Patents
Literature
33 results about "Sympathetic nerve activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
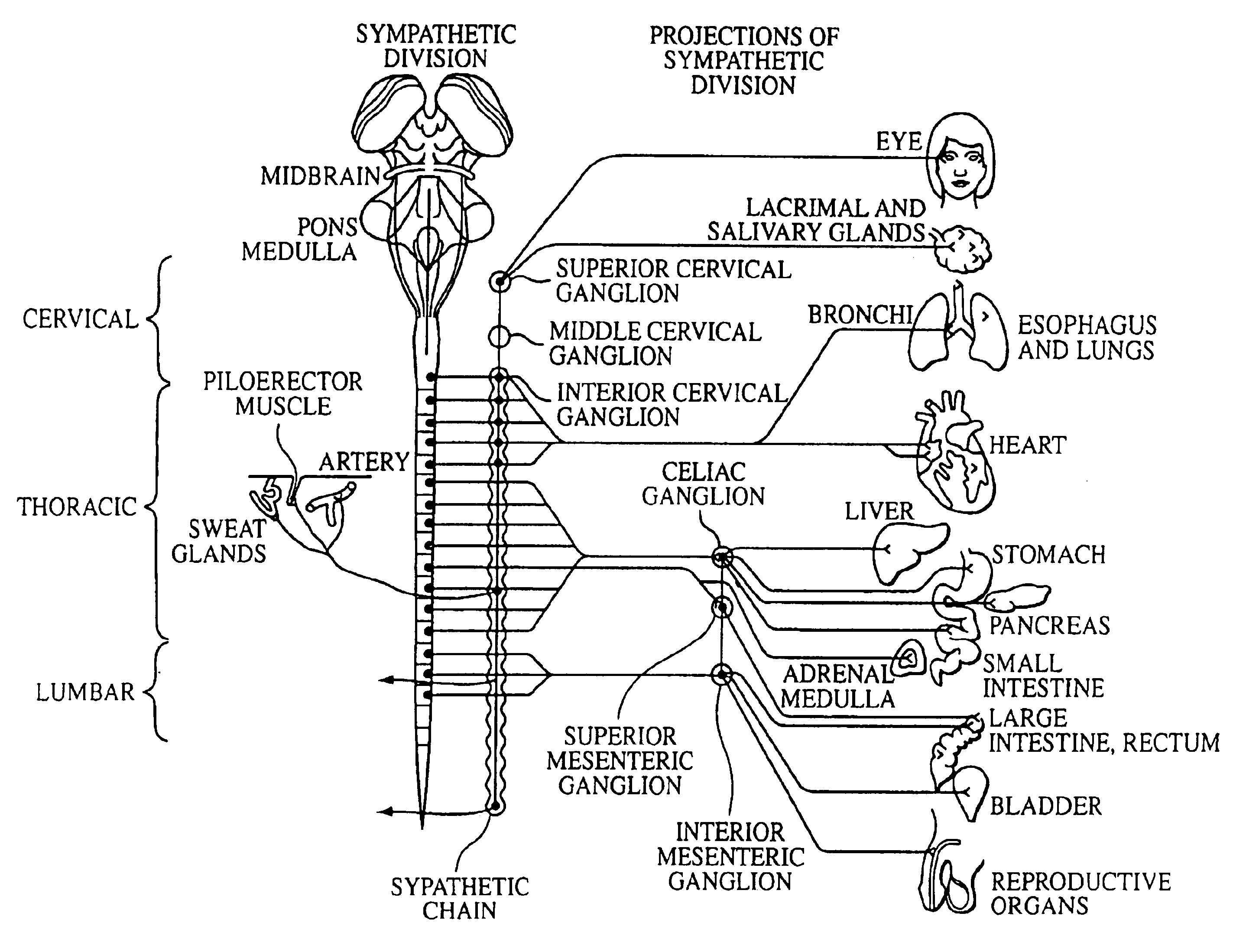
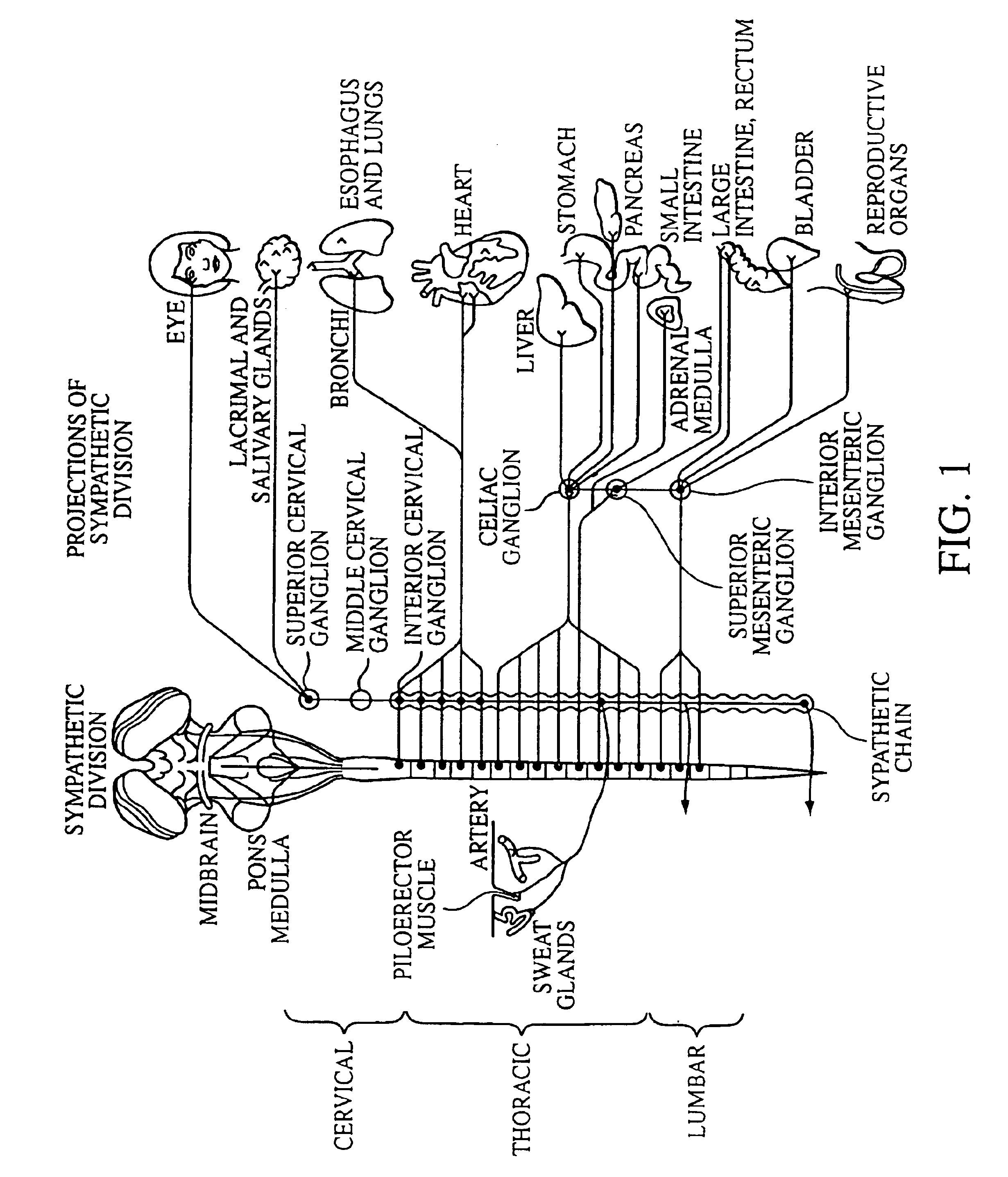
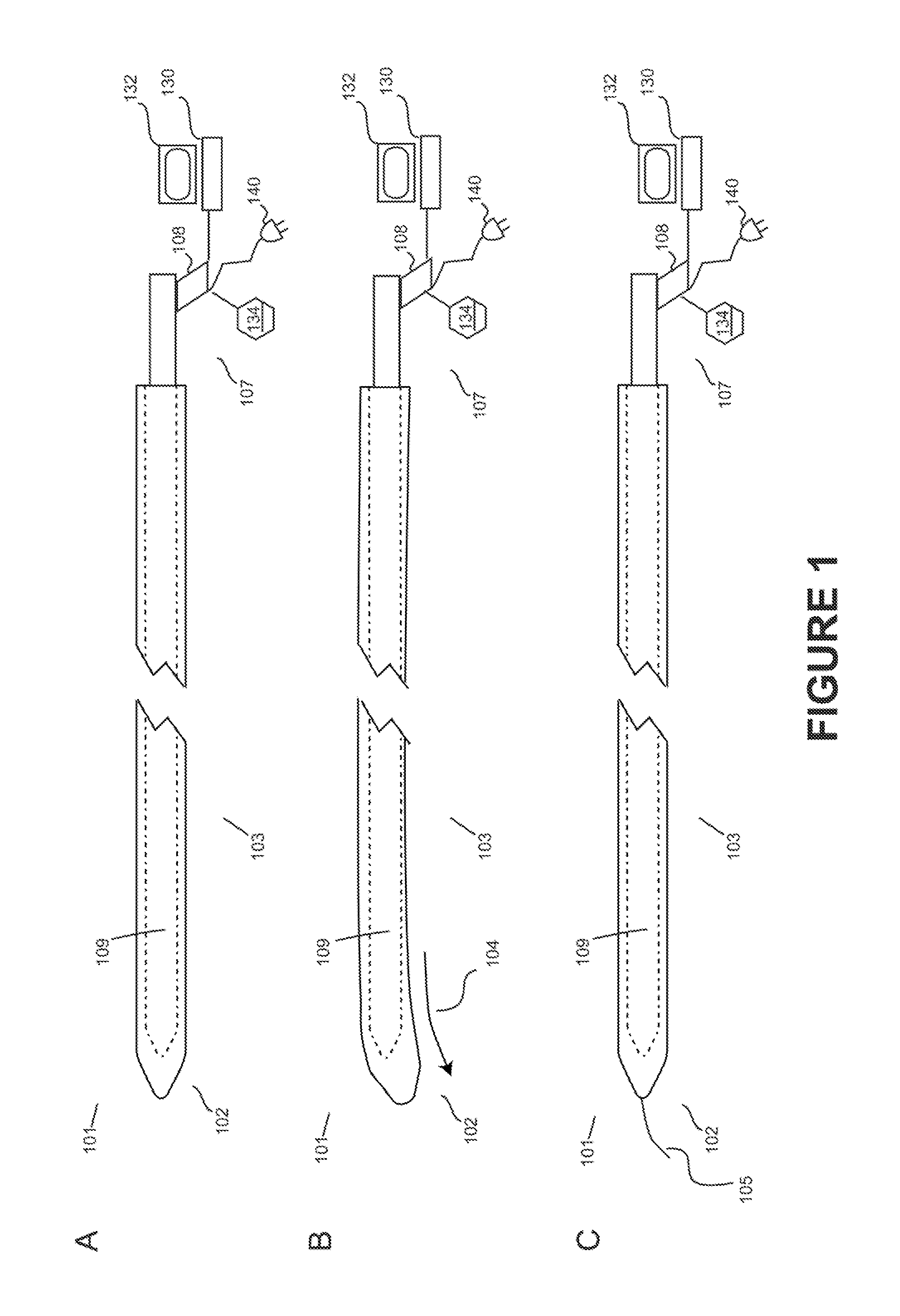
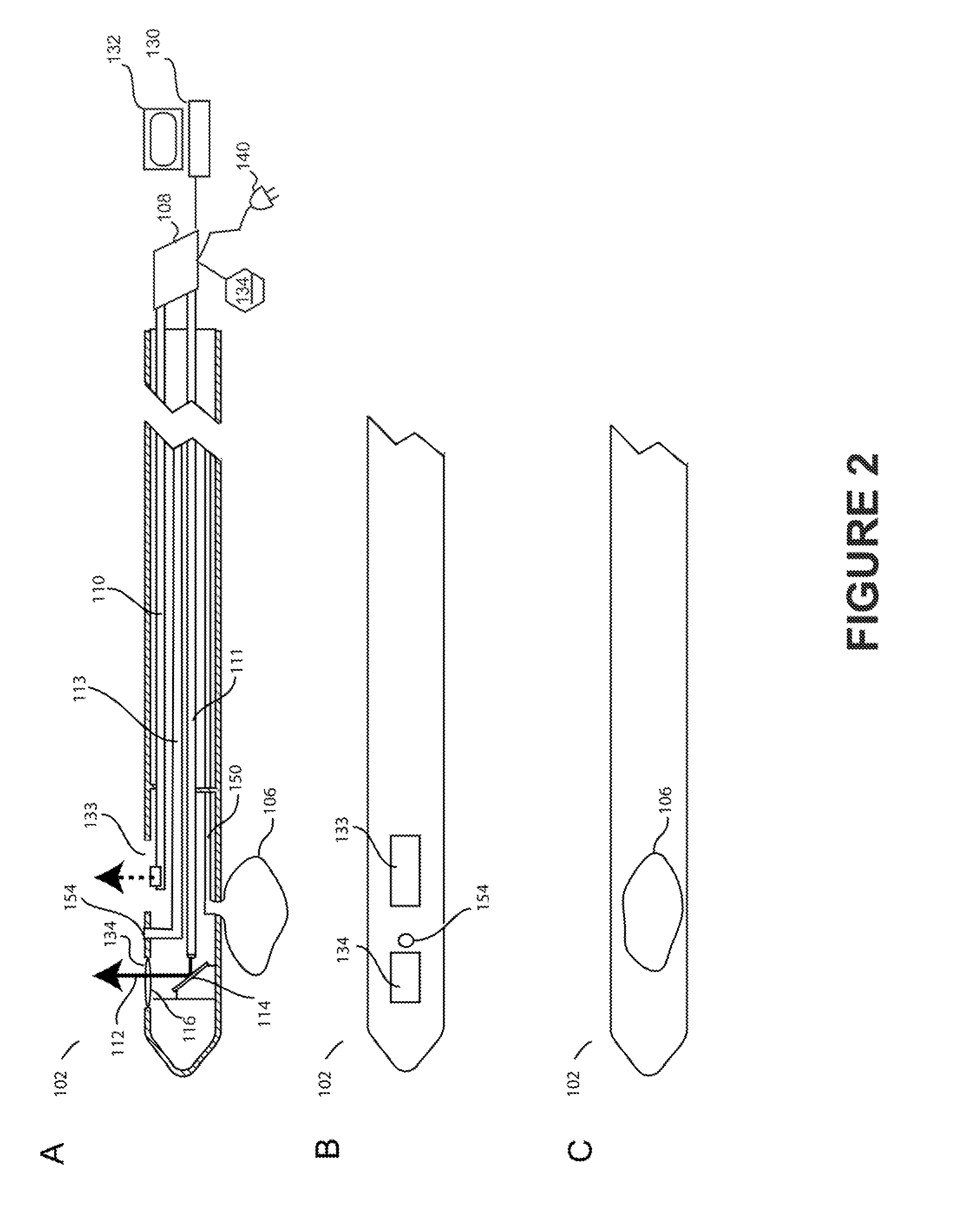
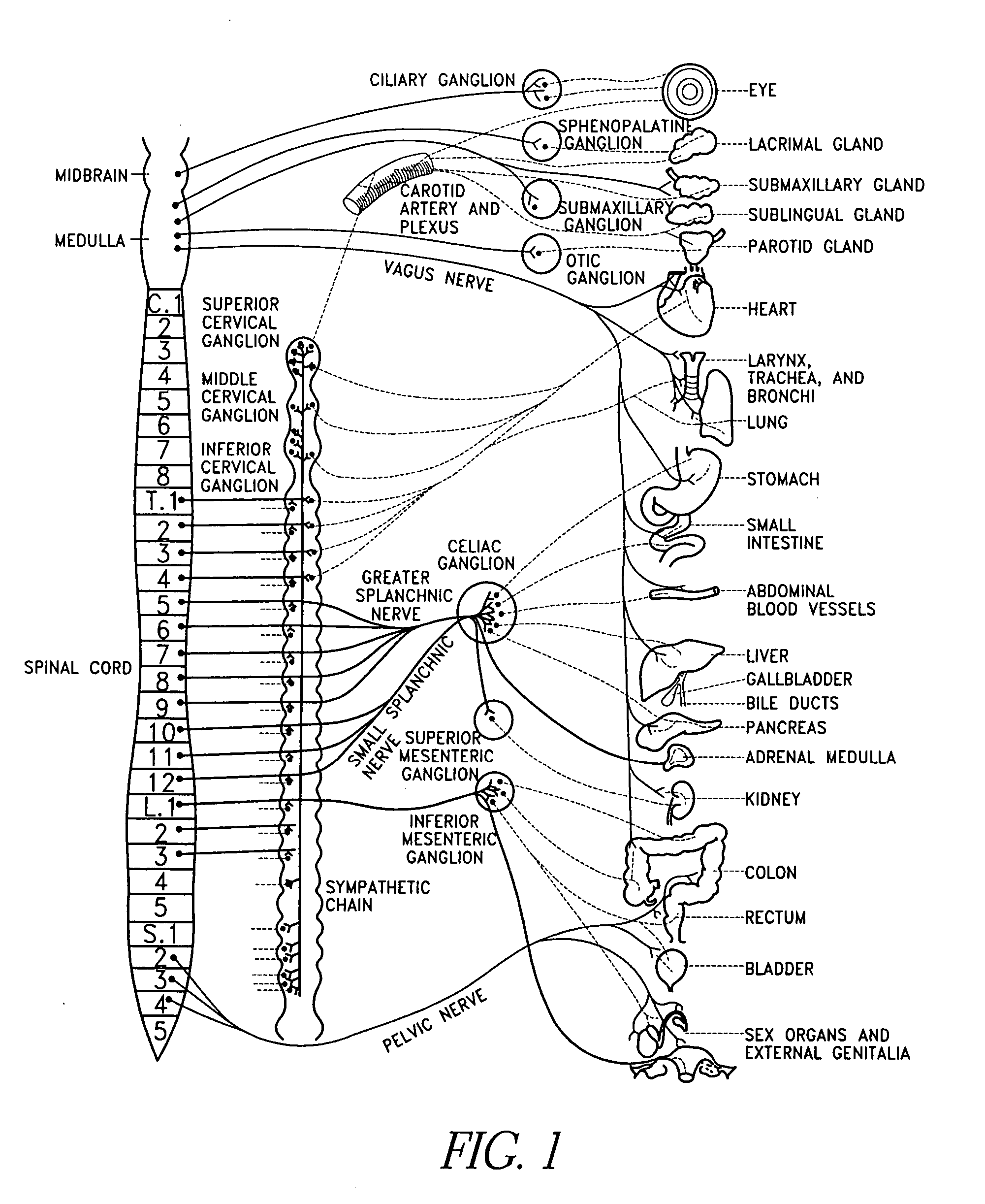
The sympathetic nervous system is a faster system as it moves along very short neurons. When the system is activated, it activates the adrenal medulla to release hormones and chemical receptors into the bloodstreams. The target glands and muscles get activated.
