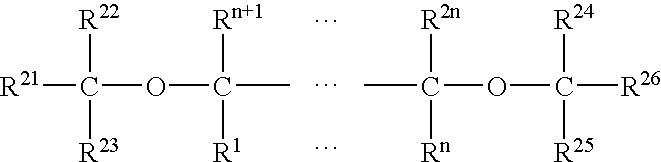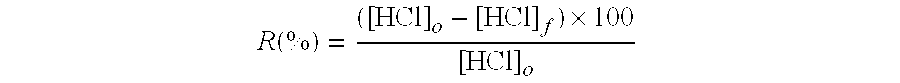Patents
Literature
65 results about "Debye" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The debye (symbol: D) (/dɛˈbaɪ/; Dutch: [dəˈbɛiə]) is a CGS unit (a non-SI metric unit) of electric dipole moment named in honour of the physicist Peter J. W. Debye. It is defined as 1×10⁻¹⁸ statcoulomb-centimeters. Historically the debye was defined as the dipole moment resulting from two charges of opposite sign but an equal magnitude of 10⁻¹⁰ statcoulomb (generally called e.s.u. (electrostatic unit) in older literature), which were separated by 1 Ångström. This gave a convenient unit for molecular dipole moments.
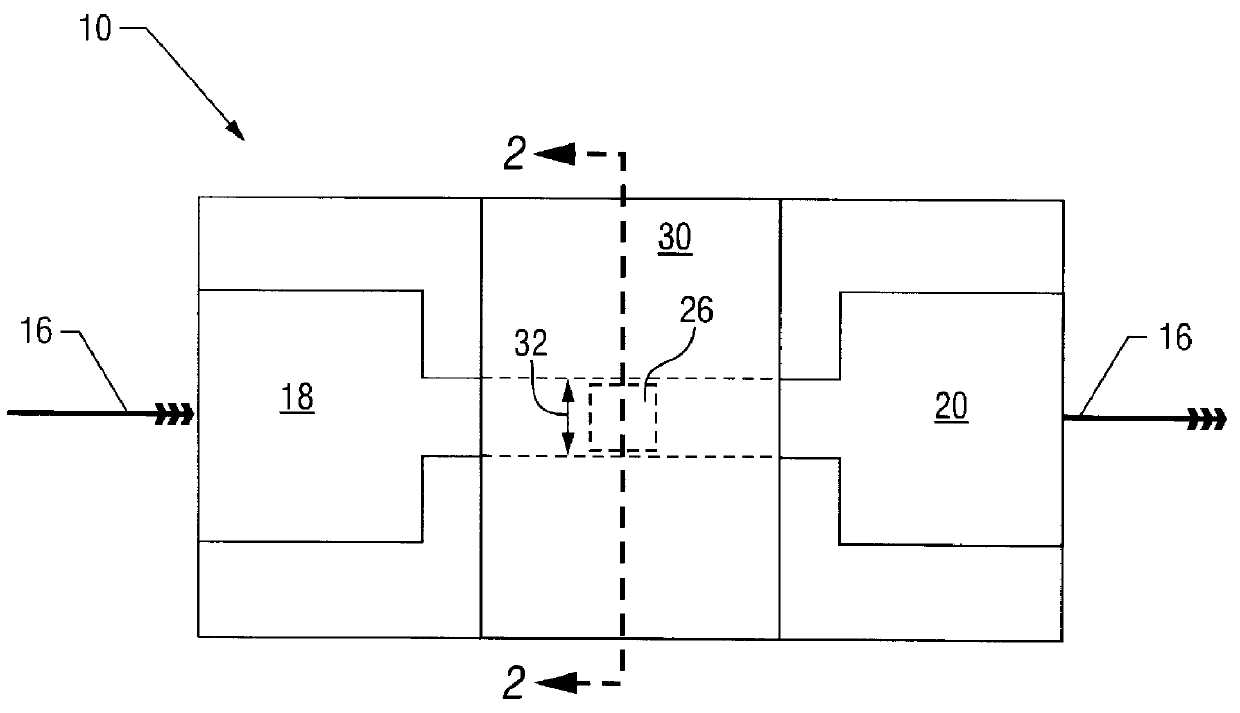
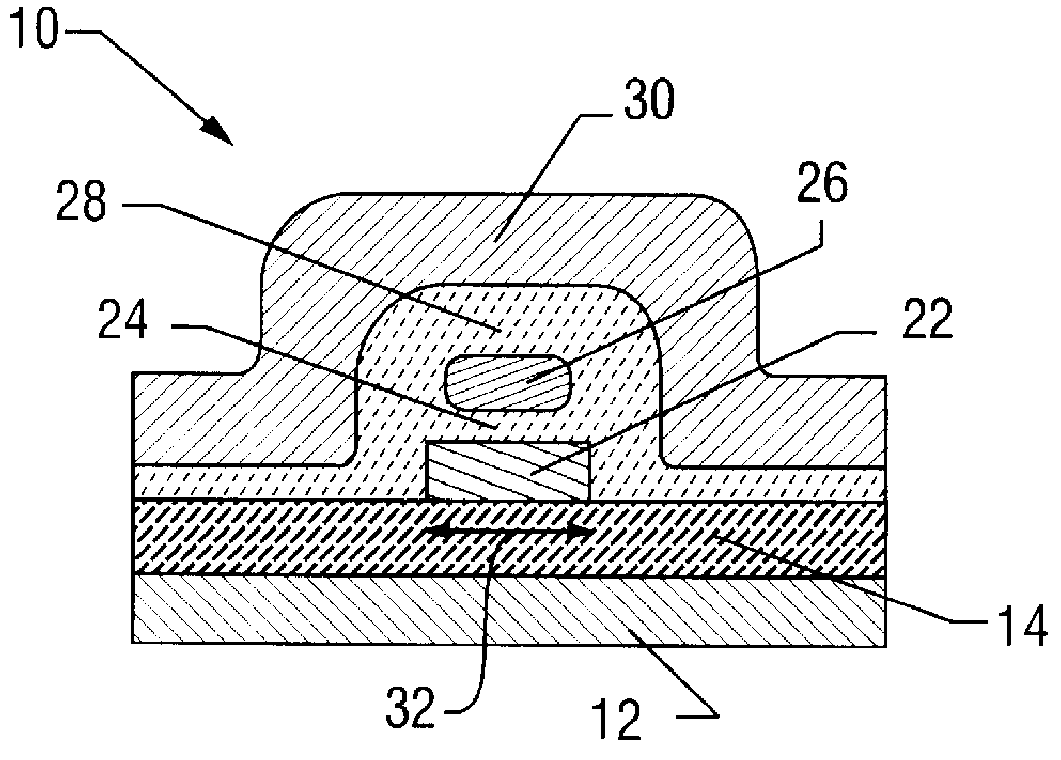
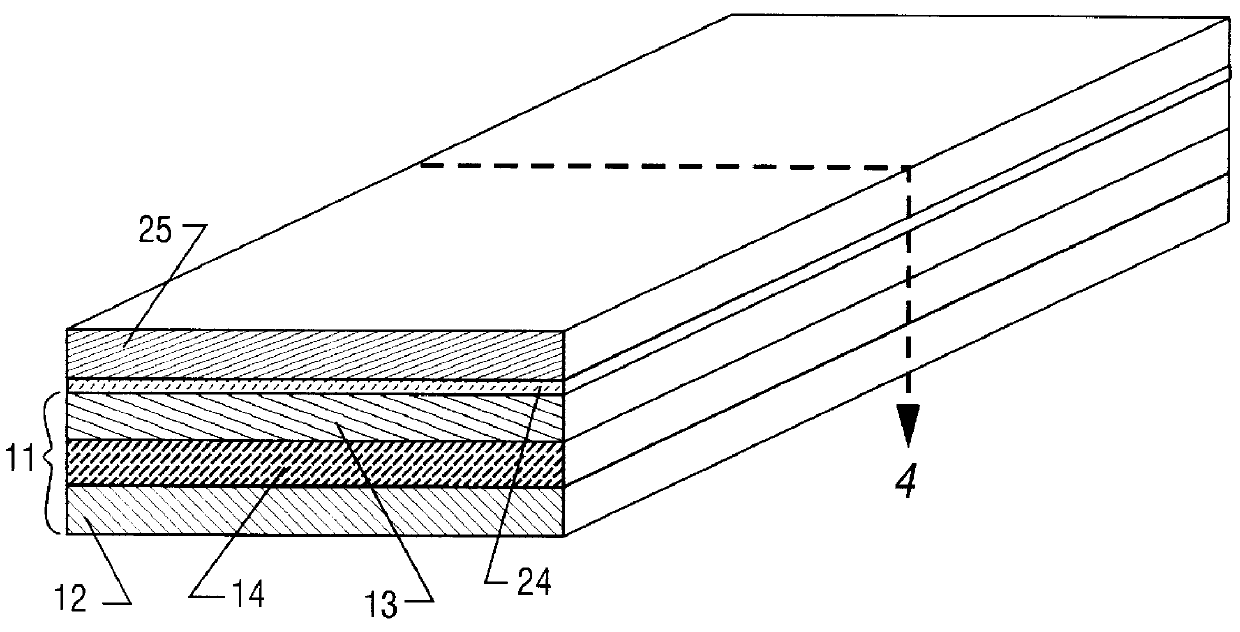
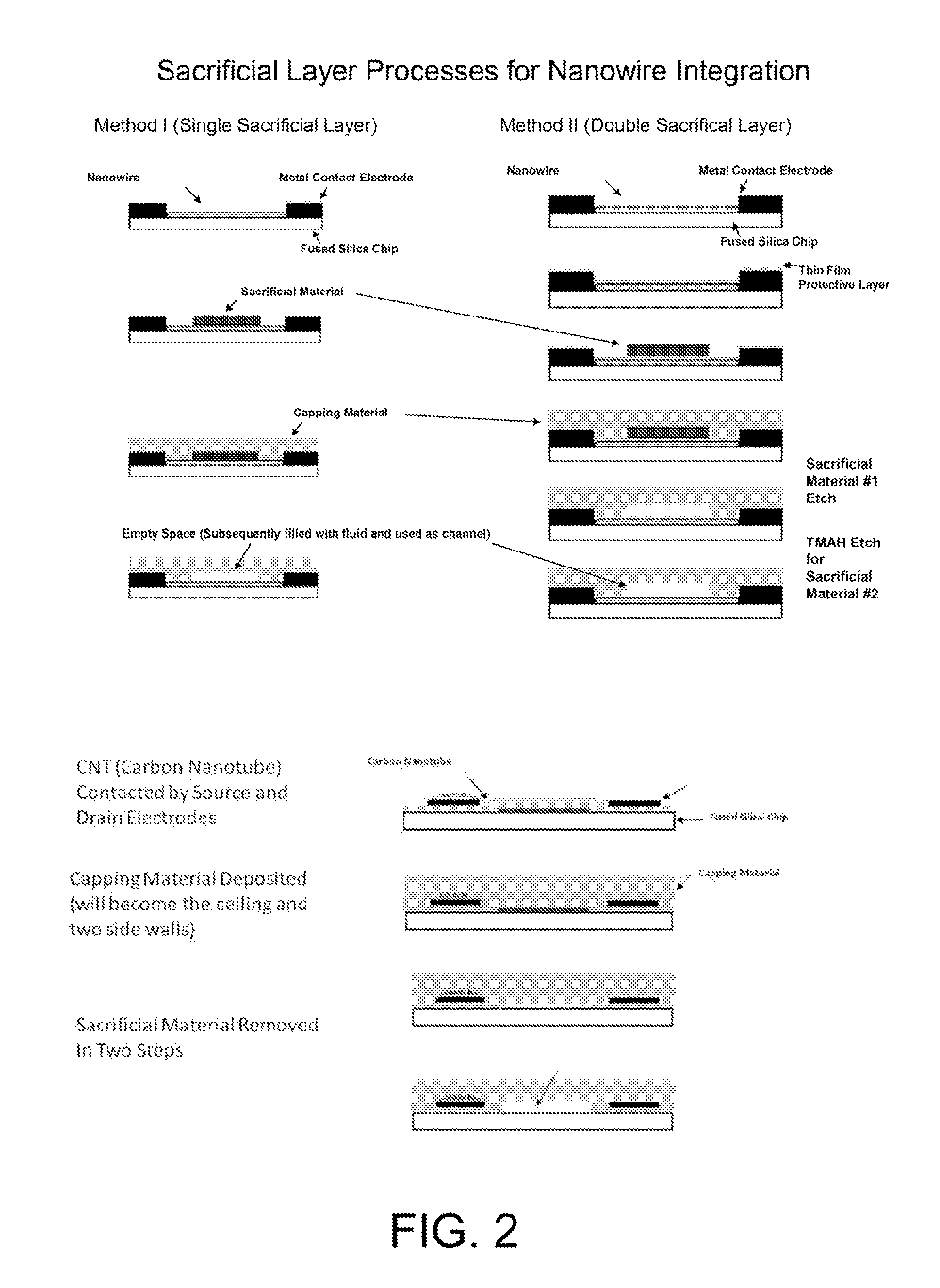
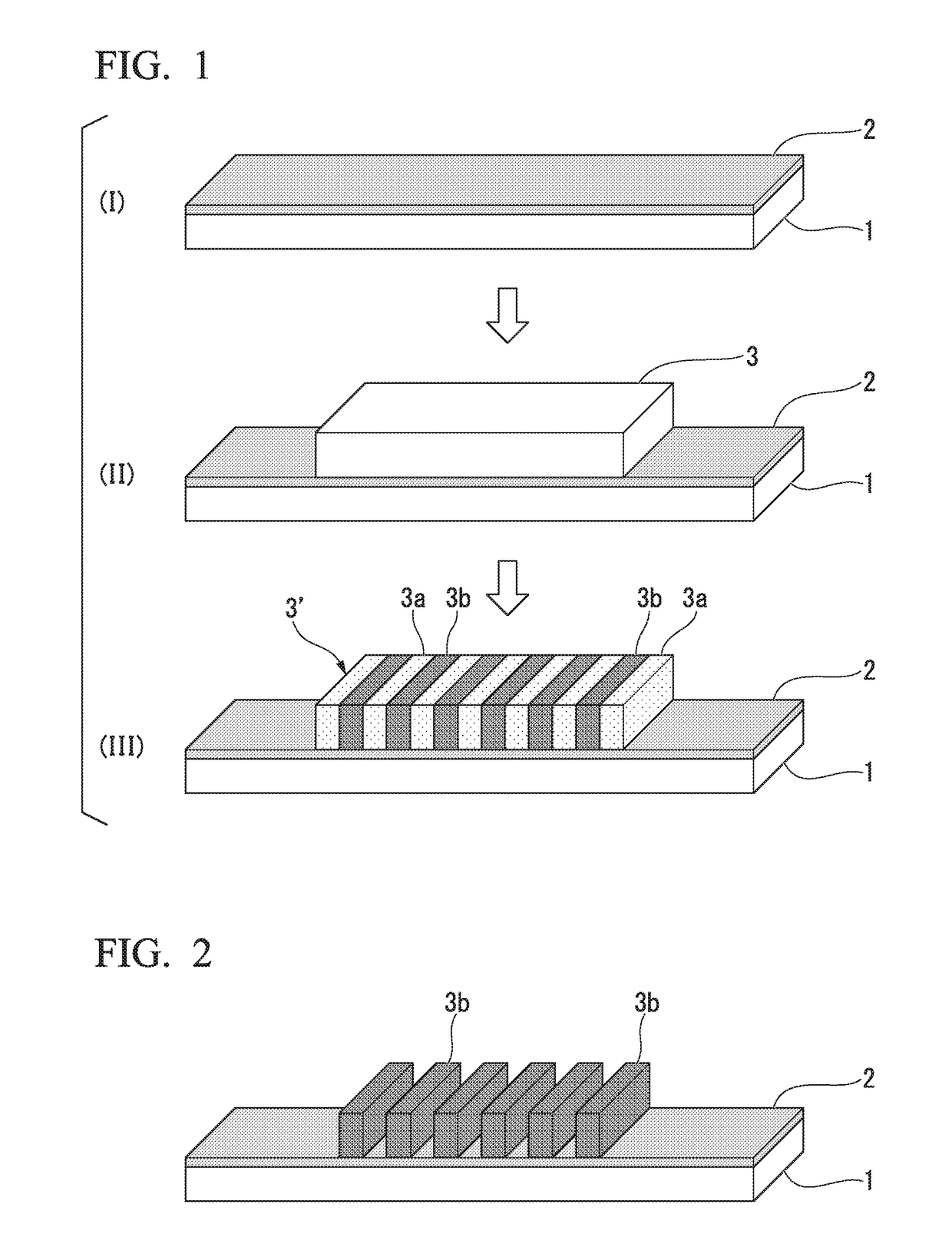
Single-electron floating-gate MOS memory
A Single Electron MOS Memory (SEMM), in which one bit of information is represented by storing only one electron, has been demonstrated at room temperature. The SEMM is a floating gate Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) transistor in silicon with a channel width (about 10 nanometers) which is smaller than the Debye screening length of a single electron stored on the floating gate, and a nanoscale polysilicon dot (about 7 nanometers by 7 nanometers by 2 nanometers) as the floating gate which is positioned between the channel and the control gate. An electron stored on the floating gate can screen the entire channel from the potential on the control gate, and lead to: (i) a discrete shift in the threshold voltage; (ii) a staircase relation between the charging voltage and the shift; and (iii) a self-limiting charging process. The structure and fabrication of the SEMM is well adapted to the manufacture of ultra large-scale integrated circuits.
Owner:MINNESOTA RGT UNIV OF A CORP OF MN
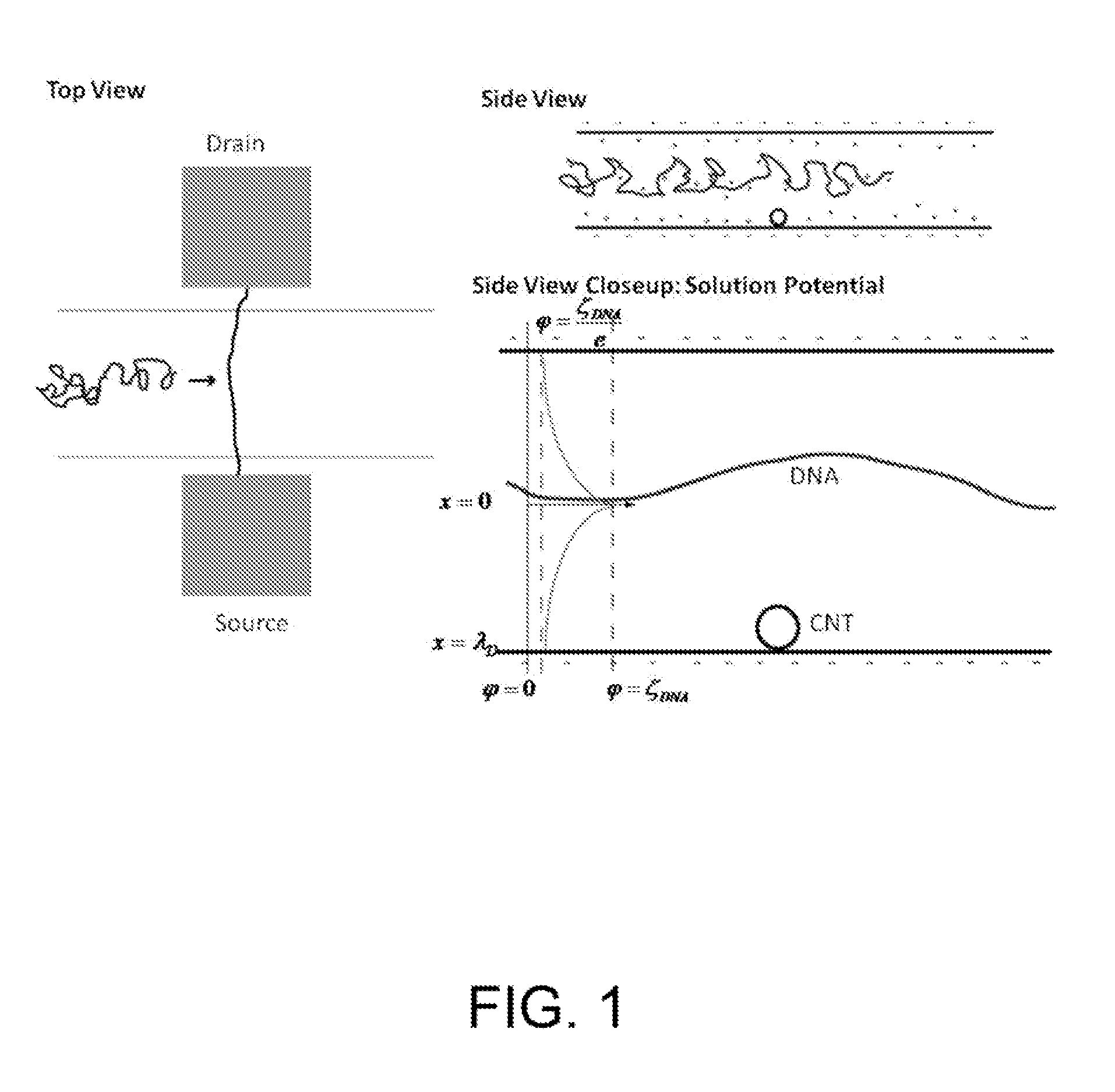
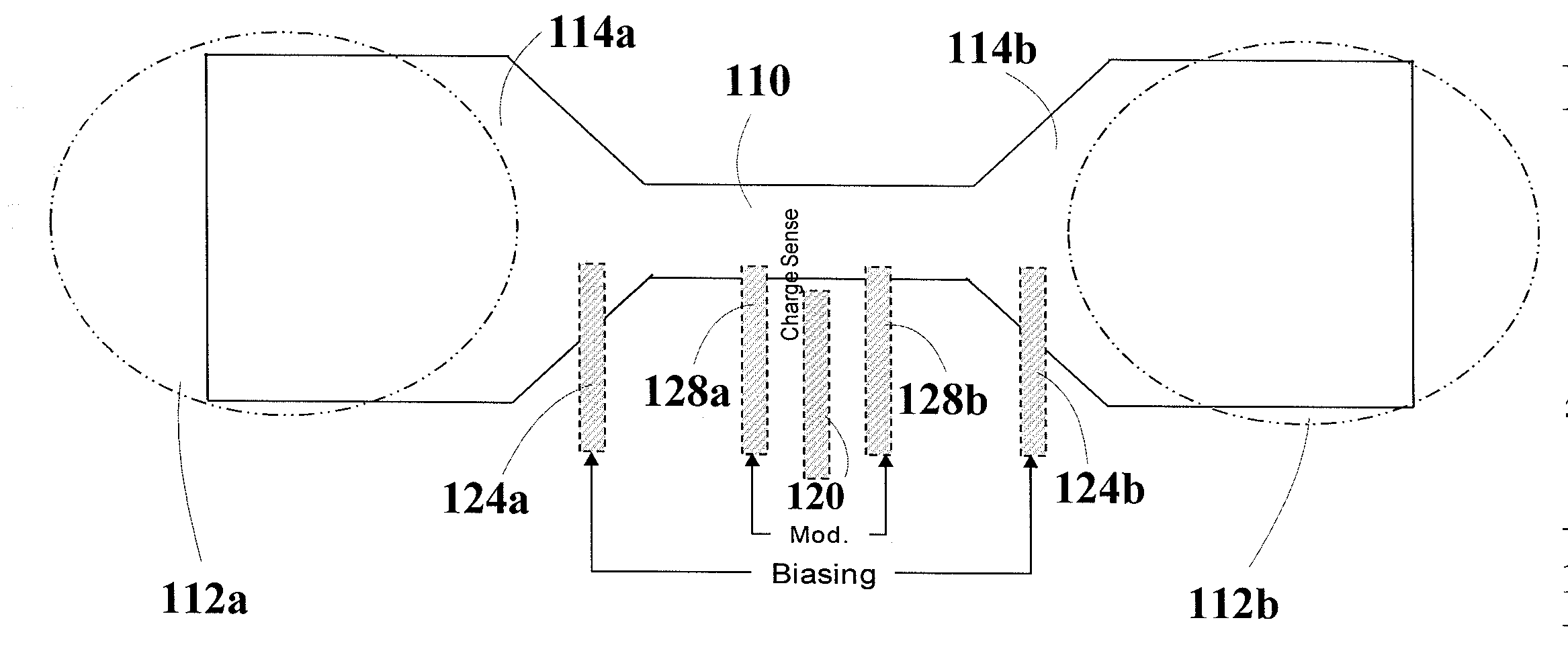
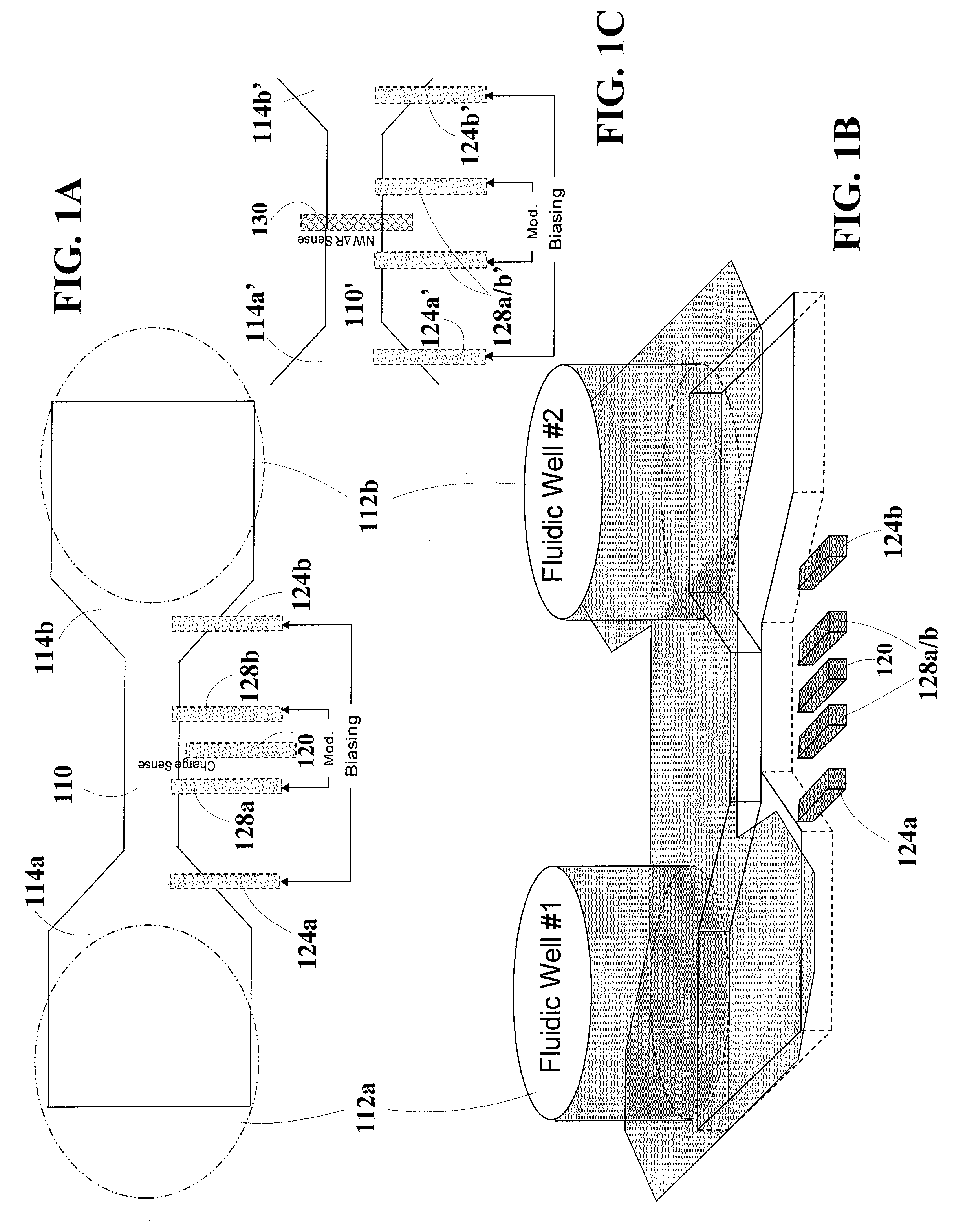
Nanofluidic channels with integrated charge sensors and methods based thereon
An electrical detector is provided that comprises a nanofluidic channel with an integrated nanoscale charge sensor. The charge sensor can be an unfunctionalized nanowire, nanotube, transistor or capacitor and can be of carbon, silicon, carbon / silicon or other semiconducting material. The nanofluidic channel depth is on the order of the Debye screening length. Methods are also provided for detecting charged molecules or biological or chemical species with the electrical detector. Charged