Patents
Literature
3119results about How to "Reduce inflammation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
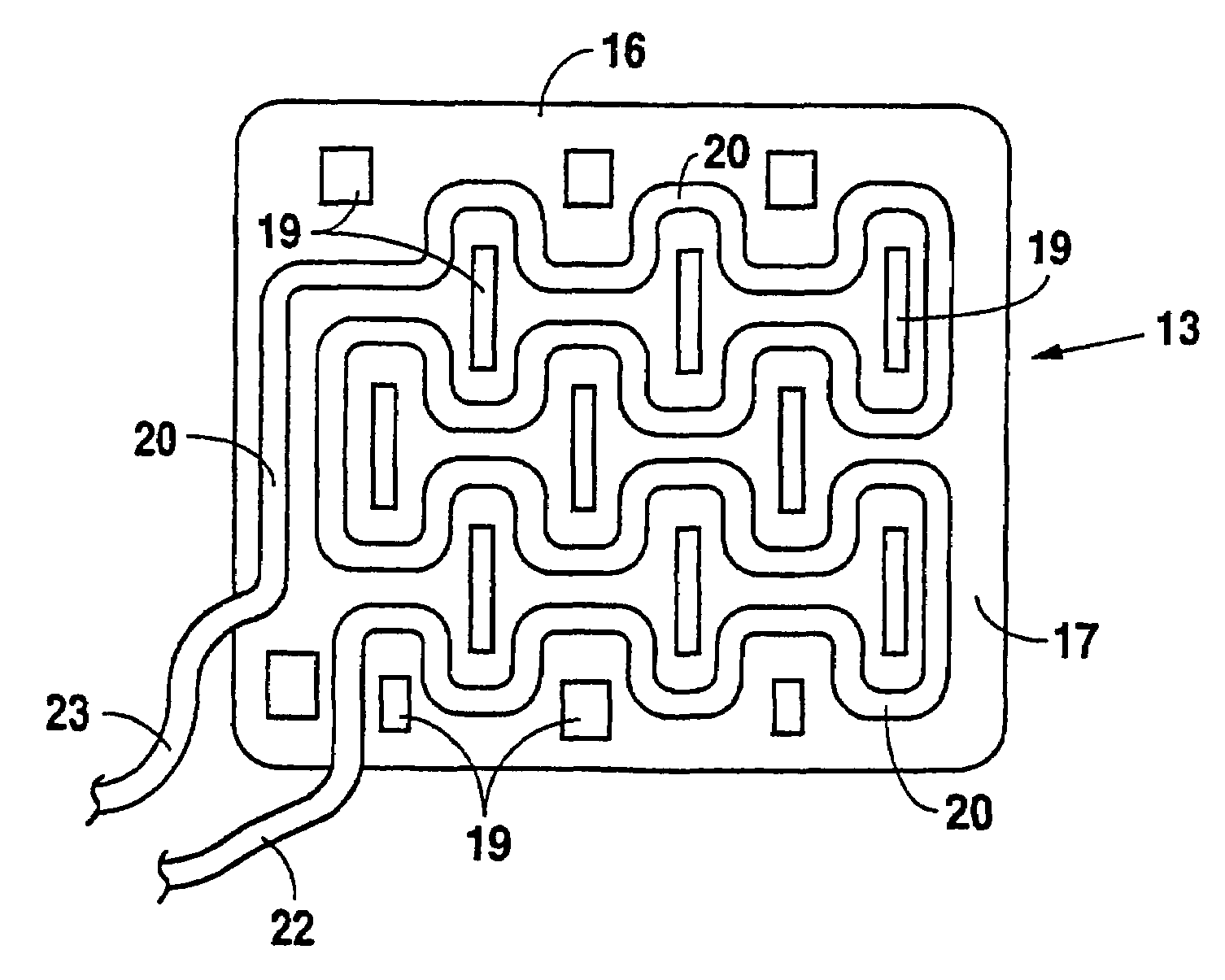
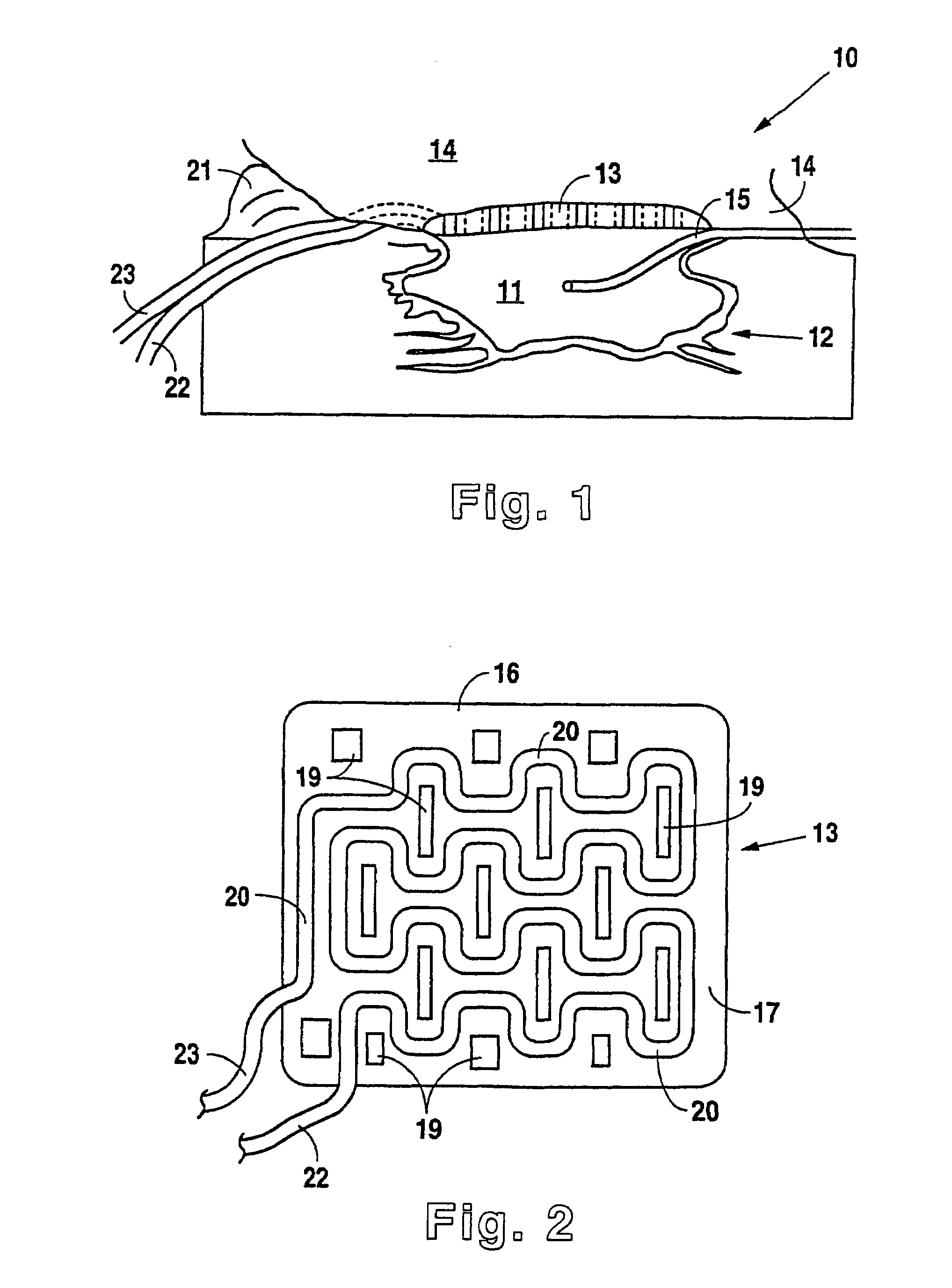
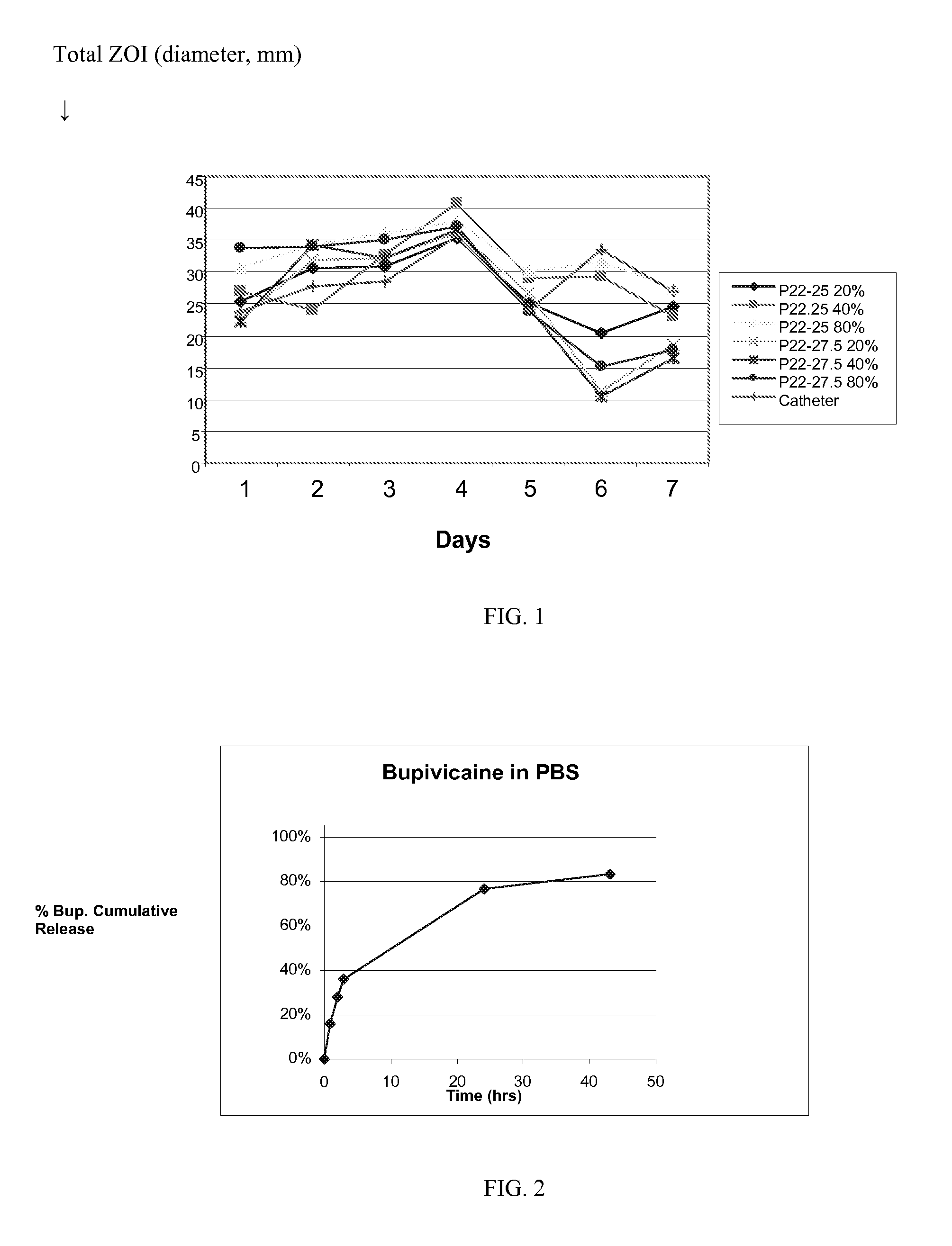
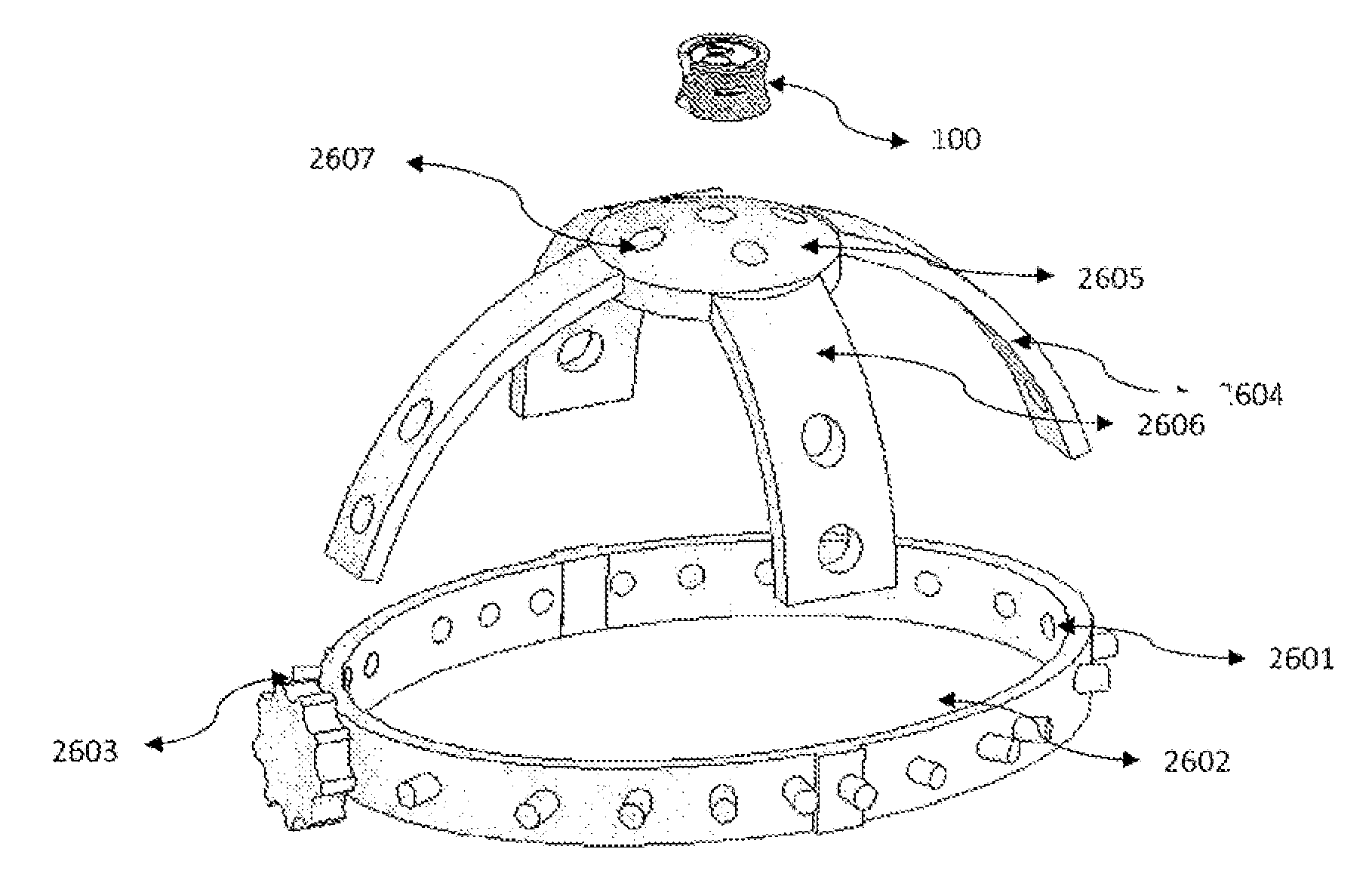
Drug depot implant designs
ActiveUS7727954B2Uniform drug distributionMinimal disruptionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal injuryChronic pain
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
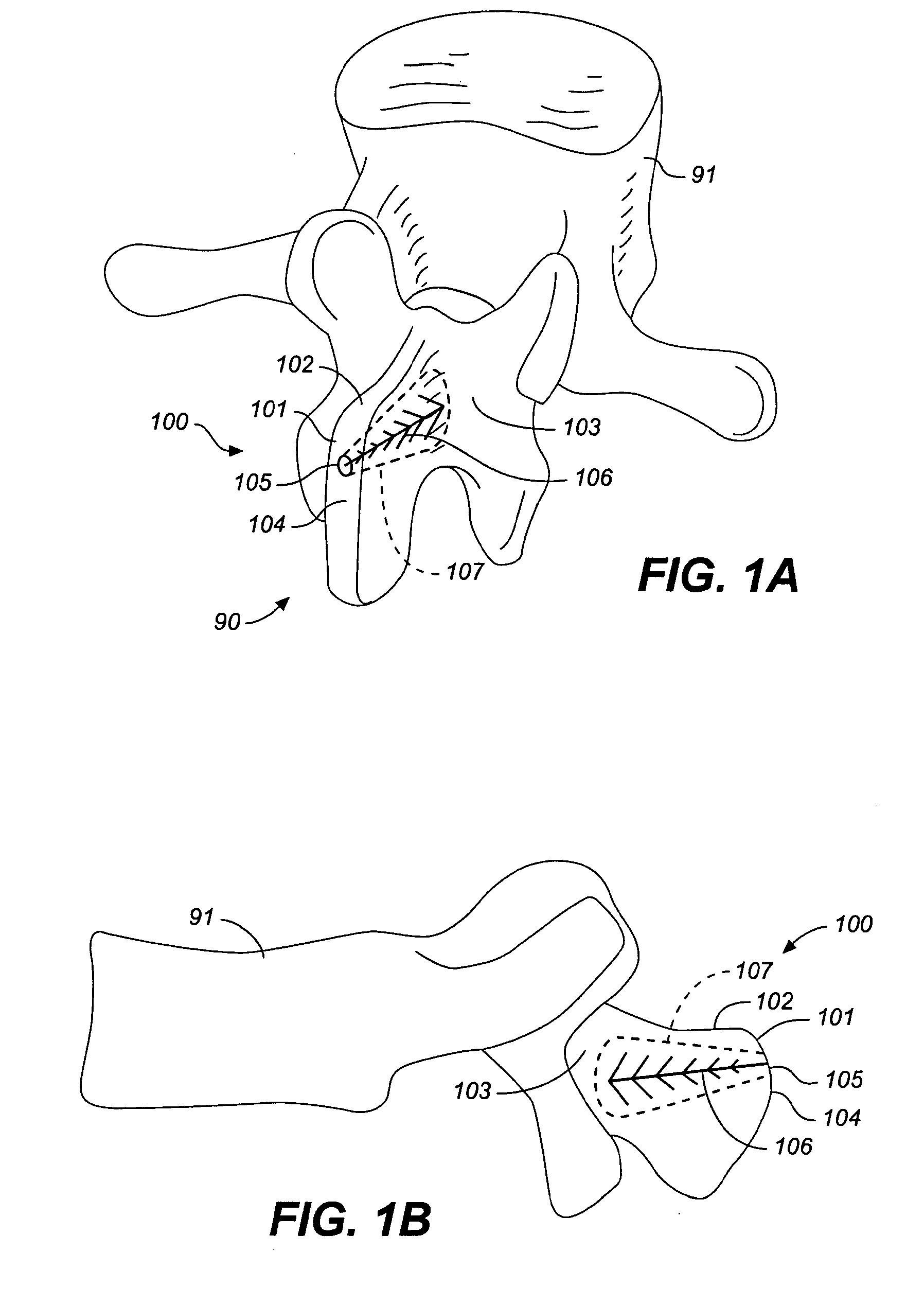
Facet device and method
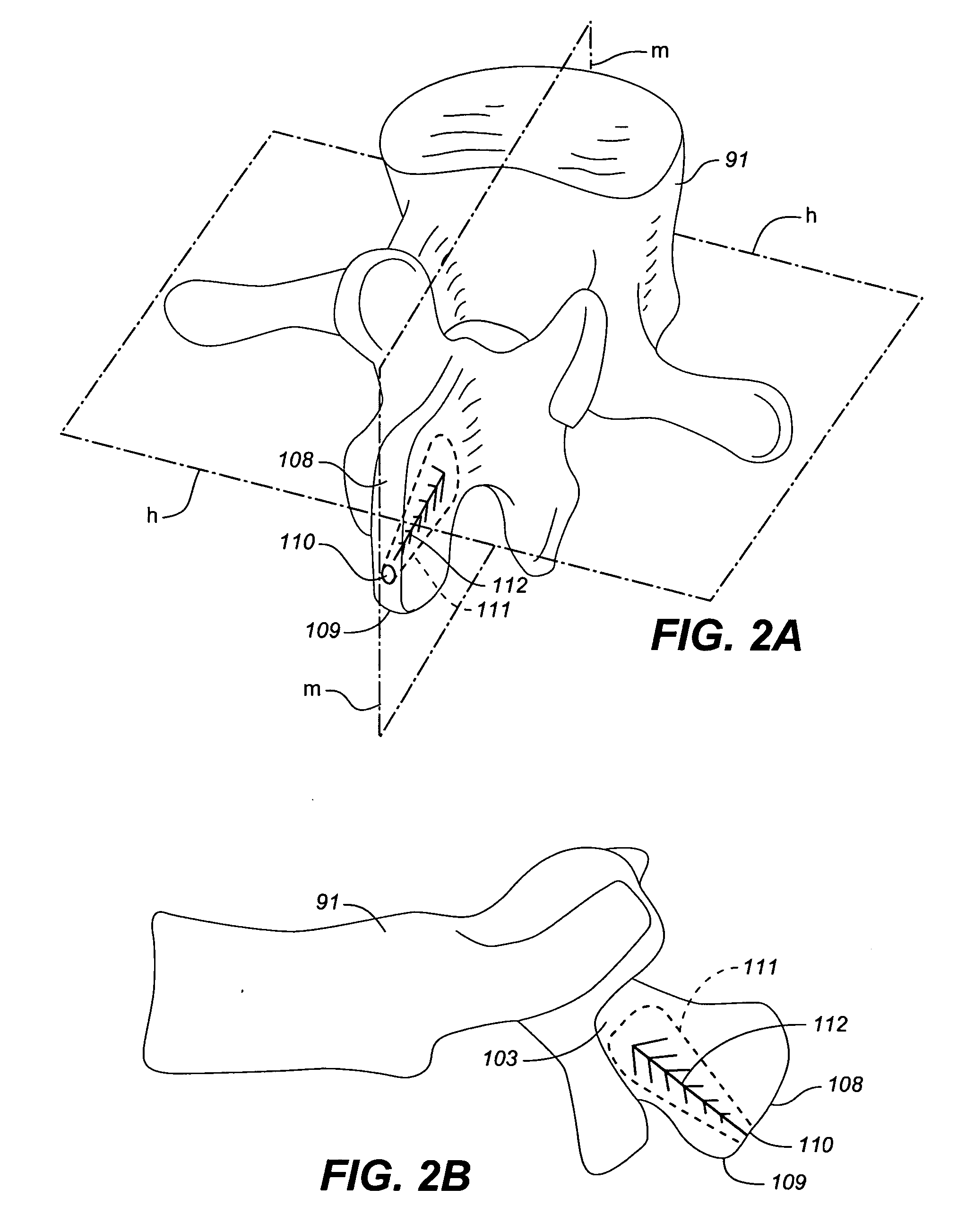
InactiveUS20060036323A1Alleviating discomfort and or deformityLess discomfortInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsProsthesisSacroiliac joint
Owner:K2M +1
Spine treatment devices and methods
InactiveUS20060036259A1Reduce deformityAvoid damageInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsBiomedical engineering
Owner:ALBANY MEDICAL COLLEGE +1
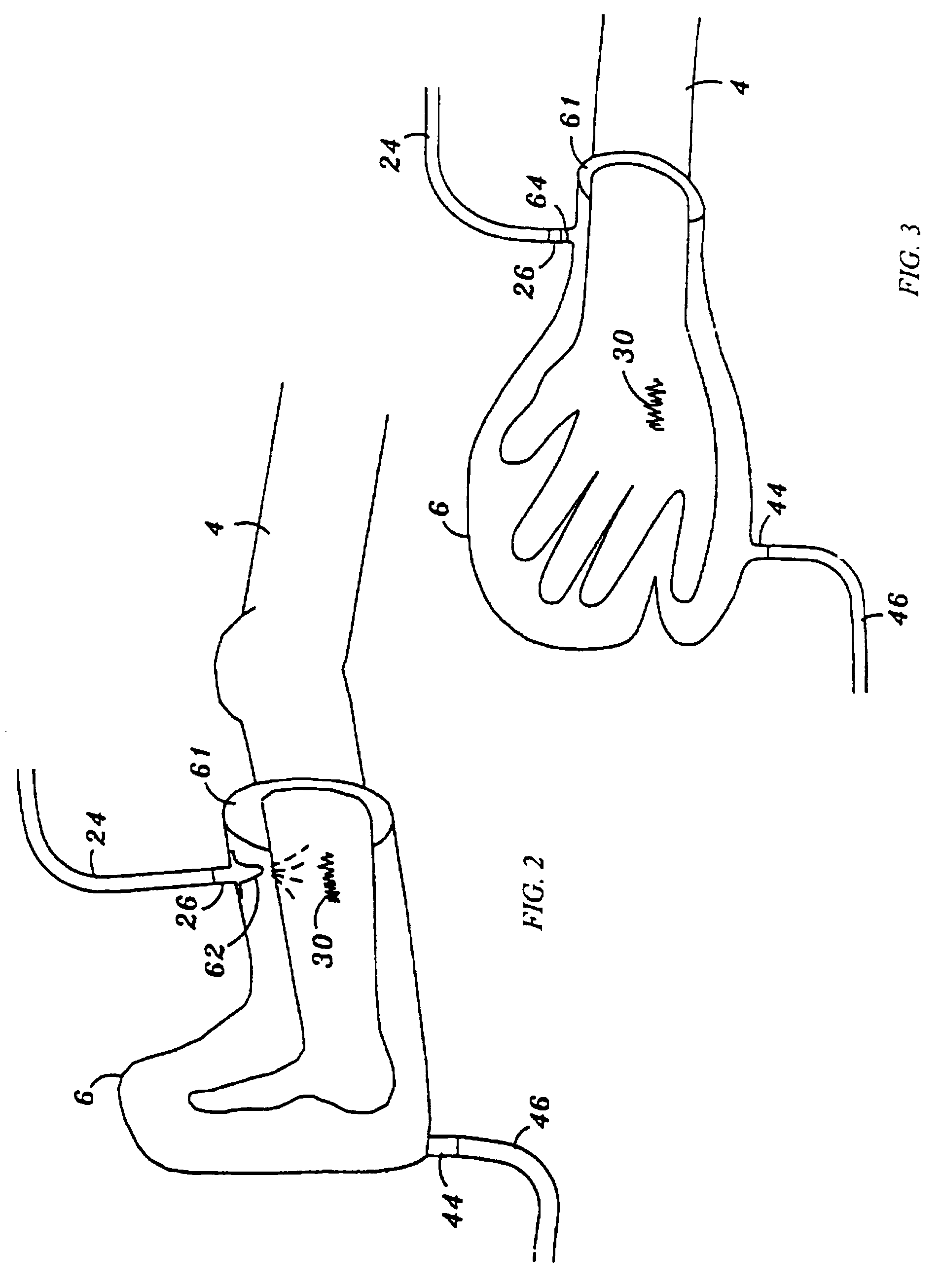
Sandwiched stapler type alimentary tract anastomosis dissecting sealer
The invention discloses a sandwiched stapler type alimentary tract anastomosis dissecting sealer, relating to the surgical instruments. The invention provides a sandwiched stapler type alimentary tract anastomosis dissecting sealer which can prevent the alimentary tract anastomotic stoma from tearing, leaking and errhysis from the cut section in surgical operations. The sandwiched stapler type alimentary tract anastomosis dissecting sealer is provided with a nail anvil (which is also called as a bottom needle holder), a nail cartridge (which is also called as a nail anvil box), a sealer body, a movable handle, an adjusting button, a cutter cushion and an anastomosing nail (which is also called as a suturing nail), wherein the nail anvil is connected with the front end of the sealer body, the adjusting button is arranged at the tail part of the sealer body, the movable handle is arranged at the back of the sealer body, a safety button is arranged at the connection of the movable handle and the sealer body, the cutter cushion is arranged on the nail anvil, the anastomosing nail is arranged at the front end part of the sealer body, a membrane is arranged on the surface of the nail anvil (which is also called as the bottom needle holder), and a membrane is also arranged on the surface of the nail cartridge (which is also called as the nail anvil box); and after stapling, a sandwich structure consisting of the membrane, an intestinal wall and the membrane is formed.
Owner:刘忠臣
Negative pressure treatment system with heating and cooling provision
InactiveUS7144390B1Prevent vacuum leakageReduce inflammationSurgical needlesPlastersWound siteSurgery
