Patents
Literature
31569results about How to "Increase the area" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
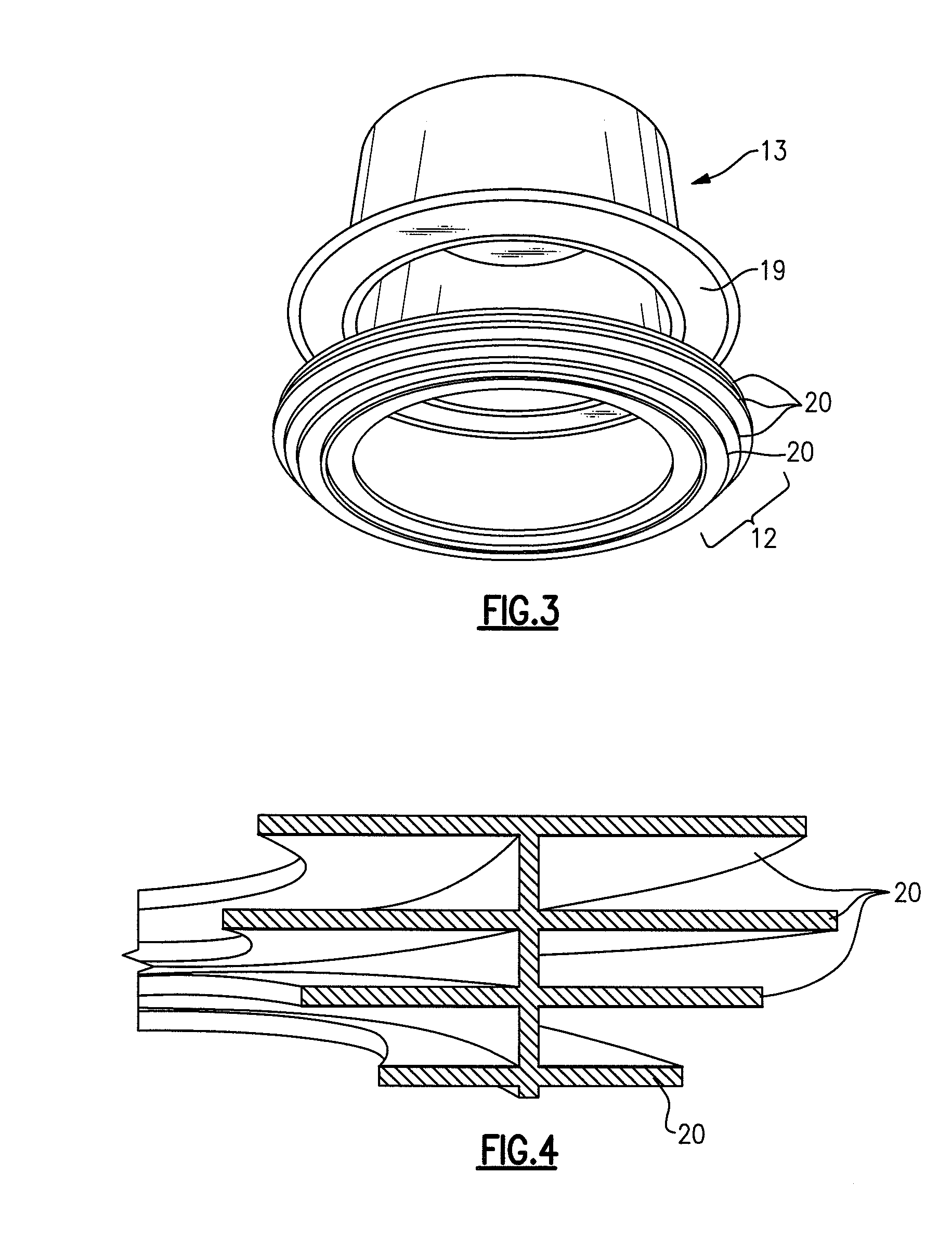
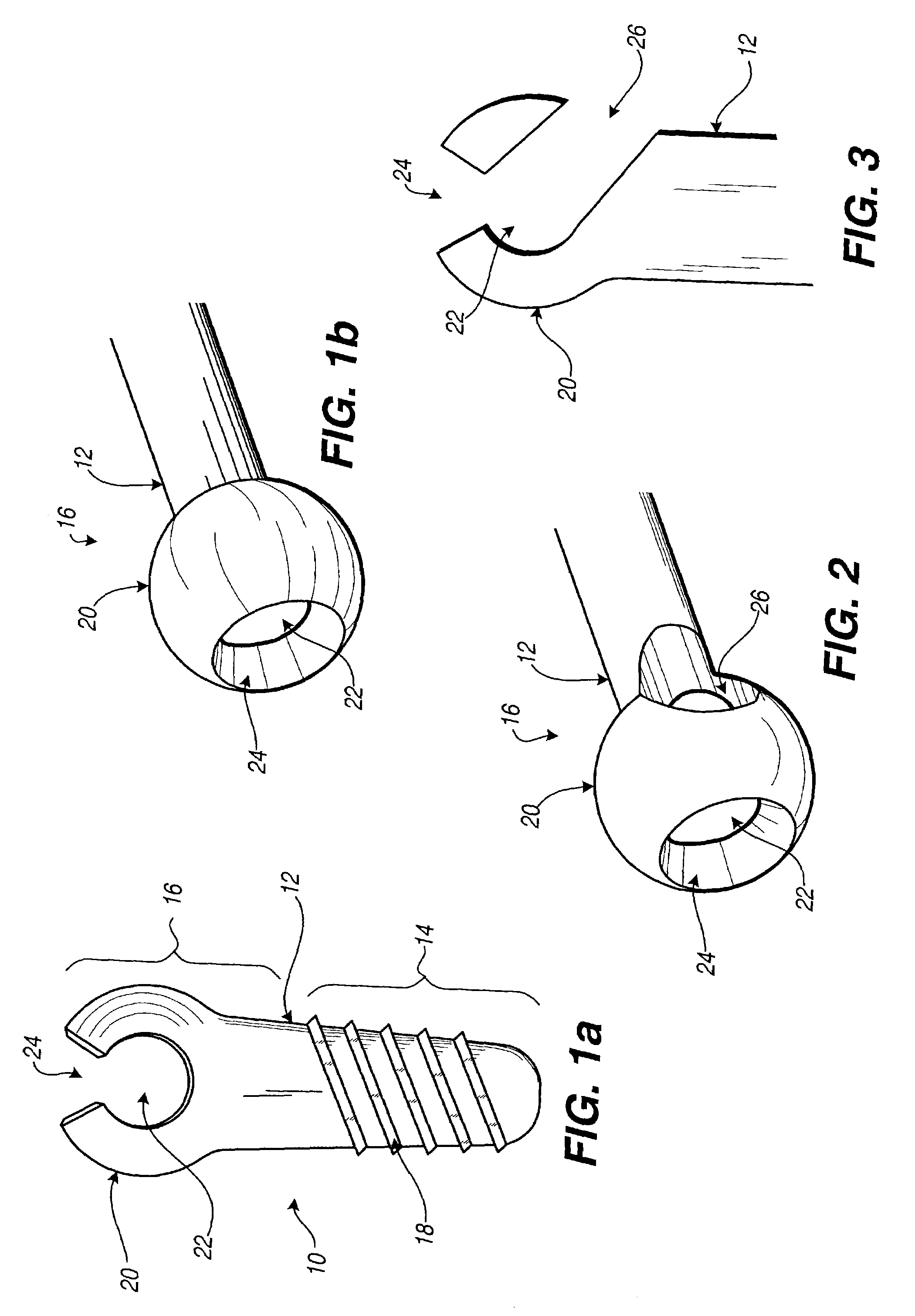
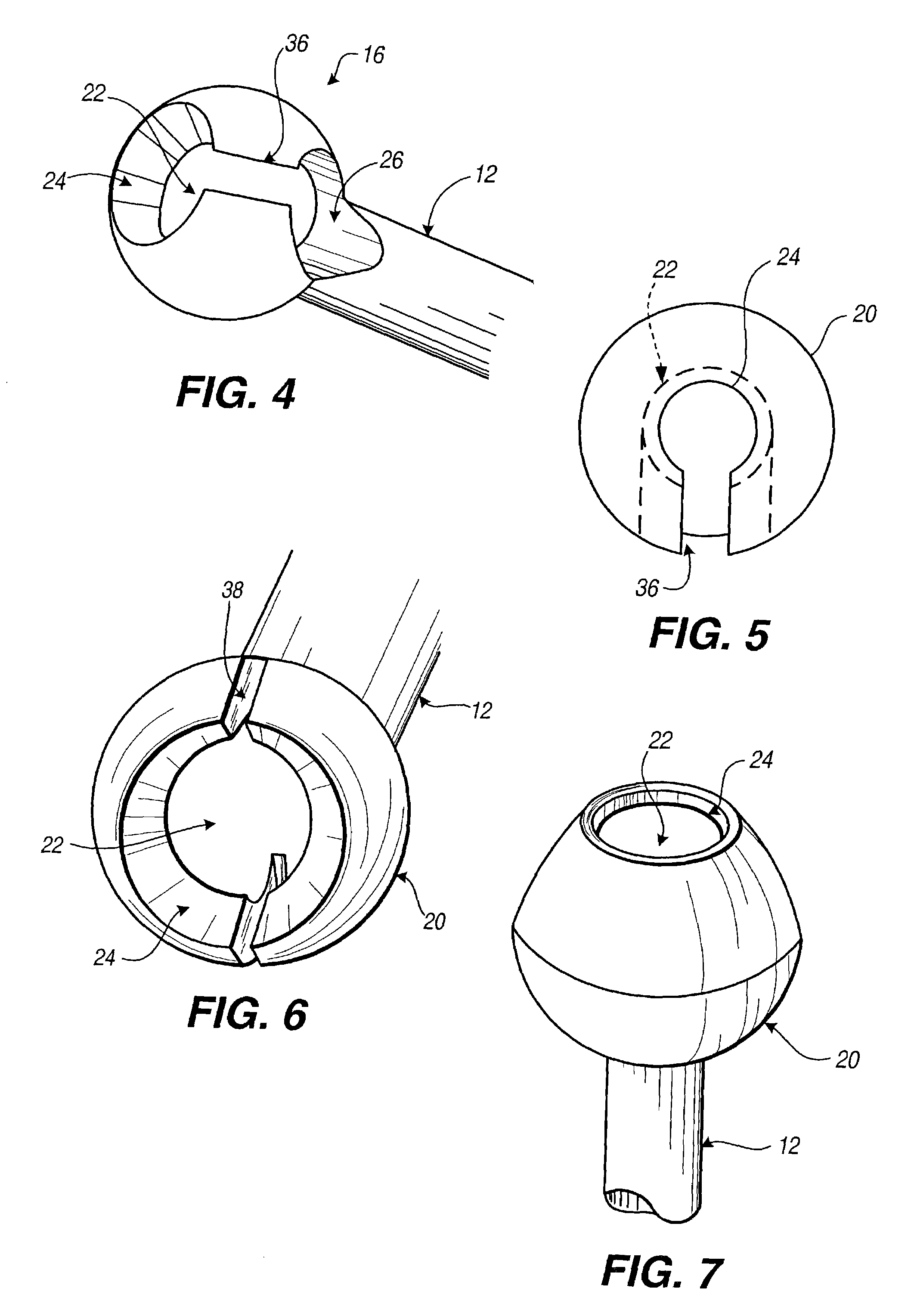
Surgical stapler anvil with nested staple forming pockets
InactiveUS6953138B1Increased lateral widthLittle lateral spaceSuture equipmentsStapling toolsMirror imageBiomedical engineering
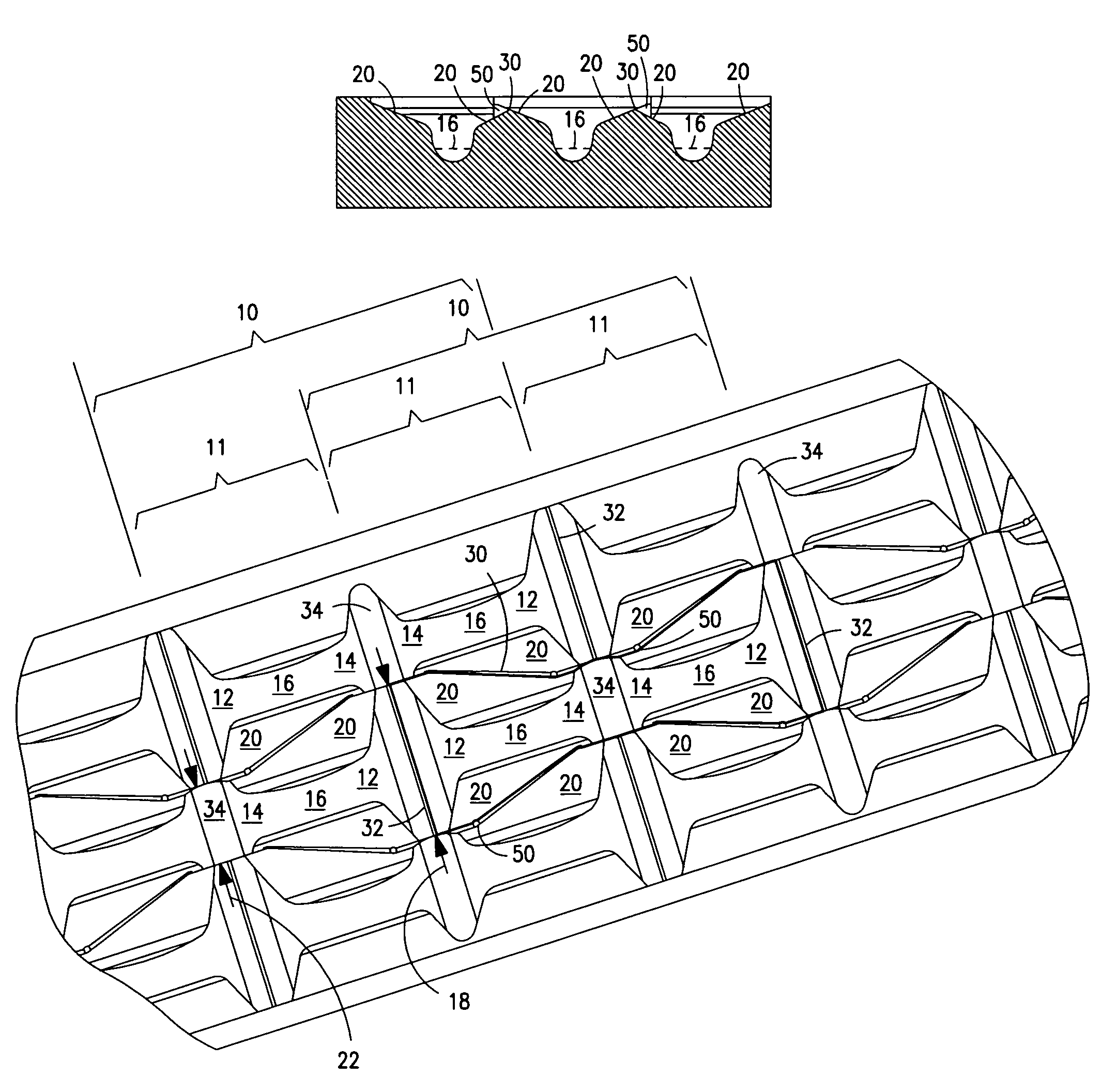
A surgical stapler anvil provides an expanded leg-receiving target area for a staple forming pocket in a compact staggered array by narrowing the lateral width of the leg-clinching portion of a laterally adjacent pocket. Advantageously, the lateral spacing between adjacent rows of staple forming pockets can remain small, while the leg-receiving target area for laterally adjacent rows of pockets is significantly expanded. The staple forming pockets include two mirror image leg-forming cups. The cups are longitudinally aligned with their respective ascending leg clinching portions adjoining in the center of the pocket. Laterally spaced guide surfaces extend upwardly and outwardly from the clinching surface at the bottom of the cup to define an expanded leg-receiving target area at the distal ends of the pocket. Substantially planar laterally outward portions of the guide surface intersect with the guide surface of a laterally adjacent pocket to form a non-linear ridge.
Owner:DWORAK FR W
Articulate and swapable endoscope for a surgical robot
InactiveUS20060178556A1Simple processIncrease the areaEndoscopesSurgical manipulatorsSurgical robotEngineering
The present invention is directed to an articulate minimally invasive surgical endoscope with a flexible wrist having at least one degree of freedom. When used with a surgical robot having a plurality of robot arms, the endoscope can be used with any of the plurality of arms thereby allowing the use a universal arm design. The endoscope in accordance to the present invention is made more intuitive a to a user by attaching a reference frame used for controlling the at least one degree of freedom motion to the flexible wrist for wrist motion associated with the at least one degree of freedom. The endoscope in accordance to the present invention attenuates undesirable motion at its back / proximal end by acquiring the image of the object in association with the at least one degree of freedom based on a reference frame rotating around a point of rotation located proximal to the flexible wrist.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Tissue fastening devices and processes that promote tissue adhesion
ActiveUS8241308B2Improve adhesionOptimize allocationStaplesNailsEndoscopic ProcedureEndoscopic surgery
The invention in certain aspects relates to a surgical fastener for fastening tissue segments having tissue surfaces. The fastener includes a first fastener member having a base and a piercing element connected to the base for piercing the tissue segments to be fastened, a second fastener member having an opening for receiving and retaining the piercing element of the first fastener member such that the tissue segments to be fastened are retained between the first and second fastening members, and means for promoting adhesion between the tissue surfaces. The invention also relates to related methods and devices for promoting adhesion of tissue segments and preventing fastener migration, especially in an endoscopic procedure for the treatment of GERD.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for optimization of wireless multipoint electromagnetic communication networks
InactiveUS20040095907A1Improve signal qualityReduce interference energyPower managementSpatial transmit diversityGlobal optimizationDiversity scheme
Exploiting the substantive reciprocity of internode channel responses through dynamic, adaptive modification of receive and transmit weights, enables locally enabled global optimization of a multipoint, wireless electromagnetic communications network of communication nodes. Each diversity-channel-capable node uses computationally efficient exploitation of pilot tone data and diversity-adaptive signal processing of the weightings and the signal to further convey optimization and channel information which promote local and thereby network-global efficiency. The preferred embodiment performs complex digital signal manipulation that includes a linear combining and linear distribution of the transmit and receive weights, the generation of piloting signals containing origination and destination node information, as well as interference-avoiding pseudorandom delay timing, and both symbol and multitione encoding, to gain the benefit of substantive orthogonality at the physical level without requiring actual substantive orthogonality at the physical level.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
Conductive line communication apparatus and conductive line radar system and method
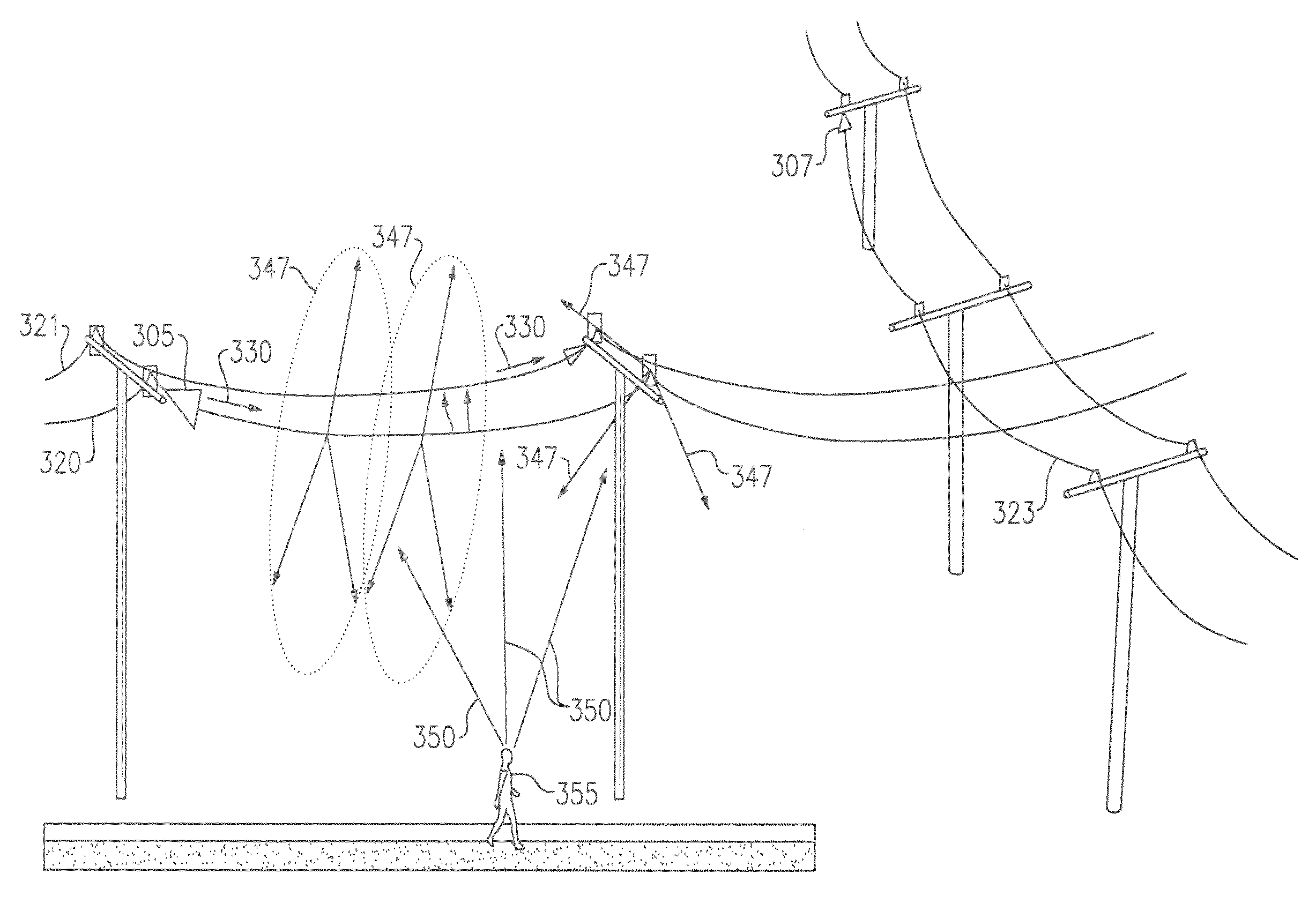
InactiveUS8159385B2Eliminate the effects ofIncrease the areaDuplex signal operationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTransceiverRadar systems
A conductive line radar comprising at least one signal surface wave launcher, which comprises a signal surface wave transceiver, which is physically attached to a power line. The signal surface wave transceiver transmits a wave signal along the power line with another signal radiating from the wave signal in a plurality of directions along the power line. The at least one signal surface wave transceiver receives reflected signals from a target within a distance of the power line. The at least one signal surface wave launcher includes at least one RF communications transceiver and can be inductively powered from the power line.