molecules or species in solution are driven through the nanofluidic channel of the electrical detector and contact the charge sensor, thereby producing a detectable signal. Methods are also provided for detecting a local solution potential of interest. A solution flowing through the nanofluidic channel of the electrical detector contacts the charge sensor, thereby producing a detectable local solution potential signal.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
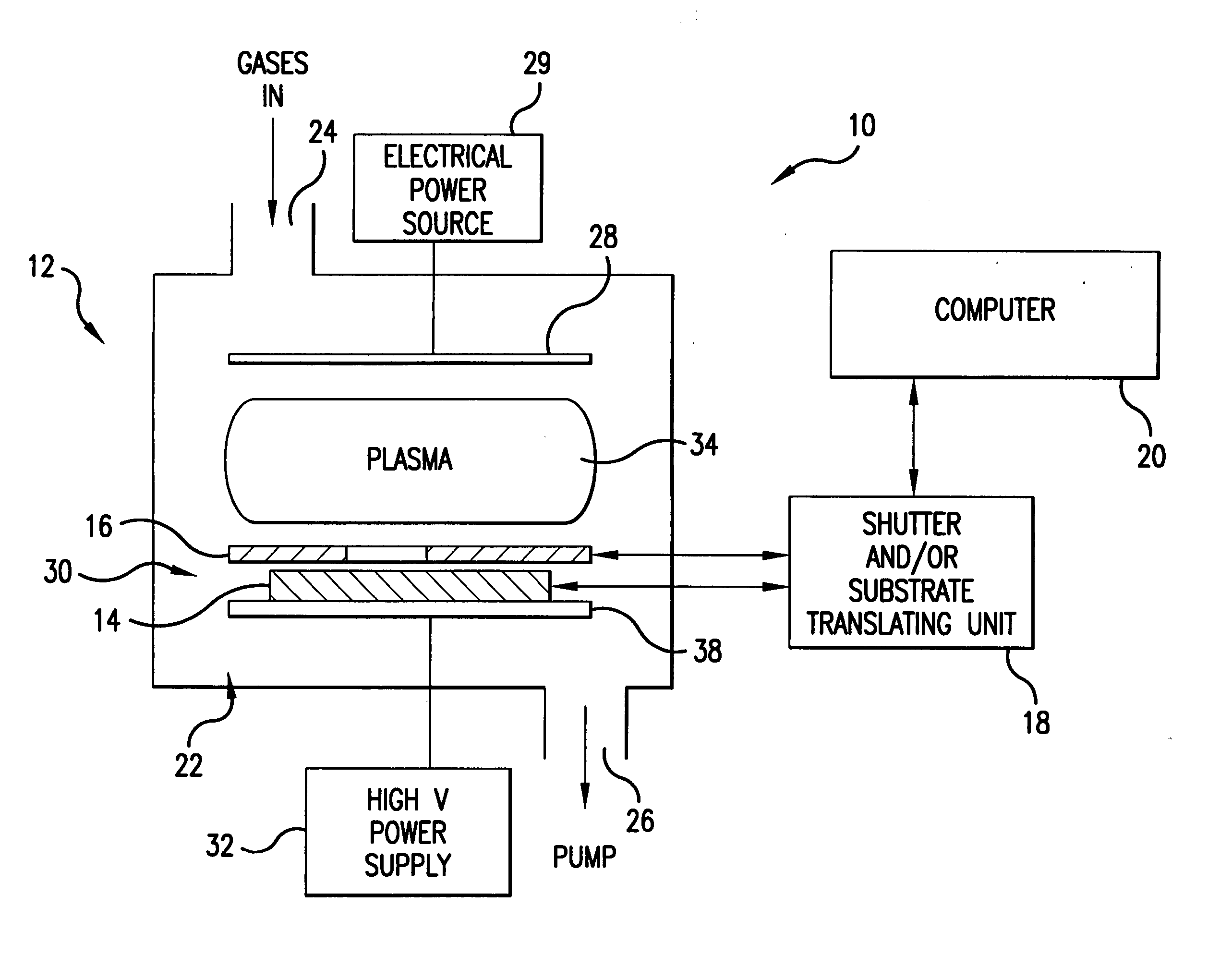
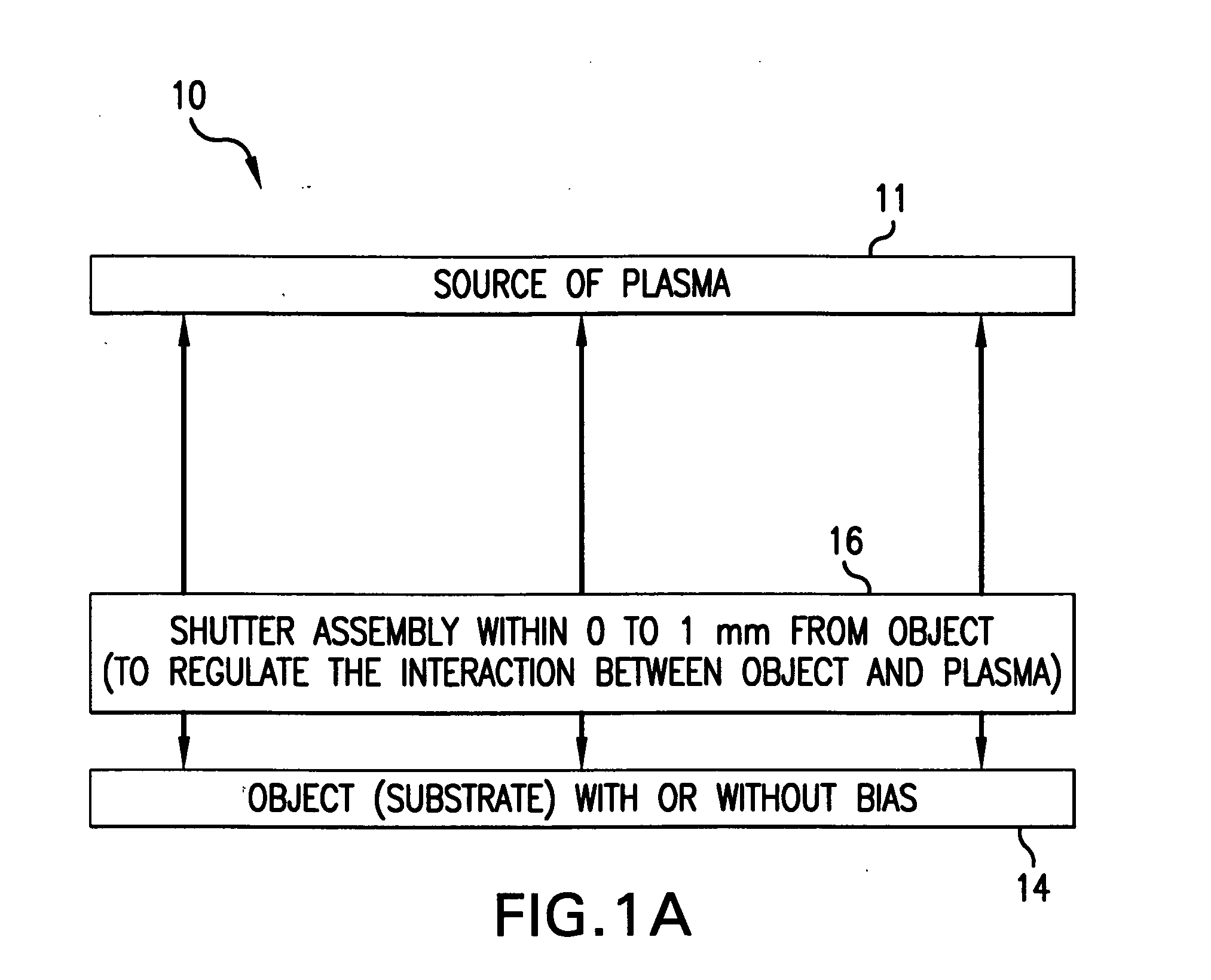
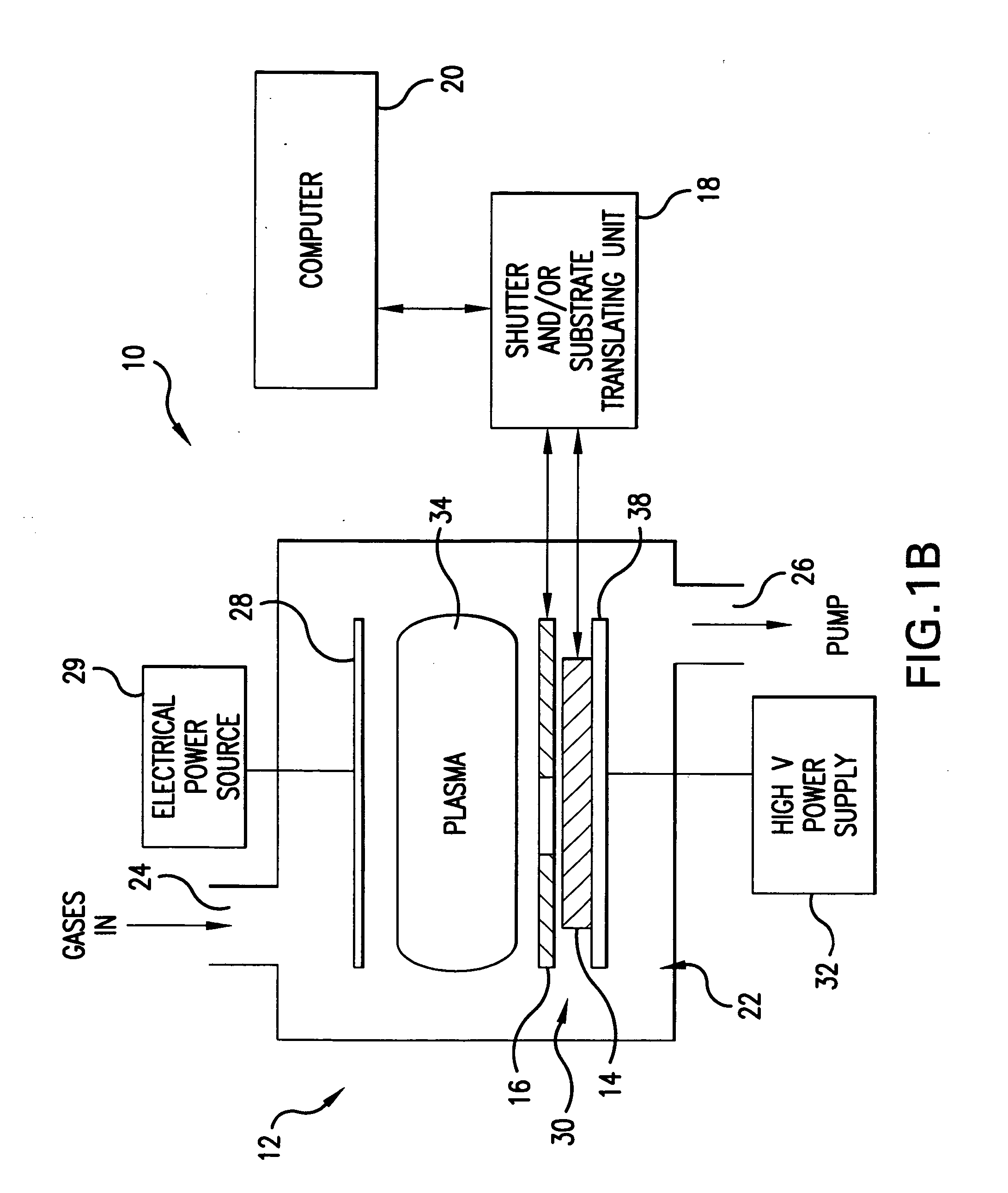
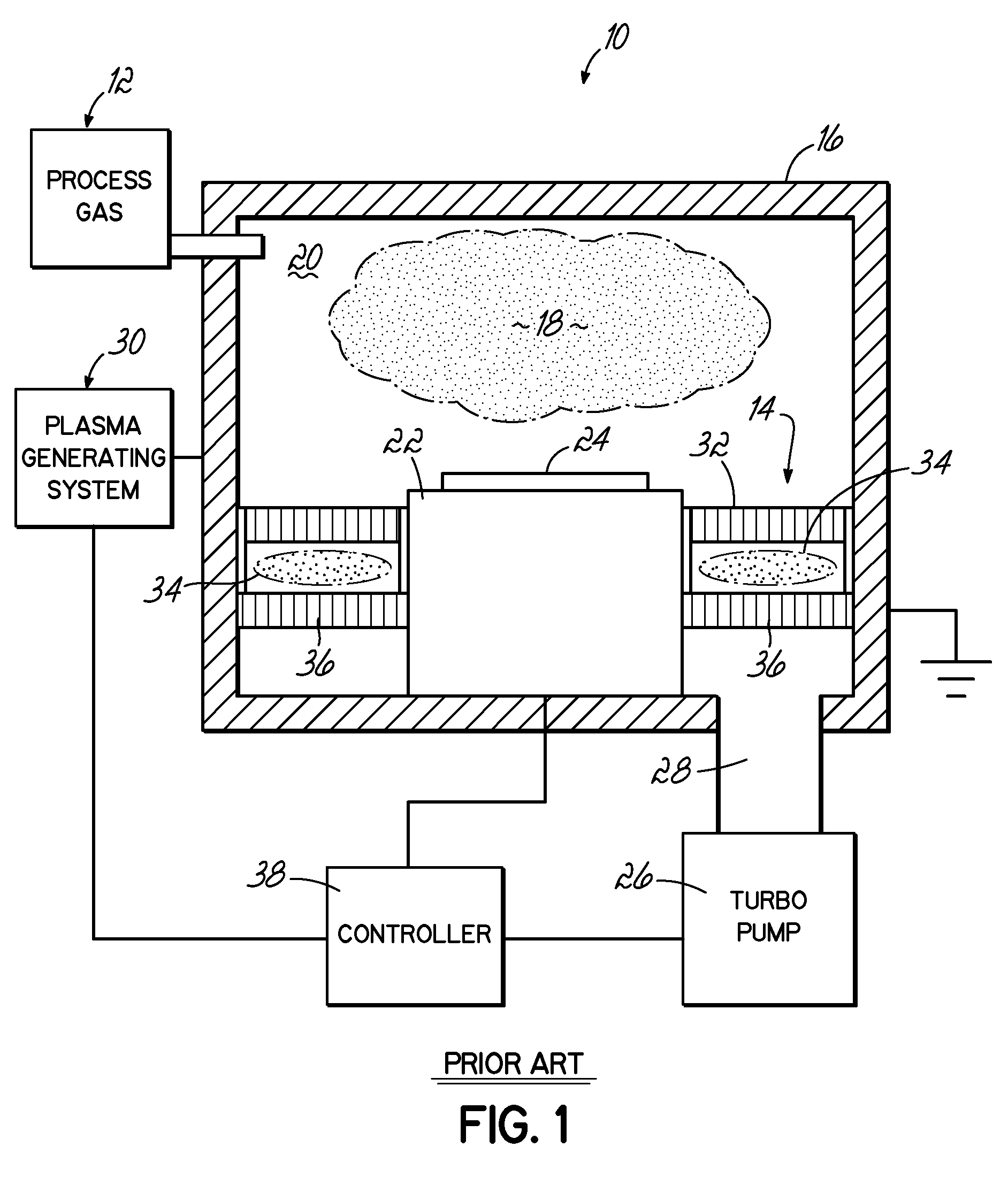
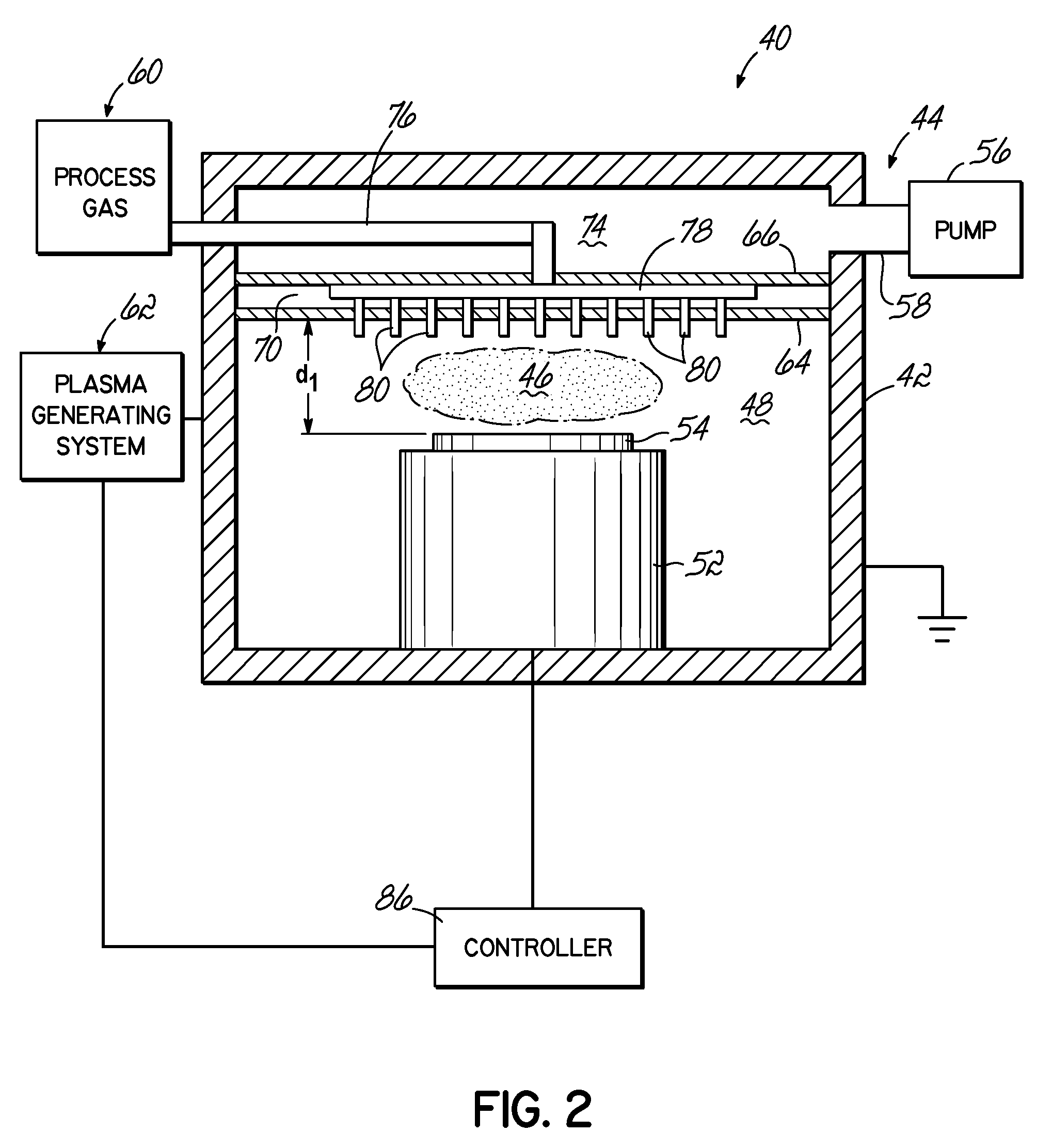
Method and system for nanoscale plasma processing of objects
InactiveUS20050051517A1Permit control of interactionPrecise, short time, nanoscale plasma processingCellsElectric discharge tubesInteraction timeDebye
A plasma processing system includes a source of plasma, a substrate and a shutter positioned in close proximity to the substrate. The substrate / shutter relative disposition is changed for precise control of substrate / plasma interaction. This way, the substrate interacts only with a fully established, stable plasma for short times required for nanoscale processing of materials. The shutter includes an opening of a predetermined width, and preferably is patterned to form an array of slits with dimensions that are smaller than the Debye screening length. This enables control of the substrate / plasma interaction time while avoiding the ion bombardment of the substrate in an undesirable fashion. The relative disposition between the shutter and the substrate can be made either by moving the shutter or by moving the substrate.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
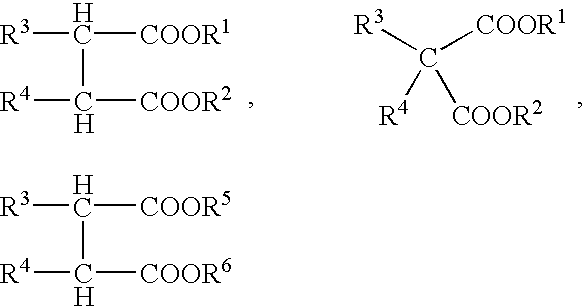
Solid titanium catalyst component, process for preparing same, olefin polymerization catalyst containing same, and olefin polymerization process
InactiveUS6521560B1QuantityHigh stereoregularityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPolyolefinElectron donor
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Composite microporous film, and production method and use thereof
ActiveCN1882436AGood adhesionHigh mechanical strengthSemi-permeable membranesFinal product manufactureDebyePolyolefin
