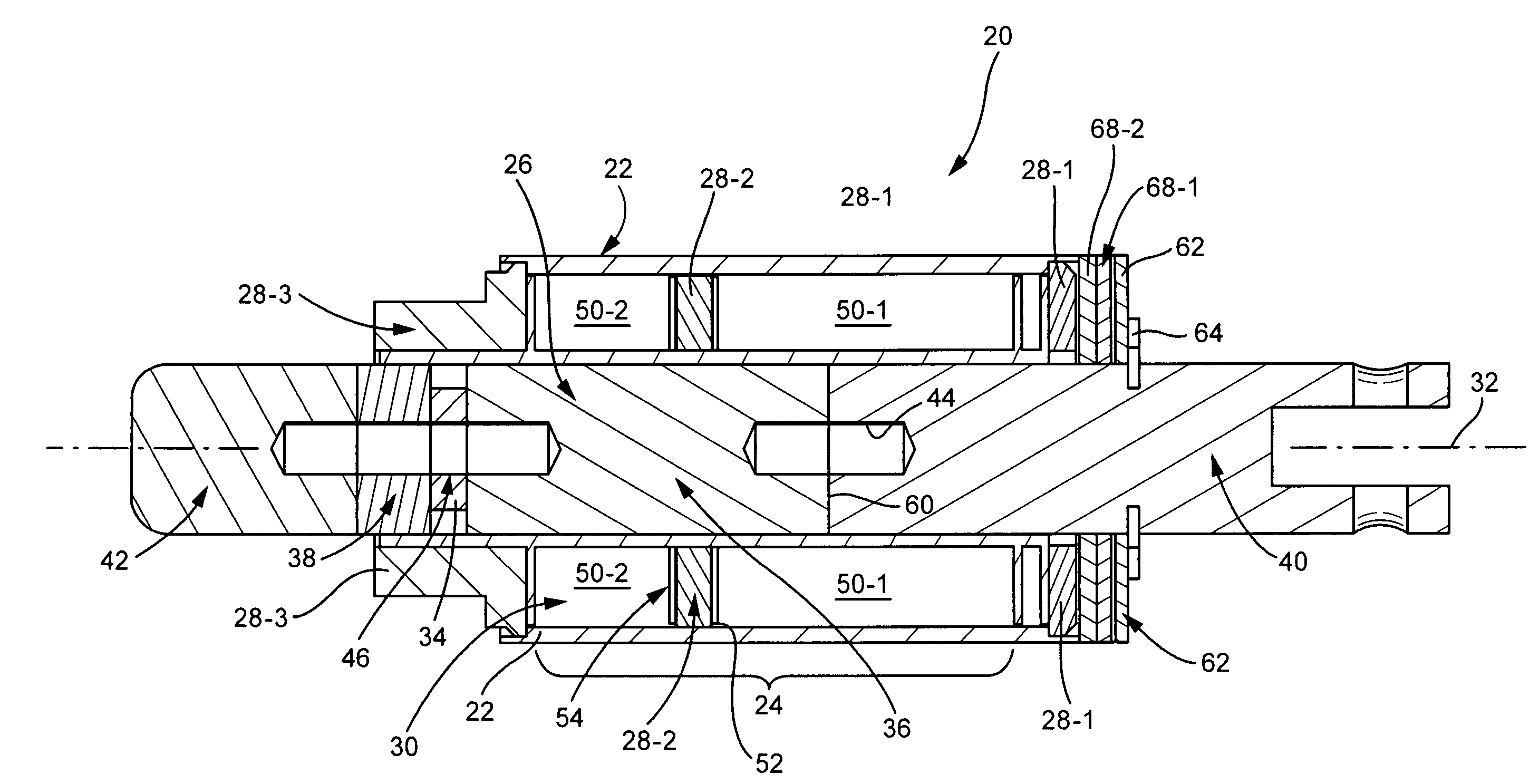
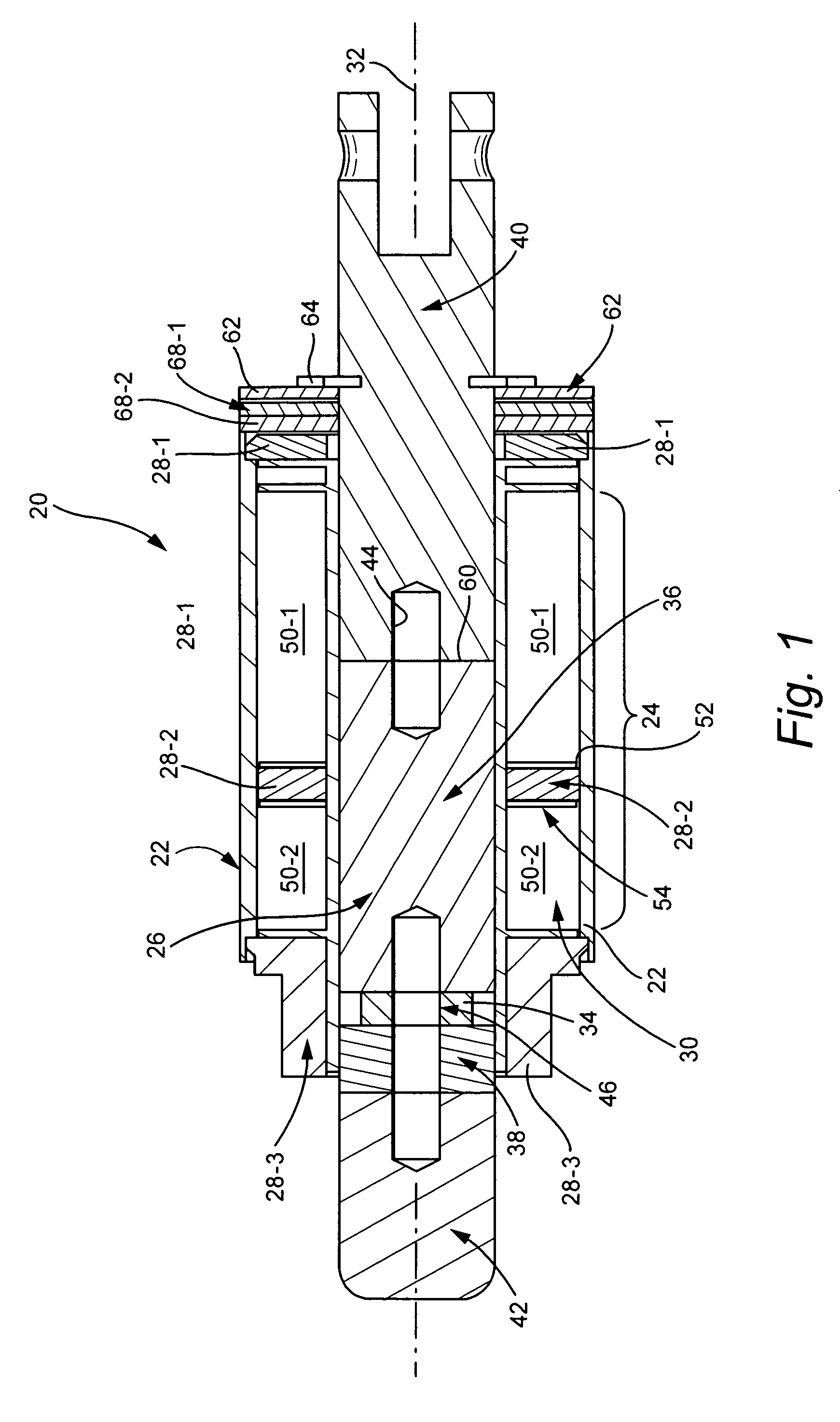
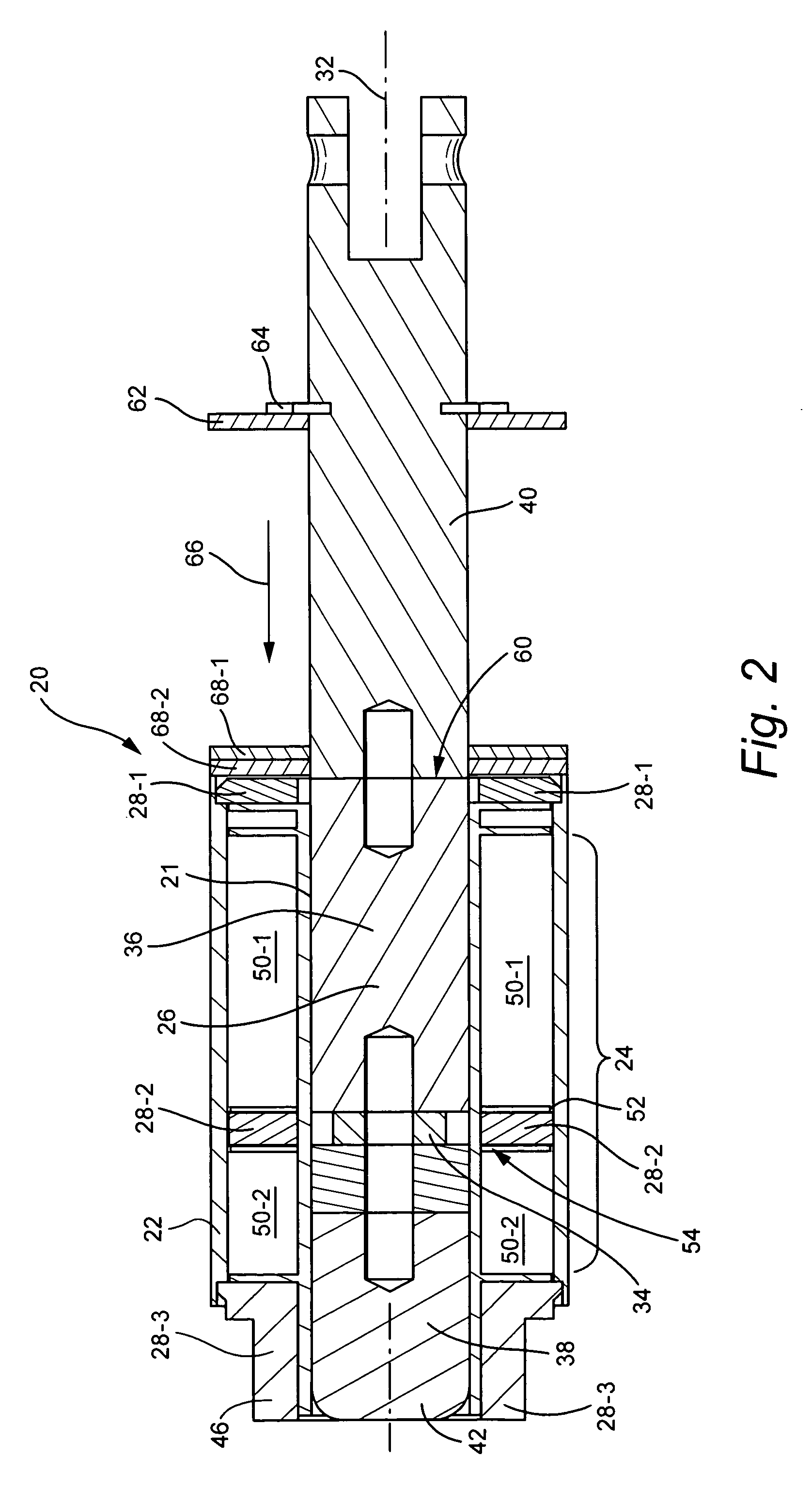
ActiveUS20080297288A1Facilitates holdingCores/yokesElectromagnets with armaturesElectrical conductorDetent
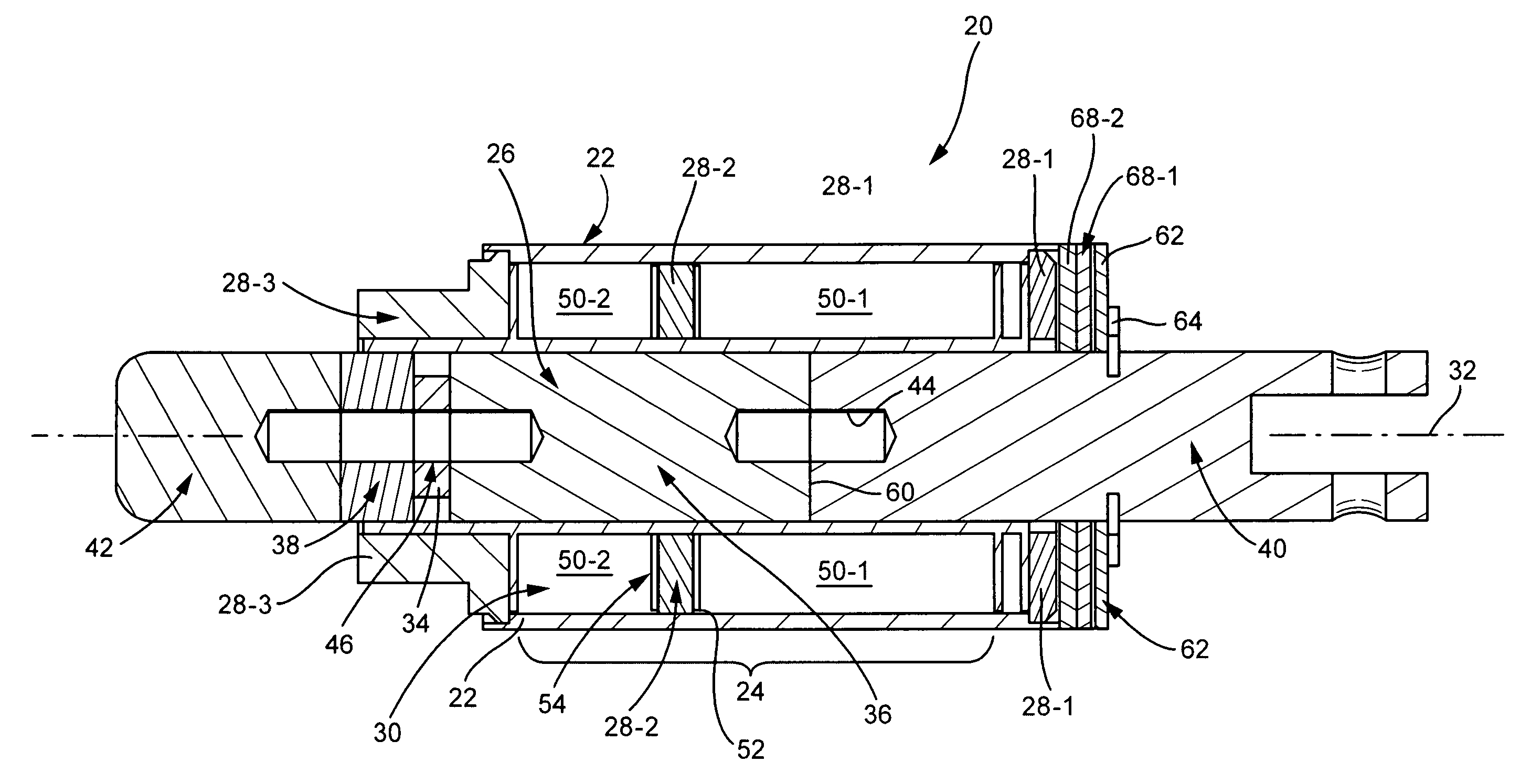
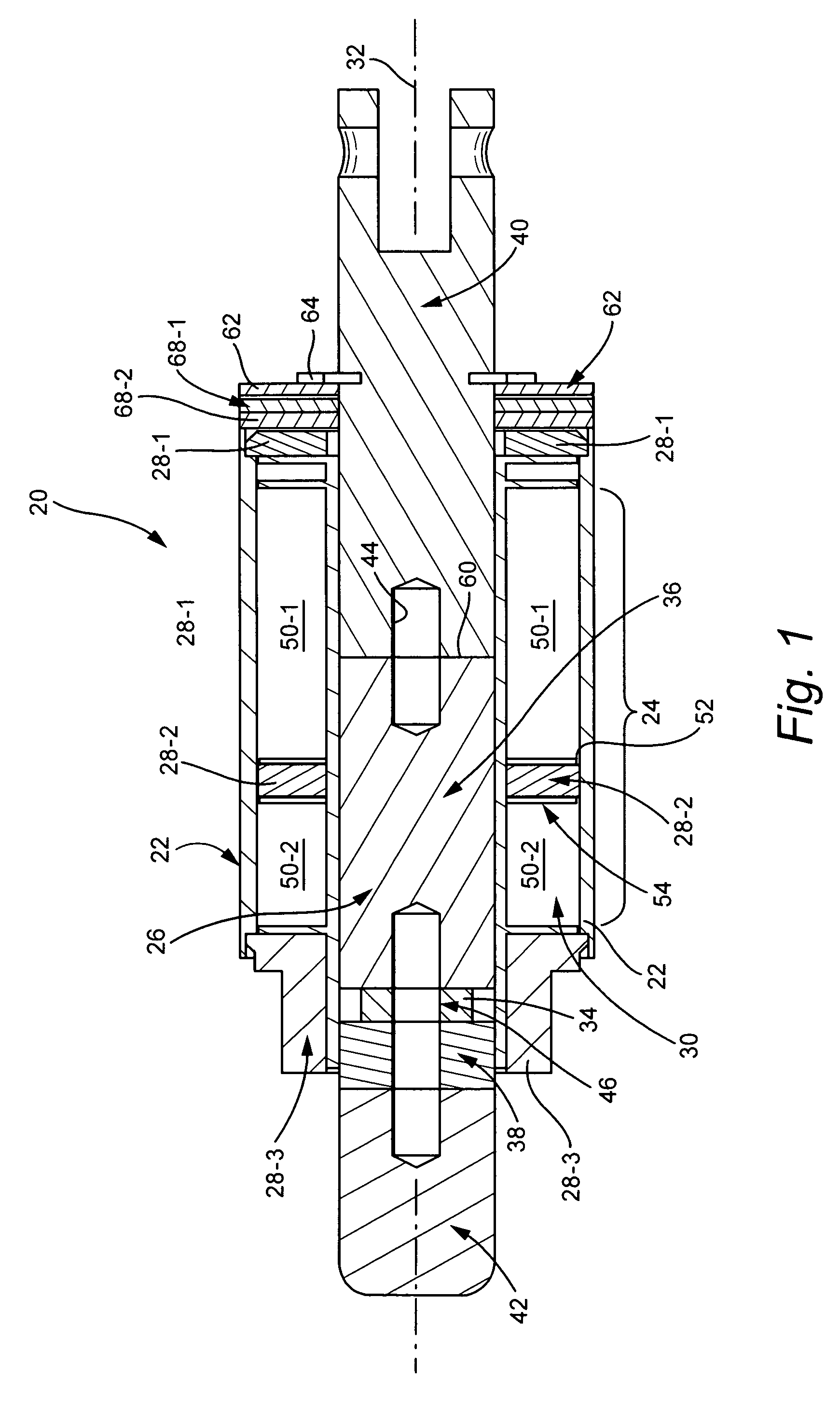
Embodiments of soft latching solenoids comprise a coil assembly (24); a plunger assembly (26); at least one flux conductor (28) comprising a flux circuit. The coil assembly (24) is fixedly situated with respect to a solenoid frame (21). The plunger assembly (26) is configured to linearly translate in a first direction along a plunger axis (32) upon application of a pulse of power to the coil assembly (24). The flux conductor(s) (28) is / are positioned radially exteriorly to the plunger assembly (26) to form the flux circuit. The flux circuit comprises the solenoid frame (21), the plunger assembly (26), and the at least one flux conductor (28). The flux circuit is arranged and configured so that the plunger assembly (26) is held in a plunger detent position upon cessation of the pulse of power.
Owner:SAIA BURS
Open MRI magnetic field generator
ActiveUS8077002B2Reduce leakageImprove efficiencyMagnetic measurementsPermanent magnetsWhole bodyFlux distribution
A magnet primarily for use in MRI applications comprises a pair of poles oriented about a plane of symmetry parallel to each therebetween defining an air gap region, magnetic field sources secured on the surfaces of the poles opposite the air gap that have yokes disposed on them, the yokes connected to each other by returns so that the entire magnet assembly can form a closed magnetic flux circuit to substantially confine the magnetic fields generated by the apparatus in the air gap where an imaging region is formed to place subjects for the purposes of examination. The main assembly being cylindrical in geometry has permanent magnets for magnetic field sources that are composed of two regions, a central disk-like portion magnetized substantially along the axial direction and an outer ring-like region magnetized substantially along the radial direction extending axially to form part of the pole together producing a very efficient and even flux distribution throughout the entire magnet assembly with minimal flux leakage. A further means of reducing flux leakage is incorporated in the yokes which have two sections, a disk-like region and an ring-like section to enclose the permanent magnets. The poles are made of multiple sections with a central disk-like region and an outer ring-like region that is a combination of permanent magnets and high permeability materials. This magnet assembly can achieve 1.0 Tesla or greater magnetic fields for whole-body scanning without saturating the magnet pole and other structures.
Owner:LIAN JIANYU +2
Shorting rings in dual-coil dual-gap loudspeaker drivers
InactiveUS6847726B2Reduce Harmonic DistortionPromote reductionTransducer detailsDeaf-aid setsFlux loopDual coil