A method, and apparatus (10) for the controlled acceleration, and / or retardation of the body's inflammatory response generally comprises a foam pad (11) for insertion substantially into a wound site, a heating, a cooling pad (13) for application over the wound site (12), a wound drape (14) or sealing enclosure of the foam pad (11), the heating, and cooling pad (13) at wound site (12). The foam pad (11) is placed in fluid communication with a vacuum source for promotion of the controlled acceleration or retardation of the body's inflammatory response. The heating, and cooling provision controls the local metabolic function as part of the inflammatory response.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
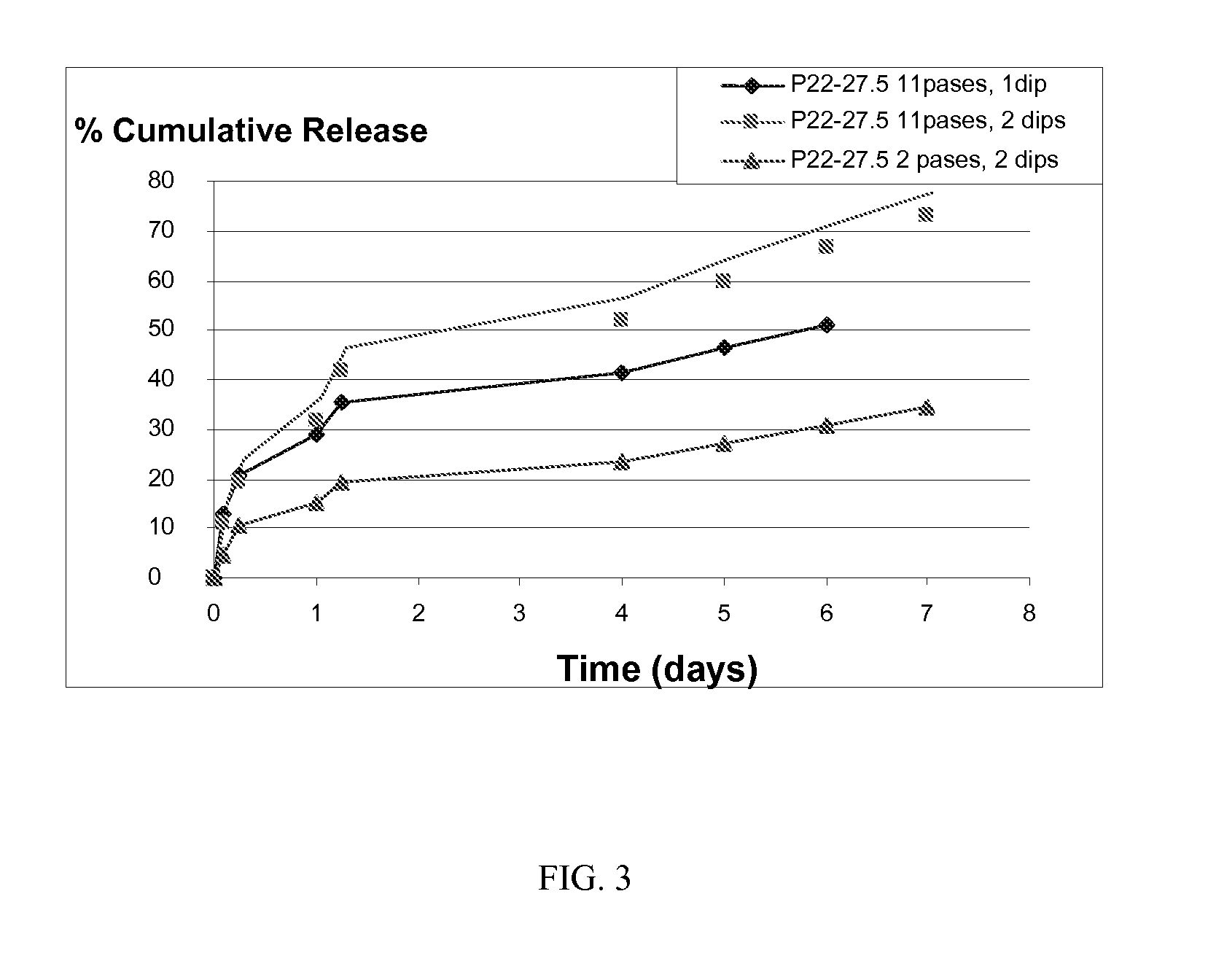
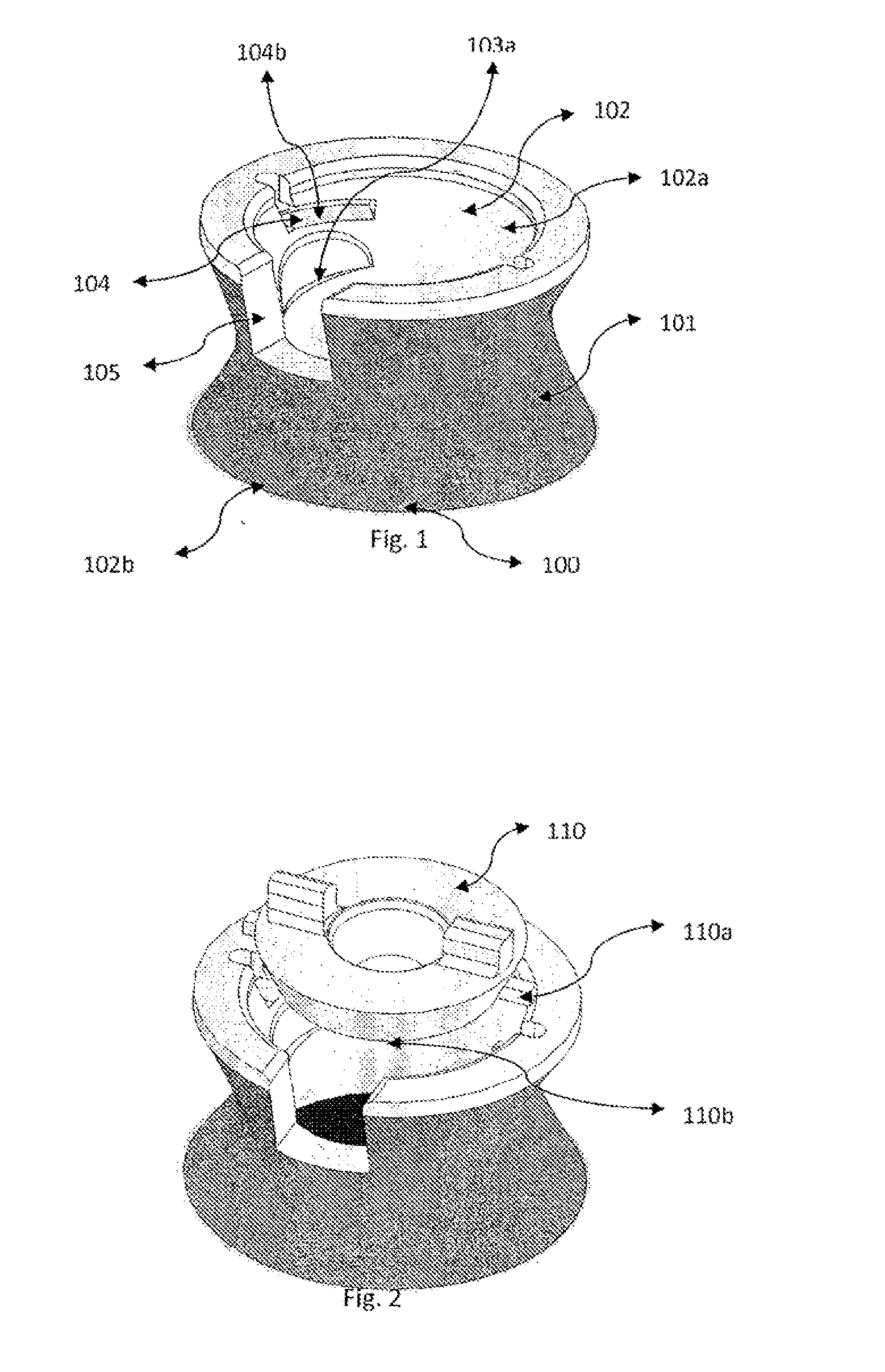
Drug depot implant designs and methods of implantation
ActiveUS20070243225A1Uniform drug distributionMinimal disruptionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal injurySacroiliac joint
The present invention relates to novel drug depot implant designs for optimal delivery of therapeutic agents to subjects. The invention provides a method for alleviating pain associated with neuromuscular or skeletal injury or inflammation by targeted delivery of one or more therapeutic agents to inhibit the inflammatory response which ultimately causes acute or chronic pain. Controlled and directed delivery can be provided by drug depot implants, comprising therapeutic agents, specifically designed to deliver the therapeutic agent to the desired location by facilitating their implantation, minimizing their migration from the desired tissue location, and without disrupting normal joint and soft tissue movement.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Antibodies that specifically bind to TIM3
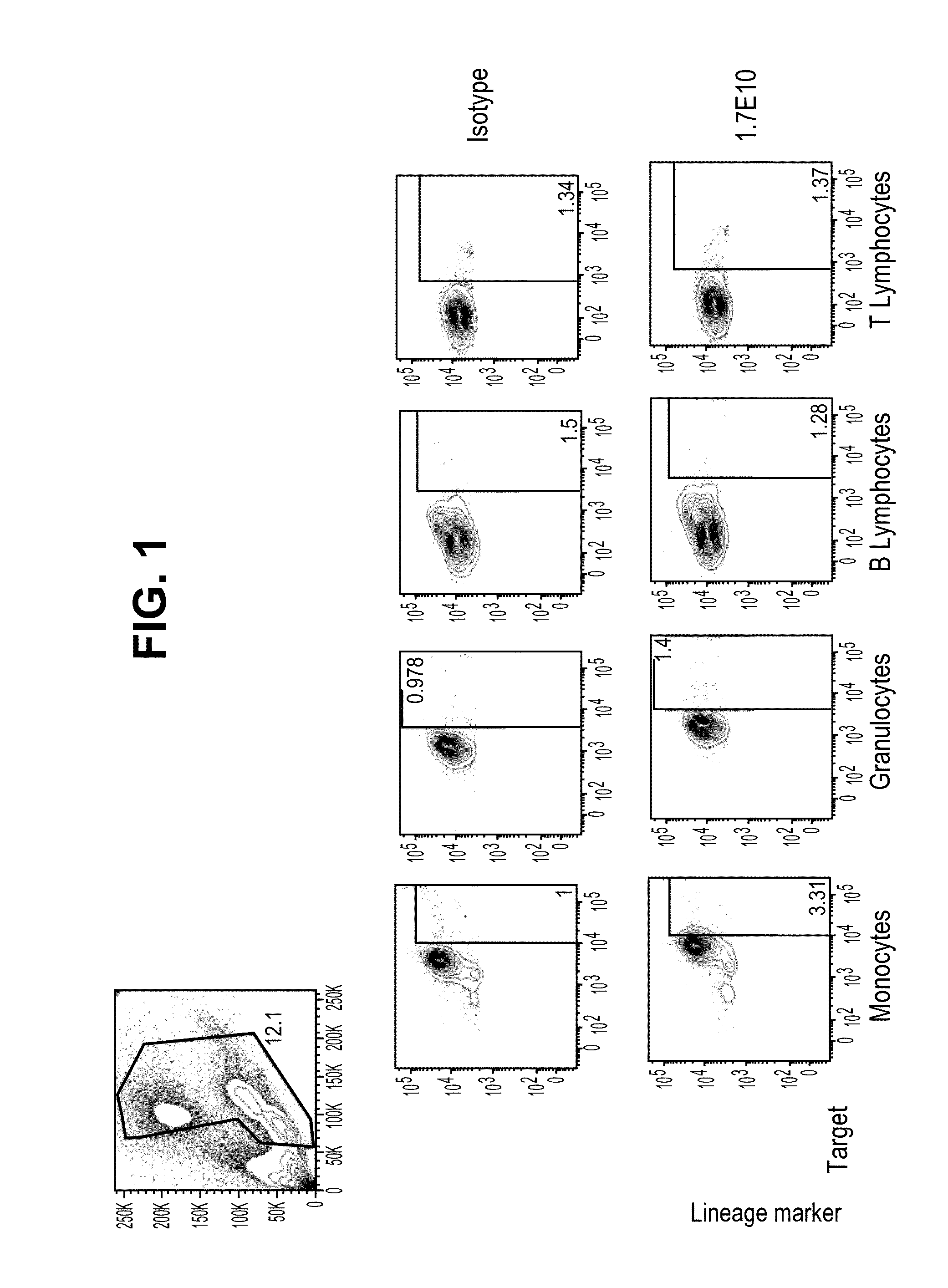
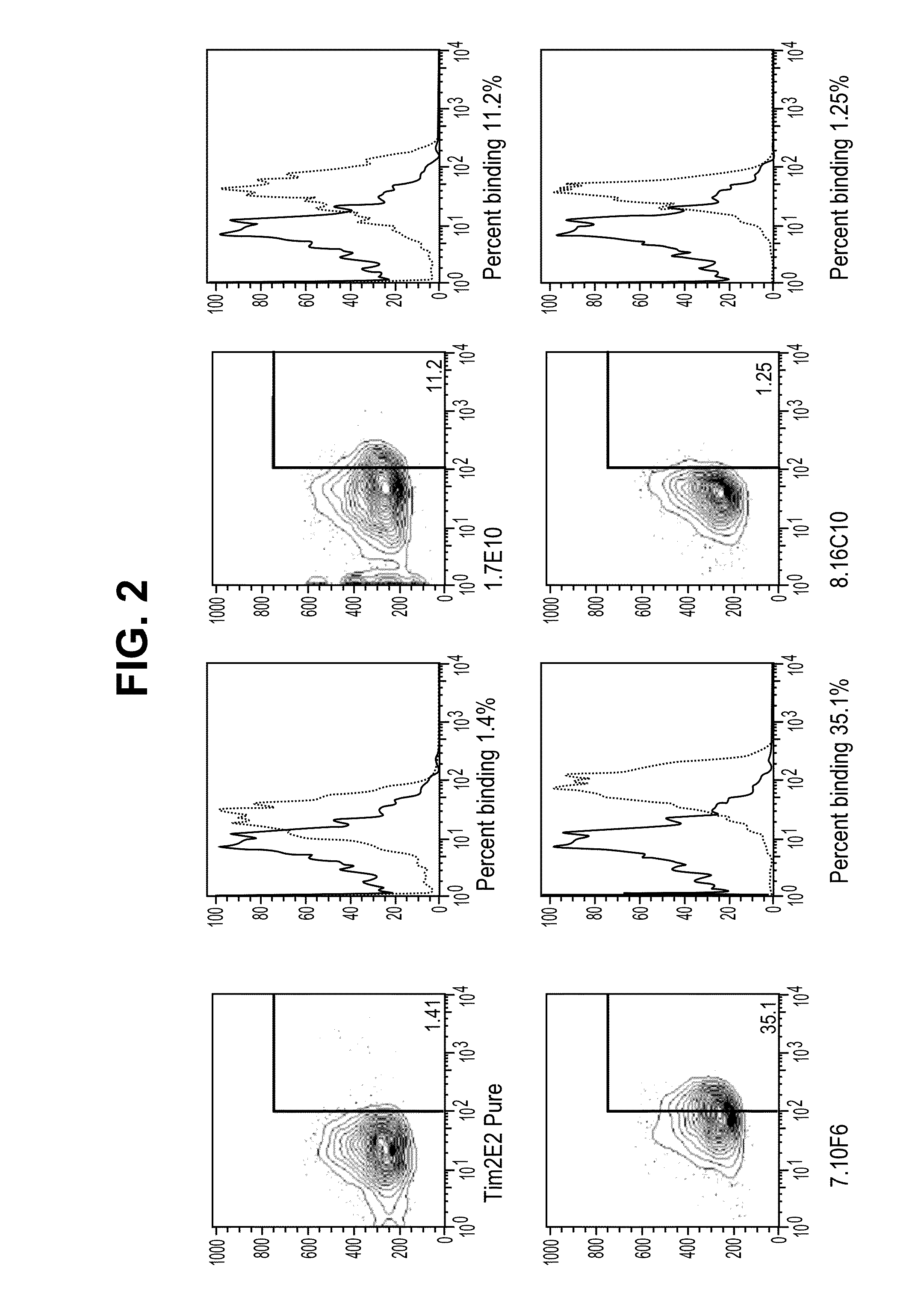
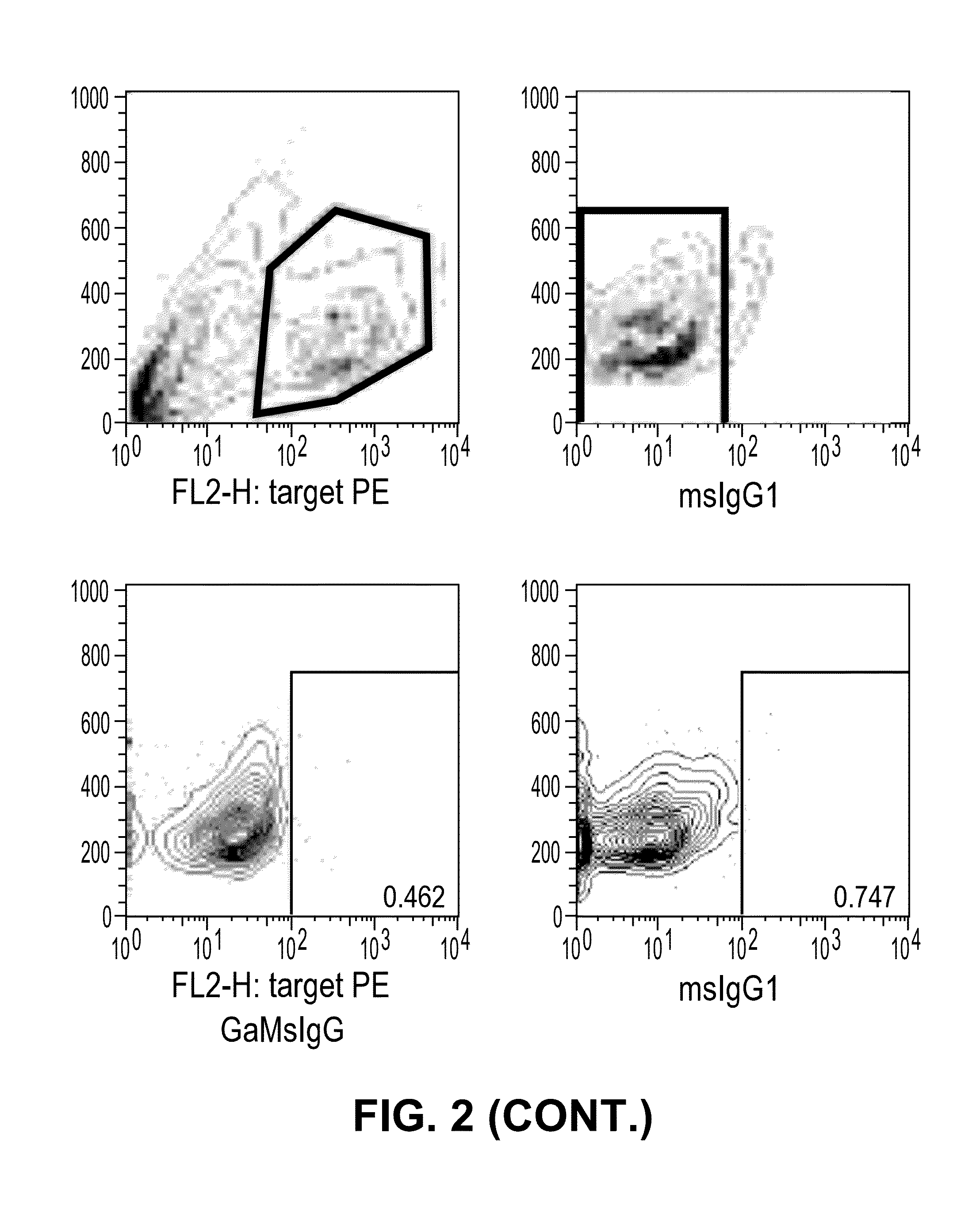
ActiveUS8841418B2Promote growthReduce inflammationHeavy metal active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellAntibody
Provided herein are antibodies specific for TIM3 that can be used to detect cancer cells, in particular, cancer stem cells. The antibodies can also be used in therapeutic compositions for treating cancer and reducing inflammation.
Owner:ONK THERAPEUTICS LTD
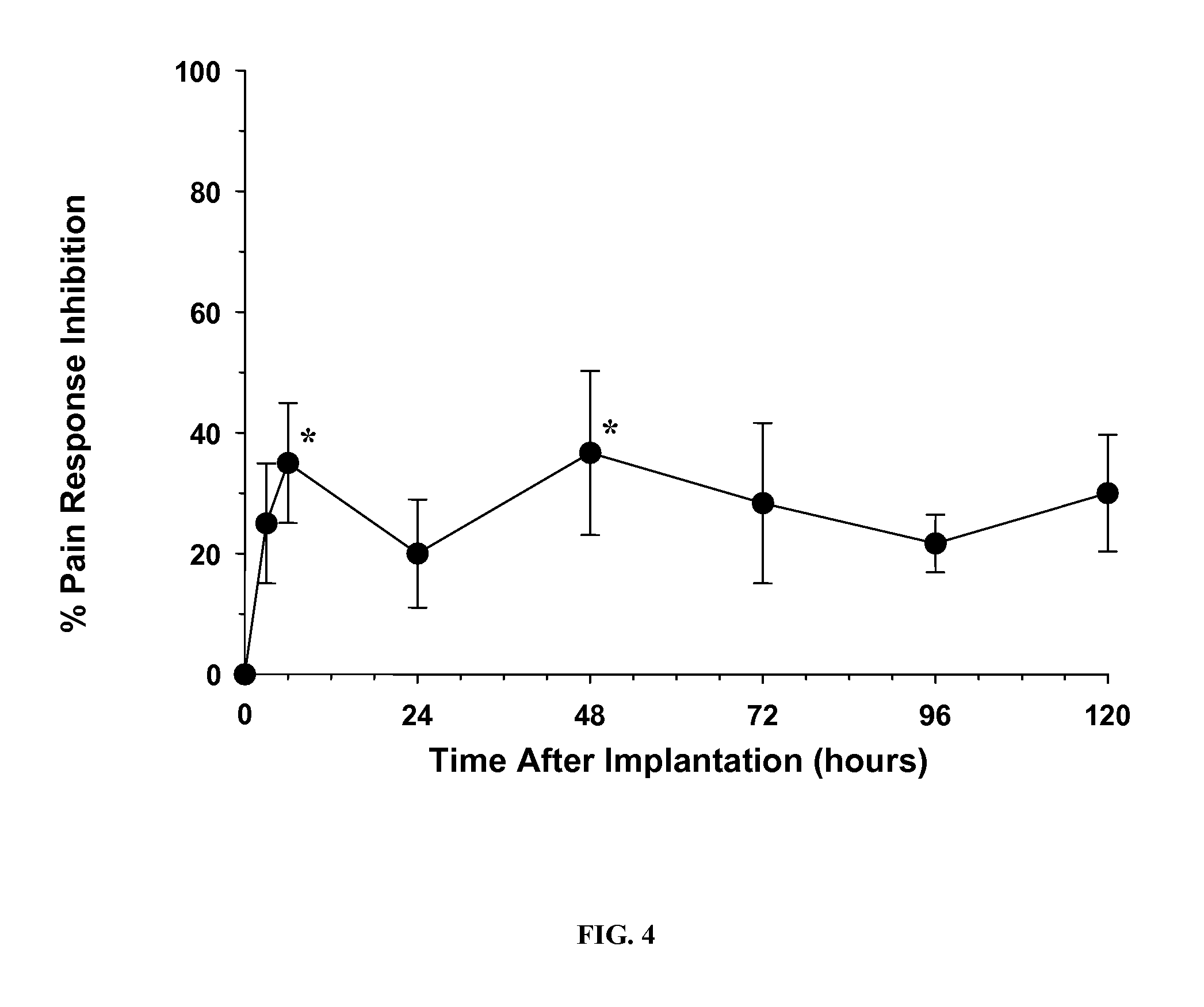
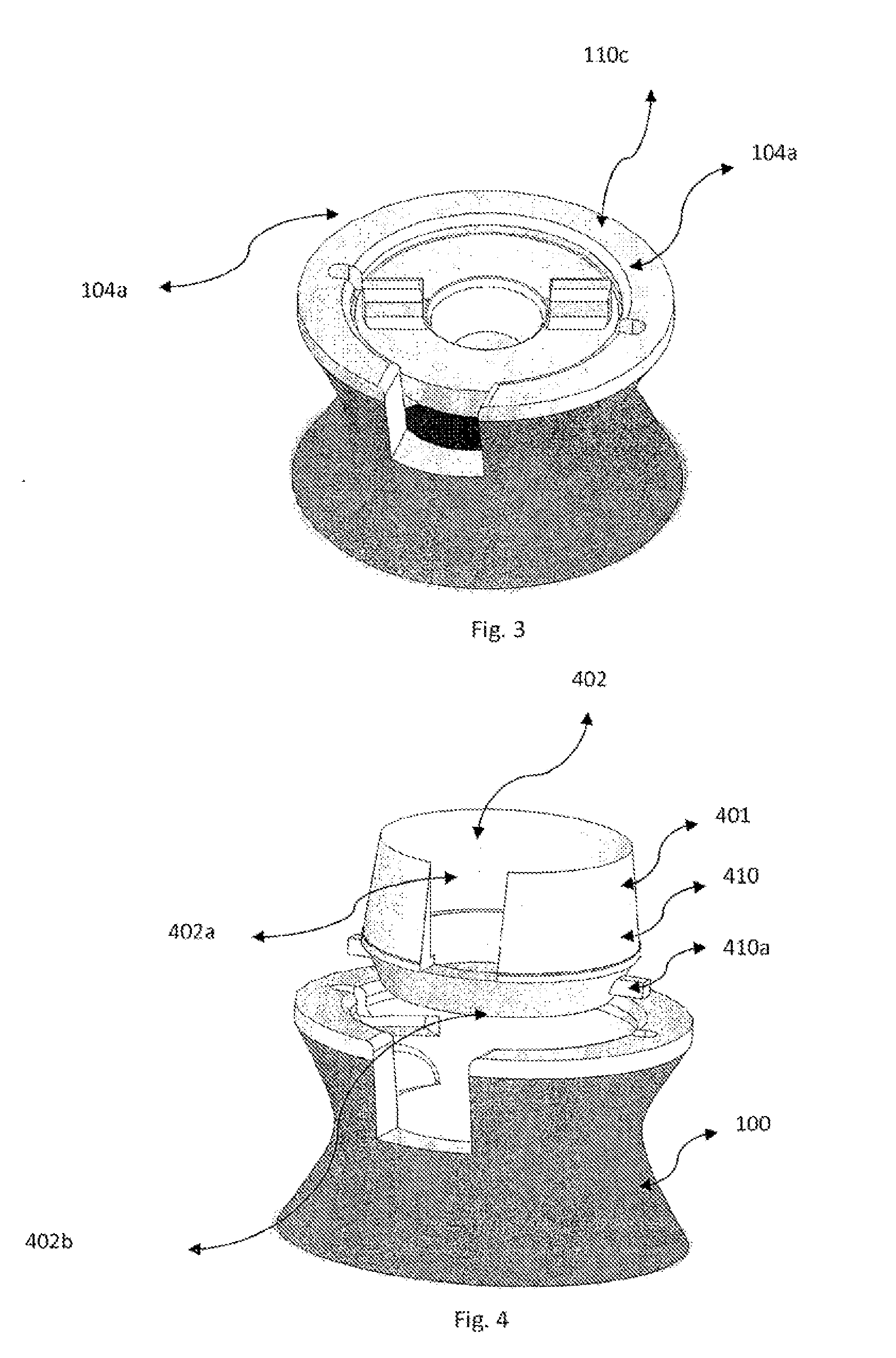
Drug depot implant designs and methods of implantation
ActiveUS20070243228A1Uniform drug distributionMinimal disruptionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal injurySacroiliac joint
