Patents
Literature
1462 results about "Thermoforming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process where a plastic sheet is heated to a pliable forming temperature, formed to a specific shape in a mold, and trimmed to create a usable product. The sheet, or "film" when referring to thinner gauges and certain material types, is heated in an oven to a high-enough temperature that permits it to be stretched into or onto a mold and cooled to a finished shape. Its simplified version is vacuum forming.
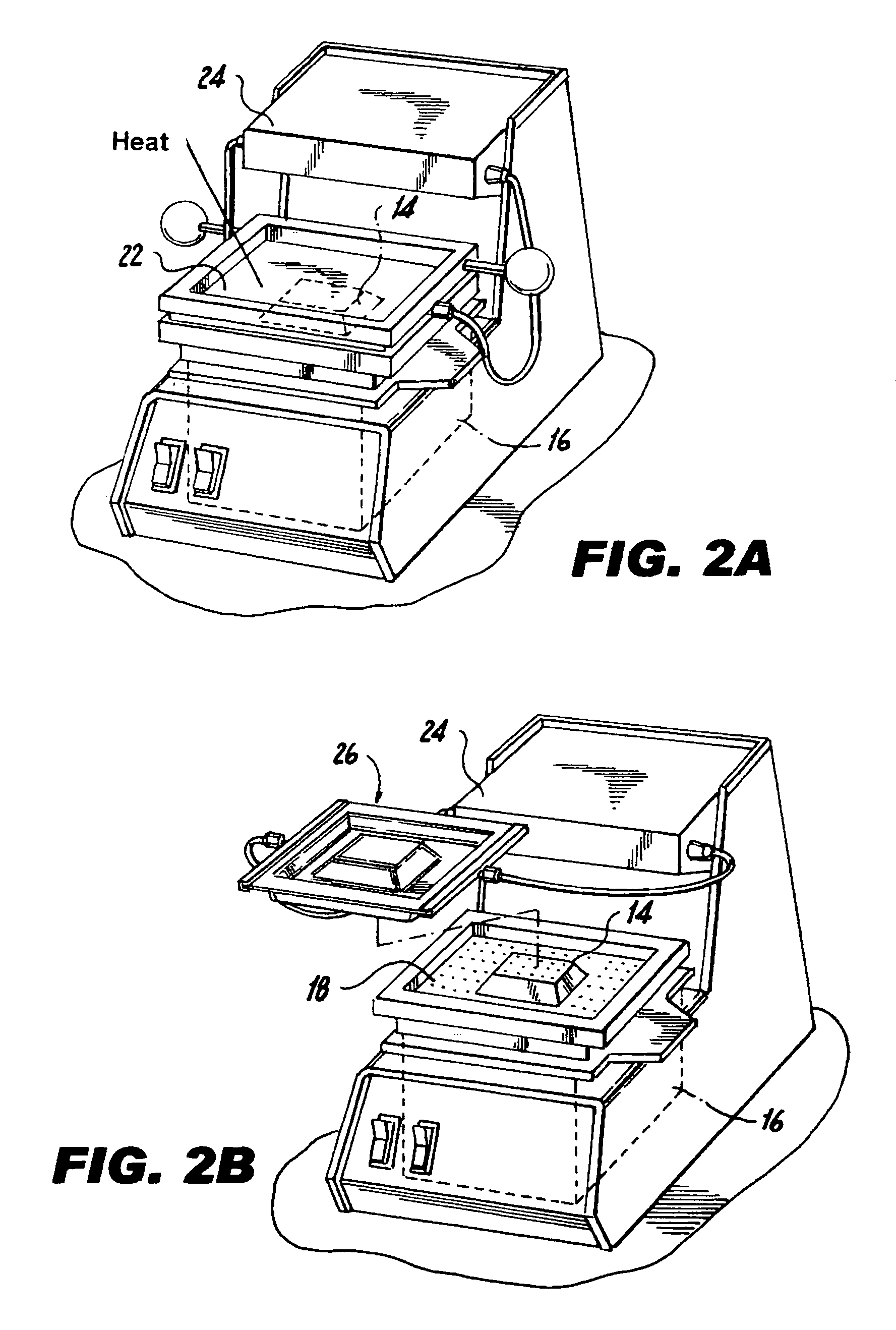
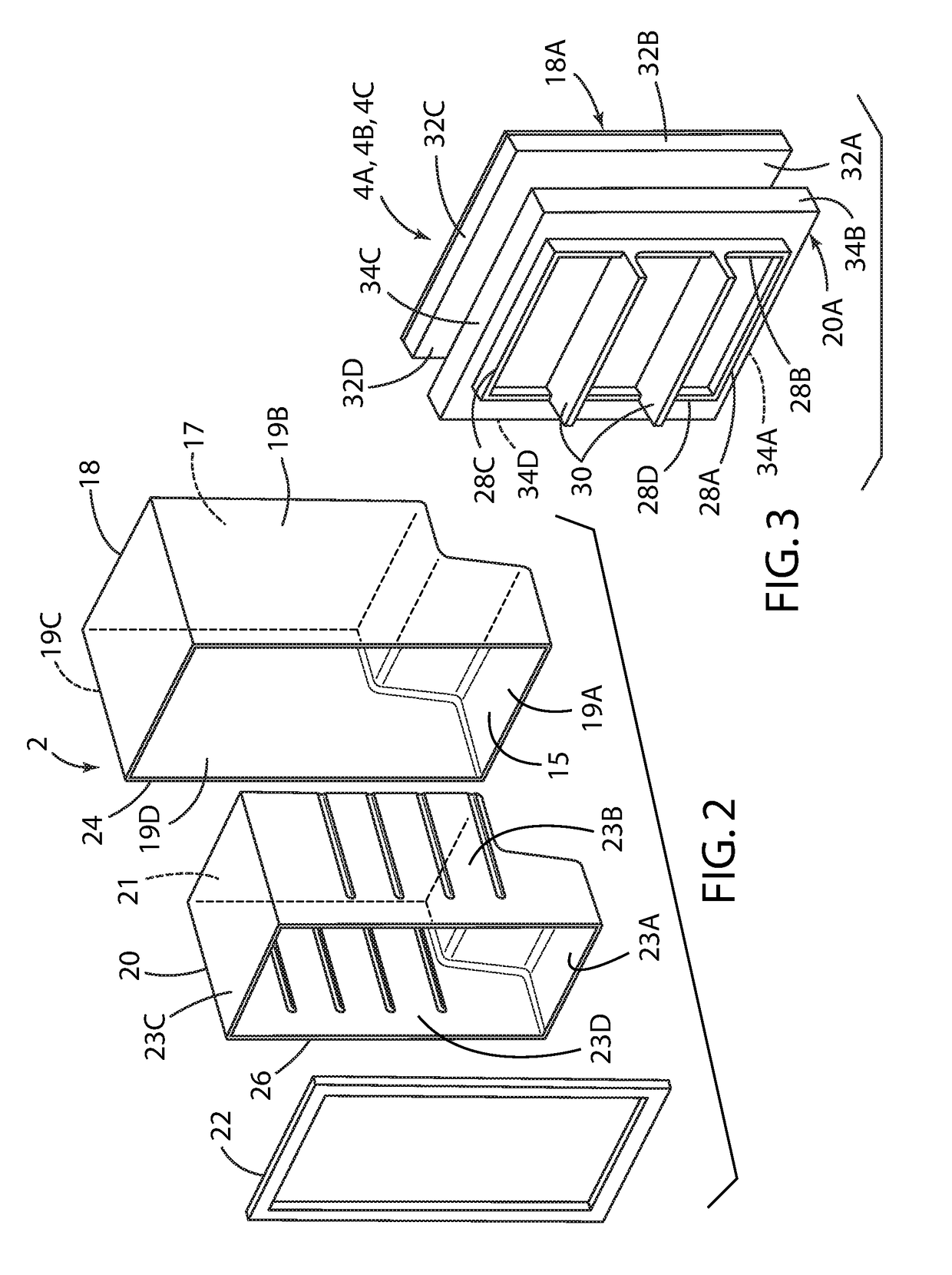
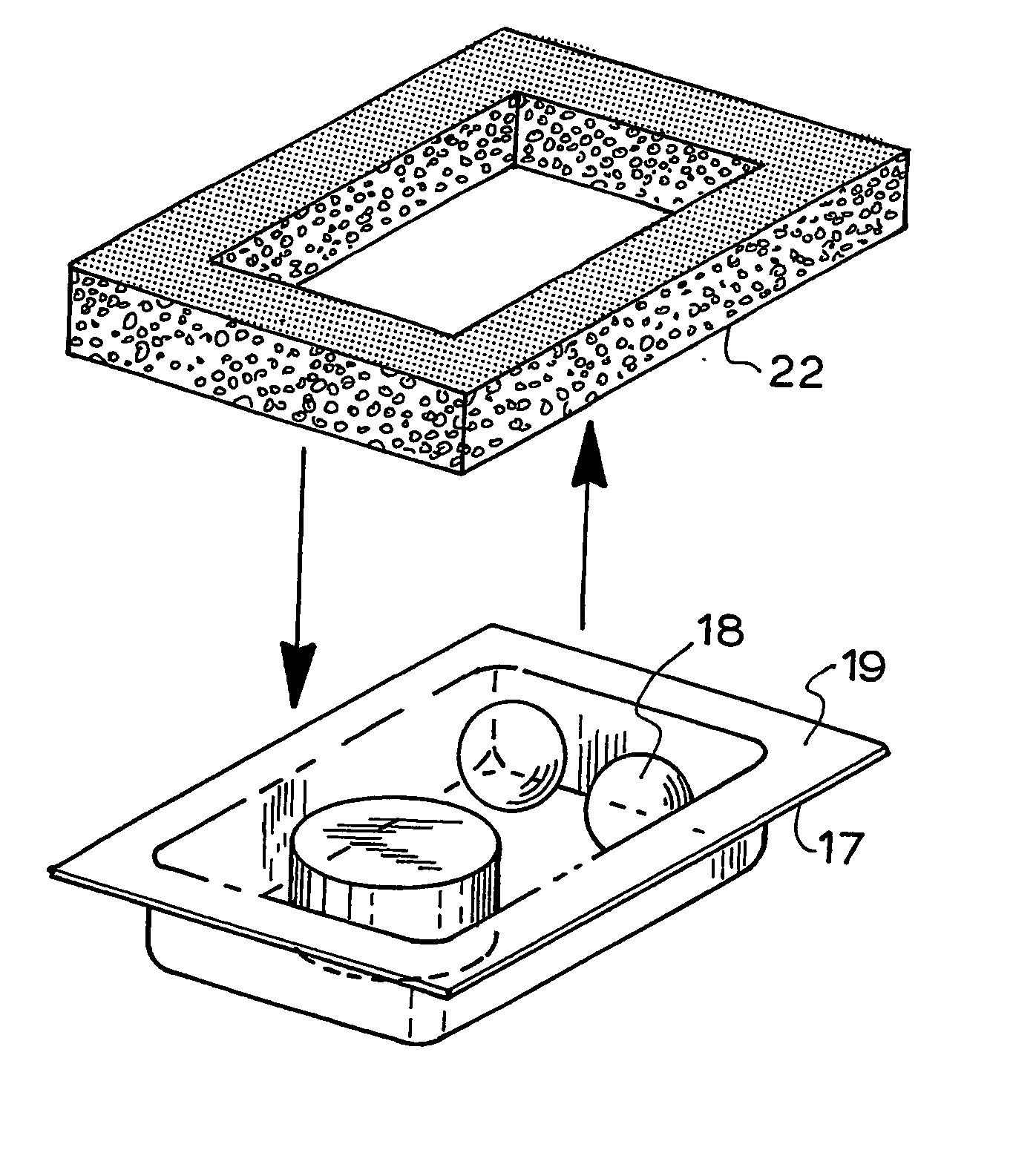
Thermoformed apparatus having a communications device
InactiveUS6943678B2Improve protectionIncreased durabilityRecord carriersDigital data processing detailsThermoformingEngineering
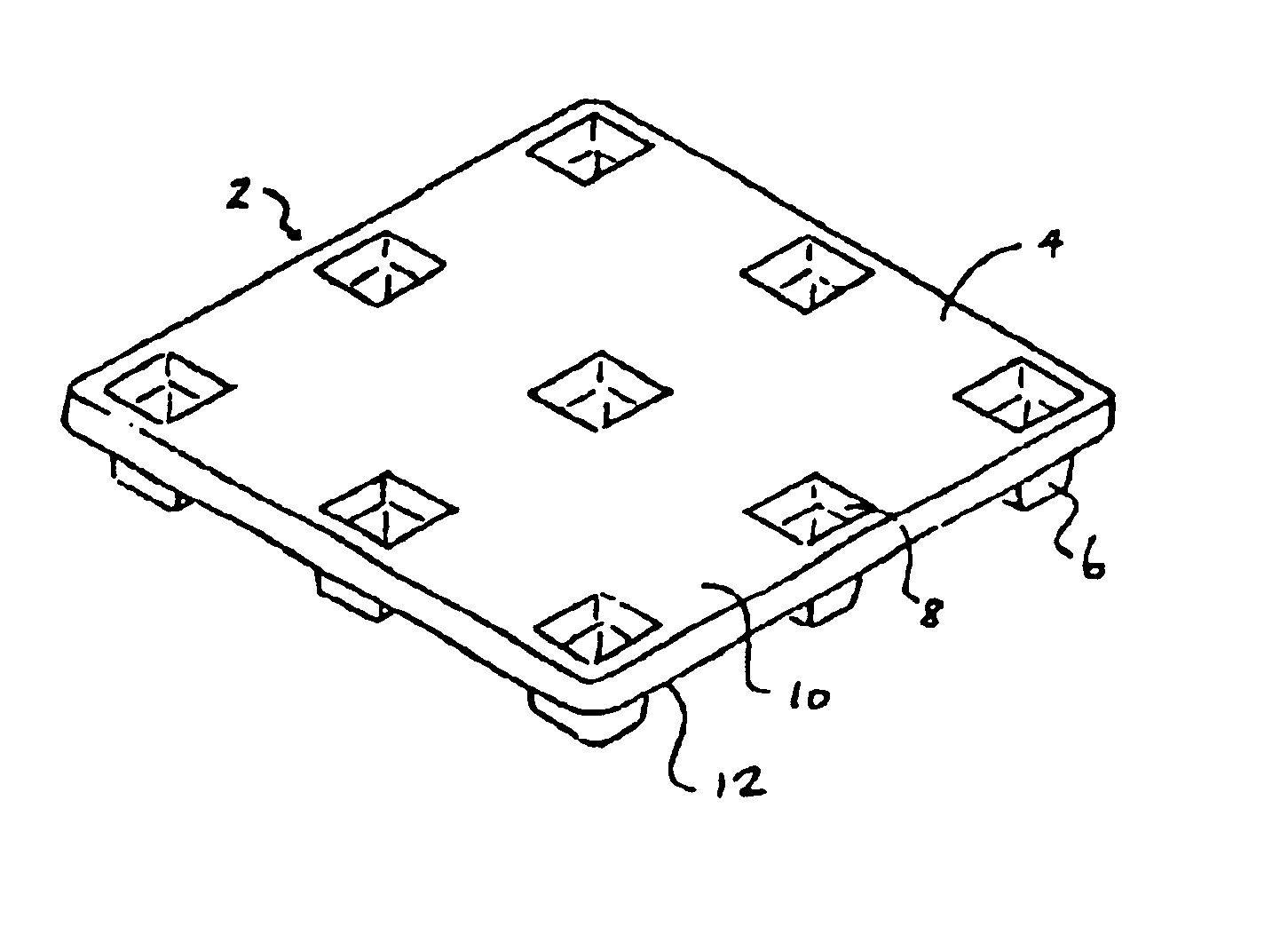
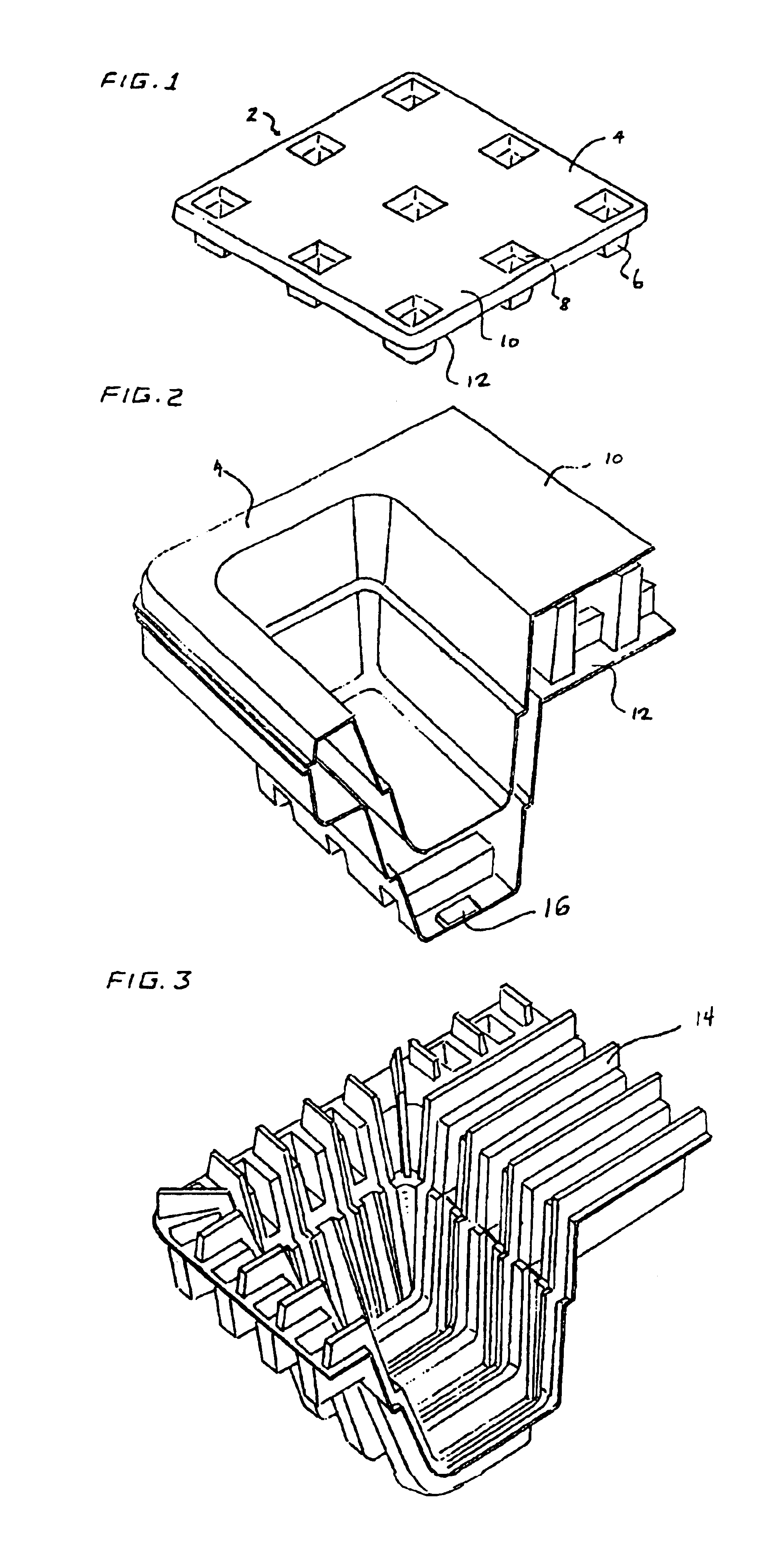
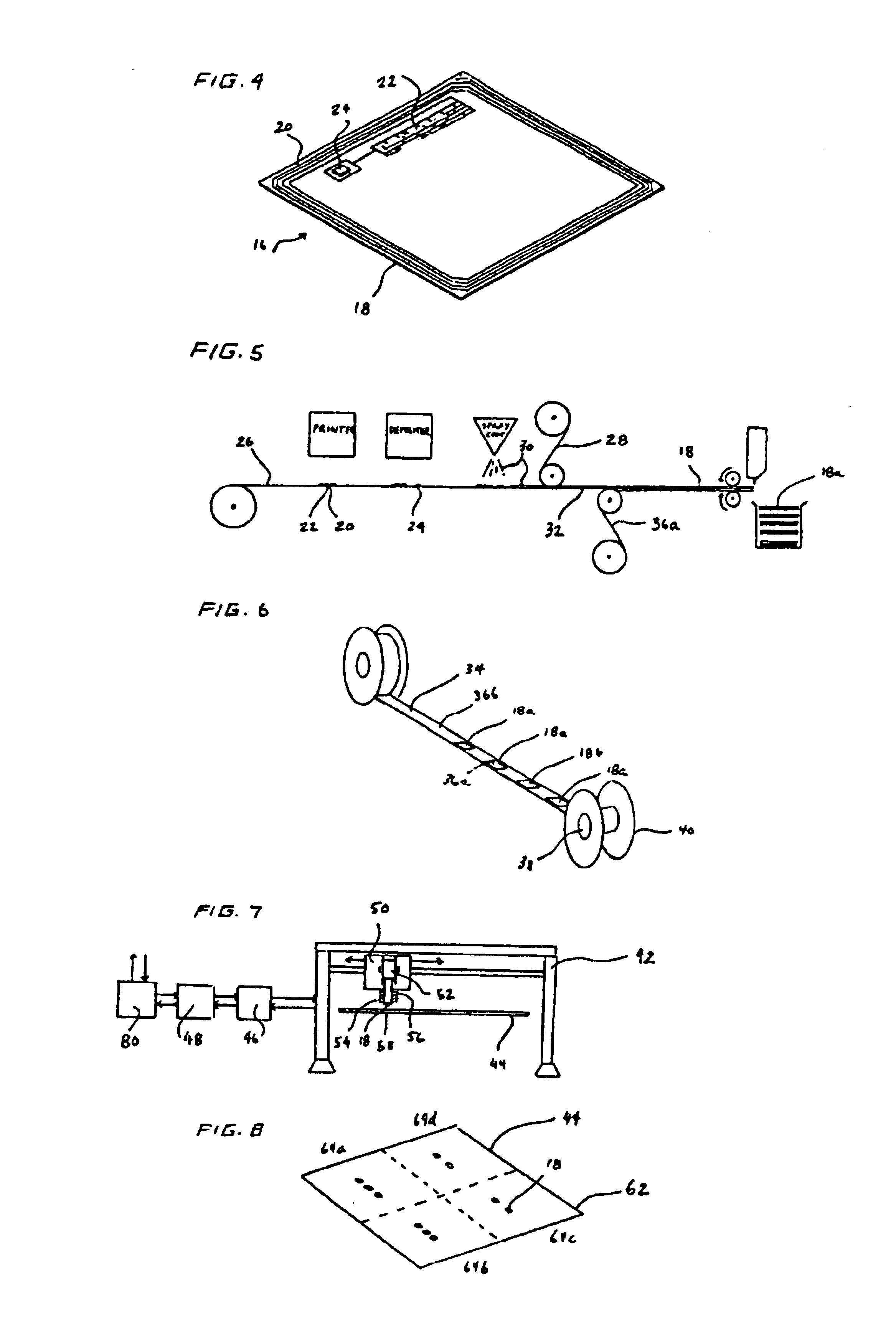
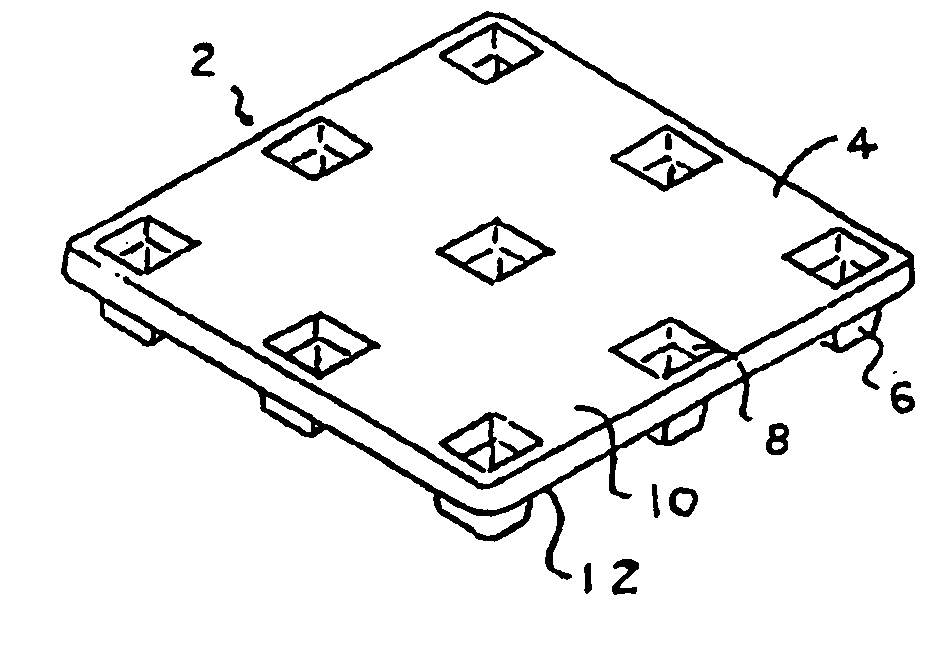
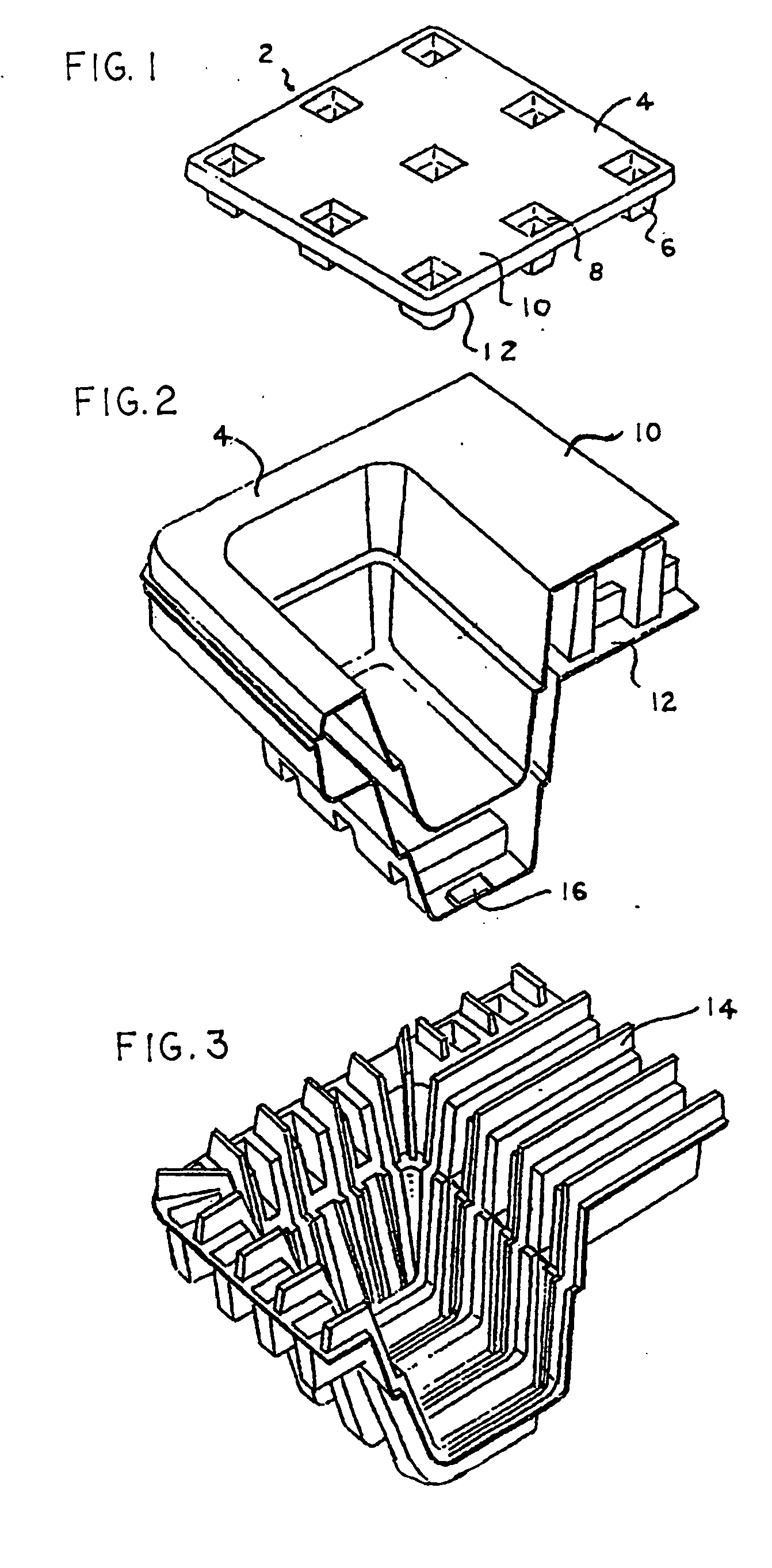
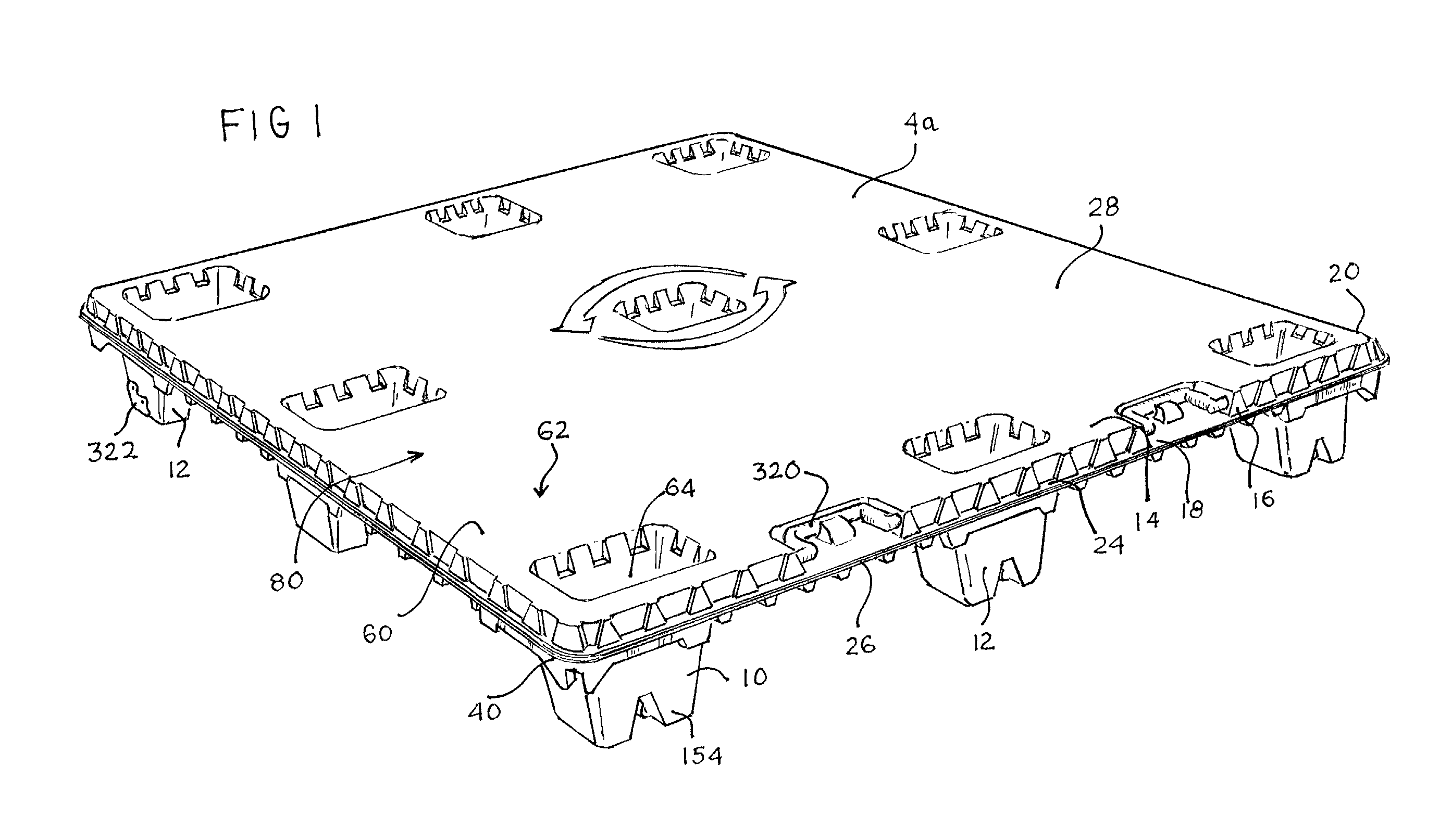
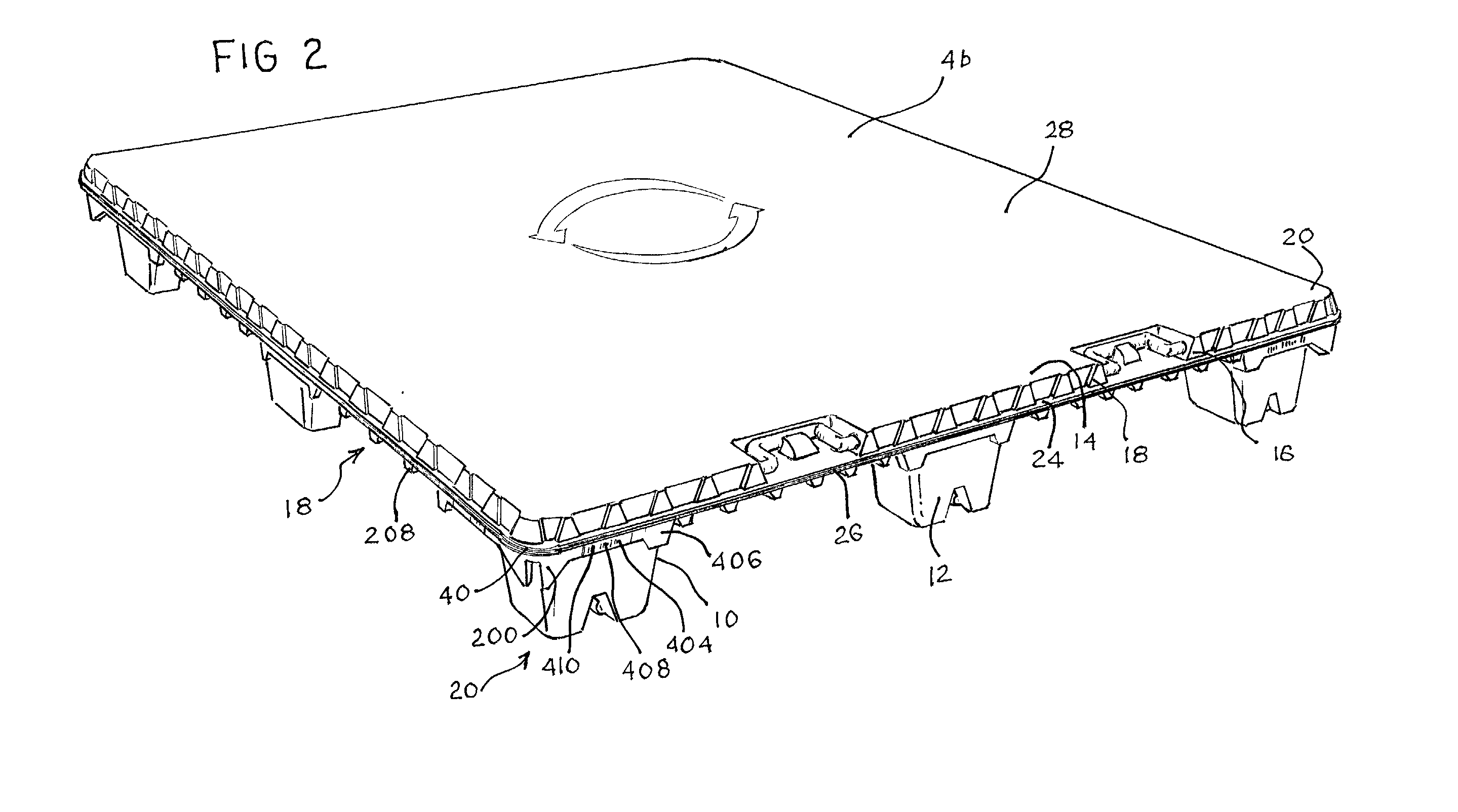
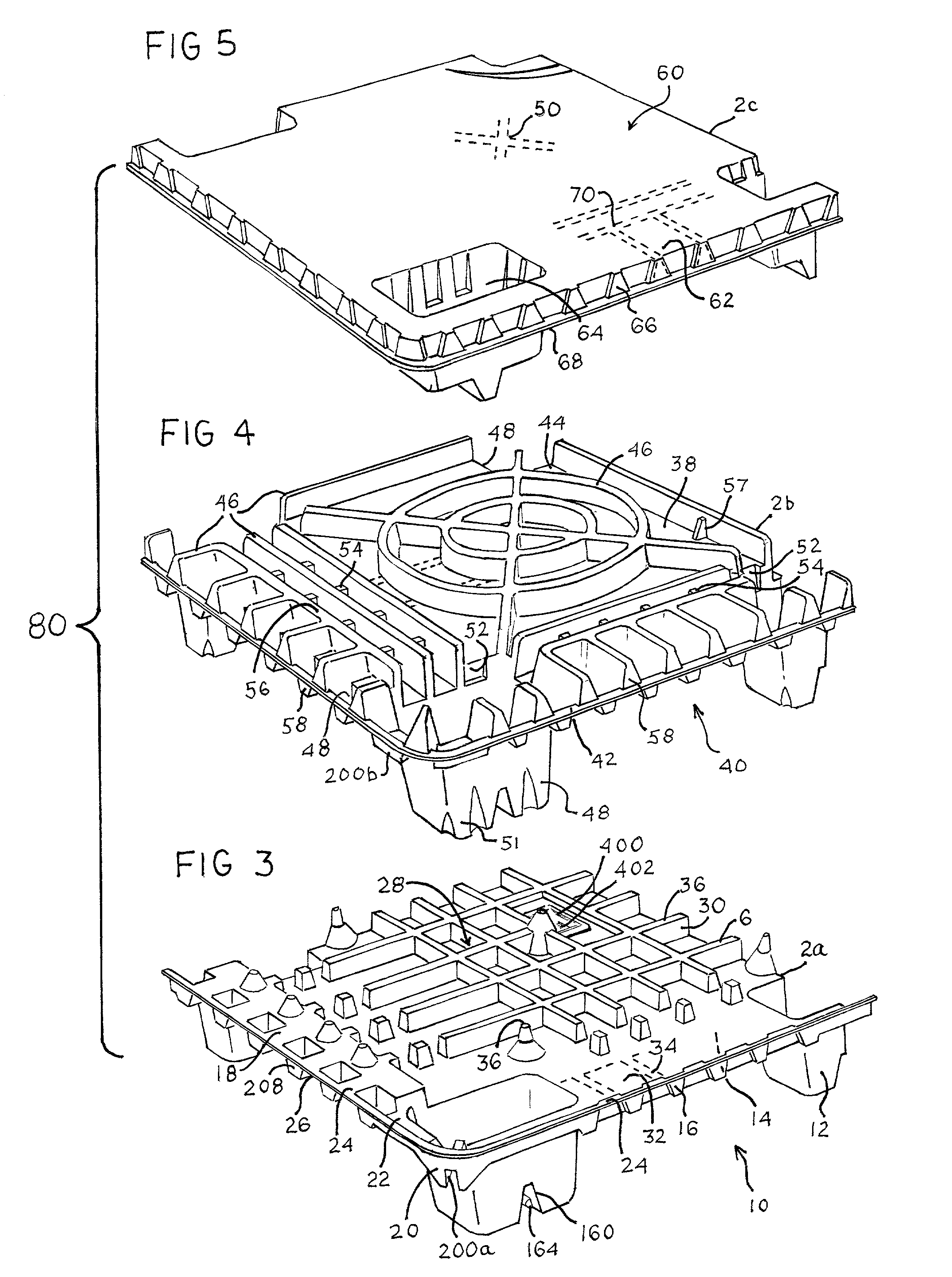
An apparatus has a communications device associated therewith. In another aspect of the present invention, a pallet is made from thermoformed polymeric sheets with an attached communications device. A further aspect of the present invention provides a radio frequency identification device attached to an apparatus. In still another aspect of the present invention, a communications device is incorporated into one or more sheets of a pallet or other container prior to forming. Methods of making and using a thermoformed pallet and container, having a communications device, are also provided.
Owner:NEXTREME
Thermoformed platform having a communications device
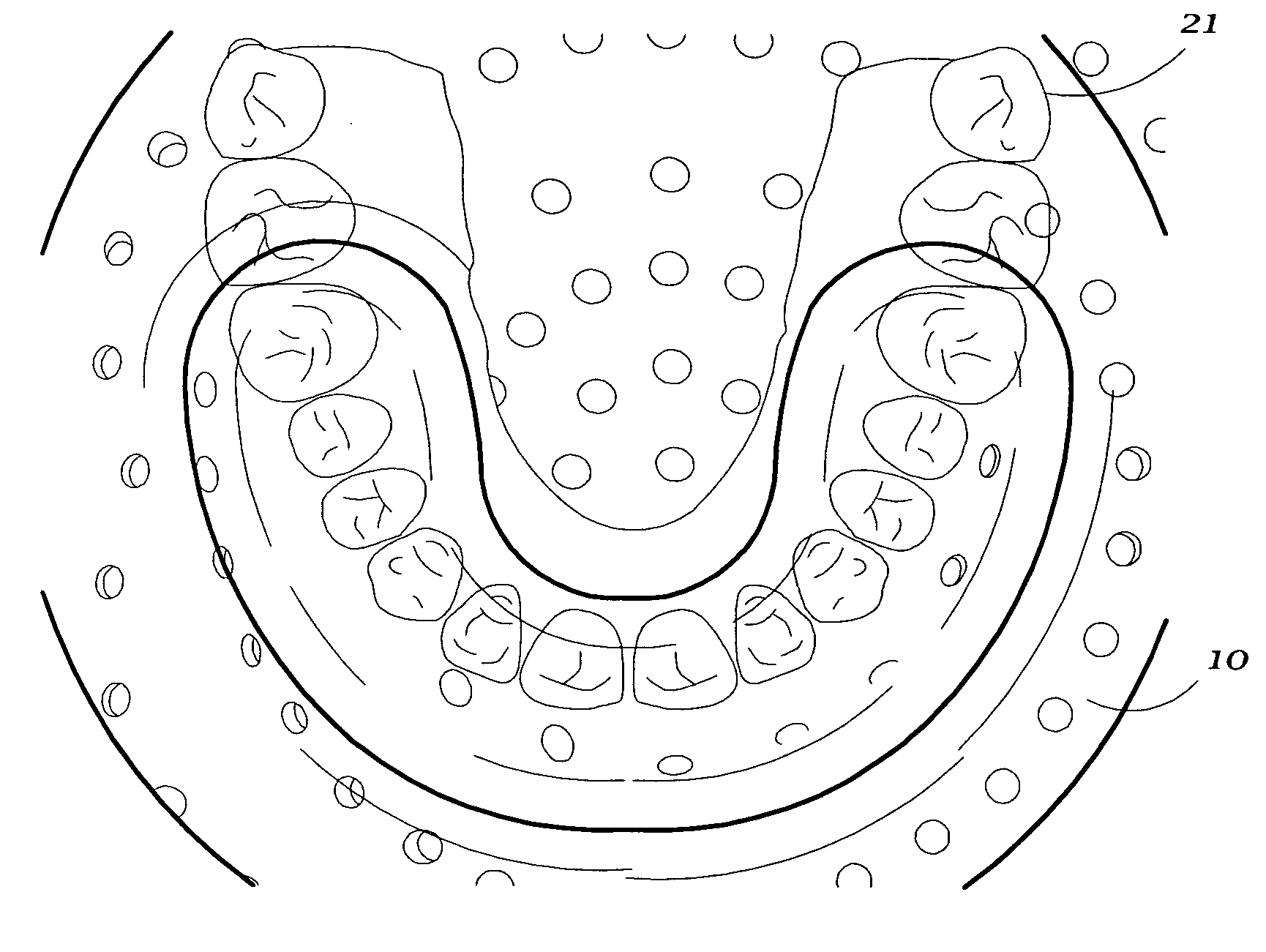
InactiveUS20050241548A1Improve protectionImprove reliability and durabilityContainer decorationsLevel indicationsThermoformingEngineering
An apparatus has a communications device associated therewith. In another aspect of the present invention, a pallet is made from thermoformed polymeric sheets with an attached communications device. A further aspect of the present invention provides a radio frequency identification device attached to an apparatus. In still another aspect of the present invention, a communications device is incorporated into one or more sheets of a pallet or other container prior to forming. Methods of making and using a thermoformed pallet and container, having a communications device, are also provided.
Owner:NEXTREME
Method for creating features in orthodontic aligners
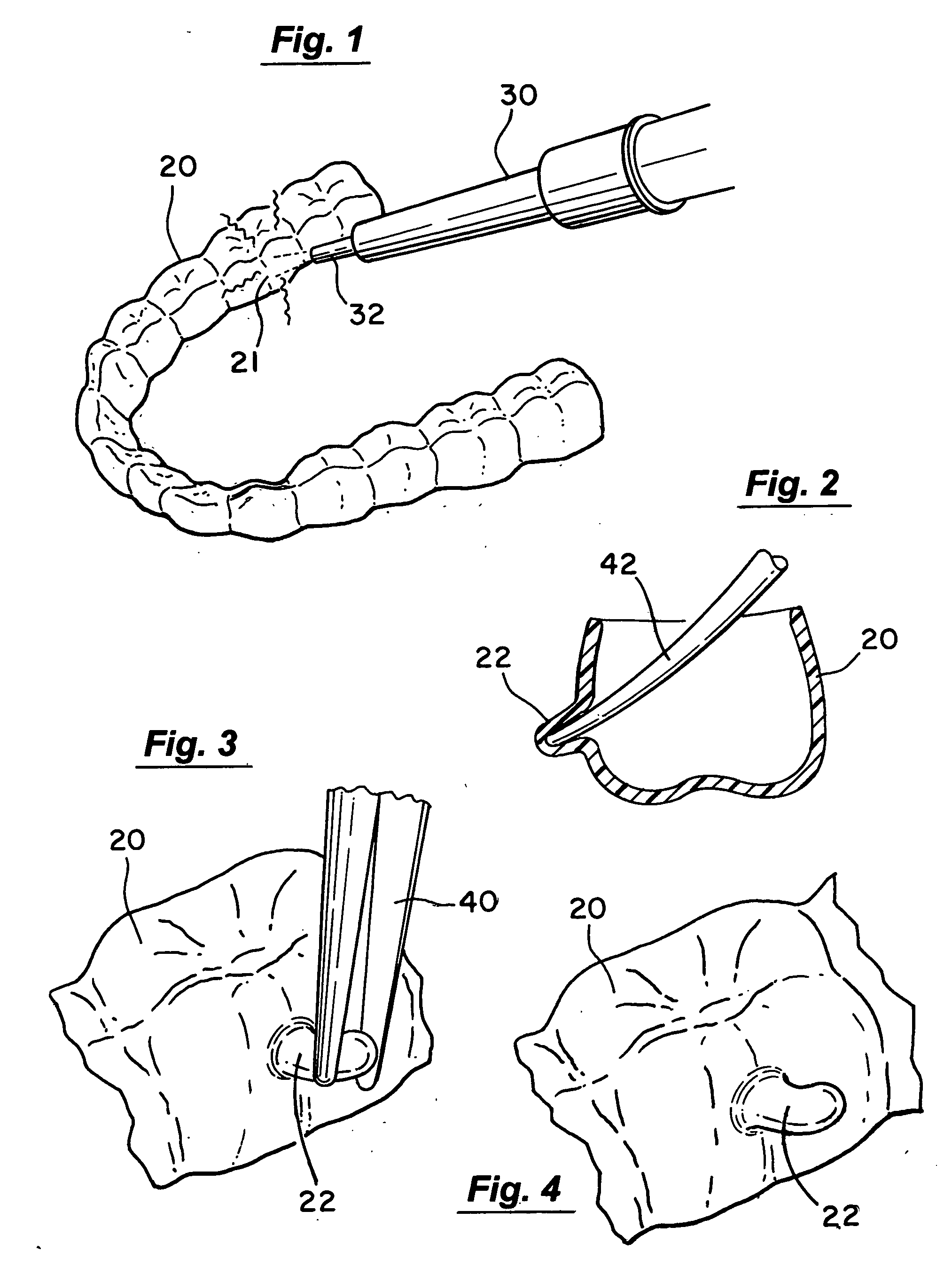
A method for creating features in an orthodontic aligner employs a hot air source having a maximum flow rate of approximately 10 liters per minute to selectively heat a small local region of the aligner above the thermoforming temperature of the aligner material. The heated region of the aligner is manipulated to form the desired feature, and then allowed to cool to solidify the feature. These features can be used, for example, to directly impart therapeutic forces on teeth, or for attachment of aligner auxiliaries to the aligner.
