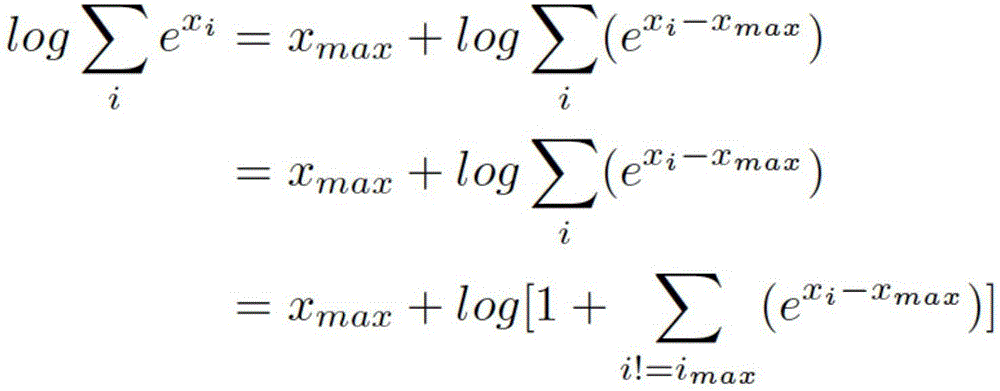Patents
Literature
1293 results about "Artificial neural network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
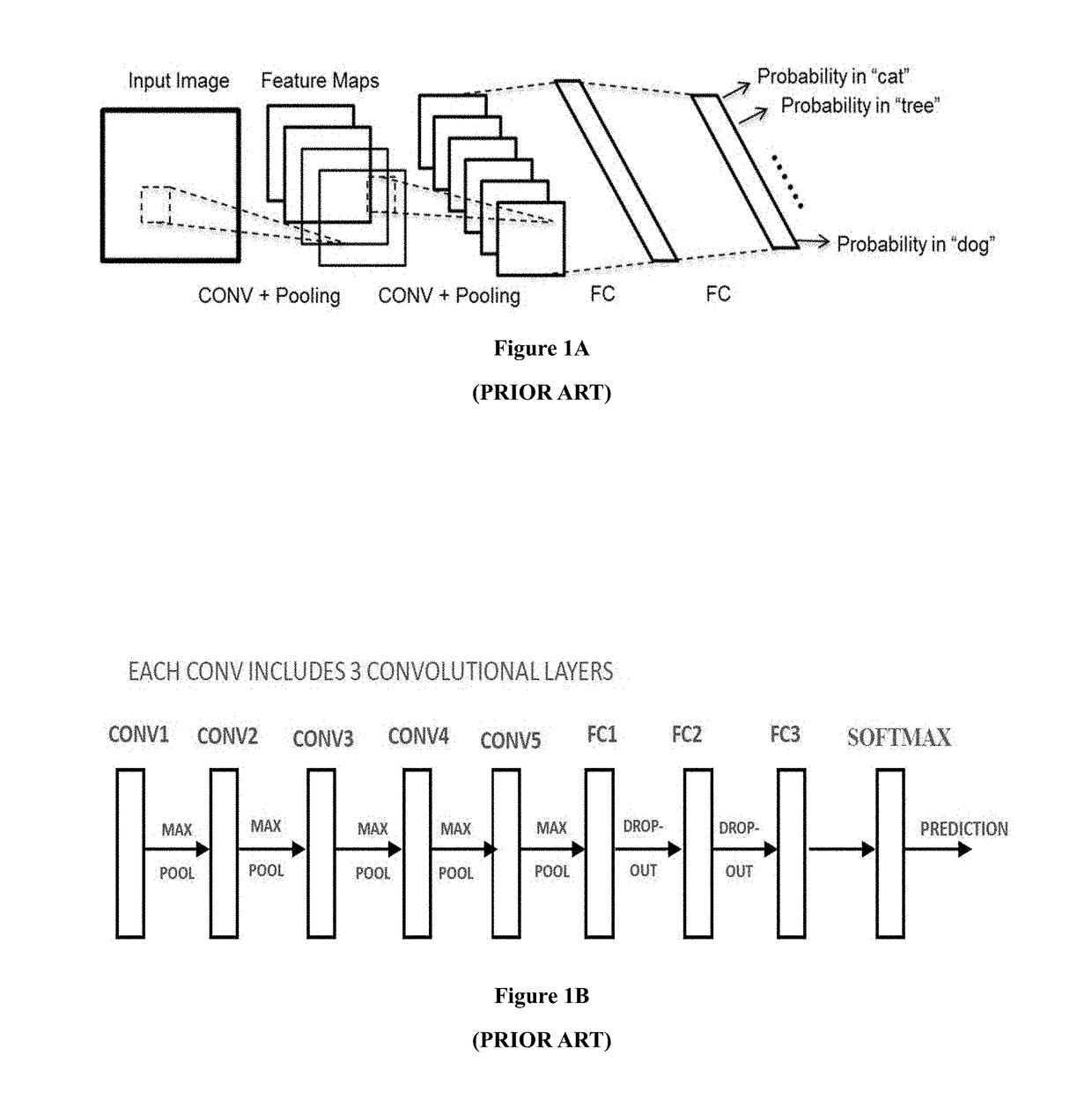
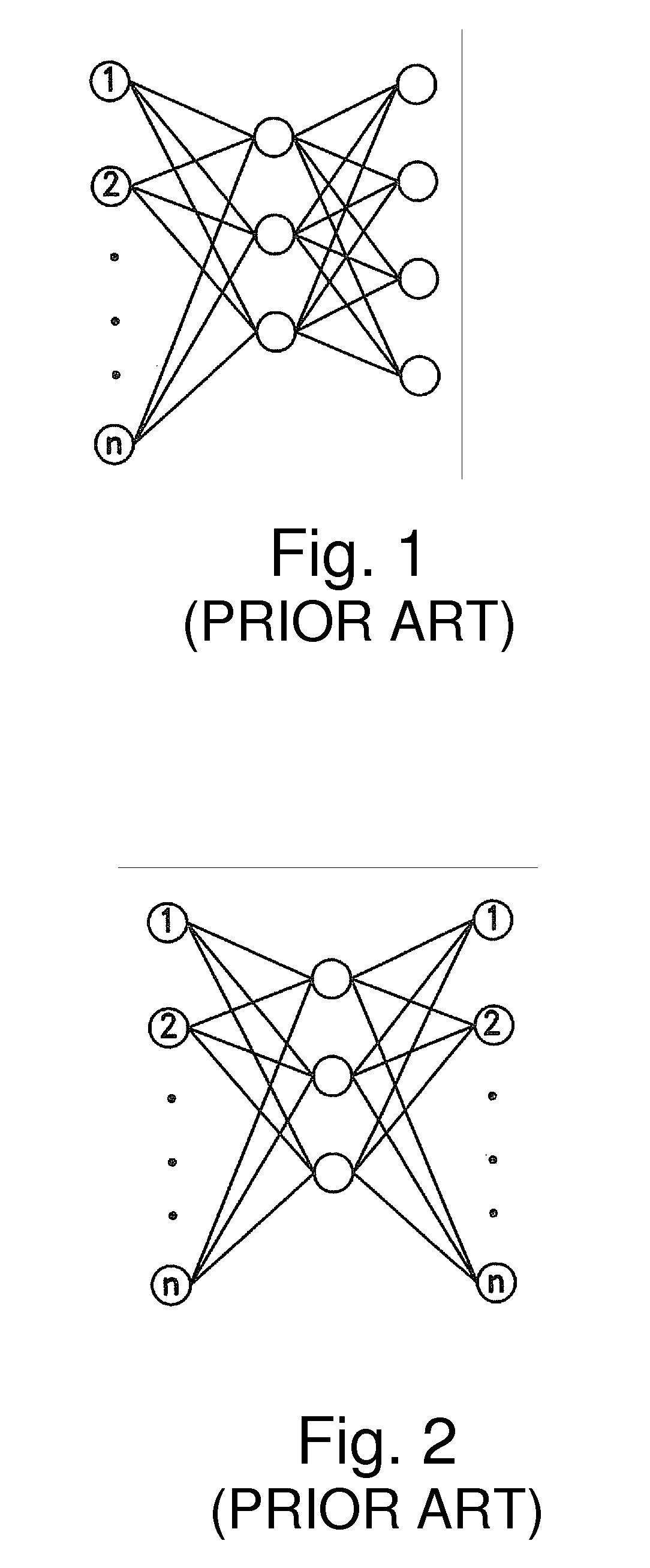
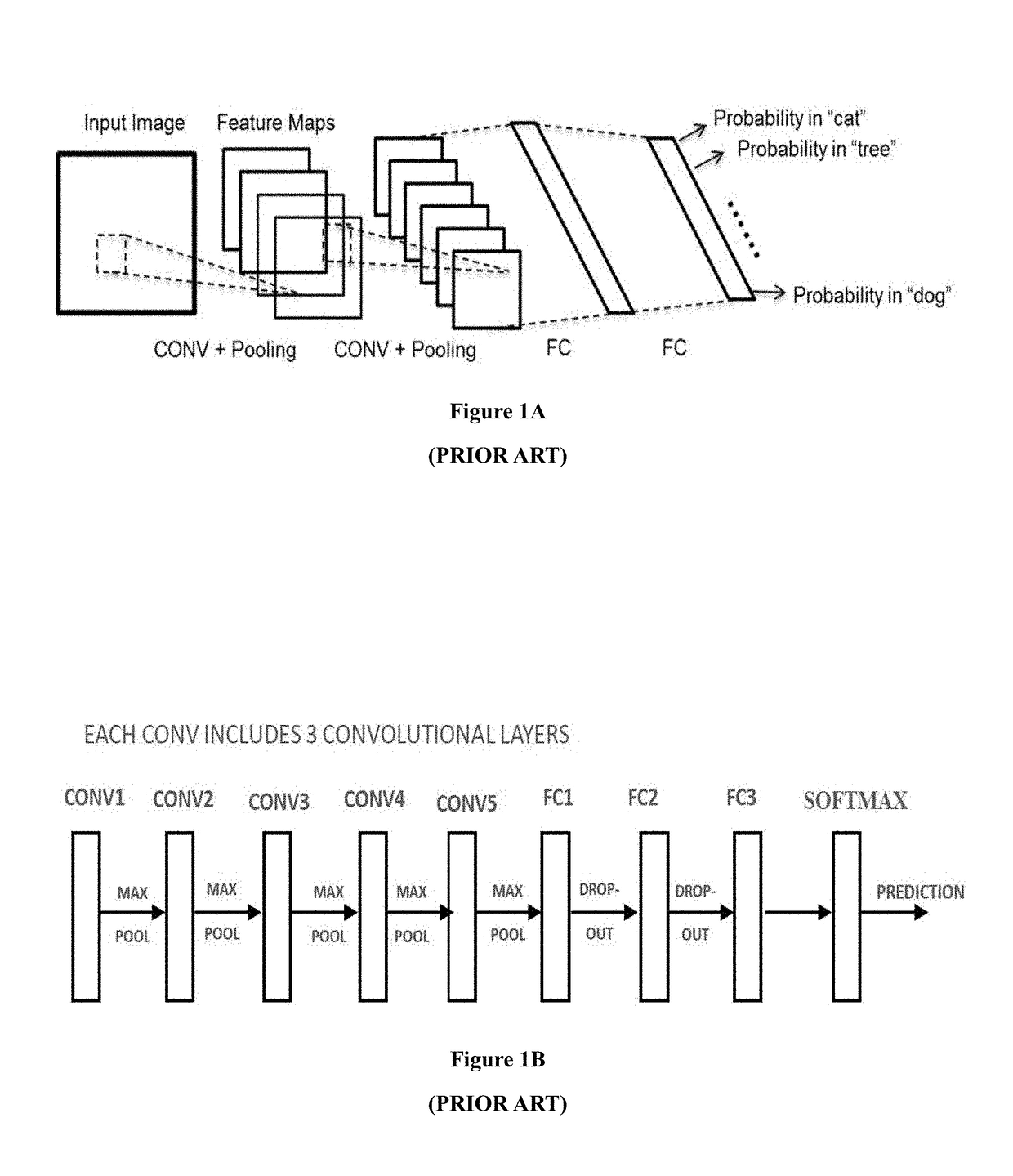
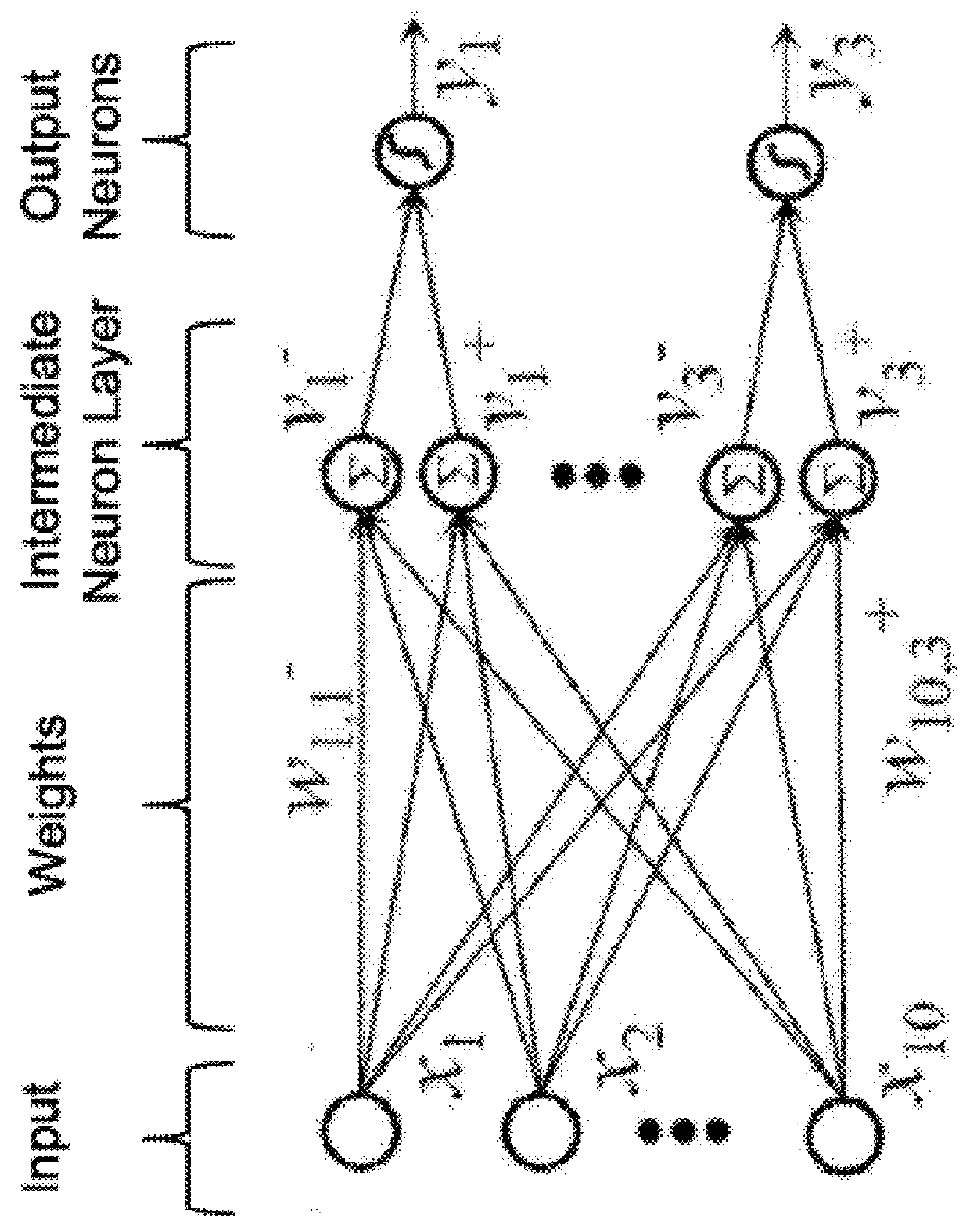
Artificial neural networks (ANN) or connectionist systems are computing systems that are inspired by, but not identical to, biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. Such systems "learn" to perform tasks by considering examples, generally without being programmed with task-specific rules. For example, in image recognition, they might learn to identify images that contain cats by analyzing example images that have been manually labeled as "cat" or "no cat" and using the results to identify cats in other images. They do this without any prior knowledge of cats, for example, that they have fur, tails, whiskers and cat-like faces. Instead, they automatically generate identifying characteristics from the examples that they process.
Patient condition display
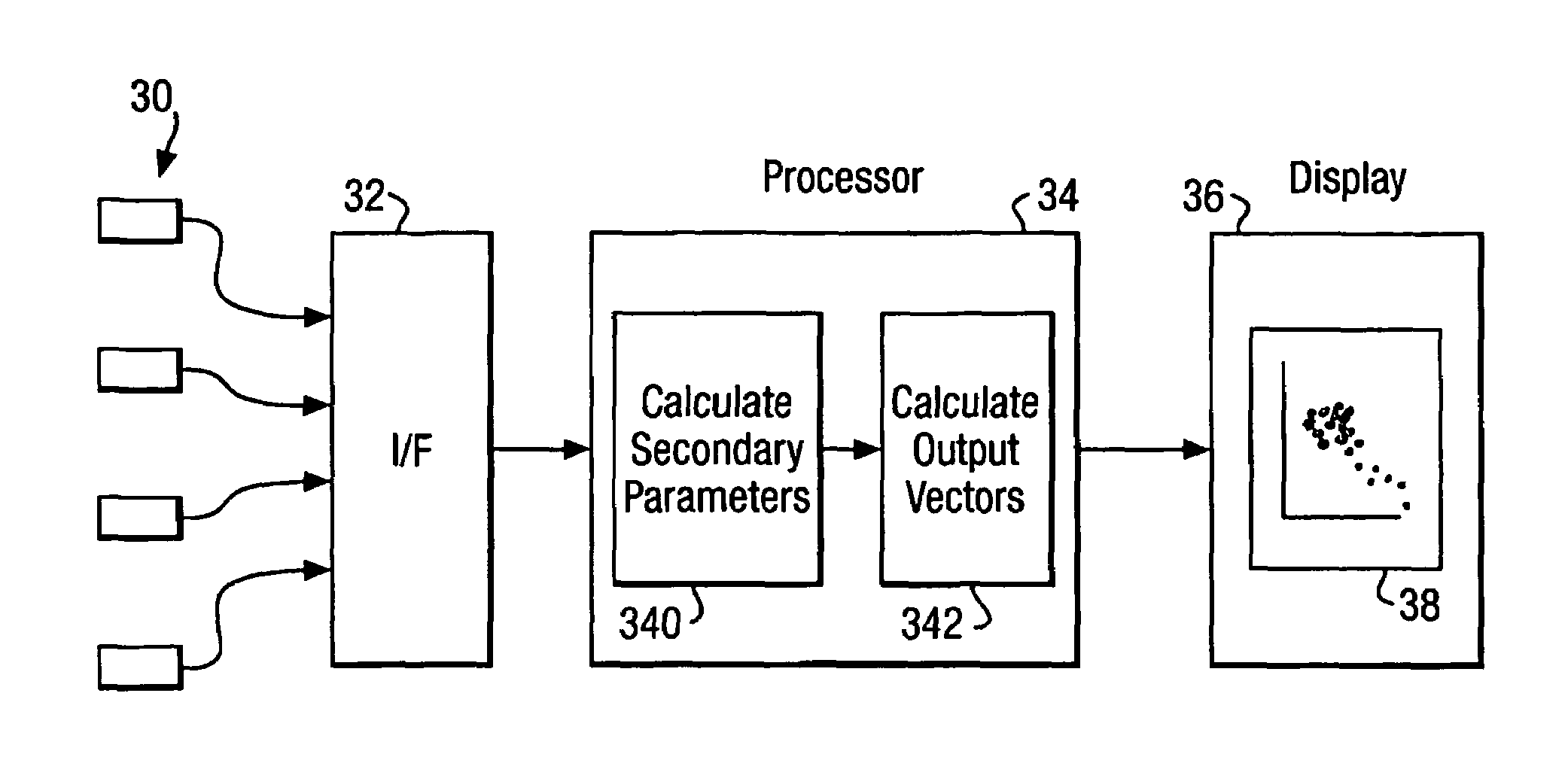
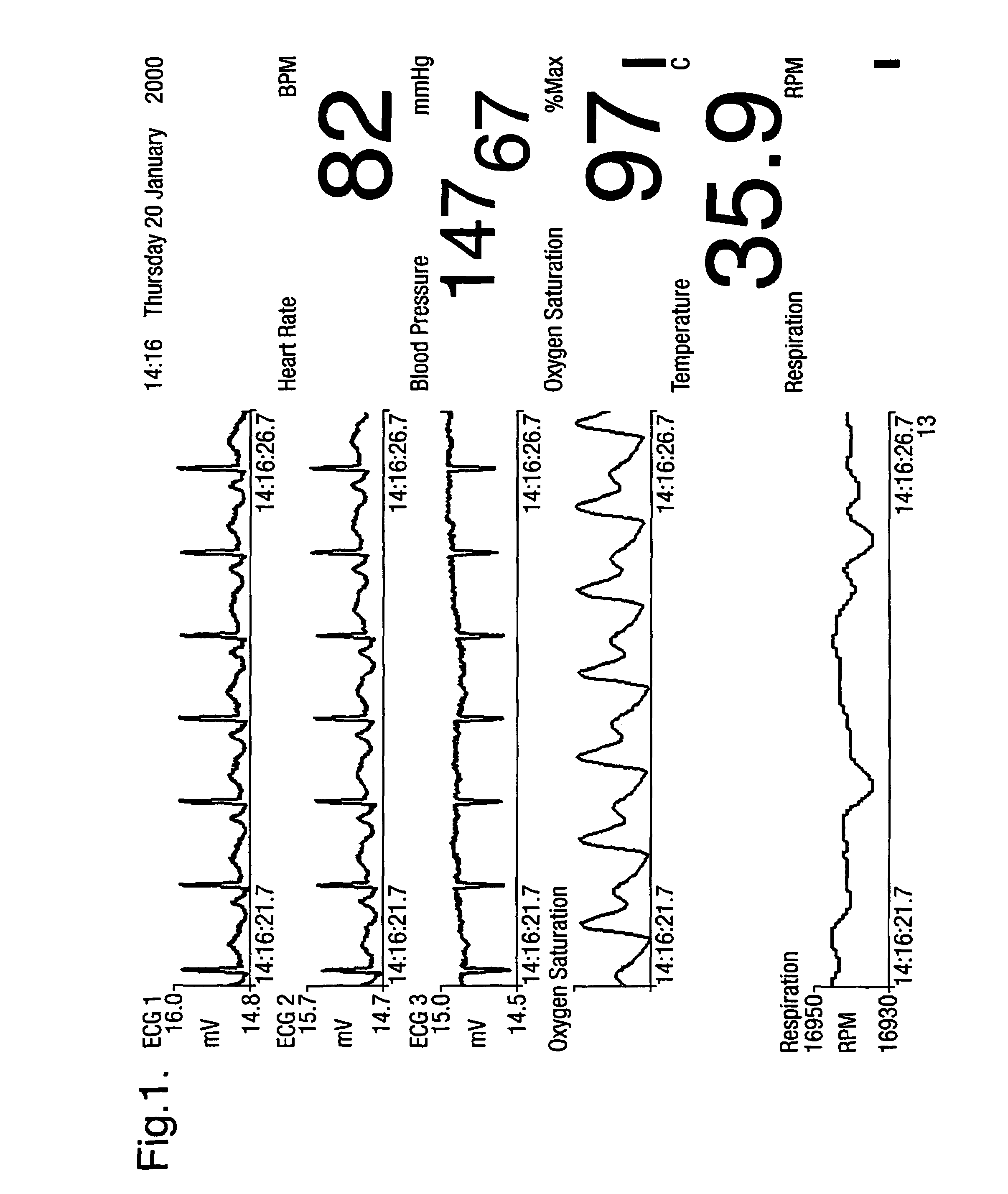
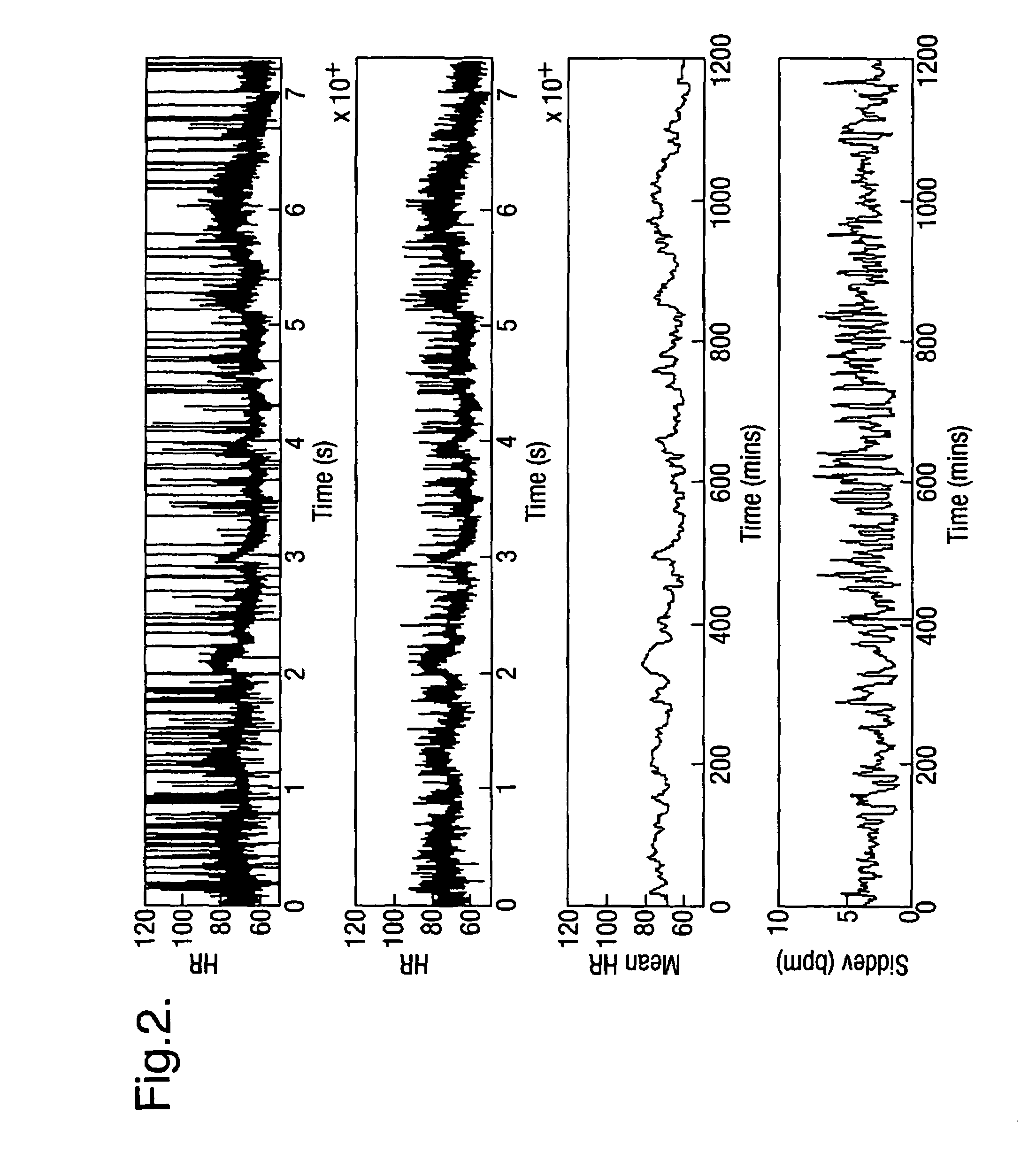
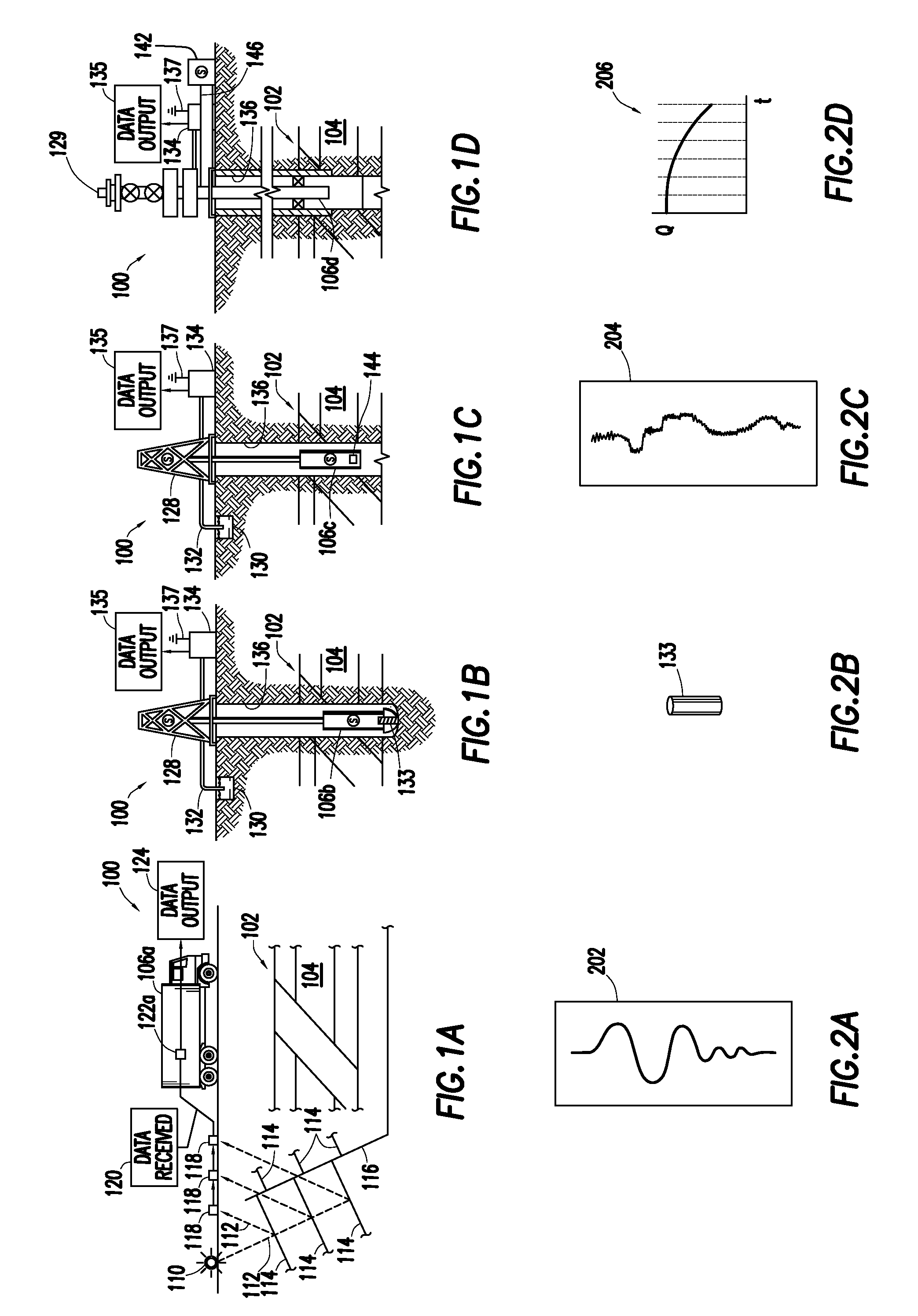
InactiveUS7031857B2Improve clinical outcomesDecreased heart rateDigital variable displayDiagnostic recording/measuringMulti dimensionalArtificial neural network
Data from a plurality of sensors representing a patient's condition, including measurement signals and also secondary parameters derived from the measurement signals, are displayed in a simple way by calculating a novelty index constituting a one-dimensional visualization space. The novelty index is based on the distance of the current data point in a multi-dimensional measurement space, whose coordinates are defined by the values of the measurement signals and secondary parameters, from a predefined normal point. This may be achieved by using a suitably trained artificial neural network to sum the distance between the current data point in the measurement space and a plurality of prototype points representing normality.
