Patents
Literature
126results about "Esophageal electrodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
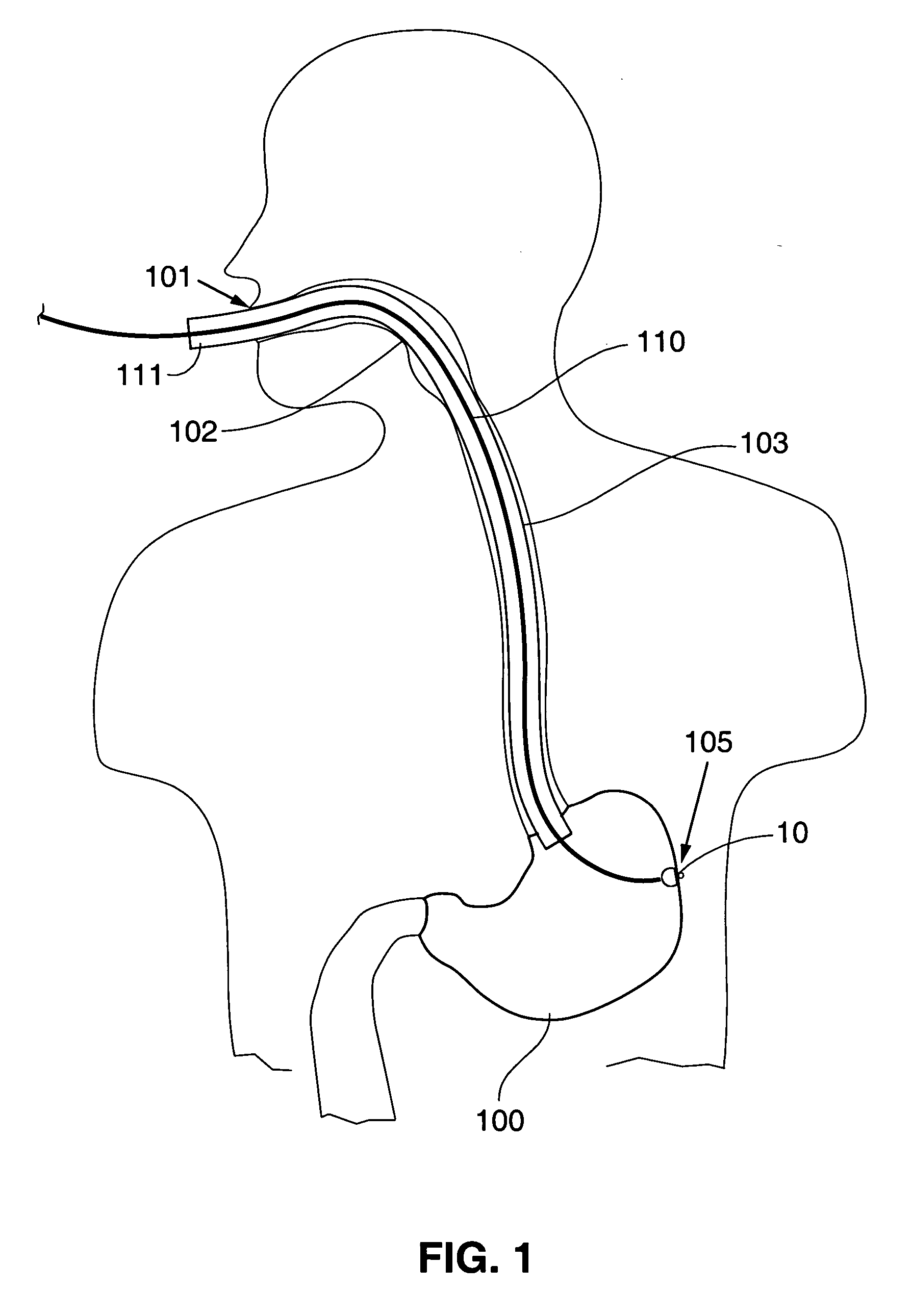
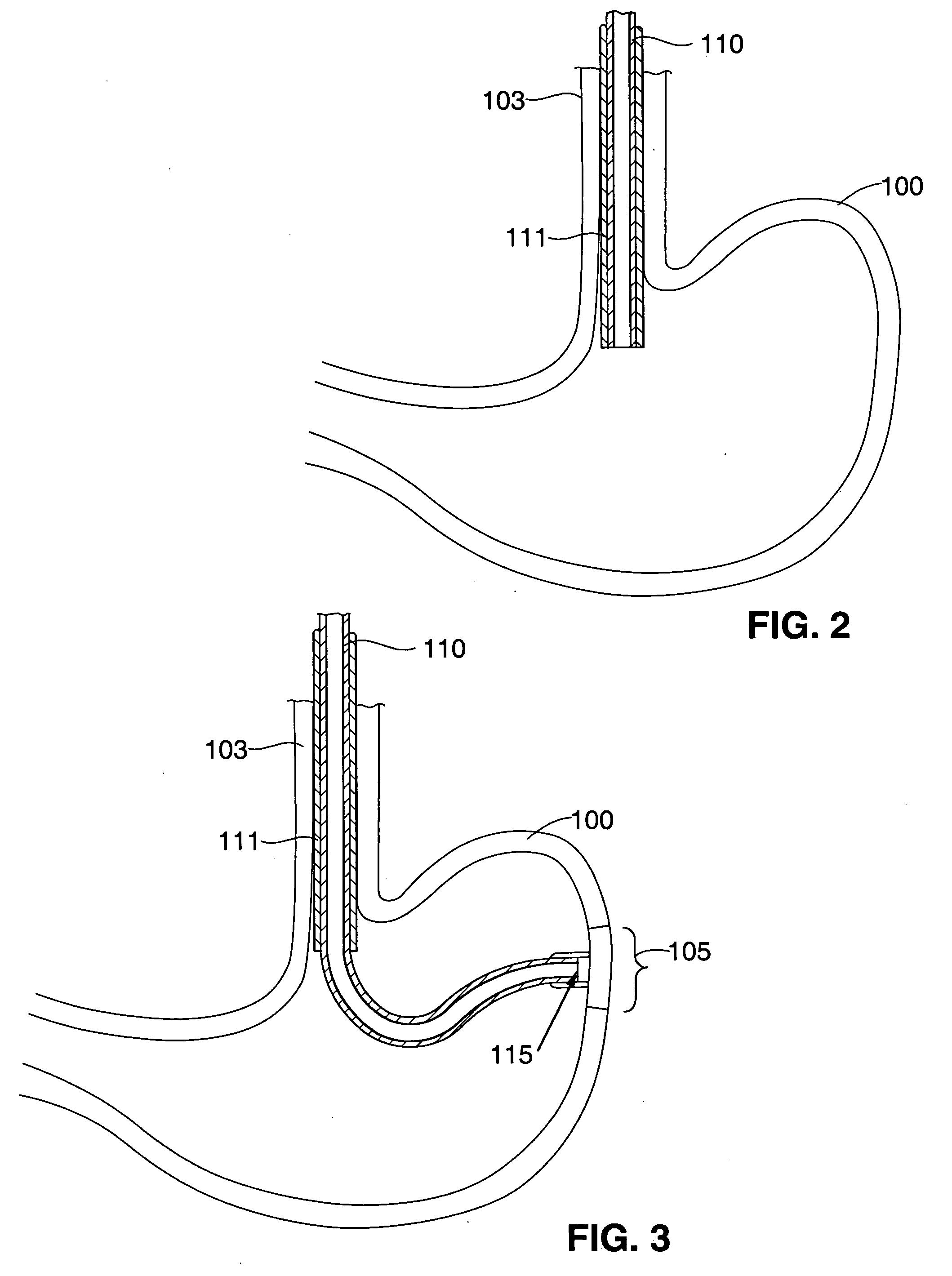
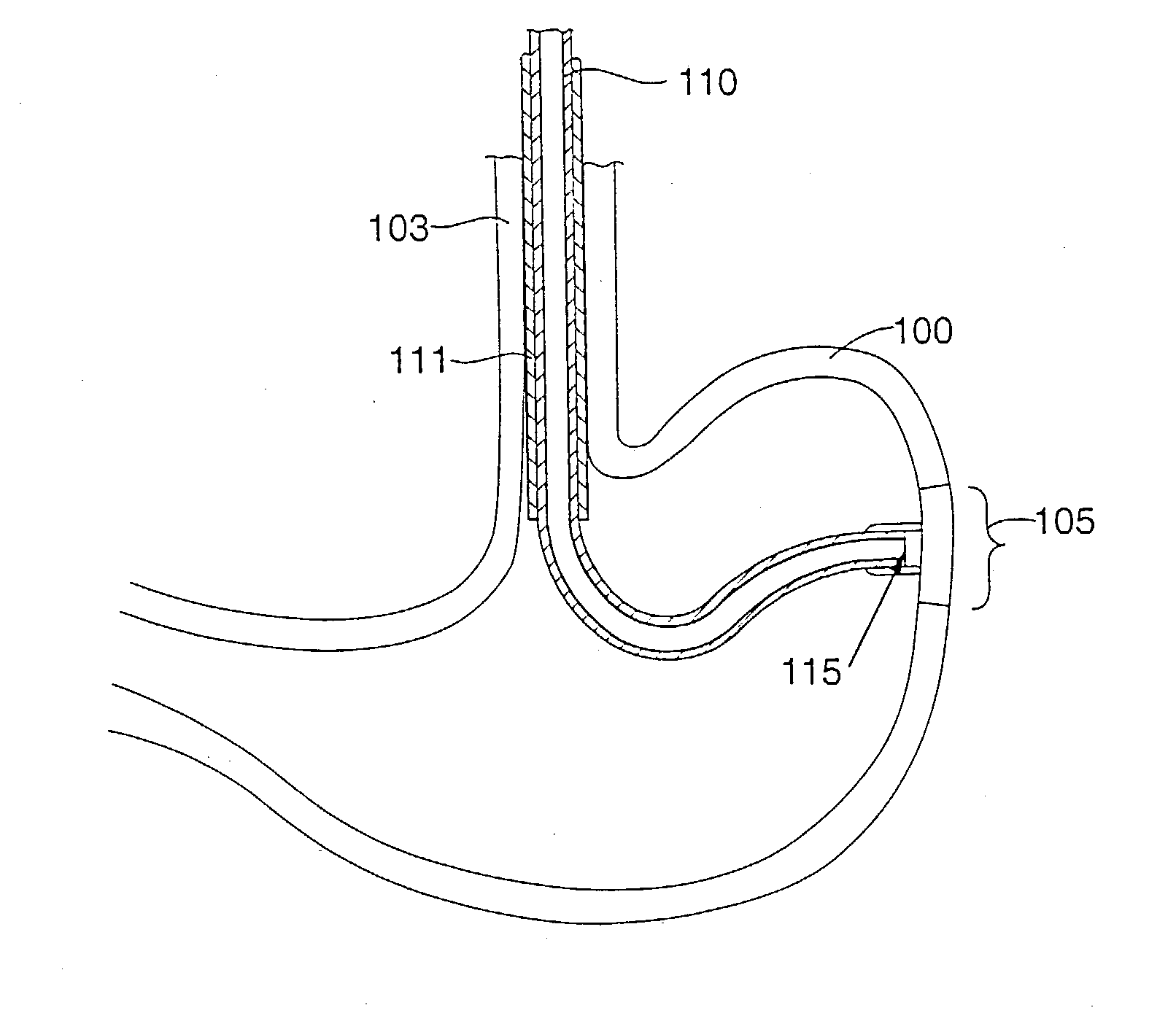
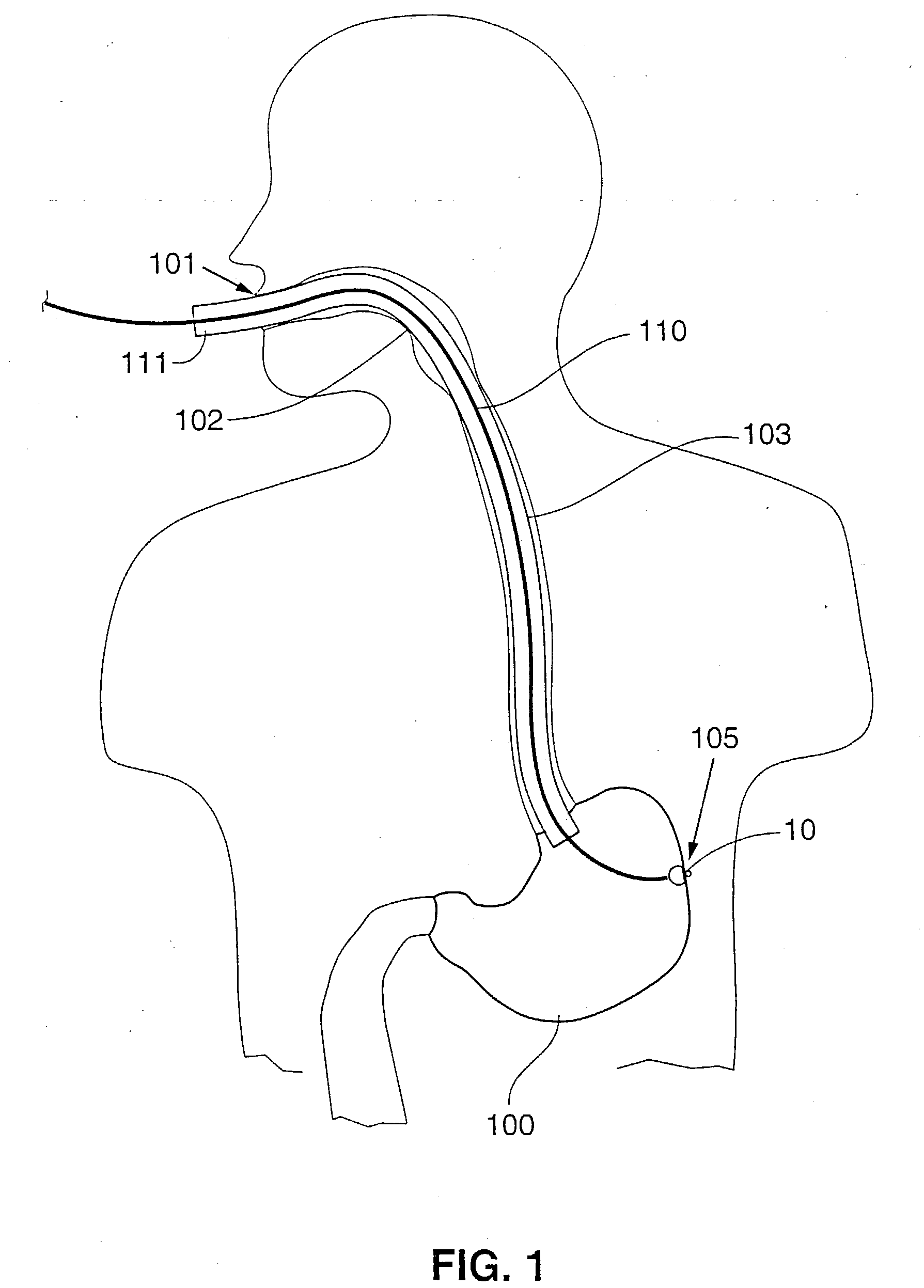
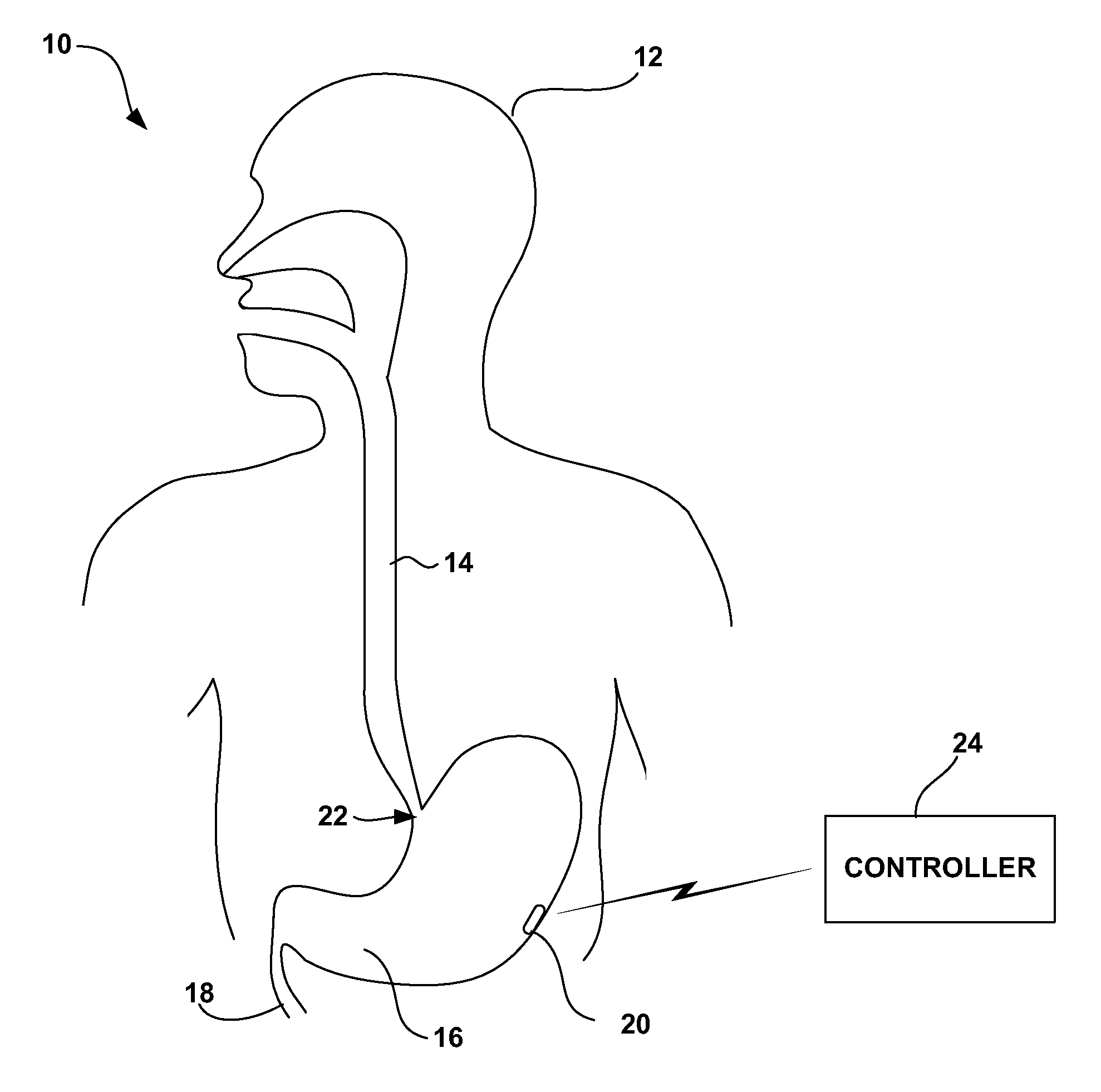
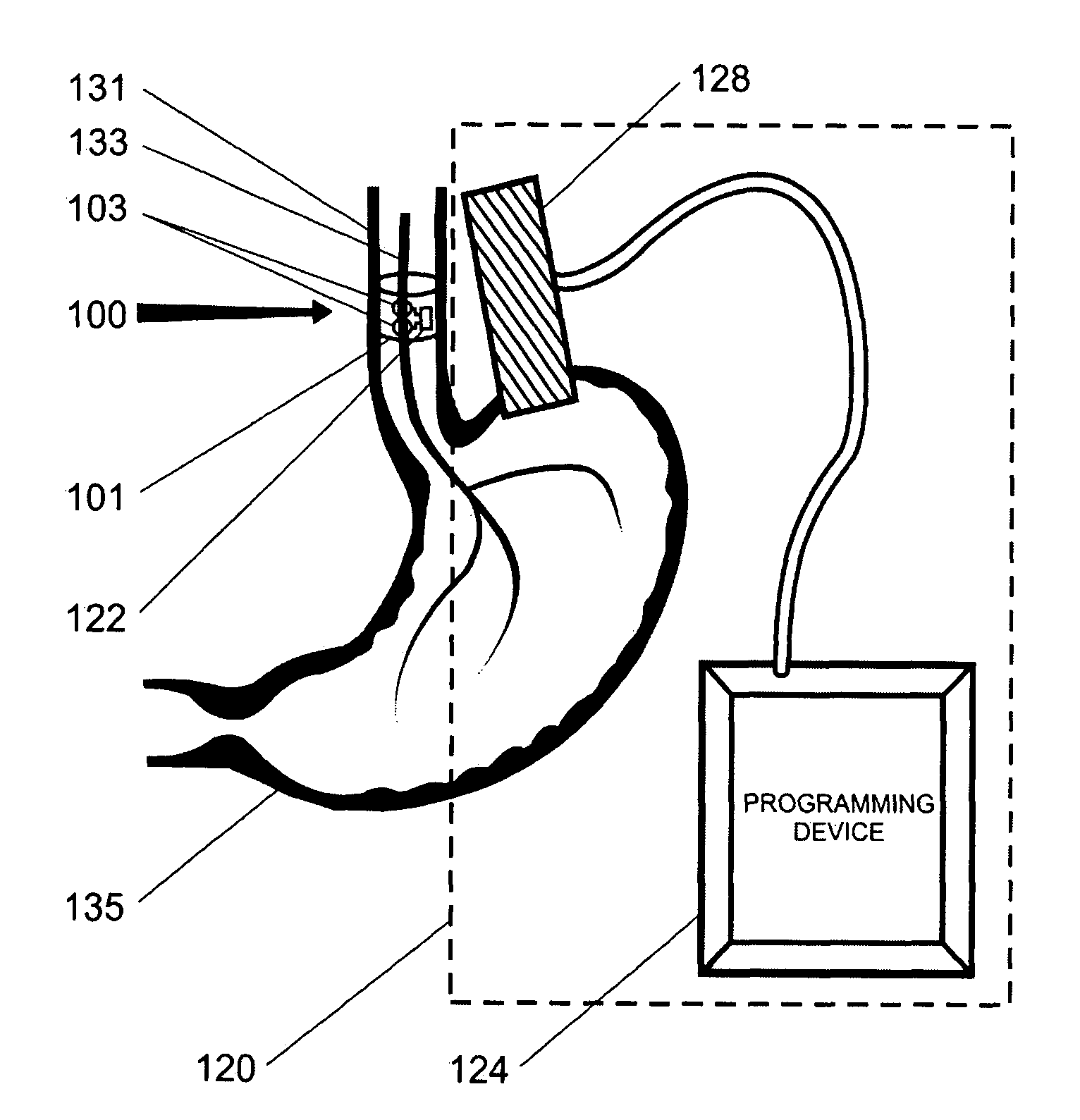
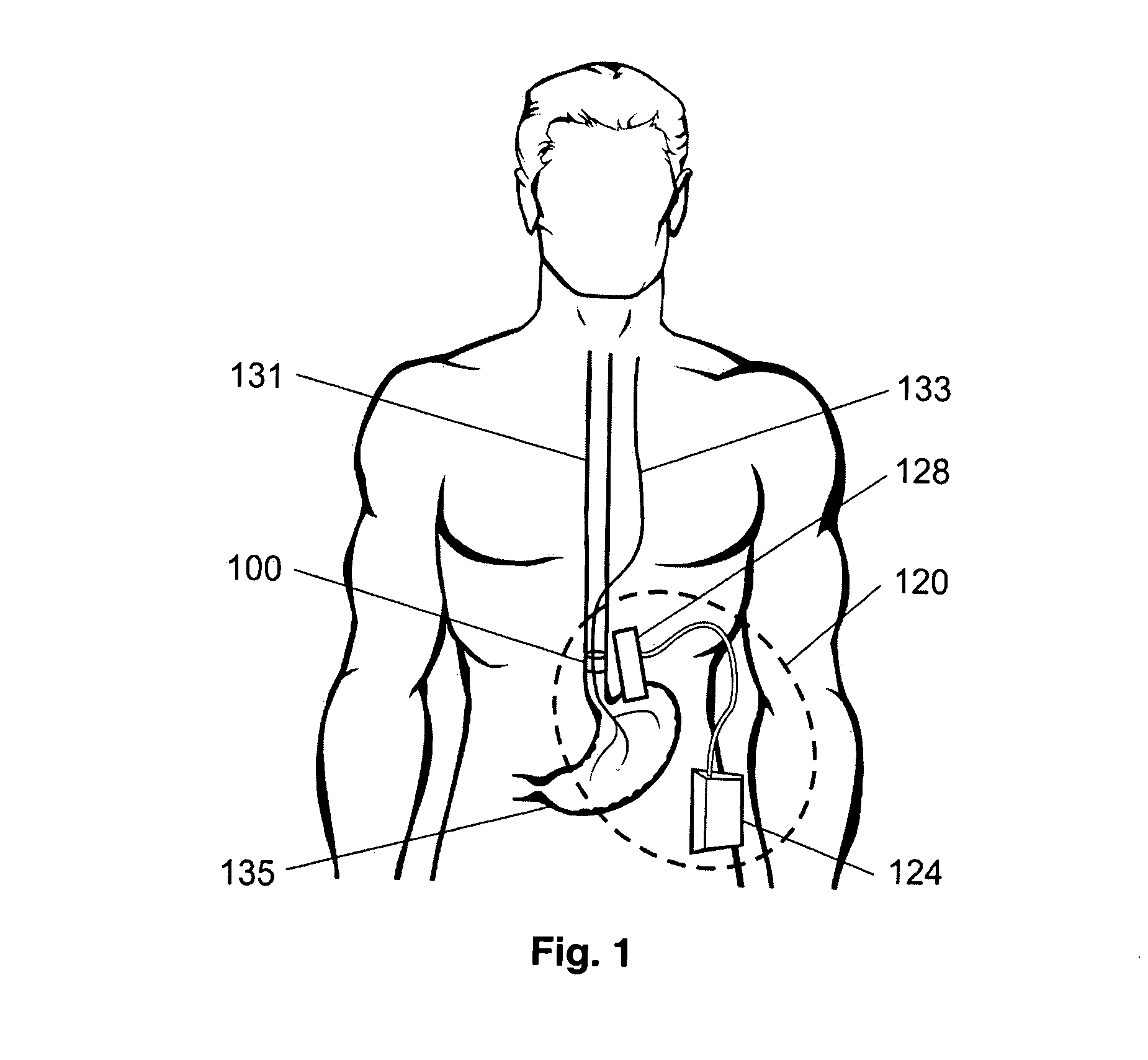
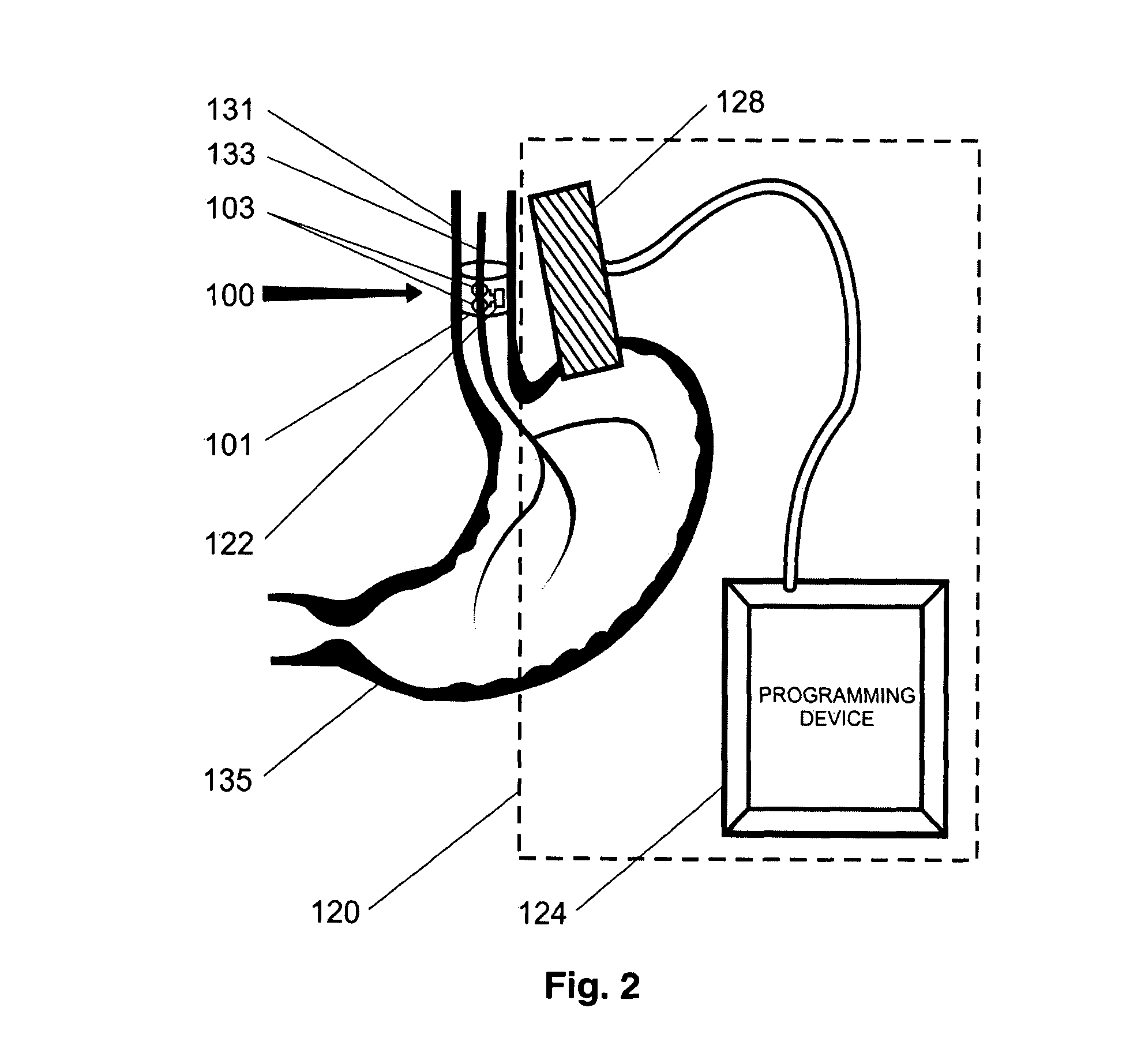
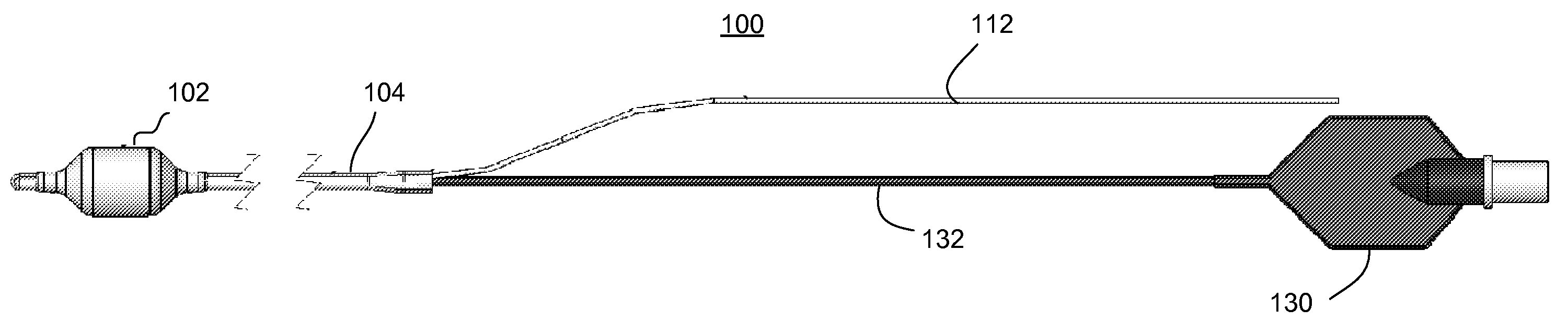
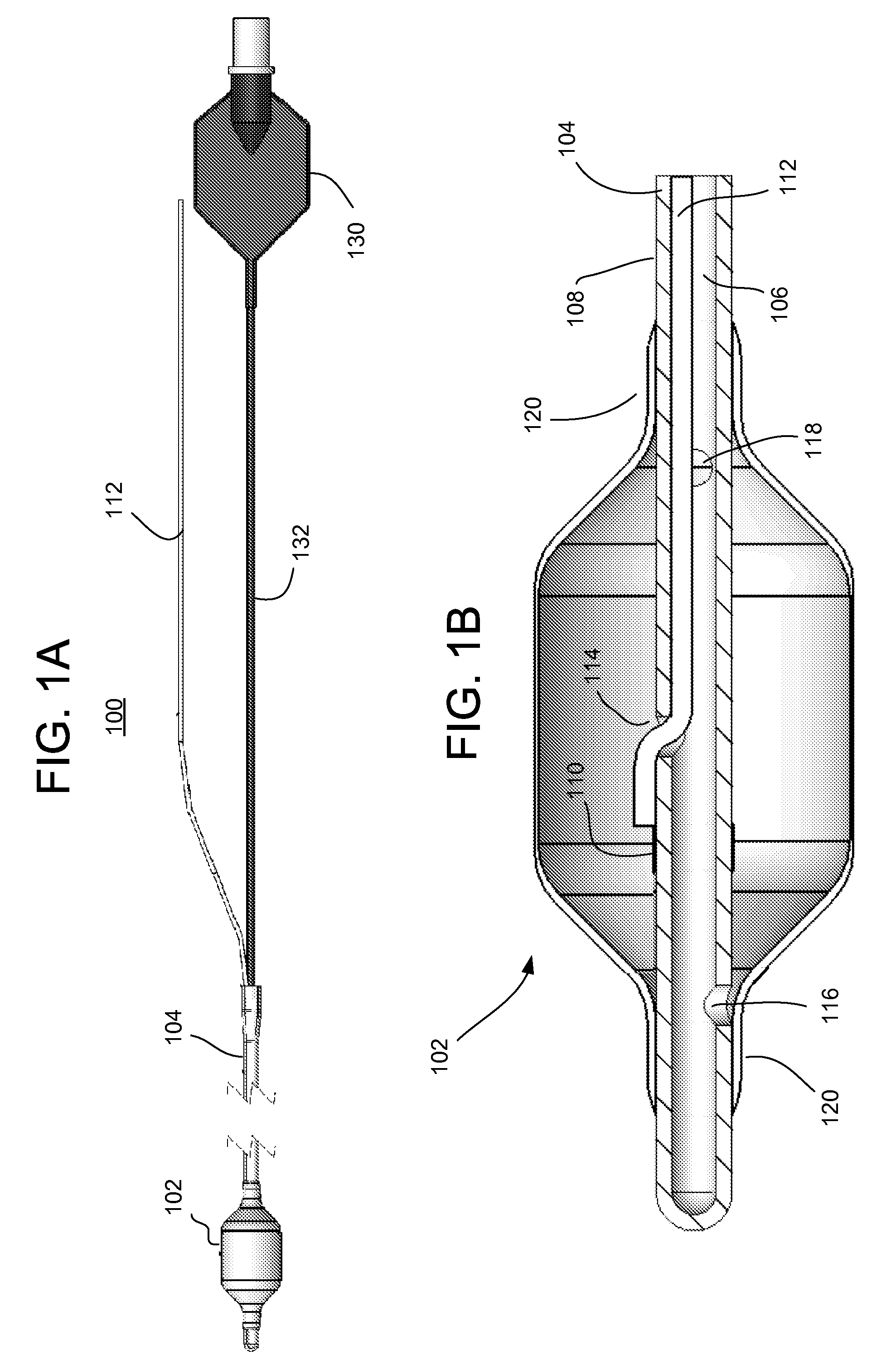
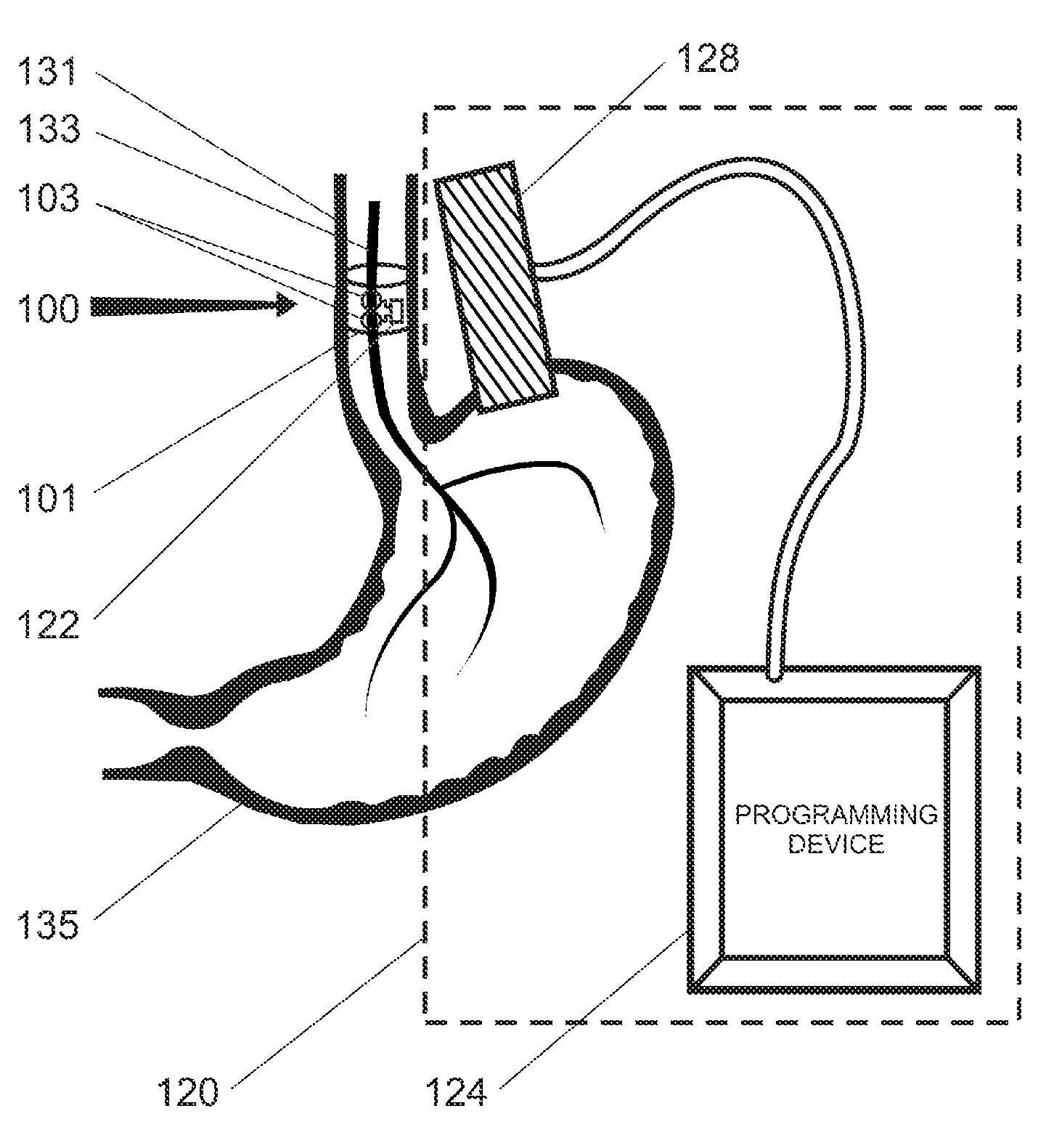
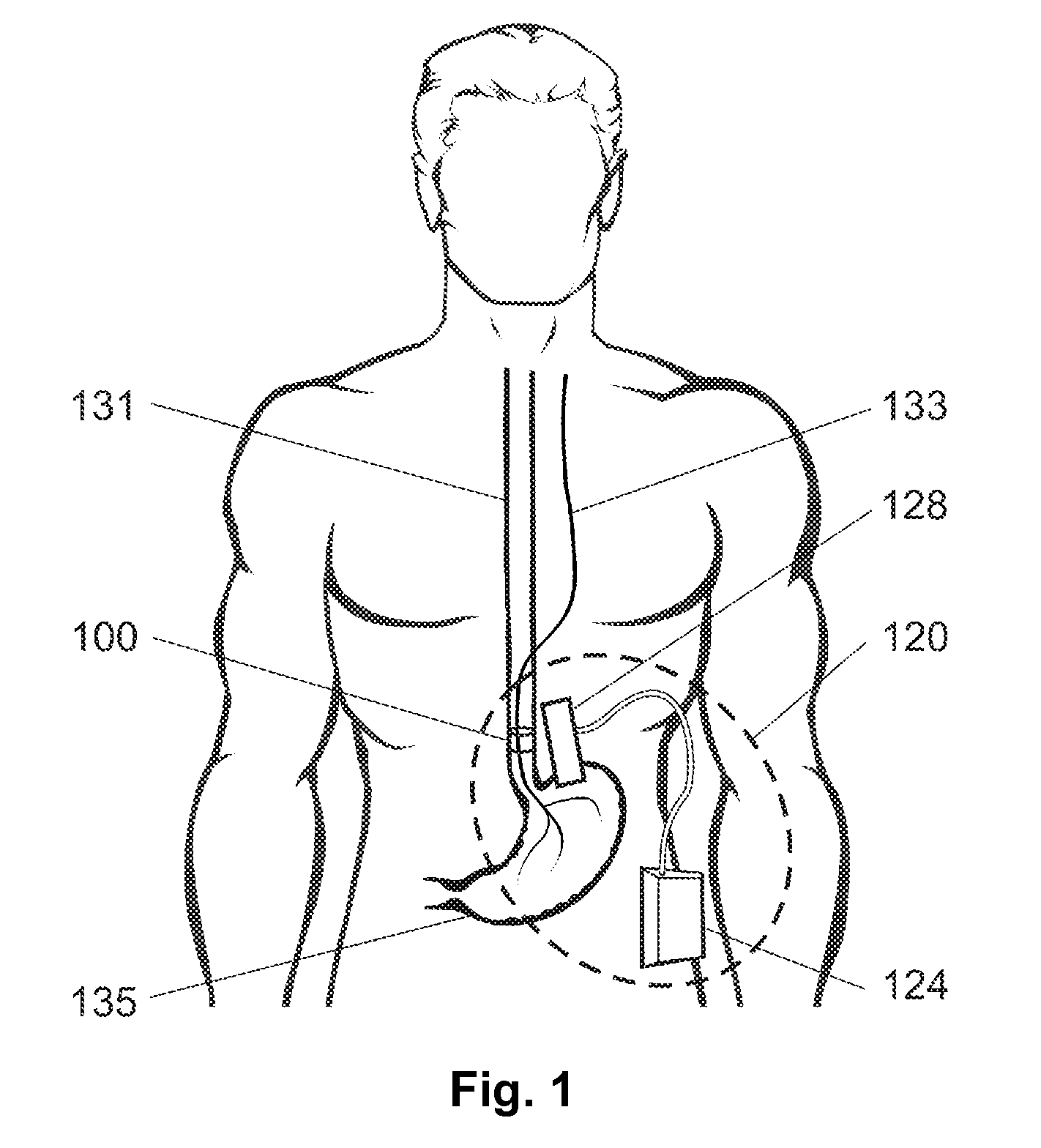
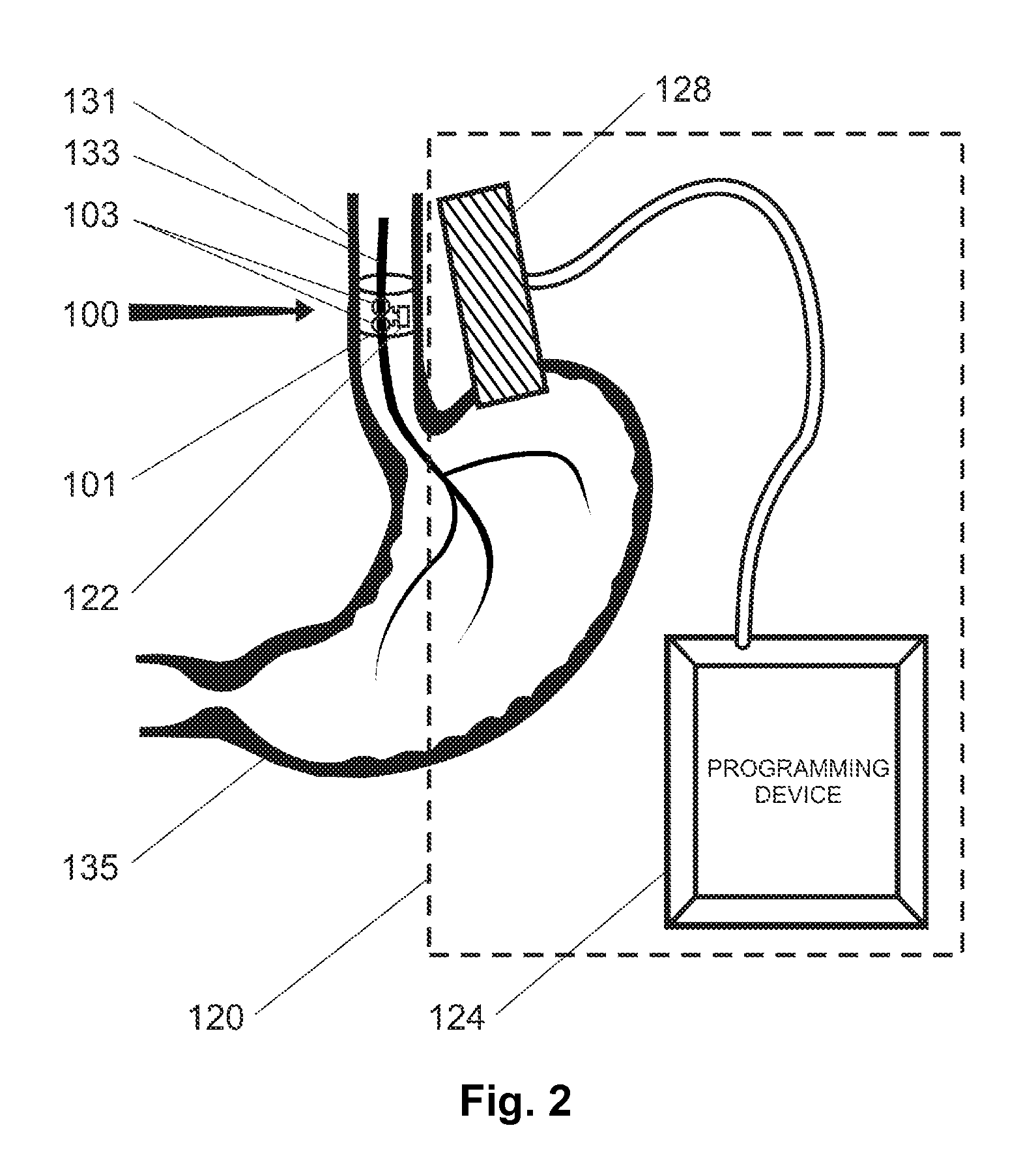
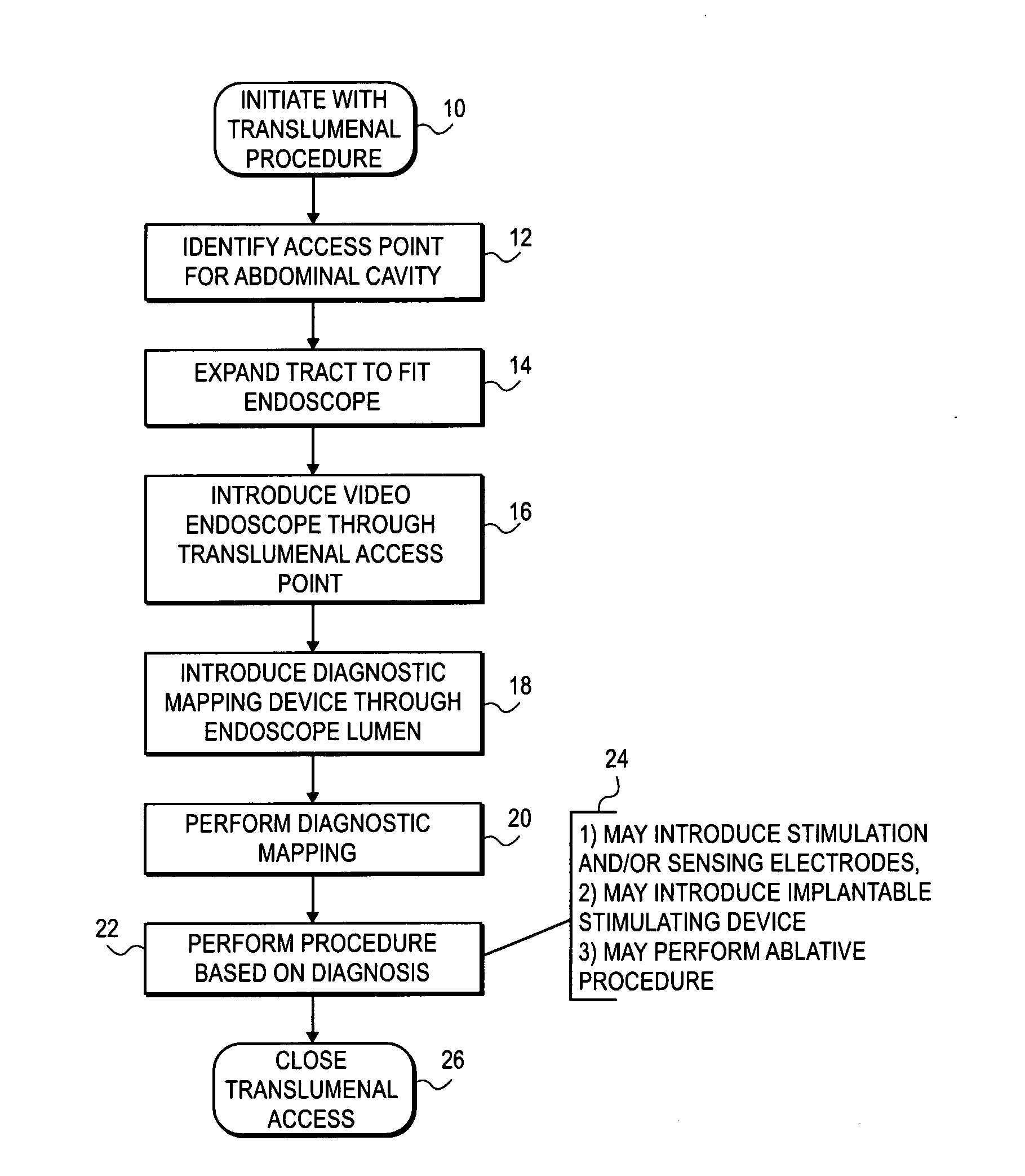
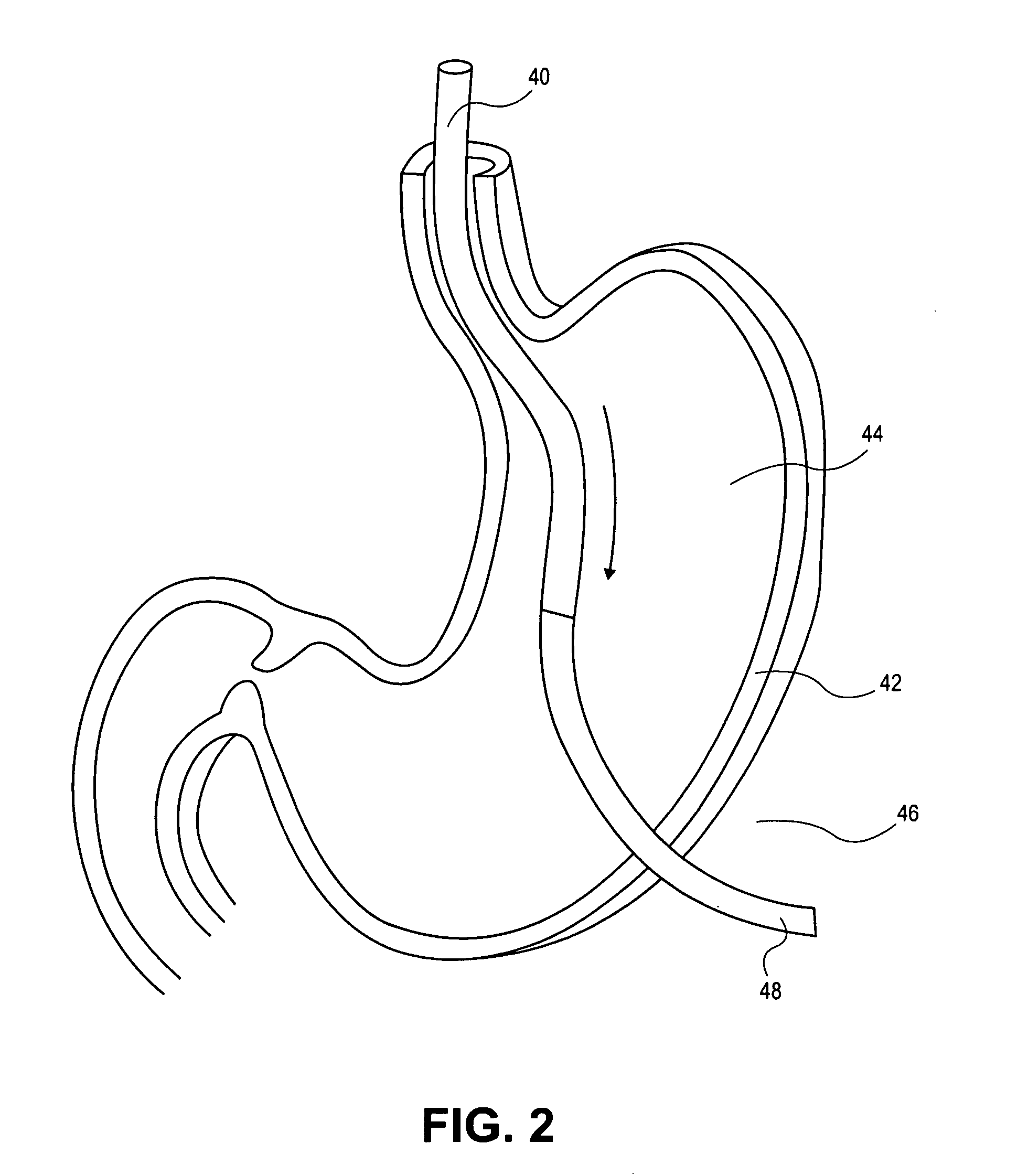
Gastric treatment and diagnosis device and method
InactiveUS20040088023A1Minimize stressReduce potential tissue damageCannulasSurgical needlesStomach wallsGastric Disorders
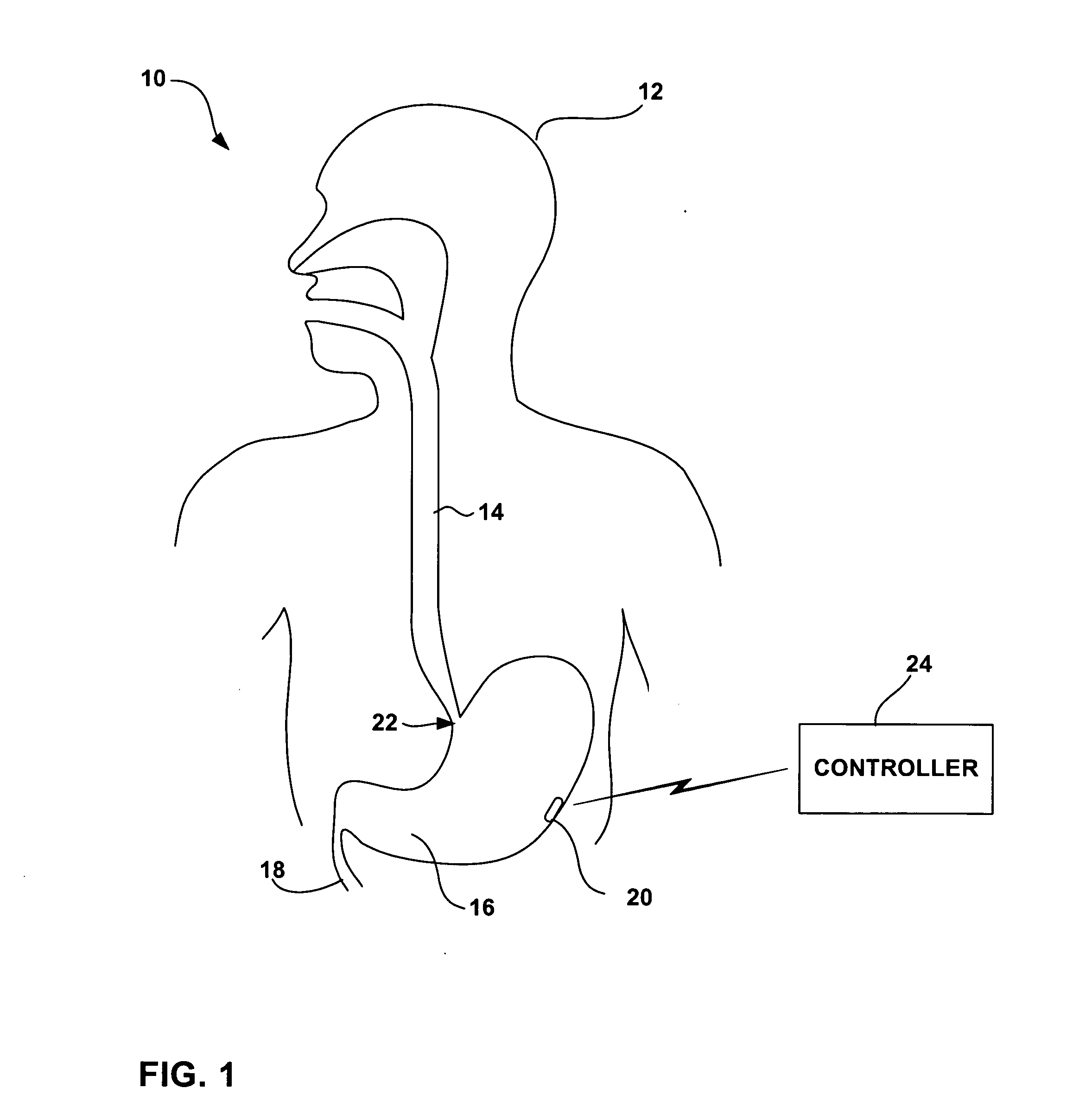
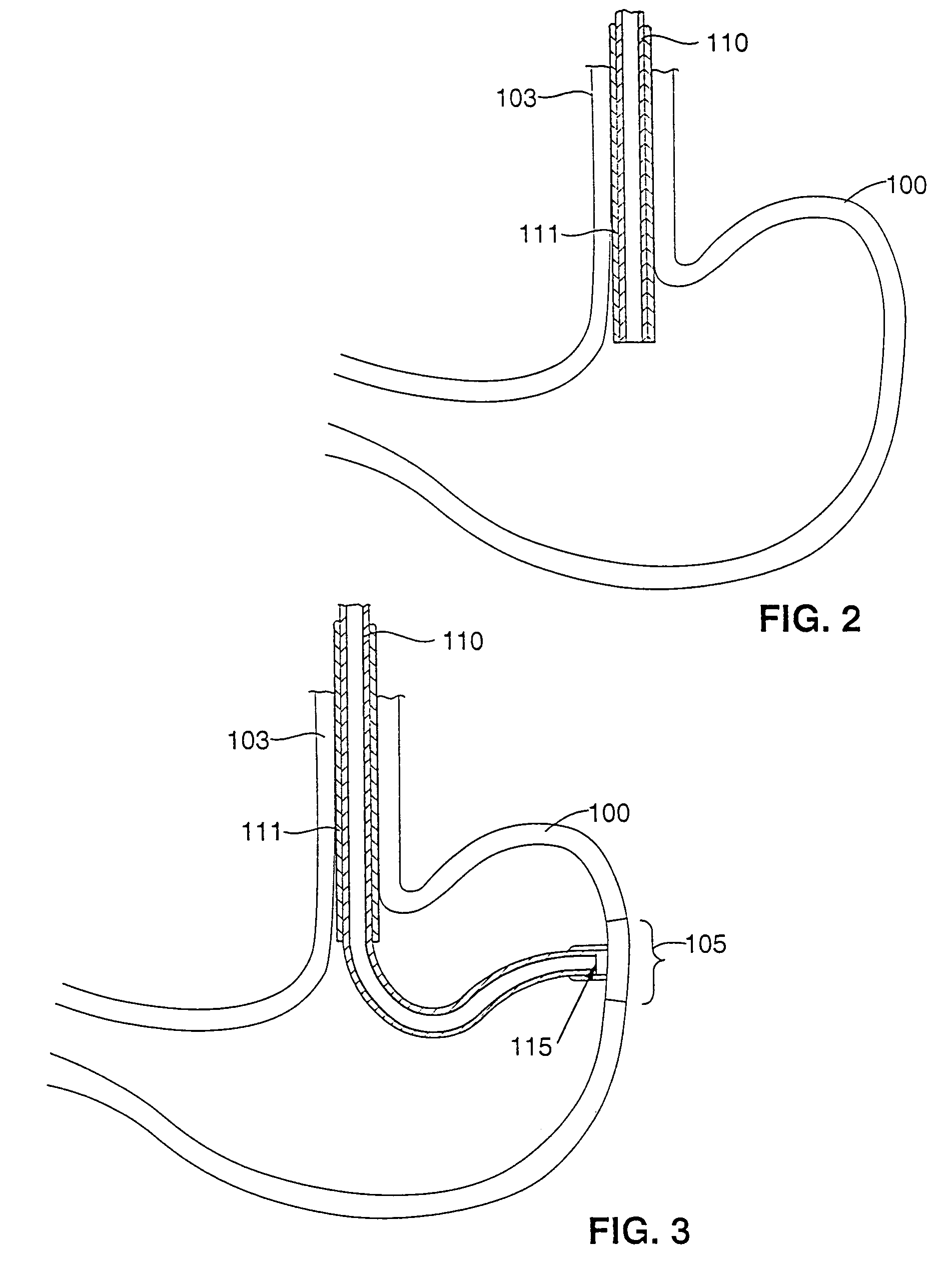
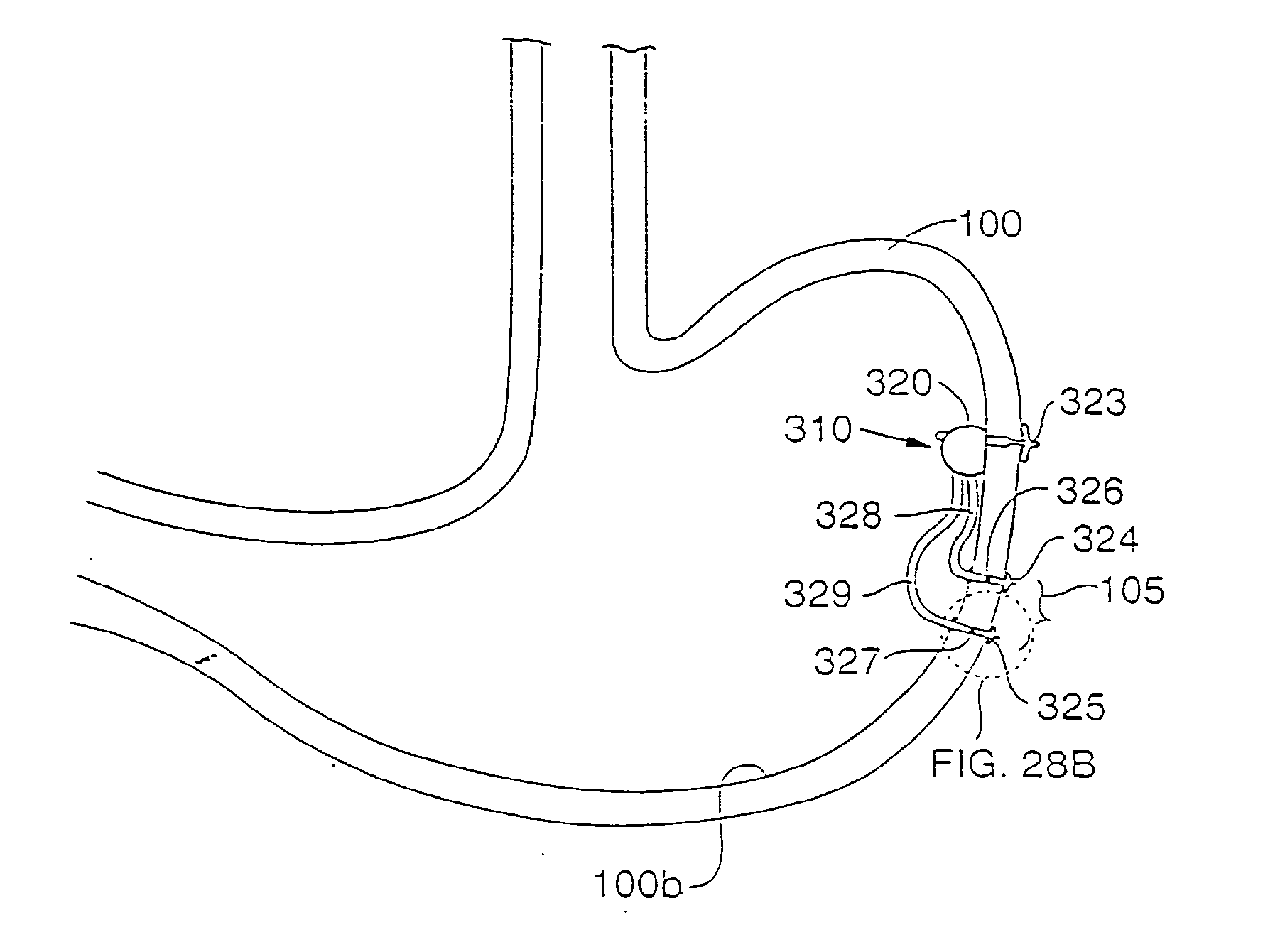
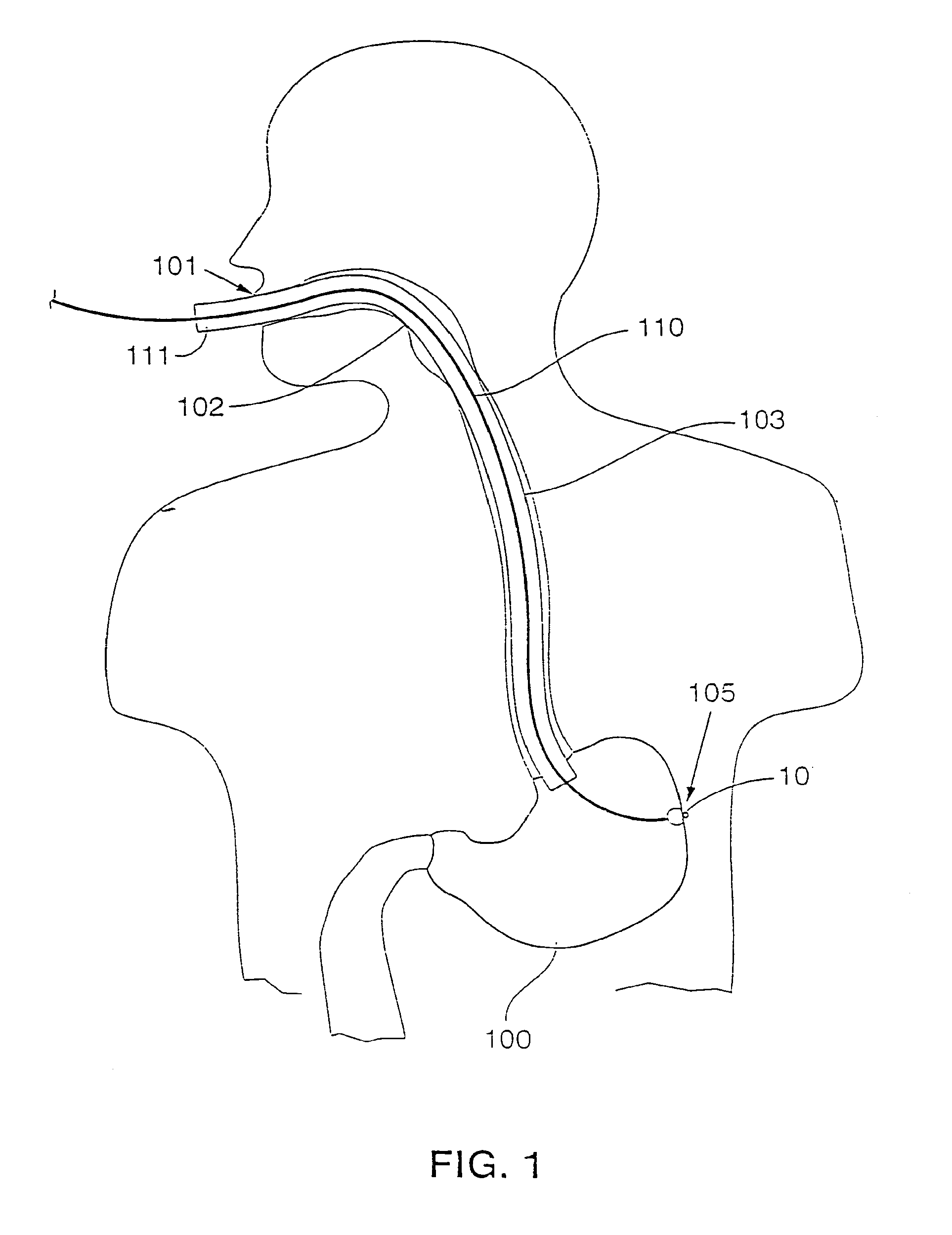
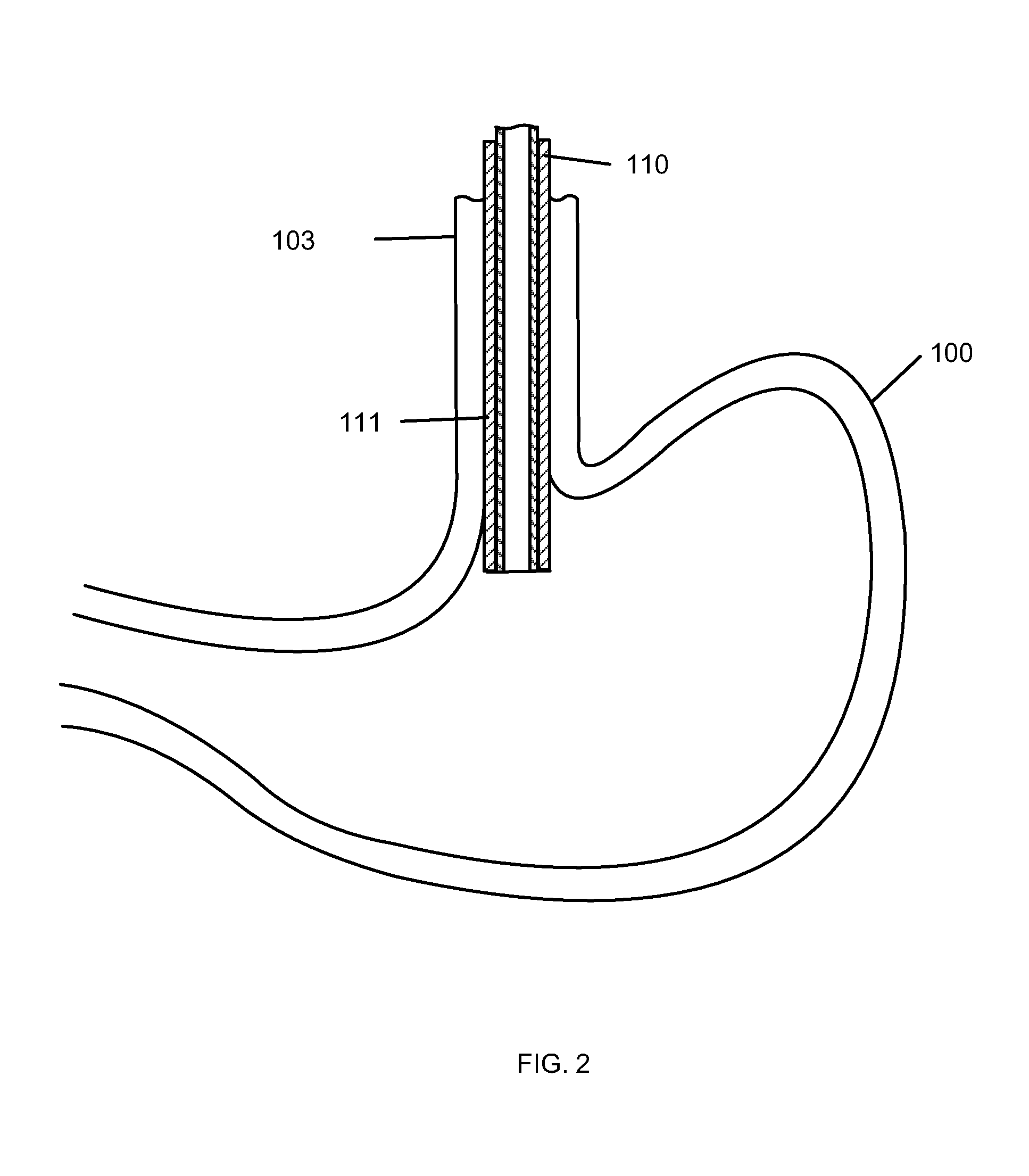
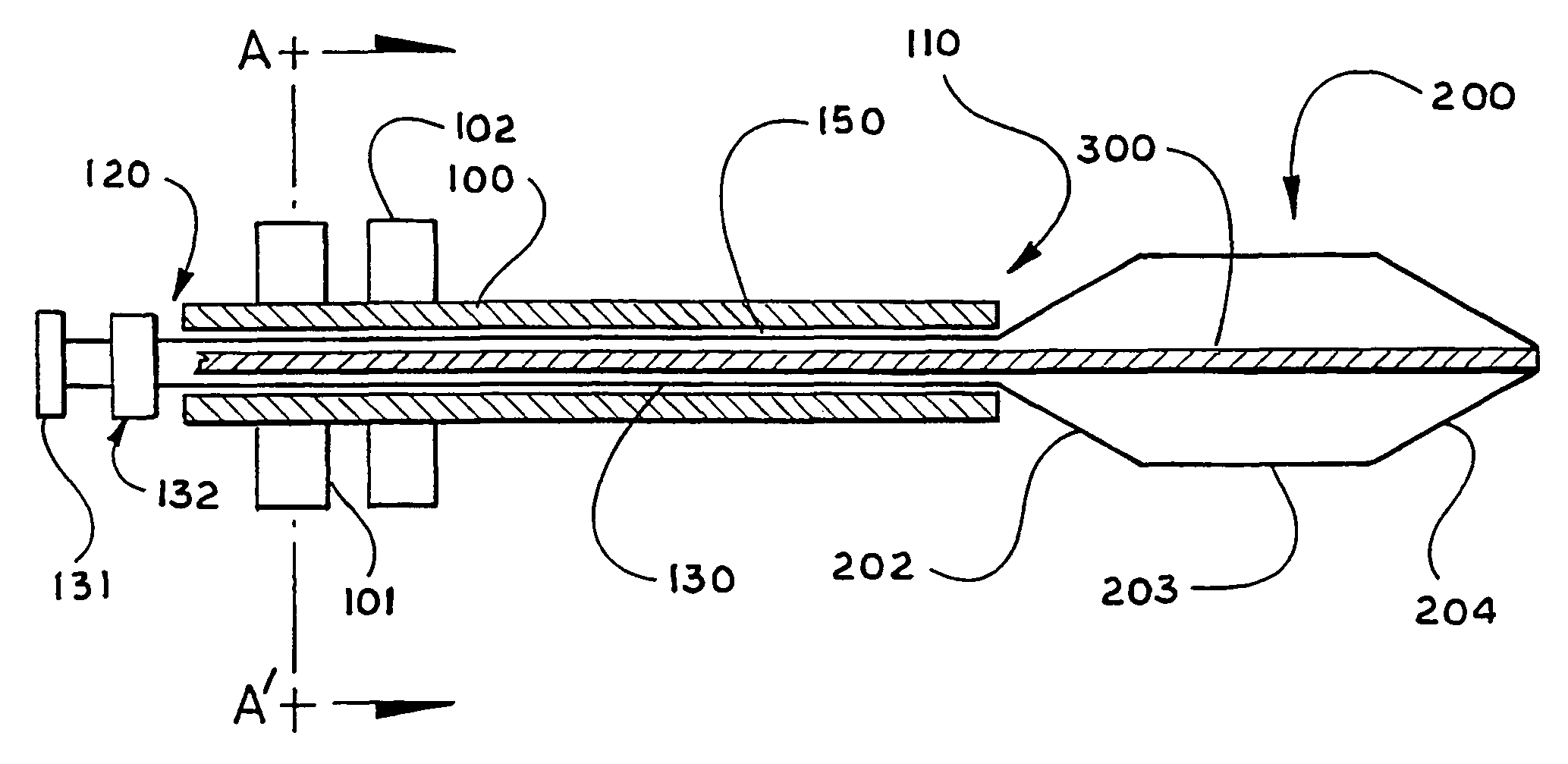
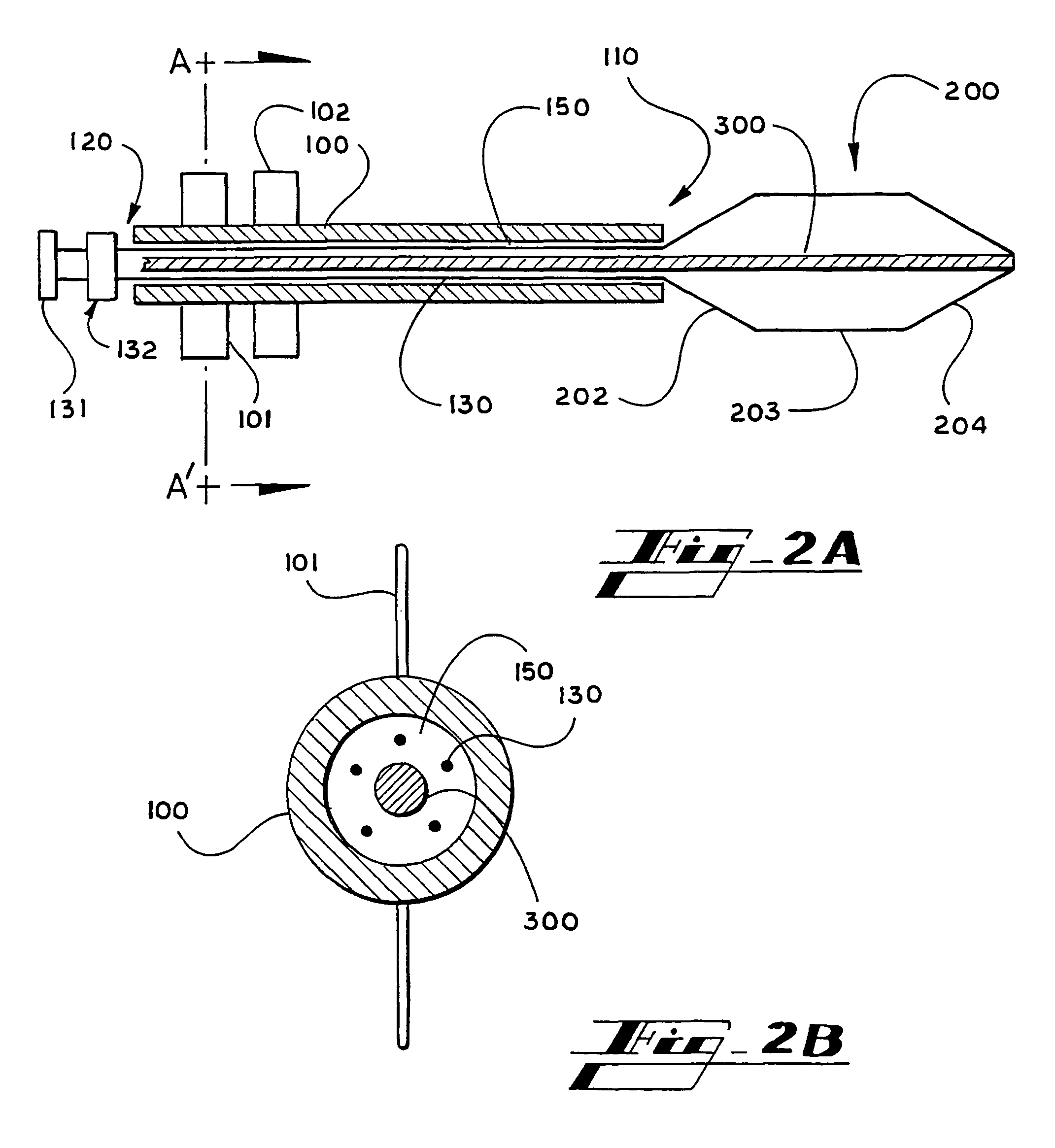
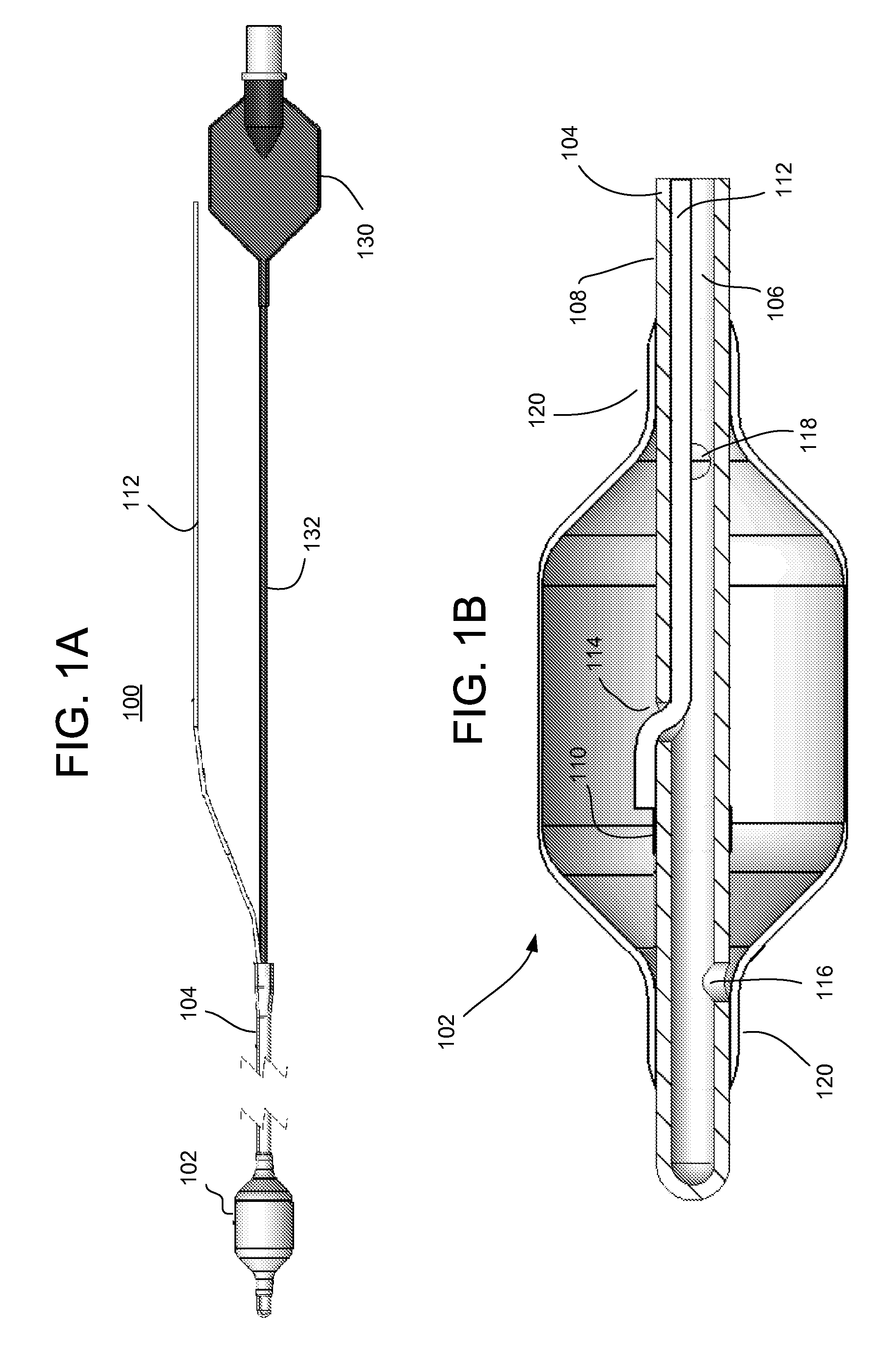
A device, system and method for diagnosing and treating gastric disorders is provided. A functional device resides within the patient's stomach and is secured to the stomach wall by an attachment device. The functional device may be a sensor for sensing various parameters of the stomach or stomach environment, or may be a therapeutic delivery device. The functional device in one embodiment provides a device, system and method for gastric electrical stimulation where stimulating electrodes are secured to the wall of the stomach