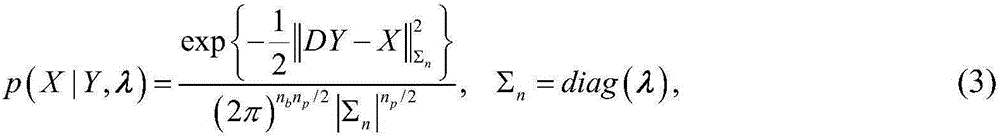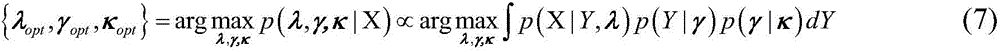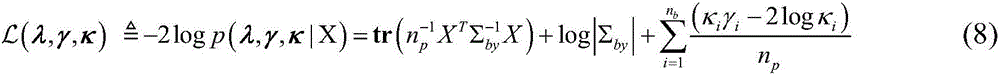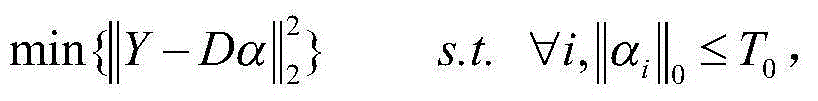Patents
Literature
297 results about "Sparse vector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A vector with sparse storage, intended for very large vectors where most of the cells are zero. The sparse vector is not thread safe. The enumerator will include all values, even if they are zero. The enumerator will include all values, even if they are zero.
Device and method for fast block-matching motion estimation in video encoders
InactiveUS20060245497A1Reduce complexityQuick estimateColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorVideo sequence
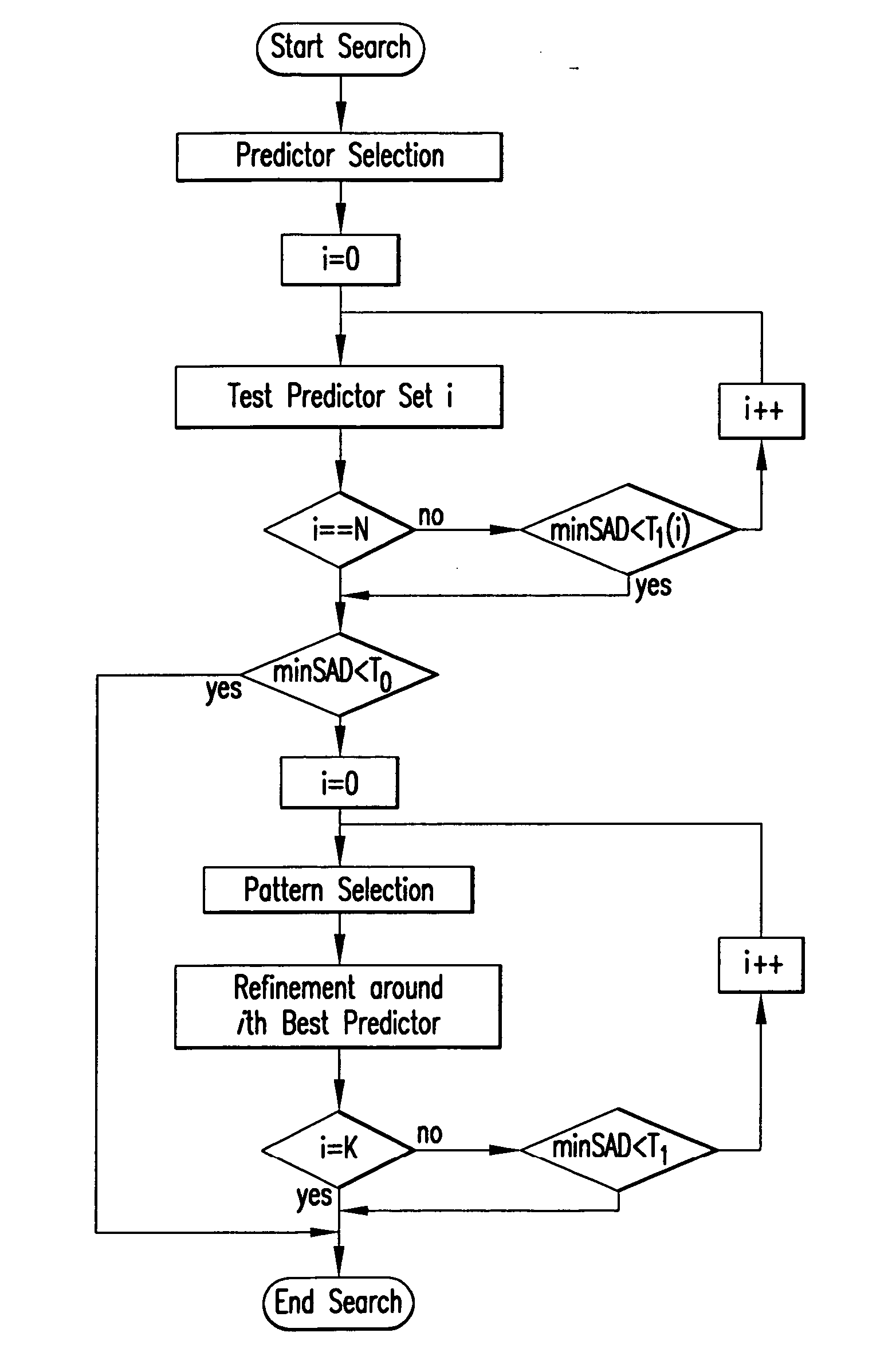
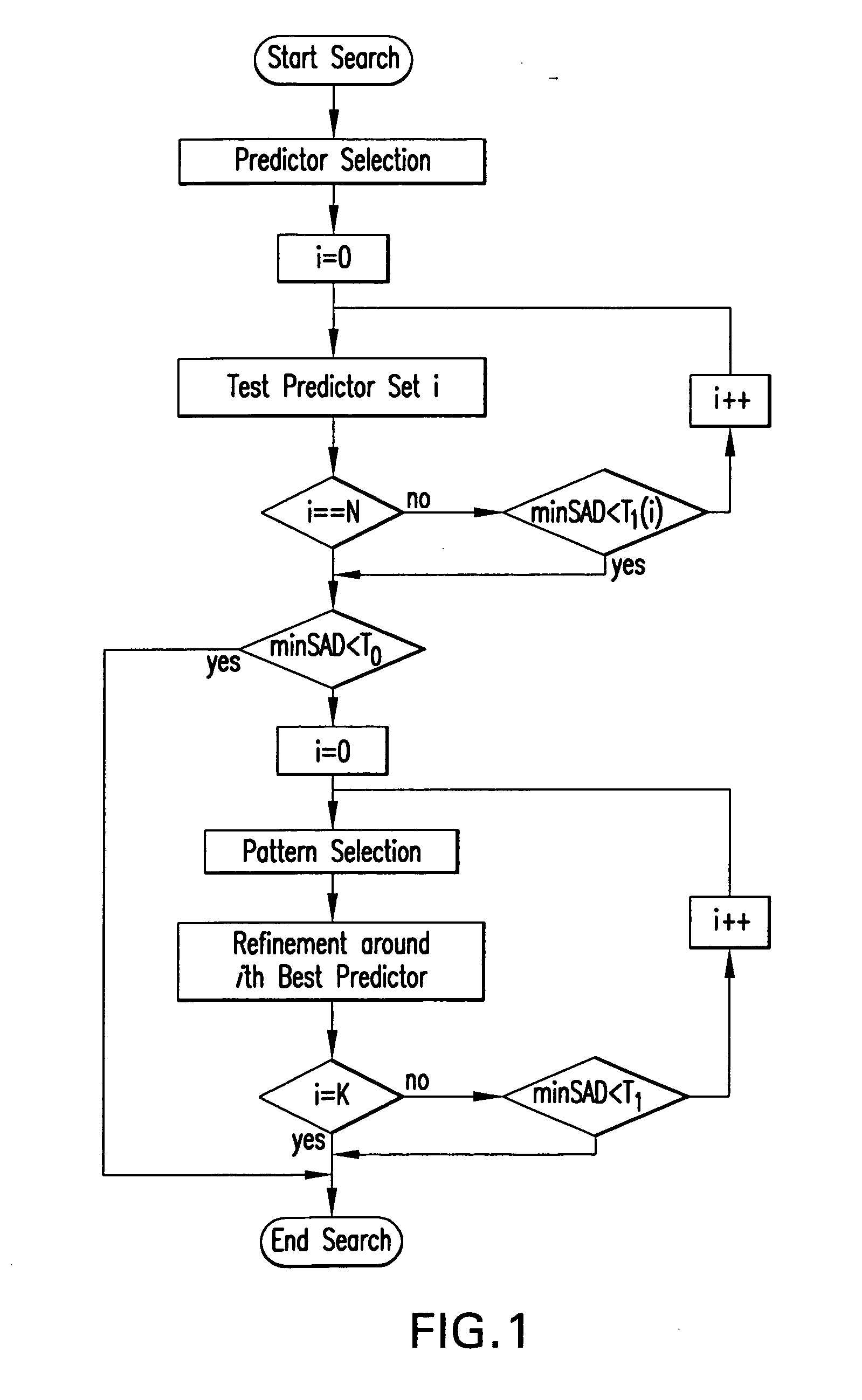
Motion estimation is the science of predicting the current frame in a video sequence from the past frame (or frames), by slicing it into rectangular blocks of pixels, and matching these to past such blocks. The displacement in the spatial position of the block in the current frame with respect to the past frame is called the motion vector. This method of temporally decorrelating the video sequence by finding the best matching blocks from past reference frames—motion estimation—makes up about 80% or more of the computation in a video encoder. That is, it is enormously expensive, and methods do so that are efficient are in high demand. Thus the field of motion estimation within video coding is rich in the breadth and diversity of approaches that have been put forward. Yet it is often the simplest methods that are the most effective. So it is in this case. While it is well-known that a full search over all possible positions within a fixed window is an optimal method in terms of performance, it is generally prohibitive in computation. In this patent disclosure, we define an efficient, new method of searching only a very sparse subset of possible displacement positions (or motion vectors) among all possible ones, to see if we can get a good enough match, and terminate early. This set of sparse subset of motion vectors is preselected, using a priori knowledge and extensive testing on video sequences, so that these “predictors” for the motion vector are essentially magic. The art of this method is the preselection of excellent sparse subsets of vectors, the smart thresholds for acceptance or rejection, and even in the order of the testing prior to decision.
Owner:FASTVDO
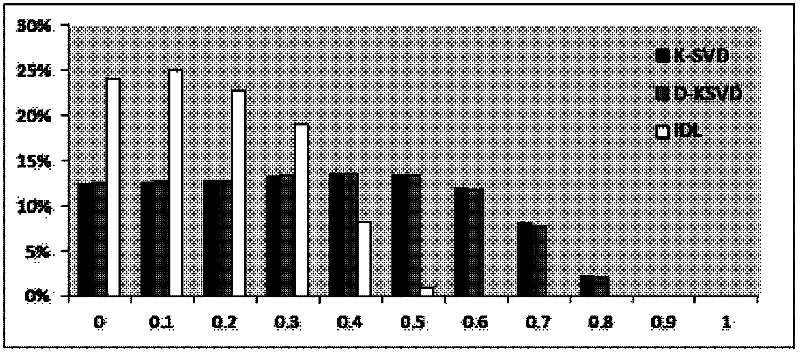
Face recognition method based on dictionary learning models
InactiveCN102609681AImprove the accuracy of face recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningPattern recognition
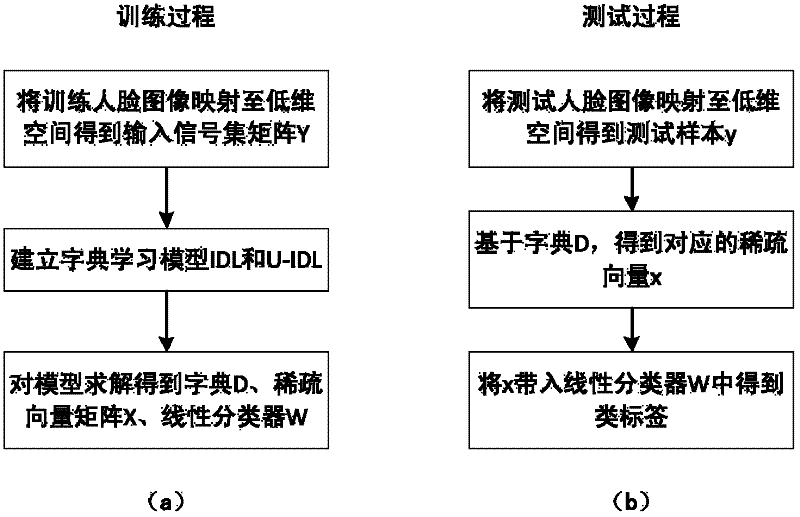
The invention discloses a face recognition method based on dictionary learning models. The method comprises the following steps of: mapping trained and tested face images to a low-dimension space to acquire a training signal set matrix; establishing the dictionary learning models which comprise an irrelevant dictionary learning (IDL) model and an unconstrained irrelevant dictionary learning (U-IDL) model; inputting the training signal set matrix into the IDL and U-IDL models, and solving the models to acquire an irrelevant dictionary and a linear classifier; acquiring a corresponding sparse vector of each picture belonging to a test sample based on the dictionary acquired in the last step by using a sparse expression algorithm; and inputting the sparse vectors into the linear classifier to acquire category labels of test sample pictures, wherein the result expressed by the category labels is used as the face recognition result. The invention provides the new models and the new method for dictionary learning problems in sparse expression, and the models and the method can be applied to mode identification and image classification problem under common conditions; and particularly, aiming at face recognition application, the dictionary learning method can achieve relatively high face recognition accuracy.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
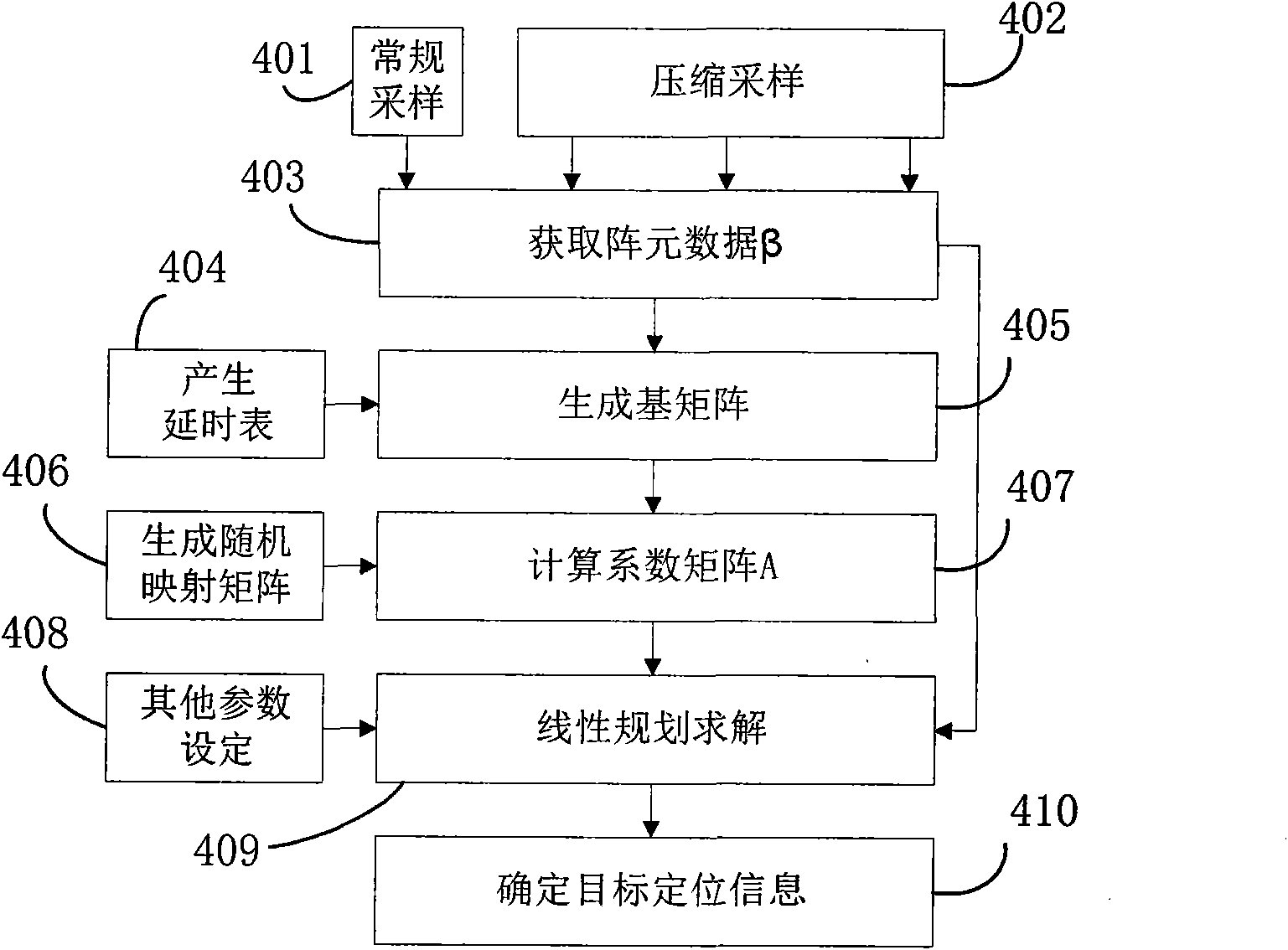
Method based on linear programming for locating near-field targets and system thereof
InactiveCN101644774AIncrease profitReduce energy consumptionAcoustic wave reradiationResource utilizationTarget signal
The invention provides a method based on linear programming for locating near-field targets and a system thereof, particularly a method for locating near-field targets on the basis of the compressivesensing theory. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a reference array element under the condition that the signal form is unknown, allowing the reference array element to work at the normal sampling frequency, and the other array elements to work at far below the Nyquist sampling frequency; taking the output signal of the reference array element as the reference target signal, to acquire the sample data of all the array elements; generating a time-delay table and a sparse basis array; generating a random mapping array and obtaining a coefficient array; obtaining a sparse vectorby linear programming solution; and acquiring the location information of the near-field target from the predetermined location-distance collection on the basis of the acquired estimation results ofthe sparse vector. According to the invention, the sensor does not need to work beyond the Nyquist sampling frequency, thereby greatly reducing the sampling rate, reducing the operating energy consumption of the sensor and improving the resource utilization rate of the system; and the method has no limits to the target bandwidth, so that the method is applicable to the target location of both narrowband and wideband, and the method is further applicable to non-Gaussian target location.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Demographic and media preference prediction using media content data analysis
ActiveUS20140195544A1Low accuracyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData setPopulation statistics
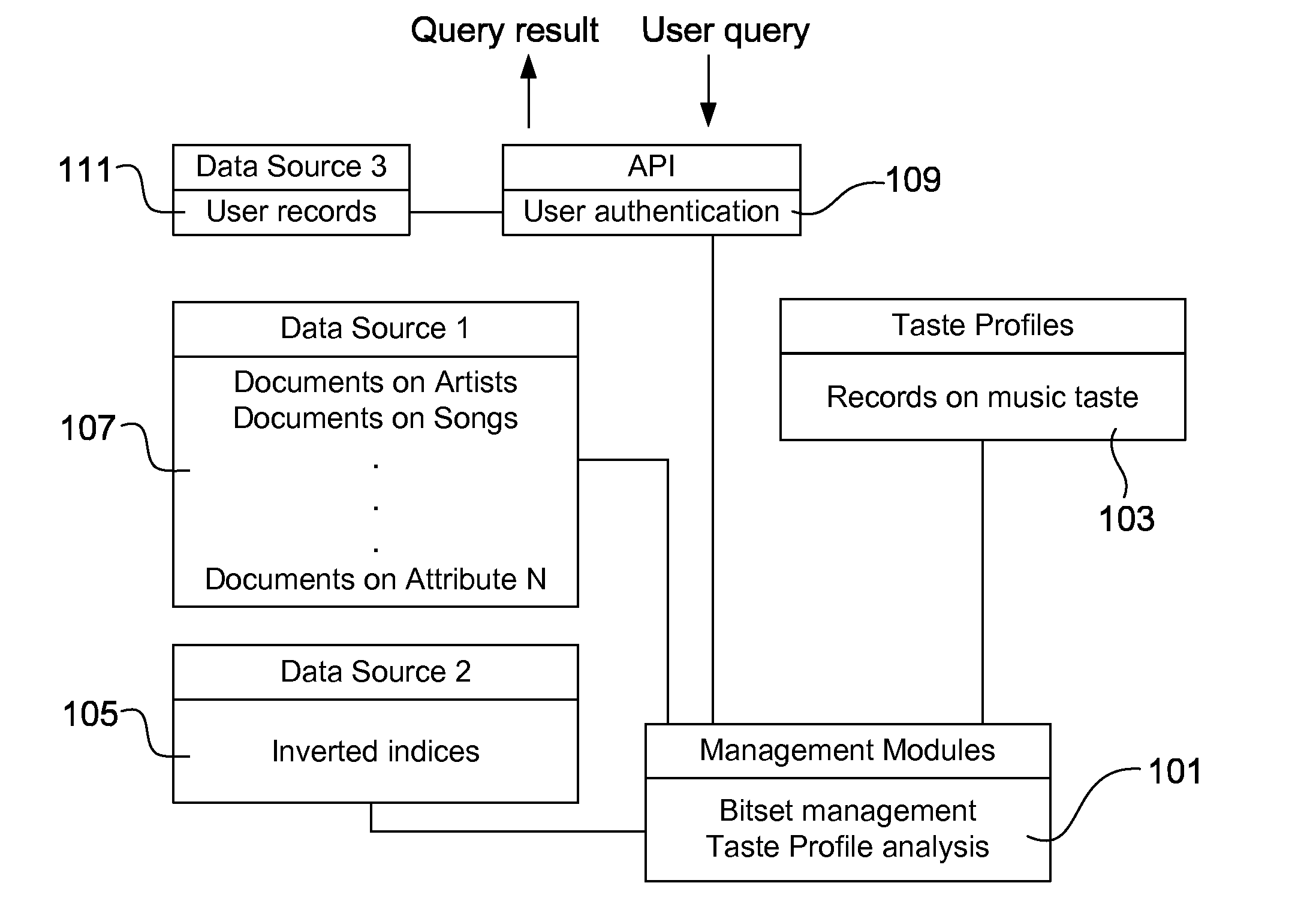
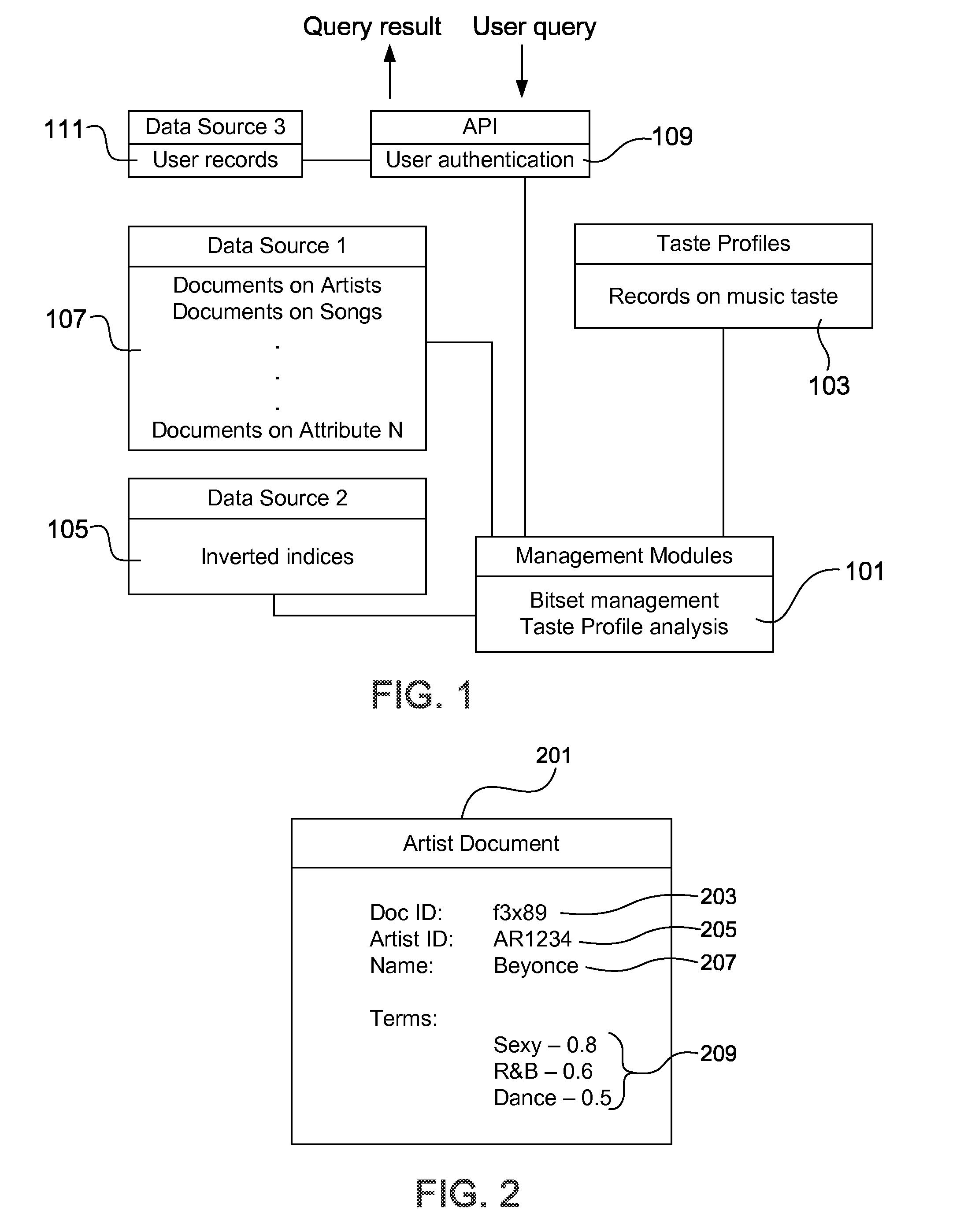
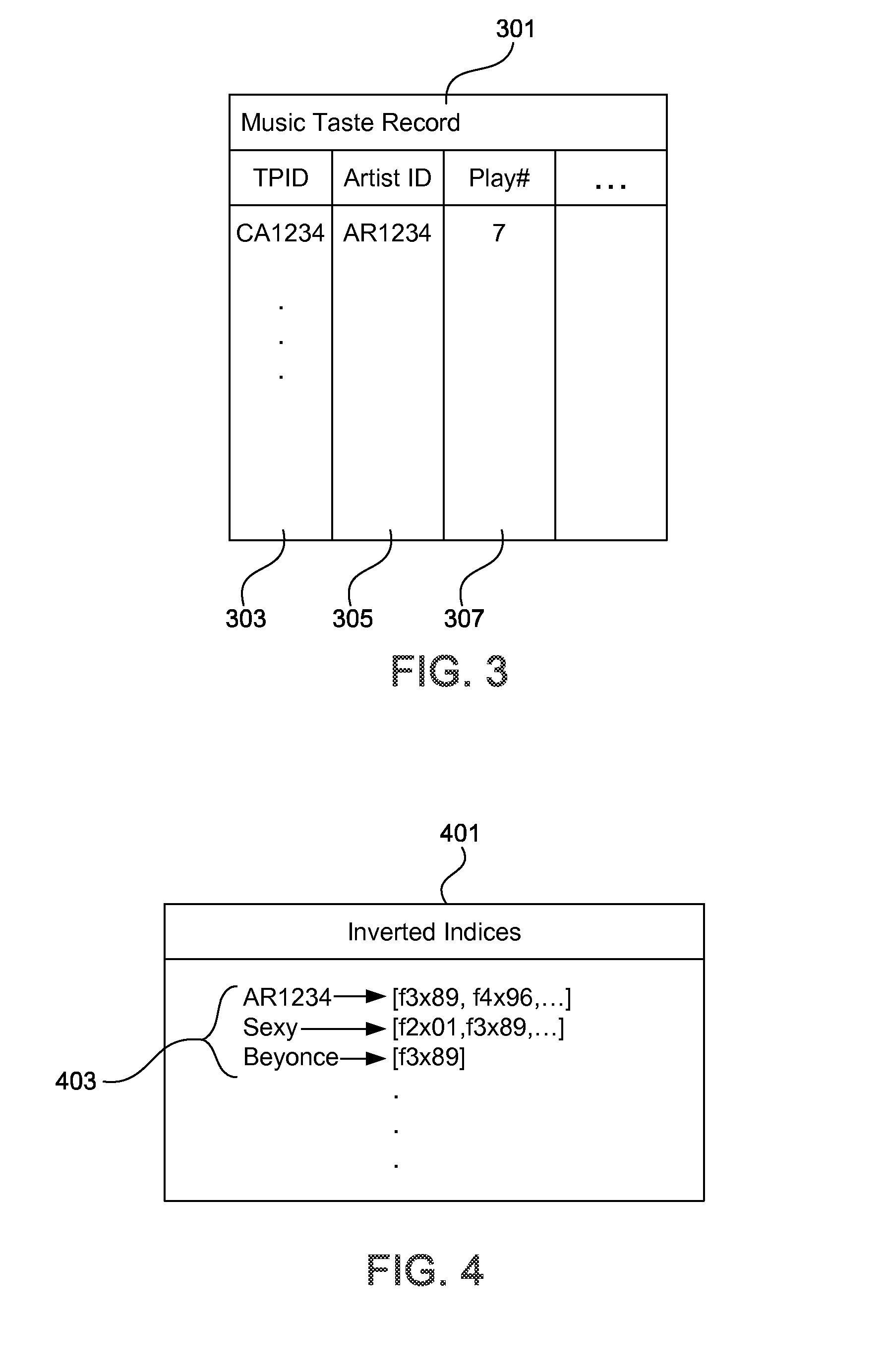
Methods, systems and computer program products are provided for predicting data. A name or title is obtained from a taste profile. There is an index into a data set based on the name or title, and a set of terms and corresponding term weights associated with the name or title are retrieved. A sparse vector is constructed based on the set of terms and term weights. The sparse vector is input to a training model including target data. The target data includes a subset of test data which has a correspondence to a predetermined target metric of data. A respective binary value and confidence level is output for each term, corresponding to an association between the term and the target metric.