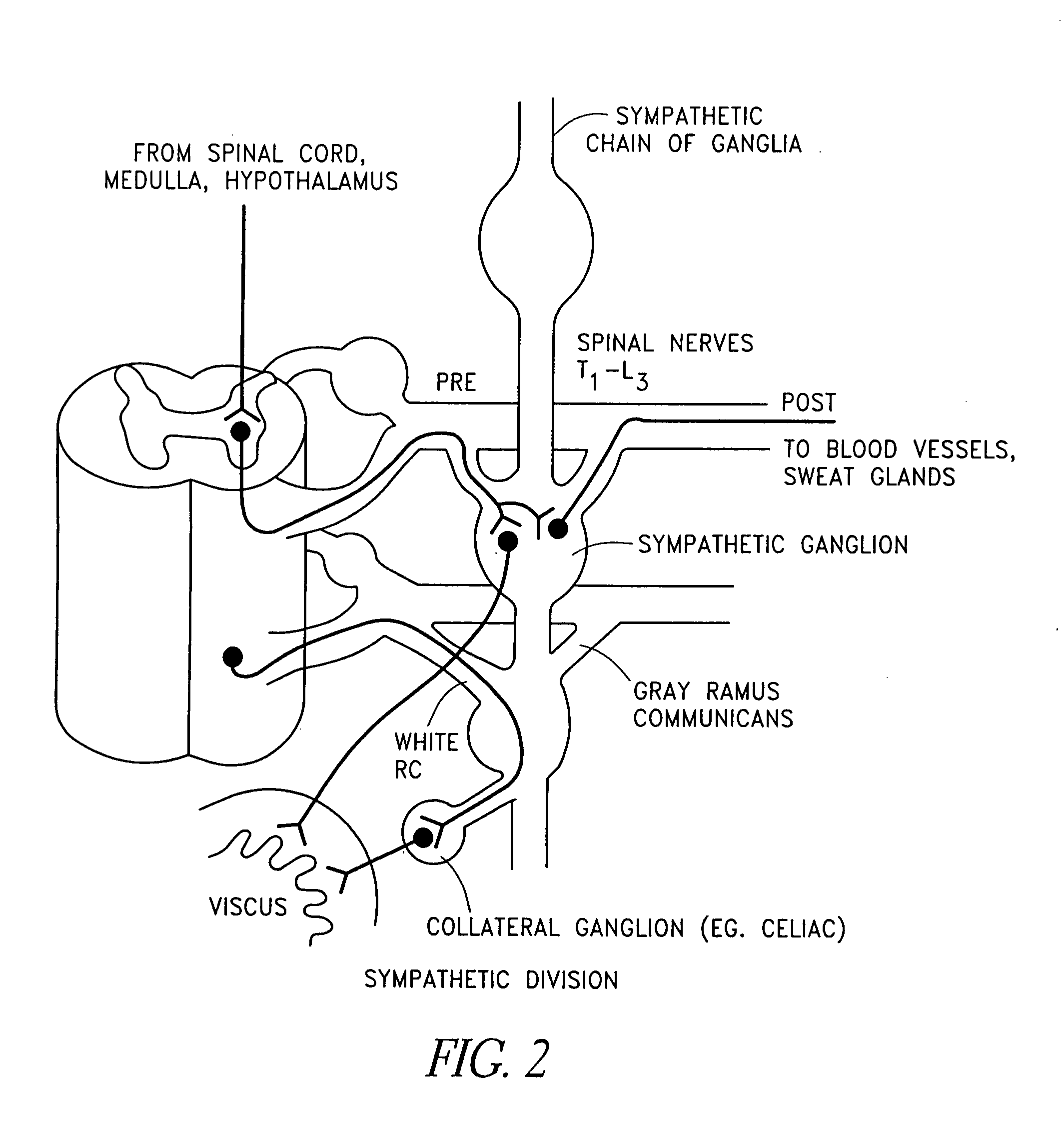
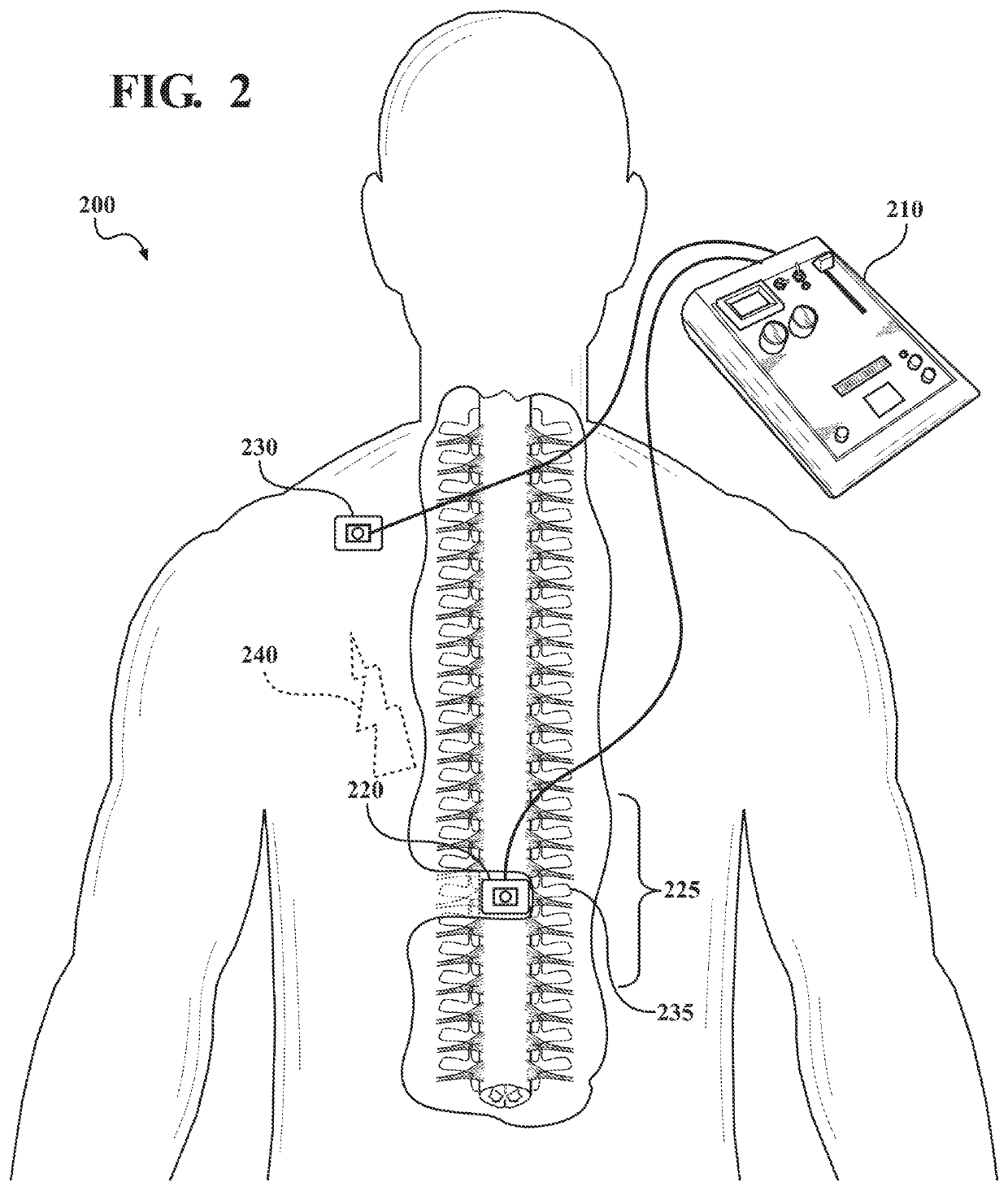
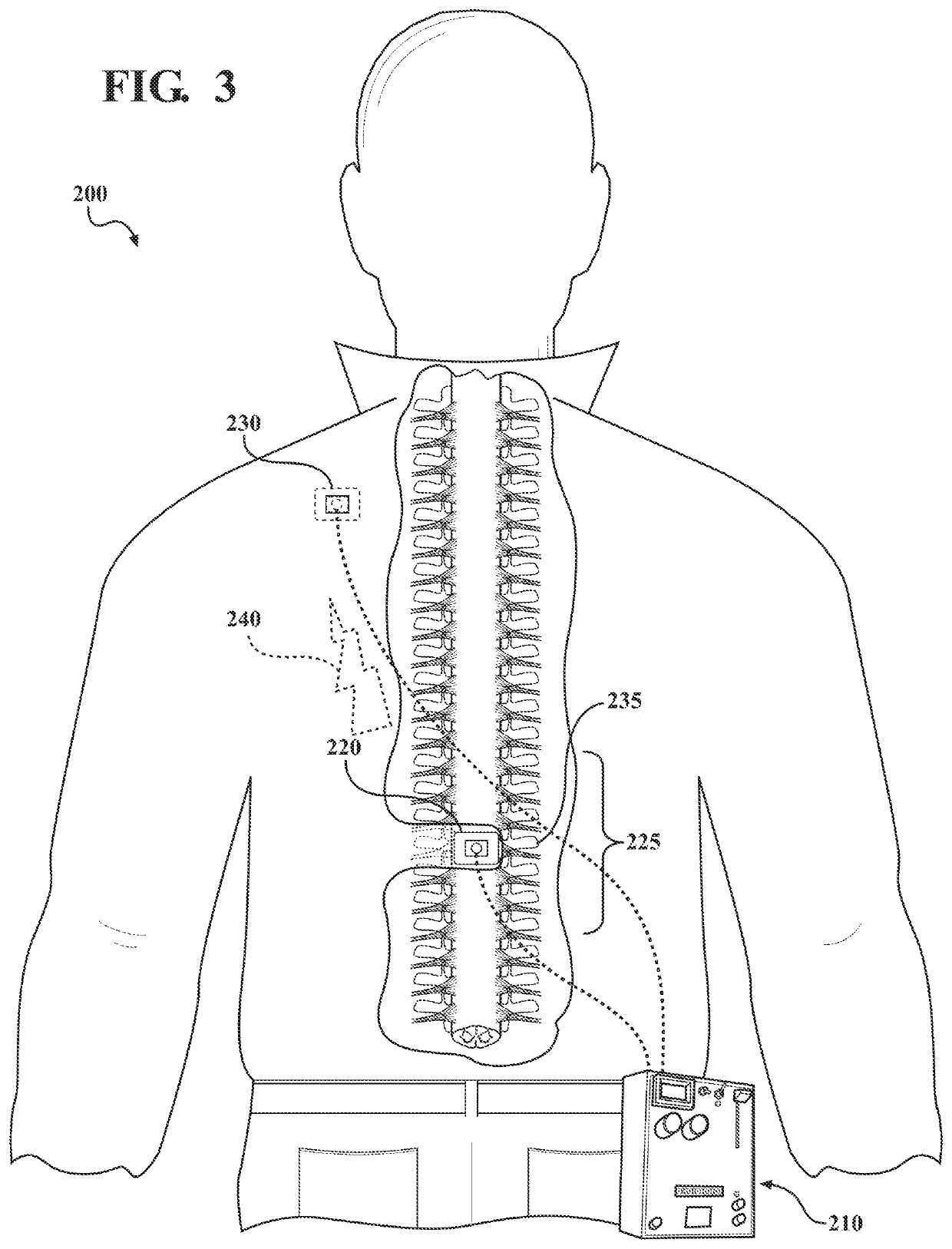
Electrical stimulation of the sympathetic nerve chain
InactiveUS6885888B2Minimizing stimulationMinimize complicationsSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSympathetic nerveSacral sympathetic chain
The present invention provides a method of affecting physiological disorders by stimulating a specific location along the sympathetic nerve chain. Preferably, the present invention provides a method of affecting a variety of physiological disorders or pathological conditions by placing an electrode adjacent to or in communication with at least one ganglion along the sympathetic nerve chain and stimulating the at least one ganglion until the physiological disorder or pathological condition has been affected.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
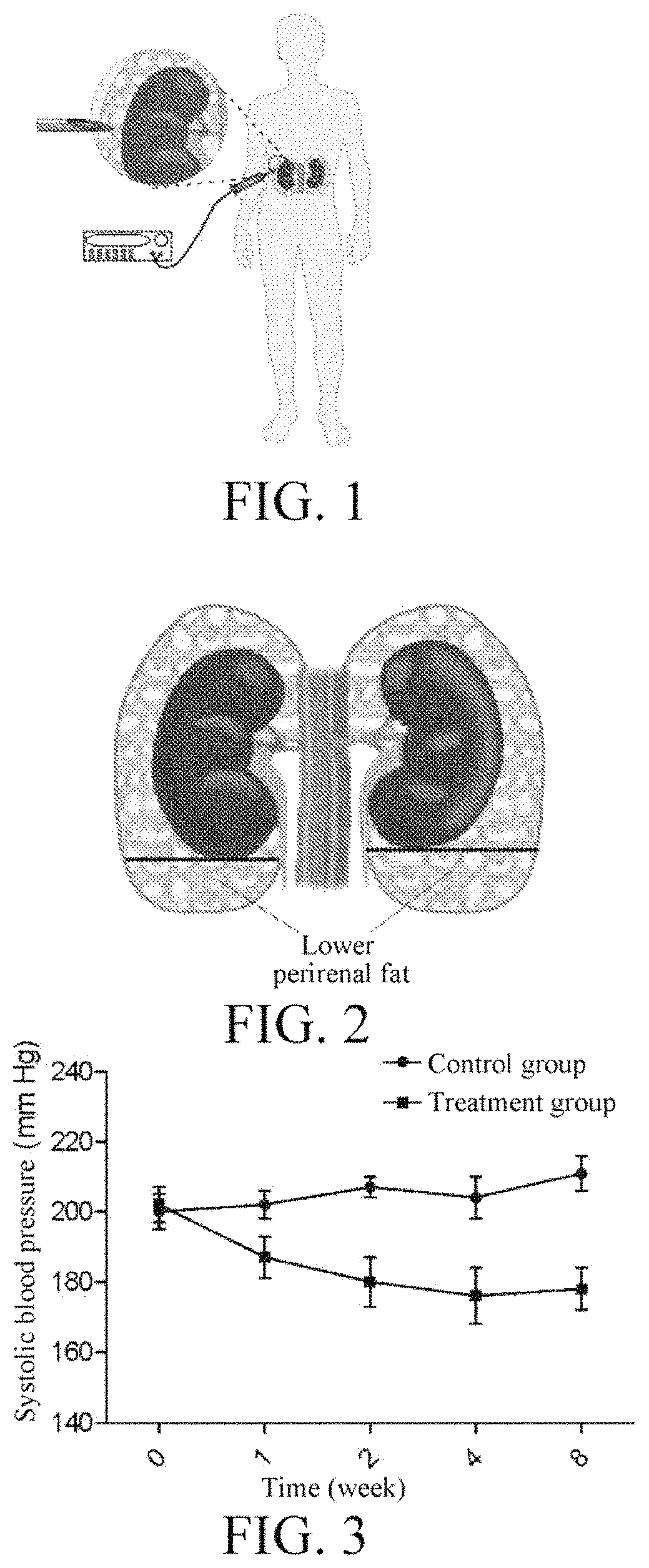
Device for reducing renal sympathetic nerve activity
The present invention provides devices and methods for modulating or blocking renal sympathetic nerve activity by applying laser energy to the renal artery wall to effect ablation of the renal nerve or nerves. The devices and methods of the invention may be useful in the treatment of cardiovascular and renal disease resulting from hypertension. In addition the devices and methods of the invention may be useful for reducing reflex hypertension following cyclosporine administration after organ transplantation.
Owner:LAMBERT DAVID +1
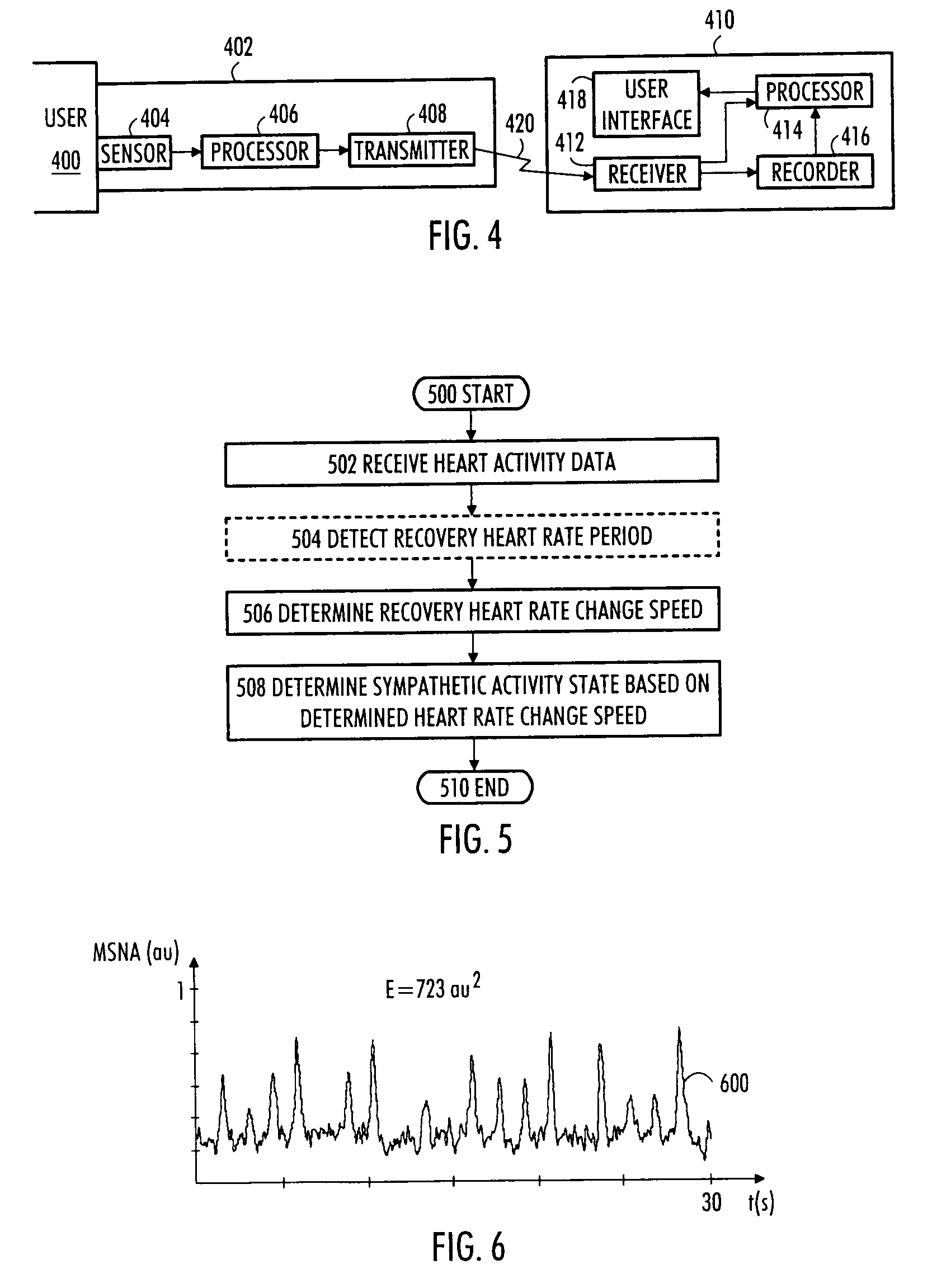
Determination of Sympathetic Activity
ActiveUS20090216143A1SensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateHeart rate changeSympathetic nerve activity
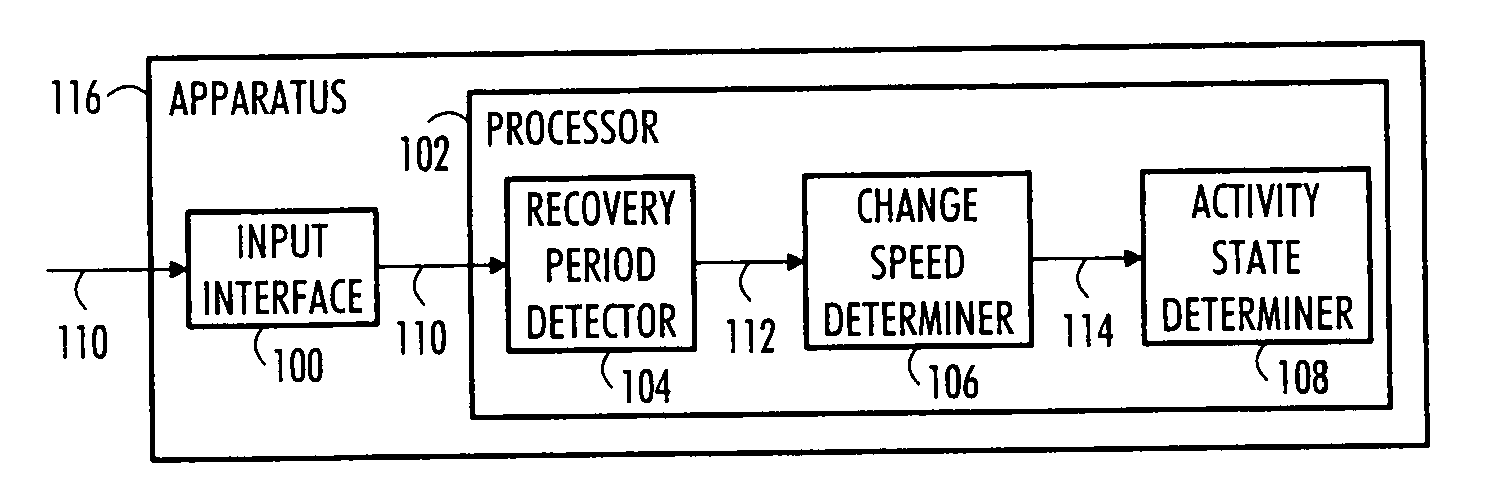
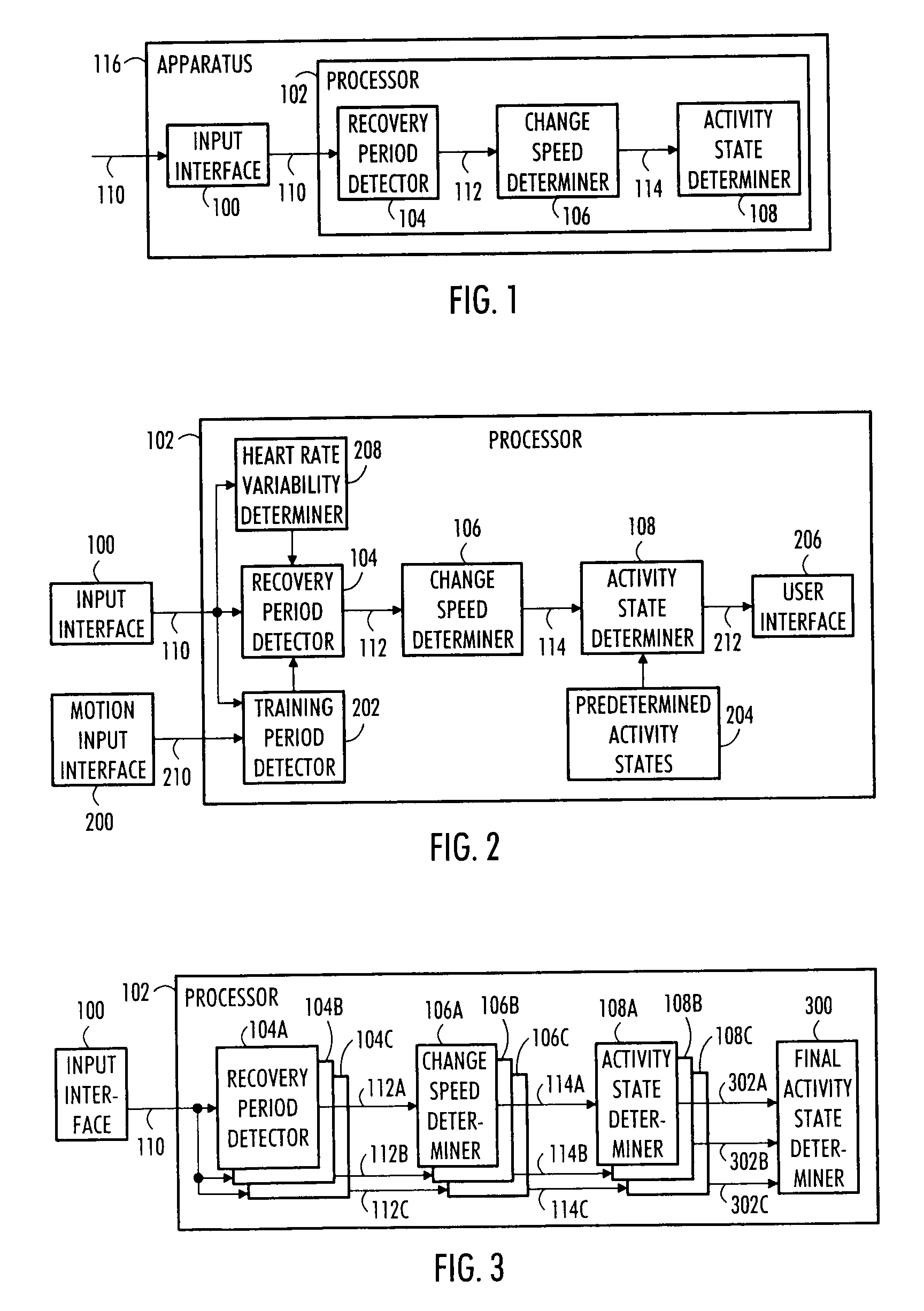
An apparatus, a method and a computer program for the determination of sympathetic activity are disclosed. The method comprises: receiving heart activity data of a person; determining a recovery heart rate change speed during a recovery heart rate period in the heart activity data; and determining a sympathetic activity state of the sympathetic nervous system of the person based on the determined recovery heart rate change speed.