by the attachment device or otherwise. A preferred device includes: at least one stimulating electrode in electrical contact with the stomach wall; an electronics unit containing the electronic circuitry of the device; and an attachment mechanism for attaching the device to the stomach wall. The functional devices may be programmed to respond to sensed information or signals. An endoscopic delivery system delivers the functional device through the esophagus and into the stomach where it is attached the stomach wall. The endoscopic instruments attach or remove the attachment devices and functional devices from the stomach and may be used to assist in determining the optimal attachment location.
Owner:INTRAPACE
Intra-luminal device for gastrointestinal electrical stimulation
InactiveUS20050209653A1Reduce deliveryRelieve symptomsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsShort termsElectrical stimulations
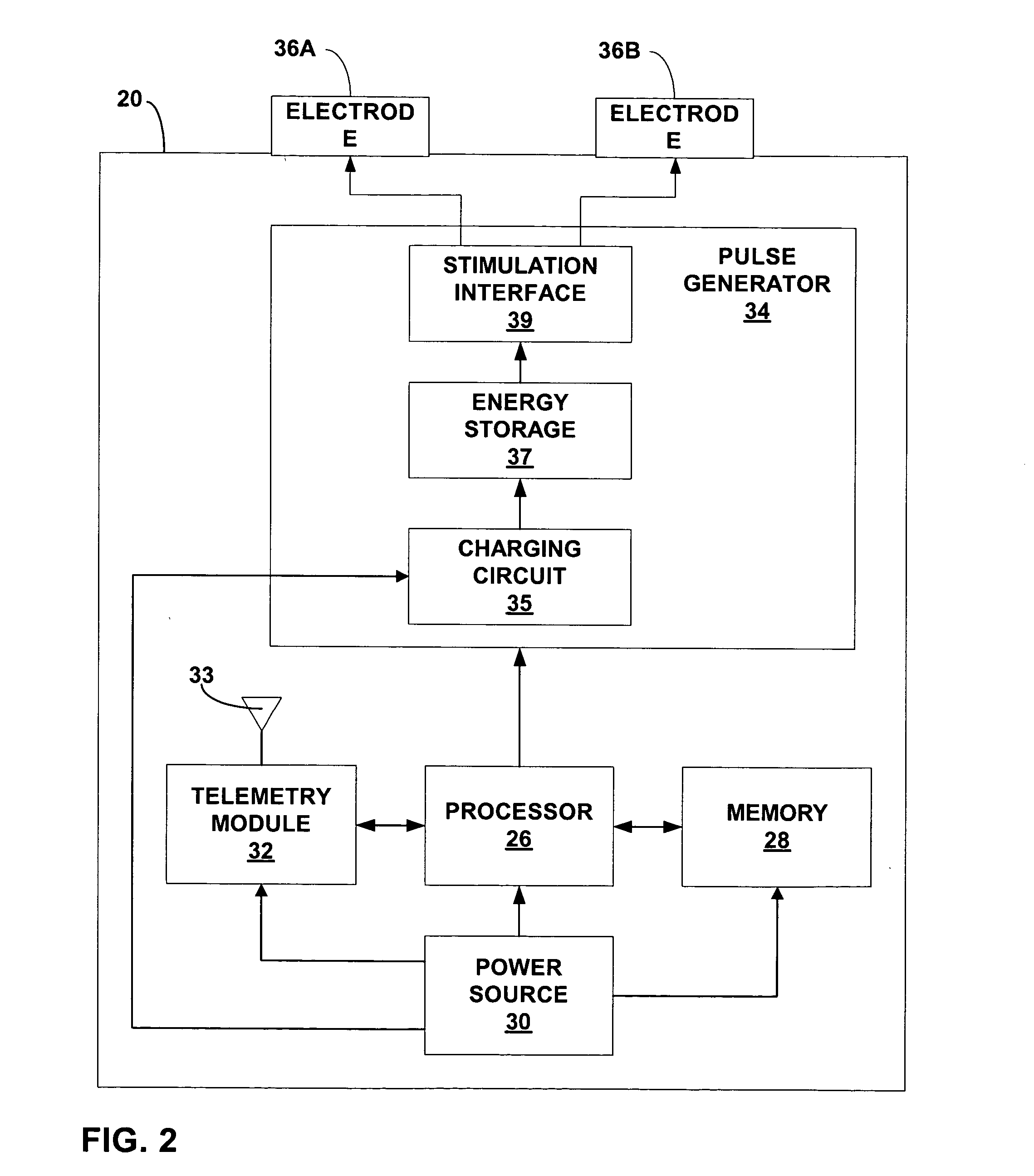
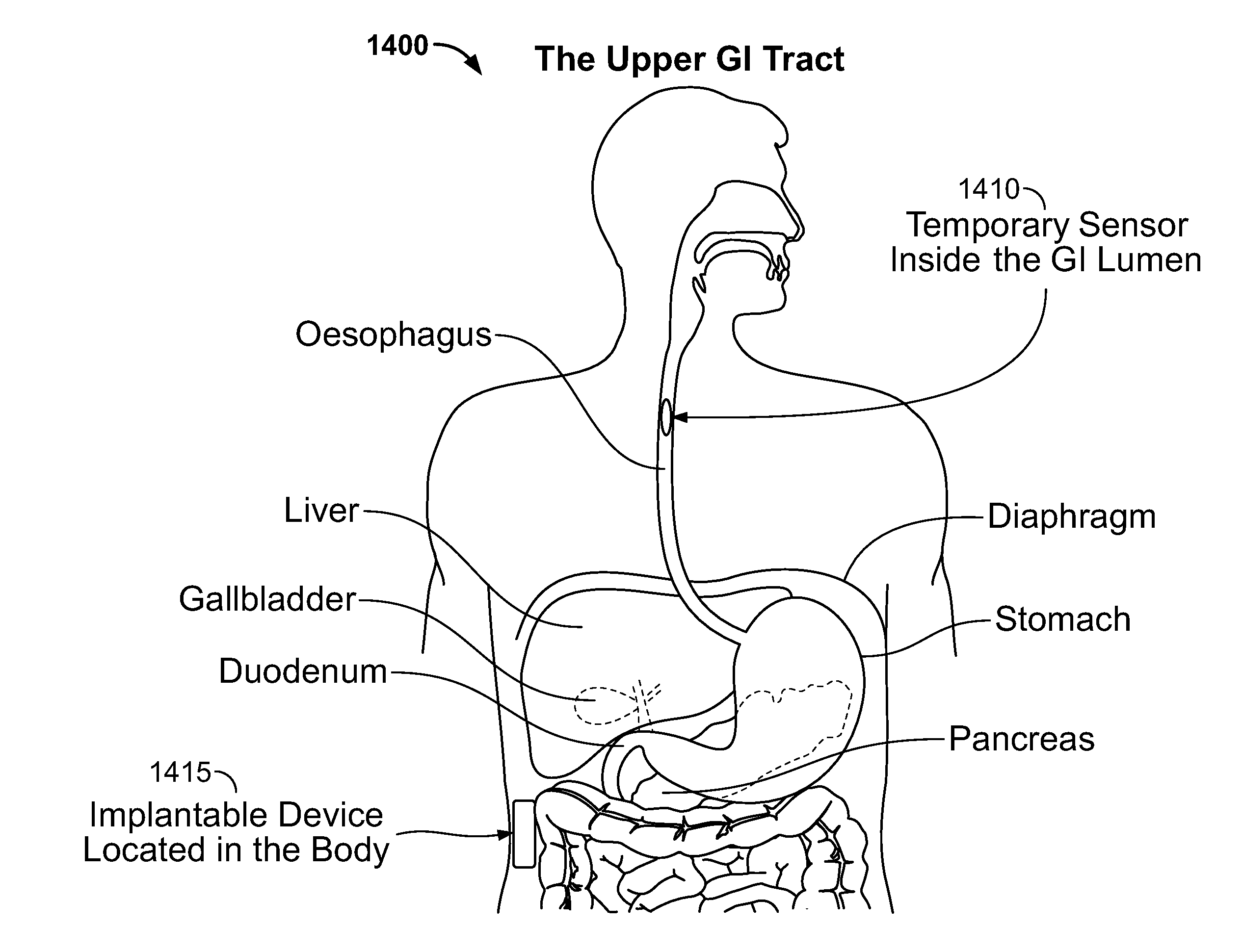
An intra-luminal device for gastrointestinal electrical stimulation is self-powered and self-contained within a capsule-like housing, and is capable of non-surgical implantation within the patient. The device includes an implantable pulse generator and one or more electrodes mounted within a common device housing. The device housing is capable of endoscopic introduction to a desired location within the gastrointestinal tract, such as the stomach, via the esophagus. The device may be appropriate for short-term, mid-term or trial stimulation applications.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Gastric anchor and method
Owner:INTRAPACE
Gastric Simulation Anchor and Method
InactiveUS20100305656A1Minimize stressAvoid foldingCannulasSurgical needlesStomach wallsGeneral surgery