Owner:SPOTIFY
Image classification method based on MapReduce
InactiveCN104392250AFast classificationNo low classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionExperimental validationImage extraction
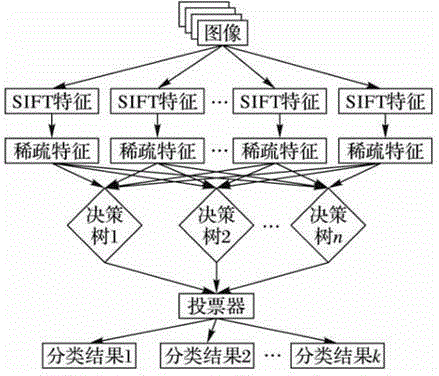
The invention discloses an image classification method based on MapReduce, on Hadoop platform, firstly, using the MapReduce frame for parallel extracting image SIFT characteristic; using the MapReduce frame for sparse coding for extracted SIFT characteristic of each image and obtaining the corresponding sparse vector of the image, generating the sparse characteristic of the image; then, based on the sparse characteristic of the image, using MapReduce frame for training the decision-making tree, generating the random forest aiming at the image characteristic set; using MapReduce combined with the random forest for classified counting each image. Through experimental verification, the image classification method based on MapReduce can obviously raise the classification speed while guaranteeing not lower than single platform classification precision.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Demographic and media preference prediction using media content data analysis
ActiveUS20130262469A1Low accuracyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData setData mining
Methods, systems and computer program products are provided for predicting data. A name or title is obtained from a taste profile. There is an index into a data set based on the name or title, and a set of terms and corresponding term weights associated with the name or title are retrieved. A sparse vector is constructed based on the set of terms and term weights. The sparse vector is input to a training model including target data. The target data includes a subset of test data which has a correspondence to a predetermined target metric of data. A respective binary value and confidence level is output for each term, corresponding to an association between the term and the target metric.
Owner:SPOTIFY
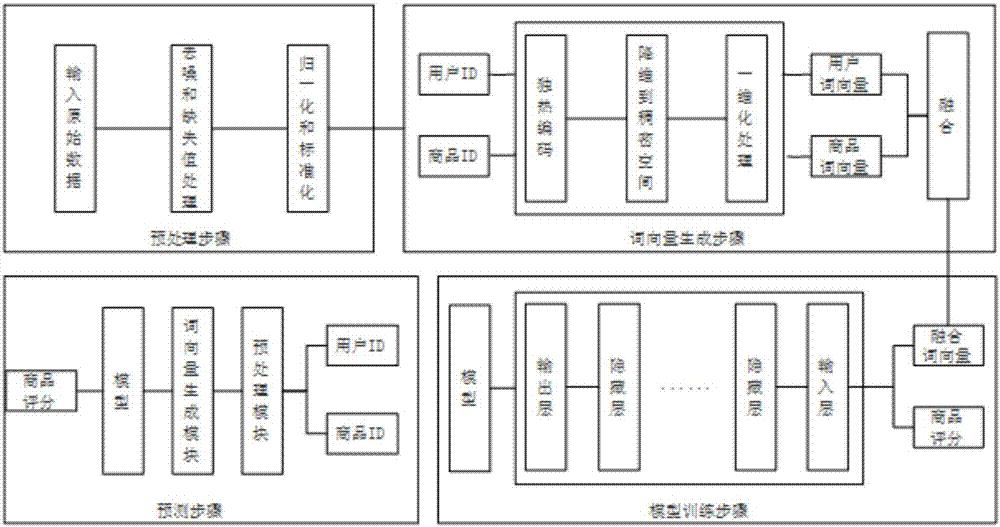
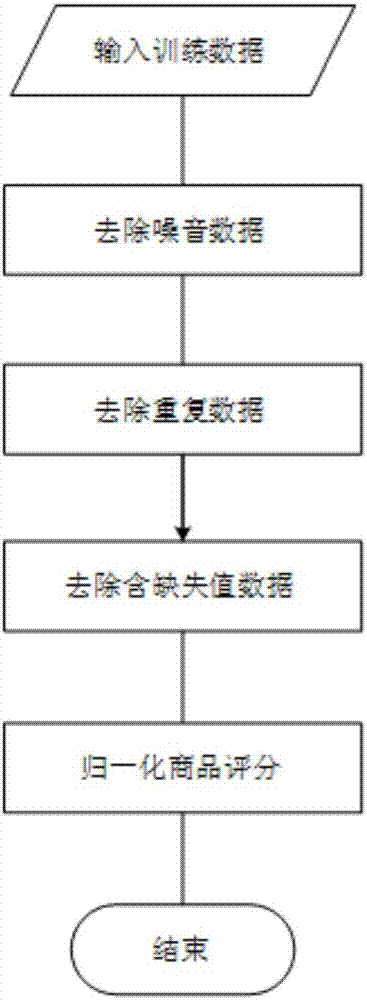
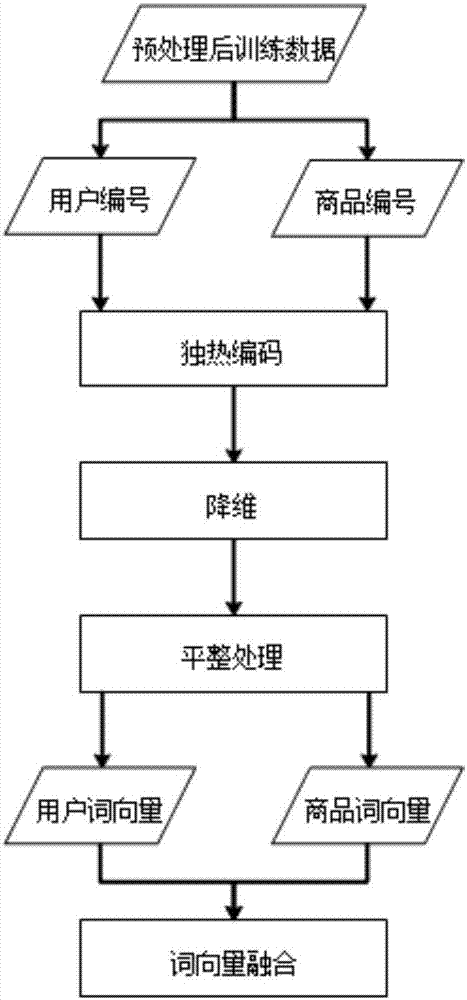
Intelligent commodity recommending method based on word vector data driving
InactiveCN106920147AHigh precisionImprove interpretabilityBuying/selling/leasing transactionsNeural architecturesText categorizationOne-hot
The invention discloses an intelligent commodity recommending method based on word vector data driving. The method includes the following steps: data pre-processing, word vector generation, score prediction constructing, model training and score prediction. The method includes the following steps: using a word vector method to take user numbers, commodity numbers and commodity scores as semantic words, changing the semantic words to a sparse vector by conducting one-hot encoding, then multiplying the sparse vector and a weight matrix and mapping a high-dimension and sparse original vector to a dense, continuous and fixed and low-dimension feature space, then inputting the original vector to a deep model for carrying out training to obtain weight parameters of each layer of a model, predicting and scoring a new user's favor to the commodity by using a well-used model so as to complete intelligent recommendation of the commodity to the user. According to the invention, the method applies the word vector method which classifies texts to score prediction and commodity recommendation which is based on favor of the user of an e-commerce platform to the commodity. The method can ensures precision and provide better explanation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
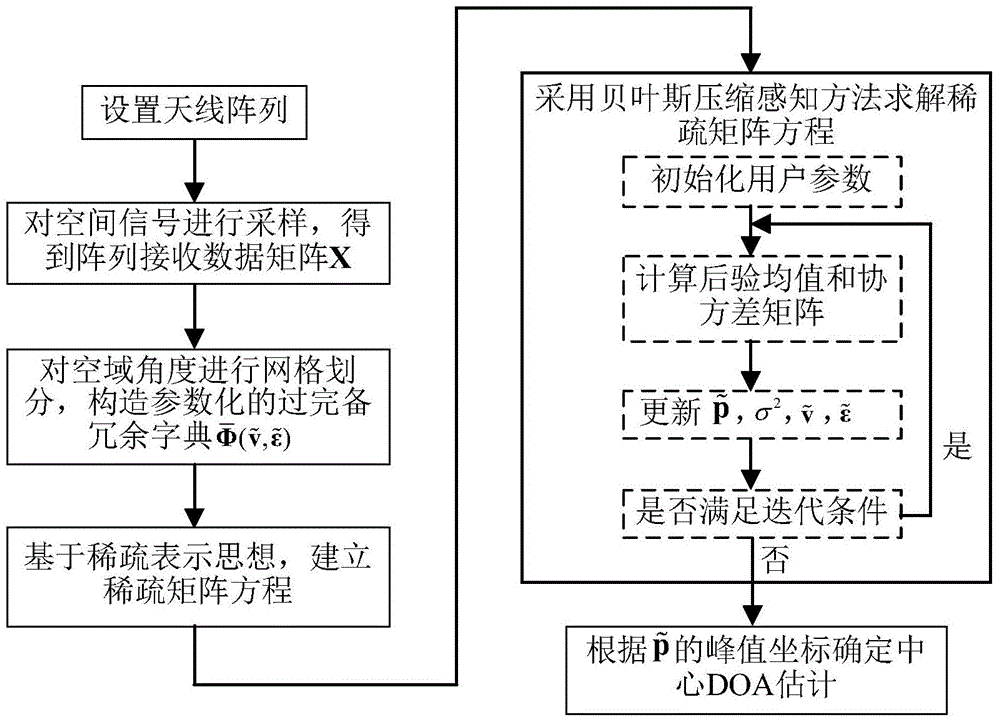
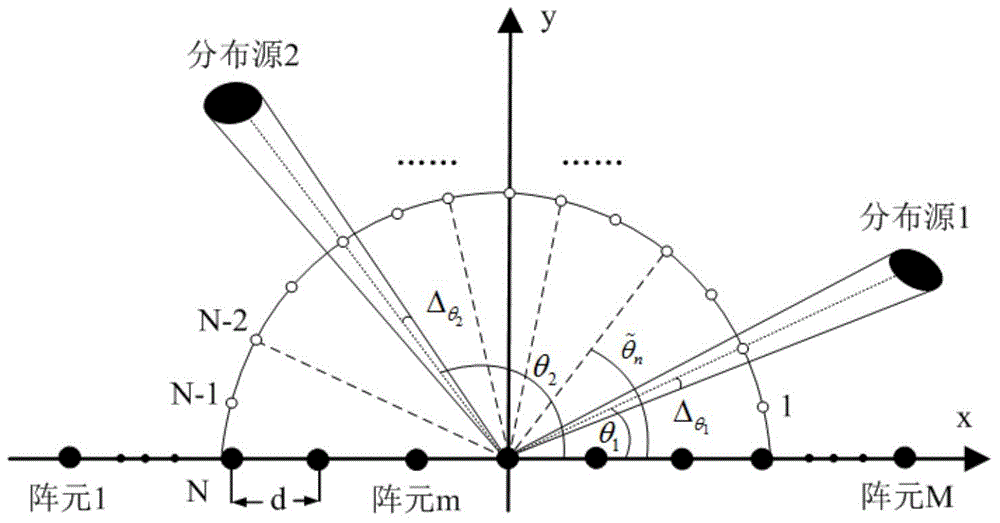
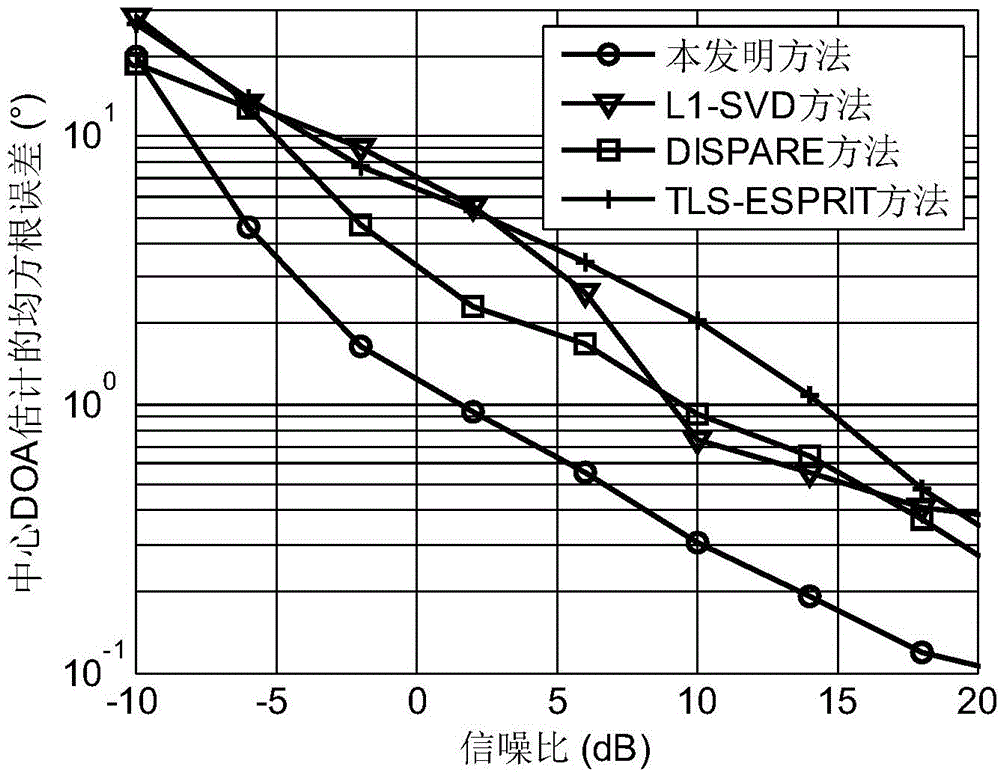
Distributed source center direction-of-arrival estimation method based on Bayesian compressed perception
InactiveCN104977558AAvoid estimating constraintsImprove estimation accuracyRadio wave finder detailsDistributed sourceEuclidean vector
The invention provides a distributed source center direction-of-arrival estimation method based on Bayesian compressed perception, and belongs to the technical field of wireless mobile communication. The invention mainly aims to solve the problem concerning inherent error of center direction-of-arrival estimation when the center angle of arrival of an information source is not on an angle sampling grid. According to the invention, an antenna array composed of parallel uniform linear arrays is arranged; an approximate array data reception model of a distribution source is established; the space-domain angle is sampled; a parameterized over-complete redundant dictionary is constructed by using an array steering vector so as to make the problem of distributed source center direction-of-arrival estimation converted into the problem of sparse matrix equation solving; a Bayesian compressed perception method is adopted to solve the equation set and obtain the most sparse solution of an unknown sparse vector; and the estimated value of the center direction of arrival is obtained according to the one-to-one correspondence relationship between sparse solutions and space-domain angles. The method of the invention is low in computing complexity, and has the characteristics of high resolution and accuracy under the condition of a small number of snapshots.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High-spectrum abnormal object detection method based on background dictionary learning and structure sparse expression
