Patents
Literature
43 results about "Hypovolemia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A condition in which the volume of blood plasma is too low.
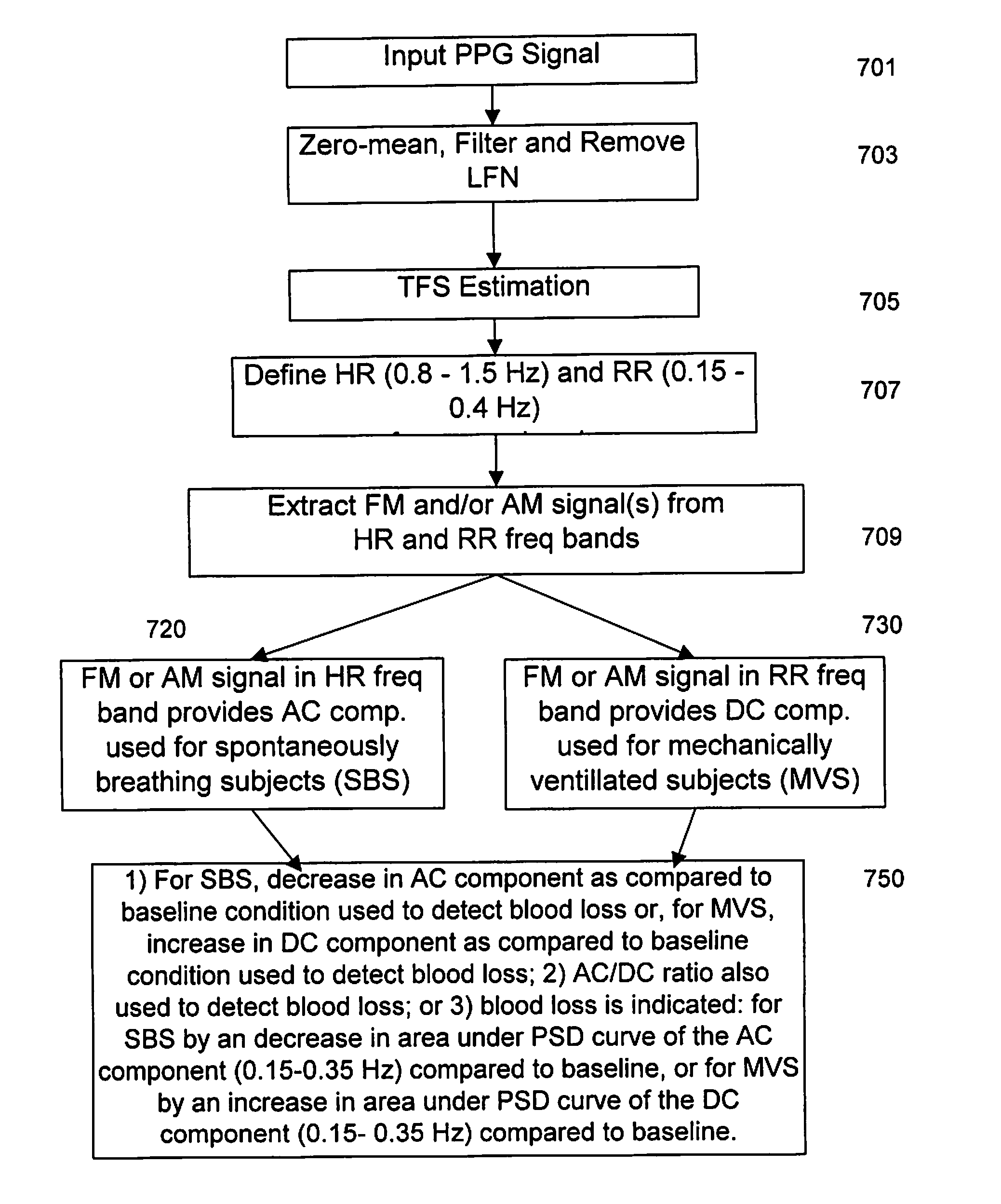
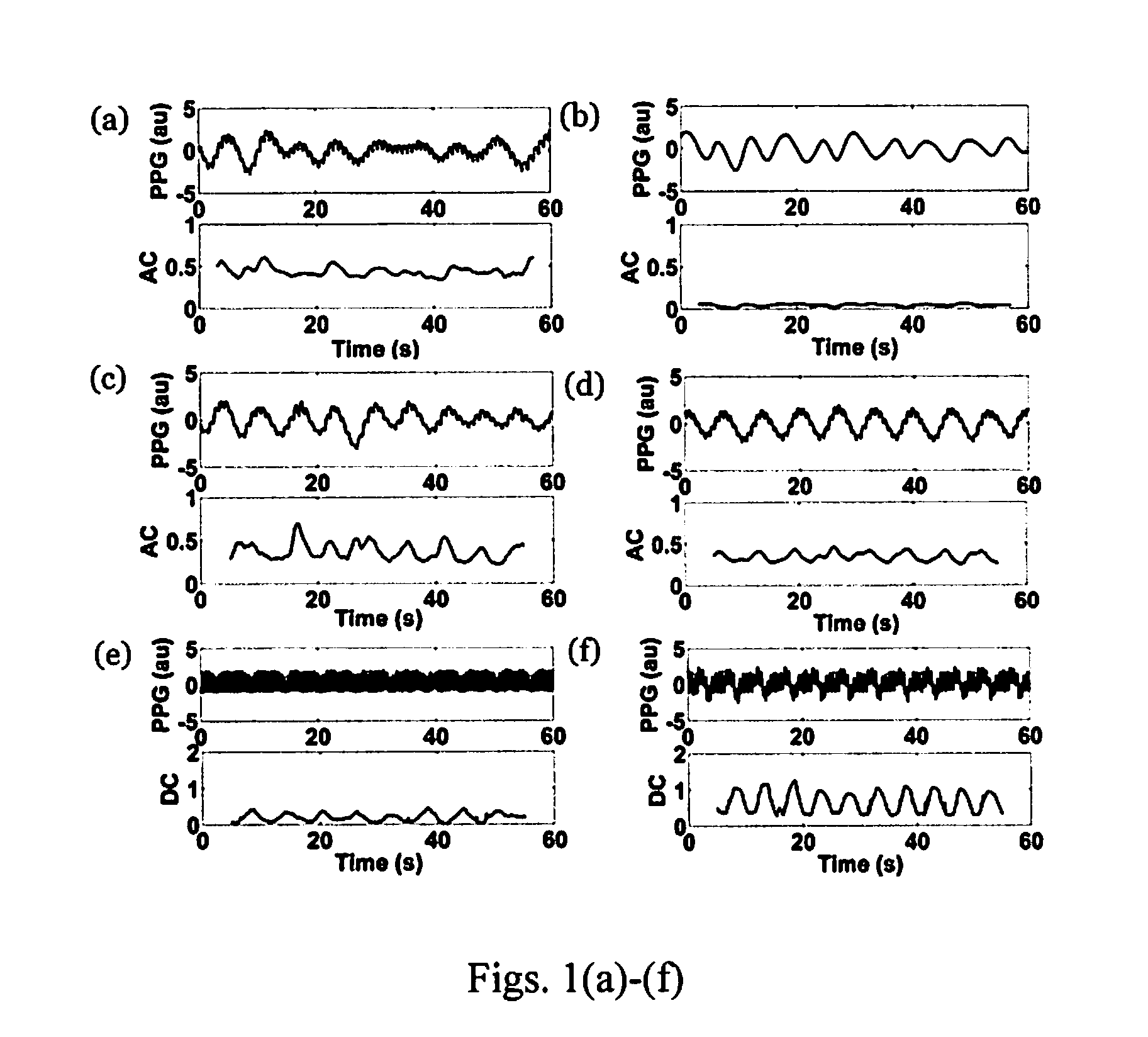
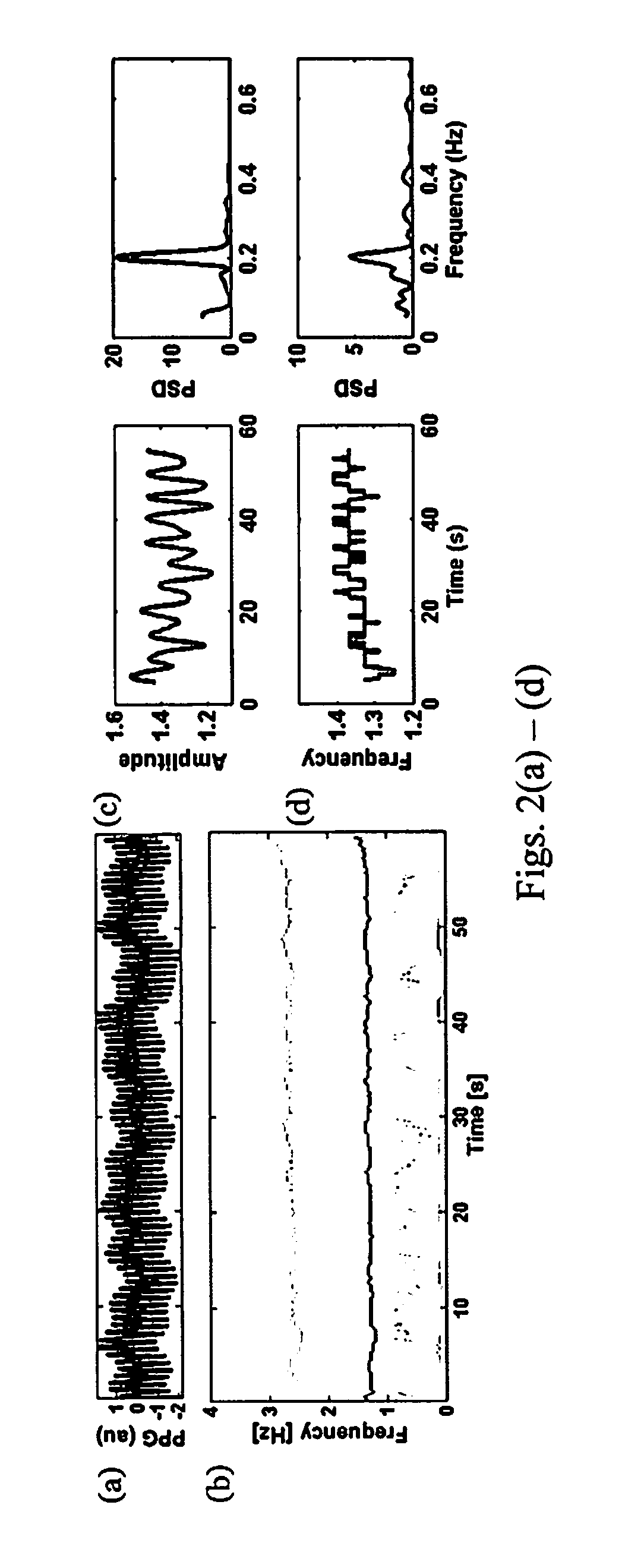
Apparatus and method for respiratory rate detection and early detection of blood loss volume
ActiveUS20120296219A1Accurate detectionEasy diagnosisEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterNon invasiveHypovolemia
An apparatus and method is provided that provide, in real-time, an accurate detection and warning of dangerous blood or fluid loss to warn of impending hypovolemia, by non-invasive monitoring and processing of photoplethysmography data.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Reduced side-effect hemoglobin compositions
The invention relates to novel hemoglobin compositions, particularly novel recombinant mutant hemoglobin compositions, which eliminate or substantially reduce 1) the creation of heart lesions, 2) gastrointestinal discomfort, 3) pressor effects, and 4) endotoxin hypersensitivity associated with the administration of extracellular hemoglobin compositions in various therapeutic applications. Applications described include treatments for anemia, head injury, hemorrhage or hypovolemia, ischemia, cachexia, sickle cell crisis and stroke; enhancing cancer treatments; stimulating hematopoiesis; improving repair of physically damaged tissues; alleviating cardiogenic shock; and shock resuscitation.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
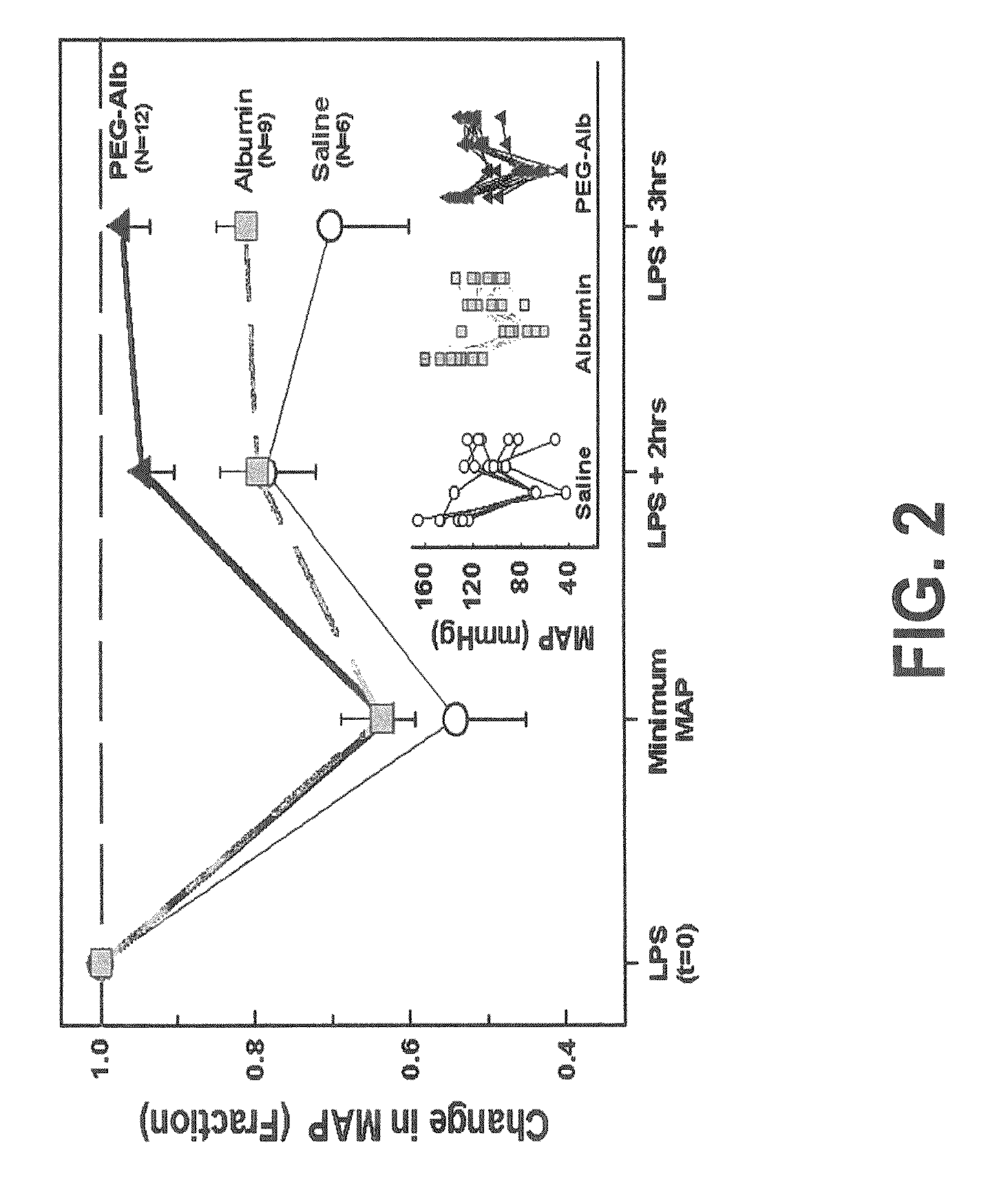
Volume Status Monitor: Peripheral Venous Pressure, Hypervolemia and Coherence Analysis
ActiveUS20100191128A1Reduce blood volumeEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterFluid replacementCoherence analysis
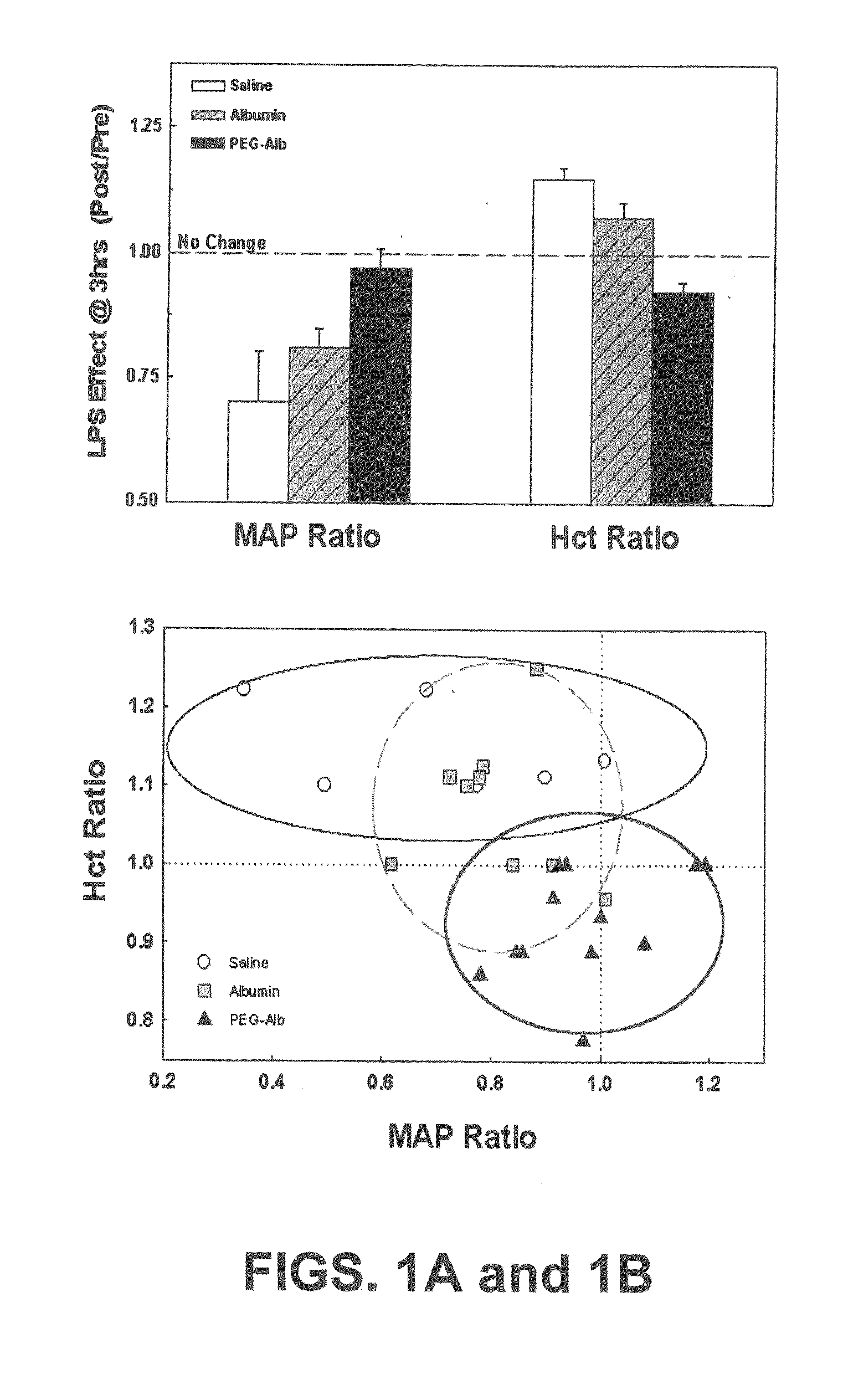
Systems and methods are provided for monitoring changes in blood volume using waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. In particular, the systems and methods relate to detecting ventilation-induced variation (VIV) of waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. Advantageously, the systems and methods may relate to analyzing VIV in peripheral venous pressure (PVP). Thus, the VIV of PVP may be measured, wherein decreased VIV is indicative of decreased blood volume In exemplary embodiments, such as involving spontaneous breathing, it may be necessary to account for changes in respiratory signal strength. Thus systems and methods are also provided for assessing coherence between ventilation and VIV for a flow or pressure waveform. Specifically, coherence is evaluated by comparing the waveform to a detected respiratory signal. Finally, systems and method are provided for distinguishing the impact of respiration on the PG signal during hypervolemia as compared to hypovolemia. Such systems and methods may advantageously be utilized to monitor fluid status during fluid replacement.