Owner:SENSIS CORPORATION
Fully implantable microstimulator for spinal cord stimulation as a therapy for chronic pain
An implantable stimulator(s), small enough to be located near or within an area of the spine responsible for sensations in a region experiencing chronic pain uses a power source / storage device, such as a rechargeable battery. Periodic recharging of such a power source / storage device is accomplished, for example, by inductive coupling with an external appliance. The small stimulator provides a means of stimulating a nerve(s) or other tissue when desired, without the need for external appliances during the stimulation session. When necessary, external appliances are used for the transmission of data to and / or from the stimulator(s) and for the transmission of power, it necessary. In a preferred embodiment, the system is capable of open- and closed-loop operation. In closed-loop operation, at least one implant includes at least one sensor, and the sensed condition is used to adjust stimulation parameters.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Seamless, maskless lithography system using spatial light modulator
InactiveUS6312134B1Eliminate needImprove processing throughputMirrorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusRadiation DosagesSpatial light modulator
The invention is a seamless projection lithography system that eliminates the need for masks through the use of a programmable Spatial Light Modulator (SLM) with high parallel processing power. Illuminating the SLM with a radiation source (1), which while preferably a pulsed laser may be a shuttered lamp or multiple lasers with alternating synchronization, provides a patterning image of many pixels via a projection system (4) onto a substrate (5). The preferred SLM is a Deformable Micromirror Device (3) for reflective pixel selection using a synchronized pulse laser. An alternative SLM is a Liquid Crystal Light Valve (LCLV) (45) for pass-through pixel selection. Electronic programming enables pixel selection control for error correction of faulty pixel elements. Pixel selection control also provides for negative and positive imaging and for complementary overlapping polygon development for seamless uniform dosage. The invention provides seamless scanning by complementary overlapping scans to equalize radiation dosage, to expose a pattern on a large area substrate (5). The invention is suitable for rapid prototyping, flexible manufacturing, and even mask making.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Lamp having outer shell to radiate heat of light source
InactiveUS20060227558A1Efficient transferImprove thermal conductivityCoupling device connectionsPoint-like light sourceEffect lightThermal radiation
Owner:TOSHIBA LIGHTING & TECH CORP
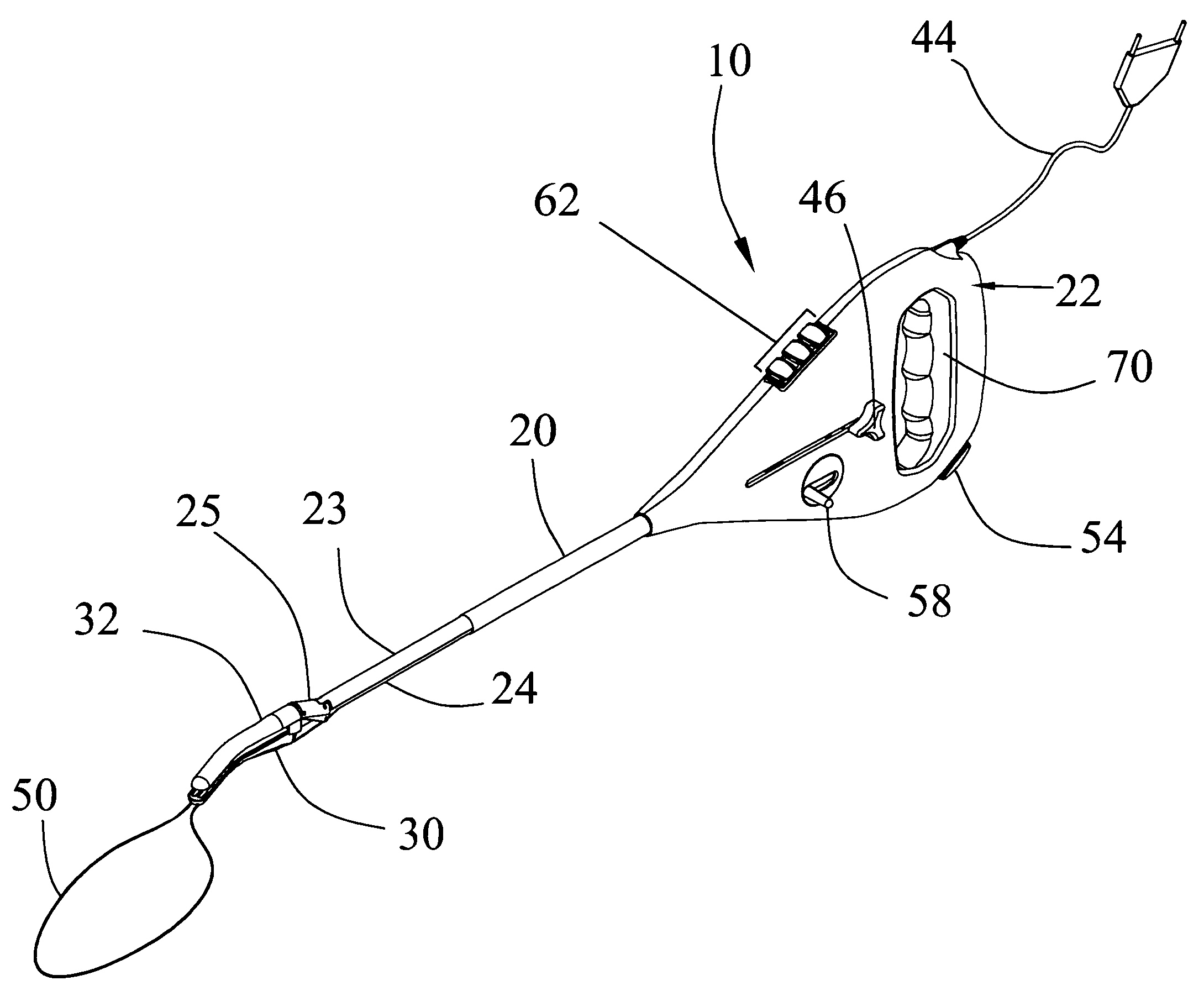
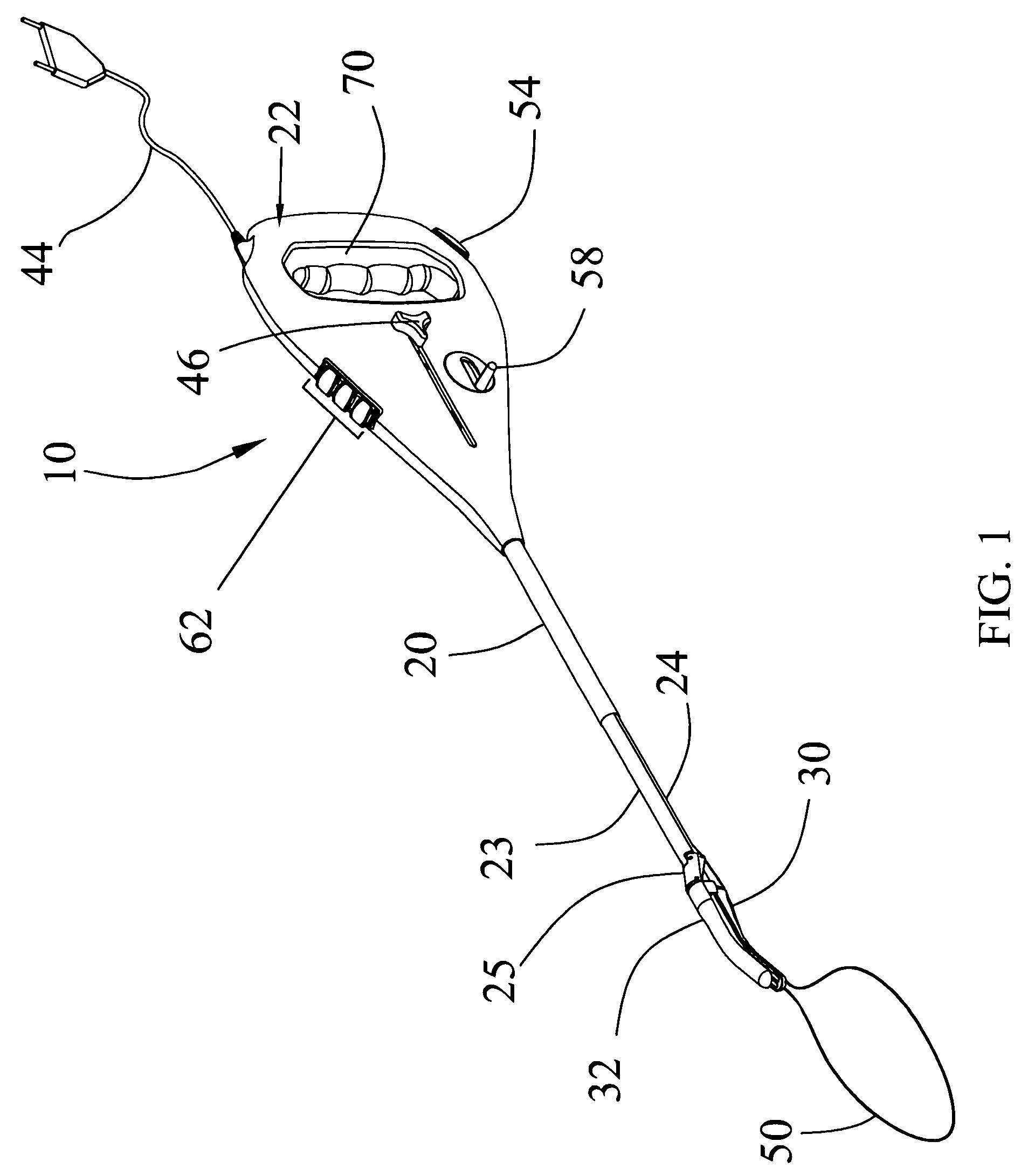
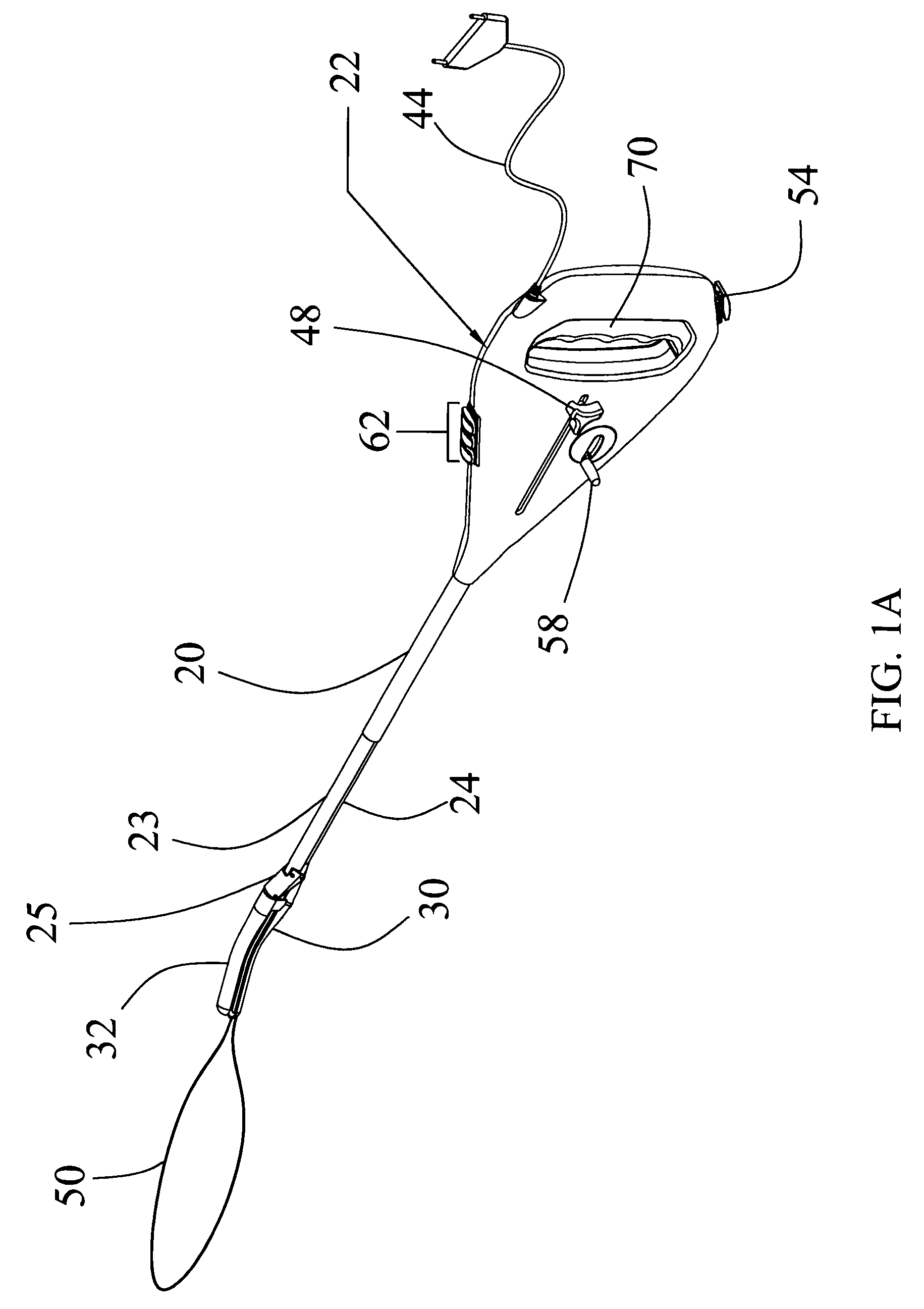
Golf club with interchangeable head-shaft connections
ActiveUS7083529B2Improve performanceQuick and reliable and disassemblySpace saving gamesGolf clubsEngineeringGolf Ball
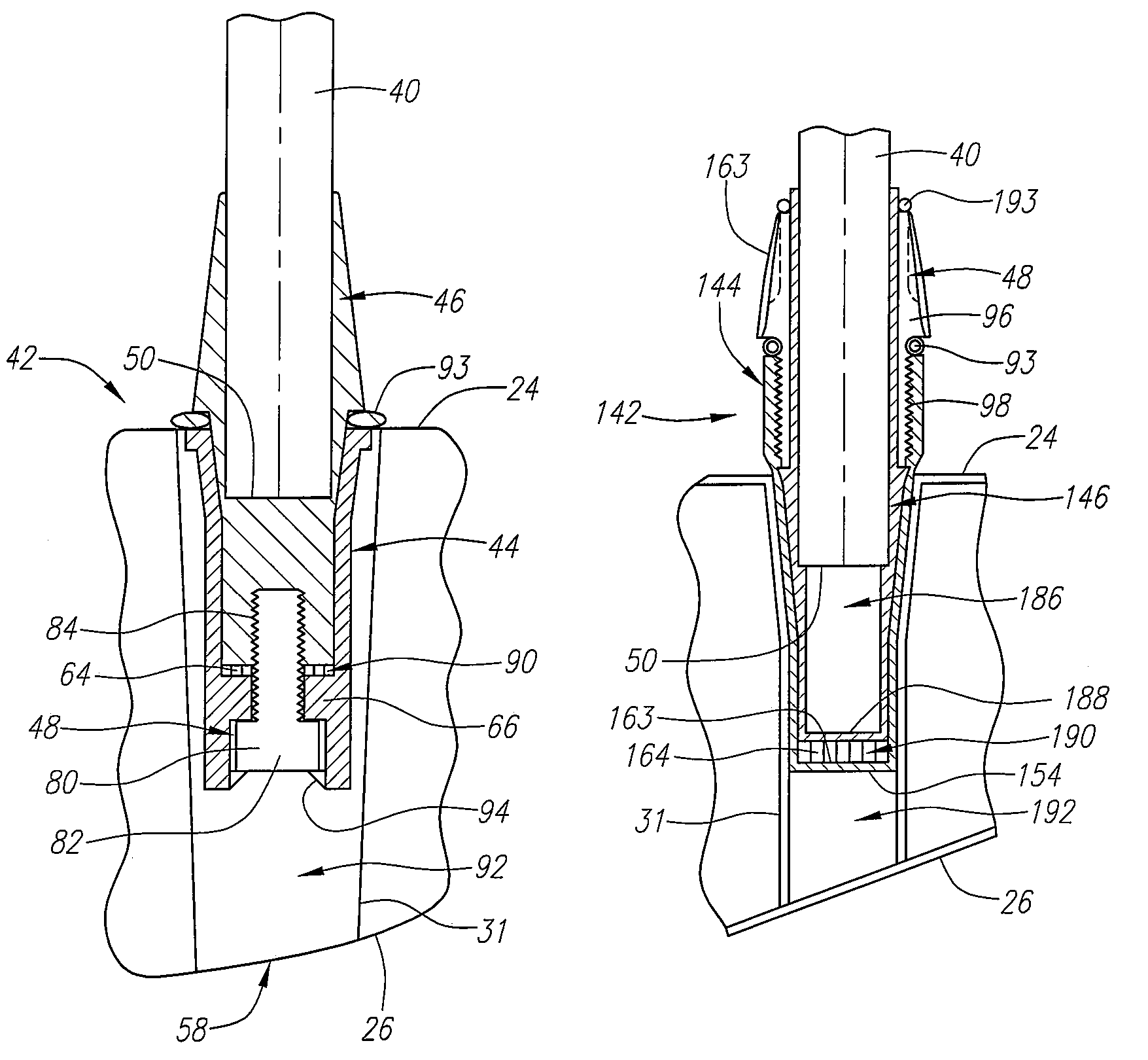
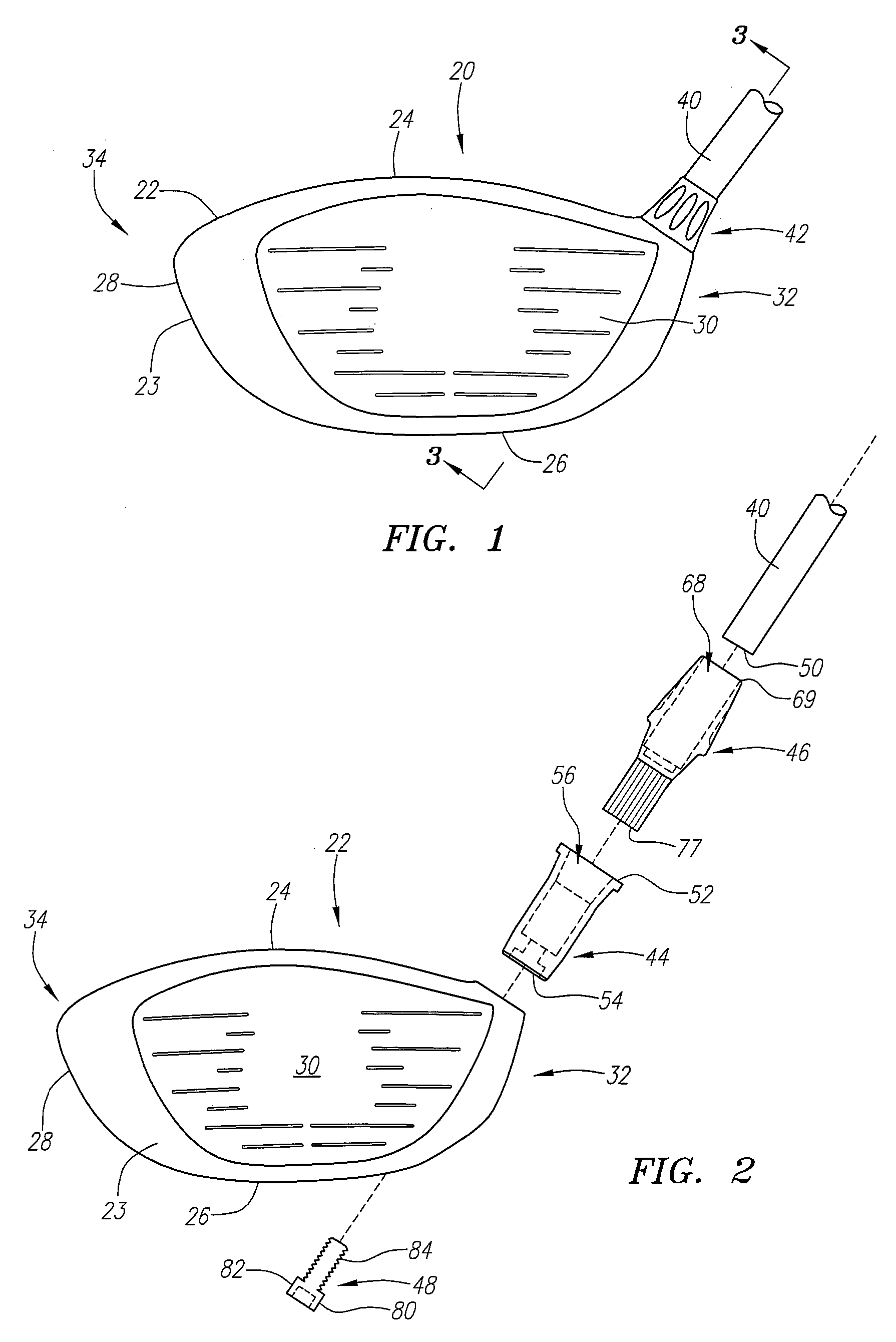
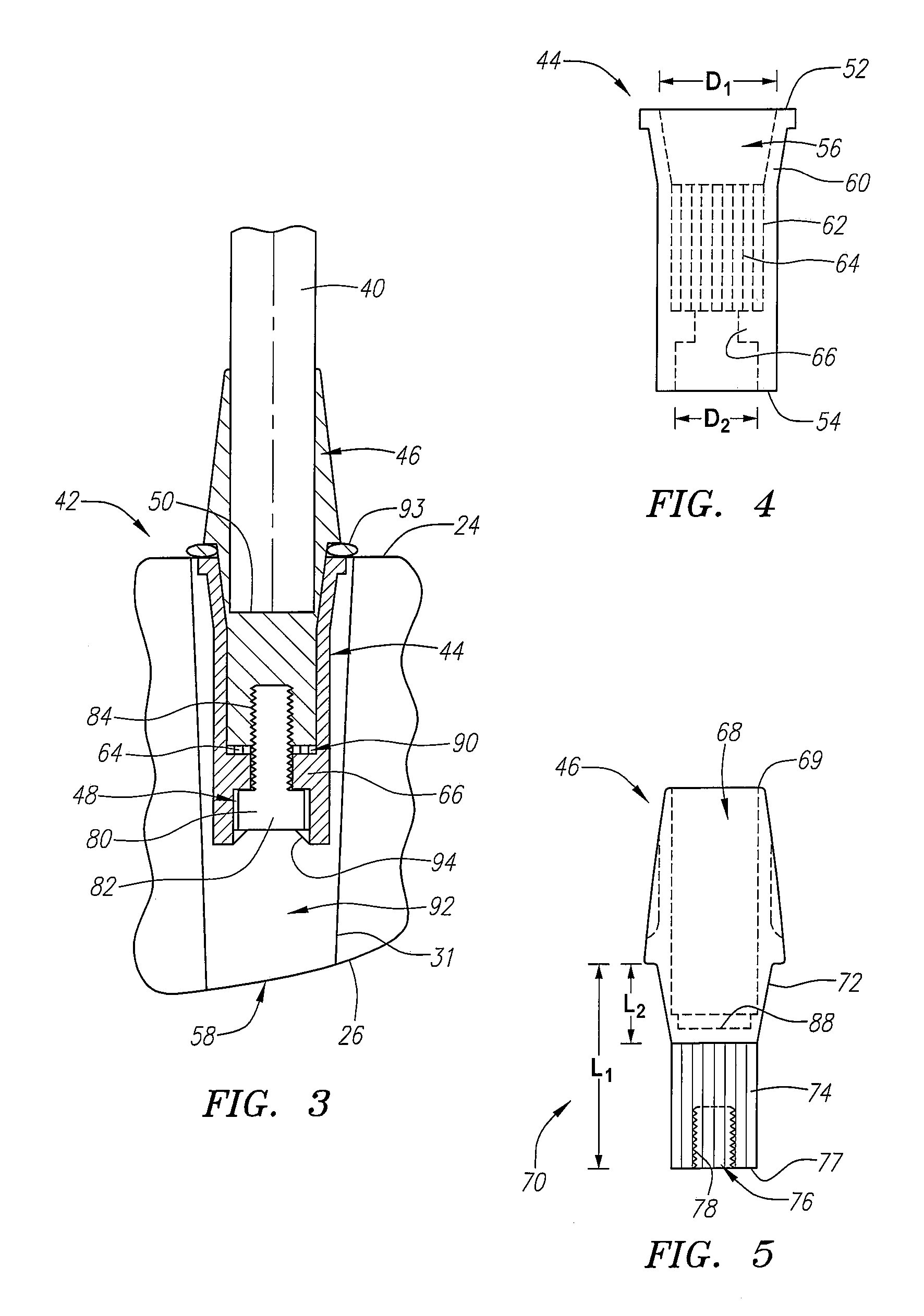
A golf club (20) having a club head (22) with an interchangeable shaft (40) is disclosed herein. The golf club (20) includes a tube (44, 144) mounted in the club head (22), and a sleeve (46, 146) mounted on a tip end (50) of the shaft (40). The tube (44, 144) includes a tapered portion (60, 160) and a rotation prevention portion (62, 162). The sleeve (46, 146) has a frustoconical portion (72, 172) and a keyed portion (74, 174) that are respectively received in the tapered portion (60, 160) and the rotation prevention portion (62, 162) of the tube (44, 144). The golf club (20) further includes a mechanical fastener (48, 148) for removably securing the shaft (40) to the club head (22).