Owner:POLAR ELECTRO
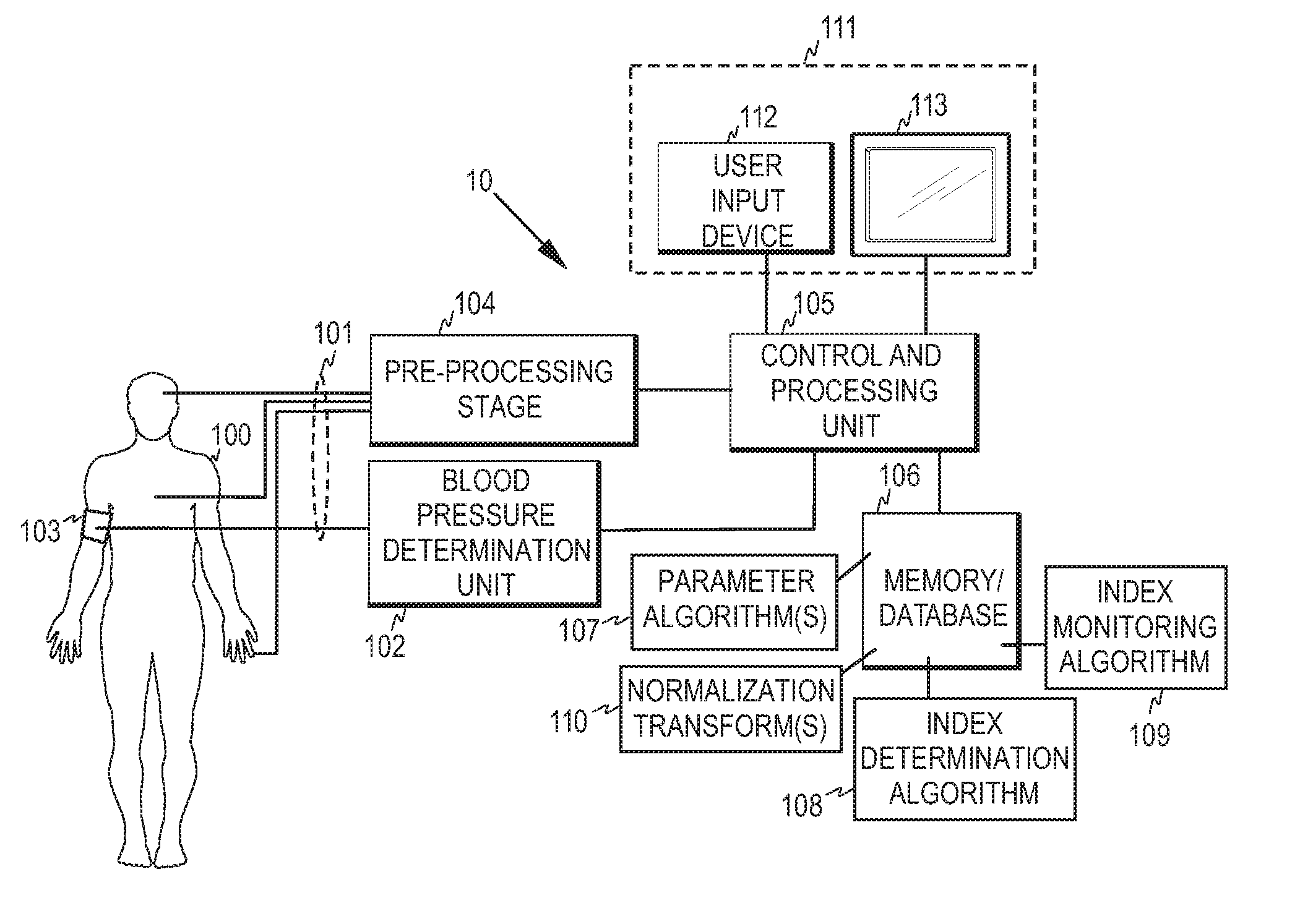
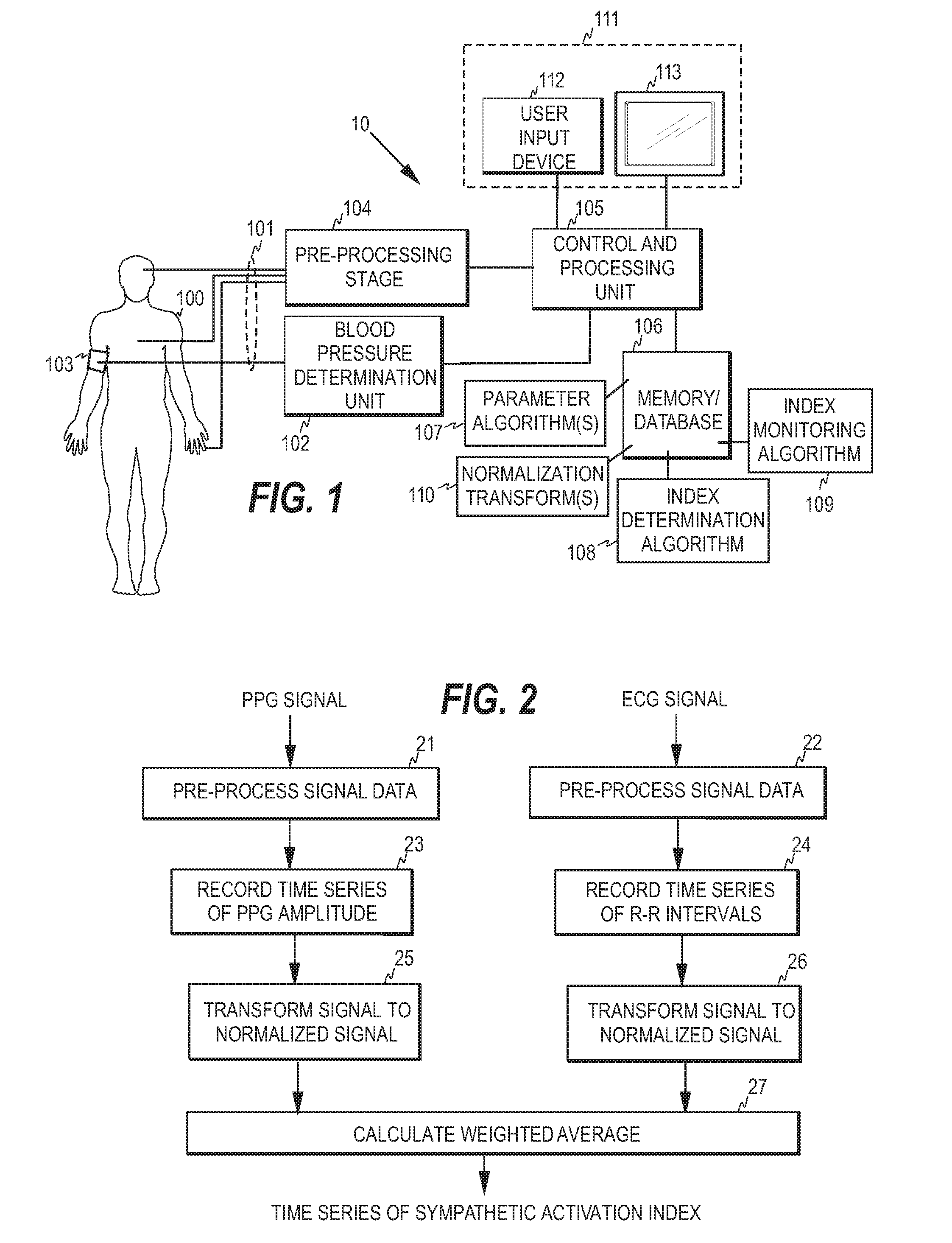
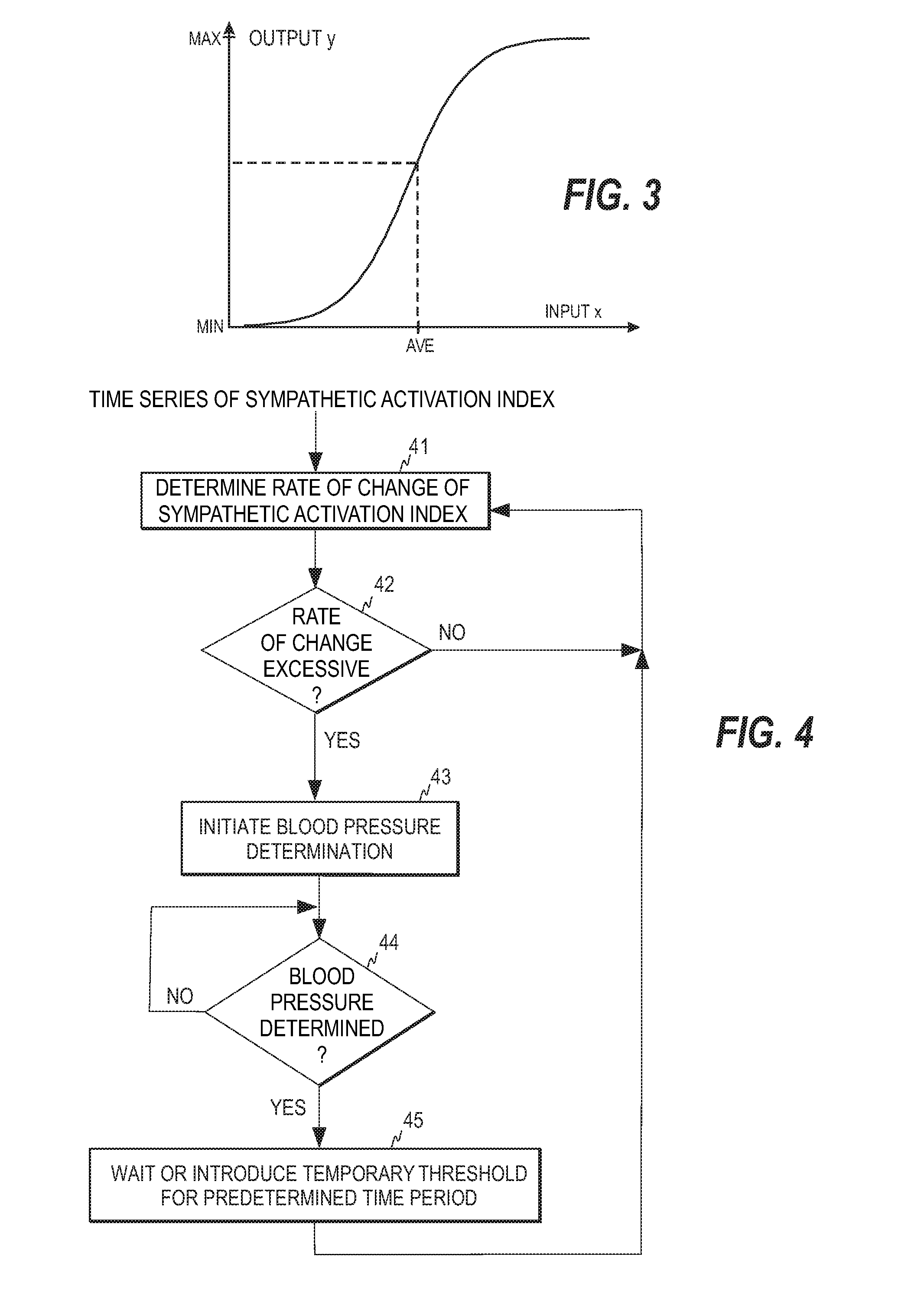
Method, apparatus and computer program for automatic non-invasive blood pressure measurement
InactiveUS20130158417A1Evaluation of blood vesselsCatheterBlood Pressure DeterminationsEmergency medicine
A method, apparatus and computer program product are disclosed for non-invasively determining blood pressure of a subject. To improve the specificity of automatic blood pressure determinations in a patient monitor provided with a non-invasive blood pressure determination unit, a physiological index indicative of sympathetic activity is derived from a subject, variations in the physiological index are monitored, and the blood pressure determination unit is instructed to initiate blood pressure determination when the variations fulfill a predetermined condition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Use of Antagonists of Hepatic Sympathetic Nerve Activity
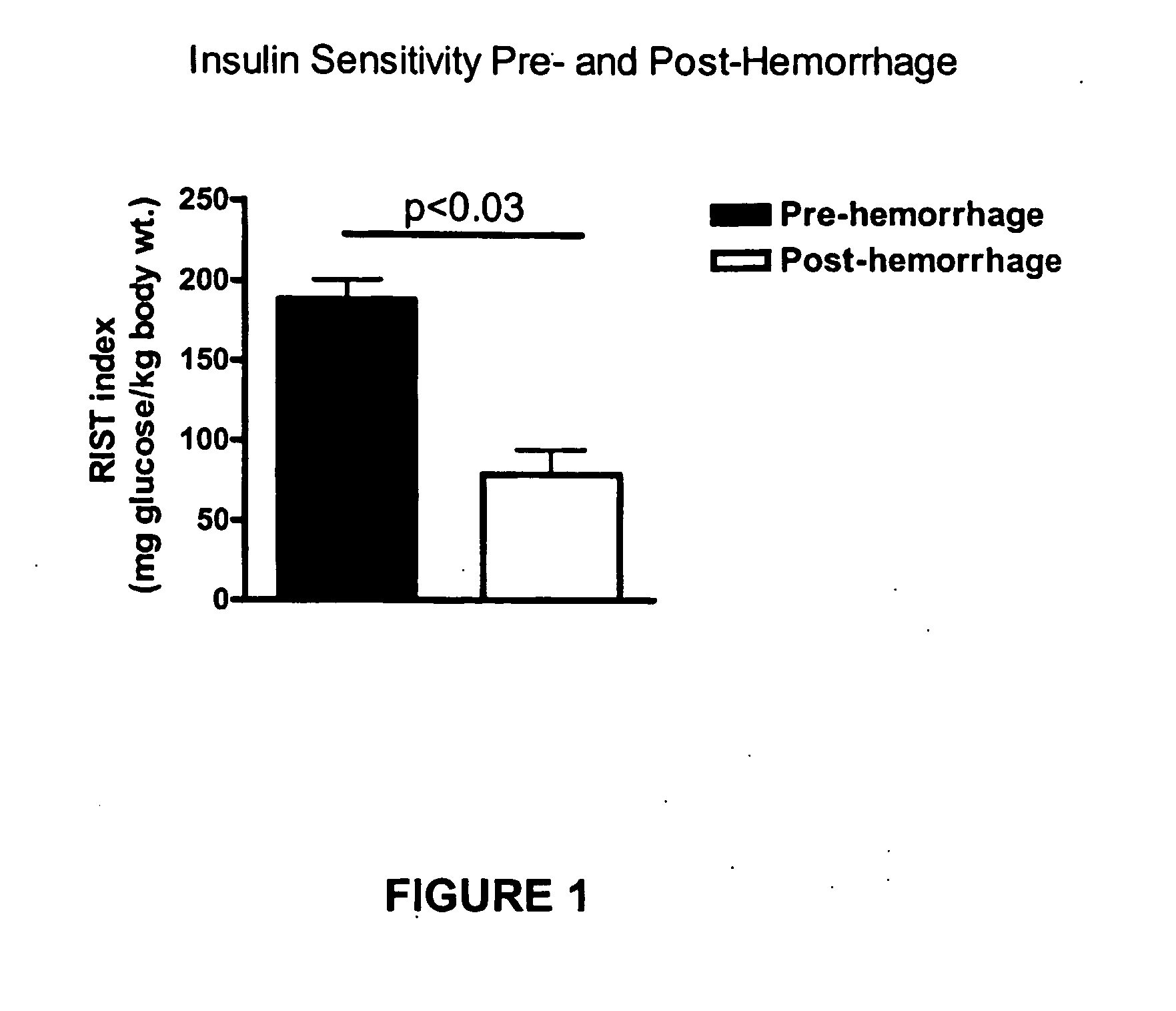
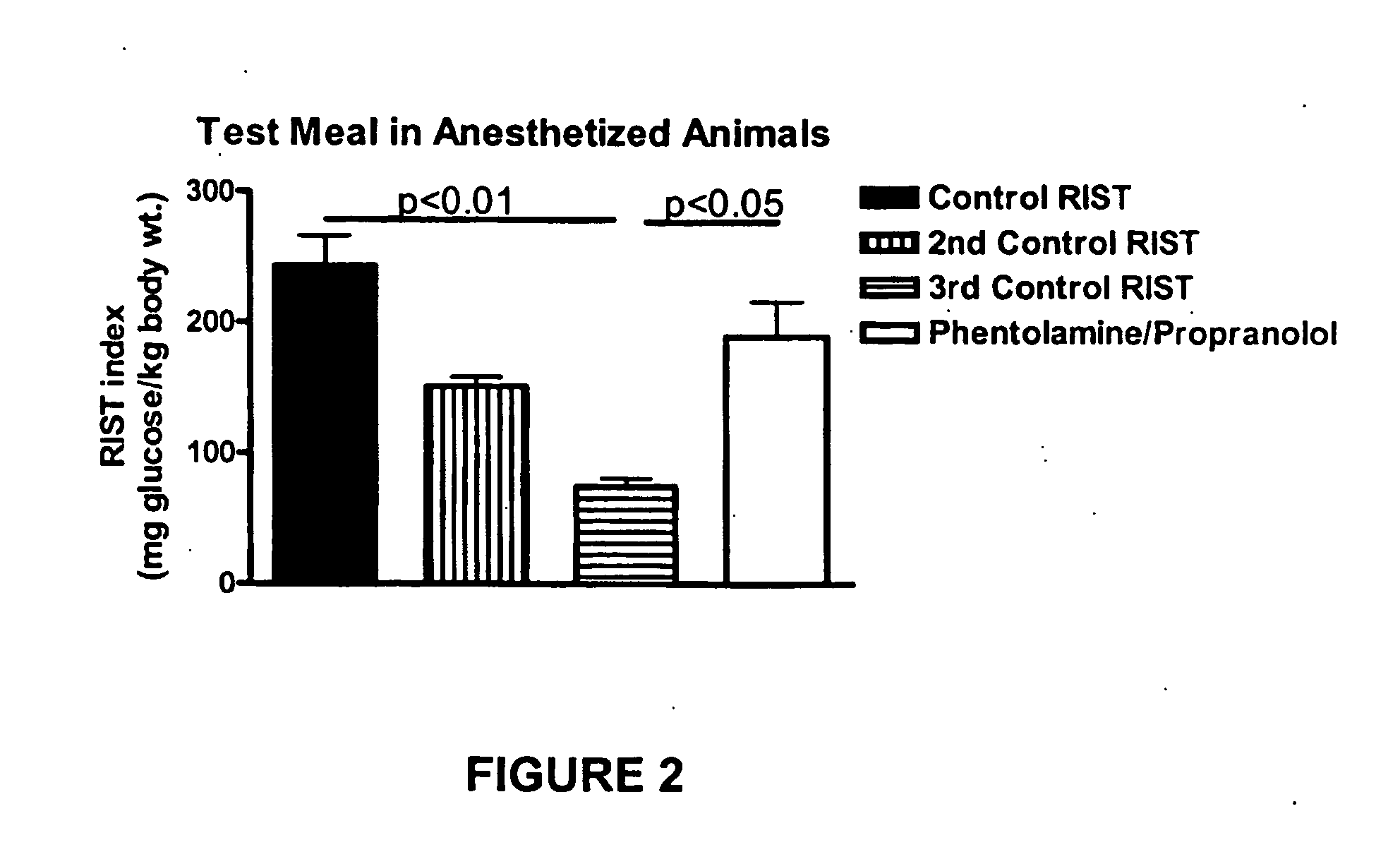
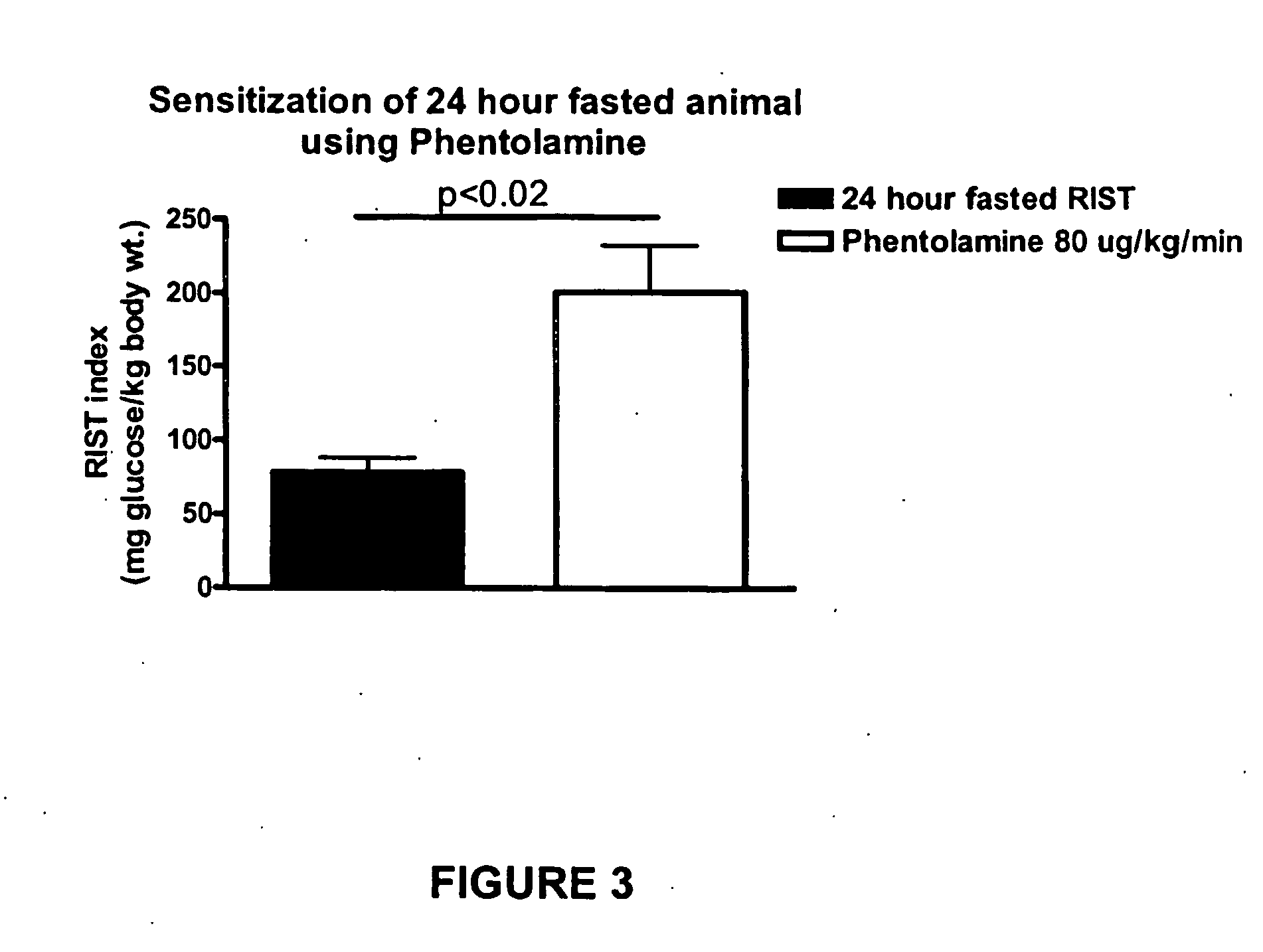
InactiveUS20070238762A1Increasing skeletal muscle glucose uptakeReduce insulin resistanceBiocideMetabolism disorderSympathetic nerve activityDiabetic nephropathy
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising antagonists of hepatic sympathetic activity and methods for using said pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinaemia, hyperlipidaemia, hypertriglyceridaemia, diabetes, insulin resistance, impaired glucose metabolism, conditions of impaired glucose tolerance, conditions of impaired fasting plasma glucose, obesity, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy, glomerulosclerosis, diabetic neuropathy, syndrome X, renal failure, sexual dysfunction, chronic stress, and anxiety.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
Forehead cooling method and device to stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system for the treatment of insomnia
InactiveUS20170252534A1Improve sleepingShortened sleep latencyElectrotherapyPneumatic massageReflexNervous system
Preclinical and clinical studies have shown that the autonomic nervous system (parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems) show reliable changes across the sleep wake cycle. Most importantly, the parasympathetic nervous system shows increased activity during sleep consistent with its role in regulating rest. Further, patients with insomnia show reduced parasympathetic activity and / or increased sympathetic activity during sleep consistent with a neurobiological model of “hyperarousal”. Described herein are methods and apparatuses that activate the parasympathetic nervous system in response to a diving reflex; a sustained diving reflex may, surprisingly, lead to enhancing sleep. The apparatuses and methods described herein may specifically and / or selectively activate this reflex may play a therapeutic role in the modulation of sleep in insomnia patients.
Owner:EBB THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Electric modulation of sympathetic nervous sytem
InactiveUS20070219596A1Increased energy expenditureReducing food intakeInternal electrodesExternal electrodesDiseaseNervous system
A method is described for the treatment of obesity or other disorders, by electrical activation or inhibition of the sympathetic nervous system. This activation or inhibition can be accomplished by electrically stimulating the greater splanchnic nerve or other portion of the sympathetic nervous system using an implantable pulse generator. This nerve activation can result in reduced food intake and increased energy expenditure. Reduced food intake may occur through a variety of mechanisms that reduce appetite and cause satiety. Increased adrenal gland hormone levels will result in increased energy expenditure. Fat and carbohydrate metabolism, which are also increased by sympathetic nerve activation, will accompany the increased energy expenditure.
Owner:LEPTOS BIOMEDICAL
Implants using ultrasonic communication for modulating splenic nerve activity
PendingUS20190321640A1Desired effectReduce concentrationSpinal electrodesCircuit arrangementsTreatment hypertensionMedical treatment
Described herein are methods for monitoring or modulating an immune system in a subject; treating, reducing or monitoring inflammation; monitoring blood pressure; treating hypertension; or administering or adjusting a therapy for inflammation or hypertension in a patient by electrically stimulating the splenic nerve or detecting splenic nerve activity using an implanted medical device. Also described herein are implantable medical devices for performing such methods. The implanted medical device includes an ultrasonic transducer configured to receive ultrasonic waves and convert energy from the ultrasonic waves into an electrical energy that powers the device, two or more electrodes in electrical communication with the ultrasonic transducer that are configured to electrically stimulate a splenic nerve or detect a splenic nerve activity, and optionally a splenic nerve attachment member.