Owner:SHELLEY KIRK H +2
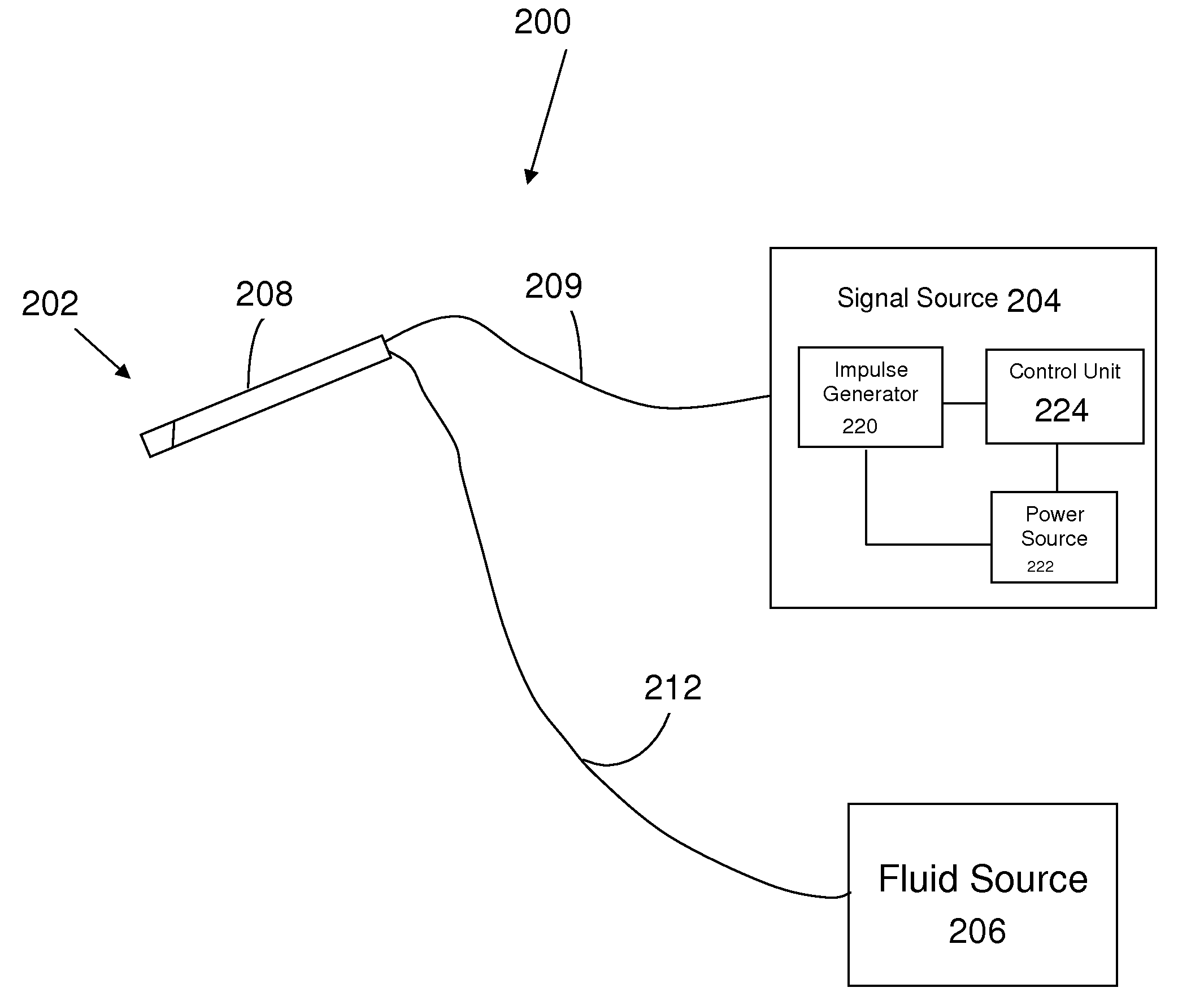
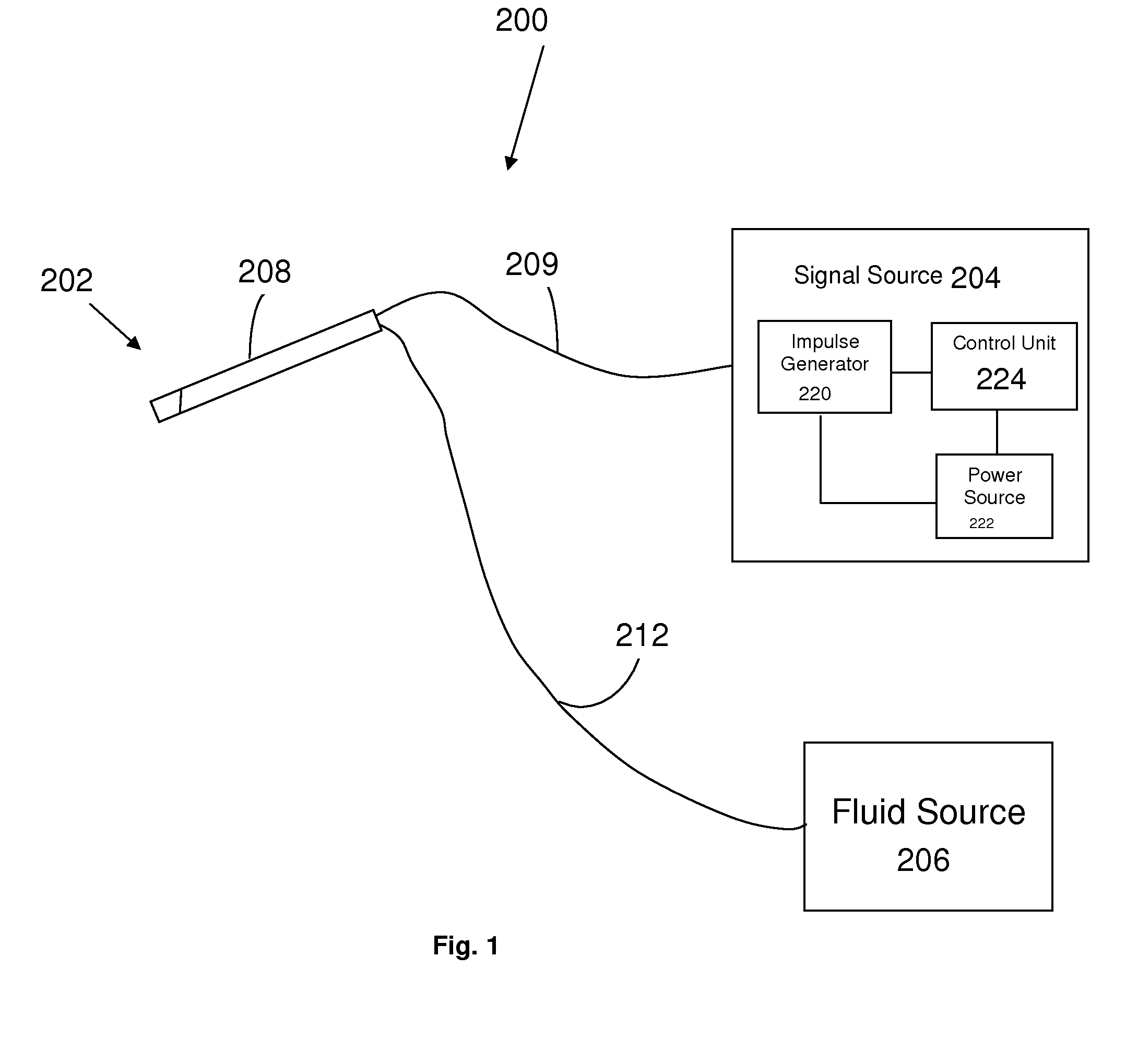
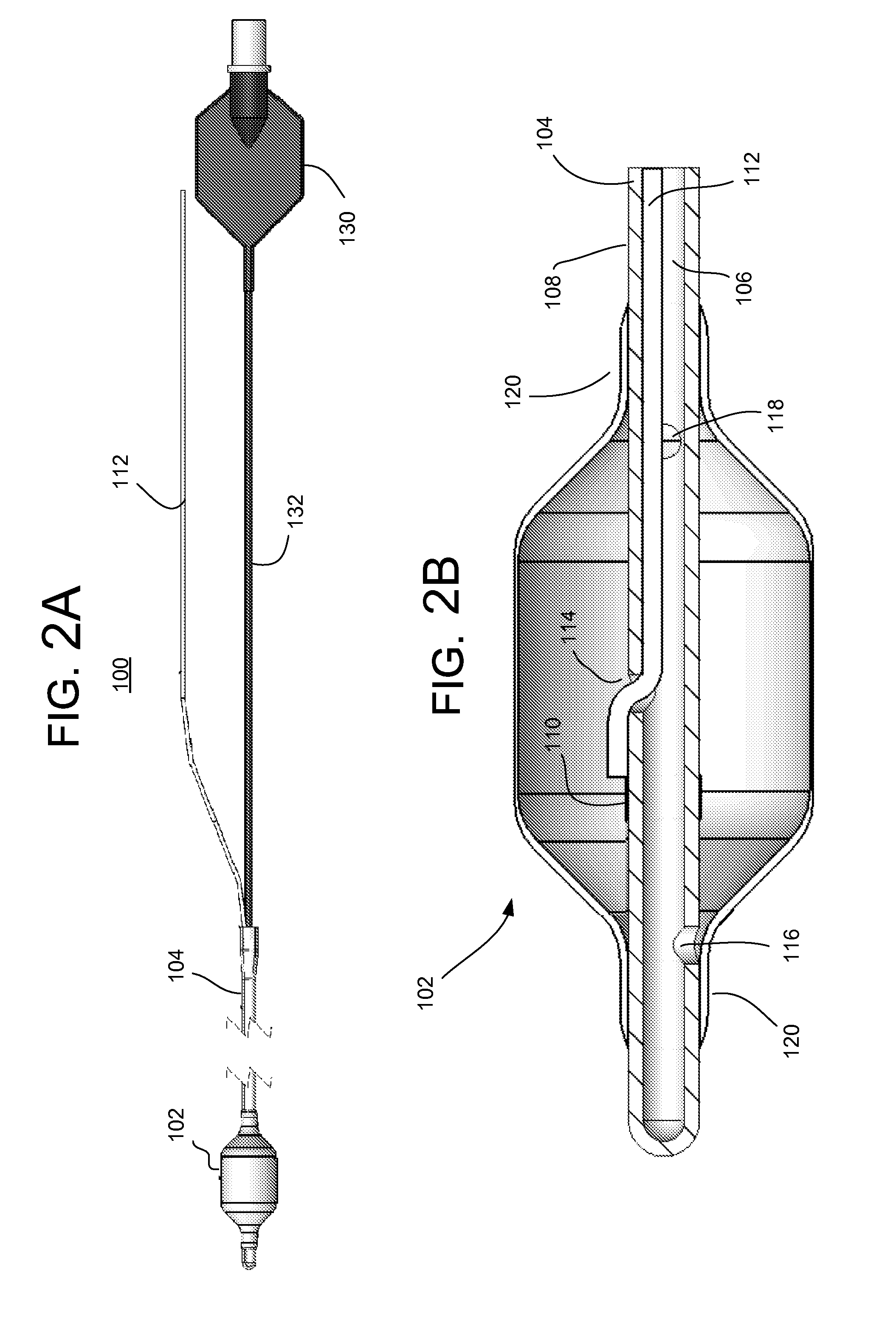
Electrical stimulation treatment of hypotension
ActiveUS8041428B2Raise the ratioSlow down heart rateEsophageal electrodesEndotracheal electrodesNervous systemMedicine
The present invention includes methods and devices for treating hypotension, such as in cases of shock, including septic shock, anaphylactic shock and hypovolemia. The method includes the step of applying at least one electrical impulse to at least one selected region of a parasympathetic nervous system of the patient. The electrical impulse is sufficient to modulate one or more nerves of the parasympathetic nervous system to increase the ratio of blood pressure to heart rate and relieve the condition and / or extend the patient's life.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
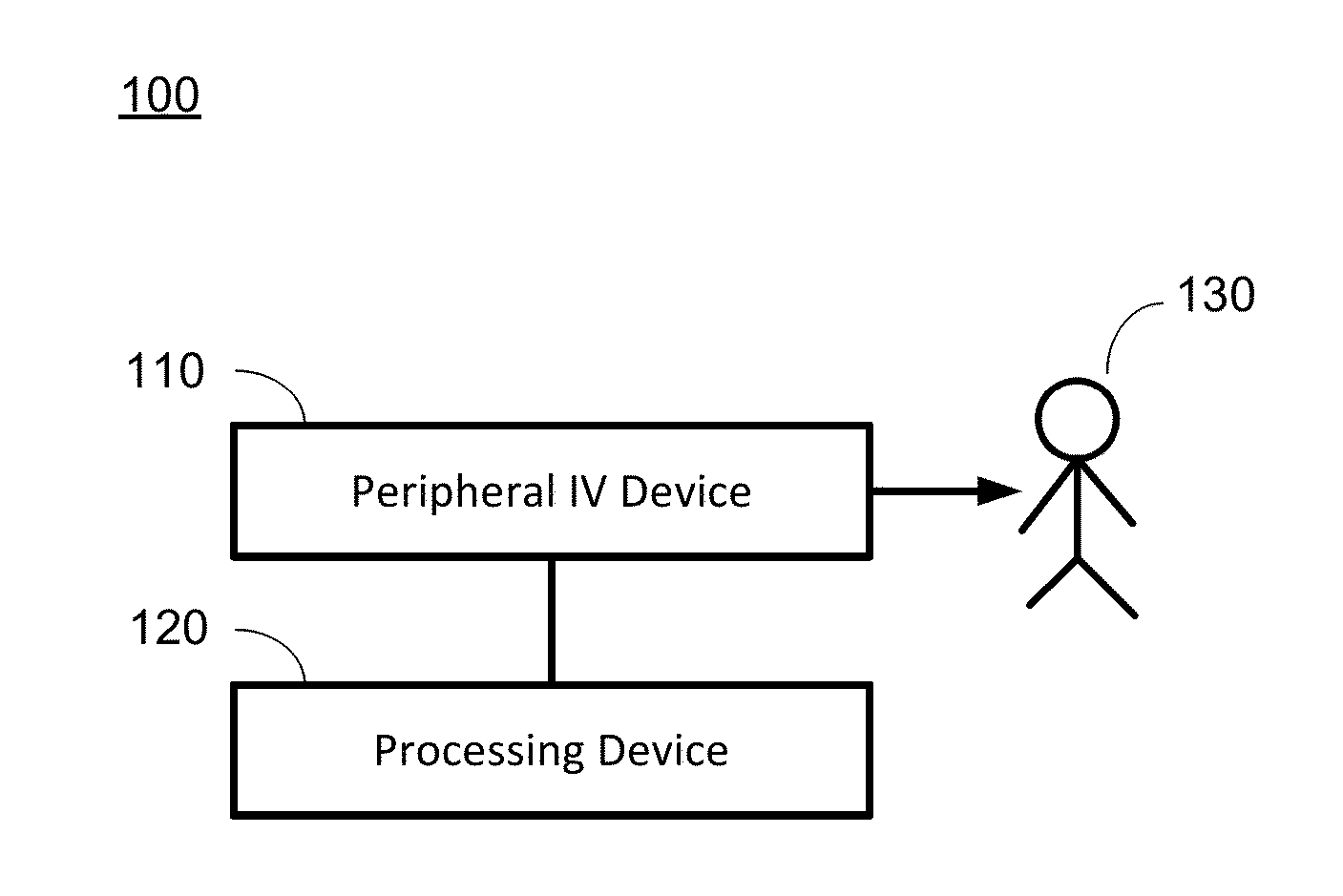
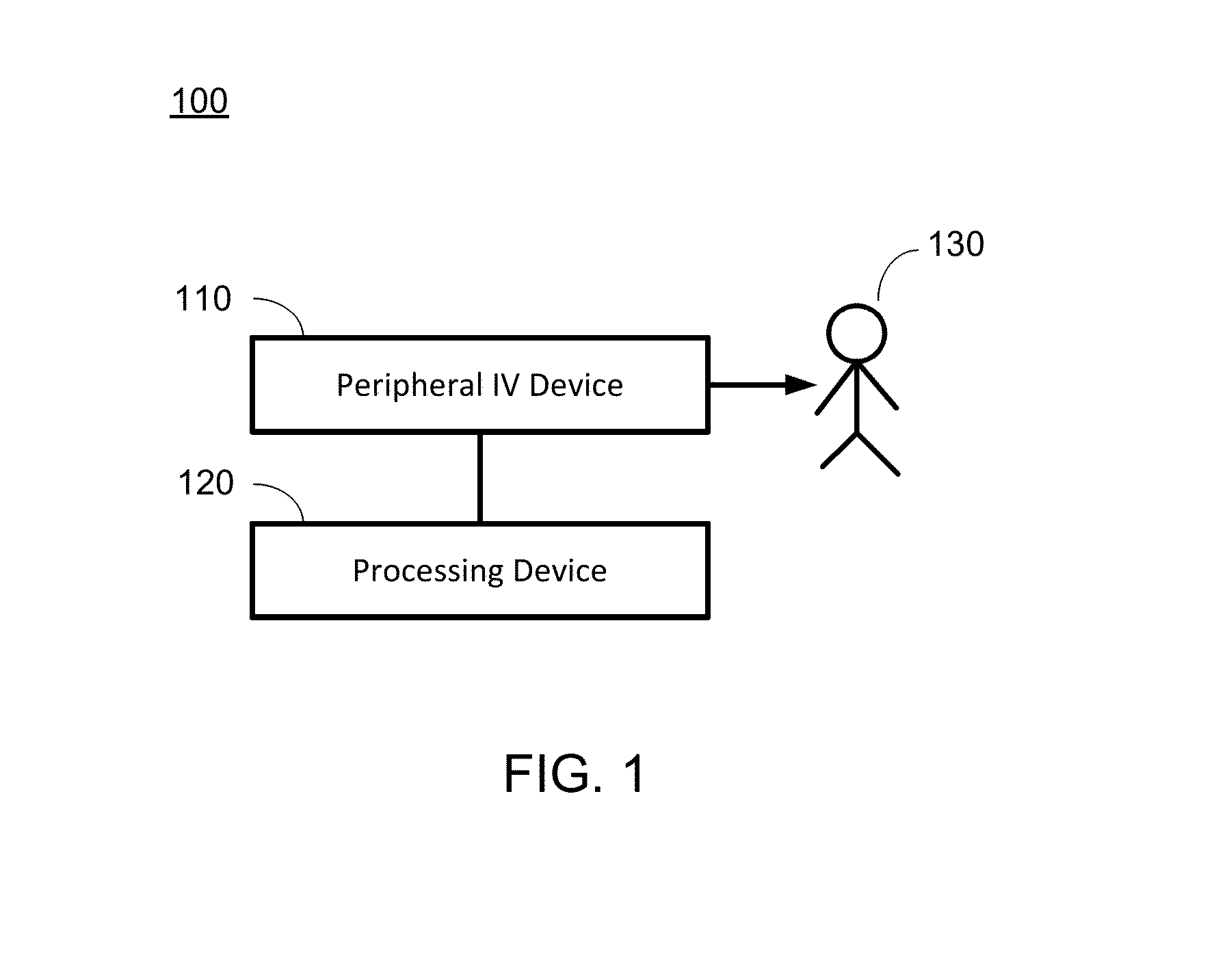
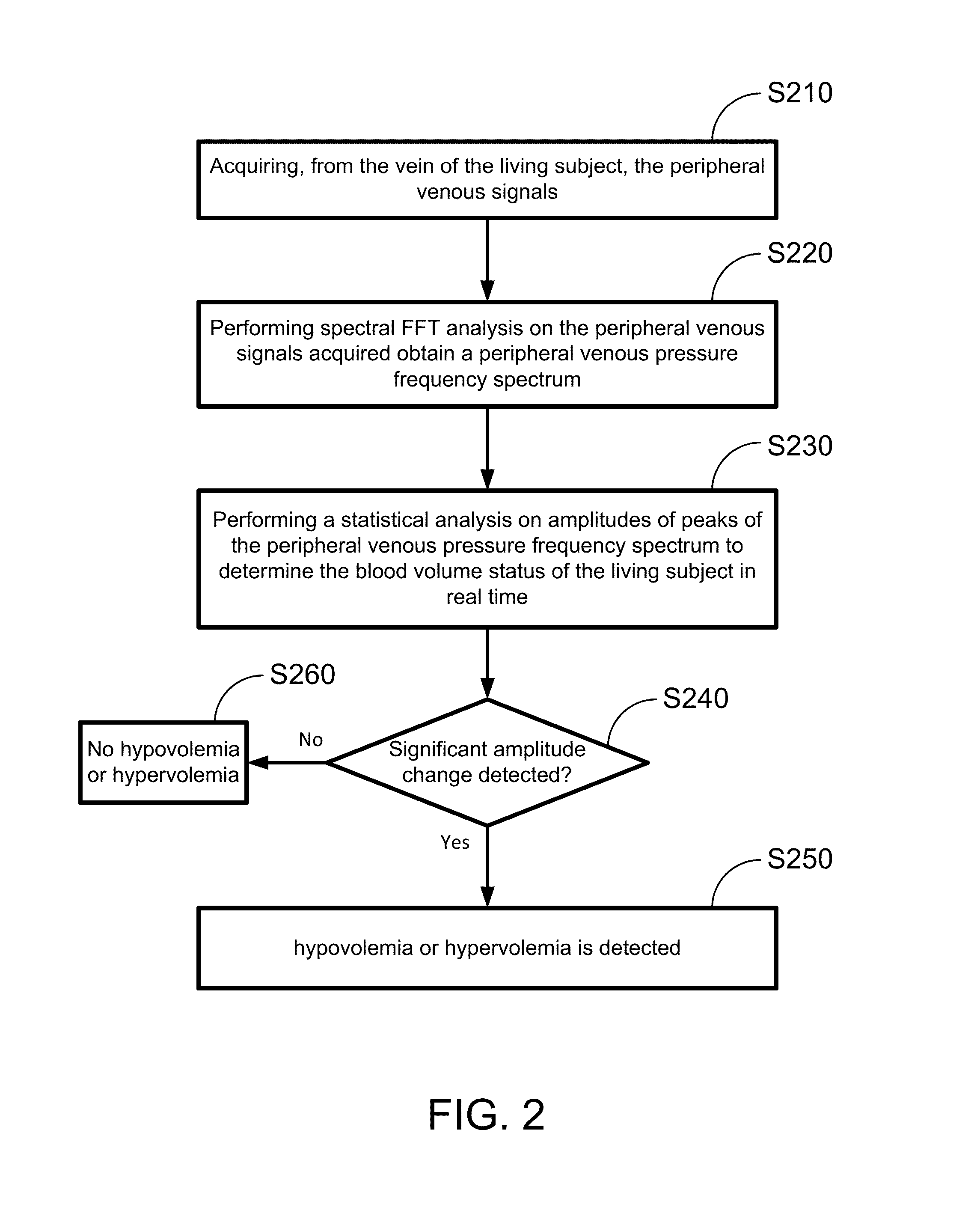
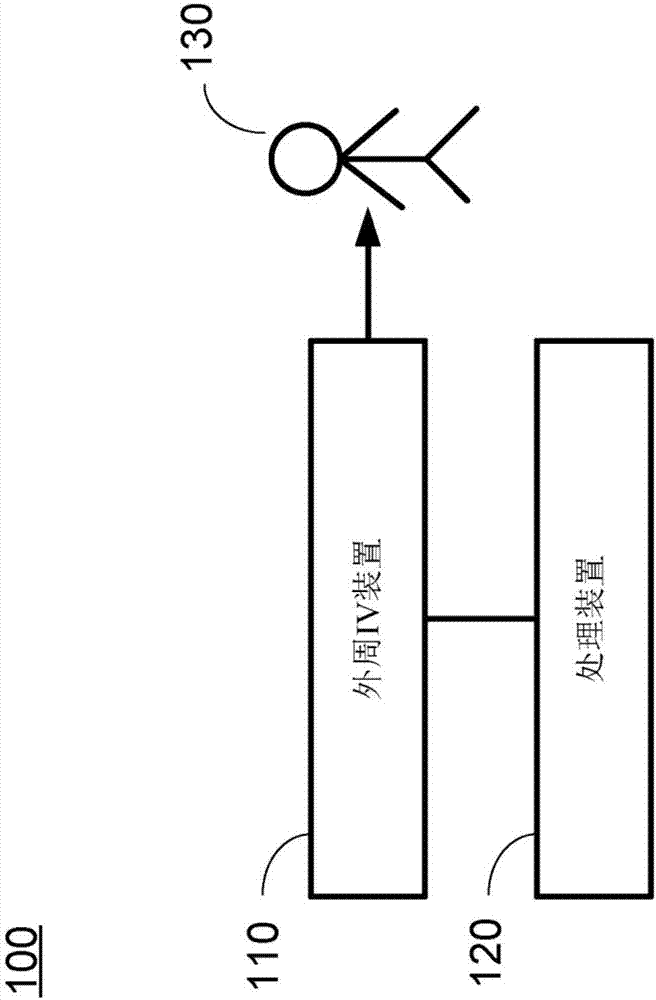
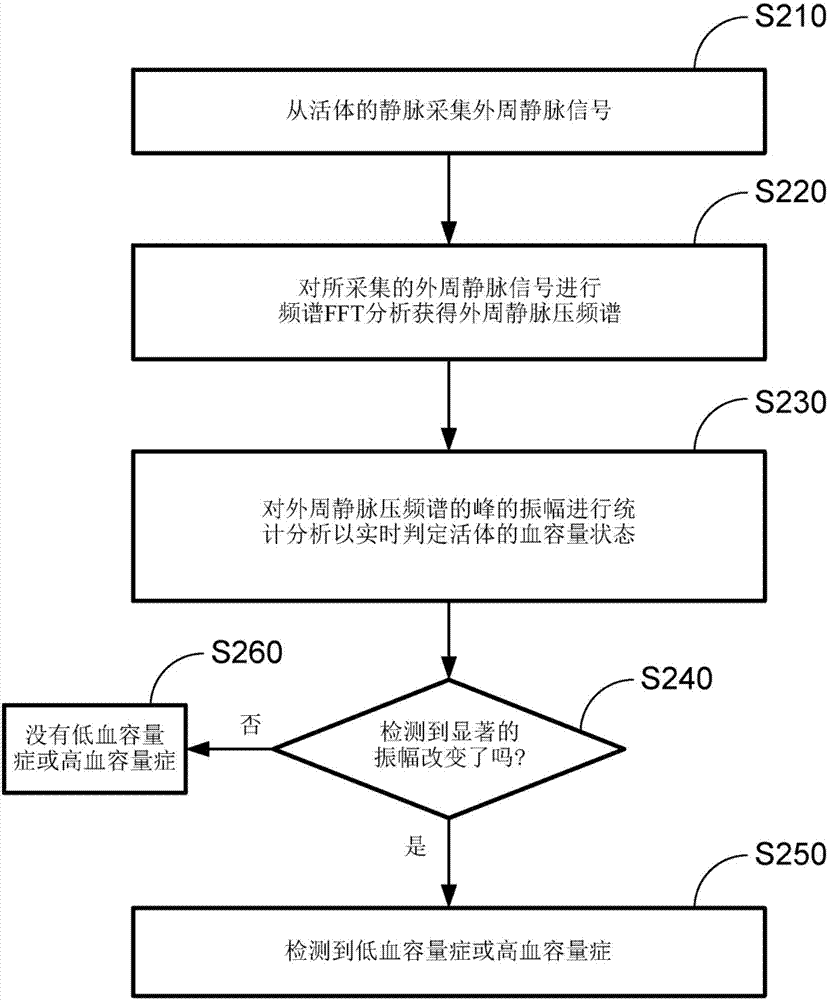
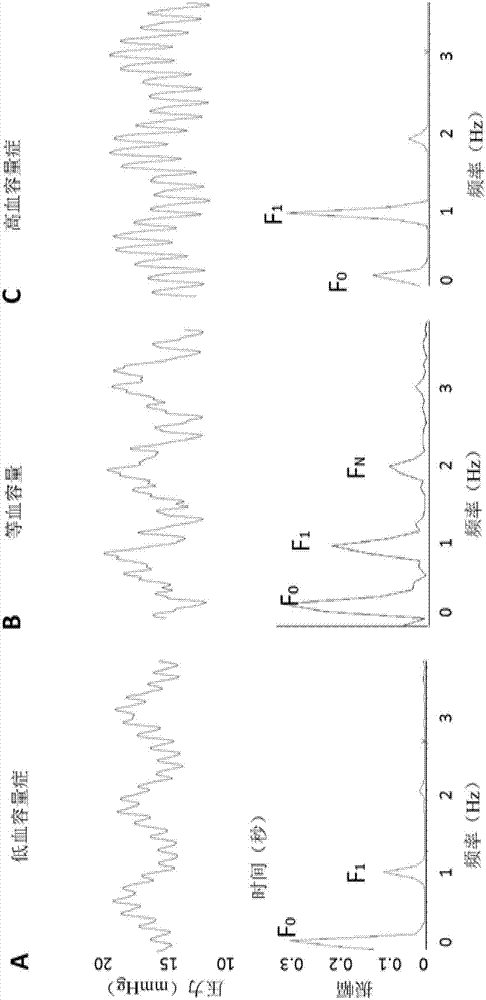
Hypovolemia/hypervolemia detection using peripheral intravenous waveform analysis (PIVA) and applications of same
Aspects of the invention relates to systems and methods for hypovolemia and / or hypervolemia detection of a living subject using peripheral intravenous waveform analysis. In one embodiment, the method includes: acquiring, from a vein of the living subject, peripheral venous signals; performing a spectral analysis on the acquired peripheral venous signals to obtain a peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum; and performing a statistical analysis on amplitudes of peaks of the peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum to determine the blood volume status of the living subject in real time. Specifically, at least two peaks, respectively corresponding to a first frequency and a second frequency, are obtained on the peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum. Amplitude change of the second peak is used to determine the blood volume status of the living subject. Hemorrhage may be detected when a significant amplitude decrease is detected from the second baseline peak to the second peak.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