Owner:INTRAPACE
System and method for monitoring esophagus proximity
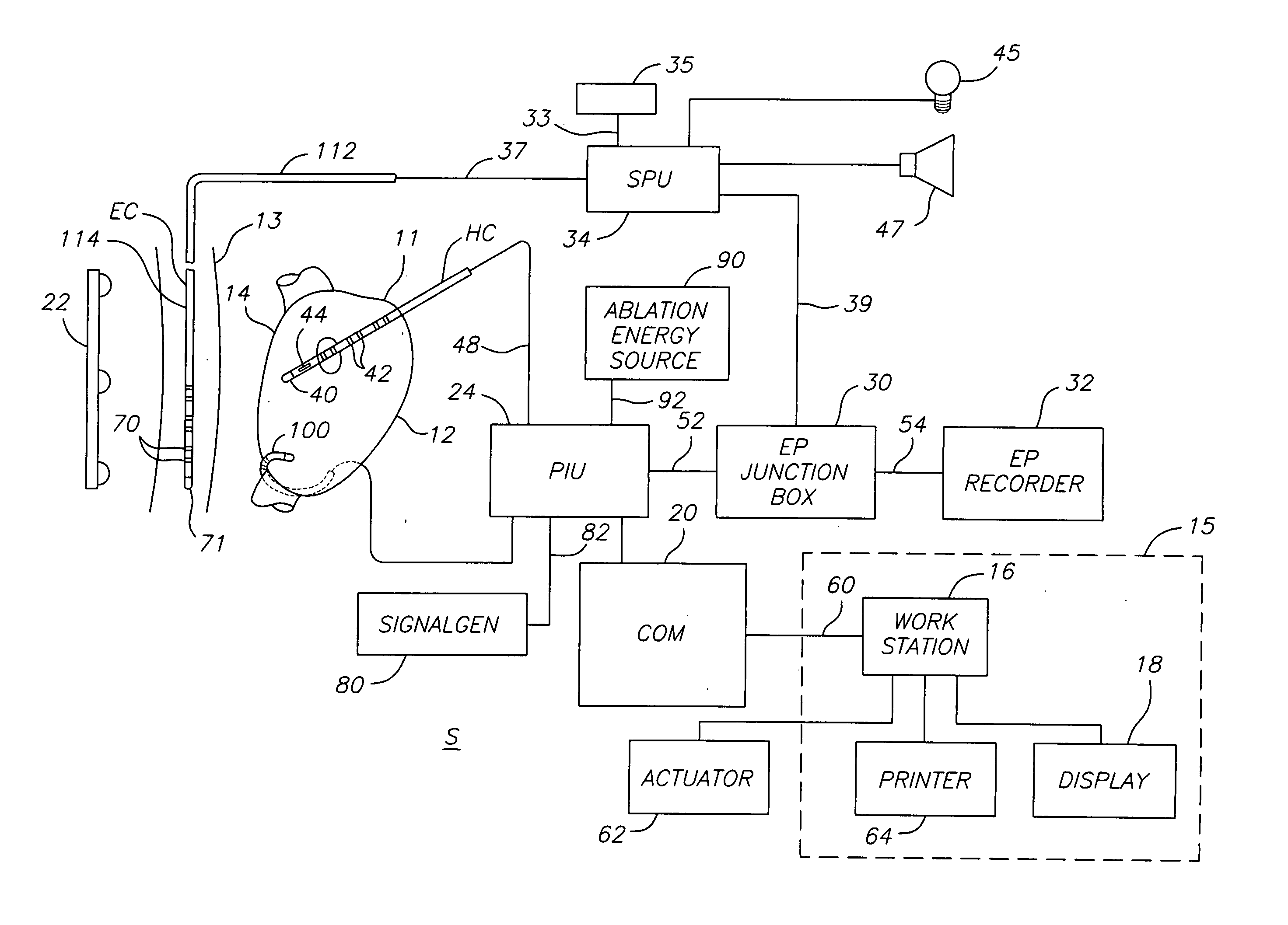
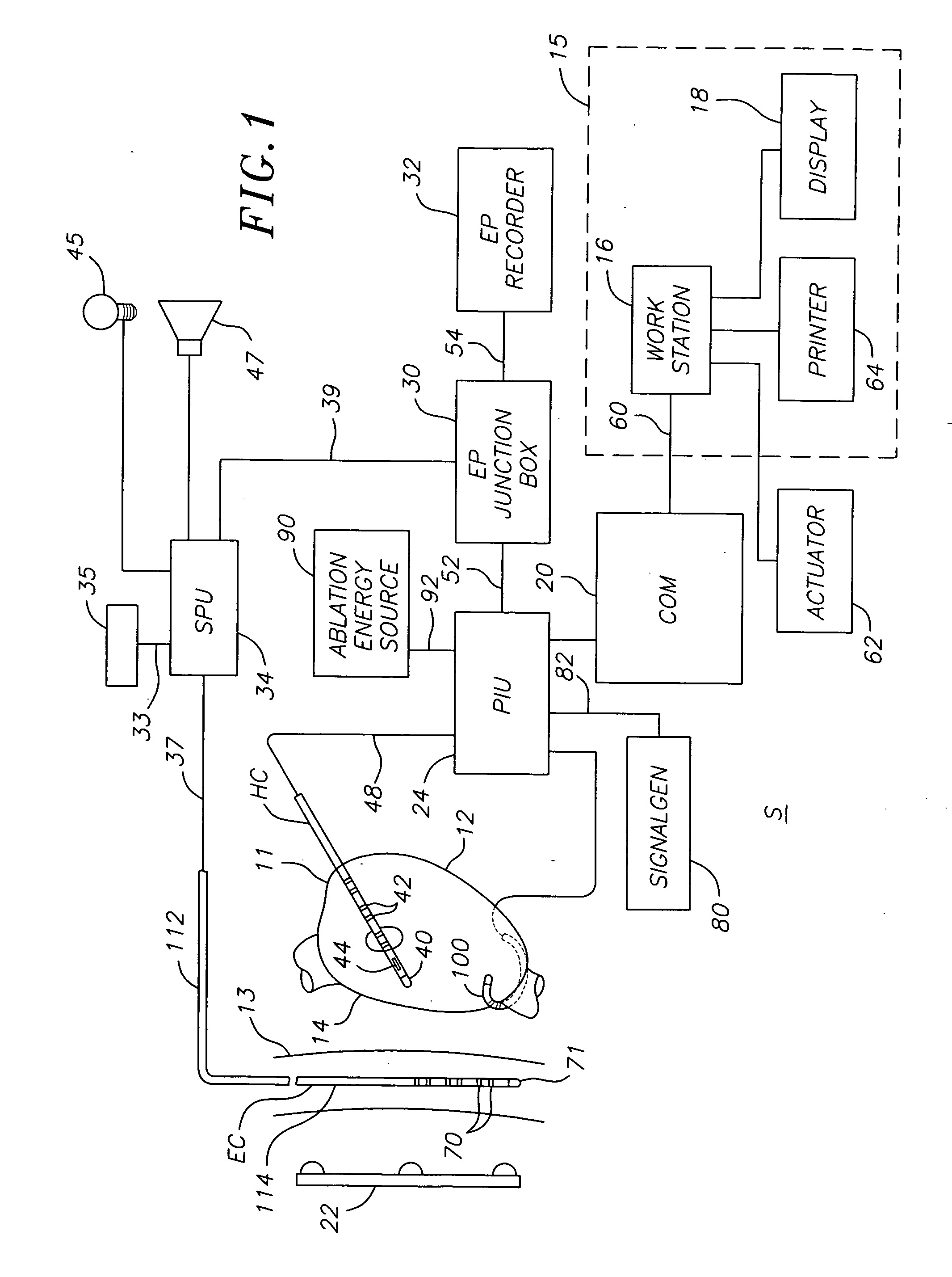
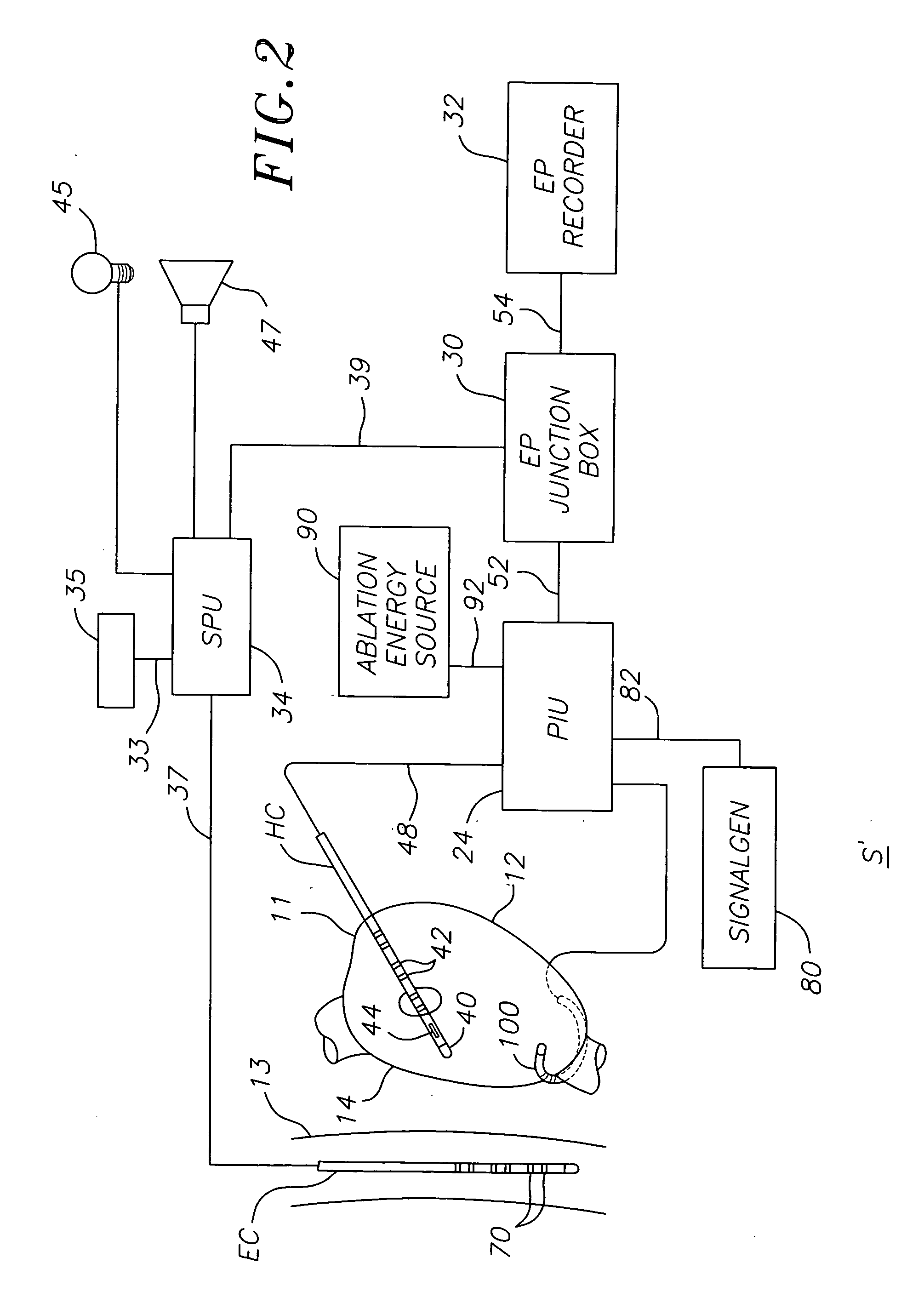
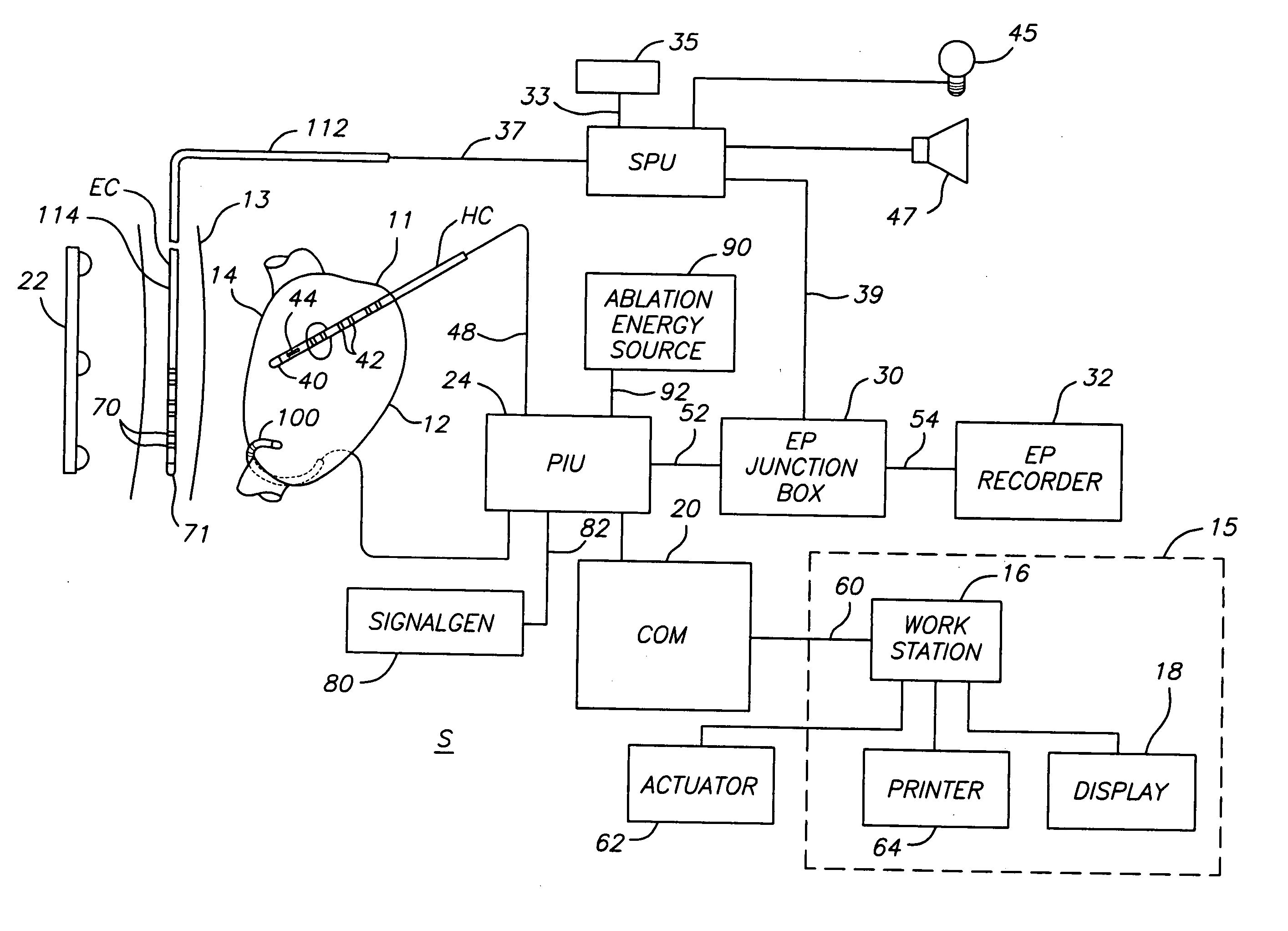
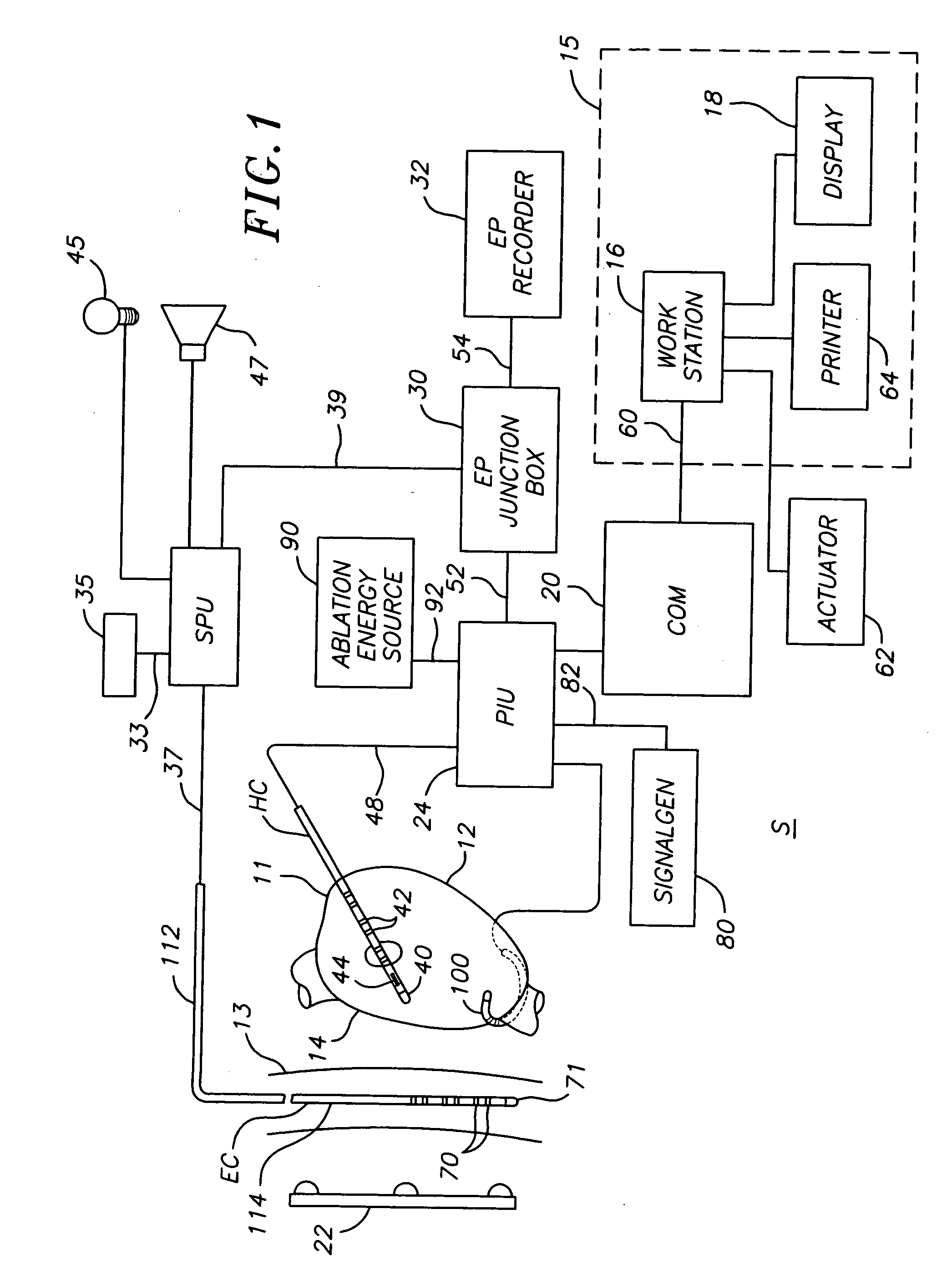
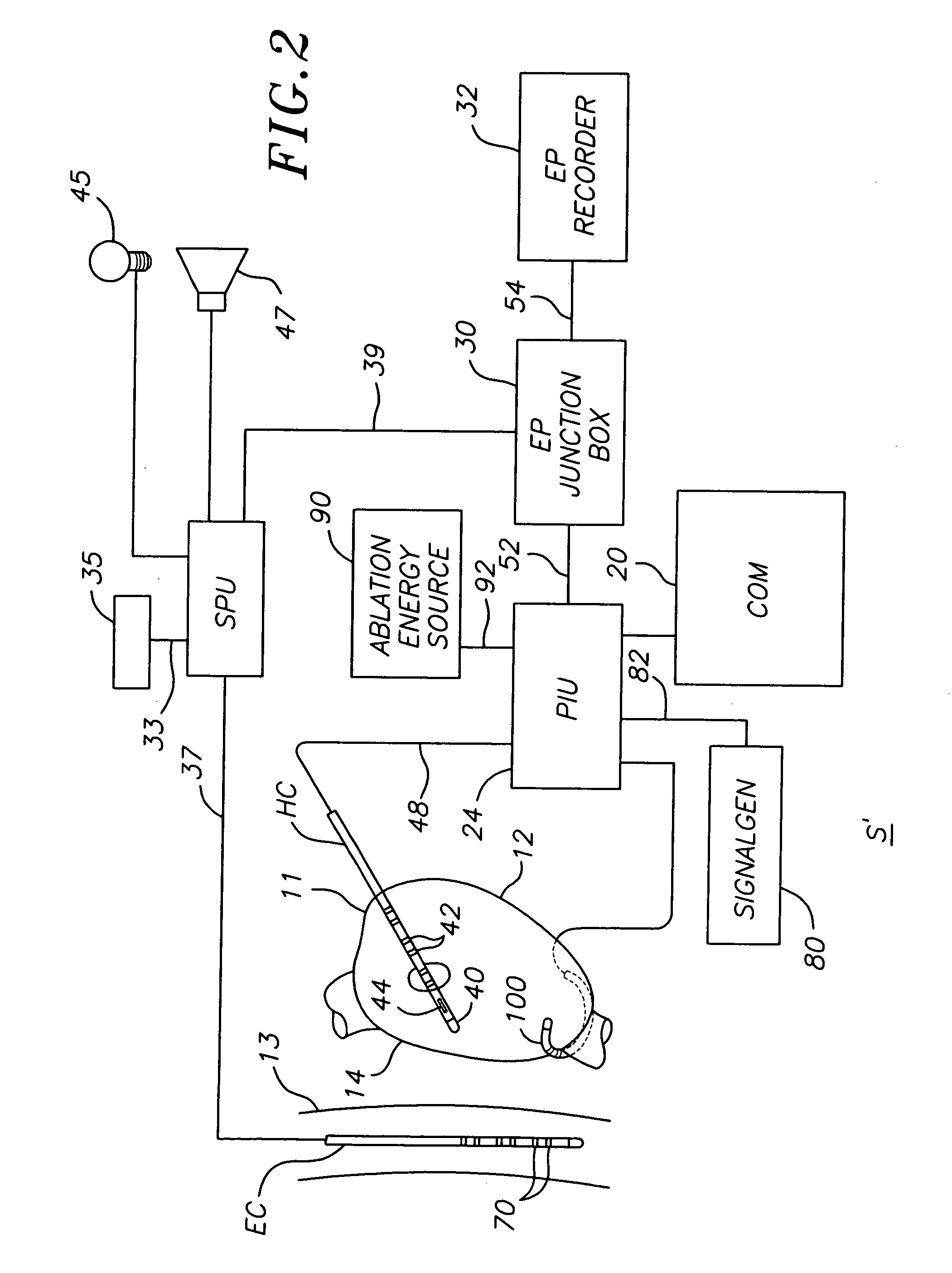
ActiveUS20070106289A1Reduce riskRisk minimizationSurgical navigation systemsSurgical instrument detailsAnesthesiaSignal processing
A system for determining the proximity of the esophagus to the ablation electrode of an ablation catheter during an ablation procedure is disclosed. The system comprises an ablation catheter having at least one ablation electrode, an esophageal probe catheter having at least one electrode, and a signal processing unit. Both the ablation electrode and the esophageal probe catheter are electrically connected to the signal processing unit. The signal processing unit receives electrical signals from the ablation electrode on the ablation catheter and the electrode on the esophageal probe catheter and compares the signals to determine the proximity of the esophagus to the ablation electrode.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Gastrointestinal anchor with optimal surface area
InactiveUS20050143784A1Equally distributedUneven distributionCannulasSurgical needlesOptimal weightArea ratio
A device, system and method for anchoring a device to a stomach is provided. The device may be, among other things, a sensor for sensing various parameters of the stomach or stomach environment, or may be a therapeutic delivery device. The anchor of the device is constructed to resist pull out forces. An anchor has an optimal weight to surface area ratio.