Disclosed is a composite microporous film which is obtained by applying a liquid mixture containing (a) a fluororesin which can be gelated, (b) a good solvent therefor and (c) a poor solvent therefor having a dipole moment of not more than 1.8 Debye to at least one surface of a polyolefin microporous film and drying it, thereby forming a coating layer composed of a porous body of the fluororesin on the surface. The composite microporous film has columnar through holes in the coating layer, and has an excellent balance among permeability, adhesion to electrodes, mechanical strength, thermal shrinkage resistance, shutdown characteristics and meltdown characteristics.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Method and apparatus for ion mobility spectrometry with alignment of dipole direction (IMS-ADD)
ActiveUS7170053B2Low ion lossesHigh sensitivityTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDebyeFree rotation
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
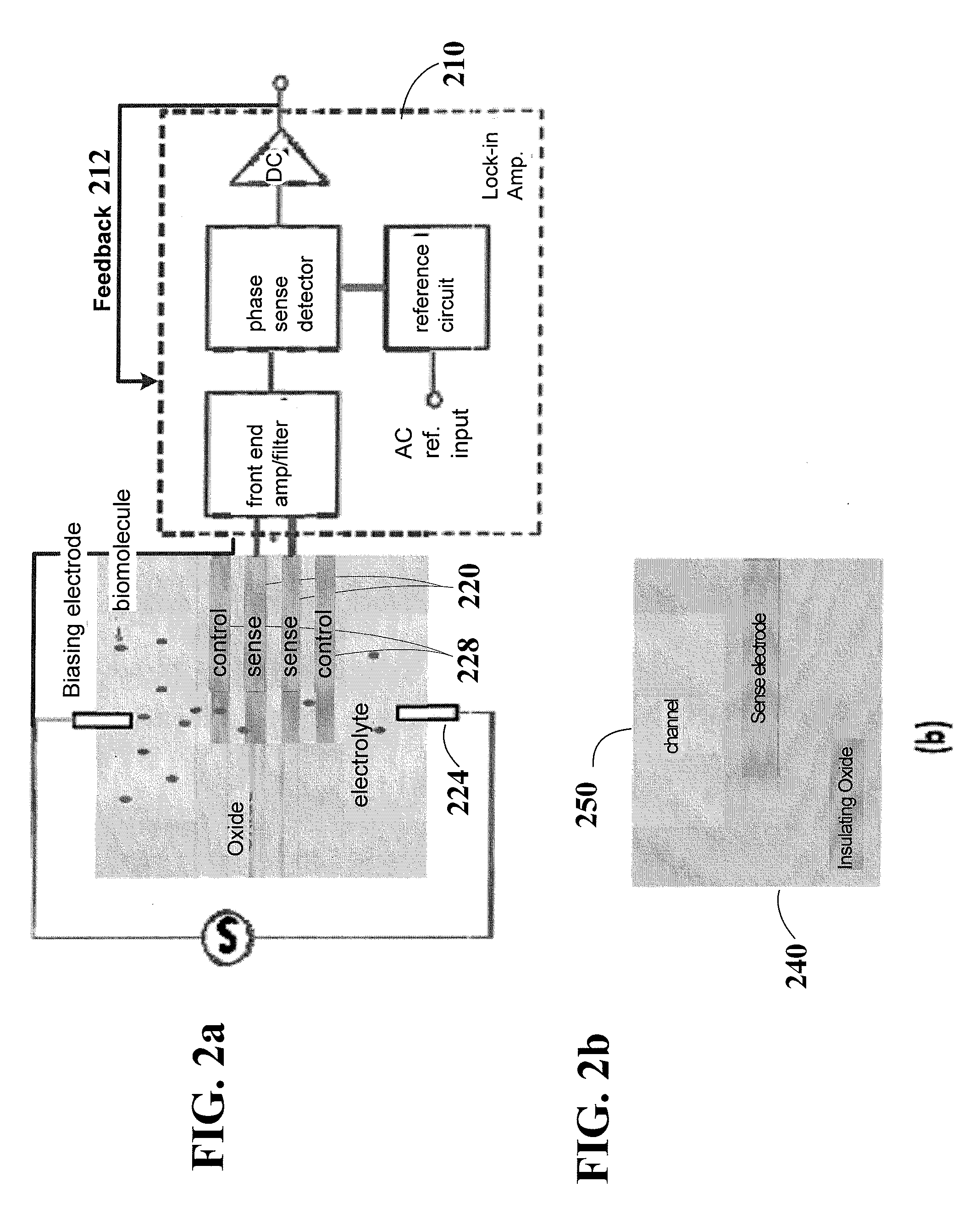
Electro-diffusion enhanced bio-molecule charge detection using electrostatic interaction
According to one aspect, the disclosure is directed to an example embodiment in which a circuit-based arrangement includes a circuit-based substrate securing a channel, with an effective width that is not limited by the Debye screening length, along a surface of the substrate. A pair of reservoirs are included in or on the substrate and configured for containing and presenting a sample having bio-molecules for delivery in the channel. A pair of electrodes electrically couple a charge in the sample to enhance ionic current flow therein (e.g., to overcome the electrolyte screening), and a sense electrode is located along the channel for sensing a characteristic of the biological sample by using the electrostatic interaction between the enhanced ionic current flow of the sample and the sense electrode. Actual detection occurs by using a charge-signal processing circuit to process the sensed charge signal and, therefrom, provide an output indicative of a signature for the bio-molecules delivered in the channel.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and apparatus for ion mobility spectrometry with alignment of dipole direction (IMS-ADD)
ActiveUS20060219889A1Low ion lossesHigh sensitivityTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDebyeFree rotation
Techniques and instrumentation are described for analyses of substances, including complex samples / mixtures that require separation prior to characterization of individual components. A method is disclosed for separation of ion mixtures and identification of ions, including protein and other macromolecular ions and their different structural isomers. Analyte ions are not free to rotate during the separation, but are substantially oriented with respect to the drift direction. Alignment is achieved by applying, at a particular angle to the drift field, a much