Owner:HILLIARD JACK KEITH
Robotic system for forming features in orthodontic aligners
A robotic system for forming features in orthodontic aligners includes a control system, a platen for three-dimensional positioning of the aligner, a heating station for selectively heating a small region of the aligner, and a thermoforming station for manipulating the heated region to form a desired feature in the aligner. Optionally, a laser cutting and trimming station can also be included to trim excess material from the aligner or to cut features into the aligner. The control system can include a processor with CAD software to enable a user to design features for aligners.
Owner:HILLIARD JACK KEITH
Vehicle interior trim panel with a soft-touch foam layer, and a method and apparatus for making the same
InactiveUS6136415ALow densityFlexible of partLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsDashboardPolyolefin
An interior trim component such as a vehicle dashboard includes a substantially rigid and form-stable substrate of polypropylene and natural fibers, a supporting halo skeleton and other frame components heat fused onto the backside of the substrate, and a polyolefin foam layer as well as a decorative polyolefin cover film laminated onto the front side of the substrate. The foam layer has an increased thickness and a decreased foam density at sharply contoured or curved areas of the trim component, in comparison to the flat surfacial areas. As a result, the trim component has a desirable soft-touch characteristic and impact absorbing properties at all areas including protruding curves and edges. A method for forming such a trim component involves steps of pre-molding the foam layer and cover film by vacuum thermoforming, pre-molding the substrate by vacuum thermoforming, and then heat laminating the pre-heated, pre-molded substrate onto the pre-molded foam layer and cover film. The sharply curved or contoured areas of the component are provided with a greater tolerance spacing between the substrate and the cover film, which are held to the respective mold contours by vacuum. Under the effect of heat and the applied vacuum, the foam layer expands to have a greater thickness and a lower density in these sharply contoured areas.
Owner:HERBERT OLBRICH
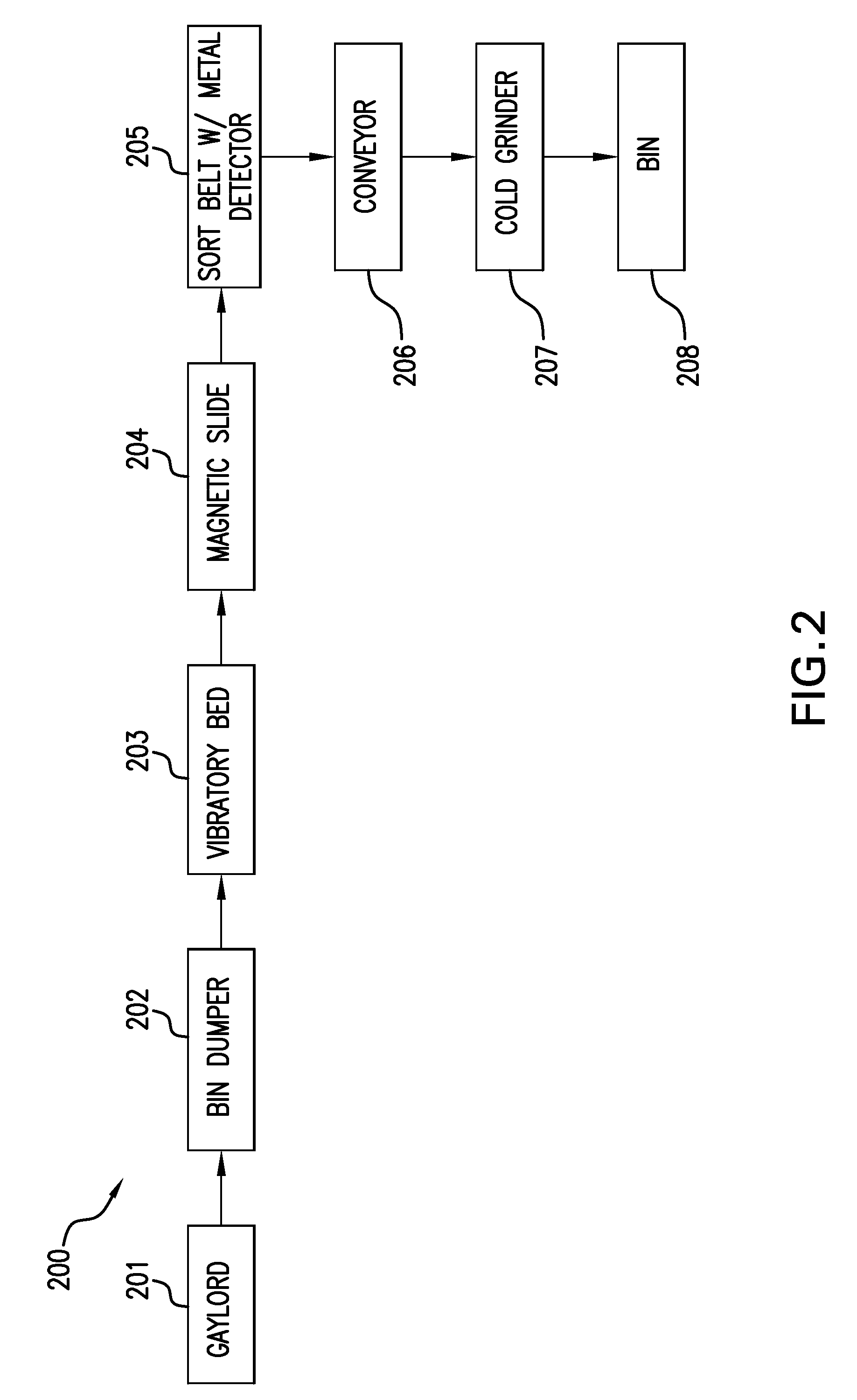
Thermoformed platform
Articles constructed of a plurality of scuffed sheets have improved sheet-to-sheet bond strength and surfaces with high coefficients of friction. Articles constructed out of three scuffed sheets include exterior intumescent polymeric surfaces resisting the spread of combustion flames and insulating the interior surfaces from the high temperature of fire. Articles include electronic apparatus sending an emergency 911 call to a remote monitoring station. Articles are advantageously reinforced with optional rigidifying structures without article modification. Members are joined with snap together features providing an assembled article. Articles include handles for ergonomic manipulation by workers. Articles include elements amenably receiving unitization accessories. The article improvements are demonstrated in the form of industrial platforms, particularly material handling pallets.