InactiveCN105825200AHigh precisionImprove detection resultsImage enhancementImage analysisDictionary learningData set
The invention discloses a high-spectrum abnormal object detection method based on background dictionary learning and structure sparse expression, for solving the technical problem of low object detection efficiency by use of a conventional high-spectrum abnormal object detection method. The technical scheme is as follows: after an initial background pixel is selected based on a local RX algorithm, a robust background dictionary is obtained through learning by use of a principle component analysis dictionary learning method. In a sparse vector solving and image reconstructing process, heavy-weight Laplace prior is introduced, and thus the sparse vector solving precision is improved. Finally, according to errors between an original image and a reconstructed image, accurate extraction of an abnormal object is realized. Test results on a real high-spectrum satellite image AVIRIS and a simulated high-spectrum data set show that the detection rate of a detection result obtained by use of the method is improved by 8% to 15% under the condition of a constant fault alarm rate compared to background arts.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Direction-of-arrival estimation method based on sample covariance matrix sparsity
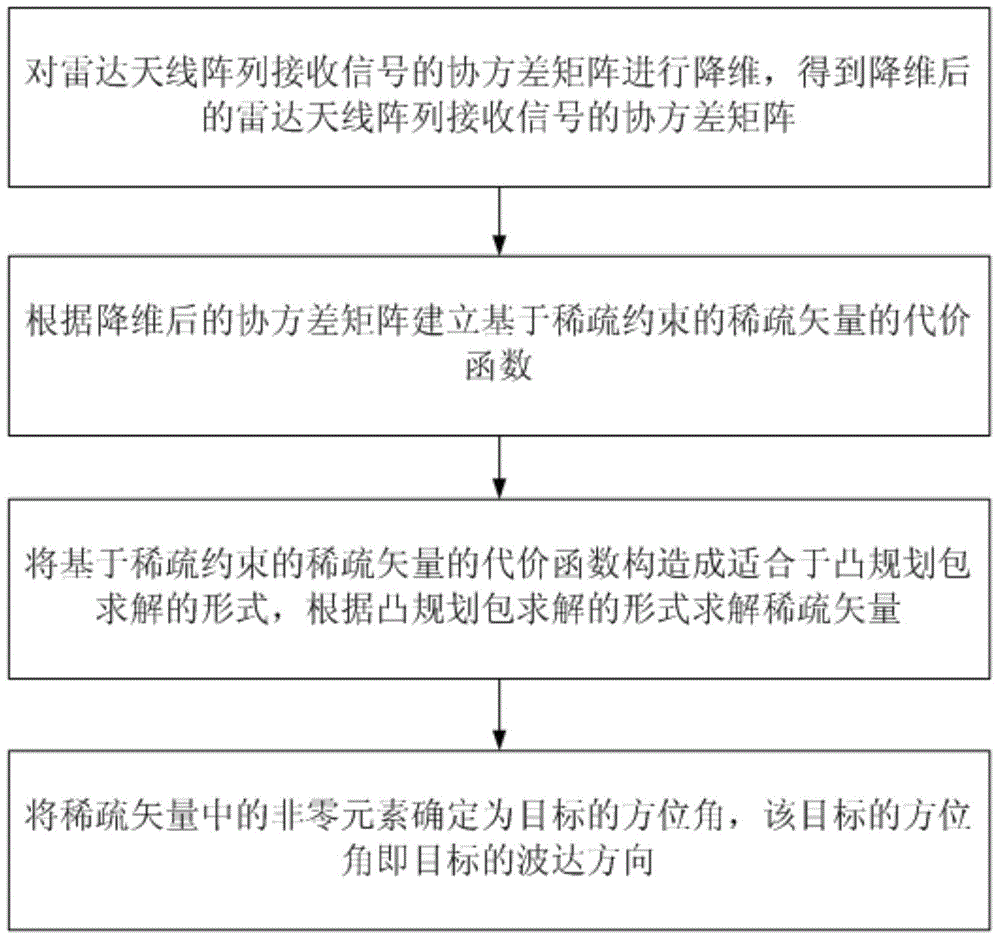
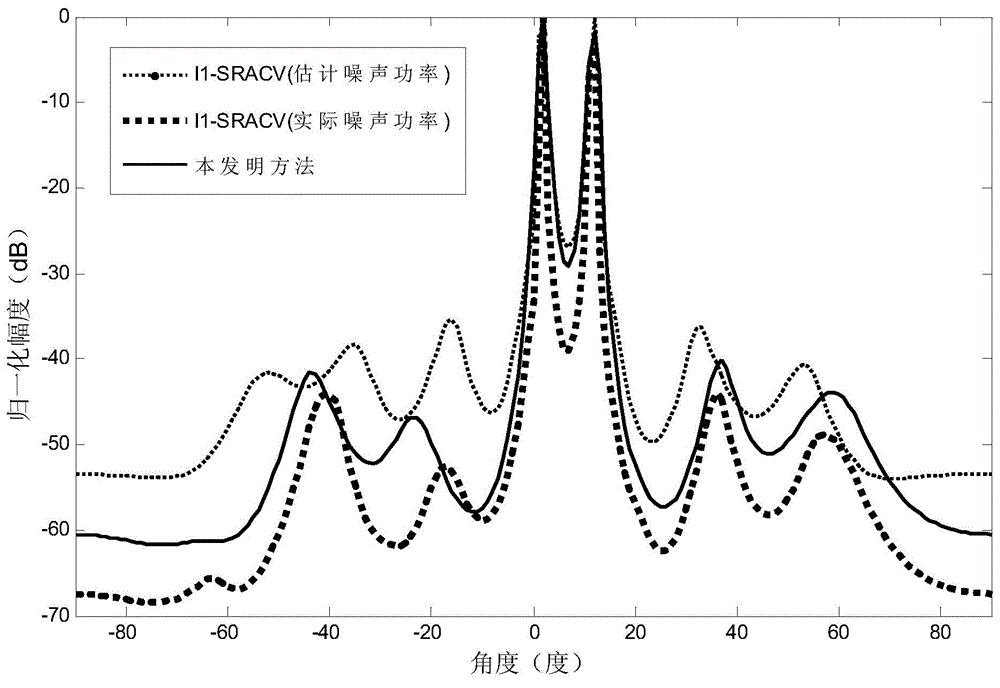
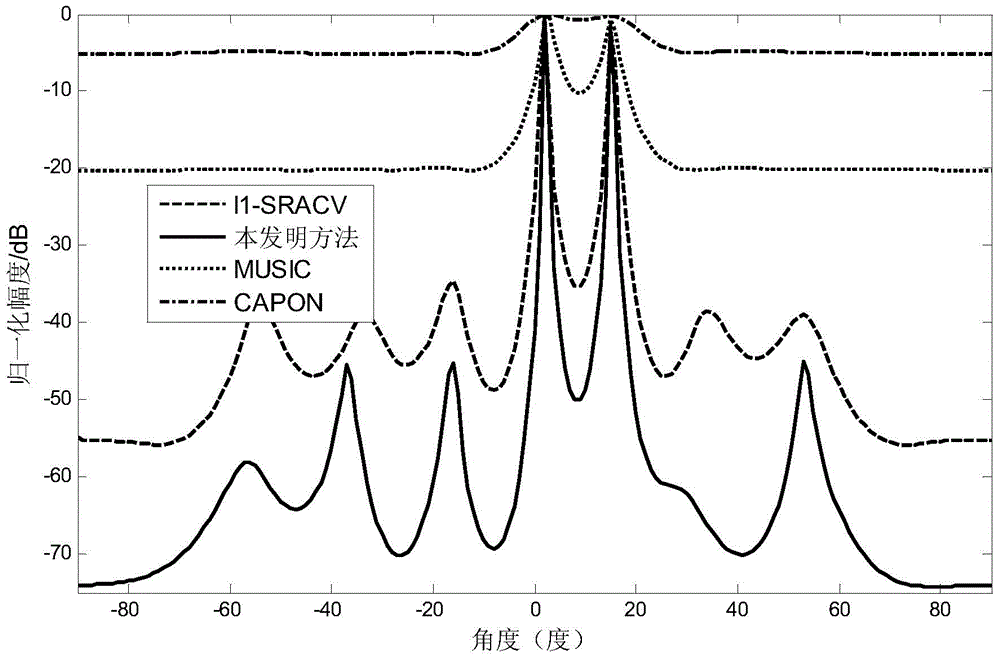
InactiveCN103954950AImprove resolutionImprove estimation accuracyWave based measurement systemsSparse constraintDimensionality reduction
The invention discloses a direction-of-arrival estimation method based on sample covariance matrix sparsity, and relates to the field of array signal processing. The method comprises the steps that firstly, dimensionality reduction is carried out on a covariance matrix, receiving signals, of a radar antenna array, and the covariance matrix, receiving the signals, of the radar antenna array is obtained after dimensionality reduction; secondly, a sparse vector cost function based on sparse constraints is built according to the covariance matrix after dimensionality reduction; thirdly, the sparse vector cost function based on the sparse constraints is constructed to be the mode suitable for convex programming package solving, and a sparse vector is solved according to the mode of convex programming package solving; fourthly, a non-zero element in the sparse vector is determined as a target azimuth angle, and the target azimuth angle is a target arrival direction. The method mainly solves the problems that in the prior art, known noise power is needed, and the calculated amount is large, and the method is mainly used for scenes of array signal processing.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
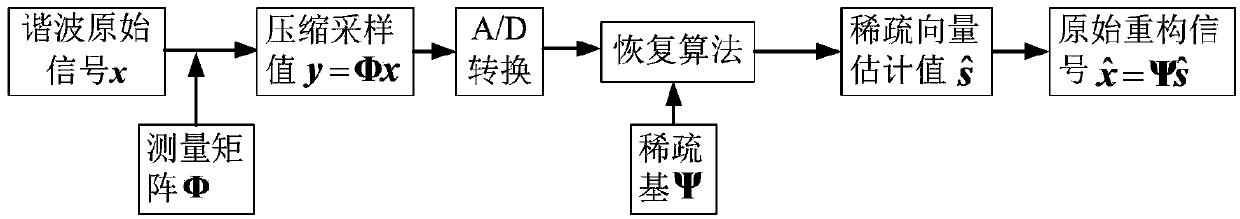
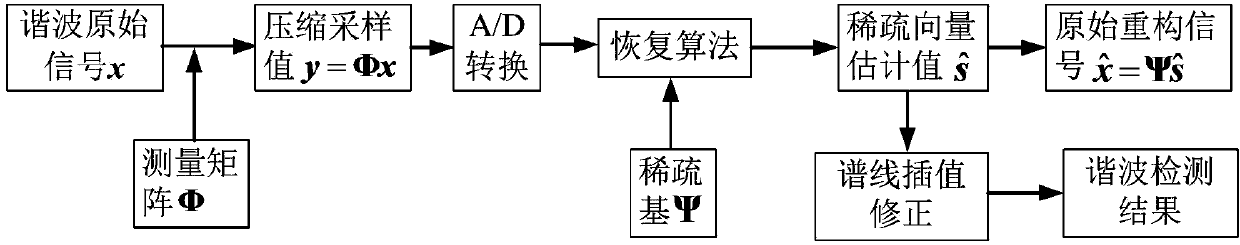
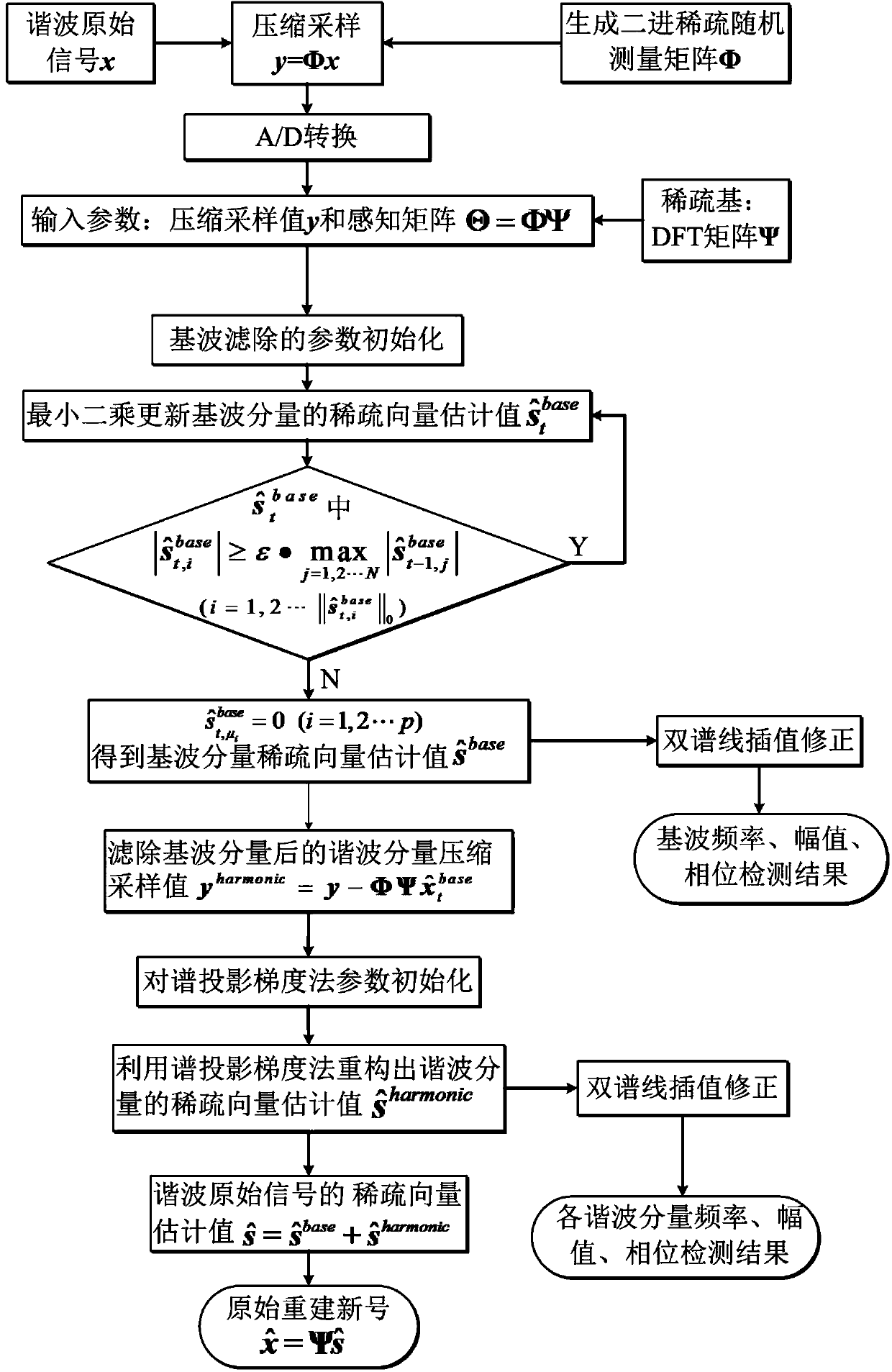
Power system harmonious wave compressed signal reconstruction and detection method based on compressed sensing
The invention discloses a power system harmonious wave compressed signal reconstruction and detection method based on compressed sensing. The power system harmonious wave compressed signal reconstruction and detection method based on compressed sensing comprises the steps that harmonious wave original signals of a power system and a measurement matrix with a binary sparse random measurement matrix serving as a power system harmonious wave data compressed sample are sent to a frequency mixer for compressed sampling in a simulation domain, then A / D conversion is carried out on the simulation signals, and a compressed sampling value is obtained; it is determined that a compressed sensing sparse base is a discrete Fourier transform base; initialization of fundamental wave filtering is carried out; fundamental wave filtering is carried out; the frequency, amplitude and phase of a fundamental component are detected; the fundamental wave constituent in the compressed sampling value is filtered away; parameter initialization is carried out on a spectrum projection gradient method; a sparse vector estimation value of a harmonious wave component is reconstructed through the spectrum projection gradient method; the frequency, amplitude and phase of the harmonious wave component are detected; reconstruction of the harmonious wave original signals of the power system is finished. The power system harmonious wave compressed signal reconstruction and detection method based on compressed sensing overcomes the defect that all existing recovery algorithms do not take the influence of the fundamental wave component in the harmonious wave signals on signal reconstruction into account, so that the recovery effect is not ideal.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
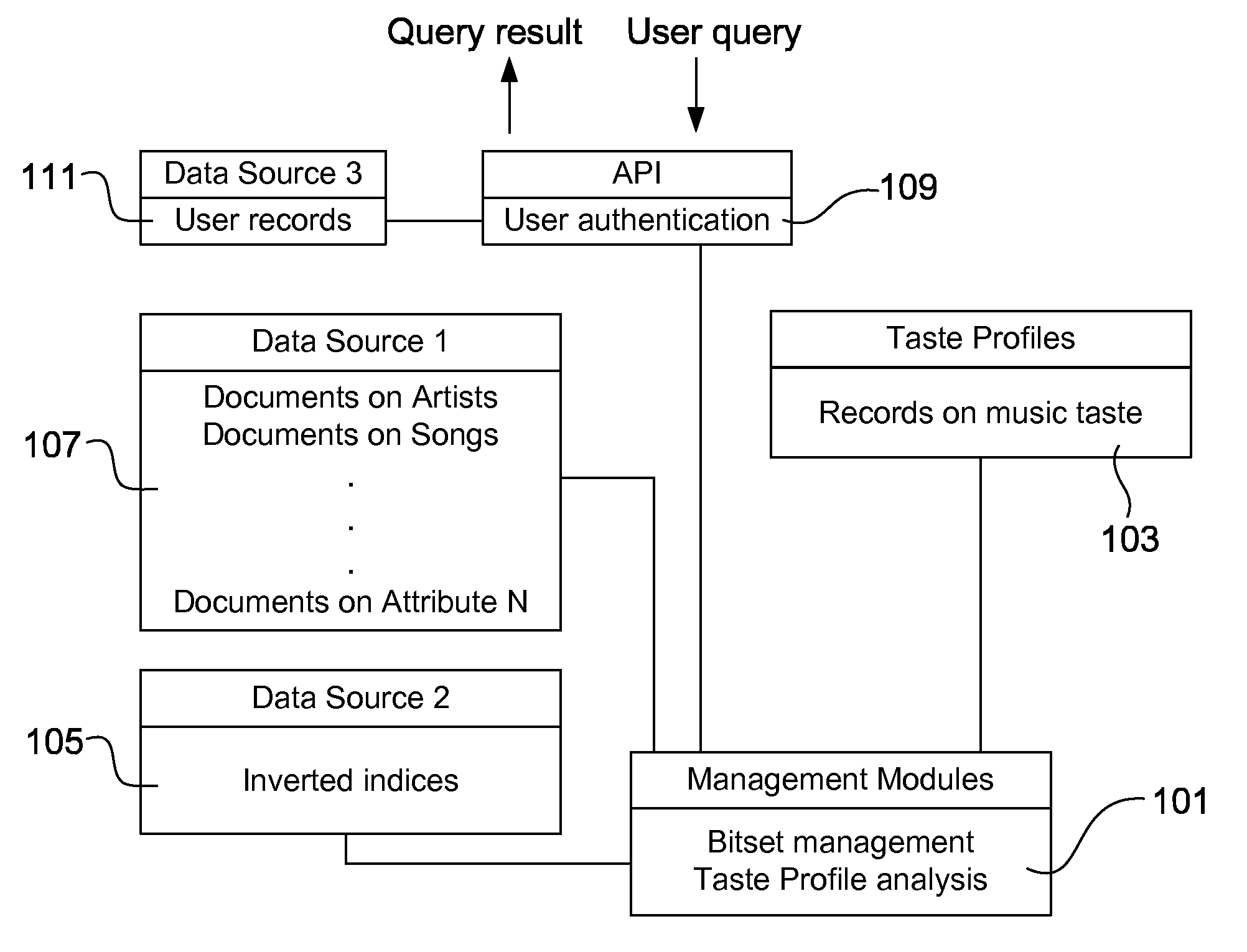
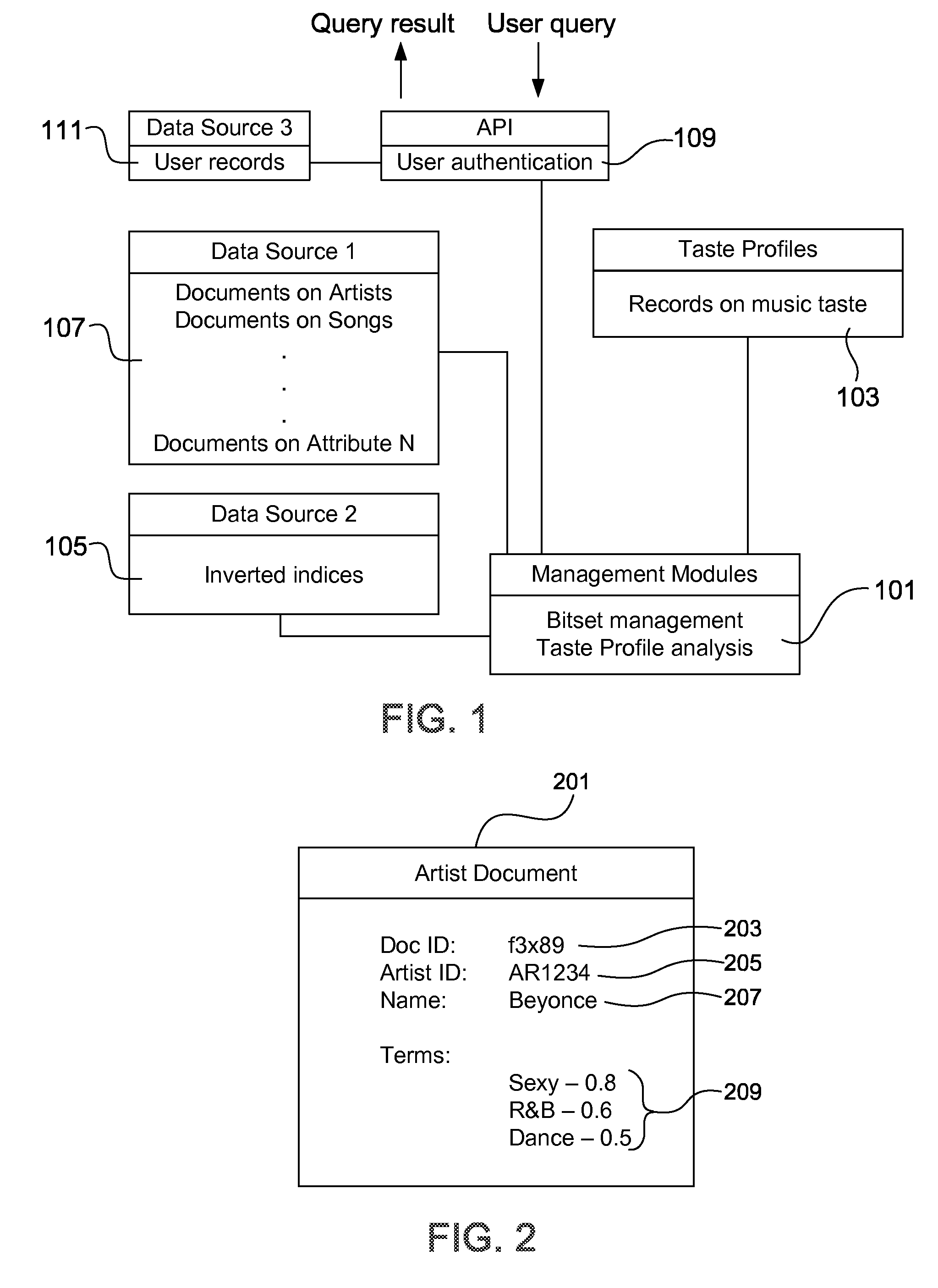
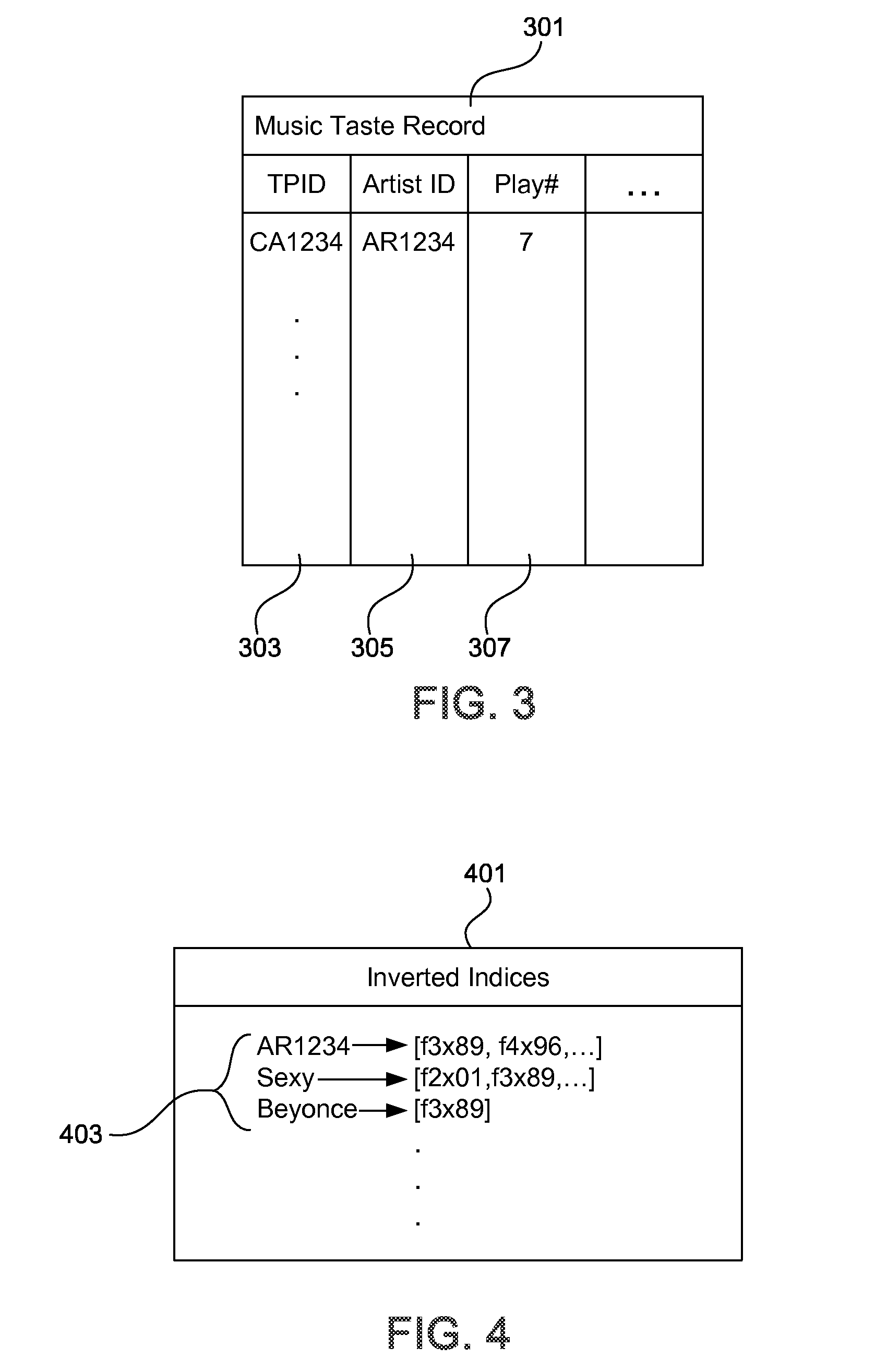
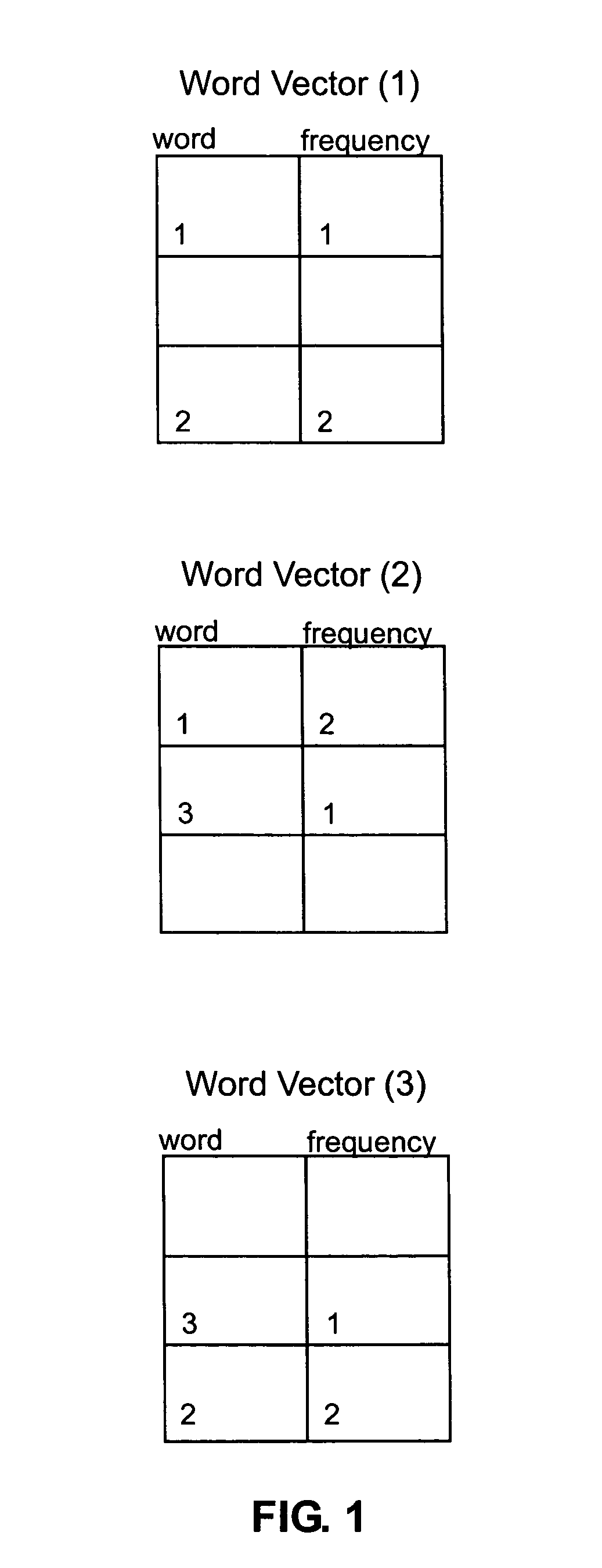
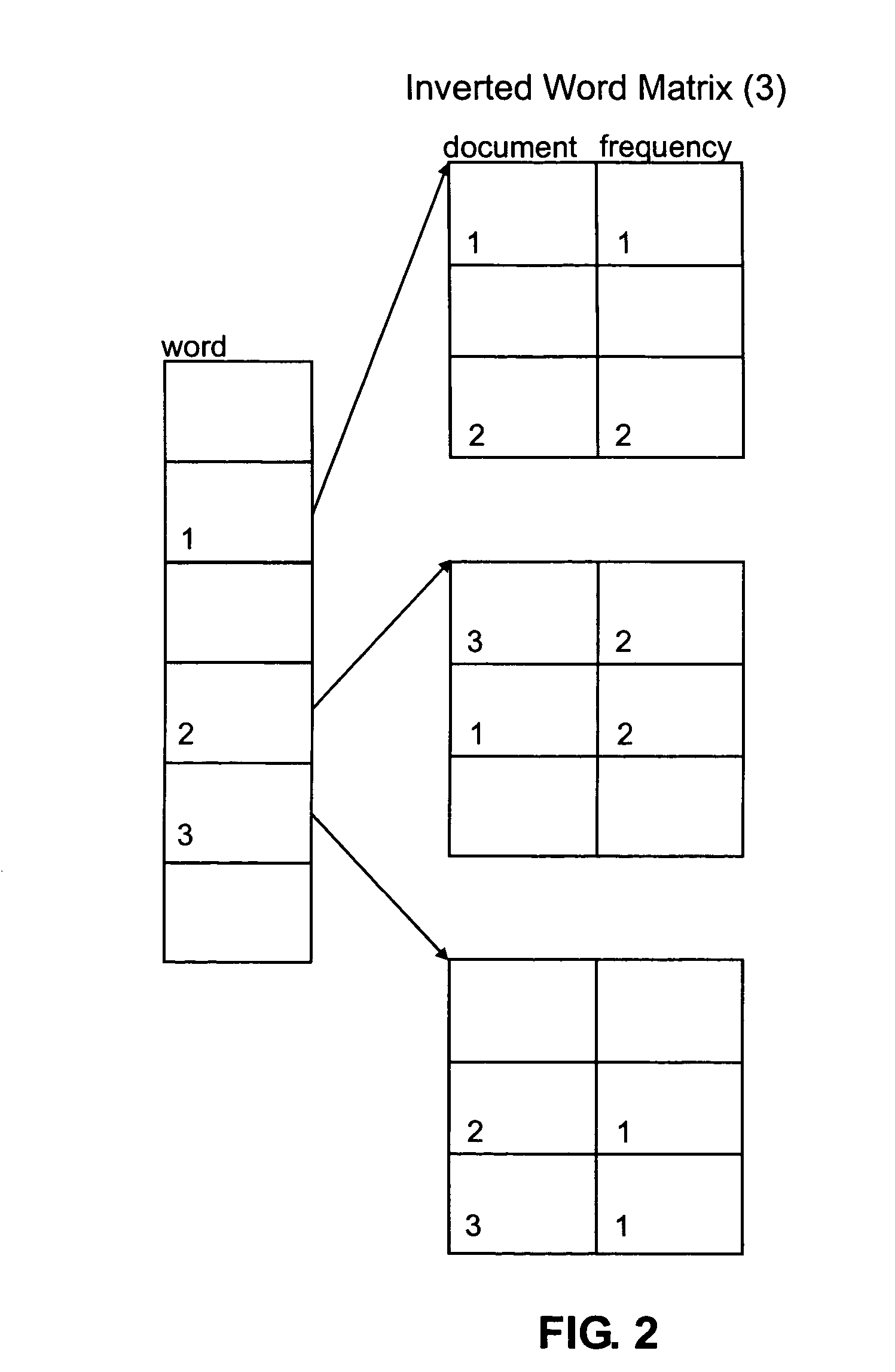
Process and system for sparse vector and matrix representation of document indexing and retrieval
InactiveUS7328204B2Easy to calculateFast document indexData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDocumentationDocument retrieval
A new data structure and algorithms which offer at least equal performance in common sparse matrix tasks, and improved performance in many. This is applied to a word-document index to produce fast build and query times for document retrieval.