stronger alternating electric field that “locks” the ion dipoles with moments exceeding a certain value. That value depends on the buffer gas composition, pressure, and temperature, but may be as low as ˜3 Debye under certain conditions. The presently disclosed method measures the direction-specific cross-sections that provide the structural information complementing that obtained from known methods, and, when coupled to those methods, increases the total peak capacity and specificity of gas-phase separations. Simultaneous 2-D separations by direction-specific cross sections along and orthogonally to the ion dipole direction are also possible.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Radiation curable compositions
InactiveUS20030149127A1Enhanced reactivity and photosensitivityGlass optical fibreAdditive manufacturing apparatusDebyeHigh dielectric permittivity
The invention relates to a radiation curable composition comprising radiation curable components wherein at least one component of the radiation curable composition contains a functional group which, when attached to an acrylate group has a calculated Boltzmann average dipole moment of higher than 3.5 Debye. The invention further relates to radiation curable optical fiber coating compositions having a high dielectric constant.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Complex index refraction tomography with sub lambda/6-resolution
The present invention discloses a method to improve the image resolution of a microscope. This improvement is based on the mathematical processing of the complex field computed from the measurements with a microscope of the wave emitted or scattered by the specimen. This wave is, in a preferred embodiment, electromagnetic or optical for an optical microscope, but can be also of different kind like acoustical or matter waves. The disclosed invention makes use of the quantitative phase microscopy techniques known in the sate of the art or to be invented. In a preferred embodiment, the complex field provided by Digital Holographic Microscopy (DHM), but any kind of microscopy derived from quantitative phase microscopy: modified DIC, Shack-Hartmann wavefront analyzer or any analyzer derived from a similar principle, such as multi-level lateral shearing interferometers or common-path interferometers, or devices that convert stacks of intensity images (transport if intensity techniques: TIT) into quantitative phase image can be used, provided that they deliver a comprehensive measure of the complex scattered wavefield. The hereby-disclosed method delivers superresolution microscopic images of the specimen, i.e. images