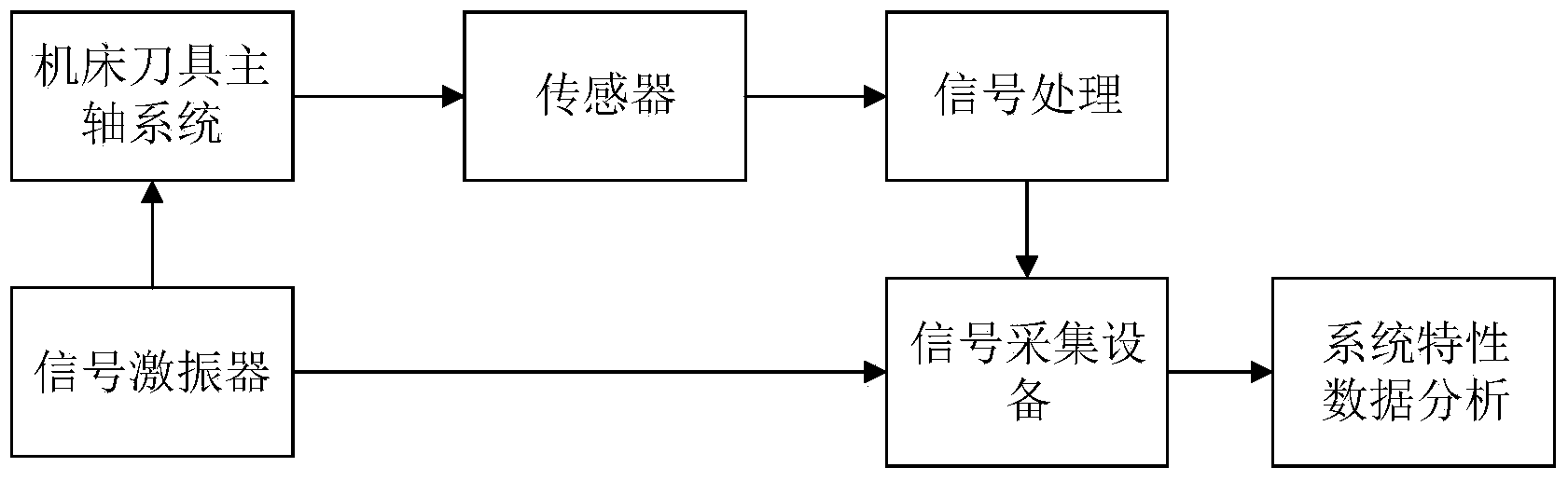
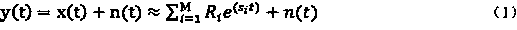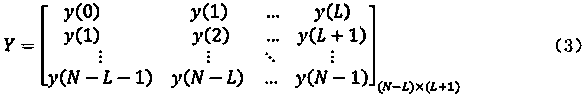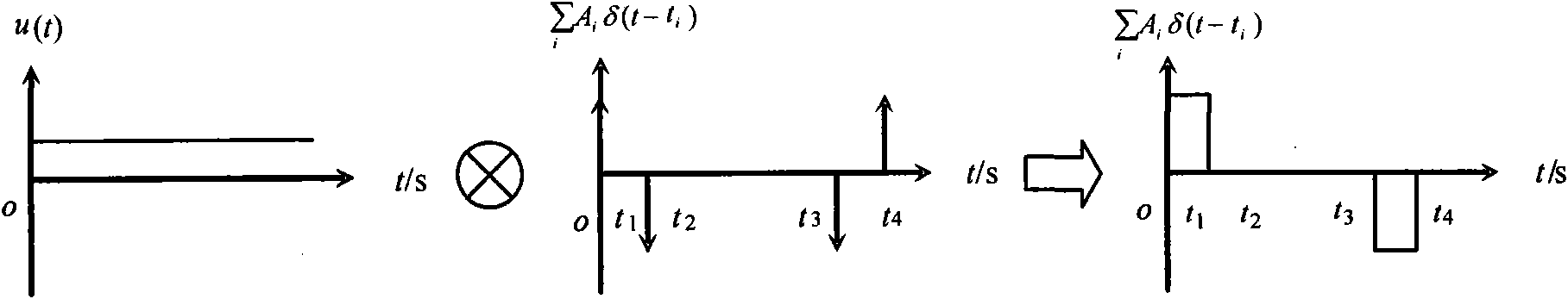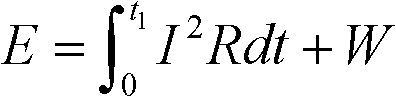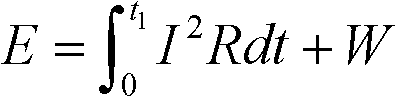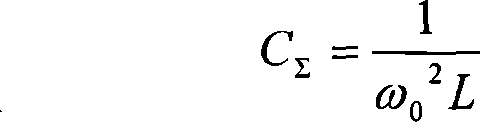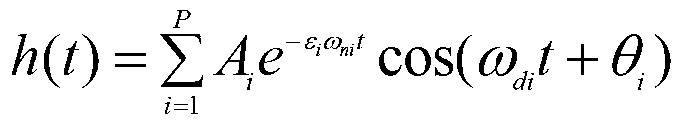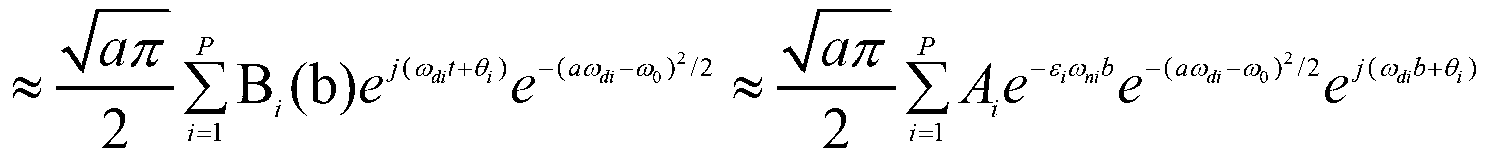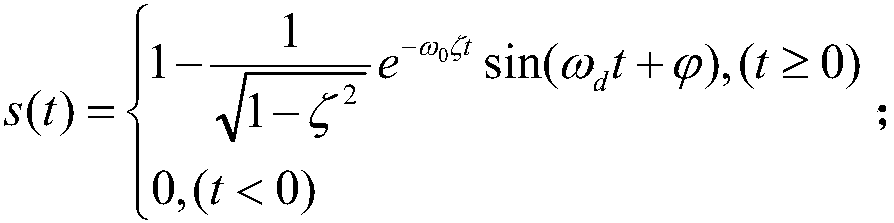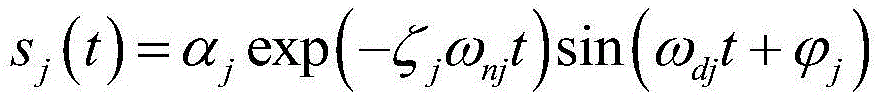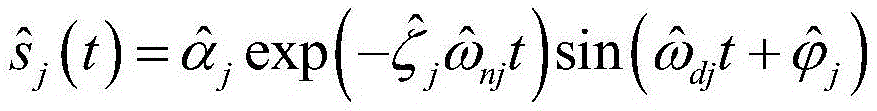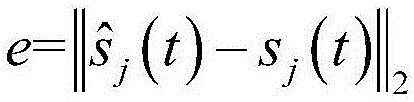Patents
Literature
818 results about "Damping ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Damping is an influence within or upon an oscillatory system that has the effect of reducing, restricting or preventing its oscillations. In physical systems, damping is produced by processes that dissipate the energy stored in the oscillation. Examples include viscous drag in mechanical systems, resistance in electronic oscillators, and absorption and scattering of light in optical oscillators. Damping not based on energy loss can be important in other oscillating systems such as those that occur in biological systems and bikes.
Damping ratio adjustable tuning quality damper
ActiveCN101457554AChange the damping ratioDamping Ratio OptimizationSpringsSolid based dampersDamping ratioEngineering
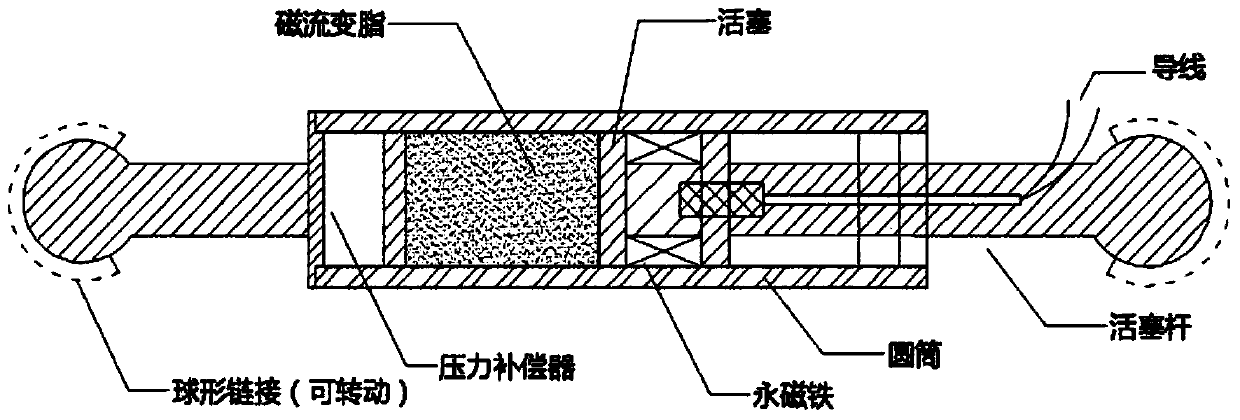
The invention specifically relates to a mass tuned vibration reducer used for regulating the subsidence ratio of the vibration of the related structures. The mass tuned vibration reducer comprises a mass block, a spring, a damper and a base, and is characterized in that the damper is an adhesion-type damper formed by a damping cylinder, adhesive damping fluid and a piston, wherein, the piston and the adhesive damping fluid are arranged in the damping cylinder, and at least part of the piston is immerged into the adhesive damping fluid. The mass tuned vibration reducer adopts the adhesion-type damper formed by the adhesive damping fluid and the piston and can provide three dimensional damping, so as to effectively prevent side tumbling and ensure the vibration reducer realizes smooth actions; vibration mass is not needed to be provided with a special guide device, so that the mass tuned vibration reducer has reliable work and higher cost performance, and basically needs no maintenance. Meanwhile, the mass tuned vibration reducer realizes the aim of regulating the natural frequency and the subsidence ratio at any time, thus better exerting the vibration absorption performance of the mass tuned vibration reducer, ensuring stableness and safety of the pedestrians and vehicles on the large-span bridge and the thin and high building, contributing to prolonging the service lives of the thin and high building and the bridge, and having remarkable economic and social benefits.
Owner:尹学军 +1
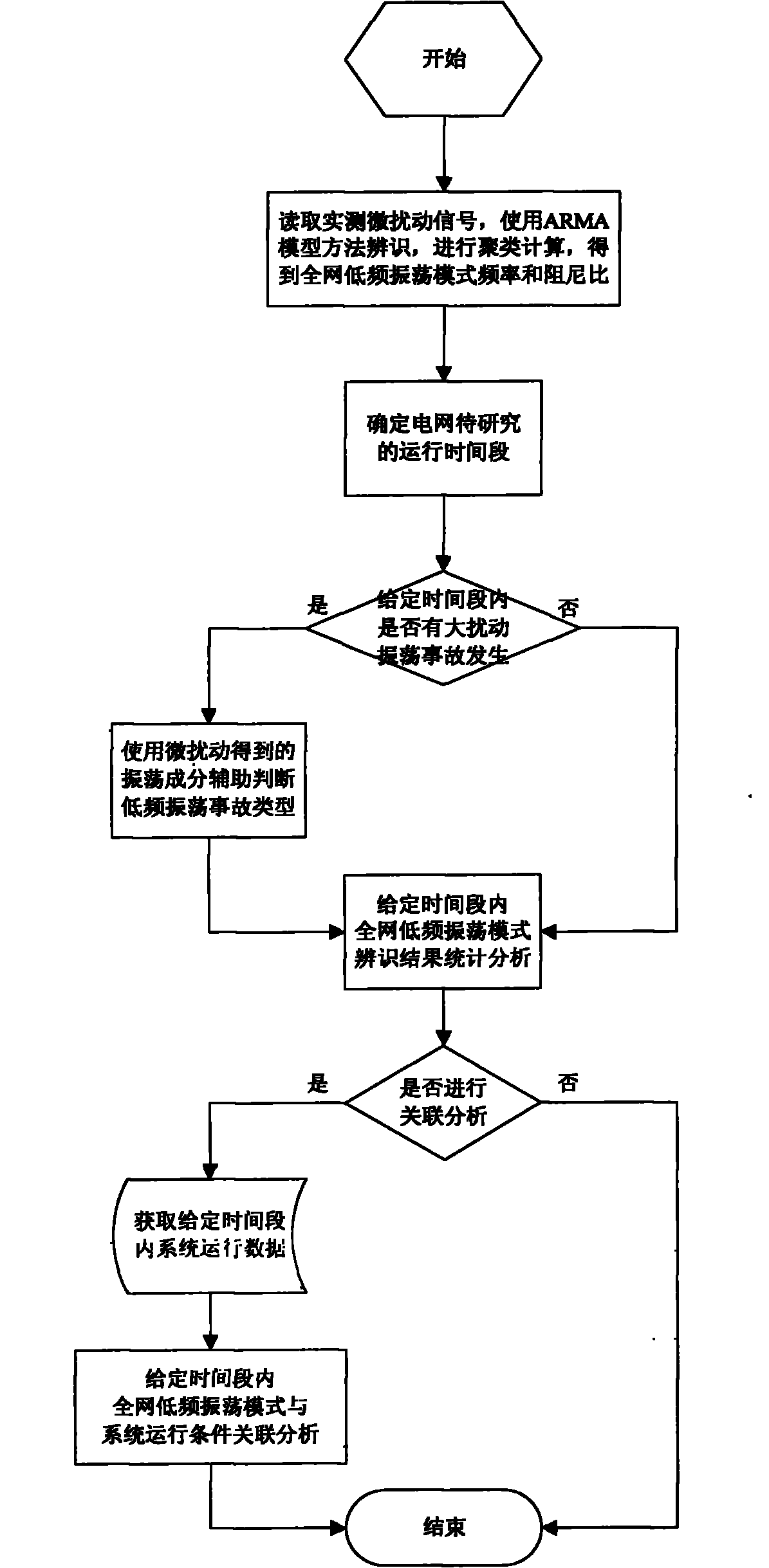
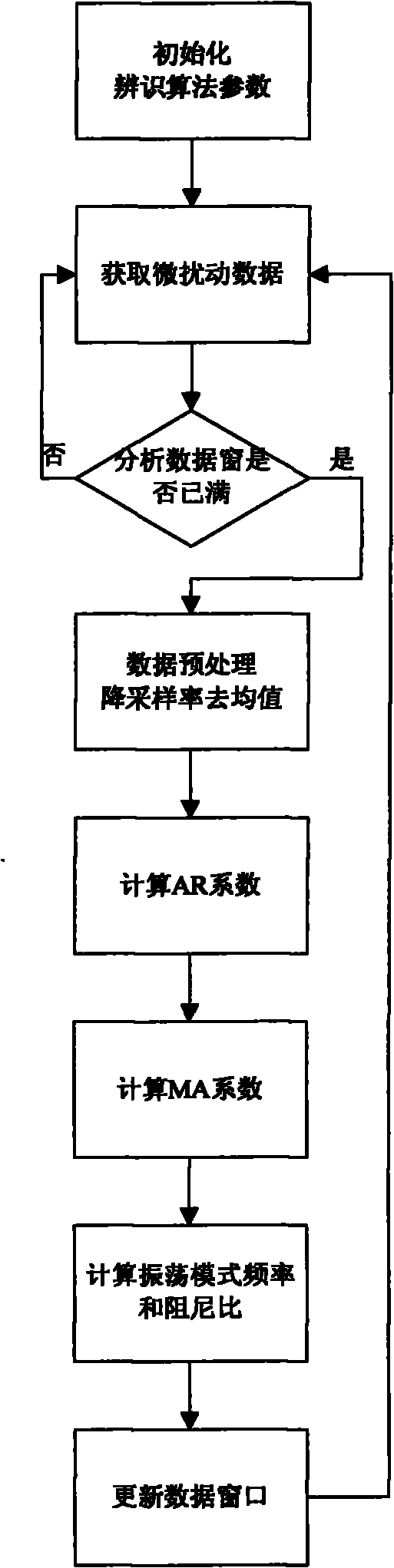
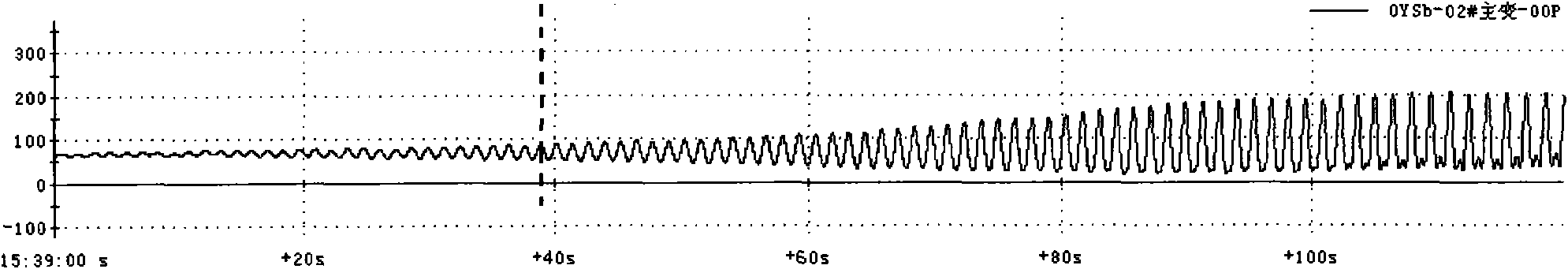
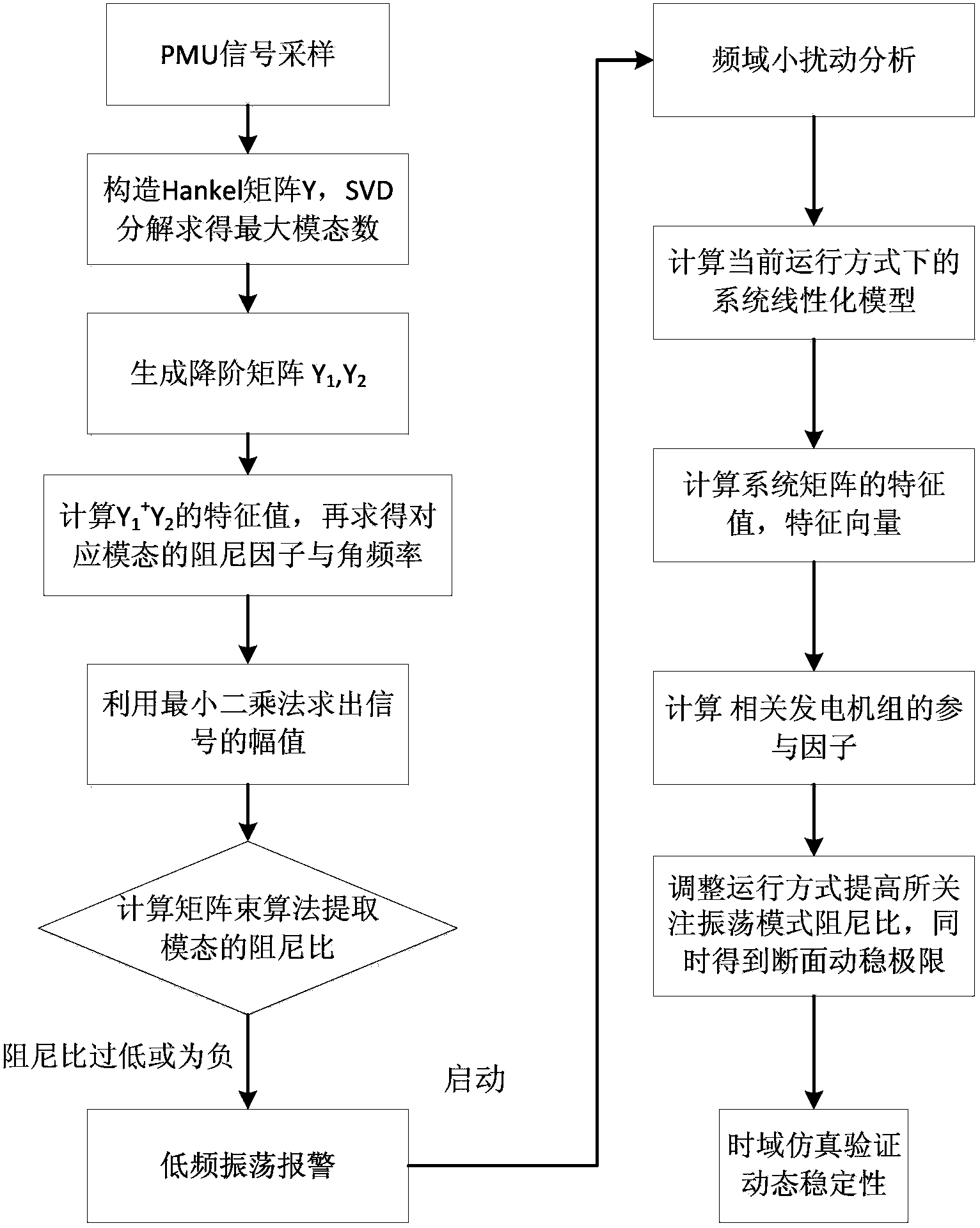
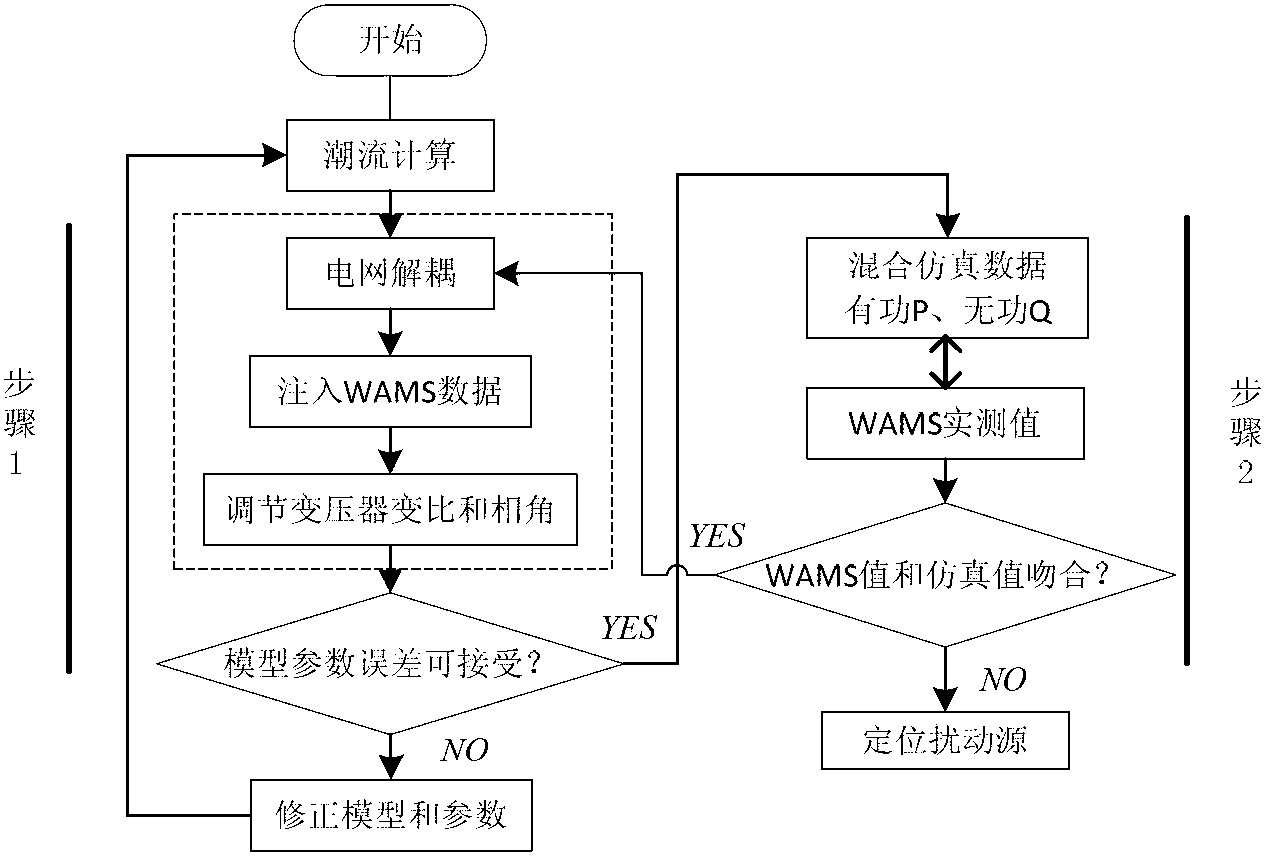
Power system low-frequency oscillation mechanism analysis method based on micro-disturbance signal oscillation mode recognition
ActiveCN102055201AExplain Oscillation PhenomenaPower oscillations reduction/preventionFault locationStatistical analysisTime segment
The invention discloses a power system low-frequency oscillation mechanism analysis method based on micro-disturbance signal oscillation mode recognition. The method comprises the following steps of: providing a basis for judgment of oscillation mechanism types of power grid low-frequency oscillation accidents by using oscillation components provided by micro-disturbance recognition result in the process of a low-frequency oscillation accident; timely discovering a system running weak link and a potential oscillation source by performing statistic analysis on an entire-grid low-frequency oscillation mode oscillation frequency and damping ratio result which is calculated by micro-disturbance recognition in the given running time period; and establishing a corresponding relation between entire-grid oscillation mode characteristic change and system running condition parameter change to provide a basis for system running adjustment by performing multi-variable association analysis on the entire-grid low-frequency oscillation mode oscillation frequency and damping ratio result which is calculated by micro-disturbance recognition in the given running time period and the system running condition parameter.