Loudspeaker and other transducers of the dual-voice-coil / dual-magnetic-gap type can be improved by the addition of one or more annular shorting rings strategically located in the vicinity of the two magnetic gaps. The shorting rings have no effect on a steady state magnetic field but act in opposition to any change in flux density or any displacement of the flux lines such as those that occur under the loading imposed when the voice coils are driven hard with audio frequency current. The location of the shorting rings determines their effect: location close to a voice coil reduces the voice coil inductance, location entirely within the magnetic flux loop centerline favors reduction of second harmonic distortion and higher order even harmonic distortion, a centered location on the flux loop centerline, i.e. centered in the magnetic gap, favors reduction of third harmonic and higher odd order harmonic distortion, while location outside the flux loop as defined by its center line but near the voice coil acts to generally reduce harmonic distortion and reduce the voice coil inductance. Thus a plurality of rings can be strategically deployed at different locations so as to optimally suppress both even and odd order harmonic distortion and to reduce the voice coil inductance.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
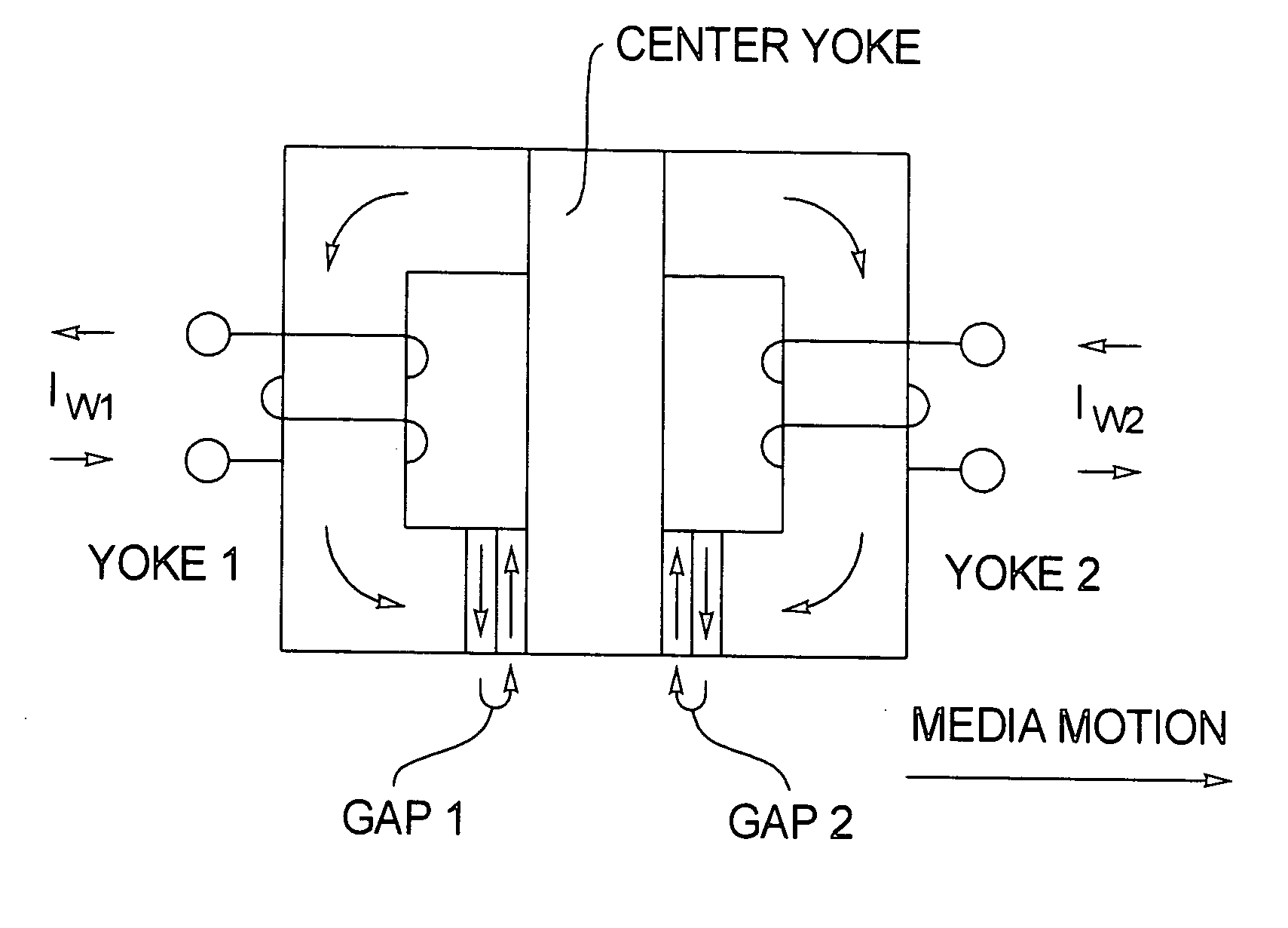
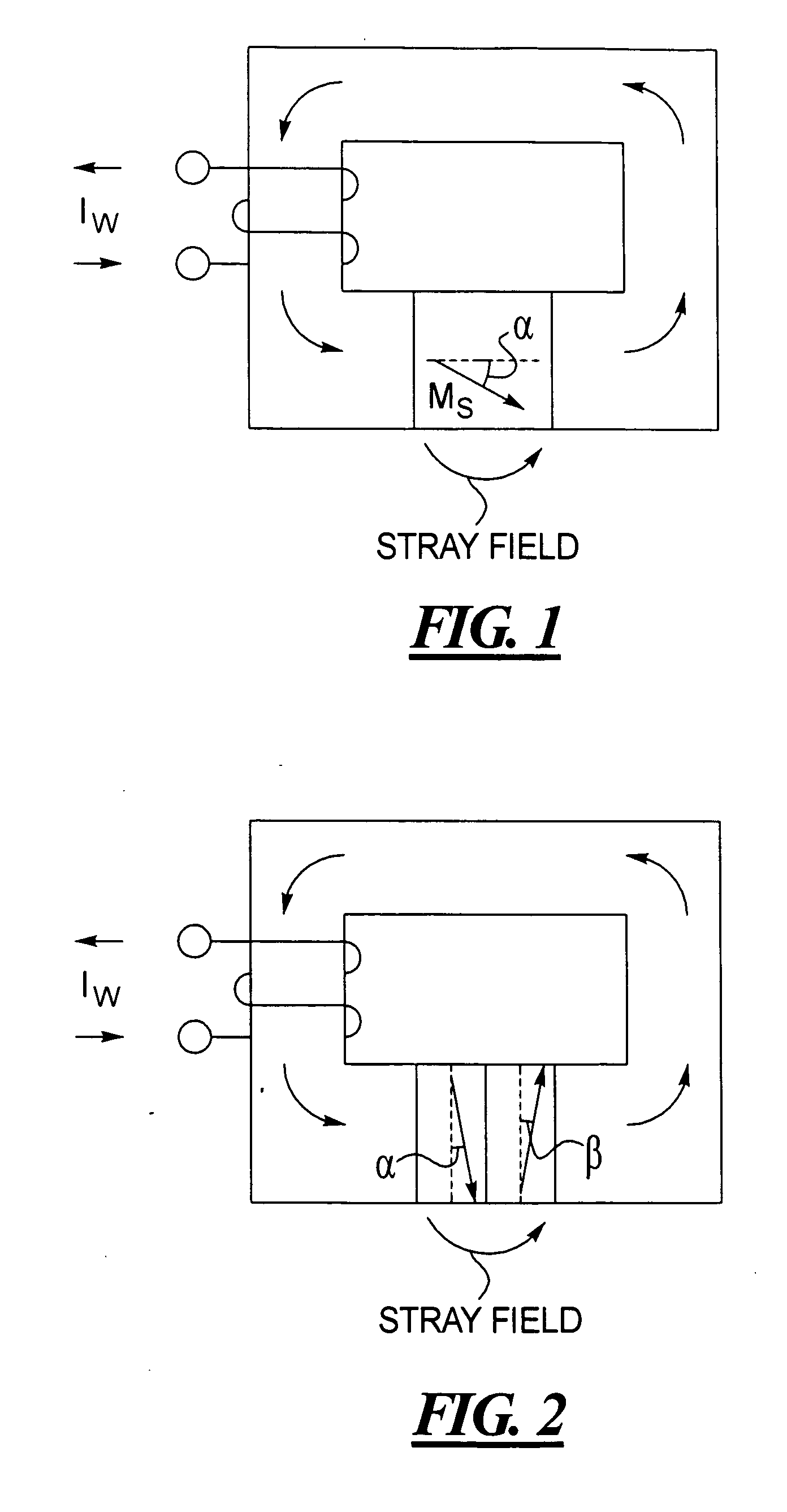
Magnetic recording head and method for high coercivity media, employing concentrated stray magnetic fields
InactiveUS20060187580A1High gradientImprove coercive forceMagnetic bodiesRecord information storageFlux loopMagnetization
In methods and arrangements for concentrating stray magnetic fields, a pair of permanent magnets is employed in combination with a magnetic flux circuit, the permanent magnets in the pair having respective magnetizations that are oriented oppositely to each other. The permanent magnets produce a stray magnetic field that adds to a magnetic field produced by the magnetic flux circuit.
Owner:TANDBERG DATA STORAGE
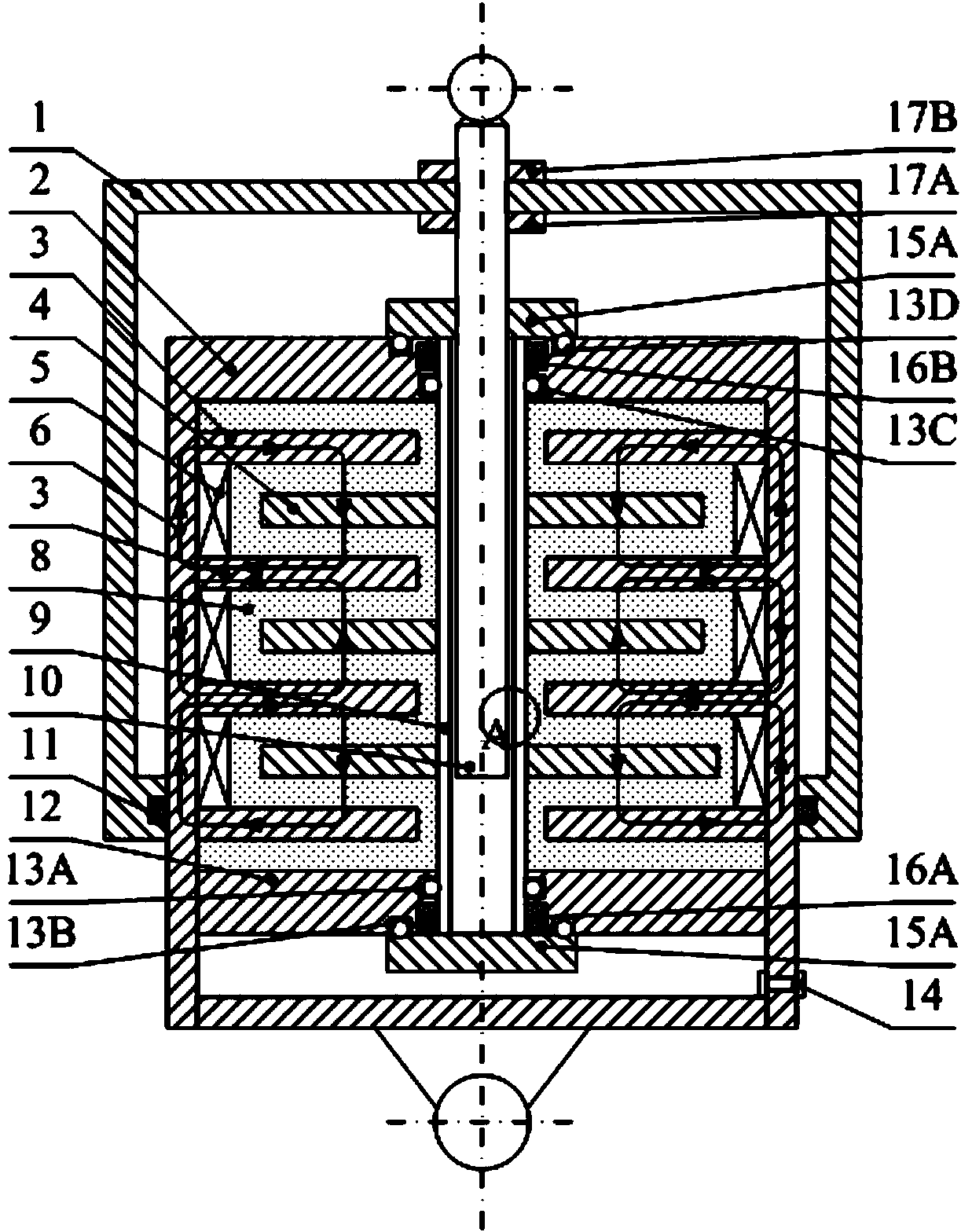
All-shearing type magneto-rheological damper
ActiveCN104179877AEffective control rangeIncreased controllable damping ratio rangeNon-rotating vibration suppressionViscous dampingVibration control
The invention discloses an all-shearing type magneto-rheological damper. The all-shearing type magneto-rheological damper is characterized by comprising an outer cylinder, an inner cylinder and a ball screw pair, wherein the inner cylinder is coaxially arranged with the outer cylinder, shearing discs are fixed by the ball screw pair, the inner wall of the inner cylinder is provided with electromagnetic coils and sharing ring sets corresponding to the shearing discs one by one, magneto-rheological liquid is filled in a cavity of the inner cylinder, at least one electromagnetic coil is arranged between adjacent shearing rings fixed on the inner wall of the inner cylinder, and the shearing discs, the shearing rings and the inner cylinder form a closed flux loop. On the premise of keeping same external size and energy consumption of a magneto-rheological damper, null-field viscous damping of the magneto-rheological damper is reduced, controllable damping ratio range is enlarged, and the all-shearing type magneto-rheological damper is added with potential for application to a high-speed impact / vibration control system. Besides, service efficiency of the magneto-rheological liquid in the magneto-rheological damper is improved, and cost of the magneto-rheological damper is effectively reduced.
