Patents
Literature
153 results about "Denervation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
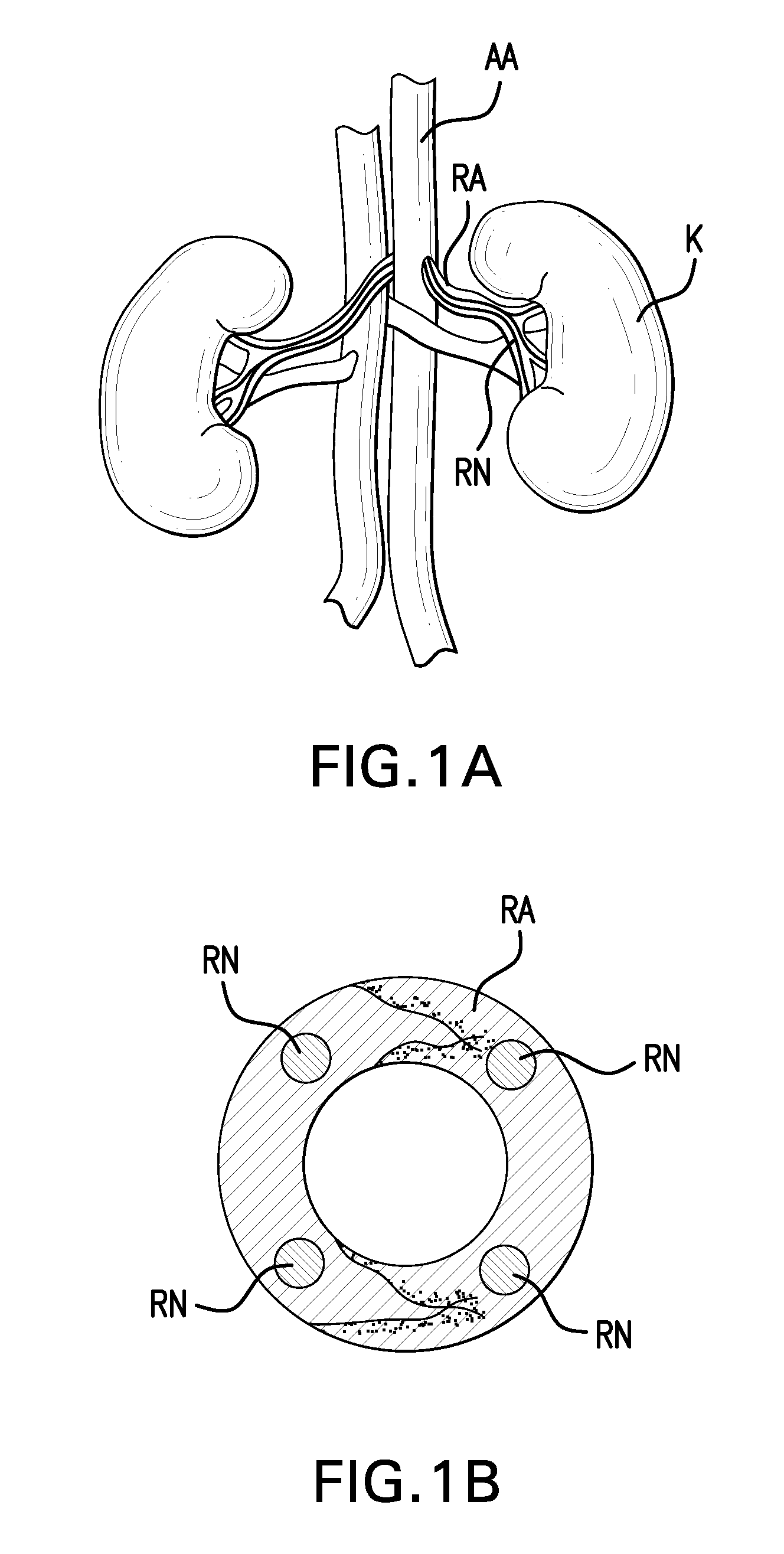
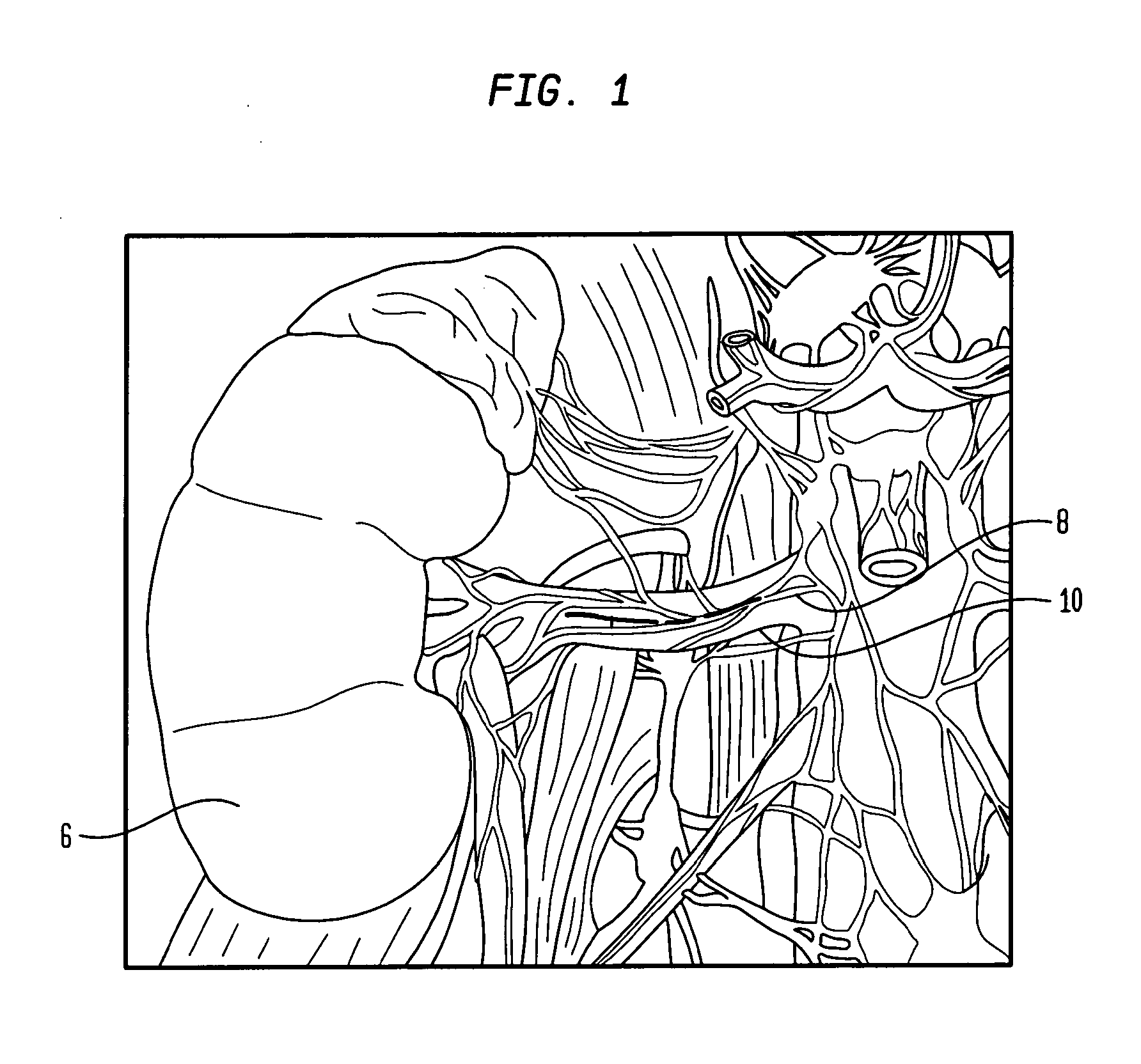
Denervation is any loss of nerve supply regardless of the cause. If the nerves lost to denervation are part of the neuronal communication to a specific function in the body then altered or a loss of physiological functioning can occur. Denervation can be caused by injury or be a symptom of a disorder like ALS and post-polio syndrome. Additionally, it can be a useful surgical technique to alleviate major negative symptoms, such as in renal denervation. Denervation can have many harmful side effects such as increased risk of infection and tissue dysfunction.
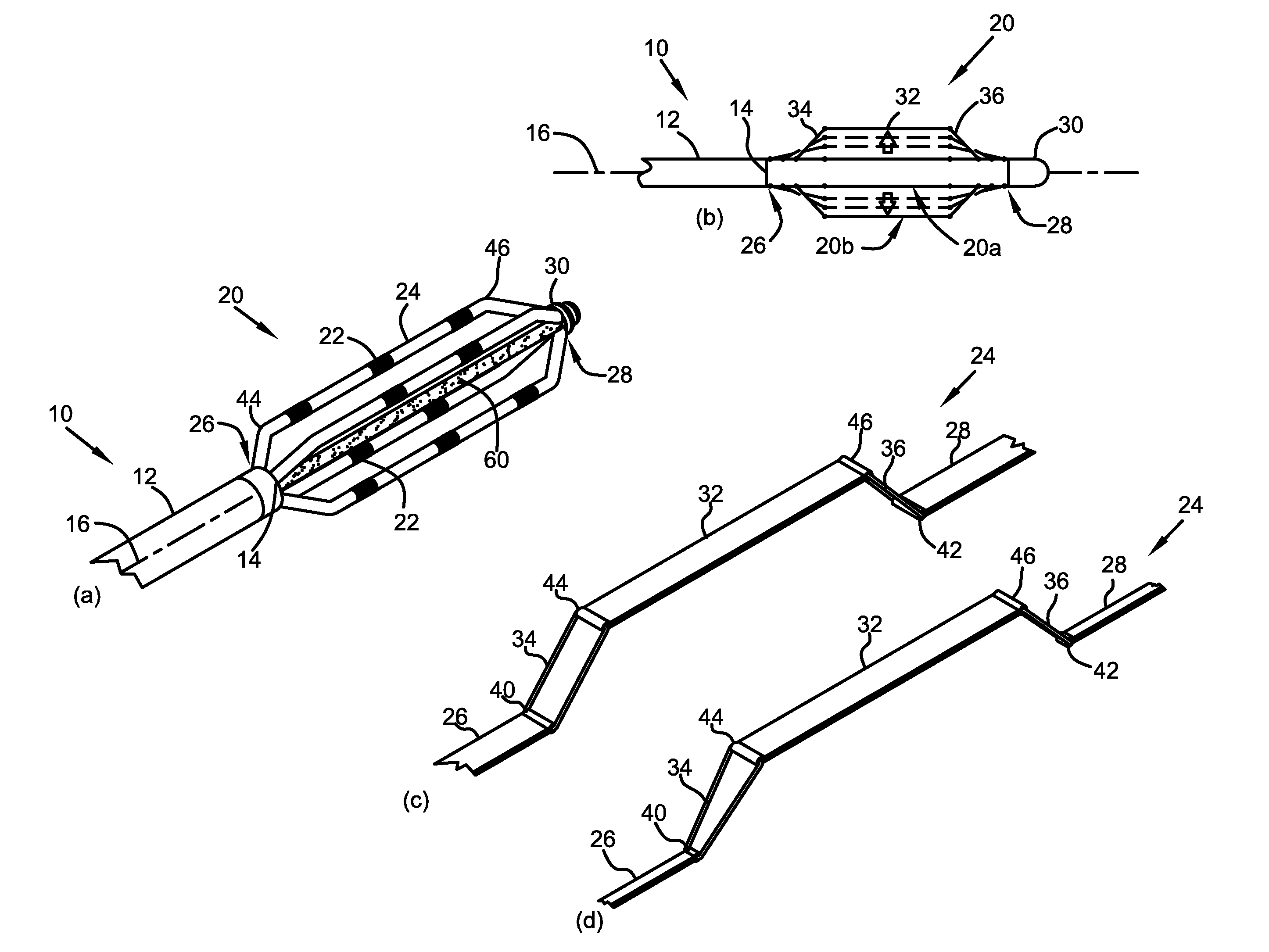
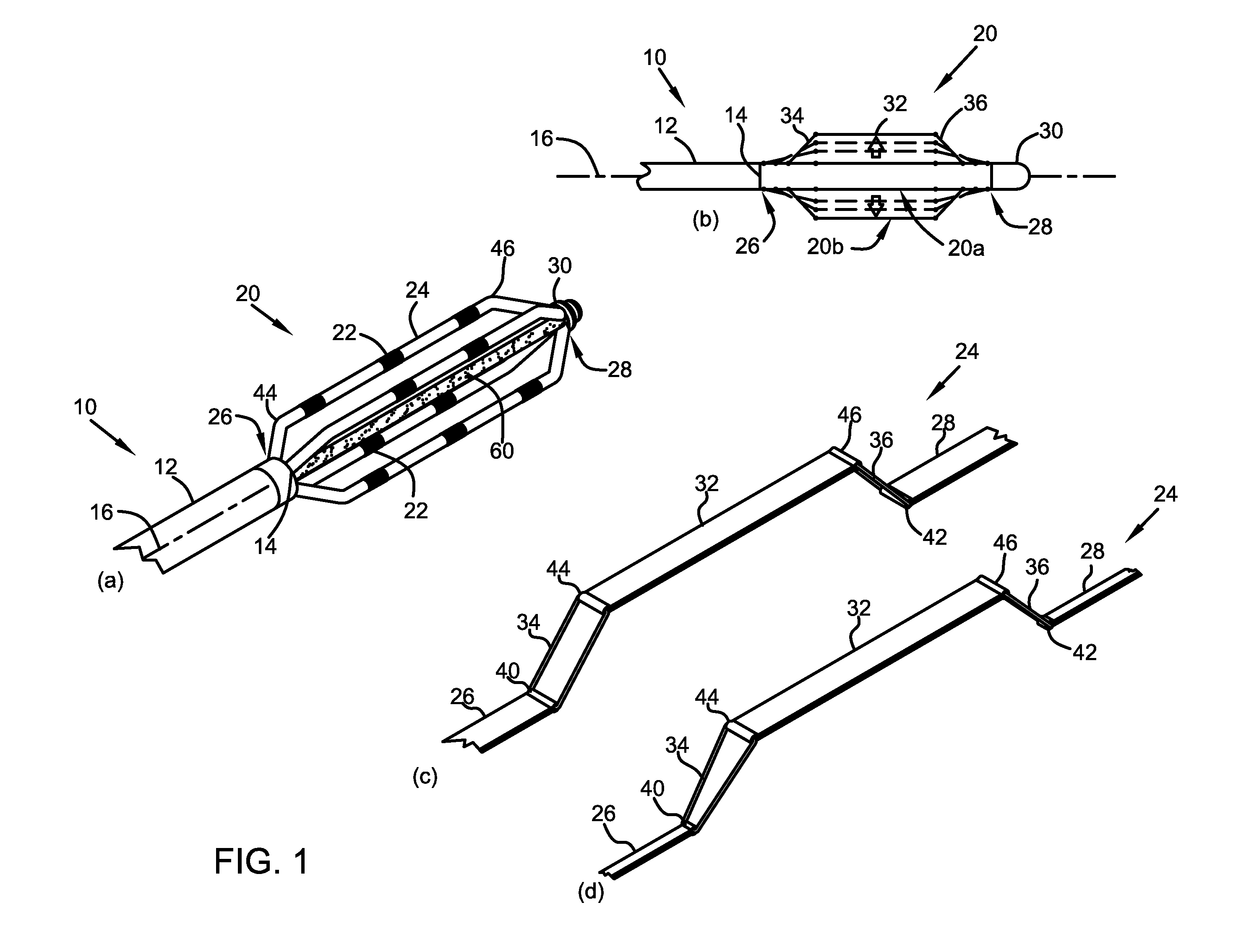
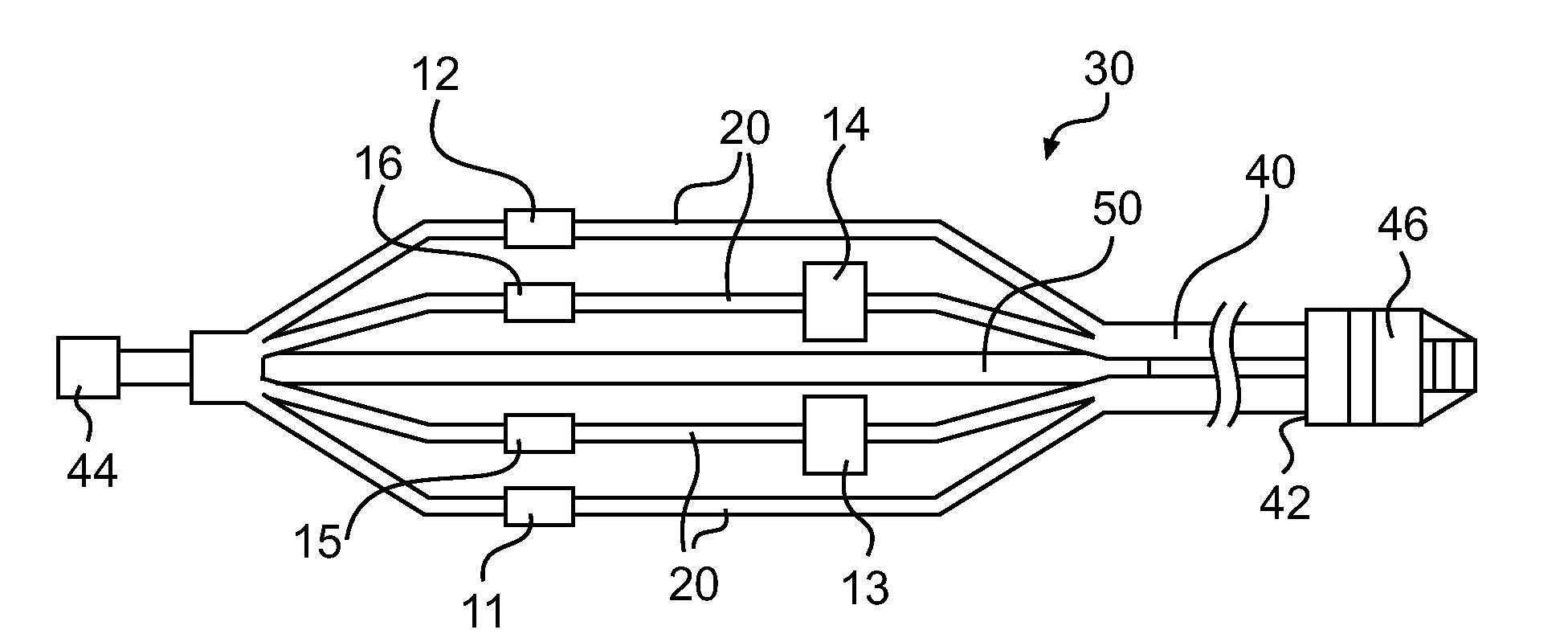
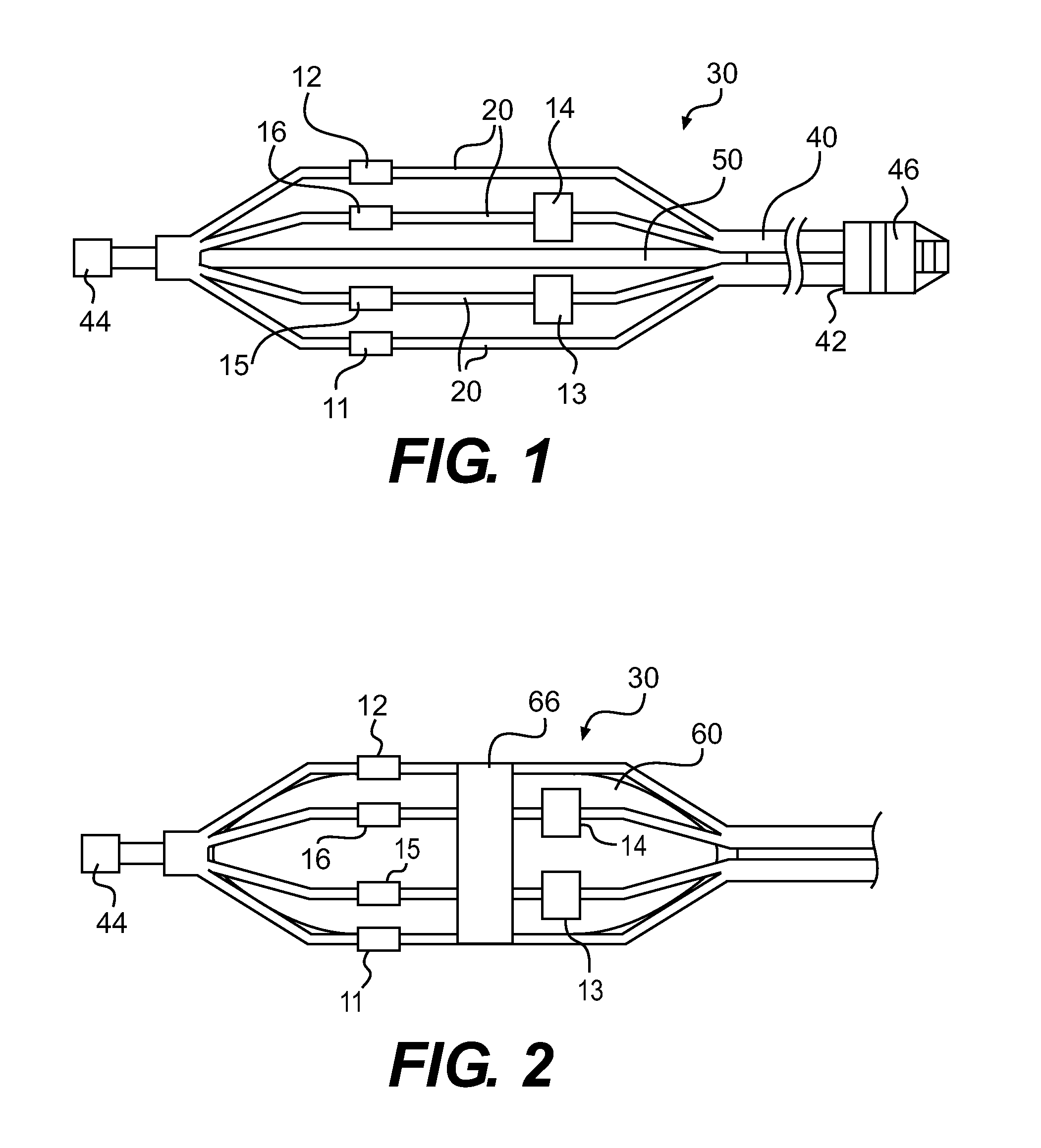
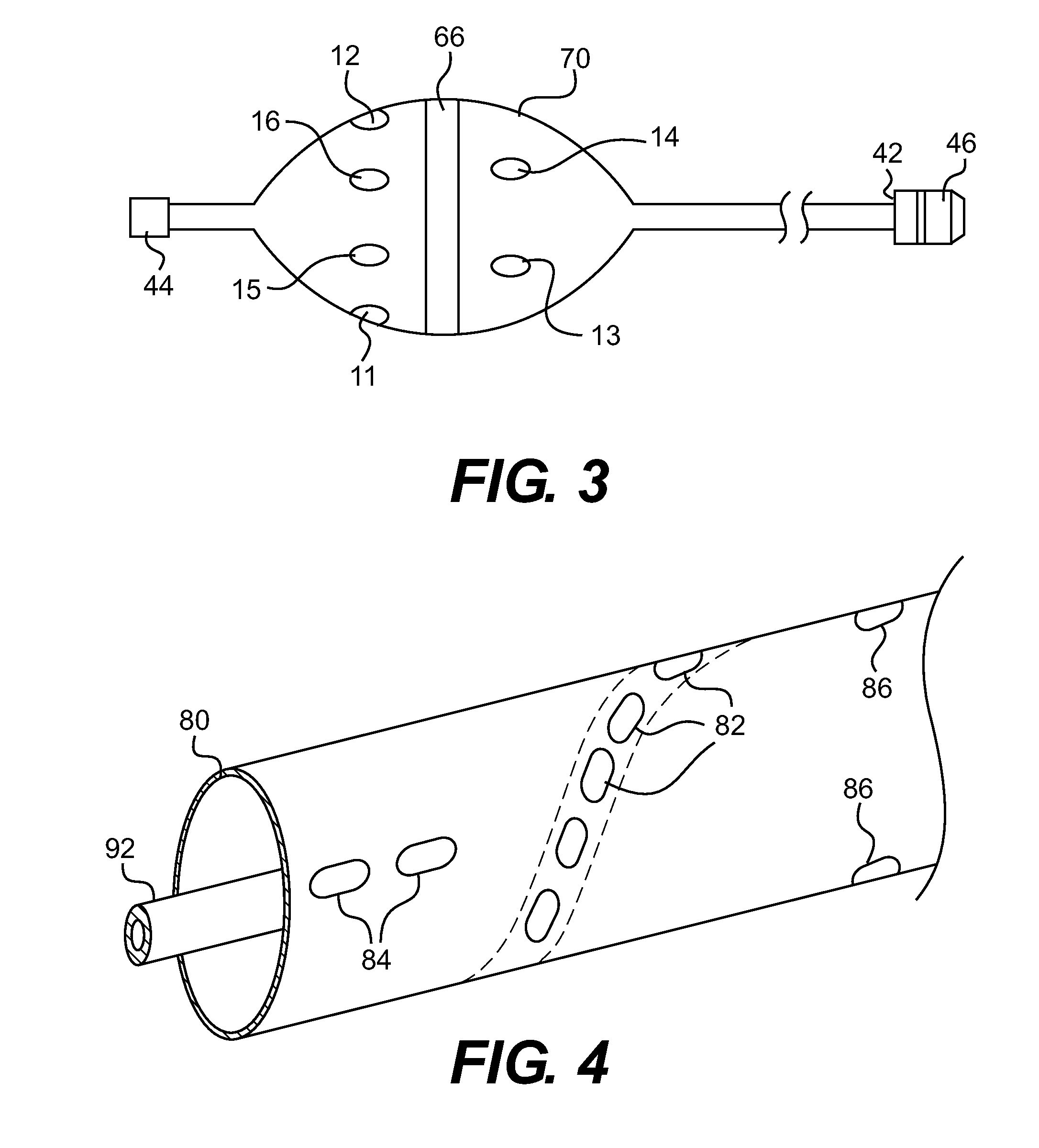
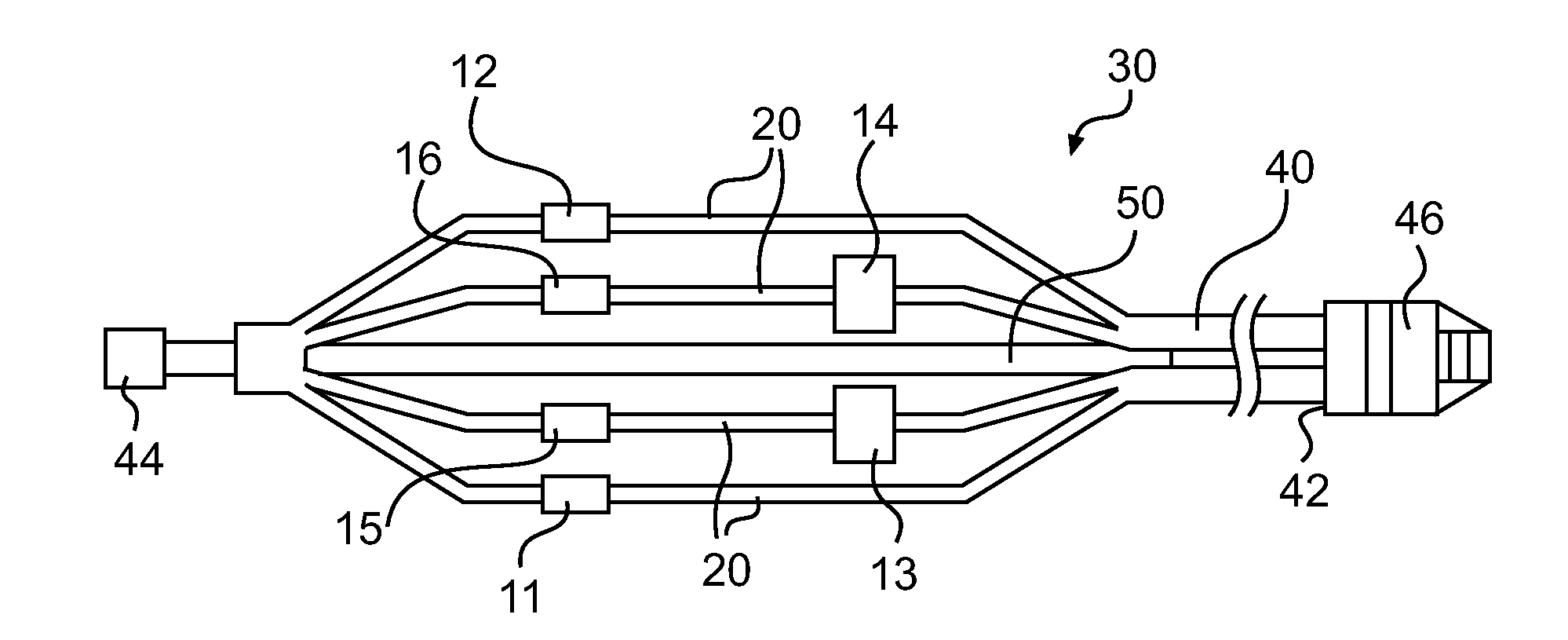
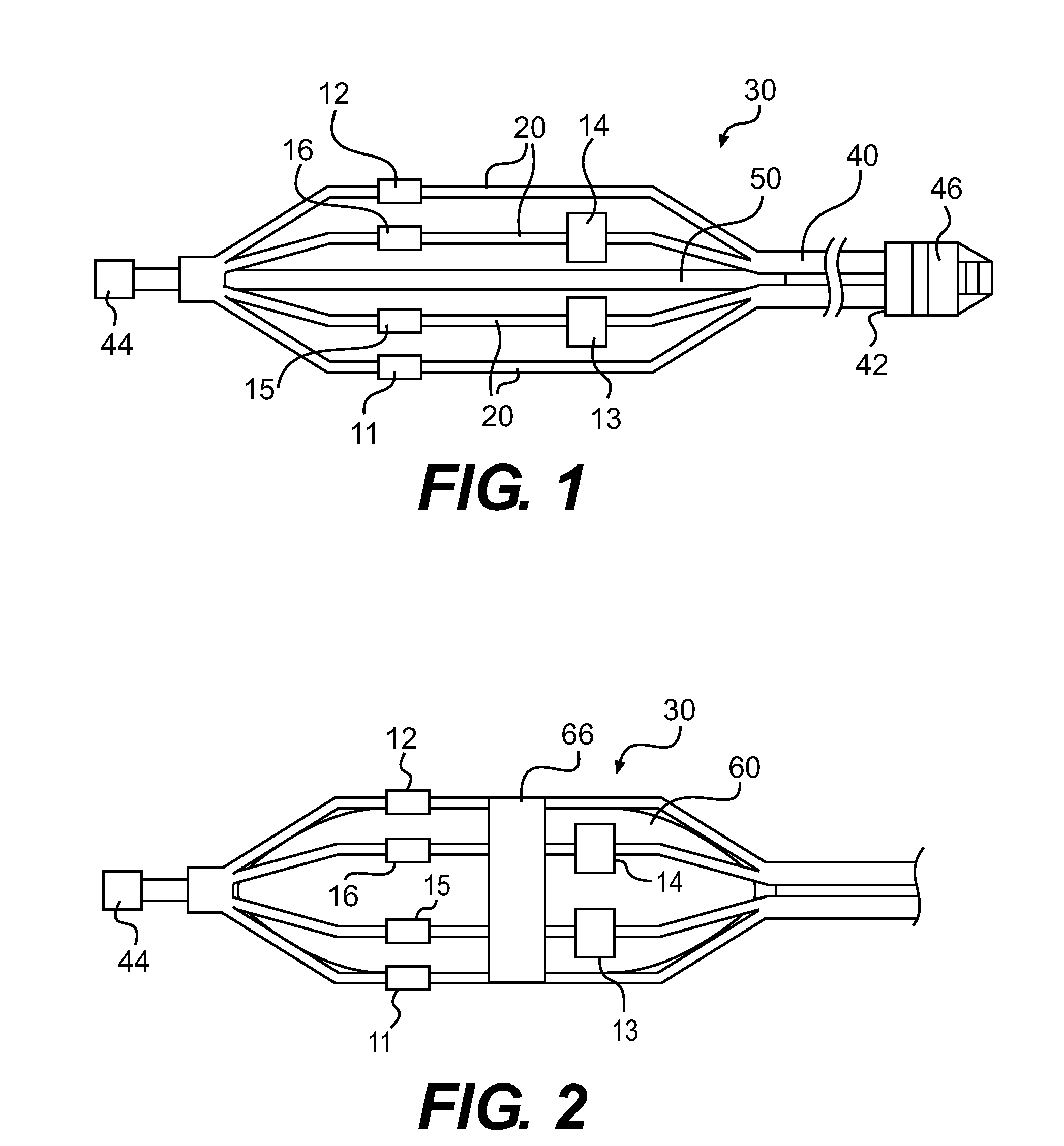
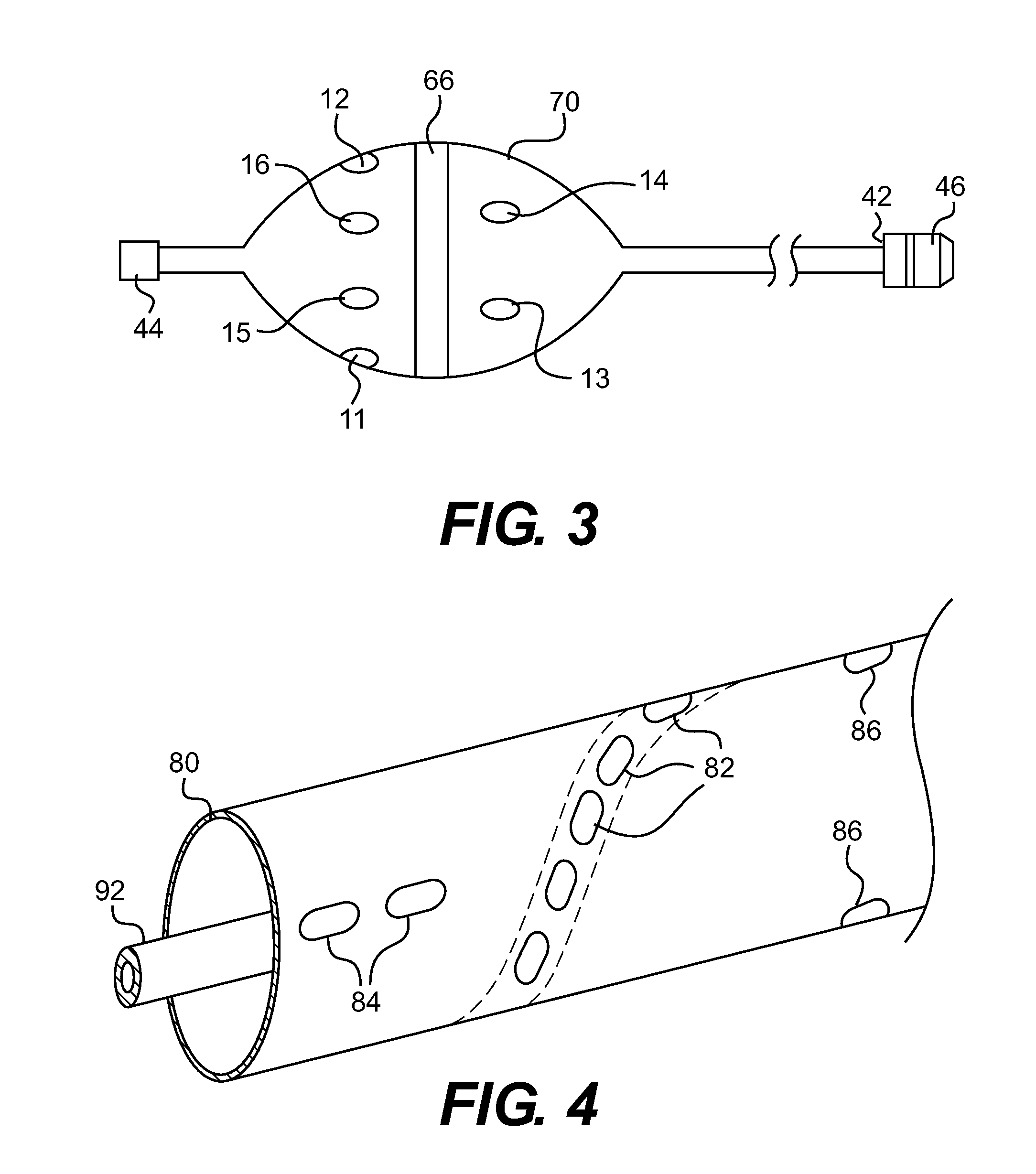
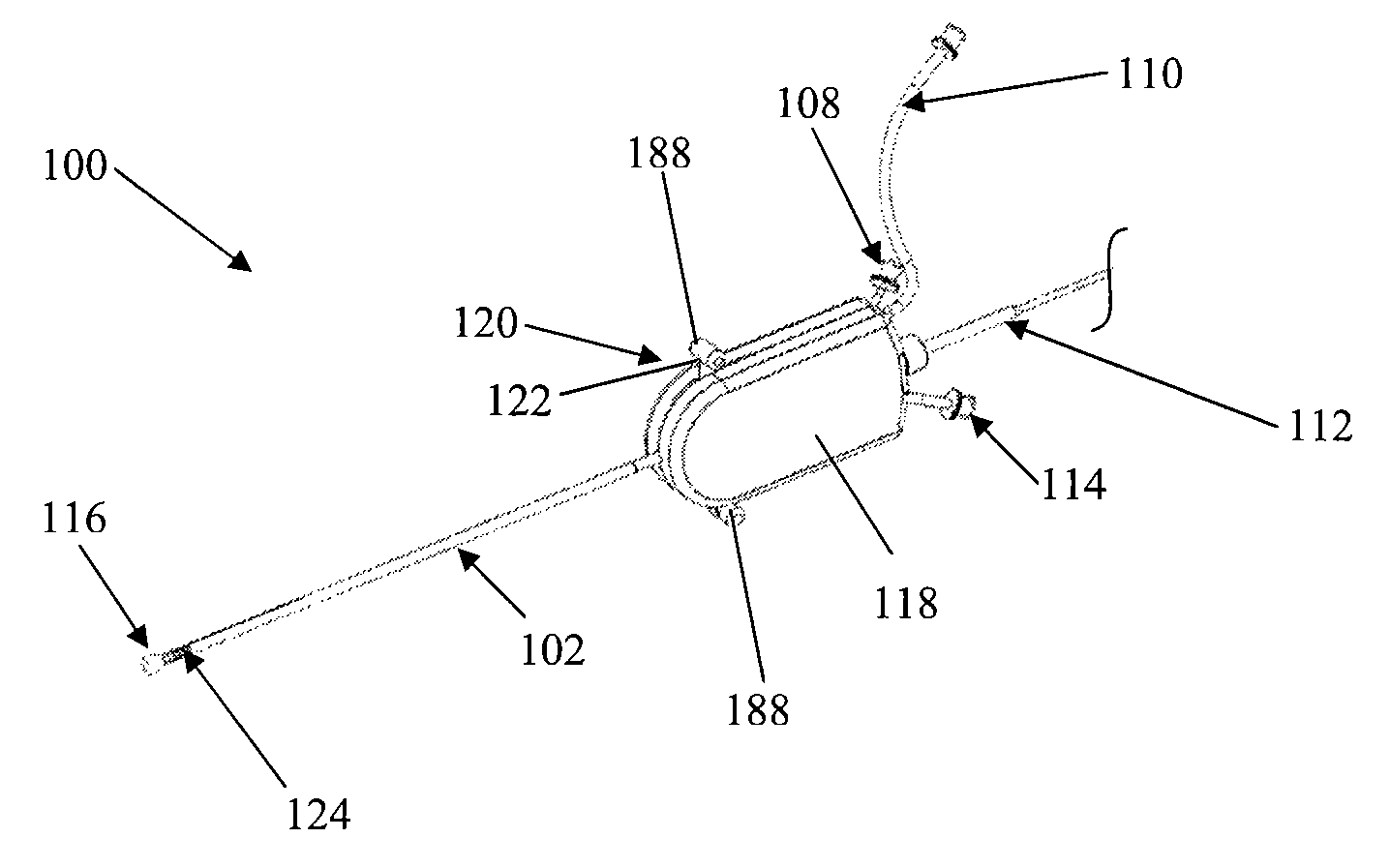
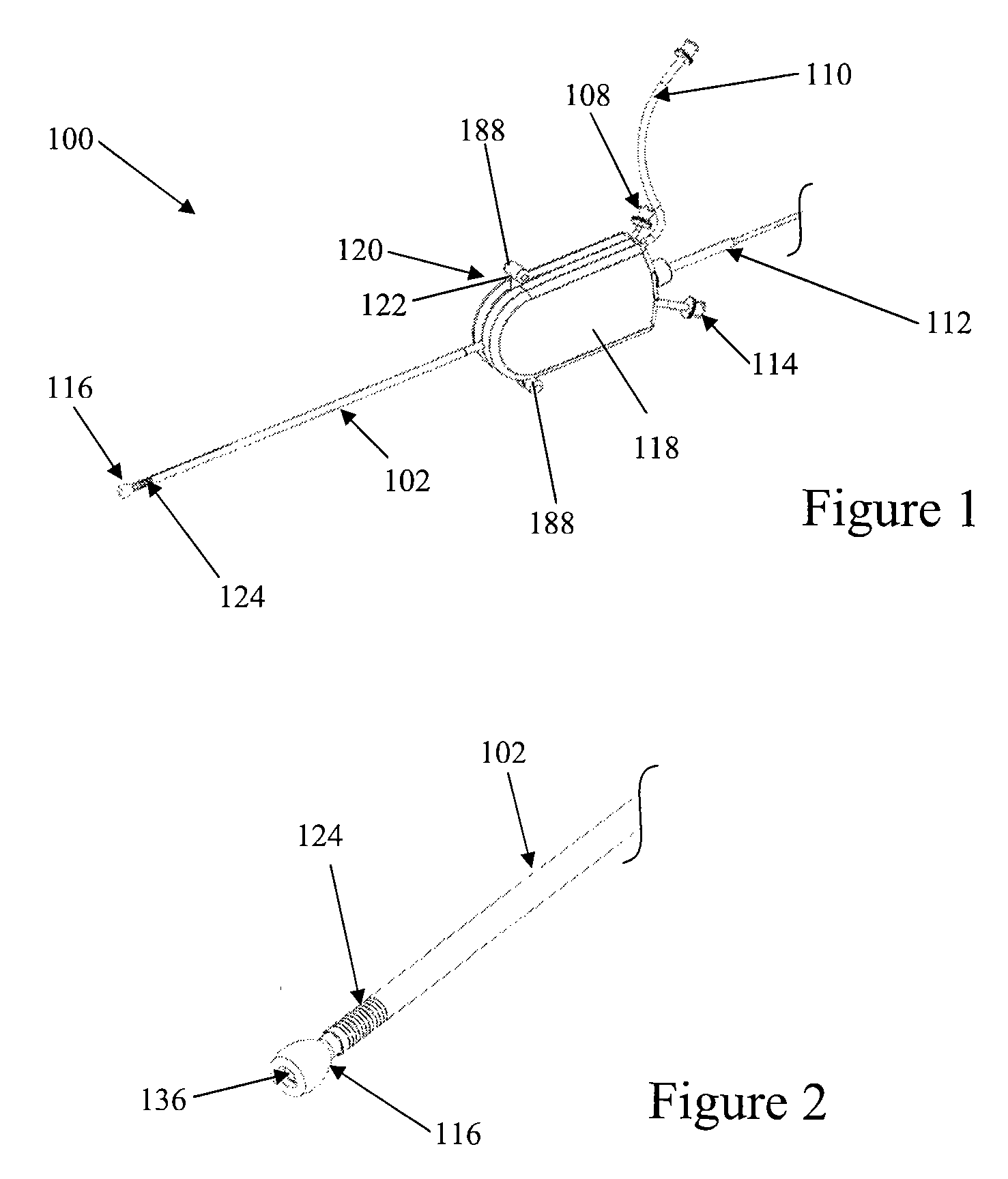
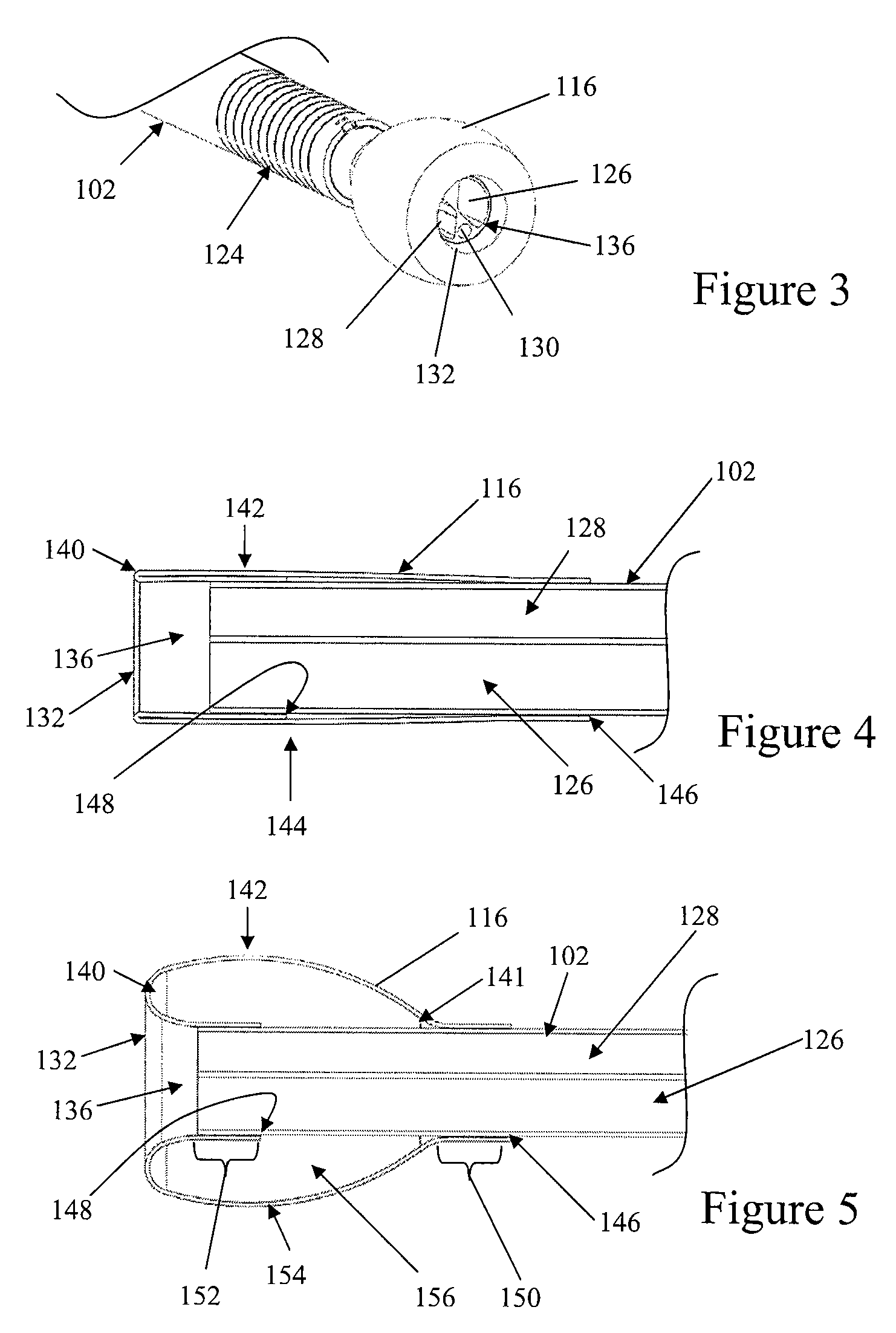