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG JIBAO AUTOMATION +1
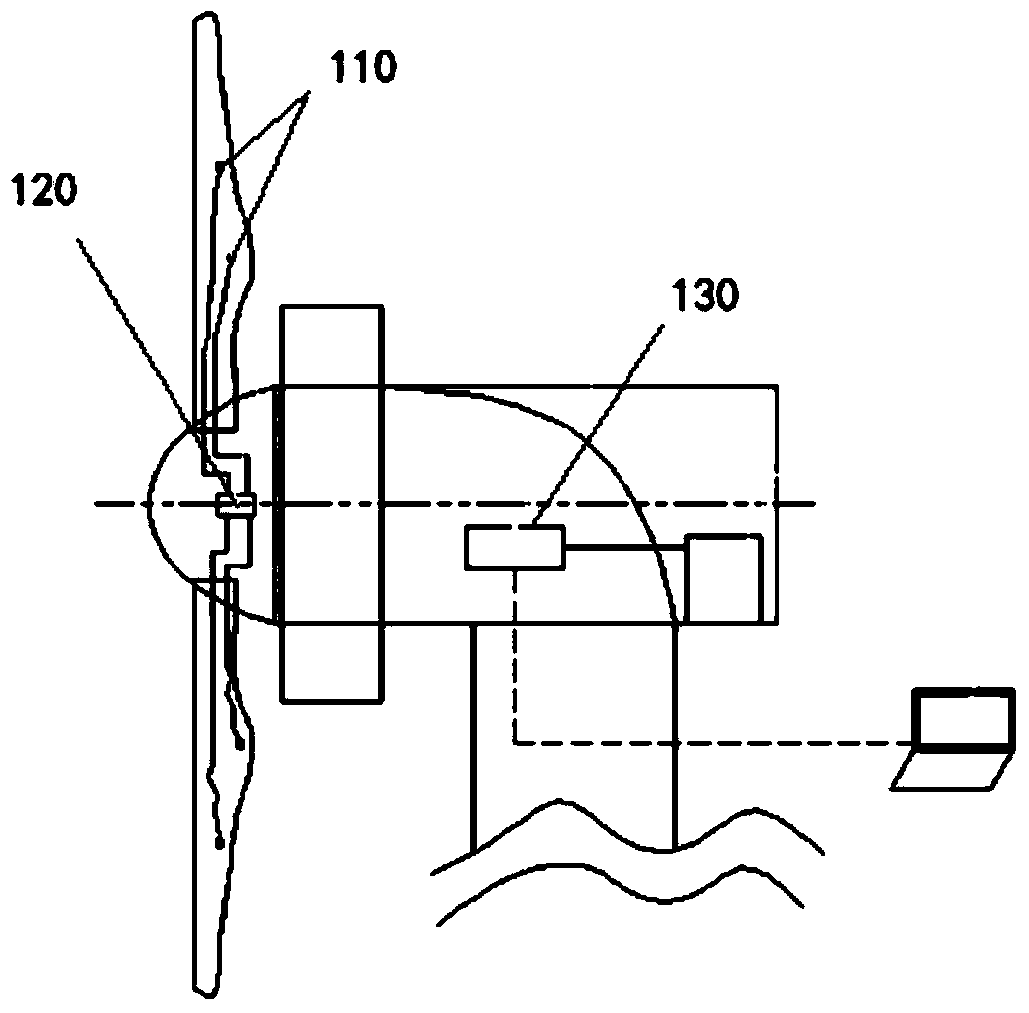
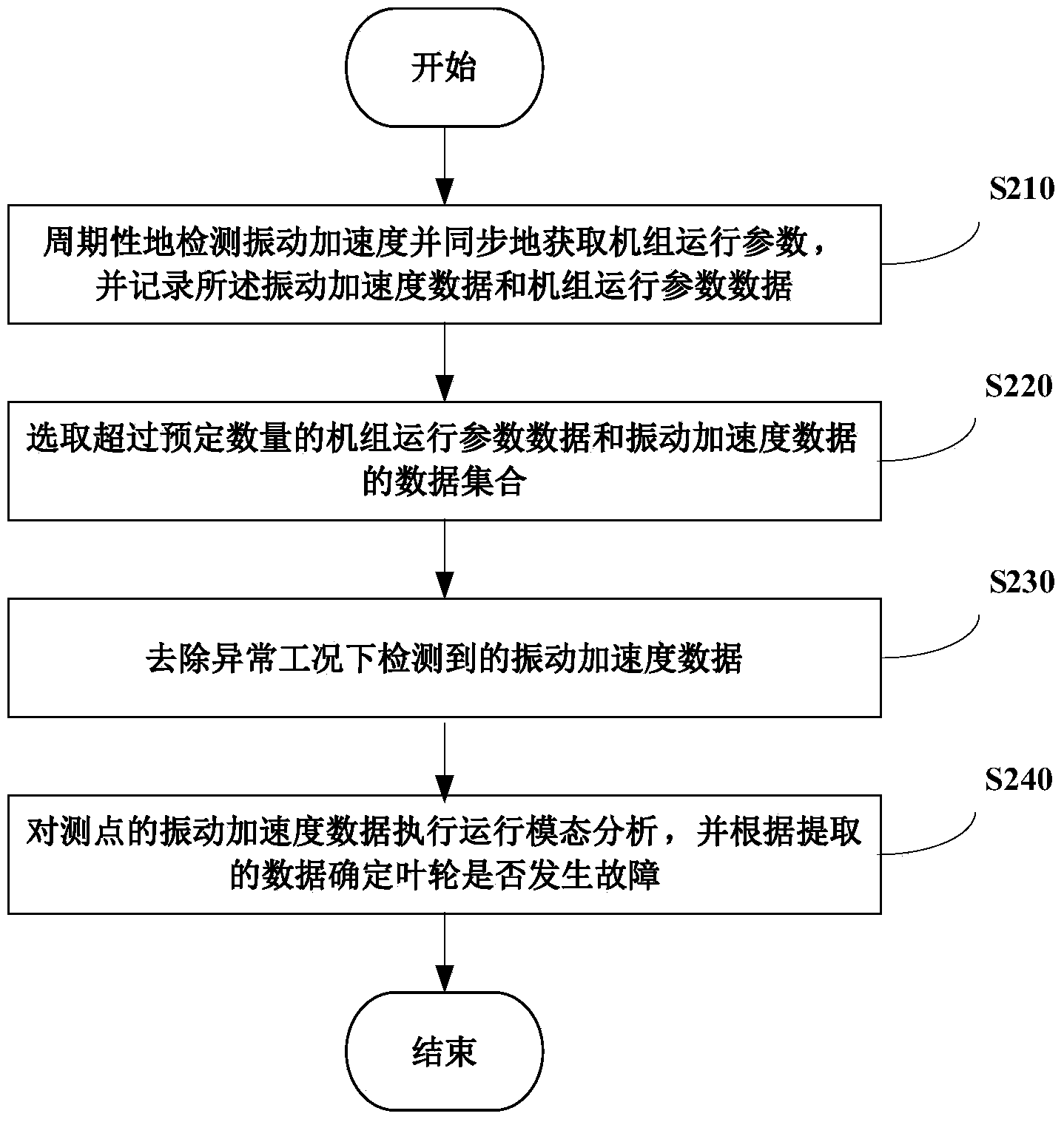
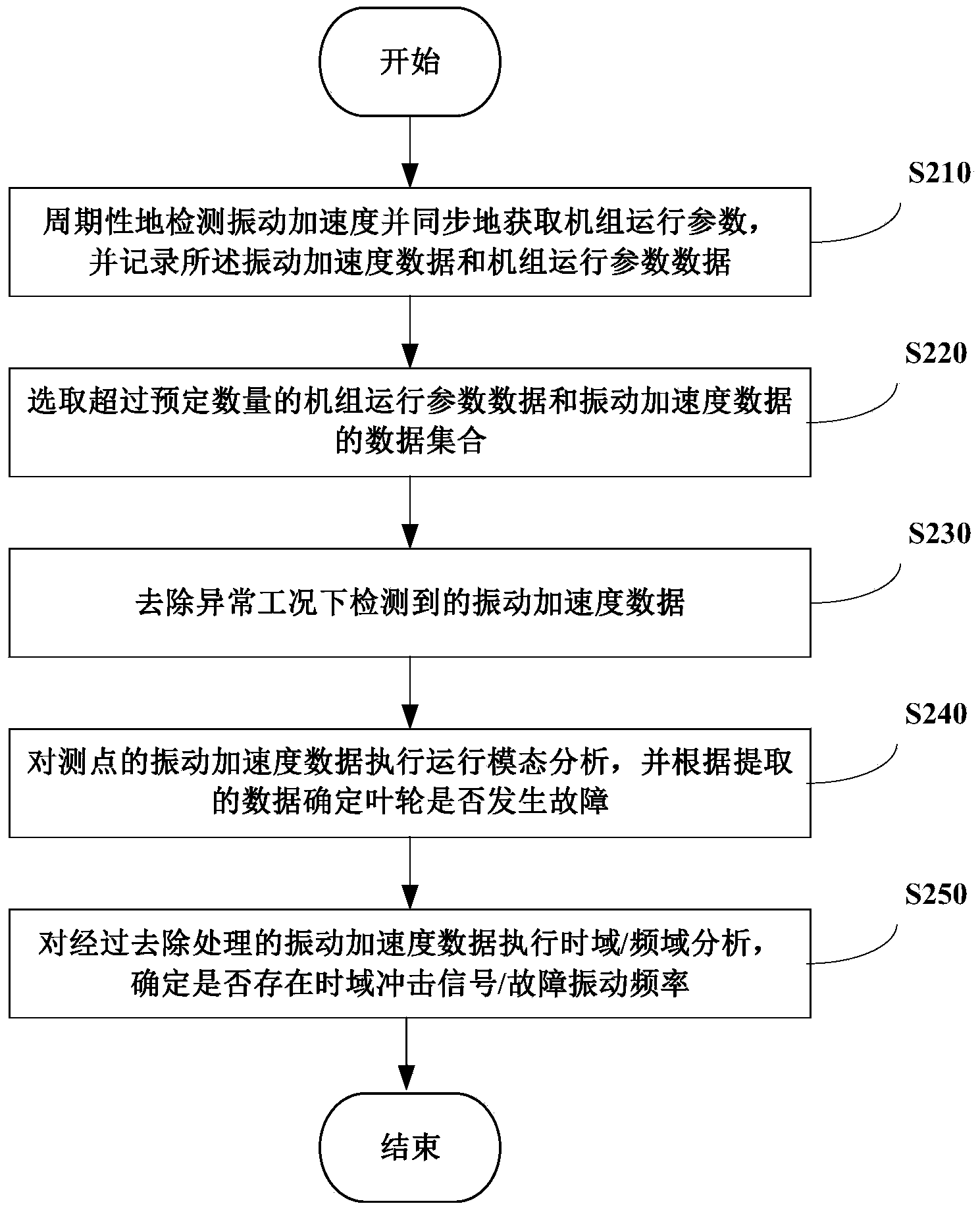
Method and system used for monitoring vibration states of impellers of wind generating sets
ActiveCN104075795ALow priceAnalysis method is simpleVibration measurement in solidsVibration testingImpellerData set
The invention provides a method and system used for monitoring the vibration states of impellers of wind generating sets. The method includes the steps that the vibration acceleration of a predetermined measuring point on a vane of each wind generating set in at least one direction is detected according to a preset detection period, data of operating parameters of at least one of the wind generating sets are synchronously acquired, and the acquired data of the operating parameters of the set and the detected vibration acceleration data are recorded; data sets of recorded operating parameter data and recorded vibration acceleration data exceeding the preset amount are selected; according to the operating parameters of the wind generating sets, vibration acceleration data detected when the wind generating sets are in abnormal working conditions are removed from the data sets; operating mode analysis is carried out on the vibration acceleration data detected at the measuring points of the vanes, at least one of the inherent frequency, the damping ratio and the vibration mode of each vane in the operating state is extracted, and whether the impellers of the wind generating sets break down or not are determined according to the extracted inherent frequency, damping ratio and vibration mode.
Owner:BEIJING GOLDWIND SCI & CREATION WINDPOWER EQUIP CO LTD
Method for vibration analysis
InactiveUS6779404B1Vibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingSingular value decompositionModal testing
Output-only modal testing of an object. Vibrations are excited in said object and measured by a number of vibration sensitive detectors. From the data of the measurements, a spectral density matrix function is determined. From this density matrix, auto spectral densities for the individual modes are identified performing a decomposition based on the Singular Value Decomposition technique. From the auto spectral densities of the individual modes, natural frequencies and damping ratios for the modes can be estimated, and from the singular vectors of the Singular Value Decomposition, the modes shapes can be estimated.
Owner:STRUCTURAL VIBRATIONS SOLUTIONS
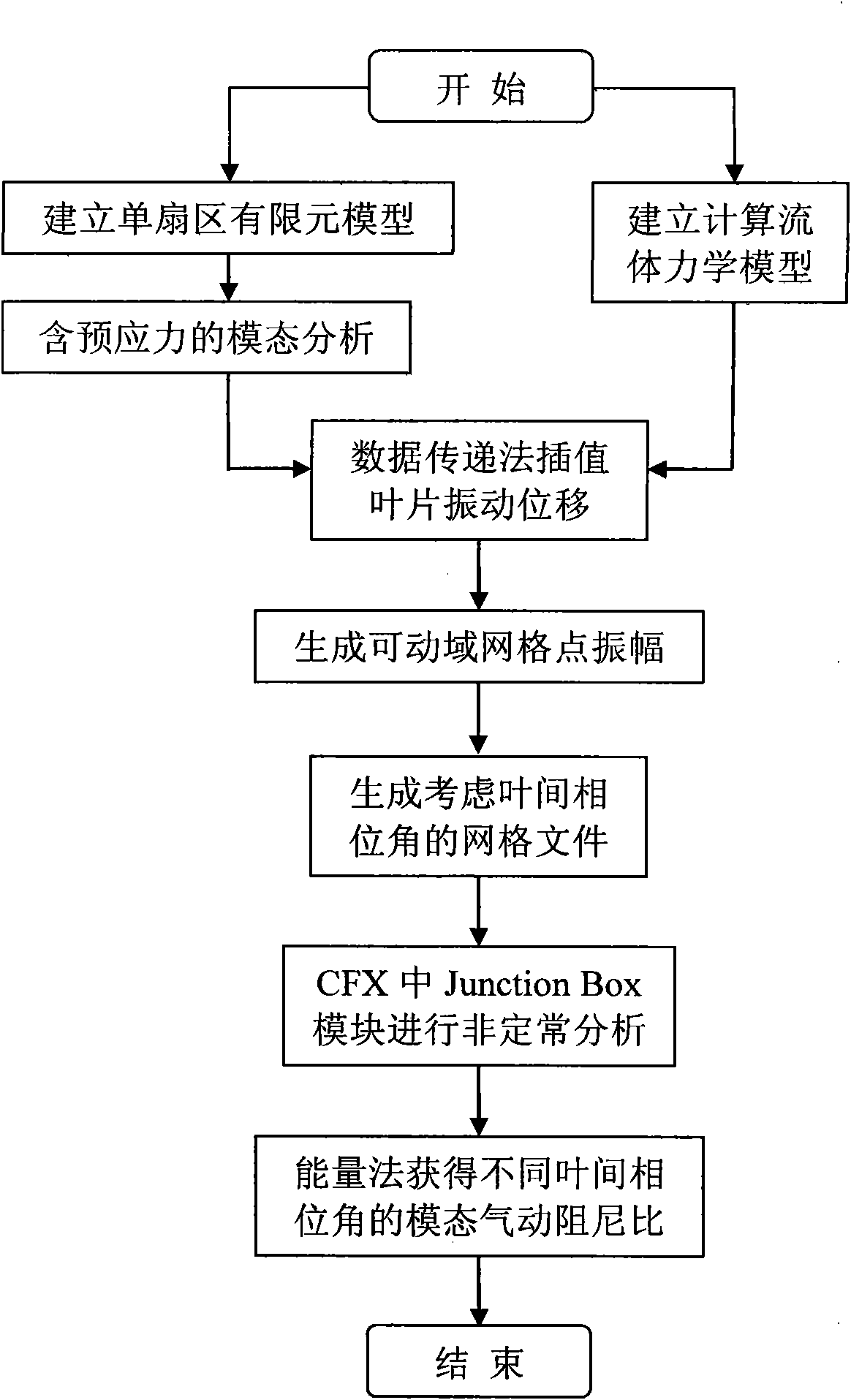
Aeroelastic stability fluid-structure interaction prediction method of turbo-machine changed interblade phase angles
InactiveCN101882177AReduce computing costCoupling calculation simplificationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelPredictive methods
The invention relates to an aeroelastic stability fluid-structure interaction prediction method of turbo-machine changed interblade phase angles, which predicts the aeroelastic stability of a turbo-machine through the modal pneumatic damping ratio of different interblade phase angles by adopting an energy method. The method adopts the modal analysis containing prestress on established single-sector finite element models, realizes the vibration displacement transfer on the fluid-structure interaction interface through a data transfer method, adopts the dynamic mesh technology for obtaining mesh files taking the interblade phase angles into consideration, is used for unsteady computation fluid mechanic analysis of Junction Box modules in CFX, further obtains the modal pneumatic damping ratio of each interblade phase angle, and is used for predicting the aeroelastic stability. The method based on the fluid-structure interaction fully utilizes the cutting edge technology of the computational structural mechanics and the computation fluid mechanics, ensures the computation precision in each sub system, and improves the computation efficiency through the division of a fixed region and a movable region. The invention has good practical value and wide application prospects in the technical field of turbo-machine simulation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
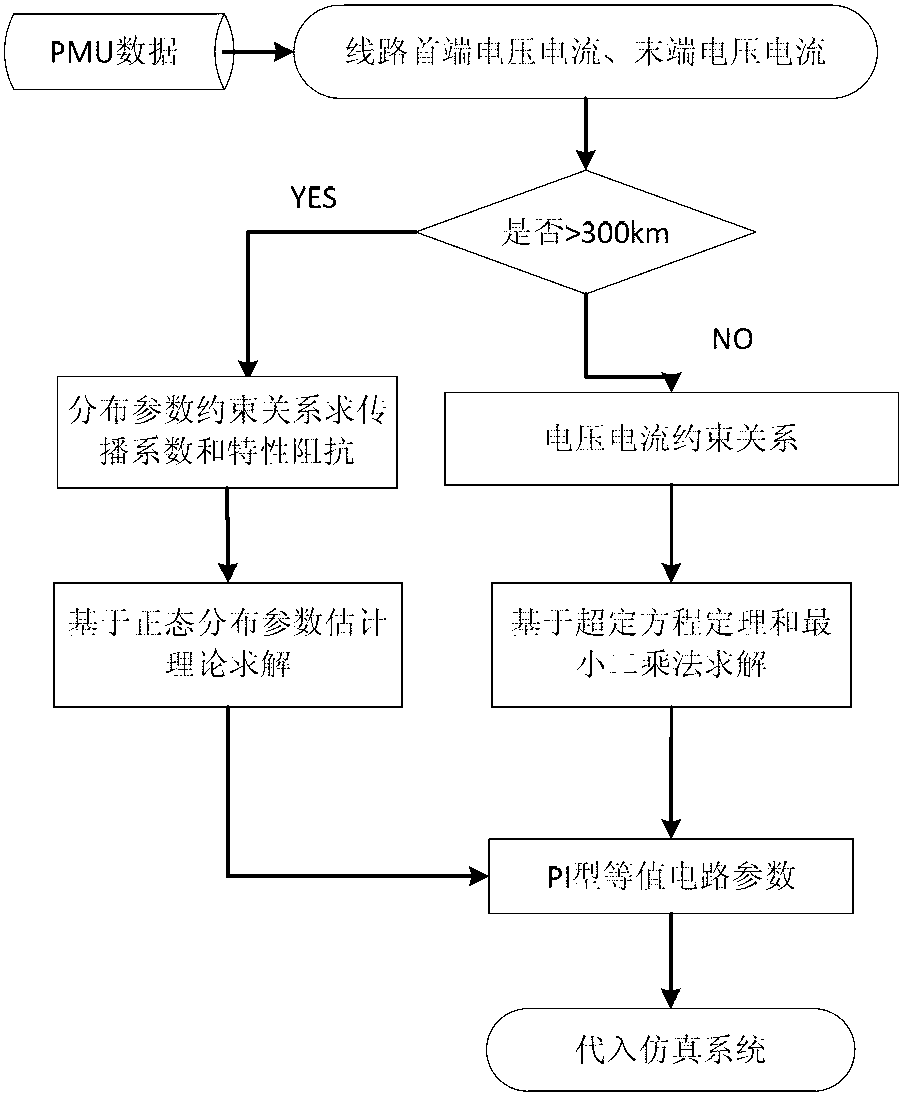
Application of phasor measurement units (PMU) for controlled system separation
This invention relates to a PMU-based controlled system separation method to protect against a catastrophic blackout. The method includes the steps of performing an offline analysis of an electrical transmission network to partition generators into a number of coherent groups, performing online monitoring of the transmission network to determine a separation interface and frequencies and damping ratios of dominant inter-area modes, and estimating the risk of system separation to perform real-time control.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST INC
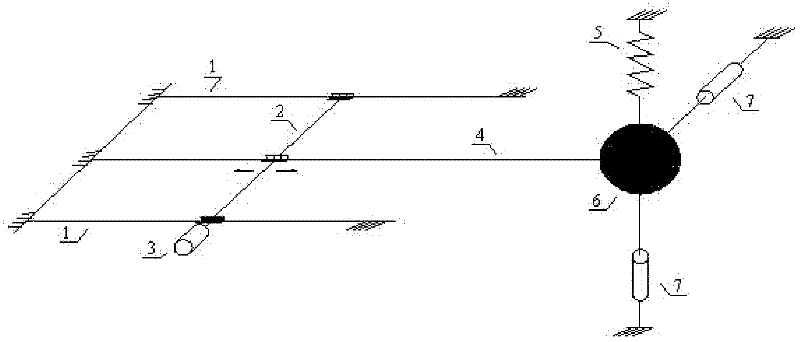
Big-tonnage cantilever type horizontal tuned mass damper for regulating eddy-current damping
ActiveCN102031751AAchieve fine-tuningRealize continuously adjustableBridge structural detailsShock proofingVibration controlEngineering
The invention relates to a horizontal vibration energy-absorbing and vibration-damping device used for large engineering structures such as a longspan foot bridge, belonging to the field of vibration control of civil engineering structures. The horizontal vibration energy-absorbing and vibration-damping device comprises a constant strength cantilever beam consisting of struts at two sides and a cross beam, two ends of the cross beam are respectively and correspondingly connected with the struts at two sides, and the bottom ends of the struts at two sides are fixed on a foundation. The horizontal vibration energy-absorbing and vibration-damping device is characterized in that the upper end of a mass block is connected with the cross beam, the lower end of the mass block is provided with a rectangular permanent magnet; and one side of the lower part of the mass block is provided with a copper plate fixedly arranged on the foundation through a supporting member, and a gap is reserved between the copper plate and the rectangular permanent magnet. The invention ensures that the rigidity and the dampness of the tuned mass damper system realize complete separation, easily realizes that the damping ratio of TMD is continuously adjustable within a larger range though regulating the gap between the permanent magnet and the copper plate, and effectively solves the problems of oil leakage failure in the conventional TMD, difficult regulation of the damping parameters and interference on the frequency.
