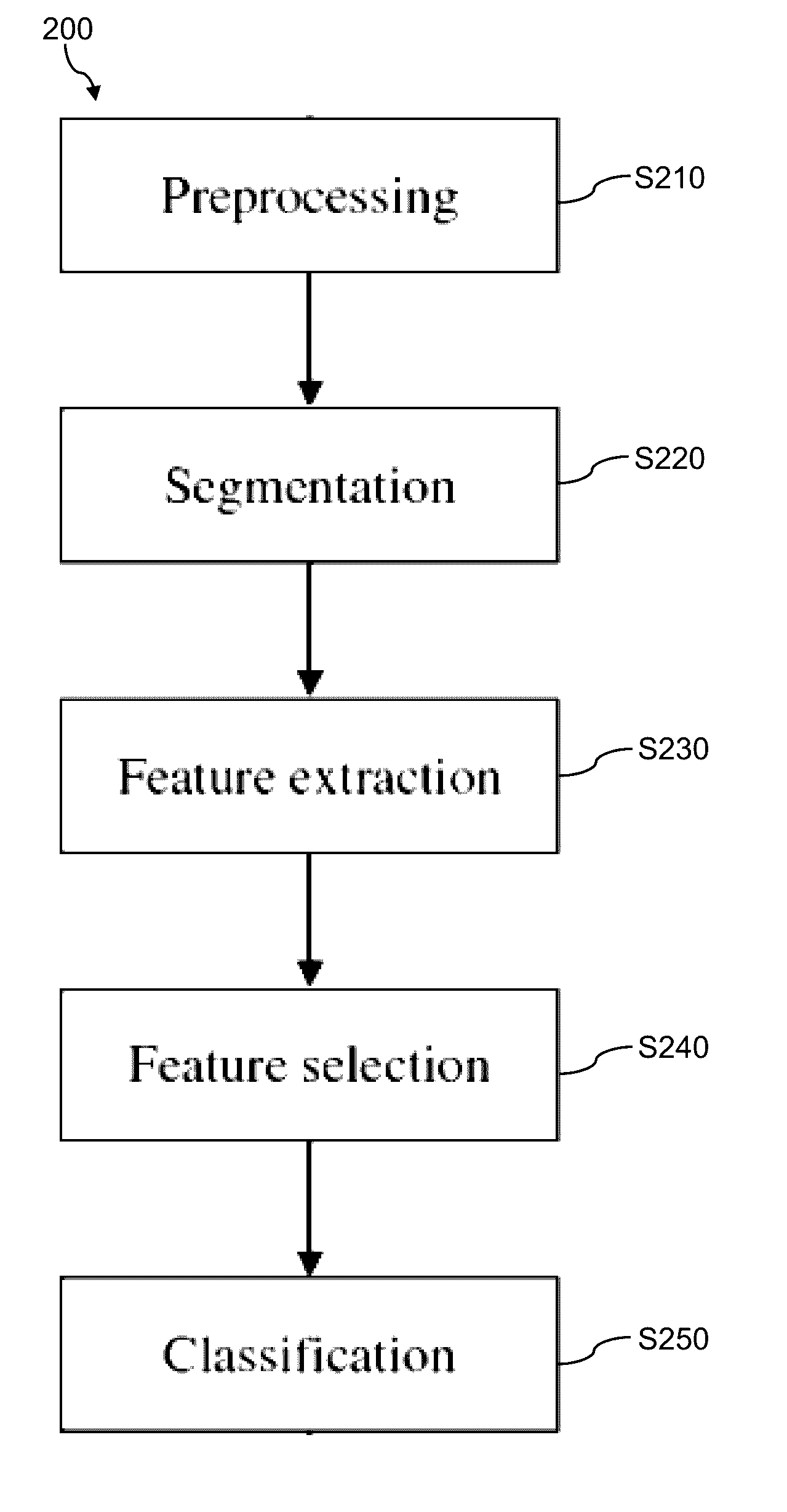
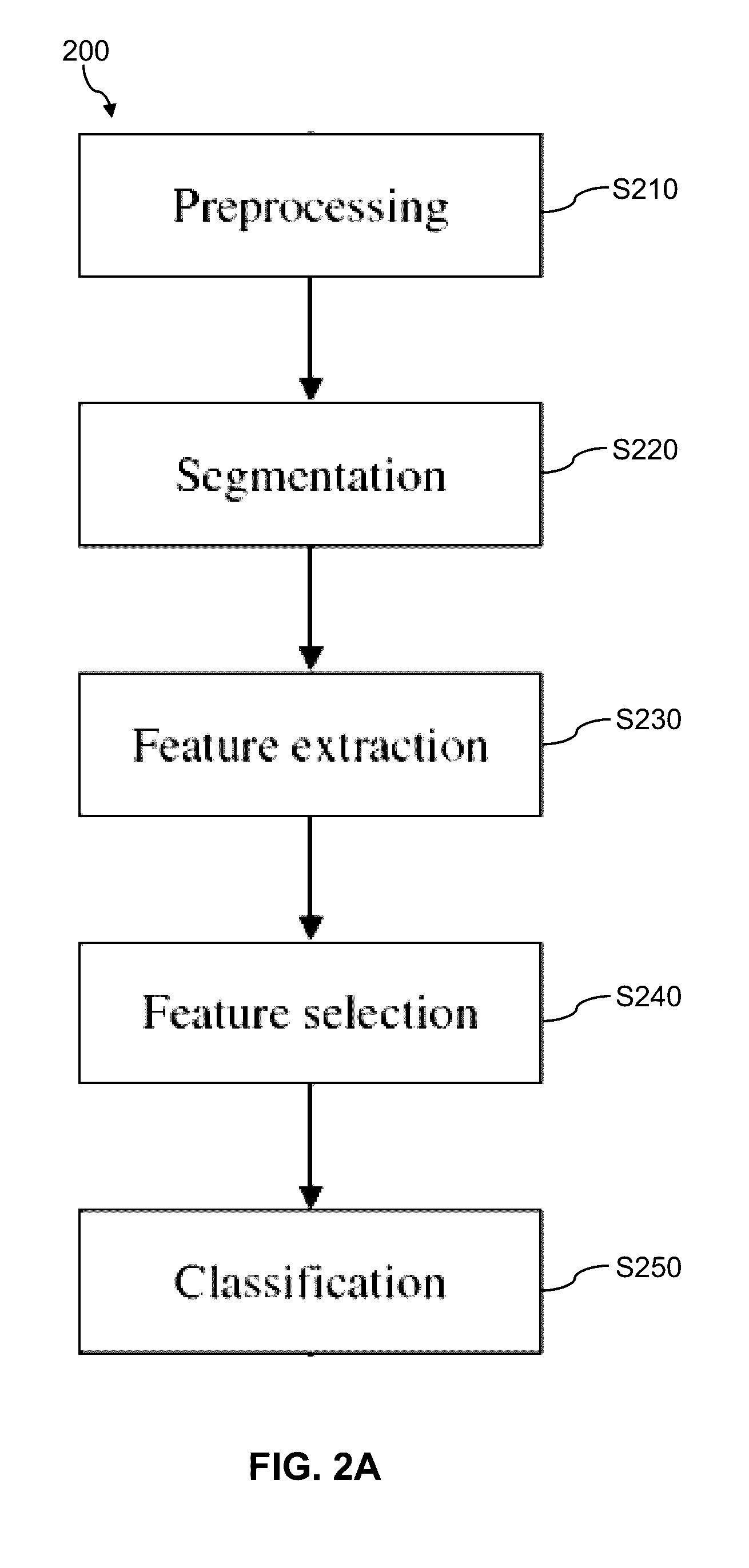
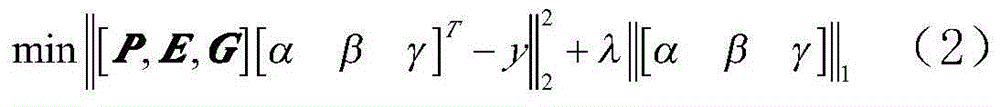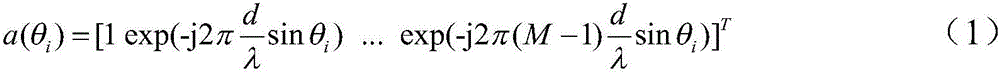Patents
Literature
348 results about "Sparse constraint" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Broadband signal DOA estimation method based on co-prime array
ActiveCN106324558AHigh-resolutionEasy to detectDirection findersSparse constraintSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
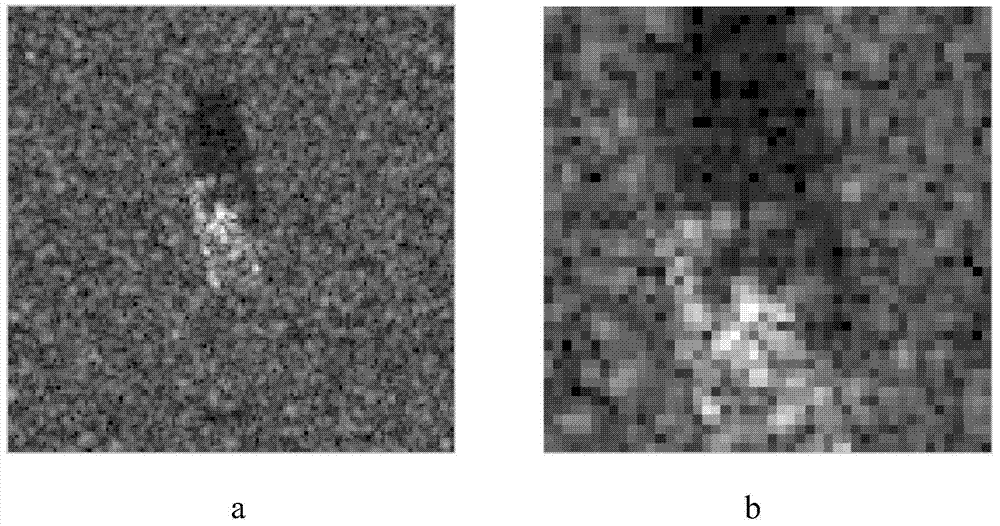
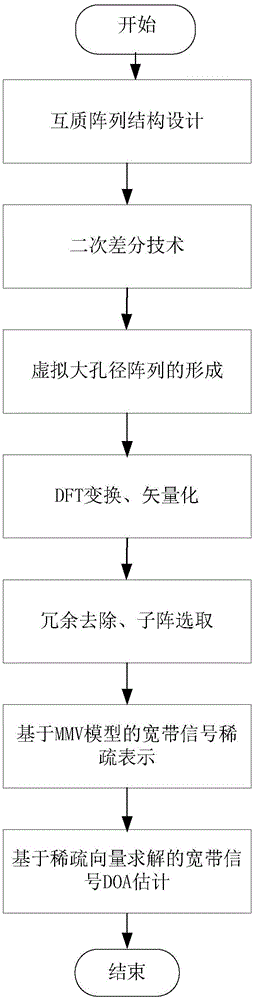
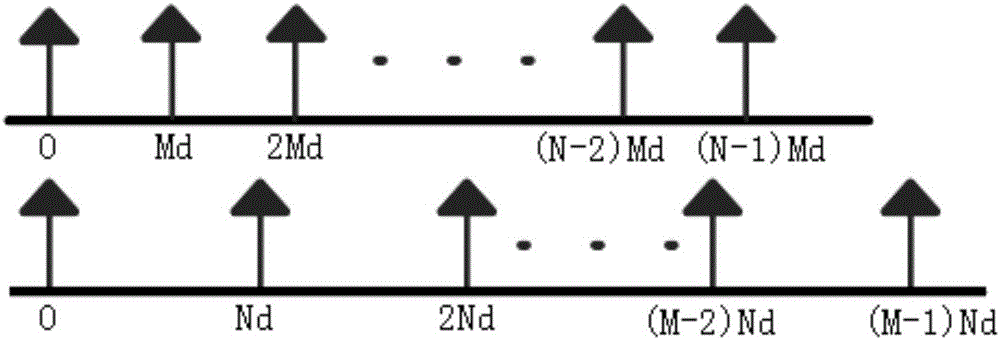
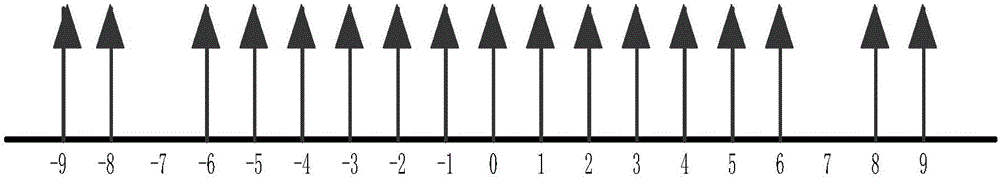
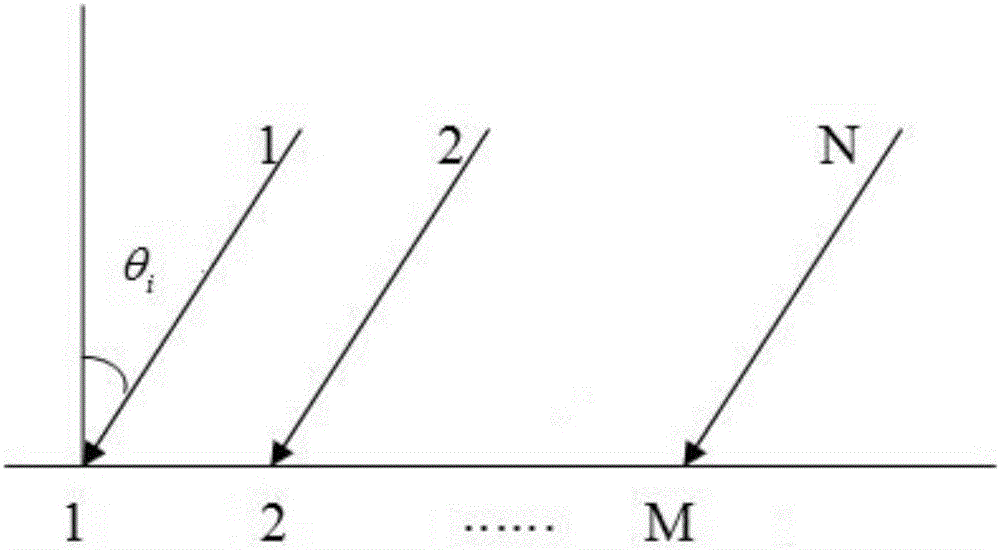
The invention discloses a broadband signal DOA estimation method based on a co-prime array, and the method comprises the steps: S1, designing a co-prime array structure through an antenna; S2, carrying out the sampling and discrete Fourier transform of a broadband signal received by an antenna in the co-prime array, and obtaining a frequency domain signal output model; S3, calculating an autocorrelation matrix of the frequency domain signal output model, carrying out the vectorization of the frequency domain signal output model, and obtaining a new signal model; S4, carrying out the processing of the new signal model, and obtaining a spatial smooth covariance matrix of the broadband signal; Sa5, dividing a space domain grid, constructing a dictionary, carrying out the sparse representation of the spatial smooth covariance matrix through employing the dictionaries of a plurality of frequency points of the broadband signal, and forming a multi-measurement-vector sparse representation model of a plurality of dictionaries of the broadband signal; S6, achieving the arrival direction estimation of the broadband signal in a mode of solving a sparse inverse problem through the joint sparse constraint of the sparse representation coefficients of the plurality of dictionaries. The method can improve the estimation precision of the direction angle of the broadband signal under the condition of low signal to noise ratio, and reduces the direction finding error.