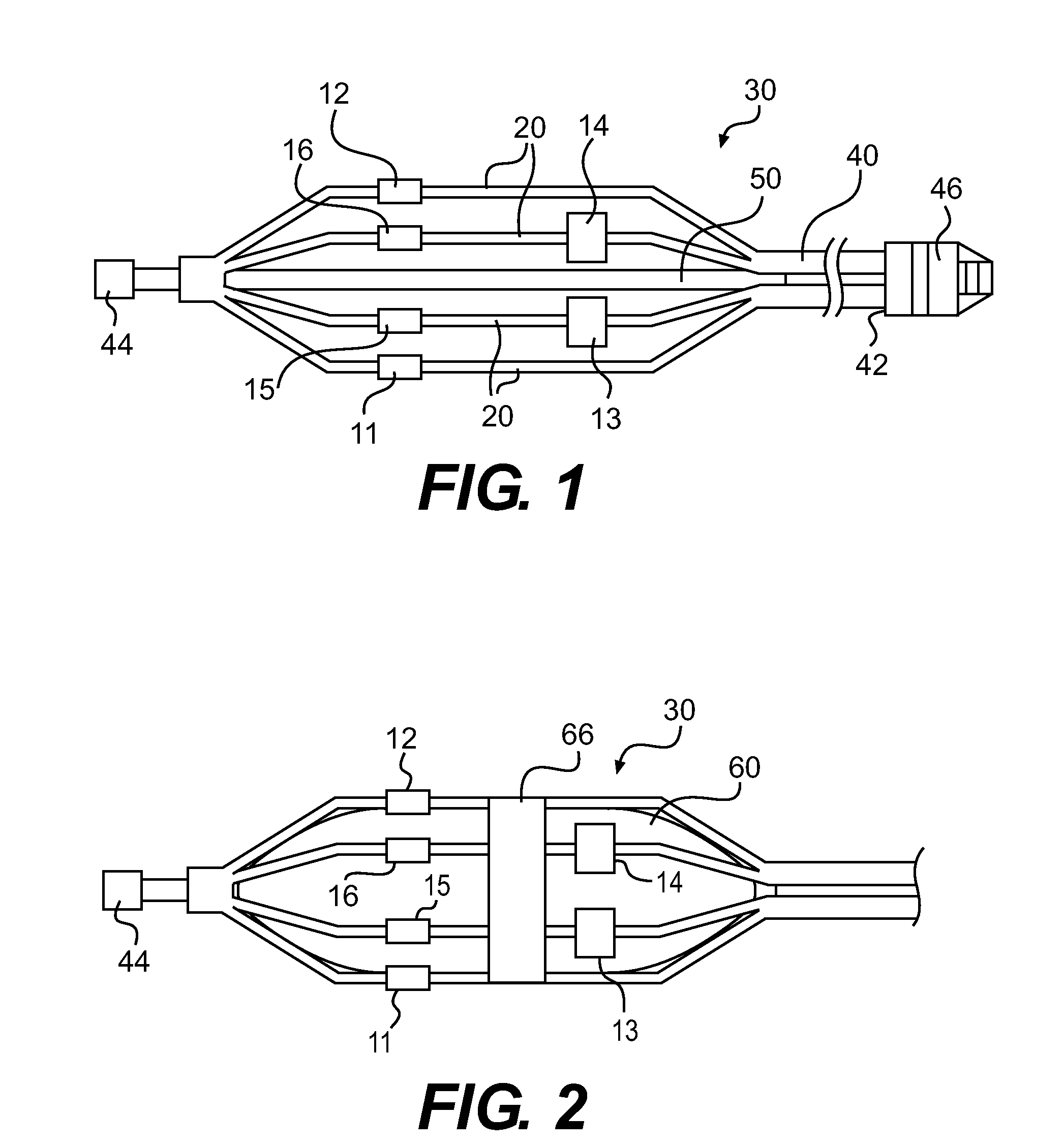
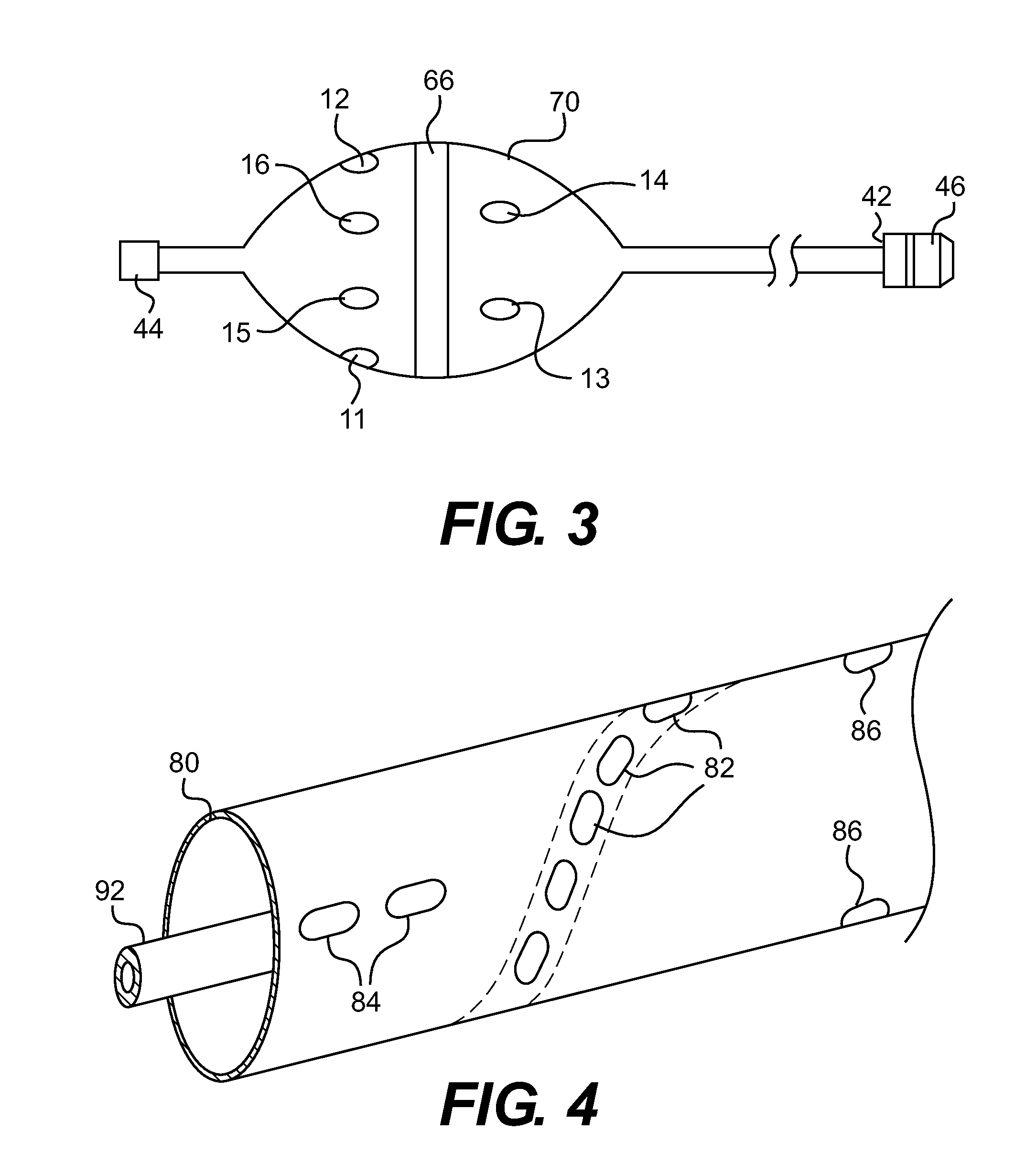
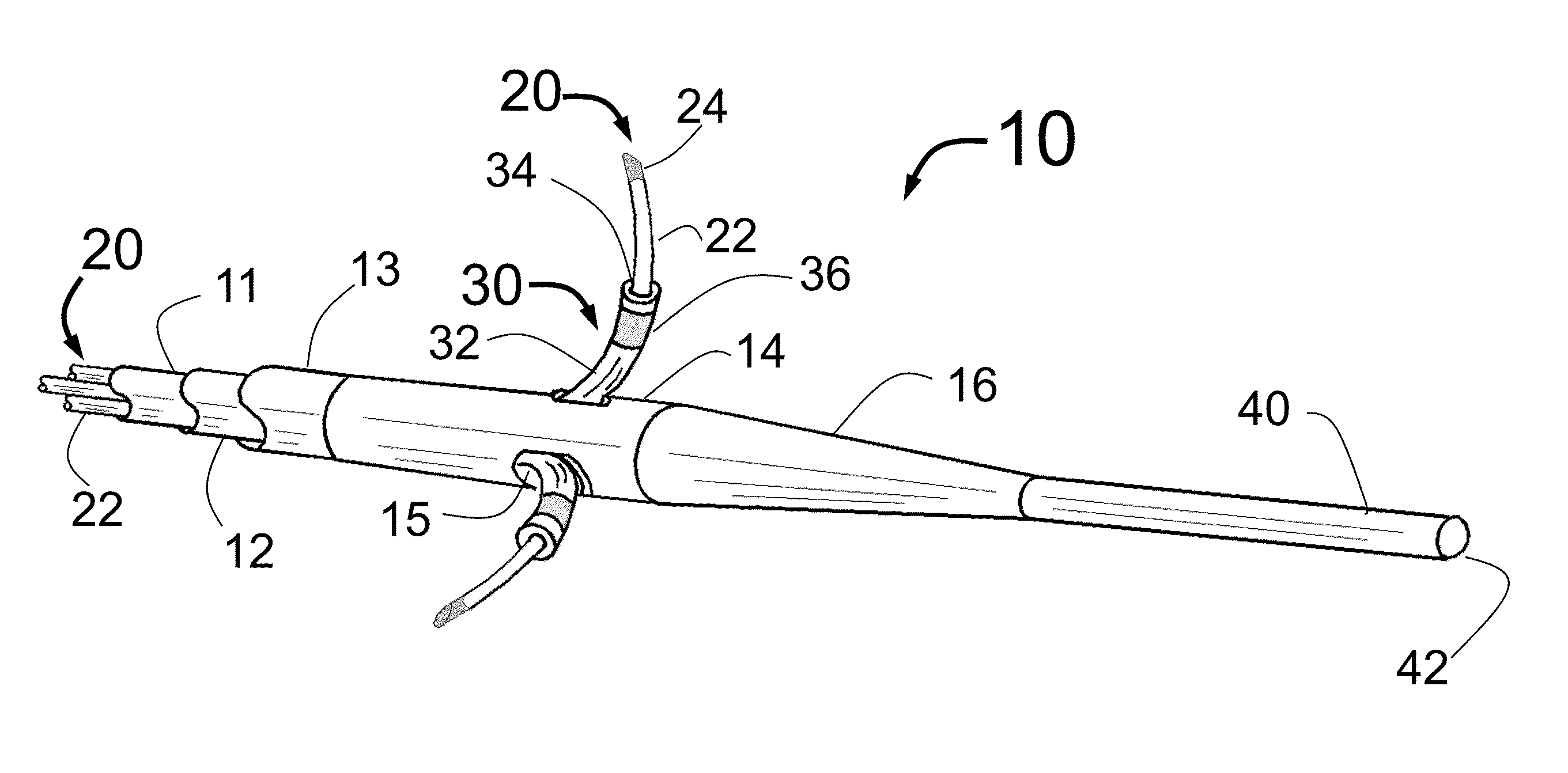
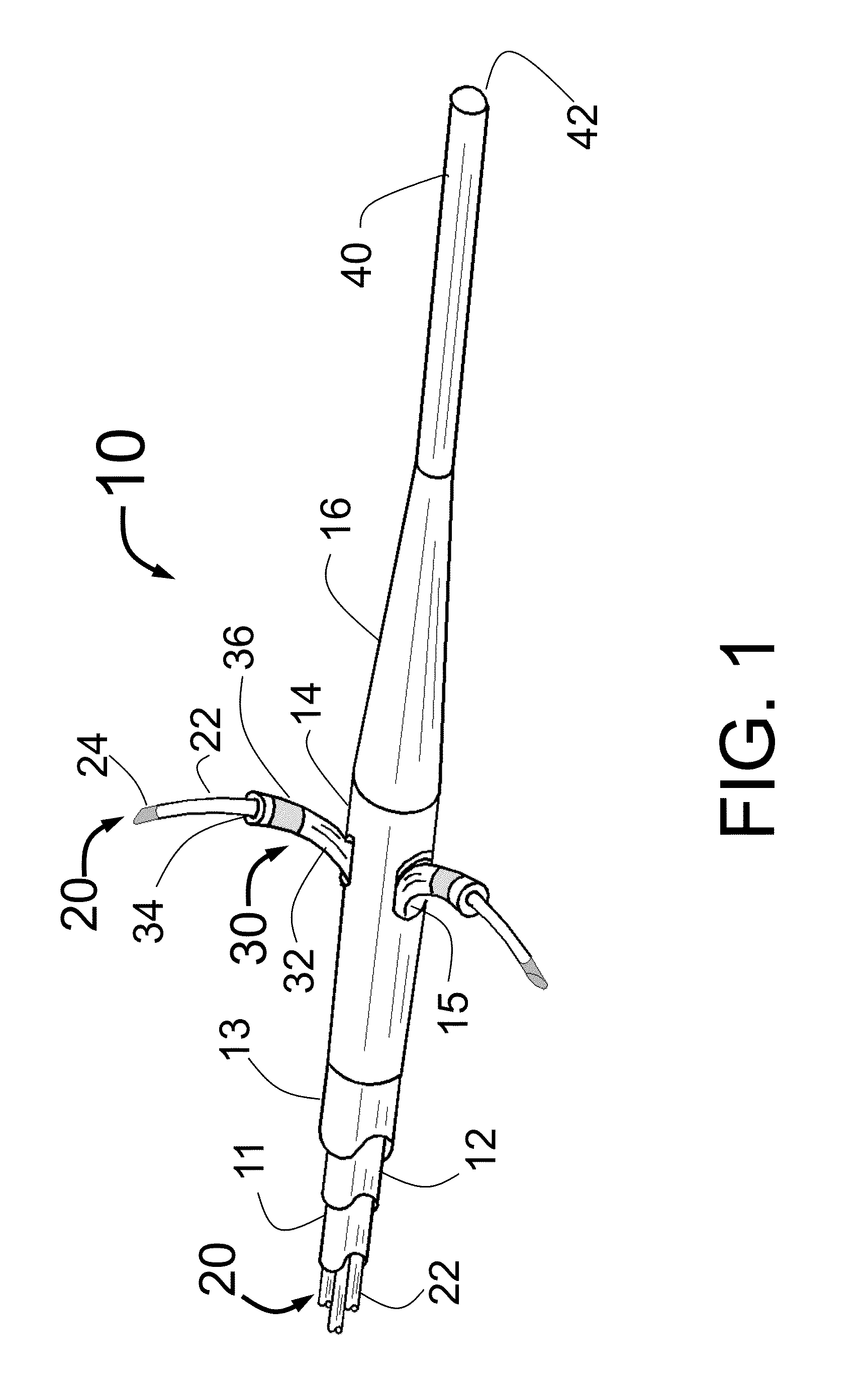
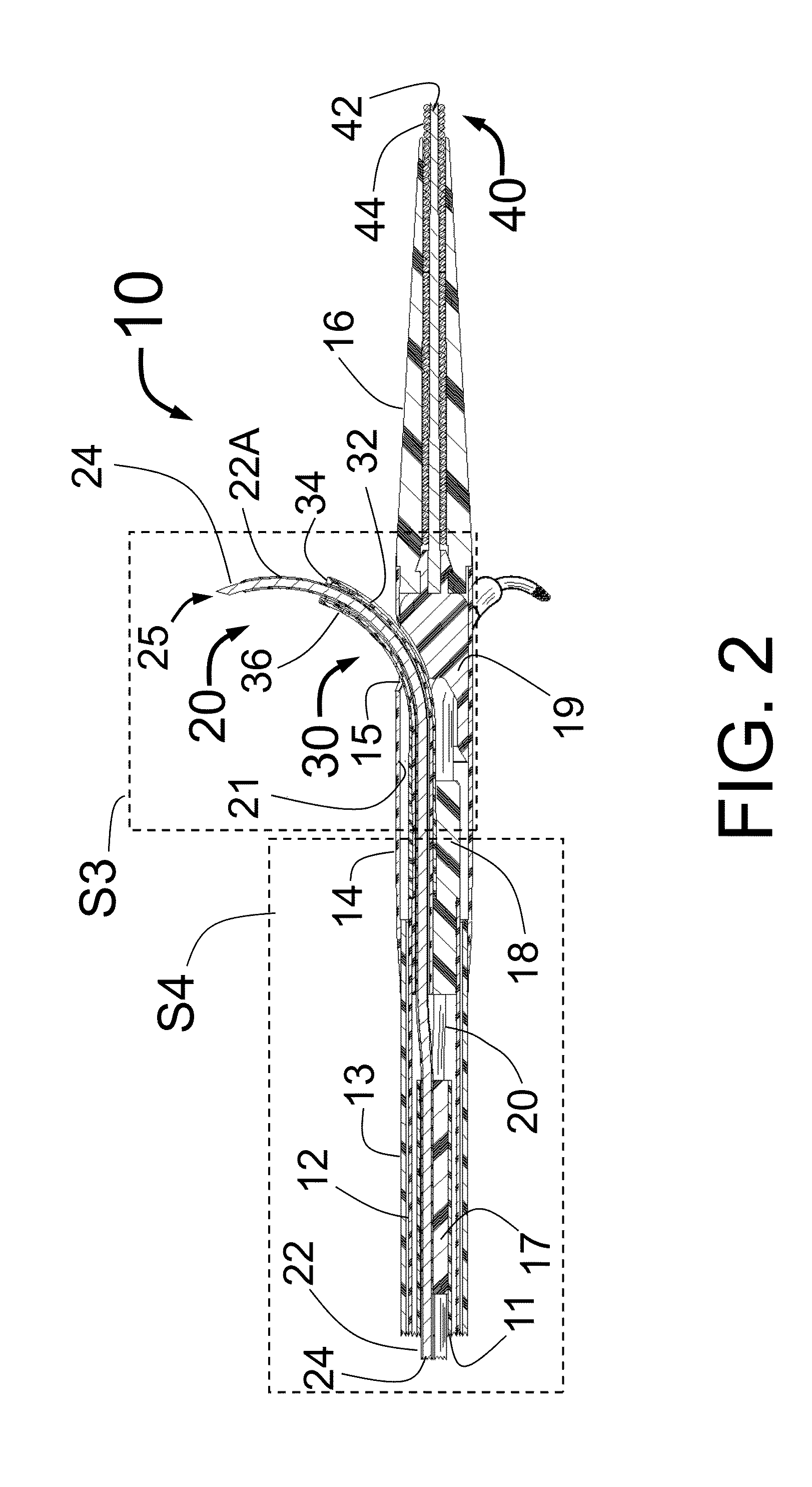
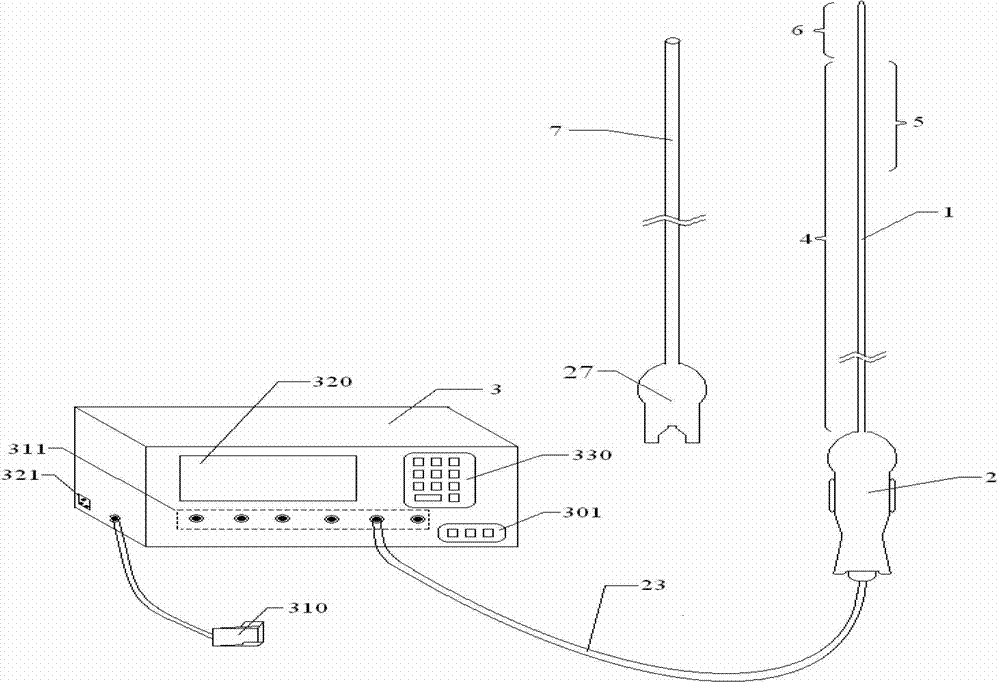
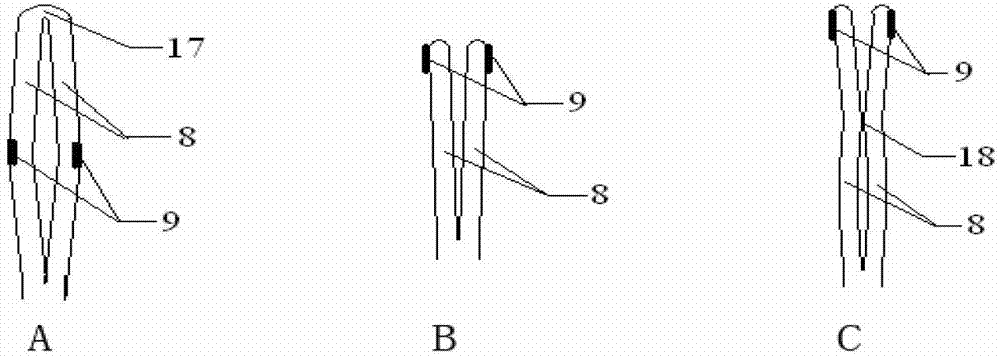
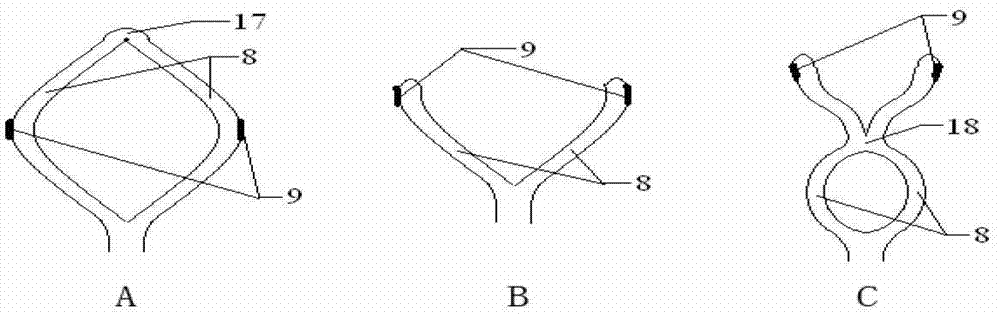
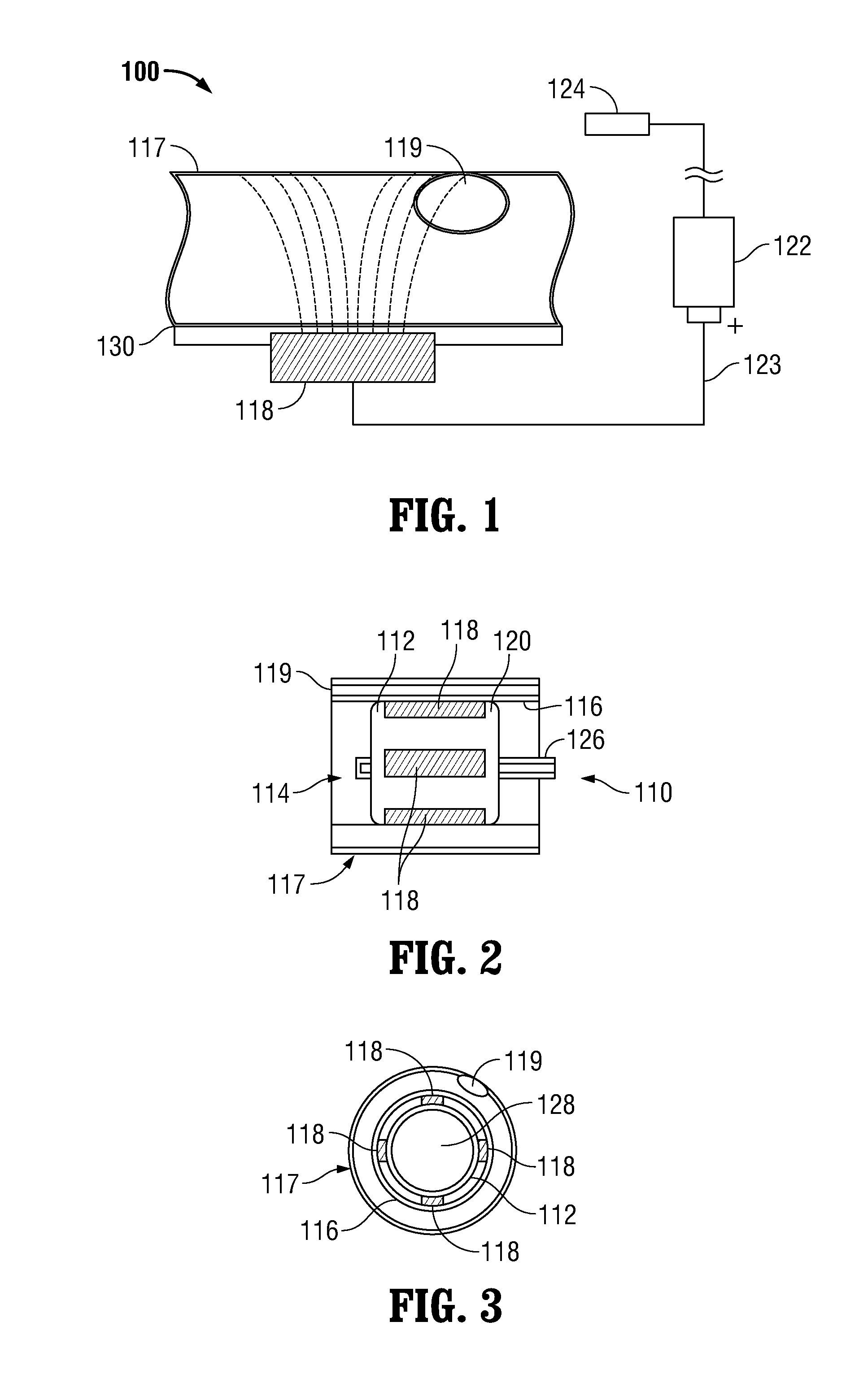
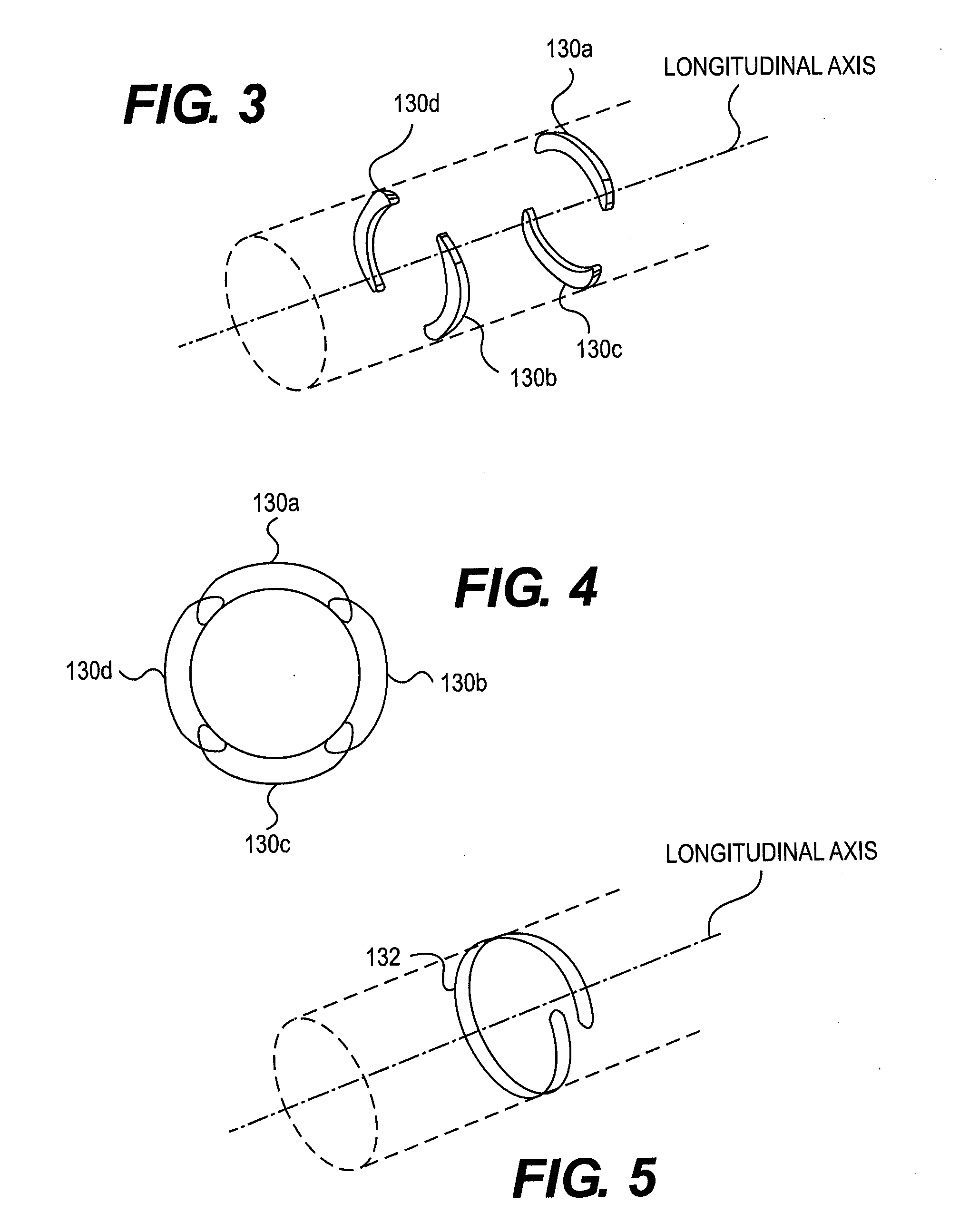
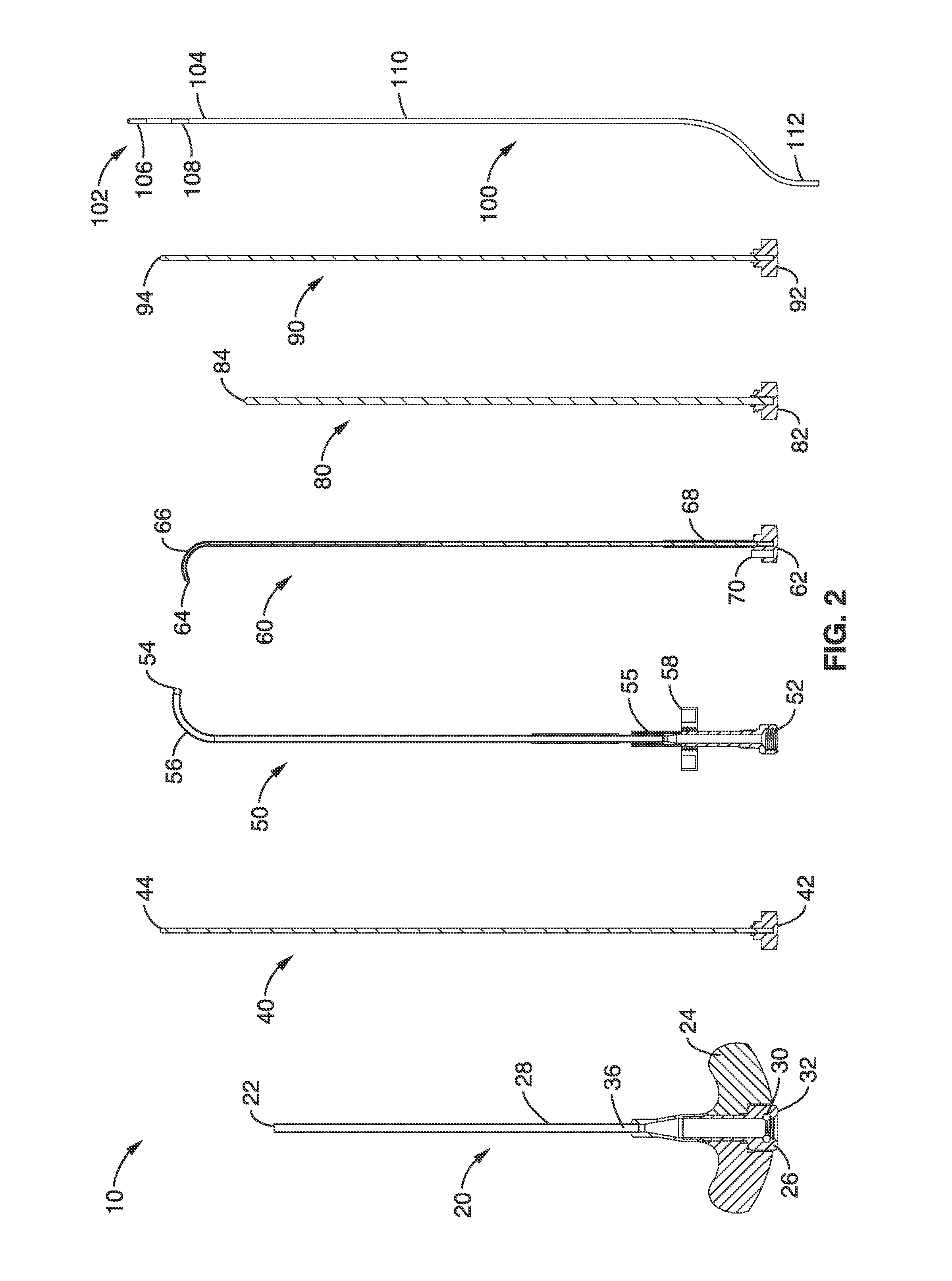
Assembly of staggered ablation elements
ActiveUS20110118726A1Reducing and eliminating riskSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for irrigation of substancesVeinClosed loop
An ablation catheter comprises a catheter body extending longitudinally between a proximal end and a distal end along a longitudinal axis; and an ablation element assembly comprising ablation elements connected to the catheter body, each ablation element to be energized to produce an ablation zone. The ablation elements are distributed in a staggered configuration such that the ablation zones of the ablation elements span one or more open arc segments around the longitudinal axis, but the ablation zones of all ablation