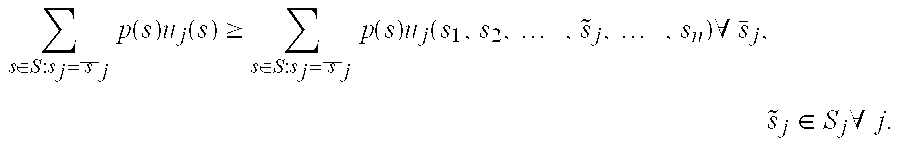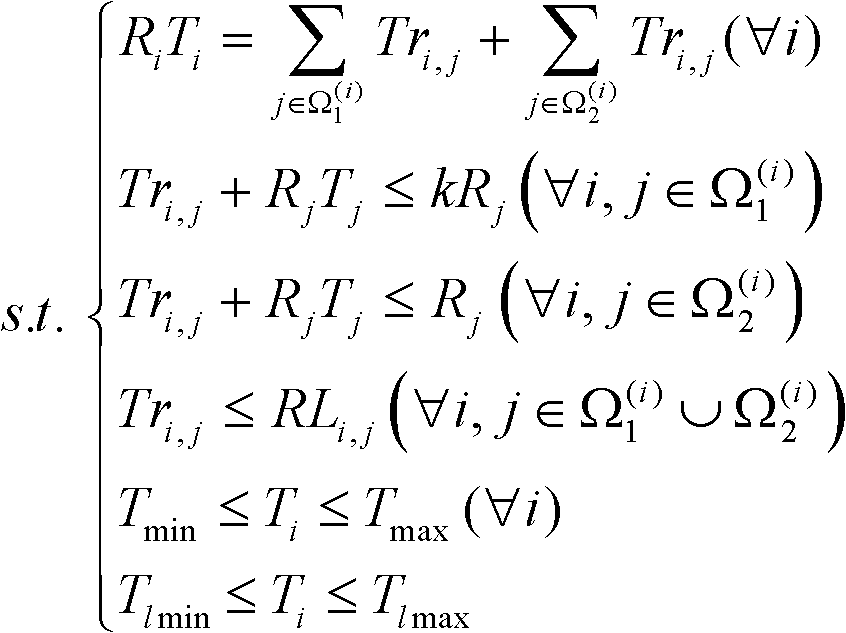Patents
Literature
1553 results about "Linear programming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Linear programming (LP, also called linear optimization) is a method to achieve the best outcome (such as maximum profit or lowest cost) in a mathematical model whose requirements are represented by linear relationships. Linear programming is a special case of mathematical programming (also known as mathematical optimization).
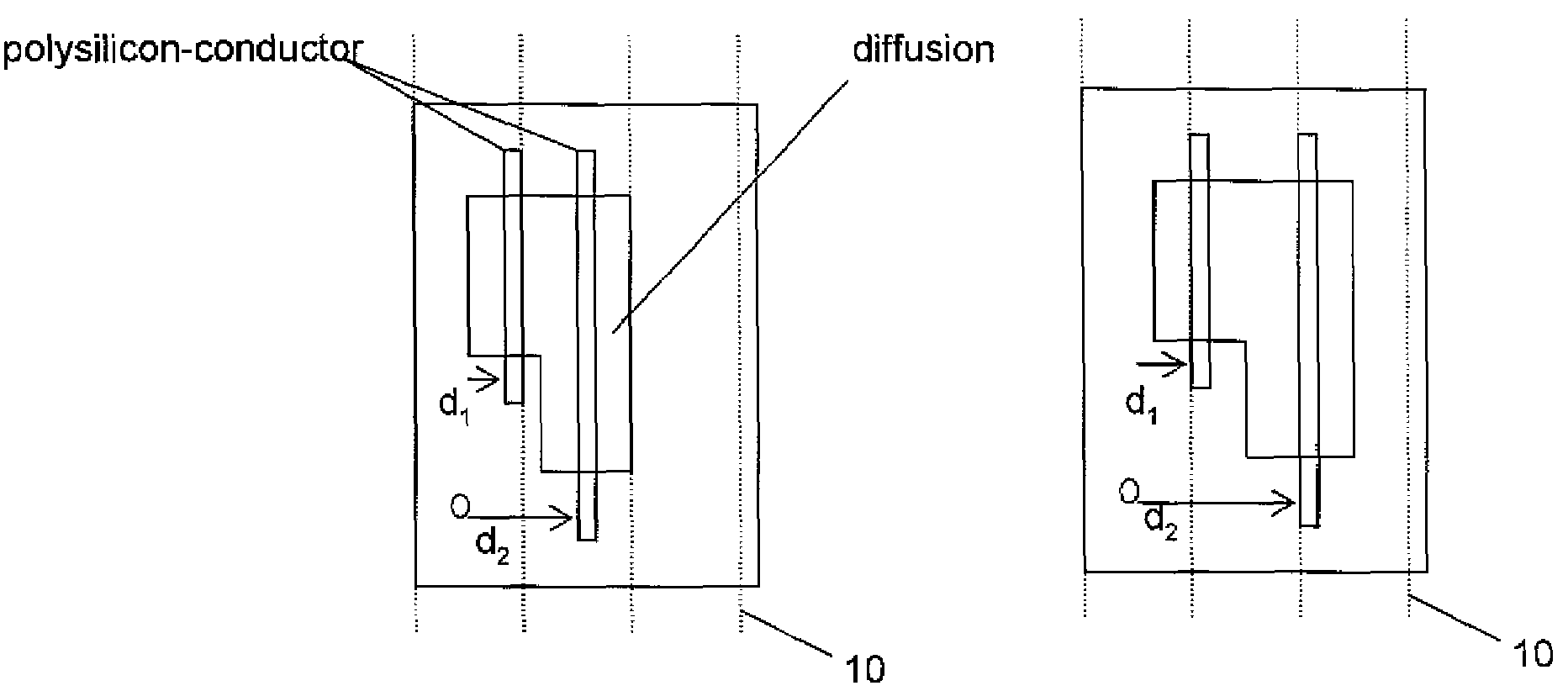
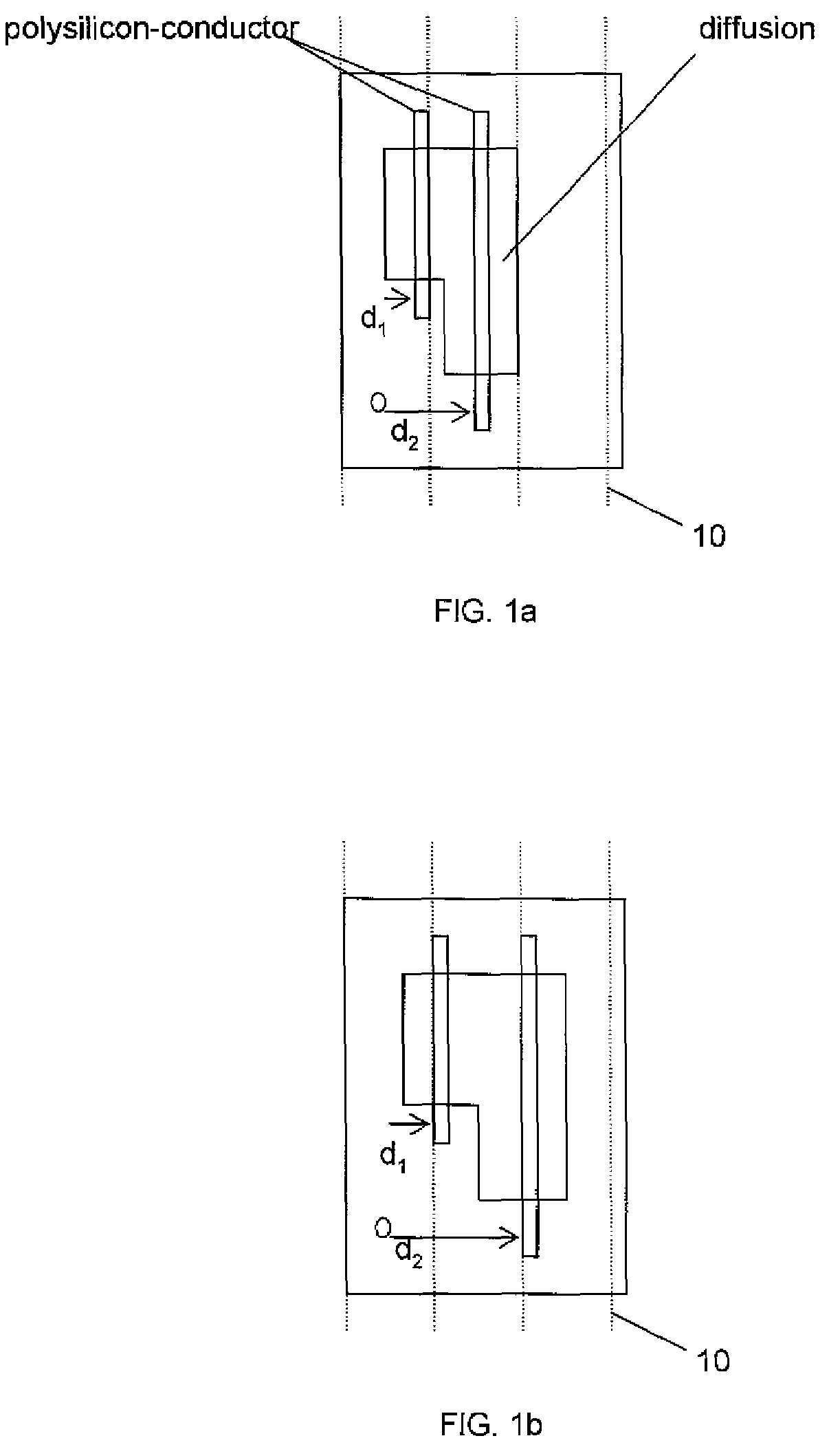
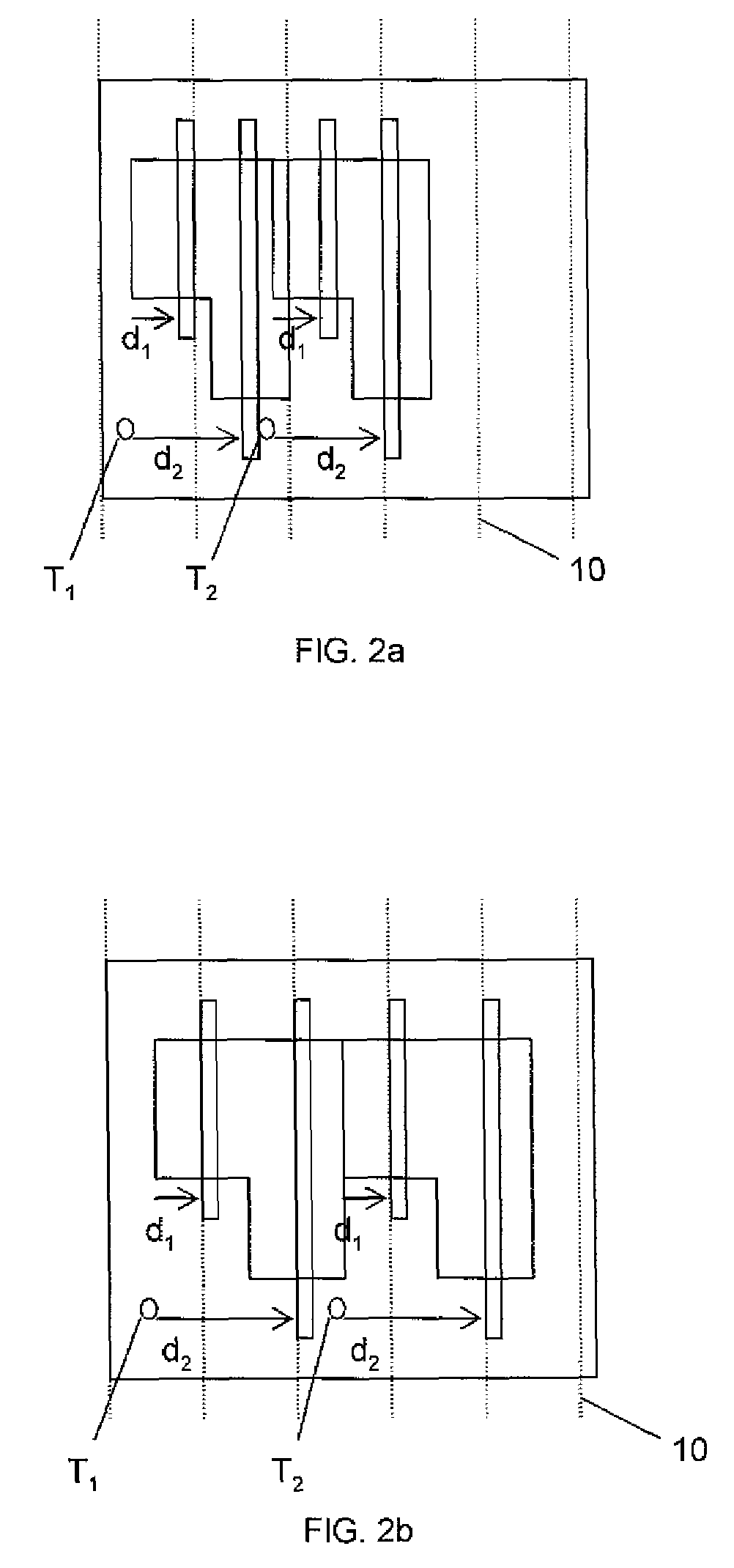
Minimum layout perturbation-based artwork legalization with grid constraints for hierarchical designs
InactiveUS7484197B2Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTheoretical computer scienceHierarchical design
A method comprises extracting a hierarchical grid constraint set and modeling one or more critical objects of at least one cell as a variable set. The method further comprises solving a linear programming problem based on the hierarchical grid constraint set with the variable set to provide initial locations of the critical objects of the at least one cell and determining target on-grid locations of the one or more critical objects in the at least one cell using the results of the linear programming solution.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
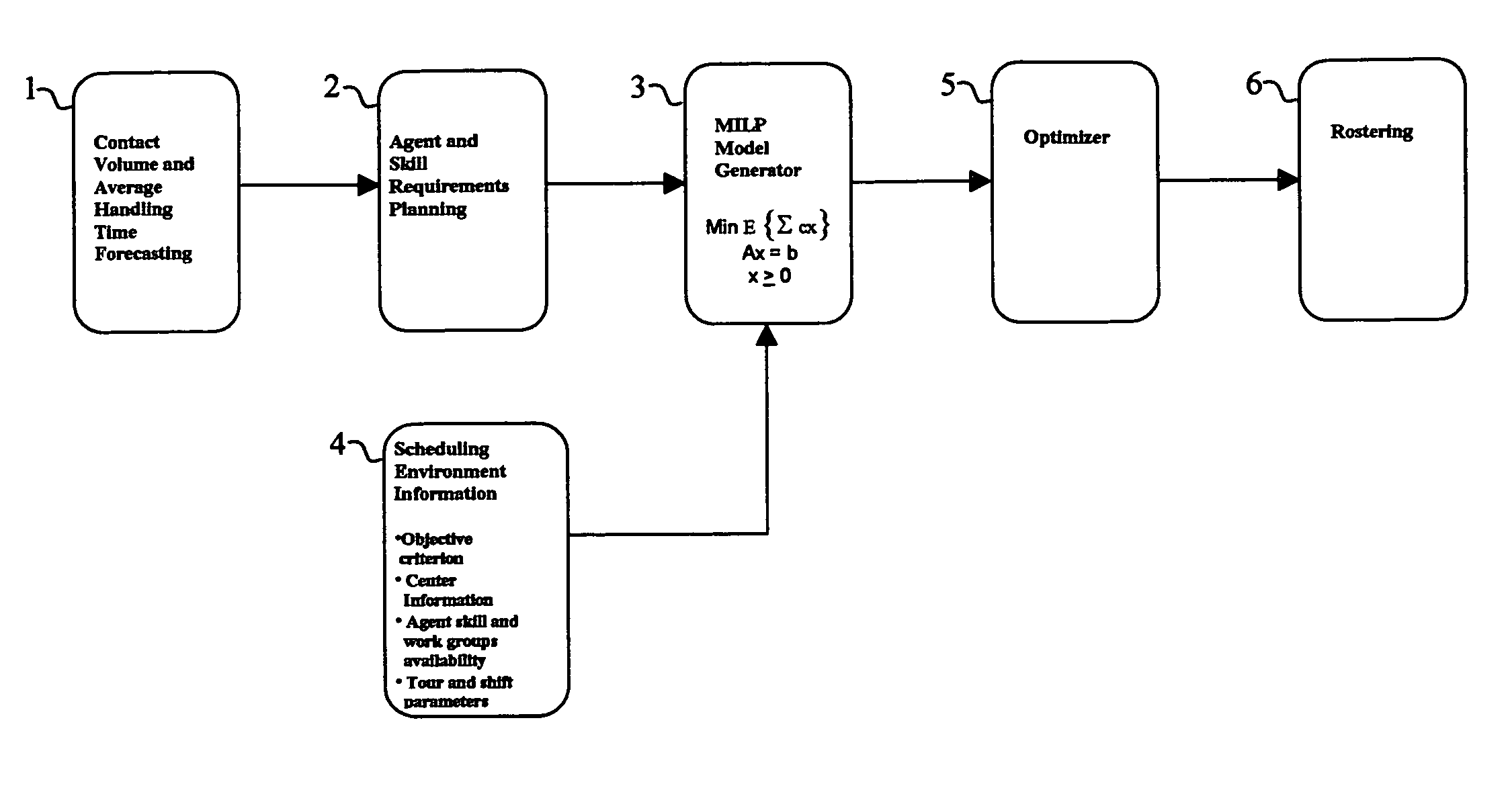
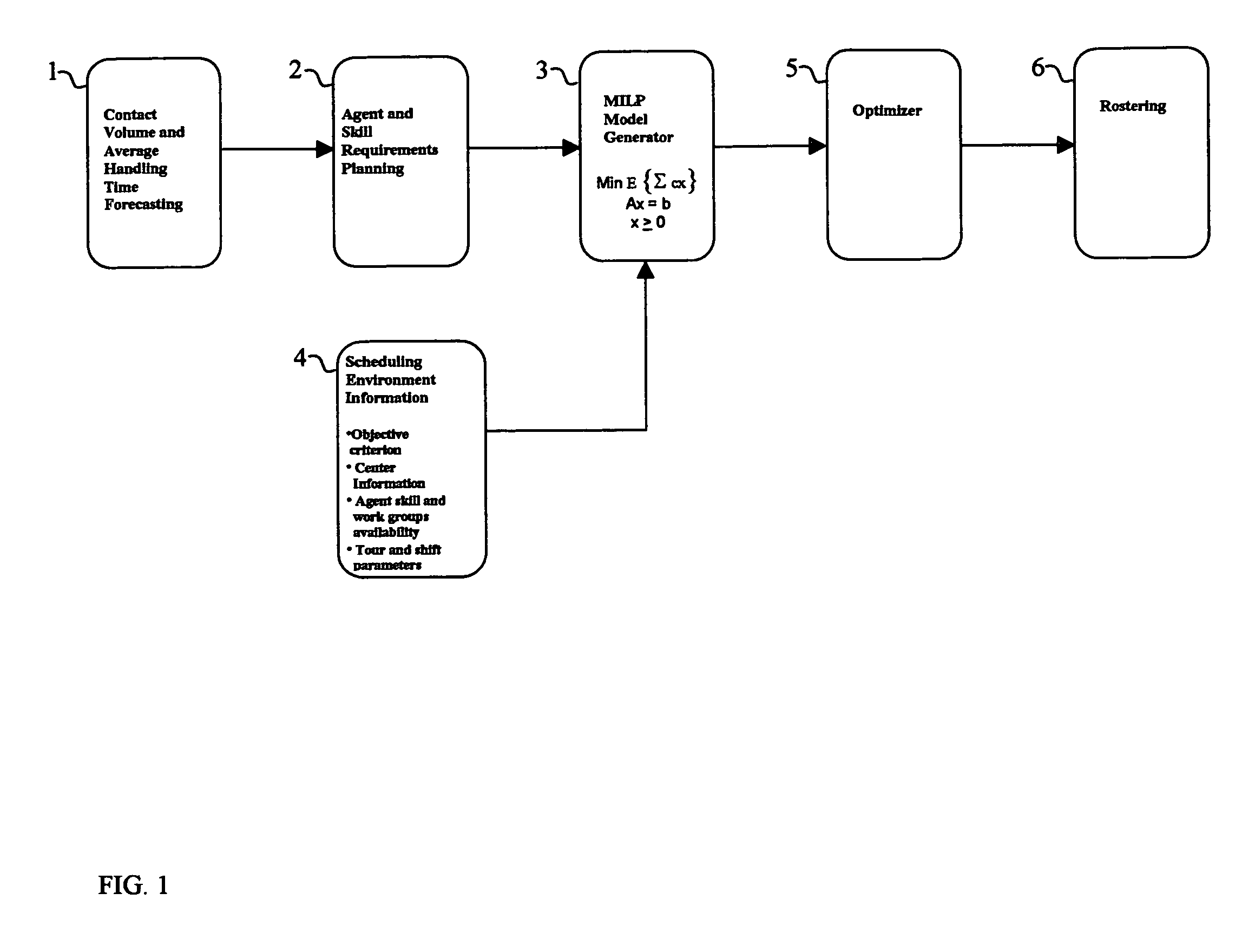
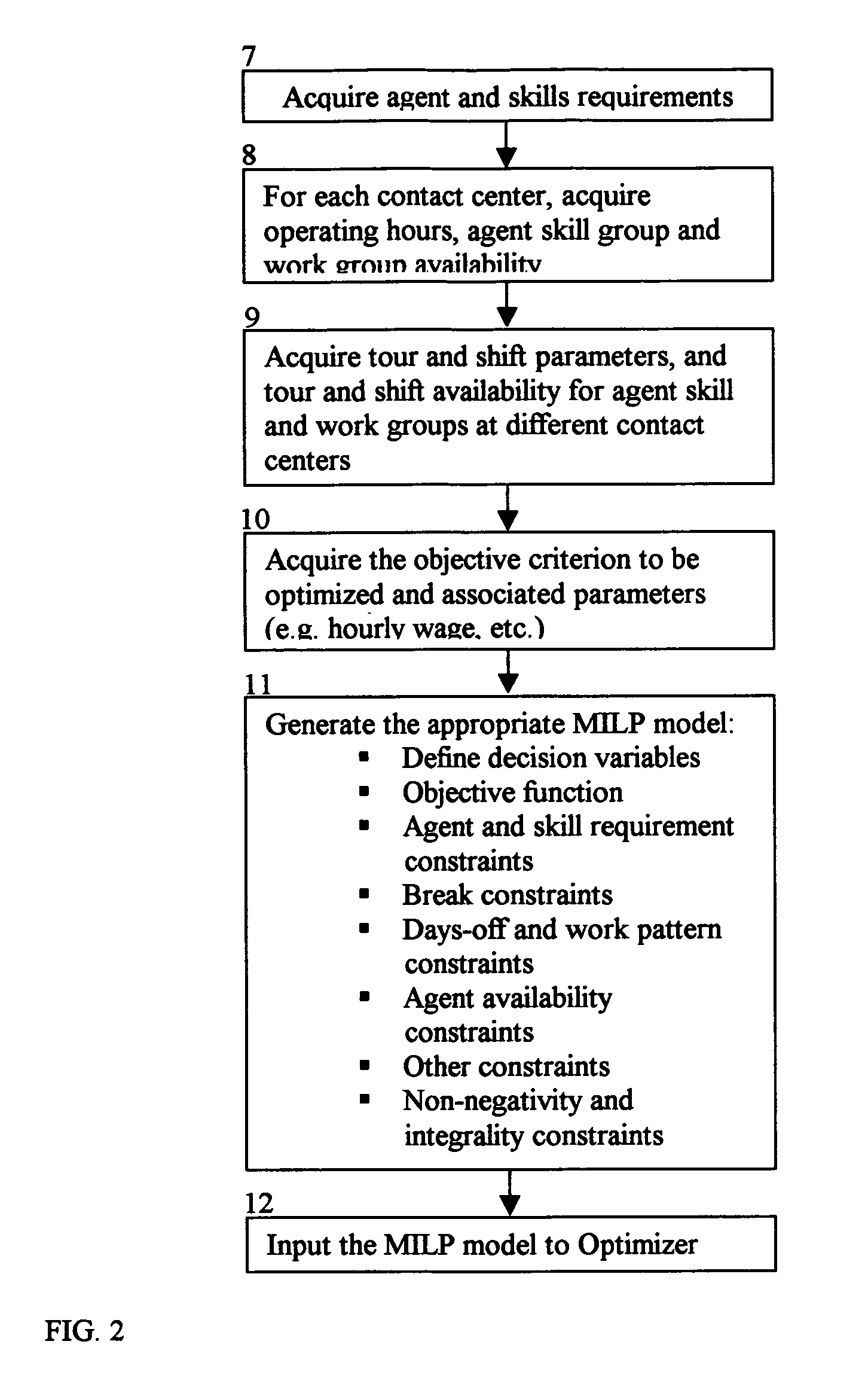
Contact center scheduling using integer programming
ActiveUS7725339B1Easy to solveFavorable objective valueOffice automationSpecial data processing applicationsContact centerWorkforce scheduling
The present invention relates to a method for workforce scheduling in which workload and workload types vary during scheduling period. The method acquires agent and skill requirements for all periods and contact types; acquires the contact center information including agent skill groups, agent work groups, tour and shift scheduling rules, agent availability, objective criterion to be optimized and its parameters; develops a Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) model for the scheduling environment; applied an optimization algorithm that uses the Branch and Bound algorithm with a Rounding Algorithm to improve performance; and locates a globally optimal or near optimal workforce schedule in total cost or paid time or agent satisfaction. Detailed schedules may be developed by assigning daily shifts to work patterns, and breaks scheduled to daily shifts.