Owner:OXFORD BIOSIGNALS
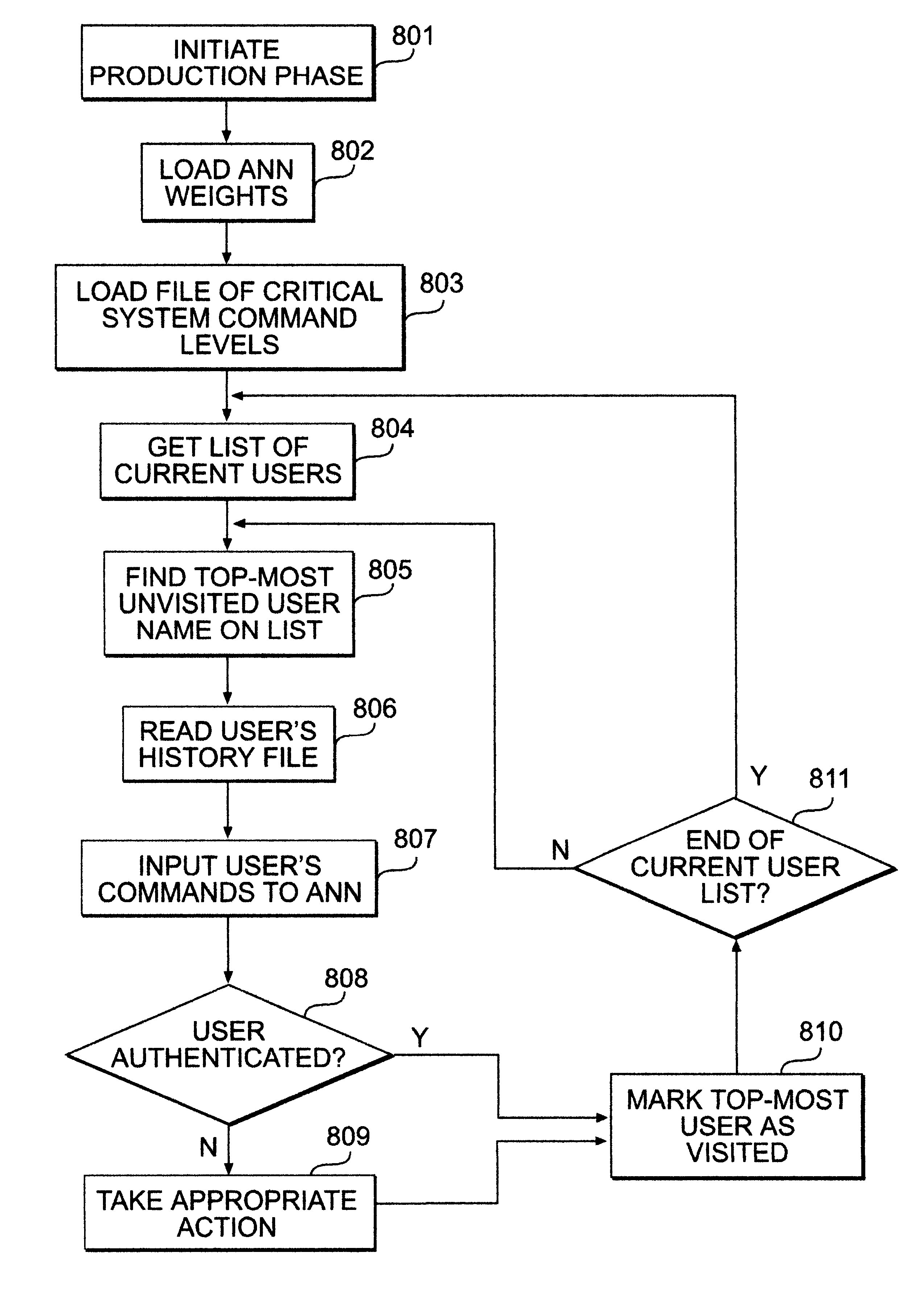
Usage pattern based user authenticator
InactiveUS6334121B1Control damagePreventing executionDigital computer detailsComputer security arrangementsOperational systemOperating system level
A usage based pattern authenticator for monitoring and reporting on user usage patterns in an operating system using a set of security rules and user usage patterns. This computer system security tool authenticates users at the operating system level in multi-user operating systems. It supports system administrators in limiting the ability of unauthorized users to disrupt system operations using a neural network and set of rules to track usage patterns and flag suspicious activity on the system. The data collection mode collects and stores usage patterns of authenticated users. The training mode trains an artificial neural network and sets the interconnection weights of the network. The production mode monitors and reports on usage patterns, and optionally performs automatic responses when confronted with non-authenticated users.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
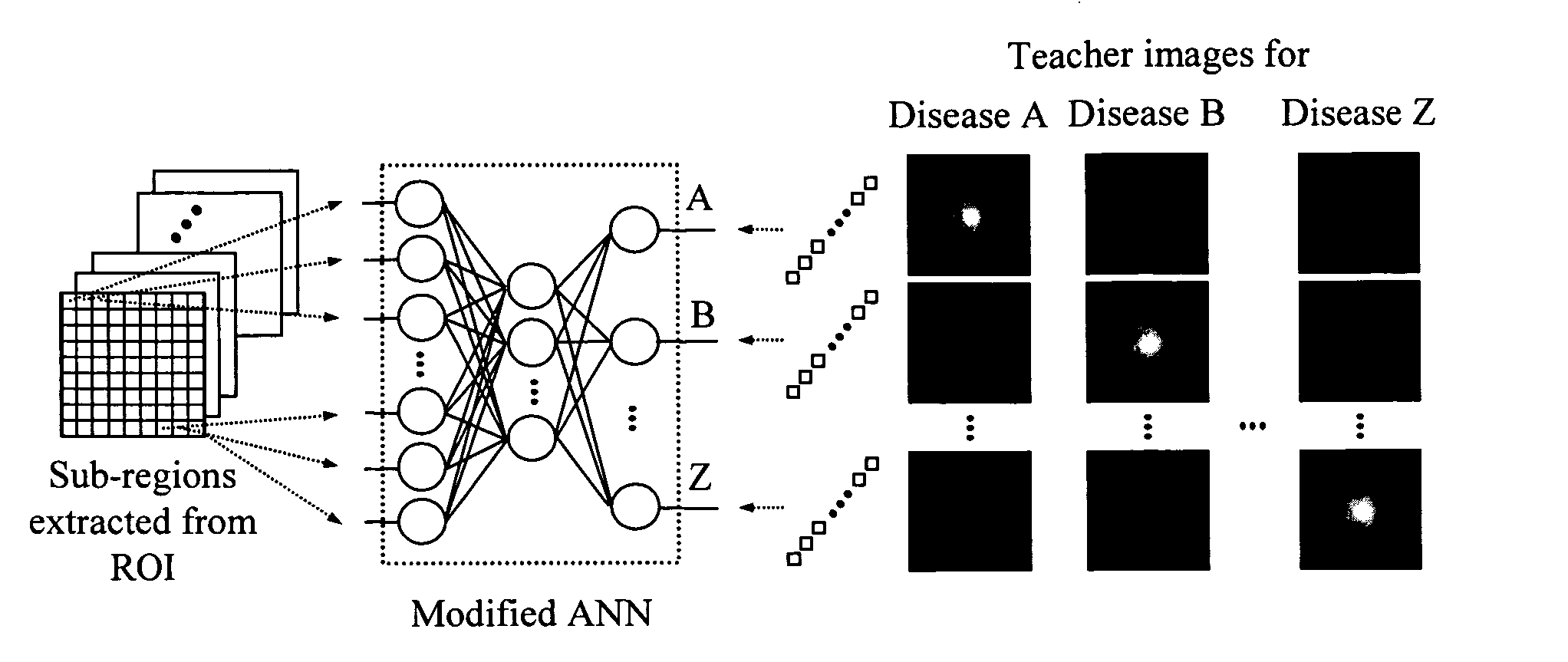
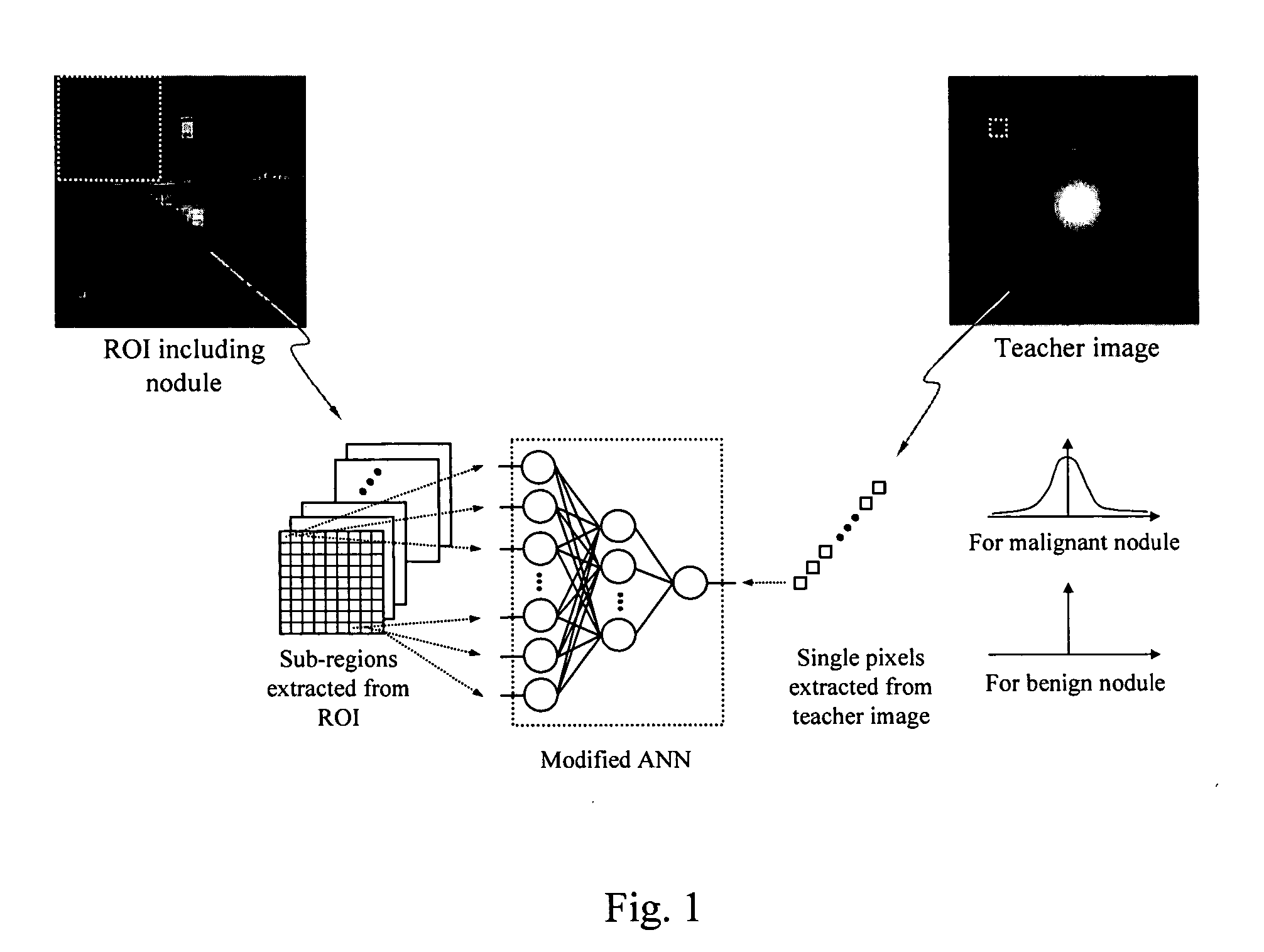
Image modification and detection using massive training artificial neural networks (MTANN)
ActiveUS20050100208A1Suppressing contrastModify their appearanceImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityAnatomical structures
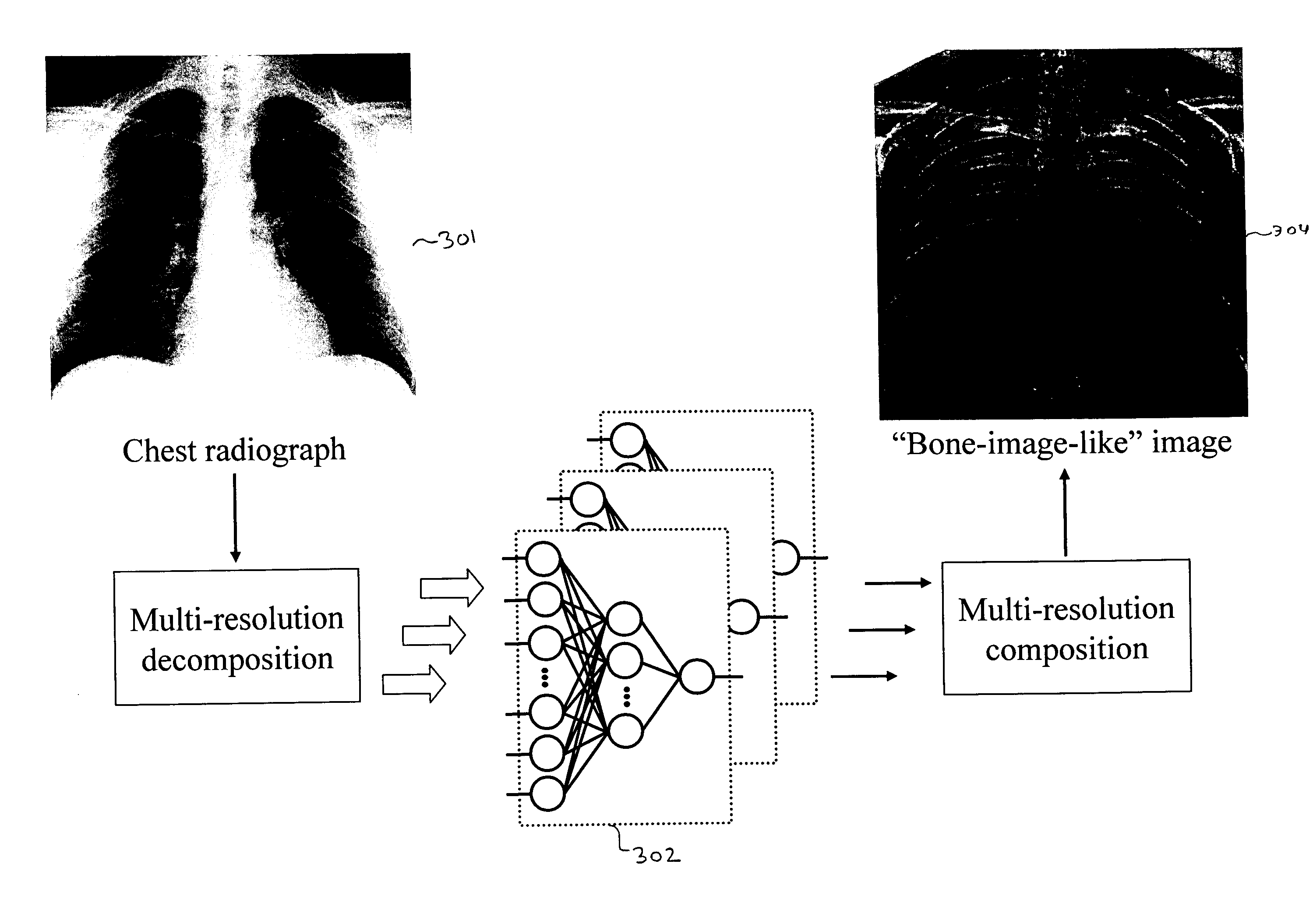
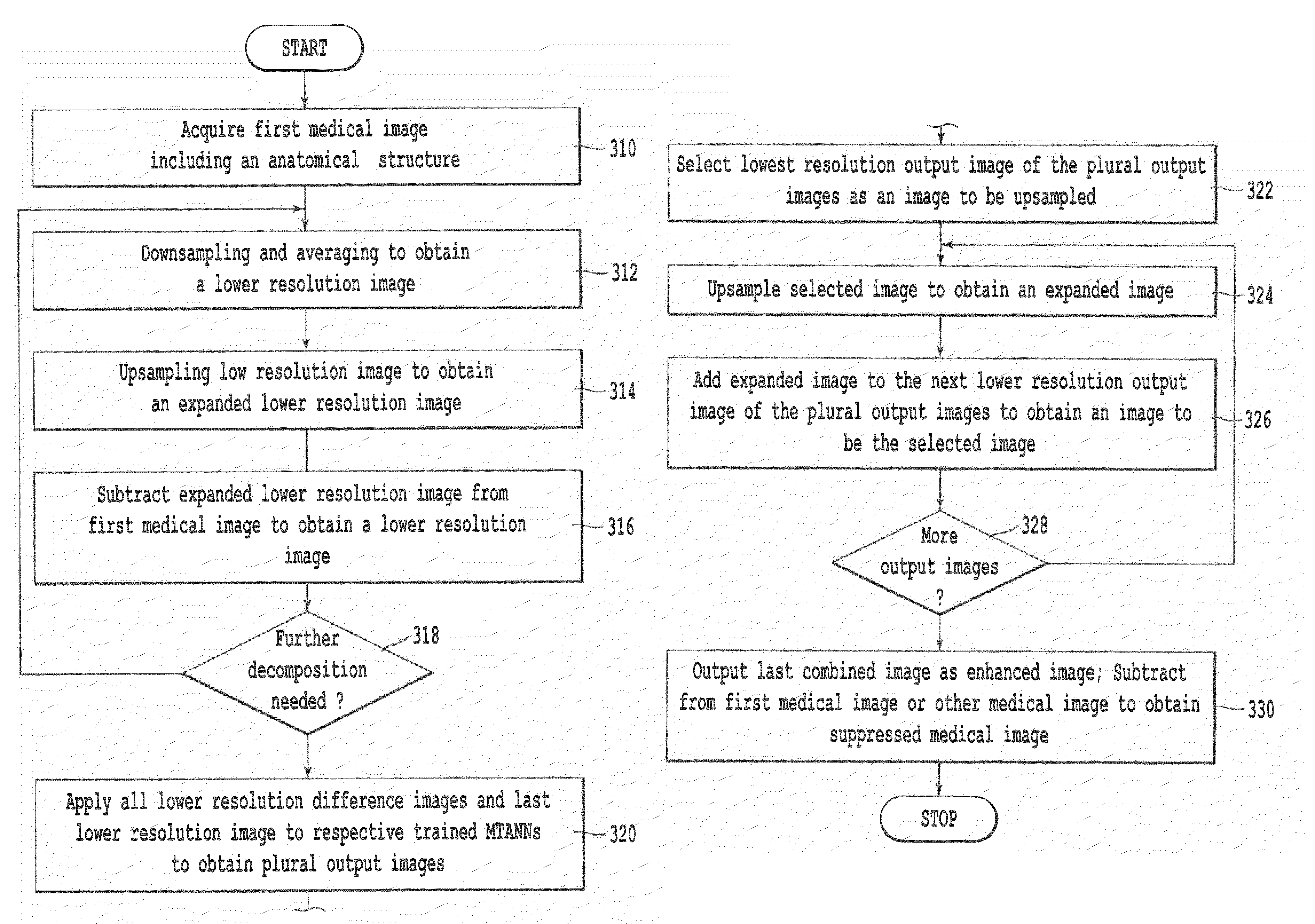
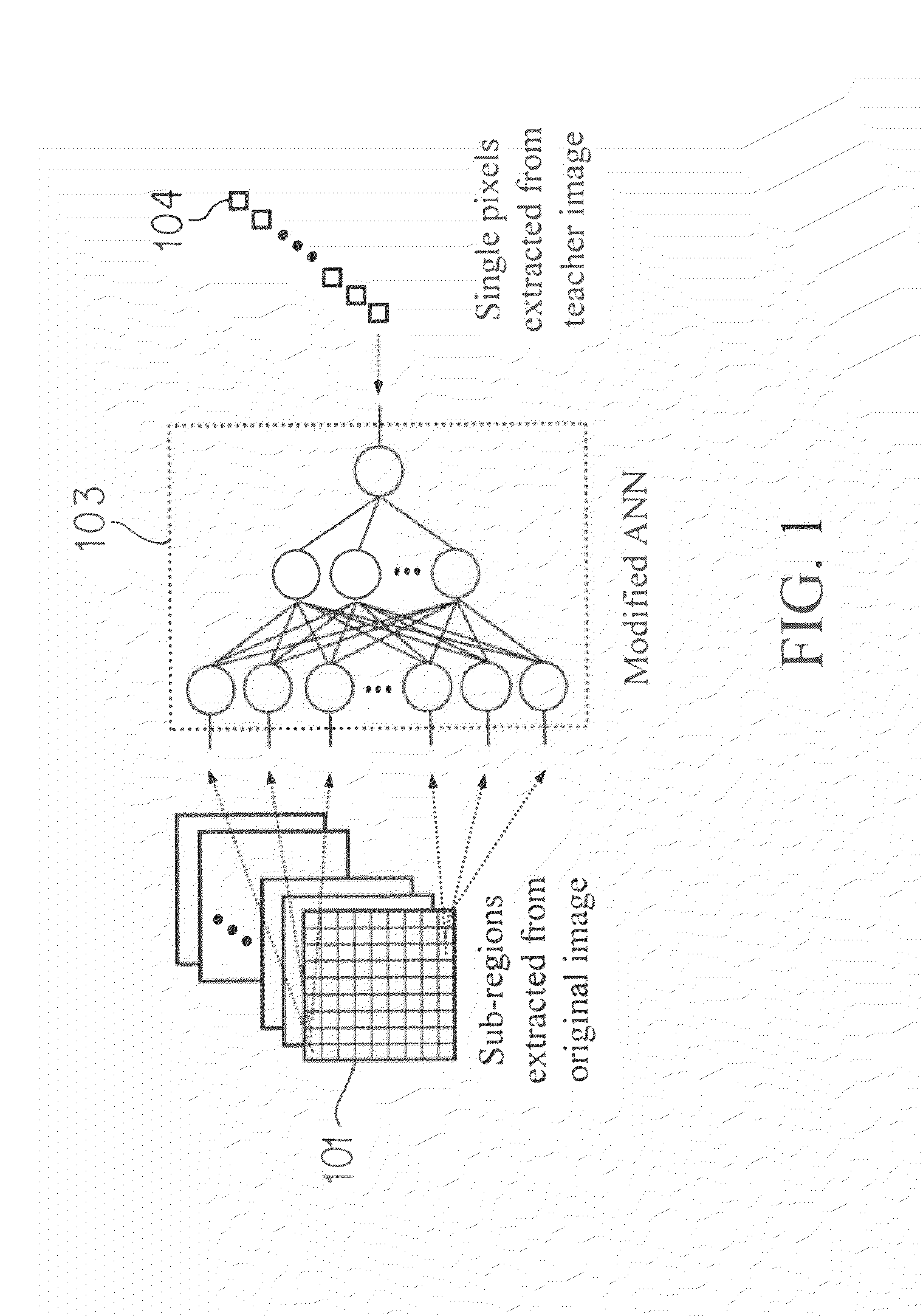
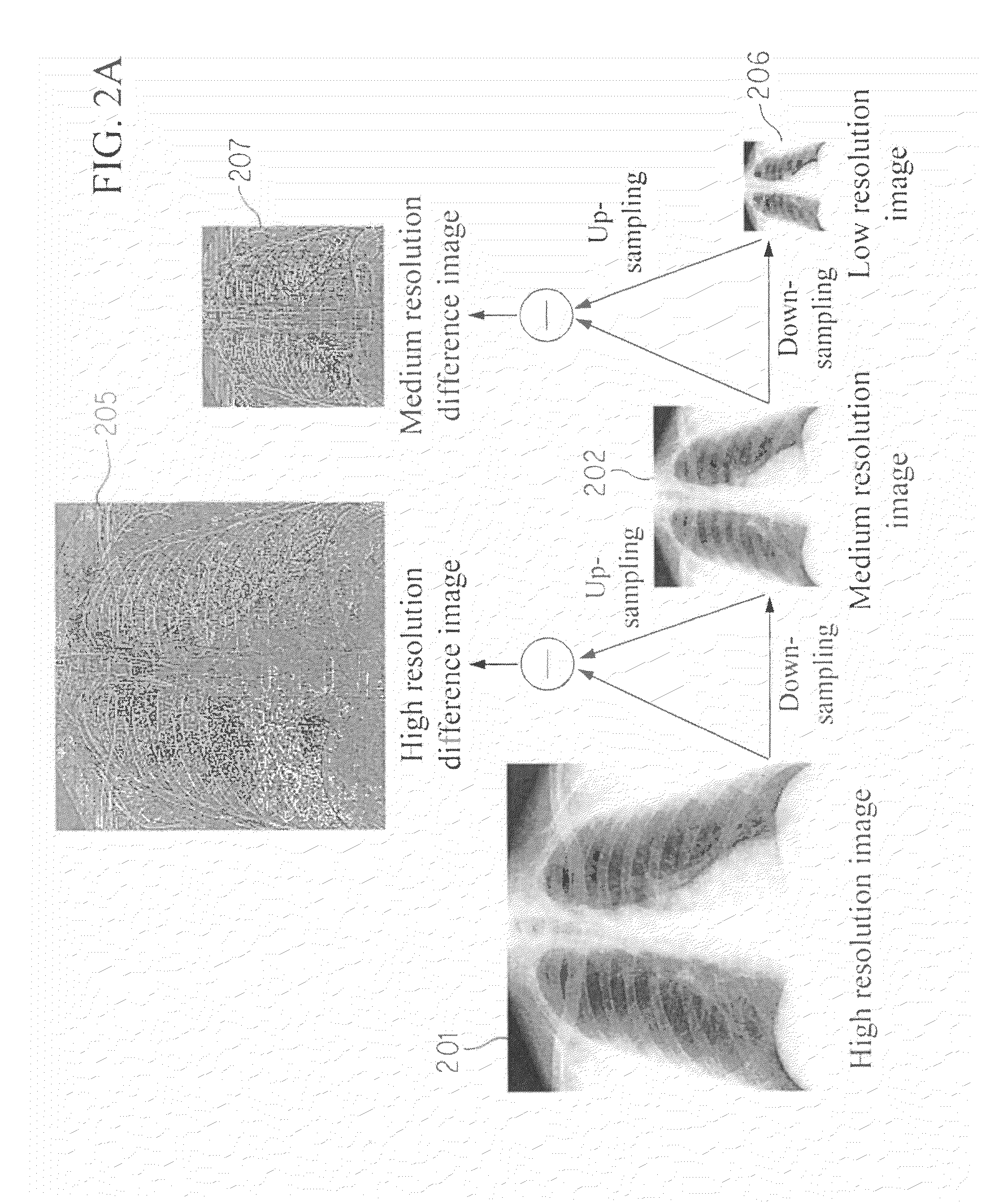
A method, system, and computer program product for modifying an appearance of an anatomical structure in a medical image, e.g., rib suppression in a chest radiograph. The method includes: acquiring, using a first imaging modality, a first medical image that includes the anatomical structure; applying the first medical image to a trained image processing device to obtain a second medical image, corresponding to the first medical image, in which the appearance of the anatomical structure is modified; and outputting the second medical image. Further, the image processing device is trained using plural teacher images obtained from a second imaging modality that is different from the first imaging modality. In one embodiment, the method also includes processing the first medical image to obtain plural processed images, wherein each of the plural processed images has a corresponding image resolution; applying the plural processed images to respective multi-training artificial neural networks (MTANNs) to obtain plural output images, wherein each MTANN is trained to detect the anatomical structure at one of the corresponding image resolutions; and combining the plural output images to obtain a second medical image in which the appearance of the anatomical structure is enhanced.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
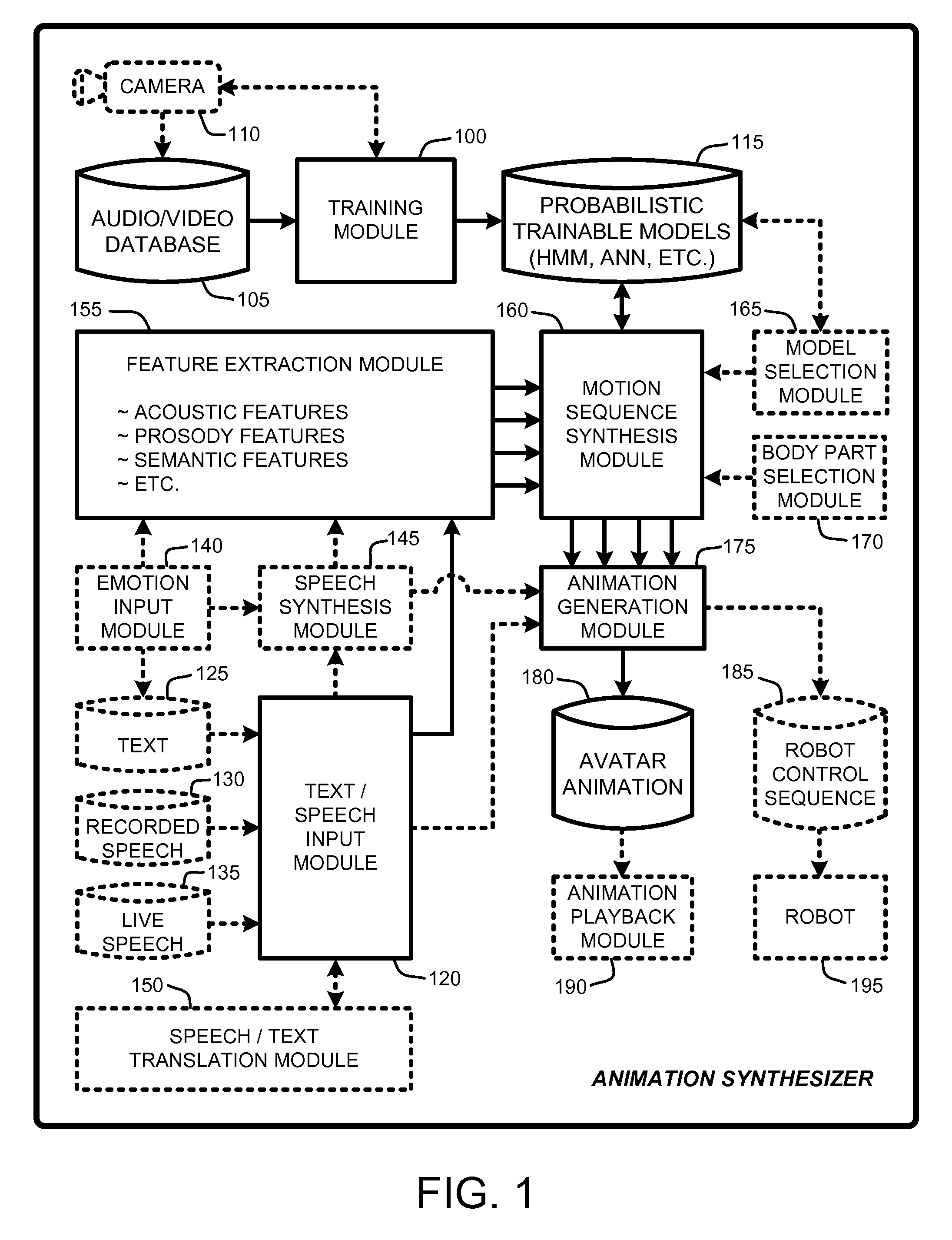
Speech and text driven hmm-based body animation synthesis
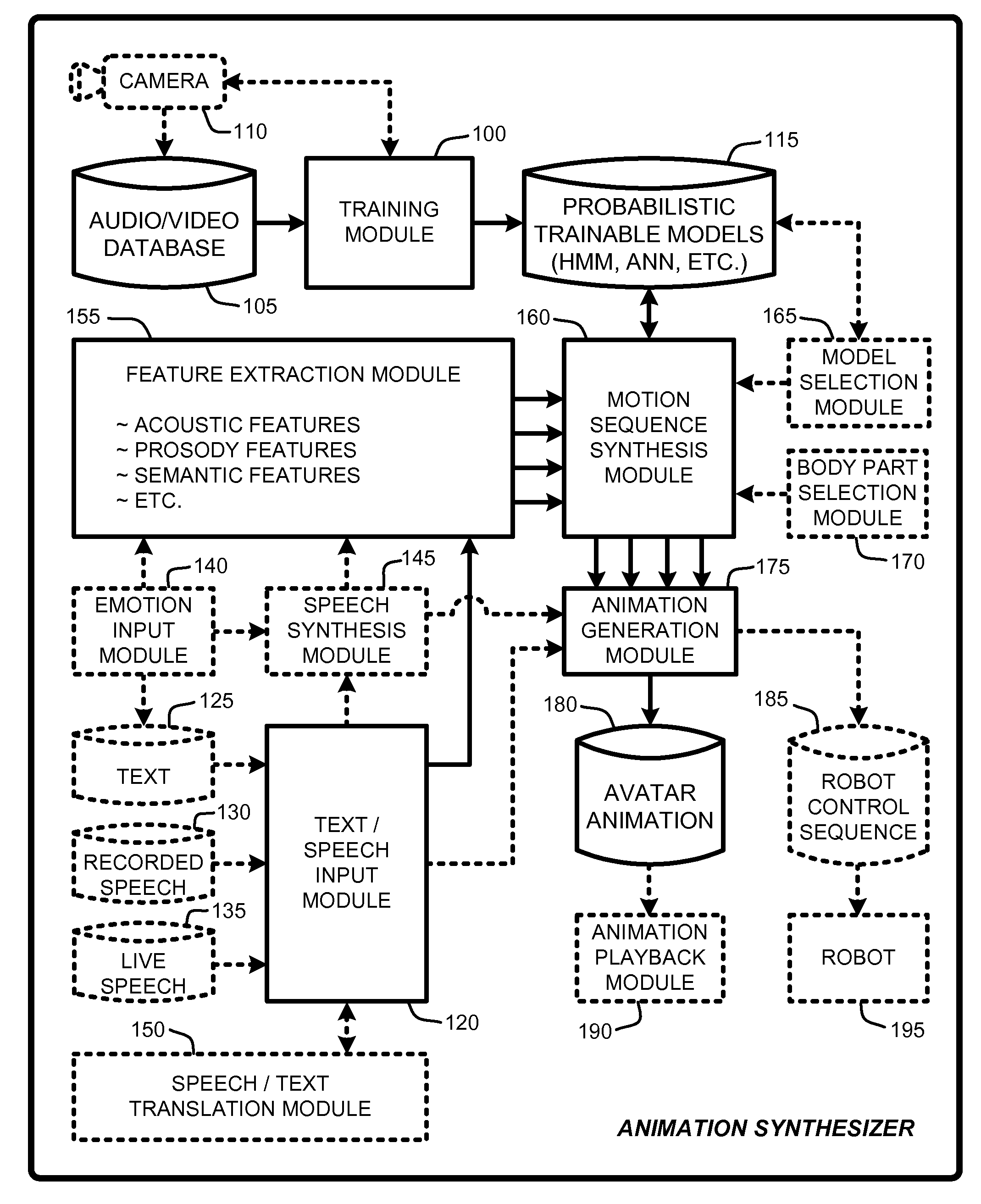
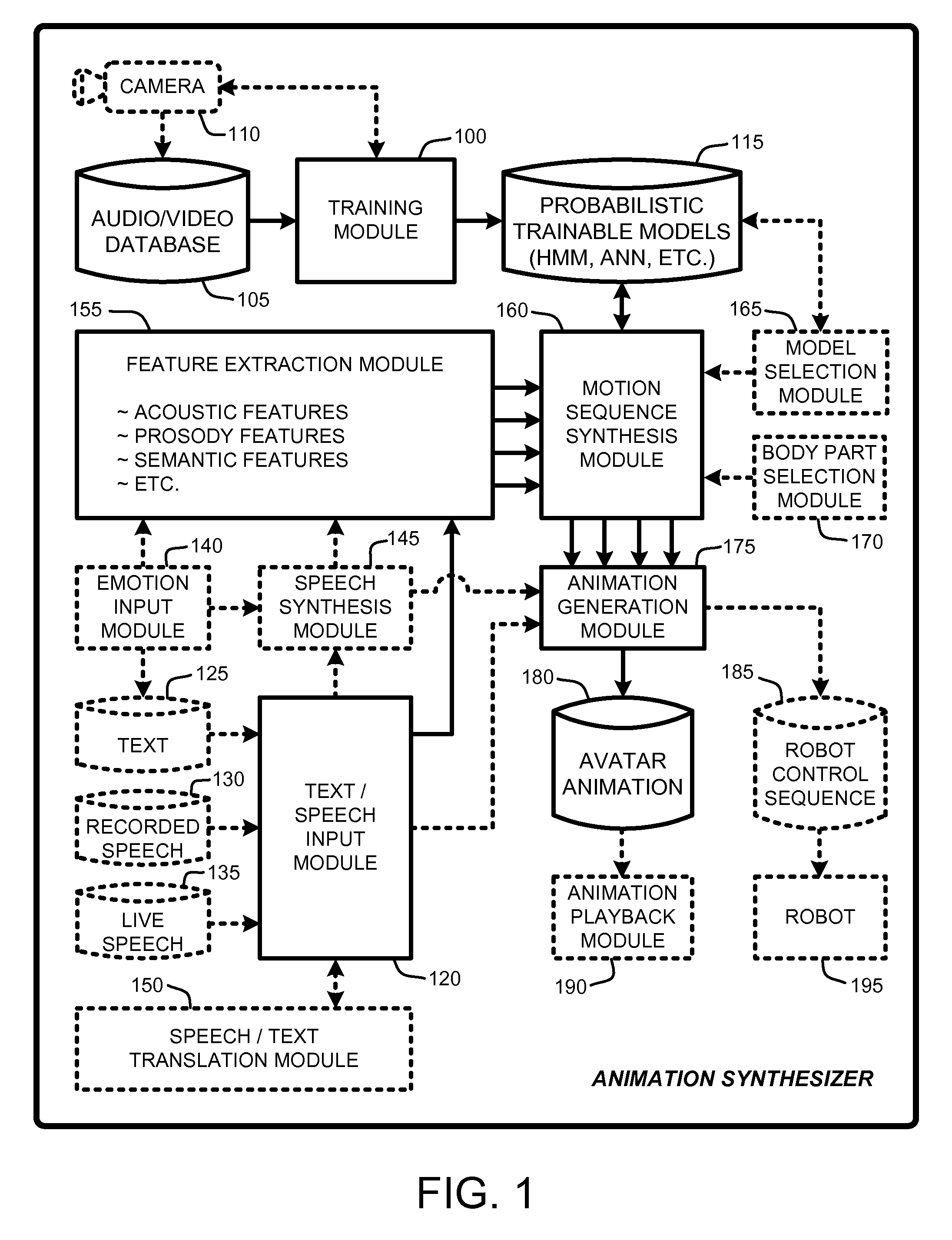
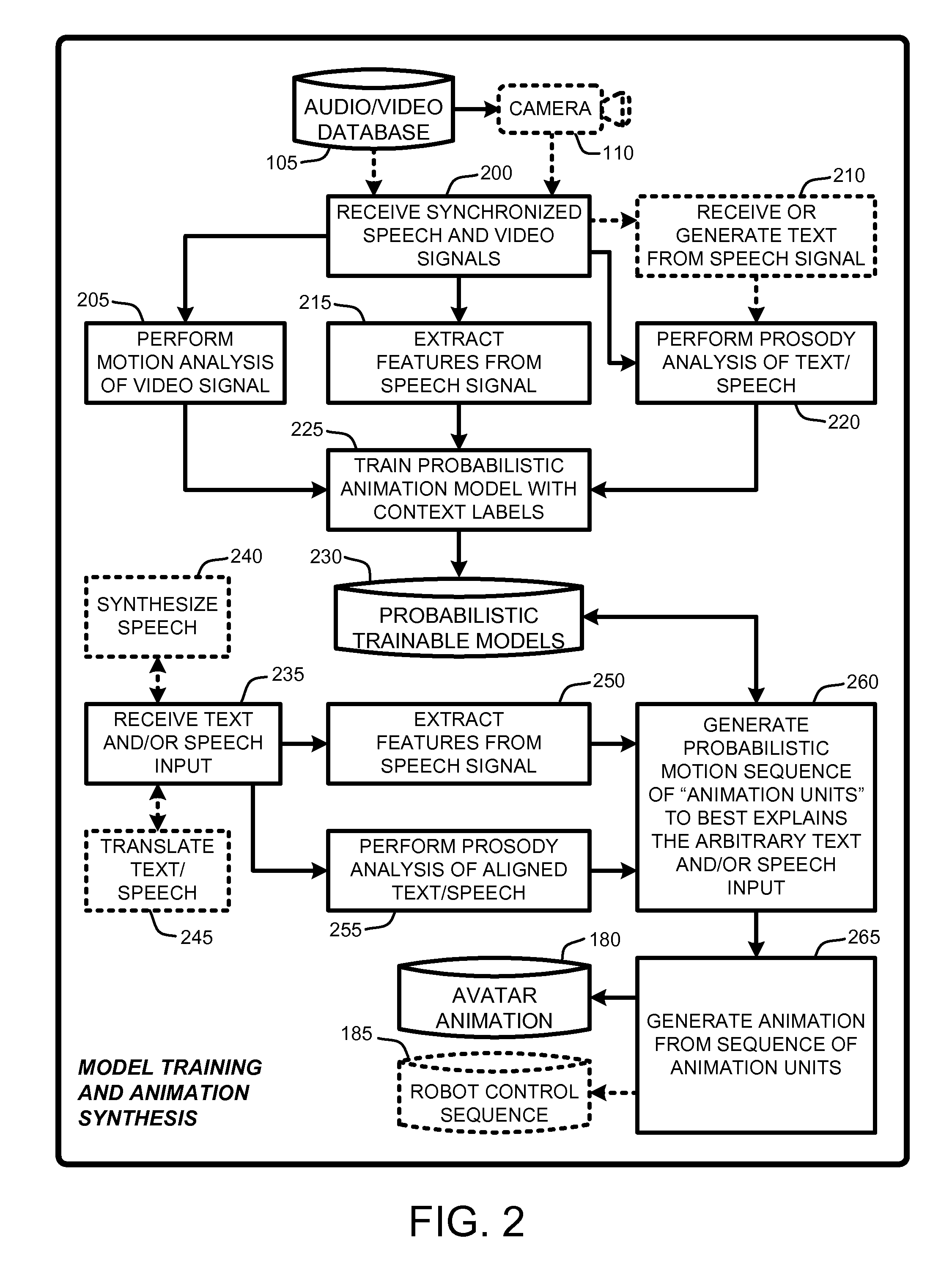
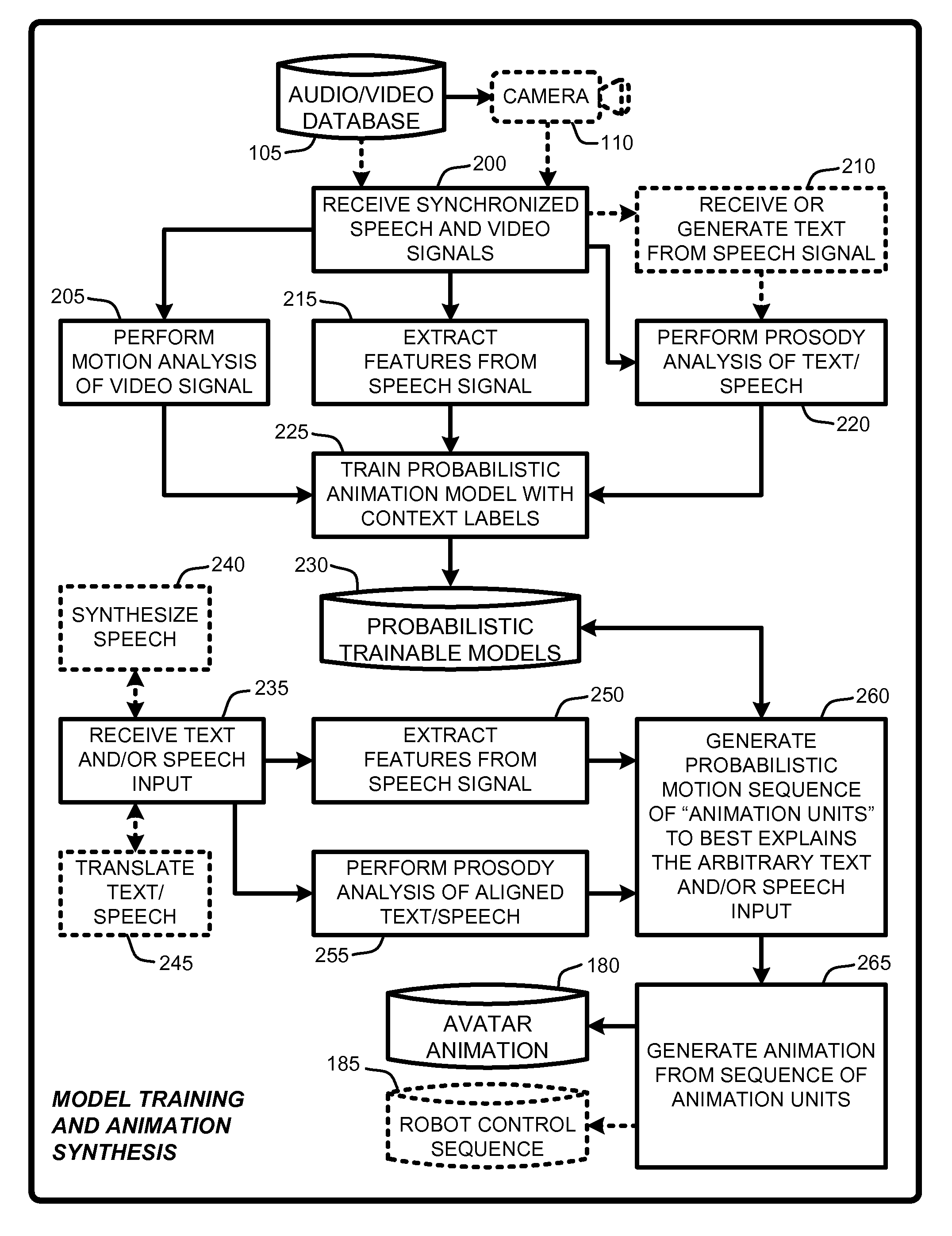
