Patents
Literature
6546 results about "Neuron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A neuron, also known as a neurone (old British spelling) or nerve cell, is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. It is the main component of nervous tissue. All animals except sponges and placozoans have neurons, but other multicellular organisms such as plants do not.
Neural regeneration peptides and methods for their use in treatment of brain damage
InactiveUS7563862B2High expressionEasy SurvivalPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNervous systemInjury brain
The invention discloses a family of peptides termed NRP compounds or NRPs that can promote neuronal migration, neurite outgrowth, neuronal proliferation, neural differentiation and / or neuronal survival, and provides compositions and methods for the use of NRPs in the treatment of brain injury and neurodegenerative disease. NRP compounds can induce neurons and neuroblasts to proliferate and migrate into areas of damage caused by acute brain injury or chronic neurodegenerative disease, such as exposure to toxins, stroke, trauma, nervous system infections, demyelinating diseases, dementias, and metabolic disorders. NRP compounds may be administered directly to a subject or to a subject's cells by a variety of means including orally, intraperitoneally, intravascularly, and directly into the nervous system of a patient. NRP compounds can be formulated into pharmaceutically acceptable dose forms for therapeutic use. Methods for detecting neural regeneration, neural proliferation, neural differentiation, neurite outgrowth and neural survival can be used to develop other neurally active agents.
Owner:CURONZ HLDG
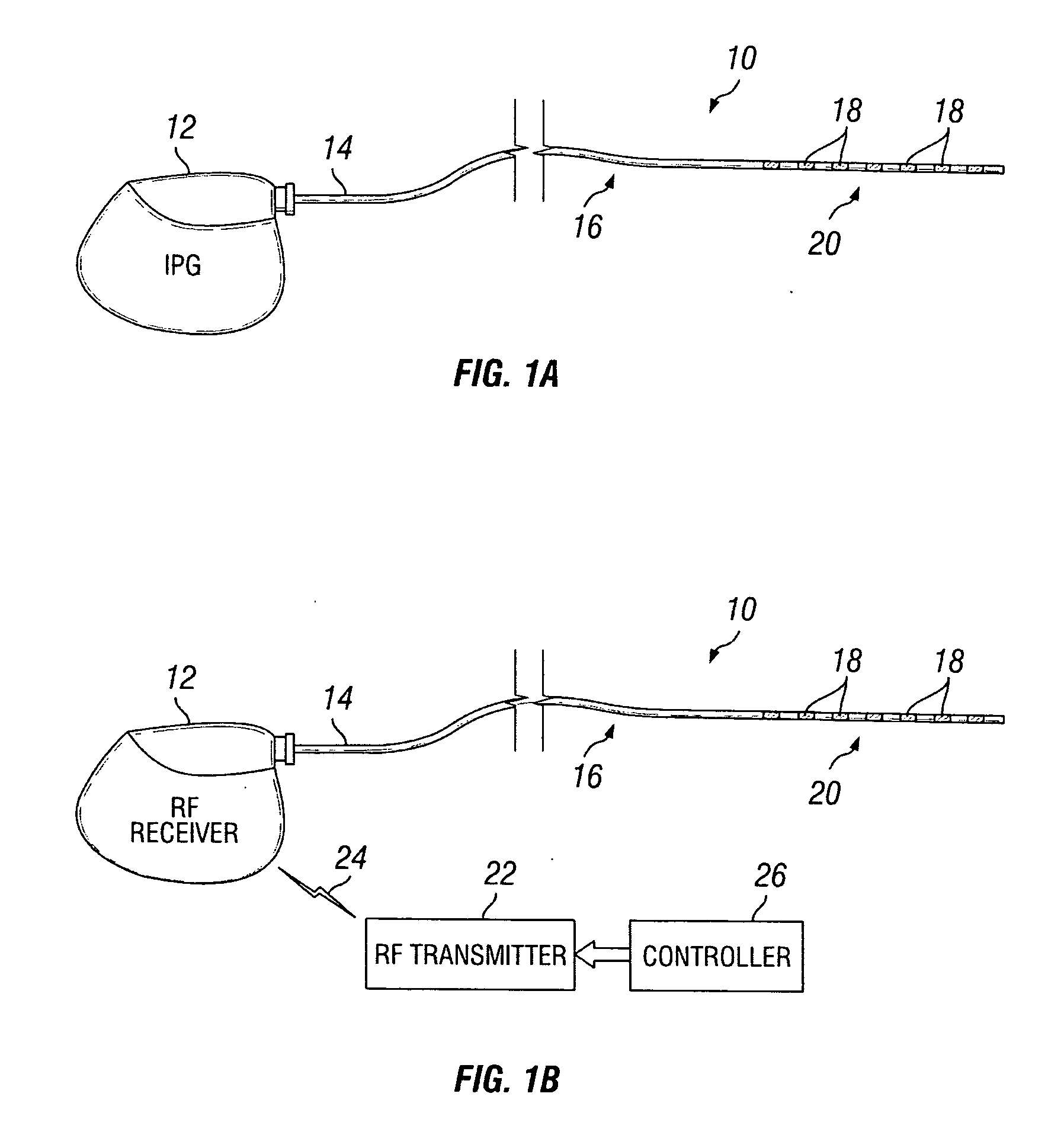
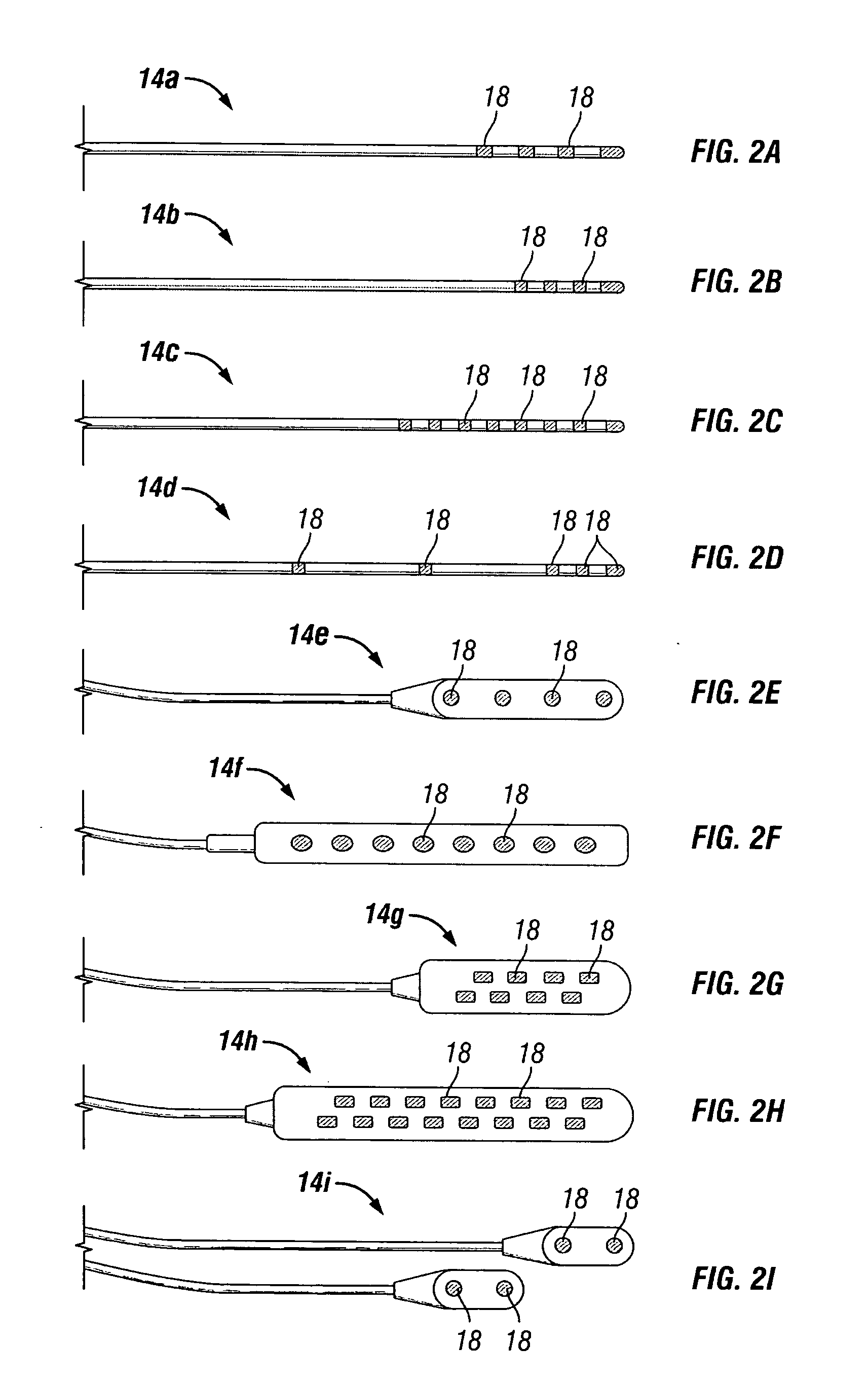
New stimulation design for neuromodulation
The present application relates to a new stimulation design which can be utilized to treat neurological conditions. The stimulation system produces a burst mode stimulation which alters the neuronal activity of the predetermined site, thereby treating the neurological condition or disorder.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Method, apparatus, and surgical technique for autonomic neuromodulation for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20060167498A1Reduce or prevent conditionReducing and preventing symptomSpinal electrodesSurgical needlesSplanchnic nervesDisease
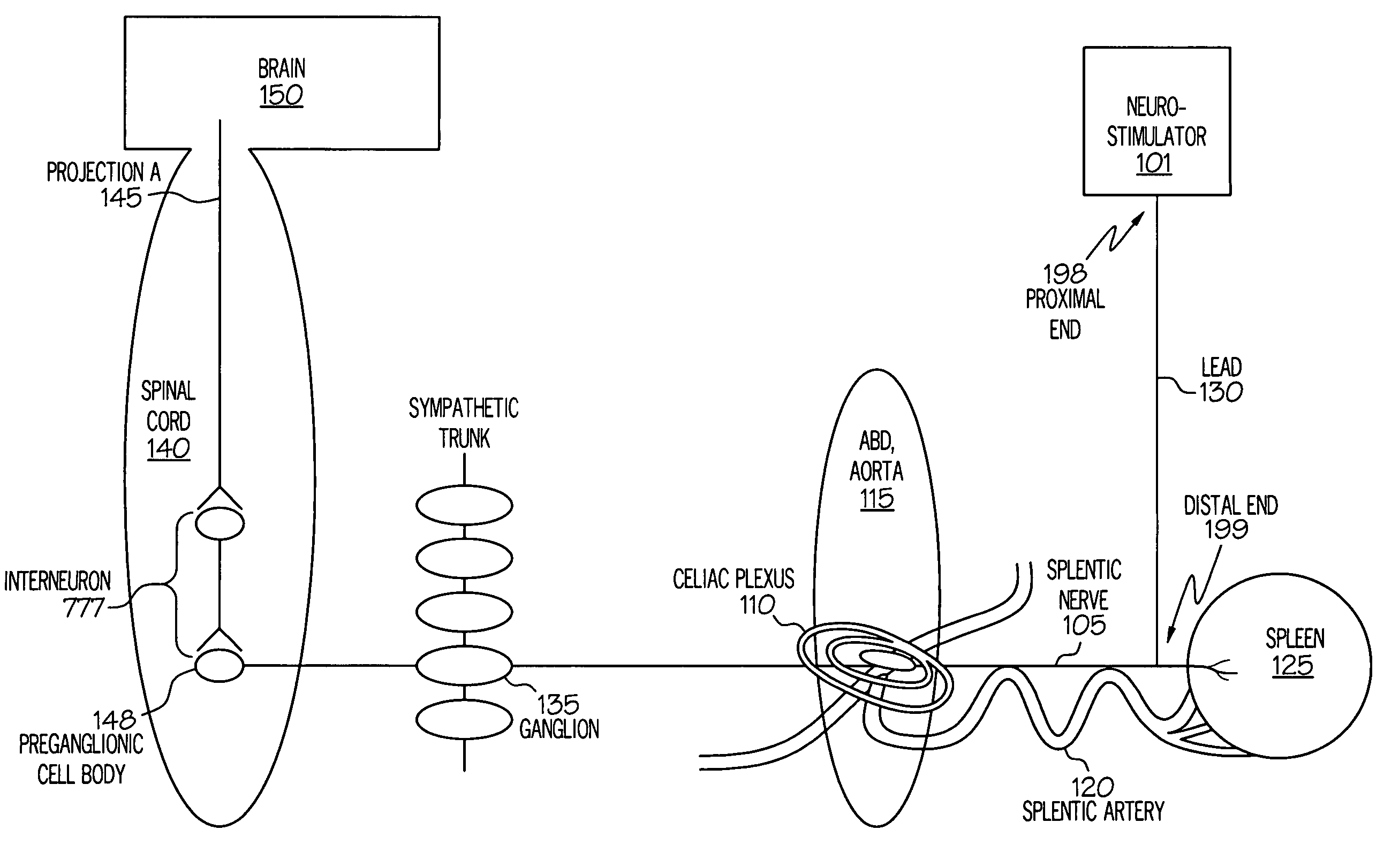
The present invention teaches a method and apparatus for physiological modulation, including neural and gastrointestinal modulation, for the purposes of treating several disorders, including obesity, depression, epilepsy, and diabetes. This includes chronically implanted neural and neuromuscular modulators, used to modulate the afferent neurons of the sympathetic nervous system to induce satiety. Furthermore, this includes neuromuscular stimulation of the stomach to effect baseline and intermittent smooth muscle contraction to increase gastric intraluminal pressure, which induces satiety, and stimulate sympathetic afferent fibers, including those in the sympathetic trunk, splanchnic nerves, and greater curvature of the stomach, to augment the perception of satiety.
Owner:DILORENZO BIOMEDICAL
Device and method for attenuating an immune response