Owner:IOTA BIOSCI INC
Method of early detection of Duchenne muscular dystrophy and other neuromuscular disease
InactiveUS6875418B2Compounds screening/testingDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseDecreasing heart rate
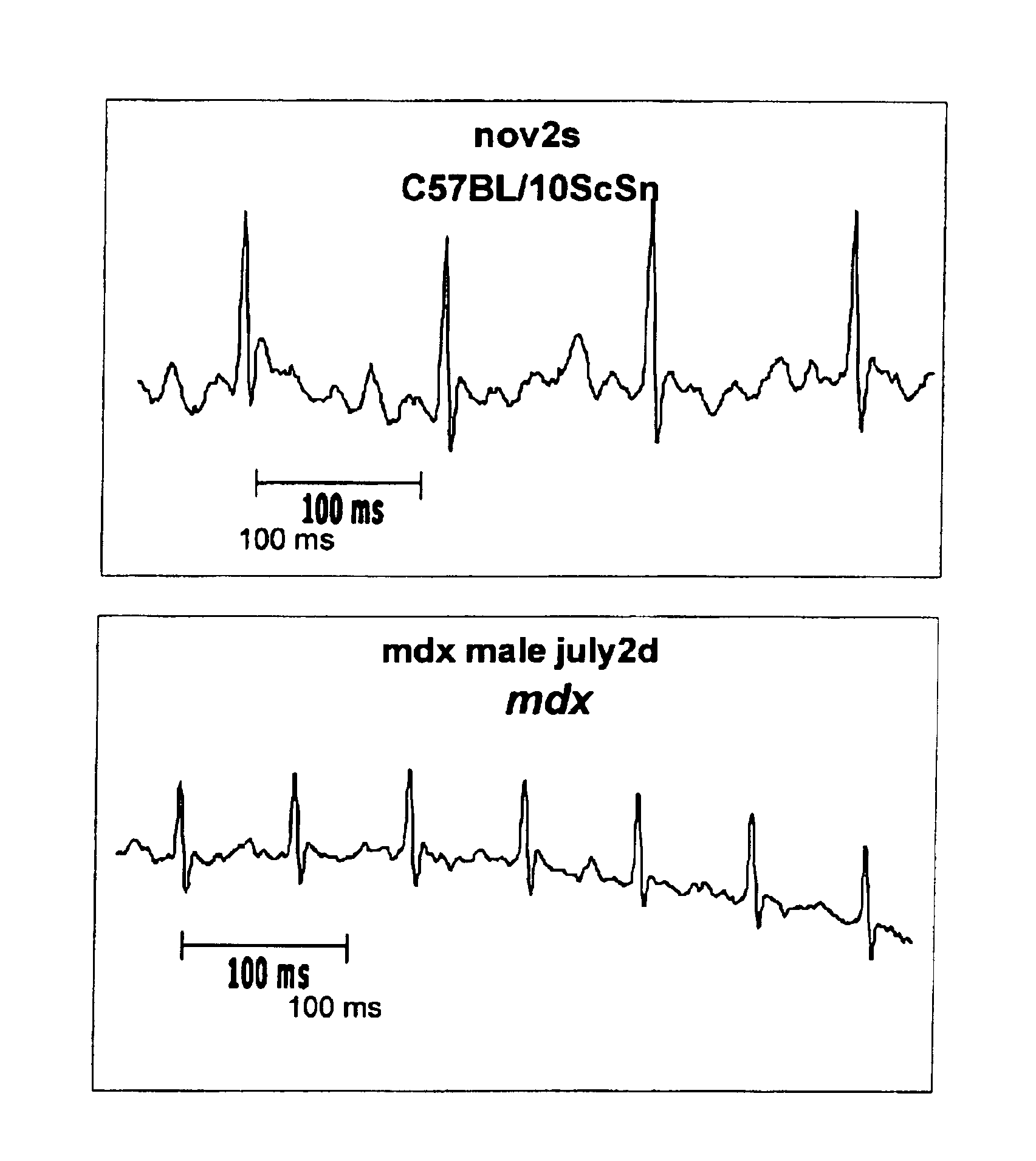
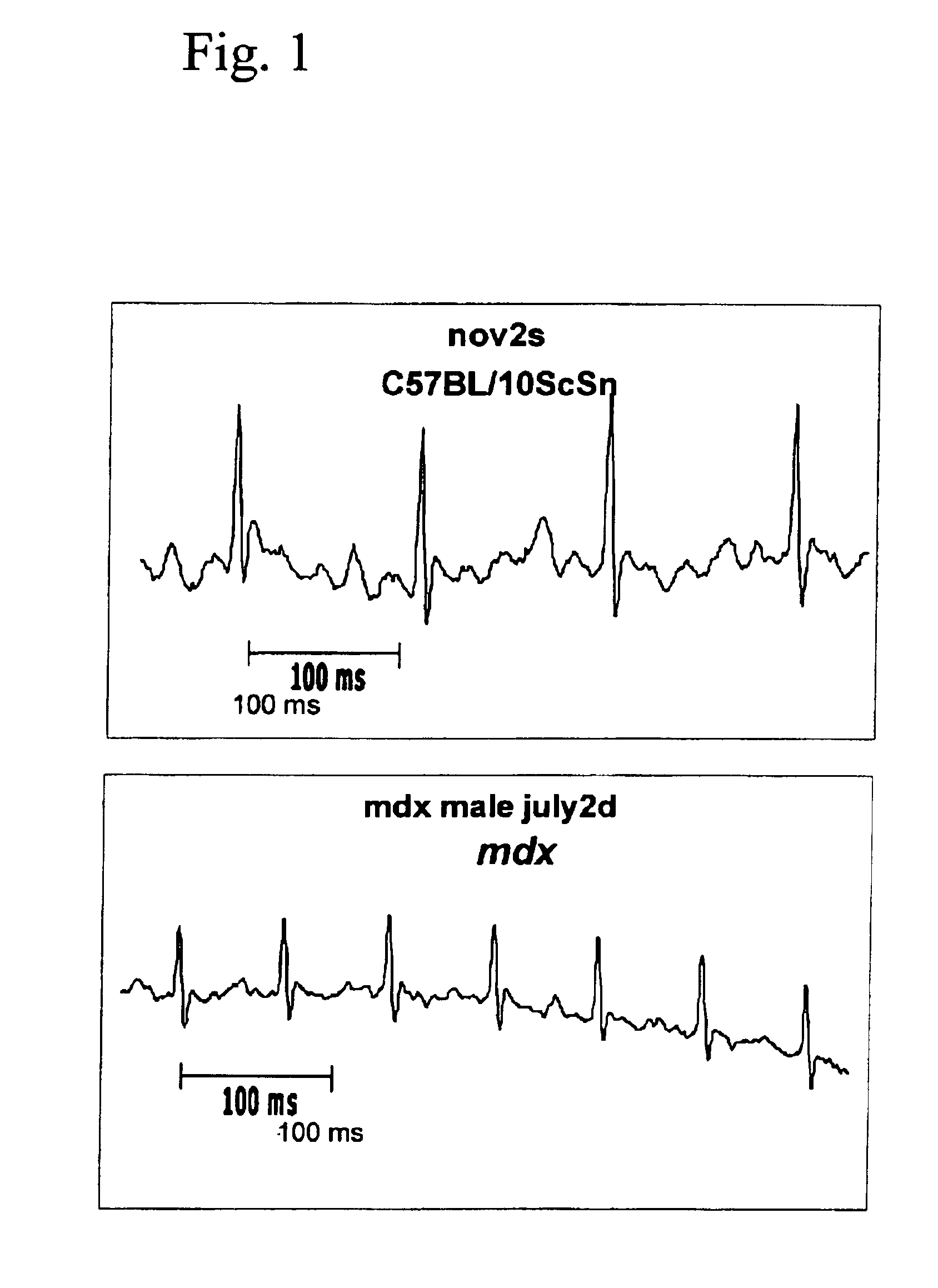
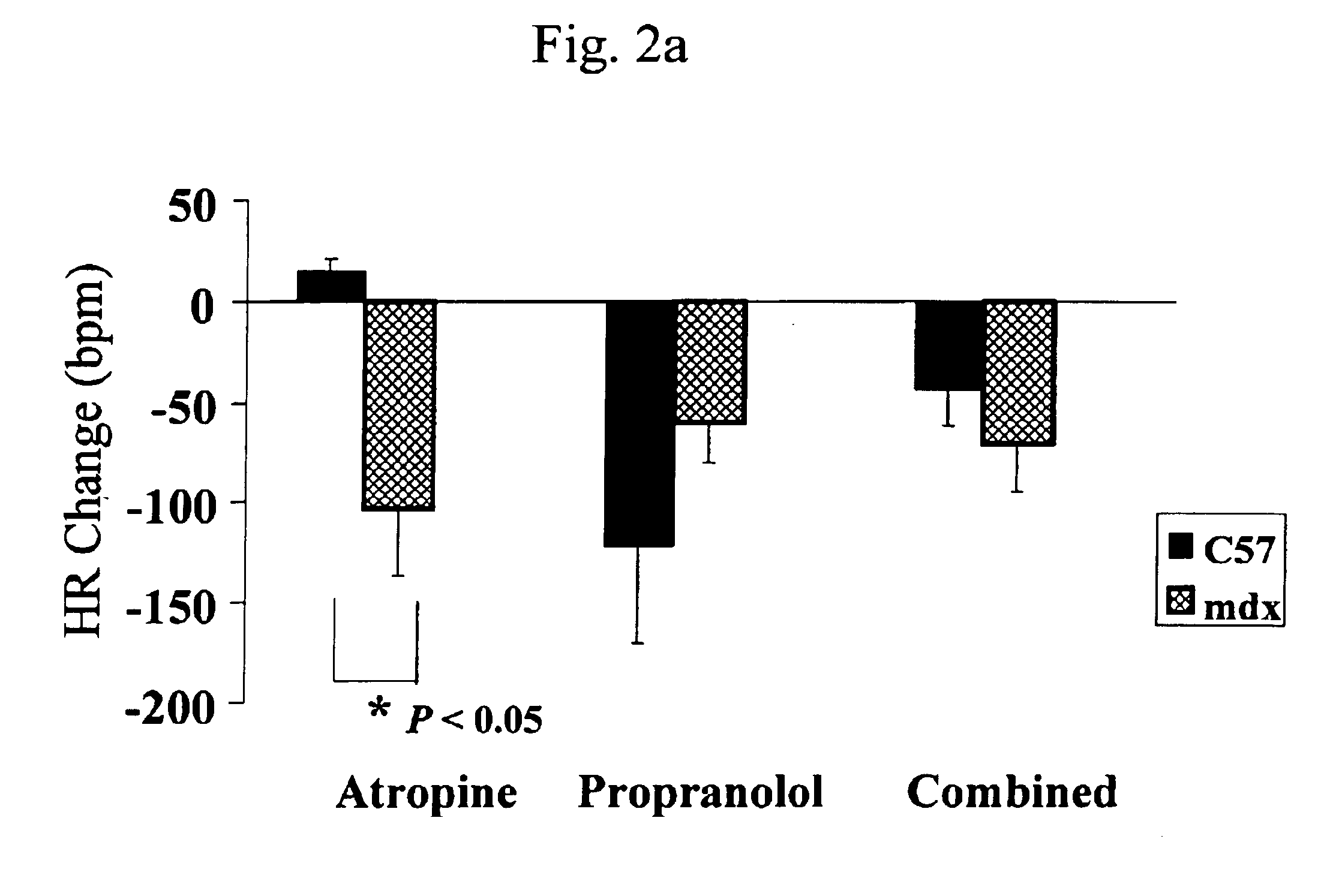
The mdx mouse is a model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The present invention describes that mdx mice exhibited clinically relevant cardiac phenotypes. A non-invasive method of recording electrocardiograms (ECGs) was used to a study mdx mice (n=15) and control mice (n=15). The mdx mice had significant tachycardia, consistent with observations in patients with muscular dystrophy. Heart-rate was nearly 15% faster in mdx mice than control mice (P<0.01). ECGs revealed significant shortening of the rate-corrected QT interval duration (QTc) in mdx mice compared to control mice (P<0.05). PR interval duration were shorter at baseline in mdx compared to control mice (P<0.05). The muscarinic antagonist atropine significantly increased heart-rate and decreased PR interval duration in C57 mice. Paradoxically, atropine significantly decreased heart-rate and increased PR interval duration in all mdx mice. Pharmacological autonomic blockade and baroreflex sensitivity testing demonstrated an imbalance in autonomic nervous system modulation of heart-rate, with decreased parasympathetic activity and increased sympathetic activity in mdx mice. These electrocardiographic findings in dystrophin-deficient mice provide new bases for diagnosing, understanding, and treating patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Owner:MOUSE SPECIFICS
Method of Conditioning a Living Body to Respond Appropriately to Stimuli
InactiveUS20190030279A1Reduced activityModifying the physiological reactionVibration massageMedical devicesPaired stimuliMedicine
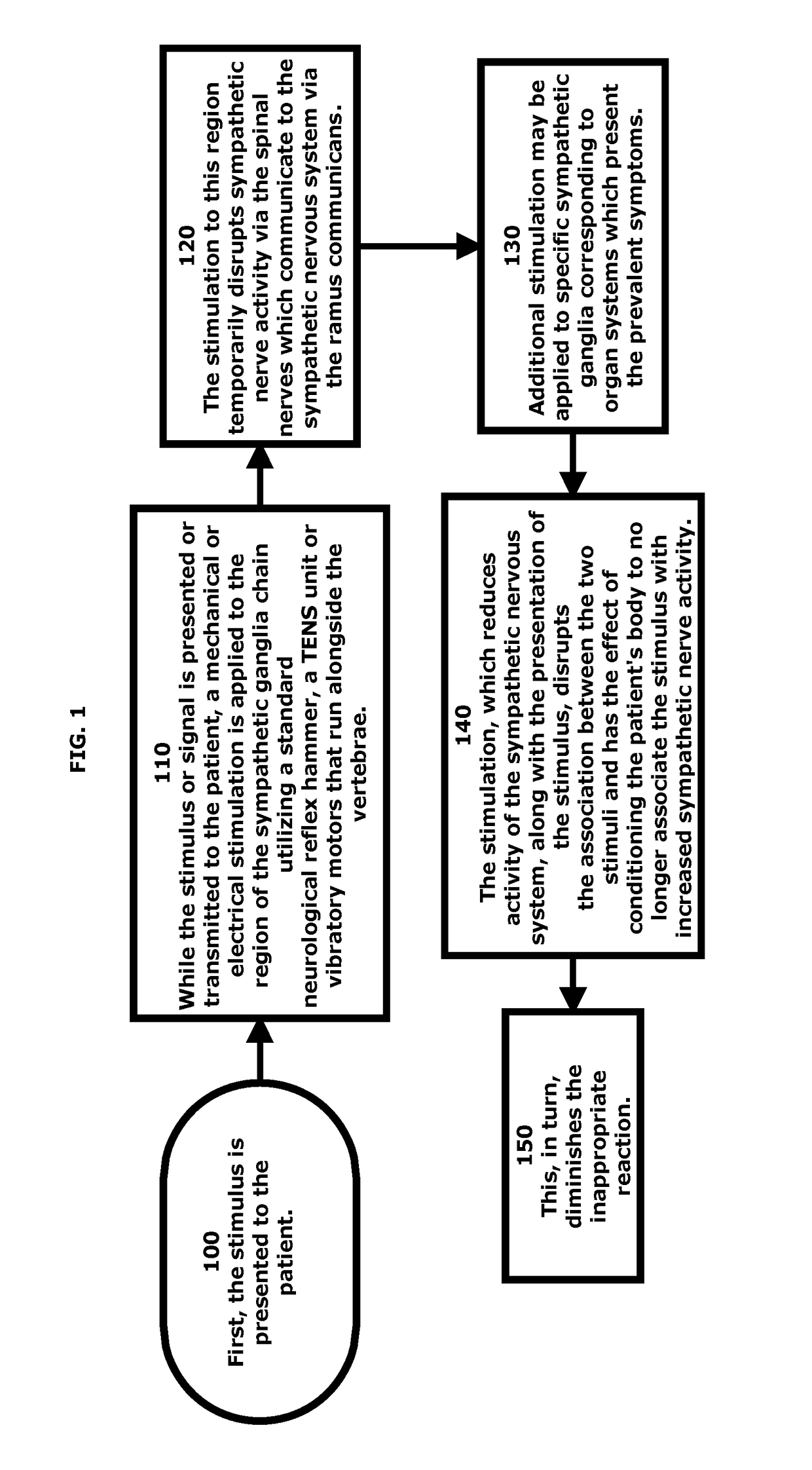
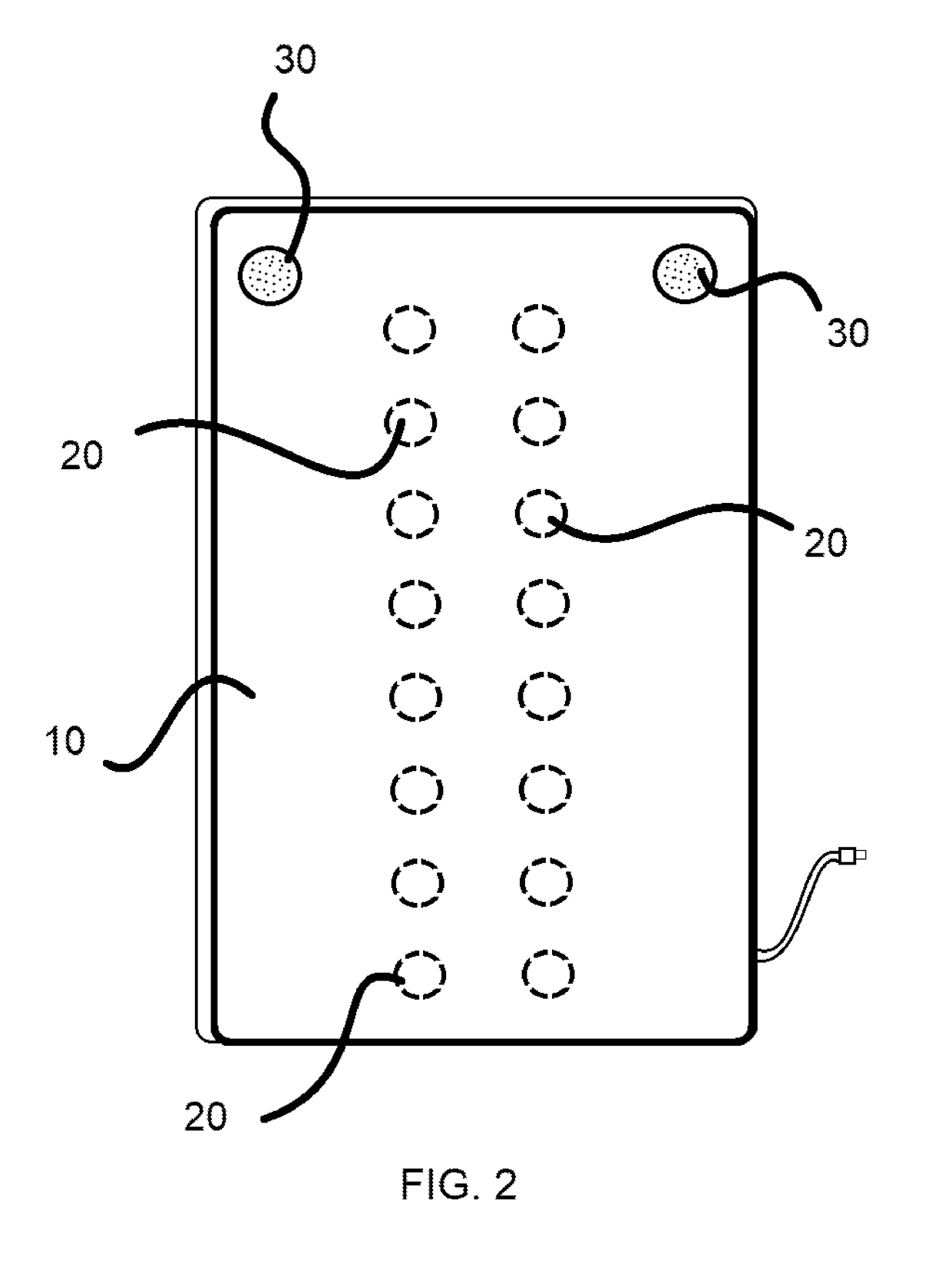
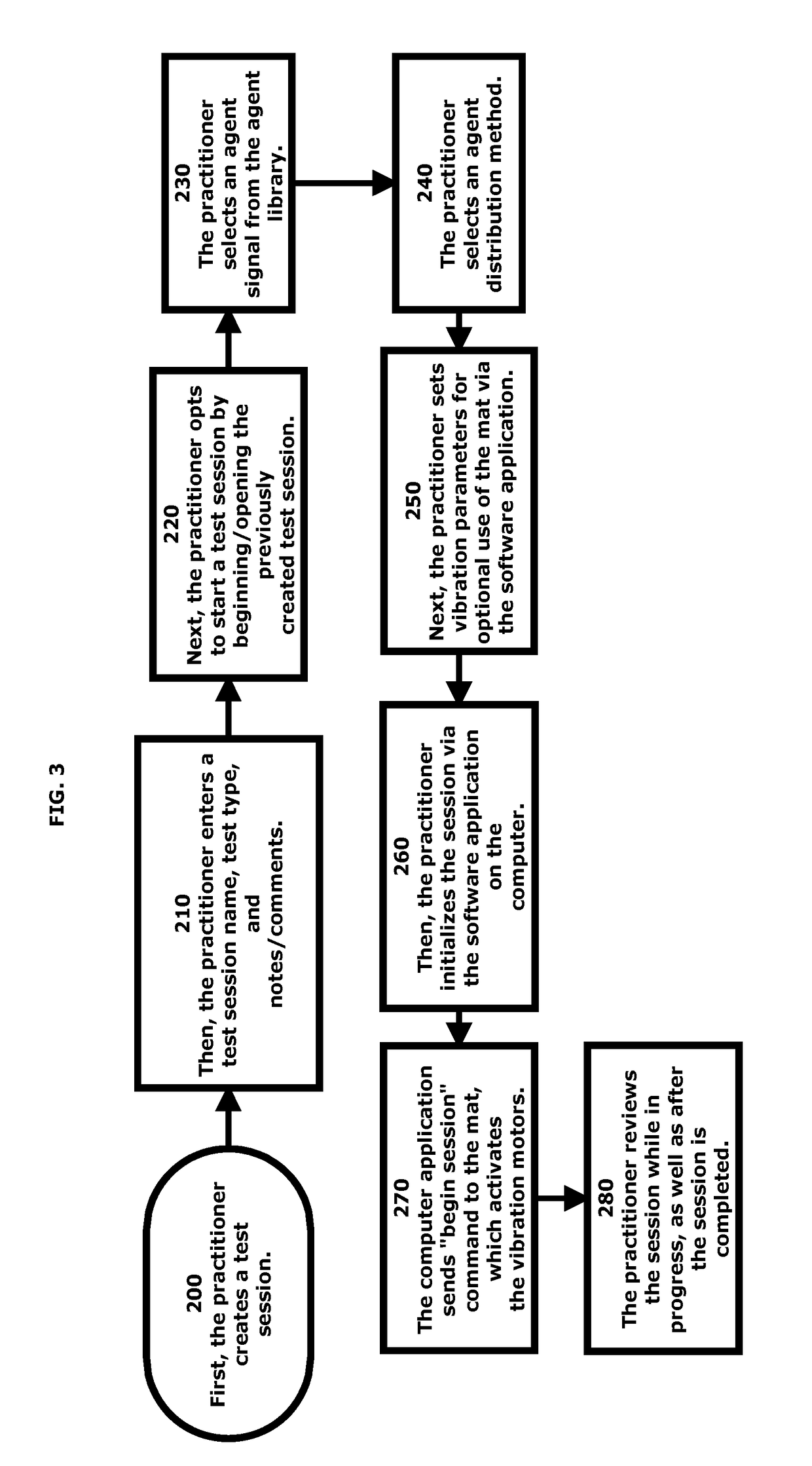
A method of conditioning a living body of a patient to associate the unconditioned stimulus (US) of decreased sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) with the conditioned stimulus (CS) or offending agent to cease or reduce defensive reactions or symptoms. The US involves non-invasive, mechanical stimulation of the sympathetic ganglia, which is paired with the offending stimuli or representation of the offending stimuli to modify pathologically conditioned reflexes of various systems involved in a reaction. In addition, conditions are treated by using digital representations, preferably provided via a computer, to represent the offending stimulus in order to engage the multimodal functioning of the brain. Sensory stimulation is used in conjunction with the various modalities of stimuli to condition the body to respond more appropriately to the stimulus.