Owner:湖南省潇振工程科技有限公司
Online evaluation method of electric power system dynamic stability
ActiveCN103368175AAvoid Sensitive ConsQuick calculationSystems intergating technologiesSpecial data processing applicationsDamping ratioMatrix pencil
The invention discloses an online evaluation method of electric power system dynamic stability. The online evaluation method comprises the steps of step 1, carrying out high-frequency sampling by utilizing a PMU (Power Management Unit), and extracting an oscillation mode for sampling data by utilizing a matrix pencil identification method; step 2, detecting low-frequency oscillation, and emitting low-frequency oscillation warning if a damping ratio of the detected oscillation mode is lower than a set threshold value; step 3, carrying out small perturbation calculation on a system model in a current running mode through a frequency domain analysis method, and obtaining a characteristic value, a characteristic vector, a corresponding unit and participated factor information; and step 4, screening out information of a low-frequency oscillation mode from a small perturbation calculation result according to the low-frequency oscillation mode which is determined by the matrix pencil identification method, regulating a related electric power generator to output, and obtaining tide stability limit of call lines between related domains through time-domain simulation at the same time. According to the online evaluation method disclosed by the invention, the influence of noise is effectively avoided, the identification accuracy is improved, the calculating speed and the calculating efficiency are increased, and the online dynamic safety evaluation effect of the electric power system is obviously improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
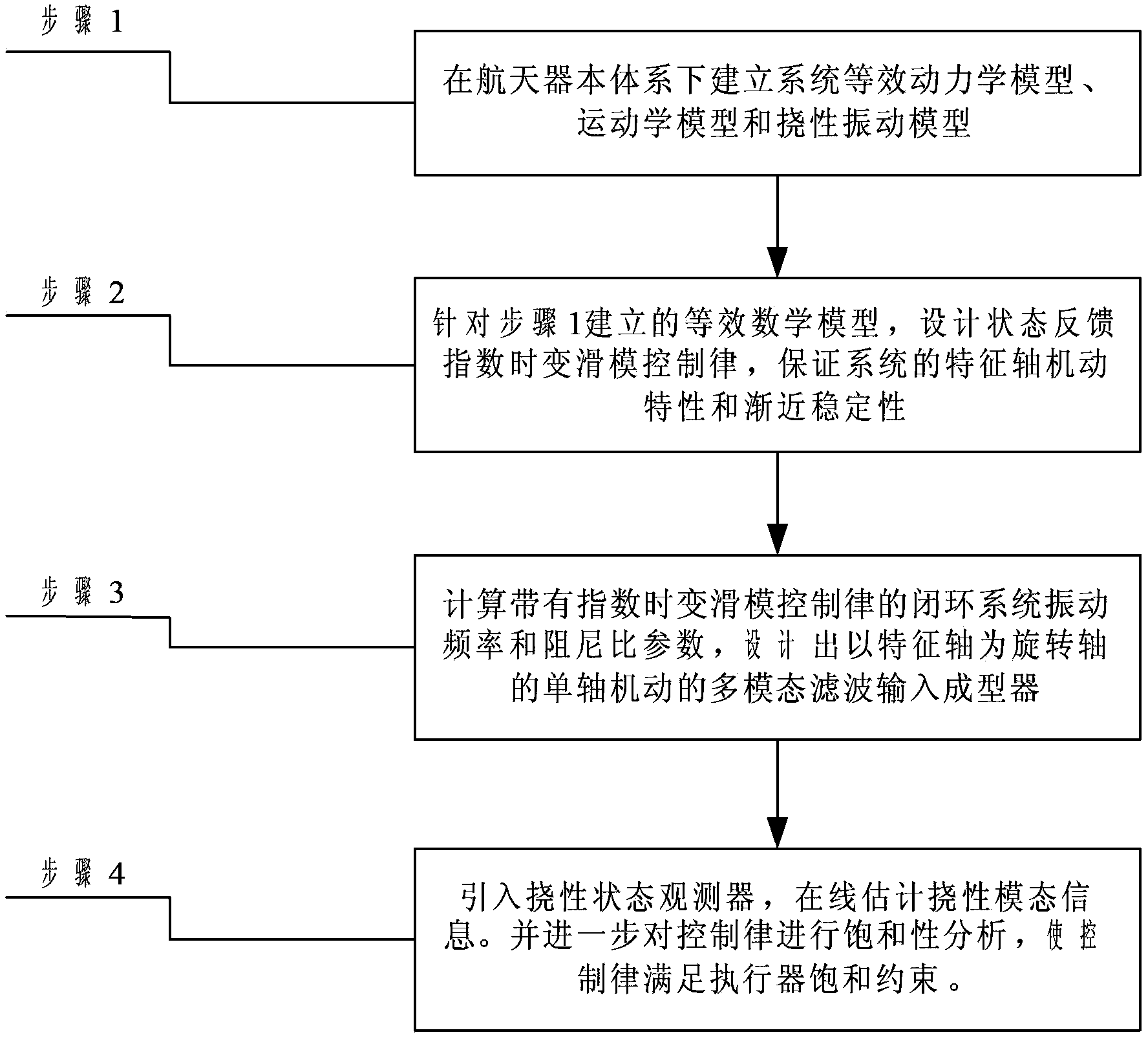
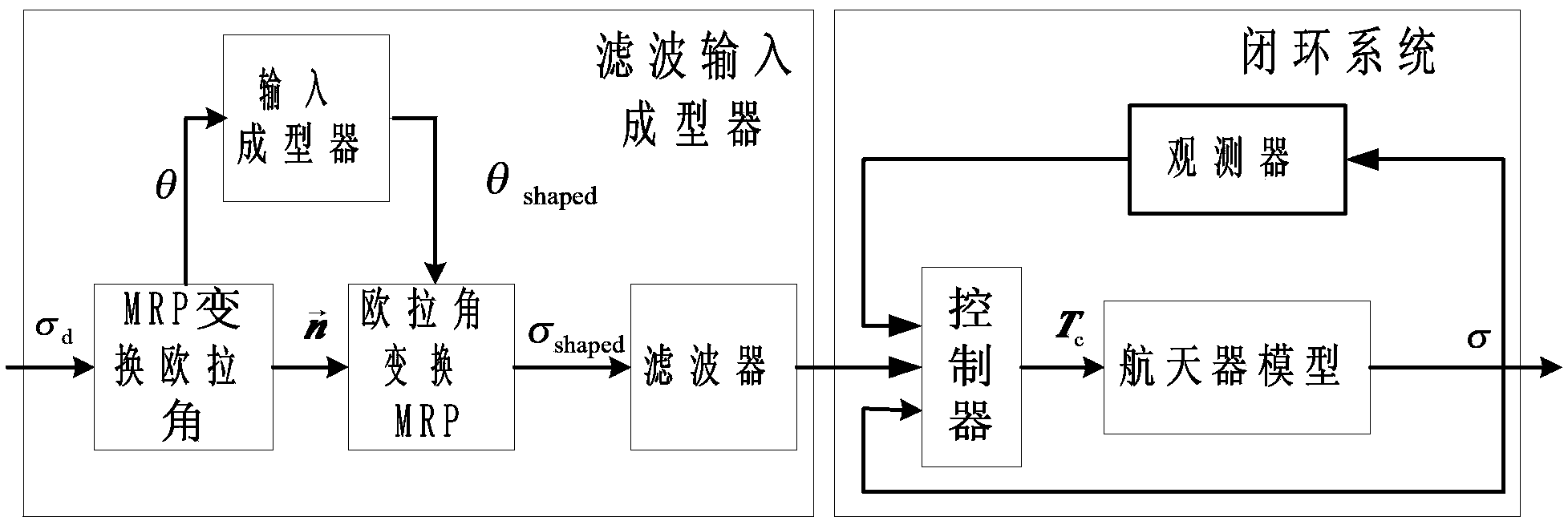
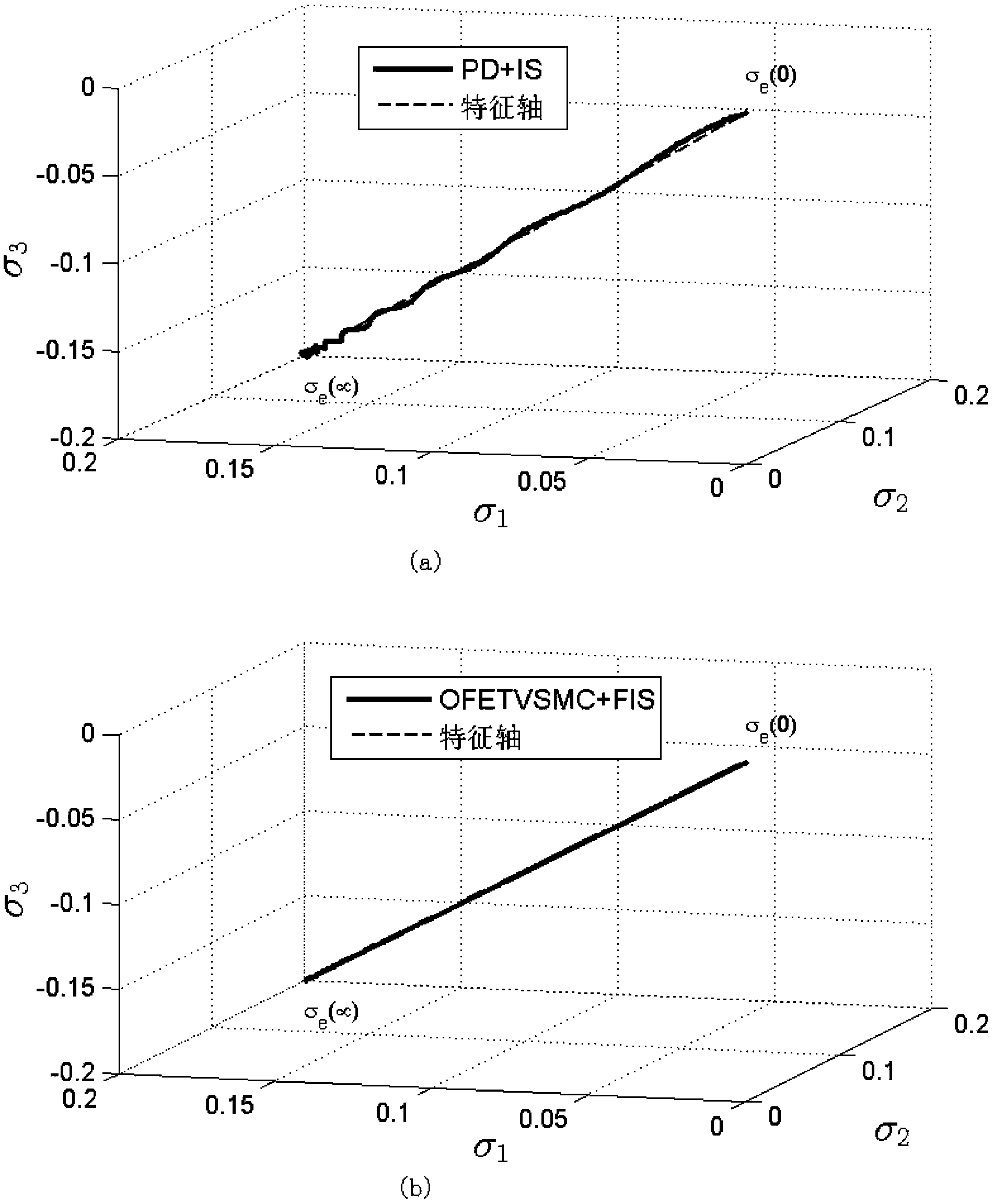
Method for controlling index time-varying slide mode of flexible spacecraft characteristic shaft attitude maneuver
ActiveCN103412491ASuppress residual vibrationAvoid complex coupling relationshipsAdaptive controlDynamic modelsSpace vehicle control
The invention relates to a method for controlling an index time-varying slide mode of flexible spacecraft characteristic shaft attitude maneuver, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft control. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a system dynamically equivalent model, a dynamic model and a flexible vibration model are established under a spacecraft system, then, the vibration frequency and the damping ratio parameter of a closed loop system with the index time-varying slide mode control law are calculated, and a single-shaft multi-modality filtering input shaping device with a characteristic shaft as a rotary shaft is designed according to the designing method of the single-shaft input shaping device to restrain flexible vibration in three-shaft motion. Meanwhile, a state observer is designed to estimate flexible modal information in real time, and the method for controlling an output feedback index time-varying slide mode is formed. At last, saturability analysis is conducted on control torque so as to satisfy the physical saturation constraint of the control torque. By means of the method, the application range of existing input shaping is expanded, the input shaping technology is expanded from single-shaft maneuver to three-shaft maneuver, the self-robustness of filter input shaping is enhanced, and the purpose that the attitude maneuver path of the spacecraft is the shortest is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
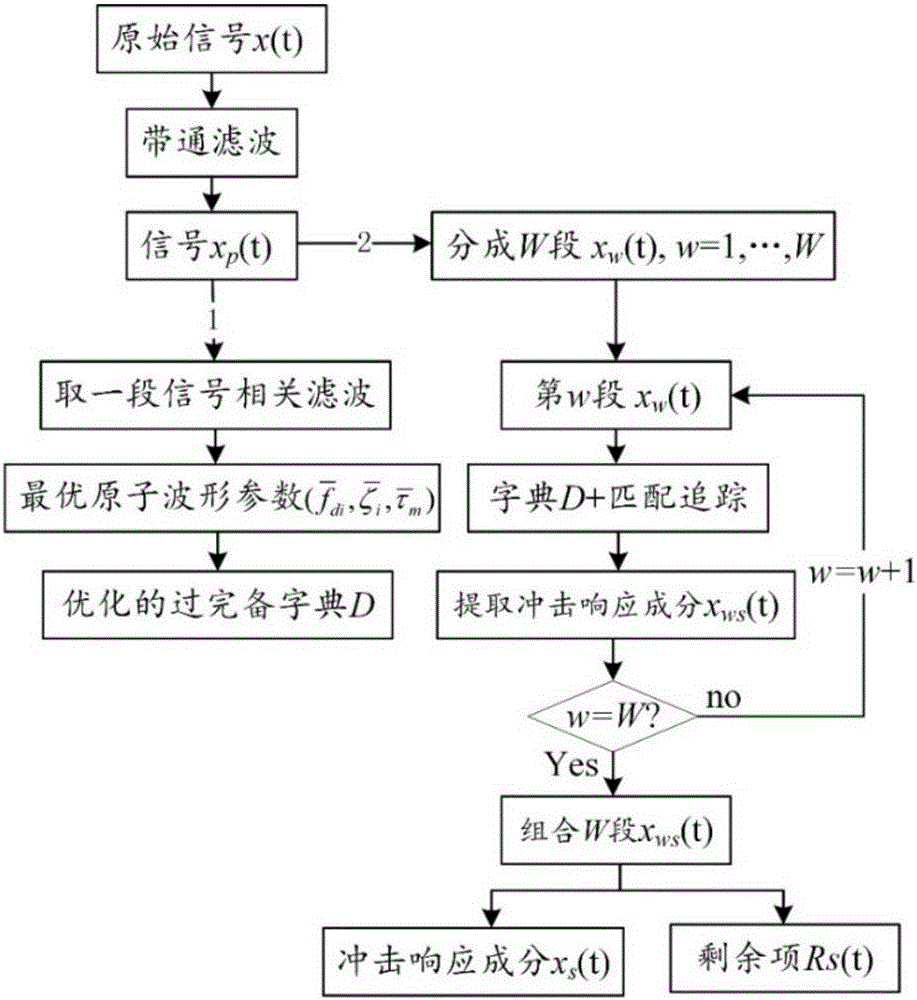
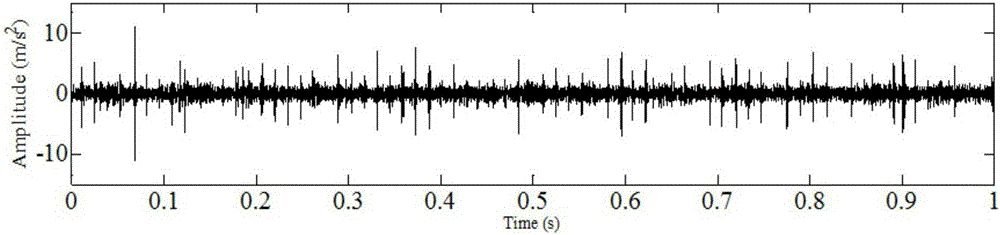
Rolling bearing fault feature extraction method based on signal sparse representation theory
InactiveCN105241666AWide versatilityReduce pointsMachine bearings testingDamping ratioAdaptive method
The invention discloses a rolling bearing fault feature extraction method based on the signal sparse representation theory, and the method comprises the following steps: constructing an over-complete dictionary representing local damages of a rolling bearing through employing a multi-stage inherent frequency unit impulse response function; recognizing the multi-stage inherent frequency and damping ratio of the rolling bearing and a sensor system from a vibration response signal through a related filtering method, and obtaining an optimized dictionary; solving a sparse coefficient through employing a matching tracking algorithm, and improving the solving speed and precision through reasonable segmentation; reconstructing an impact response signal of each segment, and obtaining the sparse representation of a fault feature signal; carrying out time domain index statistic characteristic analysis of time intervals of adjacent impact response components in a sparse signal, and diagnosing the type of a fault through combining a mean value and a mean square deviation value. The method has the advantages of an analytical method and an adaptive method, improves the precision of waveform features, and can iron out the defects that a conventional method based on Fourier transform is not suitable for rotating speed fluctuation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
PLC frequency-converting speed-governing control system for eliminating tower-type crane load
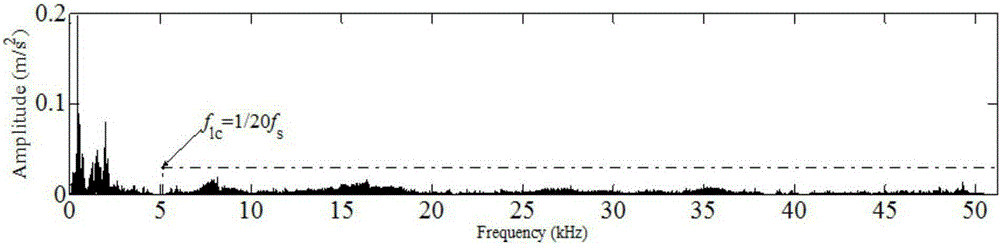
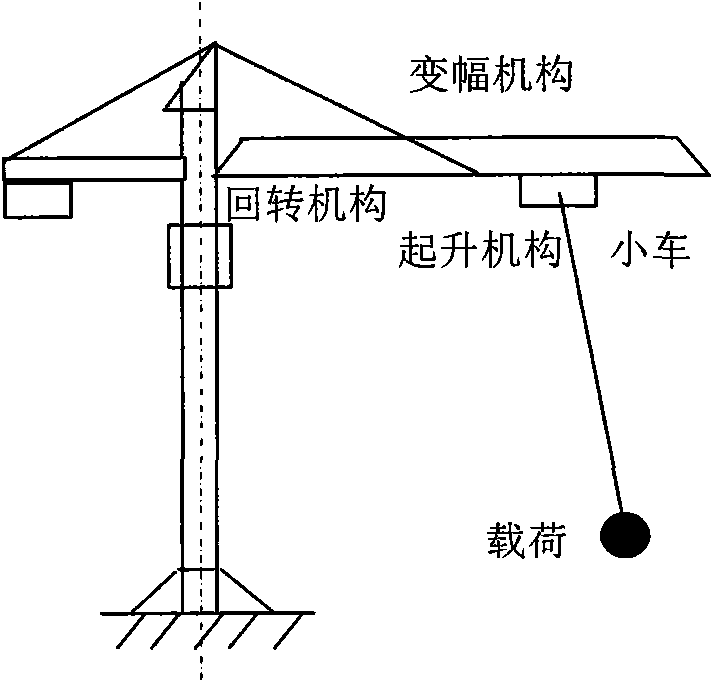
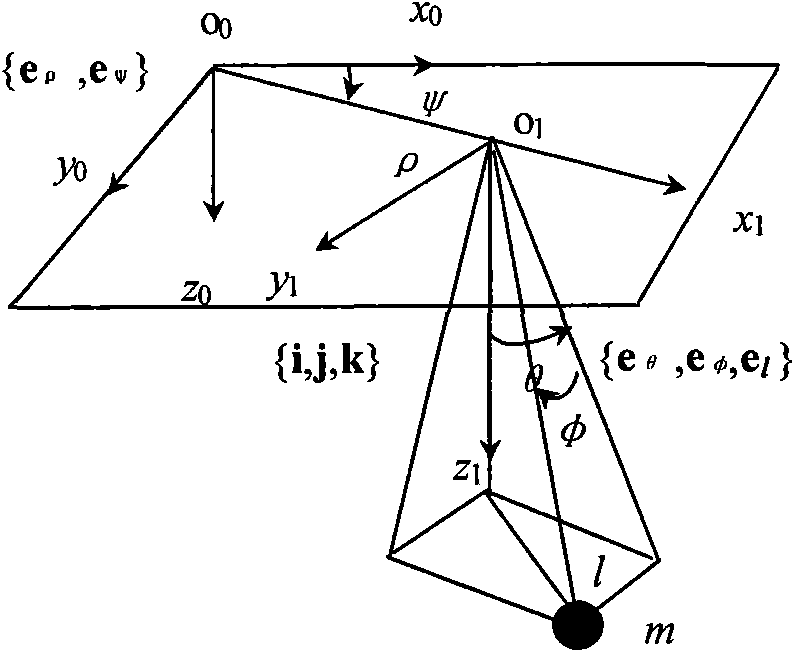
InactiveCN101659375AImprove work efficiencyImprove securityLoad-engaging elementsDynamic modelsControl system
The invention discloses a PLC frequency-converting speed-governing control system for eliminating tower-type crane load, based on an E1 time-delayed filter, which is developed by the following steps:establishing an inertia pole coordinate system, a non-inertia cartesian coordinate system and a non-inertia sphere coordinate system; establishing a nonlinear dynamics model and a linear dynamics model of a tower-type crane. The control system comprises an operation console, a controller, a PLC, a frequency-converting set, a hoisting mechanism motor, a brake, a hoisting mechanism, an amplitude varied mechanism motor, an amplitude varied mechanism, a swing mechanism motor and a swing mechanism. The controller consists of a load swing frequency and damping ratio calculation unit, a system parameter calculation unit and a time-delayed filter calculation unit. The invention provides the PLC frequency-converting speed-governing control system based on the dynamic property and the time-delayed filter principle of the tower-type crane, which has simple structure, low cost, convenient operation and effective elimination of load swing.