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
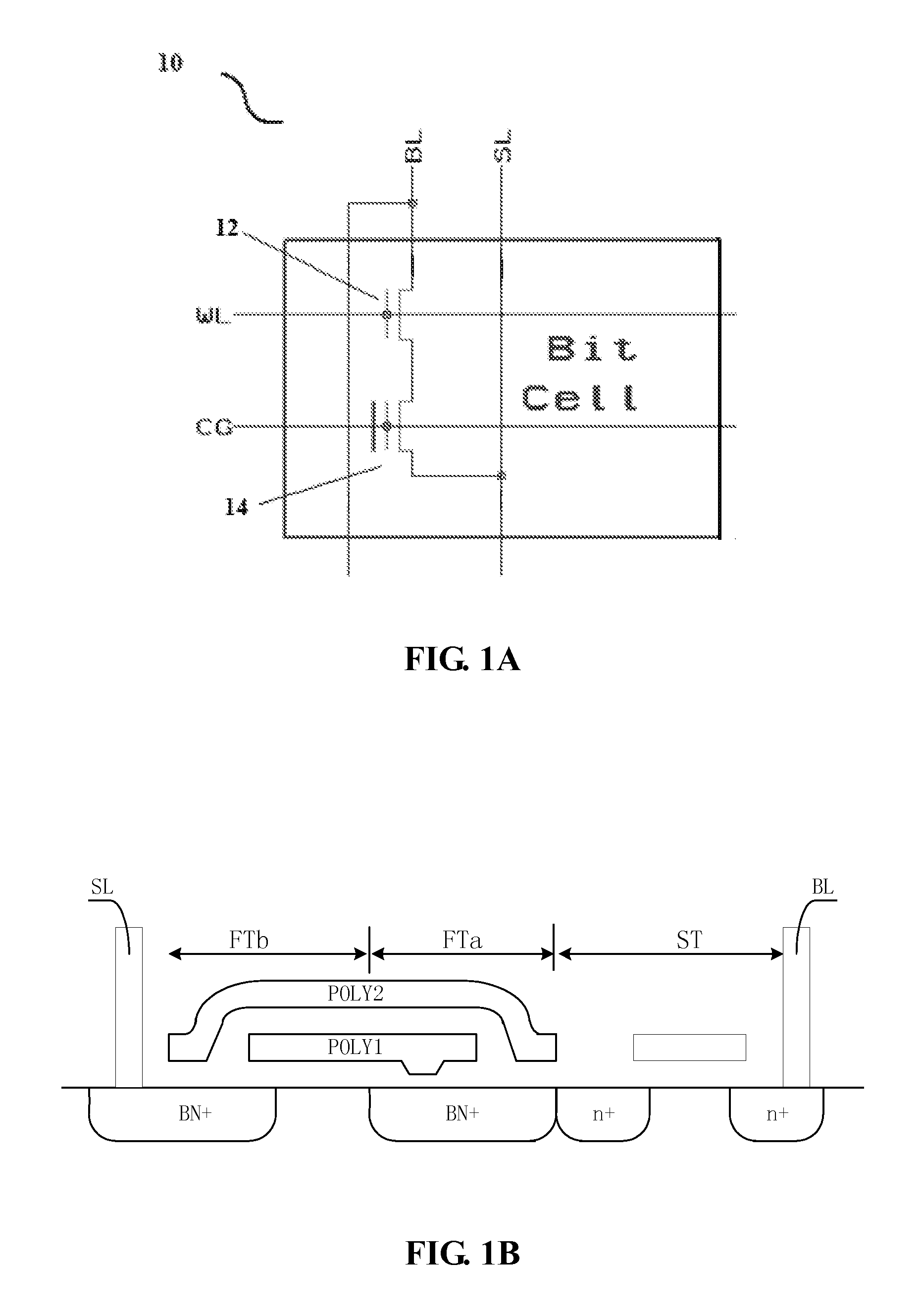
Dram-like nvm memory array and sense amplifier design for high temperature and high endurance operation
InactiveUS20110267883A1Improve threshold voltage sensing marginLarge silicon areaRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
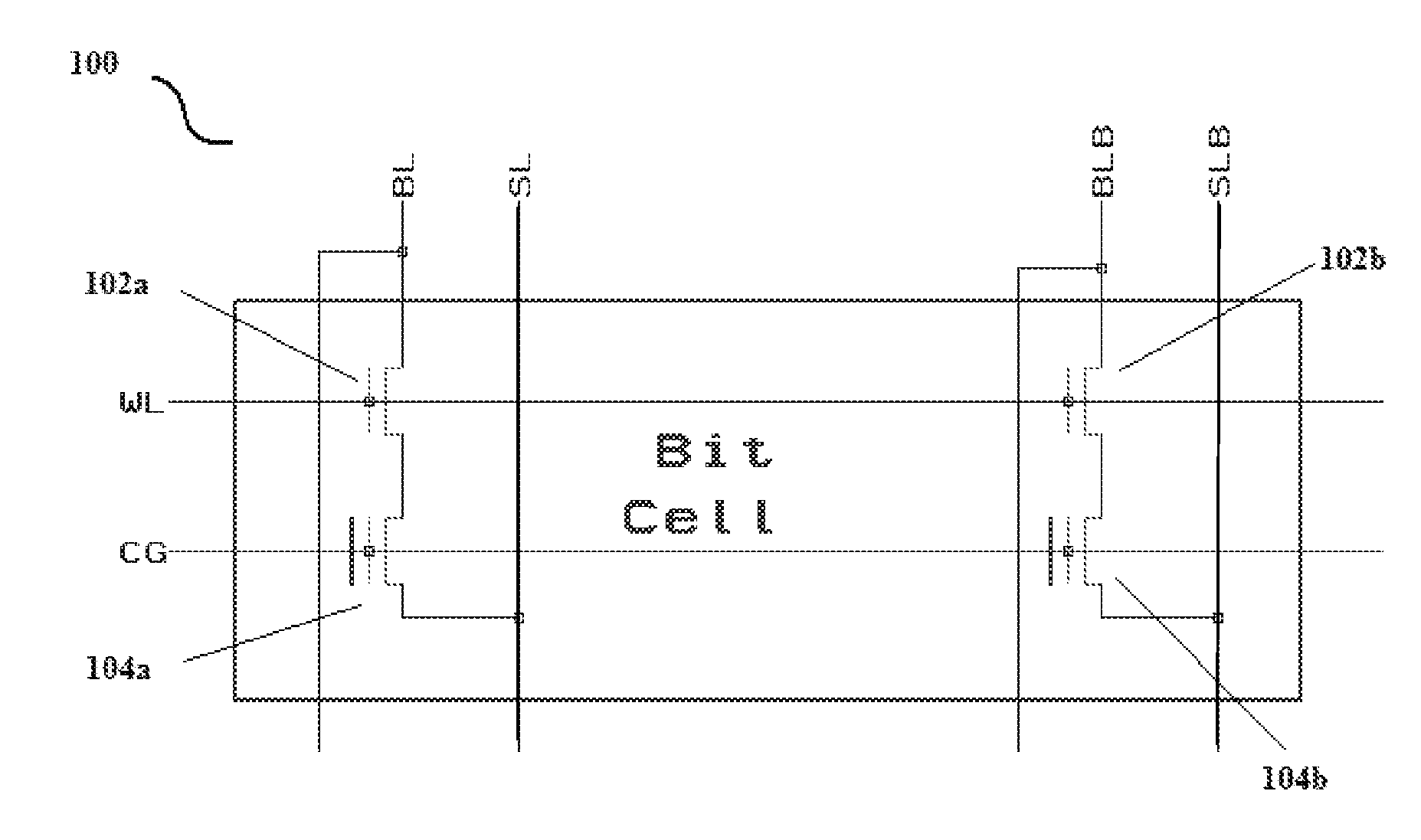
A DRAM-like non-volatile memory array includes a cell array of non-volatile cell units with a DRAM-like cross-coupled latch-type sense amplifier. Each non-volatile cell unit has two non-volatile cell devices with respective bit lines and source lines running in parallel and laid out perpendicular to the word line associated with the non-volatile cell unit. The two non-volatile cell devices are programmed with erased and programmed threshold voltages as a pair for storing a single bit of binary data. The two bit lines of each non-volatile cell unit are coupled through a Y-decoder and a latch device to the two respective inputs of the latch-type sense amplifier which provides a large sensing margin for the cell array to operate properly even with a narrowed threshold voltage gap. Each non-volatile cell device may be a 2 T FLOTOX-based EEPROM cell, a 2 T flash cell, 11 T flash cell or a 1.5 T split-gate flash cell.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Lighting assemblies and components for lighting assemblies
ActiveUS20080112170A1Add additional massIncrease surface areaPlanar light sourcesMechanical apparatusInterior spaceEffect light
A lighting assembly, comprising a light engine assembly and a room-side element. The room-side element is in contact with the light engine assembly. The light engine assembly comprises at least one trim element and a light engine. The trim element defines a trim element internal space. The light engine comprises at least one solid state light emitter, and is positioned within the trim element internal space. Also, a lighting assembly, comprising a light engine assembly and means for dissipating heat from the light engine assembly.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
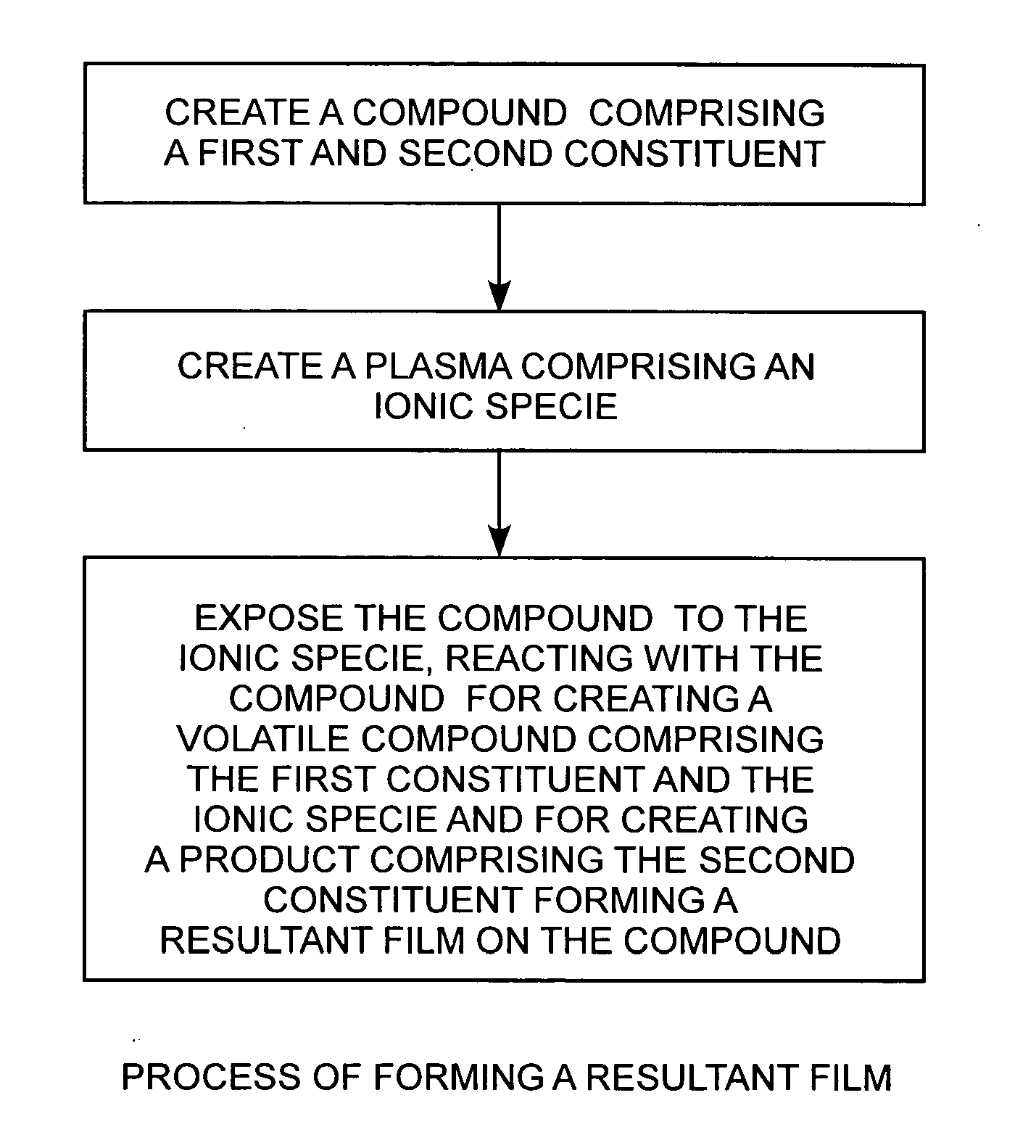
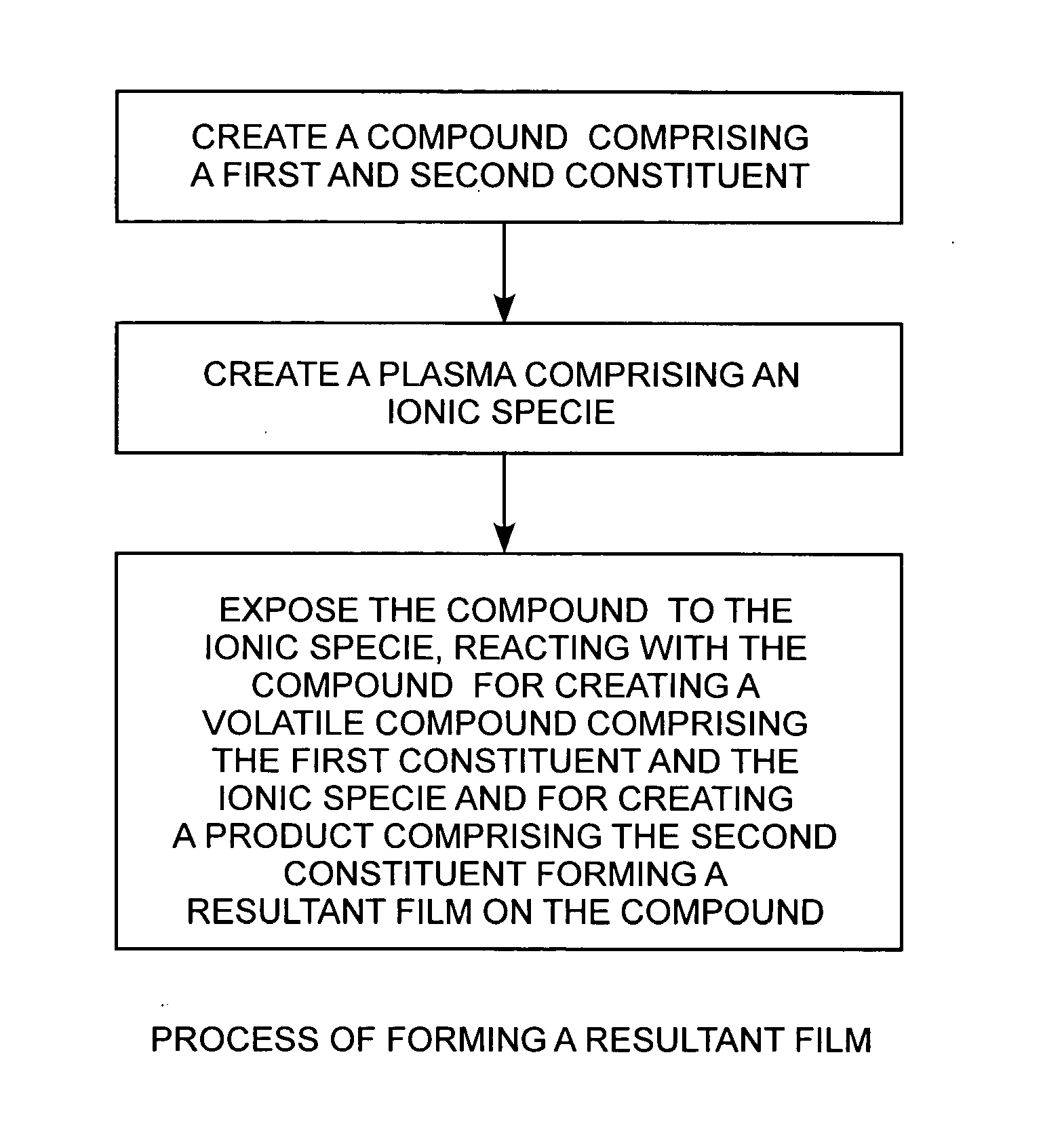
Method for producing carbon surface films by plasma exposure of a carbide compound
InactiveUS20060068125A1Reduce frictionEasy to controlChemical vapor deposition coatingFlexible microstructural devicesCarbon filmCarbon coating
Reactive halogen-ion plasmas, having for example, generating chloride ions, generated from low-pressure halogen gases using a radio-frequency plasma are employed for producing low-friction carbon coatings, such as a pure carbon film, at or near room temperature on a bulk or thin film of a compound, such as titanium carbide.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
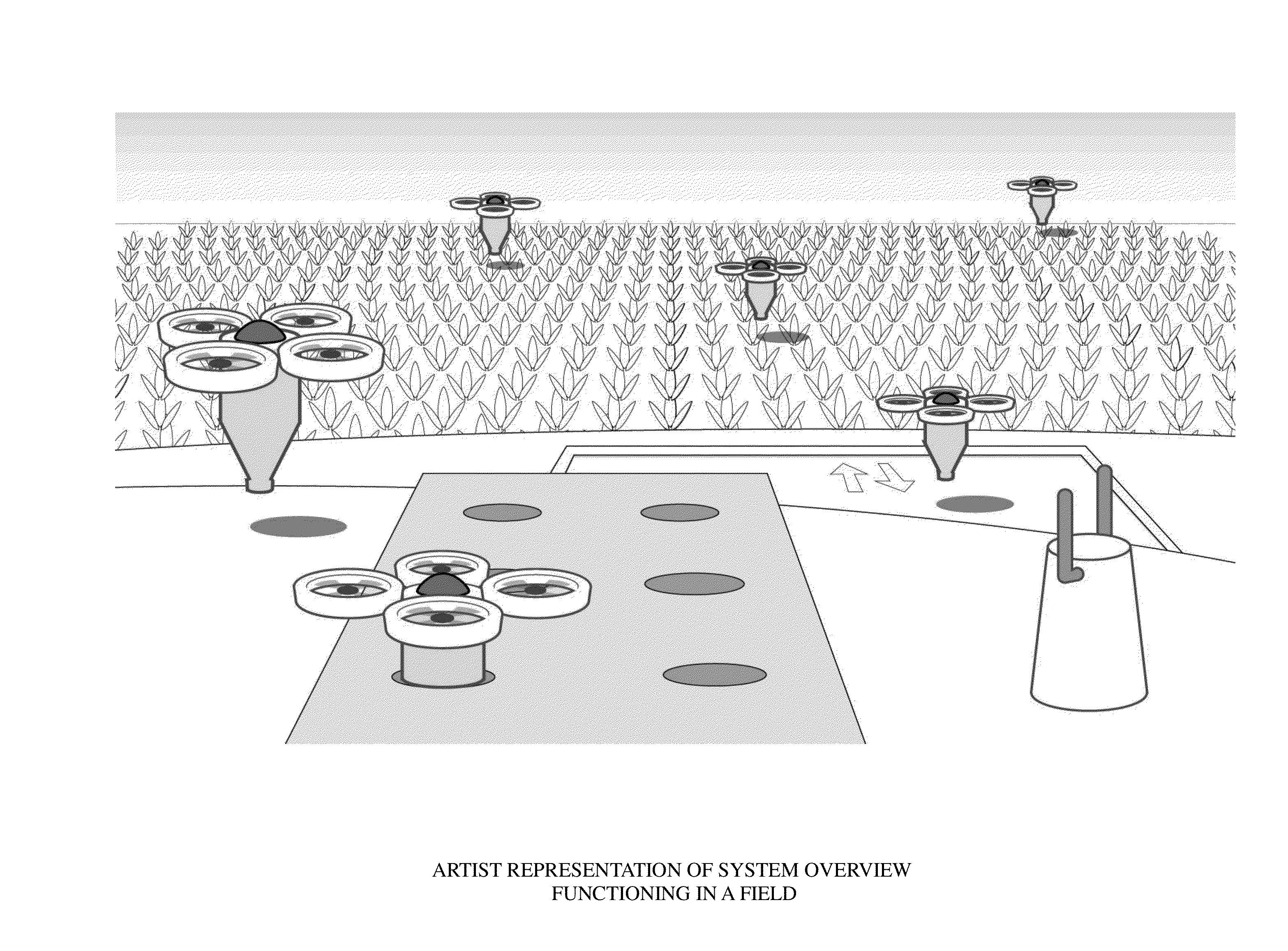
Aerial farm robot system for crop dusting, planting, fertilizing and other field jobs
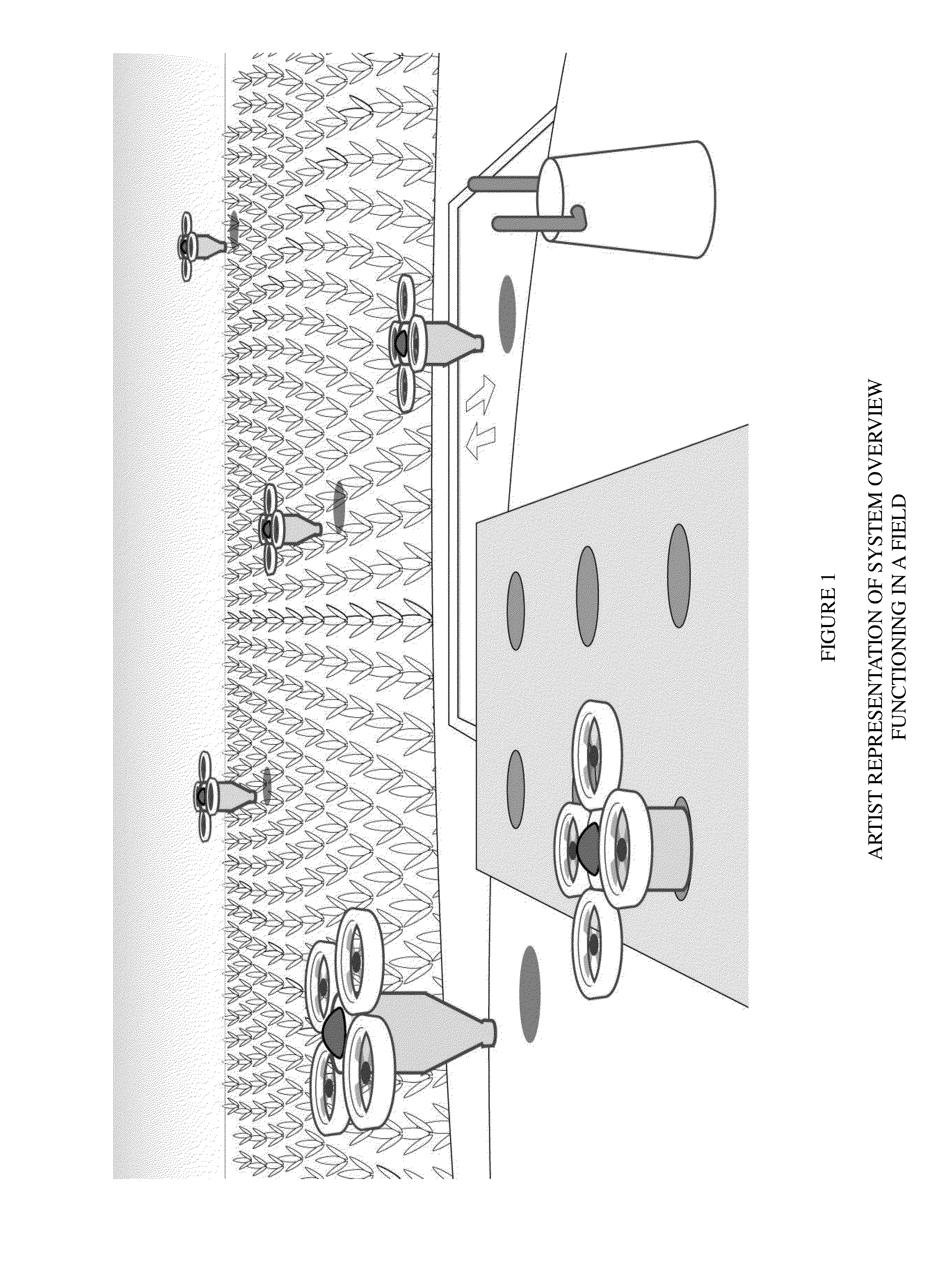
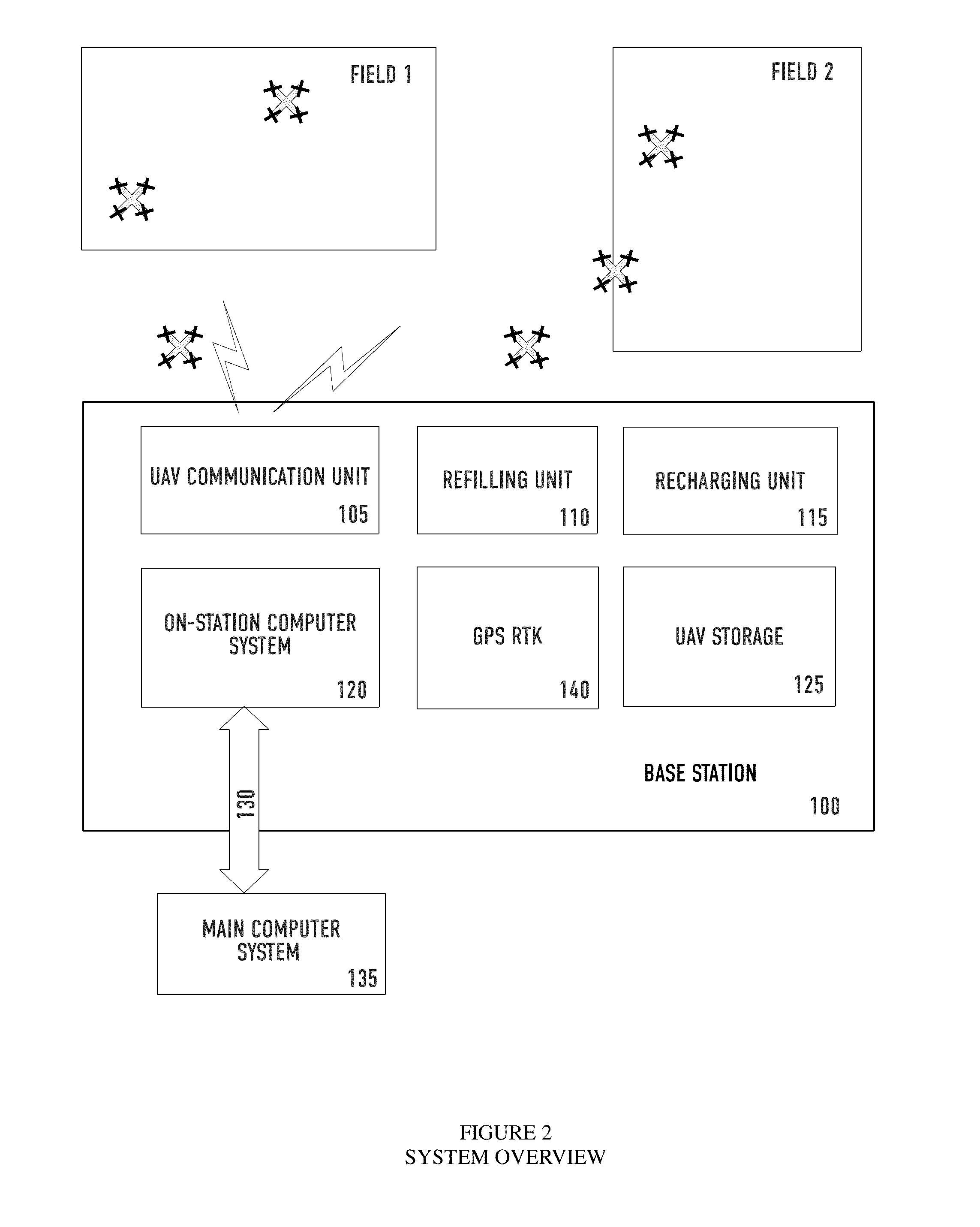
InactiveUS20140303814A1Increase the areaIncrease productionAircraft componentsDigital data processing detailsHectareRobotic systems