Owner:东北大学秦皇岛分校
Tensor structural missing filling method based on joint low rank and sparse representation
PendingCN109241491ARealize the solutionAccurate fillingComplex mathematical operationsData dredgingFiber
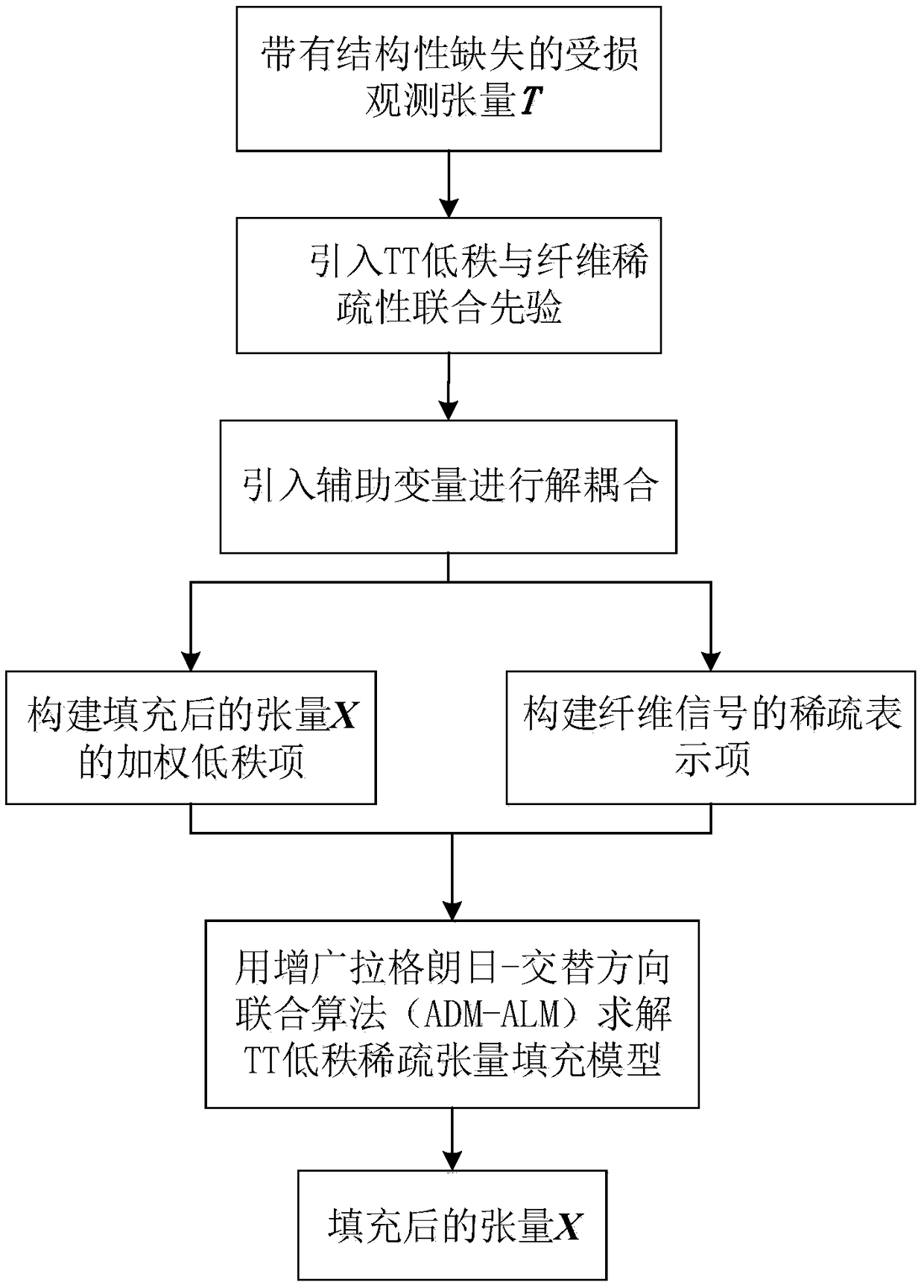
The invention relates to the field of computer vision. In order to propose a tensor structural missing filling method and realize the accurate filling of the structural missing tensor, the tensor structural missing filling method based on the combination of low rank and sparse representation and the TT low rank tensor filling theory are introduced into the TT low rank prior to constrain the potential tensor. At the same time, considering that the fiber signal along each dimension of the tensor can be sparsely represented by a dictionary, and the missing fiber of the previous dimension can be recovered by sparse constraint on the fiber signal in the next dimension, sparse constraint is introduced for each dimension of the fiber signal; based on the sparse apriori of the combined TT low rankand each dimension, the tensor filling problem with structural defects is formulated as a constrained optimization problem, so that the tensor filling problem with structural defects can be realized.The invention is mainly applied to video image inpainting, recommendation system, data mining and multi-classification learning occasions.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar imaging based on dual sparse constraints
InactiveCN104111458ARealize high-resolution imagingHigh imaging speed requirementsSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSparse constraintHigh resolution imaging
The invention discloses a method for compressed sensing synthetic aperture radar imaging based on dual sparse constraints. The method mainly solves the problems that a complete SAR image cannot be obtained in imaging through a traditional synthetic aperture radar imaging method and time loss is large. The method comprises a first step of utilizing radar to irradiate a ground sparse scene D and obtain echo signals r of the scene; a second step of constructing an orientation direction base matrix A of the scene and a distance direction base matrix B of the scene; a third step of obtaining an orientation direction measurement matrix theta, a distance direction measurement matrix omega and an echo measurement matrix S according to the orientation direction base matrix and the distance direction base matrix; a fourth step of constructing a Lagrangian function f(Y,U) according to the orientation direction measurement matrix, the distance direction measurement matrix and the echo measurement matrix; and a fifth step of using an alternate iteration multiplier method to solve the Lagrangian function f(Y,U) in the fourth step and obtaining an image of the scene D. The method can achieve high-resolution imaging of synthetic aperture radar in downsampling, is quick in imaging speed and can be used for large-area topographic mapping and cartography.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
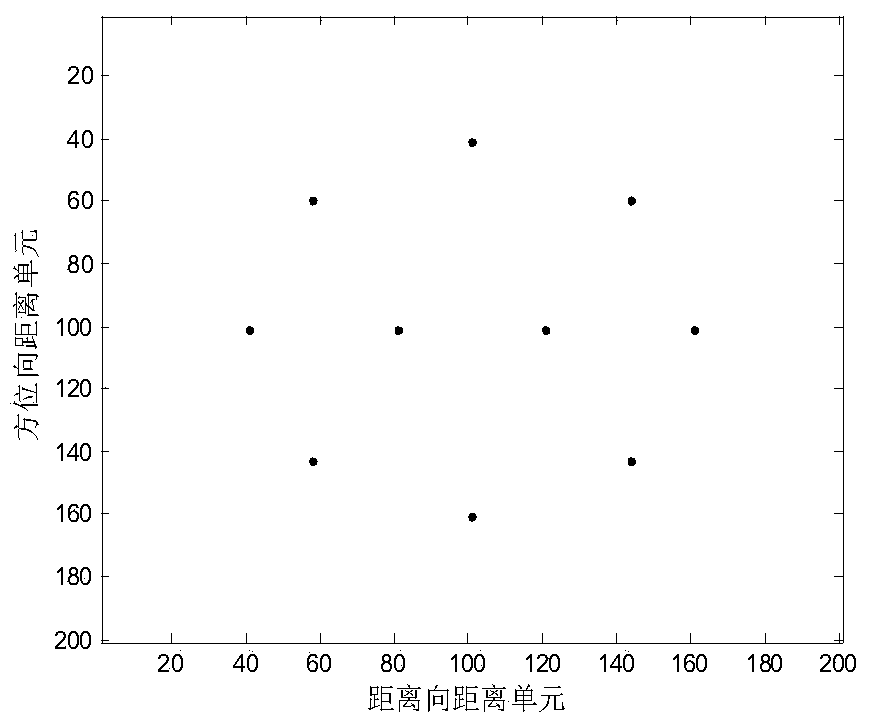
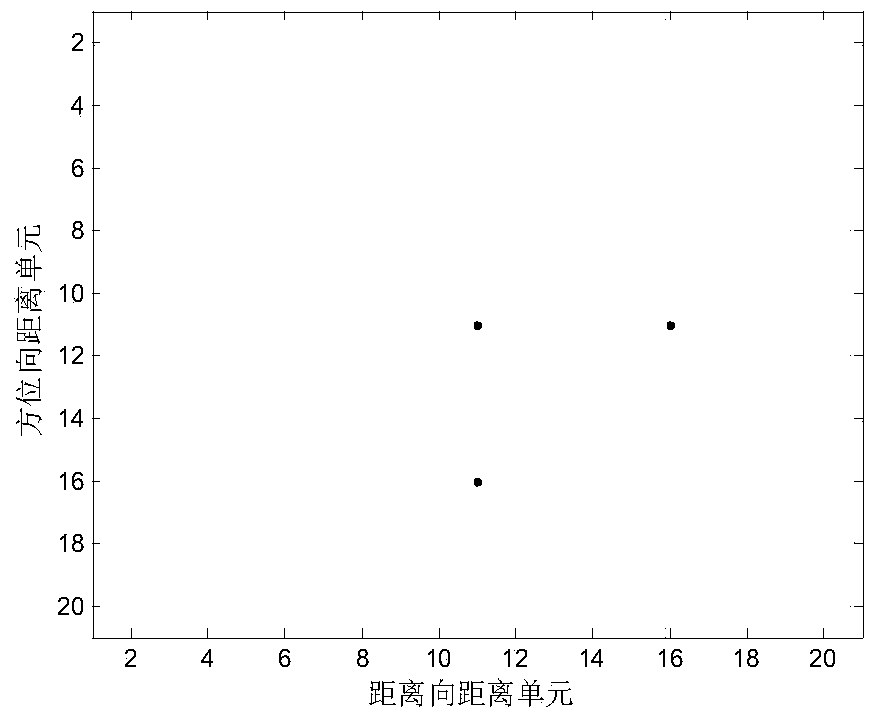
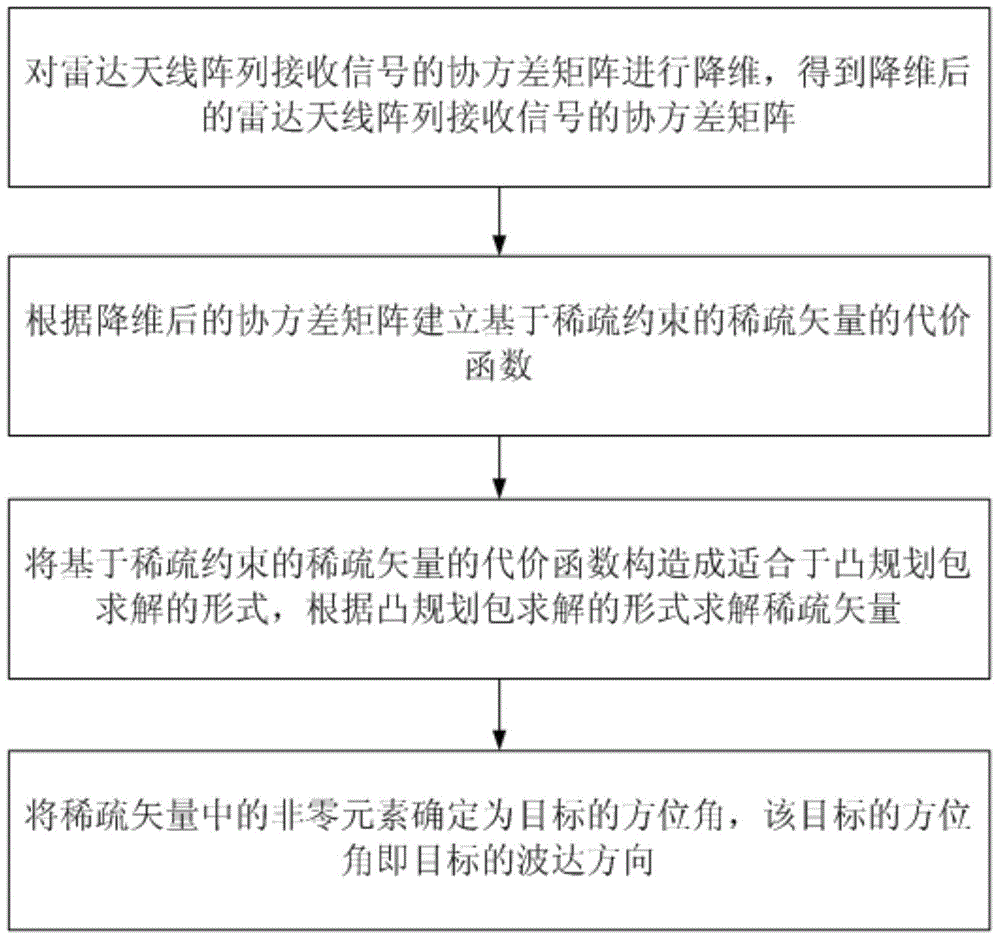
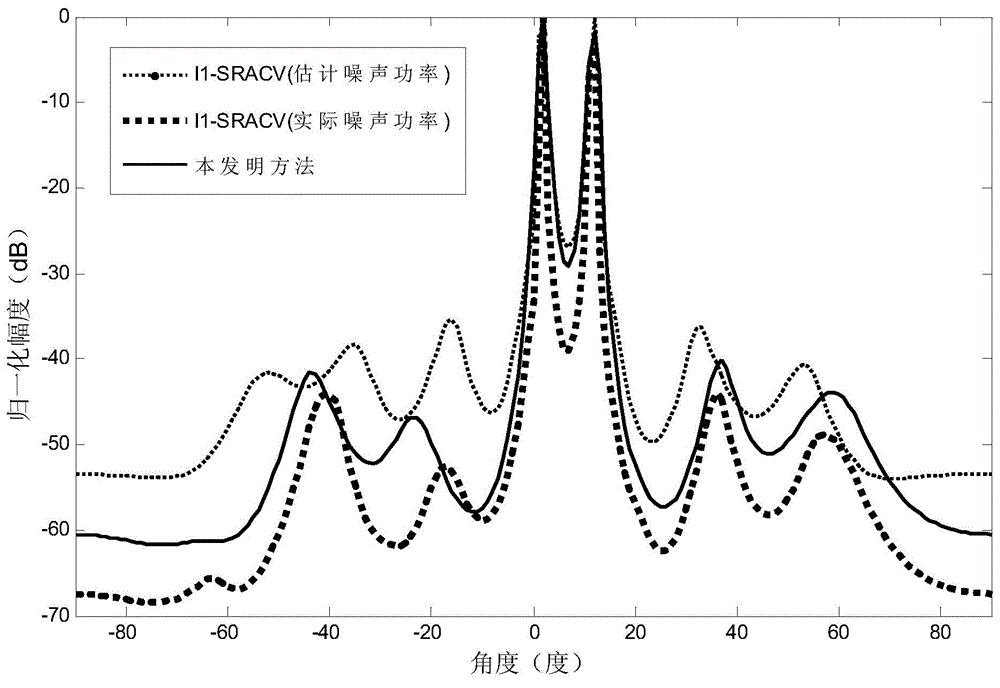
Direction-of-arrival estimation method based on sample covariance matrix sparsity
InactiveCN103954950AImprove resolutionImprove estimation accuracyWave based measurement systemsSparse constraintDimensionality reduction
The invention discloses a direction-of-arrival estimation method based on sample covariance matrix sparsity, and relates to the field of array signal processing. The method comprises the steps that firstly, dimensionality reduction is carried out on a covariance matrix, receiving signals, of a radar antenna array, and the covariance matrix, receiving the signals, of the radar antenna array is obtained after dimensionality reduction; secondly, a sparse vector cost function based on sparse constraints is built according to the covariance matrix after dimensionality reduction; thirdly, the sparse vector cost function based on the sparse constraints is constructed to be the mode suitable for convex programming package solving, and a sparse vector is solved according to the mode of convex programming package solving; fourthly, a non-zero element in the sparse vector is determined as a target azimuth angle, and the target azimuth angle is a target arrival direction. The method mainly solves the problems that in the prior art, known noise power is needed, and the calculated amount is large, and the method is mainly used for scenes of array signal processing.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
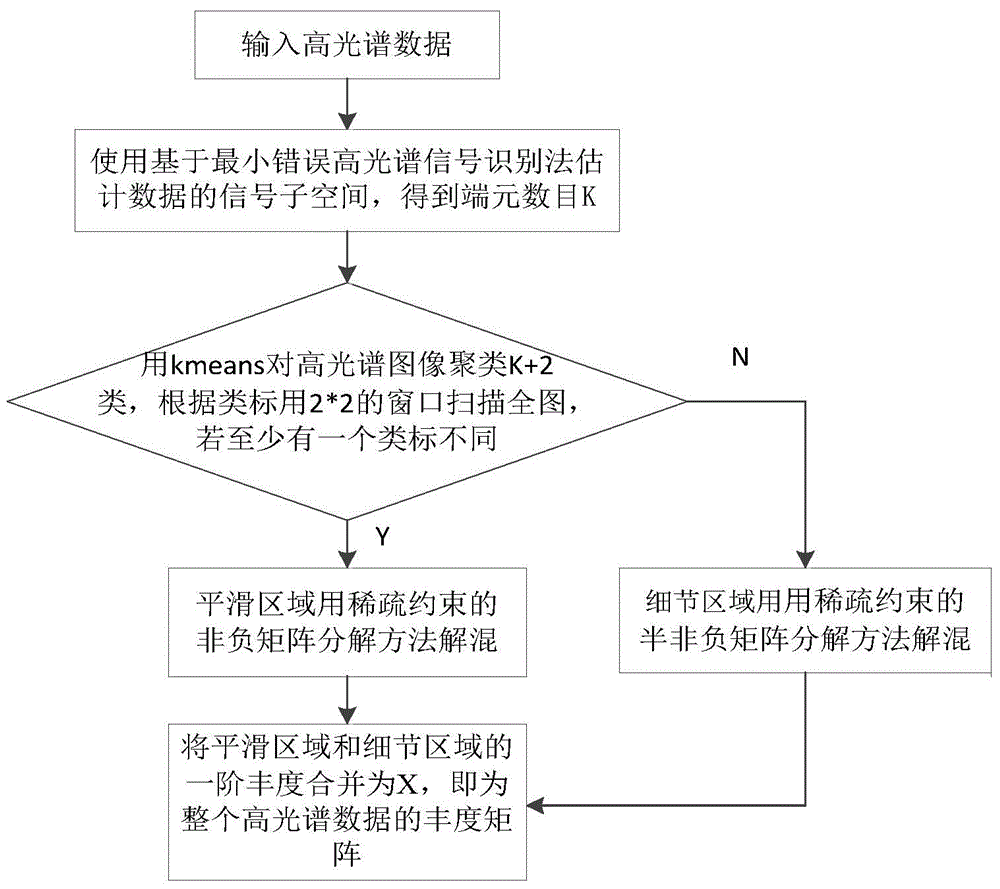
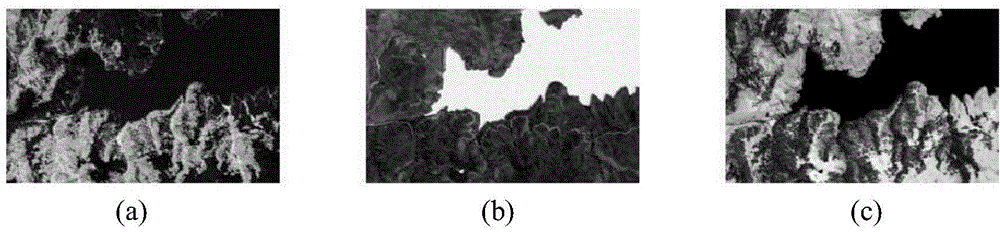
Self-adaptive hyperspectral image unmixing method based on region segmentation
ActiveCN104952050AUnmixing AccurateAccurate representationImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationNonnegative matrix
The invention discloses a self-adaptive hyperspectral image unmixing method based on region segmentation. In consideration of coexistence of linear mixing and bilinear mixing, the method is implemented by adopting the following steps: inputting a hyperspectral image; estimating the number of end elements with a minimum error based hyperspectral signal recognition method; extracting end element matrixes with a vertex component analysis algorithm; clustering hyperspectral data with a K-means clustering method, and segmenting the image into a homogeneous region and a detail region; adopting a linear model for the homogeneous region and performing unmixing with a sparse-constrained non-negative matrix factorization method, and adopting a generalized bilinear model for the detail region and performing unmixing with a sparse-constrained semi-non-negative matrix factorization method. According to the method, characteristics of the hyperspectral data and abundance are combined, the hyperspectral image is represented more accurately, and the unmixing accuracy rate is increased. The sparse constraint condition is added to the abundance, the defect of high probability of local minimum limitation of the semi-non-negative matrix factorization method is overcome, more accurate abundance is obtained, and the method is applied to ground-object recognition for the hyperspectral image.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
