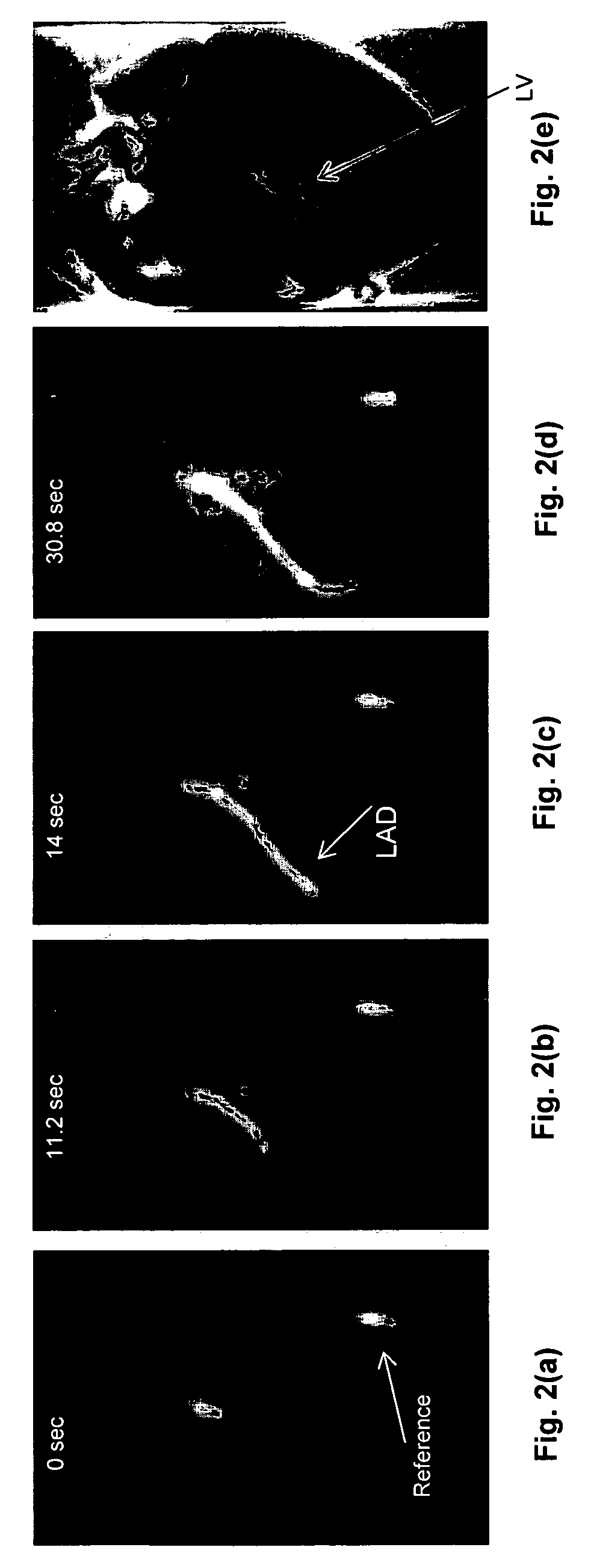
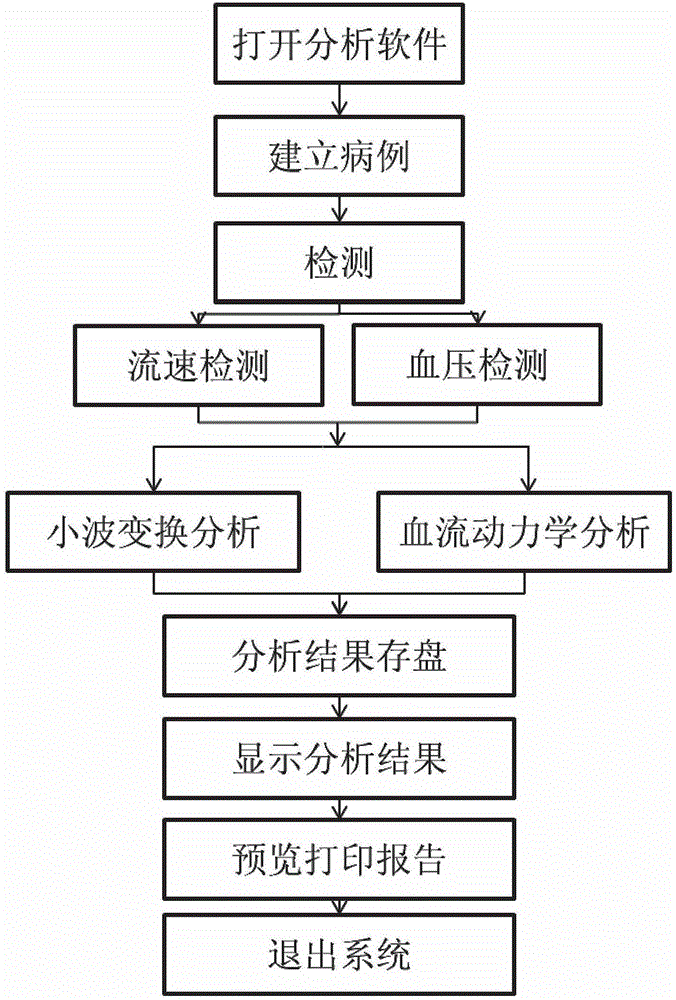
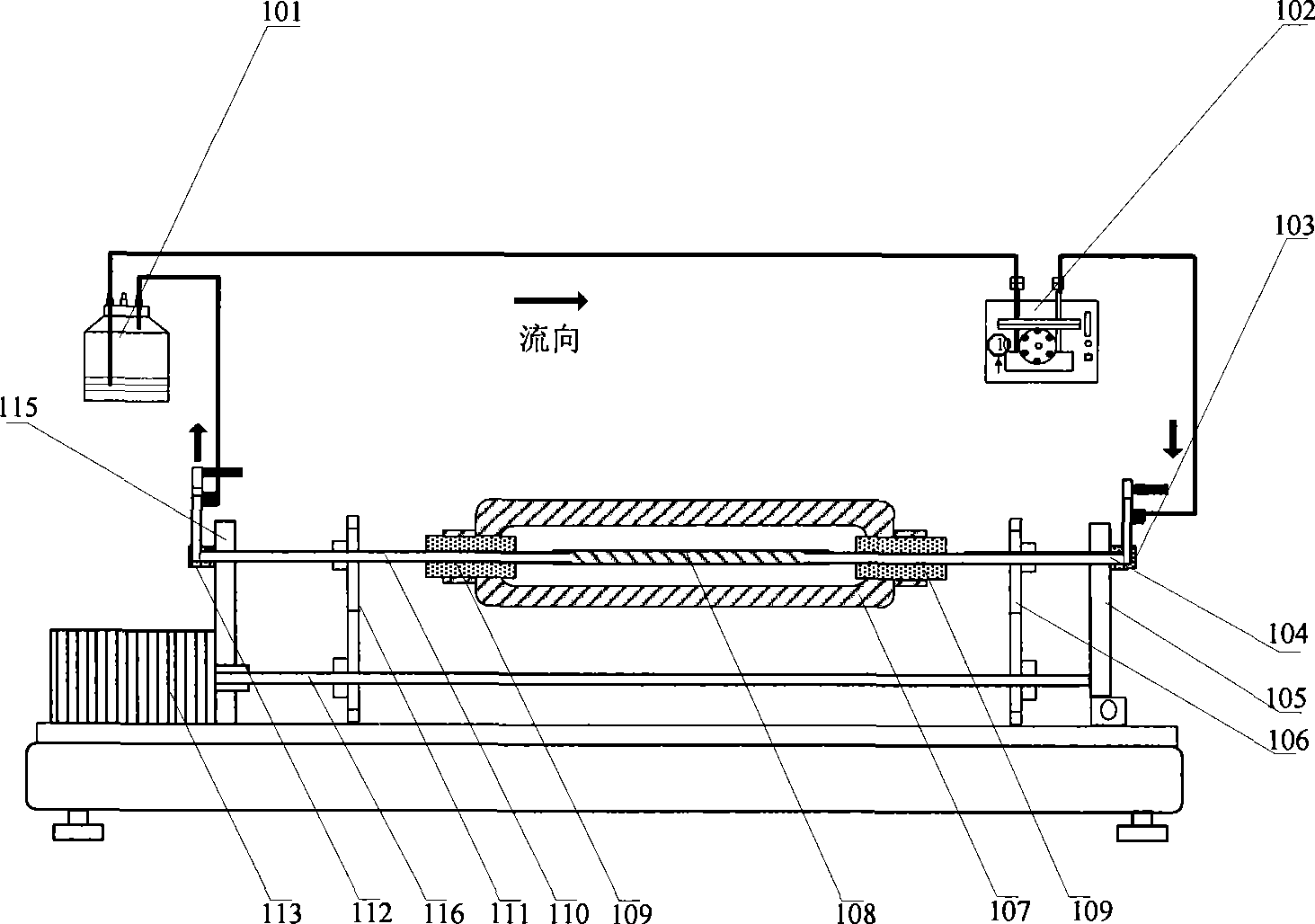
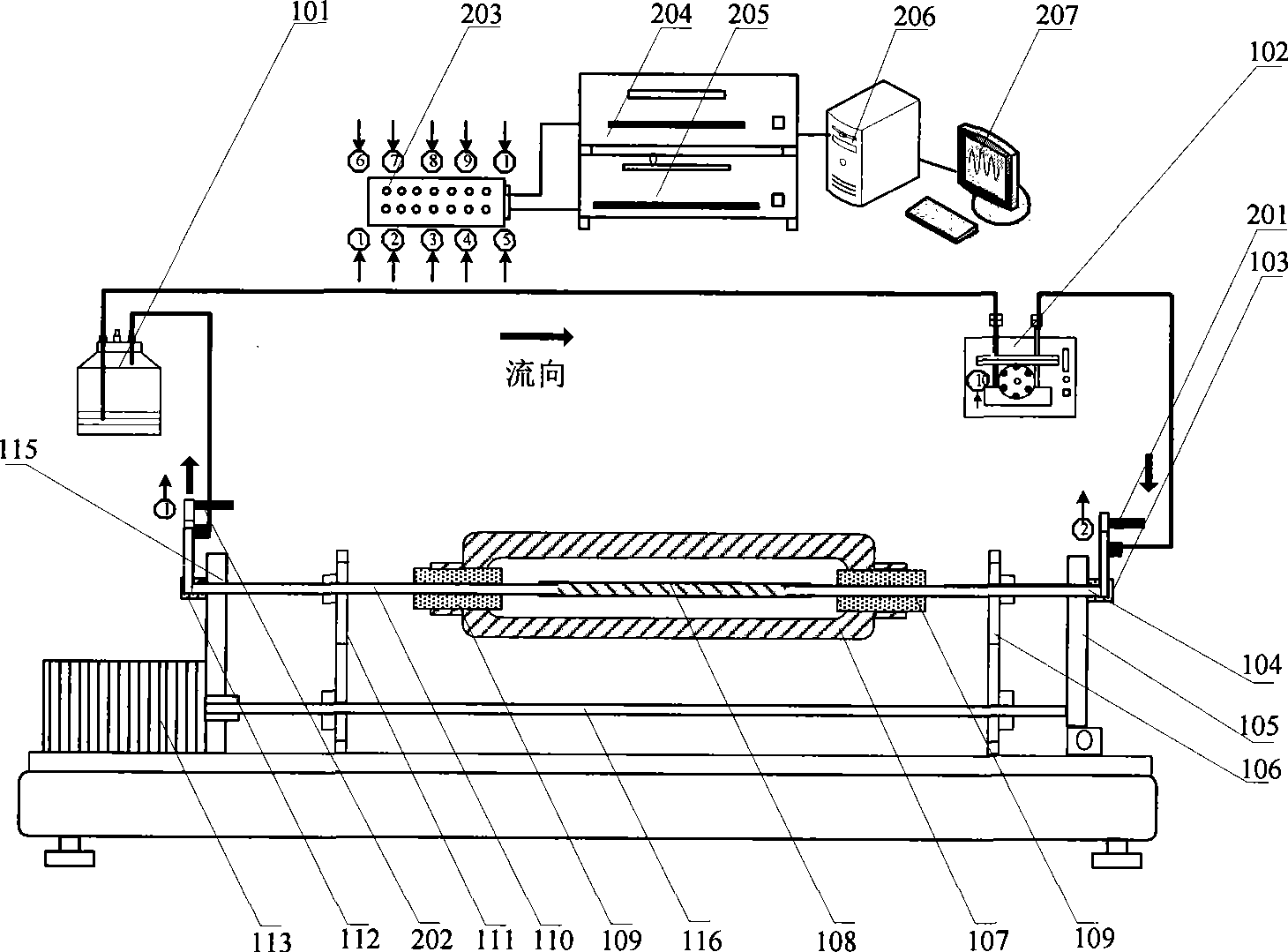
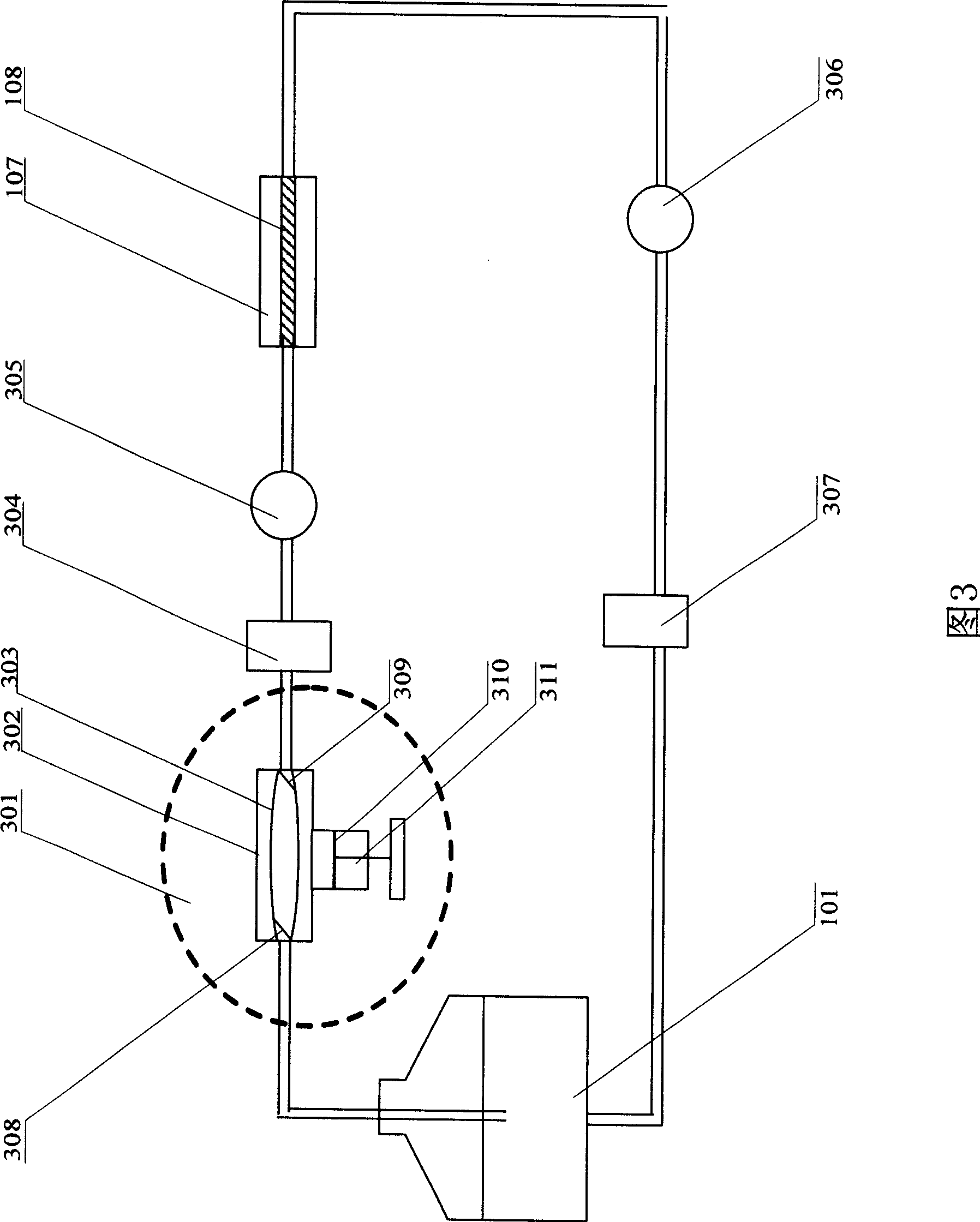
Patents
Literature
285 results about "Arterial blood" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Arterial blood is the oxygenated blood in the circulatory system found in the pulmonary vein, the left chambers of the heart, and in the arteries. It is bright red in color, while venous blood is dark red in color (but looks purple through the translucent skin). It is the contralateral term to venous blood.
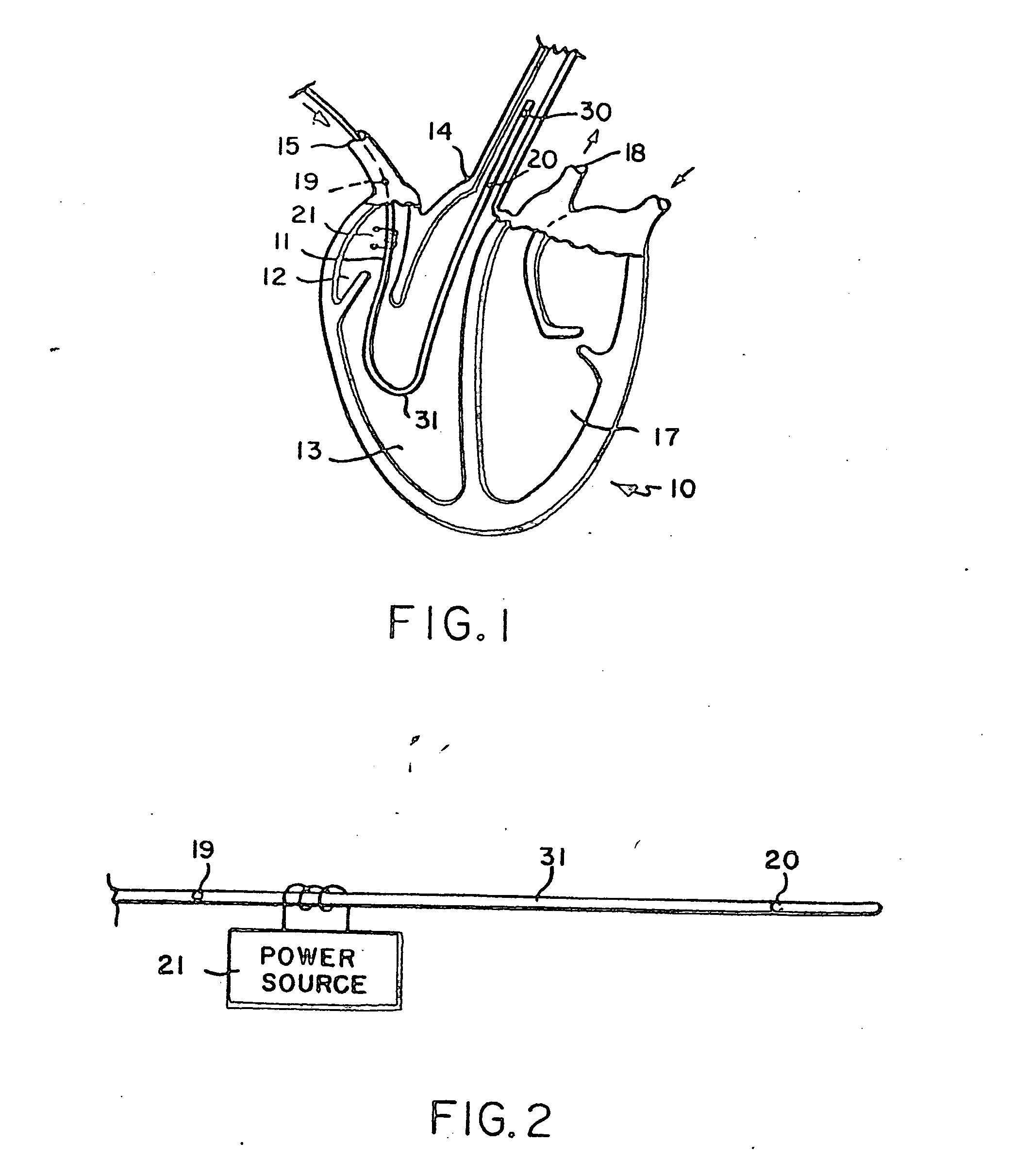
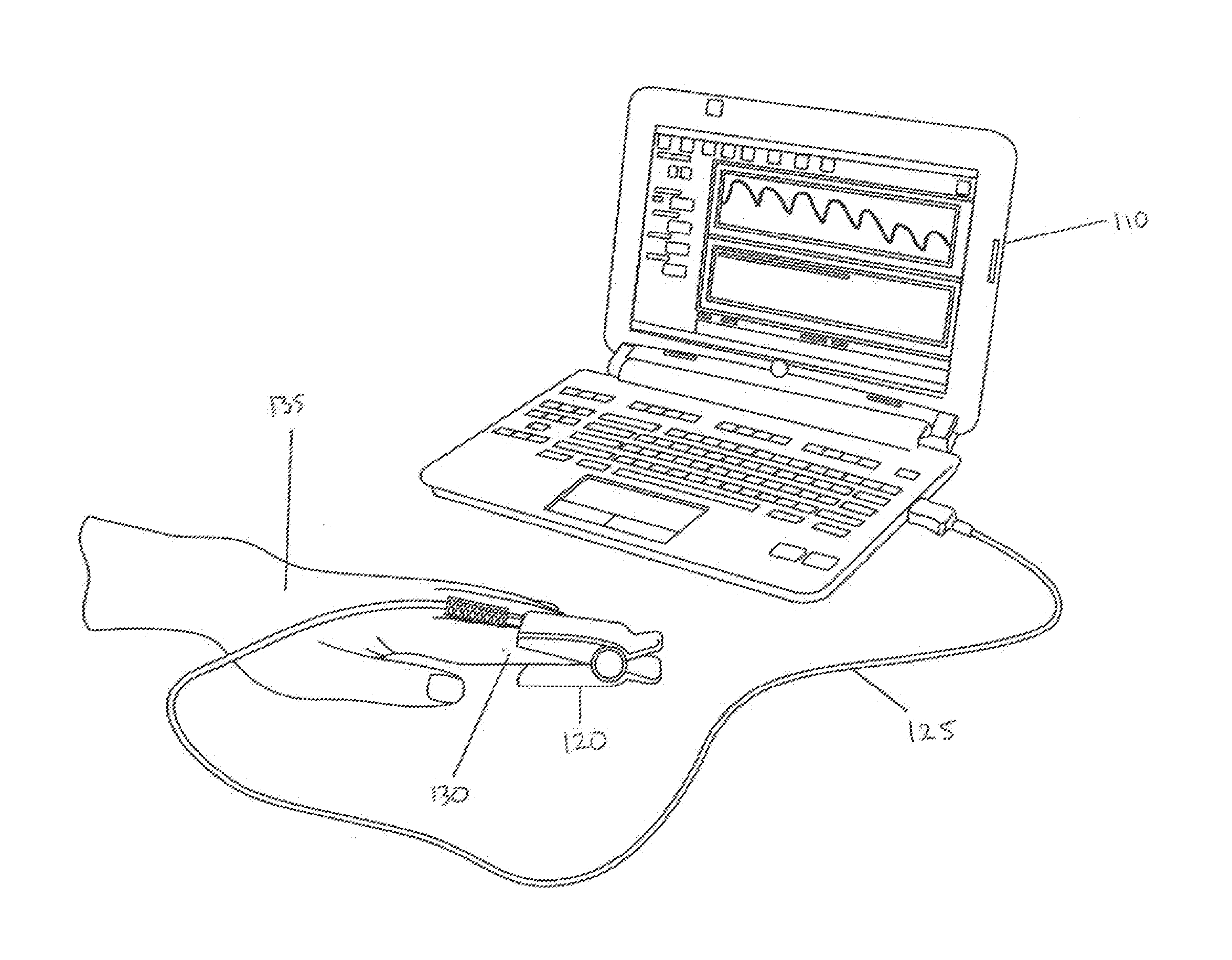
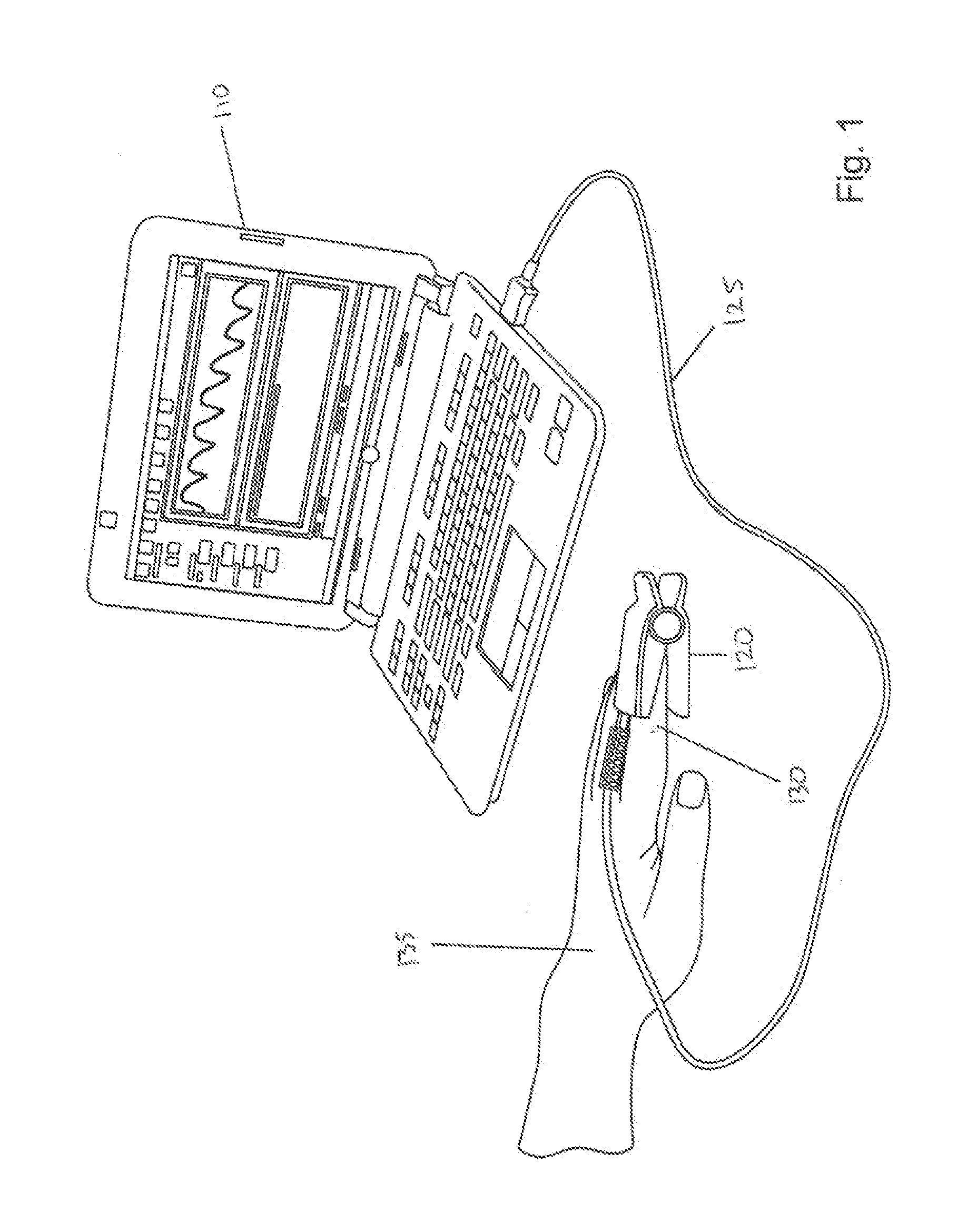
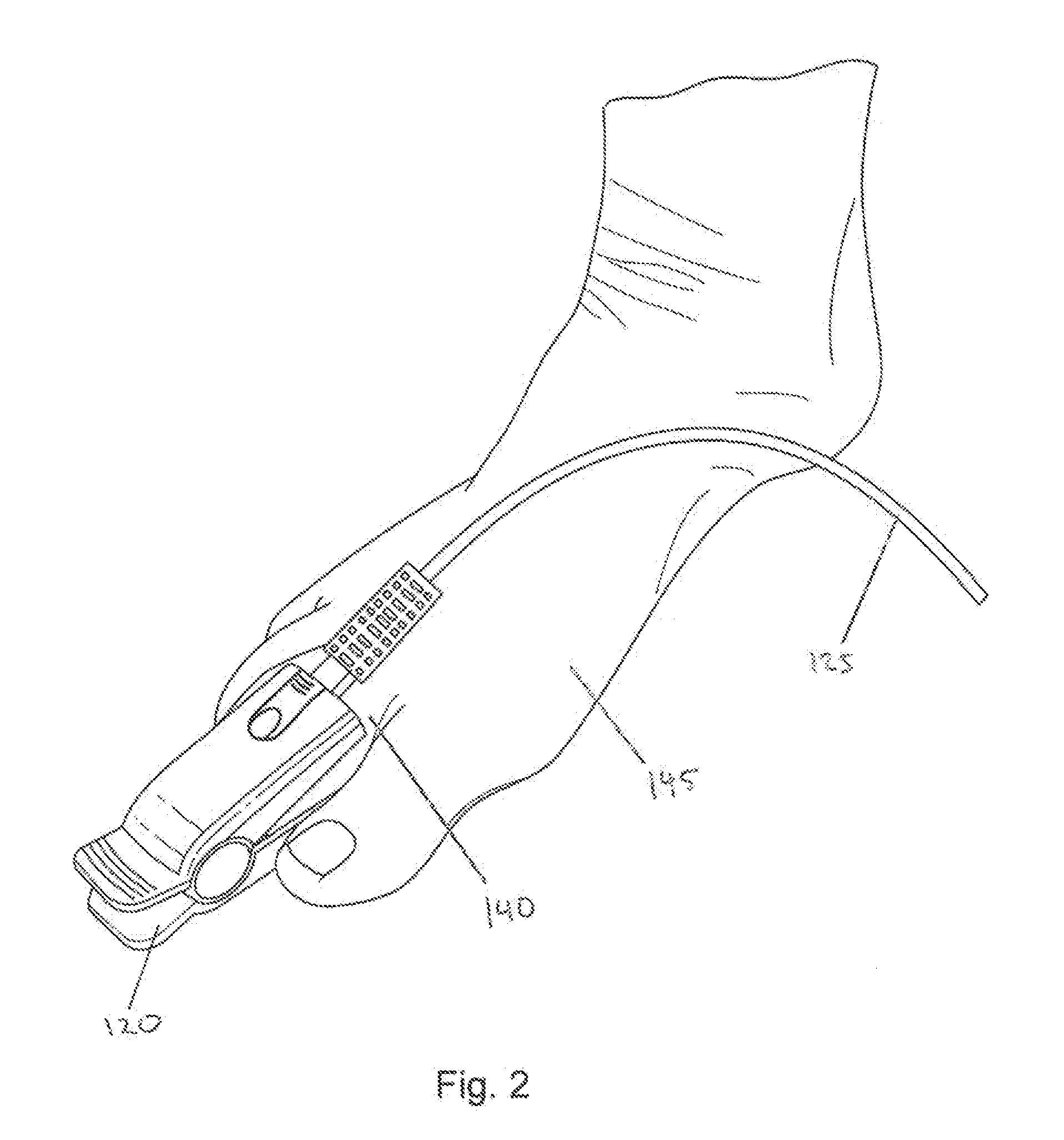
Method and apparatus for processing signals reflecting physiological characteristics from multiple sensors
InactiveUS20070260132A1Improve accuracyEnhanced signalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineMultiple sensor
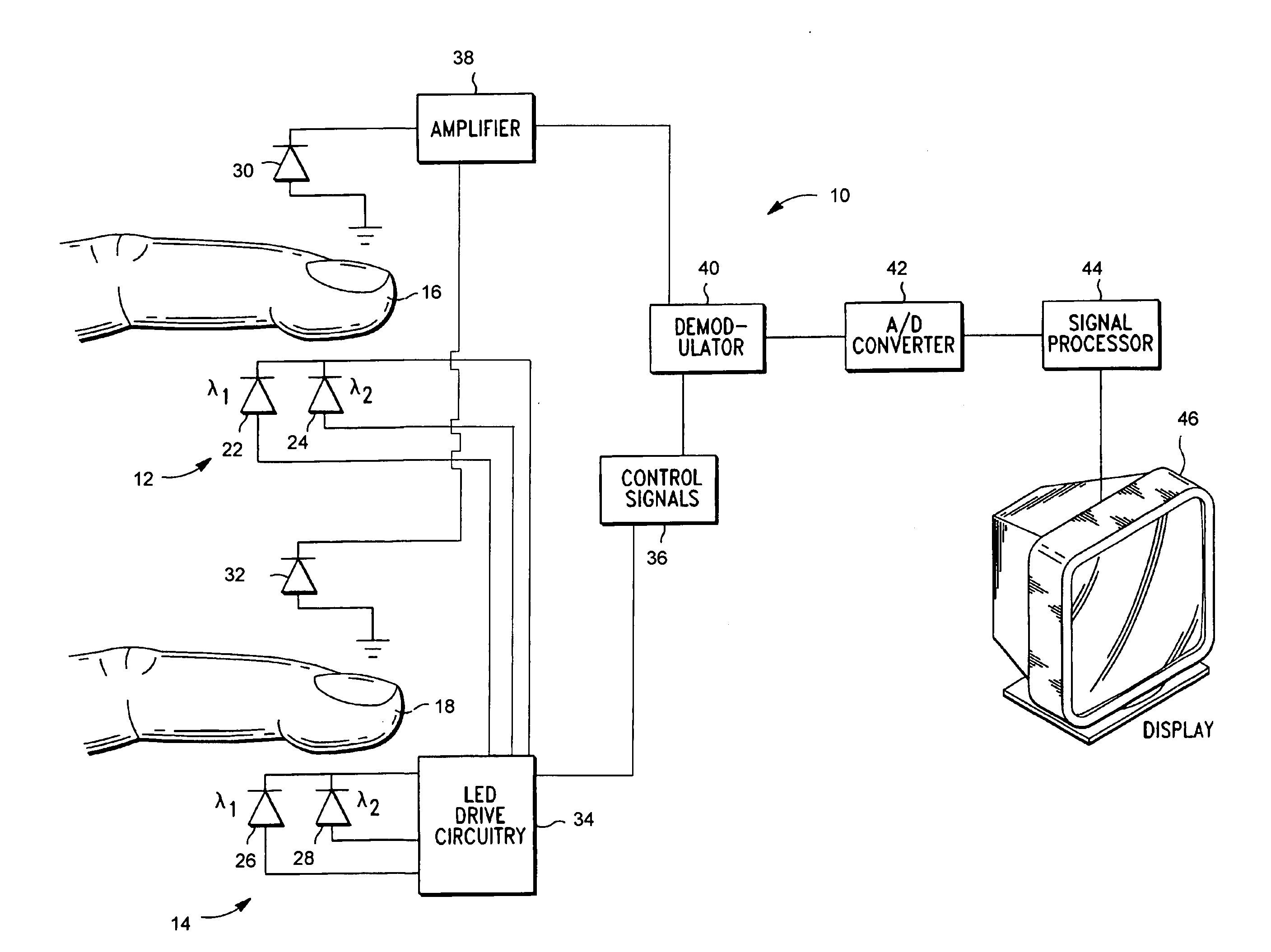
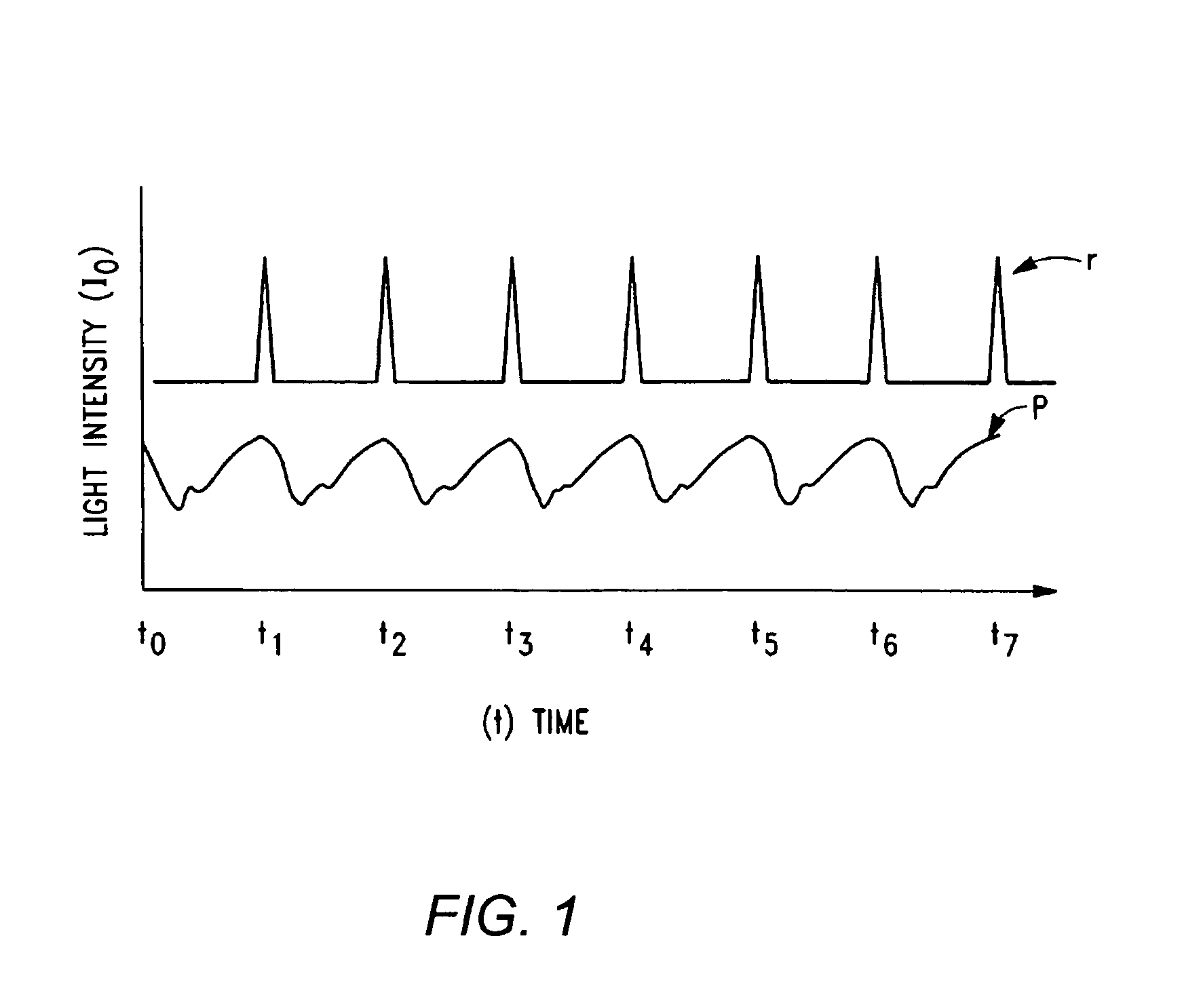
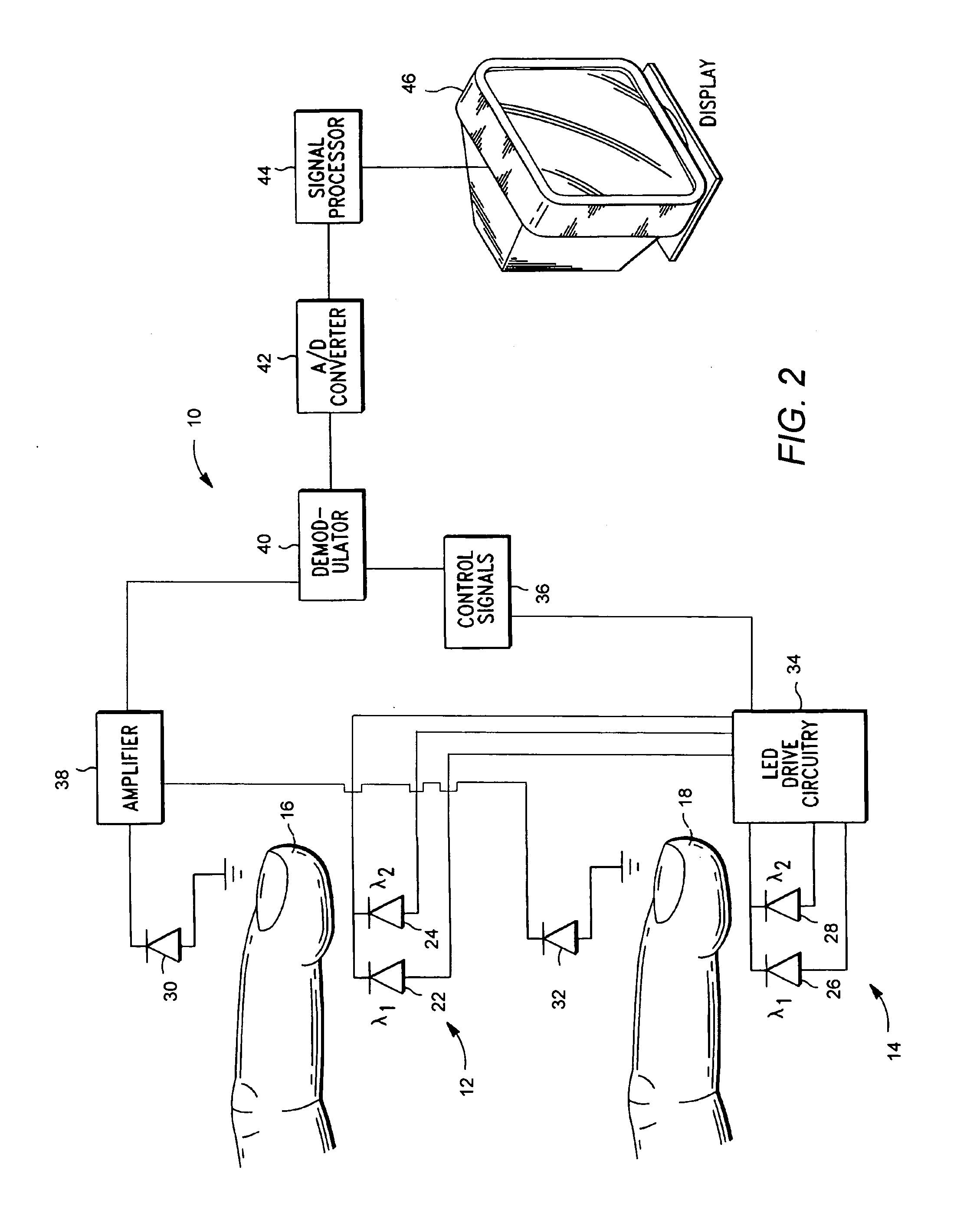
The invention comprises a method and apparatus for processing signals reflecting a physiological characteristic by performing an error minimizing mathematical combination between signals from at least two independent sensors. For example, the intensity of light is detected following tissue absorption at two wavelengths and the signals are corrected. Preferably, corrected intensity signals are derived by orthogonal regression. In one embodiment, the method and apparatus are used to determine arterial oxygen saturation.
Owner:WOOLSTHORPE TECH
