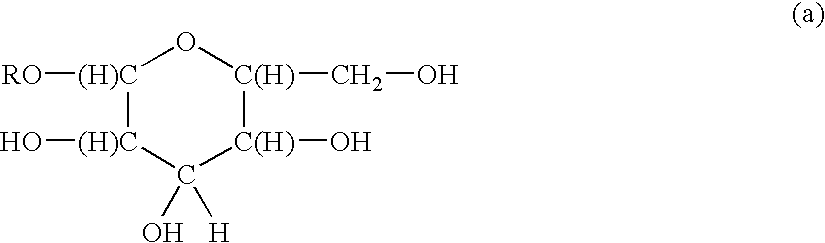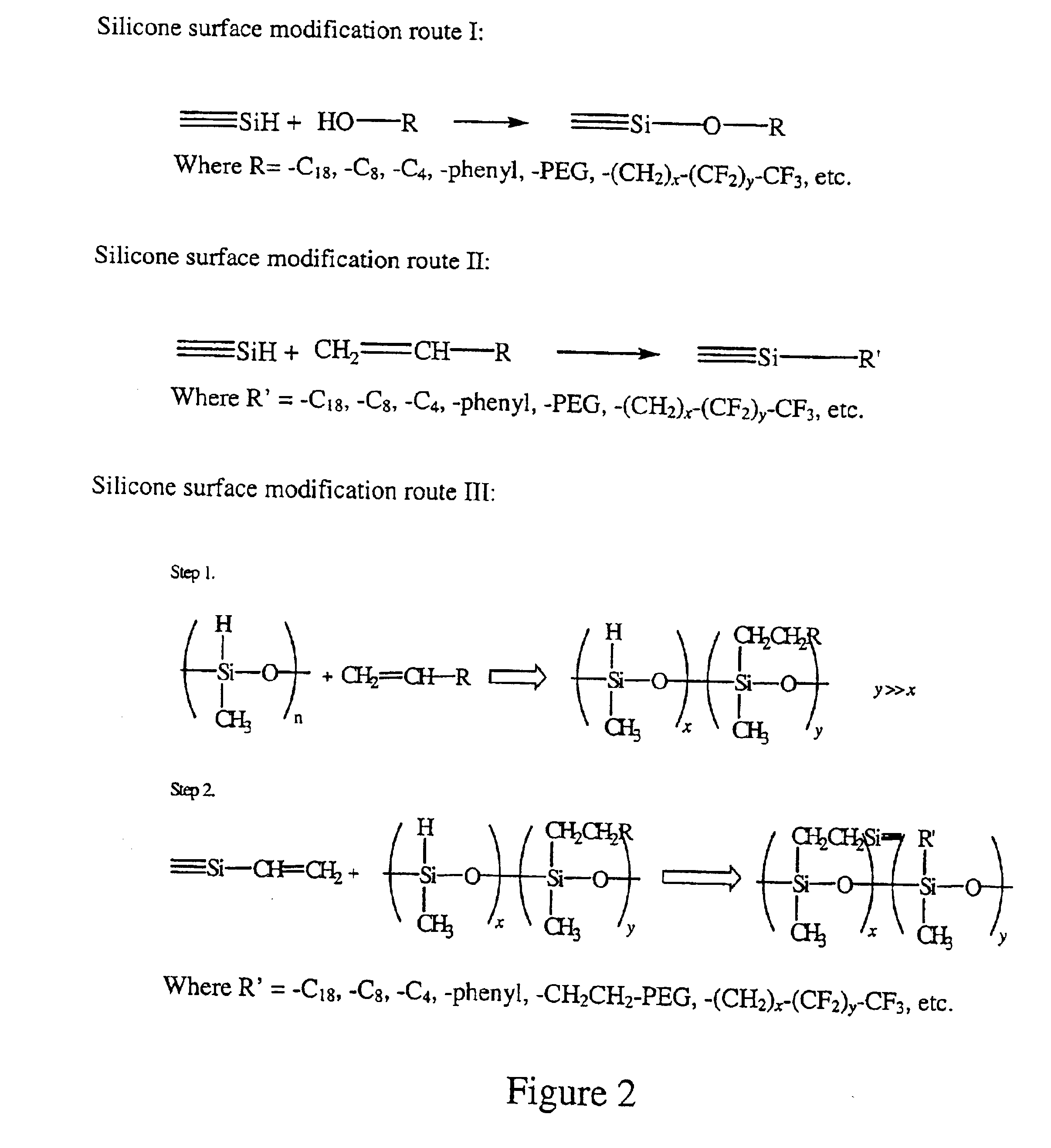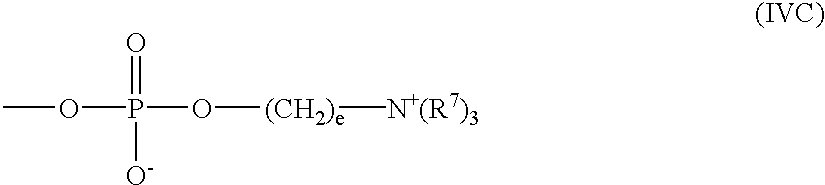Patents
Literature
1209 results about "Polymeric surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymeric materials have widespread application due to their versatile characteristics, cost-effectiveness, and highly tailored production. The science of polymer synthesis allows for excellent control over the properties of a bulk polymer sample. However, surface interactions of polymer substrates are an essential area of study in biotechnology, nanotechnology, and in all forms of coating applications. In these cases, the surface characteristics of the polymer and material, and the resulting forces between them largely determine its utility and reliability. In biomedical applications for example, the bodily response to foreign material, and thus biocompatibility, is governed by surface interactions. In addition, surface science is integral part of the formulation, manufacturing, and application of coatings.
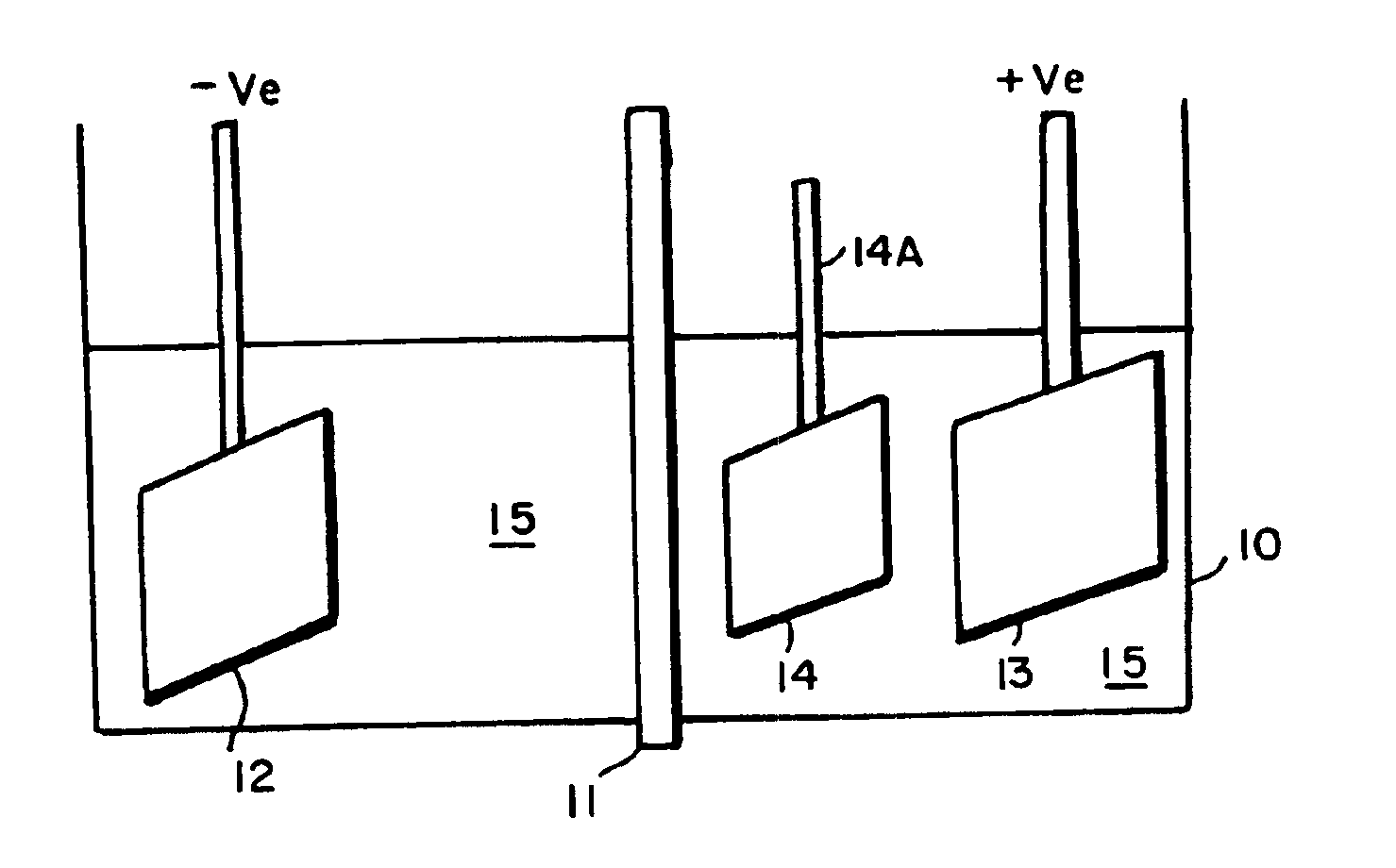
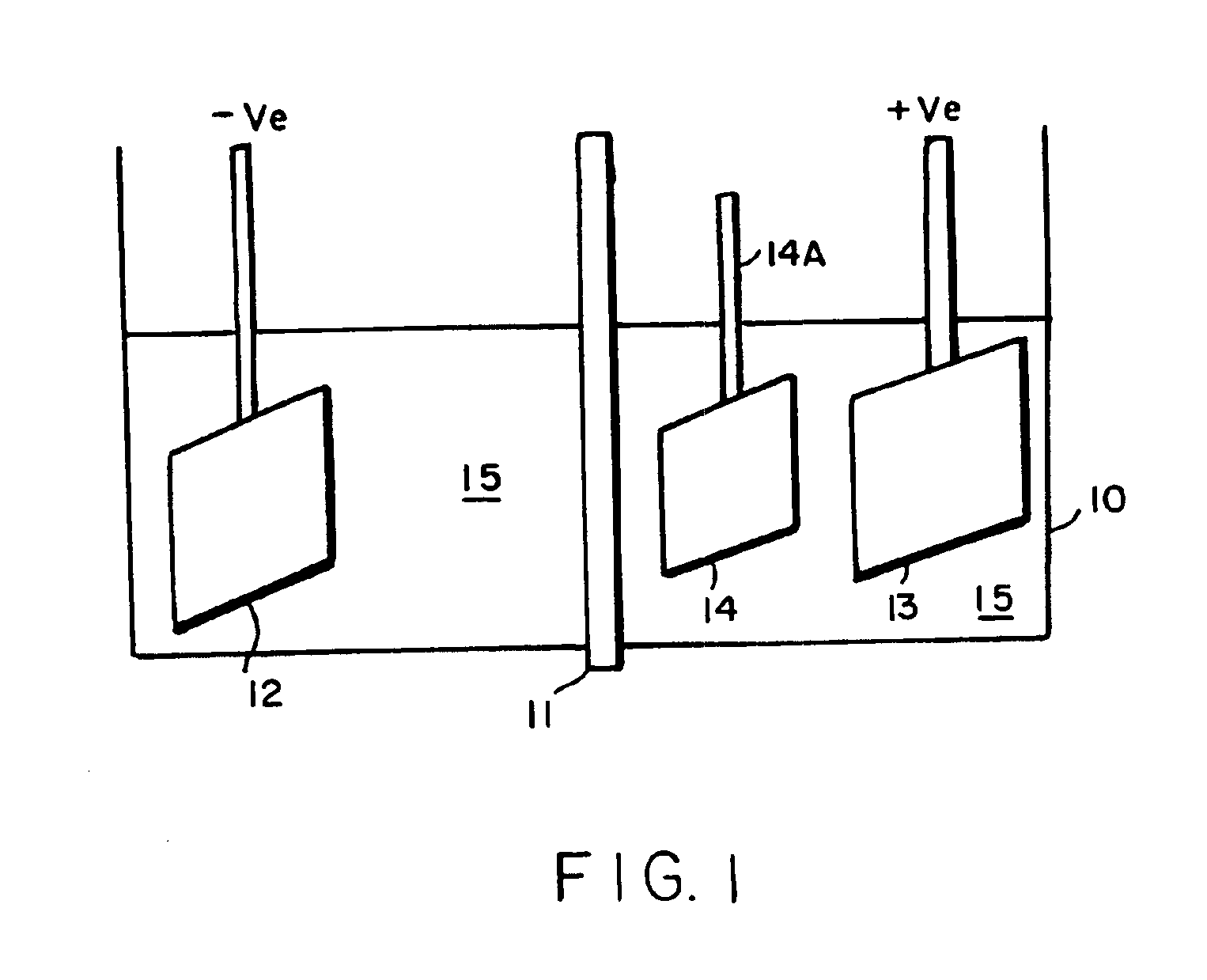
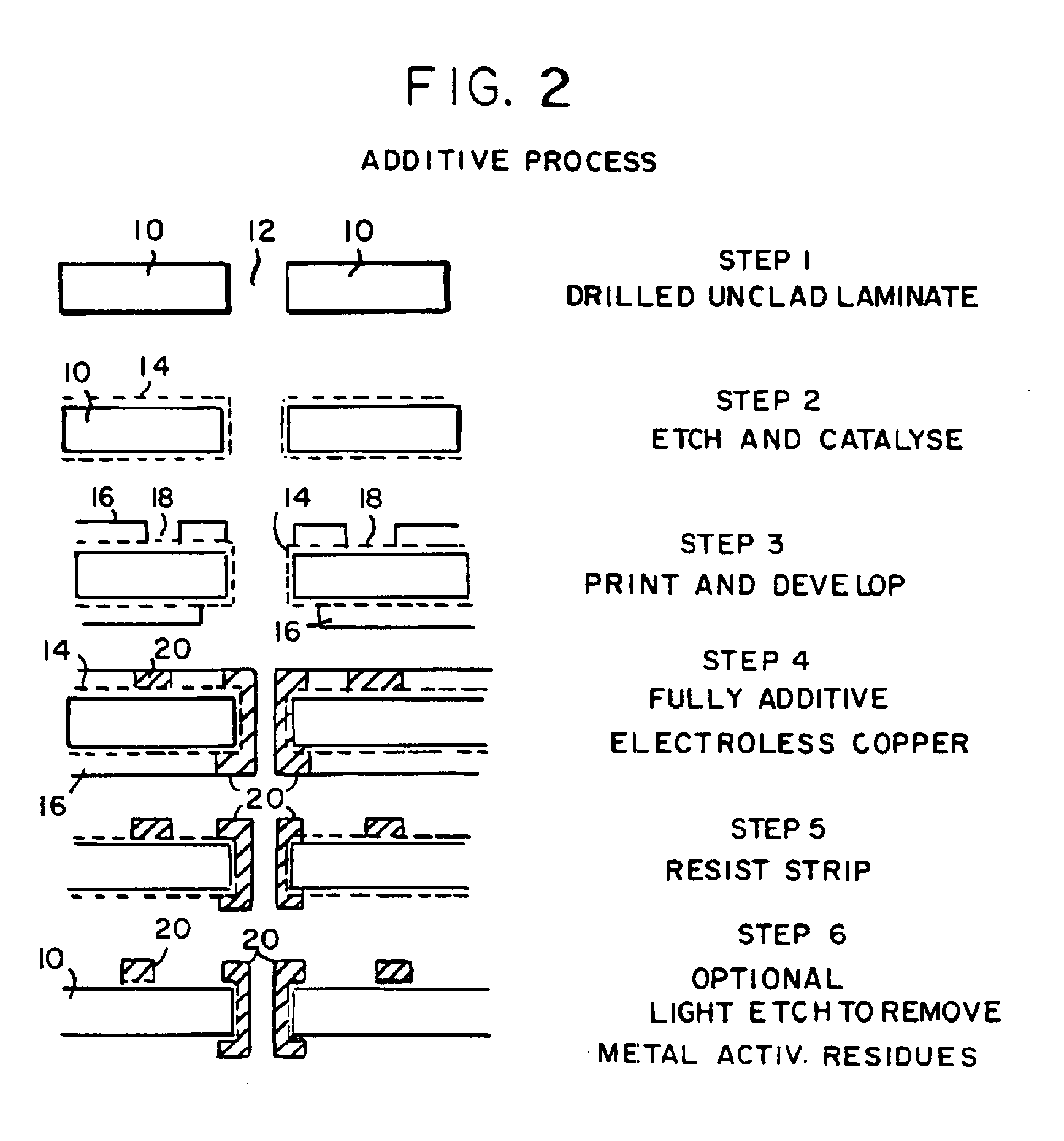
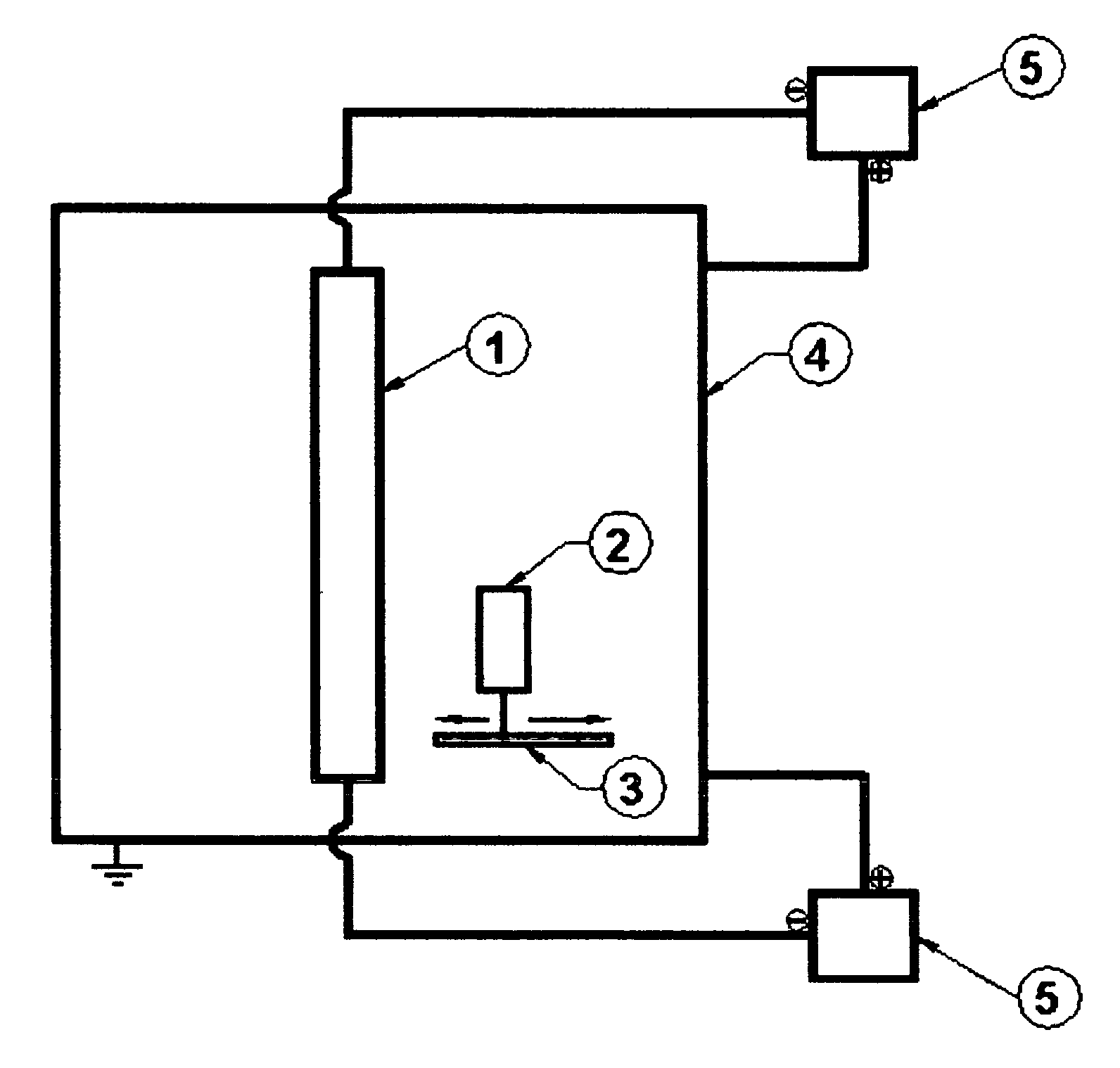
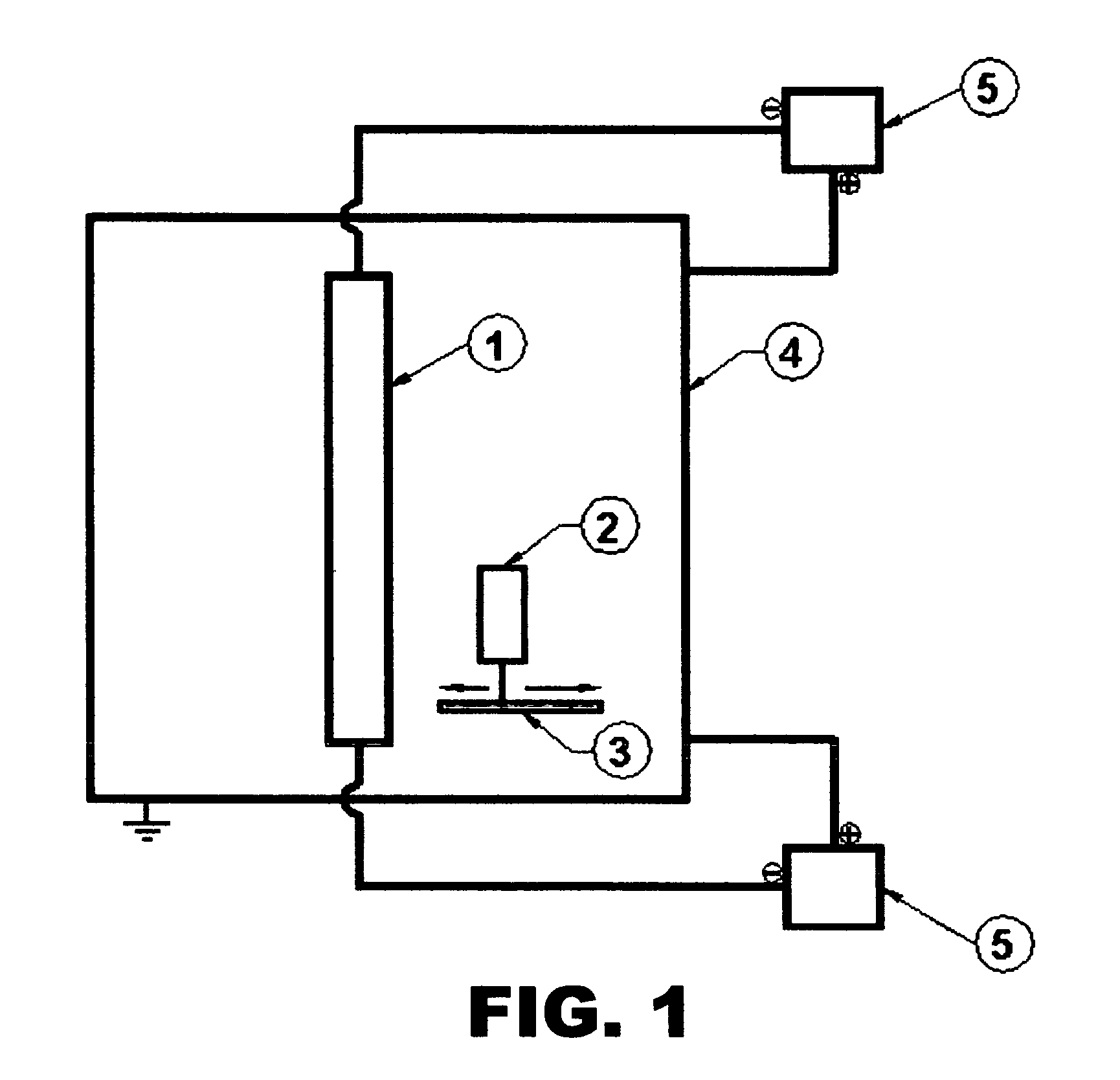
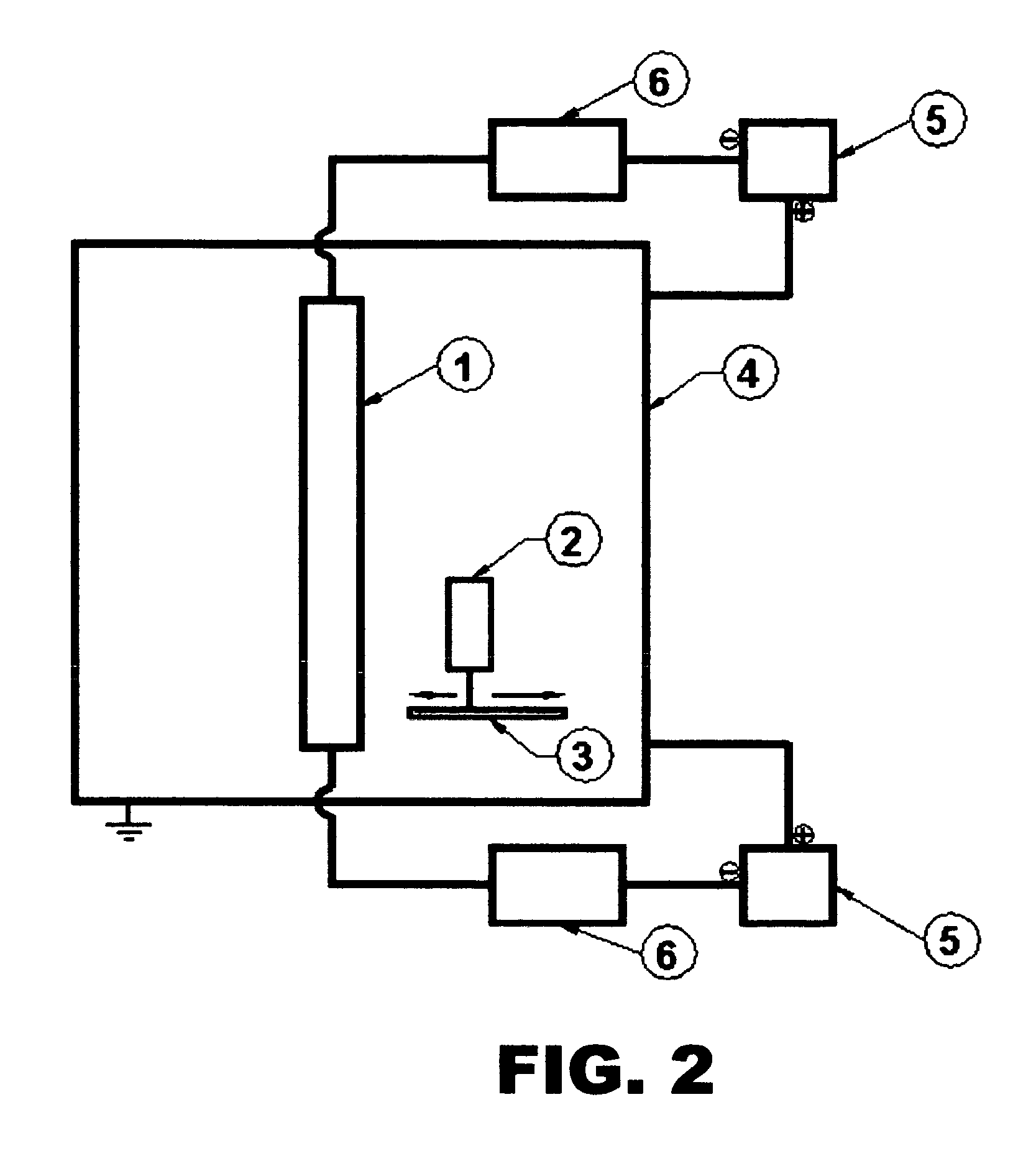
Electroless plating processes