elements projected longitudinally onto any lateral plane which is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis span a substantially closed loop around the longitudinal axis. Since the ablation zones do not form a closed loop, the risk of renal artery / vein stenosis is reduced or eliminated. Since the ablation zones of all ablation elements projected longitudinally onto any lateral plane span a substantially closed loop, substantially complete renal denervation is achieved.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
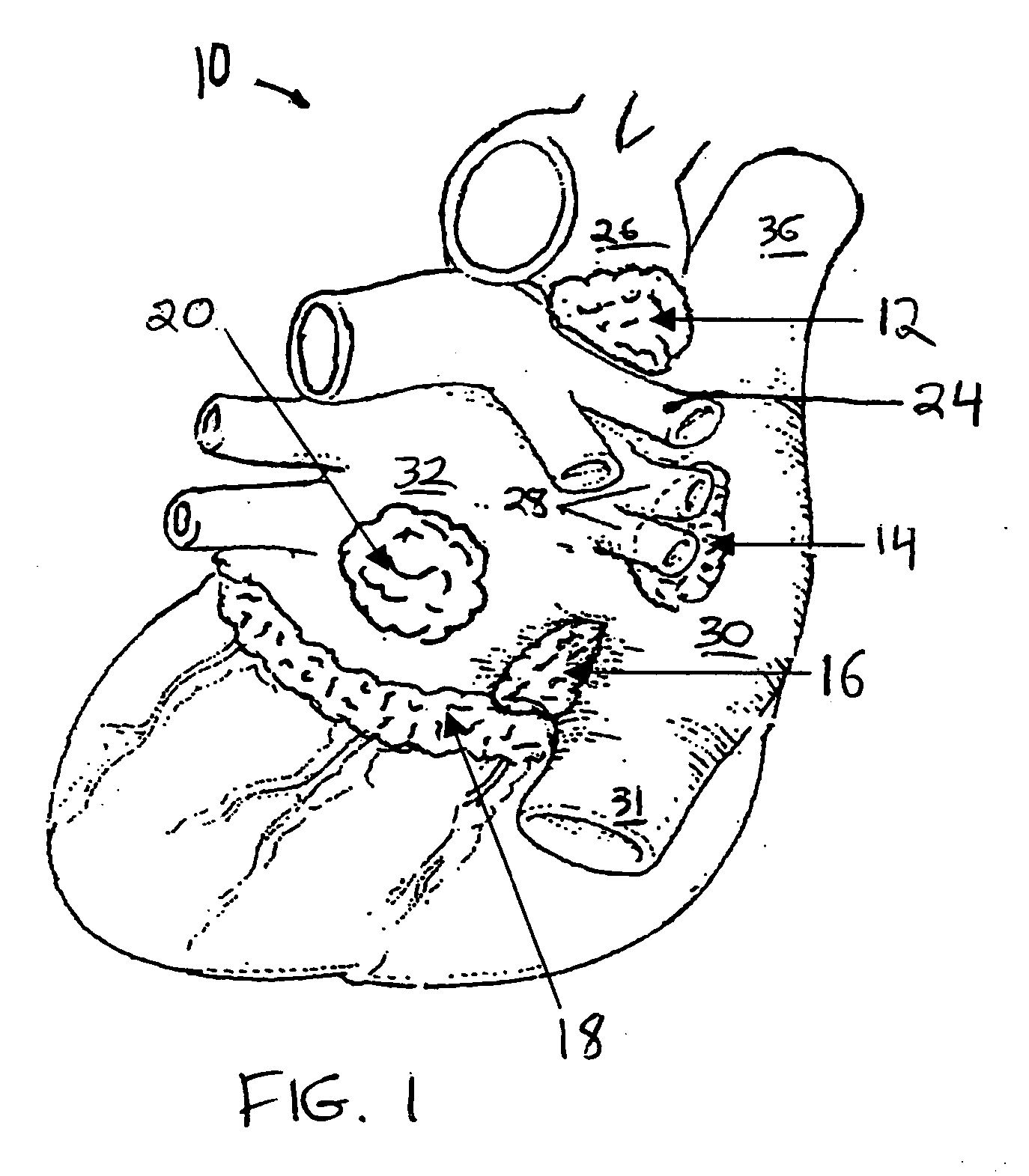
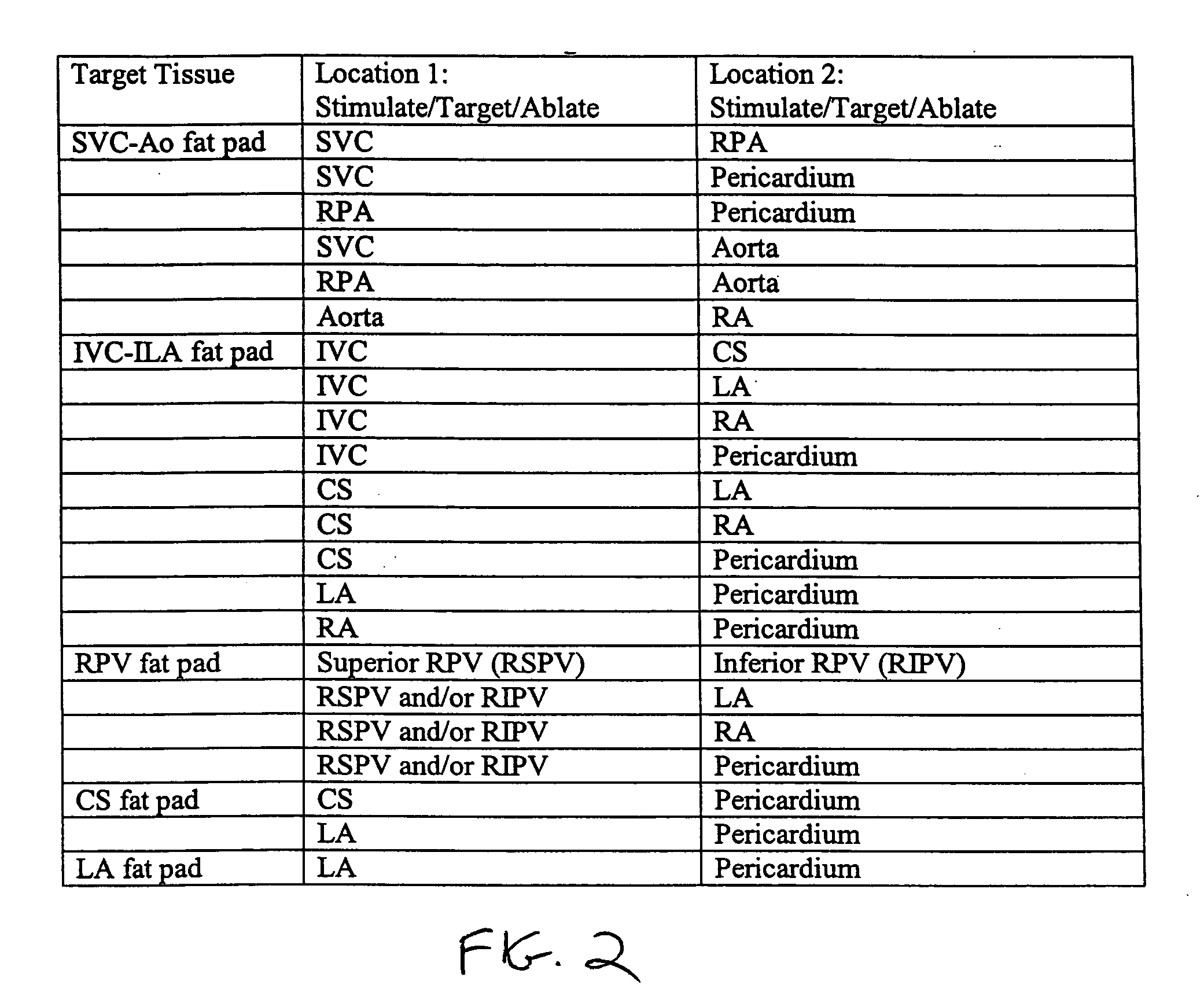
Systems and methods for selective denervation of heart dysrhythmias
InactiveUS20050261672A1Reduce sympathovagal toneAltering autonomic burdenElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingConduction pathwayElectroporation
Methods and apparatus are provided for selective denervation of conduction pathways in the heart for the treatment of dysrhythmias, including one or more ablation or electroporation catheters having electrodes for stimulating, targeting, and ablating fat pad tissue and other cardiac tissue to selectively denervate heart tissue.
