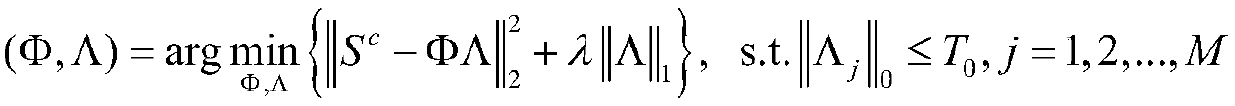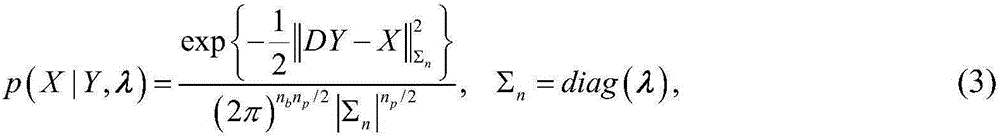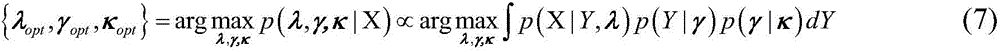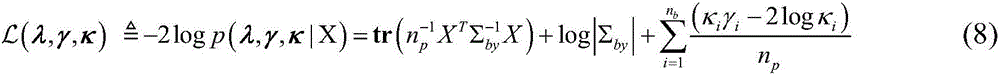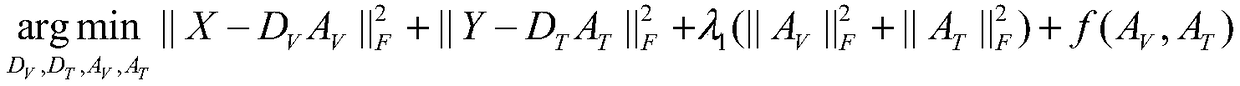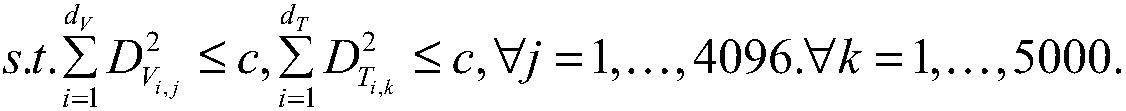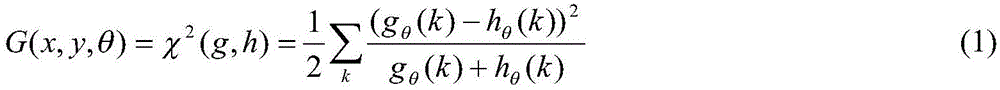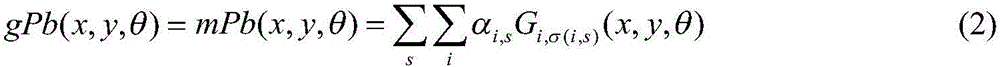Patents
Literature
972 results about "Dictionary learning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dictionary learning is a branch of signal processing and machine learning that aims at finding a frame (called dictionary) in which some training data admits a sparse representation.
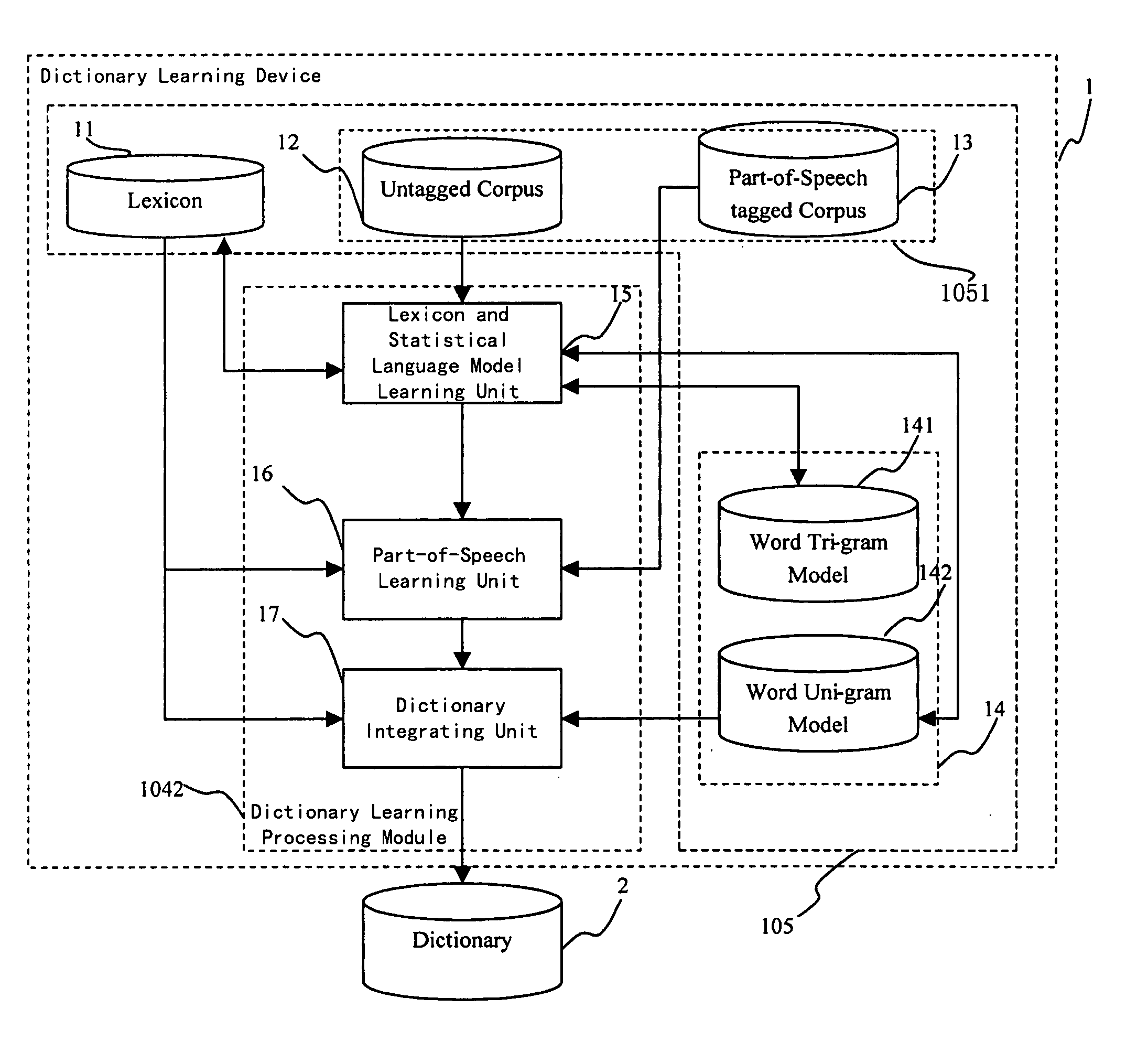
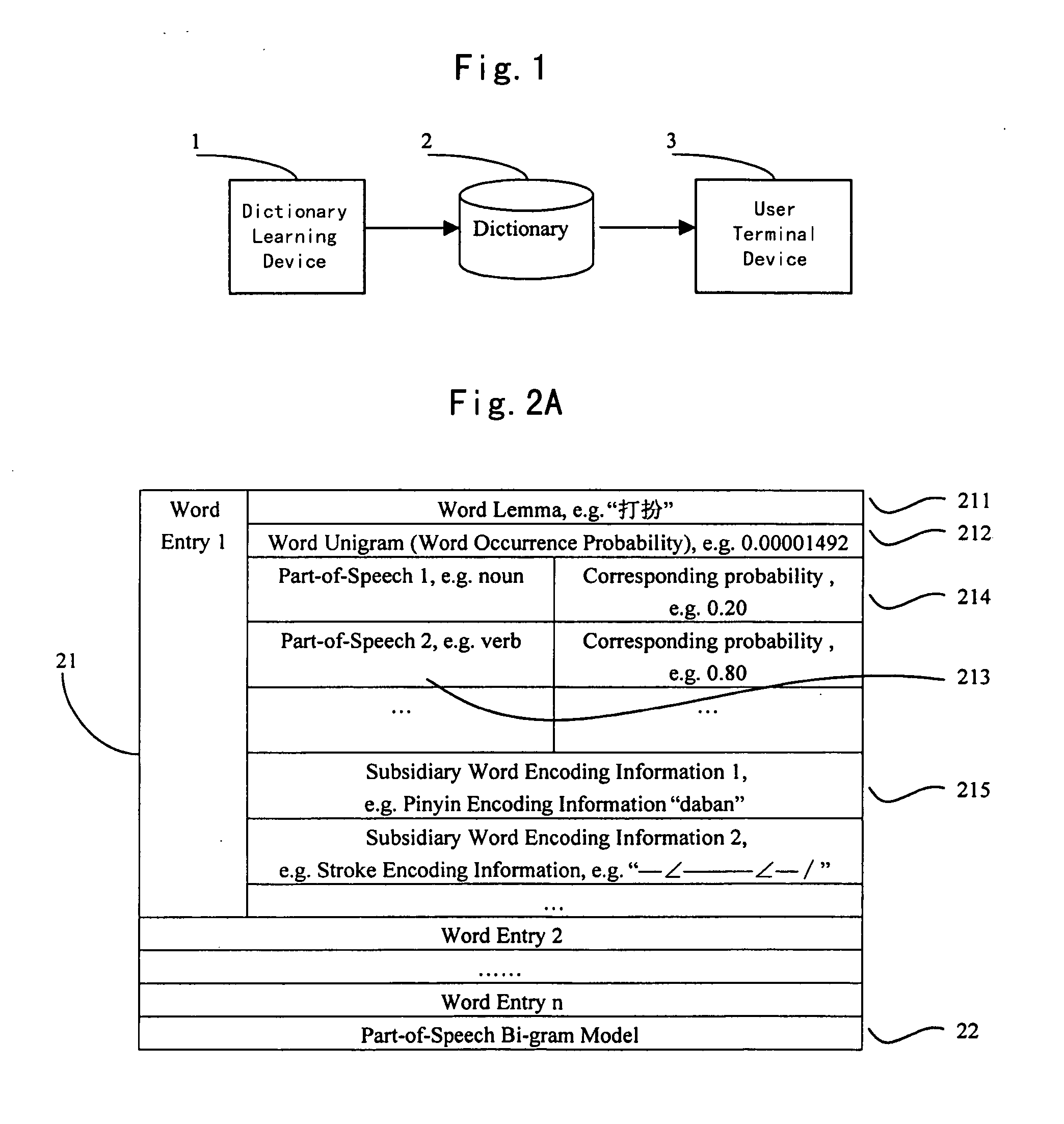
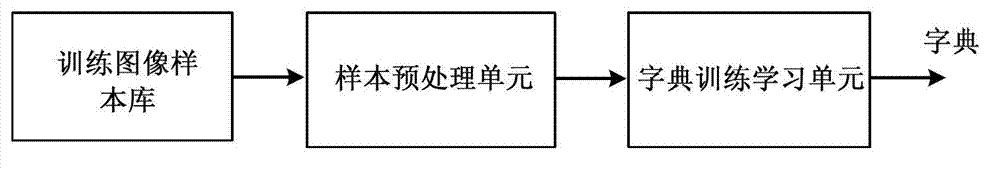
Dictionary learning method and device using the same, input method and user terminal device using the same
InactiveUS20060206313A1Increase typing speedSmall sizeConveyorsCleaningDictionary learningPart of speech
This invention provides a dictionary learning method, said method comprising the steps of: learning a lexicon and a Statistical Language Model from an untagged corpus; integrating the lexicon, the Statistical Language Mode and subsidiary word encoding information into a small size dictionary. And this invention also provides an input method on a user terminal device using the dictionary with Part-of-Speech information and a Part-of-Speech Bi-gram Model added, and a user terminal device using the same. Therefore, sentence level prediction and word level prediction can be given by the user terminal device and the input is speeded up by using the dictionary which is searched by a Patricia Tree index of a dictionary index.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
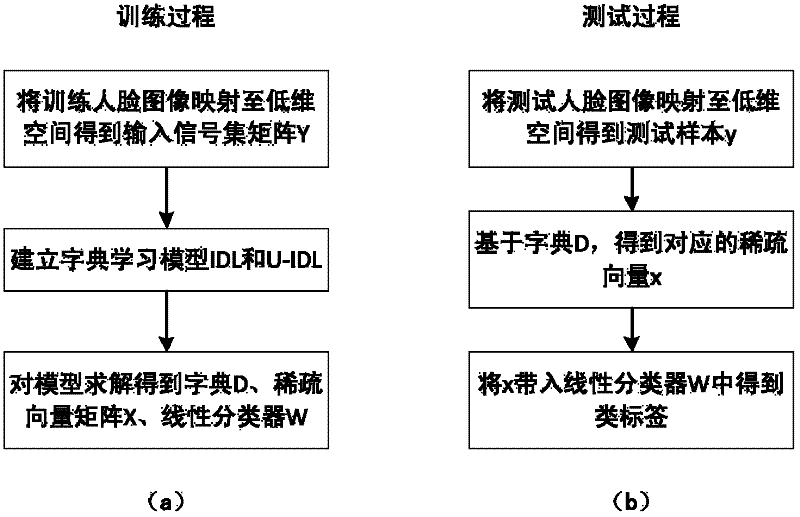
Face recognition method based on dictionary learning models
InactiveCN102609681AImprove the accuracy of face recognitionCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningPattern recognition
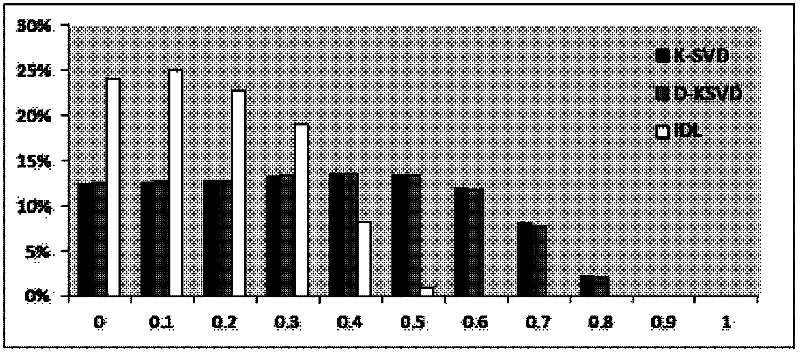
The invention discloses a face recognition method based on dictionary learning models. The method comprises the following steps of: mapping trained and tested face images to a low-dimension space to acquire a training signal set matrix; establishing the dictionary learning models which comprise an irrelevant dictionary learning (IDL) model and an unconstrained irrelevant dictionary learning (U-IDL) model; inputting the training signal set matrix into the IDL and U-IDL models, and solving the models to acquire an irrelevant dictionary and a linear classifier; acquiring a corresponding sparse vector of each picture belonging to a test sample based on the dictionary acquired in the last step by using a sparse expression algorithm; and inputting the sparse vectors into the linear classifier to acquire category labels of test sample pictures, wherein the result expressed by the category labels is used as the face recognition result. The invention provides the new models and the new method for dictionary learning problems in sparse expression, and the models and the method can be applied to mode identification and image classification problem under common conditions; and particularly, aiming at face recognition application, the dictionary learning method can achieve relatively high face recognition accuracy.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
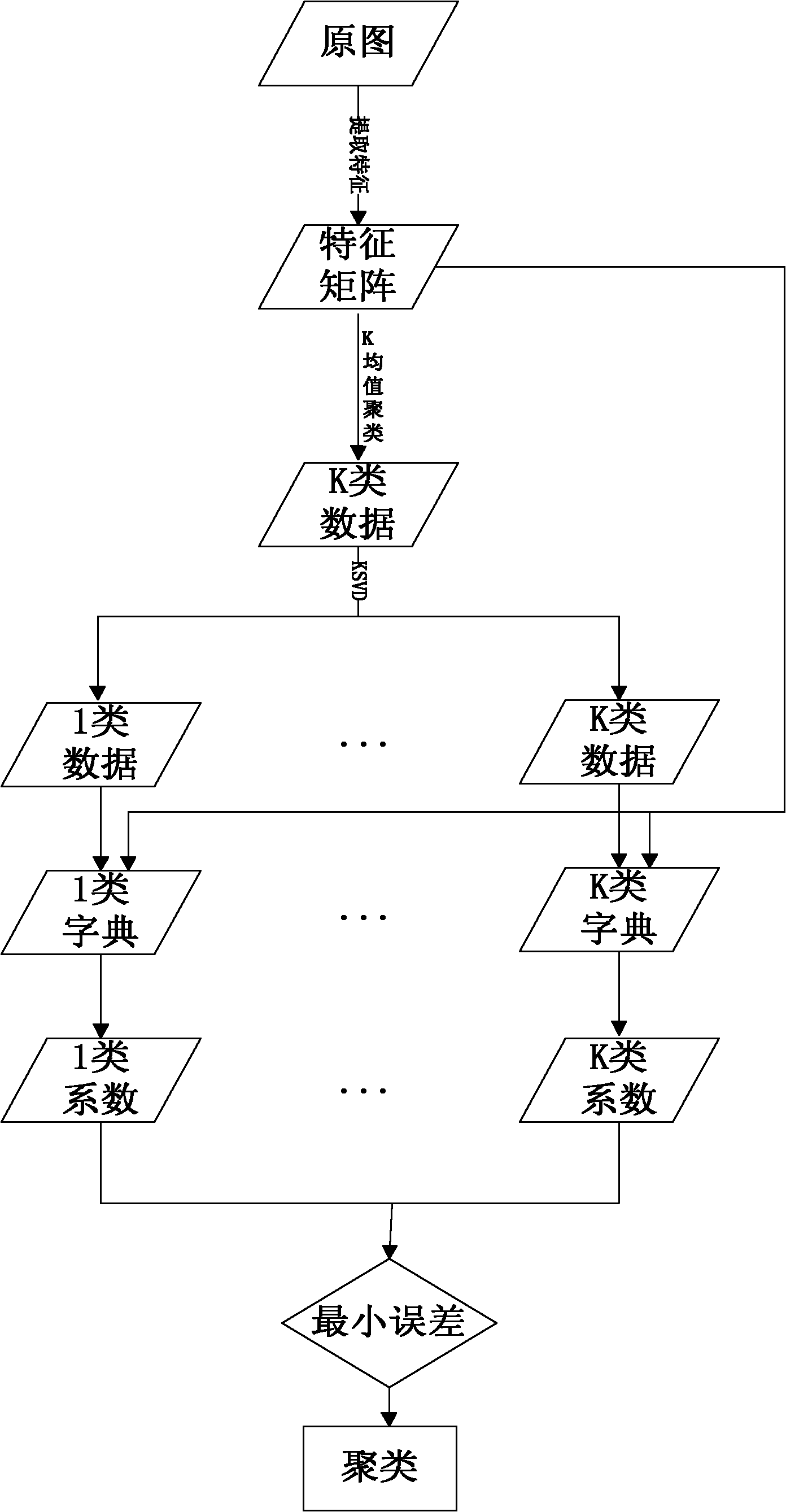
Multi-task super-resolution image reconstruction method based on KSVD dictionary learning
ActiveCN101950365AReduce refactoring timeQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDictionary learning
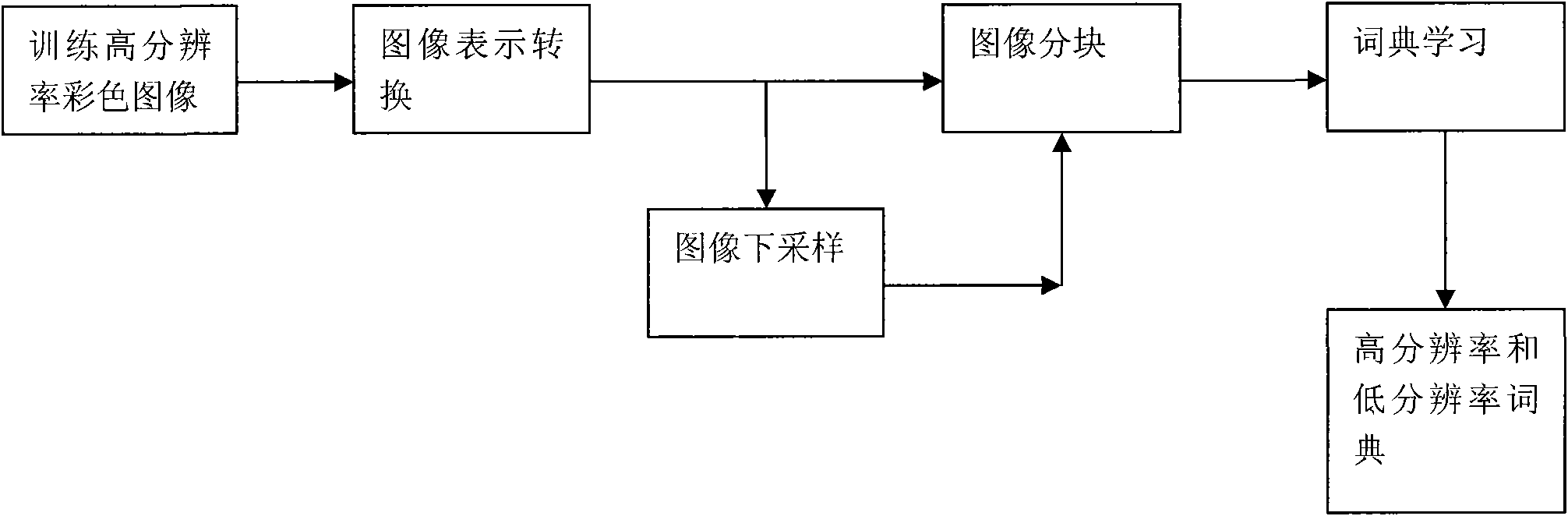
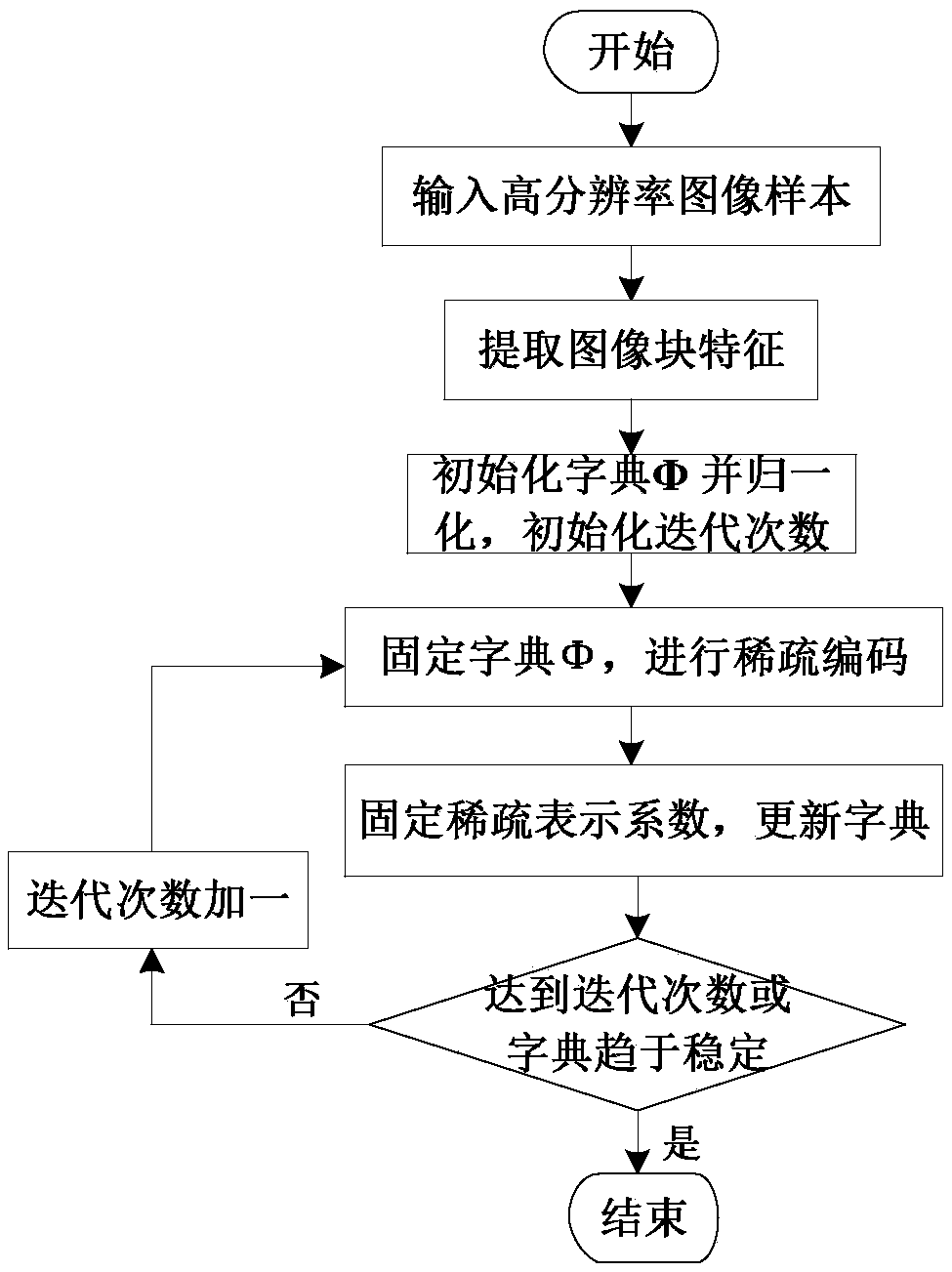
The invention discloses a multi-task super-resolution image reconstruction method based on KSVD dictionary learning, which mainly solves the problem of relatively serious quality reduction of the reconstructed image under high amplification factors in the existing method. The method mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, inputting a training image, and filtering the training image to extract features; extracting image blocks to construct a matrix M, and dividing the matrix M into K classes to acquire K pairs of initial dictionaries H1, H2...Hk and L1, L2...Lk; then, training the K pairs of initial dictionaries H1, H2...Hk and L1, L2...Lk into K pairs of new dictionaries Dh1, Dh2...Dhk and Dl1, Dl2...Dlk by utilizing a KSVD method; and finally, carrying out super-resolution reconstruction on the input low-resolution image by utilizing a multi-task algorithm and the dictionaries Dh1, Dh2...Dhk and Dl1, Dl2...Dlk to acquire a final reconstructed image. The invention can reconstruct various natural images containing non-texture images such as animals, plants, people and the like and images with stronger texture features such as buildings and the like, and can effectively improve the quality of the reconstructed image under high amplification factors.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Single image super-resolution rebuilding method
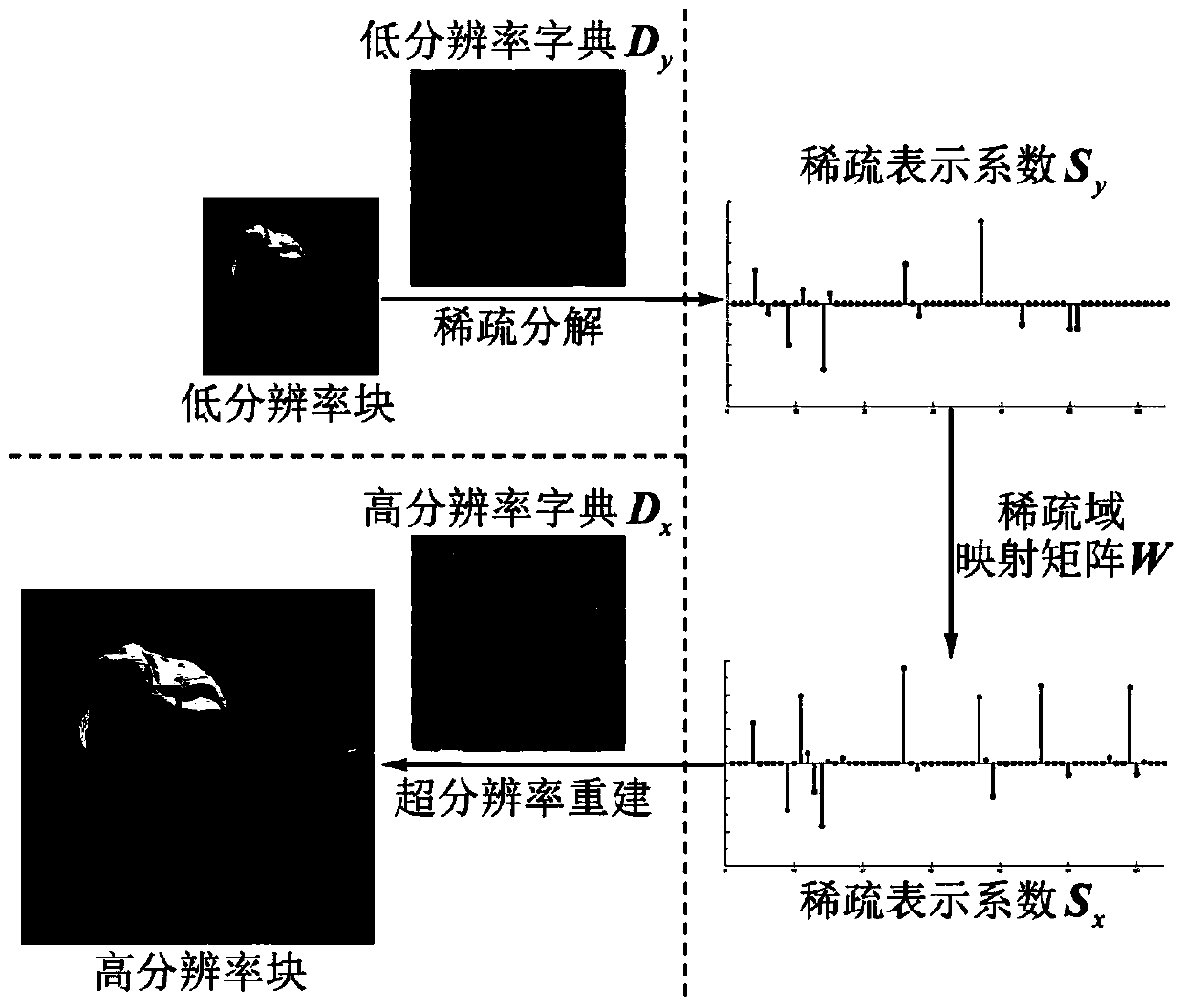
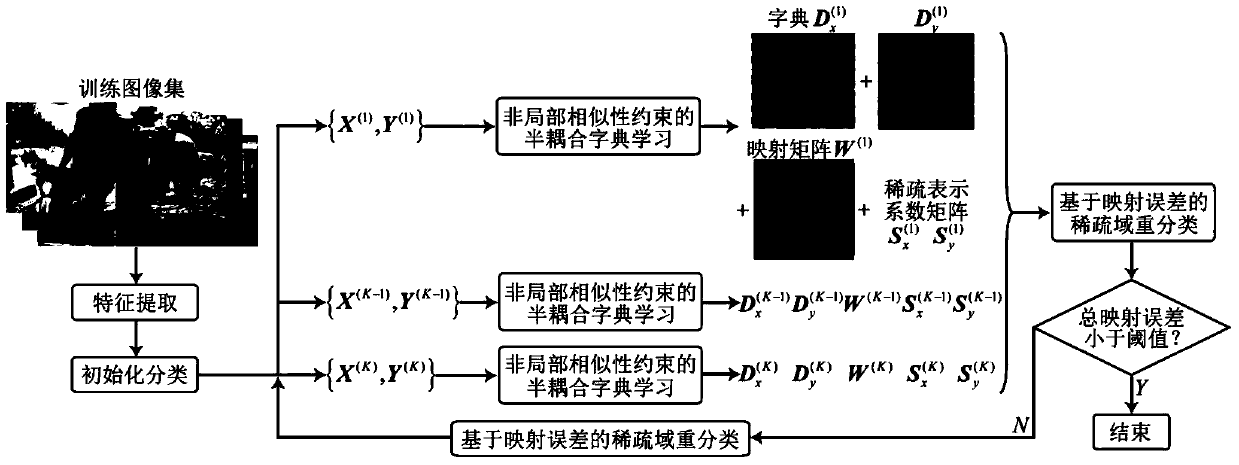
InactiveCN103617607AGood effectImprove visual effectsImage enhancementGeometric image transformationDictionary learningPattern recognition