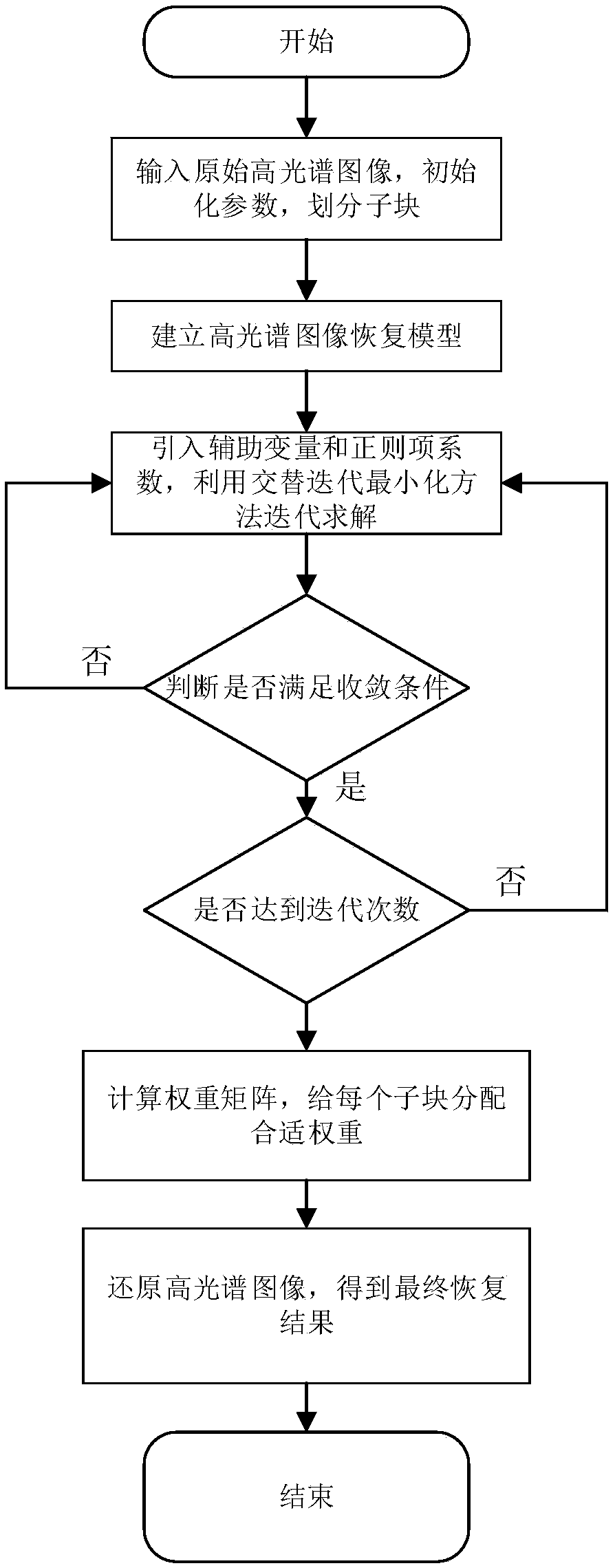
A hyperspectral remote sensing image restoration method based on non-convex low rank sparse constraint
ActiveCN109102477AImprove recovery qualitySolve the problem of not effectively removing noiseImage enhancementImage analysisSparse constraintWeight coefficient
A method for restoring hyperspectral remote sensing image based on non-convex and low-rank sparse constraint belongs to the field of hyperspectral remote sensing image processing in remote sensing image processing. In order to solve the problem that the existing hyperspectral remote sensing image restoration technology can not effectively remove noise and improve the image restoration quality, themethod comprises the following steps: inputting a hyperspectral remote sensing image; initializing a weight coefficient matrix, iterative times and a convergence threshold, initializing sub-image size and scanning step, partitioning sub-blocks; establishing an image restoration model; the auxiliary variable and the coefficient of the regular term being introduced, and the maximum-minimum algorithm being used to solve the problem iteratively; judging whether the restoration result satisfies the convergence condition; obtaining a hyperspectral restored image that meets the requirements by iterative times, otherwise returning to corresponding steps to continue the iterative operation; calculating a weight coefficient matrix and assigning appropriate weights to each sub-block; hyperspectral remote sensing images being restored to obtain the final restored hyperspectral remote sensing images. The effect of denoising is obvious and the image details are preserved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
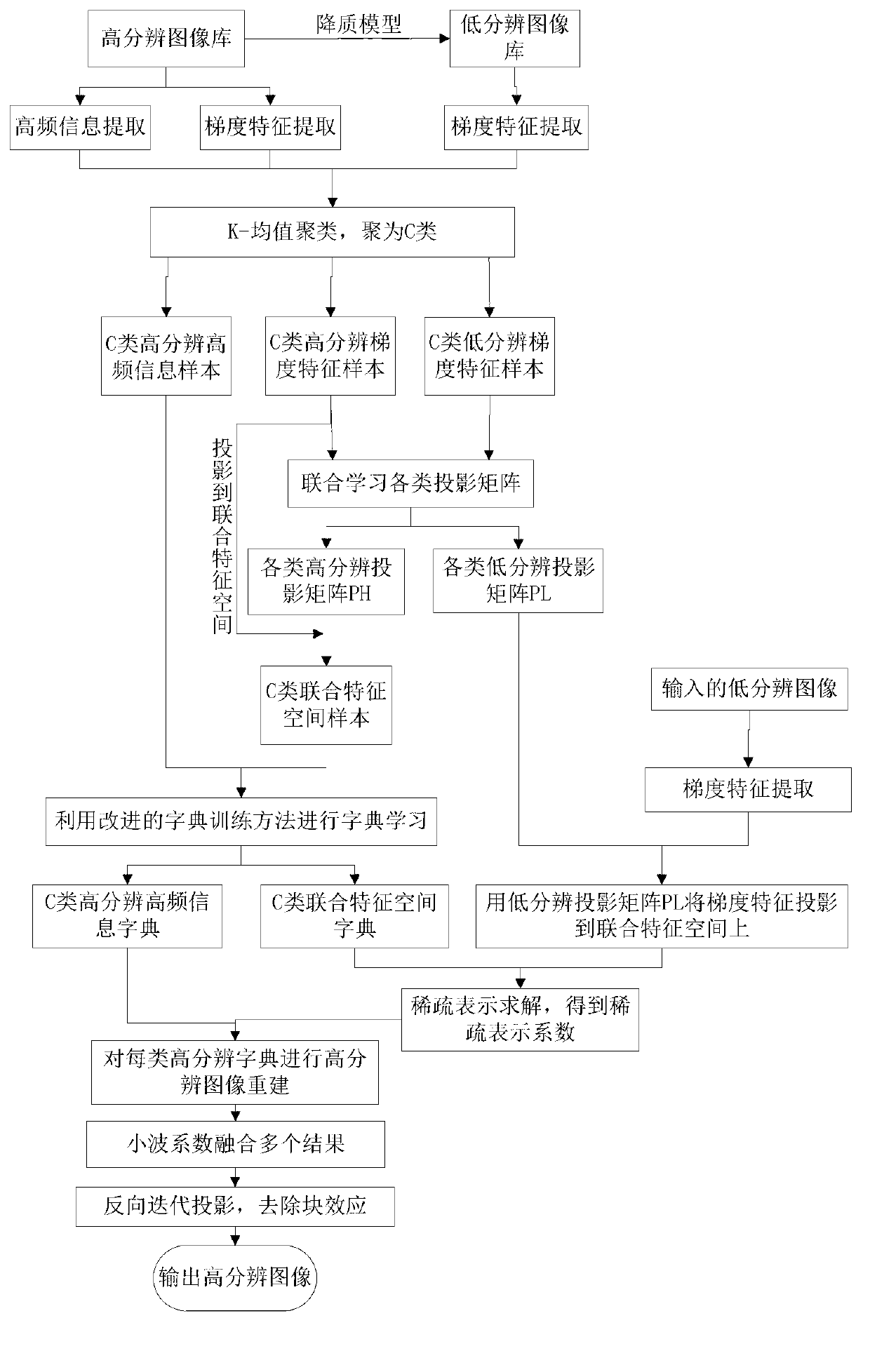
Unified feature space image super-resolution reconstruction method based on joint sparse constraint
ActiveCN103093445AGuaranteed sparse representation of coefficientsMaintain structure informationImage enhancementGeometric image transformationHat matrixDictionary learning
The invention discloses a united feature space image super-resolution reconstruction method based on joint sparse constraint. The feature space image super-resolution reconstruction method based on the joint sparse constraint comprises the achieving steps: (1) taking z images from a natural image base, and constructing a sample set; (2) gathering samples into C types, utilizing joint learning to obtain a low-resolution projection matrix and a high-resolution projection matrix of each type; (3) projecting high-resolution gradient feature samples of each type, and obtaining a sample set Mj; (4) with the joint sparse constraint adopted, carrying out dictionary learning on the Mj and high-resolution details, and obtaining dictionaries of each type; (5) partitioning an input low-resolution image Xt, carrying out projection on an image block with the projection matrixes of each type adopted, obtaining united features of each type, and obtaining a coefficient through the united features and the dictionaries of each type; (6) obtaining reconstruction results with the coefficient and the dictionaries of each type adopted; (7) mixing the reconstruction results through wavelet alternation, and obtaining a high-resolution result rh; (8) repeating from the step (5) to the step (7) to obtain a high-resolution image R0, processing the high-resolution image R0 through use of an iterative back projection (IBP) algorithm, and obtaining a reconstruction result RH. The united feature space image super-resolution reconstruction method has the advantages that the edges of the reconstruction result are clear, and the united feature space image super-resolution reconstruction method can be used for image recognition and target classification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
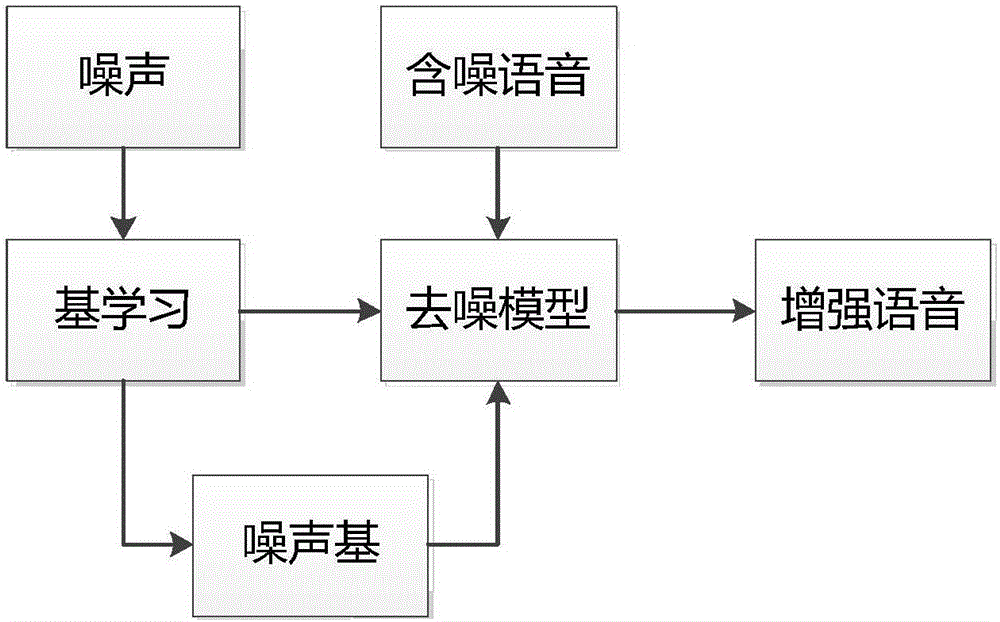
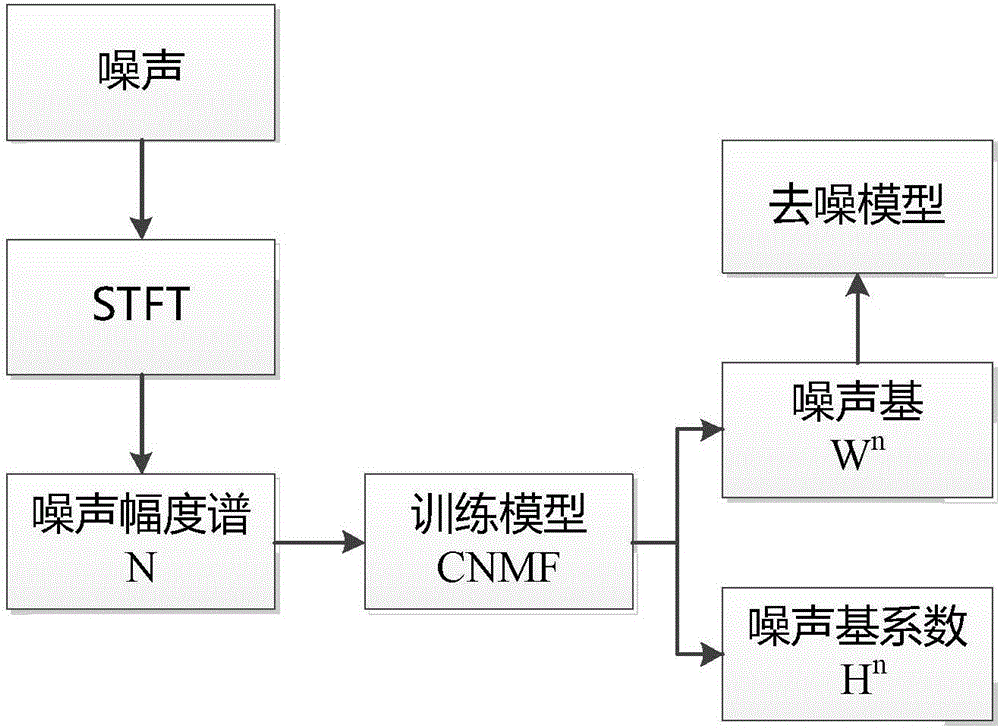
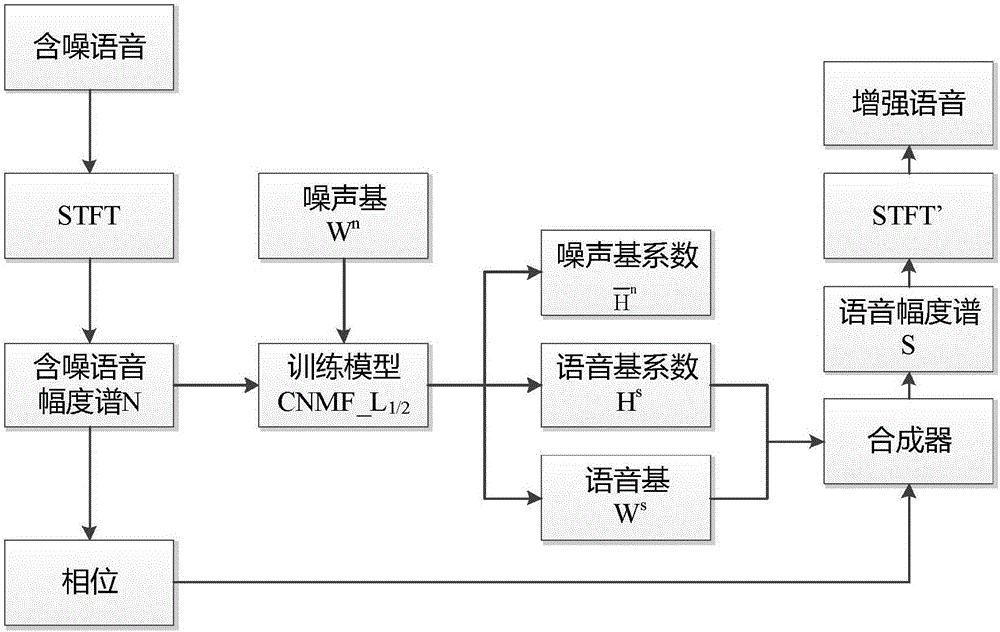
Voice denoising method and system based on L1/2 sparse constraint convolution non-negative matrix decomposition
ActiveCN105957537ALess residual noiseImprove intelligibilitySpeech analysisMatrix decompositionSpectral subtraction
The invention discloses a voice denoising method and system based on L1 / 2 sparse constraint convolution non-negative matrix decomposition. In single-channel voice enhancement, it is assumed that noised voice signals v(i) are additively relevant to noise signals n(i) and voice signals s(i), i.e., v(i)=n(i)+s(i), and noise-base information is obtained by training specific noise by use of a CNMF method; and then by taking a noise base as prior information, a voice base is obtained by decomposing noised voice by use of a CNMF_L1 / 2 method, and finally, voice after denoising is synthesized. According to the method, correlation of voice between frames can be better described; and strong-sparse constraining is performed on a voice-base coefficient matrix by use of L1 / 2 regular item, and the voice after separation comprises less residual noise. Compared to conventional methods such as a spectral subtraction method, a wiener filtering method and a minimum mean square deviation logarithm domain spectrum estimation method and the like, the voice after enhancement can be understood more easily.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
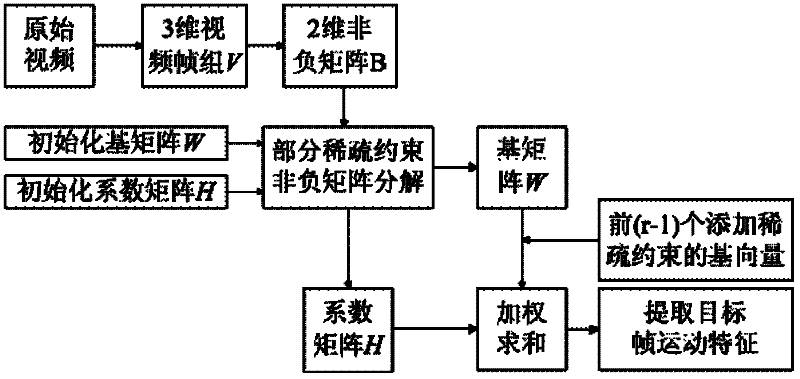
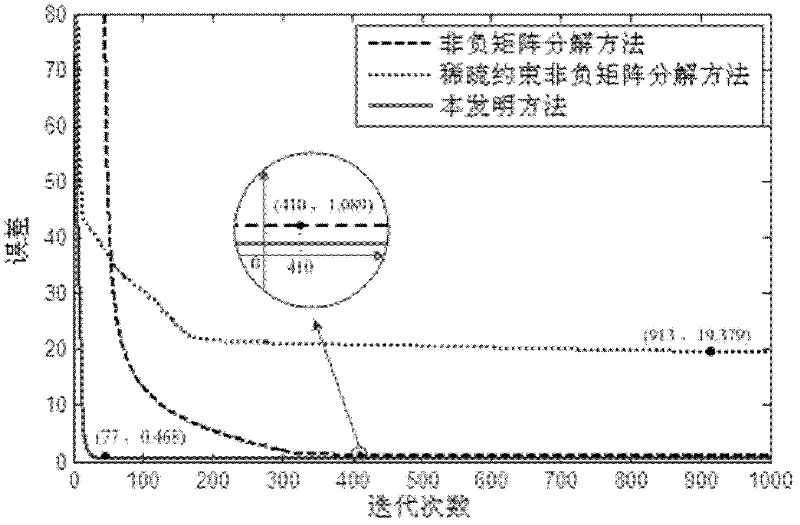
Video motion characteristic extracting method based on local sparse constraint non-negative matrix factorization
InactiveCN102254328AAccurate extractionNot affected by flash pointsImage analysisPattern recognitionVideo monitoring