InactiveUS6861097B1Reducing problem encounteredSimple methodPaper/cardboard articlesDecorative surface effectsPolymeric surfaceOxidation state
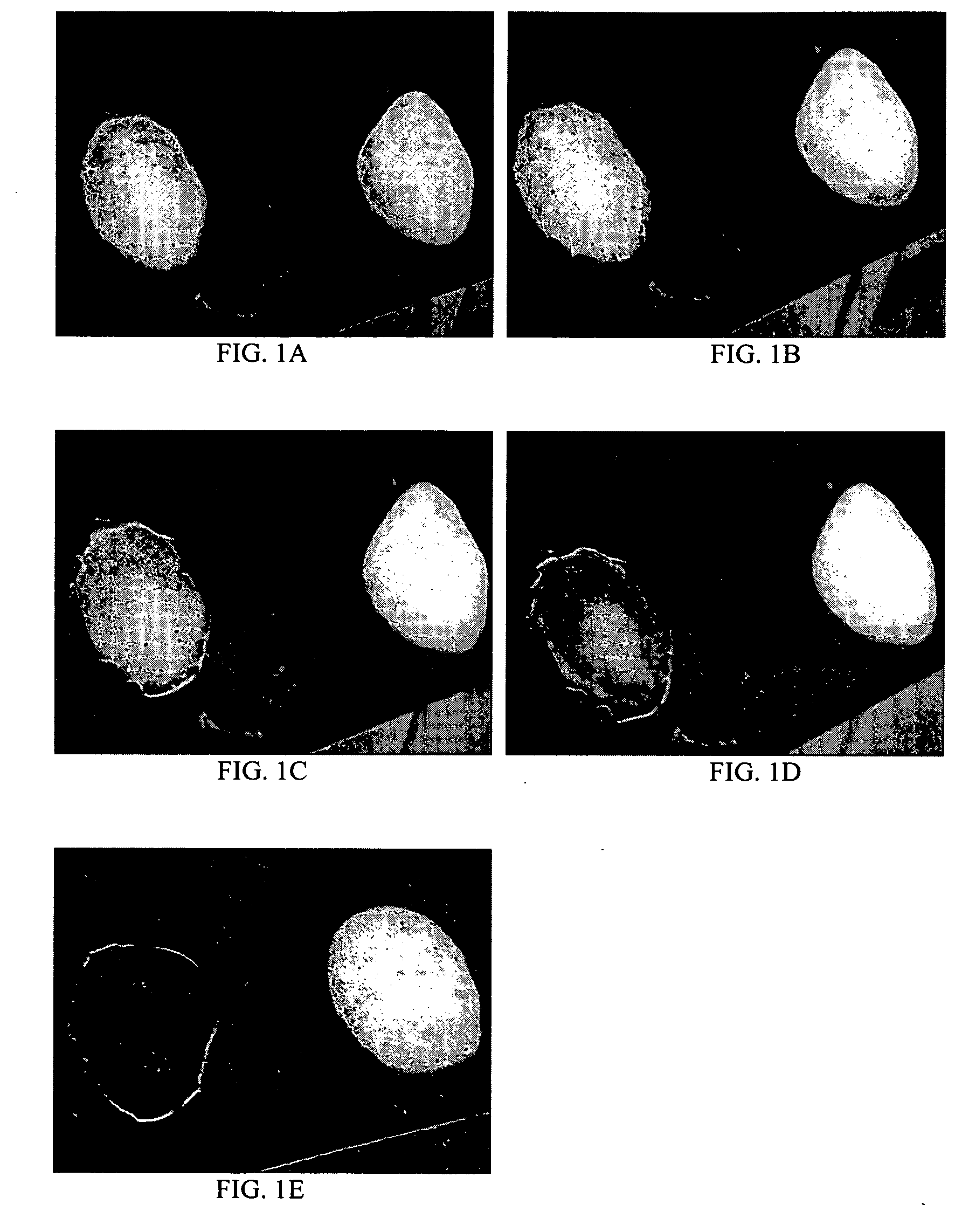
The invention includes processes for combined polymer surface treatment and metal deposition. Processes of the invention include forming an aqueous solution containing a metal activator, such as an oxidized species of silver, cobalt, ruthenium, cerium, iron, manganese, nickel, rhodium, or vanadium. The activator can be suitably oxidized to a higher oxidation state electrochemically. Exposing a part to be plated (such as an organic resin, e.g. a printed circuit board substrate) to the solution enables reactive hydroxyl species (e.g. hydroxyl radicals) to be generated and to texture the polymer surface. Such texturing facilitates good plated metal adhesion. As part of this contacting process sufficient time is allowed for both surface texturing to take place and for the oxidized metal activator to adsorb onto said part. The part is then contacted with a reducing agent capable of reducing the metal activator to a lower ionic form, or a lower oxidation state. That reduction can result in the formation of metallic catalytic material over the surface of the part. The reduced metal activator can then function to catalyze the electroless deposition of metal such as copper from solution by contacting the part with the plating solution.