The invention discloses a single image super-resolution rebuilding method. Based on non-local similarity and a classification half-coupling dictionary learning algorithm, the method comprises a training stage and a rebuilding stage. According to the method, the half-coupling dictionary learning algorithm is used as a framework, training image block sparse domain classification based on mapping errors is introduced, and a heuristic method strategy conducted alternatively through the sparse domain classification and the half-coupling dictionary learning is adopted; sparse domain non-local similarity restriction items are introduced, structural information of training image block space is excavated in the sparse domain so as to rebuild more high-frequency details; the sparse representation algorithm based on non-local restriction is improved to meet the requirements of the half-coupling dictionary learning algorithm overall framework; further, an error compensation mechanism is introduced into the rebuilding stage to further improve the super-resolution rebuilding quality. Compared with the prior art, the method improves rebuilt texture details and forge edge and saw tooth removal, achieves good effects, and achieves best subjective visual effect in the prior art.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
RGB-D image classification method and system
ActiveCN105224942AAccurate classificationFast classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningRgb image
The invention relates to an RGB-D image classification method and system. The method comprises the steps of: S1, utilizing a convolution neural network (CNN) to process a source RGB image and a Depth image respectively, and extracting low level characteristics; S2, utilizing a recursion neural network (RNN) to carry out feedback learning on the image low level characteristics, and extracting image middle level characteristics; S3, adopting a block interior constraint dictionary learning method, carrying out characteristic set sparse expression on the image middle level characteristics, and obtaining high level characteristics of the RGB-D images; and S4, inputting the high level characteristics of the RGB-D images into a linear SVM to complete the classified identification of the RGB-D images. According to the invention, automatic characteristic extraction of the images is realized, learning RGB-D image characteristic expressions can effectively distinguish classification of noise data from high similarity images, and the classification precision of the RGB-D images is improved; in addition, the linear SVM is utilized, and the image classification speed is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image segmentation method based on dictionary learning and sparse representation
InactiveCN102129573AShorten the timeImage segmentation results are goodCharacter and pattern recognitionSingular value decompositionInverse synthetic aperture radar
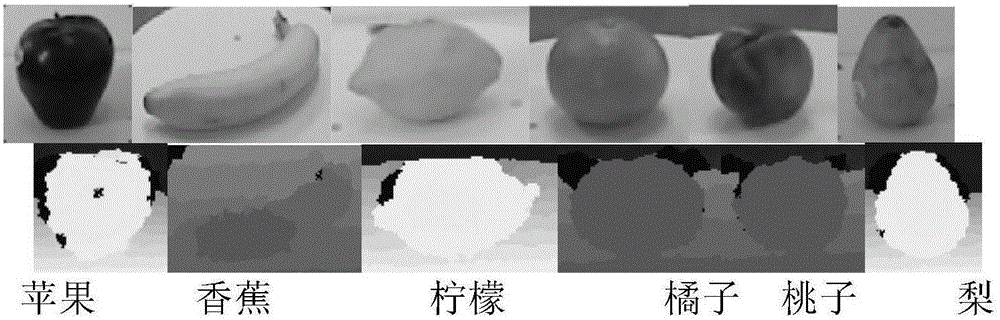
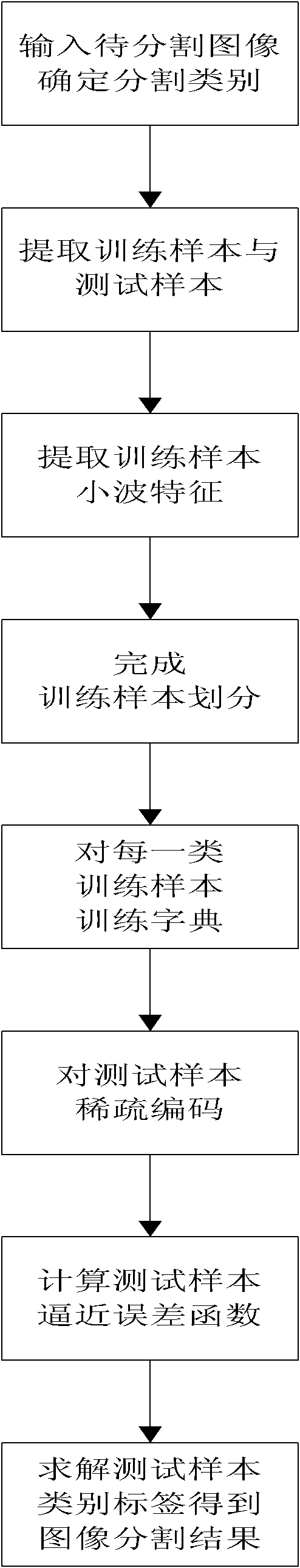
The invention discloses a SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image segmentation technique based on dictionary learning and sparse representation, and mainly solves the problems that the existing feature extraction needs a lot of time and some defects exist in the distance measurement. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inputting an image to be segmented, and determining a segmentation class number k; (2) extracting a p*p window for each pixel point of the image to be segmented so as to obtain a test sample set, and randomly selecting a small amount of samples from the test sample set to obtain a training sample set; (3) extracting wavelet features of the training sample set; (4) dividing the training sample set by using a spectral clustering algorithm; (5) training a dictionary by using a K-SVD (Kernel Singular Value Decomposition) algorithm for each class of training samples; (6) solving sparse representation vectors of the test sample on the dictionary; (7) calculating a reconstructed error function of the test sample; and (8) calculating a test sample label according to the reconstructed error function to obtain the image segmentation result. The invention has the advantages of high segmentation speed and favorable effect; and the technique can be further used for automatic target identification of SAR images.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Image super-resolution method based on overcomplete dictionary learning and sparse representation
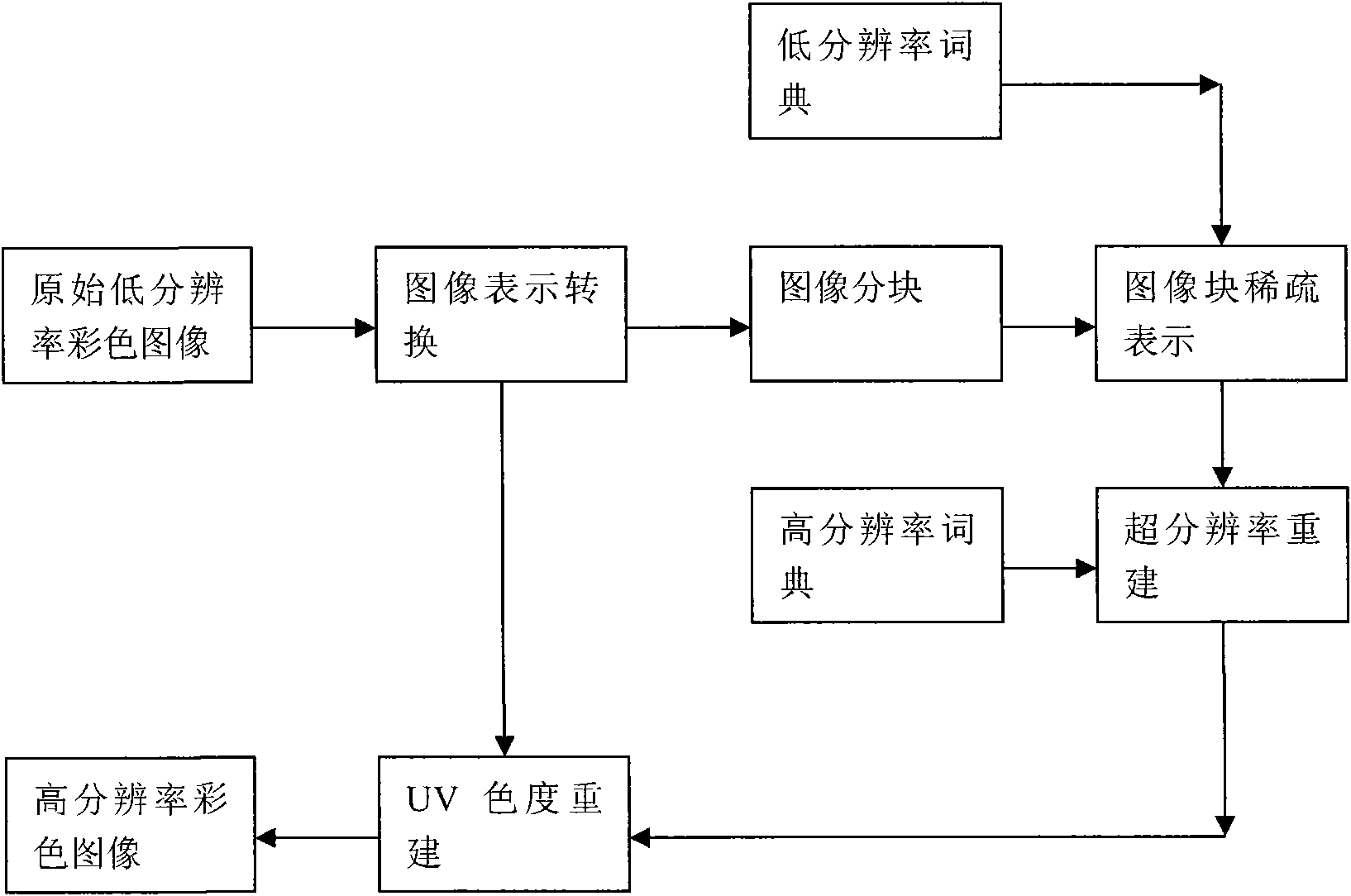
The invention relates to an image super-resolution method based on overcomplete dictionary learning and sparse representation. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting two overcomplete dictionaries (a low-resolution image block dictionary and a high-resolution image block dictionary) in a large-scale dataset and utilizing the two overcomplete dictionaries to realize super-resolution reconstruction of image sparse representation. Simultaneously, in order to further improve the super-resolution effect of color images, the invention also proposes UV chromaticity super-resolution reconstruction based on super-resolution luminance information. The image super-resolution method has wide application prospect in the fields of video monitoring, medical imaging, remote sensing image and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Sentiment dictionary learning based text sentiment analysis method and system
ActiveCN107301171AAvoid the cost problem of manual establishmentSolve the costNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsLearning basedDictionary learning
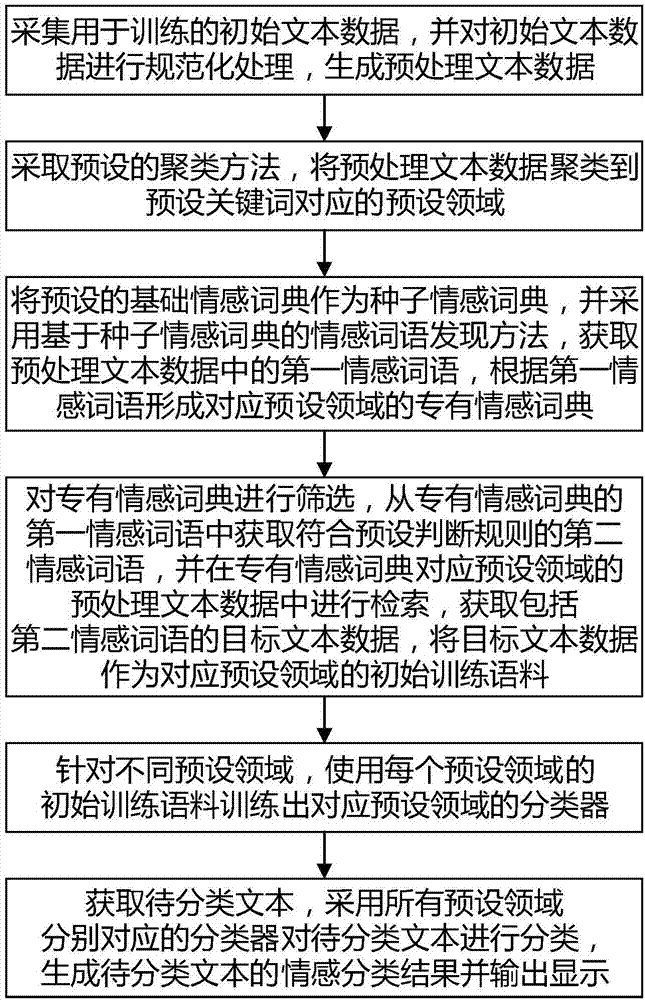
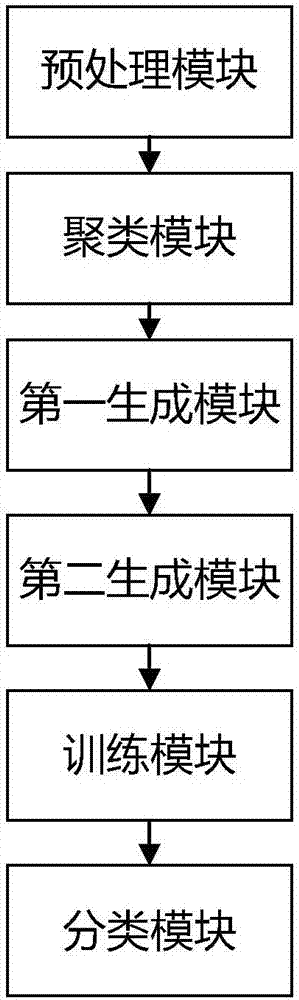
