Patents
Literature
3845 results about "Electrical stimulations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
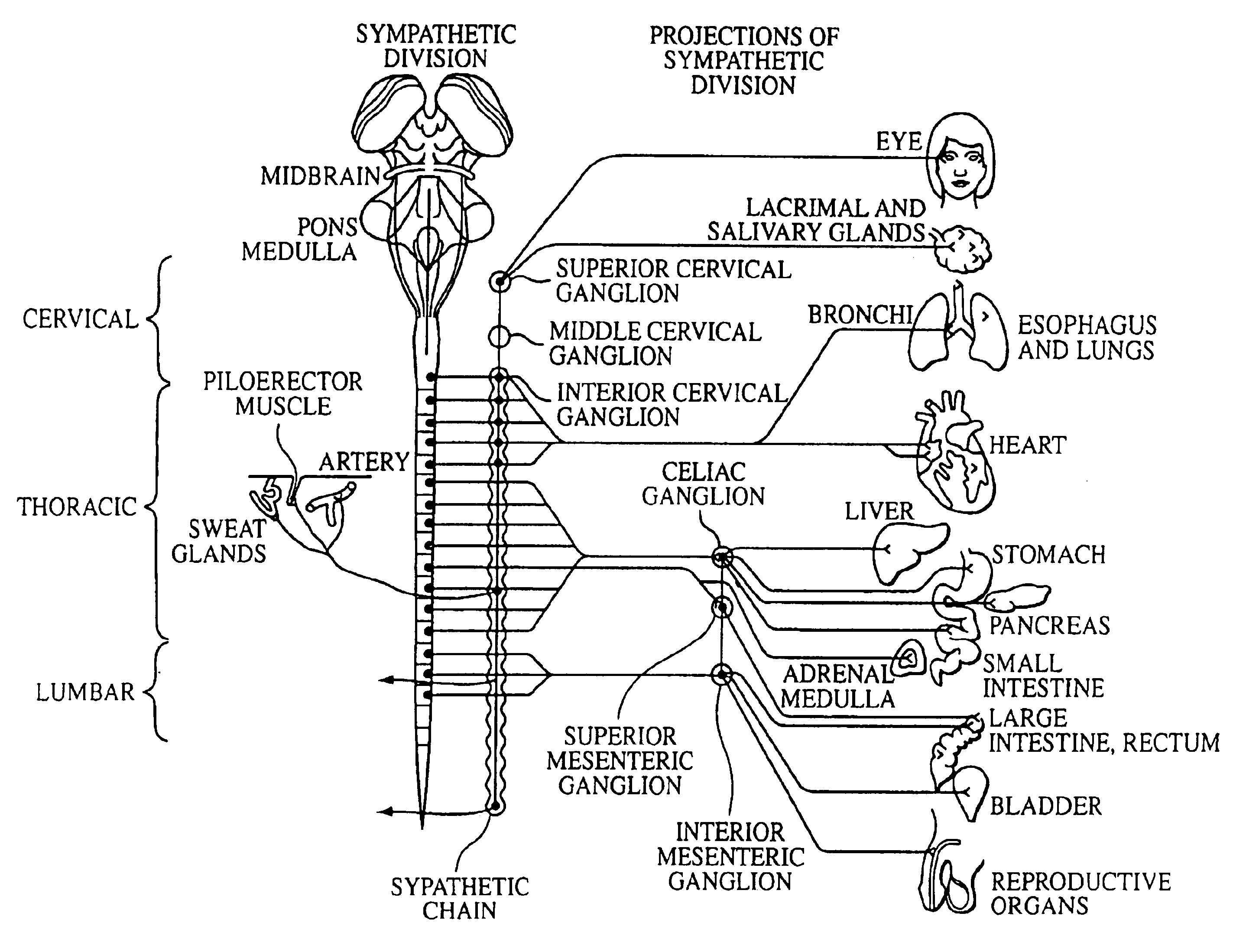
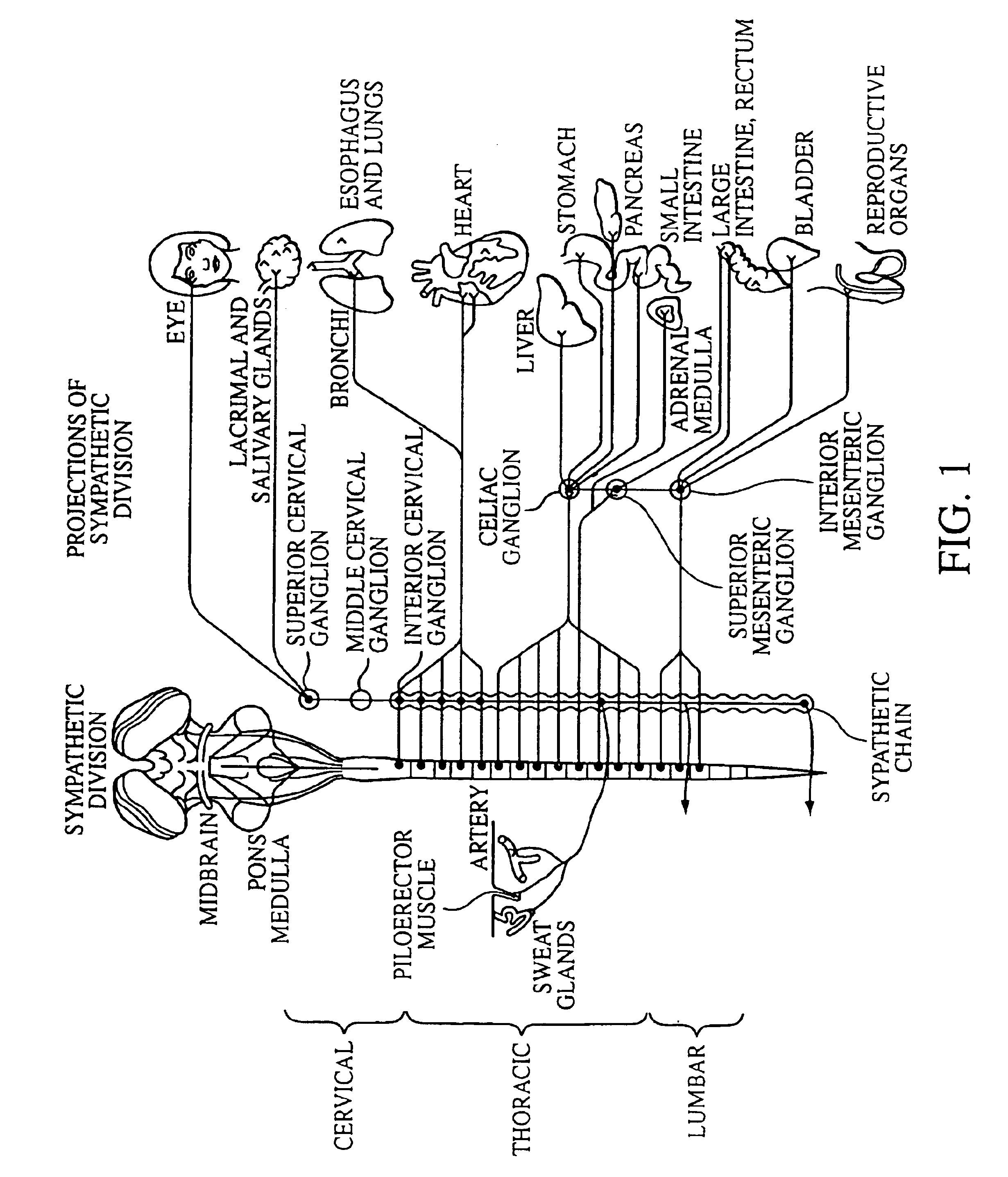
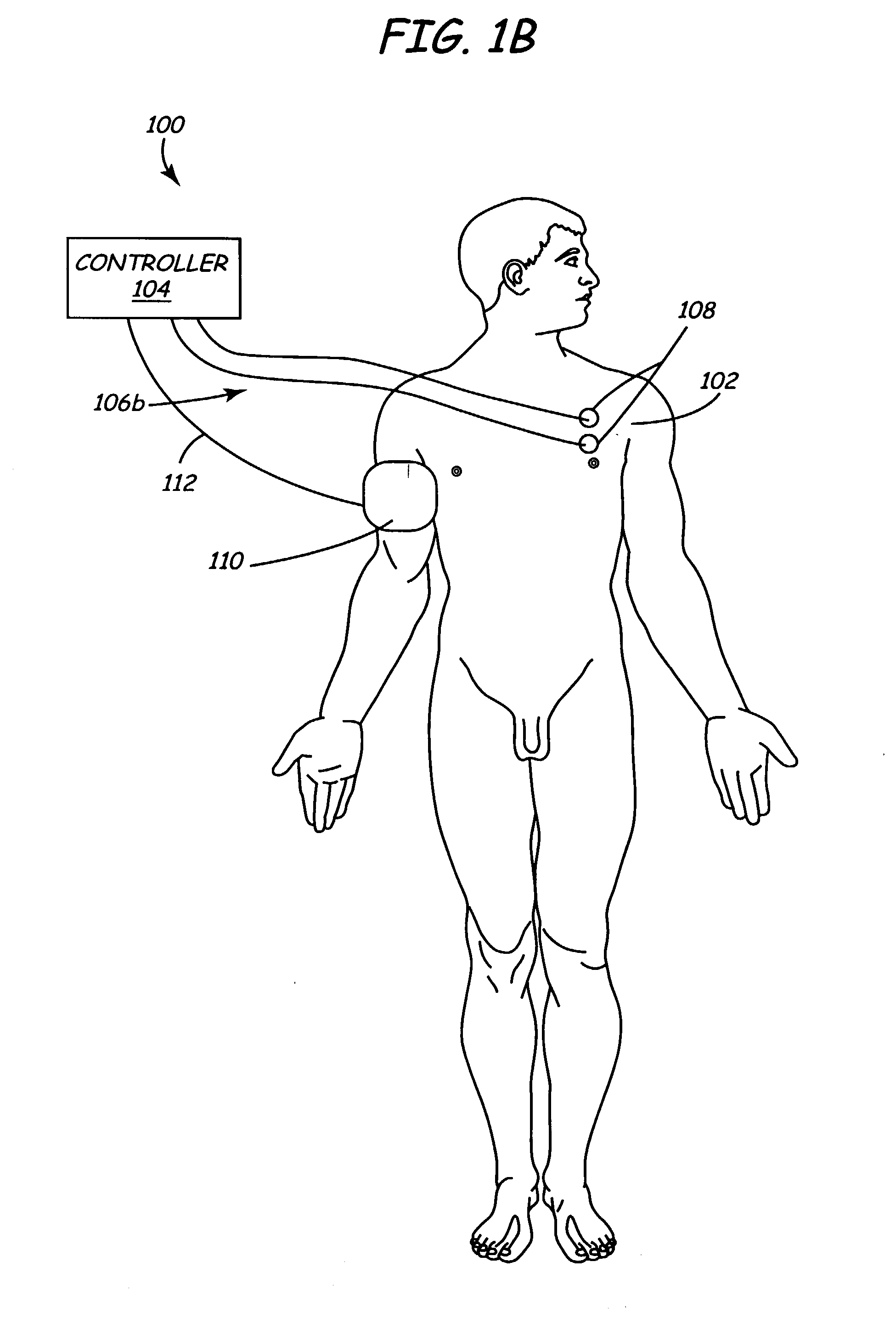
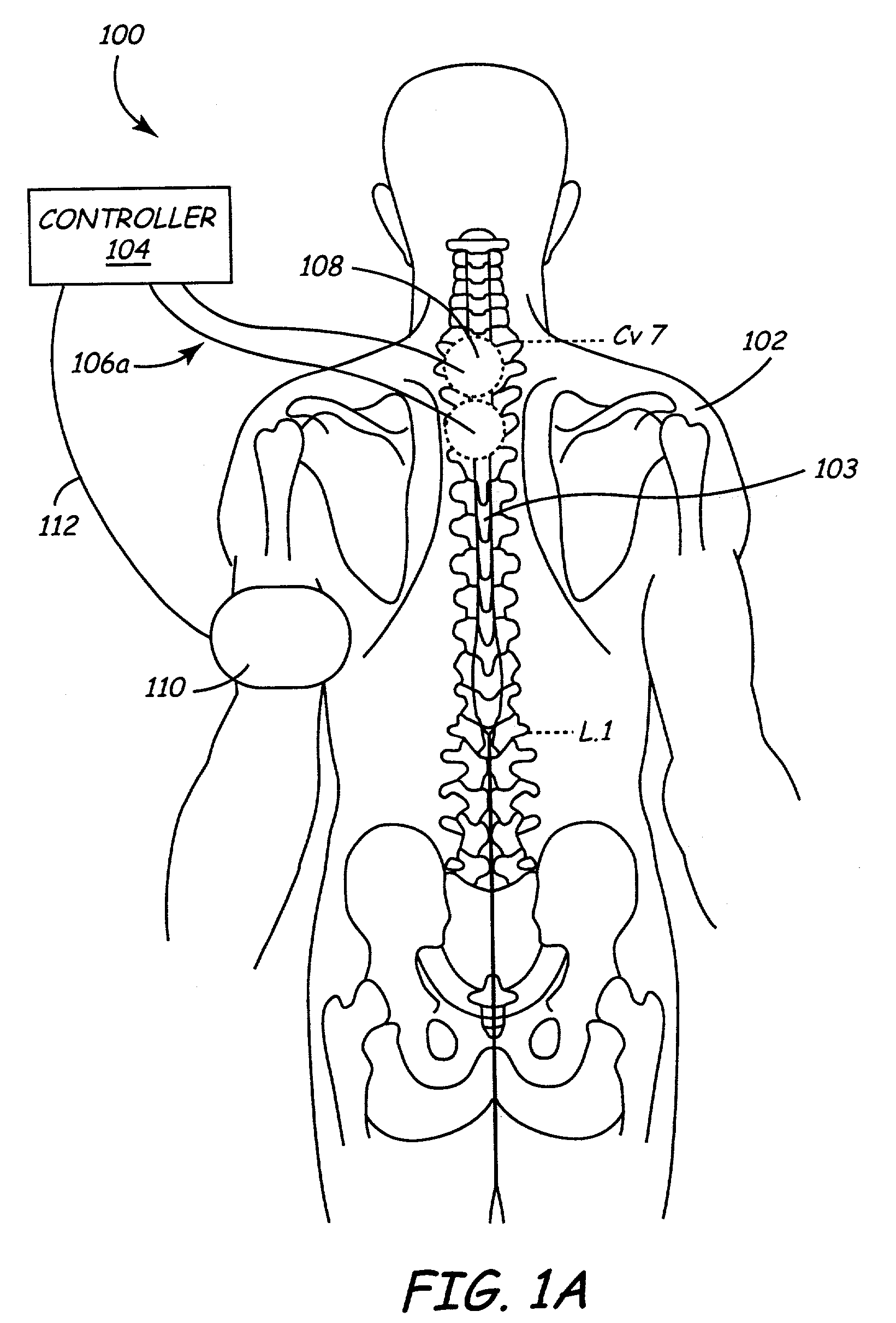
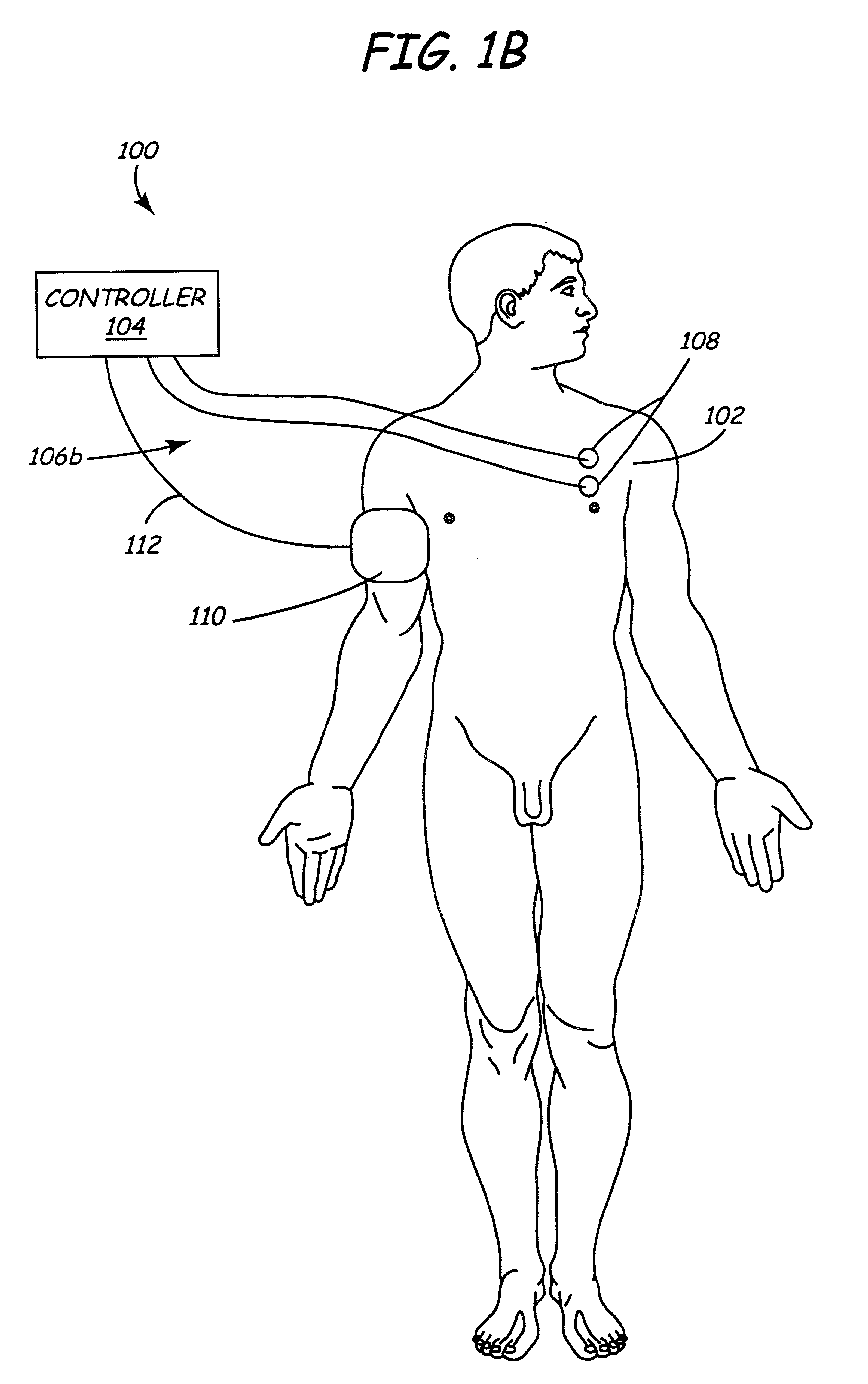
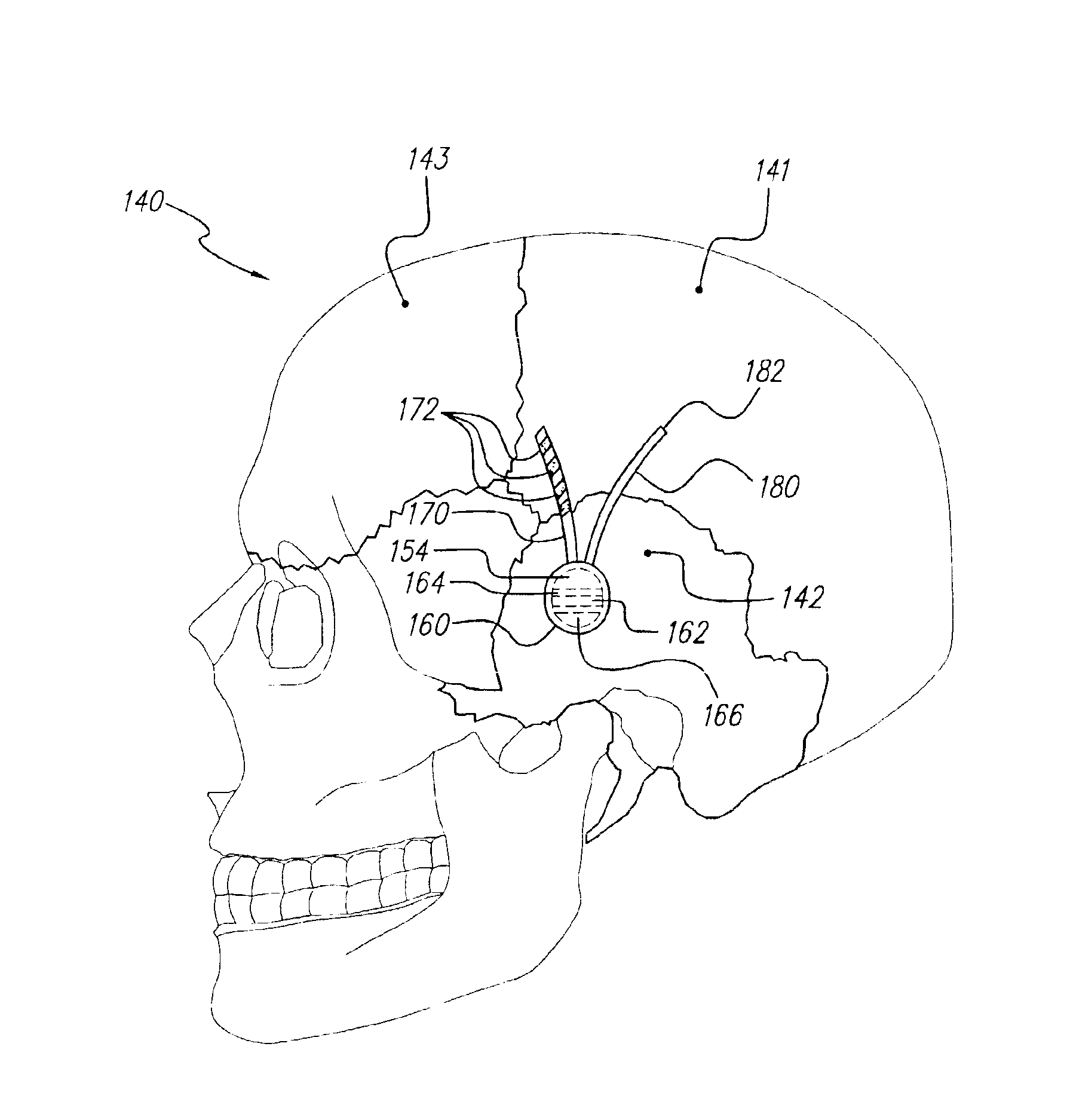
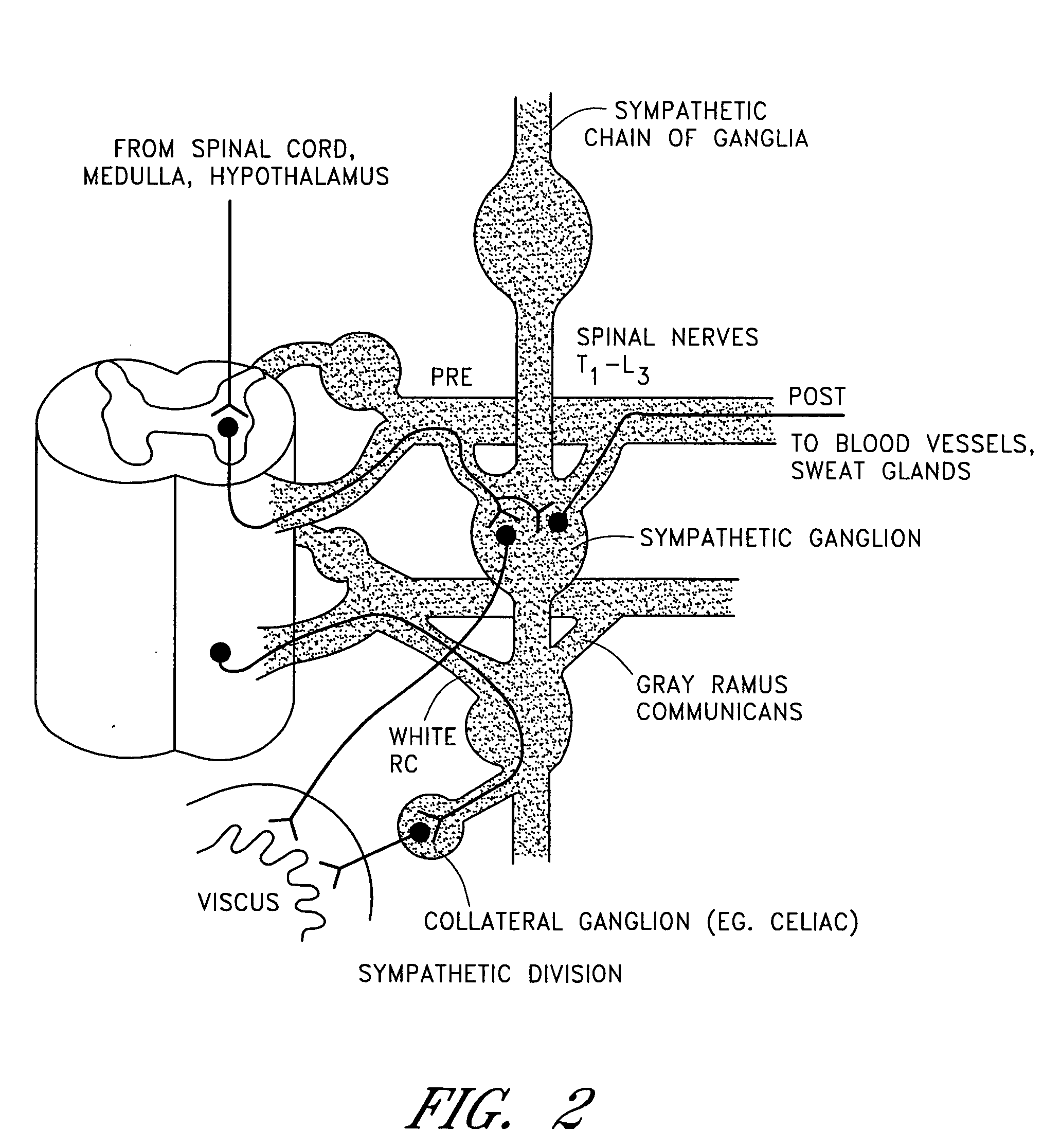
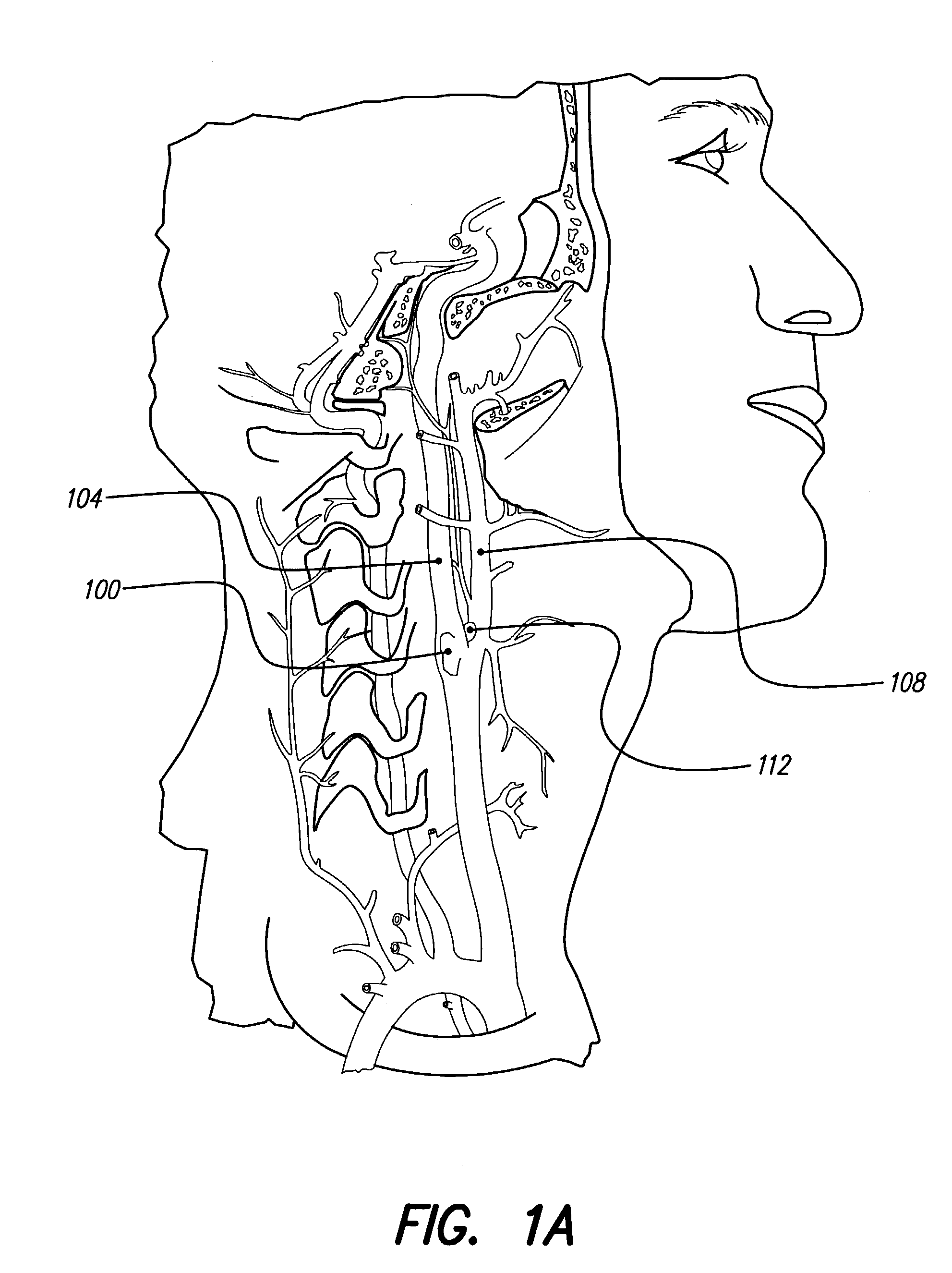
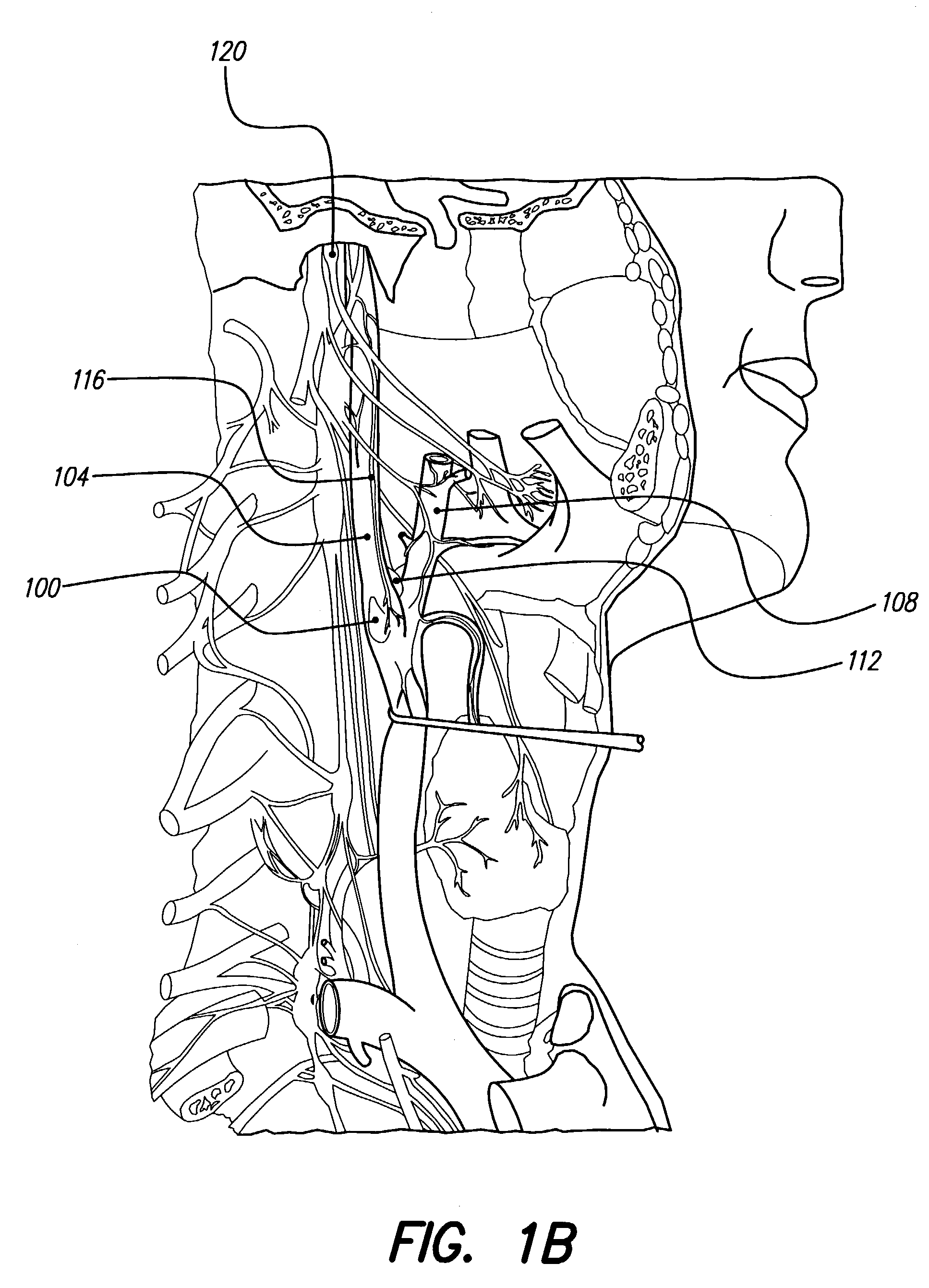
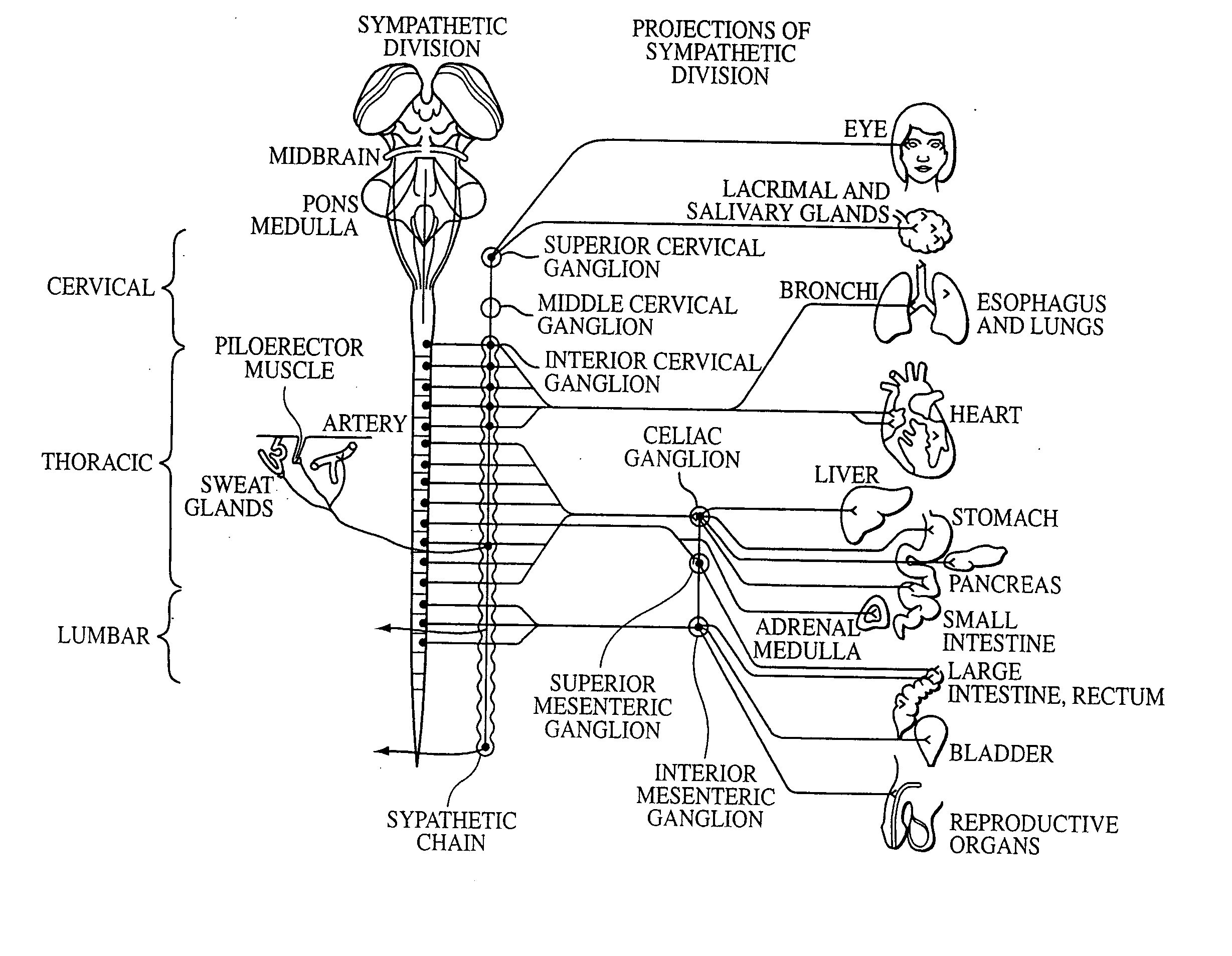
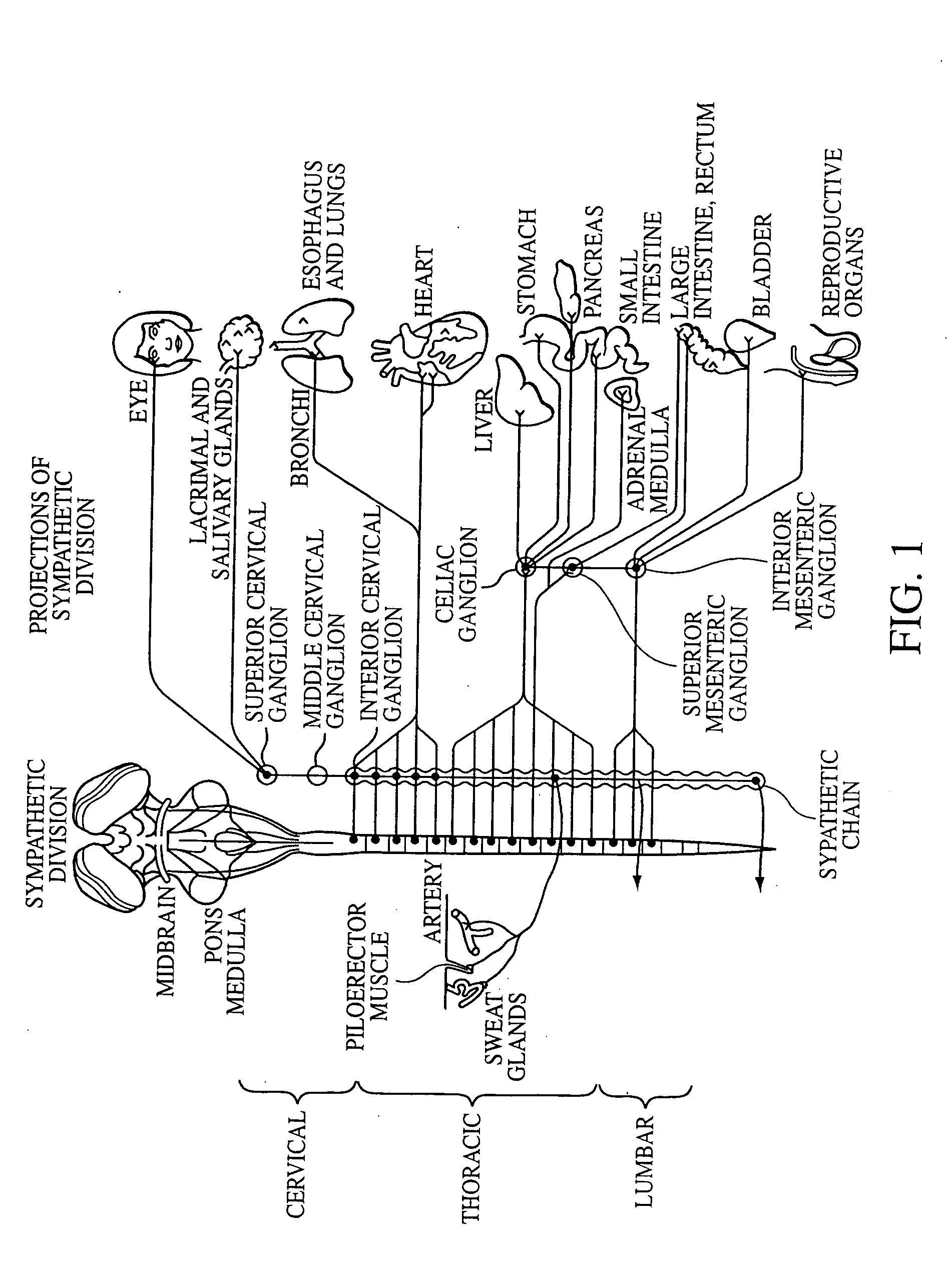
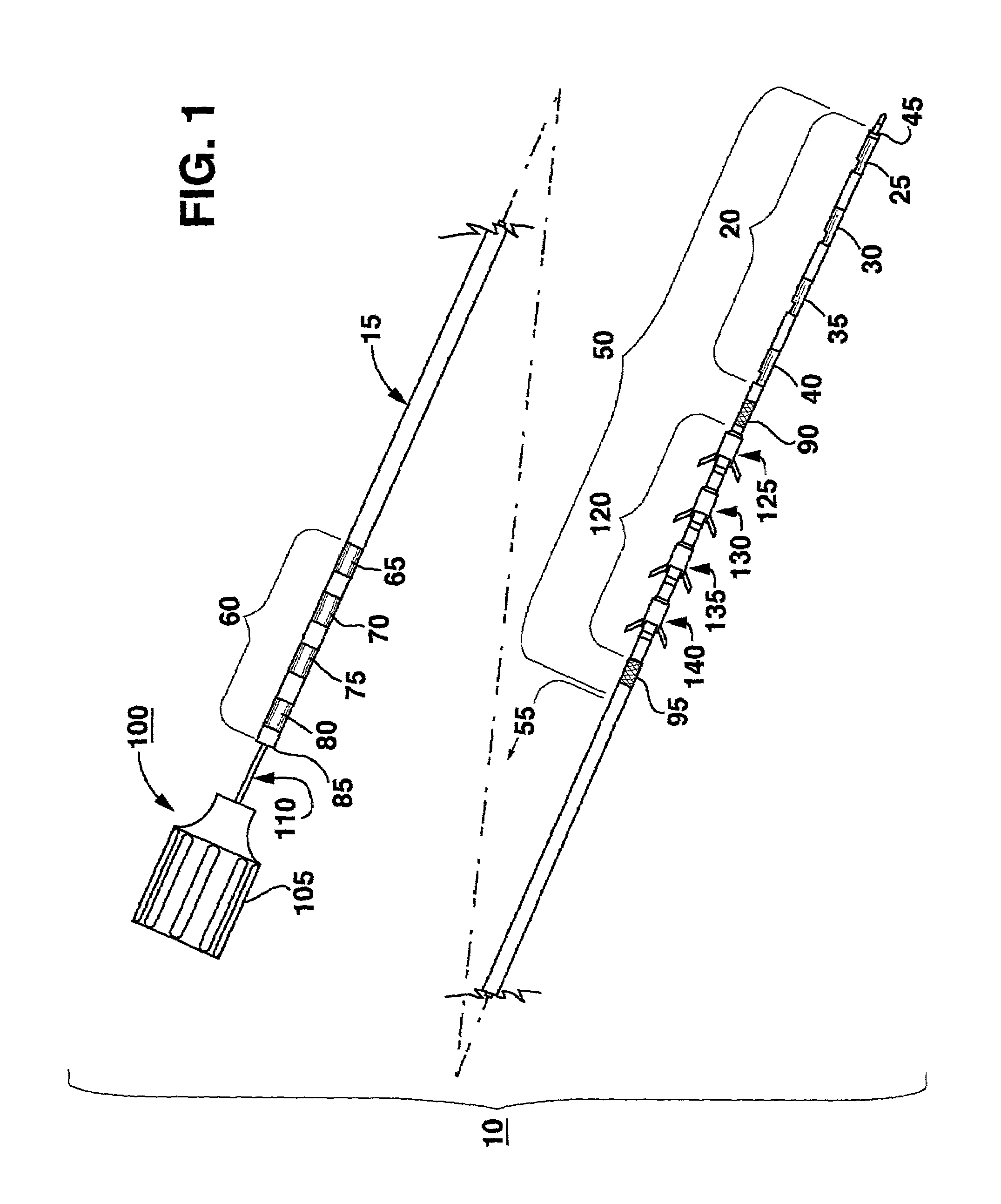
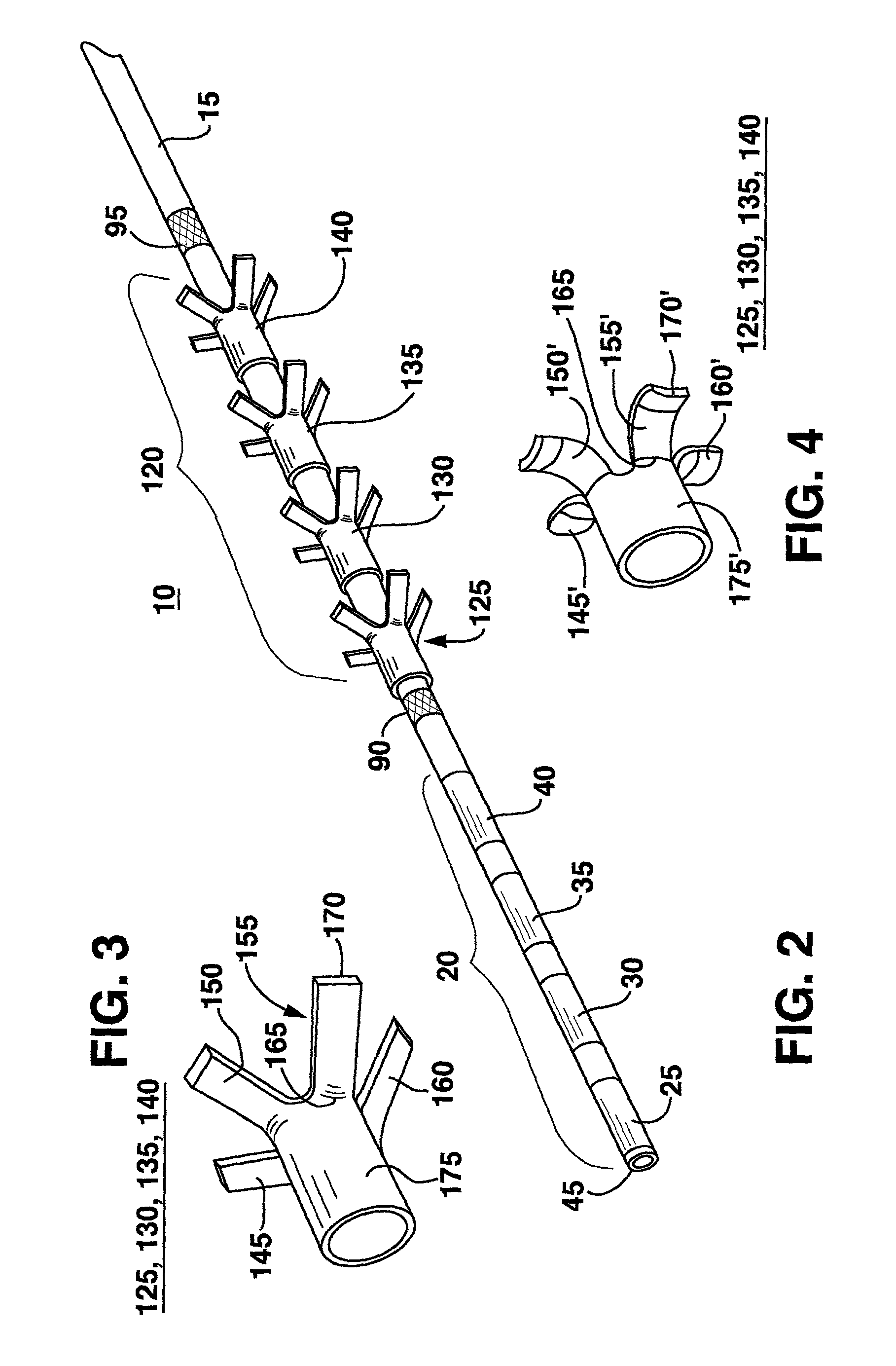
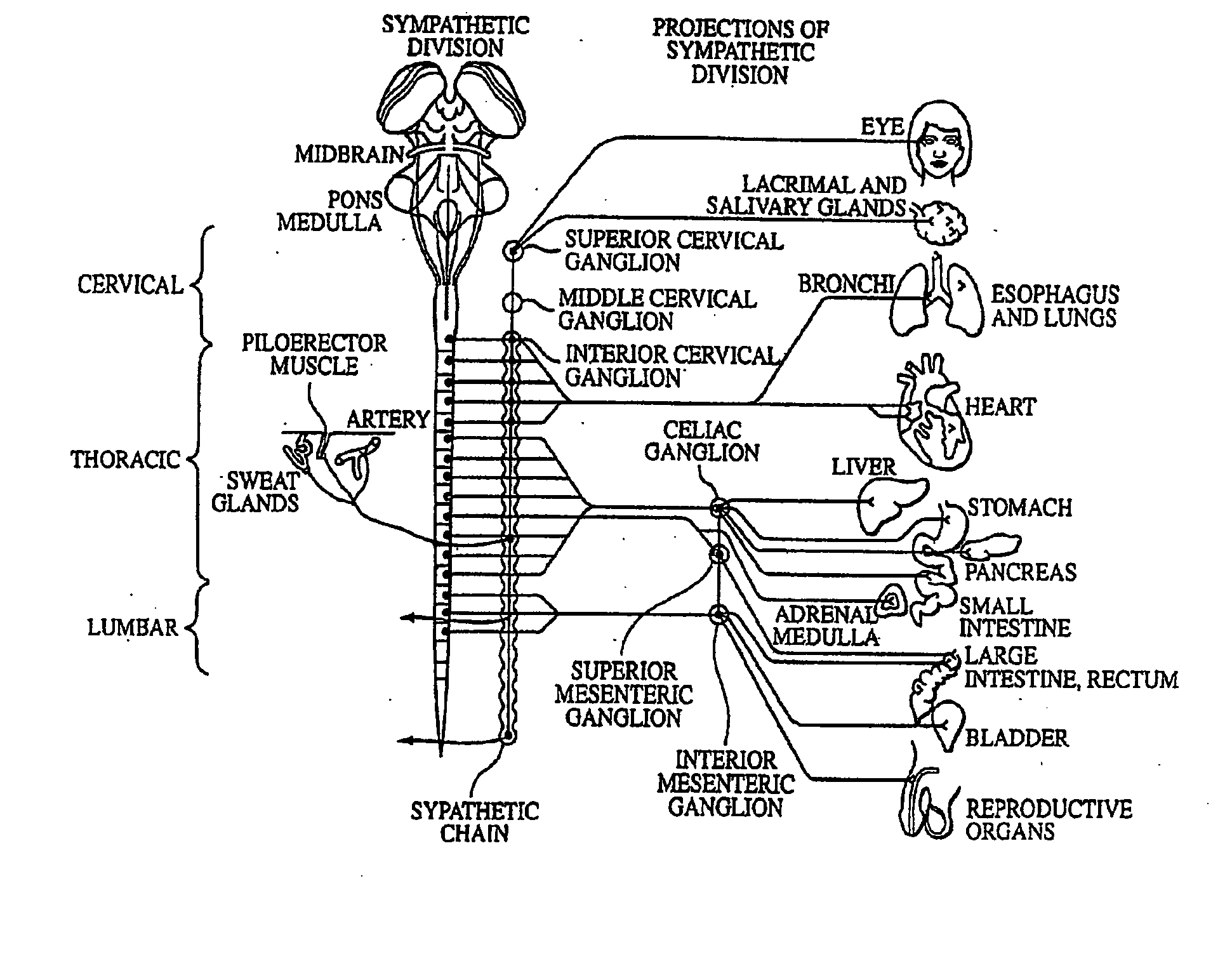
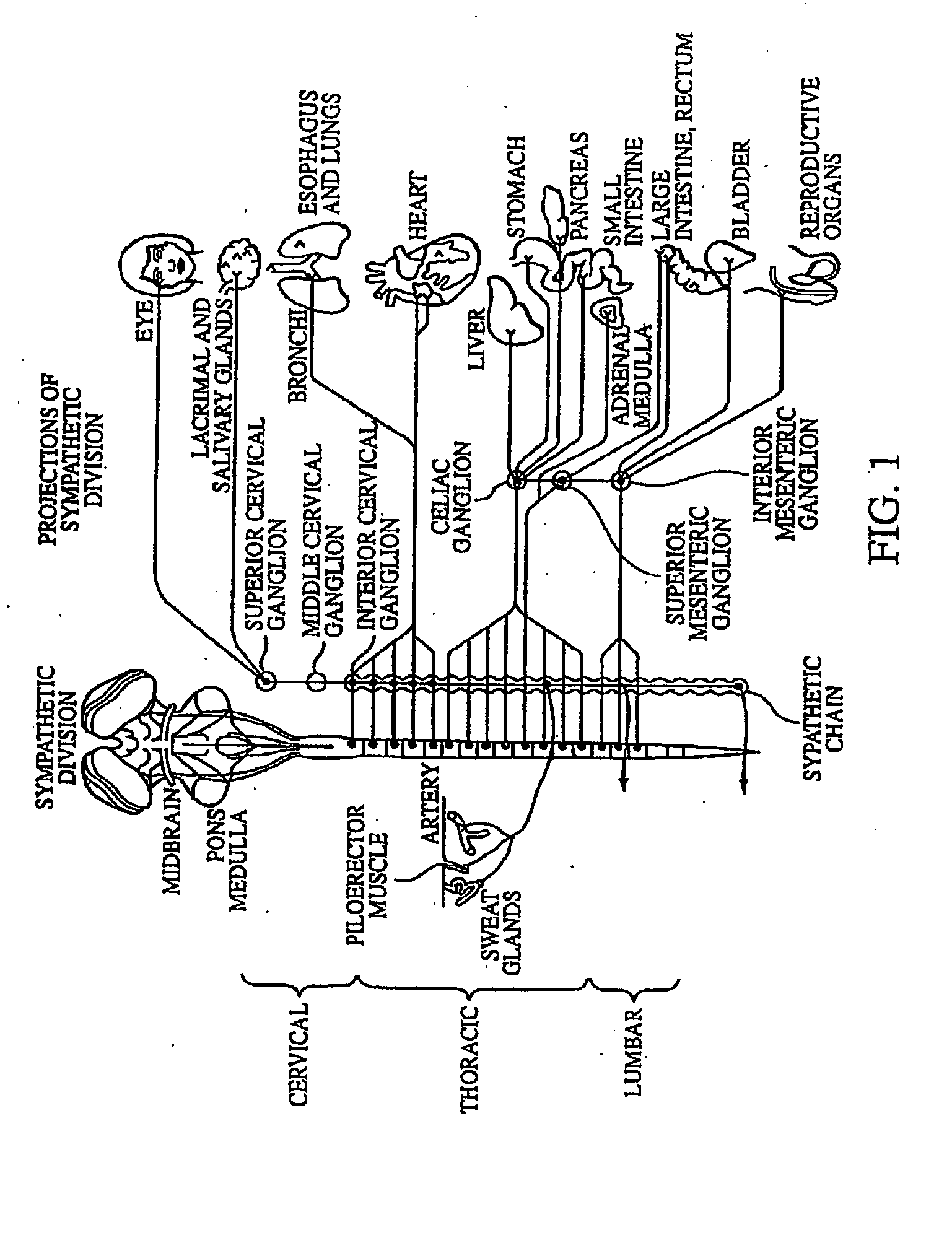
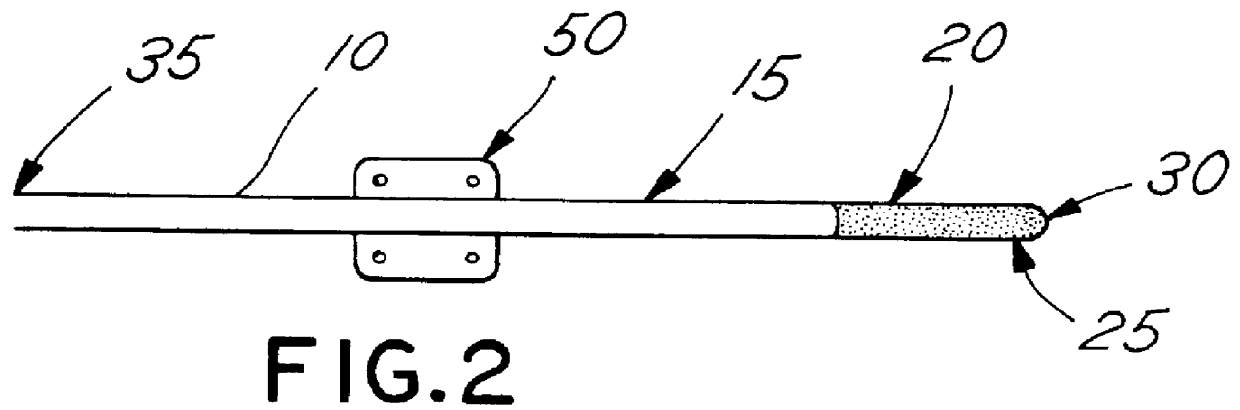
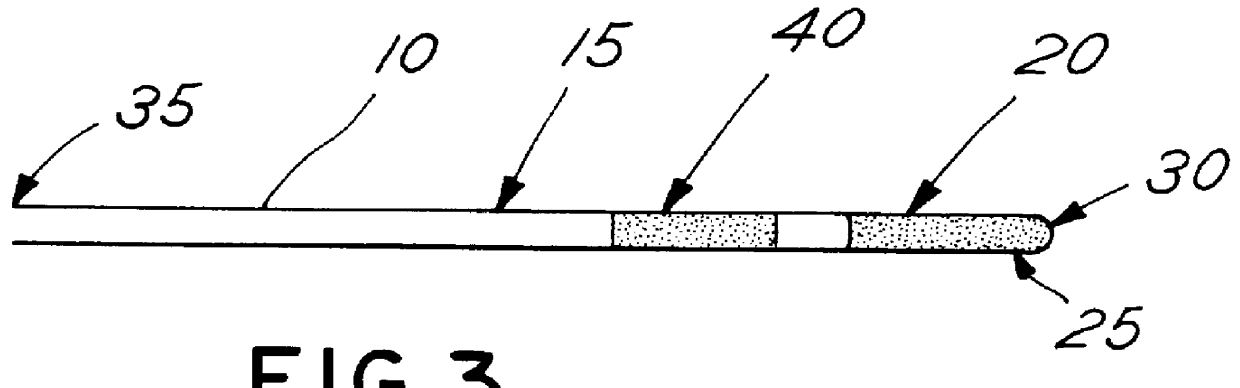
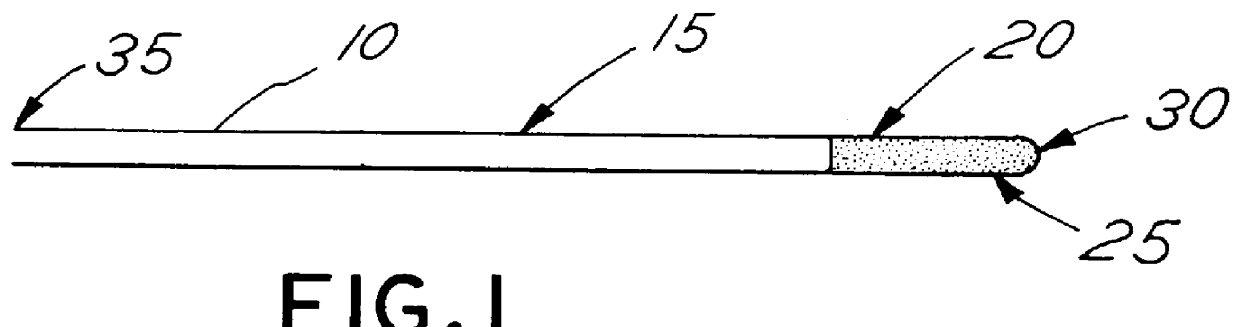
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS6885888B2Minimizing stimulationMinimize complicationsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
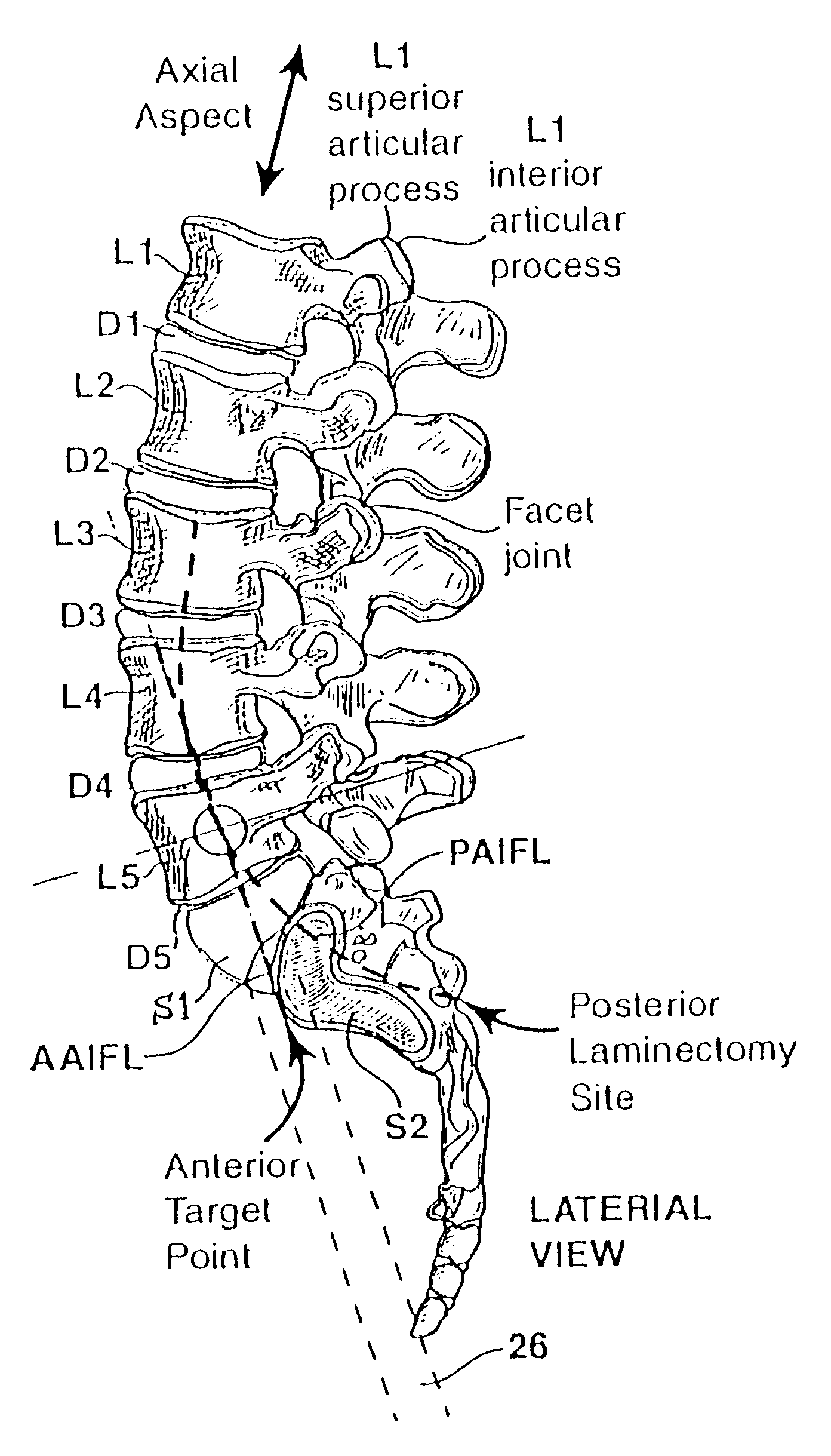
Methods and apparatus for performing therapeutic procedures in the spine
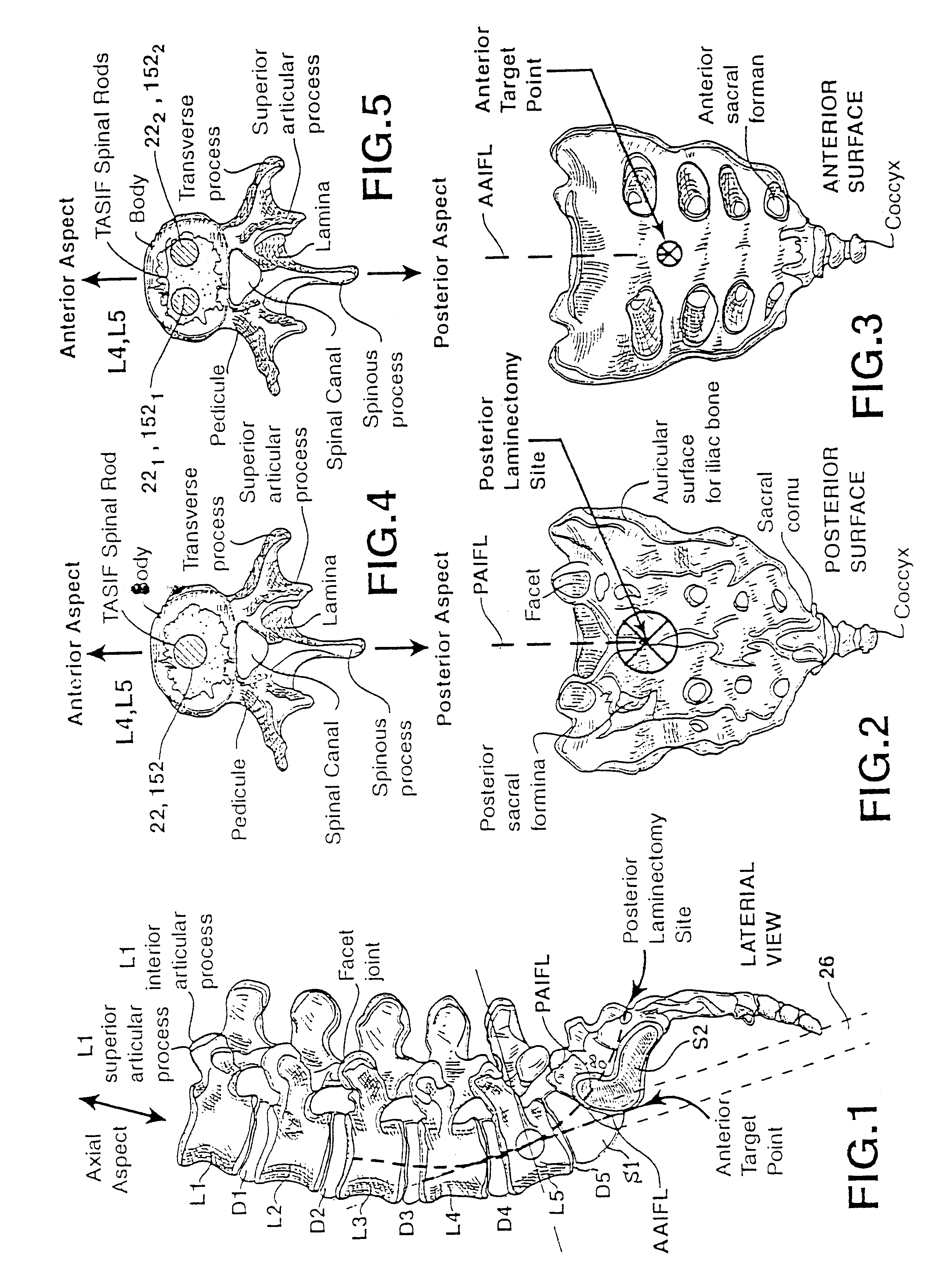
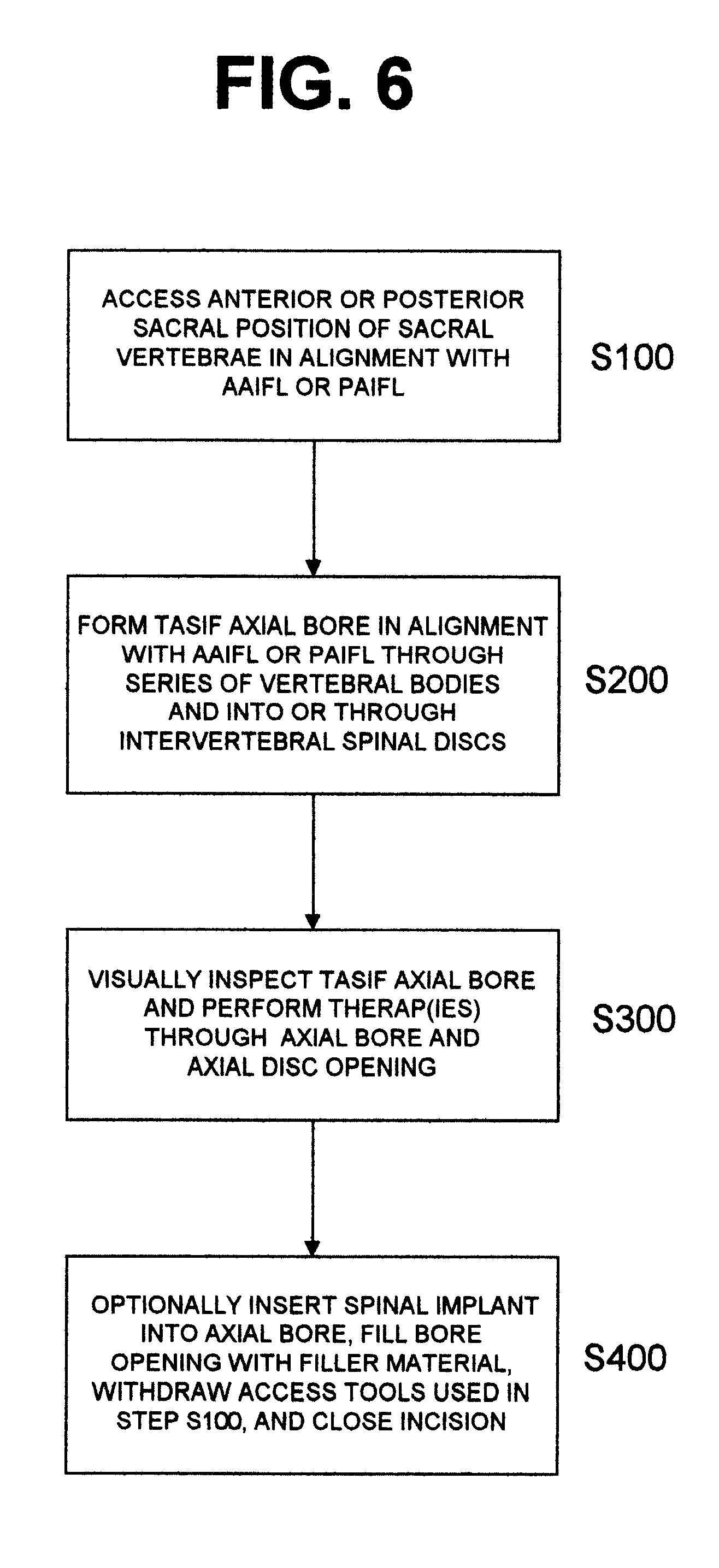
Methods and apparatus for forming one or more trans-sacral axial instrumentation / fusion (TASIF) axial bore through vertebral bodies in general alignment with a visualized, anterior or posterior axial instrumentation / fusion line (AAIFL or PAIFL) in a minimally invasive, low trauma, manner and providing a therapy to the spine employing the axial bore. Anterior or posterior starting positions aligned with the AAIFL or PAIFL are accessed through respective anterior and posterior tracts. Curved or relatively straight anterior and curved posterior TASIF axial bores are formed from the anterior and posterior starting positions. The therapies performed through the TASIF axial bores include discoscopy, full and partial discectomy, vertebroplasty, balloon-assisted vertebroplasty, drug delivery, electrical stimulation and various forms of spinal disc cavity augmentation, spinal disc replacement, fusion of spinal motion segments and implantation of radioactive seeds. Axial spinal implants and bone growth materials can be placed into single or multiple parallel or diverging TASIF axial bores to fuse two or more vertebrae, or distract or shock absorb two or more vertebrae.