with a resolution beyond the Rayleigh limit of the microscope. It is shown that the limit of resolution with coherent illumination can be improved by a factor of 6 at least. It is taught that the gain in resolution arises from the mathematical digital processing of the phase as well as of the amplitude of the complex field scattered by the observed specimen. In a first embodiment, the invention teaches how the experimental observation of systematically occurring phase singularities in phase imaging of sub-Rayleigh distanced objects can be exploited to relate the locus of the phase singularities to the sub-Rayleigh distance of point sources, not resolved in usual diffraction limited microscopy. In a second, preferred embodiment, the disclosed method teaches how the image resolution is improved by complex deconvolution. Accessing the object's scattered complex field—containing the information coded in the phase—and deconvolving it with the reconstructed complex transfer function (CTF) is at the basis of the disclosed method. In a third, preferred embodiment, it is taught how the concept of “Synthetic Coherent Transfer Function” (SCTF), based on Debye scalar or Vector model includes experimental parameters of MO and how the experimental Amplitude Point Spread Functions (APSF) are used for the SCTF determination. It is also taught how to derive APSF from the measurement of the complex field scattered by a nanohole in a metallic film. In a fourth embodiment, the invention teaches how the limit of resolution can be extended to a limit of λ / 6 or smaller based angular scanning. In a fifth embodiment, the invention teaches how the presented method can generalized to a tomographic approach that ultimately results in super-resolved 3D refractive index reconstruction.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Aggregates of ceric oxide crystallites and reduction of vehicular emissions therewith
InactiveUS6093223ASmall sizeImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyDispersed particle separationDebyeCerium
Vehicular emissions are reduced / purified via combustion of the hydrocarbon fuel therefor, e.g., diesel fuel, in the presence of a cerium compound, preferably a cerium (IV) compound, to produce soots having depressed ignition temperatures that contain effective purifying amounts of aggregates of ceric oxide crystallites, the largest particle size dimension of which ranging from 50 ANGSTROM (5 nanometers) to 10,000 ANGSTROM (1,000 nanometers) and the crystallite sizes of which, measured by Debye-Scherrer technique, ranging from 50 ANGSTROM (5 nanometers) to 250 ANGSTROM (25 nanometers).