An “Animation Synthesizer” uses trainable probabilistic models, such as Hidden Markov Models (HMM), Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), etc., to provide speech and text driven body animation synthesis. Probabilistic models are trained using synchronized motion and speech inputs (e.g., live or recorded audio / video feeds) at various speech levels, such as sentences, phrases, words, phonemes, sub-phonemes, etc., depending upon the available data, and the motion type or body part being modeled. The Animation Synthesizer then uses the trainable probabilistic model for selecting animation trajectories for one or more different body parts (e.g., face, head, hands, arms, etc.) based on an arbitrary text and / or speech input. These animation trajectories are then used to synthesize a sequence of animations for digital avatars, cartoon characters, computer generated anthropomorphic persons or creatures, actual motions for physical robots, etc., that are synchronized with a speech output corresponding to the text and / or speech input.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Image modification and detection using massive training artificial neural networks (MTANN)
A method, system, and computer program product for modifying an appearance of an anatomical structure in a medical image, e.g., rib suppression in a chest radiograph. The method includes: acquiring, using a first imaging modality, a first medical image that includes the anatomical structure; applying the first medical image to a trained image processing device to obtain a second medical image, corresponding to the first medical image, in which the appearance of the anatomical structure is modified; and outputting the second medical image. Further, the image processing device is trained using plural teacher images obtained from a second imaging modality that is different from the first imaging modality. In one embodiment, the method also includes processing the first medical image to obtain plural processed images, wherein each of the plural processed images has a corresponding image resolution; applying the plural processed images to respective multi-training artificial neural networks (MTANNs) to obtain plural output images, wherein each MTANN is trained to detect the anatomical structure at one of the corresponding image resolutions; and combining the plural output images to obtain a second medical image in which the appearance of the anatomical structure is enhanced.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
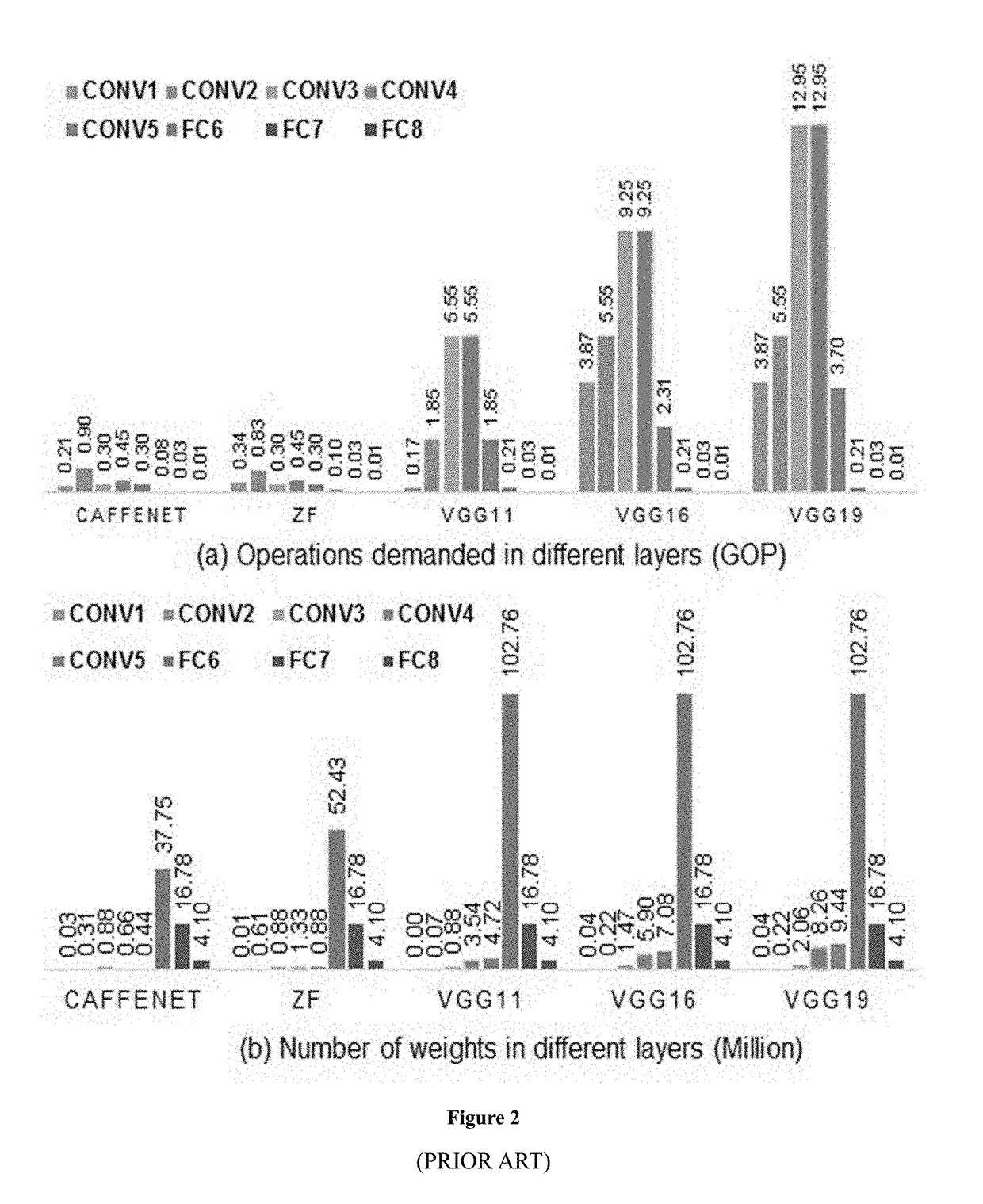
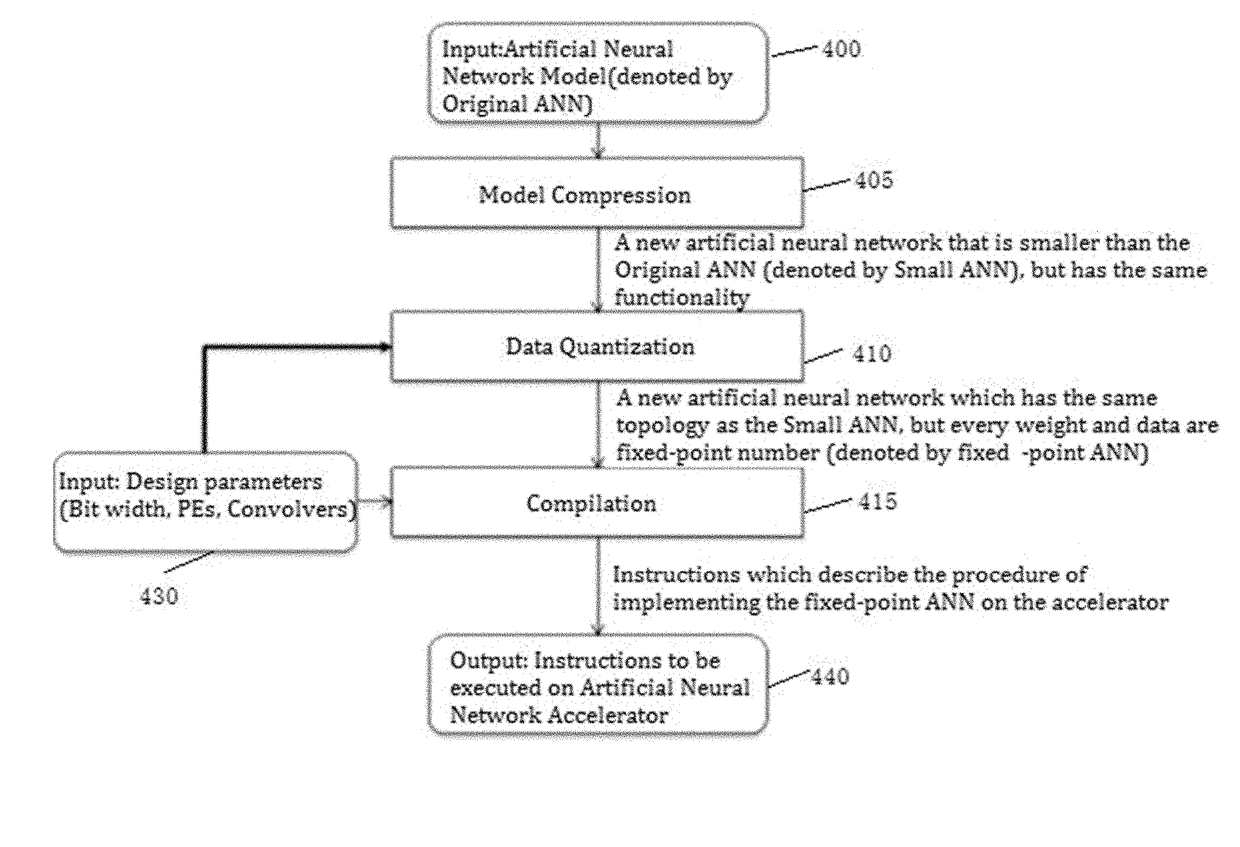
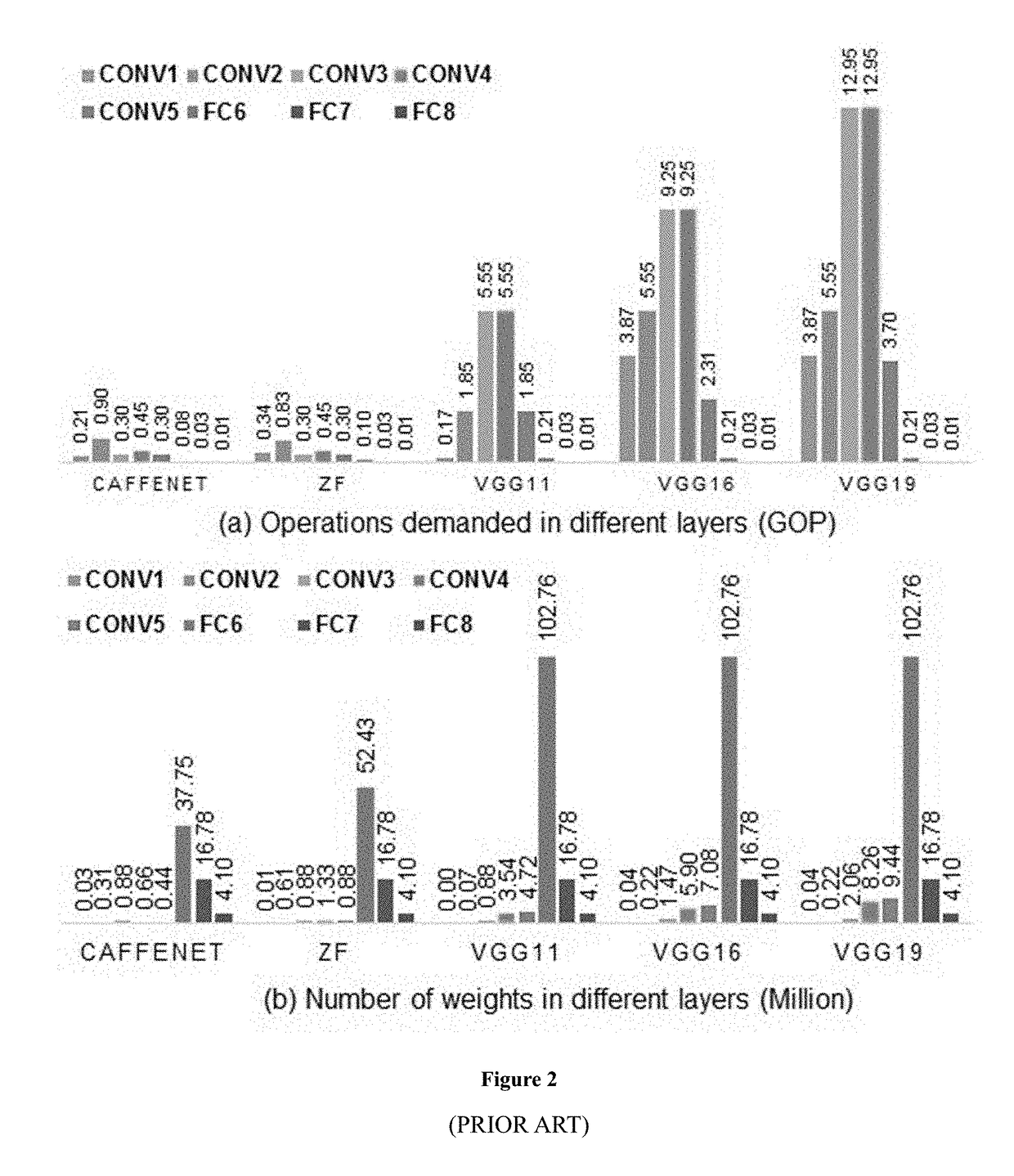
Method for optimizing an artificial neural network (ANN)
ActiveUS20180046894A1Digital data processing detailsSpeech analysisNetwork modelArtificial neural network
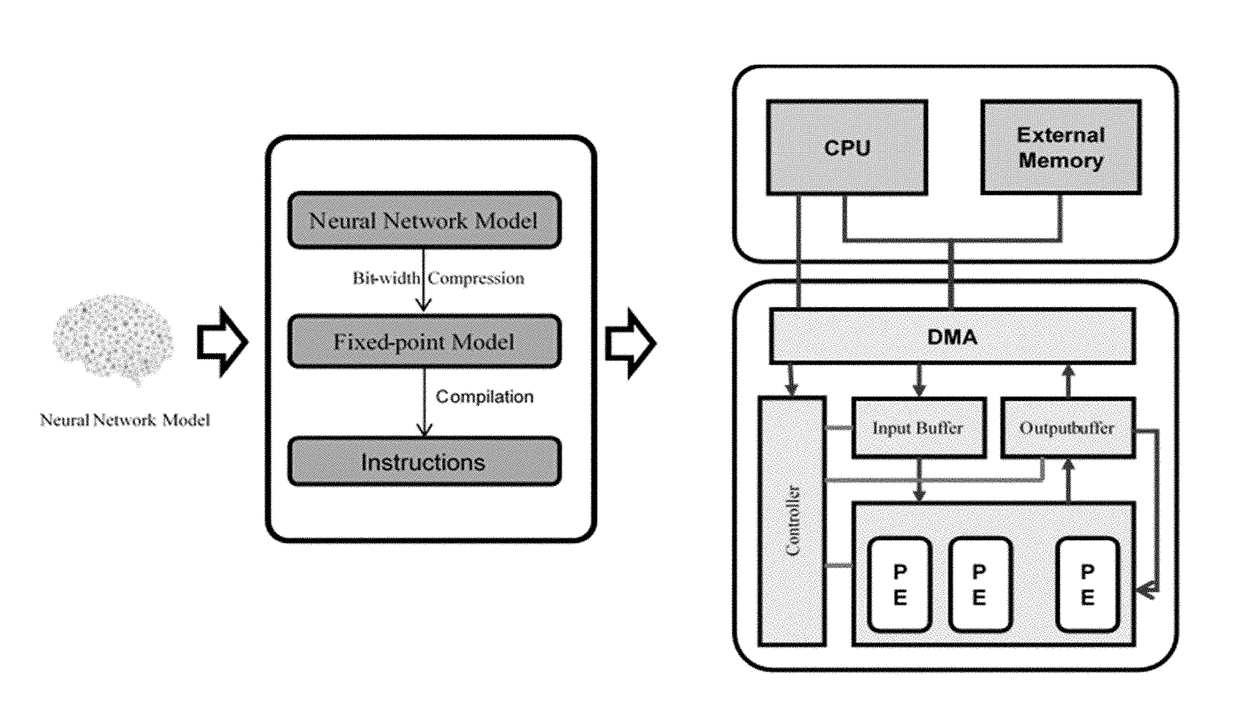
The present invention relates to artificial neural network, for example, convolutional neural network. In particular, the present invention relates to how to implement and optimize a convolutional neural network based on an embedded FPGA. Specifically, it proposes an overall design process of compressing, fix-point quantization and compiling the neural network model.
Owner:XILINX TECH BEIJING LTD
Method and system for detecting malicious behavioral patterns in a computer, using machine learning
InactiveUS20080184371A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer wormTheoretical computer science
Method for detecting malicious behavioral patterns which are related to malicious software such as a computer worm in computerized systems that include data exchange channels with other systems over a data network. According to the proposed method, hardware and / or software parameters that can characterize known behavioral patterns in the computerized system are determined. Known malicious code samples are learned by a machine learning process, such as decision trees, Naïve Bayes, Bayesian Networks, and artificial neural networks, and the results of the machine learning process are analyzed in respect to these behavioral patterns. Then, known and unknown malicious code samples are identified according to the results of the machine learning process.