Owner:INCONTACT
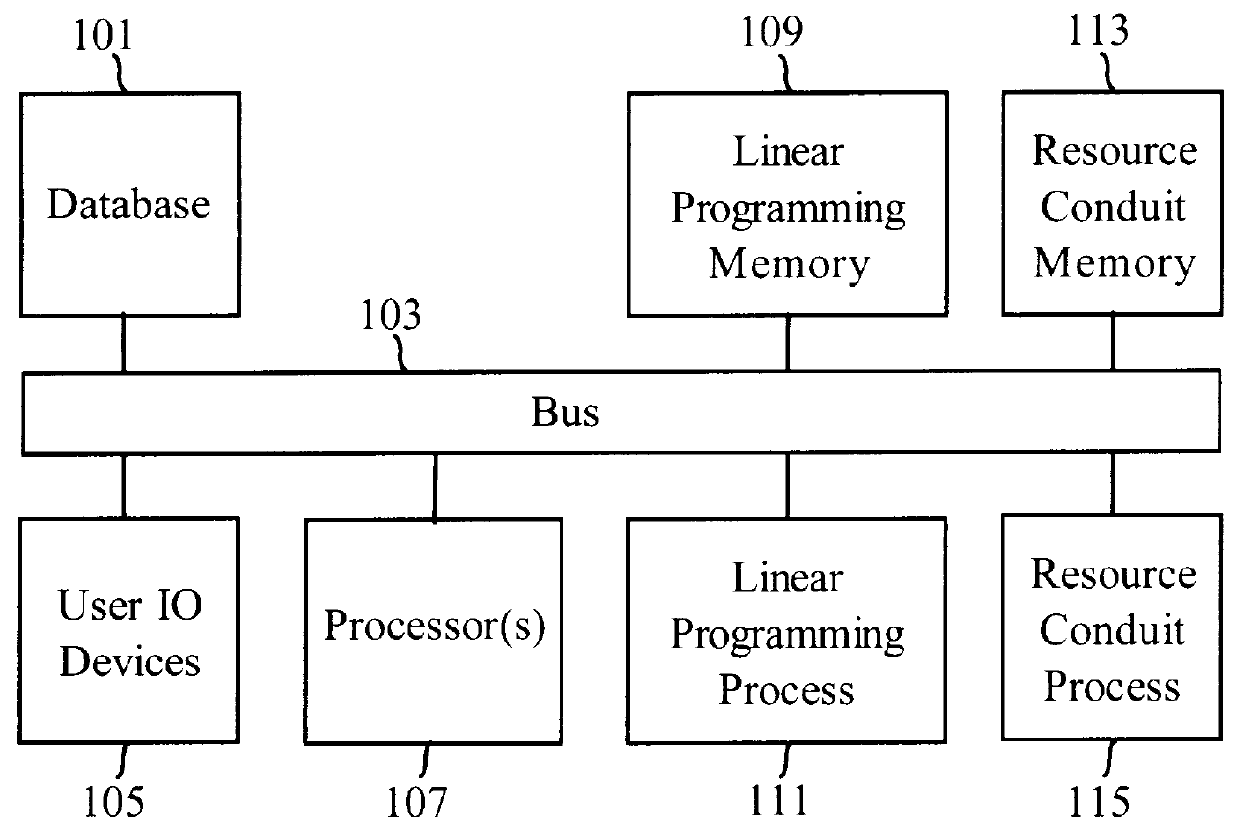
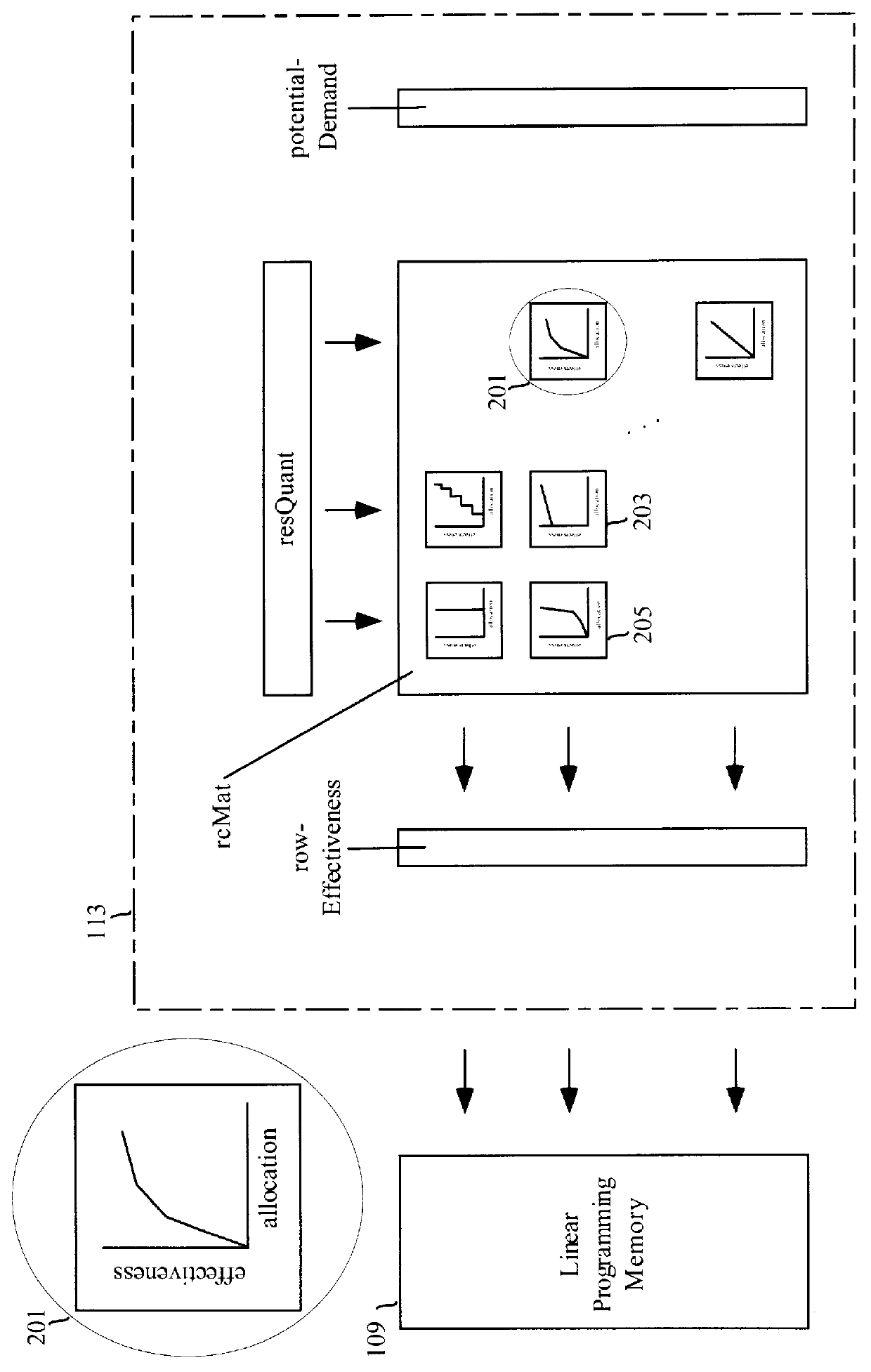
Method and apparatus for allocating, costing, and pricing organizational resources
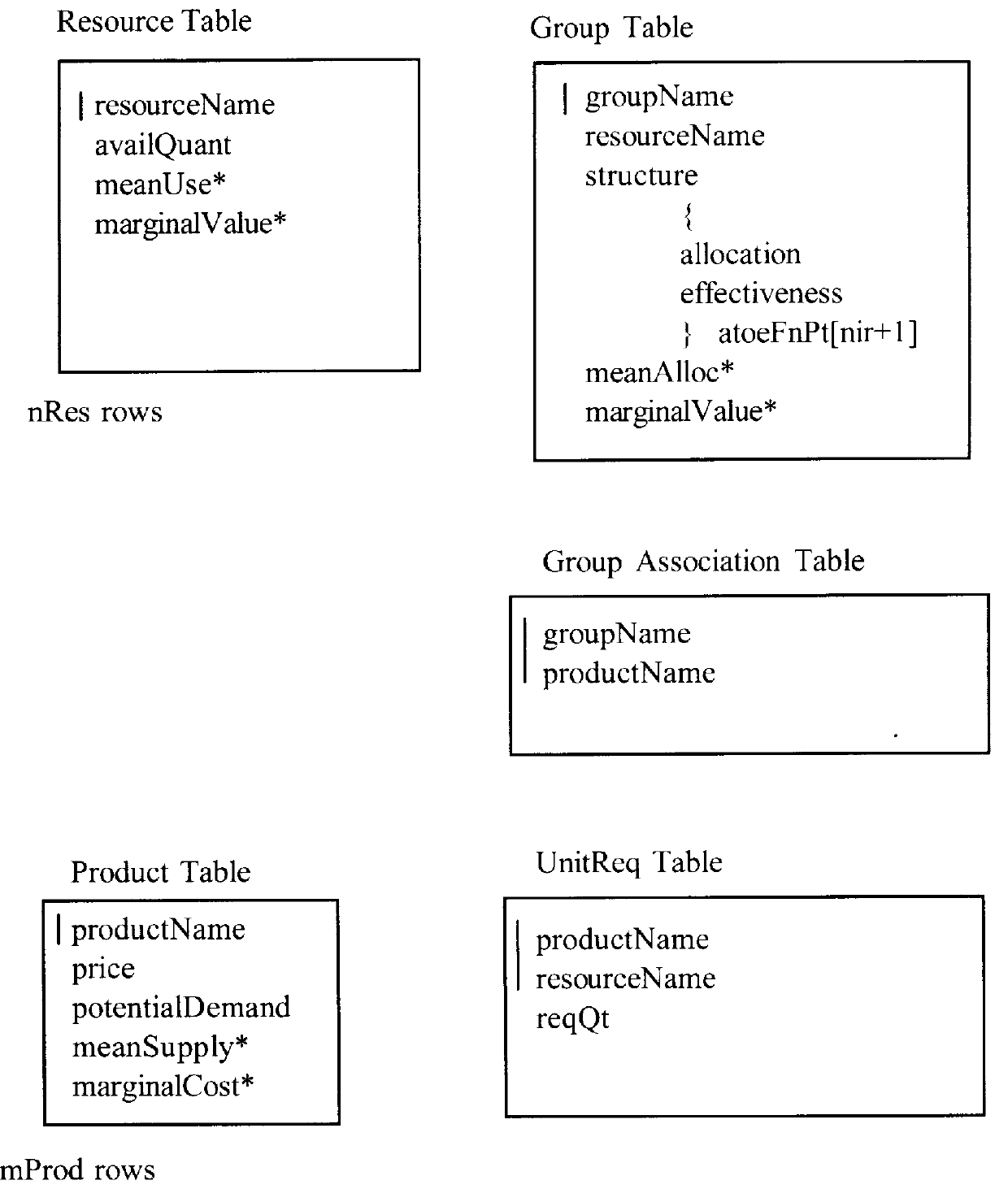
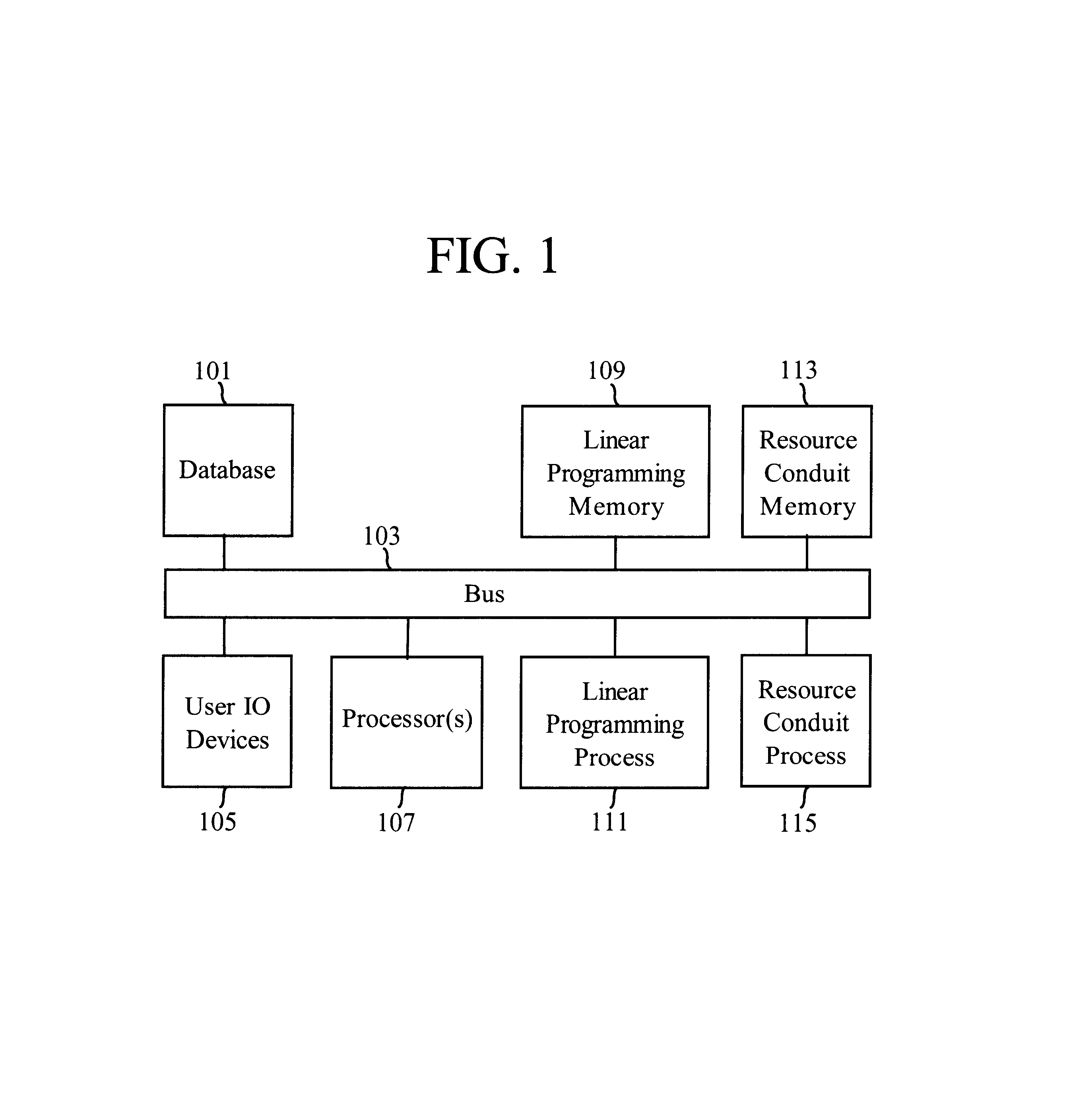
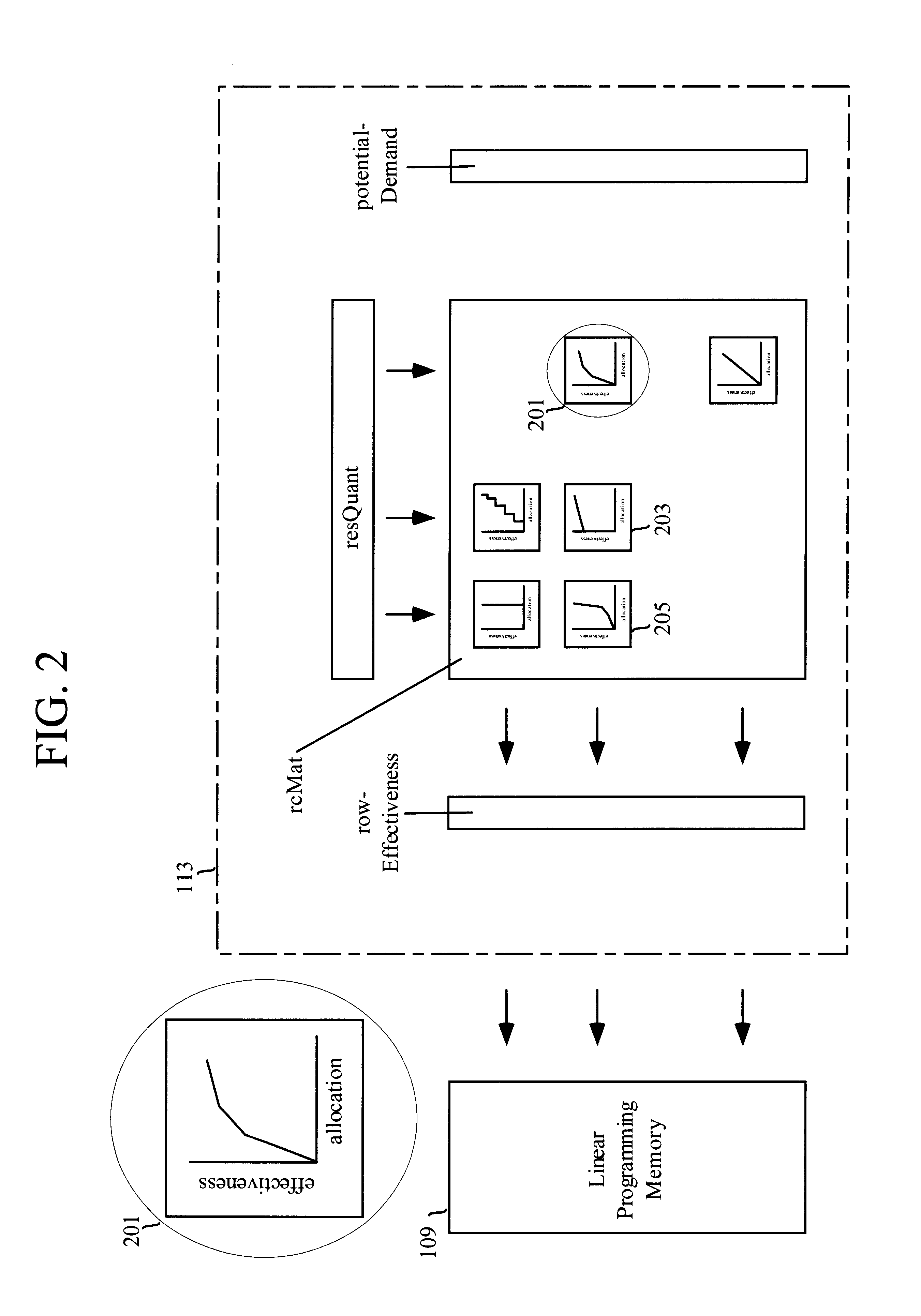
This invention is a means both to allocate all types of resources for commercial, governmental, or non-profit organizations and to price such resources. A linear programming process makes fulfillment allocations used to produce product units. A Resource-conduit process governs the linear programming process, uses two-sided shadow prices, and makes aperture allocations to allow Potential-demand to become Realized-demand. A strict opportunity cost perspective is employed, and the cost of buyable resources is deemed to be the opportunity cost of tying up cash. Resource available quantities, product resource requirements, and Potential-demand as a statistical distribution are specified in a database. The invention reads the database, performs optimization, and then writes allocation directives to the database. Also determined and written to the database are resource marginal (incremental) values and product marginal costs. The database can be viewed and edited through the invention's Graphical User Interface. Monte Carlo simulation, along with generation of supply and demand schedules, is included to facilitate analysis, explore "what if," and interact with the user to develop product offering, product pricing, and resource allocation strategies and tactics.
Owner:JAMESON JOEL
Systems and methods for generating a user profile based customized media guide that includes an internet source
ActiveUS20130305287A1Television system detailsColor television detailsUser-generated contentThe Internet
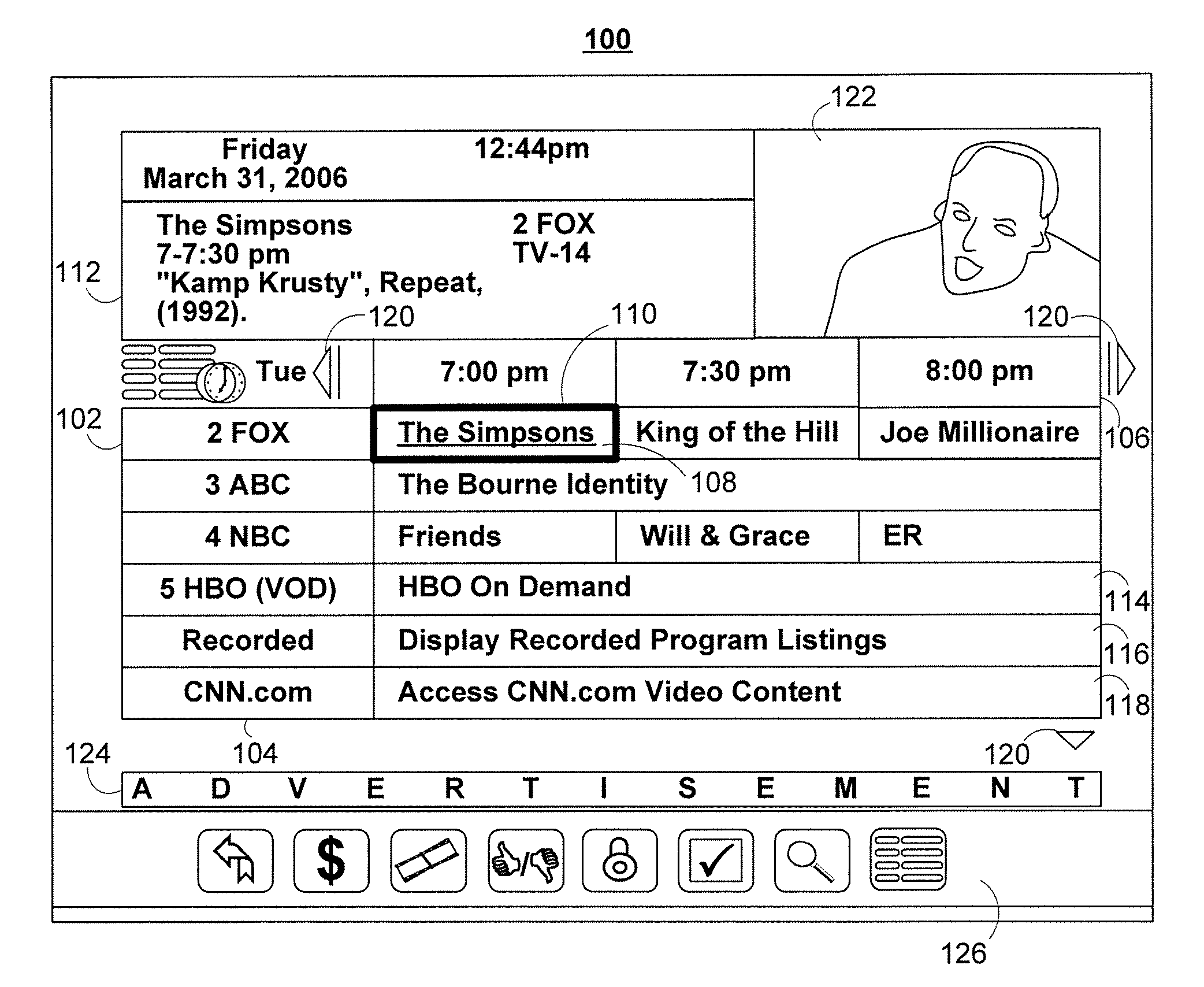
Systems and methods for presenting user-generated content in an easily accessible manner using an interactive media guide are provided. In particular, a user may be able to peruse user-generated content through an interactive media guide which is also used to access non-user-generated media content such as linear programming (e.g., over-the-air broadcast, cable, and satellite scheduled programming) and on-demand media. The interactive media guide may include a provider of user-generated content populated with user-generated content according to the user's interests or most recently added to the provider.