Owner:NEXTREME
Method for forming footwear structures using thermoforming
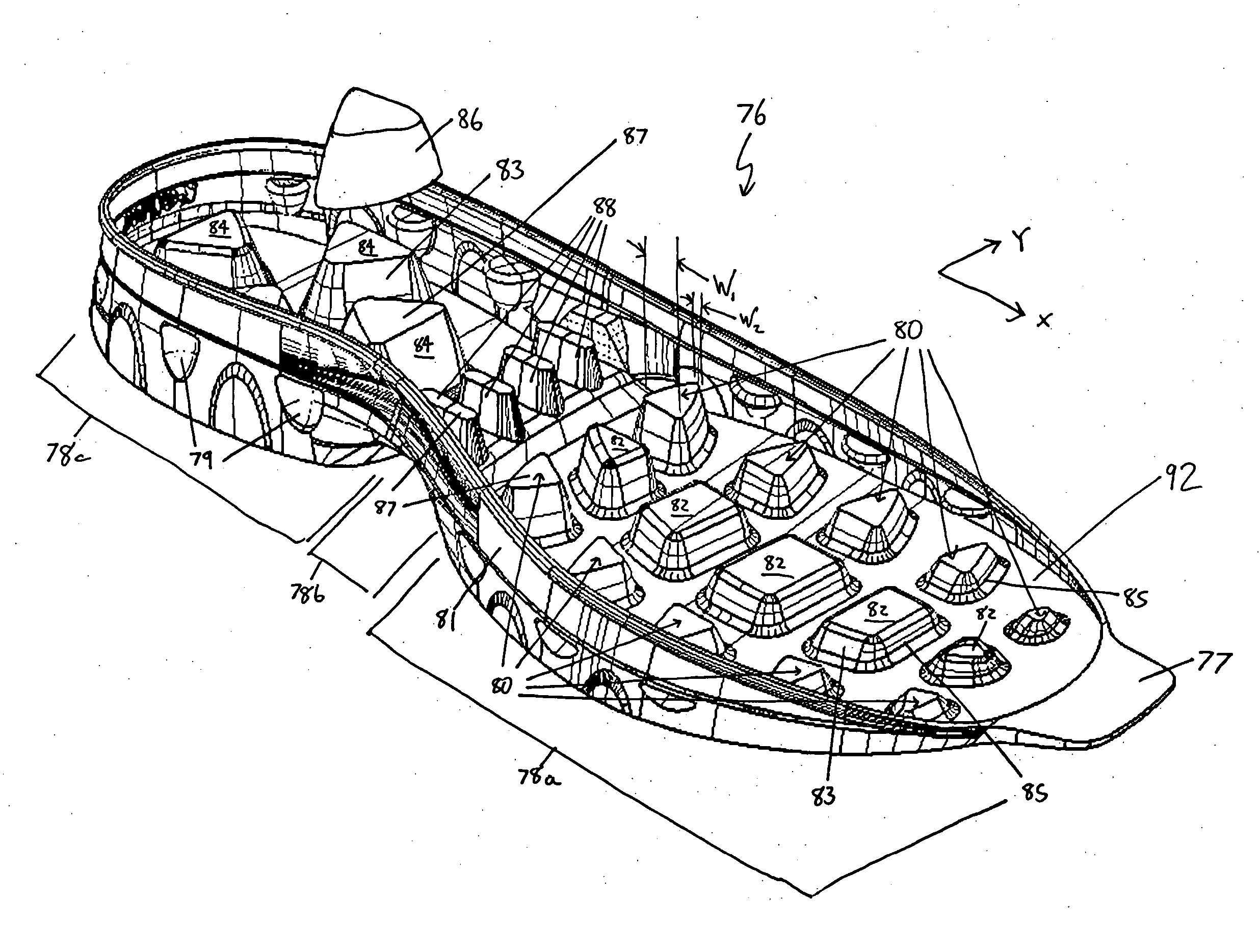
Footwear and footwear structures are provided as well as methods for forming composite components for footwear or footwear structures. In forming the structures, two material layers are overlaid such that the two material layers are in contact with one another. The two material layers are heated to a forming temperature and are then vacuum-formed together to form a composite material layer in a three-dimensional form of the footwear structure. A provided footwear structure includes an upper and a sole assembly attached to the upper. The sole assembly includes a first material layer made of a thermoplastic, and a second material layer attached to the first material layer. The first material layer includes a recessed area including a flat support portion, and is transparent or translucent. The second material layer includes a portion that is positioned on a surface of the recessed area, and a color of the second material layer indicates a location and / or a function of the second material layer.
Owner:POLYWORKS
Internal heater for thermoform plastic sheet
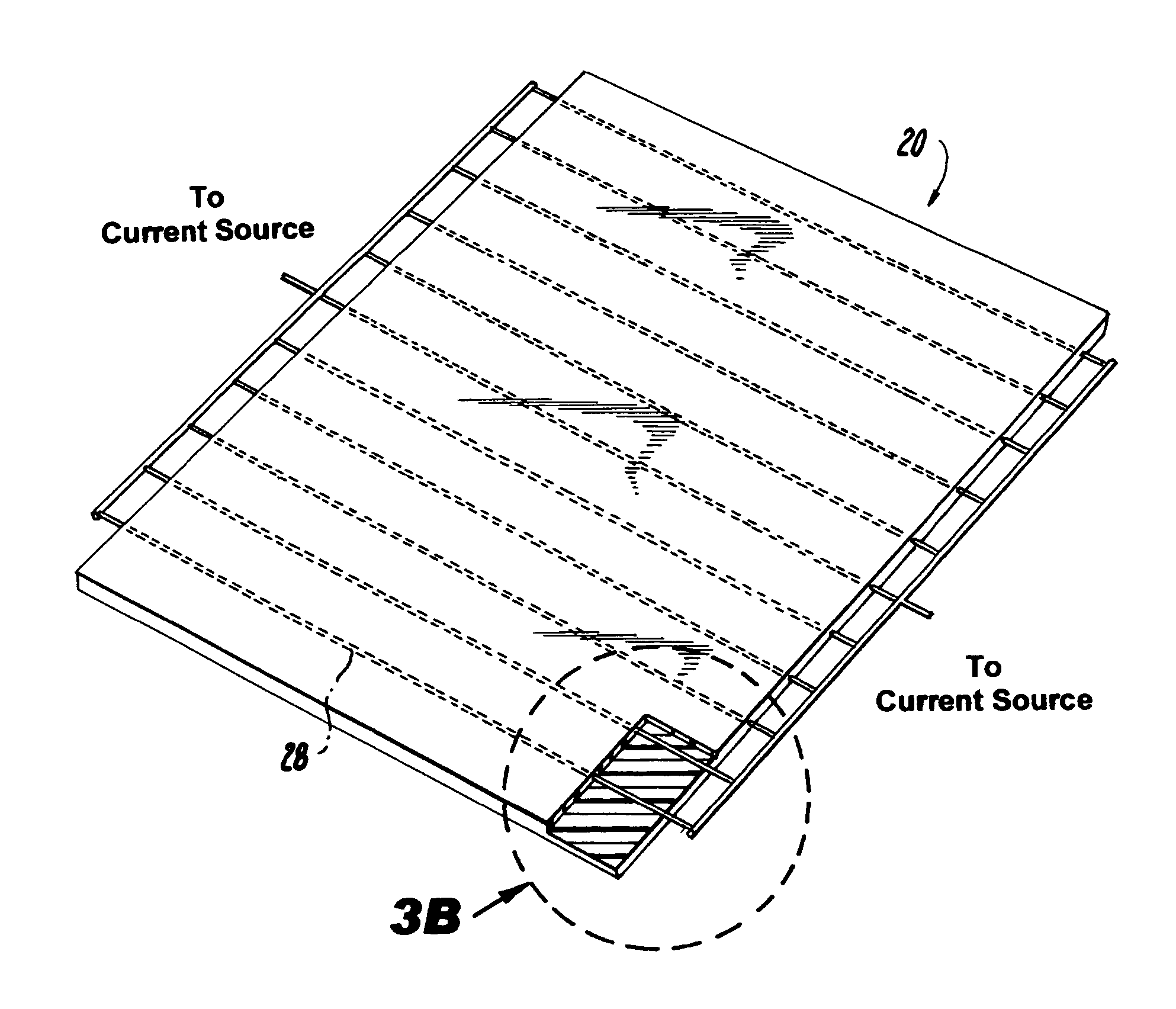
InactiveUS8017891B2Eliminate needHeating element shapesDomestic articlesElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
A plastic material sheet for use in vacuum thermoforming is formed of polymer material. Electrically conductive resistance elements, at least a portion of which are situated within sheet, conduct electrical current to heat the sheet. The elements are generally parallel to each other. They may be straight, have a generally zigzag configuration, a generally serpentine configuration, an arcuate configuration, or a grid-like configuration. The elements may each have a section that extends substantially beyond the edge of the sheet. They may be frangible. They may be embedded deeply within the sheet or may be situated proximate a surface of the sheet.
Owner:NEVIN DONALD
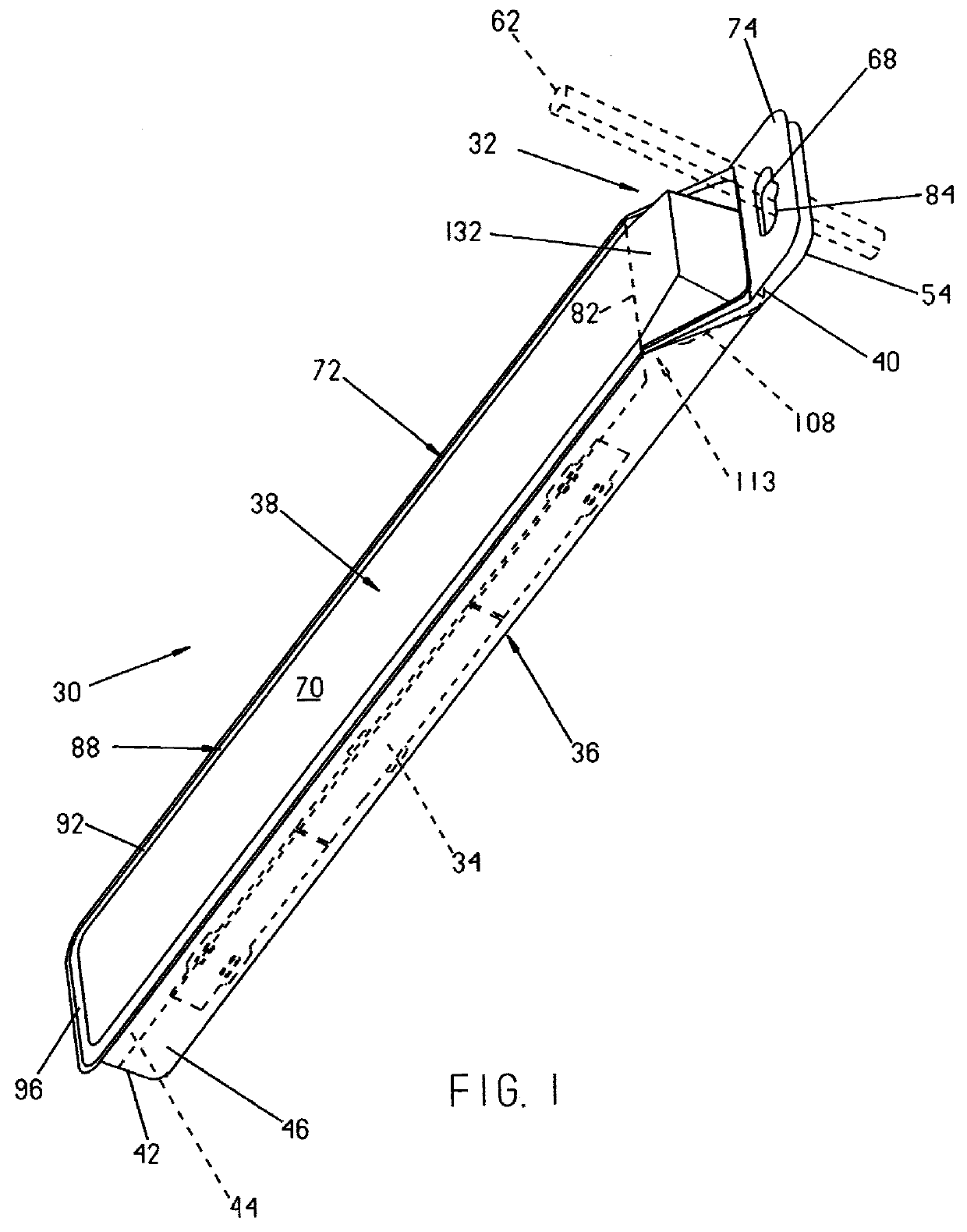
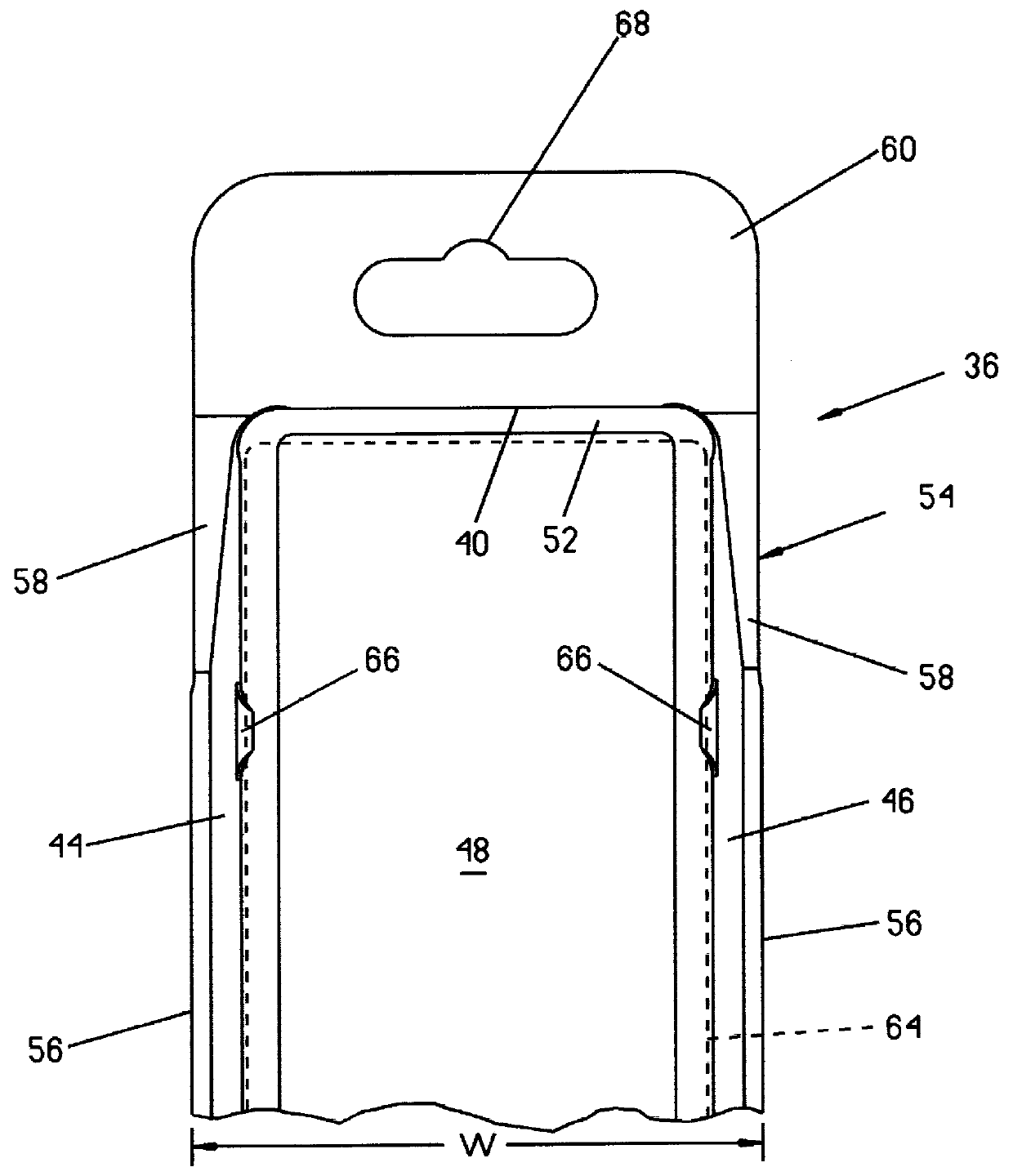
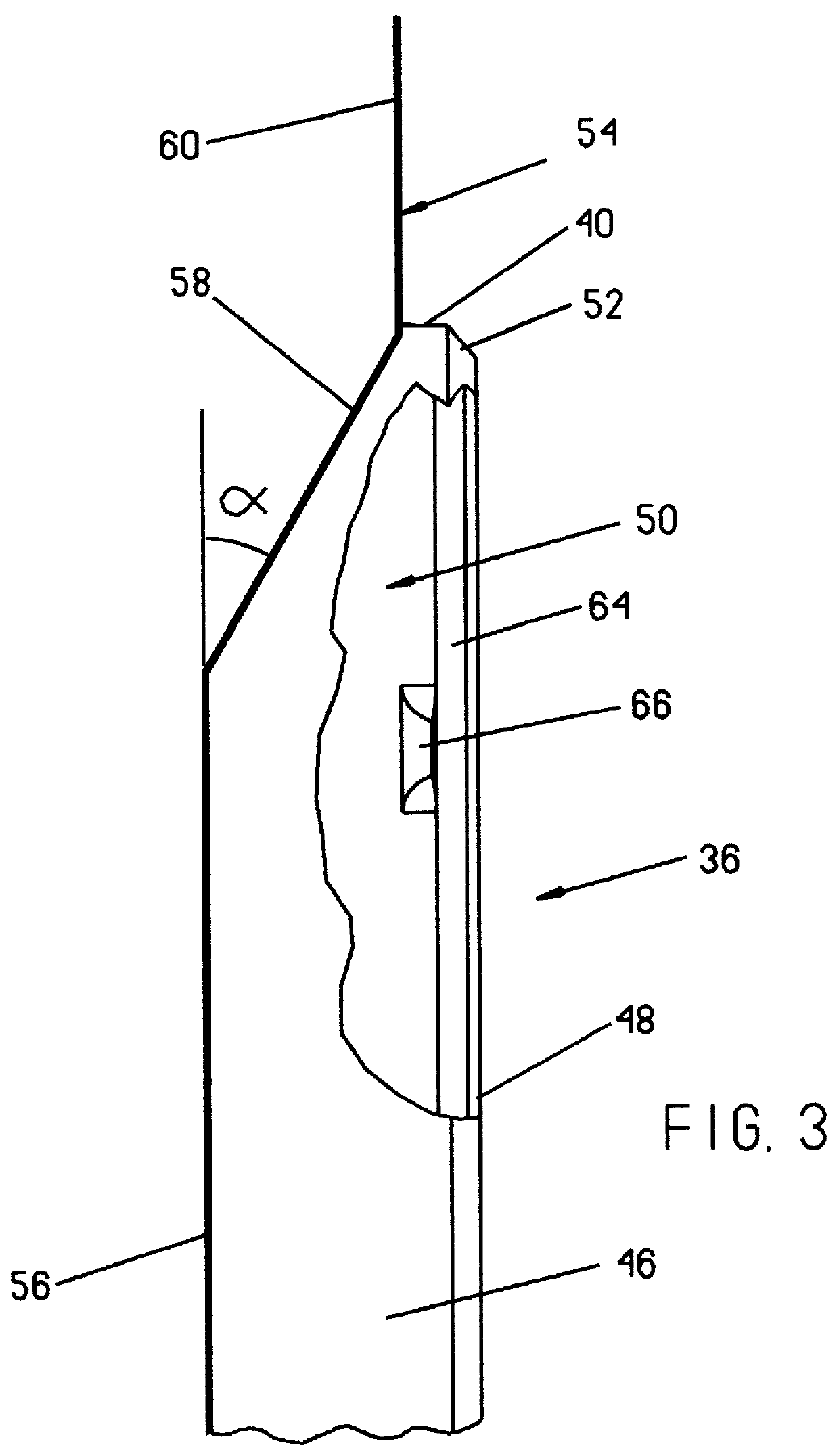
Reclosable package and method
InactiveUS6070723AWidth minimizedMaximizing usable package volumePackaging vehiclesContainers for machinesEngineeringBlisters
A reclosable package and method having an integral reclosable door adjacent one end that permits article removal from the end of the package. The package is comprised of a thermoformed blister body joined to a thermoformed backing body. The blister body has sidewalls, endwalls and a peripheral flange broken into a first section adjacent the door where the height of the sidewalls decrease and a second section opposite the door with the first section angled relative to the second section. The backing body carries the door and has an integral peripheral rib inboard of a peripheral flange with the flange having a first section about the door and a second section disposed away from the door. The rib has a pair of longitudinally-extending sections divided by a notch that preferably is a transverse rib that causes the door to bend about a desired fold line that runs generally through or adjacent the ribs or notches when urged away from a closed position. In a preferred method, after performing a multilevel trim operation to trim the multiplanar flanges of one or both the blister body and the backing body, the two bodies are joined at the flange sections about a portion of the periphery to adjacent the fold line using an energy welding process, preferably RF welding, that produces a narrow tear seam that enables finished package flange width to be minimized to thereby also minimize package width.