The present invention relates to novel drug depot implant designs for optimal delivery of therapeutic agents to subjects. The invention provides a method for alleviating pain associated with neuromuscular or skeletal injury or inflammation by targeted delivery of one or more therapeutic agents to inhibit the inflammatory response which ultimately causes acute or chronic pain. Controlled and directed delivery can be provided by drug depot implants, comprising therapeutic agents, specifically designed to deliver the therapeutic agent to the desired location by facilitating their implantation, minimizing their migration from the desired tissue location, and without disrupting normal joint and soft tissue movement.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method for repairing intervertebral discs
ActiveUS20080103564A1Increase pressureHalt leakageDiagnosticsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismIntervertebral discBiomedical engineering
A method of repairing a defect in an annulus fibrosus of an intervertebral disc, without excising the entire nucleus pulposus of the disc. The method includes inserting an introducer needle through the annulus fibrosus by puncturing the annulus fibrosus with the introducer needle, injecting an in situ curable, bio-compatible polymerizable or polymeric material composition into the disc through the introducer needle directly or indirectly so that the in situ curable composition contacts a defect in the annulus fibrosus; and curing said material in situ.
Owner:PAUZA KEVIN
Anti-inflammatory supplement compositions and regimens to reduce cardiovascular disease risks
InactiveUS20060172012A1Relieve symptomsPromotes fast digestionOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBlueberry extractApple extract
Disclosed are improvements in human nutrition involving a unique combination of natural products constituting anti-inflammatory compositions which can reduce cardiovascular disease risks as well as play a positive role in other conditions and diseases for which key indicators, especially selected from the group consisting of C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), 5-lypoxygenase (5-LOX) expression and prostaglandin E2 (PGE-2) biosynthesis or any combination of these, are indicators. Therapeutic compositions preferably comprise curcumin, bilberry extract, grape seed extract, green tea extract and apple extract, in effective amounts individually and combined to provide a therapeutically significant reduction in one or more key indicators. Another exemplified therapeutic composition comprises: omega-3 rich refined fish oil, resveratrol, blueberry extract, grape seed extract, green tea extract and gamma and / or delta tocopherol, in effective amounts individually for the above benefits.