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
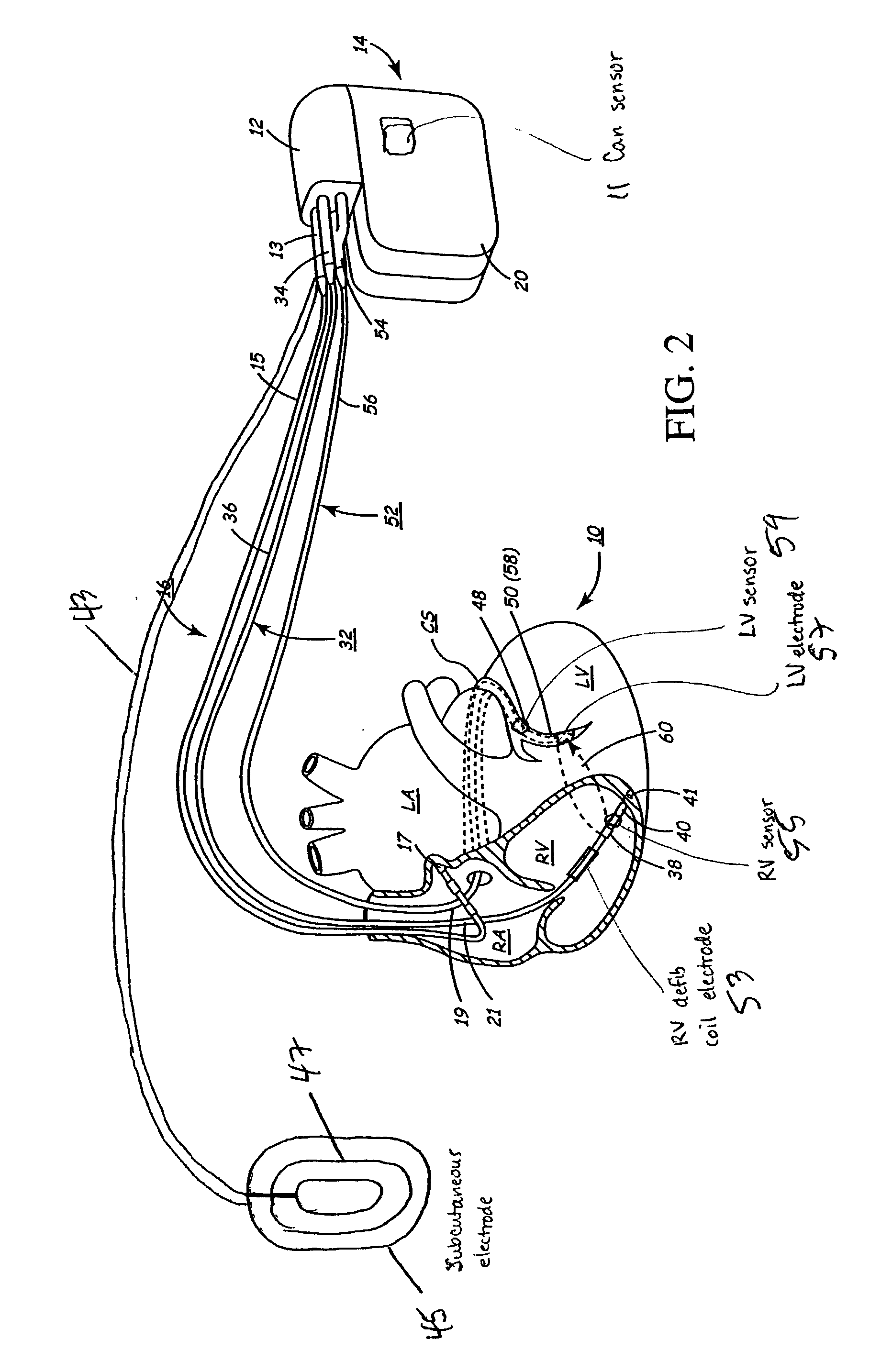
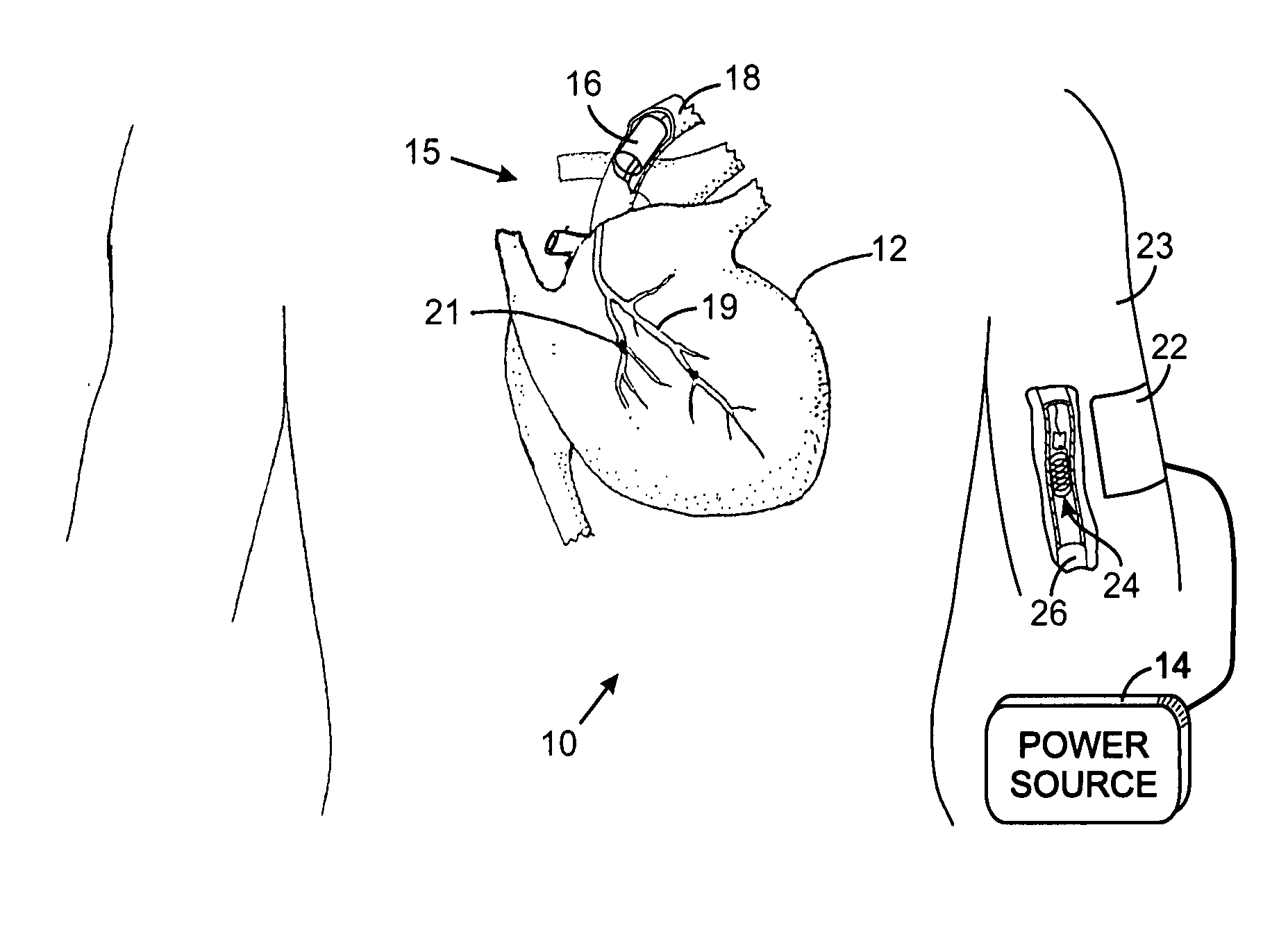
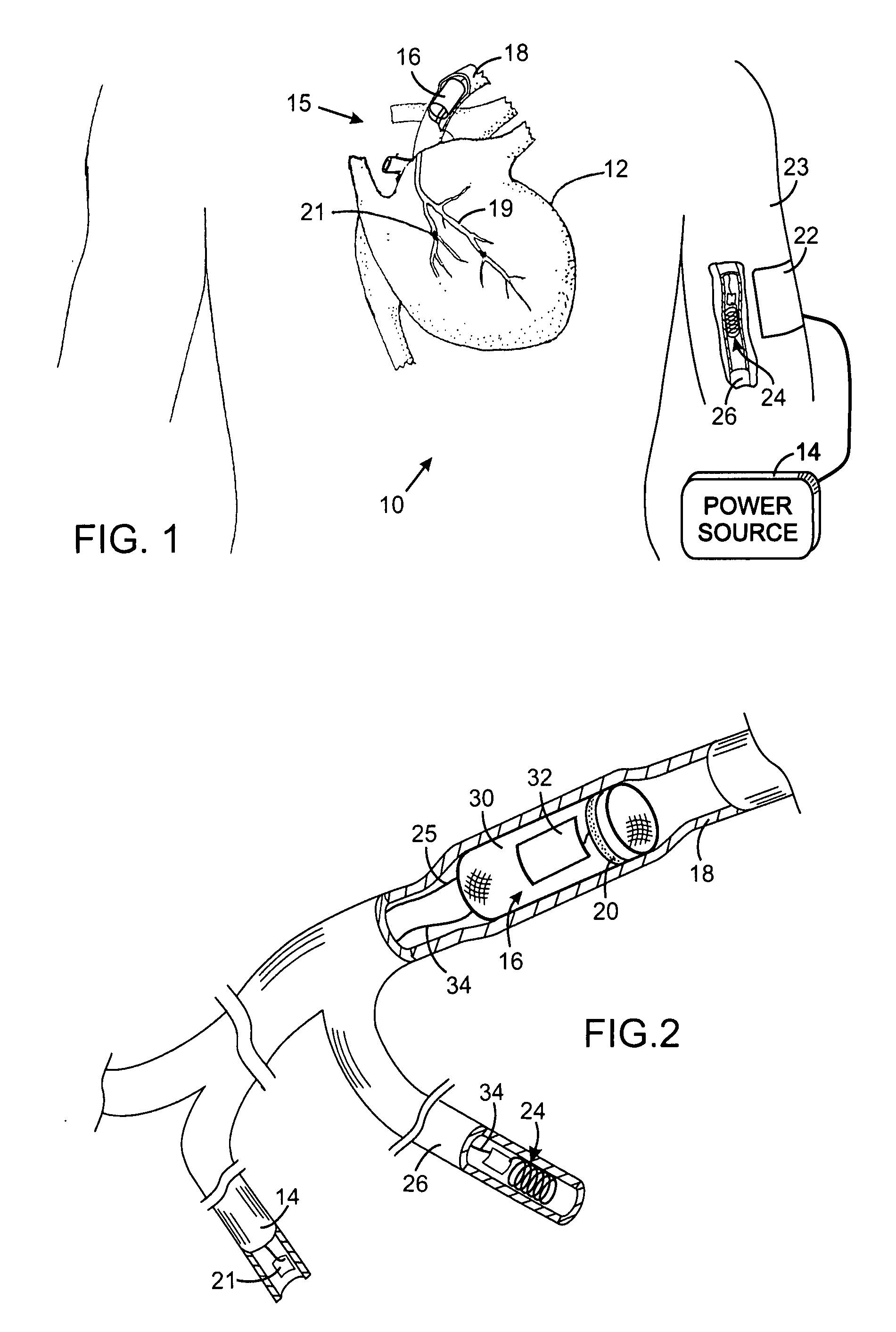
Method and apparatus for electrically stimulating the nervous system to improve ventricular dysfunction, heart failure, and other cardiac conditions
A method and apparatus are used to provide therapy to a patient experiencing ventricular dysfunction or heart failure. At least one electrode is located in a region associated with nervous tissue, such as nerve bundles T1-T4, in a patient's body. Electrical stimulation is applied to the at least one electrode to improve the cardiac efficiency of the patient's heart. One or more predetermined physiologic parameters of the patient are monitored, and the electrical stimulation is adjusted based on the one or more predetermined physiologic parameters.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Ablation apparatus having reduced nerve stimulation and related methods
InactiveUS7862560B2Mitigating and eliminating undesired electrical stimulationTrend downSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesSacral nerve stimulationPhysical therapy
Apparatus and methods for reducing nerve stimulation in electrosurgical instruments utilizing electrically isolated pairs of electrodes are disclosed. At least two pairs of electrodes may be configured to create at least two opposing currents which effectively cancel one another such that a net current flow is inhibited from developing within surrounding tissue structures to mitigate or eliminate undesired electrical stimulation of the tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
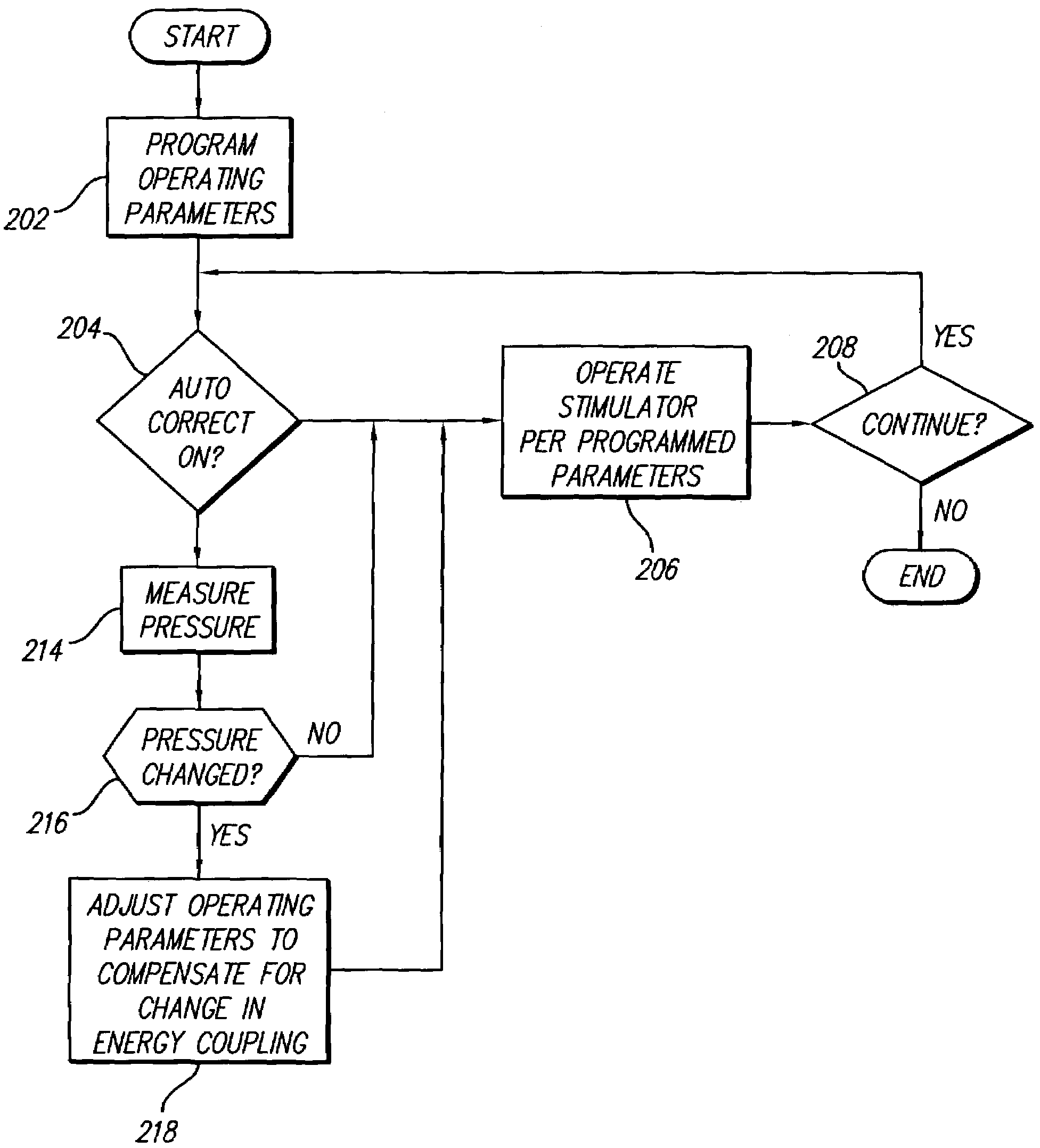
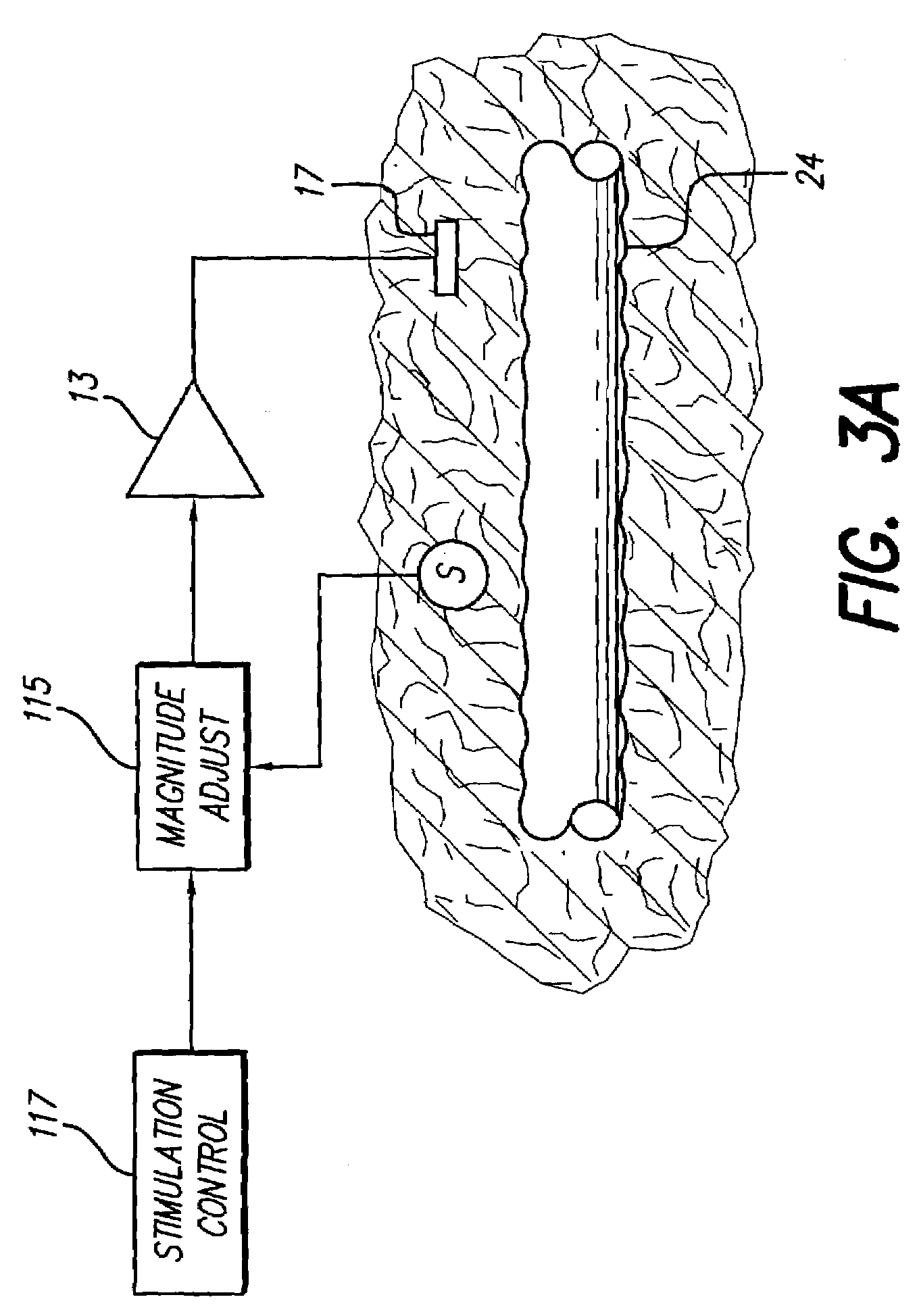