Modern farming is currently being done by powerful ground equipment or aircraft that weigh several tons and treat uniformly tens of hectares per hour. Automated farming can use small, agile, lightweight, energy-efficient automated robotic equipment that flies to do the same job, even able to farm on a plant-by-plant basis, allowing for new ways of farming. Automated farming uses unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that are equipped with detachable implements and reservoirs and that we call “aerial farm robots.” Automated farming uses high-precision GPS and other precision positioning and vision technology to autonomously and precisely perform crop dusting, planting, fertilizing and other field related farming or husbandry tasks. The subsystems for the control, refill, recharge and communication subsystems of the aerial farm robots are part of the overall automated farming system, and can autonomously handle most of the husbandry tasks on a farm.
Owner:BEE ROBOTICS
Systems and methods for electrosurgical treatment of obstructive sleep disorders
InactiveUS7131969B1Increase surface areaImprove sealingCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsThroatSleeping disorders
The present invention provides systems and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within the head and neck of a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the ear, nose and throat. The present invention applies high frequency (RF) electrical energy to one or more electrode terminals in the presence of electrically conductive fluid to remove and / or modify the structure of tissue structures. The present invention is particularly useful for treating sleep obstructive disorders, such as sleep apnea and snoring.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Controlled deployment of a medical device
A prosthesis delivery system having a balloon catheter with an inflatable balloon on its exterior. The balloon is inflatable by injection of fluid through a lumen in the catheter and the balloon is initially partially constrained against inflation by a constraint. A tubular prosthesis is disposed on the catheter over at least a portion of the balloon and a portion of the constraint. The tubular prosthesis has a contracted condition and an expanded condition. The tubular prosthesis is initially disposed on the catheter in the contracted condition. Further, a balloon catheter includes a constraint so that the balloon may be sequentially inflated for dilatation purposes such as in a valvuloplasty operation.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for executing a function within a composite icon and operating an object thereby
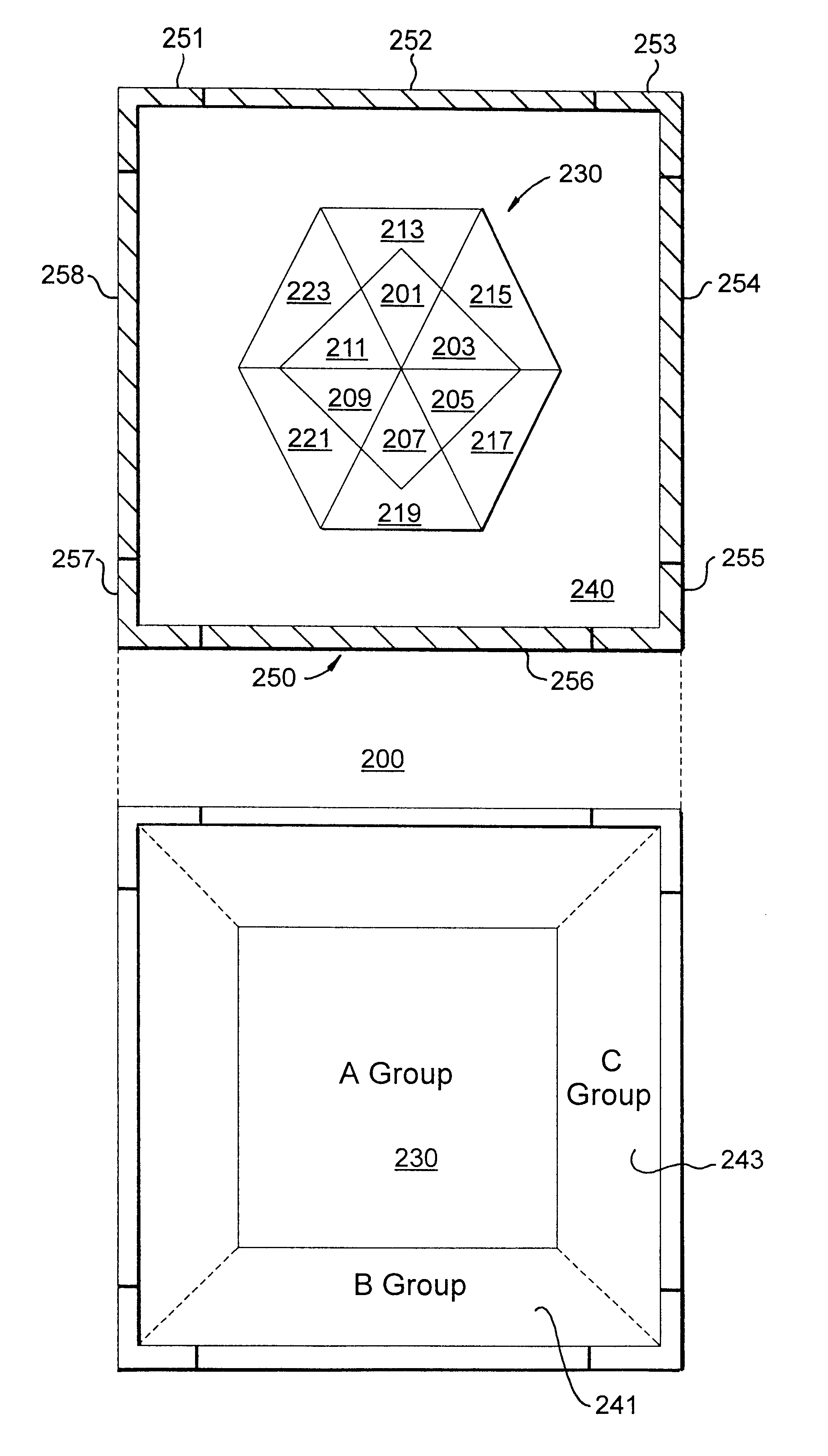
InactiveUS6469722B1Easy to operateIncrease the areaDigital output to display deviceComputer visionSoftware
The present invention is directed to explaining functions with a rich graphical expression even when the number of kinds of functions required for a software increases.More particularly, a plurality of function areas 201-223 are defined in a composite icon area of the present invention. An appearance image is associated to each function area and, when a mouse pointer comes across a function area, appearance images associated to that function area are displayed as appearance images of a composite icon. A function is also associated to each function area and, when a mouse is clicked on a function area, a function which is associated to that function area is executed. The set of the function area may be changed by changing the size of a composite icon, an operation to switch the group of functions, or selection of an object to be operated upon.