Owner:SHIPLEY CO LLC
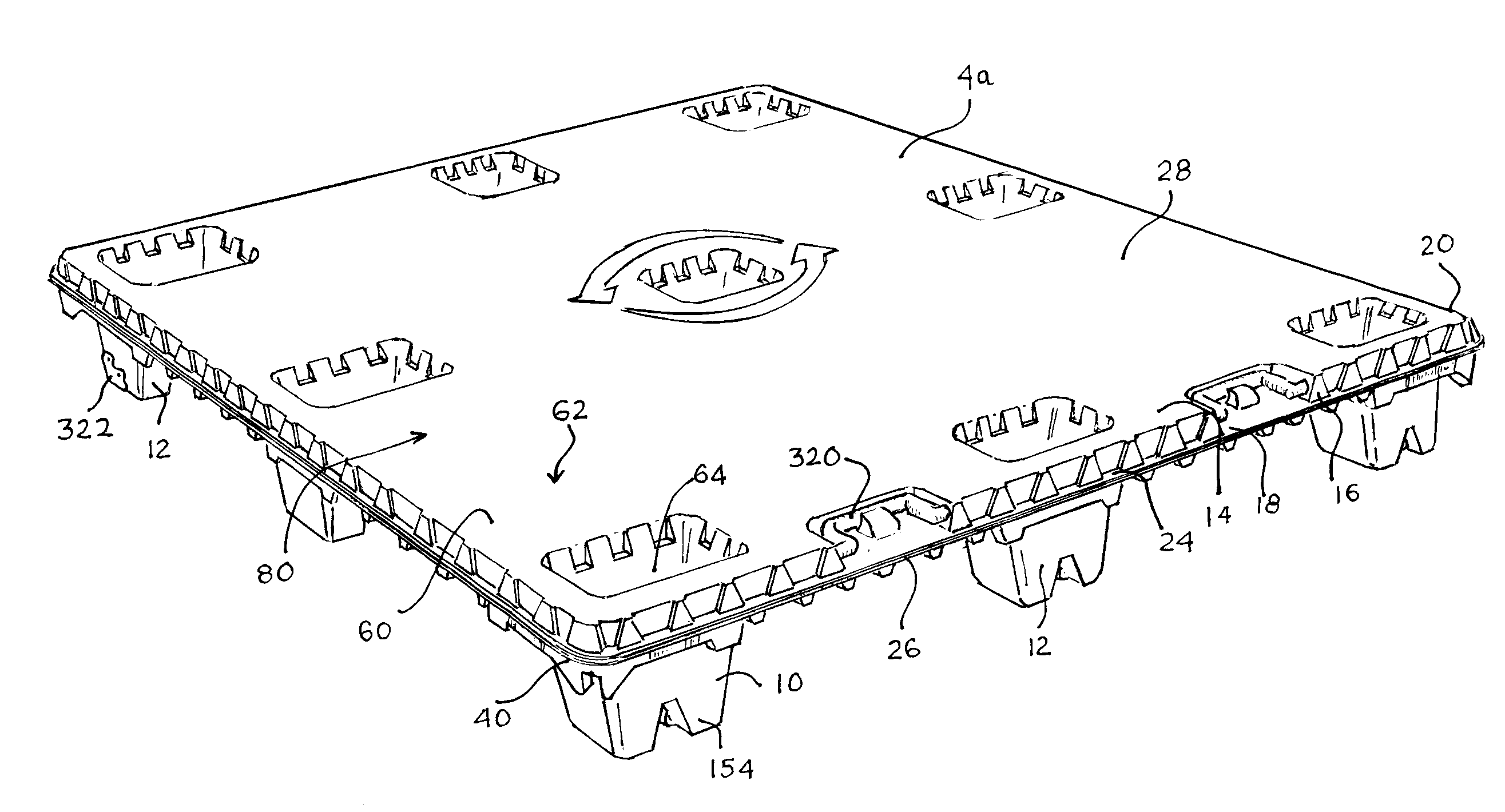
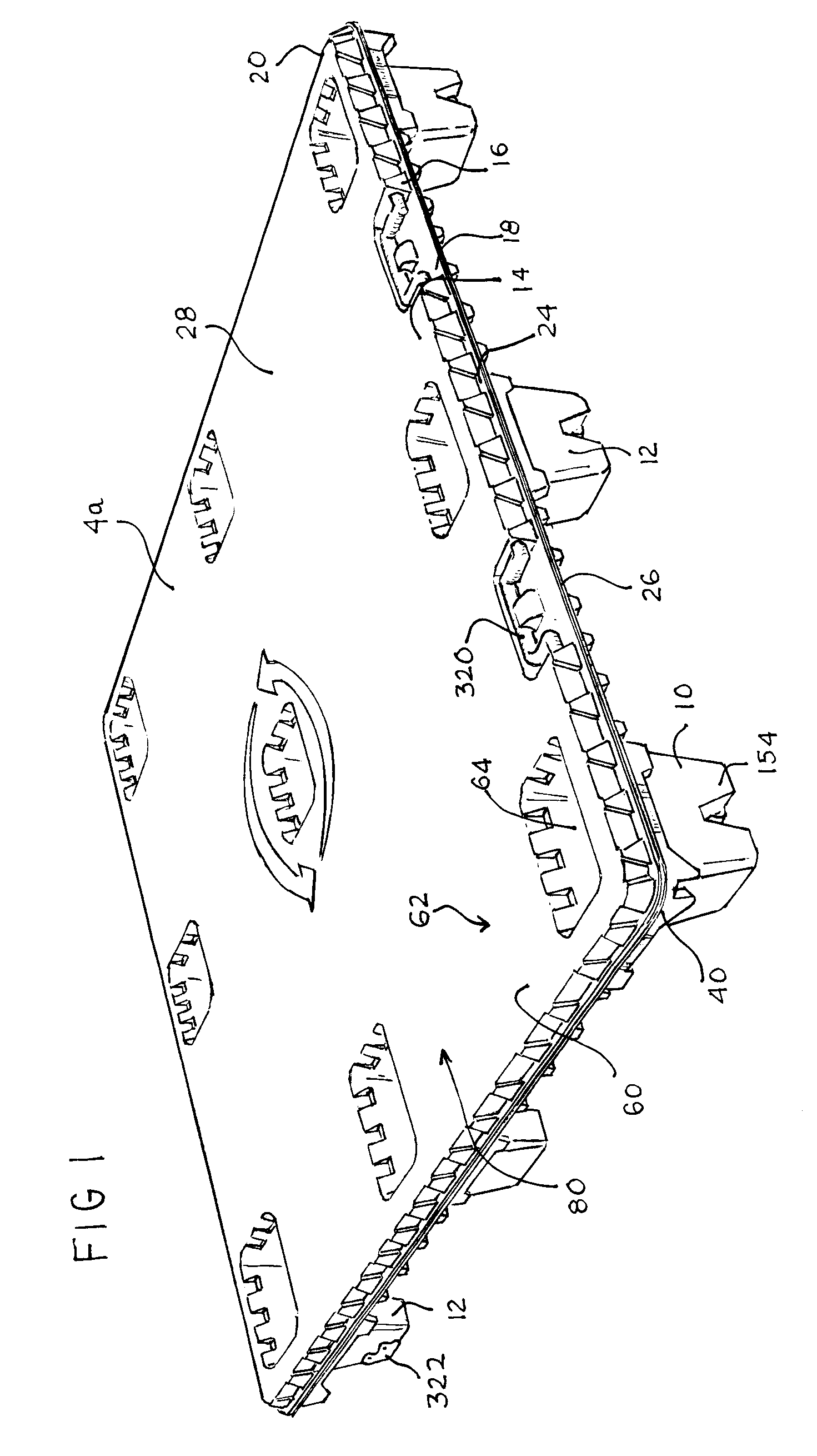
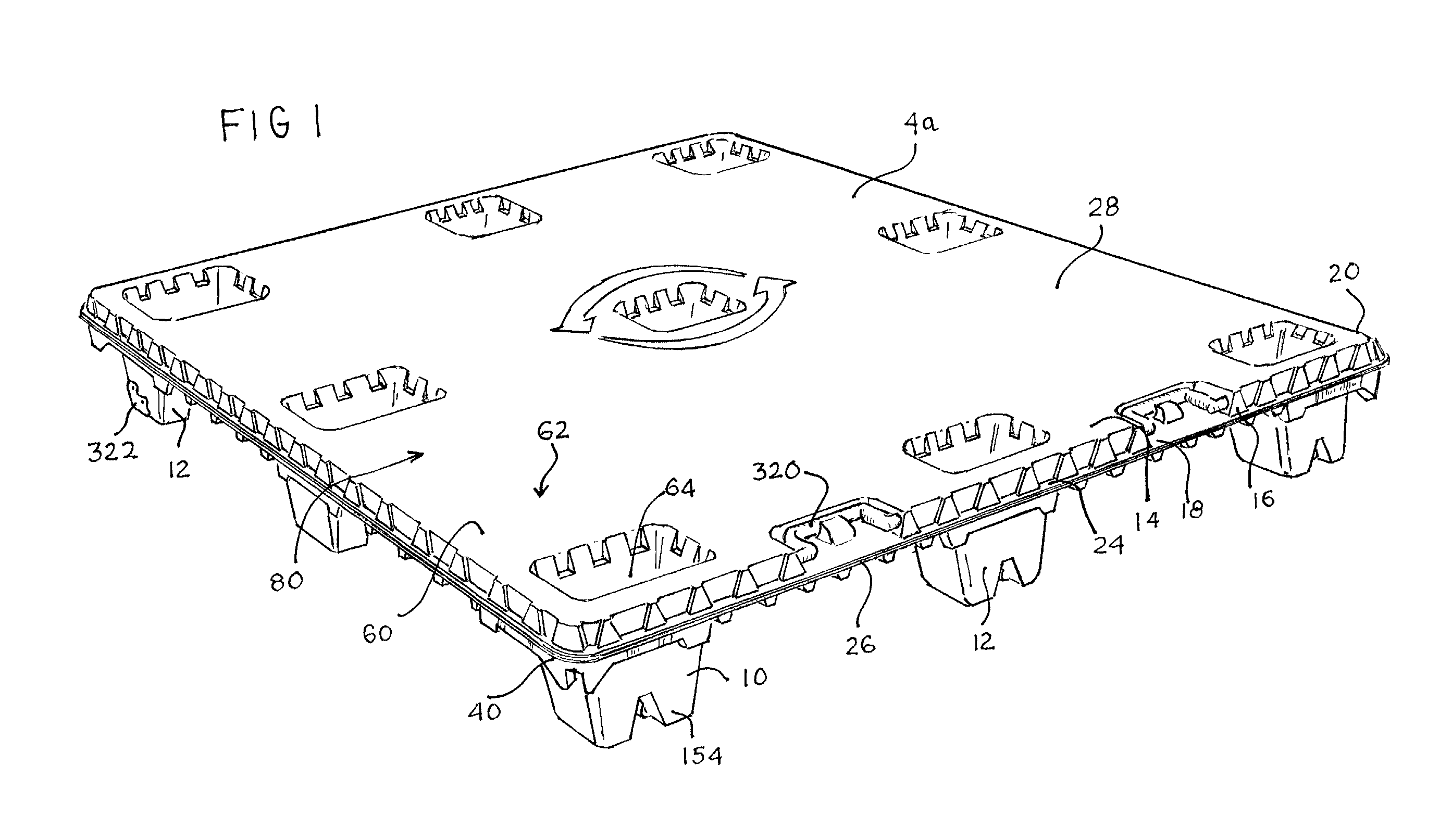
Thermoformed platform
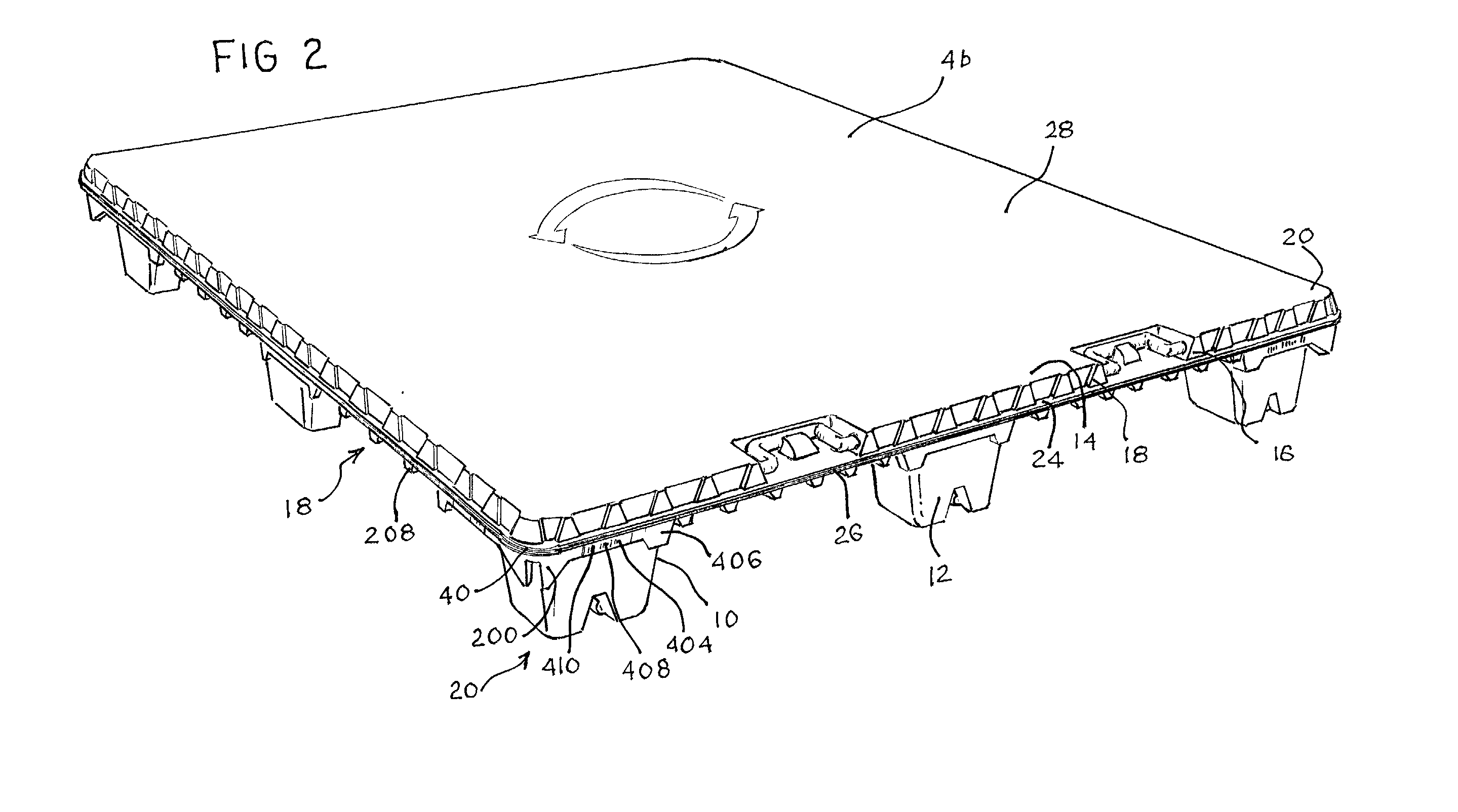
Articles constructed of a plurality of scuffed sheets have improved sheet-to-sheet bond strength and surfaces with high coefficients of friction. Articles constructed out of three scuffed sheets include exterior intumescent polymeric surfaces resisting the spread of combustion flames and insulating the interior surfaces from the high temperature of fire. Articles include electronic apparatus sending an emergency 911 call to a remote monitoring station. Articles are advantageously reinforced with optional rigidifying structures without article modification. Members are joined with snap together features providing an assembled article. Articles include handles for ergonomic manipulation by workers. Articles include elements amenably receiving unitization accessories. The article improvements are demonstrated in the form of industrial platforms, particularly material handling pallets.
Owner:NEXTREME
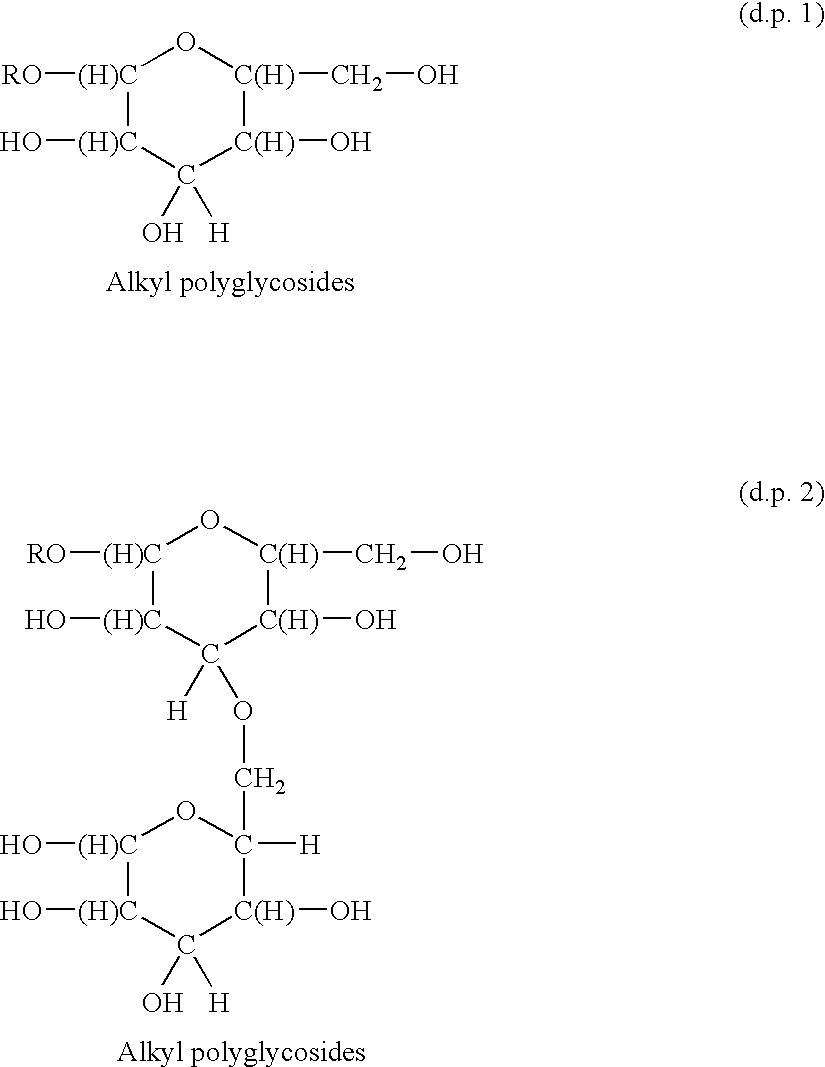
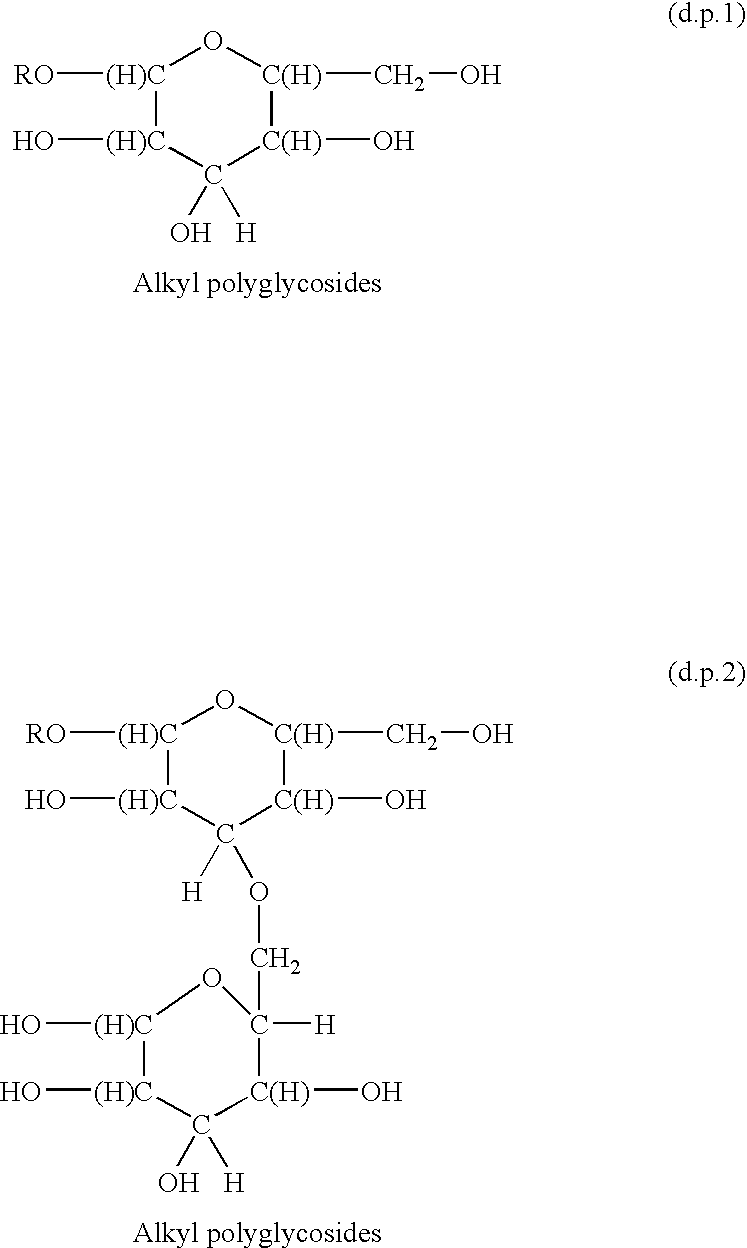
Functionalized polymeric surfactants based upon alkyl polyglycosides
The invention relates to a series of multifunctional polyglycosides derivatives that are made by the polymerized by the reaction of 1,3 dichloro isopropanl and polyglycosides, together with a functionalizing agent that contains a sulfate, sulfonate, quaternary nitrogen, or a phosphate group. The preferred polymers are cross linked having more than one group per molecule. They are made with mild reagents to avoid discoloration and mal odor.