Neural stimulation system providing auto adjustment of stimulus output as a function of sensed impedance
InactiveUS7317948B1Effectively auto correct output amplitudeMinimize occurrenceElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringLead impedanceElectricity
A neural stimulation system automatically corrects or adjusts the stimulus magnitude (stimulation energy) in order to maintain a comfortable and effective stimulation therapy. Because the changes in impedance associated with the electrode-tissue interface can indicate obstruction of current flow and positional lead displacement, lead impedance can indicate the quantity of electrical stimulation energy that should be delivered to the target neural tissue to provide corrective adjustment. Hence, a change in impedance or morphology of an impedance curve may be used in a feedback loop to indicate that the stimulation energy needs to be adjusted and the system can effectively auto correct the magnitude of stimulation energy to maintain a desired therapeutic effect.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Closed-loop neuromodulation for prevention and treatment of cardiac conditions
A method and apparatus to provide therapy to a patient for protecting cardiac tissue from insult is disclosed. The method comprises delivering electrical stimulation to one or more predetermined portions of the nervous system in a patient's body; and monitoring one or more physiologic indices of the body to determine whether the delivered therapy is effective. That is, a closed-loop feedback controller is used to apply electrical stimulation to preselected regions of the patient's body, and then the physiologic response of the patient is monitored to determine the efficacy of the stimulation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Capsule and method for treating or diagnosing the intestinal tract
ActiveUS7160258B2Comprehensive knowledgeElectrotherapyPerson identificationMedicineElectrical stimulations