Owner:DEUTSCHE TELEKOM AG
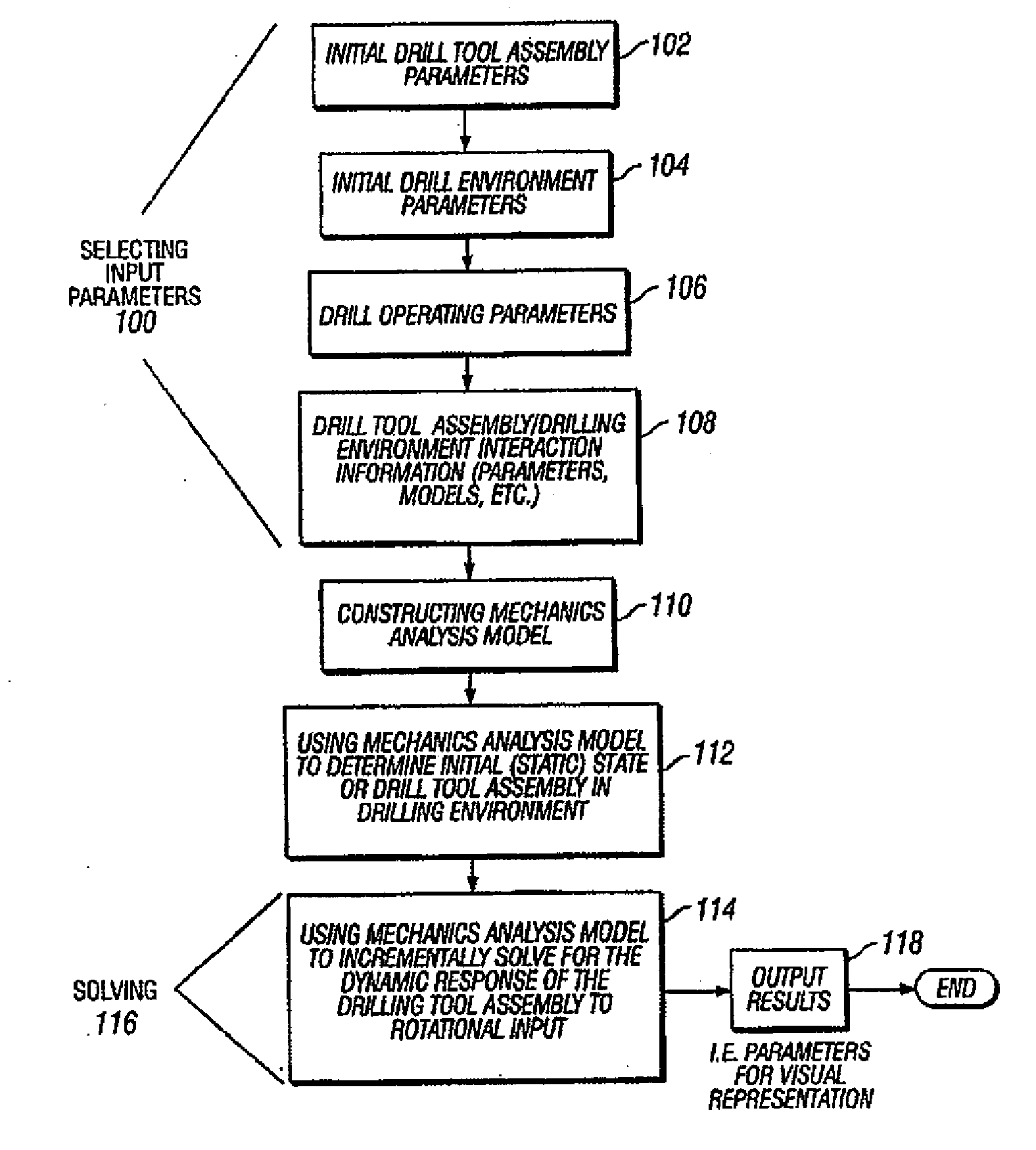
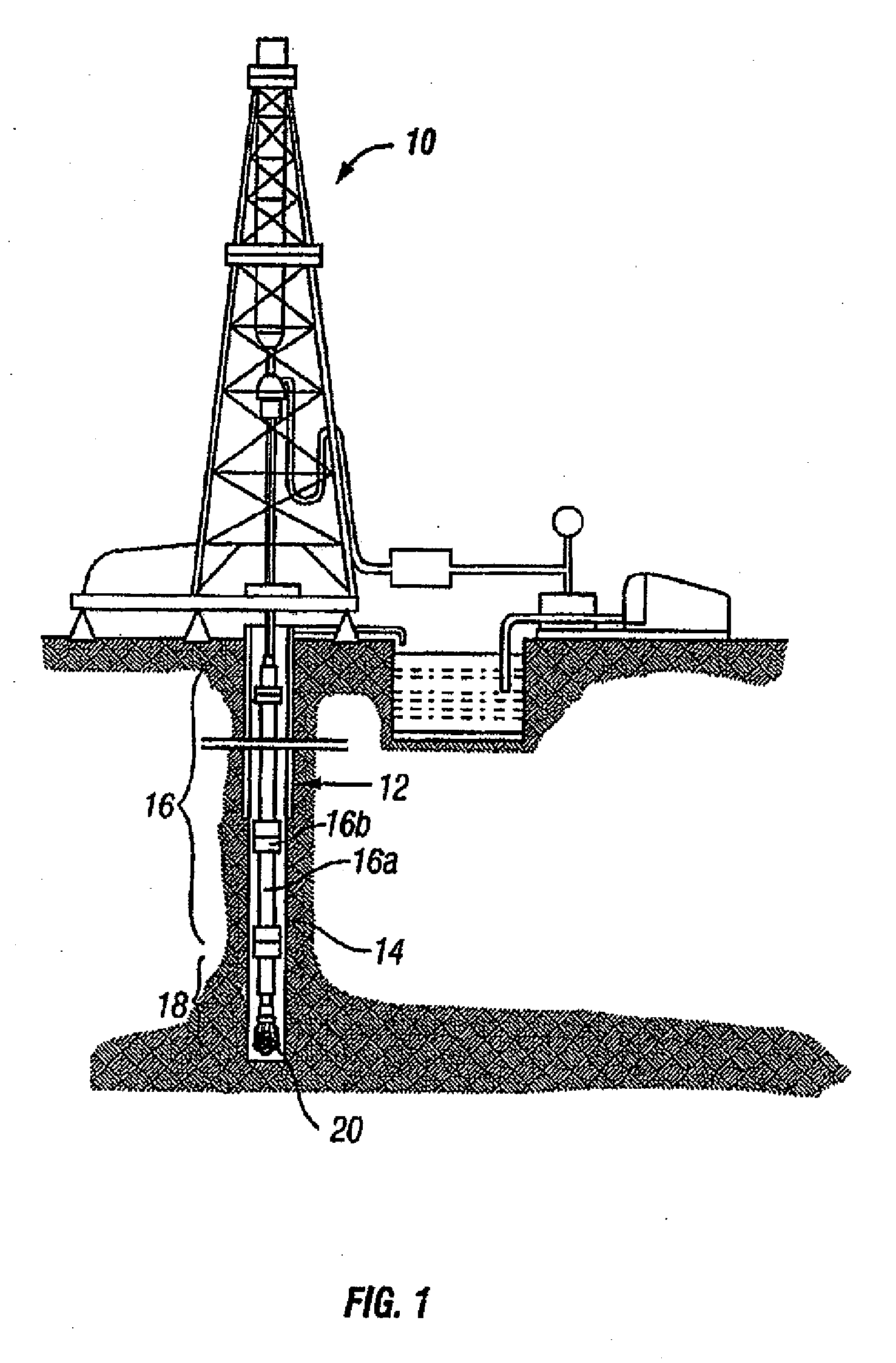
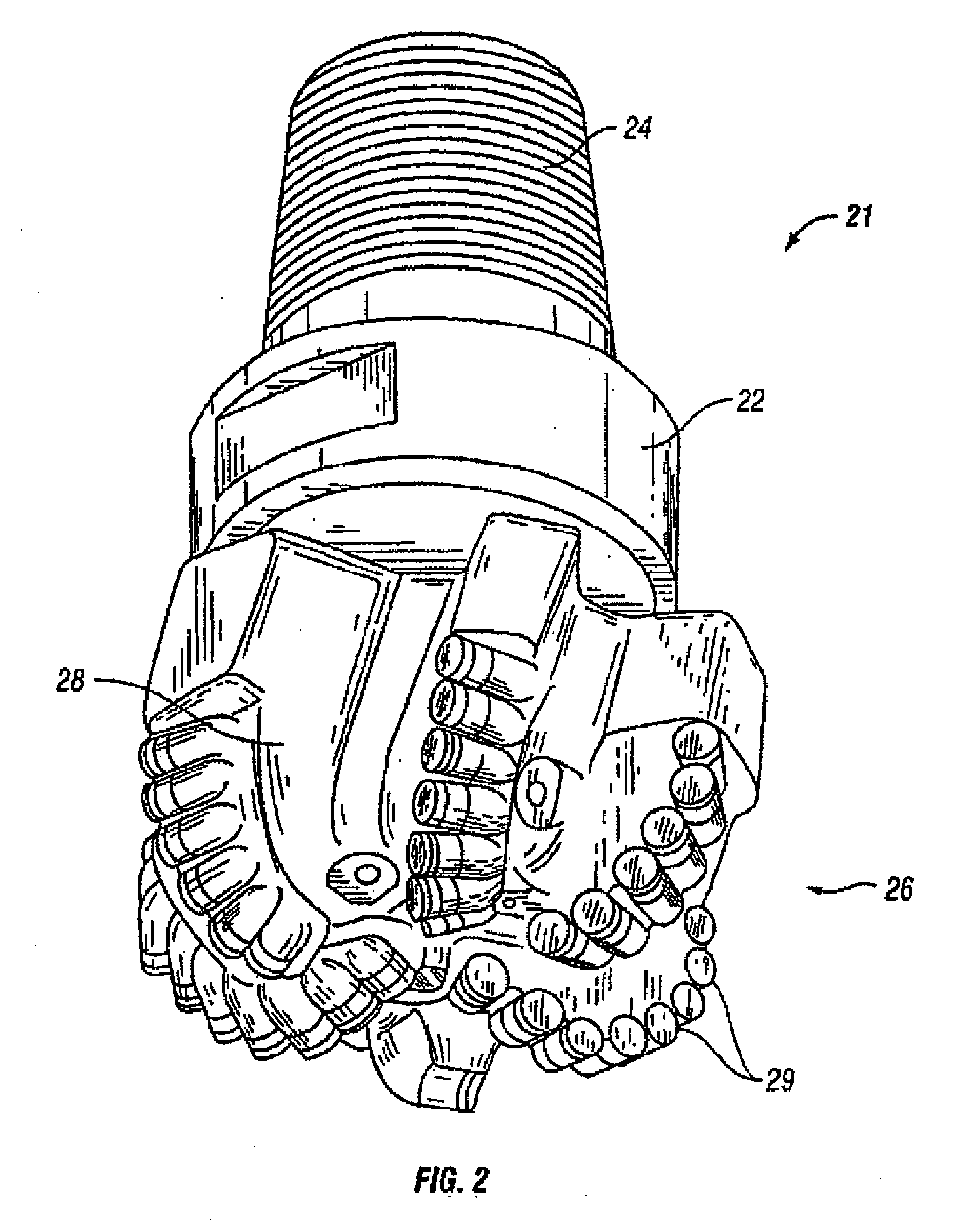
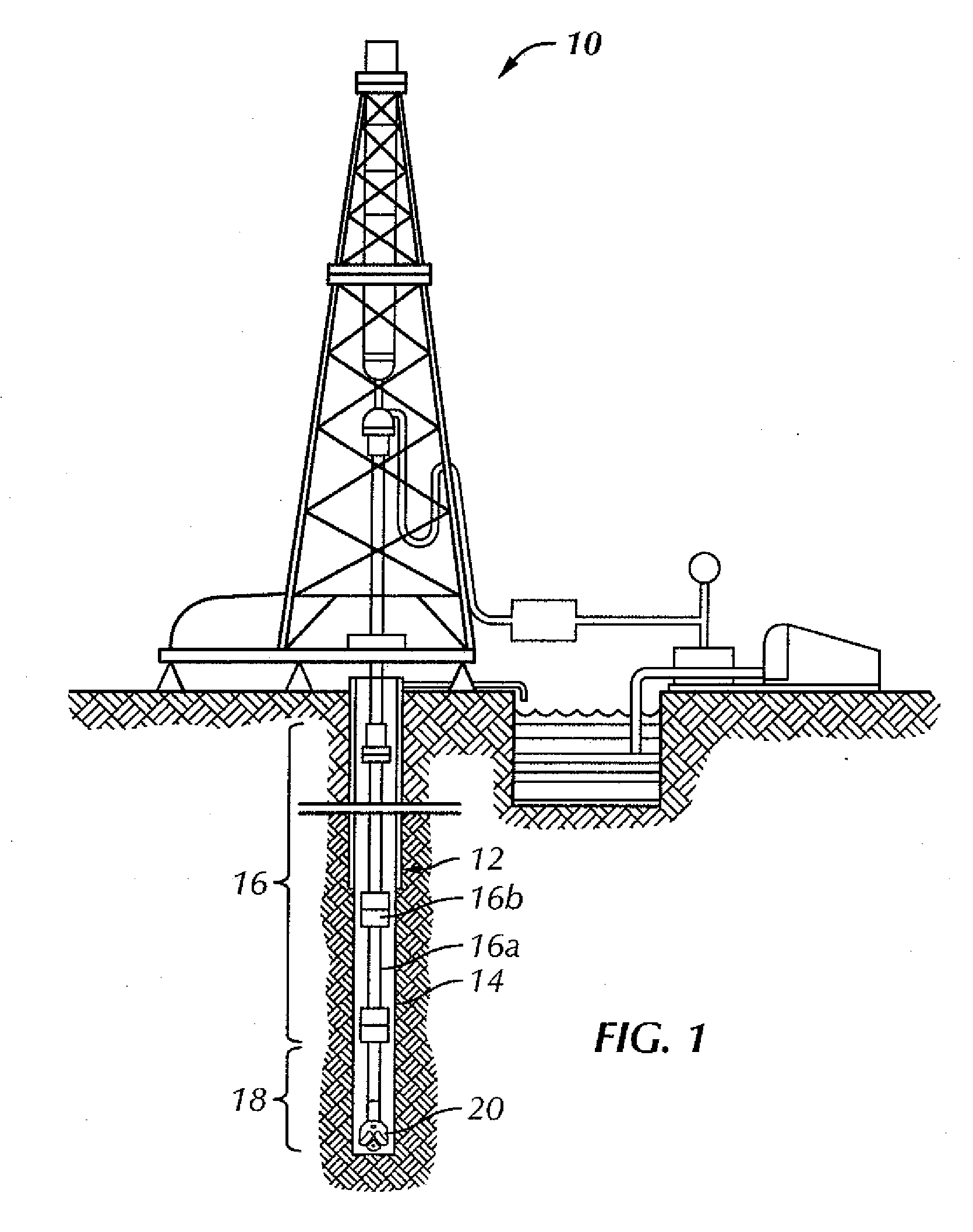
Method of real-time drilling simulation
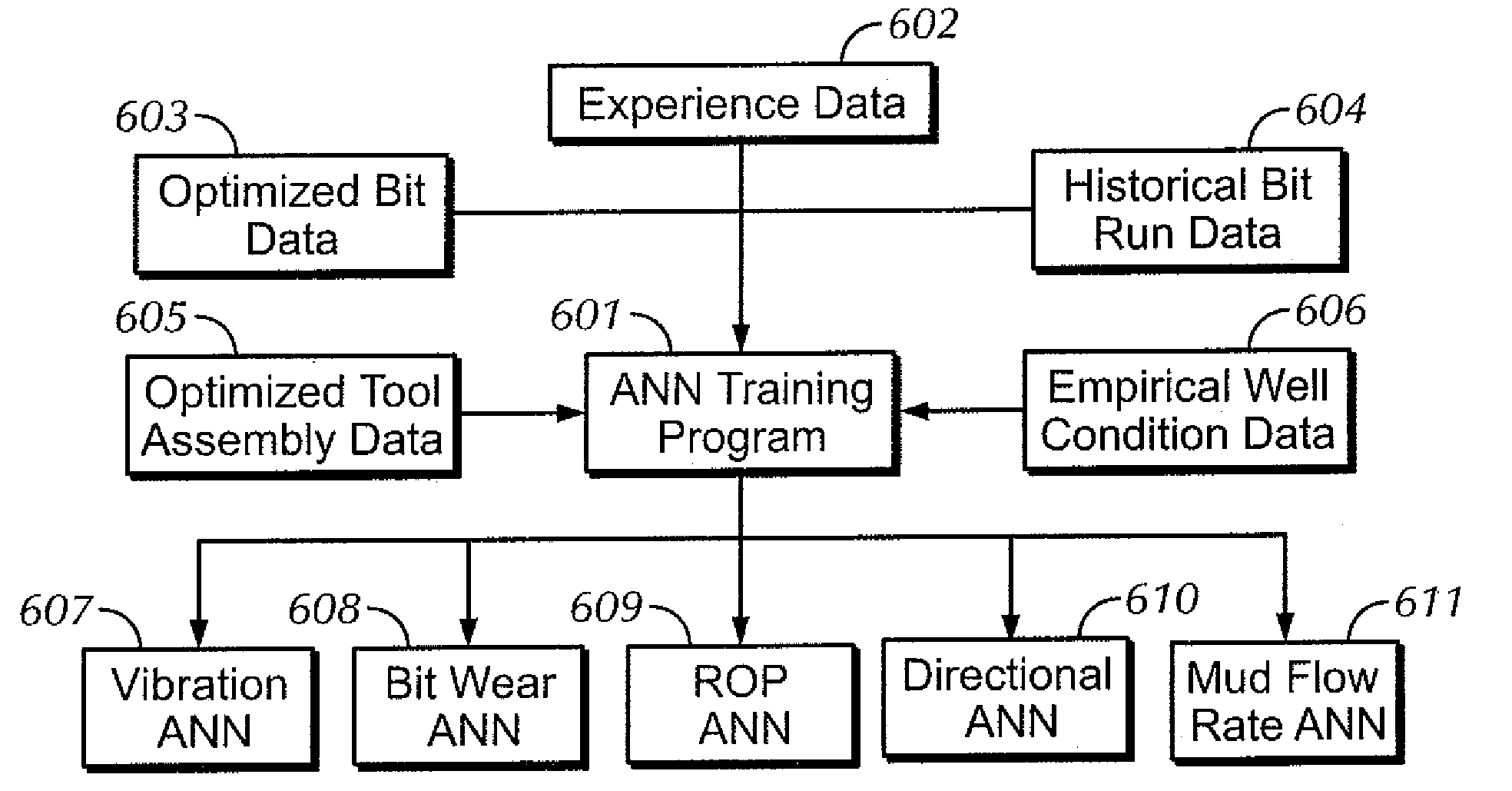
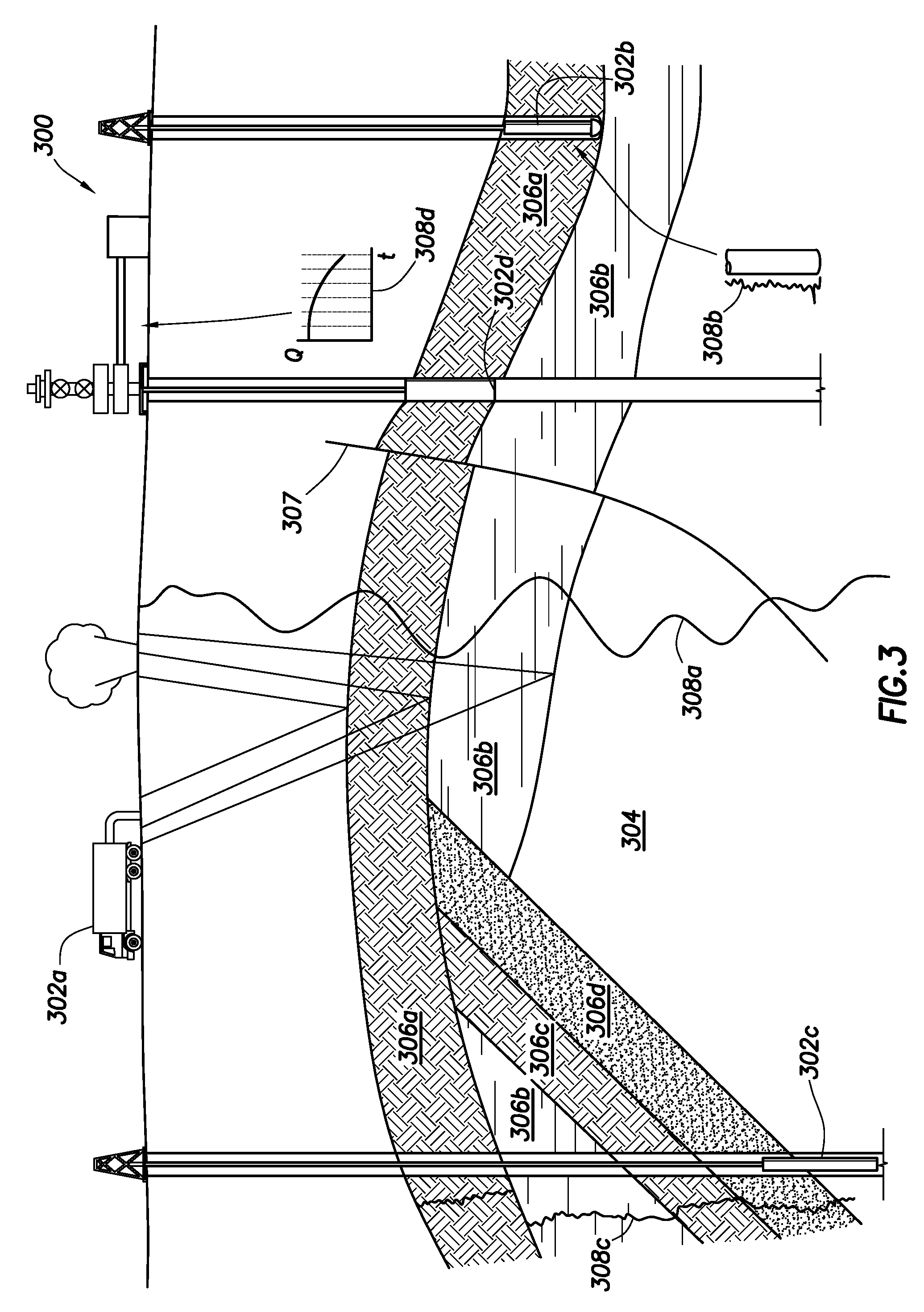
A method of optimizing drilling including identifying design parameters for a drilling tool assembly, preserving the design parameters as experience data, and training at least one artificial neural network using the experience data. The method also includes collecting real-time data from the drilling operation, analyzing the real-time data with a real-time drilling optimization system, and determining optimal drilling parameters based on the analyzing the real-time date with the real-time drilling optimization system. Also, a method for optimizing drilling in real-time including collecting real-time data from a drilling operation and comparing the real-time data against predicted data in a real-time optimization system, wherein the real-time optimization includes at least one artificial neural network. The method further includes determining optimal drilling parameters based on the comparing the real-time data with the predicted data in the real-time drilling optimization system.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
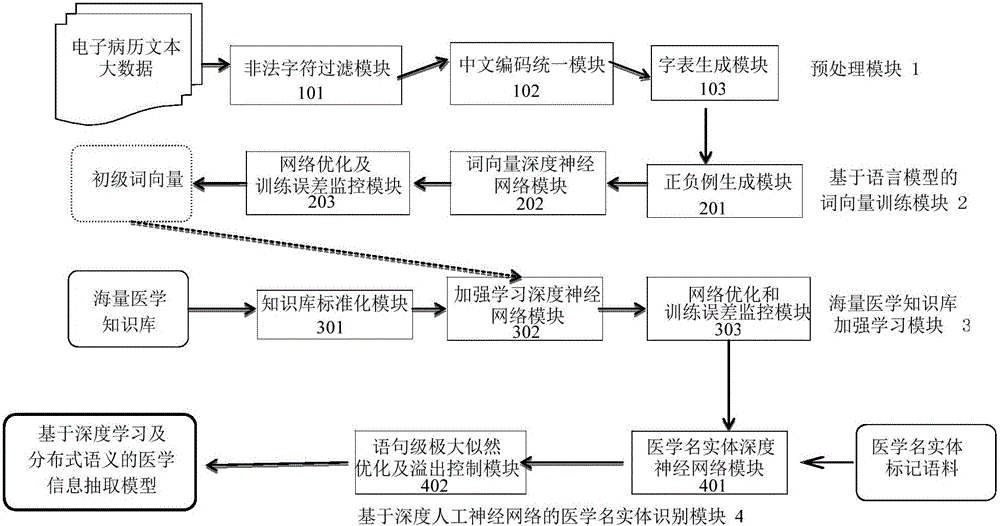
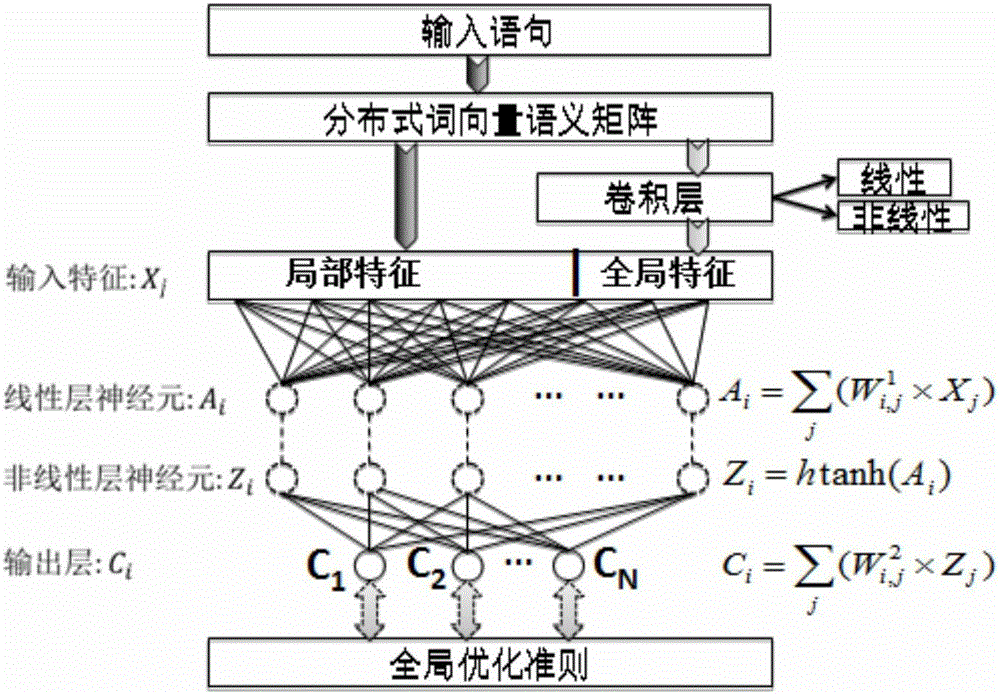
Medical information extraction system and method based on depth learning and distributed semantic features
ActiveCN105894088AAvoid floating point overflow problemsHigh precisionNeural learning methodsNerve networkStudy methods
he invention discloses a medical information extraction system and method based on depth learning and distributed semantic features. The system is composed of a pretreatment module, a linguistic-model-based word vector training module, a massive medical knowledge base reinforced learning module, and a depth-artificial-neural-network-based medical term entity identification module. With a depth learning method, generation of the probability of a linguistic model is used as an optimization objective; and a primary word vector is trained by using medical text big data; on the basis of the massive medical knowledge base, a second depth artificial neural network is trained, and the massive knowledge base is combined to the feature leaning process of depth learning based on depth reinforced learning, so that distributed semantic features for the medical field are obtained; and then Chinese medical term entity identification is carried out by using the depth learning method based on the optimized statement-level maximum likelihood probability. Therefore, the word vector is generated by using lots of unmarked linguistic data, so that the tedious feature selection and optimization adjustment process during medical natural language process can be avoided.
Owner:神州医疗科技股份有限公司 +1
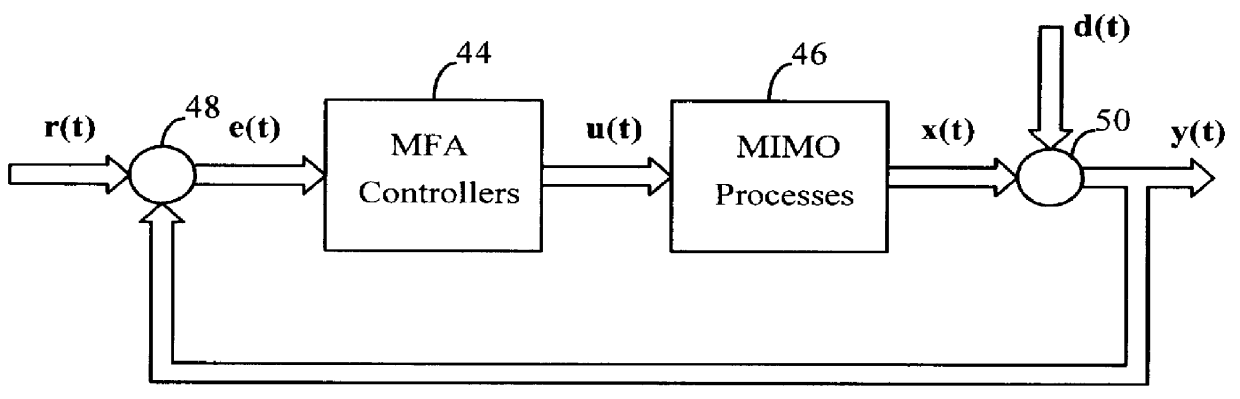
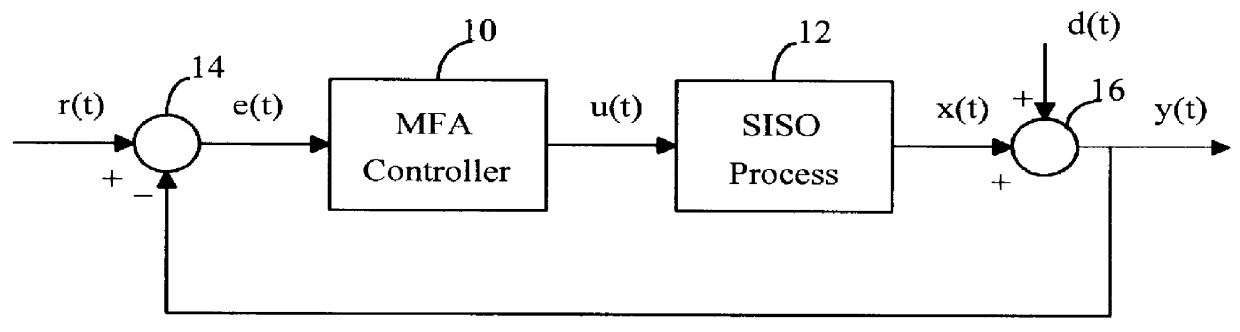
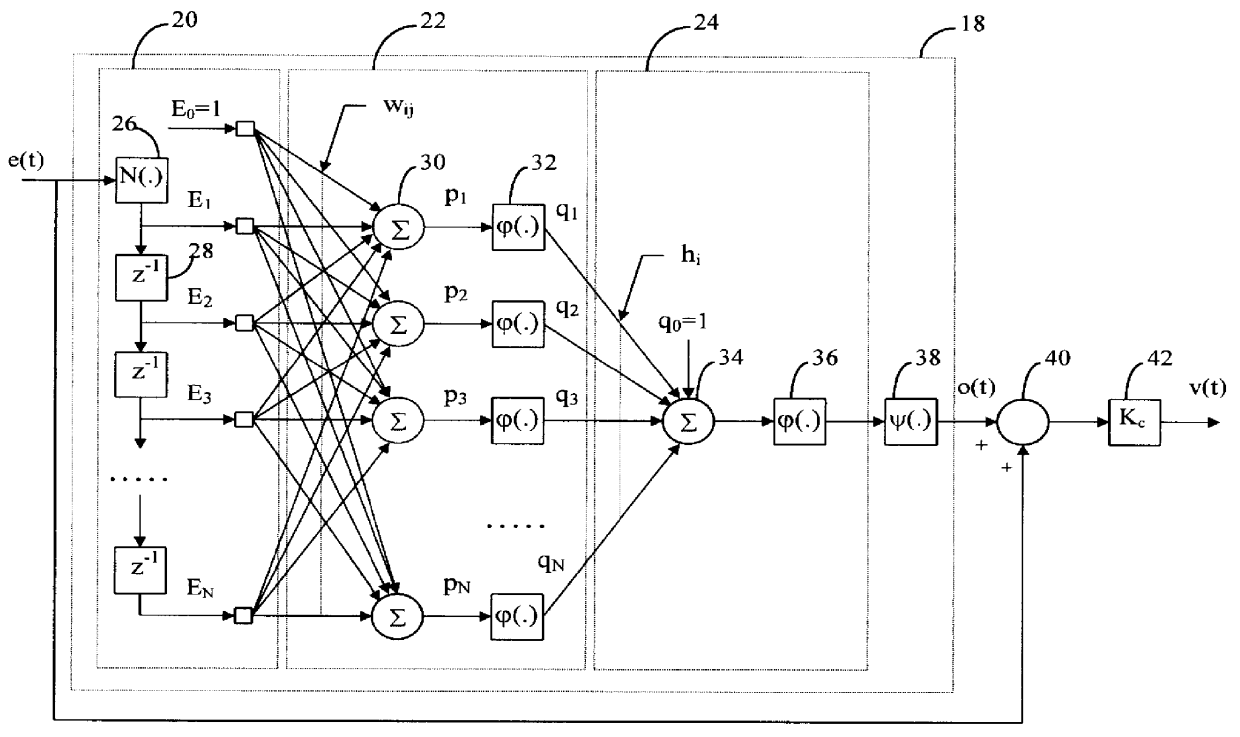
Model-free adaptive process control
InactiveUS6055524ALong response delayOvercome limitationsDigital computer detailsDigital dataData miningSelf adaptive
A model-free adaptive controller is disclosed, which uses a dynamic artificial neural network with a learning algorithm to control any single-variable or multivariable open-loop stable, controllable, and consistently direct-acting or reverse-acting industrial process without requiring any manual tuning, quantitative knowledge of the process, or process identifiers. The need for process knowledge is avoided by substituting 1 for the actual sensitivity function .differential.y(t) / .differential.u(t) of the process.