Owner:SURFATECH
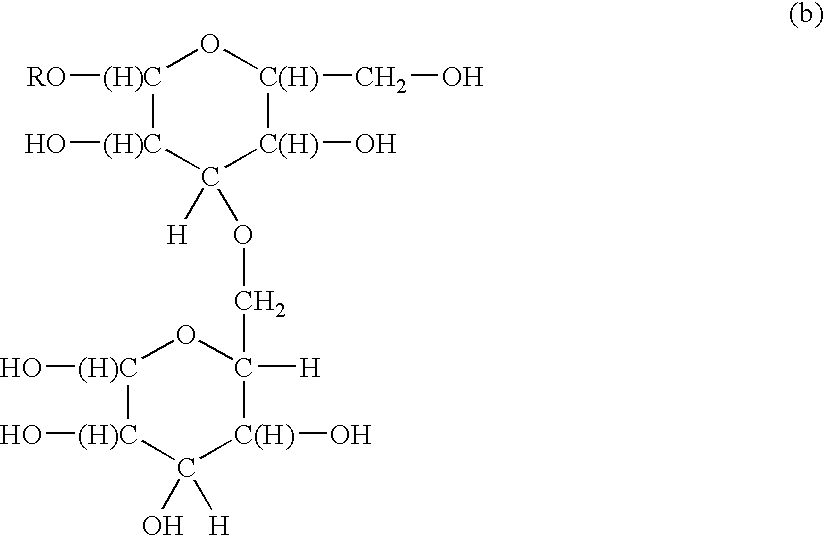
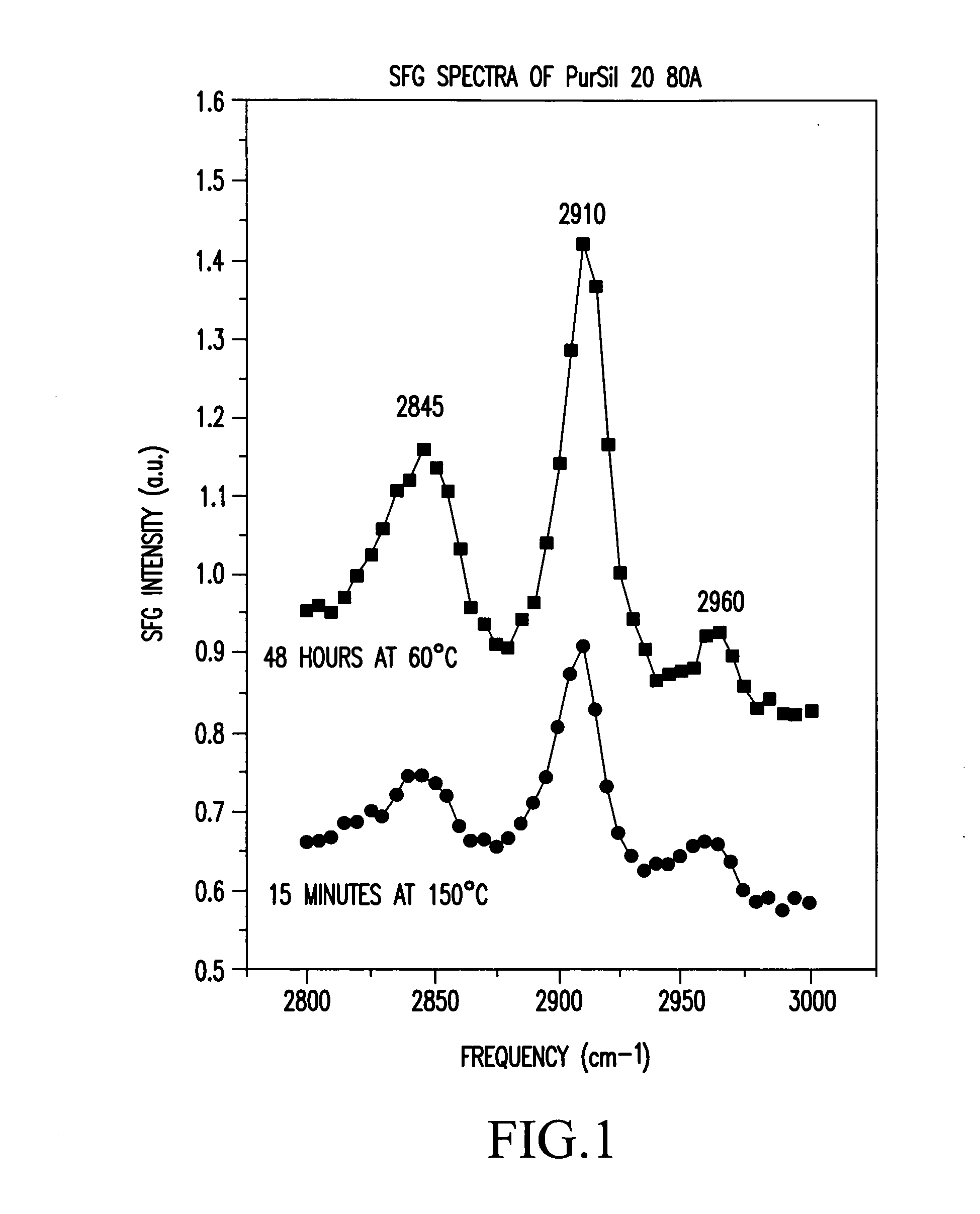
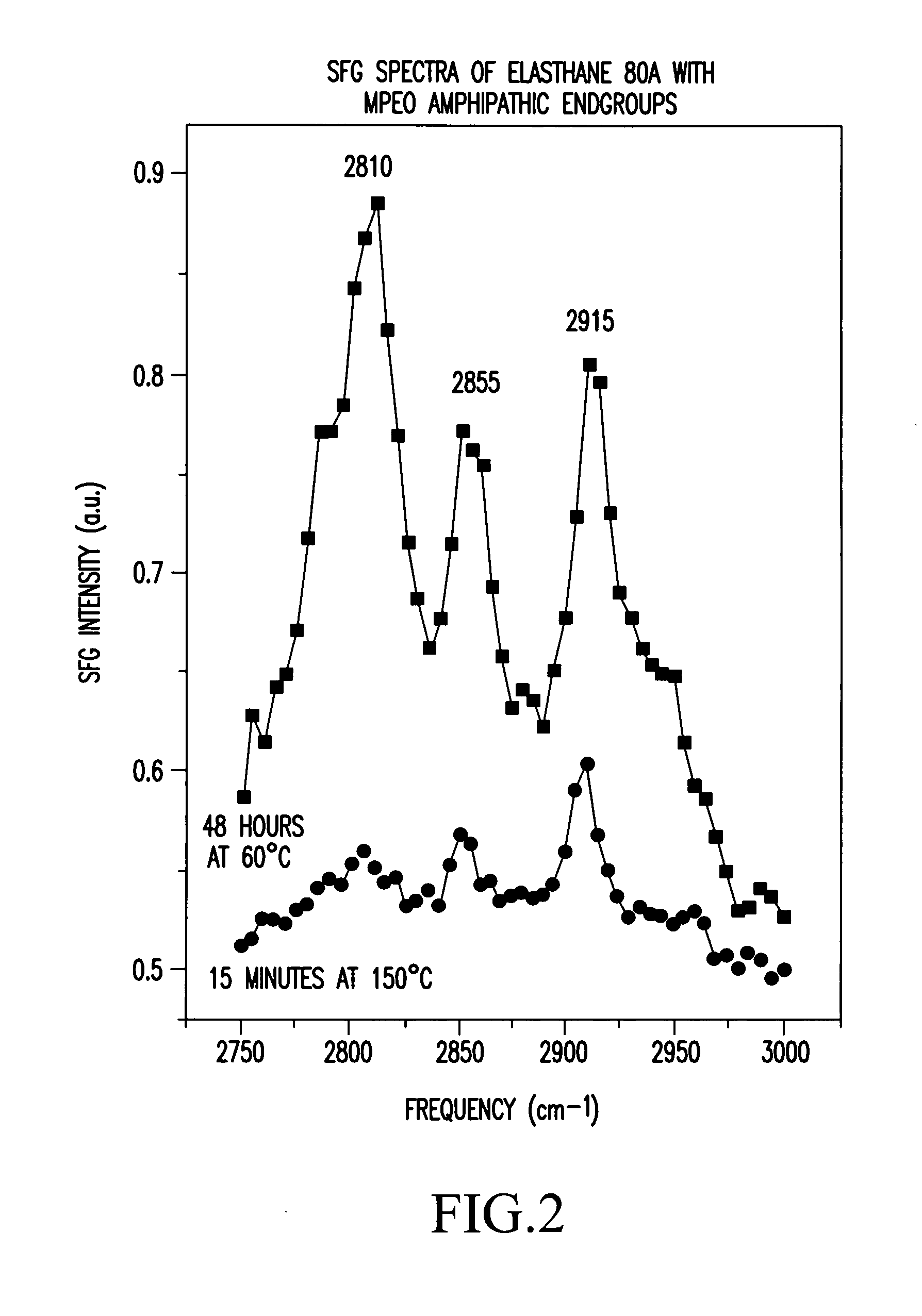
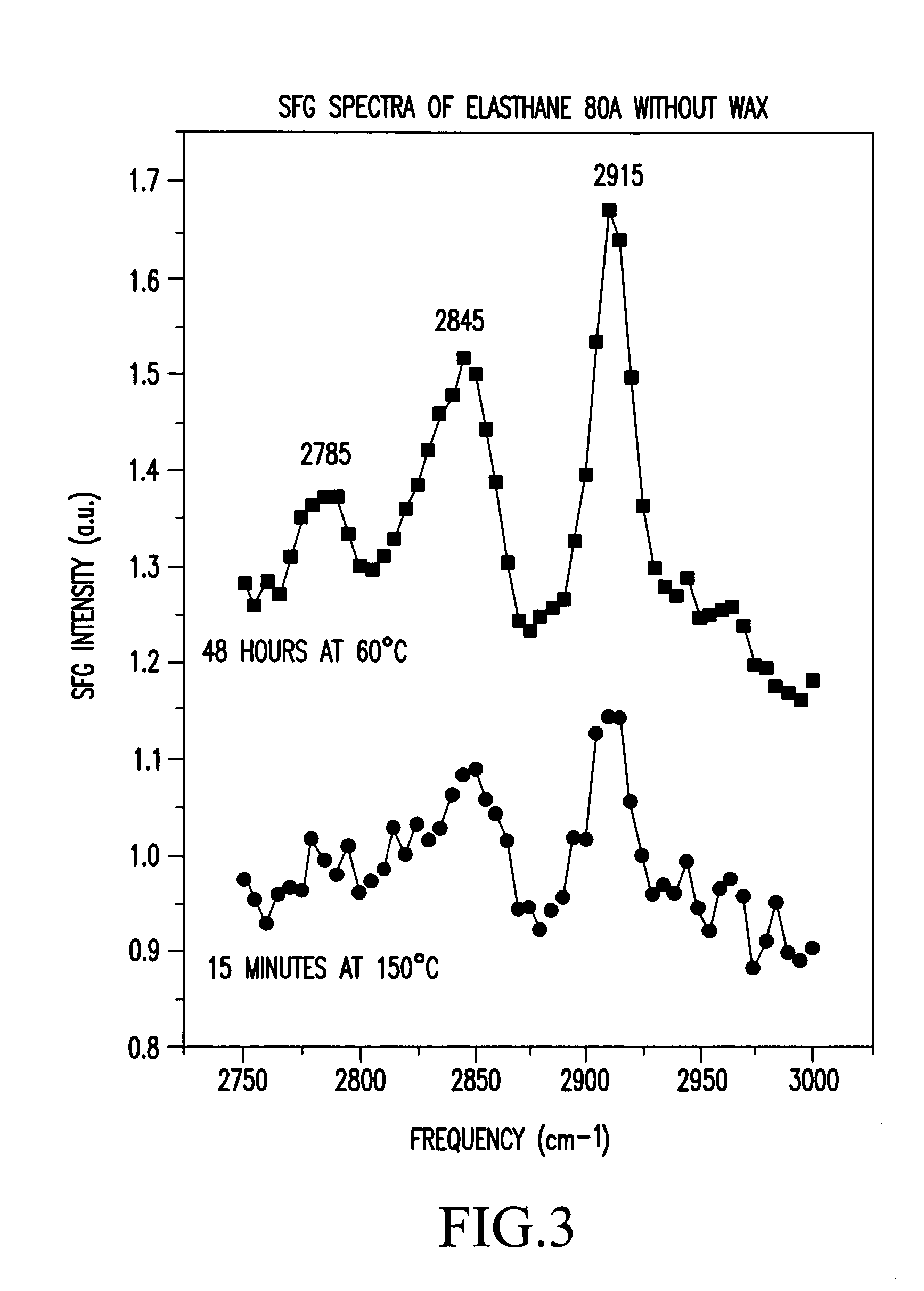
Control of polymer surface molecular architecture via amphipathic endgroups
ActiveUS20050282997A1Promote resultsReduce signal to noise ratioSurgeryCatheterPolymeric surfacePolyethylene oxide
Polymers whose surfaces are modified by endgroups that include amphipathic surface-modifying moieties. An amphipathic endgroup of a polymer molecule is an endgroup that contains at least two moieties of significantly differing composition, such that the amphipathic endgroup spontaneously rearranges its positioning in a polymer body to position the moiety on the surface of the body, depending upon the composition of the medium with which the body is in contact, when that re-positioning causes a reduction in interfacial energy. An example of an amphipathic surface-modifying endgroup is one that has both a hydrophobic moiety and a hydrophilic moiety in a single endgroup. For instance, a hydrophilic poly(ethylene oxide) terminated with a hydrophilic hydroxyl group is not surface active in air when the surface-modifying endgroup is bonded to a more hydrophobic base polymer. If the hydroxyl group on the oligomeric poly(ethylene oxide) is replaced by a hydrophobic methoxy ether terminus, the poly(ethylene oxide) becomes surface active in air, and allows the poly(ethylene oxide) groups to crystallize in the air-facing surface. In this example, immersion in water destroys the crystallinity as the poly(ethylene oxide) sorbs water and the hydrophobic methoxy group retreats below the surface of the polymer. Also disclosed are methods and articles of manufacture that make use of these polymers.