Owner:DTI OF WASHINGTON
Hyperspectral abnormal object detection method based on structure sparse representation and internal cluster filtering
InactiveCN106919952AAccurate extractionImprove detection rateCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a hyperspectral abnormal object detection method based on structure sparse representation and internal cluster filtering, aiming at addressing the technical problem of low object detection effciency of current hyperspectral abnormal object detection methods. The technical solution involves: after selecting an initial background pixel, using the dictionary learning method which is based on principal component analysis to study a background dictionary which obtains rebustness, in the course of sparse vector resolution and image reconstruction, introducing re-weighted laplacian prior to increase the solution precision of sparse vector, computing the errors betwen an original image and a reconstructed image to obtain a sparse representation error, using the internal cluster filtering to represent space spectrum characteristics of hyperspectral data, obtaining the internal cluster error by computing the error between a to-be-tested pixel and other pixel linear representation result, and finally combining the sparse representation error and the linear weighting of the internal cluster error and implementing precise extraction of an abnormal object. According to the invention, the method increases 10-15% of detection rate with the proviso of a constant false alarm rate compared with prior art.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method and system for fast similarity computation in high dimensional space
InactiveUS20130031059A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFeature vectorAlgorithm
Method, system, and programs for computing similarity. Input data is first received from one or more data sources and then analyzed to obtain an input feature vector that characterizes the input data. An index is then generated based on the input feature vector and is used to archive the input data, where the value of the index is computed based on an improved Johnson-Lindenstrass transformation (FJLT) process. With the improved FJLT process, first, the sign of each feature in the input feature vector is randomly flipped to obtain a flipped vector. A Hadamard transformation is then applied to the flipped vector to obtain a transformed vector. An inner product between the transformed vector and a sparse vector is then computed to obtain a base vector, based on which the value of the index is determined.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Demographic and media preference prediction using media content data analysis
ActiveUS9406072B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsData setComputer program
Methods, systems and computer program products are provided for predicting data. A name or title is obtained from a taste profile. There is an index into a data set based on the name or title, and a set of terms and corresponding term weights associated with the name or title are retrieved. A sparse vector is constructed based on the set of terms and term weights. The sparse vector is input to a training model including target data. The target data includes a subset of test data which has a correspondence to a predetermined target metric of data. A respective binary value and confidence level is output for each term, corresponding to an association between the term and the target metric.
Owner:SPOTIFY
Electric power system data reconfiguration decompressing method based on orthogonal matching pursuit
The invention discloses an electric power system data reconfiguration decompressing method based on orthogonal matching pursuit. A compressed sensing theory is adopted for conducting parallel data compression of sampling and compression on an electric power quality signal. The method includes that first, a line with the largest correlation with margin is selected in a sensing matrix, and simultaneously a selected space is updated. By solving a least square problem, residual is guaranteed to be minimum, sparse vector elements are obtained, then, the residual is updated, selected lines in the sensing matrix are removed, and finally sparse elements are obtained through loop iteration. By means of the method, the compressed sensing theory is adopted for conducting sparse decomposition on electric power quality data, then gauss measuring coding is conducted on sparse signals, and finally a signal is reconfigured through an orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm. The method breaks through a traditional data compression method framework of first sampling and then compressing, sampling and compression are conducted parallelly, a small amount of sampling can recover an original electric power quality signal well, a requirement for hardware is reduced, and compression efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
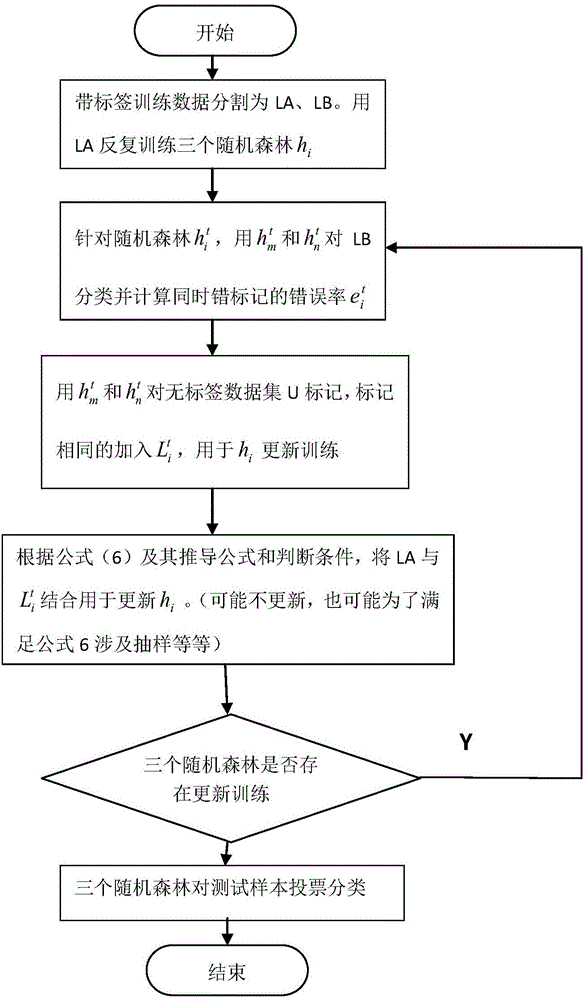
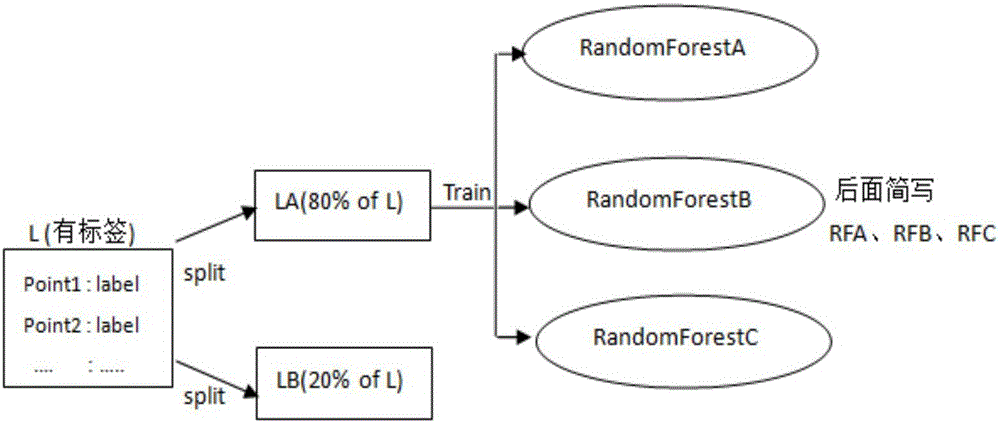
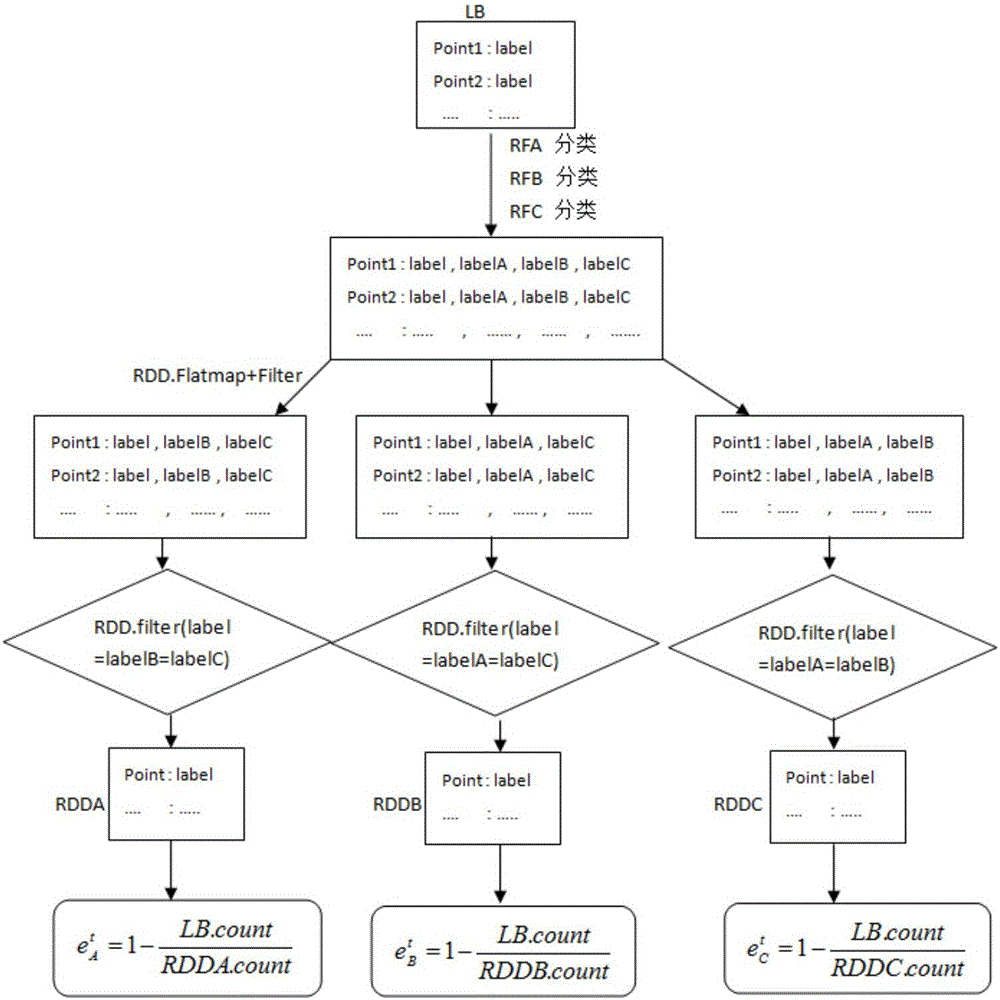
Semi-supervised random forests classification method based on Spark
InactiveCN106056134ADiversity guaranteedReduce the average error rateCharacter and pattern recognitionTree diversityData set
The invention discloses a semi-supervised random forest classification method based on Spark, which utilizes a random forests algorithm to employ replacement sampling on a training data set and column attributes, so that randomness is added in both row and column directions to ensure decision-making tree diversity, and to avoid tree pruning; in addition, a category is determined in a voting method, and accuracy is greatly improved. Accordingly, the random forests algorithm does not need to perform dimensionality reduction in processing high-dimensional data samples, and has sound effects for a sparse vector as well as a dense vector. According to the verification of a plurality of sets of experiments, the semi-supervised learning algorithm reduces a classification model error rate mean value, and improves calculating performance.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
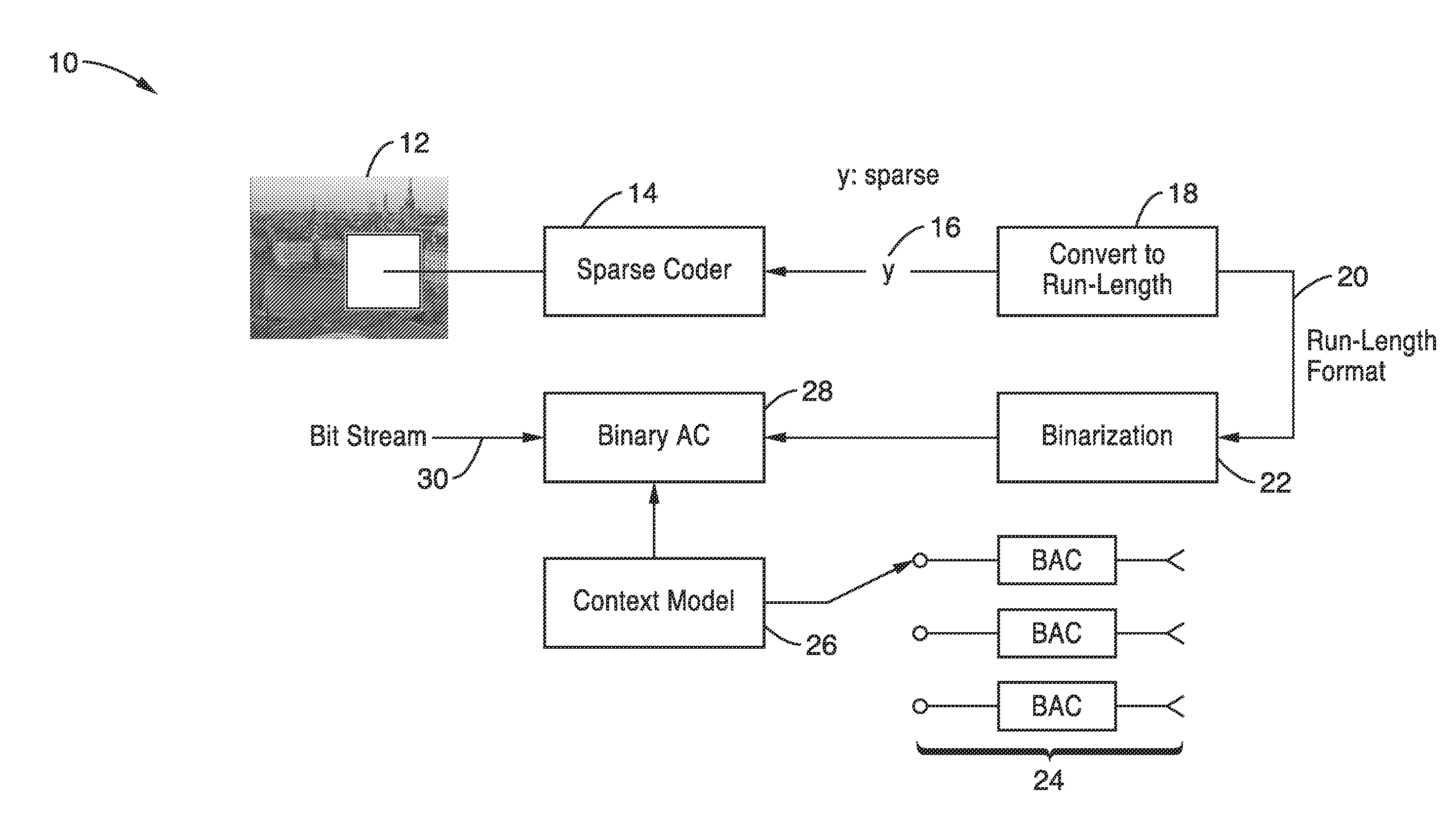
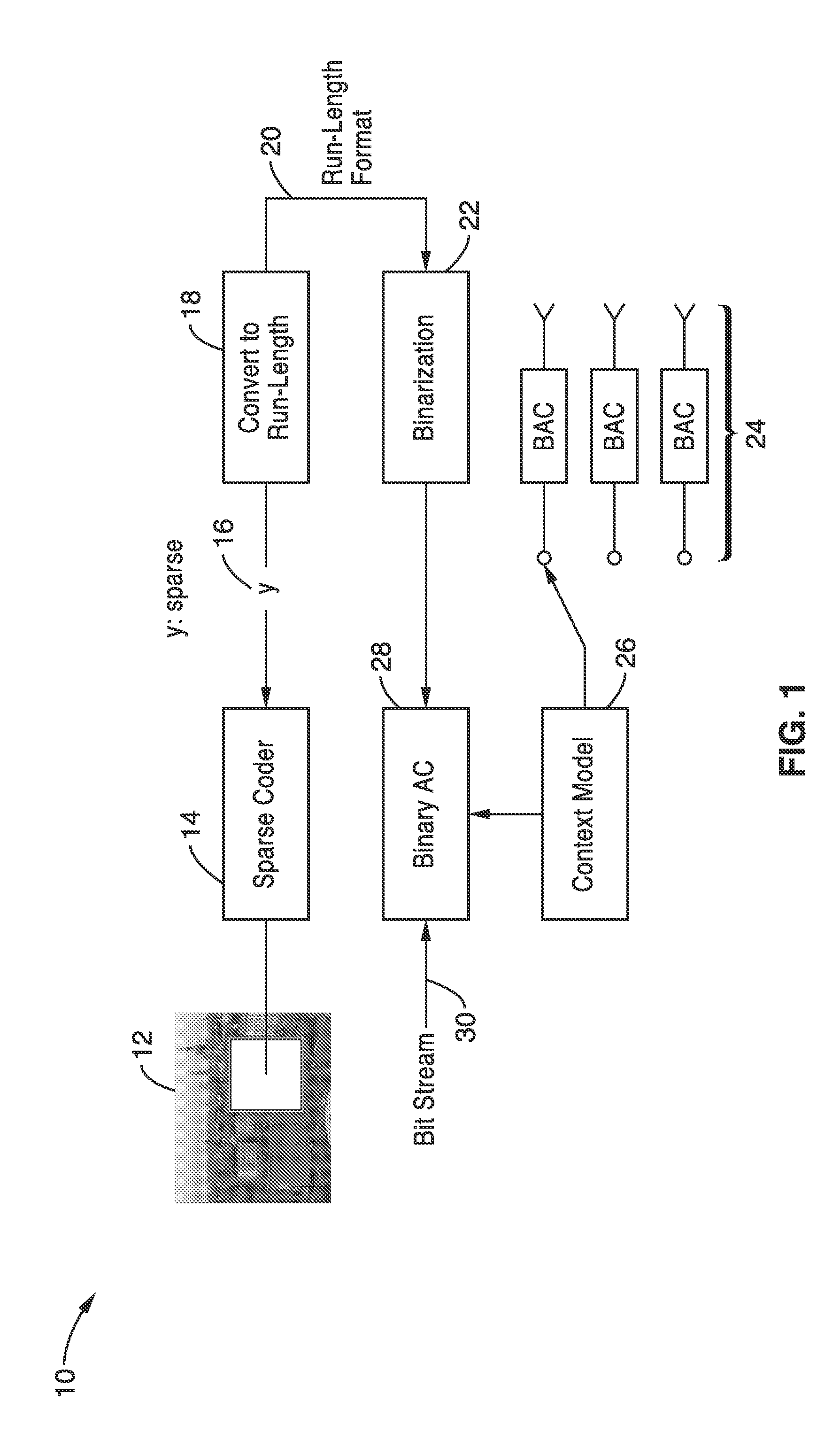
Run length coding with context model for image compression using sparse dictionaries
InactiveUS20120057799A1Reduce impactIncrease productionCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionContext modelAlgorithm
Apparatus and methods for coding images geometric vector quantization (GVQ) having an over-complete dictionary which produces a sparse vector of coefficients as it contains large runs of zeros. The sparse encoding is particularly well suited for use with run-length entropy coding techniques. Image blocks are sparse coded using GVQ, with the vector of coefficients converted to RUN-LENGTH symbols, and binarized into a set of binary symbols. At least a portion of the binary symbols are used as contexts which can be selected when performing binary arithmetic coding of the binary coded RUN and LENGTH data to generate a bit stream containing the encoded image that provides enhanced compression.