Owner:SHANDONG JIANZHU UNIV
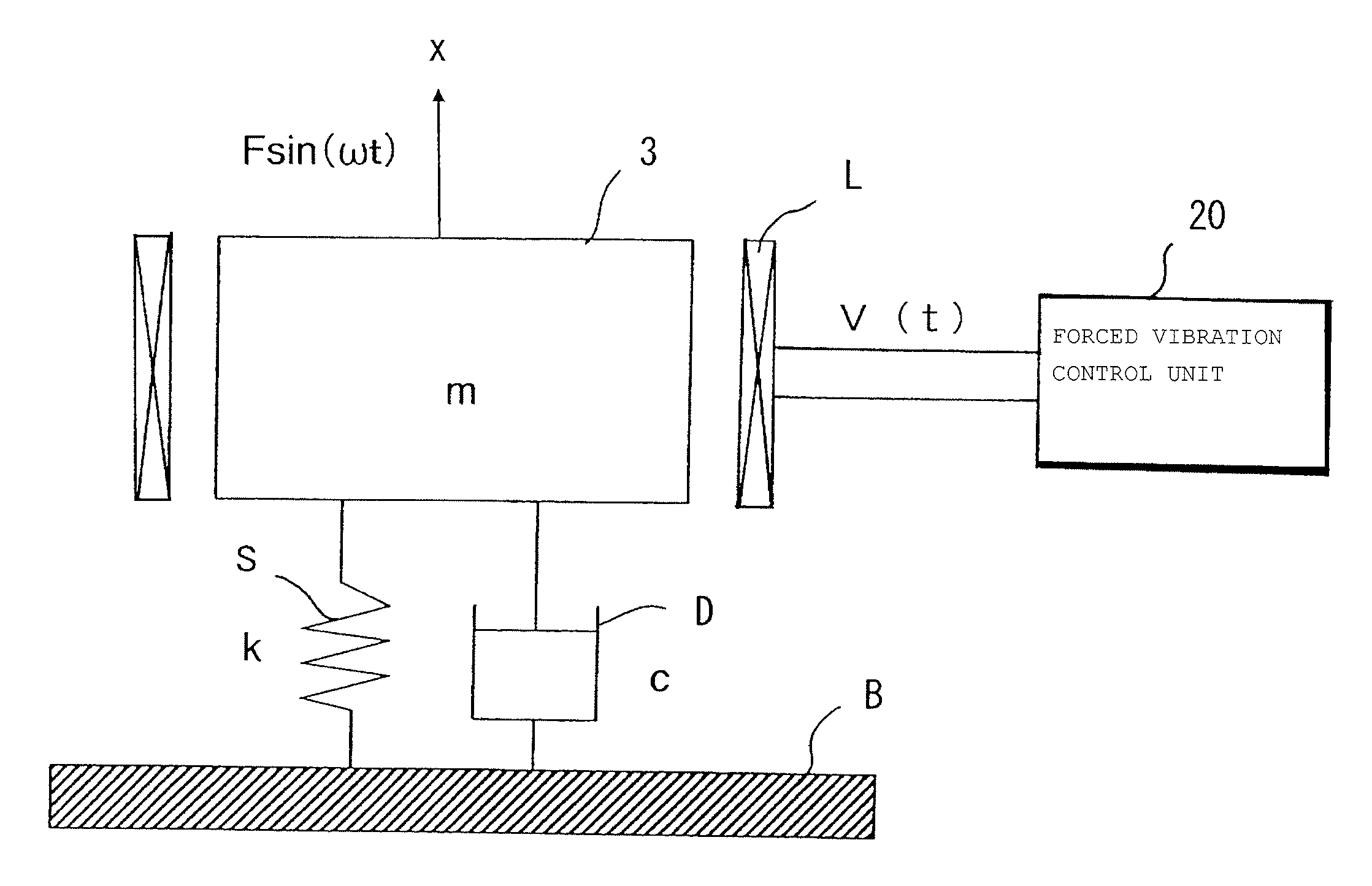
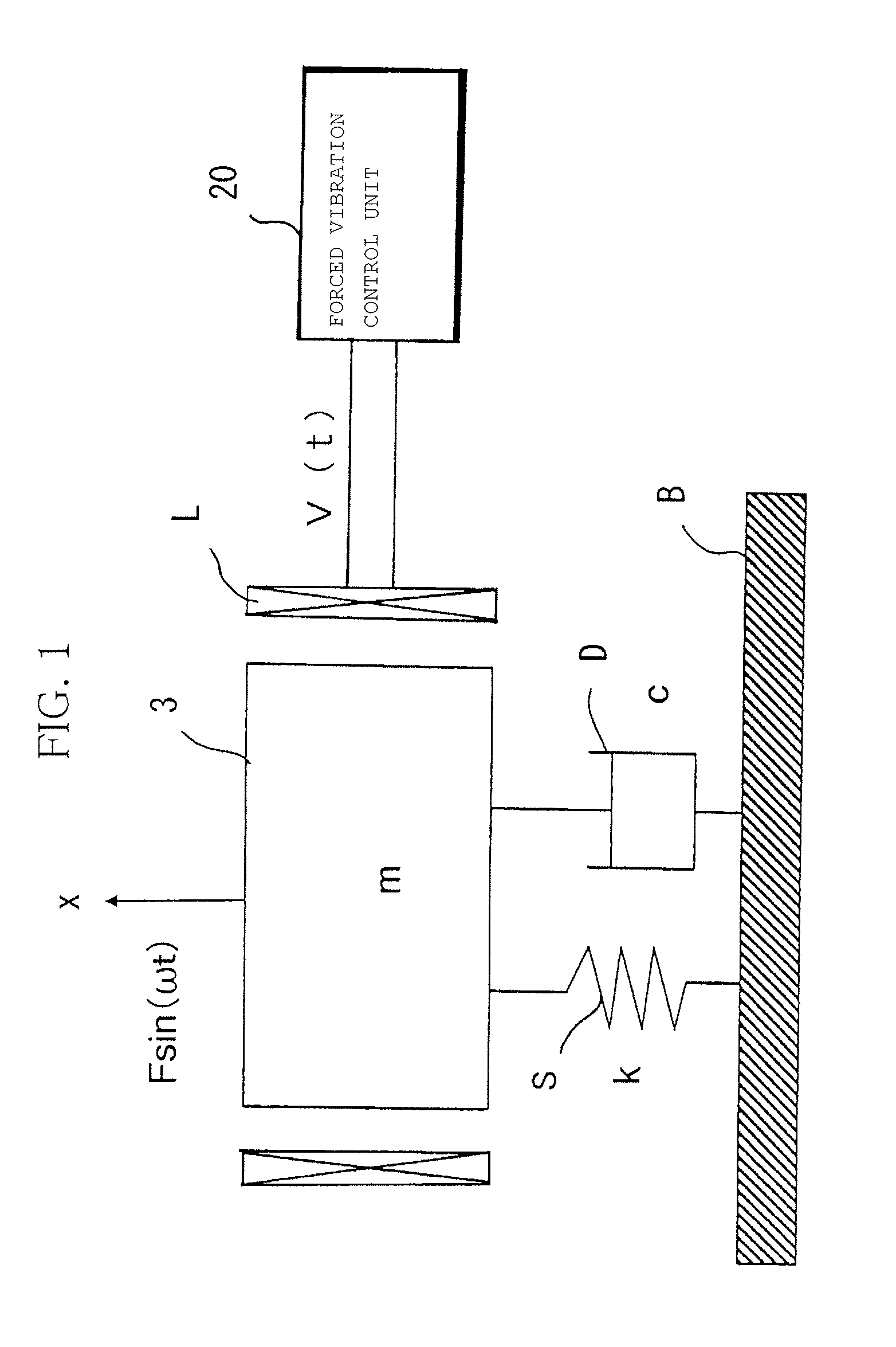
Vibration generating apparatus
InactiveUS20120025742A1High yieldLow costMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlVibration controlEngineering
A vibration generating apparatus with high yield, low cost, and can exhibit vibration tactile haptic effects even with variation in the natural frequency of a mechanical vibrator, including a damping system having a damping ratio ζ<1 to support a mechanical vibrator to a fastening part, and a magnetizing unit generating a dynamic magnetic field to vibrate the mechanical vibrator by non-contact, the mechanical vibrator generating a beat vibration by making the frequency of a drive voltage applied to the magnetizing unit, from a drive start or middle of drive, to be a non-resonant frequency out of a damped natural frequency of the mechanical vibrator, wherein the apparatus comprises a forced vibration control unit controlling to stop application of the drive voltage, in a beat wave defining an amplitude of the beat vibration, at a second valley part after a first peak part from the side of the drive start.
Owner:SANYO SEIMITSU
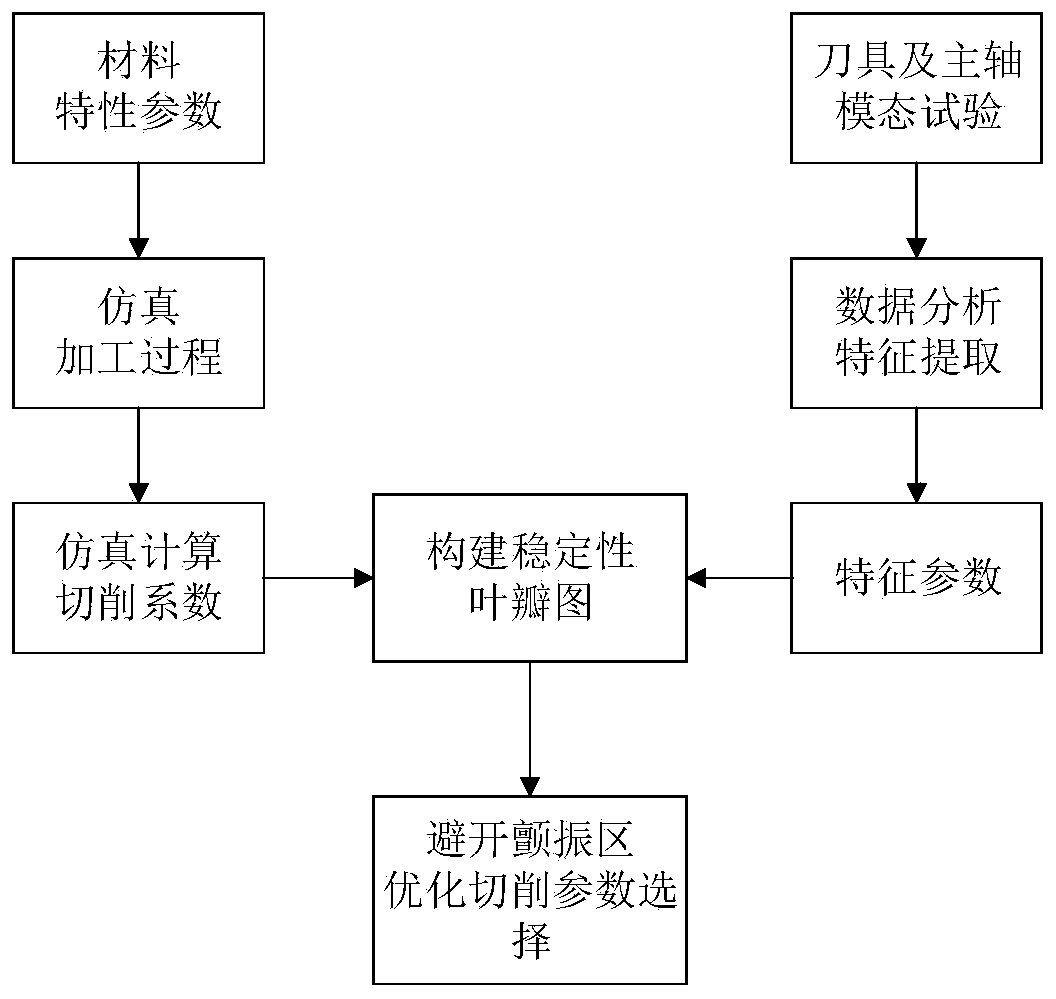
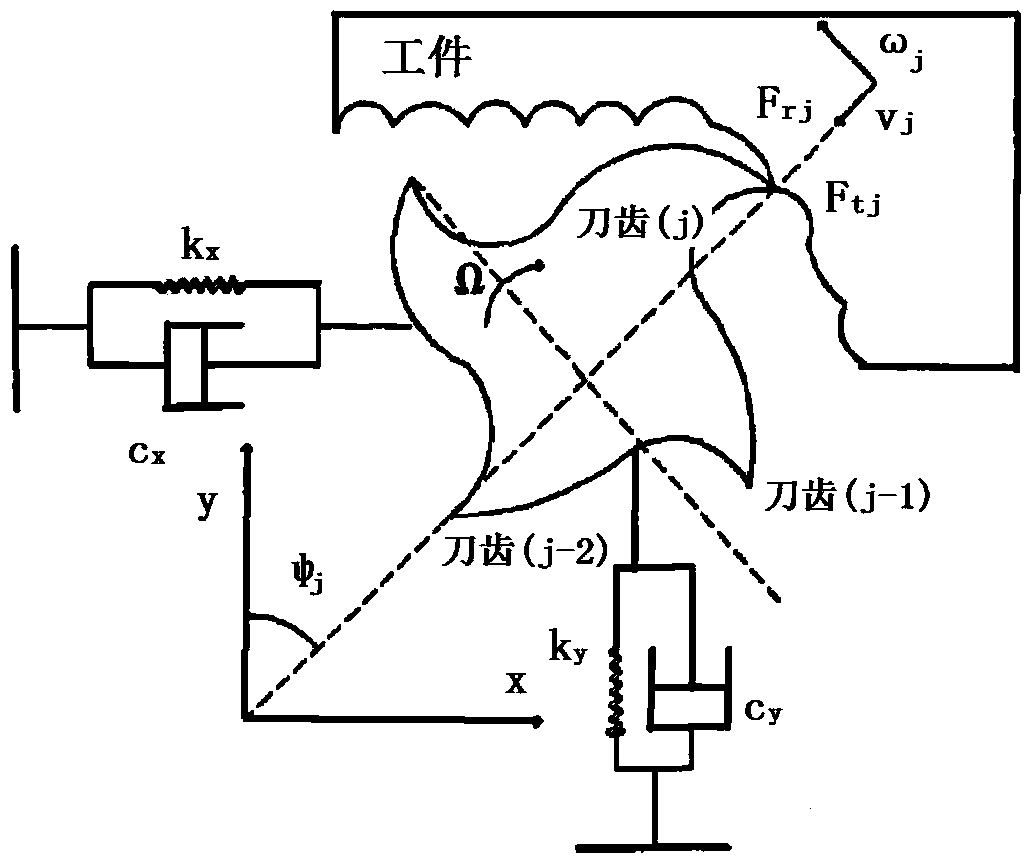
Flutter stability domain modeling approach for face cutting process
The invention belongs to the technical fields of simulating computational analysis and modal testing, and relates to a flutter stability domain modeling approach for a face cutting process. After all kinds of characteristic parameters of a material are known, a computer simulates a machining cutting process, calculates the cutting force in the machining process and analyzes the corresponding cutting coefficient. After the cutting coefficient is obtained, a modal experiment is utilized, modal testing is carried out on a machine tool spindle tool system, and the modal characteristic parameters of the machine tool spindle tool system are analyzed and comprise a multiple-order inherent frequency, a damping ratio, dynamic stiffness and the like. According to a flutter cutting theory, a stability lobe graph is drawn through combining the cutting coefficient and the system characteristic parameters and utilizing a computer assemble program, and is used for selecting the reasonable cutting parameter to avoid a flutter region, the processing precision and quality are improved, and a machine tool system is protected.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Adjustable damping energy storage type tuned mass damper
ActiveCN102493572AReduce wearNo need to worry about oil spillsShock proofingDamping ratioEngineering
The invention provides an adjustable damping energy storage type tuned mass damper. A damping adjusting device of a damper of consists of a permanent magnet, coils, auxiliary rods, an energy storage battery, an adjustable resistor, a light-emitting diode (LED) pre-warning indicator light; in the reciprocating motion process that the damper absorbs the vibration energy of a main structure so as to generate inertial mass, a cylindrical spiral spring provides damping, the permanent magnet generates a variable magnetic field, induced electromotive force is generated in the coils so as to generate induction current, and the induction current generates electromagnetic damping to inhibit the movement of the permanent magnet; the adjustable resistor in the damping adjusting device is adjusted, so the magnitude of the electromagnetic damping is changed, and the damping ratio of a structure reaches the optimum damping ratio; and residual energy is recovered by using the energy storage battery, the LED pre-warning indicator light provides a pre-warning indication for a pedestrian and a vehicle, and multiple effects of vibration controlling, clean energy recovery, pre-warning and alarming of vibration conditions and the like.