Owner:INTRAPACE
Aendoscopic instrument system@
InactiveUS20050236277A9Minimize stressAvoid foldingCannulasSurgical needlesStomach wallsGastric Disorders
A device, system and method for diagnosing and treating gastric disorders is provided. A functional device resides within the patient's stomach and is secured to the stomach wall by an attachment device. The functional device may be a sensor for sensing various parameters of the stomach or stomach environment, or may be a therapeutic delivery device. The functional device in one embodiment provides a device, system and method for gastric electrical stimulation where stimulating electrodes are secured to the wall of the stomach by the attachment device or otherwise. A preferred device includes: at least one stimulating electrode in electrical contact with the stomach wall; an electronics unit containing the electronic circuitry of the device; and an attachment mechanism for attaching the device to the stomach wall. The functional devices may be programmed to respond to sensed information or signals. An endoscopic delivery system delivers the functional device through the esophagus and into the stomach where it is attached the stomach wall. The endoscopic instruments attach or remove the attachment devices and functional devices from the stomach and may be used to assist in determining the optimal attachment location.
Owner:INTRAPACE
Electrical Treatment Of Bronchial Constriction
ActiveUS20090281593A9Dilation increaseFunction increaseSpinal electrodesHead electrodesNerve fiber bundleSmooth muscle
Owner:ELECTROCORE
System and method for measuring esophagus proximity
ActiveUS20070106287A1Risk minimizationReduce riskSurgical navigation systemsSurgical instrument detailsTunica intimaNavigation system
A system and method for determining on a continuous, real-time basis the proximity of the esophagus to an endocardial catheter during mapping, ablation or other endocardial catheter-based procedures, comprising an esophagus probe catheter and an endocardial catheter adapted for proximal signal transmission between each other. A signal processing unit is included to process and compare a characteristic of the proximity signal that is changes or attenuates with distance between the two catheters, such as impedance, amplitude and / or phase. Audio and / or optical outputs are provided to alert an operator when the distance between the catheters changes or is below a baseline measurement to avoid damage to the esophagus by the endocardial catheter. The system and method may include adaptations of the catheters with location sensor, and a mapping / navigational system for nonfluoroscopic location determination of the catheters.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Intra-Luminal Device for Gastrointestinal Electrical Stimulation
InactiveUS20060265021A1Reduce deliveryRelieve symptomsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedicineShort terms
An intra-luminal device for gastrointestinal electrical stimulation is self-powered and self-contained within a capsule-like housing, and is capable of non-surgical implantation within the patient. The device includes an implantable pulse generator and one or more electrodes mounted within a common device housing. The device housing is capable of endoscopic introduction to a desired location within the gastrointestinal tract, such as the stomach, via the esophagus. The device may be appropriate for short-term, mid-term or trial stimulation applications.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
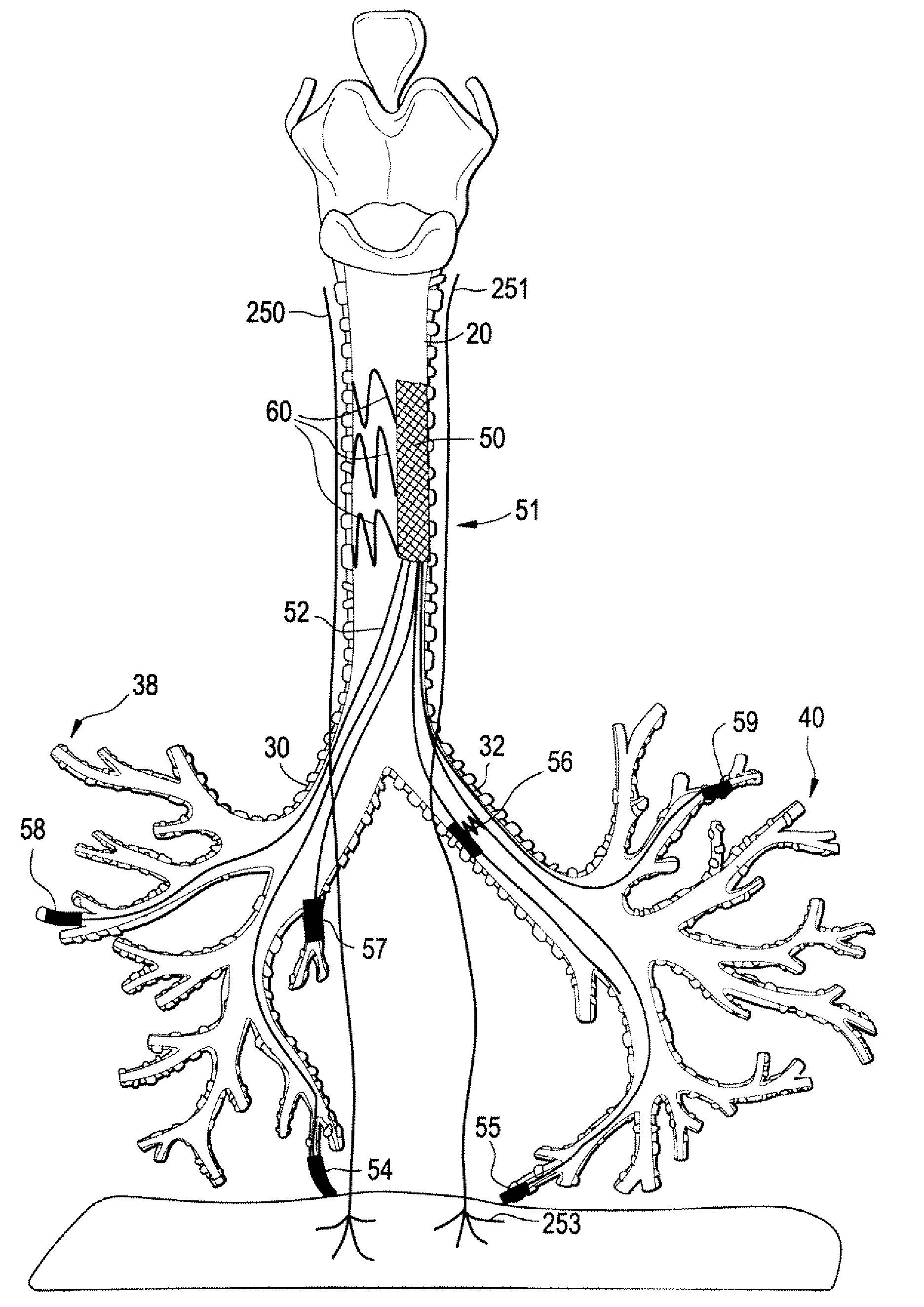
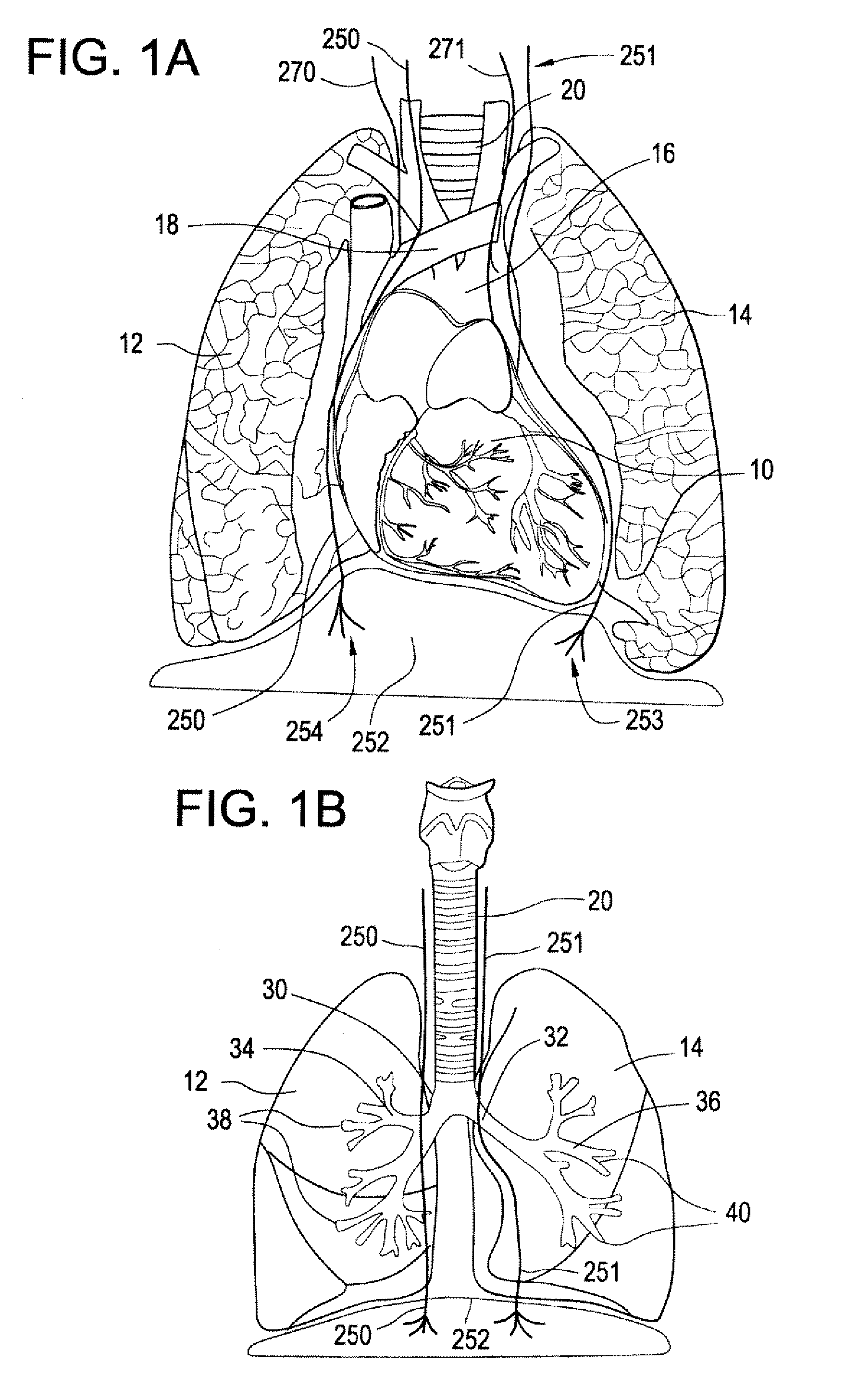
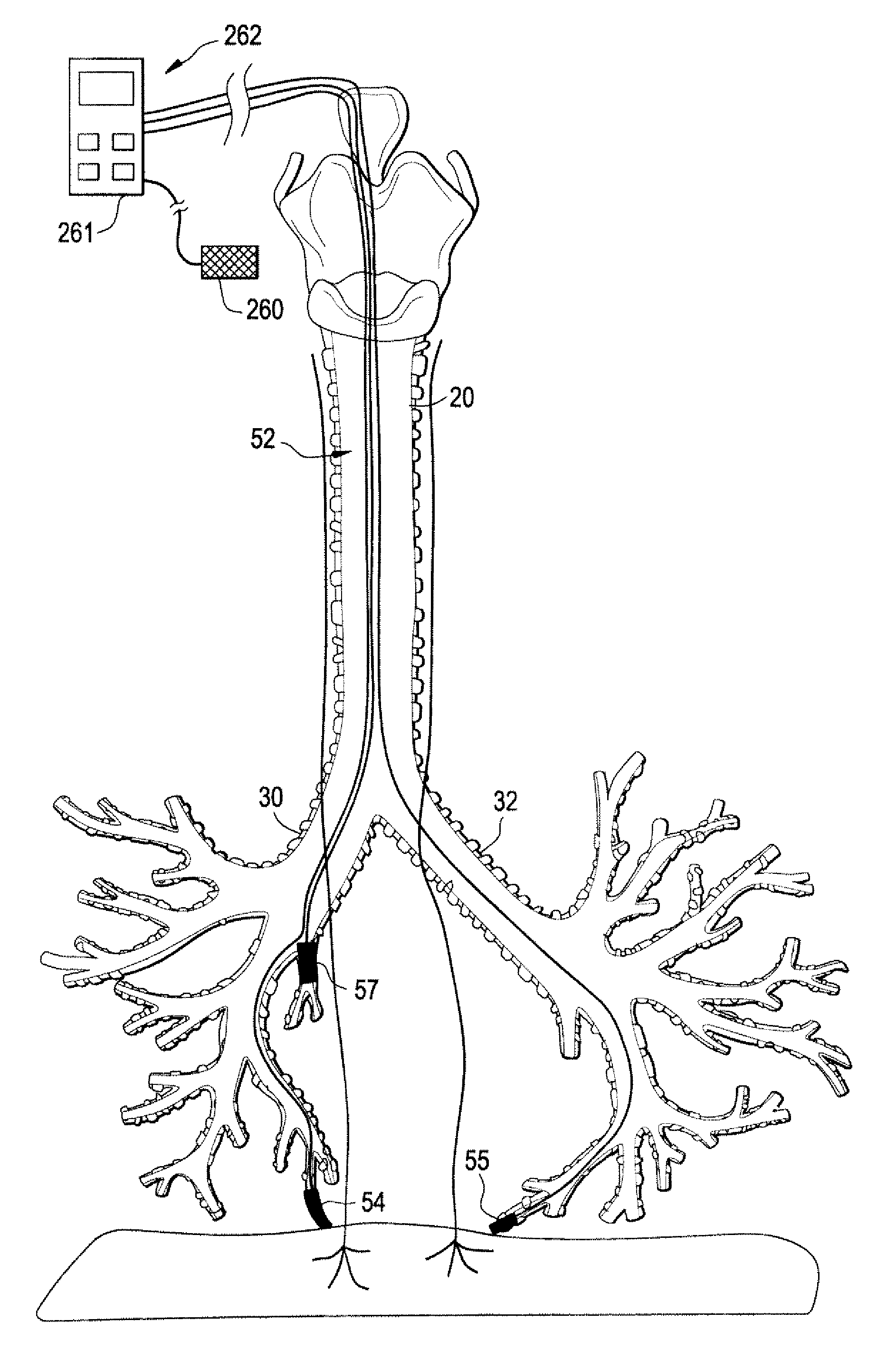
Devices and methods for electrical stimulation of the diaphragm and nerves
Medical devices, systems, and methods are provided for providing respiratory therapy by electrically stimulating the phrenic nerves and / or the thoracic diaphragm. In one embodiment, at least one electrode is deployed to a position within the patient's airway and placed in proximity to a phrenic nerve or to the diaphragm. The electrode may be attached to a controller housing including a pulse generator using one or more electrical lead or leads or may be in wireless communication with the pulse generator. The controller housing may be implanted at a position within the patient or the controller housing may reside external to the patient.