ActiveUS20050075701A1Good flexibilityMore levelsSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsNervous systemNeuron
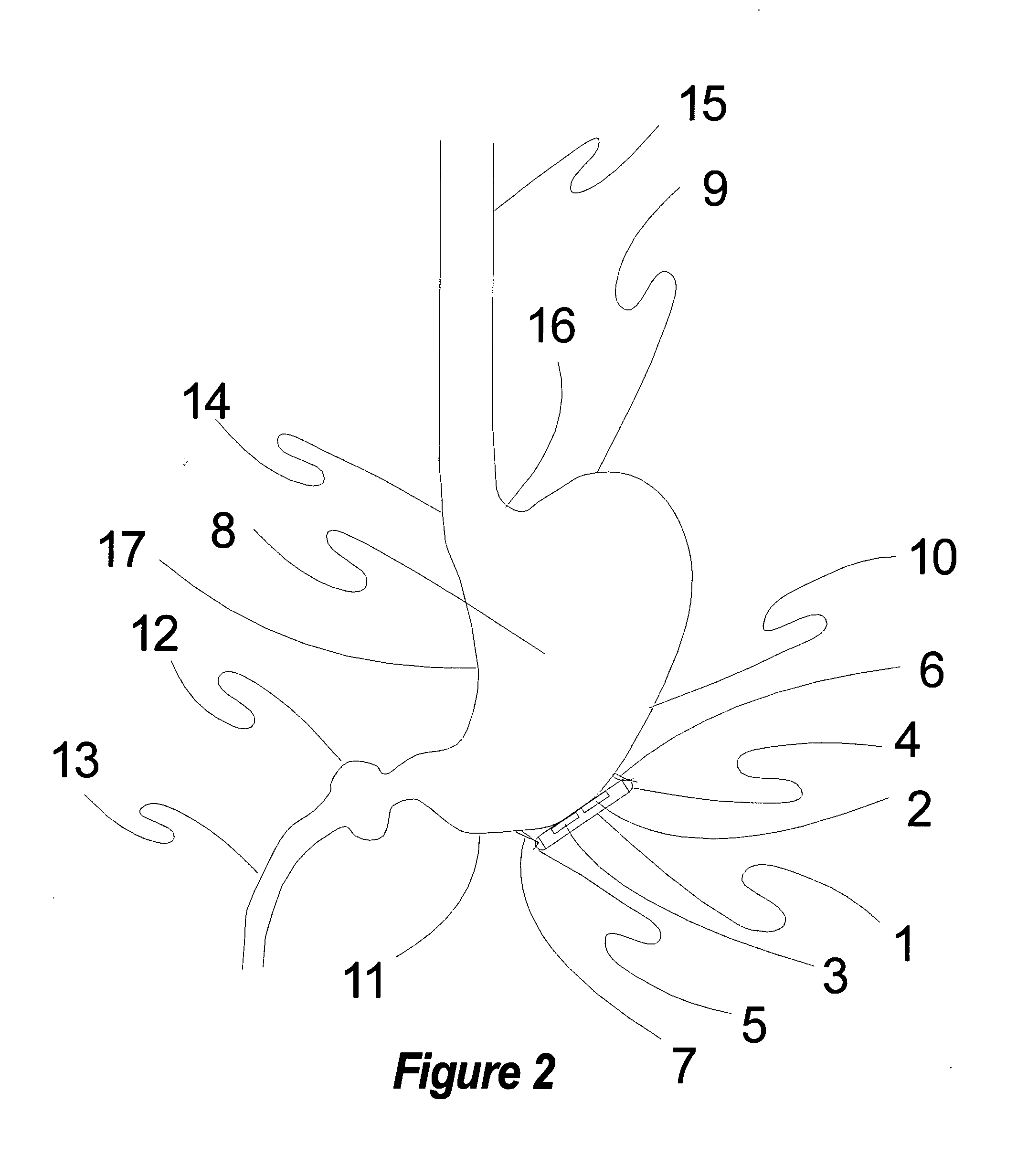
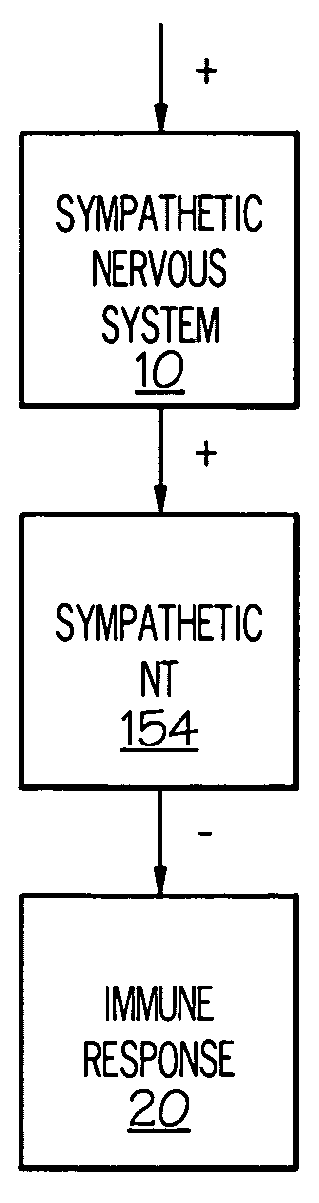
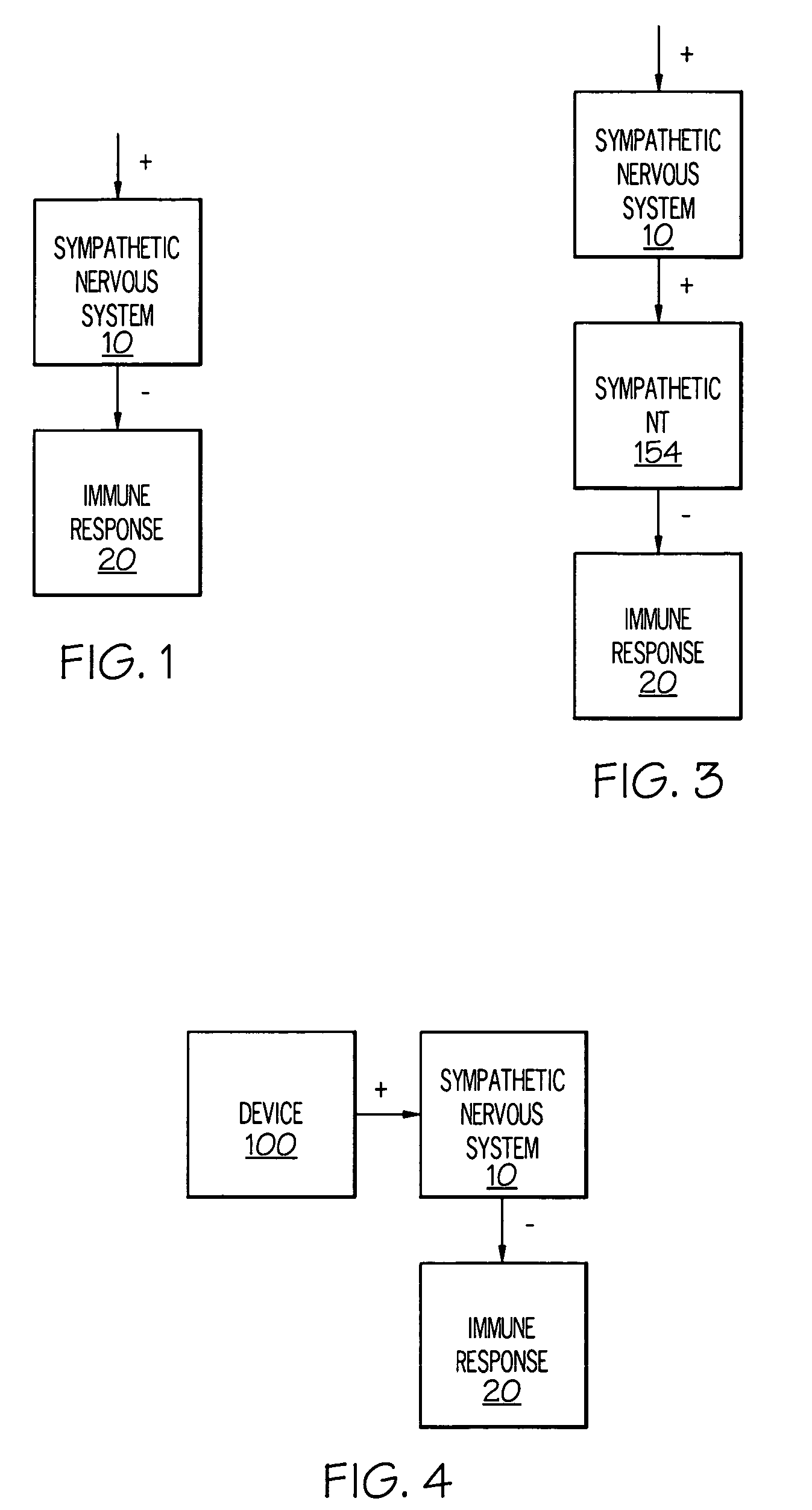
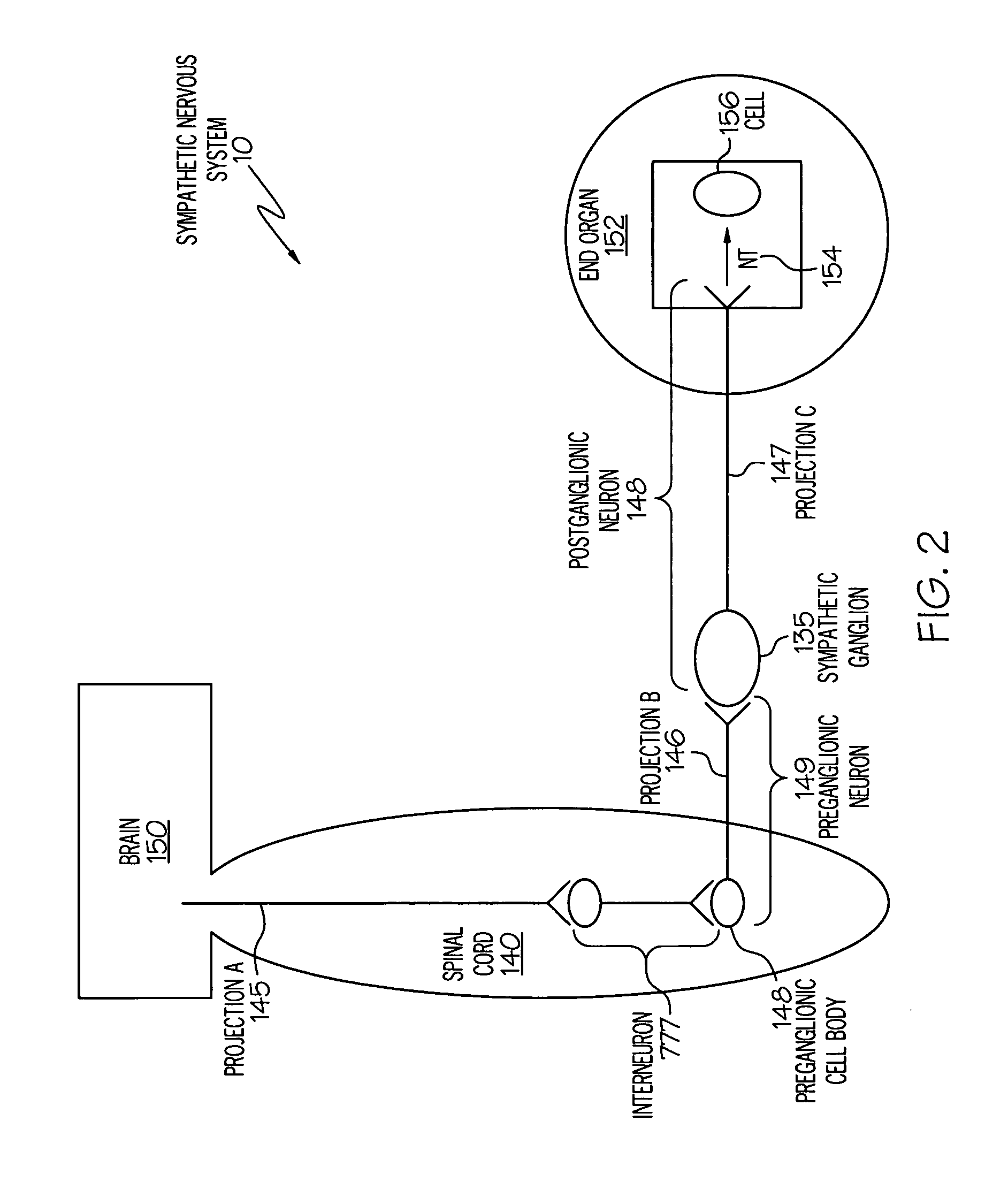
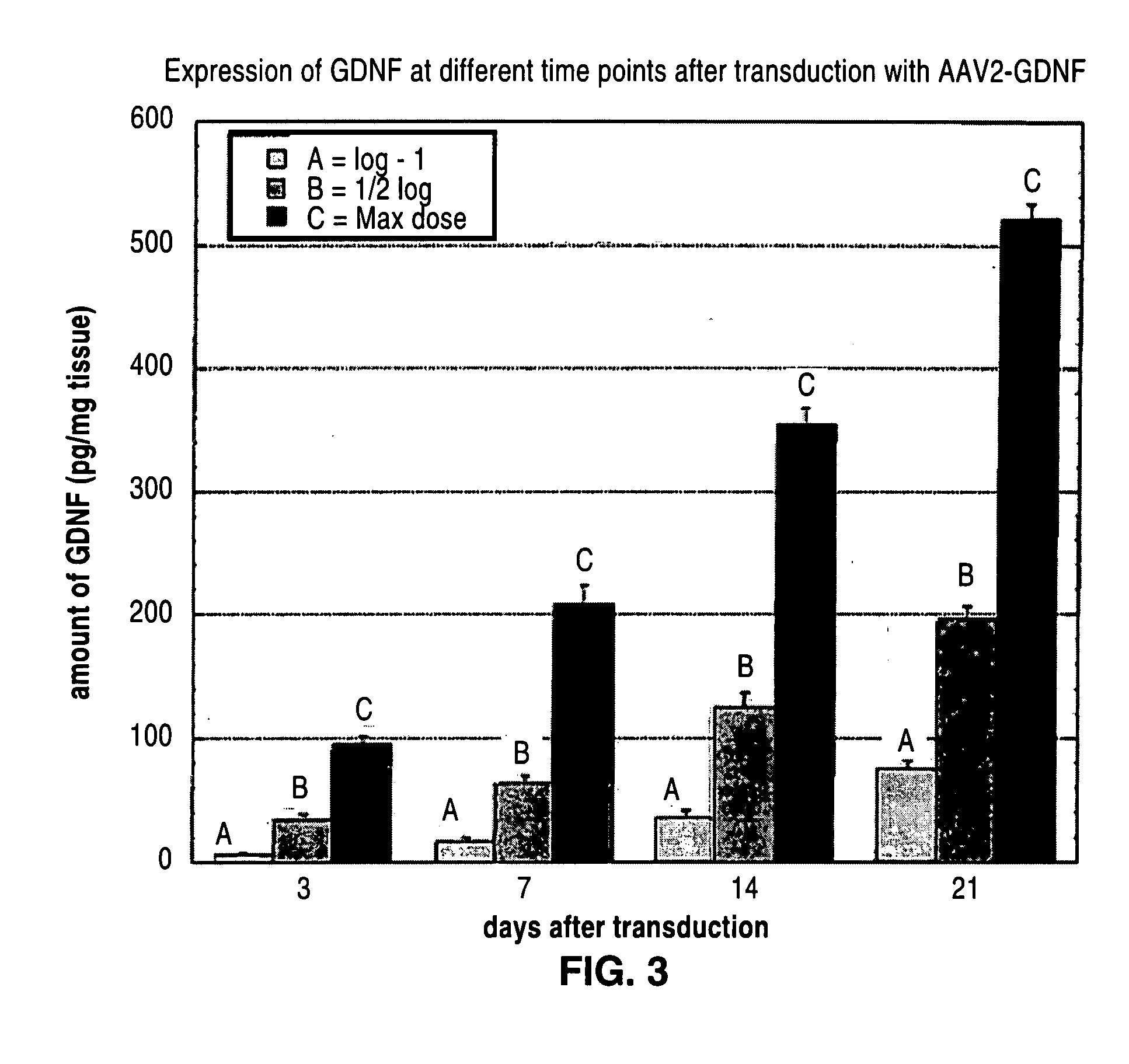
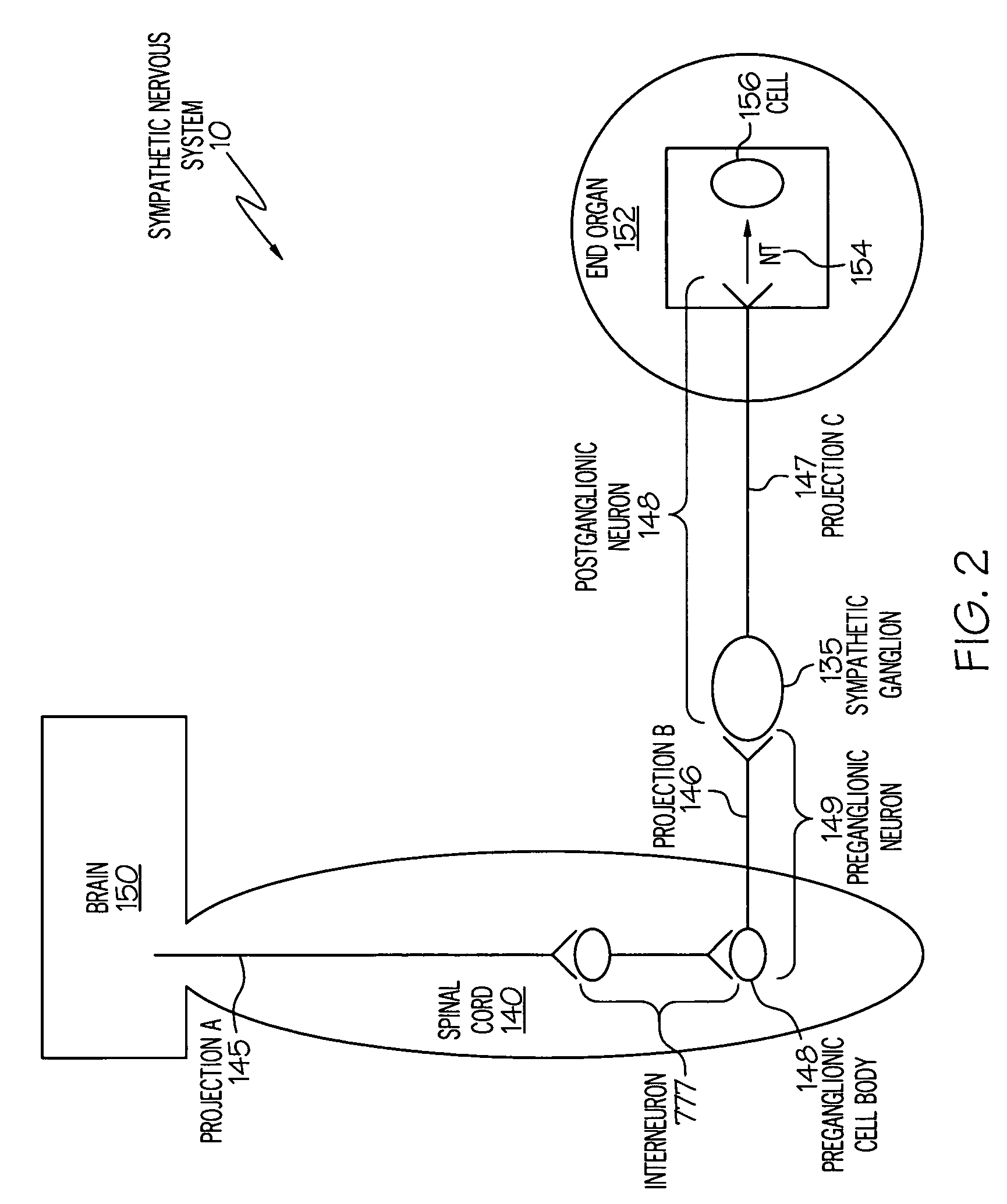
Stimulation of one or more neurons of the sympathetic nervous system, including the splenic nerve, to attenuate an immune response, including an inflammatory immune response, is discussed. Devices and systems to stimulate the sympathetic nervous system to attenuate an immune response are also discussed. Devices discussed include pulse generators and drug pumps. Systems are described as optionally having one or more sensors and operator instructions. In specific examples, stimulation of the splenic nerve of pigs with a pulse generator is shown to be safe and effective in attenuating a lipopolysaccharide-induced immune response.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods and devices for optical stimulation of neural tissues
InactiveUS6921413B2Increasing electrical field sizeHighly specificElectrotherapySurgeryPHYSICAL MANIPULATIONSOptical stimulation
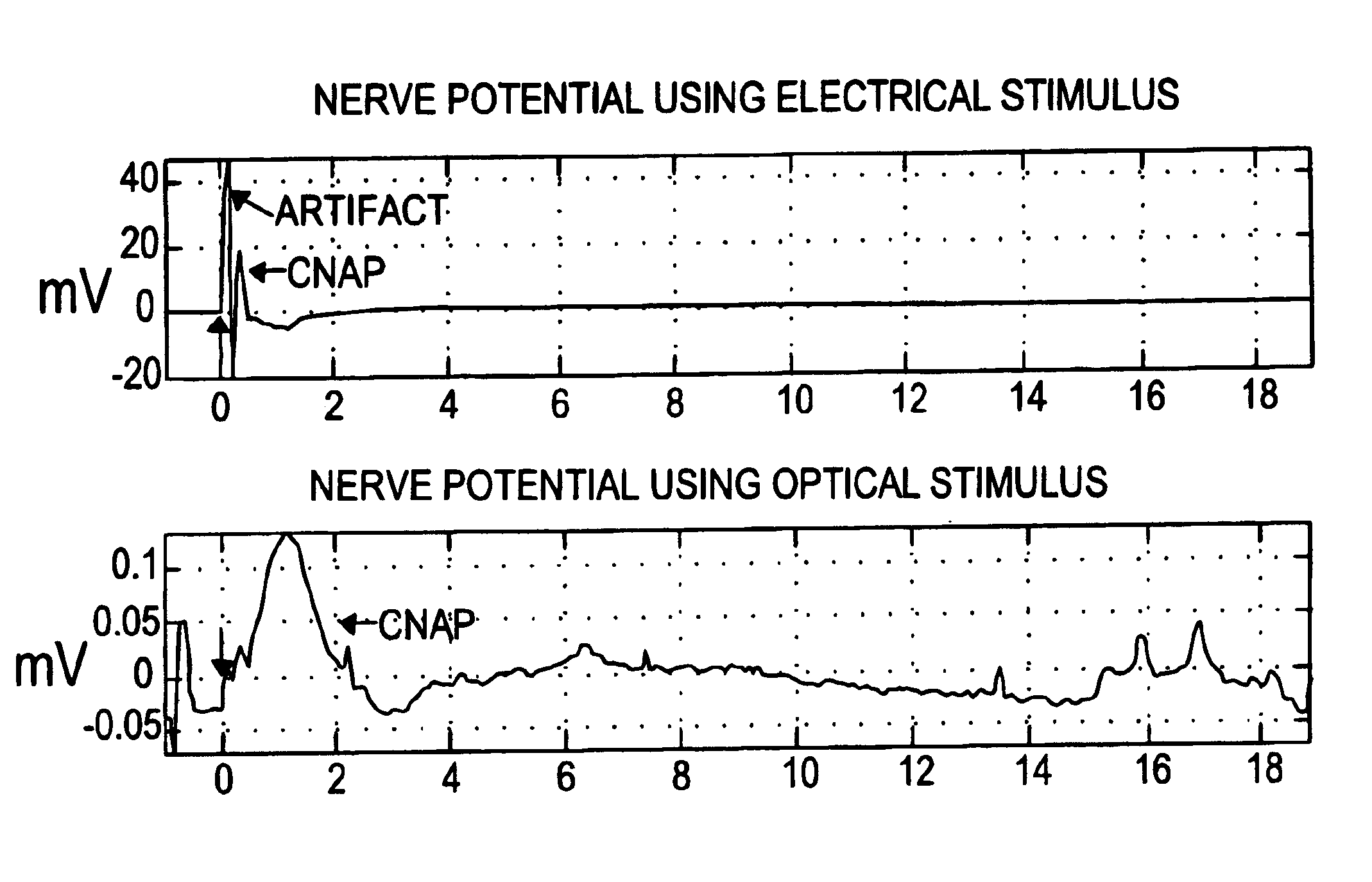
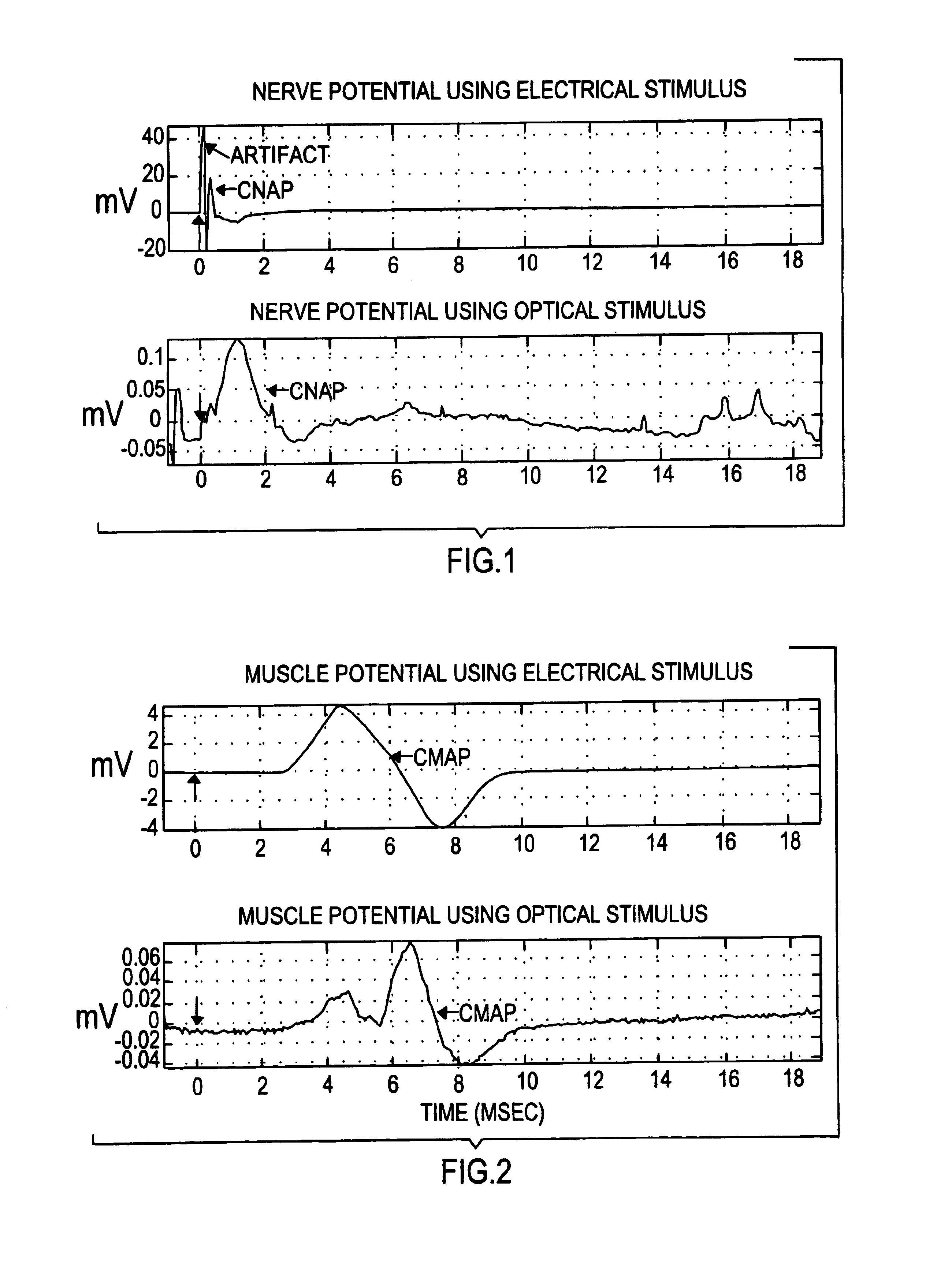
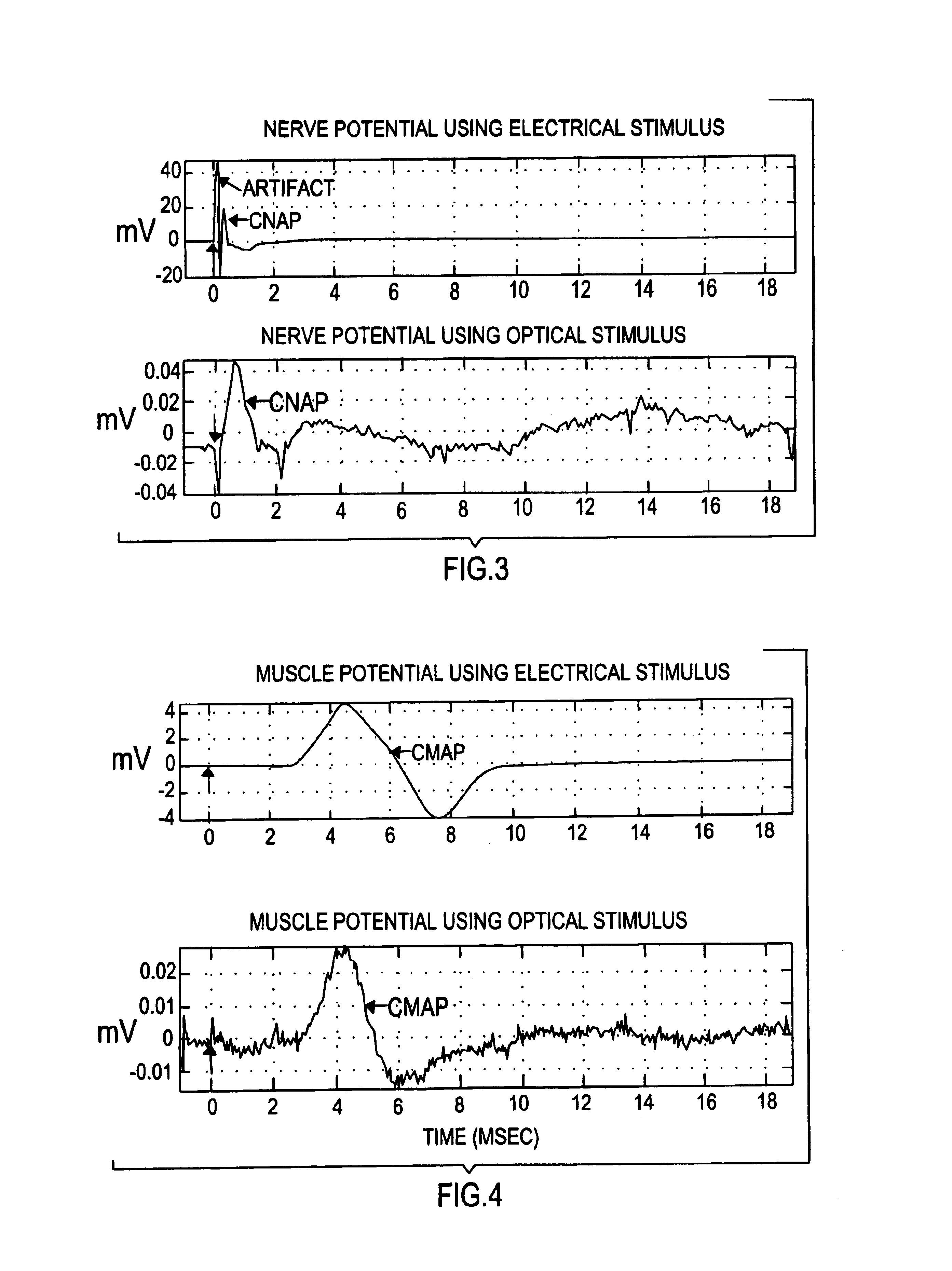
The present invention provides methods of directly stimulating neural tissue with optical energy. By stimulating neural tissue at wavelengths, laser pulses, and spot sizes disclosed herein, nerve stimulation may be used to uniquely stimulate neural tissue in way not afforded by other means of stimulation. It can allow basic scientists to study the properties of individual neurons or populations of neurons without piercing tissue with fragile microelectrodes. Furthermore, responses of neural tissue can be studied in a pure fashion without contamination by electrical artifact commonly seen with electrical stimulation. With respect to clinical uses, optical stimulation can be used to map function in subsections of peripheral nerves as an aid to operative repair. Finally, stimulation with optical energy does not require physical contact with the nerve which may be an advantage clinically when physical manipulation of neural tissue is not desired.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
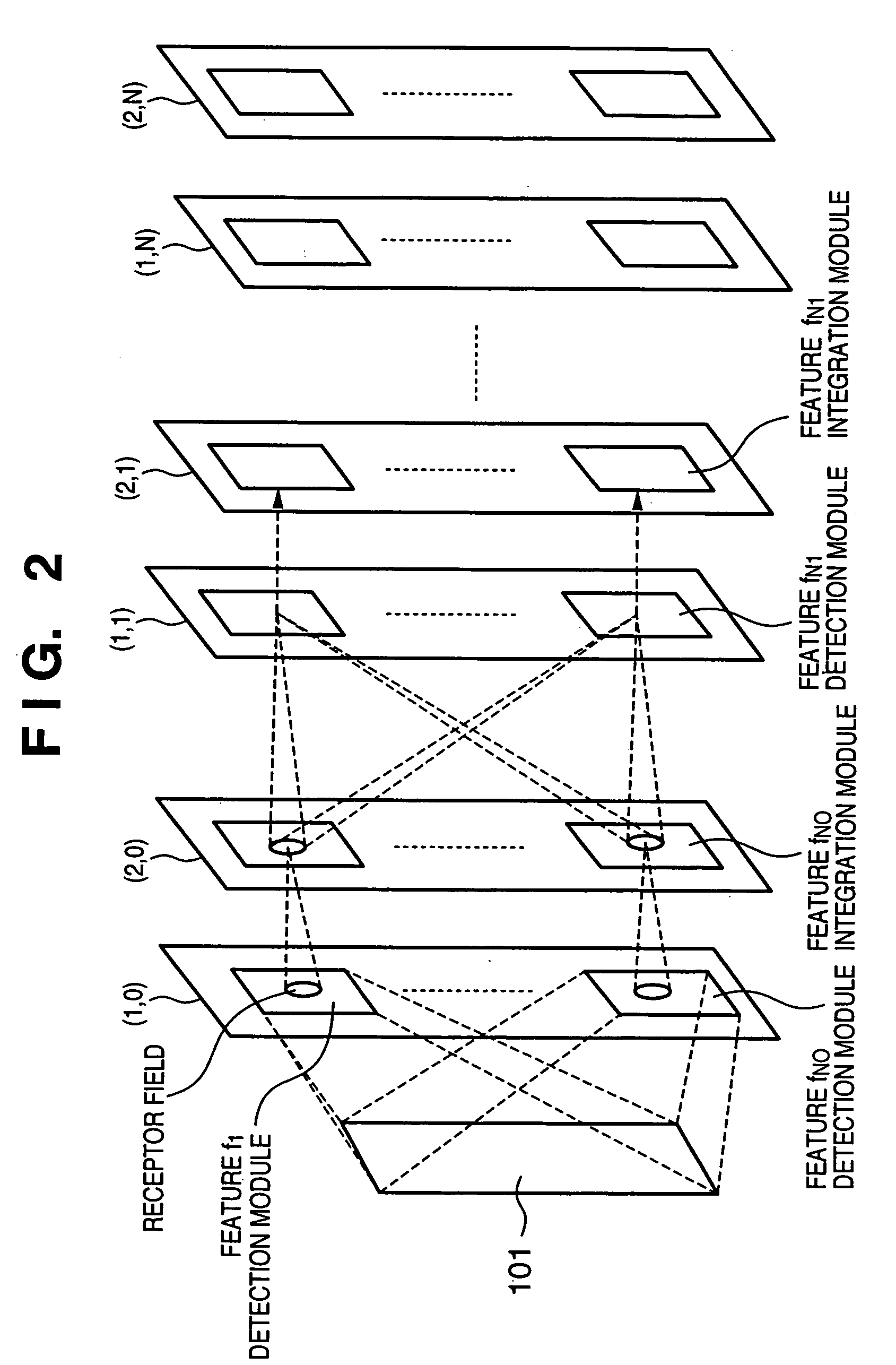
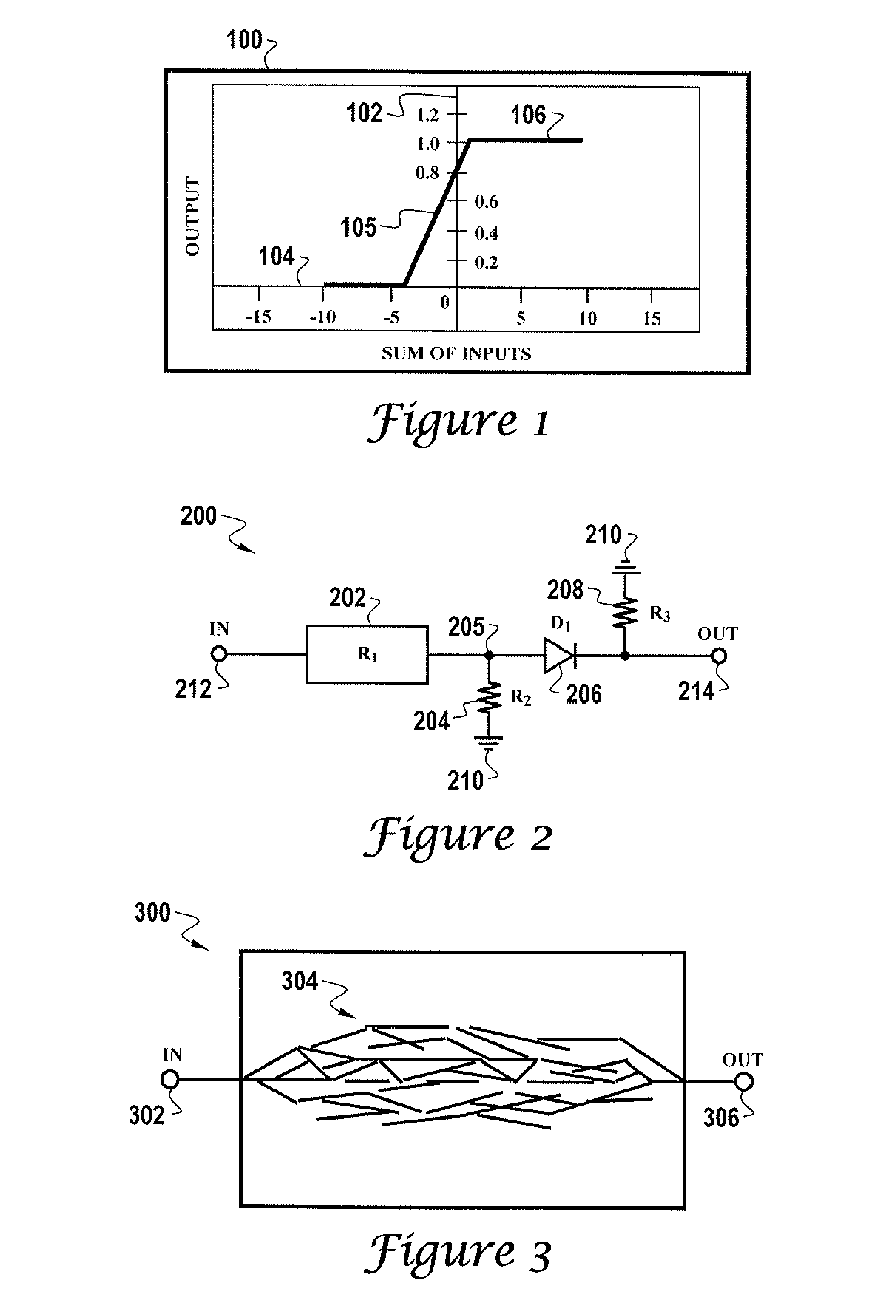
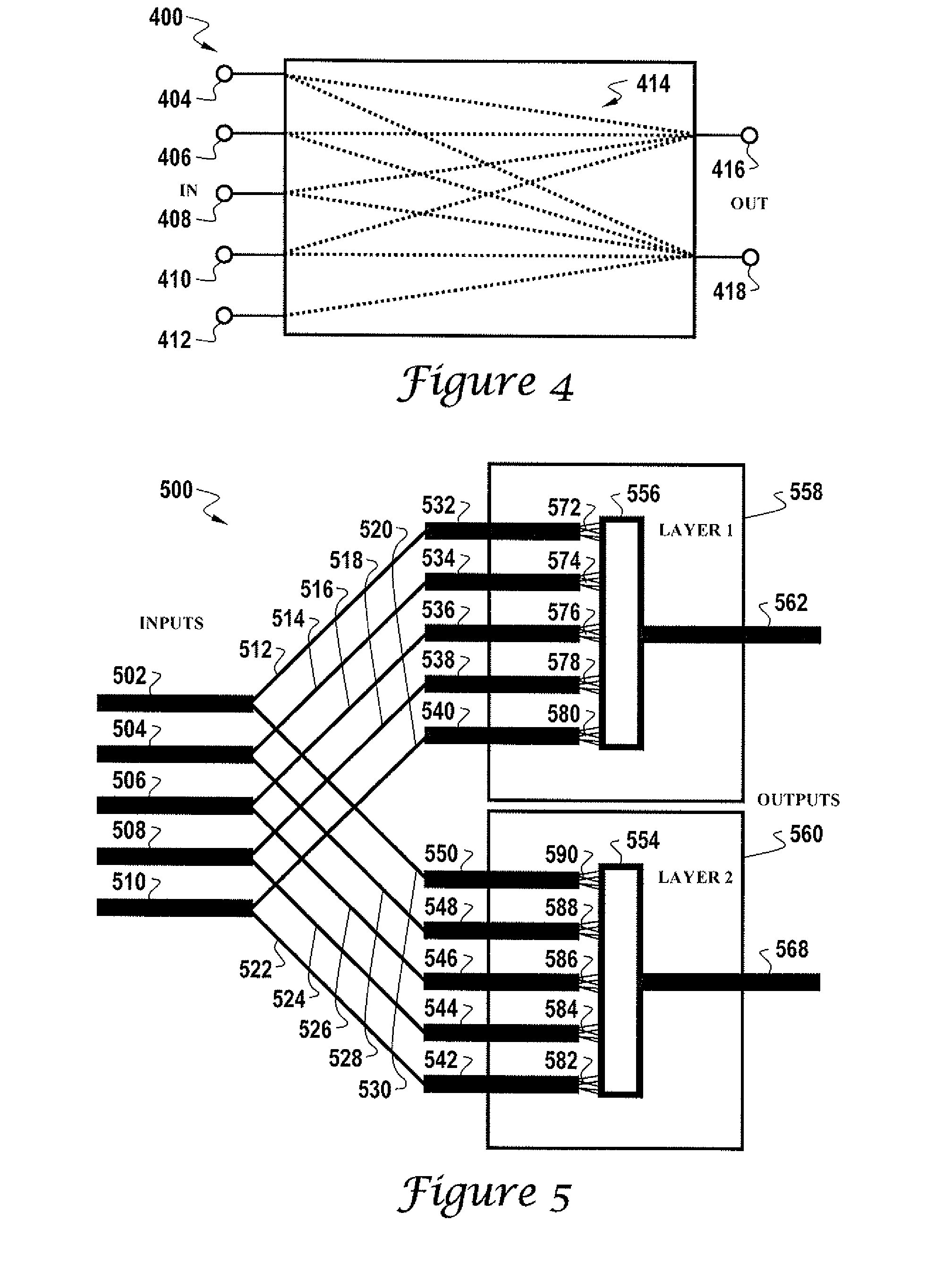
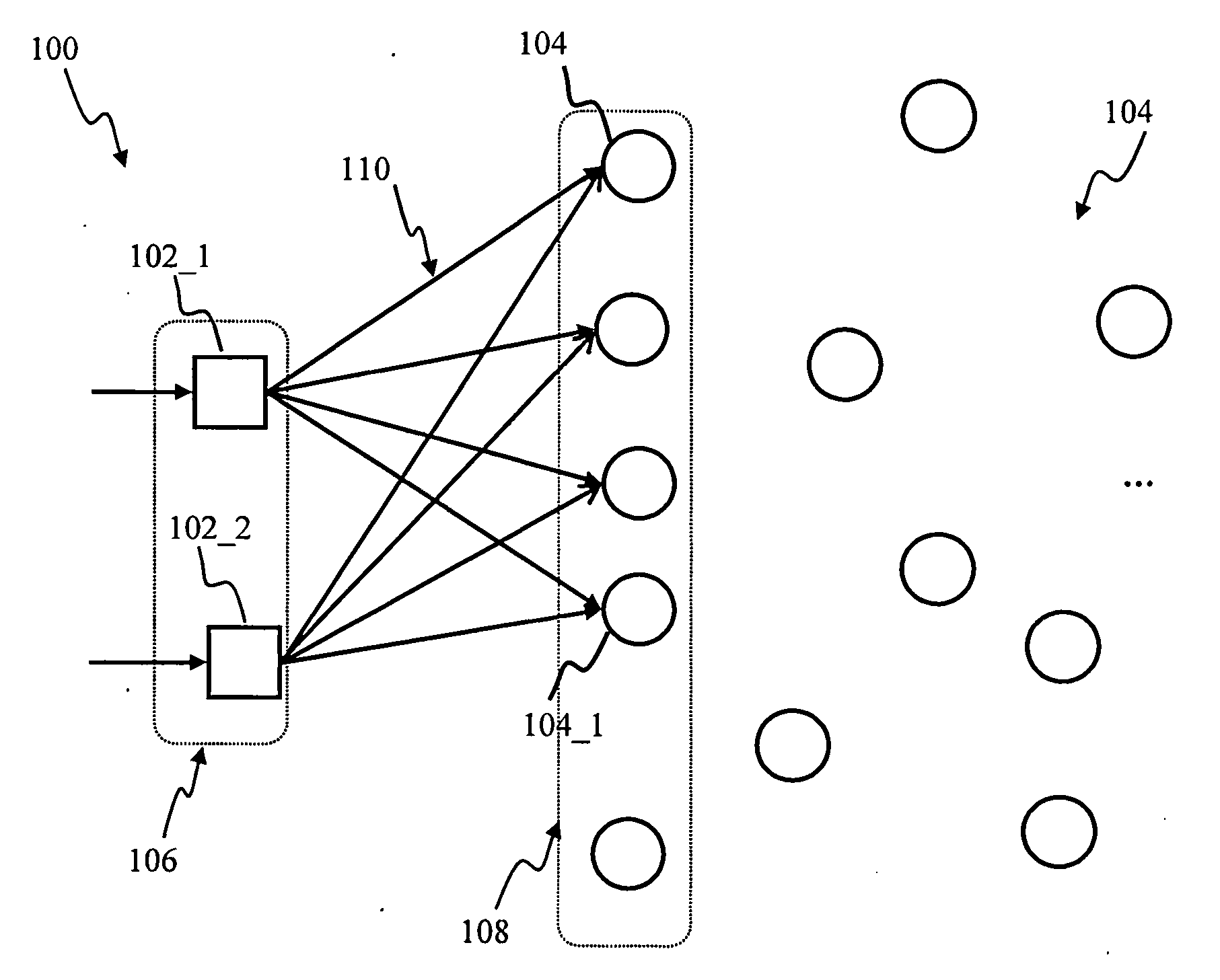
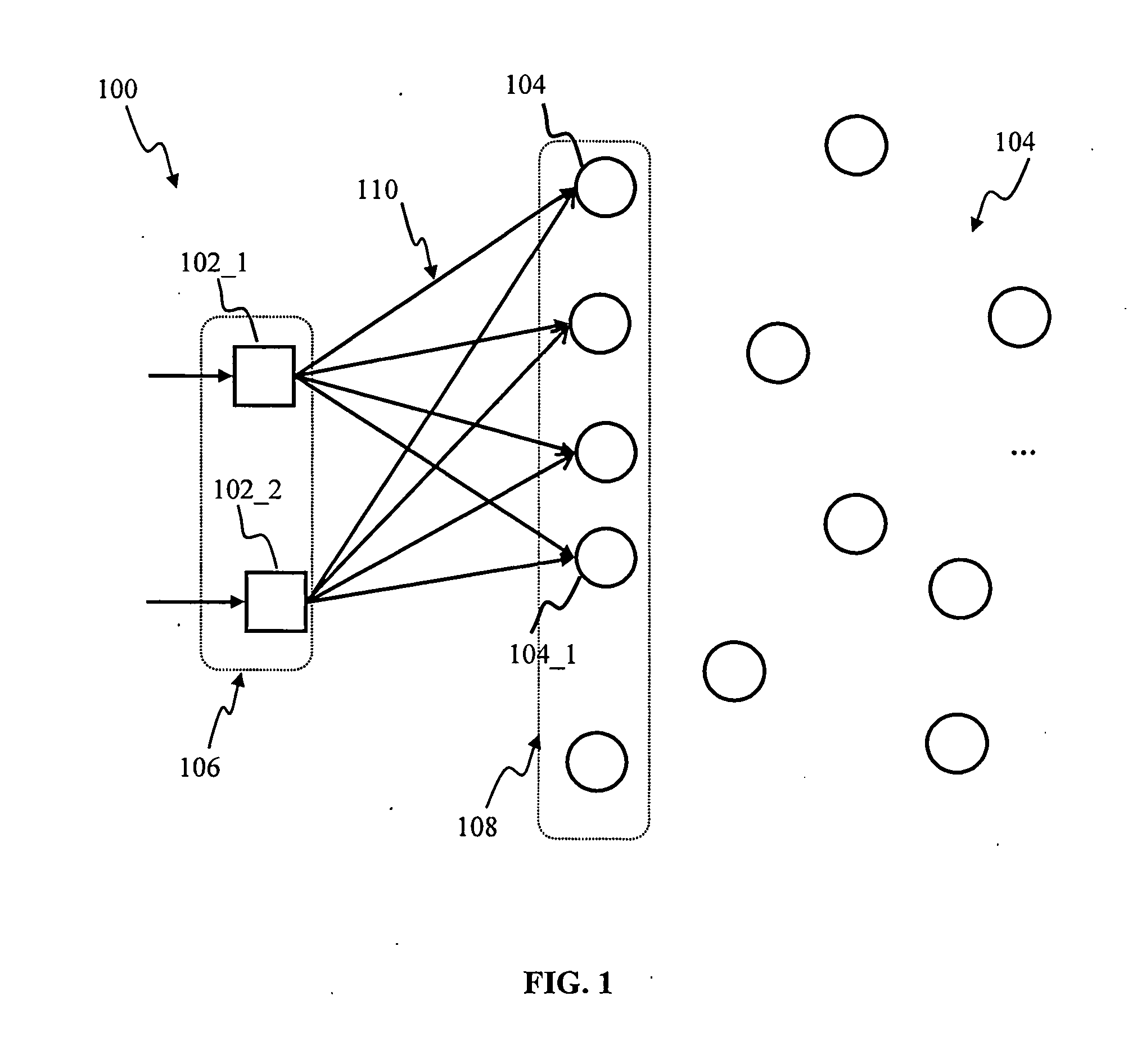
Apparatus and method for detecting or recognizing pattern by employing a plurality of feature detecting elements
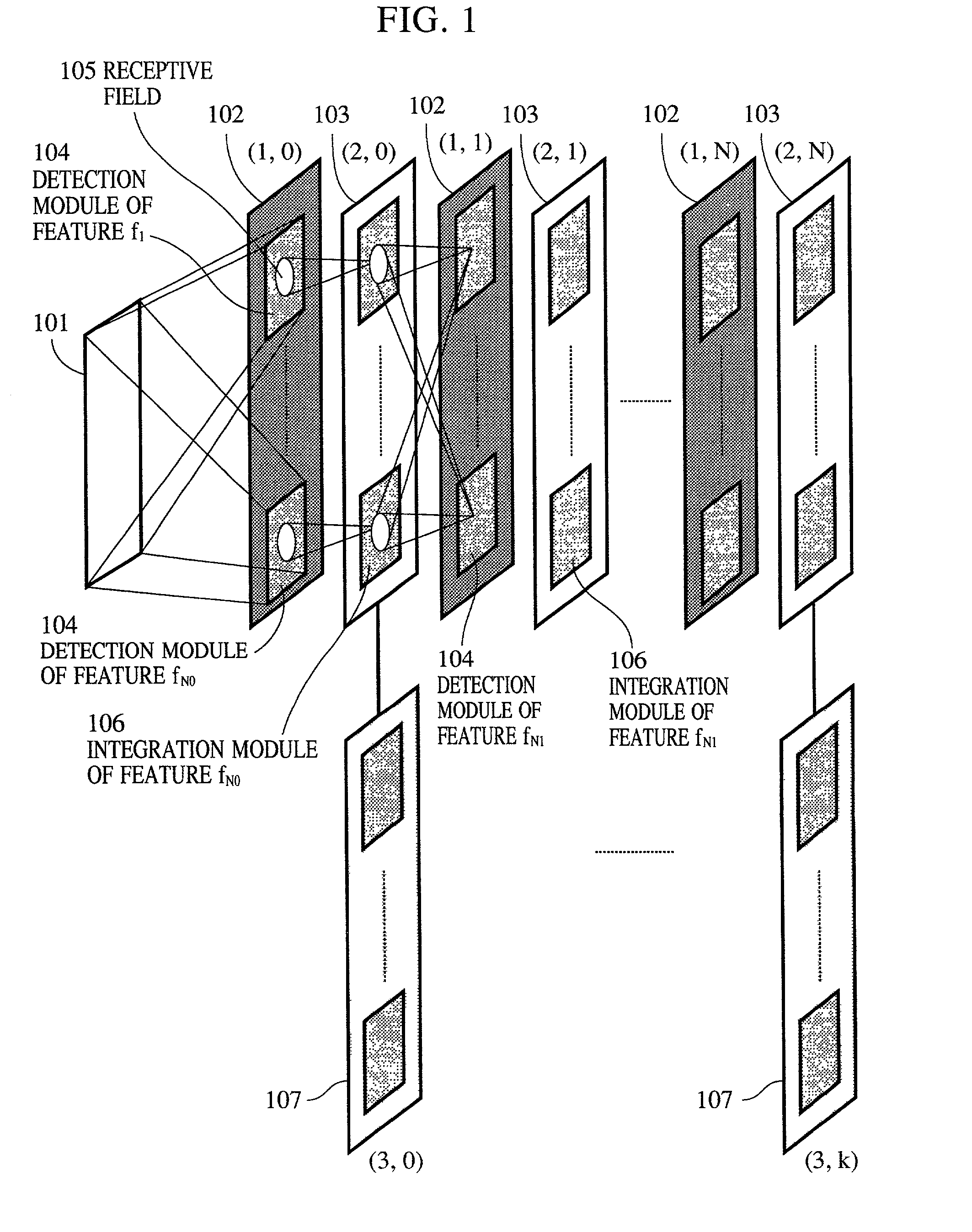
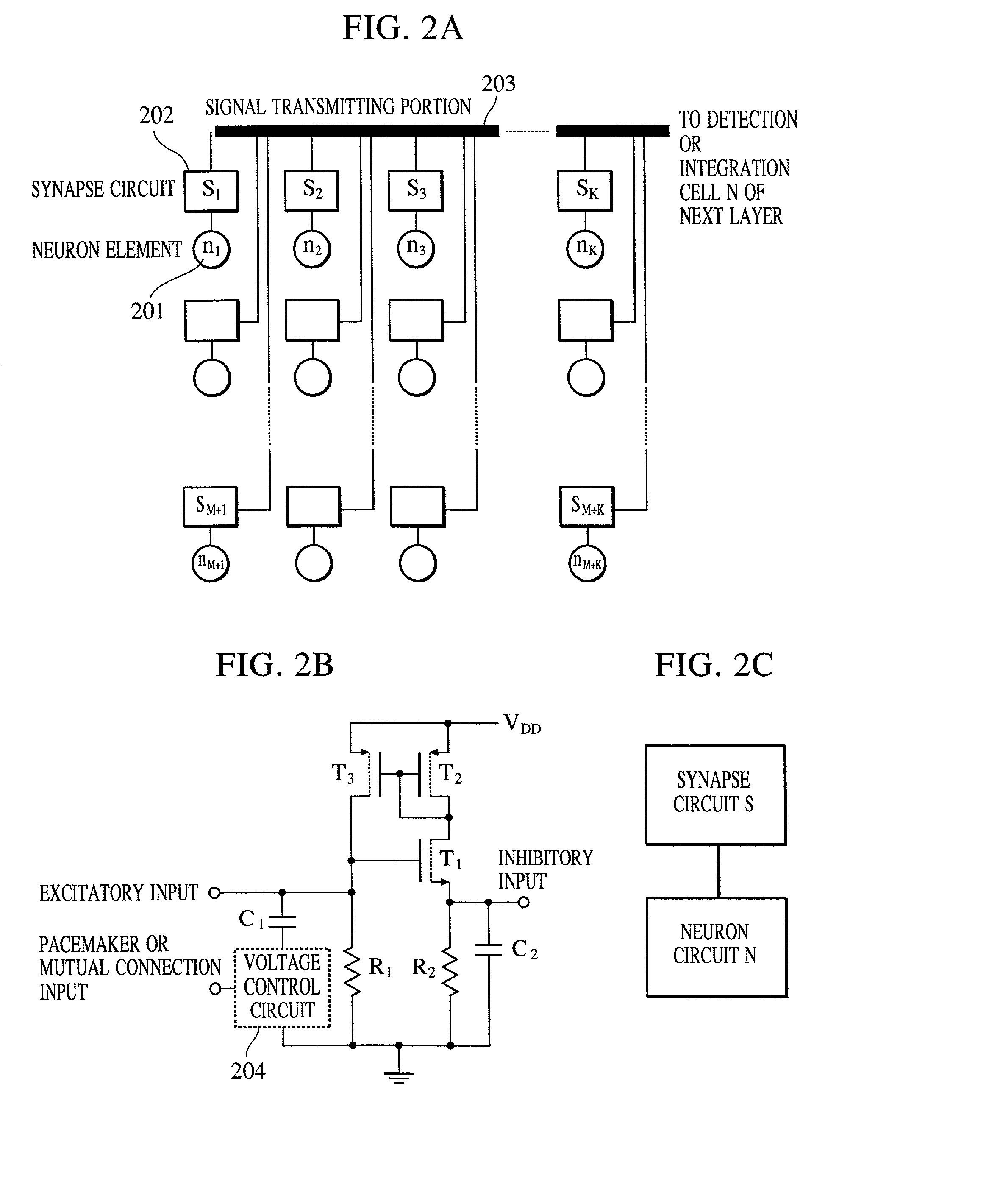
InactiveUS20020038294A1Easy constructionReduce in quantityDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSynapsePattern detection
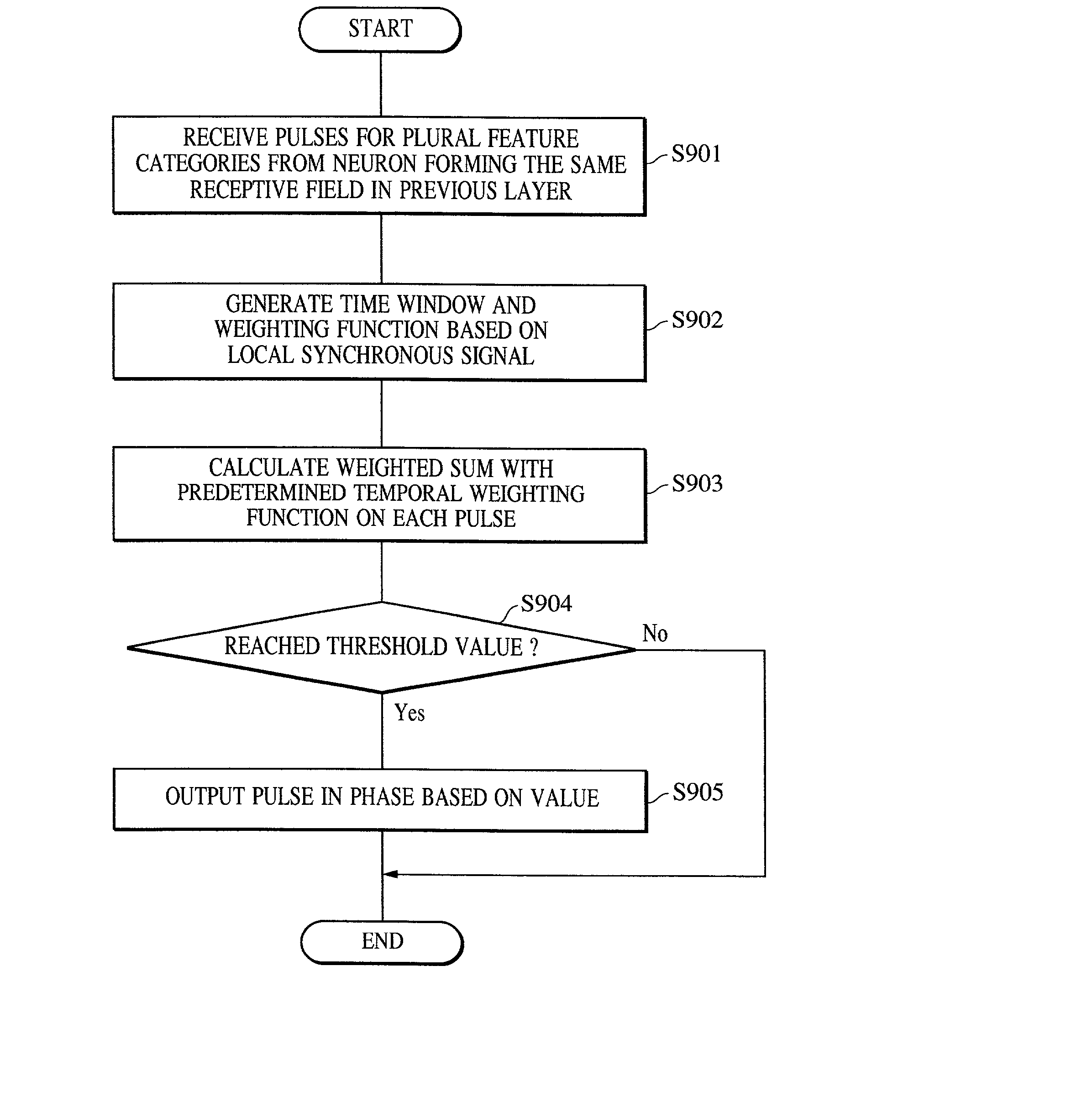