Owner:NOWLIN DAWN
Pharmaceutical composition, food or beverage capable of enhancing sympathetic nerve activity
InactiveCN101707910APromote combustionHyperactivityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderComorbidityObesity
It is intended to provide a safe composition for preventing or treating obesity or related complications which has an autonomic nervous control effect, in particular, an effect of enhancing sympathetic nervous activity and an effect of promoting energy metabolism. Thus, a medicinal composition, a food or a drink containing 2,3-dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4H-pyran-4-one and having an autonomic nervous control effect and an effect of promoting energy metabolism is provided.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Medicinal composition, food or drink having effect of enhancing sympathetic nervous activity
It is intended to provide a safe composition for preventing or treating obesity or related complications which has an autonomic nervous control effect, in particular, an effect of enhancing sympathetic nervous activity and an effect of promoting energy metabolism. Thus, a medicinal composition, a food or a drink containing 2,3-dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4H-pyran-4-one and having an autonomic nervous control effect and an effect of promoting energy metabolism is provided.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
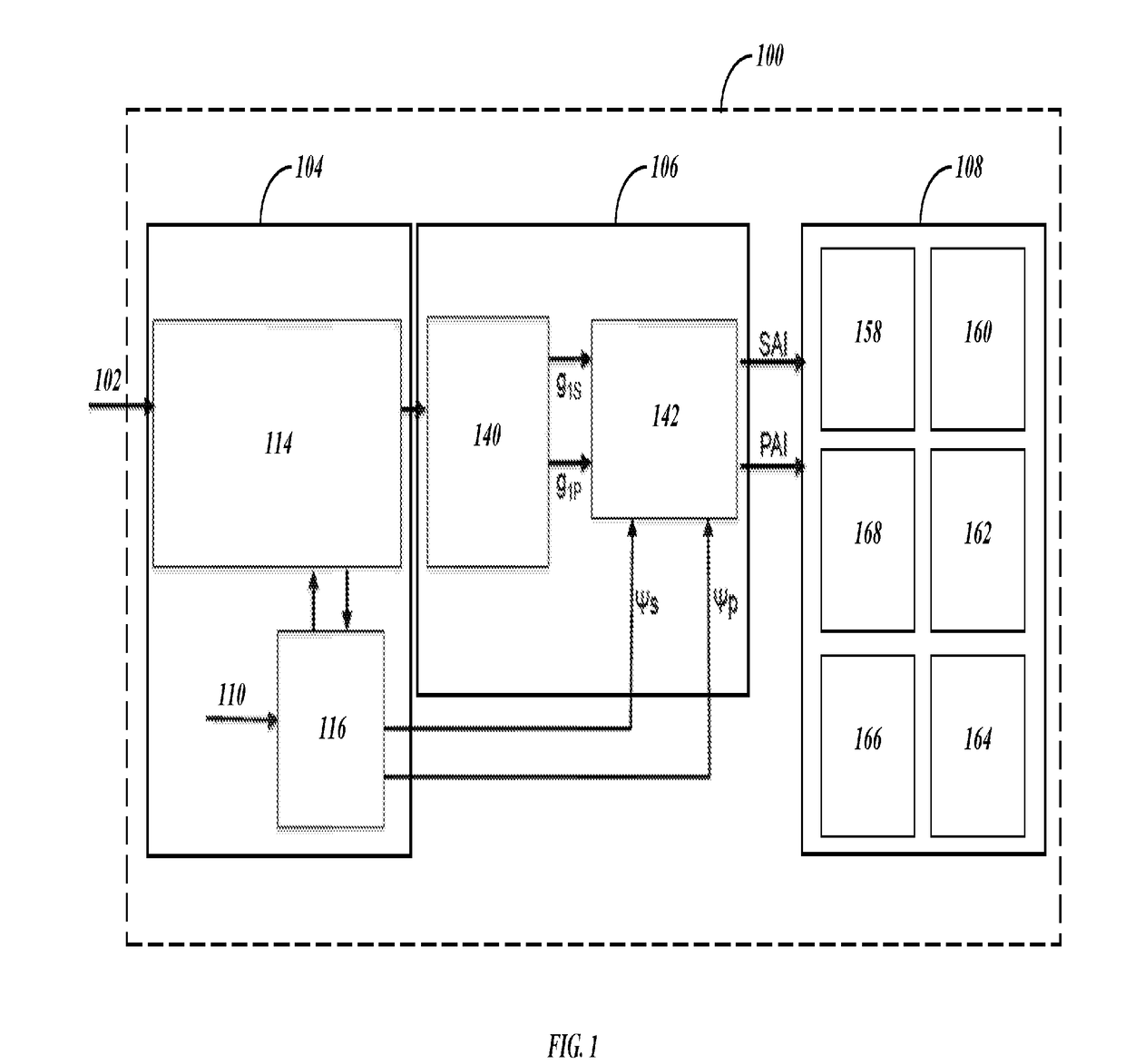
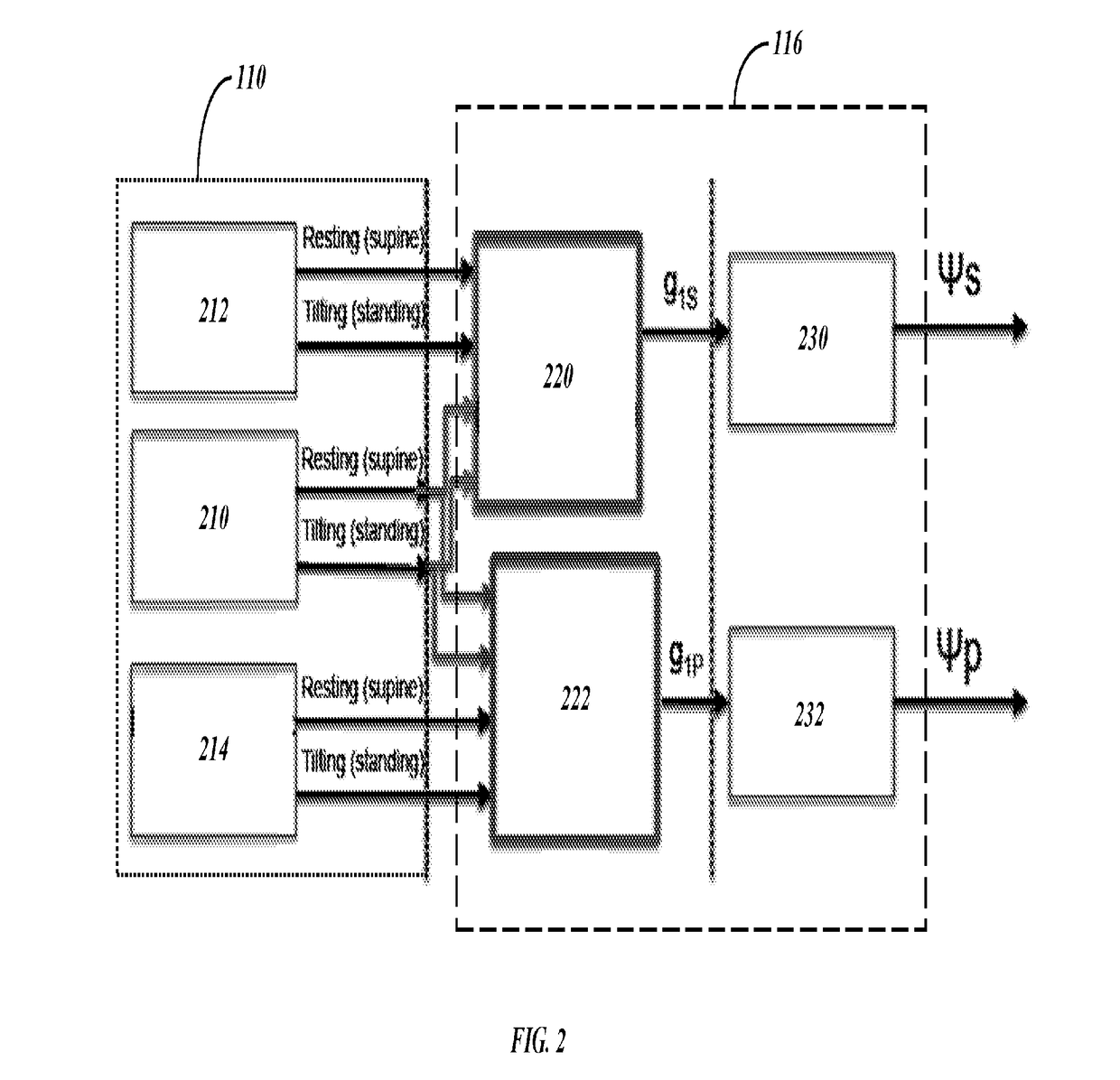
System and Method for Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Activity Monitoring by Heartbeat
A system and method for analyzing a subject health condition based on an input signal comprising subject heartbeat data recorded from the subject over a time period. Using the subject heartbeat data, a sympathetic activity index value in a sympathetic activity index (SAI) determined, where the SAI represents an influence, on a mean heart rate of the subject, of sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) of the subject.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
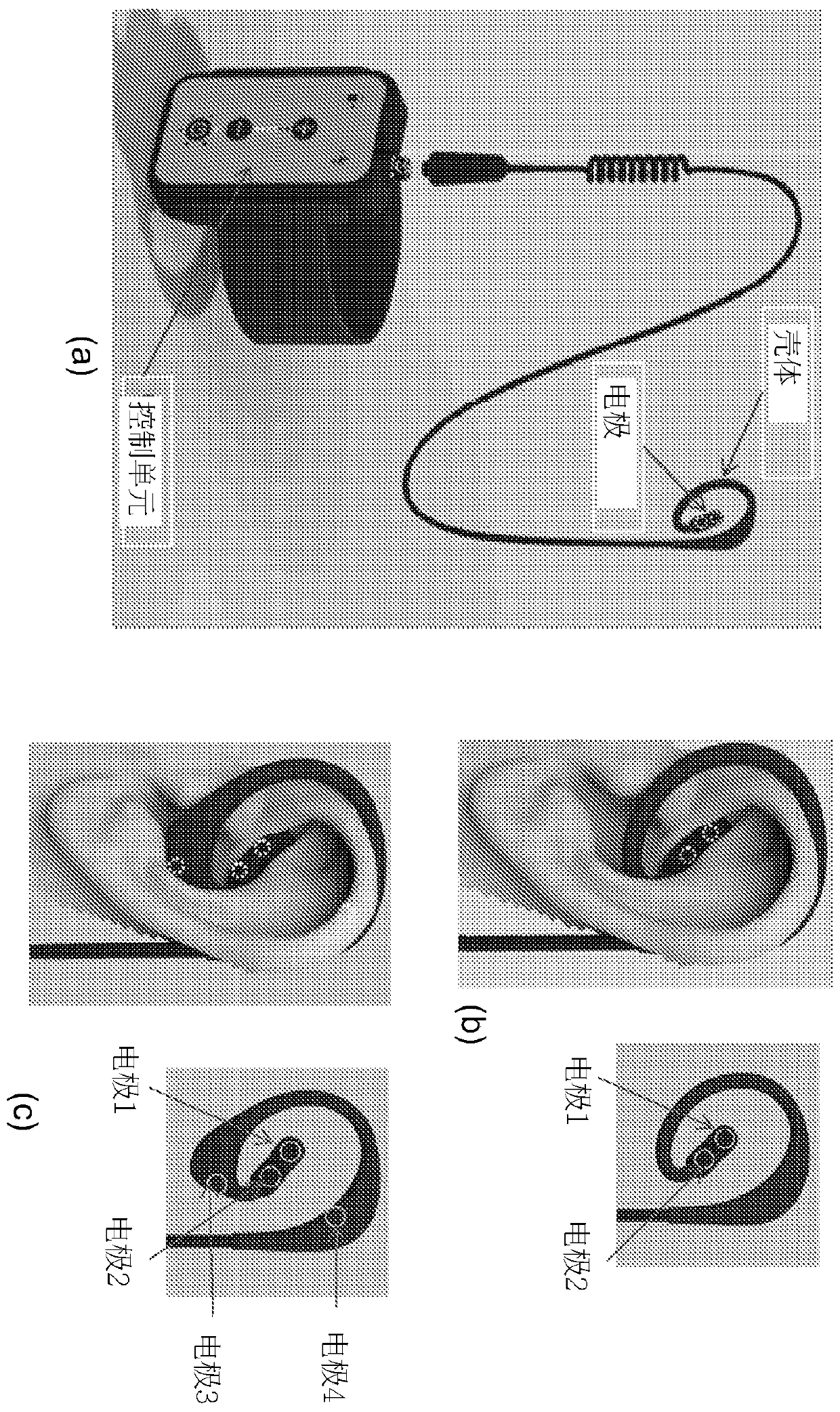
Peripheral nerve stimulation device for affecting parasympathetic and sympathetic activity to achieve therapeutic effects
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for stimulating peripheral nerves in a patient via electrical, optical, mechanical, or other stimulation, in order to change the balance between parasympathetic and sympathetic activity by selectively increasing or decreasing each of parasympathetic and sympathetic activity. In a particular application, the present disclosure relates to a device for transdermal stimulation of the vagus nerve (including the auricular branch) to selectively affect the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system to achieve the desired therapeutic effect ina human subject.
Owner:넥스트센스인크
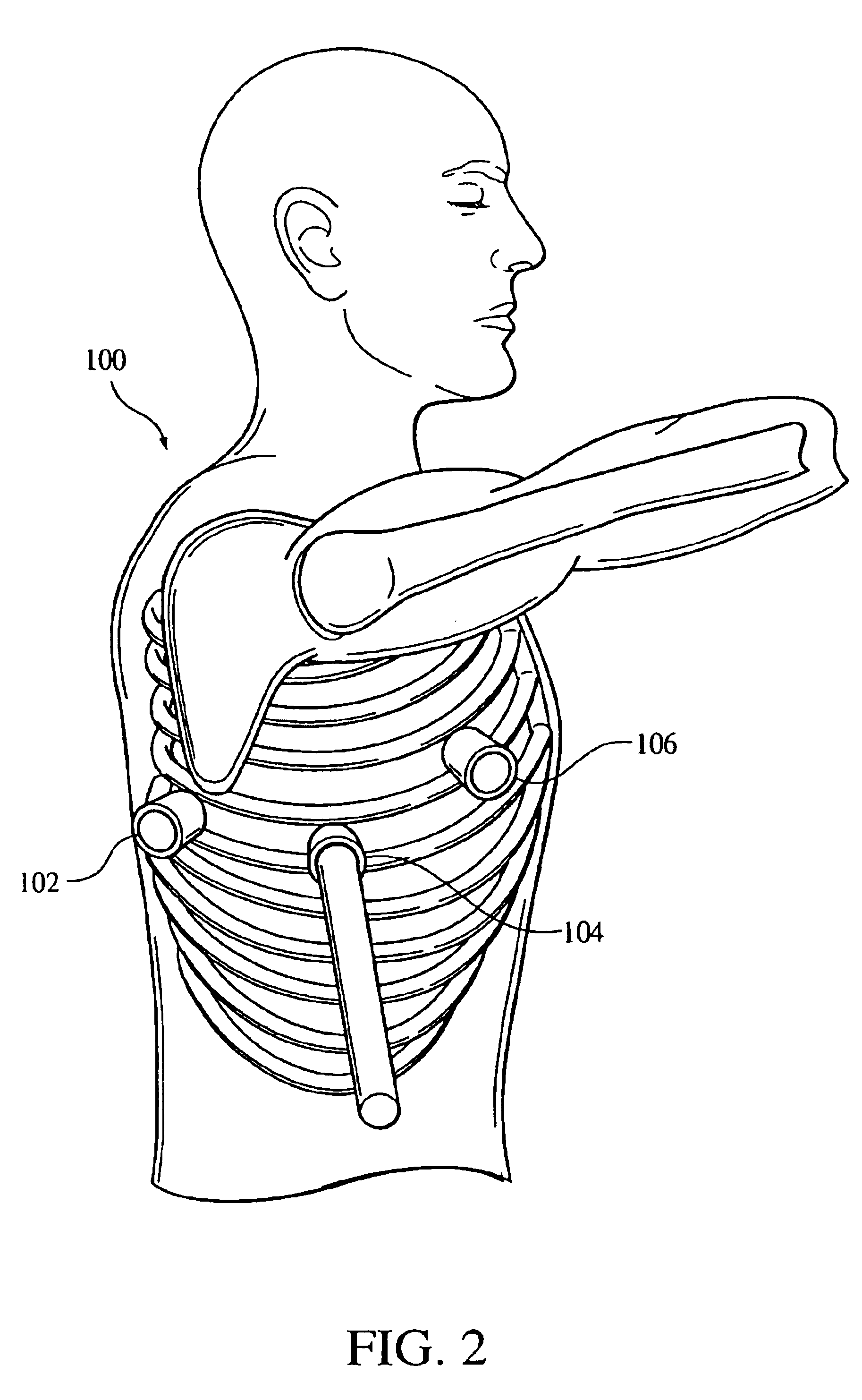
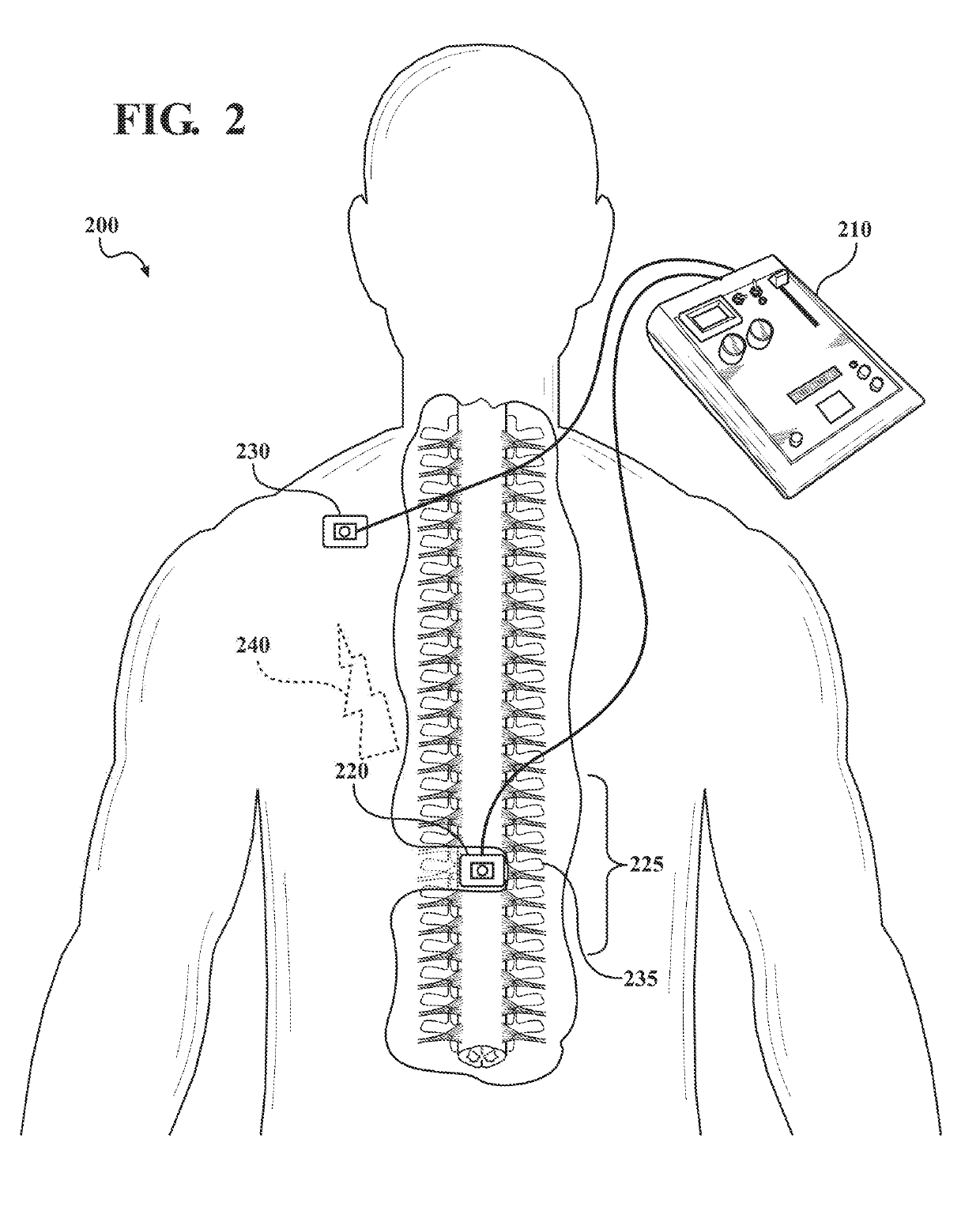
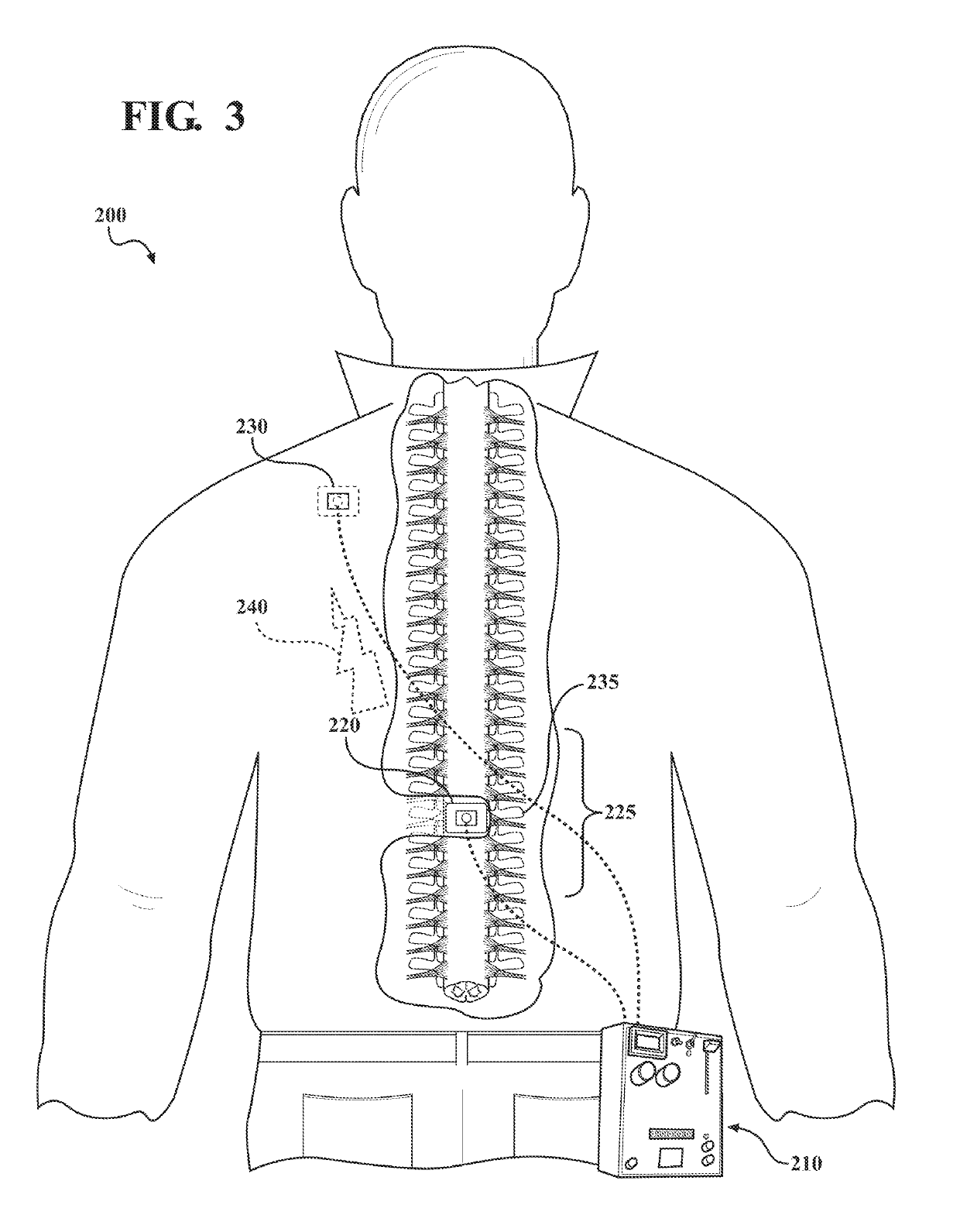
Implantable spinal cord electric simulation system for treating obesity and use method thereof
InactiveCN105498085AReduce emptyingLose weightSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSpinal cordElectrical impulse
The invention discloses an implantable spinal cord electric simulation system for treating obesity. The implantable spinal cord electrical simulation system for treating obesity includes an electrode implanted in a patient spinal cord epidural gap, a simulator for giving out an electric pulse and implanted in an abdomen or under haunch skin, and an extending wire for connecting the electrode and the simulator. The electrode is a bipolar electrode or a multi-polar electrode. The electrode implantable positions are fixed at T1 / T2 and T5 / T6. A heart rate is monitored in real time when the multi-polar electrode gives out the electric simulation. The current intensity is adjusted through the automatic feedback. Through the spinal cord electric simulation, the gastric emptying is delayed, thus the feeling of repletion is increased, and the intake is reduced. The sympathetic nerve activity is excited, and the basic metabolism and energy consumption are increased. The heart rate is monitored in real time. The electric simulation is adjusted timely through automatic feedback of the variation of the heart rate. The weights of fat patients are safely and effectively reduced.