Owner:E PACING
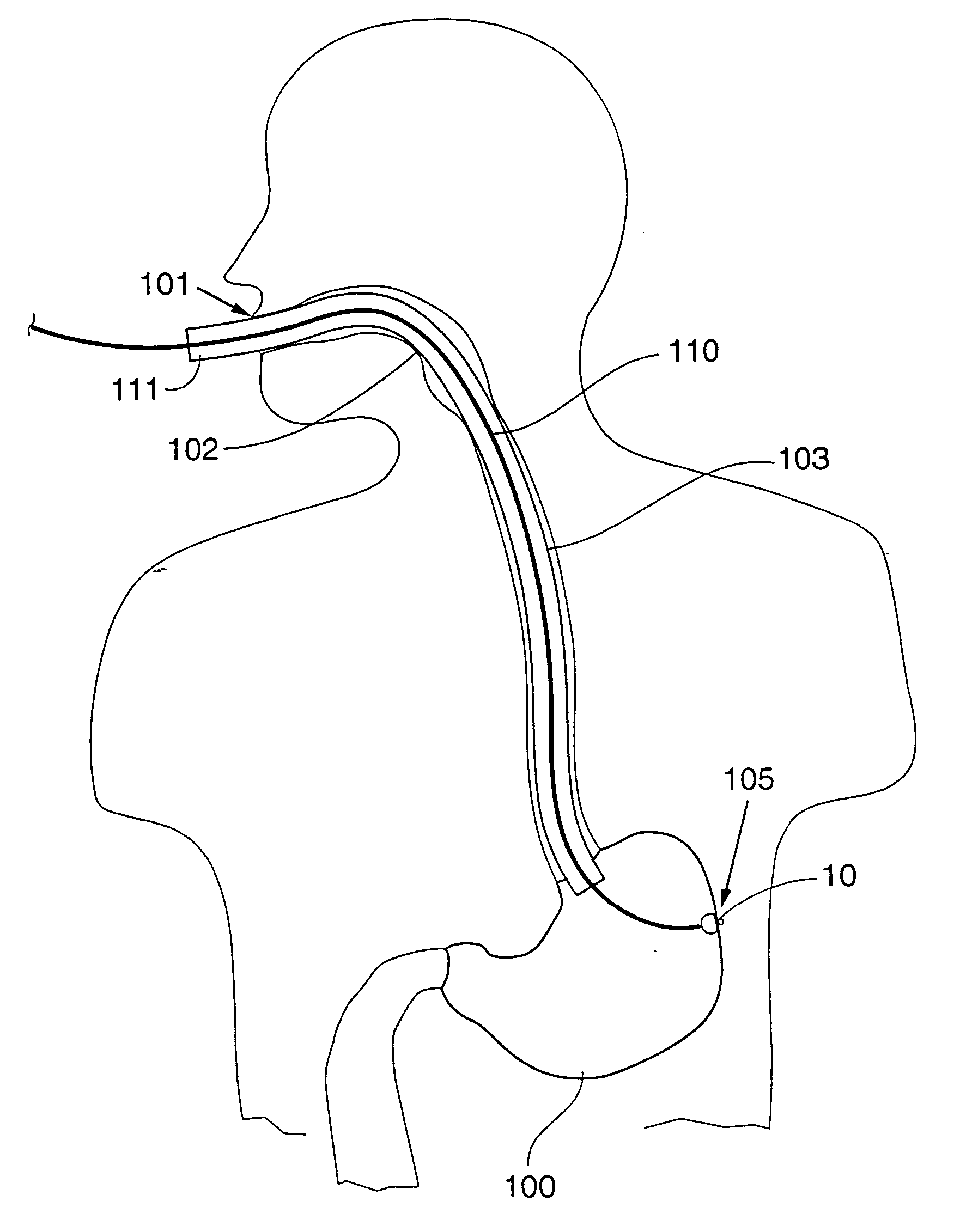
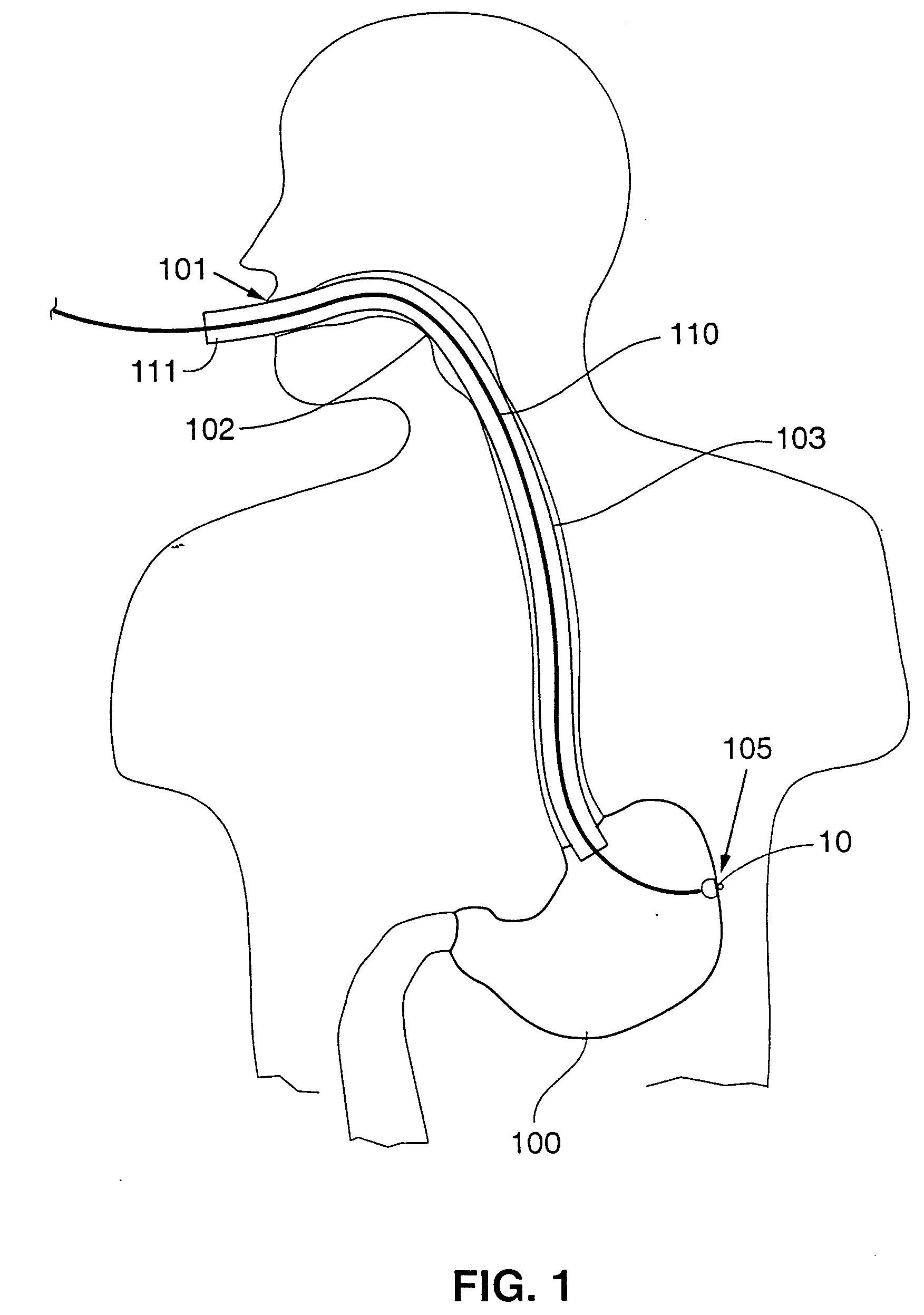
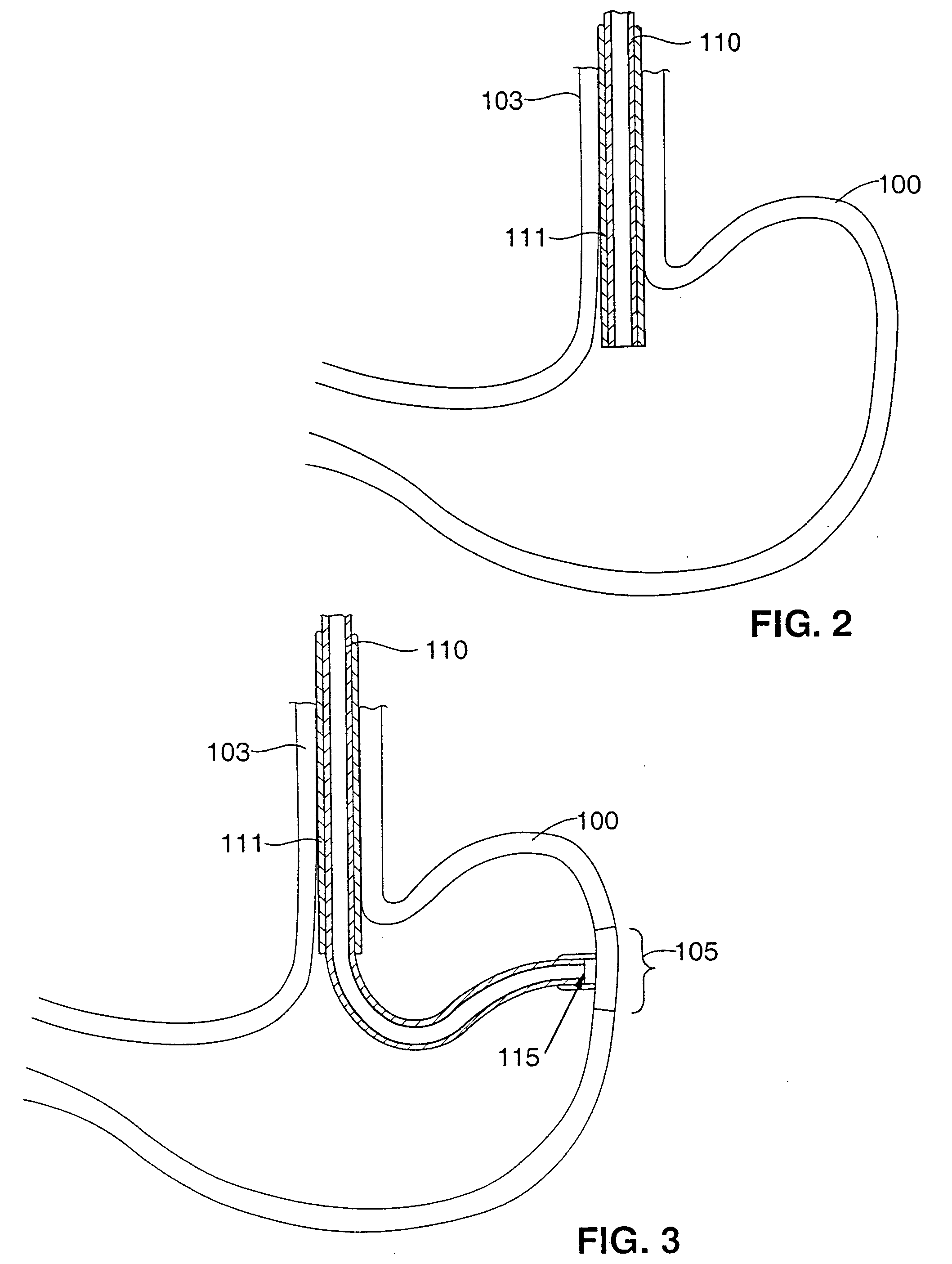
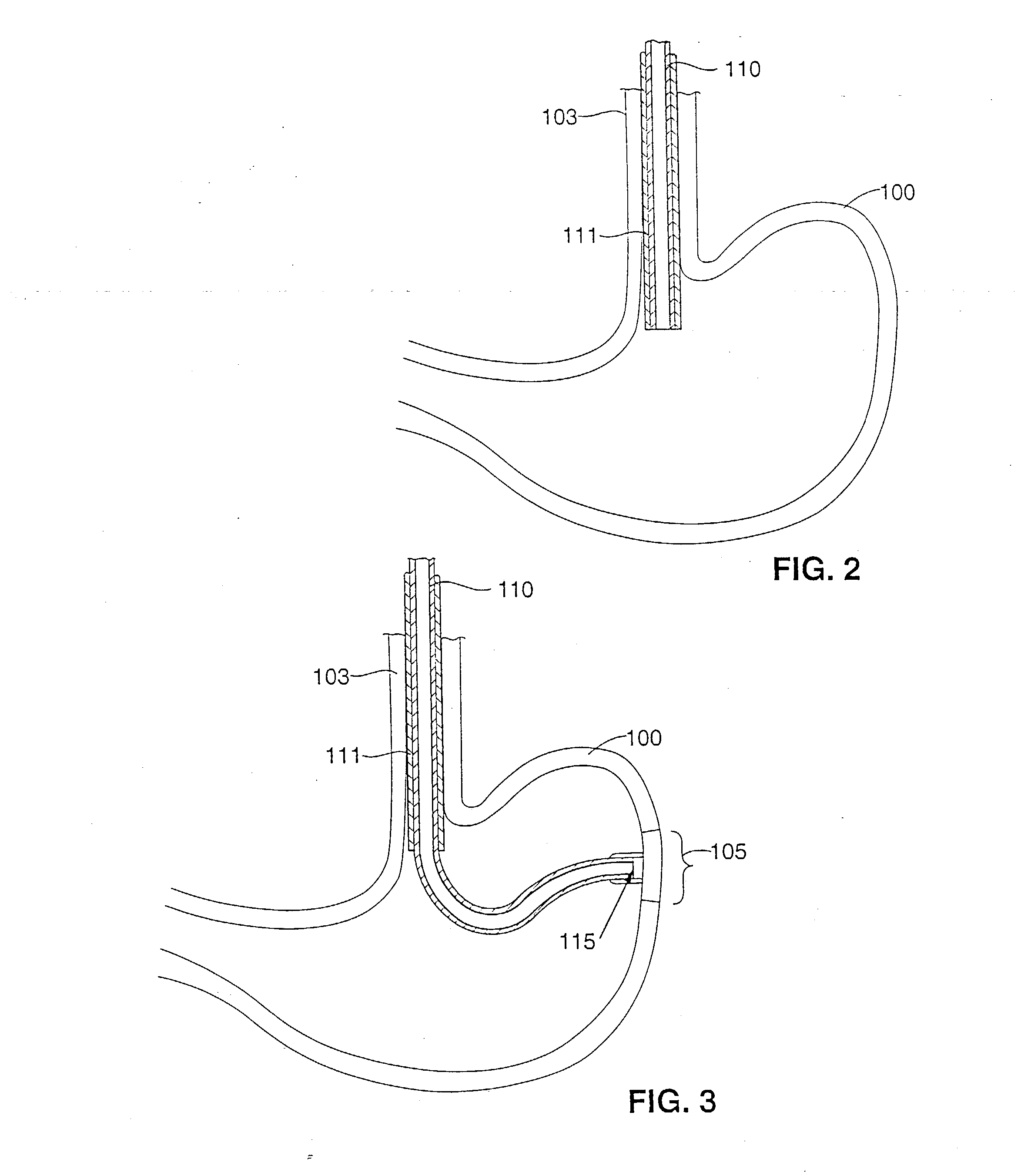
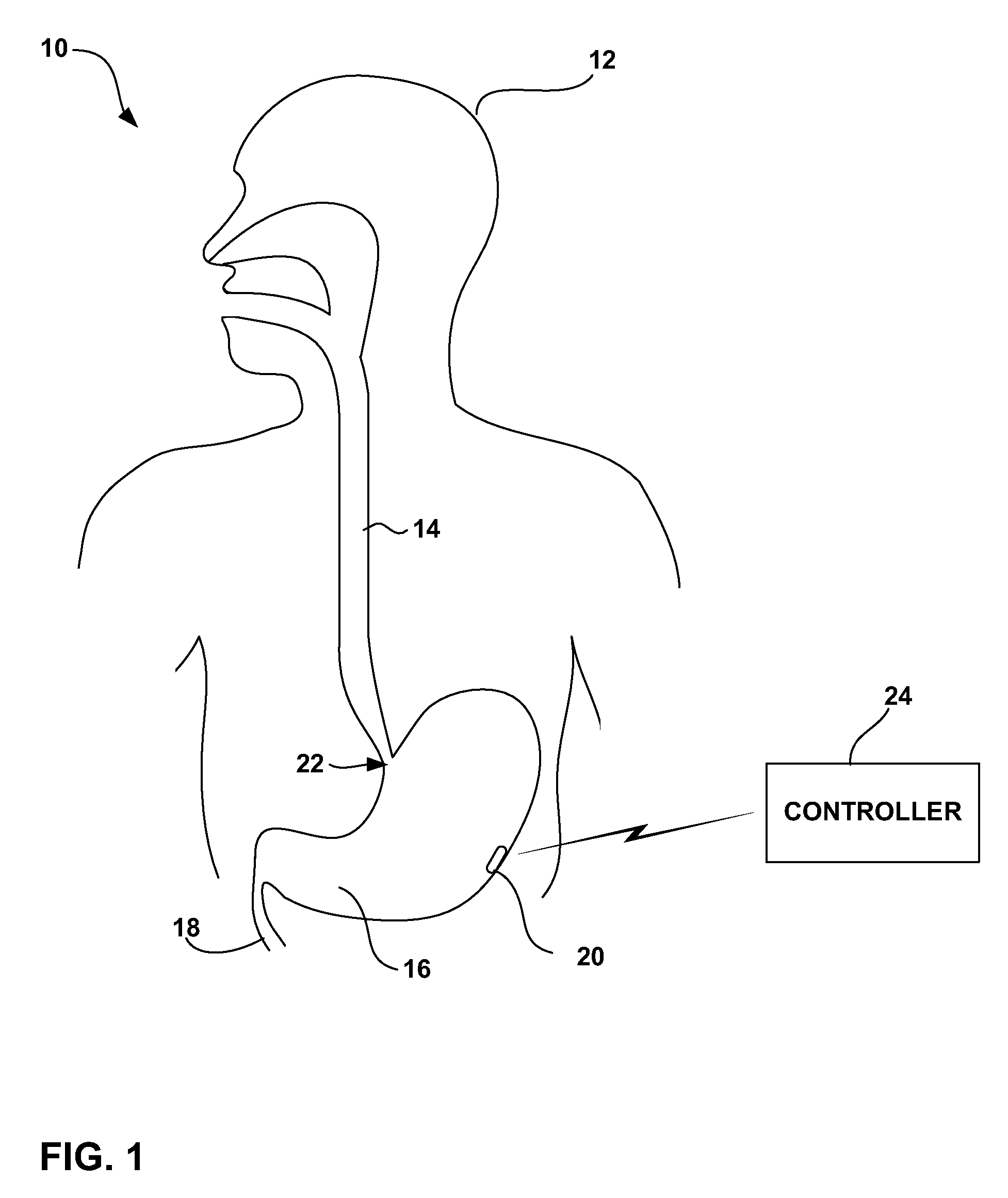
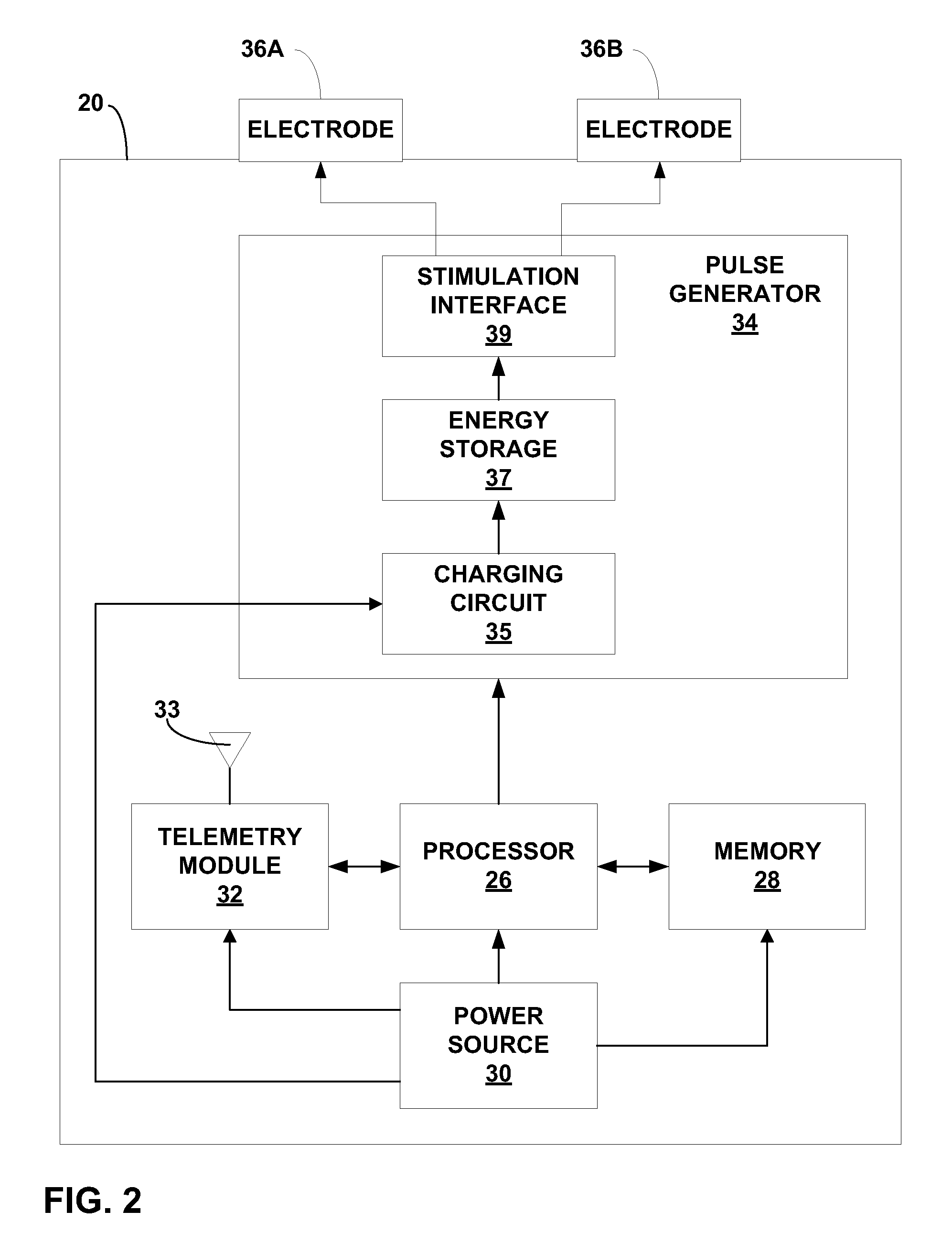
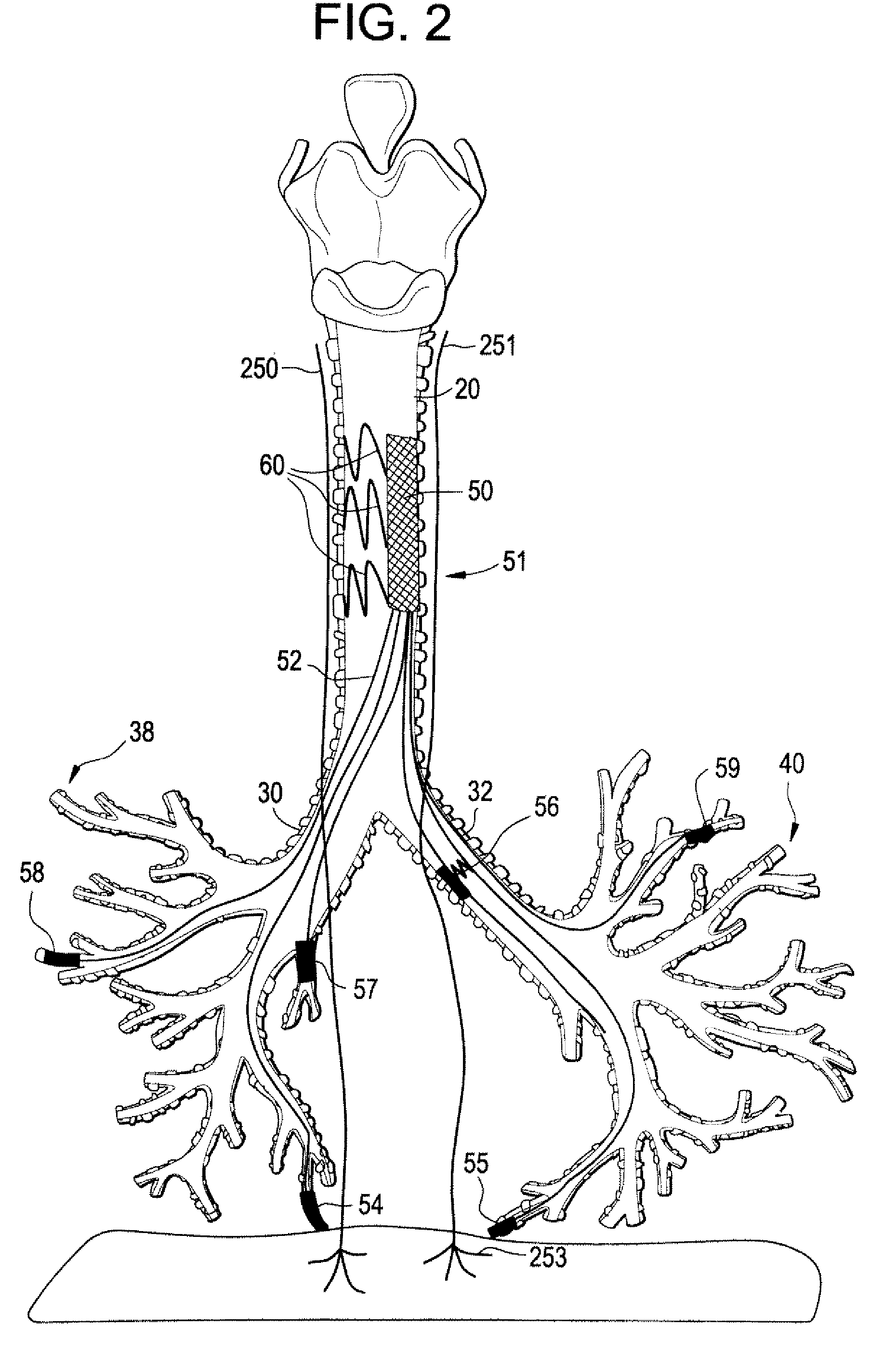
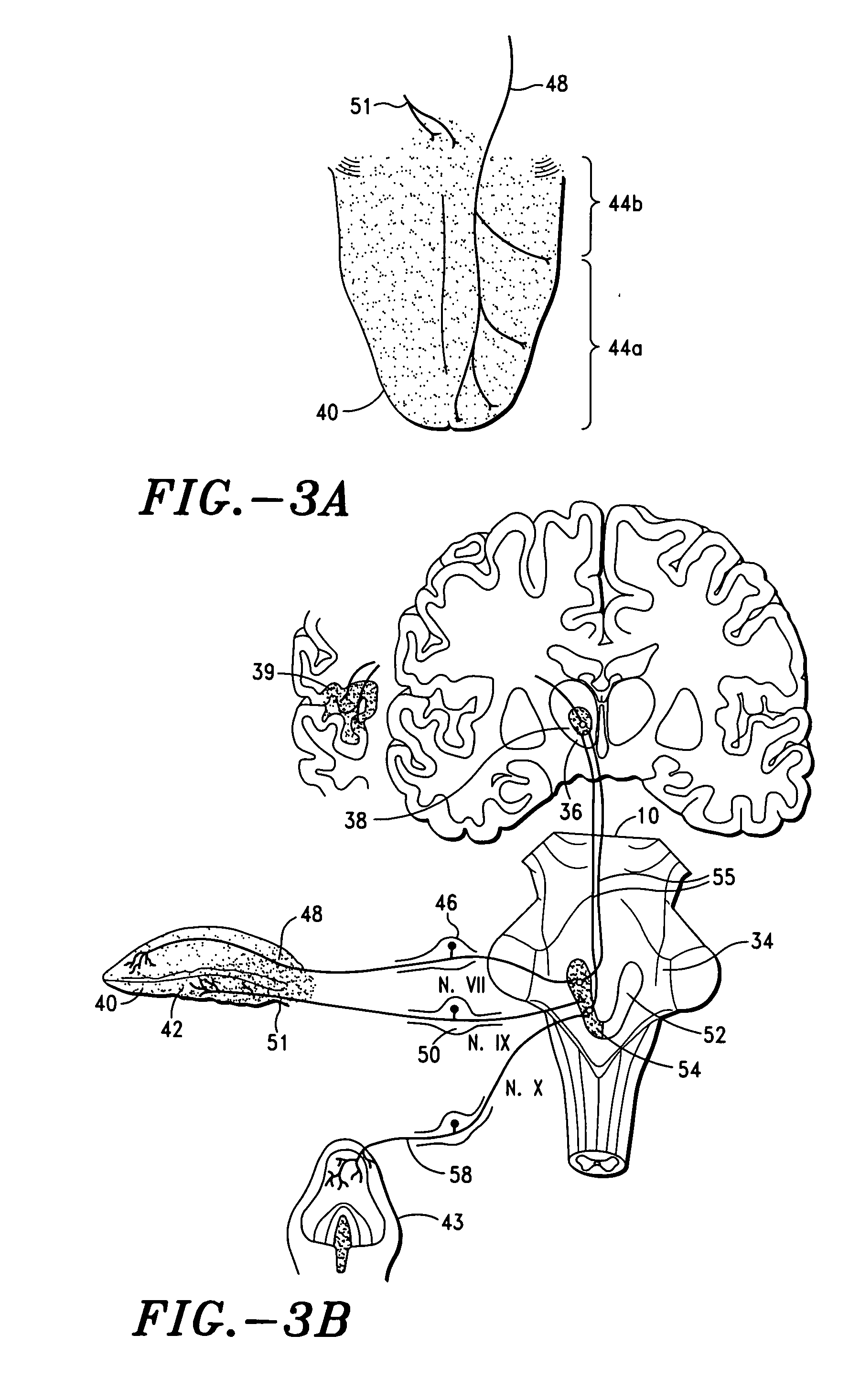
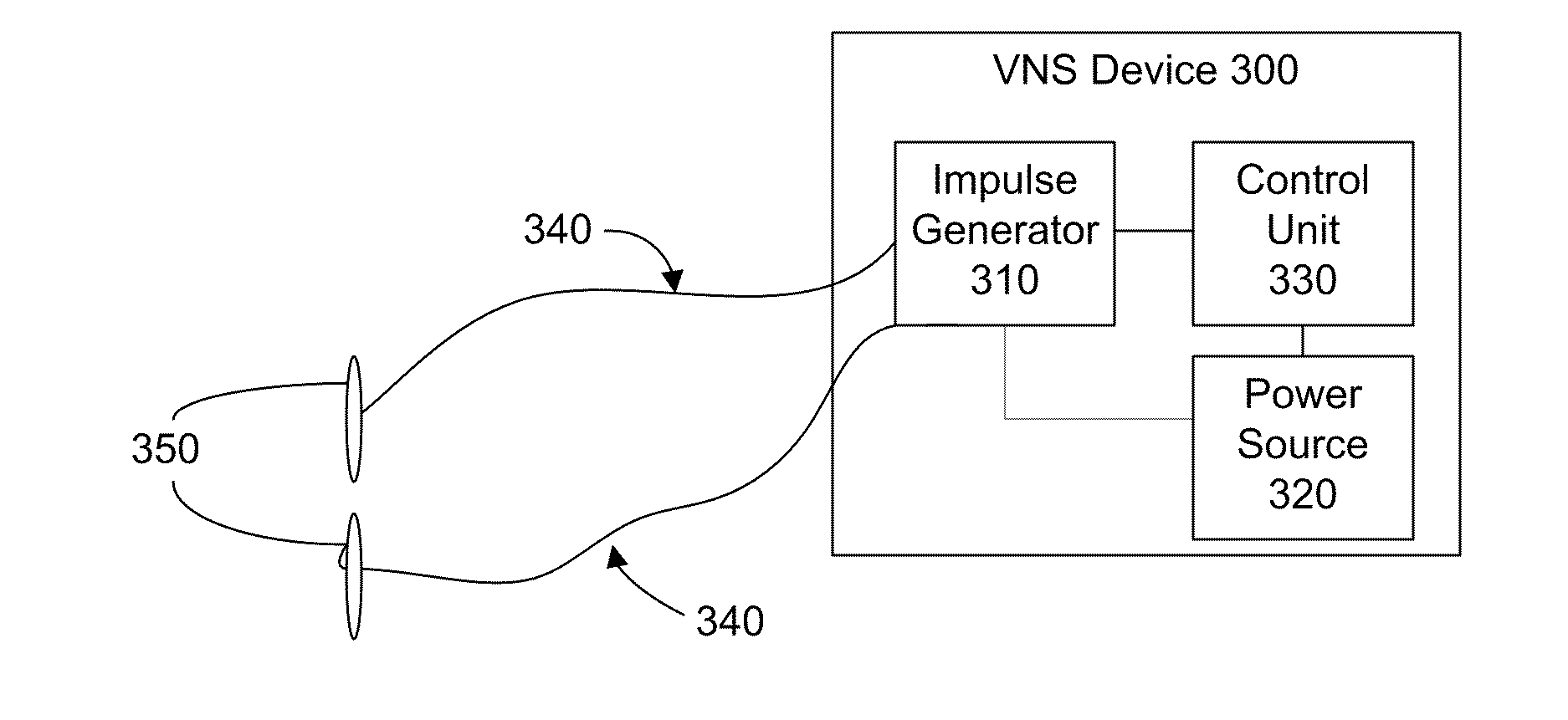
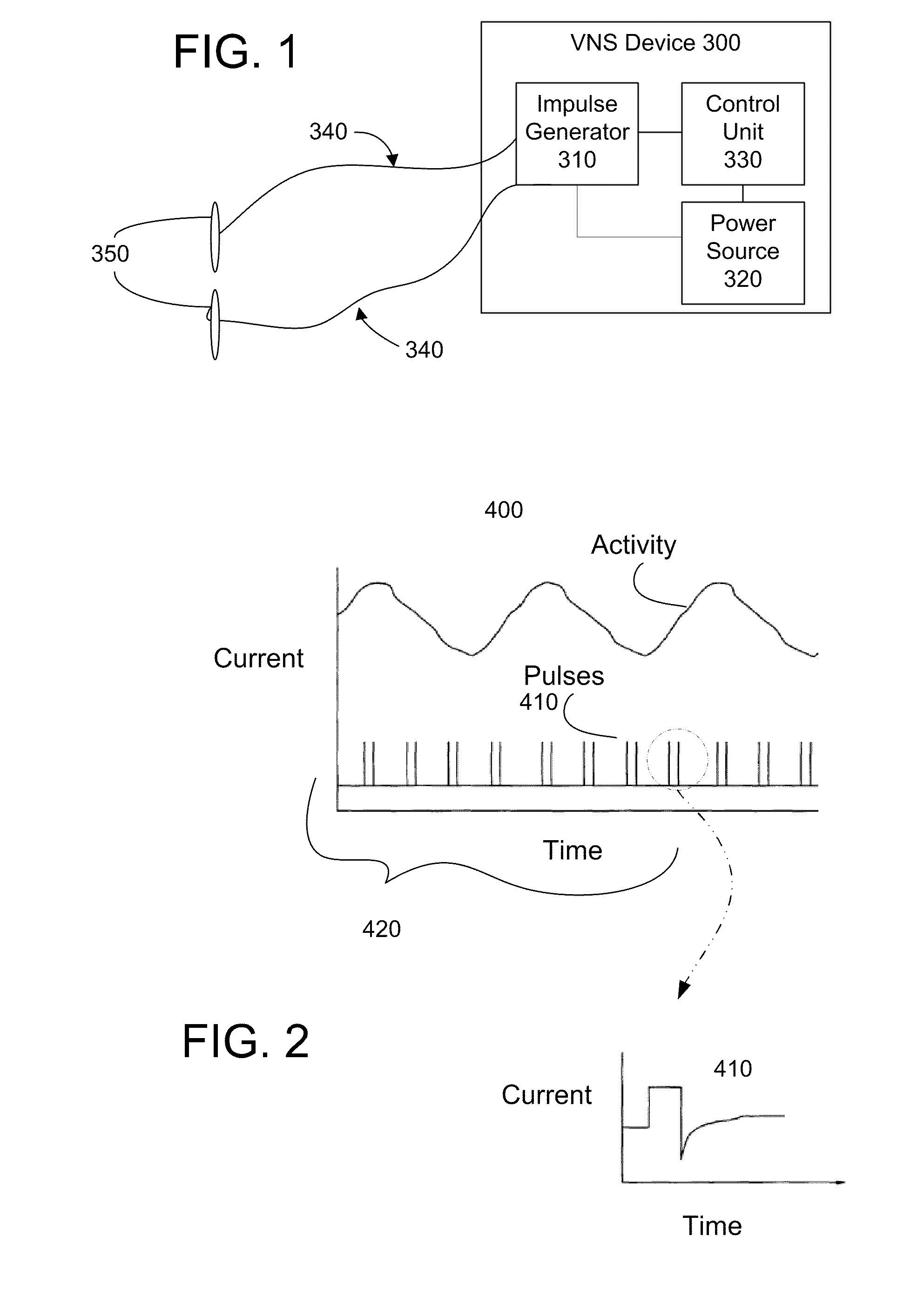
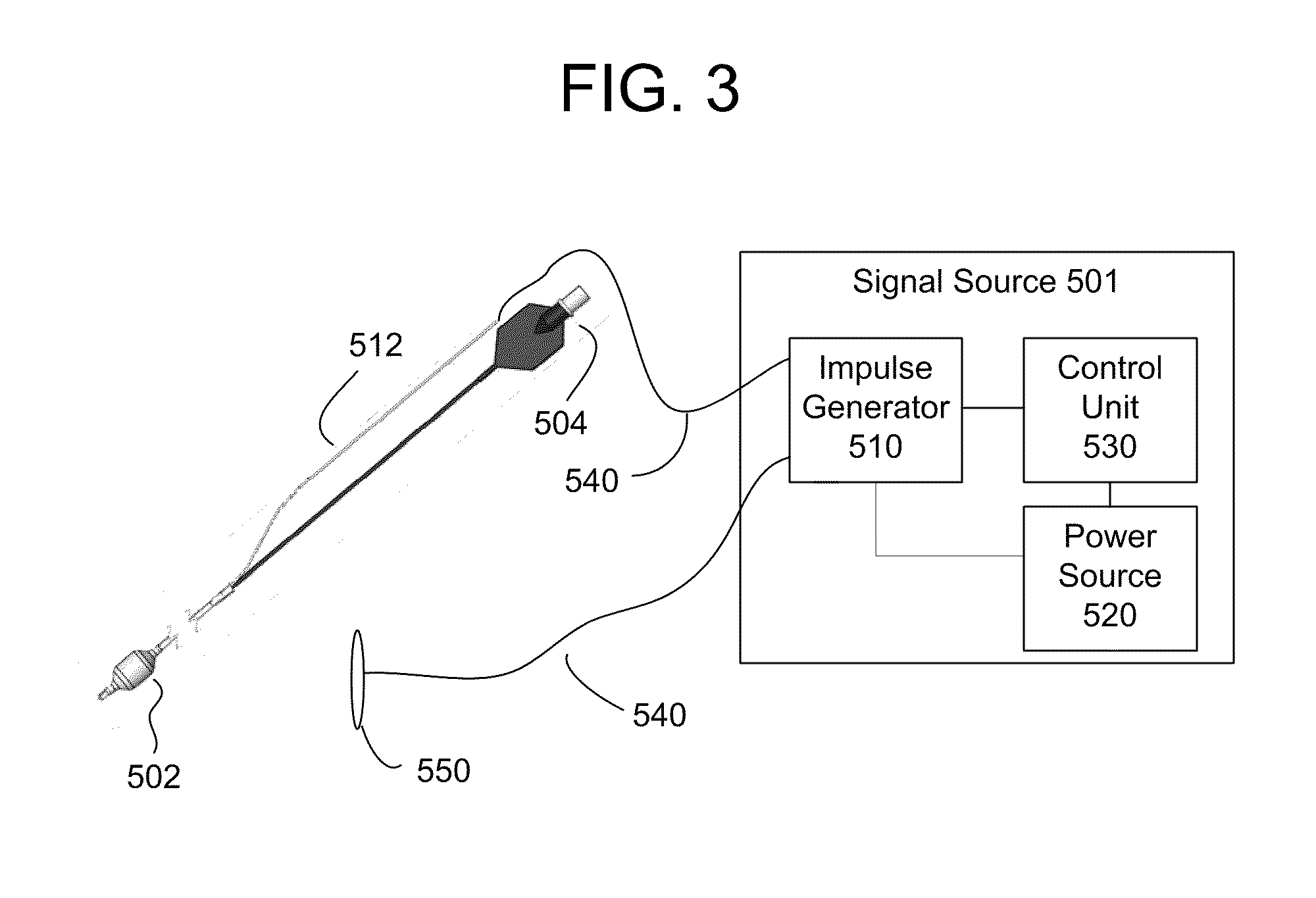
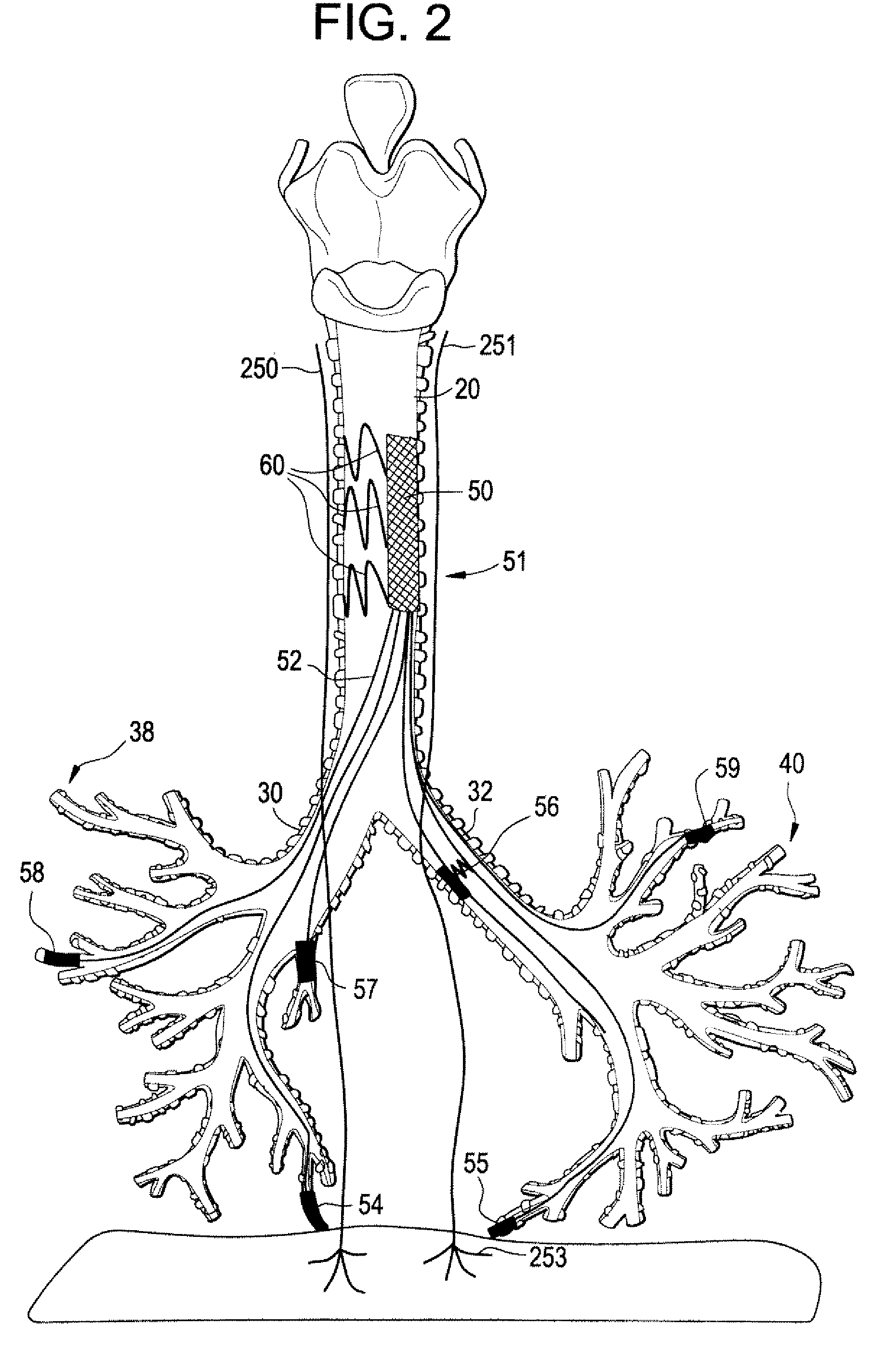
Trans-esophageal vagus nerve stimulation
Devices and methods of non-surgically providing vagus nerve therapy trans-esophageally to treat a variety of medical conditions are disclosed herein. In an embodiment, an implantable medical device comprises a support member having an outer surface. The support member is adapted to engage the inner wall of an esophagus. The IMD also comprises at least one electrode disposed on the outer surface of the support member. The at least one electrode is capable of applying a trans-esophageal electrical signal to the vagus nerve through the wall of the esophagus from the inner lumen thereof. The implantable medical device further comprises a signal generator coupled to the support member and to the at least one electrode. The signal generator causes the at least one electrode to apply an electrical signal to the vagus nerve to treat a medical condition.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Methods And Apparatus For Electrical Treatment Using Balloon And Electrode
InactiveUS20090259274A1Minimize tissue necrosis tissueMinimize tissue collateral tissue damageSpinal electrodesBalloon catheterSurgeryBody tissue
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Non-surgical device and methods for trans-esophageal vagus nerve stimulation
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Method and system for modulating eating behavior by means of neuro-electrical coded signals
InactiveUS20060206169A1Limitation for transferTransmission limitHead electrodesEsophageal electrodesEngineeringElectric signal
A method for modulating eating behavior comprising (i) generating at least one confounding neuro-electrical signal that is adapted to modulate the sense of taste in the body, (ii) generating at least one confounding neuro-electrical signal that is adapted to modulate the sense of smell in the body, and (ii) transmitting at least one of the confounding neuro-electrical signals to a subject to modulate the subject's sense of taste or smell. In a preferred embodiment, both confounding neuro-electrical signals are transmitted to the subject to modulate the subject's sense of taste and smell.