The invention particularly relates to a sentiment dictionary learning based text sentiment analysis method and system. The method includes steps: subjecting initial text data to normalization processing to generate preprocessed text data, and clustering the preprocessed text data to a preset field; adopting a seed sentiment dictionary based sentiment word discovery method to form a special sentiment dictionary in the preset field; subjecting the preprocessed text data to retrieval according to the special sentiment dictionary to acquire target text data serving as initial training corpus in the corresponding preset field, and classifying inputted to-be-classified texts through formed multiple classifiers. Labor cost is reduced, the problem of overfitting caused by a single classifier is avoided, and accuracy in text sentiment analysis is improved by consideration of the text related fields.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image bionic recognition method based on sample generation and nuclear local feature fusion
InactiveCN103020654AEfficient extractionSolve the problem of unstable extracted featuresCharacter and pattern recognitionSynthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
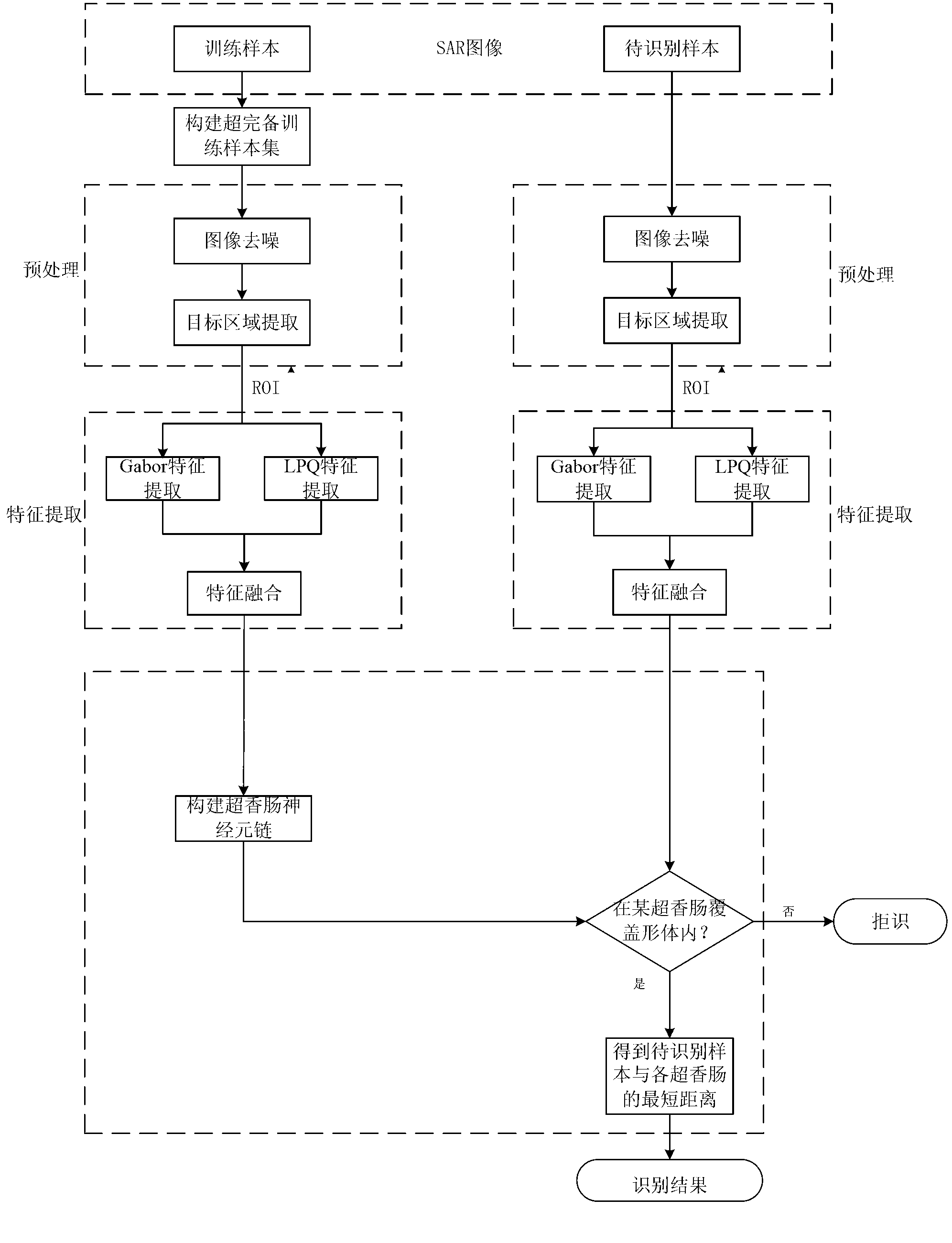
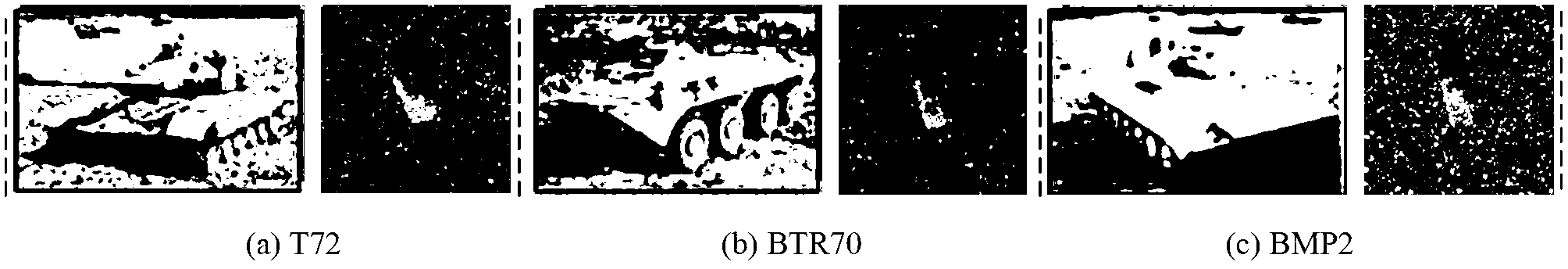
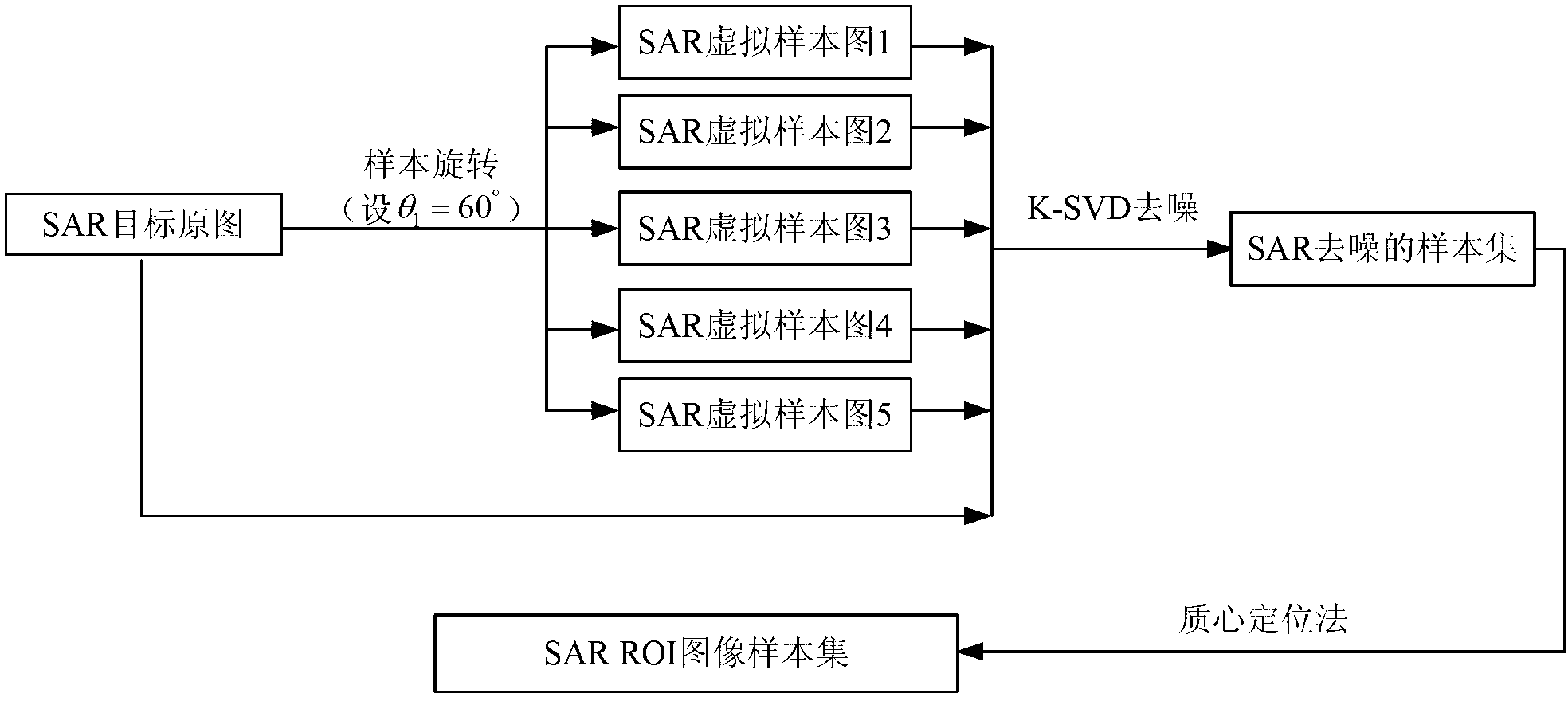
The invention provides a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image bionic recognition method based on sample generation and nuclear local feature fusion and belongs to the field of image processing technologies and SAR target recognition. According to the method, a super complete training sample set is firstly constructed for training to obtain geometry manifold, then a sample to be recognized is recognized, specifically, each sample is firstly subjected to image denoising by a K-SVD dictionary learning method, and object region extraction is achieved by means of an object centroid method; and feature extraction is performed respectively by combining local phase quantization (LPQ) and a Gabor filtering method, feature fusion is performed, finally, classification is performed by covering of high-dimensional geometry manifold, and recognition is performed by a bionic mode. According to the SAR image bionic recognition method based on sample generation and nuclear local feature fusion, inhibiting effects of image coherent noises are obvious, SAR image features can be effectively extracted, the problem of the unstable extracted features, which is caused by changes of attitude angles of SAR images, is solved, the recognition accuracy is high, and the method has good robustness.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Regularized parameter adaptive sparse representation image reconstruction method
PendingCN109064406AImprove effectivenessMaintain structureGeometric image transformationDictionary learningMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention provides a regularized parameter adaptive sparse representation image reconstruction method, comprising the following steps: adopting a sparse dictionary learning algorithm, extracting image edge features to train a compact sparse dictionary, and adaptively allocating sub-dictionaries to each image block for sparse coding; Learning the Sparse Estimation of Sparse Coding from an Overcomplete Dictionary; Making full use of the local structure similarity of images, the regularization parameters are adaptively solved by using the method based on the maximum a posteriori probability.Adaptive sparse representation model of regularized parameters is established. The invention improves the effectiveness of sparse representation by utilizing the local structure similarity, and the edge and the structure of the image are well maintained. Adaptively adjusting the regularization parameters based on the maximum a posteriori probability, updating the regularization parameters in eachiteration process, better adapting to the current situation, greatly reducing the workload of manual selection of the regularization parameters; It has good image reconstruction effect and strong robustness to noise and motion blur.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Super-resolution image reconstruction method based on non-local dictionary learning and biregular terms
ActiveCN103295196AOvercome the shortcomings of being unable to effectively supplement the missing information of low-resolution imagesComplementary efficient and directionalImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningPrior information
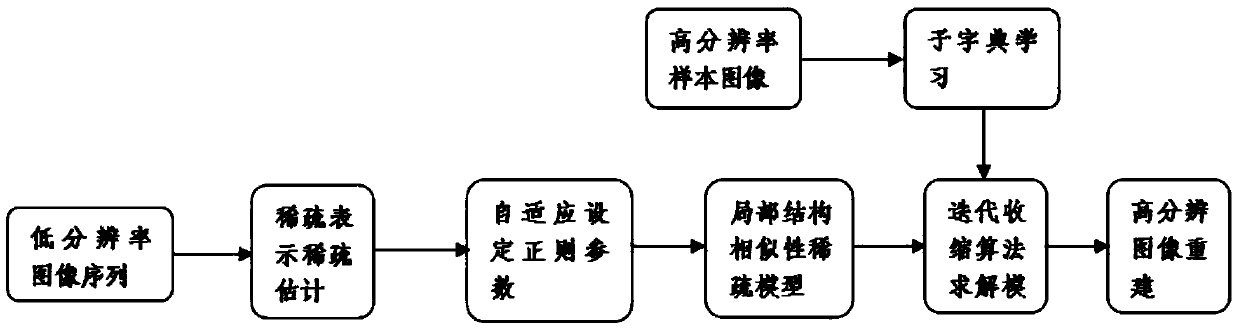
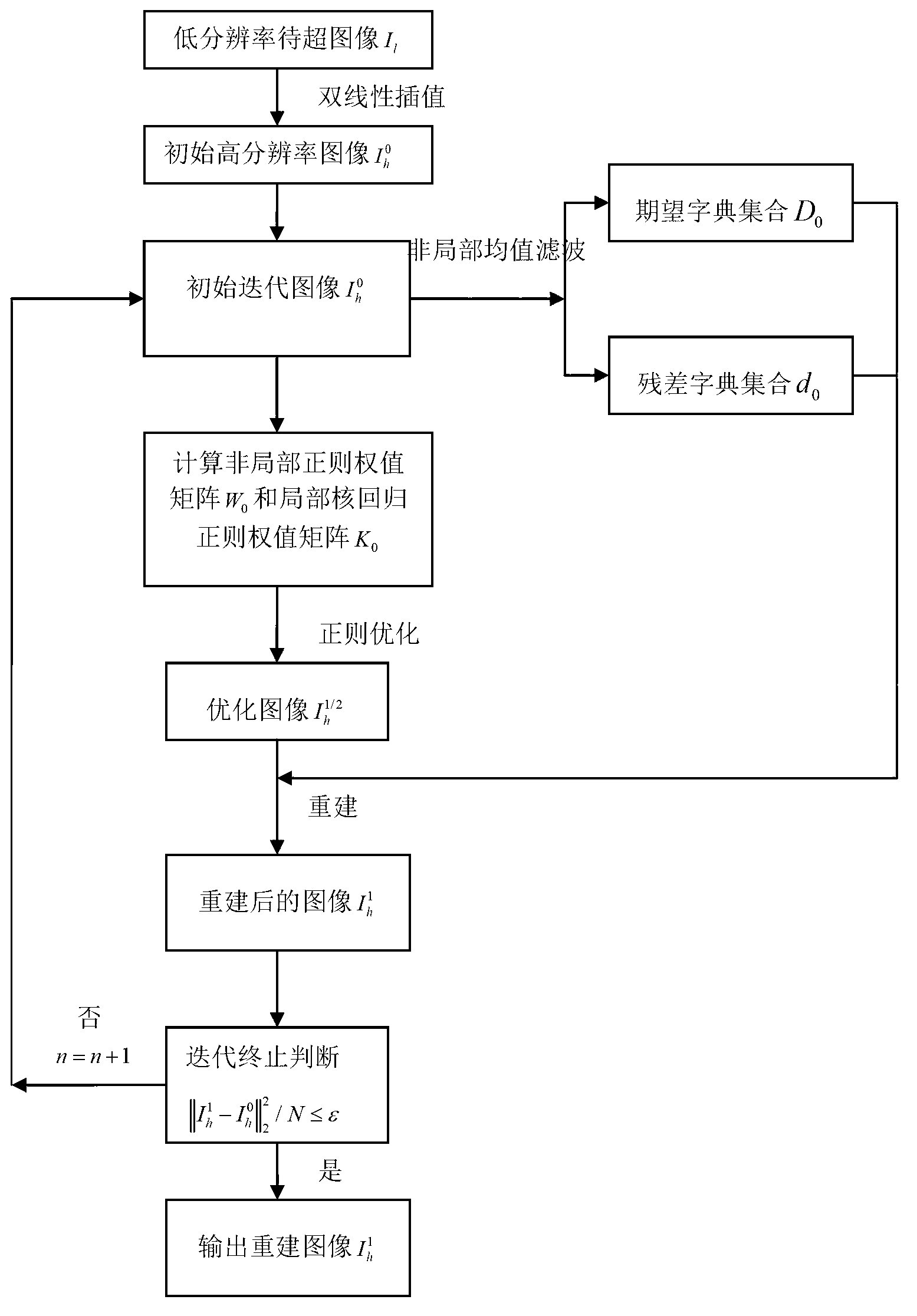
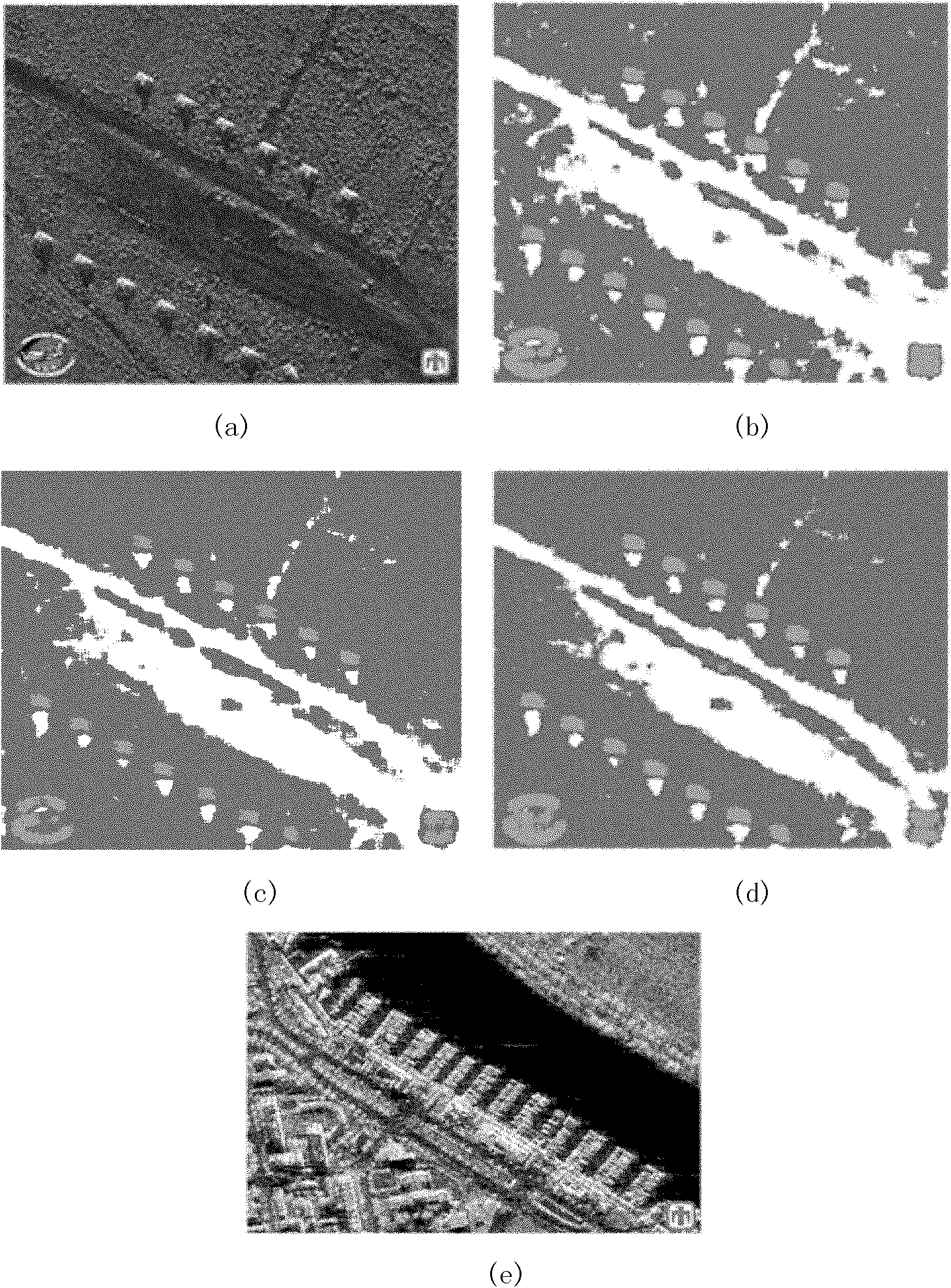
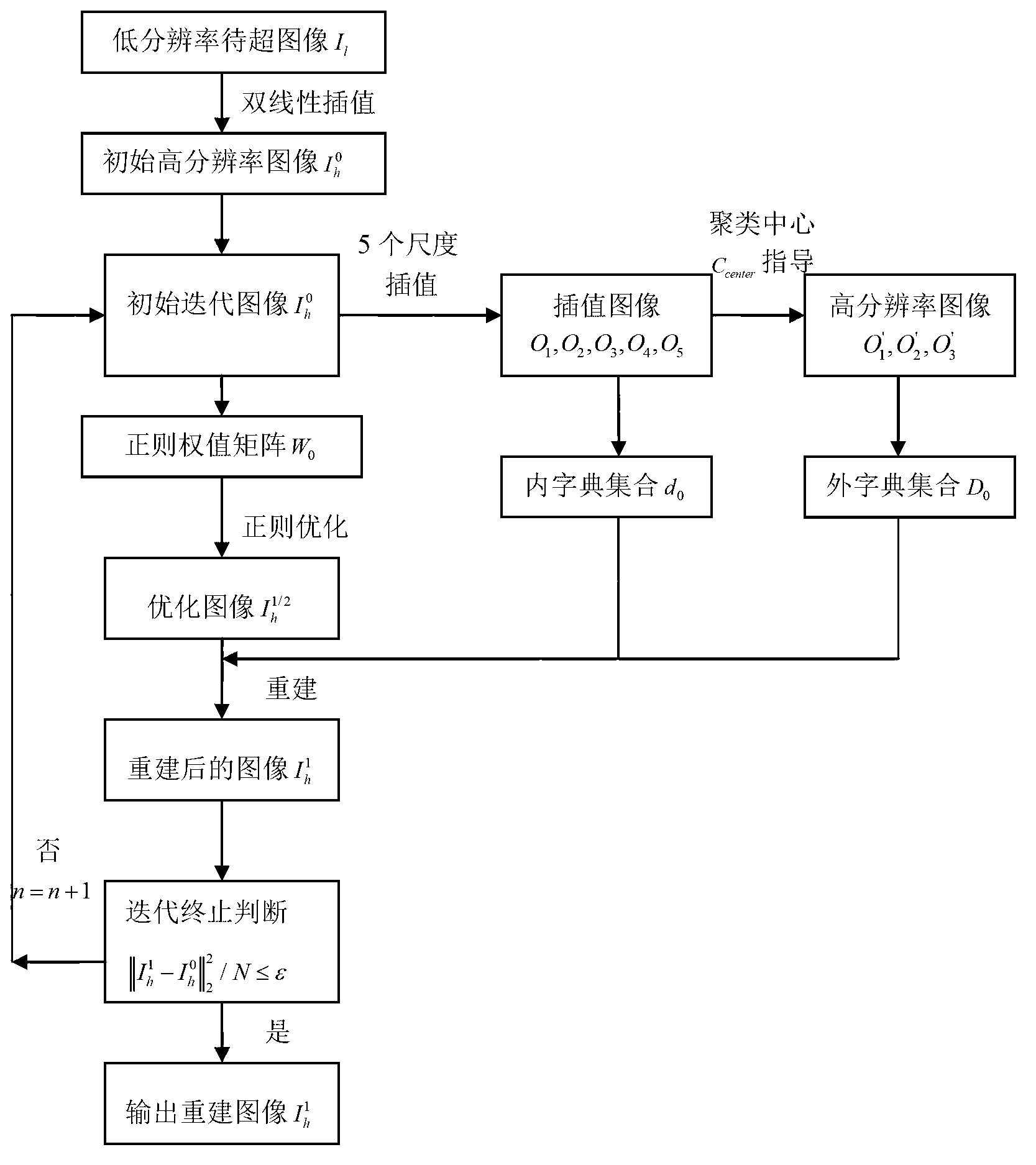
The invention discloses a super-resolution image reconstruction method based on non-local dictionary learning and biregular terms, and mainly aims to solve the problem that reconstructed images are unnatural due to the fact that prior information of ultralow-resolution images cannot be fully utilized in existing dictionary learning methods. The method includes the main steps: (1), obtaining an initial high-resolution image; (2) training an initial residual dictionary set d0 and an initial expected dictionary set D0; (3) computing an initial non-local regular weight matrix W0 and an initial local kernel regression regular weight matrix K0 on the initial high-resolution image; (4) performing regular optimization processing on an inputted initial high-resolution image to obtain an optimized image; and (5) applying the initial residual dictionary set d0 and the initial expected dictionary set D0 for reconstructing the optimized image to obtain a reconstructed image. The method is capable of reconstructing remote sensing images and effectively maintaining marginal and texture information of the images, and can be used for satellite monitoring and remote-sensing imagery.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
High-spectrum abnormal object detection method based on background dictionary learning and structure sparse expression