Owner:SONY CORP
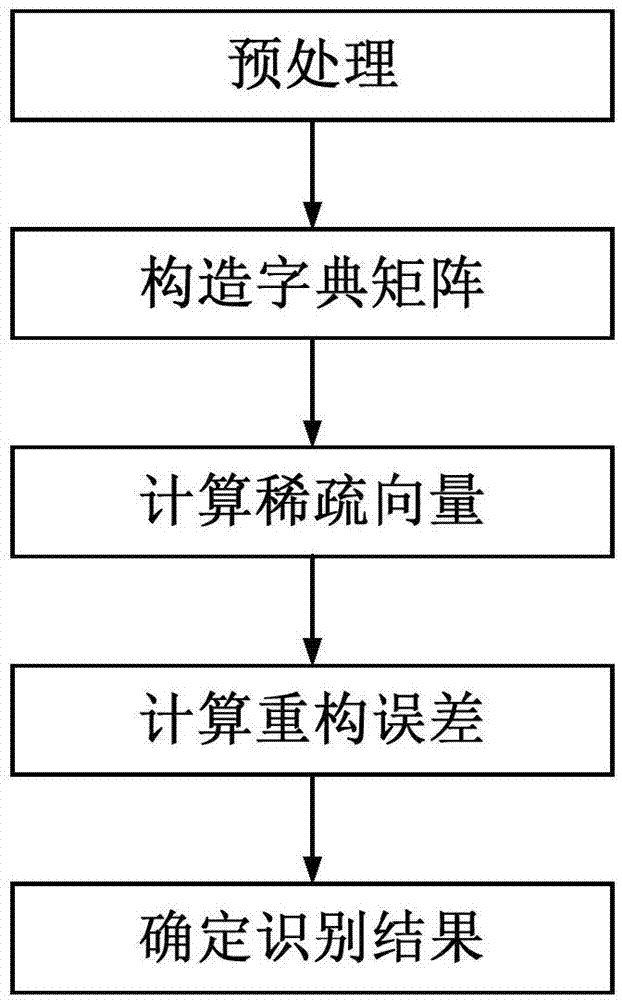
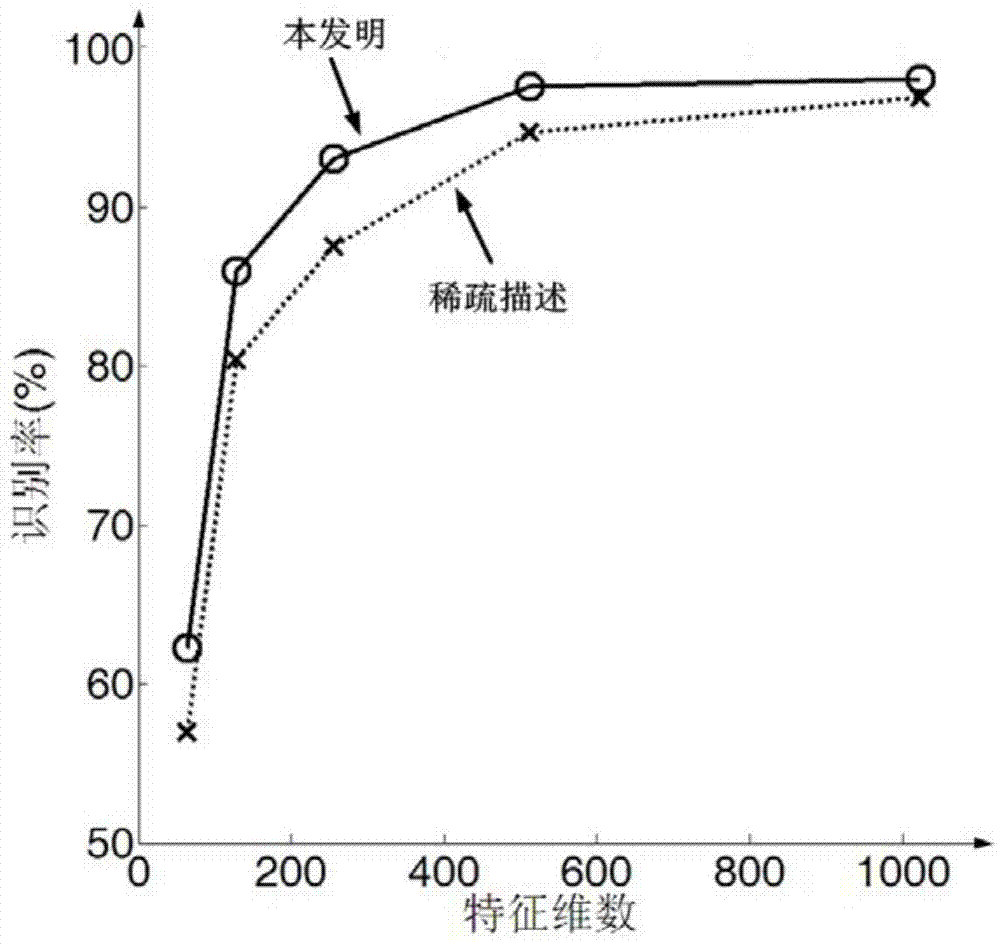
Nearest neighbor subspace SAR target identification method based on multiple sparse descriptions
InactiveCN103886337AHigh precisionEnhanced description abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionTest sampleNear neighbor
The invention discloses a nearest neighbor subspace SAR target identification method based on multiple sparse descriptions and aims at mainly solving the problem that the accuracy is low during target identification and the identification effect on locally-changing targets are poor in the prior art. The nearest neighbor subspace SAR target identification method comprises the steps of 1 performing preprocessing to obtain training samples and normalized sub-images of test sample images; 2 establishing dictionary matrixes to obtain multiple dictionary matrixes identical to categories in number; 3 calculating sparse vectors; 4 calculating reconstruction errors; 5 confirming identification results, utilizing a nearest neighbor subspace formula to use a target category corresponding to a reconstruction error minimum value as an identification result. Compared with the prior art, the identification accuracy of the locally-changing targets is improved. The description capacity and the identification rate of test sample detail features are improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
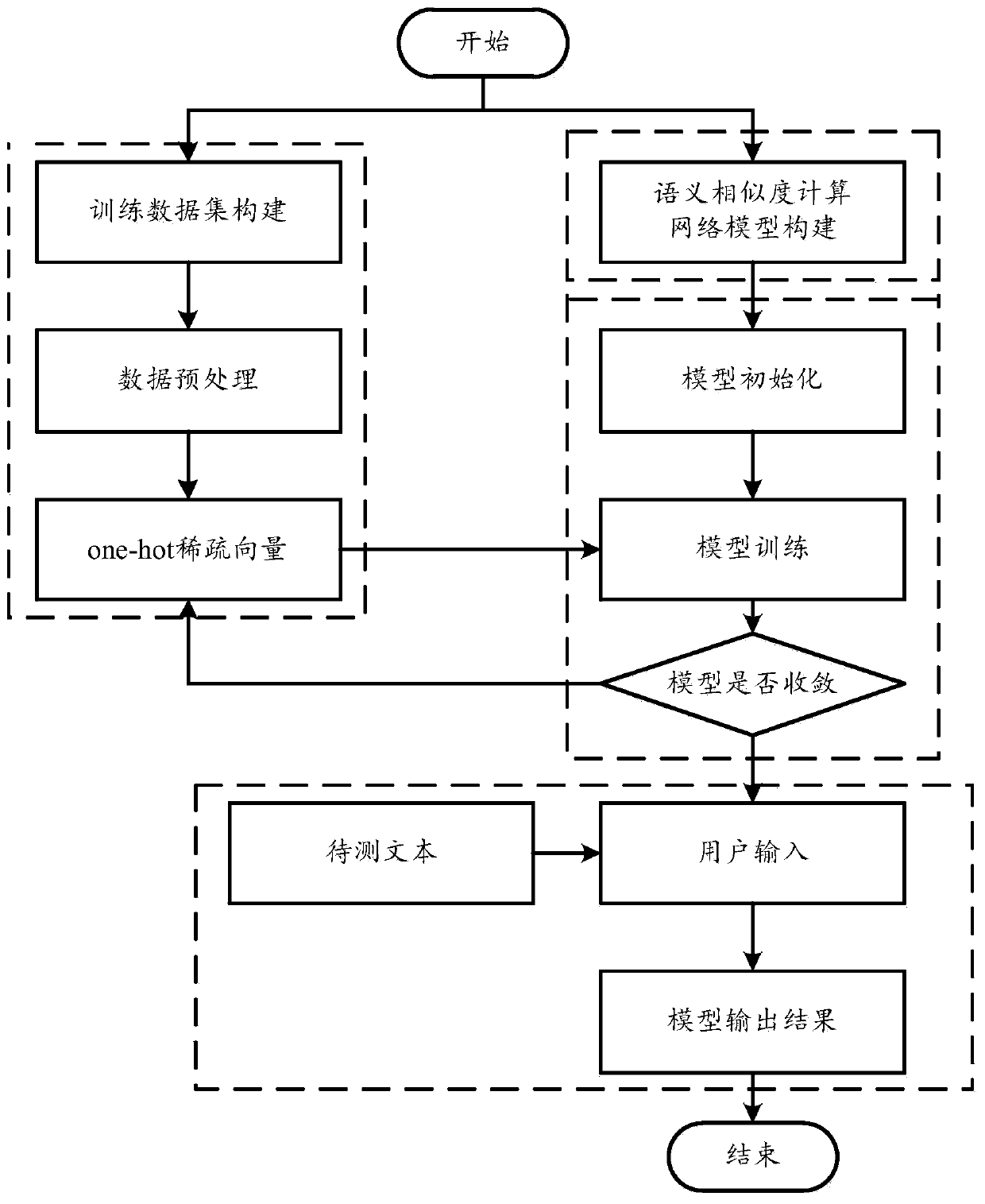
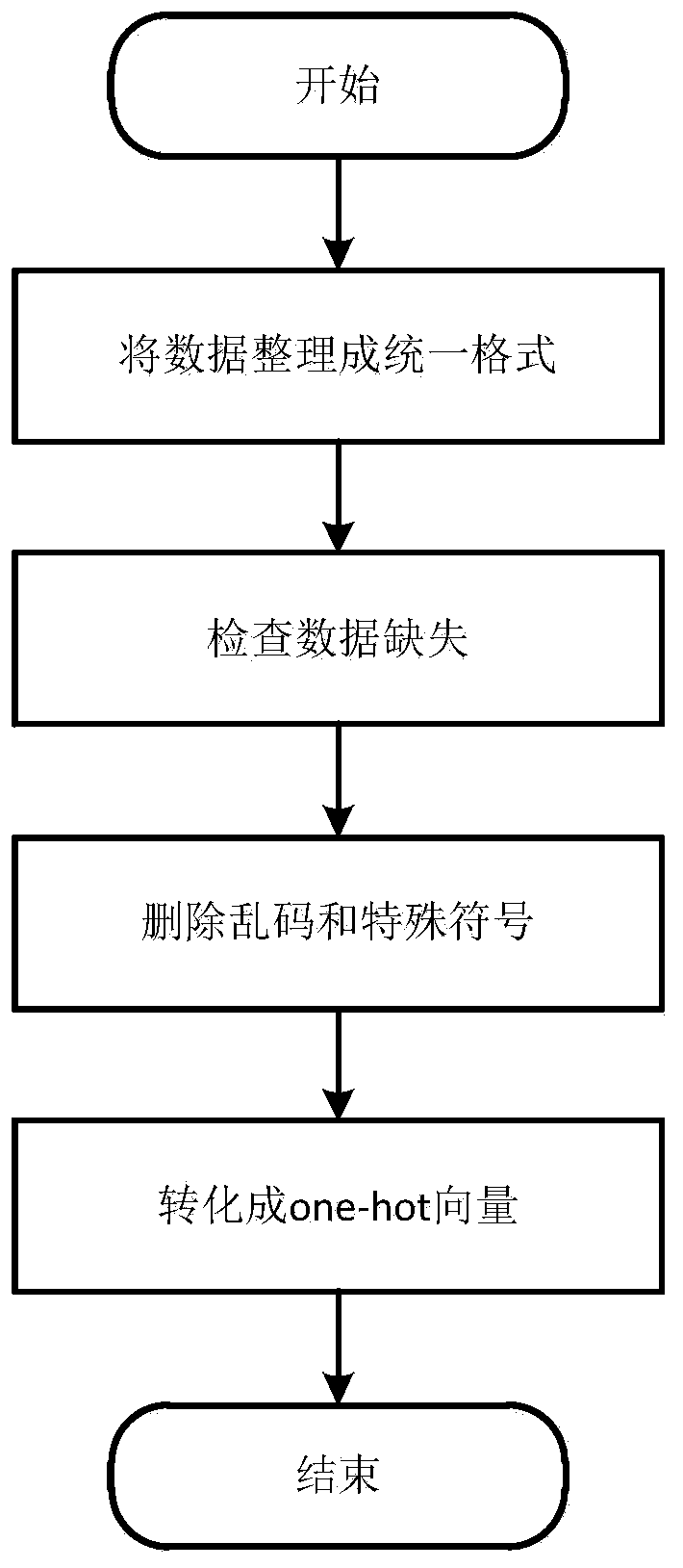
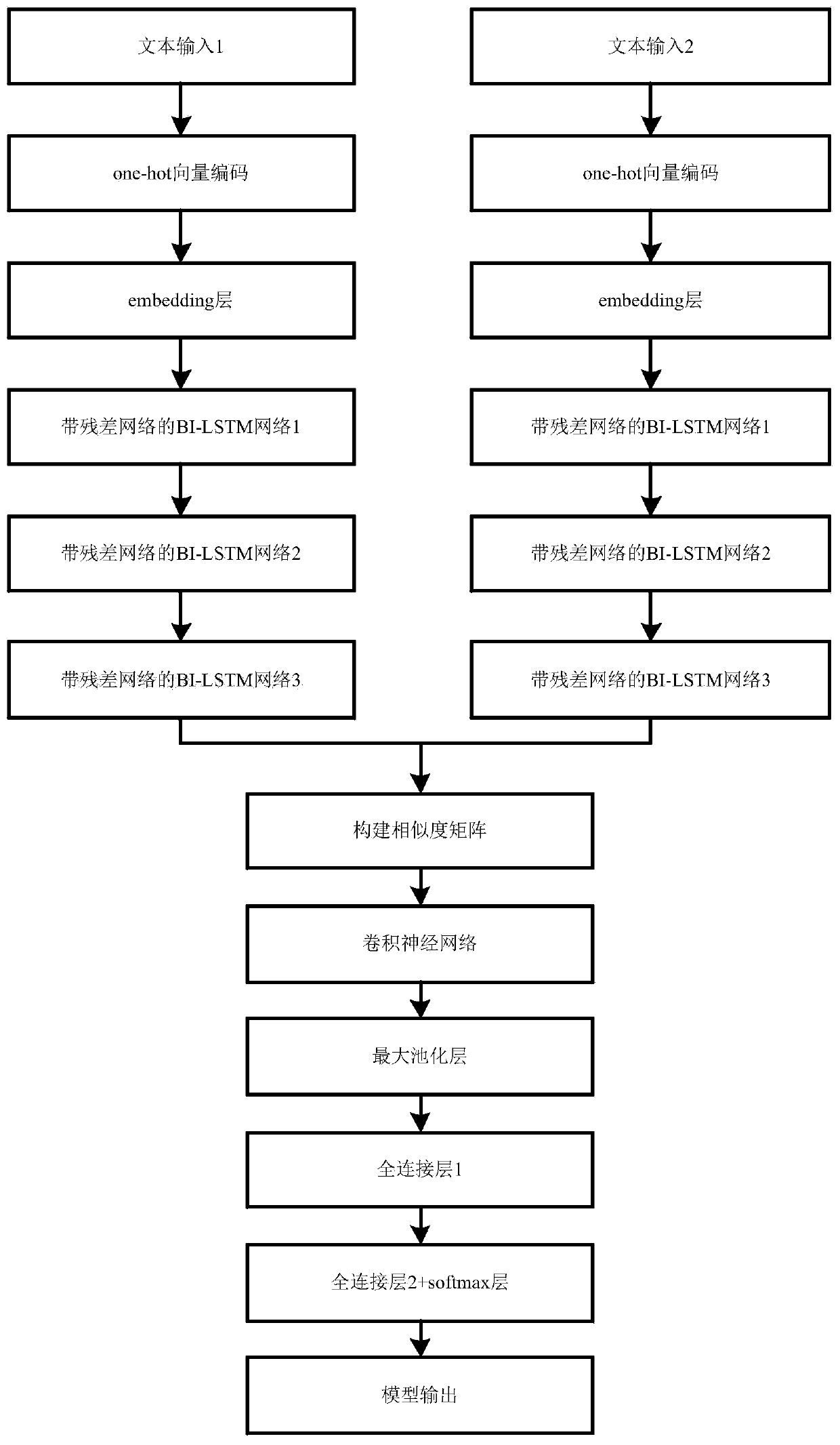
Semantic similarity calculation method based on deep learning
ActiveCN110348014AAvoid vanishing gradientsImprove feature extractionSemantic analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionData setNetwork model
The invention discloses a semantic similarity calculation method based on deep learning, and relates to the field of semantic similarity calculation. The method comprises the following steps: step 1,constructing a training data set, and preprocessing training data to obtain one-hot sparse vectors; step 2, constructing a semantic similarity calculation network model comprising N layers of BI-LSTMnetworks, a residual network, a similarity matrix, a CNN convolutional neural network, a pooling layer and a full connection layer; step 3, inputting the one-hot sparse vector into the network model,and training parameters by using a training data set to complete supervised training; and step 4, inputting a text to be tested into the trained network model, judging whether the text to be tested isa similar text or not, and outputting a result. The semantic similarity calculation network model comprises a multi-layer BI-LSTM network, a residual network, a CNN convolutional neural network, a pooling layer and a full connection layer. Meanwhile, a BI-LSTM network and a CNN convolutional neural network are used, and a residual network is added into the BI-LSTM network, so that the problem ofgradient disappearance caused by a multi-layer network is solved, and the feature extraction capability of the model is enhanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
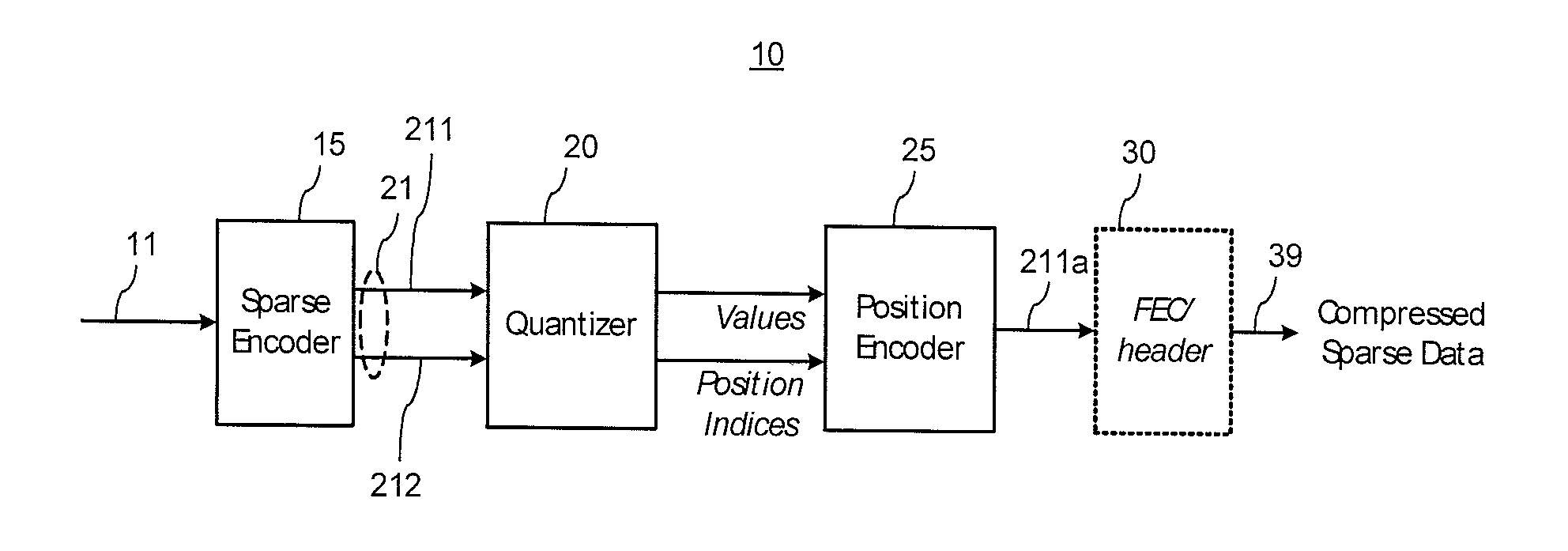
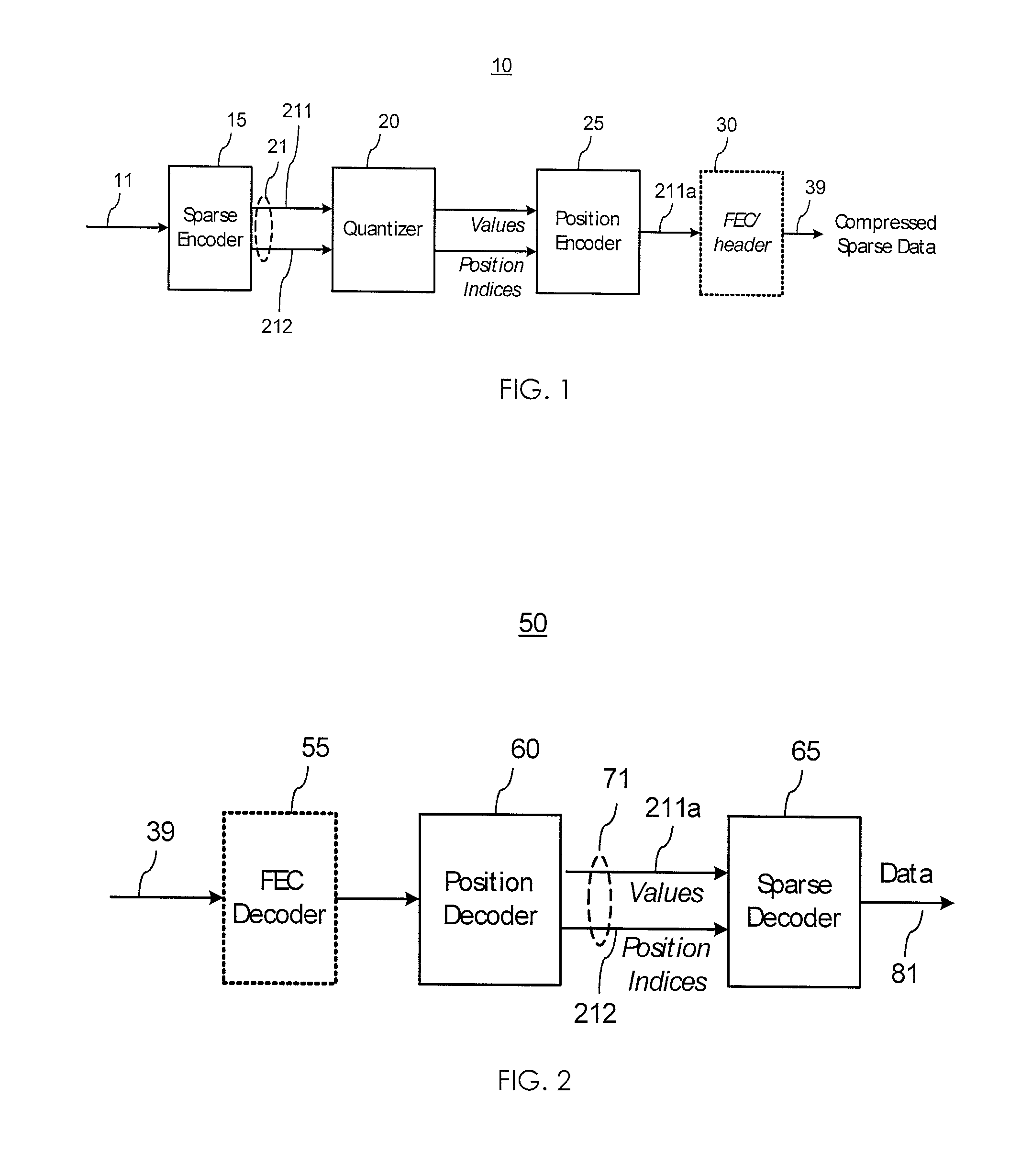
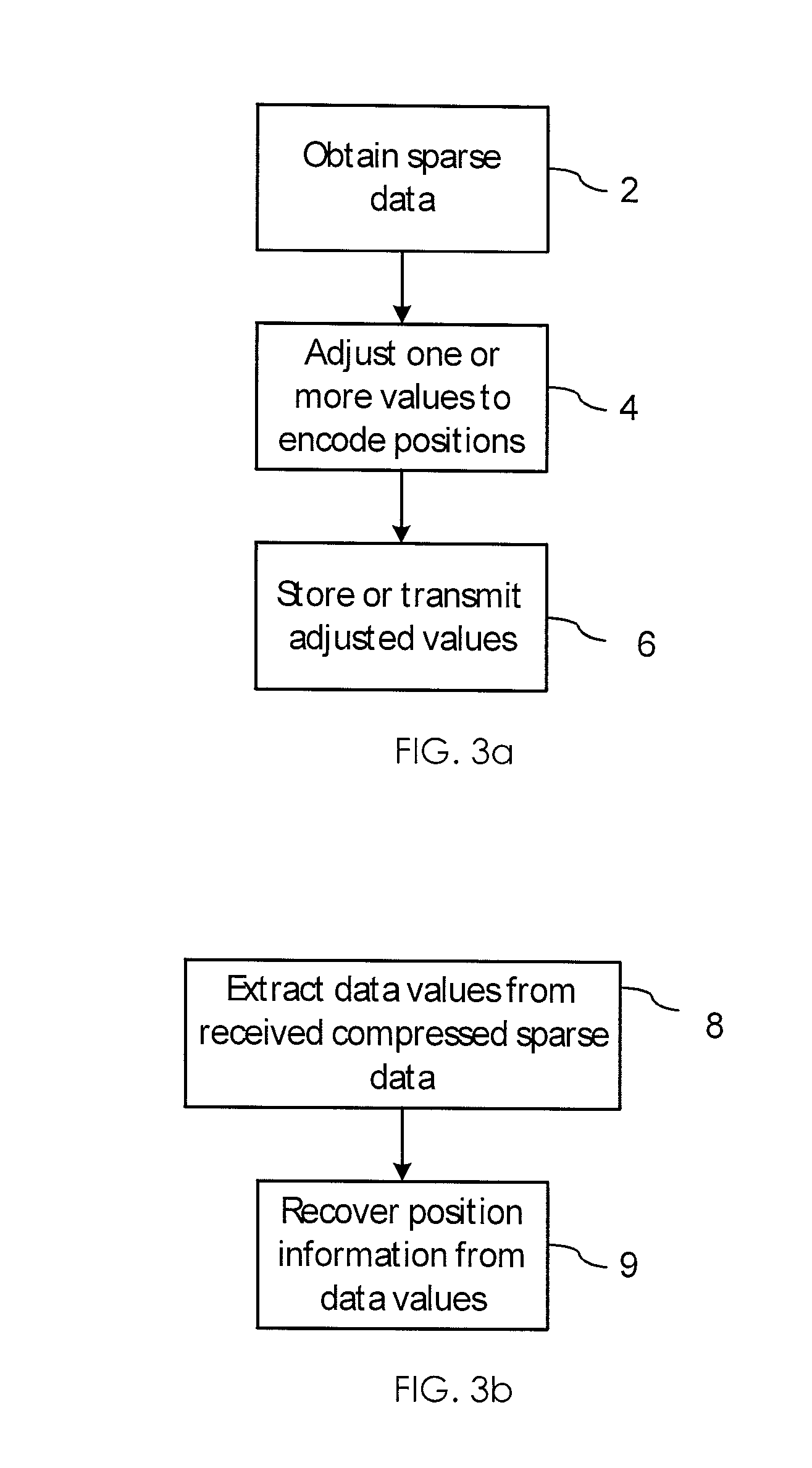
Sparse data compression
The invention relates to compressing of sparse data sets contains sequences of data values and position information therefor. The position information may be in the form of position indices defining active positions of the data values in a sparse vector of length N. The position information is encoded into the data values by adjusting one or more of the data values within a pre-defined tolerance range, so that a pre-defined mapping function of the data values and their positions is close to a target value. In one embodiment, the mapping function is defined using a sub-set of N filler values which elements are used to fill empty positions in the input sparse data vector. At the decoder, the correct data positions are identified by searching though possible sub-sets of filler values.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
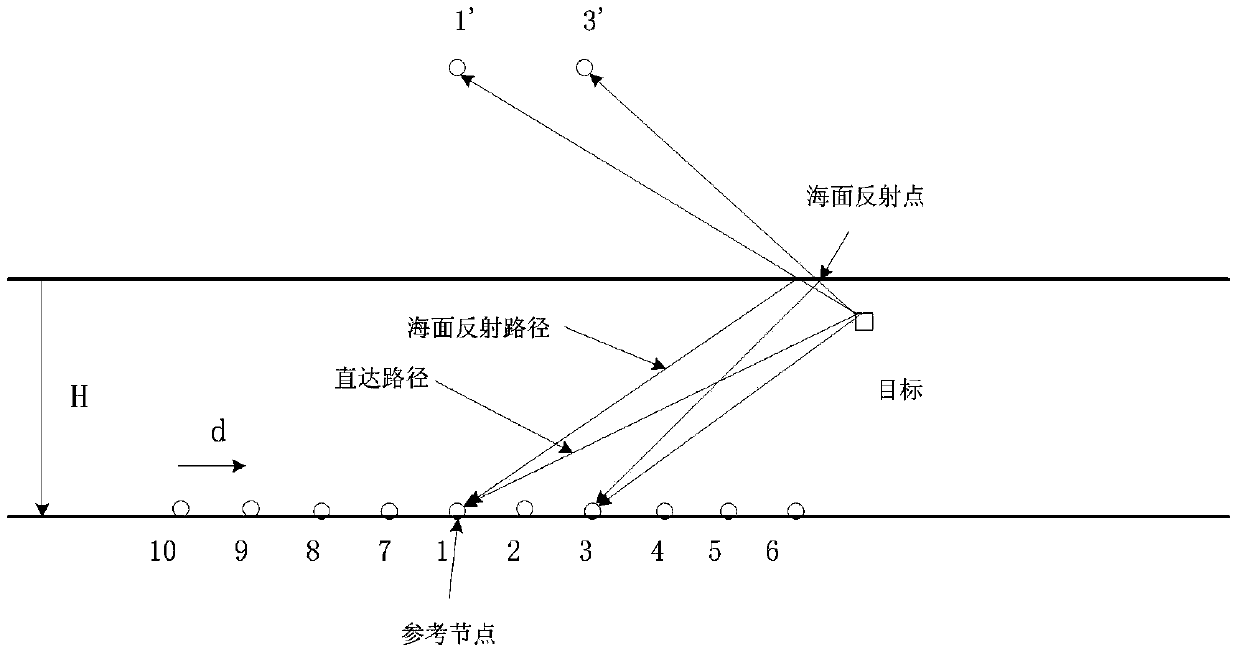
Passive underwater target positioning method based on compressed sensing of multipath time delay structure