Owner:中铁桥研科技有限公司 +2
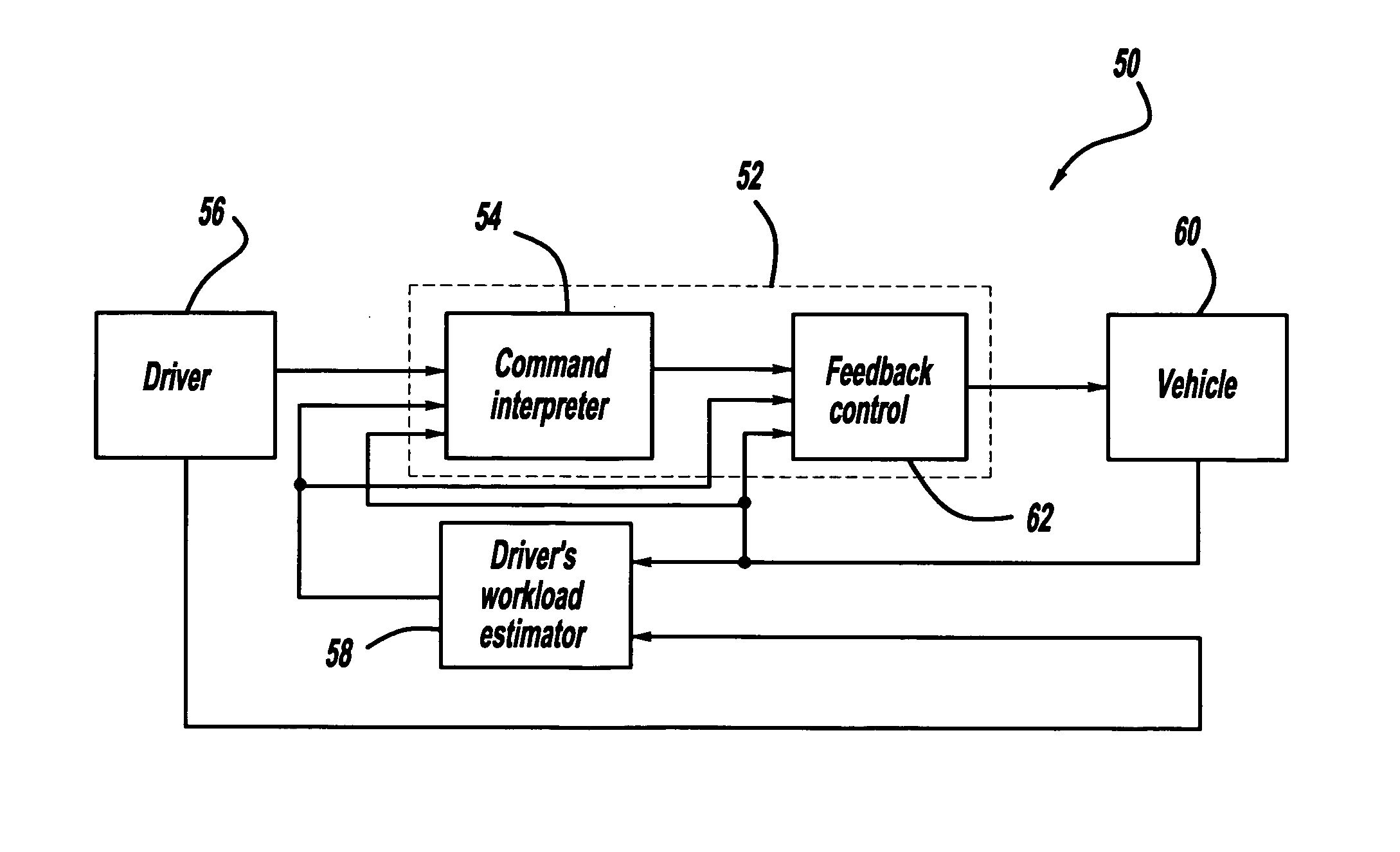
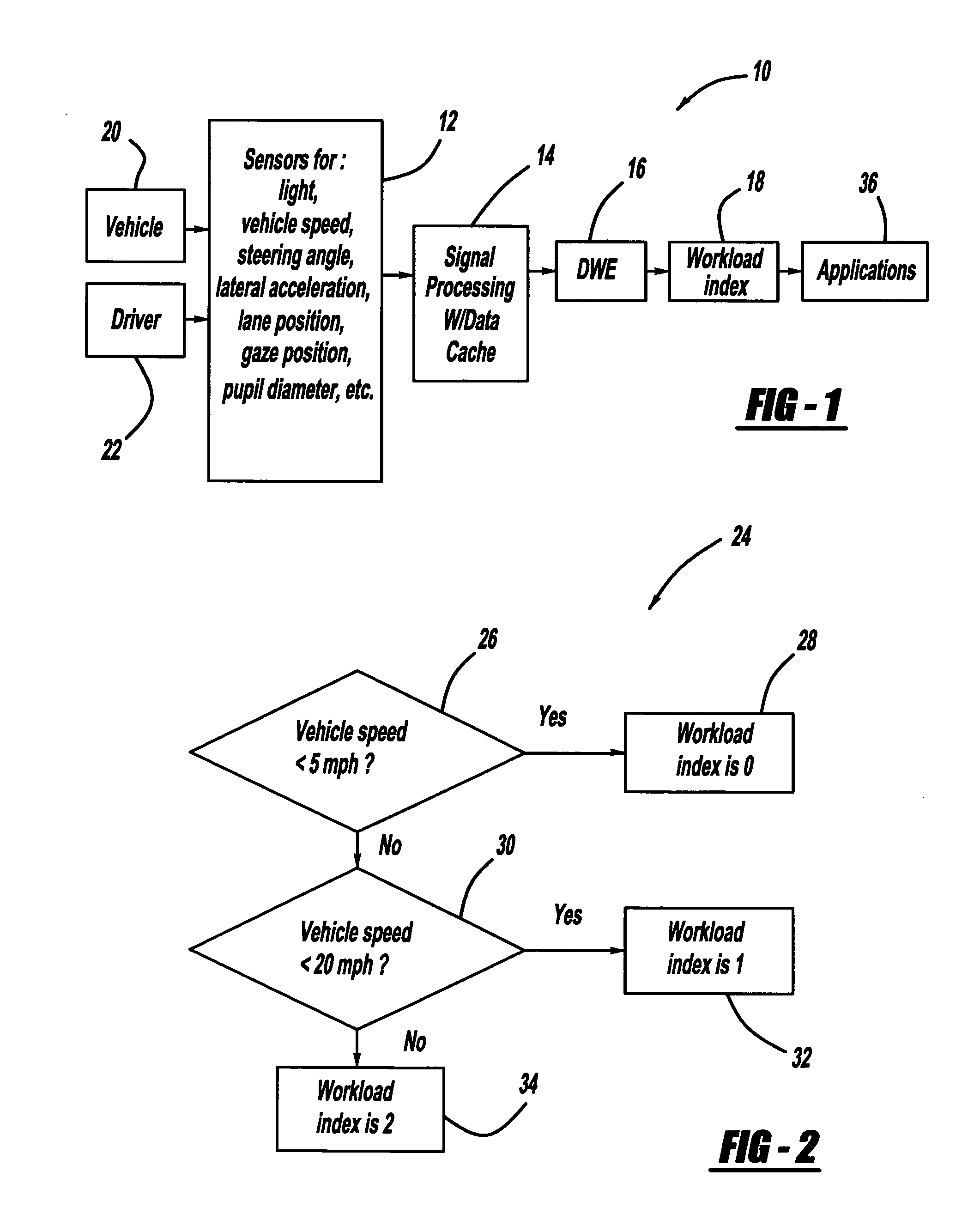
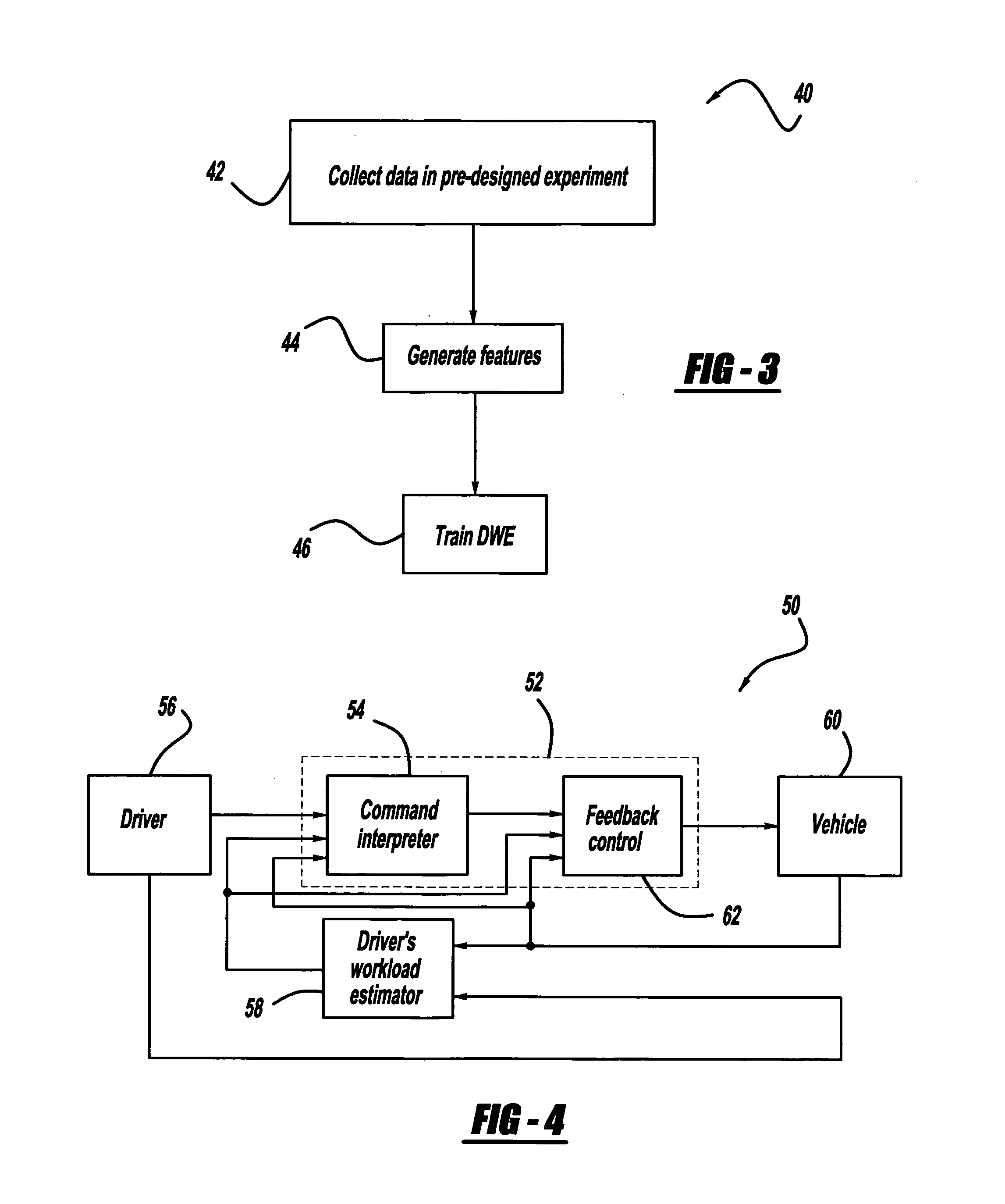
Driver workload-based vehicle stability enhancement control
InactiveUS20070244606A1Hand manipulated computer devicesAnalogue computers for trafficDriver/operatorControl signal
A vehicle stability enhancement system that is adapted for an estimated driver workload. The system includes a driver workload estimation processor that estimates the driver workload based on certain factors, such as the vehicle speed or driver-behavior factors. The driver workload estimation is used to adjust the damping ratio and natural frequency in dynamic filters in a command interpreter to adjust a desired yaw rate signal and a desired side-slip signal. The driver workload estimation is also used to generate a yaw rate multiplication factor and a side-slip multiplication factor that modify a yaw rate stability signal and a side-slip stability signal in a feedback control processor that generates a stability control signal.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Test bench of comprehensive performance of air spring
InactiveCN103364161AReduce testing costsReflect the stressMachine part testingVibration testingDynamic stiffnessAir spring
The invention discloses a test bench of the comprehensive performance of an air spring, and belongs to the technical field of vehicle engineering. The test bench can effectively achieve the aims of carrying out the vertical, transverse and twisting tests of the air spring at the same time and simulating the actual working states of the air spring. A rack of the test bench is in a four stand column type, a bearing platform is arranged in the middle of the rack, a device for bearing balance weight is arranged above the rack, a sensor is arranged below the rack, each stand column of the rack is provided with a cone-shaped fixing nut, a vertical hydraulic actuator which is arranged in a plane triangle mode is arranged below a workbench, and the volume of an additional air chamber is adjustable. The influence to the dynamics performance of the air spring by regional environment with different temperatures can be simulated by an external air conditioner system, multi-dimensional simulation is applied to the air spring through a shock excitation source, changes of loads and deflection of the air spring under the conditions with different environment temperatures and physical parameters are measured, and parameters such as dynamic stiffness, static stiffness, damping ratio and transfer ratio of the air spring are calculated through parameters of vibration characteristics. The test bench is mainly used for testing the comprehensive performance of the air spring.
Owner:CRRC QINGDAO SIFANG CO LTD
Distribution network earth insulation parameter measuring and controlling method
InactiveCN101021556AReduce displacement voltageAccelerate offEarth resistance measurementsFault locationCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
This invention discloses a measuring and controlling method of the direct earth insulating parameter of the distribution network. It has such steps as setting a high inductive-value reactor at the neutral point of the distribution network and a capacity-adjusting ground fault neutralizer injecting the frequency-changing current signal to the distribution network via the reactor, real-time measuring the back current signal and computing the direct earth capacitance, resistance and damping ratio of the distribution network. It detects the single-phase ground fault according to the displacement voltage and the damping ratio and instantly shuts the switch of ground fault neutralizer when the single-phase ground fault occurs and inputting proper ground fault neutralizer, compensating the network capacitance current and accelerating the extinguishing of the fault voltaic arc. This measuring and controlling method has high measuring accuracy and good real time and specially being appropriate to the single-phase loading distribution network. It thoroughly settles the neutral-point displacement voltage of the high-symmetry distribution network, fault arc blowout and the on-line puzzle of the targeted insulating parameter which is good to improve the indices of the reliability of the distribution network.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Autonomous control method for small unmanned helicopter
InactiveUS20060060694A1Easy to carryBroaden applicationPropellersDigital data processing detailsDead timeControl signal
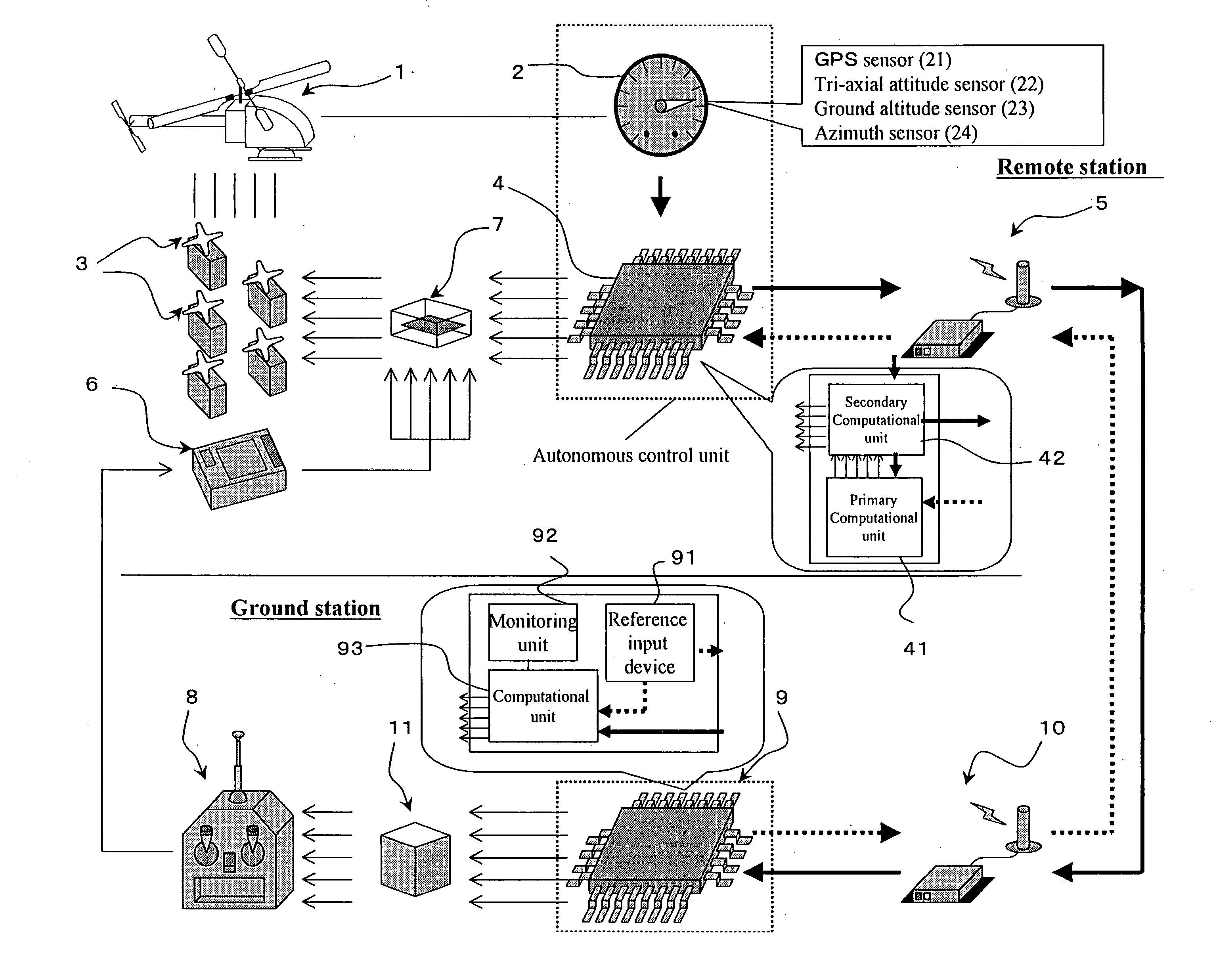
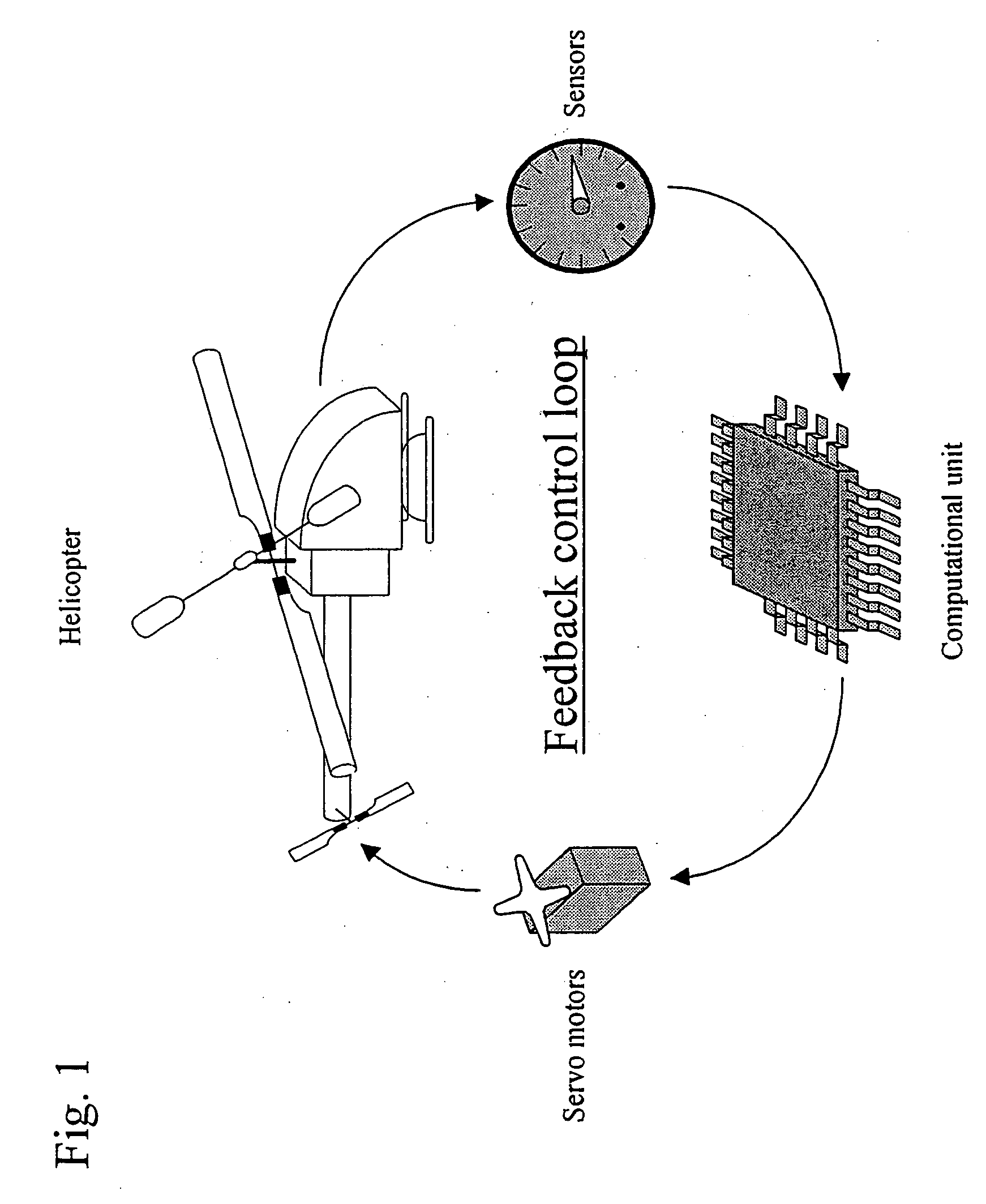
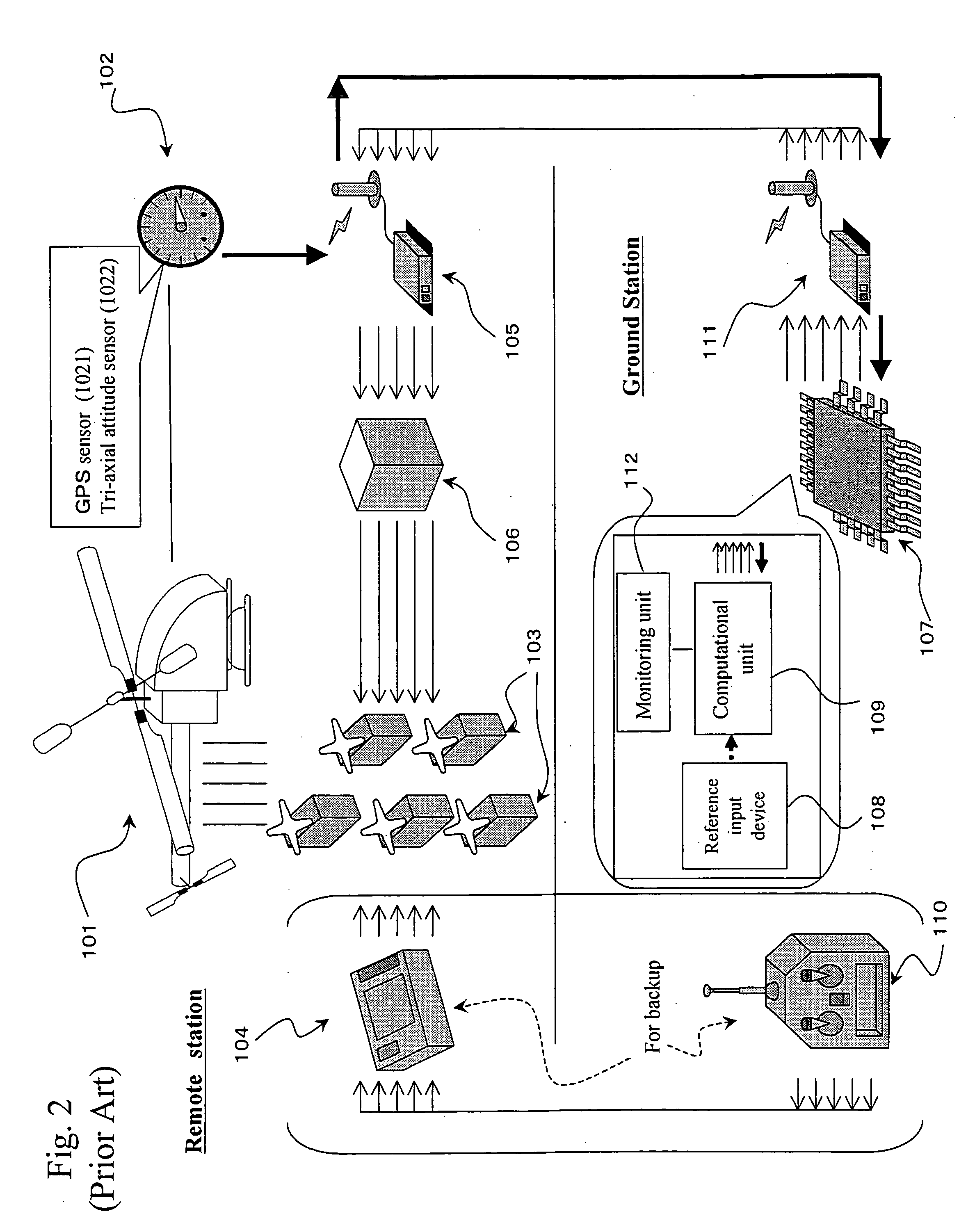
An objective of the present invention is to provide an autonomous control method that autonomously controls a small unmanned helicopter toward target values, such as a set position and velocity, by deriving model formulas that are well suited for the autonomous control of small unmanned helicopters, by designing an autonomous control algorithm based on the model formulas, and by calculating the autonomous control algorithm. The autonomous control system for a small unmanned helicopter of the present invention comprises: sensors that detect the current position, the attitude angle, the altitude relative to the ground, and the absolute azimuth of the nose of the aforementioned small unmanned helicopter; a primary computational unit that calculates optimal control reference values for driving the servo motors that move five rudders on the helicopter from target position or velocity values that are set by the ground station and the aforementioned current position and attitude angle of the small unmanned helicopter that are detected by the aforementioned sensors; an autonomous control system equipped with a secondary computational unit that converts the data collected by said sensors and the computational results as numeric values that are output by said primary computational unit into pulse signals that can be accepted by the servo motors, such that these components are assembled into a small frame box, thereby achieving both size and weight reductions; a ground station host computer that can also be used as the aforementioned computational unit for the aforementioned autonomous control system; if the aforementioned ground station host computer is used as the aforementioned computational unit for the aforementioned autonomous control system, in the process of directing the computational results that are output from said ground station host computer to said servo motors through a manual operation transmitter, a radio control generator that converts said computational results as numerical values into pulse signals that said manual operation transmitter can accept; a servo pulse mixing / switching apparatus, on all said servo motors for said small unmanned helicopter, that permits the switching of manual operation signals and said control signals that are output from said autonomous control system or mixing thereof in any ratio; an autonomous control algorithm wherein the mathematical model for transfer function representation encompassing pitching operation input through pitch axis attitude angles in the tri-axis orientation control for said small unmanned helicopter is defined as Gθ(s)=e-LsKθωns2(s2+2sωn ss+ωn s2)(Tθs+1)swherein Gθ: parameter e−Ls: dead time element Kθ: model gain Tθ: model gain ωns: natural frequency s: laplace operator ξs: damped ratio such that the aforementioned small unmanned helicopter is controlled autonomously based on the aforementioned mathematical model.