The invention discloses a video motion characteristic extracting method based on local sparse constraint non-negative matrix factorization. The video motion characteristic extracting method mainly solves the problems that static background interference and flash points of a video cannot be filtrated, the convergence rate is low, and the factorization error is over-serious in the prior art. The video motion characteristic extracting method comprises the steps of: firstly converting a video into a video frame group by taking a target frame as the center, and converting the video frame group into a non-negative matrix; next, factorizing the non-negative matrix by a local sparse constraint non-negative matrix factorization method, carrying out sparse constraint on part of base matrix column vectors, and calculating a motion vector of the target frame through weighted summarization of the part of the base matrix column vectors undergoing sparse constraint and the corresponding coefficient matrixes; and finally converting the motion vector of the target frame into the motion characteristic of the target frame. The video motion characteristic extracting method disclosed by the invention is applicable to target tracking and video monitoring, and can be used for extracting the video motion characteristic quickly, accurately and effectively.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
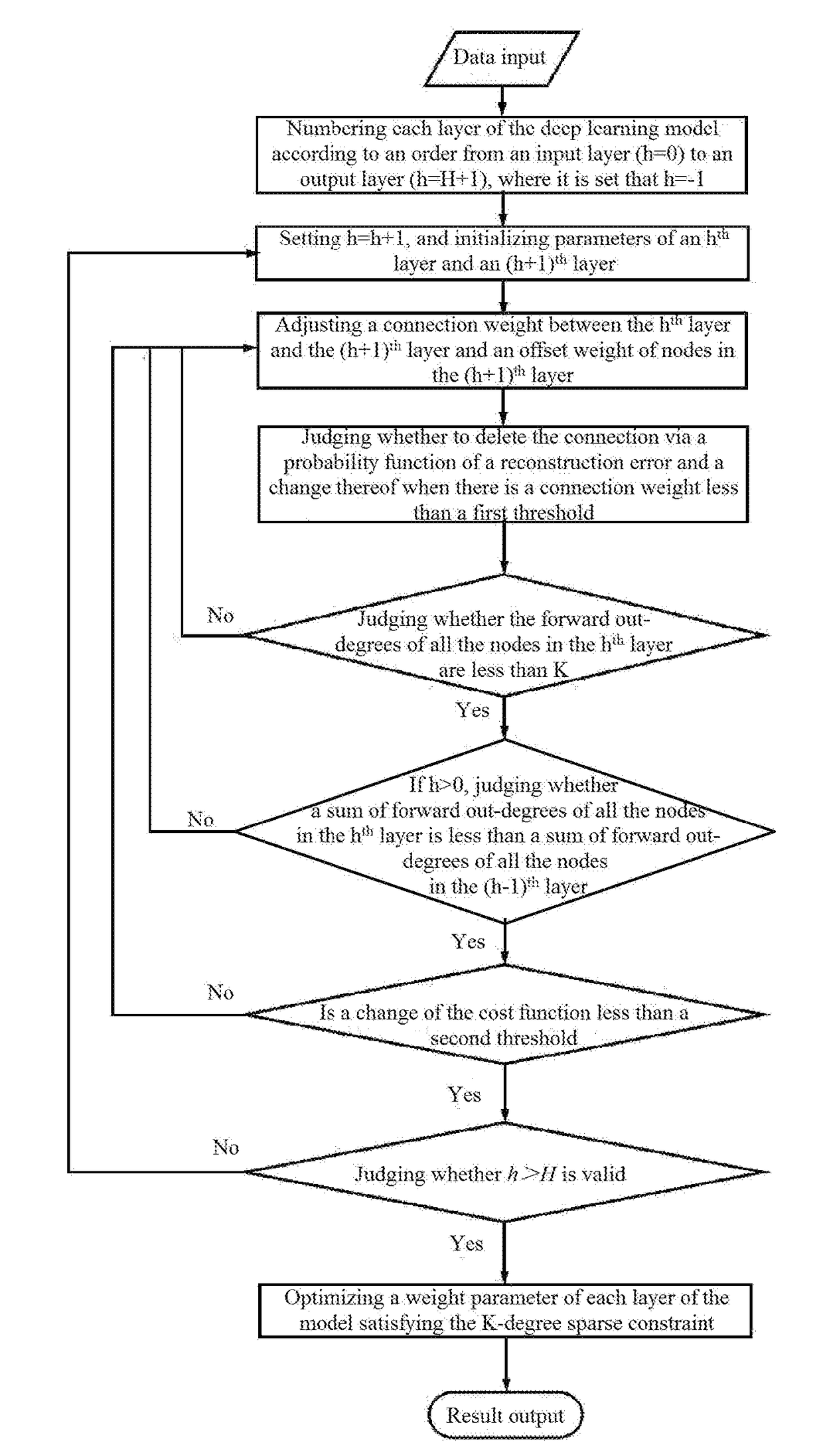
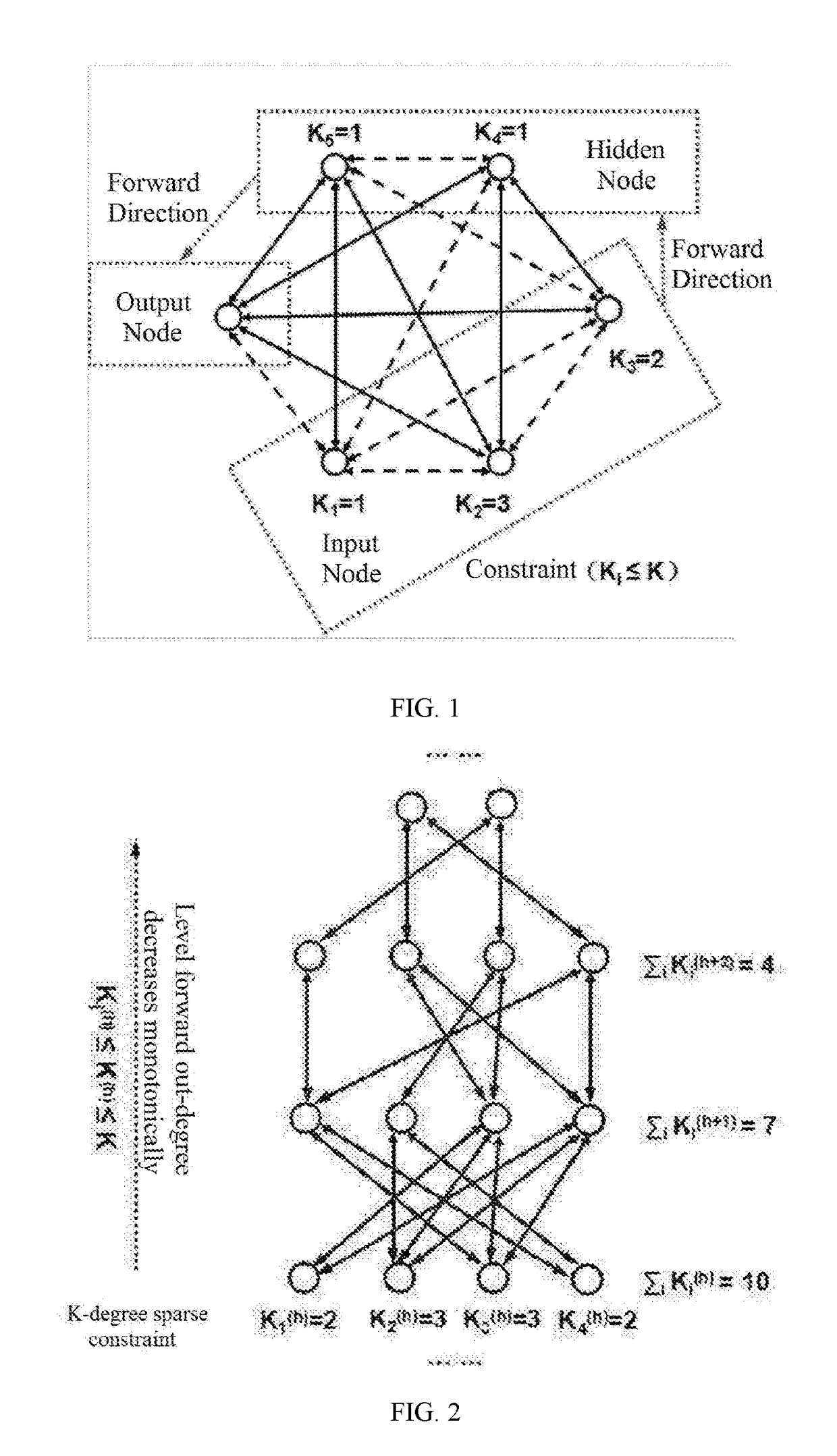
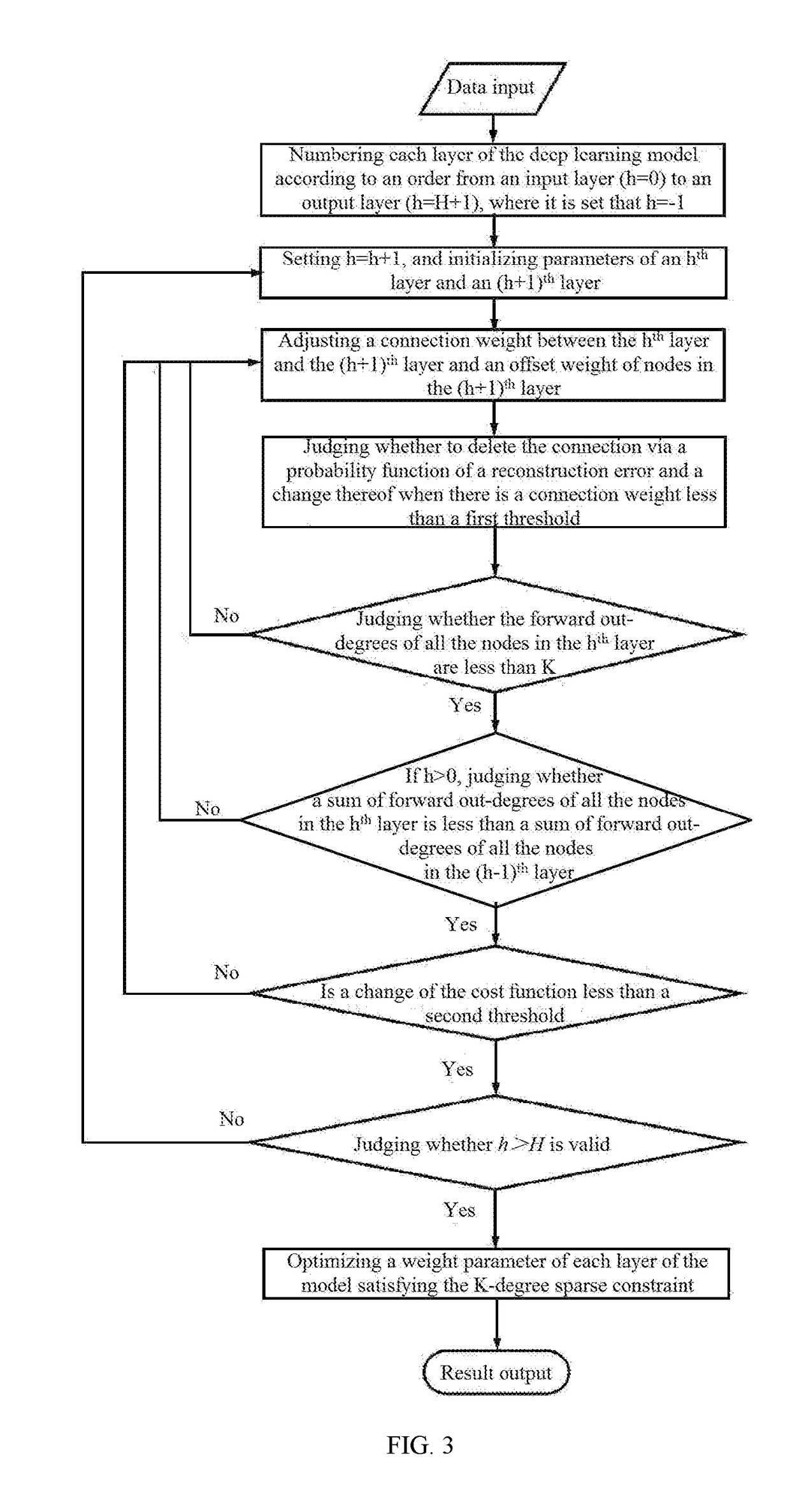
Big data processing method based on deep learning model satisfying k-degree sparse constraint
ActiveUS20180068216A1Increase expansion capabilityImprove generalization abilityNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsNODALSparse constraint
A big data processing method based on a deep learning model satisfying K-degree sparse constraints comprises: step 1), constructing a deep learning model satisfying K-degree sparse constraints using an un-marked training sample via a gradient pruning method, wherein the K-degree sparse constraints comprise a node K-degree sparse constraint and a level K-degree sparse constraint; step 2), inputting an updated training sample into the deep learning model satisfying the K-degree sparse constraints, and optimizing a weight parameter of each layer of the model, so as to obtain an optimized deep learning model satisfying the K-degree sparse constraint; and step 3), inputting big data to be processed into the optimized deep learning model satisfying the K-degree sparse constraints for processing, and finally outputting a processing result. The method in the present invention can reduce the difficulty of big data processing and increase the speed of big data processing.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method and system for reconstructing magnetic resonance parameters
ActiveCN102663701AQuality improvementAvoid mistakesImage enhancementSparse constraintMathematical model
A method for reconstructing magnetic resonance parameters includes the steps: acquiring diffusion-weighted imaging K space data according to a random descending acquisition matrix; establishing a diffusion-weighted imaging mathematical model containing a dispersion tensor coefficient; defining an objective function, fitting the dispersion tensor coefficient by solving an optimization problem and adding sparse constraint; and solving the dispersion tensor coefficient according to the descending acquired data to minimize the objective function. In the method for reconstructing the magnetic resonance parameters, DWI (diffusion-weighted imaging) images do not need to be reconstructed, the dispersion tensor coefficient is directly obtained from the descending acquired K space data by means of calculation, mistaken fitting of the dispersion tensor coefficient caused by errors introduced in reconstruction of the DWI images is avoided, and error propagation is prevented. The invention further provides a system for reconstructing the magnetic resonance parameters.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
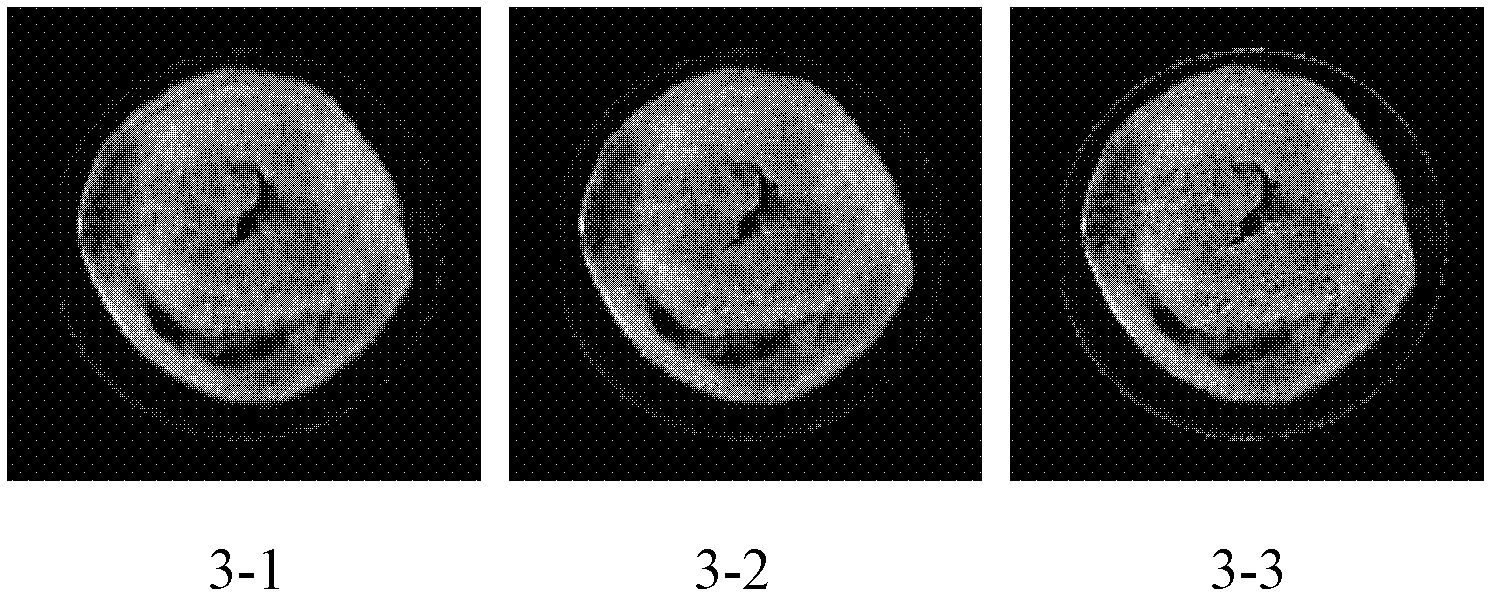
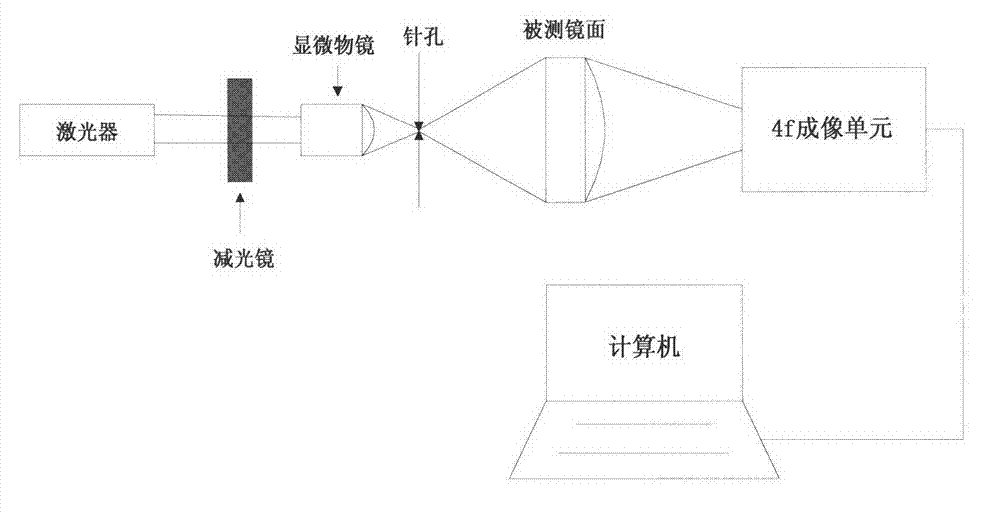
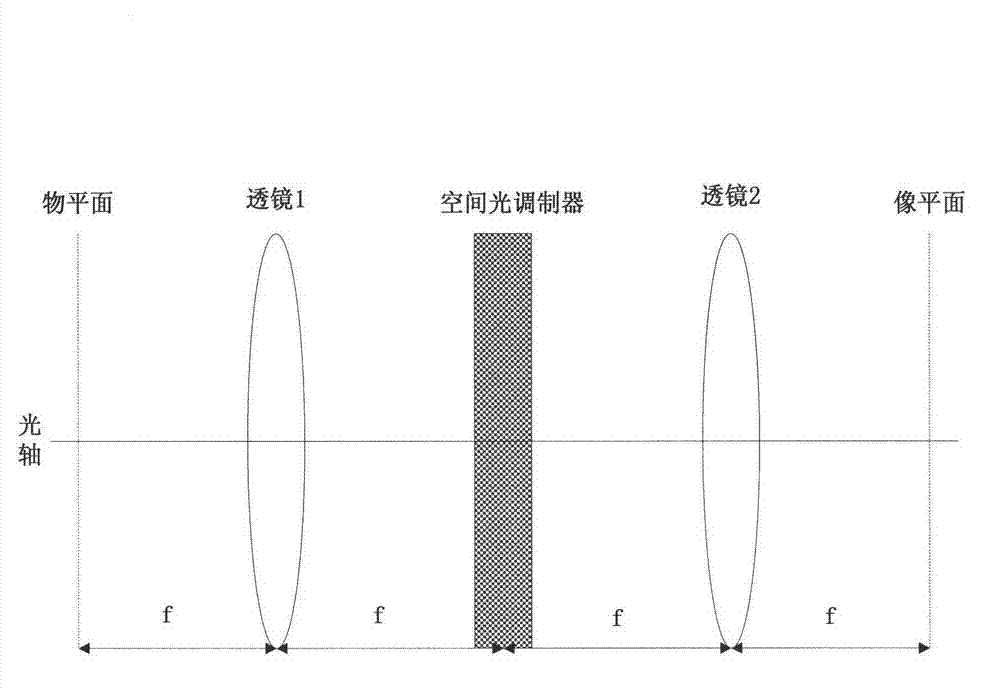
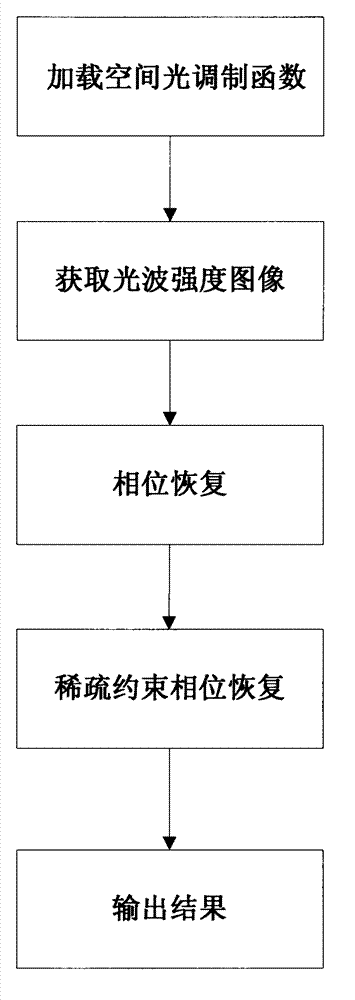
Phase retrieval based 4f mirror surface detection imaging system and phase retrieval based 4f mirror surface detection imaging method
InactiveCN102865832ARealize multiple modulation samplingOvercome the disadvantage of poor stability of strengthUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesSpatial light modulatorSparse constraint
The invention discloses a phase retrieval based 4f mirror surface detection imaging system and a phase retrieval based 4f mirror surface detection imaging method. The system comprises a laser, a neutral density filter, a microobjective, a pinhole, a measured mirror surface, a 4f imaging unit and a computer, wherein the 4f imaging unit comprises a lens 1, a space light modulator, a lens 2 and a charge coupled device (CCD) camera. The light emitted by the laser irradiates the measured mirror surface after passing through the neutral density filter, the microobjective and the pinhole. The CCD camera arranged in the 4f imaging unit is used for acquiring a plurality of times of a light wave modulation image, and then the image is sent into the computer for sparse constraint phase recovery treatment. Based on the acquired light wave intensity image of the measured mirror surface, the method utilizes the sparse constraint phase recovery treatment to obtain the phase position of the light wave on the measured mirror surface, thus realizing the error detection for the measured mirror surface. The invention has the advantages of being high in accuracy, good in stability, simple in operation and good in noise robustness.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
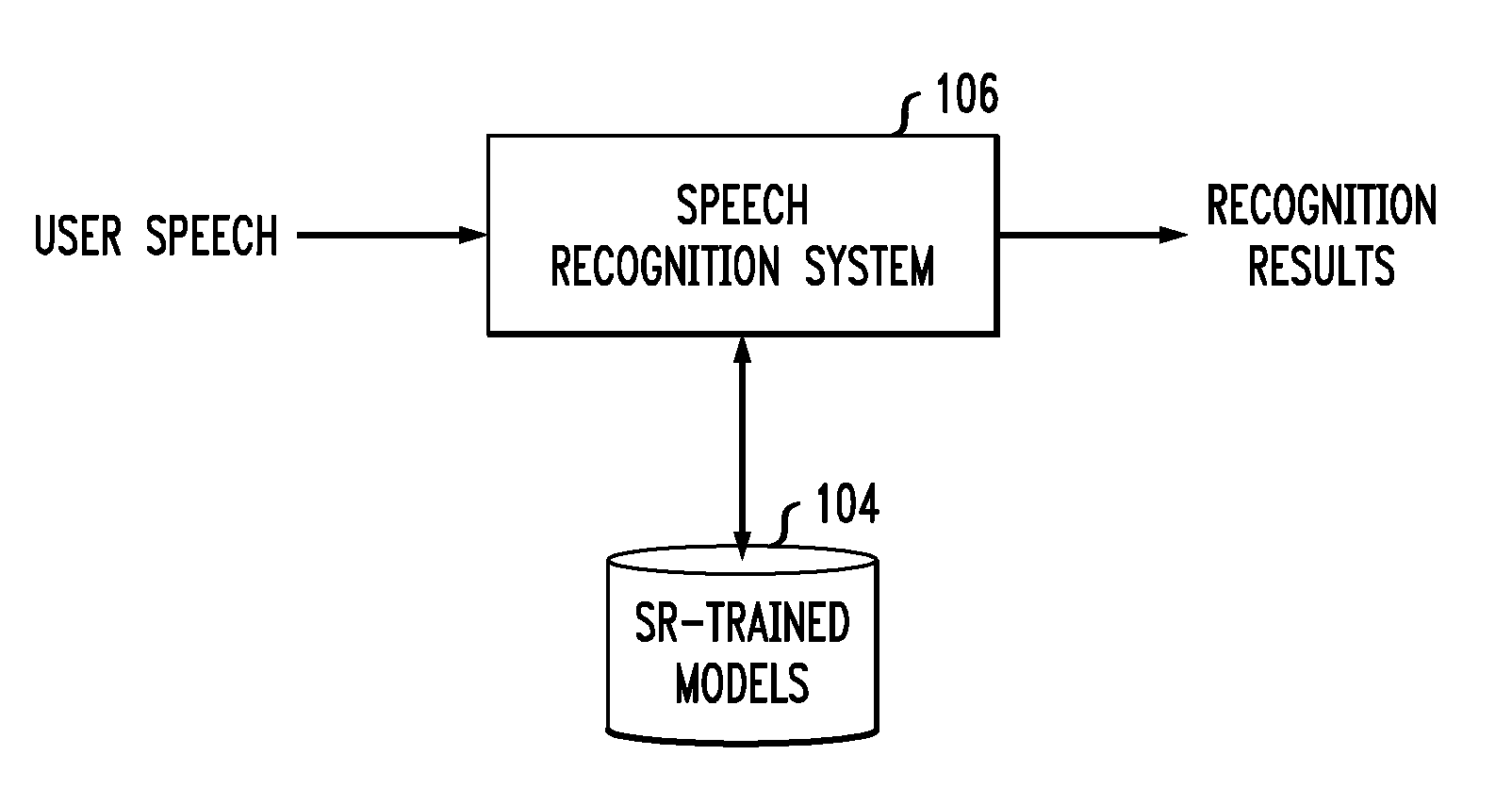
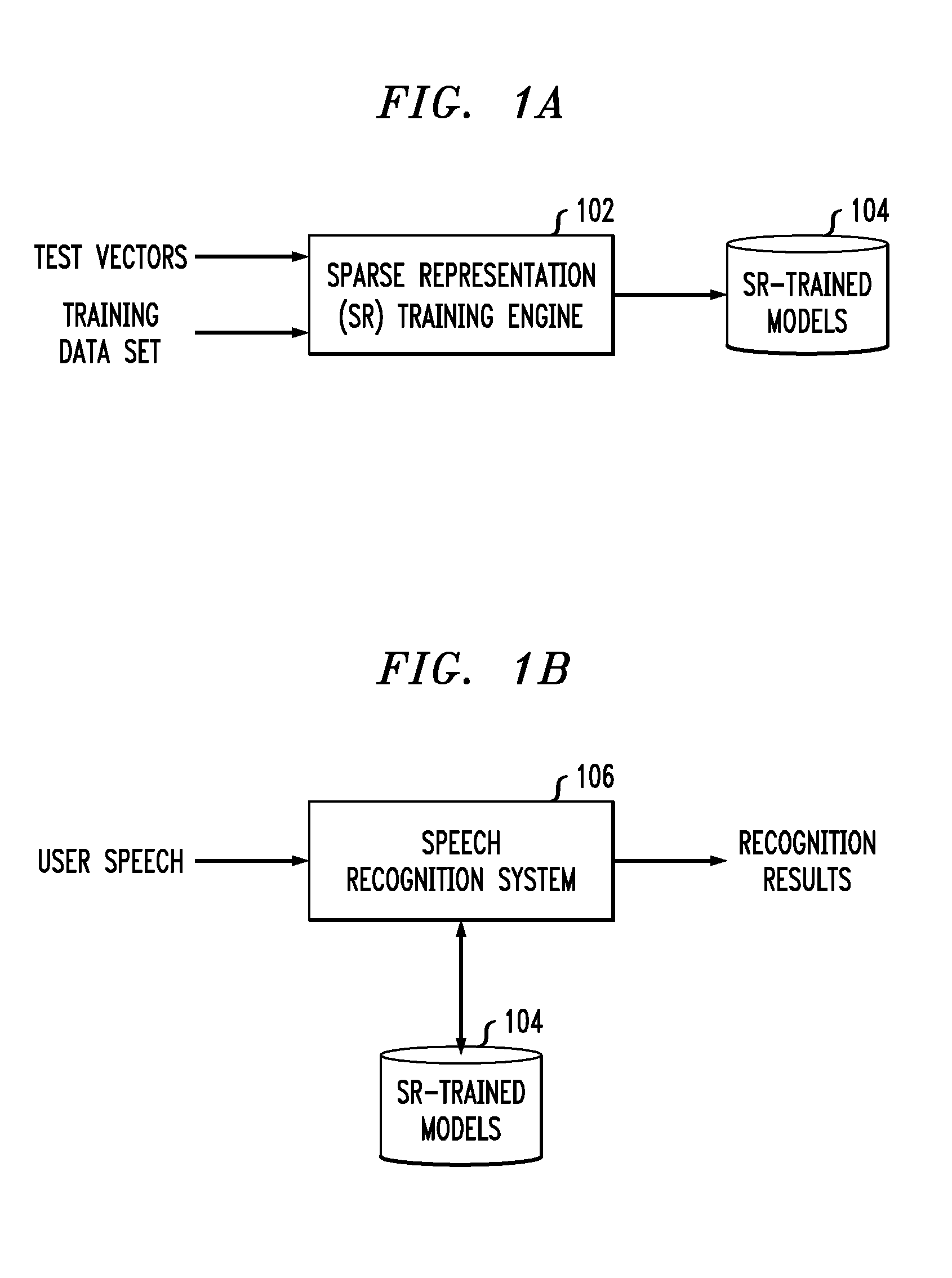
Sparse representation features for speech recognition
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Non-negative matrix factorization method applied to hyperspectral image processing
The present invention discloses a Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) based on sparse and correlation constraints and the method is applied to processing of decomposition of mixed pixels of a hyper-spectral remote sensing image. According to the method, finally, a given non-negative matrix Vm*n is factorized into a product of a basis matrix Wm*r and a coefficient matrix Hr*n, i.e. Vm*n is approximately equal to Wm*r Hr*n ; firstly, the non-negative matrix V is selected, W and H are randomly initialized, then the minimum correlation constraint is applied to the coefficient matrix H in a target function, the sparse constraint is applied to the basis matrix W and the coefficient matrix H and then iteration is carried out according to an iteration formula until the matrices W and H are converged.