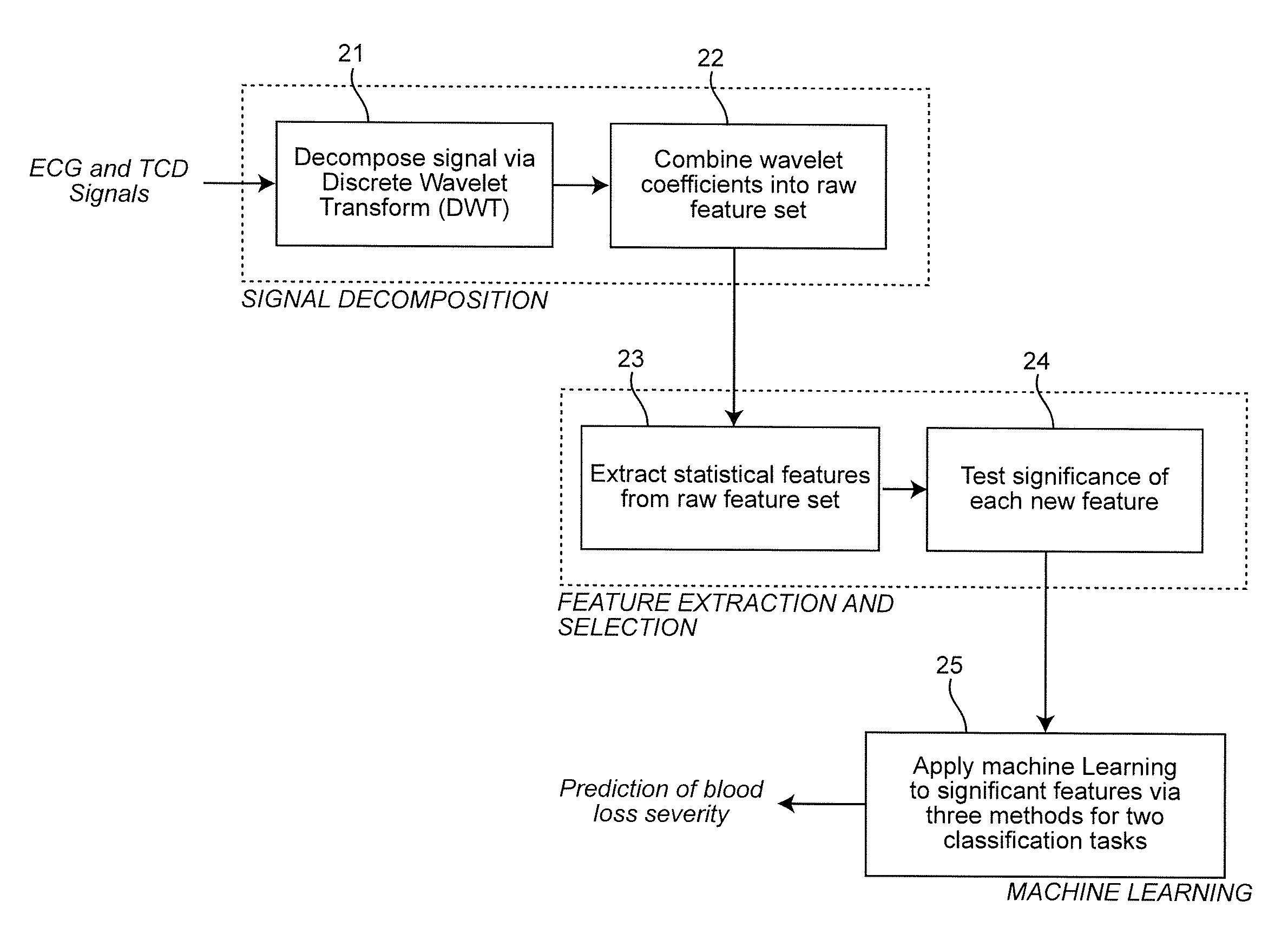
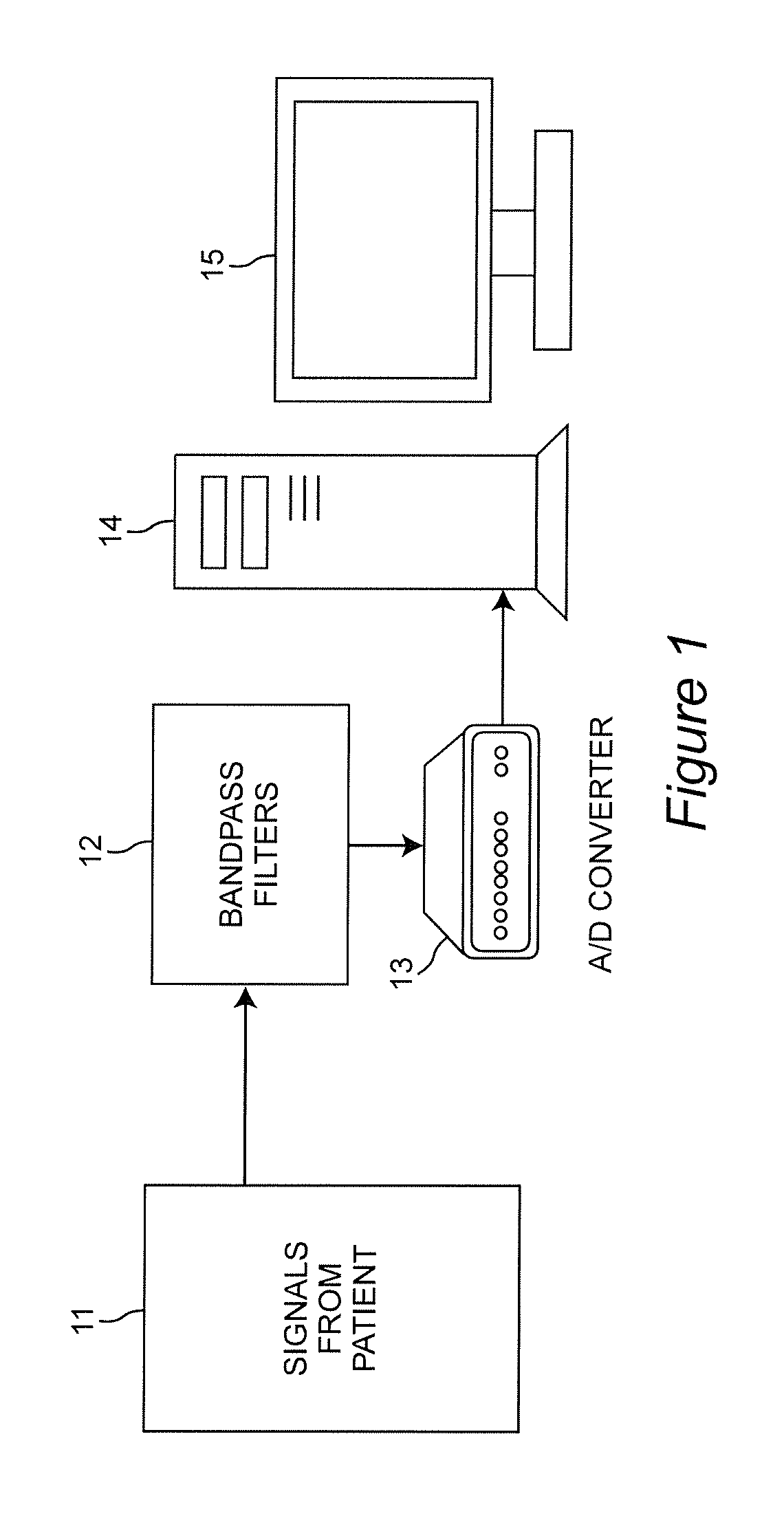
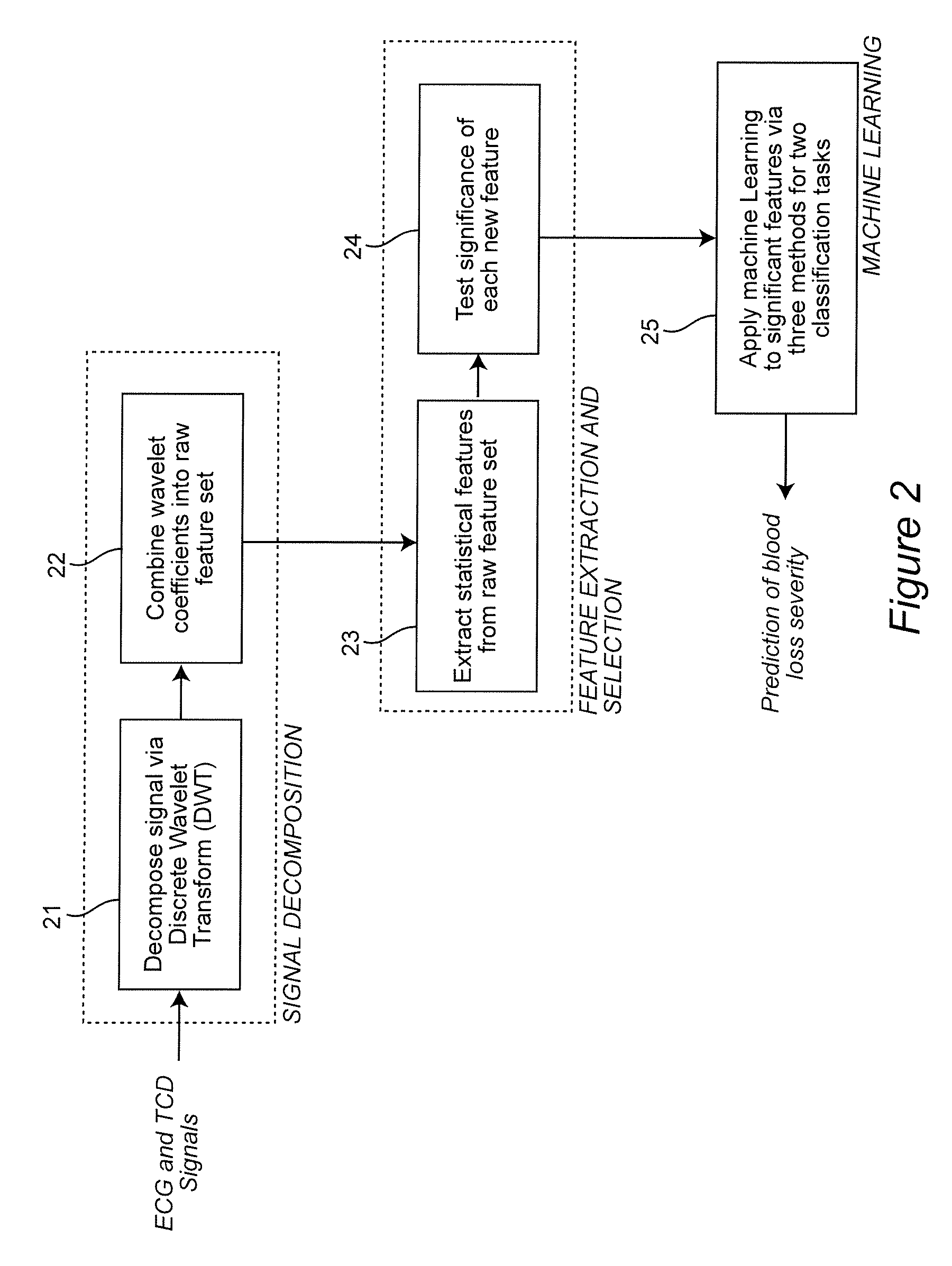
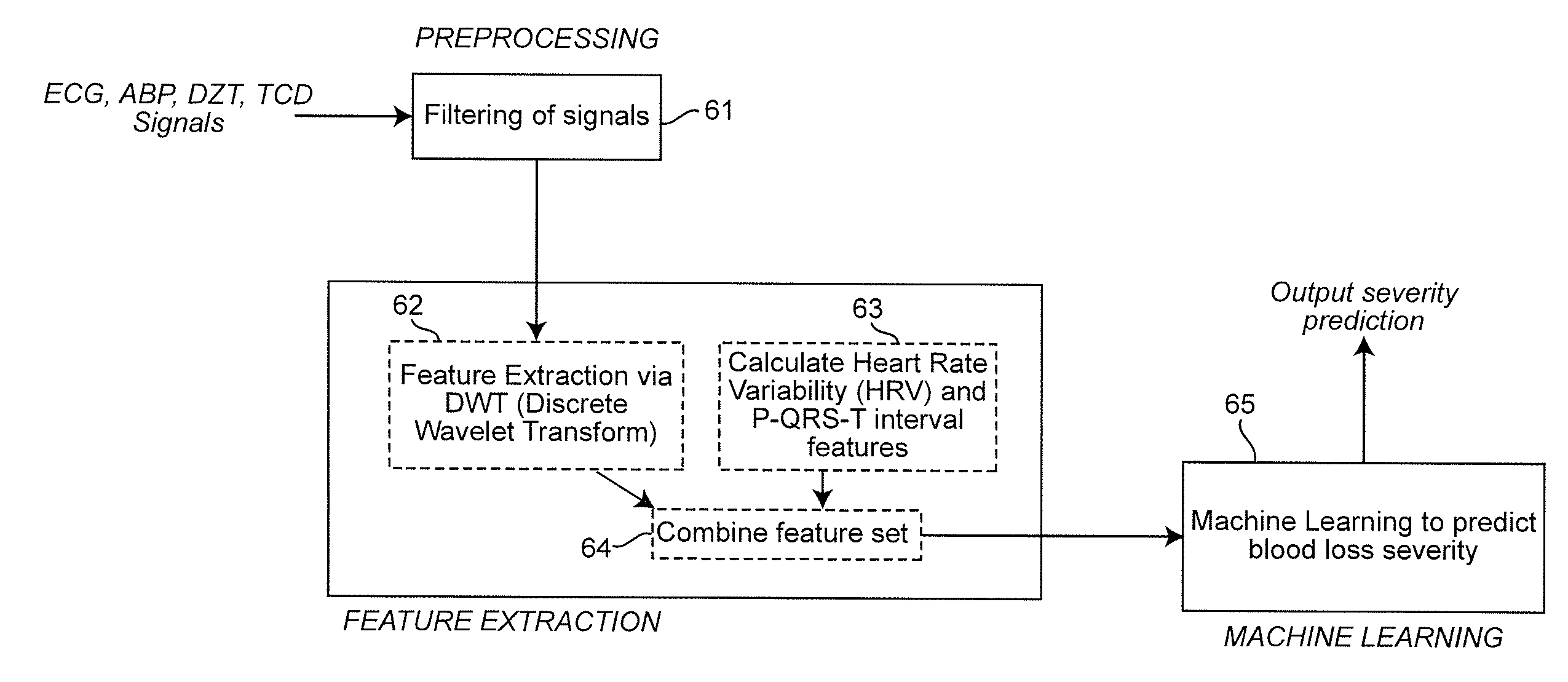
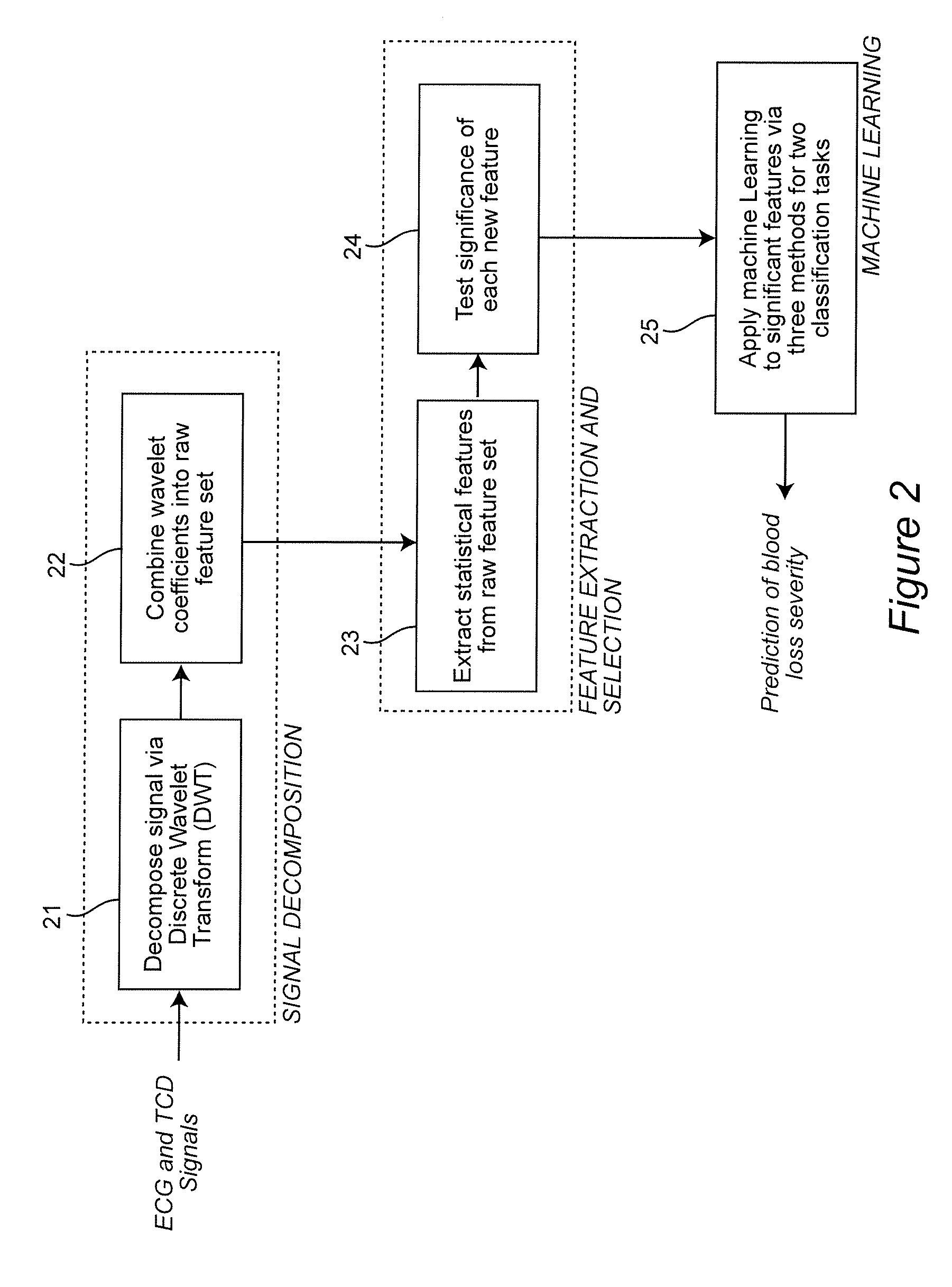
Combining predictive capabilities of Transcranial Doppler (TCD) with Electrocardiogram (ECG) to predict hemorrhagic shock
InactiveUS8762308B2Maximization of survival rateElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesDecompositionHypovolemia
A real-time decision-support system predicts hemorrhagic shock of a patient by analysis of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals and transcranial Doppler (TCD) signals from the patient. These signals are subject to signal decomposition using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to sets of wavelet coefficients and selecting significant signal features. Machine learning is applied to the significant features to evaluate and classify hypovolemia severity based on the input ECG and TCD signals from the patient. The classification of blood loss severity is displayed in real-time. An extension of the decision-support system integrates Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) signals and thoracic electrical bio-impedance (DZT) signals with the ECG and TCD signals from the patient to evaluate severity of hypovolemia.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
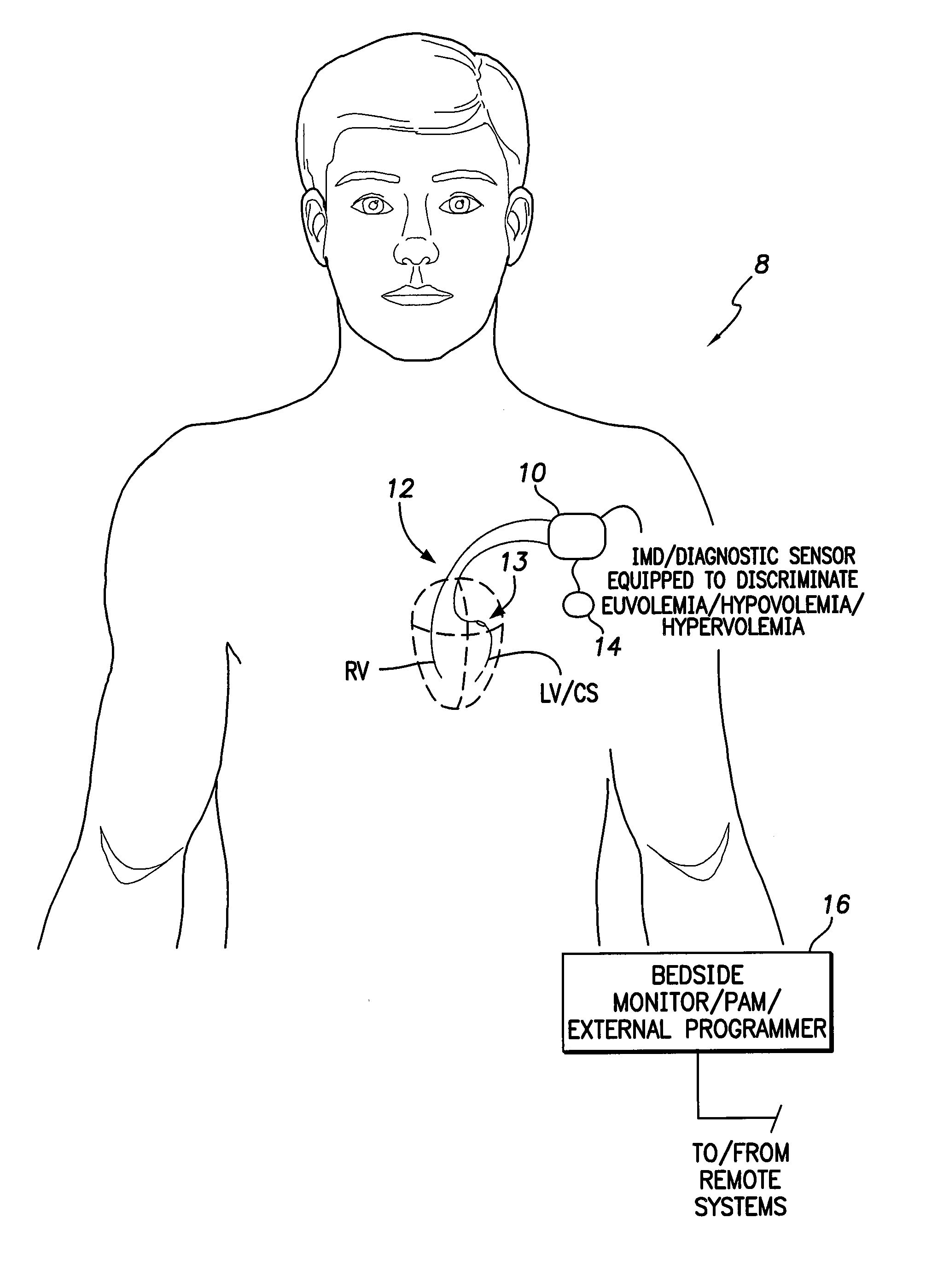
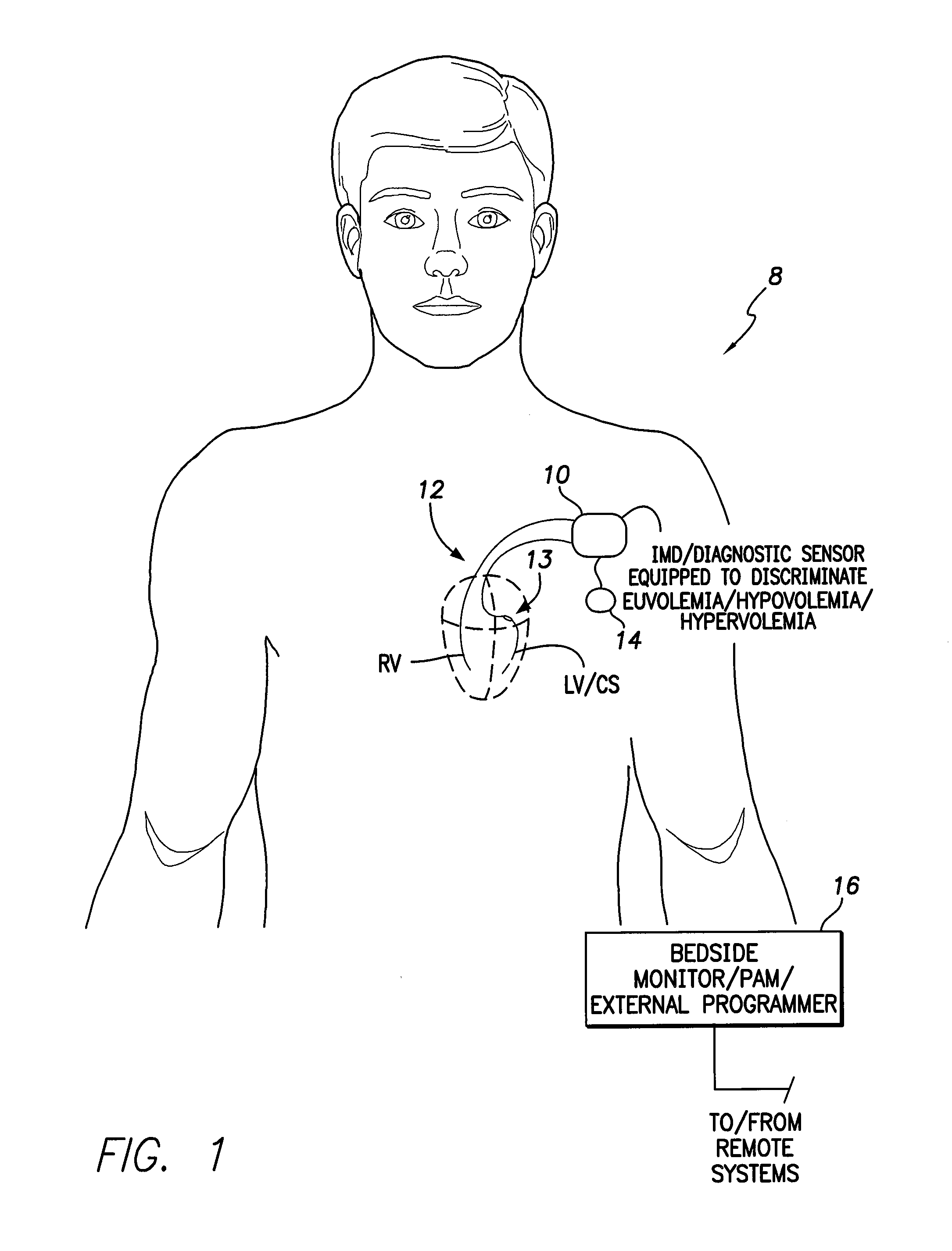
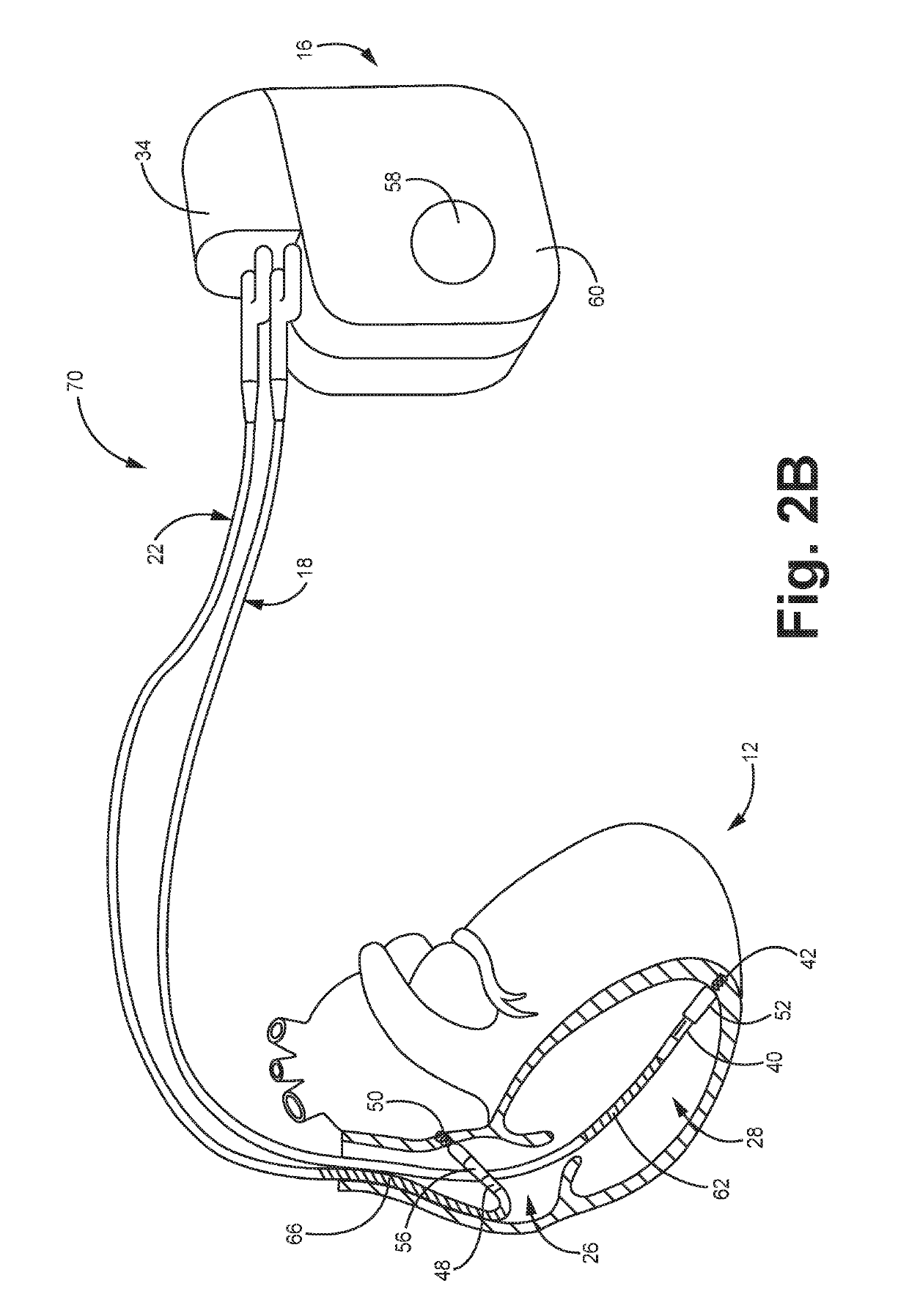
System and method for discriminating hypervolemia, hypovolemia and euvolemia using an implantable medical device
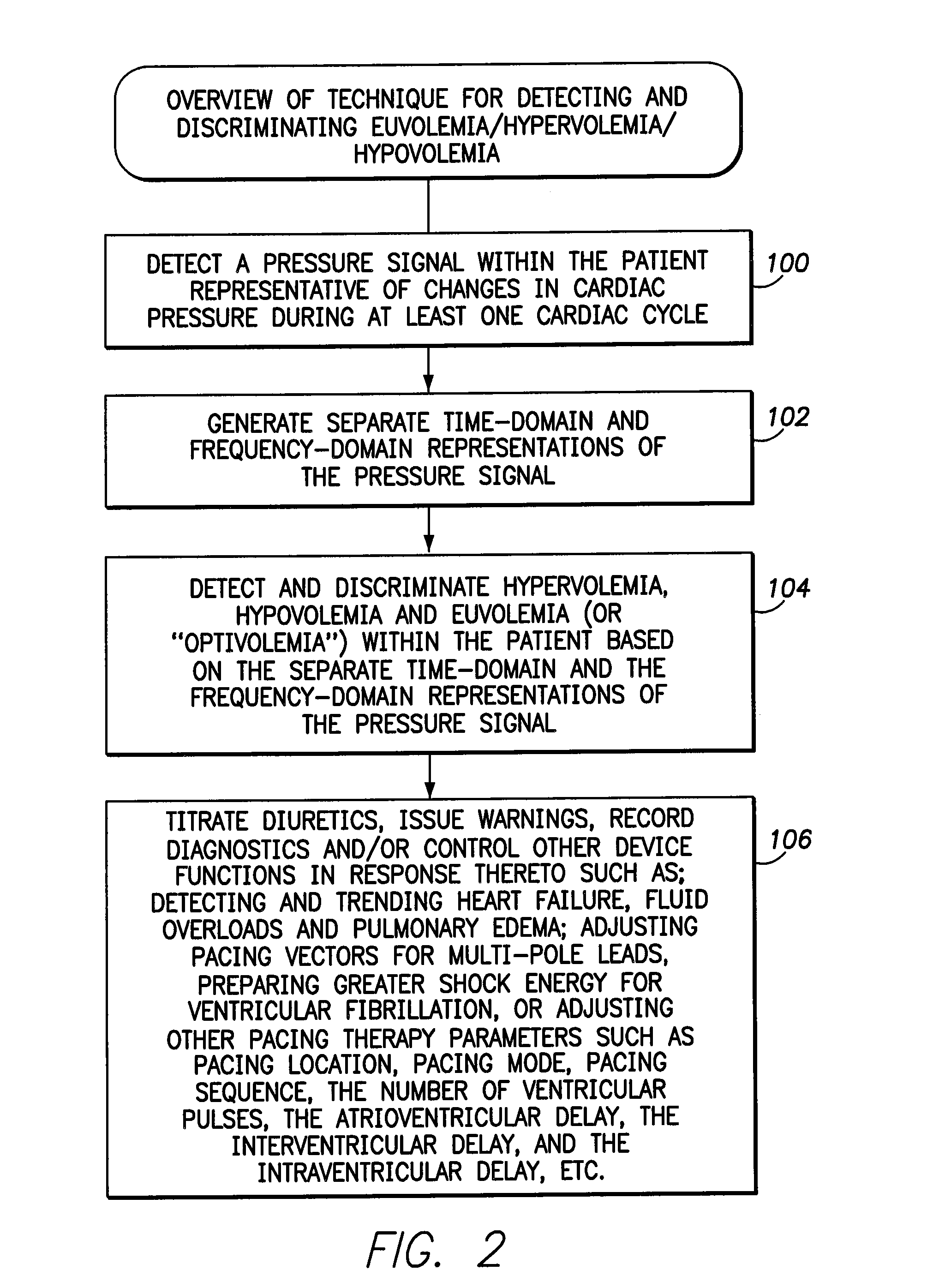
Techniques are provided for use by an implantable medical device or diagnostic sensor for detecting and discriminating euvolemia, hypervolemia and hypovolemia. In one example, the device detects a pressure signal within the patient representative of changes in cardiac pressure overall several cardiac cycles. The device generates separate time-domain and frequency-domain representations of the pressure signal and then discriminates among euvolemia, hypervolemia and hypovolemia