Owner:ARDIAN
Methods and apparatus for treating back pain
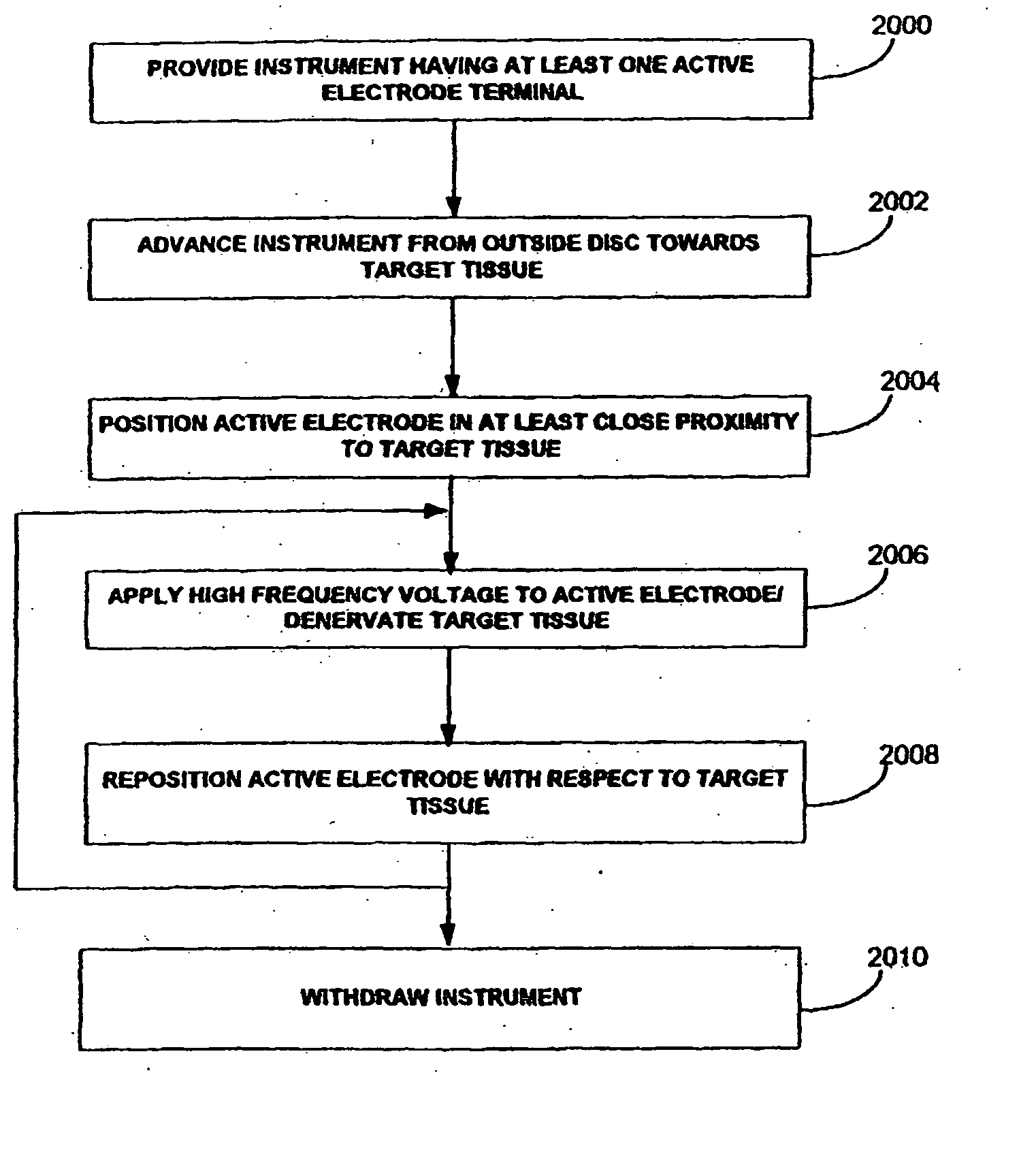
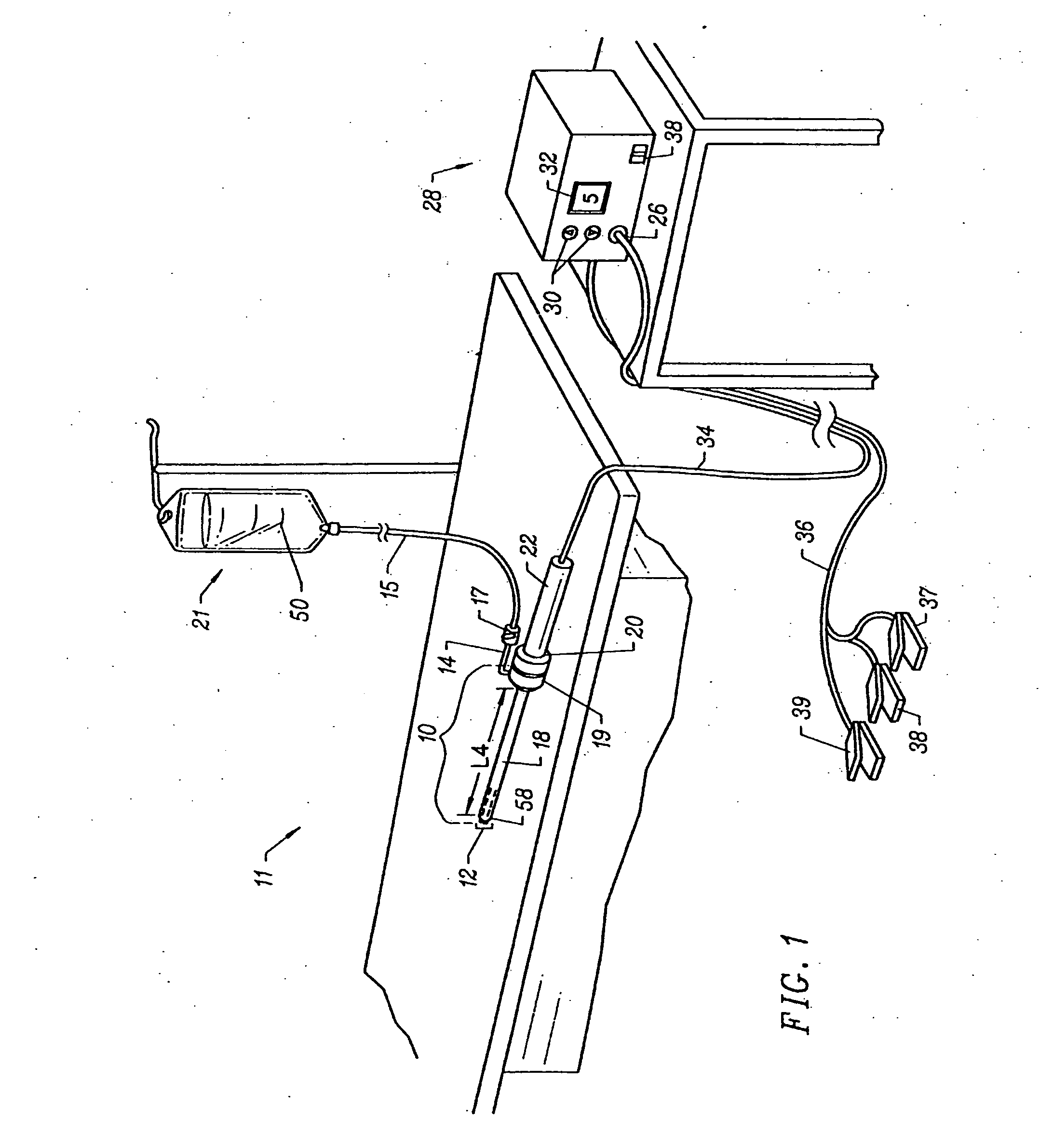
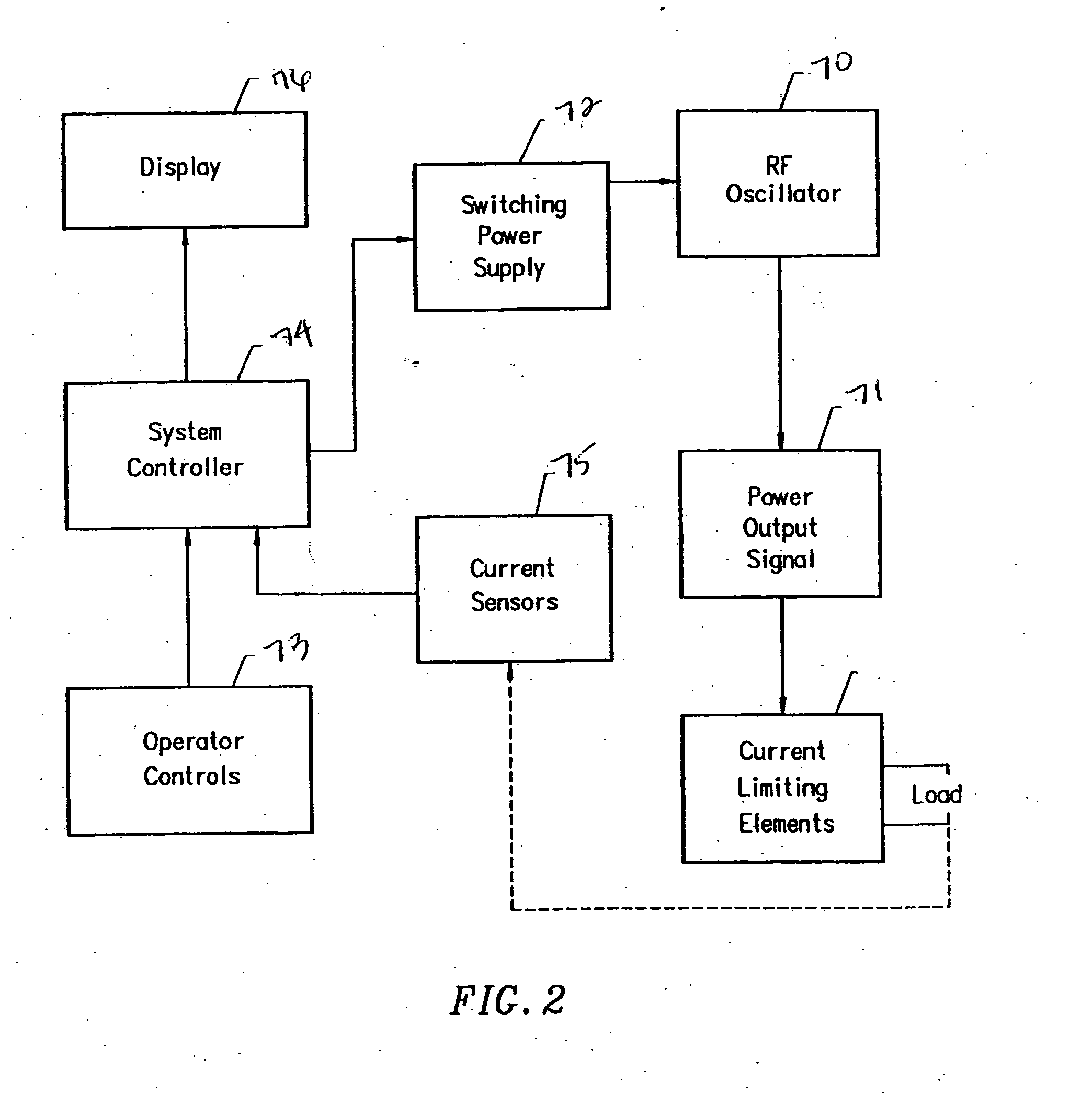
Apparatus and methods for treating back pain of a patient by denervation of an intervertebral disc or a region of the posterior longitudinal ligament by the controlled application of heat to a target tissue. In one embodiment, the invention may include a procedure combining both decompression of a disc, and denervation of the annulus fibrosus. In one embodiment, a method of the invention includes positioning an active electrode of an electrosurgical instrument in at least close proximity to an intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode and a return electrode, wherein nervous tissue within the annulus fibrosus is inactivated, and discogenic pain of the patient is alleviated. In one embodiment, the invention includes positioning a first electrode of a dual-shaft electrosurgical instrument at a first location in relation to a target disc, positioning a second electrode of the instrument at a second location, and applying a high frequency voltage between the first and second electrodes, wherein the first and second electrodes are disposed on separate shafts of the instrument.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
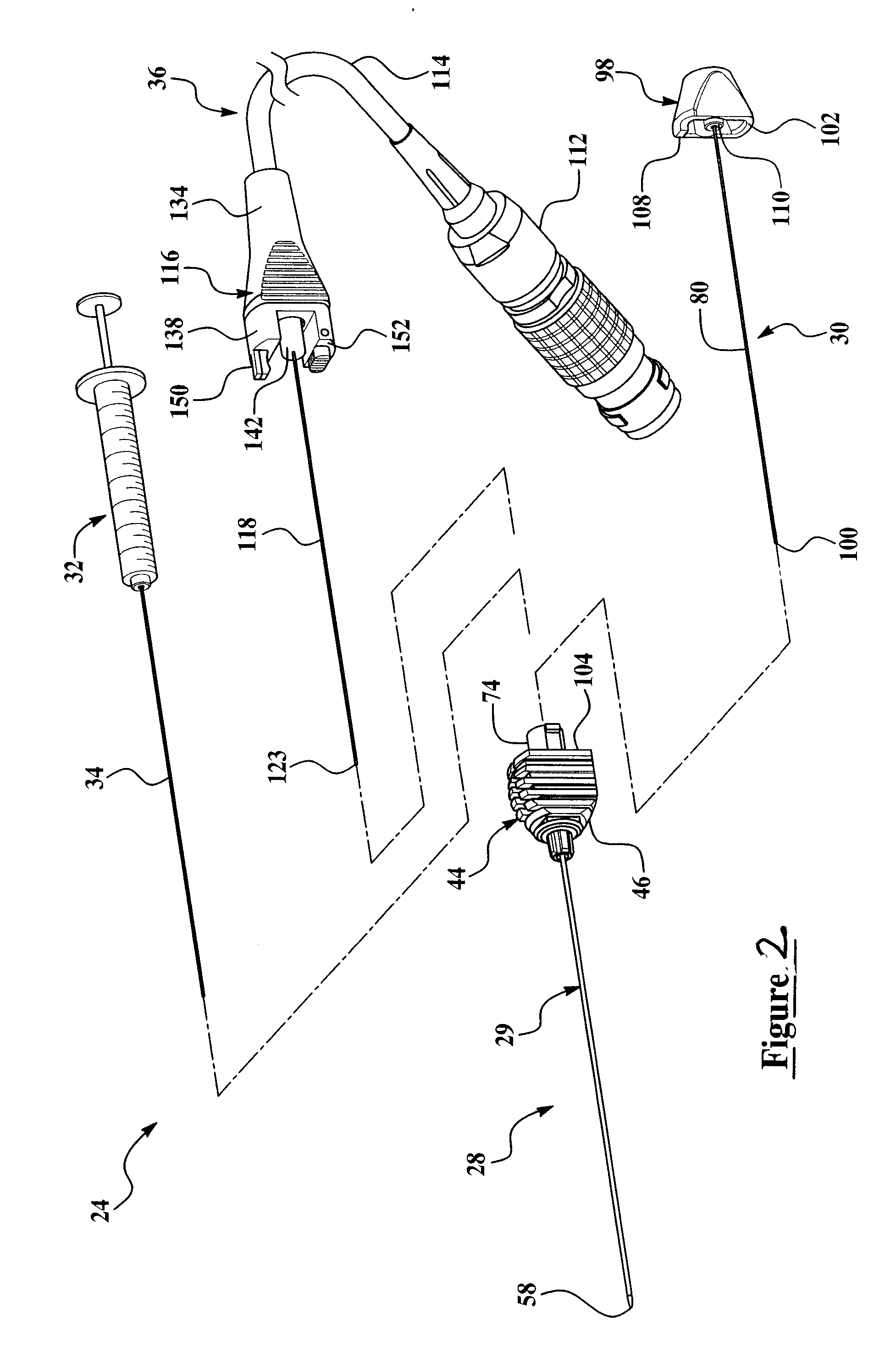
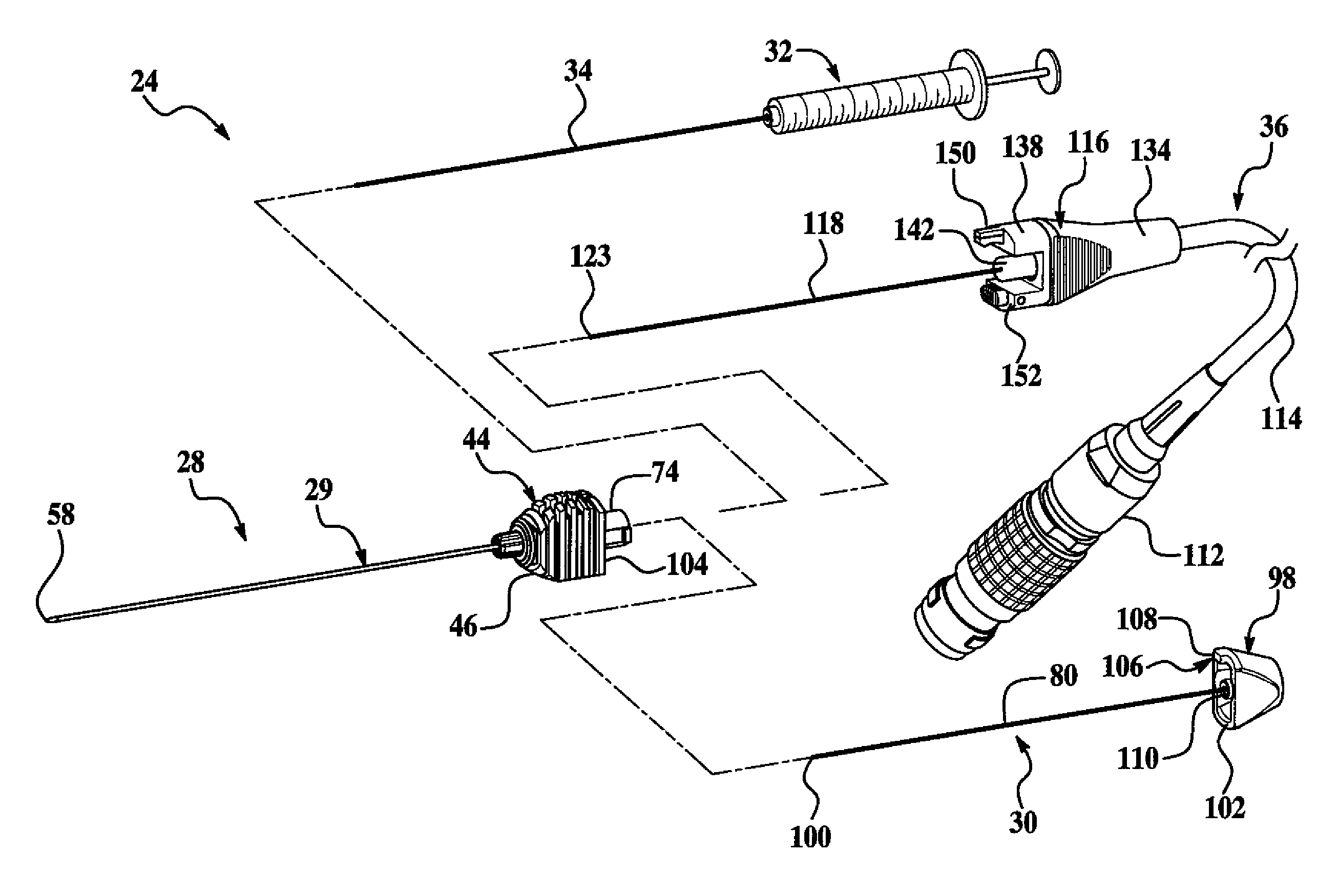
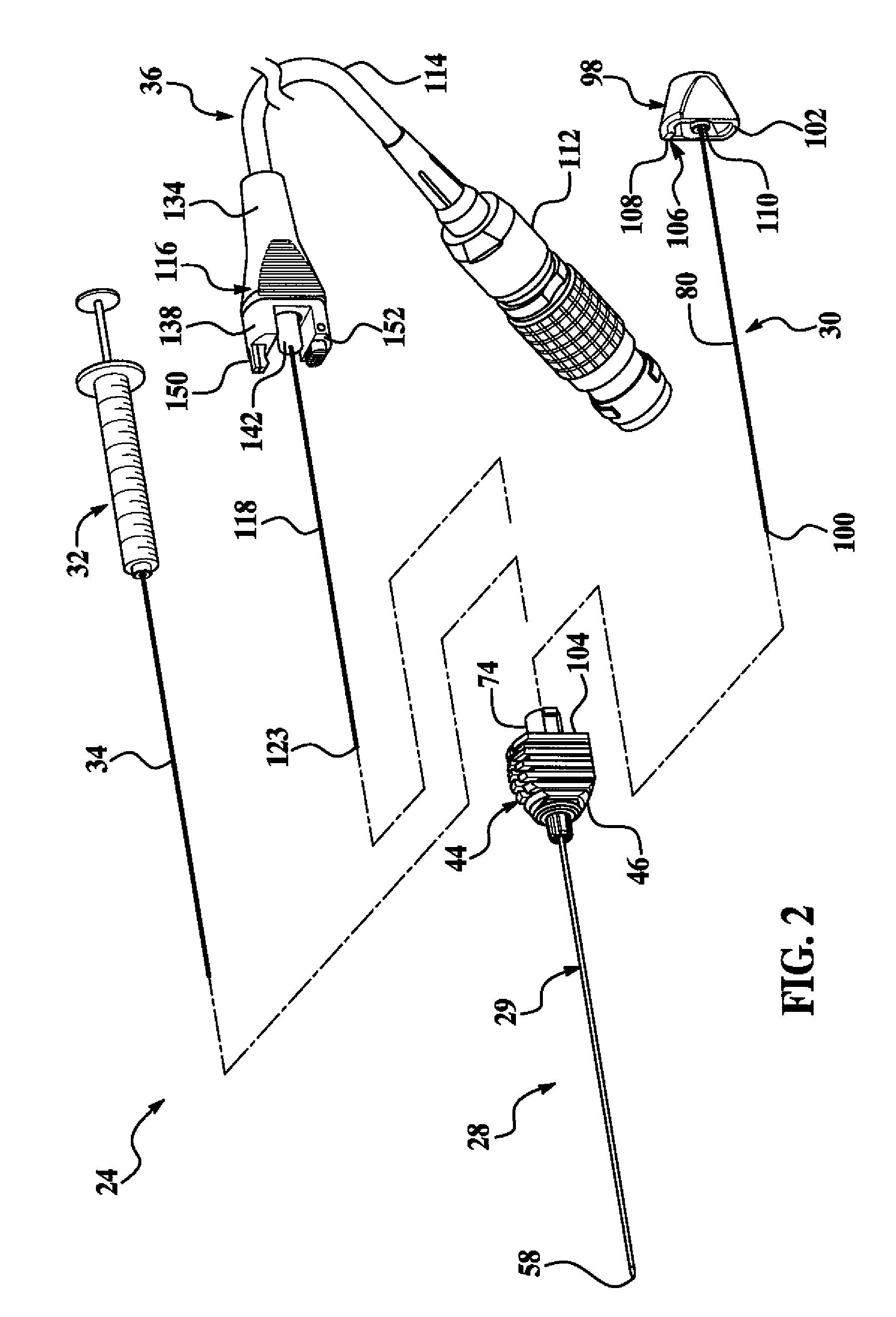
Medical Bipolar Electrode Assembly With A Cannula Having A Bipolar Active Tip And A Separate Supply Electrode And Medical Monopolar Electrode Assembly With A Cannula Having A Monopolar Active Tip And A Separate Temperature-Transducer Post
An electrosurgical system preferably used for denervation procedures of nerve tissue has a control unit and a pluggable electrode assembly. The electrode assembly has a preferably disposable cannula and a preservable supply electrode assembly. The cannula has a tubular body that projects axially from a preferably pointed distal end for piercing tissue to a proximal end engaged to a first coupling assembly of the cannula. The body carries a first contact exposed directly to the nerve tissue and connected electrically to a terminal of the first coupling assembly. The supply electrode assembly has a second coupling assembly and a supply electrode that projects axially and removably into a through-bore of the body when the tool is in an operating state. The second coupling assembly carries a terminal that abuts the first coupling assembly when the coupling assemblies are mated. Preferably the supply electrode carries a temperature sensor for temperature measurement of the targeted tissue and processing by the control unit. Preferably, the electrode assembly also includes a stylet having a rod that fits into the through-bore of the body when the supply electrode assembly is removed and the tool is in a tissue penetrating state.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
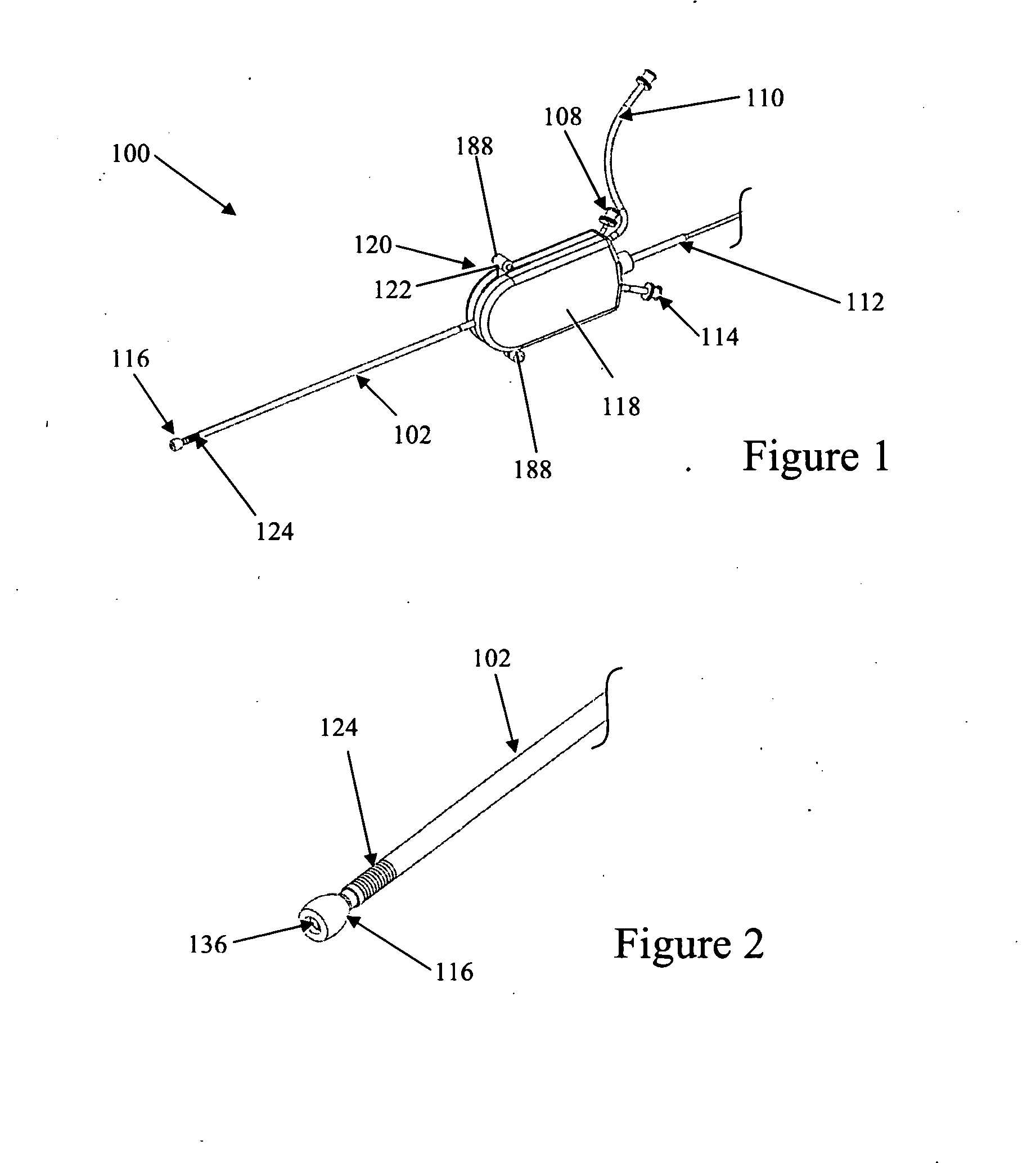
Method and apparatus of assessing transvascular denervation
InactiveUS20120296232A1Smooth connectionEnhanced signalSurgical instrument detailsCatheterDenervationIntravascular catheter
Embodiments of the invention provide catheter devices for assessing transvascular denervation. A method of assessing denervation comprises: introducing intravascularly a catheter to a vessel of a patient, the catheter including one or more recording elements; performing a baseline recording of responses by supplying nerve stimulation to the vessel and recording responses of the vessel to the nerve stimulation; denervating at least some tissue proximate the vessel after performing the baseline recording; performing a post-denervation recording of responses, after the denervating, by supplying nerve stimulation to the vessel and recording responses of the vessel to the nerve stimulation; and assessing denervation of the vessel based on a comparison of the responses of the baseline recording and the responses of the post-denervation recording.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
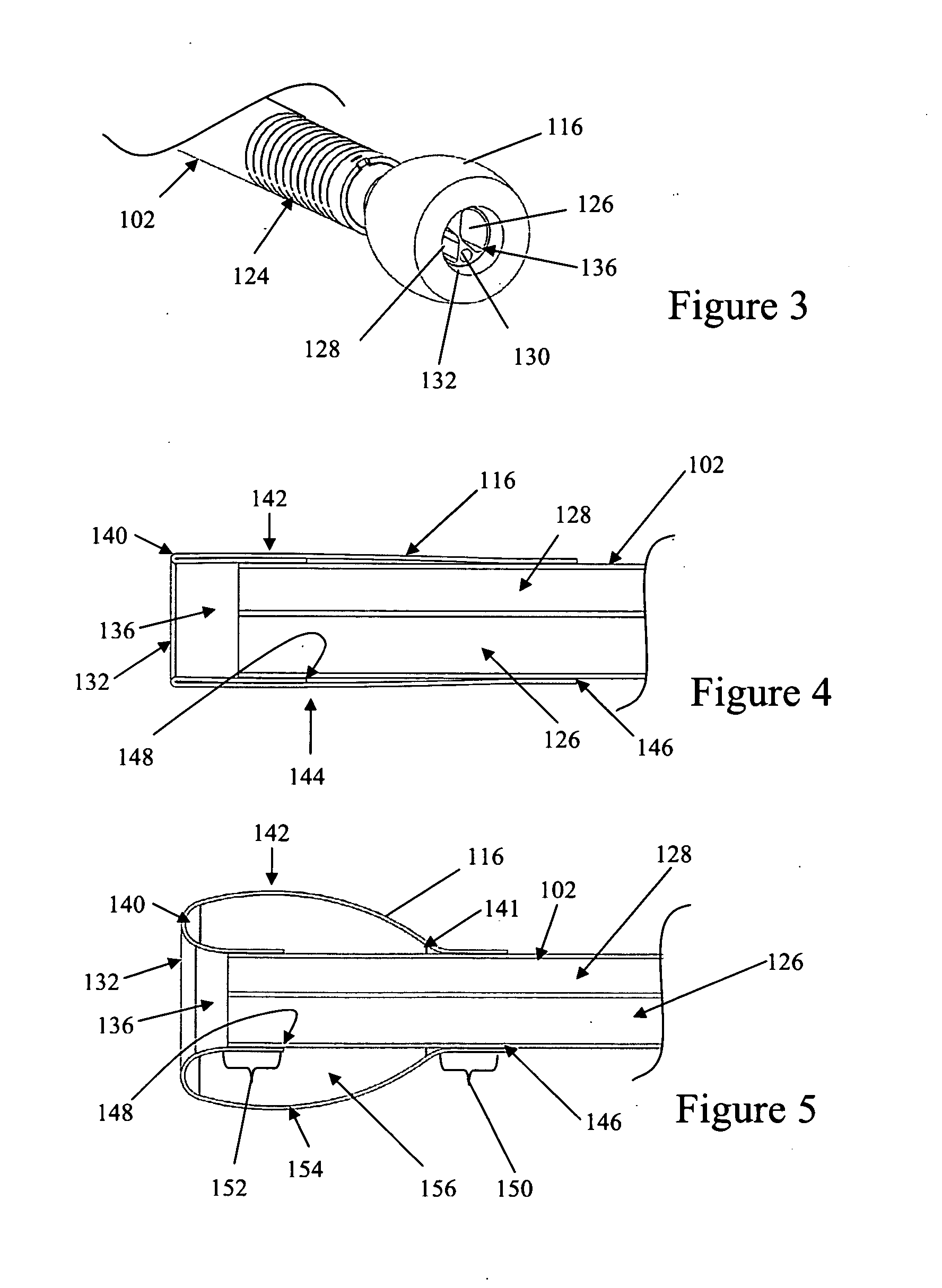
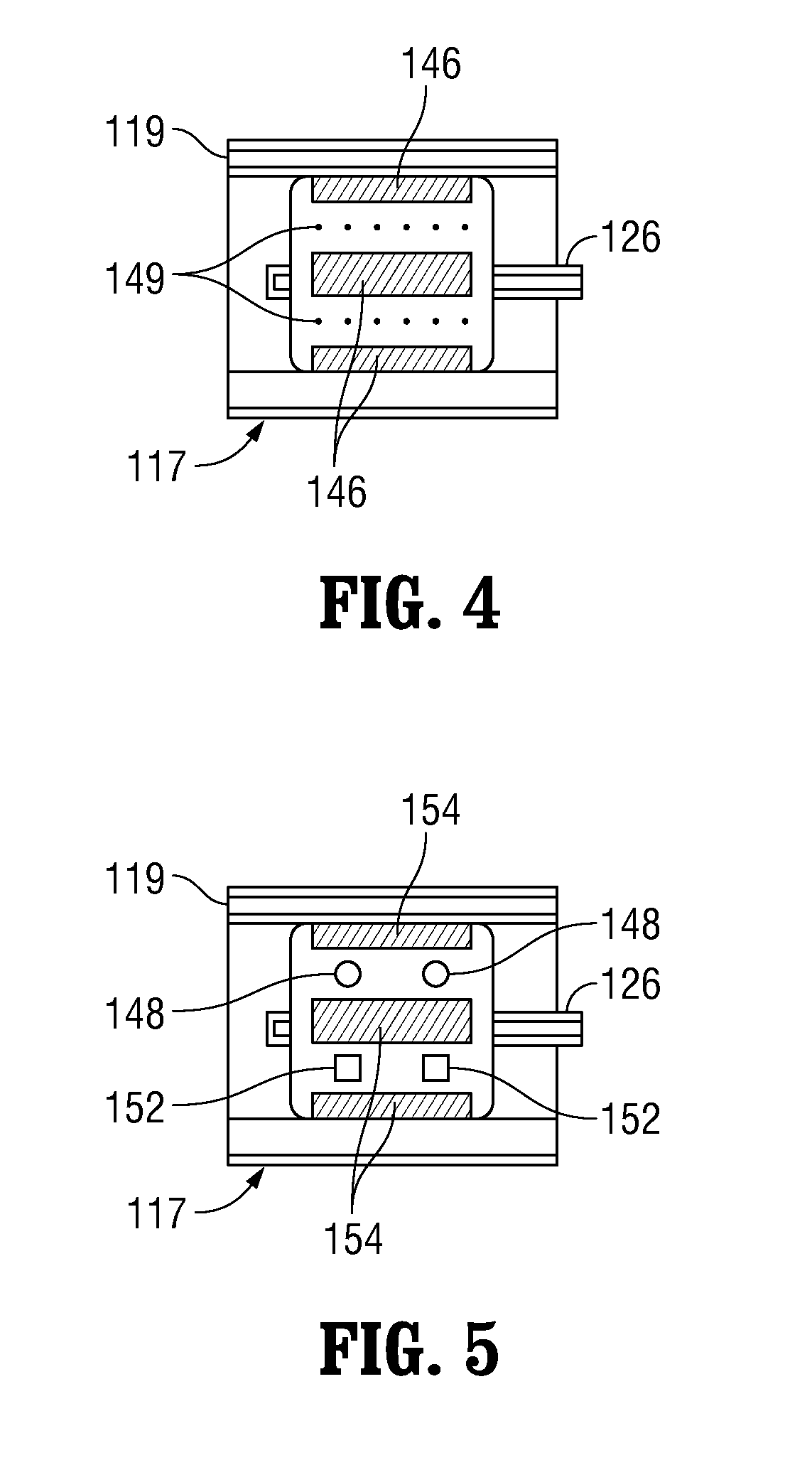
Apparatus and method of assessing transvascular denervation
ActiveUS20120296329A1Smooth connectionEnhanced signalCatheterSurgical instrument detailsElement spaceDenervation
A catheter apparatus for assessing denervation comprises: an elongated catheter body; a deployable structure coupled to the catheter body, the deployable structure being deployable outwardly from and contractible inwardly toward the longitudinal axis of the catheter body; one or more ablation elements disposed on the deployable structure to move outwardly and inwardly with the deployable structure; one or more stimulation elements spaced from each other and disposed on the deployable structure to move with the deployable structure, the stimulation elements being powered to supply nerve stimulating signals to the vessel; and one or more recording elements spaced from each other and from the stimulation elements, the recording elements being disposed on the deployable structure to move with the deployable structure, the recording elements configured to record response of the vessel to the nerve stimulating signals.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Balloon cannula system for accessing and visualizing spine and related methods