Owner:ANQING HUITONG AUTOMOTIVE PARTS
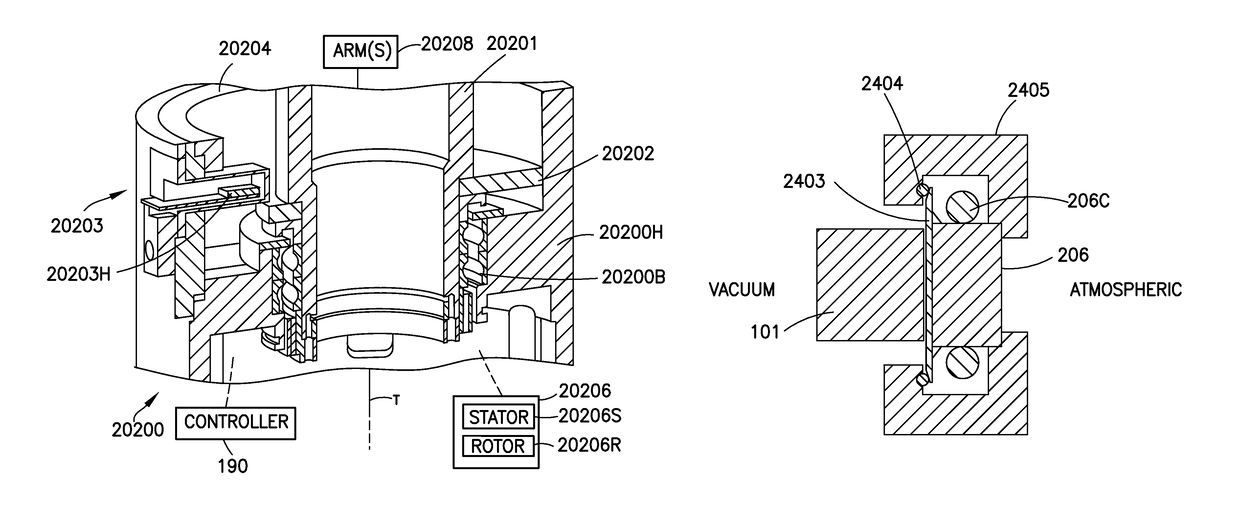
Sealed robot drive
ActiveUS9948155B2Improve motor efficiencyAvoid excessive deflectionMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorsFlux loopEngineering
A transport apparatus including a housing, a drive mounted to the housing, and at least one transport arm connected to the drive where the drive includes at least one rotor having at least one salient pole of magnetic permeable material and disposed in an isolated environment, at least one stator having at least one salient pole with corresponding coil units and disposed outside the isolated environment, where the at least one salient pole of the at least one stator and the at least one salient pole of the rotor form a closed magnetic flux circuit between the at least one rotor and the at least one stator, and at least one seal configured to isolate the isolated environment where the at least one seal is integral to the at least one stator.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
Lightweight solenoid-operated spray gun
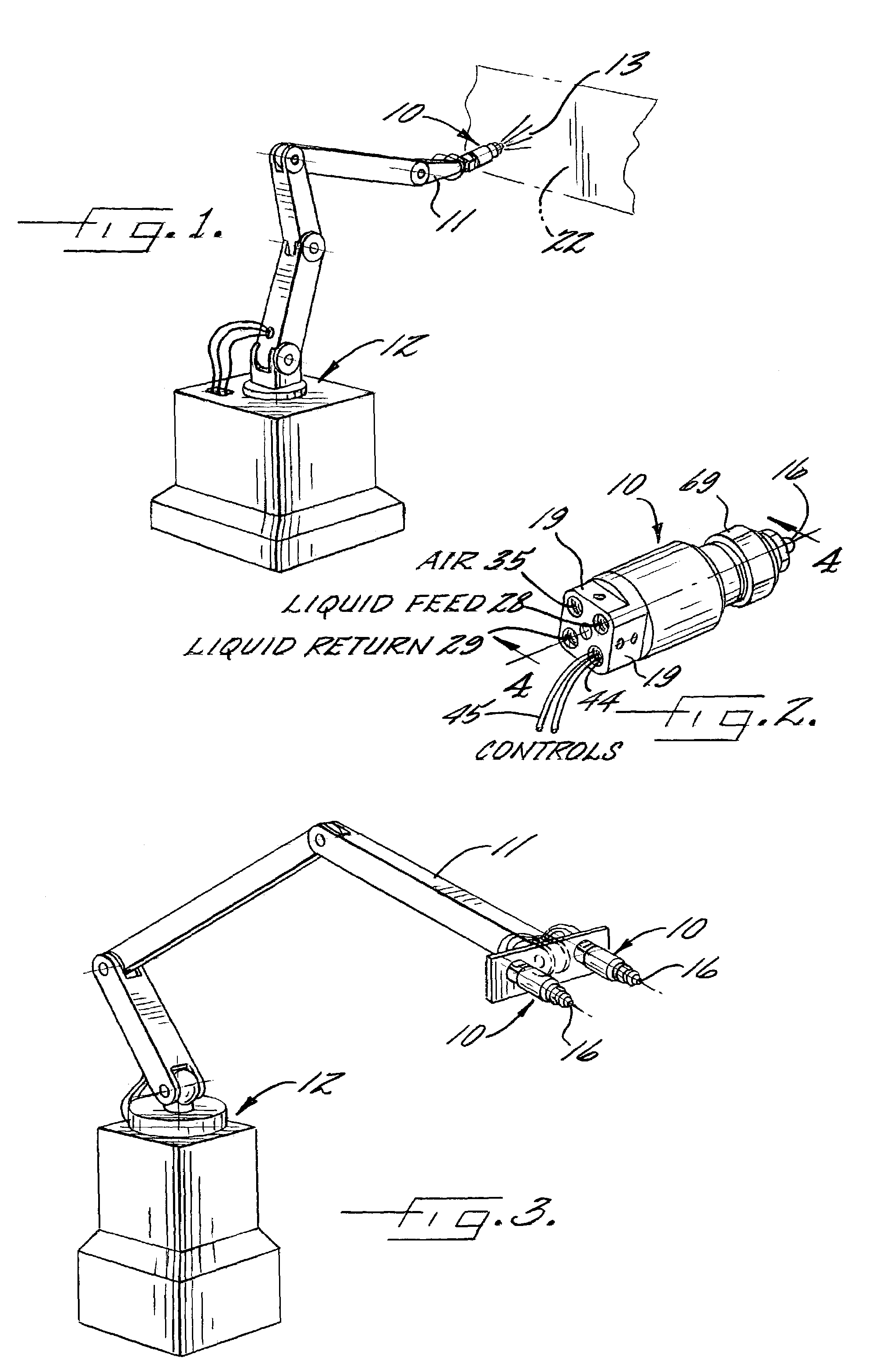
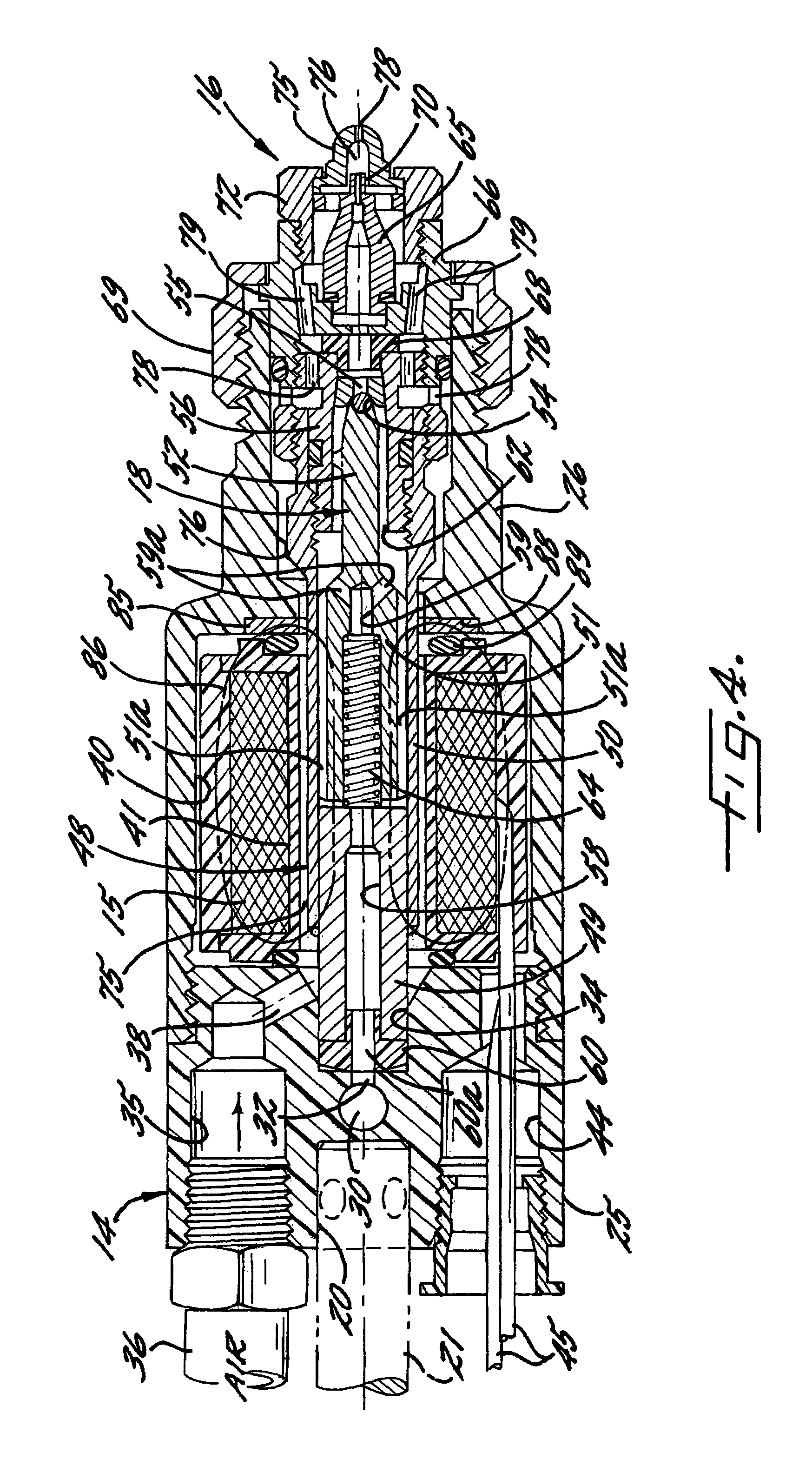
InactiveUS7086613B2Add supportPrecise positioningOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSpray nozzlesReciprocating motionFlux loop
A solenoid-operated liquid spray gun having a lightweight, corrosion resistant plastic housing which enables the spray gun to be mounted on and be more easily moved by robotic transfer devices. To effect the necessary flux loop within the plastic-housed spray gun for reciprocating a valve plunger in response to energization of the solenoid coil, the spray gun includes a radially disposed flux-directing member adjacent at least one end of the coil. The flux-directing member, while extending radially outwardly a distance less than the diameter of solenoid coil, effects efficient flux direction for operating the solenoid notwithstanding the lack of a magnetic conductive medium provided by the metal housing of conventional solenoid-operated spray guns.
Owner:SPRAYING SYST
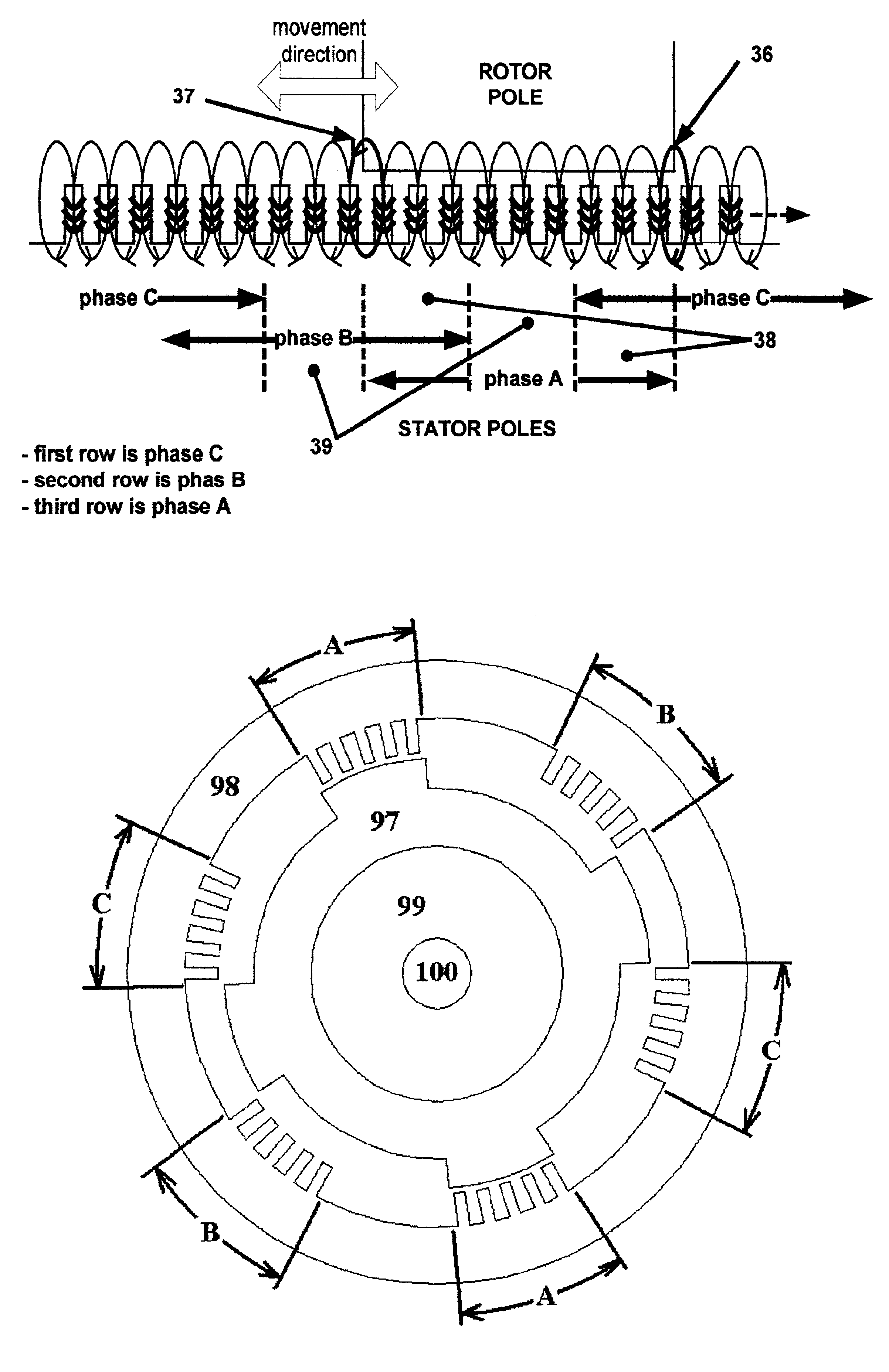
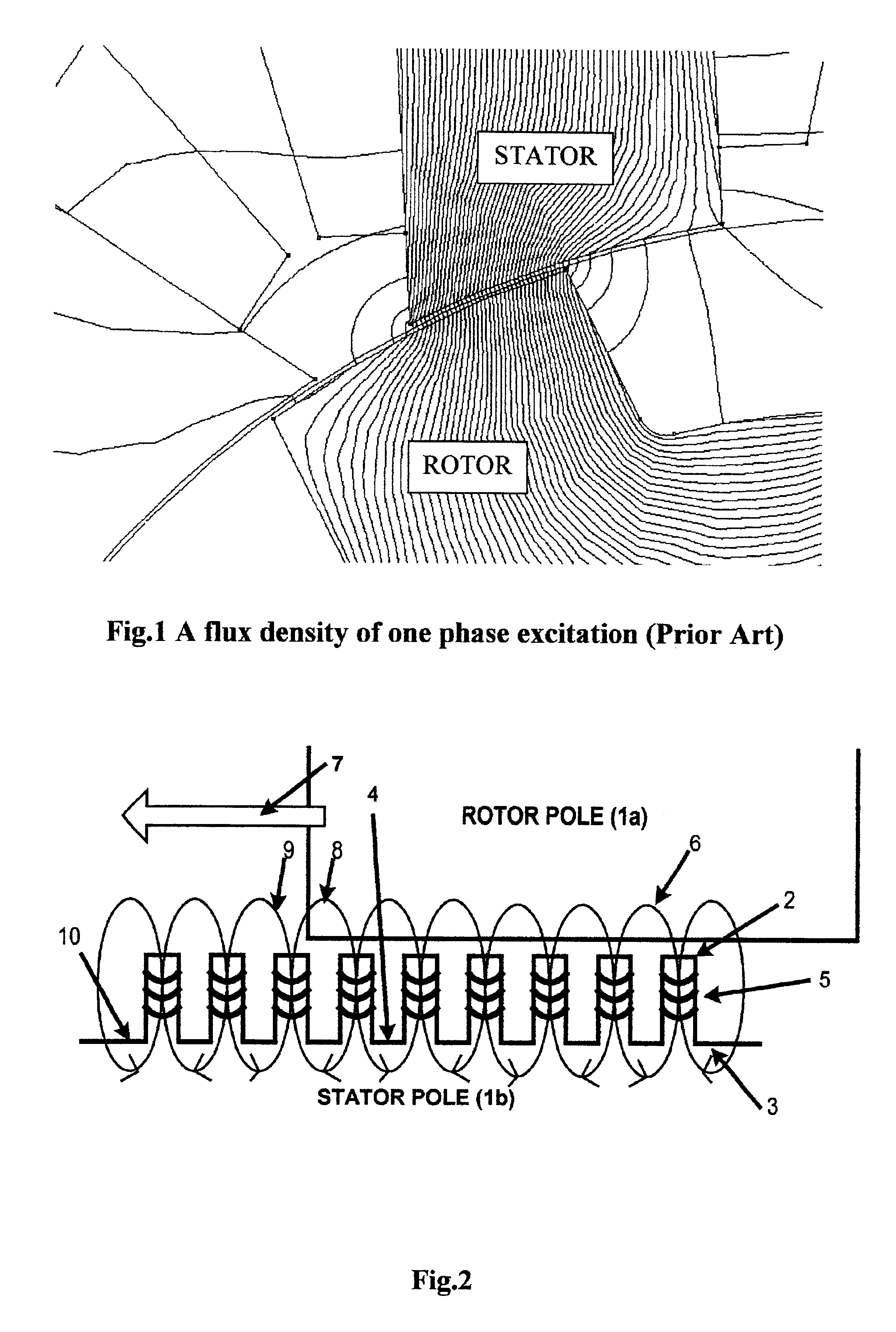
Multi-circular flux motor
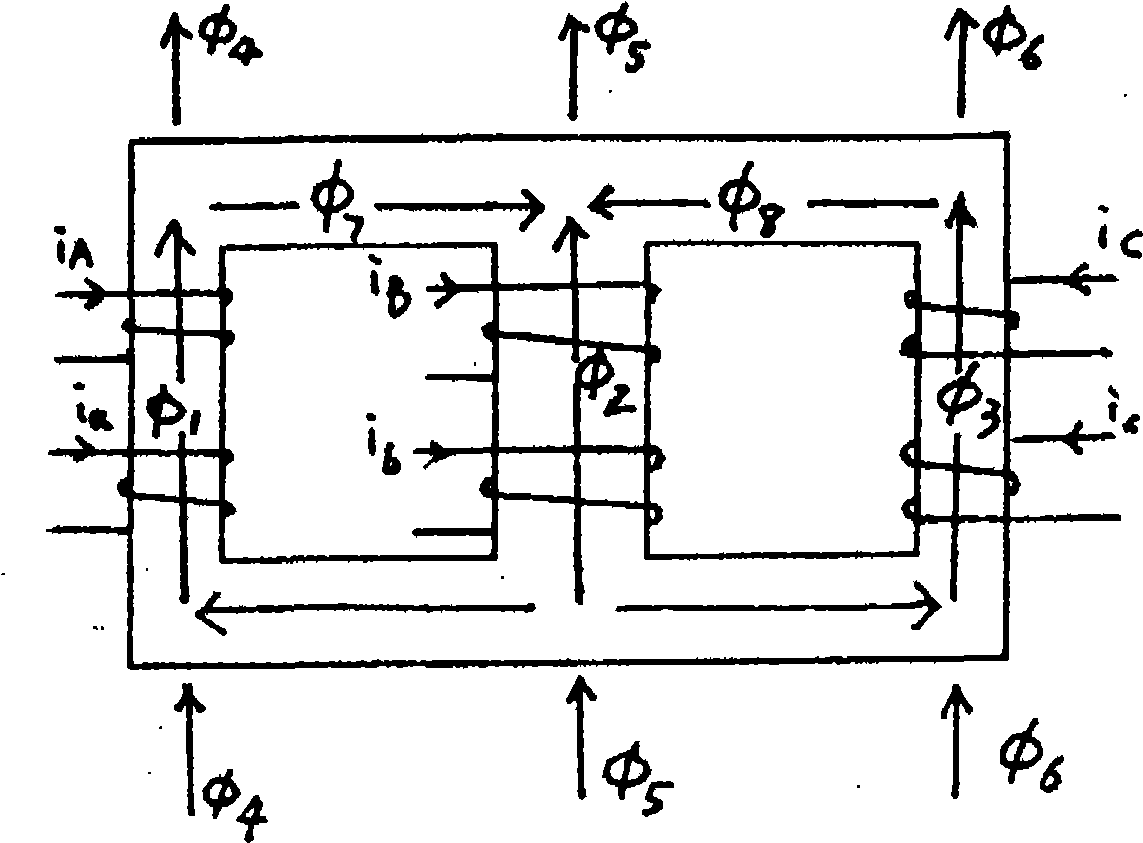
An invention is a new type of motor, a multi-circular flux motor. The invention has simple structure and comprises of a salient pole rotor and the silent pole stator. The stator pole is subdivided into plural teeth with the individual winding. A group of windings of each stator pole is connected in either series or parallel and is driven by one excitation phase. The movement of the invention uses multi-circular flux loops to produce reluctance torque to make the rotor moves. The multi-circular flux loops comprise of a series of flux loops that every flux loop is inversely rotation direction to each other adjacent. The invention can apply in a linear and rotating machine. By having plural winding poles and phases, the invention can be a poly-phase machine. The invention can be designed to be any number of poles and phases because all flux loops are separated. The invention is applied in both AC and DC machine and both linear and rotating machine. The rotor core can be replaced with a lightweight material or hollowed out to be a lightweight rotor. The invention can be designed to be a toothless-stator or toothless-rotor machine.