Owner:南京博曼环保设备有限公司
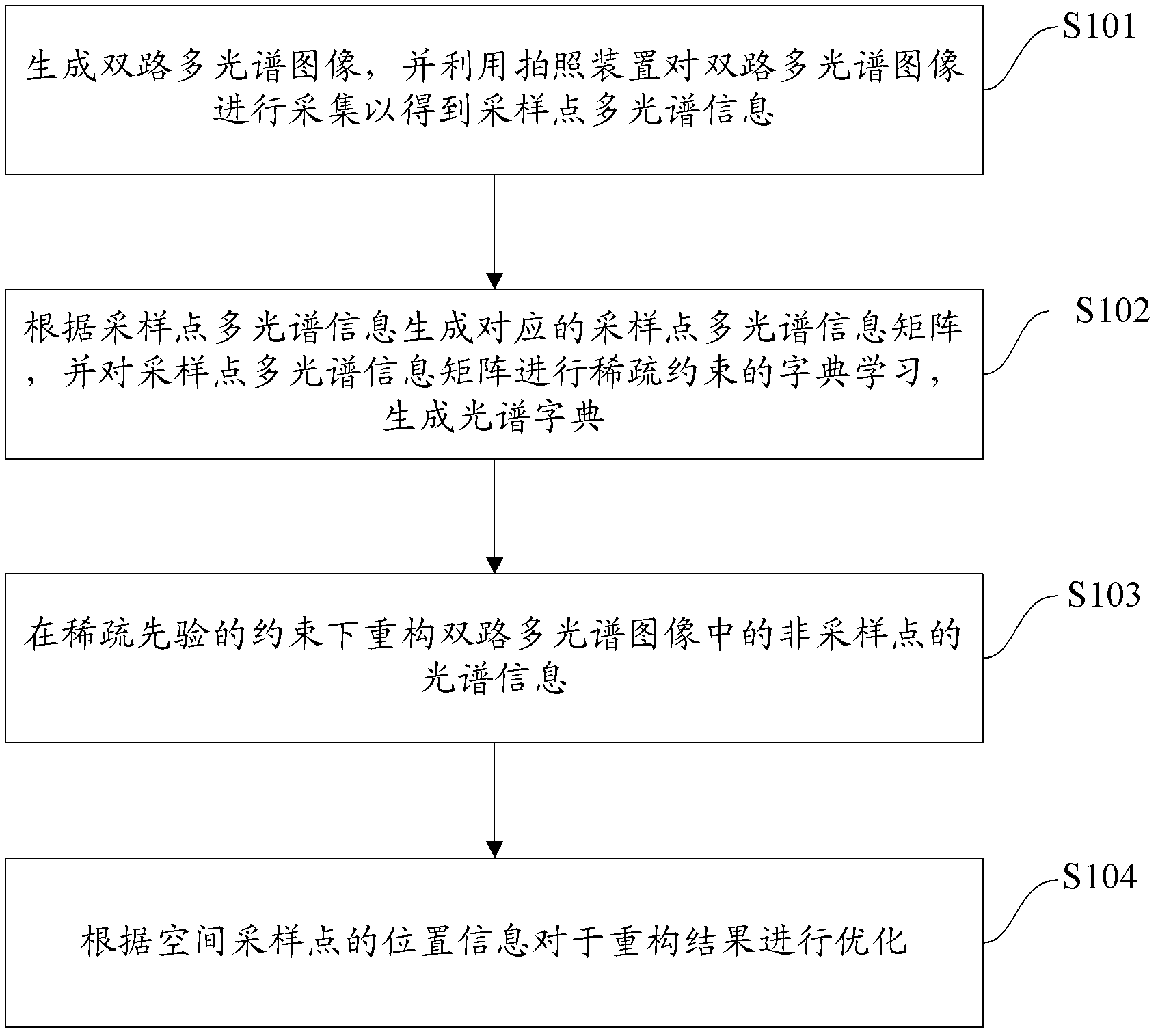
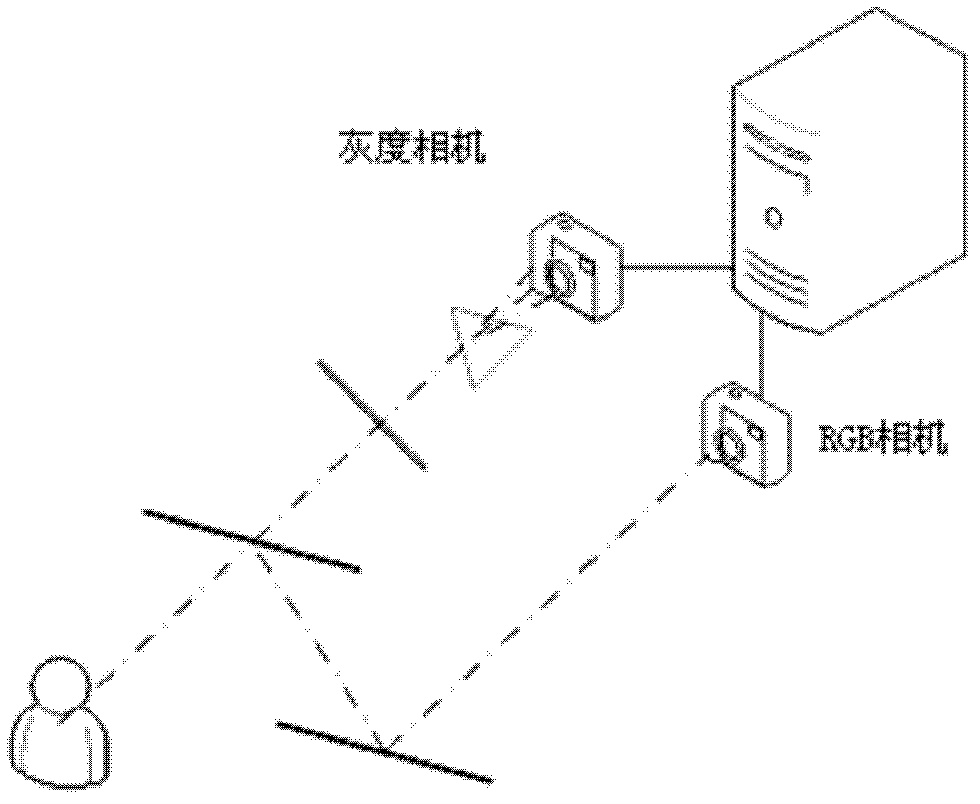
Multispectral calculation reconstruction method and system
ActiveCN102661794AEasy to refactorRefactoring is intuitiveSpectrum investigationDictionary learningHigh dimensionality
The invention provides a multispectral calculation reconstruction method which comprises the steps of generating a two-way multispectral image and employing a photographing device toacquire the two-way multispectral image to obtainmultispectral information of sampling points; according to the multispectral information of the sampling points generating a corresponding multispectral information matrix of the sampling points and allowing the multispectral information matrix of the sampling points to be subjected to dictionary learning with sparse constraint to generate a spectral dictionary; and reconstructing the spectral information of non-sampling points in the two-way multispectral image under sparse prior constraint. The invention also provides a multispectral calculation reconstruction system which comprises an image acquisition device, a dictionary learning device and a spectral information reconstruction device. The method and the system provided by the invention employthe inherent law of the multispectral information, scene materials and the sparsity of light source spectrum, thus the reconstruction of the multispectral informationbeing simple and intuitive, the needed scene spectrum sampling points being less, and realizing high dimension multispectral data collection based on a compression perception theory.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
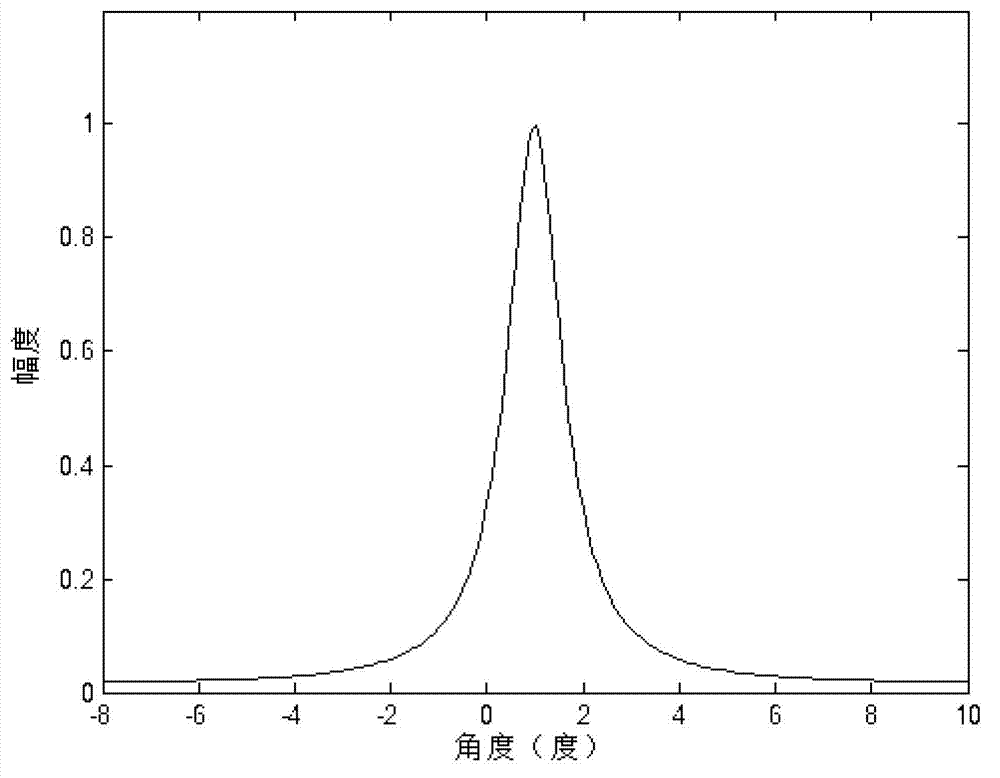
Real beam scanning radar angle super-resolution imaging method based on sparse constraint
ActiveCN104950305AInhibition effectImprove estimation accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSparse constraintRadar
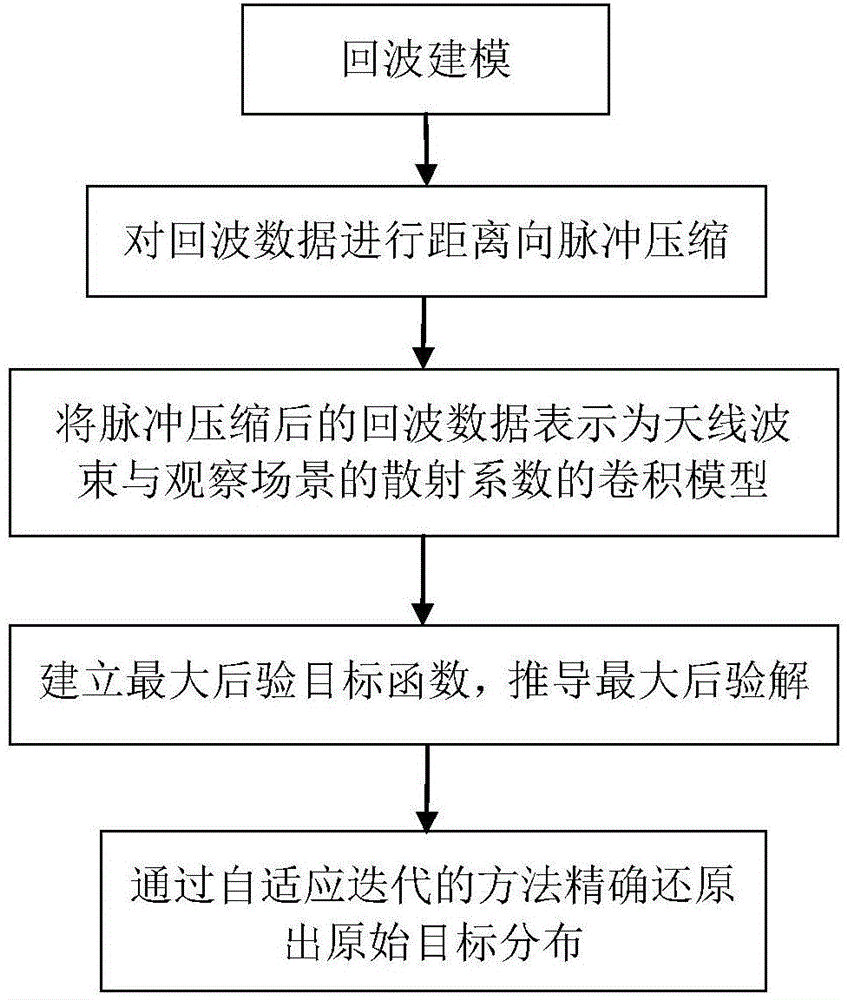
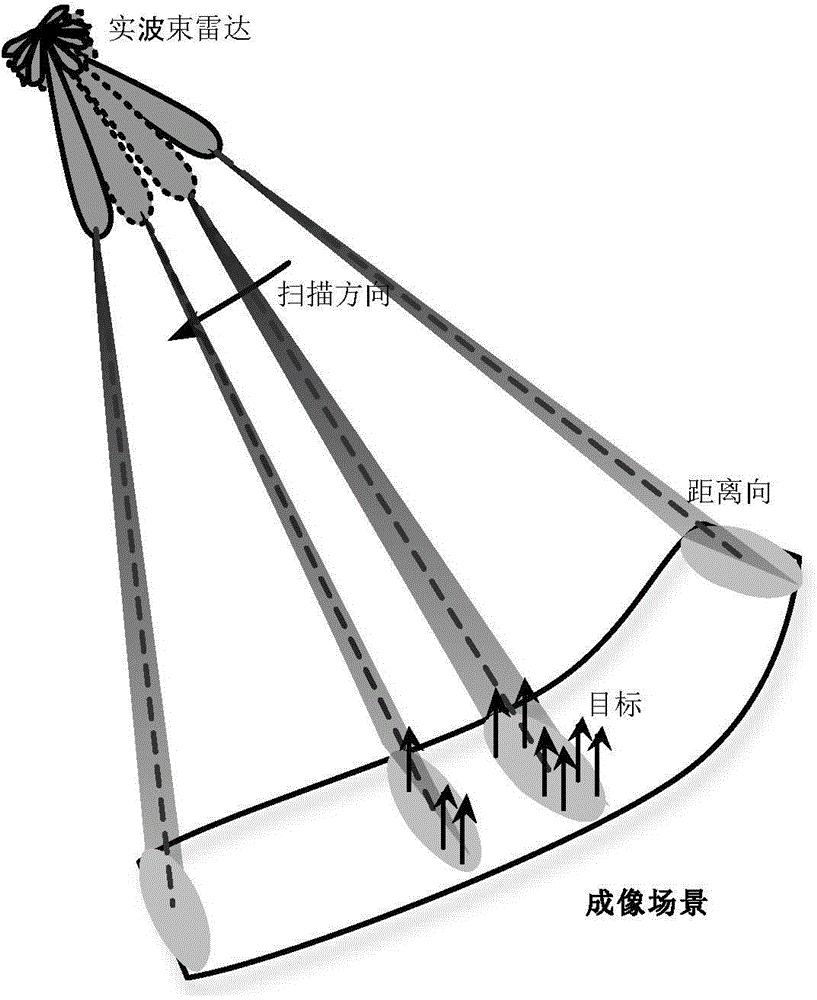
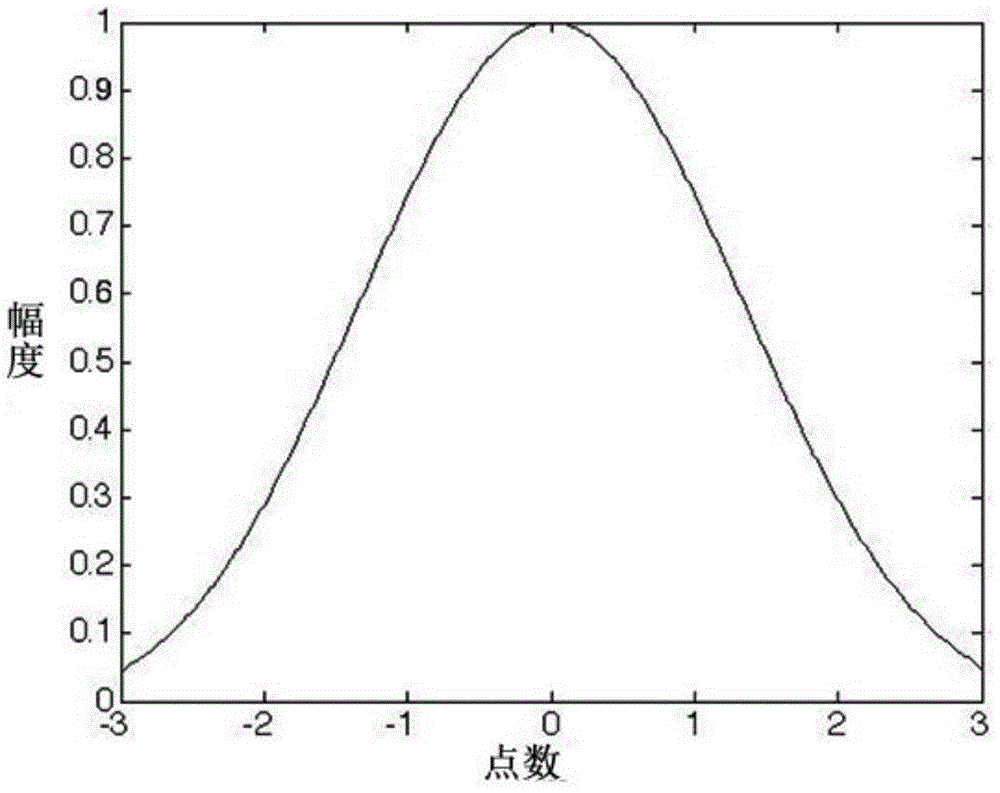
The invention discloses a real beam scanning radar angle super-resolution imaging method based on sparse constraint. The real beam scanning radar super-resolution imaging method comprises the following steps of S1 performing echo modeling, and establishing an echo data model of a scanning radar on the basis of a geometrical relationship of a real beam scanning radar and a target; S2 performing range pulse compression on echo data, so as to realize range high resolution; S3 expressing the echo data after pulse compression to a convolution model of scattering coefficients of an antenna beam and an observation scene; S4 establishing a maximum posterior objective function according to the convolution model obtained in the step S3, and deducing a maximum posterior solution; S5 precisely reducing original target distribution through an adaptive iteration method. According to the real beam scanning radar angle super-resolution imaging method, clutter characteristics are expressed by using rayleigh distribution, target distribution characteristics are reflected by utilizing the sparse constraint, target distribution is inverted, and additionally, the influence of noise on imaging results is inhibited, so that radar angle super resolution processing results are close to actual target distribution, and real beam scanning radar angle super-resolution imaging is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Combined medical science image fusion denoising method based on discrimination dictionary learning
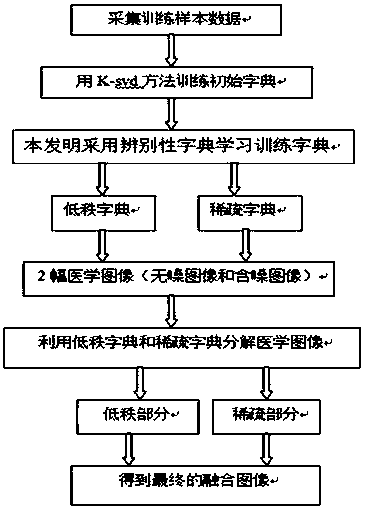
ActiveCN107563968AEasy to integrateAvoid spreadingImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionDictionary learning
The invention relates to a combined medical science image fusion denoising method based on discrimination dictionary learning, which belongs to the technical field of digital image processing. Firstly, medical science images are collected. Secondly, the collected medical science images undergo training, obtaining a sparse dictionary and a low-rank dictionary. Thirdly, image decomposition is conducted on the sparse dictionary and the low-rank dictionary, obtaining sparse element and low-rank element. The sparse element is added with sparse constraint and weighted kernel norm constraint, and thelow-rank element is added with kernel norm, obtaining low-rank coefficient and sparse coefficient. Iteration is conducted on the low-rank dictionary and the low-rank coefficient, obtaining the updated low-rank component. Iteration is conducted on the sparse dictionary and the sparse coefficient, obtaining sparse component. Finally, the low-rank component and the sparse component are fused, obtaining the final fusion image. The invention is advantageous in that when source images have noise are input, the fusion effect can still be good, and thereby effect is obviously raised.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
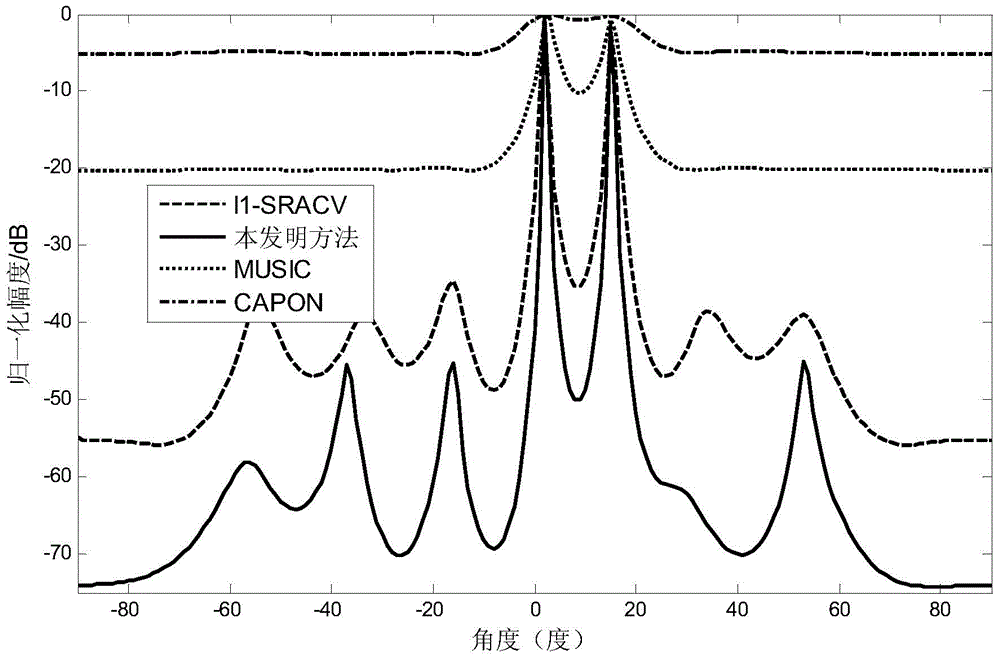
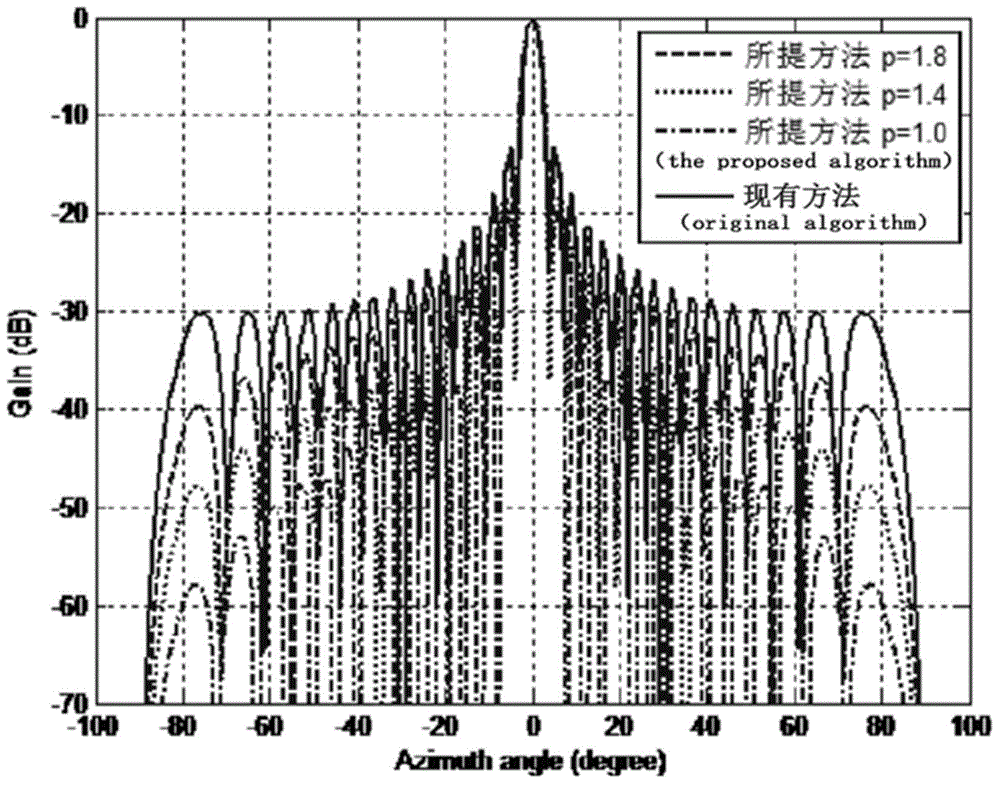
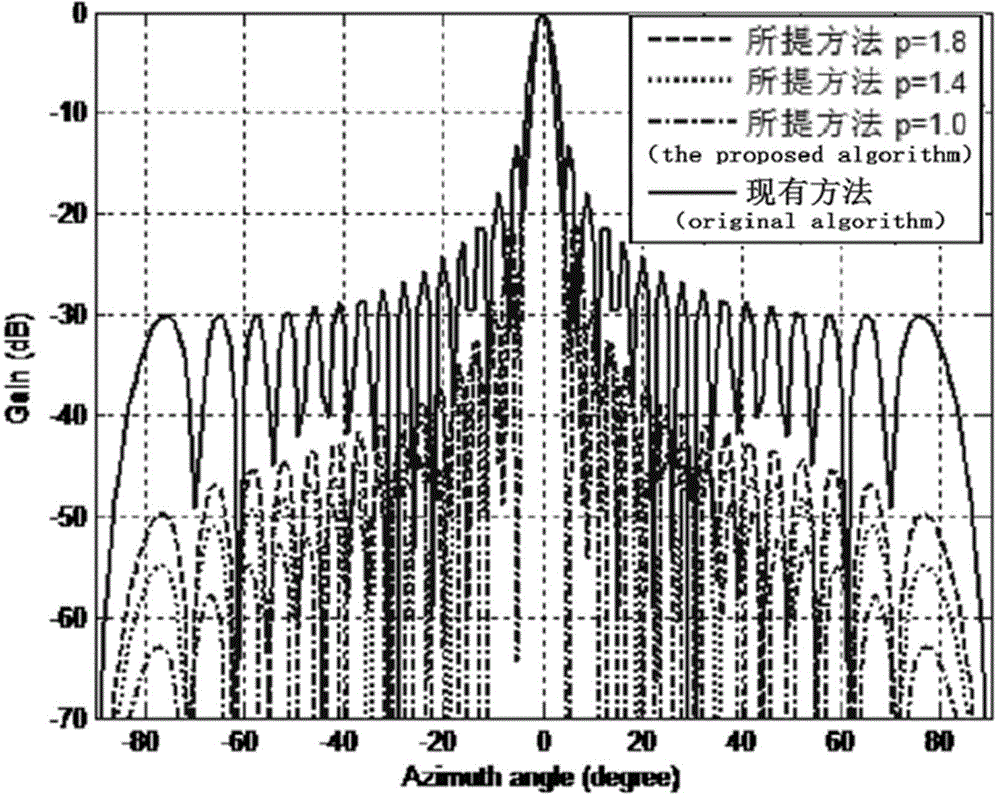
Beam broadening and sidelobe suppression method based on sparse constraint
InactiveCN104615854AEnhanced inhibitory effectReduce sidelobeSpecial data processing applicationsWireless transmissionSparse constraint