Owner:RHONE POULENC CHEM SA
Microporous composite membrane and its production method and use
InactiveUS20070072069A1Adhesive electrodeMechanical strengthSemi-permeable membranesFinal product manufacturePorous coatingDebye
A microporous composite membrane obtained by coating at least one surface of a microporous polyolefin membrane with a solution of a gelable fluororesin in a mixed solvent of a good solvent for the fluororesin, and a poor solvent having a dipole moment of 1.8 Debye or less and drying to form a porous coating layer of the above fluororesin has cylindrical penetrating pores formed in the above coating layer, with well-balanced permeability, adhesion to electrodes, mechanical strength, heat shrinkage resistance, shutdown properties and meltdown properties.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Preparation of liquid mixtures
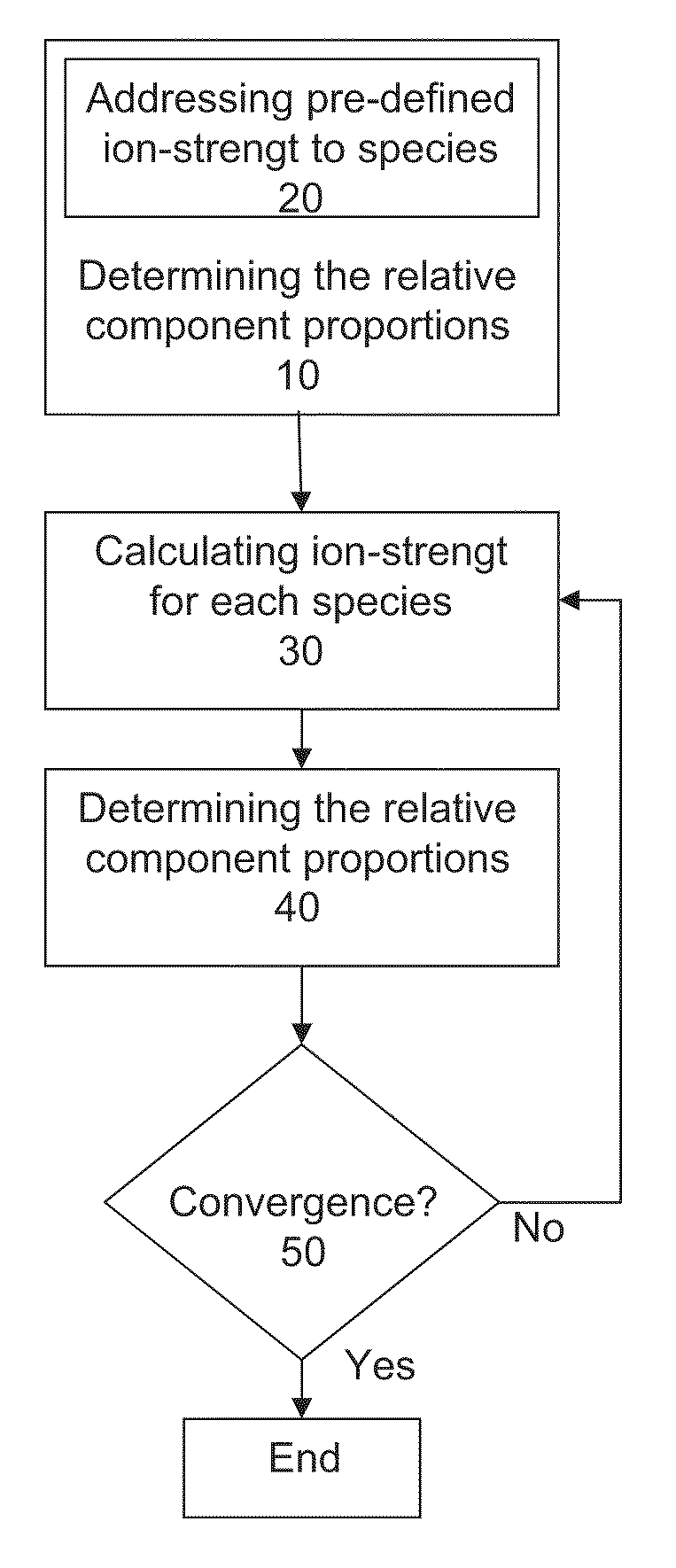
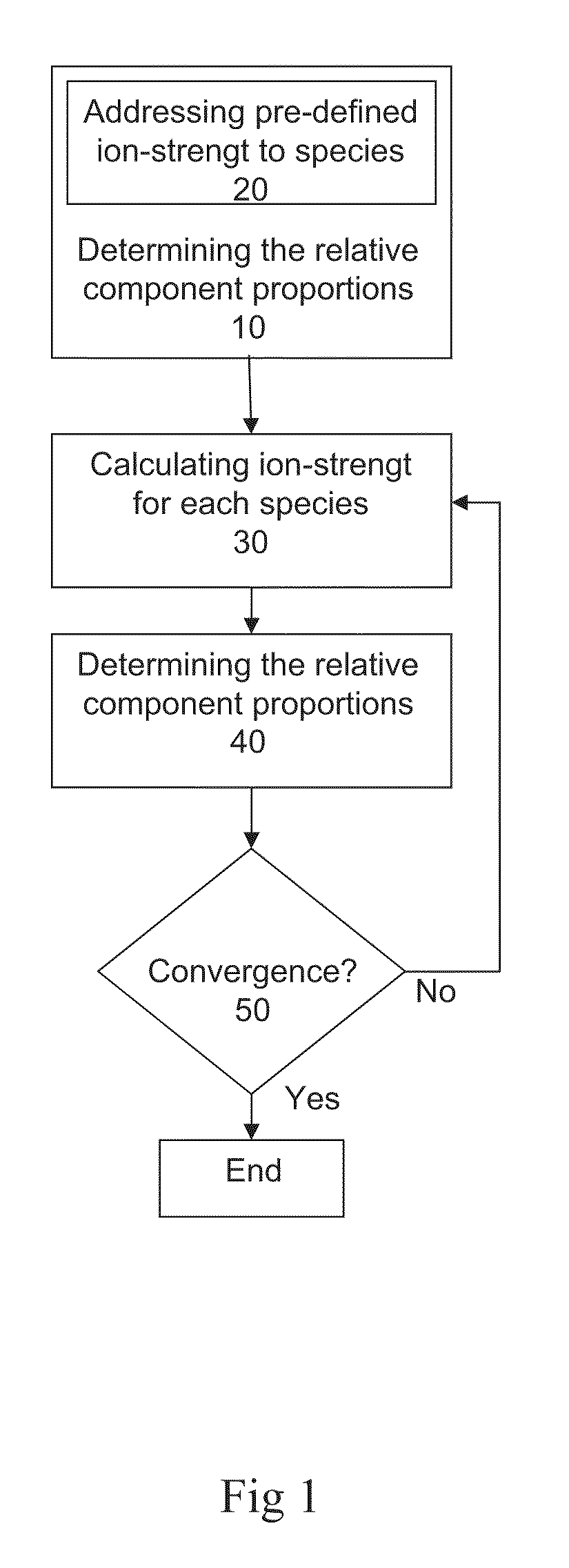
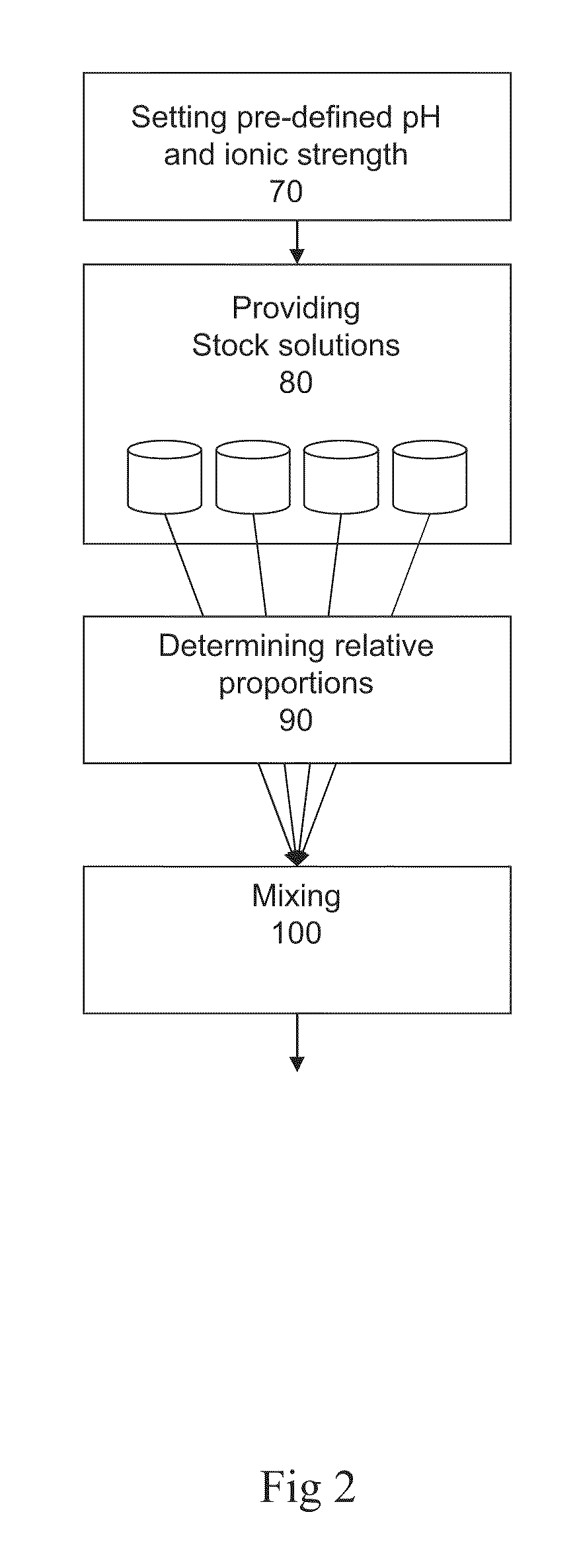
ActiveUS20110039712A1Avoid false convergenceFast convergenceIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationDebyeIonic strength
A method of determining the relative component proportions of at least one each of: a buffer; an acid or a base; a solvent; and optionally a salt, for providing a liquid mixture of pre-defined pH and ionic strength, wherein the relative component proportions are determined using the equation of Debye-Hückel, wherein the ion size parameter a in the Debye-Hückel equation is determined as the weighted mean ion size of all species contributing to the ionic strength of the liquid mixture, and wherein the ionic strength of each species is used as weighting parameter. The present method is also applicable in a method of providing a liquid mixture. Further there is provided a buffer preparation device.