Owner:A M TODD
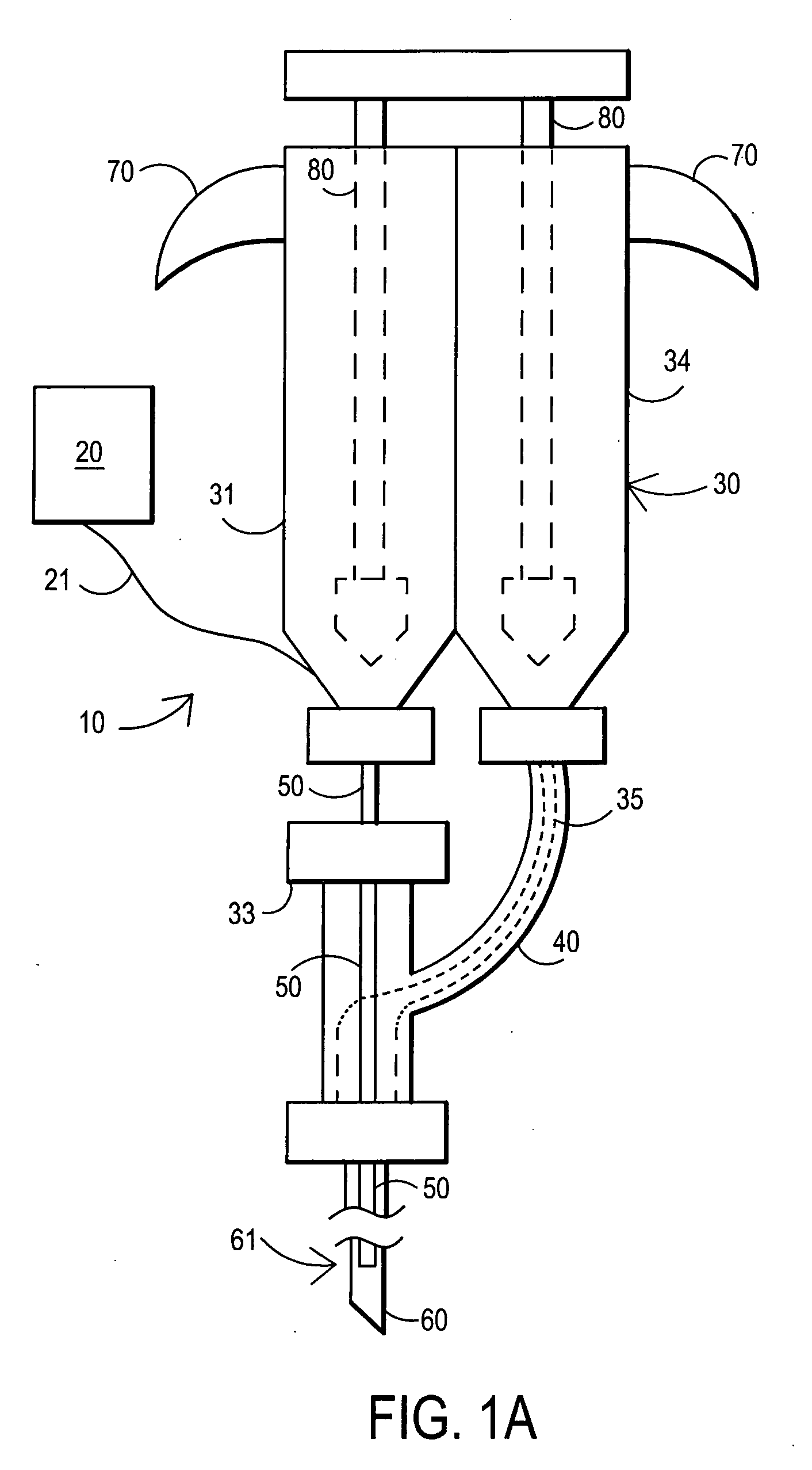
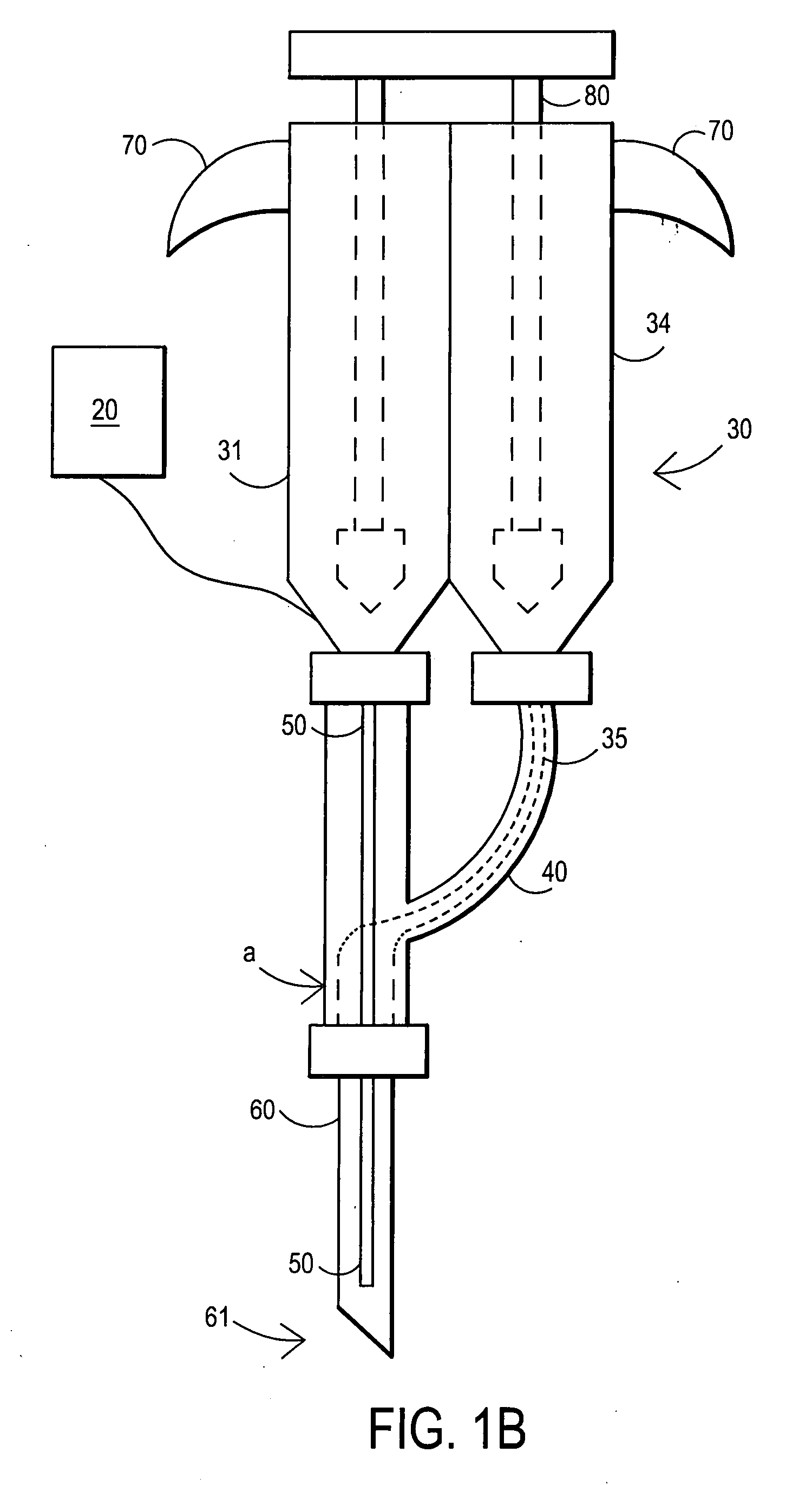
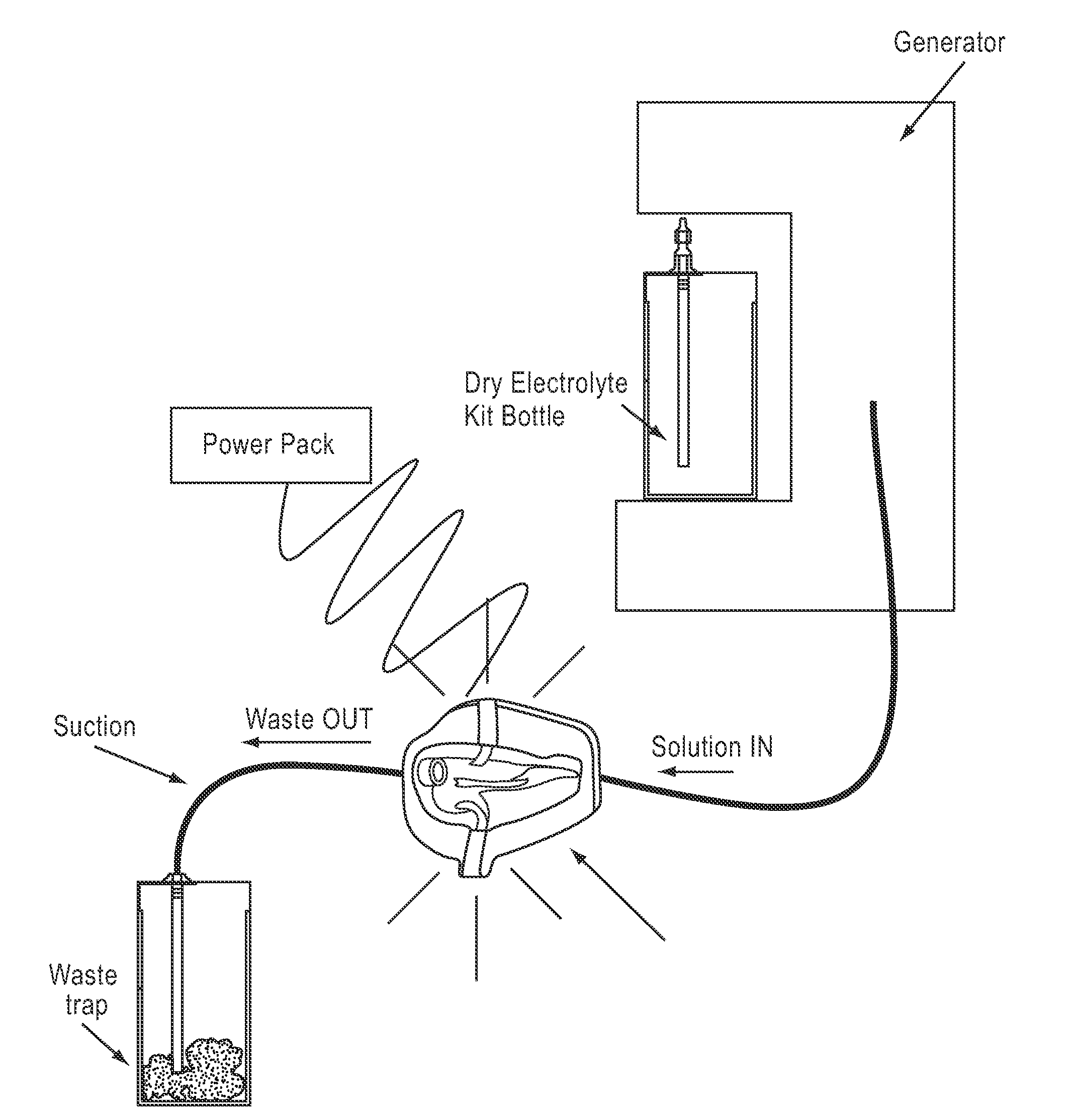
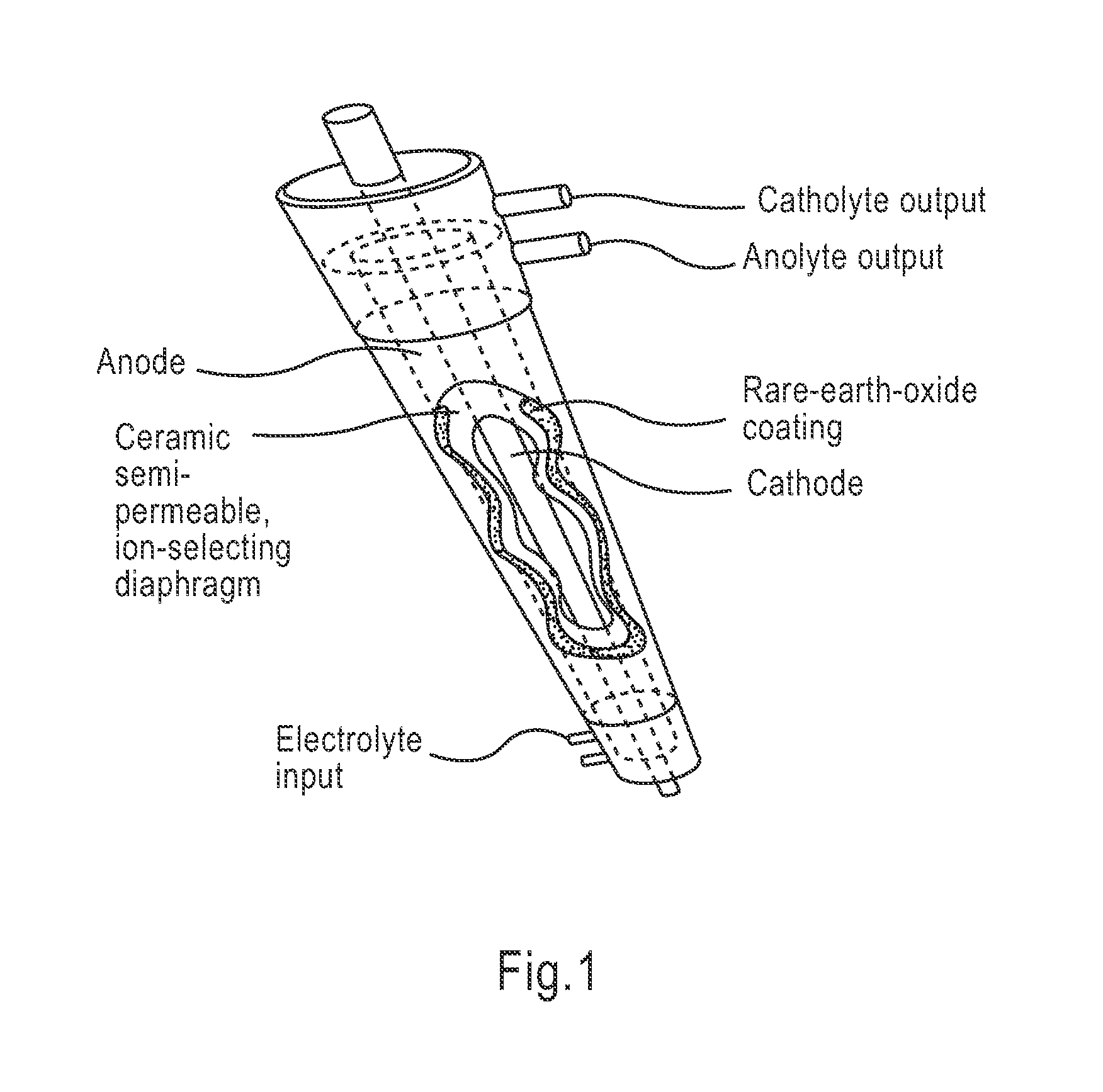
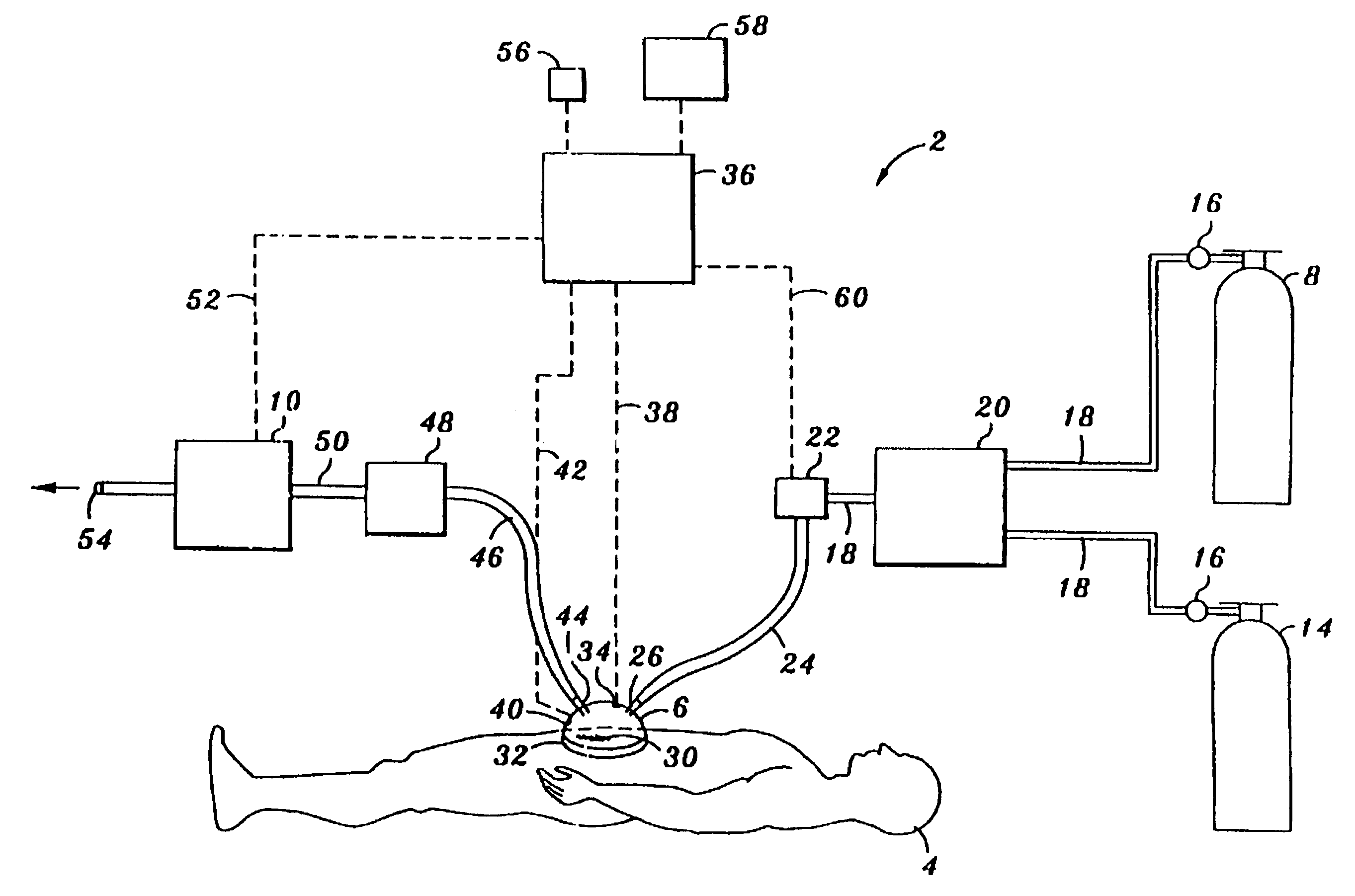
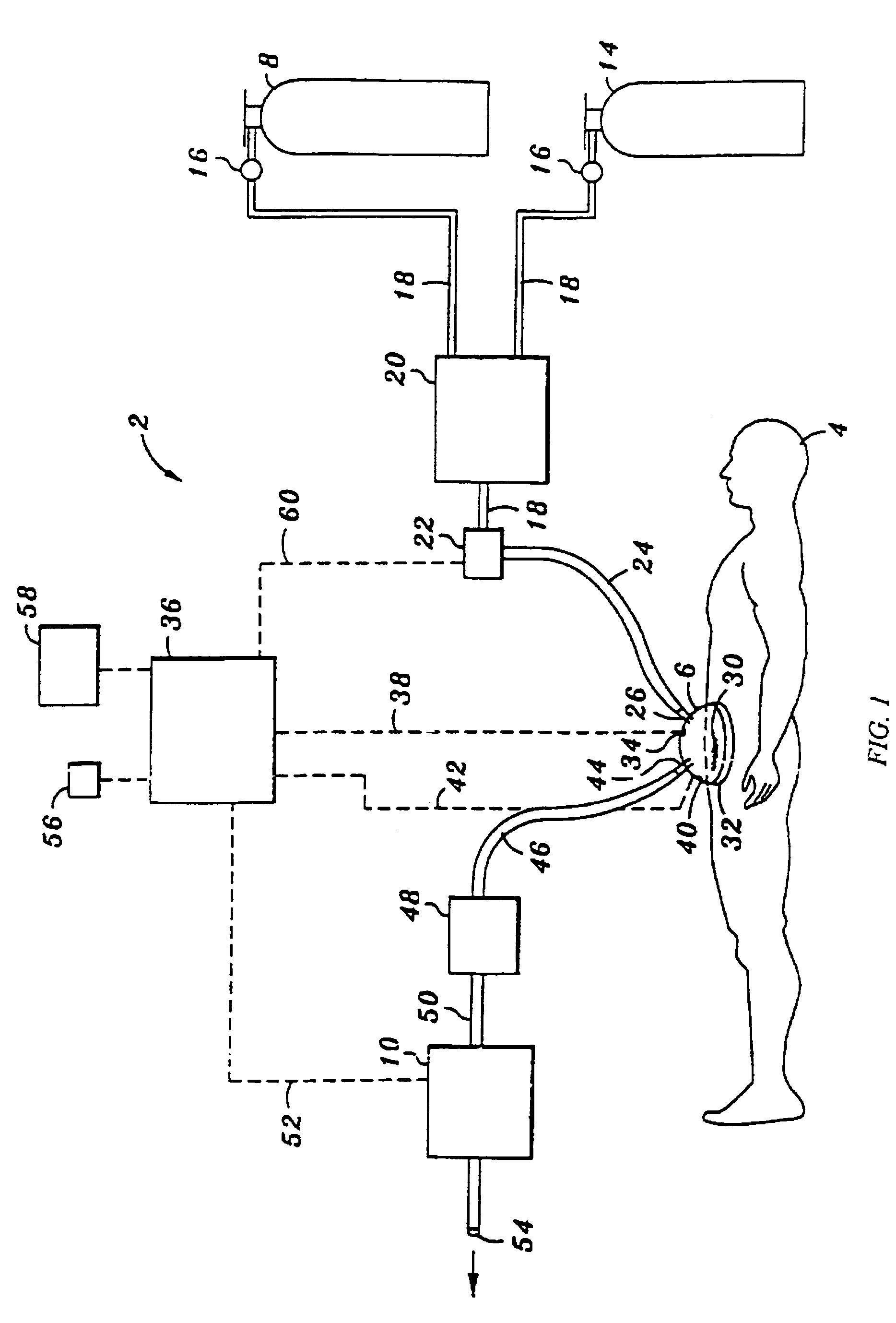
Apparatus and method for wound, cavity, and bone treatment
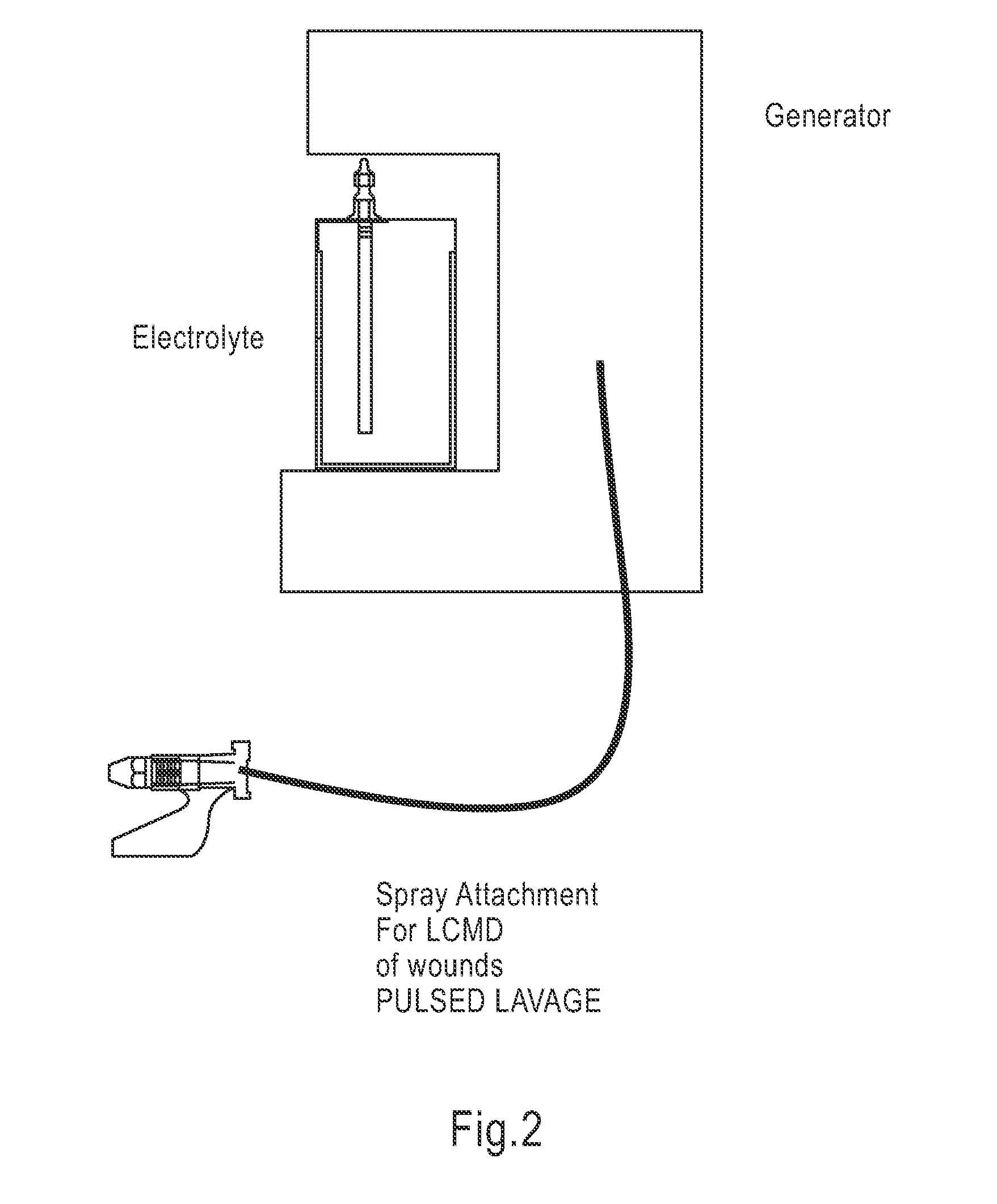
InactiveUS20100030132A1Quicker wound closureSafer wound care environmentElectrolysis componentsCannulasNeed treatmentBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides a treatment apparatus. The apparatus contains a reservoir or generator for a treatment solution, a mechanism for delivering the treatment solution to a wound site, and a mechanism for applying the solution to a wound, tissue, bone or surgical cavity for treatment. The apparatus may apply the solution (e.g., a solution containing hypohalous acid) with, for example, an occlusive wound dressing, pulsative lavage device, hydrotherapy, hydrosurgical device, and / or ultrasound. A waste container may be operably connected to the apparatus for collecting waste from the wound by run-off, or by applying negative pressure (e.g. a vacuum). Because the apparatus of the invention can optionally be portable or mobile, the invention is suitable for use in hospitals and nursing homes, as well as for home wound care. The invention also provides a method for treating a wound (or other area needing treatment), and / or for reducing wound bioburden, by supplying a hypochlorous acid solution to the site, such as a wound colonized or infected with drug resistant bacteria, before, during, or after negative pressure wound therapy.
Owner:PURICORE
Immunization-free methods for treating antigen-stimulated inflammation in a mammalian host and shifting the host's antigen immune responsiveness to a Th1 phenotype
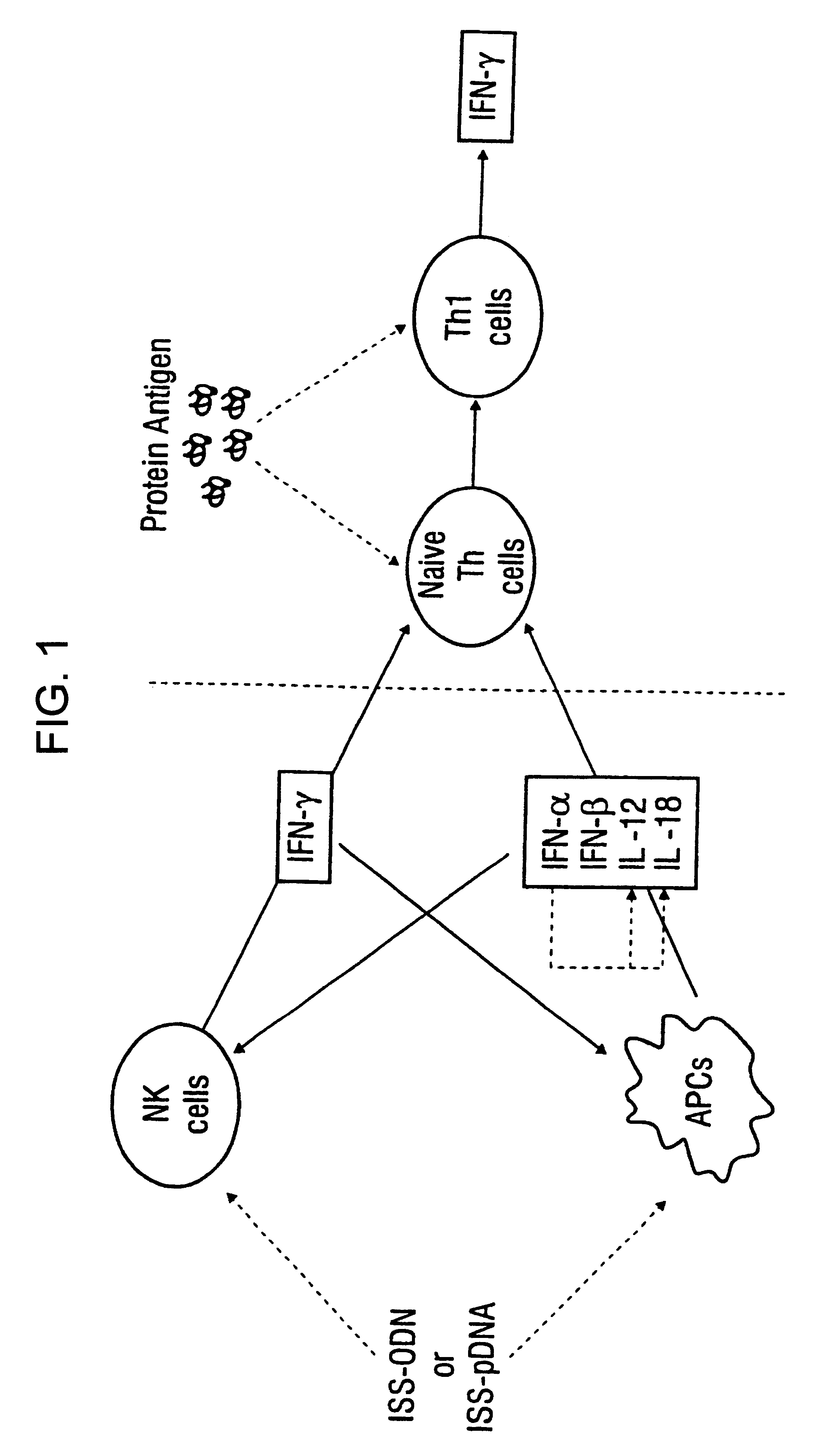
InactiveUS6498148B1Treatment and prevention of inflammationSuppresses antigen-stimulated granulocyte infiltrationOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderAntigen stimulationTherapeutic intent
The invention relates to methods for preventing or reducing antigen-stimulated, granulocyte-mediated inflammation in tissue of an antigen-sensitized mammal host by delivering an immunostimulatory oligonucleotide to the host. In addition, methods for using the immunostimulatory oligonucleotides to boost a mammal host's immune responsiveness to a sensitizing antigen (without immunization of the host by the antigen) and shifting the host's immune responsiveness to a Th1 phenotype to achieve various therapeutic ends are provided. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Temporarily Stiffened Mesh Prostheses
ActiveUS20070198040A1Low experience requirementReduce implantationPretreated surfacesAdhesive dressingsFiberSide effect
The present invention relates to medical prostheses and methods of manufacturing those devices. In particular, the prostheses are temporarily stiffened meshes with particular coatings to provide initial stiffness and thereby permit easier surgical handling for treatment or reconstruction of soft tissue defects. Preferred embodiments include surgical meshes coated with one or more biodegradable polymers that can act as a stiffening agent by coating the filaments or fibers of the mesh to temporarily immobilize the contact points of those filaments or fibers and / or by increasing the stiffness of the mesh by at least 1.1 times its original stiffness. The devices of the invention can also provide relief from various post-operative complications associated with their implantation, insertion or surgical use. By including biologically active agents and / or drugs in the coating, the devices provide prophylaxis for and can alleviate side effects or complications associated with the surgery or use of prostheses in general.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods for using a three-dimensional stromal tissue to promote angiogenesis
InactiveUS20030007954A1Reduce inflammationPromotes rapid endothelializationSuture equipmentsBiocideSmooth muscleCardiac muscle
The present invention relates to a method for promoting blood vessel formation in tissues and organs. In particular, the method relates to implantation or attachment of an engineered three-dimensional stromal tissue to promote endothelialization and angiogenesis in the heart and related tissues. The three-dimensional stromal tissue of the present invention may be used in a variety of applications including, but not limited to, promoting repair of and regeneration of damaged cardiac muscle, promoting vascularization and healing during cardiac surgery, promoting blood vessel formation at anastomosis sites, and promoting vascularization and repair of damaged skeletal muscle, smooth muscle or connective tissue.