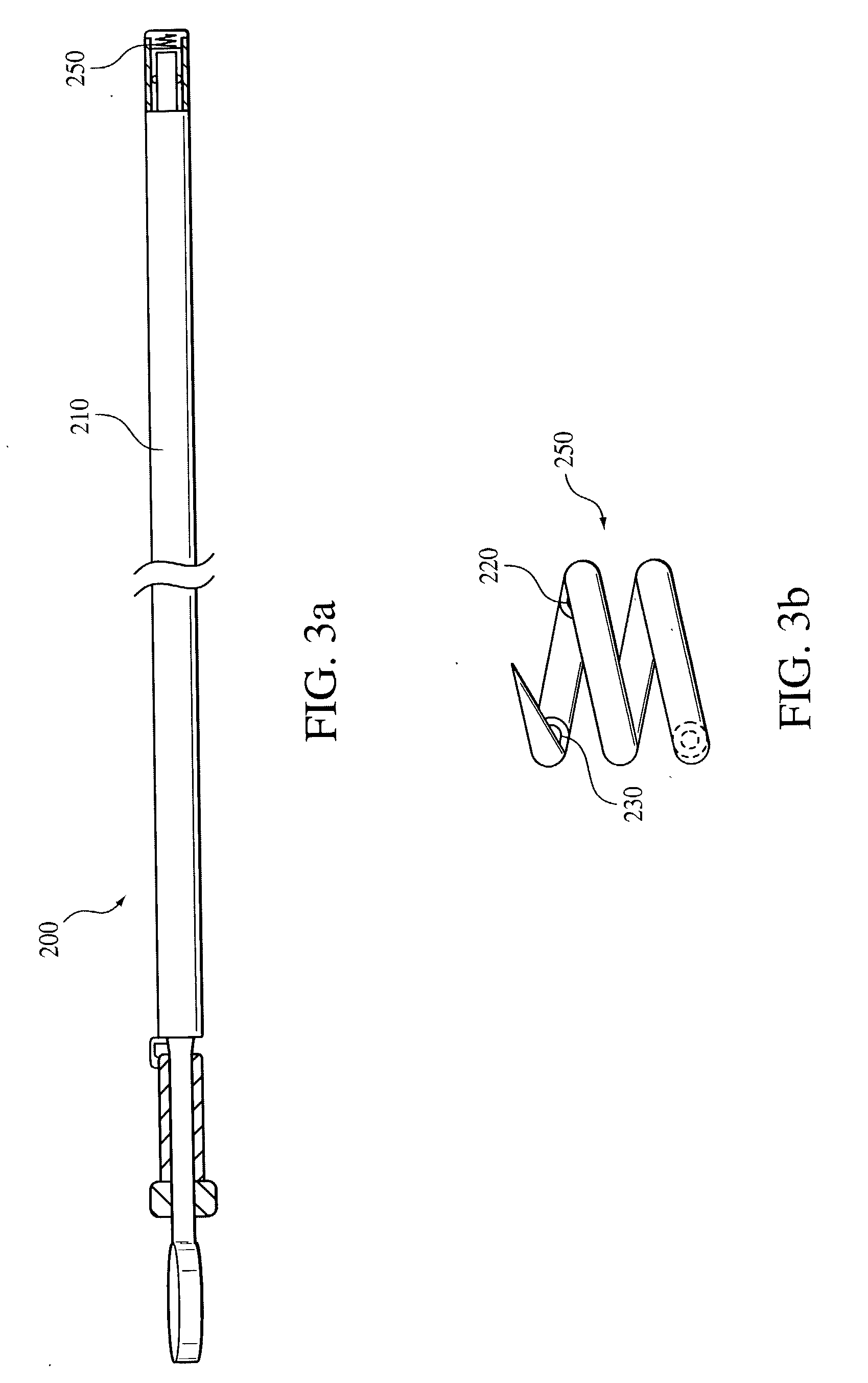
Vibratory venous and arterial oximetry sensor
A method and an apparatus for distinguishing concentrations of blood constituents among distinct vascular components in situ. The method has steps of inducing periodic vibration, characterized by a frequency, in a limb of a person in such as manner as to selectively excite a resonant response in a specified blood vessel of the person, an artery or a vein, illuminating the limb of the person with a light source, and synchronously detecting a plethysmographic signal for discriminating response attributable to the specified blood vessel.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
Apparatus and method for treatment of cerebral aneurysms, arterial-vascular malformations and arterial fistulas
An apparatus and method for stabilization of aneurysm is disclosed. The apparatus comprises an ultraviolet radiation generator for generating UV radiation having a wavelength, strongly absorbed by the DNA and a catheter including means for delivering the ultraviolet radiation to the aneurysm. The distal end of the catheter is placed inside the aneurysm. Stabilization of the aneurysm is achieved by forming a mural arterial thrombus inside the aneurysm. To make irradiation possible, the blood is displaced from the aneurysm by a steady stream of UV radiation transparent fluid. The injury to the endothelium that triggers the thrombus formation is caused by UV radiation delivered to the aneurysm. In several days after intervention the thrombus becomes fully organized, leaving on the inside surface of the aneurysm a thick layer of fibrotic tissue that stabilizes the aneurysm.