Owner:THE POLYMER TECH GROUP
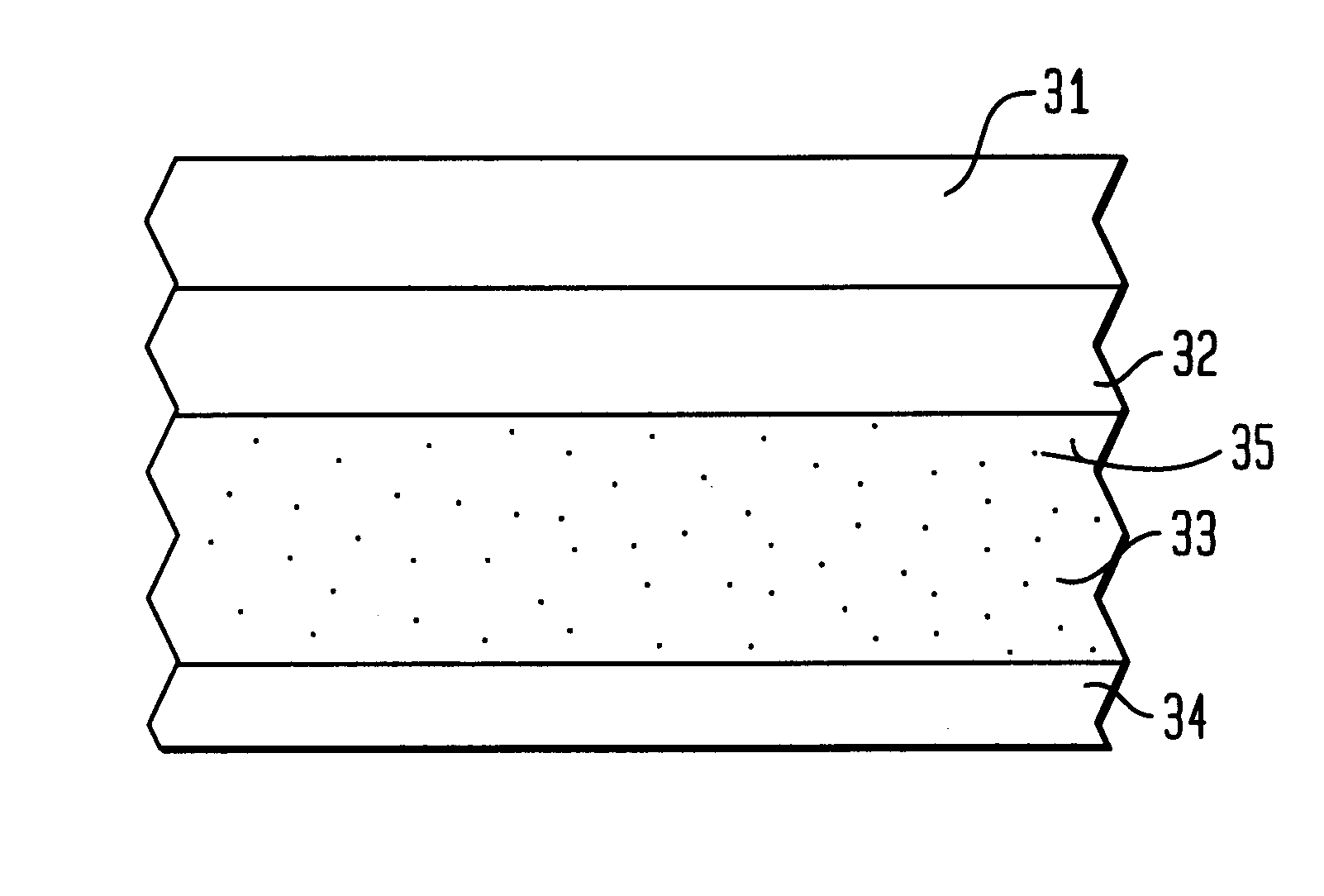
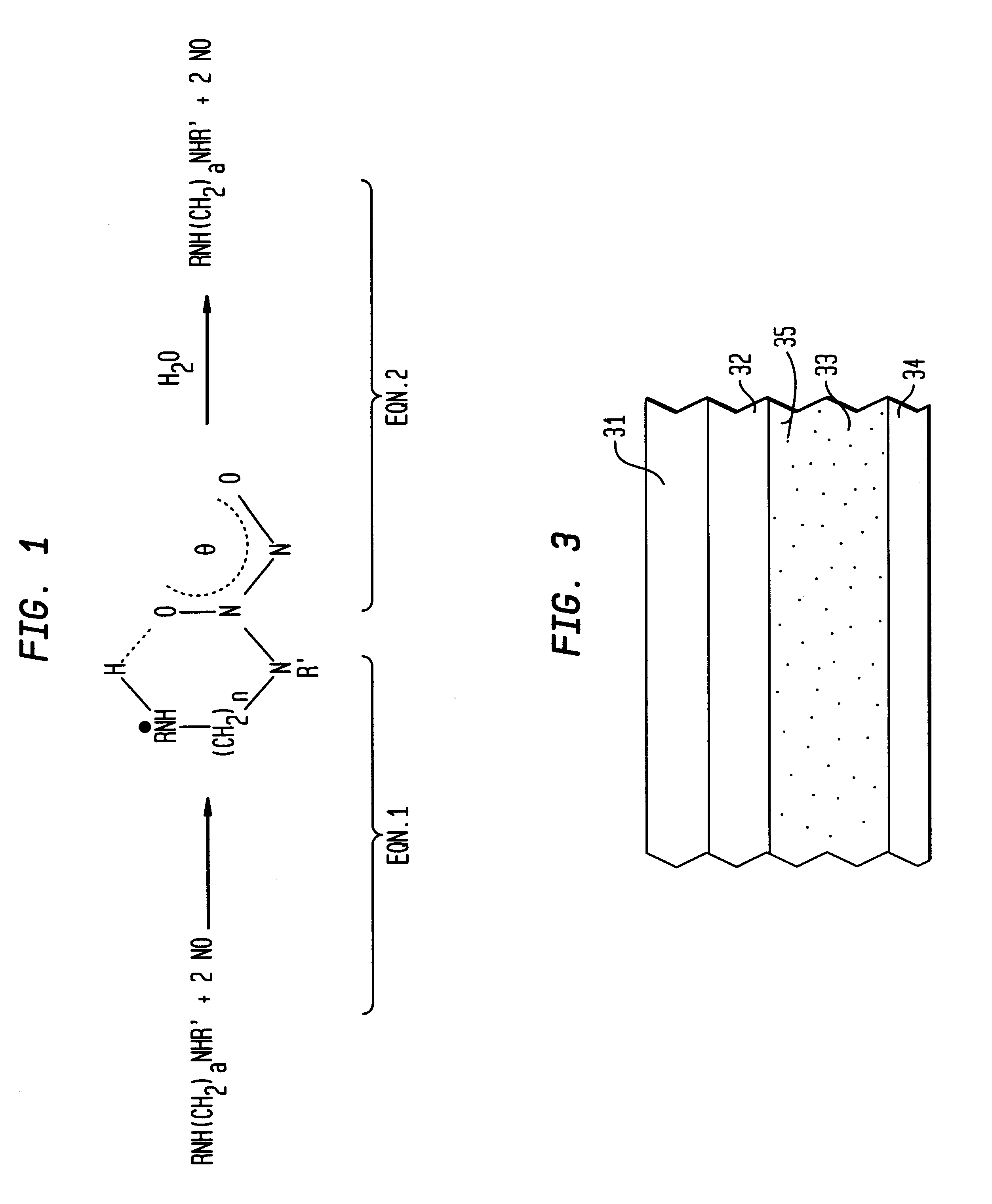
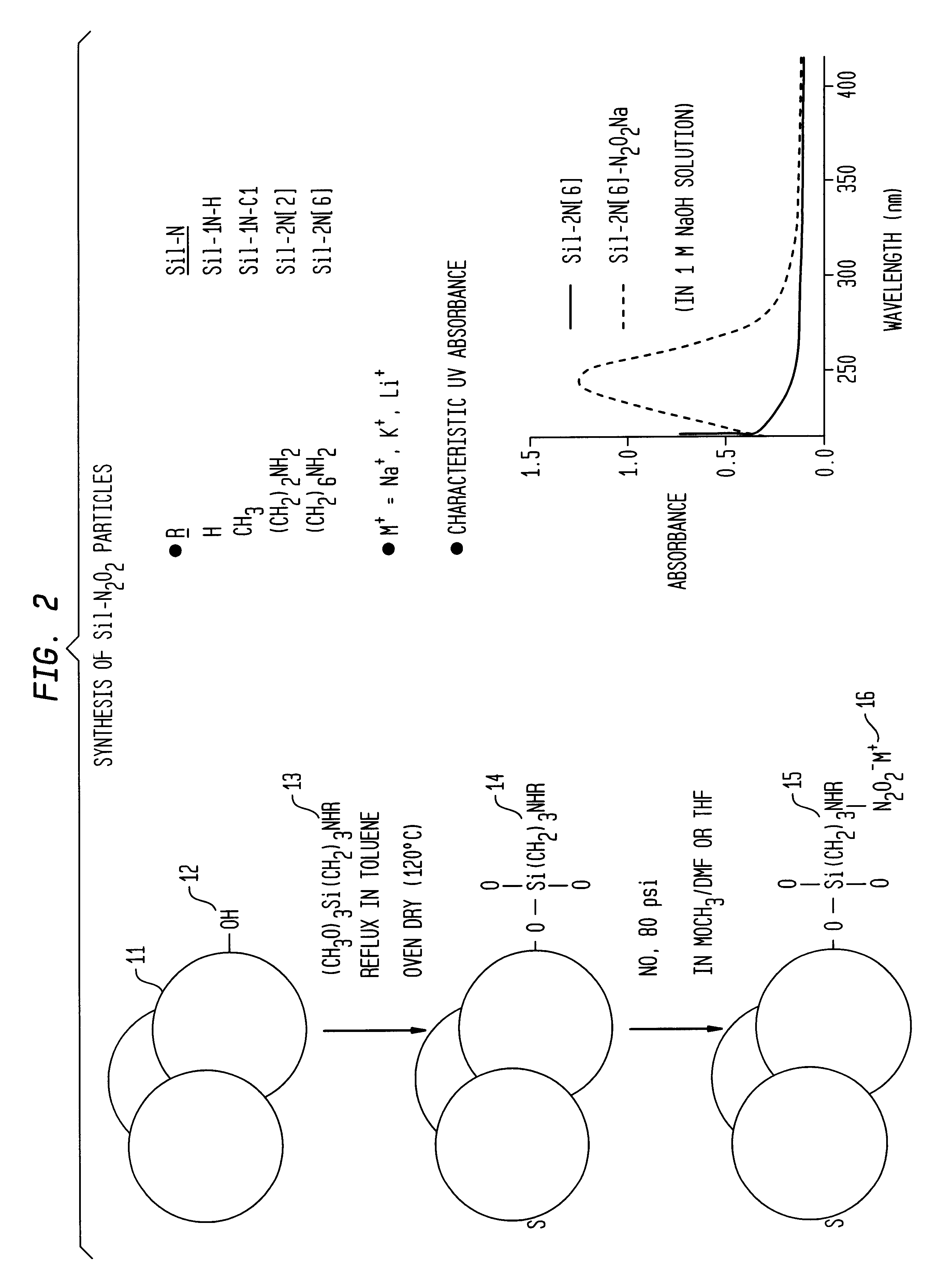
Nitric oxide-releasing polymers incorporating diazeniumdiolated silane derivatives
InactiveUS6841166B1Reduce activationReduce aggregationBiocideInorganic active ingredientsPolymeric surfaceSilanes
Biocompatible polymeric materials capable of providing in situ release of nitric oxide (NO) included diazeniumdiolated fumed silica as a filler in a multilayer polymer structure to release NO upon contact with water (blood). The blood-contacting polymer surface is preferably multi-layered so that the NO-releasing layer, containing the diazeniumdiolated fumed silica, is shielded from blood contact by one or more top (or base) coats. When in contact with blood, the NO released at the surface of the polymer prevents platelet activation and adhesion to the surface, thereby reducing platelet consumption, risk of thrombus formation and other clinical complications associated with interactions between blood and foreign materials.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Foamable alcoholic composition
A stable foam composition includes greater than about 40 weight percent of an alcohol, based upon the total weight of the alcoholic composition, and a foaming surfactant selected from fluorosurfactants, siloxane polymer surfactants, and combinations thereof. When the foaming surfactant includes a fluorosurfactant, the alcoholic composition further includes a polymeric or oligomeric foam stabilizer.
Owner:GOJO IND INC
Surfaces which are self-cleaning by hydrophobic structures, and a process for their production
A process for producing self-cleaning surfaces, in which an at least partially hydrophobic, surface structure is formed by securing particles on a polymer surface, which comprises applying, to the polymer surface, at least one solvent which comprises the particles and which solvates the polymer surface, and securing at least part of the particles to the polymer surface by removing the solvent; self-cleaning surfaces obtained by the process; and objects containing self-cleaning surfaces obtained by the process.
Owner:CREAVIS GES FUER TECH
Polypropylene type aqueous dispersion, polypropylene type composite aqueous emulsion composition and its use
A polypropylene type aqueous dispersion comprising the following components (a) to (c): (a) a polypropylene type polymer100parts by weightand / or a modified polypropylene typepolymer(b) a surfactant1 to 100parts by weight, and(c) water100 to 1,000parts by weight,wherein the component (a) has a main chain having the following features (1) and (2) and dispersion particles in the dispersion have an average particle size of at most 0.5 μm, Feature (1) when observing a peak derived from a carbon atom of a methyl group in a propylene unit chain part comprising a head-to-tail bond by 13C-NMR and fixing a chemical shift of a peak top at a peak attributable to pentad expressed by mmmm to 21.8 ppm, a ratio (S1 / S) of an area S1 of a peak of a peak top at 21.8 ppm to a total area S of peaks at from 19.8 ppm to 22.1 ppm is at least 10% and at most 60%, and when an area of a peak (mmmr) of a peak top at 21.5 to 21.6 ppm is expressed as S2, 4+2S1 / S2>5, and Feature (2) a content ratio (mol ratio) of propylene unit (A): other olefin unit (B) is from 100:0 to 90:10.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Process for extracting bitumen
Bitumen extraction done using a process comprising: (a) preparing a bitumen froth comprising particulate mineral solids and hydrocarbons dispersed in aqueous lamella in the form of an emulsion; (b) adding a sufficient amount of a paraffinic solvent to the froth to induce inversion of the emulsion and precipitate asphaltenes from the resultant hydrocarbon phase; (c) mixing the froth and the solvent for a sufficient time to dissolve the solvent into the hydrocarbon phase to precipitate asphaltenes; and (d) subjecting the mixture to gravity or centrifugal separation for a sufficient period to separate substantially all of the water and solids and a substantial portion of the asphaltenes from the bitumen; wherein a separation enhancing additive is present in the process. The separation enhancing additive is a polymeric surfactant that has multiple lipophilic and hydrophilic moieties, which can effect easier handling of asphaltene sludges and less foaming during solvent recovery.
Owner:MARATHON OIL SANDS +2
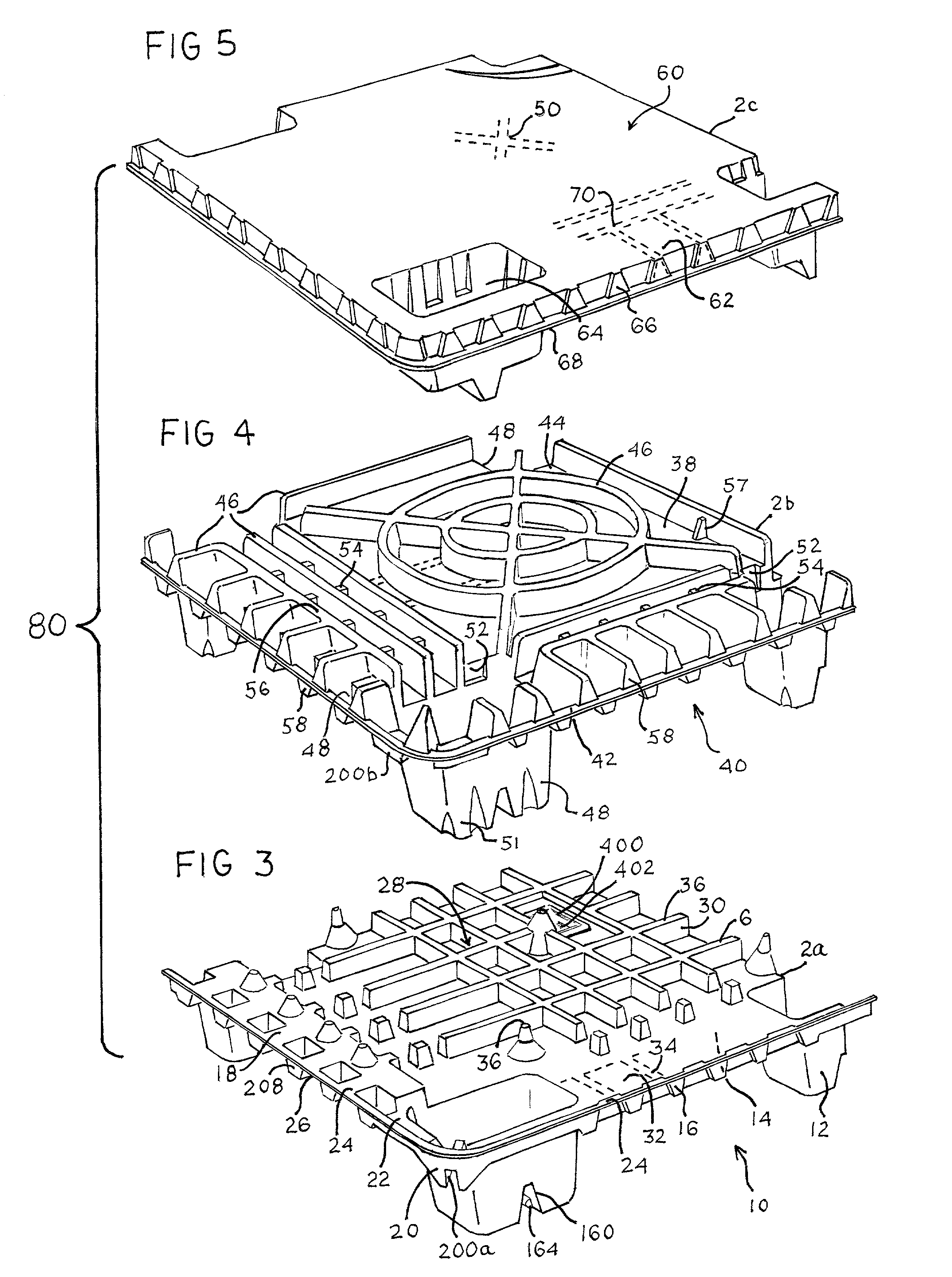
Thermoformed platform
Articles constructed of a plurality of scuffed sheets have improved sheet-to-sheet bond strength and surfaces with high coefficients of friction. Articles constructed out of three scuffed sheets include exterior intumescent polymeric surfaces resisting the spread of combustion flames and insulating the interior surfaces from the high temperature of fire. Articles include electronic apparatus sending an emergency 911 call to a remote monitoring station. Articles are advantageously reinforced with optional rigidifying structures without article modification. Members are joined with snap together features providing an assembled article. Articles include handles for ergonomic manipulation by workers. Articles include elements amenably receiving unitization accessories. The article improvements are demonstrated in the form of industrial platforms, particularly material handling pallets.