Owner:NEUROX CORP +1
Electrical Treatment Of Bronchial Constriction
ActiveUS20090187231A1Immediate airway dilationImmediate heart function increaseSpinal electrodesHead electrodesNerve fiber bundleSmooth muscle
Devices, systems and methods for treating bronchial constriction related to asthma, anaphylaxis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease wherein the treatment includes stimulating selected nerve fibers responsible for smooth muscle dilation at a selected region within a patient's neck, thereby reducing the magnitude of constriction of bronchial smooth muscle.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Devices and methods for electrical stimulation of the diaphragm and nerves
Medical devices, systems, and methods are provided for providing respiratory therapy by electrically stimulating the phrenic nerves and / or the thoracic diaphragm. In one embodiment, at least one electrode is deployed to a position within the patient's airway and placed in proximity to a phrenic nerve or to the diaphragm. The electrode may be attached to a controller housing including a pulse generator using one or more electrical lead or leads or may be in wireless communication with the pulse generator. The controller housing may be implanted at a position within the patient or the controller housing may reside external to the patient.
Owner:E PACING
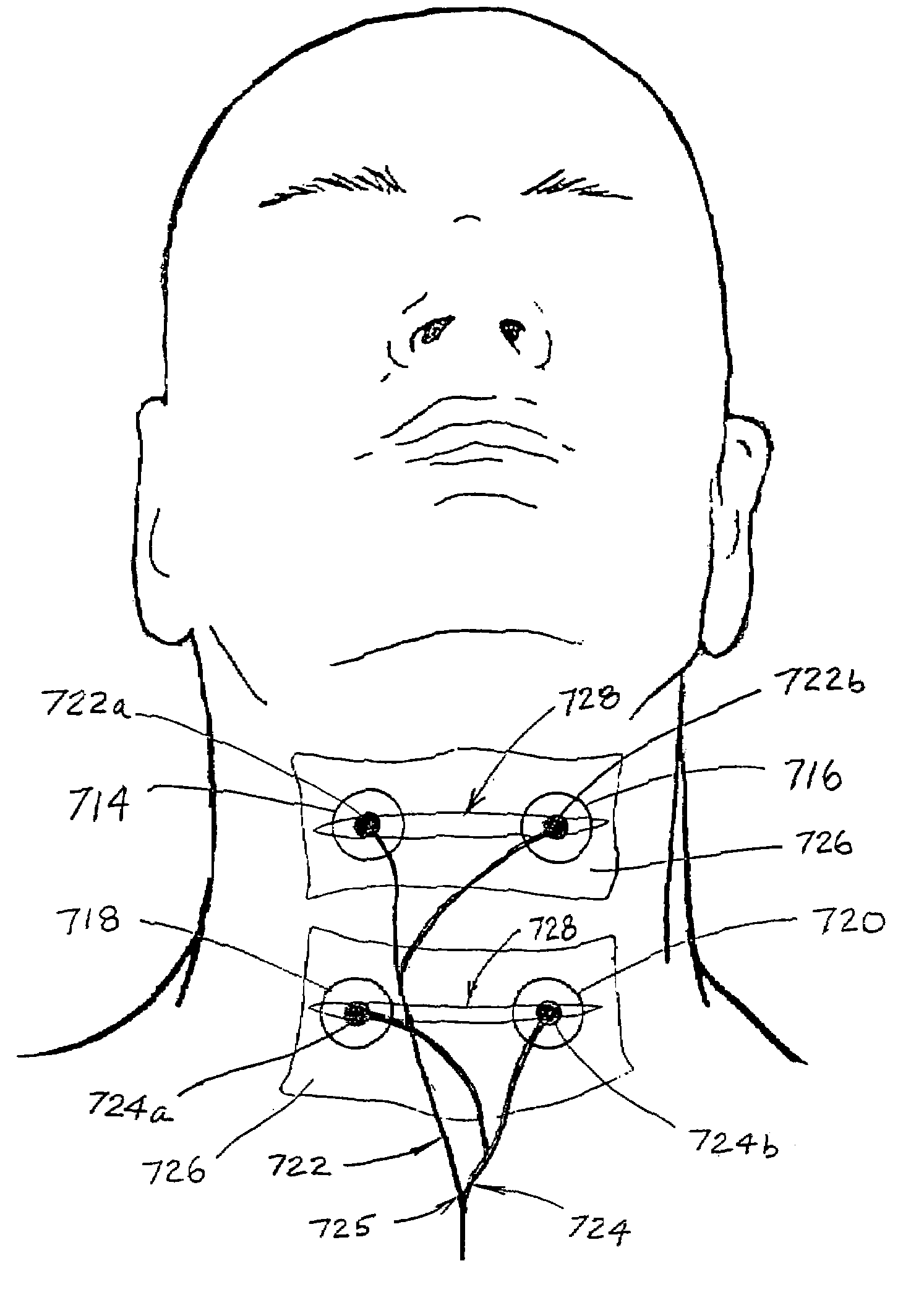
Treatment of oropharyngeal disorders by application of neuromuscular electrical stimulation
InactiveUS7280873B2Easy to swallowEnhanced advantageHead electrodesEsophageal electrodesElectricityDisease
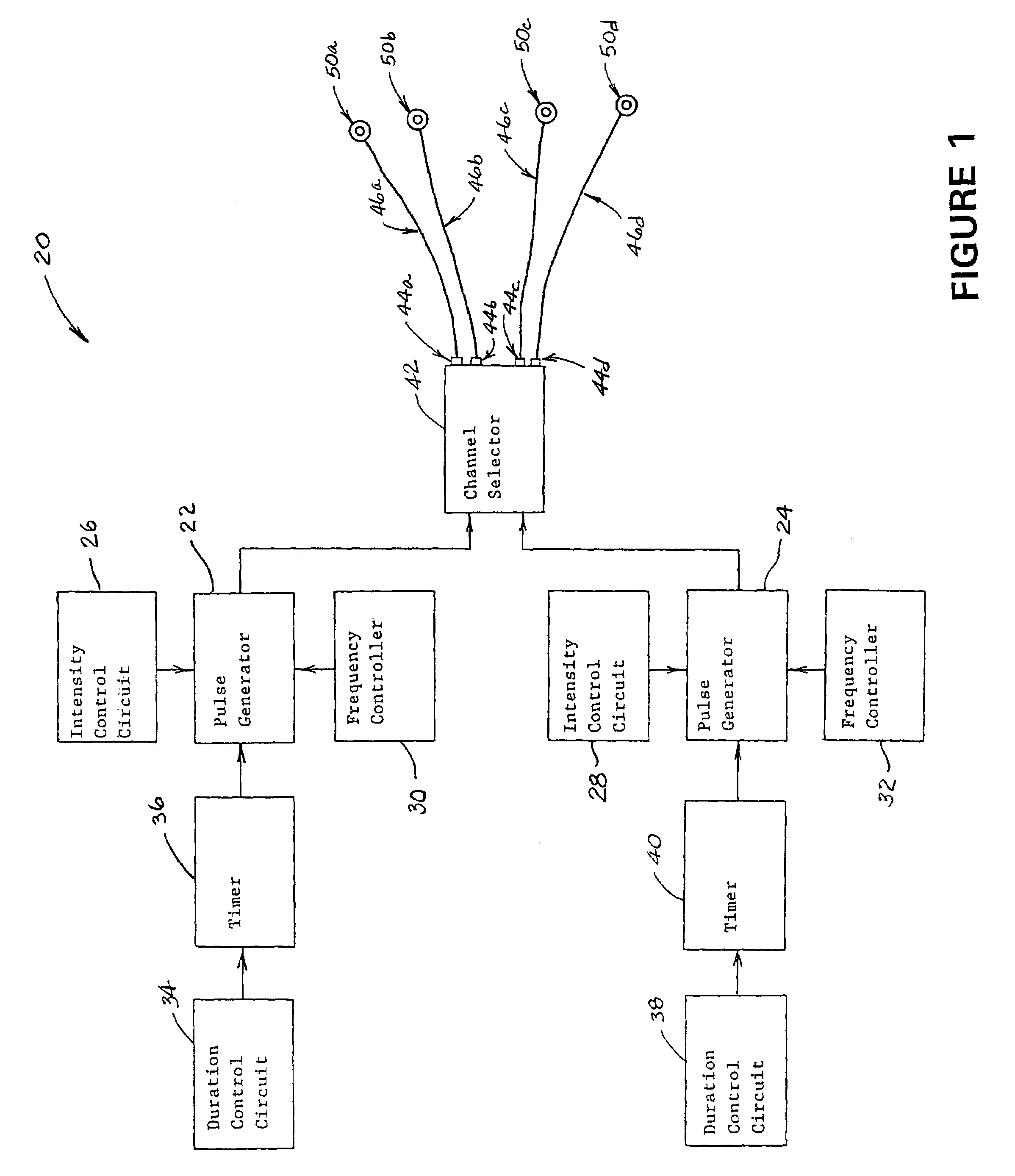
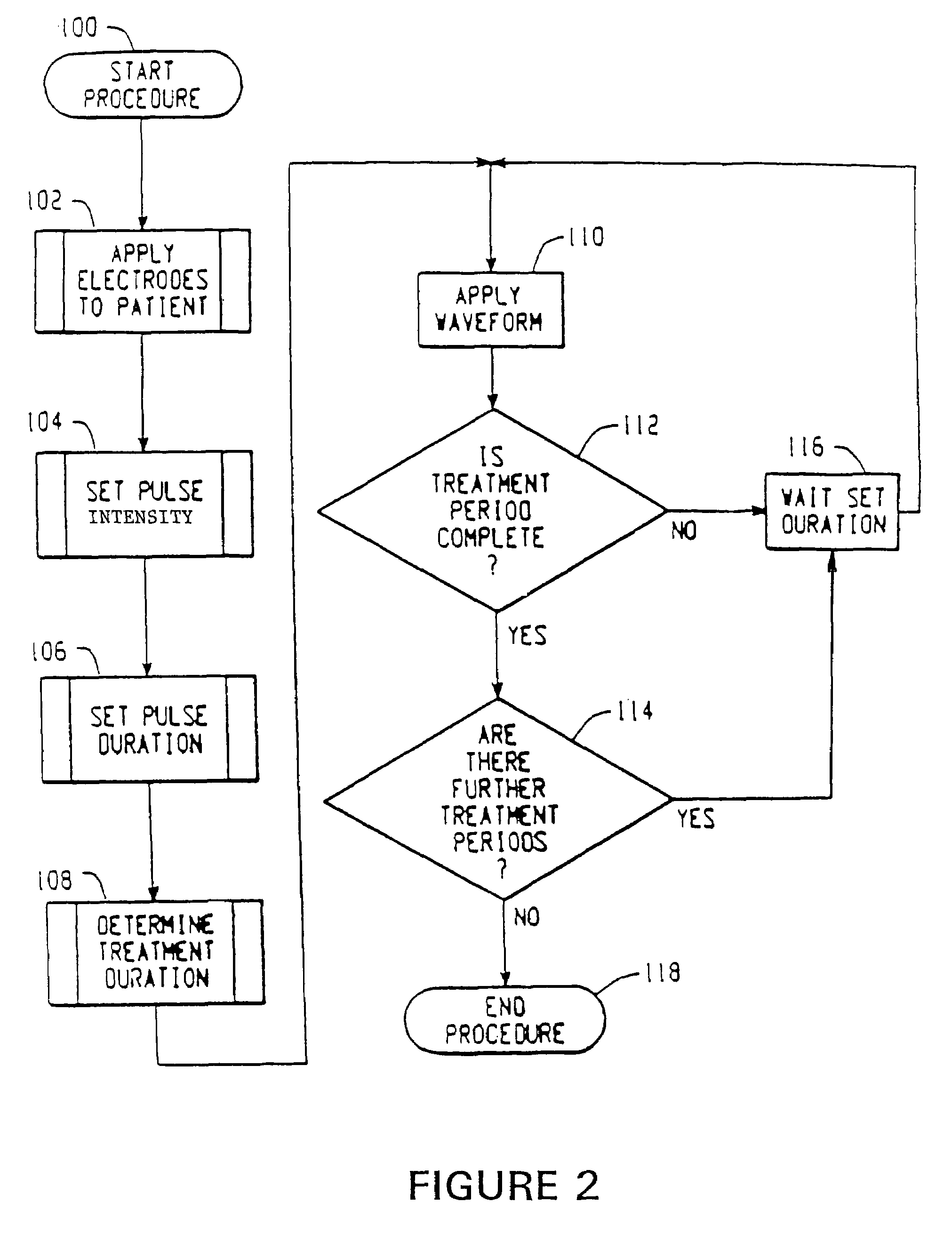
A method for treating an oropharyngeal disorder in a patient by neuromuscular electrical stimulation includes selectively placing a plurality of electrodes in electrical contact with tissue of a pharyngeal region of the patient. The method also includes the steps of providing a pulse generator for generating a series of electrical pulses, each of which comprises a biphasic symmetrical waveform with an interval between the two phases, and attaching the plurality of electrodes to the pulse generator so that the series of electrical pulses may be provided to the patient through the plurality of electrodes. According to the method, a series of electrical pulses, each of which comprises a biphasic symmetrical waveform with an interval between the two phases, is generated, and said series of electrical pulses is provided to the patient through the plurality of electrodes. An apparatus for generating a series of electrical pulses for application of electrical neuromuscular stimulation to a patient through a plurality of electrodes for treatment of oropharyngeal disorders includes a pulse generator which generates a series of electrical pulses, each of which pulses comprises a biphasic symmetrical waveform with an interval between the two phases. The apparatus includes an intensity control circuit for regulating the series of electrical pulses such that the intensity of the electrical pulses does not exceed a predetermined value, a frequency controller for controlling the frequency at which the series of electrical pulses is generated so that such pulses are generated at a predetermined frequency, and a duration control circuit for controlling the duration of each such electrical pulse.
Owner:ESD
Endospoic Sheath with Illumination Systems
A protective sheath adapted to cover an elongate medical probe. The sheath includes an elongate sheath adapted to receive an insertion tube of a medical probe and isolate the insertion tube from body tissue and at least one light generating element mounted on the sheath.
Owner:COGENTIX MEDICAL
Intraluminal sleeve with active agents
ActiveUS20120232460A1Effective obesityEffecting weight lossMedical devicesEndoradiosondesControlled releaseActive agent
An intraluminal sleeve system is provided, which generally includes an intraluminal sleeve capable of dispensing an active agent to a patient, for example, a metabolic agent or satiety inducing agent. The intraluminal sleeve may be structured to contain the active agent and permit controlled release of the active agent to the patient while the intraluminal sleeve is positioned within the patient's intestine. Methods for treating obesity are also provided which include positioning an intraluminal sleeve in a patient's intestine, the intraluminal sleeve being capable of dispensing an active agent to the patient. In one embodiment, the active agent may be contained in a reservoir and dispensed to a portion of the patient's body.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
Transvisceral neurostimulation mapping device and method
The invention provides a method and device for providing electrical stimulation to a patient's diaphragm (or other organ or tissue) including the steps of: introducing an endoscope transviscerally (e.g., transgastrically) into the patient's body cavity; delivering an electrode into the patient's body cavity through a lumen of the endoscope; applying suction to attach the electrode to a stimulation site on the diaphragm (or other organ or tissue); and delivering a stimulation pulse to the stimulation site. The stimulation may be repeated at multiple stimulation sites.
Owner:SYNAPSE BIOMEDICAL INC
Electrical stimulation treatment of hypotension
ActiveUS8041428B2Raise the ratioSlow down heart rateEsophageal electrodesEndotracheal electrodesNervous systemMedicine
The present invention includes methods and devices for treating hypotension, such as in cases of shock, including septic shock, anaphylactic shock and hypovolemia. The method includes the step of applying at least one electrical impulse to at least one selected region of a parasympathetic nervous system of the patient. The electrical impulse is sufficient to modulate one or more nerves of the parasympathetic nervous system to increase the ratio of blood pressure to heart rate and relieve the condition and / or extend the patient's life.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
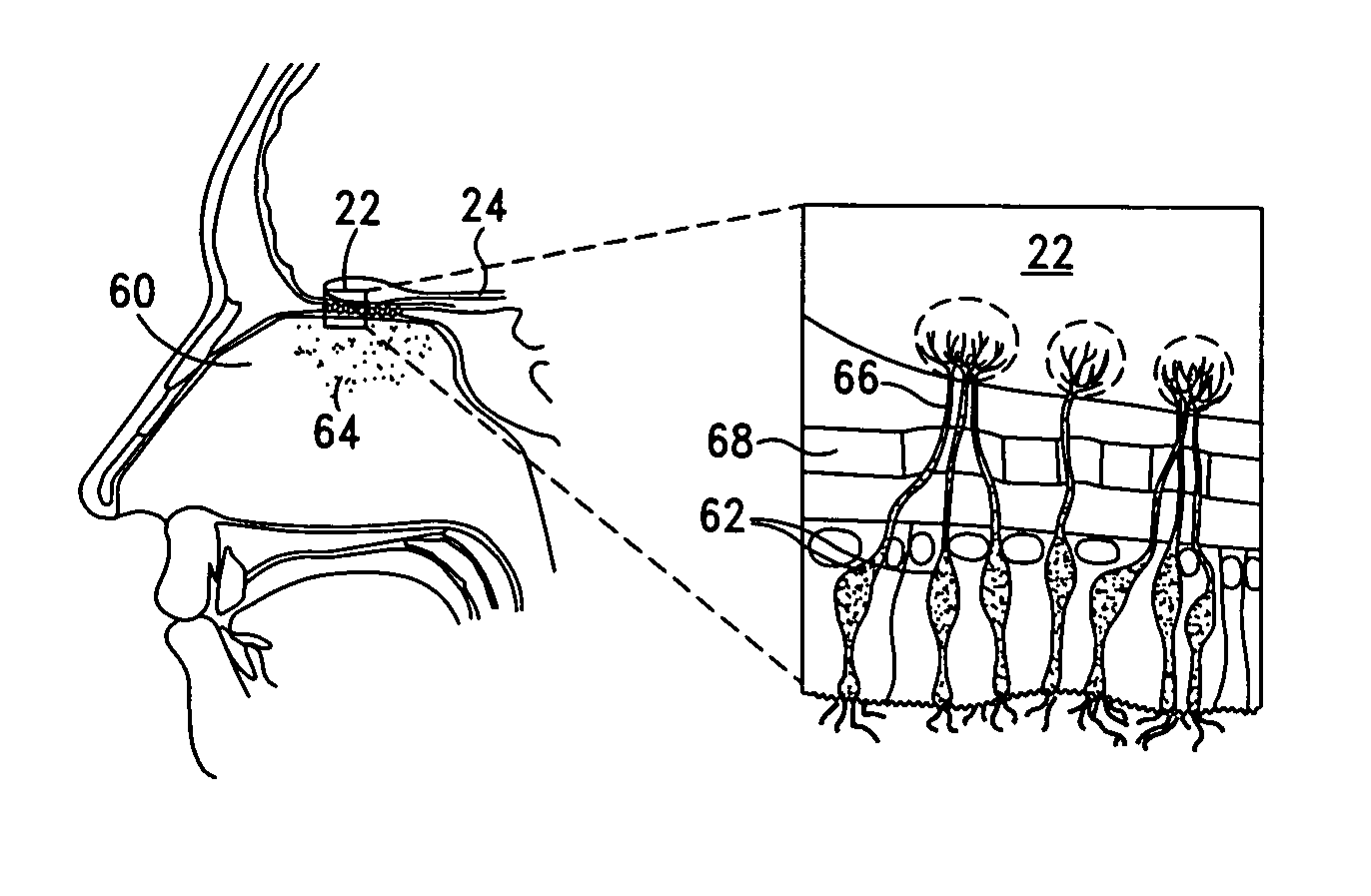
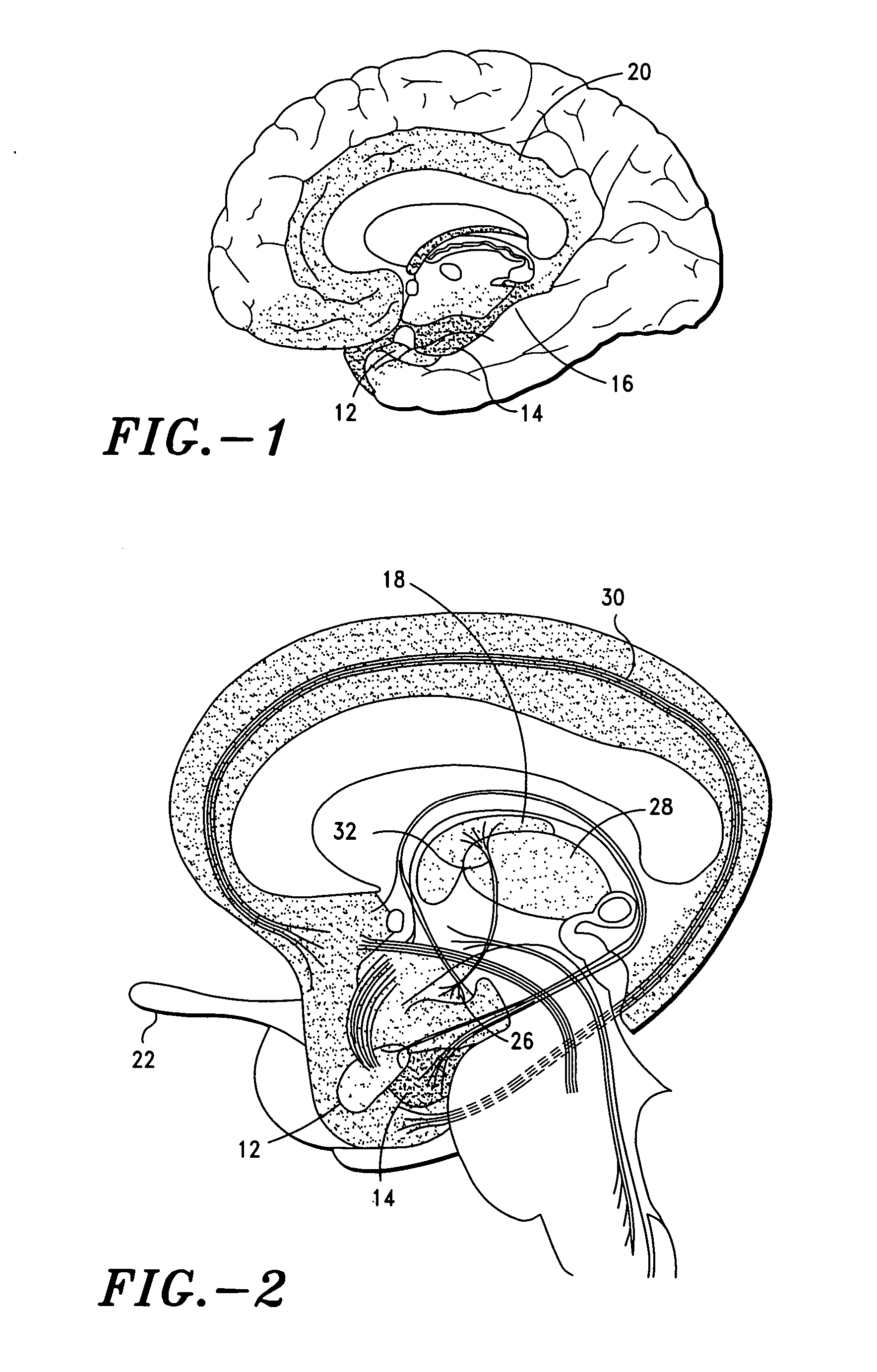
Methods and apparatus for deep brain stimulation
InactiveUS20100010564A1Precise positioningLower potentialSpinal electrodesBalloon catheterMedicineElectrical impulse
The present invention provides systems, apparatus and methods for treating nerve disorders in the brain. An electrode is introduced into a patient's sinus cavity and an electrical impulse is applied to the electrode to modulate one or more target nerves in the brain to treat the disorder. In preferred embodiments, the electrode is positioned within a sinus cavity adjacent to or near the frontal cortex of the brain and the electrical signal is sufficient to modulate, stimulate and / or inhibit nerves within the frontal cortex. The electrode may be movable between a collapsed or compact configuration for introduction into the sinus cavity and an expanded configuration for contacting tissue within the sinus cavity to deliver the electrical impulse through the tissue to the target nerves in the brain.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Add-On For Invasive Probe
InactiveUS20080255441A1Simpler and cheapIncrease the diameterEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsBiomedical engineering
An invasive probe assembly including an invasive probe having a surface area and a tool carrier removably mounted on the invasive probe, including a substrate having an area smaller than 25% of the surface area of the probe and at least one tool mounted on the substrate. The layout of the substrate or of one or more of the at least one tool is optionally substantially different in different sectors of the circumference of the probe.
Owner:HADANI RON
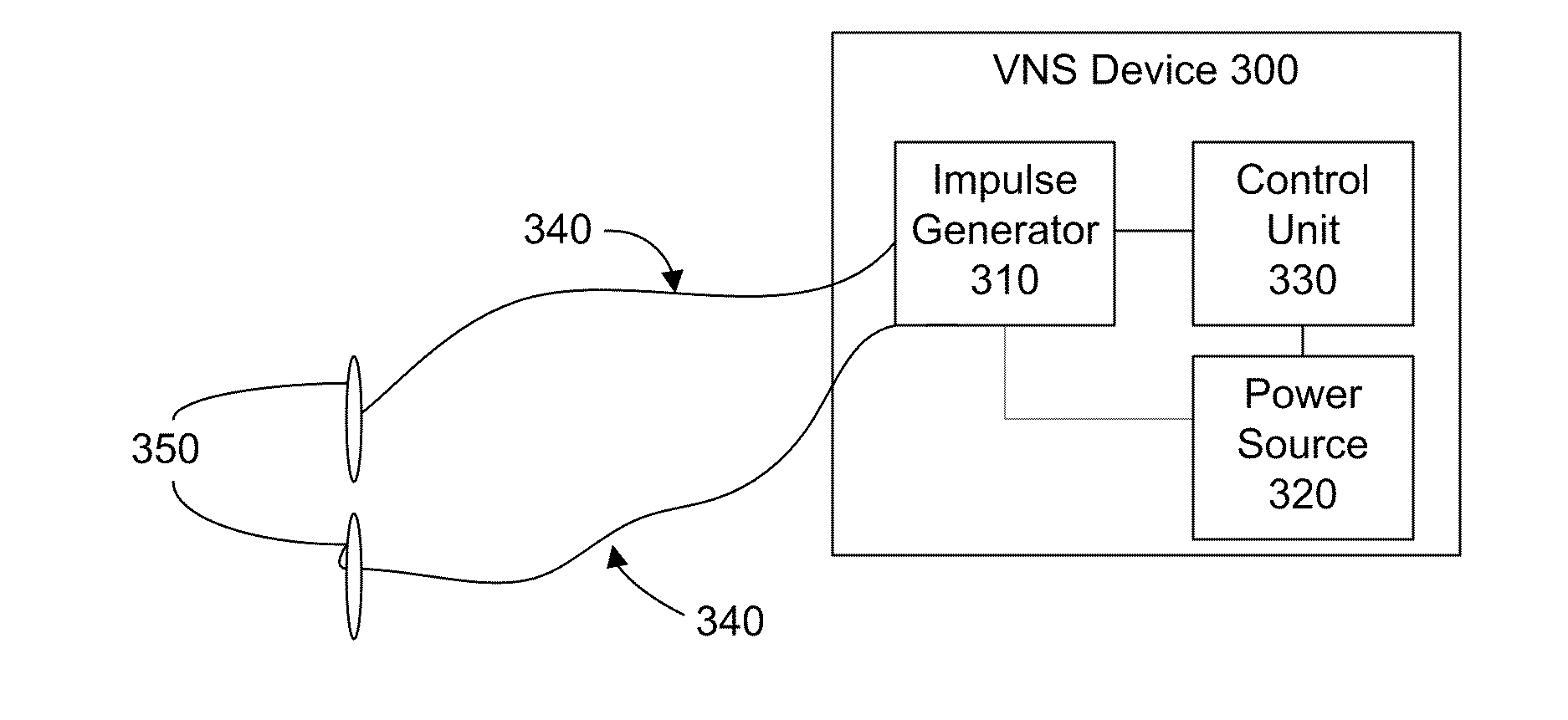
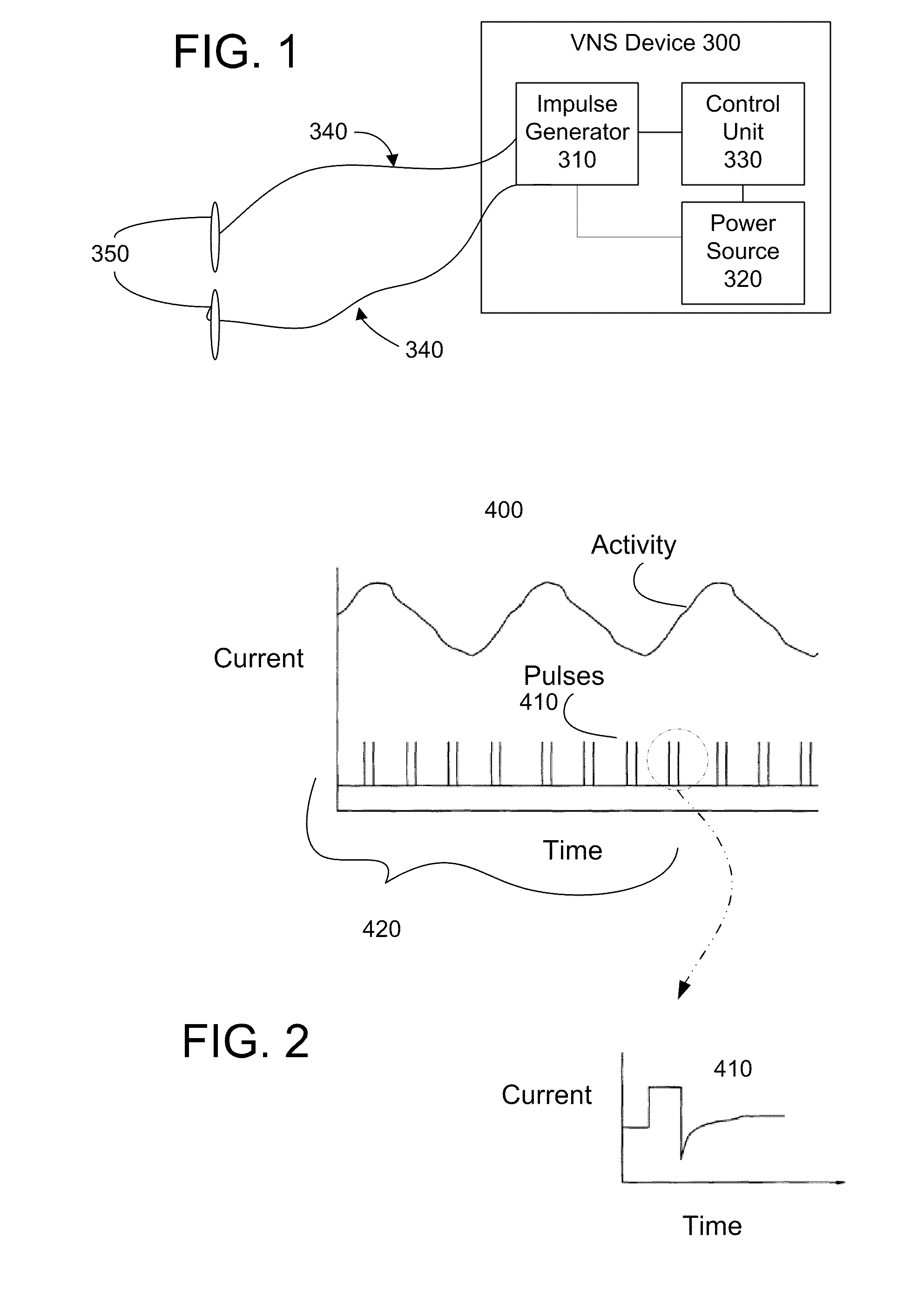
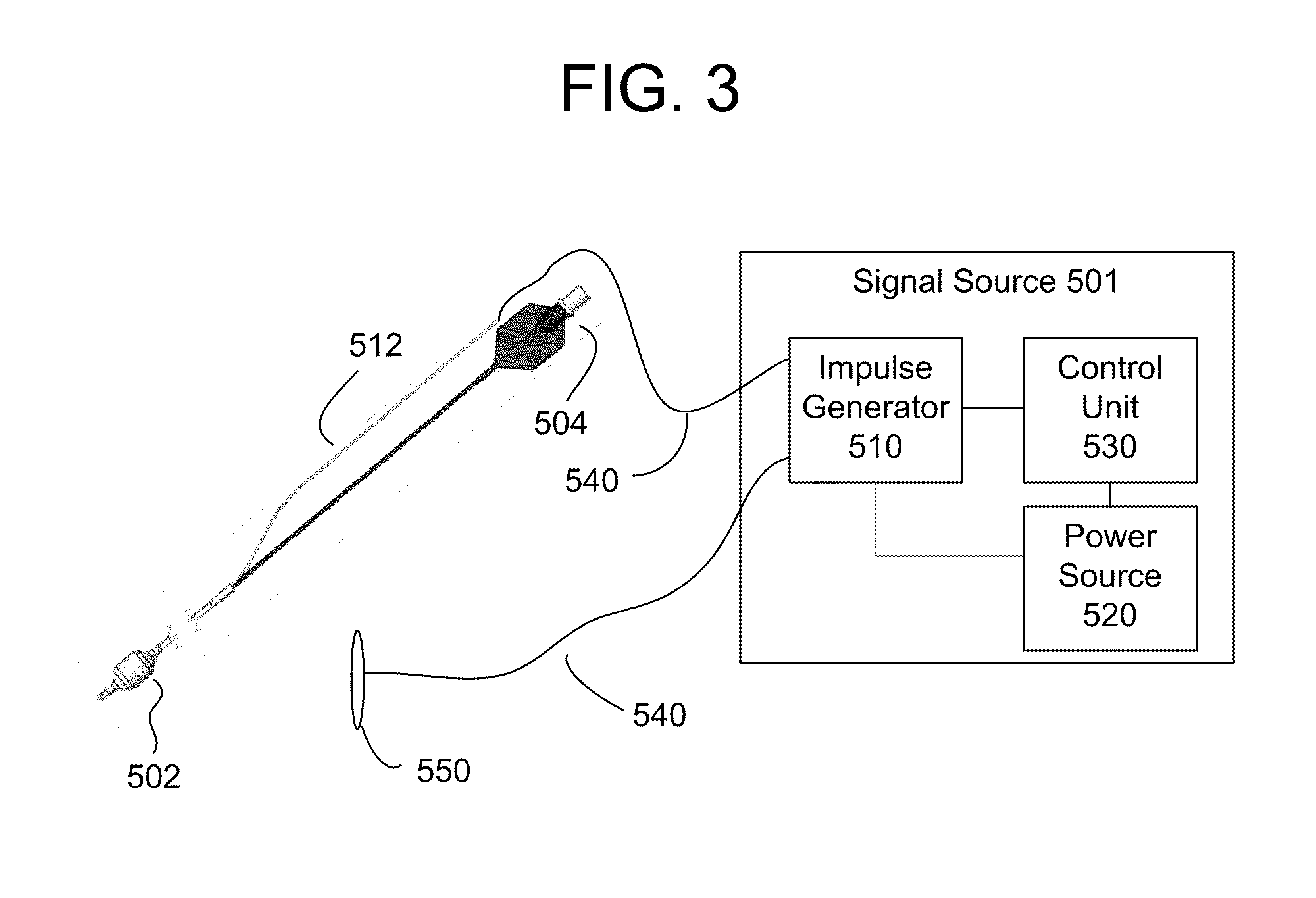
Devices and methods for vagus nerve stimulation
InactiveUS7840278B1Increase stimulationEasy to superviseSpinal electrodesHead electrodesNon invasiveBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to apparatus and methods for electrically inducing, pharmacologically maintaining cardiac asystole. The present invention also provides cutaneous array electrodes (900) that may be used non-invasive to stimulate the vagus nerve.