Owner:宁波贝思转化医学研究中心有限公司
Methods and materials for treating elevated sympathetic nerve activity conditions
InactiveUS20170065327A1Relieve symptomsDisrupt pathophysiologySpinal electrodesPressure infusionDiseaseNephrosis
This document provides methods and materials involved in treating hypertension (e.g., age-associated hypertension, resistant hypertension, or chronic refractory hypertension), heart failure (e.g., congestive heart failure), or kidney disease (e.g., chronic kidney disease). For example, methods and materials involved in administering one or more sympatholytic agents to a patient to identify the patient as having an elevated baseline level of sympathetic nerve activity and treating the identified patient with a sympatholytic therapy to reduce the symptoms of hypertension (e.g., resistant hypertension), heart failure (e.g., congestive heart failure), or kidney disease (e.g., chronic kidney disease) are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
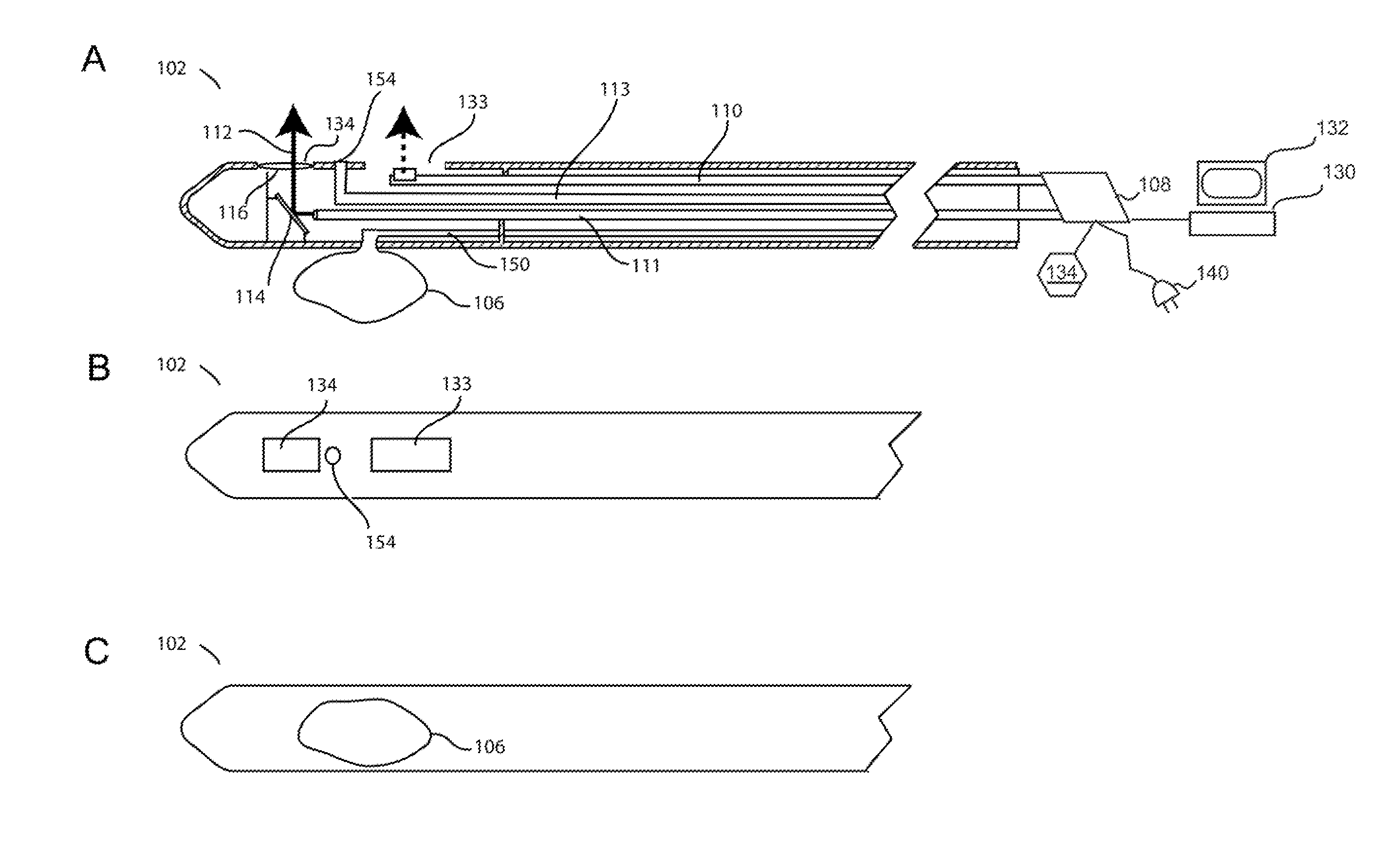
Medical device for sympathetic nerve ablation with printed components
A medical device for sympathetic nerve ablation may include an elongate shaft and an expandable member. A printed ablation electrode assembly may be disposed on an outer surface of the expandable member, the printed ablation electrode assembly including a positive electrical pathway and a ground electrical pathway printed directly on the outer surface of the expandable member. A temperature sensor may be printed directly on the outer surface of the expandable member. A method of manufacturing a medical device for sympathetic nerve ablation may include printing a conductive ink network directly on a surface of a polymeric balloon material in a flat configuration, printing at least one temperature sensor directly on the surface of the polymeric balloon material, forming the polymeric balloon material into an inflatable balloon, and attaching the inflatable balloon to an elongate catheter shaft.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method of Training a Living Body to Not React to Substances
InactiveUS20160129215A1Decreased sympathetic nerve activityPhysical therapies and activitiesElectrotherapyReflexPaired stimuli
A method of conditioning a living body of a patient to associate the unconditioned stimulus (US) of decreased sympathetic nerve activity SNA) with the conditioned stimulus (CS) of a representation of an offending agent to cease or reduce defensive reactions or symptoms. The US involves non-invasive, transcutaneous sensory stimulation of the sympathetic ganglia, which is paired with the CS of digital audio representations of offending substances to modify pathologically conditioned. reflexes of various systems involved. in a reaction. In addition, a patient's allergies or sensitivities are treated by using digital representations, preferably provided via a computer, to represent the actual substances in order to engage the multimodal functioning of the brain. Sensory stimulation is used in conjunction with the digital audio signals to condition the body to respond more appropriately to the substance.
Owner:NOWLIN DAWN
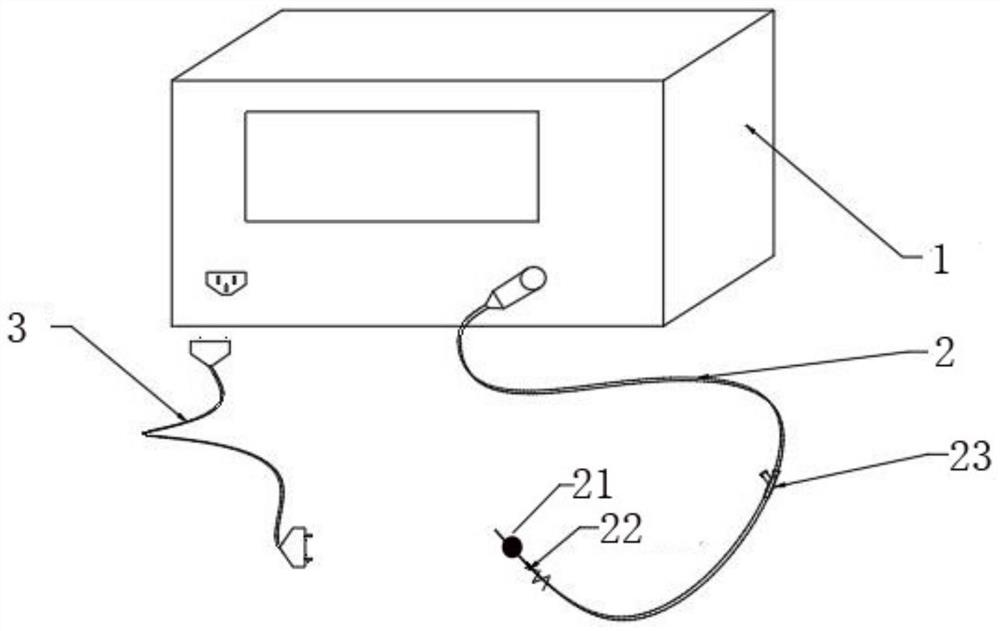
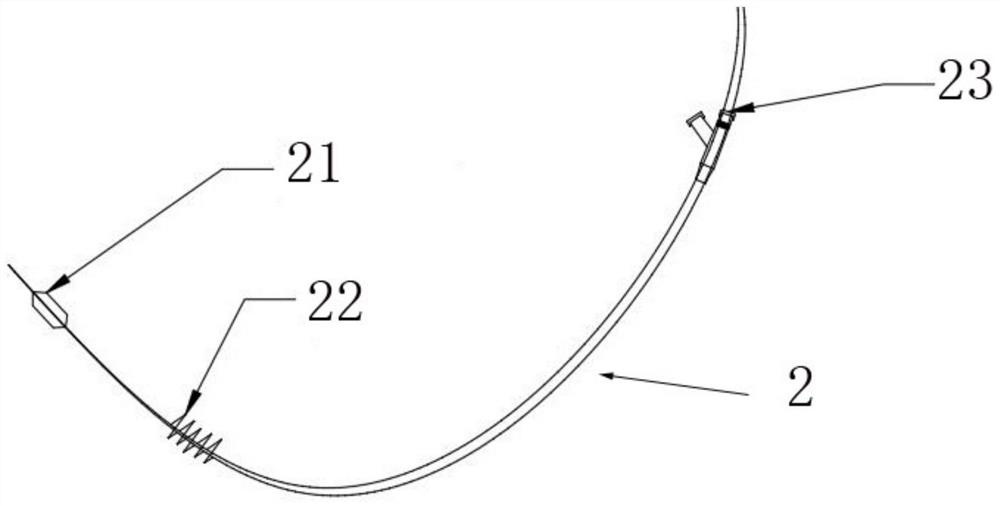
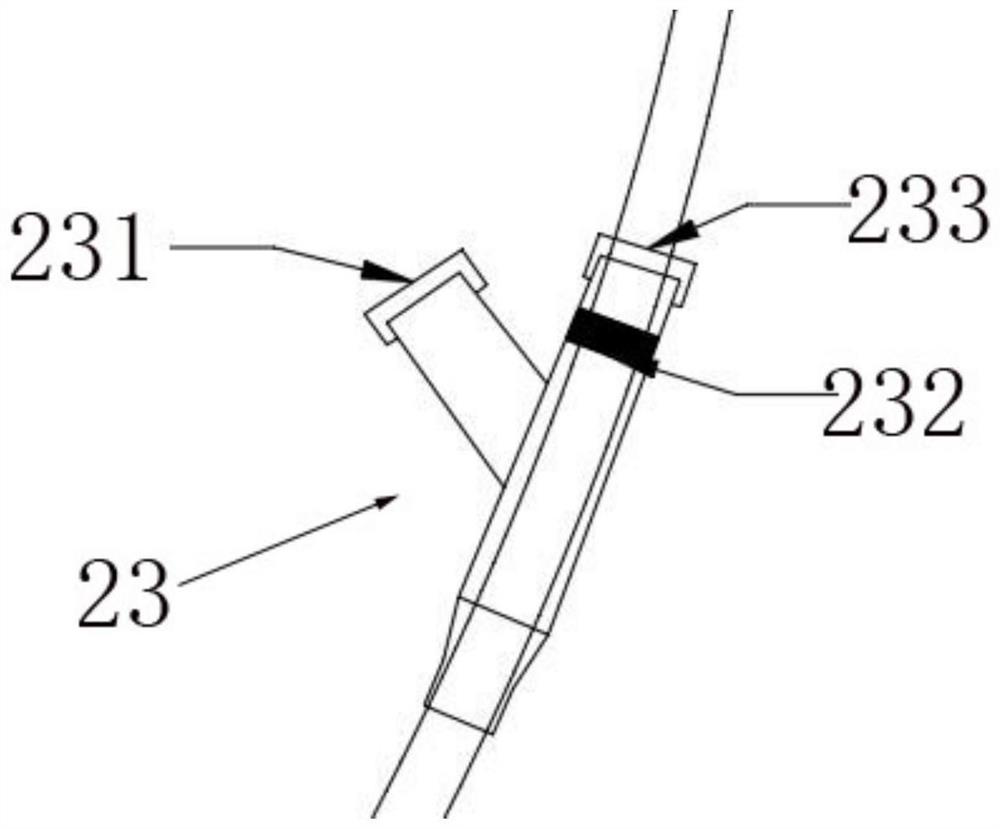
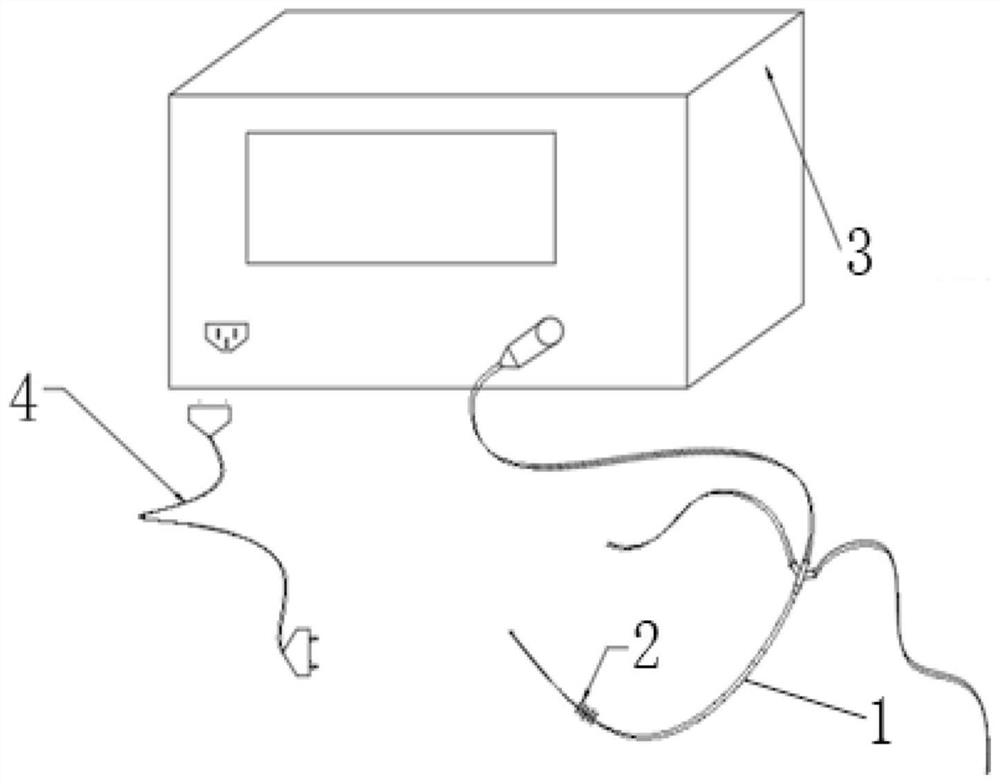
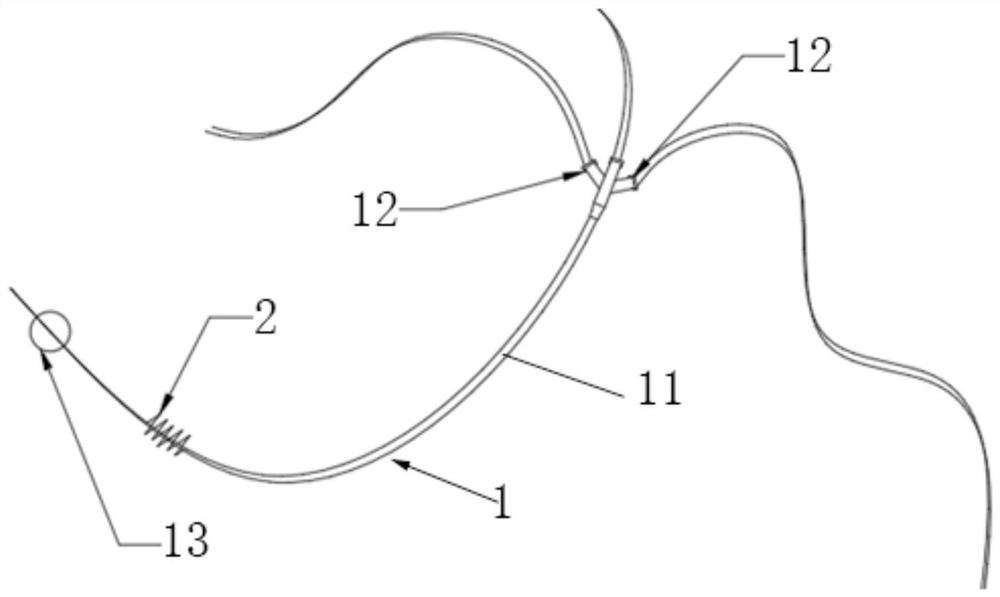
Renal artery sympathetic nerve activity measurement system
PendingCN113633282AEfficient detection processEasy to operateCatheterSensorsSympathetic nerveAnatomy
The invention provides a renal artery sympathetic nerve activity measurement system. The system comprises blood analysis and measurement equipment, an interventional catheter, a flexible expansion part which is arranged at the position close to the other end part of the interventional catheter, is communicated with the interventional catheter and is used for controllably stimulating the renal artery sympathetic nerve activity through expansion at the renal artery so as to promote secretion to form related to-be-tested blood, and various blood detection sensors which are arranged on the interventional catheter, are close to the flexible expansion part and are used for collecting to-be-detected blood, converting the to-be-detected blood into various corresponding signals and feeding the various corresponding signals back to the blood analysis and measurement equipment, wherein various signals of the blood to be measured are analyzed through the blood analysis and measurement equipment to form corresponding physicochemical indexes reflecting renal artery sympathetic nerve activity. The technical scheme has the beneficial effects that the whole measurement system is high in controllability, simple in testing condition as long as the flexible expansion part is expanded to the wall of the renal arterial blood vessel. Furthermore, the activity of renal artery sympathetic nerves can be accurately determined based on specific physicochemical indexes.
Owner:SHANGHAI ANTONG MEDICAL TECH
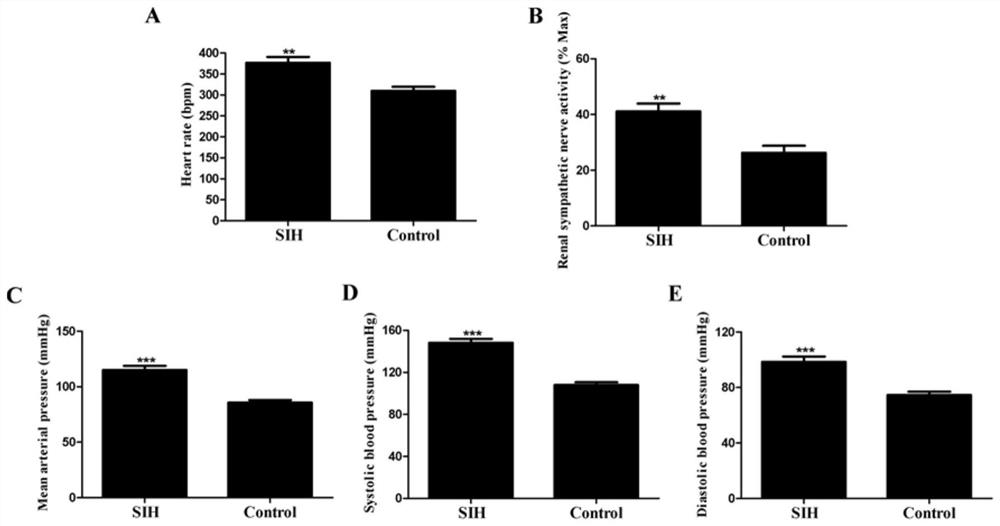
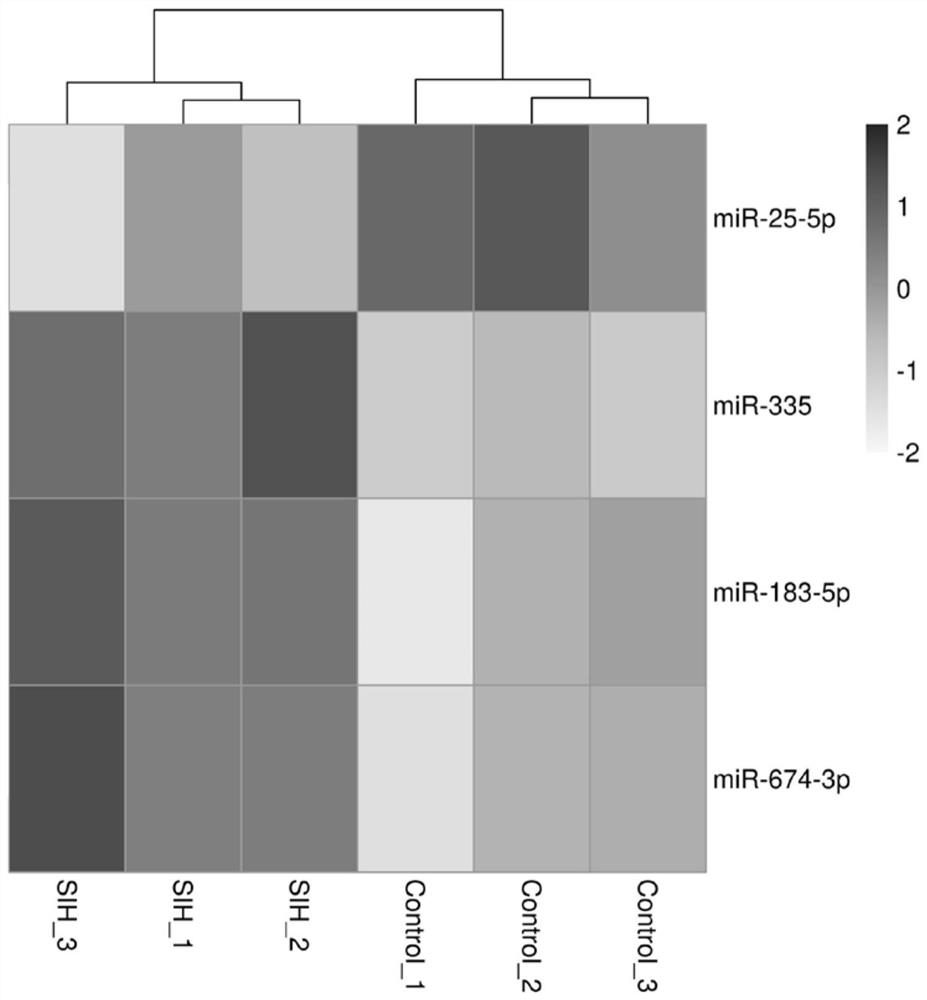
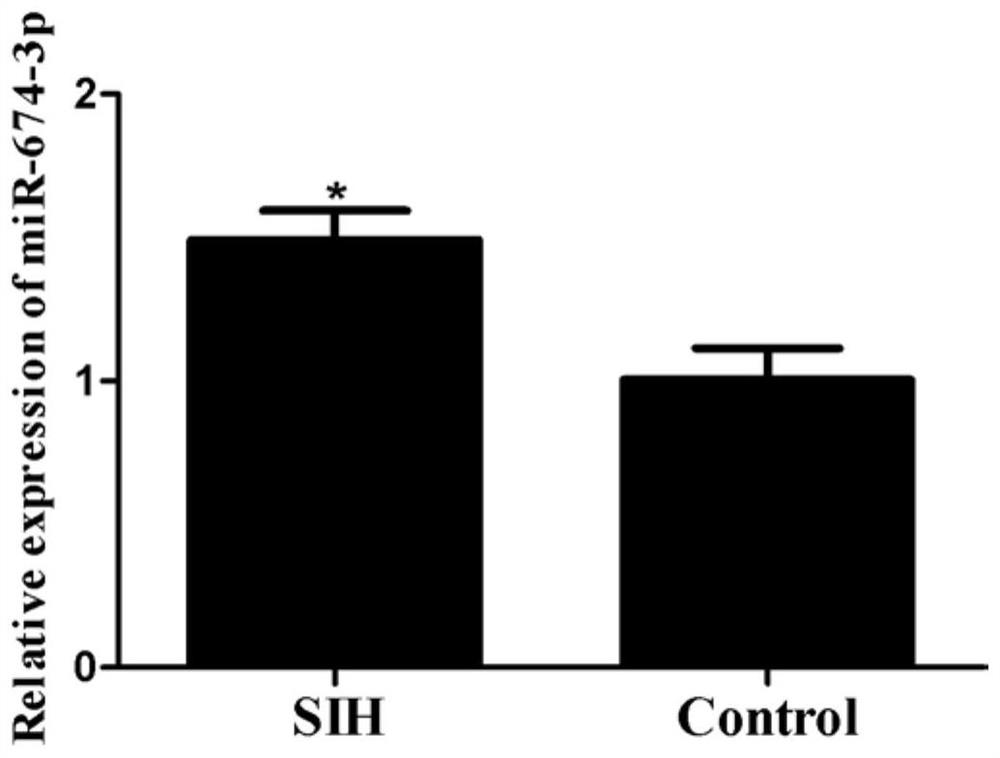
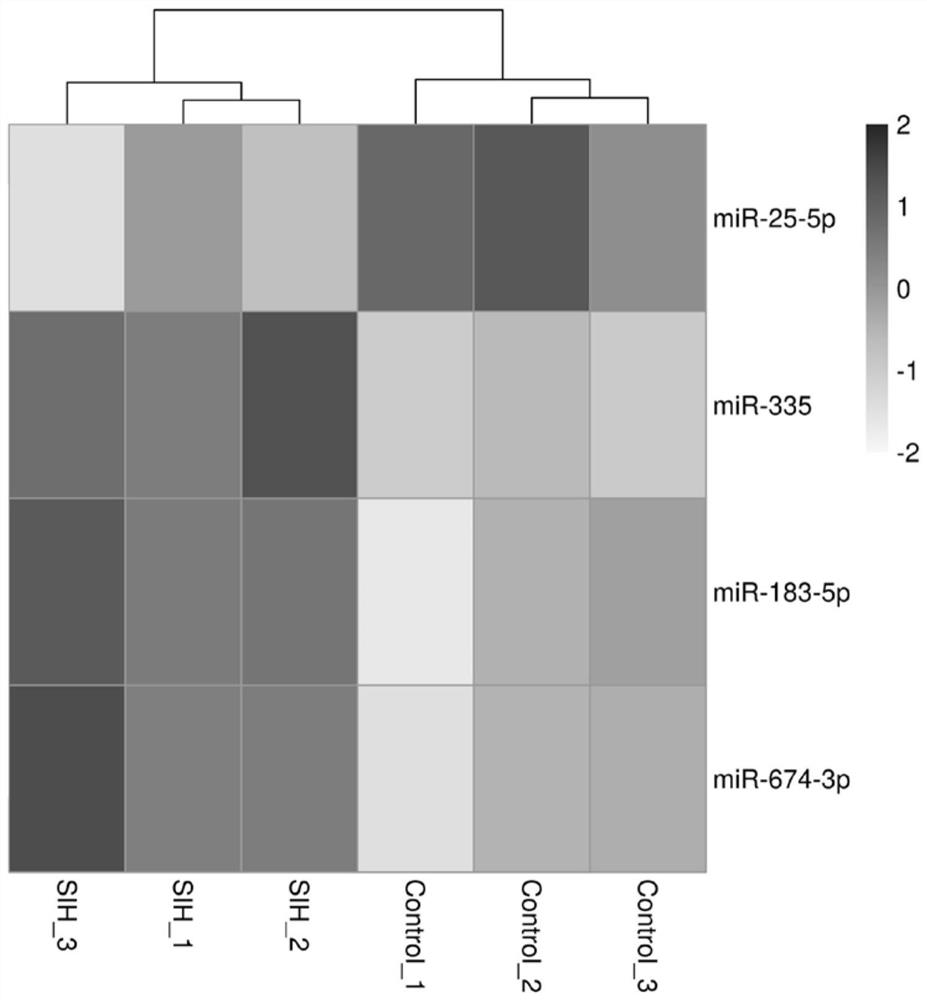
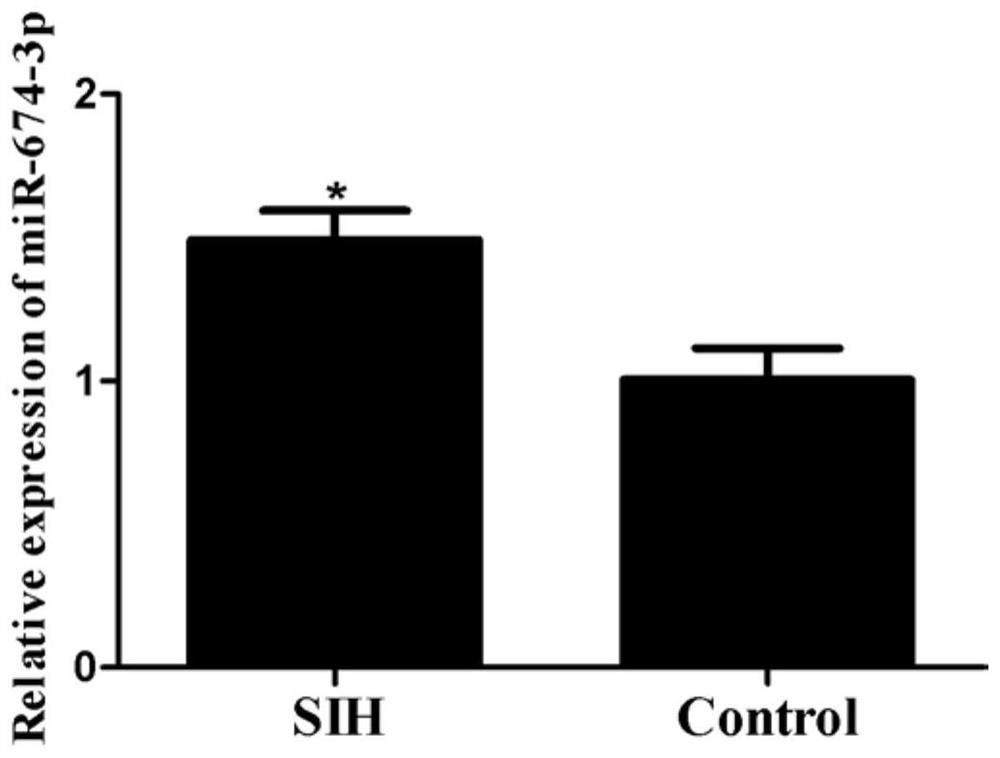
Application of miR-674-3p in preparation of drugs for preventing or treating stress hypertension
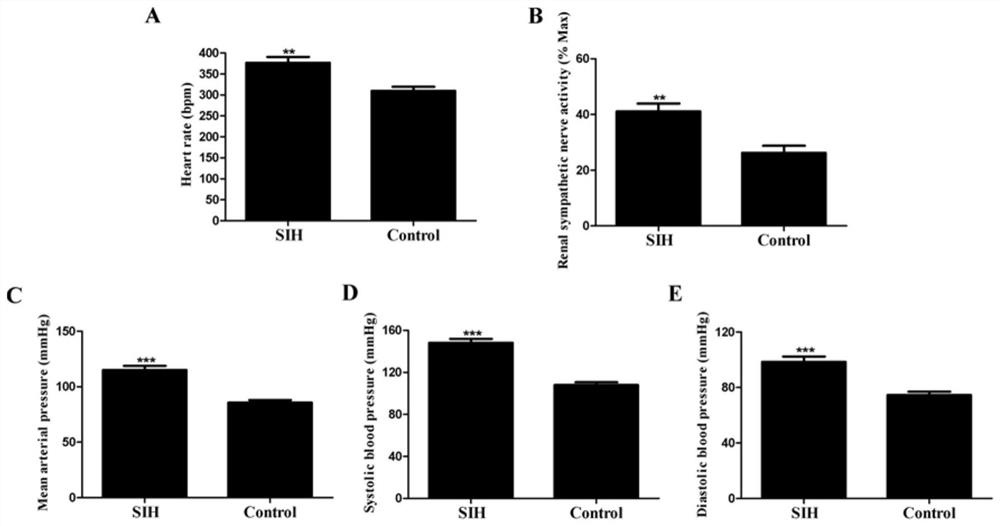
ActiveCN113384595ASlow down heart rateDecreased renal sympathetic nerve activityOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderHypertension medicationsSympathetic nerve
The invention discloses an application of miR-674-3p in preparation of drugs for preventing or treating stress hypertension. The application of the miR-674-3p in preparation of the drugs for preventing or treating the stress hypertension reveals that the heart rate, renal sympathetic nerve activity, mean arterial pressure, systolic pressure and diastolic pressure of a rat with the stress hypertension can be effectively reduced by inhibiting the expression of the miR-674-3p. The miR-674-3p can be used as a new molecular target for treating the stress hypertension and is used for guiding the screening, research and development of related drugs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Interventional renal artery sympathetic nerve activity detection system
The invention provides an interventional renal artery sympathetic nerve activity detection system. The system comprises an interventional catheter, a various-blood detection sensor and blood analysis and detection equipment, an interventional end structure of the interventional catheter is communicated with a catheter, and chemical substances are conveyed to a preset position through the interventional end structure, wherein renal artery sympathetic nerves sense the concentration of the input chemical substances and then feed back through a RAAS system so as to secrete and form related blood to be detected; the various-blood detection sensor is arranged on the interventional catheter and close to the interventional end structure of the interventional catheter, and the various-blood detection sensor is used for detecting the blood to be detected to form detection signals; and the blood analysis and detection equipment is connected with the blood detection sensor and is used for receiving the detection signals and analyzing various signals of the blood to be detected to form corresponding physicochemical indexes reflecting the activity of the renal artery sympathetic nerves. The technical scheme has the beneficial effects that the activity of the renal artery sympathetic nerves can be accurately determined through the cooperative operation of the whole set of system.