Owner:ROVI GUIDES INC
Layout decomposition for double patterning lithography
ActiveUS20110078638A1Low costAvoids small jogging line-endsOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputer aided designLithographic artistDecomposition
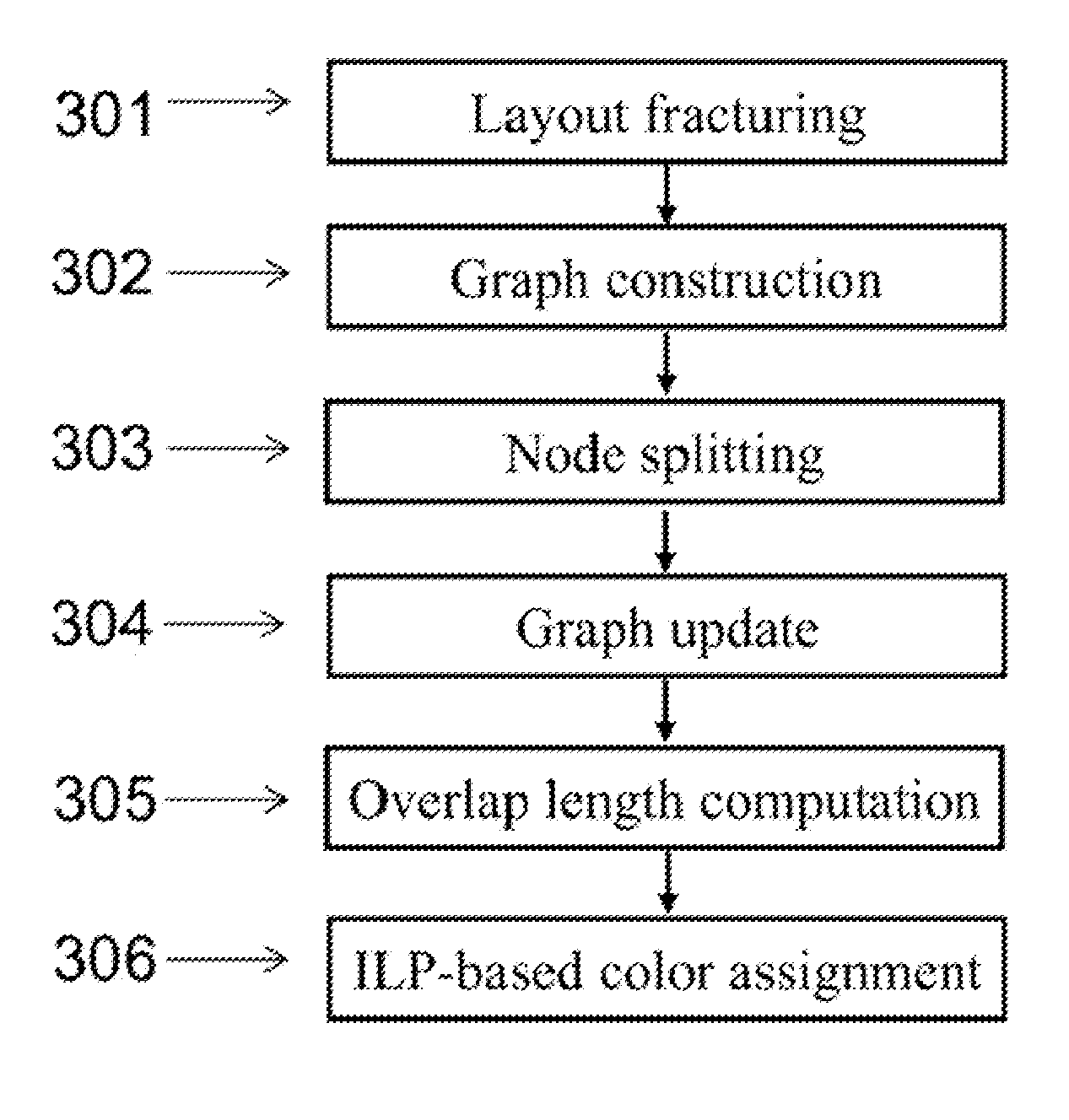
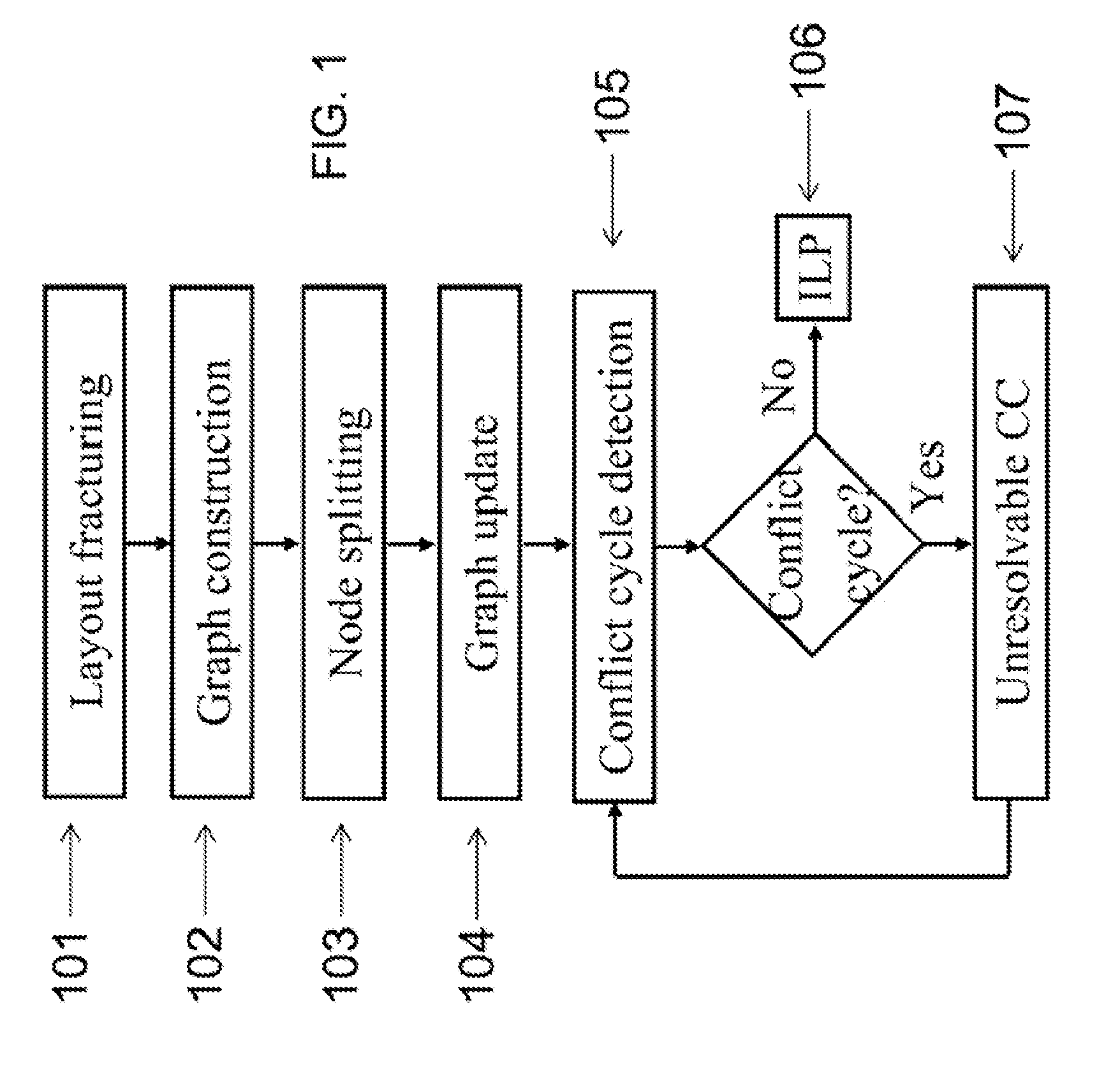
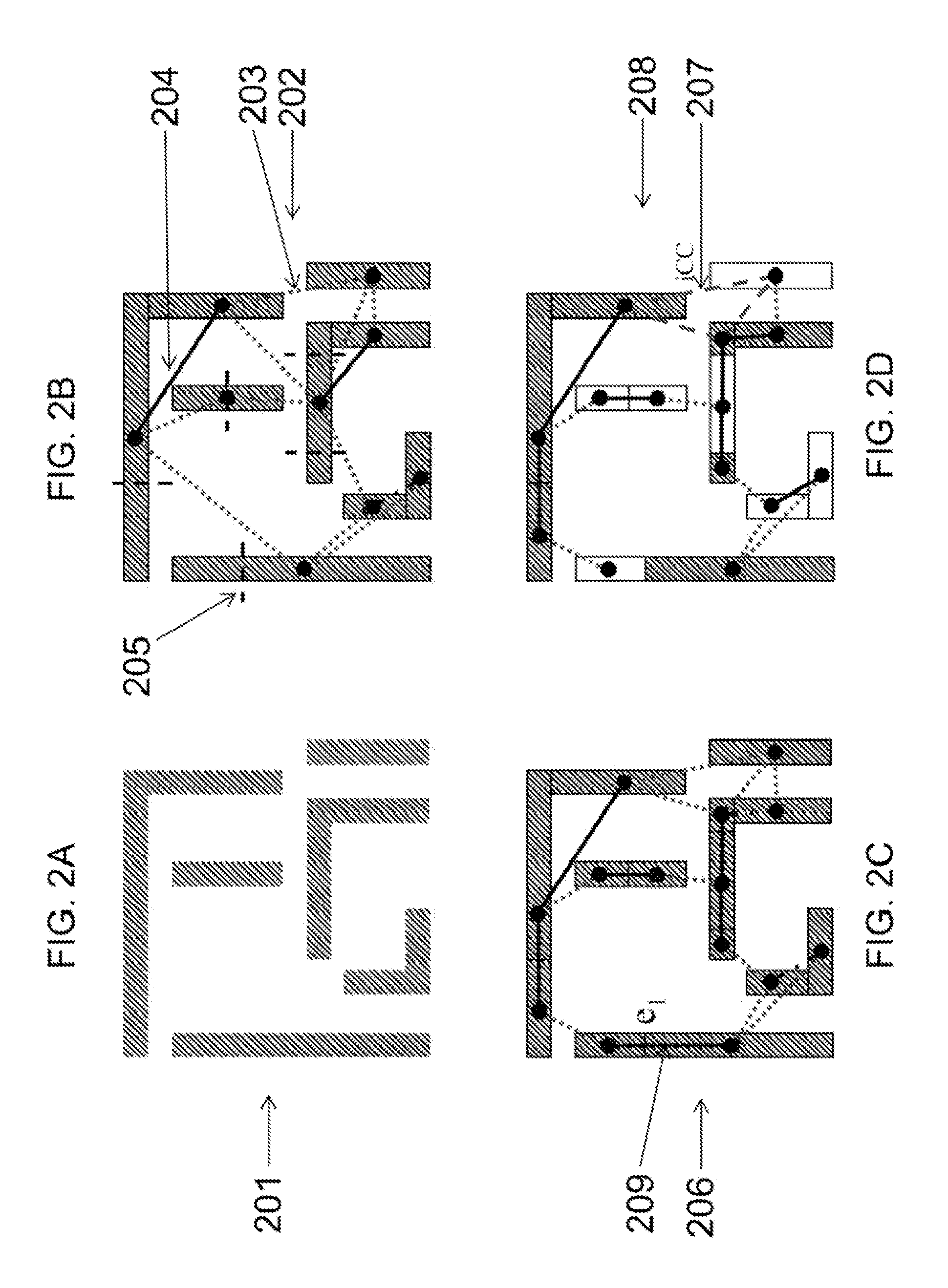
The invention provides systems and methods for layout decomposition to produce exposure layouts that can be used to perform double patterning lithography (DPL). Preferred embodiment methods of the invention are executed by a computer and provide alternate methods for layout decomposition for double patterning lithography (DPL) using integer linear programming (ILP) formulations. Embodiments of the invention meet a key optimization goals, which is to reduce the total cost of layout decomposition, considering the abovementioned aspects that contribute to cost of prior conventional DPL techniques. Embodiments of the invention provide integer linear programming (ILP), phase conflict detection (PCD) and node election bipartization (NBD) formulations for the optimization of DPL layout decomposition, with a process-aware cost function that avoids small jogging line-ends, and maximizes overlap at dividing points of polygons. The cost function can also make preferential splits at landing pads, junctions and long runs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
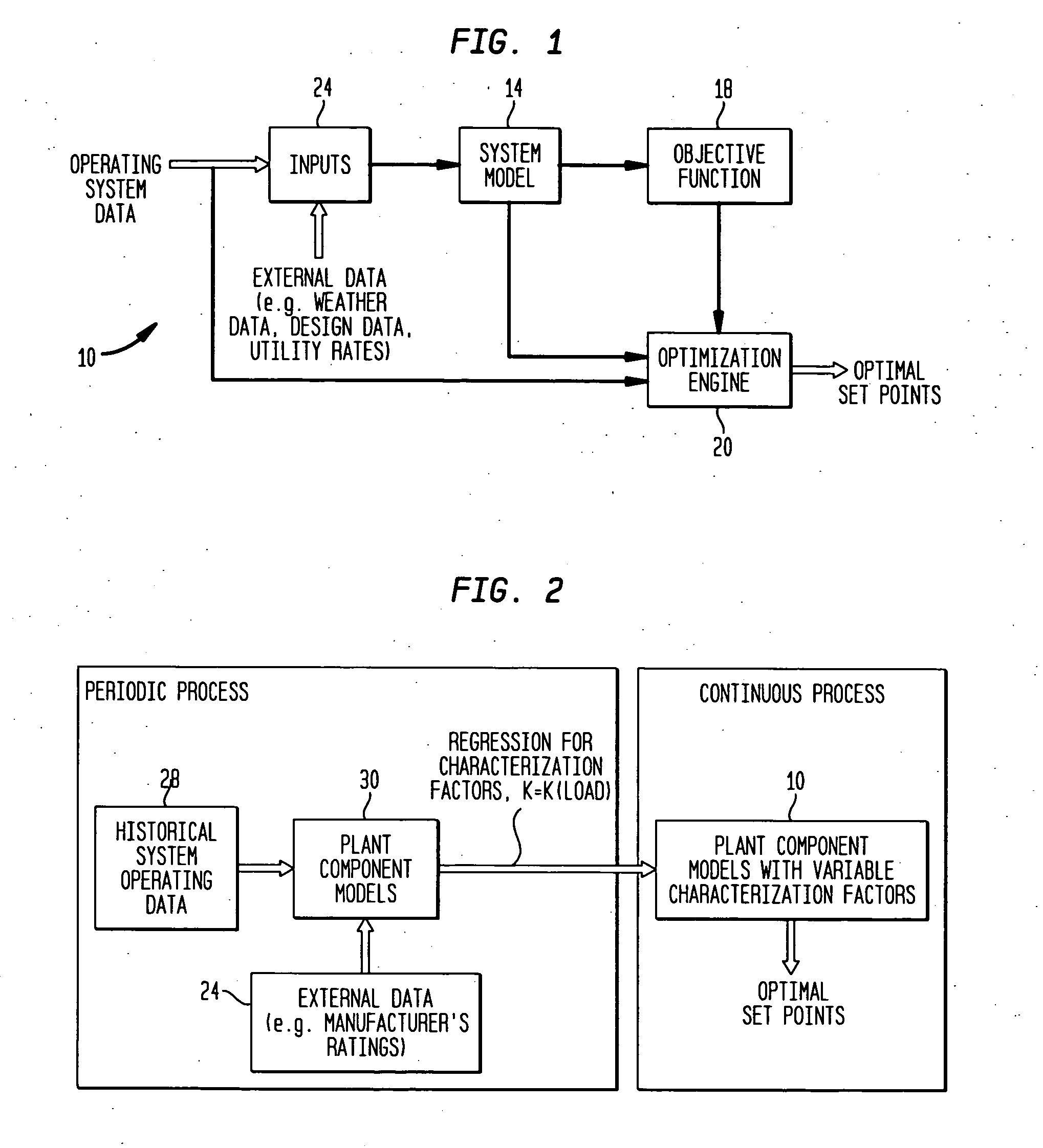
System and method for optimizing global set points in a building environmental management system
InactiveUS20050192680A1Point to optimizationReduce operating costsSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlFuzzy ruleComponent modeling
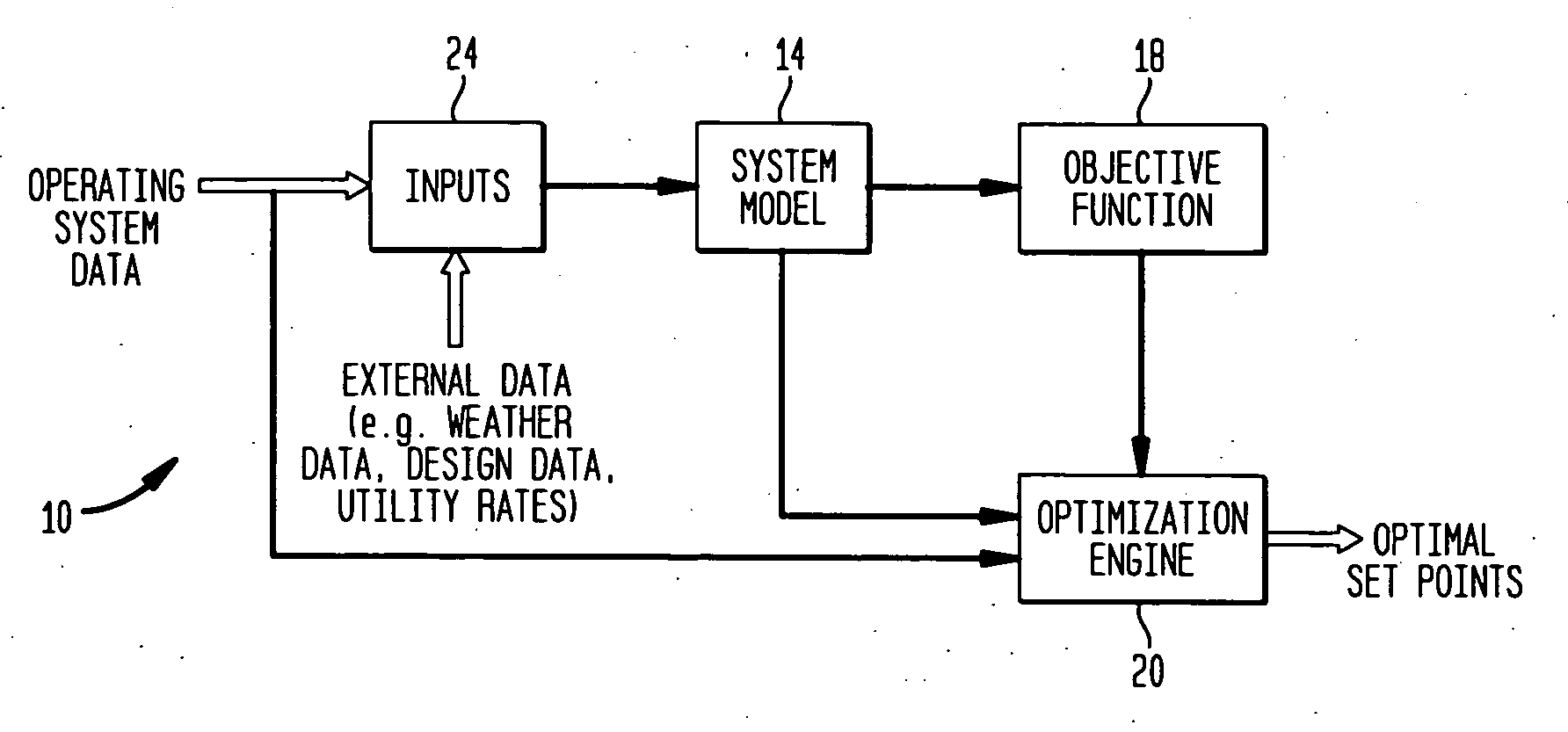
A system generates optimal global set points for an environmental management system. The system comprises a system model for modeling components of a thermal plant, an objective function for modeling a parameter of the thermal plant, and an optimization engine for optimizing the parameter modeled by the objective function. The system model is coupled to an input data collector for receiving building data and weather data corresponding to a particular site. The system model includes models for thermal plant system components that may be implemented using classical models or artificial intelligence models. Classical models are those models that are implemented using linear programming, unconstrained non-linear programming, or constrained non-linear programming methodologies. The artificial intelligence models are those models that may be implemented using a fuzzy expert control system with crisp and fuzzy rules, genetic algorithms for optimization, or neural networks.
Owner:SIEMENS IND INC
Decomposition system and method for solving a large-scale semiconductor production planning problem
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Vehicle dispatching method and system
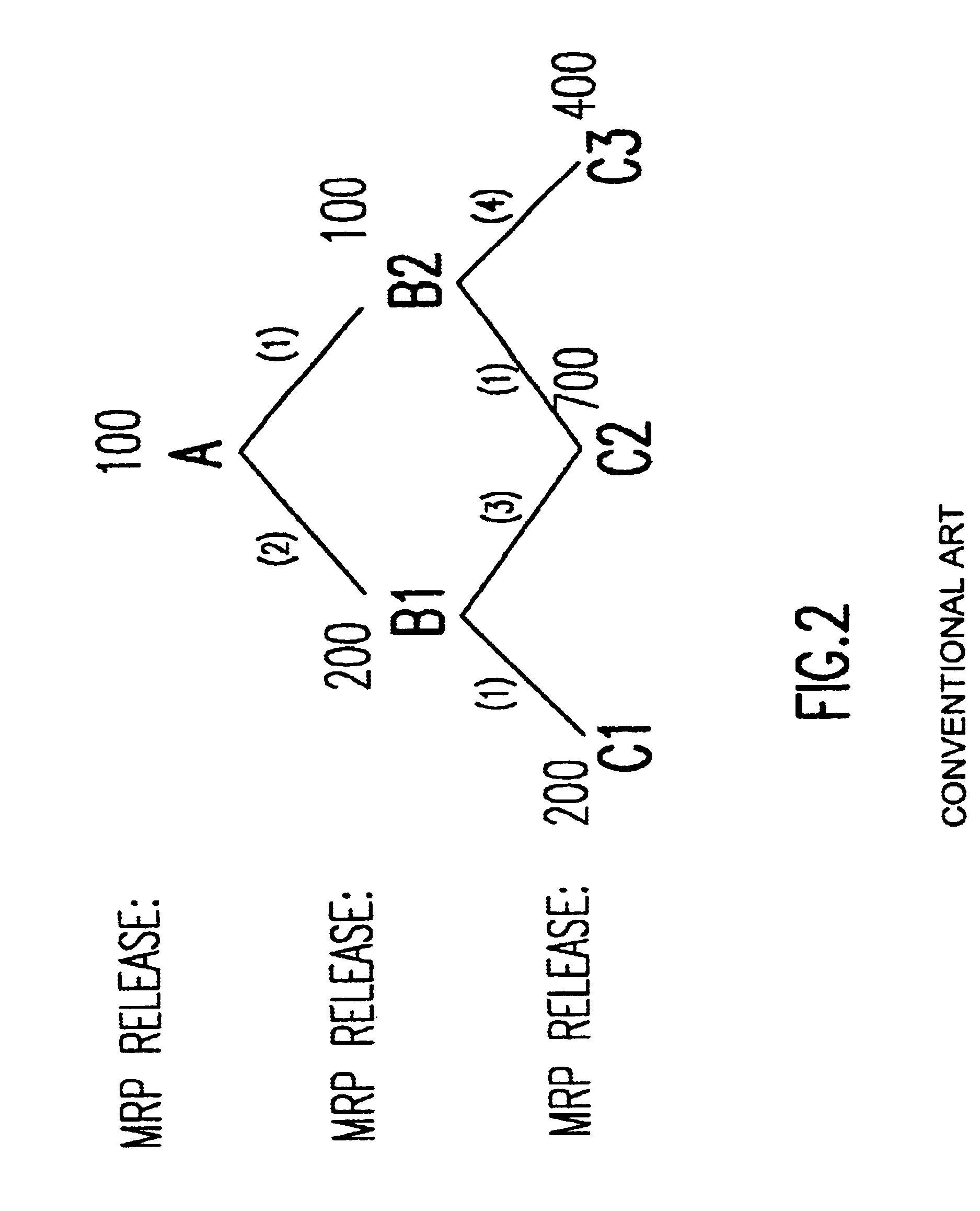
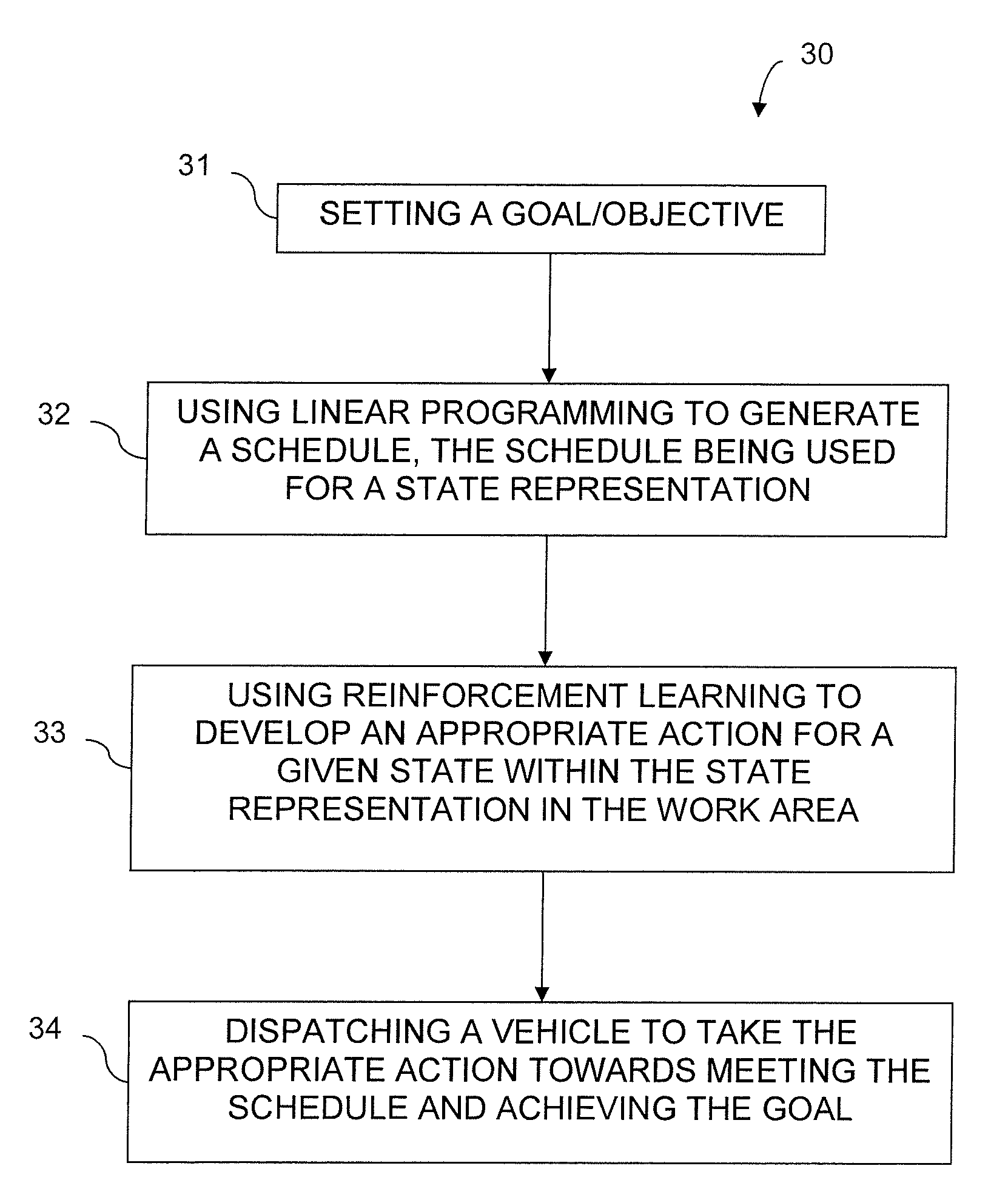
ActiveUS20090327011A1Autonomous decision making processTransportation facility accessTime scheduleReinforcement learning algorithm
A system and method for dispatching a plurality of vehicles operating in a work area among a plurality of destination locations and a plurality of source locations includes implementing linear programming that takes in an optimization function and constraints to generate an optimum schedule for optimum production, utilizing a reinforcement learning algorithm that takes in the schedule as input and cycles through possible environmental states that could occur within the schedule by choosing one possible action for each possible environmental state and by observing the reward obtained by taking the action at each possible environmental state, developing a policy for each possible environmental state, and providing instructions to follow an action associated with the policy.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS SOLUTIONS
Method and apparatus for distributing media content
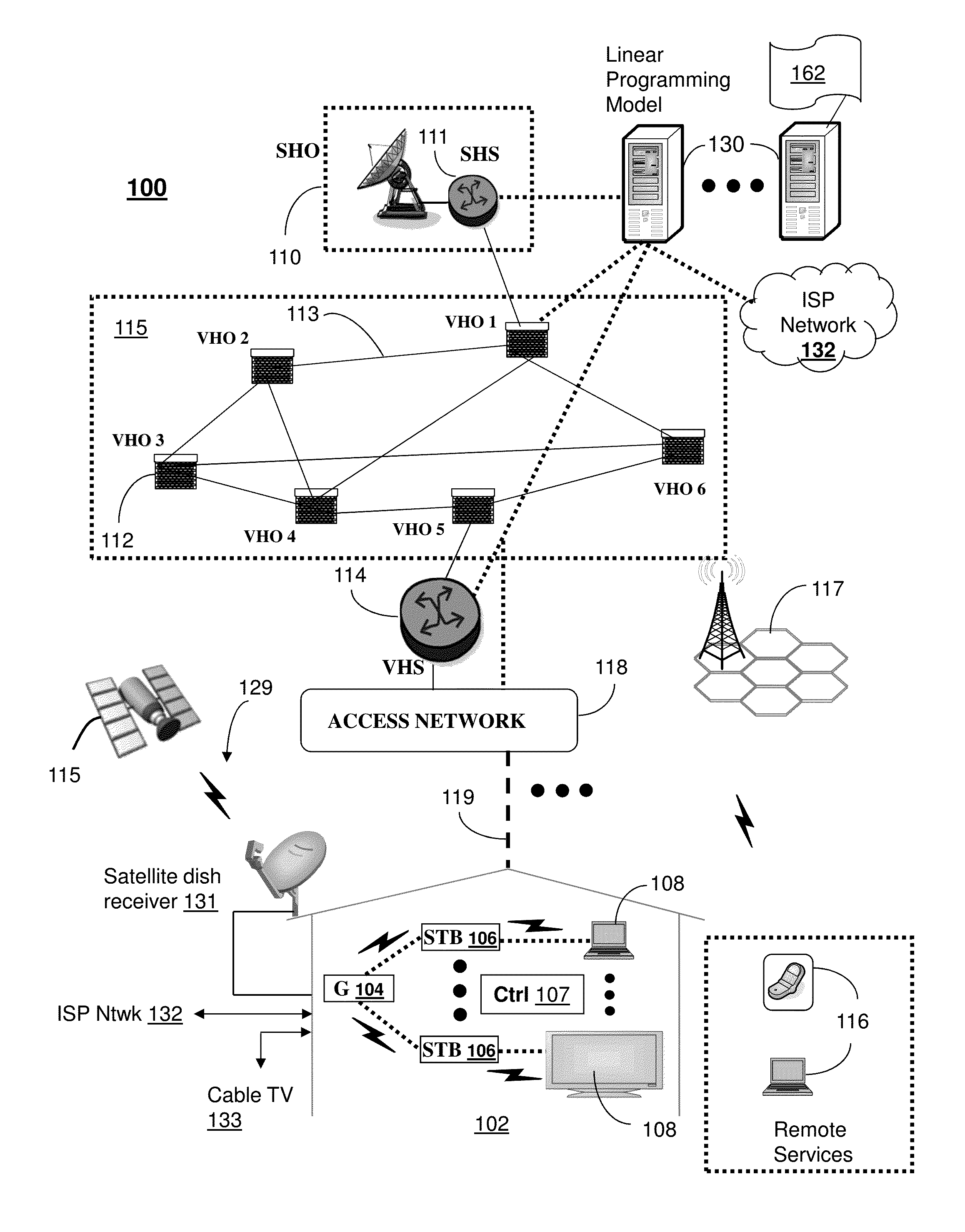
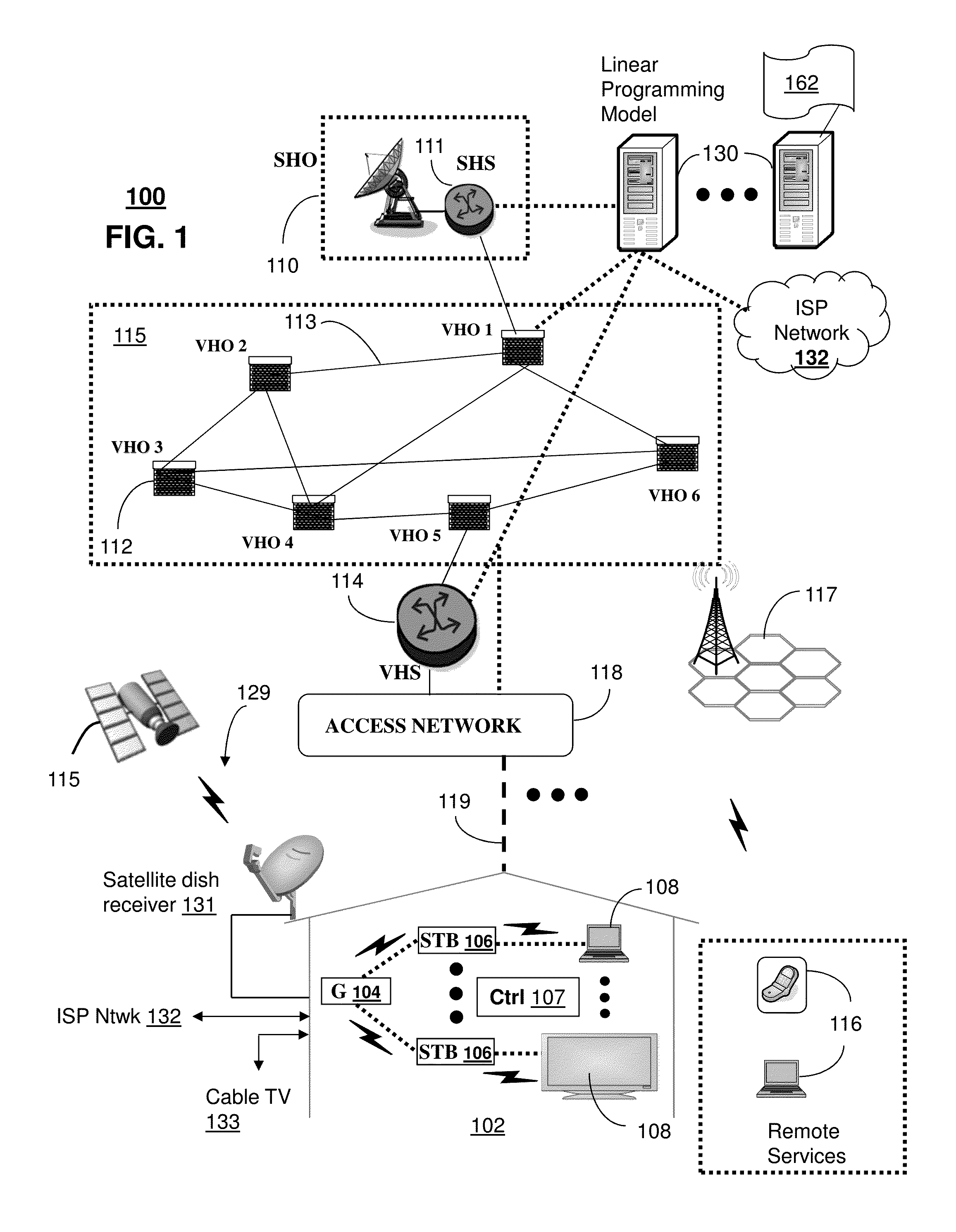
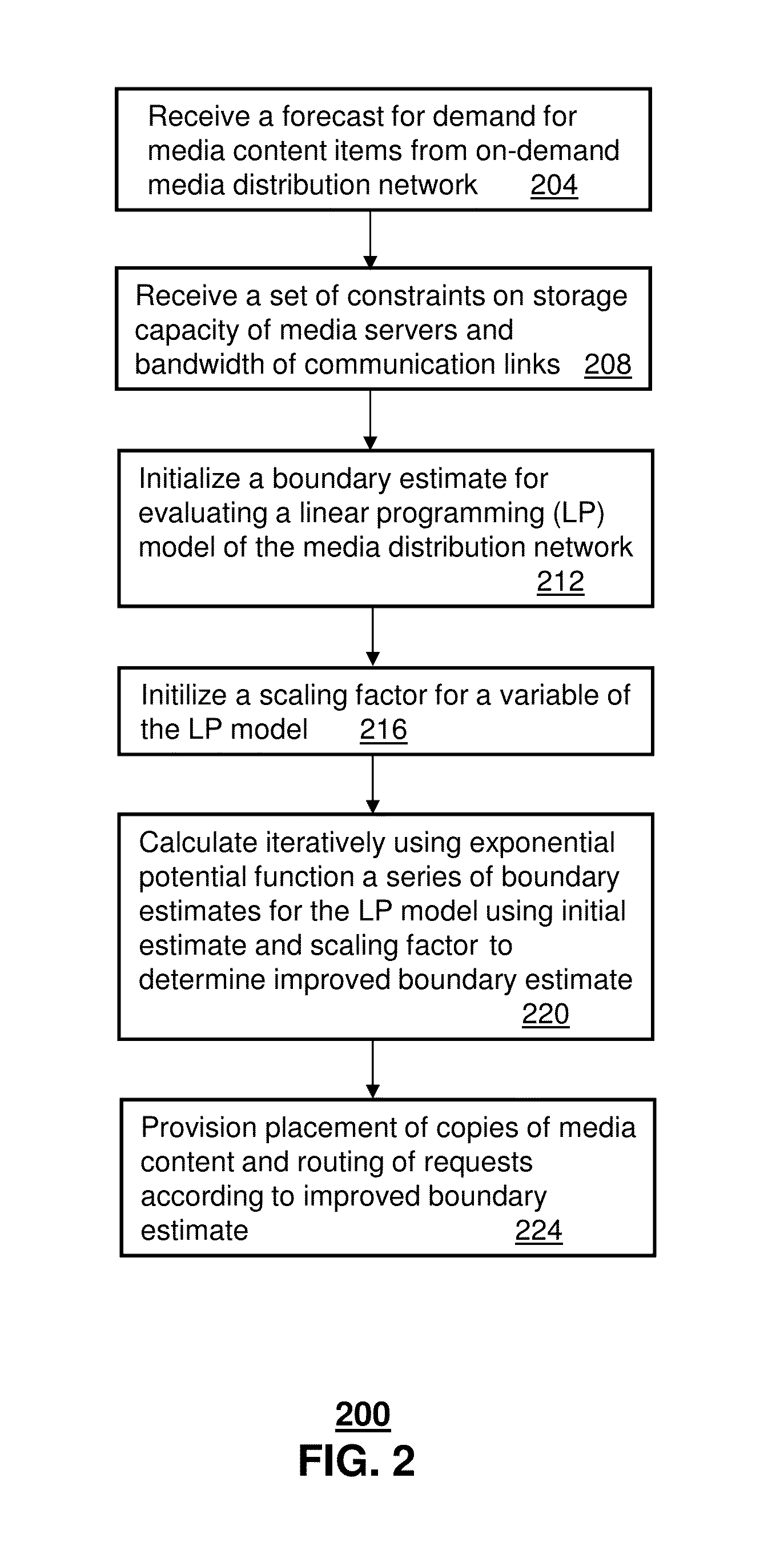
ActiveUS9407676B2Resource allocationDesign optimisation/simulationTelecommunications linkExponential potential
A system that incorporates teachings of the present disclosure may include, for example, initializing a boundary estimate for an optimization of a linear programming model describing a network of media servers for servicing requests for media content items from subscriber devices, where the boundary estimate is an estimate of an infeasible solution of the linear programming model, and calculating iteratively, using an exponential potential function, additional boundary estimates for the linear programming model, wherein the calculating resolves to an improved boundary estimate that corresponds to placement of copies of the media content items at the media servers subject to a set of constraints on storage capacity of media servers and on bandwidth for communication links in the network. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Methods and apparatus for allocating, costing, and pricing organizational resources