Owner:NONAMI KENZO +4
Modal test method of large draught fan blade based on photography measurement technology
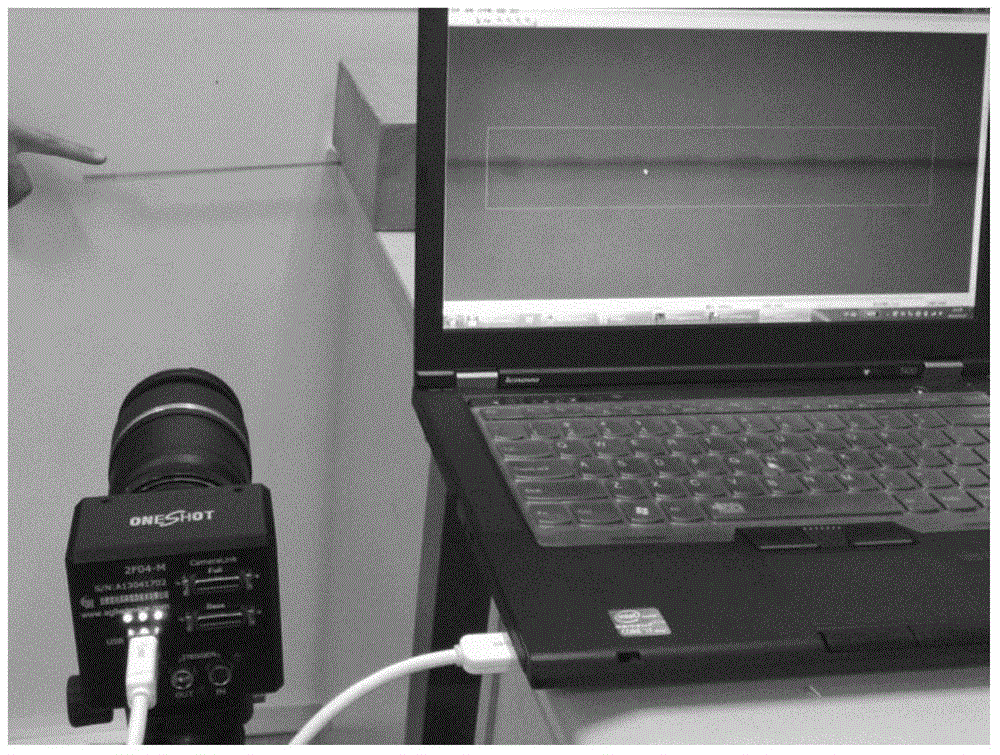
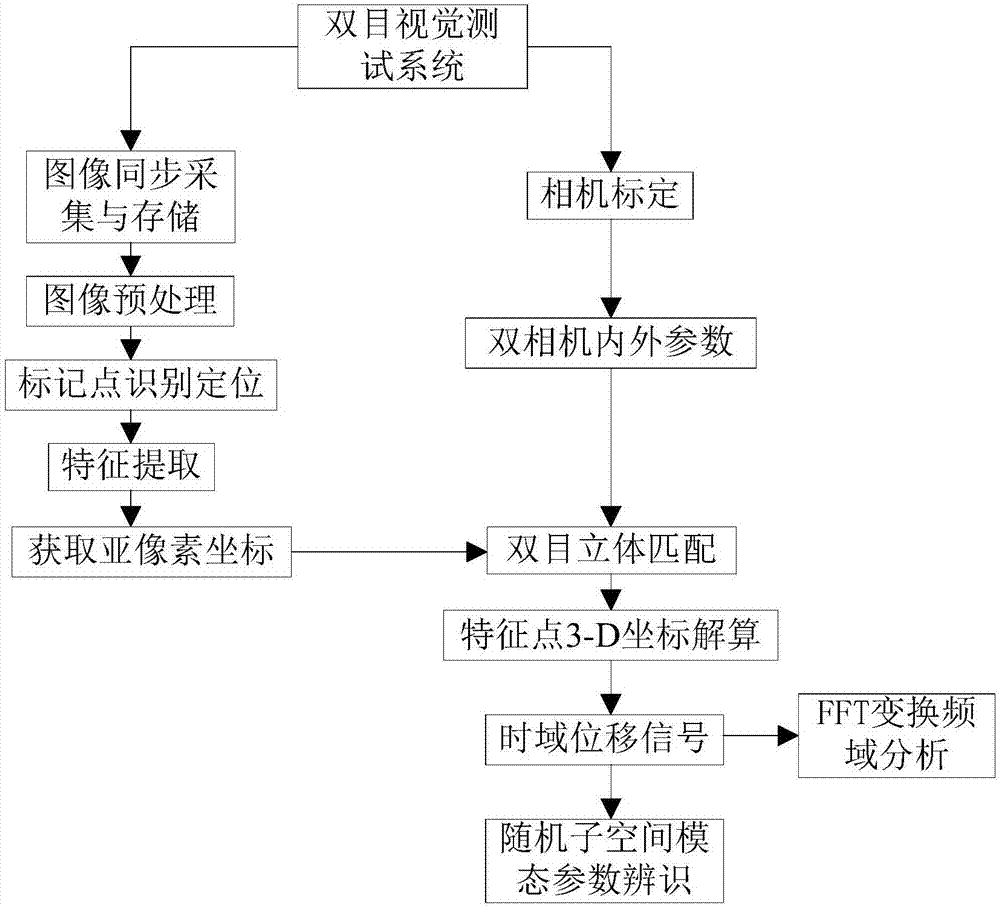
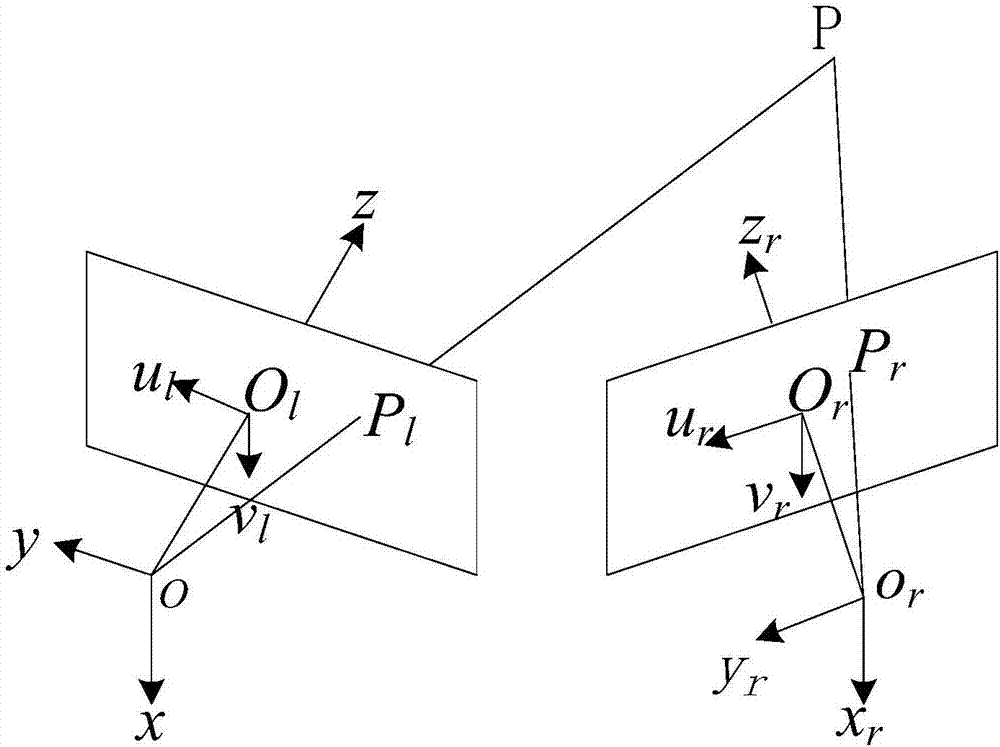
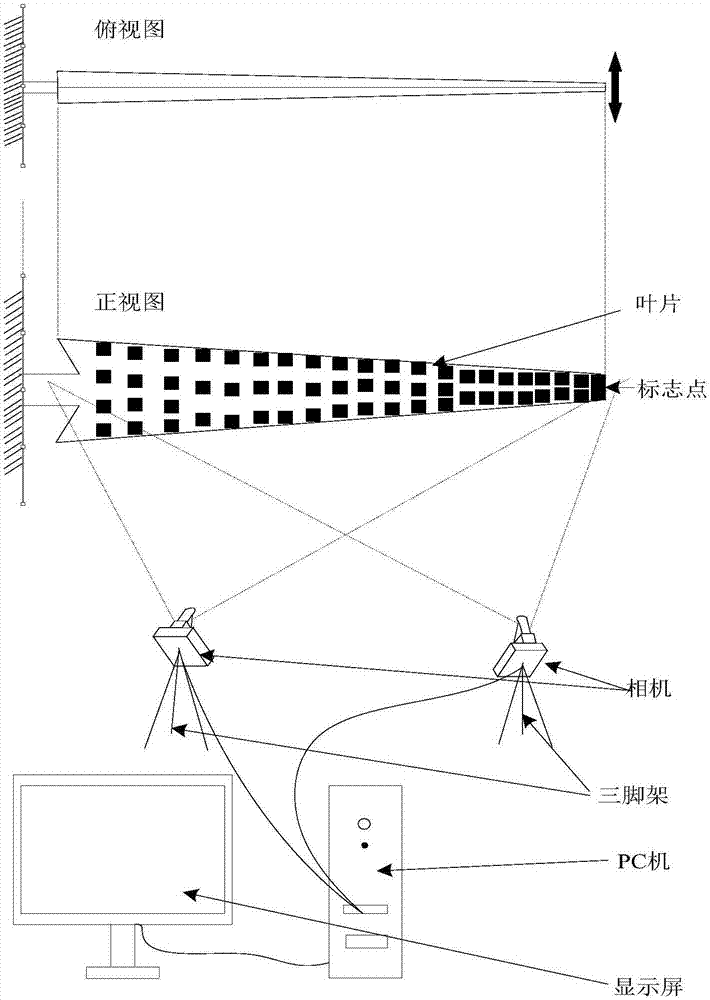
ActiveCN106989812AThe influence of dynamic characteristicsRealize non-contact measurementSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansMeasurement pointFourier transform on finite groups
The invention discloses a modal test method of a large draught fan blade based on the photography measurement technology. The method comprises steps of using a pair of CMOS / CCD industrial cameras to carry out synchronous shooting on surface images of the draught fan blade under random excitation vibration; identifying and positioning multiple marking points in the images; extracting central sub-pixel level coordinates of the marking points and carrying out stereo matching of the double cameras; calculating three-dimensional coordinates of each measurement point through the three-dimensional reconstruction technology; carrying out micro-division processing on displacement data to obtain required vibration response (speed and accelerated speed) signals; through the Fourier transform, converting time domain signals into observation peak values in frequency domains to find corresponding modal frequencies; by combining analyzed frequency values, further using the stochastic subspace identification method (SSI) to precise calculate modal parameters of the blade; and acquiring the fixed frequency, the vibration mode and the damping ratio of the blade. According to the invention, by use of non-contact type multi-point synchronous vibration measurement, rapid high-precision model test on the draught fan blade can be achieved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
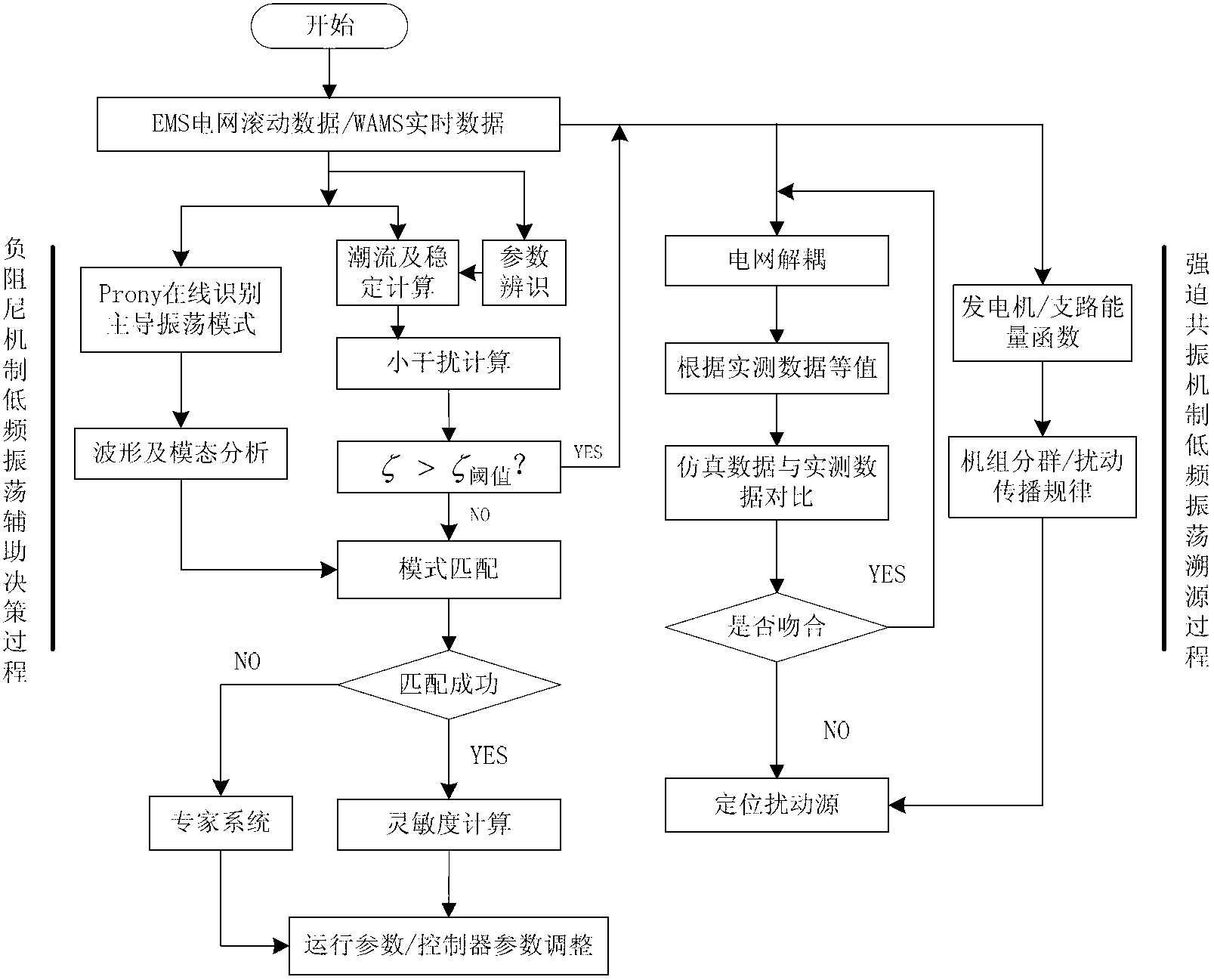
Online prevention and control method for low-frequency oscillation of electric power system on basis of two types of mechanisms
ActiveCN103178535ARealize communicationImprove real-time performancePower oscillations reduction/preventionDamping ratioElectric power
The invention relates to an online prevention and control method for low-frequency oscillation of an electric power system on the basis of two types of mechanisms. By the method, according to the idea of online pre-decision and real-time matching, low-frequency oscillation of a negative damping mechanism and low-frequency oscillation of a forced resonance mechanism can be monitored, the low-frequency oscillation of the negative damping mechanism can be monitored online and decision supporting information can be provided by utilizing a time-domain online Prony algorithm, a real-time small interference frequency-domain QR (quadrature right-triangle)algorithm, an IRA(irregular repeat-accumulate) algorithm and a characteristic value sensitivity principle; and further, when damping ratio of a capstan oscillation mode is higher than a damping threshold while oscillation exists, transmission rules of the low-frequency oscillation of the forced resonance mechanism and disturbance sources are recognized by a direct method and a hybrid dynamic simulation method which is implemented on the basis of PSD-FDS whole process stability analysis software. By the online prevention and control method which is high in credibility, real-time data source communication is guaranteed, and the low-frequency oscillation of the two types of mechanisms are monitored on line.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
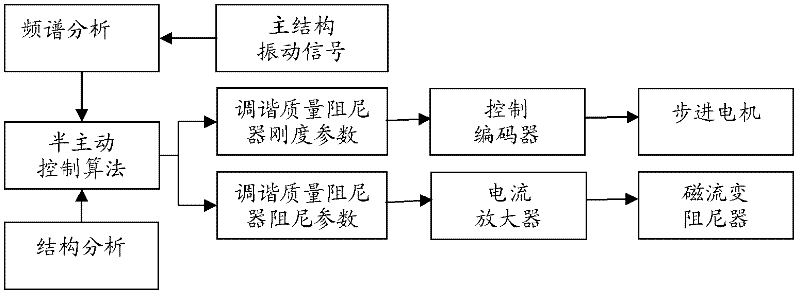
Variable-rigidity and variable-damping tuned mass damper
ActiveCN102345333AWorking principle is clearGood vibration reduction effectArtificial islandsBridge structural detailsSemi activePower flow
The invention discloses a variable-rigidity and variable-damping tuned mass damper, which is mainly applied to vibration control over multi-frequency structures such as high-rise buildings or long-span bridges, ocean platforms and the like. The tuned mass damper comprises a mass block, wherein a vertical spring is connected to the upside of the mass block in a vertical direction, and magnetorheological dampers are respectively arranged on the mass block in a horizontal direction and a vertical direction; and a cantilever spring is arranged horizontally and longitudinally, one end of the cantilever spring is connected with the mass block, the other end of the cantilever is connected with a traveling mechanism. Two ends of the traveling mechanism are placed on a rigid guide rail, and the traveling is driven by a stepping motor to move longitudinally. The length of the cantilever spring is regulated by the movement of the stepping motor, so that the tuning frequency of the tuned mass damper is further regulated; and by regulating currents of the magnetorheological dampers to change the damping ratio of the tuned mass damper, the rigidity and the damping are regulatable continuously, so that the vibration control in the vertical direction and the horizontal direction. The variable-rigidity and variable-damping tuned mass damper disclosed by the invention has a clear working principle and has the advantages of easiness for realizing semi-active control property, good damping effect, fast response, high precision and the like in engineering application.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for performing bridge monitoring by using multiple strapdown inertial systems
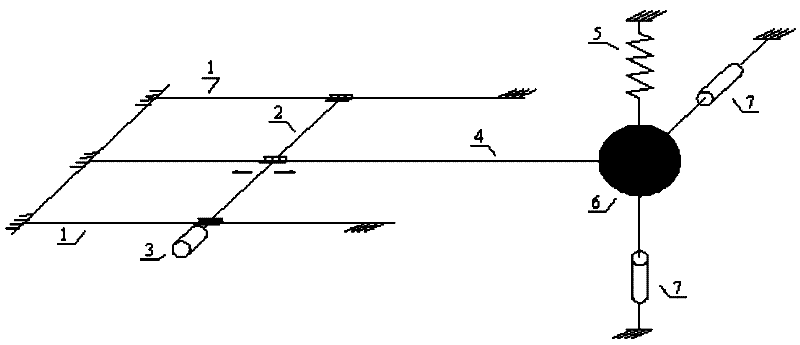
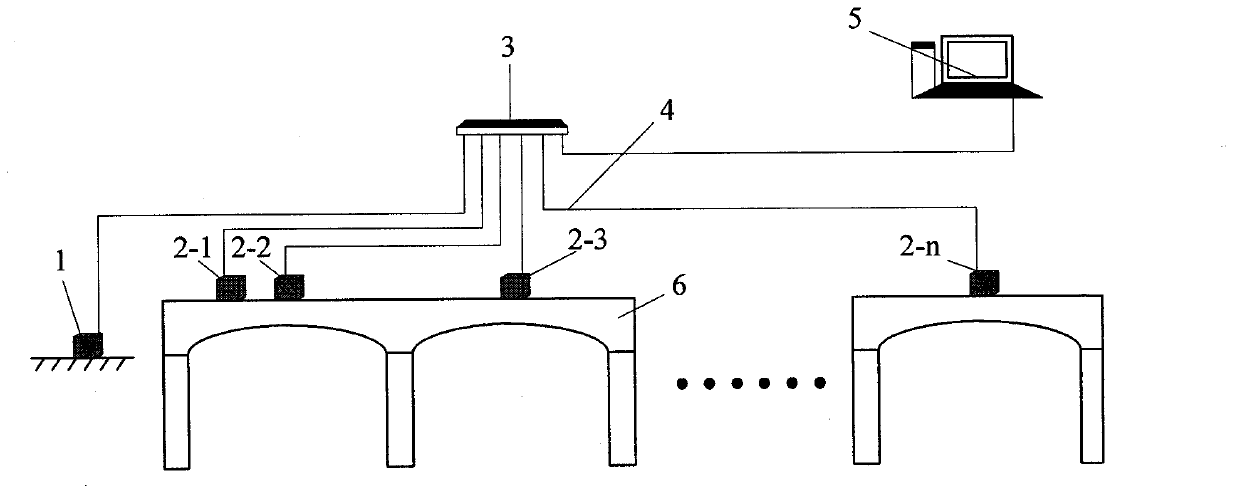
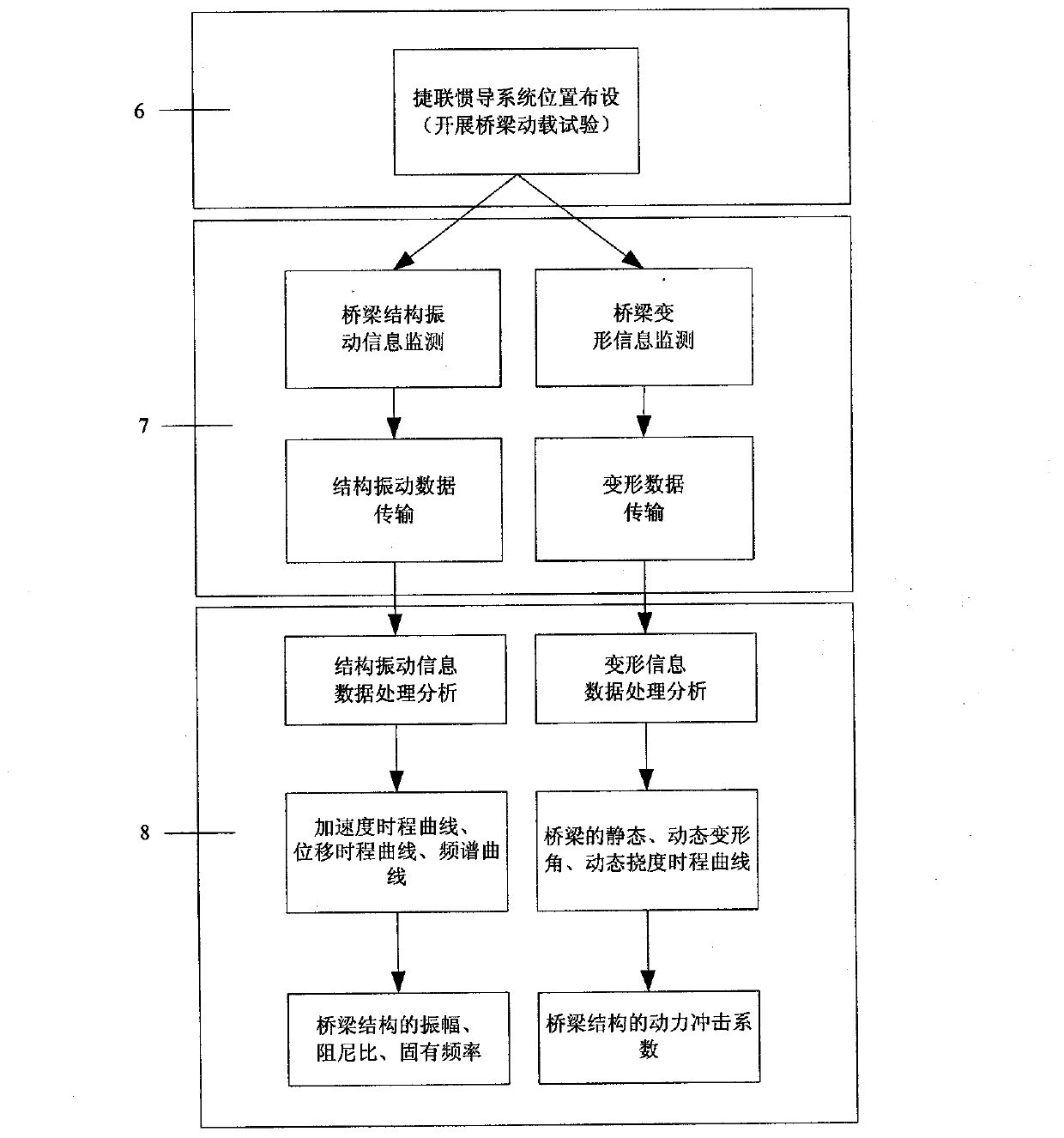
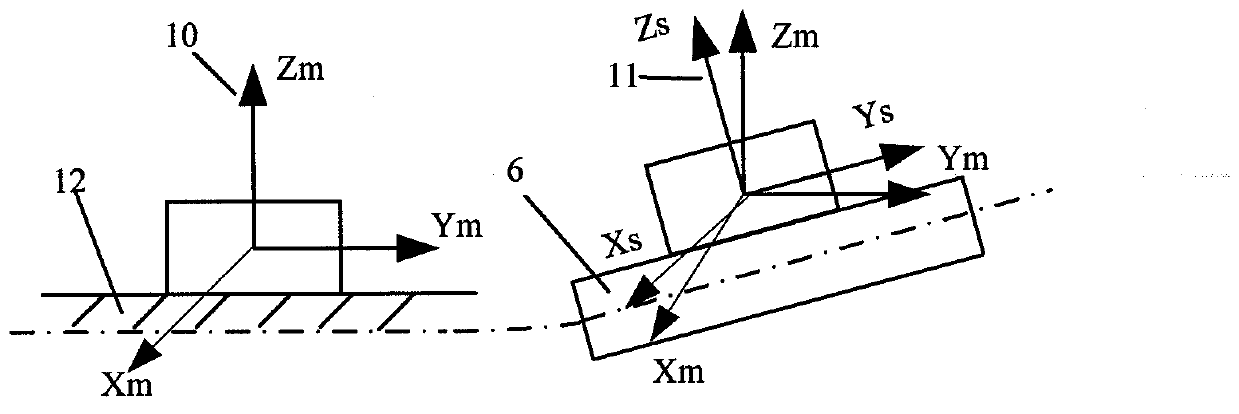
InactiveCN102998081AReal-time acquisitionHigh short-term accuracySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementVibration testingContinuous measurementMeasurement point