A device and method for mapping, diagnosing and treating the intestinal tract is provided using a capsule passing through the intestinal tract. Further, a capsule tracking system is provided for tracking a capsule's location along the length of an intestinal tract as various treatment and / or sensing modalities are employed. In one variation, an acoustic signal is used to determine the location of the capsule. A map of sensed information may be derived from the pass of a capsule. Capsules may be subsequently passed through to treat the intestinal tract at a determined location along its length. One variation uses an electrical stimulation capsule to treat and / or diagnose a condition in the intestinal tract.
Owner:ENTRACK INC
Medical devices for the detection, prevention and/or treatment of neurological disorders, and methods related thereto
ActiveUS20060173510A1Avoid detectionMinimal invasionElectroencephalographyHead electrodesSubstance abuserTranscranial Electrical Stimulations
Disclosed are devices and methods for detecting, preventing, and / or treating neurological disorders. These devices and methods utilize electrical stimulation, and comprise a unique concentric ring electrode component. The disclosed methods involve the positioning of multiple electrodes on the scalp of a mammal; monitoring the mammal's brain electrical patterns to identify the onset of a neurological event; identifying the location of the brain electrical patterns indicative of neurological event; and applying transcutaneous or transcranial electrical stimulation to the location of the neurological event to beneficially modify brain electrical patterns. The disclosed methods may be useful in the detection, prevention, and / or treatment of a variety of indications, such as epilepsy, Parkinson's Disease, Huntington's disease, Alzheimer's disease, depression, bipolar disorder, phobia, schizophrenia, multiple personality disorder, migraine or headache, concussion, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, eating disorder, substance abuse, and anxiety. The disclosed methods may also be used in combination with other peripheral stimulation techniques.