Owner:CYTIVA SWEDEN AB
Radiation curable compositions
InactiveUS6916855B2Enhanced reactivity and photosensitivityGlass optical fibreAdditive manufacturing apparatusDebyeHigh dielectric permittivity
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Sample enrichment chip, manufacturing method and enrichment method and on micronano structure
InactiveCN101000290ARich sourcesMature processing technologyComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationDebyeEnrichment methods
The invention relates to sample enrichment chip, manufacturing method and enrichment method based on micro nanostructure. Its feature is that the enrichment chip is used quartz glass as backing material, formed by enrichment nanometer channel and micro sample transmitting pipeline. It applies MEMS technique to process the channel and pipeline one the quartz glass, strictly control channel depth to make it satisfy ion falling demand, utilizes low temperature bonding method to process for the substrate and covering piece, fills sample into chip pipeline, adds direct voltage in the sample pool to form electric field in nanometer channel. Because of Debye layers in the channel are superposed, while ion falling zoon is formed beside the channel. The sample moved under the action of the electric field is enriched beside the channel to form sample enrichment zoon. The chip has small volume, will not destroy enrichment component while enriching.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for liquid phase aromatics alkylation comprising in-situ catalyst reactivation with polar compounds
The catalyst becomes at least partially deactivated by sorbing catalyst poisons present in the feed during a process for alkylating aromatics by contacting a feed containing benzene, toluene, xylenes, alkylbenzenes, naphthalene or substituted naphthalenes under liquid phase alkylating conditions with C2-C16 olefins in the presence of MCM-22, MCM-36, MCM-49, MCM-56, ZSM-5, ZSM-11, ZSM-12, ZSM-23, ZSM-35, ZSM-48, ZSM-50, ZSM-4, ZSM-18, ZSM-20, Zeolite X, Zeolite Y, USY, mordenite or offretite to provide an alkylated aromatic product. The at least partially deactivated catalyst can be treated in situ by contacting with at least one polar compound having a dipole moment of at least 0.05 Debyes and selected from the group consisting of acetic acid, formic acid, water, and carbon monoxide, under conditions of temperature and pressure employed in the liquid phase alkylating conditions which are sufficient to at least partially desorb the catalyst poison from the catalyst.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CORP (US)
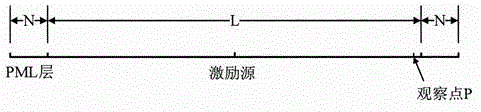
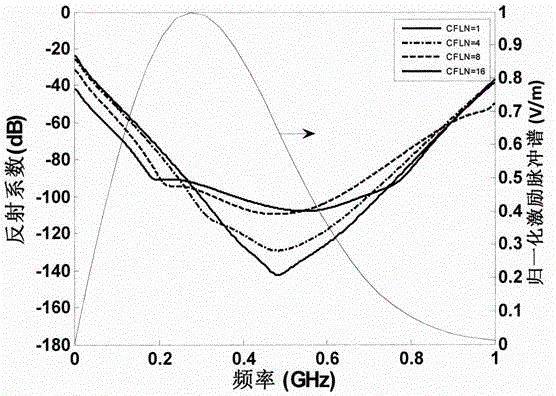
Implementation algorithm for truncating one dimensional Debye medium Crank-Nicolson perfectly matched layer
The invention provides an implementation algorithm for truncating a one dimensional Debye medium Crank-Nicolson perfectly matched layer, belongs to the technical field of numerical simulation, and aims to truncate a Debye dispersive medium by using the perfectly matched layer and simulate a limited memory space of a computer into an infinite space to simulate the propagation characteristic of electromagnetic wave in the Debye dispersive medium. The algorithm is characterized by comprising the following steps: a plurality of stretch coordinate variables are converted from a frequency domain to a z domain by using a bilinear transformation method, then a maxwell equation is dispersed in the time domain by using a Crank-Nicolson finite difference time domain method, an explicit iterative equation of an electric field is induced, and finally a value of an electromagnetic field component is solved. The algorithm has the advantages of unconditional stability and capabilities of improving the electromagnetic field calculation speed and saving memory.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