A method for performing bridge monitoring by using multiple strapdown inertial systems belongs to the bridge monitoring technology and includes: performing position setting for the strapdown inertial systems according to the dynamic characteristic of a bridge structure and performing installation calibration and initial calibration for the strapdown inertial systems; carrying out bridge dynamic load tests which include a pulsating test, a sports car test and a bumping test, and performing continuous monitoring by using deformation and vibration information of the strapdown inertial systems relative to a reference point and measurement points; obtaining static deformation angles and dynamic deformation angles of the measurement points of the bridge at each moment by using the deformation information obtained in an inertial test matching method; obtaining a girder deflection curve of the bridge by using the dynamic deformation angles of the inertial systems calculated at the reference point and the measurement points, and obtaining an impact coefficient of the bridge through further processing; using accelerometer output information to obtain acceleration time history curves of all the measurement points and obtaining displacement time history curves through integration; and analyzing the acceleration time history curves and the displacement time history curves in a time domain analysis method and a frequency domain analysis method to obtain structural parameters including bridge amplitude, damping ratio and vibration mode. The method has the advantages of being free of weather variation interference, little in manual operation, high in automatic degree and capable of performing continuous measurement.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BOKAI TECH DEV
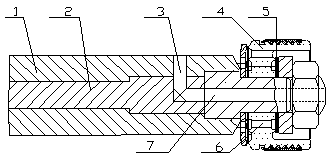
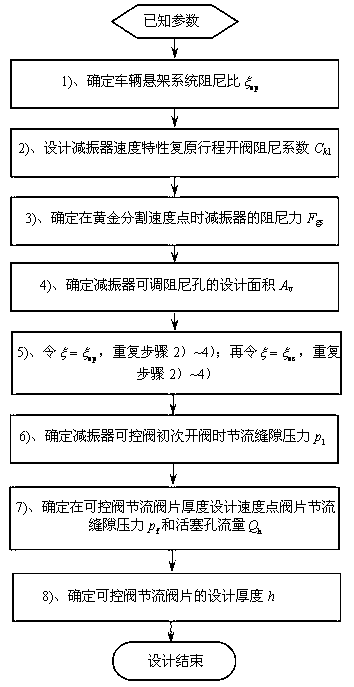
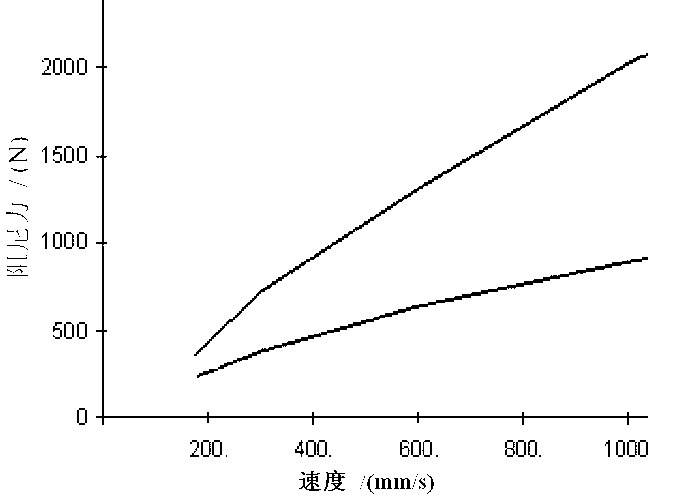
Optimal design method for parameter of controllable cylinder type hydraulic buffer of semi-active suspension
InactiveCN102840265AReduce design costShorten the development cycleSpringsShock absorbersSemi activeDamping ratio
The invention relates to an optimal design method for a parameter of a controllable cylinder type hydraulic buffer of a semi-active suspension. The optimal design method is characterized by adopting the following steps: 1), determining the damping ratio of a vehicular suspension system; 2), designing an open valve damping coefficient of a buffer speed property recover route; 3), determining the damping force of the reducer at a golden cutting speed point; 4), determining the design area of an adjustable damping hole of the reducer; 5), repeating the steps 2) to 4), calculating the adjustable damping hole area required by the thickness of the design valve block is calculated; repeating the steps 2) to 4) again, and calculating the minimum area of the adjustable damping hole; 6), determining the throttle seam pressure when a controllable valve of the buffer is opened at the first time; 7), determining the throttle seam pressure and the piston hole flow rate at the thickness designed speed point of the controllable valve throttle valve block; 8), determining the design thickness of the controllable valve throttle valve block. By adopting the design method, the design value of the valve parameter is exact and reliable; the repeatedly test and modification are avoided; the design cost of the controllable buffer is reduced; and the development cycle of the buffer is shortened.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for identifying modal parameters of transformer coil
InactiveCN103267907AEasy to design and manufactureTimely maintenanceSpectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceMorlet waveletEngineering
The invention discloses a method for identifying modal parameters of a transformer coil. The method includes the following steps: vibration signals of all measure points of the transformer coil are collected; Fourier transformation is carried out on the vibration signals, and a vibration frequency response curve of the transformer coil is obtained; Fourier inversion is carried out, and free vibration signals of the transformer coil are obtained; wavelet conversion is carried out on the free vibration signals through Morlet wavelets, and a wavelet transformation time-frequency diagram is made; wavelet ridges are extracted from the wavelet transformation time-frequency diagram, and the vertical coordinate of each wavelet ridge is inherent frequency of each step of the transformer coil; the damping ratio of inherent frequency of all the steps is calculated; a coil vibration mode of the inherent frequency of each step is calculated. With the method, the mode parameters of the transformer coil can be accurately and efficiently identified. Design, manufacturing, coil deformation detection and state evaluation are convenient to carry out on a coil structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
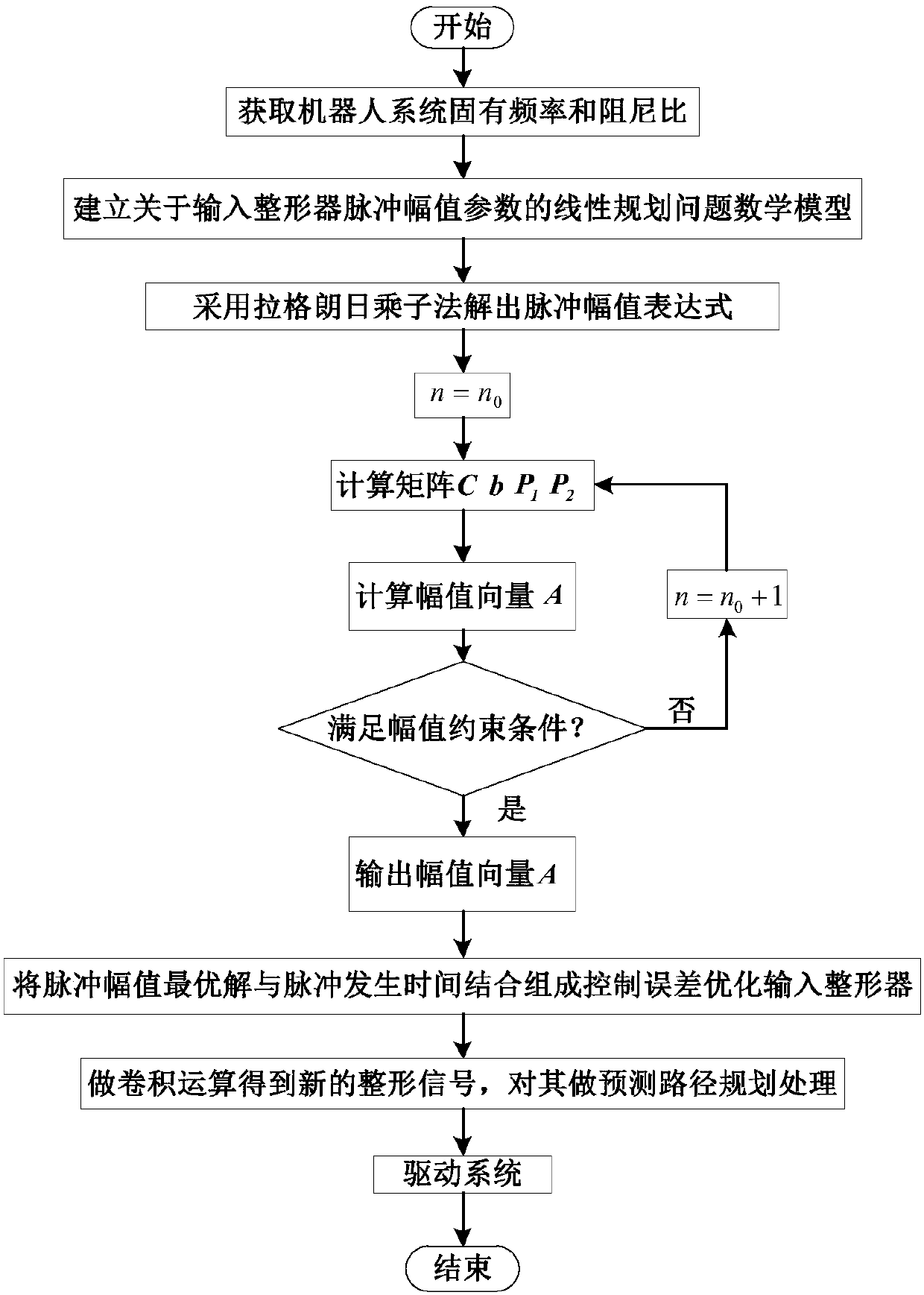
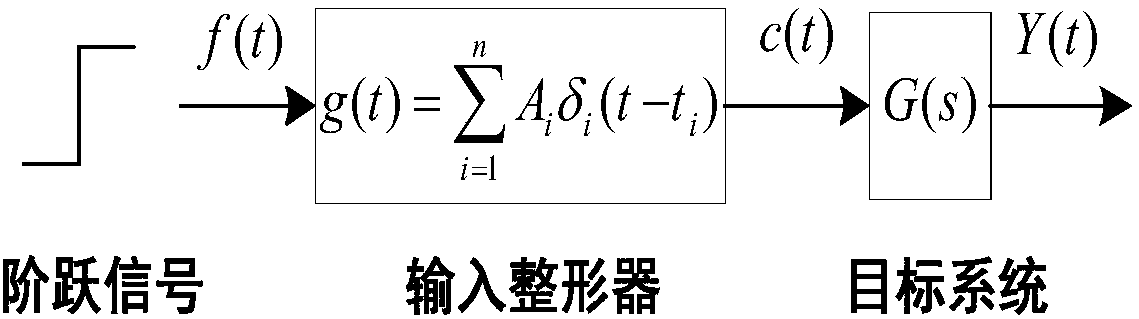
Robot joint tail end residual vibration restraining method based on input shaper
The invention discloses a robot joint tail end residual vibration restraining method based an input shaper. The robot joint tail end residual vibration restraining method based the input shaper comprises the steps that firstly, the undamped inherent frequency omega0 and the damping ratio zeta of a robot system are obtained; secondly, a linear programming problem mathematic model about the pulse amplitude parameter of the input shaper is established; thirdly, a pulse amplitude expression is solved through a lagrangian multiplier method, and the optimal solution of the pulse amplitude is workedout through iteration; fourthly, the optimal solution of the pulse amplitude and the pulse generation time are combined to form the control error optimization input shaper; and fifthly, a reference signal and the control error optimization input shaper are subjected to convolution operation, so that a novel shaping signal is obtained, and after a predicted path is planned for the novel shaping signal, the system is driven by the signal to restrain robot tail end residual vibration. According to the robot joint tail end residual vibration restraining method based the input shaper, the robustness of the input shaper is enhanced, and a process control error and a positioning error are minimized; and the predicted path is planned for the shaped signal, and thus the system lag time caused by input shaping is compensated and reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Working modal identification method based on time-frequency domain single-source-point sparse component analysis
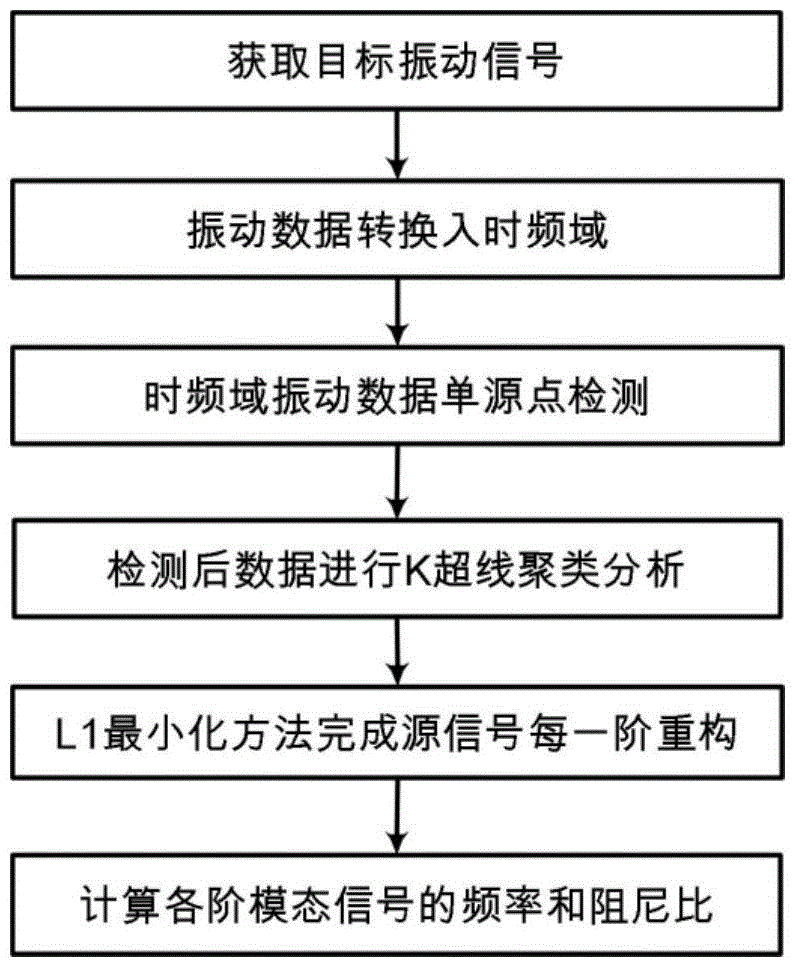
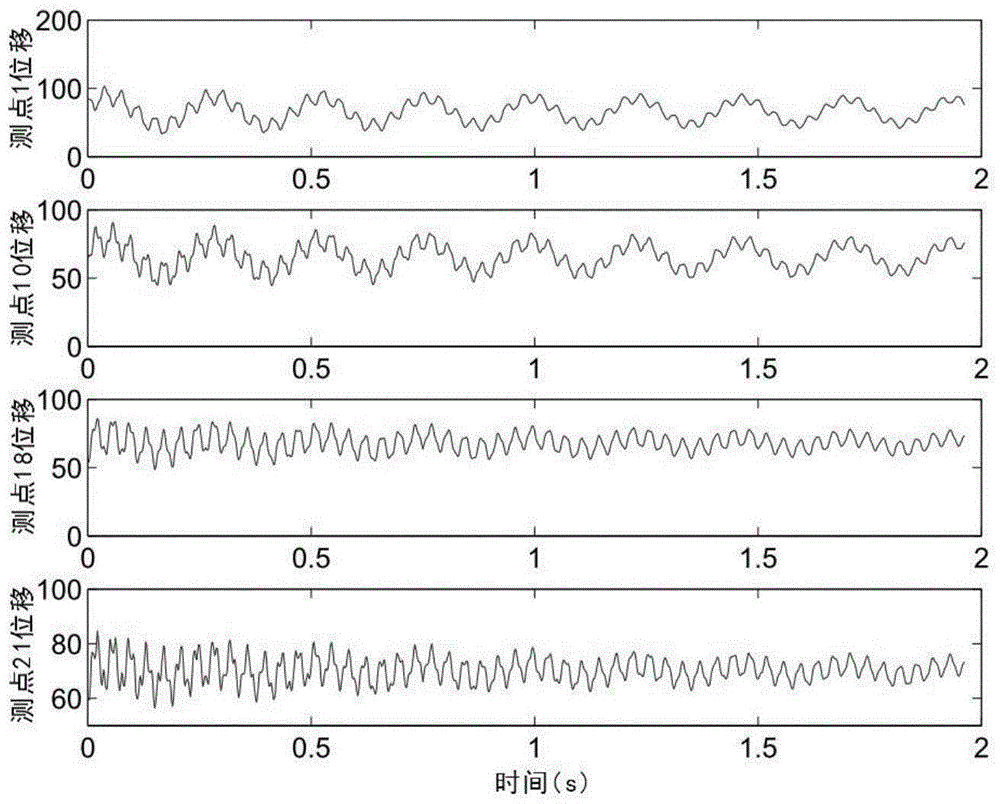
ActiveCN104166804ASmall amount of calculationEfficient identificationSpecial data processing applicationsL1 minimizationMeasurement point