Owner:ENERGY DEVICES
Quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with positive and negative stiffness in parallel connection
ActiveCN109139760AImprove bearing capacityImprove stabilitySprings/dampers functional characteristicsMagnetic springsFlux loopMagnetic stiffness
The invention discloses a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with positive and negative stiffness in parallel connection. The vibration isolator comprises a base, an upper cover, a supporting rod, spiral springs, spacers, an annular iron core, fan-shaped permanent magnet bodies, stators, a permanent magnet body clamping mechanism, working air gaps and a guide plate. The fan-shaped permanent magnet bodies, stators, permanent magnet body clamping mechanism, and working air gaps form a magnetic flow loop, and form magnetic springs with negative magnetic stiffness. The spiral springs are connected with the supporting rod and the upper cover, and initial positive stiffness of the vibration isolator is provided and is in parallel connection with magnetic negative stiffness. The dynamic stiffness of the annular iron core in the equilibrium position is reduced. The guide plate is mounted on the lower portion of the base, and is in sliding-fit with the supporting rod. Compared with an existing quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator, the vibration isolator has the advantages that load bearing is high, and the mechanism is compact; and as a passive vibration isolator, the vibration isolator can effectively reduce the natural frequency of the vibration isolation system, broaden a vibration isolation frequency band, and has the advantages of easy maintenance and high reliability.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Magnetic element with permanent magnetic bias
InactiveCN101789304AReduce the cross-sectional areaShorten the lengthPermanent magnetsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresDc currentFlux loop
The invention relates to a magnetic element with permanent magnetic bias, which comprises a magnetic core which is used for forming a magnetic flux loop and provided with at least one air gap fracture. The magnetic element is characterized in that a working coil is wound on the magnetic core, at least one lateral surface of the air gap fracture of the magnetic core is provided with a pair of permanent magnets, the permanent magnets are provided with at least one soft magnetic core for communicating the two permanent magnets so as to form a permanent magnet containing magnetic branch connected in parallel with the air gap fracture, and the reluctance of the permanent magnet containing magnetic branch connected in parallel with the air gap fracture is more than 5 times as high as the reluctance of the air gap fracture of the magnetic element. The direct-current bias resistance of the magnetic core of the magnetic element can be effectively improved, the inductance under certain direct-current bias current is improved, or the section area of the magnetic core is reduced, and the volume is reduced or the length and electric resistance of the copper used for the working coil is reduced; and meanwhile, the defects that the traditional magnetic element with the permanent magnet is easy to be demagnetized by the current pulse and the eddy-current loss of the permanent magnet under the high-frequency flux causes temperature rise to result in failure of the permanent magnet at the high temperature.