Owner:GEN CYBERNATION GROUP
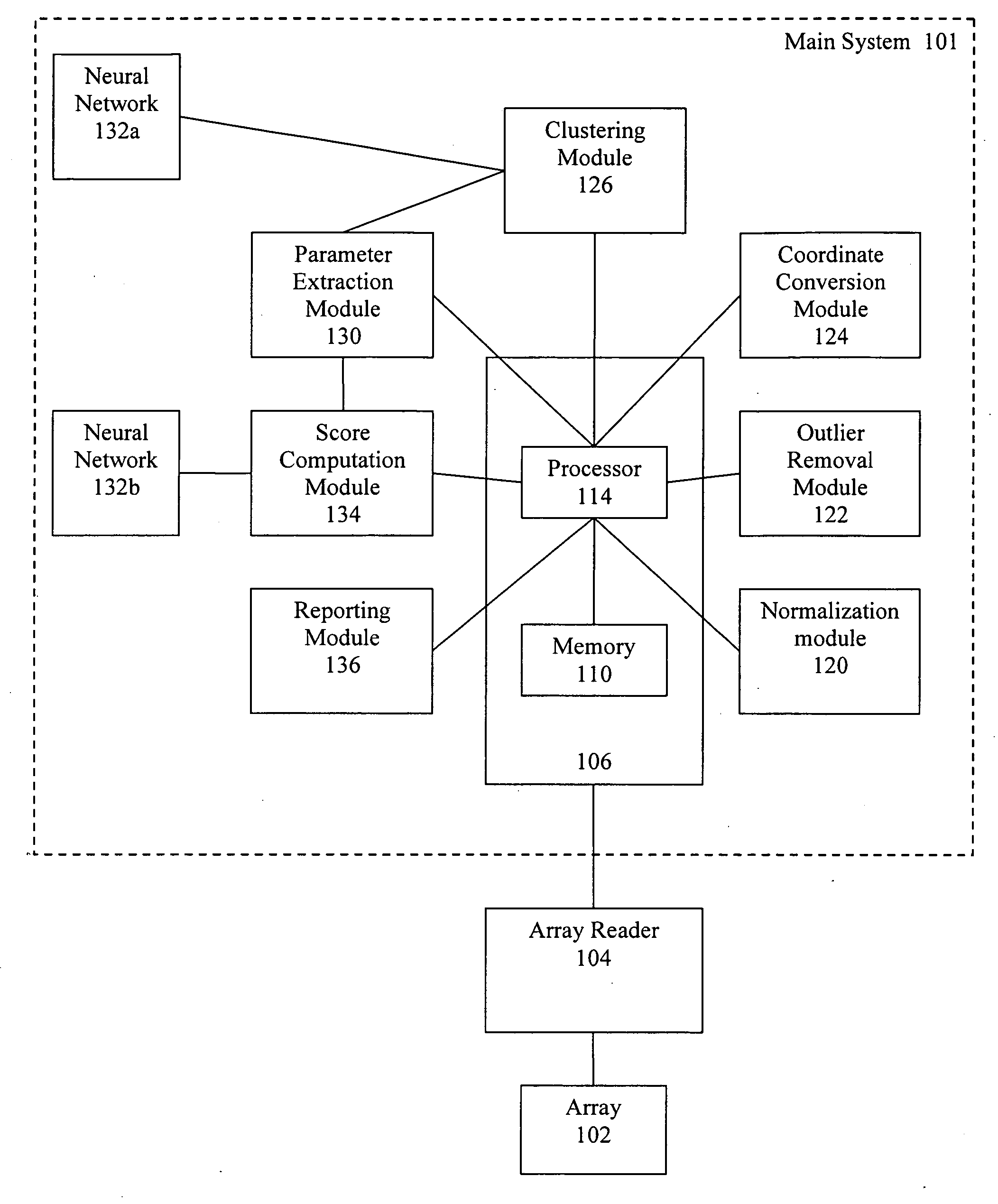
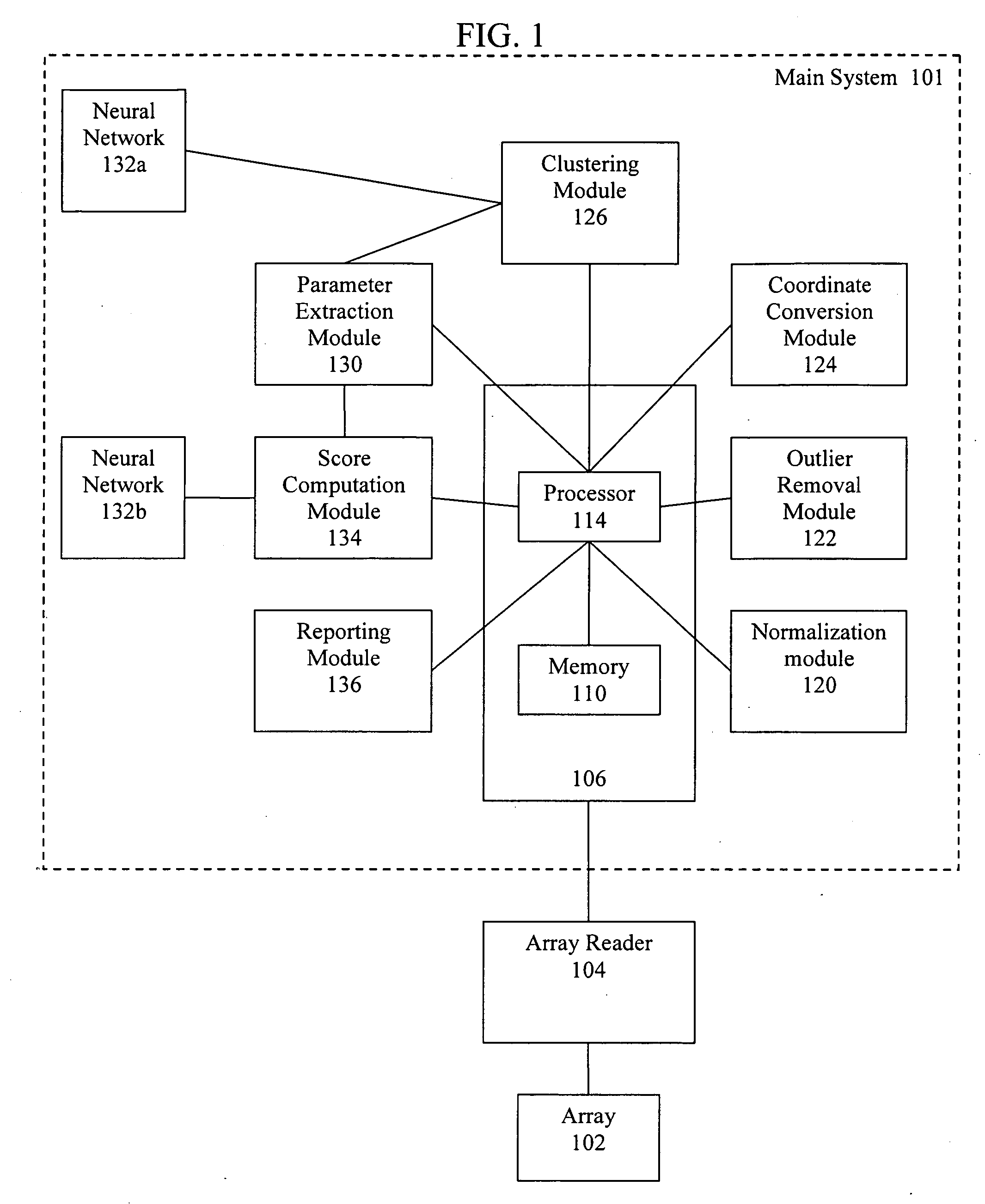
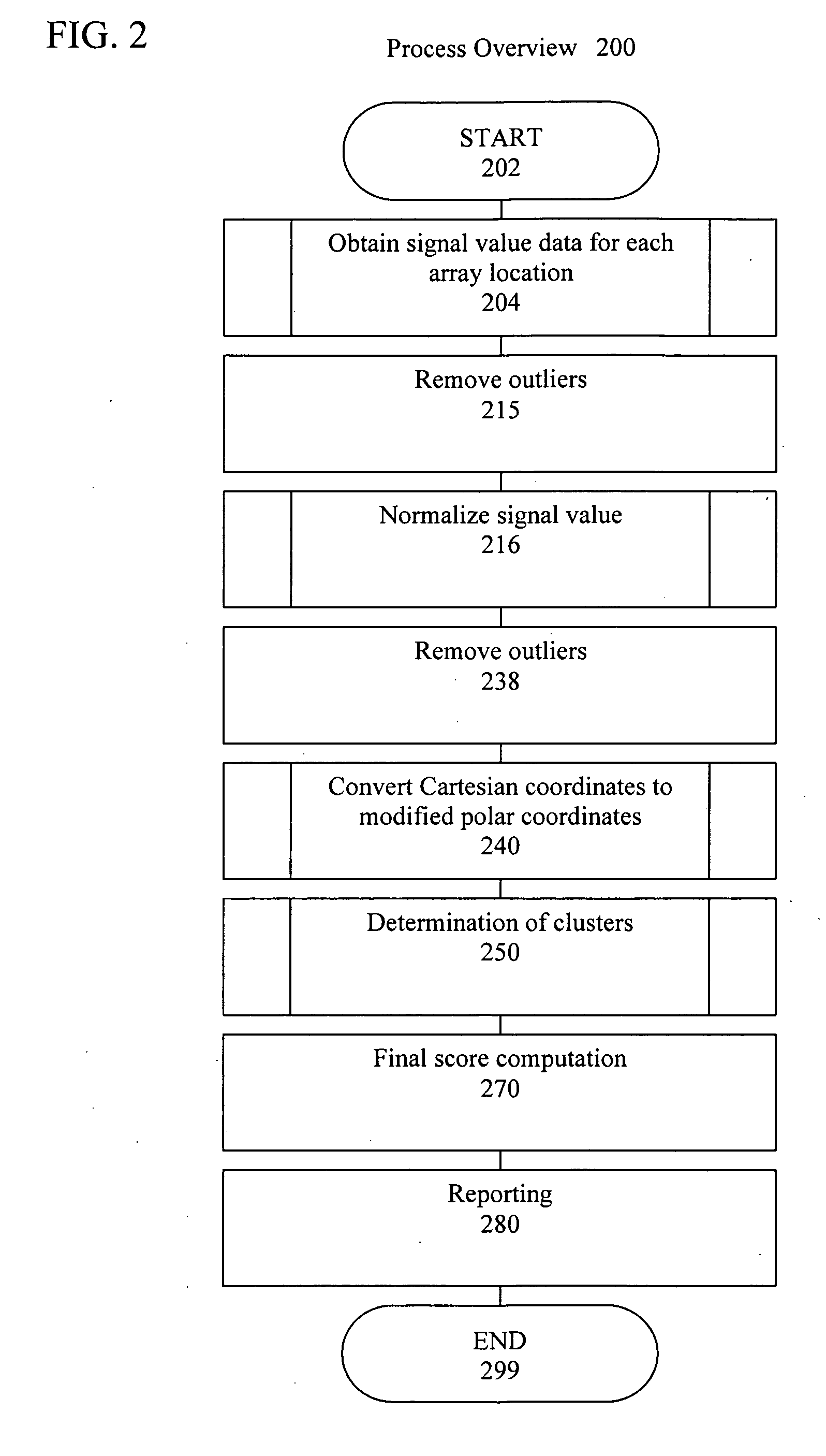
Artificial intelligence and global normalization methods for genotyping
Described herein are systems and methods for normalizing data without the use of external controls. Also described herein are systems and methods for analyzing cluster data, such as genotyping data, using an artificial neural network.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Digital object recognition audio-assistant for the visually impaired
InactiveUS20050208457A1Character and pattern recognitionTeaching apparatusDECIPHERVisually Impaired Persons
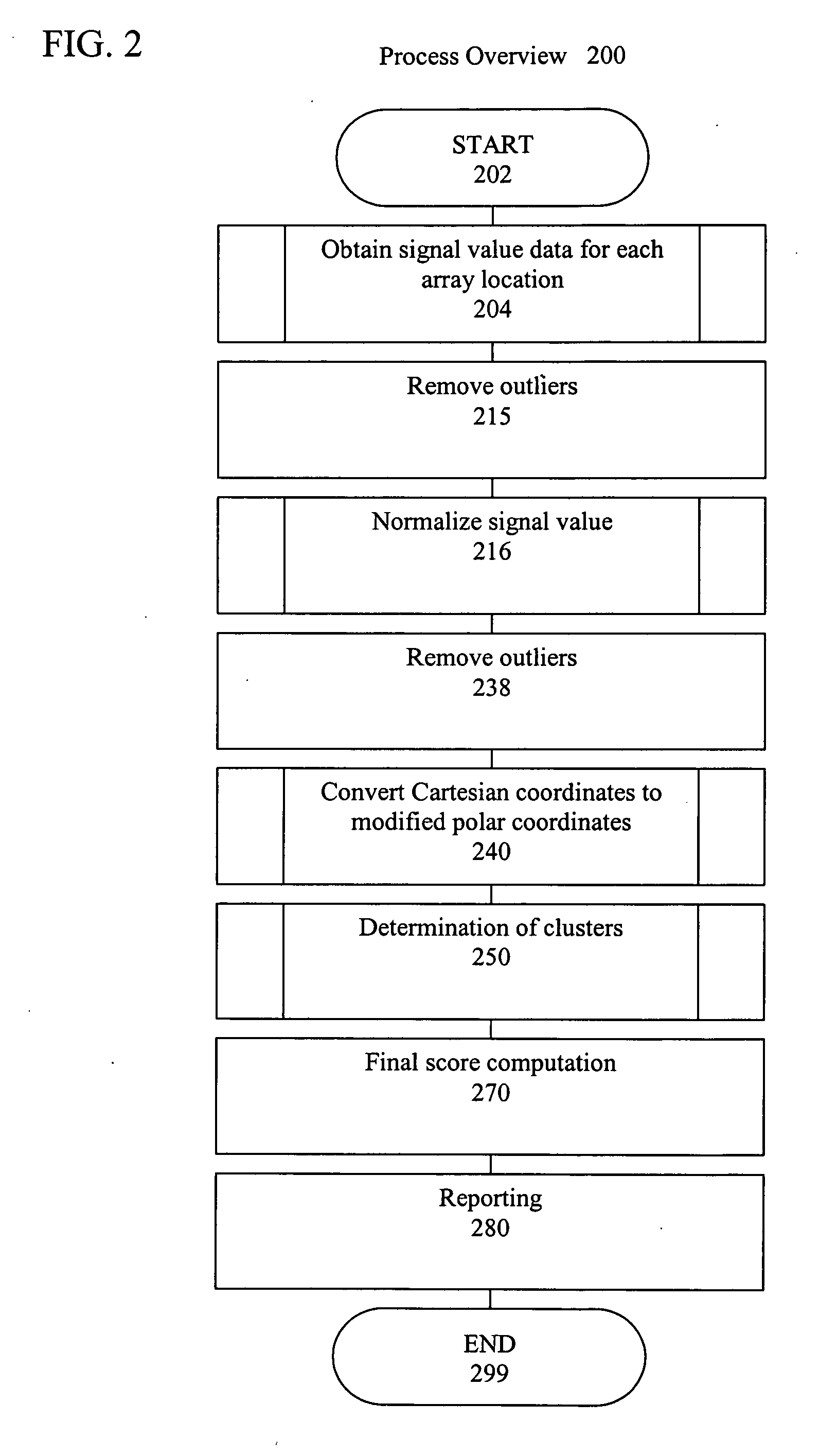
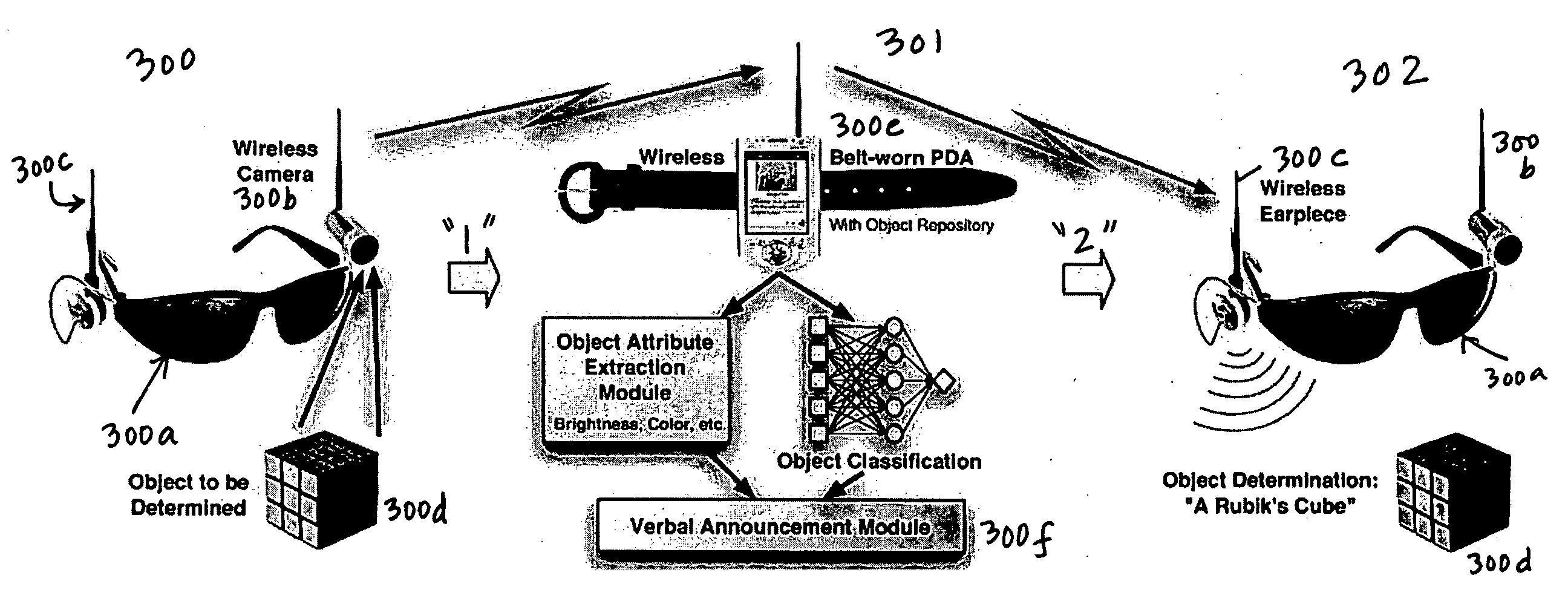
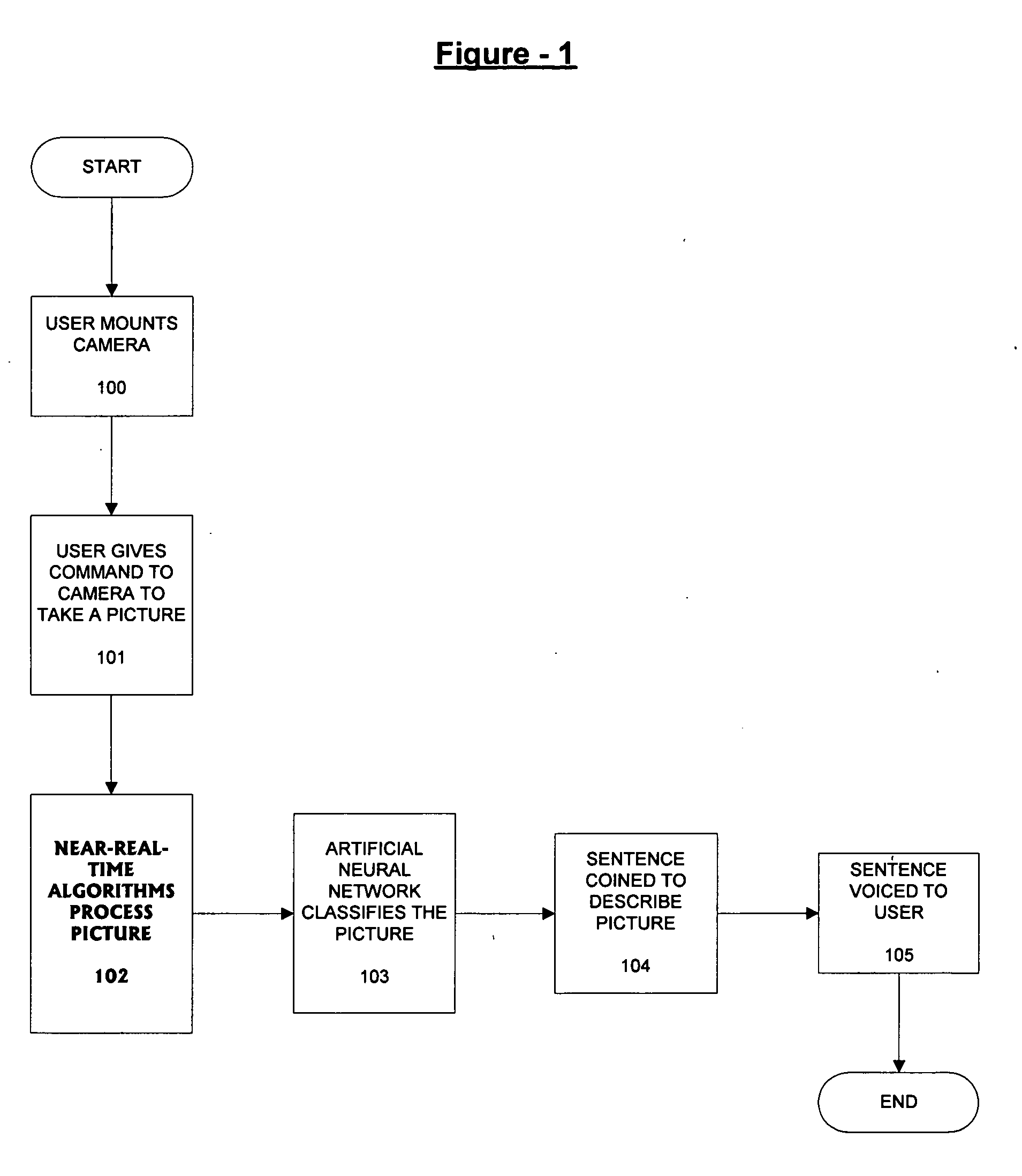
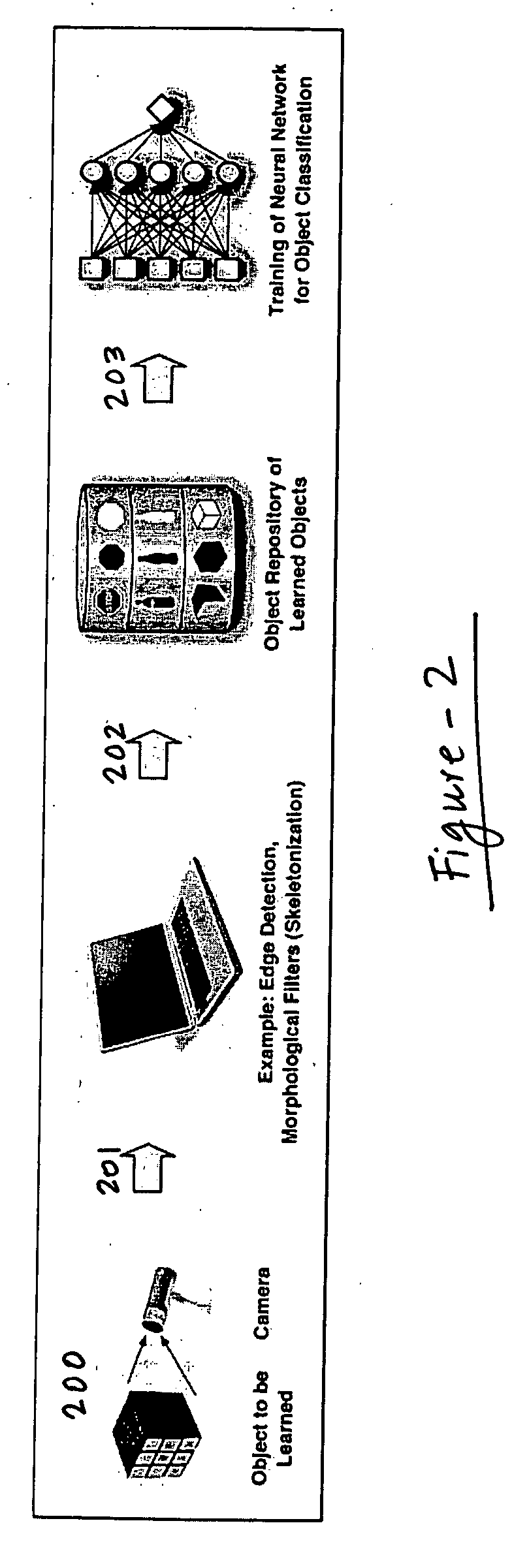
A camera-based object detection system for a severely visually impaired or blind person consisting a digital camera mounted on the person's eyeglass or head that takes images on demand. Near-real time image processing algorithms decipher certain attributes of the captured image by processing it for edge pattern detection within a central region of the image. The results are classified by artificial neural networks trained on a list of known objects, in a look up table, or by a threshold. Once the pattern is classified a descriptive sentence is constructed of the object and its certain attributes and a computer-based voice synthesizer is used to verbally announce the descriptive sentence. The invention is used to determine the size of an object, or its distance from another object, and can be used in conjunction with an IR-sensitive camera to provide “sight” in poor visibility conditions, or at night.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Deep processing unit (DPU) for implementing an artificial neural network (ANN)
The present invention relates to artificial neural network, for example, convolutional neural network. In particular, the present invention relates to how to implement and optimize a convolutional neural network based on an embedded FPGA. Specifically, it proposes a CPU+FPGA heterogeneous architecture to accelerate ANNs.
Owner:XILINX TECH BEIJING LTD
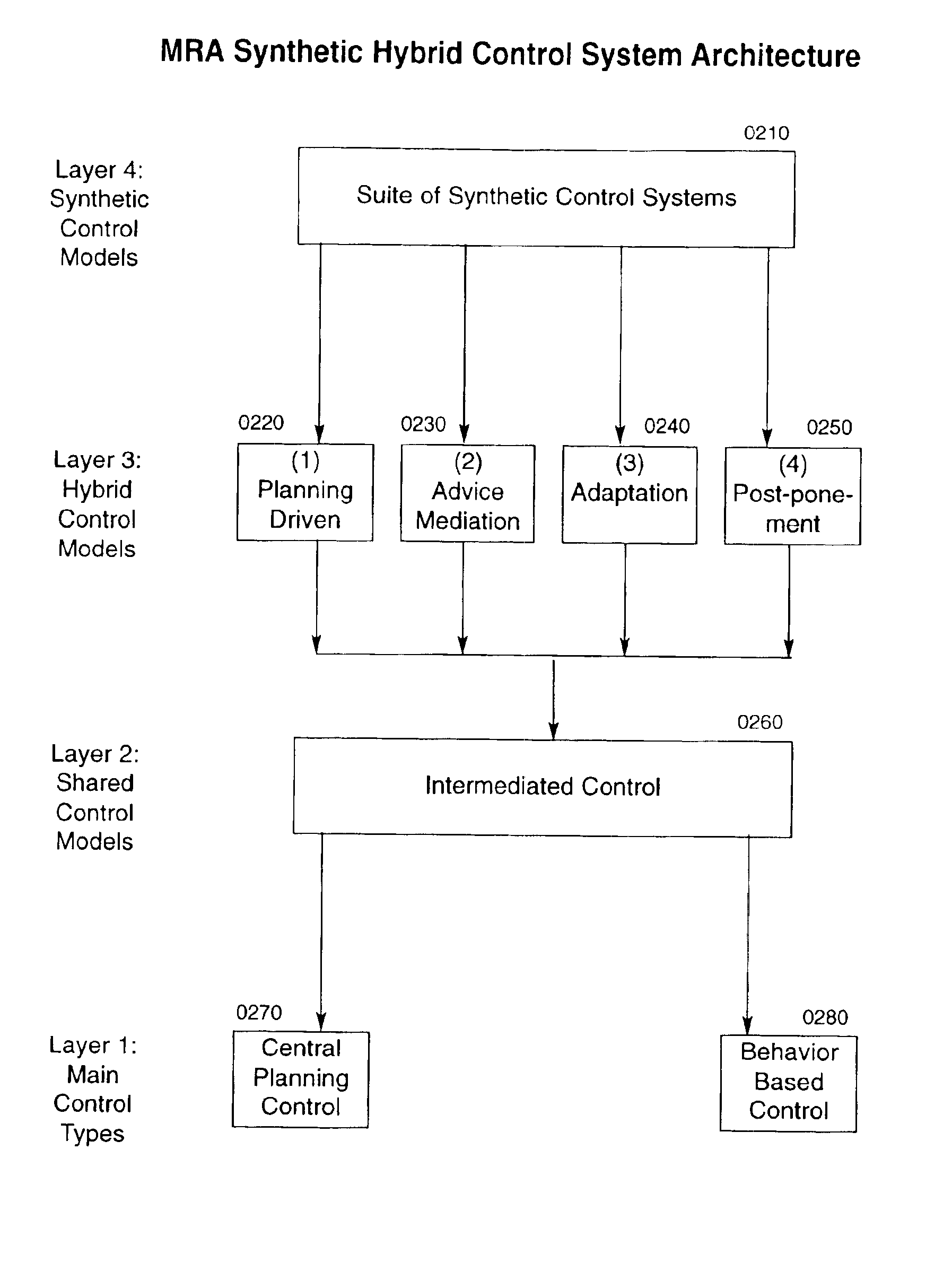
System, method and apparatus for organizing groups of self-configurable mobile robotic agents in a multi-robotic system
InactiveUS6904335B2Severe resource restrictionComplex behaviorProgramme-controlled manipulatorAutonomous decision making processRobotic systemsMultirobot systems
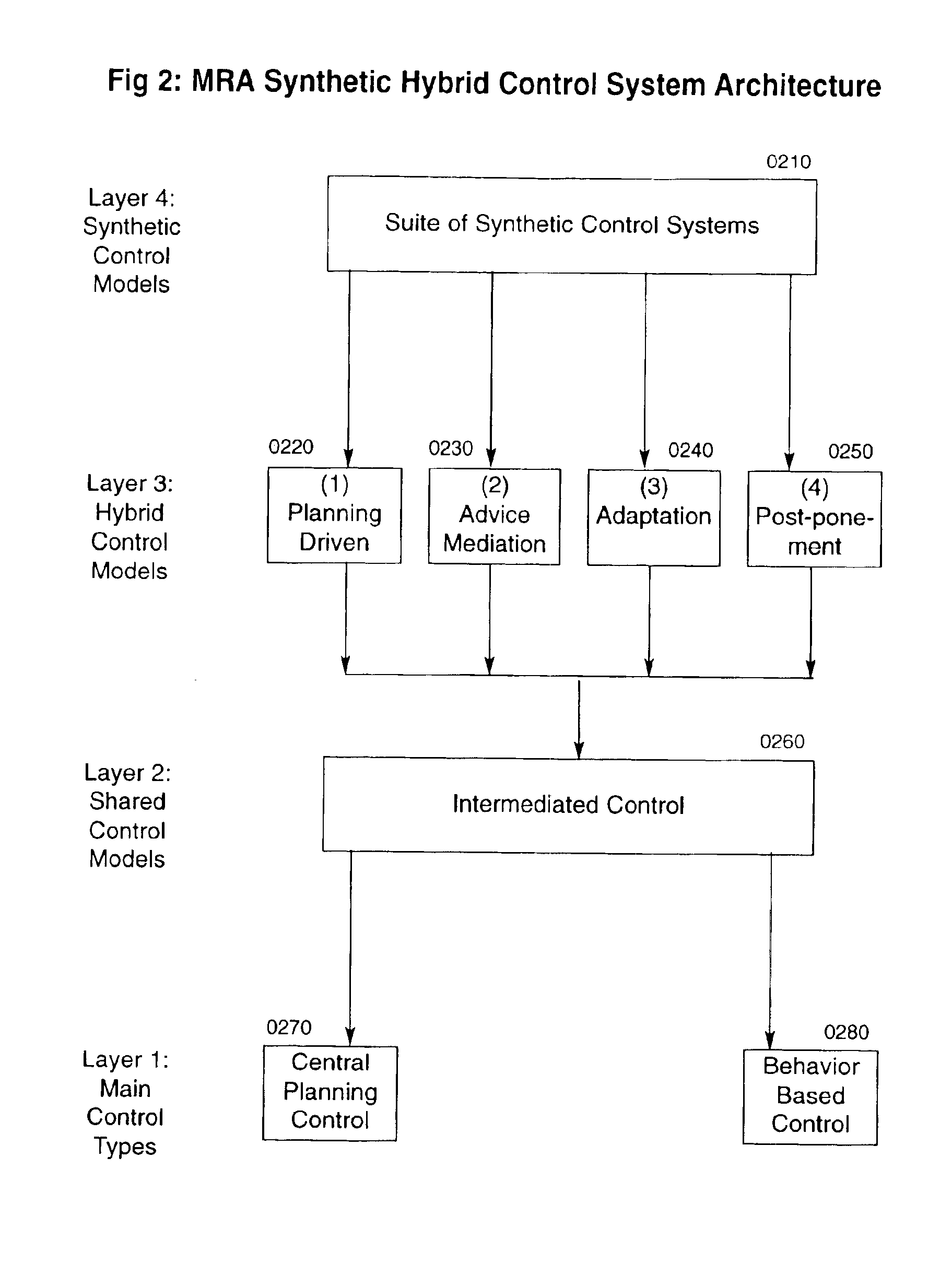
A system of self-organizing mobile robotic agents (MRAs) in a multi-robotic system (MRS) is disclosed. MRAs cooperate, learn and interact with the environment. The system uses various AI technologies including genetic algorithms, genetic programming and evolving artificial neural networks to develop emergent dynamic behaviors. The collective behaviors of autonomous intelligent robotic agents are applied to numerous applications. The system uses hybrid control architectures. The system also develops dynamic coalitions of groups of autonomous MRAs for formation and reformation in order to perform complex tasks.