InactiveCN105825200AHigh precisionImprove detection resultsImage enhancementImage analysisDictionary learningData set
The invention discloses a high-spectrum abnormal object detection method based on background dictionary learning and structure sparse expression, for solving the technical problem of low object detection efficiency by use of a conventional high-spectrum abnormal object detection method. The technical scheme is as follows: after an initial background pixel is selected based on a local RX algorithm, a robust background dictionary is obtained through learning by use of a principle component analysis dictionary learning method. In a sparse vector solving and image reconstructing process, heavy-weight Laplace prior is introduced, and thus the sparse vector solving precision is improved. Finally, according to errors between an original image and a reconstructed image, accurate extraction of an abnormal object is realized. Test results on a real high-spectrum satellite image AVIRIS and a simulated high-spectrum data set show that the detection rate of a detection result obtained by use of the method is improved by 8% to 15% under the condition of a constant fault alarm rate compared to background arts.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
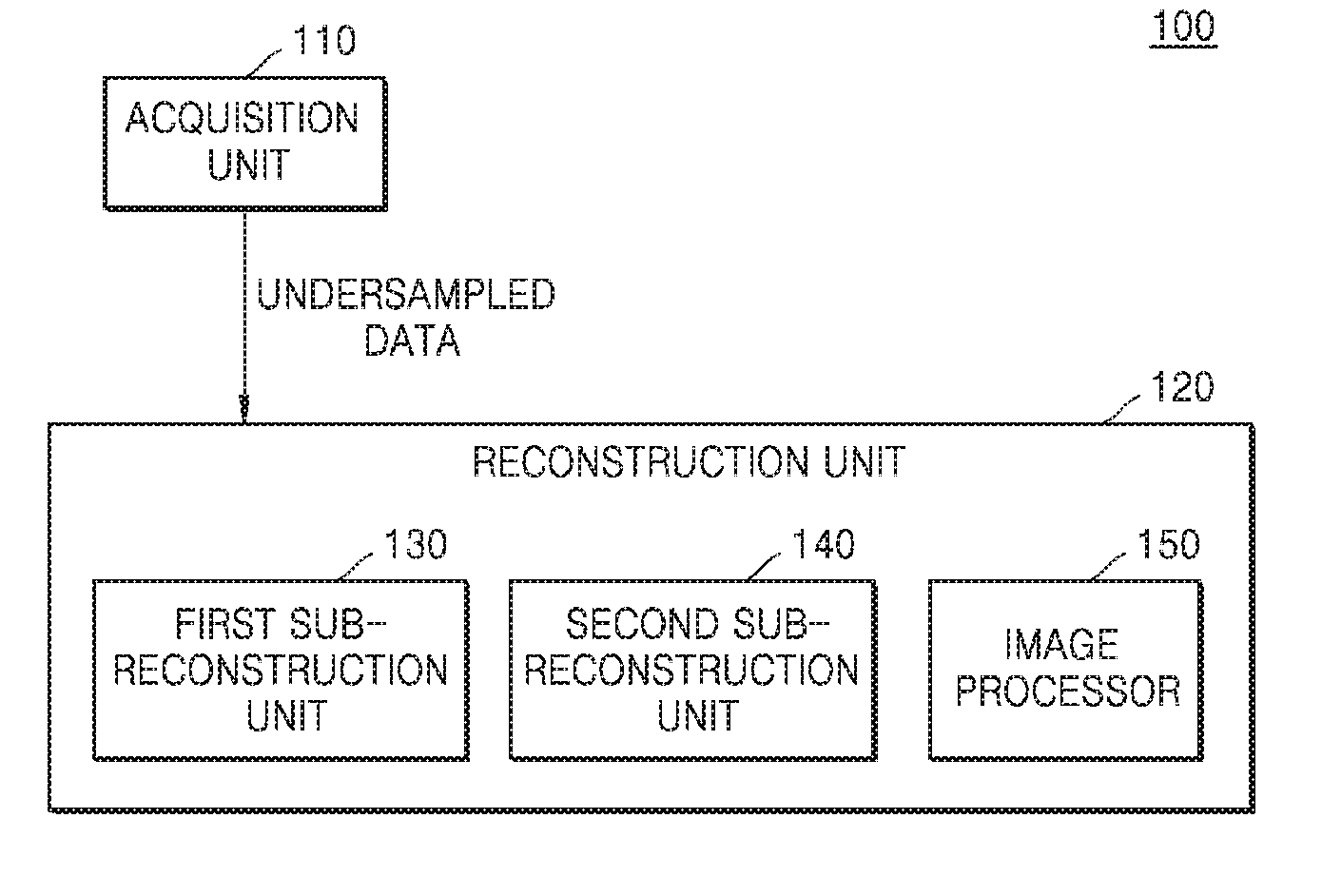
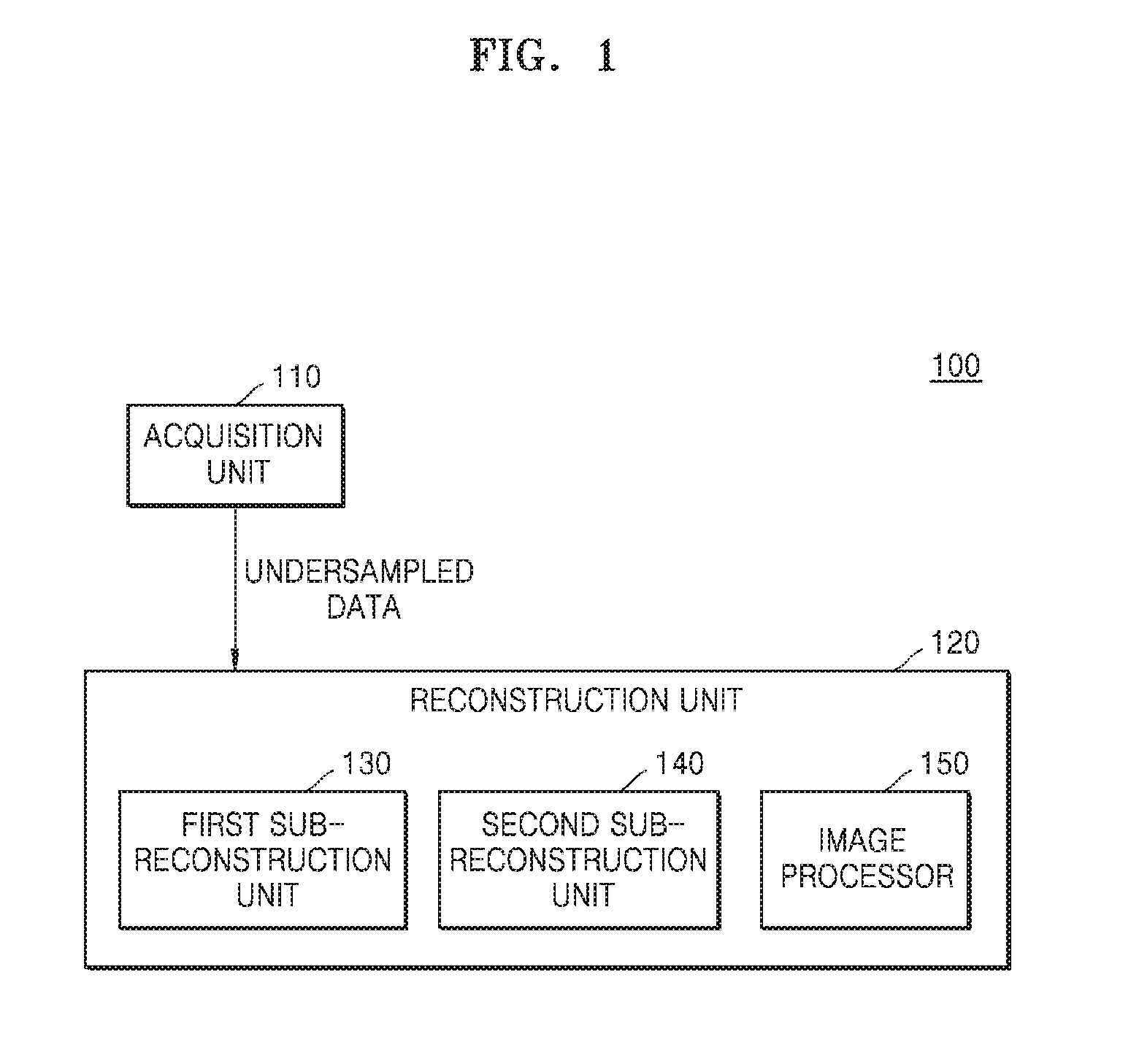
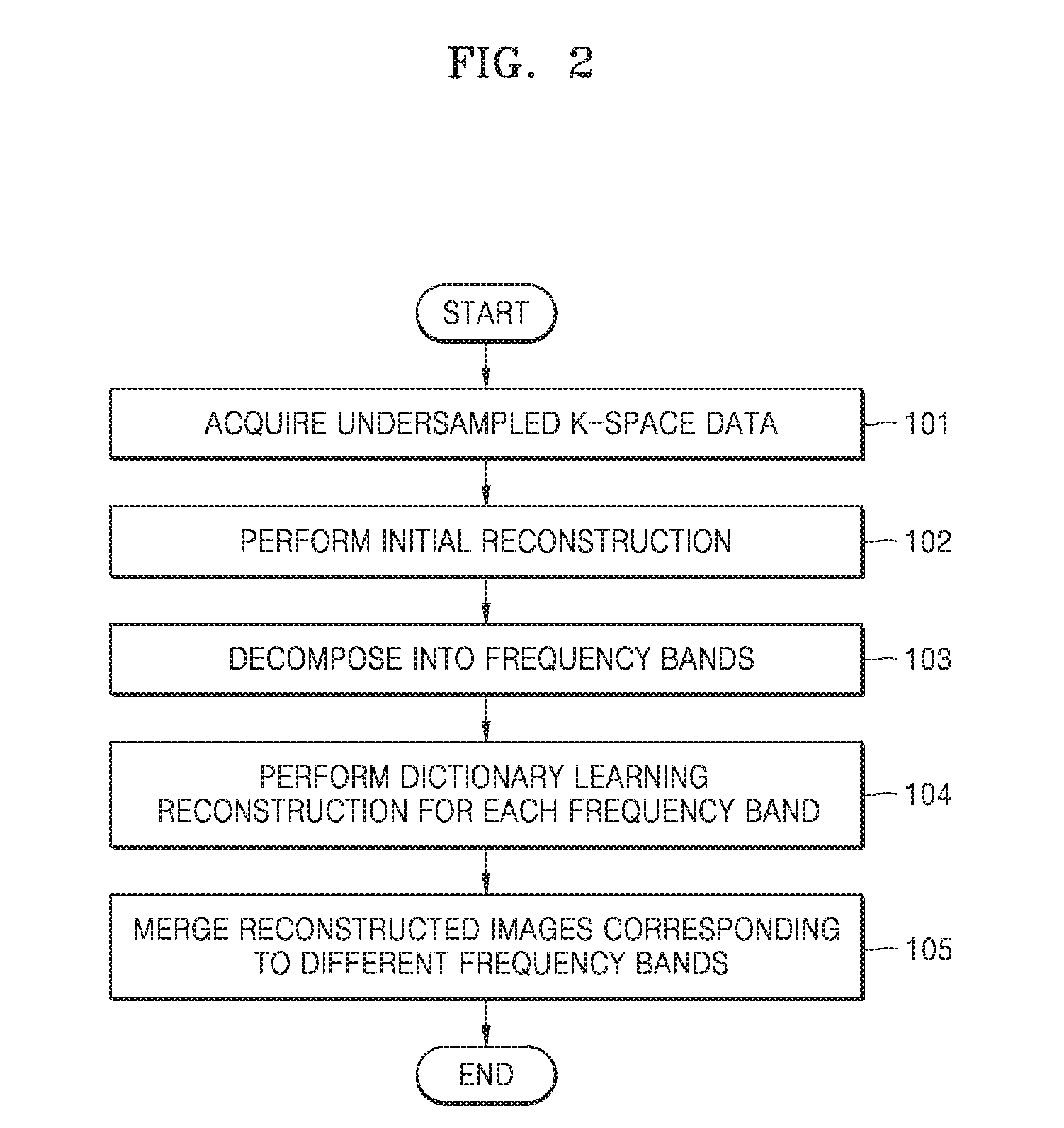
Magnetic resonance imaging device and method for generating magnetic resonance image
ActiveUS20170053402A1Increase speedAccelerate the computational algorithmsImage enhancementMedical imagingDictionary learningFrequency spectrum
Provided is a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus including an acquisition unit configured to acquire an undersampled spectrum in a k-space and a reconstruction unit configured to generate a target image based on the undersampled spectrum, wherein the reconstruction unit includes: a first sub-reconstruction unit configured to perform initial reconstruction on data corresponding to unsampled positions in the k-space by using a Split Bregman algorithm or approximate sparse coding; a second sub-reconstruction unit configured to decompose the initially reconstructed spectrum in the k-space into multiple frequency bands to thereby generate a plurality of individual spectra and perform dictionary learning reconstruction on images respectively corresponding to the decomposed multiple frequency bands by alternating sparse approximation and reconstructing of measured frequencies; and an image generator configured to generate a target image by merging together the reconstructed images respectively corresponding to the multiple frequency bands.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
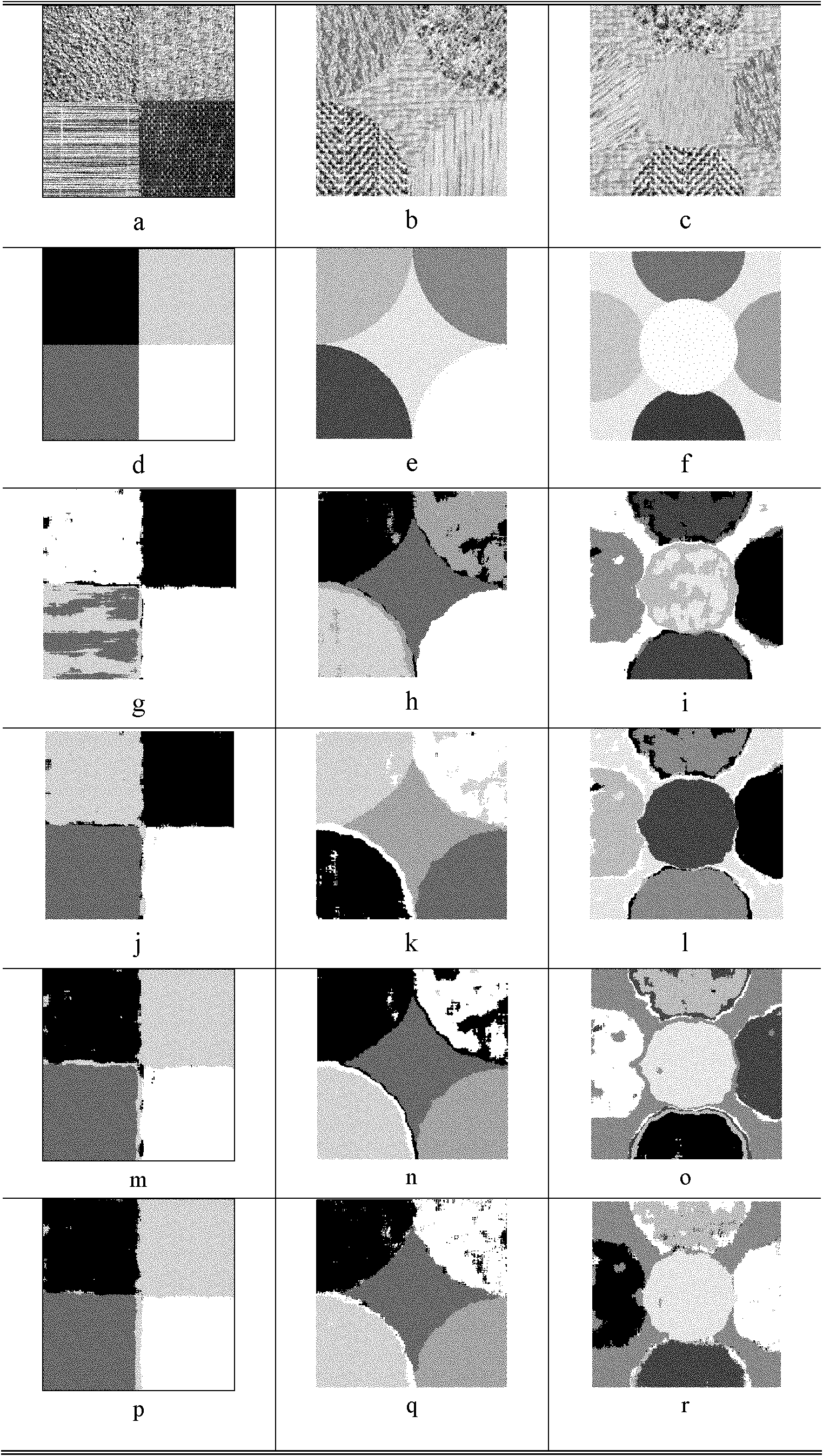
Method for segmenting images by utilizing sparse representation and dictionary learning
ActiveCN102096819AThe image segmentation effect is stableThe segmentation result is accurateCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningSingular value decomposition
The invention discloses a method for segmenting images by sparse representation and dictionary learning, and the method is mainly used for solving the problem of unstable division result under the condition of no sample label in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inputting an image to be segmented, and extracting the gray co-occurrence features and wavelet features of the image to be segmented; (2) carrying out K-means clustering on the image to be segmented by utilizing the features so as to obtain K-feature points; (3) acquiring K dictionaries corresponding to the K-feature points by an KSVD (K-clustering with singular value decomposition) method; (4) carrying out sparse decomposition on all the features of the K dictionaries by a BP (back propagation) algorithm to obtain a sparse coefficient matrix; (5) calculating the sparse representation error of each dictionary according to each feature point, and dividing the point corresponding to the feature to the type with the smallest dictionary error; and (6) repeating the step (5) until all the points have label values, and finishing final segmentation. Compared with the prior art, the method can be used for significantly improving the image stability and the segmentation performance, and can be used for target detection and background separation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Single image rain removal method based on convolutional neural network
ActiveCN106204499AOvercome the problem of taking too longGuaranteed clarityImage enhancementImage analysisDictionary learningImaging processing
The invention provides a single image rain removal method based on a convolutional neural network and relates to image processing. The method includes the following steps that firstly, manual rain addition is conducted on clean and clear images through a screen blend model to form corresponding rain images, and an image library is built; secondly, the system structure of the convolutional neural network is determined; thirdly, corresponding rain image blocks and rain-free image blocks with the size being 64*64 are obtained from the first step and serve as training samples for training; fourthly, the single image blocks are obtained in an overlapped mode and input in a trained rain removal filter system to obtain the corresponding rain-free image blocks, and weighted averaging is conducted on the image blocks to obtain rain-free images. The method solves the problem that a single image rain removal method based on dictionary learning is long in consumed time, achieves rain removal and guarantees definition of background images, the rain-free images can be quickly obtained after the rain images are input, and the requirement of embedded equipment for real-time processing is met.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Integration method for face recognition by using sparse representation