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Multi-circular flux motor
An invention is a new type of motor, a multi-circular flux motor. The invention has simple structure and comprises of a salient pole rotor and the silent pole stator. The stator pole is subdivided into plural teeth with the individual winding. A group of windings of each stator pole is connected in either series or parallel and is driven by one excitation phase. The movement of the invention uses multi-circular flux loops to produce reluctance torque to make the rotor moves. The multi-circular flux loops comprise of a series of flux loops that every flux loop is inversely rotation direction to each other adjacent. The invention can apply in a linear and rotating machine. By having plural winding poles and phases, the invention can be a poly-phase machine. The invention can be designed to be any number of poles and phases because all flux loops are separated. The invention is applied in both AC and DC machine and both linear and rotating machine. The rotor core can be replaced with a lightweight material or hollowed out to be a lightweight rotor. The invention can be designed to be a toothless-stator or toothless-rotor machine.
Owner:ENERGY DEVICES
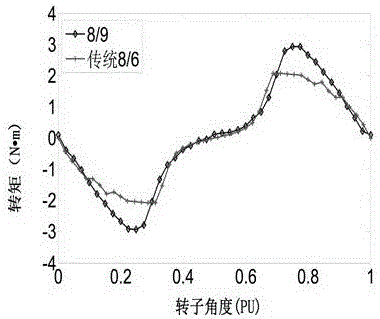
Switched reluctance motor with 8/9 structure
PendingCN106026434ALarge output torqueIncrease output torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineFlux loop
The present invention relates to a switched reluctance motor with 8 / 9 structure. The switched reluctance motor provided by the invention is a block rotor equipped switched reluctance motor having a four-phase eight-pole stator and a nine-pole rotor. Fixedly arranged on the motor shell, the stator is provided with exciting poles and auxiliary poles alternately; the rotor comprises nine independent rotor poles and a non-conductive magnet. All the rotor poles are embedded in the non-conductive magnet evenly; each of the independent rotor poles forms an independent magnetic flux circuit with its adjacent exciting pole and auxiliary pole. The internal part of the rotor is provided with a motor shaft penetrating through the rotor center and driving the rotor to move. Because of the short flux path, there is no reversal of magnetic flux in the stator and rotor. In the process of motor rotating and phase changing, no negative torque will be generated. In addition, the motor adopts single-phase concentrated winding. The number of motor turns decreases; and required end winding is reduced so much that it can be neglected. Under the same input condition, the motor copper consumption is small, the core loss is small, the output torque is large, and therefore, the output efficiency of the motor is increased.