Owner:SOLOMON RES
Signal processing method and system for noise removal and signal extraction
InactiveUS7519488B2Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainDecomposition
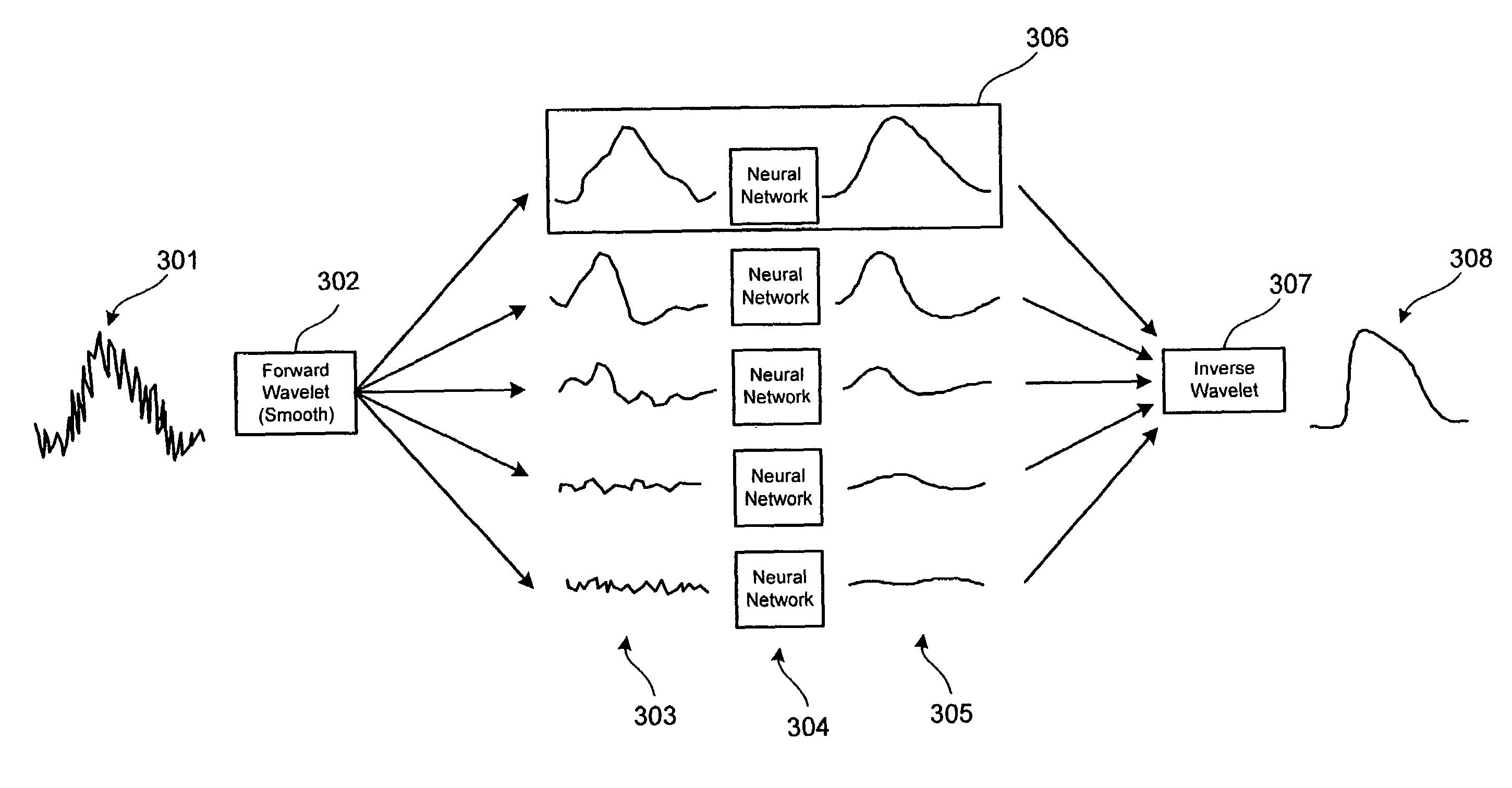
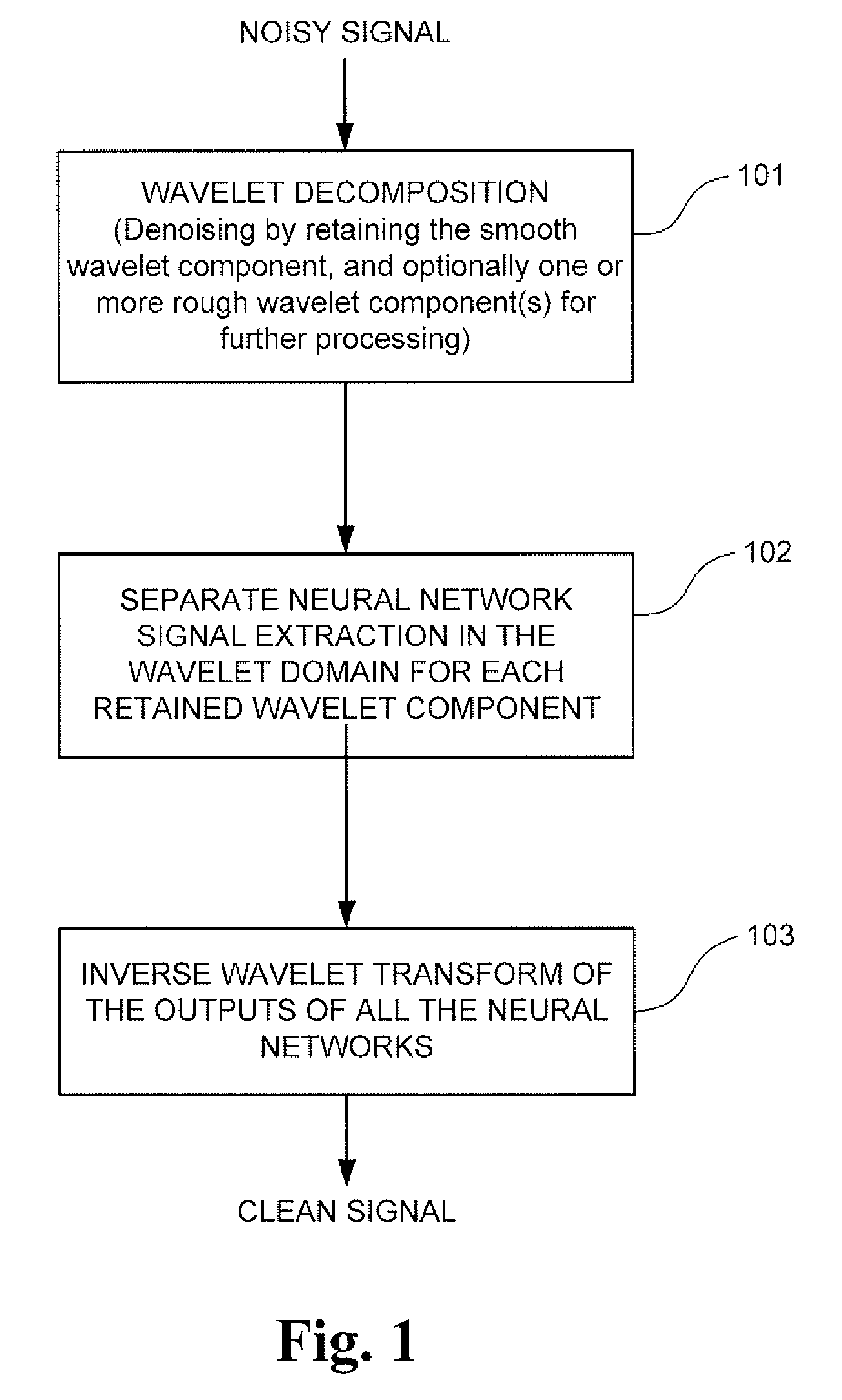
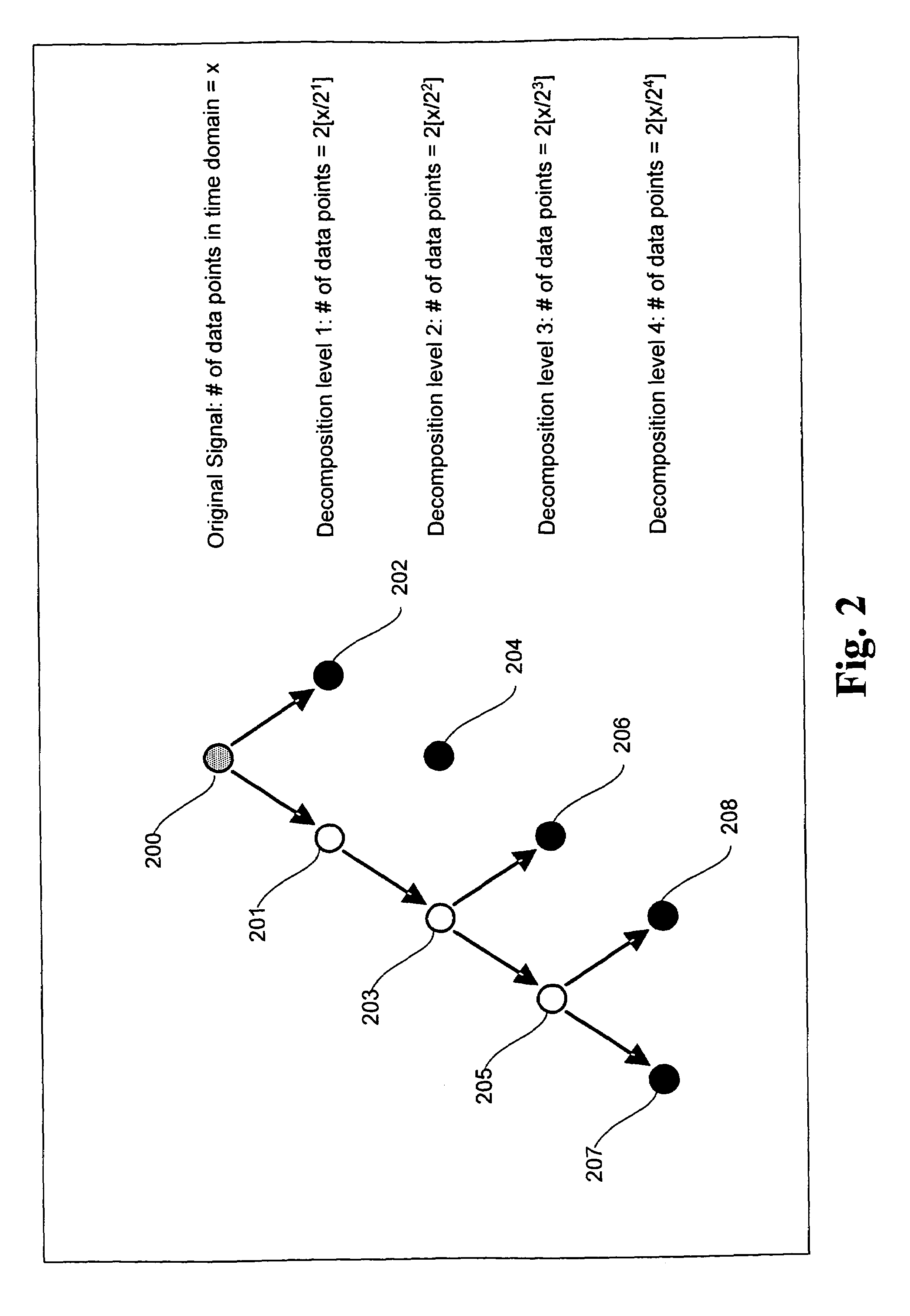
A signal processing method and system combining smooth level wavelet pre-processing together with artificial neural networks all in the wavelet domain for signal denoising and extraction. Upon receiving a signal corrupted with noise, an n-level decomposition of the signal is performed using a discrete wavelet transform to produce a smooth component and a rough component for each decomposition level. The nth level smooth component is then inputted into a corresponding neural network pre-trained to filter out noise in that component by pattern recognition in the wavelet domain. Additional rough components, beginning at the highest level, may also be retained and inputted into corresponding neural networks pre-trained to filter out noise in those components also by pattern recognition in the wavelet domain. In any case, an inverse discrete wavelet transform is performed on the combined output from all the neural networks to recover a clean signal back in the time domain.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
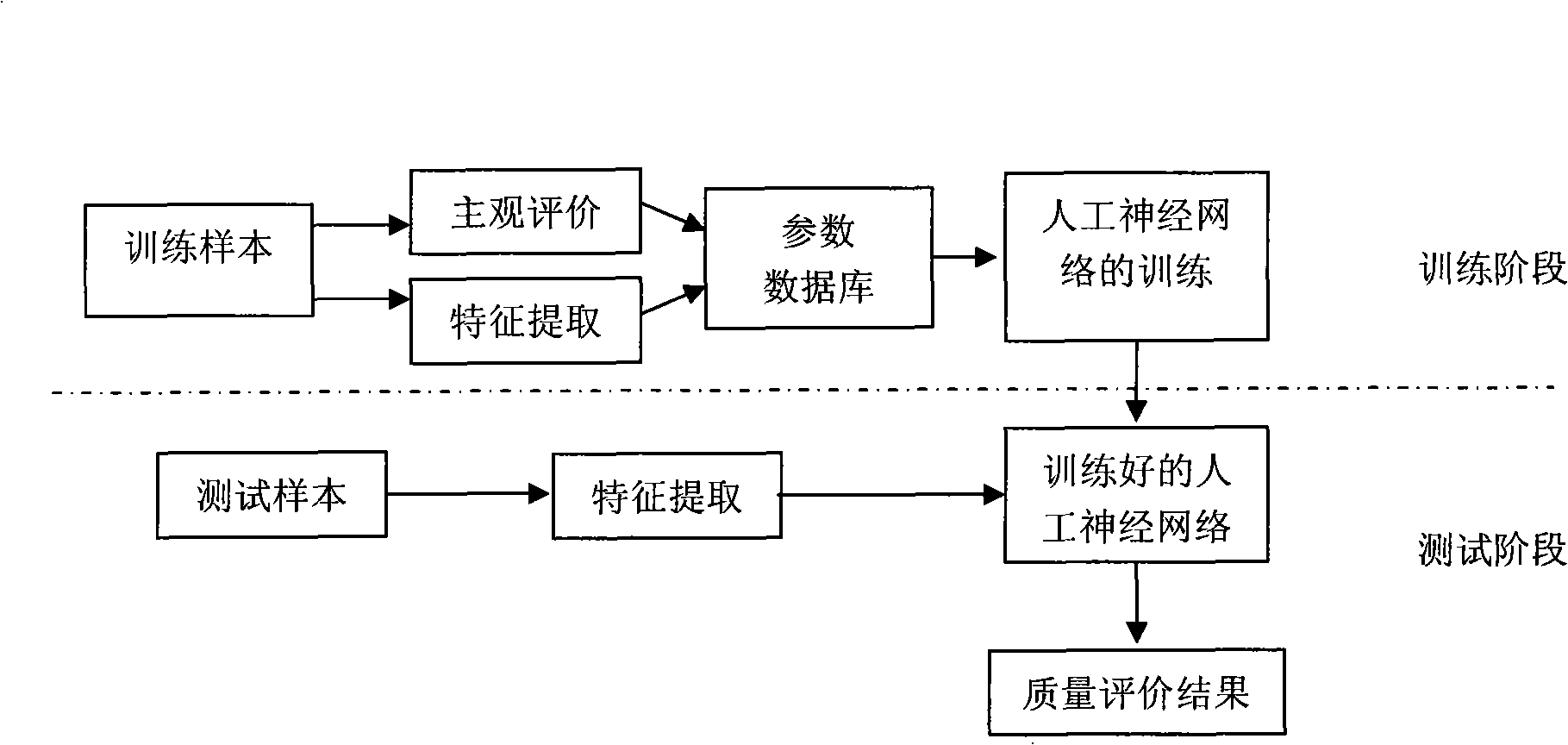
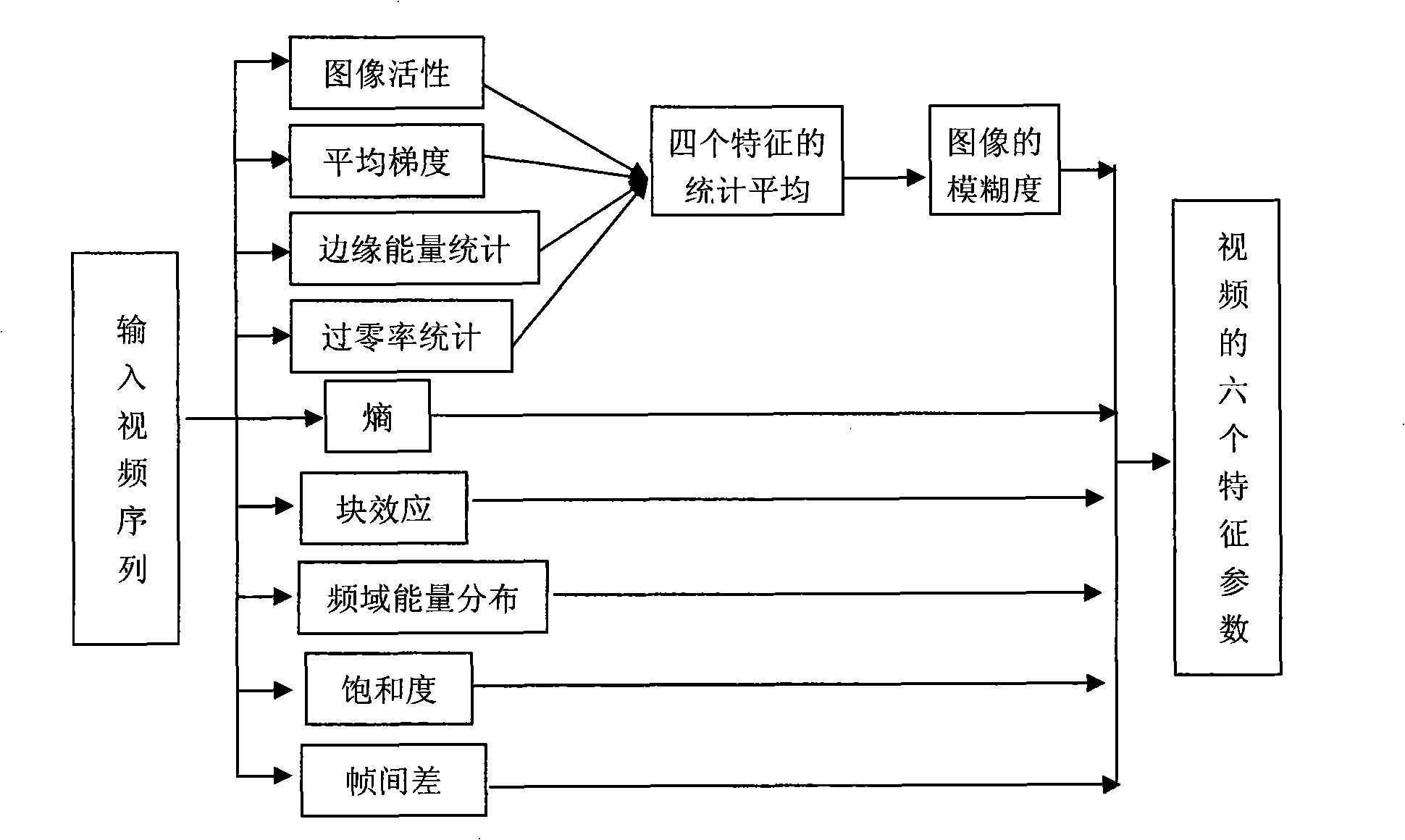
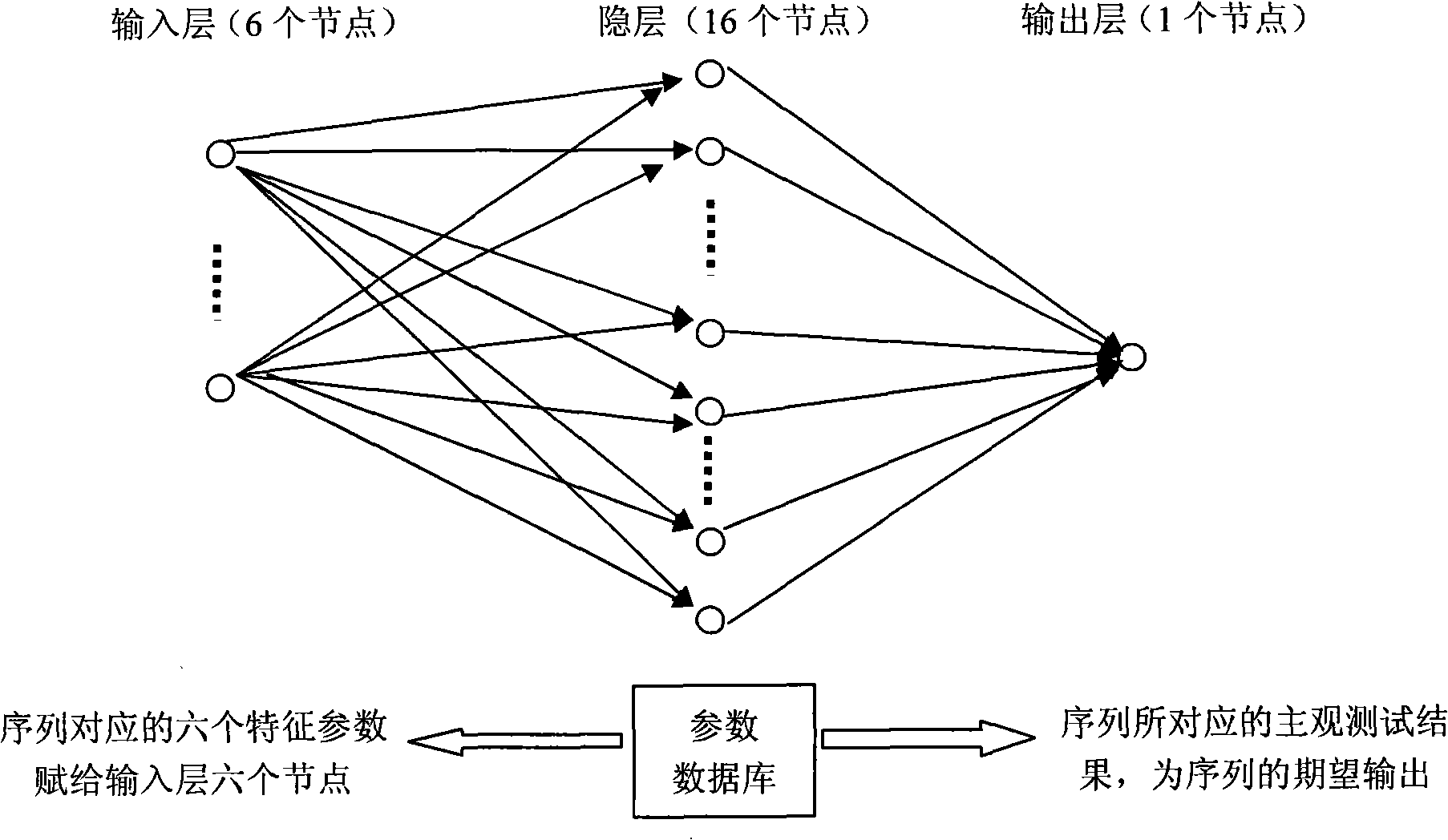
Method for evaluating video quality based on artificial neural net
InactiveCN101282481AImprove evaluation resultsBiological neural network modelsTelevision systemsDigital videoAlgorithm
A video quality evaluation method based on artificial neural network, which belongs to the field of computer digital video processing. The evaluation algorithm computes damage extent of an image by analyzing spatial characters (blur, entropy, blocking effect, frequency-domain energy analysis, saturation) and time behaviors (frame-to-frame differences). Evaluation effect of the algorithm can be effectively modified by using colour space saturation as one of the parameters for non-reference evaluation algorithm. The system is designed based on artificial neural network, therefore, training process and testing process of the network are included in realization of the algorithm. To the selected training sample (video image sequence), firstly extracts six parameters of the sample, then obtains expected output (subjective evaluation result) in training through subjective evaluation. Characteristic parameters of the training sample and the corresponding subjective evaluation result are inputted to the artificial neural network as training parameters. The experiment shows that evaluation result obtained by the objective evaluation system is highly-consistent with visual sense of human eyes.
Owner:COMMUNICATION UNIVERSITY OF CHINA
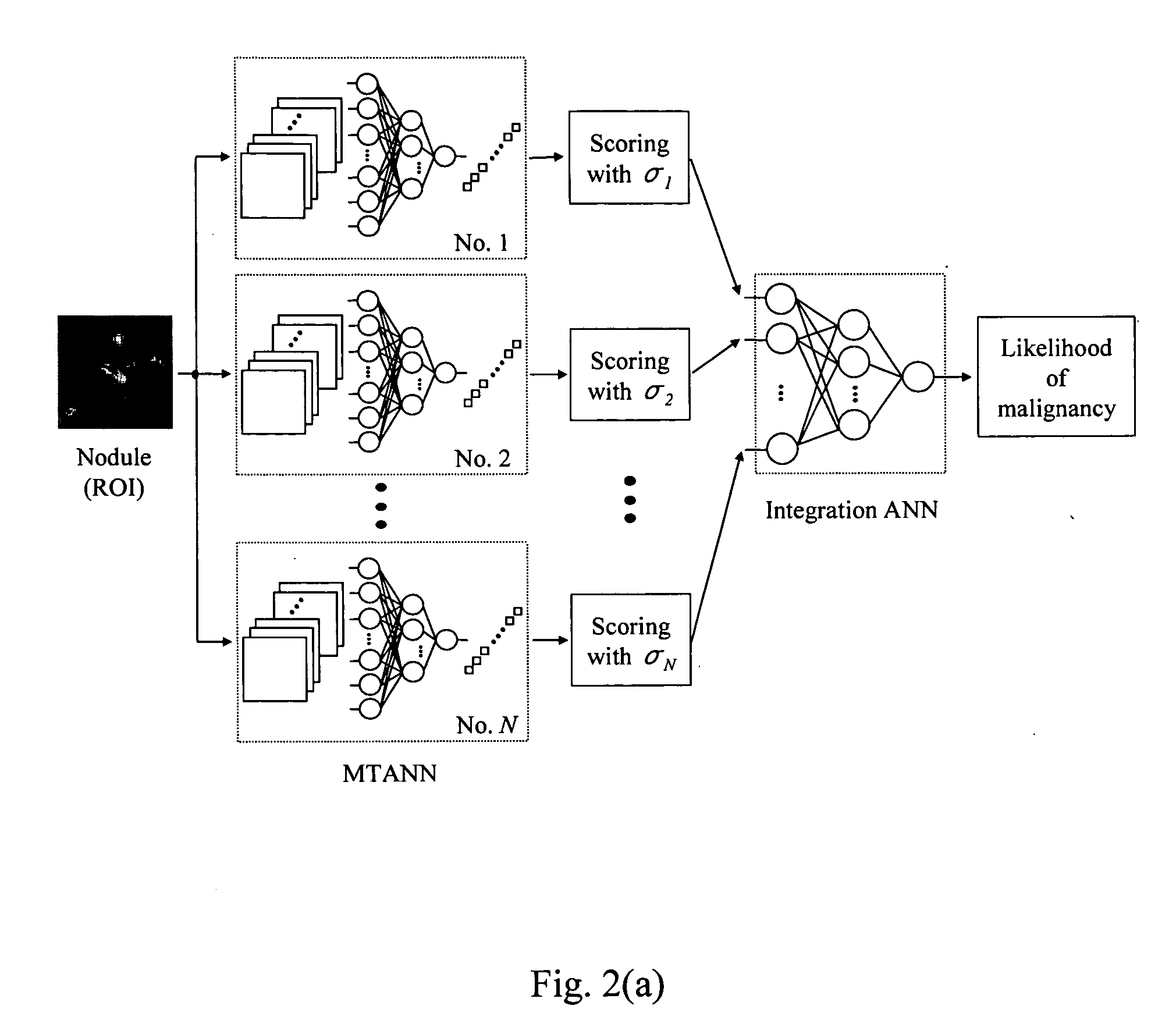
Computerized scheme for distinction between benign and malignant nodules in thoracic low-dose CT
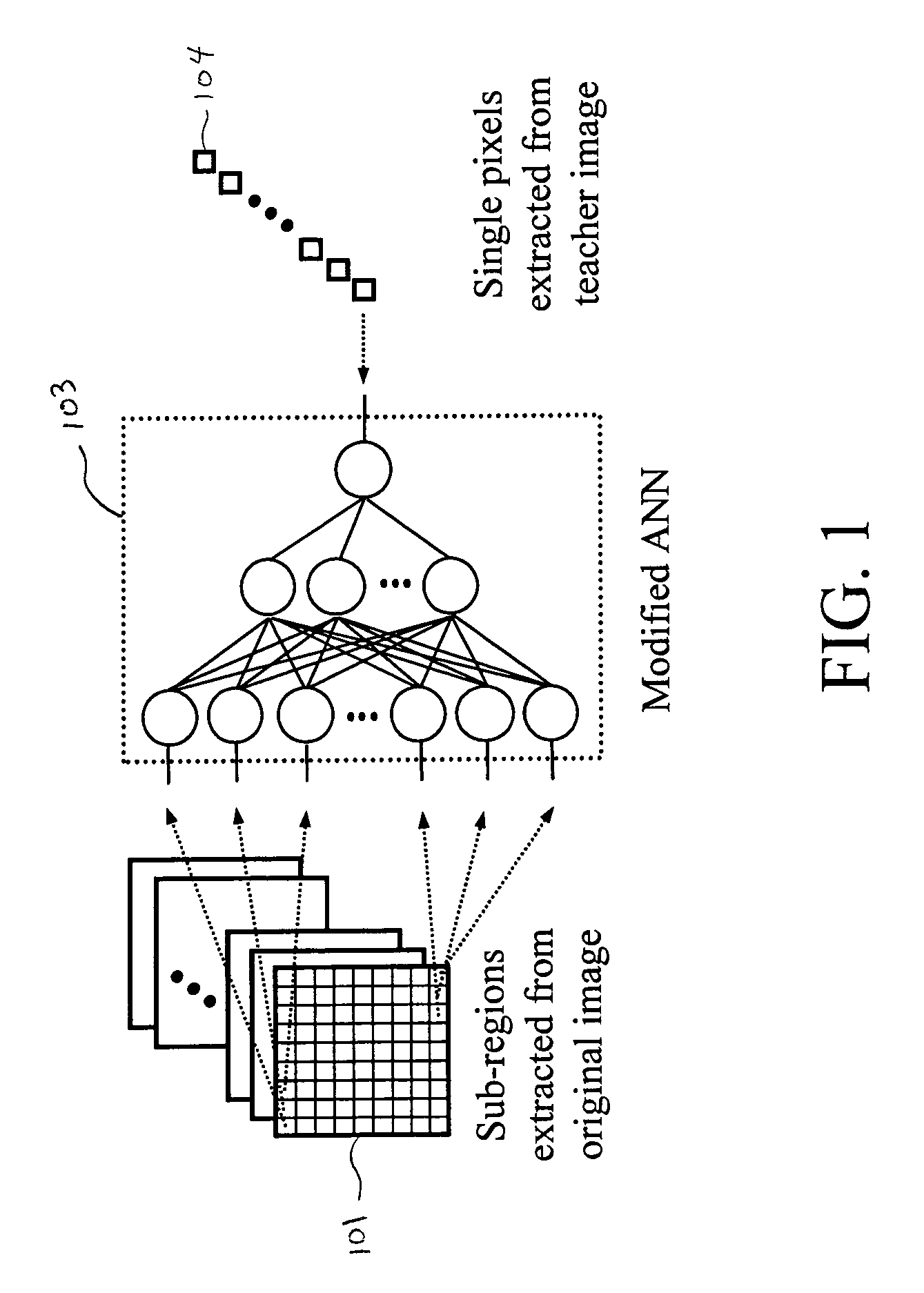
A system, method, and computer program product for classifying a target structure in an image into abnormality types. The system has a scanning mechanism that scans a local window across sub-regions of the target structure by moving the local window across the image to obtain sub-region pixel sets. A mechanism inputs the sub-region pixel sets into a classifier to provide output pixel values based on the sub-region pixel sets, each output pixel value representing a likelihood that respective image pixels have a predetermined abnormality, the output pixel values collectively determining a likelihood distribution output image map. A mechanism scores the likelihood distribution map to classify the target structure into abnormality types. The classifier can be, e.g., a single-output or multiple-output massive training artificial neural network (MTANN).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Method and system for detecting malicious behavioral patterns in a computer, using machine learning
InactiveUS20070294768A1Memory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer wormComputerized system
Method for detecting malicious behavioral patterns which are related to malicious software such as a computer worm in computerized systems that include data exchange channels with other systems over a data network. Accordingly, hardware and / or software parameters are determined in the computerized system that is can characterize known behavioral patterns thereof. Known malicious code samples are learned by a machine learning process, such as decision trees and artificial neural networks, and the results of the machine learning process are analyzed in respect to the behavioral patterns of the computerized system. Then known and unknown malicious code samples are identified according to the results of the machine learning process.