Owner:ADVANCED TISSUE SCIENCES INC
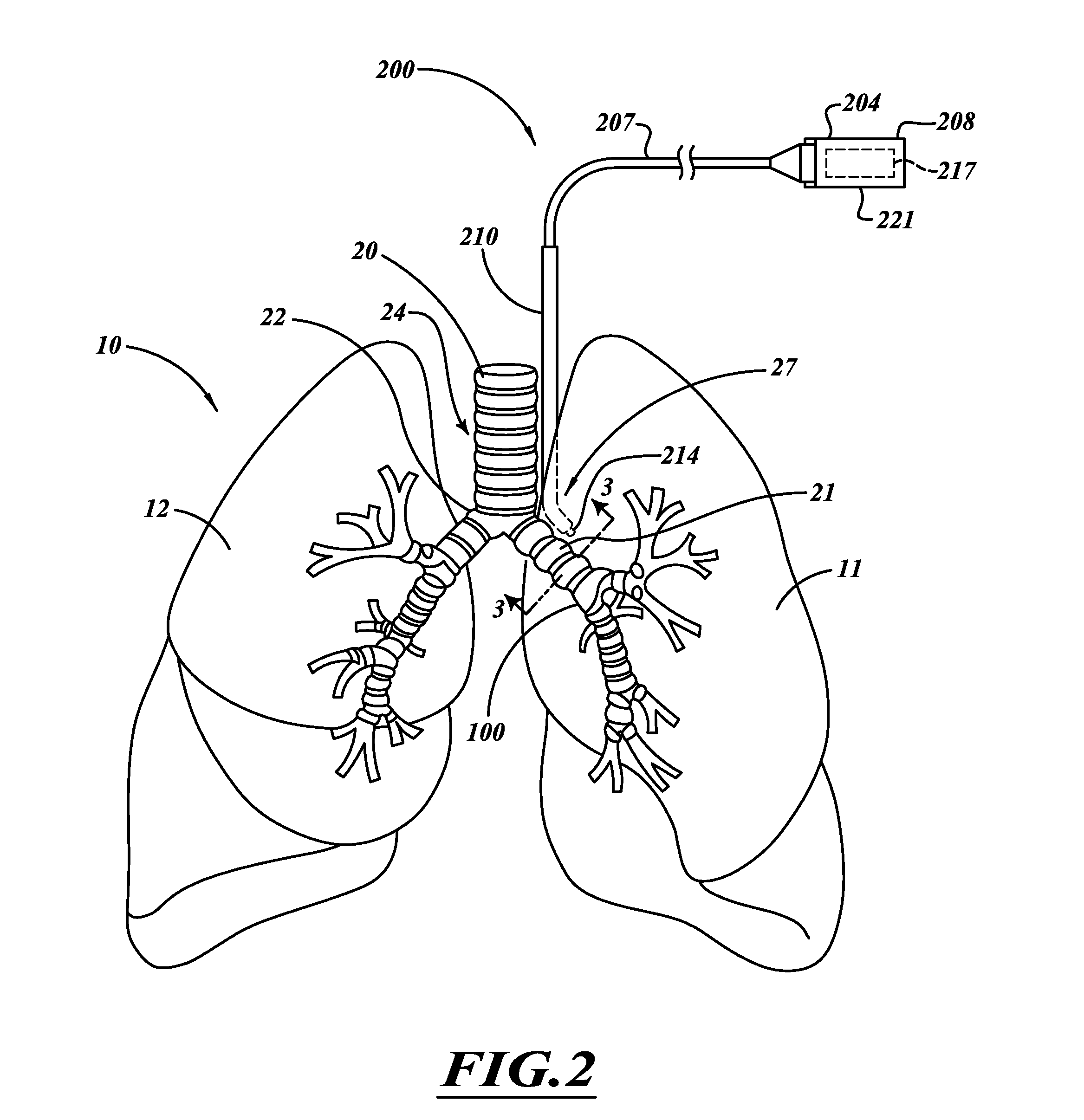
Non-invasive and minimally invasive denervation methods and systems for performing the same
ActiveUS20110118725A1Reduce harmReduce obstructionUltrasound therapySurgical needlesCOPDPartial denervation
A system and method can be used to denervate at least a portion of a bronchial tree. An energy emitter of an instrument is percutaneously delivered to a treatment site and outputs energy to damage nerve tissue of the bronchial tree. The denervation procedure can be performed without damaging non-targeted tissue. Minimally invasive methods can be used to open airways to improve lung function in subjects with COPD, asthma, or the like. Different sections of the bronchial tree can be denervated while leaving airways intact to reduce recovery times.
Owner:NUVAIRA INC
Bioprosthetic tissue preparation with synthetic hydrogels
ActiveUS20050119736A1Reduce calcificationReduce stiffnessSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCross-linkIn situ polymerization
Methods for treating xenogenic tissue for implantation into a human body including in-situ polymerization of a hydrogel polymer in tissue, and tissue treated according to those methods, where the polymerization takes place in tissue that has not been fixed with glutaraldehyde. The polymerization may only fill the tissue, bind the polymer to the tissue, or cross-link the tissue through the polymer, depending on the embodiment. One method includes free radical polymerization of a first vinylic compound, and can include cross-linking through use of a second compound having at least two vinyl groups. Another method utilizes nucleophilic addition polymerization of two compounds, one of which can include PEG and can further include hydrolytically degradable regions. In one embodiment, applicants believe the in-situ polymerization inhibits calcification, and that the polymerization of tissue un-fixed by glutaraldehyde allows for improved penetration of the polymer. The methods find one use in the treatment of porcine heart valve tissue, intended to extend the useful life of the valves by inhibiting calcification. The incorporation of degradable hydrogel regions may initially fill the tissue and reduce any initial inflammatory response, but allow for later infiltration by cells to remodel the tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods for Reducing Discomfort During Electrostimulation, and Compositions and Apparatus Therefor
ActiveUS20110319975A1Reduce inflammationReduce injuriesPowder deliveryExternal electrodesSkin surfaceElectrode gel
An electrode assembly for neuro-cranial stimulation includes an electrode, a conductive gel, and an adapter including an interior compartment for positioning the electrode relative to the adapter and for receiving and retaining the conductive gel. The conductive gel contacts the electrode along an electrode-gel interface. An orifice at one end of the interior compartment and adjacent to a positioning surface of the adapter for positioning the electrode assembly against a skin surface of a user enables the conductive gel is able to contact the skin surface of the user to define a gel-skin interface, such that a minimum distance between the electrode-gel interface and the gel-skin interface is maintained between 0.25 cm and 1.3 cm. An electrode assembly mounting apparatus is provided for adjustably positioning a plurality of electrode assemblies against target positions on the cranium.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
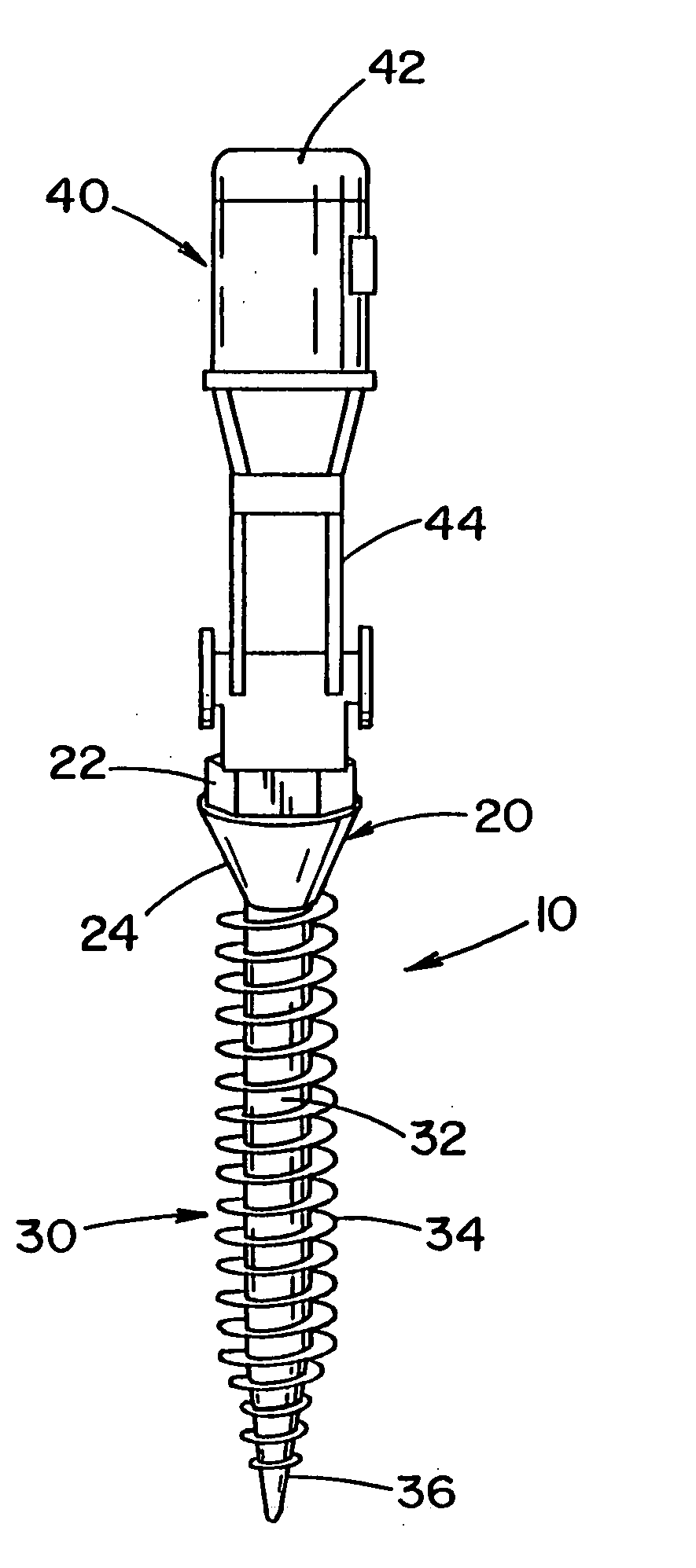
Implant device
InactiveUS20060036253A1Minimal chanceEasy to insertSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisImplanted deviceCartilage
Owner:SPINECO
Polypeptide and immune modulation
ActiveUS20150071957A1Strong elevationReduced gene expressionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideRoseburia
The present invention relates to Roseburia flagellin, and / or a polynucleotide sequence encoding said Roseburia flagellin, and / or a vector comprising said polynucleotide sequence, and / or a host cell, including bacteria, comprising said vector, and / or a host cell, including bacteria, comprising said polynucleotide sequence, for use in modulating the inflammation of a tissue or an organ in a subject.