Owner:MINNESOTA MEDICAL PHYSICS LLC
Methods for vascular reconstruction of diseased arteries
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
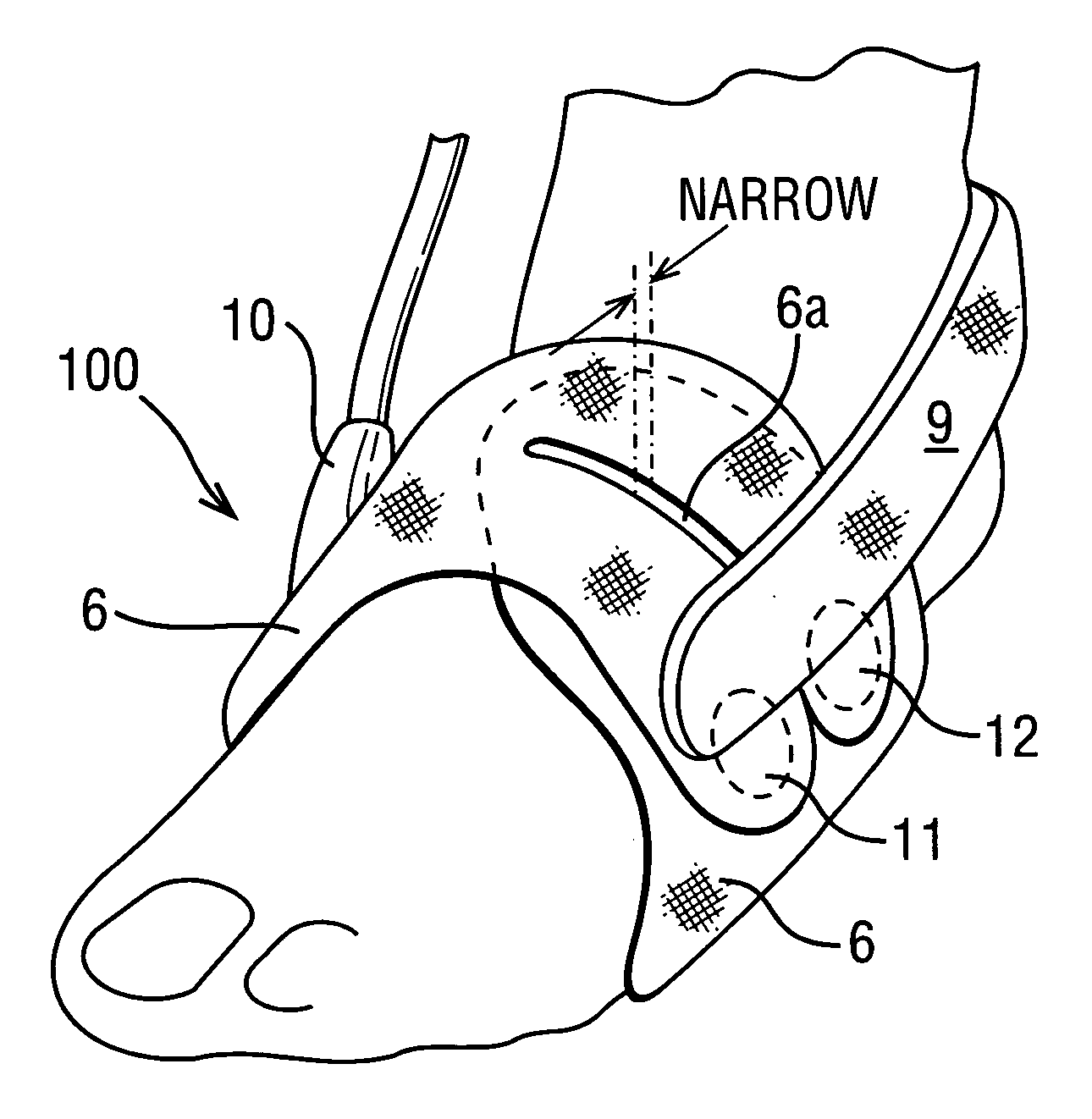
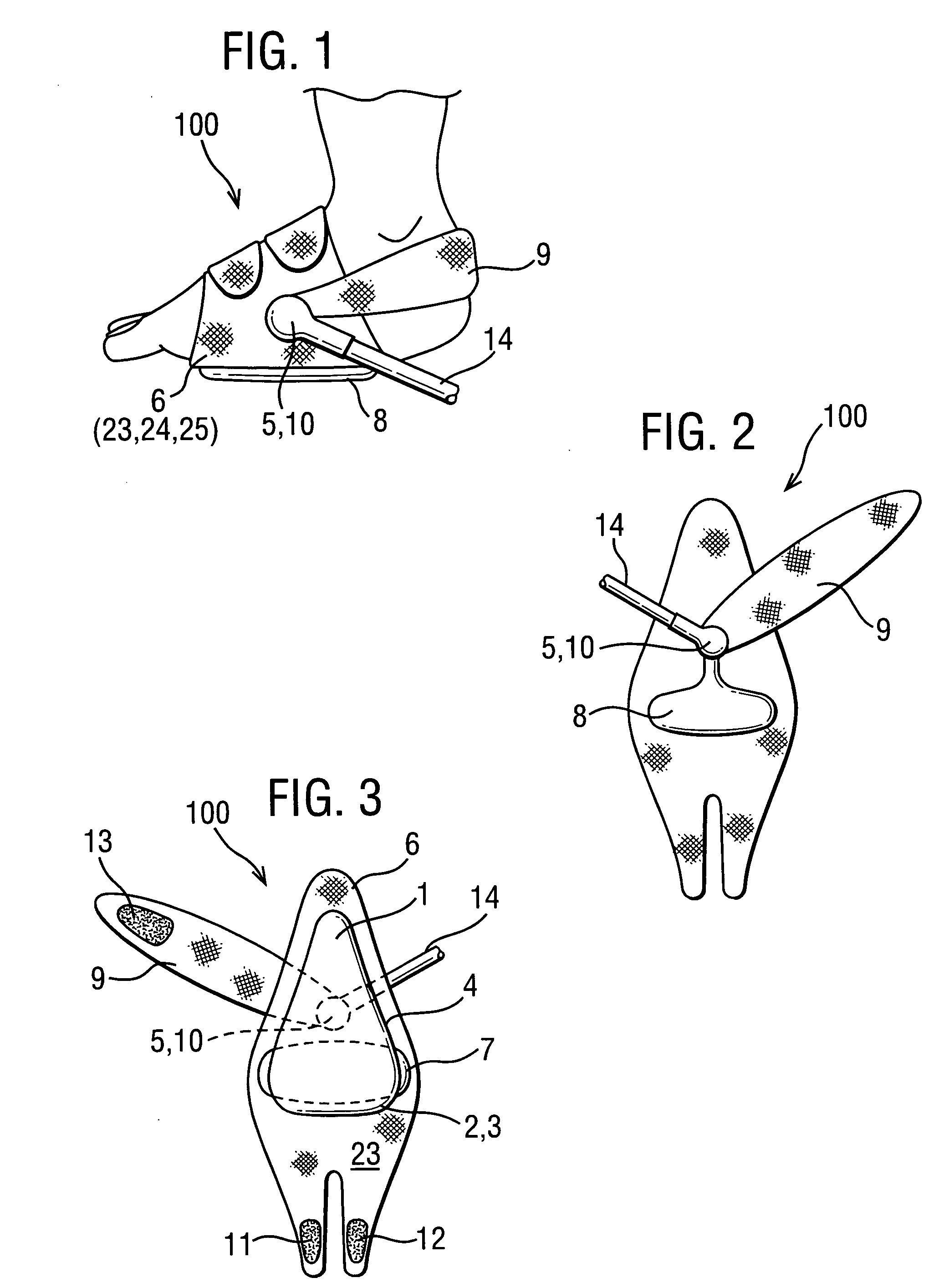
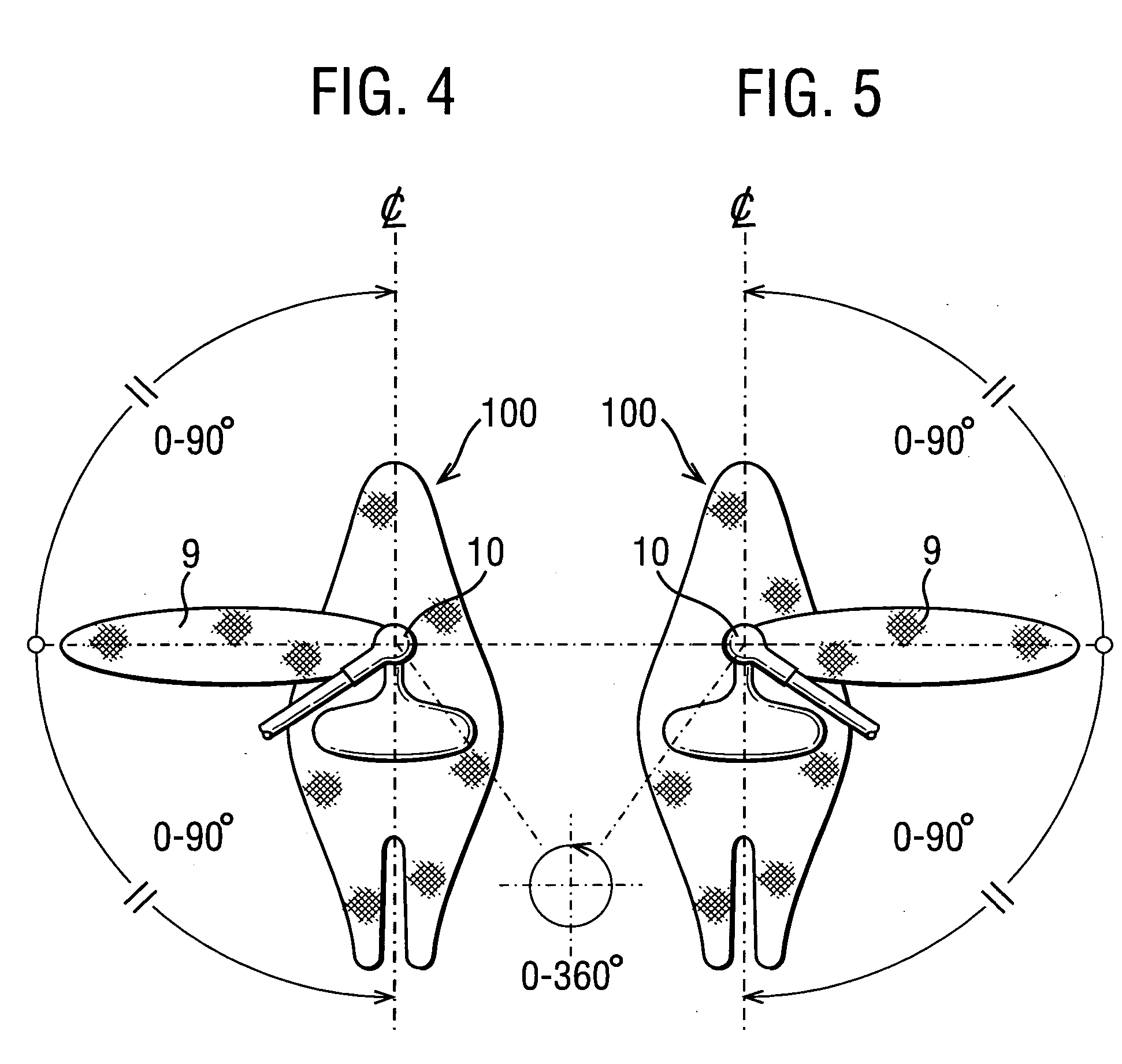
Garment for use in pump therapy for enhancing venous and arterial blood flow
ActiveUS20050143682A1Improves patient comfortImprove treatment complianceVibration massageGenitals massageVeinPulse therapy
Disclosed herein are exemplary embodiments of an impulse therapy garment for use in pump therapy for enhancing venous and arterial blood flow. The garment may be advantageously fitted to a human foot, and may include a rotationally positionable heel-strap, an air inlet connector, separate dorsum straps, or other features. For example, other garments may include a washer having a center hole locatable around the stem and configured to be forcibly retained against the outer surface of the fabric by snap-fit using annular stem protrusions extending from an external surface of the stem. In further embodiments, a garment may include a bladder retention fastener configured to retain an end of the bladder to the fabric to allow substantially differential movement between the fabric and non-retained portions of the bladder during inflation and deflation of the bladder.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH IRELAND UNLTD
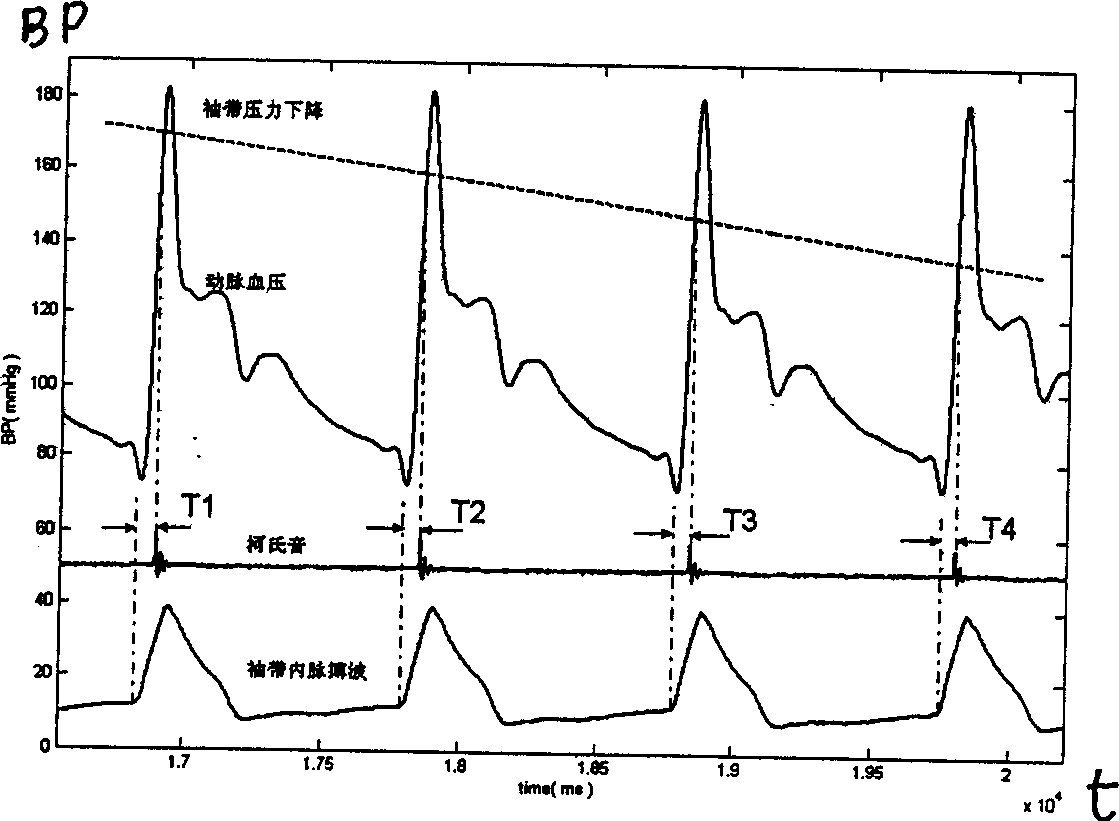
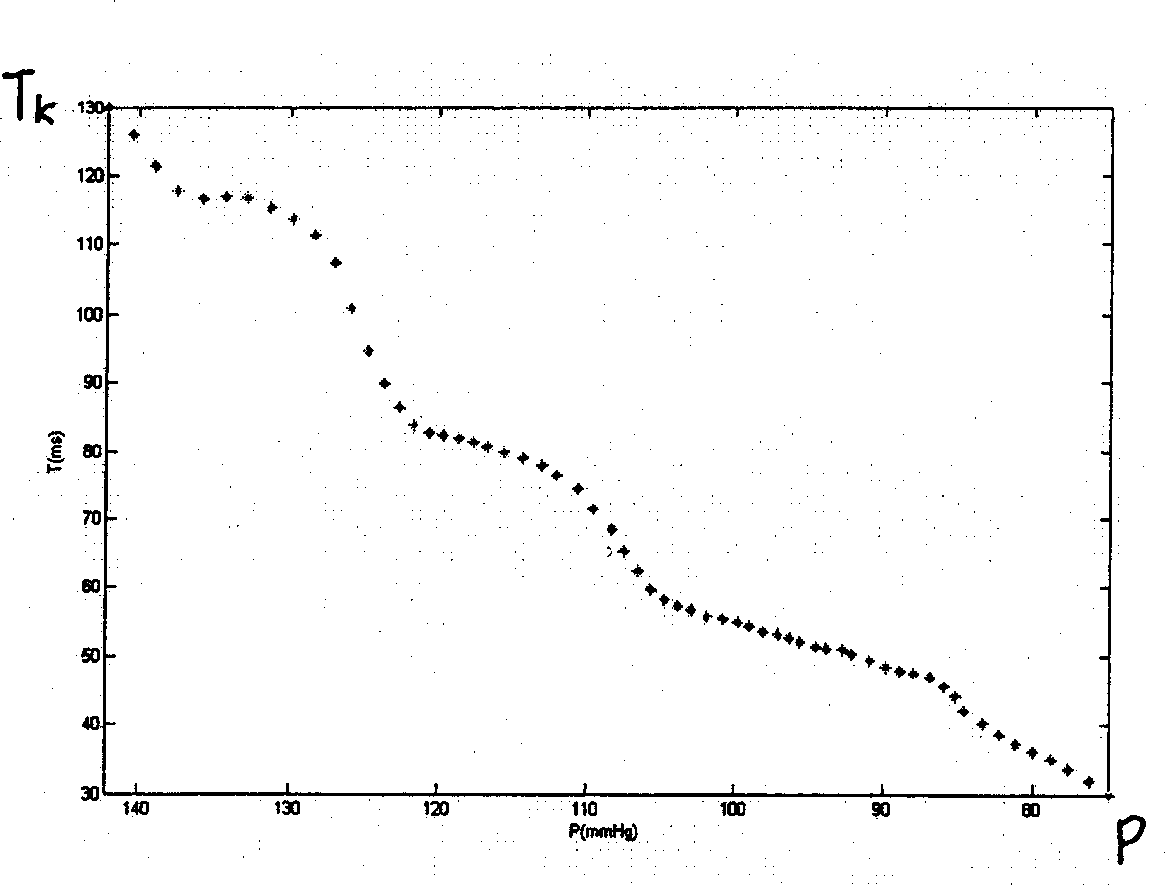
Method for measuring arterial pressure, apparatus and individual correction tech. therefor
InactiveCN1868399AHigh implementabilityReduce mistakesEvaluation of blood vesselsAngiographyContinuous measurementPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
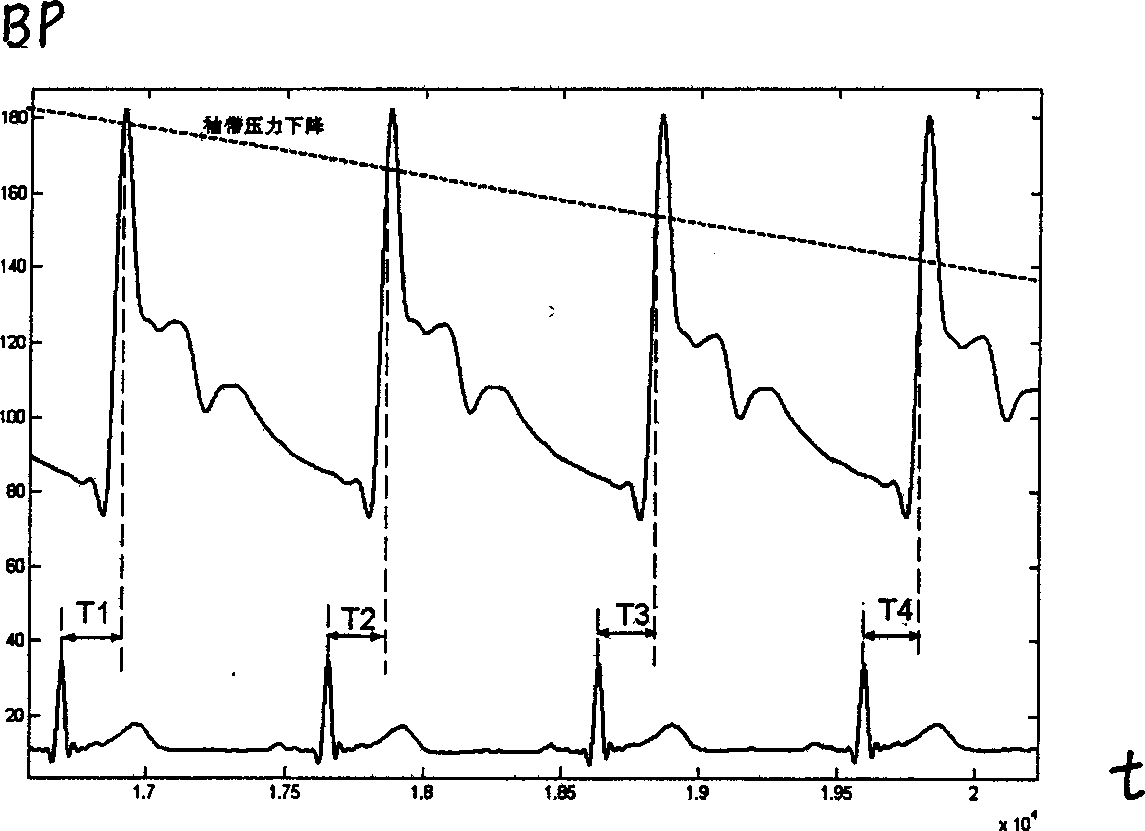
A method and device for measuring the blood pressure of artery and its personalized correction technique are disclosed. A series of the pressure values (P) for sleeve band and the time delay values (Tk) of the relative remote Ke's sounds are obtained. The function relation Tk(P) between said pressure change and sound delay is in turn obtained. Measuring a Tk relative to a P can calculate out the blood pressure change. A regression equation for continuous measurements of arteral blood pressure is used to obtain a personalized correction coefficient.