Owner:PORTAGE PLASTICS
Method for producing upsized frp member
InactiveUS20040130072A1Improve mass productionReduce manufacturing costLamination ancillary operationsLaminationAir cycleFiber
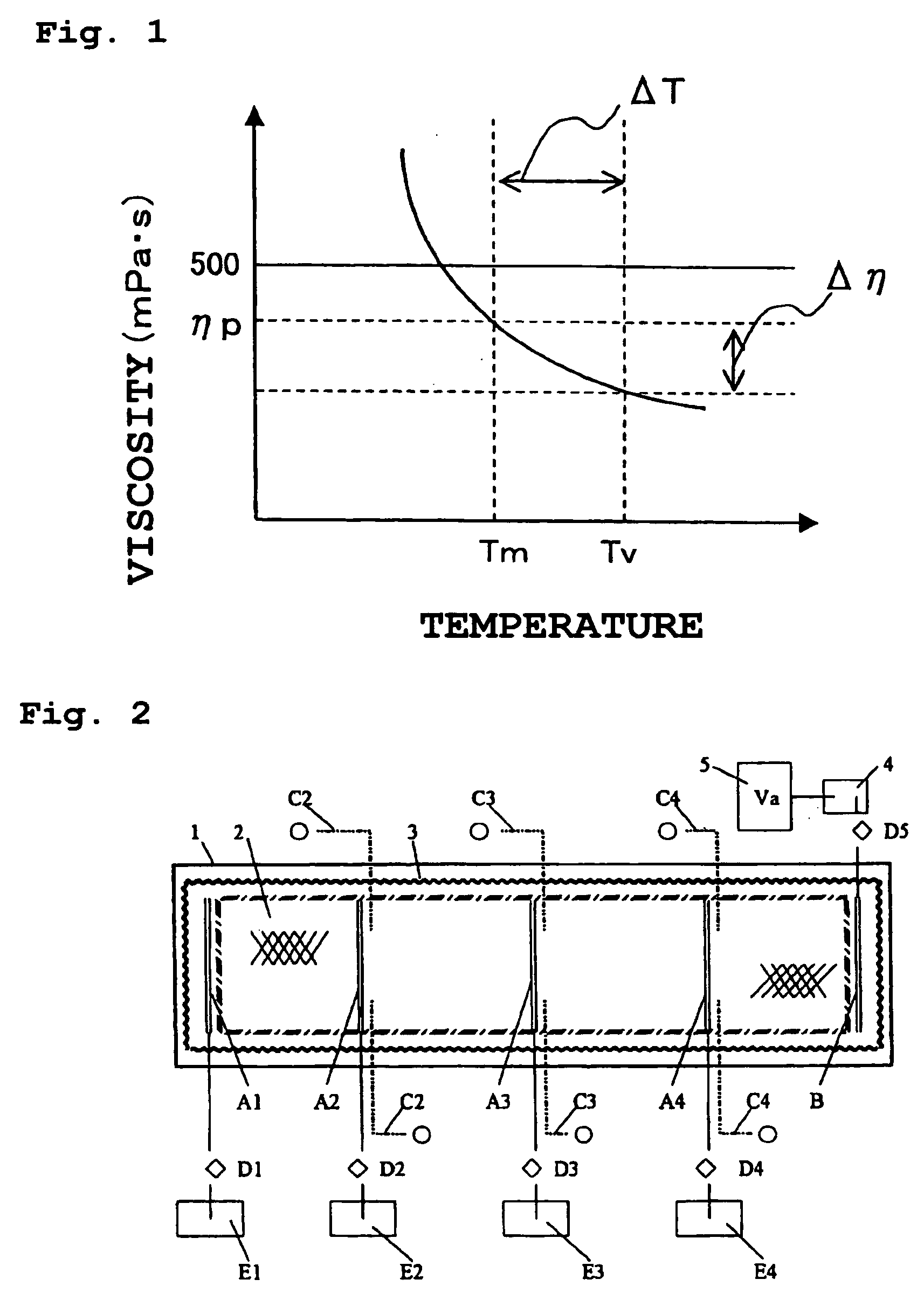
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a large FRP member and has the following structure. The method for manufacturing a large FRP member, comprising the following steps (A) to (F). They are: setting step (A) of disposing a preform containing a reinforcing fiber base material on a surface of a molding die; sealing step (B) of covering a molding portion with a bagging material or a mold and providing at least one suction port and at least one resin injection port for sealing; evacuating step (C) of evacuating the molding portion through the suction port; hot-air heating step (D) of heating the molding portion by hot air; resin injection step (E) of injecting a thermosetting resin from the resin injection port for impregnating the reinforcing fiber base material with the resin while a temperature Tm of the molding die and a temperature Tv of the bagging material or the mold are both set to room temperature or more, and a difference DeltaT in temperature between the Tm and the Tv is set to 10° C. or less; and curing step (F) of curing the resin by maintaining the molding portion at a predetermined temperature Tpc which is equal to or more than room temperature. Preferably, the preform described above includes the reinforcing fiber base material and a resin distribution medium. In addition, it is preferable that in the hot-air heating step (D), the molding die be placed in a sealed chamber which is heat insulated with a heat insulating material, the hot air be circulated and supplied, and timing of starting the injection of the resin from a plurality of the resin injection ports be controlled in accordance with signals supplied from resin detection sensors provided in the molding die. The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a large FRP member having superior quality at an inexpensive cost and with high production yield, in which non-impregnated portions and voids are unlikely to be formed.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
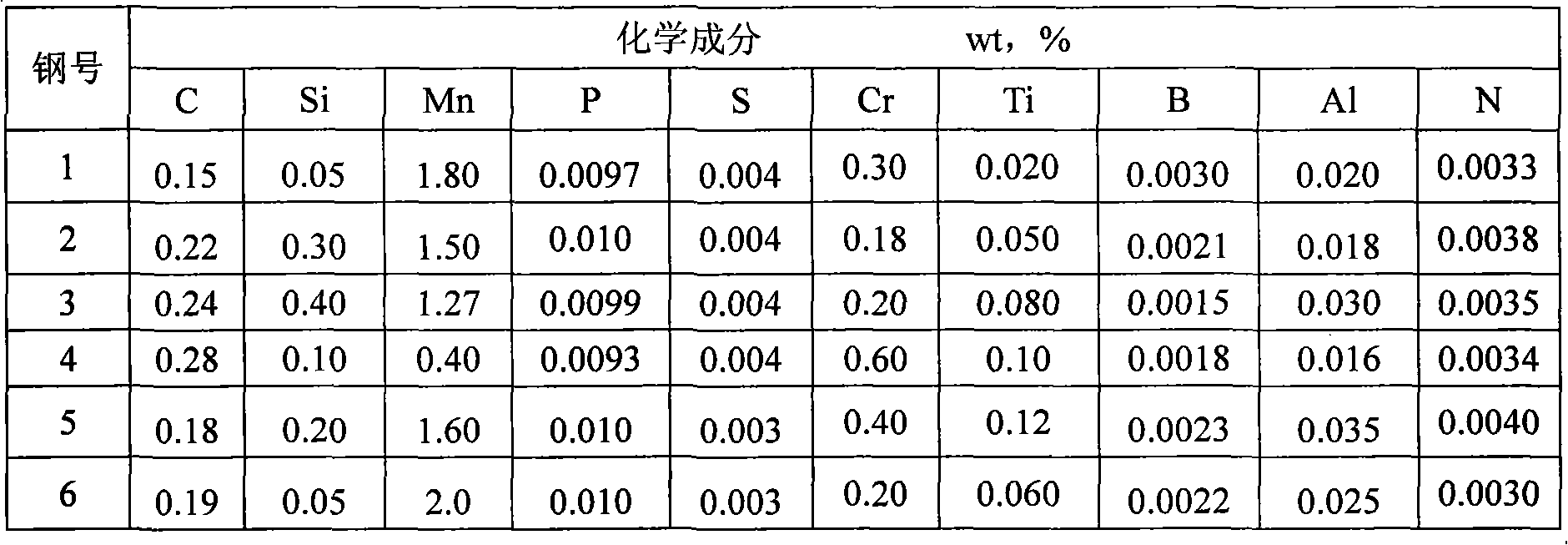
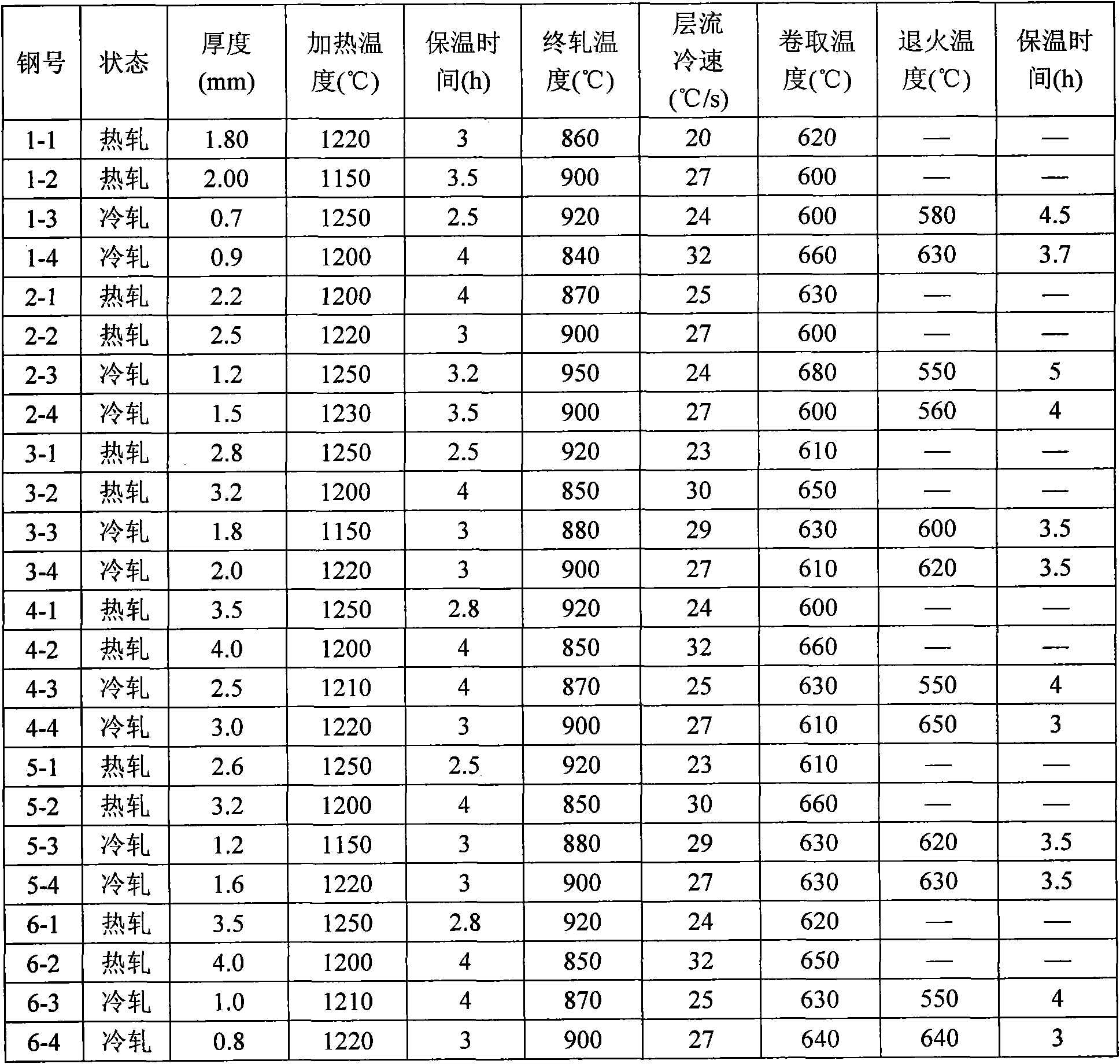
Steel plate for stamping and quenching and thermoforming method of steel plate
ActiveCN102031456ASimple compositionPlay the effect of weight reduction and energy savingHot stampingSimple component
The invention discloses a steel plate for stamping and quenching and a thermoforming method of the steel plate. The steel plate comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.14-0.28% of C, less than 0.40% of Si, 0.4-2.0% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.010% of P, less than or equal to 0.004% of S, 0.016-0.040% of Al, 0.15-0.8% of Cr, 0.015-0.12% of Ti, 0.0001-0.005% of B, less than or equal to 0.005% of N, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The thermoforming method comprises the following steps: blanking by