This invention is a means both to allocate all types of resources for commercial, governmental, or non-profit organizations and to price such resources. A linear programming process makes fulfillment allocations used to produce product units. A Resource-conduit process governs the linear programming process, uses two-sided shadow prices, and makes aperture allocations to allow Potential-demand to become Realized-demand. A strict opportunity cost perspective is employed, and the cost of buyable resources is deemed to be the opportunity cost of tying up cash. Resource available quantities, product resource requirements, and Potential-demand as a statistical distribution are specified in a database. The invention reads the database, performs optimization, and then writes allocation directives to the database. Also determined and written to the database are resource marginal (incremental) values and product marginal costs. The database can be viewed and edited through the invention's Graphical User Interface. Monte Carlo simulation, along with generation of supply and demand schedules, is included to facilitate analysis, explore “what if,” and interact with the user to develop product offering, product pricing, and resource allocation strategies and tactics.
Owner:JAMESON JOEL
Method of simplifying & automating enhanced optimized decision making under uncertainty
InactiveUS20060117303A1Simple interfaceSuccessful applicationOffice automationSpecific program execution arrangementsProgram calculationSensitivity analyses
Many business problems involve too many complex and interacting variables for a person to solve them, unassisted. Linear programming, statistical and probability analyses provide effective tools for solving such problems, but until now, use of these tools has not been practical for persons without extensive mathematical training. The present invention provides an understandable user interface to these tools, enabling even mathematically unsophisticated users to effectively solve complex problems. The invention also incorporates sensitivity analyses, thereby permitting the user to explore how changes in input data would affect the results of the program calculations. In addition to a data-input program module, respective program modules are disclosed for managing a company product line, a securities portfolio, and a short-selling portfolio.
Owner:GIZINSKI GERARD H
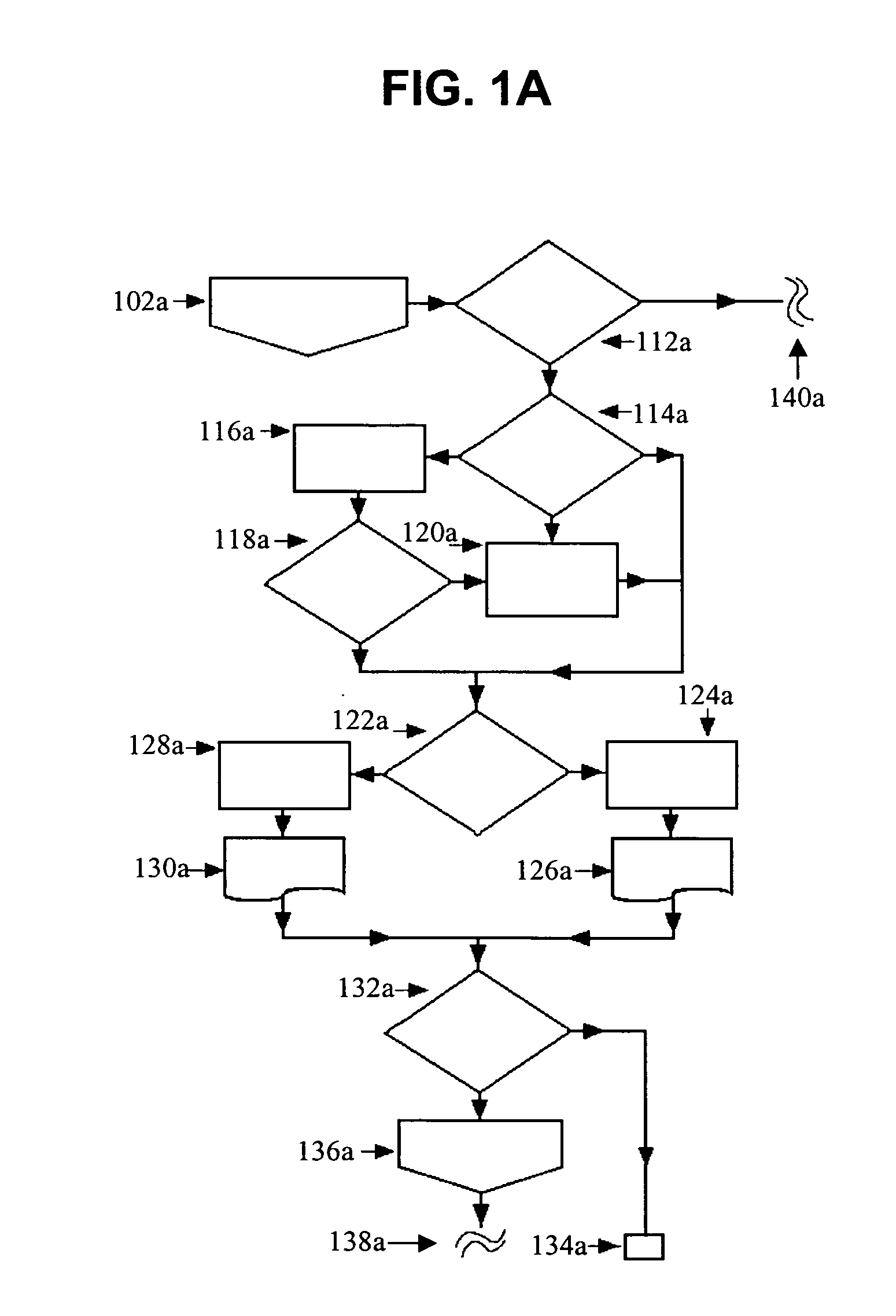
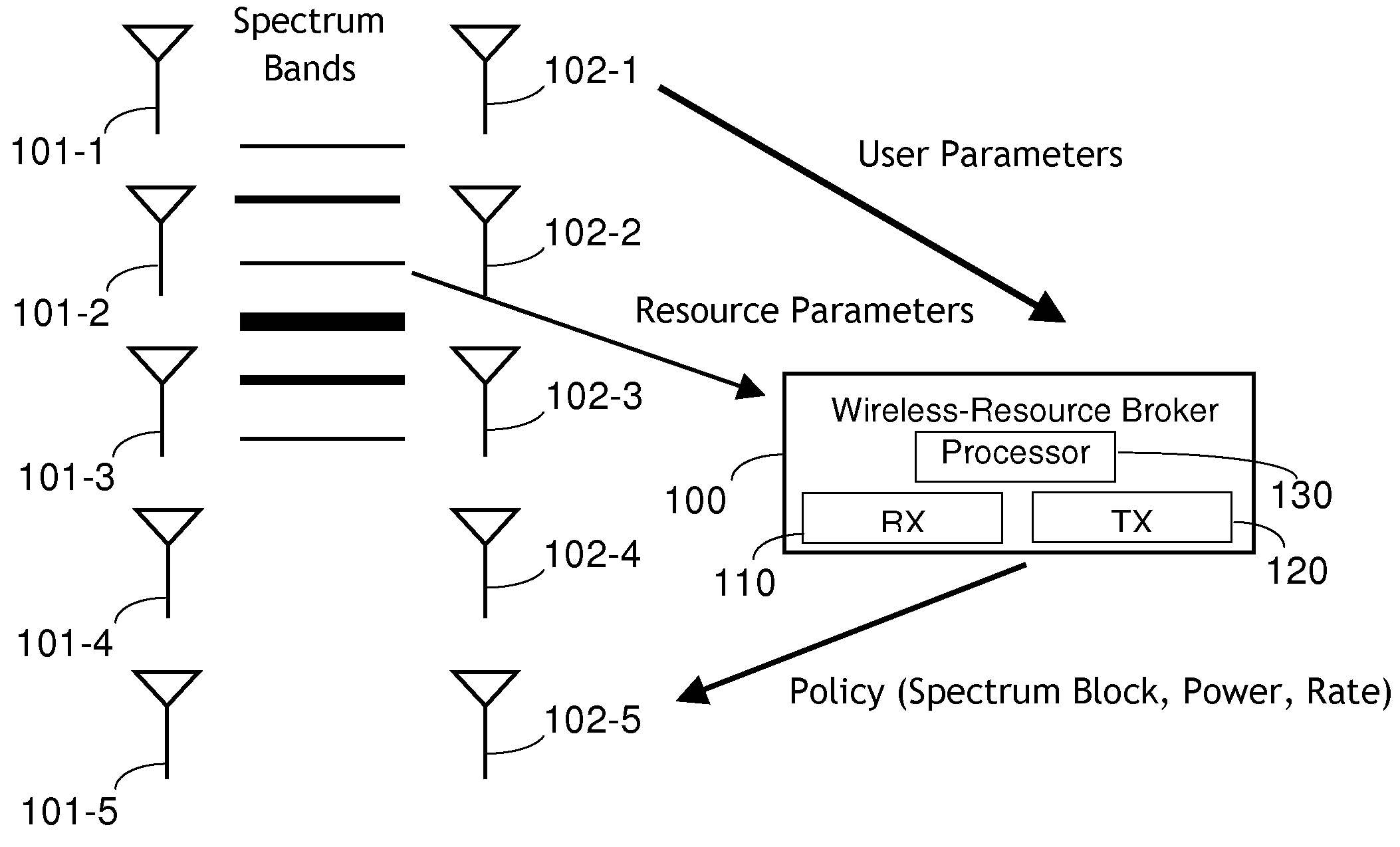
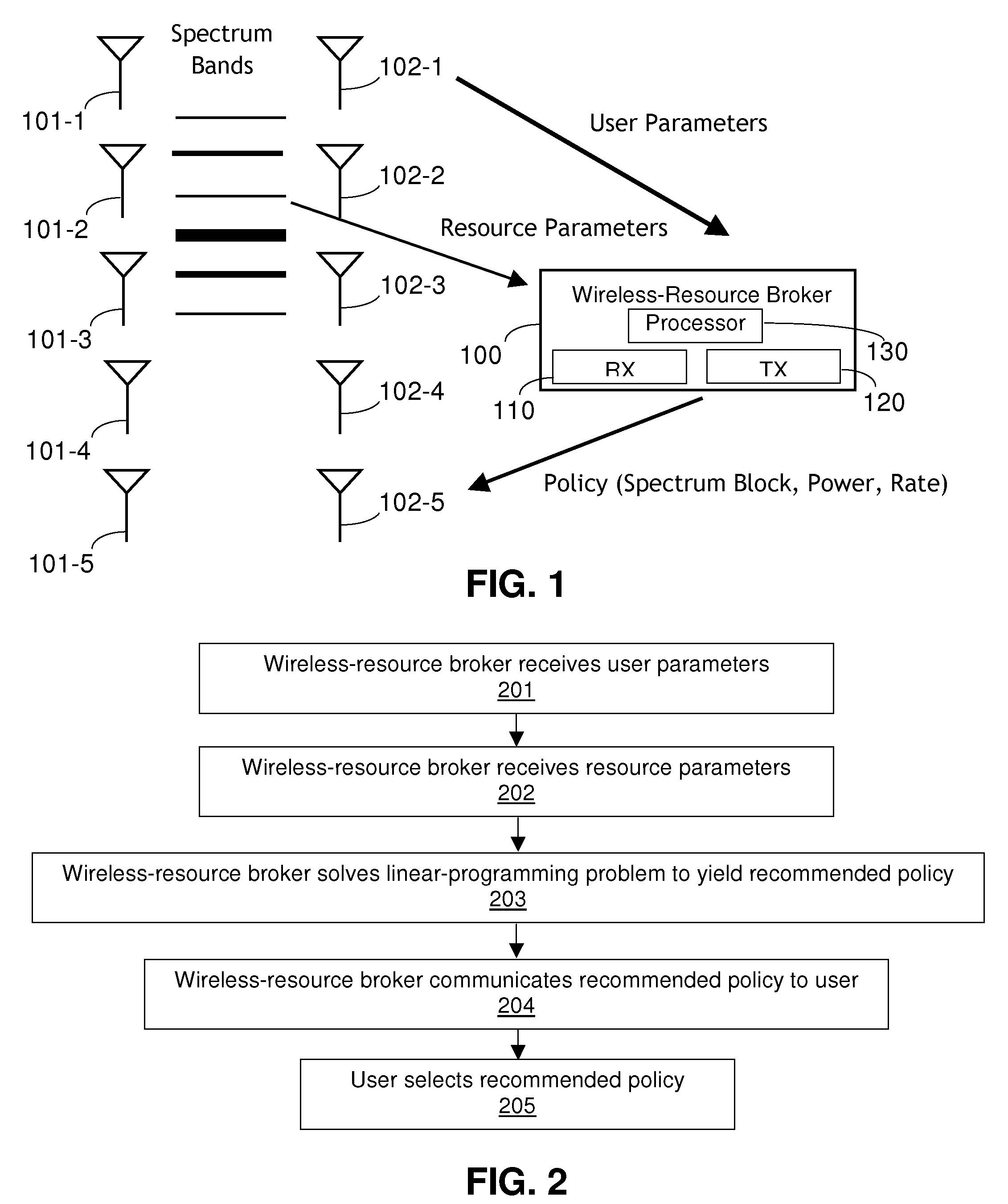
Wireless-resource broker
InactiveUS20100069074A1Network traffic/resource managementServices signallingResource brokerTransmitter
In one embodiment, a wireless-resource broker employs a self-enforcing spectrum-sharing policy, e.g., the expected utility (e.g., rate) a user obtains by following the policy provided by the broker is not less than the expected utility that the user obtains by switching to some other strategy. Each user is associated with one or more transmitter-receiver pairs, e.g., a transmitter of a wireless device and a receiver of a base station in communication via a wireless channel. The broker receives, as input, user parameters characterizing one or more of the transmitters and / or receivers and resource parameters characterizing one or more available spectrum blocks. The broker solves a linear-programming problem to generate and transmit a recommended policy for one or more users. The policy for each user includes information such as the spectrum block(s) to which the user is assigned, the transmission power for the user, and the transmission rate for the user.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
System, Method and Apparatus for Allocating Resources by Constraint Selection
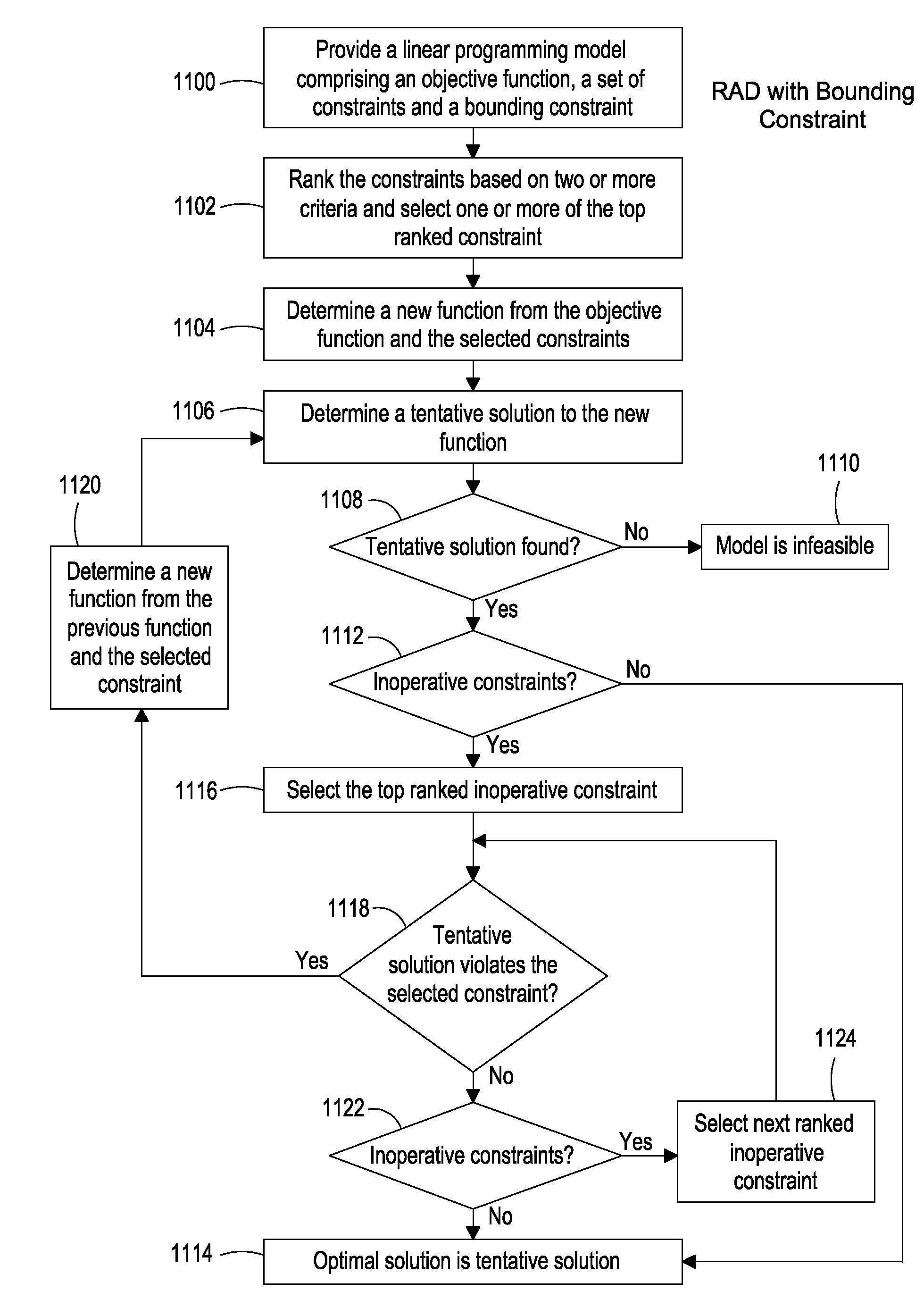
ActiveUS20080134193A1Efficient memory usageGood decisionProgram synchronisationDigital computer detailsObject functionResource allocation
The present invention provides a system, method and apparatus for allocating resources with a linear programming model comprising an objective function and a set of constraints describing feasible allocations of the resources. The method ranks constraints based on a numerical measure derived from criteria selected from at least a first and second group and selects one or more of the top-ranked constraints. A new problem is determined from the model's objective function, the previously selected constraints, and the newly selected constraints, and a tentative resource allocation is determined based on the new problem. Whenever the tentative resource allocation violates a model constraint not in the current problem, one or more of the top-ranked such violated constraints are selected, and the new problem determination and tentative resource allocation steps are repeated. The resources are allocated according to the tentative resource allocation when it does not violate any model constraints.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Decomposition system and method for solving a large-scale semiconductor production Planning problem
A method and system for efficient allocation of limited manufacturing resources over time to meet customer demand. At the enterprise planning level this typically requires determination of a feasible production schedule for an extended supply chain. The method and system utilizes a new and unique type of systematic decomposition based on both product and process considerations. This approach simultaneously reduces the model size (and therefore computation time) and increases modeling flexibility from strictly linear programming based decision making to include more general nonlinear programming characteristics.