A pattern detecting apparatus has a plurality of hierarchized neuron elements to detect a predetermined pattern included in input patterns. Pulse signals output from the plurality of neuron elements are given specific delays by synapse circuits associated with the individual elements. This makes it possible to transmit the pulse signals to the neuron elements of the succeeding layer through a common bus line so that they can be identified on a time base. The neuron elements of the succeeding layer output the pulse signals at output levels based on a arrival time pattern of the plurality of pulse signals received from the plurality of neuron elements of the preceding layer within a predetermined time window. Thus, the reliability of pattern detection can be improved, and the number of wires interconnecting the elements can be reduced by the use of the common bus line, leading to a small scale of circuit and reduced power consumption.
Owner:CANON KK
Deep Learning Neural Network Classifier Using Non-volatile Memory Array
ActiveUS20170337466A1Input/output to record carriersRead-only memoriesSynapseNeural network classifier
An artificial neural network device that utilizes one or more non-volatile memory arrays as the synapses. The synapses are configured to receive inputs and to generate therefrom outputs. Neurons are configured to receive the outputs. The synapses include a plurality of memory cells, wherein each of the memory cells includes spaced apart source and drain regions formed in a semiconductor substrate with a channel region extending there between, a floating gate disposed over and insulated from a first portion of the channel region and a non-floating gate disposed over and insulated from a second portion of the channel region. Each of the plurality of memory cells is configured to store a weight value corresponding to a number of electrons on the floating gate. The plurality of memory cells are configured to multiply the inputs by the stored weight values to generate the outputs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
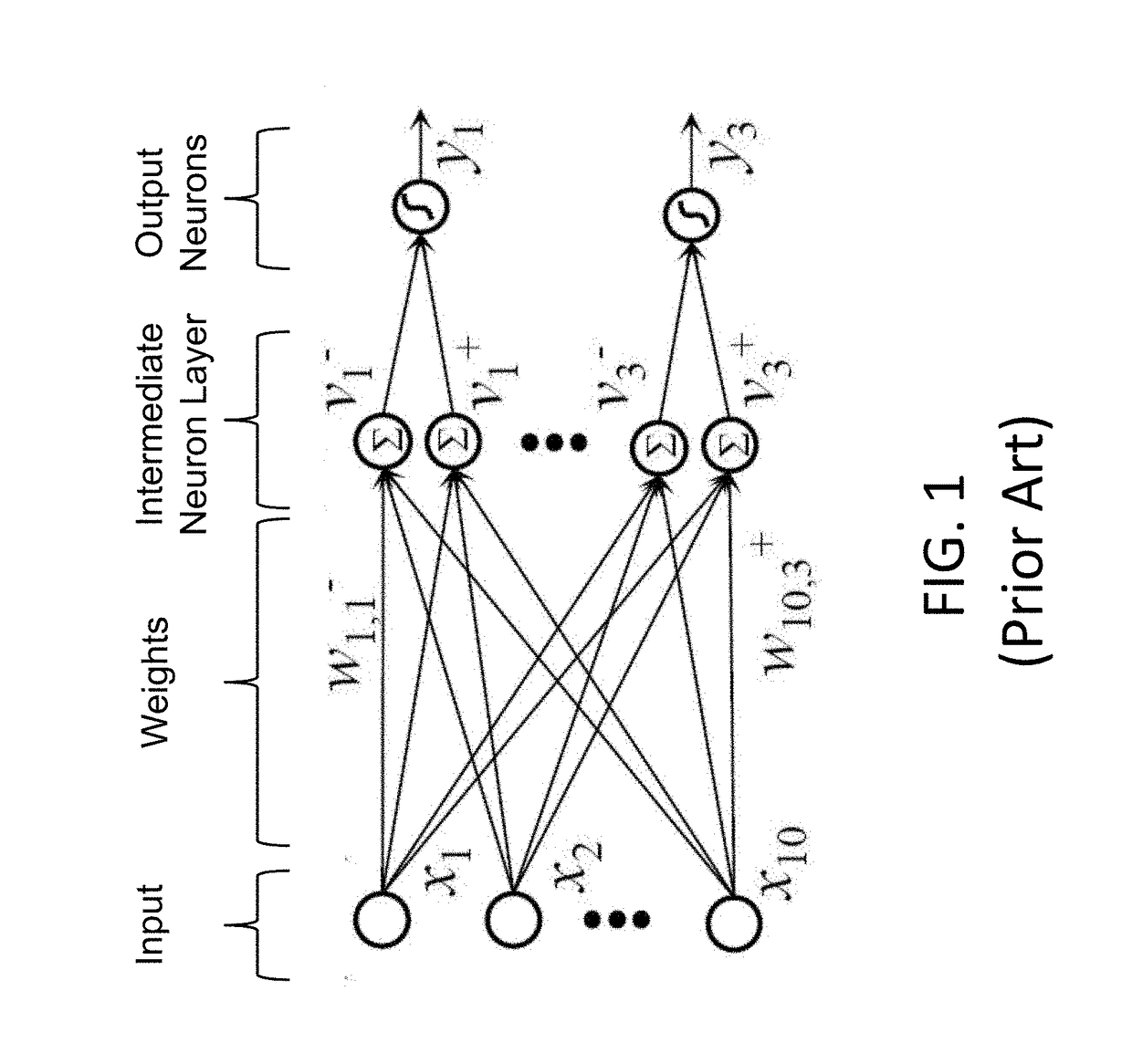
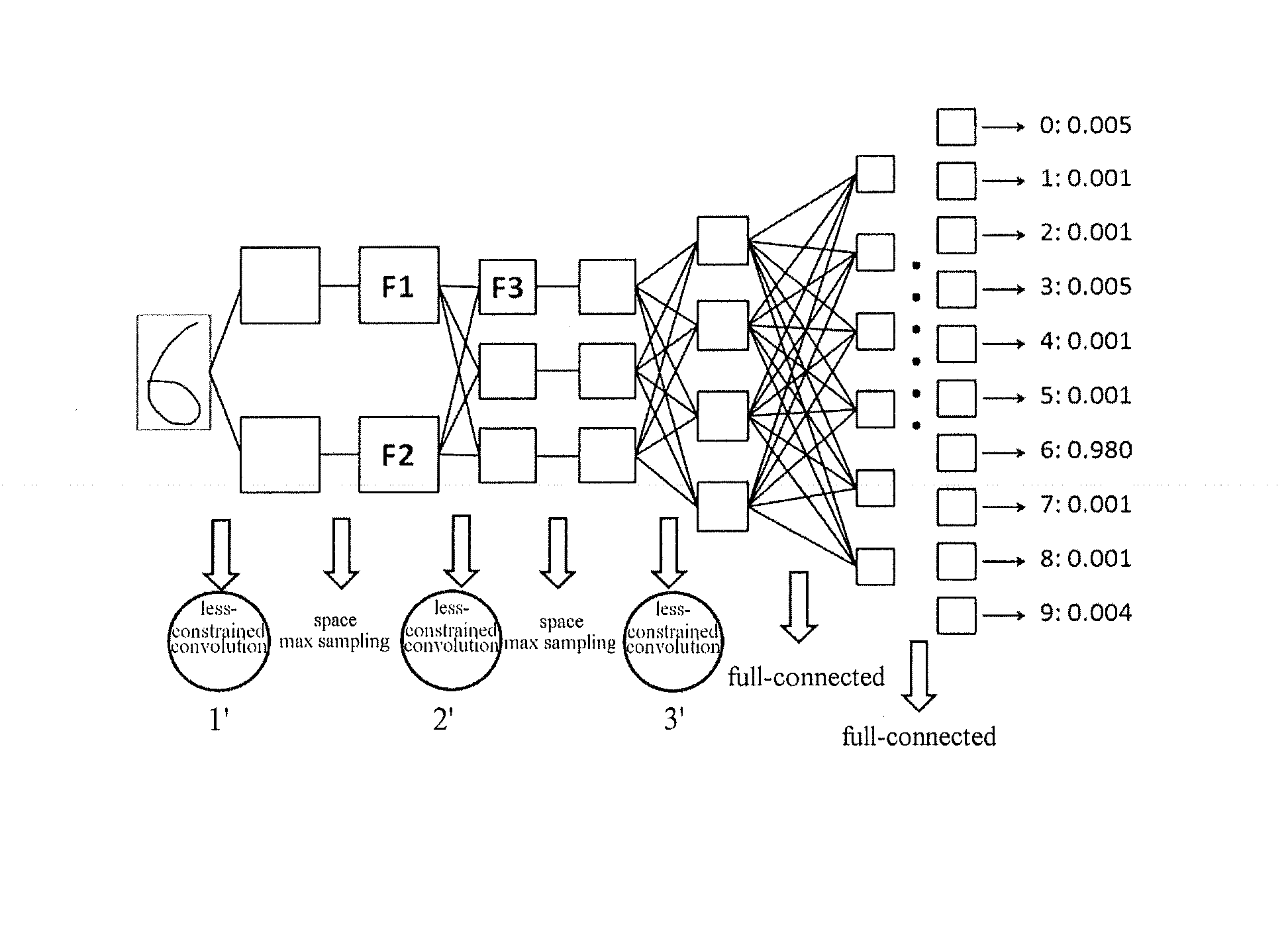
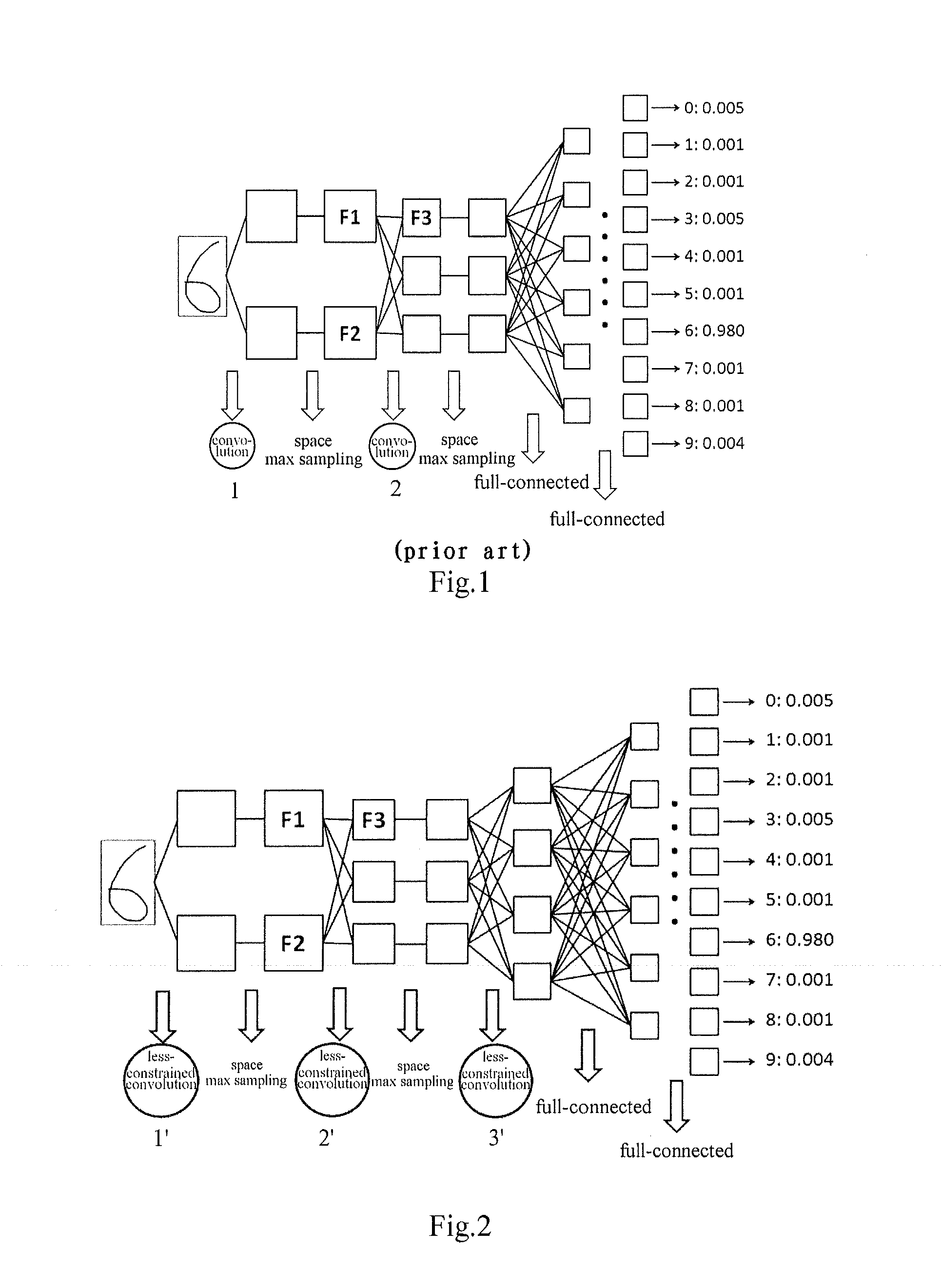
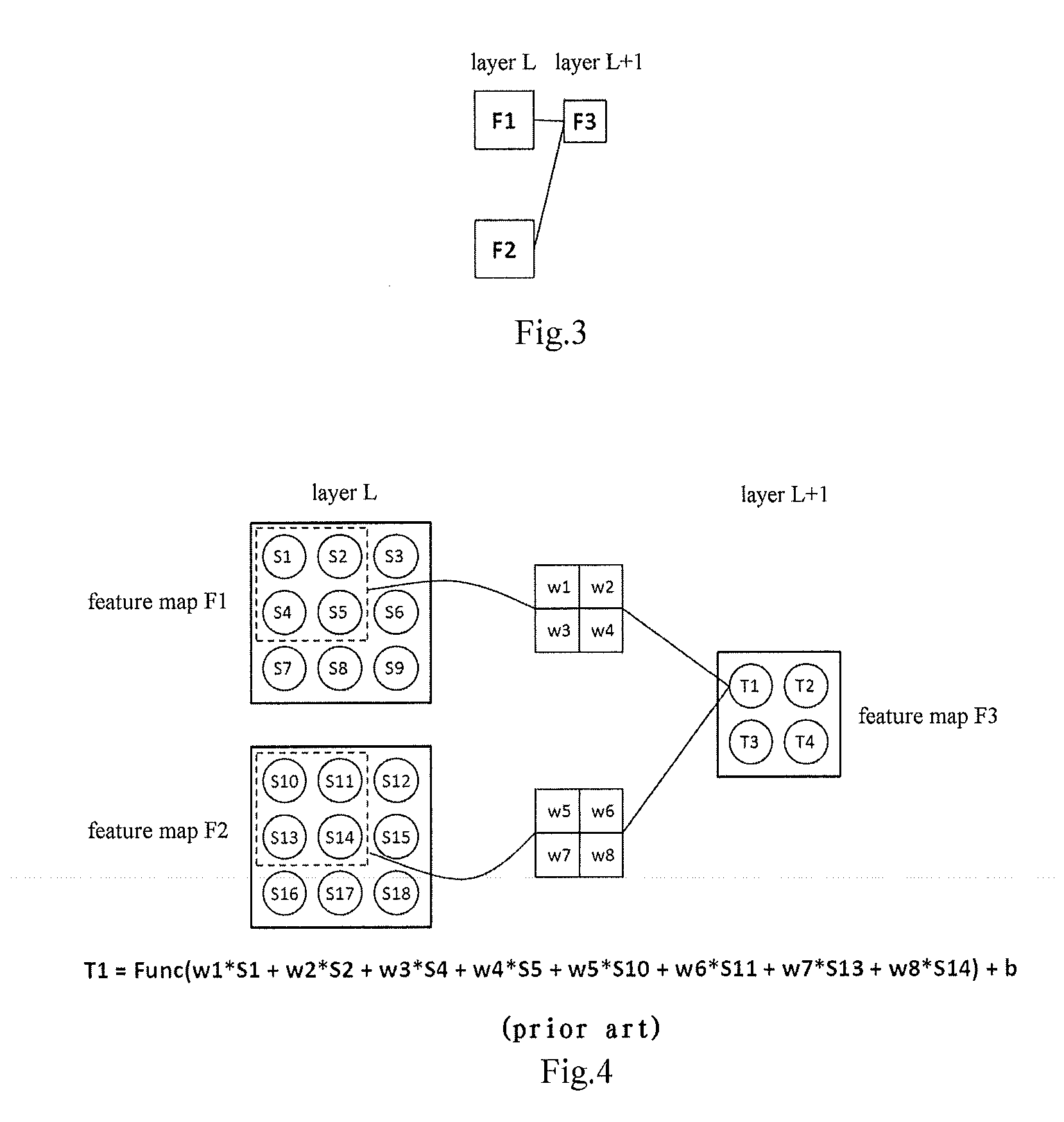
Convolutional-neural-network-based classifier and classifying method and training methods for the same
InactiveUS20150036920A1Character and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsClassification methodsNeuron
The present invention relates to a convolutional-neural-network-based classifier, a classifying method by using a convolutional-neural-network-based classifier and a method for training the convolutional-neural-network-based classifier. The convolutional-neural-network-based classifier comprises: a plurality of feature map layers, at least one feature map in at least one of the plurality of feature map layers being divided into a plurality of regions; and a plurality of convolutional templates corresponding to the plurality of regions respectively, each of the convolutional templates being used for obtaining a response value of a neuron in the corresponding region.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
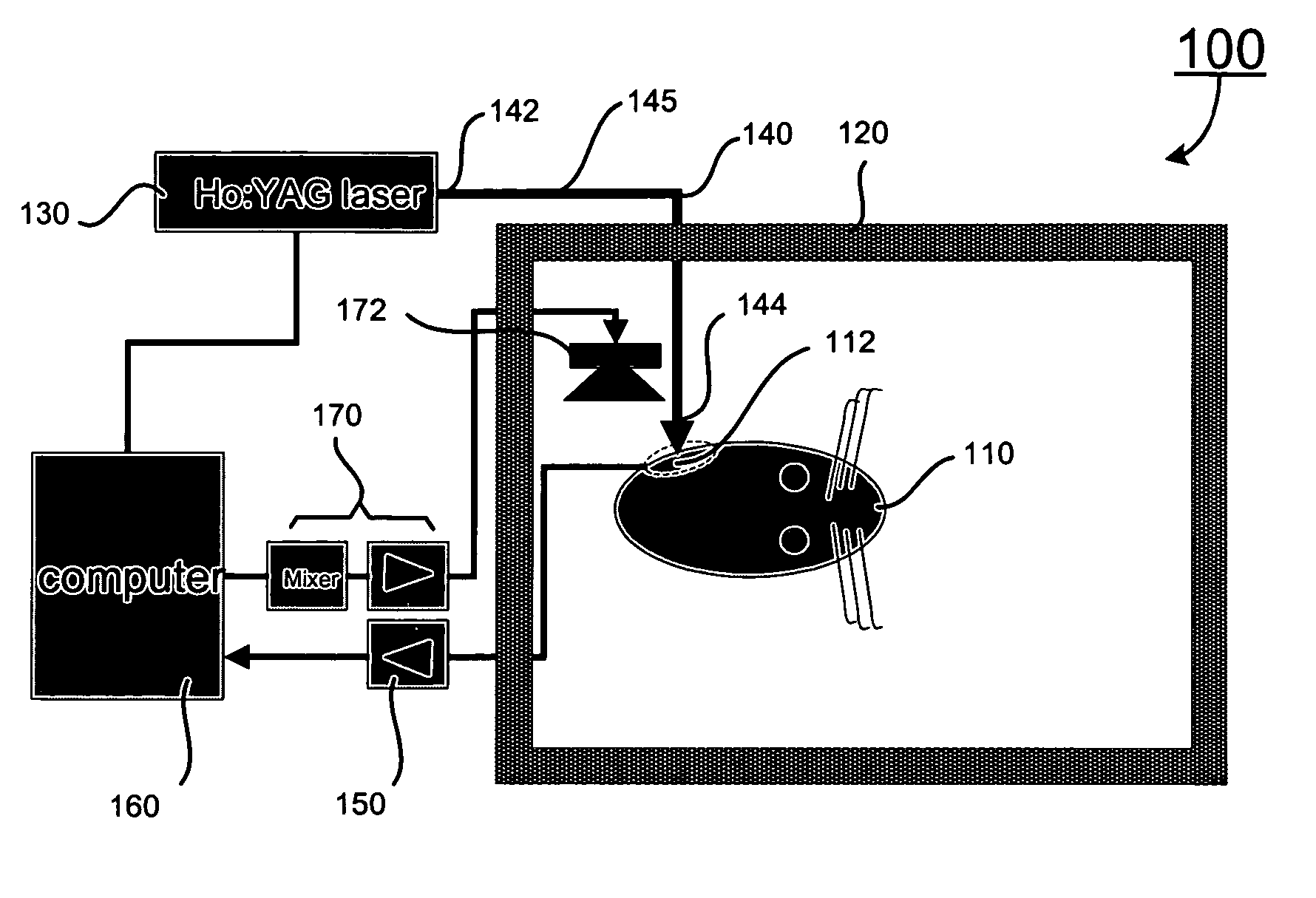
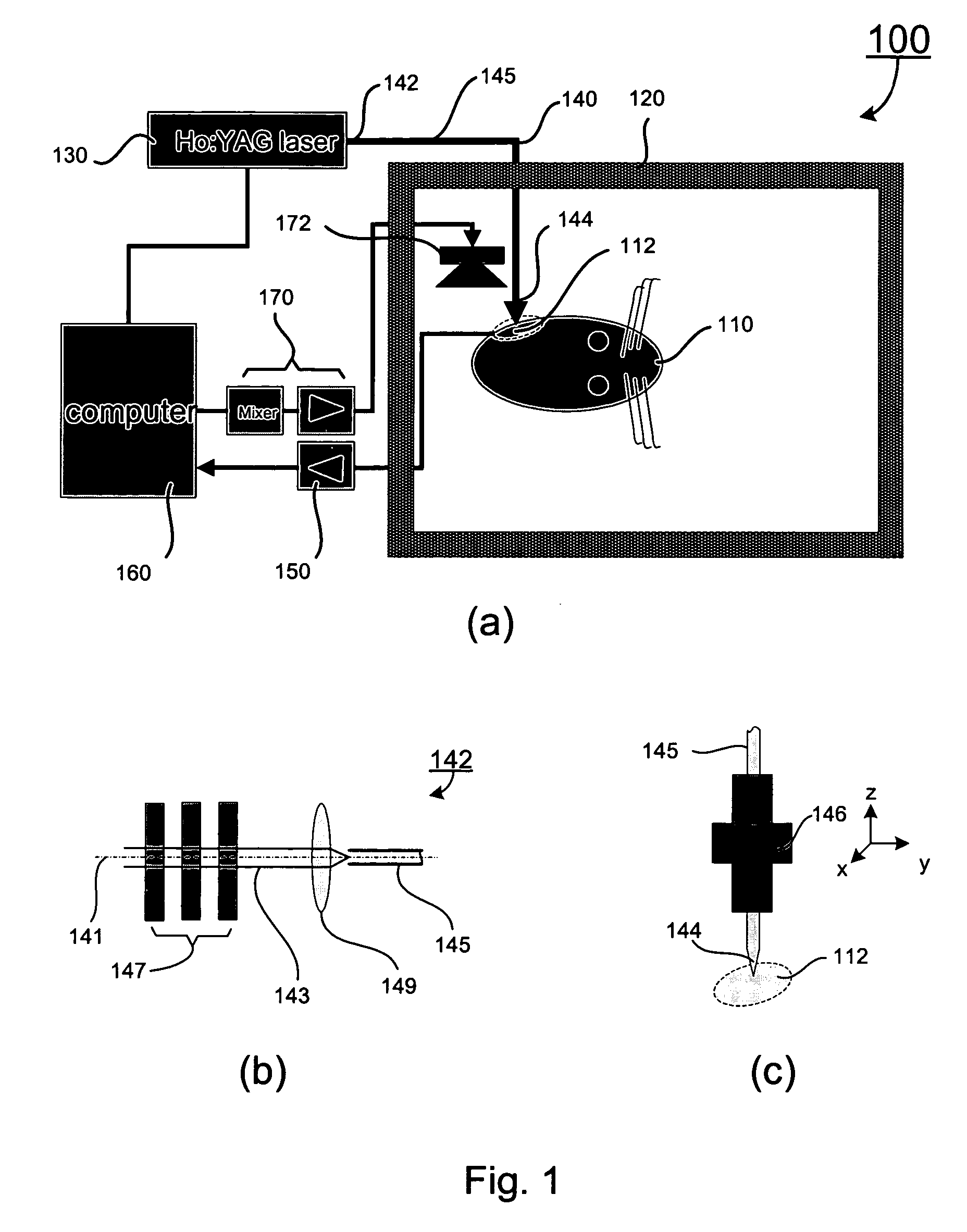
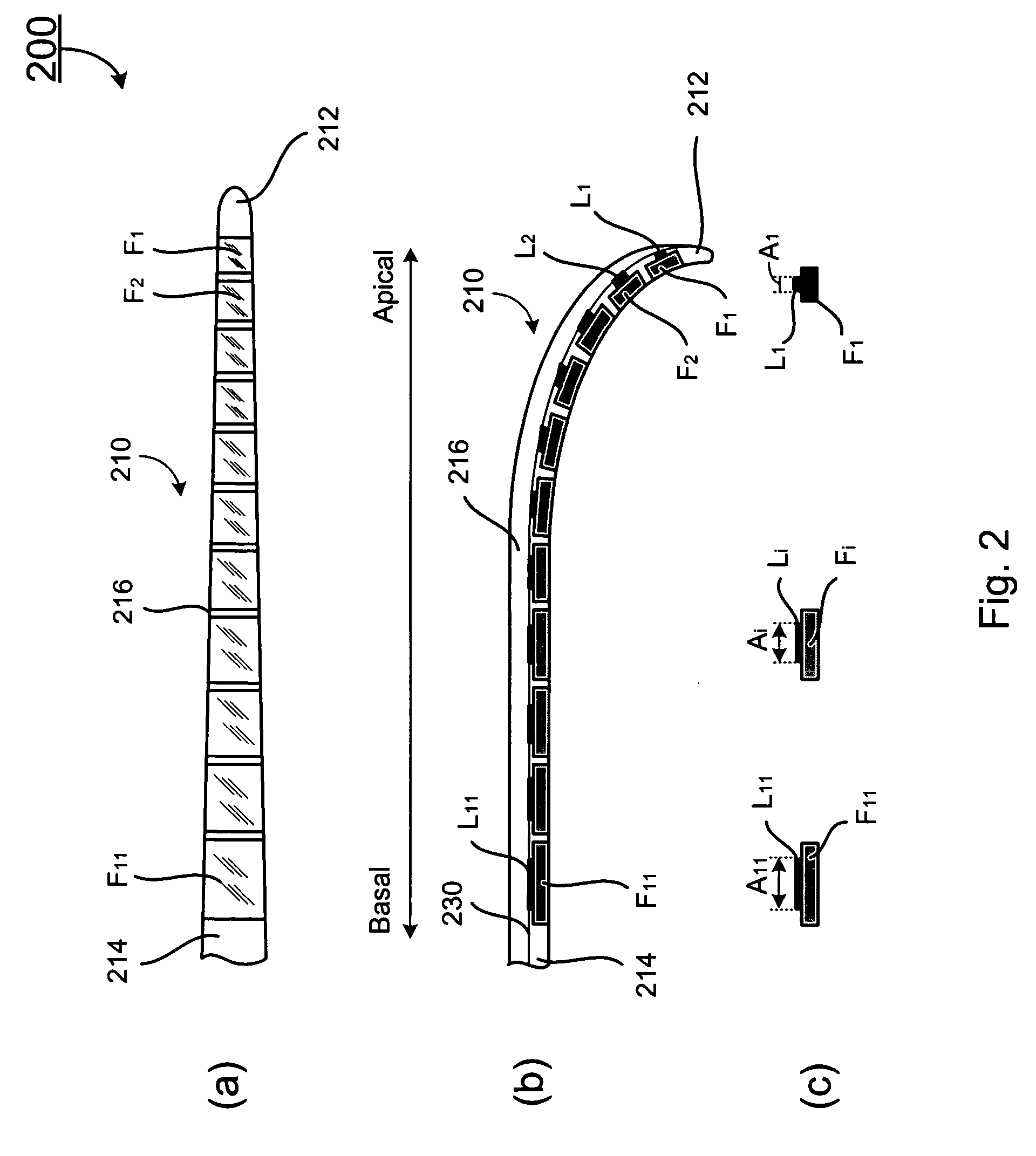
Apparatus and methods for optical stimulation of the auditory nerve