InactiveCN102073880AEasy to distinguishImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningOriginal data
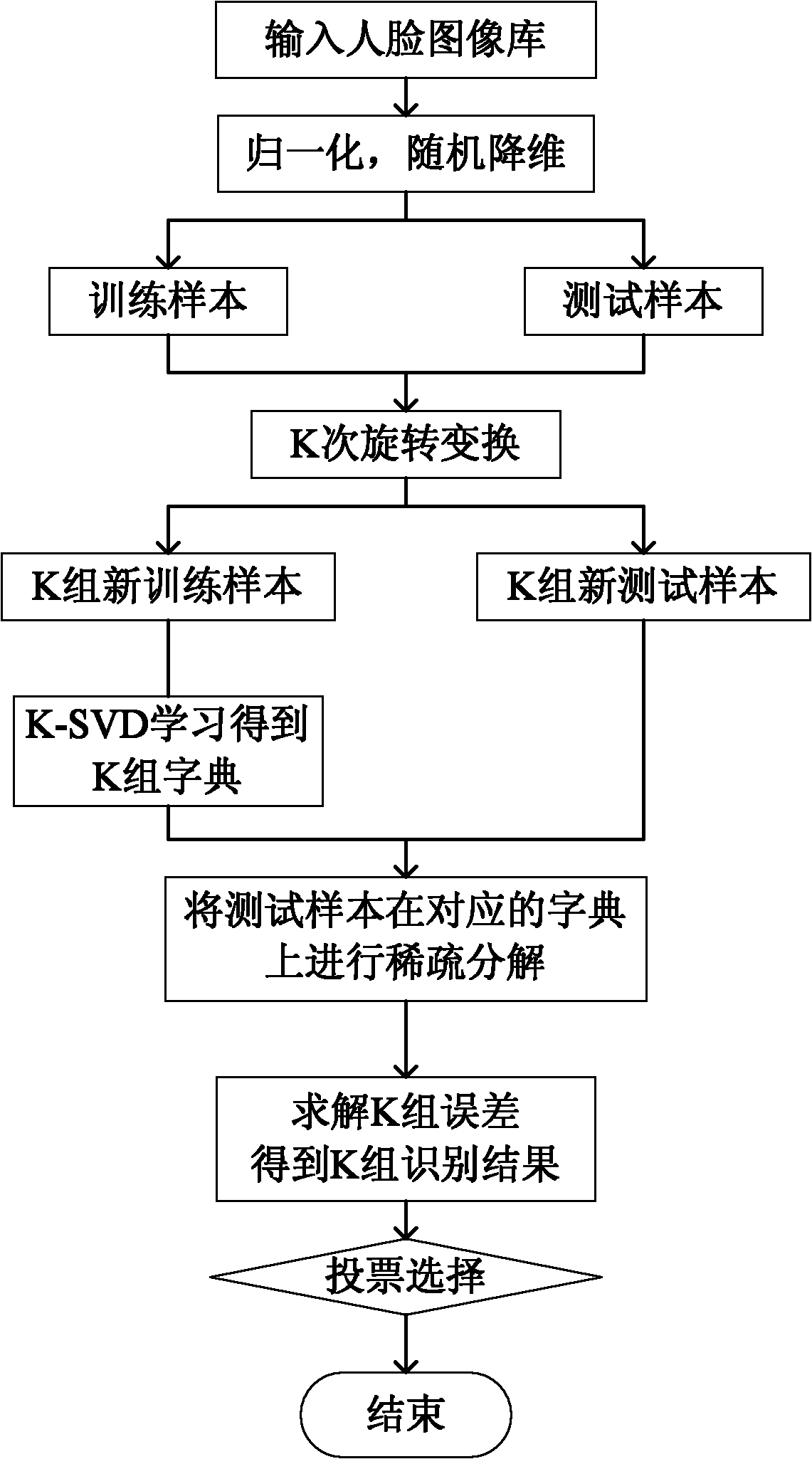
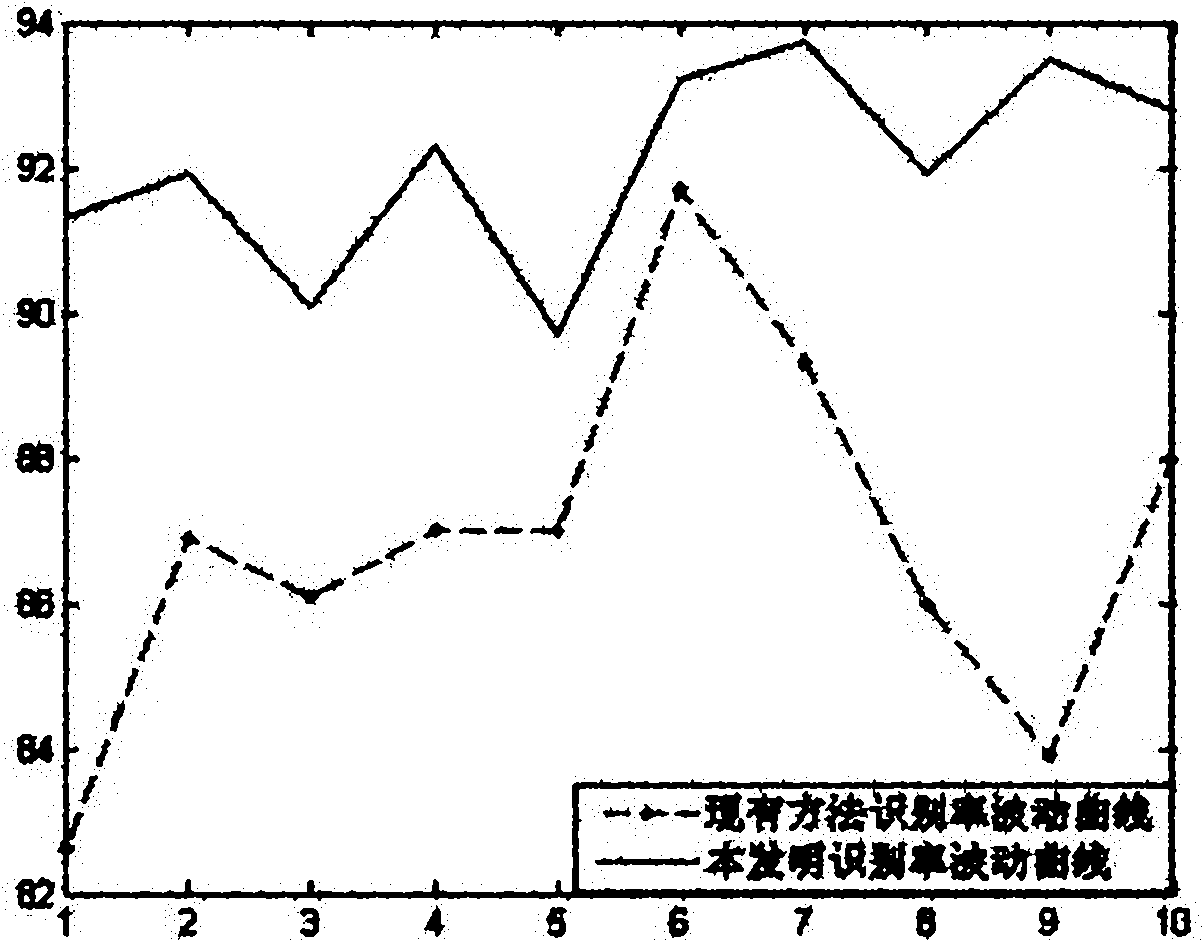
The invention discloses an integration method for face recognition by using sparse representation, which mainly solves the problem of low recognition stability in the conventional K-SVD dictionary learning method. The integration method is realized by the following steps of: generating a rotation matrix by a rotation forest algorithm; randomly projecting the same face sample data to different coordinate systems through the rotation matrix, wherein the projected face sample data is easier to distinguish than the original data; recognizing the projected face sample data by a sparse representation classification method; and voting to select the recognition result of a projected face sample to acquire the recognition result of the original face sample. Compared with the conventional sparse representation-based classification method, the integration method has the characteristics of improving the recognition correctness and the recognition stability, and can be used for a safety verification system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
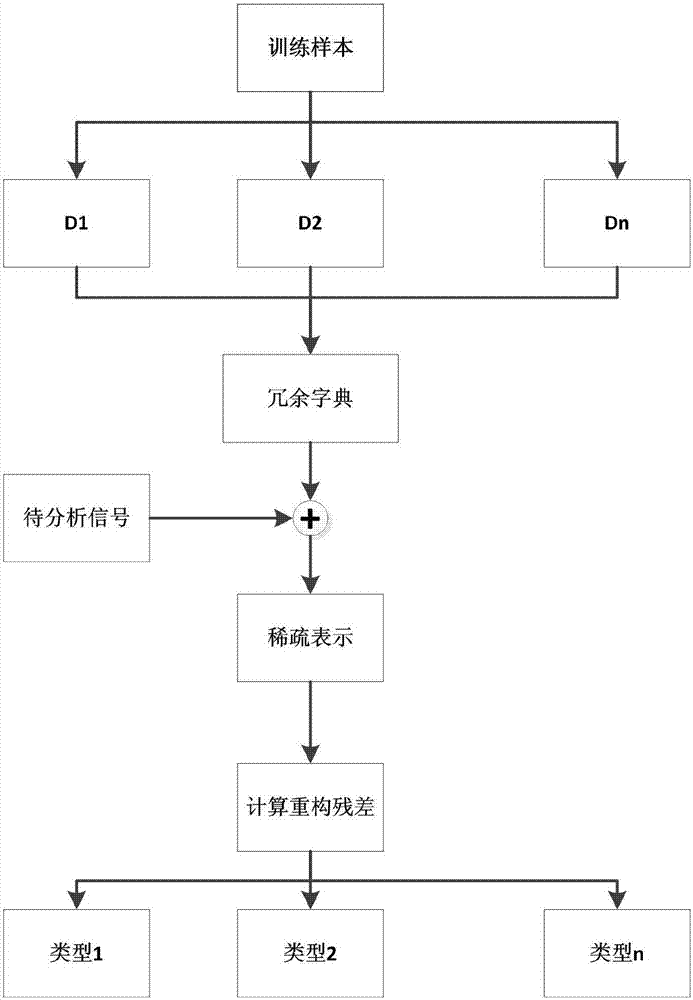
Sparse representation and dictionary learning-based bearing fault classification method
ActiveCN107368809AEnhance expressive abilityQuality assuranceCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningDecomposition
The invention discloses a sparse representation and dictionary learning-based bearing fault classification method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preprocessing acquired history bearing vibration signals to obtain vibration signals under different working states, respectively constructing corresponding sub-dictionaries and combining the sub-dictionaries into a redundant dictionary; and online acquiring a bearing vibration signal by using a sensor, solving a sparse coefficient of the signal under the redundant dictionary by using a generalized orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm, and classifying the vibration signal through a reconstruction error so as to identify the bearing working state. According to the method, relatively good classification effect can be obtained, the dictionary training process can be accelerated and the ability, of being adapted to target signals, of the dictionary is improved, so that the method is capable of realizing the sparse decomposition of complex vibration signals more efficiently and is used for fault identification.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Image coding method and system based on dictionary learning
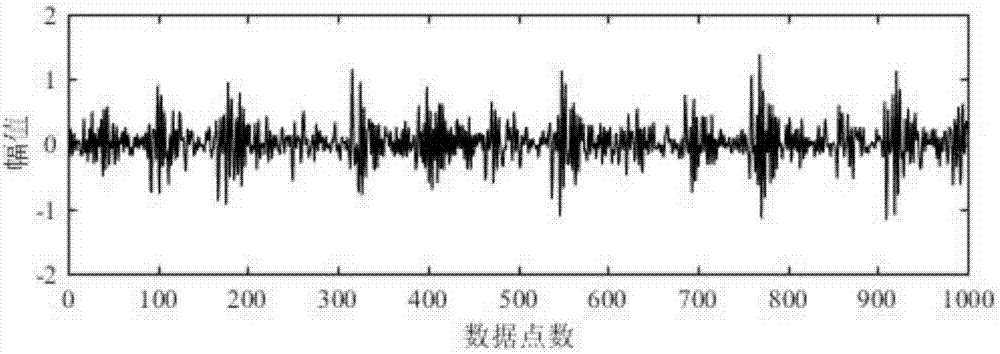
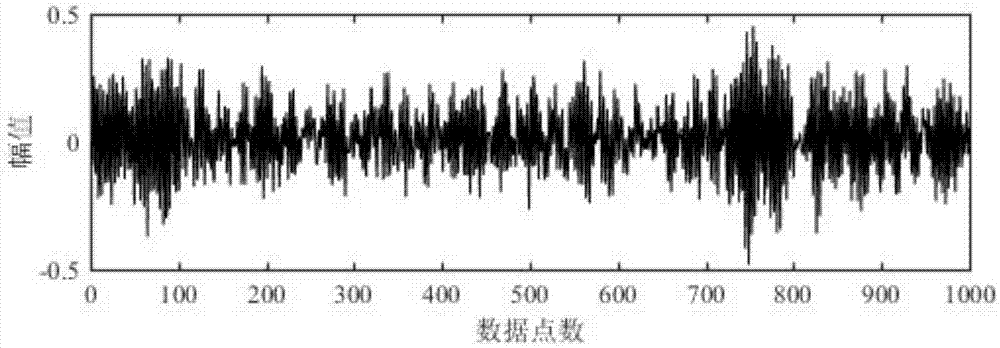
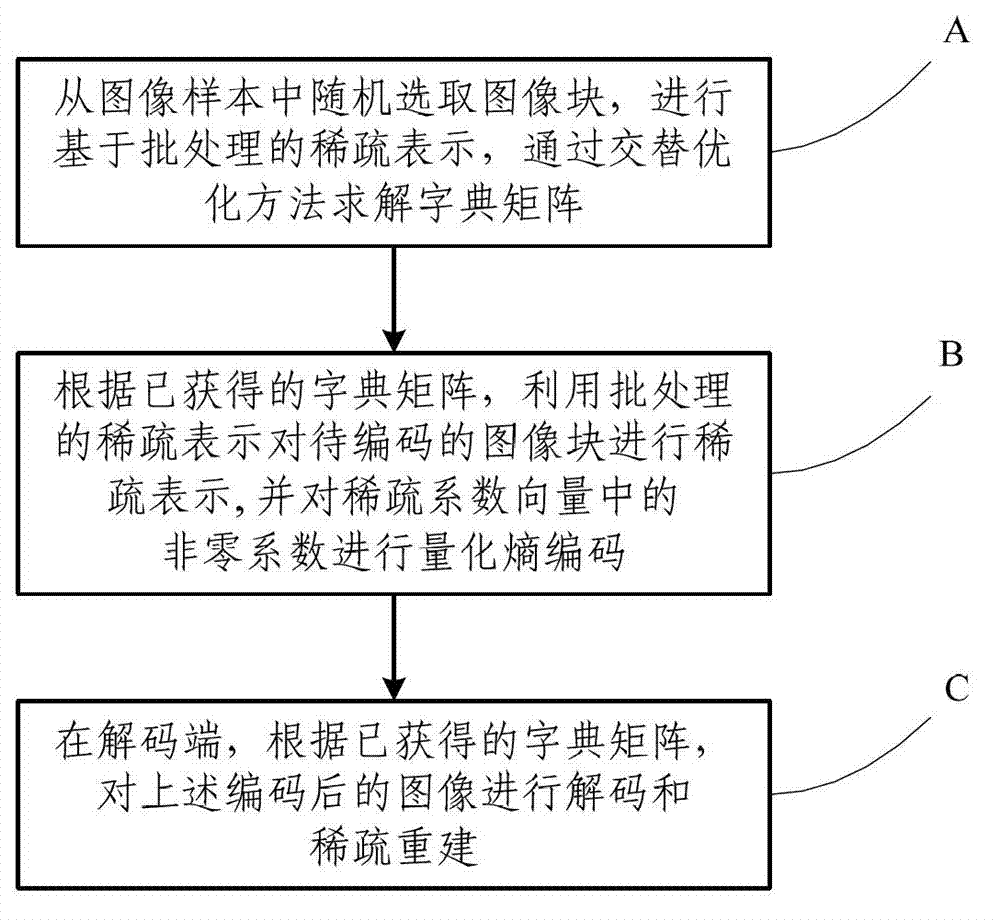
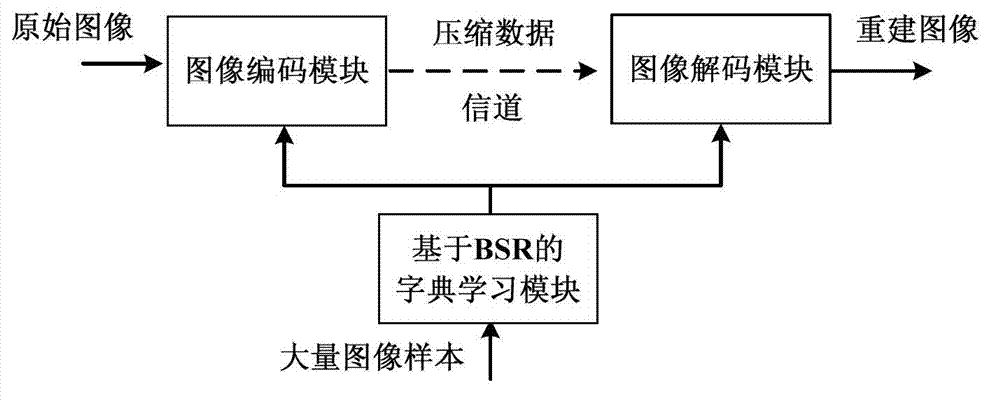
InactiveCN103489203AIn line with subjective feelingsExcellent rate-distortion compression performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingDictionary learningNonzero coefficients
The invention discloses an image coding method and system based on dictionary learning. The method comprises the steps that image blocks are randomly selected from an image sample to carry out sparse representation based on batch processing, and a dictionary matrix is solved through an alternative optimization method; according to the obtained dictionary matrix, the sparse representation processed in batch is utilized to carry out sparse representation on the image blocks to be coded, and quantification entropy coding is carried out on nonzero coefficients in sparse coefficient vectors; decoding and sparse reconstruction are carried out on the coded image at a decoding end according to the obtained dictionary matrix. The system comprises a dictionary learning module of sparse representation based on batch processing, an image coding module and an image decoding module. According to the method and system, the problem that the training sample in dictionary learning is large in scale is resolved, meanwhile reconstruction errors of the image sample are reduced, and rate-distortion performance of image compression is significantly promoted.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Distributed microphone array sound source positioning method based on space sparsity
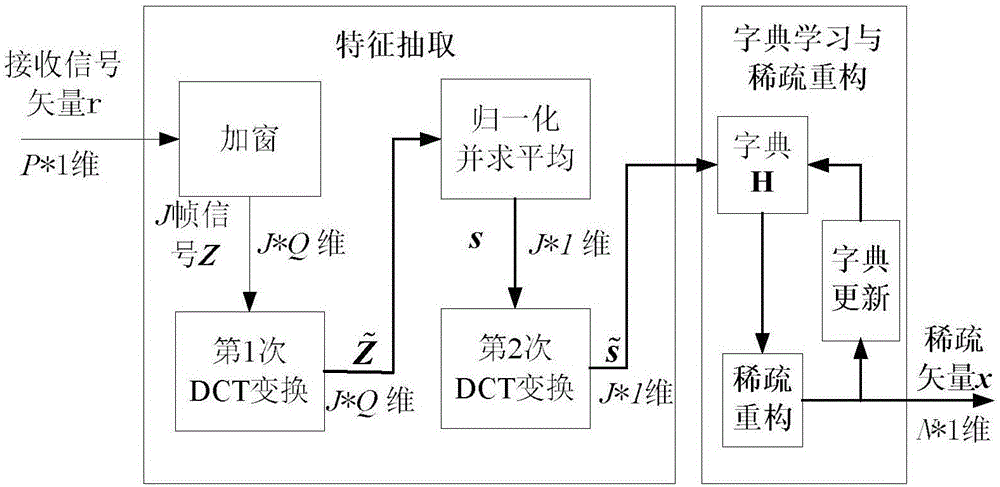
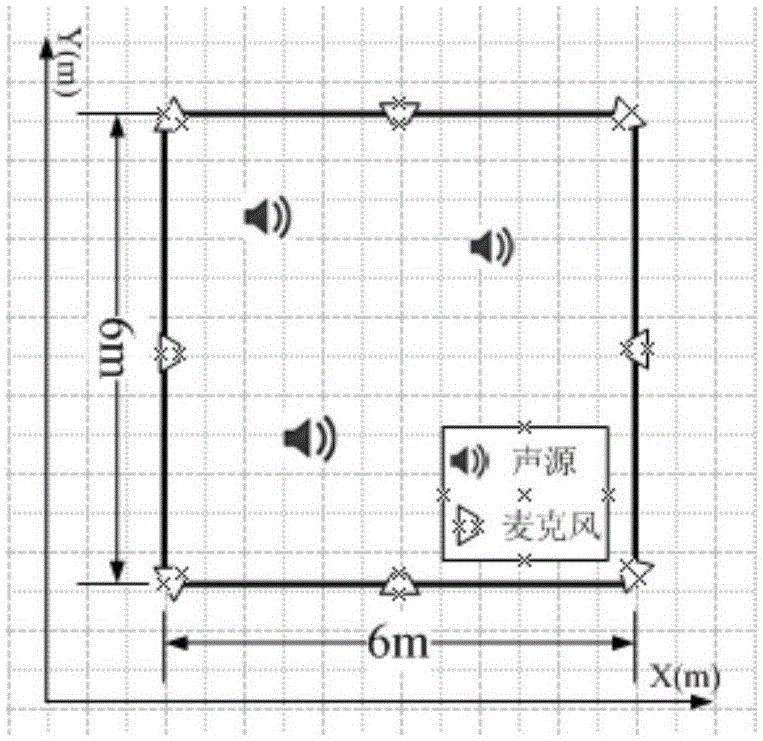
ActiveCN105068048AImprove noise immunityImprove robustnessPosition fixationSound sourcesReconstruction algorithm
The invention discloses a distributed microphon array sound source positioning method based on space sparsity, comprising steps of performing signal characteristic extraction through two steps of discrete cosine transform (discrete cosine transform DCT), utilizing the characteristics to construct a sparsity positioning model in order to comprehensively utilize the short time or long time characteristics of the voice signal, reducing the dimension of the model, utilizing a dictionary learning method to perform correction on the model, adopting an approximating I0 norm reconstruction algorithm to perform reconstruction on a sparse signal to find a sound source. The invention has no special requirement on the array structure, requires less calculation, effectively improves the capability of resisting noise and reverberation and positioning accuracy, and is suitable for indoor sound positioning and widely applicable to the video conference system, the voice recognition system and the intelligent robots.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Sparse-coding license plate character recognition method based on shape and contour features