Owner:DEUTSCHE TELEKOM AG
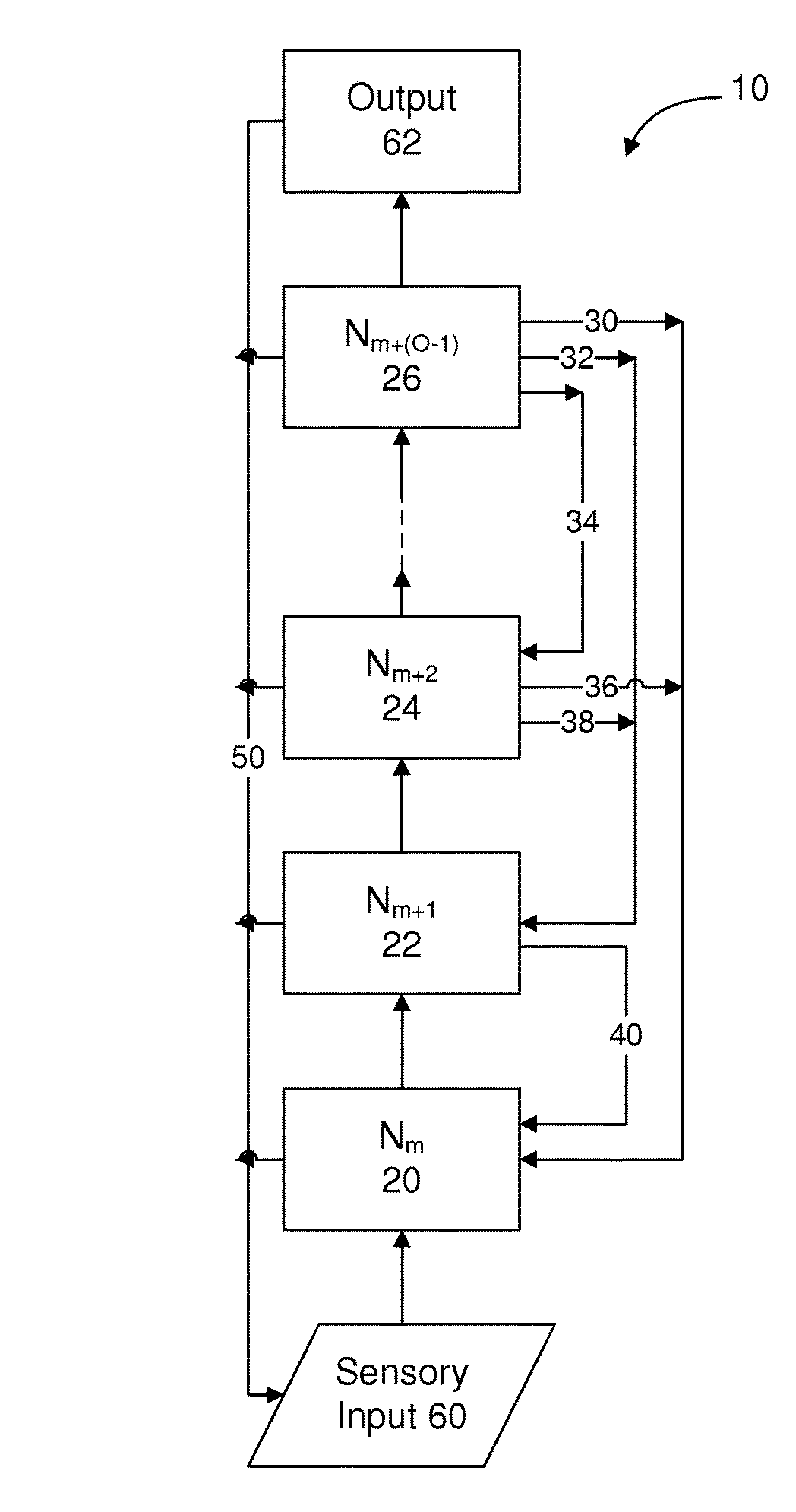
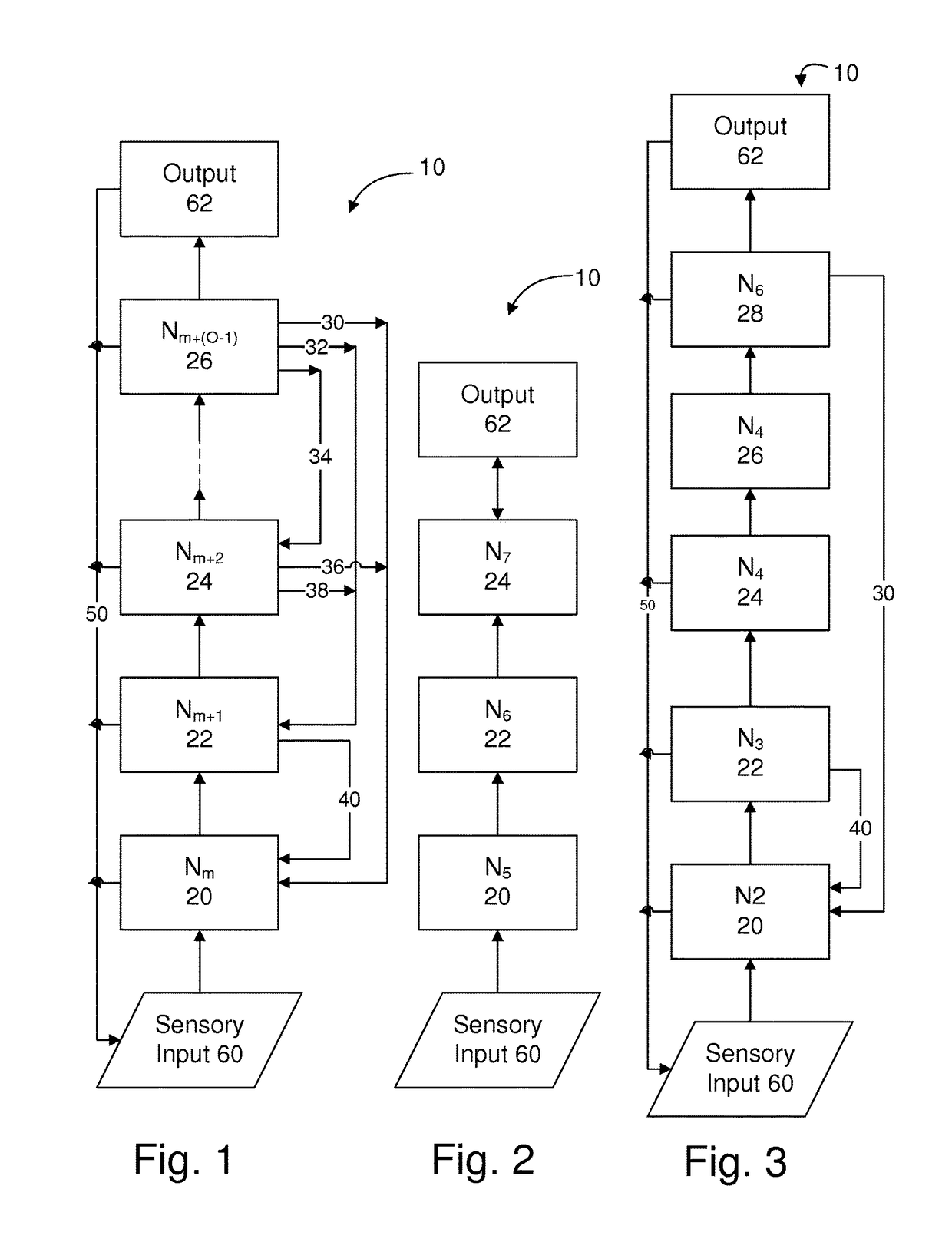
Method and apparatus for providing real-time monitoring of an artifical neural network
ActiveUS20150106316A1Overcome deficienciesDigital computer detailsNeural architecturesProcessor registerMulti dimensional
A circuit element of a multi-dimensional dynamic adaptive neural network array (DANNA) may comprise a neuron / synapse select input functional to select the circuit element to function as one of a neuron and a synapse. In one embodiment of a DANNA array of such circuit elements, (wherein a circuit element may be digital), a destination neuron may be connected to a first neuron by a first synapse in one dimension a second destination neuron may be connected to the first neuron by a second synapse in a second dimension to form linked columns and rows of neuron / synapse circuit elements. In one embodiment, the rows and columns of circuit elements have read registers that are linked together by signal lines and clocked and controlled so as to output columnar data to an output register when a neuron / synapse data value is stored in the read register.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
High Precision And Highly Efficient Tuning Mechanisms And Algorithms For Analog Neuromorphic Memory In Artificial Neural Networks
An artificial neural network device that utilizes analog neuromorphic memory that comprises one or more non-volatile memory arrays. The embodiments comprise improved mechanisms and algorithms for tuning the non-volatile memory arrays such that the floating gates of the memory cells can be quickly and accurately injected with the desired amount of charge to signify an analog value utilized as a weight by the artificial neural network.
Owner:SILICON STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
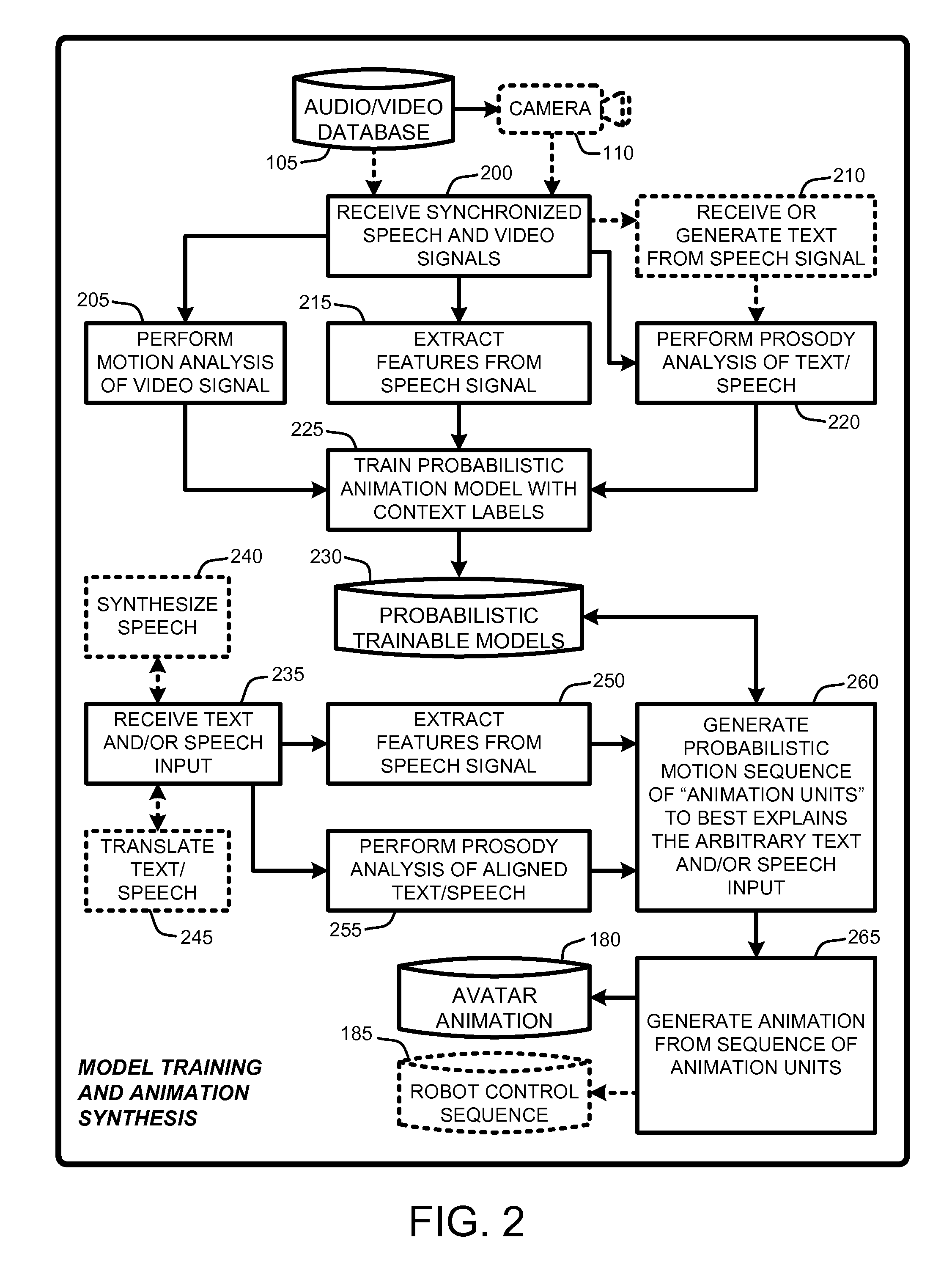
Speech and text driven HMM-based body animation synthesis
An “Animation Synthesizer” uses trainable probabilistic models, such as Hidden Markov Models (HMM), Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), etc., to provide speech and text driven body animation synthesis. Probabilistic models are trained using synchronized motion and speech inputs (e.g., live or recorded audio / video feeds) at various speech levels, such as sentences, phrases, words, phonemes, sub-phonemes, etc., depending upon the available data, and the motion type or body part being modeled. The Animation Synthesizer then uses the trainable probabilistic model for selecting animation trajectories for one or more different body parts (e.g., face, head, hands, arms, etc.) based on an arbitrary text and / or speech input. These animation trajectories are then used to synthesize a sequence of animations for digital avatars, cartoon characters, computer generated anthropomorphic persons or creatures, actual motions for physical robots, etc., that are synchronized with a speech output corresponding to the text and / or speech input.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Intelligent control with hierarchical stacked neural networks
ActiveUS9875440B1Simple taskProgramme controlElectrical controlData miningArchitecture of Integrated Information Systems
A method of processing information is provided. The method involves receiving a message; processing the message with a trained artificial neural network based processor, having at least one set of outputs which represent information in a non-arbitrary organization of actions based on an architecture of the artificial neural network based processor and the training; representing as a noise vector at least one data pattern in the message which is incompletely represented in the non-arbitrary organization of actions; analyzing the noise vector distinctly from the trained artificial neural network; searching at least one database; and generating an output in dependence on said analyzing and said searching.
Owner:COMMONS MICHAEL LAMPORT
Method for coding pixels or voxels of a digital image and a method for processing digital images
InactiveCN101189641AAuxiliary diagnosis possibleCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingVoxelImaging processing
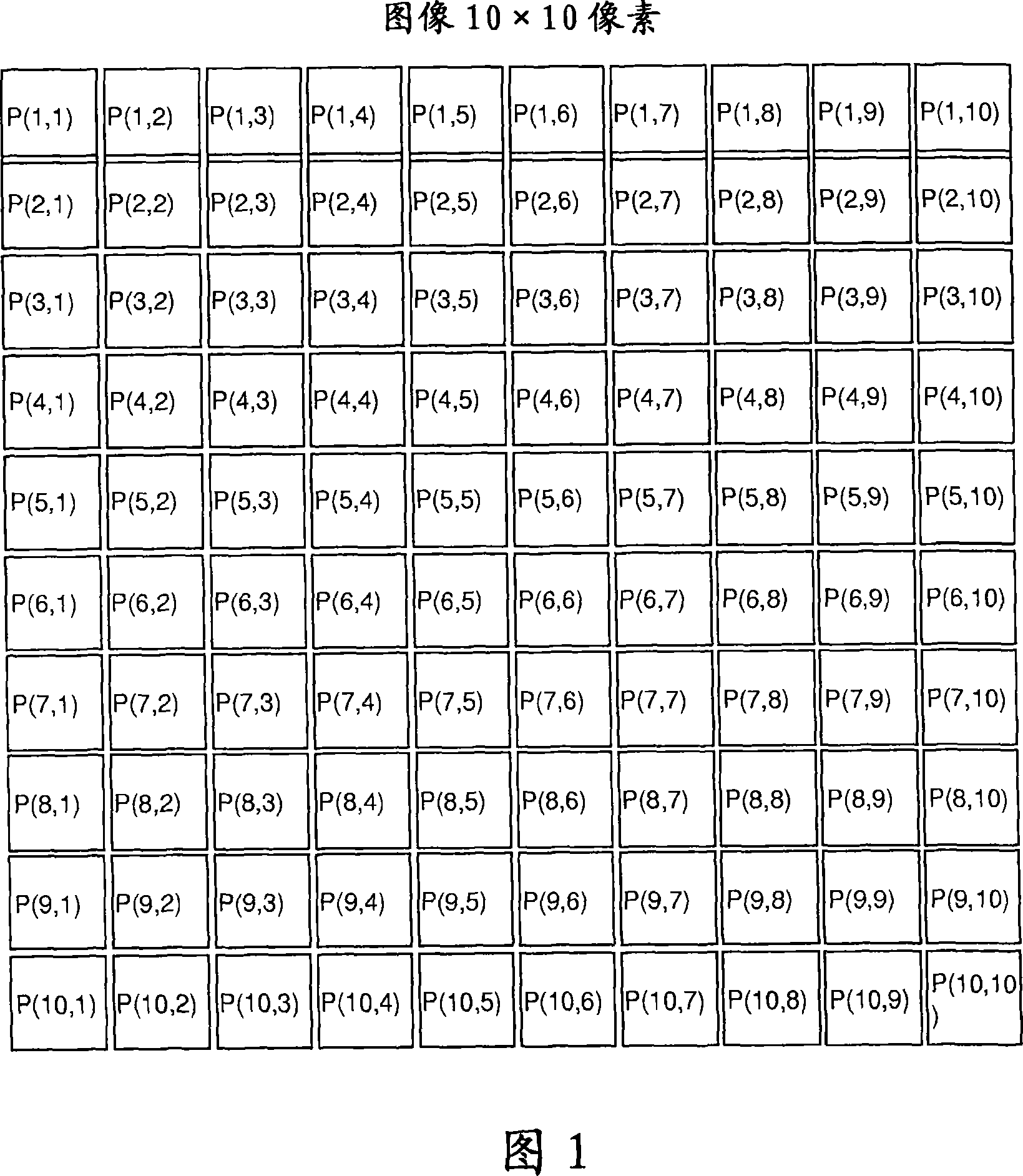
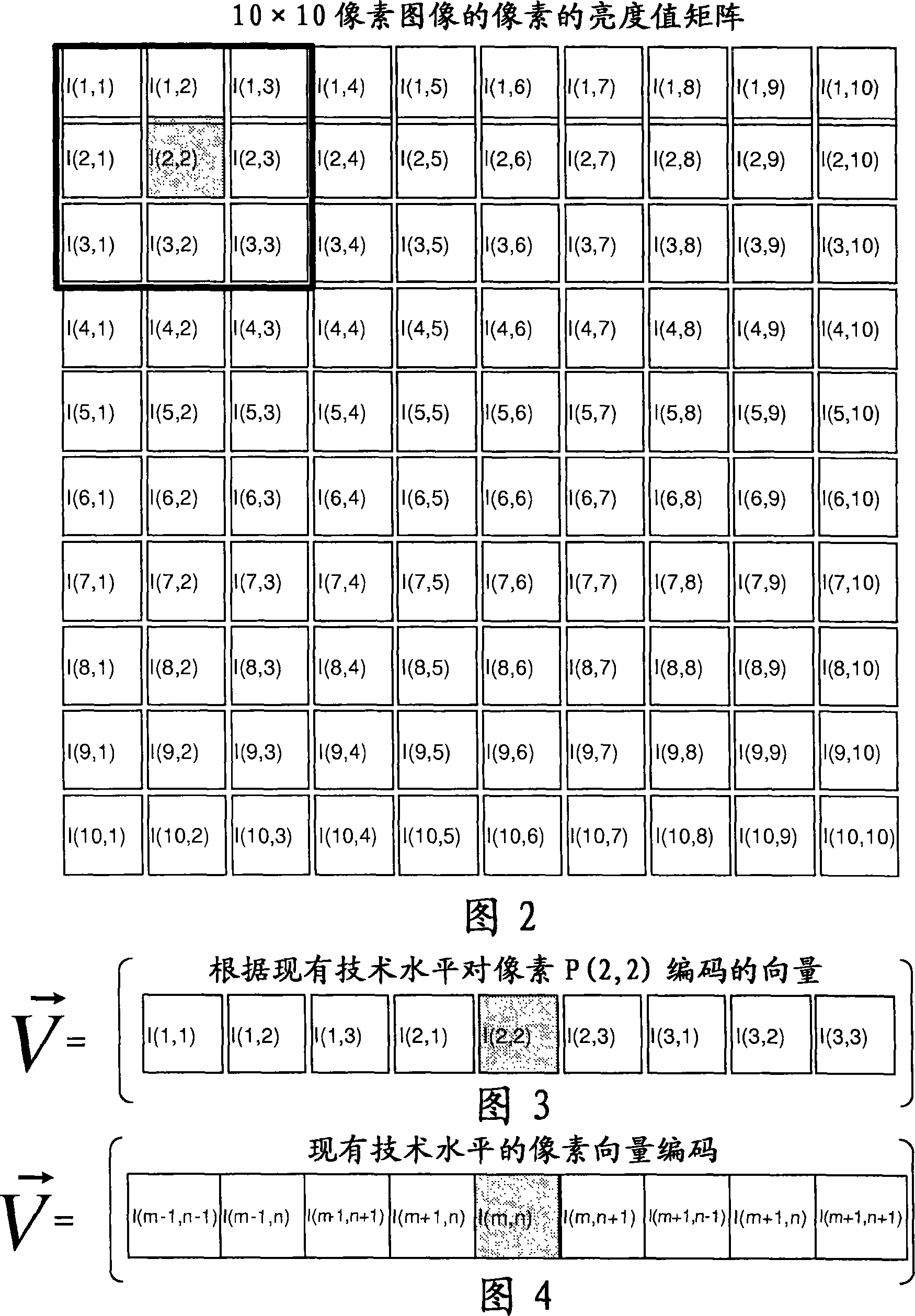
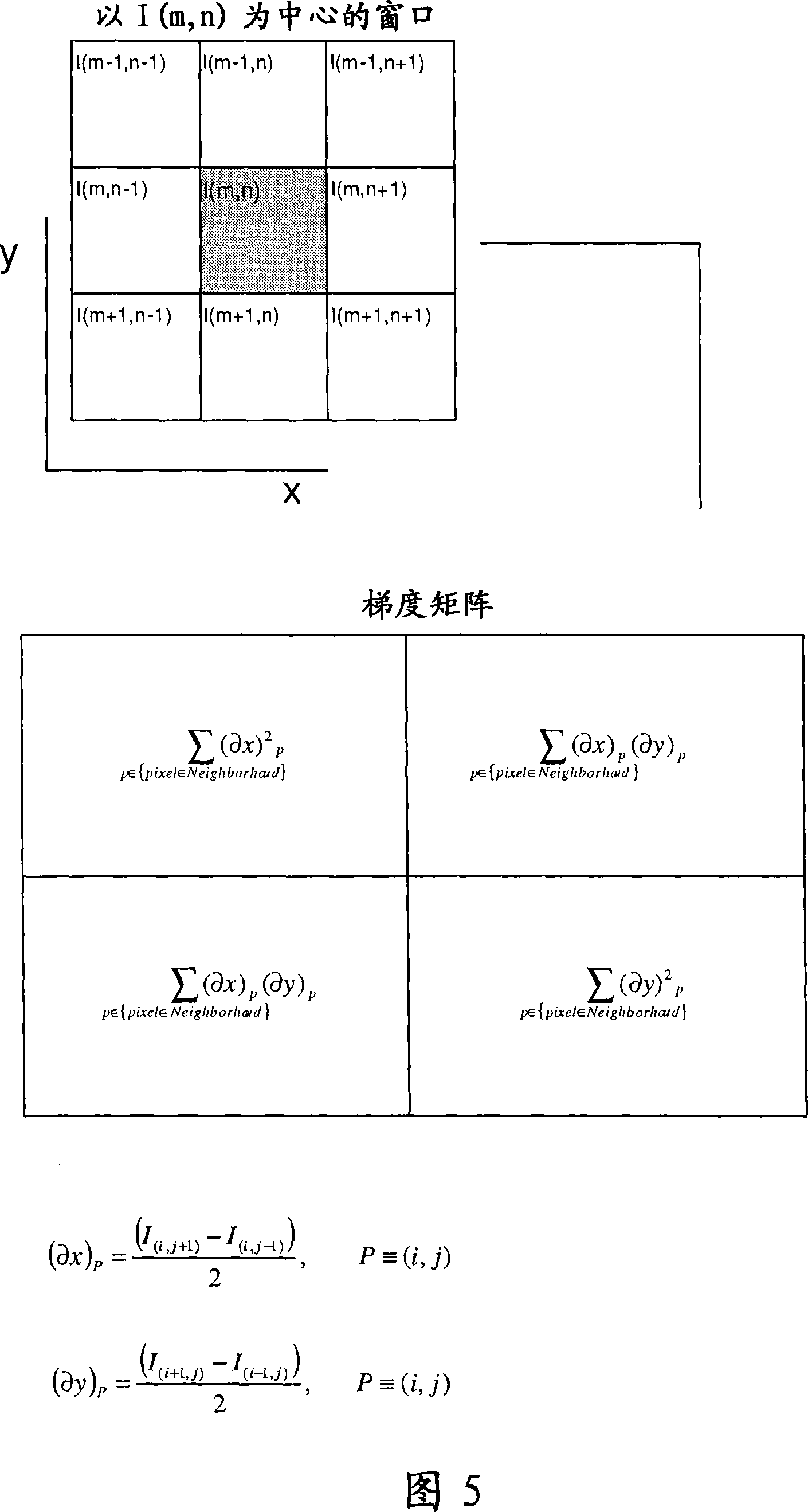
A method for coding pixels or voxels of a digital or digitalized two dimensional or three dimensional image, comprises the steps of: providing a digital image consisting in a two dimensional array of pixels or in a three dimensional array of voxels, each pixel or voxel being defined by at least one variable as its intensity in a grey scale image or the HSV (Hue, Saturation and Value) or the RGB values in a colour image; each pixel or voxel of the image being considered as a target pixel or voxel and for each target pixel or voxel a neighborhood being formed by a pixel or voxel windows comprising the said target pixel or voxel and a certain number of surrounding pixels or voxels for each target pixel or voxel generating a vector univocally associated to the said target pixel or voxel, the components of the said vectors being generated as a function of the values of the said target pixel or voxel and of each of the pixels or voxels of the said pixel or voxel window. The function of the values of the said target pixel or voxel and of each of the pixels or voxels of the said pixel or voxel window correspond to the characteristic parameters of the numerical matrix representing the pixels or voxels of the said window or of a transformation of the said numerical matrix. The invention relates also to an image processing method in which image data coded according to the above method are processed by means of a predictive algorithm as for example an artificial neural network.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Artificial intelligence and global normalization methods for genotyping
Described herein are systems and methods for normalizing data without the use of external controls. Also described herein are systems and methods for analyzing cluster data, such as genotyping data, using an artificial neural network.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Neural net for use in drilling simulation
A method of optimizing a drilling tool assembly including inputting well data into an optimization system, the optimization system having an experience data set and an artificial neural network. The method further including comparing the well data to the experience data set and developing an initial drilling tool assembly based on the comparing the well data to the experience data, wherein the drilling tool assembly is developed using the artificial neural network. Additionally, the method including simulating the initial drilling tool assembly in the optimization system and creating result data in the optimization system based on the simulating.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