A cochlear implant placed in a cochlea of a living subject for stimulating the auditory system of the living subject, where the auditory system comprises auditory neurons. In one embodiment, the cochlear implant includes a plurality of light sources, {Li}, placeable distal to the cochlea, each light source, L1, being operable independently and adapted for generating an optical energy, Ei, wherein i=1, . . . , N, and N is the number of the light sources, and delivering means placeable in the cochlea and optically coupled to the plurality of light sources, {Li}, such that in operation, the optical energies {Ei} generated by the plurality of light sources {Li} are delivered to target sites, {Gi}, of auditory neurons, respectively, wherein the target sites G1 and GN of auditory neurons are substantially proximate to the apical end and the basal end of the cochlea, respectively.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
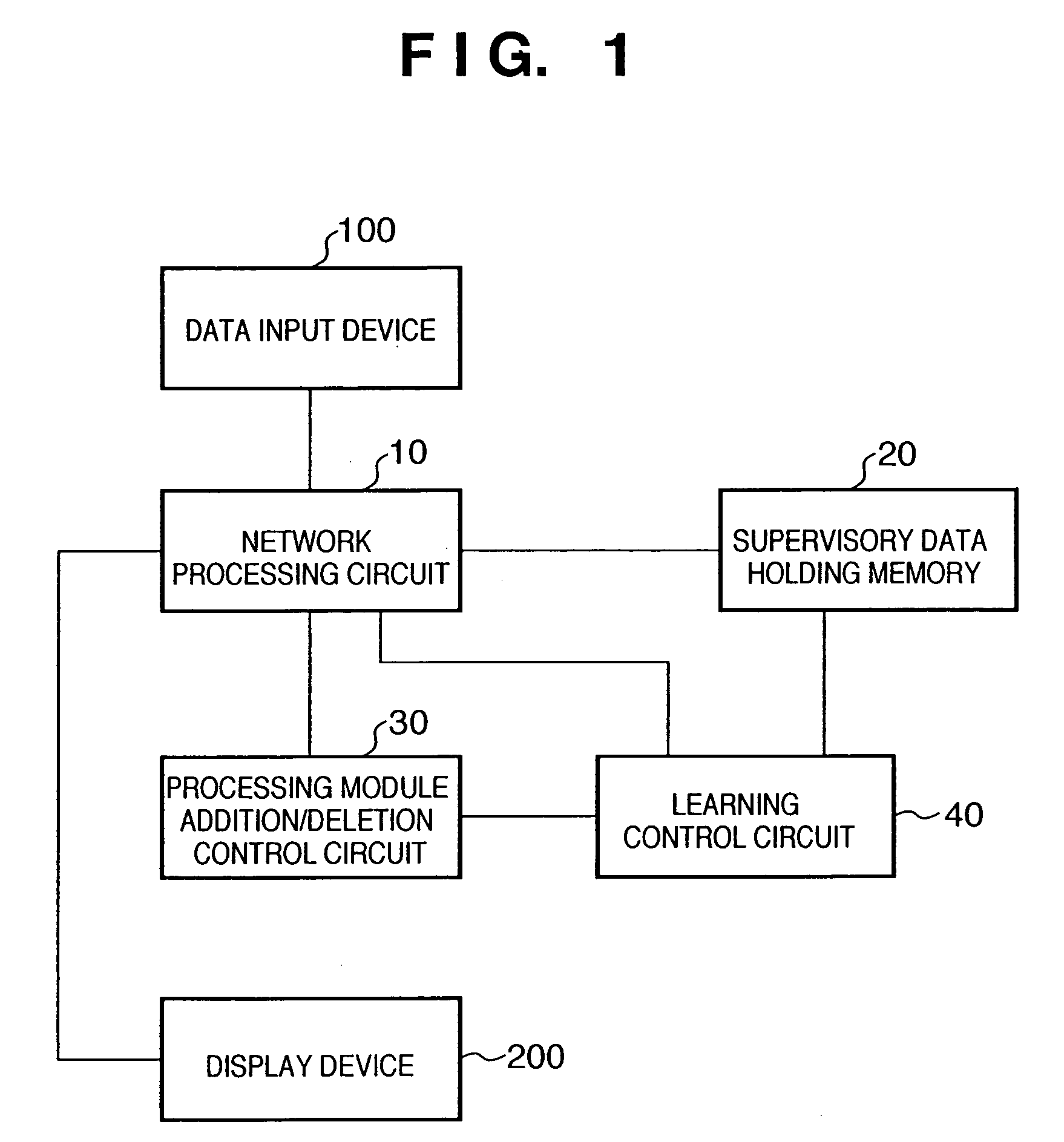
Information processing apparatus, information processing method, pattern recognition apparatus, and pattern recognition method
InactiveUS20050283450A1Image analysisDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionInformation processing
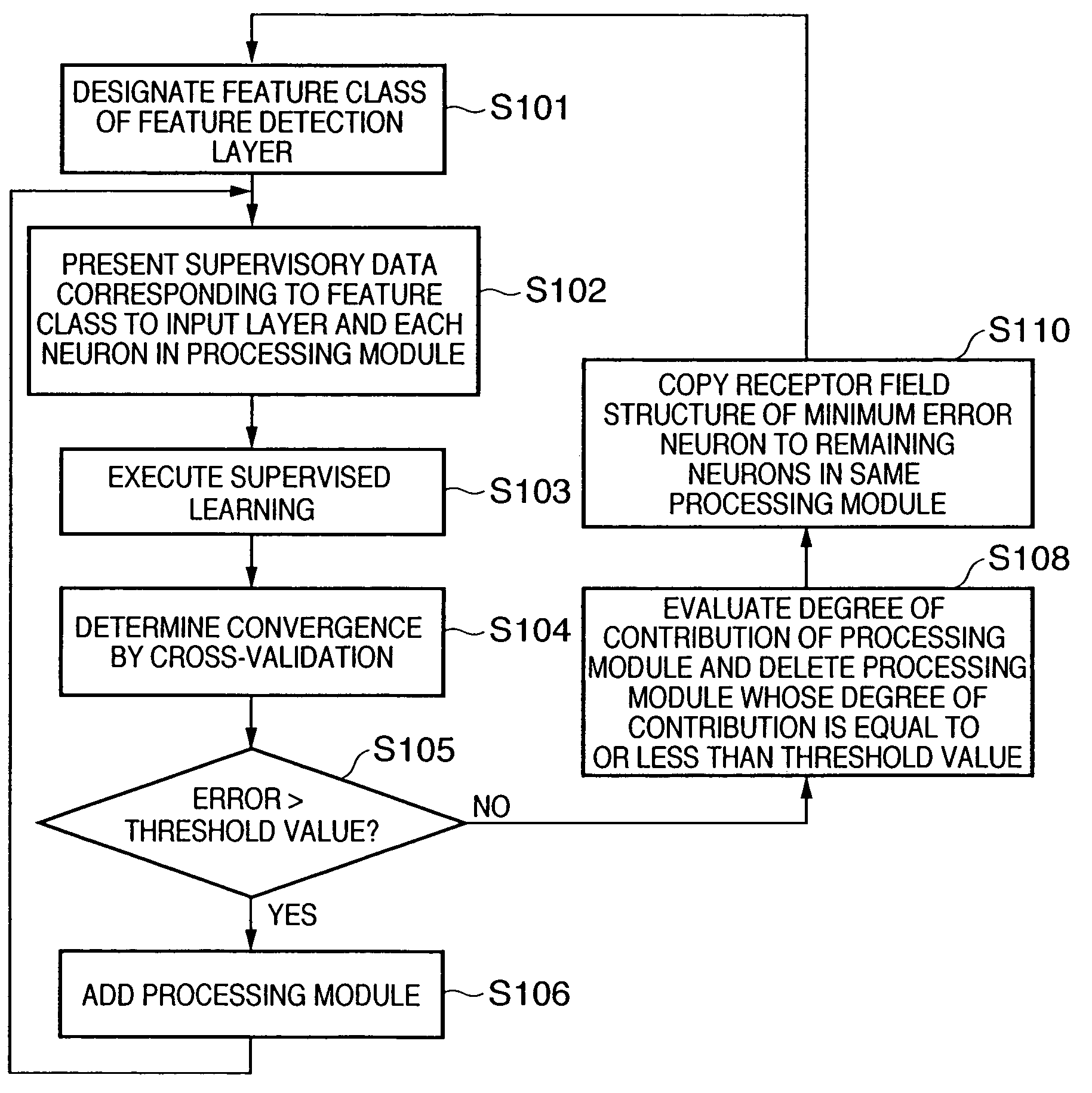
In a hierarchical neural network having a module structure, learning necessary for detection of a new feature class is executed by a processing module which has not finished learning yet and includes a plurality of neurons which should learn an unlearned feature class and have an undetermined receptor field structure by presenting a predetermined pattern to a data input layer. Thus, a feature class necessary for subject recognition can be learned automatically and efficiently.
Owner:CANON KK
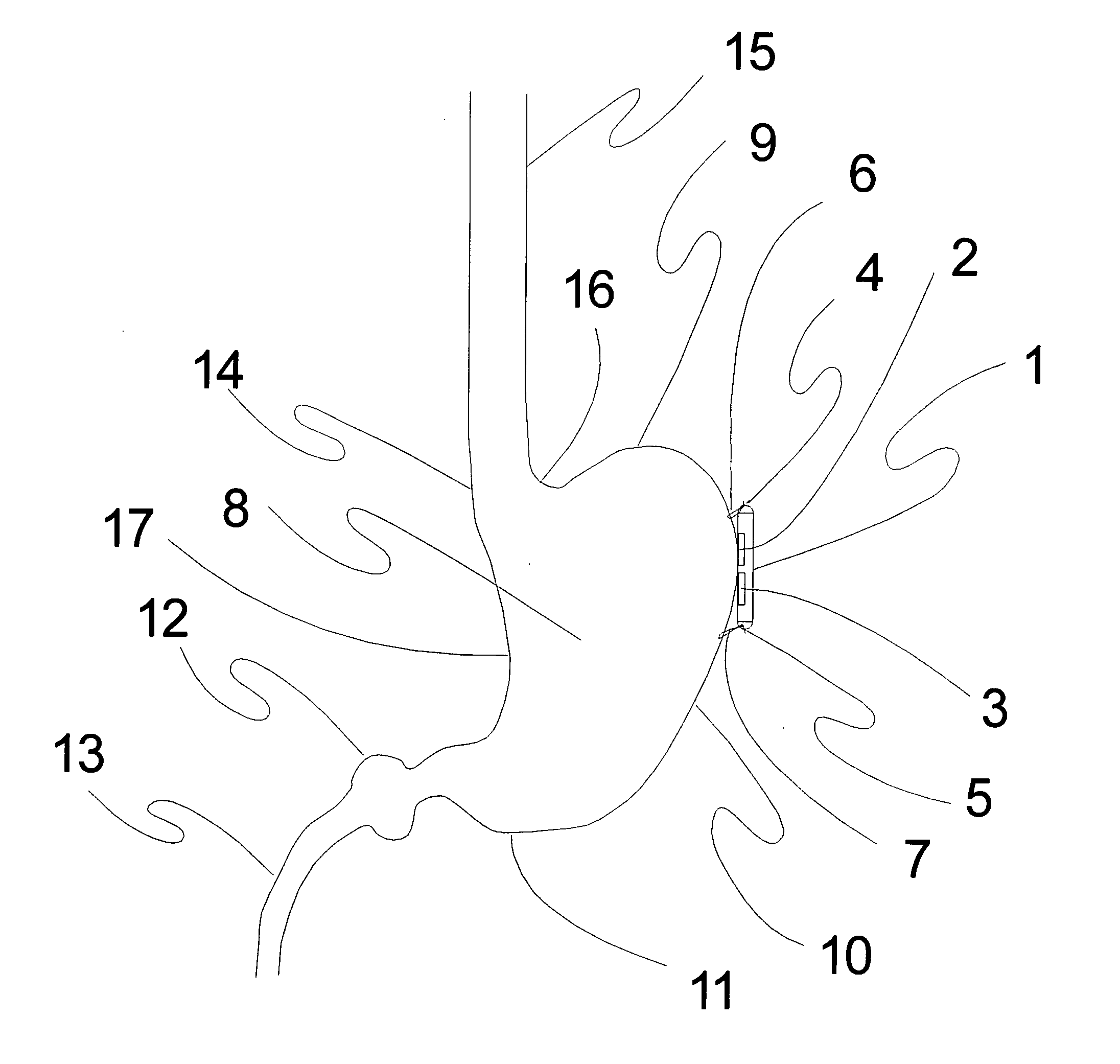
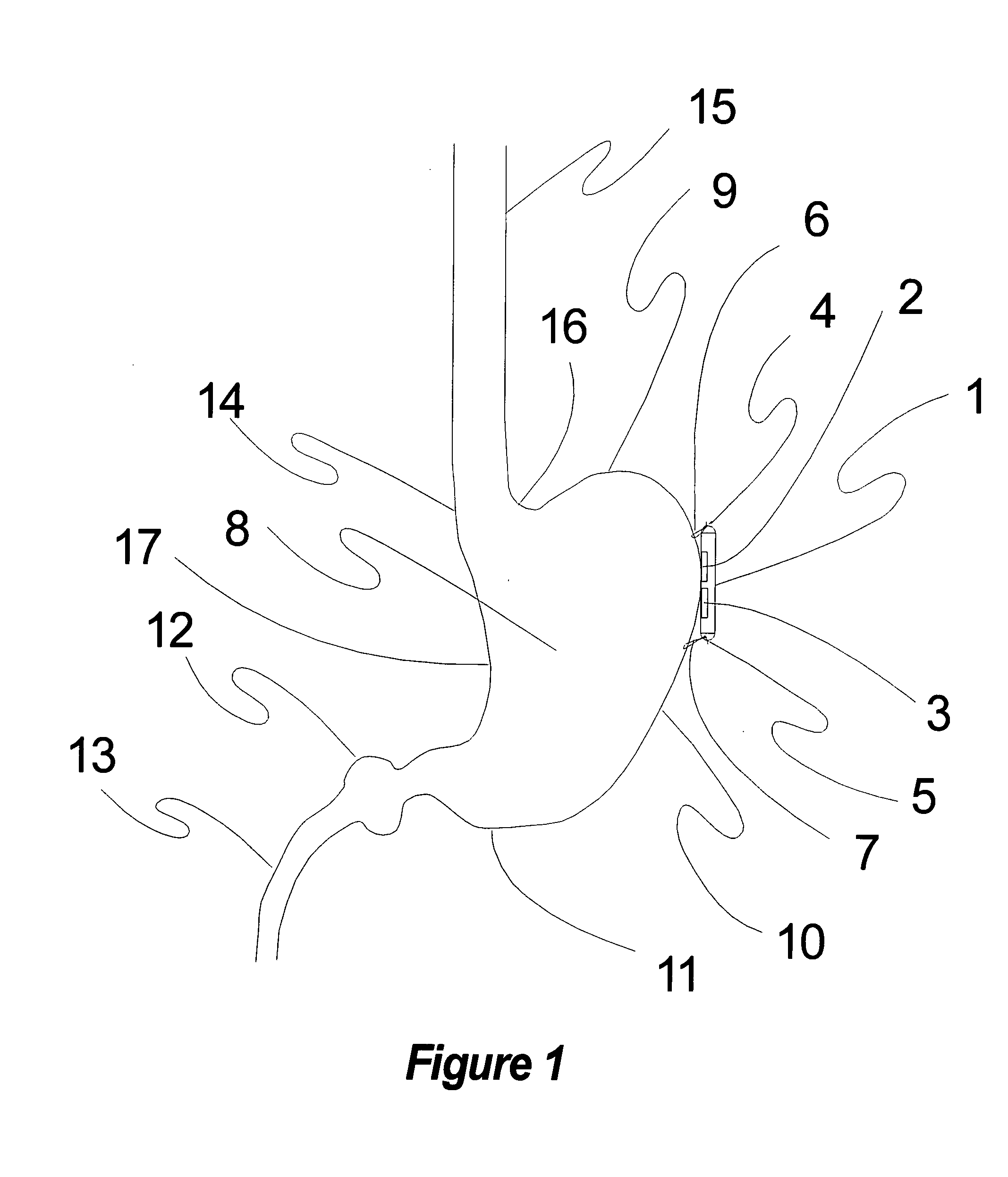
Selective neurostimulation for treating epilepsy
A method and device for treating epilepsy are disclosed which provide for electrical, chemical or magnetic stimulation of certain areas of the brain to modulate neuronal activity of areas associated with symptoms of epilepsy. Deep brain stimulation is combined with vagus nerve stimulation to enhance symptomatic relief of the disorder. Some embodiments also employ a sensing capability to optimize the therapeutic treatment regimen.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
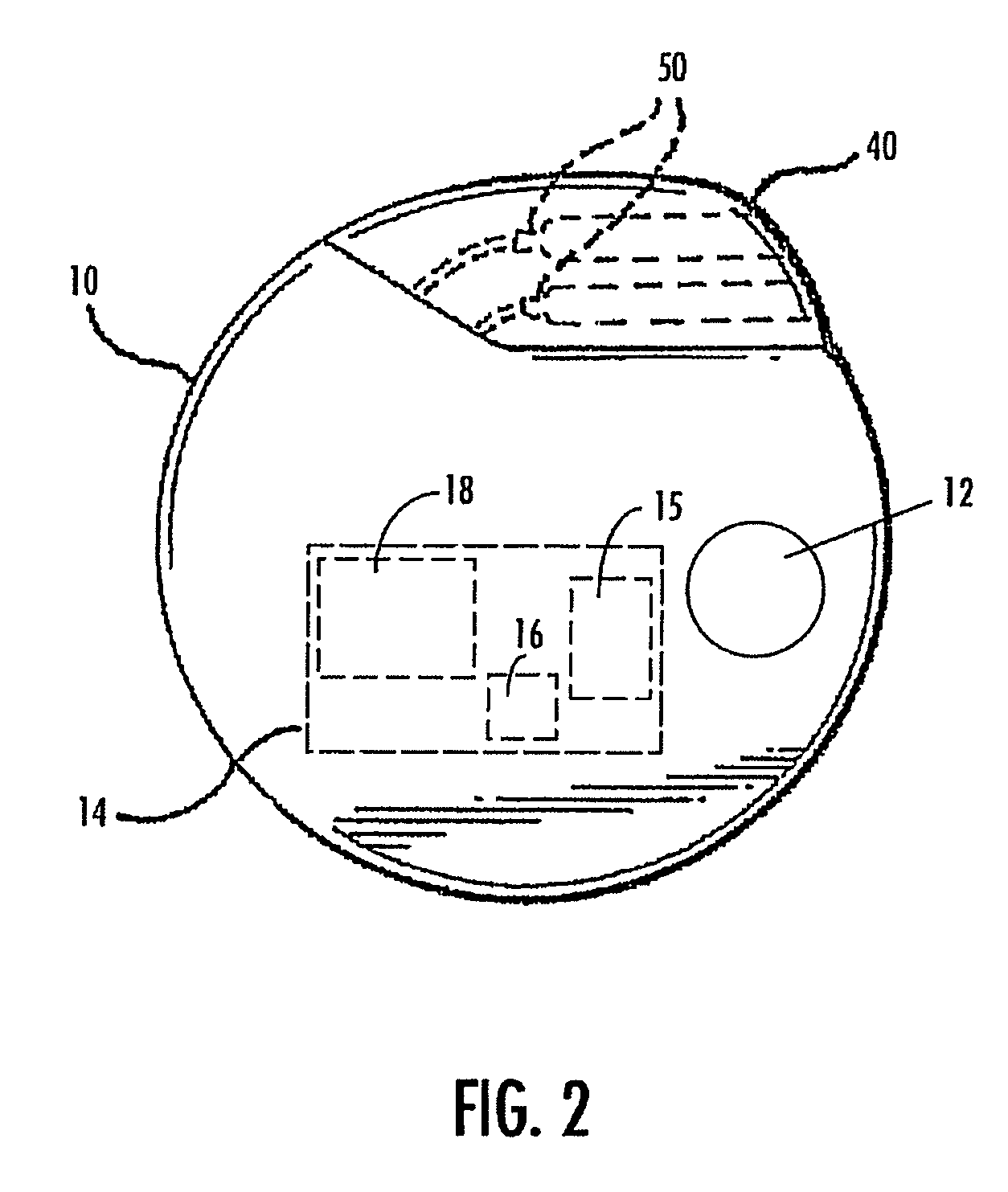
Externally activated neuro-implant which directly transmits therapeutic signals
InactiveUS20060142822A1Enhances inductive couplingMinimized in sizeElectrotherapyArtificial respirationImplantable ElectrodesElectrical stimulations
An externally powered and controlled neuro-implant system for transmission of stimulating therapeutic signals to an implantable electrode. The system basically consists of two coils, one external active coil and one internal passive coil each housed in a ferrite pot core which enhances inductive coupling and minimizes the coils in size, thus facilitating the construction of a passive coils array to enable the usage of multi-contact electrodes for swithching of the electrical stimulation between a number of sites along the target neurons. The implanted part of the system, comprising only a coil housed in a ferrite pot core, is fully passive. The passive coil, that is implanted under the skin, is connected with the electrode placed in neighbouring of the target neural tissue via implanted thin medical grade wires. The active coil is placed on the skin overlying the passive coil. Therapeutic signals produced by the transmitter outside the body are transmitted through the coils by inductive coupling across the skin of the patient.