Owner:SHANGHAI ANTONG MEDICAL TECH
Application of radiofrequency catheter ablation system to treatment of essential hypertension
ActiveUS20180125572A1Blood pressure level be reduceReduce activitySurgical needlesCatheterNervous systemDisease
An application of a radiofrequency catheter ablation system to treatment of essential hypertension. The treatment process is under ultrasonic guidance, an electrode needle is made to penetrate into target tissue of a patient, electrification is conducted to start ablation, the needle is withdrawn or made to penetrate into the other side of the target tissue for target ablation after reaching ablation temperature and duration time, and overall ablation treatment is completed. The system can treat a secondary center for regulating the activity of a whole-body sympathetic system to reduce its activity, thus, the blood pressure level of a patient can be reduced, and fewer kinds and smaller dosage of antihypertensive drugs taken or ceased altogether. By treating the secondary center, the activity of the whole-body sympathetic system, insulin resistance and whole-body fibrosis is reduced, and other diseases characterized in activity abnormity of the sympathetic system might be treated too.
Owner:NANJING GUANGCI MEDICAL TECH
Transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation for treatment of psychiatric disorders
ActiveUS20190134386A1Decreasing sympathetic activityReduced activityExternal electrodesArtificial respirationSympathetic activityVertebra
Methods of treating a psychiatric disorder in a subject are provided which include placing at least one anode on an area of the subject's back over the dorsal spinal cord at the level of one or more of: thoracic vertebra 7 (T7), 8 (T8), 9 (T9), 10 (T10), 11 (T11), and 12 (T12) and lumbar vertebra 1 (L1); placing at least one cathode on an area of the subject's back which is generally rostral with reference to the anode; connecting the anode and the cathode to at least one source of direct and / or alternating electrical current; delivering direct current to the anode for a treatment period of time, the treatment period of time defining a tsDCS and / or tsACS treatment session, thereby modulating spinal input to the brain of the subject, decreasing sympathetic activity and reducing one or more symptoms and / or comorbidities associated with the psychiatric disorder.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Application of radiofrequency catheter ablation system to treatment of essential hypertension
An application of a radiofrequency catheter ablation system to treatment of essential hypertension. The treatment process is under ultrasonic guidance, an electrode needle is made to penetrate into target tissue of a patient, electrification is conducted to start ablation, the needle is withdrawn or made to penetrate into the other side of the target tissue for target ablation after reaching ablation temperature and duration time, and overall ablation treatment is completed. The system can treat a secondary center for regulating the activity of a whole-body sympathetic system to reduce its activity, thus, the blood pressure level of a patient can be reduced, and fewer kinds and smaller dosage of antihypertensive drugs taken or ceased altogether. By treating the secondary center, the activity of the whole-body sympathetic system, insulin resistance and whole-body fibrosis is reduced, and other diseases characterized in activity abnormity of the sympathetic system might be treated too.
Owner:NANJING GUANGCI MEDICAL TECH
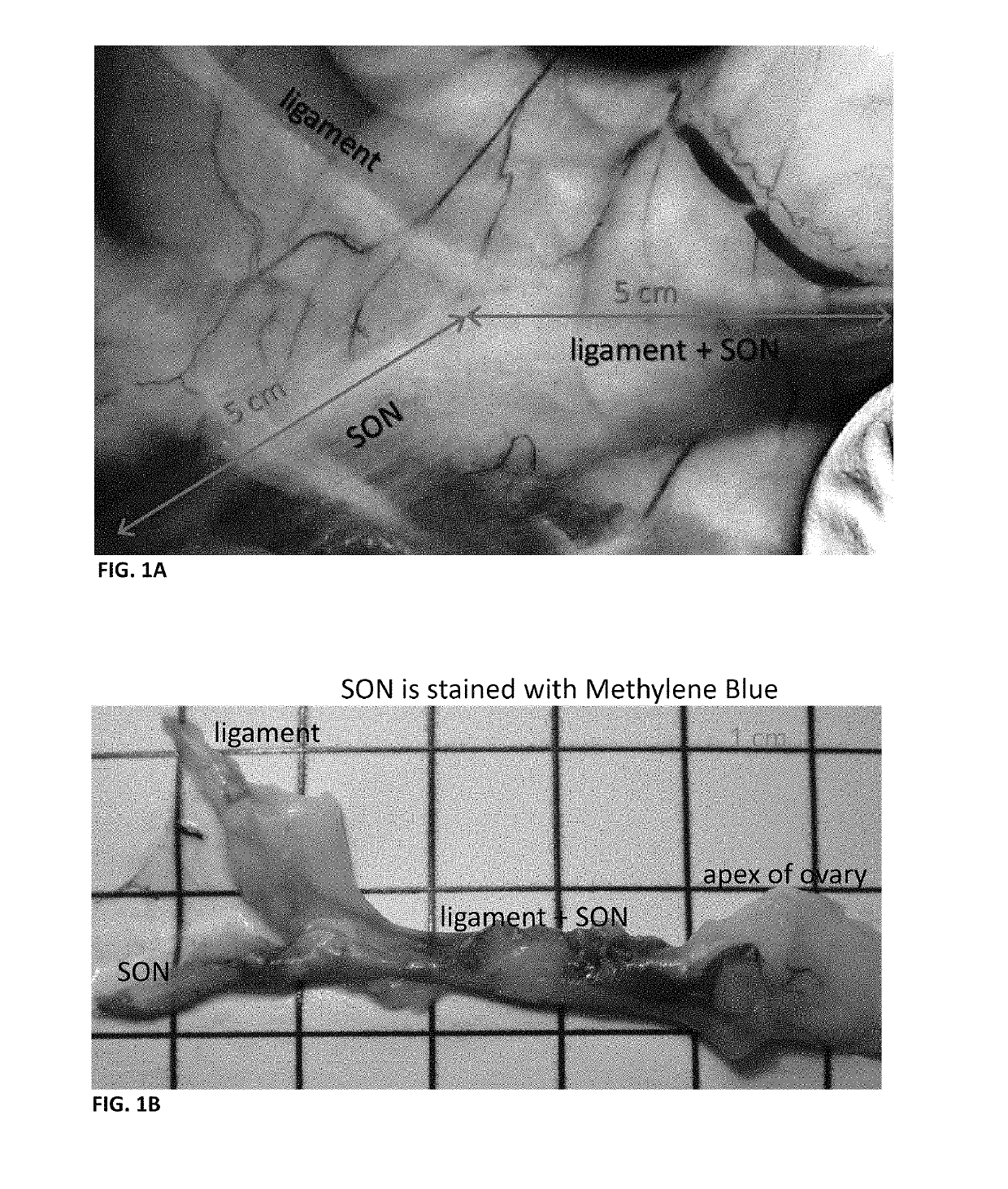
Neuromodulation device
ActiveUS10406362B2Effective treatmentFormation of cysts is amelioratedSpinal electrodesUltrasound therapyMedicineControl signal
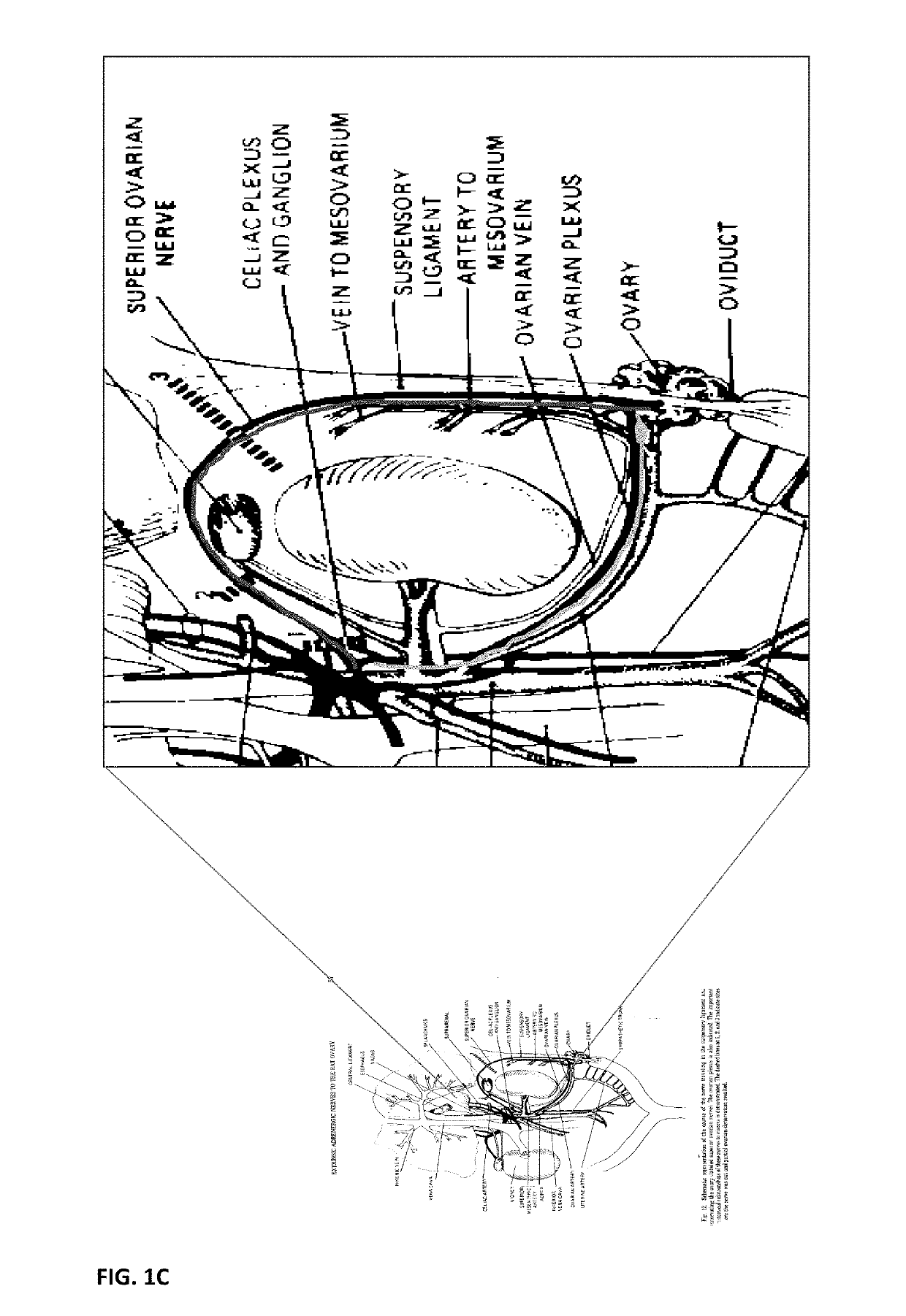
Methods for treating polycystic ovarian syndrome with a neuromodulation device that modulates sympathetic neural activity are described herein. The neuromodulation device is an apparatus for the treatment of polycystic ovarian syndrome. In one aspect, the apparatus decreases the neural activity of a postganglionic ovary-innervating sympathetic nerve. Modulation in neural activity may be achieved using an apparatus comprising one or more stimulators each configured to apply a signal to a postganglionic ovary-innervating sympathetic nerve of the patient, a controller coupled to the one or more stimulators, the controller controlling the signal to be applied by each of the one or more stimulators, such that the signal decreases the neural activity of the nerve to produce a physiological and / or biochemical response in the patient, wherein the physiological and / or biochemical response comprises an improvement in one or more symptoms of polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHILE +2
Application of a kind of mir-674-3p in the preparation of drugs for preventing or treating stress-induced hypertension
ActiveCN113384595BSlow down heart rateDecreased renal sympathetic nerve activityOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderHypertension medicationsSympathetic nerve
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
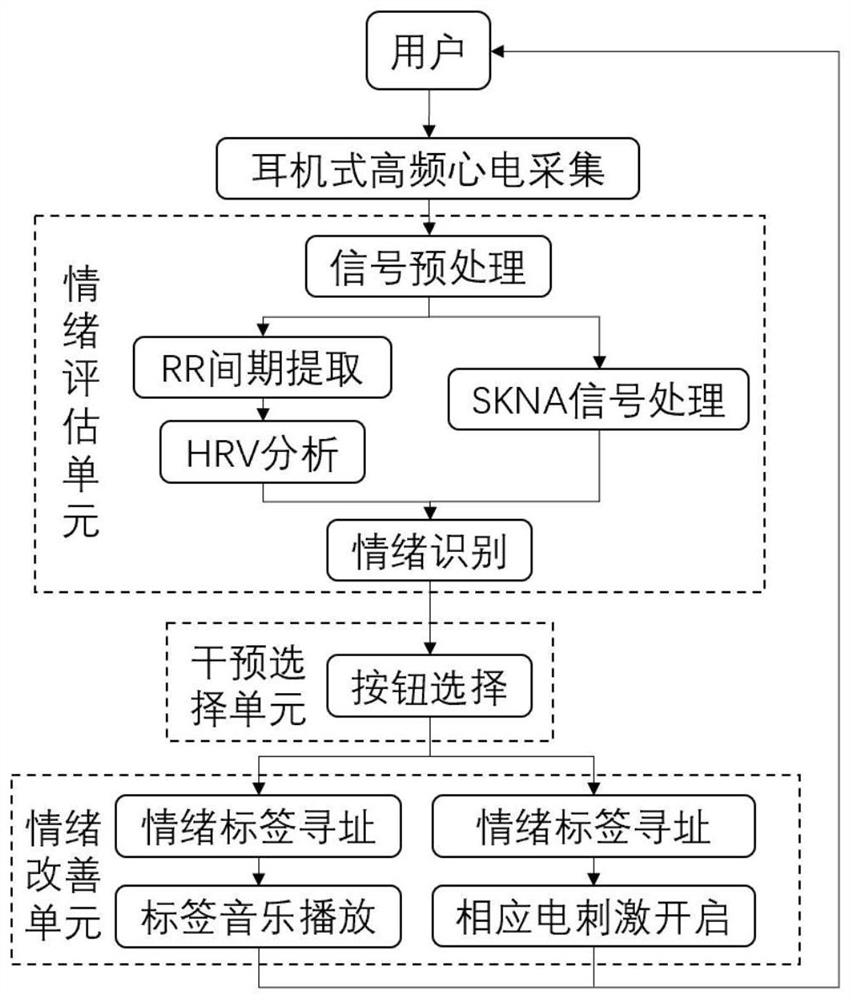
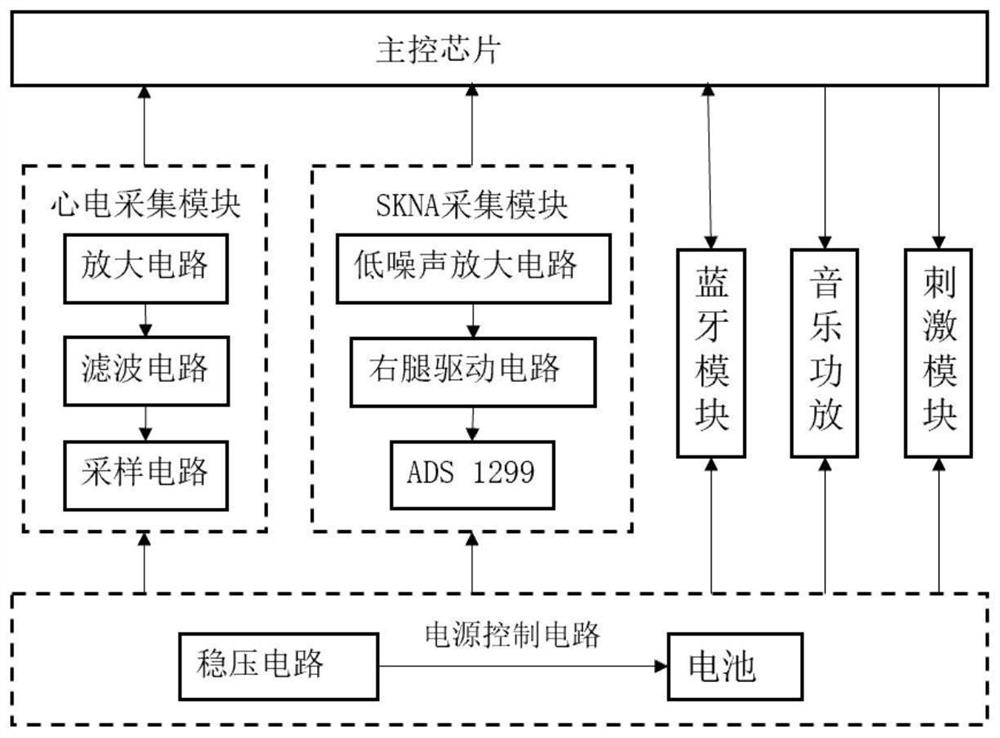
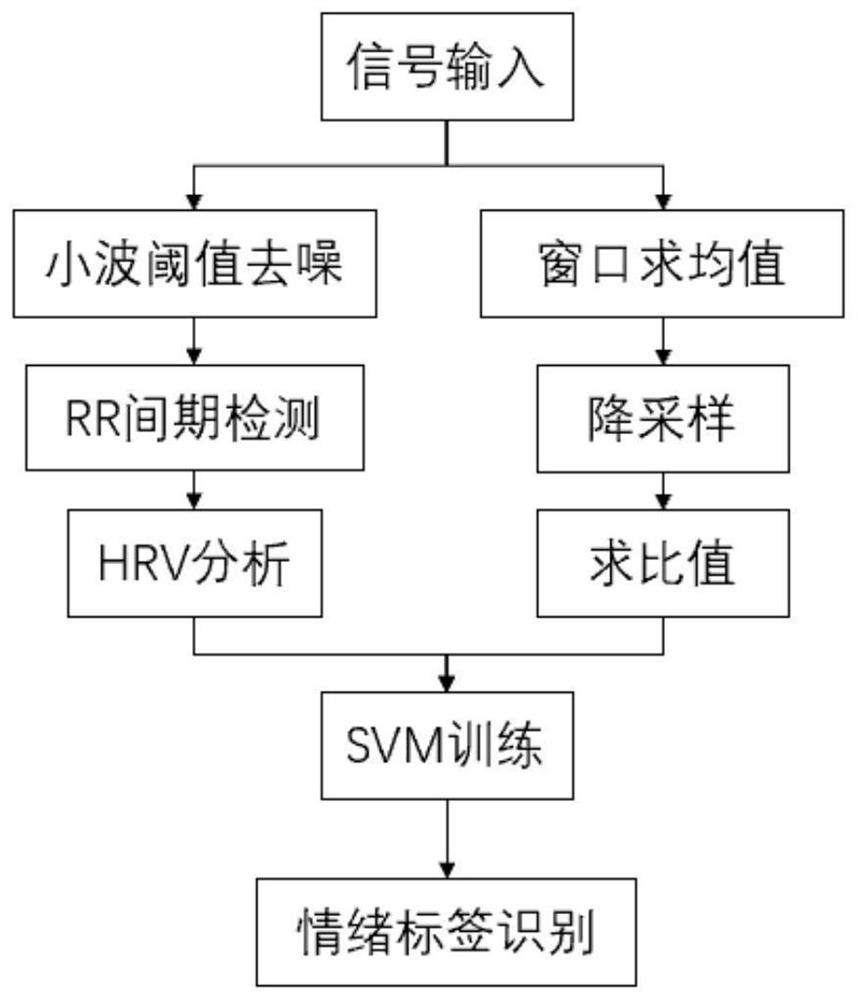
Earphone type emotional pressure adjusting device based on high-frequency electrocardio