InactiveUS20090062871A1Enhance direct visualizationImprove visualizationStentsBalloon catheterSpinal stenosisMedicine
Balloon cannula systems may be used for accessing and visualizing the spine and related methods of treatment, including a forward-looking balloon system for creating a working space and the balloon system having atraumatic dissection capability to allow visualization in spine. The devices and methods described may be used, for example, to perform annulus repair, herniated disc excision, and denervation of neurological tissue; to dispense pharmacological agents and / or cell or tissue therapy agents; to diagnose disc degeneration and bony degeneration, spinal stenosis, and nucleus decompression, and to perform disc augmentation.
Owner:SPINE VIEW INC
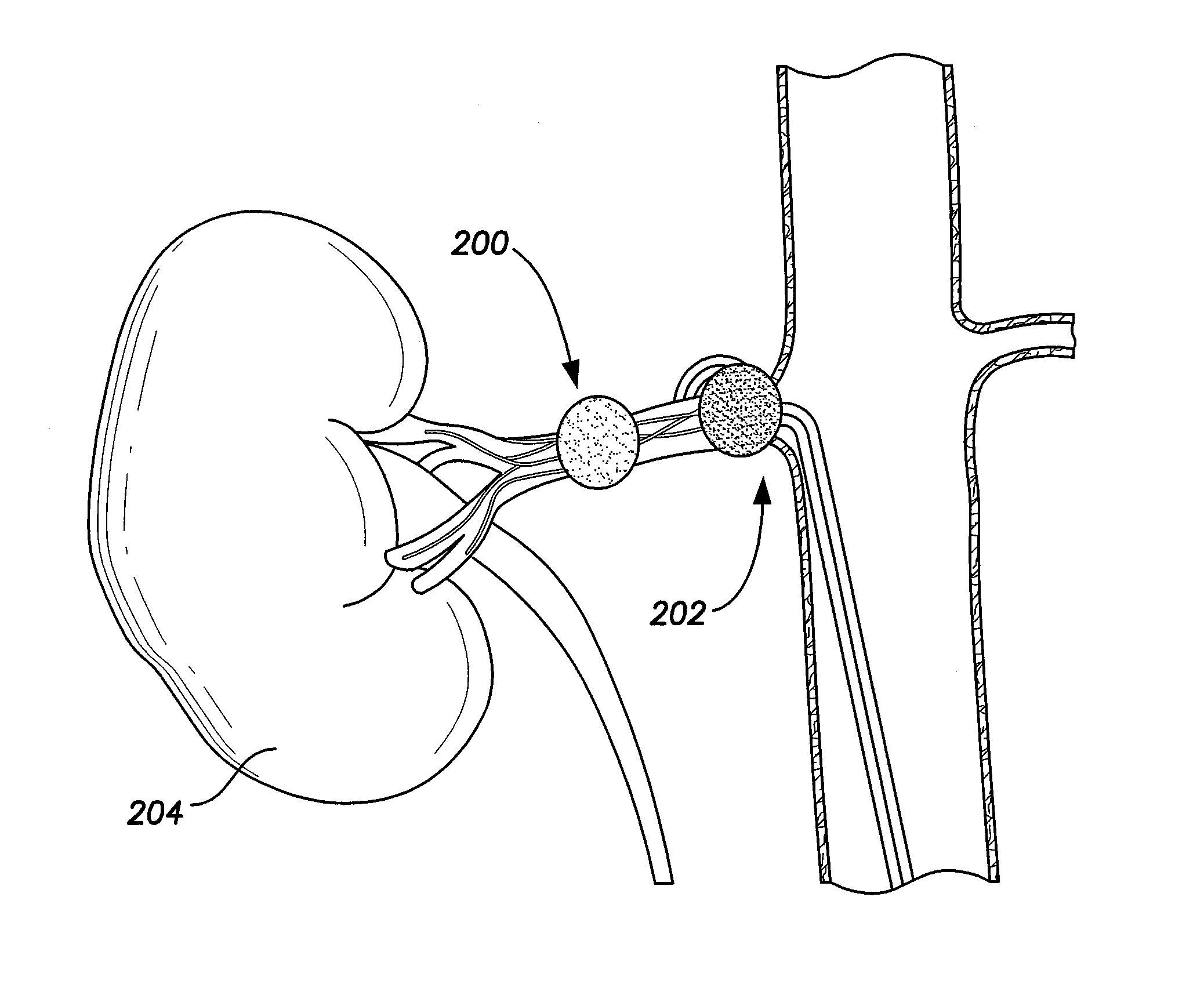
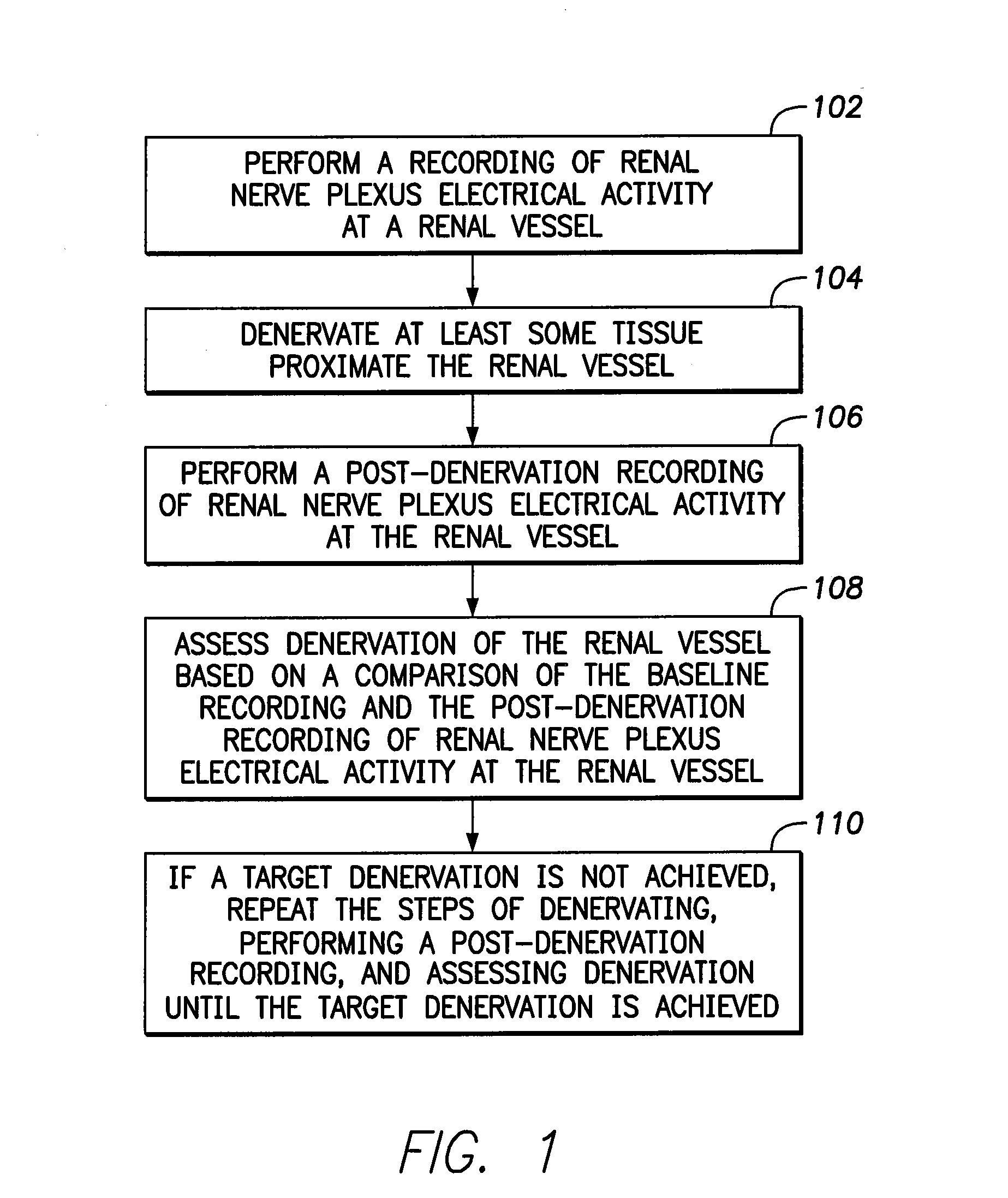
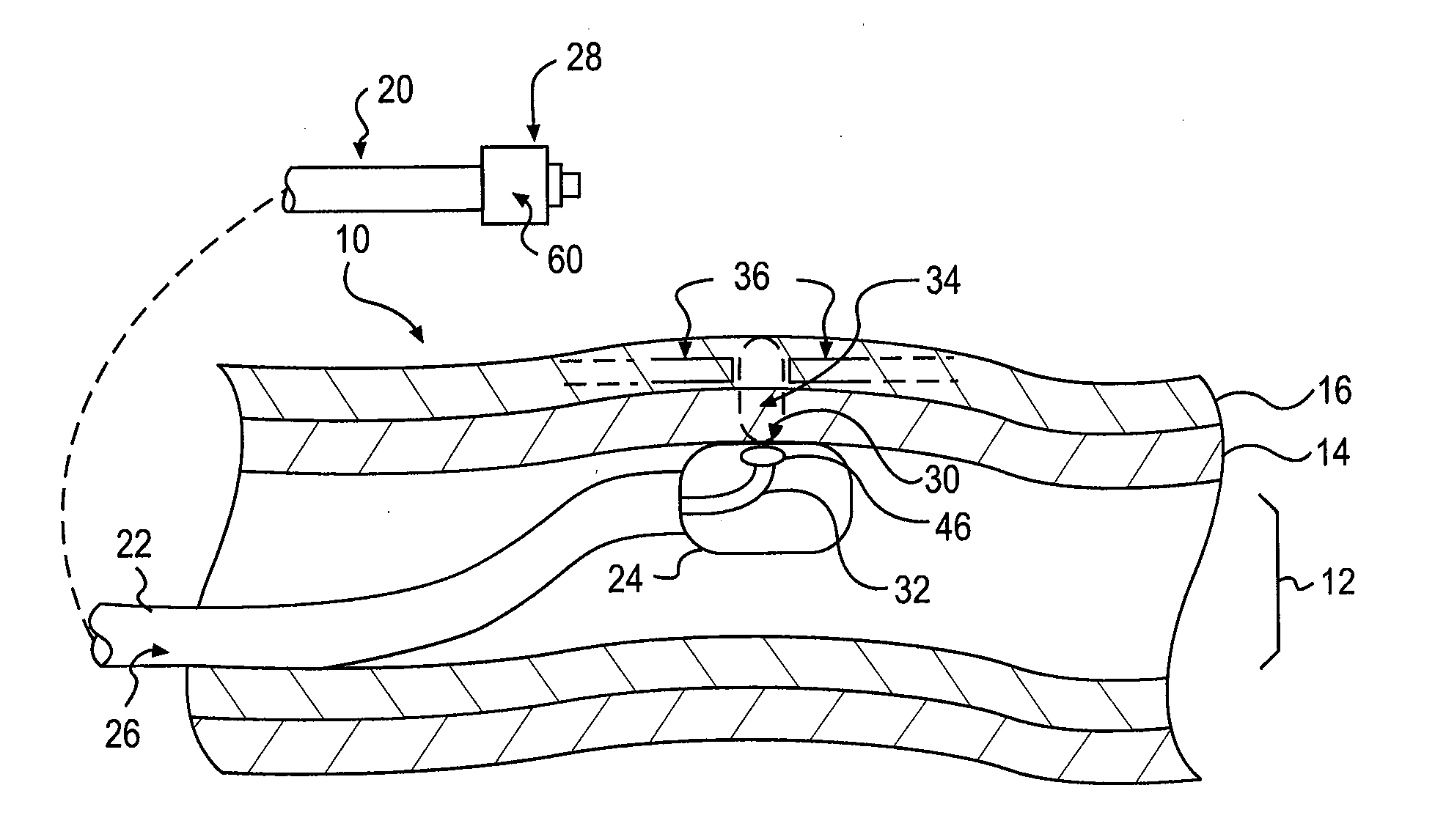
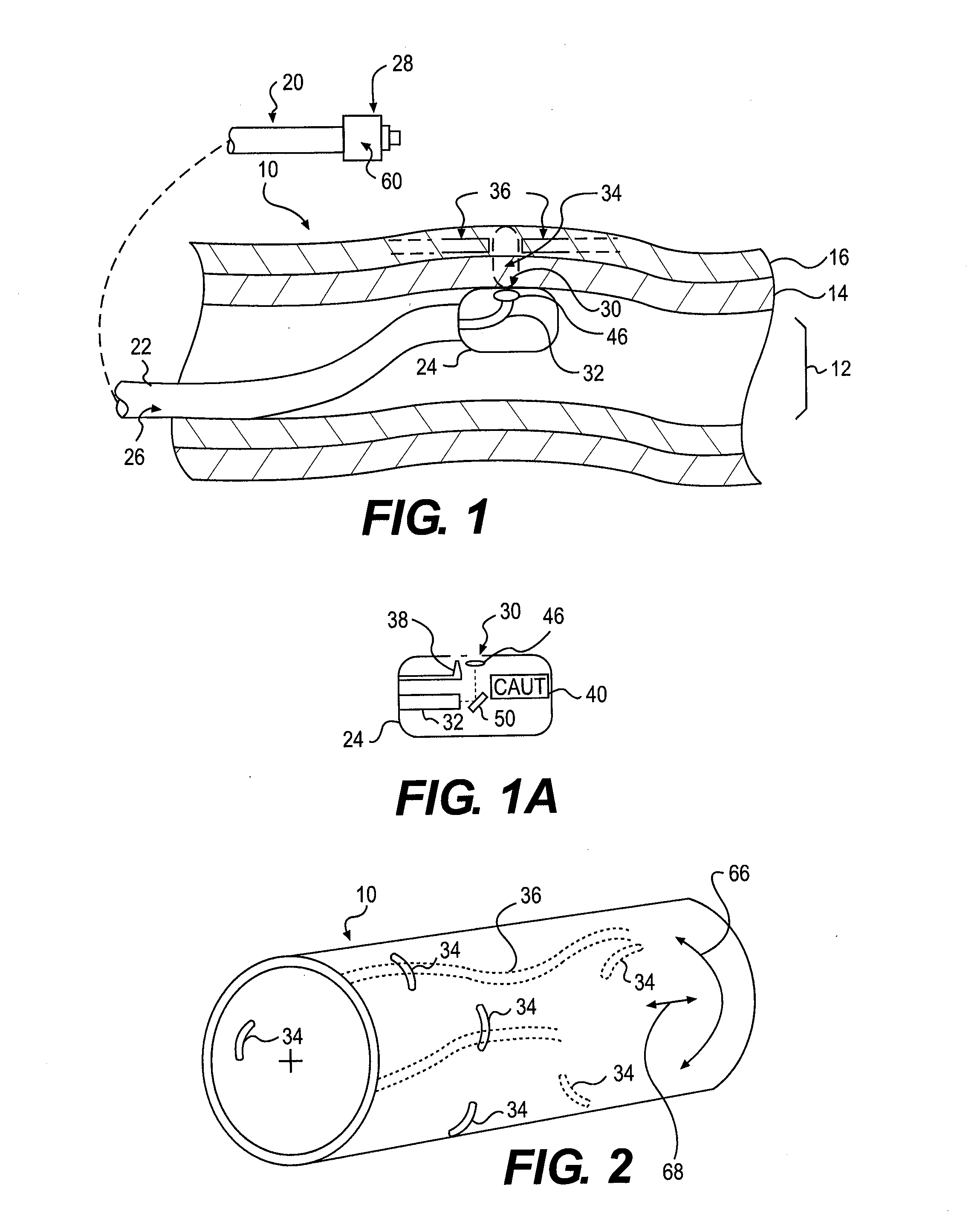
System and method for performing renal denervation verification
ActiveUS20130085489A1Avoid excessivePrevent unnecessary ablationSpinal electrodesSensorsRenal vesselsDenervation
A renal denervation feedback method is described that performs a baseline measurement of renal nerve plexus electrical activity at a renal vessel; denervates at least some tissue proximate the renal vessel after performing the baseline measurement; performs a post-denervation measurement of renal nerve plexus electrical activity at the renal vessel, after the denervating; and assesses denervation of the renal vessel based on a comparison of the baseline measurement and the post-denervation measurement of renal nerve plexus electrical activity at the renal vessel.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Methods and apparatus for treating back pain
InactiveUS20050261754A1Relieve back painSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingIntervertebral discBACK DISCOMFORT
Apparatus and methods for treating back pain of a patient by denervation of an intervertebral disc or a region of the posterior longitudinal ligament by the controlled application of heat to a target tissue. In one embodiment, the invention may include a procedure combining both decompression of a disc, and denervation of the annulus fibrosus. In one embodiment, a method of the invention includes positioning an active electrode of an electrosurgical instrument in at least close proximity to an intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode and a return electrode, wherein nervous tissue within the annulus fibrosus is inactivated, and discogenic pain of the patient is alleviated. In one embodiment, the invention includes positioning a first electrode of a dual-shaft electrosurgical instrument at a first location in relation to a target disc, positioning a second electrode of the instrument at a second location, and applying a high frequency voltage between the first and second electrodes, wherein the first and second electrodes are disposed on separate shafts of the instrument.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Methods and apparatus for treating back pain
Apparatus and methods for treating back pain of a patient by denervation of an intervertebral disc or a region of the posterior longitudinal ligament by the controlled application of heat to a target tissue. In one embodiment, the invention may include a procedure combining both decompression of a disc, and denervation of the annulus fibrosus. In one embodiment, a method of the invention includes positioning an active electrode of an electrosurgical instrument in at least close proximity to an intervertebral disc, and applying at least a first high frequency voltage between the active electrode and a return electrode, wherein nervous tissue within the annulus fibrosus is inactivated, and discogenic pain of the patient is alleviated. In one embodiment, the invention includes positioning a first electrode of a dual-shaft electrosurgical instrument at a first location in relation to a target disc, positioning a second electrode of the instrument at a second location, and applying a high frequency voltage between the first and second electrodes, wherein the first and second electrodes are disposed on separate shafts of the instrument.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Methods and devices for denervation
Various delivery devices are described to deliver an agent locally to the renal nerves. The delivery devices are positioned in the renal artery and penetrate into the wall of the renal artery to deliver the agent to the renal nerves. The delivery devices may be used to deliver the agent according to longitudinal position, radial position, and depth of the renal nerves relative to the renal artery. In addition, various methods are described to denervate, modulate, or otherwise affect the renal nerves and other neural tissue. Also, various agents are described to denerve, modulate, or otherwise affect the renal nerves and other neural tissue.