Owner:BEIJING XINXING YANGSHENG TECHN CORP +1
MR coronary angiography with a fluorinated nanoparticle contrast agent at 1.5 T
InactiveUS20060239919A1Reduce eliminateHigh and low oxygen tensionDispersion deliveryNanomedicine3d imageNon invasive
Disclosed herein is a medical imaging technique that uses a fluorinated nanoparticle contrast agent for imaging of an interior portion of a body. The fluorinated nanoparticles preferably comprise nontargeted intravascular fluorocarbon or perfluorocarbon nanoparticles. The interior body portion may be a patient's vasculature, and the medical imaging is preferably noninvasive MR angiography, which may encompass (either for 2D imaging or 3D imaging) MR coronary angiography, MR carotid angiography, MR peripheral angiography, MR cerebral angiography, MR arterial angiography, and MR venous angiography. Coils tuned to match to the 19F signal can be used, or dual tuned coils for 19F and 1H imaging can be used. Clinical field strengths (e.g. 1.5 T) and clinical doses may be used while still providing effective images.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
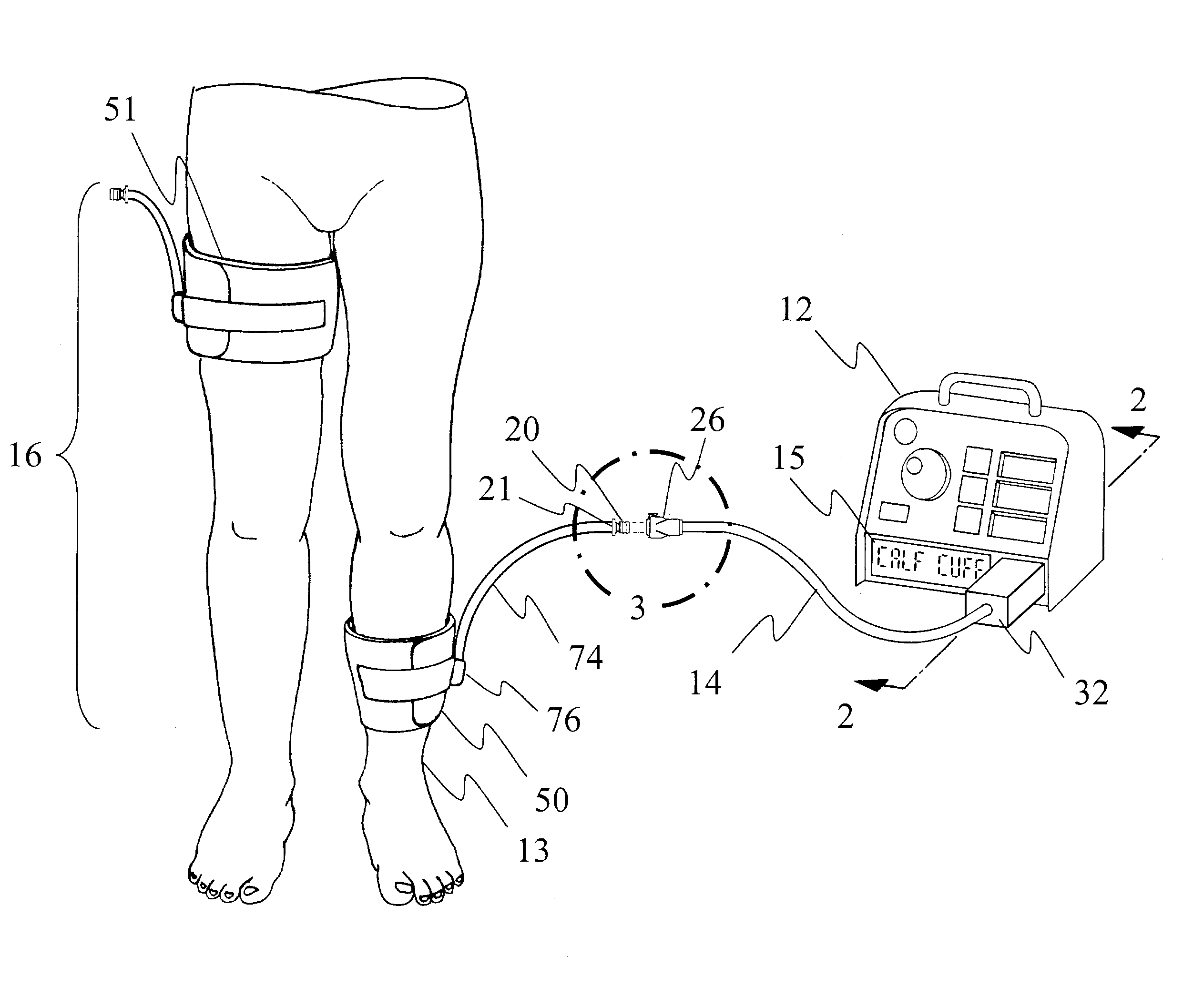
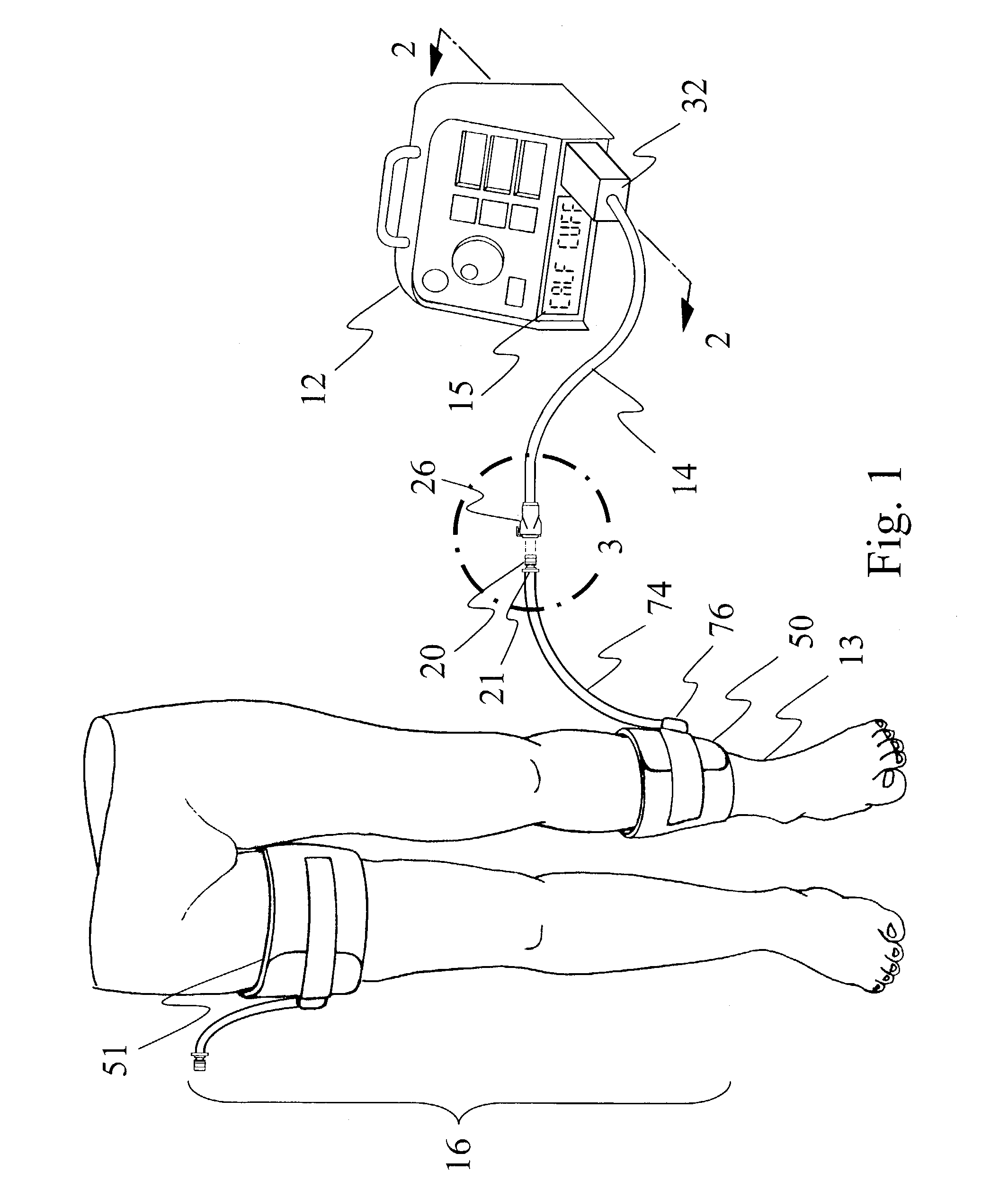
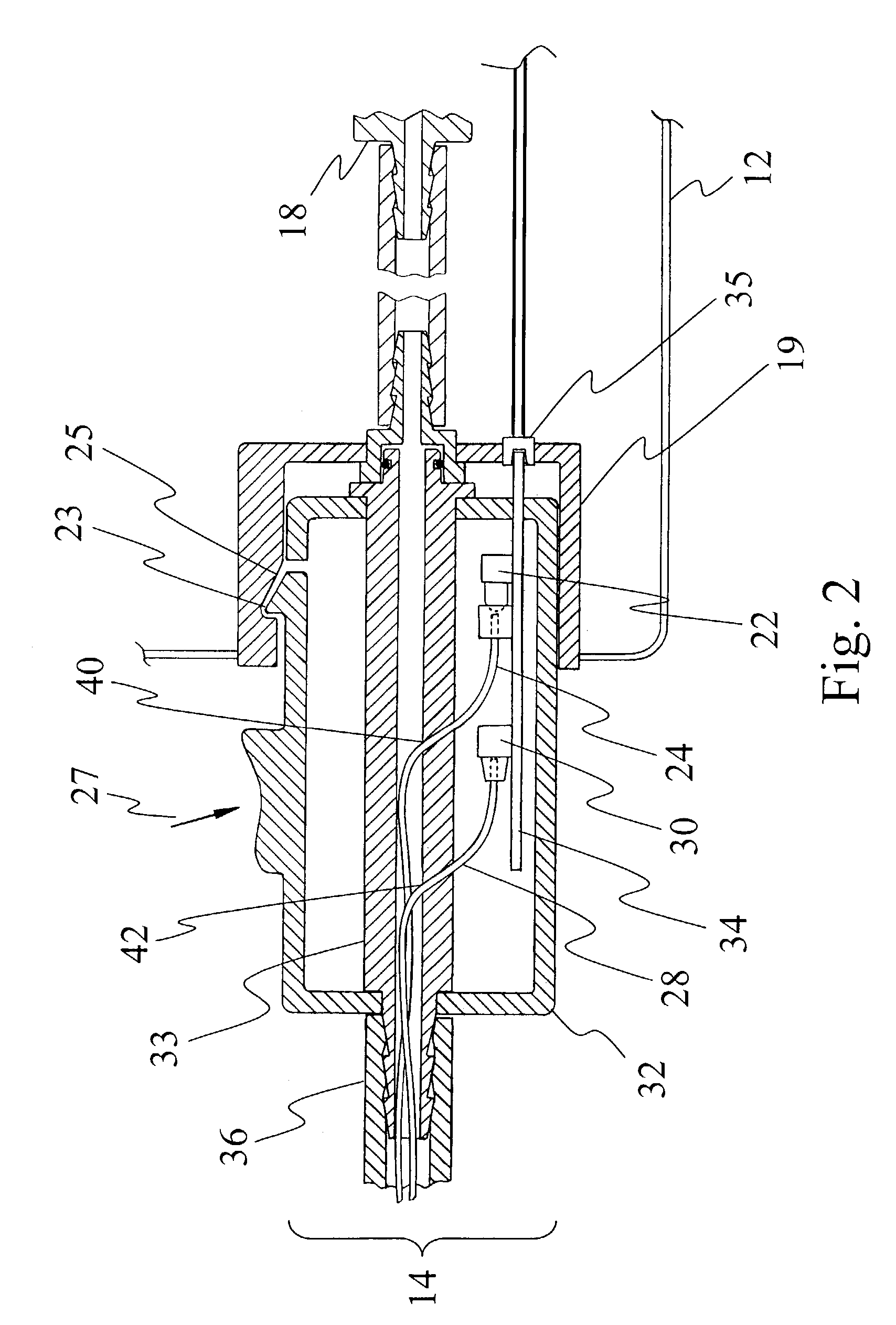
Adaptive tourniquet cuff system
An adaptive tourniquet cuff system comprises: a tourniquet cuff having a physical characteristic and including an inflatable bladder of a length greater than the circumference of a limb at a selected location; a cuff connector carried on the cuff and communicating pneumatically with the bladder for releasably connecting to a tourniquet instrument to establish a gas-tight passageway between the bladder and the tourniquet instrument; and an identifying collar including identification means indicative of the physical characteristic and detectable by the tourniquet instrument upon establishment of the gas-tight passageway. The tourniquet instrument may supply gas to the bladder through the gas-tight passageway at a pressure sufficient to stop arterial blood flow into the limb distal to the cuff at the selected location, and may adapt its operation in response to the detected physical characteristic of the cuff.
Owner:WESTERN CLINICAL ENG
Blood flow monitor with venous and arterial sensors
Owner:THERMAL TECH
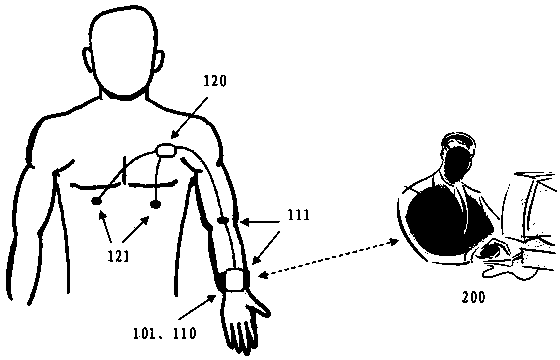
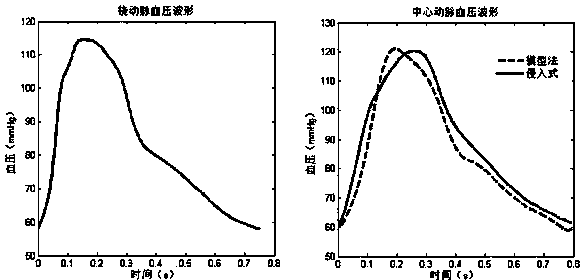
Non-invasive central aortic blood pressure measuring method and device
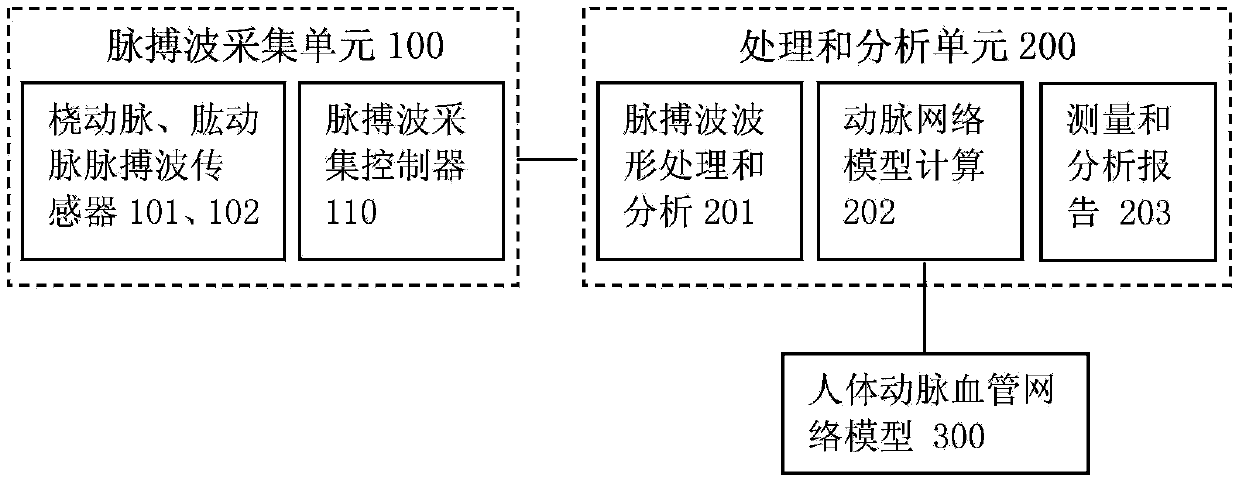
The invention discloses a non-invasive central aortic blood pressure measuring method and device. The non-invasive central aortic blood pressure measuring method includes, according to a human artery network model based on viscous fluid mechanics, a method of calculating artery network model personalized parameters of a measured person through measured radial artery and brachial artery pulse wave signals and arm blood pressure values, a method of calculating an ascending aorta-radial artery transfer function and a method of calculating central arterial pressure waveforms through measured central arterial pressures. The non-invasive central aortic blood pressure continuous measuring device comprises a pulse wave signal processing and analysis unit and a radial artery and brachial artery pulse wave signal acquisition unit worn on a wrist. The method is different from an existing general transfer function method, the artery network model parameters of each person to be measured are measured and calculated and the artery network model parameters are numerical characteristics of the cardiovascular system states of the person to be measured with the calculated central arterial pressure waveforms, and the method and device has important meanings in prevention, curing and control of cardiovascular diseases, especially high-risk diseases, such as hypertensions and coronary heart diseases.
Owner:南京茂森电子技术有限公司
Data mining system for noninvasive intracranial pressure assessment
InactiveUS8821408B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPerson identificationData setBlood pressure
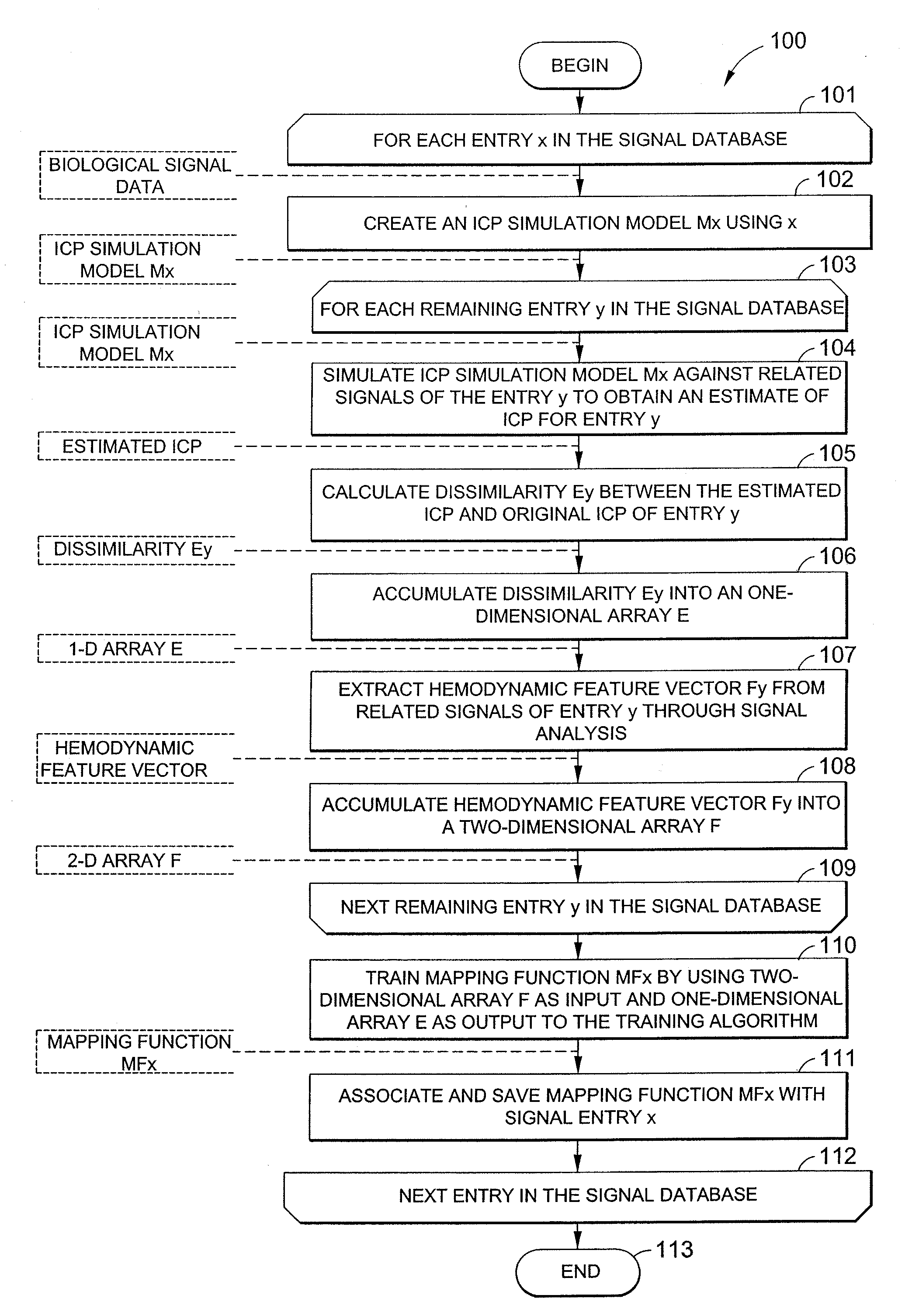
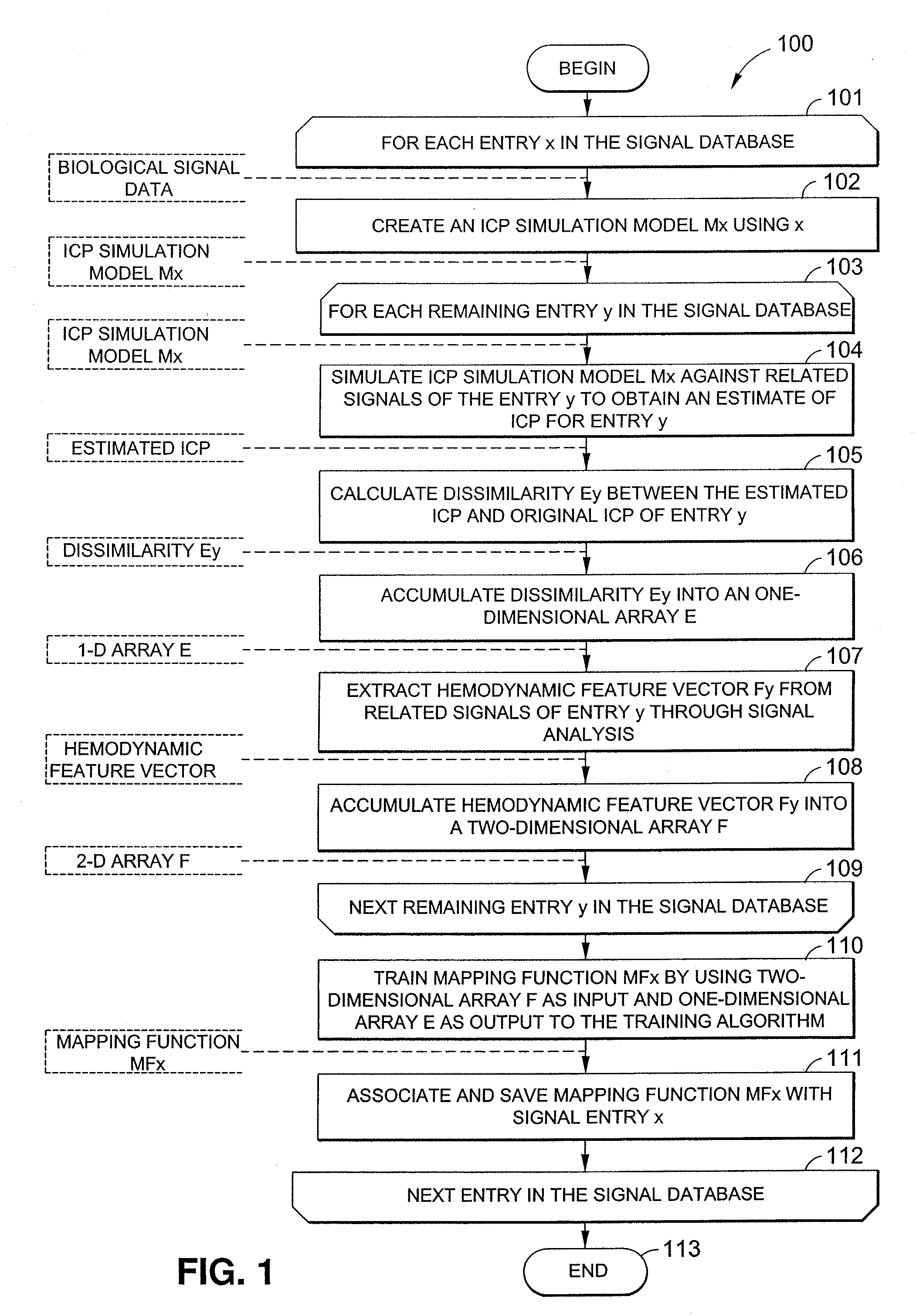
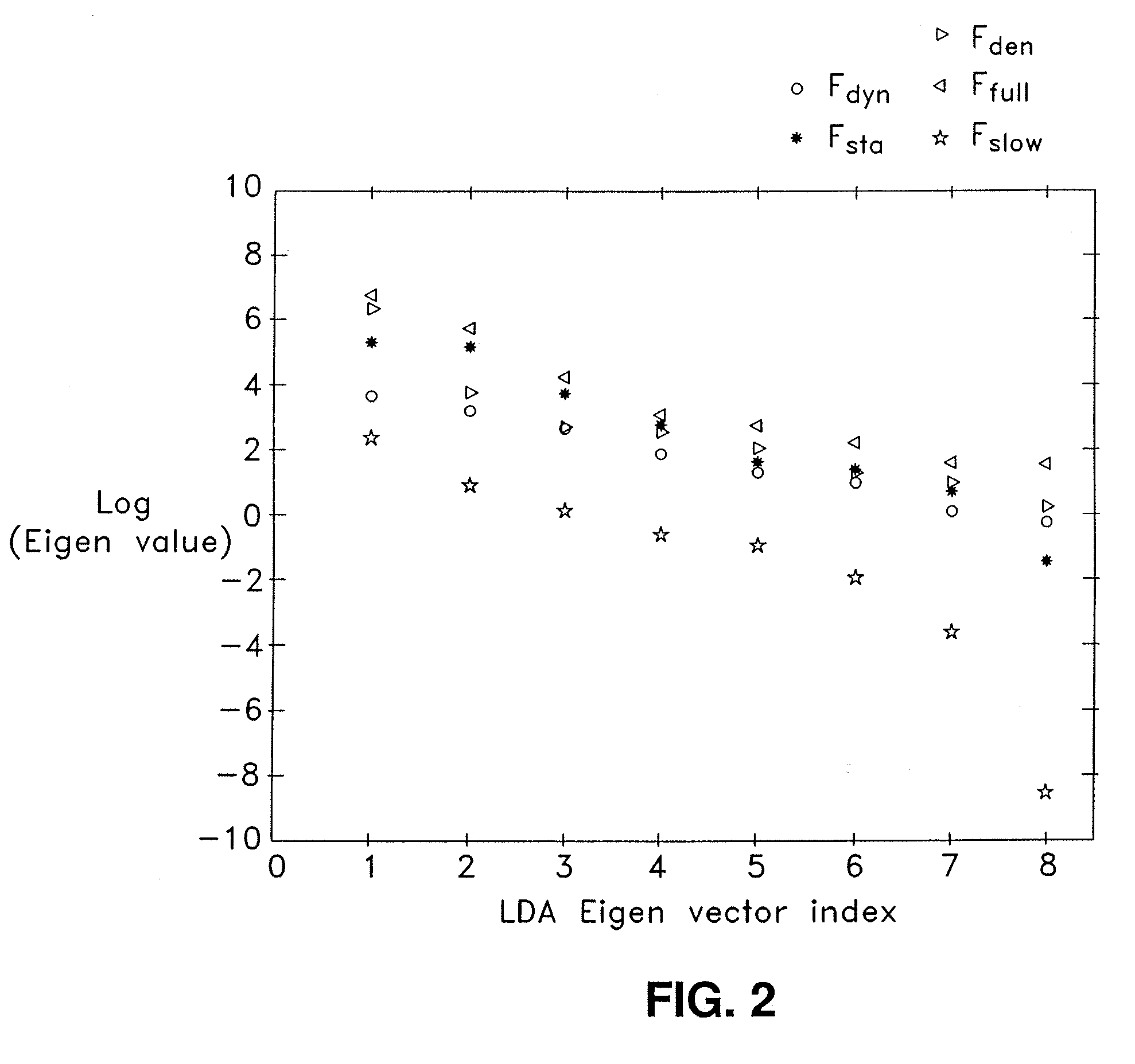