Owner:TULGAR METIN
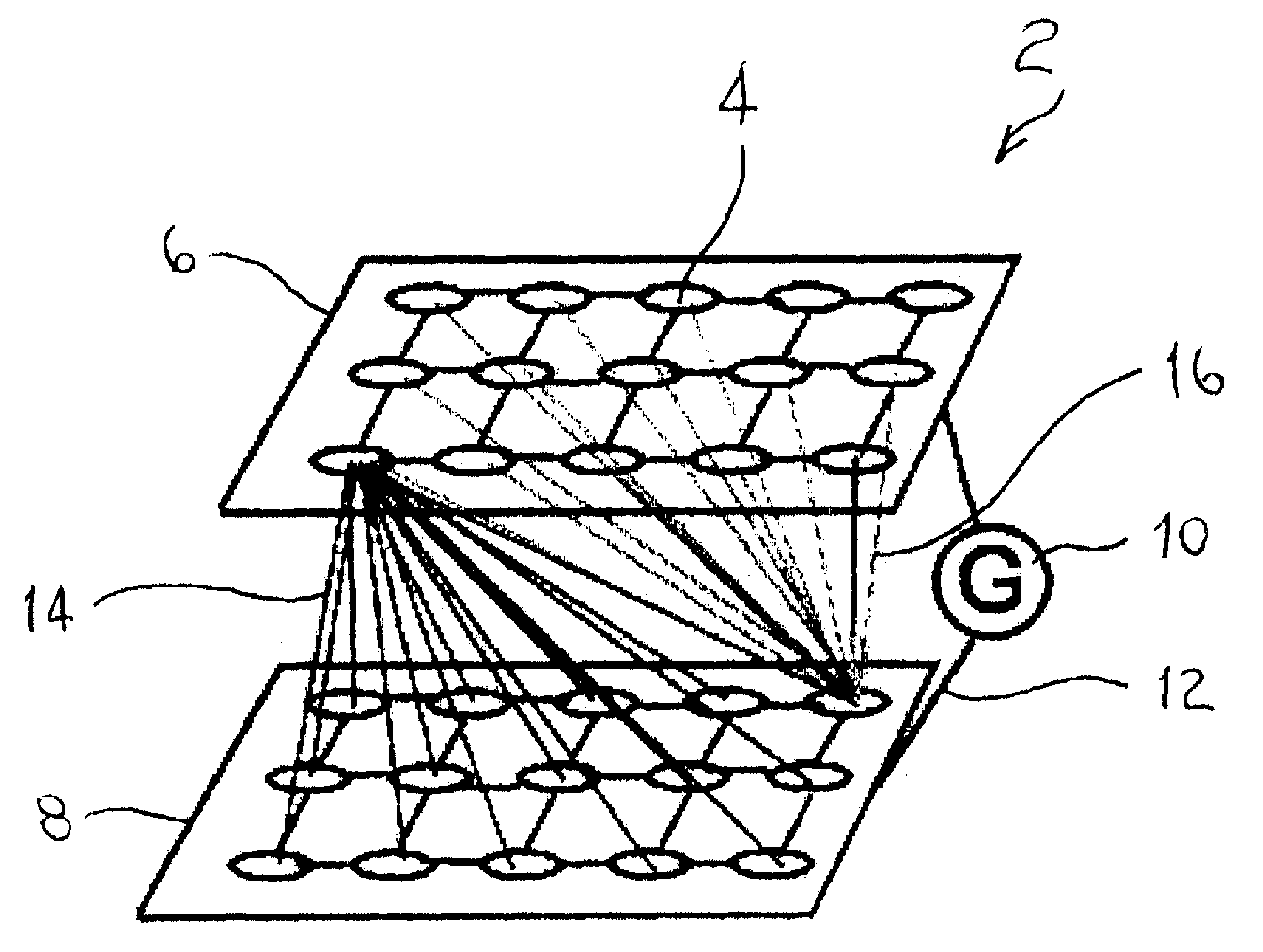
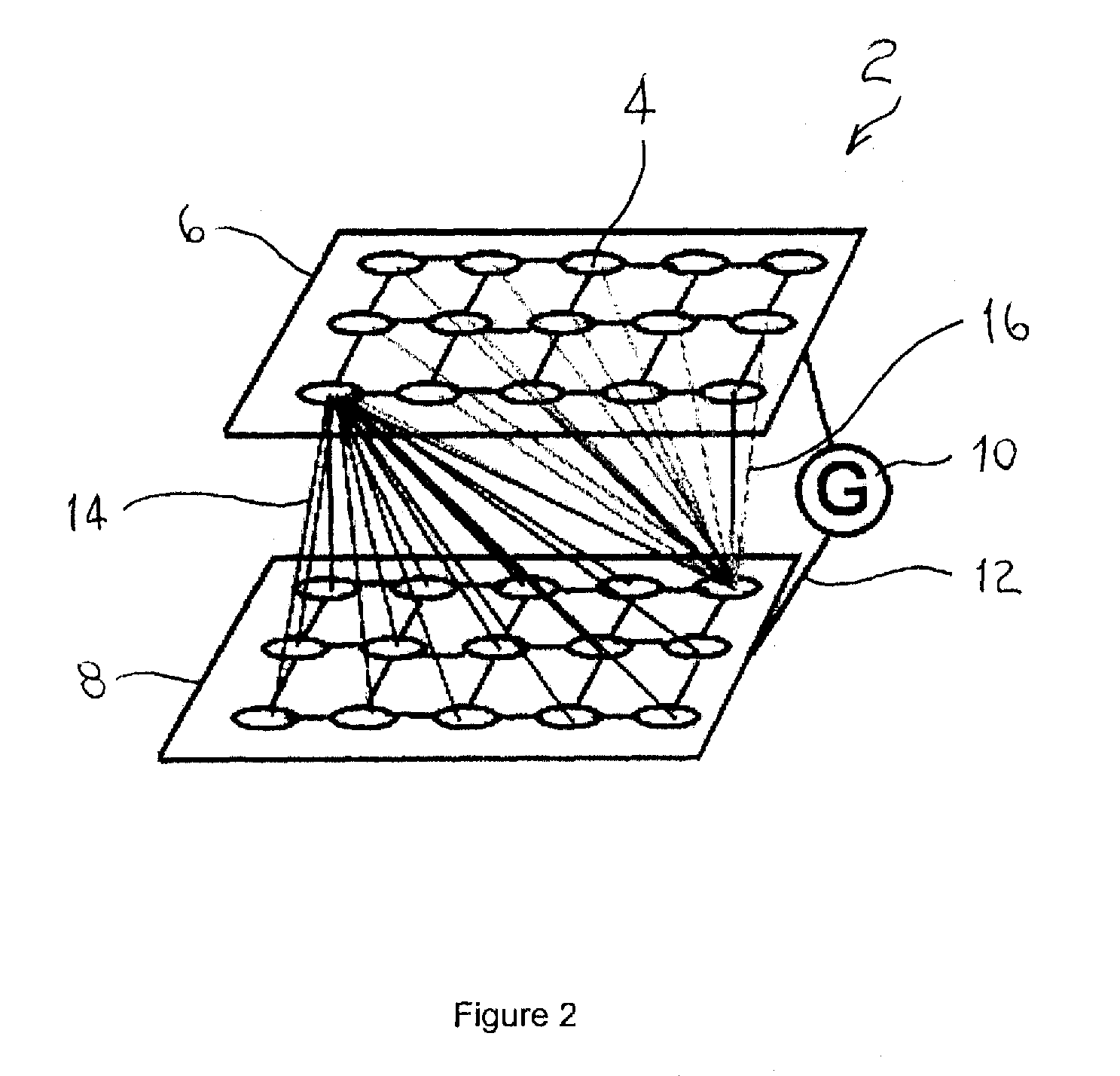
Spatio-temporal pattern recognition using a spiking neural network and processing thereof on a portable and/or distributed computer
ActiveUS20090287624A1Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSpiking neural networkNeuron
A system and method for characterizing a pattern, in which a spiking neural network having at least one layer of neurons is provided. The spiking neural network has a plurality of connected neurons for transmitting signals between the connected neurons. A model for inducing spiking in the neurons is specified. Each neuron is connected to a global regulating unit for transmitting signals between the neuron and the global regulating unit. Each neuron is connected to at least one other neuron for transmitting signals from this neuron to the at least one other neuron, this neuron and the at least one other neuron being on the same layer. Spiking of each neuron is synchronized according to a number of active neurons connected to the neuron. At least one pattern is submitted to the spiking neural network for generating sequences of spikes in the spiking neural network, the sequences of spikes (i) being modulated over time by the synchronization of the spiking and (ii) being regulated by the global regulating unit. The at least one pattern is characterized according to the sequences of spikes generated in the spiking neural network.
Owner:ROUAT JEAN +2
Sensor assembly for monitoring an infant brain
InactiveUS20040030258A1Risk minimizationGood flexibilityElectroencephalographyDiagnostics using lightNeuronal swellingTreatment effect
A flexible, conformable, sensor assembly is provided, including an electrode array especially adapted for stable, long-term recording of EEG signals from a pre-term or neonatal infant in intensive care. A kit or sterile pack includes guidance for placement of the electrodes over a designated area of the infant's brain, an area likely to be injured. The sensor assembly includes a left-side and a right-side flexible strip bearing at least electrodes and optional temperature, motion, and optical sensors provide for the monitoring of an extended range of parameters including aspects of cerebral perfusion and metabolism. Optional impedance measurements provide an indication of neuronal swelling. Stable performance over from three days to about a week is intended so that progress, effects of treatment, and outcome can be considered.
Owner:TRU TEST
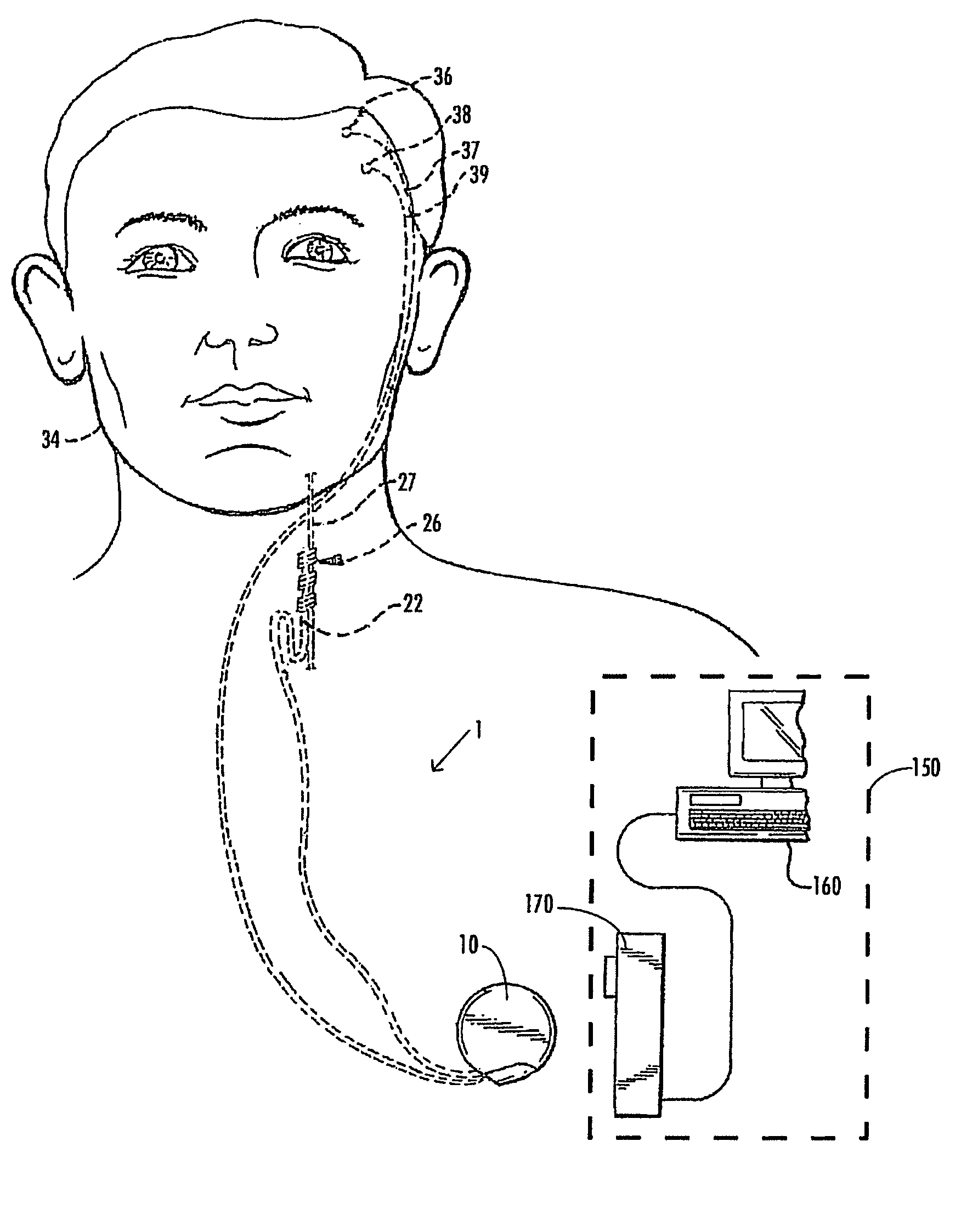
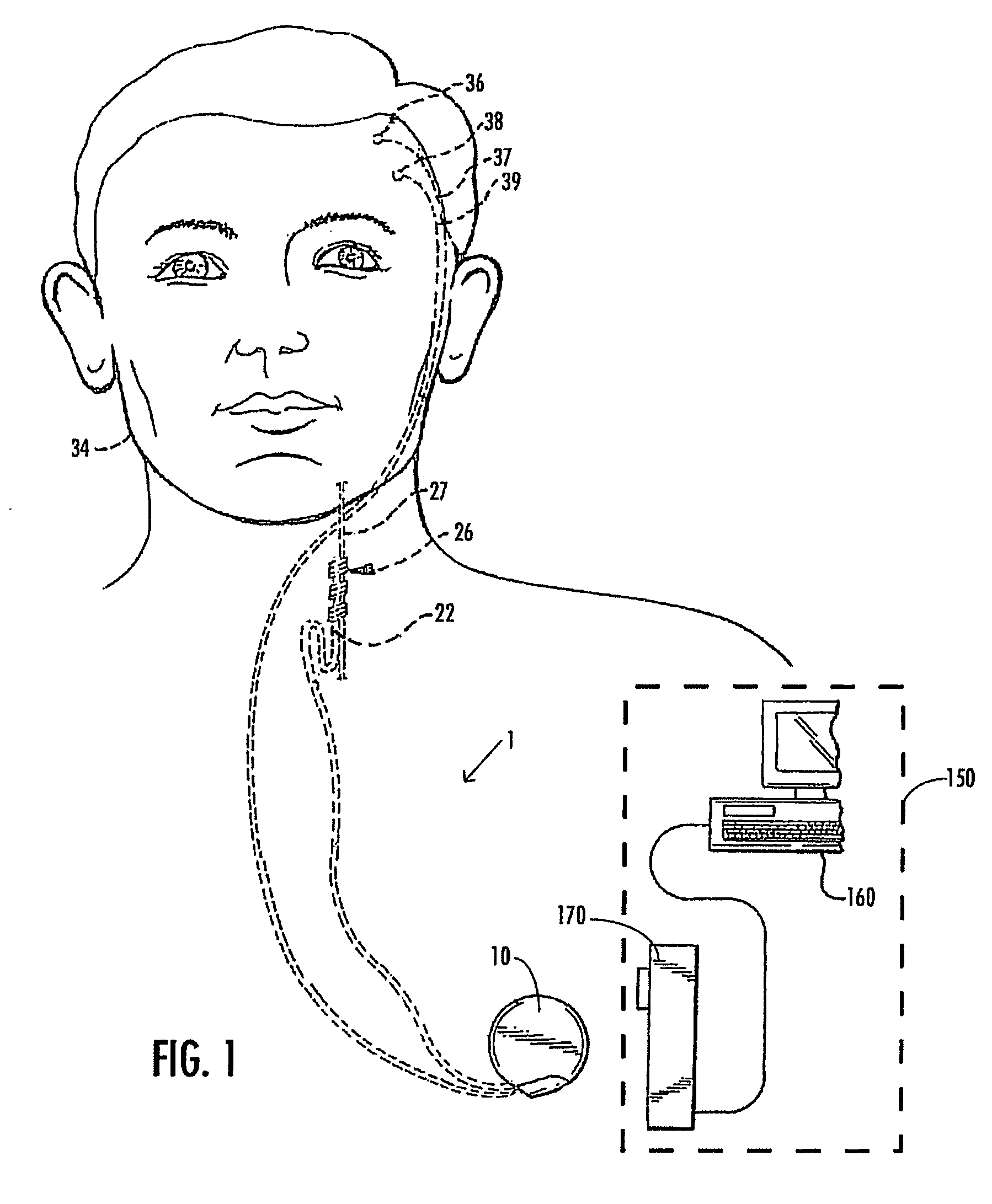
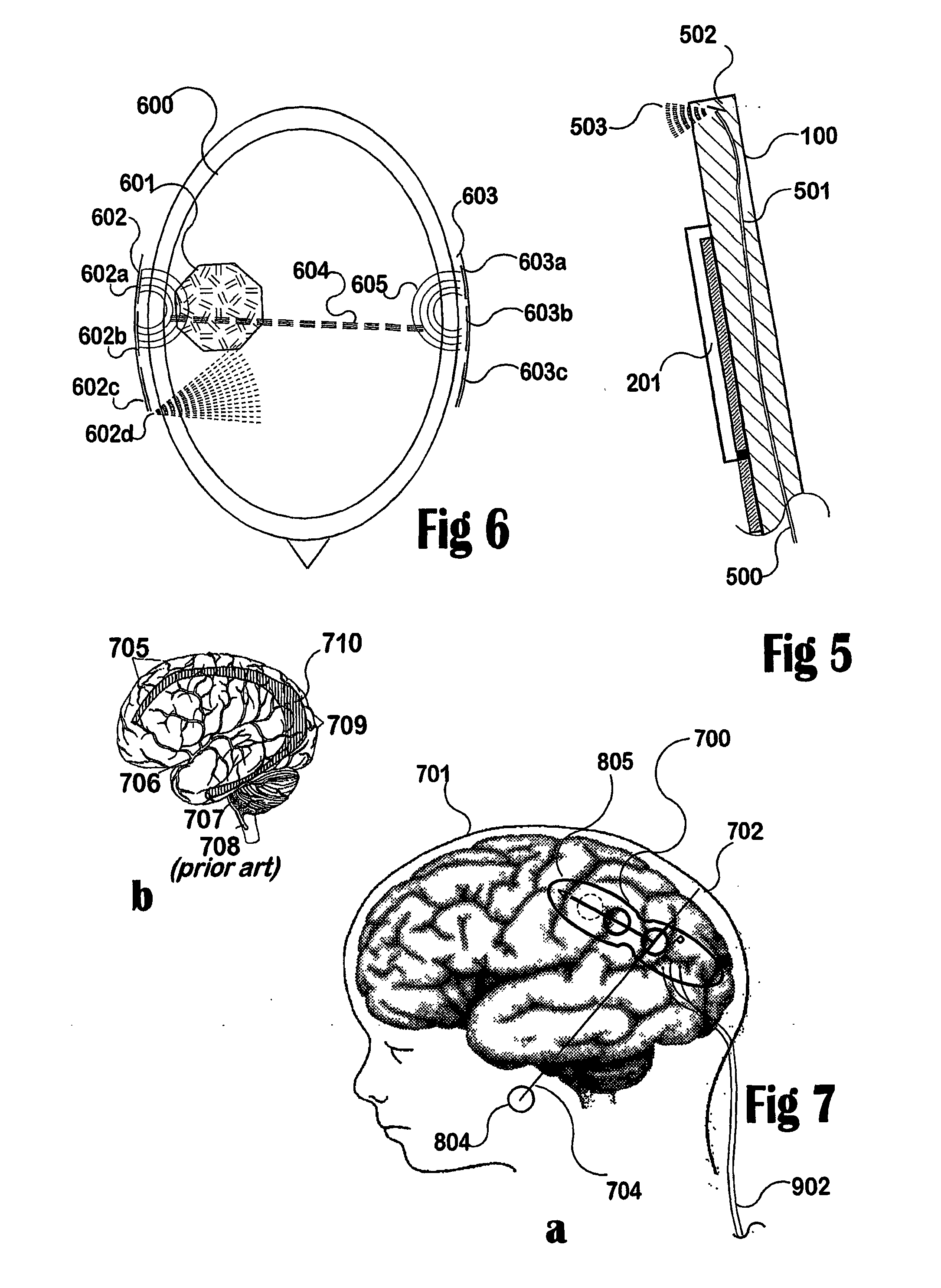
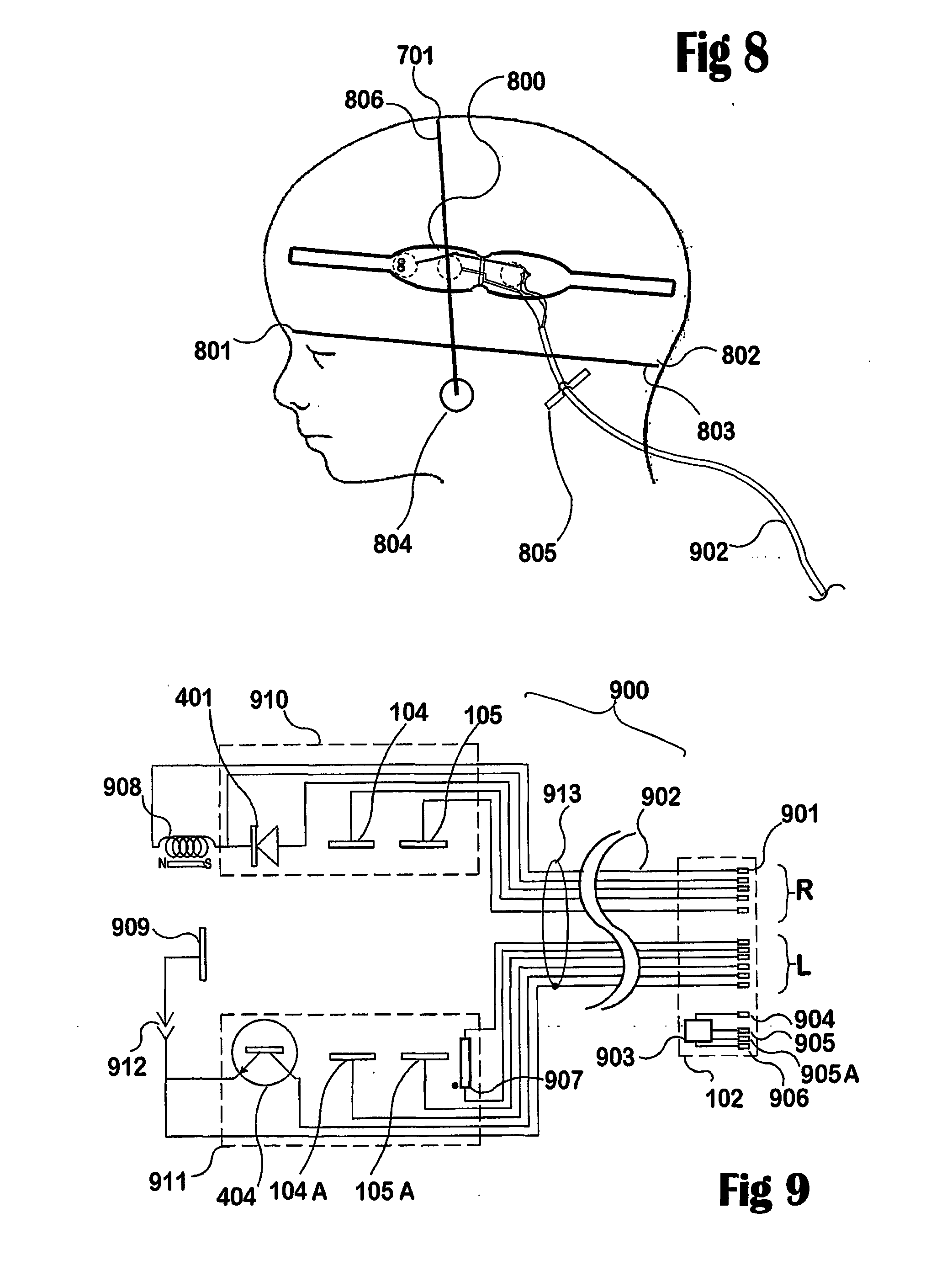
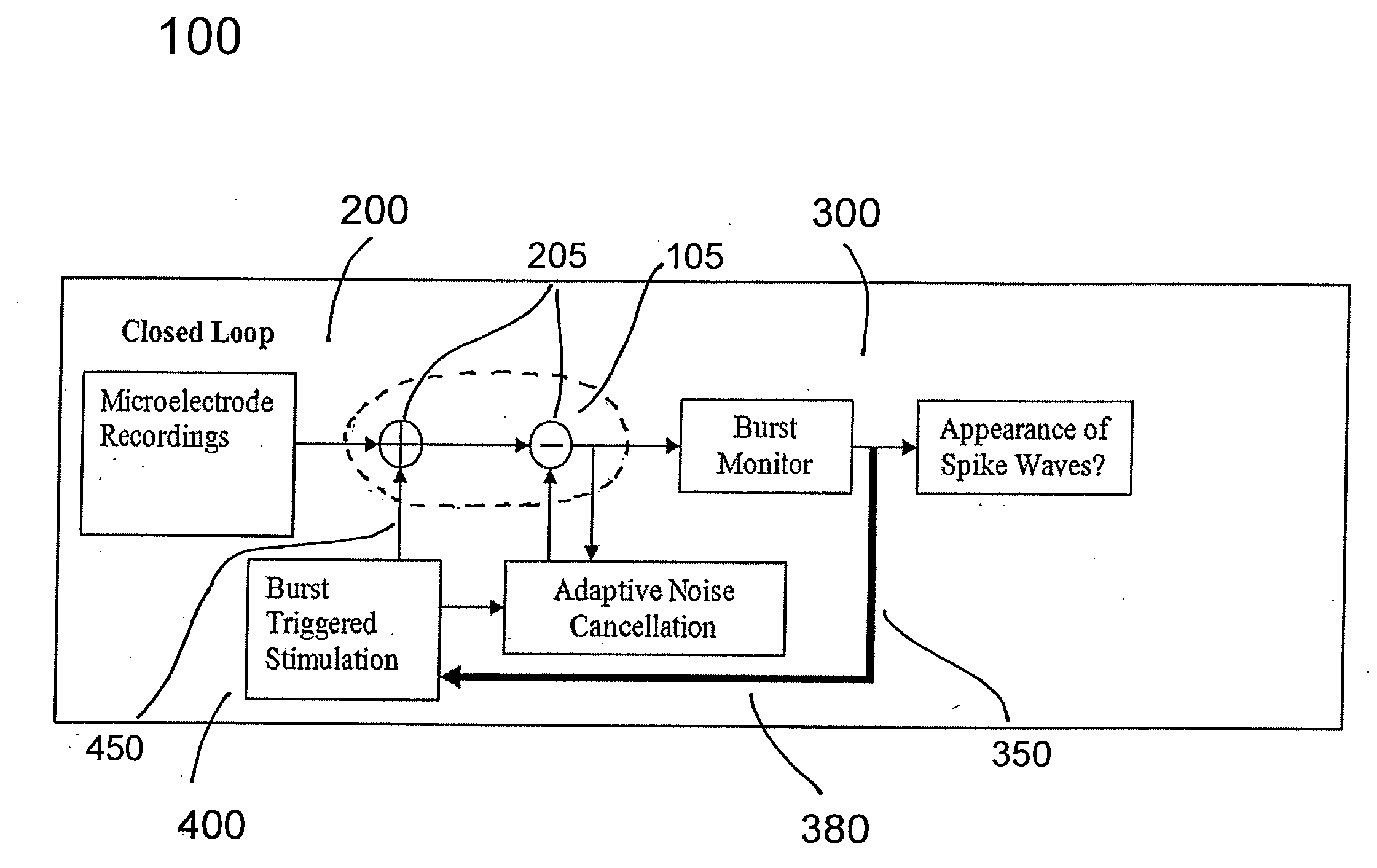
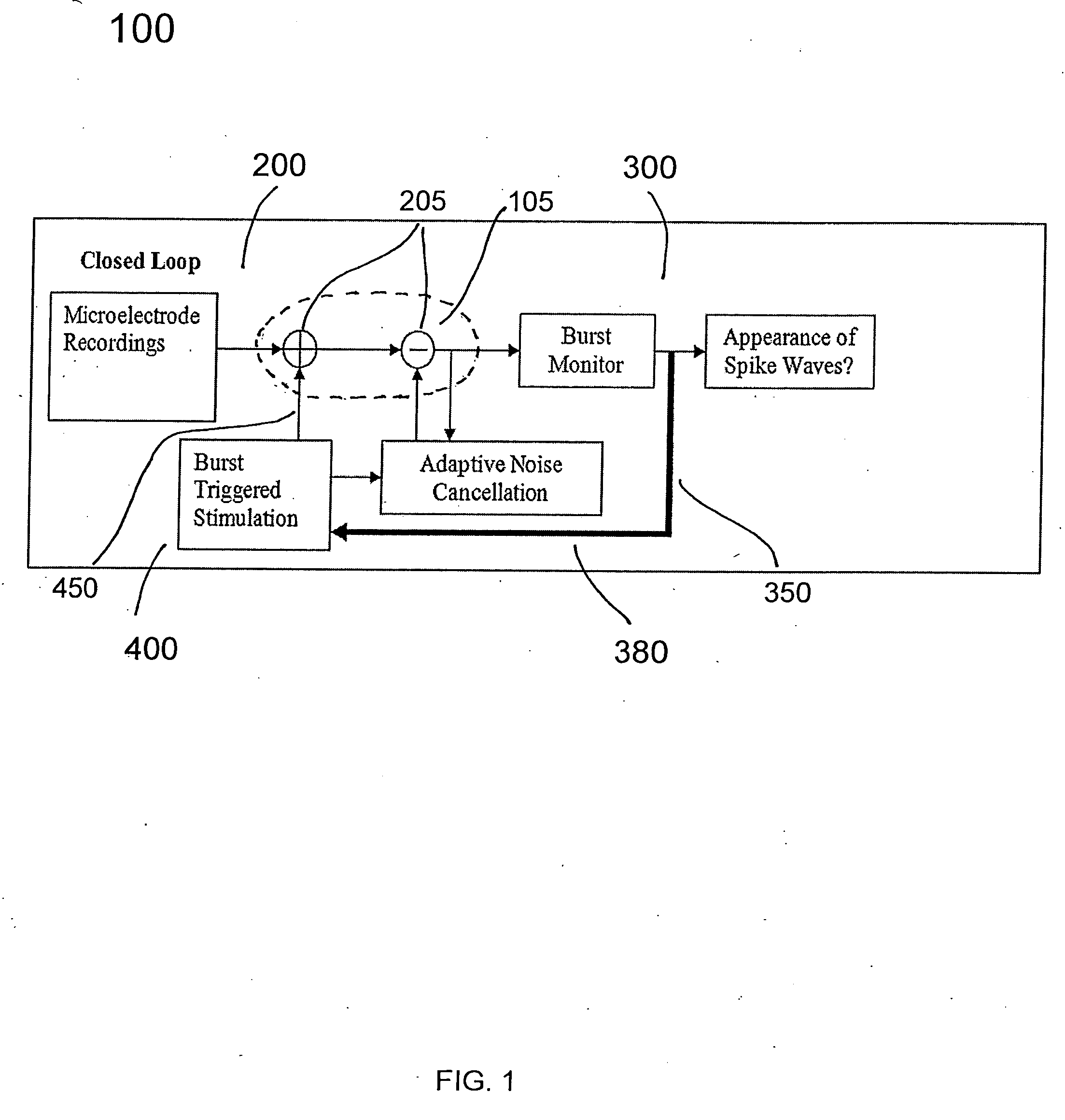
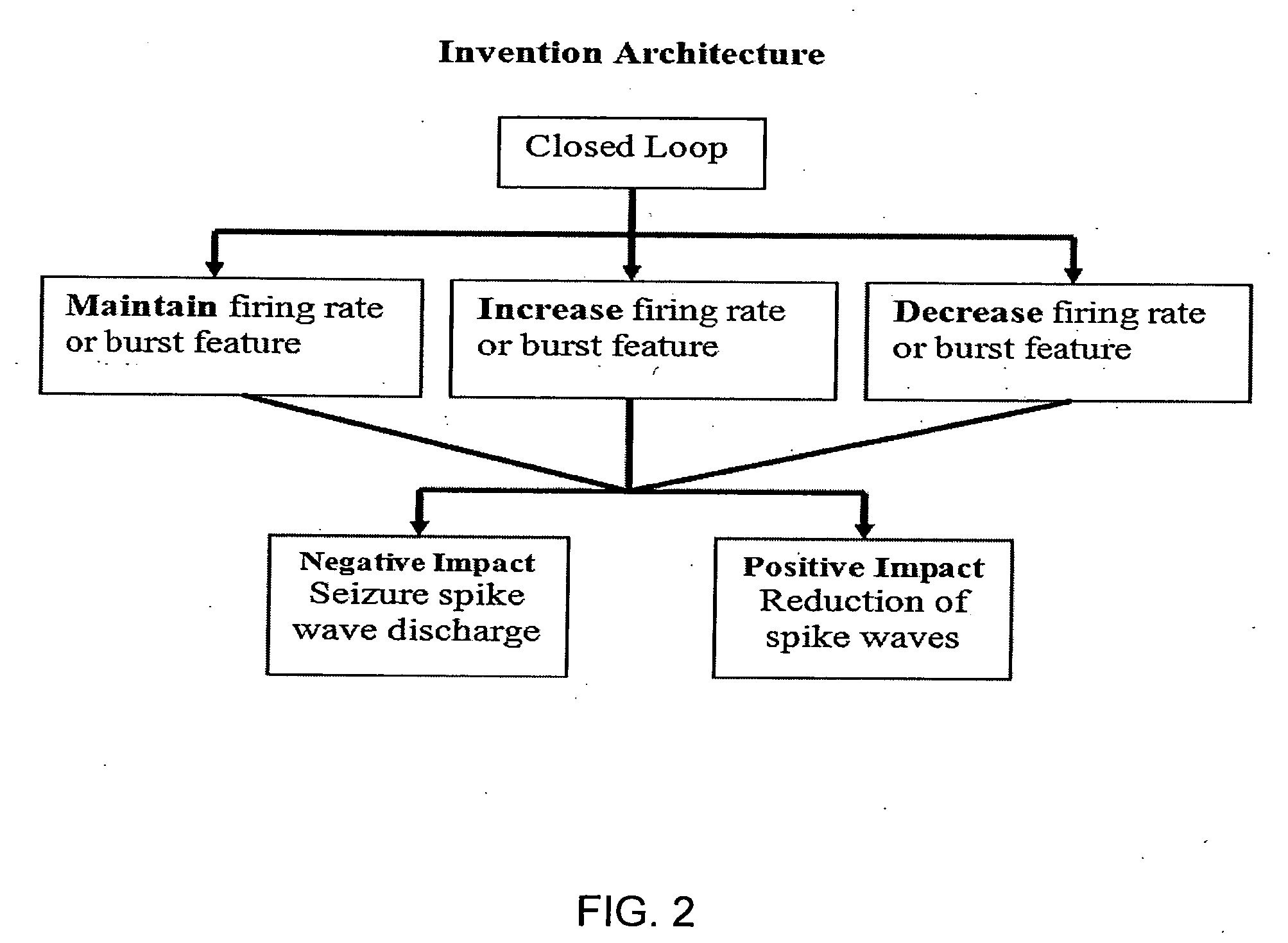
Closed-loop micro-control system for predicting and preventing epilectic seizures
InactiveUS20070067003A1Prevention and reduction of severityHigh resolutionHead electrodesMedicineControl system
The invention provides a micro-control neuroprosthetic device and methods for predicting and controlling epileptic neuronal activity. The device includes a detection system that detects and collects electrophysiological information comprising action potentials from single neurons and ensembles of neurons in a neural structure such as an epileptogenic region of the brain in a subject. An analysis system included in the neuroprosthetic device evaluates the electrophysiological information and performs a real-time extraction of neuron firing features from which the system determines when stimulus intervention is required. The neuroprosthetic device further comprises a stimulation intervention system that provides stimulus output signals having a desired stimulation frequency and stimulation intensity directly to the neural structure in which abnormal neuronal activity is detected. The analysis system further analyzes collected electrophysiological information during or following stimulus intervention to assess the effects of the stimulation intervention and to provide outputs to maintain or modify the stimulation intervention.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Nanotechnology neural network methods and systems