Owner:NORTHWIND MEDICAL
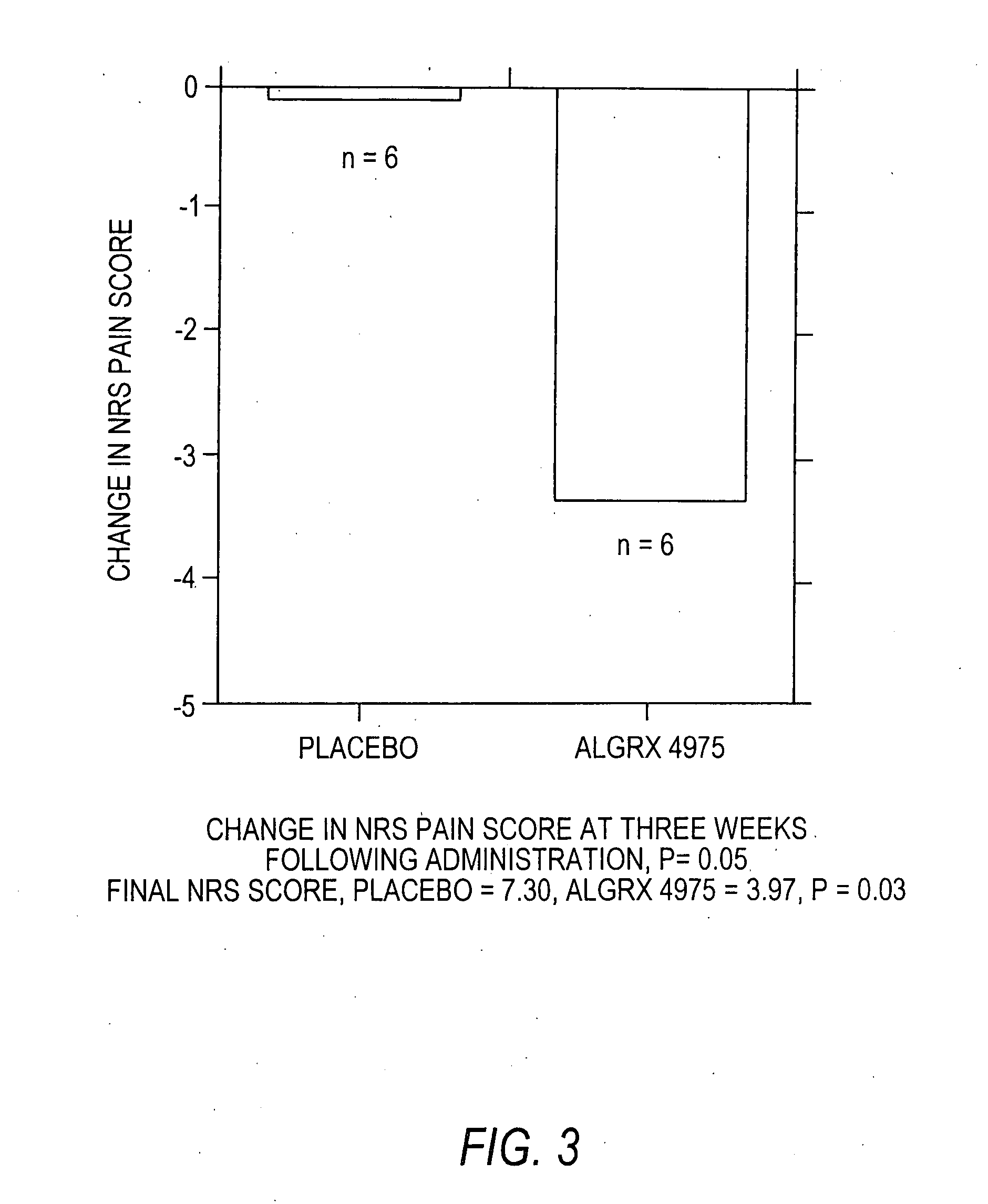
Injectable capsaicin
InactiveUS20050019436A1Reducing and eliminating painMinimizing adverse consequenceBiocideNervous disorderCapsaicinAnesthesia
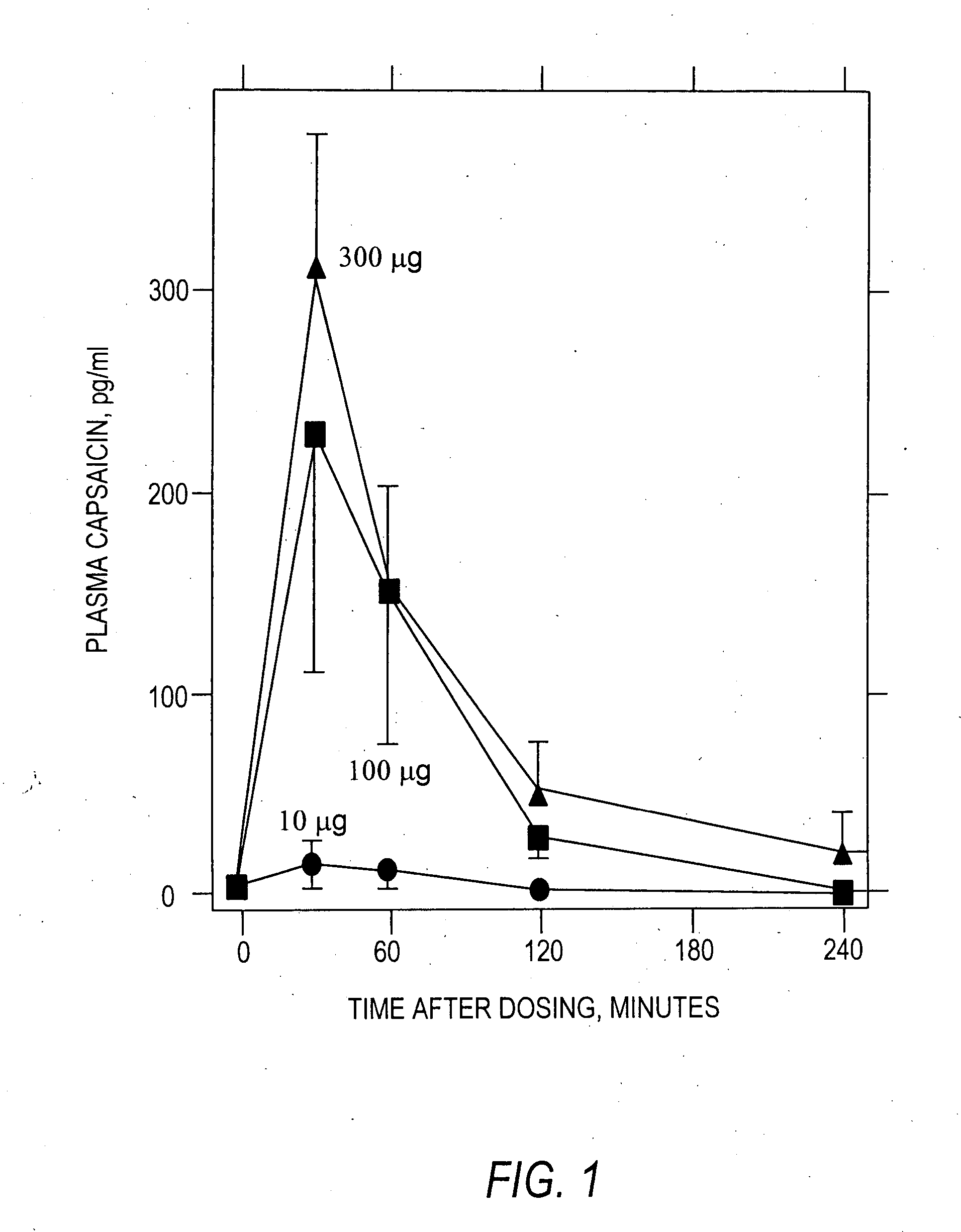
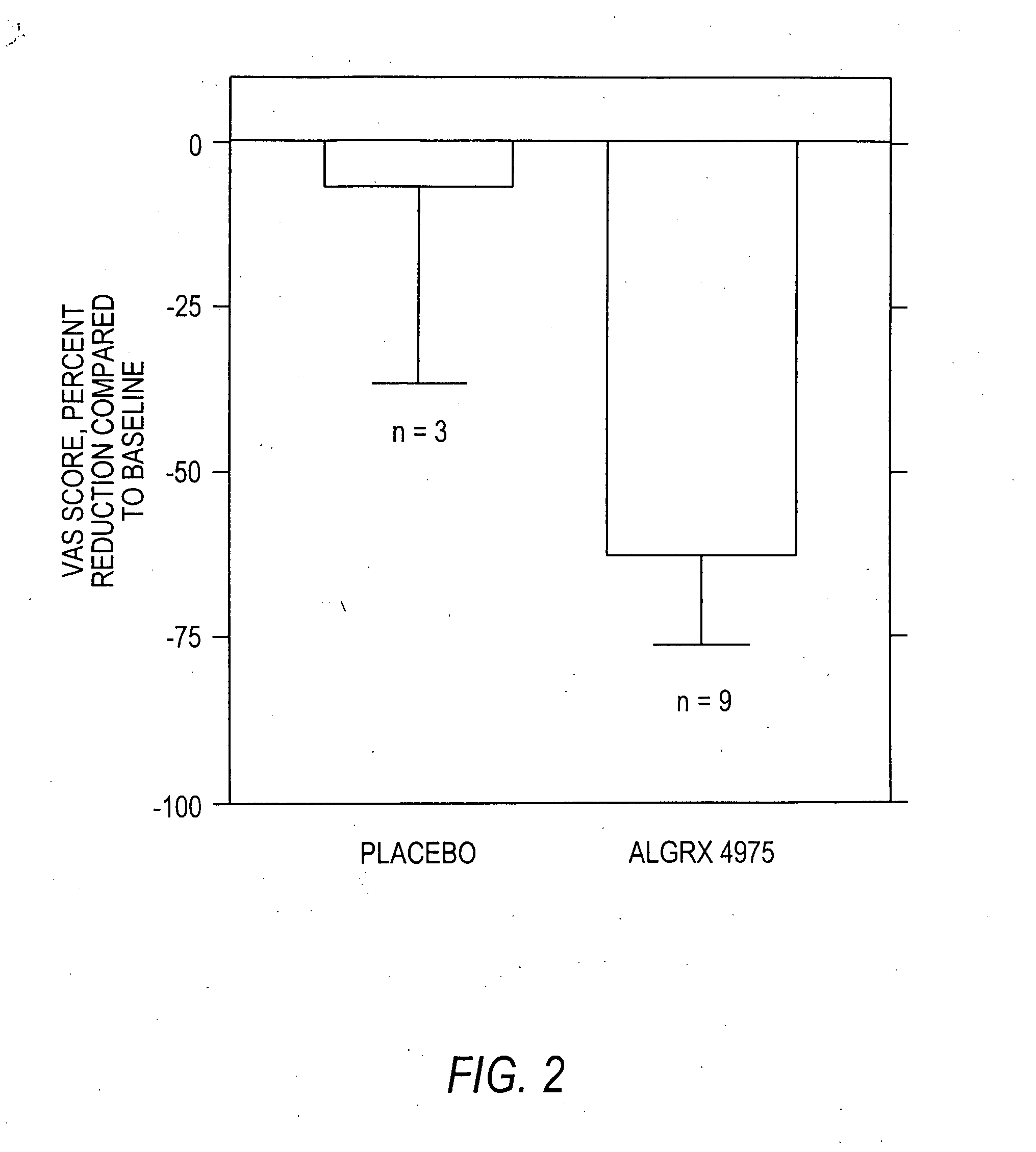
The present invention provides compositions and methods for relieving pain at a site in a human or animal in need thereof by administering at a discrete site in a human or animal in need thereof a dose of capsaicin in an amount effective to denervate a discrete site without eliciting an effect outside the discrete location, the dose of capsaicin ranging from 1 μg to 3000 μg.
Owner:ALGORX PHARMA INC
Balloon cannula system for accessing and visualizing spine and related methods
Balloon cannula systems may be used for accessing and visualizing the spine and related methods of treatment, including a forward-looking balloon system for creating a working space and the balloon system having atraumatic dissection capability to allow visualization in spine. The devices and methods described may be used, for example, to perform annulus repair, herniated disc excision, and denervation of neurological tissue; to dispense pharmacological agents and / or cell or tissue therapy agents; to diagnose disc degeneration and bony degeneration, spinal stenosis, and nucleus decompression, and to perform disc augmentation.
Owner:SPINE VIEW INC
Balloon cannula system for accessing and visualizing spine and related methods
Balloon cannula systems may be used for accessing and visualizing the spine and related methods of treatment, including a forward-looking balloon system for creating a working space and the balloon system having atraumatic dissection capability to allow visualization in spine. The devices and methods described may be used, for example, to perform annulus repair, herniated disc excision, and denervation of neurological tissue; to dispense pharmacological agents and / or cell or tissue therapy agents; to diagnose disc degeneration and bony degeneration, spinal stenosis, and nucleus decompression, and to perform disc augmentation.
Owner:SPINE VIEW INC
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Bone marrow stromal cells (BMSC) differentiate into neuron-like phenotypes in vitro and in vivo, engrafted into normal or denervated rat striatum. The BMSC did not remain localized to the site of the graft, but migrated throughout the brain and integrated into specific brain regions in various architectonic patterns. The most orderly integration of BMSC was in the laminar distribution of cerebellar Purkinje cells, where the BMSC-derived cells took on the Purkinje phenotype. The BMSC exhibited site-dependent differentiation and expressed several neuronal markers including neuron-specific nuclear protein, tyrosine hydroxylase and calbindin. BMSC can be used to target specific brain nuclei in strategies of neural repair and gene therapy.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Method and apparatus for stimulating a denervated muscle
A method of stimulating a subject having a denervated muscle and a corresponding functional muscle that are responsible for producing actions, such as blinking, on first and second portions, respectively, of the subject's body. The method includes determining whether the functional muscle has contracted, generating a contraction signal if it is determined that it has contracted, and causing the denervated muscle to contract following the generation of the contraction signal. Also, an apparatus for stimulating such a subject including one or more sensing devices operatively associated with the functional muscle and one or more stimulating devices operatively associated with the denervated muscle. One or more of the sensing devices generates one or more first signals in response to activity indicating functional muscle contraction. The one or more stimulating devices are made to cause the denervated muscle to contract in response to the generation of the first signals.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Apparatus and method of assessing transvascular denervation
A catheter apparatus for assessing denervation comprises: an elongated catheter body; a deployable structure coupled to the catheter body, the deployable structure being deployable outwardly from and contractible inwardly toward the longitudinal axis of the catheter body; one or more ablation elements disposed on the deployable structure to move outwardly and inwardly with the deployable structure; one or more stimulation elements spaced from each other and disposed on the deployable structure to move with the deployable structure, the stimulation elements being powered to supply nerve stimulating signals to the vessel; and one or more recording elements spaced from each other and from the stimulation elements, the recording elements being disposed on the deployable structure to move with the deployable structure, the recording elements configured to record response of the vessel to the nerve stimulating signals.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Apparatus for effective ablation and nerve sensing associated with denervation
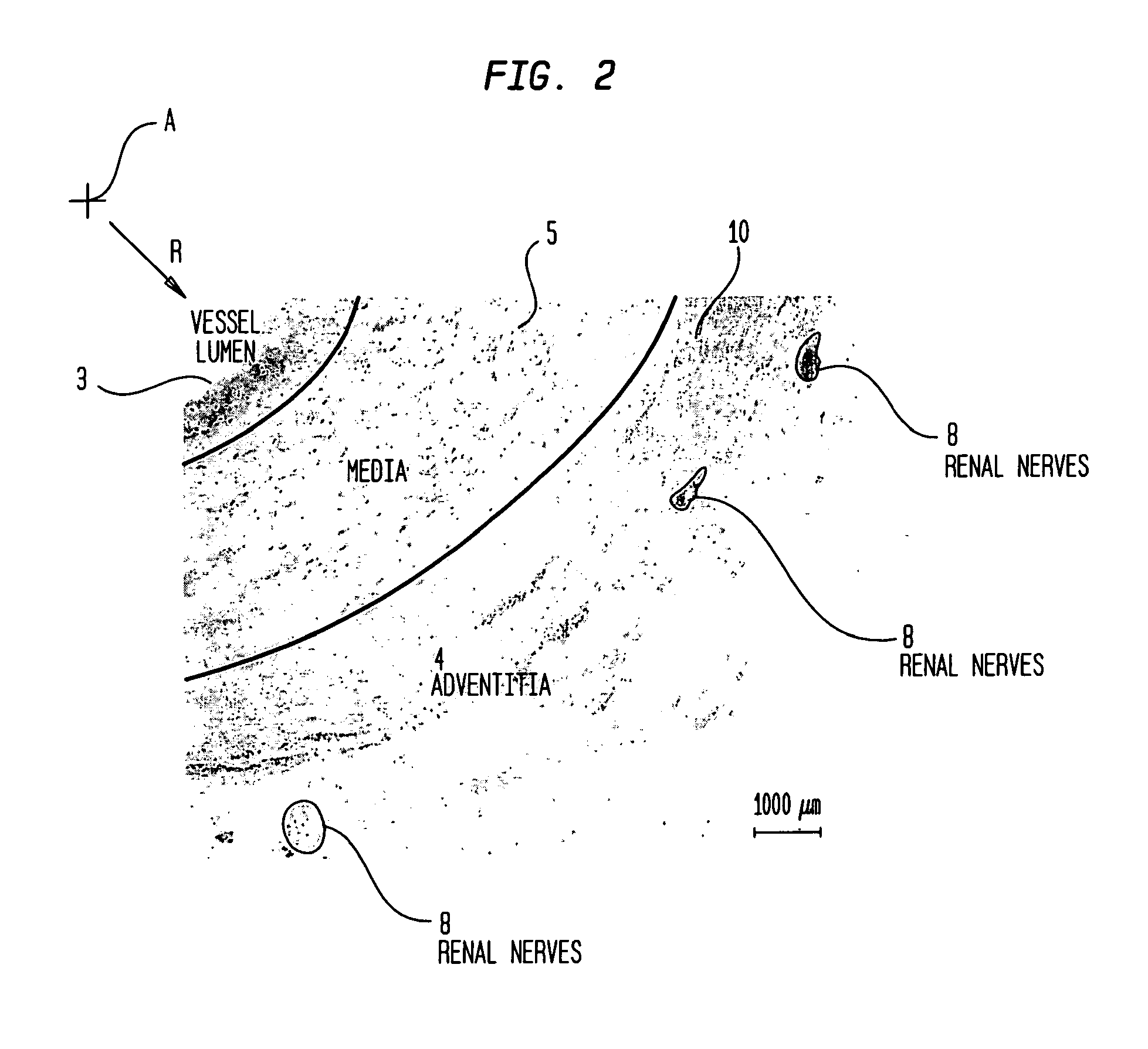
An intravascular catheter for nerve activity ablation and / or sensing includes one or more needles advanced through supported guide tubes (needle guiding elements) which expand to contact the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the needles to be advanced though the vessel wall into the extra-luminal tissue including the media, adventitia and periadvential space. The catheter also includes structures which provide radial and lateral support to the guide tubes so that the guide tubes open uniformly and maintain their position against the interior surface of the vessel wall as the sharpened needles are advanced to penetrate into the vessel wall. Electrodes near the distal ends of the needles allow sensing of nerve activity before and after attempted renal denervation. In a combination embodiment ablative energy or fluid is delivered from the needles in or near the adventitia to ablate nerves outside of the media while sparing nerves within the media.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
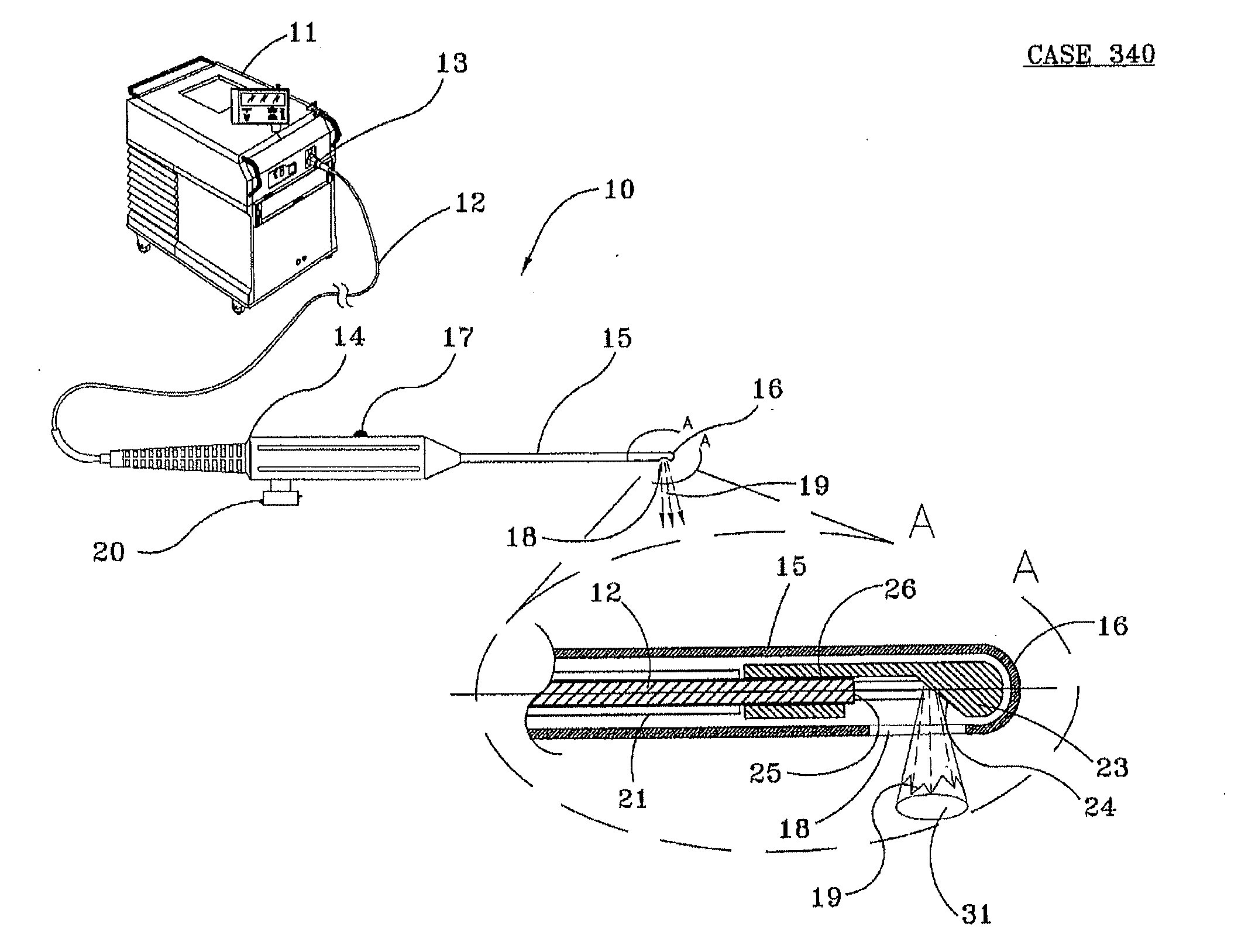
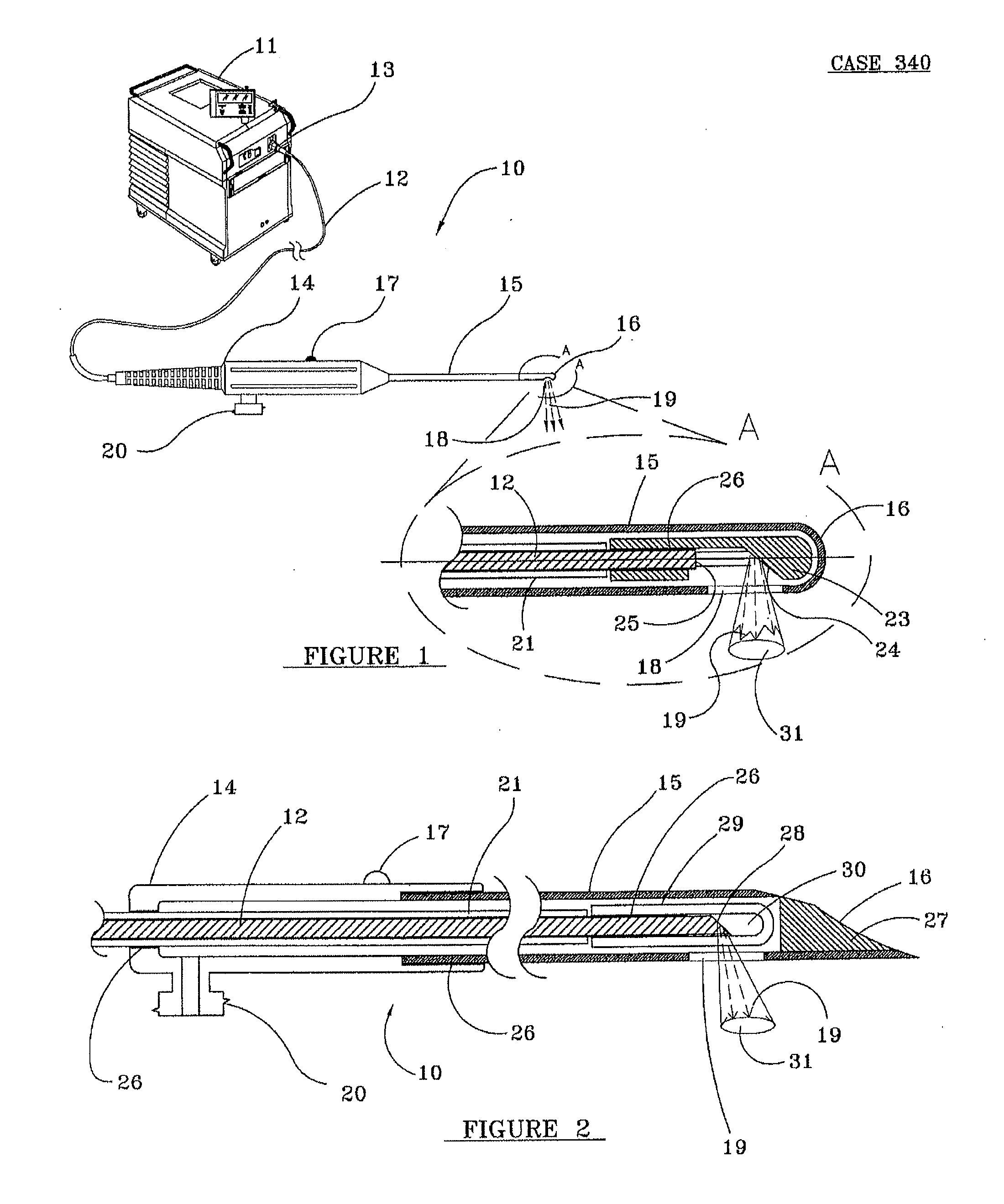
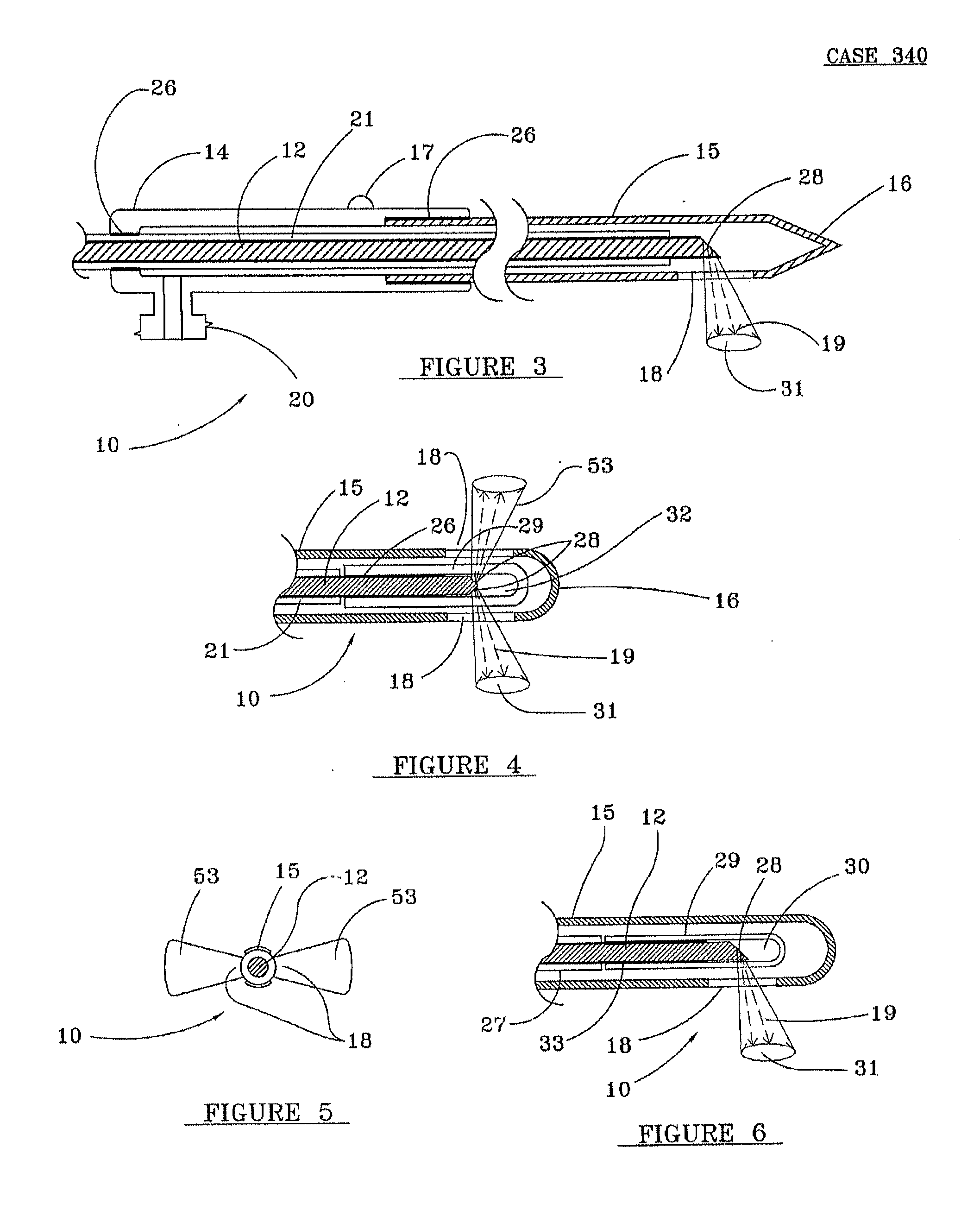
Devices for effective and uniform denervation of nerves and unique methods of use thereof
Apparatus for delivering laser energy suitable for denervation, such as renal denervation and the like, comprises an optical fiber inside a cannula and defining a channel therebetween for delivery of a liquid to cool and clean the tip of the optical fiber and to cool tissue subjected to laser irradiation, while the apparatus is Stationed, Moved, Rotated and or Swept during the emission of laser energy.