Owner:4D PHARMA RES LTD +1
Method of biochemical treatment of persistent pain
InactiveUS20050152905A1Reduce releaseAvoid exposureBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInterleukin 6Interleukin-1beta
This invention relates to a method for the biochemical treatment of persistent pain disorders by inhibiting the biochemical mediators of inflammation in a subject comprising administering to said subject any one of several combinations of components that are inhibitors of biochemical mediators of inflammation. Said process for biochemical treatment of persistent pain disorders is based on Sota Omoigui's Law, which states: ‘The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response’. Sota Omoigui's Law of Pain unifies all pain syndromes as sharing a common origin of inflammation and the inflammatory response. The various biochemical mediators of inflammation are present in differing amounts in all pain syndromes and are responsible for the pain experience. Classification and treatment of pain syndromes should depend on the complex inflammatory profile. A variety of mediators are generated by tissue injury and inflammation. These include substances produced by damaged tissue, substances of vascular origin as well as substances released by nerve fibers themselves, sympathetic fibers and various immune cells. Biochemical mediators of inflammation that are targeted for inhibition include but are not limited to: prostaglandin, nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1-alpha, interleukin 1-beta, interleukin-4, Interleukin-6 and interleukin-8, histamine and serotonin, substance P, Matrix Metallo-Proteinase, calcitonin gene-related peptide, vasoactive intestinal peptide as well as the potent inflammatory mediator peptide proteins neurokinin A, bradykinin, kallidin and T-kinin.
Owner:OMOIGUI OSEMWOTA SOTA
Bioeffective krill oil compositions
InactiveUS20080274203A1Increasing flesh colorationPromote growthBiocideMetabolism disorderInsulin resistanceAnti oxidant
This invention discloses new krill oil compositions characterized by having high amounts of phospholipids, astaxanthin esters and / or omega-3 contents. The krill oils are obtained from krill meal using supercritical fluid extraction in a two stage process. Stage 1 removes the neutral lipid by extracting with neat supercritical CO2 or CO2 plus approximately 5% of a co-solvent. Stage 2 extracts the actual krill oils by using supercritical CO2 in combination with approximately 20% ethanol. The krill oil materials obtained are compared with commercially available krill oil and found to be more bioeffective in a number of areas such as anti-inflammation, anti-oxidant effects, improving insulin resistances and improving blood lipid profile.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ANTARCTIC
Antibodies that specifically bind to tim3
ActiveUS20130022623A1Promote growthReduce inflammationHeavy metal active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellAntibody
Provided herein are antibodies specific for TIM3 that can be used to detect cancer cells, in particular, cancer stem cells. The antibodies can also be used in therapeutic compositions for treating cancer and reducing inflammation.
Owner:ONK THERAPEUTICS LTD
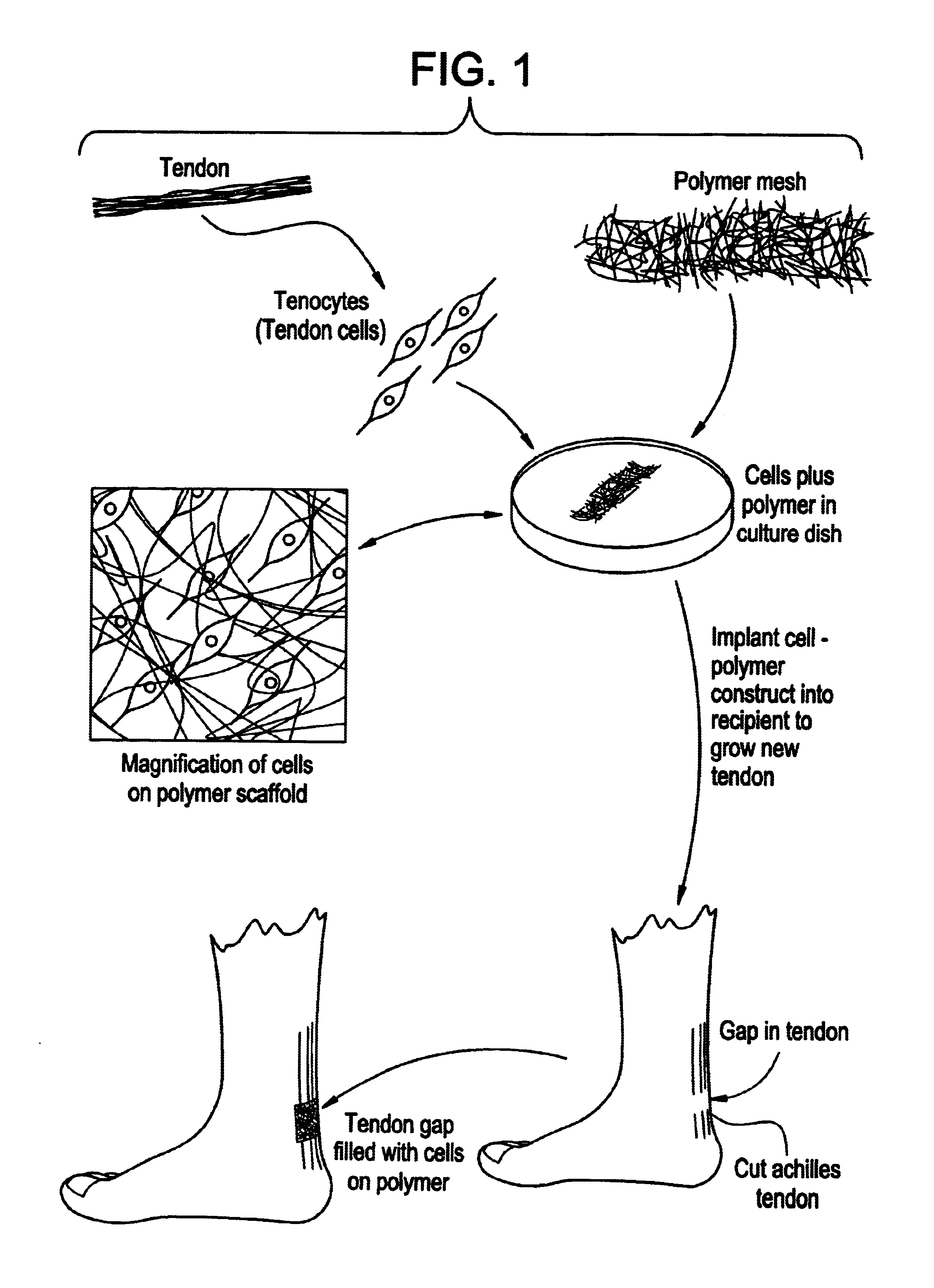
Tissue engineered tendons and ligaments
InactiveUS6840962B1Moderate strengthReduce inflammationLigamentsMusclesEnzymatic digestionLigament structure
Connective tissue, including neo-tendons and ligaments, has been constructed using biodegradable synthetic scaffolds seeded with tenocytes. The scaffolds are preferably formed from biodegradable fibers formed of a polymer such as polyglycolic acid-polylactic acid copolymers, and seeded with cells isolated from autologous tendon or ligament by means of enzymatic digestion or direct seeding into tissue culture dishes from explants. The cell polymer constructs are then surgically transplanted to replace missing segments of functioning tendon or ligament.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES WITH ALTERED AFFINITIES FOR HUMAN FCyRI, FCyRIIIa, AND C1q PROTEINS
InactiveUS20130149300A1Good curative effectLow toxicitySugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsDiseaseFc-Gamma Receptor
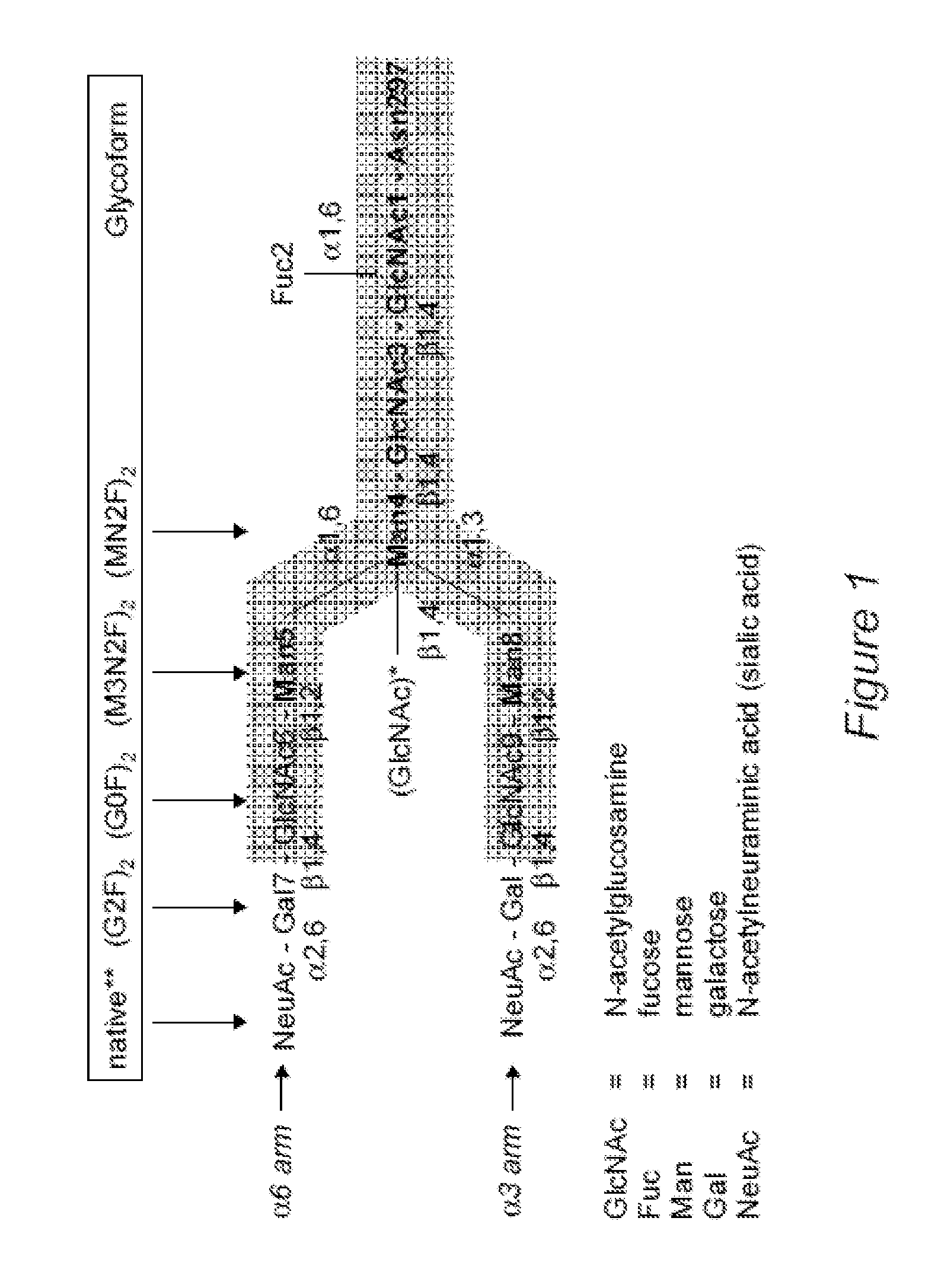
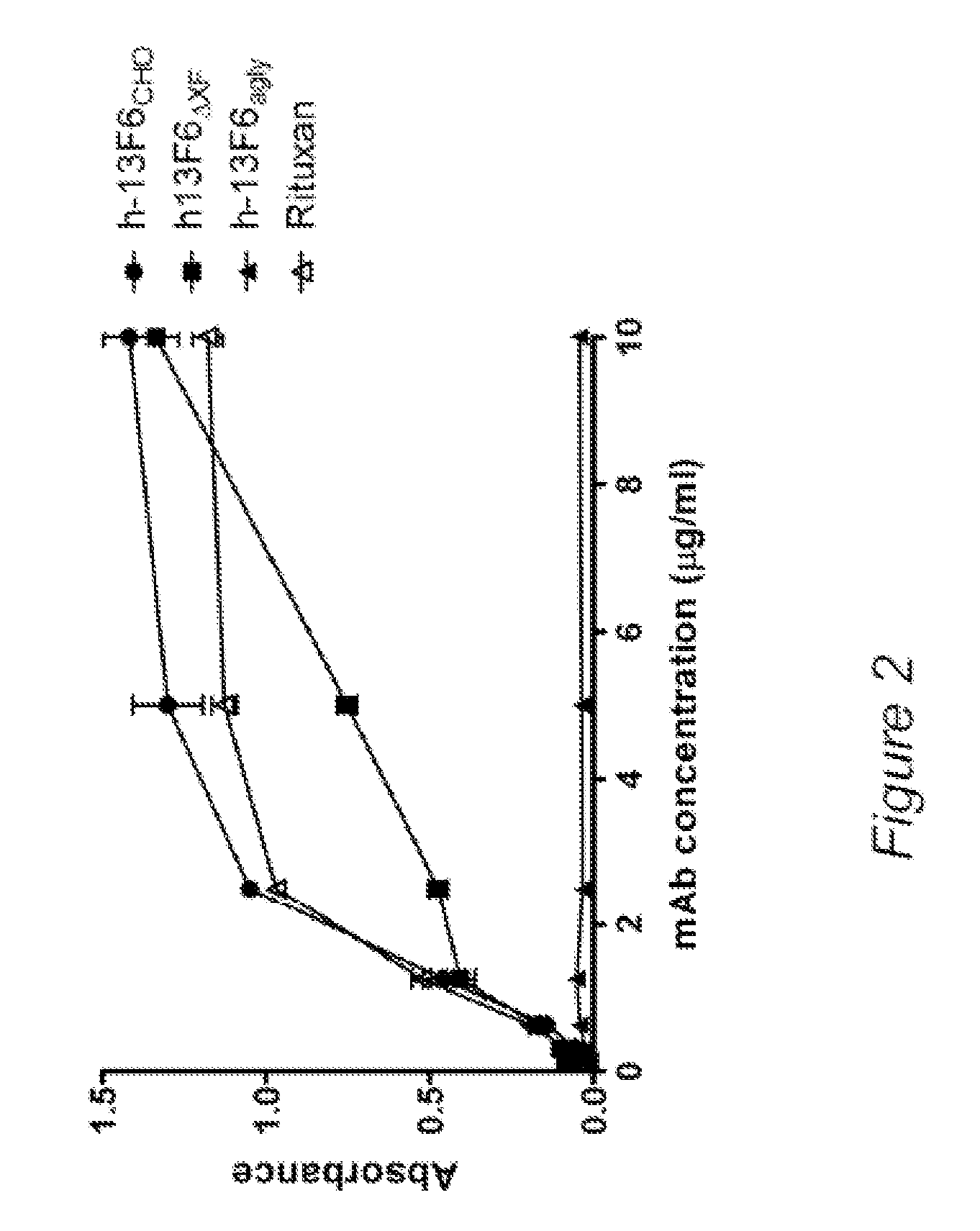
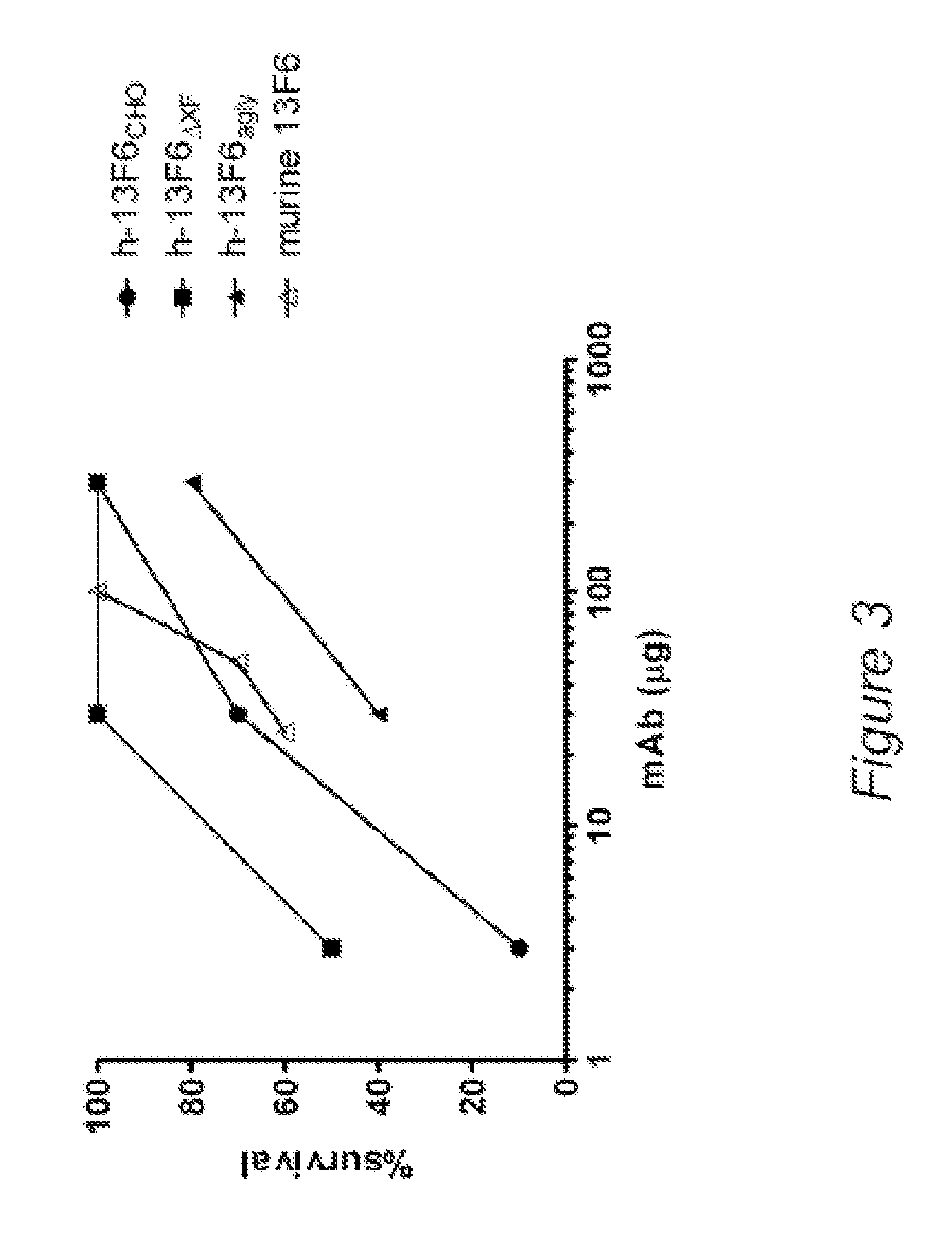
Disclosed herein are GNGN and G1 / G2 antibodies that recognize and bind various FcRs and C1q. Also disclosed herein are glycan-optiminzed antibodies, predominantly of the GNGN or G1 / G2 glycoform, with enhanced Fcγ receptor binding achieved through CHO, Nicotiana benthamiana and yeast manufacturing systems. Nucleic acids encoding these antibodies, as well as expression vectors and host cells including these nucleic acids are also disclosed herein. Methods and pharmaceutical compositions including the monoclonal antibodies are provided herein for the prevention and / or therapeutic treatment of viral infections, cancers and inflammatory diseases.