Owner:PUSKAS JOHN D
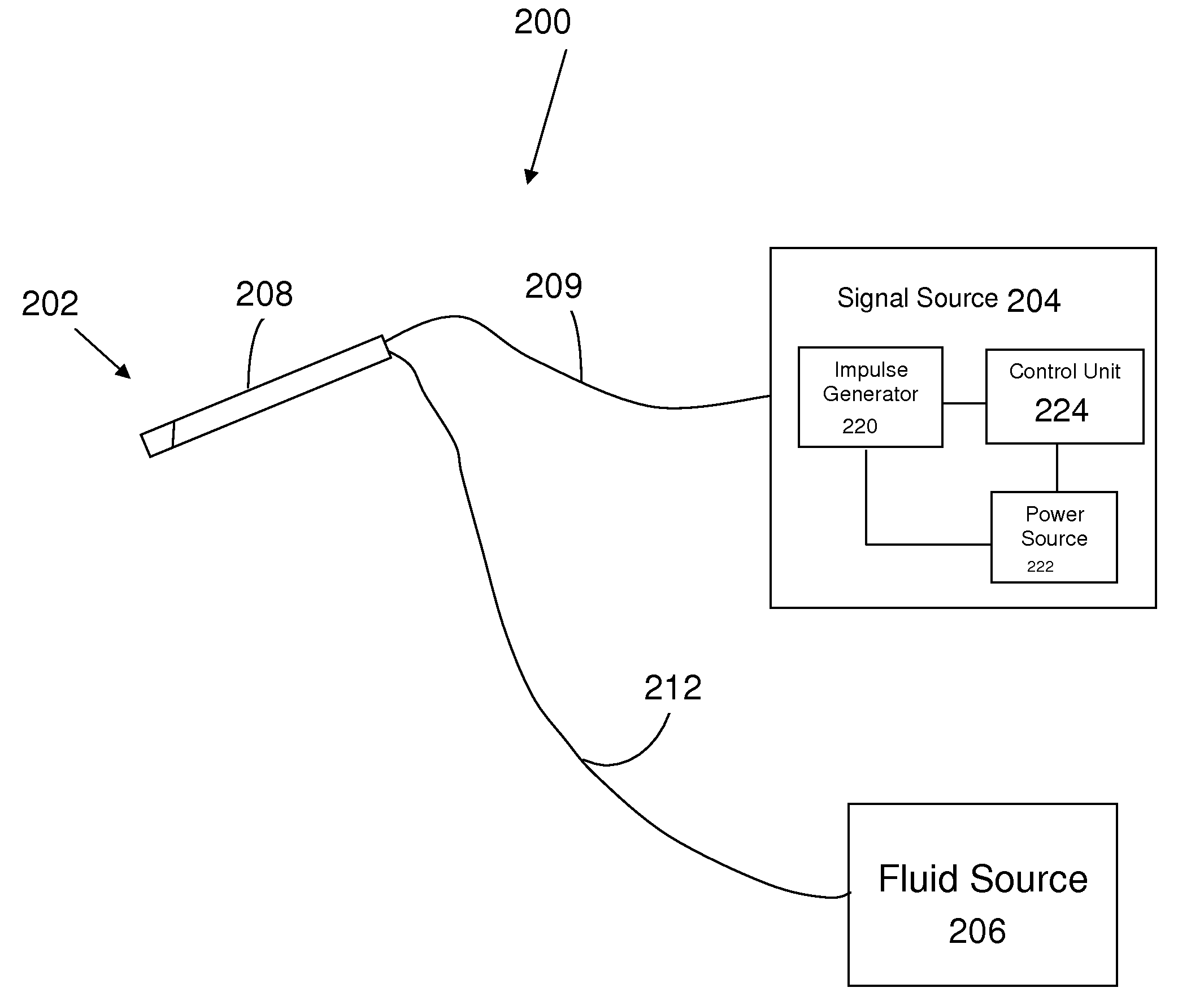
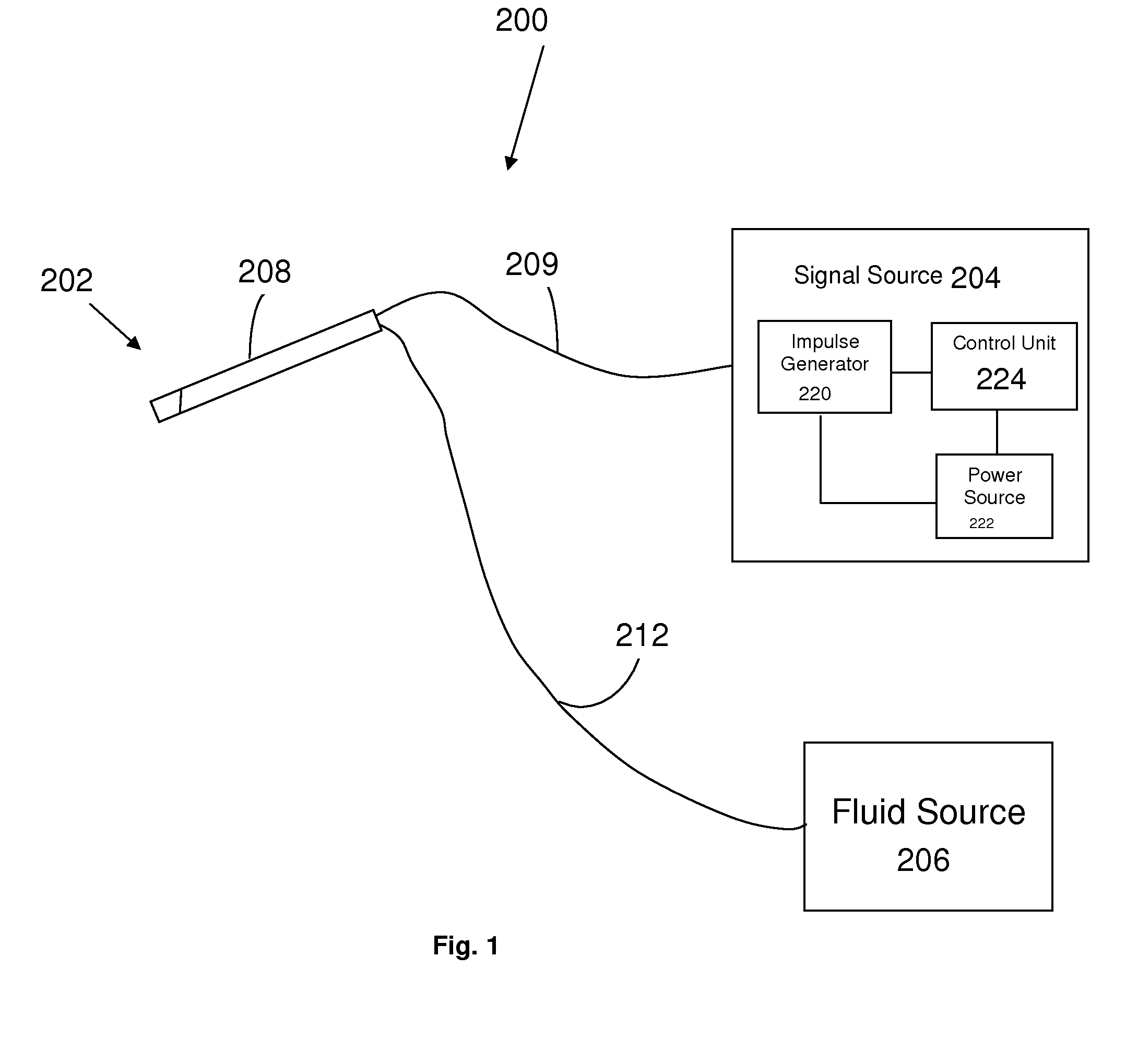
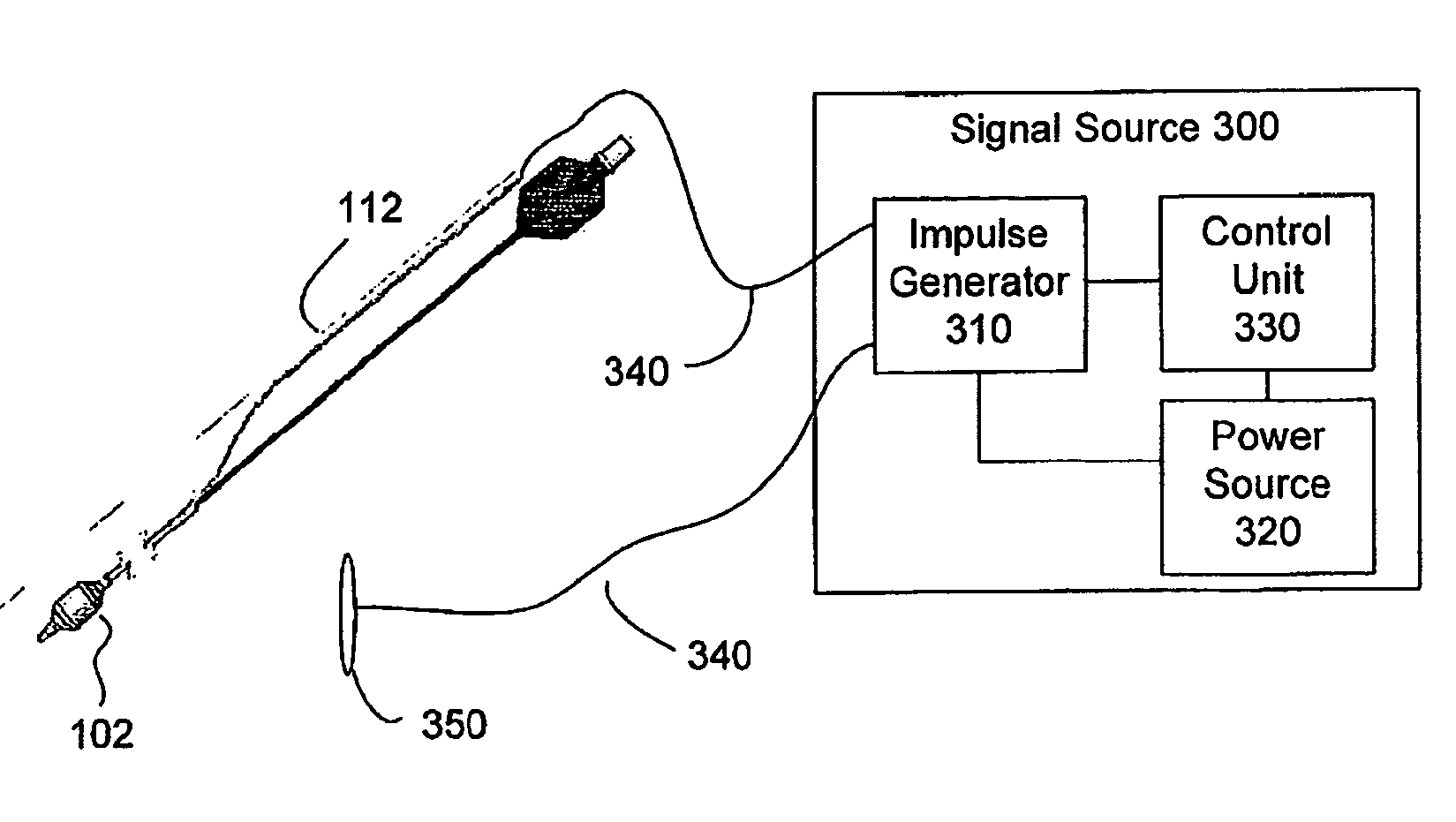
Methods and apparatus for electrical stimulation treatment using esophageal balloon and electrode
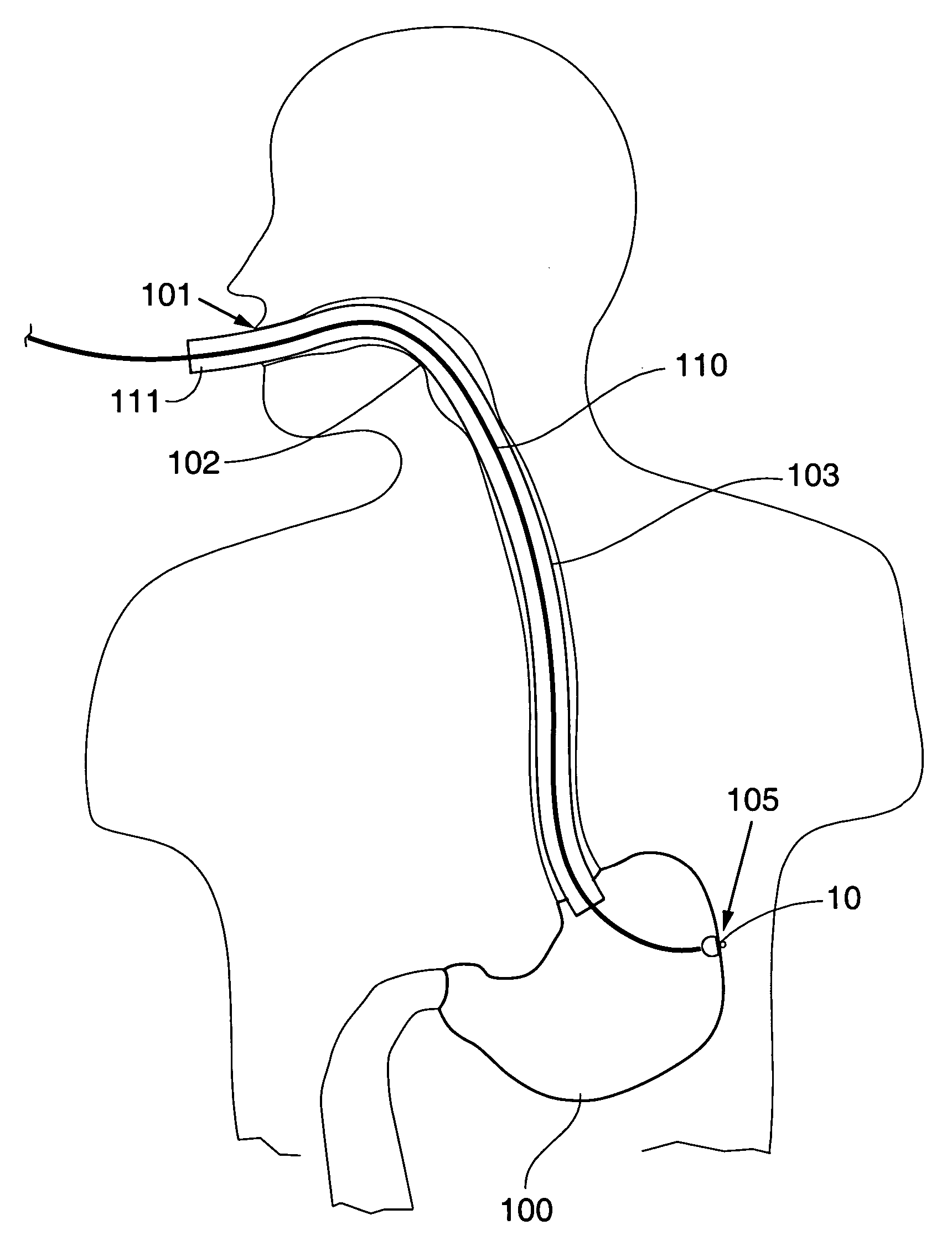
InactiveUS20100160996A1ConstrictionConstriction of smoothExternal electrodesEsophageal electrodesDiseaseElectrical conductor
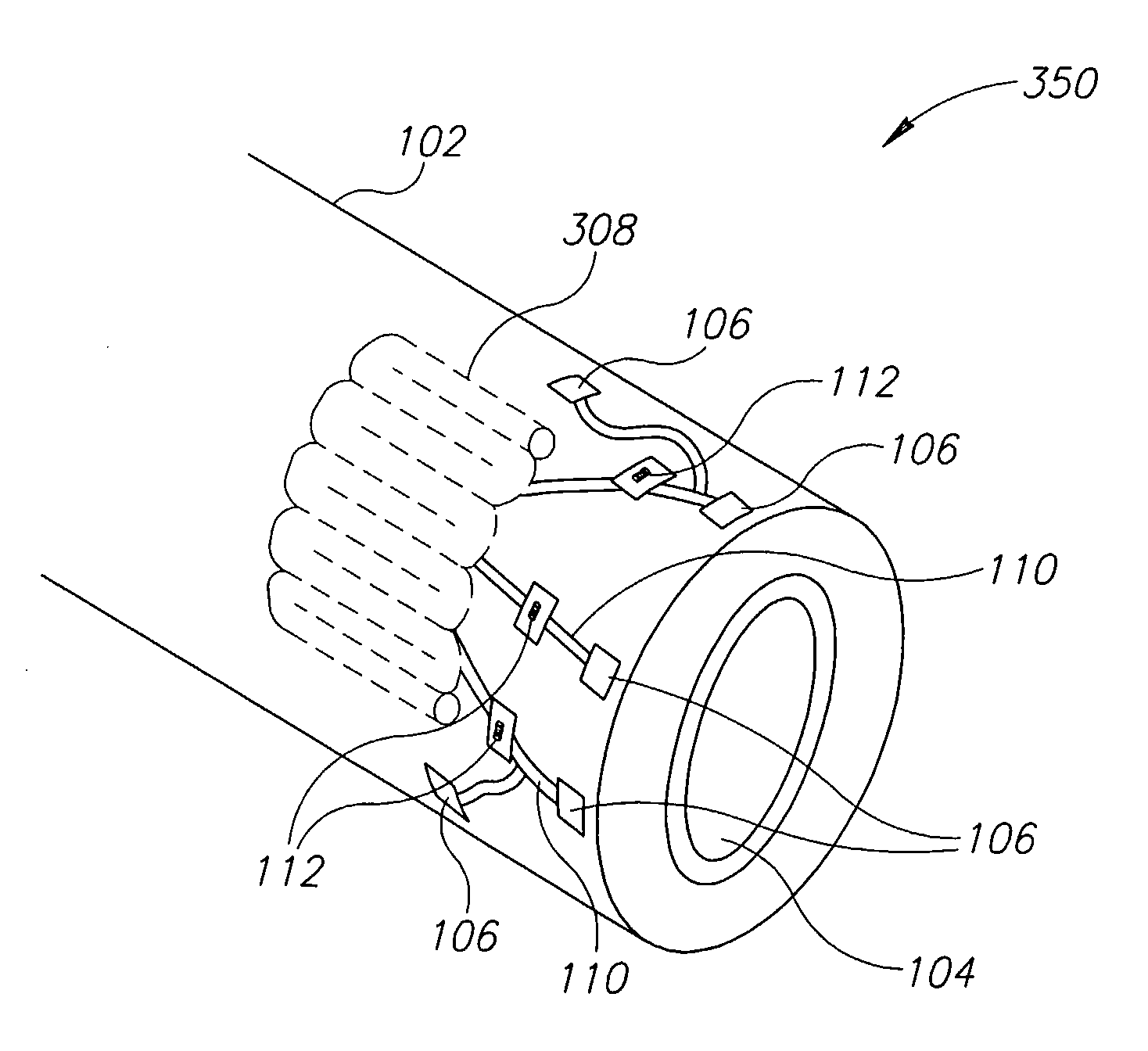
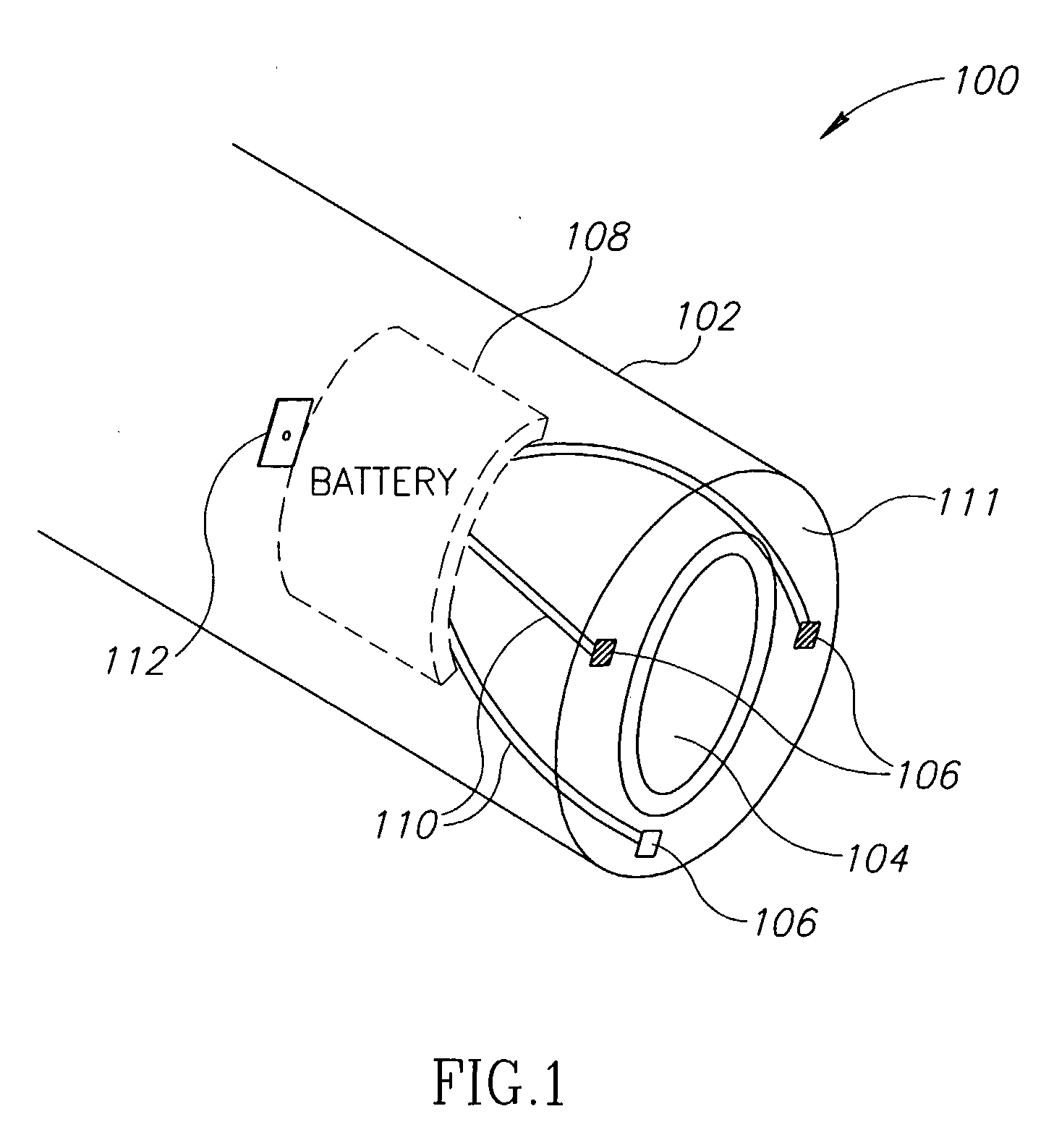
Methods and apparatus for treating ailments provide for: inserting a balloon-electrode device into an esophagus of a mammal, the balloon-electrode device including: (i) a nasogastral (NG) having an internal passageway and an external surface, (ii) at least one electrode coupled to the external surface of the NG tube, (iii) a conductor extending through the internal passageway of the NG tube and electrically connecting to the electrode, and (iv) a balloon surrounding the electrode and a portion of the NG tube; inflating the balloon with fluid such that the electrode is substantially centrally located within an interior volume of the balloon; and applying at least one electrical signal to the electrode via the conductor such that an electromagnetic field emanates from the electrode to at least one of nerves and muscles of the mammal.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Device and Implantation System for Electrical Stimulation of Biological Systems
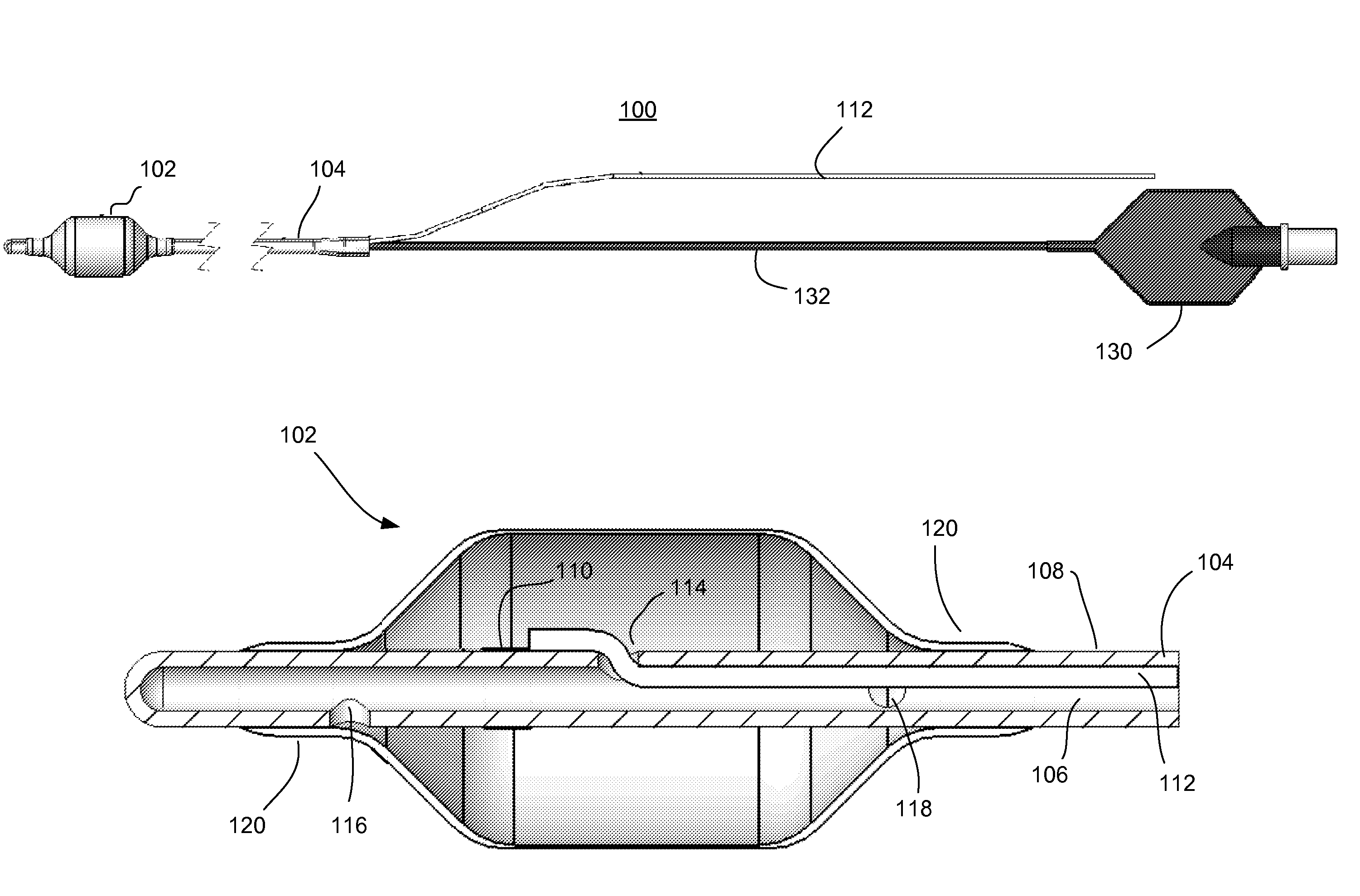
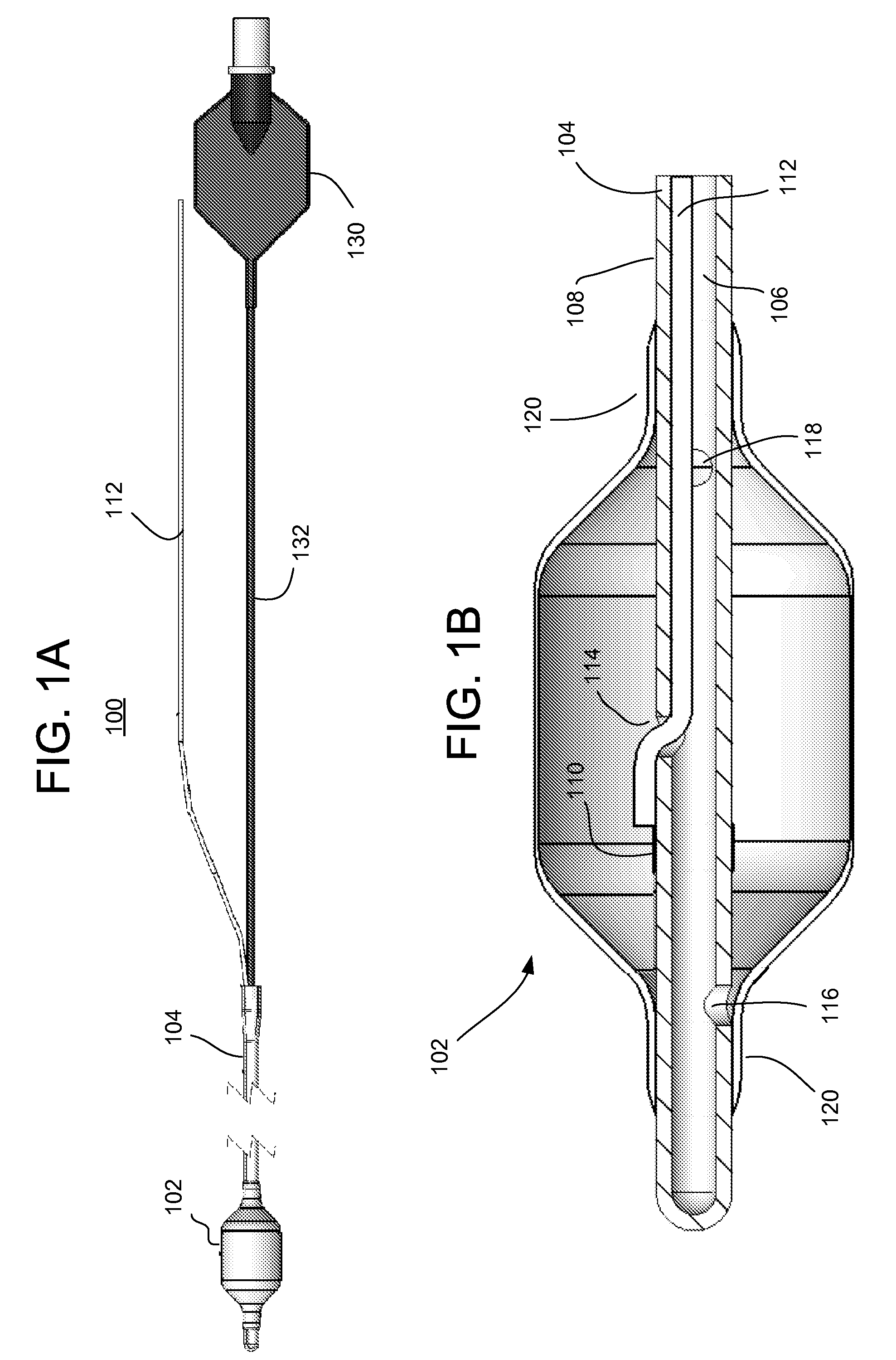
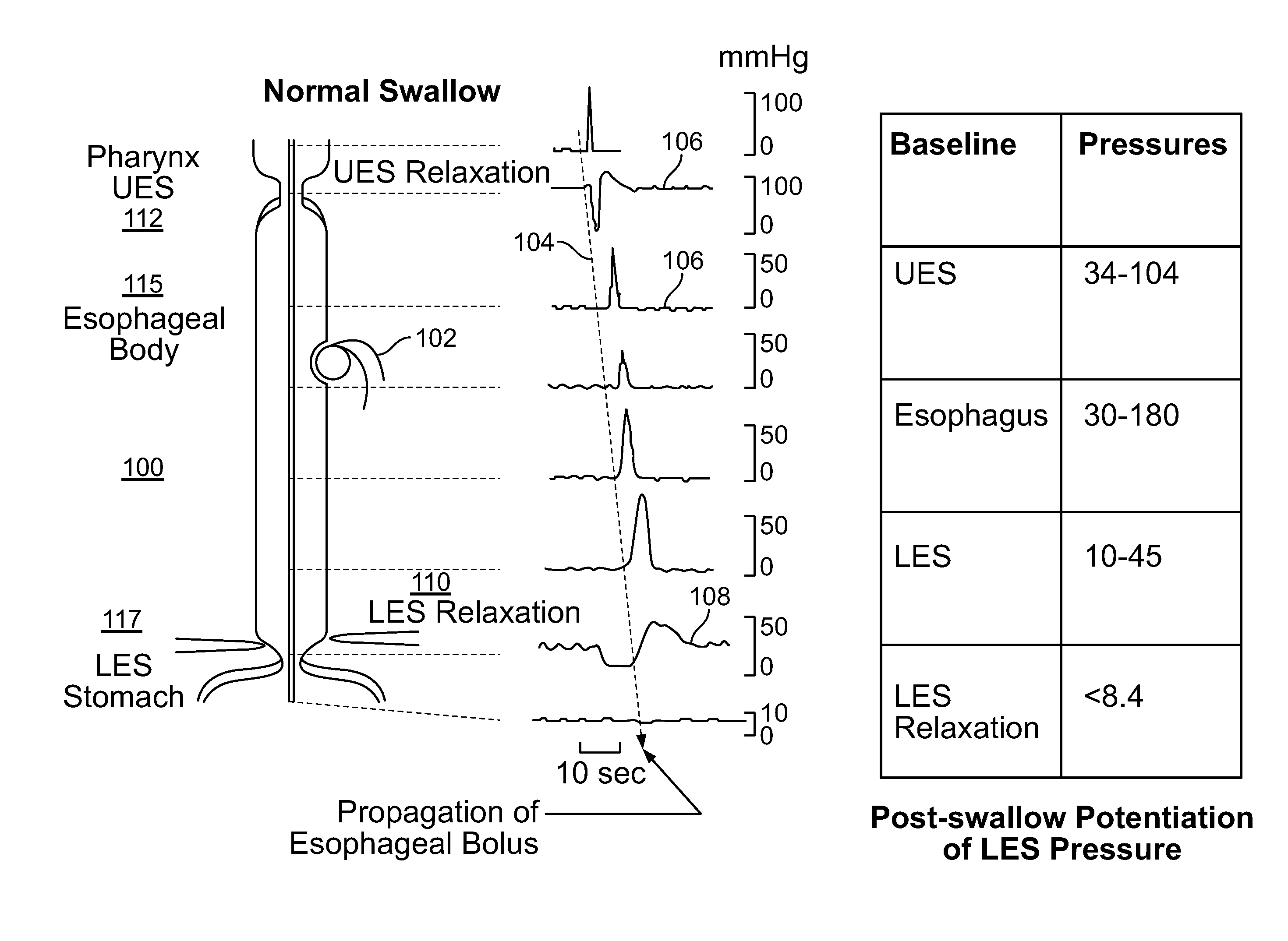
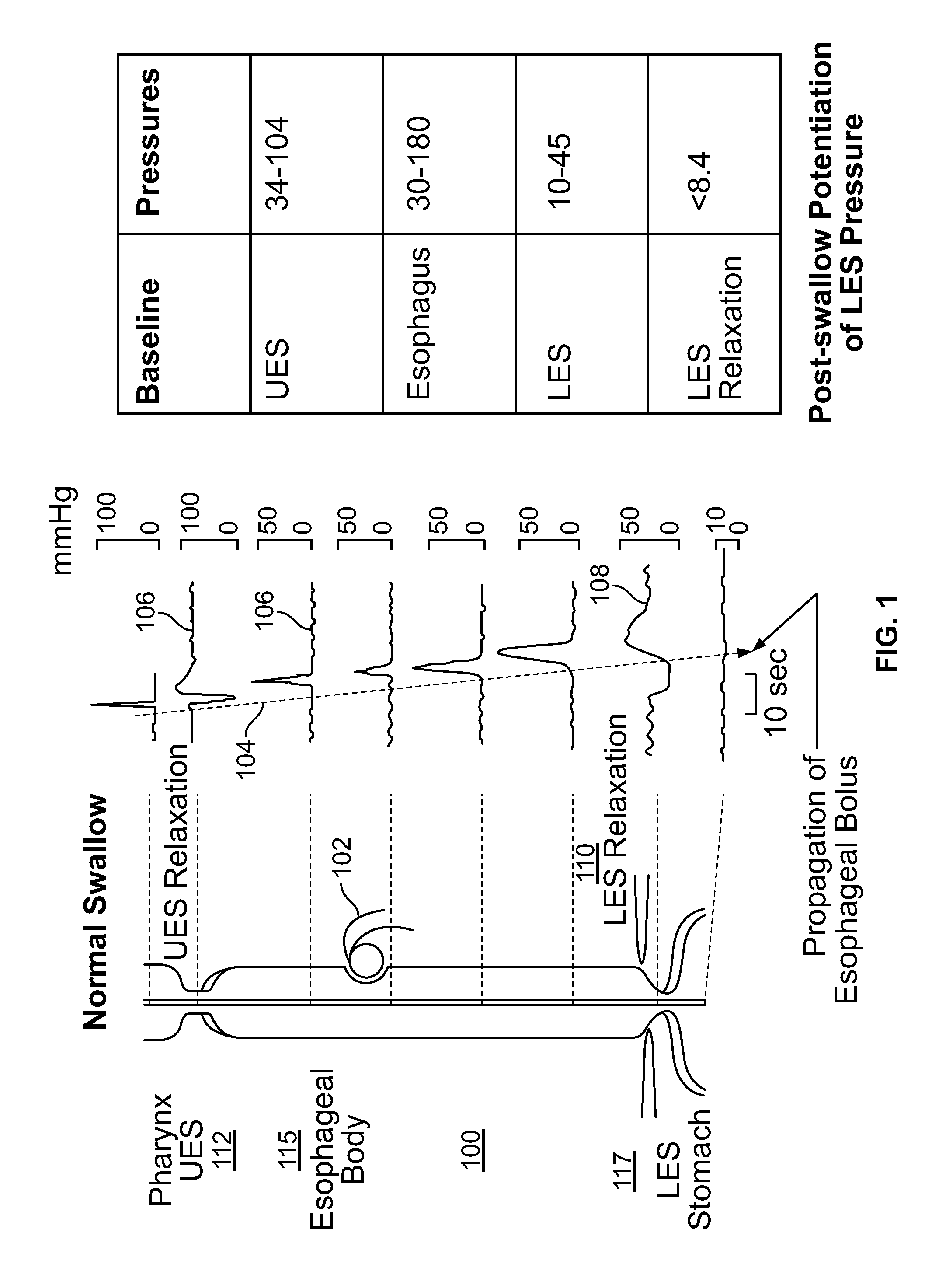
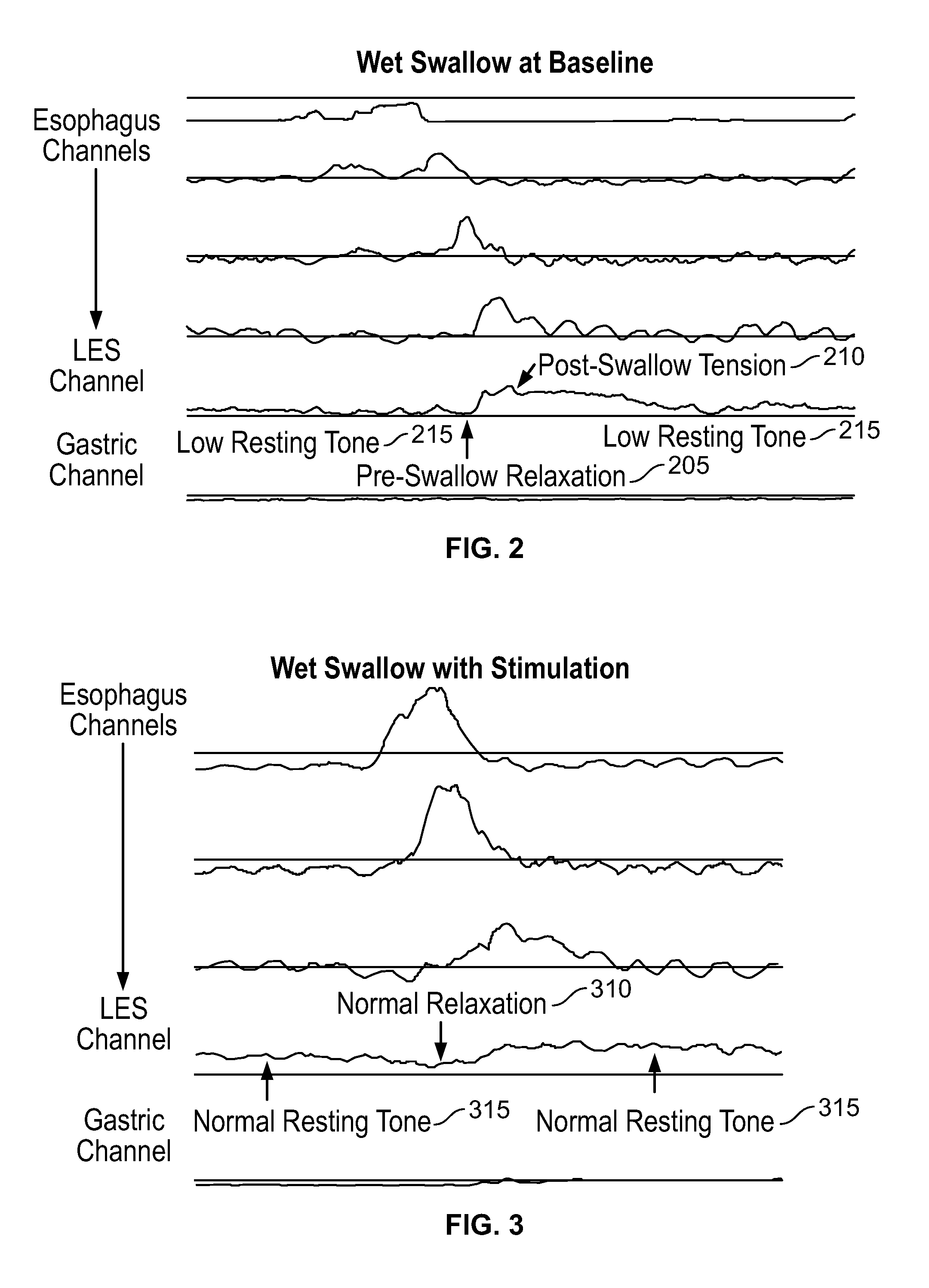
ActiveUS20140228911A1Not induce dysphagiaIncrease pressureImplantable neurostimulatorsCatheterLower esophagusSphincter
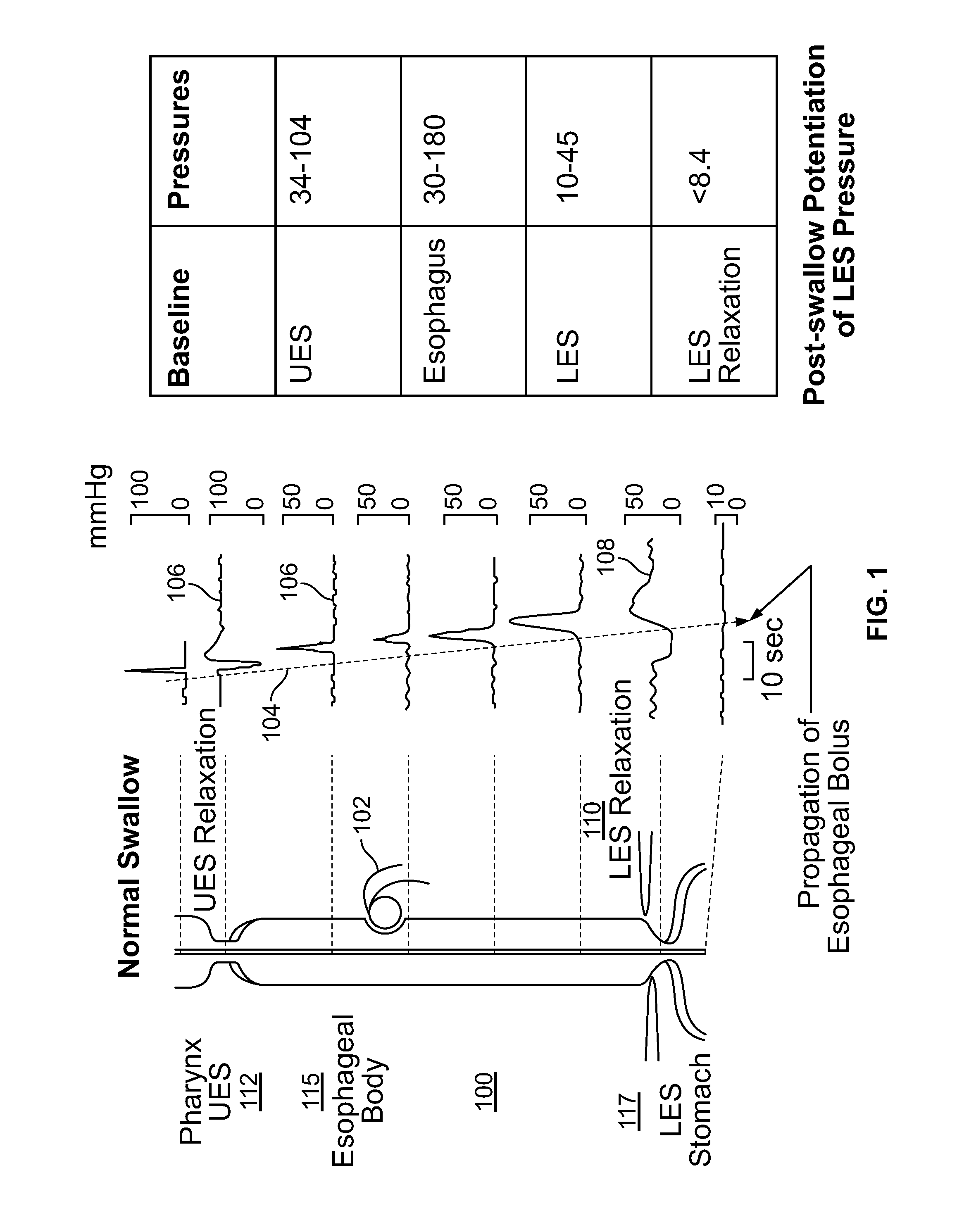
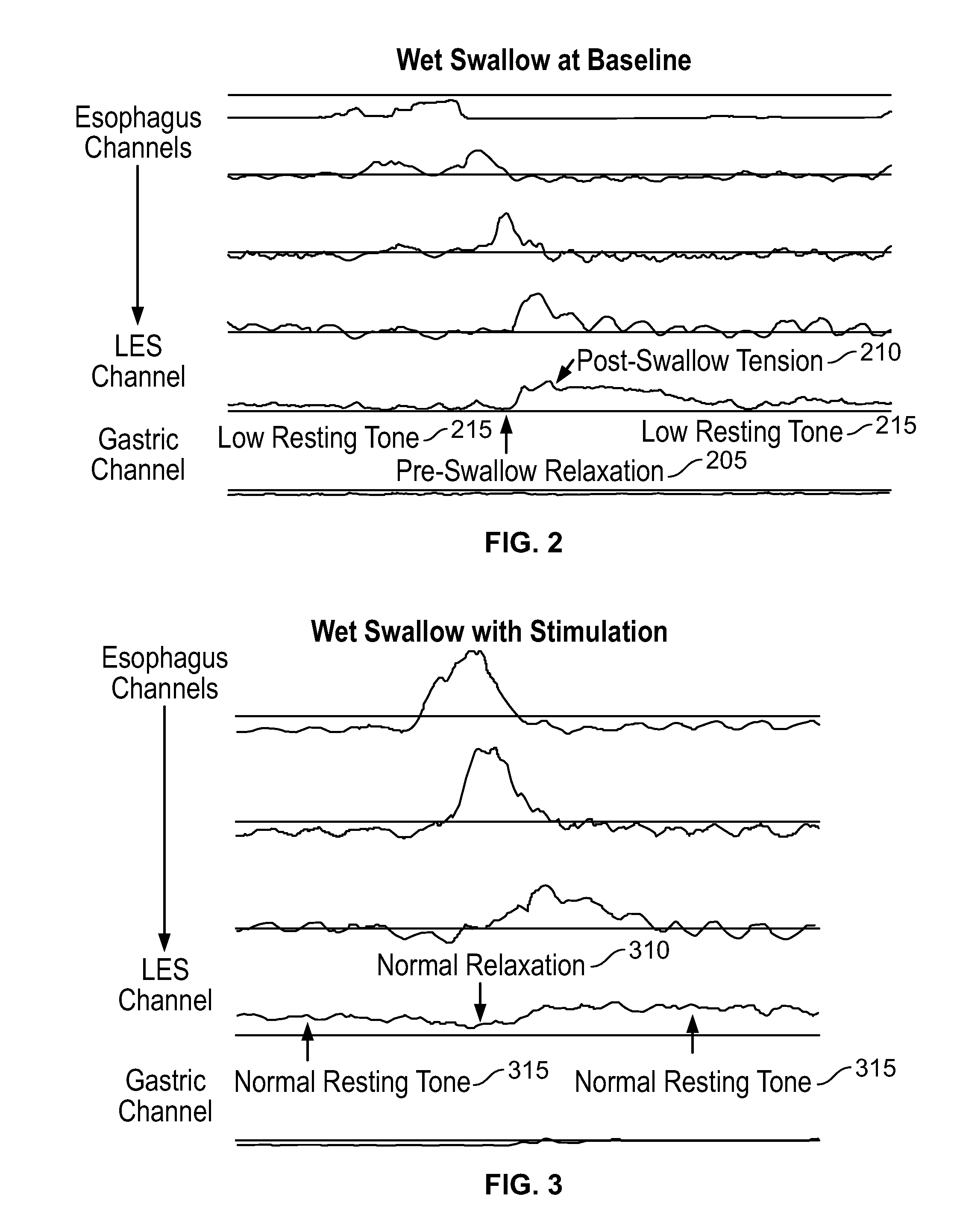
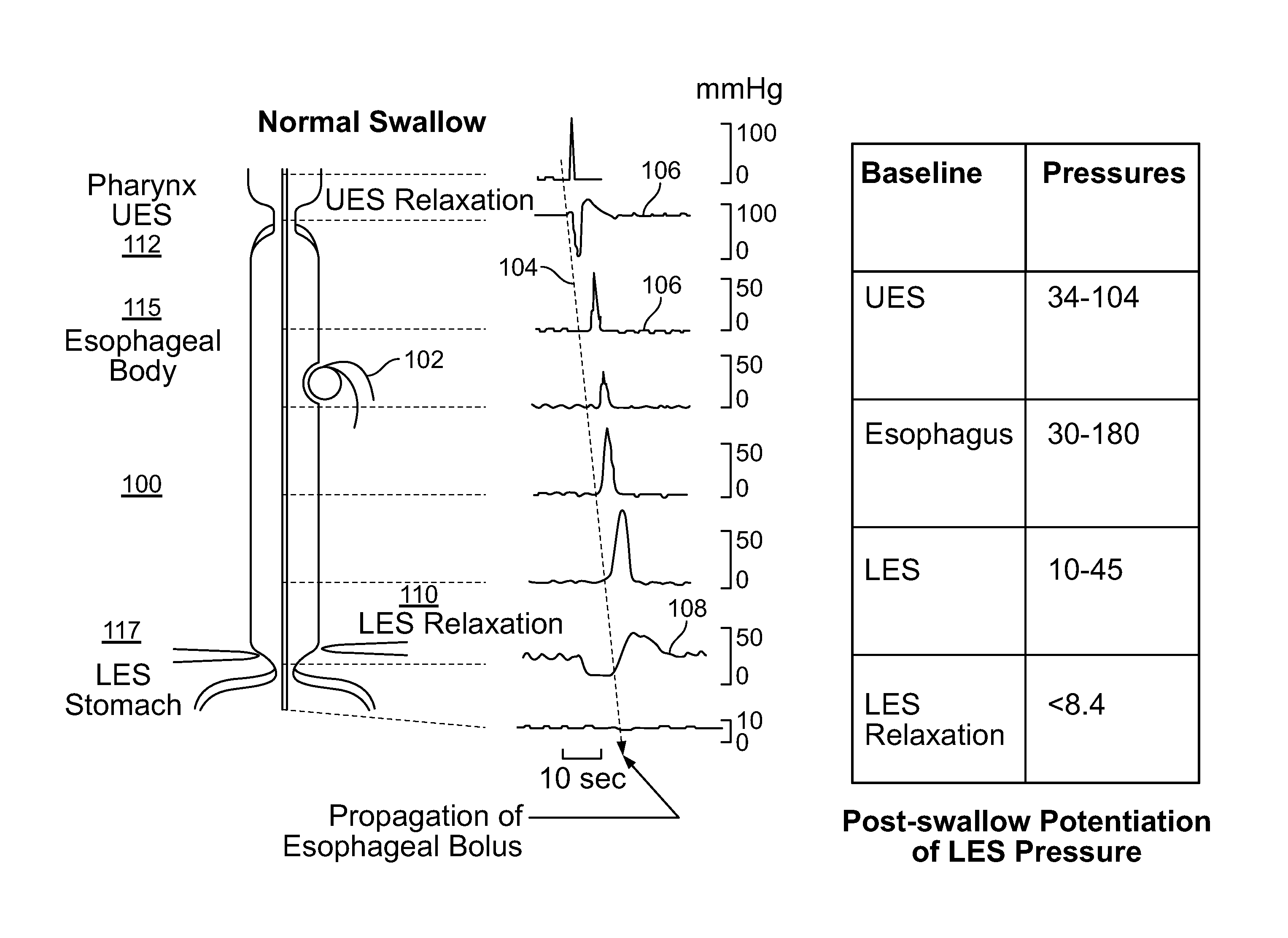
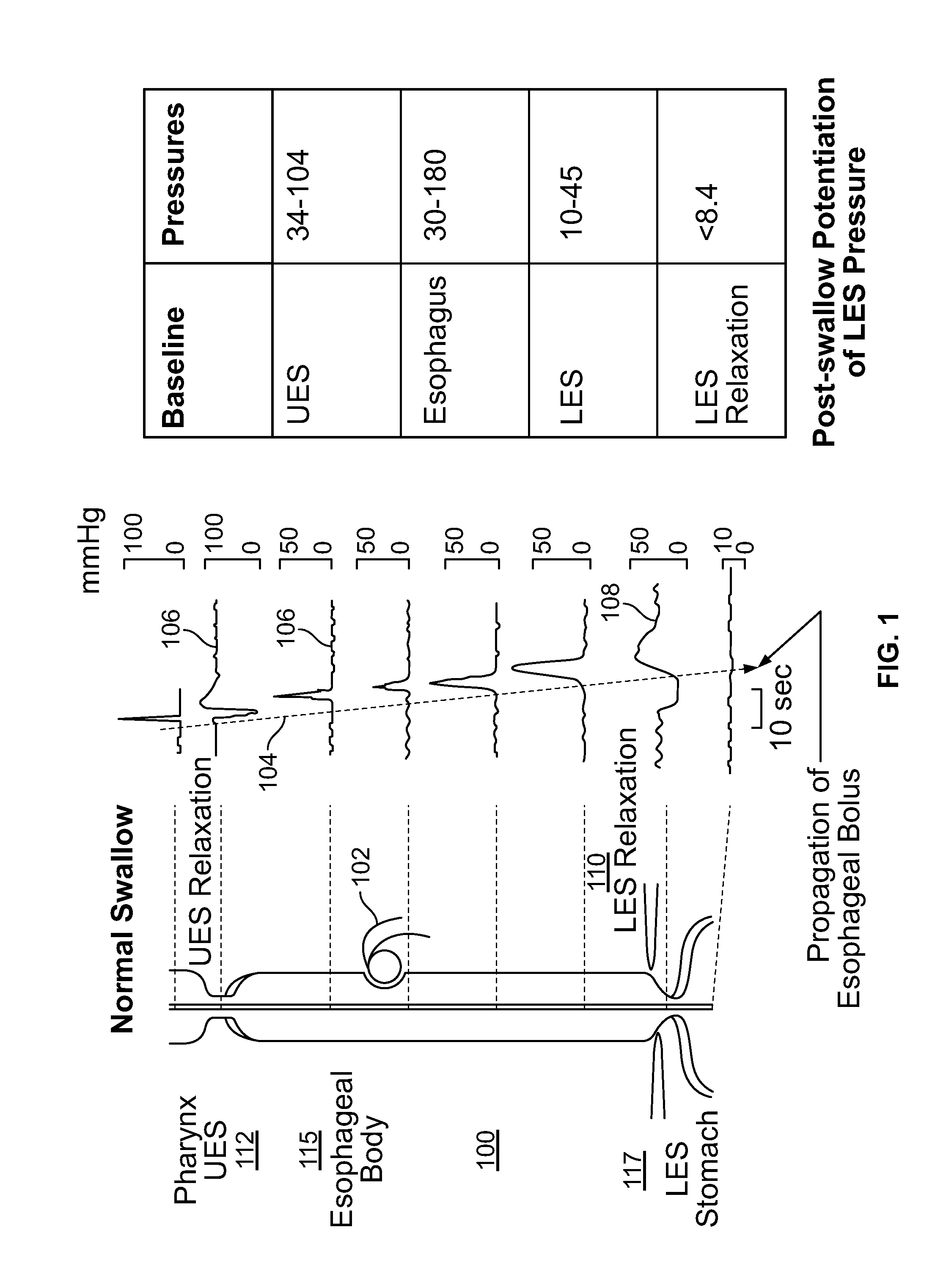
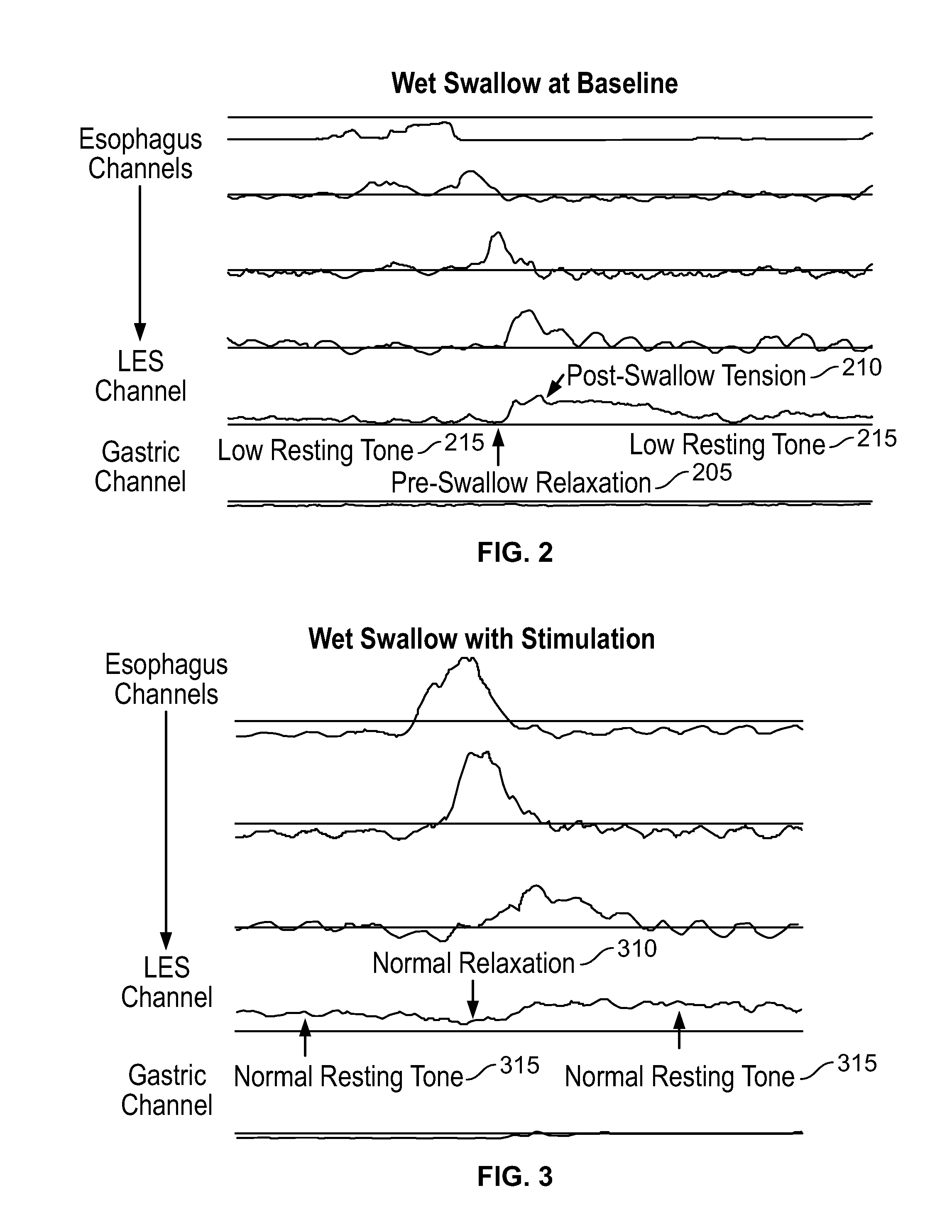
The present specification discloses devices and methodologies for the treatment of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations (tLESRs). Individuals with tLESRs may be treated by implanting a stimulation device within the patient's lower esophageal sphincter and applying electrical stimulation to the patient's lower esophageal sphincter, in accordance with certain predefined protocols. The presently disclosed devices have a simplified design because they do not require sensing systems capable of sensing when a person is engaged in a wet swallow and have improved energy storage requirements.