Systems and methods are described for noninvasively assessing an intracranial pressure of a patient. Some embodiments include providing a simulation model with a measured arterial blood pressure of the patient. Some embodiments further include providing the simulation model with a measured cerebral blood flow velocity of the patient. The simulation model correlates arterial blood pressure values, cerebral blood flow velocity values, and intracranial pressure values. Some embodiments further includes determining an intracranial pressure of the patient based on the simulation model. Some embodiments further includes creating an output data set indicative of the determined intracranial pressure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
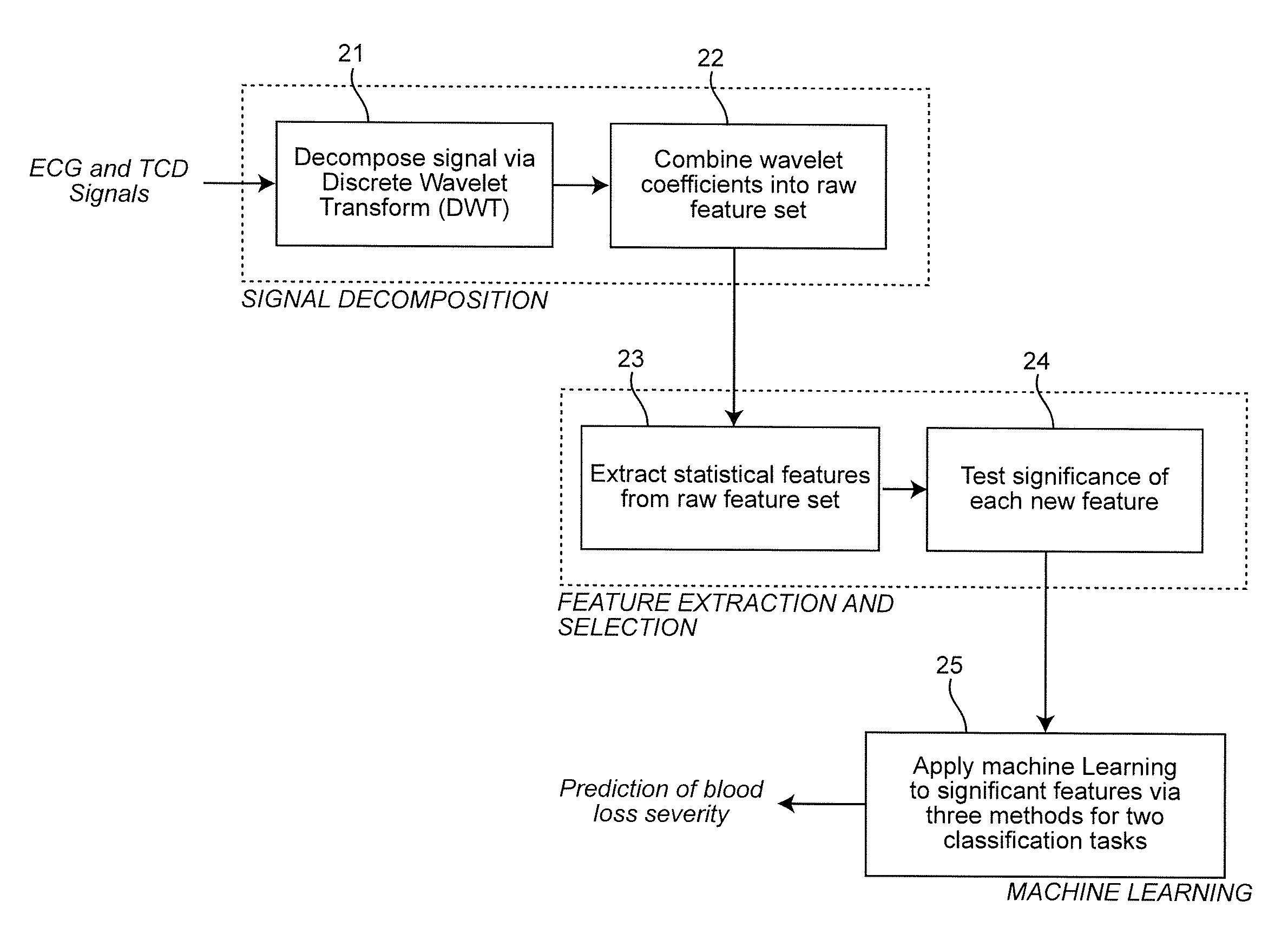
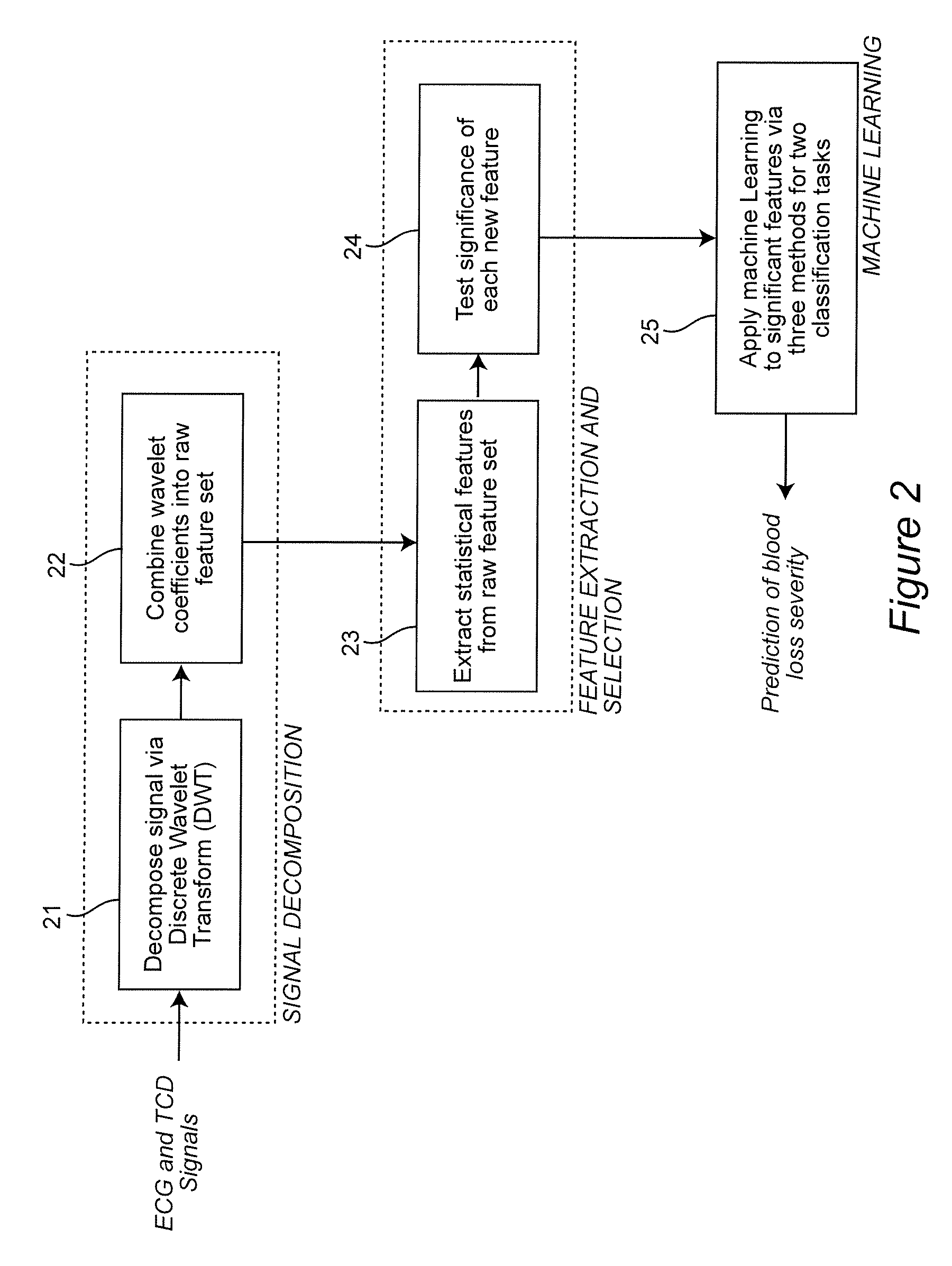
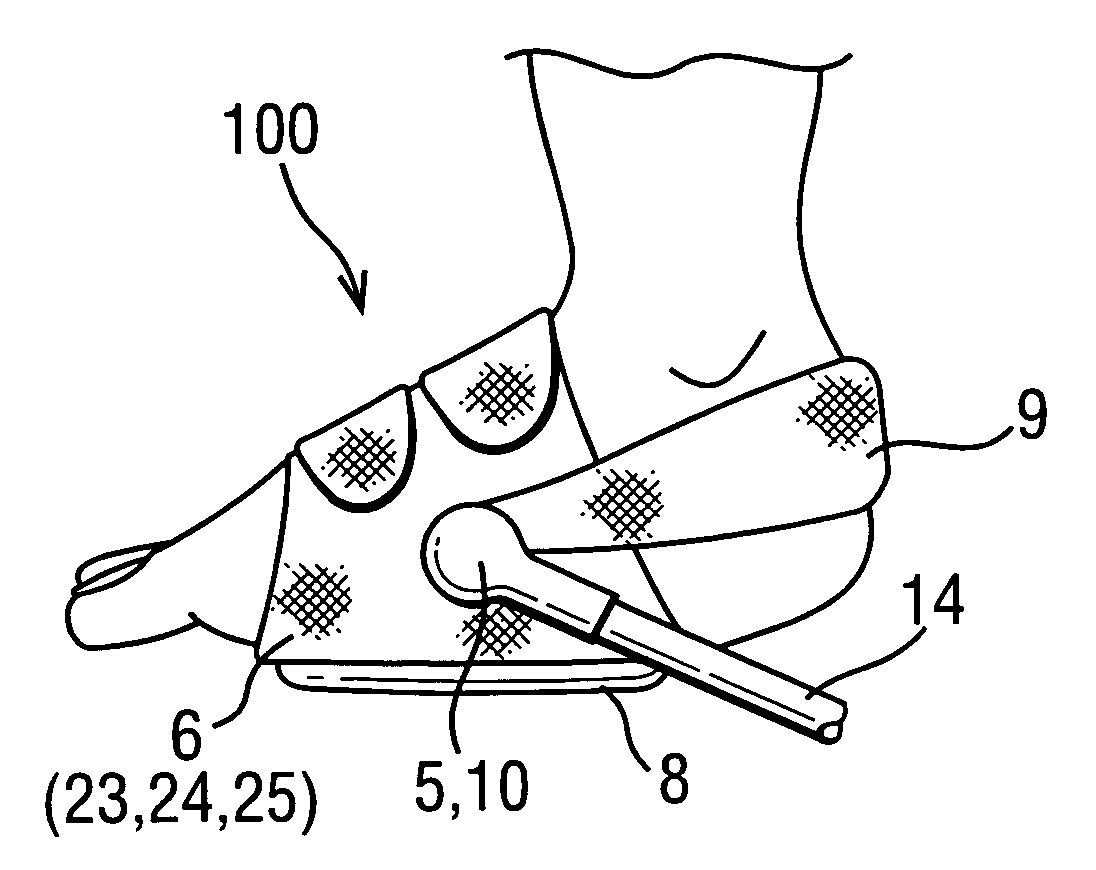
Combining predictive capabilities of Transcranial Doppler (TCD) with Electrocardiogram (ECG) to predict hemorrhagic shock
InactiveUS8762308B2Maximization of survival rateElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesDecompositionHypovolemia
A real-time decision-support system predicts hemorrhagic shock of a patient by analysis of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals and transcranial Doppler (TCD) signals from the patient. These signals are subject to signal decomposition using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to sets of wavelet coefficients and selecting significant signal features. Machine learning is applied to the significant features to evaluate and classify hypovolemia severity based on the input ECG and TCD signals from the patient. The classification of blood loss severity is displayed in real-time. An extension of the decision-support system integrates Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) signals and thoracic electrical bio-impedance (DZT) signals with the ECG and TCD signals from the patient to evaluate severity of hypovolemia.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Garment for use in pump therapy for enhancing venous and arterial blood flow
ActiveUS7452340B2Improve complianceAvoid insufficient lengthVibration massageGenitals massageVeinPulse therapy
Disclosed herein are exemplary embodiments of an impulse therapy garment for use in pump therapy for enhancing venous and arterial blood flow. The garment may be advantageously fitted to a human foot, and may include a rotationally positionable heel-strap, an air inlet connector, separate dorsum straps, or other features. For example, other garments may include a washer having a center hole locatable around the stem and configured to be forcibly retained against the outer surface of the fabric by snap-fit using annular stem protrusions extending from an external surface of the stem. In further embodiments, a garment may include a bladder retention fastener configured to retain an end of the bladder to the fabric to allow substantially differential movement between the fabric and non-retained portions of the bladder during inflation and deflation of the bladder.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH IRELAND UNLTD
Micro-volume blood transfer device
ActiveUS20140296745A1Reduce the risk of infectionMinimize the numberAnimal teeth treatmentCatheterBody weightPediatrics
A micro-volume blood transfer device to facilitate the collection of small volumes of clean arterial blood from patients who may be volume restricted for blood loss such as low-birth weight infants.
Owner:HUMMINGBIRD MED DEVICES INC
Circulation Monitoring System
Owner:SEMLER SCI
Apparatus and methods for dilating vasospasm of small intracranial arteries
A device and method for treatment of intracranial vasospasm is provided. The device is a microcatheter having a steeply tapered end and is thicker walled, and in a preferred embodiment is braided to provide greater pushability. In order to achieve a thicker walled catheter, in one embodiment, the inner lumen diameter can be reduced, leaving the outer diameter the same while in another embodiment the catheter is larger in outer diameter. In one embodiment, the microcatheter is coated with performance enhancing lubricant, such as a hydrophilic coating. Further, the microcatheter can also be coated with drugs and serve as a drug delivery device, drugs being embedded into vessel intima. In the use of the method of treatment, the device is fed into the smaller arterial vessels in the brain simultaneously dilating arteries of various caliber along the path of the catheter to relieve vasospasm; pharmacological agents can then be delivered by the microcatheter to further effect treatment.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