Owner:NEXTREME
Surface deformation electroactive polymer transducers
InactiveUS20080289952A1Augments out-of-plane deflectionsIncrease awarenessPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEfficient propulsion technologiesPolymeric surfaceVisibility
The present invention provides electroactive polymer transducers that produce out-of-plane deflections. The transducers form a set of surface features based on deflection of an electroactive polymer. The set of surface features may include elevated polymer surface features and / or depressed electrode surface features. Actuation of an active area may produce the polymer deflection that creates one or more surface features. A passive layer may operably connect to a polymer. The passive layer may comprise a thicker and softer material to amplify polymer thickness changes and increase surface feature visibility.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Deposition of calcium-phosphate (CaP) and calcium-phosphate with bone morphogenic protein (CaP+BMP) coatings on metallic and polymeric surfaces
InactiveUS20080097618A1Reduce the amount of solutionHigh densityImpression capsBone implantPolymeric surfaceSolubility
The invention is a medical implantable device which is coated by the method according to the invention. The surface of the substrate used for the implantable device, in the raw condition, following a cleaning regime and physiochemical pretreatments, is coated using a biomimetic process in a supersaturated calcium phosphate solution (SCPS) to obtain the desired coating coverage and morphology maintaining a ratio of calcium to phosphorus pH, as well as solution temperature plays a major role in yielding precipitation of the proper phase of CaP so that composition, morphologies, crystal structures, and solubility characteristics are optimal for the deposition process. The biomimetic coating adds the attribute of osteoconductivity to the implant device. To maximize bone growth, the implant must also induce bone growth, or possess the attribute of osteoinductivity. This attribute is acquired by the use of therapeutic agents, i.e. bone morphogenic proteins (BMP), growth factors, stem cells, etc. The preparation of the SCPS solution is slightly altered so that during the immersion of the implant in the SCPS, the therapeutic agents are co-precipitated and bonded with the CaP directly on the underlying surface of the implant device. A final dipping process into a BMP solution provides an initial burst of cellular activity. For delivering stem and / or progenitor cell, after drying the dipped solution of BMP, the cells are cultured on the surface of the implant.
Owner:HERKOWITZ HARRY N
Radiopaque coatings for polymer substrates
InactiveUS20070178222A1Improve radiopacityImprove adhesionElectric discharge tubesPharmaceutical containersPolymeric surfacePolymer science
Improved radiopaque coatings particularly suitable for polymer substrates are described. A modified ion plasma deposition (IPD) method is used to provide coatings with macroparticle-dense surfaces that have excellent radiopacity. The coatings are particularly adapted to polymer surfaces because of high adherence and resistance to peeling and flaking.
Owner:NANOSURFACE TECH
Functionalized polymeric surfactants based upon alkyl polyglycosides
The invention relates to a series of multifunctional polyglycosides derivatives that are made by the polymerized by the reaction of polyoxyalkylene containing crosslinking reagent and polyglycosides, together with a functionalizing agent that contains a sulfate, sulfonate, quaternary nitrogen, or a phosphate group. The preferred polymers are cross linked having more than one group per molecule. They are made with mild reagents to avoid discoloration and mal odor.
Owner:SURFATECH
Implantable valve and method
Implantable valve for treating venous insufficiency having a self-expanding frame encased in polymer having a distal section for blood in-flow, a bulbous center section and a proximal section for blood out-flow. Polymeric leaflets have proximal ends forming a valve outlet which opens and closes in response to venous blood flow and distal portions integral with the inner polymer surface of the distal end of said bulbous section. The leaflets define a predominantly biomimetic sinus region with the bulbous section. Opening of the valve induces flushing of blood from the sinus region for smooth non-traumatic blood flow through said valve.
Owner:VENARUM MEDICAL LLC
Nanoparticle and surface-modified particulate coatings, coated balloons, and methods therefore
Devices, coatings, and methods therefore comprise a medical device for delivering nanoparticles of an active agent to a treatment site. A coating on the medical device comprises active agent nanoparticles, which delivers coating to the treatment site and releases active agent nanoparticles into the treatment site over at least one day. A coating may comprise a polymer, a surfactant, and the nanoparticles. The coating may be prepared by forming a nanoemulsion. A coating may comprise encapsulated active agent nanoparticles which comprise active agent nanoparticles encapsulated in a polymer. The coating may have a positive surface charge. The coating may deliver active agent nanoparticles into the treatment site over at least about one day. The coating may be formed of a surfactant and nanoparticles mixture. The active agent nanoparticles may be deposited on the medical device using electrostatic capture.
Owner:MICELL TECH INC
Preparation method of graphene solution phase
The invention relates to a preparation method of graphene solution phase. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) oxidizing graphite, (2) stripping mother liquid of the oxidized graphite, (3) reducing graphene oxide, wherein, polymer surface-active agent added into colloidal solution of graphene oxide is used as stabilizing agent and hydrazine hydrate is used as reducing agent. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that the obtained graphene has large area which can reach thousands or more square microns; the effective control of the sizes of graphene product can be realized only by selecting the size of the raw material of graphite, and the size of graphene can be effectively controlled between 20-200 microns; the concentration of the obtained graphene soliquid is high, which can be up to 5-10g / l, the stability of the graphene soliquid is good, and the graphene soliquid can not be subsided when being stewed for months; the method has the advantages of simple whole process, strong controllability and low price of adopted polymer surface active agent, thus being applicable to low-cost and large-scale production.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Coacervate systems having soil anti-adhesion and anti-deposition properties on hydrophilic surfaces
InactiveUS20060276371A1Organic detergent compounding agentsAnionic surface-active compoundsPolymeric surfaceSurface cleaning
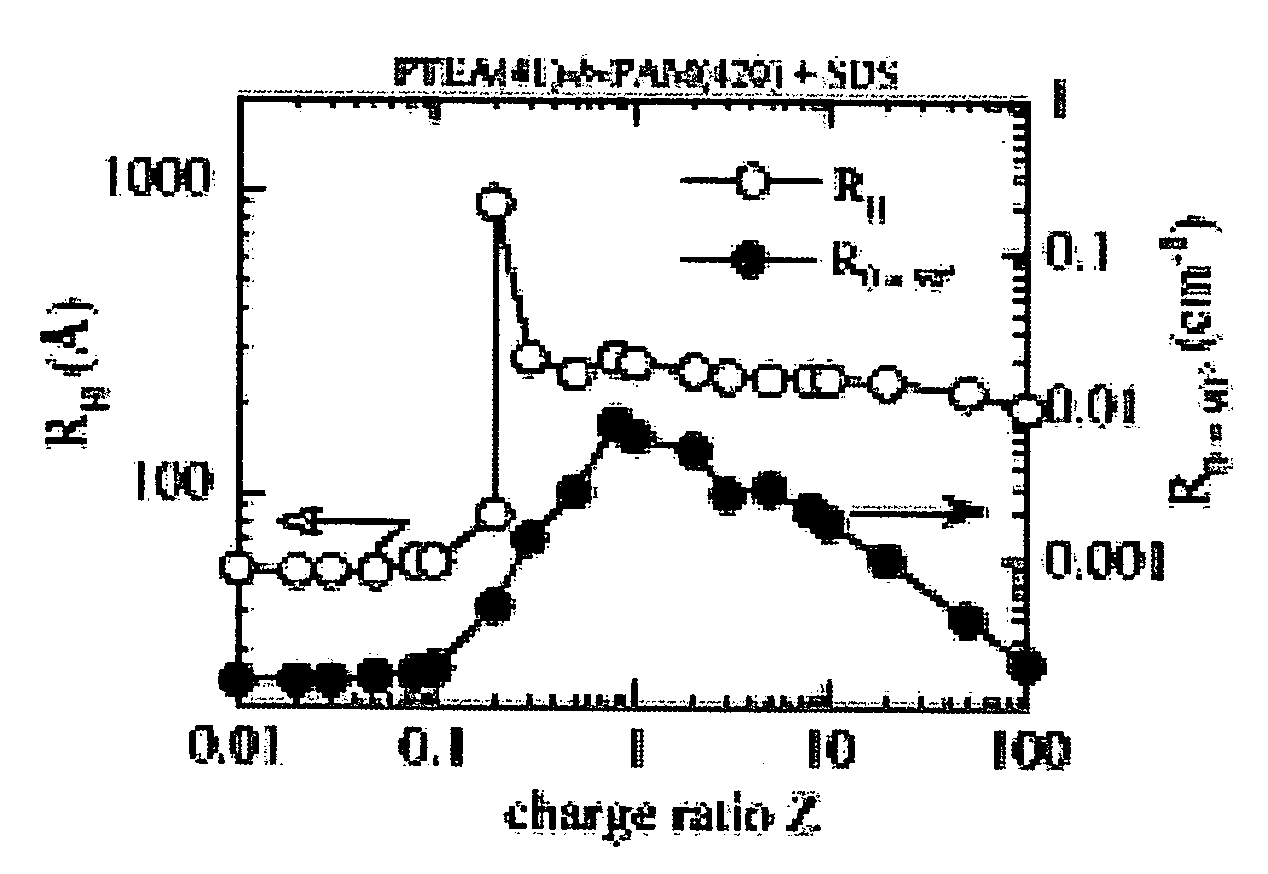
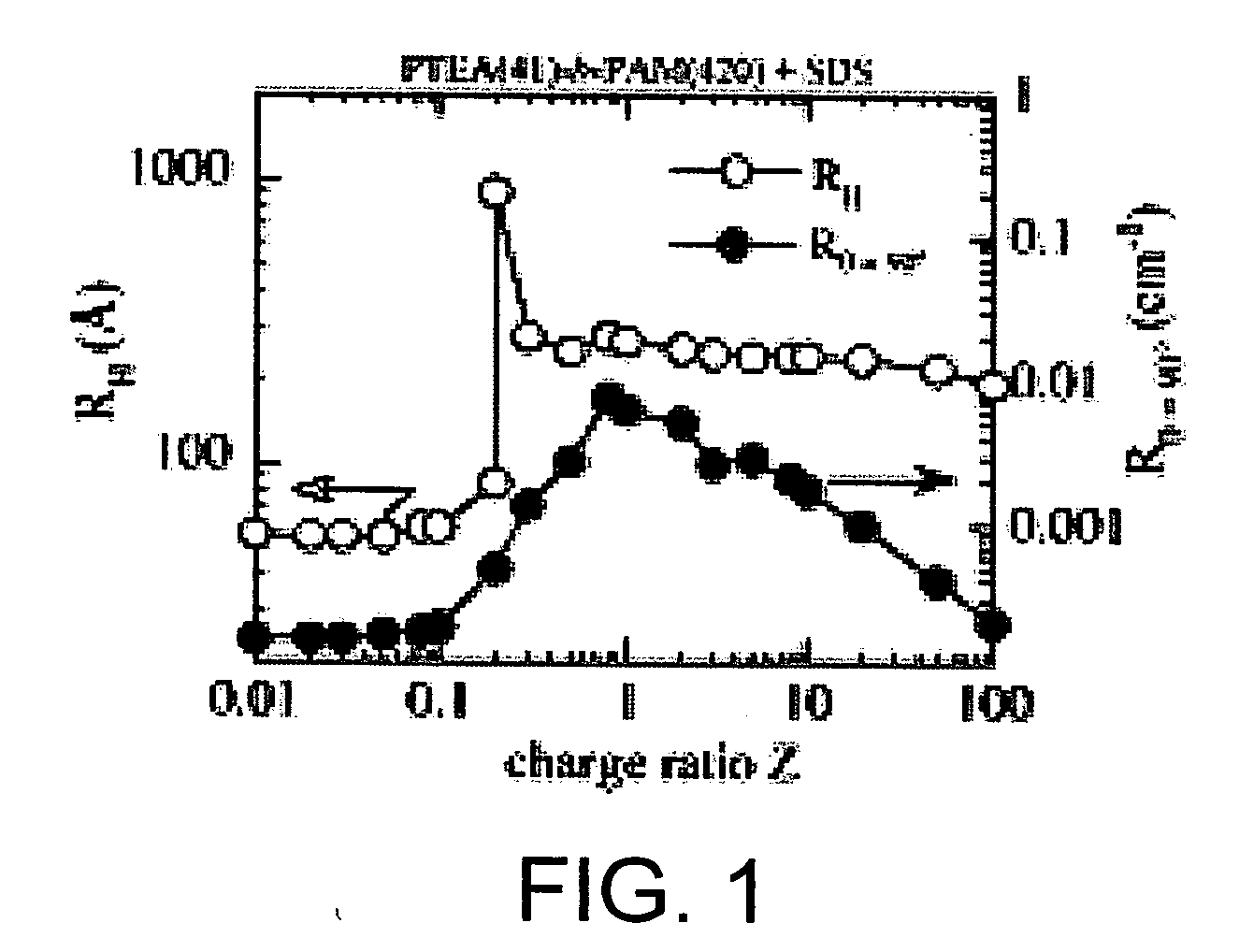
A hard surface cleaning composition comprising a coacervate complex having a molar charge ratio Z greater than 0.1, wherein said coacervate complex comprises a copolymer and at least one of two components selected from a surfactant or a polymer, whereby the copolymer is cationic if the polymer, surfactant, or combination of polymer and surfactant is anionic, or the copolymer is anionic if the polymer, surfactant, or combination of polymer and surfactant is cationic, and a method of cleaning hard surfaces, are disclosed.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