Owner:LINKEDIN
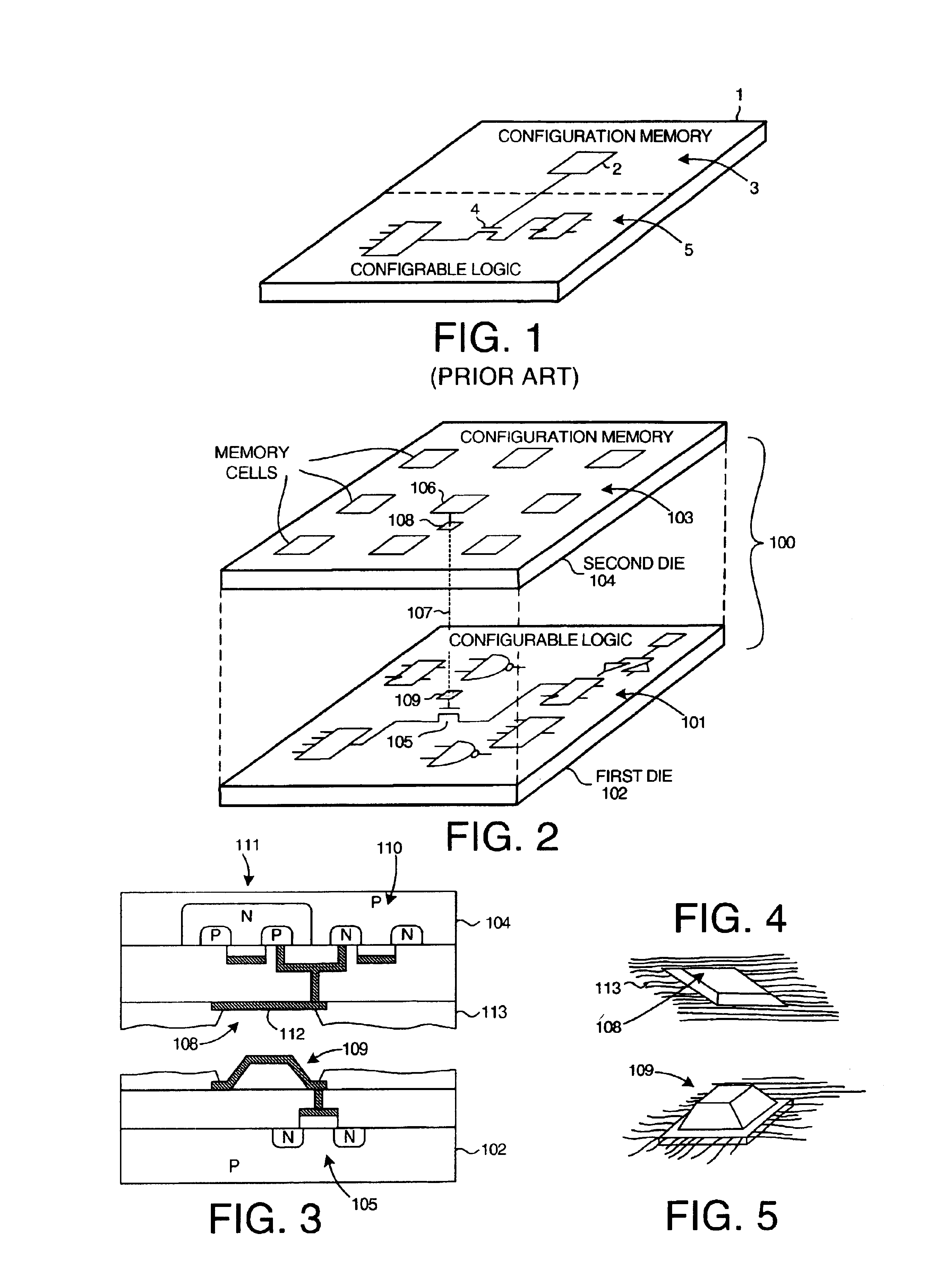
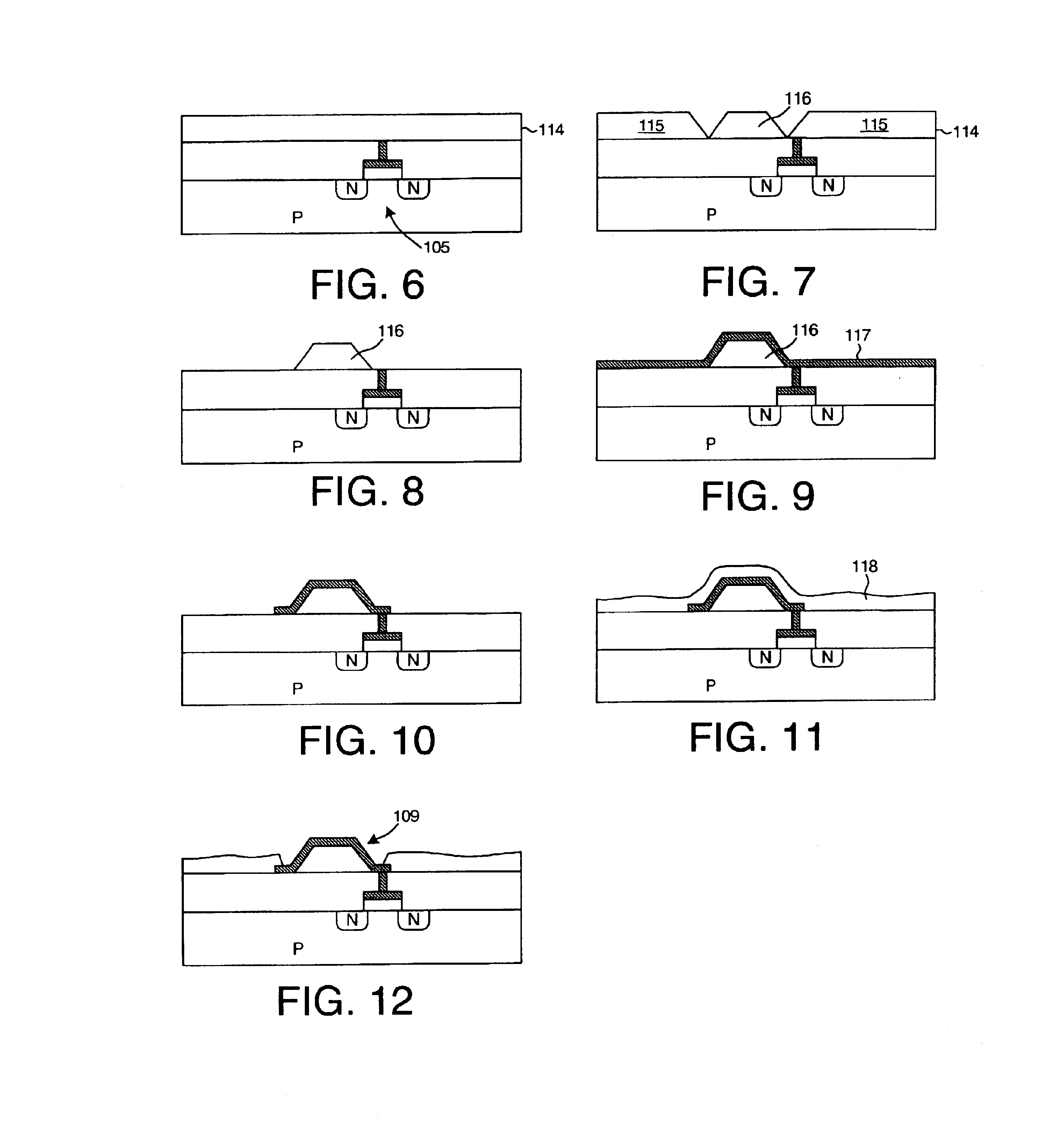
Multi-chip programmable logic device having configurable logic circuitry and configuration data storage on different dice
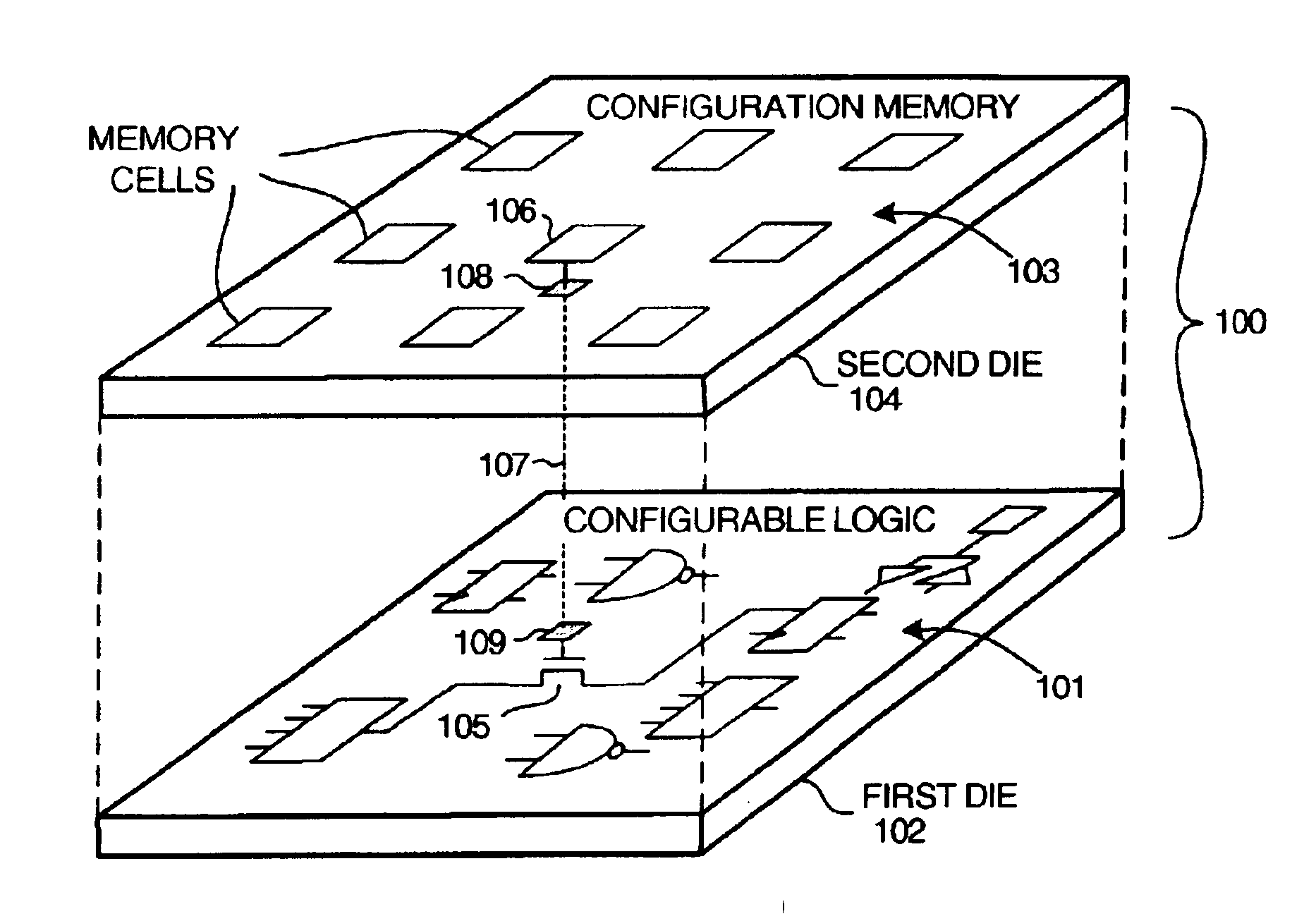
InactiveUS6917219B2Increase volumeIncrease productionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceLogical part
The circuitry of a programmable logic device (for example, an FPGA) includes a configurable logic portion and a configuration memory. The configuration memory stores configuration data that configures the configurable logic portion to realize a user-defined circuit. The configurable logic portion is disposed on a first die whereas the configuration memory is disposed on a second die. The second die is bonded to the first die in stacked relation. Each bit of configuration data passes from the second die to the first die through a pair of micropads. One micropad of the pair is disposed on the first die and the other micropad of the pair is disposed on the second die. When the first die and second die are brought together in face-to-face relation, the two micropads form an electrical connection through which the configuration data bit passes from the second die to the first die.
Owner:XILINX INC
Methods for reducing hollow organ volume
ActiveUS20050192599A1Reducing stomach volumeLarge anchor surface areaStaplesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesOrgan VolumeBody organs
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Foldable electronic device and a flexible display device
ActiveUS20060146488A1Easy to applyIncrease the areaSubstation equipmentDetails for portable computersDisplay deviceFlexible display
An electronic device, which comprises: at least two parts foldable in relation to each other, which can be turned into a first position and into a second position around a rotation axis; and a flexible display device, which extends over at least two foldable parts, covering them either entirely or partly. The flexible display device comprises: a folded position, to which the display device settles in the first position, and in which it folds around a first direction, which is parallel in relation to the rotation axis; and a curved position, to which the display device settles in the second position, and in which it curves around a second direction, which is transverse in relation to the rotation axis. A flexible display device can also be used with an electronic device.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
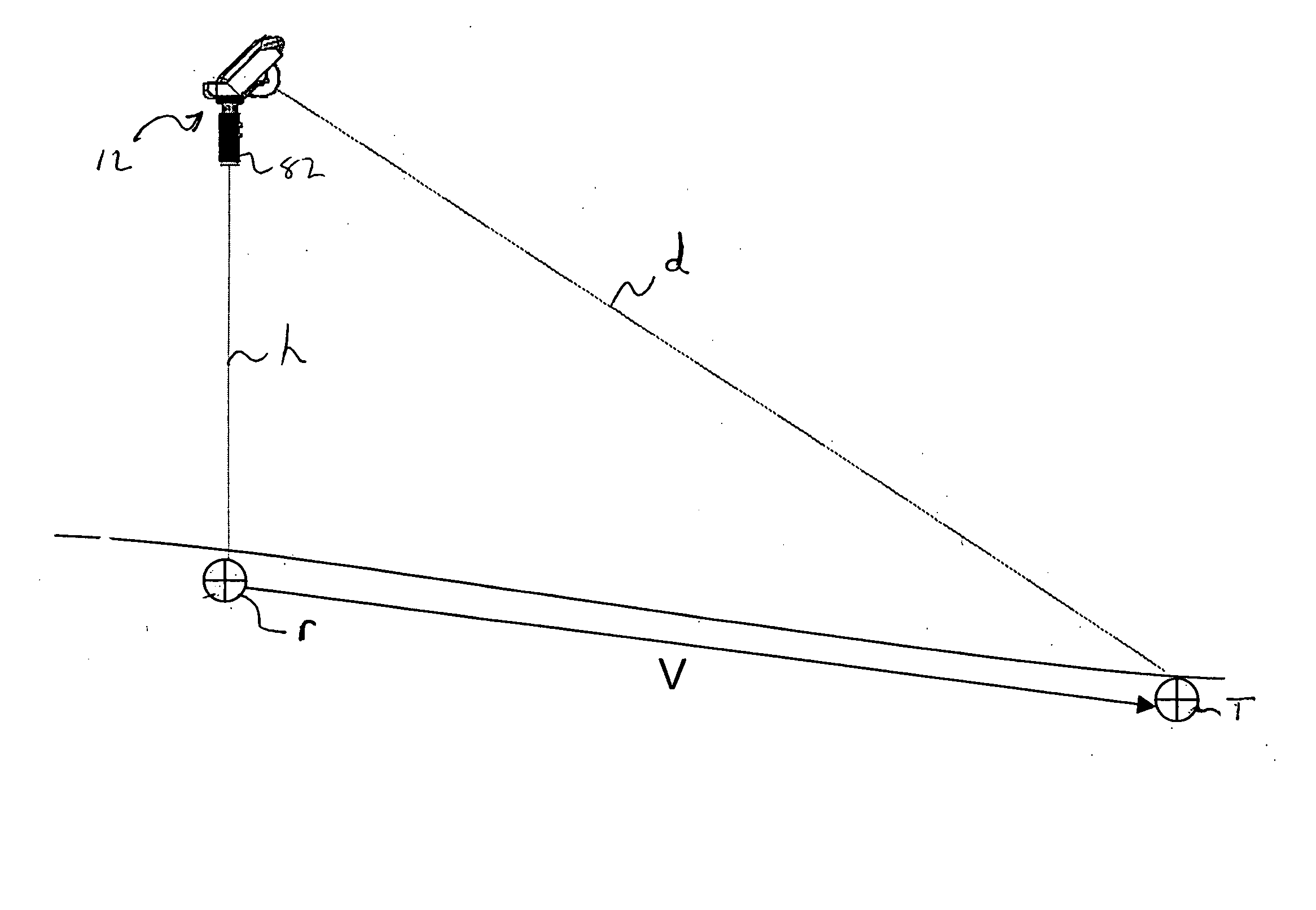
Measurement methods and apparatus
InactiveUS20050057745A1Precise positioningImprove viewing effectAngle measurementActive open surveying meansMeasurement deviceLocation determination
A measurement device is provided that allows for determining distance, range and bearing of a target of interest. The distance, range and bearing to the target of interest are determined relative to the position of the measurement device and are stored in memory. The device is further operative to translate these relative positions of the target to an absolute position at the time of measurement, or, when the position of the measurement device becomes known. The absolute position of the measurement device may be determined utilizing GPS technologies or through the measurement of geophysical reference points. Measurement of the relative location of target(s) of interest is performed utilizing an electronic range finding device and elevation and heading sensors. The resulting information is stored in memory for conversions to vector information that may be utilized to generate, for instance, topographical images.
Owner:GEOSCAN TECH
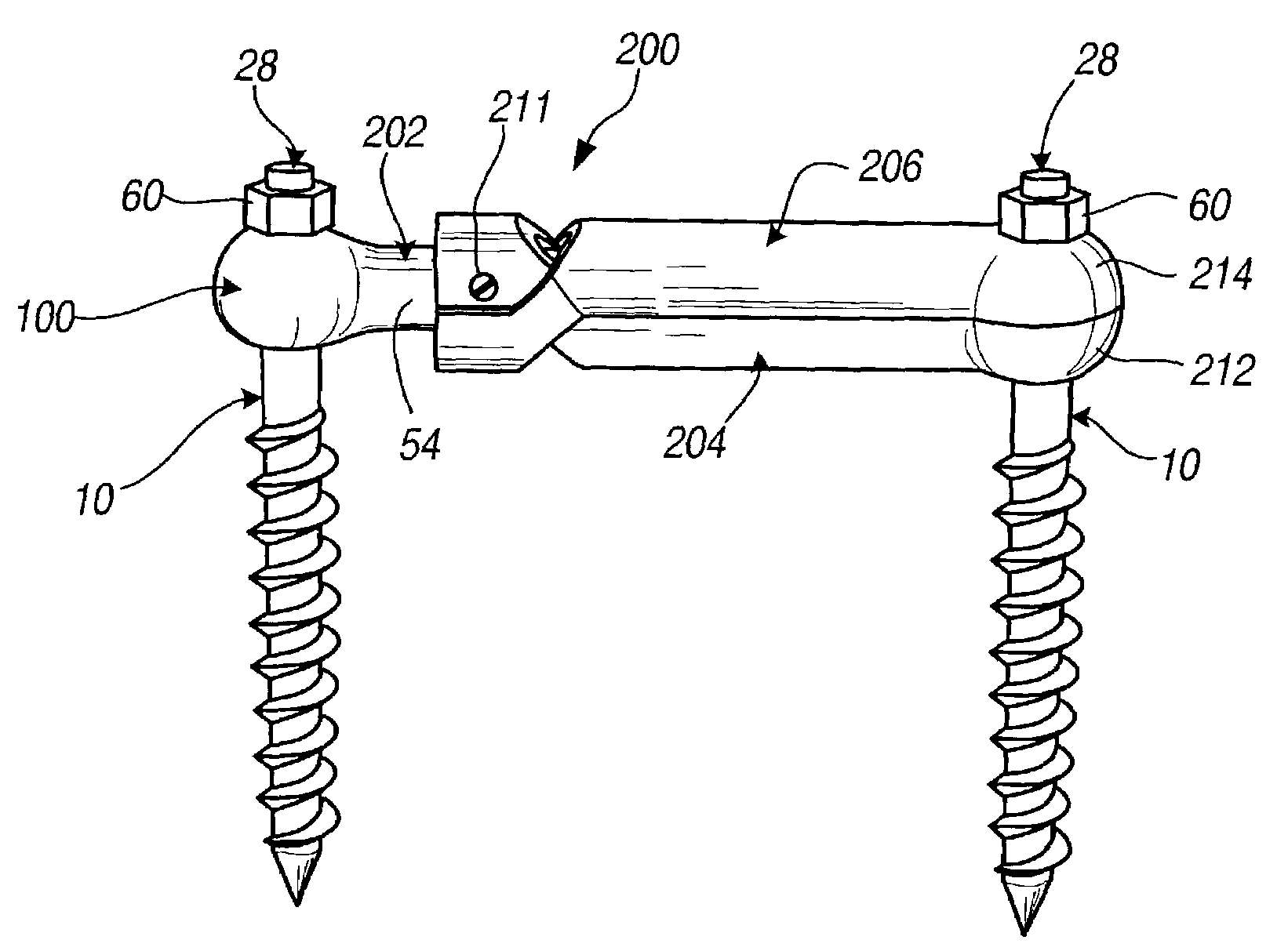
Connection rod for screw or hook polyaxial system and method of use
InactiveUS7207992B2Increase the areaPrevent rotationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsCouplingPedicle screw
A low-profile surgical implant assembly is provided that includes a connector device that is an integral part of a rod, the connector device allowing the rod to be attached directly to a bone screw, such as a pedicle screw. Another aspect of the invention is a clamp device that allows the length of a rod spanning to attachment devices to be adjusted at the time of implantation, and further allows the clamp device to be secured by tightening a securing end of the clamp at the attachment device. The assemblies are useful for insertion into bone and connecting a foreign object to bone via a polyaxial coupling mechanism. A method for implanting the assembly is also provided.
Owner:RITLAND STEPHEN
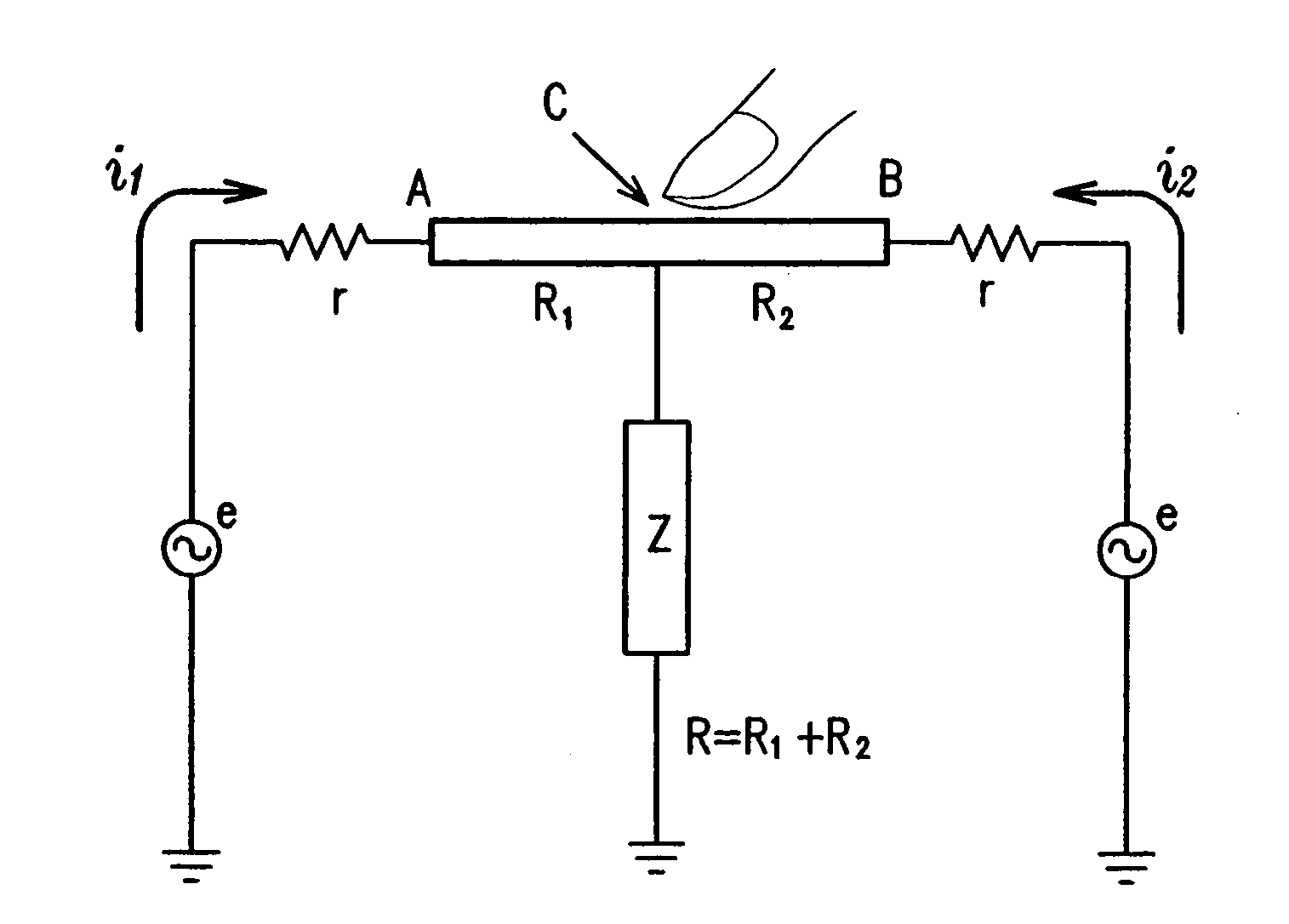
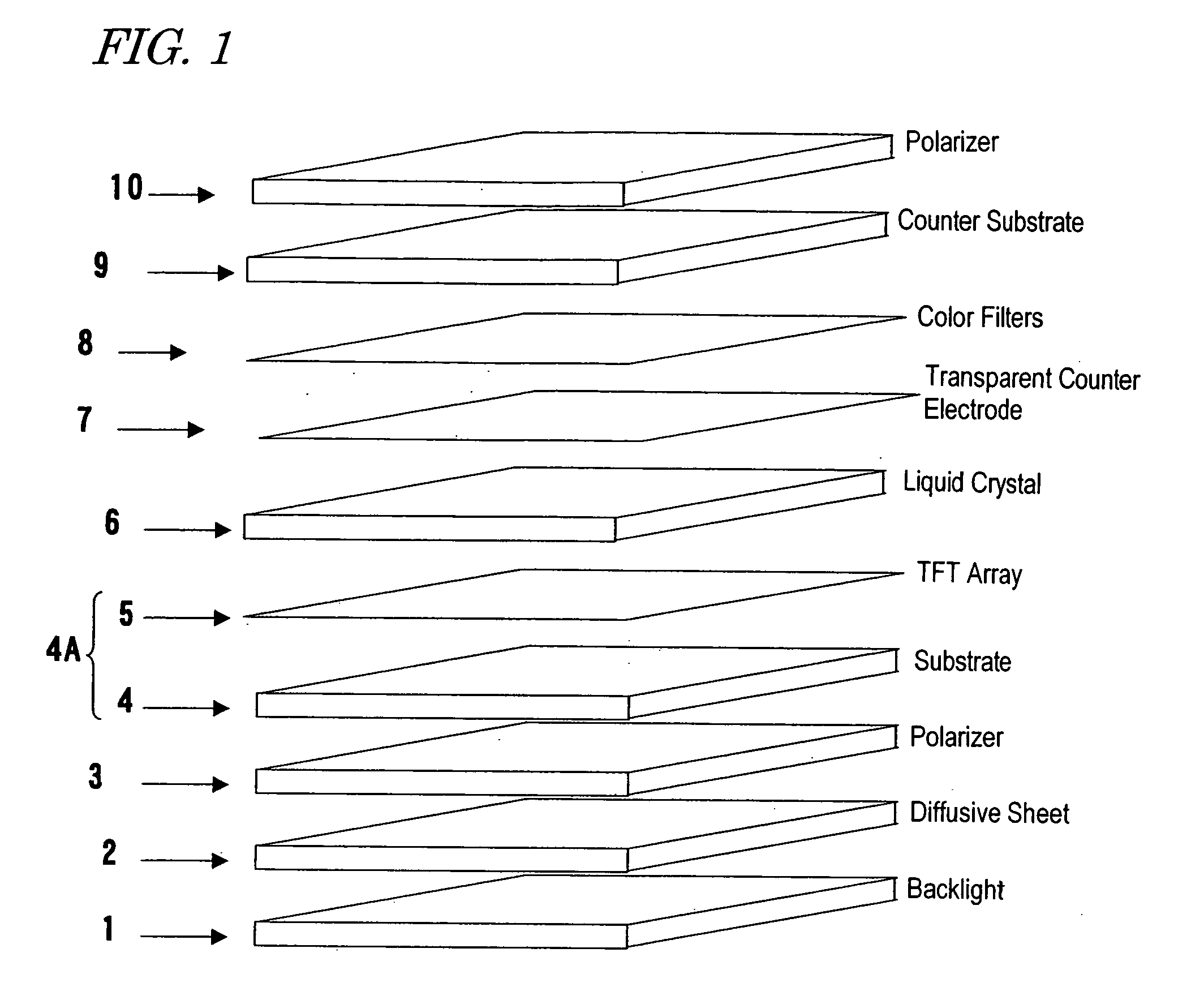
Touch sensor, display with touch sensor, and method for generating position data
ActiveUS20040217945A1Not deteriorate display performanceEffectively downsizedCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsElectricityVoltage
A display device with a touch sensor according to the present invention includes an active matrix substrate 4A and a transparent counter electrode 7. On a first surface of the active matrix substrate, multiple pixel electrodes are arranged in matrix. The transparent counter electrode is opposed to the first surface of the active matrix substrate. The display device further includes a first circuit, a second circuit and a switching circuit. The first circuit supplies a voltage or a current to the transparent counter electrode for display purposes. The second circuit detects currents flowing from a number of points on the transparent counter electrode. And the switching circuit selectively connects electrically one of the first and second circuits to the transparent counter electrode.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Vertical LED lamp with a 360-degree radiation and a high cooling efficiency
InactiveUS20070159828A1Improve cooling efficiencyIncrease the areaPoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsEngineeringConductive materials
A vertical LED lamp with a 360-degree radiation and a high cooling efficiency includes a lampshade, a lamp base and a LED module. The LED module is contained in a chamber surrounded by the lampshade and the lamp base. The lamp base is able to provide DC for the LED module to work. The LED module is composed of a cooling column and a preset number of LED boards. The cooling column, shaped as a triangle or a tetragon or polygon and made of a thermal conductive material, is provided with a plugging slot on each surface for fitting with the LED bulb board, and plural fins formed on each surface for increasing areas to contact air Therefore, the LED lamp has 360-defree radiation and can perform with a better brightness and obtain a longer life.