A physical neural network is disclosed, which includes a connection network comprising a plurality of molecular conducting connections suspended within a connection gap formed between one or more input electrodes and one or more output electrodes. One or more molecular connections of the molecular conducting connections can be strengthened or weakened according to an application of an electric field across said connection gap. Thus, a plurality of physical neurons can be formed from said molecular conducting connections of said connection network. Additionally, a gate can be located adjacent said connection gap and which comes into contact with said connection network. The gate can be connected to logic circuitry which can activate or deactivate individual physical neurons among said plurality of physical neurons.
Owner:KNOWM TECH
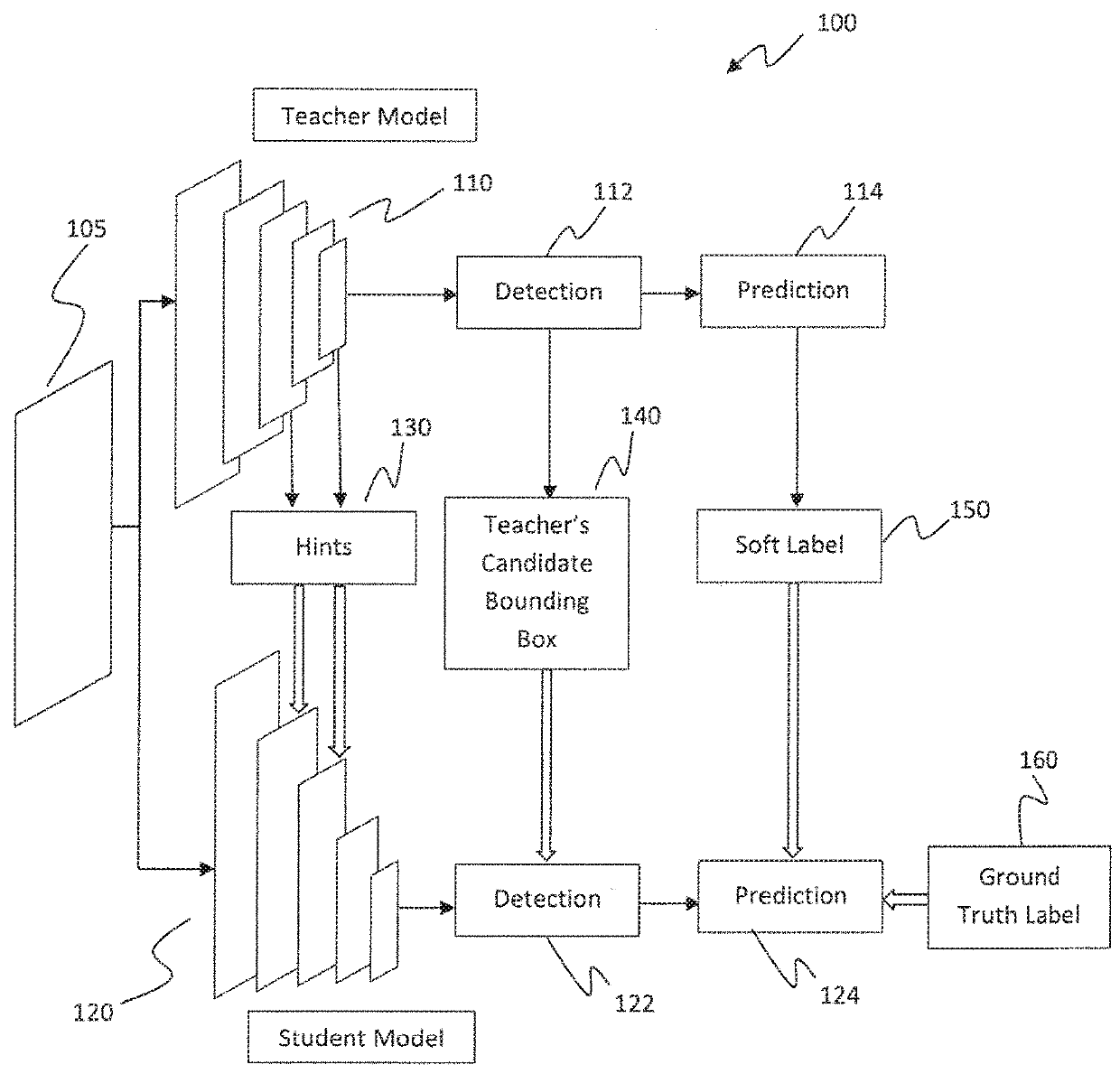
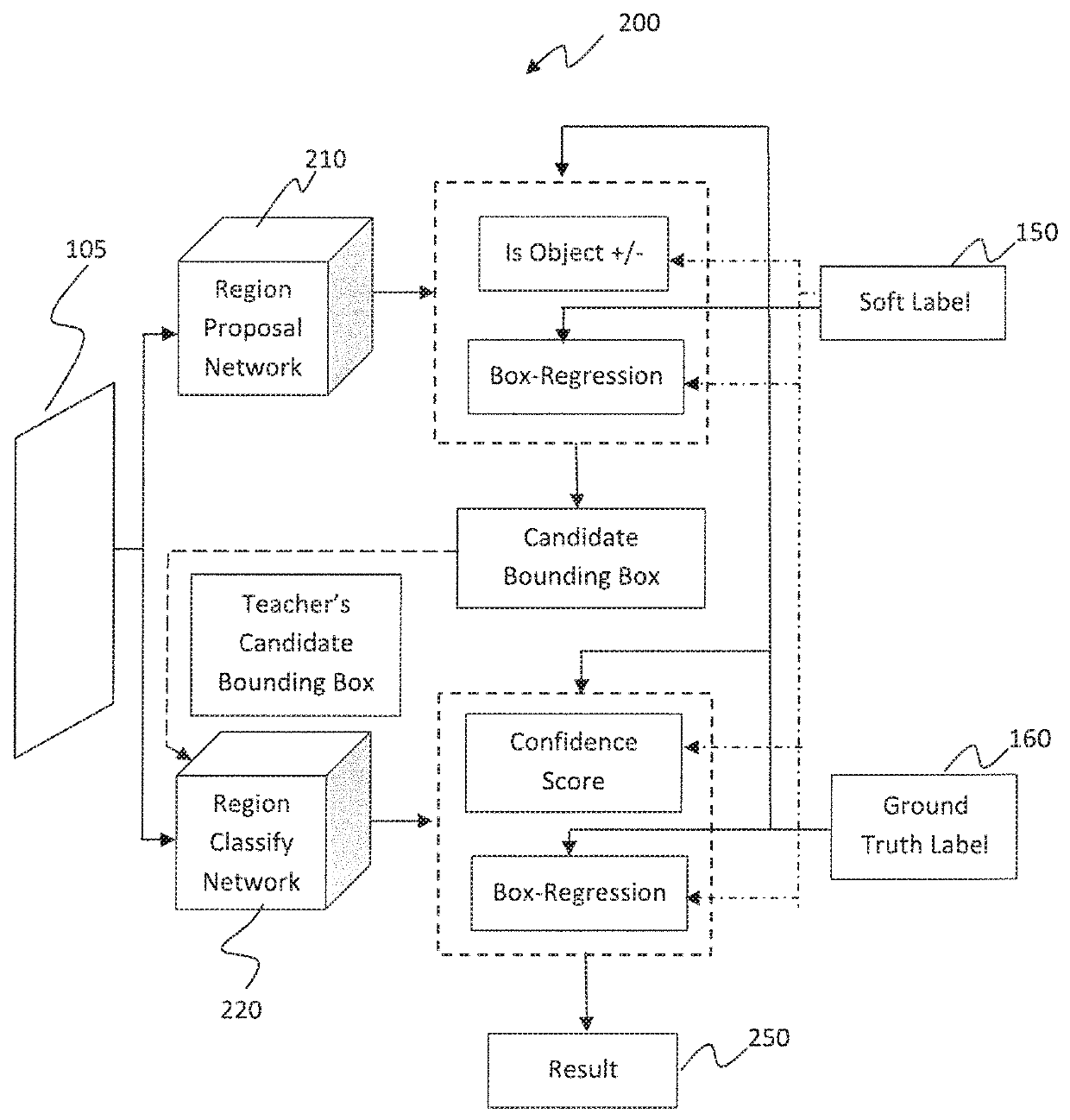
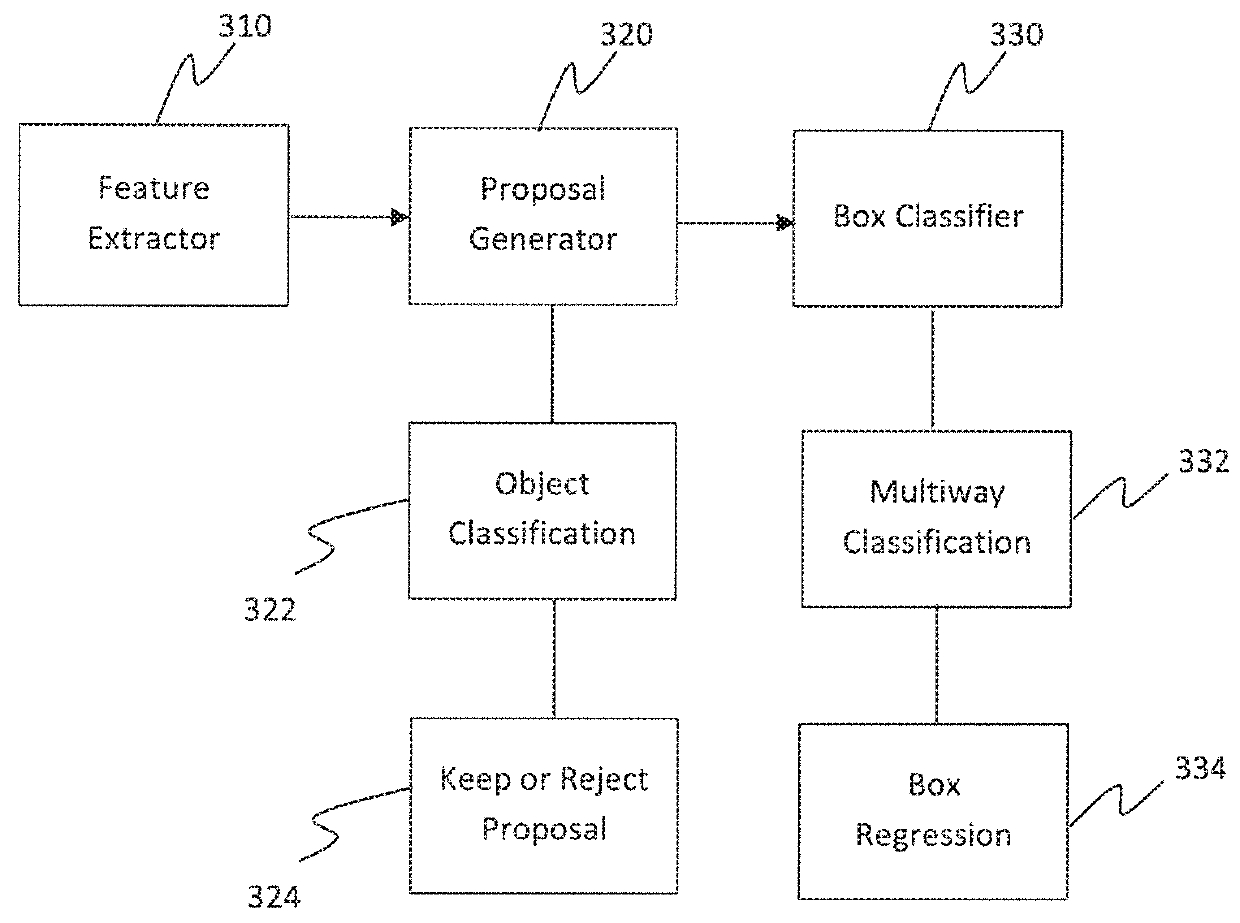
Learning efficient object detection models with knowledge distillation
InactiveUS20180268292A1Character and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsObject ClassDistillation
A computer-implemented method executed by at least one processor for training fast models for real-time object detection with knowledge transfer is presented. The method includes employing a Faster Region-based Convolutional Neural Network (R-CNN) as an objection detection framework for performing the real-time object detection, inputting a plurality of images into the Faster R-CNN, and training the Faster R-CNN by learning a student model from a teacher model by employing a weighted cross-entropy loss layer for classification accounting for an imbalance between background classes and object classes, employing a boundary loss layer to enable transfer of knowledge of bounding box regression from the teacher model to the student model, and employing a confidence-weighted binary activation loss layer to train intermediate layers of the student model to achieve similar distribution of neurons as achieved by the teacher model.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Systems and methods for phase measurements
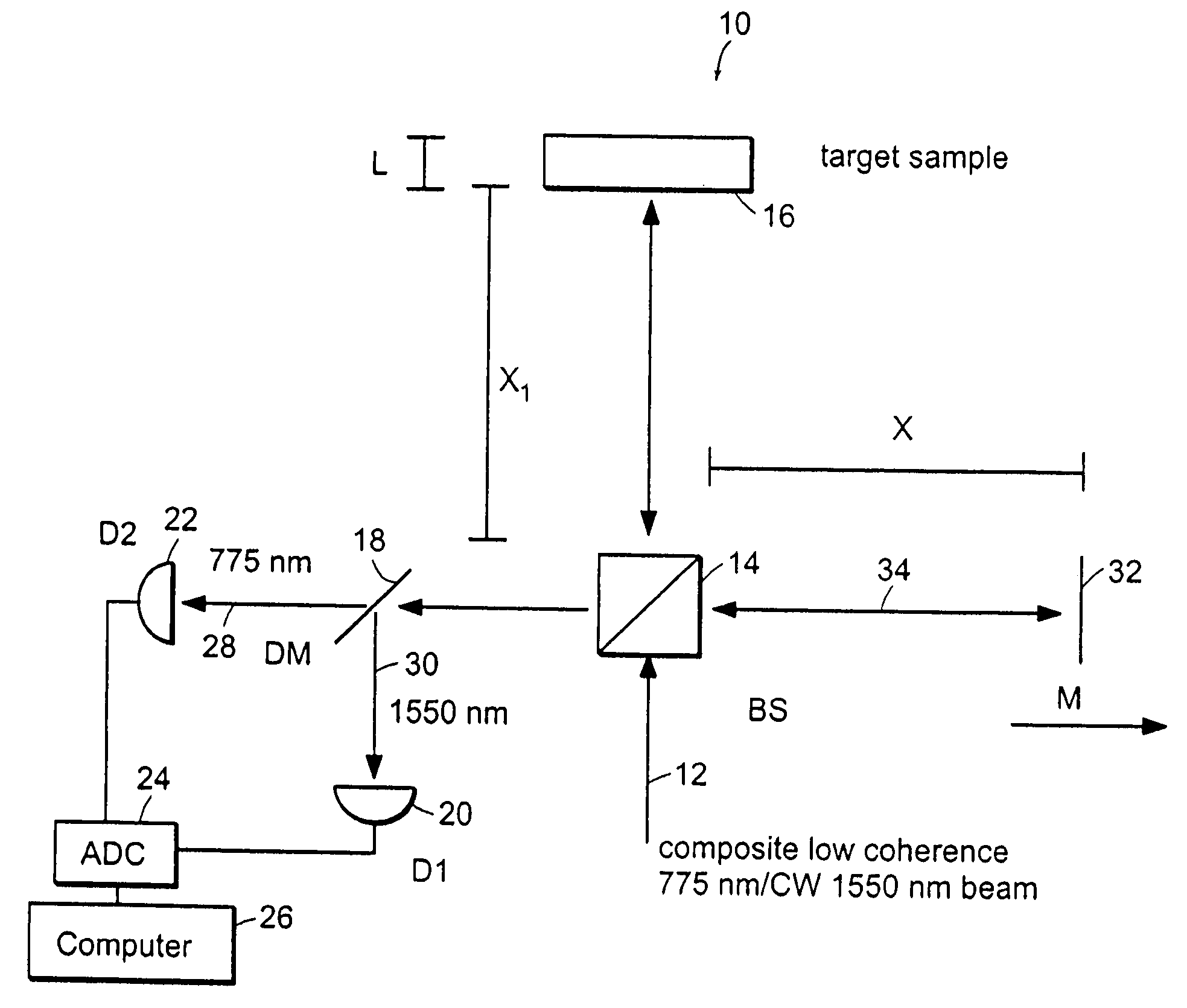
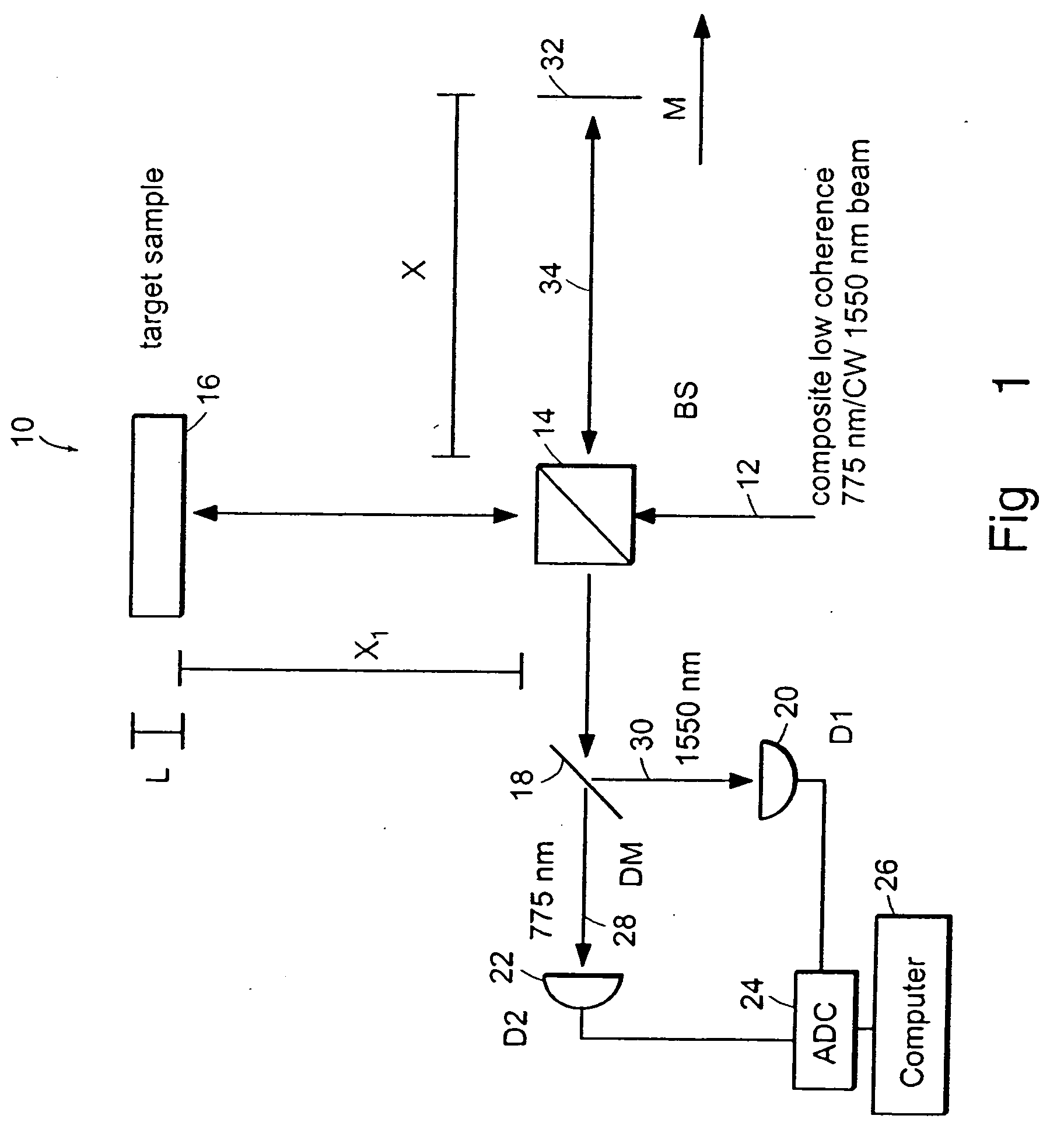
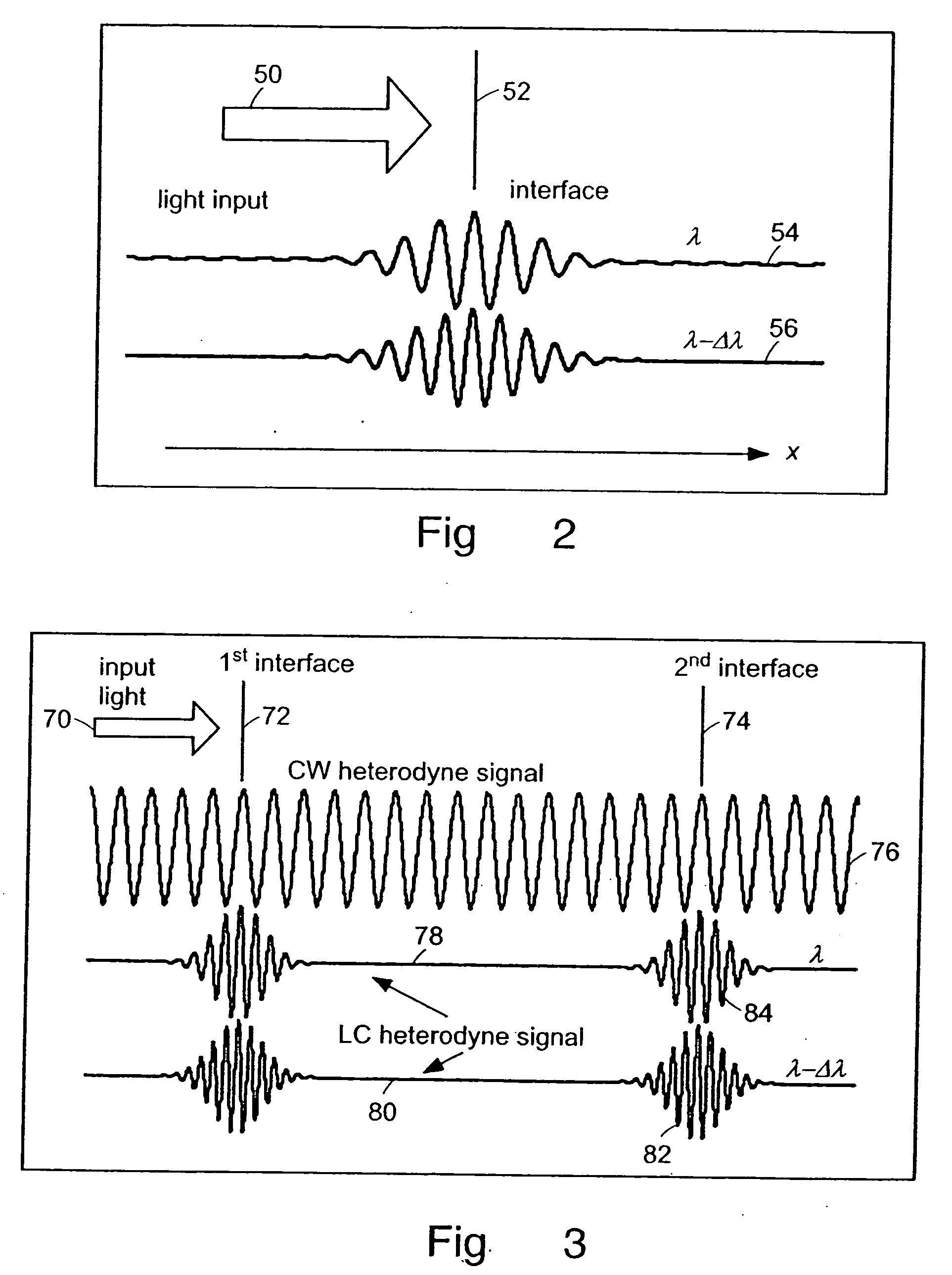
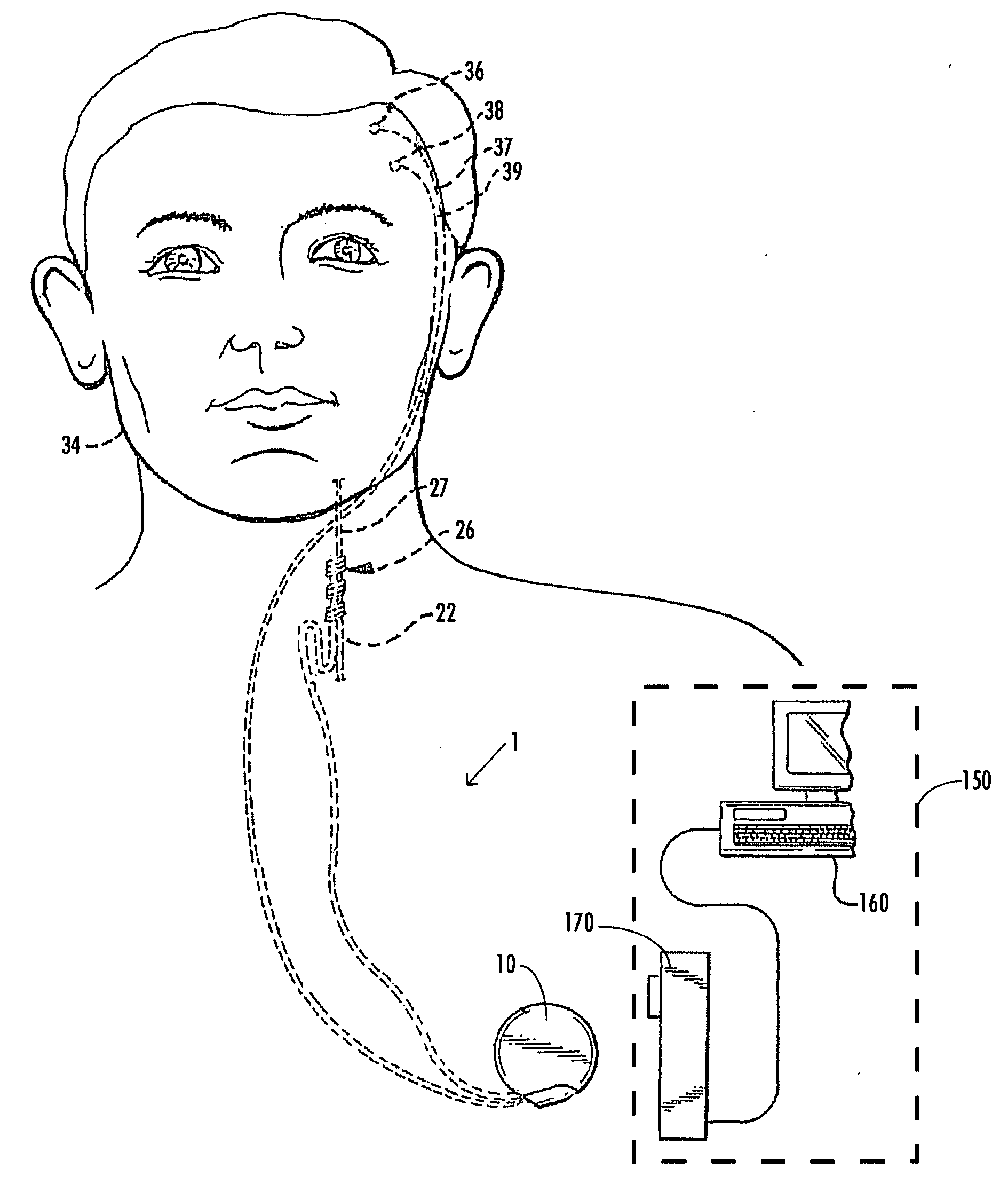
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Selective neurostimulation for treating mood disorders
ActiveUS20070027500A1Relieve symptomsAlter modulation of neuronal activityHead electrodesDiseaseRegimen
A method and device for treating a mood and / or anxiety disorder are disclosed which comprise electrical, chemical or magnetic stimulation of certain areas of the brain to modulate neuronal activity of areas associated with symptoms of mood disorders. In certain embodiments, deep brain stimulation is combined with cranial nerve stimulation to enhance symptomatic relief of the disorder. Certain embodiments also employ a sensing capability to optimize the therapeutic treatment regimen.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Method and apparatus for neuromodulation and physiologic modulation for the treatment of metabolic and neuropsychiatric disease
InactiveUS7529582B1Delay is slowIncrease pressureUltrasound therapySpinal electrodesSplanchnic nervesAfferent Neurons
A method and apparatus for physiological modulation, including neural and gastrointestinal modulation, for the purposes of treating several disorders, including obesity, depression, epilepsy, and diabetes. This includes chronically implanted neural and neuromuscular modulators, used to modulate the afferent neurons of the sympathetic nervous system to induce satiety. Furthermore, this includes neuromuscular stimulation of the stomach to effect baseline and intermittent smooth muscle contraction to increase gastric intraluminal pressure, which induces satiety, and stimulate sympathetic afferent fibers, including those in the sympathetic trunk, splanchnic nerves, and greater curvature of the stomach, to augment the perception of satiety.