within the patient based on an analysis of the time-domain and the frequency-domain representations of the signal. Depending upon the capabilities of the device, suitable warnings may be generated to alert the patient or caregiver. Diuretics or other medications can be titrated to address abnormal fluid conditions such as a fluid overload during hypervolemia. Techniques for detecting a pressure alternans pattern indicative of imminent decompensation are also described.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
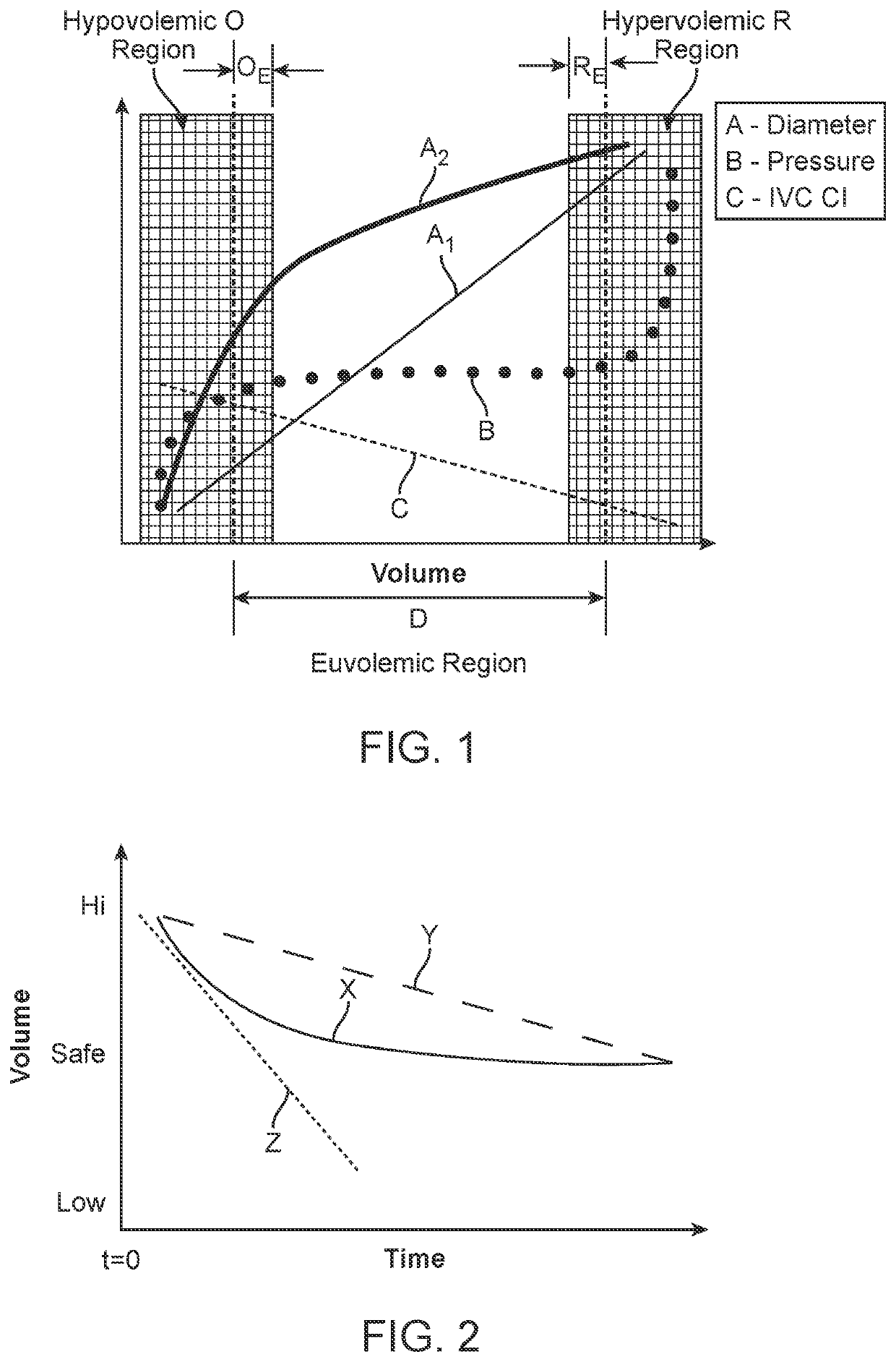
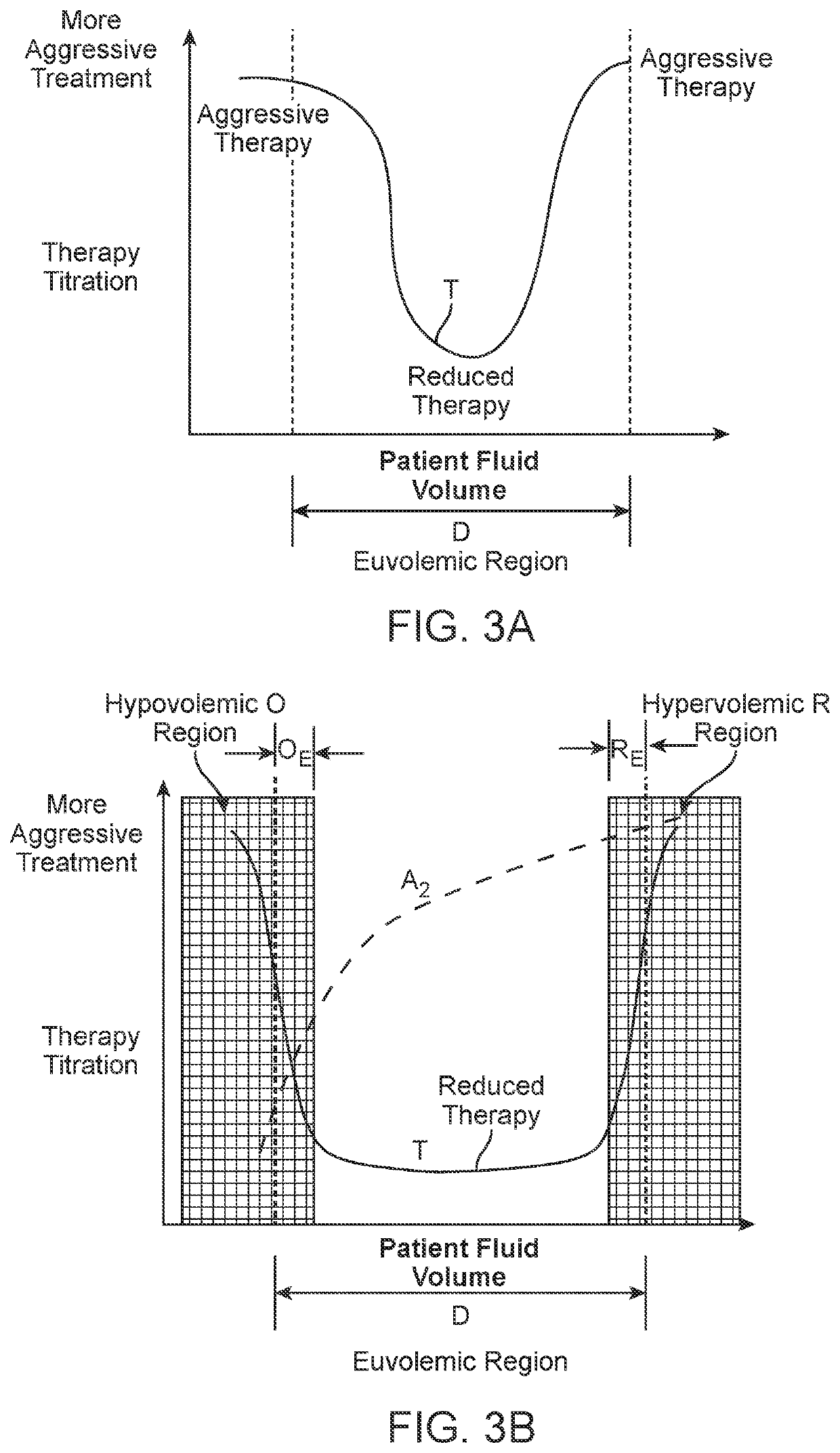
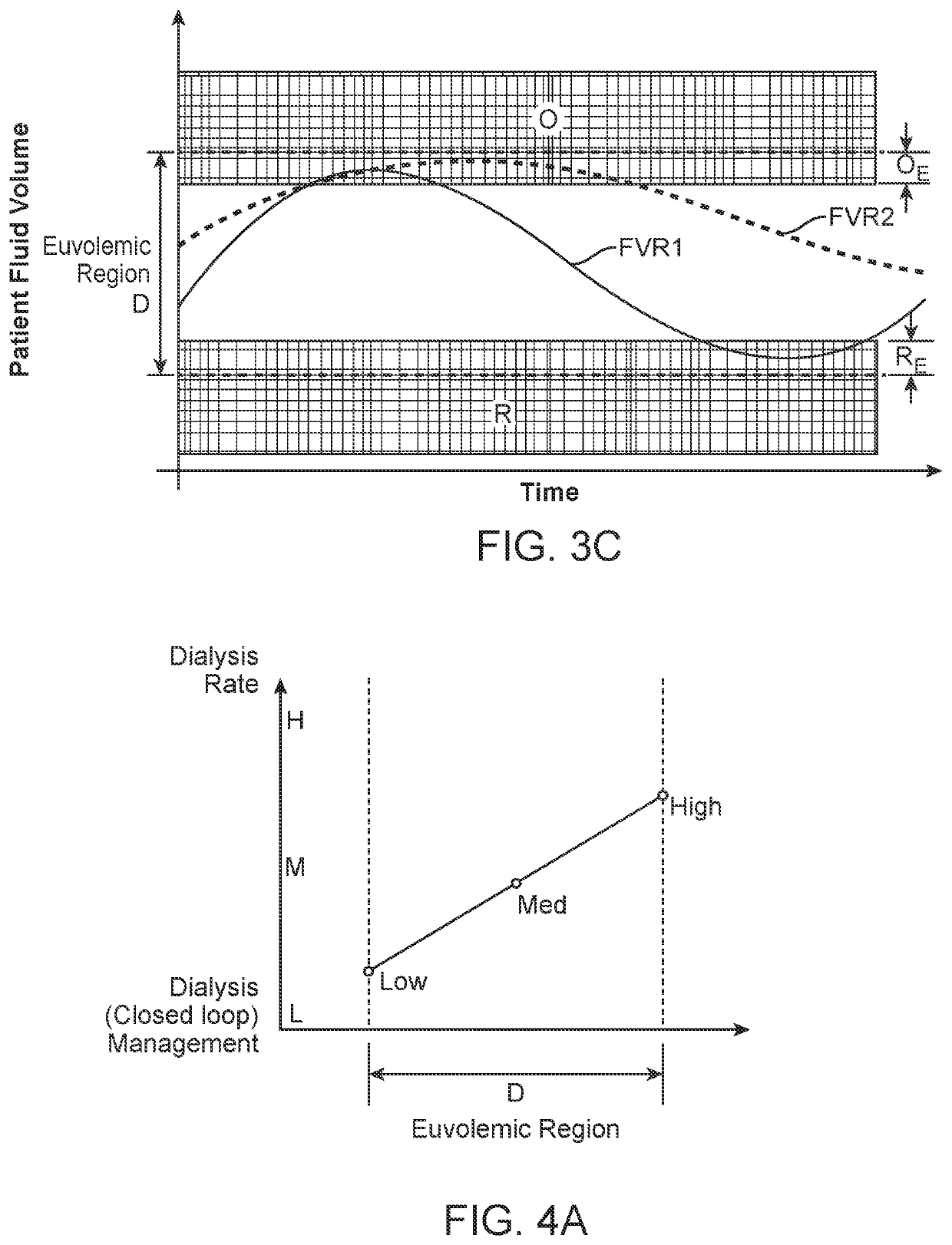
Systems and Methods for Patient Fluid Management
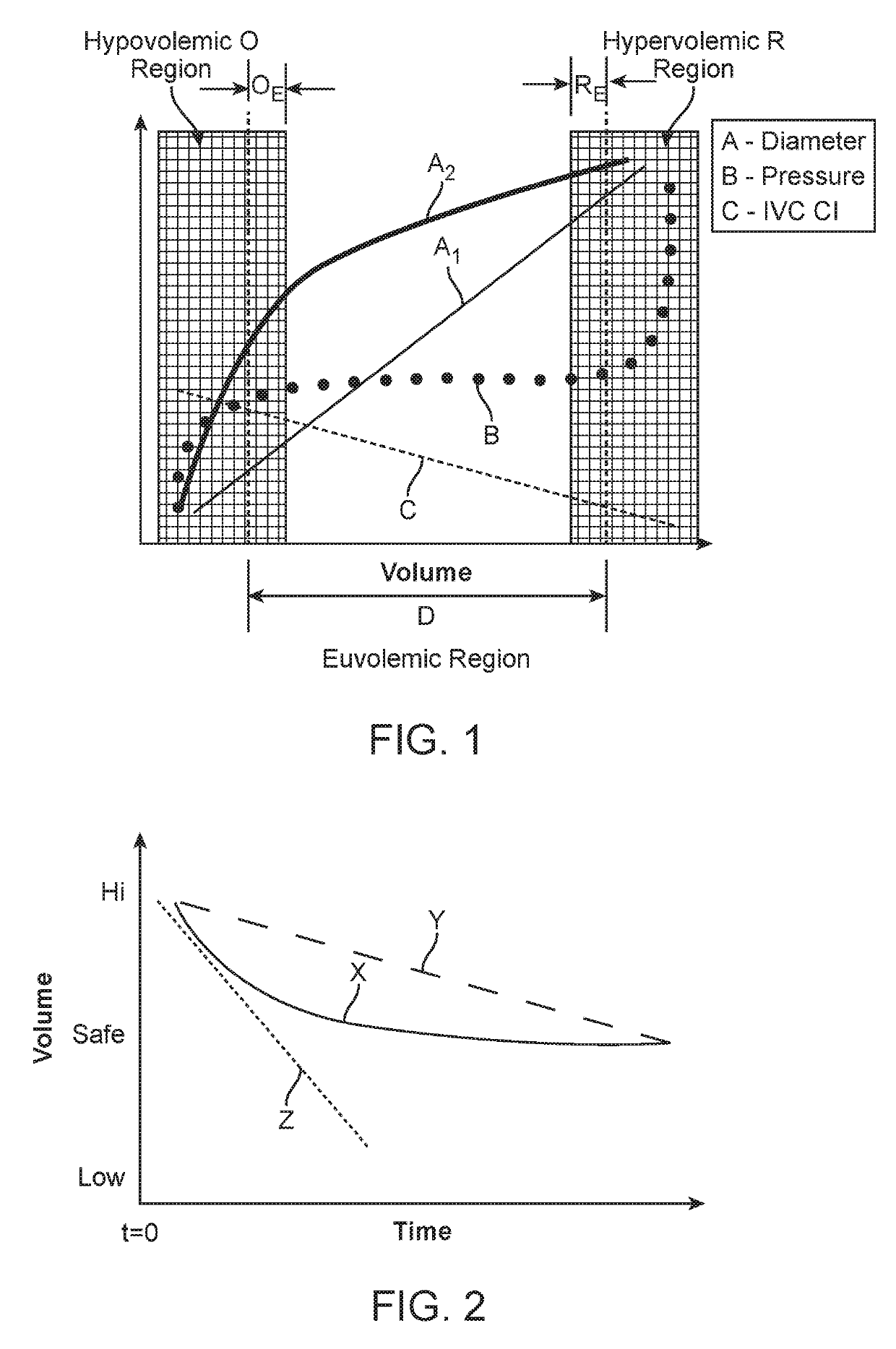
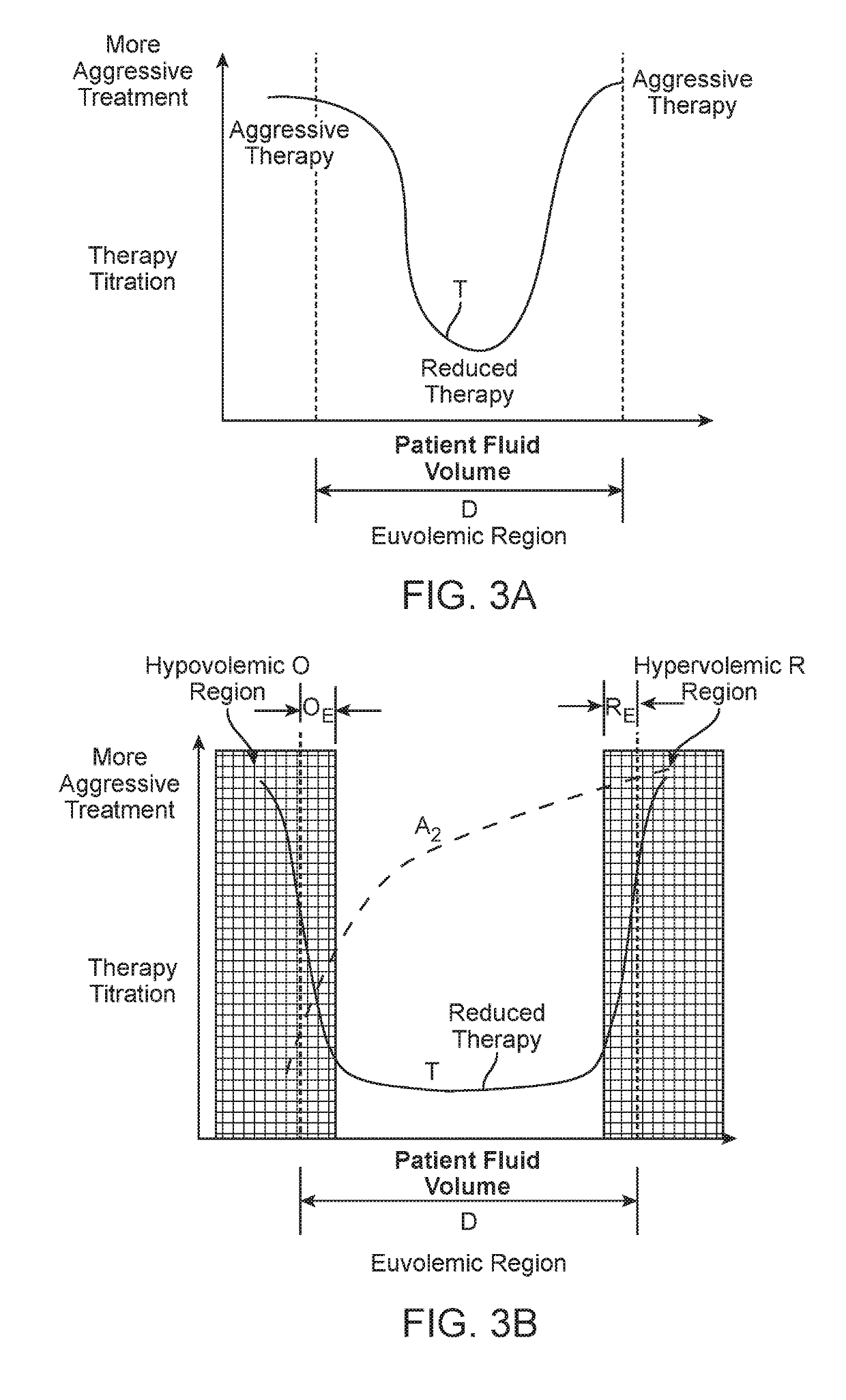
Systems and methods are disclosed that provide for regular, periodic or continuous monitoring of fluid volume based on direct measurement of an inferior vena cava (IVC) physical dimension using a wireless measurement sensor implanted in the IVC. By basing diagnostic decisions and treatments on changes in an IVC physical dimension, information on patient fluid state is available across the entire euvolemic range of fluid states, thus providing earlier warning of hypervolemia or hypovolemia and enabling the modulation of patient treatments to permit more stable long-term fluid management.
Owner:FOUNDRY INNOVATION & RES 1 LTD
Combining Predictive Capabilities of Transcranial Doppler (TCD) with Electrocardiogram (ECG) to Predict Hemorrhagic Shock
InactiveUS20120136224A1Maximization of survival rateElectrocardiographyBlood flow measurement devicesDecompositionHypovolemia
A real-time decision-support system predicts hemorrhagic shock of a patient by analysis of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals and transcranial Doppler (TCD) signals from the patient. These signals are subject to signal decomposition using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to sets of wavelet coefficients and selecting significant signal features. Machine learning is applied to the significant features to evaluate and classify hypovolemia severity based on the input ECG and TCD signals from the patient. The classification of blood loss severity is displayed in real-time. An extension of the decision-support system integrates Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) signals and thoracic electrical bio-impedance (DZT) signals with the ECG and TCD signals from the patient to evaluate severity of hypovolemia.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