Owner:CERAMATE TECH CO LTD
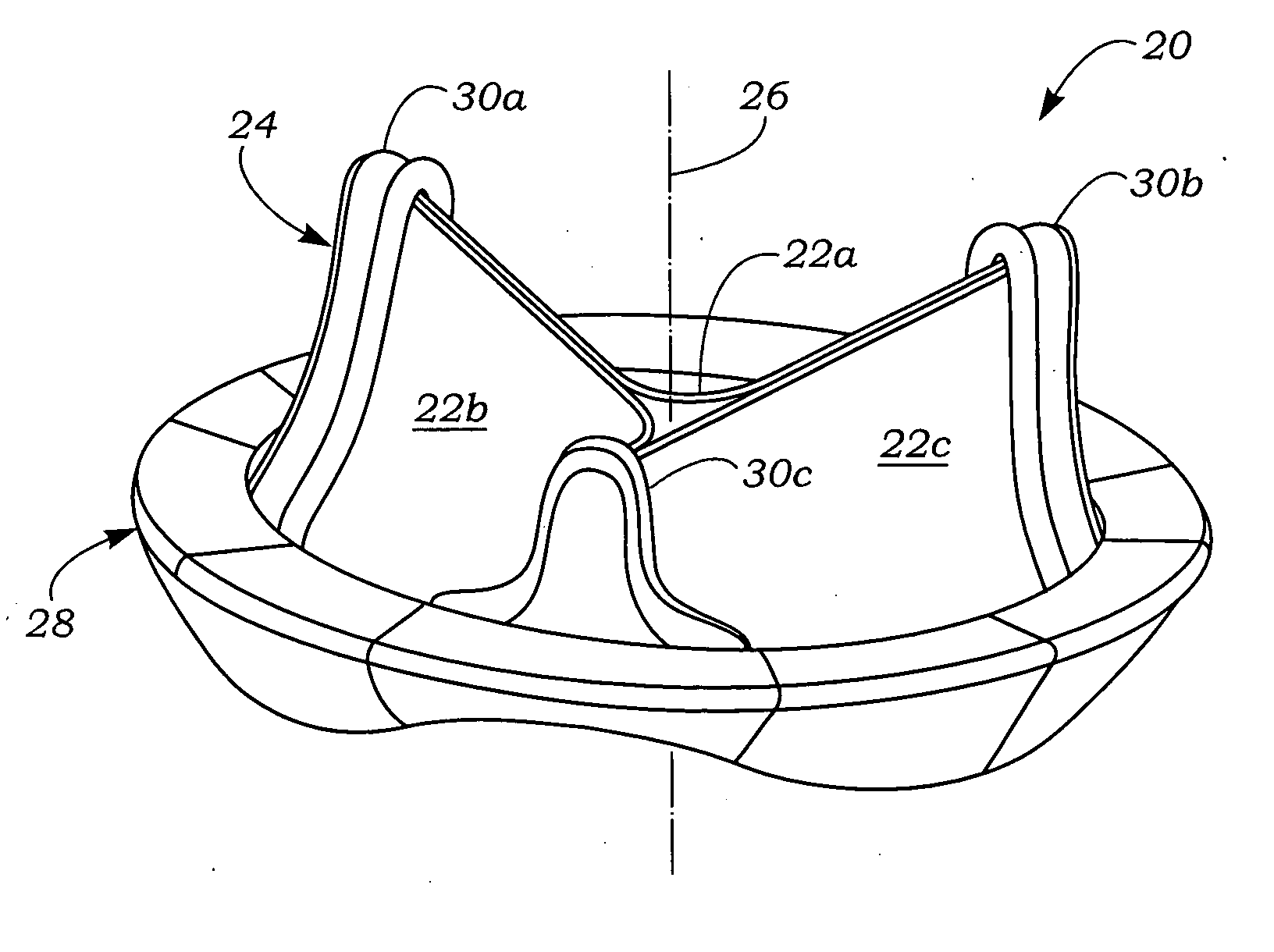
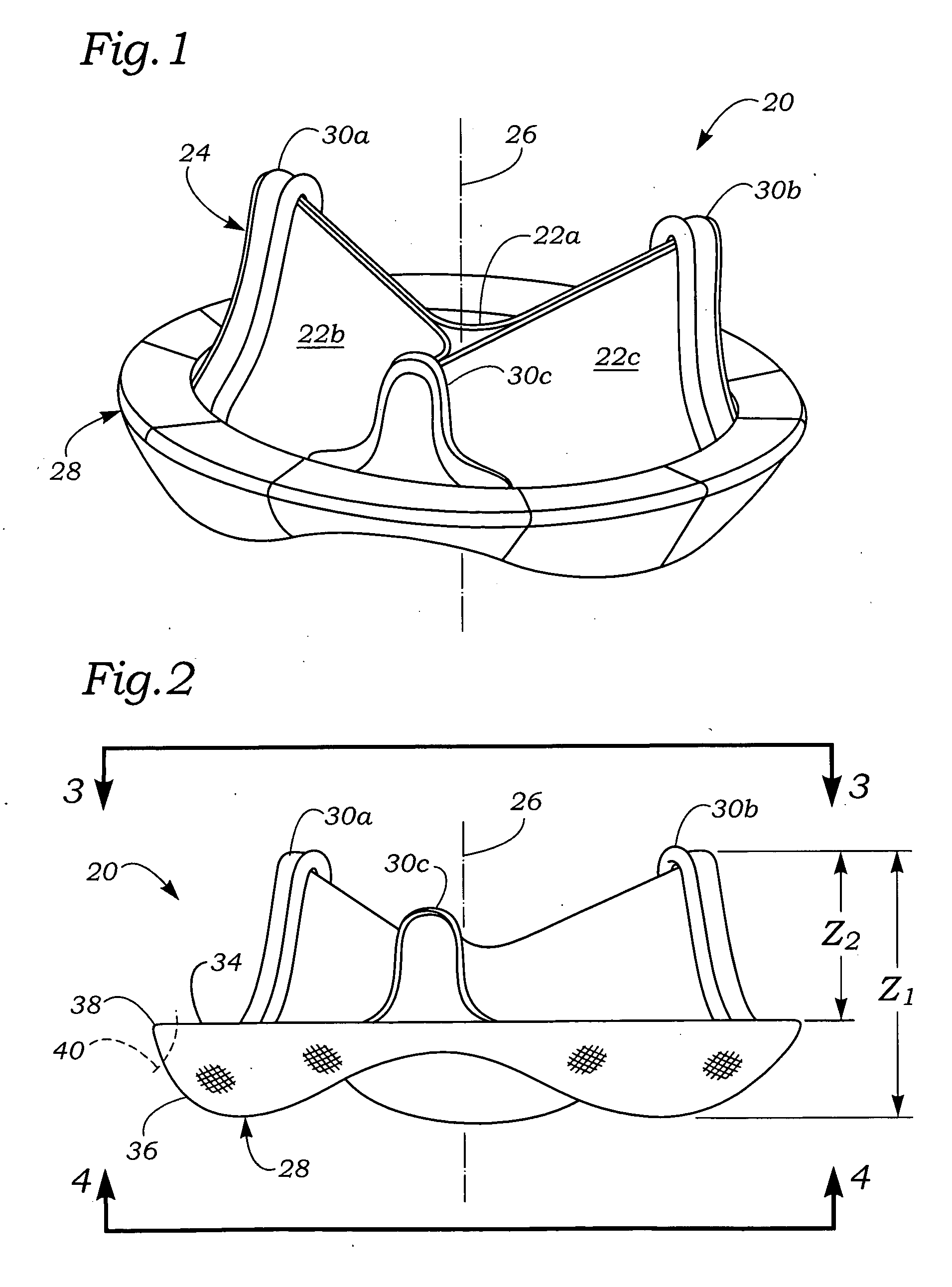
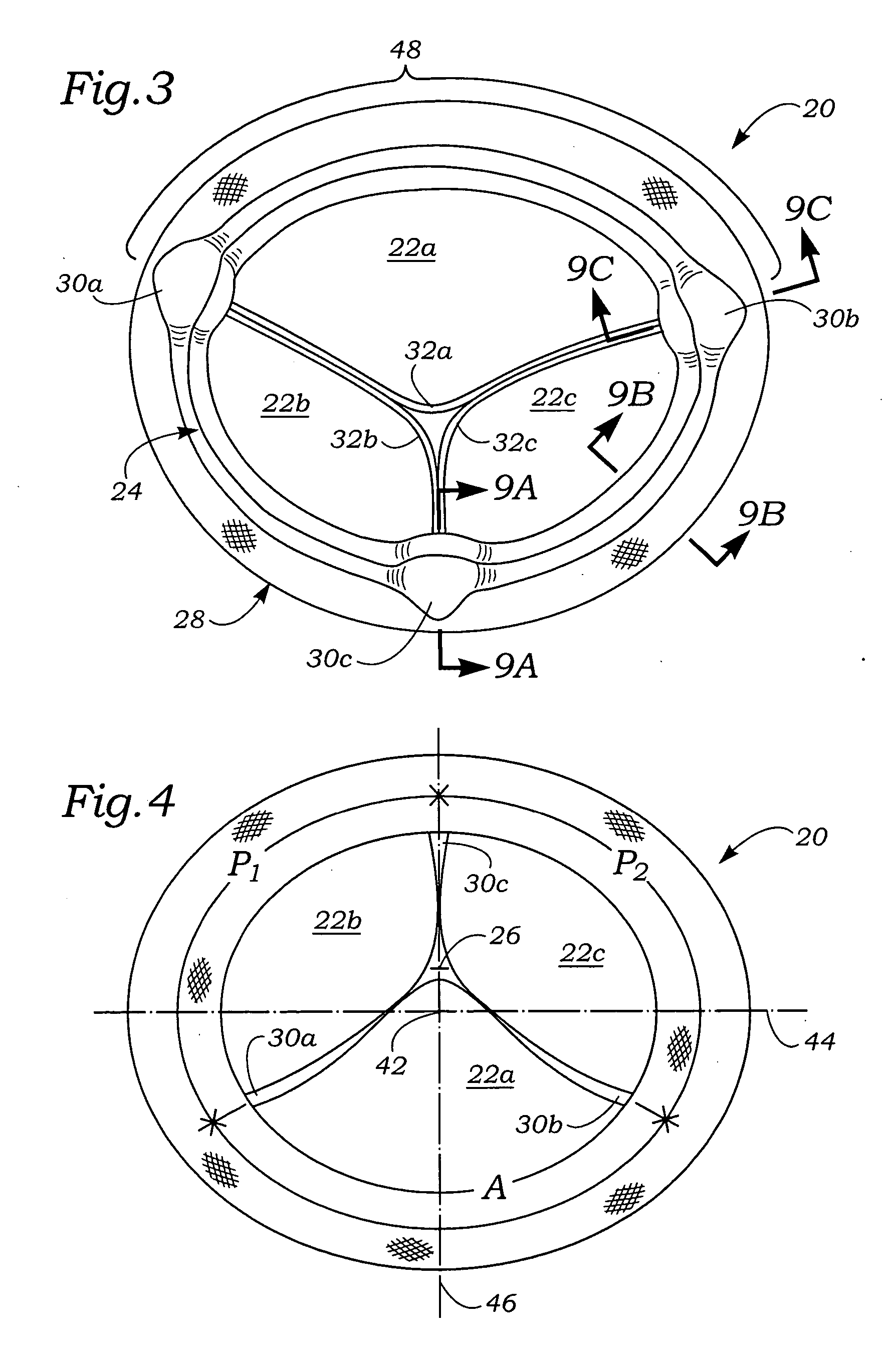
Anatomically approximate prosthetic mitral heart valve
ActiveUS20060293745A1Increase the areaReduce the overall heightAnnuloplasty ringsAnterior leafletMitral annulus
An anatomically approximate prosthetic heart valve includes dissimilar flexible leaflets, dissimilar commissures and / or a non-circular flow orifice. The heart valve may be implanted in the mitral position and have one larger leaflet oriented along the anterior aspect so as to mimic the natural anterior leaflet. Two other smaller leaflets extend around the posterior aspect of the valve. A basic structure providing peripheral support for the leaflets includes two taller commissures on both sides of the larger leaflet, with a third, smaller commissure between the other two leaflets. The larger leaflet may be thicker and / or stronger than the other two leaflets. The base structure defines a flow orifice intended to simulate the shape of the mitral annulus during the systolic phase. For example, the flow orifice may be elliptical. A relatively wide sewing ring has a contoured inflow end and is attached to the base structure in such a way that the valve can be implanted in an intra-atrial position and the taller commissures do not extend too far into the left ventricle, therefore avoiding injury to the ventricle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
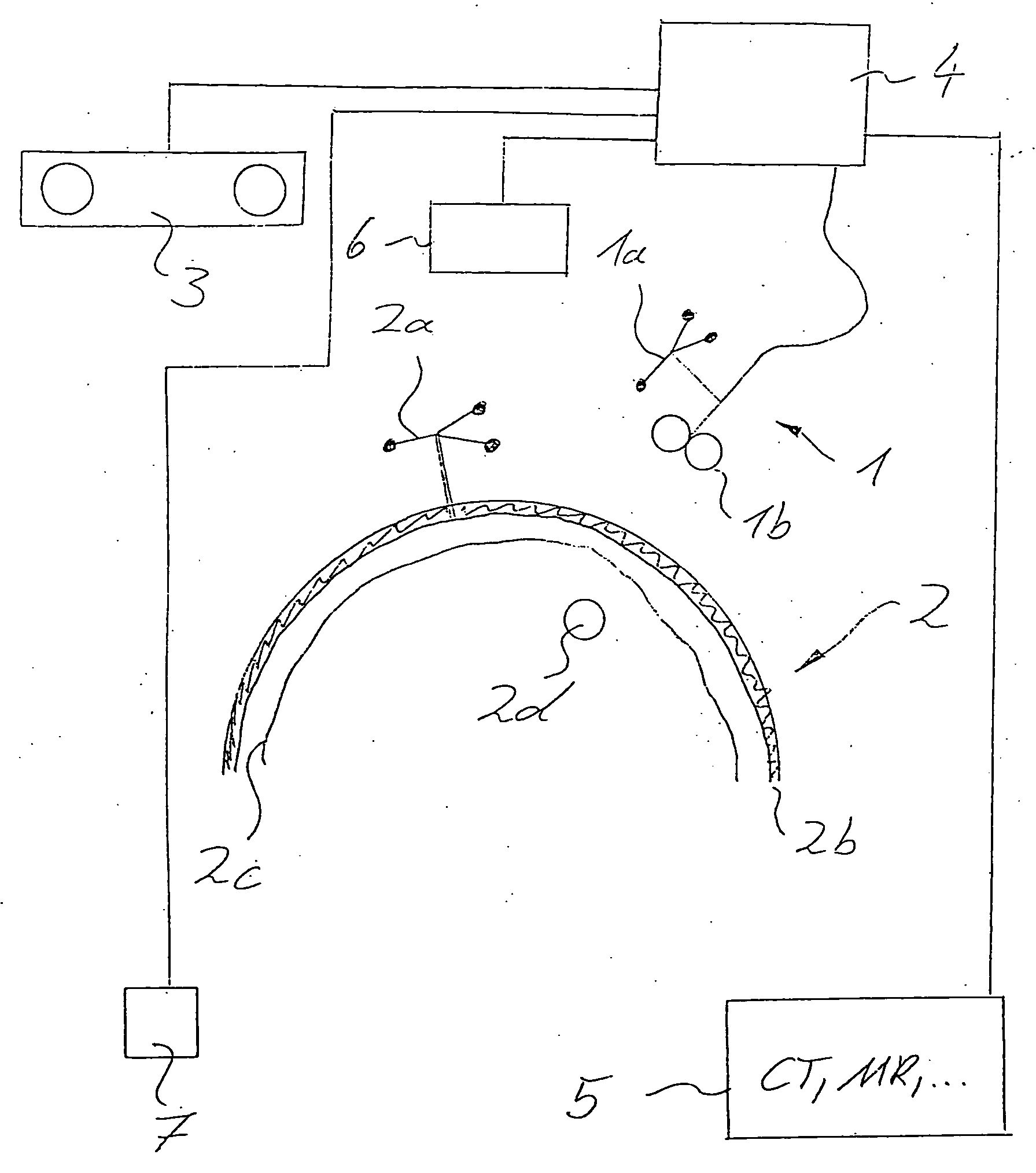
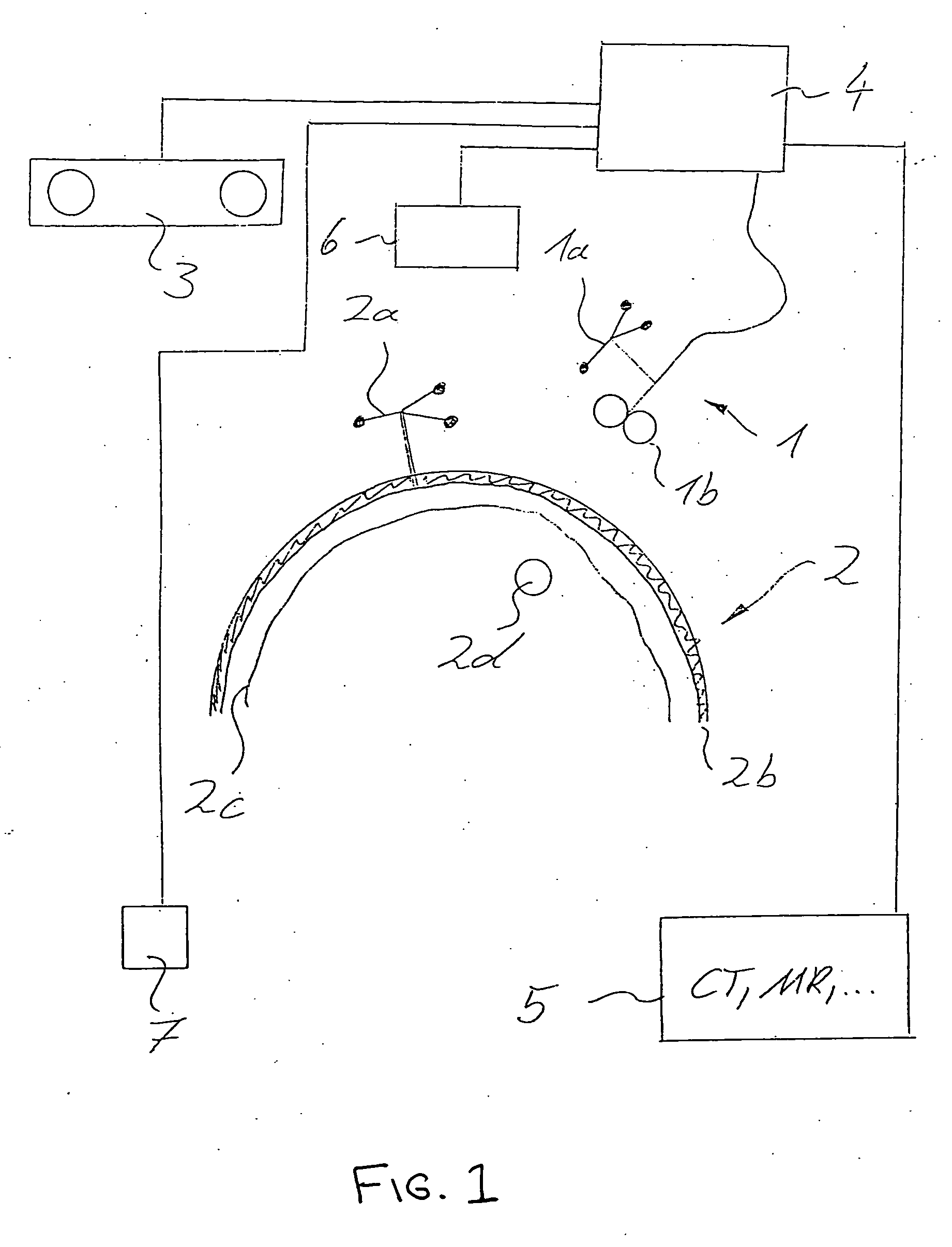
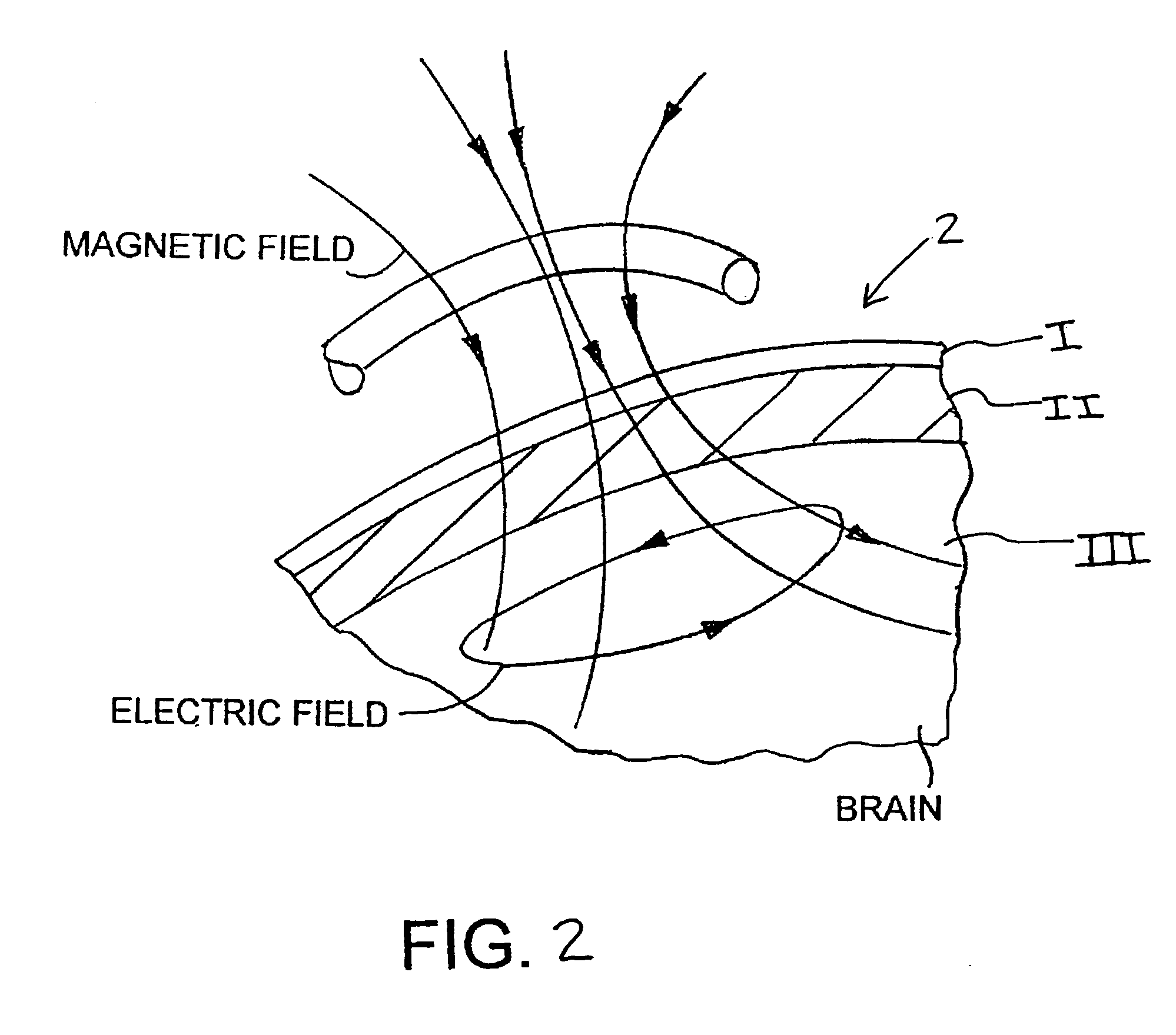
Method and device for stimulating the brain
ActiveUS20050033380A1Increase stimulationSimply localizingElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyAnatomical structuresElectricity
A method for stimulating a particular area of a brain using a stimulation device includes detecting a spatial structure of a head and determining electrical and / or magnetic properties of at least one part of anatomical structures of the head. An energy amount to be provided by the stimulation device for stimulating the particular area of the brain is calculated automatically based on the spatial structure of the head and the determined electrical and / or magnetic properties of at least one part of the anatomical structures of the head.