Owner:LOUISIANA TECH UNIV RES FOUND A DIV OF LOUISIANA TECH UNIV FOUND +1
Systems and methods for treatment of obesity and eating disorders by electrical brain stimulation and/or drug infusion
InactiveUS6950707B2Reduced activityIncrease excitementHead electrodesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismElectricityMedicine
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
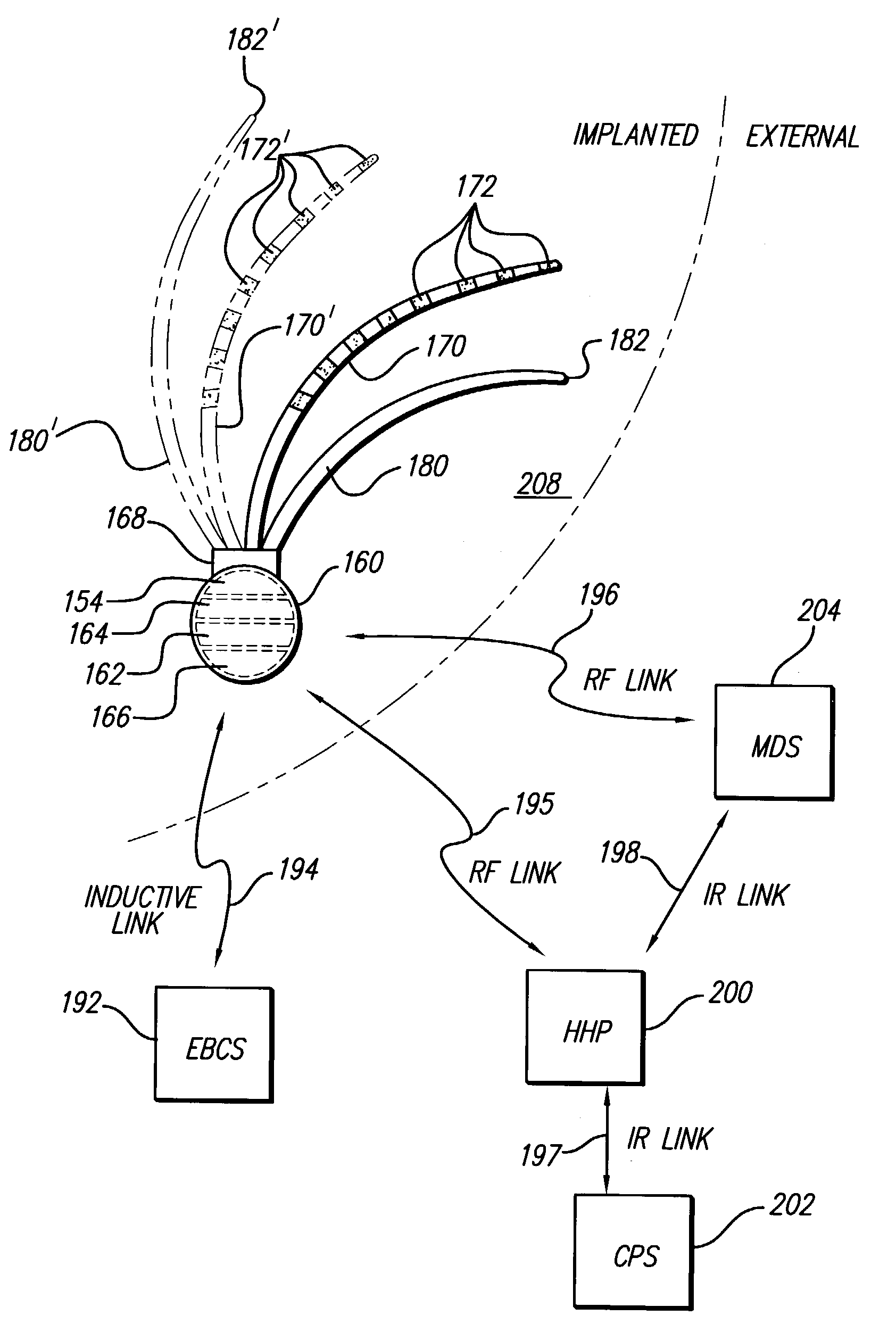
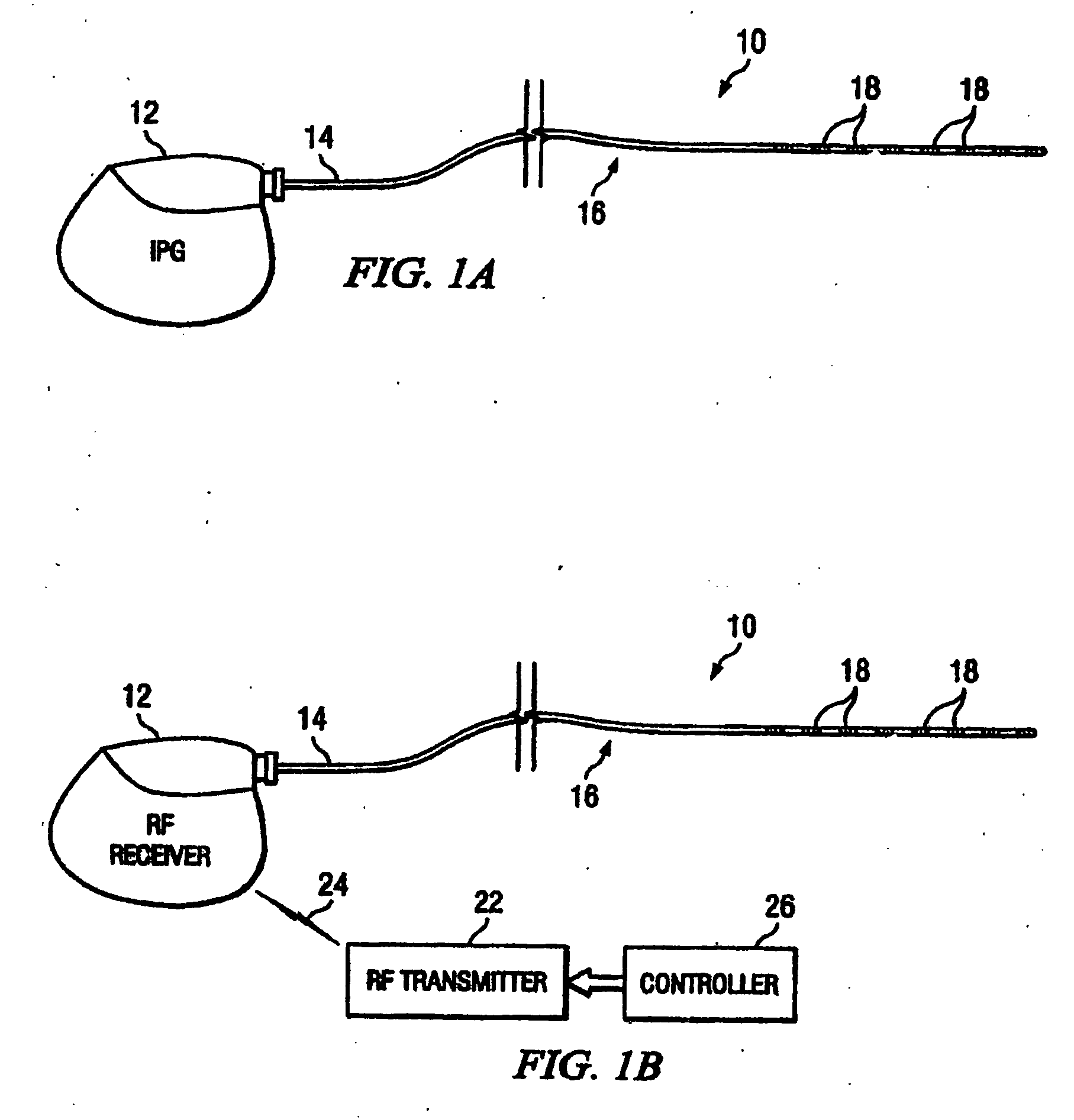
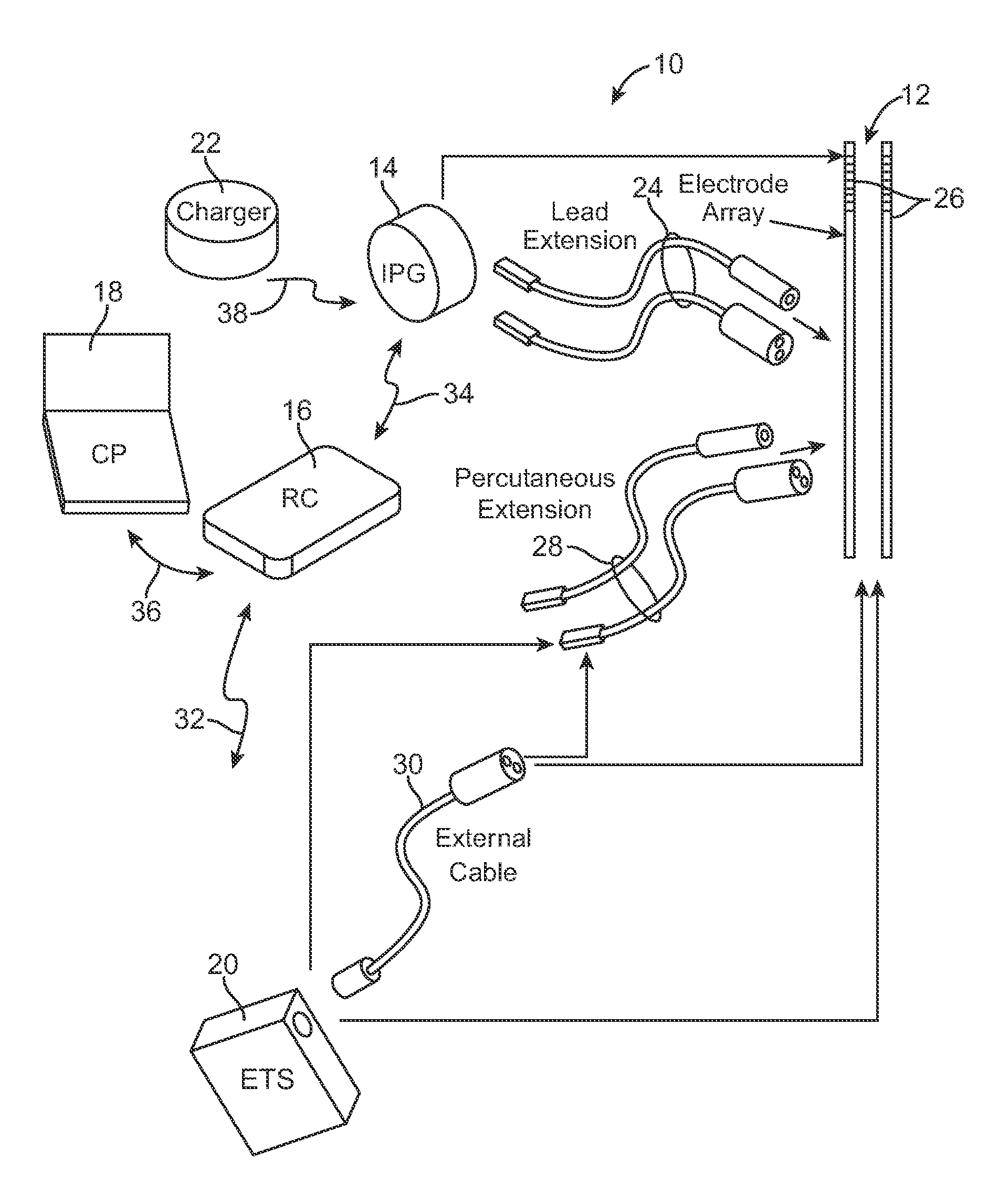
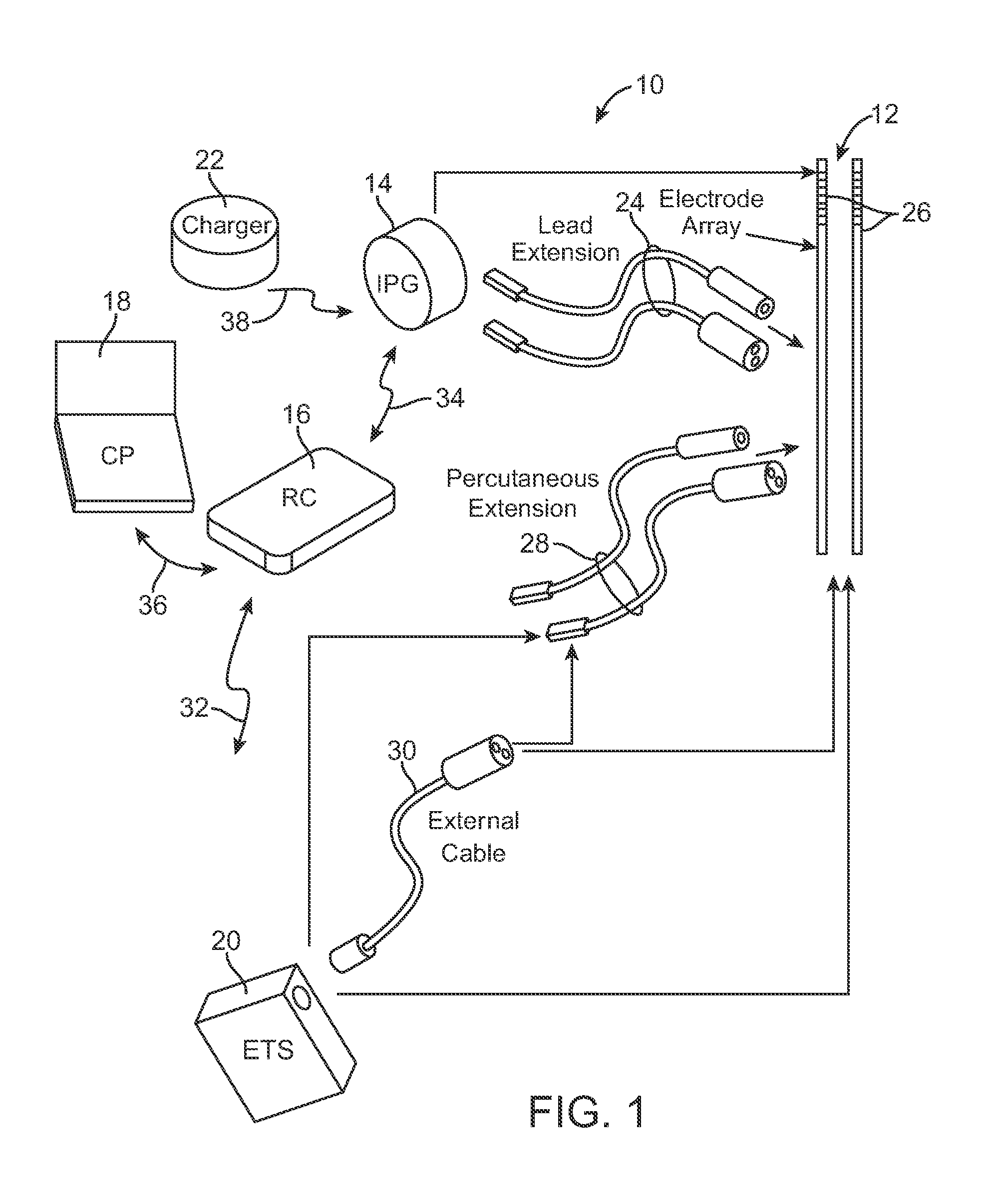
System and method for providing electrical pulses to the vagus nerve(s) to provide therapy for obesity, eating disorders, neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders with a stimulator, comprising bi-directional communication and network capabilities
InactiveUS20050049655A1Extended service lifeIncrease stimulationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationRight vagusThe Internet
A system and method for providing pulsed electrical stimulation to one or both vagus nerve(s) of a patient to provide therapy for obesity, eating disorders, neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders. The electrical pulses can be provided either unilaterally or bilaterally (left and right vagus nerves) and can be supra-diaphramatic or be sub-diaphramatic. The system comprising implantable stimulator, lead(s), an external stimulator, and a programmer. The implantable stimulator, comprising a pulse generator module, and a stimulus-receiver module which is used in conjunction with an external stimulator. Control circuitry ensures selective operation of one of the modules of the implanted stimulator, at a time. Further, the external stimulator comprises a telemetry module for remotely activating (or de-activating) programs over the internet, to arrive at the optimal program for each patient. Once the optimal “dose” is titrated using the external stimulator, the implanted pulse generator can then be programmed to similar parameters. The external stimulator in conjunction with the implanted stimulus-receiver can override the implanted pulse generator module, to provide extra dose of therapy, and also to conserve the implanted battery. The external stimulator is networked to other computers. Using the networking, a physician situated remotely can monitor and program the devices, as well as, automatically generate invoicing. In one embodiment, the external stimulator also comprises GPS circuitry for locating patient.
Owner:NEURO & CARDIAC TECH
Dynamic nerve stimulation for treatment of disorders
ActiveUS20050065575A1Provide central nervous system satietyIncreased energy expenditureSpinal electrodesDiseasePhysical therapy
A method for the treatment of obesity or other disorders by electrical activation or inhibition of nerves is disclosed. This activation or inhibition can be accomplished by stimulating a nerve using an electrode. Dynamic stimulation through ramped cycling of electrical stimulation, stimulation frequency alteration, and / or duty cycle variance can produce therapeutic benefits.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
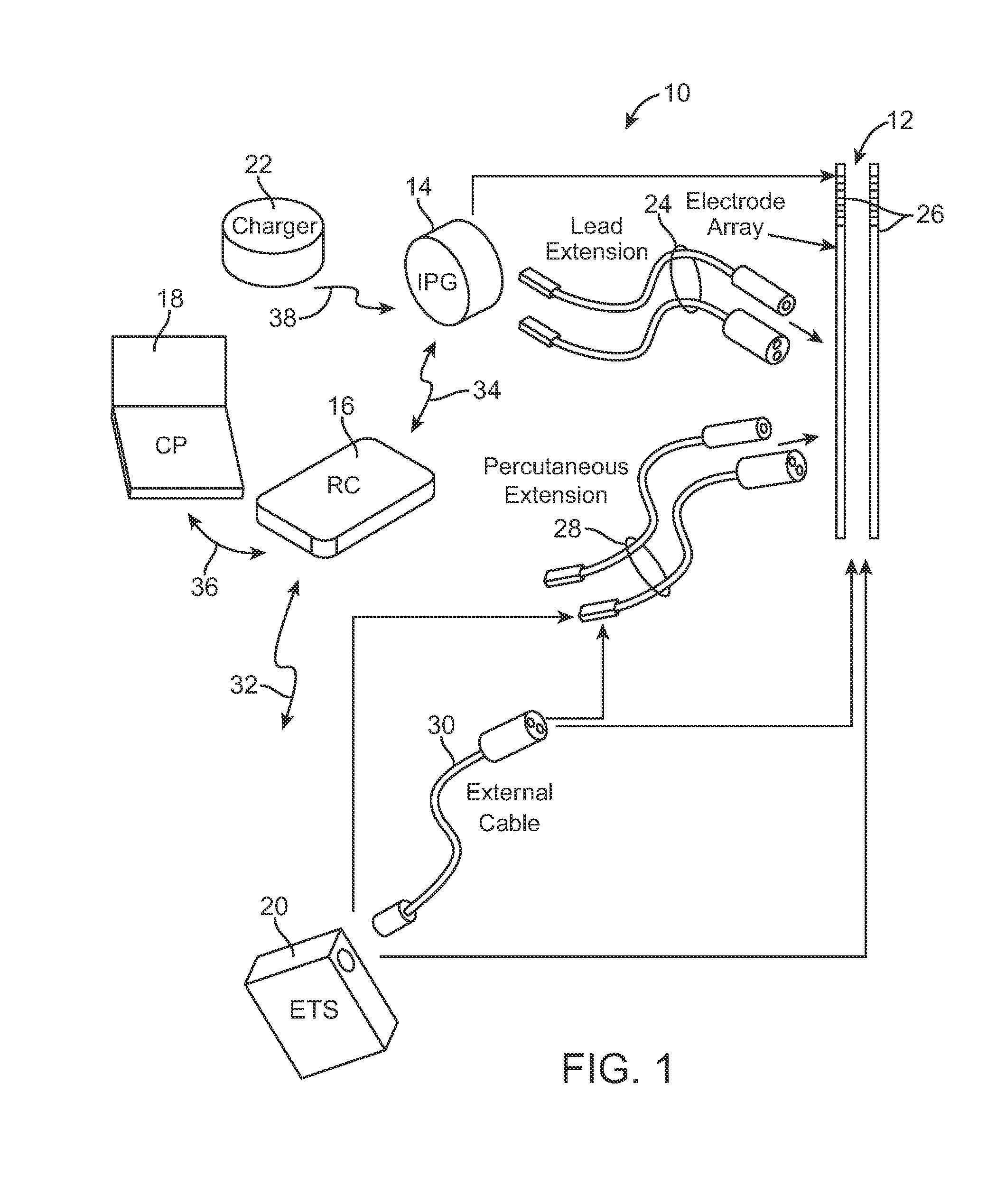
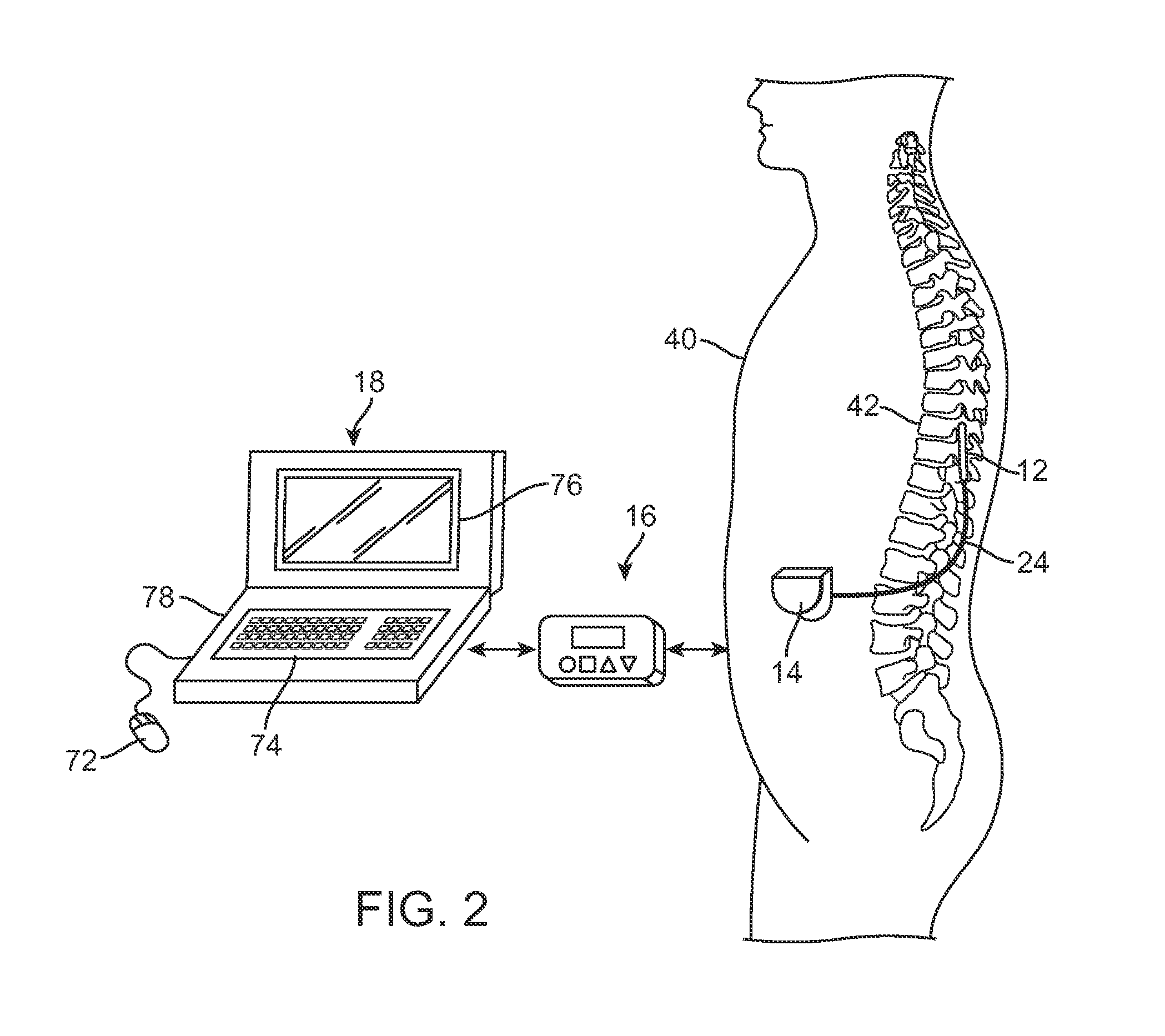
System and method for converting tissue stimulation programs in a format usable by an electrical current steering navigator
A method, computer medium, and system for programming a controller is provided. The controller controls electrical stimulation energy output to electrodes, and stores a set of programmed stimulation parameters associated with the electrodes. The programmed stimulation parameter set is compared with sets of reference stimulation parameters, each of the reference sets of stimulation parameters being associated with the electrodes. If an identical match is determined between the programmed stimulation parameter set and any one of the reference stimulation parameter sets exists based on the comparison, the identically matched stimulation parameter set is selected as an initial stimulation parameter set. If an identical match does not exist, a best between the programmed stimulation parameter set and the reference stimulation parameter sets is determined and selected as the initial stimulation parameter set. The controller is then programmed with a new set of programmable stimulation parameters based on the initial stimulation parameter set.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Treatment of hypertension
InactiveUS7155284B1Sufficient amountAvoid the needPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImplantable neurostimulatorsCarotid bodyElectrical stimulations
Treatment of hypertension includes implantation of the discharge portion(s) of a catheter and / or electrical stimulation electrode(s) adjacent the tissue(s) to be stimulated. Stimulation pulses, i.e., drug infusion pulses and / or electrical pulses, are supplied by one or more implanted stimulators, through the catheter and possibly also a lead, tunneled subcutaneously between the stimulator and stimulation site. A microstimulator(s) may also / instead deliver electrical stimulation pulses. Stimulation sites include the carotid sinus and carotid body, among other locations. Treatments include drugs used for acute and / or chronic treatment of hypertension. In a number of embodiments, a need for or response to treatment is sensed, and the electrical and / or infusion pulses adjusted accordingly.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Apparatus and method for treatment of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders using programmerless implantable pulse generator system
InactiveUS6760626B1Internal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsCranial nervesElectrical stimulations
System and method for neuromodulation therapy of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders comprises an implantable lead and pulse generator system for providing the appropriate electrical stimulation to a cranial nerve such as the vagus nerve. The implantable pulse generator having prepackaged / predetermined programs stored in the memory of the pulse generator, and means for accessing these with an external magnet. The pulse generator adapted to selectively activate predetermined programs with the external magnet, thereby eliminating the need for an external programmer. The elimination of the external programmer resulting in significant cost reduction with essentially the same functionality.