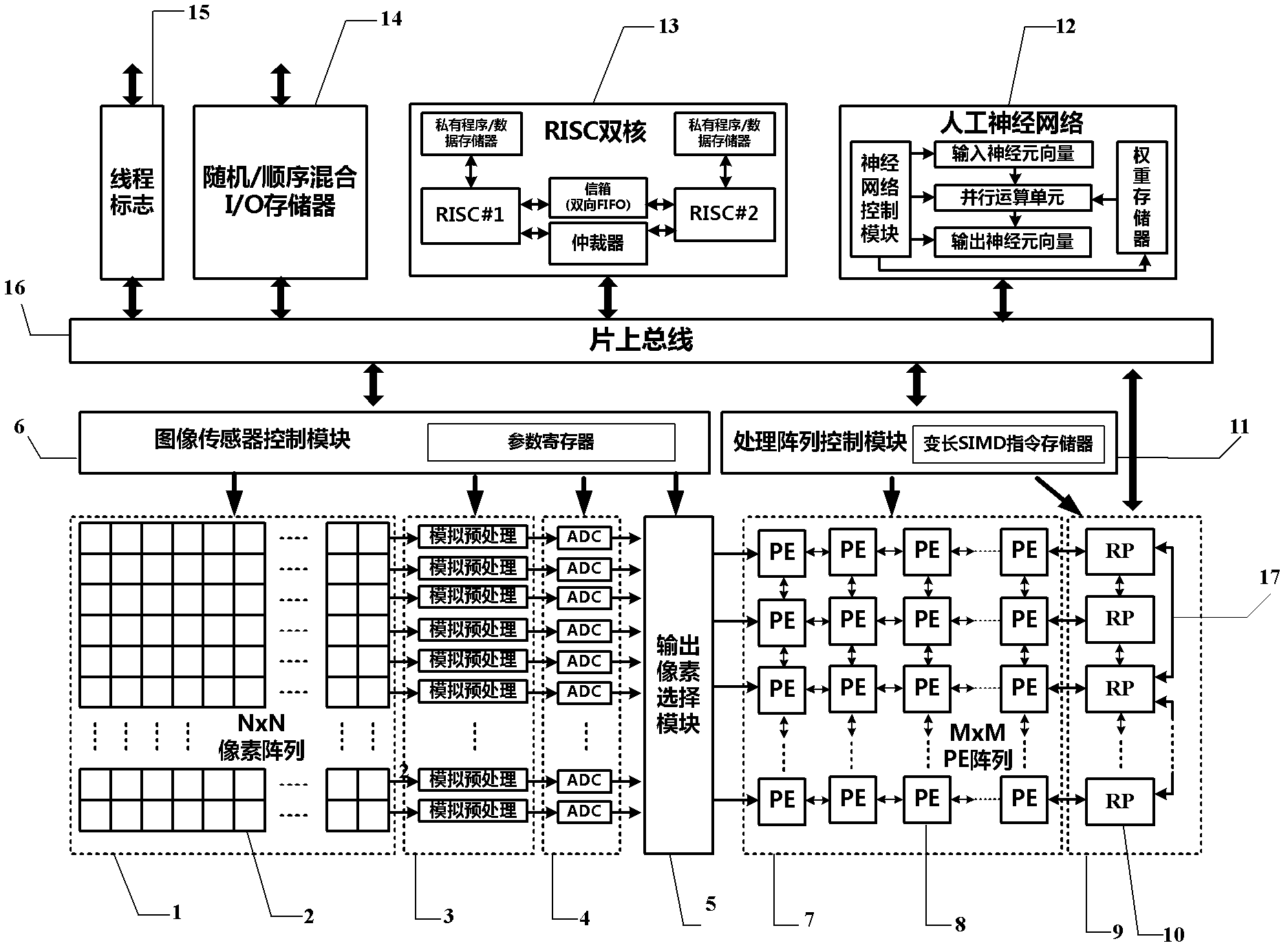
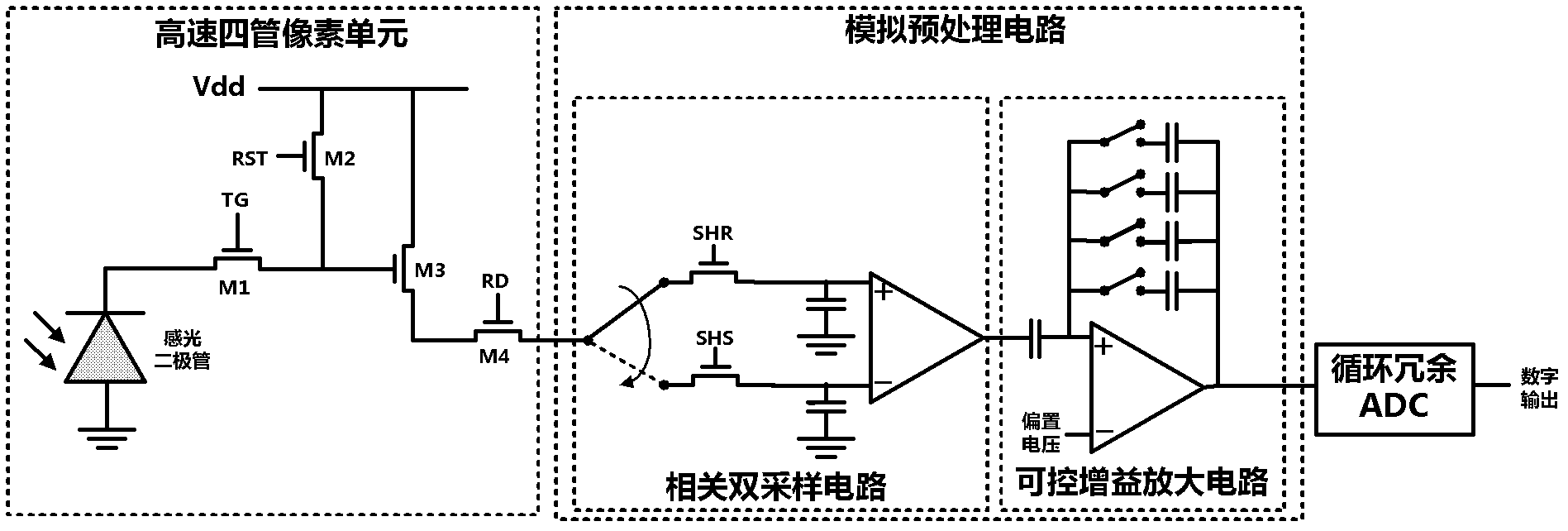
Programmable visual chip-based visual image processing system
ActiveCN102665049AFlexible handlingFlexible multi-resolution processingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFace detectionDual core
Disclosed in the invention is a programmable visual chip-based visual image processing system, comprising an image sensor and a multilevel parallel digital processing circuit. The image sensor mainly includes a pixel array, an analog preprocessing circuit array and an analog-to-digital conversion circuit array; and the digital processing circuit consists of a parallel processing unit array with an M*M pixel level, a parallel processing unit array with M*1 rows, an on-chip artificial neural network and a reduced instruction processor dual-core subsystem. According to the provided system, high quality image collection with high speed and multilevel parallel image processing are realized and several high-speed intelligent visual application can be realized by programming; and compared with a traditional image system, the provided system has advantages of high speed, high integration, low power consumption and low cost. Moreover, the invention brings forward an embodiment for realizing the above-mentioned system as well as several high-speed intelligent visual image processing algorithms based on the embodiment. High-speed motion detection, high-speed gesture identification and rapid face detection are included; and the processing speed can reach 1000 frames per second. Therefore, a requirement of high-speed real-time processing can be met.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
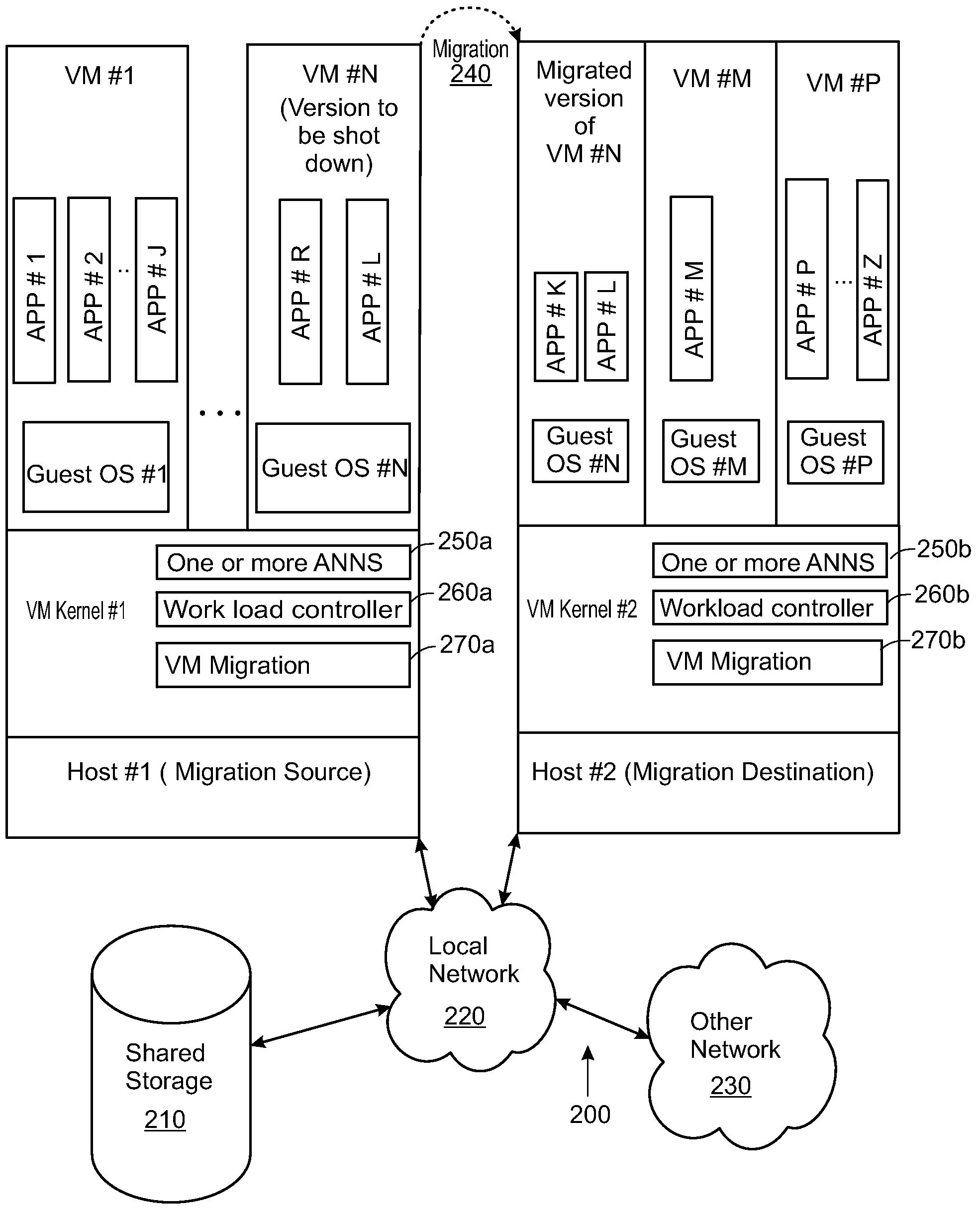
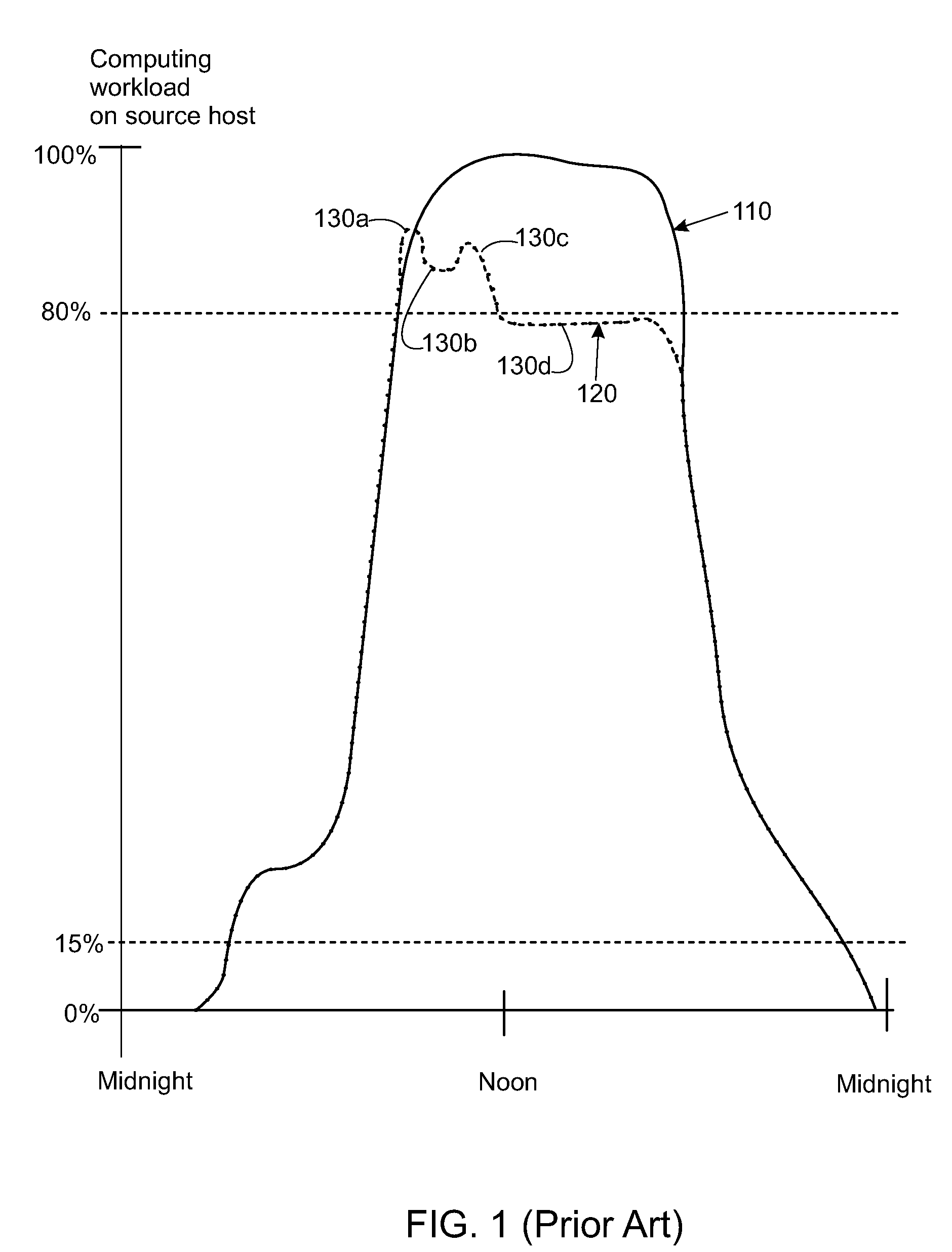
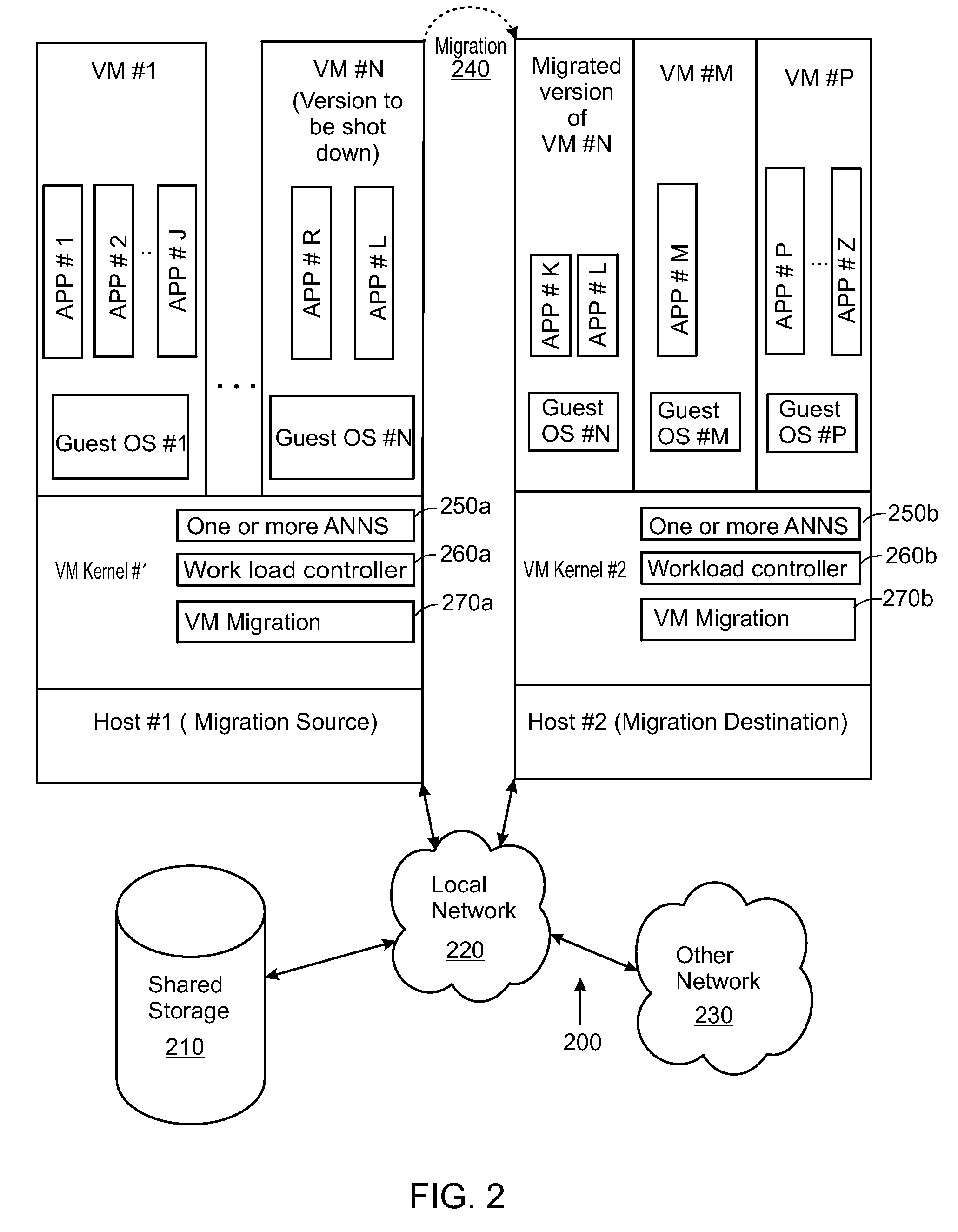
Artificial neural network for balancing workload by migrating computing tasks across hosts
Methods and apparatuses for balancing computing workload via migrating computing tasks are disclosed. An artificial neural network (ANN) is trained based on the workload distribution over time for a host. The ANN predicts the workload for the host, and an indication may be sent to migrate at least one computing task away from the host. The indication is sent when the method is operating in a proactive mode and when the predicted workload is outside of a desired operating range. Some embodiments monitor the workload; and automatically switch the method to the proactive mode, when a difference between the monitored workload and the predicted workload is small. Other embodiments monitor the workload; and automatically switch the method to a reactive mode, when the monitored workload is outside of a failsafe operating range for the particular host.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Device and method for executing forward operation of artificial neural network
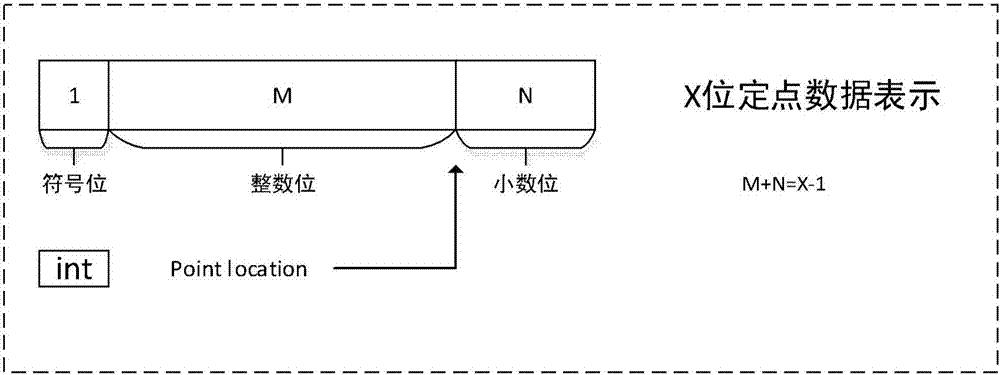
PendingCN107330515ASmall area overheadReduce area overhead and optimize hardware area power consumptionDigital data processing detailsCode conversionData operationsComputer module
The invention provides a device and a method for executing a forward operation of an artificial neural network. The device comprises the components of a floating point data statistics module which is used for performing statistics analysis on varies types of required data and obtains the point location of fixed point data; a data conversion unit which is used for realizing conversion from a long-bit floating point data type to a short-bit floating point data type according to the point location of the fixed point data; and a fixed point data operation module which is used for performing artificial neural network forward operation on the short-bit floating point data. According to the device provided by the invention, through representing the data in the forward operation of the multilayer artificial neural network by short-bit fixed points, and utilizing the corresponding fixed point data operation module, forward operation for the short-bit fixed points in the artificial neural network is realized, thereby greatly improving performance-to-power ratio of hardware.
Owner:CAMBRICON TECH CO LTD
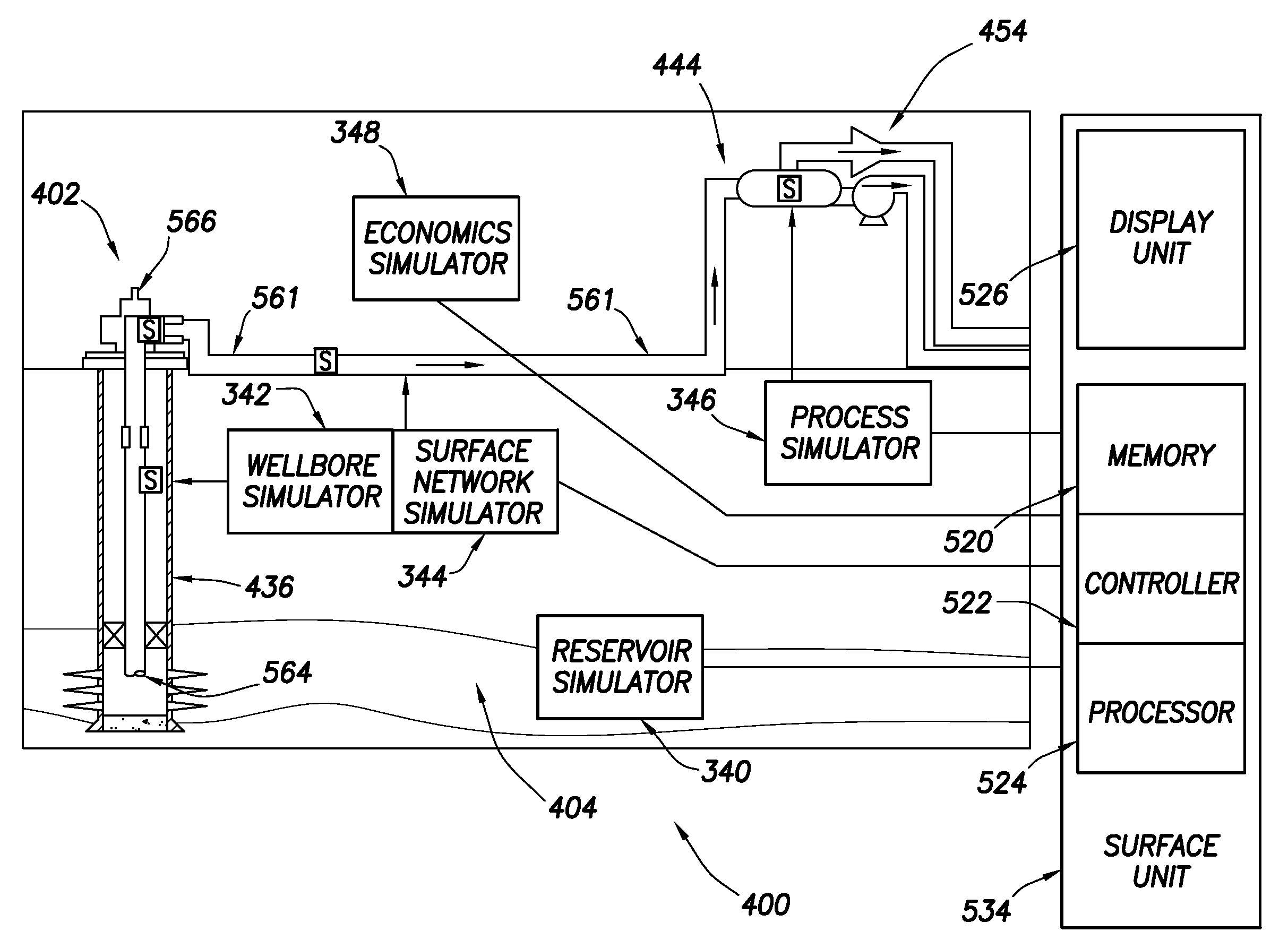
Apparatus, method and system for stochastic workflow in oilfield operations
The invention relates to a method for performing an oilfield operation. The method steps include obtaining oilfield data sets associated with oilfield entities, generating a stochastic database from the oilfield data sets based on an artificial neural network of the oilfield data sets, screening the oilfield data sets to identify candidates from the oilfield entities, wherein the screening is based on the stochastic database, performing a detail evaluation of each candidates, selecting an oilfield entity from the candidates based on the detail evaluation, and performing the oilfield operation for the selected oilfield entity.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
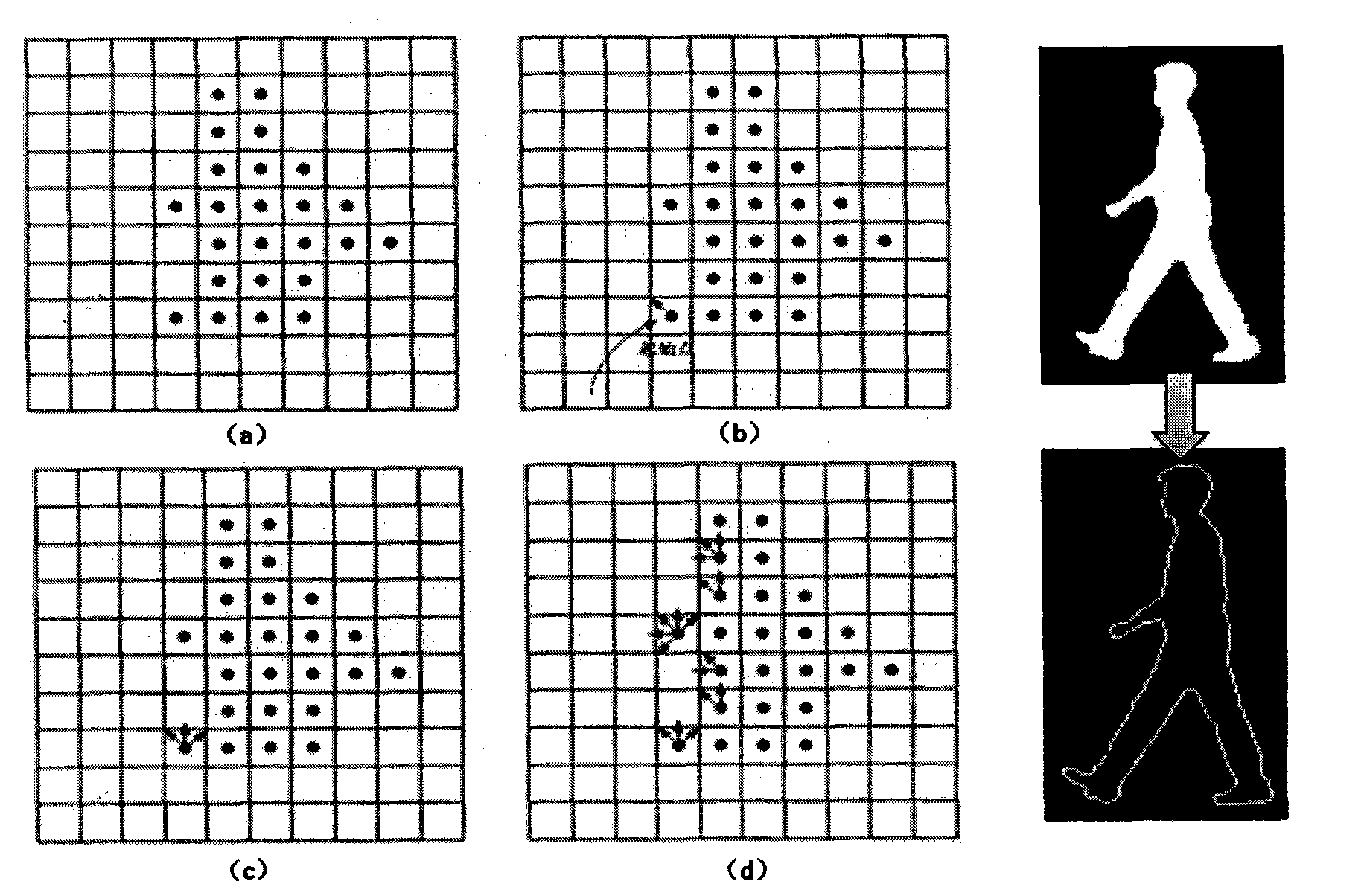
Artificial neural network-based multi-source gait feature extraction and identification method
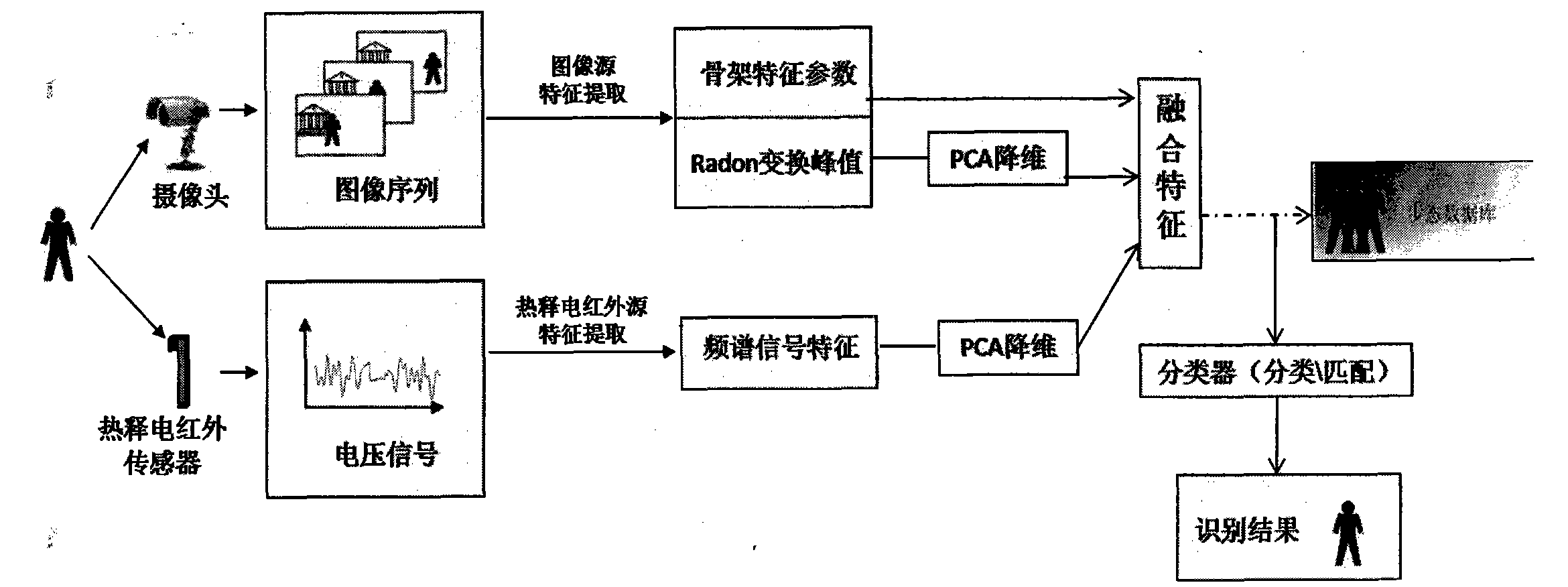
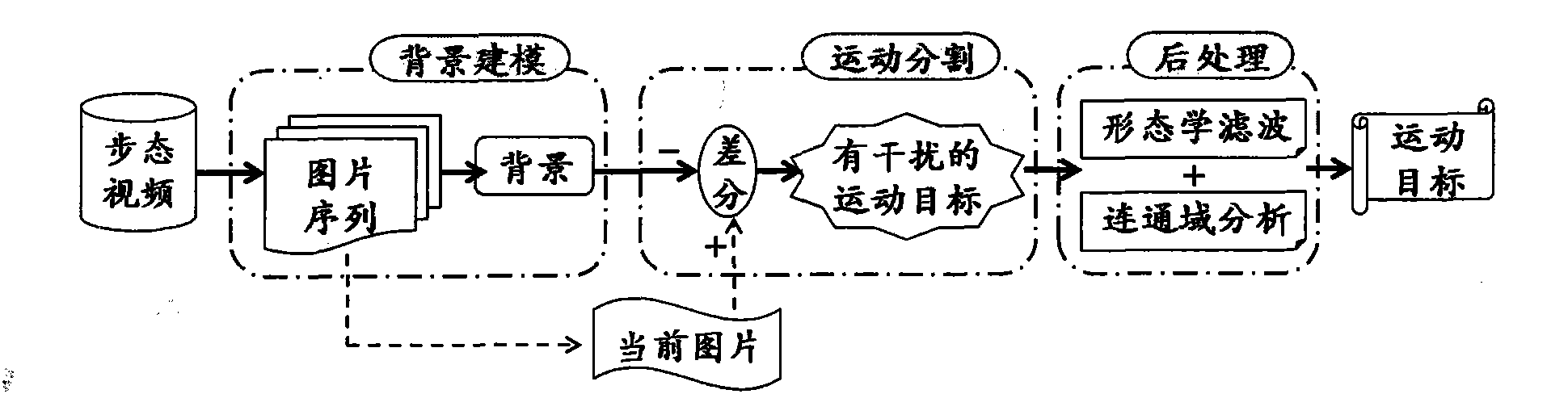
ActiveCN101807245ASuppress interferenceImprove robustnessImage analysisBiological neural network modelsImaging processingFeature extraction
The invention relates to identification, image processing and the like, in particular to an artificial neural network-based multi-source gait feature extraction and identification method, which aims to reduce inferences with external factors such as complex background and shelters so as to more accurately extract the effective information reflecting the walking characteristics of the moving people and improve the gait identification accuracy. The technical scheme of the invention comprises the following steps: separately acquiring the gait data by using a camera and a pyroelectric infrared sensor; extracting the skeleton feature parameter and Radon change peak characteristic parameter from the image source information acquired by the camera, and for the pyroelectric infrared source information, converting an acquired voltage signal into frequency domain characteristic parameter; merging the skeleton feature parameter, the Radon change peak feature parameter and the frequency domain characteristic parameter which are subjected to dimension reduction and corresponding signal process; and finally, realizing classified identification of the merged characteristics by using a BP neutralnetwork as the classifier and evaluating the identification effect. The method is mainly applied to identification.
Owner:中电云脑(天津)科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com