shearing the steel plate, and heating at Ac3 to (Ac3+80) DEG C to carry out austenization; after insulating for 5-10 minutes in the heating furnace, immediately transferring the steel plate to a metal mold the inside of which is cooled by introducing water, and stamping at the high temperature of 650-850 DEG C; cooling the formed workpiece in the closed mold, and cooling the mold by water circulation in the mold, wherein the cooling rate is greater than the critical cooling rate when austenite forms martensite, and the temperature of the workpiece leaving the hot stamping production line is below 150 DEG C; and carrying out air-cooling to room temperature. The steel plate has the advantages of simple component system and favorable hardenability; and the substrate tissues, which are ferrite and pearlite, are processed by hot stamping andquenching to obtain the all martensitic structure. The tensile strength of the steel plate can be higher than 1300 N / mm<2>.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
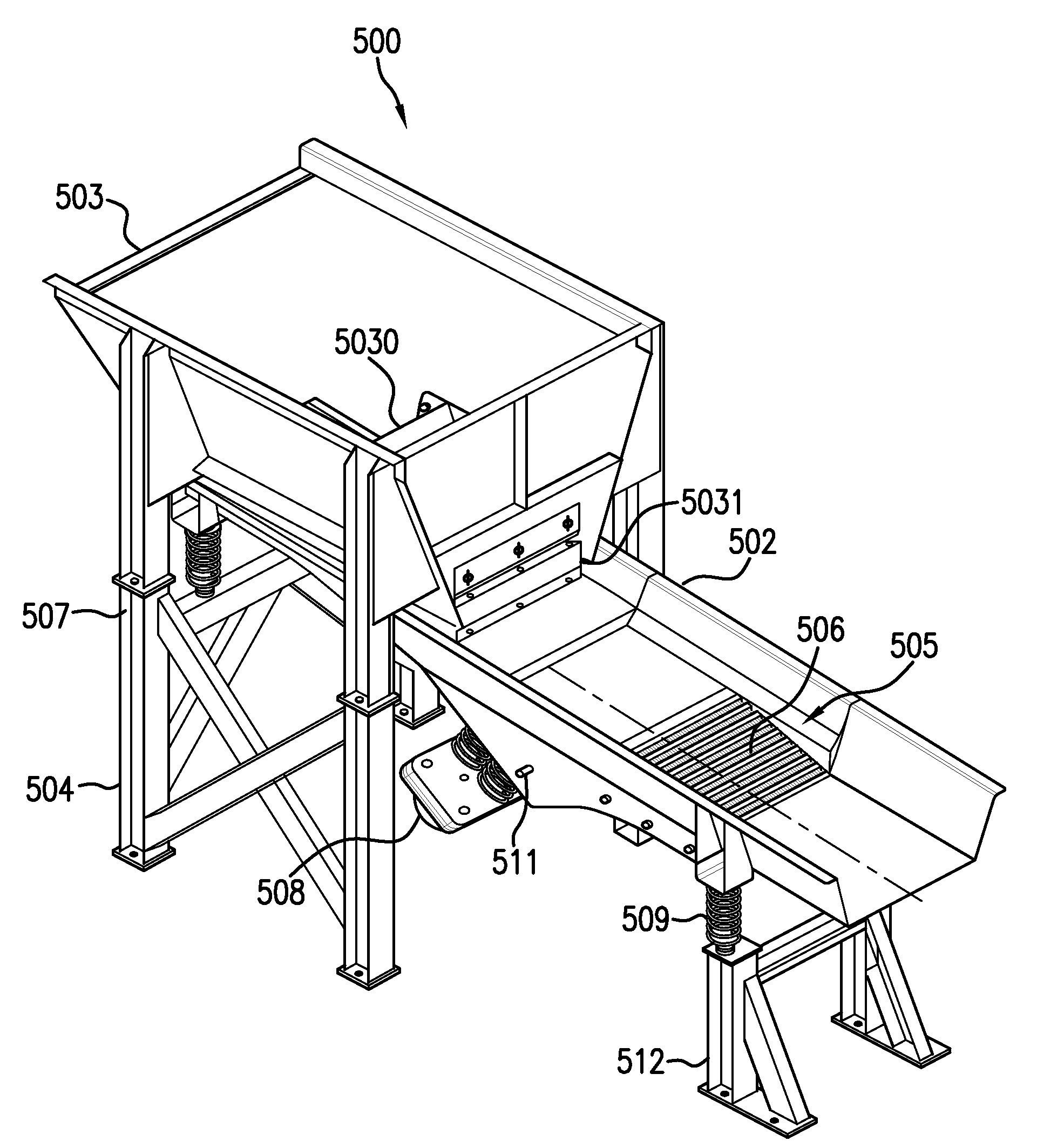
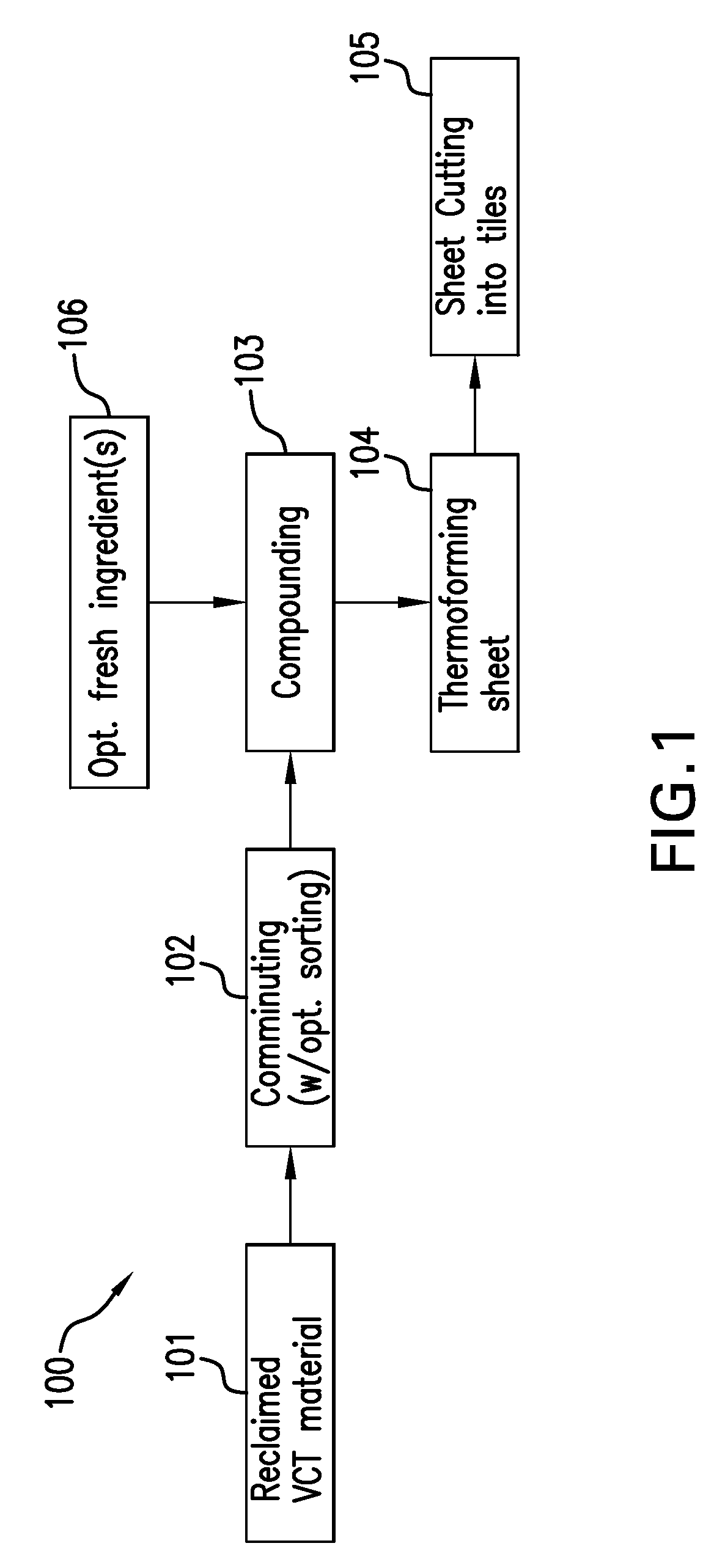
Surface Coverings Containing Reclaimed VCT Material, and Methods and Systems For Making and Using Them
InactiveUS20090226662A1Offset rising material costReduces virgin material requirementCovering/liningsWallsAdhesivePre treatment
Surface coverings, such as vinyl flooring, carpeting and the like, comprising reclaimed VCT material, are disclosed. Vinyl composition tile (VCT) having at least 5% by weight reclaimed vinyl composition tile material which can include a surface adhesive, and filler, where the mixture is a thermoformed solidified material in individual tile form is disclosed. Methods for making these surface covering materials and using them to provide floor coverings are also disclosed. A system for presorting and grinding reclaimed VCT to provide feed material for these and other uses is also disclosed.
Owner:MANNINGTON MILLS
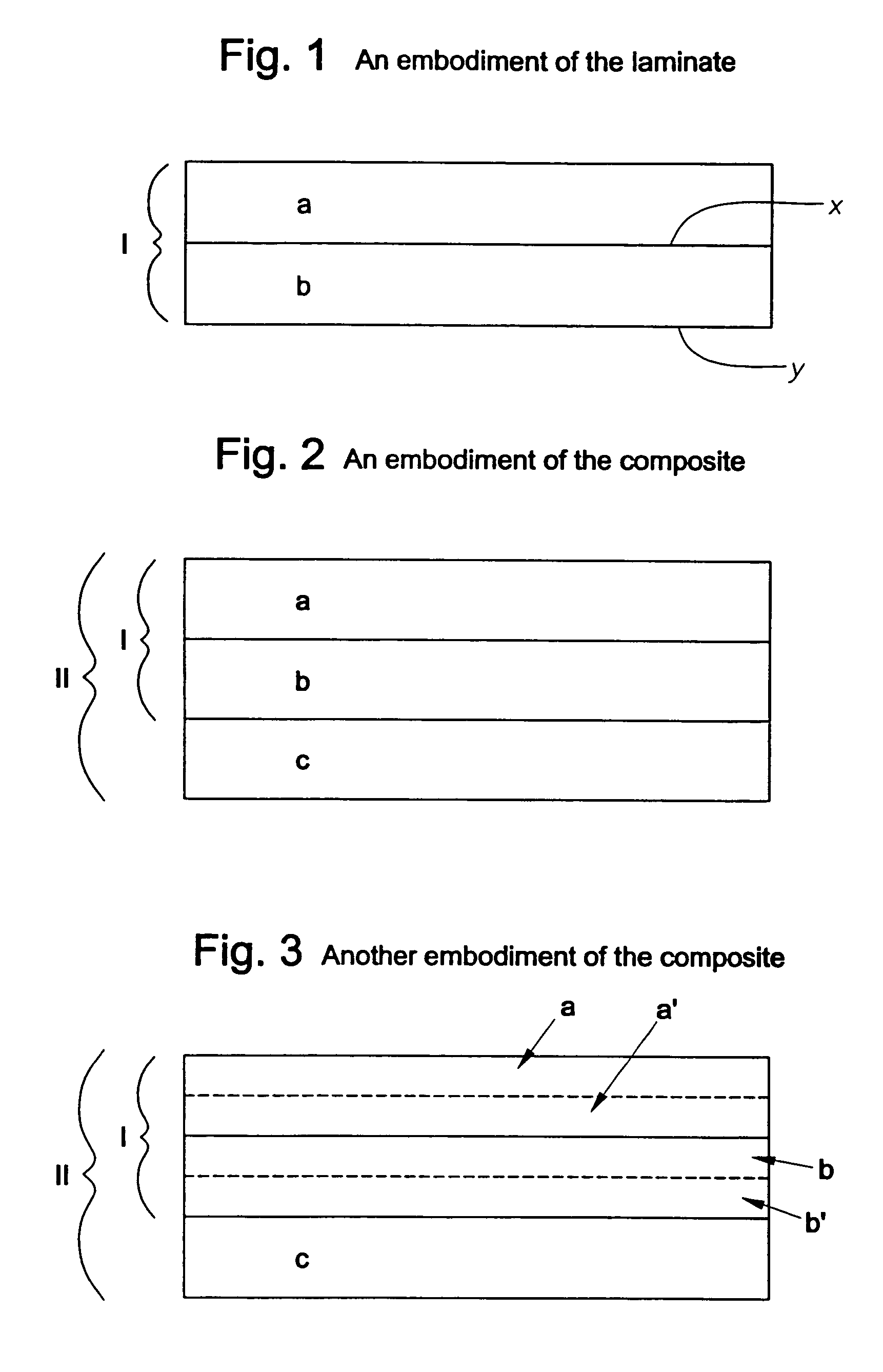
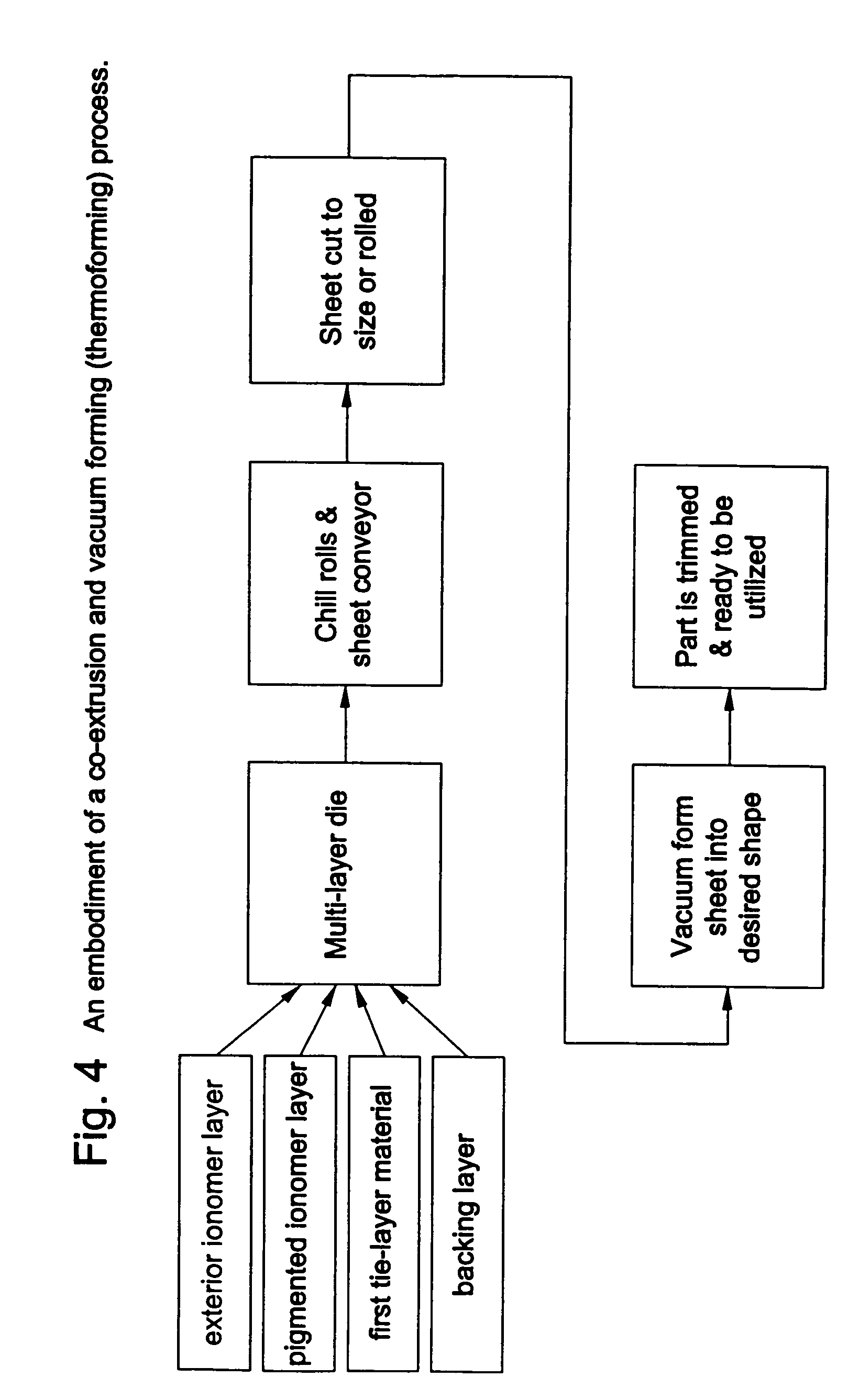
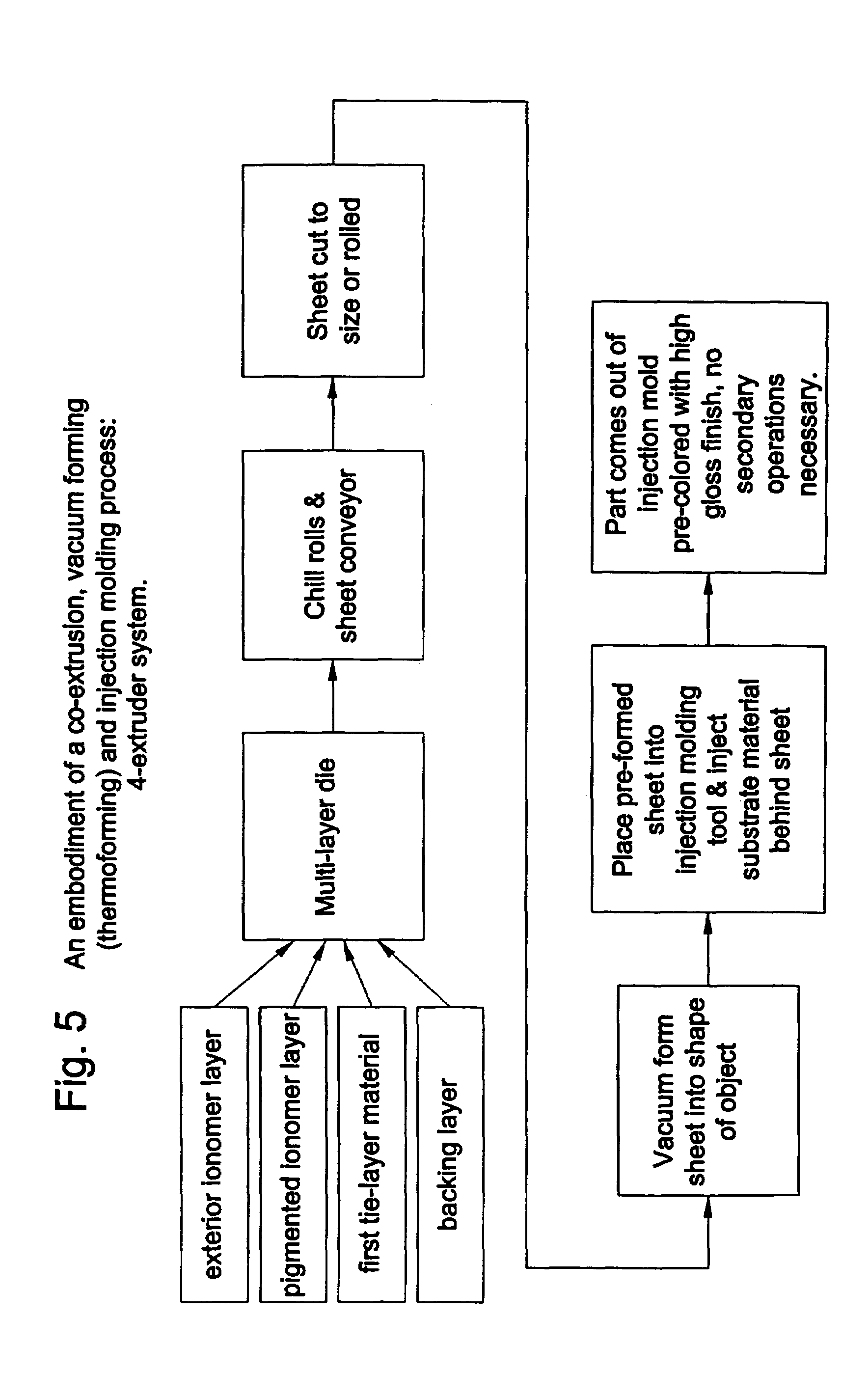
Ionomer laminates and articles formed from ionomer laminates
InactiveUS7405008B2Lamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsIonomerPolymer science
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
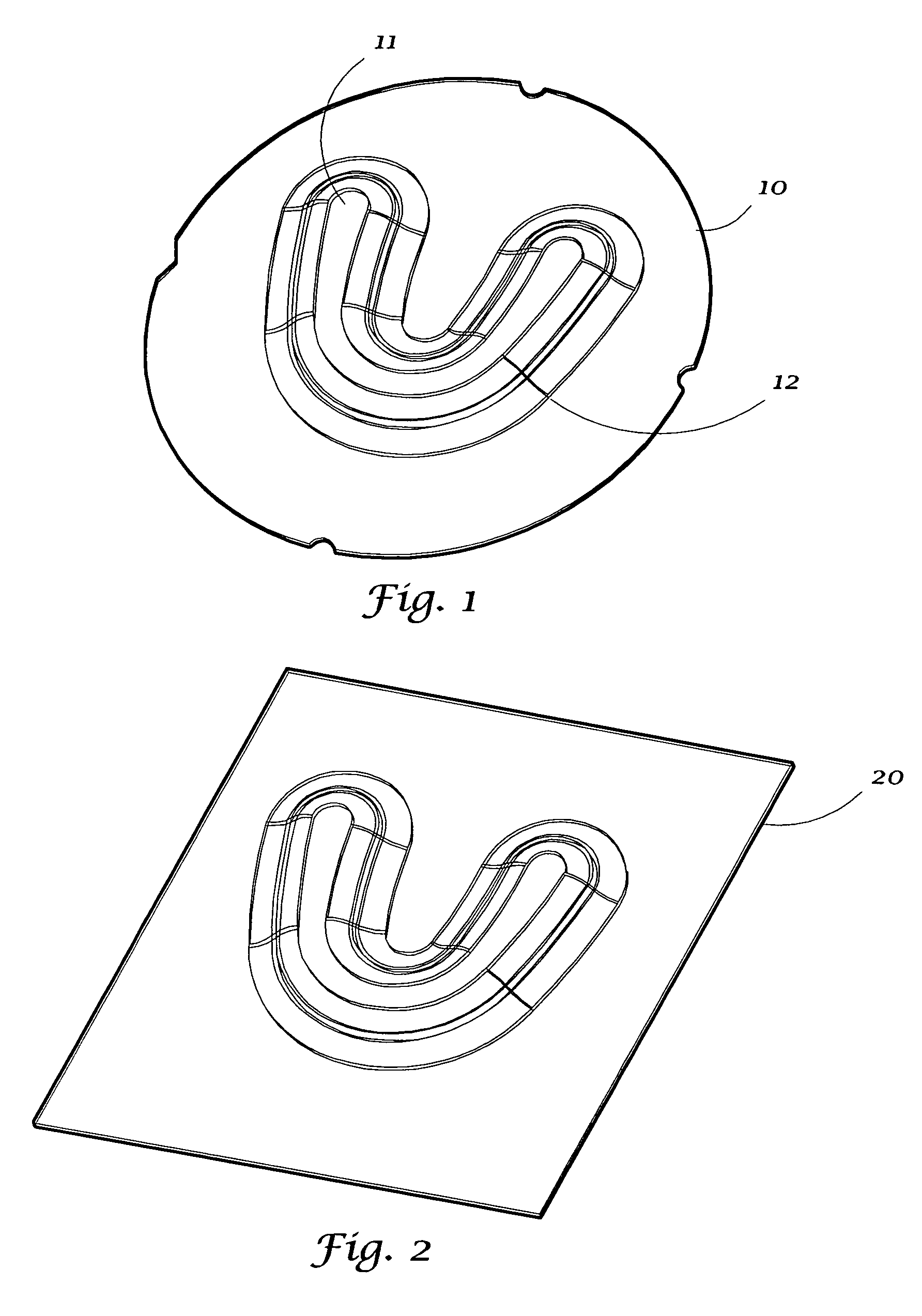
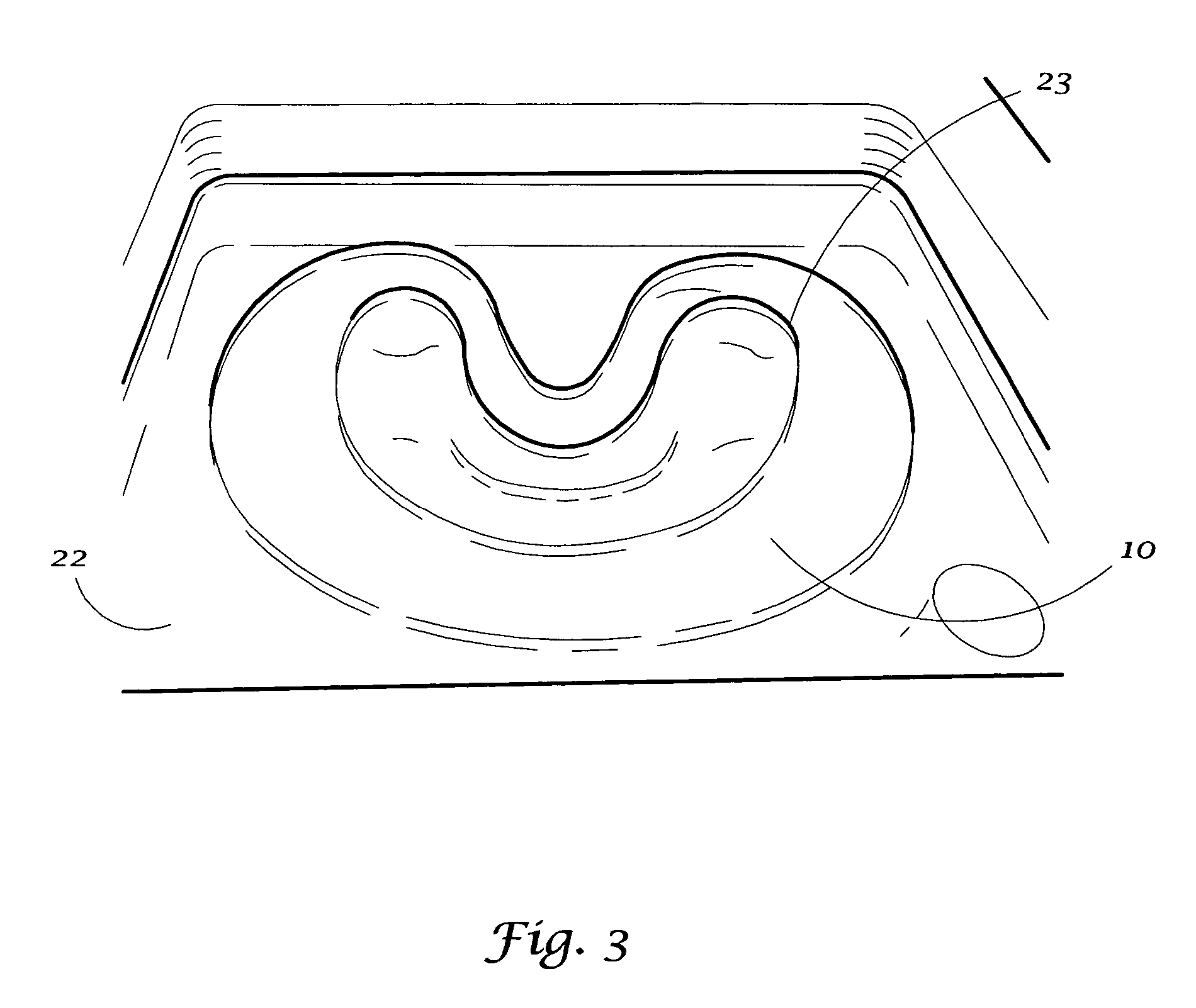
Thermoforming plastic type II
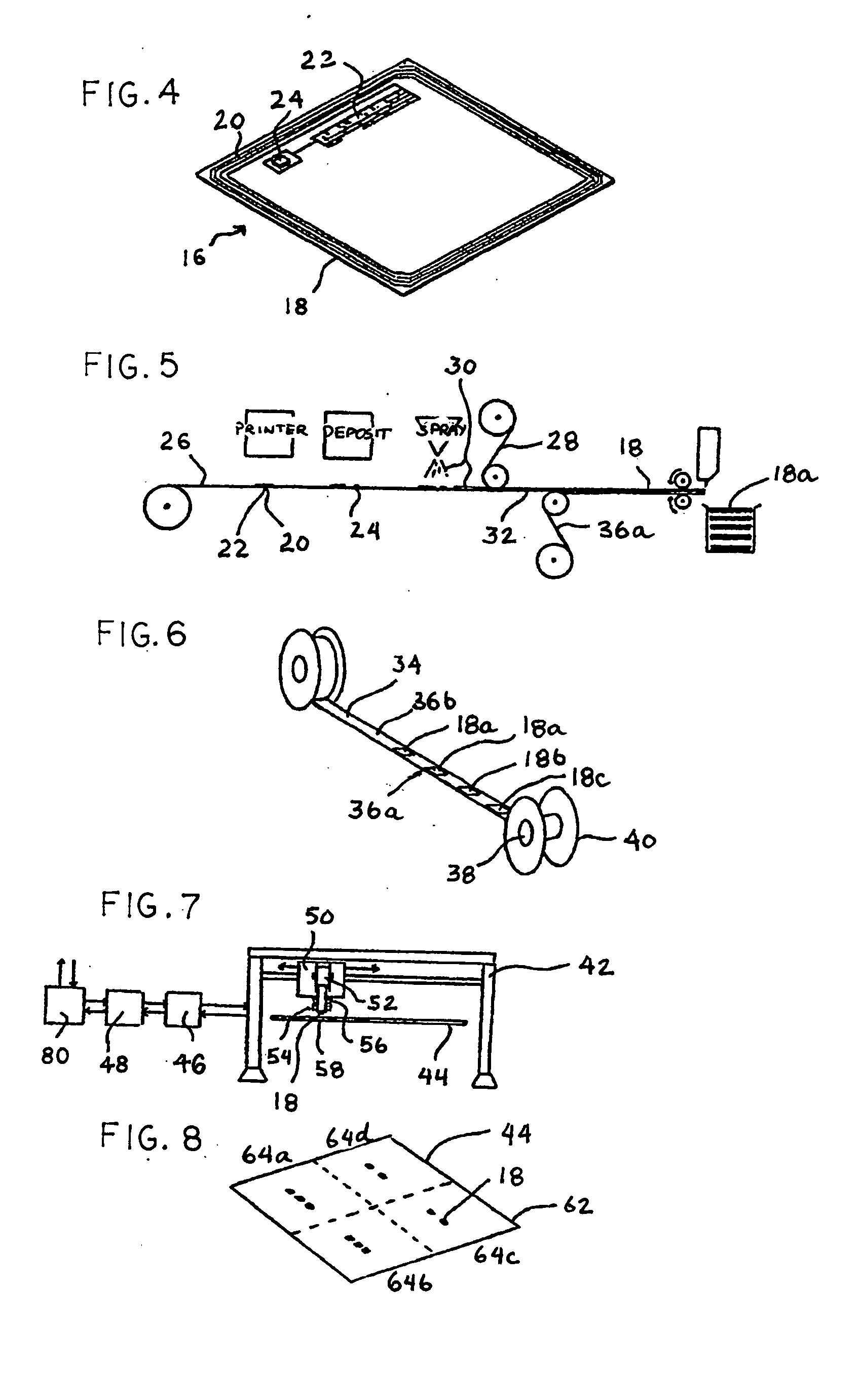
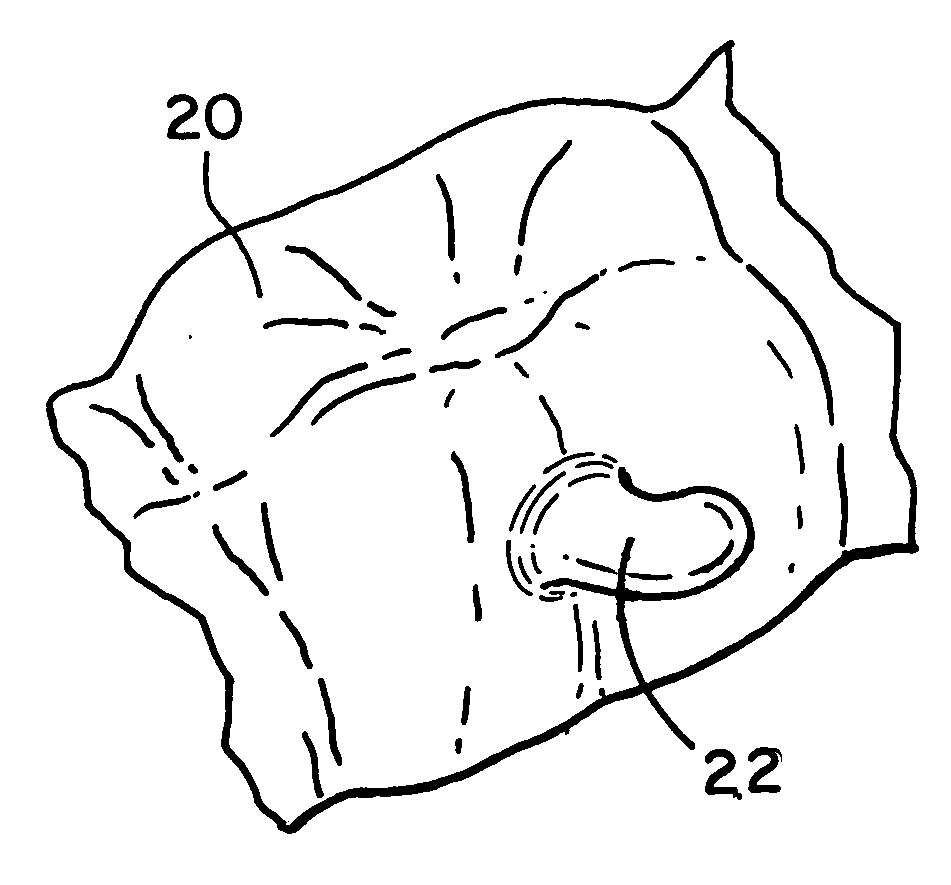
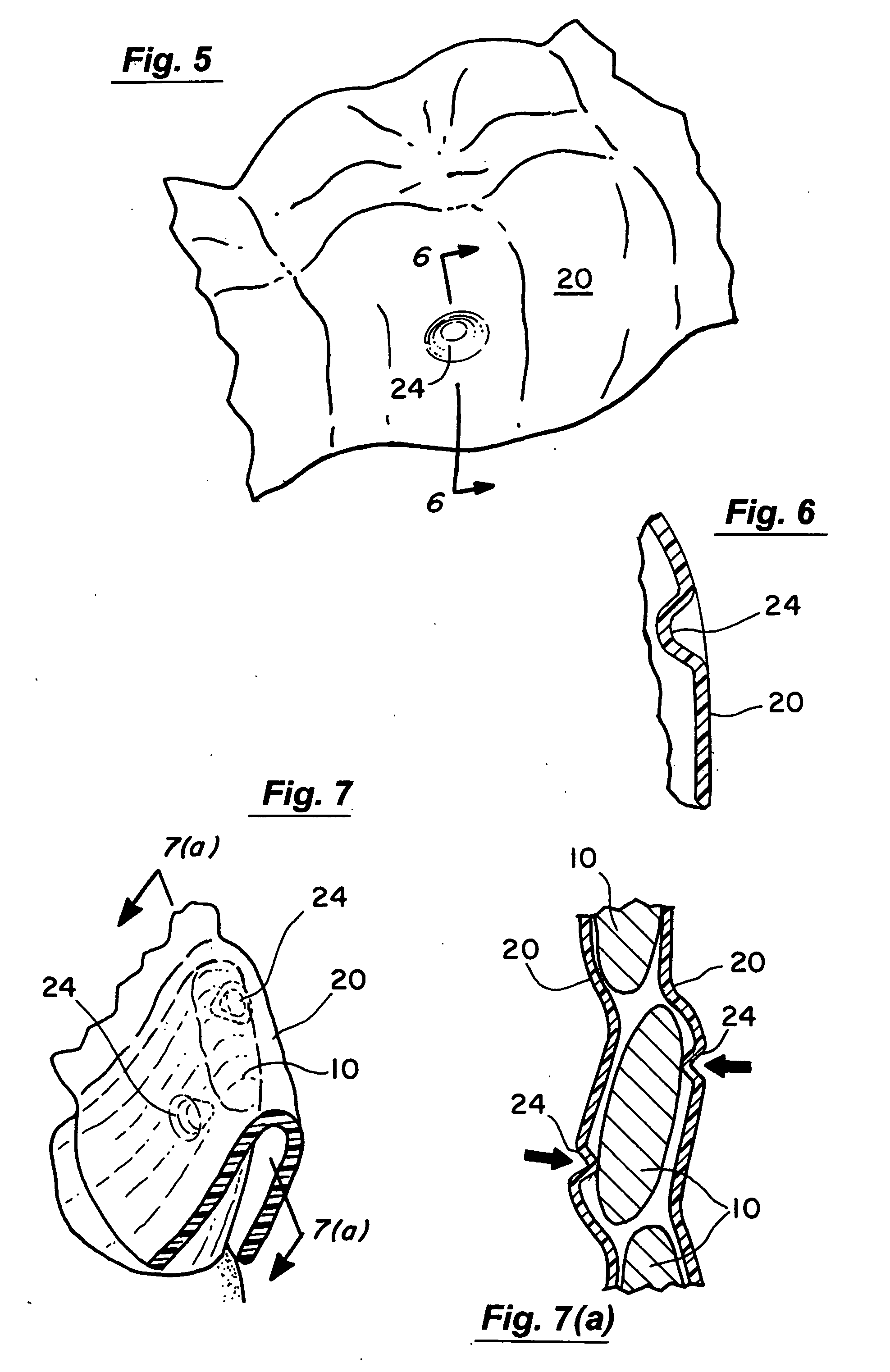
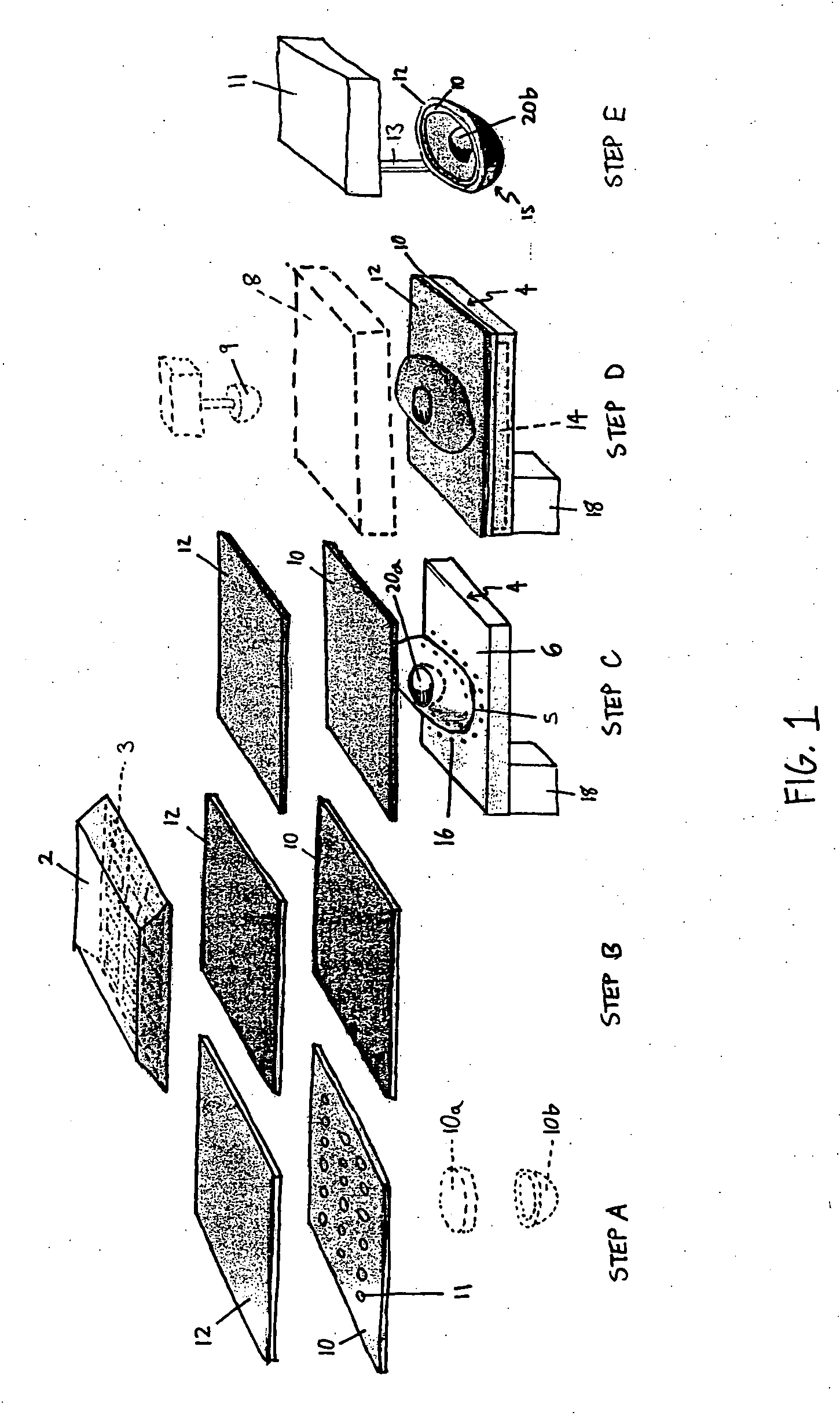
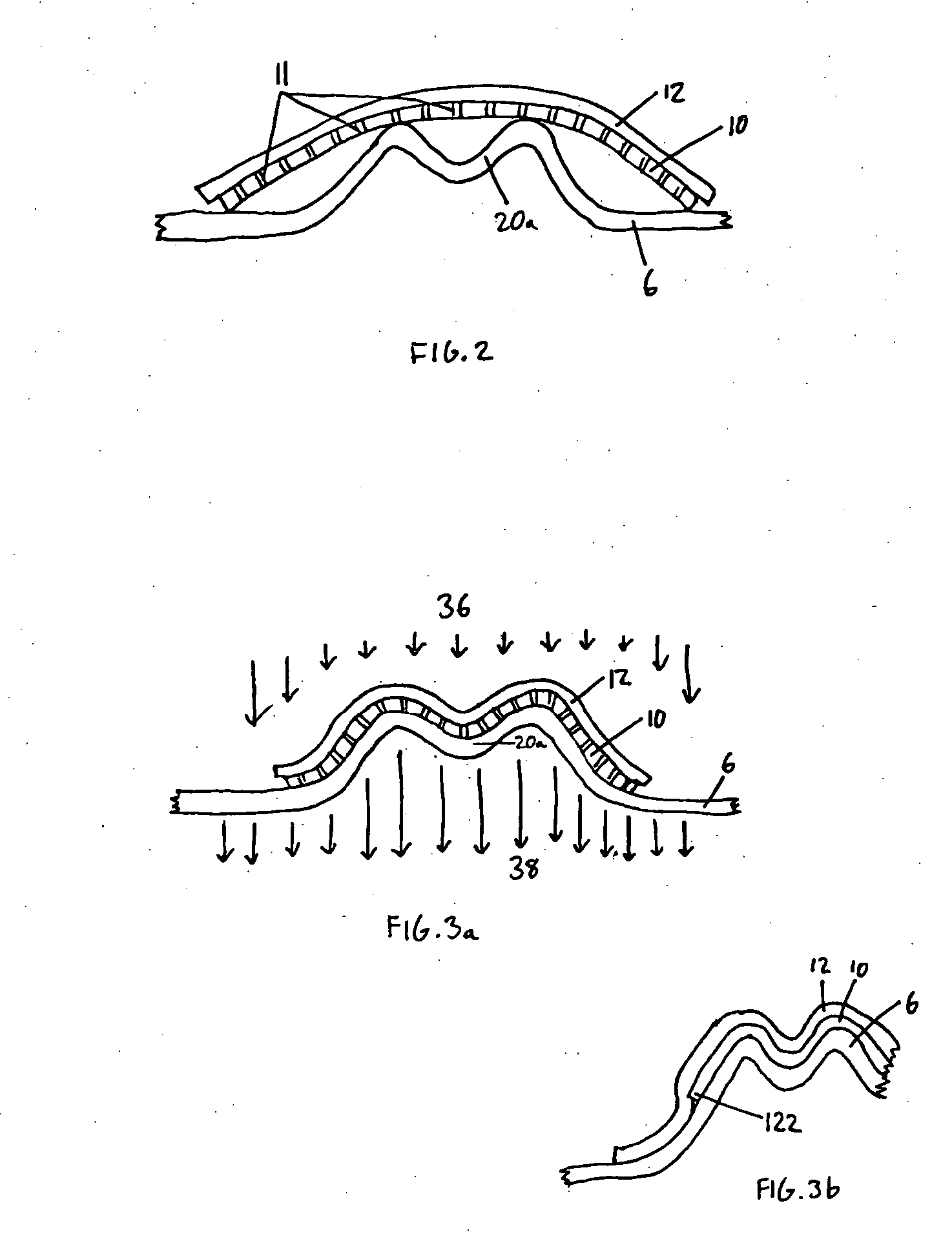
A sheet (10, 20) for use in a model vacuum thermoforming process, wherein the sheet (10, 20) has a thickened area (11) that may be in a preselected three-dimensional form such as arch-shape (12). The thickened area (11) or three-dimensional area (12) is placed over an area of the model (21) where the plastic sheet is to be stretched during the thermoforming process. This ensures a uniform or a preselected thickness in the stretched areas than would otherwise occur.