Owner:NEURO & CARDIAC TECH
Implantable medical device for treating cardiac mechanical dysfunction by electrical stimulation
InactiveUS20040049235A1Increase the number ofHigh detection specificityHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac dysfunctionElectrical stimulations
The above-described methods and apparatus are believed to be of particular benefit for patients suffering heart failure including cardiac dysfunction, chronic HF, and the like and all variants as described herein and including those known to those of skill in the art to which the invention is directed. It will understood that the present invention offers the possibility of monitoring and therapy of a wide variety of acute and chronic cardiac dysfunctions. The current invention provides systems and methods for delivering therapy for cardiac hemodynamic dysfunction.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
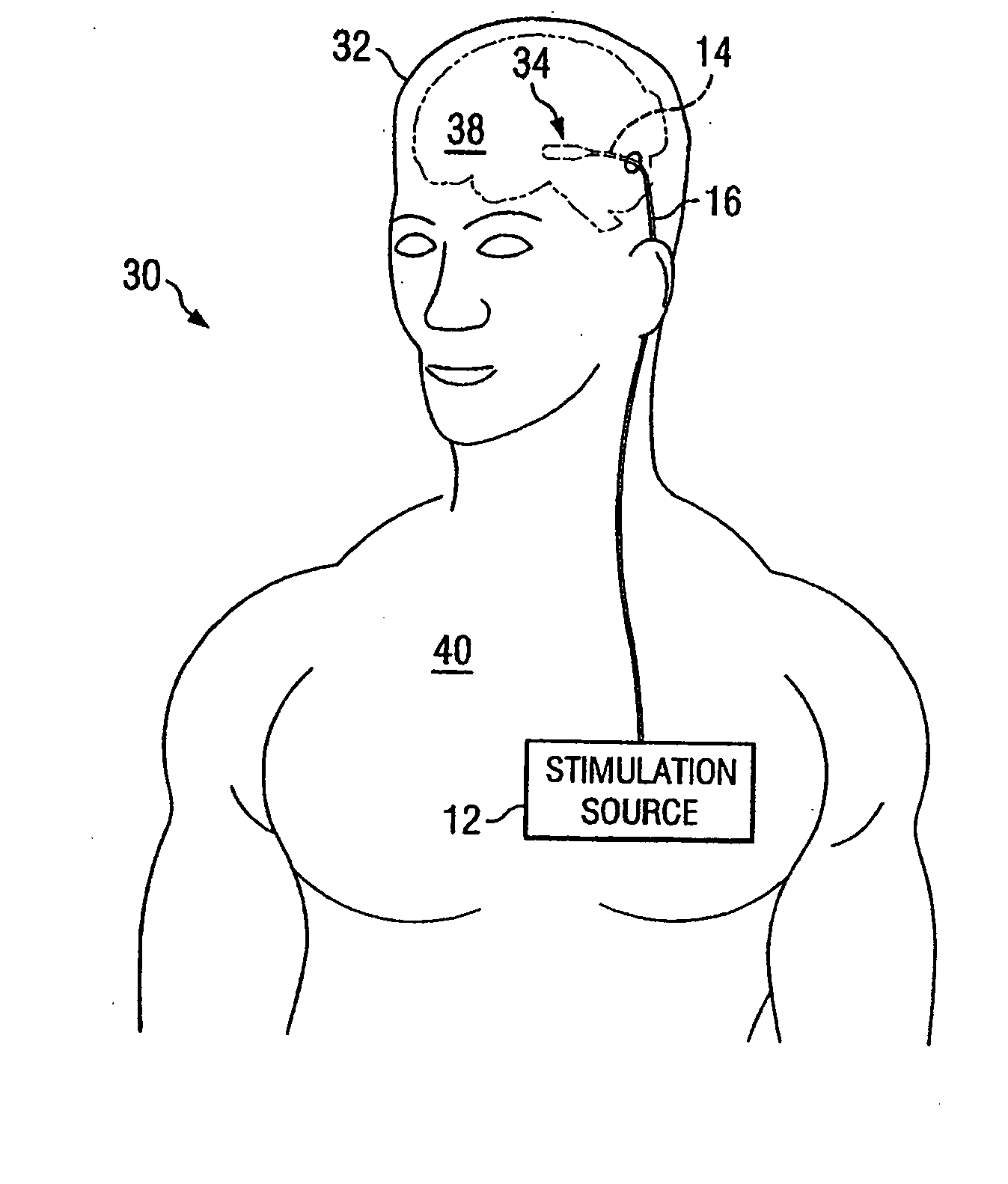
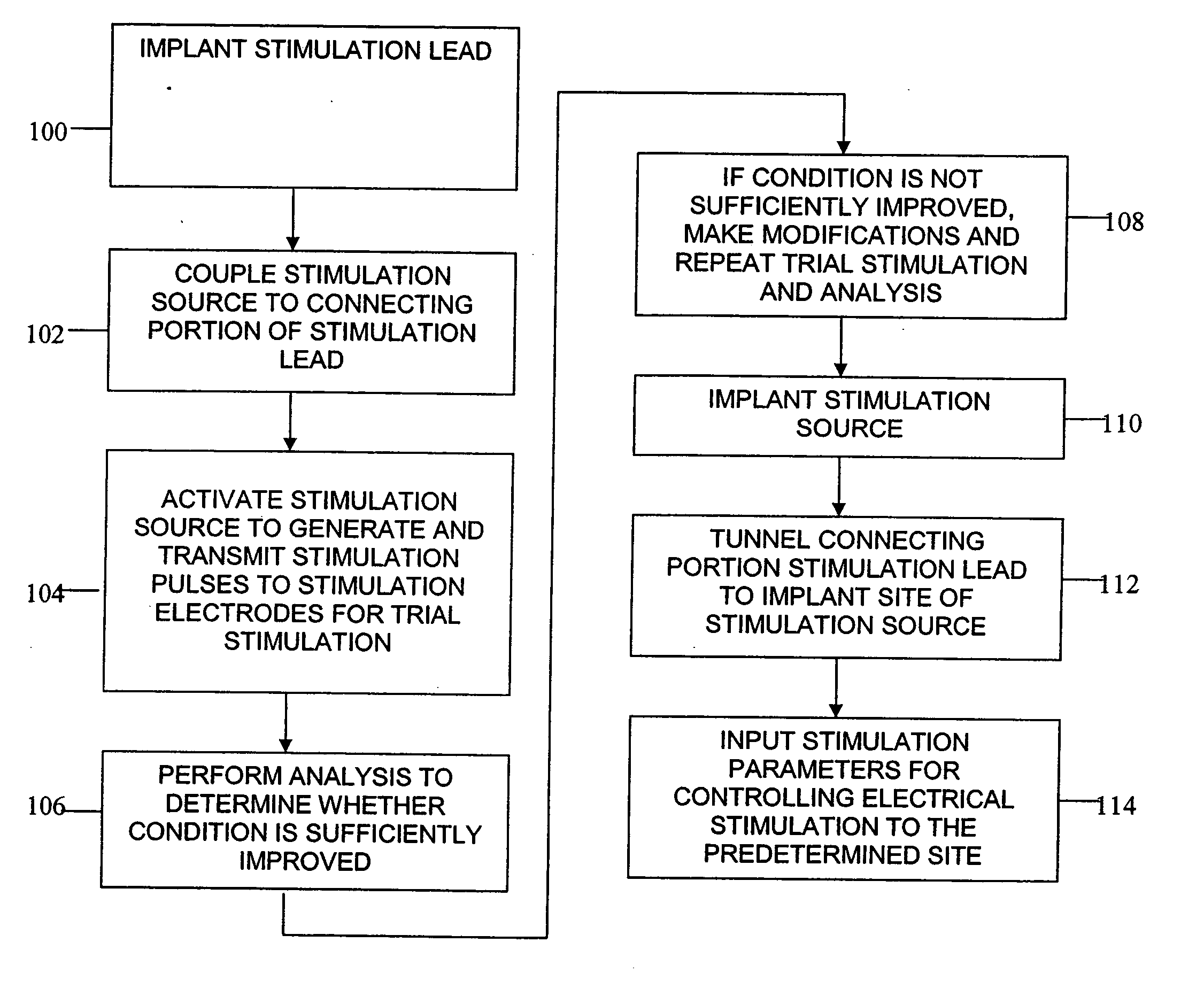
Electrical stimulation system and method for stimulating tissue in the brain to treat a neurological condition
InactiveUS20060004422A1Reduce and eliminate certain problem and disadvantageRemissionSpinal electrodesHead electrodesElectricityMedicine
According to one aspect, a stimulation system is provided for electrically stimulating a predetermined site to treat a neurological condition. The system includes an electrical stimulation lead adapted for implantation in communication with a predetermined site, wherein the site is brain tissue site. The stimulation lead includes one or more stimulation electrodes adapted to be positioned in the predetermined site. The system also includes a stimulation source that generates the stimulation pulses for transmission to the one or more stimulation electrodes of the stimulation lead to deliver the stimulation pulses to the predetermined site to treat a neurological disorder or condition.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
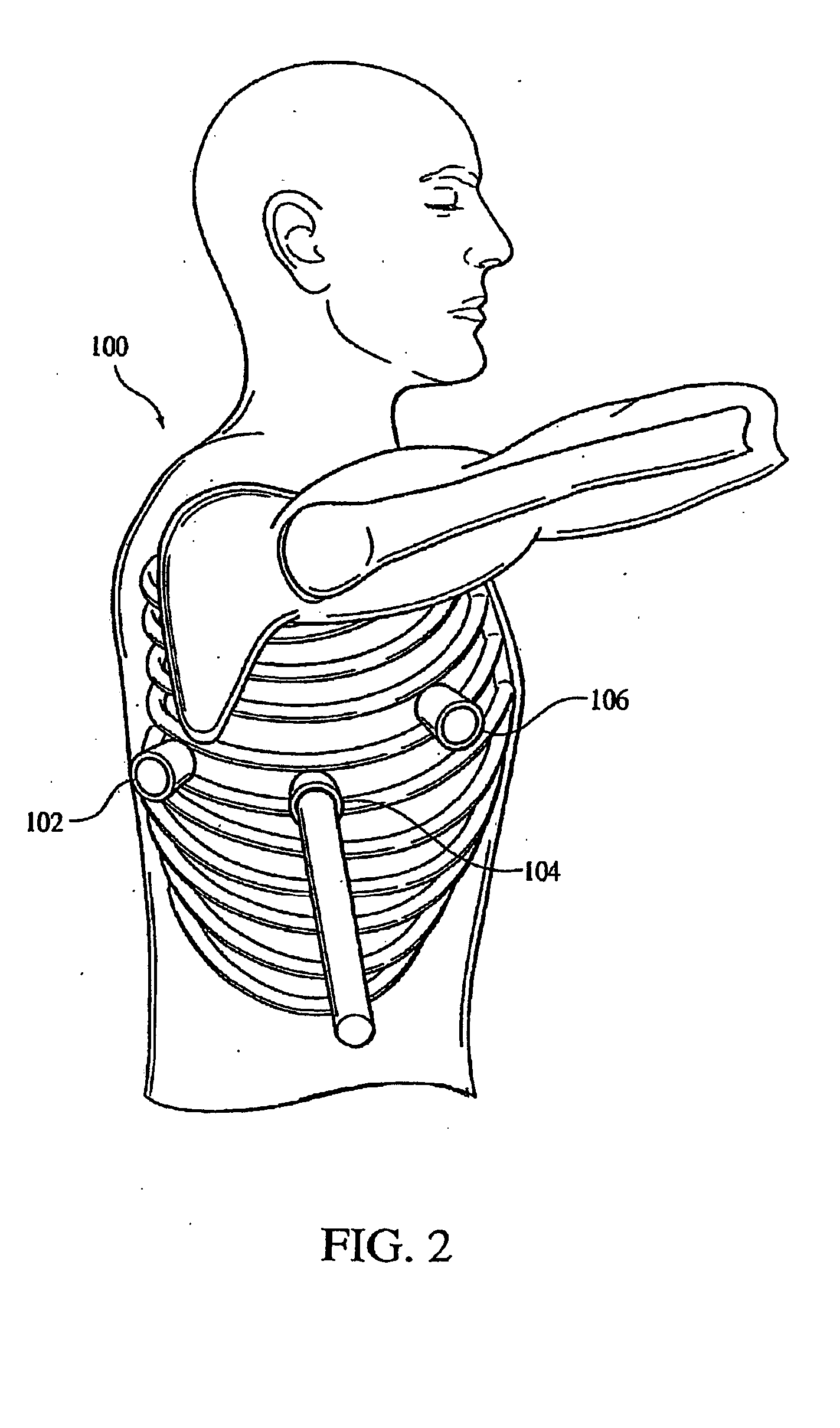
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS20050065573A1Minimizing stimulationMinimize complicationsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
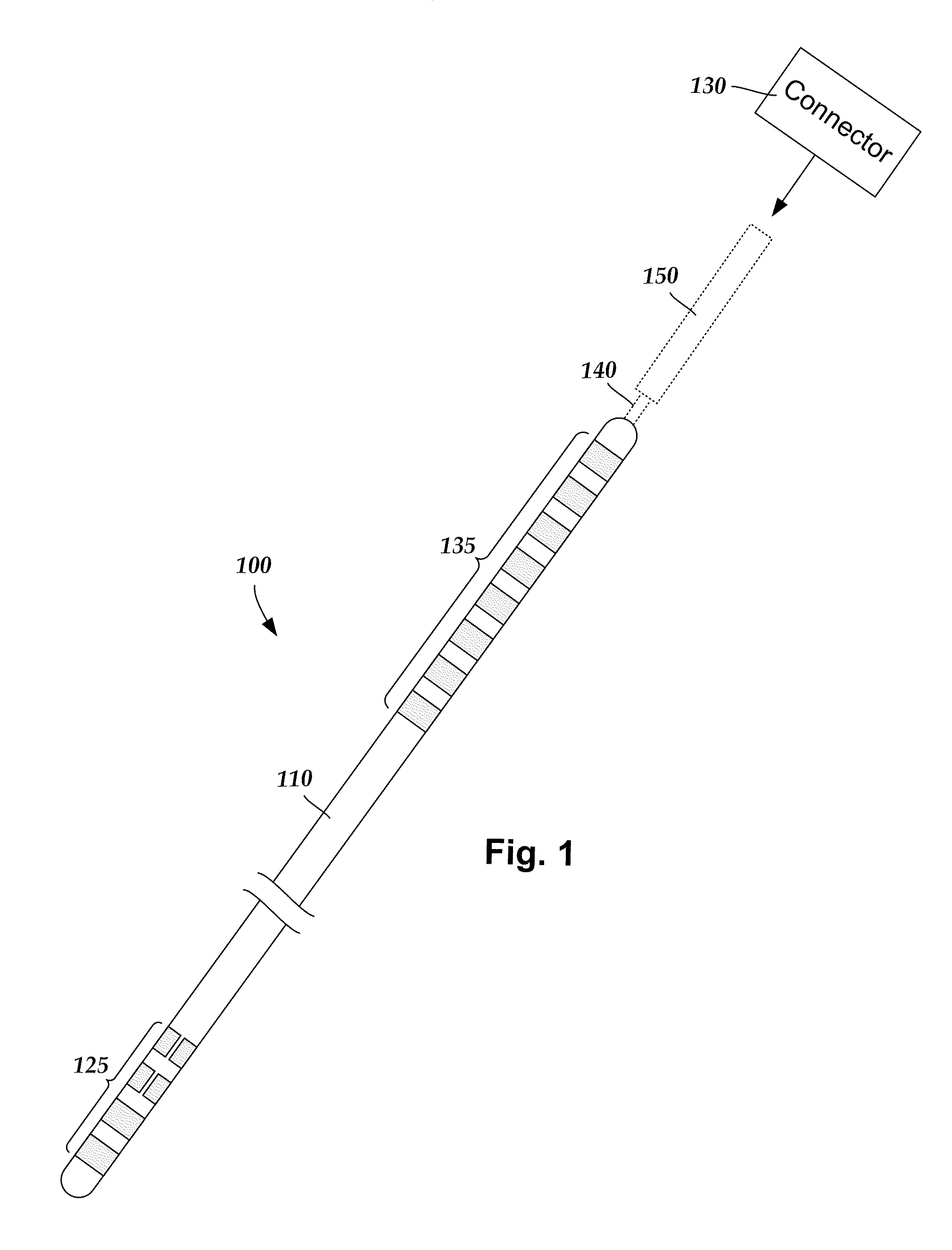
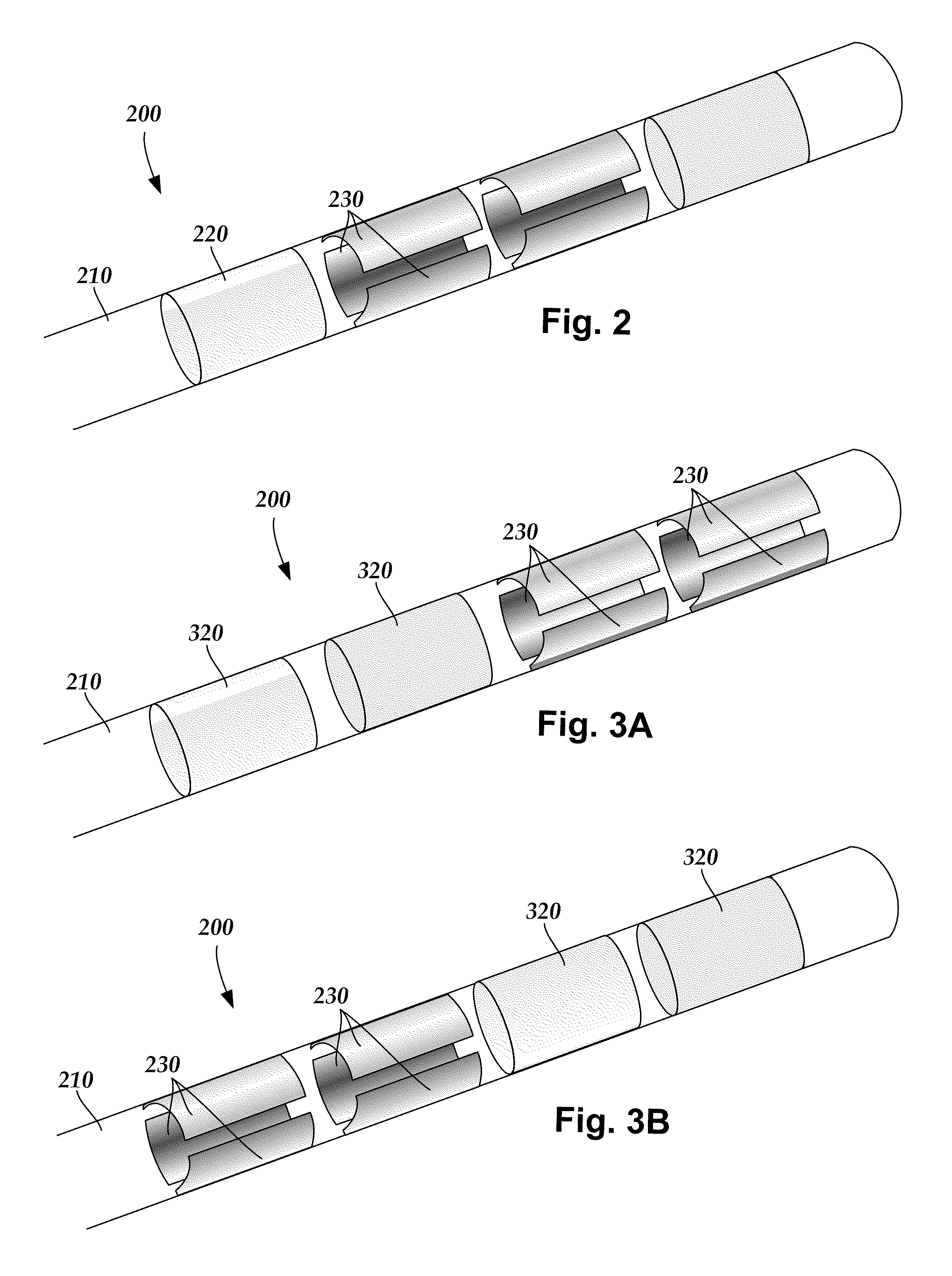
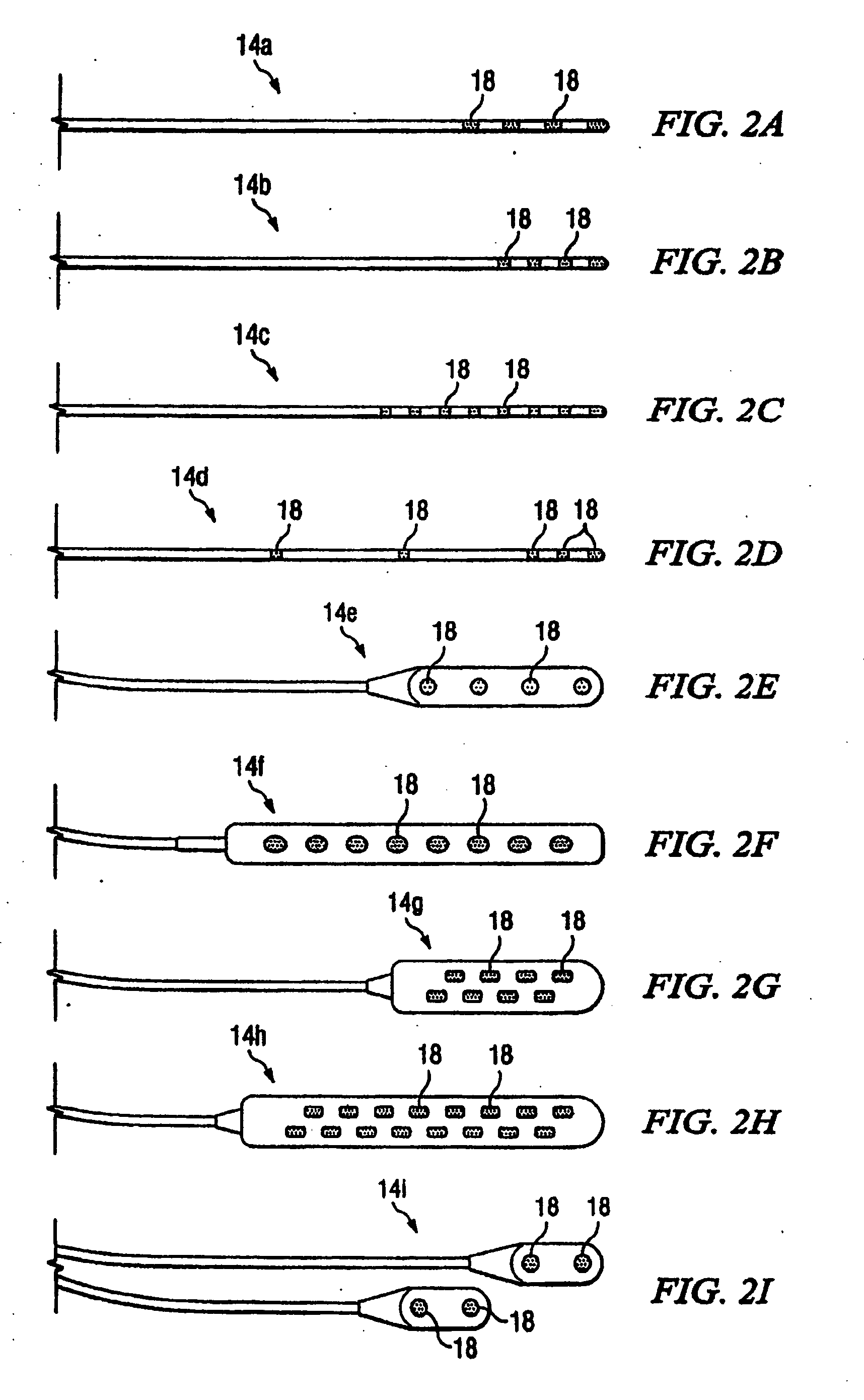
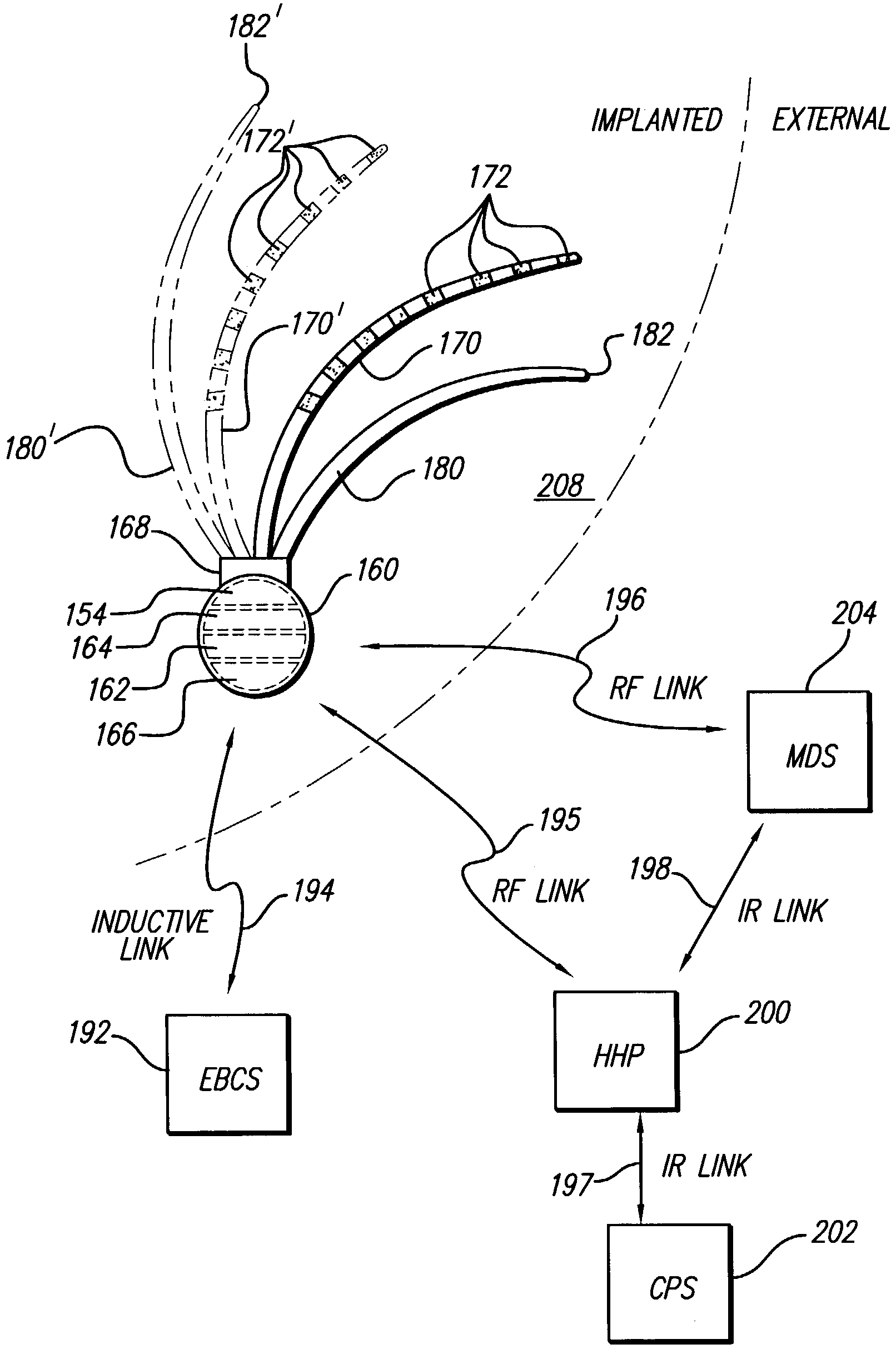
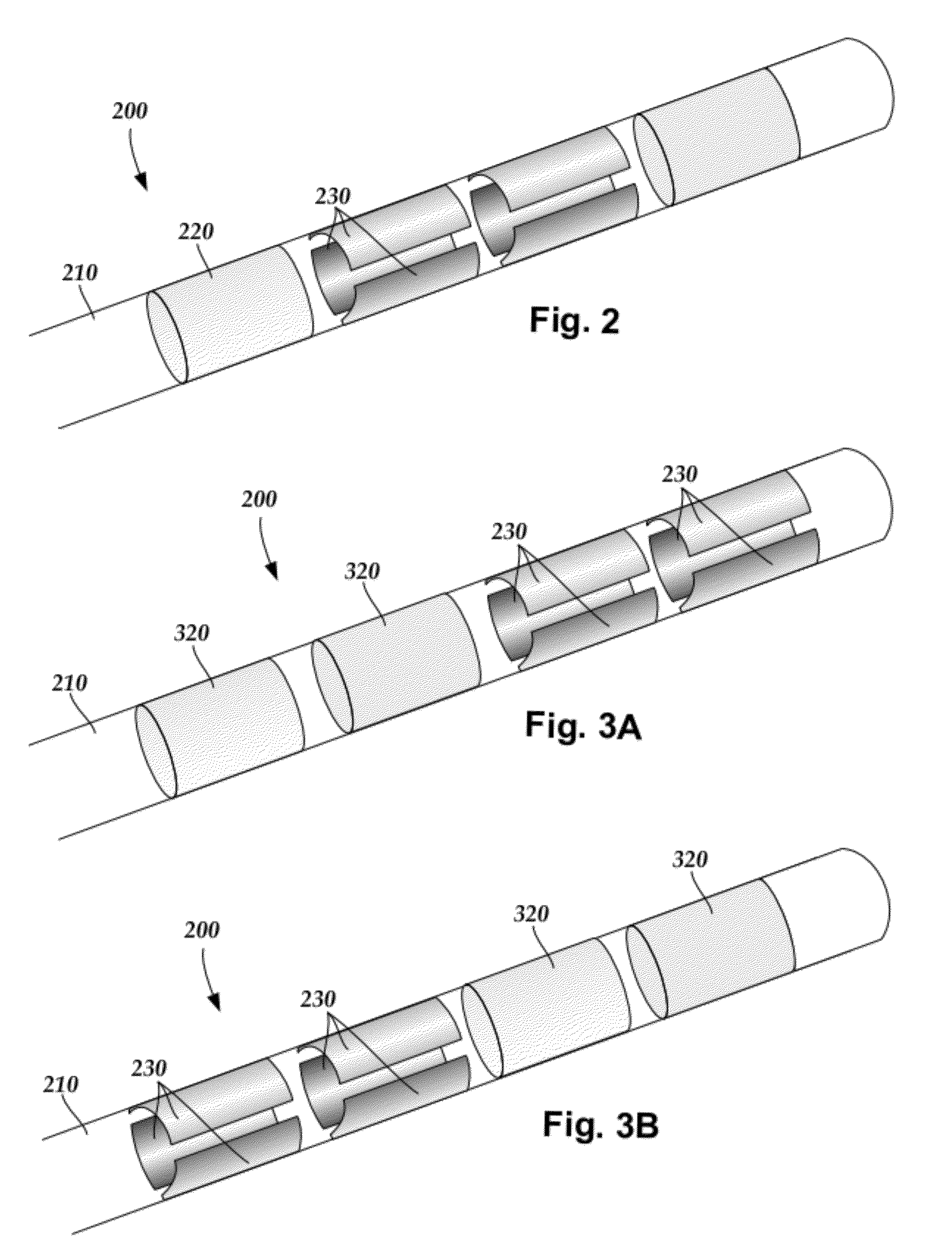
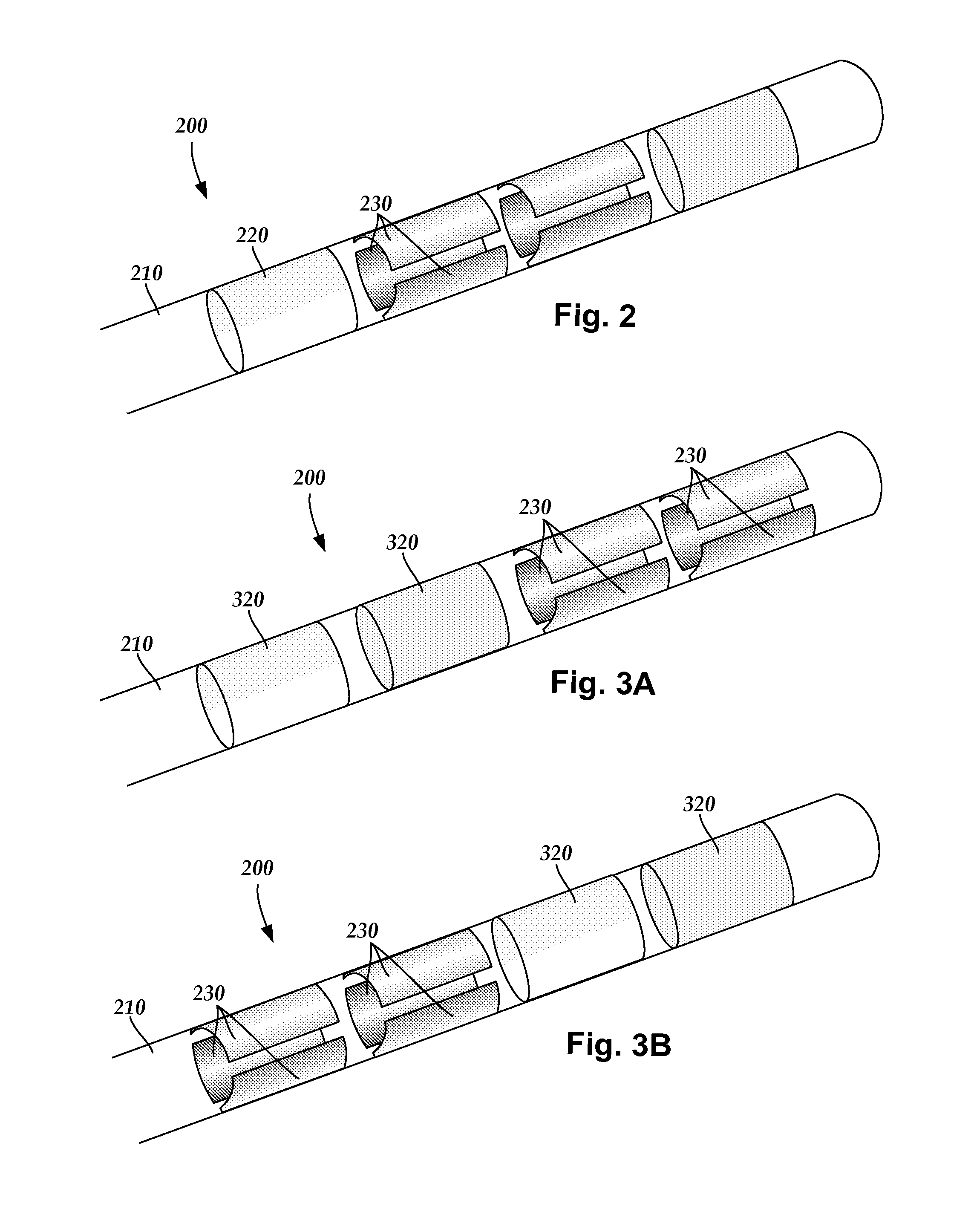
Methods for making leads with radially-aligned segmented electrodes for electrical stimulation systems
ActiveUS20110078900A1Head electrodesConnection formation by deformationElectrical conductorEngineering
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
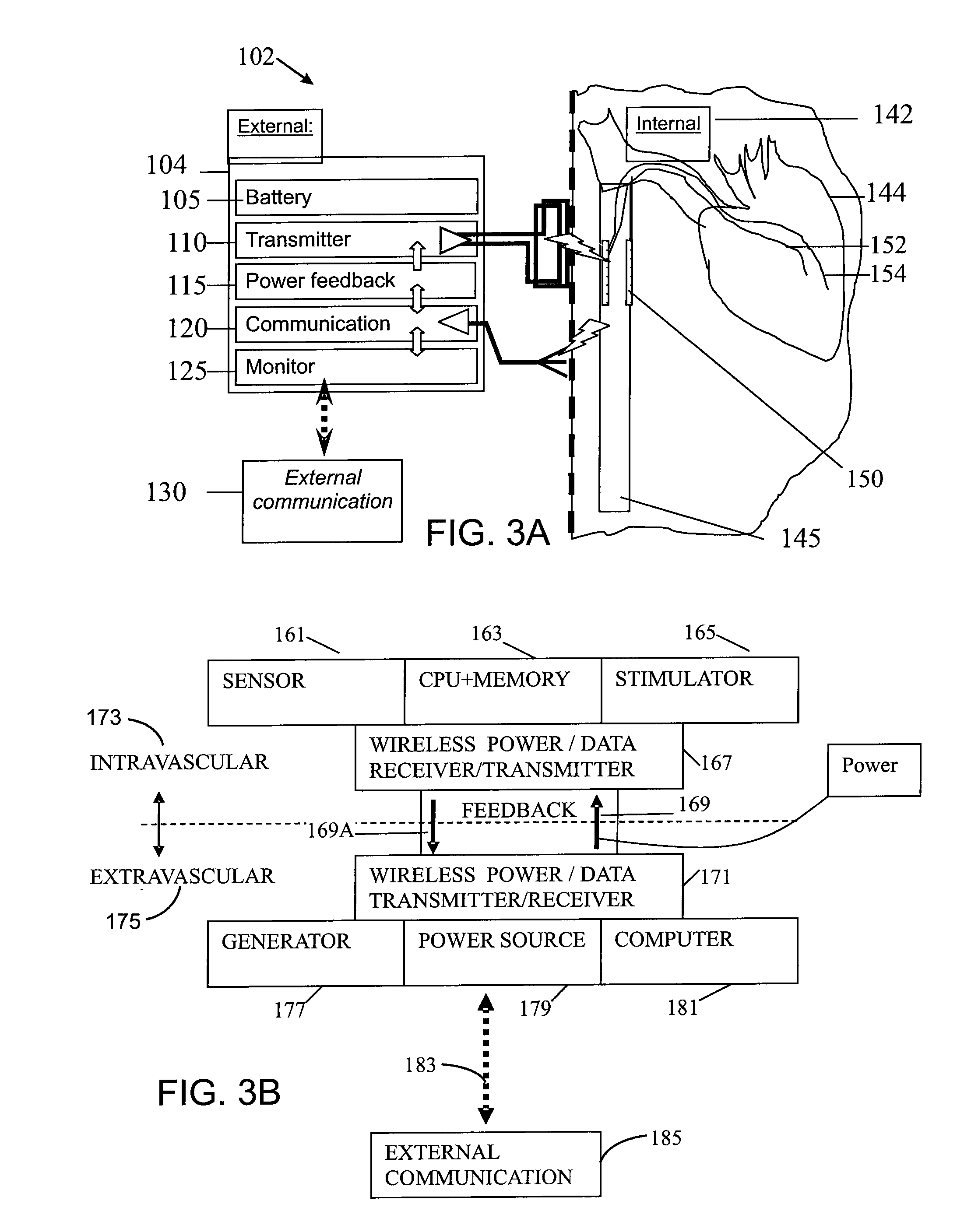
Intravascular implant system
An intravascular implantable system for providing electrical stimulation of tissue inside an animal to deal with a clinical condition is described. The system comprises a power supply module supplying energy to the implantable system, an implanted control module controlling operation of the implantable system and producing desired digital waveforms. Each desired digital waveform has an envelope with a predetermined attribute. An implanted intravascular sensing module sensing at least one parameter of interest for the purpose of dealing with the clinical condition. An intravascular stimulation module is provided to electrically stimulate the tissue with an output waveform that is substantially similar to the desired digital waveform produced by the control module.
Owner:KENERGY INC
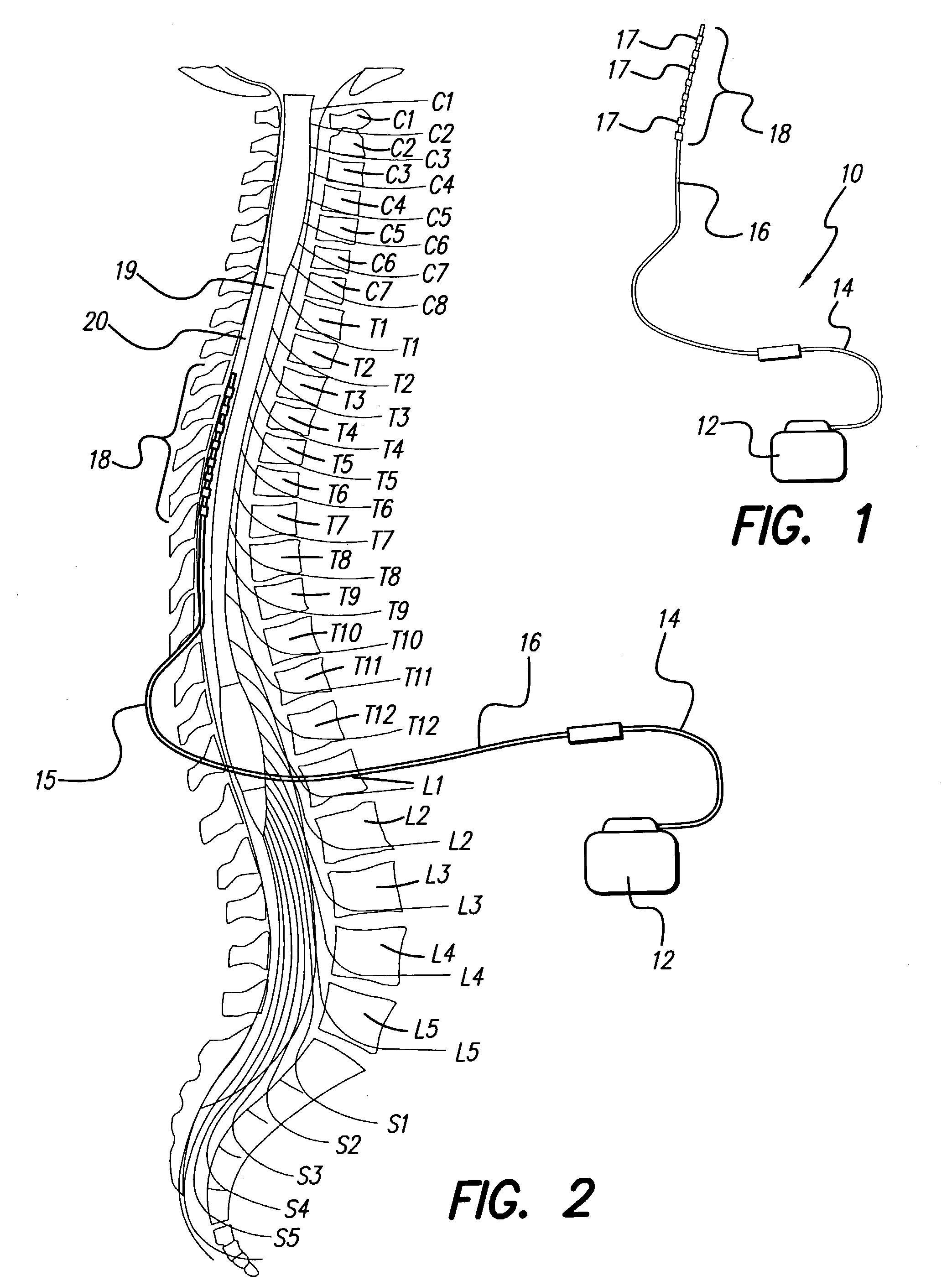
Method of using spinal cord stimulation to treat neurological disorders or conditions
InactiveUS20070060954A1Improve the quality of lifeEffectively treat lack of coordinationSpinal electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsMedicineElectrical stimulations
The present invention involves methods and systems for using electrical stimulation to treat neurological disorders. More particularly, the method comprises surgically implanting an electrical stimulation lead that is in communication with spinal nervous tissue associated with a first, second, or third cervical vertebral segment to result in spinal nervous tissue stimulation, thus treating a wide variety of neurological disorders.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