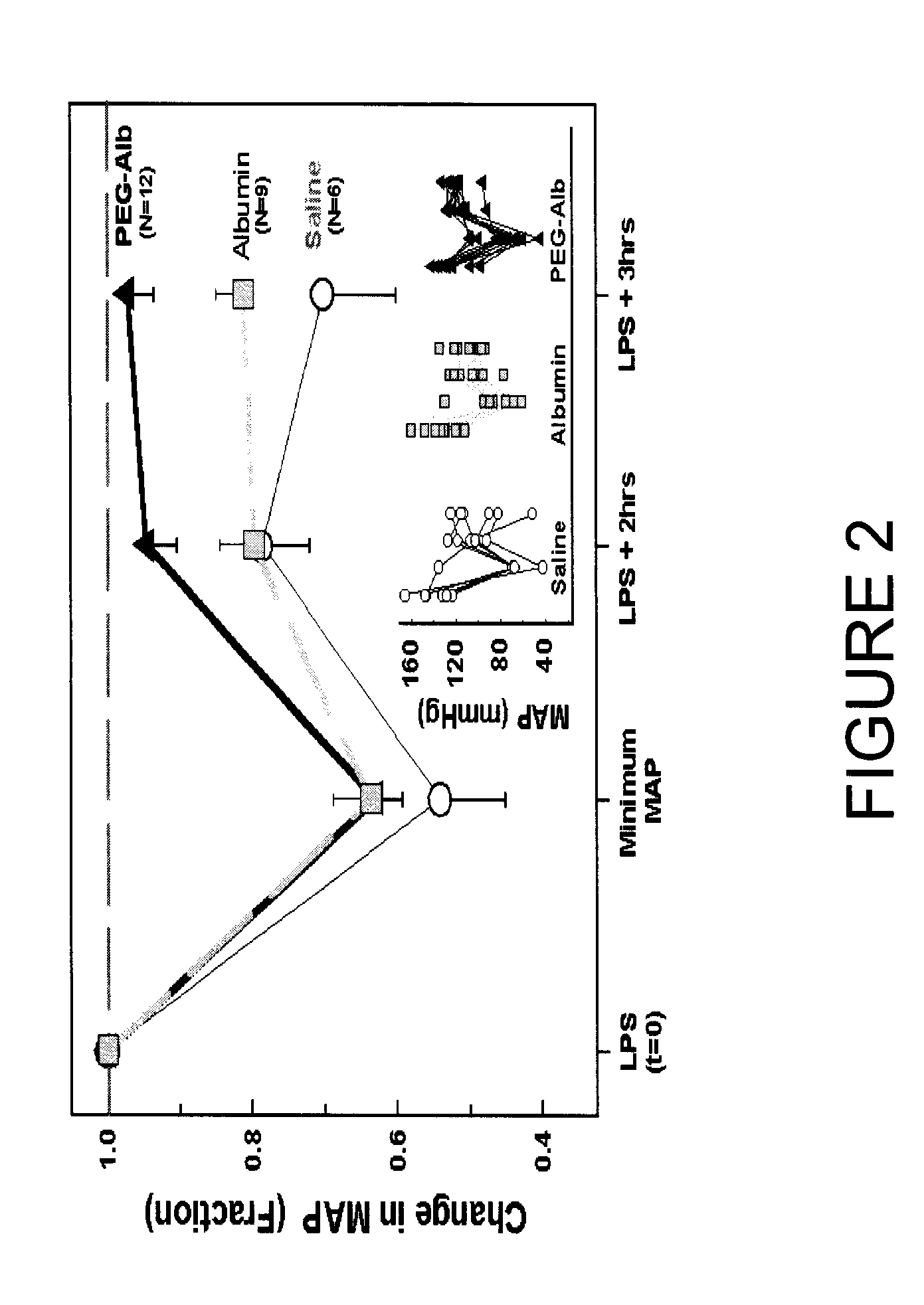
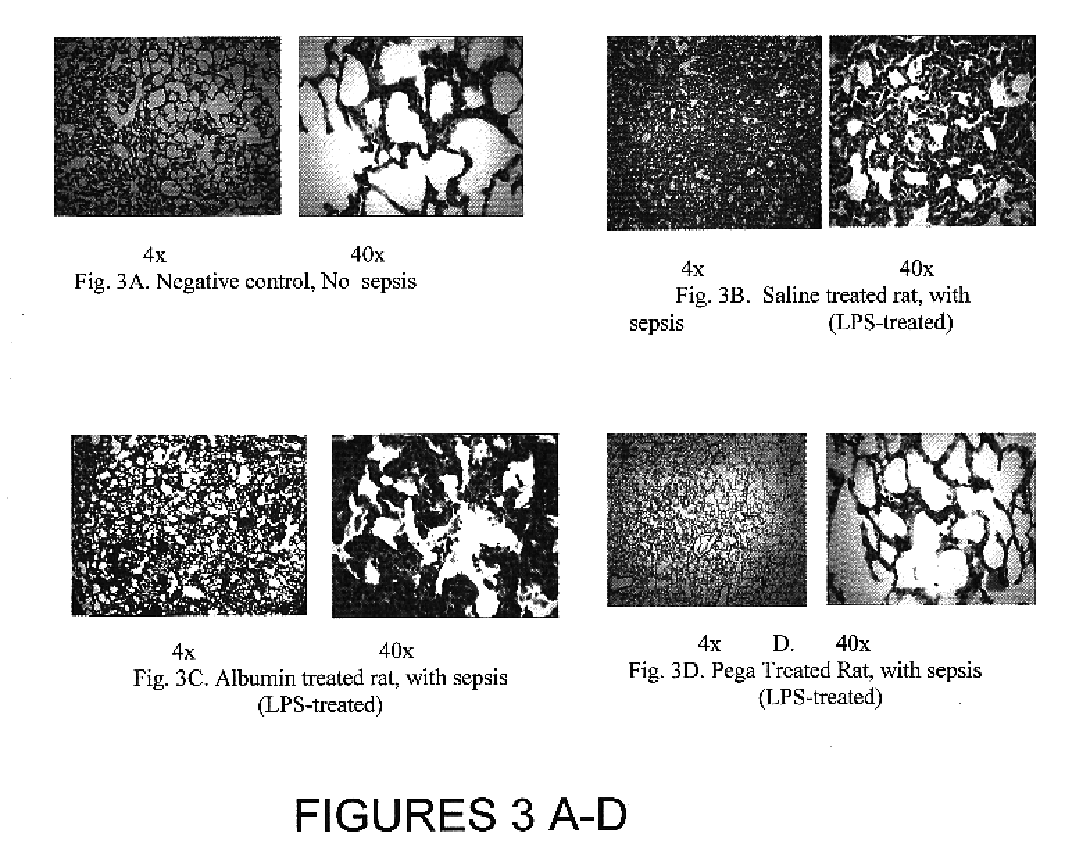
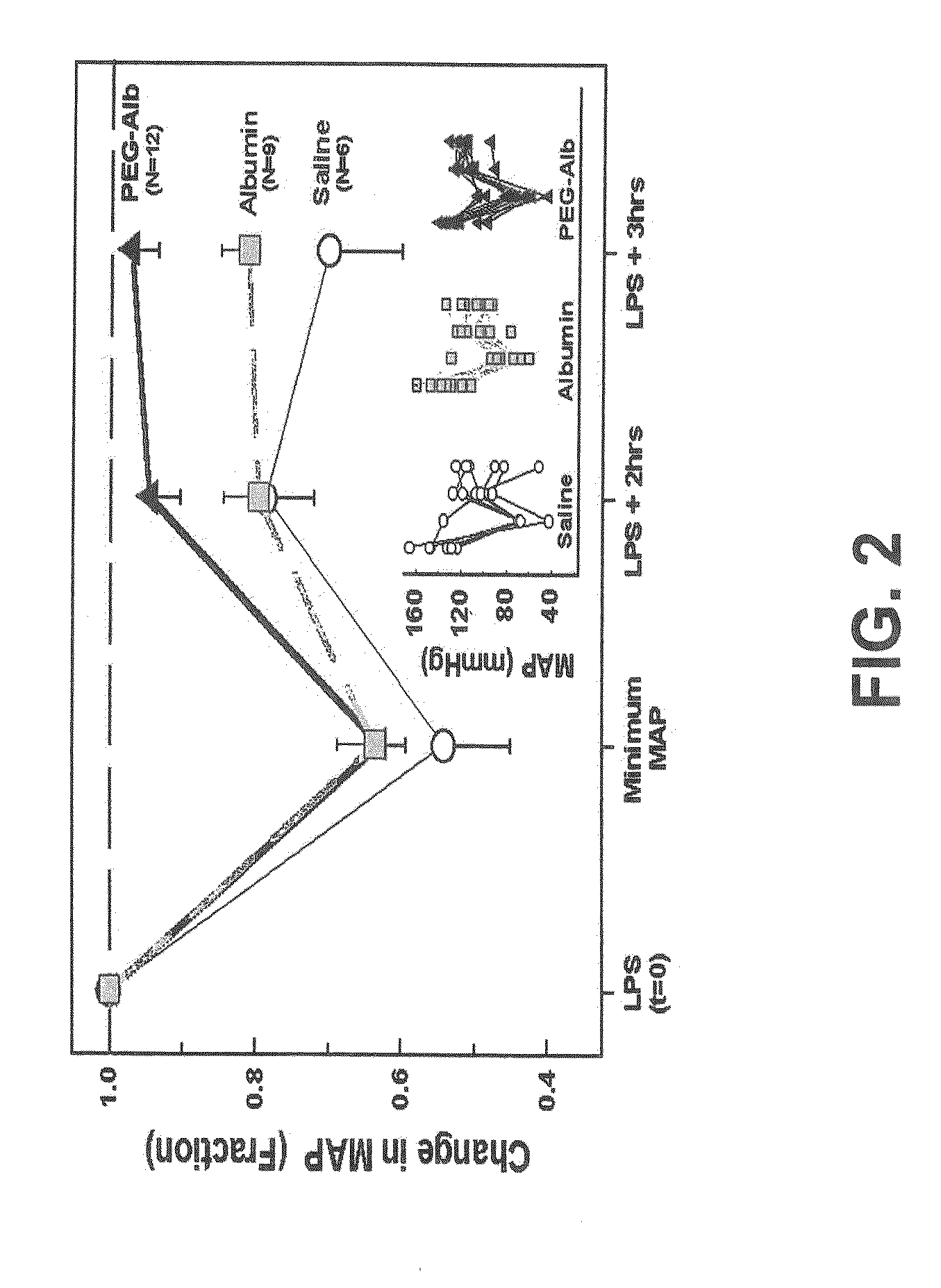
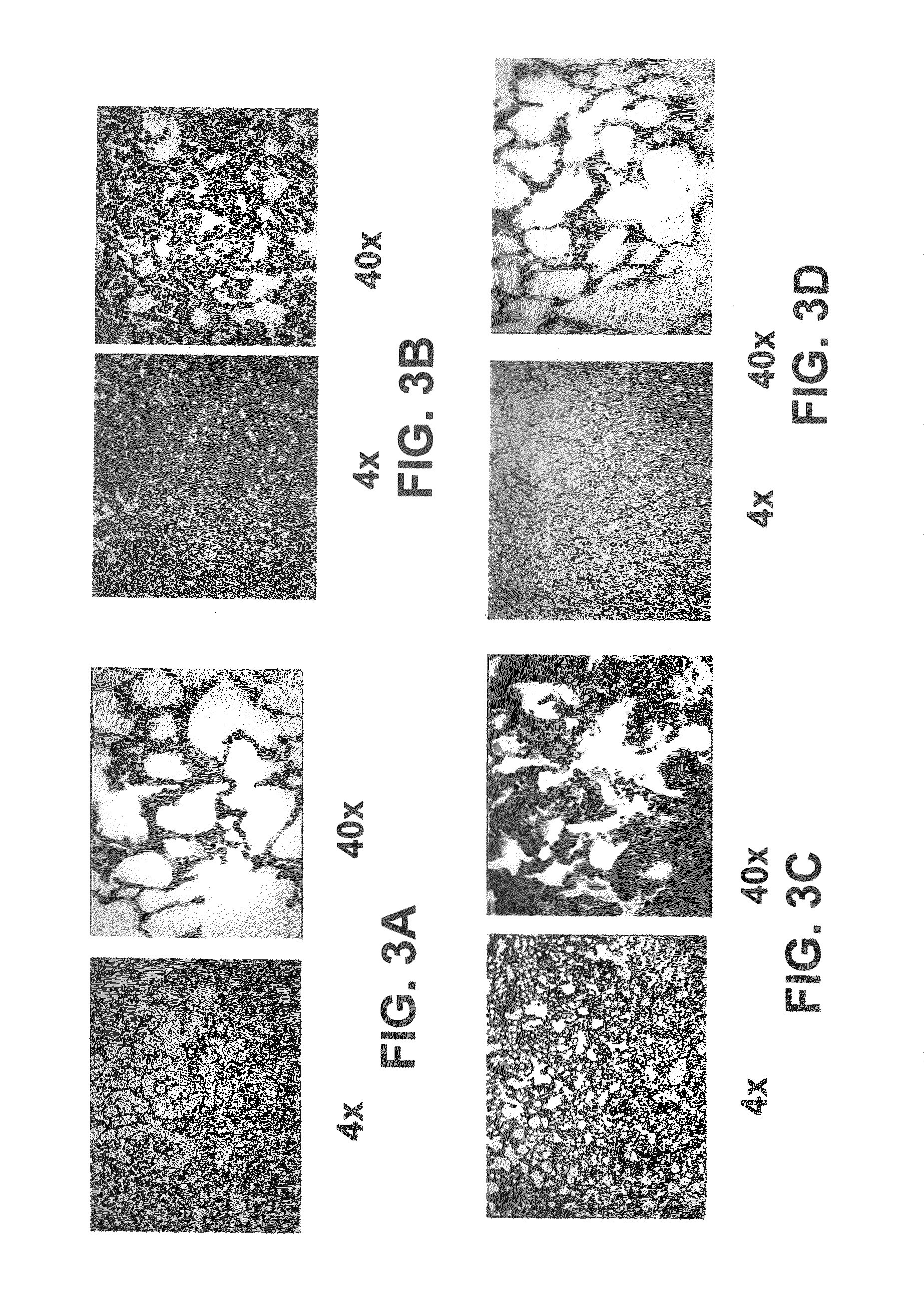
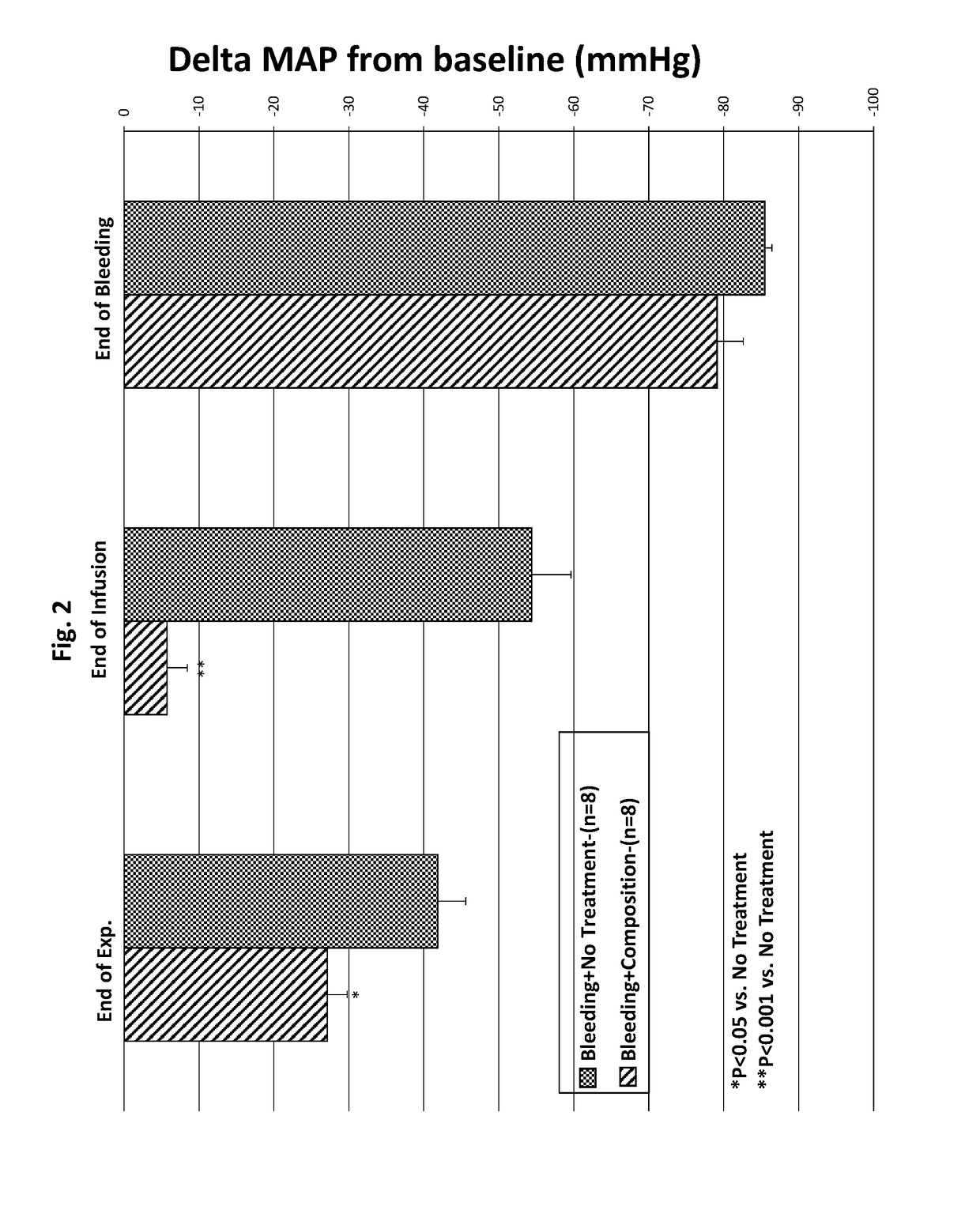
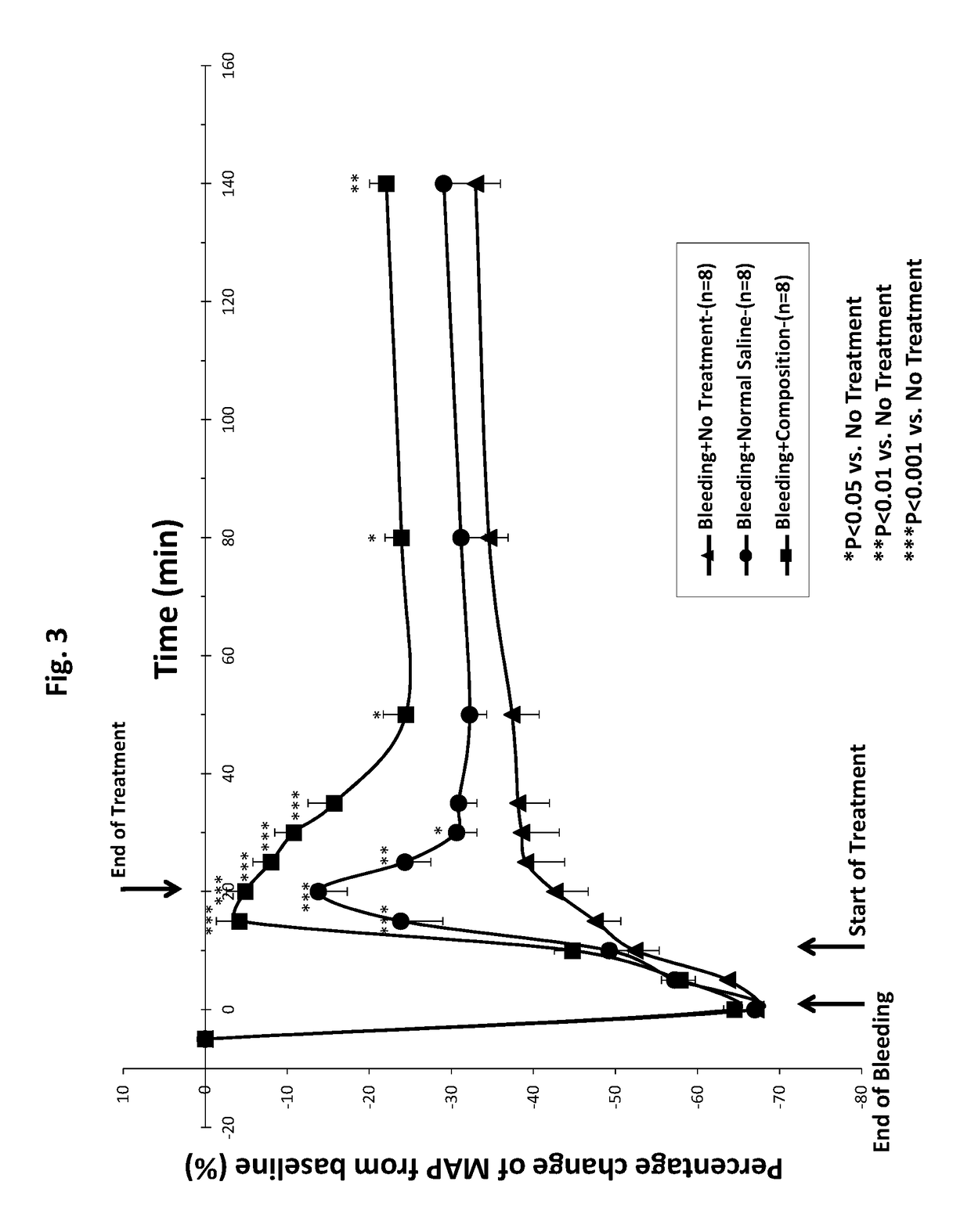
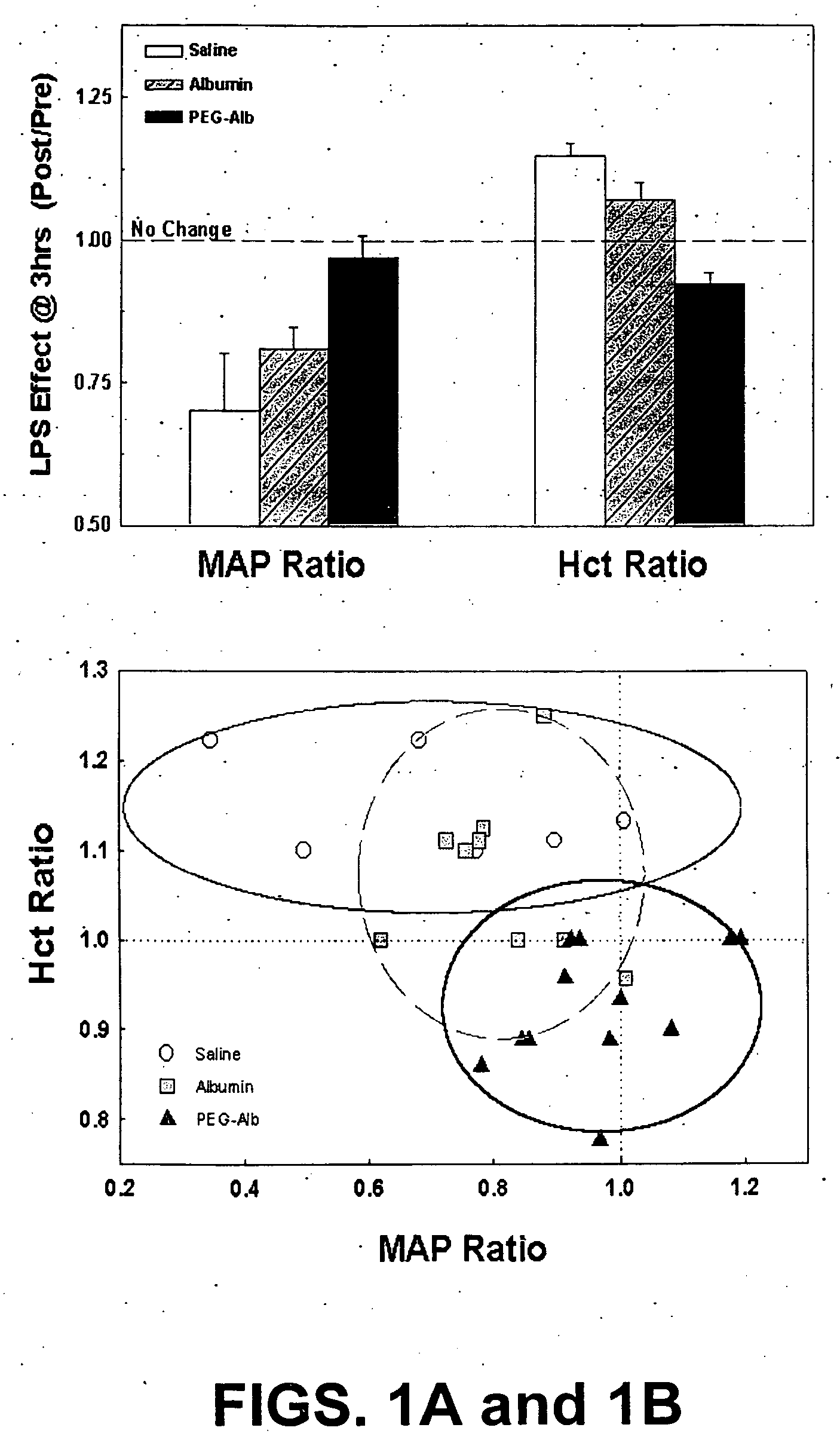
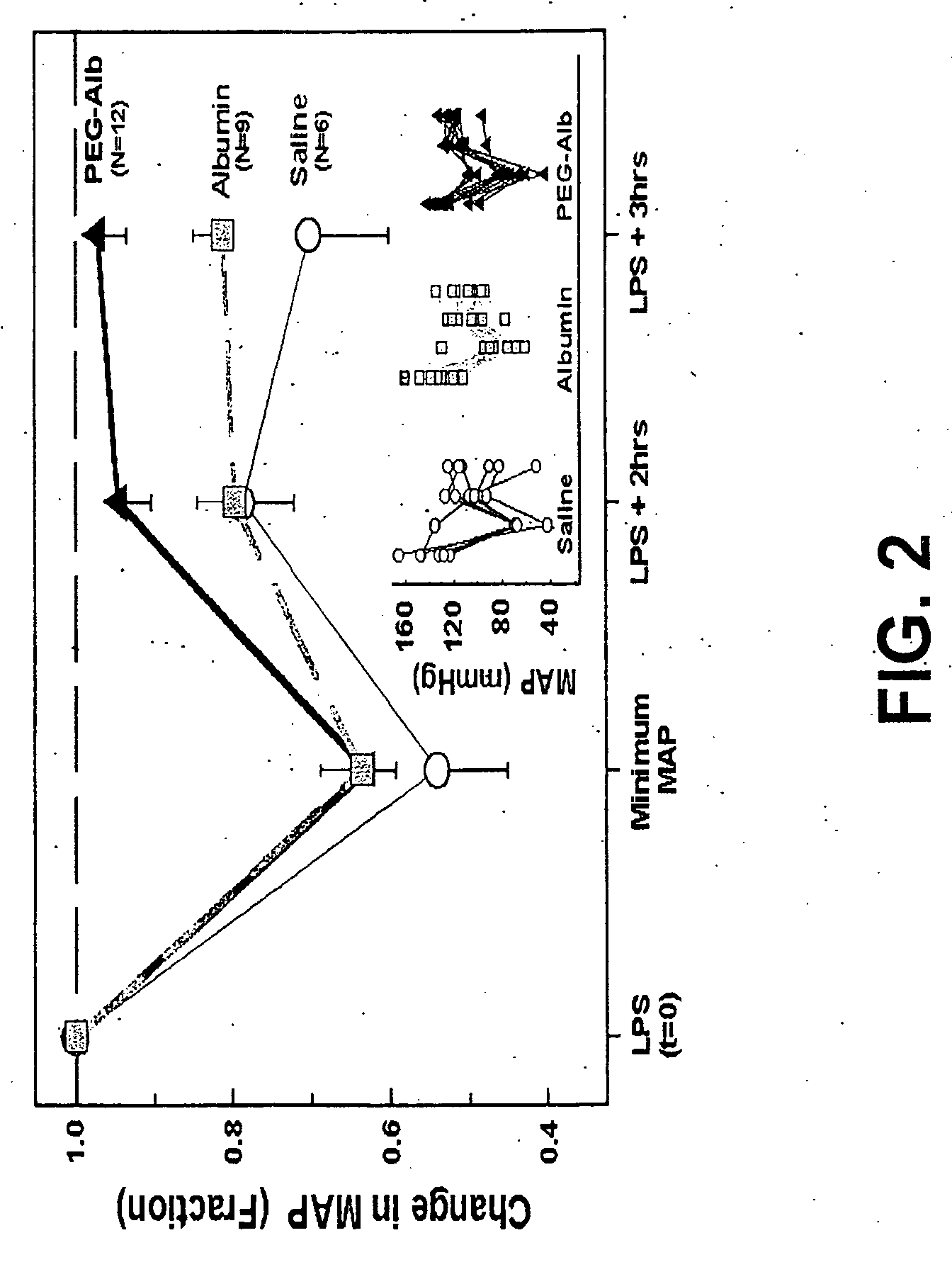
Albumin-based colloid composition and method of use in treating hypovolemia and multiorgan dysfunction
ActiveUS7037895B2No loss of biological activityNo toxicityBiocideHydrolysed protein ingredientsSystemic capillary leak syndromeMultiorgan dysfunction
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF OHIO
Absolute intrathoracic impedance based scheme to stratify patients for risk of a heart failure event
ActiveUS20170027474A1Quick confirmationAvoid and reduce probabilityHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringMoving averageIntrathoracic impedance
A health care system acquires data determines whether a patient is at risk of hypervolemia or hypovolemia. The method comprises (a) acquiring from a device memory a patient's absolute intrathoracic impedance data over a pre-specified time period, (b) determining a running average of the intrathoracic impedance data over the pre-specified time period, and (c) determining by the system whether the running average of the intrathoracic impedance data over the pre-specified time period exceeds one of a first and second range, the first range being a higher value boundary of intrathoracic electrical impedance and the second range being a lower value boundary of intrathoracic electrical impedance.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4 sodium chloride injection and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101450075AIncrease osmotic pressureRaise oxygen partial pressureOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderHydroxyethyl starchTreatment effect