Owner:BRILLIANCE AUTO
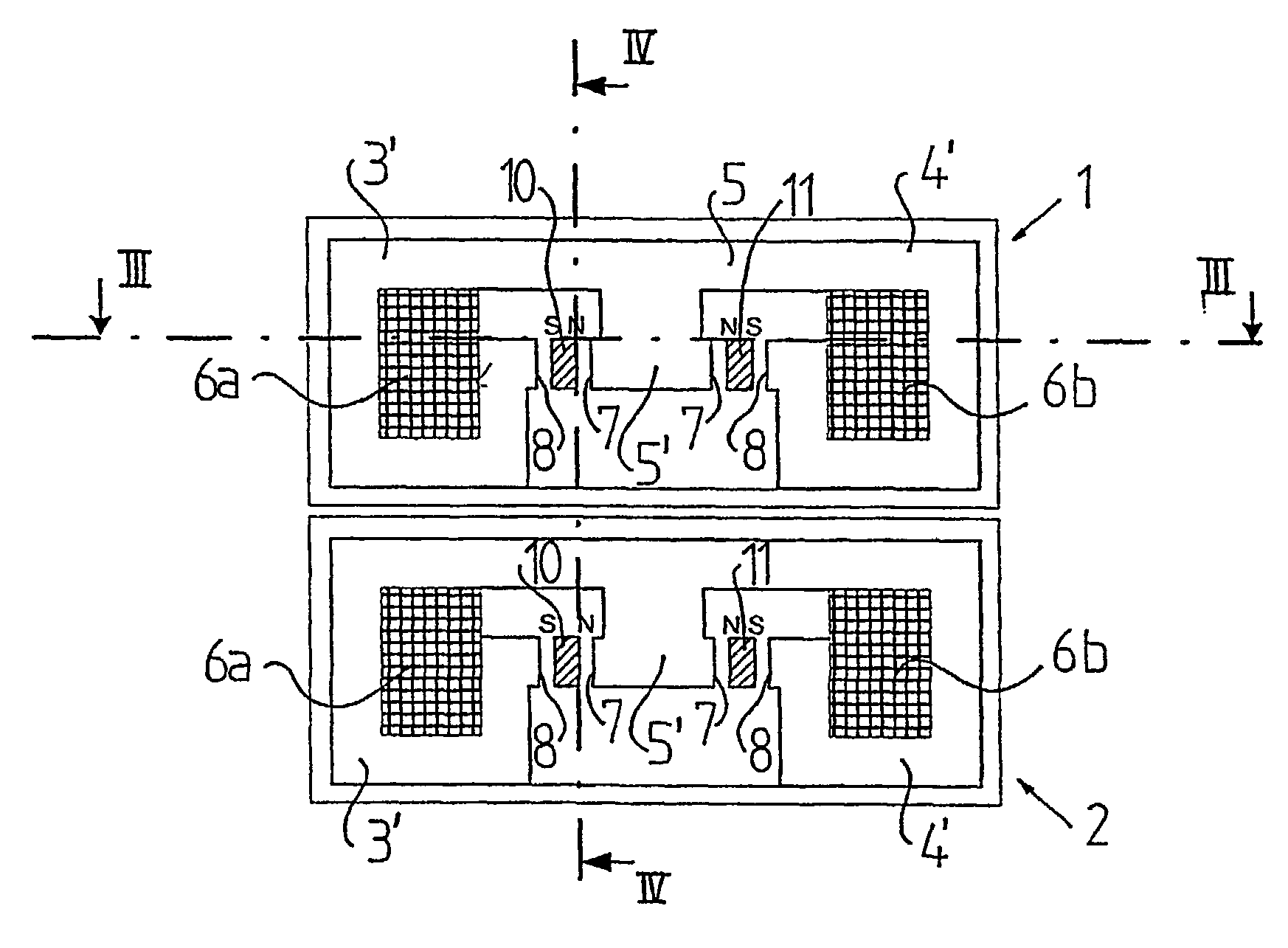
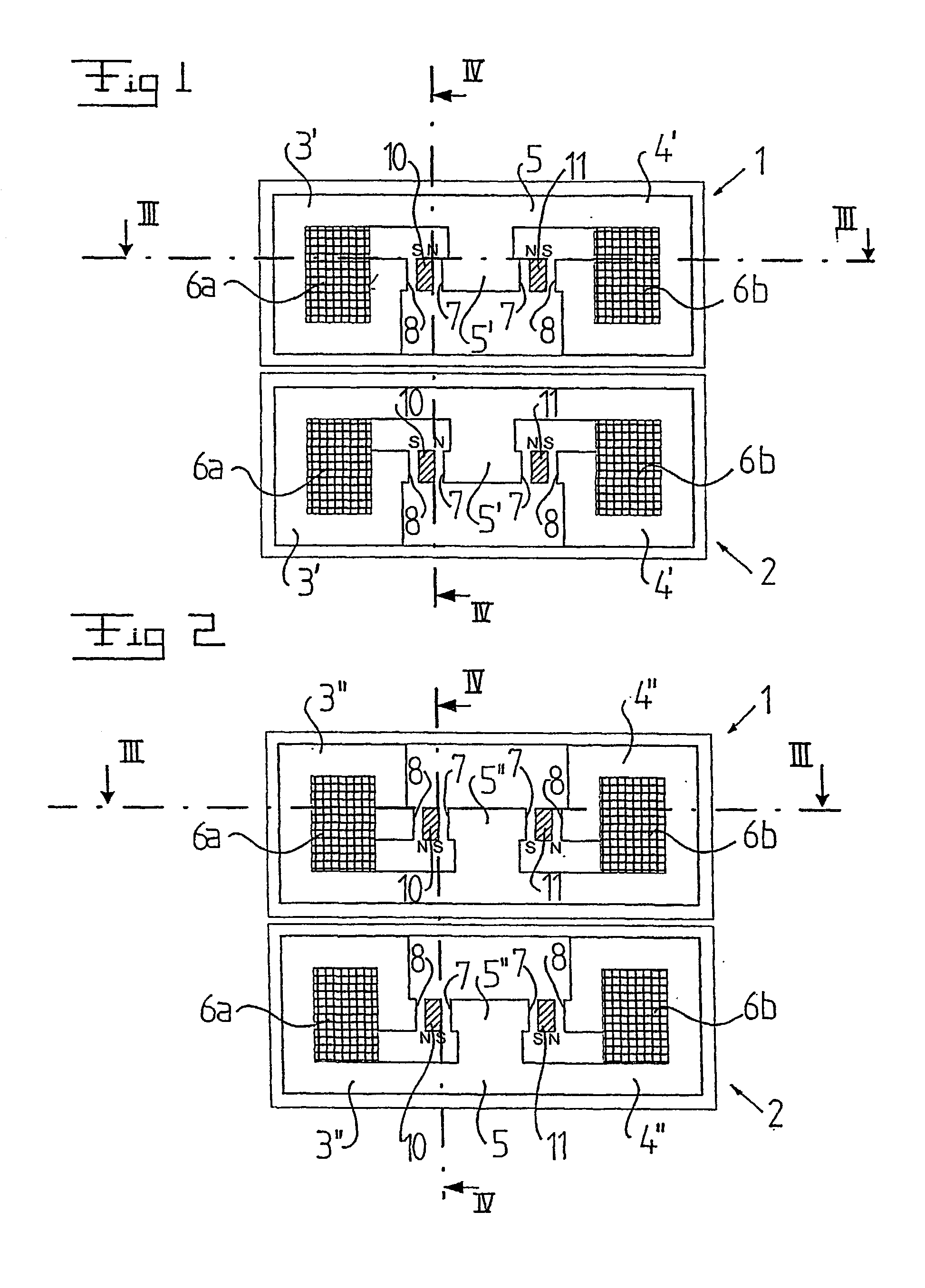
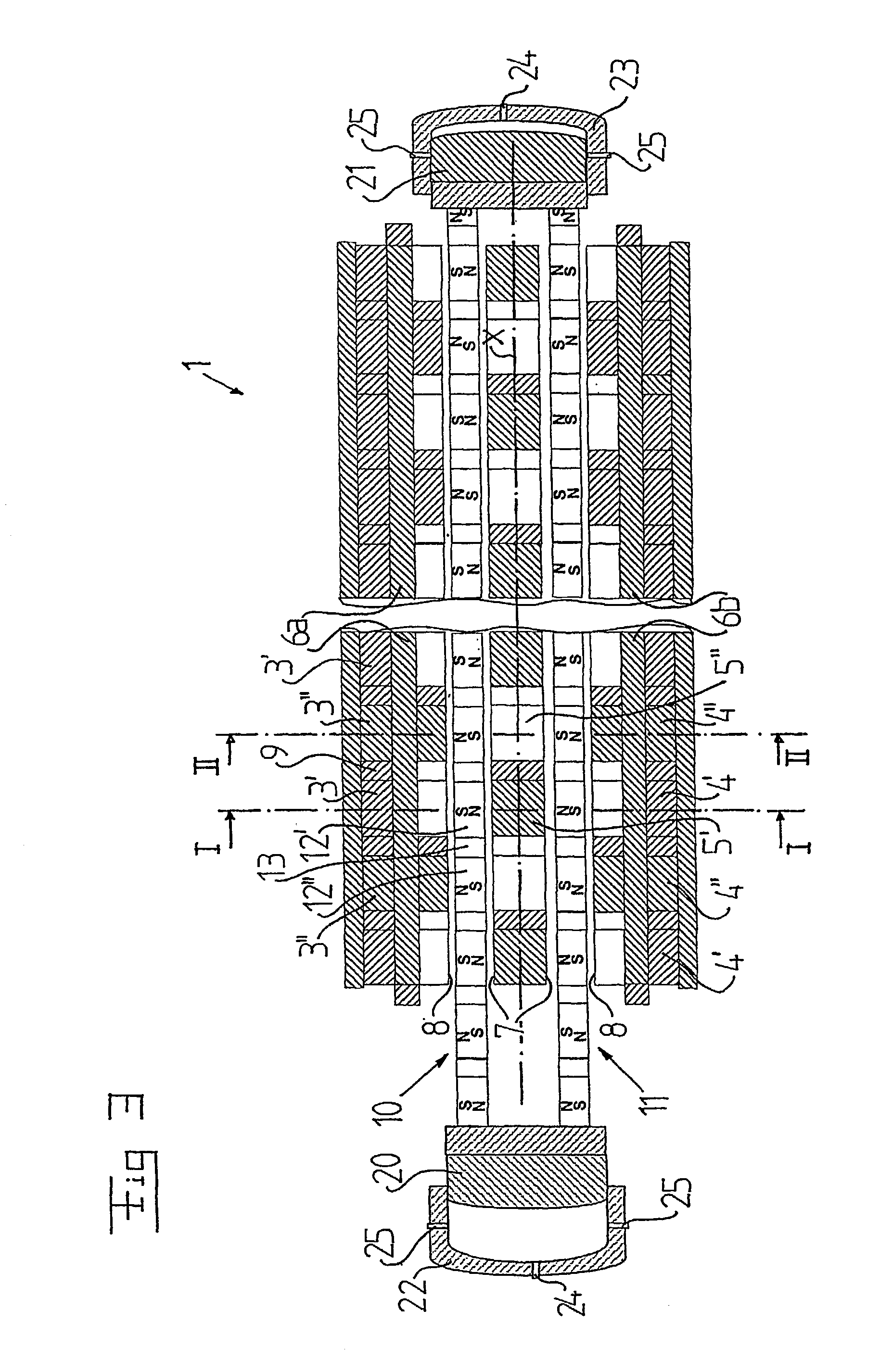
Electrical machine
InactiveUS20030048019A1Improve efficiencyReduce in quantityCombustion enginesSynchronous machinesElectrical conductorElectric machine
The invention refers to an electrical machine with at least a machine unit (1). This machine unit includes a stator, which includes a plurality of magnetic flux conductors (3', 3'') and an electric conductor forming a winding extending in a substantially closed winding path through each magnetic flux conductor, and at least one first movable element (10), which includes a number of permanent magnet elements (12', 12'') and which is movable in a reciprocating movement in relation to the stator along a first movement path in a space having a finite length and formed by at least some of said magnetic flux conductors. The winding path includes a first current carrying portion (6a), which extends substantially in parallel with the first movement path. Each magnetic flux conductor (3', 3'') is arranged to form, together with one of said permanent magnet elements (12', 12''), a closed magnetic flux circuit extending around said current carrying portion.
Owner:VOLVO TECH
Transverse flux electrical motor
A transverse flux electrical motor to produce motion from an input electric current, the electrical motor comprising: a static element having a plurality of magnets arranged in at least two rows and defining a path of movement; a magnetizable movable element having at least two openings, each opening being sized and shaped to receive a magnet from one of the rows of magnets, the movable element being movable along the path of movement such that the magnets of each row pass through one of the openings; and a plurality of windings positioned adjacent to the movable element, to receive the electric current and produce a magnetic flux circuit in the movable element and a force on the movable element in the direction of the path of movement; wherein the magnetic flux circuit in the movable element is transverse to the direction of force on the movable element.
Owner:YASKAWA EURO TECH
Method for predicting inrush current of three-phase electric power transformer
ActiveCN101488659AAccurate analysisHelp to solveEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectrical testingRemanenceHypothesis
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER +1
Soft latch bidirectional quiet solenoid
Embodiments of soft latching solenoids comprise a coil assembly (24); a plunger assembly (26); at least one flux conductor (28) comprising a flux circuit. The coil assembly (24) is fixedly situated with respect to a solenoid frame (21). The plunger assembly (26) is configured to linearly translate in a first direction along a plunger axis (32) upon application of a pulse of power to the coil assembly (24). The flux conductor(s) (28) is / are positioned radially exteriorly to the plunger assembly (26) to form the flux circuit. The flux circuit comprises the solenoid frame (21), the plunger assembly (26), and the at least one flux conductor (28). The flux circuit is arranged and configured so that the plunger assembly (26) is held in a plunger detent position upon cessation of the pulse of power.