Owner:MAPP BIOPHARM +1
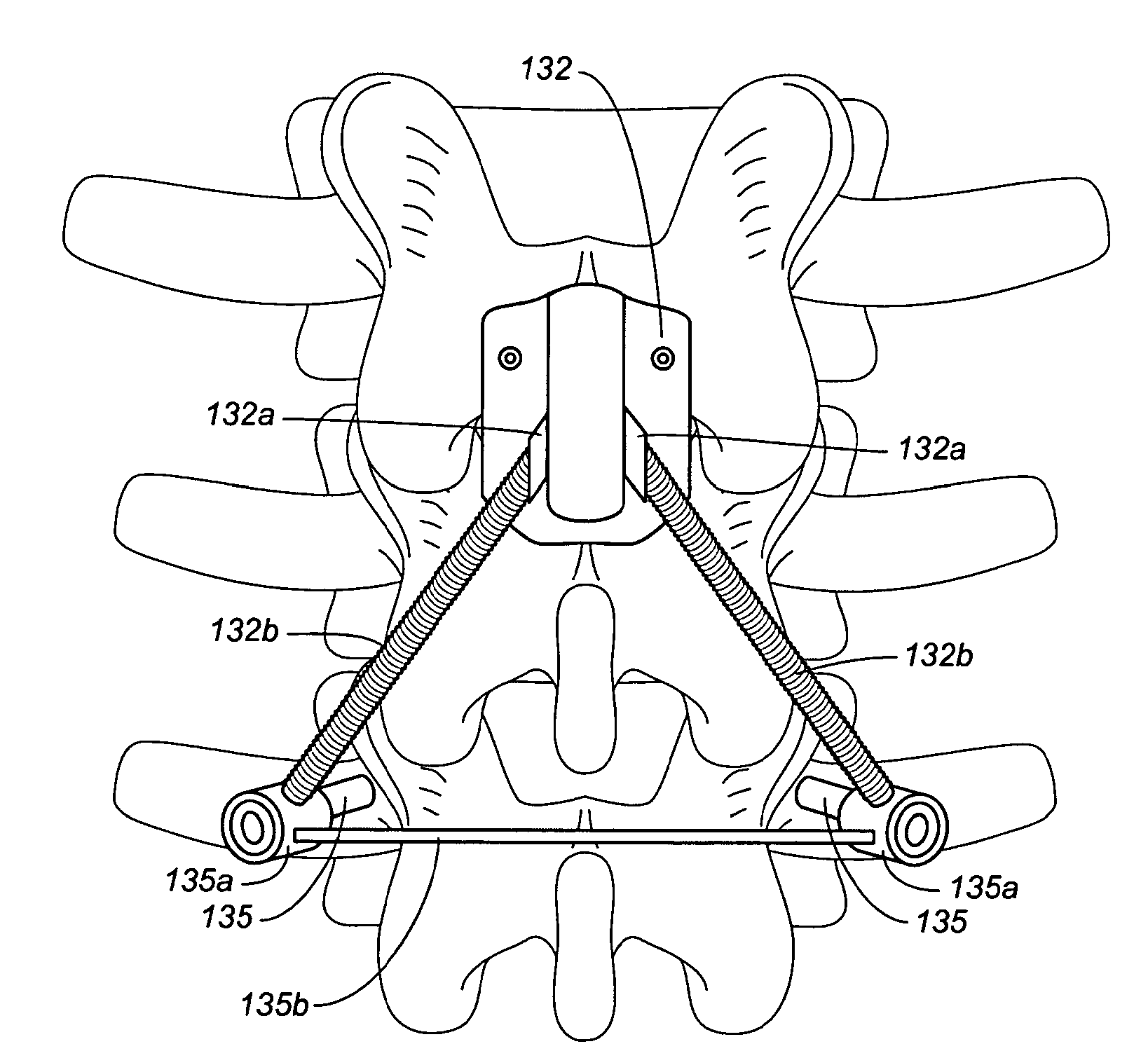
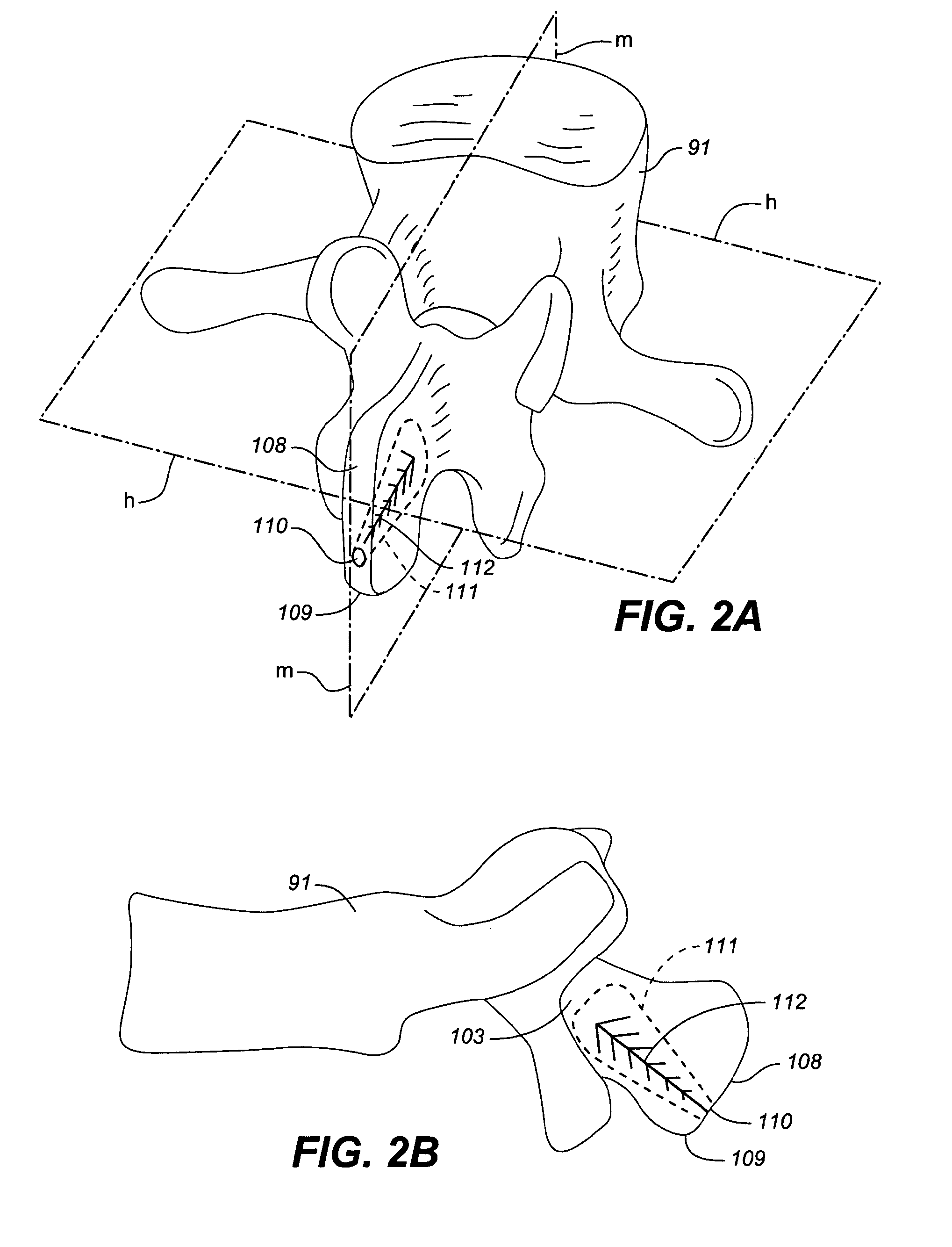
Device and method for correcting a spinal deformity
ActiveUS20100100130A1Less discomfortAlleviating or deformityAdditive manufacturing apparatusInternal osteosythesisMedicineDirect device
A device and method for correcting a spinal deformity are provided. A spinal implant for correcting a spinal deformity includes a multipoint connector that connects to at least one vertebra of a spine at a plurality of locations and a force directing device that applies a force to the vertebra through the multipoint connector. The force directing device may include a rod which extends generally along an axis of the spine and a force directing member which is adjustably coupled to both the rod and the multipoint connector and which applies a corrective force to the at least one vertebra.
Owner:K2M +1
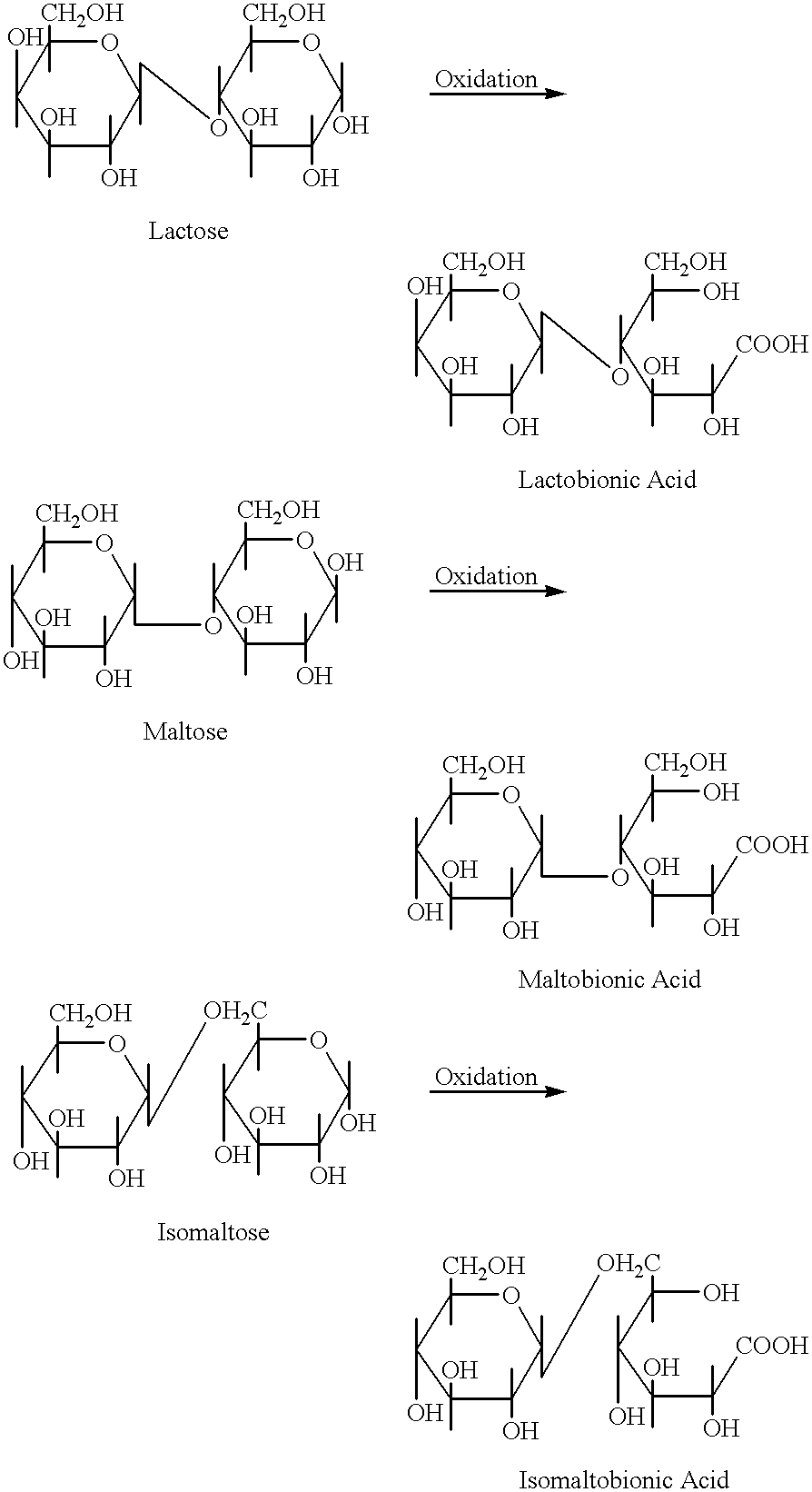
Oligosaccharide aldonic acids and their topical use
Compositions comprising oligosaccharide aldonic acids are useful for general care, as well as for treatment and prevention, of various cosmetic conditions and dermatological disorders, including those associated with intrinsic and / or extrinsic aging, as well as with changes or damage caused by extrinsic factors; general care, as well as treatment and prevention of diseases and conditions, of the oral, and vaginal mucosa; for general oral care, as well as treatment and prevention of oral and gum diseases; and for wound healing of the skin. Compositions comprising oligosaccharide aldonic acids may further comprise a cosmetic, pharmaceutical or other topical agent to enhance or create synergetic effects.