The invention provides an ethoxyl starch 130 / 0.4 sodium chloride injection, in which, 20-80g of ethoxyl starch 130 / 0.4 and 5-13g of sodium chloride is include in per litre injection. The invention further provides the preparing method and application of the injection. The ethoxyl starch 130 / 0.4 in the raw material of the medicine in the invention is an improved product of 'heas' used clinically for treating and preventing hypovolemia, acute normovolemic hemodilution and so on. A better normovolemic therapeutic effect is achieved by optimizing molecular weight and molecular weight distribution, reducing displacement grade and changing displacement manner (C2 / C6); it can stays in blood for longer time after intravenous drip, consequently, can increase plasma osmotic pressure, tissue fluid back-flow and blood volume, can improve oxygenation condition in or after major operation evidently, and can increase tissue oxygen partial pressure and improve tissue oxygenation faster and earlier, thereby can satisfy the clinic demand better.
Owner:CHENGDU ZHENGKANG PHARMA
Volume status monitor: peripheral venous pressure, hypervolemia and coherence analysis
Systems and methods are provided for monitoring changes in blood volume using waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. In particular, the systems and methods relate to detecting ventilation-induced variation (VIV) of waveforms in the peripheral vasculature. Advantageously, the systems and methods may relate to analyzing VIV in peripheral venous pressure (PVP). Thus, the VIV of PVP may be measured, wherein decreased VIV is indicative of decreased blood volume In exemplary embodiments, such as involving spontaneous breathing, it may be necessary to account for changes in respiratory signal strength. Thus systems and methods are also provided for assessing coherence between ventilation and VIV for a flow or pressure waveform. Specifically, coherence is evaluated by comparing the waveform to a detected respiratory signal. Finally, systems and method are provided for distinguishing the impact of respiration on the PG signal during hypervolemia as compared to hypovolemia. Such systems and methods may advantageously be utilized to monitor fluid status during fluid replacement.