Owner:SAIA BURS
Concentrated winding transverse flux permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN111404290AIncrease profitEasy extractionMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsTransverse fluxFlux loop
The invention discloses a concentrated winding transverse flux permanent magnet synchronous motor, which comprises stator E-shaped teeth, a stator yoke part, a stator winding, rotor magnetic steel anda rotor yoke part, the stator E-shaped teeth comprise three teeth and two grooves, and the three teeth face the air gap and are axially arranged; the stator winding is wound on the middle teeth of the stator E-shaped teeth and fills the two grooves to form a concentrated winding coil, and the winding directions of the coils of the two adjacent stator E-shaped teeth are opposite; the stator yoke part wraps the exposed windings of the two adjacent stator E-shaped teeth; each pole of rotor magnetic steel is formed by axially arranging three pieces of magnetic steel with alternate N poles and S poles, and the three pieces of magnetic steel are respectively aligned with three teeth of the E-shaped teeth of the stator; the polarities of the rotor magnetic steels of two adjacent poles are opposite; the rotor yoke part provides a magnetic flux loop and comprises a radial magnetic flux direction and a transverse magnetic flux direction. According to the invention, the utilization rate of the stator winding can be greatly improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Permanent magnet brushless machine with magnetic flux regulation
A permanent magnet machine (PMM) has a generally cylindrical permanent magnet (PM) rotor that has multiple PM rotor poles arranged around a rotor axis of rotation; and a stator with two generally cylindrical and concentric yokes, an inner yoke proximate the PM rotor with associated multiple inner poles and inner armature windings suitable for multiphase alternating current operation that form a PMM magnetic flux circuit, an outer yoke with associated multiple outer poles and outer control windings suitable for connection to a direct current source, with distal ends of the outer poles in contact with the inner yoke to form an external magnetic flux circuit that diverts magnetic flux from the PMM magnetic flux circuit; wherein application of increasing direct current to the outer windings results in increased magnetic reluctance of the external magnetic flux circuit, thereby causing the external magnetic flux circuit to divert less magnetic flux from the PMM magnetic flux circuit.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Enhanced thermal conductivity ferrite stator
ActiveUS7119461B2Increase speedQuick closeAC/DC convertorsEfficient propulsion technologiesPermanent magnet rotorHeat conducting
A permanent magnet electric machine (i.e.: motor / generator) having a magnetic flux circuit including a stator and a permanent magnet rotor mounted for rotation about an axis relative to the stator. The stator has an electric circuit with windings electro-magnetically coupled to the magnetic circuit. The stator is of material having a Curie temperature, wherein magnetic flux circulation through the stator material is impeded when the stator material acquires a temperature above the Curie temperature. The stator includes heat conducting layers and magnetic flux conducting layers, where the thermal conductivity of the heat conducting layers is greater than the thermal conductivity of the magnetic flux conducting layers. By this means the overall thermal conductivity of the stacked stator assembly is improved and means for quickly effecting shutdown of the electric machine are provided with a heat exchanger thermally coupled to the stator, thereby regulating magnetic flux circulation through the stator material. Preferably the magnetic flux conducting layers are manganese zinc ferrite, and the heat conducting layers are: insulated copper sheets; insulated aluminum sheets; thermally conductive polymer sheets; sheet metal; or plated metal layers deposited on associated magnetic flux conducting layers.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Coil component and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150145627A1Reduce lossesTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresElectrical conductorFlux loop
Disclosed herein is a coil component capable of being protected from static electricity without loss of a main magnetic flux loop. The coil component includes: a magnetic substrate; a coil layer disposed on the magnetic substrate and having conductor patterns installed therein; and an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protecting layer disposed on the coil layer and discharging static electricity introduced into the conductor patterns.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Electromagnetic induction device and manufacturing method therefor