The invention discloses a beam broadening and sidelobe suppression method based on sparse constraint, belongs to the field of processing of antenna array signals receiving wireless transmission signals, and particularly relates to a method for utilizing sparse reconstruction for achieving beam broadening and sidelobe suppression to optimize an antenna array. A sparse constraint algorithm is utilized for achieving beam broadening, and meanwhile a low sidelobe level can be obtained, so that the restraining ability to interference signals is improved. An antenna array model is built, so that a guide vector parameter is determined; an over-complete dictionary is utilized for expressing a matrix of observation and interference direction information, a weight vector of a beam former is initialized, sparse iteration is carried out on the weight vector, the weight vector meeting the condition is obtained, and therefore an output peak value obtains a lower sidelobe on the original basis. Compared with other algorithms, the super-resolution is achieved while a narrow main lobe is achieved; stability is improved while the sidelobe is low.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Inter-class inner-class face change dictionary based single-sample face identification method
The invention discloses an inter-class inner-class face change dictionary based single-sample face identification method to solve the problem of limitations of the current single-sample face identification algorithm. The method comprises the steps of step1, obtaining expressions of face images in the compression domain; step2, building a face image training sample matrix containing k classes; step3, building an average face matrix and an inter-class face change matrix of a face database; step4, adding low rank and sparse constraints into the inter-class face change matrix; step5, solving an inter-class similarity matrix and an inter-class difference matrix; step6, projecting the average face matrix, the inter-class similarity matrix and the inter-class difference matrix to low-dimensionality space; step7, performing normalization processing on the dimensionality reduced average face matrix, the inter-class similarity matrix and the inter-class difference matrix through a normalization method, and performing iterative solution on the face image training sample matrix based sparse coefficient vectors through a norm optimization algorithm; step8, selecting column vector face labels in the average face matrix, which are corresponding to the sparse coefficient maximum, to serve as the final face identification result.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
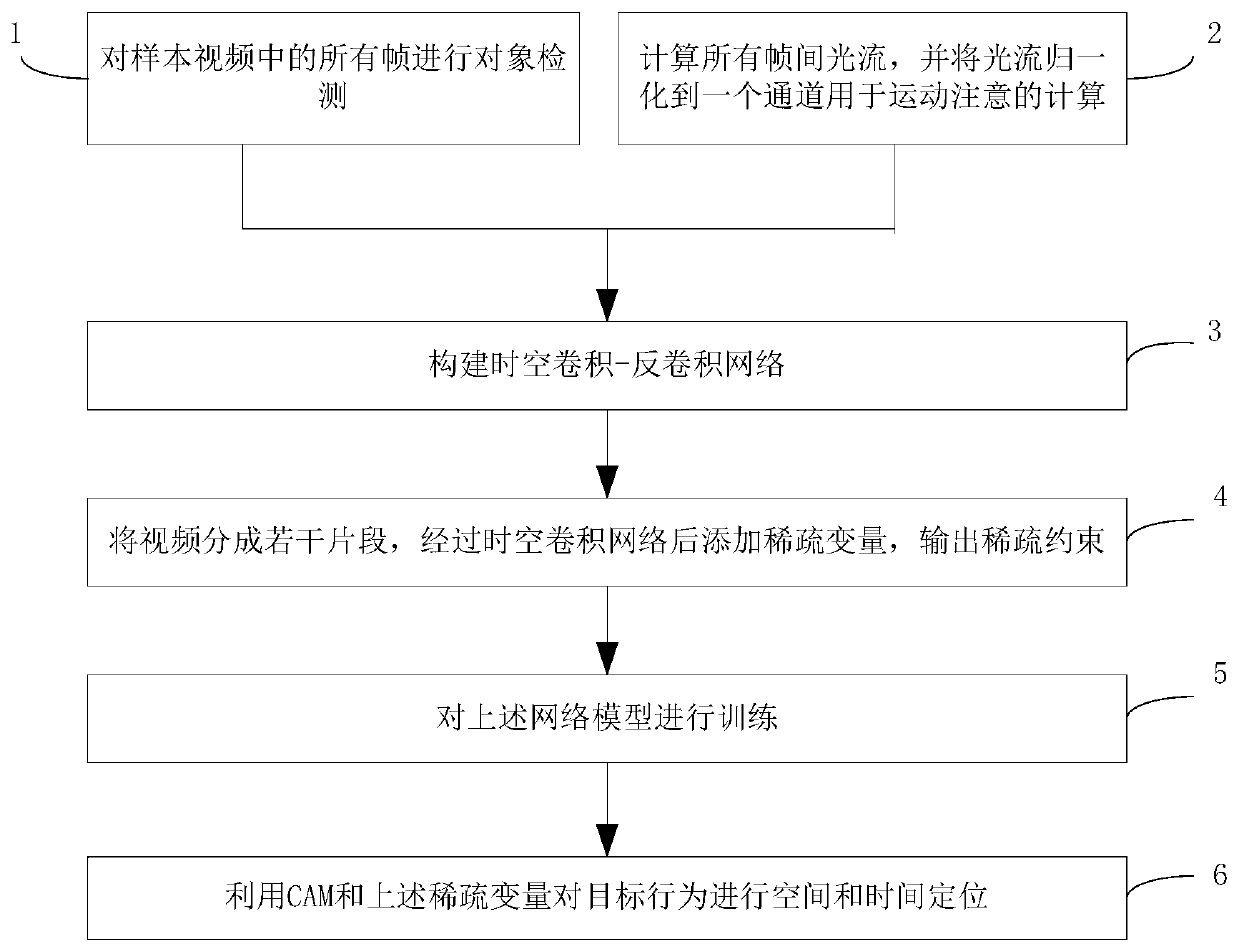
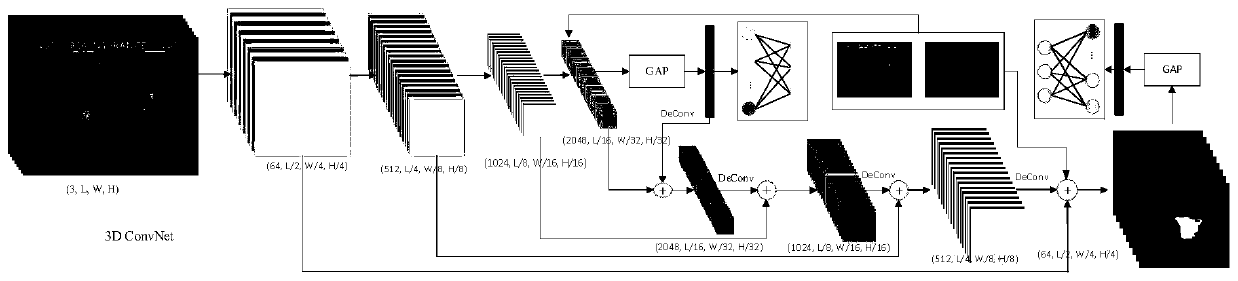
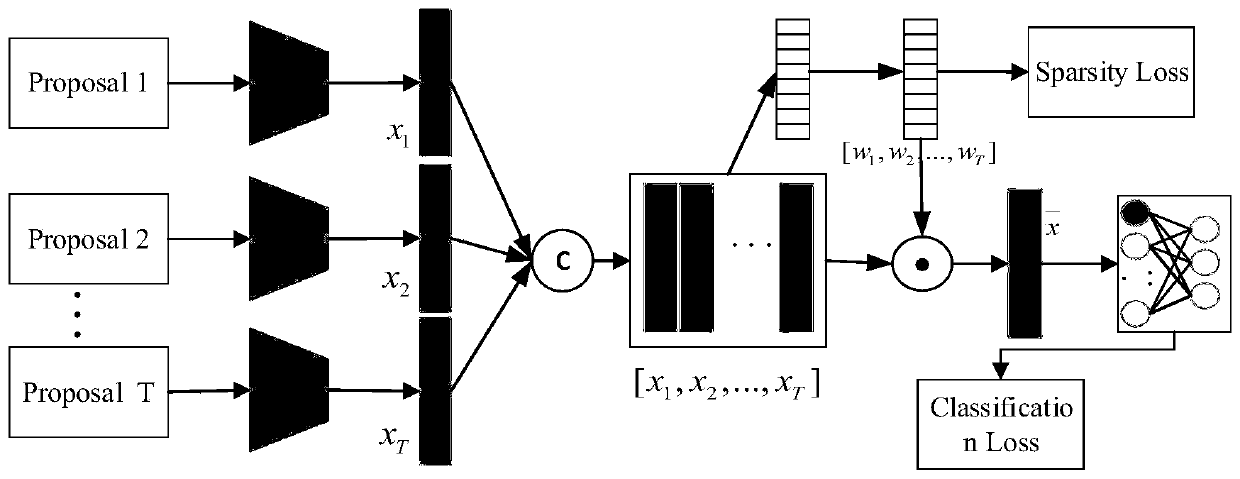
Space-time behavior detection method
InactiveCN109961019AReduce behavioral search spaceImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisOptical flowCross entropy
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method, system and computer program product for breast density classification using parts-based local features
InactiveUS20160314579A1Improve accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisPrincipal component analysisClassification methods
An automated content-based image retrieval method, a system and a computer program product for the classification of breast density from mammographic imagery. Raw digital mammogram images taken of patients are initially pre-processed to remove noise and enhance contrast, then subjected to pectoral muscle segmentation to produce region of interest (ROI) images. The ROI images are then decomposed using non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), where a non-negative sparsity constraint and reconstruction quality measures are imposed on the extracted and retained first few NMF factors. Based on the retained NMF factors, kernel matrix-based support vector machines classify the mammogram images binomially or multinomially to breast density categories. Methods of assessing and comparing the NMF-based breast classification method to principal component analysis or PCA-based methods are also described, and the NMF-based method is found to achieve higher classification accuracy and better handling of invariance in the digital mammogram images because of its parts-based factorization.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
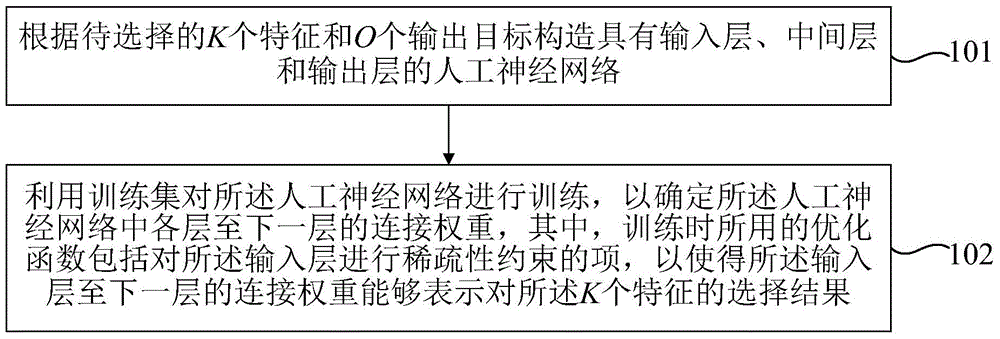
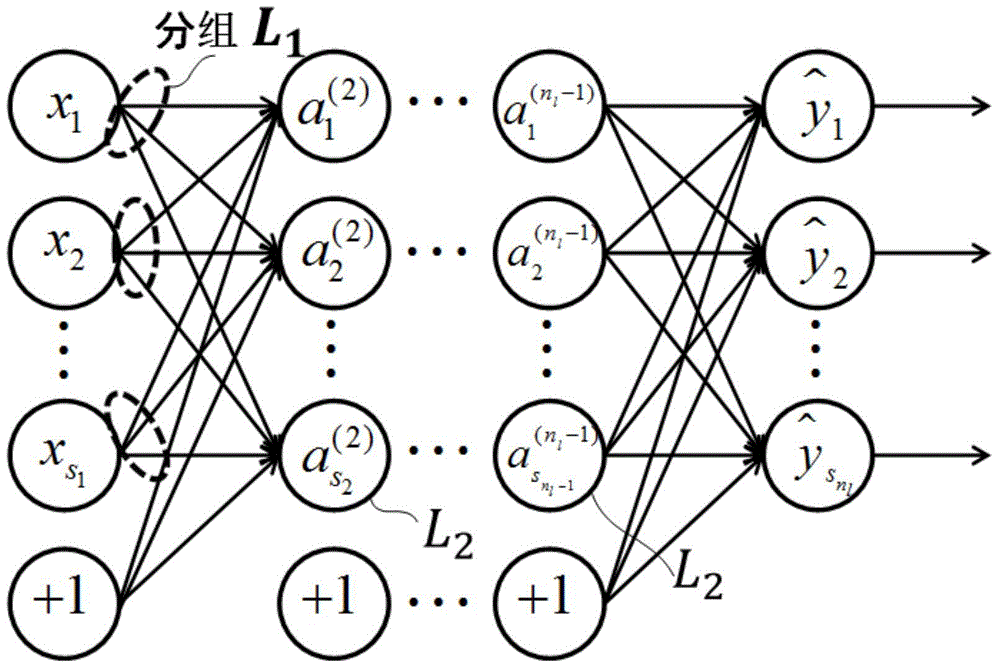
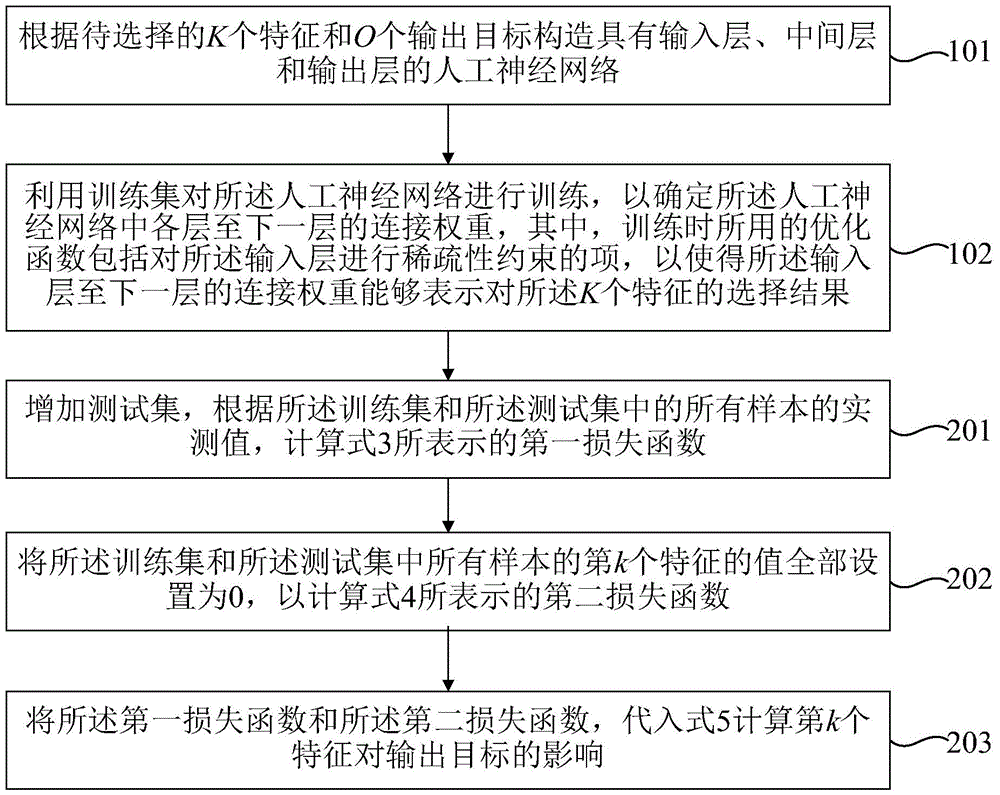
Characteristic selecting method and characteristic selecting device based on artificial neural network
InactiveCN105787500AImprove the efficiency of feature selectionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsSparse constraintData mining
The invention relates to a characteristic selecting method and a characteristic selecting device based on an artificial neural network. The characteristic selecting method is characterized in that the artificial neural network having the input layer, the middle layer, and the output layer can be formed according to K characteristics and O output targets; the artificial neural network can be trained by adopting a training set, and the connecting weight between every layer and the next layer of the artificial neural network can be determined; the optimization function used by the training comprises the items for the sparse constraint of the input layer, and then the connecting weight between the input layer and the next layer can be used to show the selecting result of the K characteristics. By adding the sparse constraint to the input layer of the artificial neural network, the training of the artificial neural network can be realized, and at the same time, the characteristic selecting result can be acquired, and then the efficiency of the characteristic selection of the artificial neural network can be improved.