InactiveCN103761531AEasy to identifyImprove scalabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningFeature set
The invention provides a sparse-coding license plate character recognition method based on shape and contour features. The method comprises a sparse dictionary learning process and a dictionary-utilizing character recognition process. The method mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, a training image set is formed by pre-processing standard license plate images; secondly, feature extraction is performed on the training image set, so that a training feature set is formed; thirdly, a sample region feature and a chain code histogram feature of the raining feature set are introduced into an objective function, sparse dictionary learning is performed on license plate character samples off line to obtain dictionaries corresponding to all characters, and a dictionary set is formed by all the dictionaries; fourthly, feature extraction is performed on test sample data; fifthly, test sample features are subjected to sparse representation in each dictionary, and license plate character recognition is performed through reconstruction errors. Since region features and boundary features of character images are considered at the same time, the sparse-coding license plate character recognition method is a fast and robust license plate character recognition method.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
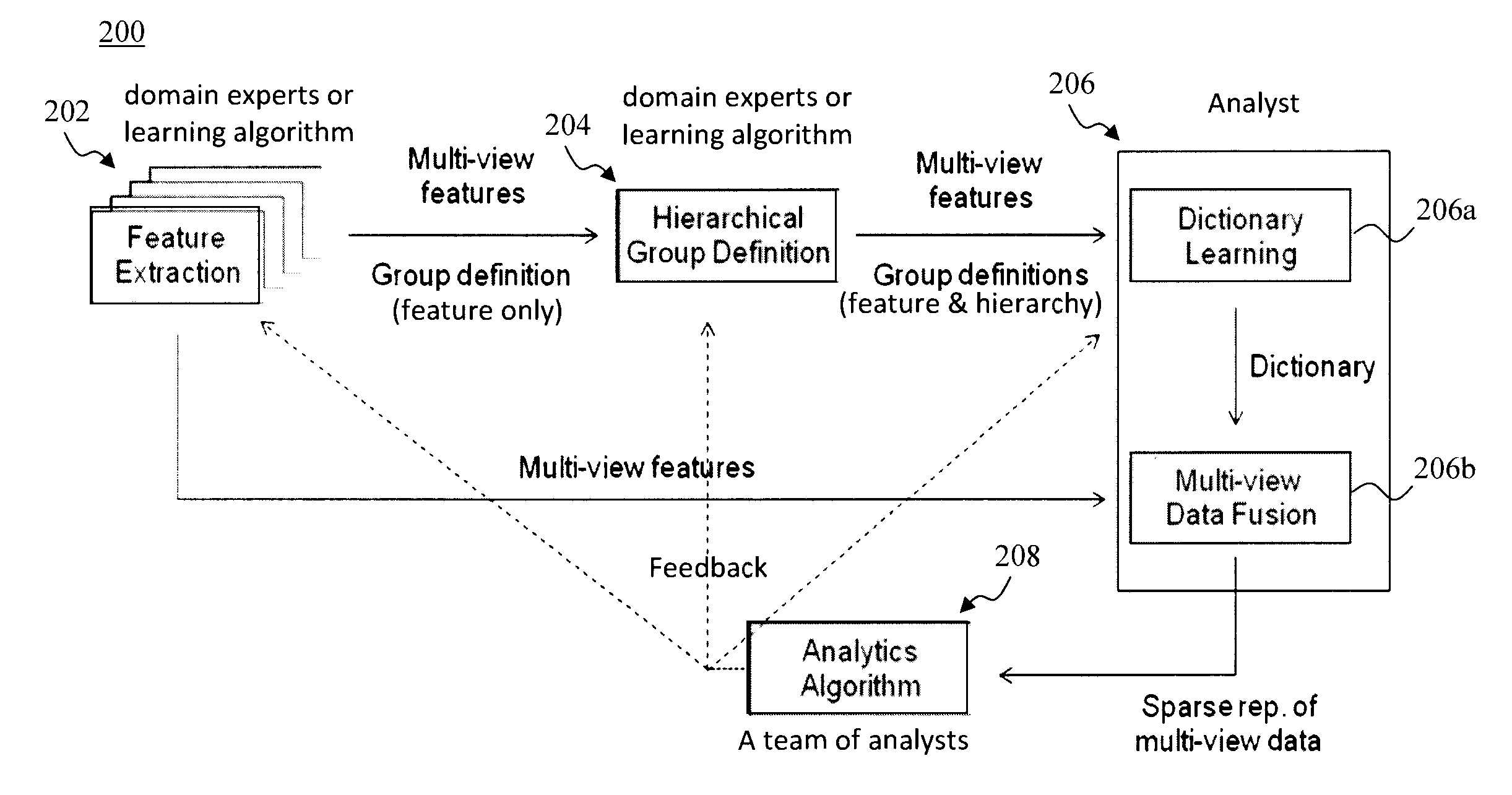
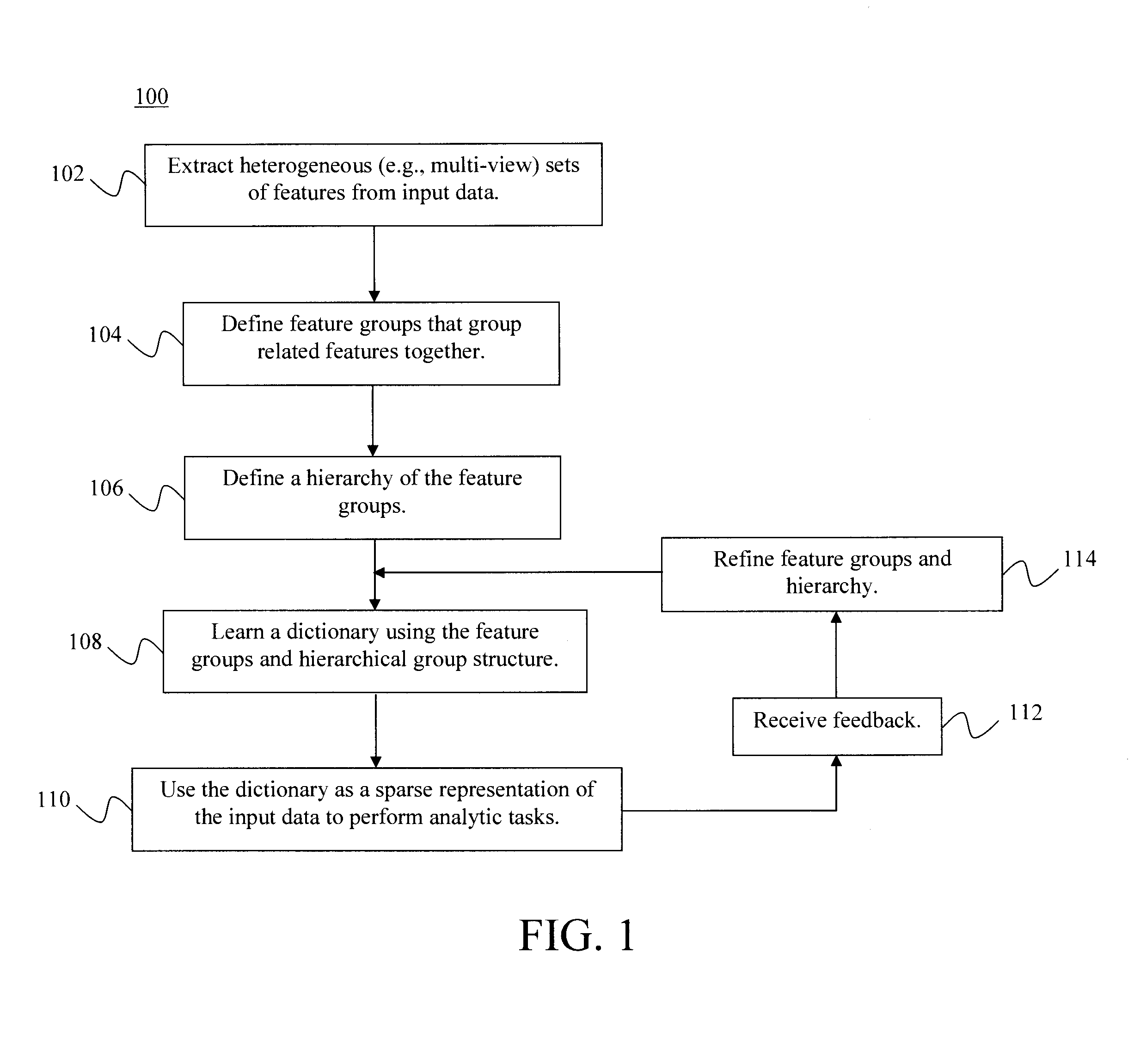
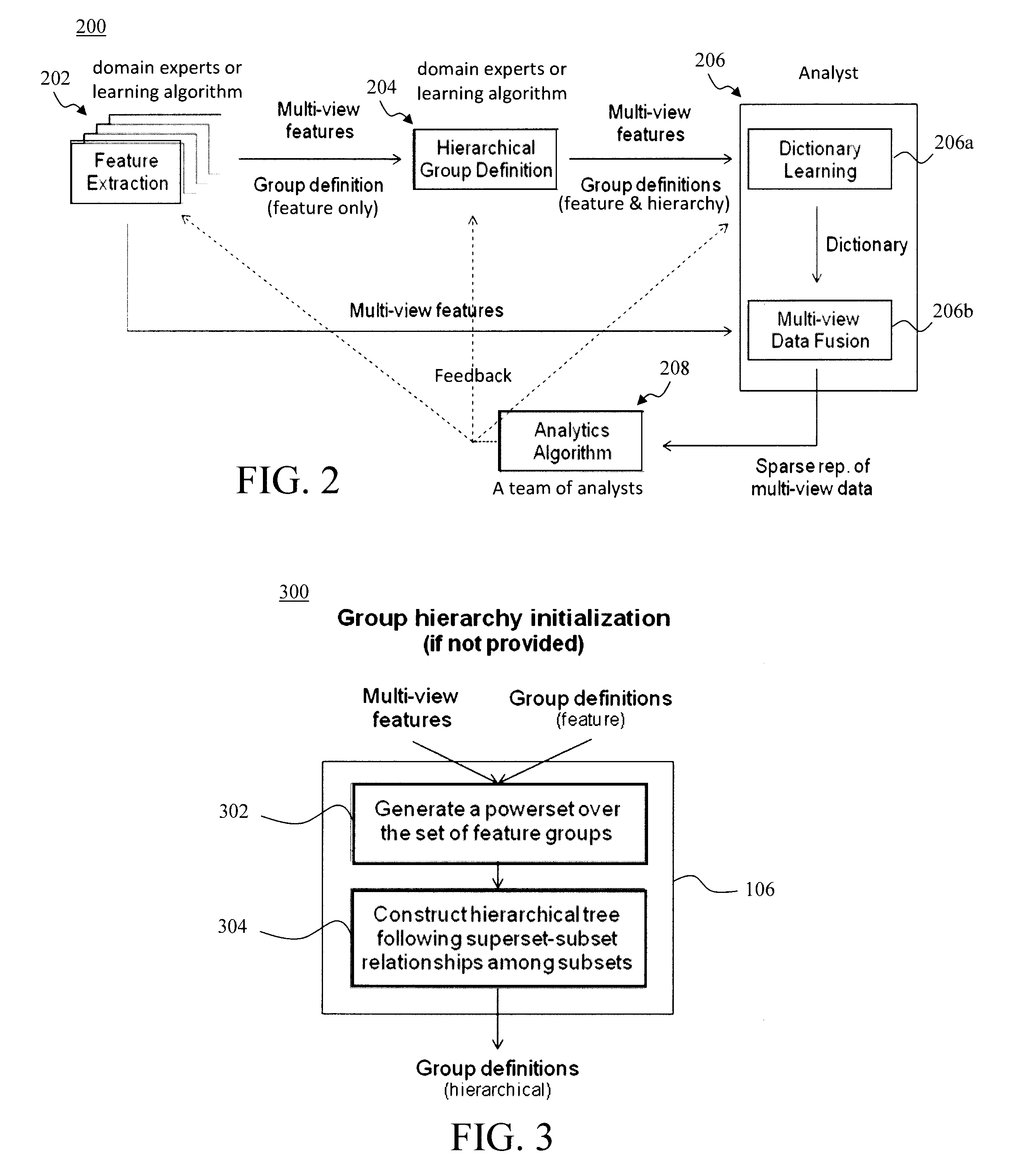
Multimodal Data Fusion by Hierarchical Multi-View Dictionary Learning
ActiveUS20160283858A1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningMultimodal data
Techniques for multimodal data fusion having a multimodal hierarchical dictionary learning framework that learns latent subspaces with hierarchical overlaps are provided. In one aspect, a method for multi-view data fusion with hierarchical multi-view dictionary learning is provided which includes the steps of: extracting multi-view features from input data; defining feature groups that group together the multi-view features that are related; defining a hierarchical structure of the feature groups; and learning a dictionary using the feature groups and the hierarchy of the feature groups. A system for multi-view data fusion with hierarchical multi-view dictionary learning is also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
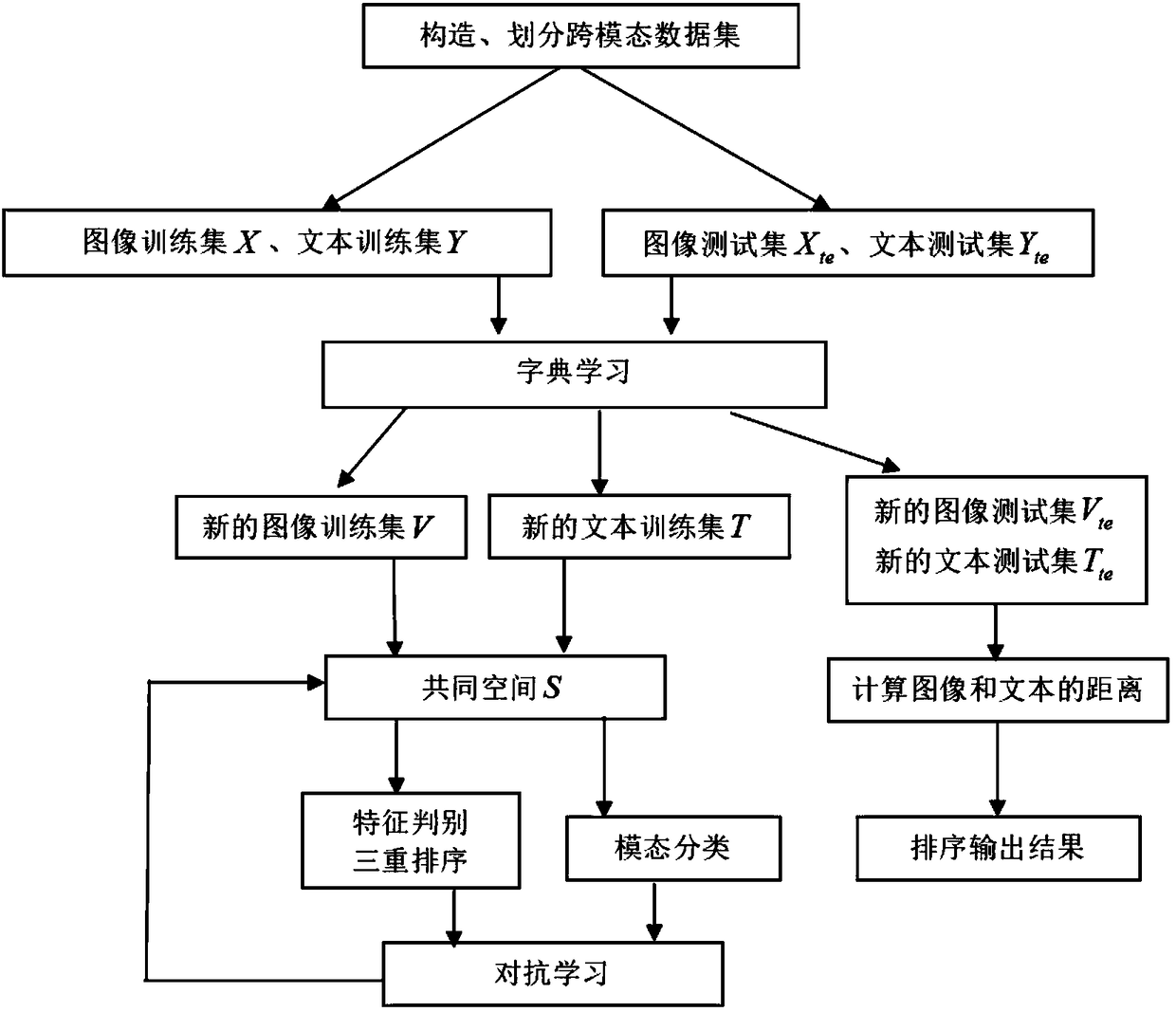
A method and system for counteracting cross-modal retrieval based on dictionary learning
InactiveCN109299341AImprove accuracyIncrease weightCharacter and pattern recognitionOther databases queryingDictionary learningFeature extraction
The invention discloses a method and a system for antagonistic cross-modal retrieval based on dictionary learning. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the bottom characteristics of image data and text data, and respectively constructing a training set and a test set of the image and text based on the bottom characteristics; Construct dictionary learning model, train based on imageand text training set, construct new training set and test set according to the obtained image dictionary and text dictionary; Projecting a training set of the new image and text onto a common representation space; According to the image and text feature data in the common representation space, the feature preserver is learned, that is, feature discrimination, triple sorting and learning modal classifier. Feature preserver and modal classifier are confronted to learn, the common representation space is optimized, and the cross-modal retrieval is carried out by test suite. The accuracy of cross-modal retrieval can be greatly improved by using dictionary learning to extract features and antagonistic learning to learn the common space of image modal and text modal.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Hyperspectral image classification method based on linear regression Fisher discrimination dictionary learning (LRFDDL)
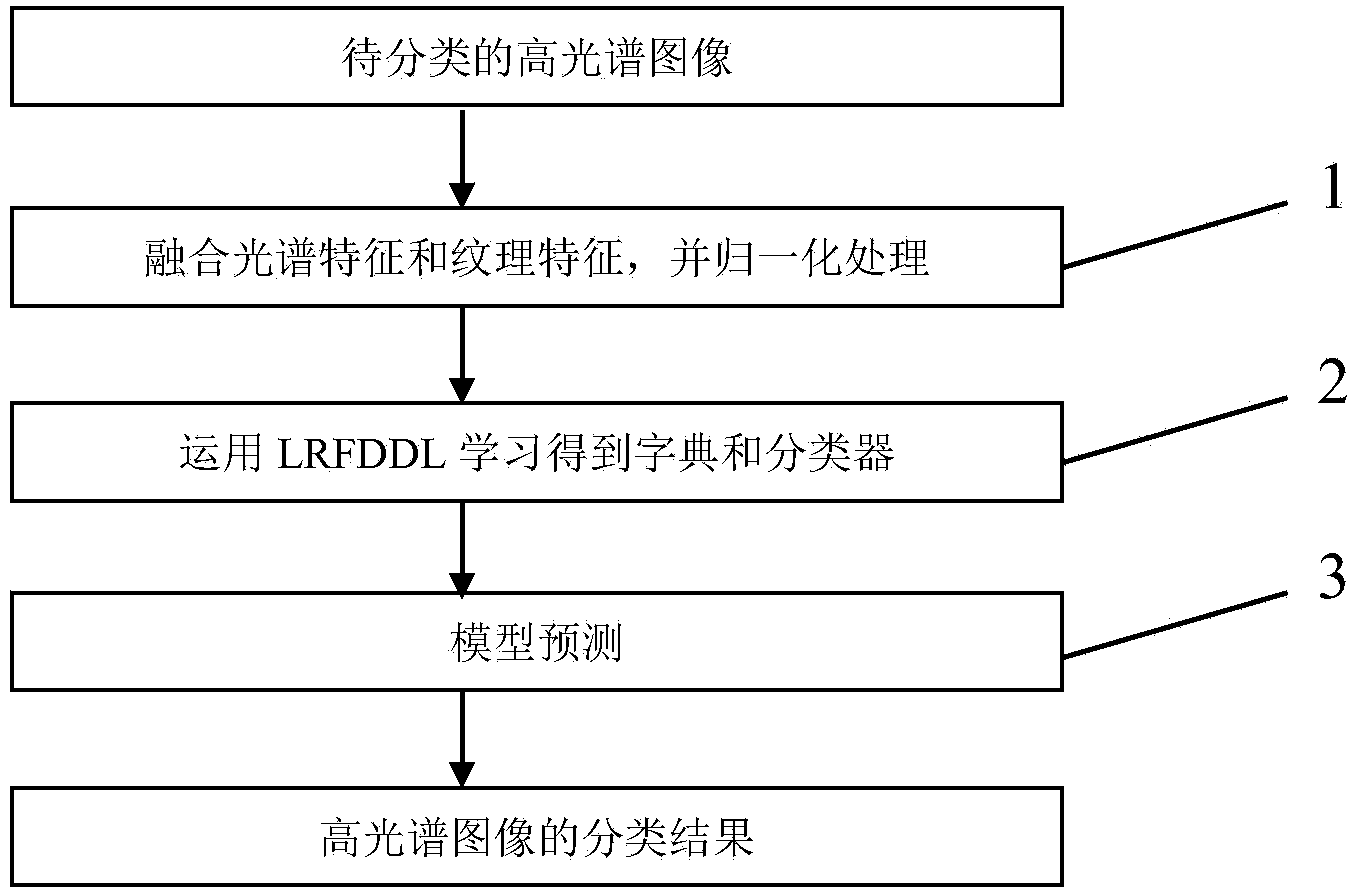
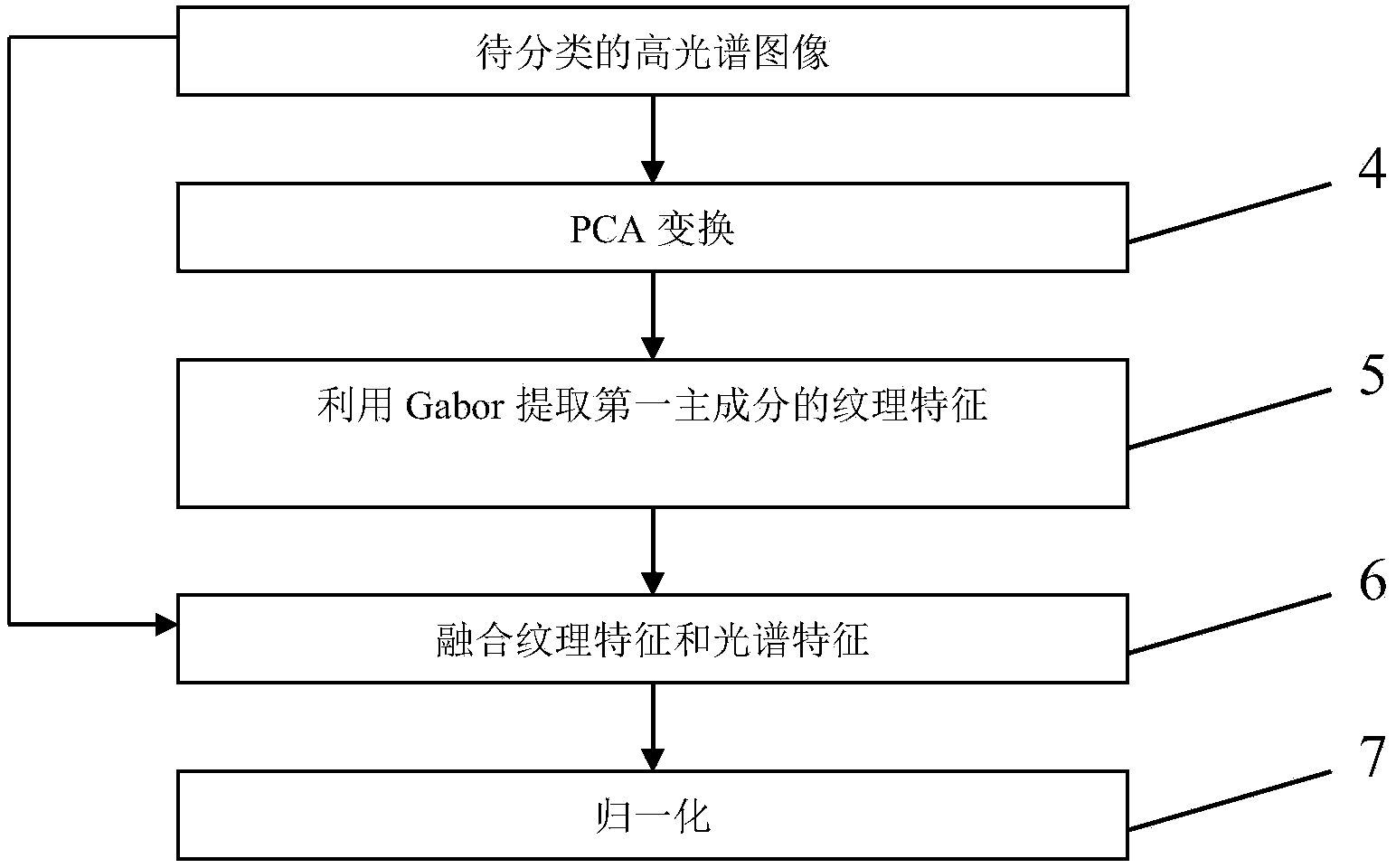
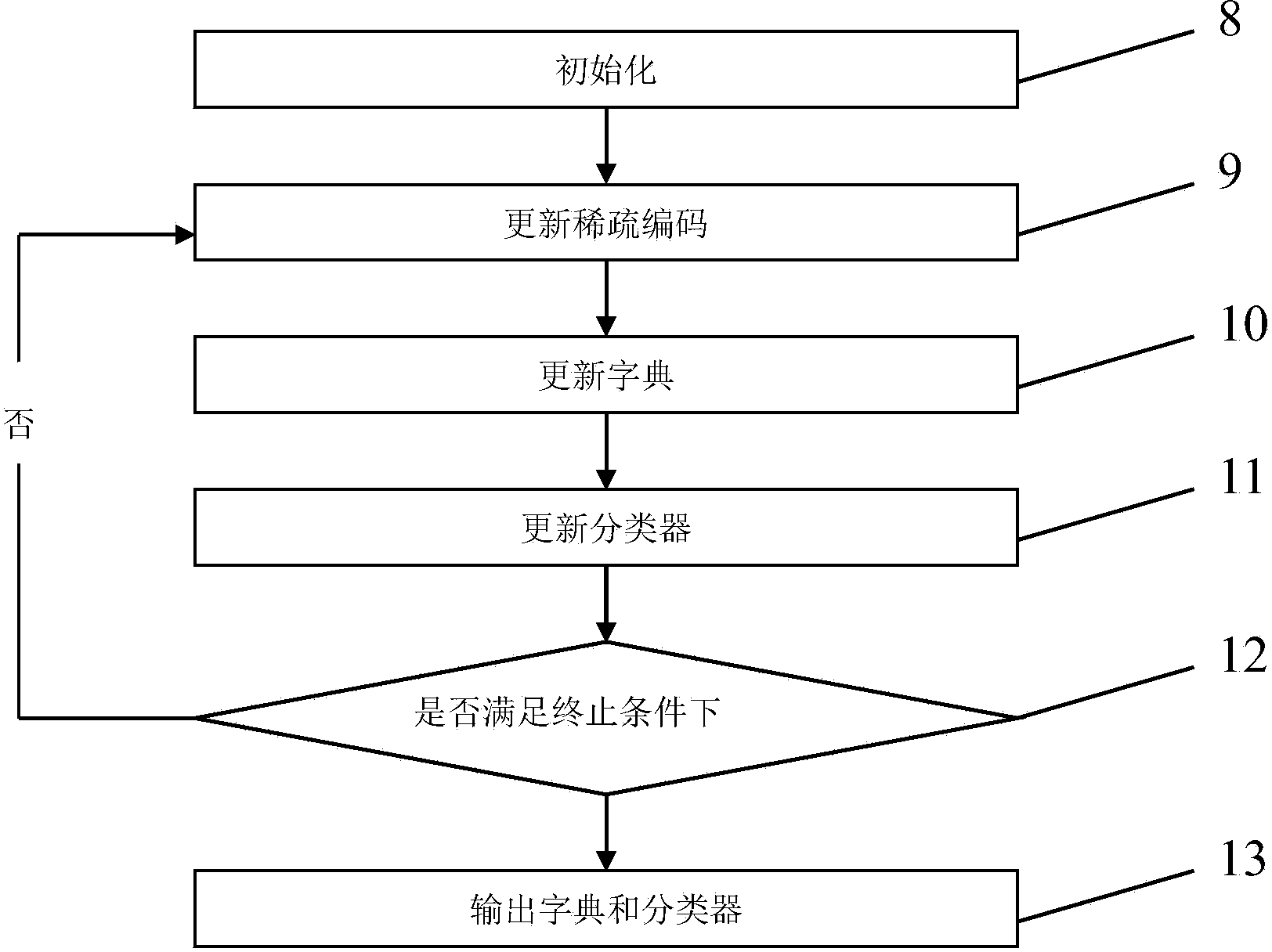
ActiveCN103971123AImprove classification performanceStrong discriminationCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningHyperspectral image classification
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method based on linear regression Fisher discrimination dictionary learning (LRFDDL). The method includes the following steps that the textural features and the spectral features of each hyperspectral image are fused and normalized; a dictionary and a linear classifier are obtained by learning through an LRFDDL algorithm; model prediction is conducted. According to the hyperspectral image classification method based on LRFDDL, the LRFDDL algorithm is applied to hyperspectral image classification, so that the classification accuracy of the hyperspectral images is improved; in addition, the textural features of the hyperspectral images are added into the classification, and thus the classification effect of the hyperspectral images is further improved.
Owner:南京词酷网络信息技术有限公司
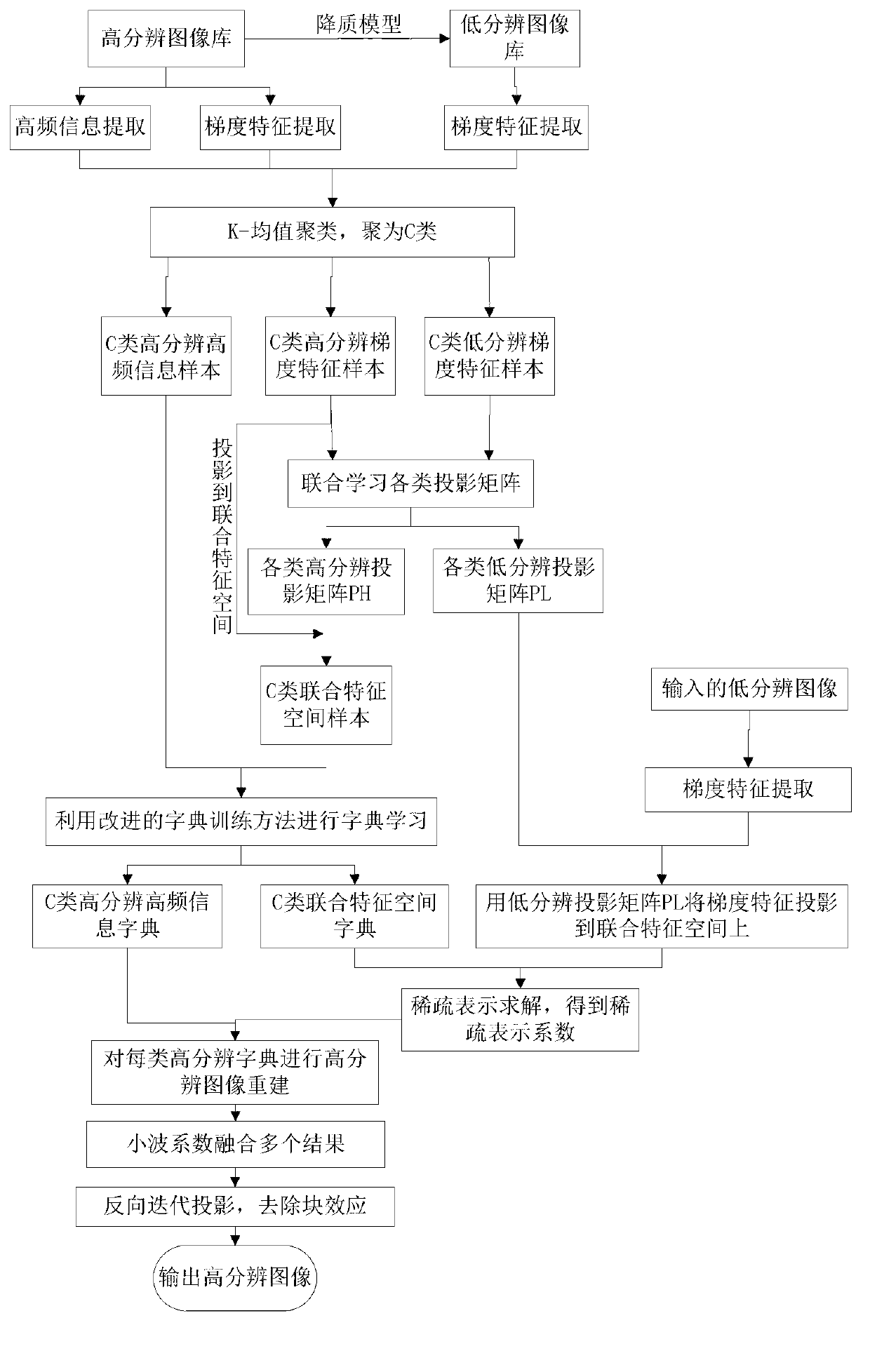
Unified feature space image super-resolution reconstruction method based on joint sparse constraint
ActiveCN103093445AGuaranteed sparse representation of coefficientsMaintain structure informationImage enhancementGeometric image transformationHat matrixDictionary learning