Owner:IBM CORP
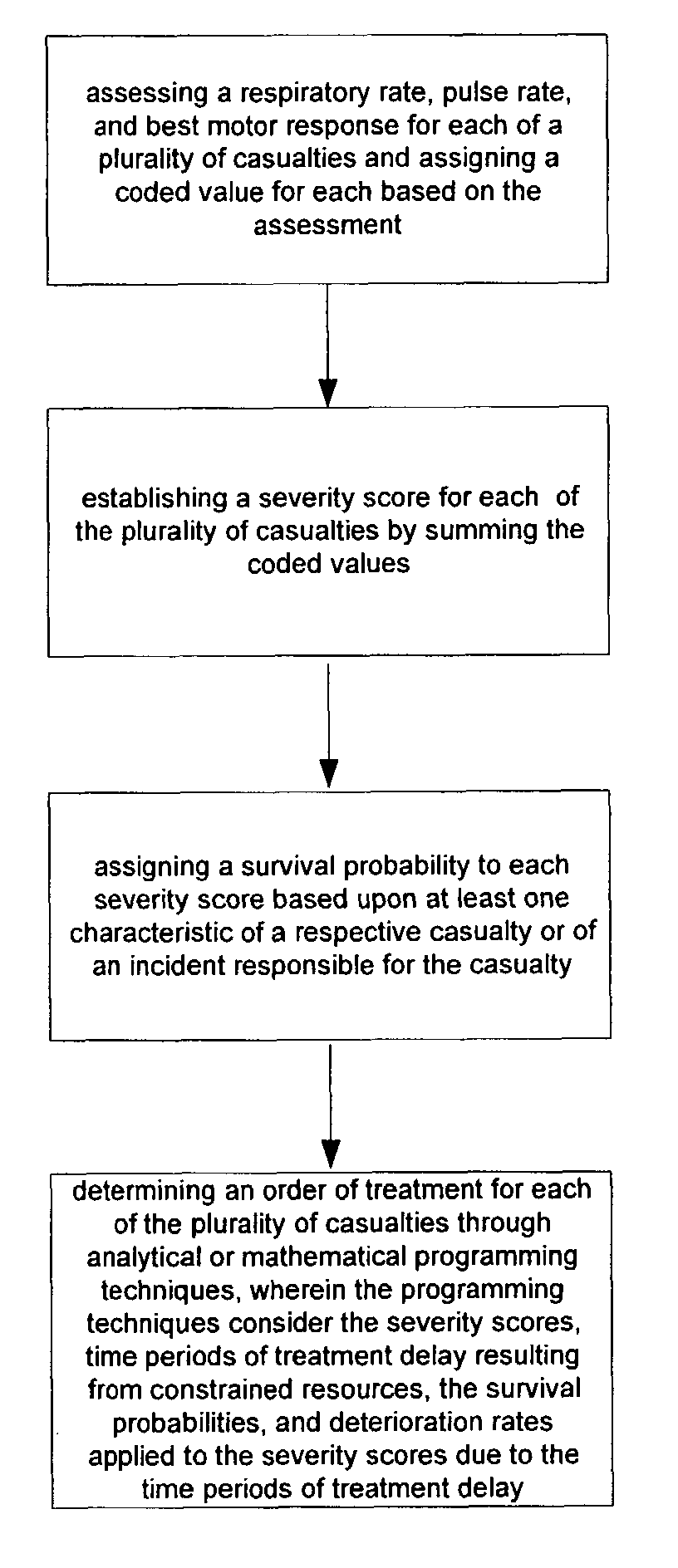
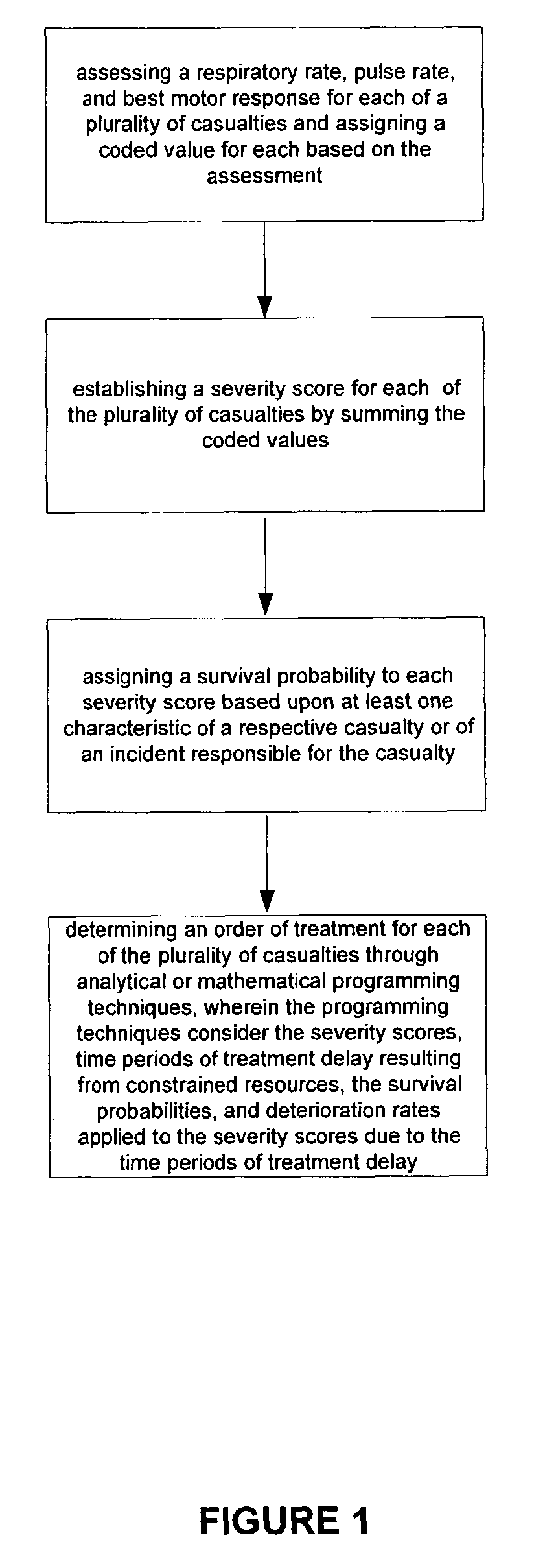
Method and system of mass and multiple casualty triage
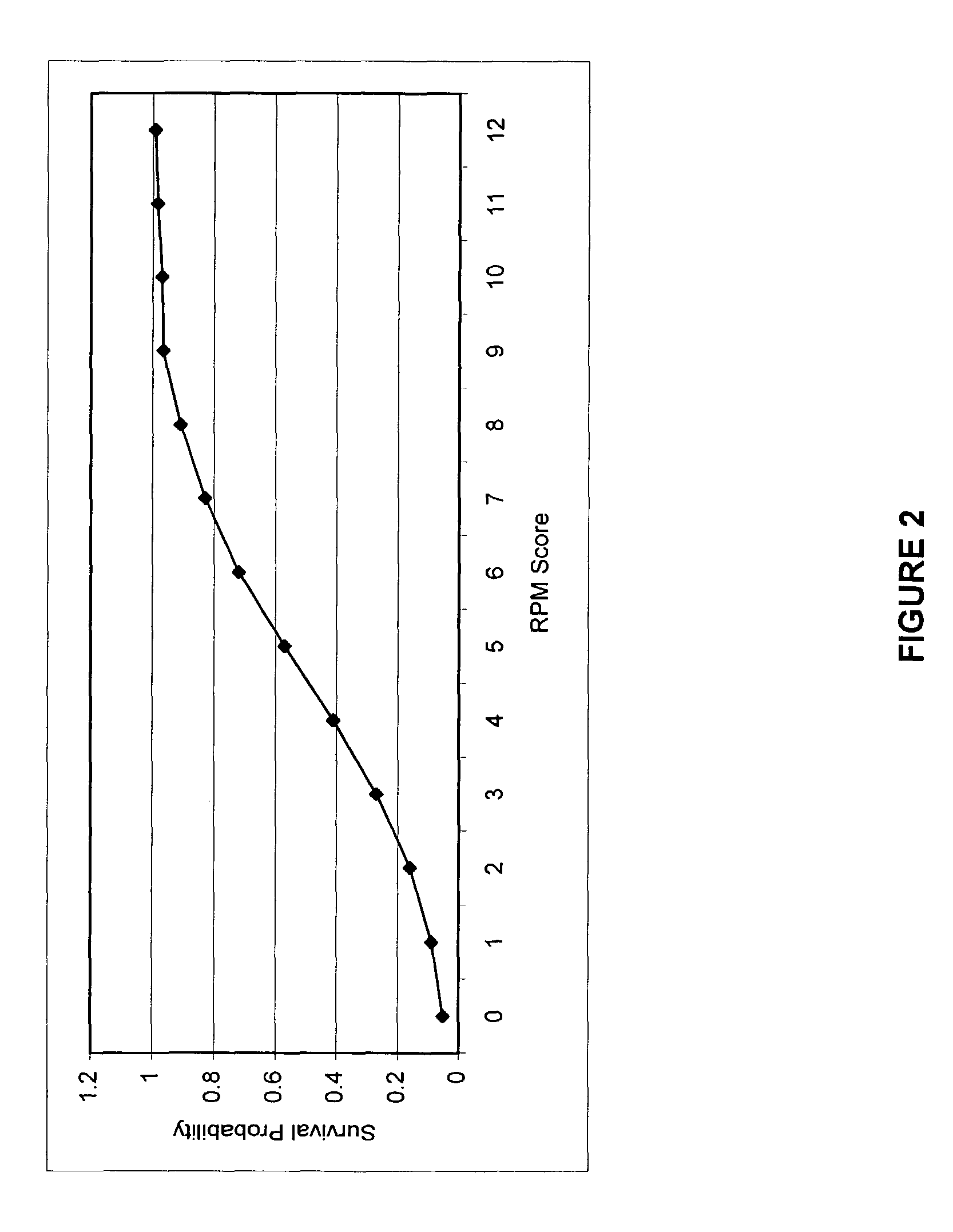
InactiveUS7761309B2Maximize survivabilityMaximize savingMental therapiesDiagnostic recording/measuringTriageDeterioration rate
The present invention is a method and system of triage that assesses a severity score for each casualty, and determines a treatment prioritization plan to maximize the number of survivors. The present invention includes a score-based mathematical algorithm for resource-constrained triage, where an optimal number of survivors is determined through a methodology that can be mathematically modeled and solved, a methodology that considers victim survival probabilities, victim deterioration rates, and resource availability. First, each casualty is assessed and an RPM severity score is assigned based upon a sum of coded values for respiratory rate, pulse rate, and best motor response. Next, treatment priorities are determined from analytical or mathematical techniques, such as dynamic or linear programming, in consideration of survival probabilities associated with each RPM score, and deterioration-with-time rates for each RPM score for victims awaiting transport and treatment and the availability and timing of transport and treatment services.
Owner:THINKSHARP
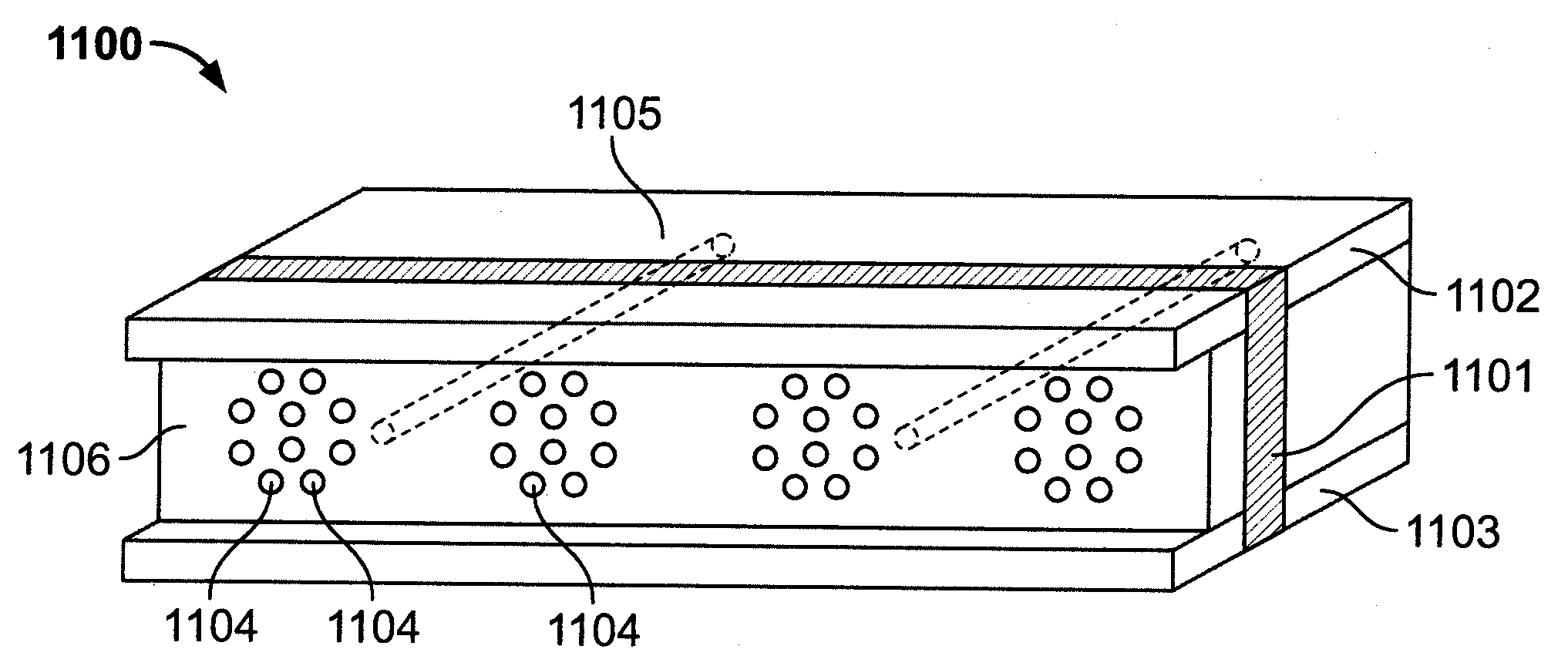
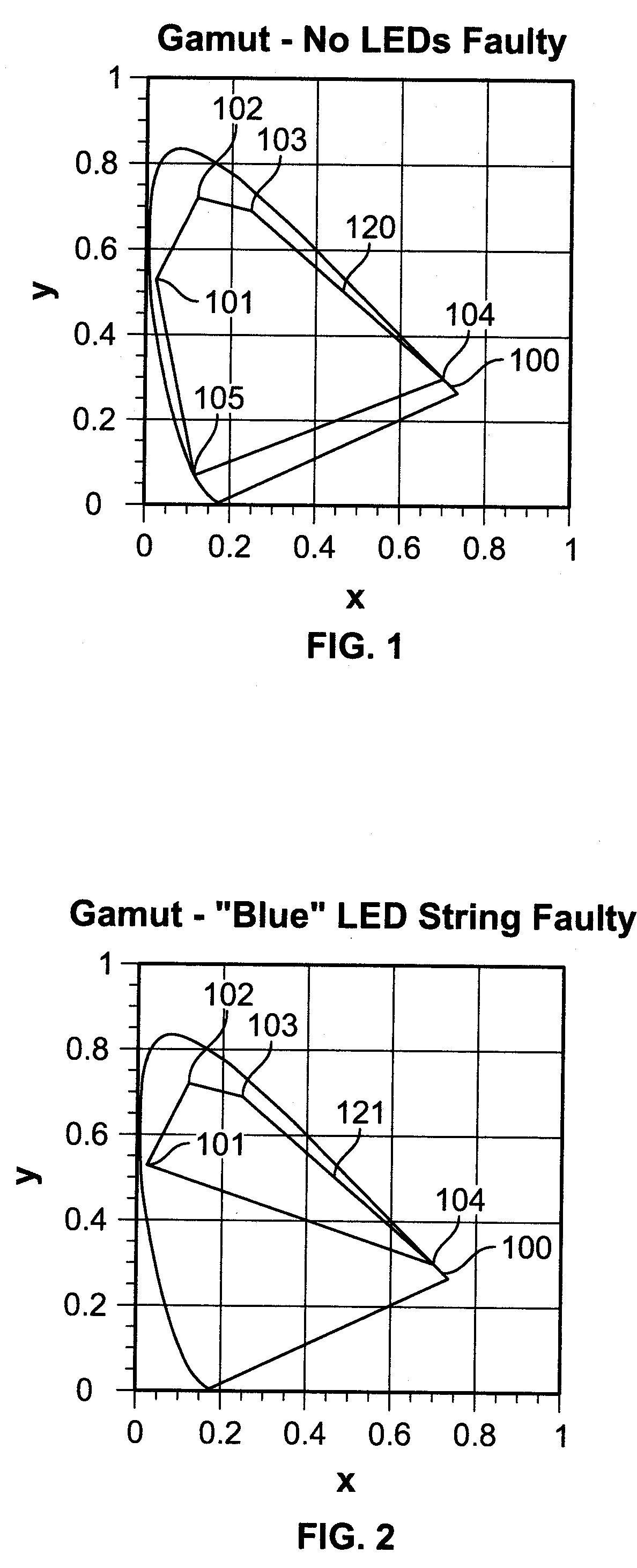
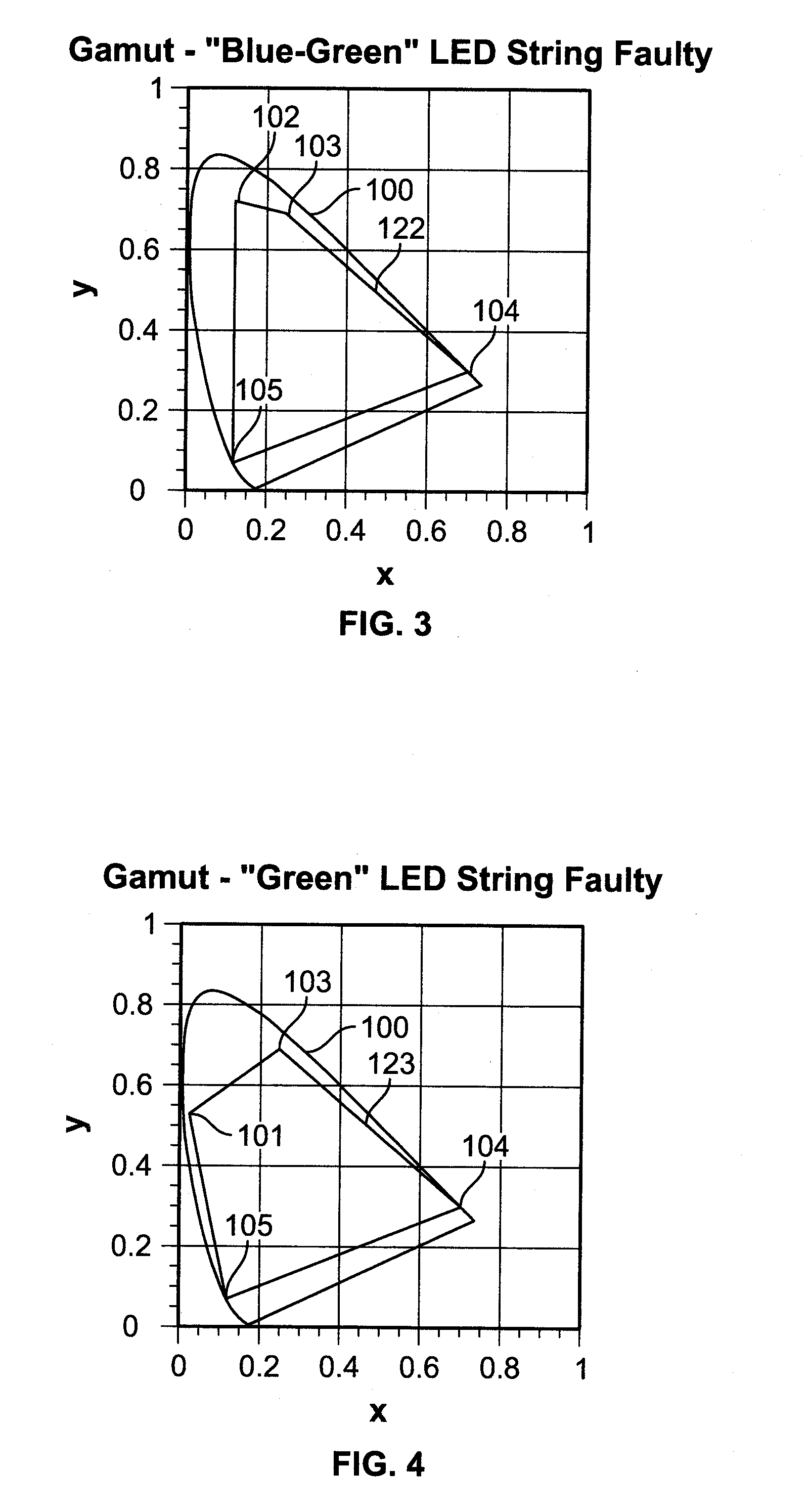
Method for computing drive currents for a plurality of leds in a pixel of a signboard to achieve a desired color at a desired luminous intensity
ActiveUS20090040154A1Improve functionalityImprove reliabilityCathode-ray tube indicatorsDriving currentGamut
A method computes drive currents for LEDs in a pixel of a signboard to achieve a desired color at a desired luminous intensity. This method is particular applicable to a signboard having pixels made up of four (4) or more primary colors. The method selects a number of colors within a color gamut, and for each selected color, the method computes drive currents for the LEDs of each basis color, such that the resulting luminous intensity of the selected color is maximum. Using the computed drive currents, the method then scales the drive currents to achieve the desired luminous intensity in the desired color. The drive currents may be computed, for example, using a constrained maximization technique, such as linear programming. In one embodiment, the drive currents for each selected color are computed subject to the constraint that none of the drive currents is negative, and that their total is less than a predetermined value. In one embodiment, the selected color is expressed in the units of a linear color space.