Owner:TRIMEDYNE
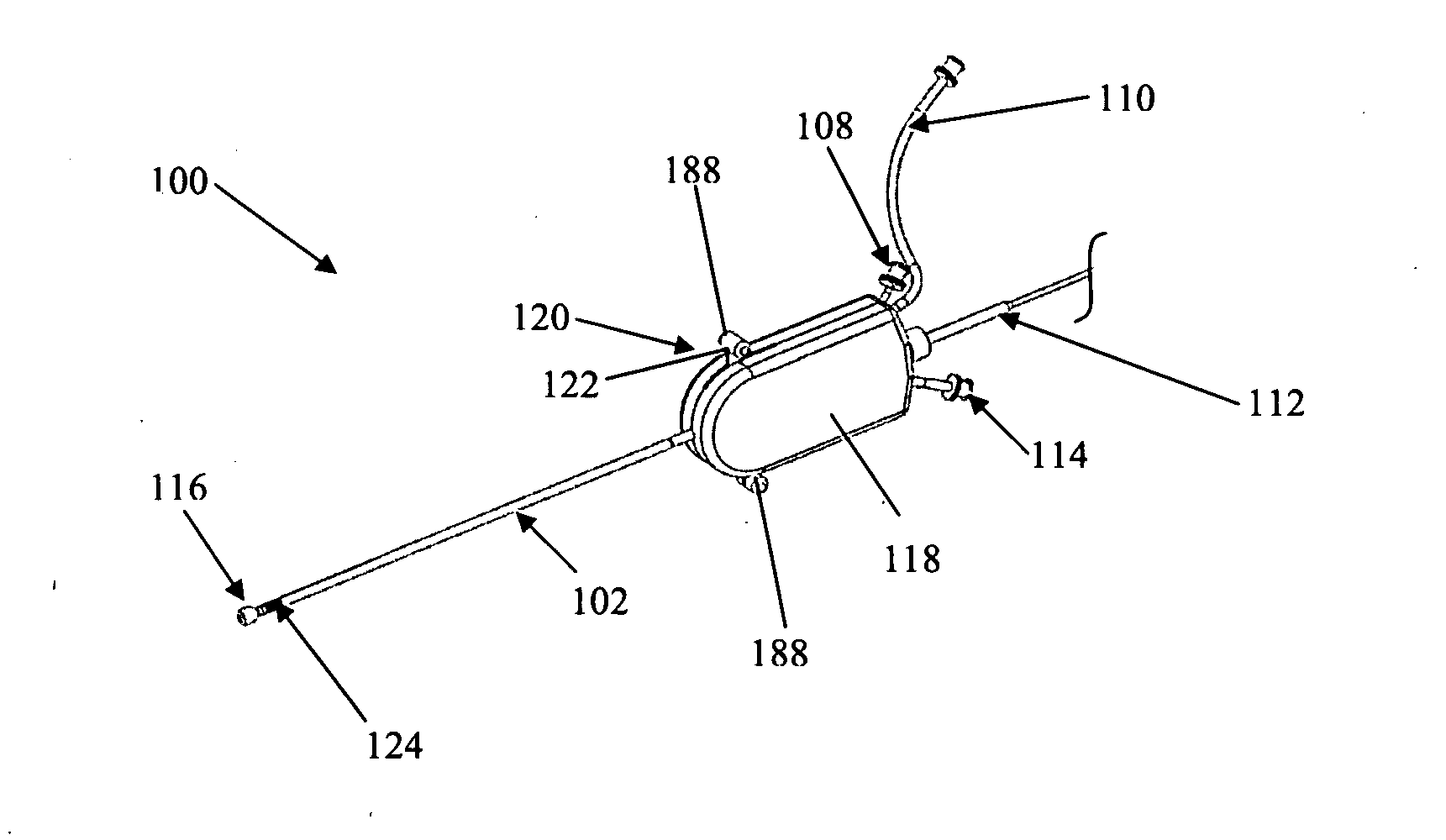
Sympathetic nerve denervation ablation catheter system for kidneys
InactiveCN102885648APrevent slidingRelieve painUltrasound therapyCatheterSympathetic nerveMechanical stability
The invention discloses a sympathetic nerve denervation ablation catheter system inside arteria renalis. The system comprises an ablation catheter, a guide catheter, a control handle, an ablation generator and a guide catheter control handle which can be arranged optionally. The ablation catheter comprises a catheter section and an ablation section from the near end to the far end in sequence, wherein the front end of the catheter body further comprises a controllable bending section and is connected with the control handle by the catheter body; and the ablation section comprises at least two independent structures, wherein an ablation head is arranged on at least one independent structure. With the adoption of the sympathetic nerve denervation ablation catheter system, multi-point ablation can be simultaneously achieved, so that the ablation effect is monitored during an operation in real time and mechanical stability is better.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Iontophoresis drug delivery system and method for denervation of the renal sympathetic nerve and iontophoretic drug delivery
InactiveUS20120259269A1Facilitate drug deliveryReduce deliveryStentsBalloon catheterMedicineDenervation
A system for denervation of the renal sympathetic nerve and iontophoresis drug delivery includes an iontophoresis catheter fitted with a drug coated balloon. The balloon contacts the vessel wall when inflated. One or more electrodes are associated with a surface of the balloon, and may be disposed on an outer surface of the balloon. The electrodes are operably coupled to an energy source configured to produce a bipolar or monopolar electric field between two balloon electrodes and / or between one balloon electrode and another electrode placed in contact with the patient's body. The drug-delivery catheter produces an electric potential gradient within adjacent tissue, that, facilitates iontophoresis delivery of a drug. The catheter can also include a store of one or more drugs to be delivered to the targeted tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Catheter device and method for denervation
InactiveUS20130090637A1Increase temperaturePotential for leakageCatheterSurgical instruments for heatingProximal pointDistal portion
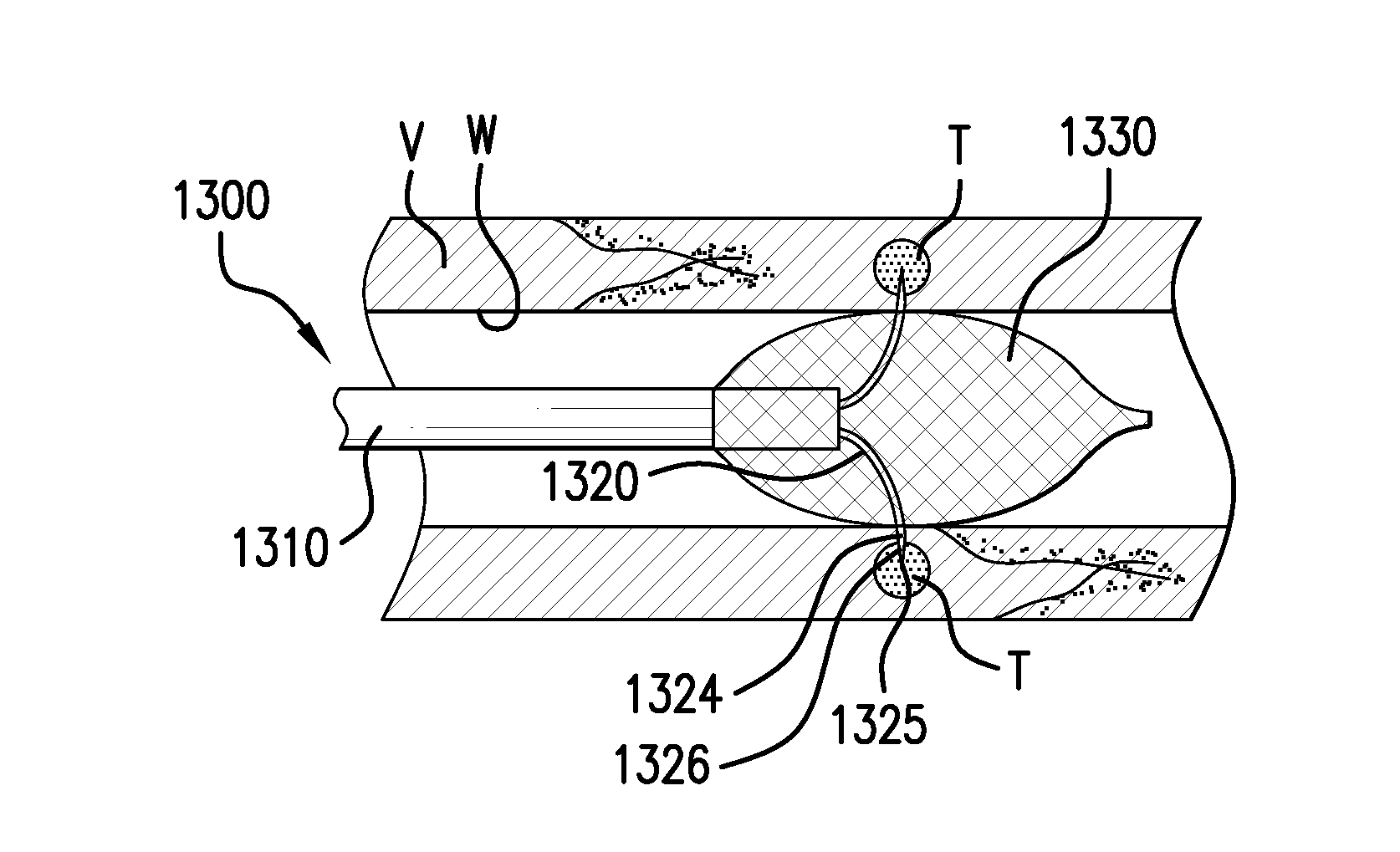
A method for denervation comprises: introducing a distal portion of a catheter to an interior of a vessel of patient, the catheter including an elongated catheter body extending longitudinally between a proximal end and a distal end along a longitudinal axis, the catheter body including the distal portion at the distal end and a catheter lumen from the proximal end to the distal end; delivering optical energy via the catheter lumen to the distal portion of the catheter body; emitting an optical beam outwardly from the distal portion, through an optical emission port disposed in the distal portion of the catheter body; and forming at least one trench using the emitted optical beam with sufficient intensity to a depth into a vessel wall of the vessel sufficient to cause tissue removal and physically sever at least one nerve associated with the vessel wall at the depth within that depth range.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
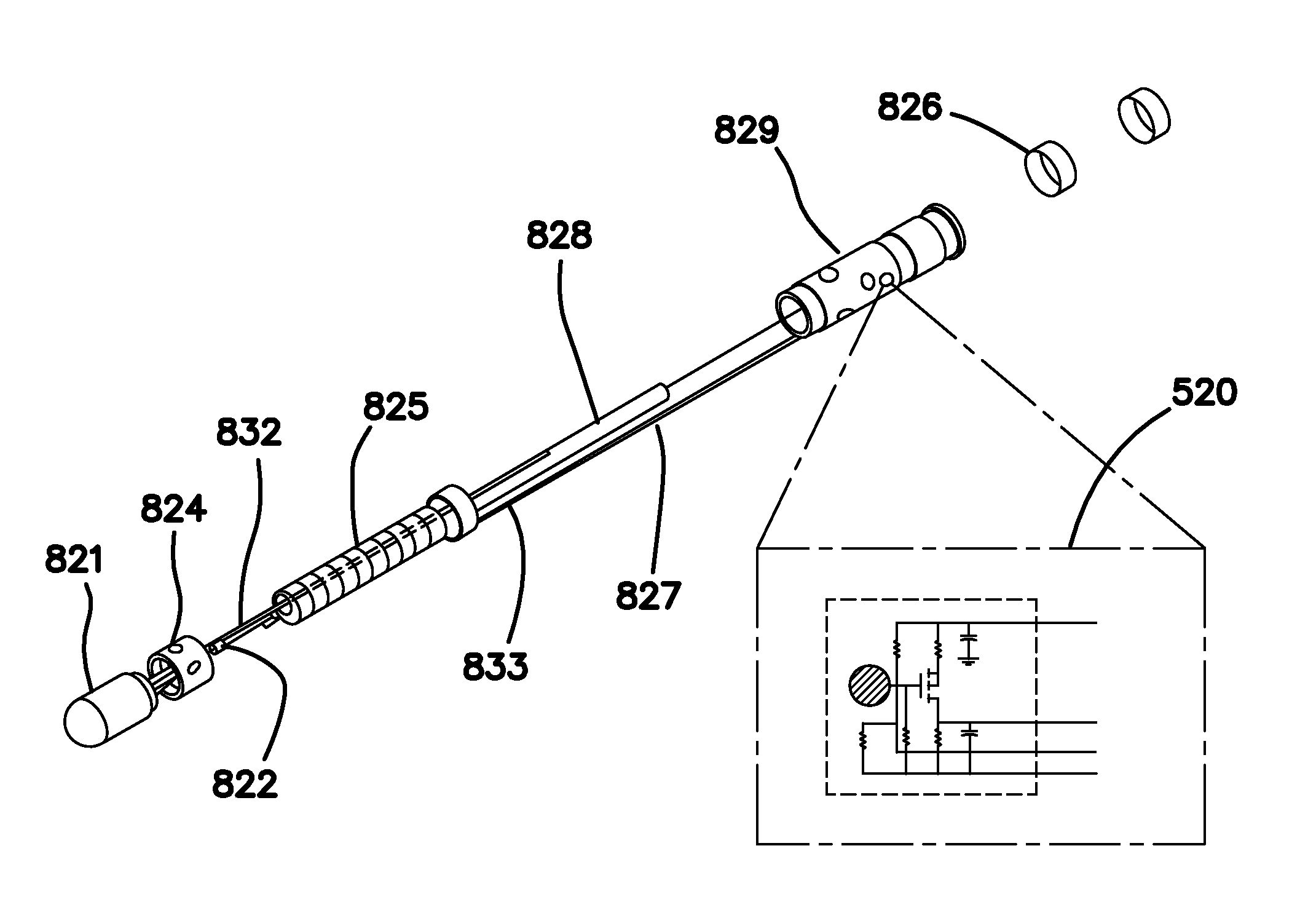
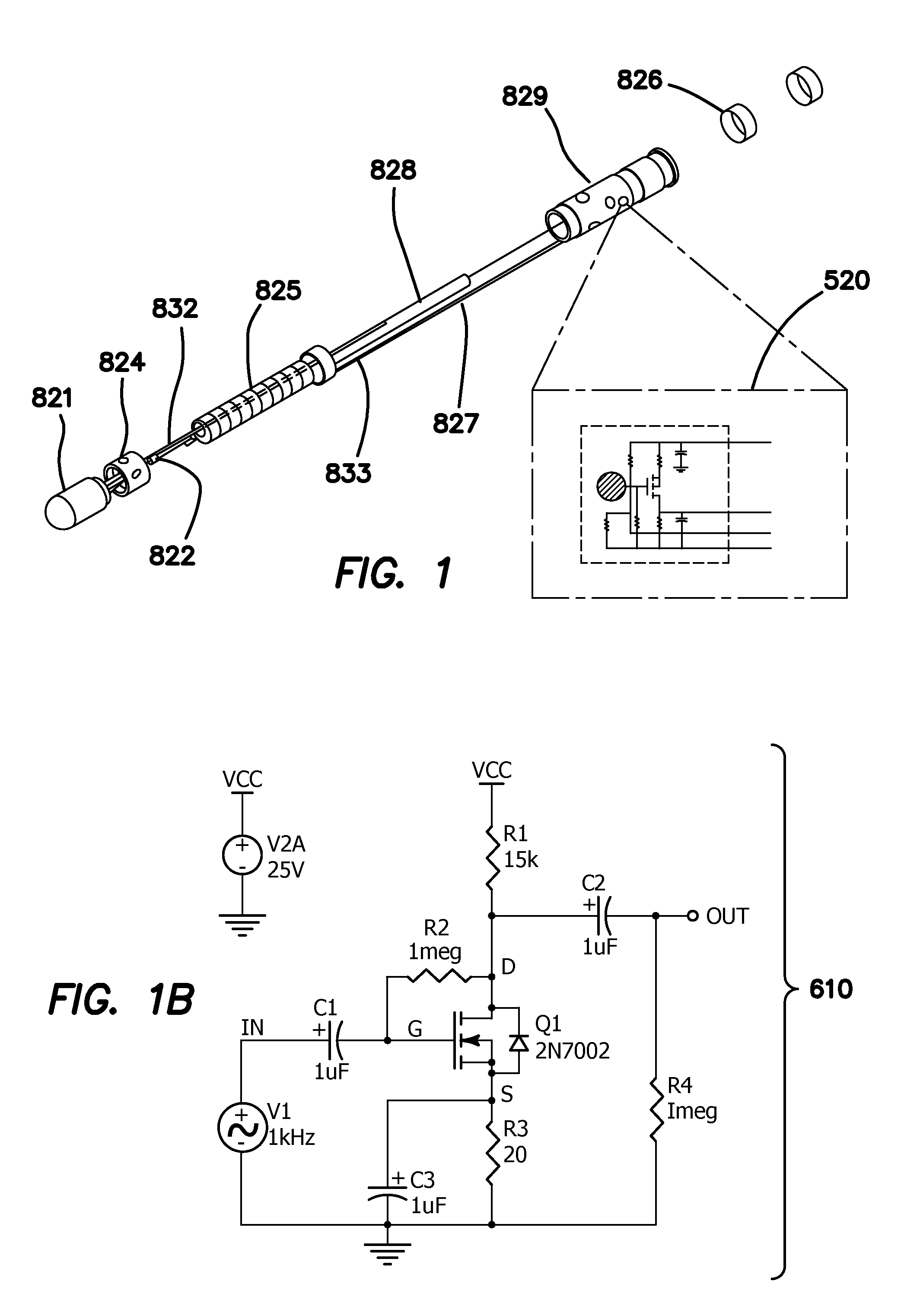
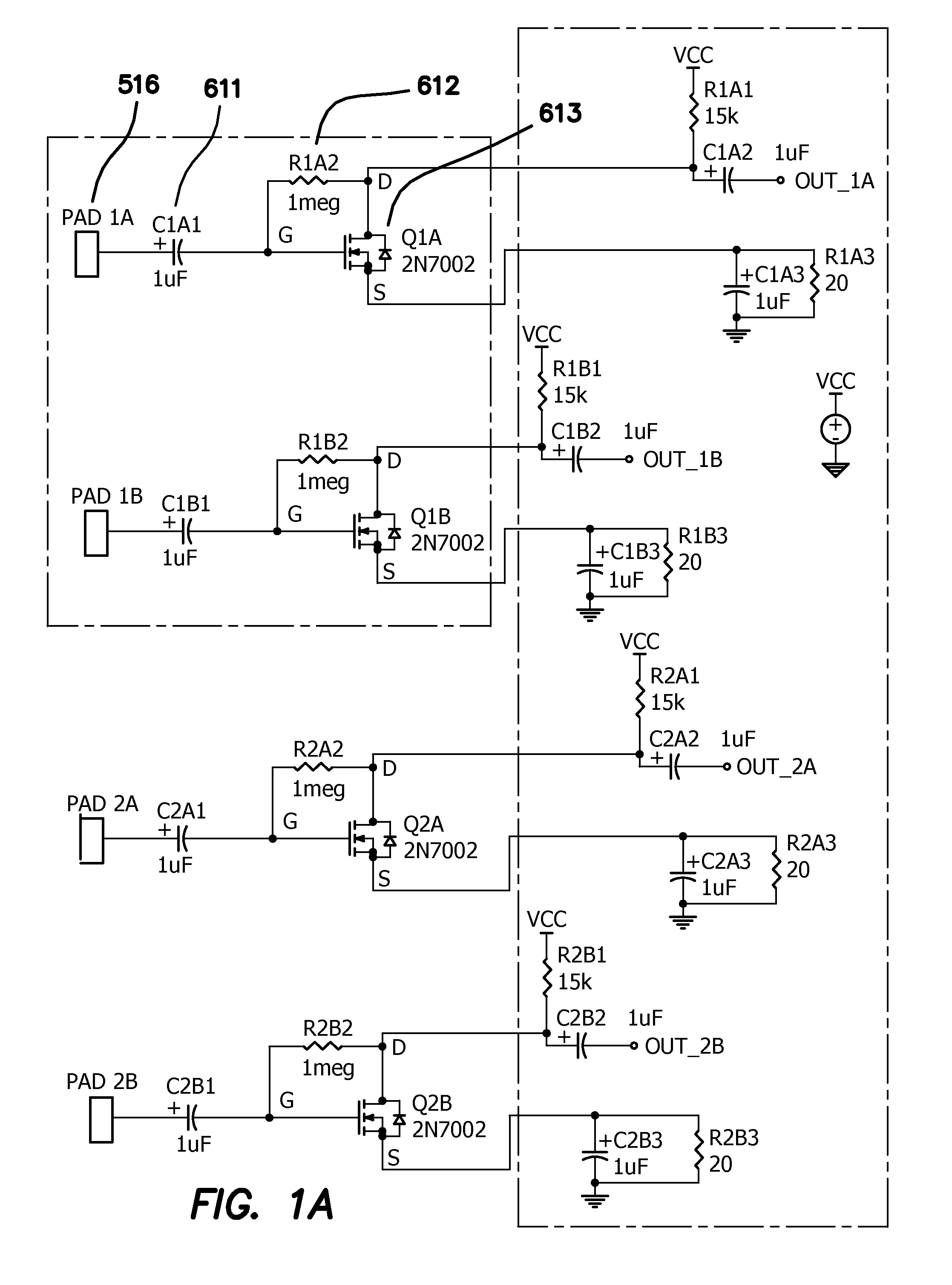
Method and apparatus for magnetically guided catheter for renal denervation employing mosfet sensor array
ActiveUS20140018792A1Improve filtering effectRapid and efficientDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSensor arrayMOSFET
A system for a mapping and ablation catheter. The catheter includes a MOSFET sensor array that provides better fidelity of the signal measurements as well as data collection and reduces the error generated by spatial distribution of the isotropic and anisotropic wave fronts and error associated with near and far field's signal averages. The system maps the change in bioelectric potential in the vicinity of an activation wave front. During measurement, the manifold carrying the sensor array translates and rotates so as to achieve a measure of high potential employing an impedance value. The system of guiding and controlling the movement of the catheter distal end is able to deliver energy for ablating the renal artery nerve and thereby providing a safe and efficient method and apparatus for neuromodulation.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Bipolar cannula for use with an electrode assembly having a separate supply electrode