Owner:DENTSPLY RES DEVMENT
Thermoformed, extruded sheeting with reduced gloss
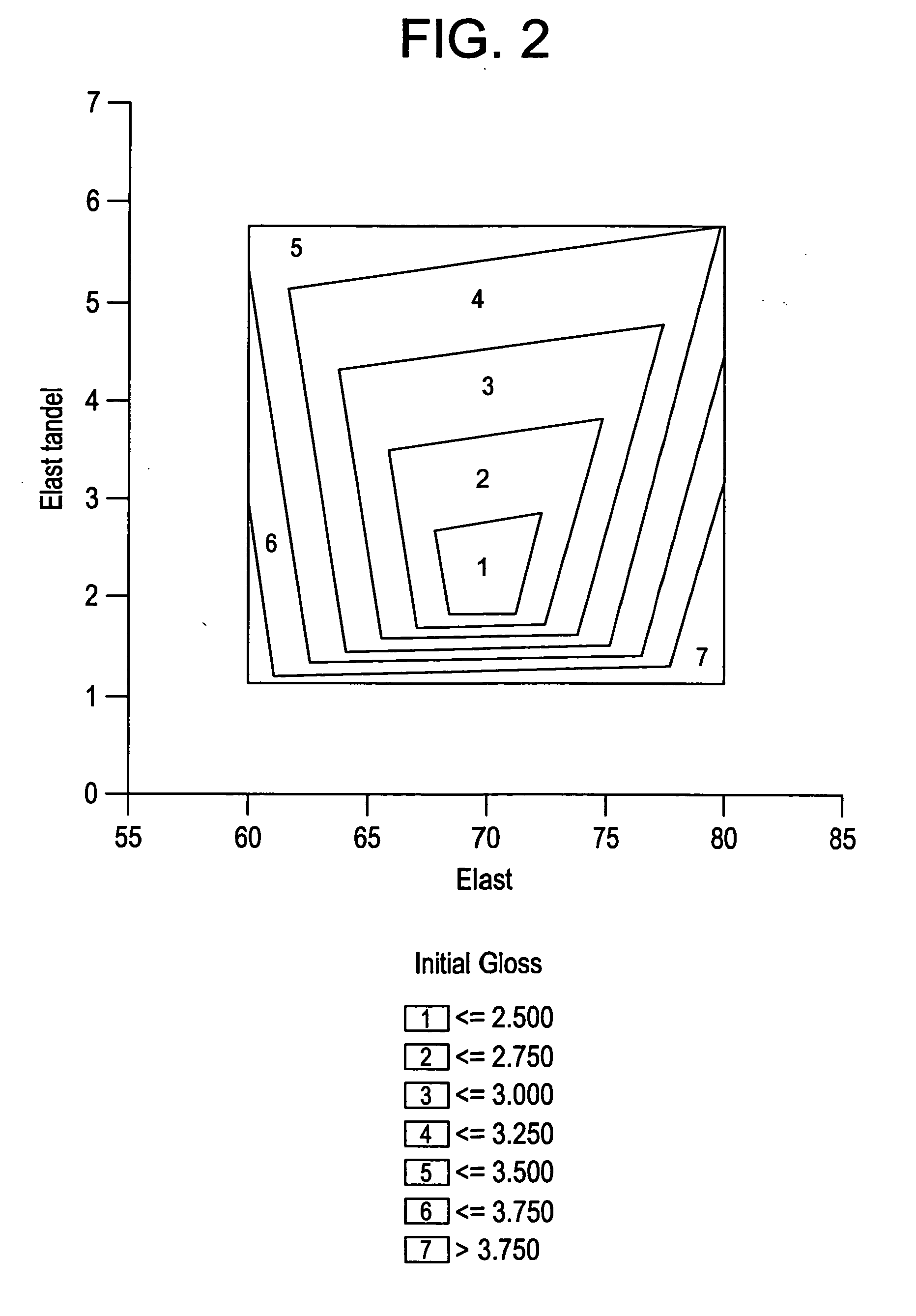
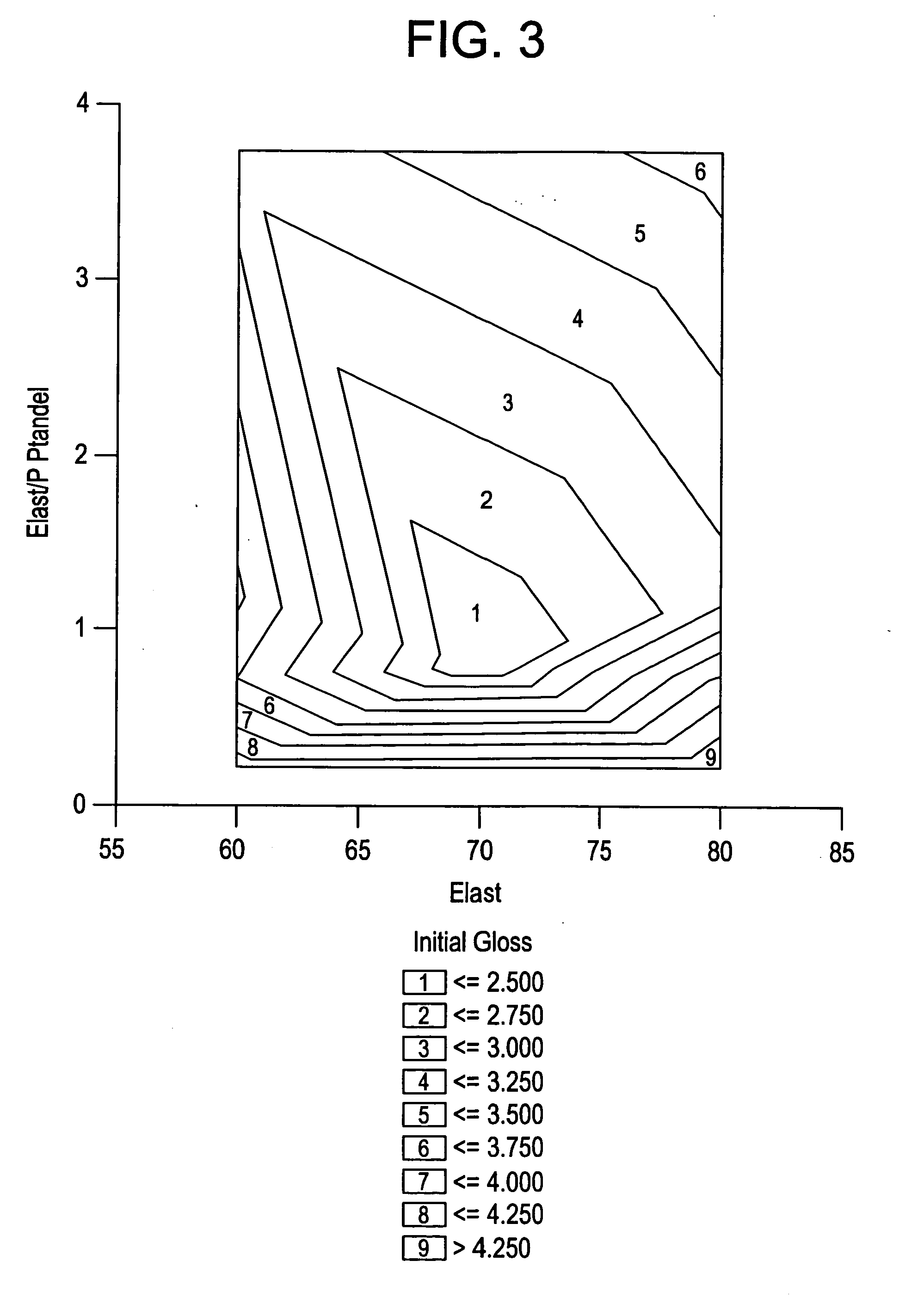
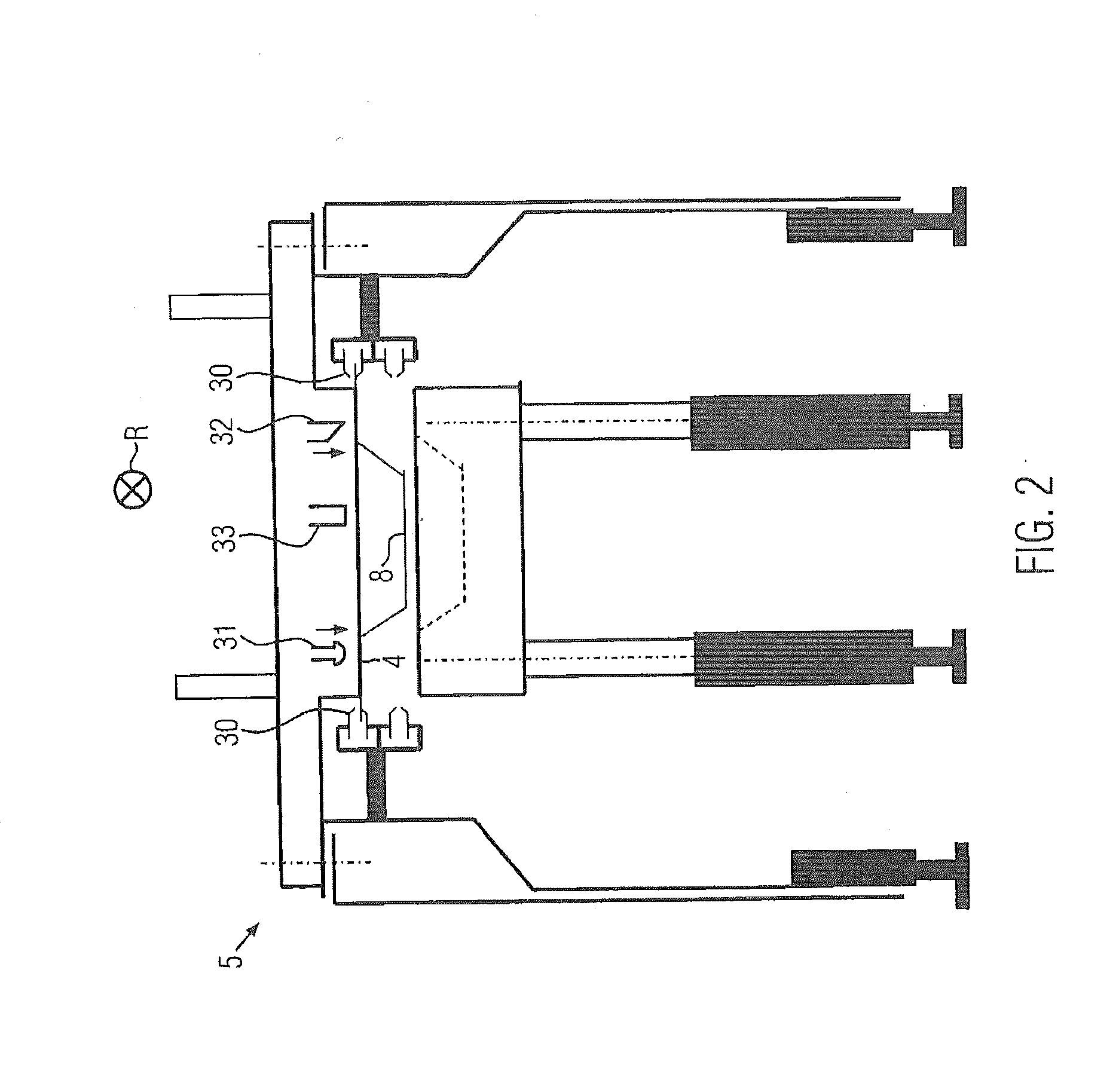
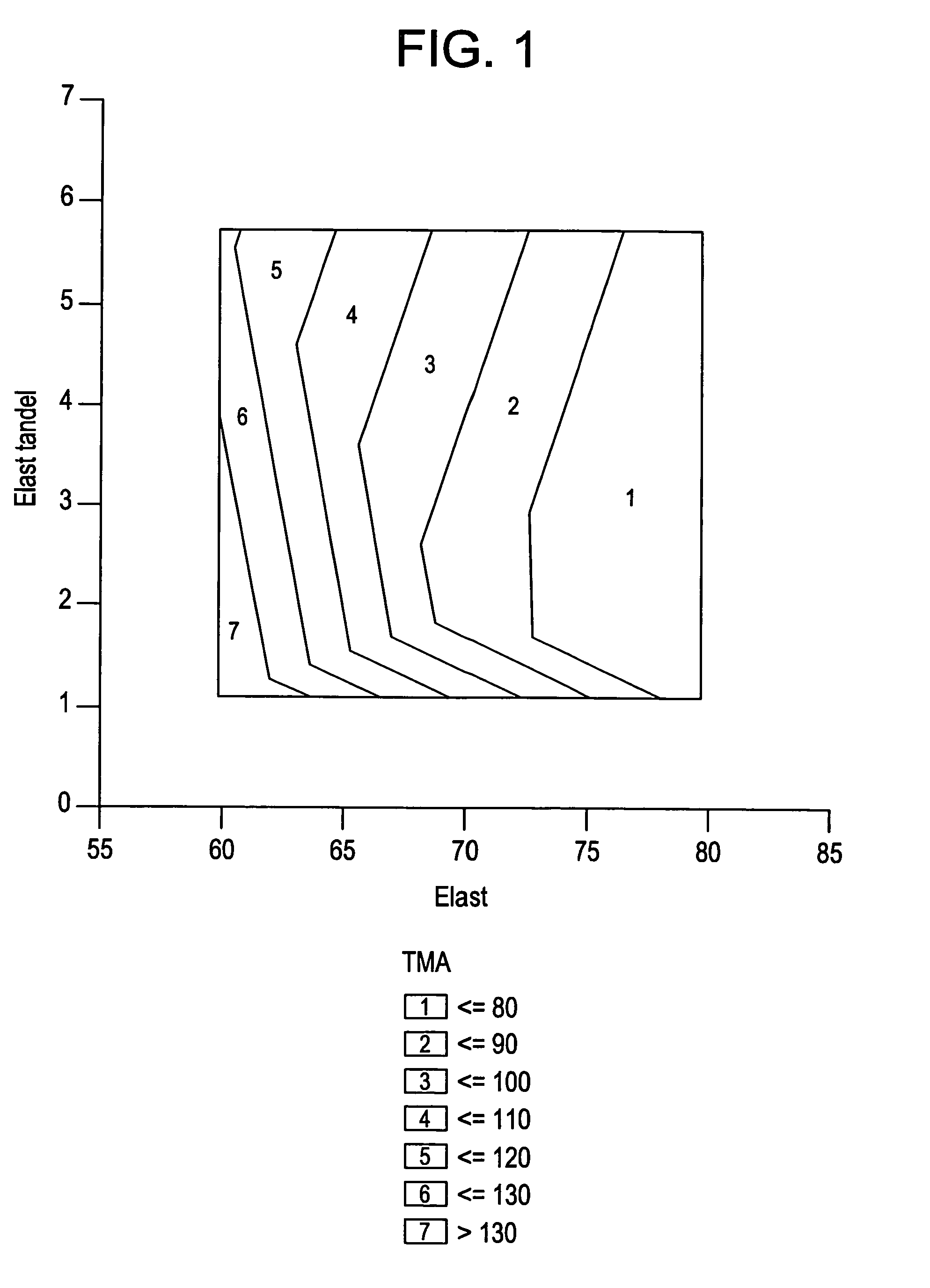
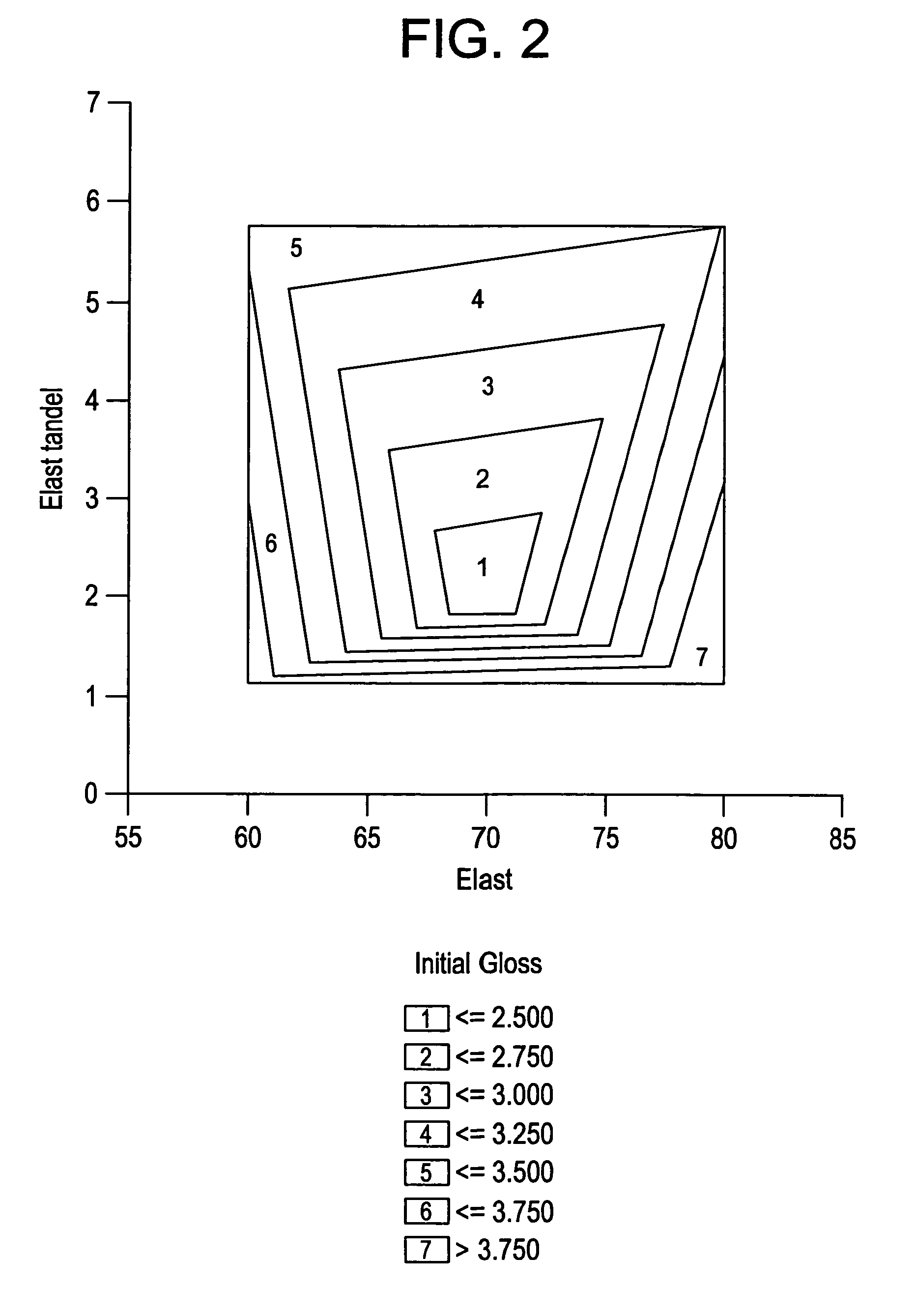
ActiveUS20070167575A1Low gloss valueHigh glossSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationElastomerAlpha-olefin
The invention is directed to compositions comprising an elastomer component and a propylene component, and in which the elastomer component comprises at least one ethylene / α-olefin polymer, optionally containing a diene, and the polypropylene component comprises at least one branched polypropylene. Preferably, the elastomer component has a melt tan delta between about 0.7 and about 8, as measured by parallel plate rheometer at 0.1 rad / sec, 190° C., and 15 percent strain; and the ratio of the “melt tan delta of the elastomer component” to the “melt tan delta of the propylene component” is from 0.5 to 4. The invention also provides for method of making such compositions, and to low gloss articles prepared from the same. The inventive compositions are particularly suitable for fabricating thermoformed sheeting with reduced gloss.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Polyester film
ActiveUS20070009750A1Poor producibilityHigh production costFlexible coversWrappersPolyesterIngested food
[Problems] The present invention provides a-polyester-film superior in heat resistance, chemical resistance, insulation property and thermal dimensional stability, and suitable for application to fields associated with boiling or retort treatment, which require tenacity, pinhole resistance, bending resistance, bag breakage resistance on dropping, impact resistance and the like, fields requiring thermoforming or vacuum forming, and various uses such as packaging bags for water-containing food, pharmaceutical products and the like. [Solving Means] The polyester film characteristically shows an initial elastic modulus in at least one direction of 2.5-10 GPa, an impact strength of 40-10000 J / mm, a thermal shrinkage in at least one direction at 150° C. of −0.5% to 6%, a haze of 0.001% to 7%, and an absolute value of the difference in the thermal shrinkage between the longitudinal direction and the transverse direction of not more than 1.1%.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Bumper system incorporating thermoformed energy absorber
A bumper system includes a tubular beam and a thermoformed energy absorber with crush boxes formed into a base flange, such as by vacuum or thermal forming processes. The crush boxes have planar energy-absorbing sidewalls a depth of about 10 mm to 35 mm, wall thicknesses of about 1 mm to 3 mm, and are formed from polyethylene or other thermoform materials having a memory. The base flange can include thermoformed features engaging recesses in the beam, and is combinable with injection-molded or foam energy absorbers for design flexibility. In one form, the energy absorber includes a thermoformed first sheet forming crush boxes and a second sheet bonded to the first sheet to define apertured air pockets. Related methods of manufacture and impacting are also disclosed.
Owner:NETSHAPE INT LLC
Fluoropolymer film structures and laminates produced therefrom
InactiveUS7070675B2Easy to useAdhesive processesFilm/foil adhesive primer layersPolymer sciencePolyolefin
Fluoropolymer films which combine the attributes of outdoor durability, chemical resistance and thermoformability with paint-like aesthetics are formed into film structures which have at least one surface coated with a primer of amine functional polymer and an overcoat of a thermoplastic adhesive of acid modified polyolefin. Fluoropolymer films so coated are securely bonded to a variety of thermoplastic substrates forming a laminated film structure which resists delamination when exposed to moisture and humidity.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Reinforced thermoplastic articles, compositions for the manufacture of the articles, methods of manufacture, and articles formed therefrom
A composition for the manufacture of a porous, compressible article, the composition comprising a combination of: a plurality of reinforcing fibers; a plurality of polysulfone fibers; and a plurality of polymeric binder fibers; wherein the polymeric binder fibers have a melting point lower than the polysulfone fibers; methods for forming the porous, compressible article; and articles containing the porous, compressible article. An article comprising a thermoformed dual matrix composite is also disclosed, wherein the composite exhibits a time to peak release, as measured by FAR 25.853 (OSU test), a 2 minute total heat release, as measured by FAR 25.853 (OSU test), and an NBS optical smoke density of less than 200 at 4 minutes, determined in accordance with ASTM E-662 (FAR / JAR 25.853).
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Multi-layer gas barrier materials for vacuum insulated structure
ActiveUS20170184339A1Thermal insulationSynthetic resin layered productsInterior spaceFilling materials
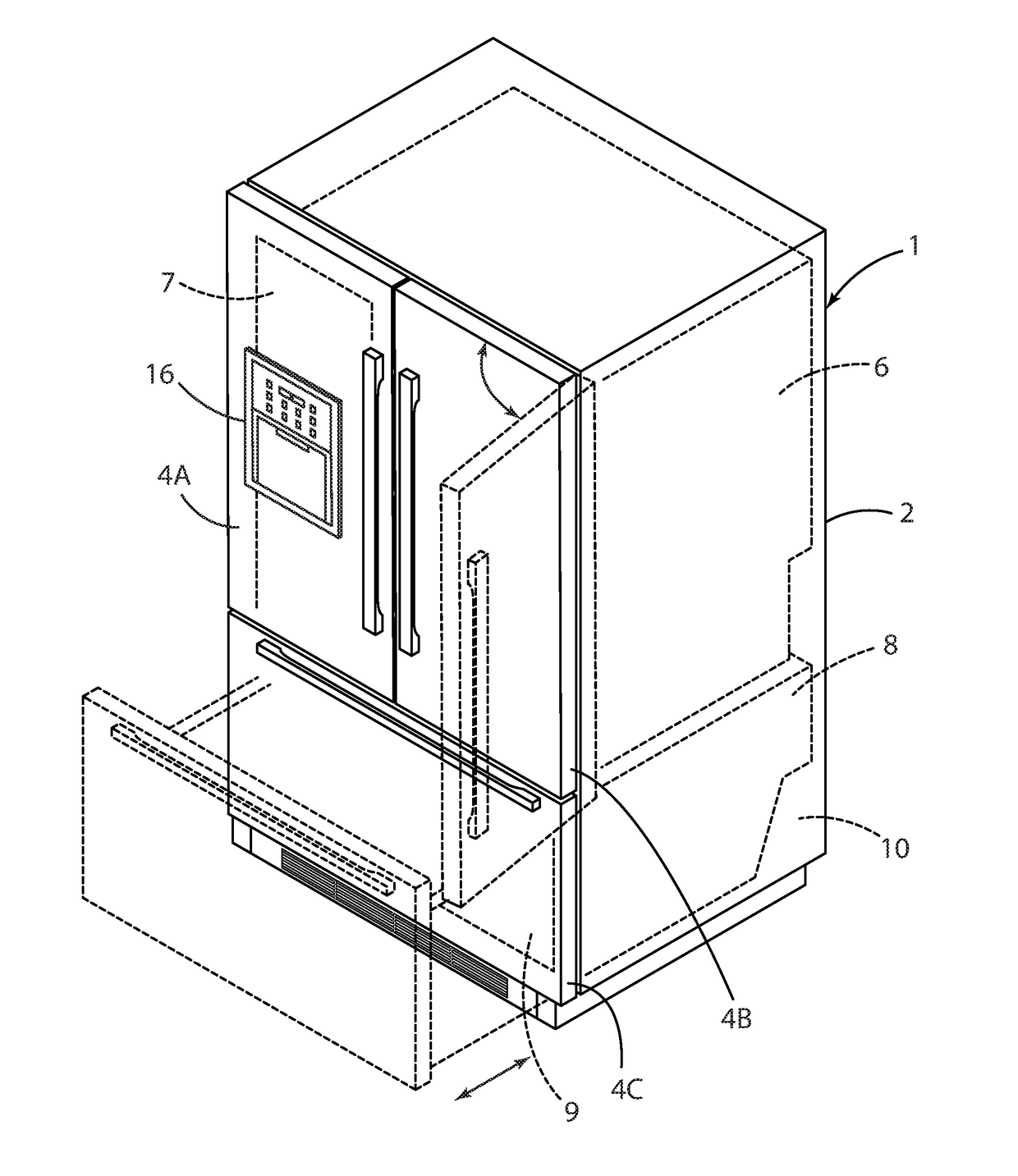
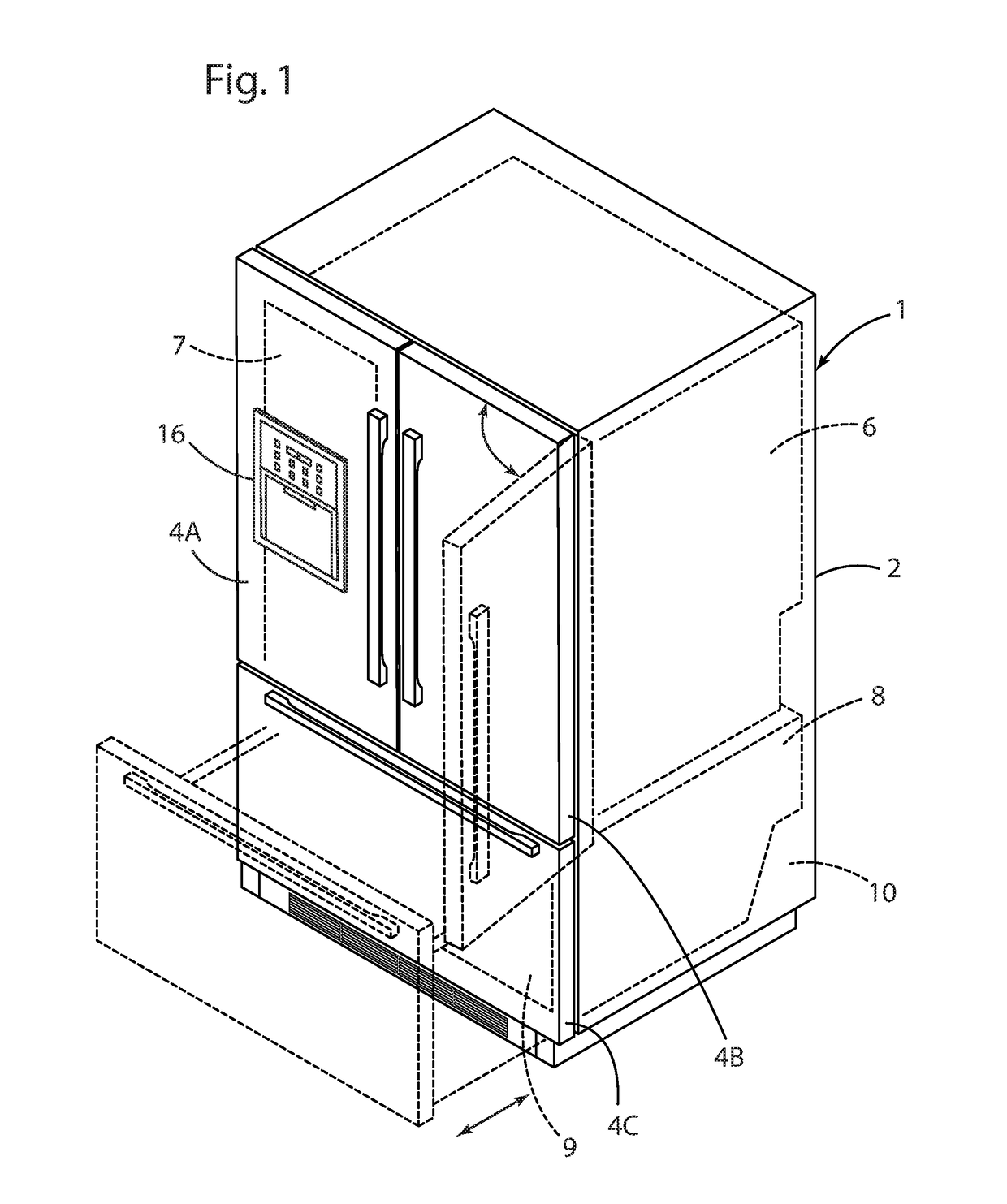
A method of forming a vacuum insulated refrigerator cabinet structure includes providing a multi-layer sheet of material comprising at least one layer of barrier material that is disposed between first and second outer structural layers. The barrier material and the first and second outer layers comprise thermoplastic polymers. The multi-layer sheet of material is thermoformed to form a non-planar first component having a central portion and four sidewalls extending transversely from the central portion. The method further includes securing a second component having a central portion and four sidewalls extending transversely from the central portion to the first component to form an interior space therebetween. Porous filler material is positioned in the interior space, and a vacuum is formed in the interior space. The first and second components are sealed together to form a vacuum insulated refrigerator cabinet structure.