Owner:LANDMARK SCREENS
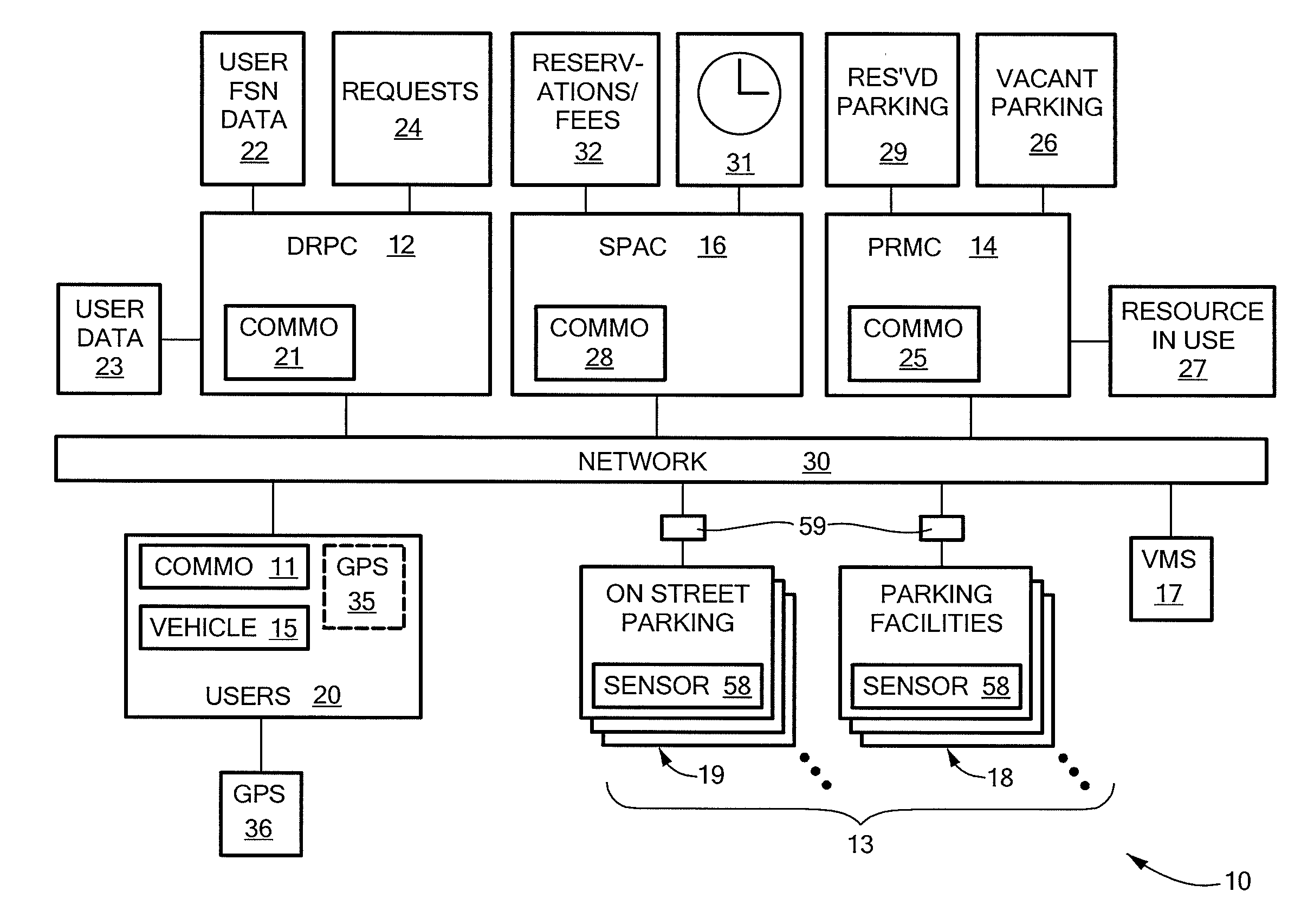
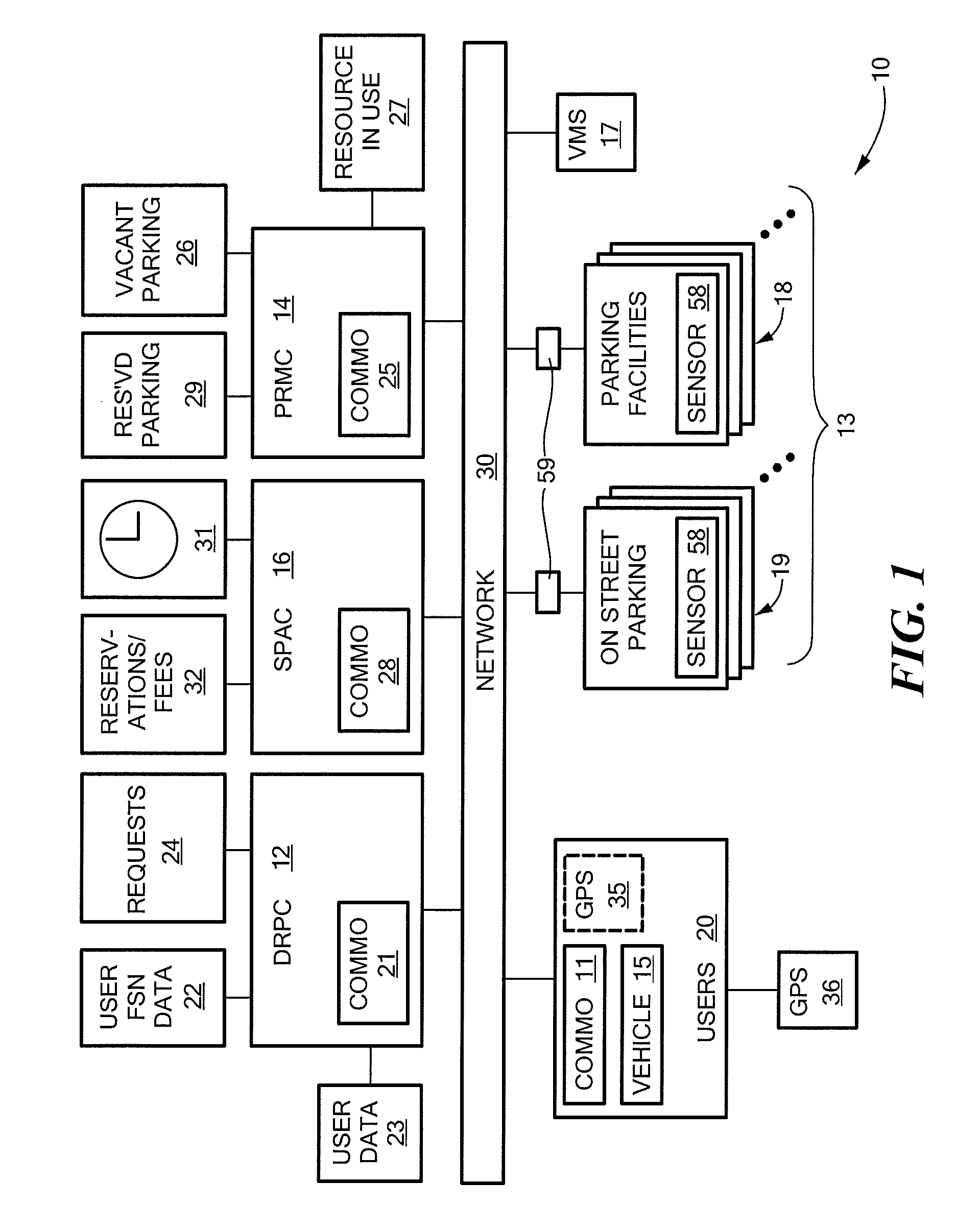
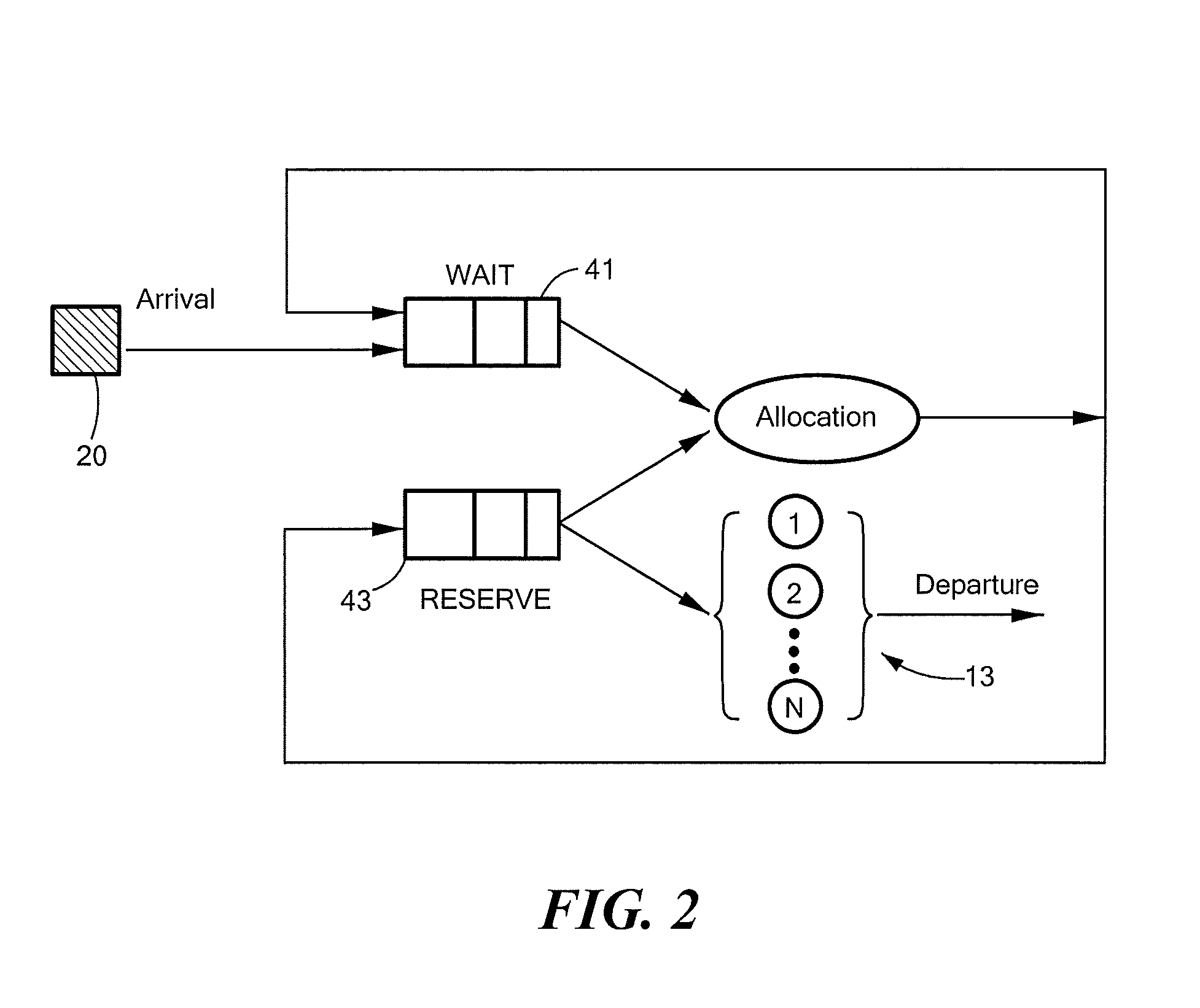
Method and system for dynamic parking allocation in urban settings
InactiveUS20140149153A1Increase opportunitiesReservationsIndication of parksing free spacesDynamic resourceParking space
A “smart parking” system and method for an urban environment based on a dynamic resource allocation approach. The system assigns and reserves an optimal resource (parking space) for a discrete user based on the user's objective function that combines proximity to destination with parking cost, while also ensuring that the overall parking capacity is efficiently utilized. The solution of each Mixed Integer Linear Program (MILP) is an optimal allocation based on current state information and subject to random events such as new user requests or parking spaces becoming available.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
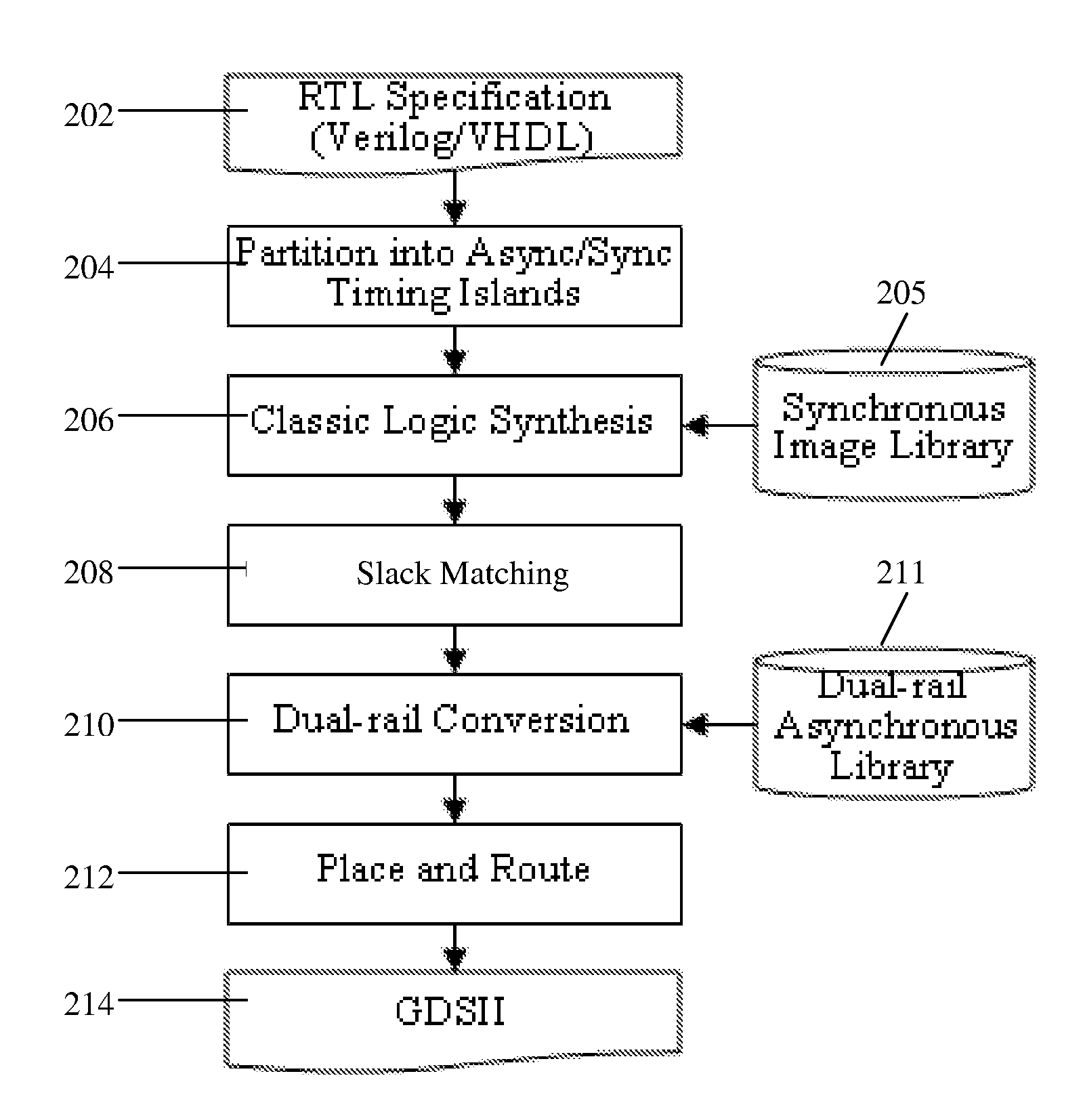
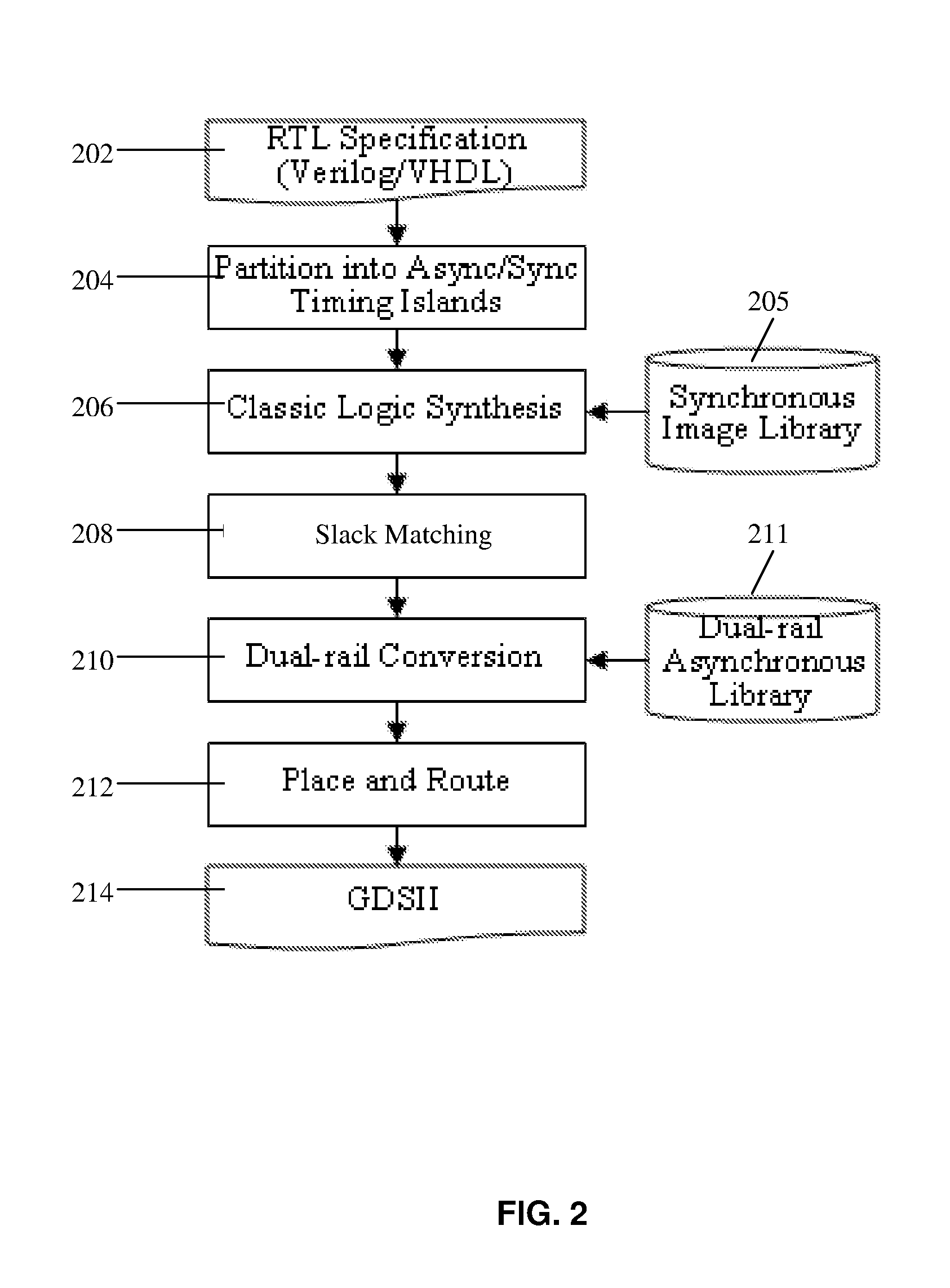
Logic synthesis of multi-level domino asynchronous pipelines
InactiveUS20090217232A1Reduce overheadNo impact on the level of performanceCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationTheoretical computer scienceLogic synthesis
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods and systems for determining resource capabilities for a lean production environment
ActiveUS20050151993A1Improve the environmentImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersProduction rateEngineering
A plurality of printing jobs associated with a printing environment can be initially evaluated. Such a printing environment can be implemented as a print shop or another lean document production environment. A set of minimal resource capacities can then be calculated as a multi-objective optimization using a linear programming (LP) analysis. Alternatively, in a generalized geometrical algorithm, at least one peak-demand production rate associated with the most critical resource can first be estimated, in response to evaluating the plurality of printing jobs. Thereafter, minimal resource capacities of the plurality of resources of the printing environment can be hierarchically calculated based on estimating the previously determined peak-demand production rate of higher priority.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and apparatus for assigning communication nodes to CMTS cards
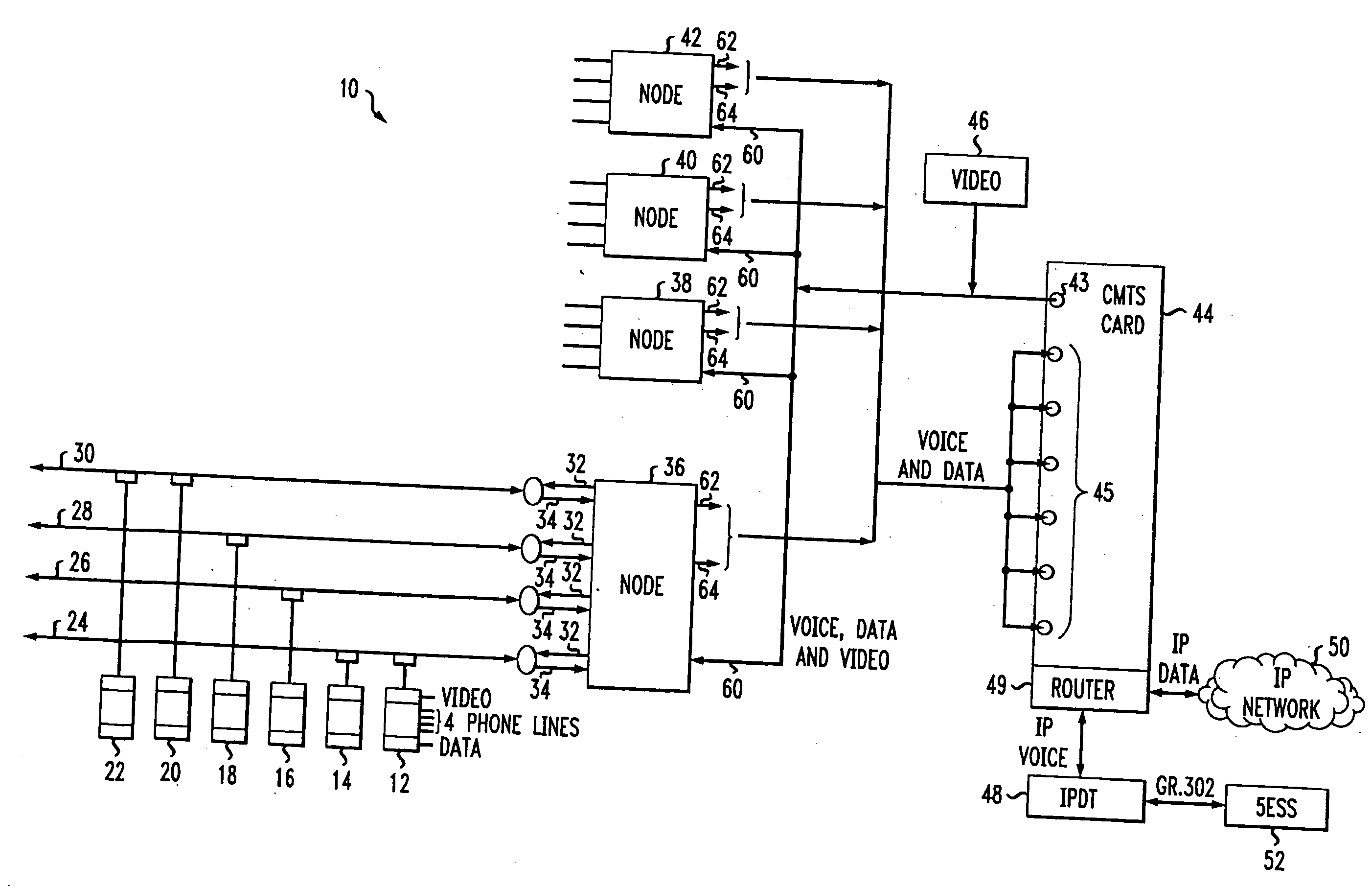
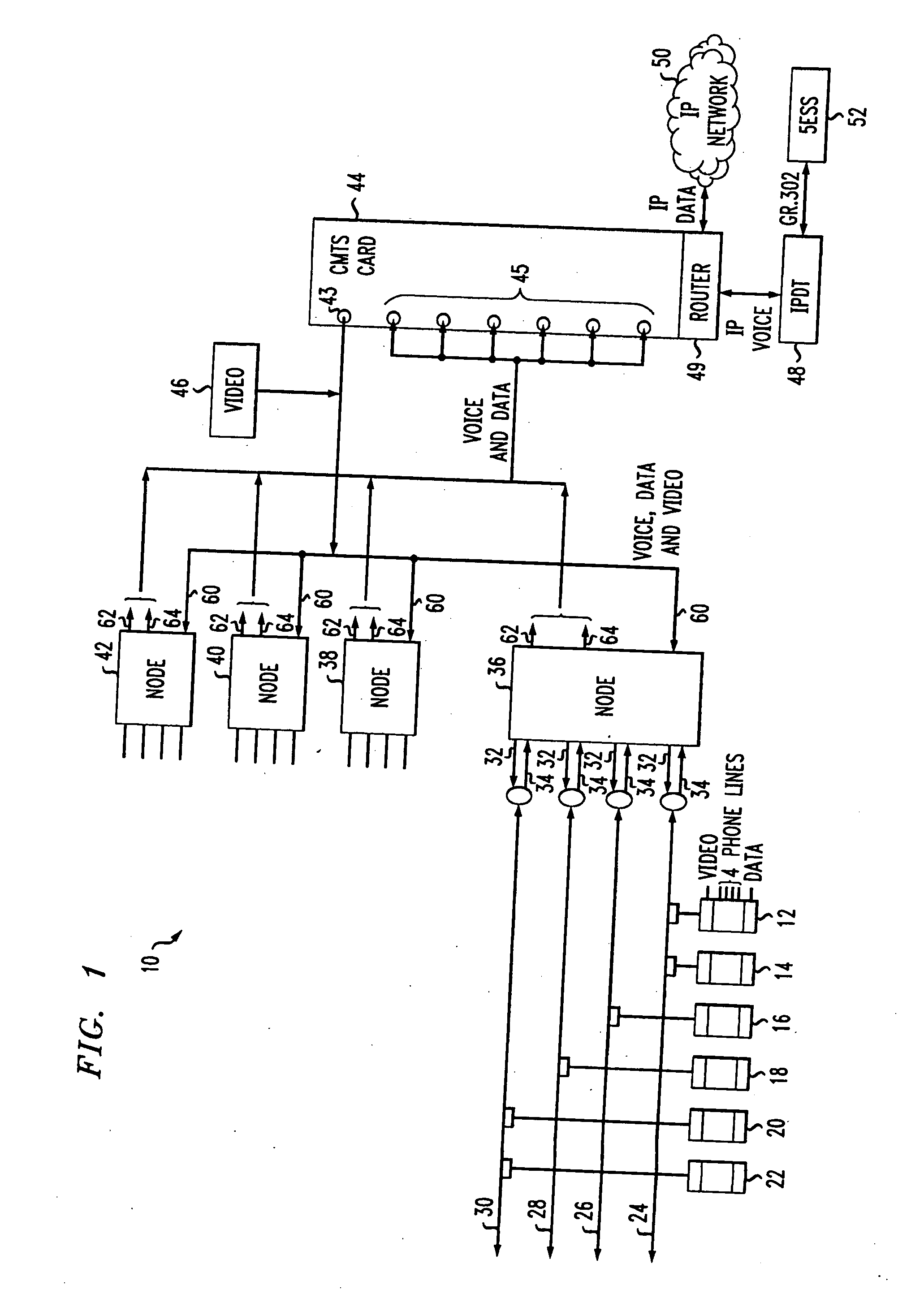
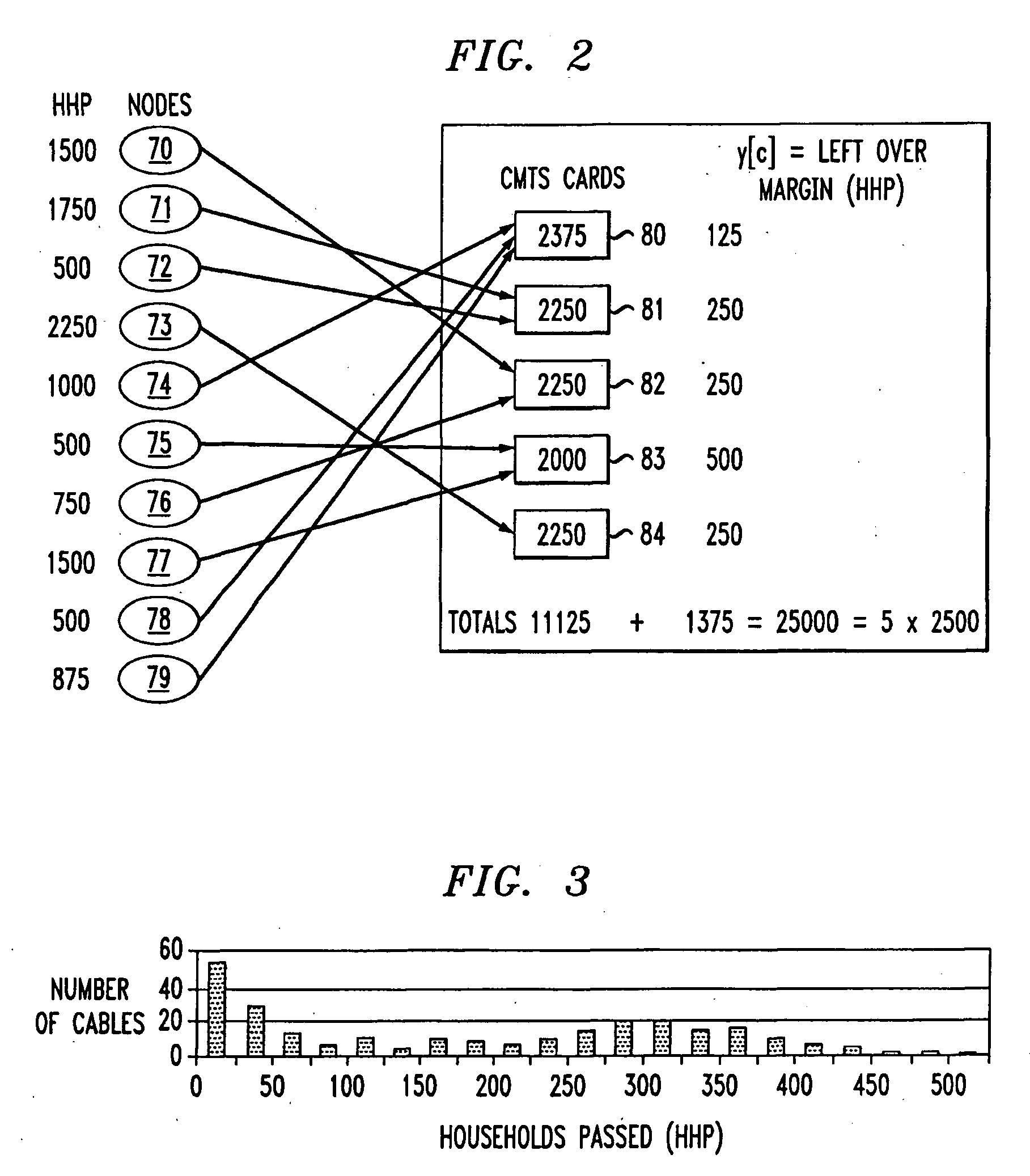
InactiveUS20080159745A1Maximize useFree capacityInterconnection arrangementsBroadband local area networksFiberCommunications system
A method and apparatus for assigning nodes to CMTS cards in a communication system. In order to avoid bottlenecks and to efficiently use resources of the cards in a hybrid fiber-coax architecture, the nodes are assigned to the cards using linear programming techniques so as to distribute the traffic load and minimize the unused capacity of each card. The number of households, nodes and cards are determined and used to establish a model which is then implemented using linear programming techniques to determine an optimal solution.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
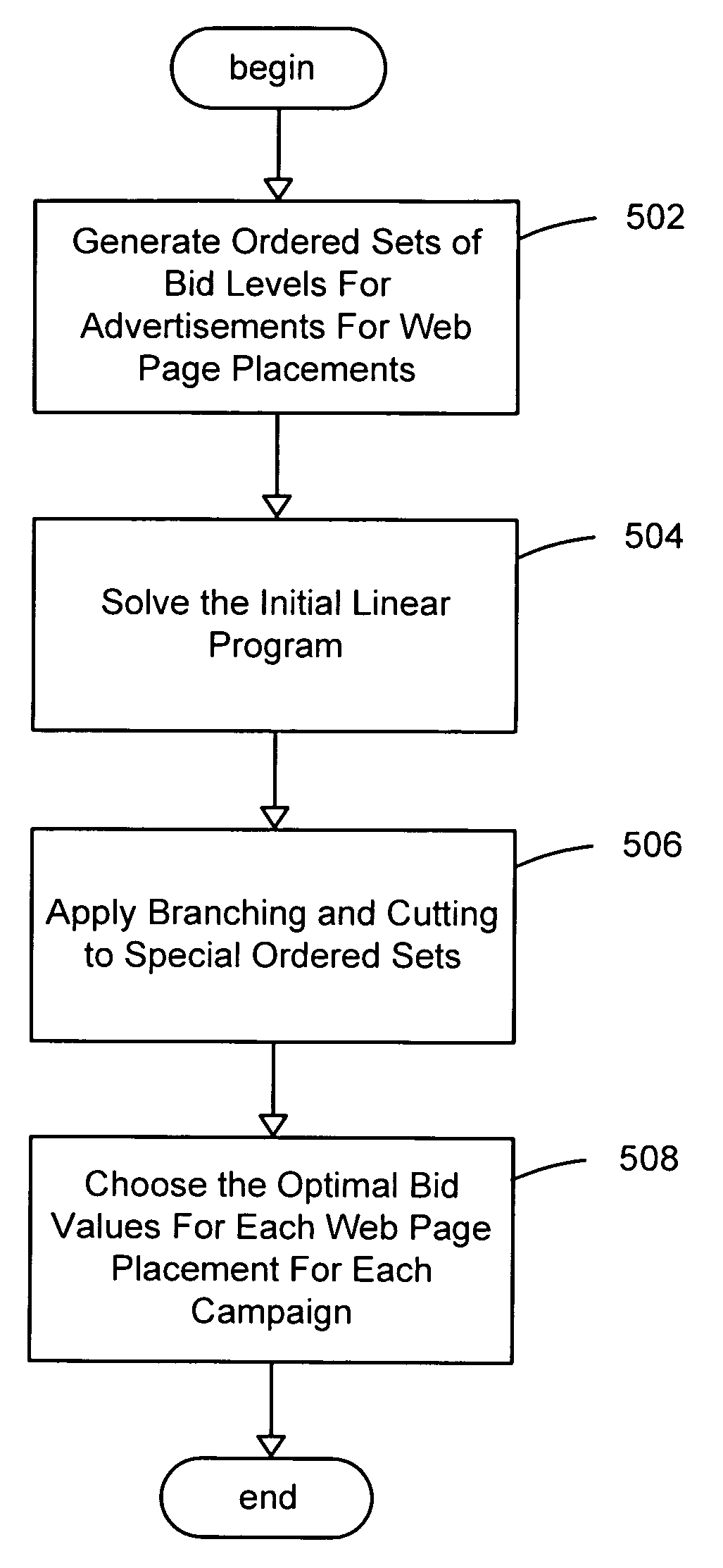
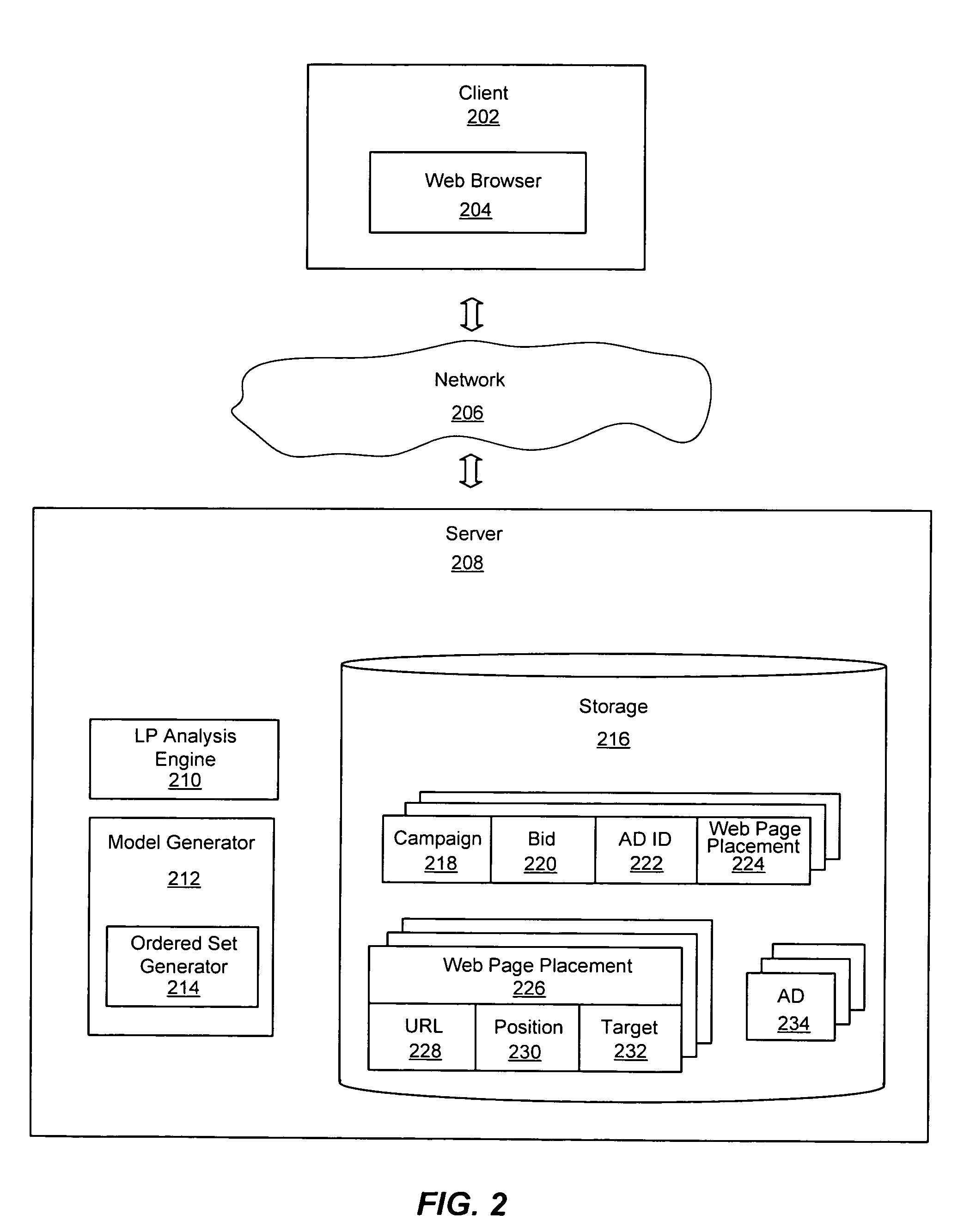
System and method for optimizing online advertisement auctions by applying linear programming using special ordered sets
InactiveUS20080065479A1Expand coverageAdvertisementsForecastingSpecial ordered setOnline advertising
An improved system and method for optimizing online advertising auctions is provided by applying linear programming using special ordered sets. A linear programming model using special ordered sets of bids may first be created offline for the web page placements of advertisements for advertising campaigns. An expected number of impressions of advertisements for alternative bid levels may be determined for web page placements for advertising campaigns for a time period. Ordered sets of bid levels may be generated for web page placements of advertising campaigns and linear programming may be applied to determine optimal bid values for web page placements of advertising campaigns. Branching and cutting techniques may also be applied to the special ordered sets of bid values to rapidly obtain an optimal bid value for each special ordered set. Advertising campaigns may be updated with the optimal bid values for bidding in an online advertising auction.
Owner:OATH INC
Method based on linear programming for locating near-field targets and system thereof
InactiveCN101644774AIncrease profitReduce energy consumptionAcoustic wave reradiationResource utilizationTarget signal
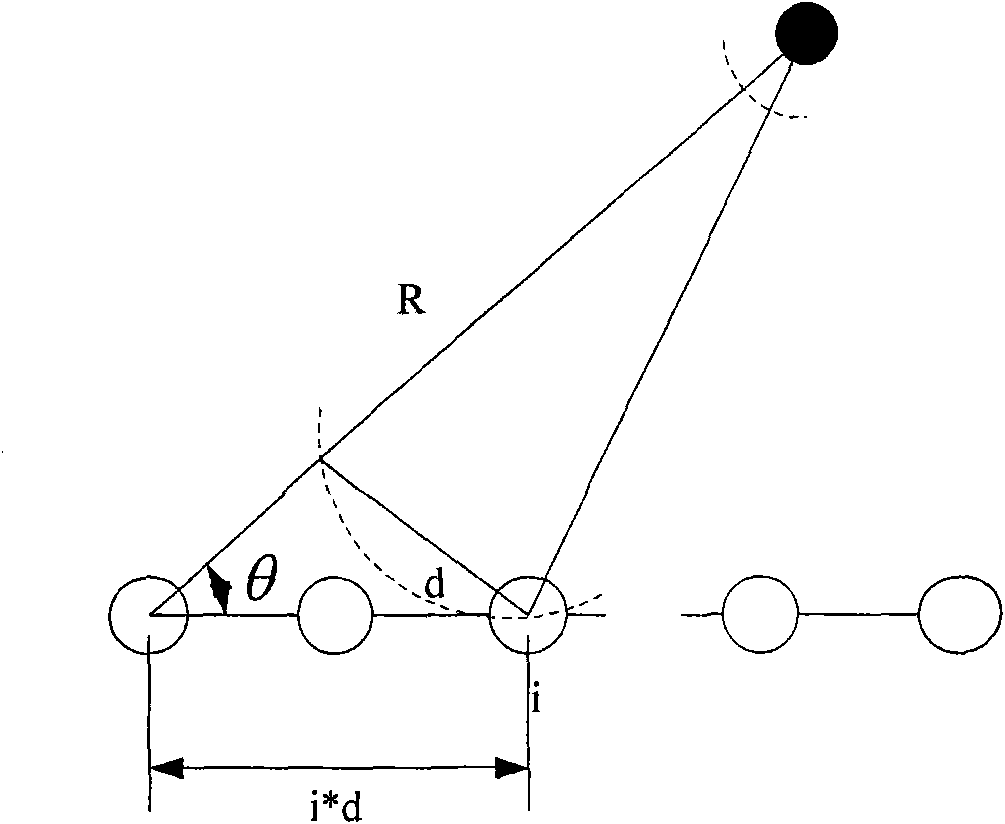