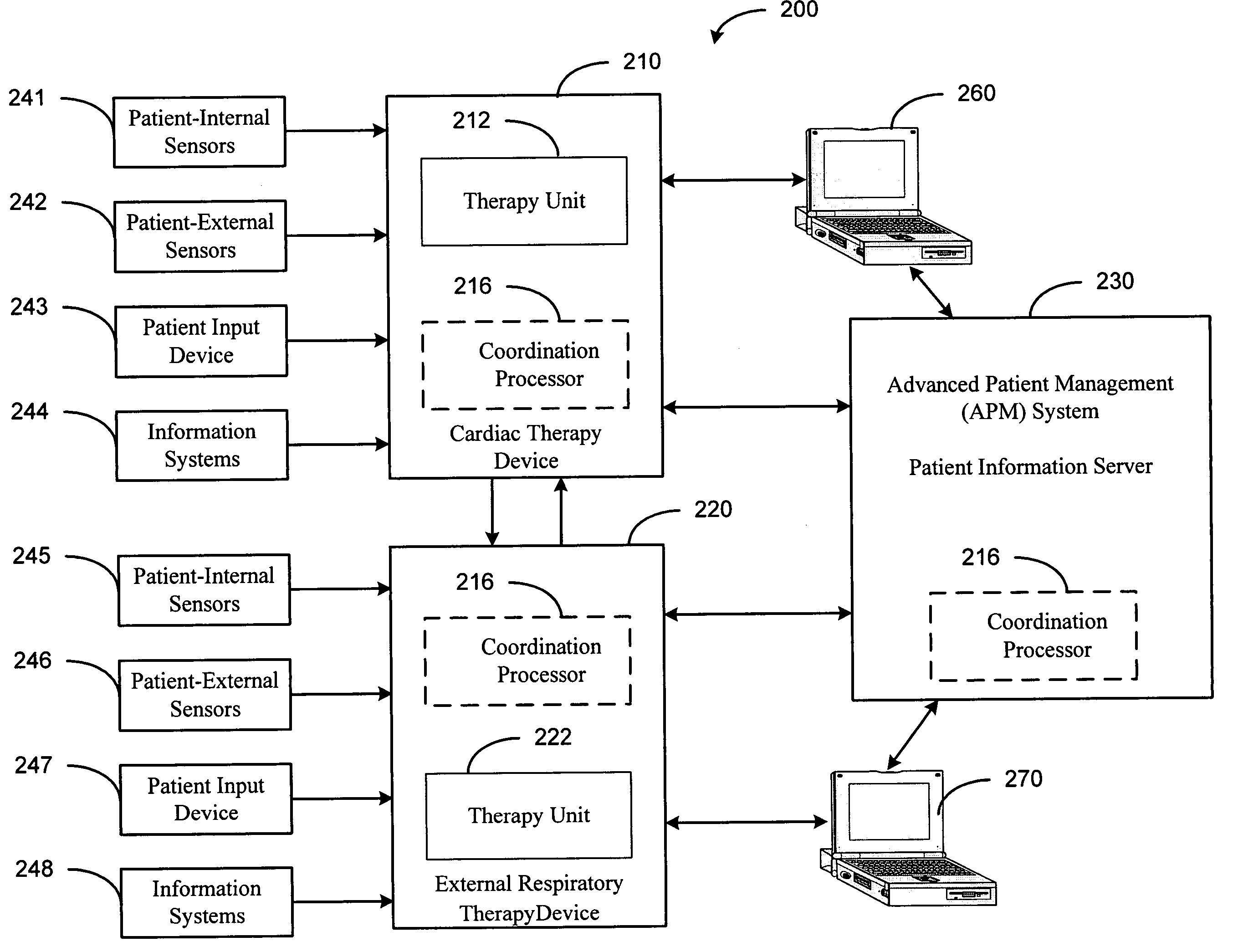
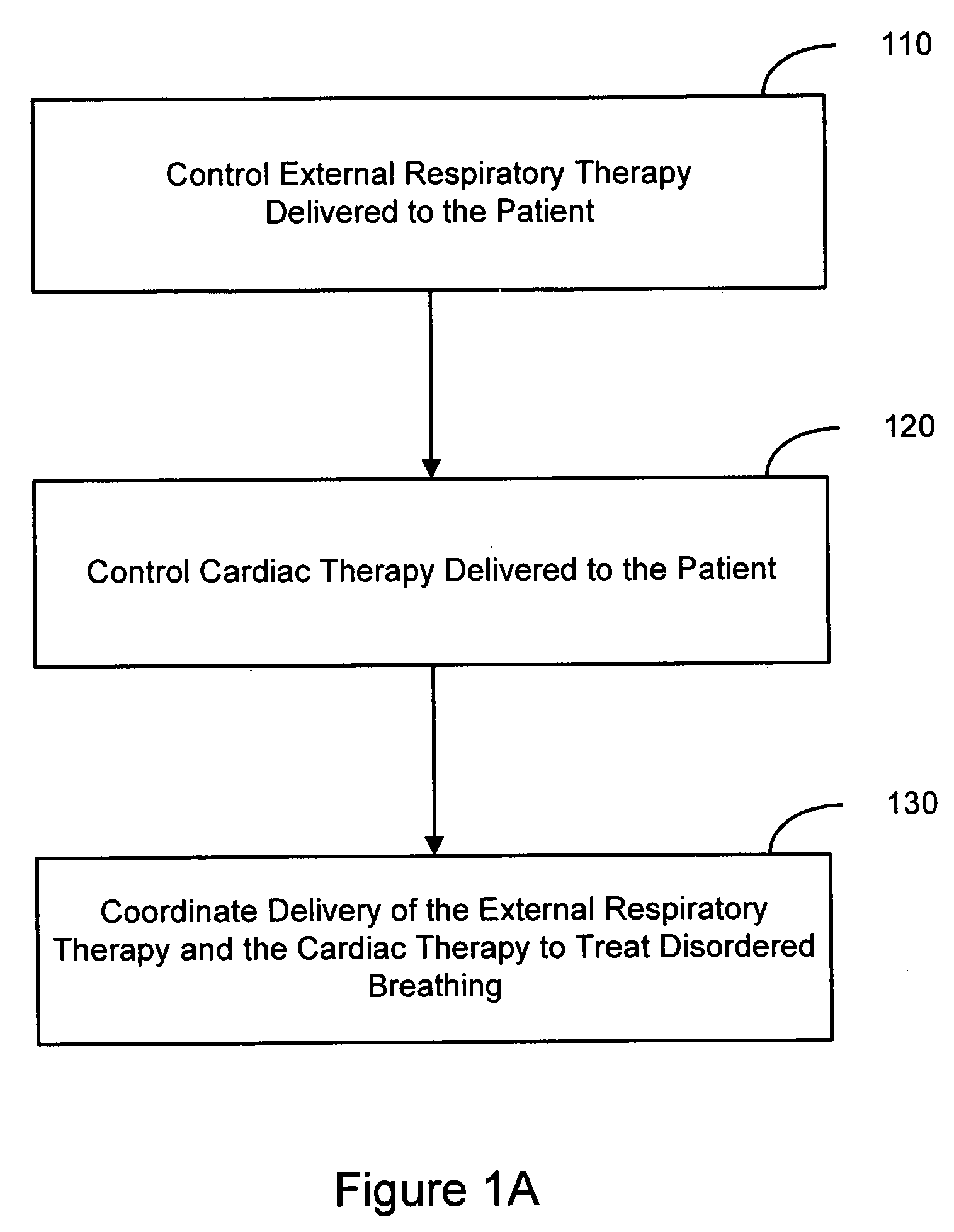
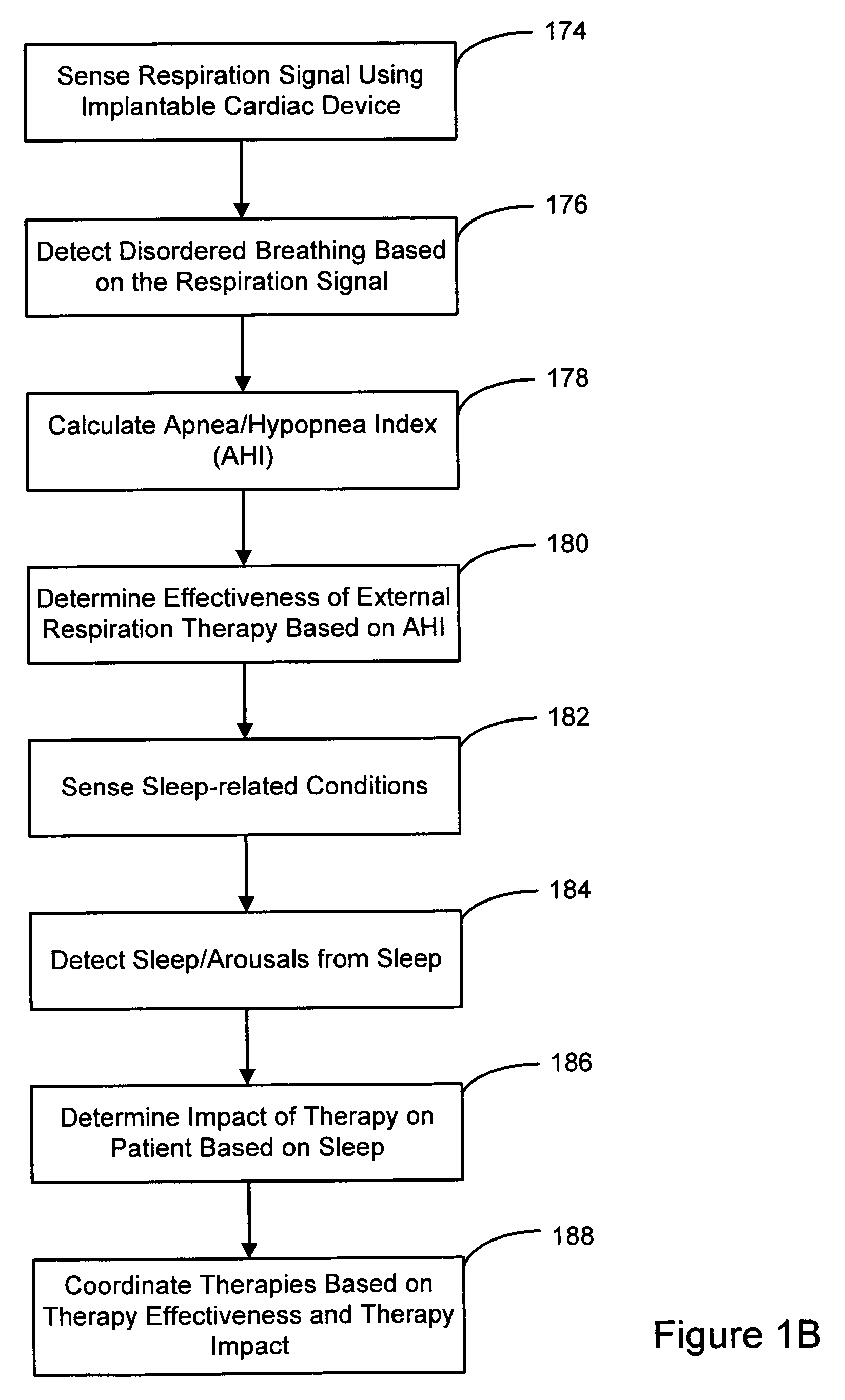
Coordinated use of respiratory and cardiac therapies for sleep disordered breathing
InactiveUS20050061320A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTherapeutic goalSleep disordered breathing
Methods and systems involve coordinating therapies used for treating disordered breathing. Disordered breathing therapies may include cardiac electrical stimulation therapy and external respiratory therapy as well as other therapies for treating disordered breathing in a patient. The therapies delivered to the patient may be coordinated to enhance effectiveness of the therapy, to reduce therapy interactions, to improve patient sleep, or to achieve other therapeutic goals.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
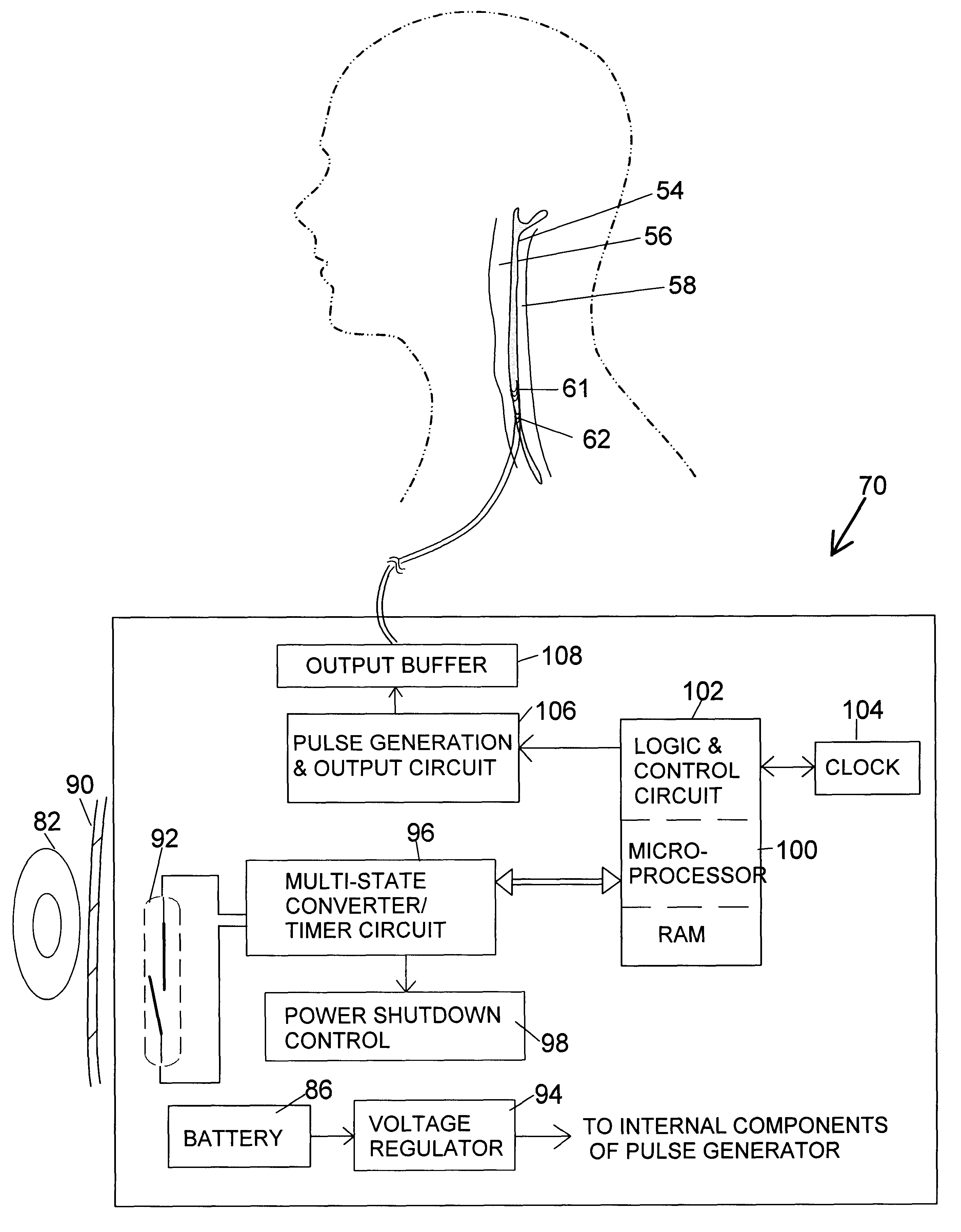
Implantable medical electrical stimulation lead fixation method and apparatus
InactiveUS6999819B2Optimize locationQuick placementSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesMuscle tissueMedicine
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC +1
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS20050065562A1Convenient treatmentModulating levelSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
System and method for determining appropriate steering tables for distributing stimulation energy among multiple neurostimulation electrodes
A method, computer medium, and system for programming a control device are provided. The control device is configured for controlling electrical stimulation energy provided to a plurality of electrode leads that are physically implanted within a patient in a side-by-side lead configuration. Electrical energy is conveying from the electrode leads to create a stimulation region within the patient. The stimulation region is automatically shifted along the electrode leads (e.g., by selecting and using at least one navigation table) in accordance with an electrical current shifting pattern that is based on a stagger of the side-by-side lead configuration. At least one stimulation parameter set is selected based on the effectiveness of the shifted stimulation region, and the control device is programmed with the selected stimulation parameter set(s).
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Single and multi-polar implantable lead for sacral nerve electrical stimulation
InactiveUS6055456ALess sensitivitySimple procedureSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical conductorSacral nerve stimulation
An implantable medical lead for stimulation of the sacral nerves comprises a lead body which includes a distal end and a proximal end, and the distal end having at least one electrode contact having a length of between 0.10 and 1.50 inches extending longitudinally from the distal end toward the proximal end. The lead body at its proximal end may be coupled to a pulse generator, additional intermediate wiring, or other stimulation device. The implantable medical lead can comprise a first and second electrode contacts. The second electrode contact has a length of between 0.030 and 1.00 extending longitudinally from a point approximately 1.00 from the distal end toward the proximal end. The first and second electrode contacts do no overlap longitudinally. The implantable lead is implanted by taking the lead and implanting near the sacral nerves and then connecting to a pulse generator.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Treatment of epilepsy by brain stimulation
InactiveUS7003352B1Small sizeInhibition amountElectrotherapyPressure infusionMedicineElectrical stimulations