Owner:WHIRLPOOL CORP
Polymeric Compositions Including Their Uses and Methods of Production
ActiveUS20070240605A1Positive performance characteristicGood processing characteristicsSynthetic resin layered productsInksElastomerFiber
Polymeric compositions and methods of making and using such compositions are provided. The compositions incorporate at least one component that is a polymer including propylene-derived units and at least one component that is a styrenic block copolymer. The polymeric compositions are found to have desirable elastomeric properties while at the same time exhibiting beneficial processabilty characteristics. The unique combination of processability and performance attributes result in the polymeric compositions useful in a variety of applications such as films, fibers, woven and non-woven fabrics, sheets, molded objects, extruded forms, thermoformed objects, and all products made from such application materials.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Polishing pads and methods relating thereto
InactiveUS6287185B1Speed up the flowFacilitate smoothing and planarizingRevolution surface grinding machinesFlexible-parts wheelsThermoformingEngineering
Polishing pads are provided having a polishing surface formed from a hydrophilic material. The polishing surface has a topography produced by a thermoforming process. The topography consists of large and small features that facilitate the flow of polishing fluid and facilitate smoothing and planarizing.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Easy open water soluble blister package
InactiveUS20060260973A1Easy to openEasy disposalSmall article dispensingFlexible coversWater solublePolymer composition
A blister package consists of a backing sheet (16) of cardboard, paper or plastic adhered to a blister (17) in which at least one or both of the backing sheet and the blister is made from a transparent water soluble thermoformable polymer composition. A tooth brush, cleaning utensil or garden utensil enclosed in the water soluble packaging material can be opened by placing it under running water. The packaging material is a starch or modified starch based polymer by direct contact with water, and that biodegrades in waste water. The preferred starch is a high amylose maize starch. The starch can also be derived from wheat, potato, rice, oats, arrowroot and pea sources. The backing sheet is adhered to water and applying the backing sheet with the use of a press plate (24).
Owner:PLANTIC TECH
Method of thermoforming fiber reinforced thermoplastic sandwich panels, thermoformed articles, and modular container structure assembled therefrom
ActiveUS20040112907A1Facilitate repair/replacementHigh weight ratioLarge containersHollow wall articlesModularityThermoplastic
A method is disclosed utilizing off the shelf constant cross section thickness sandwich panels comprised of Fiber Reinforced Thermoplastic (FRTP) resin skins and low density thermoplastic (TP) core material wherein the steps of selectively and controllably exposing the panels to heat and incrementally thermoforming the skin-core into a consolidated composite edge or intra-panel area in consideration of subsequent mating and attachment of the FRTP sandwich panel to other structures is achieved. The exact configuration of articles so thermoformed is design optimized to overcome manufacturing, assembly, weight, in-service and structural performance shortcomings of prior art and FRP sandwich panel structures. Further disclosed is an improved, load-bearing, modular design container structure assembled from such thermoformed FRTP sandwich panels in which is utilized the unique core-skin edge configuration of the present invention in consideration of improved: load bearing performance, useful load volume, reduced manufacturing costs, structural weight savings, impact and damage tolerance and repair and replace issues.
Owner:ADVANCED COMPOSITE STRUCTURES LTD
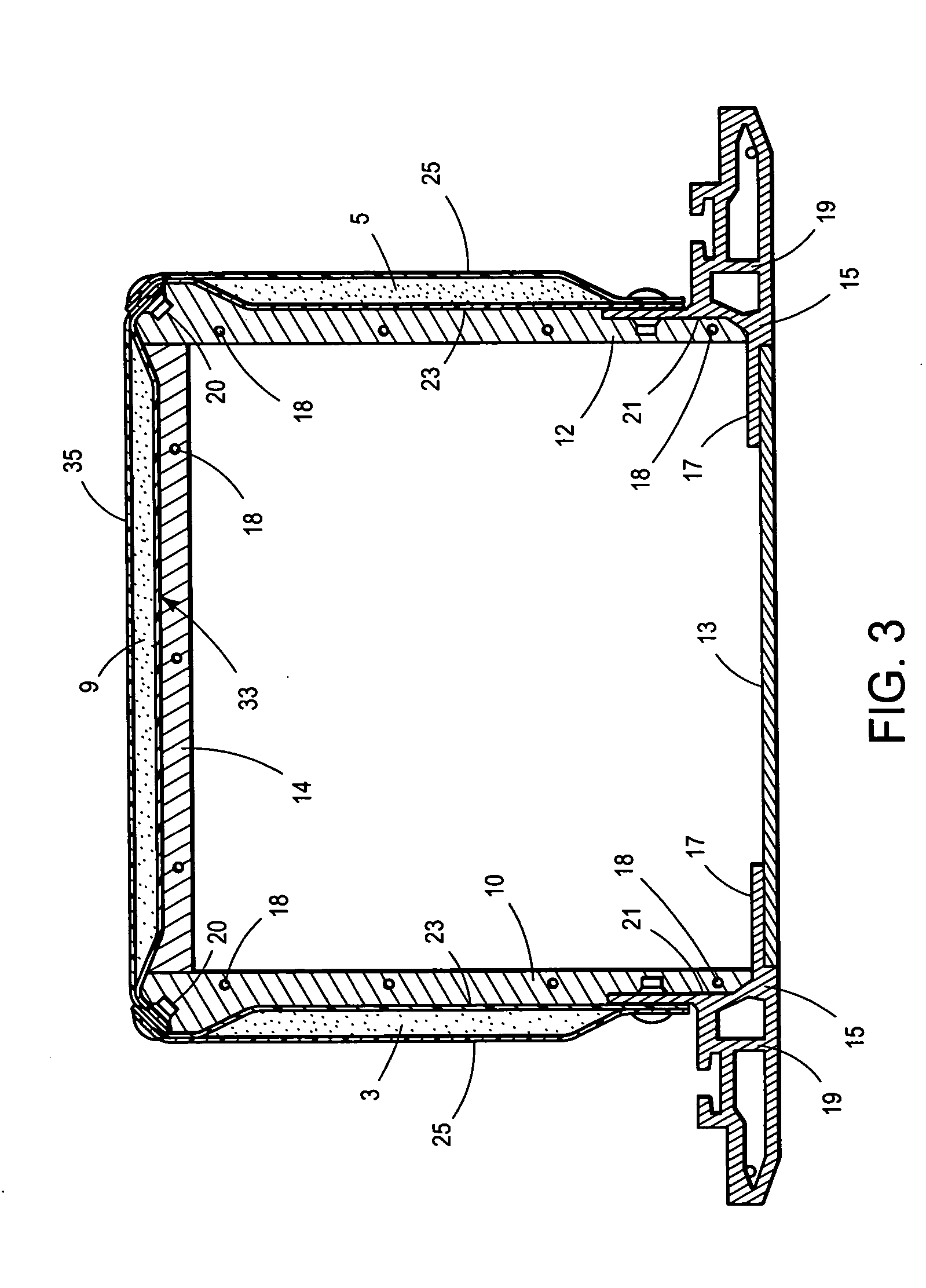
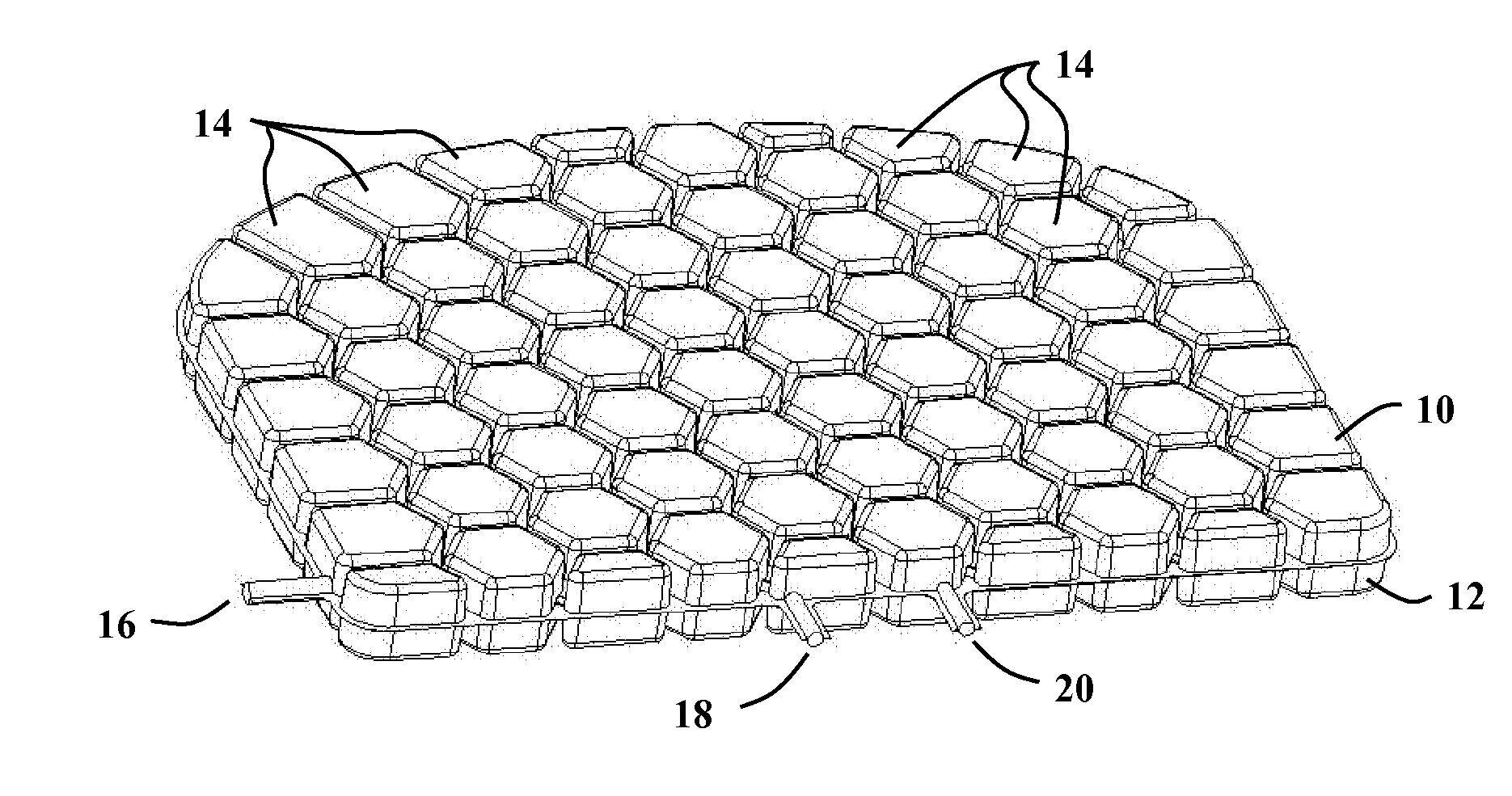
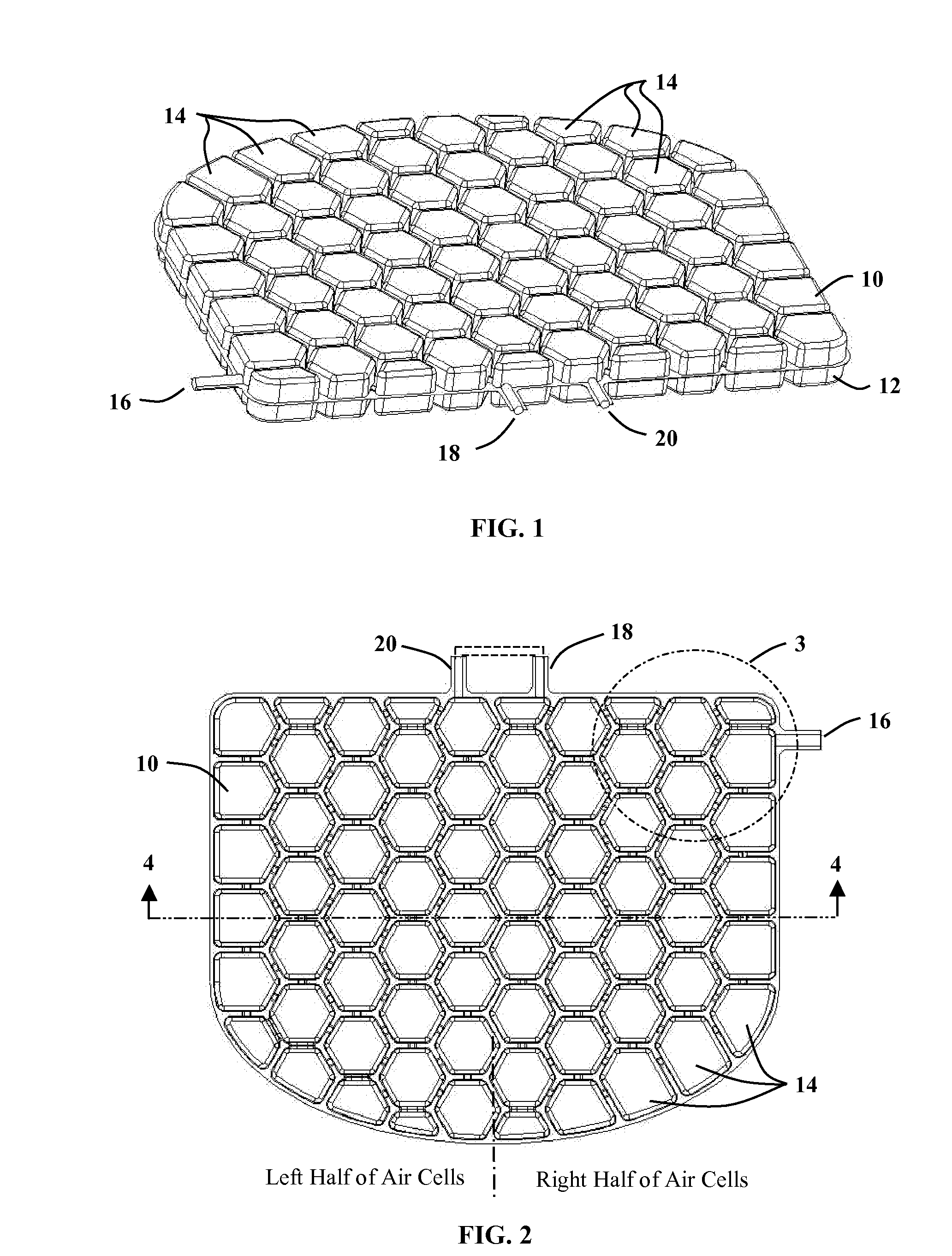
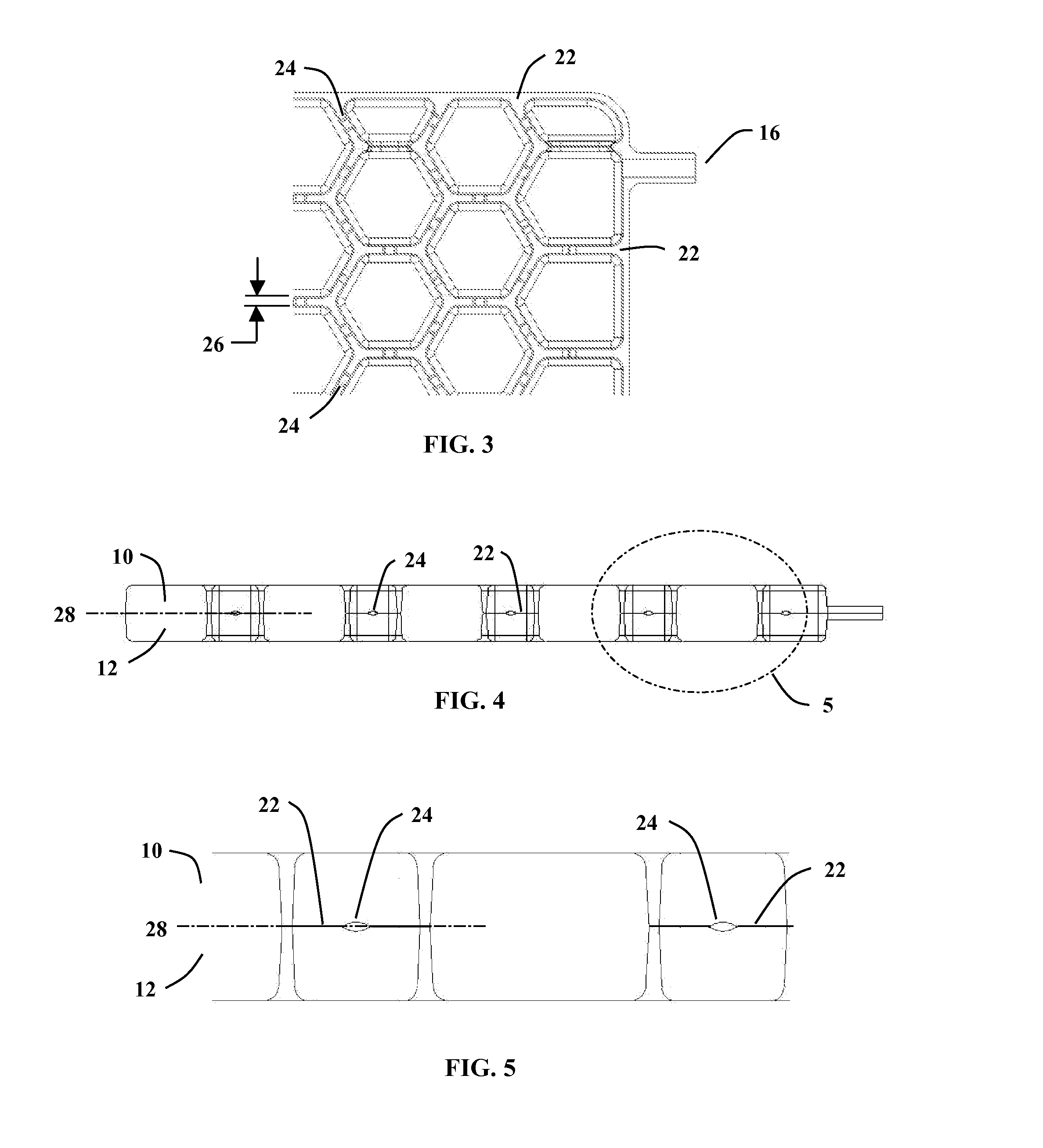
Conforming Air Cell Design and Method of Manufacture
A design and method of manufacture for a conforming air cell device to be used for seating, vibration and shock isolation, custom fitting and other applications. Interconnected air cells are formed from two thin sheets of highly resilient thermoformed plastic, so that once inflated, the air cells readily conform to the shape of the user while equalizing pressure from cell to cell. The manufacturing method simultaneously thermoforms both halves of the cell structure, followed immediately by joining these halves while still at the material's forming temperature. The result is a relatively complex matrix of air cells, interconnecting passages and one or more inflation features in a single manufacturing process, greatly simplifying the manufacturing process over previous methods. The design and method of manufacture result in an extremely lightweight, flexible and compactable system that quickly inflates and deflates, and can easily be taken and used anywhere it is needed.