The invention discloses a passive underwater target positioning method based on the compressed sensing of a multipath time delay structure. The method includes dividing a positioned three-dimensional region into N grid points; distributing a plurality of underground nodes on the shallow seabed, and positioning according to sea surface reflection path signals of nodes and delays of direct path signals of reference paths; performing sparse representation on the receive signals of the nodes under different delays of reference signal receive nodes; then comprising and sampling node data except for the reference nodes by means of random sampling matrix, positioning the central node and acquiring the target position by acquiring the target position sparse vectors by the compressed sensing recovery algorithm according to node observation data. By the aid of the method, the sampling rate of underground nodes can be decreased greatly, the requirements on underwater communication bandwidth are lowered, and the method is adaptive to target positioning in the multipath underwater environment, is easy to implement and has high practical applicant value.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
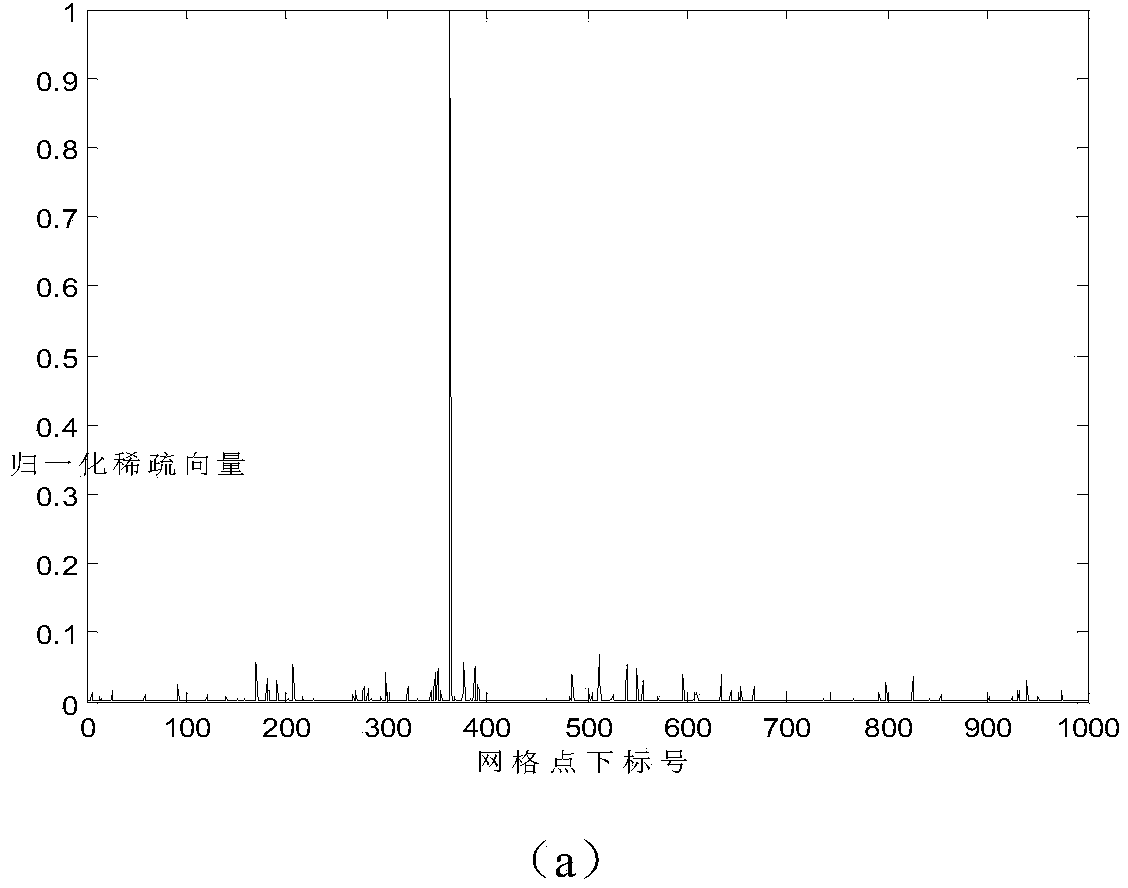
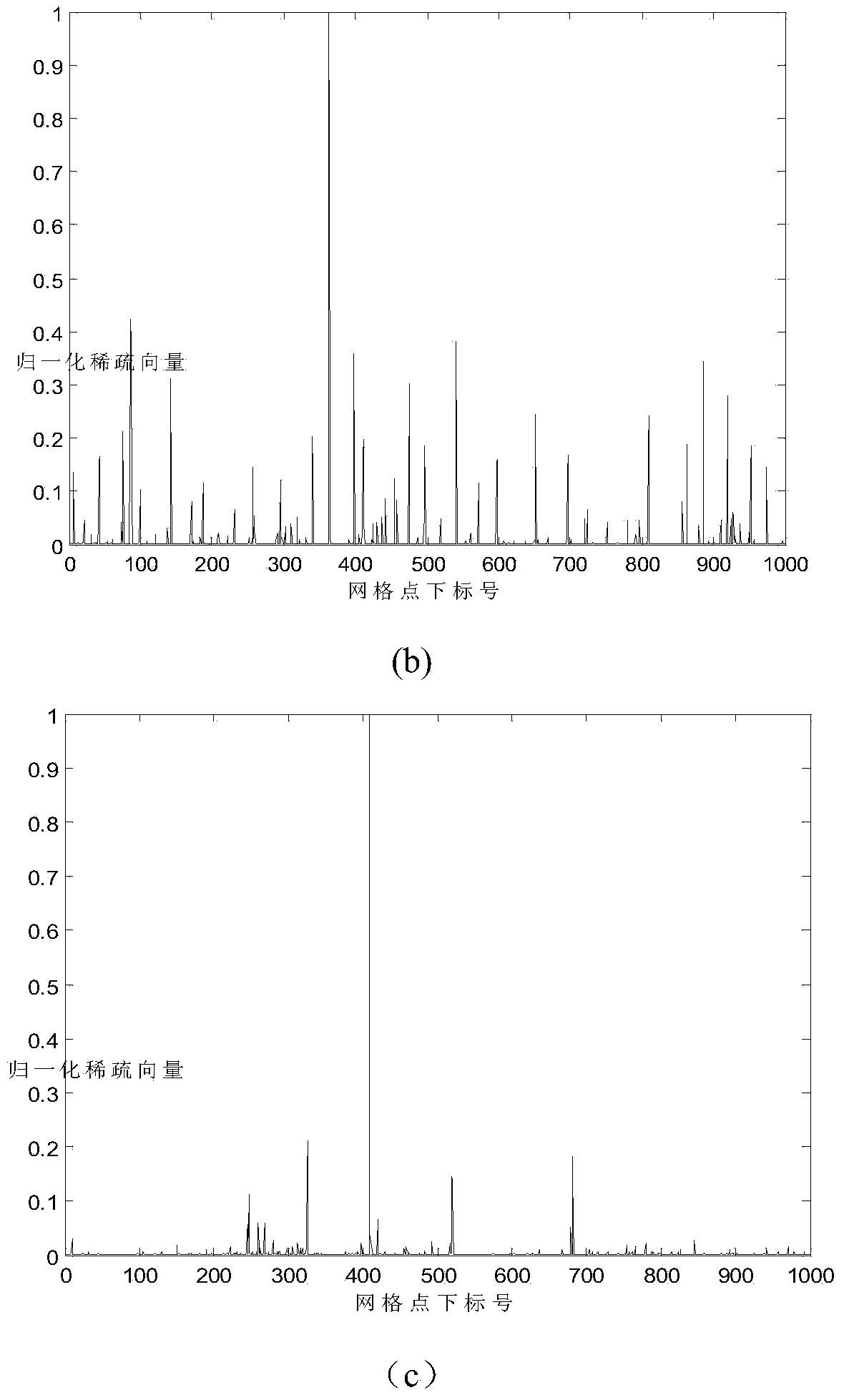
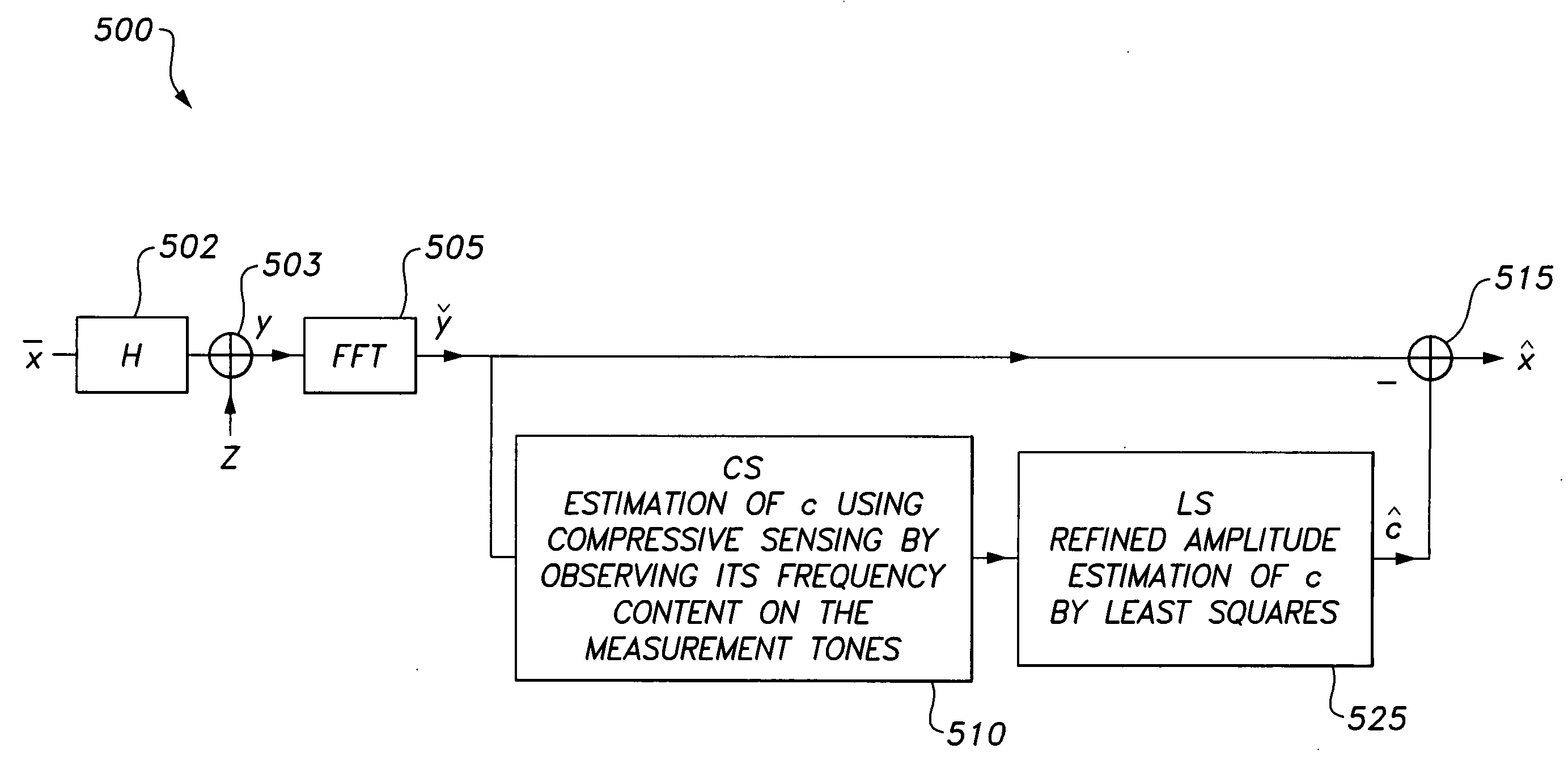
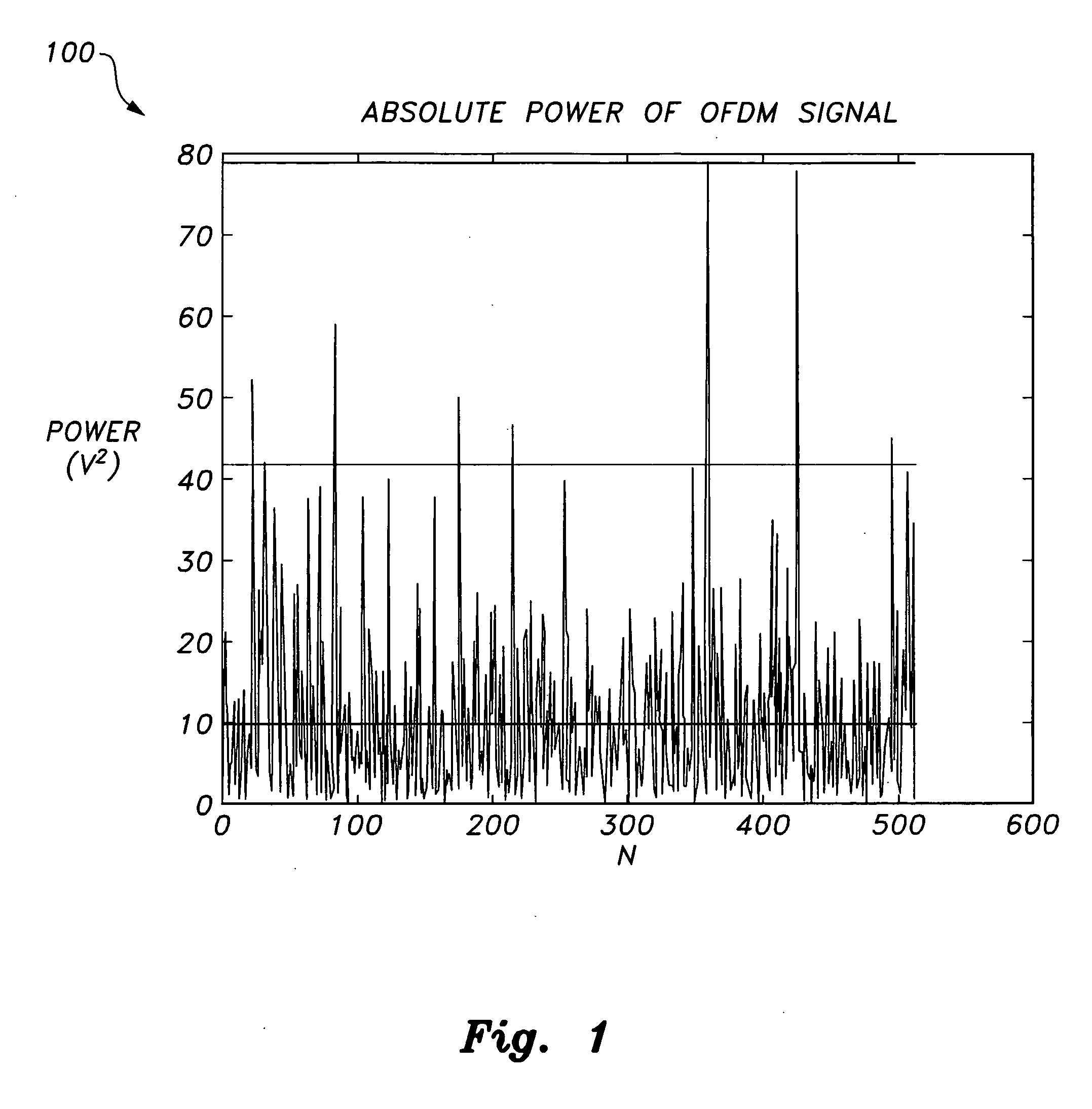
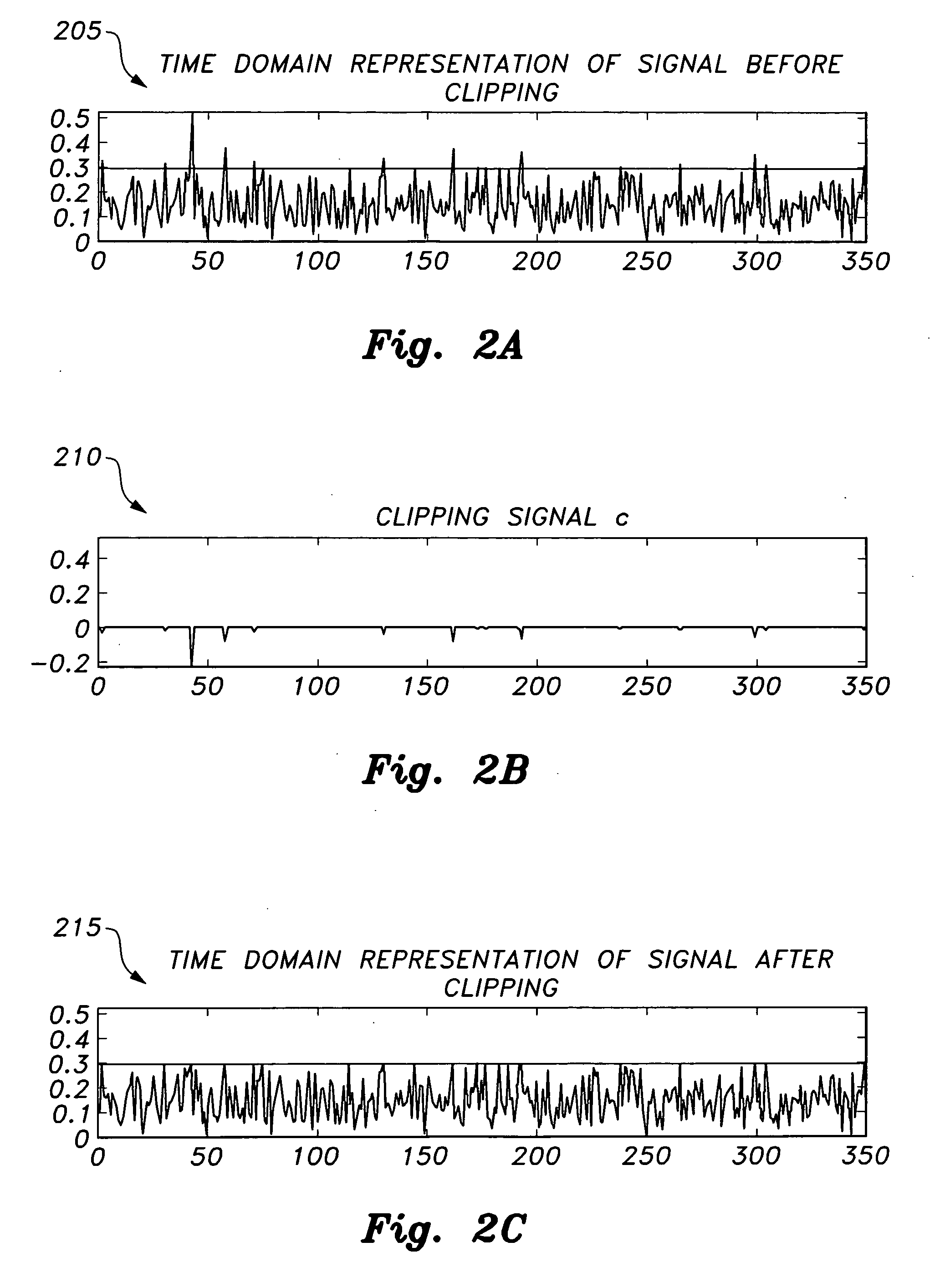
OFDM peak-to-average power ratio reduction method
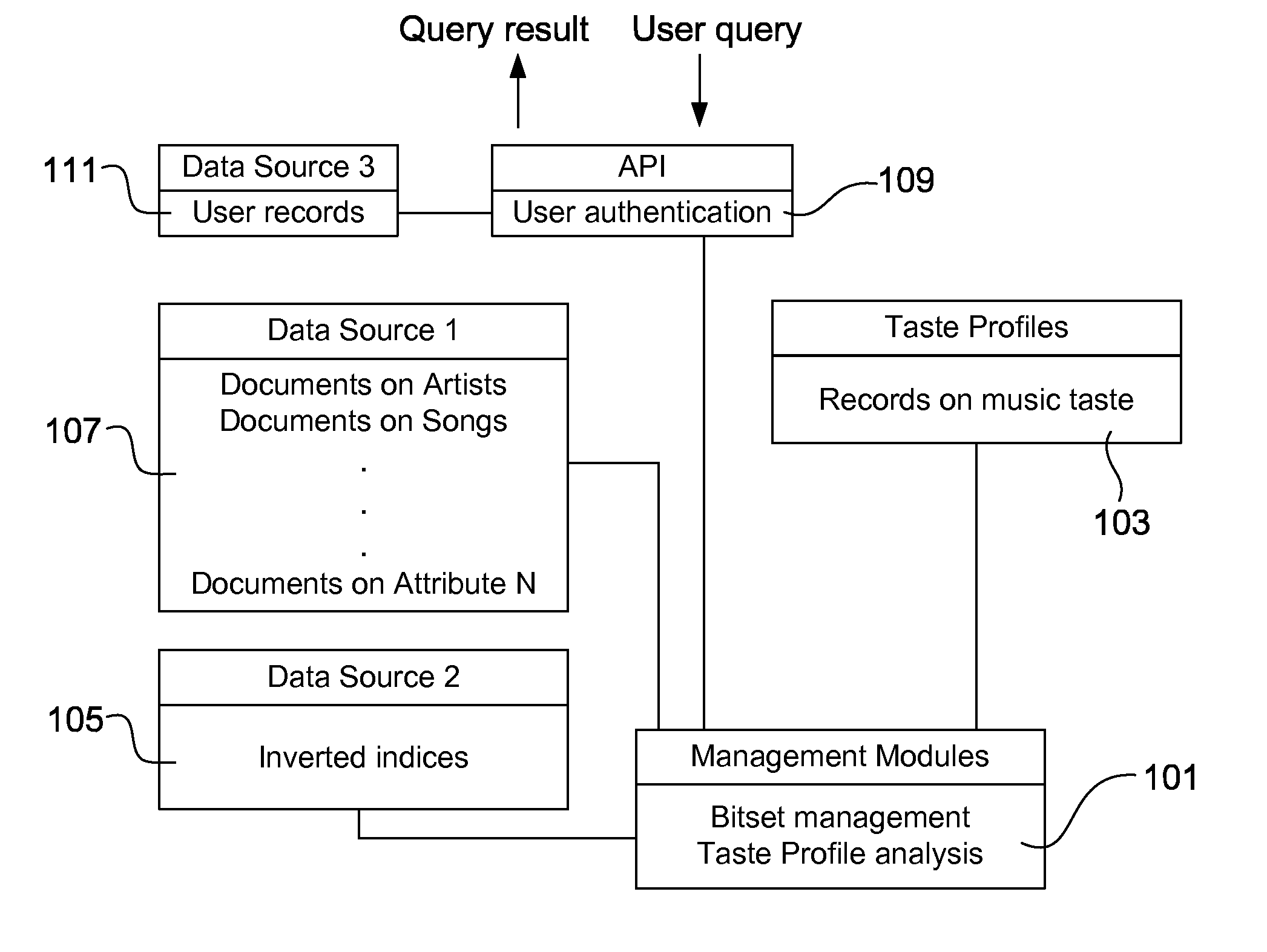
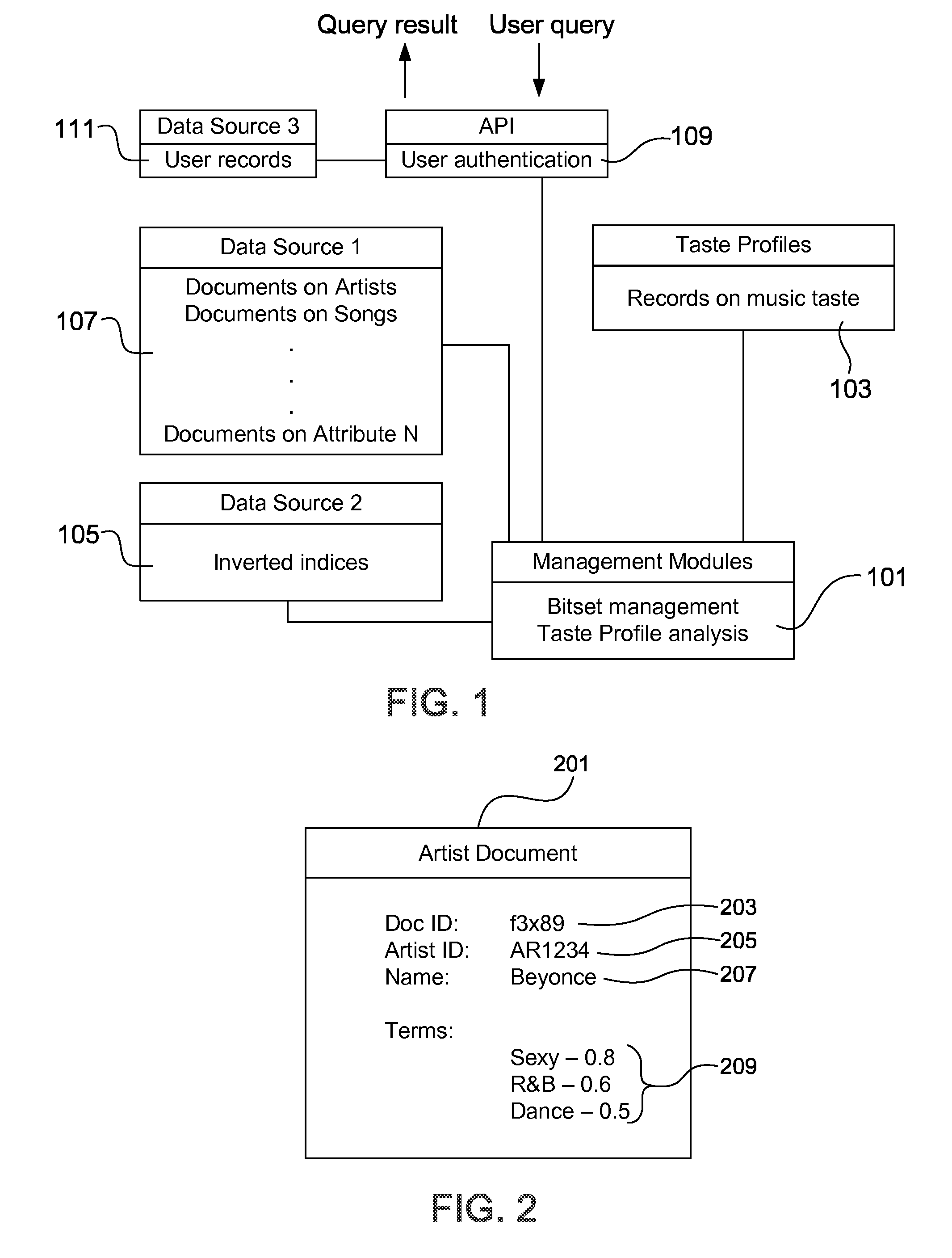
InactiveUS20110122930A1Reduce complexitySimple peak-reducing signalError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionPeak valueComputer science
The OFDM peak-to-average power ratio reduction apparatus and method provides a compressive sensing algorithm that estimates the sparsity pattern of a sparse vector by a limited number of measurements. When the positions of the clipped peaks are known beforehand by, e.g., a genie-augmented receiver, then the algorithm optimally performs amplitude estimation utilizing a least squares estimation technique. When the cardinality of the peak-reducing signal is known at the receiver at initialization, the receiver optimizes the estimated peak-reducing signal by using least squares.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
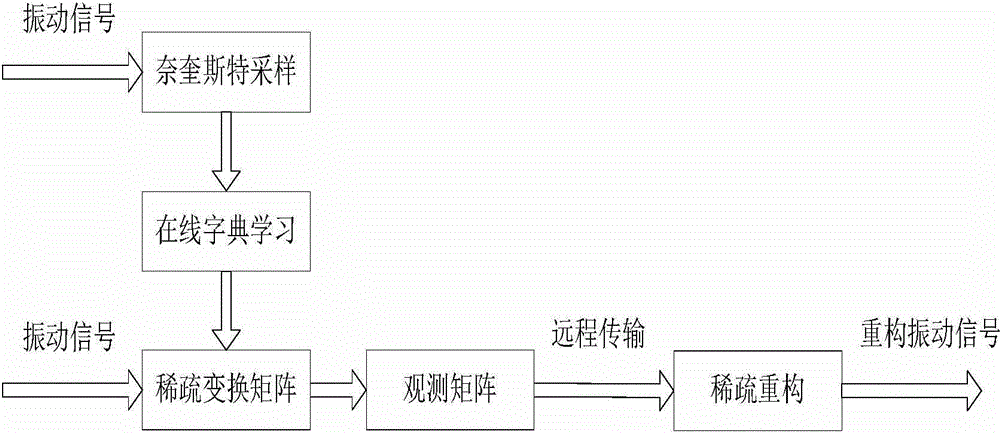
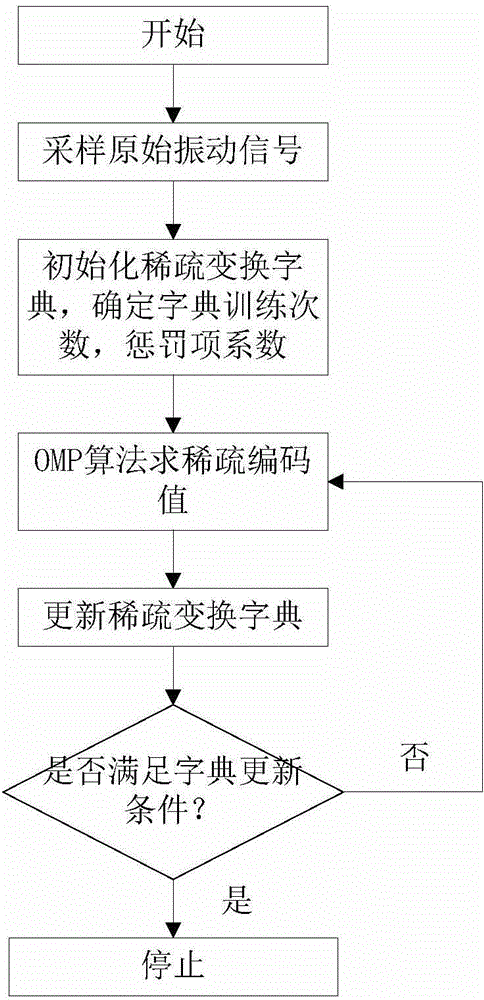
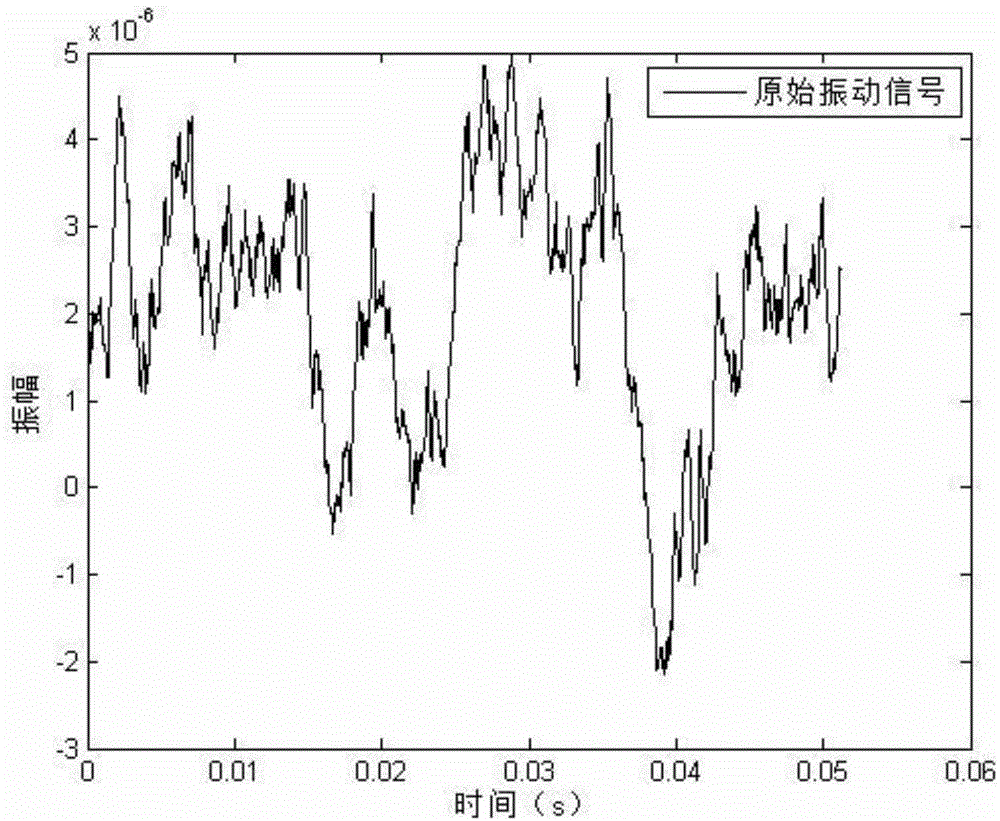
Vibration signal compressing and sampling method
InactiveCN104935349AImprove accuracySparsity is clearly concentratedCode conversionOnline learningSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a vibration signal compressing and sampling method, and belongs to the technical field of processing for mechanical vibration signals. The vibration signal compressing and sampling method can effectively solve the problem of an adaptive ability and an online learning ability. The vibration signal compressing and sampling method comprises the steps of first carrying out Nyquist sampling on continuous vibration signals Xc so as to acquire a prior signal Xp of the vibration signals; constructing a sparse transformation matrix Ds of the prior signal Xp by using an online dictionary learning algorithm; then carrying out sparse transformation on the continuous vibration signals Xc so as to acquire a sparse vector Xs, transmitting the sparse vector Xs to a perception matrix so as to carry out perception sampling to acquire a compressed signal Y; and finally, transmitting the compressed vibration signal Y to a reconstruction recovery terminal, carrying out signal reconstruction, and acquiring a vibration signal Xc with a transverse line thereon. The method disclosed by the invention is mainly applied to long-distance transmission of vibration signals.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
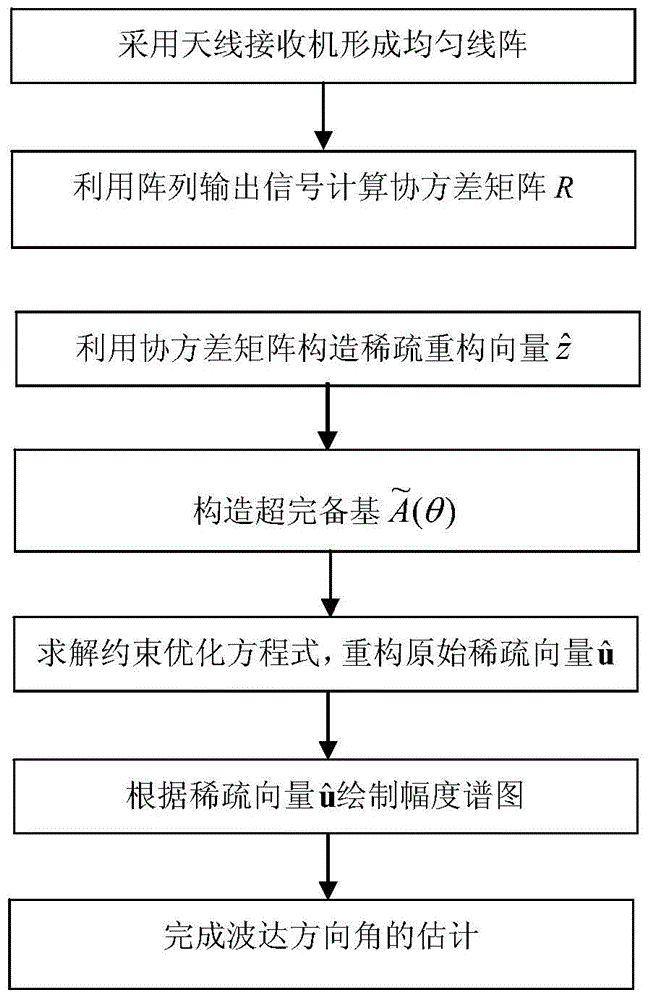
Direction-of-arrival estimation method based on sparse representation
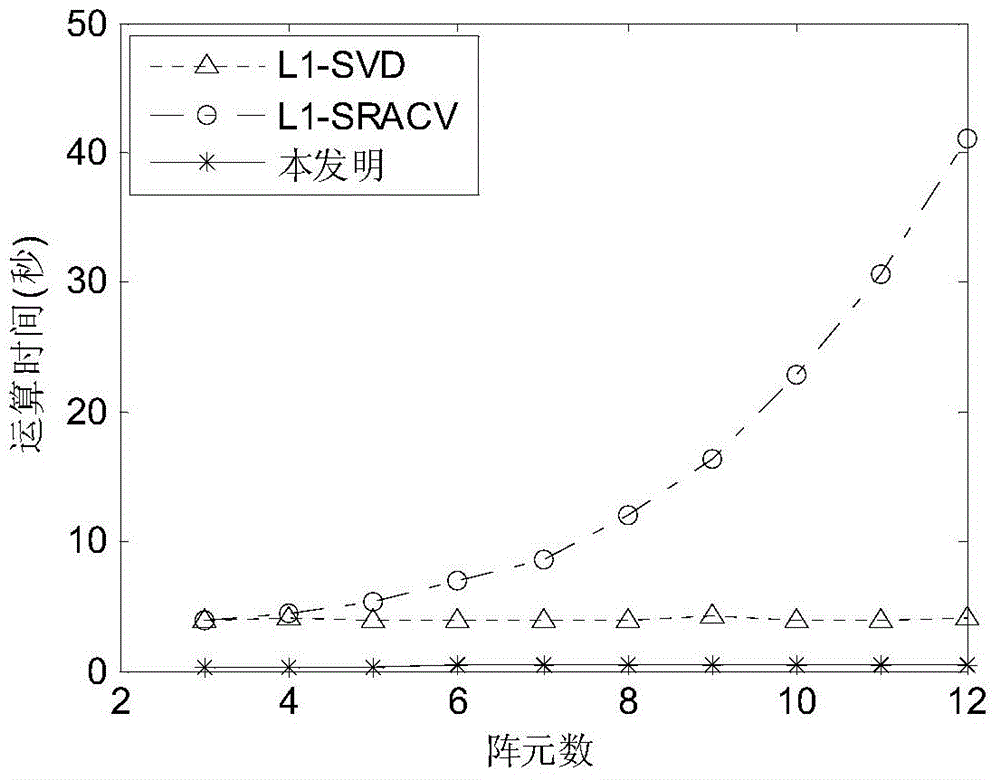
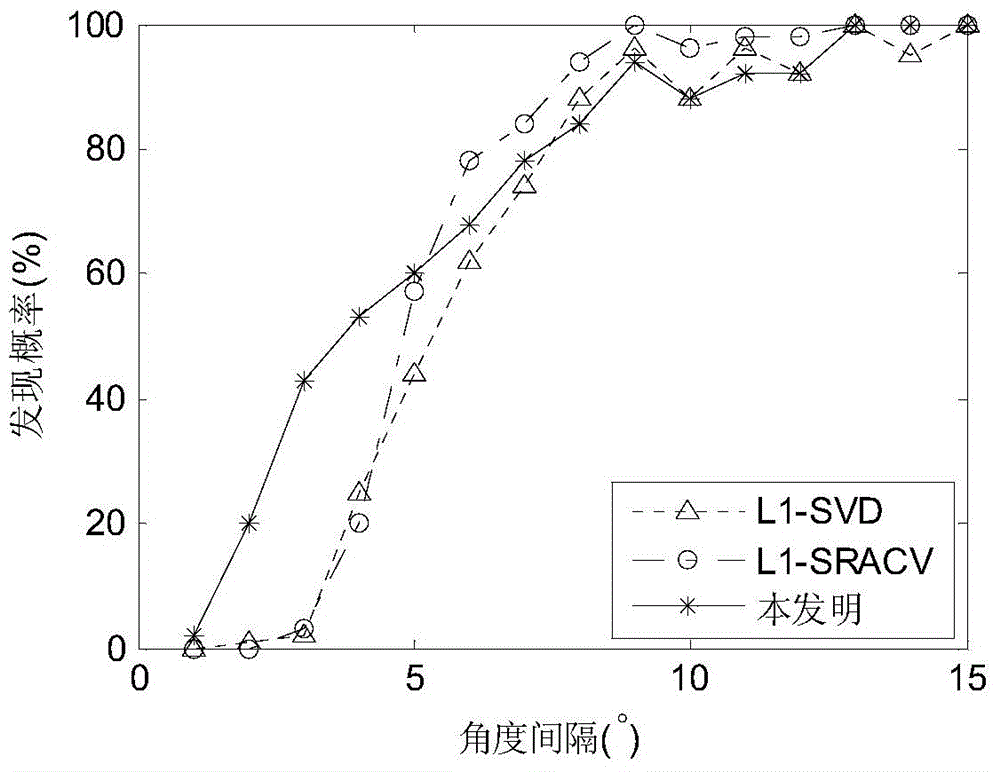
InactiveCN104020438AAvoid anglesBreaking through the Rayleigh limit of resolutionRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsEstimation methodsImage resolution
The invention discloses a direction-of-arrival estimation method based on sparse representation. The method mainly solves the problems that because a similar technology is large in calculation amount and low in angular resolution, the estimation speed of target reconnaissance and passive location is low and estimation errors in target reconnaissance and passive location are large. The method comprises the implementation steps: (1) acquiring output signals of an array and calculating a covariance matrix R of the signals, (2) constructing reconstructed sparse vectors through lower triangular elements of the covariance matrix R, (3) carrying out mesh generation on a spatial domain to construct a perfect base, (4) converting the direction-of-arrival estimation issue into the issue of solving