Owner:BRAINLAB
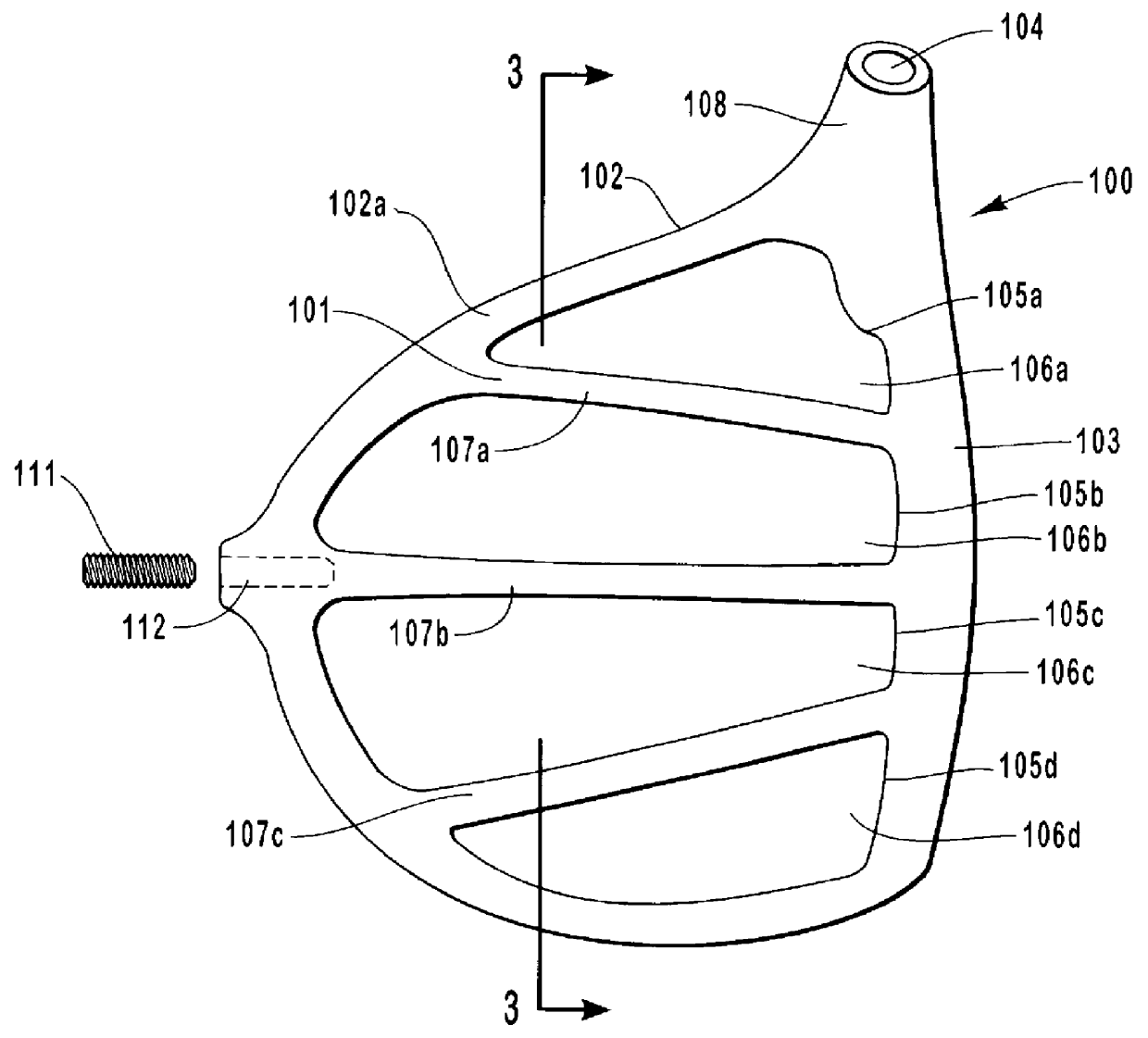
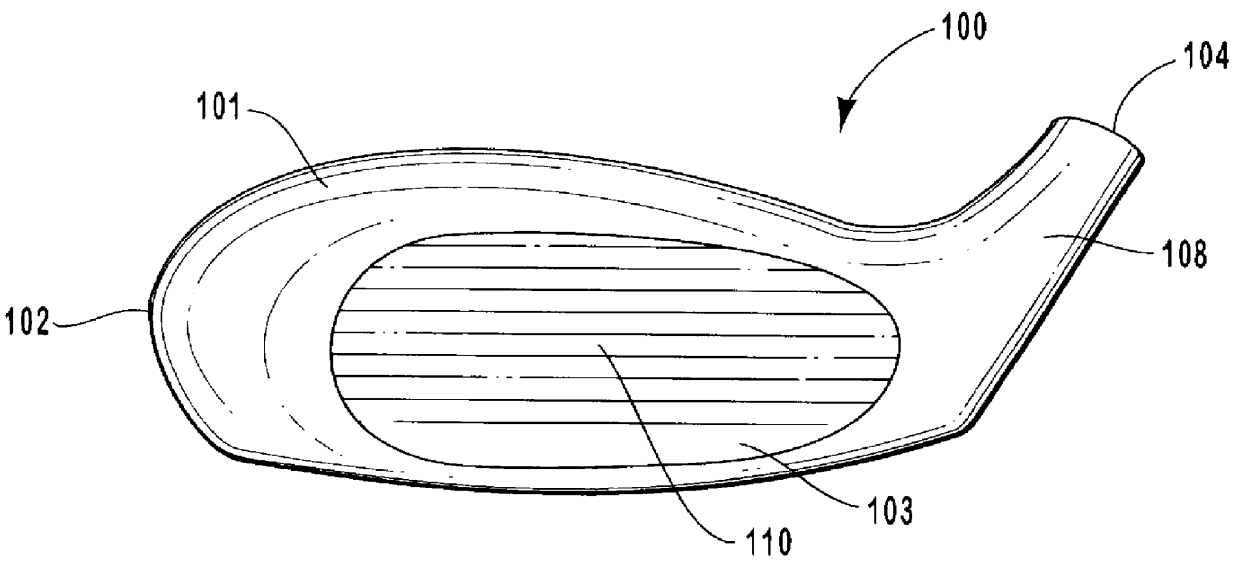
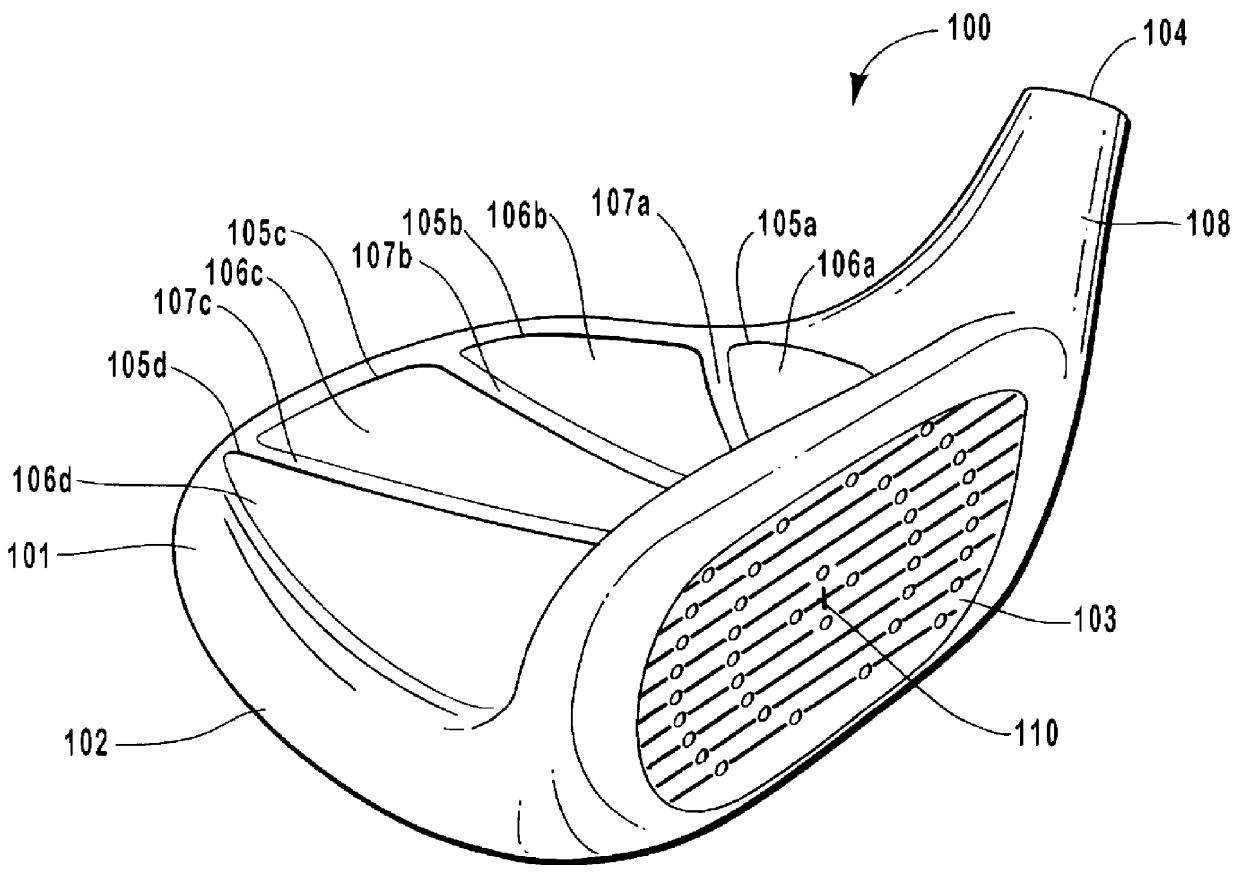
Golf club head having performance-enhancing structure
InactiveUS6059669AEconomical and labor-efficientGreat distance of ball flightGolf clubsRacket sportsFiberEngineering
A golf club that is preferably made from fiber-reinforced plastic composite by an injection molding process. The preferred golf club head includes a striking face for striking a golf ball, an outer periphery, a cavity formed between the outer periphery and the back of the striking face, a sole enclosing the bottom portion of said cavity, and at least one elongate power bar extending across the cavity from the striking face to the outer periphery. The sole is preferably integrally formed with the face plate and outer periphery. The cavity of the golf club head opens to the top of the club head. Each elongate power bar separates the cavity into receptacles. Inserts may be placed within the receptacles for aesthetic, aerodynamic, acoustic, and other purposes.
Owner:EDIZONE LC
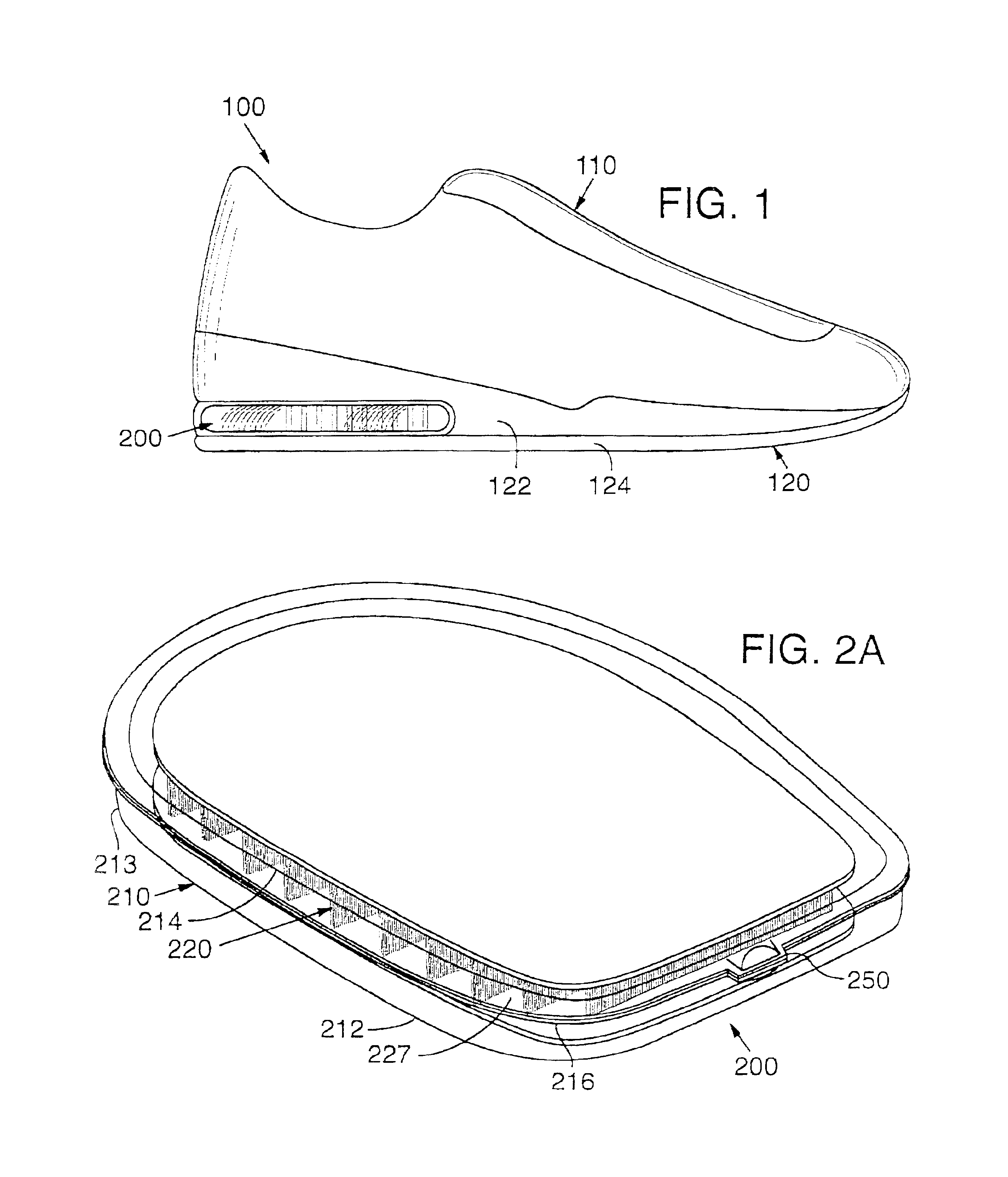
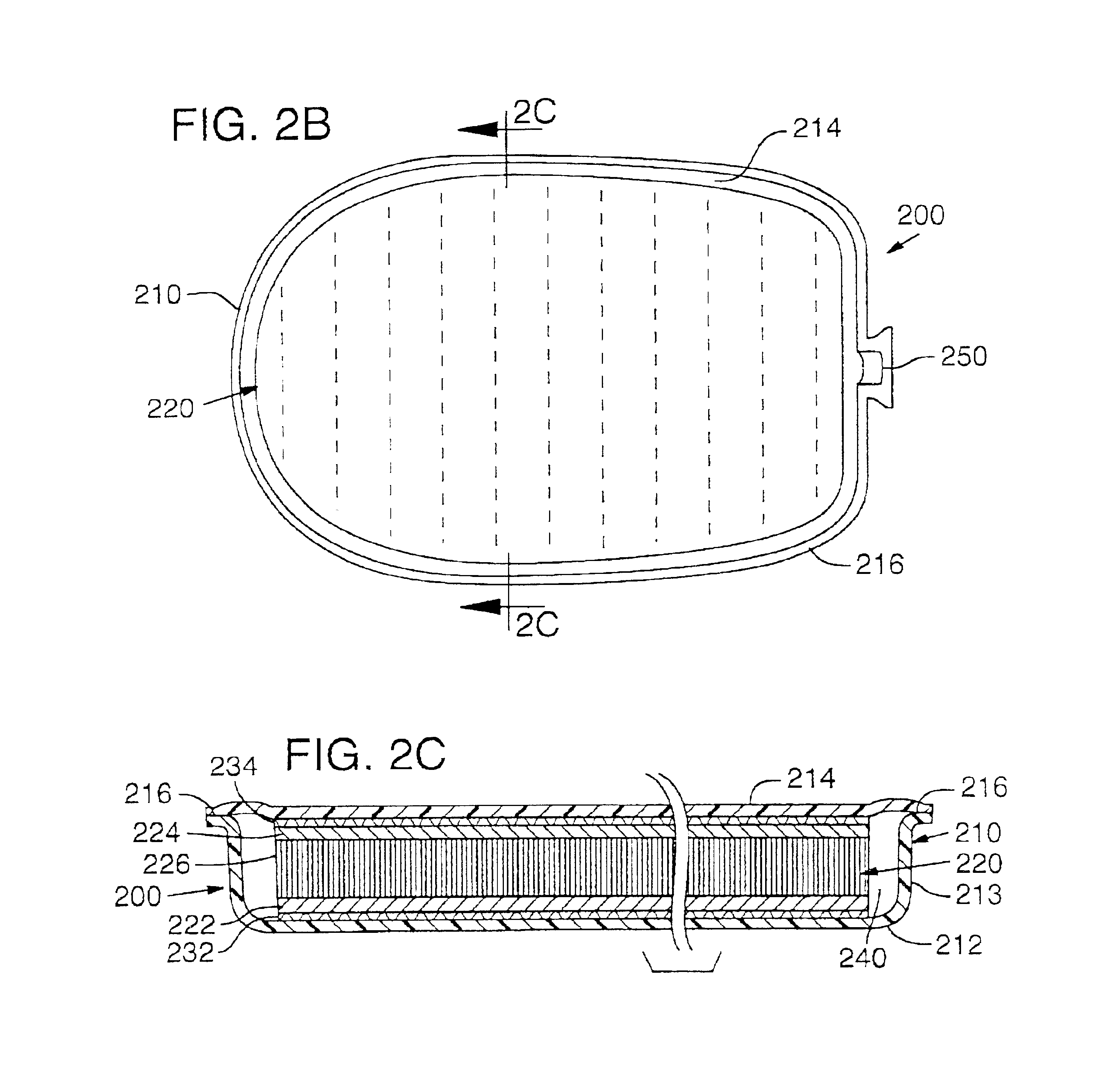
Method of thermoforming a bladder structure
InactiveUS6837951B2Increase awarenessImprove efficiencySolesOrnamental textile articlesBladder structureThermal contact
A method for thermoforming a resilient, fluid-filled bladder structure with thermal contact molding is disclosed. The bladder includes two sheets of thermoplastic material that are separated by at least one core formed of two spaced outer layers connected together by a plurality of connecting members. The bladder is formed by bonding the sheets to the core, bonding the sheets to each other around the periphery of the core and forming a sidewall between the sheets in a single mold. A fluid is then inserted into the space bounded by the peripheral bond and the two sheets such that the connecting members are extended.