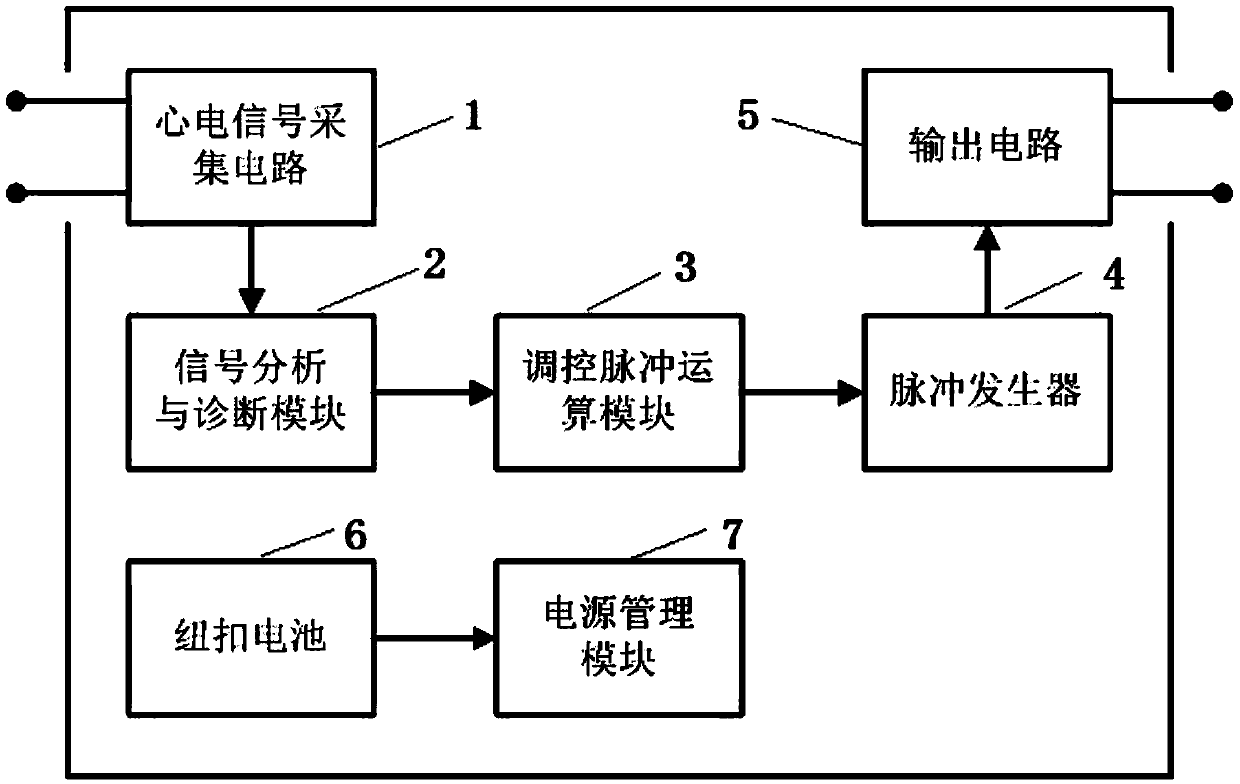
PendingCN114053550ADetermine emotional stateEmotional state real-time managementInput/output for user-computer interactionElectrotherapyEcg signalHeadphones
The invention discloses an earphone type emotional pressure adjusting device based on high-frequency electrocardio. An earphone type high-frequency electrocardio signal acquisition unit acquires an electrocardio signal and a skin sympathetic nerve activity signal of a user, and pre-processes the acquired signals. An emotion evaluation unit extracts the time domain, the frequency domain and the nonlinear indexes of the electrocardio signal of the user and the characteristics of the skin sympathetic nerve activity signal to obtain an emotional state label of the user. An emotion improvement unit is divided into two modules, wherein a music feedback module selects music of a corresponding label based on a Hevner model, an electrical stimulation module performs corresponding noninvasive electrical stimulation on the ears of the user for emotion adjustment. A selection unit performs emotion intervention by music or transcutaneous electrical stimulation or both of music and transcutaneous electrical stimulation. According to the invention, music corresponding to emotional alleviation can be played autonomously, different electrical stimulation modes are adopted to improve the emotion, and states such as emotional excitation and excessive pressure of a patient can be effectively alleviated.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
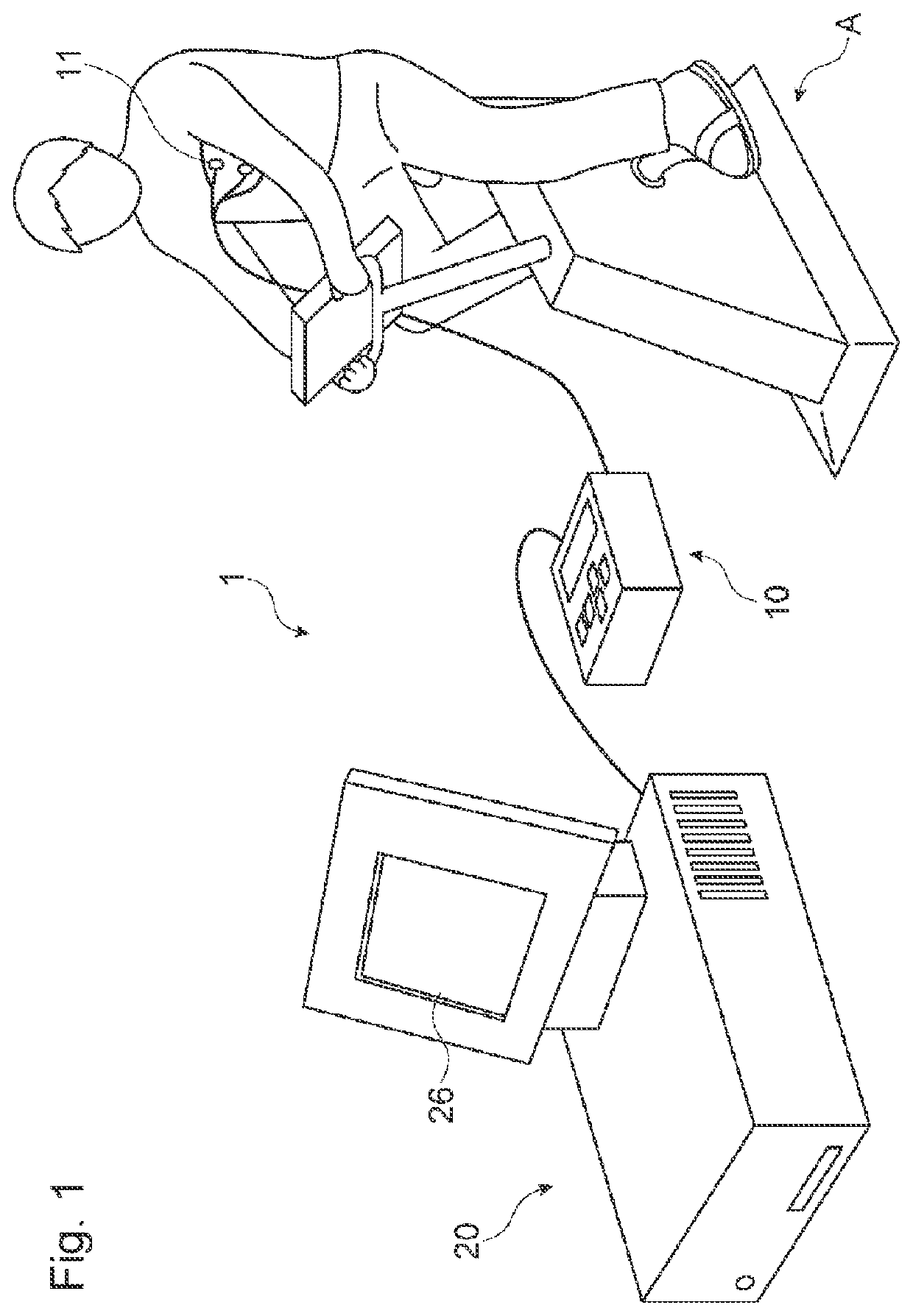
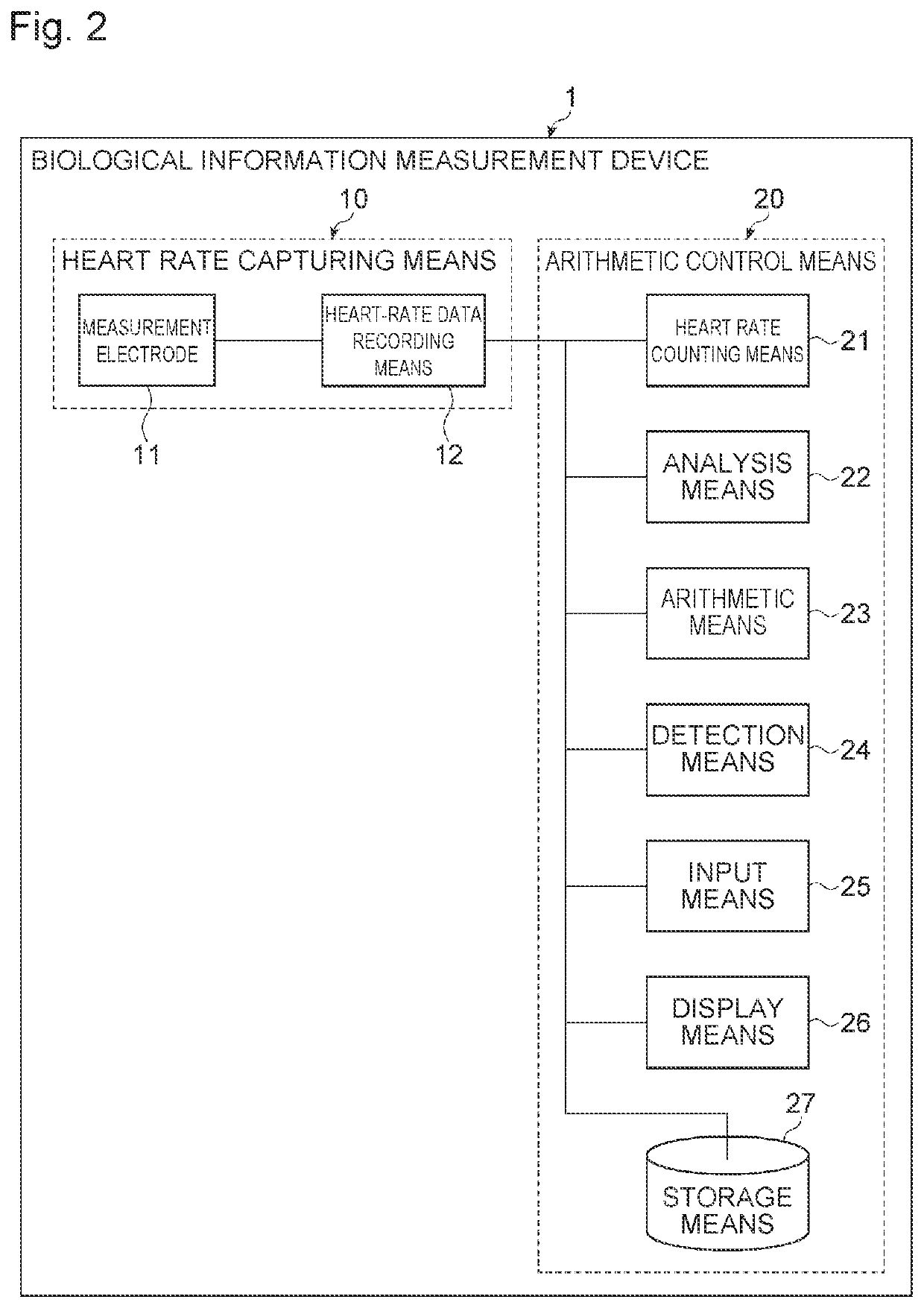
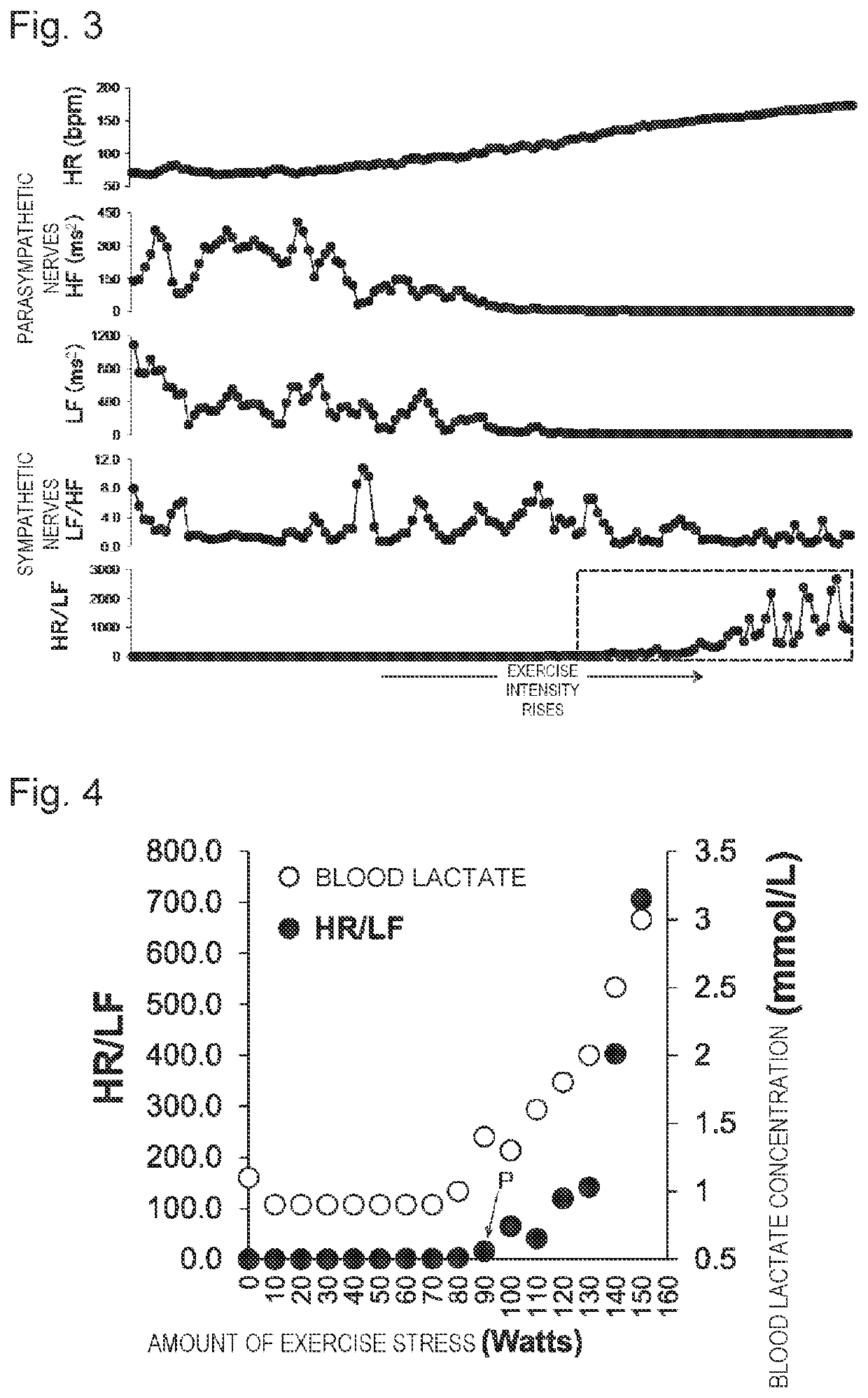
Biological information measurement device, biological information measurement method, and biological information measurement program
PendingUS20220175288A1Improve detection accuracyEasy to practiceSensorsErgometrySympathetic nerve activityExercise intensity
A biological information measurement device which is capable of improving accuracy of detection of optimal exercise intensity, a biological information measurement method, and a biological information measurement program are provided. At the biological information measurement device, heart rate counting means measures an HR value indicating a heart rate on the basis of heart-rate data obtained by capturing heartbeats when a subject to be measured exercises, and analysis means performs power spectrum analysis on a heart rate variability frequency of the heart-rate data to calculate an LF value which is an integral value of low frequency components. Detection means then detects an HR / LF value by dividing the HR value with respect to exercise intensity of the subject to be measured by an LF value. Thus, by the biological information measurement device obtaining the HR / LF value as a new index indicating sympathetic nerve activity, it is possible to obtain biological information important for health management.
Owner:FUKUOKA UNIV
Transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation for treatment of psychiatric disorders
ActiveUS10857356B2Reduced activityMany symptomExternal electrodesArtificial respirationDC - Direct currentLumbar
Methods of treating a psychiatric disorder in a subject are provided which include placing at least one anode on an area of the subject's back over the dorsal spinal cord at the level of one or more of: thoracic vertebra 7 (T7), 8 (T8), 9 (T9), 10 (T10), 11 (T11), and 12 (T12) and lumbar vertebra 1 (L1); placing at least one cathode on an area of the subject's back which is generally rostral with reference to the anode; connecting the anode and the cathode to at least one source of direct and / or alternating electrical current; delivering direct current to the anode for a treatment period of time, the treatment period of time defining a tsDCS and / or tsACS treatment session, thereby modulating spinal input to the brain of the subject, decreasing sympathetic activity and reducing one or more symptoms and / or comorbidities associated with the psychiatric disorder.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
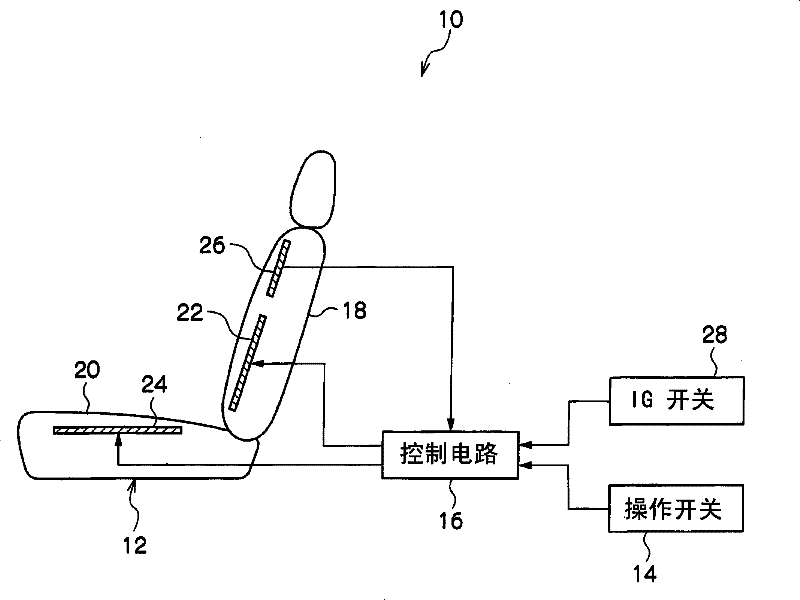
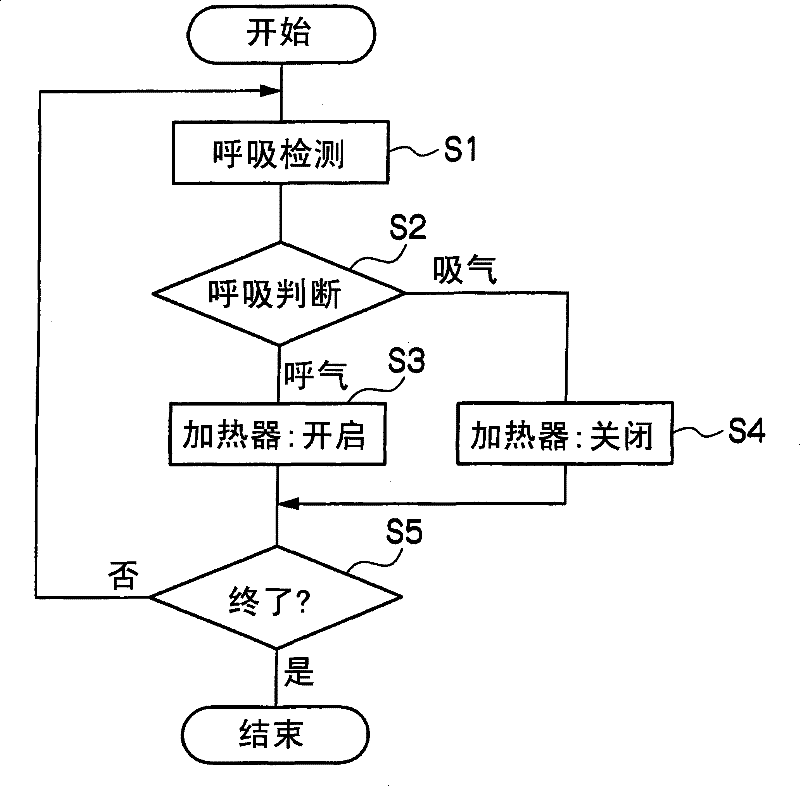
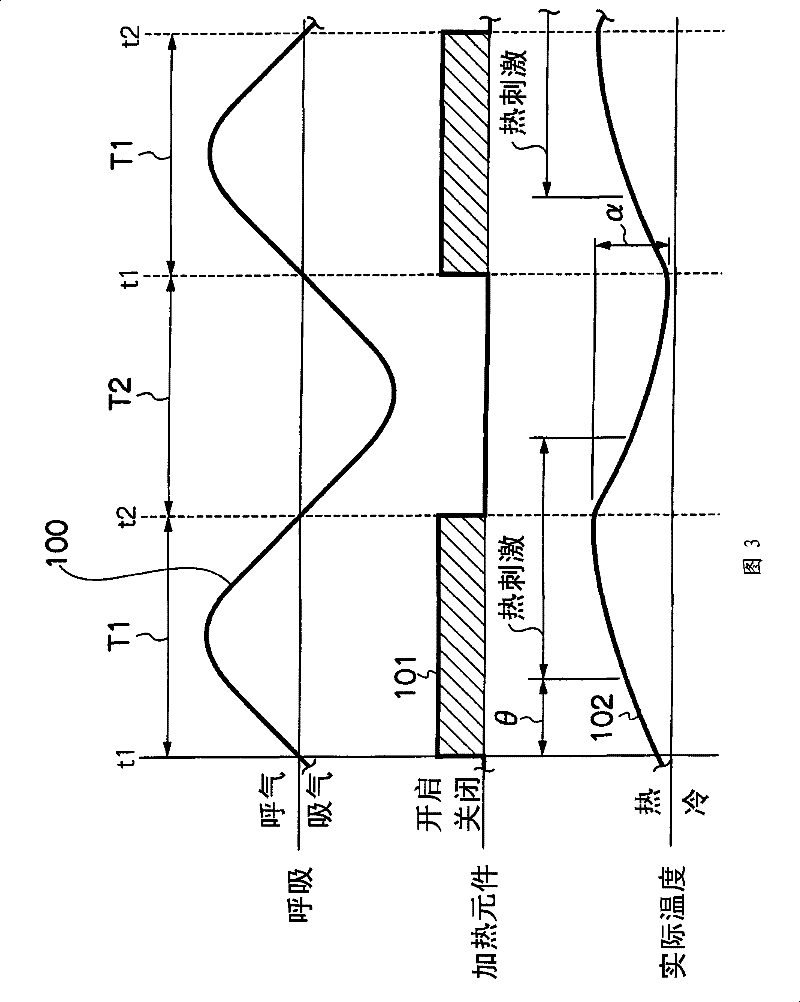
Thermal stimulation apparatus for vehicles
InactiveCN101378802BReduce fatigueEnhance physical fitnessVehicle seatsMedical devicesThermal stimulationPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
It is intended to provide a thermal stimulation apparatus for vehicles which can exert effects of, for example, reducing fatigue and improving physical conditions on a crew member in a vehicle. In a thermal stimulation apparatus for vehicles (10), when the biorhythm (for example, respiration rhythm) with periodical changes of a crewmember is detected by a piezoelectric sensor (26), heater elements (22, 24) are switched on by a control circuit (16) based on the detection data and thus thermal stimuli synchronizing the respiration rhythm of the crew member are provided to the crew member by switching on / off the heater element (22, 24). As a result, the autonomic nerve (parasympathetic nerve) activity of the crew member can be enhanced. Therefore, it becomes possible to exert effects of, forexample, reducing fatigue and improving physical conditions on a crew member in a vehicle.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com