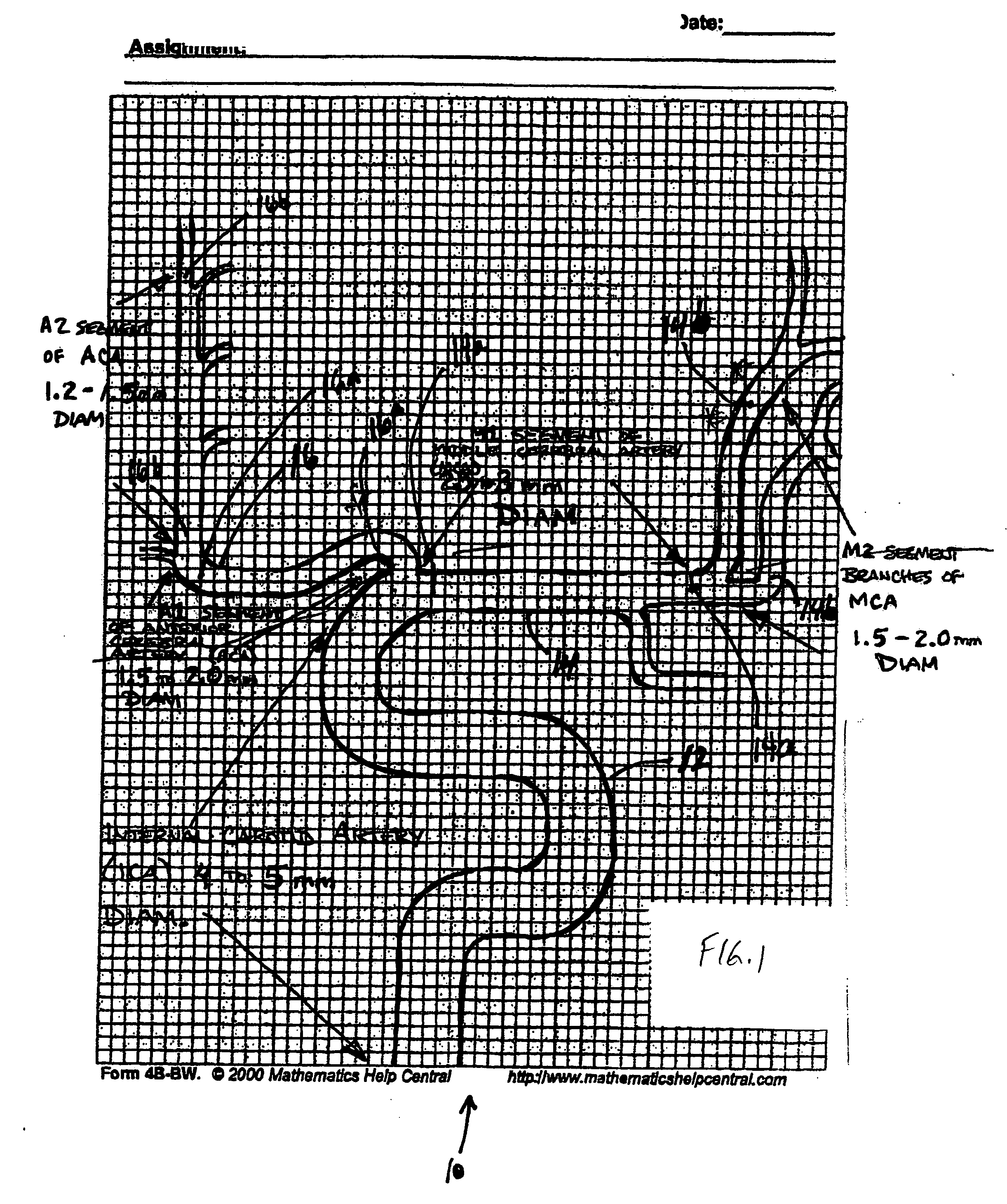
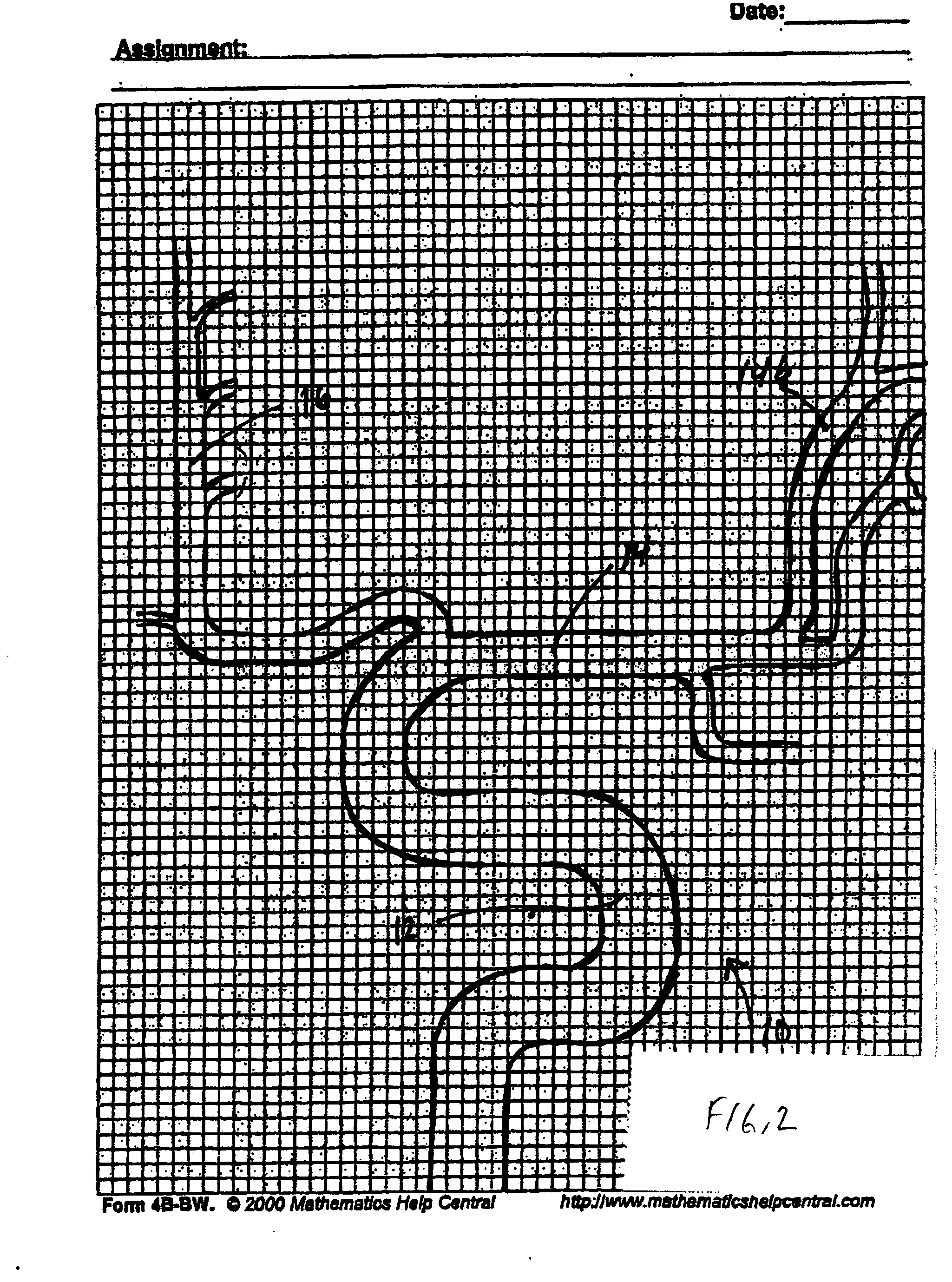
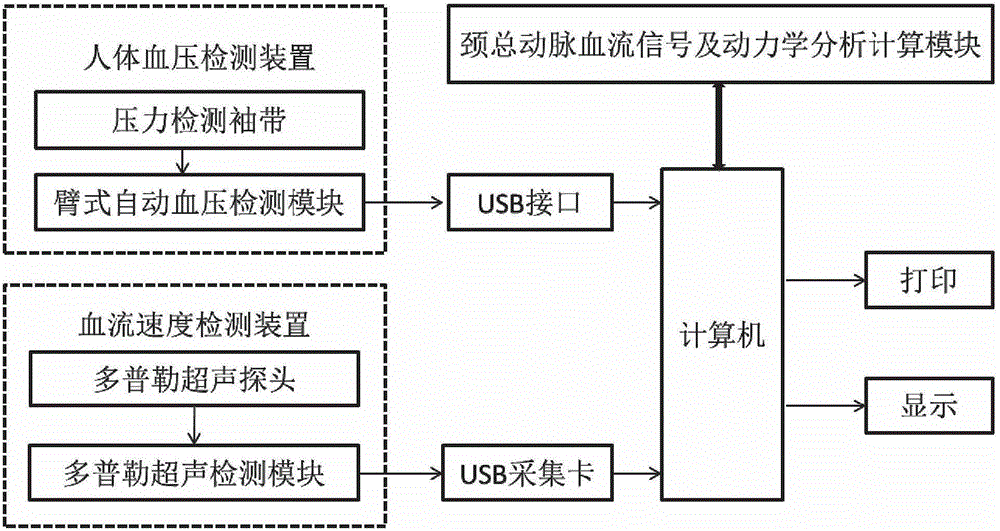
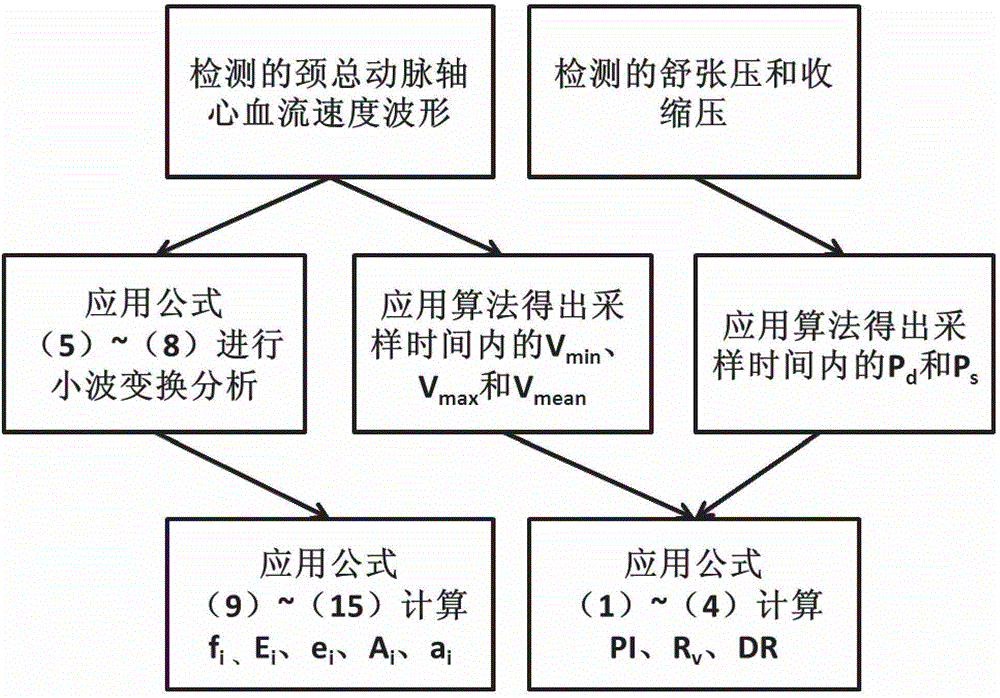
Hemodynamics and signal analysis system and method of carotid arterial system
The invention provides a simple and convenient method and a simple and convenient system for evaluating hemodynamic indexes and characteristic parameters of a blood signal of a carotid arterial system through non-invasive detection on blood pressure of brachial arteries and an axial blood velocity signal of a common carotid artery. The method comprises the following steps: detecting the waveform and a numerical value of an axial blood velocity of the common carotid artery by using a continuous Doppler blood velocity waveform detecting module, detecting diastolic pressure and systolic pressure of a human body by using an arm-type electronic blood pressure detecting module, and then calculating hemodynamic parameters of the carotid arterial system by a simplified method; and selecting Morlet mother wavelet for wavelet analysis on the waveform of the blood velocity of the common carotid artery, and calculating the characteristic parameters of the blood signal. The method is an analysis method which combines the hemodynamic principle and wavelet transformation; compared with the method adopted by the conventional cerebral hemodynamic analysis device, the signal acquisition and analysis method is simpler; and to a great extent, the defects that the conventional analysis device is complicated in structure, huge in volume, complex in operation, high in price and the like are overcome.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
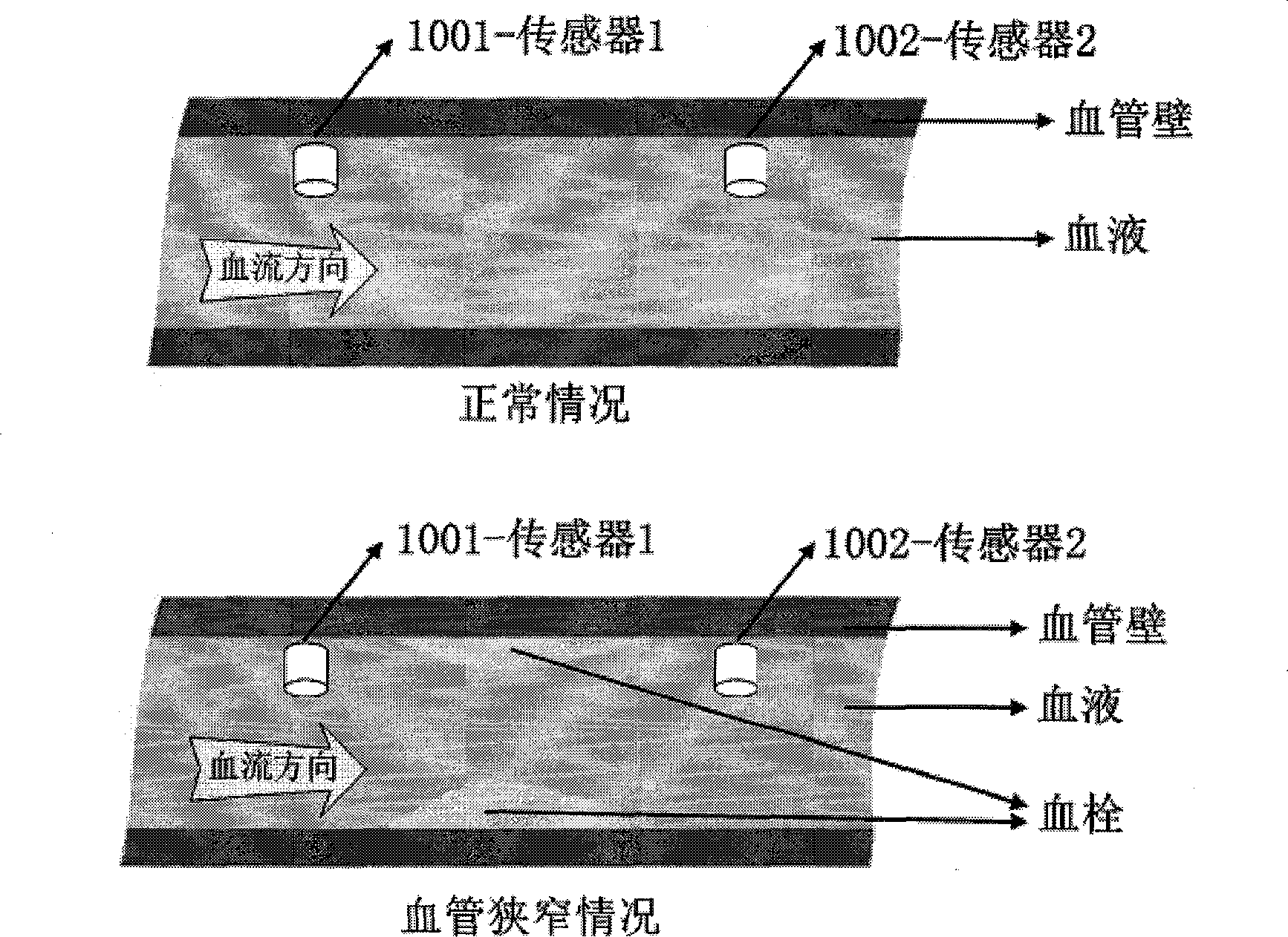
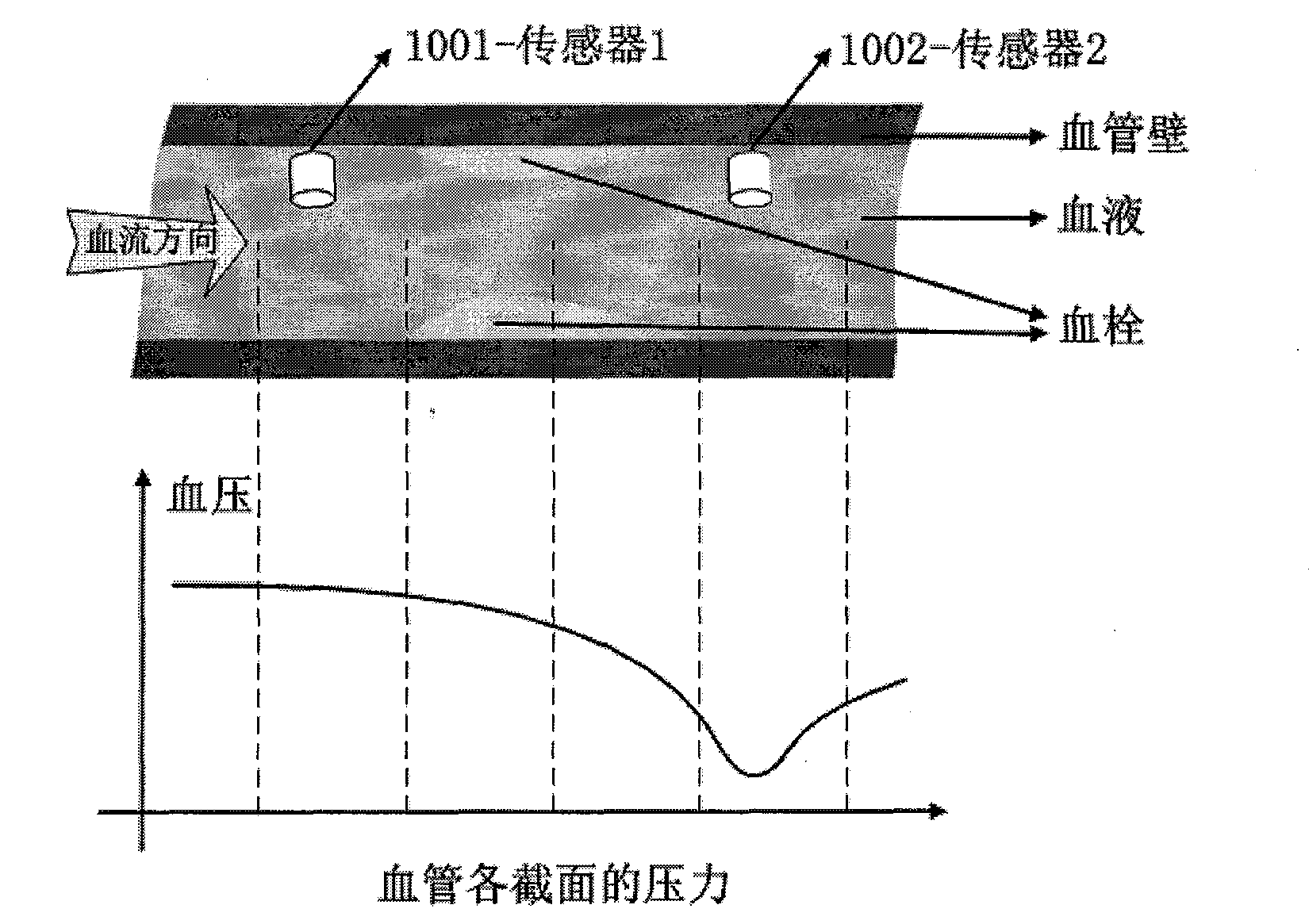
Method for detecting vessel stenosis based on double interventional pressure sensors
InactiveCN103829933AReal-time monitoring of stenosisEffective treatmentEndoradiosondesCatheterArterial vesselTubular stenosis
The invention relates to a method for detecting vessel stenosis based on double interventional pressure sensors. According to the method for detecting the vessel stenosis based on double interventional pressure sensors, the two pressure sensors are guided into a blood vessel (mainly the artery blood vessel) in an interventional mode, and whether stenosis happens to the blood vessel between the two pressure sensors can be judged by measuring the numerical values of the two pressure sensors through calculation.
Owner:任勇 +2
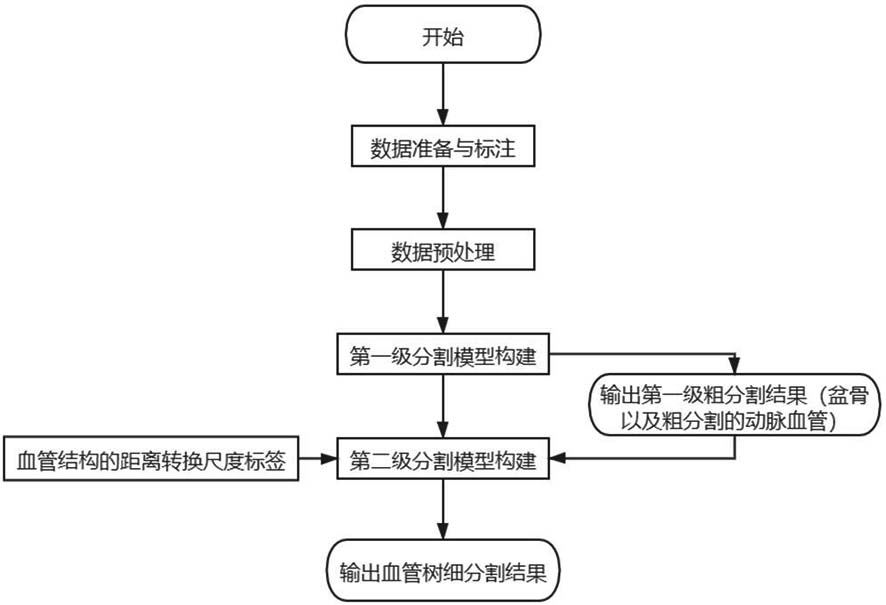
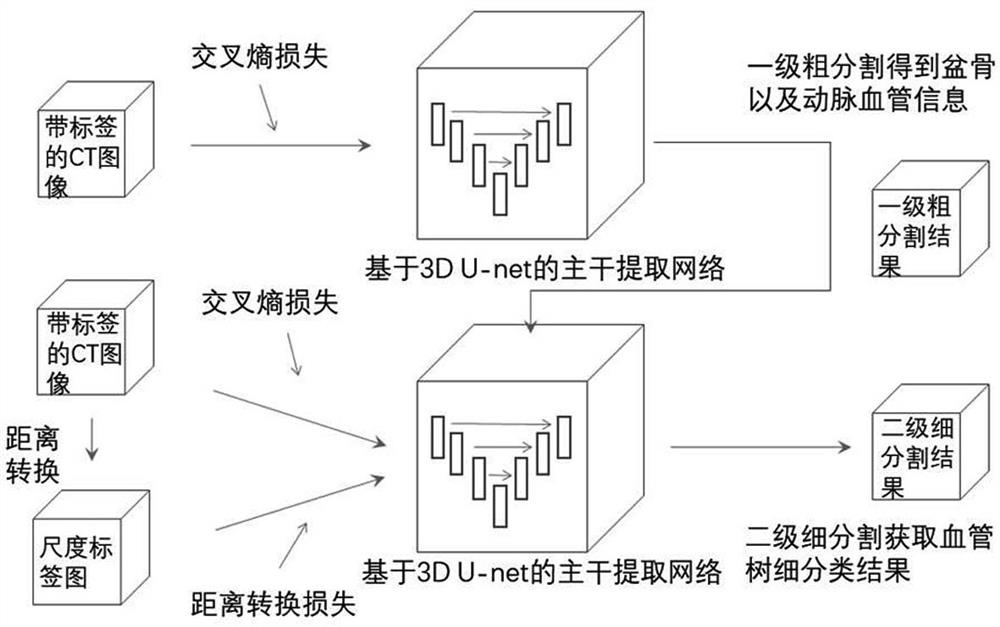
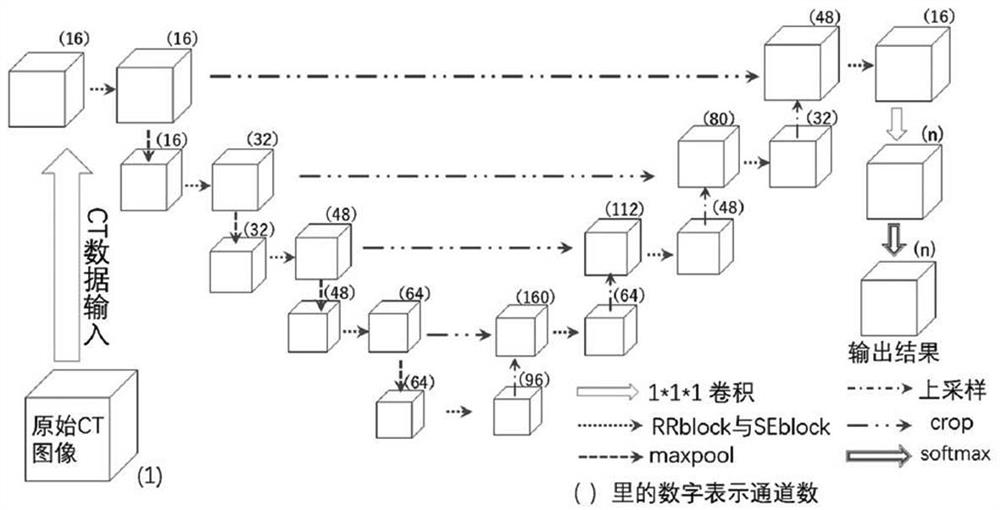
Deep learning-based multi-level segmentation method for pelvis and artery blood vessels thereof
ActiveCN112489047ASplit automaticallyAutomatically segment resultsImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageAbdomen+Pelvis
The invention relates to the technical field of pelvis and pelvis artery blood vessel tree segmentation, in particular to a deep learning-based pelvis and pelvis artery blood vessel multi-level segmentation method, which is used for solving the problem that an abdomen pelvis and a pelvis artery blood vessel tree cannot be automatically, efficiently and accurately segmented in a multi-resolution CTimage in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing and labeling data; 2, preprocessing the data; 3, constructing a first-level segmentation model of the 3D convolutional neural network based on multi-level segmentation; 4, constructing a second-stage segmentation model; 5, training a first-stage segmentation model and a second-stage segmentation model by using thecalibrated data and the synthesized loss function; and 6, performing abdomen information segmentation on the input three-dimensional CT image by using the first-stage segmentation model and the second-stage segmentation model trained in the step 5. According to the method, the abdominal pelvis and the pelvis vascular tree can be automatically, efficiently and accurately segmented in the multi-resolution CT image.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Sensor holder
The present invention is directed to holders for a sensor. The holders apply pressure to the sensor to prevent a venous blood signal without dampening the arterial blood signal and are optically opaque to shield ambient light from reaching the sensor.