Polymer surface modification
InactiveUS7005493B2Fixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementPolymeric surfacePolymer science
The present invention is directed to a surface modified polymer comprising a surface which is covalently bonded to a surface modifying compound. Formation of the covalent bond between the polymer and the surface modifying compound is achieved by a reaction between an intrinsic functional group that is present in the polymer and the functional group of the surface modifying compound. By using a polymer having an intrinsic functional group, a separate surface activation step is avoided.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Biological material using electrostatic attraction layer-layer self-assembled modified polyester material as surface with cell compatibility
InactiveCN1394901AReduce inflammationImprove biological activityMaterial nanotechnologyNanomedicinePolymeric surfacePolyester
Fistly, said ivnention utilizes polyamine aminolyzed polyester polymer surface to obtain polymer whose surface has free amine group, then uses acid to make acidification to make polymer surface possess positive charge, and utilzies electrostatic attraction layer-to-layer self-assembling method to alternatively assemble single layer or several layers of different polyanions and polycations with biological activity on its surface, and these biological activity polyelectrolytes which are layer-to-layer self-assembled still retain their original biological activity so as to obtain the invented plane membrane and three-D porous support material with cell compatibility and its product.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
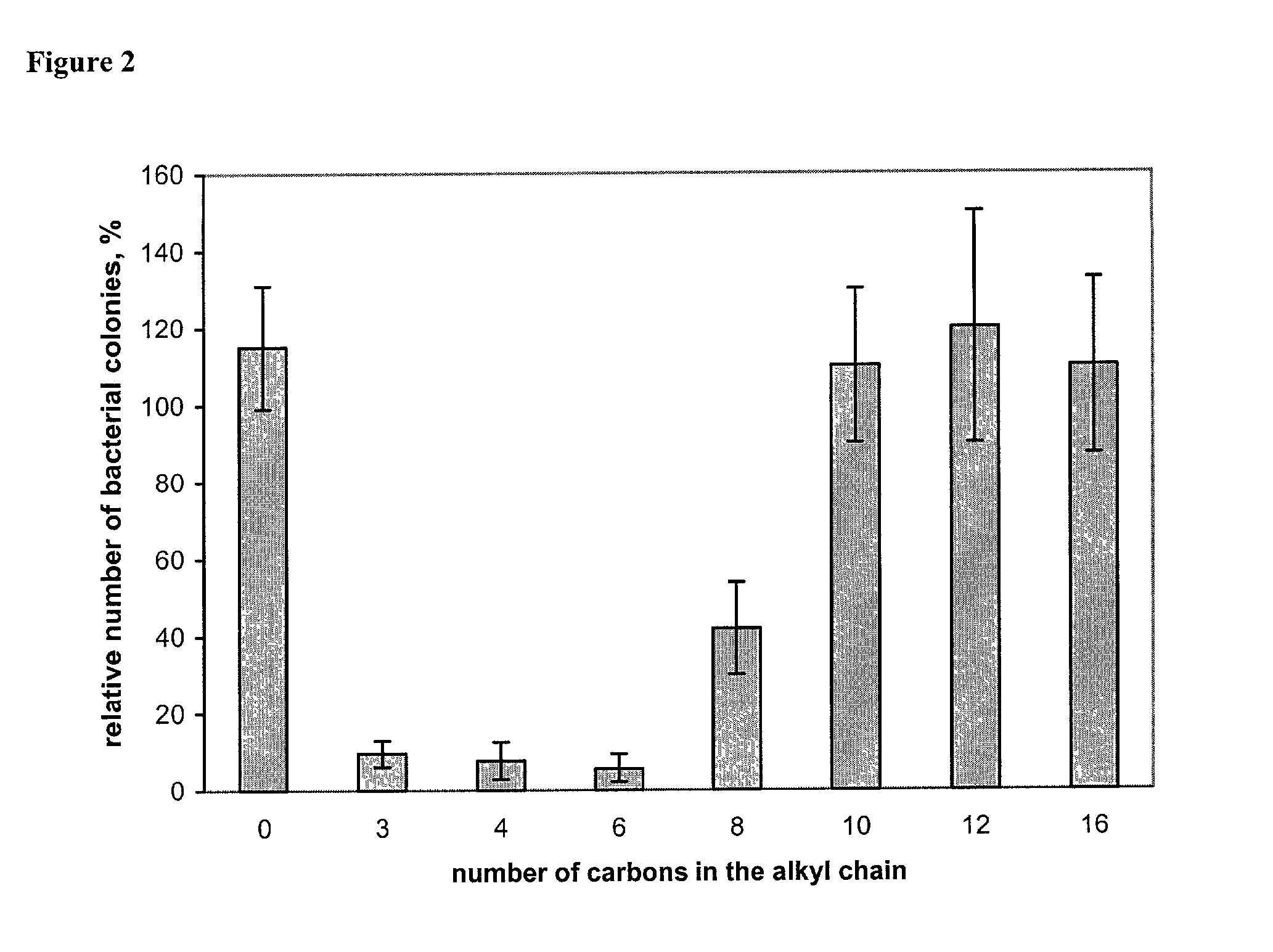
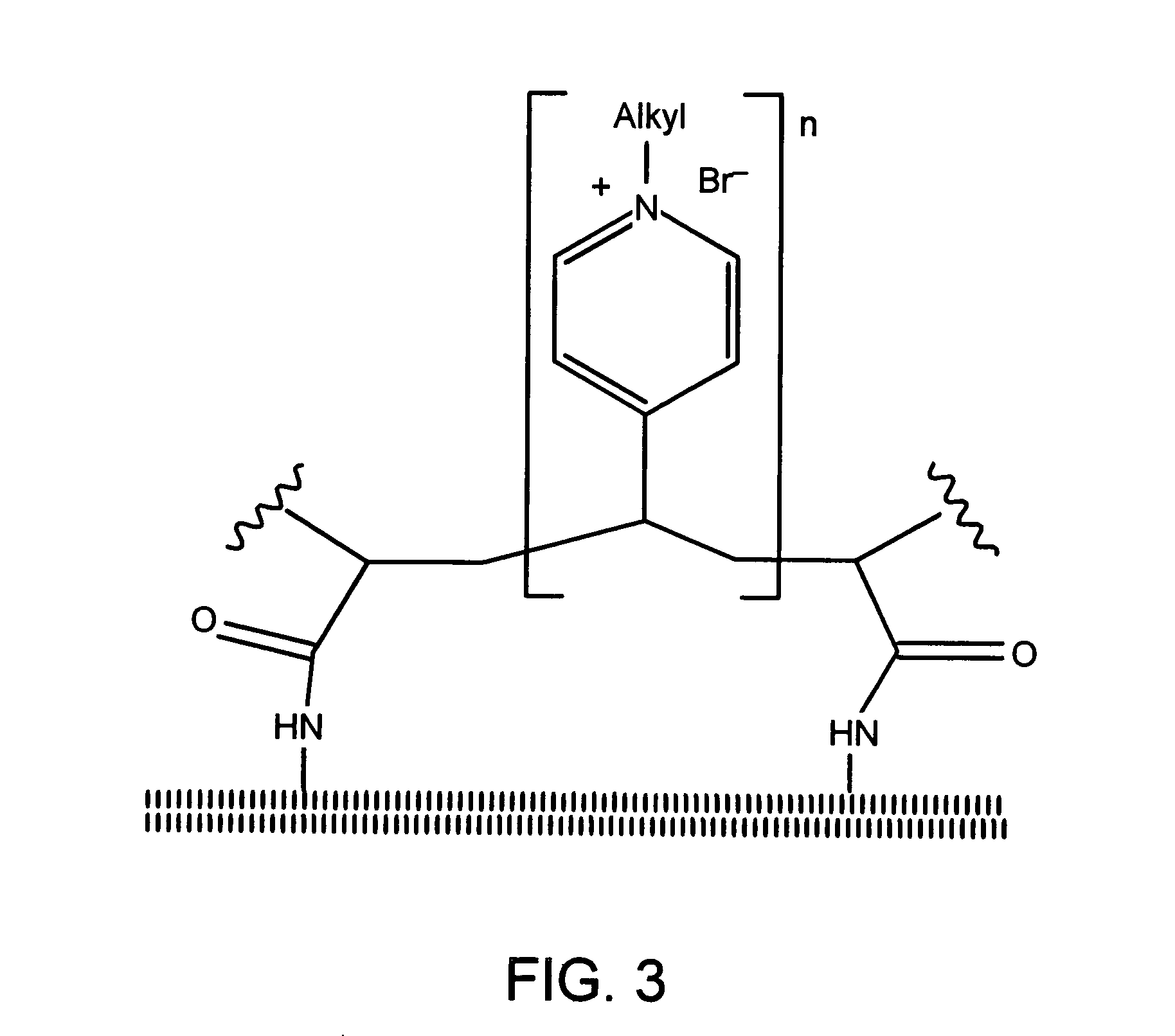
Antimicrobial polymeric surfaces
Bactericidal compositions are disclosed that comprise a polymeric compound immobilized on a material. Medical devices are also disclosed which comprise such a bactericidal composition. Methods are disclosed for covalently derivatizing the surfaces of common materials with an antibacterial polycation, e.g., poly(vinyl-N-pyridinium bromide); the first step of the methods involves coating the surface with a nanolayer of silica. Various commercial synthetic polymers derivatized in this manner are bactericidal, i.e., they kill on contact up to 99% of deposited Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, whether deposited through air or water.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE +1
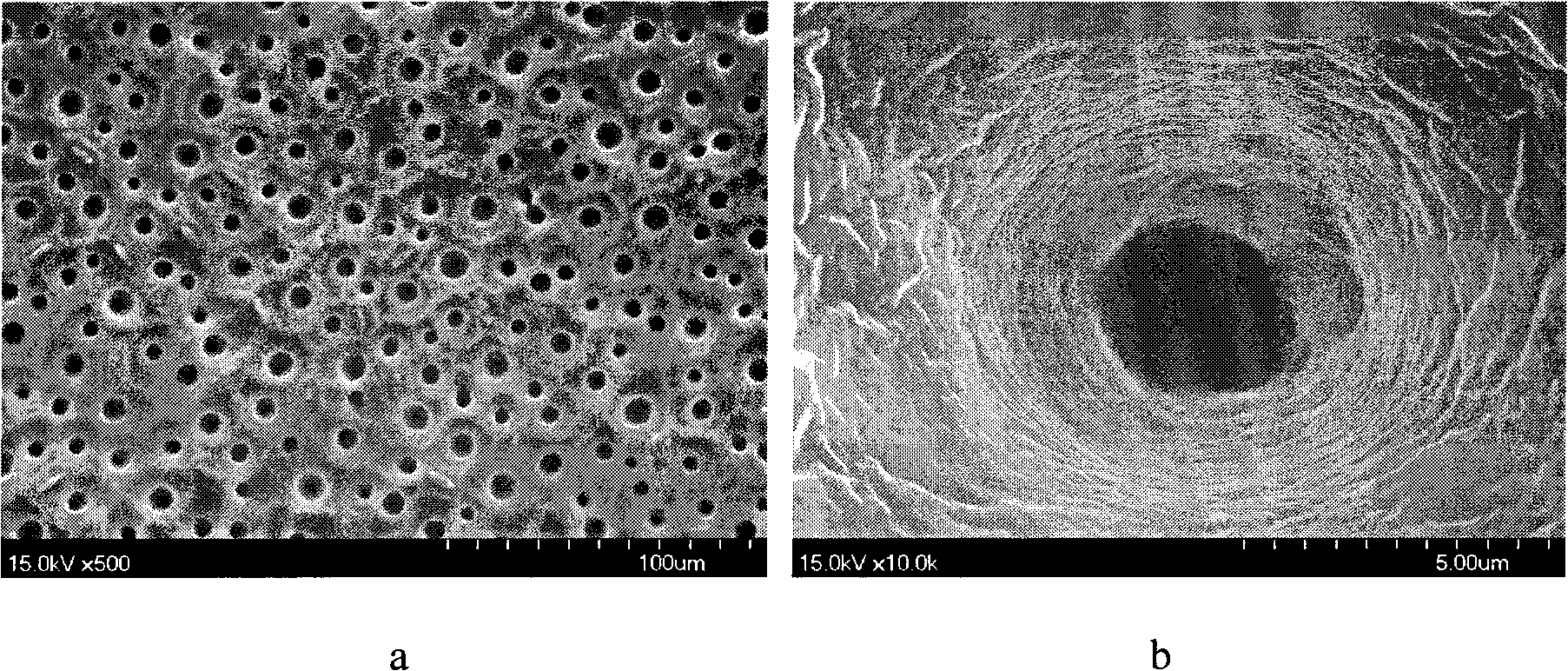
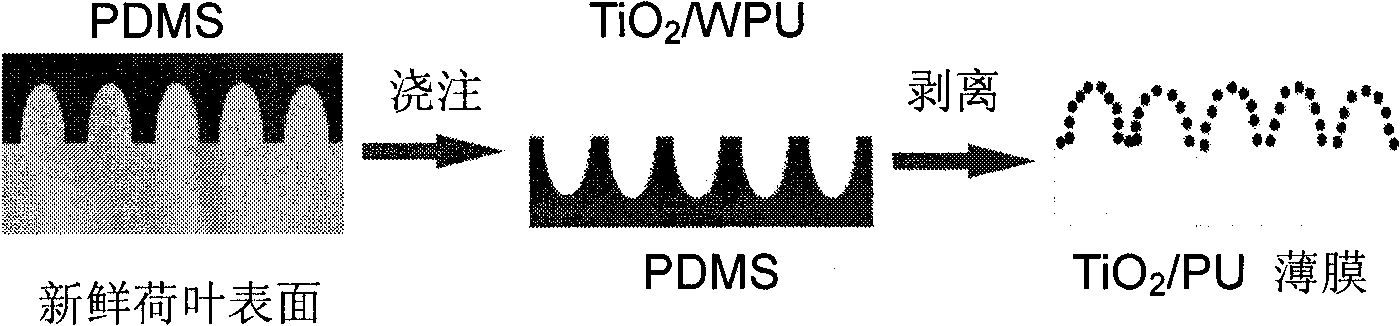
Method for preparing superhydrophobic surface by using nano-particles for assisting micromolding
The invention provides a method for preparing a polymer superhydrophobic surface by using nano-particles for assisting micromolding. The method firstly uses a PDMS as a raw material for copying a micro-structure on the surface of a fresh lotus leaf to be used as a soft template, then casts or hot presses the modified nano particles and a polymer on the surface of the PDMS soft template and strips after molding, thereby obtaining the polymer superhydrophobic surface which contains a micro / nano second-order structure on the surface and has a certain function. The method has simple operation process, high efficiency and good controllability and repeatability; as the obtained surface contains the functional nano-particles, the method not only gives the superhydrophobic property to the polymer surface, but also gives a certain function to the superhydrophobic surface, thereby providing a simple and effective way for preparing the superhydrophobic surface and having wide application value and broad market prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Polymeric coatings and methods for forming them
InactiveUS20080045686A1Achieving Reliability RequirementsPretreated surfacesCoatingsPolymeric surfaceSide chain
The present invention relates to a controllable polymeric surface coating including a macromolecule, which is covalently bound to the surface of a substrate, the macromolecule including a plurality of polymerisation initiators and a plurality of surface binding groups; and pendant polymers grafted from at least some of the polymerisation initiators.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Compositions and methods for the removal of photoresist for a wafer rework application
InactiveUS20100056410A1Organic detergent compounding agentsPolymeric surface-active compoundsPolymeric surfaceAlkaline earth metal
Compositions useful in reworking microelectronic device wafers, i.e., removing photoresist from rejected wafers, without damaging underlying layers and structures such as cap layers, interlevel dielectric layers, etch stop layers and metal interconnect material. The semi-aqueous compositions include at least one alkali and / or alkaline earth metal basic salt, at least one organic solvent, water, optionally at least one quaternary ammonium basic salt, optionally at least one metal corrosion inhibitor and optionally at least one water-soluble polymer surfactant.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Polymeric surfactants derived from cyclic monomers having pendant fluorinated carbon groups
InactiveUS20040242804A1Good optical performanceHigh glossTransportation and packagingMixingPolymeric surfacePolymer science
A fluorine containing polymer which acts as a wetting, flow or leveling agent, and has at least one polar group. The polymer has at least one pendant or ether side chain containing from about 1 to about 20 carbon atoms with at least 25% of the hydrogen atoms being replaced by fluorine atoms. The fluorinated polymers unexpectedly impart wetting, flow or leveling properties to a variety of coatings while producing little foam.
Owner:DEUT BANK AG NEW YORK BRANCH AS SUCCESSOR AGENT
Biological functionalisation of substrates
InactiveUS20100227372A1Improve surface stabilityMaintaining conformationLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsCross-linkPolymeric surface
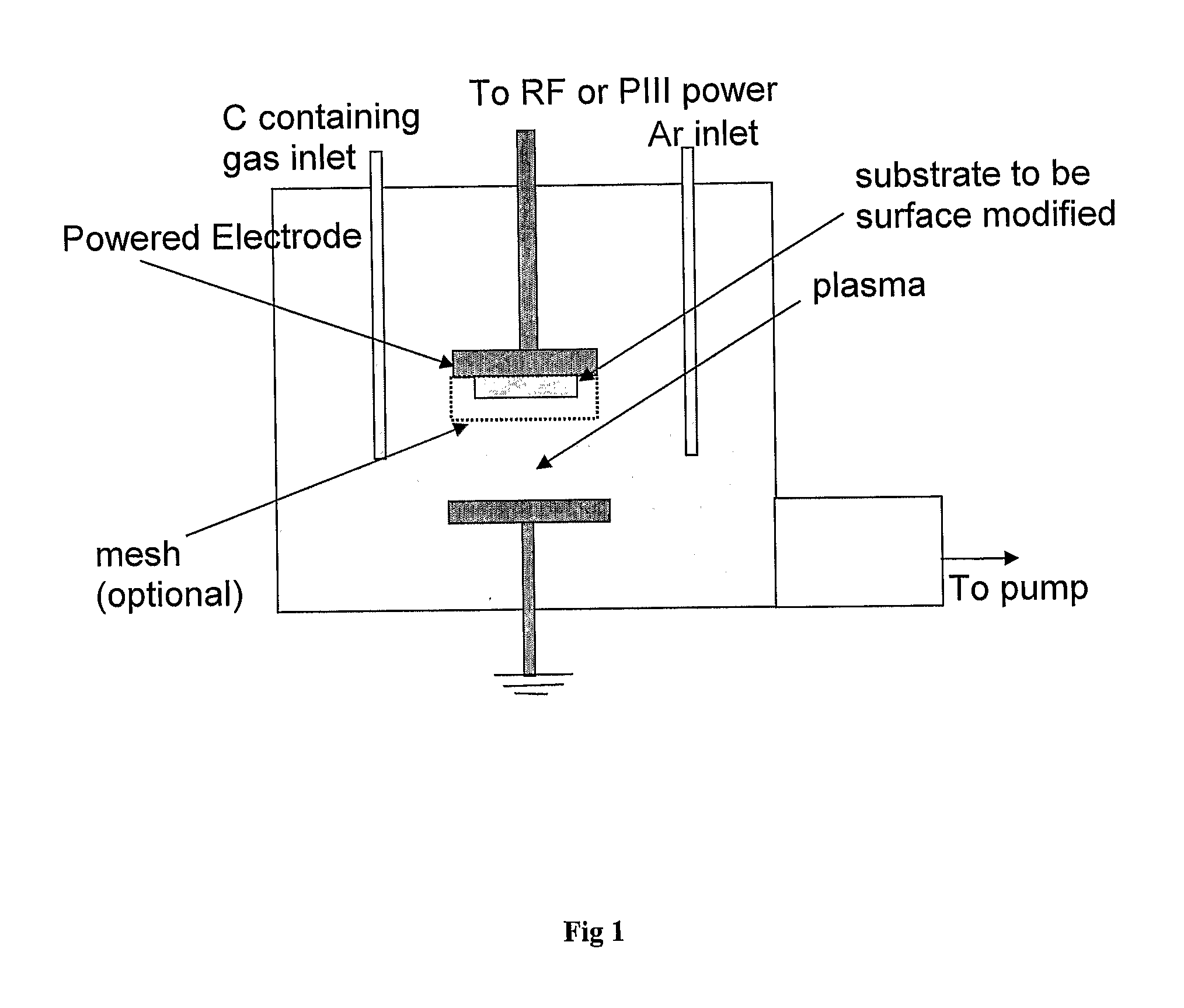
The invention relates to an activated metallic, semiconductor, polymer, composite and / or ceramic substrate, the substrate being bound through a mixed or graded interface to a hydrophilic polymer surface that is activated to enable direct covalent binding to a functional biological molecule, the polymer surface comprising a sub-surface that includes a plurality of cross-linked regions, as well as to such activated substrates that have been functionalised with a biological molecule and to devices comprising such functionalised substrates. Such substrates can be produced by a method comprising steps of: a. exposing a surface of the substrate to any or more of (i) to (iii): (i) plasma ion implantation with carbon containing species; (ii) co-deposition under conditions in which substrate material is deposited with carbon containing species while gradually reducing substrate material proportion and increasing carbon containing species proportion; (iii) deposition of a plasma polymer surface layer with energetic ion bombardment; incubating the surface treated according to step (a) with a desired biological molecule.