The invention provides a method based on linear programming for locating near-field targets and a system thereof, particularly a method for locating near-field targets on the basis of the compressivesensing theory. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a reference array element under the condition that the signal form is unknown, allowing the reference array element to work at the normal sampling frequency, and the other array elements to work at far below the Nyquist sampling frequency; taking the output signal of the reference array element as the reference target signal, to acquire the sample data of all the array elements; generating a time-delay table and a sparse basis array; generating a random mapping array and obtaining a coefficient array; obtaining a sparse vectorby linear programming solution; and acquiring the location information of the near-field target from the predetermined location-distance collection on the basis of the acquired estimation results ofthe sparse vector. According to the invention, the sensor does not need to work beyond the Nyquist sampling frequency, thereby greatly reducing the sampling rate, reducing the operating energy consumption of the sensor and improving the resource utilization rate of the system; and the method has no limits to the target bandwidth, so that the method is applicable to the target location of both narrowband and wideband, and the method is further applicable to non-Gaussian target location.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
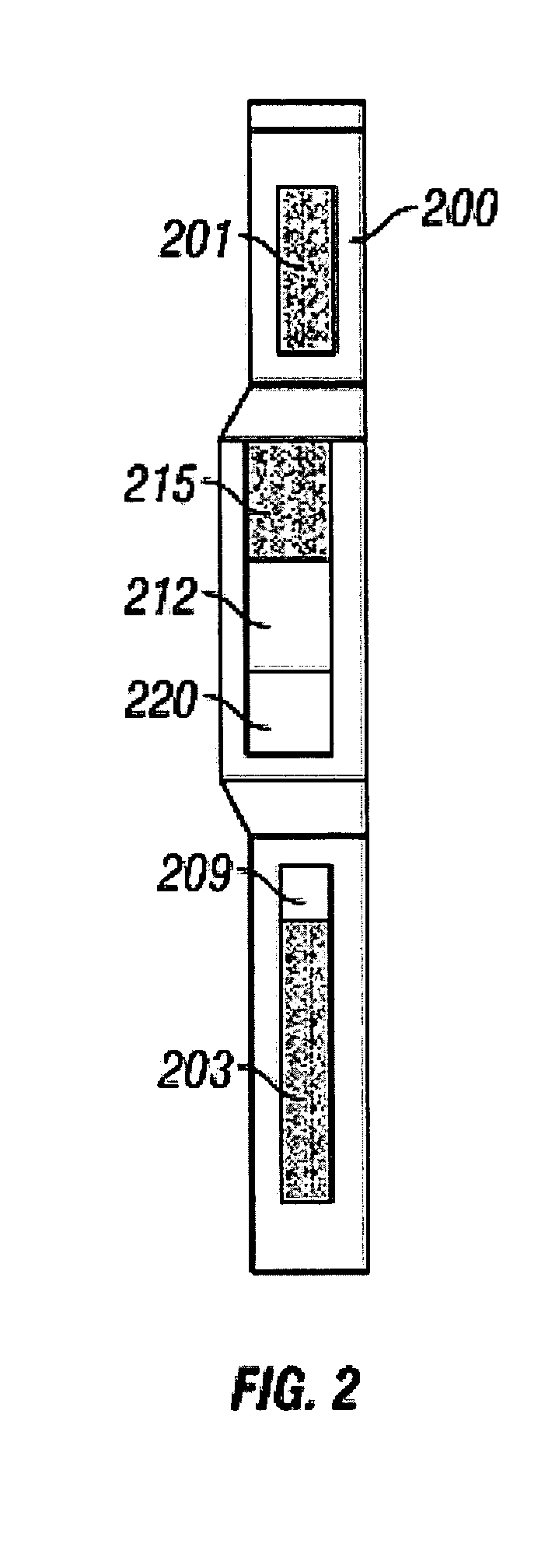
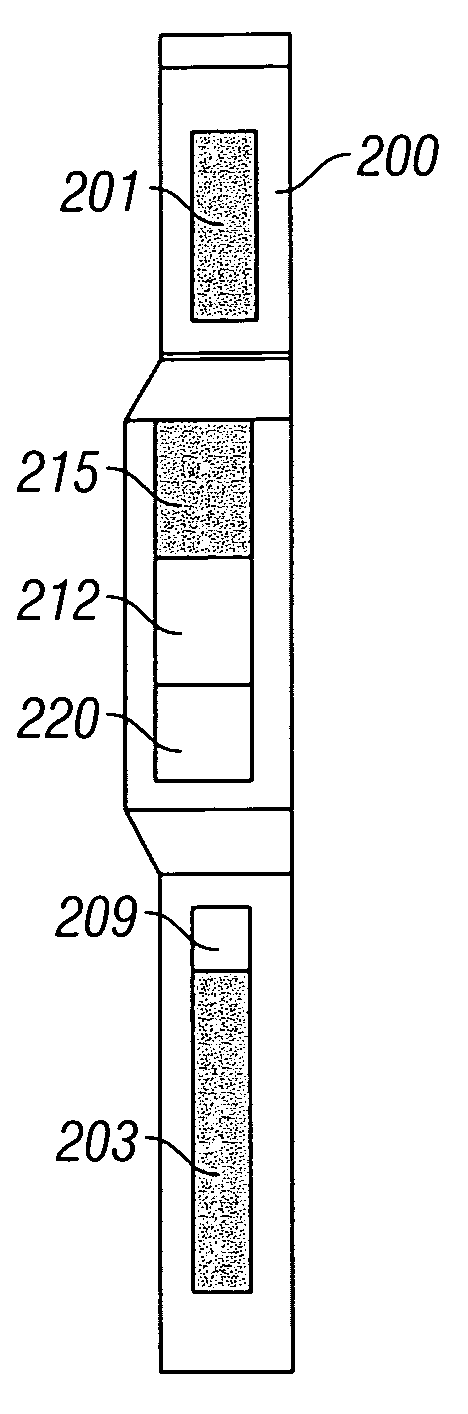
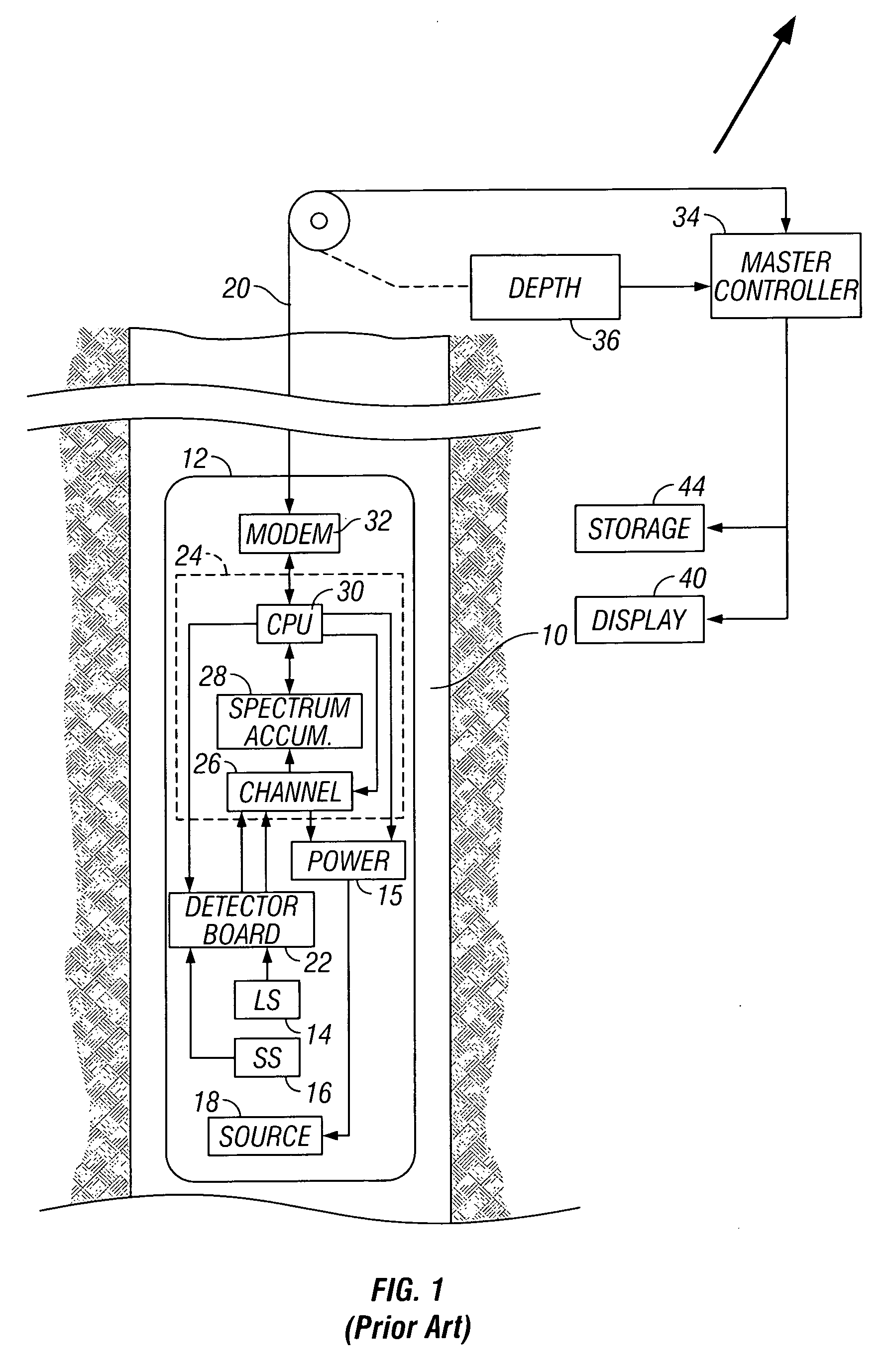
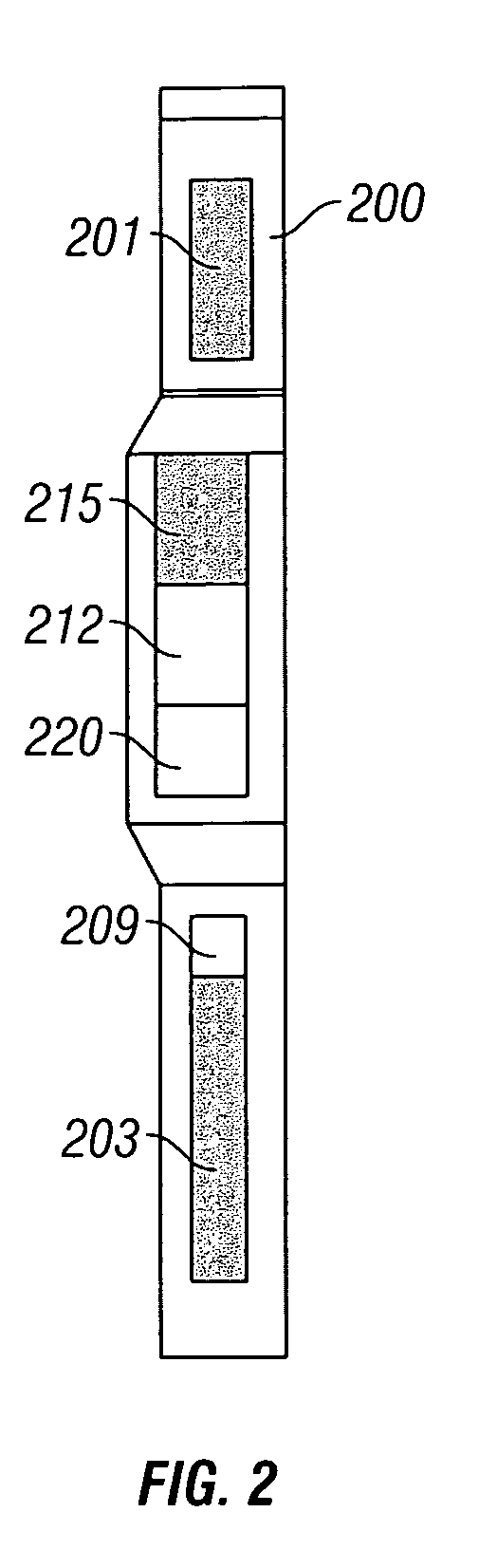
Method and apparatus for determining aluminum concentration in earth formations
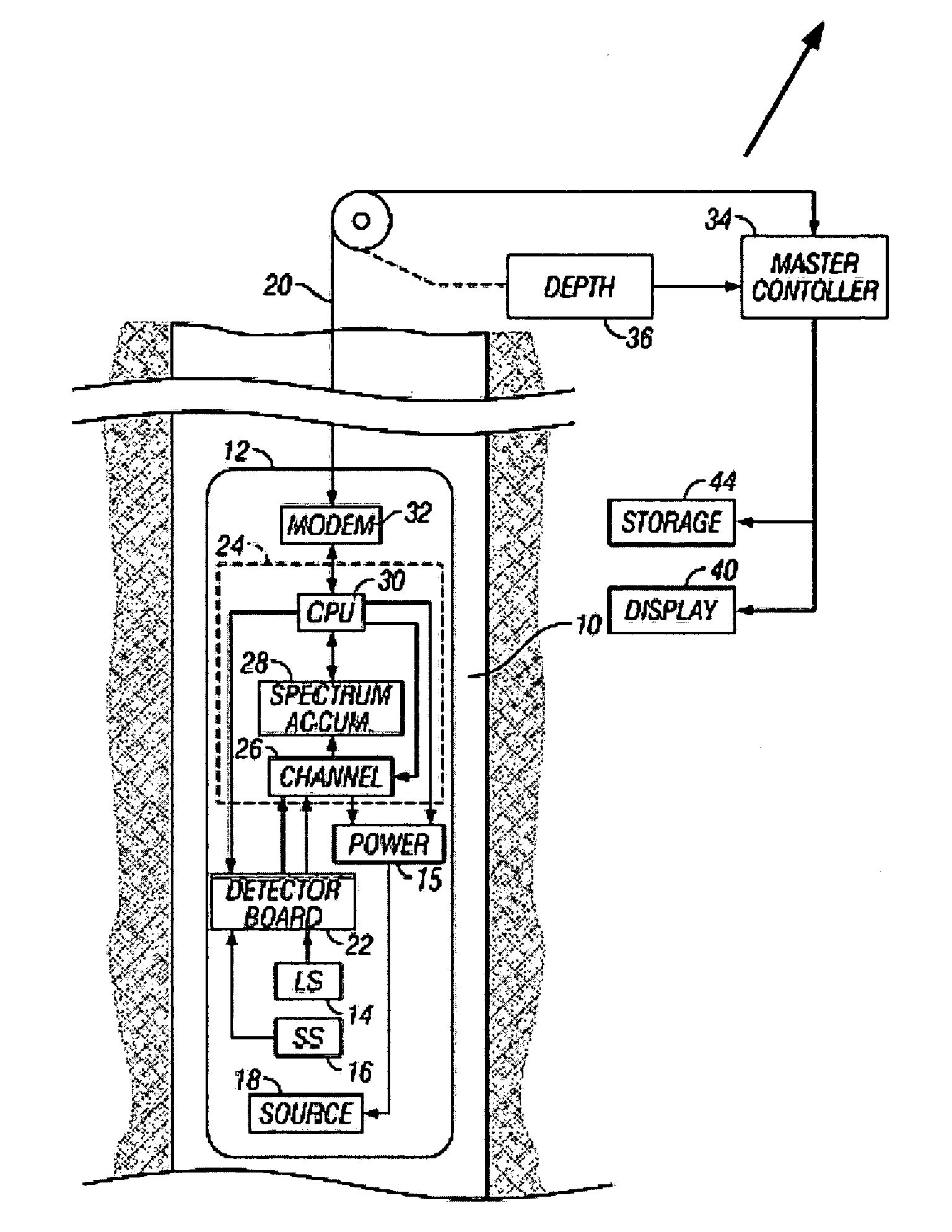
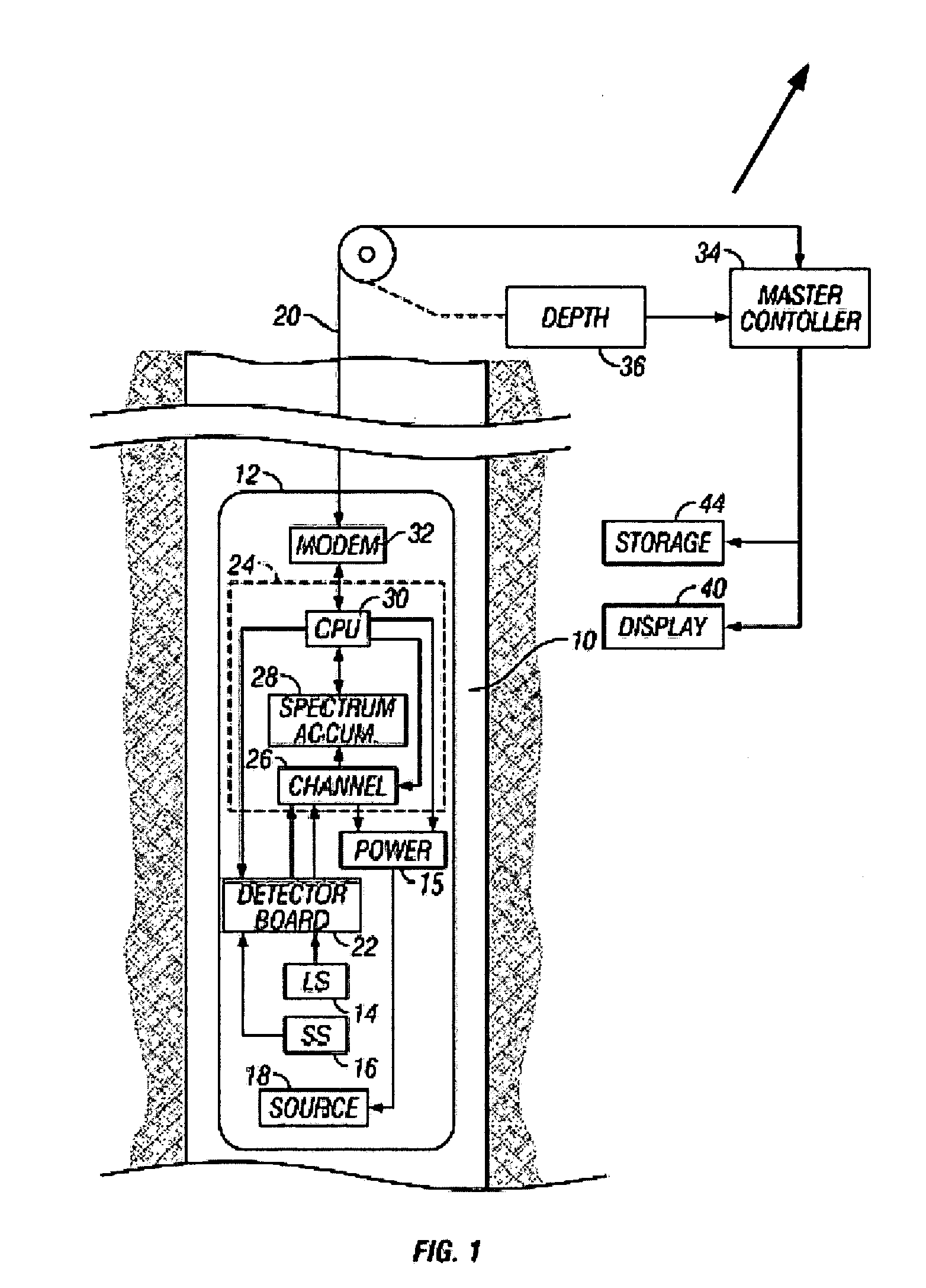
InactiveUS20060033023A1Earth material testingNuclear radiation detectionWell loggingElemental analysis
Elemental analysis of an earth formation (including Aluminum) is obtained using measurements from a gamma ray logging tool. The inelastic spectrum of Aluminum is determined from measurements made in a water tank. From the elemental analysis, an estimate of the mineralogy of the formation is made treating the problem as one of Linear Programming (maximizing an objective function subject to equality and / or inequality constraints.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Elemental gamma ray signature instrument
InactiveUS7205535B2Earth material testingNuclear radiation detectionElemental analysisLinear programming
Elemental analysis of an earth formation is obtained using measurements from a gamma ray logging tool. From the elemental analysis, an estimate of the mineralogy of the formation is made treating the problem as one of Linear Programming (maximizing an objective function subject to equality and / or inequality constraints).
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
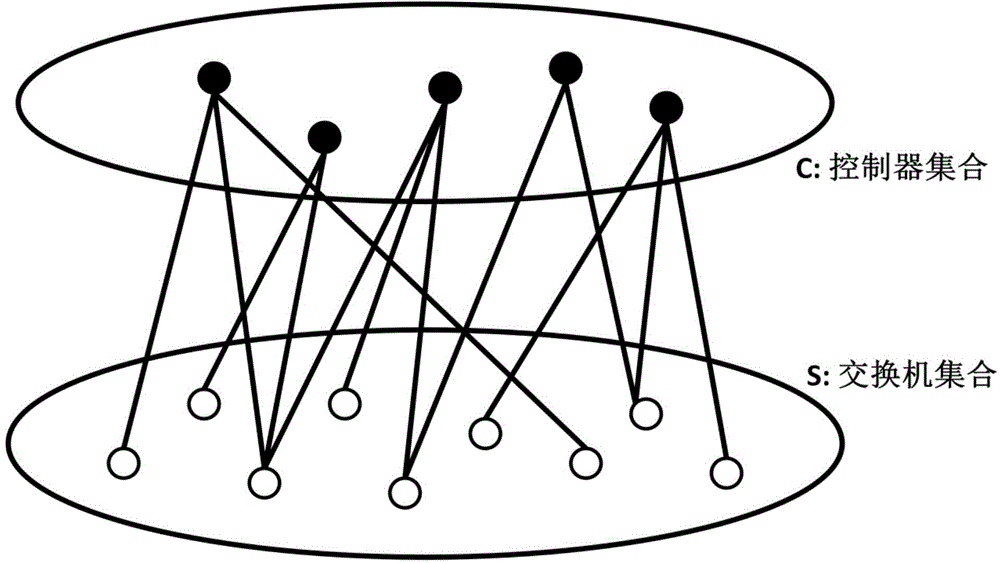
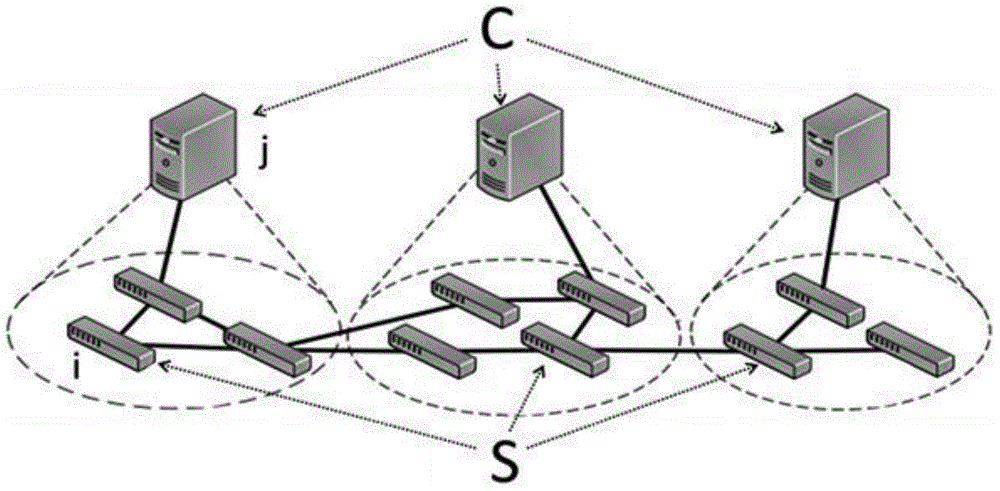
SDN multi-controller deployment method for reducing management load overhead
The invention discloses an SDN multi-controller deployment novel method for reducing management load overhead, belonging to the technical field of the software defined network (SDN). The method is characterized in that the management load of a software defined network (SDN) controller is used as a decision variable, and a mathematical model about controller management load is constructed. An original SDN network multi-controller deployment problem is abstracted to be a graph theory problem, the graph theory problem is converted into an integer linear programming problem through establishing the mathematical model, and an NP difficult problem is solved by using an approximate algorithm. According to the method, in the process of constructing the mathematical model of the multi-controller deployment problem, the network performance and the management load of the SDN controller are creatively taken into consideration, effective deployment schemes can be provided for different SDN networks, the reasonable selection and effective deployment of the number of multiple controllers are realized, and the normal and effective operation of the SDN network in the condition of the satisfaction of certain network performance and minimum cost are ensured.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
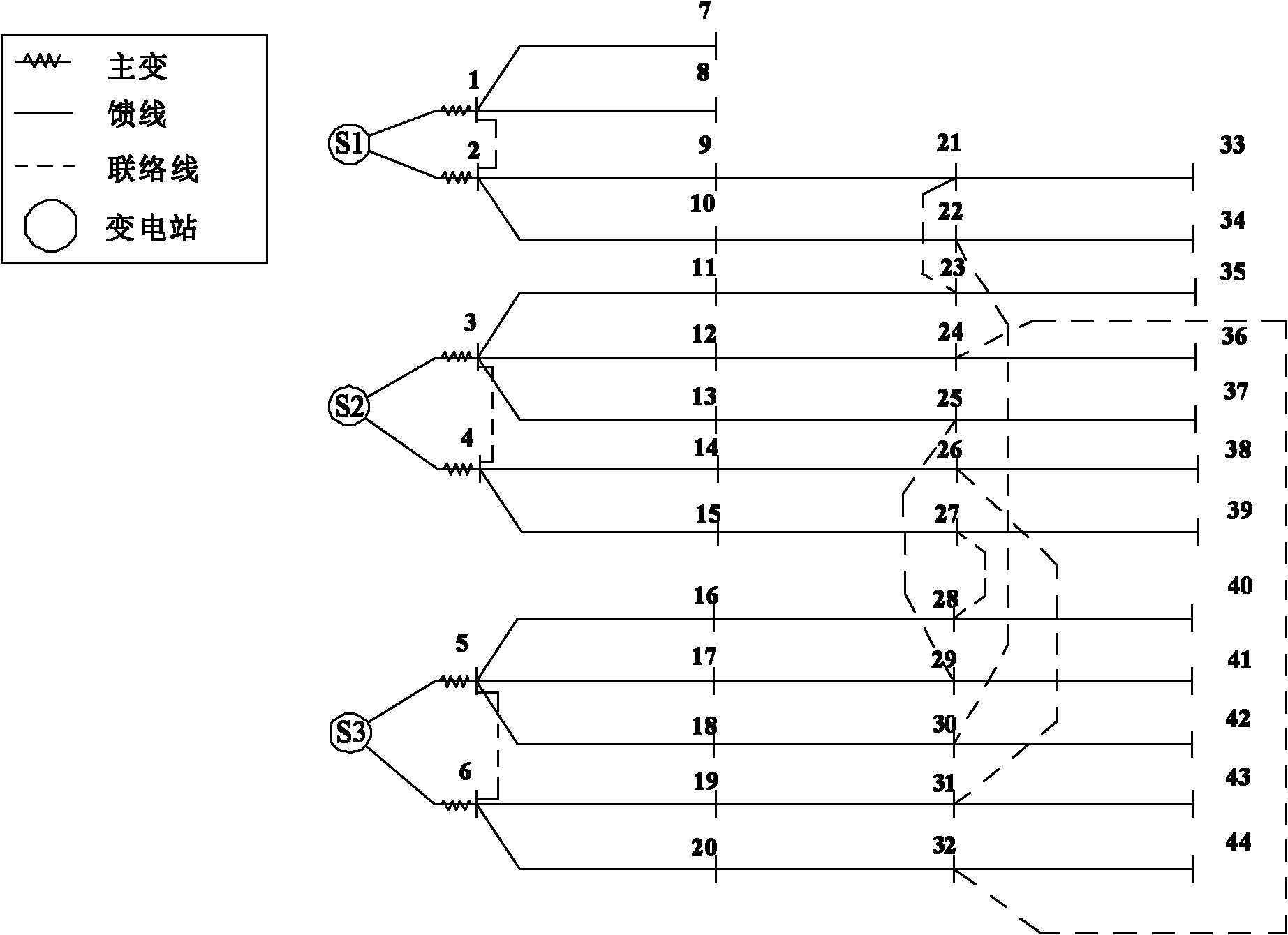
Method for accurately calculating maximum power supply capacity of medium voltage distribution network
ActiveCN102025153ACalculation method of accurate power supply capacityThe calculation result is accurateAc network circuit arrangementsMathematical modelDistribution system
The invention discloses a method for accurately calculating the maximum power supply capacity of a medium voltage distribution network, which relates to the field of calculating the index power supply capacity of a distribution network of a power distribution system. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a mathematical model taking the maximum power supply capacity TSC of the power distribution network as an objective function; converting the calculation into a problem of linear programming; and calculating the objective function by using linear programming software, wherein the calculated objective function is the accurate maximum power supply capacity under the existing 'N-1' restriction. The calculation result is more accurate, so the method can accurately calculate the power supply capacity of the power distribution network, and provides a new quantification, theory and evaluation tool for the power distribution network.
Owner:TIANDAQIUSHI ELECTRIC POWER HIGH TECH CO LTD