Owner:PARAS HLDG LLC
Device and Implantation System for Electrical Stimulation of Biological Systems
InactiveUS20140222106A1Increase pressureKeep the pressureCatheterImplantable neurostimulatorsElectricityPhysical therapy
The present specification discloses devices and methodologies for the treatment of GERD. Individuals with GERD may be treated by implanting a stimulation device within the patient's lower esophageal sphincter and applying electrical stimulation to the patient's lower esophageal sphincter, in accordance with certain predefined protocols. The presently disclosed devices have a simplified design because they do not require sensing systems capable of sensing when a person is engaged in a wet swallow and have improved energy storage requirements.
Owner:ENDOSTIM INC
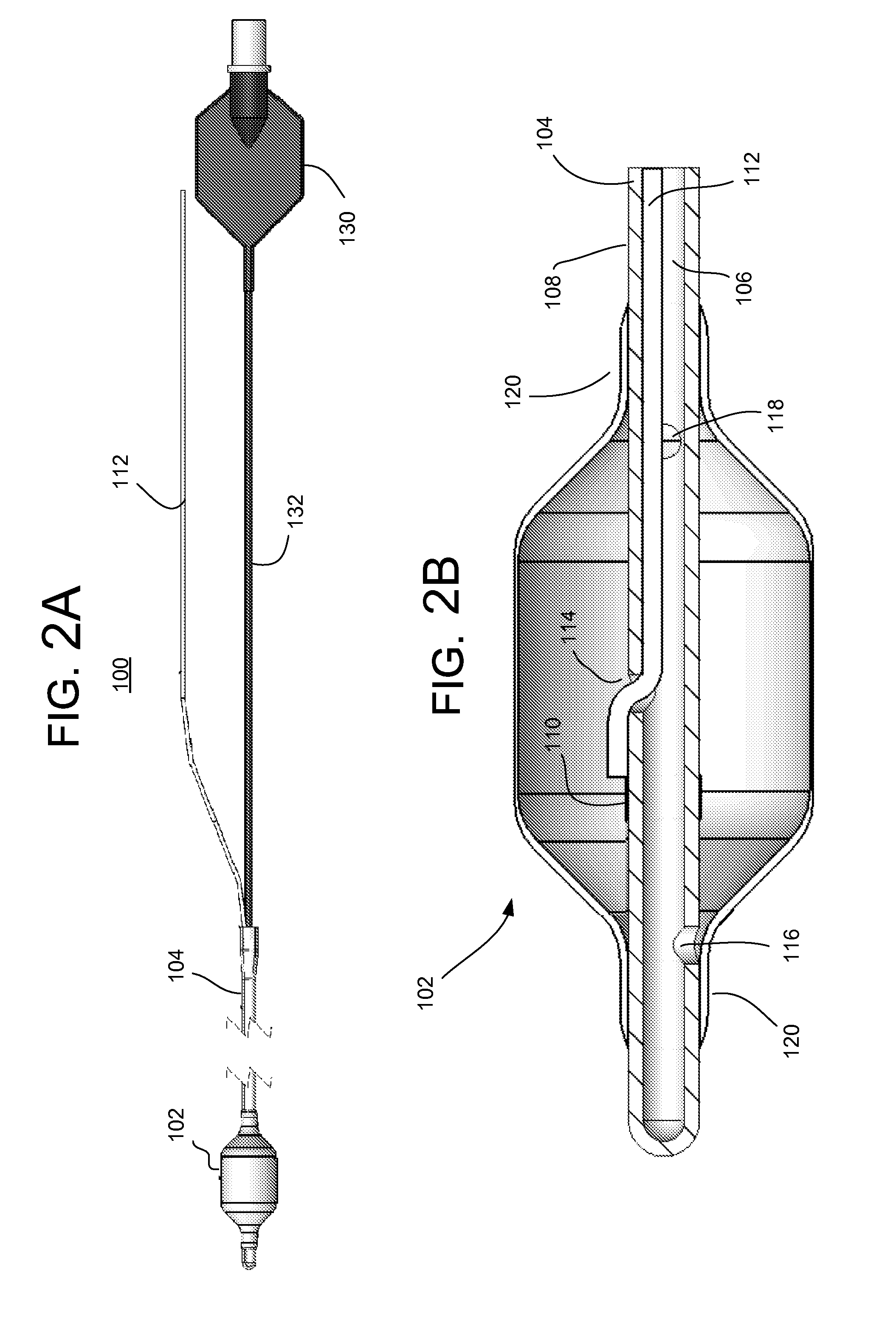
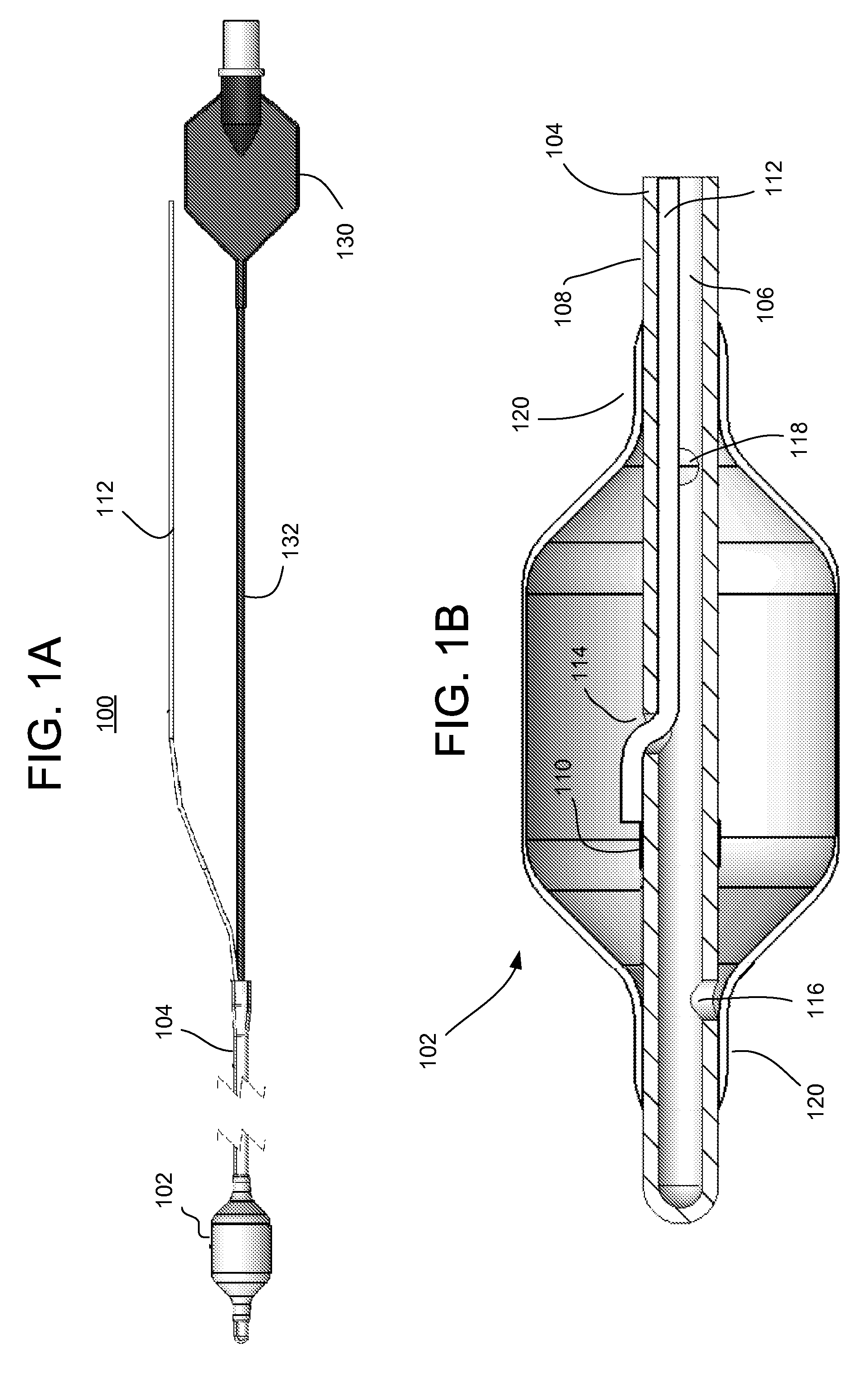
Methods and apparatus for electrical treatment using balloon and electrode
InactiveUS8401650B2Uniform applicationIncrease the areaSpinal electrodesBalloon catheterSurgeryBody tissue
The present invention provides systems, apparatus and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to body tissue. A device is provided having an enclosure within an outer wall formed from an electrically-permeable material to allow for electrical energy to pass from the interior of the enclosure through the outer wall. The device further includes an electrode positioned within the interior of the enclosure and a fluid passage coupled to the enclosure for delivery of an electrically conductive fluid into the interior of the enclosure such that the electrically conductive fluid couples the electrode with the electrically-permeable section of the outer wall. The conductive fluid allows for the passage of electrical energy from the electrode through the fluid and the outer wall of the enclosure for treatment of tissue on or in a patient. In this manner, the electrode does not directly contact the tissue of the patient, which reduces the potential for collateral tissue damage or necrosis and / or excessive electric fields in the tissue.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com