a constrained optimization equation according to the sparse representation relation between the reconstructed sparse vectors and the perfect base, (5) solving the constrained optimization equation according to the convex optimization method to obtain the optimal estimation vectors, (6) drawing a magnitude spectrum according to the one-to-one correspondence of the optimal estimation vectors and spatial domain angles to obtain the direction-of-arrival value. By means of the method, the calculation speed of target reconnaissance and passive location is decreased, and the estimation errors in target reconnaissance and passive location are reduced. The method can be applied to target reconnaissance and passive location.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
FDD large-scale MIMO channel estimation pilot frequency optimization method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN105978674AReduce mean square errorImprove estimation performanceChannel estimationPilot signal allocationMean squareGreek letter epsilon
The invention discloses an FDD large-scale MIMO channel estimation pilot frequency optimization method based on compressed sensing, and the method comprises the steps: firstly enabling a channel to be modeled into a formula in a large-scale MIMO system: Y=HX+N, wherein H (shown in the description) is a channel matrix, X (shown in the description) is a pilot frequency matrix, Y (shown in the description) is a receiving signal matrix, and N (shown in the description) is channel noise, M is the number of transmitting antennas, and T is the number of pilot frequencies; secondly carrying out the conversion of the channel matrix, and solving the conjugate matrix (shown in the description) of Y, wherein the conjugate matrix (shown in the description) of the channel matrix represents the conversion form of the channel matrix, the conjugate matrix (shown in the description) of the pilot frequency matrix represents the conversion form of the pilot frequency matrix, and the conjugate matrix (shown in the description) of the receiving signal matrix represents the conversion form of the receiving signals of a receiving end; and finally solving an optimal pilot frequency matrix. Because the conjugate matrix (shown in the description) of the channel matrix is a sparse vector, a channel estimation problem can be modeled into a compressed sensing reconstruction problem shown in the description, wherein ||*||<1> represents 1-norm, ||*||<2> represents 2-norm, and epsilon is greater than zero and less than one. The method can guarantee that the FDD MIMO downlink channel estimation based on compressed sensing can remarkably reduce the mean square error of channel estimation, and improves the channel estimation performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
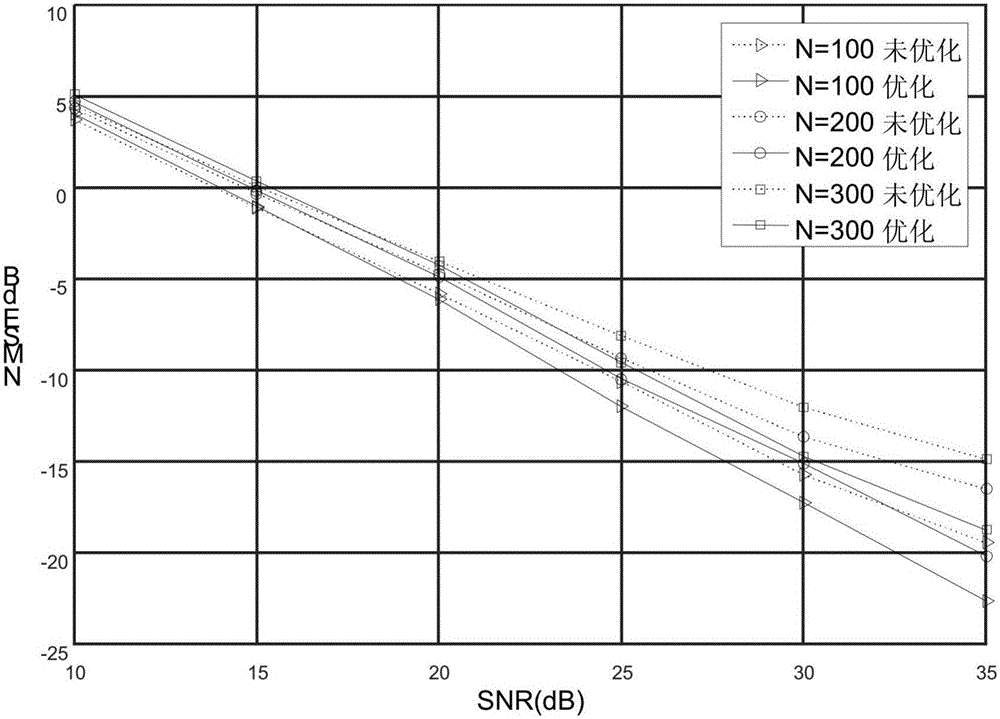
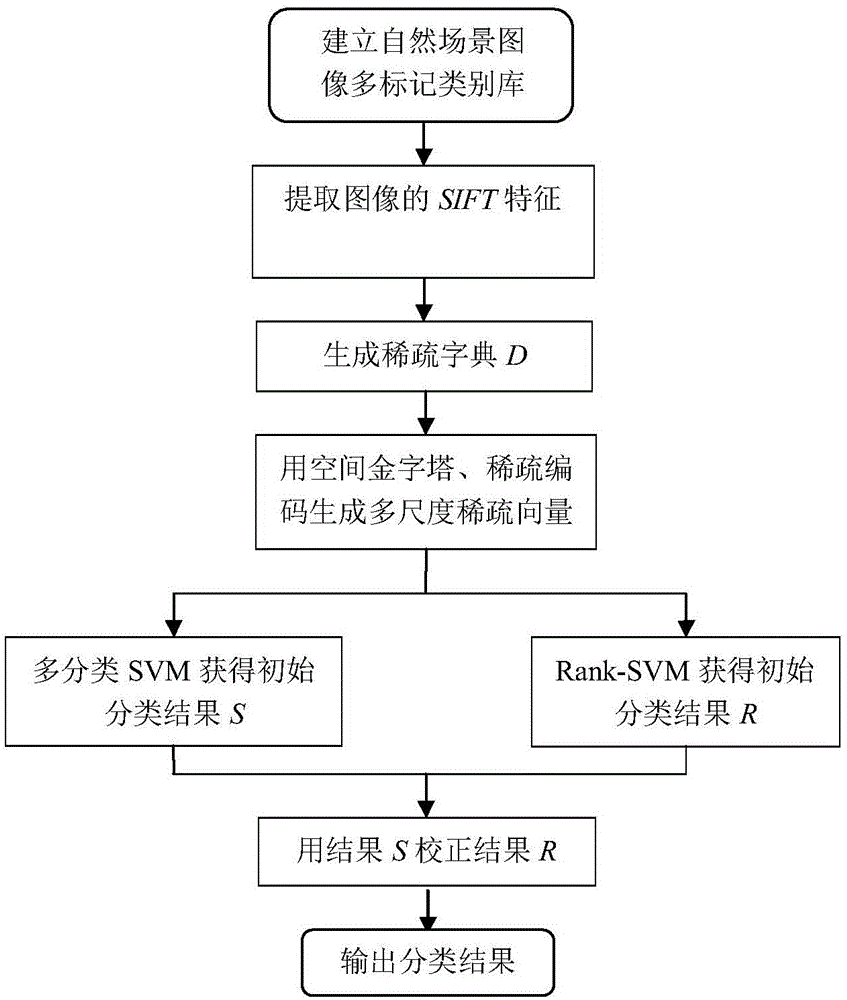
Multi-label natural scene classification method based on spatial pyramid and sparse coding
ActiveCN105069481AImprove classification accuracyImprove robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineClassification methods
The invention discloses a multi-label natural scene classification method based on spatial pyramid and sparse coding, and mainly aims at solving the problems that a present classification method cannot completely describe a natural scene and the classification accuracy is relatively low. The method comprises the steps that a multi-label class library of a natural scene is established; the scale invariant feature (SIFT) of the class library is extracted to generate a sparse dictionary D; the sparse dictionary is used to carry out dictionary mapping on the image, and the spatial pyramid and sparse coding are used to generate a multi-scale sparse vector; and a classification result of a multi-class support vector machine is used to correct and order classification results of a support vector machine, and further to obtain the final classification result of the natural scene image. The multi-scale feature, sparse coding and multi-scale classification method is used, local information of the image is extracted, characteristic information of the is enriched, the natural scene is described more comprehensively, the classification precision and robustness of the natural scene are improved, and the method can be used to match, classify and identify the natural scenes.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
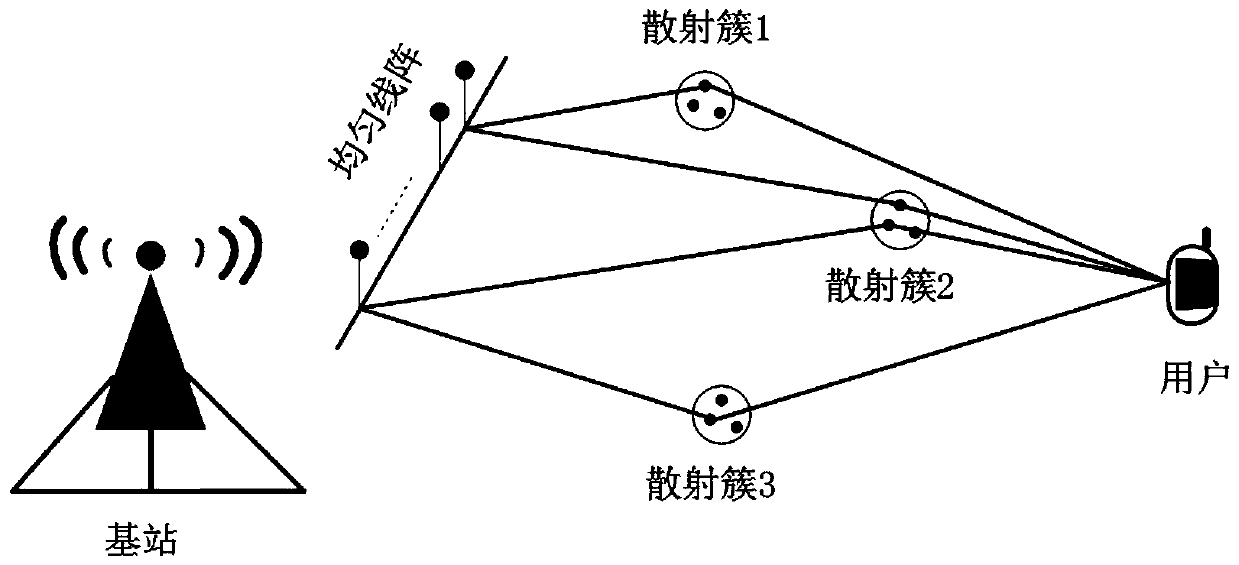
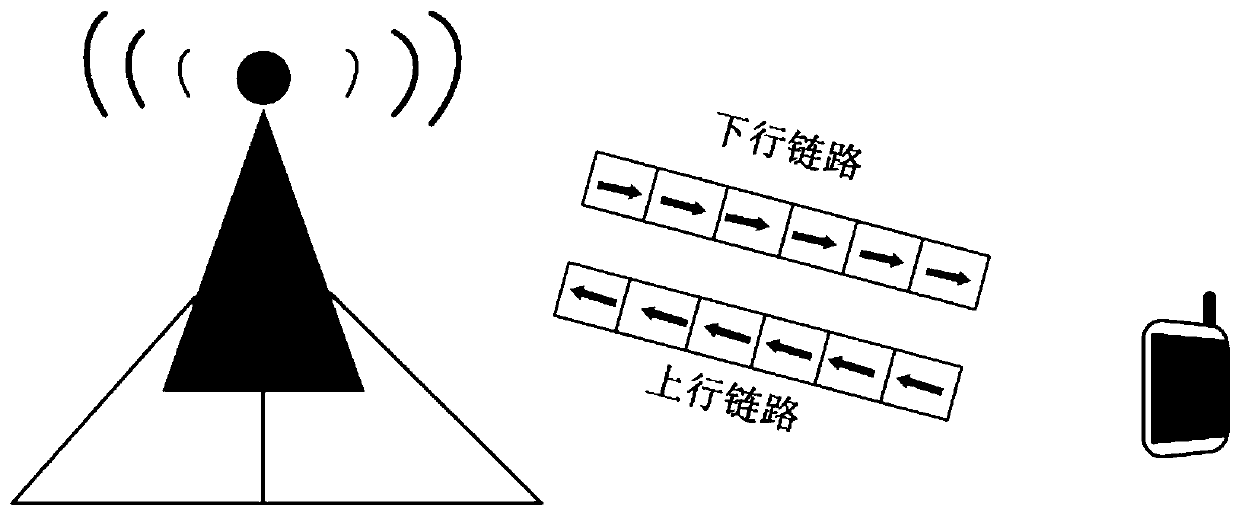
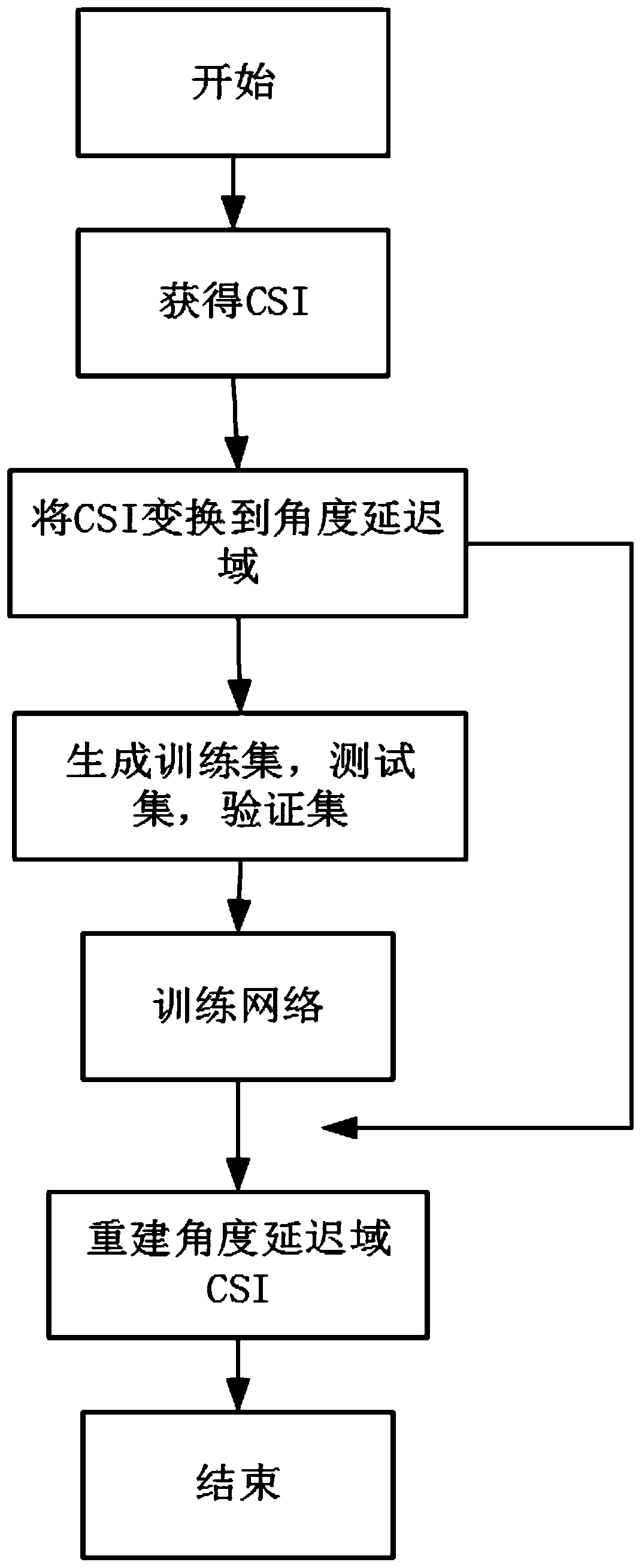
Channel state information reconstruction method based on deep learning