The invention discloses a united feature space image super-resolution reconstruction method based on joint sparse constraint. The feature space image super-resolution reconstruction method based on the joint sparse constraint comprises the achieving steps: (1) taking z images from a natural image base, and constructing a sample set; (2) gathering samples into C types, utilizing joint learning to obtain a low-resolution projection matrix and a high-resolution projection matrix of each type; (3) projecting high-resolution gradient feature samples of each type, and obtaining a sample set Mj; (4) with the joint sparse constraint adopted, carrying out dictionary learning on the Mj and high-resolution details, and obtaining dictionaries of each type; (5) partitioning an input low-resolution image Xt, carrying out projection on an image block with the projection matrixes of each type adopted, obtaining united features of each type, and obtaining a coefficient through the united features and the dictionaries of each type; (6) obtaining reconstruction results with the coefficient and the dictionaries of each type adopted; (7) mixing the reconstruction results through wavelet alternation, and obtaining a high-resolution result rh; (8) repeating from the step (5) to the step (7) to obtain a high-resolution image R0, processing the high-resolution image R0 through use of an iterative back projection (IBP) algorithm, and obtaining a reconstruction result RH. The united feature space image super-resolution reconstruction method has the advantages that the edges of the reconstruction result are clear, and the united feature space image super-resolution reconstruction method can be used for image recognition and target classification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Hyperspectral abnormal object detection method based on structure sparse representation and internal cluster filtering
InactiveCN106919952AAccurate extractionImprove detection rateCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a hyperspectral abnormal object detection method based on structure sparse representation and internal cluster filtering, aiming at addressing the technical problem of low object detection effciency of current hyperspectral abnormal object detection methods. The technical solution involves: after selecting an initial background pixel, using the dictionary learning method which is based on principal component analysis to study a background dictionary which obtains rebustness, in the course of sparse vector resolution and image reconstruction, introducing re-weighted laplacian prior to increase the solution precision of sparse vector, computing the errors betwen an original image and a reconstructed image to obtain a sparse representation error, using the internal cluster filtering to represent space spectrum characteristics of hyperspectral data, obtaining the internal cluster error by computing the error between a to-be-tested pixel and other pixel linear representation result, and finally combining the sparse representation error and the linear weighting of the internal cluster error and implementing precise extraction of an abnormal object. According to the invention, the method increases 10-15% of detection rate with the proviso of a constant false alarm rate compared with prior art.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
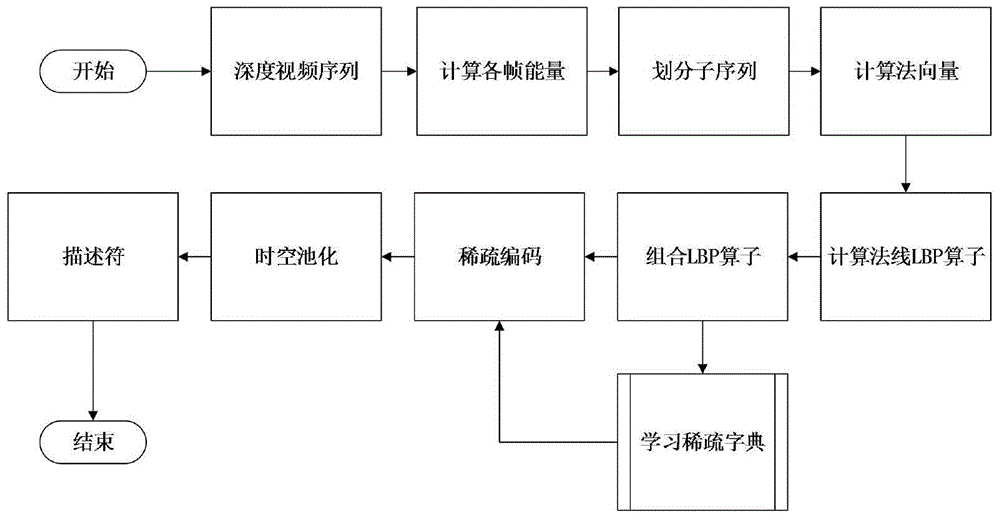
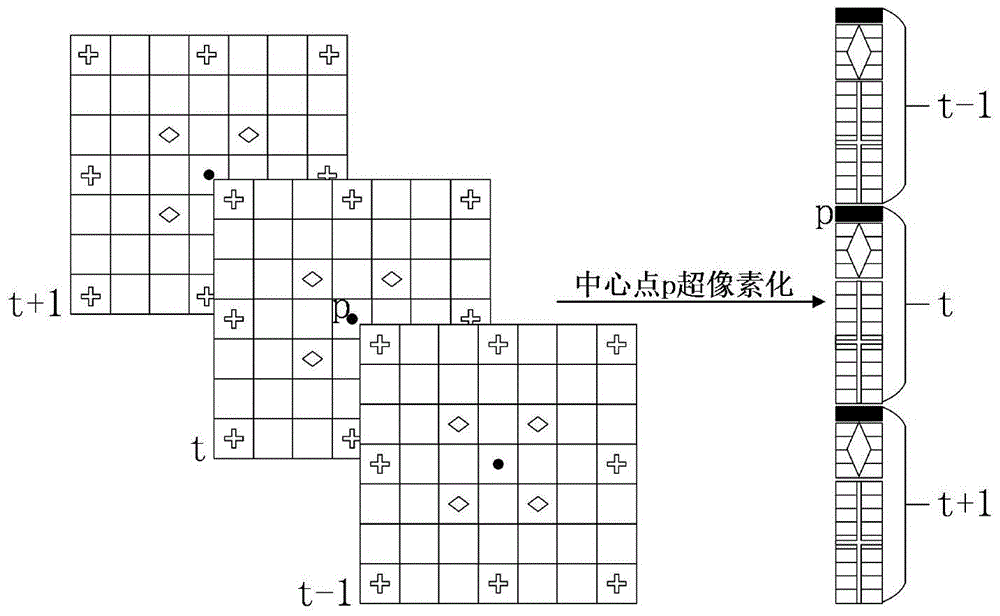
Human body behavior identification method based on depth sequence
ActiveCN105740833AStrong stickReduce data volumeCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyPattern recognition
The invention discloses a human body behavior identification method based on a depth sequence. The human body behavior identification method comprises the following steps: adopting a LBP (Local Binary Patterns) operator based on normal information; adopting a combined LBP operator of a spatial pyramid form; carrying out the sparse representation of the combined LBP operator; and carrying out the segmentation and the alignment of a behavior sequence. In order to obtain surface features which reflect different human body behavior surfaces in a depth map and further improve the robustness of human body behavior identification, a LBP description operator of normal information in the depth map is defined according to the similarity and the associated information of a human body structure in the depth map, wherein the operator keeps the geometric characteristics of a human body behavior surface on an aspect of details, extracts the local features of the surface on a local space, and expresses the local features as the human body behavior local features in the depth map. On the whole, detail information is integrated by a coding method based on dictionary learning, the local spatial structure relationship of a human body surface is kept by the pooling processing of an adaptive space-time pyramid and a thinning coefficient, and the detail and integral feature description of three-dimensional human body behaviors is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Blood vessel and fundus image segmentation method, device and equipment and readable storage medium
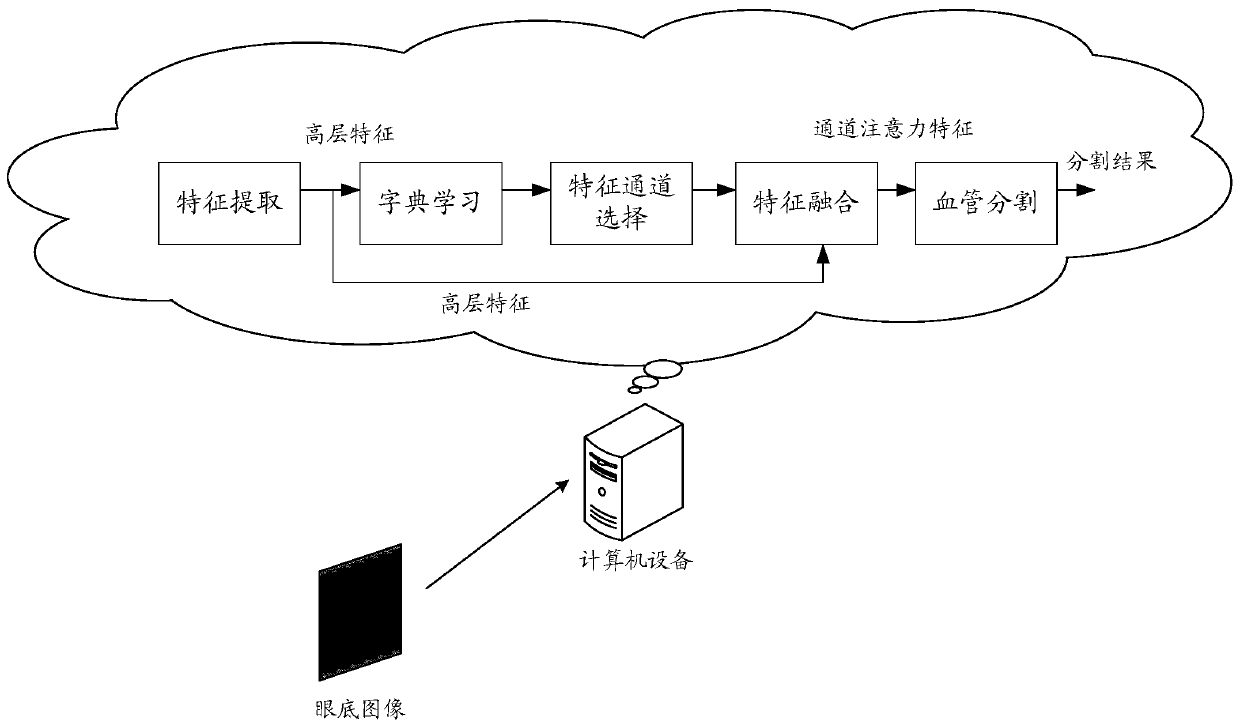
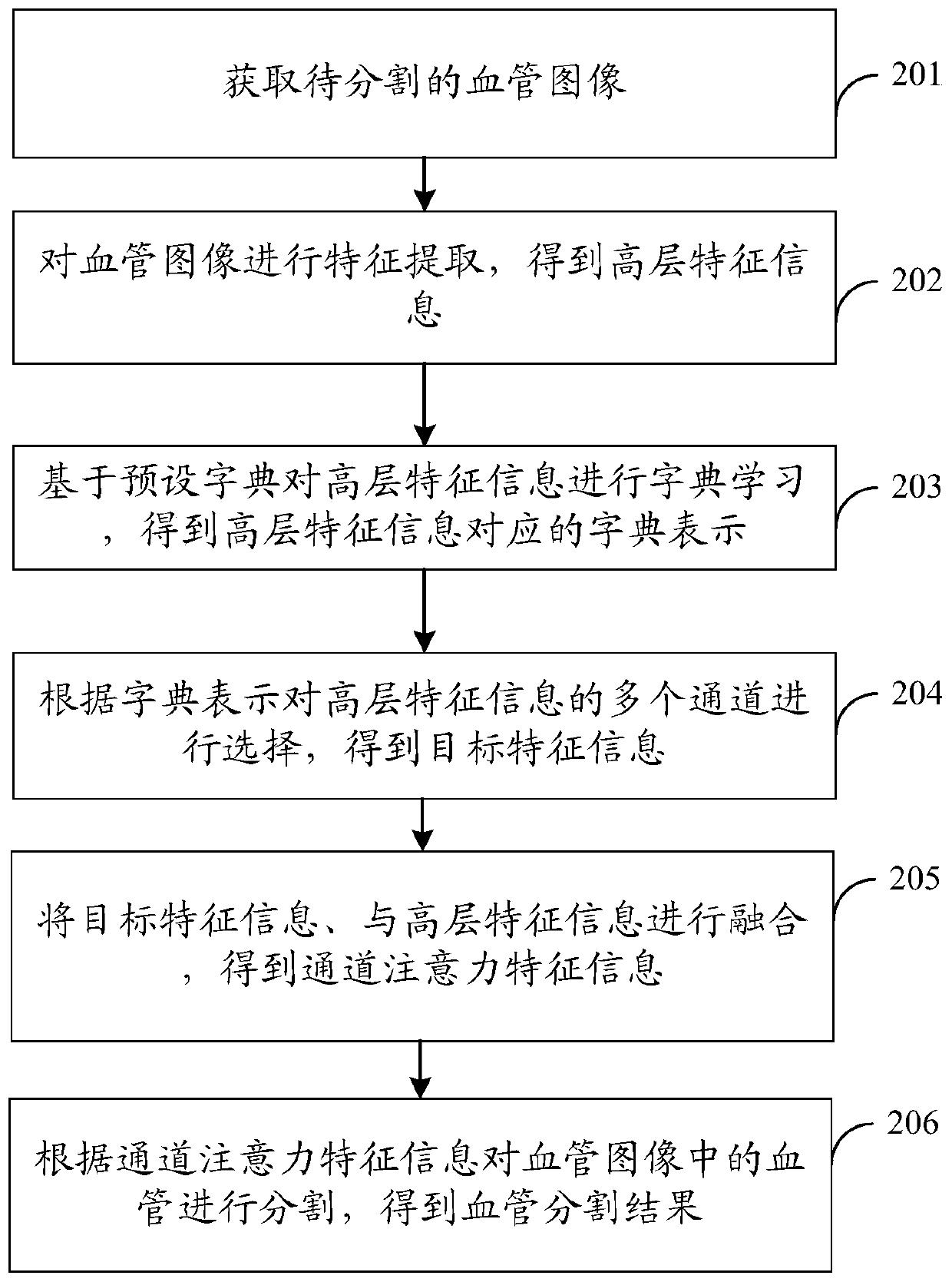
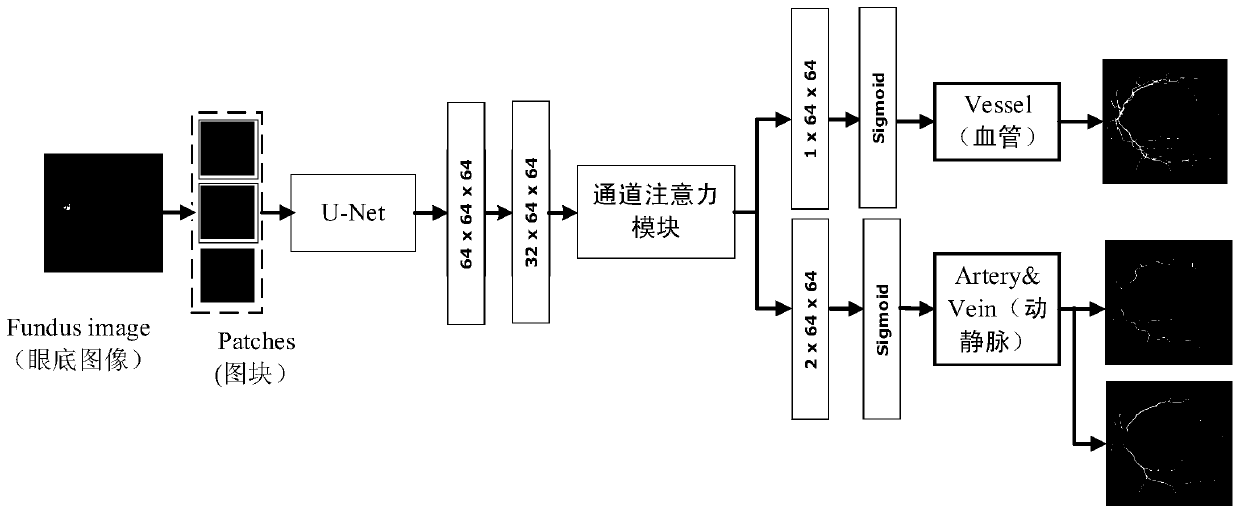
PendingCN110443813AImprove Segmentation AccuracyAvoid lossImage enhancementImage analysisDictionary learningFeature extraction