Owner:SHELLEY KIRK H +2
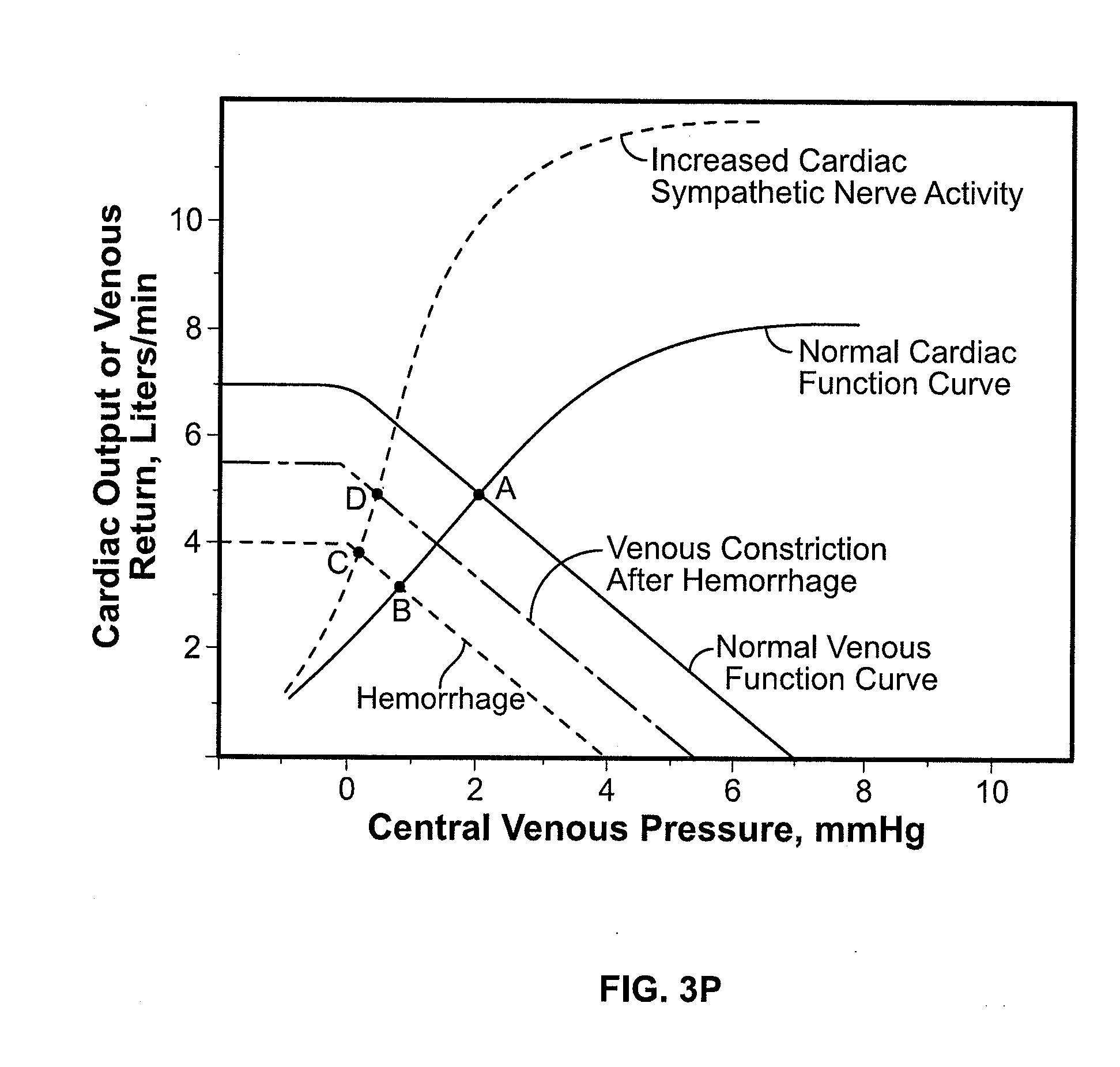
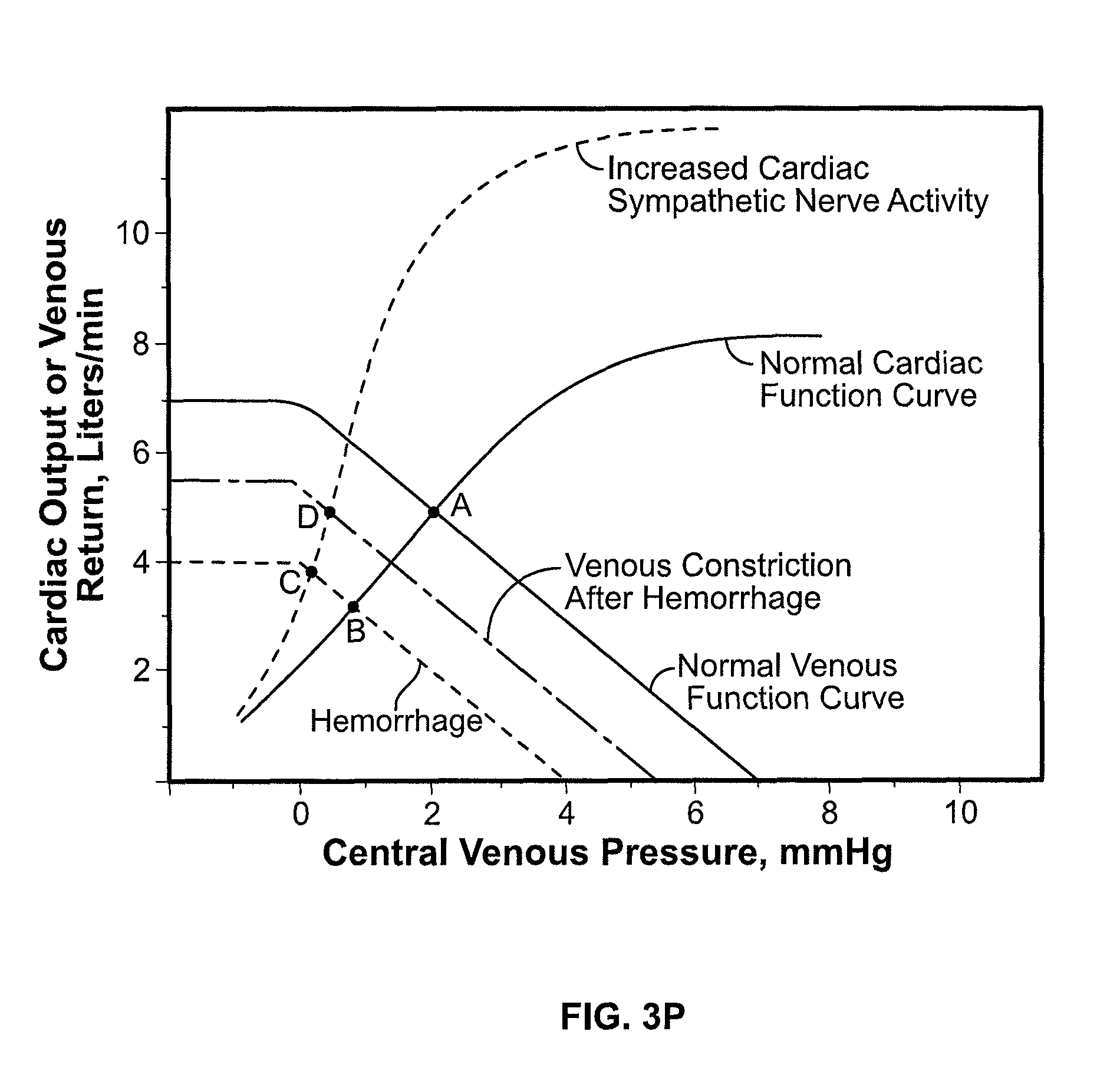
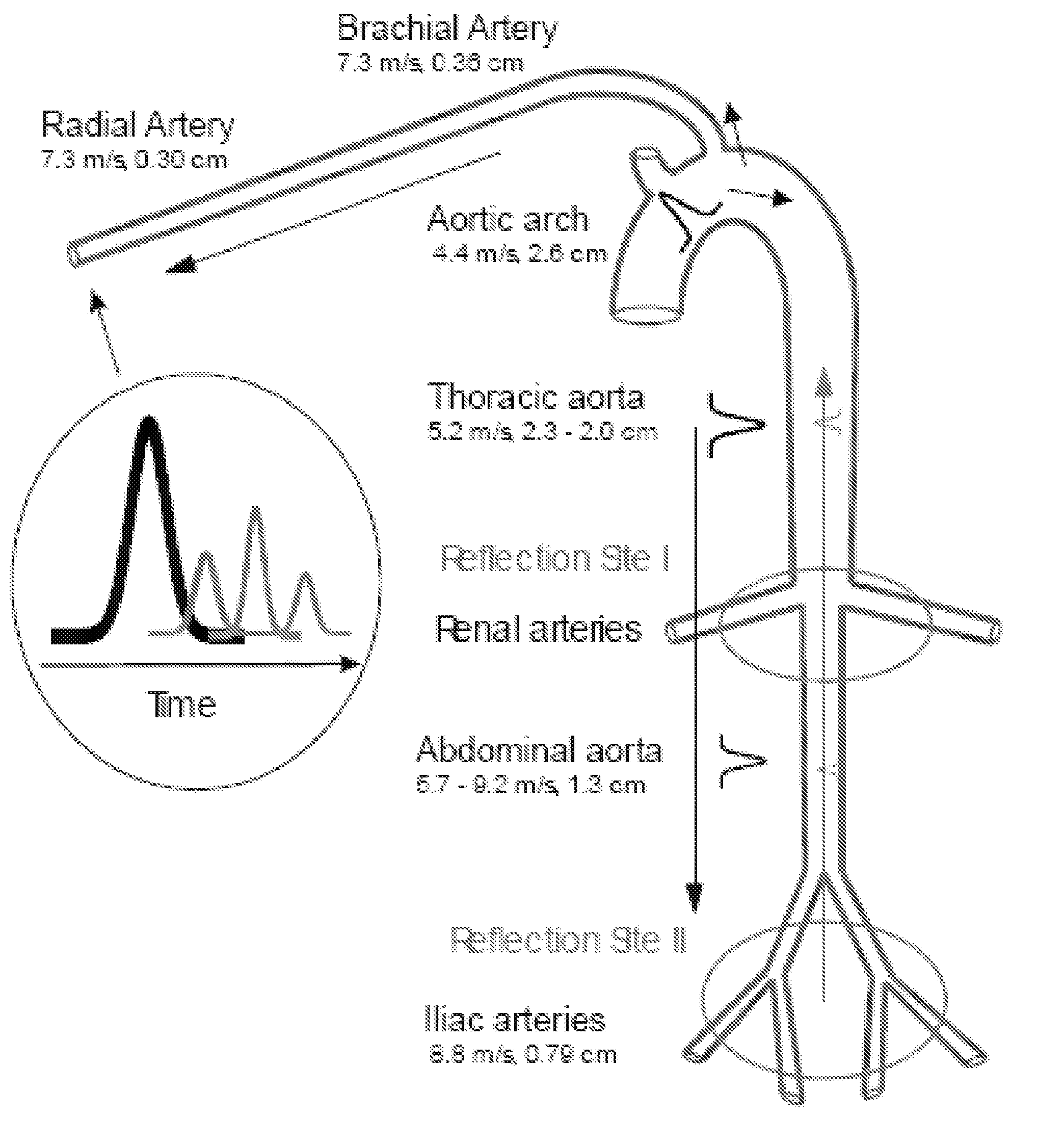
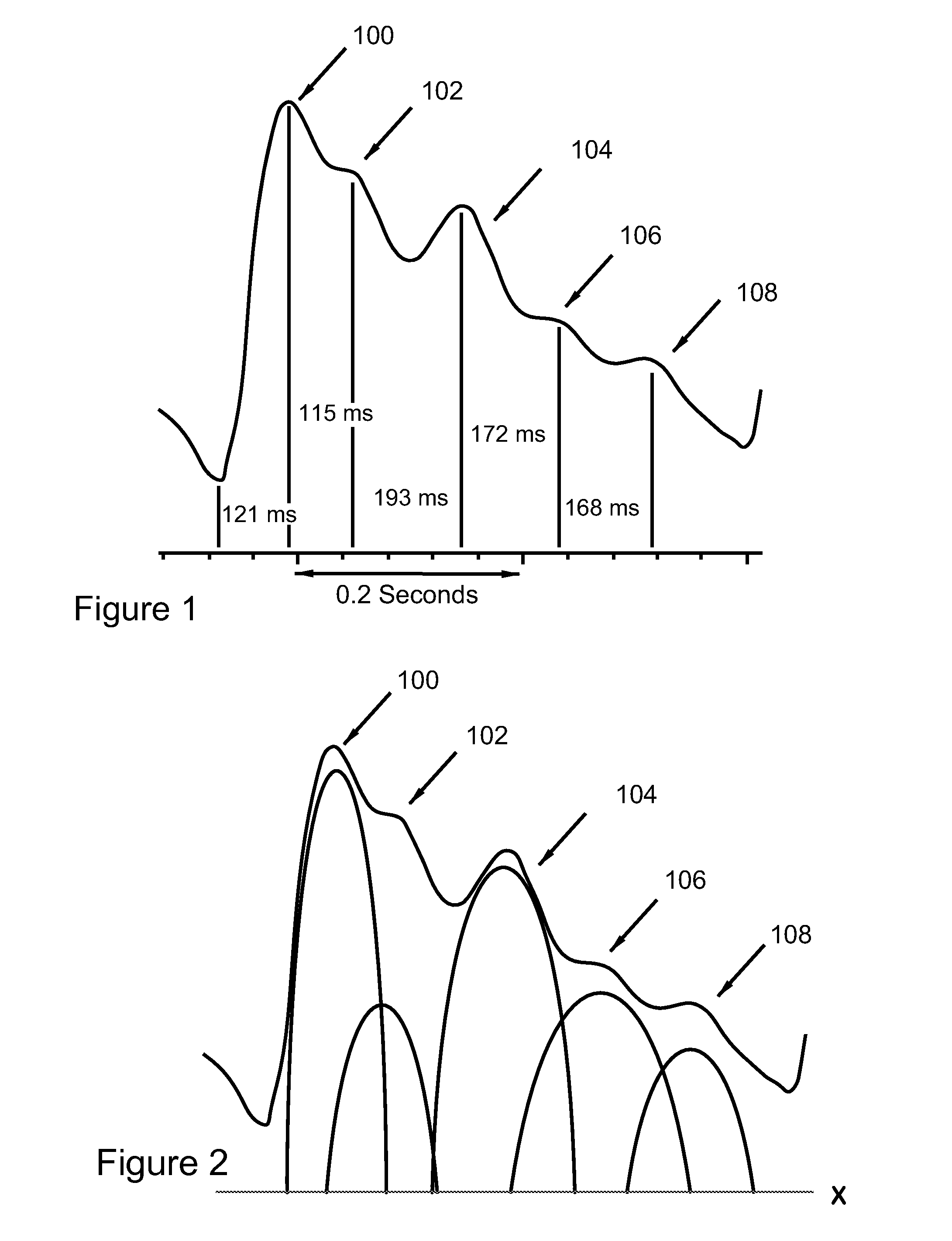
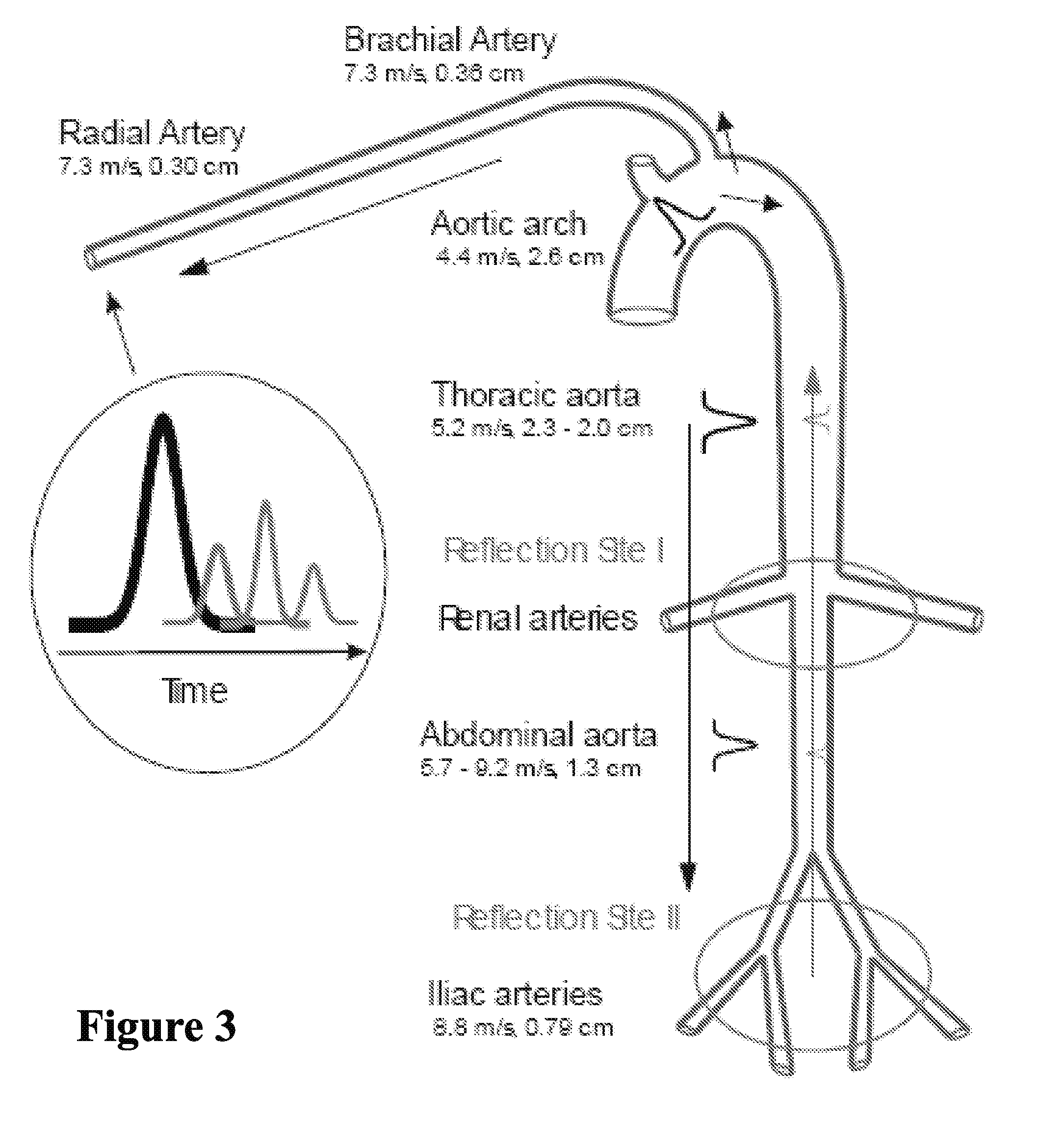
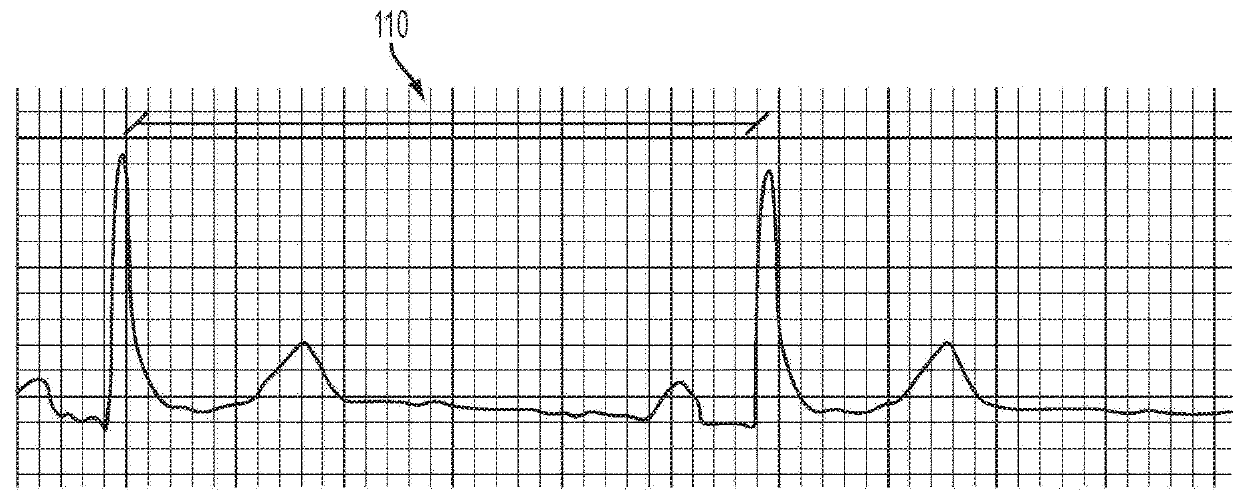
Detection of progressive central hypovolemia
ActiveUS20150148694A1Less complexLow costMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLeft ventricular ejectionNormal blood volume
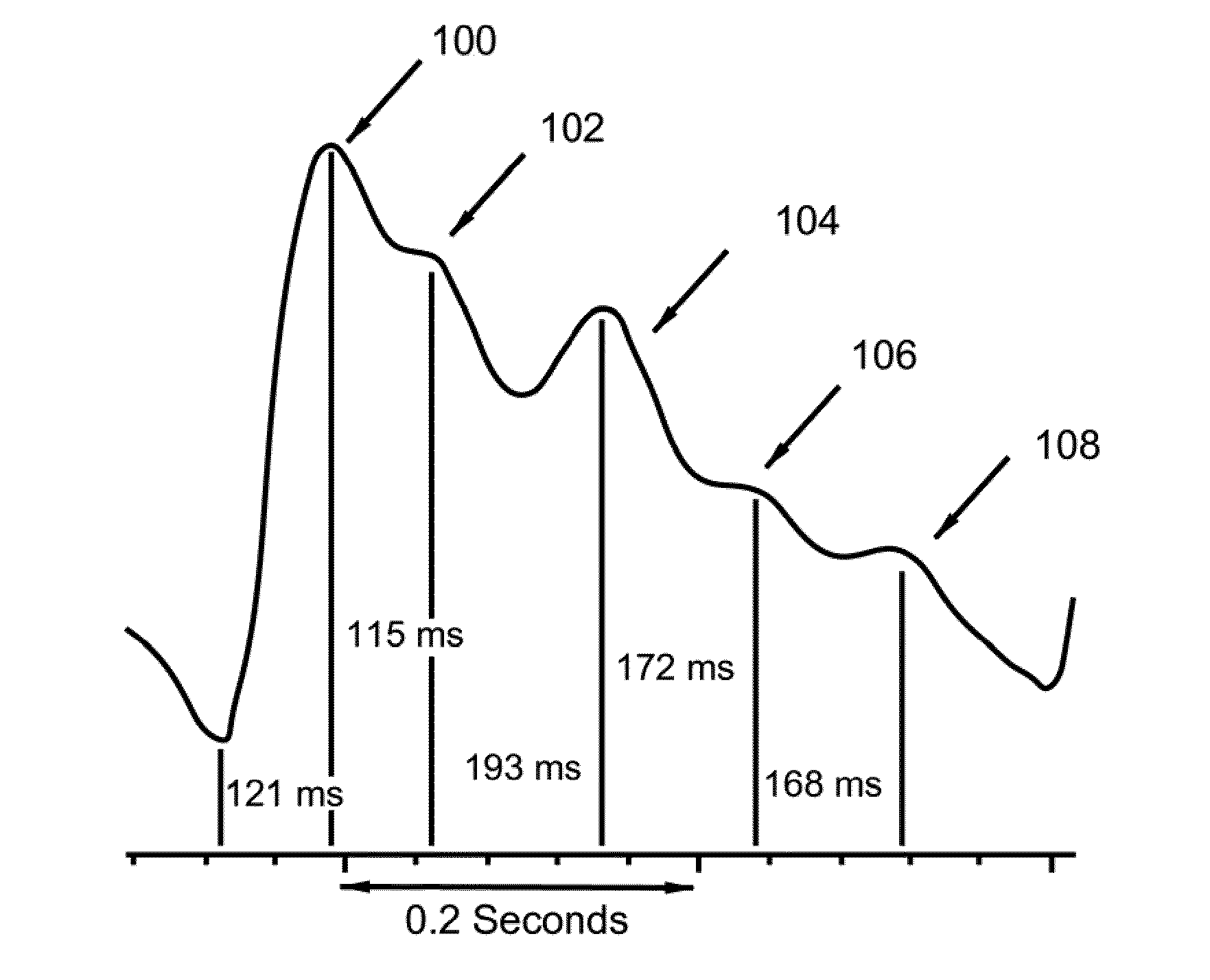
A system for detecting dehydration, hemorrhaging, and increases in blood volume comprising monitors the time difference between the arrival of the primary left ventricular ejection pulse (pulse T1) and the arrival of the iliac reflection (pulse T3) to determine an arterial pulse parameter which is the time difference between T1 T3. Changes in T3 minus T1 are indicative of something happening to blood volume. If the T1-3 value goes up and the patient is on an infusion system, it can be an indication of having too much fluid pumped and if T1-3 is lower than it should be for an individual, they are either dehydrated (which can result in decreases in blood volume), they are hemorrhaging, or they have hemorrhaged. A downtrend in T13 can tell whether someone is continuing to hemorrhage
Owner:EMPIRICAL TECH CORP
Detection of Progressive Central Hypovolemia using the System of the present invention with Pulse-Decomposition Analysis (PDA)
InactiveUS20100262022A1Less complexLow costEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterLeft ventricular ejectionMedicine
A system for detecting dehydration, hemorrhaging, and increases in blood volume comprising monitors the time difference between the arrival of the primary left ventricular ejection pulse (pulse T1) and the arrival of the iliac reflection (pulse T3) to determine an arterial pulse parameter which is the time difference between T1 T3. Changes in T3 minus T1 are indicative of something happening to blood volume. If the T1−3 value goes up and the patient is on an infusion system, it can be an indication of having too much fluid pumped and if T1−3 is lower than it should be for an individual, they are either dehydrated (which can result in decreases in blood volume), they are hemorrhaging, or they have hemorrhaged. A downtrend in T13 can tell whether someone is continuing to hemorrhage
Owner:BARUCH MARTIN +2
Albumin-based colloid composition and method of use in treating hypovolemia and multiorgan dysfunction
InactiveUS20100004178A1No loss of biological activityNo toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderSystemic capillary leak syndromeMultiorgan dysfunction
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF OHIO
Blood replacement product
A composition comprising Human Serum Albumin and an Amino Acid Solution, a method of making the same, and a method for use, including treating acute hypovolemia due to any number of medical conditions due to sepsis with shock, hemorrhagic shock, hypovolemic shock, burn injury, capillary leak syndrome, hypoalbuminemia, nephritic syndrome, or multi-organ failure with third space fluid loss from any other medical disease.