Owner:MASSMANN MARK WILLIAM
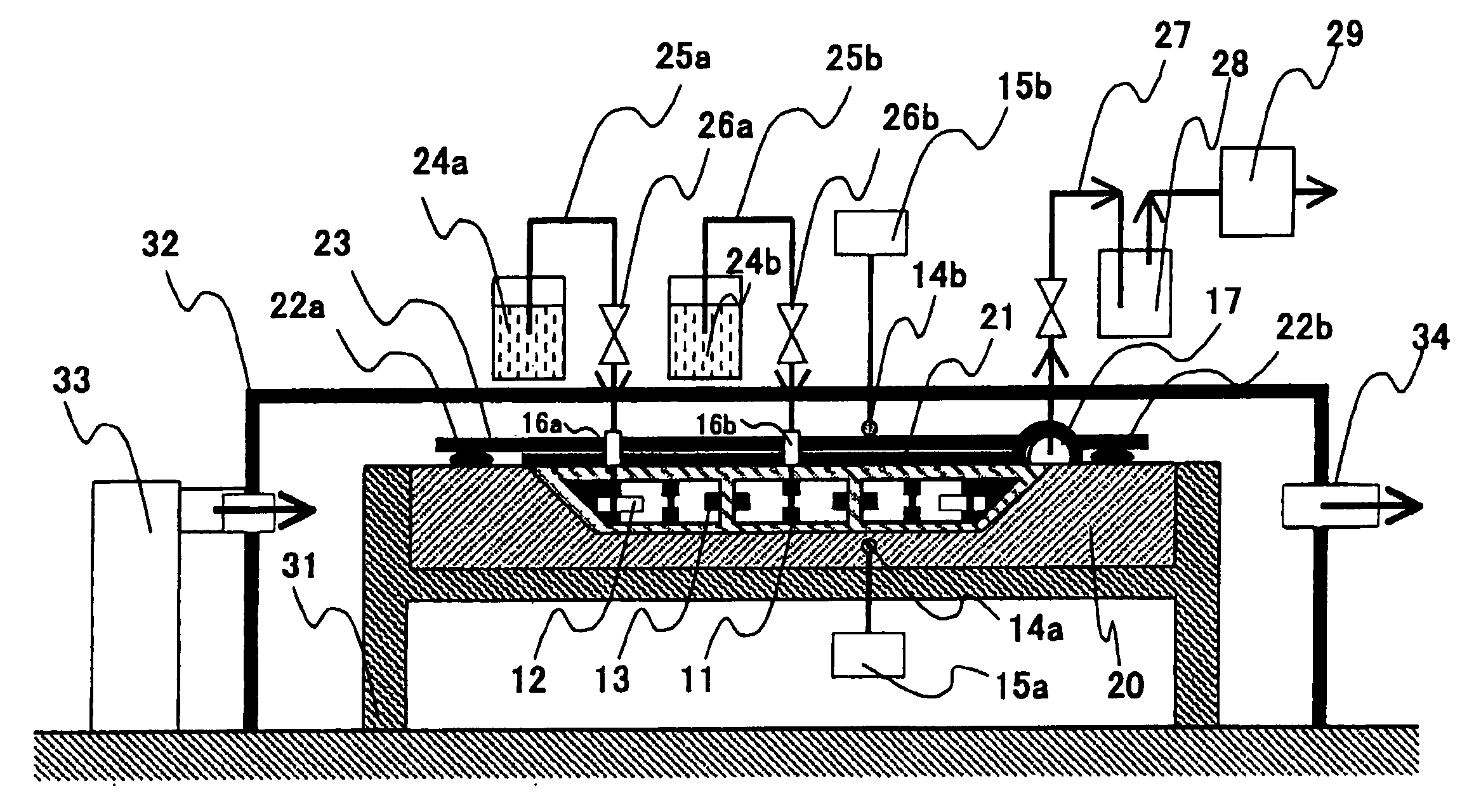
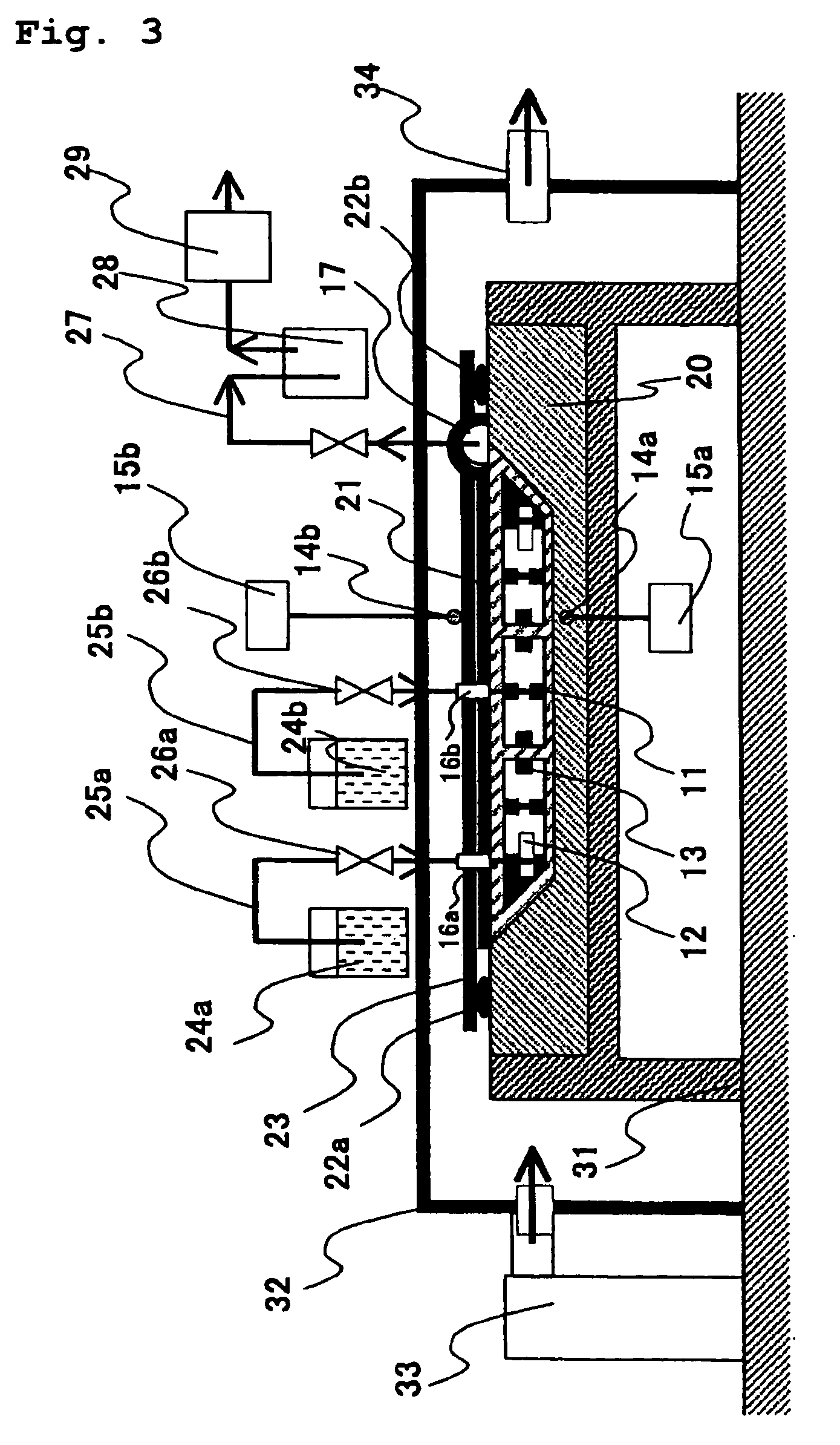
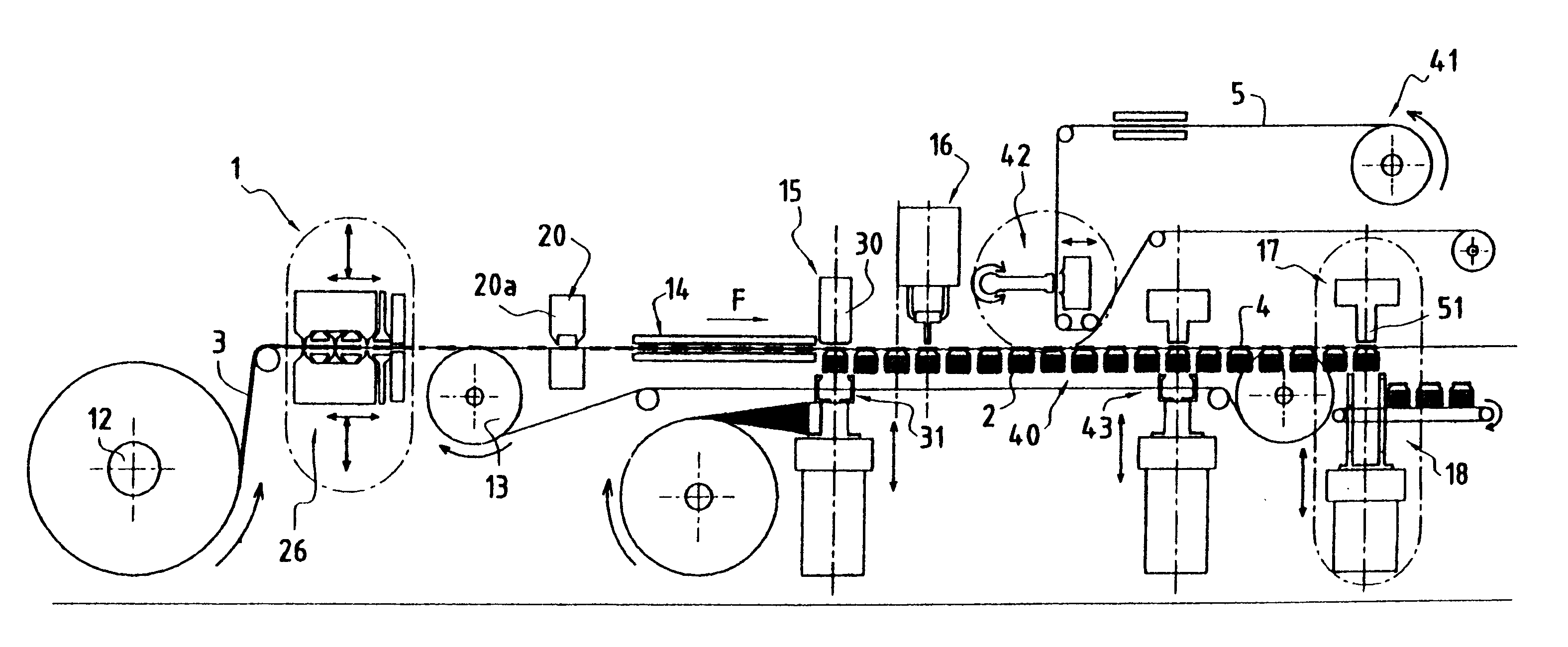
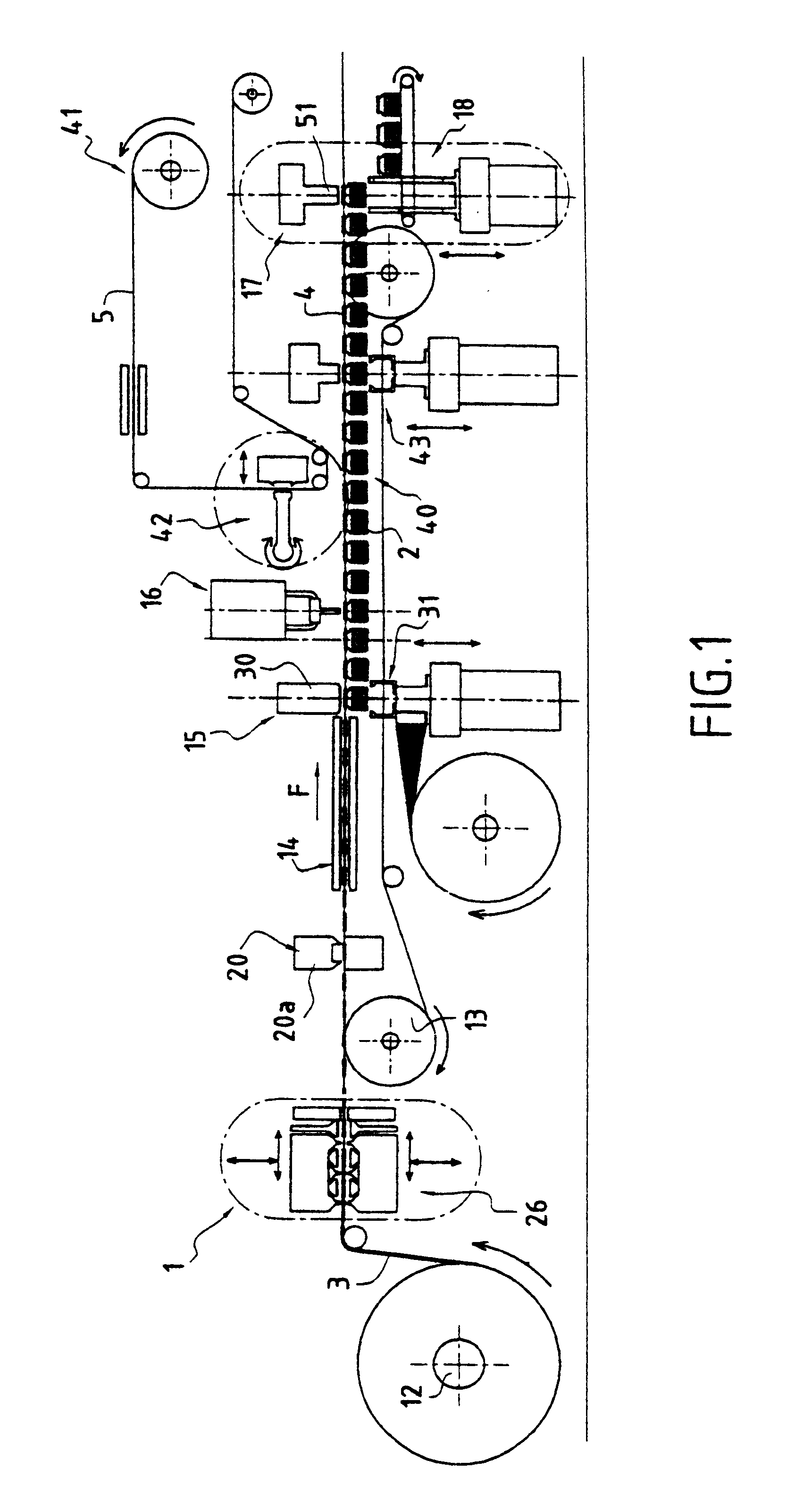
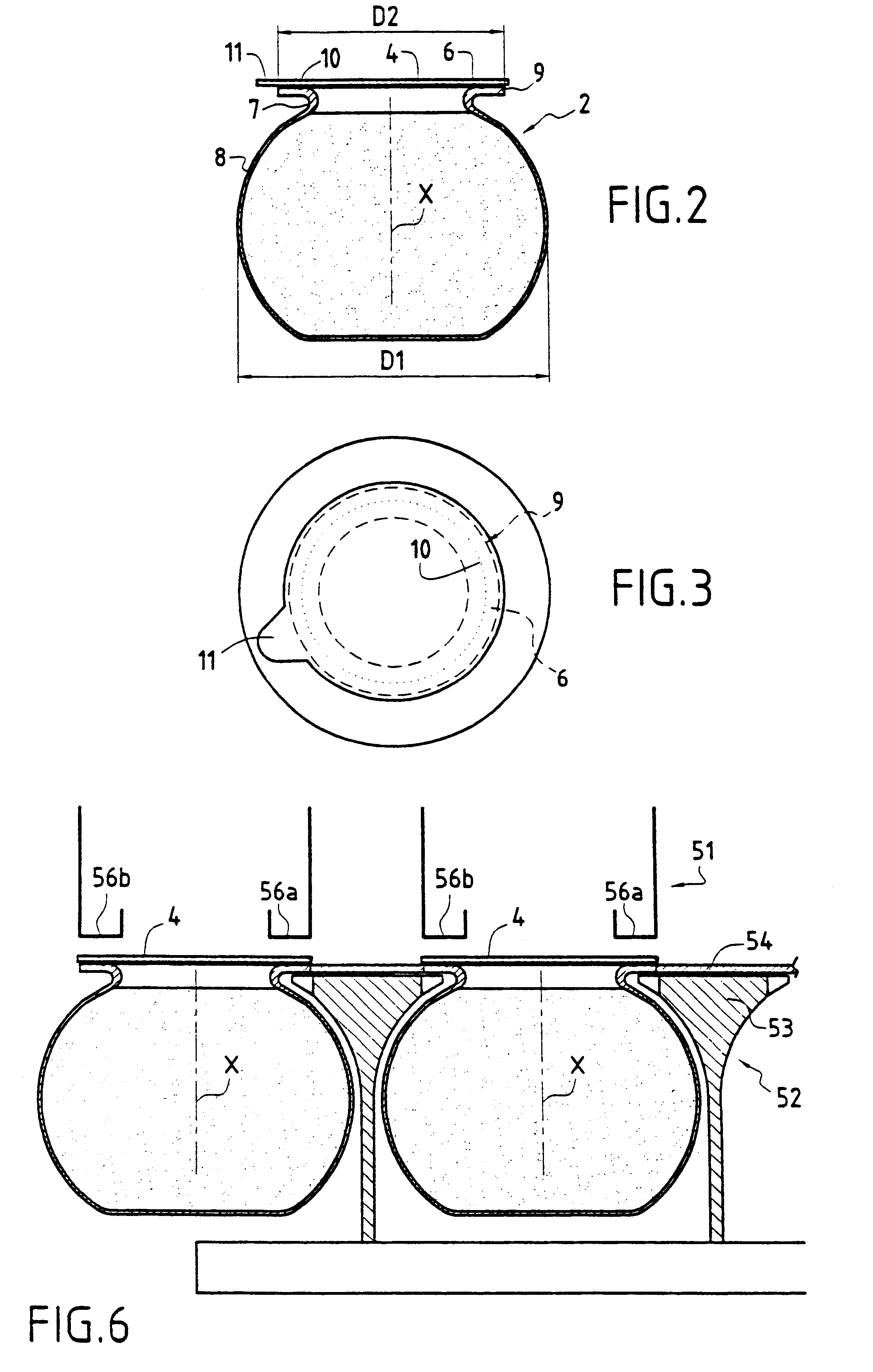
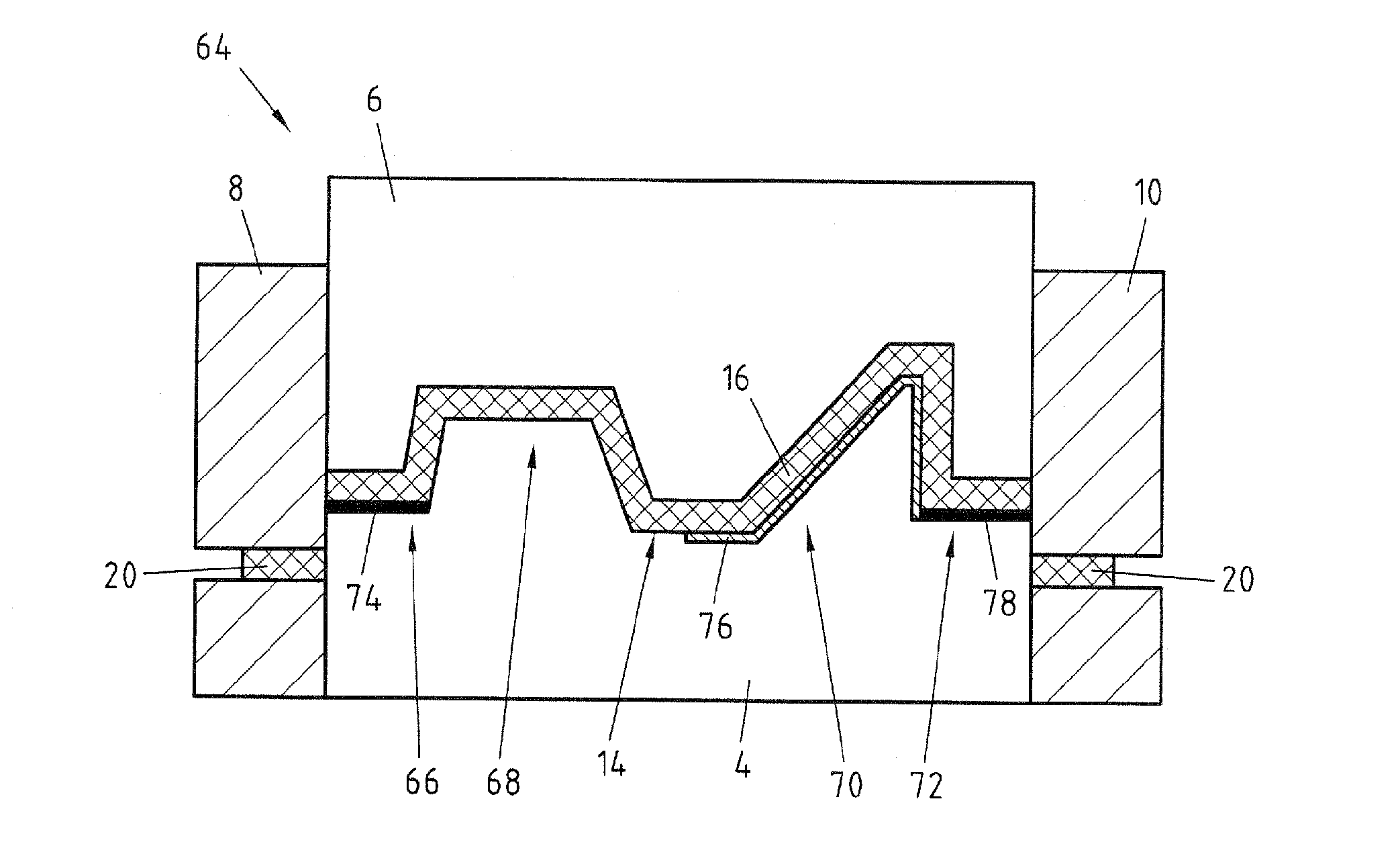
Method and an installation for thermoforming, filling, and closing re-entrant receptacles
The method and the installation of the invention enable re-entrant receptacles to be thermoformed, filled, and closed, the rim of each receptacle having a diameter that is smaller than the diameter of its body. Prior to thermoforming a row of receptacles, preliminary cuts separated by attachment points are made in a transverse stripe of the strip of the thermoplastic strip that is to be used for thermoforming in a subsequent cycle, and for each receptacle that is to be thermoformed, the cuts define practically the entire final periphery of the rim of said receptacle, the attachment points being broken when the receptacles are separated in a subsequent cycle after the filled receptacles have been closed.
Owner:ERCA FORMSEAL
Method and Device for Producing a Metal Component
The invention relates to a method for producing a metal structural component, in particular a vehicle structural component, in which a steel part is hot formed and is hardened at least over sections by contact with a tool surface, in which the steel part is during the hardening cooled in at least two partial regions at different cooling rates, so that the partial regions after the hardening differ in their microstructure, wherein the cooling rates differing from one another are produced by sections of the tool surface corresponding to the partial regions of the steel part, which differ from one another as regards their thermal conductivities. The invention also relates to a further method for producing a metal structural component, as well as a tool and a batch furnace.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG
Thermo-forming packaging machine and method
InactiveUS20150096263A1Wrapping material feeding apparatusSolid materialThin membranePackaging machine
The invention relates to a thermo-forming packaging machine with a controller, a first forming station for forming a tray into a base film and a second motor-adjustable forming station for forming a lid into a top film. A first detection device detects the marking of the base film for controlling a film advance step of the tray associated with this marking into the sealing station.
Owner:MULTIVAC SEPP HAGGENMULLER GMBH & CO KG
Thermoformed, extruded sheeting with reduced gloss
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Thermoformed litter scoop
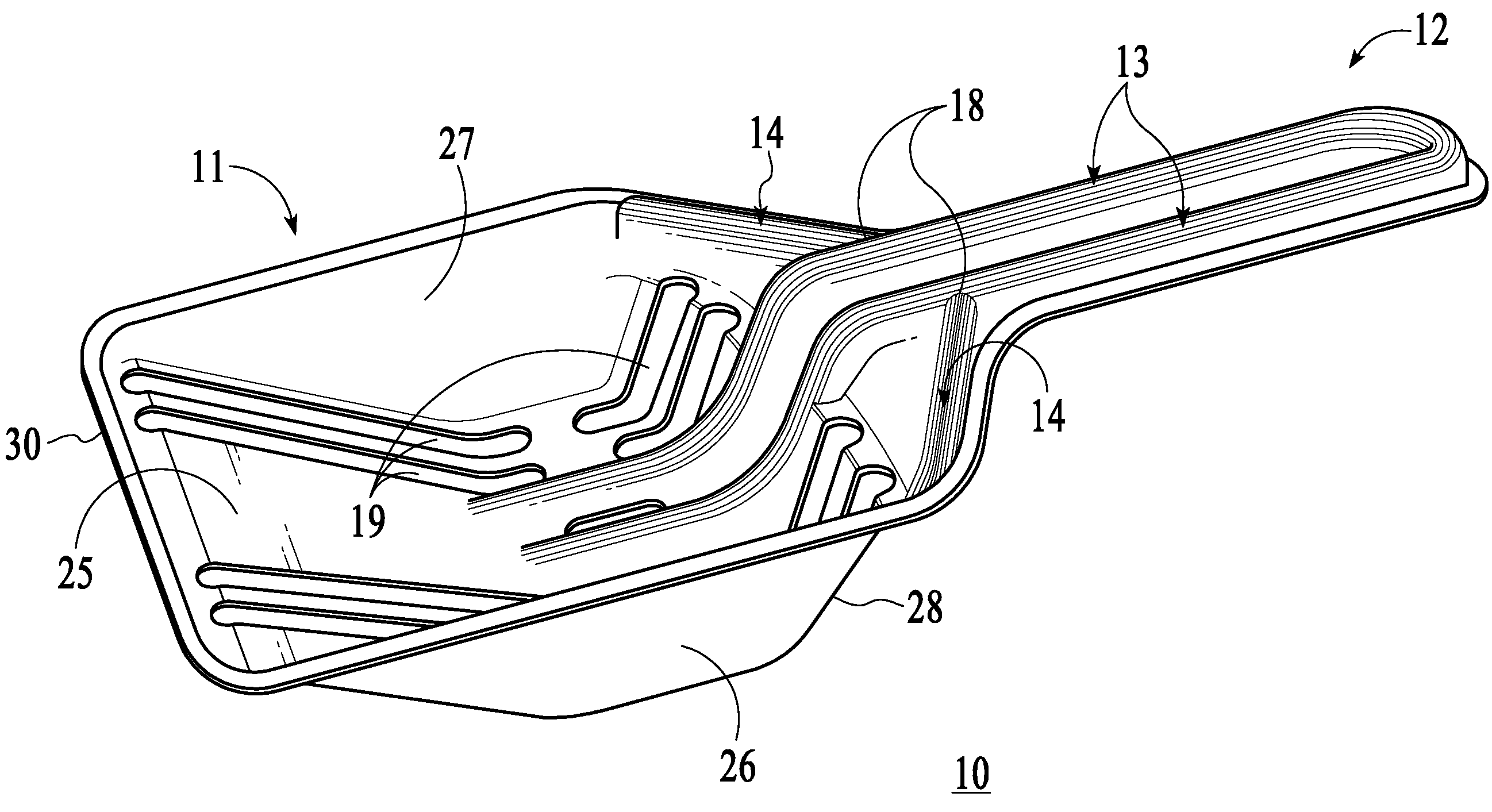
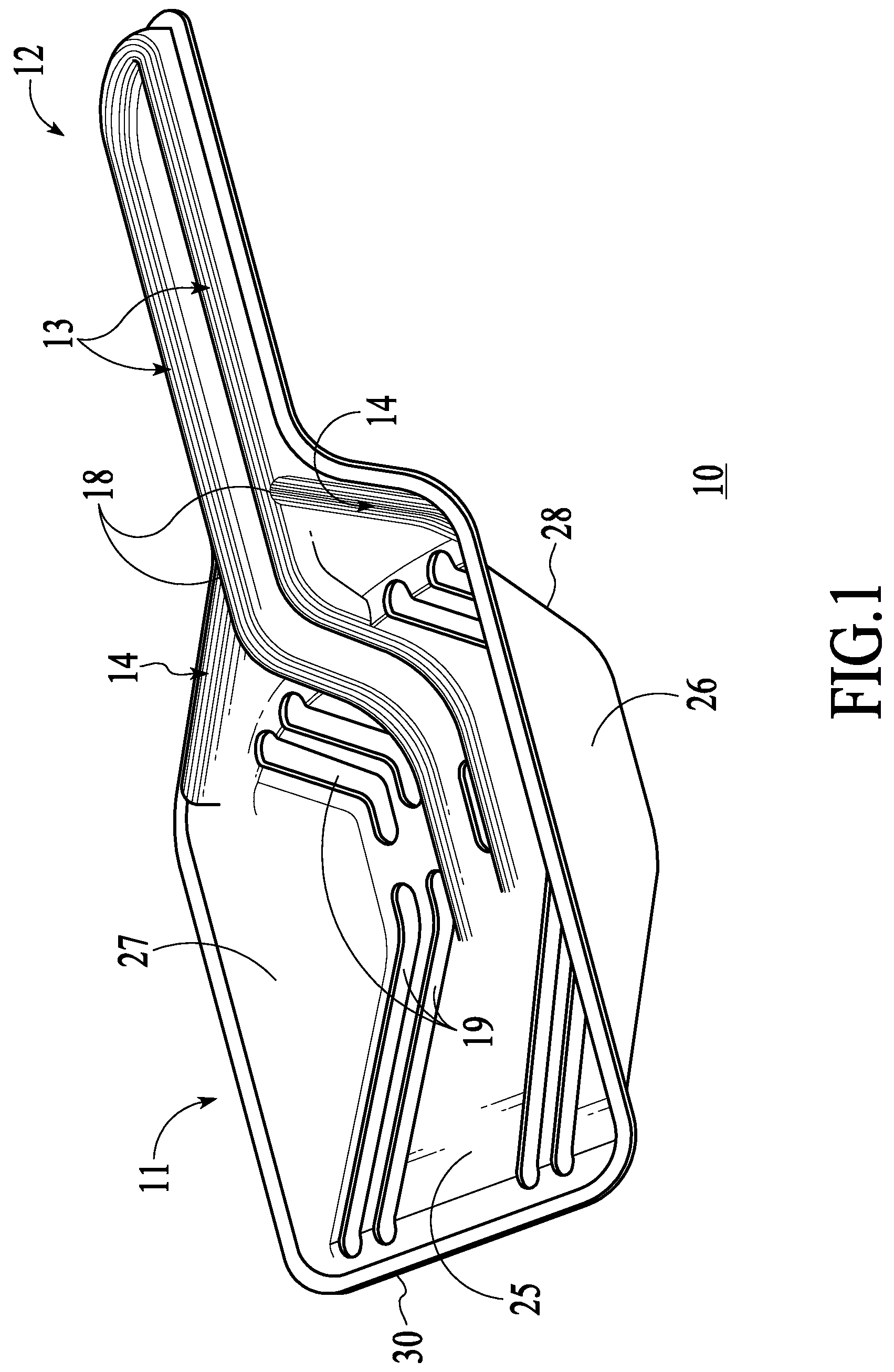
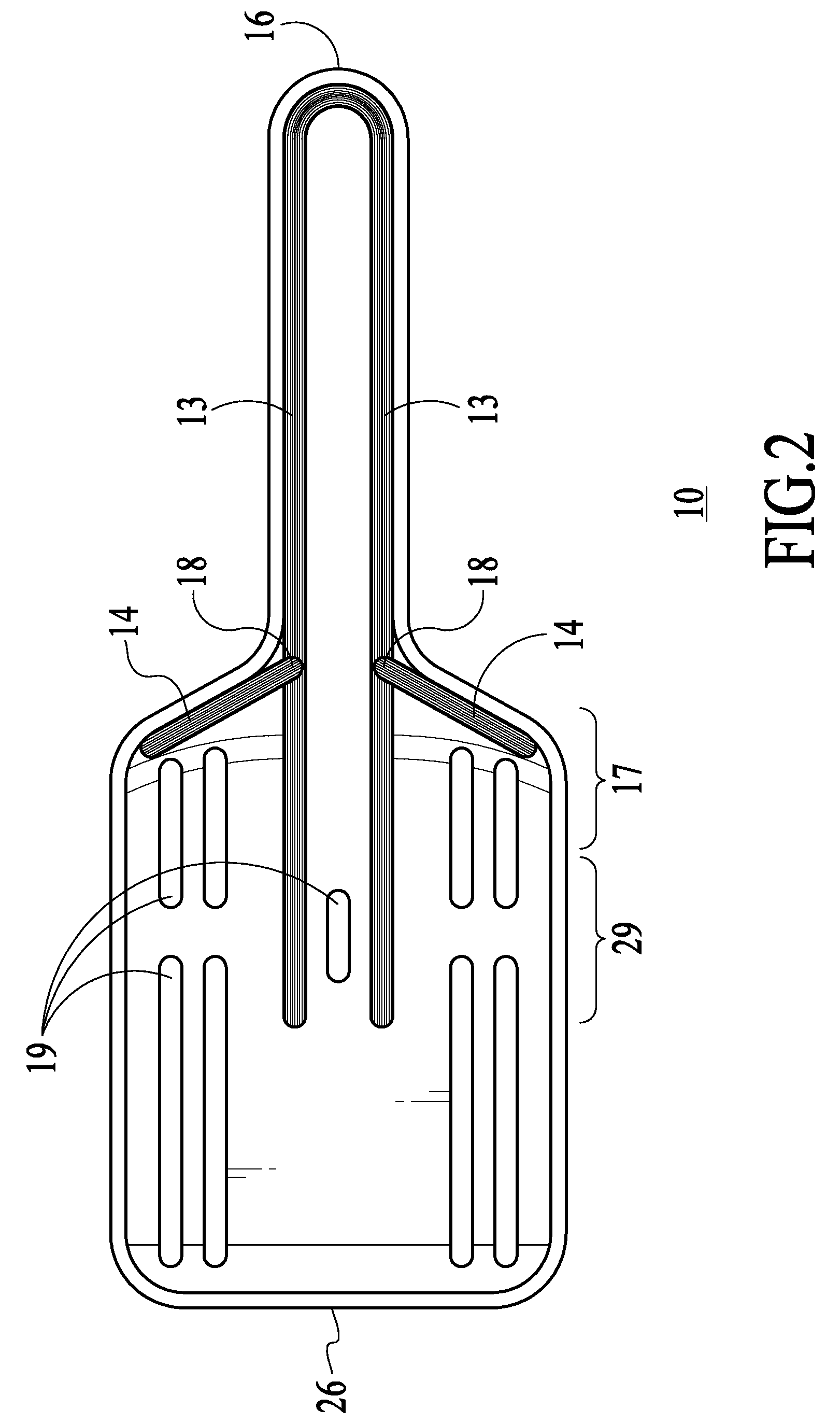
The present invention provides a thermoformed litter scoop comprising a generally concave scoop portion, and a handle portion attached to the scoop portion. The scoop portion has a bottom, sides and a rear and a plurality of openings therein. The openings are defined to allow the passage of litter granules therethrough. The handle portion has reinforcing ribs and the scoop portion has reinforcing ribs. The invention also describes a method of making a thermoformed scoop.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com