Owner:CONMED CORP
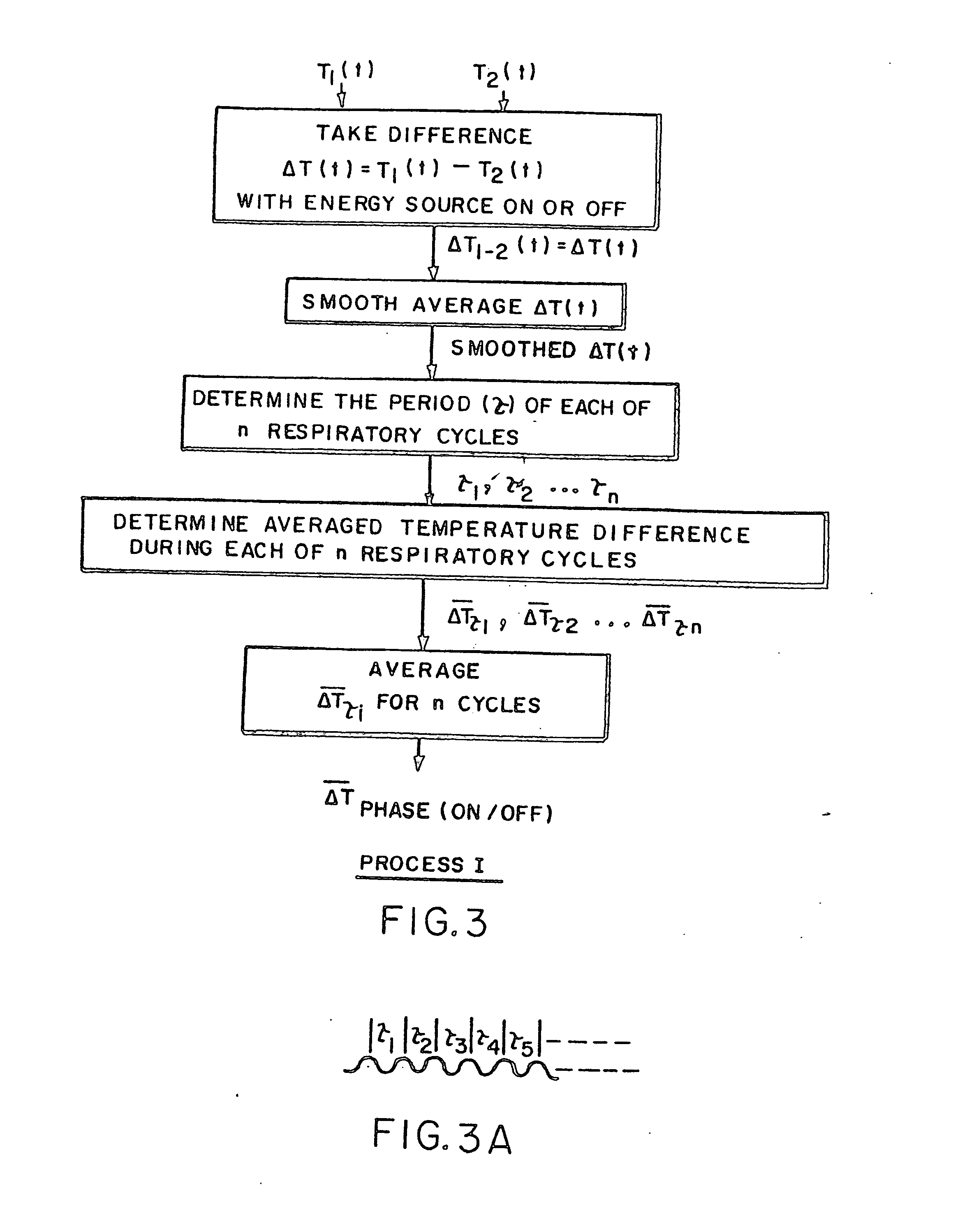
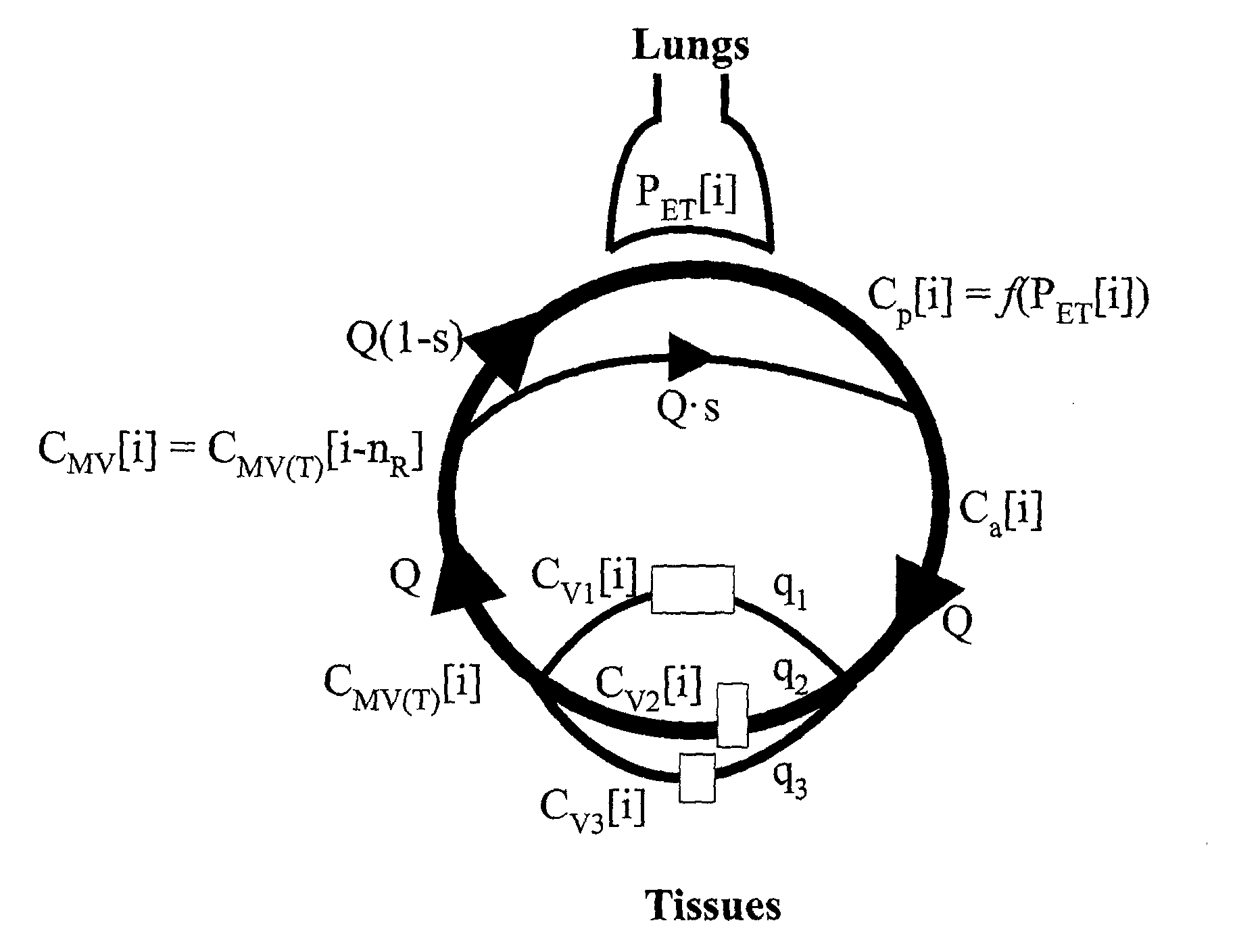
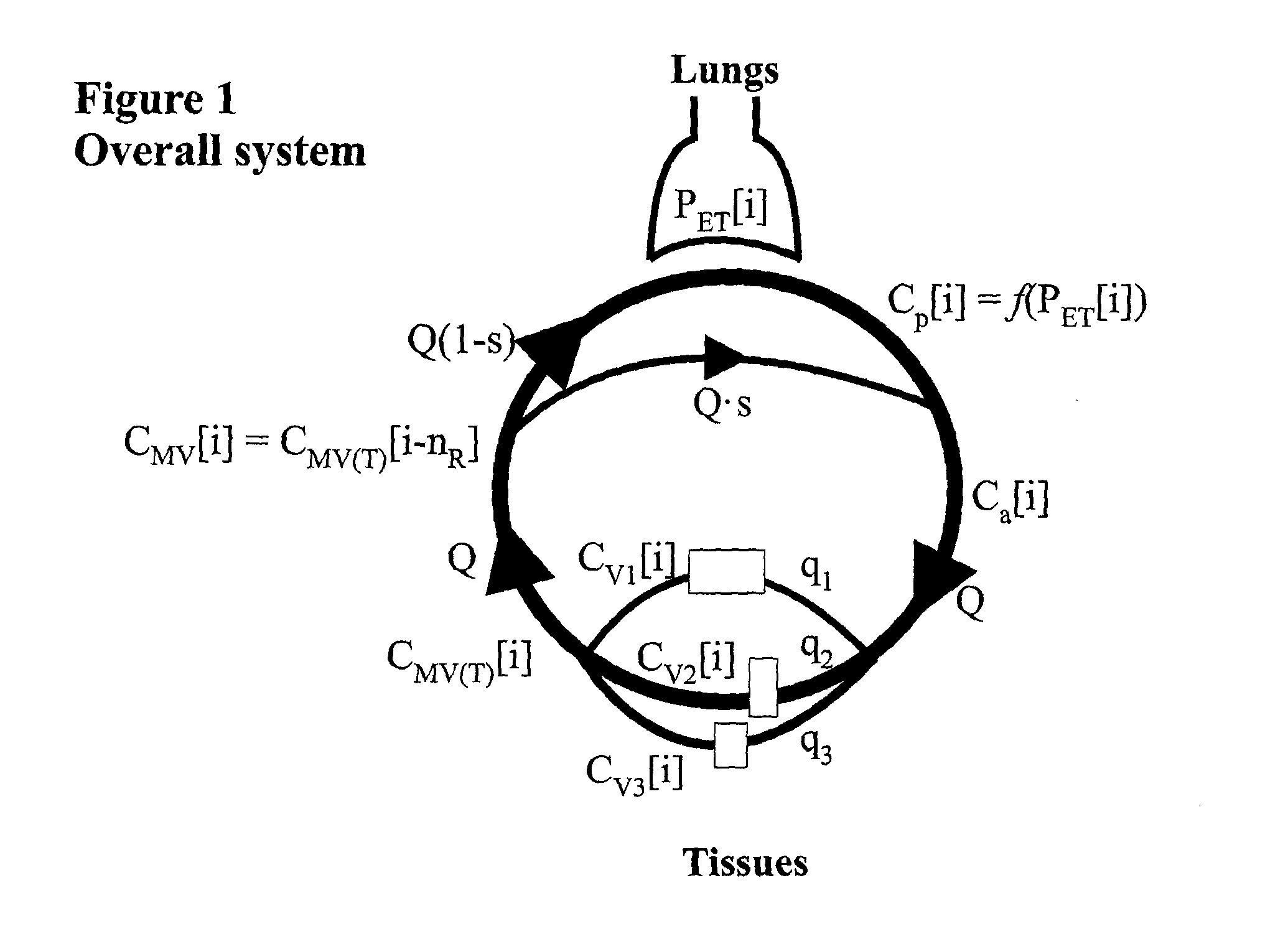
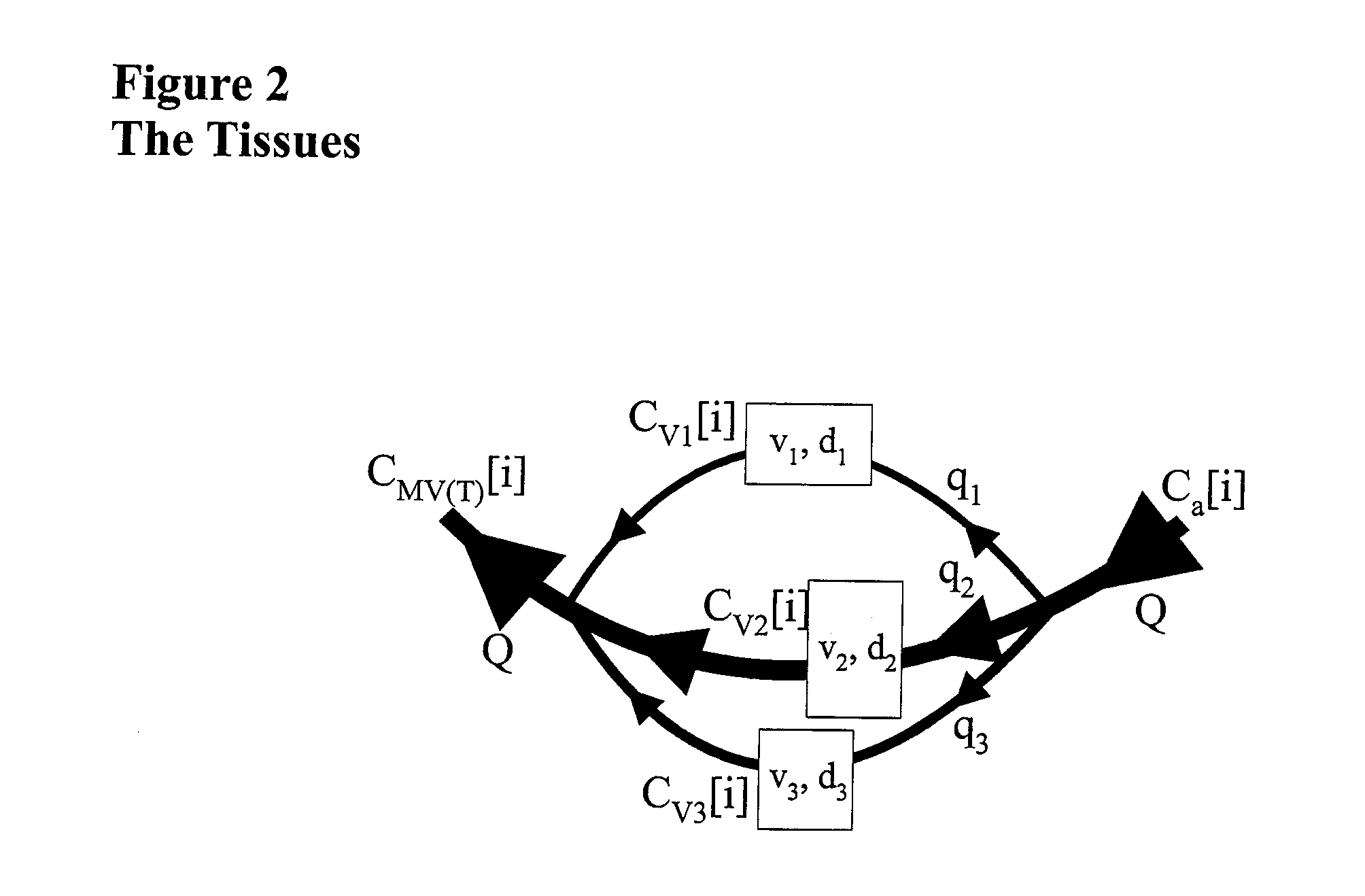
Method and apparatus to attain and maintain target arterial blood gas concentrations using ramp sequences
InactiveUS20150114394A1Ensure proper implementationReduce the differenceRespiratorsElectrocardiographyMedicineTherapeutic intent
An apparatus and method for controlling the end tidal partial pressure of a gas X in a subject's lung, and to the use of such an apparatus and method for research, diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, wherein the method consists of: obtaining input of a series of logistically attainable PetX values for a series of respective breaths: determining an amount of gas X required to be inspired by the subject in an inspired gas to target the PetX for each of said respective breaths: and controlling a gas delivery device to deliver the amount of gas in a volume of gas delivered to the subject in each of said respective breaths to target the respective PetX for that breath.
Owner:KLEIN MICHAEL +8
Pourable vascular tissue engineering reactor having rotating function
ActiveCN101372660ARealize the pulsation functionRealize axial push-pull functionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPerfusion CultureRotation function
The invention discloses a vascular tissue engineering reactor with rotation function. The reactor overcomes the disadvantages that the common arterial tissue engineering reactors can not simultaneously supply the vascular tissue with the culture conditions of intravascular perfusion and vascular rotation, and the mass transfer performance is poor. The vascular tissue engineering reactor comprises a liquid storage bottle, a liquid driving device, a vascular tissue culture cavity, a linear motor, a step motor, a vascular tissue transmission device, and the like, realizes the vascular tissue rotation in the course of intravascular perfusion culture, and has good mass transfer performance.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
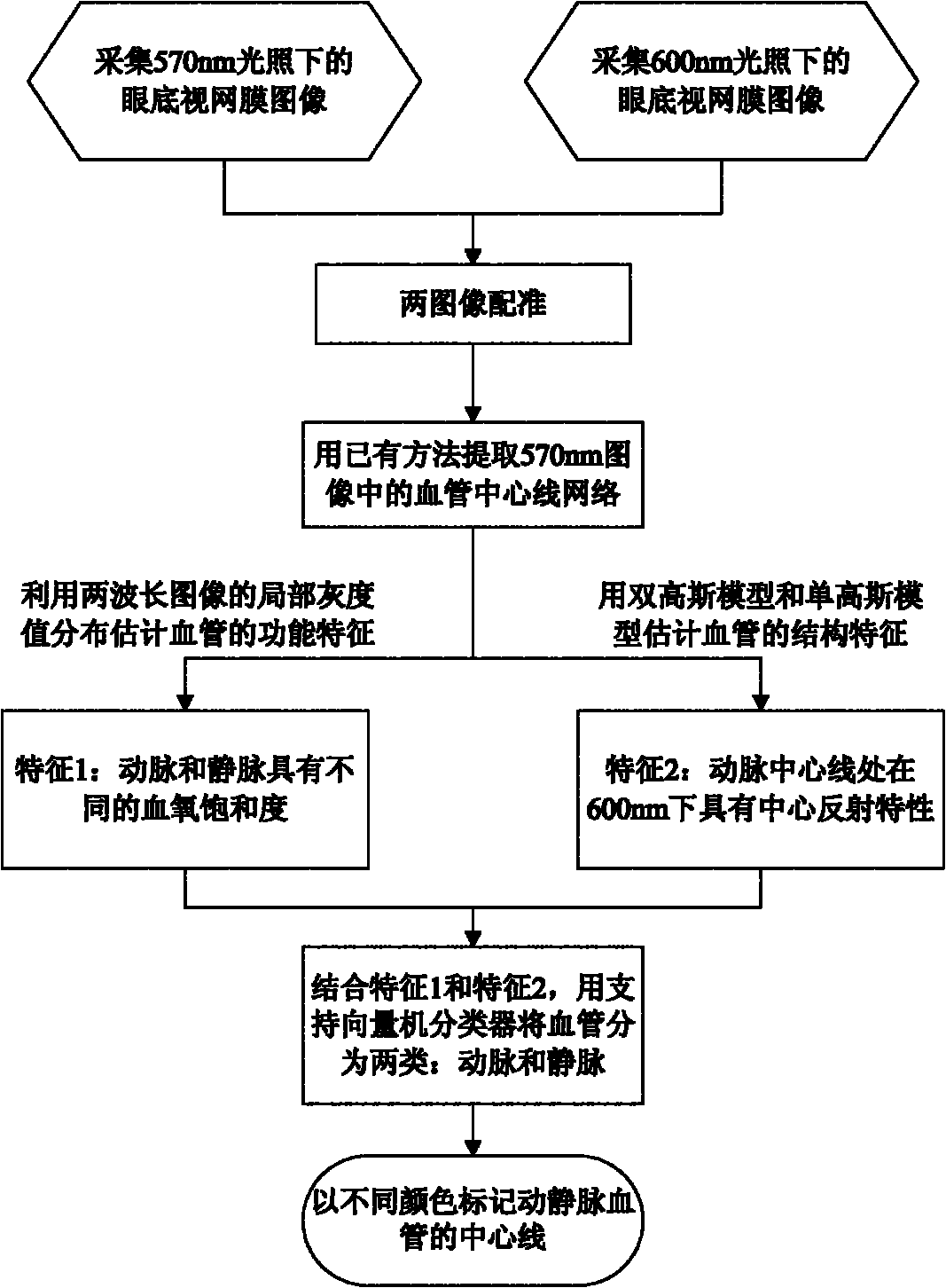
Endogenous optical imaging method for automatically separating arteries and veins
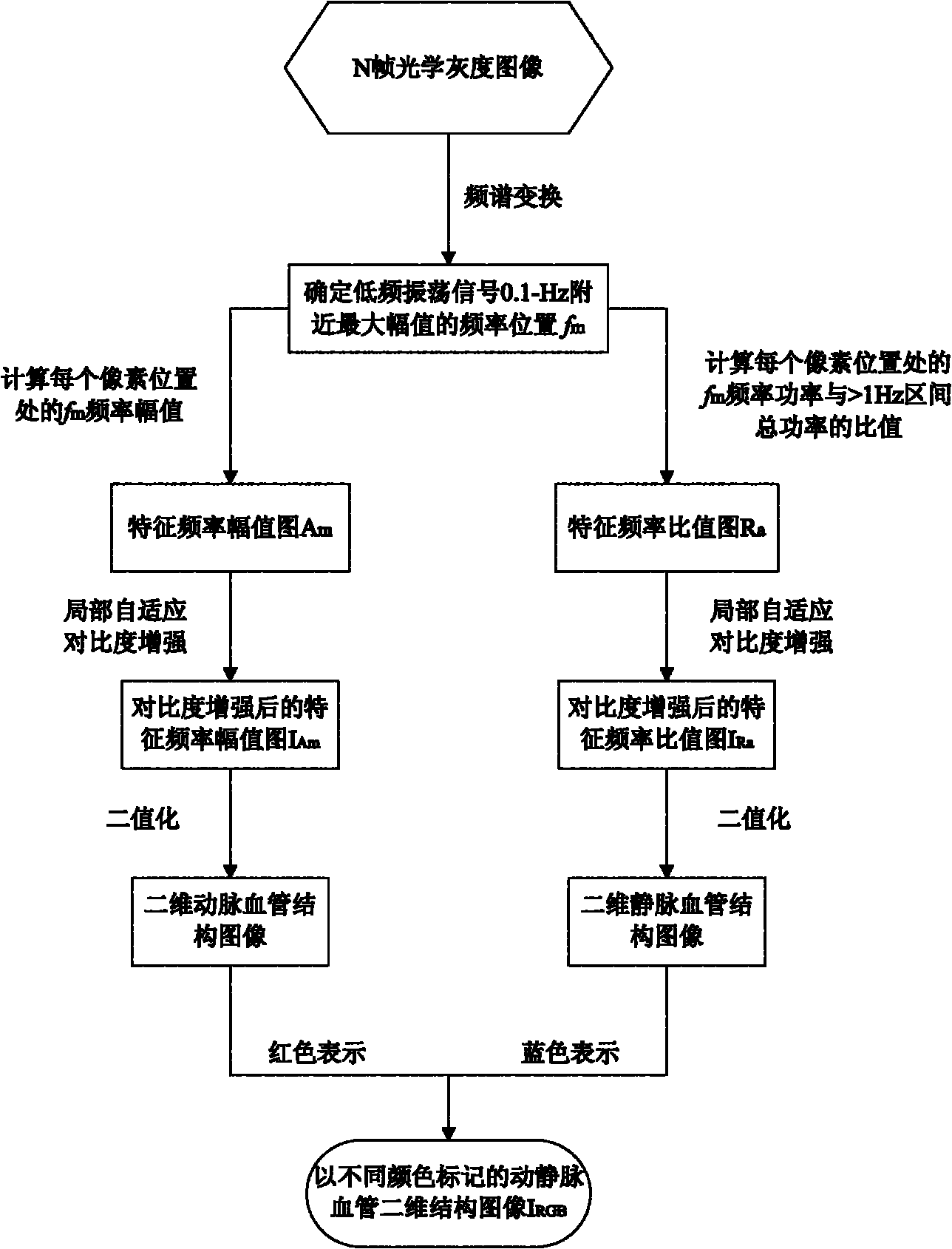
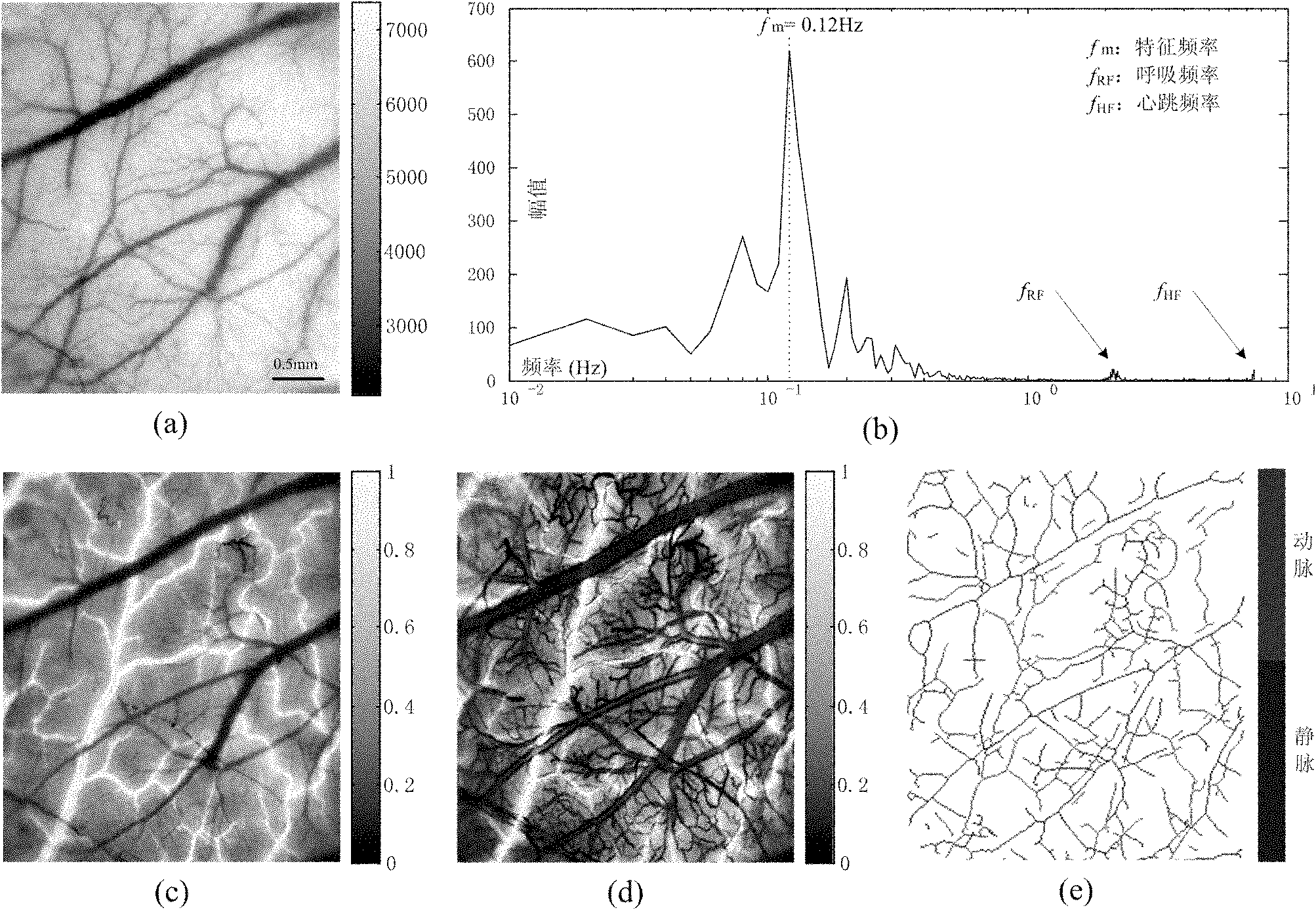
ActiveCN101999885AAvoid complexityRealize automatic separationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFrequency spectrumVenous vessel
The invention discloses an endogenous optical imaging method for automatically separating arteries and veins and aims at providing an effective endogenous optical imaging method for effectively and automatically separating arteries and veins of organisms. In the technical scheme, the endogenous optical imaging method comprises the following steps of: carrying out spectrum analysis to a collected image sequence by adopting narrow-band quasi monochromatic light for illumination, and then realizing the identification and automatic separation of the arteries and veins by utilizing the amplitude distribution features of low-frequency oscillating signals of the image sequence through the operations of frequency spectrum transformation, enhancement of a local self-adaption contrast, automatic threshold segmentation and the like. The endogenous optical imaging method can be used for automatically separating the arteries and the veins and highlighting and separating the vessel structures of many arterioles and veinlets, thereby avoiding the design complexity of the imaging device using light with various central wavelengths for illumination.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Methods and Apparatus for Segregation of Particles
InactiveUS20110065181A1Prevent movementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyMaternal blood
The disclosure relates to an apparatus for segregating particles on the basis of their ability to flow through a stepped passageway. At least some of the particles are accommodated in a passage bounded by a first step, but at least some of the particles are unable to pass through a narrower passage bounded by a second step, resulting in segregation of the particles. The apparatus and methods described herein can be used to segregate particles of a wide variety of types. By way of example, they can be used to segregate fetal-like cells from a maternal blood sample such as maternal arterial blood.