ActiveCN111464220AReduce overfittingEasy to compressSpatial transmit diversityChannel estimationOriginal dataInformation networks
The invention discloses a channel state information reconstruction method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an NBS * Nc-dimensional channel matrix H on a frequency domain at a user side; converting the obtained channel matrix H into an angle delay domain channel matrix Ha with only non-zero elements; in the angle time delay domain, acquiring a new dimension matrix by advancing in the intercepted channel matrix Ha, converting the new matrix into a non-sparse vector X with the dimension of 2N * 1, wherein the non-sparse vector X serves as to-be-compressed data, and carrying out compression through the compressed sensing technology to obtain to-be-fed back channel state information Y; reconstructing and training a channel state information network; and according to the trained ReNet network model, recovering Y as input data of the network and as output data of the network from the obtained channel state information Y to be fed back, and performinginverse Fourier transform to obtain original CSI after obtaining. The original CSI data obtained by the user side is processed, subsequent compression and feedback are facilitated, and recovery ofthe compressed data is completed through the network trained by the known samples.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
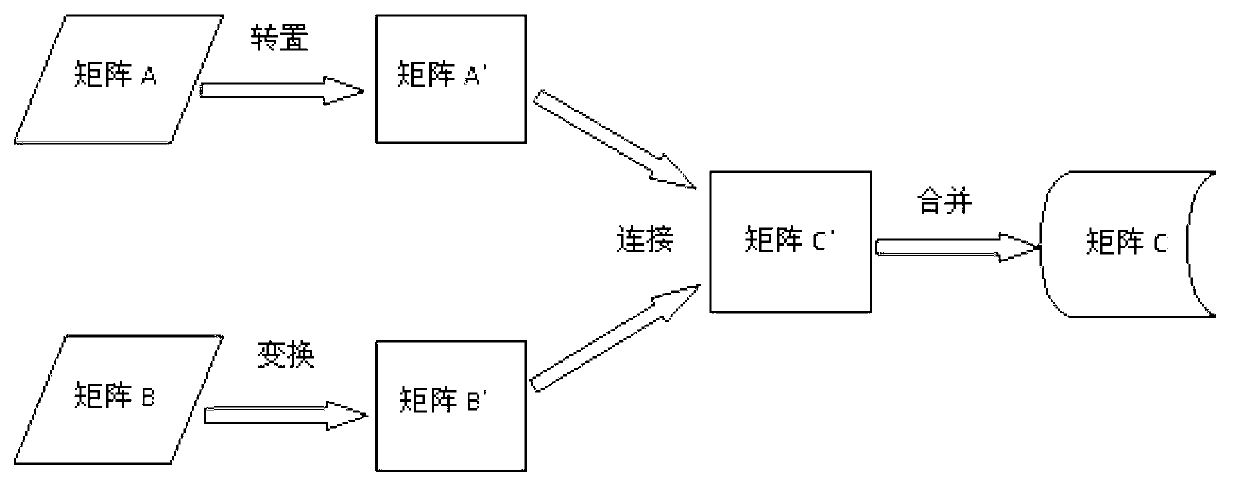
Large-scale sparse matrix multiplication method based on mapreduce
InactiveCN103106183AReduce restrictionsCalculation speedDigital data processing detailsComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmSparse matrix multiplication
The invention provides a large-scale sparse matrix multiplication method based on mapreduce. Suppose that the large-scale sparse matrixes are A and B, and a multiplication matrix of A and B is C. The method includes the following steps: step 10, a mapreduce Job finishes transposing of the matrix A and outputting of a matrix A'; step 20, a transformational matrix B converts a storage mode using the matrix B as a coordinate point into a storage mode of sparse vector, and outputs a matrix B'; step 30, connecting the matrix A' and the matrix B', calculating a product component, obtaining the product component of a column number K on the matrix A and column number K on the matrix B of Cij; step 40, merging the product components, calculating Cij through accumulation of the product components Cij_k. The large-scale sparse matrix multiplication is converted into basic operations of transposition and transformation, connection and merging and the like which are suitable for mapreduce calculation, and the problem of resource limit of a single machine large-scale sparse matrix multiplication is solved.
Owner:FUJIAN TQ DIGITAL
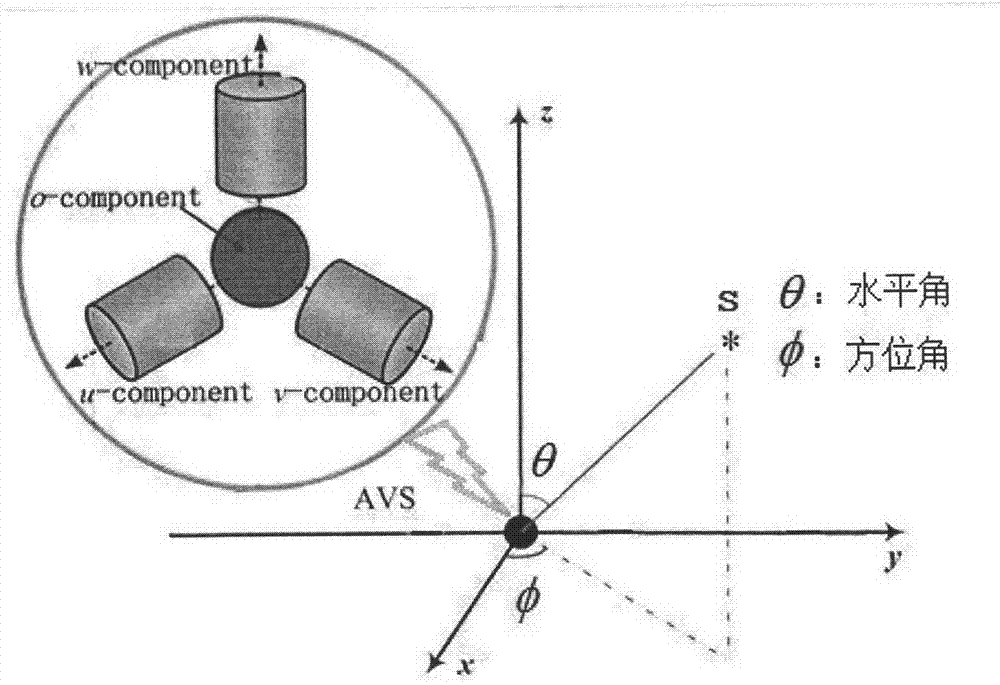
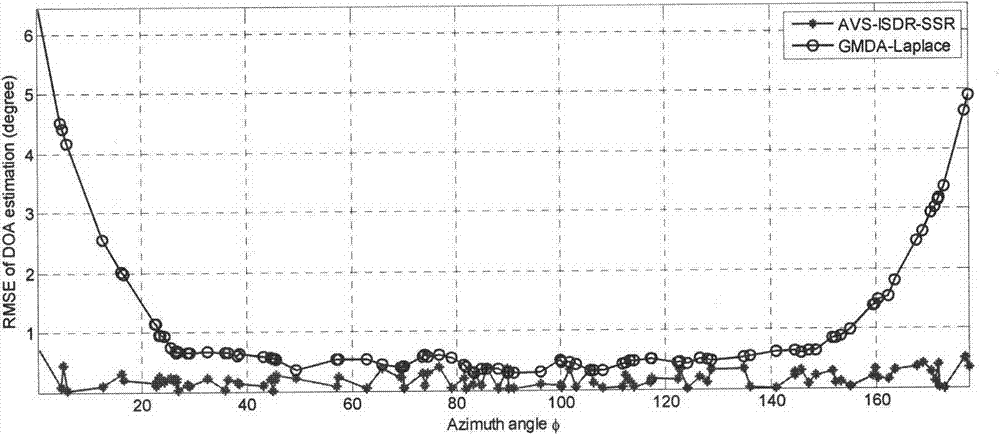
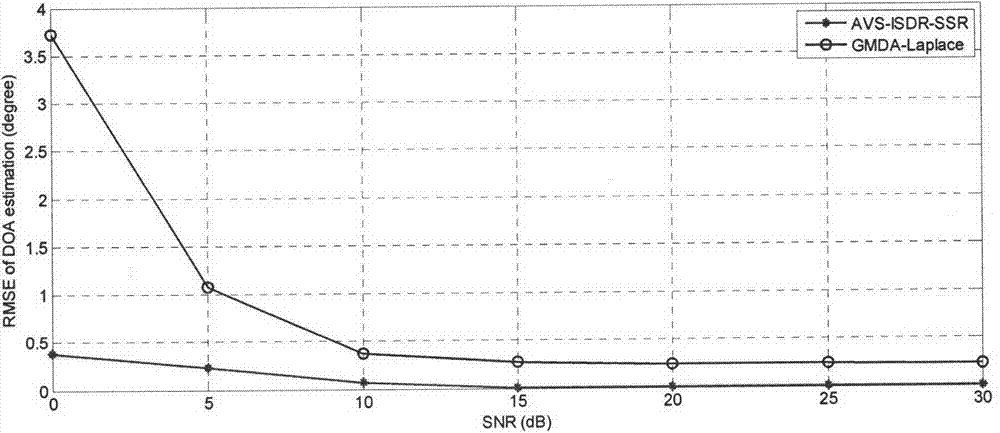
Monolingual sound source DOA estimation method based on AVS and sparse representation
ActiveCN103760520AReduce complexityEasy to integrateDirection/deviation determination systemsSound sourcesTrack algorithm
The invention provides a monolingual sound source DOA estimation method based on an AVS and sparse representation. According to the method, the acoustic vector sensor is adopted to collect audio signals, high signal-to-noise ratio time frequency points are extracted by utilizing the trigonometric function relationship between the time frequency sparse characteristic of the voice signals and the receiving component of the AVS and adopting a sine track algorithm, and the ratio of data of a pressure gradient sensor to data of an all-around pressure sensor is calculated. On the basis, an over-complete dictionary sparse representation model for the ratio of data of the sensors is acquired through the spatial sparse characteristic of a sound source, and the monolingual sound source direction-of-arrival estimation problem is converted into a sparse vector solving problem. The sparse vector is solved with the l1-SVD method, the spatial power spectrum is calculated, and the DOA of the monolingual sound source can be obtained through calculation. The DOA of the monolingual sound source can be accurately estimated under conditions of different noise intensities and room reverberations with the method. Besides, a microphone array adopted for the method is small in size and only has the area of 1 cm<3>, and thus the method is very suitable for the voice technology for portable devices.
Owner:SHENZHEN HIAN SPEECH SCI & TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com