Introducing one or more stimulating drugs to the brain and / or applying electrical stimulation to the brain is used to treat epilepsy. At least one implantable system control unit (SCU) produces electrical pulses delivered via electrodes implanted in the brain and / or drug infusion pulses delivered via a catheter implanted in the brain. The stimulation is delivered to targeted brain structures to adjust the activity of those structures. The small size of the SCUs of the invention allow SCU implantation directly and entirely within the skull and / or brain. Simplicity of the preferred systems and methods and compactness of the preferred system are enabled by the modest control parameter set of these SCU, which do not require or include a sensing feature.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
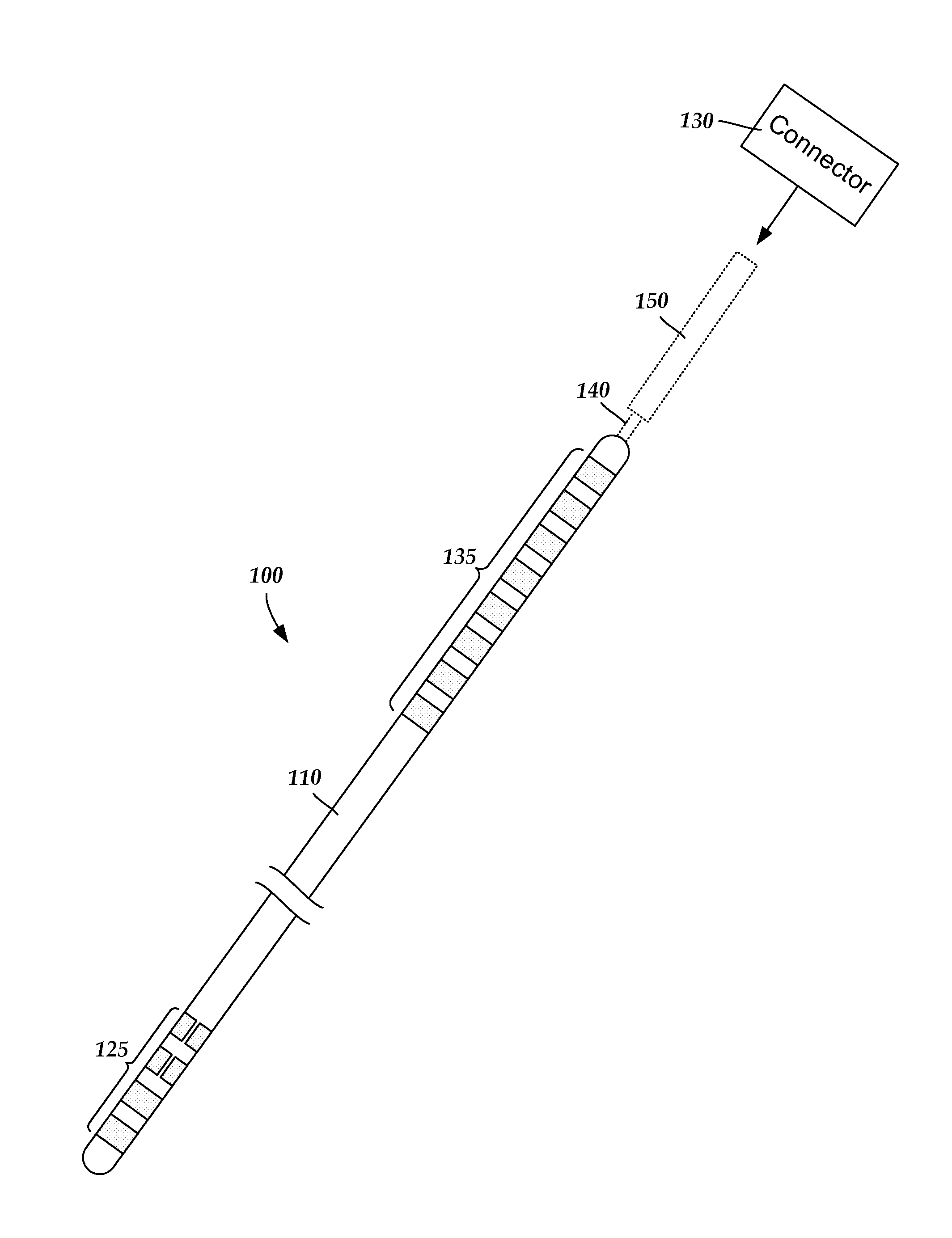
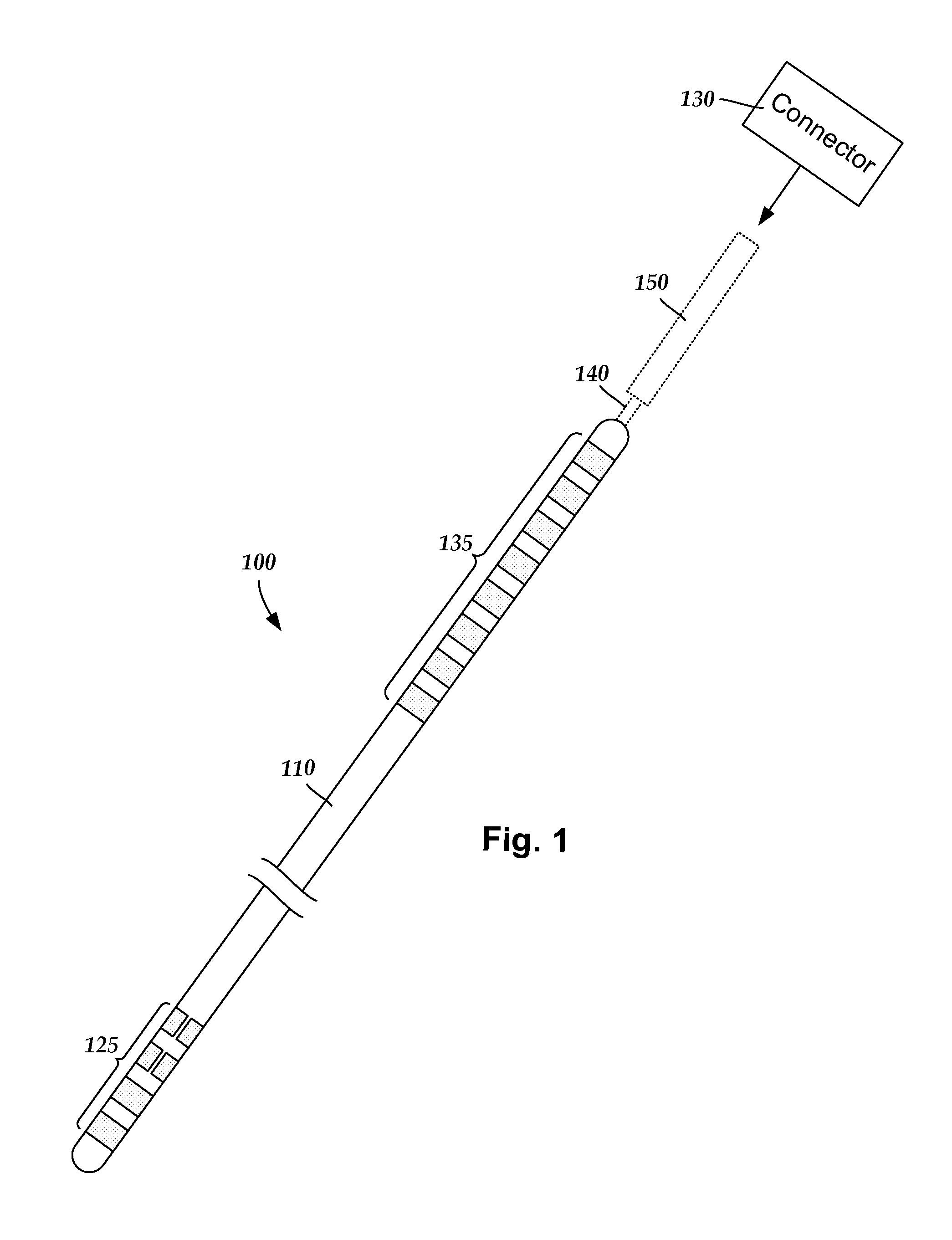
Methods for making leads with segmented electrodes for electrical stimulation systems
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Methods for making leads with segmented electrodes for electrical stimulation systems
ActiveUS20120165911A1Spinal electrodesLine/current collector detailsElectrical stimulationsBiomedical engineering
One embodiment is a method of making a stimulation lead that includes providing a pre-electrode assembly comprising a plurality of segmented electrodes and a plurality of raised connectors. Each of the segmented electrodes is coupled to at least one other of the segmented electrodes by at least one of the raised connectors. The method further includes forming the pre-electrode assembly into a tube with the tube defining a longitudinal axis. Each of the raised connectors is disposed at a radius with respect to the longitudinal axis that is greater than a radius of any of the segmented electrodes with respect to the longitudinal axis. The method also includes forming at least a portion of a lead body around the segmented electrodes of the pre-electrode assembly; and grinding the tube comprising the pre-electrode assembly and portion of the lead body to remove the plurality of raised connectors leaving the plurality of segmented electrodes and the portion of the lead body.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Implantable medical device for treating cardiac mechanical dysfunction by electrical stimulation
InactiveUS7096064B2Improve toleranceExtension of timeHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac dysfunctionElectrical stimulations
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus of particular benefit for patients suffering heart failure including cardiac dysfunction, chronic HF, and the like and all variants thereof. According to the disclosure monitoring and therapy delivery for a wide variety of acute and chronic cardiac dysfunctions are described and depicted. Various forms of paired or coupled pacing therapy delivery provided alone or in combination with neurostimulation therapy delivered by both implantable and external apparatus, including defibrillation therapy are also provided herein.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method for neurological stimulation of peripheral nerves to treat low back pain
ActiveUS7324852B2Reduce and eliminate and disadvantageReduce and eliminate problemSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesProximatePeripheral neuron
According to one embodiment, a system for neurological stimulation of peripheral nerve fibers to treat low back pain is provided. The system includes stimulation electrodes adapted to be implanted in tissue proximate a network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating a painful region of the low back area and to deliver electrical stimulation pulses to the network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating the painful region of the low back area. The system also includes a stimulation source adapted for implantation into the person's body and operable to generate electrical stimulation pulses for transmission to the electrodes for delivery to the network of peripheral nerve fibers located in and innervating the painful region of the low back area to relieve pain in the painful region of the low back area.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com