Owner:DILORENZO DANIEL J
Calculation apparatus and method for accelerator chip accelerating deep neural network algorithm
InactiveCN105488565AExtended waiting timeConsume morePhysical realisationNeural learning methodsSynaptic weightNerve network
The invention provides a calculation apparatus and method for an accelerator chip accelerating a deep neural network algorithm. The apparatus comprises a vector addition processor module, a vector function value calculator module and a vector multiplier-adder module, wherein the vector addition processor module performs vector addition or subtraction and / or vectorized operation of a pooling layer algorithm in the deep neural network algorithm; the vector function value calculator module performs vectorized operation of a nonlinear value in the deep neural network algorithm; the vector multiplier-adder module performs vector multiplication and addition operations; the three modules execute programmable instructions and interact to calculate a neuron value and a network output result of a neural network and a synaptic weight variation representing the effect intensity of input layer neurons to output layer neurons; and an intermediate value storage region is arranged in each of the three modules and a main memory is subjected to reading and writing operations. Therefore, the intermediate value reading and writing frequencies of the main memory can be reduced, the energy consumption of the accelerator chip can be reduced, and the problems of data missing and replacement in a data processing process can be avoided.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
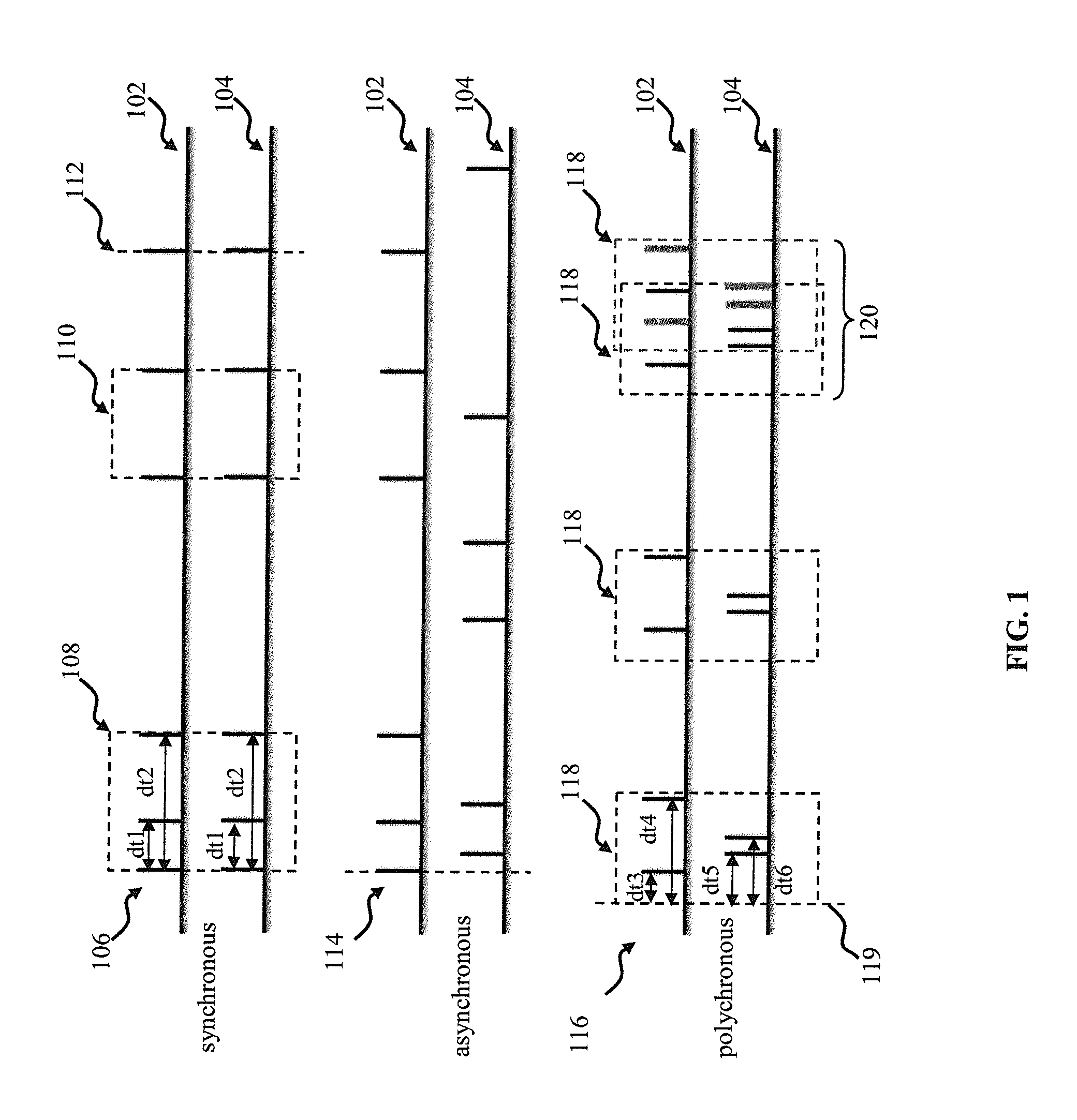
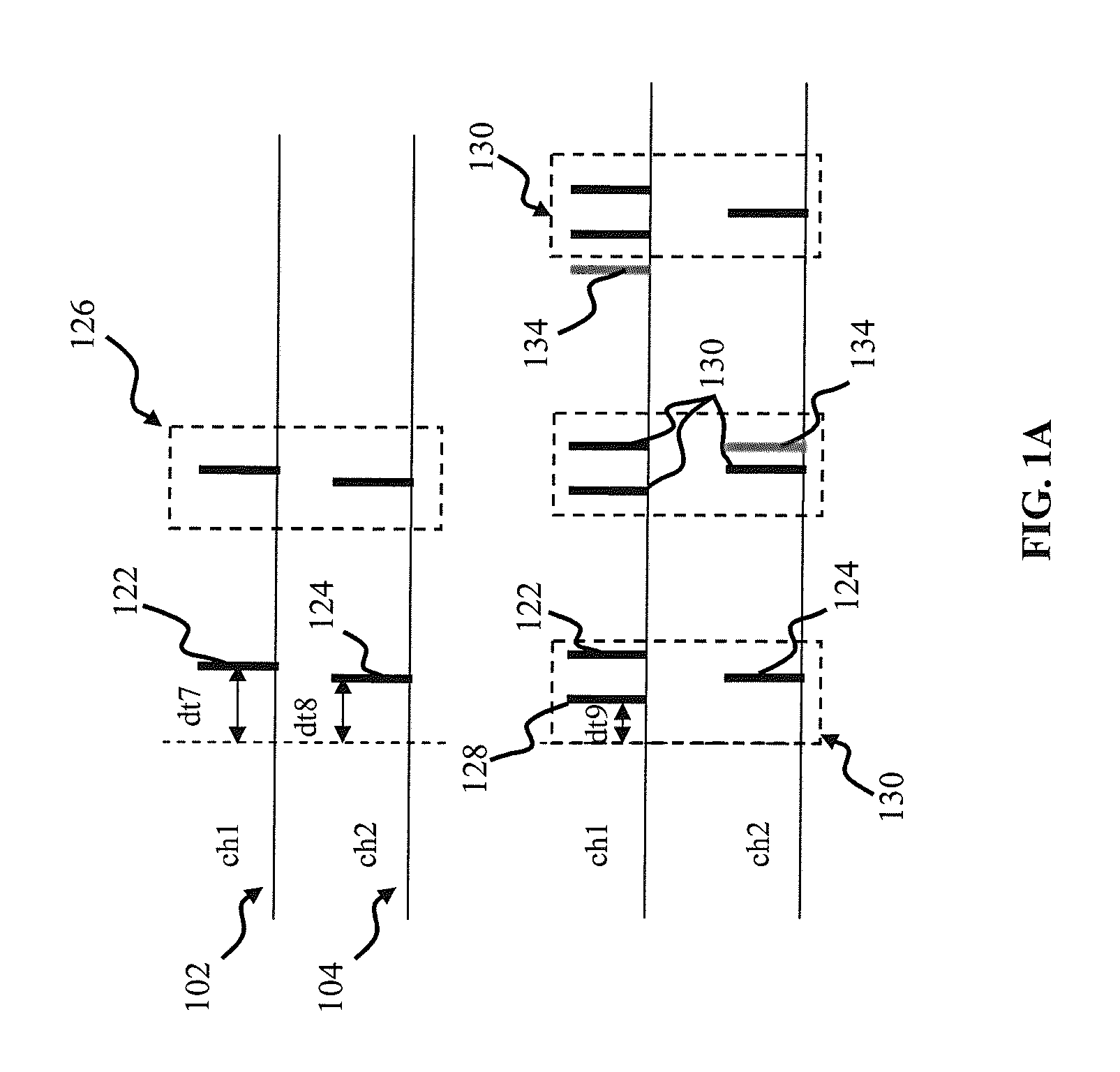
Apparatus and methods for polychronous encoding and multiplexing in neuronal prosthetic devices
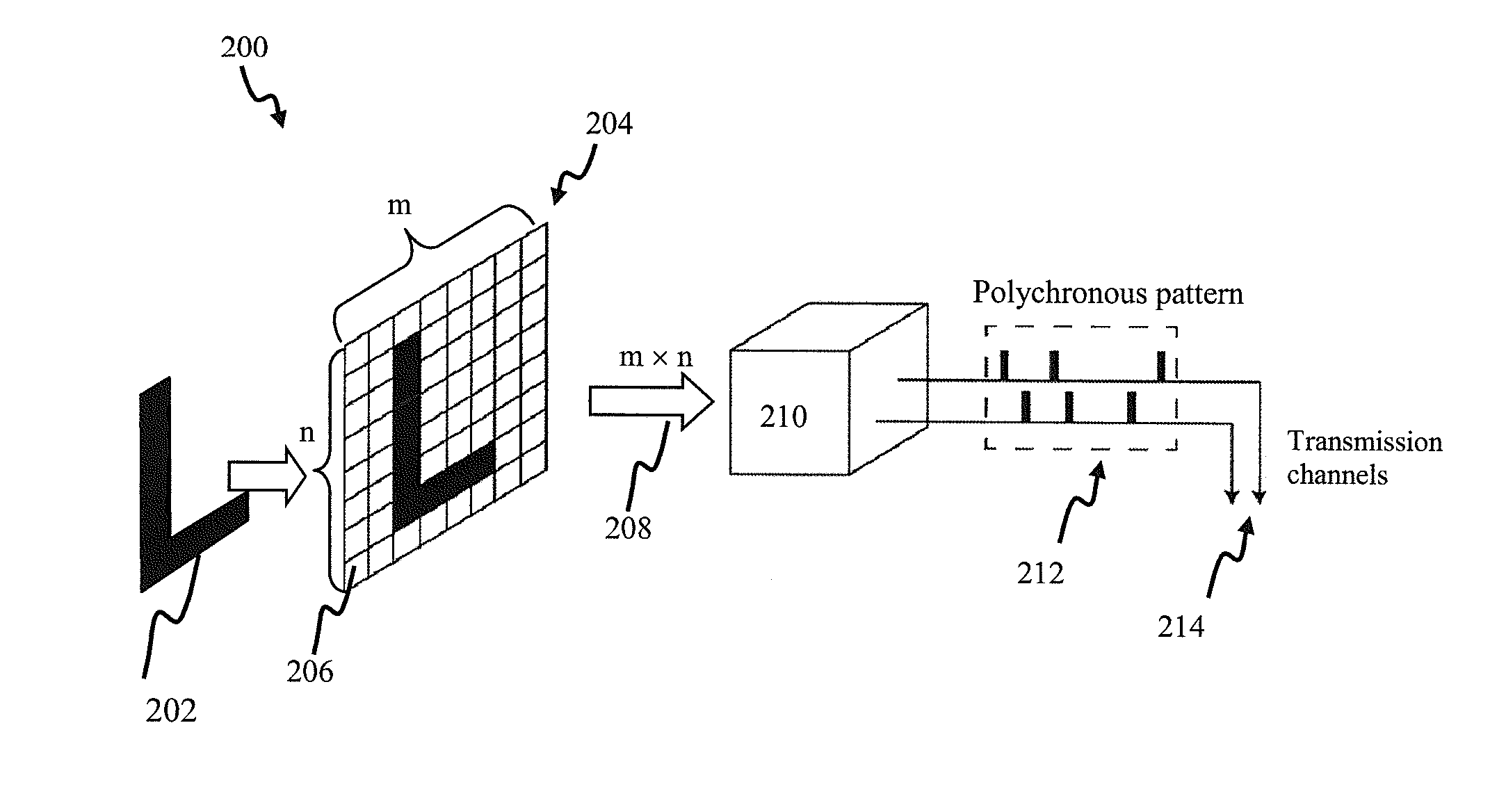
Apparatus and methods for encoding sensory input information into patterns of pulses and message multiplexing. In one implementation, the patterns of pulses are polychronous (time-locked by not necessary synchronous), and a retinal prosthetic encodes the input signal into the polychronous patterns for delivery via stimulating electrodes. Different polychronous patterns simultaneously encode different sensory signals; (such as different features of the image), thus providing for message multiplexing. Increasing data transmission capacity allows for a reduction in the number of electrodes required for data transmission. In one implementation, an adaptive feedback mechanism is employed to facilitate encoder operation. In another aspect, a computer vision system is described.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Administration of growth factors for the treatment of CNS disorders
ActiveUS20070254842A1Prevents and delay onsetReduce severityHeavy metal active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseNervous system
A method and system that is directed to the local delivery of growth factors to the mammalian CNS to treat CNS disorders associated with neuronal death and / or dysfunction is described.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Device and method for attenuating an immune response
ActiveUS7418292B2Good flexibilityMore levelsSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsNervous systemImmunity response
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
InactiveUS20050059597A1Attenuated downstream NMDAR signalingReduced infarct volumeNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
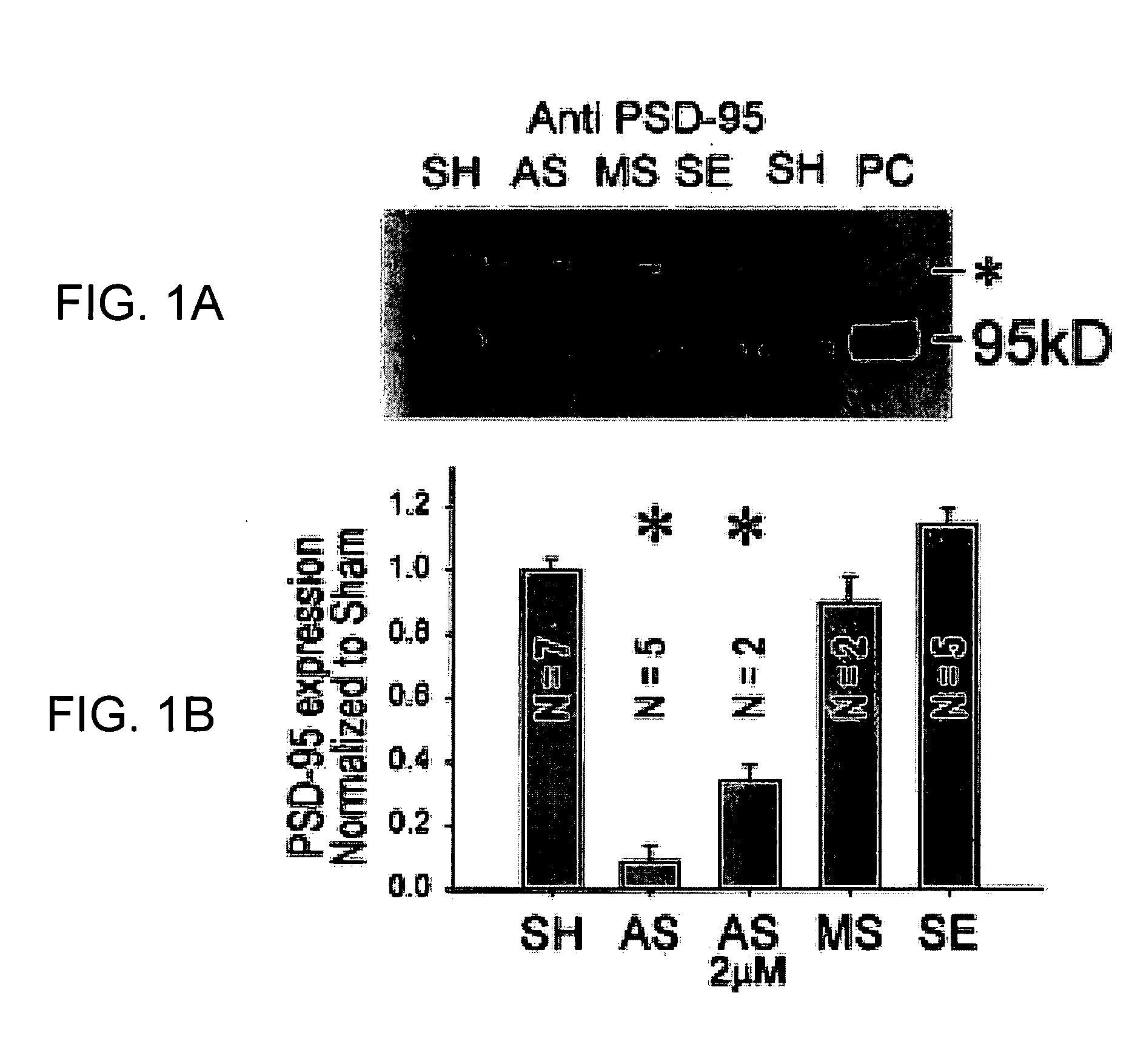
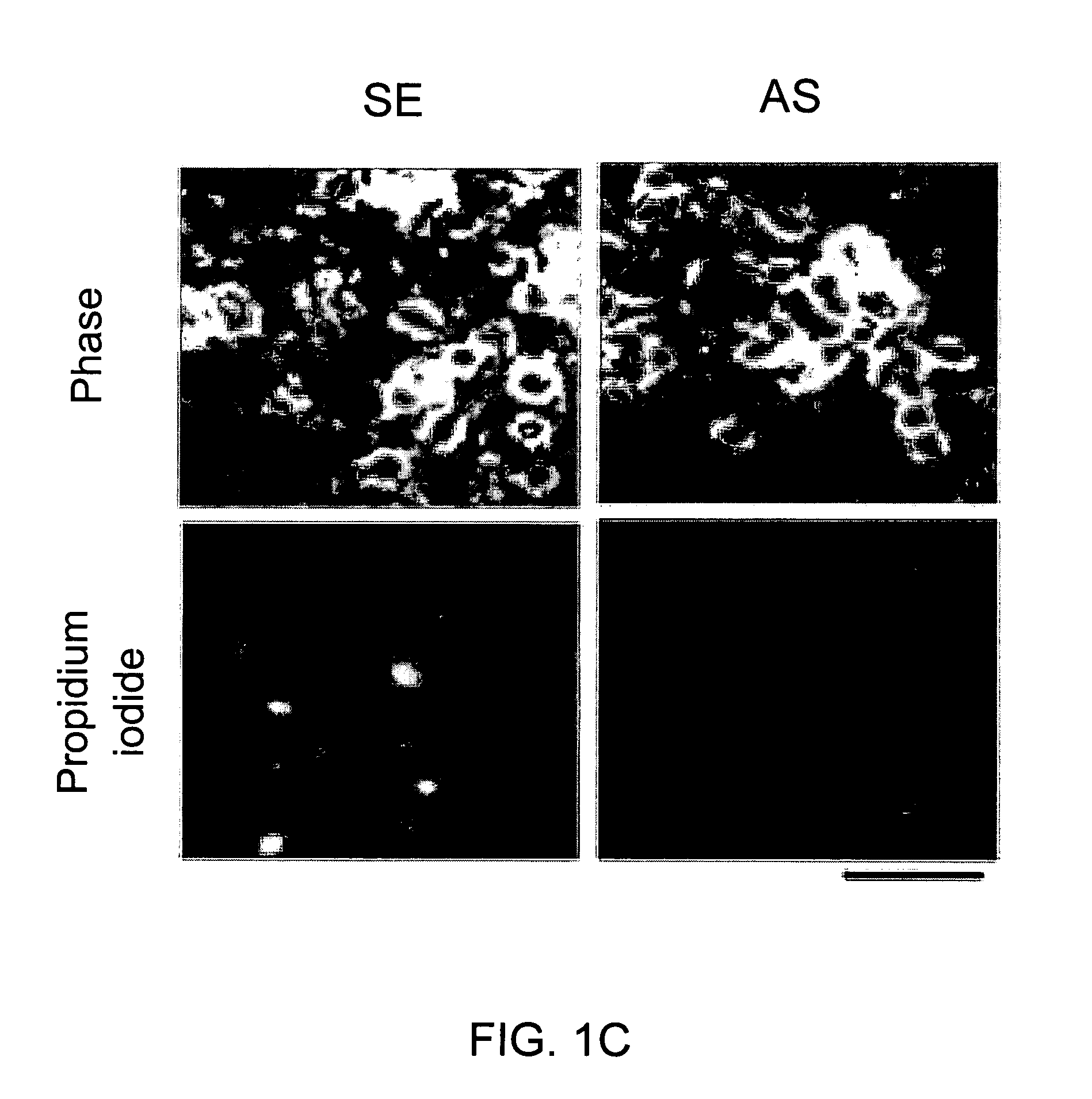
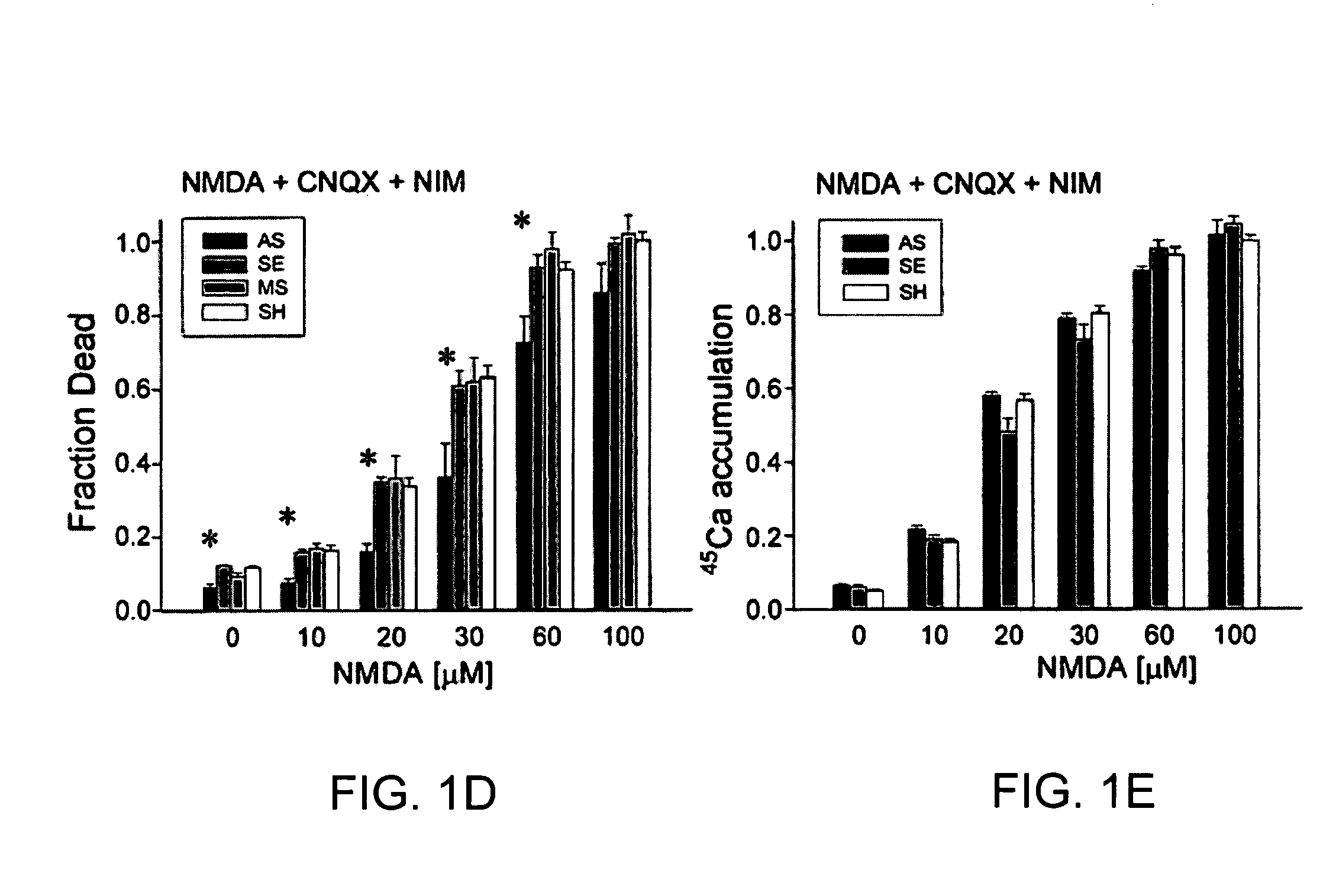
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor—neuronal protein interaction. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity, ischemic and traumatic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults, dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia, and traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats.