Owner:ANGLE NORTH AMERICA INC
Stent model matching method and device for intracranial aneurysm and stent simulation display method
ActiveCN111743625AImprove matchHigh speedMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMedical automated diagnosisIntracranial ArteryCranial aneurysm
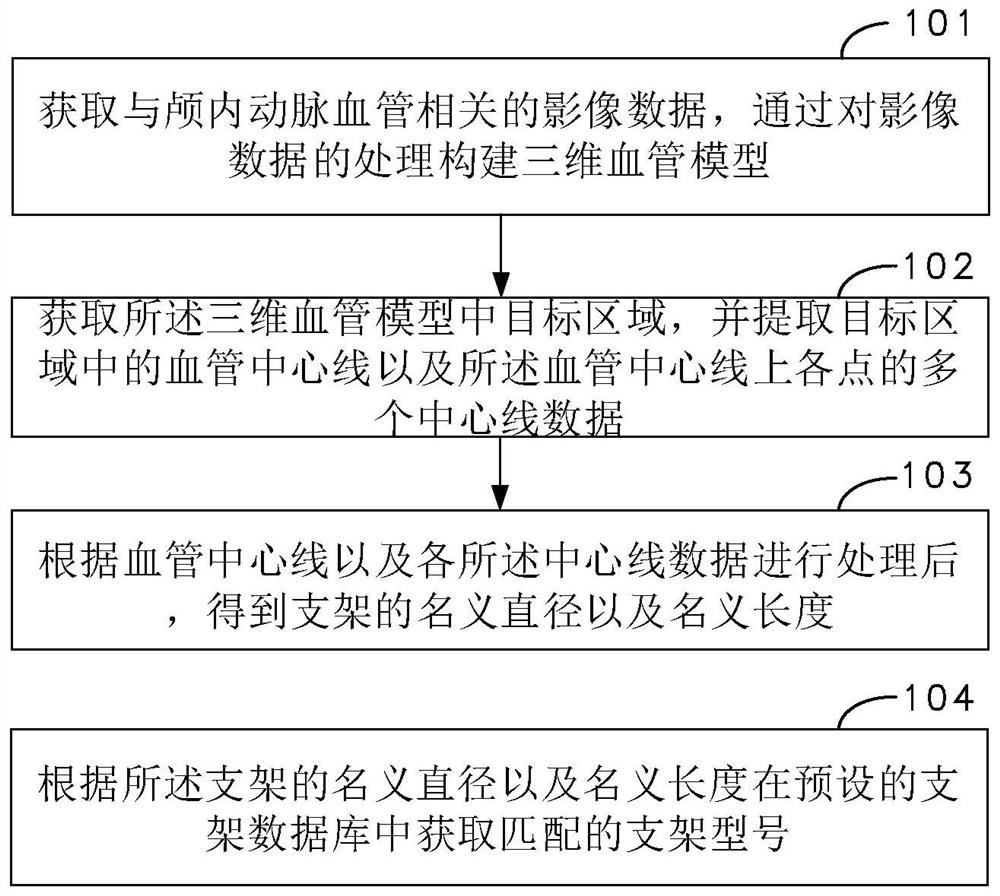
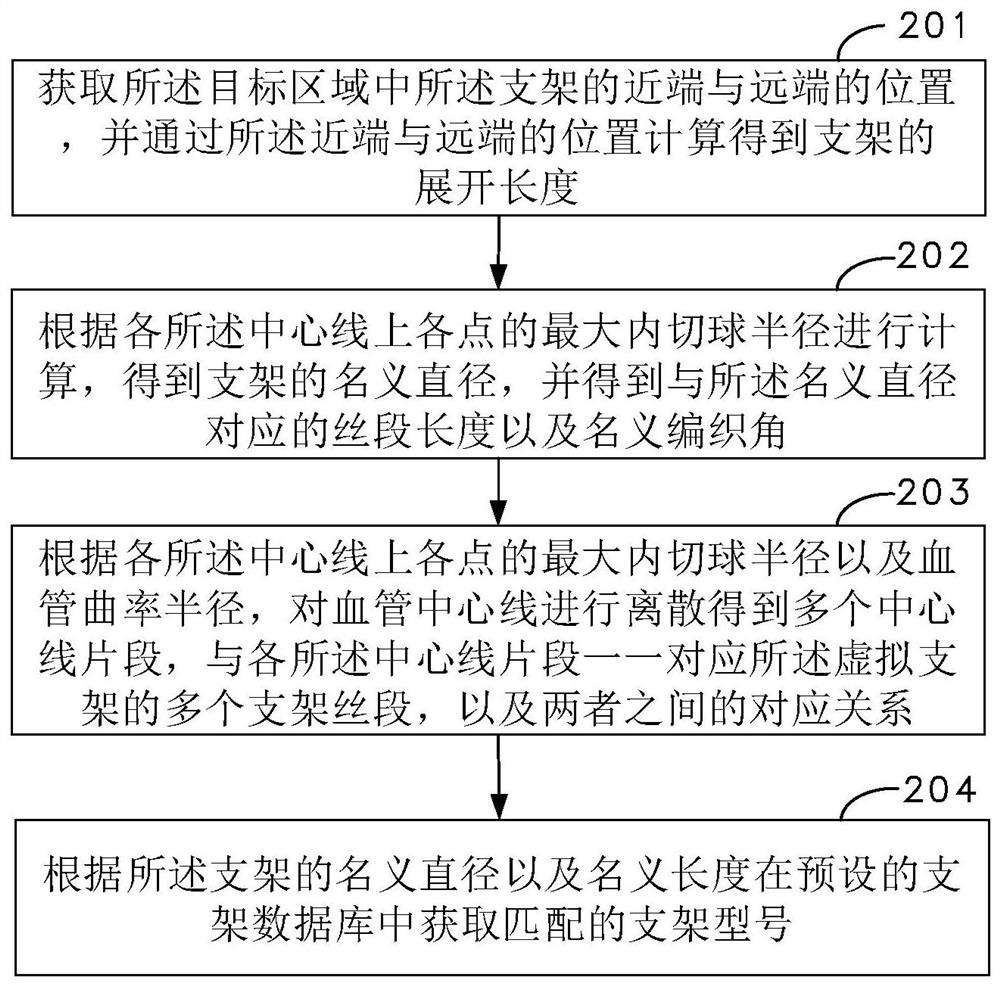
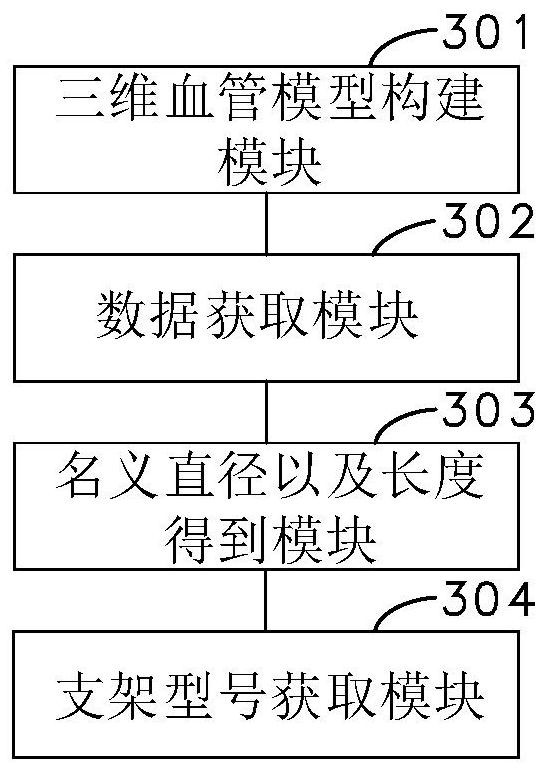
The invention relates to a stent model matching method and device for intracranial aneurysm and a stent simulation display method. The stent model matching method comprises the following steps of: acquiring image data related to intracranial artery blood vessels, and constructing a three-dimensional blood vessel model by processing the image data; obtaining a target area in the three-dimensional blood vessel model, and extracting a blood vessel center line in the target area and a plurality of pieces of center line data of points on the blood vessel center line; carrying out processing according to the blood vessel center line and the center line data to obtain a nominal diameter and a nominal length of the stent; and according to the nominal diameter and the nominal length of the stent, obtaining a matched stent model in a preset stent database. By adopting the method, the stent model matching efficiency and the blood vessel suitability can be improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU ARTERYFLOW TECH CO LTD
Physiological monitoring devices, systems, and methods
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Intracranial vascular image interception method and system based on a central line
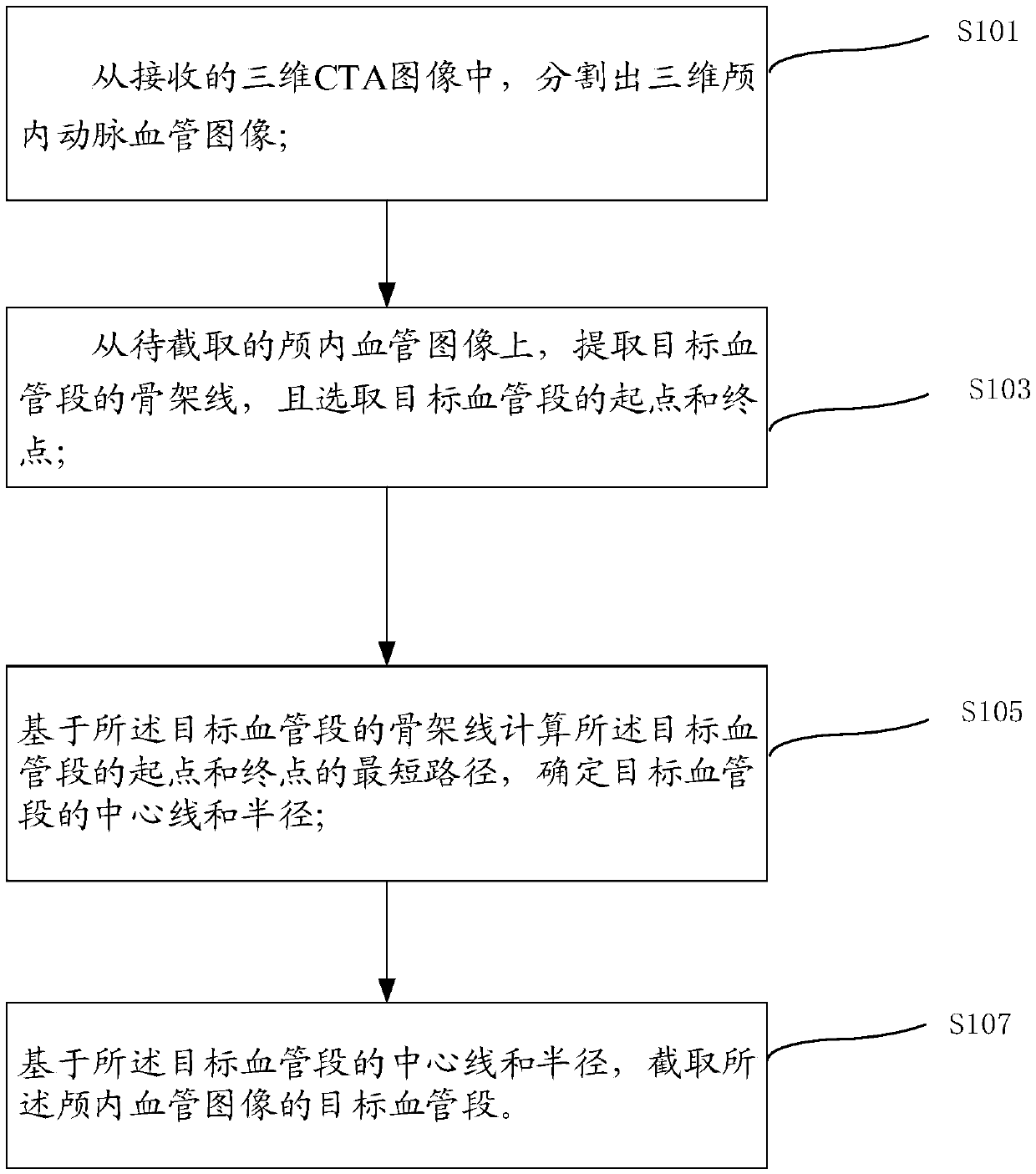
PendingCN109584169ARealize partial interceptionEasy to materializeImage enhancementImage analysisIntracranial ArteryComputer vision
The embodiment of the invention discloses an intracranial vascular image interception method and system based on a central line. The scheme comprises the steps of segmenting a three-dimensional intracranial artery blood vessel image from a received three-dimensional CTA image; Extracting a skeleton line of the target blood vessel segment from the intracranial blood vessel image to be intercepted,and selecting a starting point and a terminal point of the target blood vessel segment; Calculating the shortest path of the starting point and the ending point of the target blood vessel segment based on the skeleton line of the target blood vessel segment, and determining the center line and the radius of the target blood vessel segment; And based on the center line and the radius of the targetblood vessel segment, intercepting the target blood vessel segment of the intracranial blood vessel image. According to the scheme, the blood vessel segment image in the three-dimensional CTA image islocally captured, so that the intracranial artery blood vessel segment can be materialized, and interventional operation simulation and related teaching appliance manufacturing are facilitated.
Owner:XUANWU HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL UNIV OF MEDICAL SCI
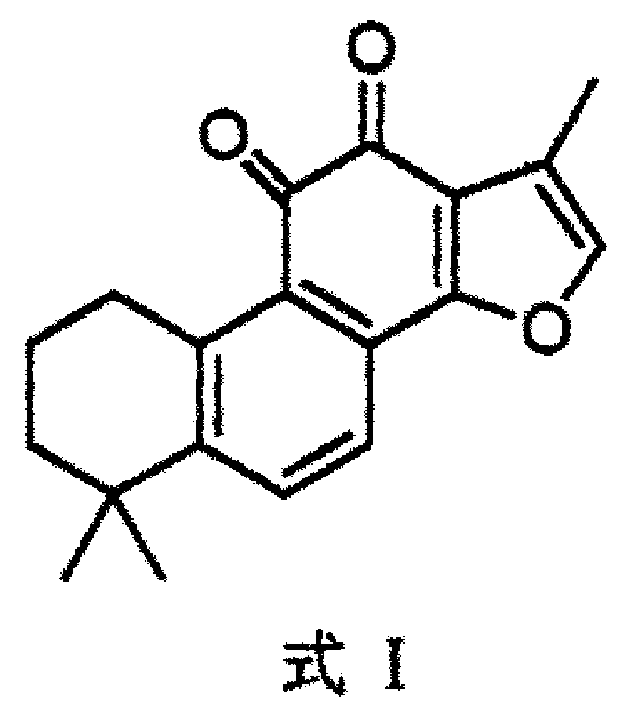
Tanshinone 11A used in preparing medicine for preventing and treating atherosclerosis
InactiveCN1426782ADeposit reduction and removalDoes not affect metabolismOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderDiseaseCholesterol
An application of tanshinone 11A to preparing the medicines for preventing and treating atherosclerosis and its related diseases is disclosed. The tanshinone 11A can reduce the deposit of cholesterol on the inner surface of artery.
Owner:广州美奇生物科技有限公司
Adaptive calibration for pulse oximetry
A method for calibrating a pulse oximeter device and an apparatus incorporating the method and a system for utilizing the method. The method is based on modeling light propagation in tissue at two wavelengths, typically, one in the red and one in the infrared range of the spectrum. A formula is derived relating the arterial oxygen saturation to a ratio R commonly measured by standard pulse oximeters. A specific parameter is identified and utilized in the calibration of the oximeter. This parameter is formulated in terms of the DC signals measured by the pulse oximeter at the two wavelengths. An empirical method for estimating this parameter based on experimental data is also described.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Method for non-invasive quantitative assessment of radioactive tracer levels in the blood stream
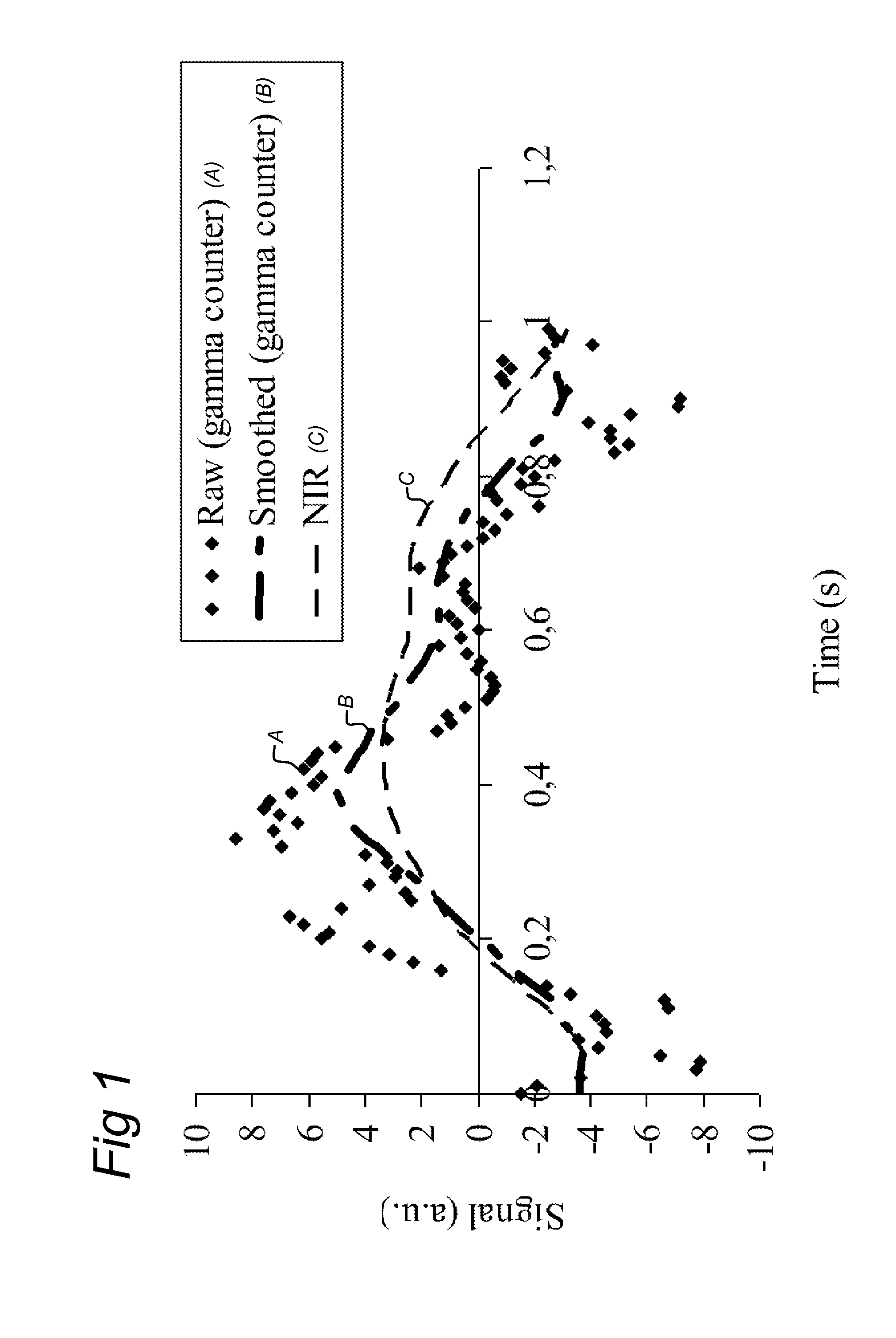
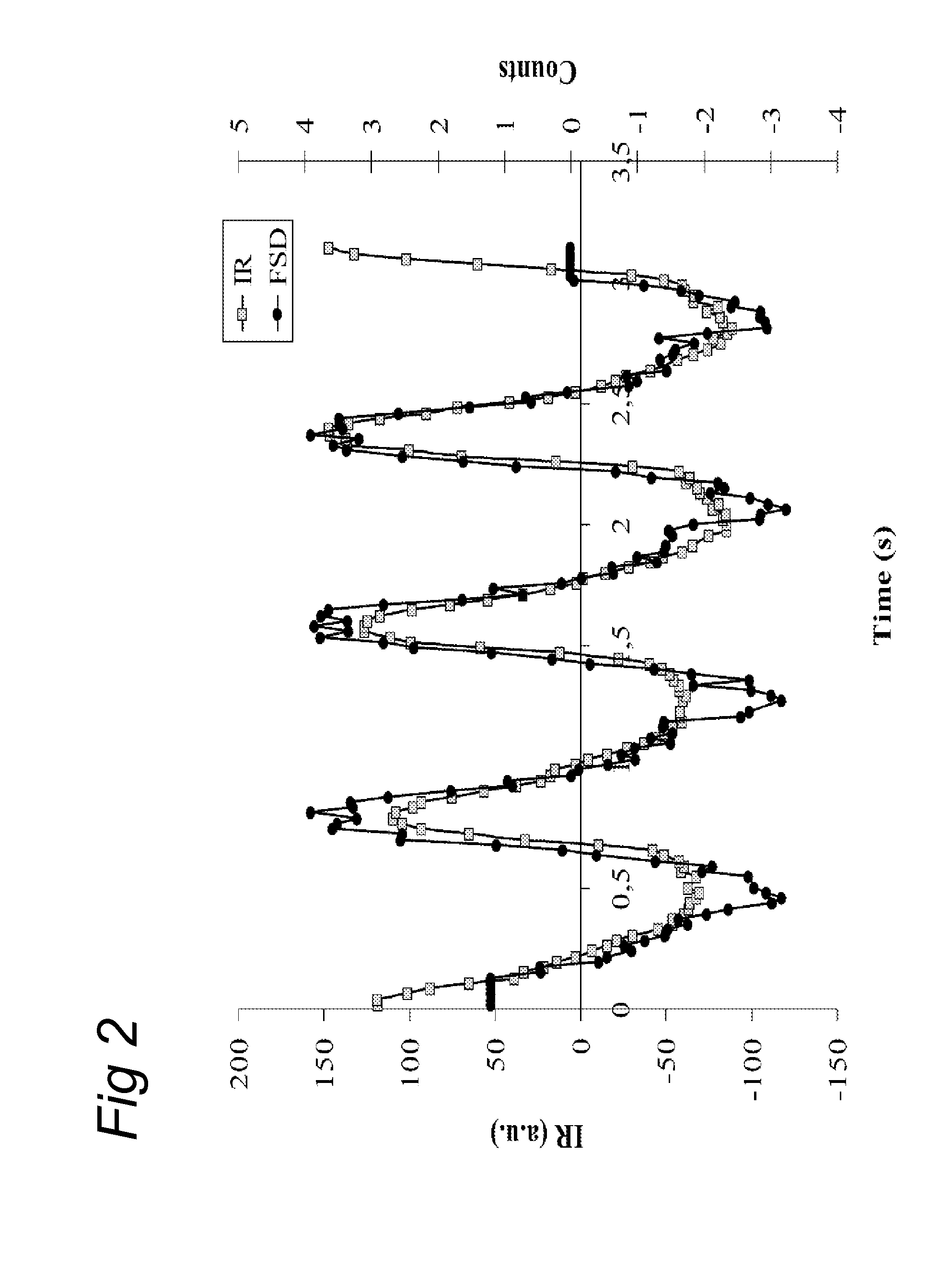
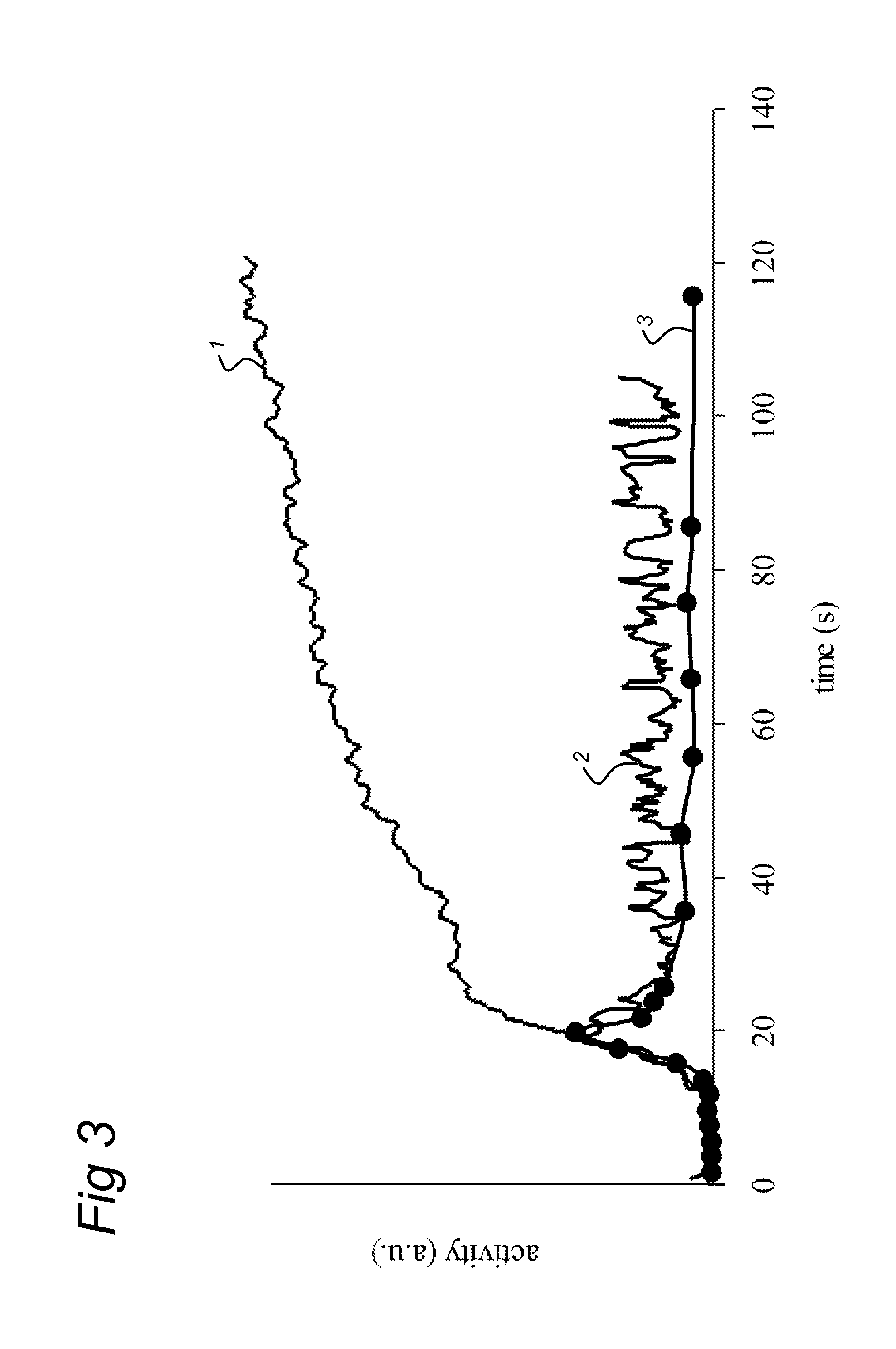
A method and system for non-invasive quantitative assessment of radionuclide tracer levels in the blood stream. The method relies on the finding that the gamma-radiation signal acquired using a gamma scintillation probe, is the resultant from a wave-component with changing amplitude, resulting from the radiotracer in the bloodstream and a non-wave background component resulting from radiotracer distributed throughout the tissue surrounding the arterial vessel. The method involves phase-sensitive conversion of the ‘input signal’, extracting there from an output signal representing the signal component originating from the bloodstream, using the changes in arterial blood volume as the reference wave-form. A particular aspect of the invention concerns methods of quantitative PET or SPECT imaging wherein the concentration of radionuclides in the blood stream as a function of time after injection is assessed using the method of the invention.
Owner:NETHERLANDS CANCER INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com