Owner:YU RUEY J +1
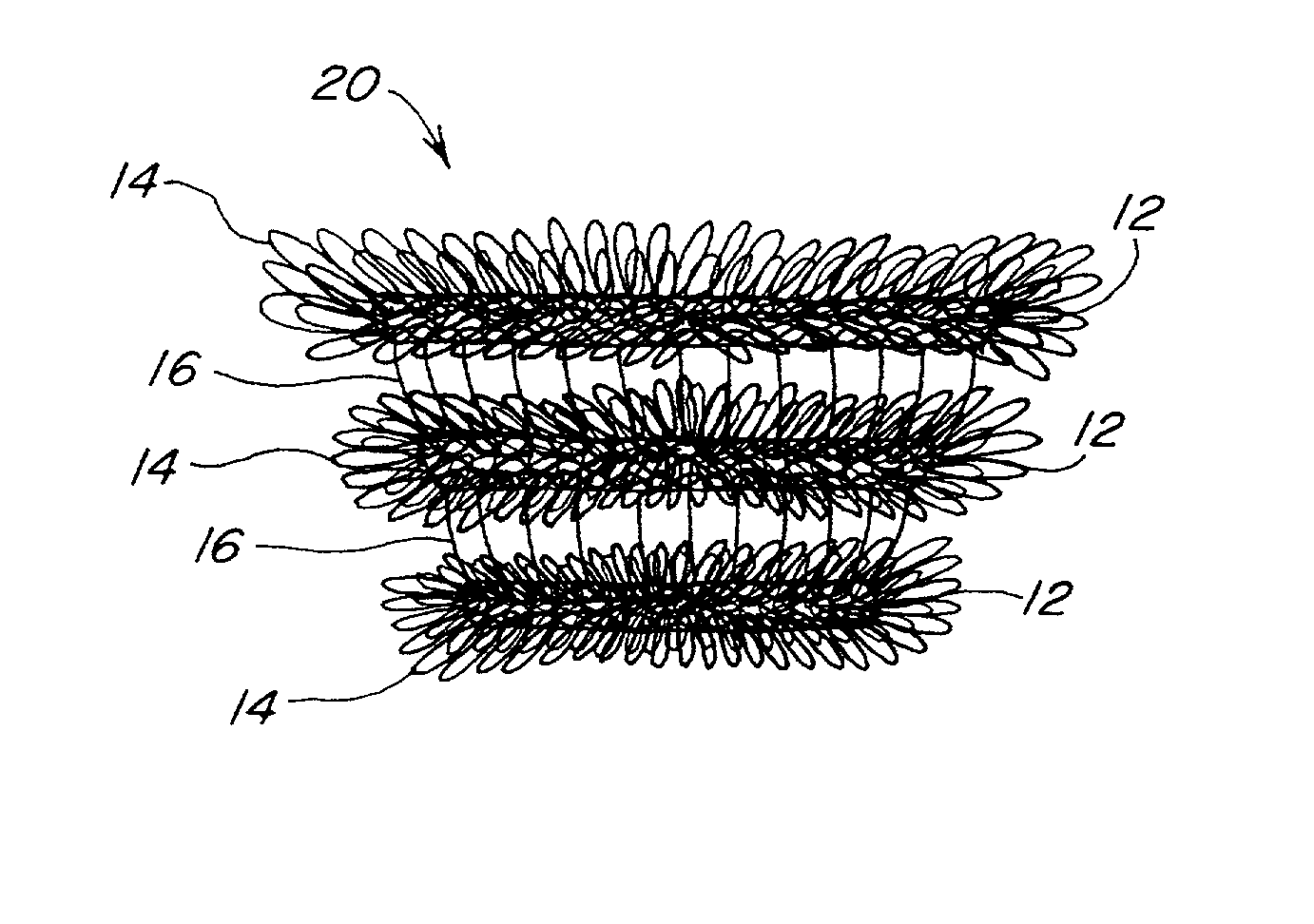
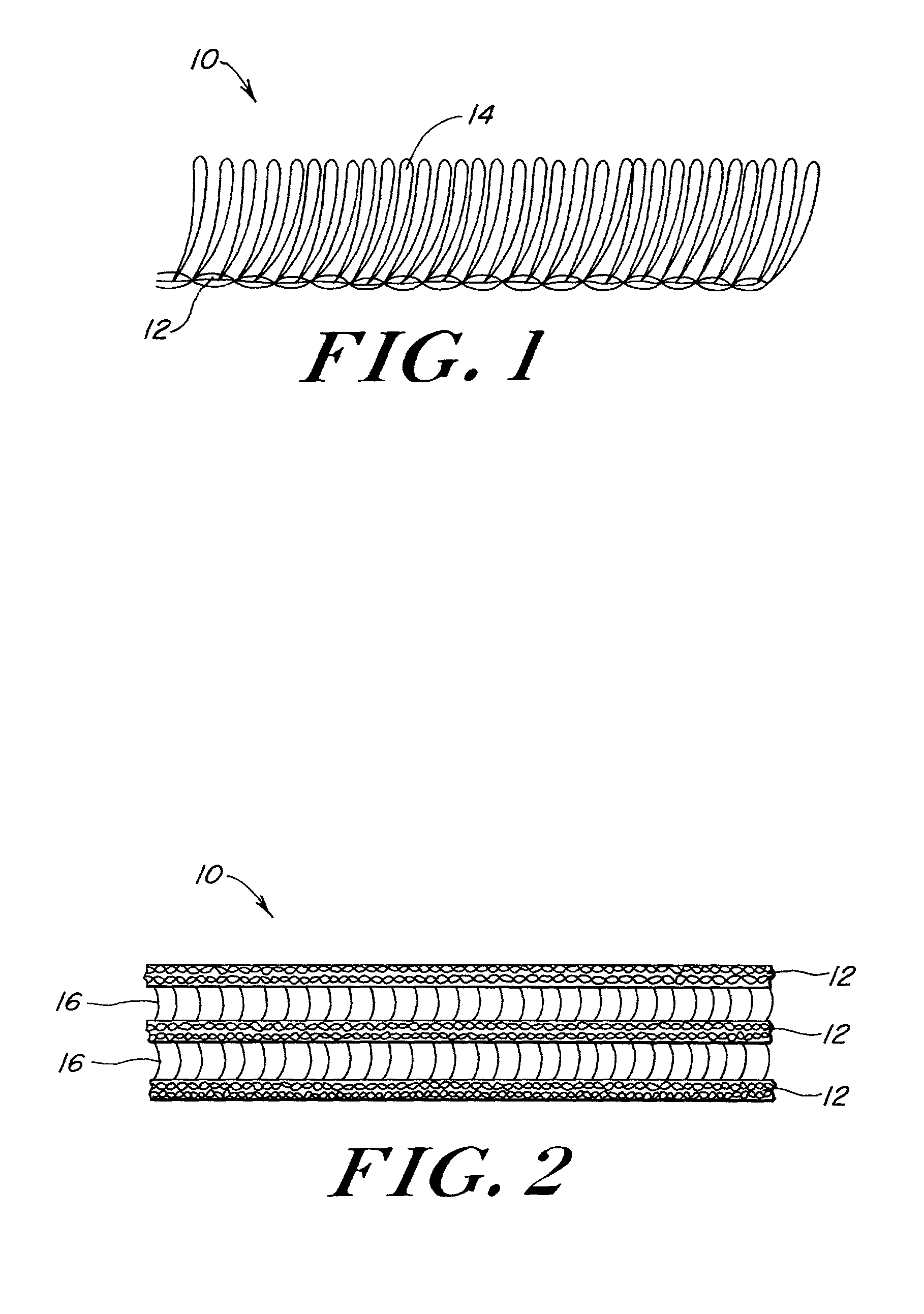
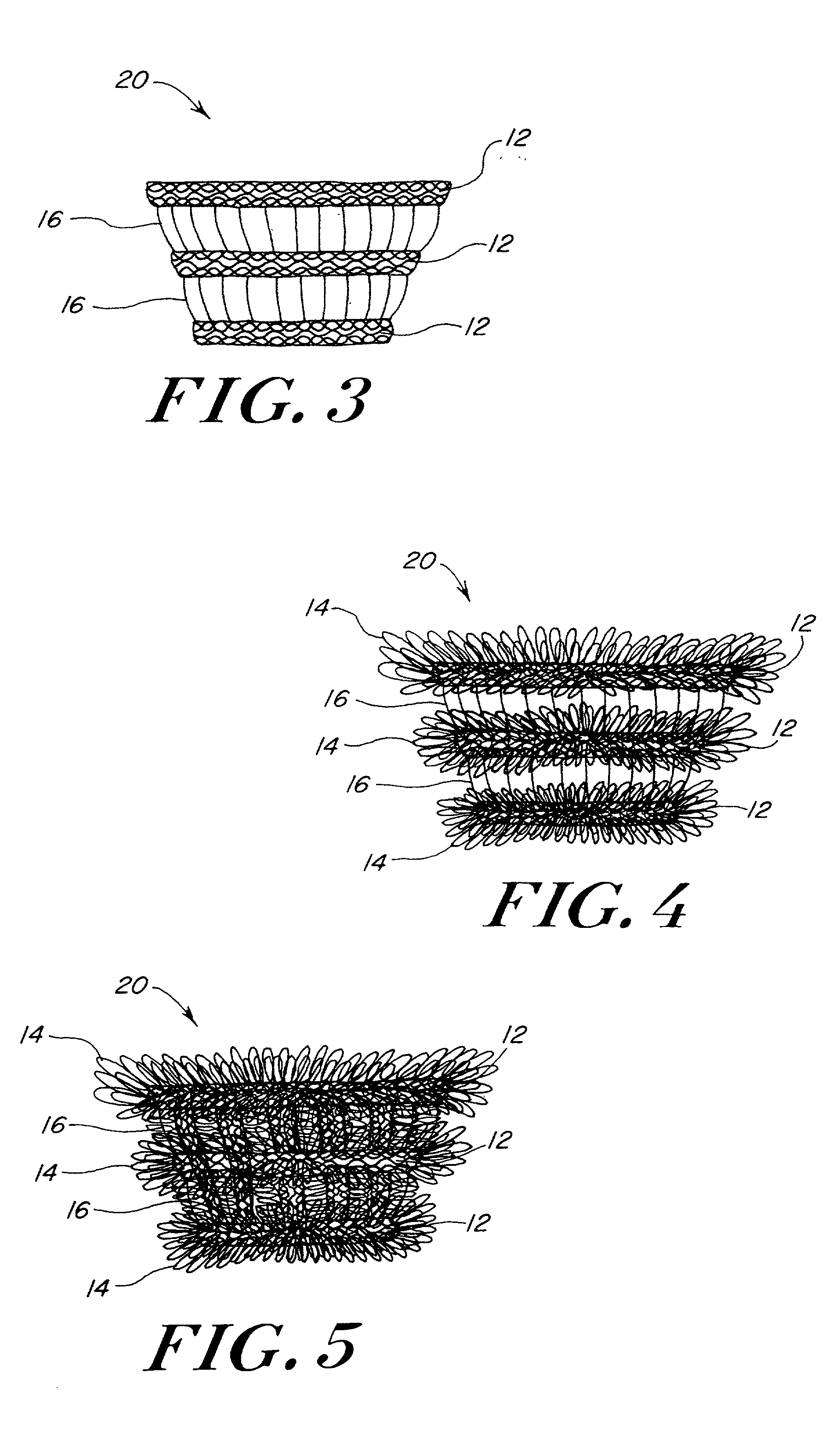
Pile mesh prosthesis
InactiveUS20020116070A1Add support structurePromoting rapid tissue in-growthWeft knittingWarp knittingRepair tissueProsthesis
A method and apparatus relating to a biocompatible soft tissue implant is disclosed. The implant, in the form of a prosthesis, is constructed of a knitted pile mesh material arranged into either a 3-dimensional structure or a planar shape or structure. The material or fabric includes a plurality of filament extensions projecting outwardly therefrom. The filament extensions can be radially projecting looping filaments from one or more rows of the knitted pile mesh material. The combination of the filament extensions with the 3-dimensional structure results in the biocompatible implant having a structural resistance to hinder anticipated crushing forces applied to the implant, and also provide a suitable 3-dimensional structure for promoting rapid tissue in-growth to anchor such implant without migration and strengthen the repaired tissue area.
Owner:ATRIUM MEDICAL
Device and method for treatment of wounds with nitric oxide
InactiveUS7122018B2Promote wound healingReduce the burden onBiocideOther blood circulation devicesHigh concentrationNitric oxide gas
Topical exposure of nitric oxide gas to wounds such as chronic non-healing wounds may be beneficial in promoting healing and preparing the wound bed for further treatment and recovery. Nitric oxide gas may be used to reduce the microbial infection, manage exudates secretion by reducing inflammation, upregulate expression of endogenous collagenase to locally debride the wound, and regulate the formation of collagen. High concentration of nitric oxide ranging from 160–400 ppm may be used without inducing toxicity in the healthy cells around a wound site. Exposure to the high concentration for a first treatment period reduces the microbial burden and inflammation, and increases collagenase expression to debride necrotic tissue at the wound site. After a first treatment period, a second treatment period at a lower concentration of nitric oxide, preferably ranging from 5–20 ppm may be used to restore the balance of nitric oxide and induce collagen expression aiding in the wound closure.
Owner:SENSORMEDICS +1
Compositions and methods for treatment of eye disorders
The present invention provides compounds and methods for the treatment of LFA-1 mediated diseases. In particular, LFA-1 antagonists are described herein and these antagonists are used in the treatment of LFA-1 mediated diseases. One aspect of the invention provides for diagnosis of an LFA-1 mediated disease and administration of a LFA-1 antagonist, after the patient is diagnosed with a LFA-1 mediated disease. In some embodiments, the LFA-1 mediated diseases treated are dry eye disorders. Also provided herein are methods for identifying compounds which are LFA-1 antagonists.
Owner:NOVARTIS PHARM CORP
Methods of neuroprotection using neuroprotective steroids and a vitamin d
InactiveUS20110306579A1Inhibiting neurodegenerationPromote physical recoveryBiocideOrganic active ingredientsNervous systemProgesterones
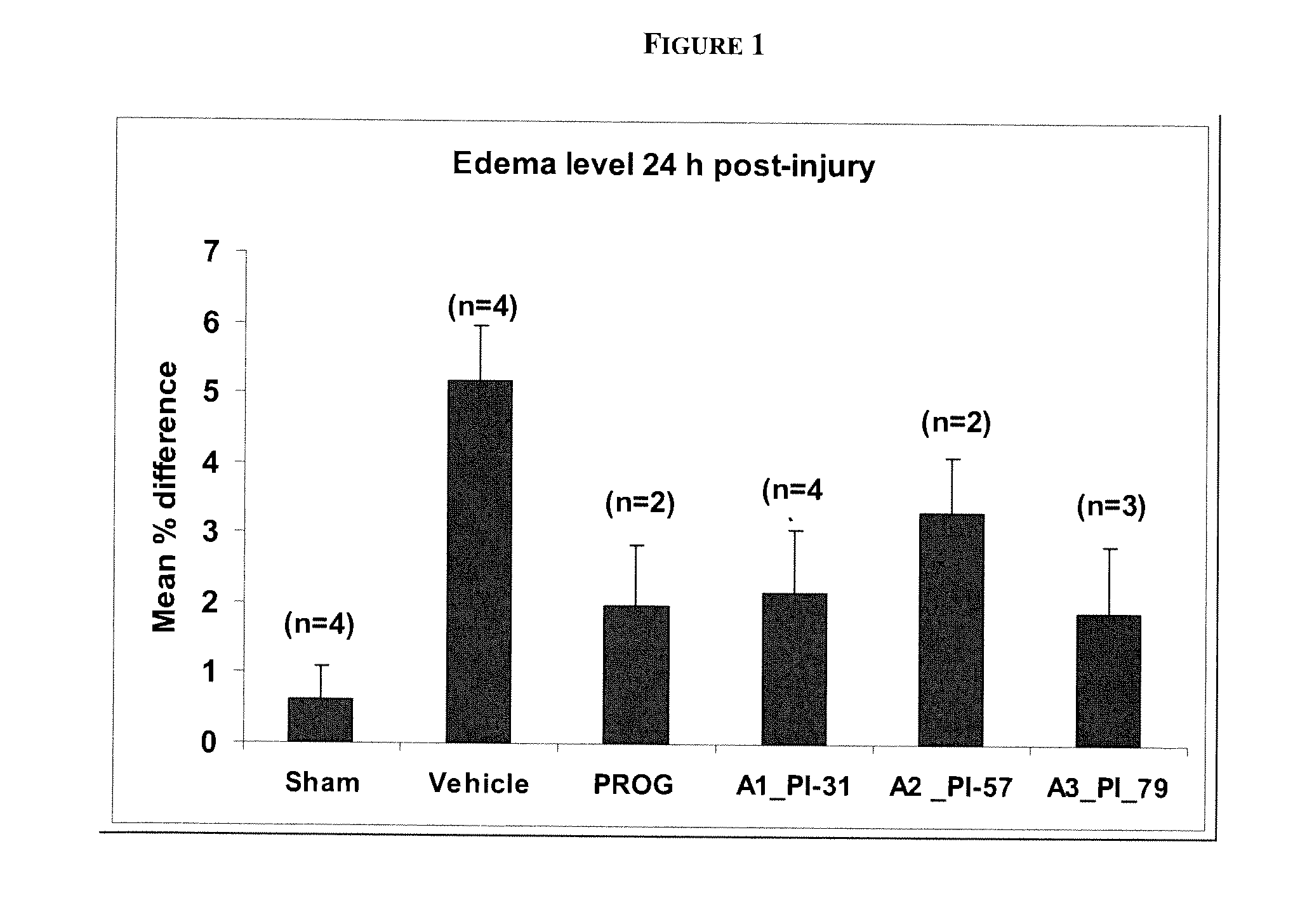
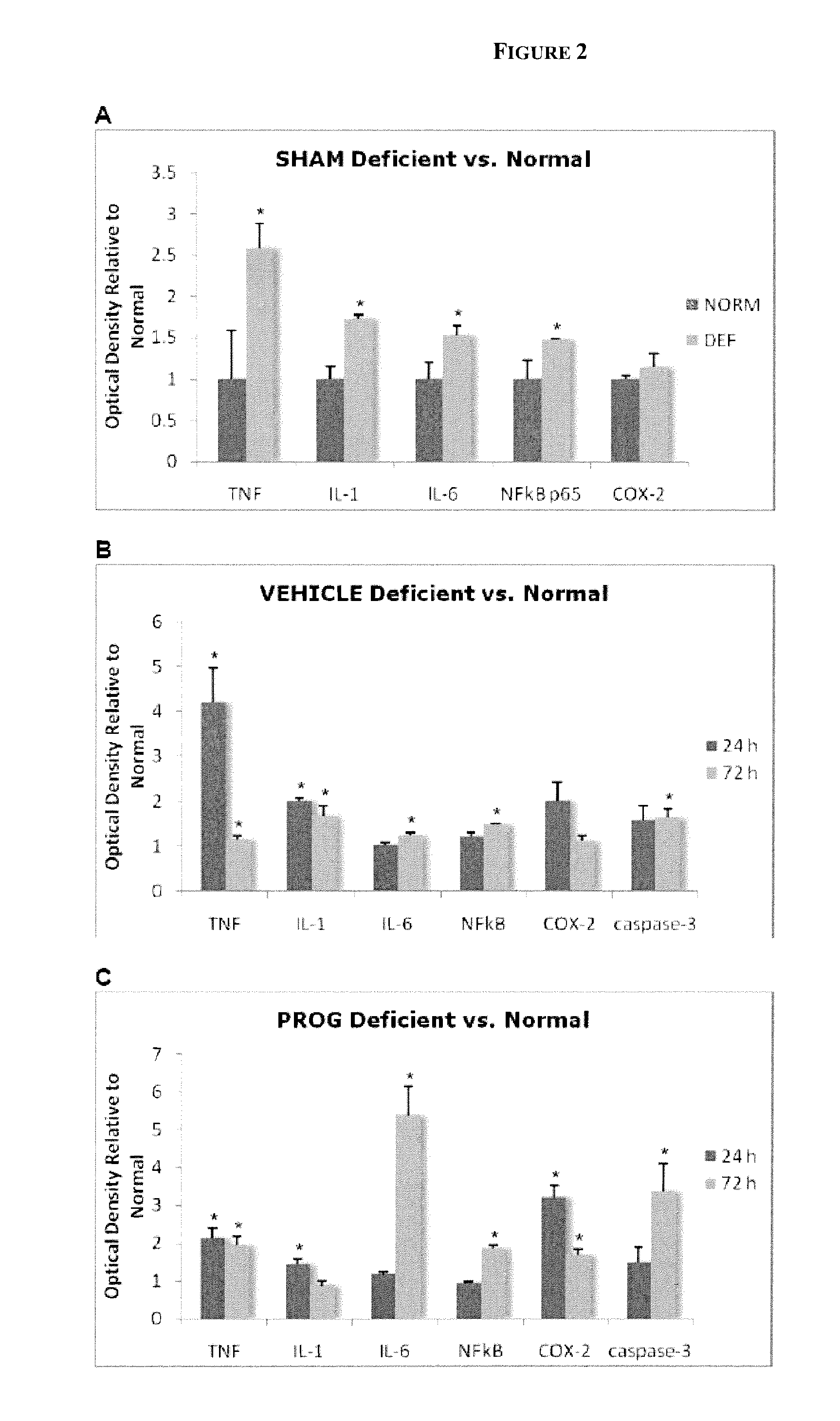
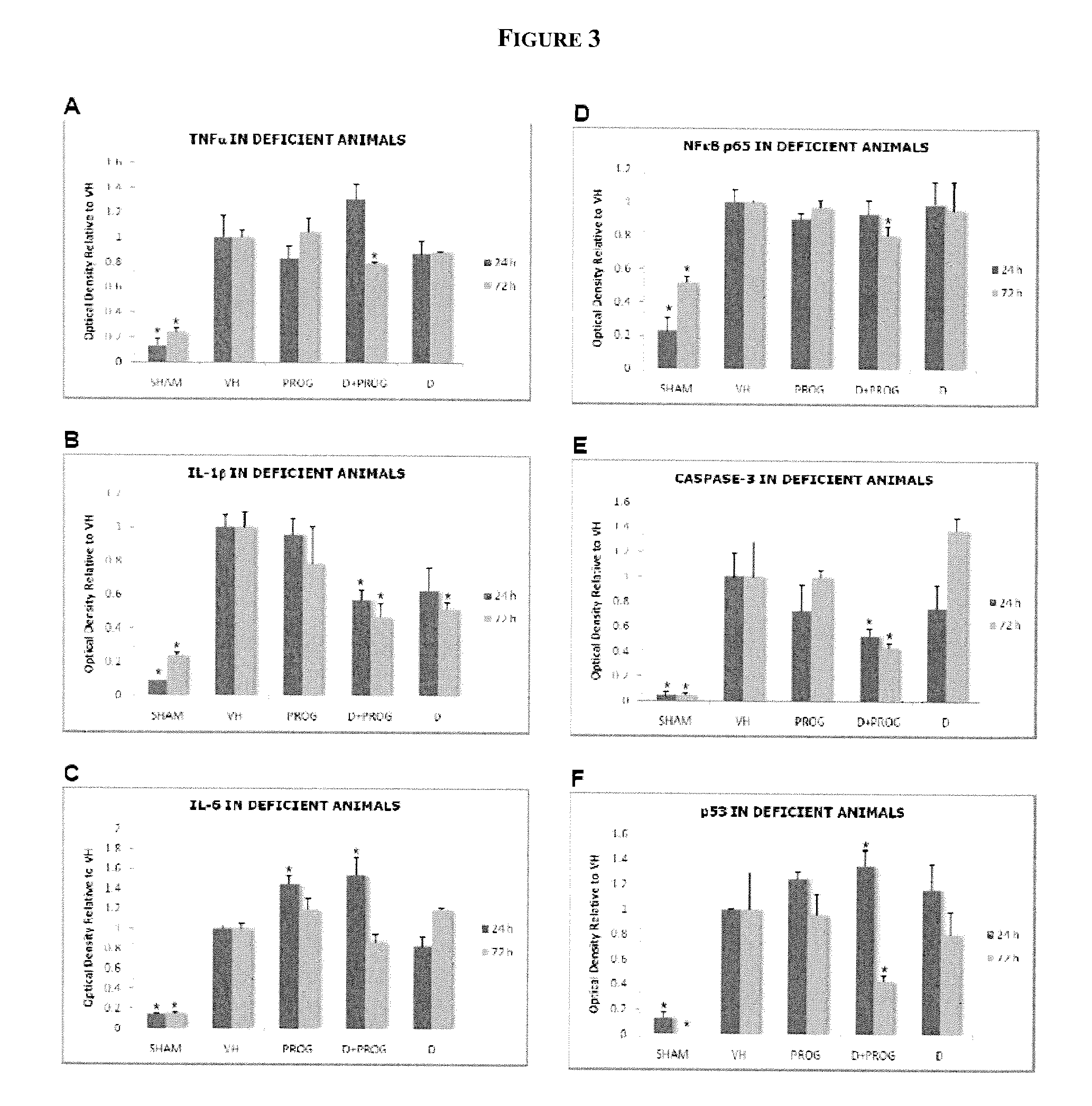
Described herein are compositions and methods for treating or preventing nervous system injury. In particular, the methods and compositions relate to the use of at least one neuroprotective steroid, such as progesterone, and vitamin D.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com