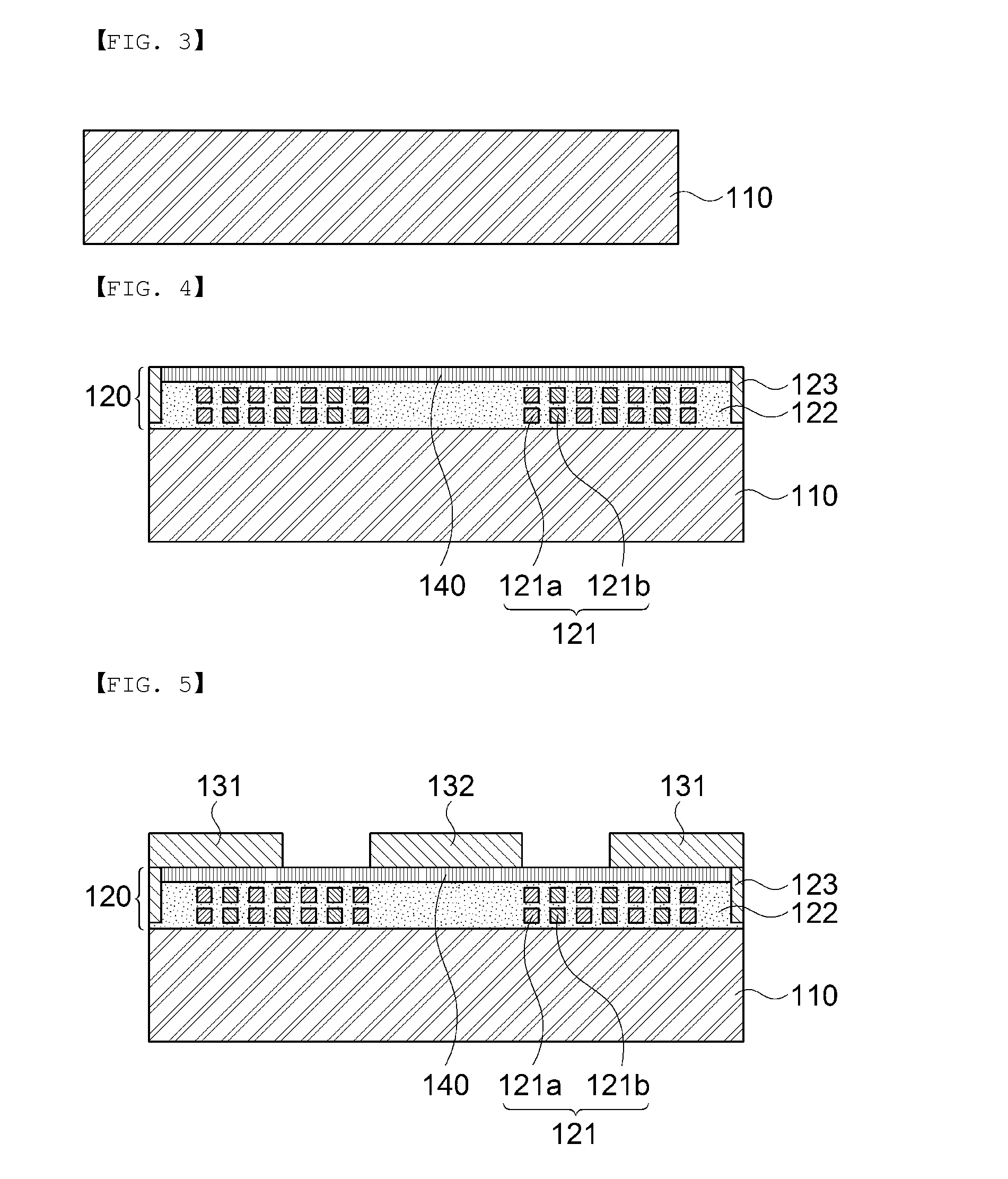
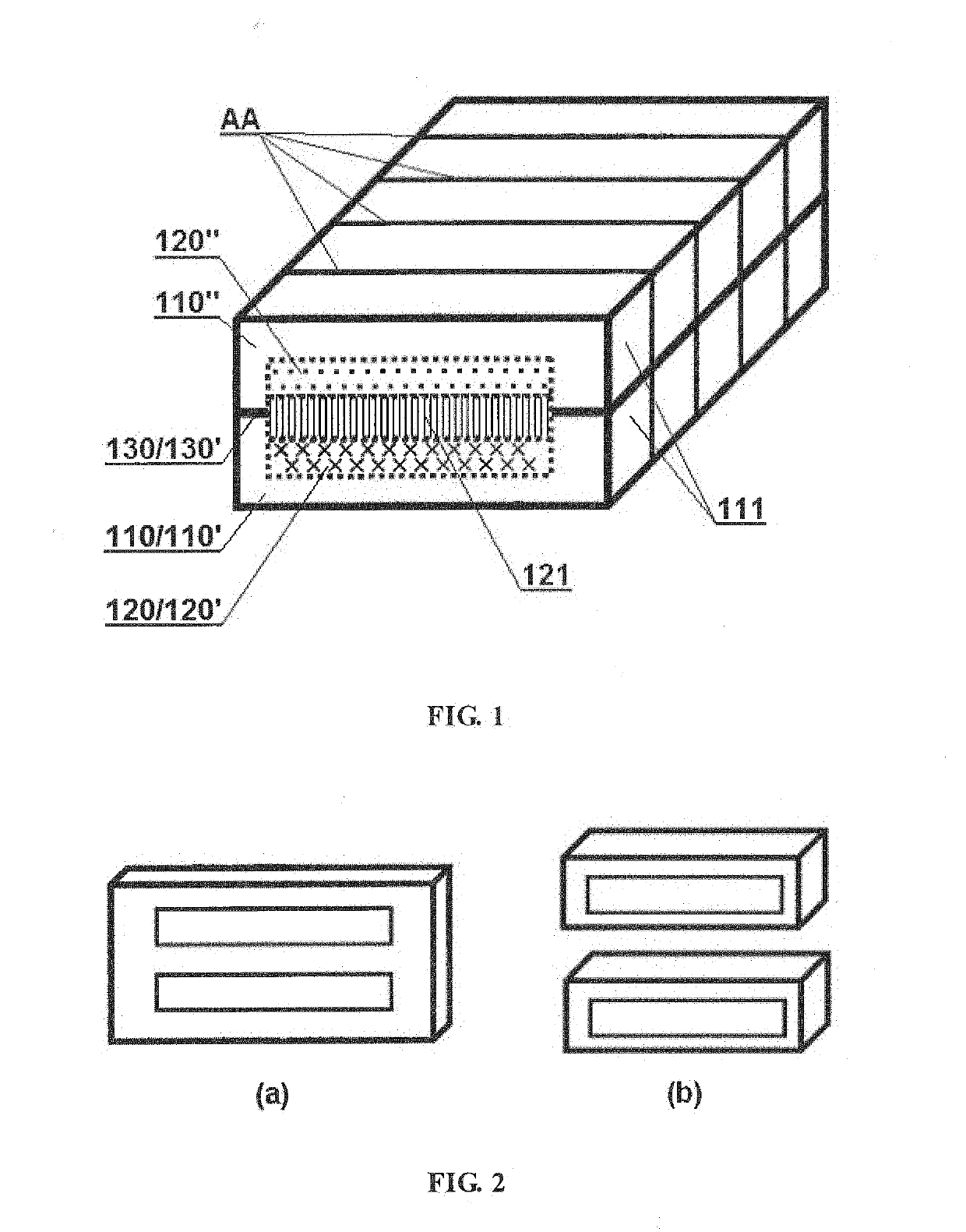
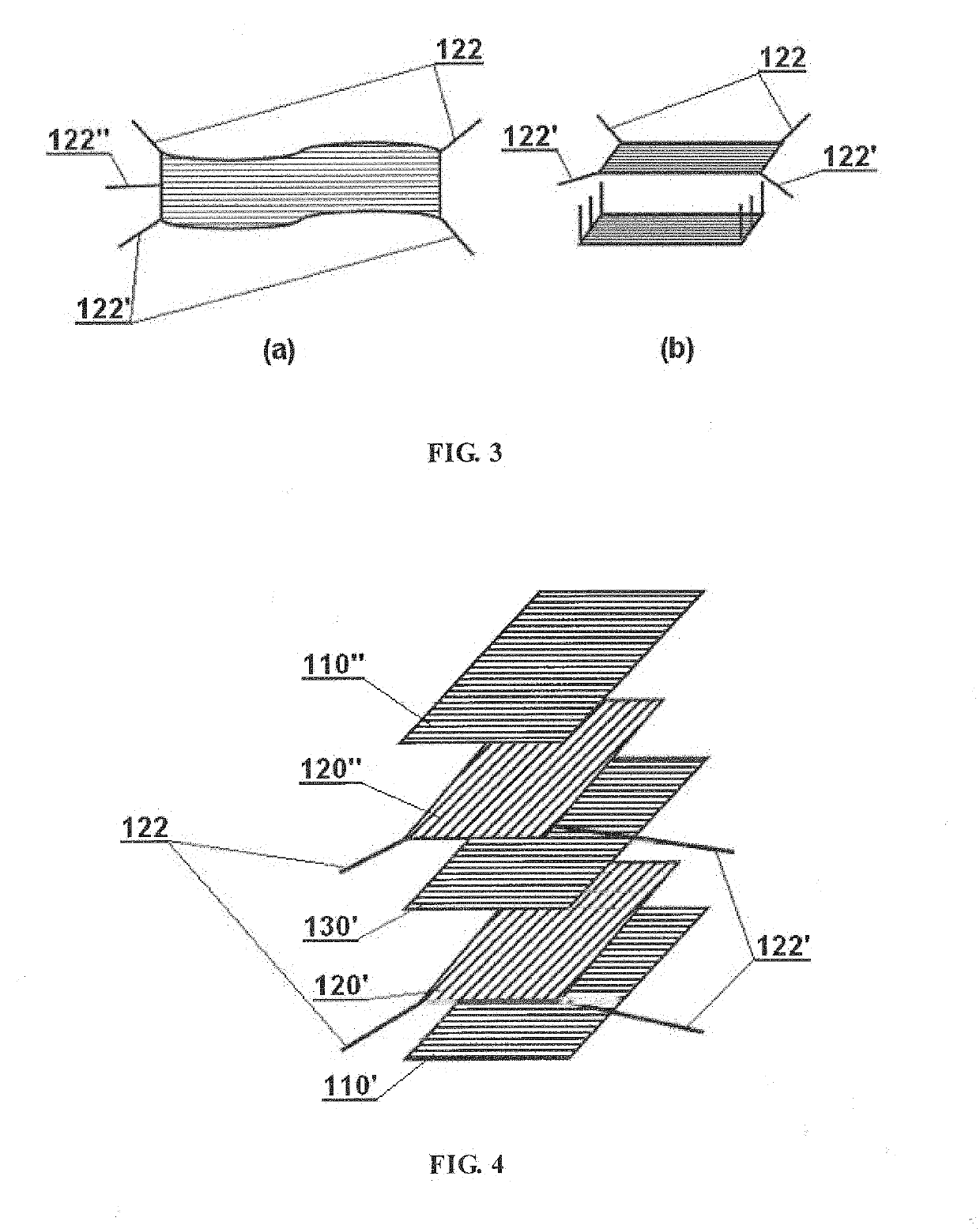
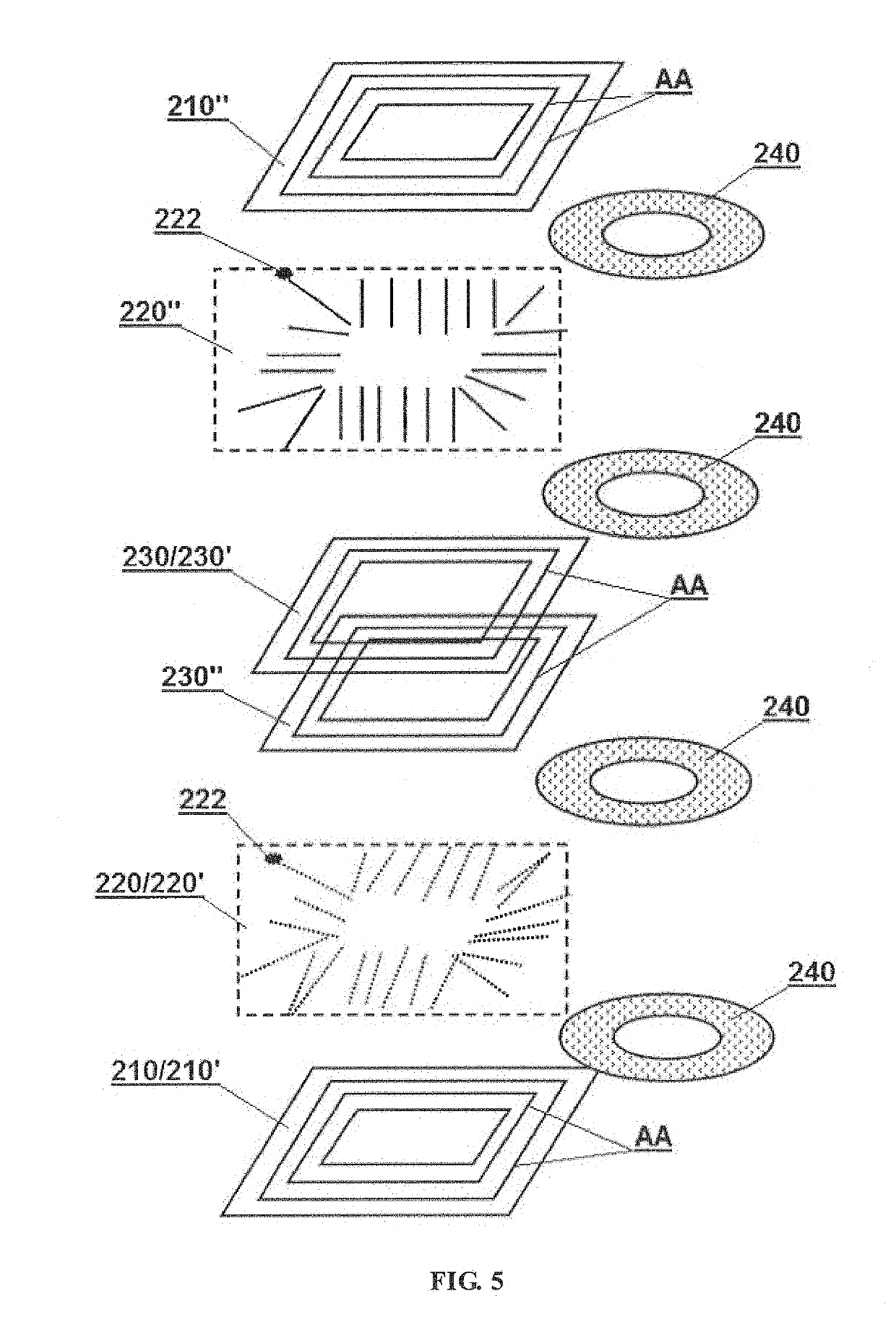
InactiveUS20190156989A1Reduce Flux LeakageReduce magnetic resistanceTransformers/inductances casingsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsMagnetic reluctanceMagnetic flux
An electromagnetic induction device, comprising a magnetic coating (110) and at least one set of coils (120). The magnetic coating (110) is formed by splicing all magnetic cells together, and is provided therein with at least one cavity. Magnetic division surfaces (AA) between each two magnetic cells are substantially arranged along a magnetic flux loop without cutting off the magnetic flux loop. The coils (120) are placed in a cavity formed by the magnetic coating (110), and the magnetic flux loop in the magnetic coating (110) is formed by the coils (120) after being energized. The overall structure of the magnetic coating (110) comprises at least two magnetically permeable layers (110′, 110″). The electromagnetic induction device, on the one hand, can be substantially closed to reduce leakage flux; on the other hand, since there is no air gap on a magnetic unit, the magnetic reluctance is effectively reduced. In addition, the magnetic coating (110) is of a layered structure so that the electromagnetic induction device can be fabricated in a superposed manner, thereby not only reducing the manufacturing difficulty, but also facilitating obtaining a high-performance flat electromagnetic induction device. Also provided is a corresponding method for manufacturing the electromagnetic induction device.
Owner:BOLYMEDIA HLDG
Transverse flux electrical motor
A transverse flux electrical motor to produce motion from an input electric current, the electrical motor comprising: a static element having a plurality of magnets arranged in at least two rows and defining a path of movement; a magnetizable movable element having at least two openings, each opening being sized and shaped to receive a magnet from one of the rows of magnets, the movable element being movable along the path of movement such that the magnets of each row pass through one of the openings; and a plurality of windings positioned adjacent to the movable element, to receive the electric current and produce a magnetic flux circuit in the movable element and a force on the movable element in the direction of the path of movement; wherein the magnetic flux circuit in the movable element is transverse to the direction of force on the movable element.
Owner:YASKAWA EURO TECH
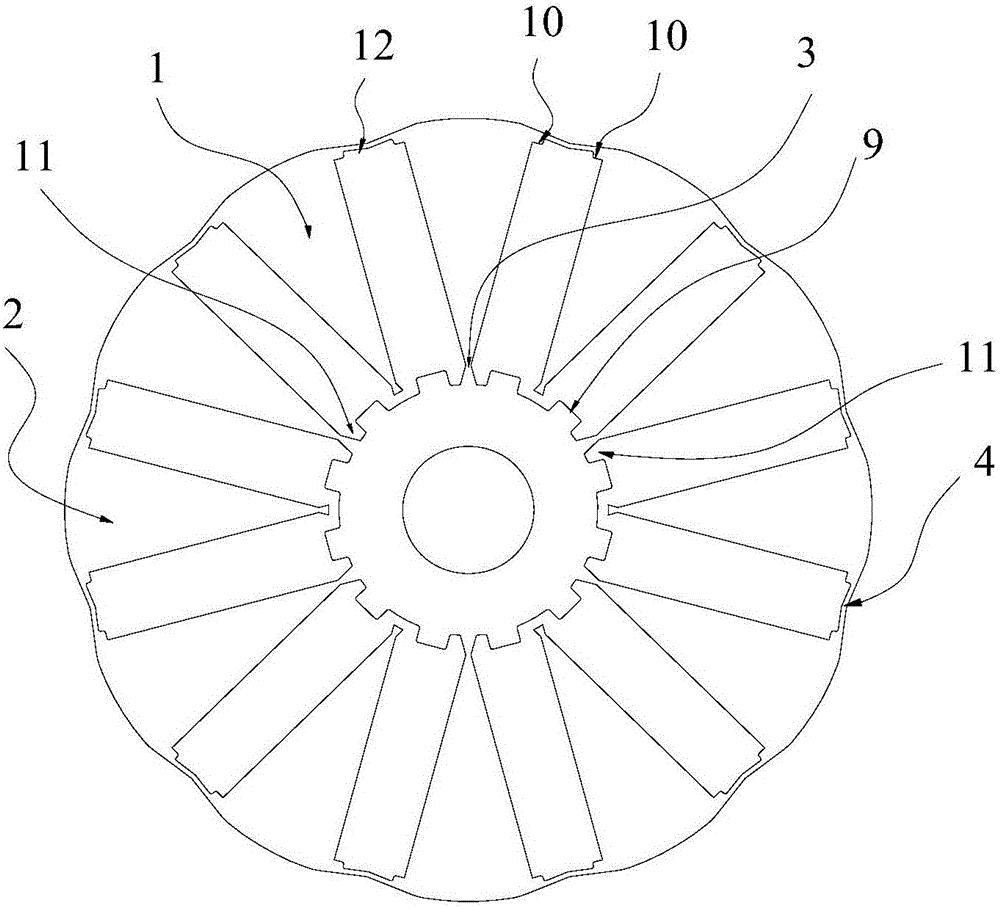
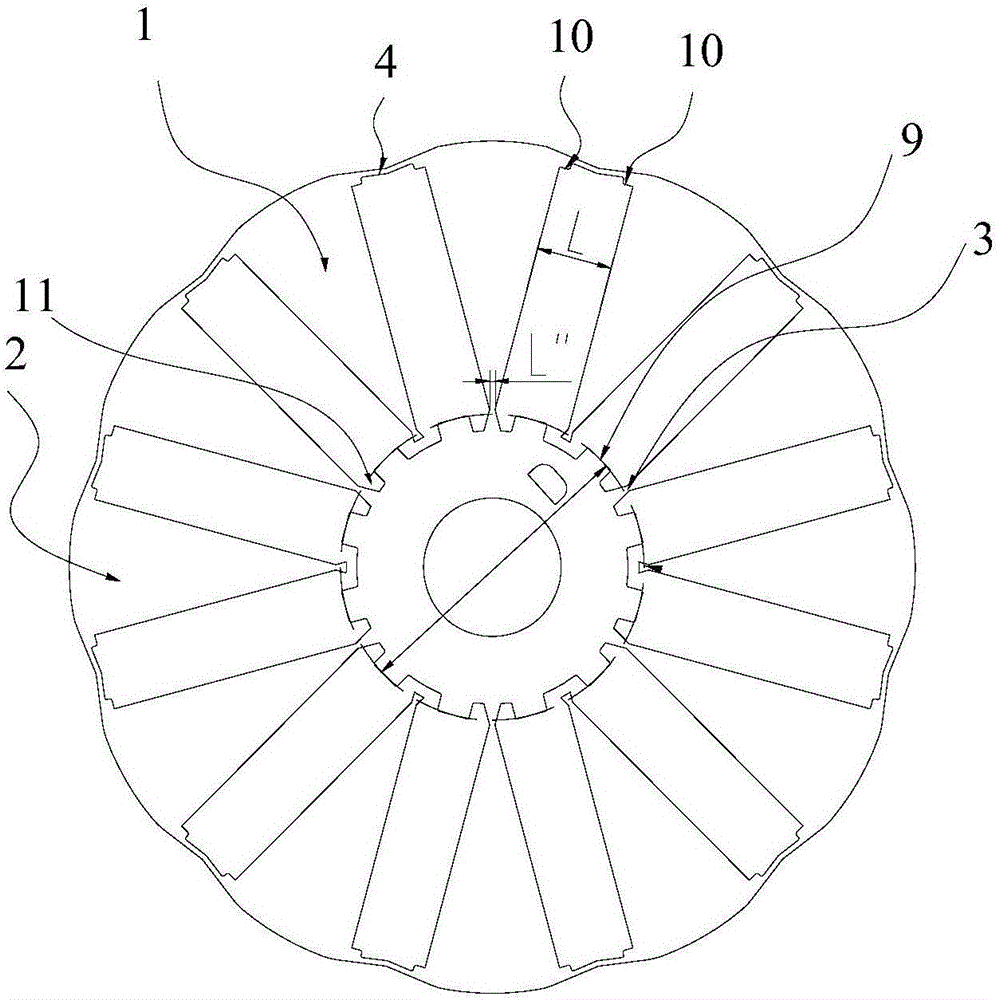
Rotor punching plate and permanent magnet motor
ActiveCN105743251ATaking into account the structural strengthReduce torque rippleMagnetic circuit rotating partsPunchingFlux loop
The invention relates to the technical field of generators, in particular to a rotor punching plate and a permanent magnet motor. The rotor punching plate comprises an iron core, wherein a plurality of magnetic shoe grooves are evenly distributed in the iron core along the circumferential direction of a rotating shaft; each magnetic shoe groove is formed along the radial direction of the rotating shaft; a magnetic shoe is arranged in each magnetic shoe groove; and inner-side magnetic isolation bridges are formed between the adjacent magnetic shoe grooves and are disconnected from one another. The invention further provides the permanent magnet motor. The permanent magnet motor comprises the rotor punching plate. The inner-side magnetic isolation bridges are disconnected from one another, so that leakage flux loops at the inner sides of the magnetic shoe grooves are blocked; and leakage flux is reduced. The optimal widths of the magnetic shoe grooves can be quickly and accurately given through the minimum inner diameters of the inner sides of the magnetic shoe grooves, the number of rotor pole pairs and the widths of the inner-side magnetic isolation bridges; and optimal configuration of the structural strength and the magnetic property is achieved. Through an iron core outer arc formed by N curves which comprise eccentric circular arcs and straight scrap edges connected with two sides of the eccentric circular arcs, the air-gap reluctance of the outer arc side of the rotor punching plate along the radial direction is changed; and sine wave counter electromotive force is achieved.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com