Owner:NORBERG WILLIAM J
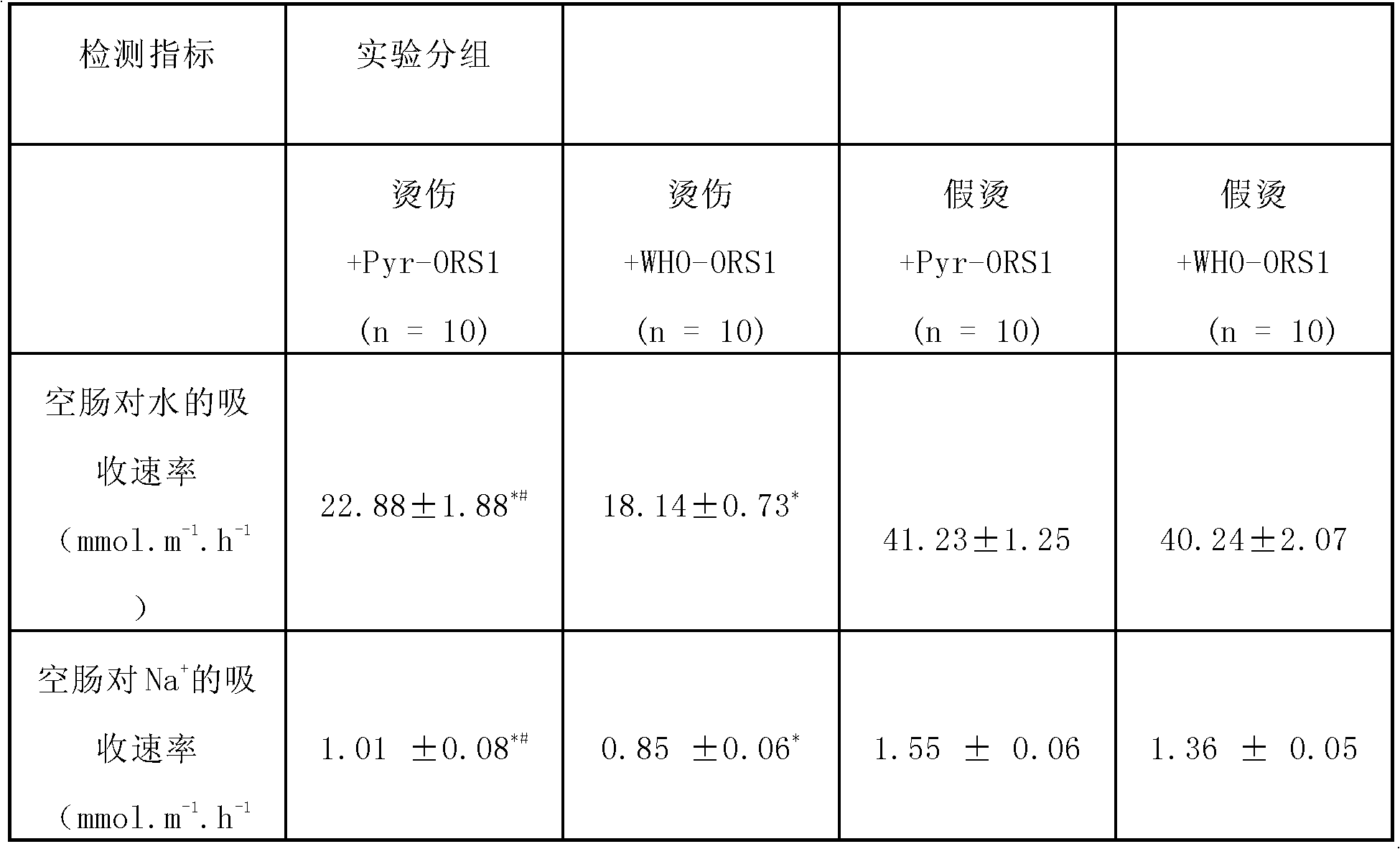
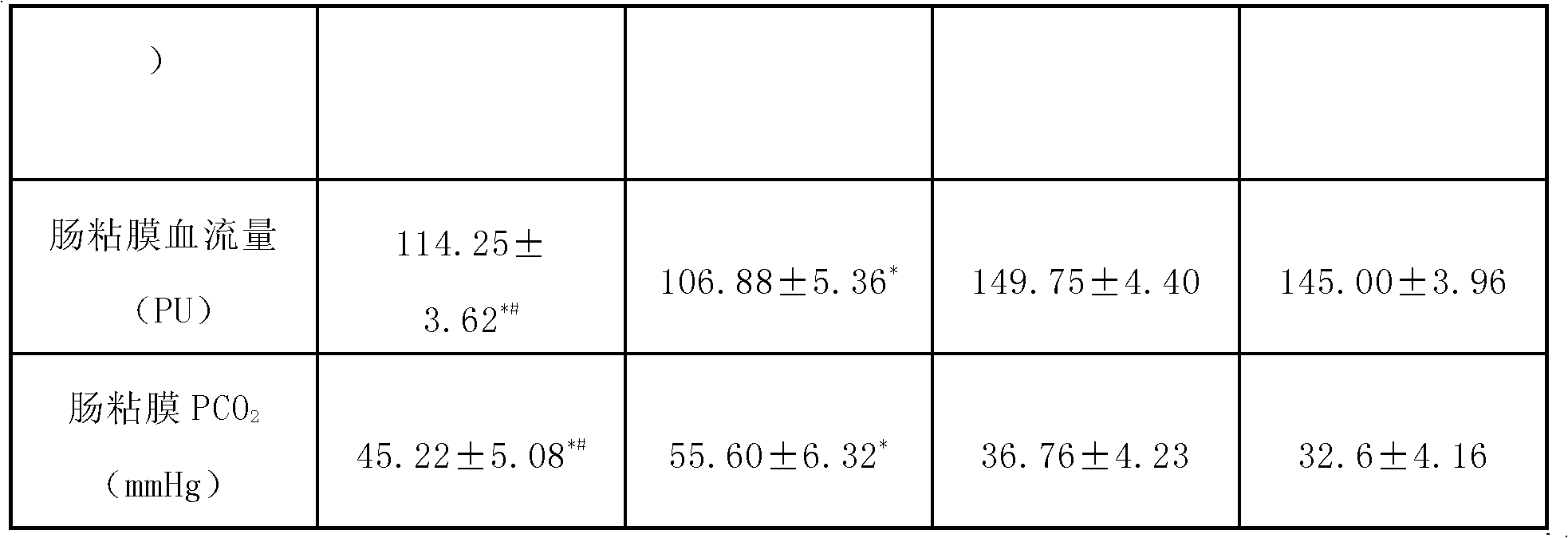
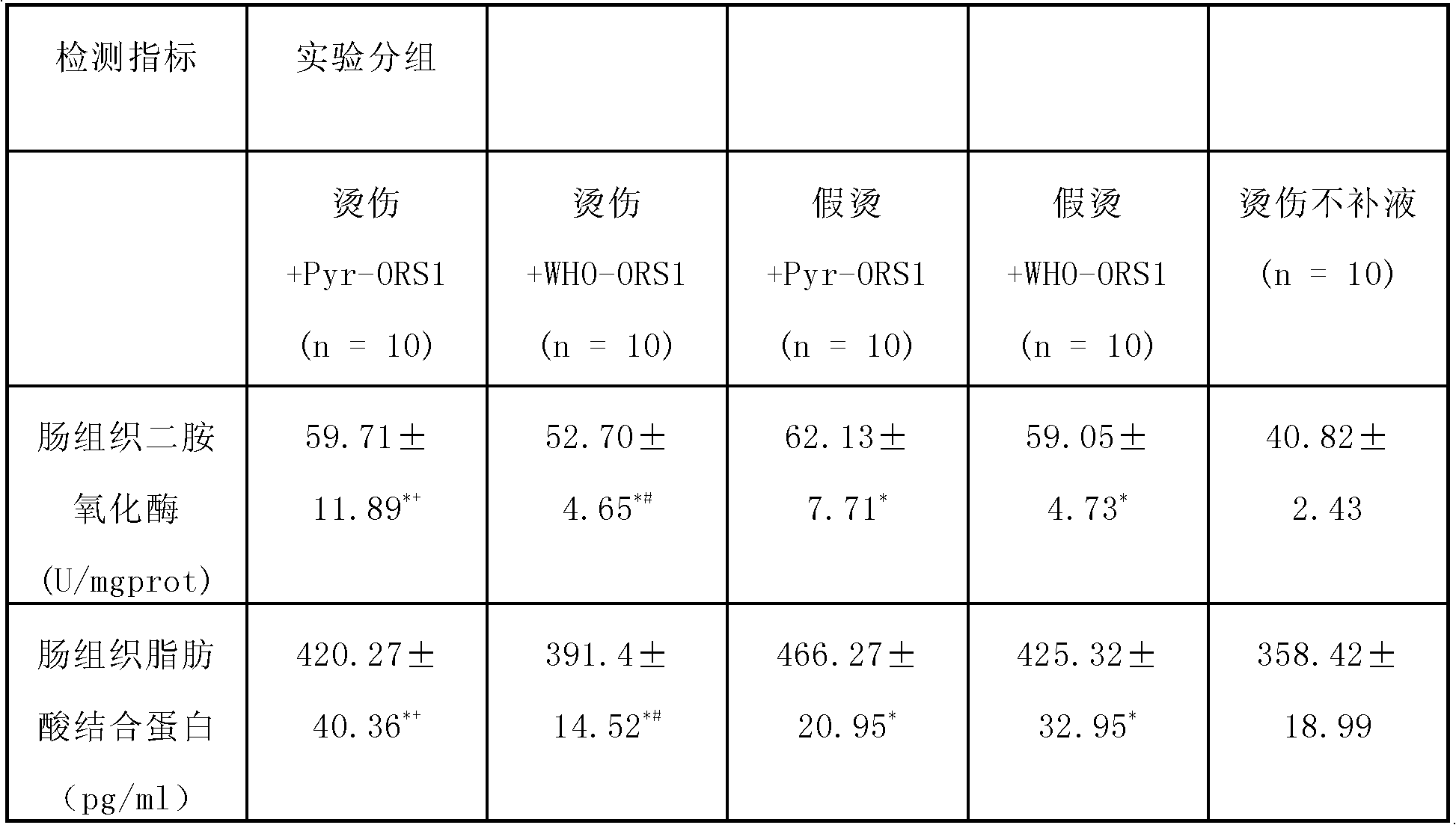
Pyruvate oral rehydration salt composition for curing circulation hypovolemia or water-losing with salt-losing
InactiveCN103316038APromote absorptionBlood volume expansionAntibacterial agentsInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsFluid replacementPotassium
The invention discloses a pyruvate oral rehydration salt composition for curing circulation hypovolemia or water-losing with salt-losing. The composition comprises the following components: (i) 2.0-6.0 parts by weight of sodium pyruvate, (ii) 1.5-17.0 parts by weight of sodium chloride, (iii) 0-2.0 parts by weight of potassium chloride, and (iv) 10.0-50.0 parts by weight of anhydrous glucose or other carbohydrates; and the sum weight of the components (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv) is 50-100 % of the total composition weight.
Owner:胡森 +1
System and method for discriminating hypervolemia, hypervolemia and euvolemia using an implantable medical device
Techniques are provided for use by an implantable medical device or diagnostic sensor for detecting and discriminating euvolemia, hypervolemia and hypovolemia. In one example, the device detects a pressure signal within the patient representative of changes in cardiac pressure overall several cardiac cycles. The device generates separate time-domain and frequency-domain representations of the pressure signal and then discriminates among euvolemia, hypervolemia and hypovolemia within the patient based on an analysis of the time-domain and the frequency-domain representations of the signal. Depending upon the capabilities of the device, suitable warnings may be generated to alert the patient or caregiver. Diuretics or other medications can be titrated to address abnormal fluid conditions such as a fluid overload during hypervolemia. Techniques for detecting a pressure alternans pattern indicative of imminent decompensation are also described.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Compositions and methods for treatment of loss of fluids leading to hypotension and/or hypovolemia
InactiveUS20200093853A1Easy to transportMaintain good propertiesPowder deliveryInorganic non-active ingredientsBlood flowLow blood pressures
The present invention is directed to a composition containing at least one salt and at least one natural or synthetic high molecular weight, non-ionic, hydrophilic polymer. When in a liquid form, the composition is ready for infusion or injection to patients that suffer from loss of fluids that causes reduced volume and / or pressure in the systemic circulation. The composition is also suitable for treatment of organ conditions where blood flow is impaired or insufficient, resulting in organ distress, including tissue loss. The invention also relates to use as a prophylaxis to prevent medical consequences of anticipated conditions where depleted circulatory fluids, low blood pressure, or impaired organ perfusion require correction.
Owner:CELLPHIRE INC
Monitoring blood distribution in a subject
PendingUS20210085280A1Avoid replacementImplemented cost-effectivelyBlood flow measurement devicesHealth-index calculationNormal blood volumeHematological test
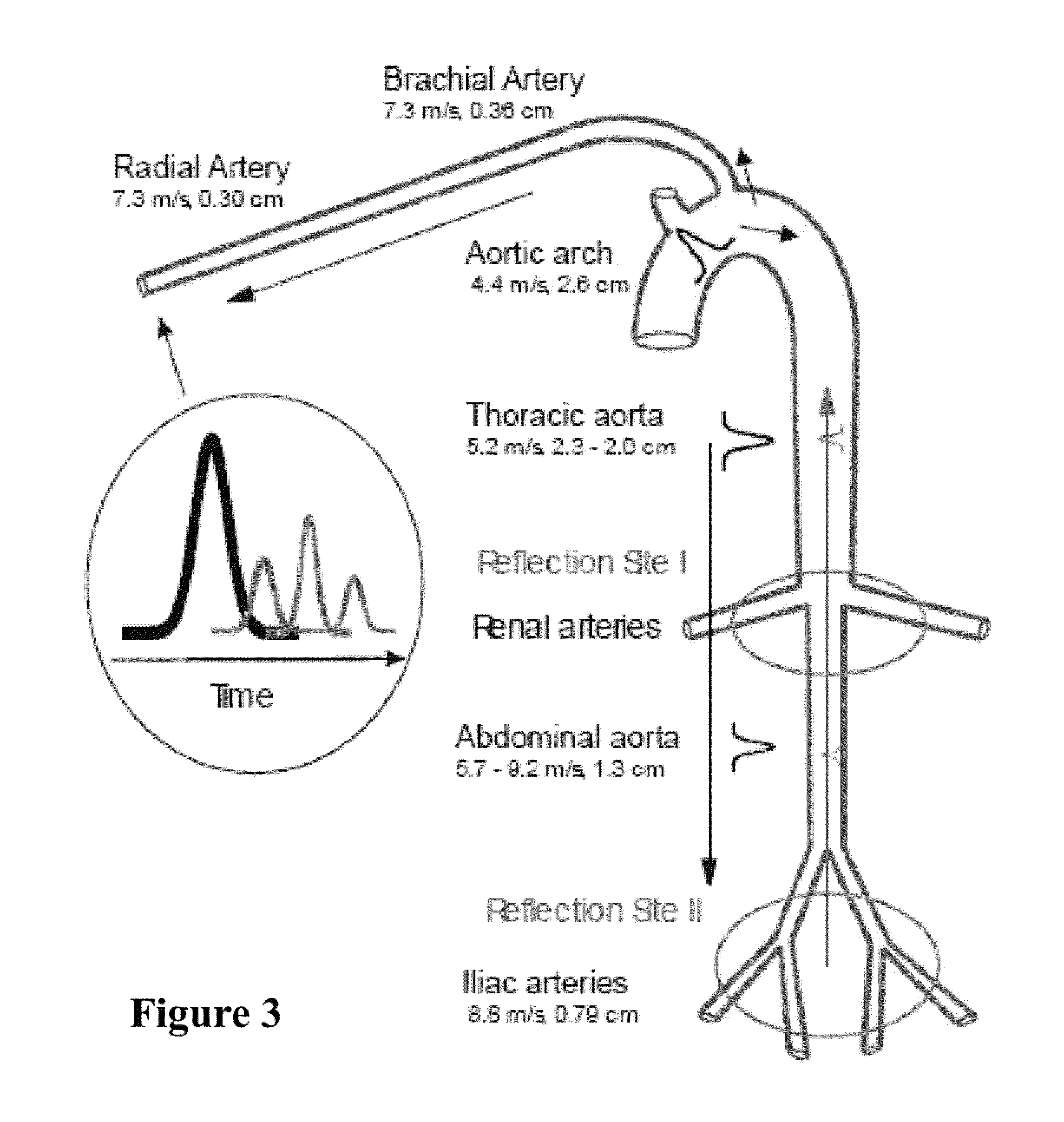
A system for monitoring blood distribution in a subject, the system comprising a processor(38) responsive to Doppler ultrasound data representing arterial blood flow in at least two different locations of the subject, such as the neck and the arm, to obtain velocity (C, B1, B2, B3) or volumetric flow rate at each location, to monitor changes in a predetermined function of the blood flows, and to provide an output indicative of the monitored changes which may result from blood volume centralization. This can indicate the onset of hypovolemia or hypervolemia.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Composition and methods for treatment of loss of fluids leading to hypotension and/or hypovolemia
InactiveUS20180169139A1Easy to transportMaintain good propertiesPowder deliveryInorganic active ingredientsMedicineHypotension shock
The present invention is directed to a composition containing at least one salt, at least one natural or synthetic saccharide, and at least one natural or synthetic high molecular weight, non-ionic, hydrophilic polymer. When in a liquid form, the composition is ready for infusion or injection to patients that suffer from loss of fluids that causes reduced volume and / or pressure in the systemic circulation. The composition is also suitable for treatment of organ conditions where blood flow is impaired or insufficient, resulting in organ distress, including tissue loss. The invention also relates to use as a prophylaxis to prevent medical consequences of anticipated conditions where depleted circulatory fluids, low blood pressure, or impaired organ perfusion require correction.
Owner:CELLPHIRE INC
Absolute intrathoracic impedance based scheme to stratify patients for risk of a heart failure event
ActiveUS10368774B2Quick confirmationAvoid and reduce probabilityHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical resistance and conductanceIntrathoracic impedance
A health care system acquires data determines whether a patient is at risk of hypervolemia or hypovolemia. The method comprises (a) acquiring from a device memory a patient's absolute intrathoracic impedance data over a pre-specified time period, (b) determining a running average of the intrathoracic impedance data over the pre-specified time period, and (c) determining by the system whether the running average of the intrathoracic impedance data over the pre-specified time period exceeds one of a first and second range, the first range being a higher value boundary of intrathoracic electrical impedance and the second range being a lower value boundary of intrathoracic electrical impedance.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Albumin-based colloid composition and method of use in treating hypovolemia and multiorgan dysfunction
InactiveUS20060166886A1No loss of biological activityNo toxicityBiocideHydrolysed protein ingredientsSystemic capillary leak syndromeMultiorgan dysfunction
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF OHIO
Methods And Systems For Predicting Hypovolemic Hypotensive Conditions Resulting From Bradycardia Behavior Using A Pulse Volume Waveform
InactiveUS20200187806A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesElectrocardiographyBlood pressure cuffsBlood pressure cuff
A method for identifying cardiac bradycardia behavior may include acquiring pulse volume wave data from a sensor associated with a patient, and calculating metrics associated with peaks detected therein. The metrics may include changes in peak amplitudes of pulse volume peaks and in the times of occurrence of pulse volume peaks. Alternative metrics may include changes in frequency domain parameters derived from the time domain pulse volume wave data. Peak amplitude values may be compared to an amplitude baseline, and differences in successive peak occurrence times may be compared to a time baseline. Cardiac bradycardia behavior may be identified by a combination of a decrease in the pulse volume peak amplitude and an increase in successive peak occurrence times. A system to implement the method may include a computing device in data communication with a photo-plethysmograph. Alternative sensors may include a blood pressure cuff and an ECG device.
Owner:INTELOMED
Sodium Pyruvate Oral Rehydration Salt Composition for Treating Hypovolemia or Hyponatration Associated with Hypohydration
InactiveUS20150105463A1Promote absorptionPromote circulationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBlood pressureD-Glucose
Disclosed in the present invention is a sodium pyruvate oral rehydration salt composition for treating hypovolemia or hyponatration associated with hypohydration, said composition containing the following components: (i) 2.0-6.0 parts by weight of sodium pyruvate; (ii) 1.5-17.0 parts by weight of sodium chloride; (iii) 0-2.0 parts by weight of potassium chloride; and (iv) 10.0-50.0 parts by weight of glucose anhydrous or other carbohydrates. The weight of components (i)+(ii)+(iii)+(iv) constitutes 50-100% of the total weight of the composition.
Owner:ZHOU FANGQIANG
Albumin-based colloid composition and method of use in treating hypovolemia and multiorgan dysfunction
InactiveUS20080113903A1No loss of biological activityNo toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAlbumin peptidesSystemic capillary leak syndromeMultiorgan dysfunction
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF OHIO
Hypovolemia/hypervolemia detection using peripheral intravenous waveform analysis (PIVA) and applications of same
Aspects of the invention relates to systems and methods for hypovolemia and / or hypervolemia detection of a living subject using peripheral intravenous waveform analysis. In one embodiment, the method includes: acquiring, from a vein of the living subject, peripheral venous signals; performing a spectral analysis on the acquired peripheral venous signals to obtain a peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum; and performing a statistical analysis on amplitudes of peaks of the peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum to determine the blood volume status of the living subject in real time. Specifically, at least two peaks, respectively corresponding to a first frequency and a second frequency, are obtained on the peripheral venous pressure frequency spectrum. Amplitude change of the second peak is used to determine the blood volume status of the living subject. Hemorrhage may be detected when a significant amplitude decrease is detected from the second baseline peak to the second peak.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4 sodium chloride injection and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101450075BIncrease osmotic pressureIncrease partial pressureOrganic active ingredientsBlood disorderHydroxyethyl starchSodium Chloride Injection
The invention provides an ethoxyl starch 130 / 0.4 sodium chloride injection, in which, 20-80g of ethoxyl starch 130 / 0.4 and 5-13g of sodium chloride is include in per litre injection. The invention further provides the preparing method and application of the injection. The ethoxyl starch 130 / 0.4 in the raw material of the medicine in the invention is an improved product of 'heas' used clinically for treating and preventing hypovolemia, acute normovolemic hemodilution and so on. A better normovolemic therapeutic effect is achieved by optimizing molecular weight and molecular weight distribution, reducing displacement grade and changing displacement manner (C2 / C6); it can stays in blood for longer time after intravenous drip, consequently, can increase plasma osmotic pressure, tissue fluid back-flow and blood volume, can improve oxygenation condition in or after major operation evidently, and can increase tissue oxygen partial pressure and improve tissue oxygenation faster and earlier, thereby can satisfy the clinic demand better.
Owner:CHENGDU ZHENGKANG PHARMA
Systems and Methods for Self-Directed Patient Fluid Management
Systems and methods are disclosed that provide for regular, periodic or continuous monitoring of fluid volume based on direct measurement of an inferior vena cava (IVC) physical dimension using a wireless measurement sensor implanted in the IVC. By basing diagnostic decisions and treatments on changes in an IVC physical dimension, information on patient fluid state is available across the entire euvolemic range of fluid states, thus providing earlier warning of hypervolemia or hypovolemia and enabling the modulation of patient treatments to permit more stable long-term fluid management.
Owner:FOUNDRY INNOVATION & RES 1 LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com