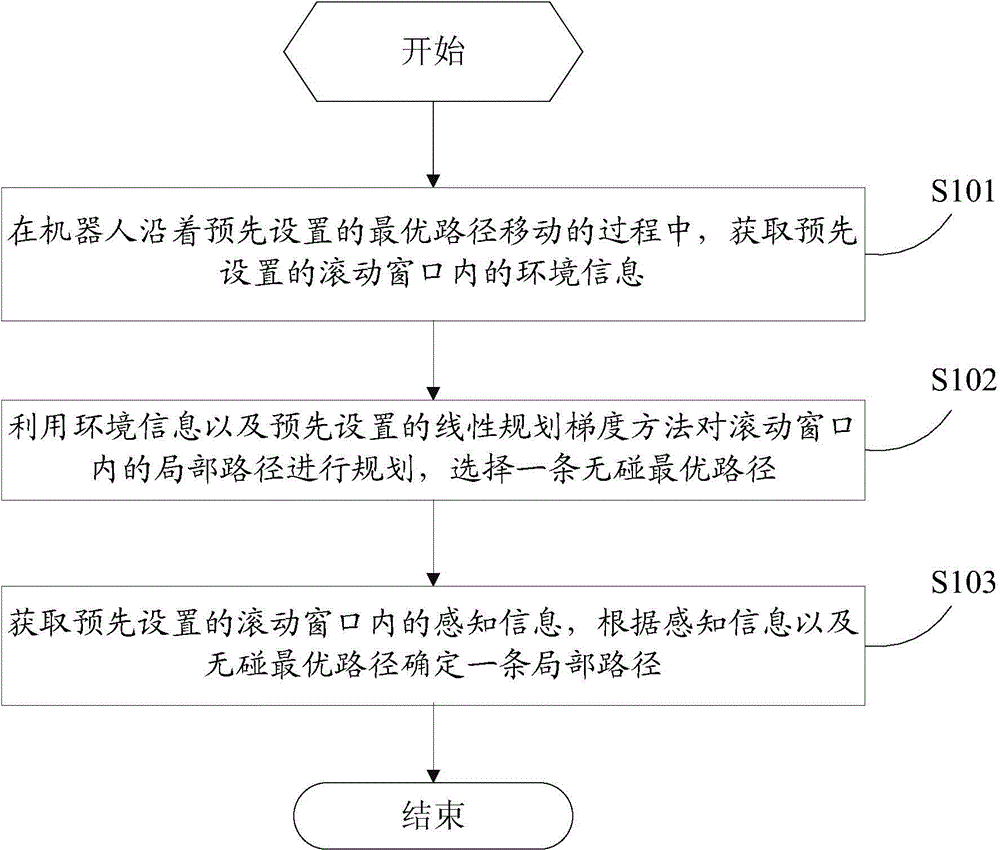
Method and device for route programming in dynamic unknown environment
InactiveCN103605368ASmall amount of calculationImprove efficiencyPosition/course control in two dimensionsComputation processPlanning approach
The invention provides a method and device for route programming in a dynamic unknown environment. In the moving process of a robot along a preset optimal route, a collision-free optimal route is obtained through calculation by using a linear programming gradient method and through environment information acquired by a preset rolling window, and then partial routes are obtained through calculation carried out on the obtained collision-free optimal route and acquired perceptual information in the rolling window. In the calculation process, the rolling window is used for reducing calculation amount and improving efficiency, and the linear programming gradient method is applied to ensure global convergence and to prevent from being caught in the problems of local minimum and oscillation.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG INST OF IND TECH SOOCHOW UNIV
Overlay network layered multicast resource optimum allocation method for scalable video stream
InactiveCN101547347APulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationAdaptive matchingMulticast communication
The invention relates to an overlay network layered multicast optimal resource allocation method for a scalable video stream, and provides a new measurement standard for the multicast performance, namely layer extensity which is used for measuring end-to-end time delay of video layers during data distribution aiming at layered multicast communication of the scalable video stream in the overlay network. In order to realize the overall minimization of the layer extensity, the method carries out the combined optimization on the network code of relay nodes, the receiving end driven flow control, and multi-path route strategy, and adopts a linear programming method to establish a layered multicast resource optimum allocation model for the overlay network. On one hand, the method adaptively matches the interlayer dependency of the scalable video code; on the other hand, the method allows a receiving node to decide and regulate the required video quality of own accord. In addition, the invention also provides a distributed heuristic algorithm which has low complexity, approaches the globally optimal solution and is applied to the construction of a scalable video flow distribution network.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Camera layout optimization method for large-scale scene monitoring
InactiveCN104469322ASimplify design stepsShorten design timeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVideo monitoringMathematical model
The invention discloses a camera layout optimization method for large-scale scene monitoring, and relates to the technical field of video monitoring. The method includes the following steps of conducting modeling of a monitoring scene, conducting modeling of monitoring requirements, and obtaining the optimal camera layout scheme through the optimization algorithm. According to the scheme, mathematical models can be established for the layout optimization problem of a whole camera, the layout optimization problem of multiple cameras is converted into the linear programming problem, and the optimal camera layout scheme meeting the monitoring requirement can be automatically achieved under the condition that multiple constraint conditions exist. The design steps can be simplified while the design effect is ensured, the design time is saved, and the scientific basis is provided for the camera layout optimization for the large-scale scene monitoring.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Optimal evaluation method of wind power capacity based on sced
ActiveCN102280878AGuaranteed uptimeWind power capacity is reasonableAc network circuit arrangementsElectricityWind power penetration
The invention discloses a wind power penetration optimization evaluation method based on SCED. The method comprises the following steps: based on a physical model and an economic model of an evaluation power grid and under a condition of knowing a turn on / turn off scheme of a routine unit, establishing a safety constraint economy scheduling model; taking a wind power station in an area as a concrete evaluation target, setting an optimization object of the safety constraint economy scheduling model to be a maximized total wind power output and acquiring an optimization model of wind power penetration evaluation; linearizing non-linear factors in the evaluation model; solving the evaluation model by adopting a linear programming method, calculating an active curve of the accepted wind powerin the research area, acquiring a wind power penetration ability of the power grid and acquiring a maximized grid-connected generation capacity of the each wind power station in an evaluation period.By using the method of the invention, carrying out precontrol to a risk of accessing large scale wind power into the power grid can be easily achieved, and security of power grid operation can be raised.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com