An electrosurgical system preferably used for denervation procedures of nerve tissue has a control unit and a pluggable electrode assembly. The electrode assembly has a preferably disposable cannula and a preservable supply electrode assembly. The cannula has a tubular body that projects axially from a preferably pointed distal end for piercing tissue to a proximal end engaged to a first coupling assembly of the cannula. The body carries a first contact exposed directly to the nerve tissue and connected electrically to a terminal of the first coupling assembly. The supply electrode assembly has a second coupling assembly and a supply electrode that projects axially and removably into a through-bore of the body when the tool is in an operating state. The second coupling assembly carries a terminal that abuts the first coupling assembly when the coupling assemblies are mated. Preferably the supply electrode carries a temperature sensor for temperature measurement of the targeted tissue and processing by the control unit. Preferably, the electrode assembly also includes a stylet having a rod that fits into the through-bore of the body when the supply electrode assembly is removed and the tool is in a tissue penetrating state.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
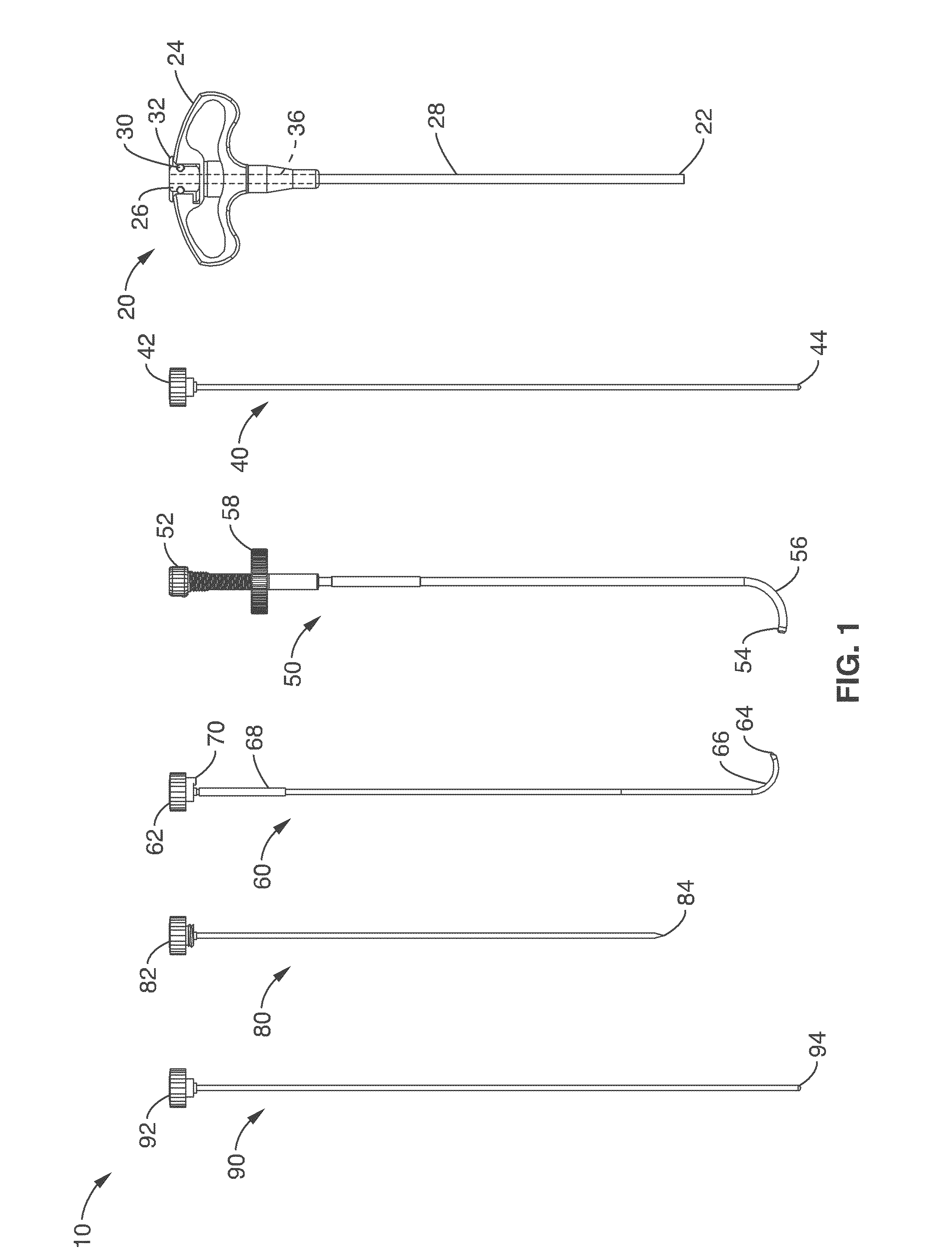
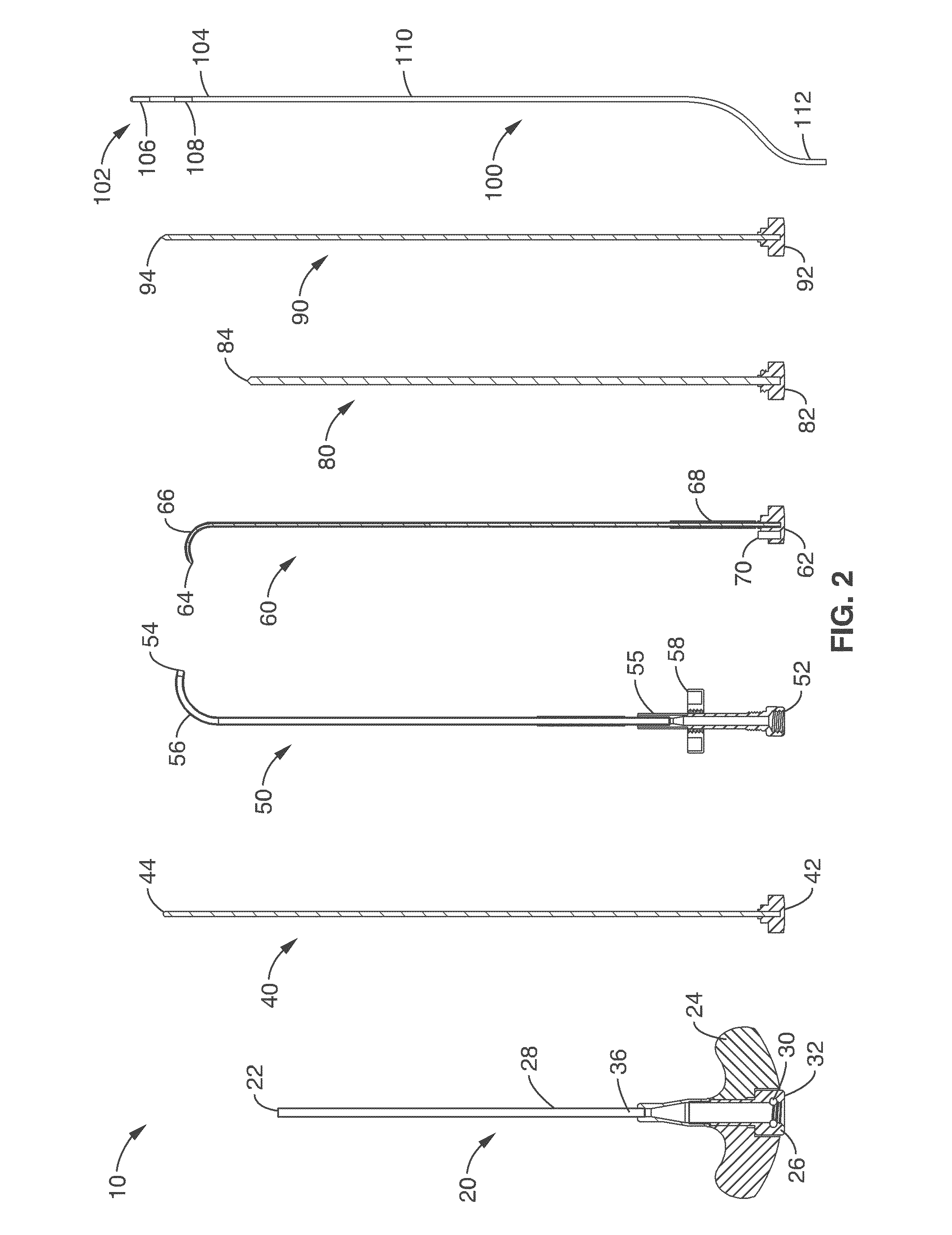
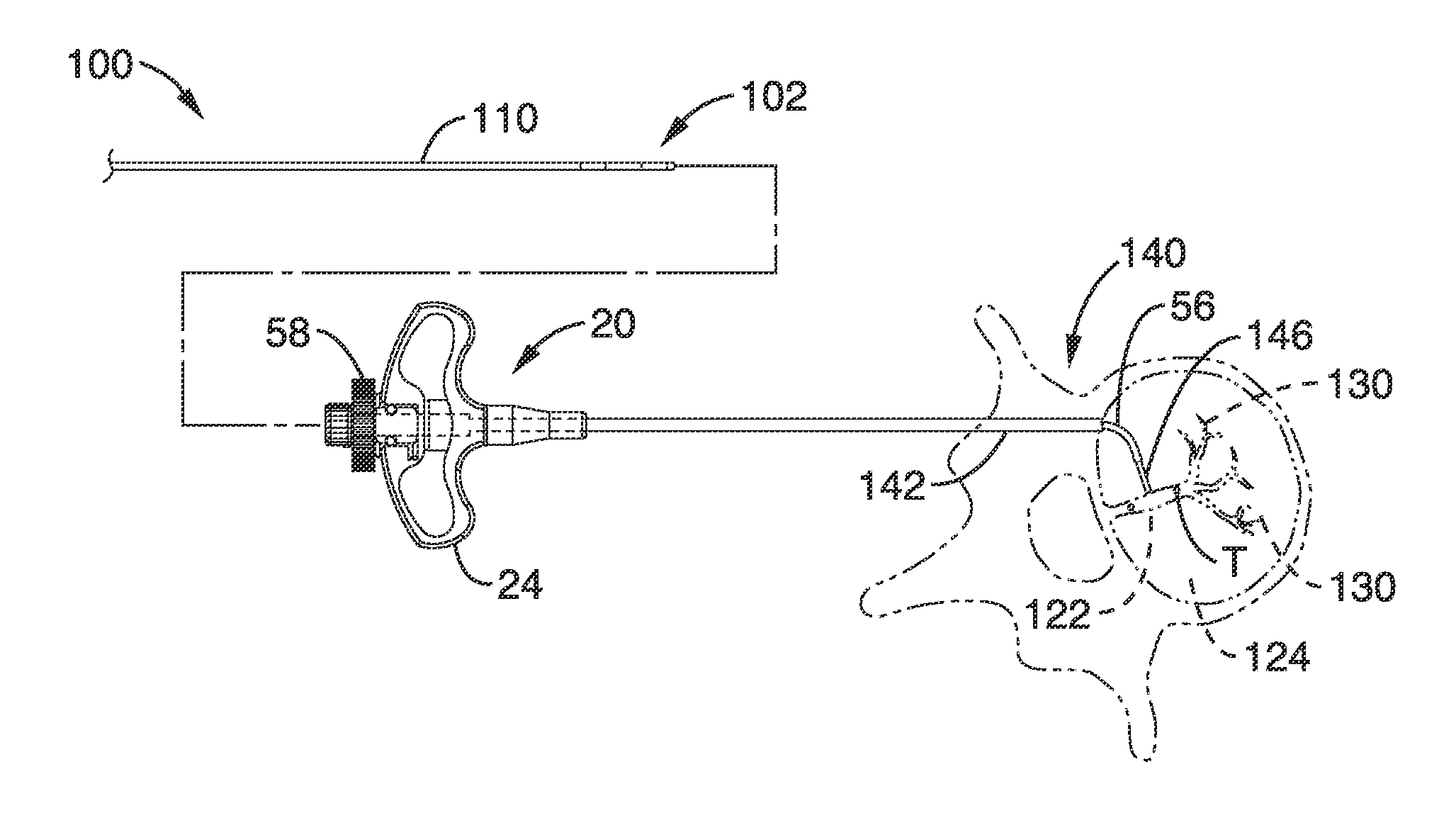
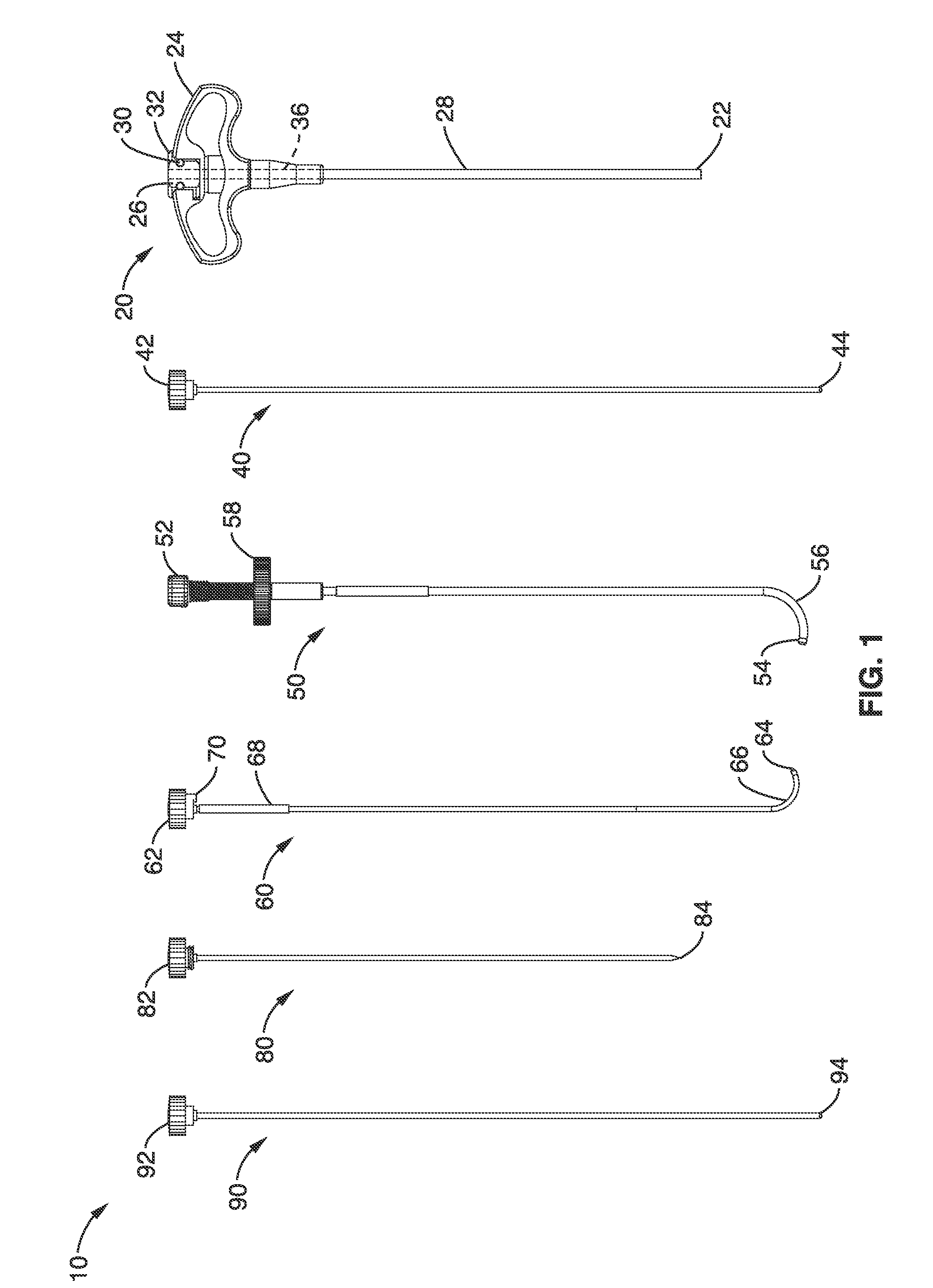
Intraosseous nerve denervation methods
System and methods for channeling a path into bone include a trocar having a proximal end, distal end and a central channel disposed along a central axis of the trocar. The trocar includes a radial opening at or near the distal end of the trocar. The system includes a curveable cannula sized to be received in the central channel, the curveable cannula comprising a curveable distal end configured to be extended laterally outward from the radial opening in a curved path extending away from the trocar. The curveable cannula has a central passageway having a diameter configured allow a probe to be delivered through the central passageway to a location beyond the curved path.
Owner:RELIEVANT MEDSYST
Basivertebral nerve denervation
System and methods for channeling a path into bone include a trocar having a proximal end, distal end and a central channel disposed along a central axis of the trocar. The trocar includes a radial opening at or near the distal end of the trocar. The system includes a curveable cannula sized to be received in the central channel, the curveable cannula comprising a curveable distal end configured to be extended laterally outward from the radial opening in a curved path extending away from the trocar. The curveable cannula has a central passageway having a diameter configured allow a probe to be delivered through the central passageway to a location beyond the curved path.
Owner:RELIEVANT MEDSYST
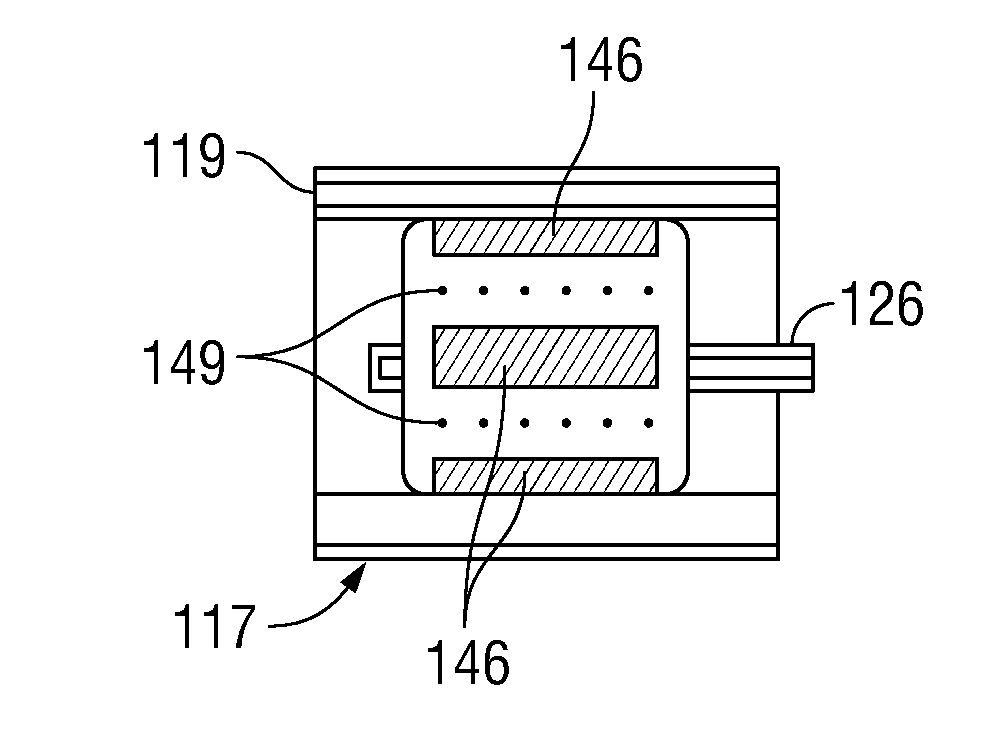
Non-electric field renal denervation electrode
ActiveUS20130282000A1Dissipating materialAvoid spreadingSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsElectrical conductorDebye length
A renal denervation device can include an elongated catheter body extending along a longitudinal axis, and an assembly connected to the catheter body. The assembly includes a plurality of heating elements connected to the catheter body. Each heating element has a conductor and a layer of an RF dissipating material such as a polymer overlying the conductor. During operation of the device, the layer of RF dissipating material is disposed between the conductor and body tissues of a subject. The layer of RF dissipating material is substantially thicker than the Debye length within the material in order to reduce the electric field reaching the tissue and to eliminate direct contact of the electrode with the body tissue.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Methods and systems for screening subjects
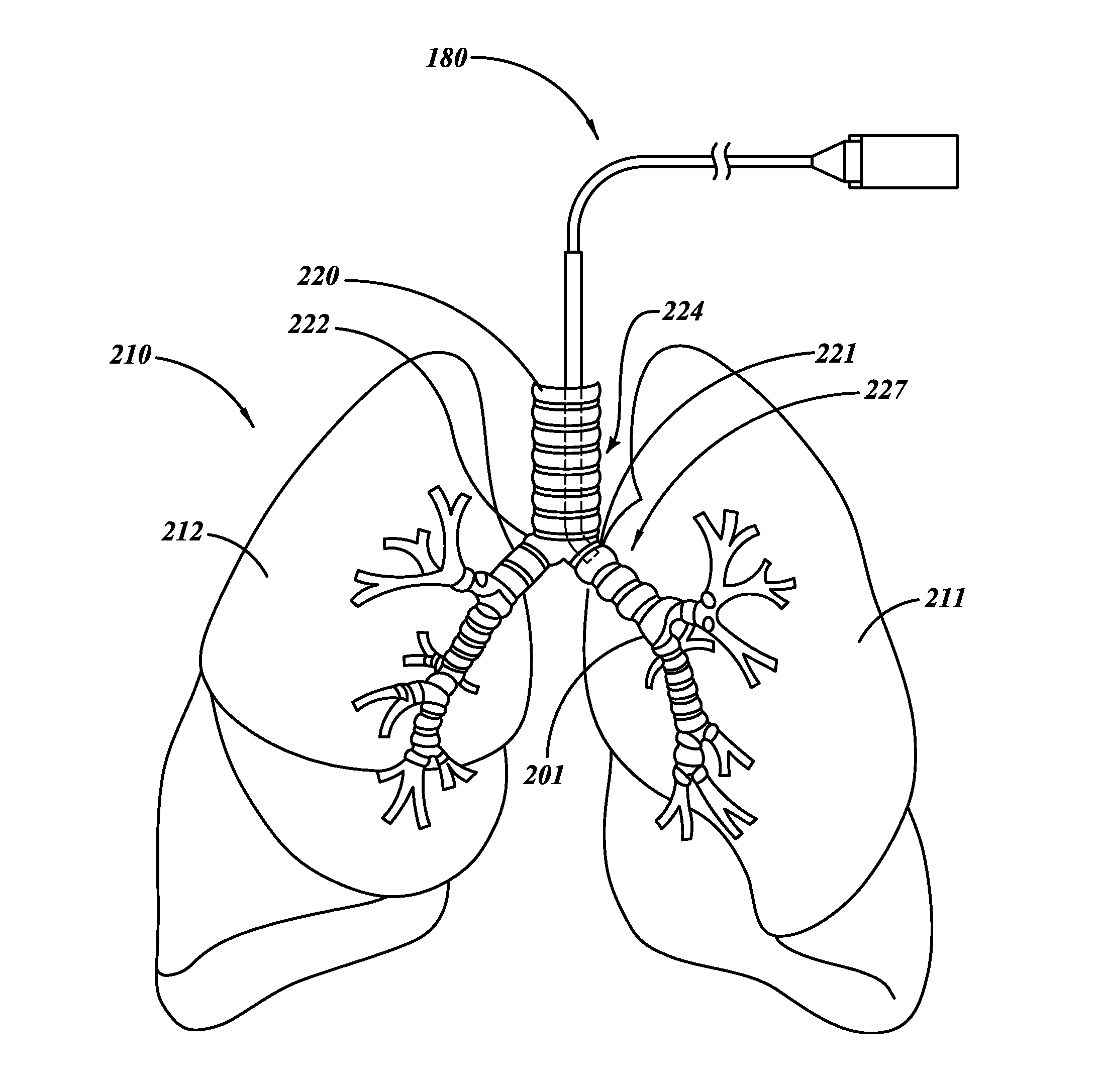
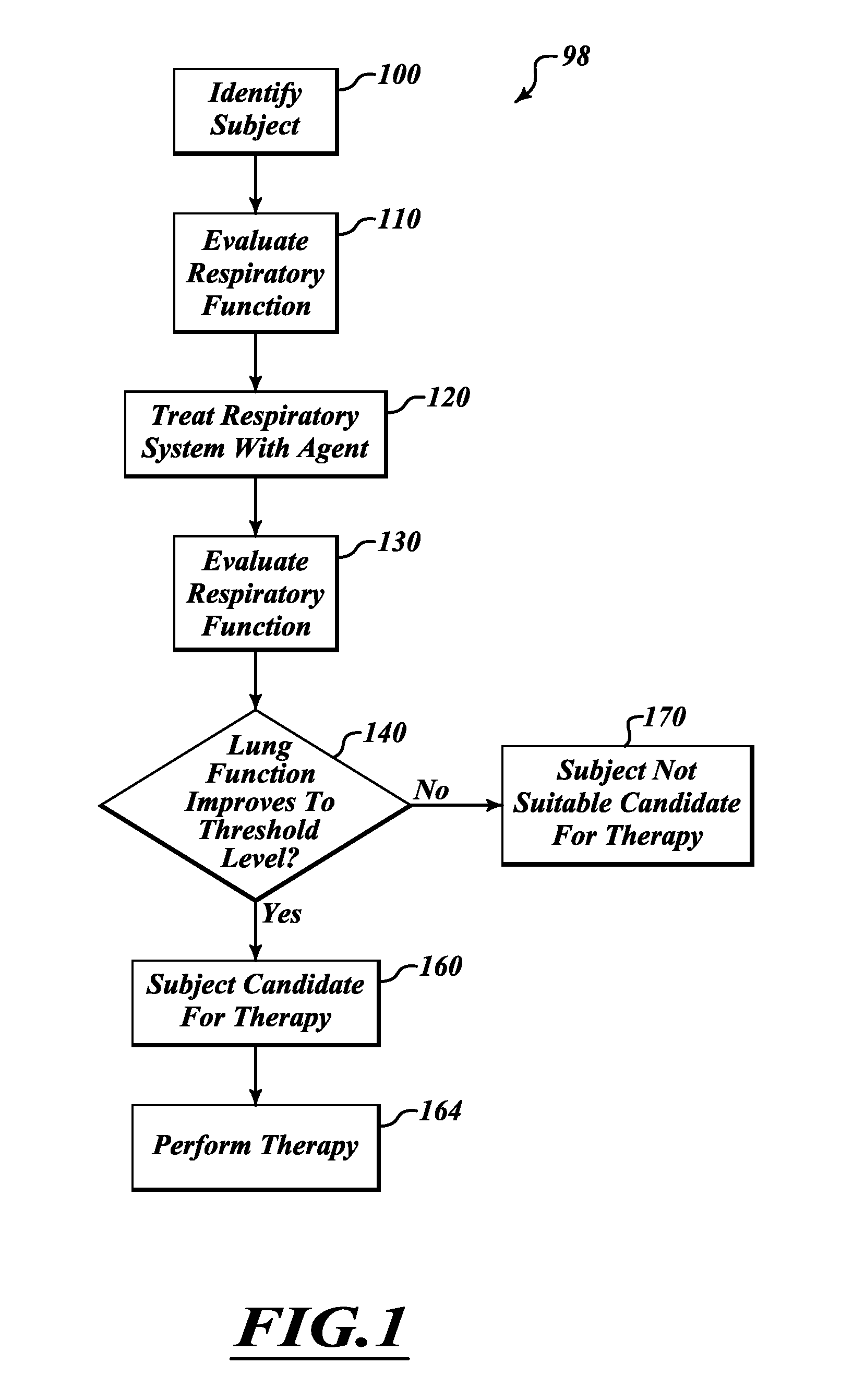
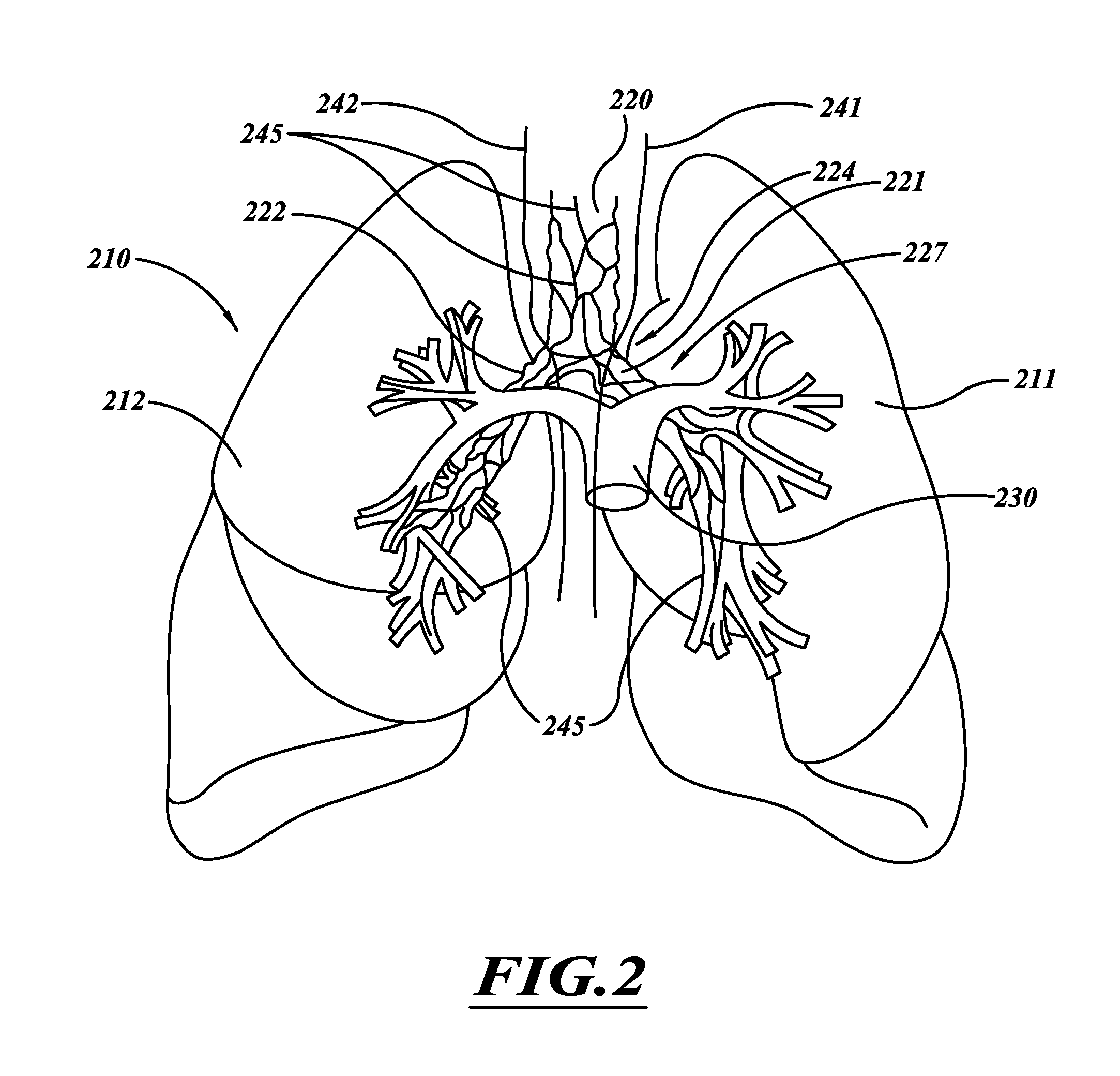
InactiveUS20120302909A1Improve exercise capacityImprove function capacityRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsTest agentScreening method
A screening method can be used to determine whether a subject is a suitable candidate for interventional therapy. The method can be used to determine the likelihood the subject will receive a therapeutic effect from denervation therapy. The determination is based, at least in part, on lung information obtained by performing lung function tests with and without treating the subject's lungs with a test agent. Based on the response to a test agent, the subject's response to a therapy is predicted.
Owner:NUVAIRA INC
Method and apparatus for non-invasive treatment of hypertension through ultrasound renal denervation
InactiveUS20120209118A1Easy to doUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorNon invasive
Non-invasive inactivation of nerve conduction in a treatment region of a mammalian subject as, for example, a region encompassing a renal artery. A therapeutic ultrasound transducer (31) is engaged with the body of the subject outside of the treatment region, preferably with the skin of the subject in proximity to the treatment region (10). The transducer is actuated to transmit therapeutically effective softly focused ultrasound energy at a level which brings tissues throughout a relatively large impact volume (22), desirably 1 cm3 or larger, to a temperature sufficient to inactivate conduction nerves but insufficient to cause rapid necrosis. The impact volume can be aligned with the treatment region using imaging techniques. The treatment can be applied without imaging or precisely locating individual nerves, and can be used, for example, to inactive renal nerves in treatment of hypertension.
Owner:OTSUKA MEDICAL DEVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com