Owner:SYDNEY THE UNIV OF
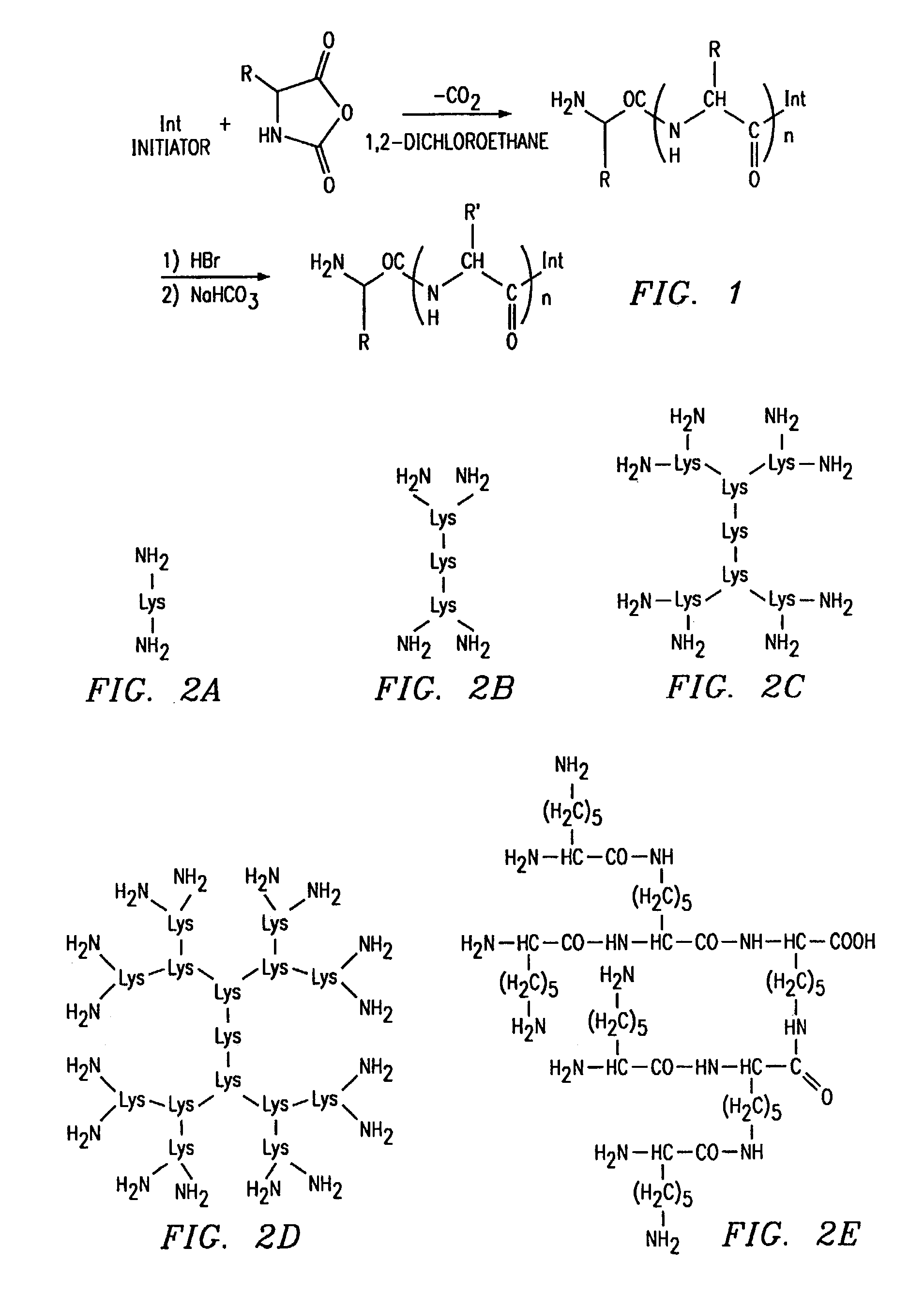
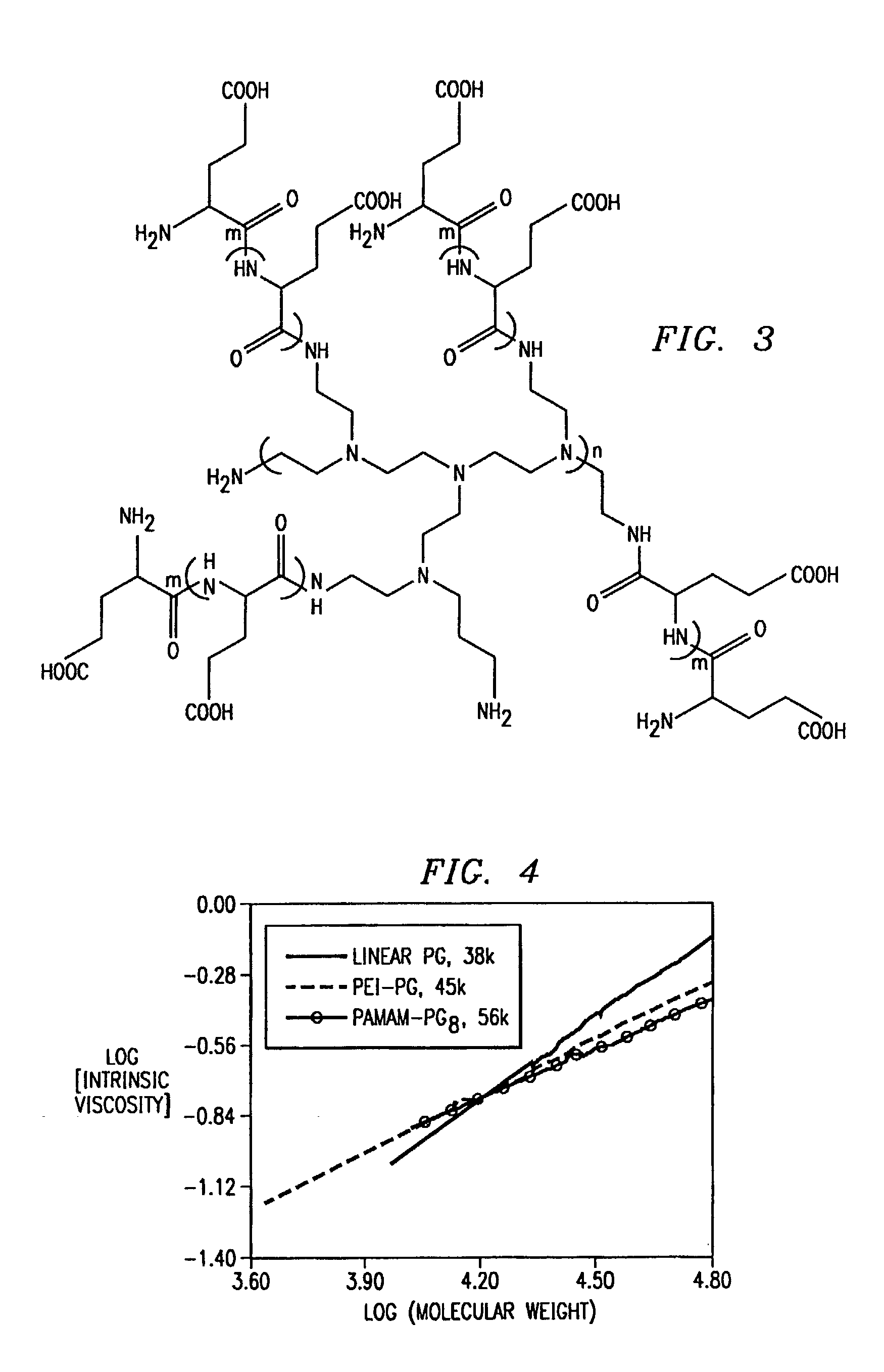
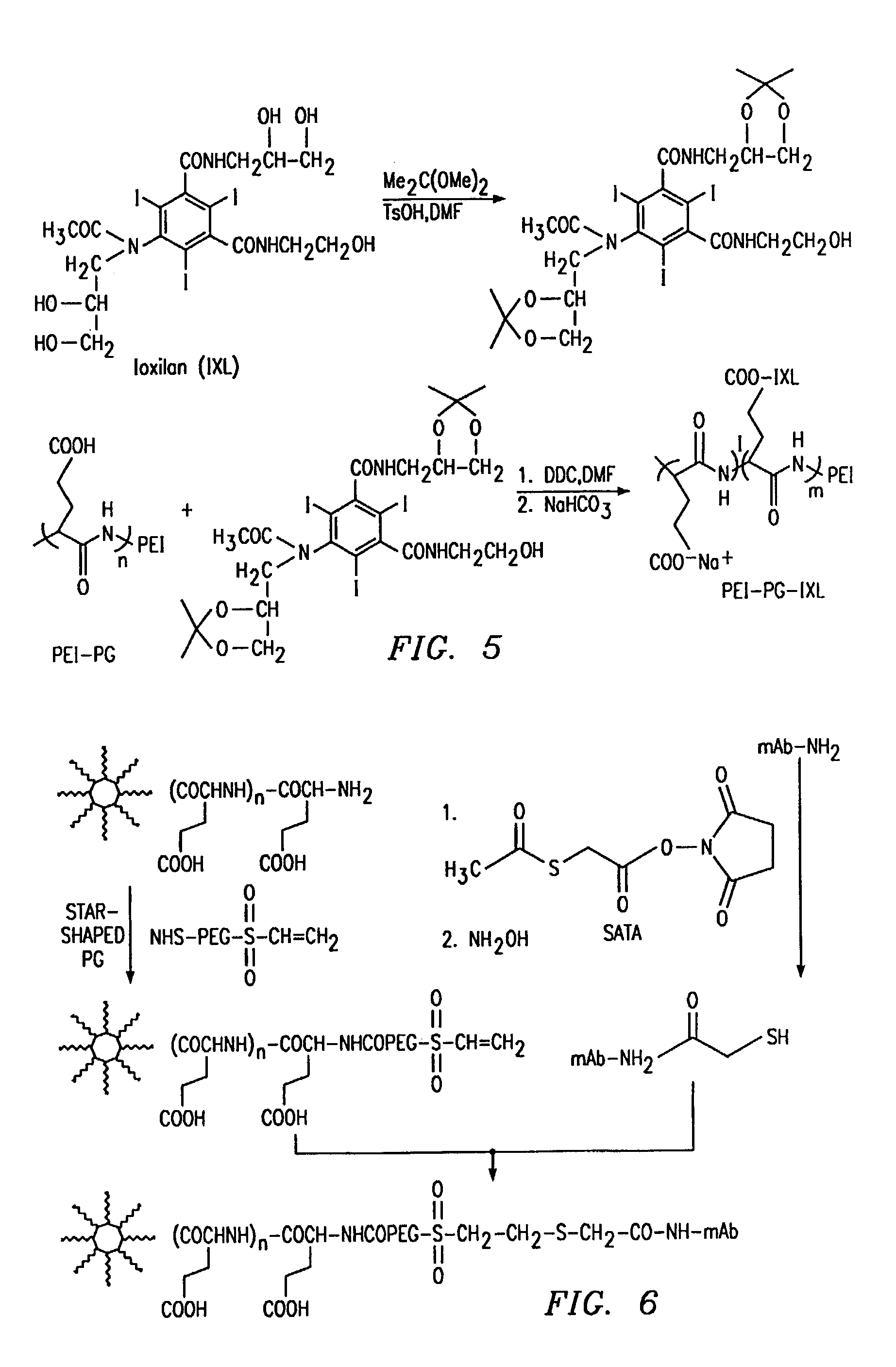
Dendritic poly (amino acid) carriers and methods of use
InactiveUS7261875B2Sufficient and improved retentionAvoid problemsNanomedicineDepsipeptidesCrystallographyPolymeric surface
The present invention concerns a design for dendritic poly(amino acid) polymer carriers, also known as nonlinear polymers, and their applications. These dendritic poly(amino acid) carriers have multiple functional groups at the polymer surface. In addition, they have heterofunctional groups on the poly(amino acid) side chains for drug or diagnostic agent attachment. They are designed to allow sufficient preservation of the binding affinity of the targeting ligand while conjugating therapeutic or diagnostic agents to the polymers. The present invention also describes methods of production of the polymer carriers and methods for the treatment or diagnosis of diseases employing the polymer carriers. The present invention also includes methods to introduce targeting moieties site-specifically to the end of polymer chains.
Owner:TEXAS SYST BOARD OF REGENTS THE UNIV OF +1
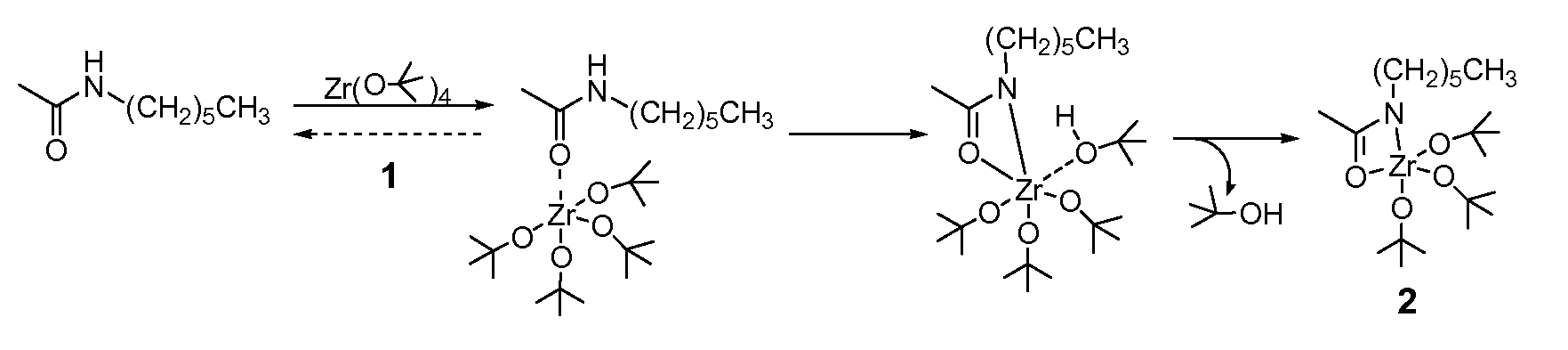
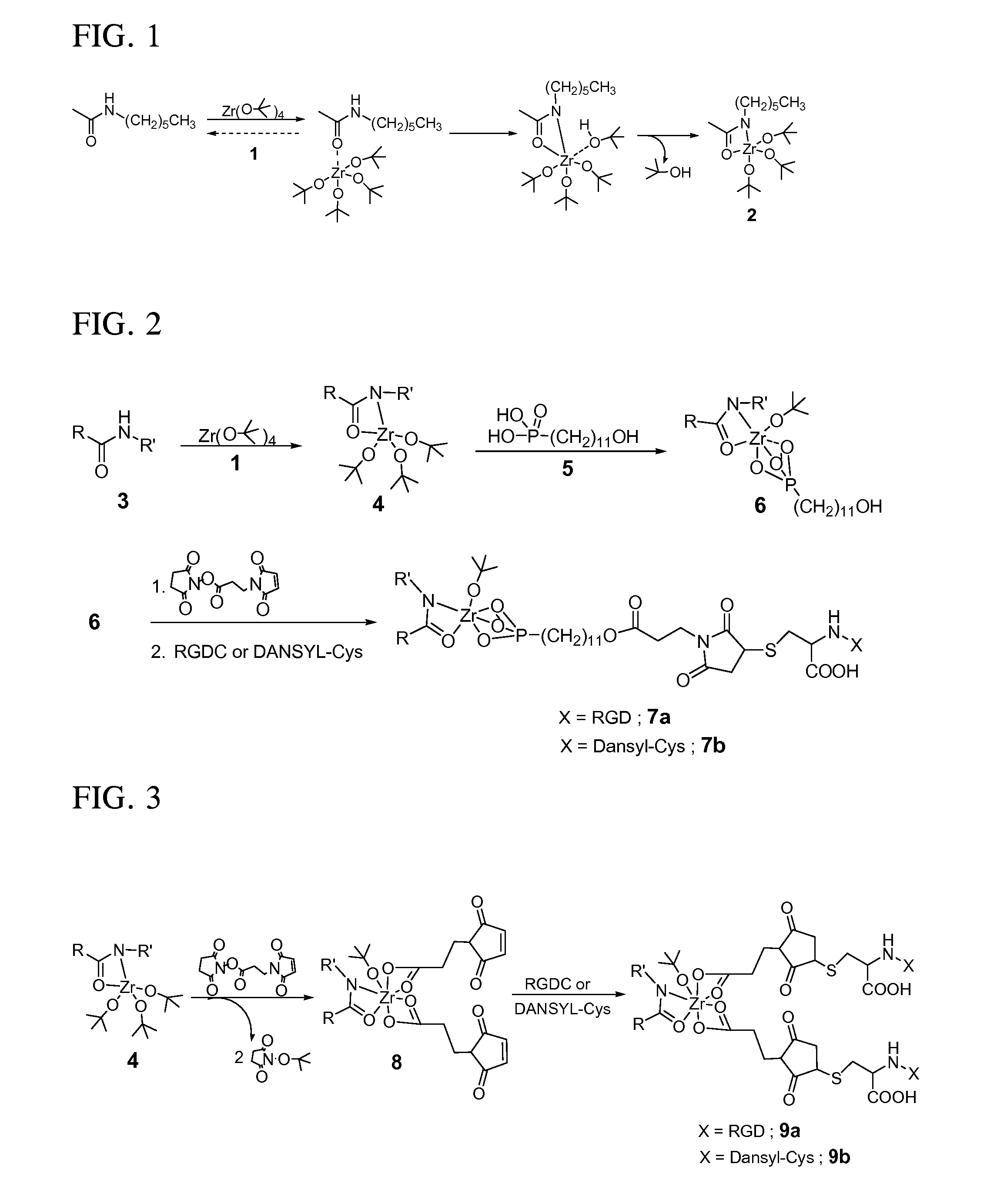
High-yield activation of polymer surfaces for covalent attachment of molecules
InactiveUS20070196663A1High yieldMild reaction conditionsSurgeryPretreated surfacesPolymeric surfaceBiological activation
Polymer surfaces coated with organometallic layers, wherein the organometallic layers and polymer surfaces have functional groups that react to bond the organometallic layer to the polymer surface with organometallic functional groups remaining unreacted for the subsequent covalent attachment of organic overlayers. Coating methods and coated articles are also disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Polymeric surface coatings
A biocompatibilising process in which a substrate having a surface which bears substrate pendant functional groups is biocompatibilised by coating it with a coating composition containing a polymer formed from a radical polymerisable monomers including a radical polymerisable zwitterionic monomer and a radical polymerisable monomer containing a reactive group to form a polymer having zwitterionic groups and pendant reactive groups and the said pendant reactive groups are reacted to form covalent bonds with said substrate pendant functional group and thereby form a stable coating of polymer on the said surface.
Owner:BIOCOMPATIBLES UK LTD
Mesostructured materials, silica mesostructured materials, preparation methods thereof and control method of mesopore orientation
A mesostructured material, which has plural tubular mesopores and is arranged on a polymer surface, characterized in that the mesopores are oriented in on direction parallel to the surface. The mesostructured material can be developed to functional devices.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com