The embodiment of the invention discloses a blood vessel and eye fundus image segmentation method, device and equipment and a readable storage medium, and relates to the computer vision technology ofartificial intelligence. Specifically, the method comprises steps of acquiring a blood vessel image to be segmented, such as a fundus image; performing feature extraction on the blood vessel image such as the fundus image to obtain high-level feature information; performing dictionary learning on the high-level feature information based on a preset dictionary to obtain dictionary representation corresponding to the high-level feature information; selecting a plurality of channels of the high-level feature information according to the dictionary representation to obtain target feature information; fusing the target feature information with the high-level feature information to obtain channel attention feature information; and segmenting blood vessels in the blood vessel image, such as the fundus image, according to the channel attention feature information to obtain a blood vessel segmentation result. According to the scheme, global information loss of the characteristic blood vessel image such as the fundus image can be avoided, and the segmentation accuracy of the blood vessel image such as the fundus image is greatly improved.
Owner:腾讯医疗健康(深圳)有限公司
Image scene labeling method based on conditional random field and secondary dictionary study
ActiveCN105844292AConsistencyImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDictionary learningConditional random field
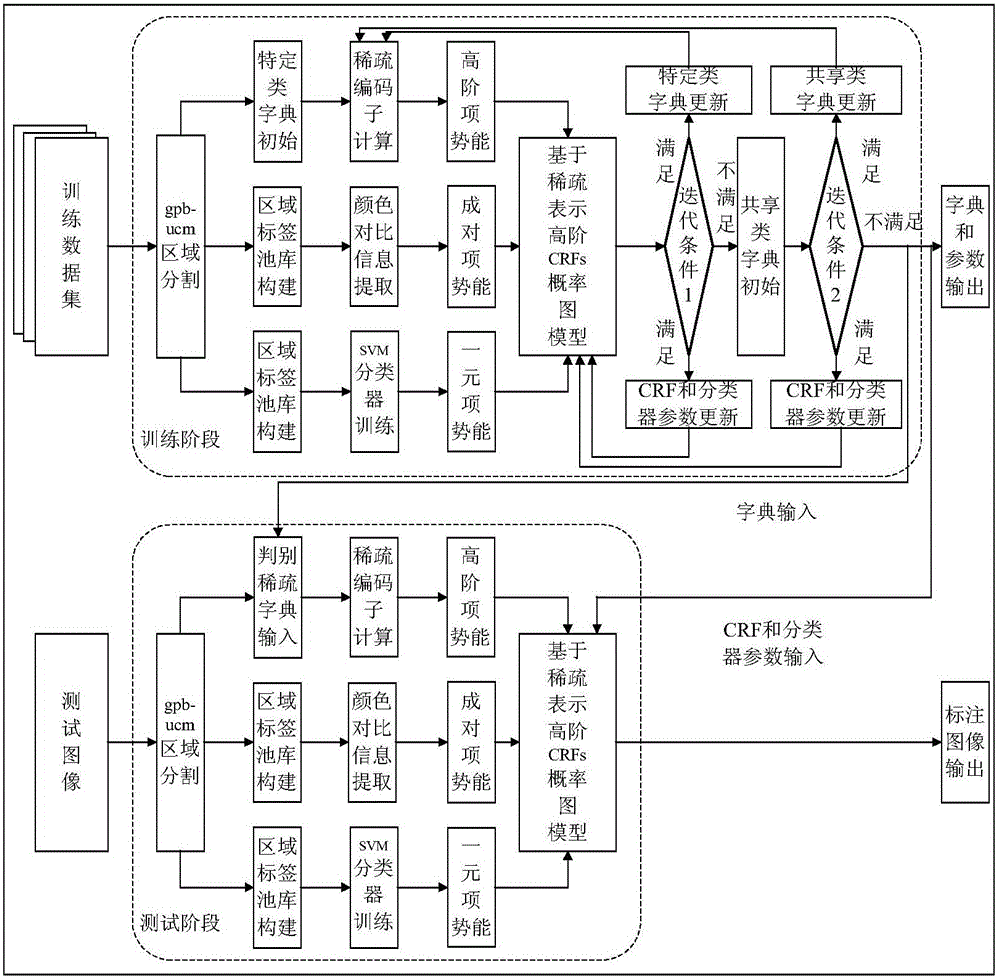
The invention discloses an image scene labeling method based on a conditional random field and a secondary dictionary study, comprising steps of performing superpixel area over-segmentation on a training set image, obtaining a superpixel over-segmentation area of each image, extracting the characteristics of each superpixel over-segmentation area, combining with a standard labeled image to construct a superpixel label pool, using the superpixel label tool to train a support vector machine classifier to calculate superpixel unary potential energy, calculating paired item potential energy of adjacent superpixels, in virtue of global classification statistic of the over-segmentation superpixel area in a training set, constructing a classifier applicable to a class statistic histogram as a classification cost, using the histogram statistic based on the sum of the sparse coders of the sparse representation of the key point characteristic in each class superpixel area as the high order potential energy of a CRF model, using two distinguishing dictionaries of a class dictionary and a shared dictionary to optimize the sparse coder through the secondary sparse representation, and updating the dictionary, the CRF parameters and the classifier parameters. The image scene labeling method improves the labeling accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
SAR (stop and reveres) image segmentation method based on dictionary migration clustering
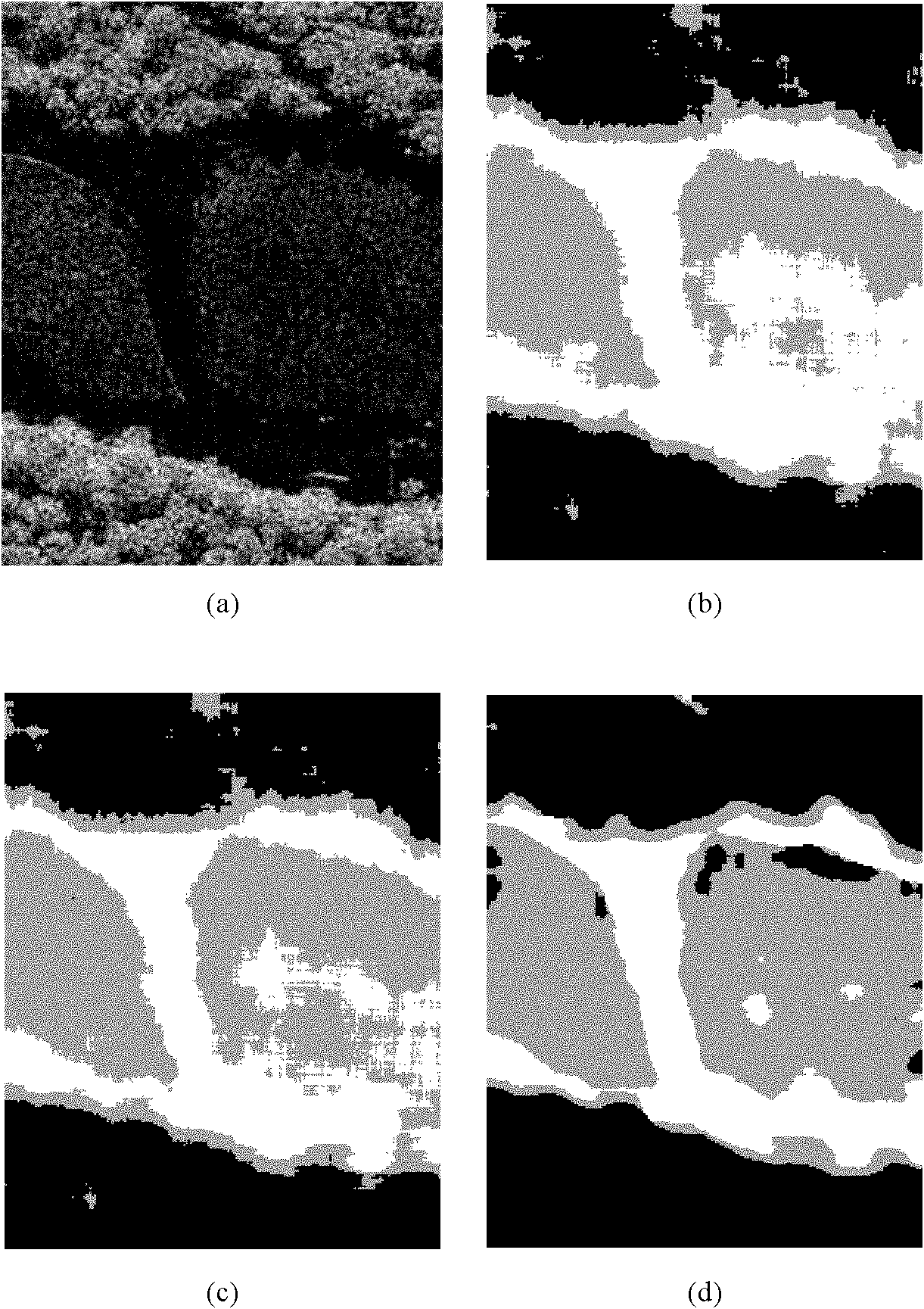
InactiveCN102122386AEasy to divideShorten the timeImage enhancementDictionary learningImage segmentation
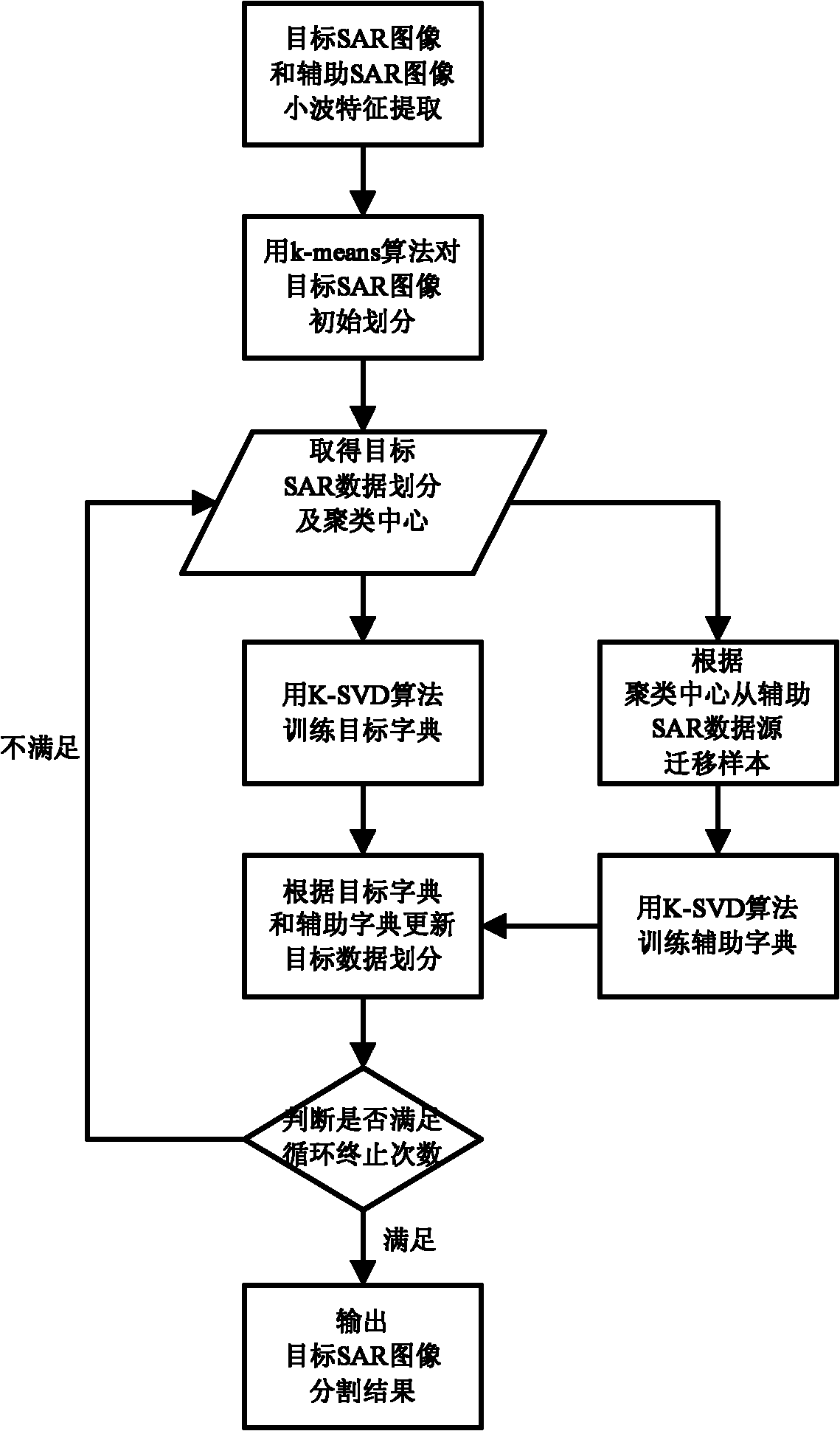
The invention discloses an SAR (stop and reveres) image segmentation method based on dictionary migration clustering, which mainly solves the problems that the existing artificial mark SAR image has high cost and the existing non-mark SAR image can not assist a target SAR image in segmenting. The method has the following realization processes: 1) extracting wavelet characteristics for the target SAR image and the non-mark assistant SAR image; 2) setting circulation ending times, and preliminarily dividing the target SAR image with a k-means method; 3) training a dictionary for each class of target SAR image data; 4) migrating a group of samples for each class of target SAR image data from the assistant SAR image data; 5) removing the assistant data sample with an unstable label by a spectral clustering integration method; 6) training an assistant dictionary by each bath of purified assistant samples; and 7) updating a sample label and outputting a clustering segmenting result according to a target dictionary, the assistant dictionary and a corresponding clustering center. The SAR image segmentation method has the advantage of good segmenting effect and can be used for further identifying the SAR image target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Image super-resolution rebuilding method based on dictionary learning and bilateral holomorphy
InactiveCN103295197AComplementary efficient and directionalOvercome the shortcomings of being unable to effectively supplement the missing information of low-resolution imagesImage enhancementVideo monitoringDictionary learning
The invention discloses an image super-resolution rebuilding method based on dictionary learning and bilateral holomorphy, and mainly solves the problem of poor quality of rebuilt images through the existing dictionary learning method. The image super-resolution rebuilding method includes: (1), acquiring initial high-definition images; (2), training initial an inner dictionary set d0 and an initial outer dictionary set D0; (3), calculating initial a holomorphy weight matrix W0 on the initial high-definition images; (4), performing holomorphy optimizing processing on the inputted initial high-definition images to acquire optimized images; and (5), applying the initial inner dictionary set d0 and the initial outer dictionary set D0 to rebuild the optimized images to acquire rebuilt images. The image super-resolution rebuilding method can rebuilt natural images, can effectively preserve edges and texture information of the images and can be used for video monitoring and video switching.
Owner:西安智慧创新信息科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com