Owner:NIKE INC
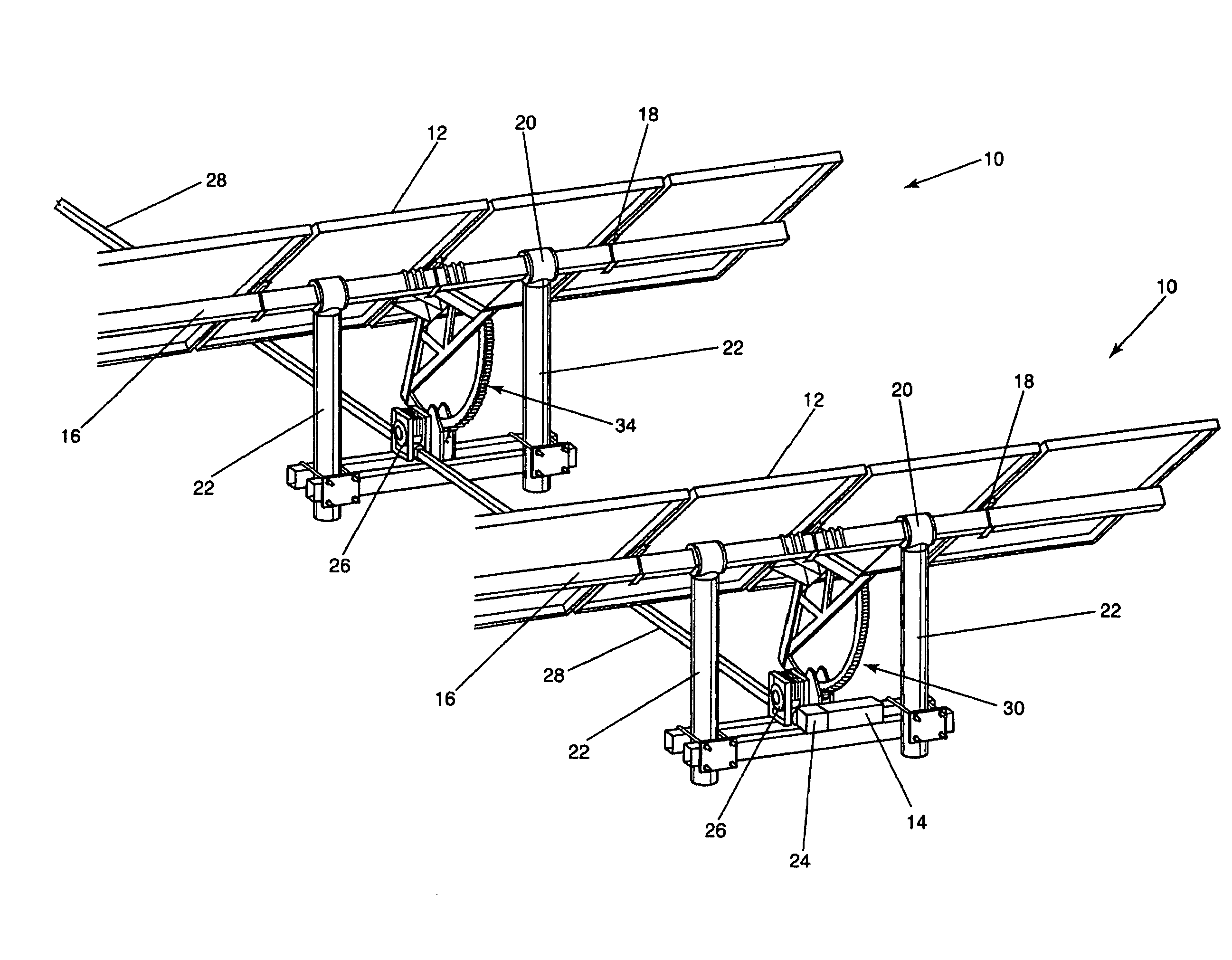
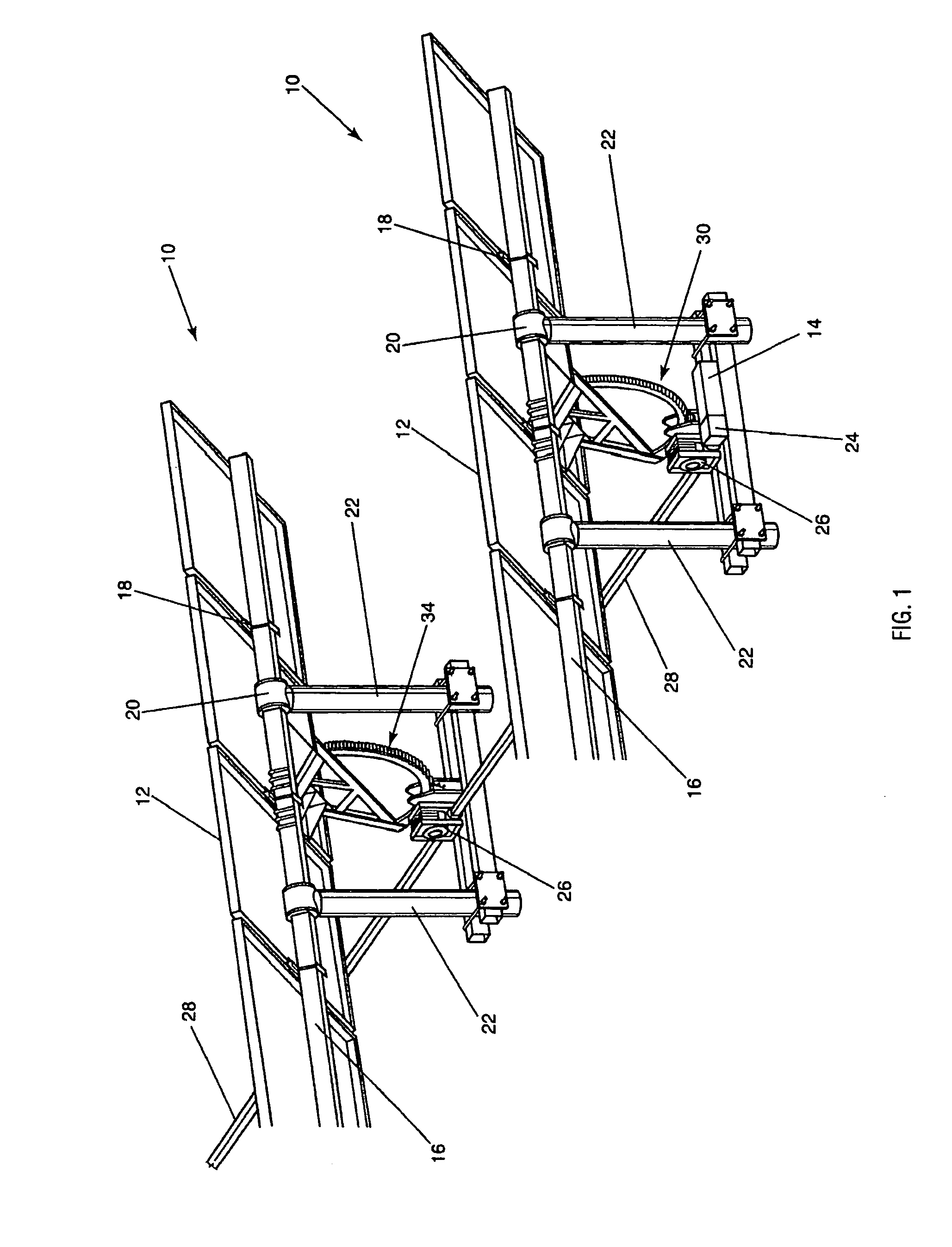
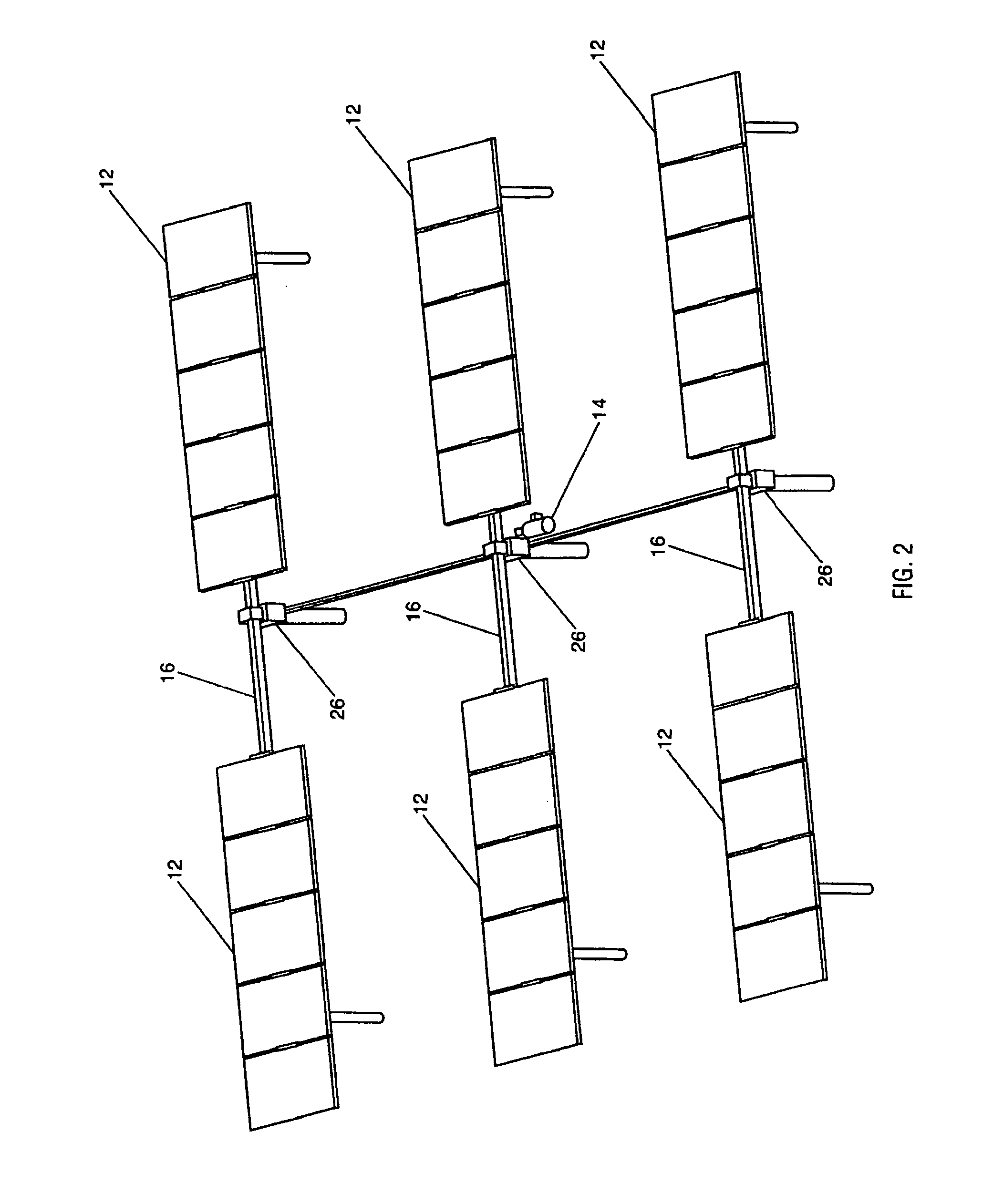
Single Axis Solar Tracking System
ActiveUS20080308091A1Maximize economic performancePerformance maximizationPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyTerrainWind force
A solar tracking system with a torque tube supporting solar panels. Columns support the system and have bearings for rotation of the torque tube. A drive is coupled to the torque tube and is driven by a gearbox, such as a worm gear assembly, for rotating the array of solar panels to follow the sun's diurnal motion. The array can rotate in an opposite direction, or backtrack, to prevent shadowing from one module row to another. Multiple gearboxes can be mechanically linked by drive shafts and driven by a single motor. The drive shafts may incorporate universal joints for uneven terrain or staggered configurations. Harmonic dampers can be affixed to the solar panels to decouple wind forces which allows the use of larger solar panels.
Owner:ARRAY TECH
Resecting device
InactiveUS7488319B2Accurate placementReduce the temperatureElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A resecting device is disclosed. The resecting device comprises: a handle having a jaw trigger slidably engaged with the handle and mechanically engaged with a spring mechanism communicating a biasing force to the jaw trigger; a fixed shaft portion having a first and a second end, wherein the fixed shaft portion first end is affixed to the housing, wherein the fixed shaft portion second end forms a first jaw member, and wherein the first jaw member has a tissue contact area; and a slidable shaft portion in communication with the spring mechanism and slidable relative to the fixed shaft portion.
Owner:YATES LEROY L
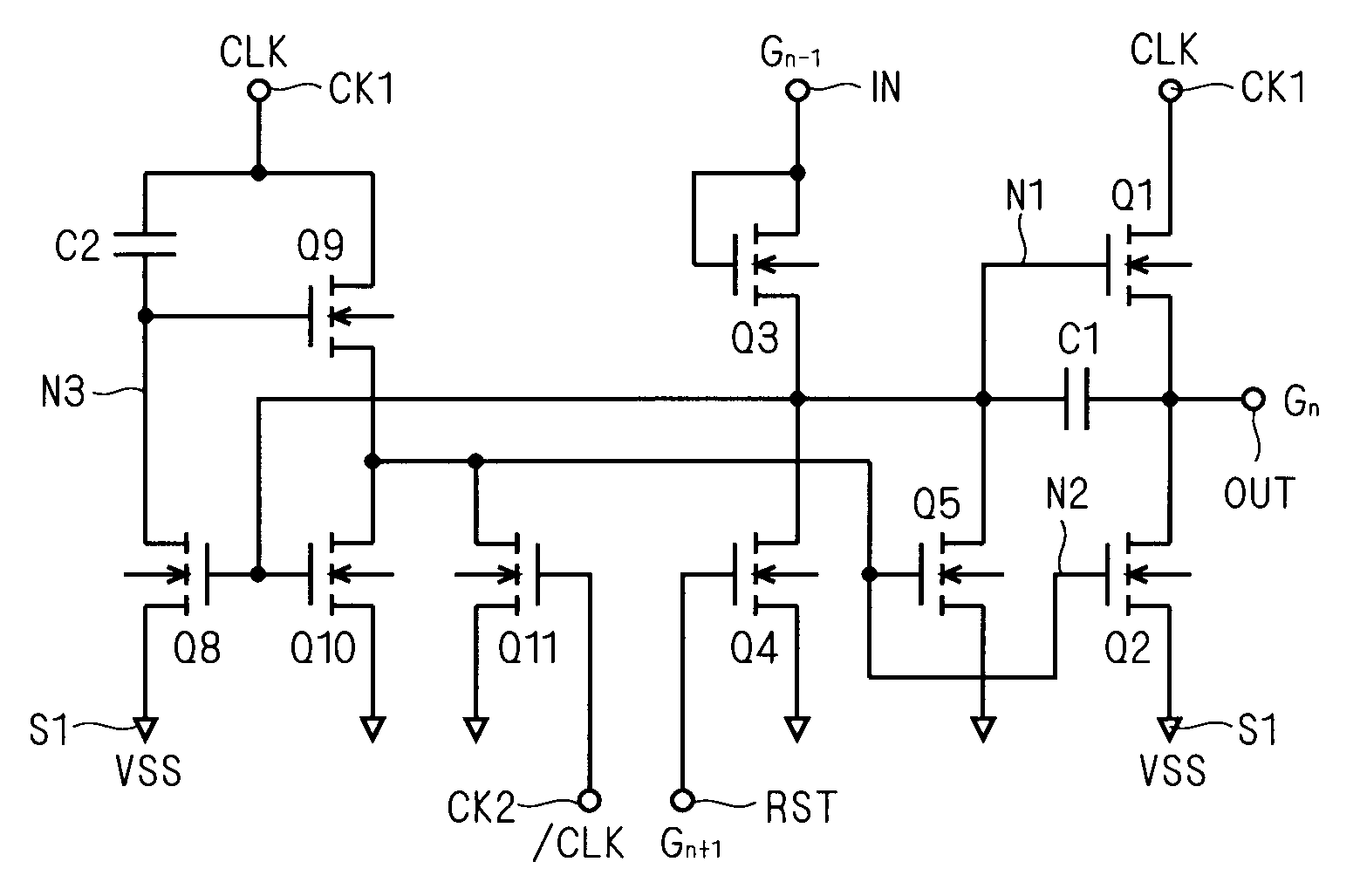
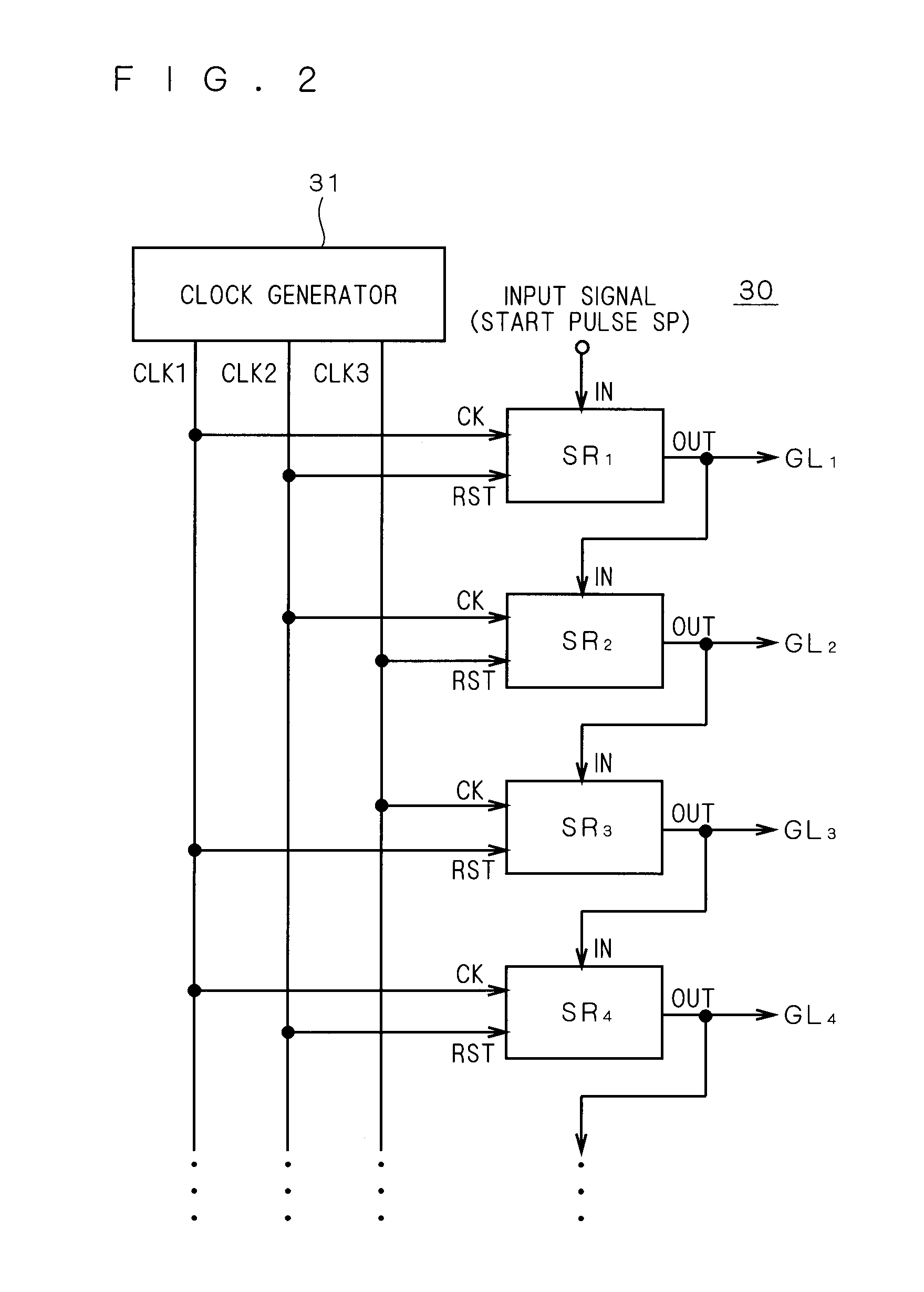
Shift register and image display apparatus containing the same
ActiveUS20080101529A1Increased circuit areaImprove driving reliabilityStatic indicating devicesDigital storagePower inverterShift register
A shift register includes a first transistor supplying an output terminal with a clock signal input to a first clock terminal and a second transistor discharging the output terminal. Defining the gate node of the first transistor as a first node, and the gate node of the second transistor as a second node, the shift register includes an inverter circuit in which the first node serves as its input node and a capacitive element serves as a load, and a buffer circuit receiving the output from the inverter circuit and outputting a signal to the second node.
Owner:TRIVALE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com