Owner:NEC CORP
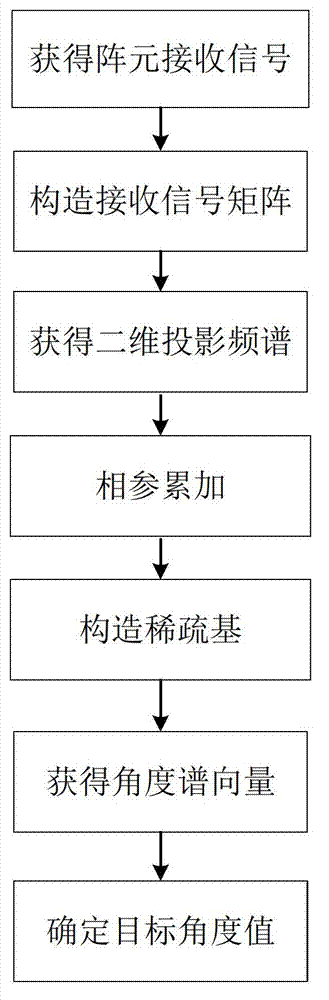
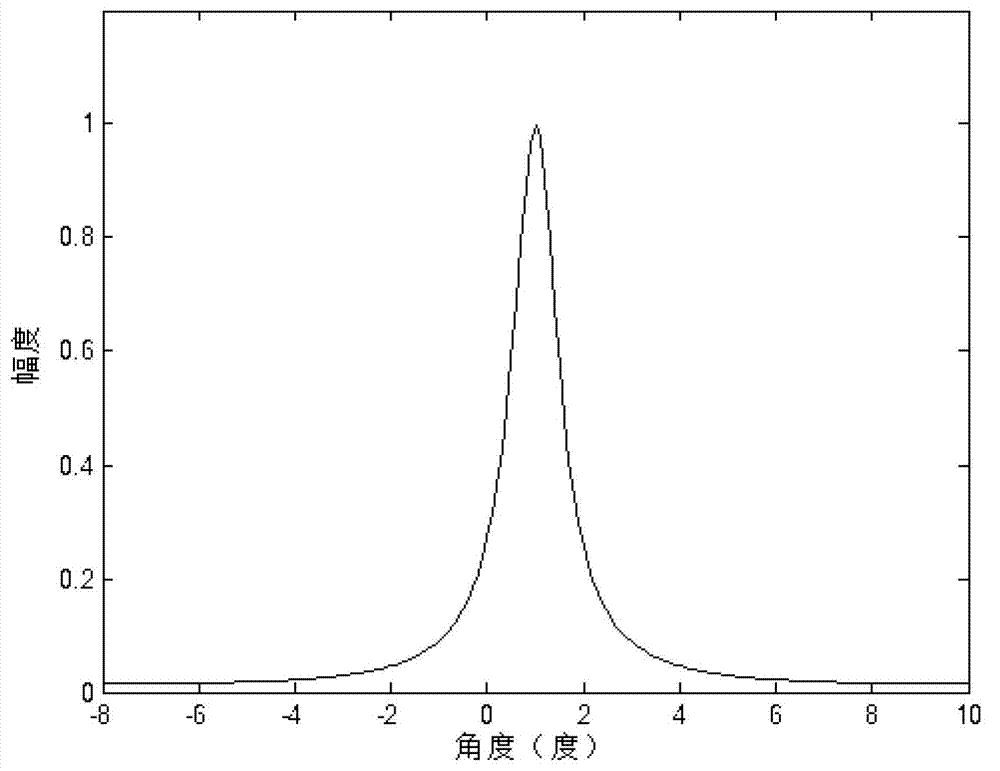
Broadband target direction finding method based on two-dimensional frequency domain sparse constraint
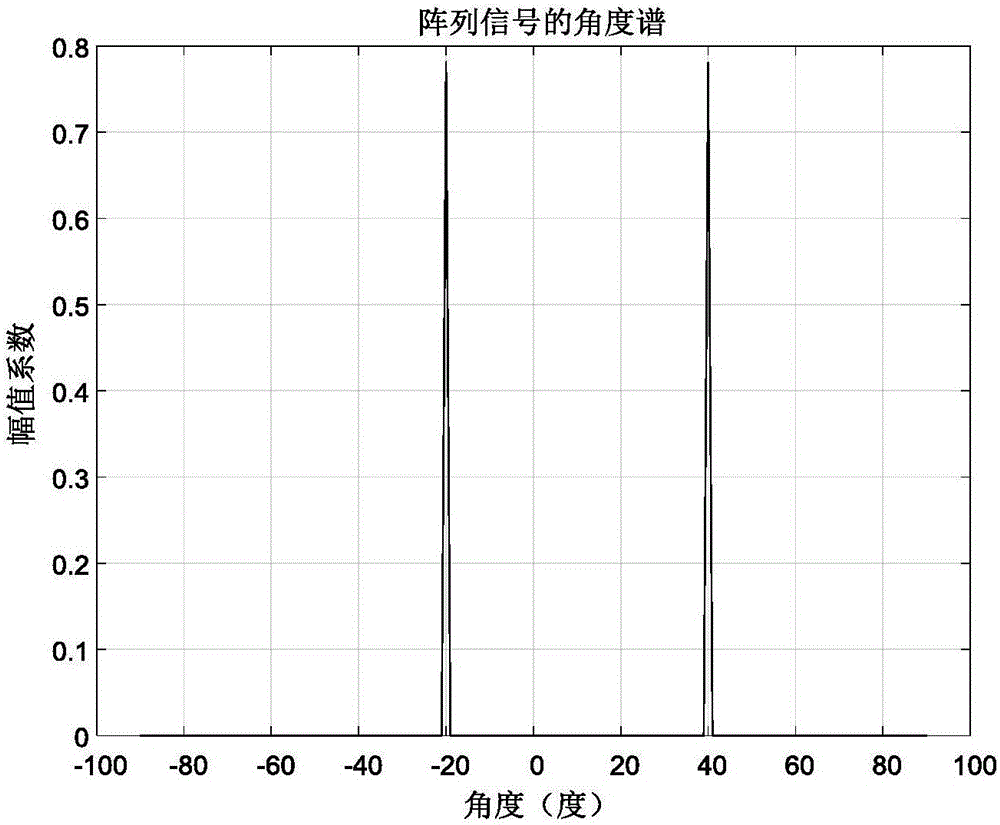
The invention discloses a broadband target direction finding method based on two-dimensional frequency domain sparse constraint. The method mainly solves the problems of a low angle resolution ratio, the poor coherent signal source estimation accuracy and a large calculation amount of common algorithms of prior methods. The technical scheme includes that the method comprises the steps of fully using target space sparseness and priori knowledge of array element receiving signals in a two-dimensional domain, and performing two-dimensional domain projection conversion on the array element receiving signals to obtain a two-dimensional projection spectrum; performing angle division on the angle measuring range, and designing a sparse base of the two-dimensional projection spectrum; solving an optimization problem through an optimization solving algorithm to obtain a high-resolution angle spectrum; and performing peak value detection on the angle spectrum through a threshold comparison method to obtain a target angle value. The broadband target direction finding method has the advantages of being small in calculation amount, high in measuring accuracy and angle resolution ratio and applicable to target angle estimation of radars and sonars.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
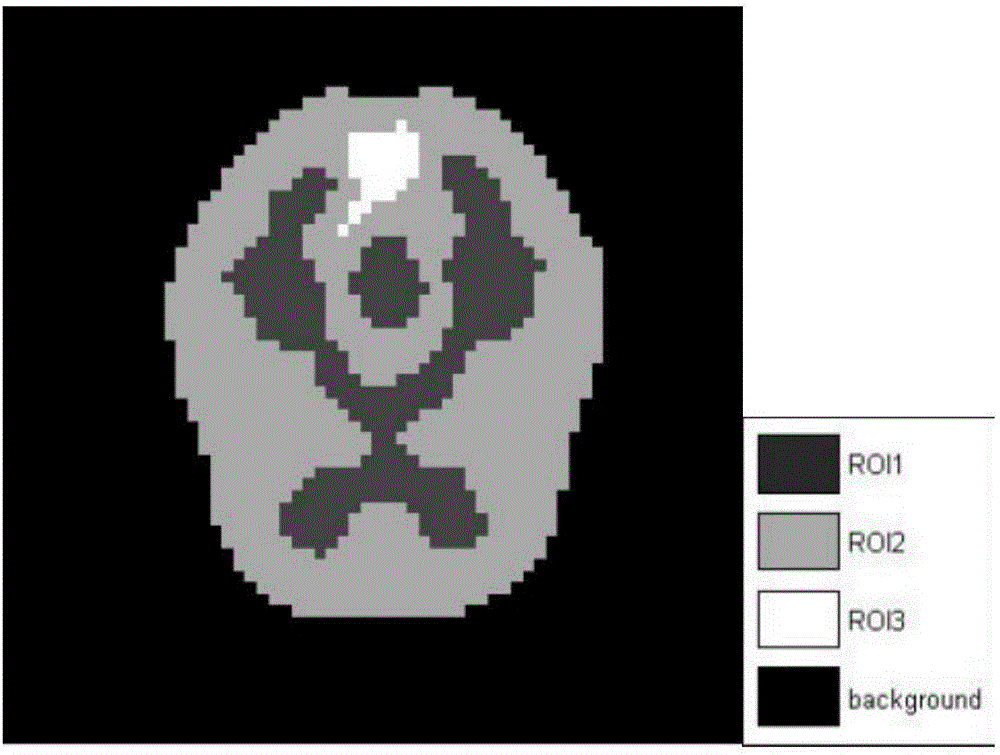
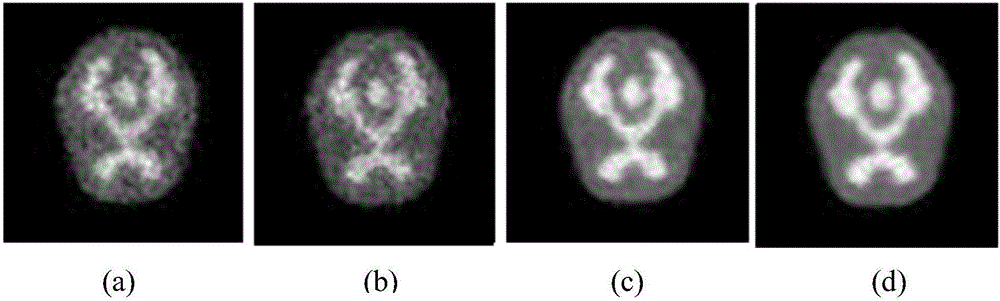
Method for synchronously reconstructing dynamic PET image and tracer kinetic parameter on the basis of TV and sparse constraint
ActiveCN105894550ASolve the estimation problemHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionImage generationSequence reconstructionSparse constraint
The invention discloses a method for synchronously reconstructing a dynamic PET image and a tracer kinetic parameter on the basis of TV (total variation) and sparse constraint. The method introduces a dictionary based on sparse constraint and a TV operator to carry out a whole reconstruction process by establishing a mathematic model for synchronously estimating the dynamic PET image and the kinetic parameter, wherein a dynamic PET sequence reconstruction subproblem provided with the total variation operator is subjected to iterative optimization solution by an ADMM algorithm, and a PET kinetic parameter estimation subproblem in combination with the dictionary based on sparse constraint is solved by a soft threshold iterative algorithm. The method solves a problem for simultaneously estimating the dynamic PET image sequence and the kinetic parameter, introduces the TV operator to improve the low result resolution and noise interference proneness in the PET image reconstruction process, and may obtain a better reconstruction result compared with other algorithms which individually reconstructs the PET image or estimates the kinetic parameter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
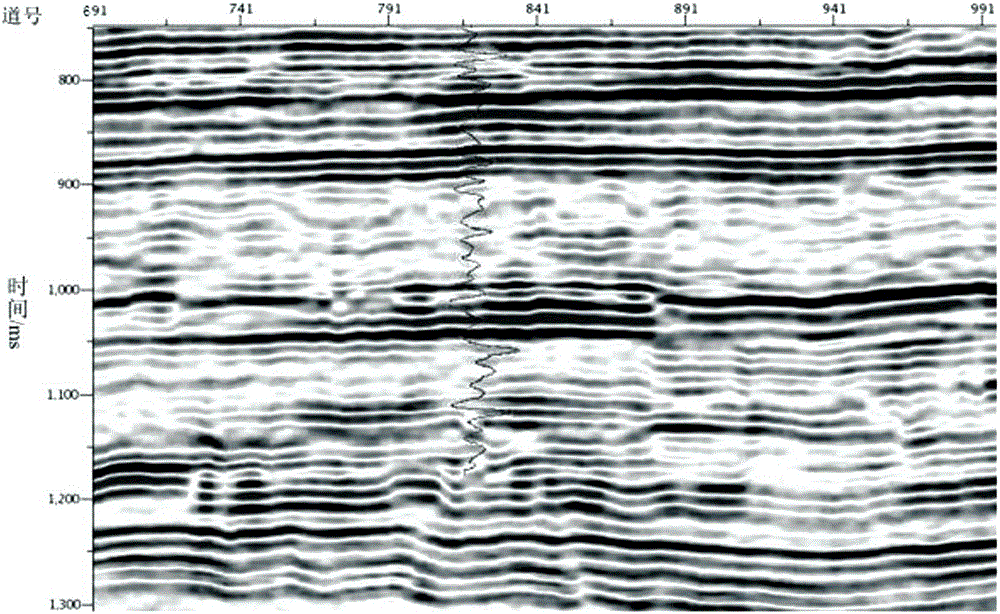
High resolution converted wave crack prediction method
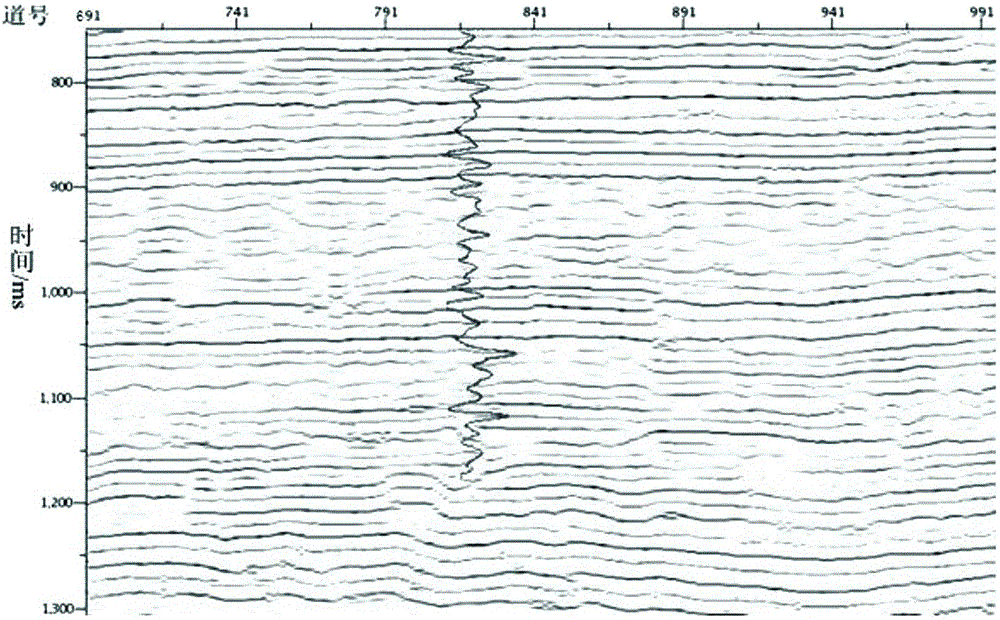
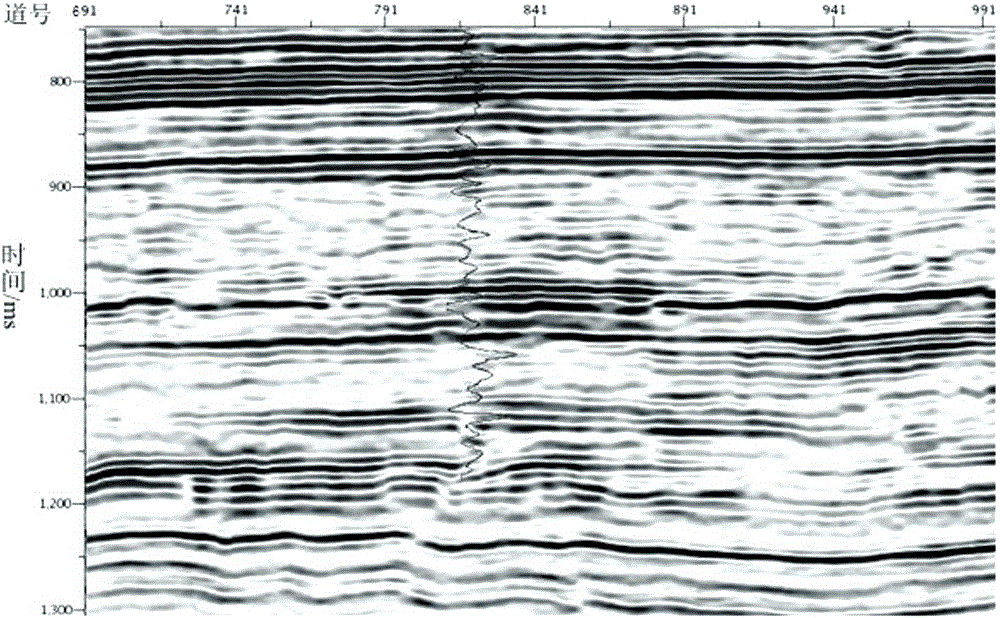
ActiveCN106443775AHigh solution accuracyImprove noise immunitySeismic signal processingSparse constraintImage resolution
The present invention provides a high resolution converted wave crack prediction method. The method comprises the steps of acquiring the converted wave seismic data, and carrying out the pre-processing and the prestack migration to obtain a converted wave migration section; establishing a multi-thin layer objective function of sparse constraint and wave impedance constraint on the migration section; for the multi-thin layer objective function, utilizing the frequency domain mapping and L1-norm joint optimization algorithm to obtain a high-precision reflection coefficient; constructing a high frequency wavelet while keeping the high frequency wavelet have a determined frequency width, obtaining a high resolution converted wave migration section according to the high frequency wavelet and the high-precision reflection coefficient; utilizing an improved third generation characteristic value coherence volume calculation method to carry out the coherence data volume slice extraction on the high resolution converted wave migration section, thereby realizing the crack prediction. According to the present invention, the resolution of the extracted crack prediction section is higher, the crack trend is more clear, and the details are depicted more obviously.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Sparse representation features for speech recognition
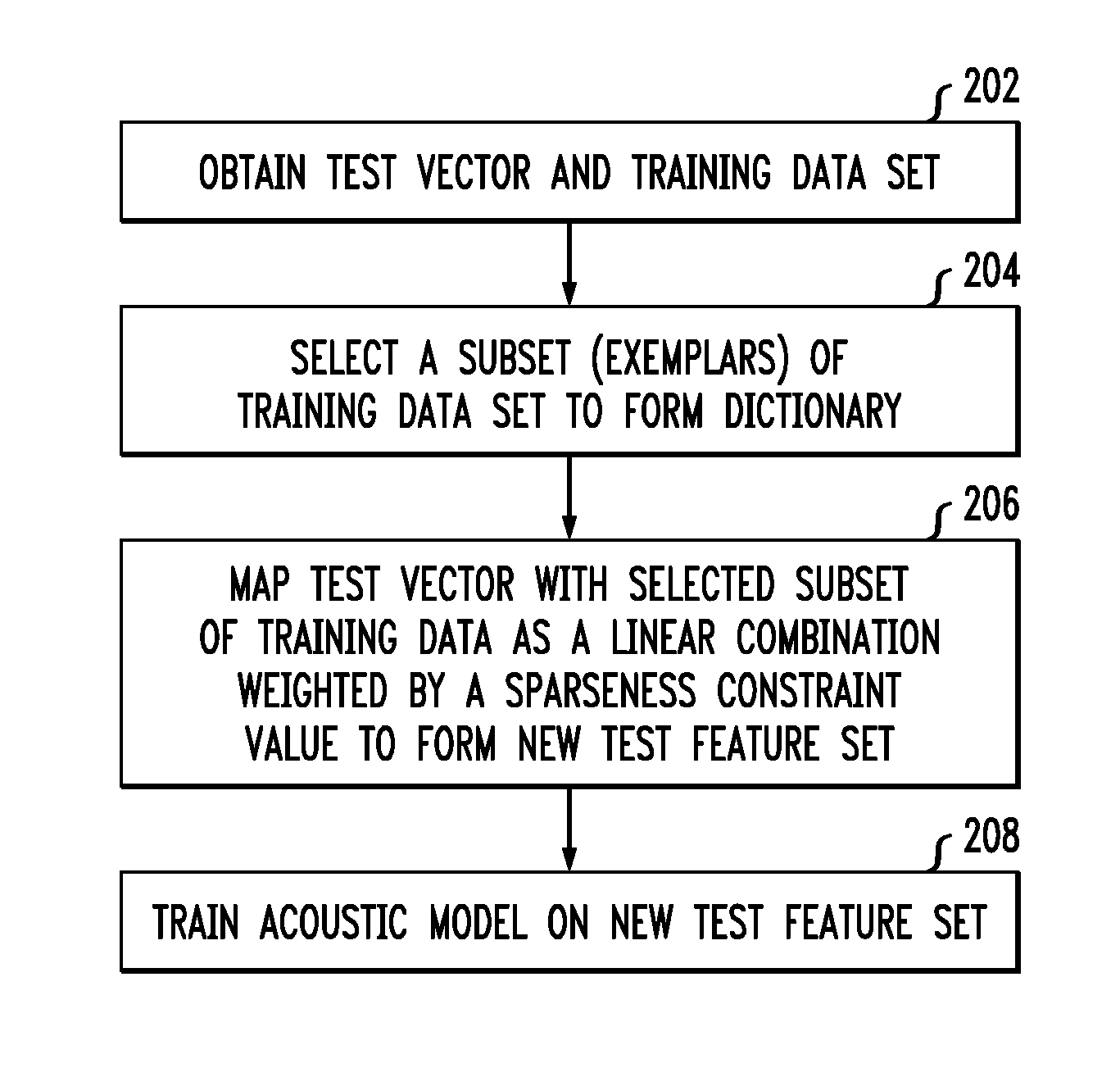
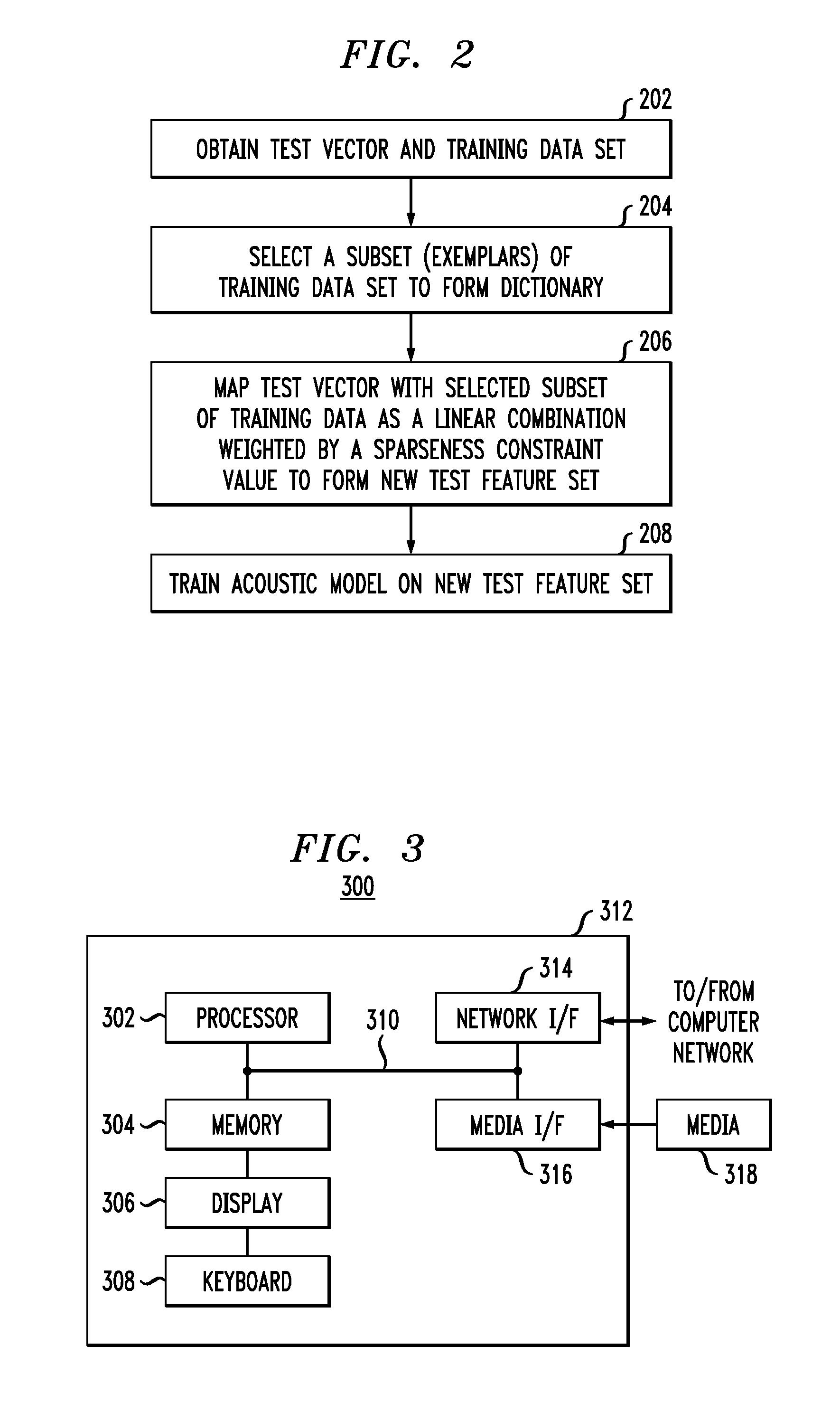
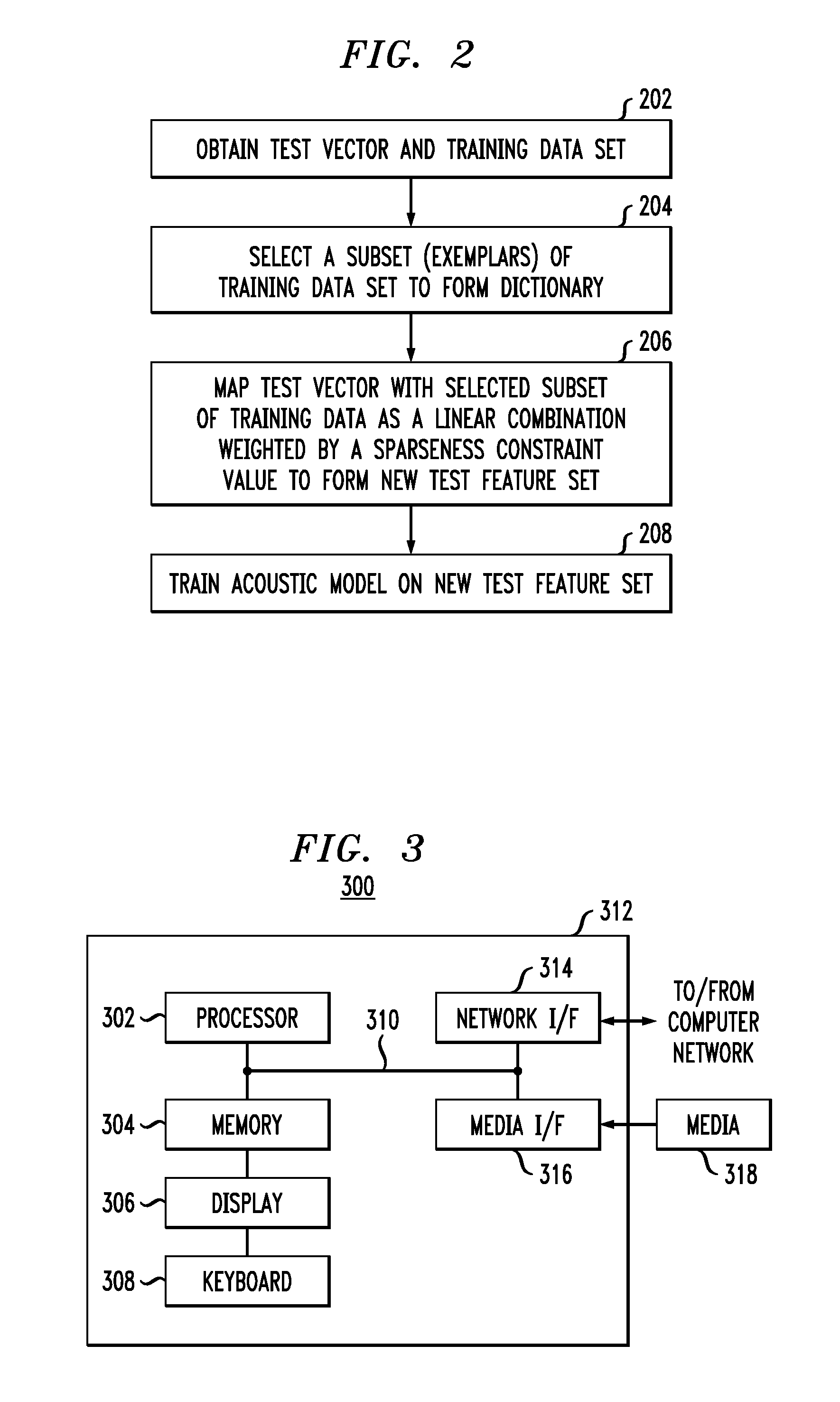
Techniques are disclosed for generating and using sparse representation features to improve speech recognition performance. In particular, principles of the invention provide sparse representation exemplar-based recognition techniques. For example, a method comprises the following steps. A test vector and a training data set associated with a speech recognition system are obtained. A subset of the training data set is selected. The test vector is mapped with the selected subset of the training data set as a linear combination that is weighted by a sparseness constraint such that a new test feature set is formed wherein the training data set is moved more closely to the test vector subject to the sparseness constraint. An acoustic model is trained on the new test feature set.The acoustic model trained on the new test feature set may be used to decode user speech input to the speech recognition system.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Signal angle-of-arrival high-precision estimation method under high sampling 1 bit quantification conditions