Owner:NONO INC
Adaptive neural network utilizing nanotechnology-based components
Methods and systems for modifying at least one synapse of a physicallelectromechanical neural network. A physical / electromechanical neural network implemented as an adaptive neural network can be provided, which includes one or more neurons and one or more synapses thereof, wherein the neurons and synapses are formed from a plurality of nanoparticles disposed within a dielectric solution in association with one or more pre-synaptic electrodes and one or more post-synaptic electrodes and an applied electric field. At least one pulse can be generated from one or more of the neurons to one or more of the pre-synaptic electrodes of a succeeding neuron and one or more post-synaptic electrodes of one or more of the neurons of the physical / electromechanical neural network, thereby strengthening at least one nanoparticle of a plurality of nanoparticles disposed within the dielectric solution and at least one synapse thereof.
Owner:KNOWM TECH
Round-trip engineering apparatus and methods for neural networks
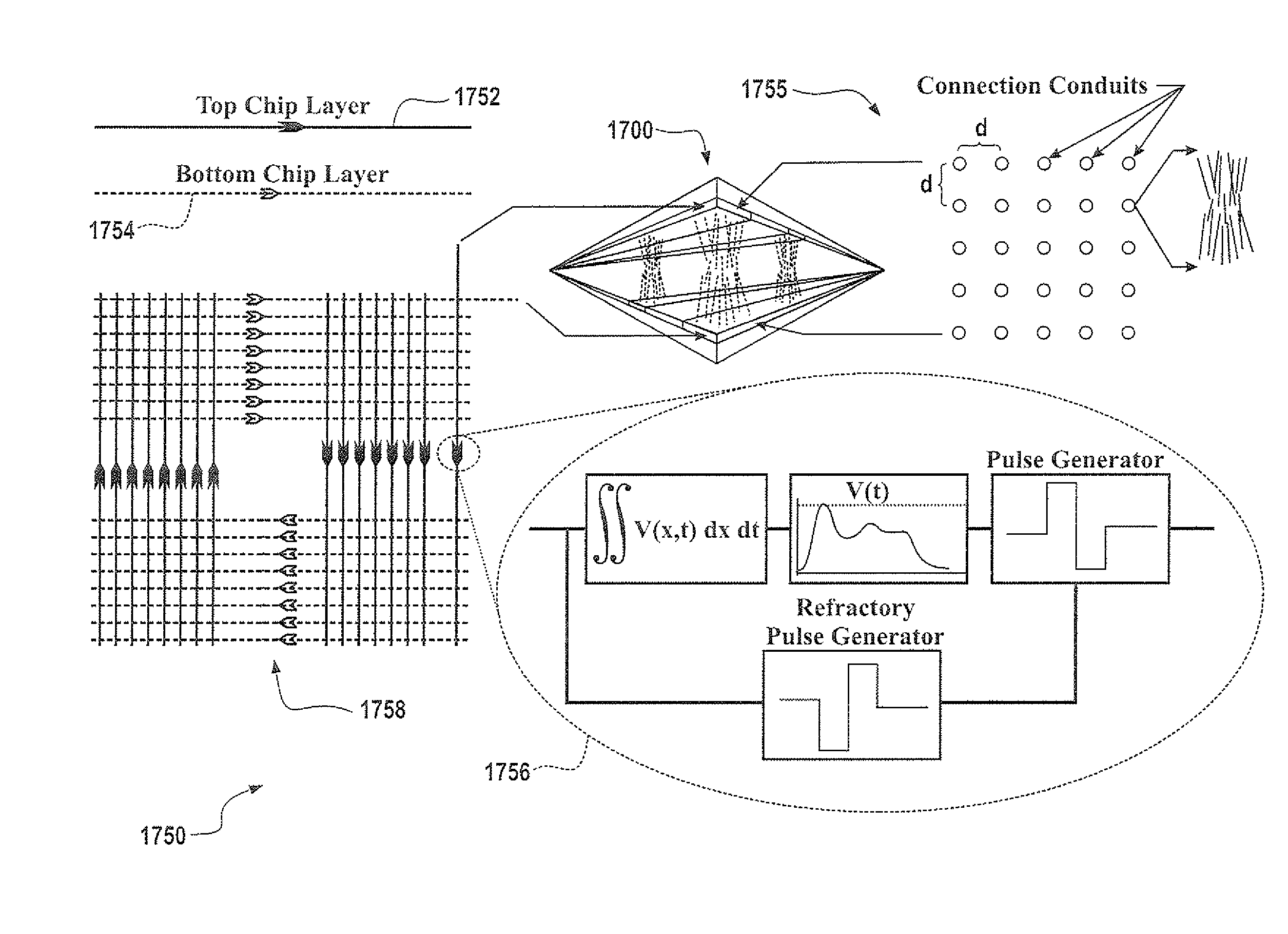
Apparatus and methods for high-level neuromorphic network description (HLND) framework that may be configured to enable users to define neuromorphic network architectures using a unified and unambiguous representation that is both human-readable and machine-interpretable. The framework may be used to define nodes types, node-to-node connection types, instantiate node instances for different node types, and to generate instances of connection types between these nodes. To facilitate framework usage, the HLND format may provide the flexibility required by computational neuroscientists and, at the same time, provides a user-friendly interface for users with limited experience in modeling neurons. The HLND kernel may comprise an interface to Elementary Network Description (END) that is optimized for efficient representation of neuronal systems in hardware-independent manner and enables seamless translation of HLND model description into hardware instructions for execution by various processing modules.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
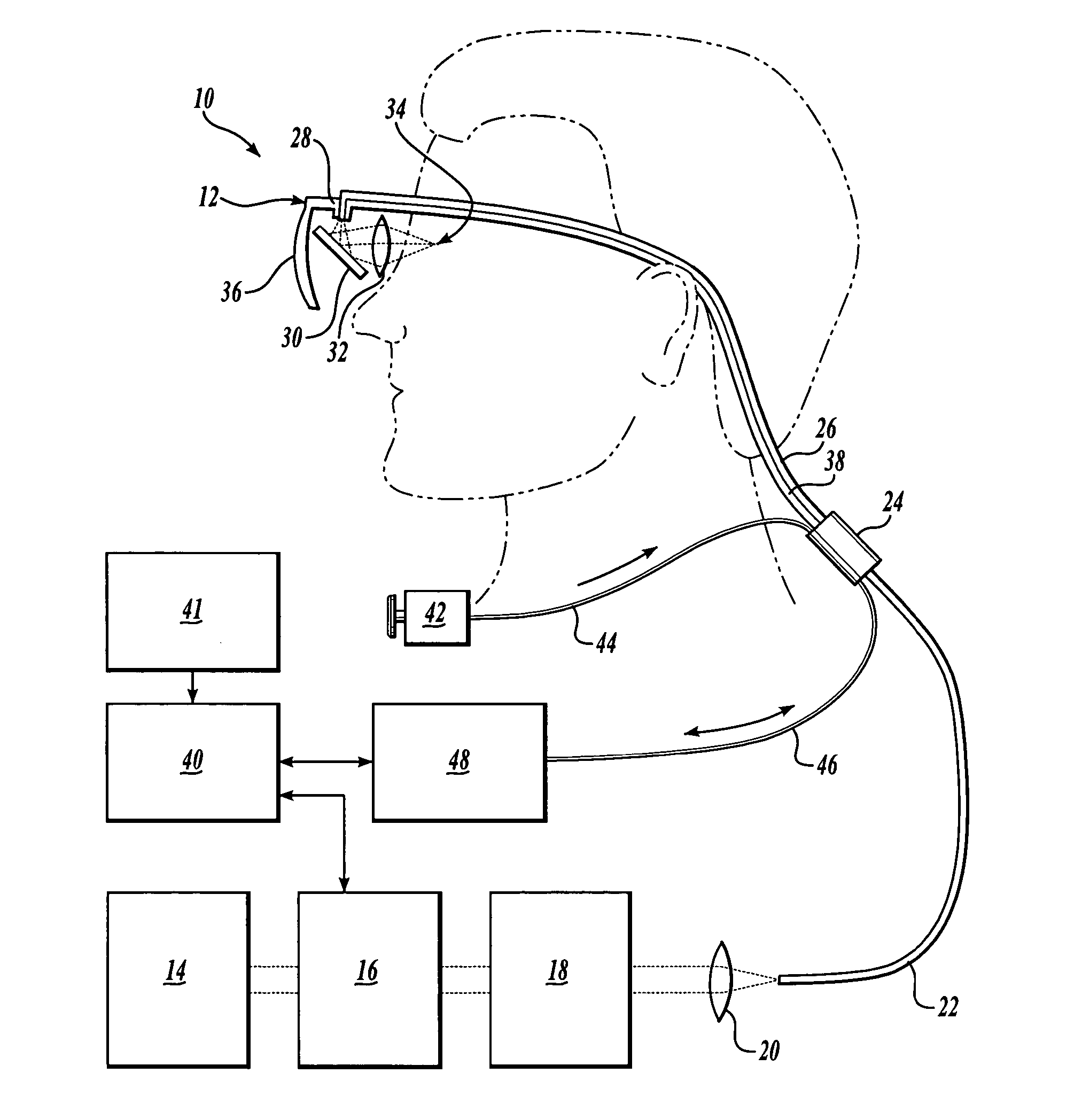
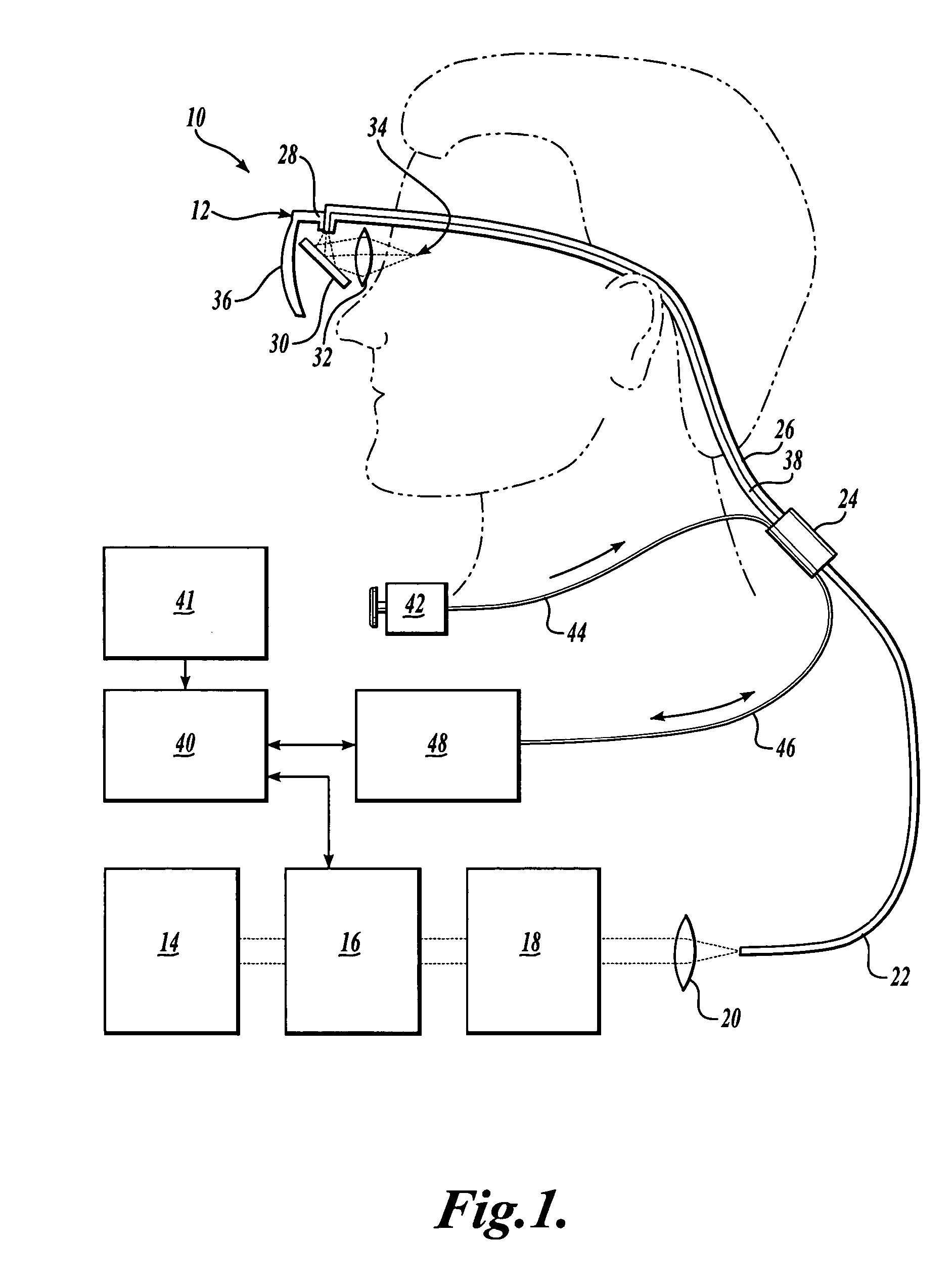
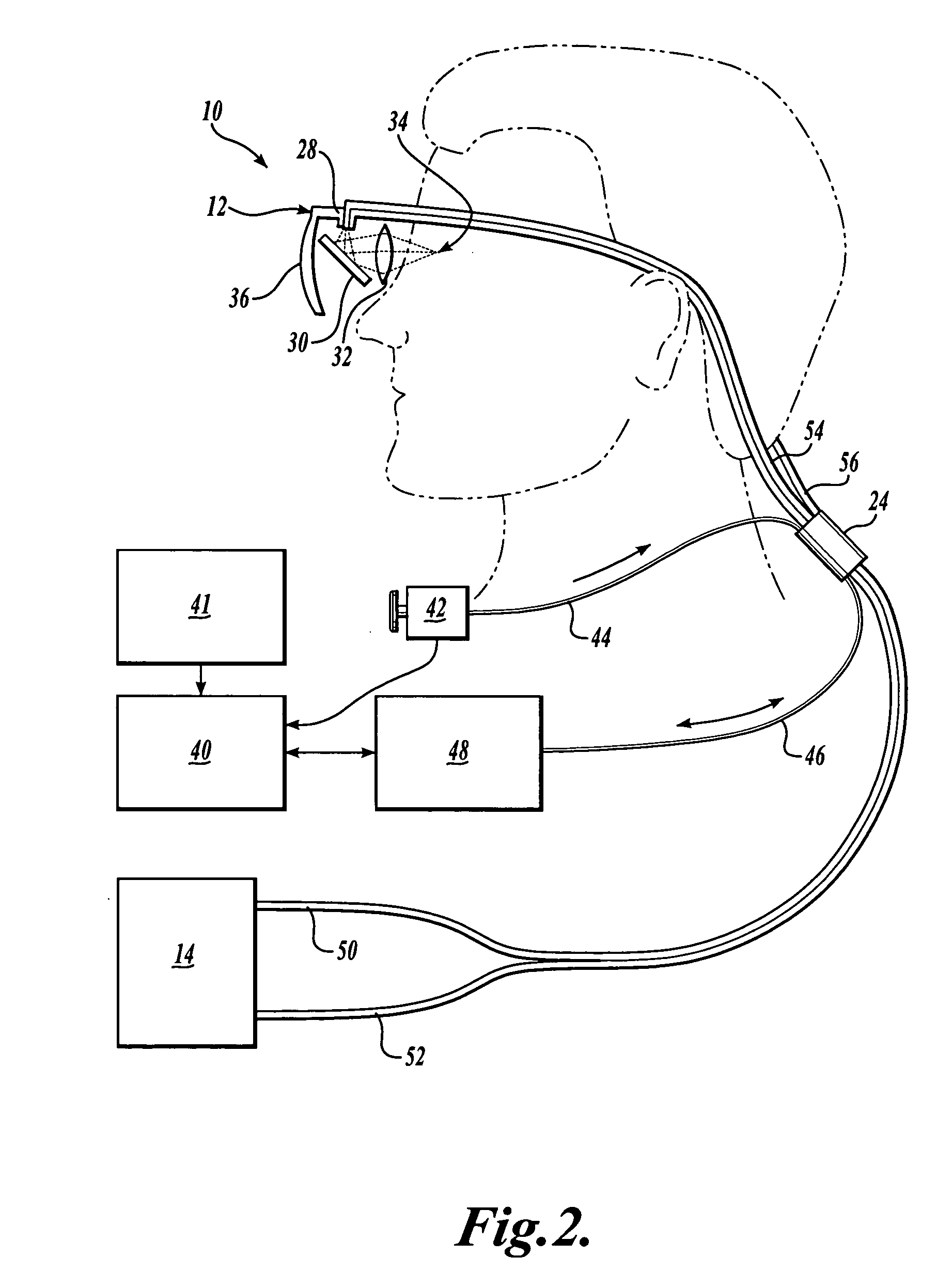
Scanning laser device and methods of use
InactiveUS20050015120A1Promote healthEasy SurvivalElectrotherapyDiagnosticsLight energyRetinal Neuron
In one aspect, the invention provides vision prosthesis systems. Exemplary vision prosthesis systems of the invention comprise a light energy generator operably connected to a wearable head piece comprising a device for directing light energy produced by the light energy generator onto a mammalian retina, wherein the light energy generator is tuned to emit light energy of sufficient power to modulate neural activity in the retina. In another aspect, the invention provides methods for irradiating neurons in the retina of the mammalian eye by directing light energy produced by a light energy generator onto a mammalian retina. The methods of the invention may be used to directly modulate the activity of retinal neurons or to introduce molecules into retinal cells.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
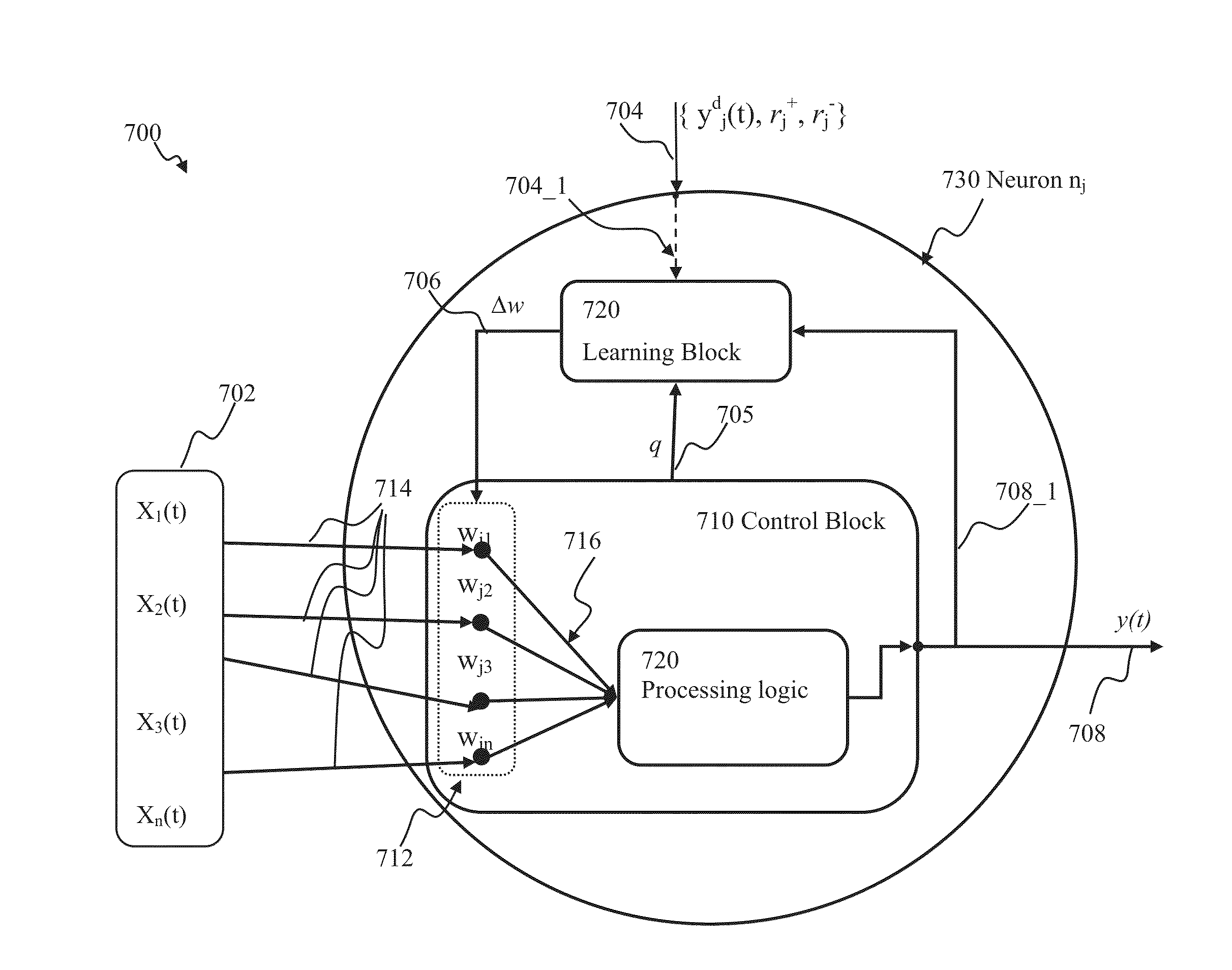
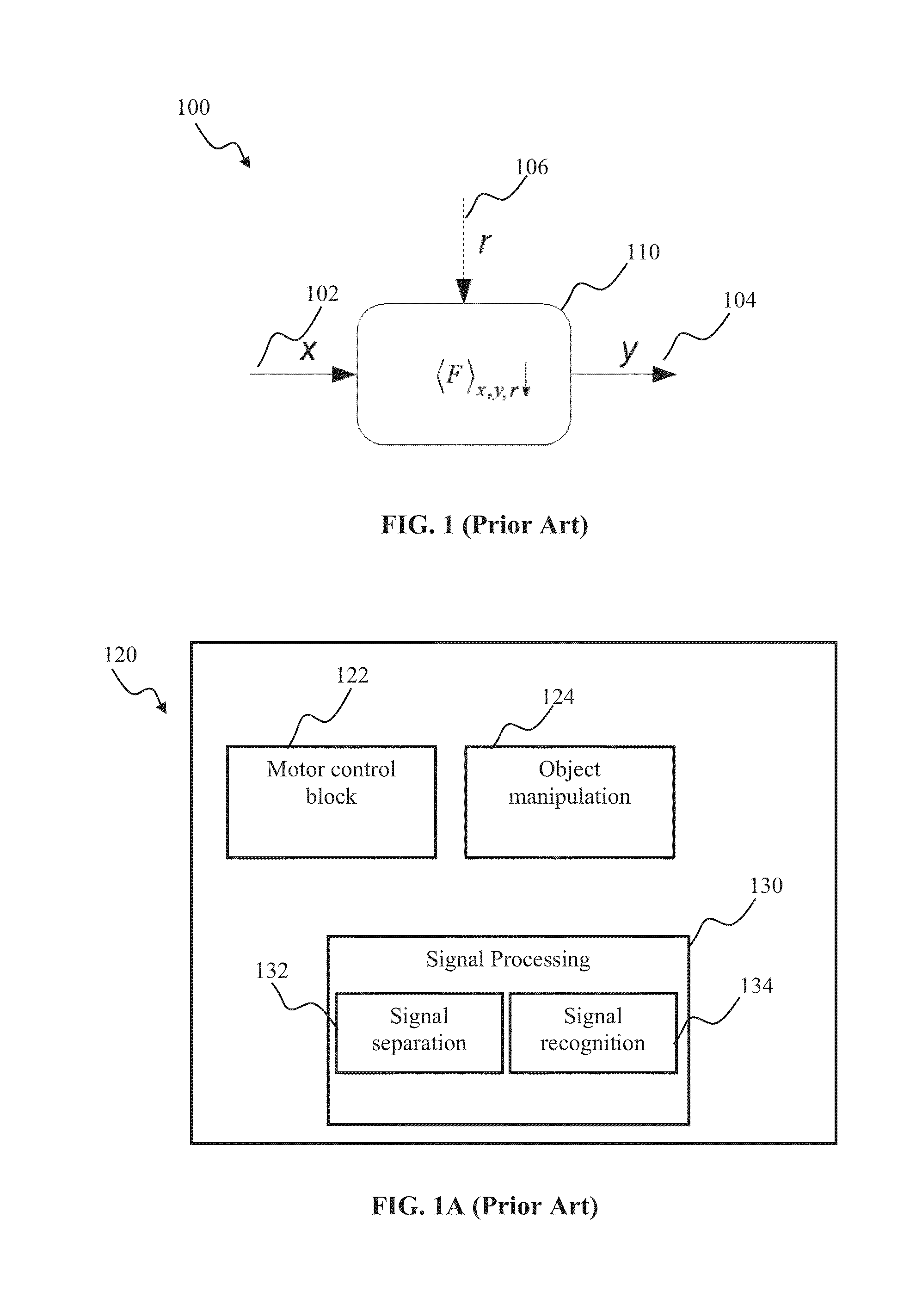
Stochastic spiking network learning apparatus and methods
Generalized learning rules may be implemented. A framework may be used to enable adaptive spiking neuron signal processing system to flexibly combine different learning rules (supervised, unsupervised, reinforcement learning) with different methods (online or batch learning). The generalized learning framework may employ time-averaged performance function as the learning measure thereby enabling modular architecture where learning tasks are separated from control tasks, so that changes in one of the modules do not necessitate changes within the other. Separation of learning tasks from the control tasks implementations may allow dynamic reconfiguration of the learning block in response to a task change or learning method change in real time. The generalized spiking neuron learning apparatus may be capable of implementing several learning rules concurrently based on the desired control application and without requiring users to explicitly identify the required learning rule composition for that task.
Owner:BRAIN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com