The invention provides a working modal identification method based on time-frequency domain single-source-point sparse component analysis. The working modal identification method specifically includes the following steps that vibration signals of an equipment target position under the working state are obtained through measurement; time-frequency domain conversion is conducted on the mixed vibration signals; a single-source-point method is used for extracting the mixed vibration signals used for estimating a hybrid matrix in a time-frequency domain; a hybrid matrix estimation method based on K hyperline clustering sparse component analysis is used for estimating the hybrid matrix; after the hybrid matrix is solved, the time-frequency domain is returned, the l1 minimization method is used for reconstructing each order of source signals, and modal vectors of a structure are extracted; then the working modal frequency and the damping ratio are obtained through signal index expression. According to the method, the calculation amount in the hybrid matrix estimation process is reduced, under the poor condition that the number of measuring points is less than that of the source signals, modal parameters are identified effectively, and the method has good anti-interference capacity for incomplete sparsity of noise, abnormal values and the source signals.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Large-damping engineering structure modal parameter identification method
InactiveCN106844935AImprove noise immunityAccurately get the modal parametersGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsFast Fourier transformStructural health monitoring
The invention belongs to the field of structural health monitoring and mainly relates to a large-damping engineering structure modal parameter identification method. Cross-correlation function responded by structure vibration under random excitation is converted into a frequency domain, a real part or a virtual part of available frequency domain data are subjected to independent component analysis to acquire modal vibration model and modal response, rough modal frequency and damping ratio of modal responses of each order are calculated by adopting fast Fourier transform and a half-power bandwidth method, the rough modal frequency and the damping ratio are taken as initial values for fitting modal response curves to have the modal responses of each order fitted by adopting a least squares iterative estimation, and accurate values of the modal frequency of the each order and the damping ratio can be finally acquired. By the arrangement, independence assumption in independent component analysis of the processed data can be met, and the modal parameters with the large-damping structure can be accurately identified.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
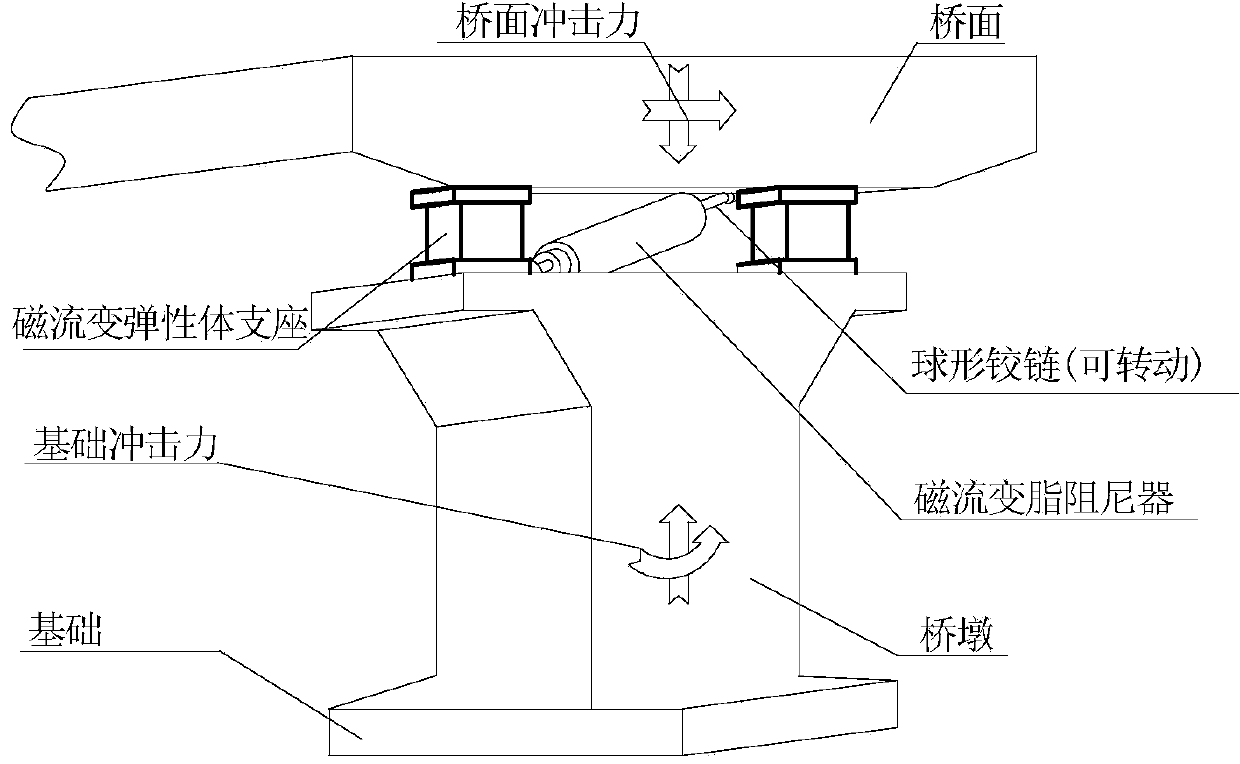
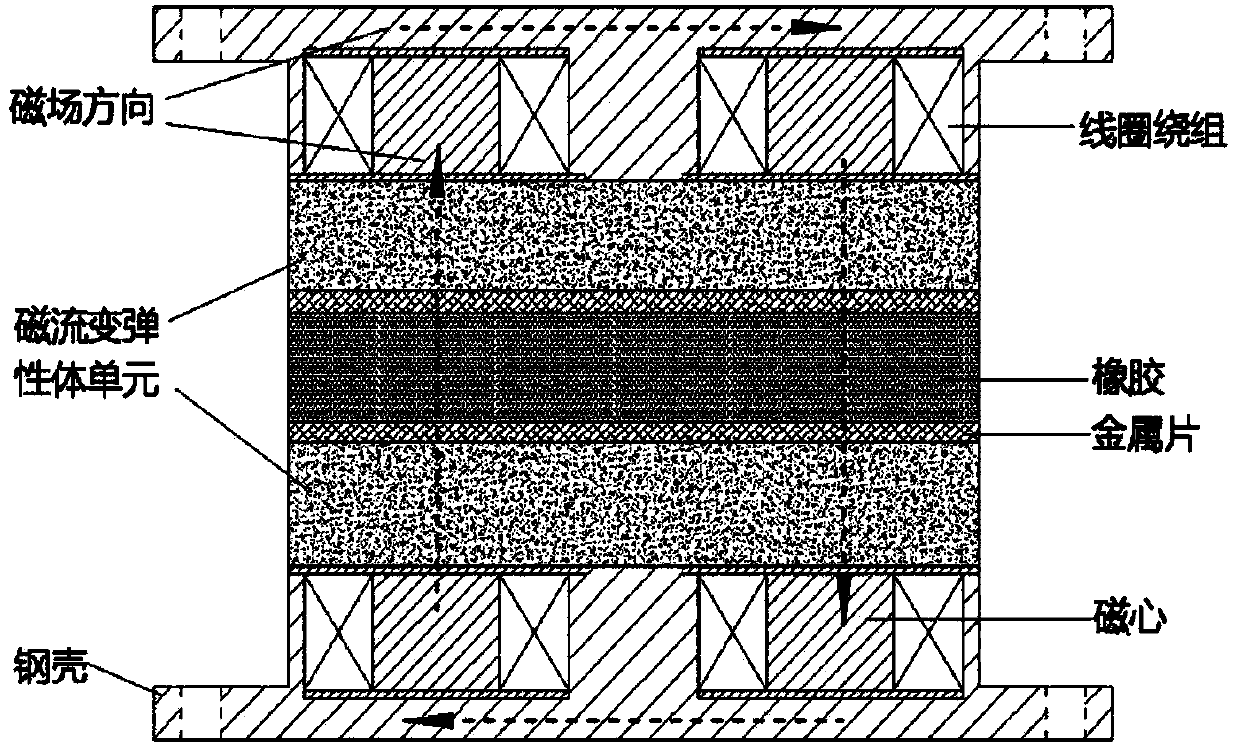
Design method and device of anti-impact vibration isolation type magnetorheological pier bearing-damper system
ActiveCN104179118AInhibition shiftEnhanced vertical strengthBridge structural detailsElastomerDamping ratio
The invention relates to a design method and a device of an anti-impact vibration isolation type magnetorheological pier bearing-damper system. According to the method, magnetorheological elastomers which are large in vertical stiffness, high in structural strength and adjustable in elasticity modulus are used as bearing bodies, and impact resistance and vibration isolation of a pier-beam structure under the action of large load are realized by adjustment of pier stiffness; a magnetorheological damper capable of providing large damping without medium settlement is used as a damping device, three-dimensional rotation capacity of the damper is improved by using a ball-and-socket joint mode at two ends thereof, and pier-beam displacement is restrained by damping adjustment for further vibration reduction and energy dissipation; magnetorheological elastomer bearings, the magnetorheological damper and a controller jointly form an anti-impact vibration-isolation pier bearing device, the controller intelligently adjusts stiffness and damping of the bearing-damper system by detecting the impact vibration of a bridge, structural strength of the pier-beam structure is improved while damping ratio thereof is increased, and when the bridge is under large-load impact vibration, impact transmission is slowed down or isolated and pier-bean displacement is restrained so as to guarantee structural safety of the bridge.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
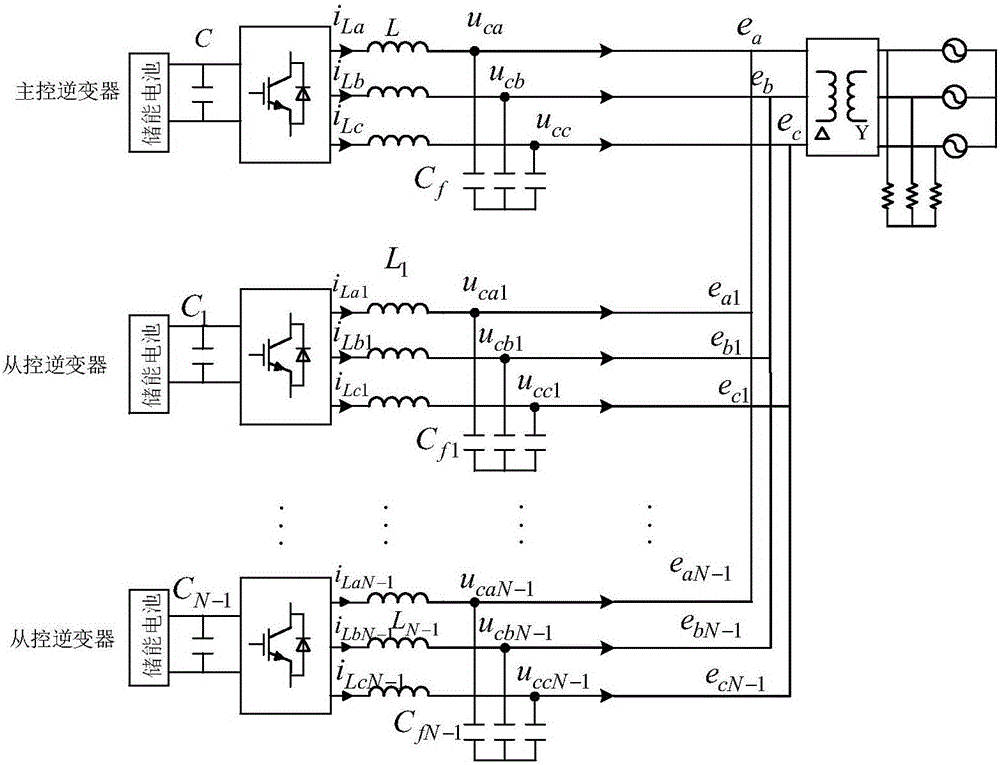
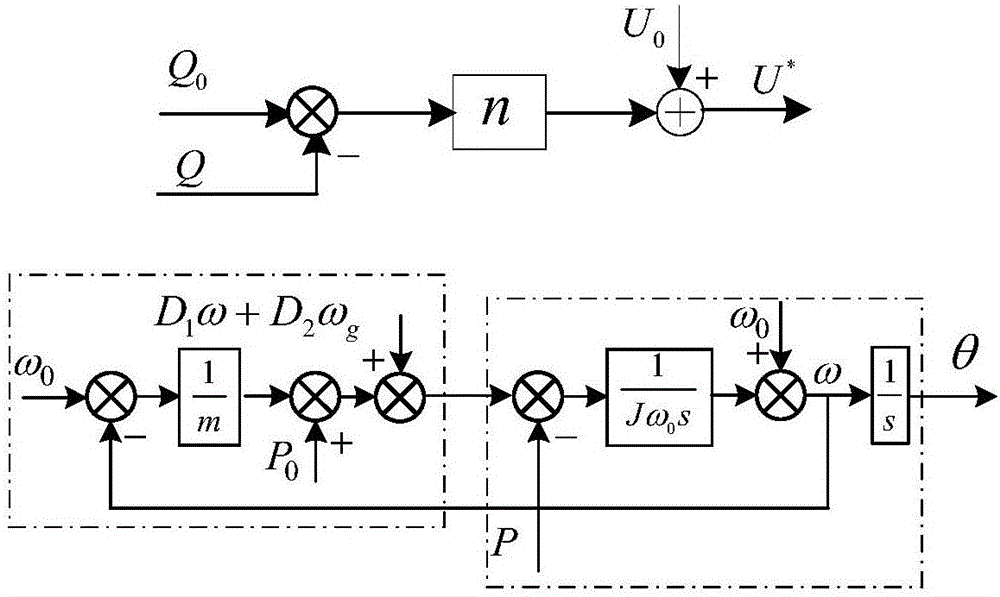
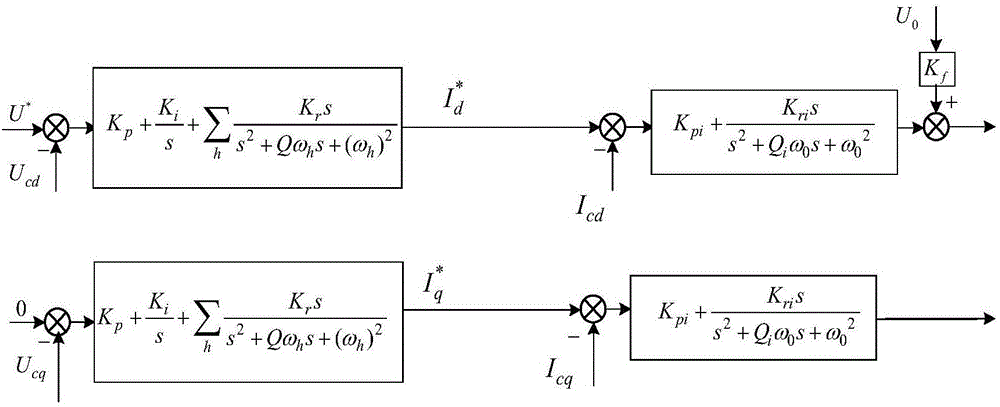
Master-slave control method for energy storage inverter based on virtual synchronous generator
ActiveCN106849186AHigh output voltage power qualityLow load unevennessSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPower qualityVirtual synchronous generator
The invention discloses a master-slave control method for an energy storage inverter based on a virtual synchronous generator. The energy storage inverter comprises a master control inverter and a slave control inverter, wherein the master control inverter adopts a voltage source output mode based on the virtual synchronous generator to provide amplitude and frequency of network voltage, provide virtual inertia and a virtual damping ratio according to the capacity of the master control inverter, and meanwhile provide static active and passive current quotas to each inverter; the slave control inverter adopts a current source output mode based on the virtual synchronous generator to receive static active and passive current quotas issued by the master control inverter, and meanwhile provide the virtual inertia according to the capacity of the slave control inverter. According to the method, in island parallel operation, a load is non-uniform and fluidity is relatively low under various load conditions, and relatively high output voltage power quality is provided; compared with traditional master-slave control, a controller structure does not need to be changed when switching between grid connection and disconnection is performed, and the master control inverter and the slave control inverter independently provide the virtual inertia without depending on communication, so that improvement on system stability under dynamic condition is facilitated, and the reliability is relatively high.
Owner:合肥庐阳科技创新集团有限公司
Storage device, memory, terminal, server, server-client system, storage medium, and control device
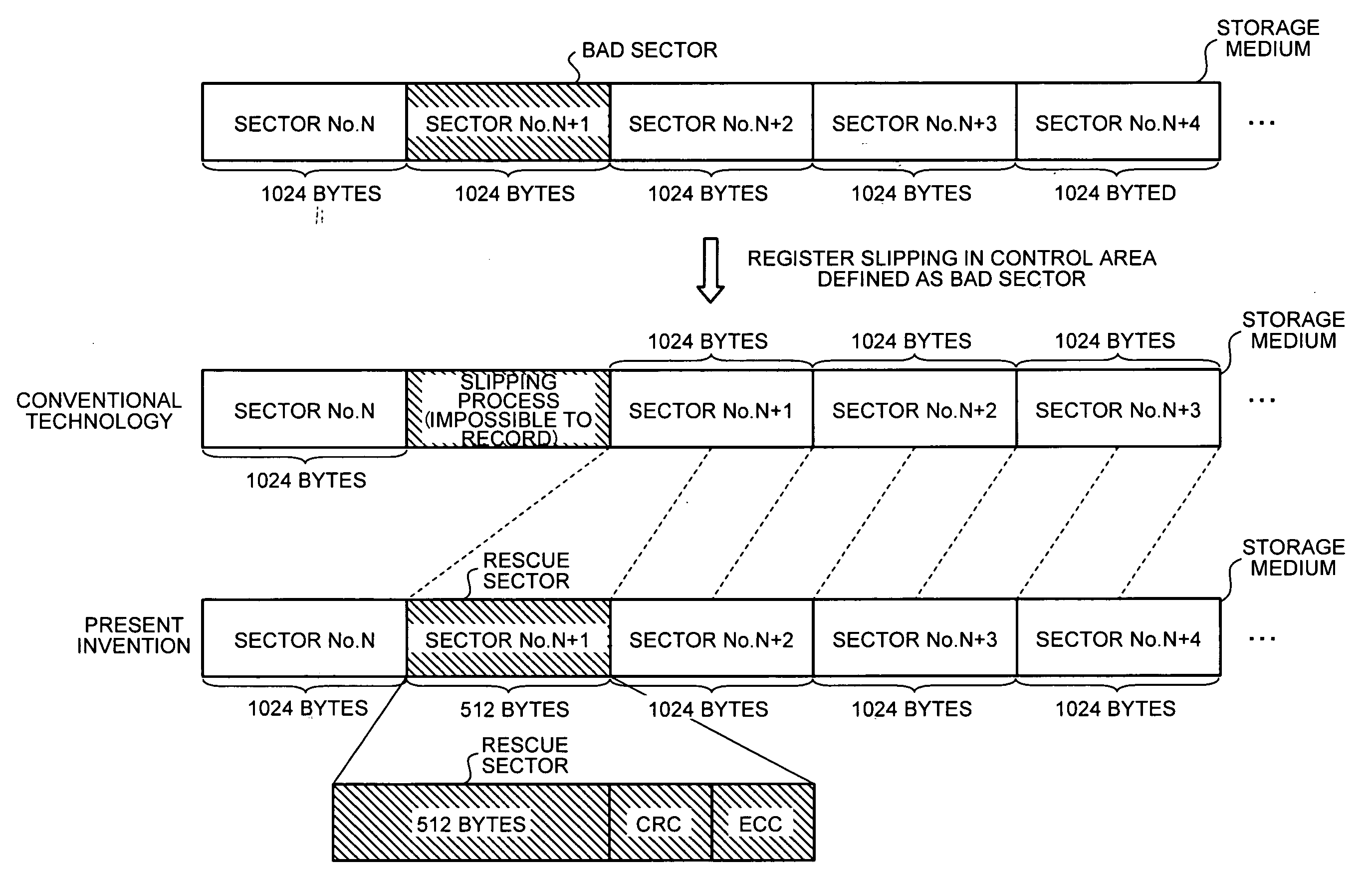
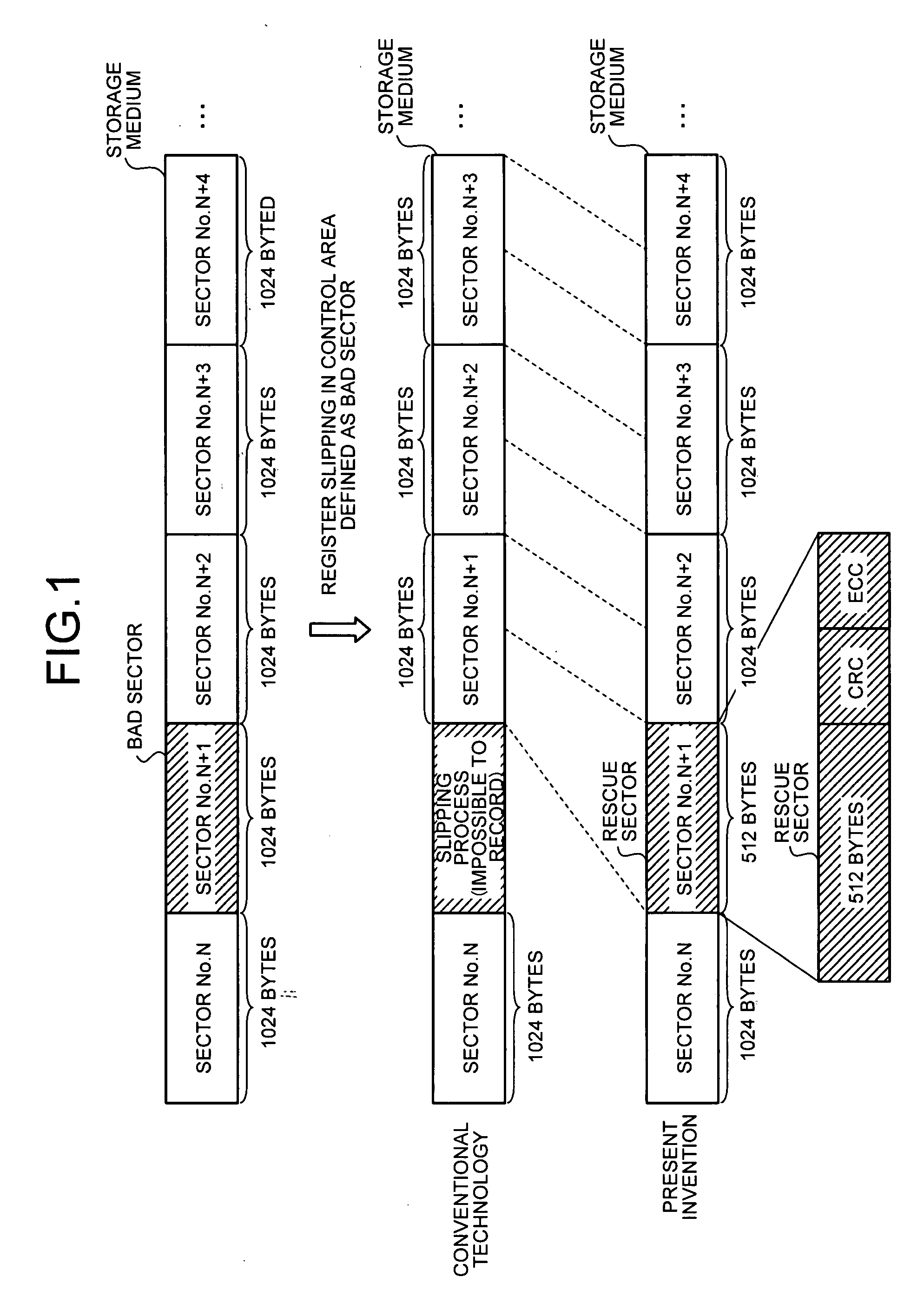
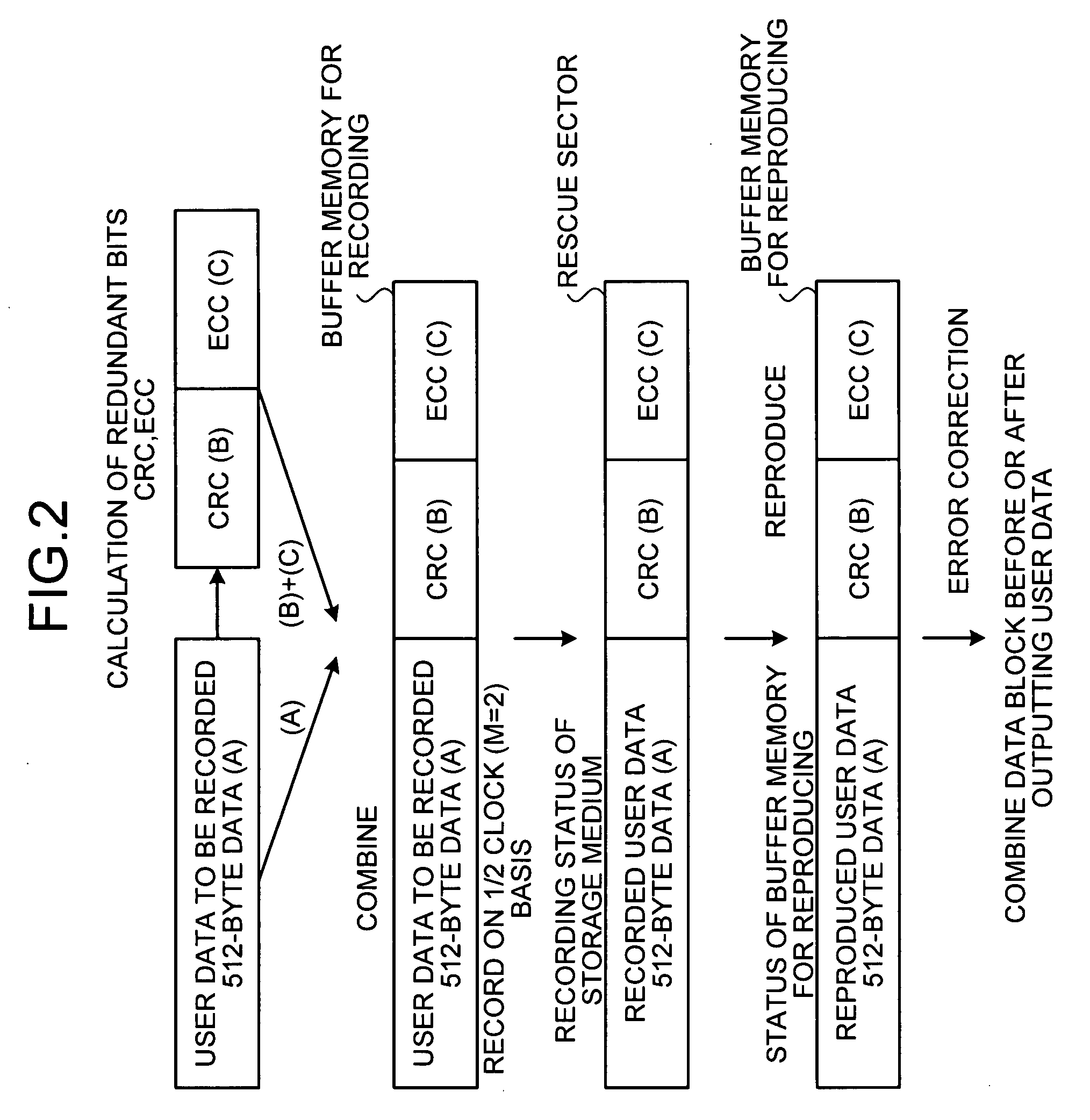
InactiveUS20080130434A1Solve problemsDisc-shaped record carriersError detection/correctionDamping ratioBad sector
In a storage device, a bad-sector detecting unit detects a bad sector, and a process determining unit determines whether rescue process is performed for the bad sector. Upon determining to perform the rescue process, the process determining unit controls a damping ratio. A table-updating control unit records various information in an alternating-process control table, and a controller records and reproduces data with respect to a rescue sector based on the alternating-process control table.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com