InactiveCN106842113AFew samplesEstimation is easy to implement in engineeringDirection findersSupport vector machineSparse constraint
The invention discloses a signal angle-of-arrival high-precision estimation method under high sampling 1 bit quantification conditions. The method includes the steps: firstly, generating a snapshot signal received by a uniform array comprising M array elements and performing 1 bit quantification sampling on the signal; secondly, building a sparse signal representation model taking a rho norm as a sparse constraint item and combining an insensitive epsilon-SVR (support vector regression) model, and performing sparse representation in original signal information by the aid of a non-convex optimization model; finally, resolving the non-convex optimization model by an ADMM (alternative direction multiplier method) to obtain a sparse representation coefficient for determining the arriving direction of the signal. According to the method, the arriving direction of the signal can be estimated in a high-precision manner without calculating an autocorrelation matrix and without reference to coherence of information sources when sampling quantity is small (such as single-snapshot), and signal arriving direction estimation based on the 1 bit quantification sampling conditions is more easily and rapidly implemented in engineering.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Ground object recognition method based on hyperspectral image unmixing
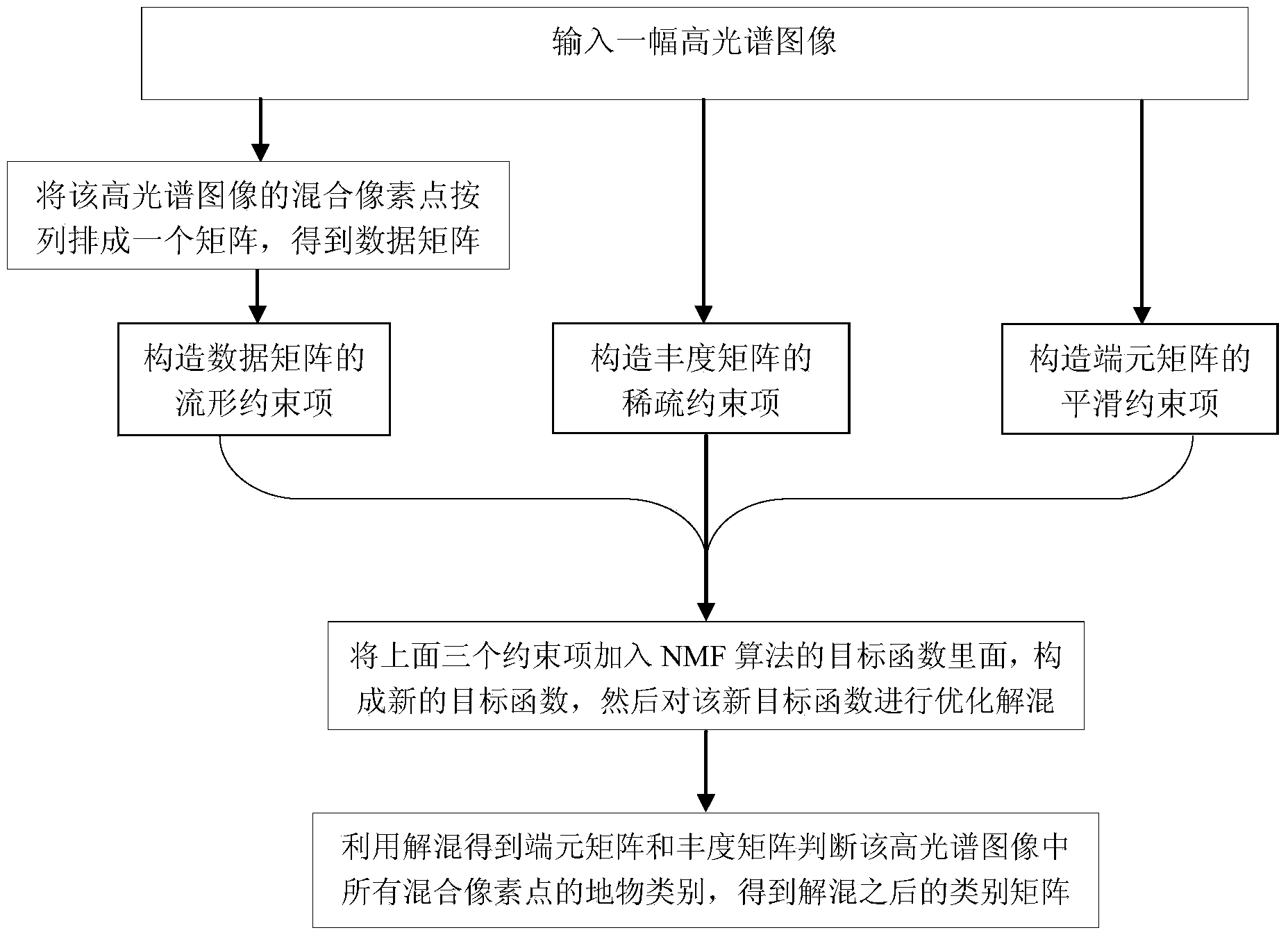
ActiveCN103679210AHigh precisionImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionSparse constraintCompositional data
The invention discloses a ground object recognition method based on hyperspectral image unmixing. The method mainly solves the problem that according to an existing method, the type of a ground object which mixed pixels belong to cannot be accurately judged. The method includes the steps of inputting a hyperspectral image, and arranging the mixed pixels in the hyperspectral image into a matrix to form a data matrix; adding a constraint term composed of a manifold constraint of a data matrix, a sparsity constraint of an abundance matrix and a smoothness constraint of an end member matrix into a target function of an NMF algorithm to form a new target function; carrying out optimal unmixing on the new target function to obtain an end member matrix and an abundance matrix of the hyperspectral image after unmixing; and judging the type of the ground object of all mixed pixels in the hyperspectral image according to the end member matrix and the abundance matrix after unmixing. The method can improve precision of an end member value and an abundance value obtained through unmixing, and accordingly precision of hyperspectral image ground object recognition is improved and the method can be used for target tracking.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
SAR image target recognition method based on non-negative matrix factorization of sparse constraint
ActiveCN104268510AReflect sparsityReflect the differenceCharacter and pattern recognitionSparse constraintImaging processing
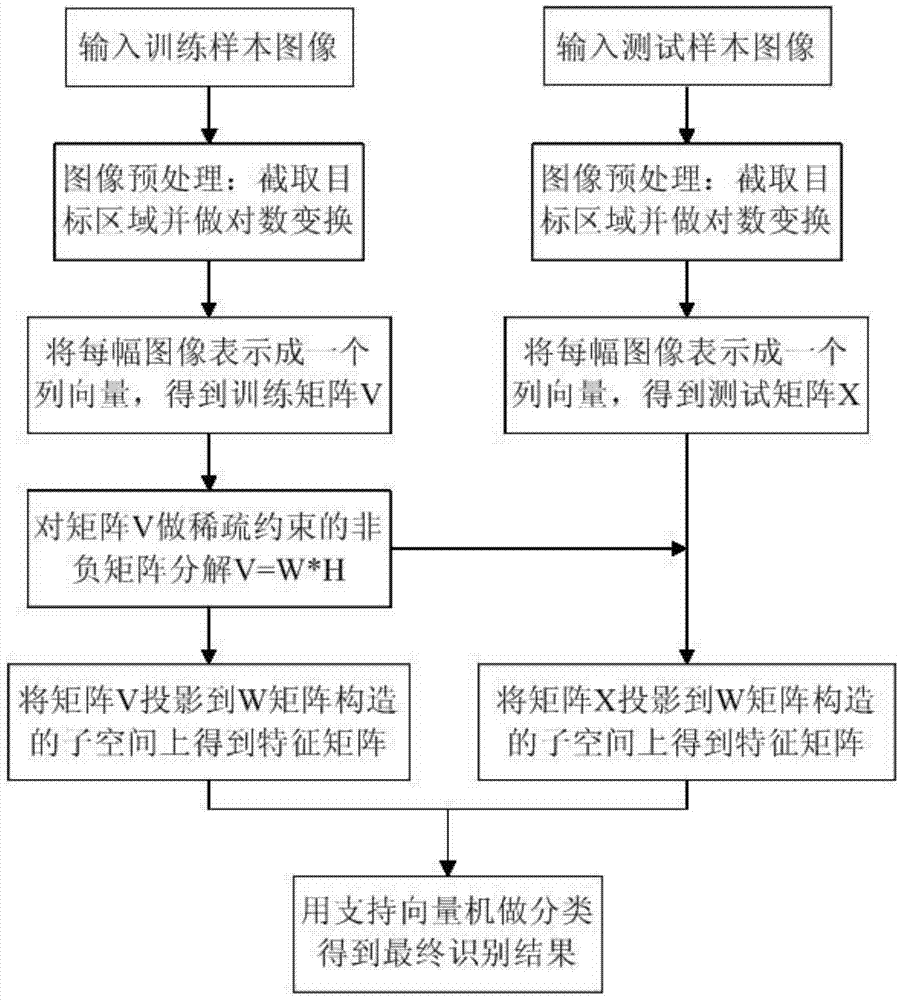
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, and particularly discloses an SAR image target recognition method based on non-negative matrix factorization of sparse constraint. According to the method, more effective features are extracted by improving a non-negative matrix factorization method to improved recognition precision, and the problems that features extracted in the prior art are not typical and recognition precision is not high are solved. According to the method, a training sample image and a test sample image are pre-processed in the same way, logarithmic transformation is carried out, a pre-processed training sample set is factorized through non-negative matrix factorization of sparse constraint to obtain a basis matrix and a coefficient matrix, a test sample set is projected in a sub space of a basis matrix structure, classification is carried out through an SVM after a feature matrix is obtained, and then classification accuracy is obtained ultimately. Compared with the prior art, the extracted features are more effective and recognition precision can be effectively improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Radar antenna array steady beam forming method based on sparse constraint
InactiveCN106443594AReduce computational complexityWave based measurement systemsSparse constraintTarget signal
The invention belongs to the field of radar array signal processing and discloses a radar antenna array steady beam forming method based on sparse constraint. The method includes the steps that L receiving signals of a radar antenna array are acquired, and a covariance matrix estimated value (please see the formula in the specification) of the receiving signals is obtained through calculation according to the L receiving signals; an assumed target signal guide vector is s, and a target signal guide vector estimated value (please see the formula in the specification) is obtained according to the covariance matrix estimated value (please see the formula in the specification) of the receiving signals and the assumed target signal guide vector s; a complete interference and signal subspace is determined according to the covariance matrix estimated value (please see the formula in the specification) of the receiving signals and the target signal guide vector estimated value (please see the formula in the specification); an optimal adaptive beam forming weight vector of a radar antenna array output end is established according to the complete interference and signal subspace.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com