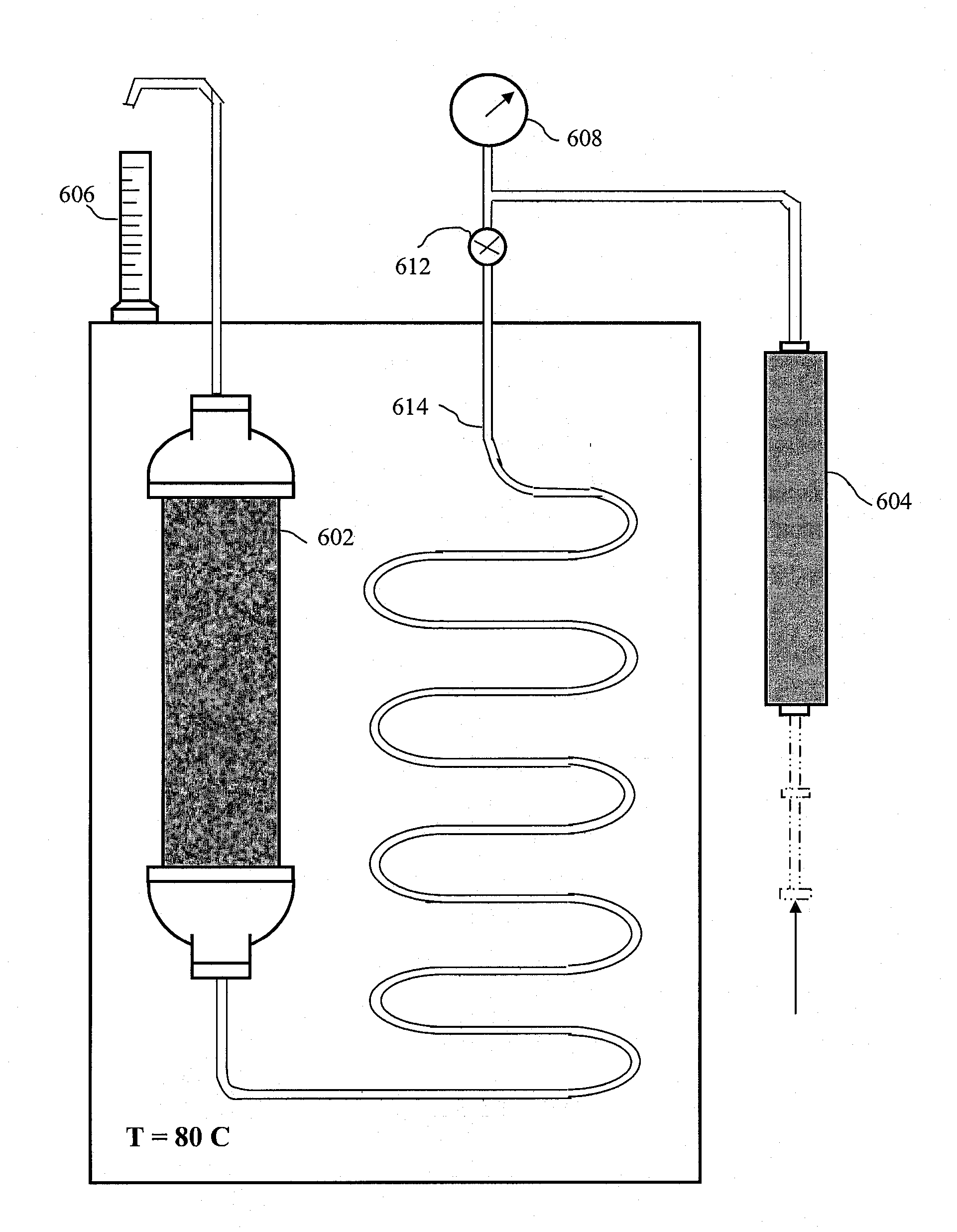
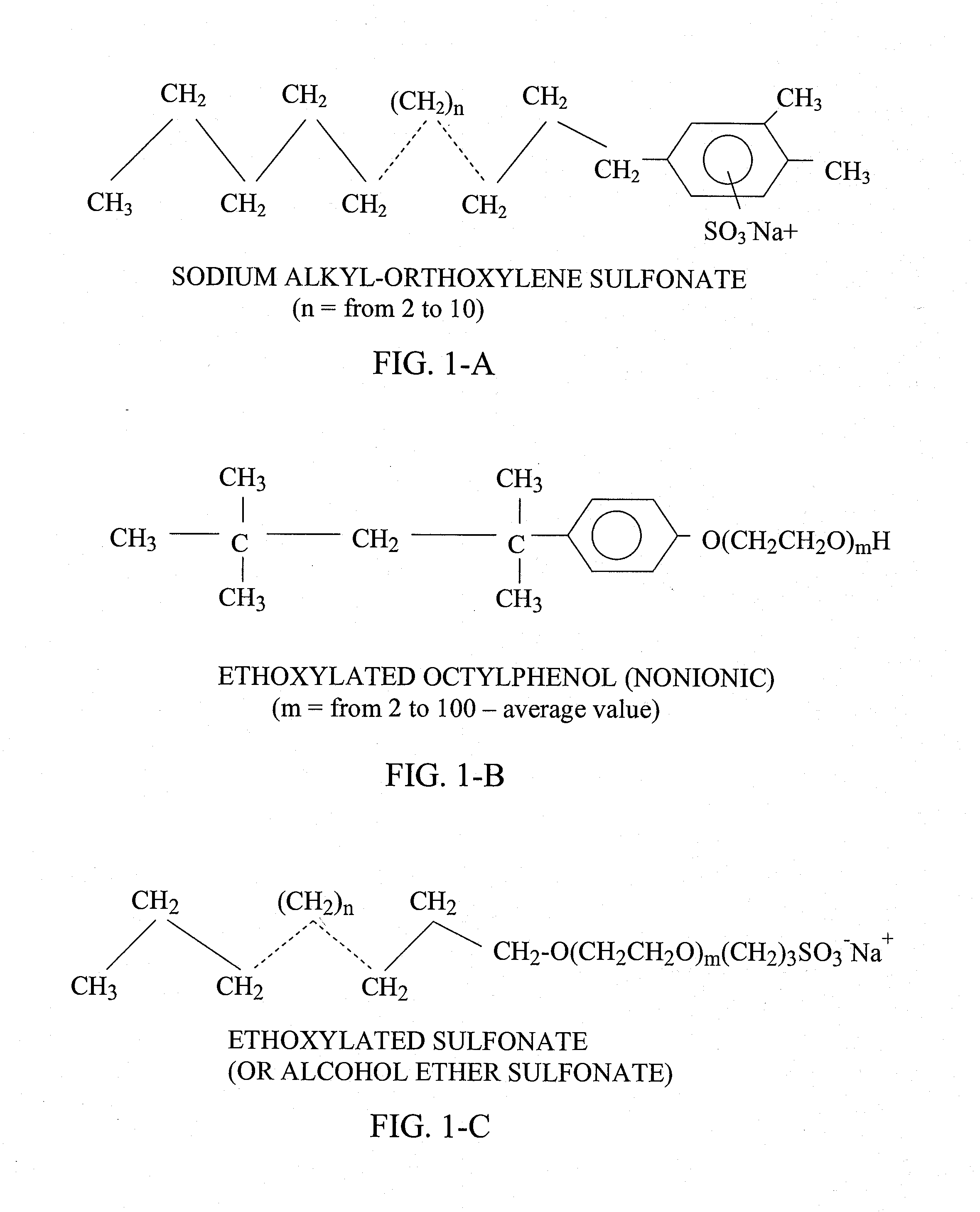
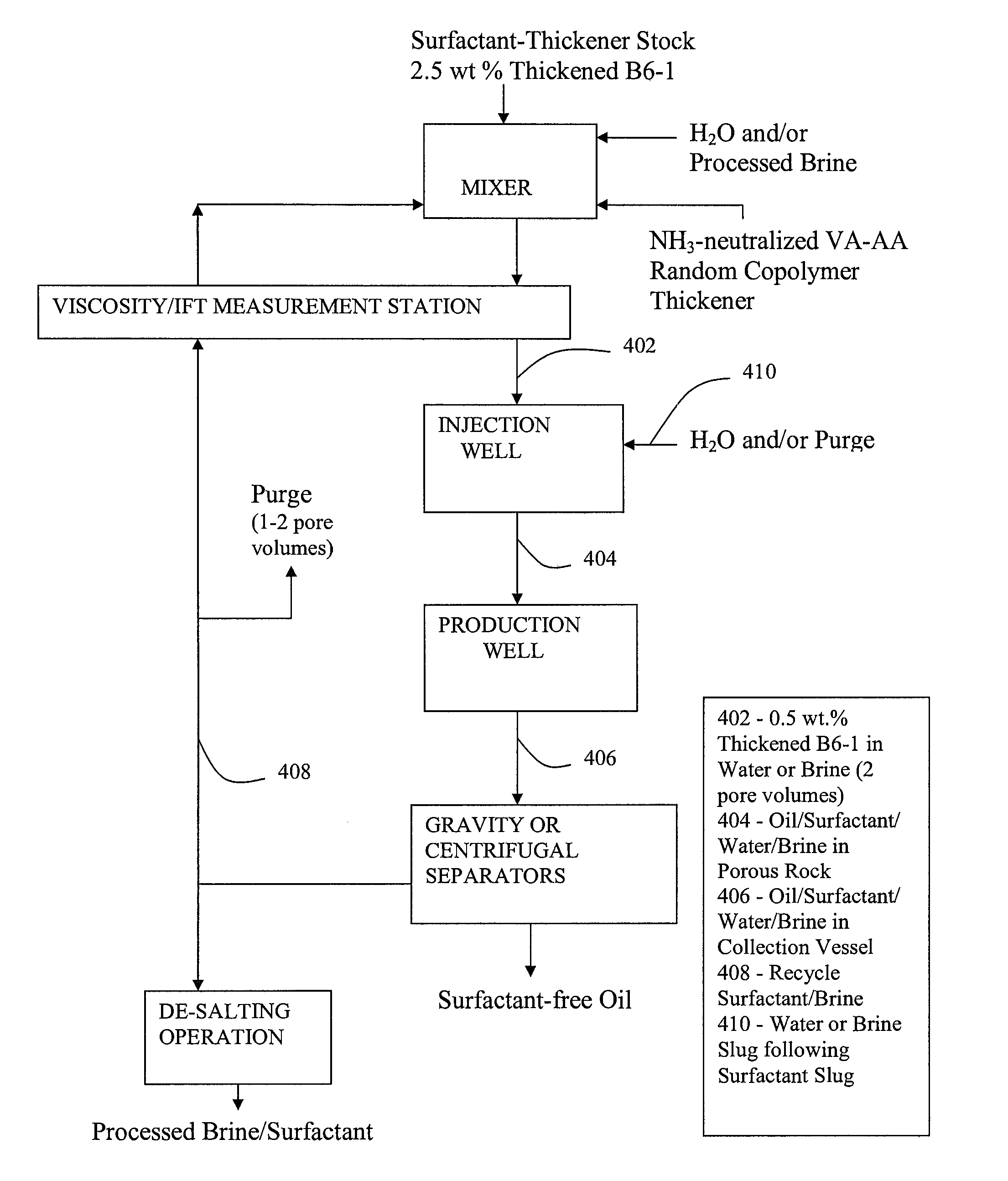
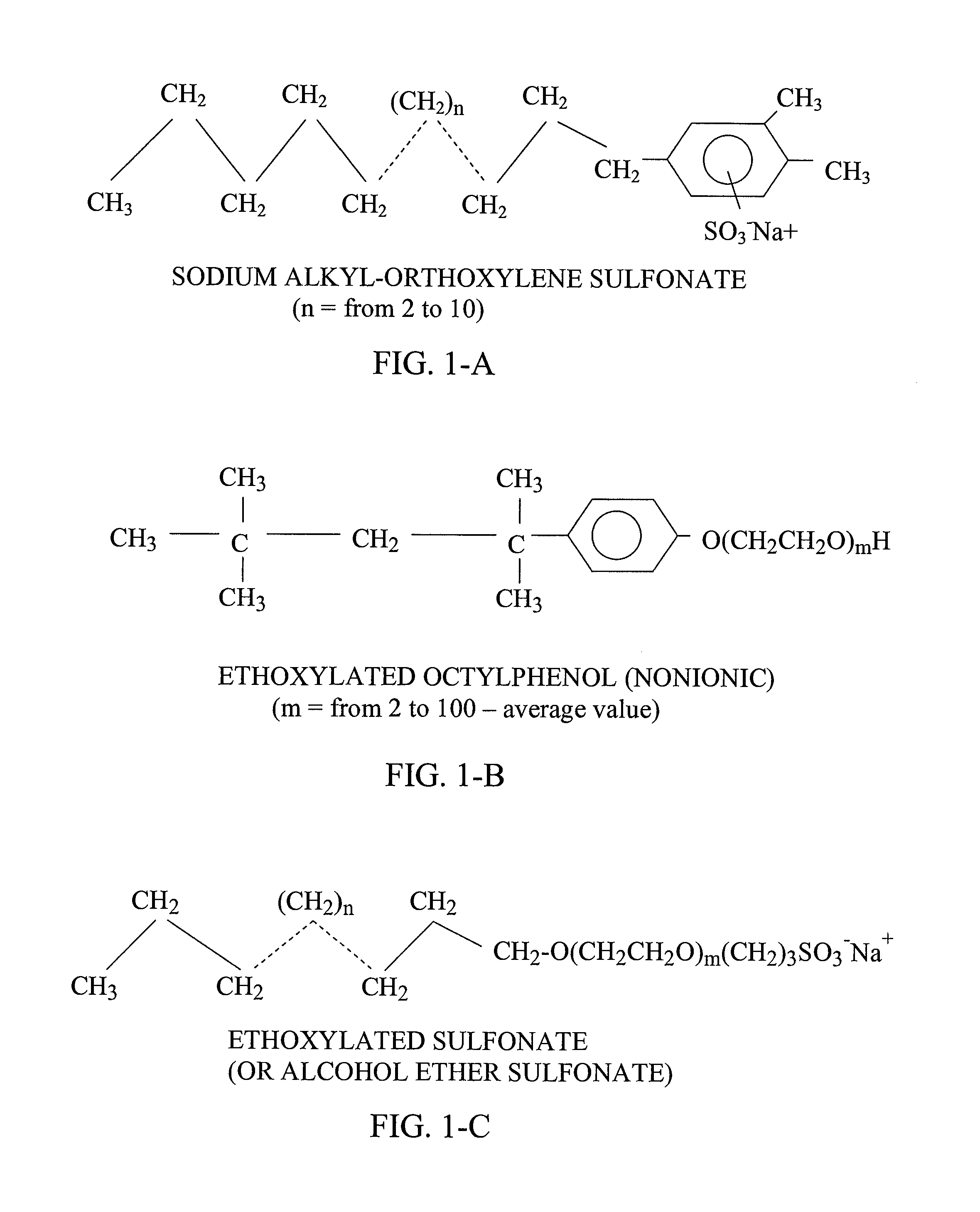
Multifunctional multipolymeric surfactants for oil and bitumen recovery and other applications
InactiveUS20080190814A1Reduce lossesReduces cost of and complexity of and timeOther chemical processesLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionDebyePolymeric surface
The present invention provides method for recovering fossil-based materials from oil sources using multifunctional, multipolymer surfactants. The invention also provides methods for reducing the loss of volatile organic compoiunds (VOCs) from oil storage containers using multifunctional, multipolymer surfactants. The multifunctional, multipolymer surfactants are characterized by a hydrophobic part and a hydrophilic part. The hydrophobic part of the polymer surfactants includes functionalities that impart a polarity of greater than 0 Debye to the hydrophobic part. The polymer surfactants are further characterized by molecular weights that are above their entanglement weights. The result is polymer surfactants with demulsifying characteristics.
Owner:NANOCHEM OIL
Multifunctional multipolymeric surfactants for oil and bitumen recovery and other applications
InactiveUS7691260B2Reduce lossesReduces cost of and complexity of and timeOther chemical processesLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionPolymeric surfaceDebye
Owner:NANOCHEM OIL
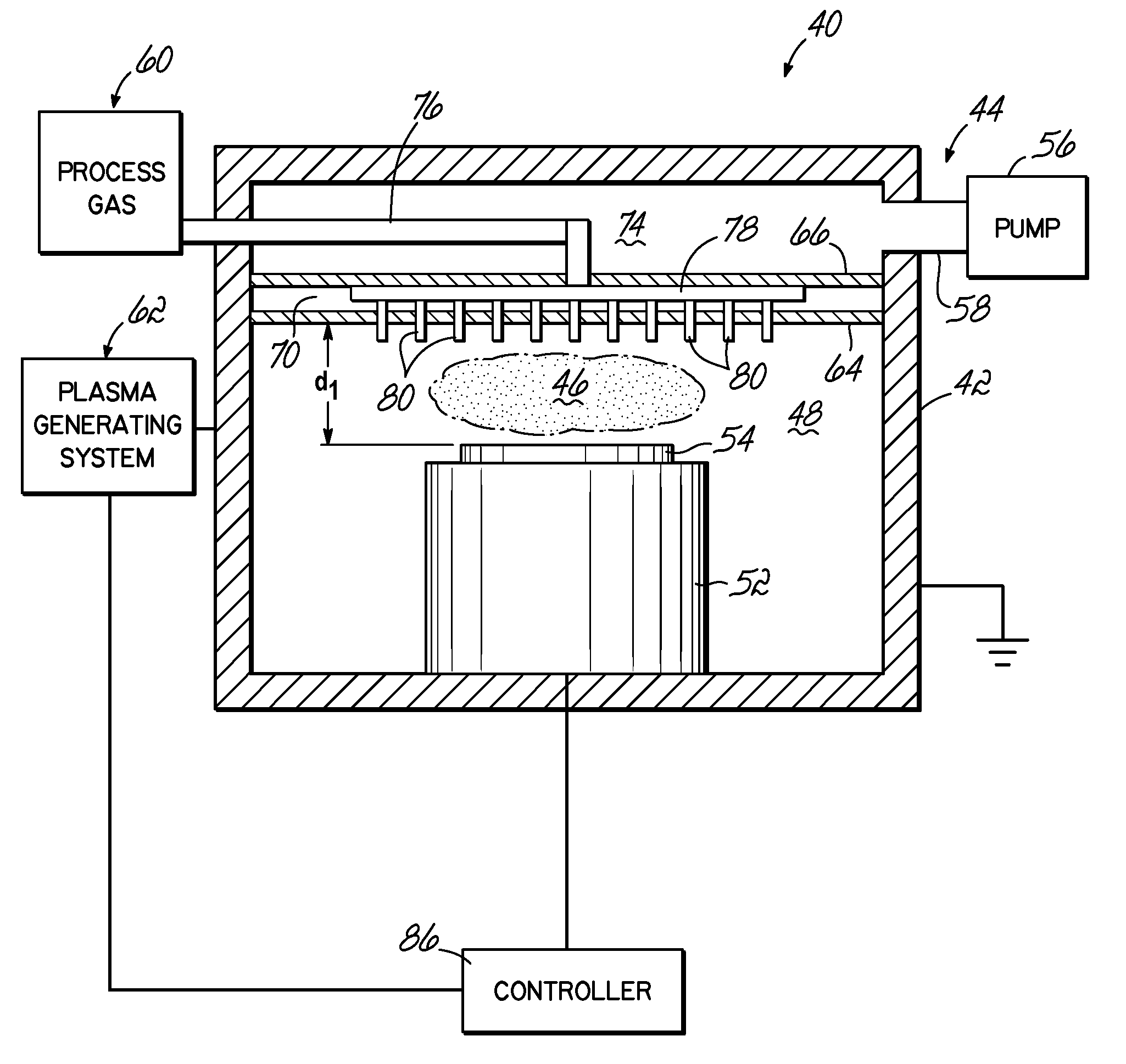
Plasma source pumping and gas injection baffle
A plasma processing system. The processing system comprises a process chamber having first and second ends arranged such that the first end opposes the second end. A substrate support is positioned at the first end of the process chamber and is configured to support a substrate. An exhaust system is positioned proximate the second end of the process chamber and draws a vacuum on the process chamber. Between the exhaust system and substrate support there is a plurality of super-Debye openings, and between the exhaust system and the plurality of super-Debye openings is a plurality of sub-Debye openings. The super-Debye openings are configured to limit diffusion of plasma while the sub-Debye openings are configured to quench plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Microporous composite membrane and its production method and use
InactiveUS7781094B2Well-balanced permeabilitySemi-permeable membranesFinal product manufacturePorous coatingDebye
A microporous composite membrane obtained by coating at least one surface of a microporous polyolefin membrane with a solution of a gelable fluororesin in a mixed solvent of a good solvent for the fluororesin, and a poor solvent having a dipole moment of 1.8 Debye or less and drying to form a porous coating layer of the above fluororesin has cylindrical penetrating pores formed in the above coating layer, with well-balanced permeability, adhesion to electrodes, mechanical strength, heat shrinkage resistance, shutdown properties and meltdown properties.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Resin composition for forming a phase-separated structure, and method of producing structure containing phase-separated structure
ActiveUS20170240766A1Improve phase separationImprove performancePhotomechanical apparatusNanotechnologyDebyeIonic liquid
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD +1
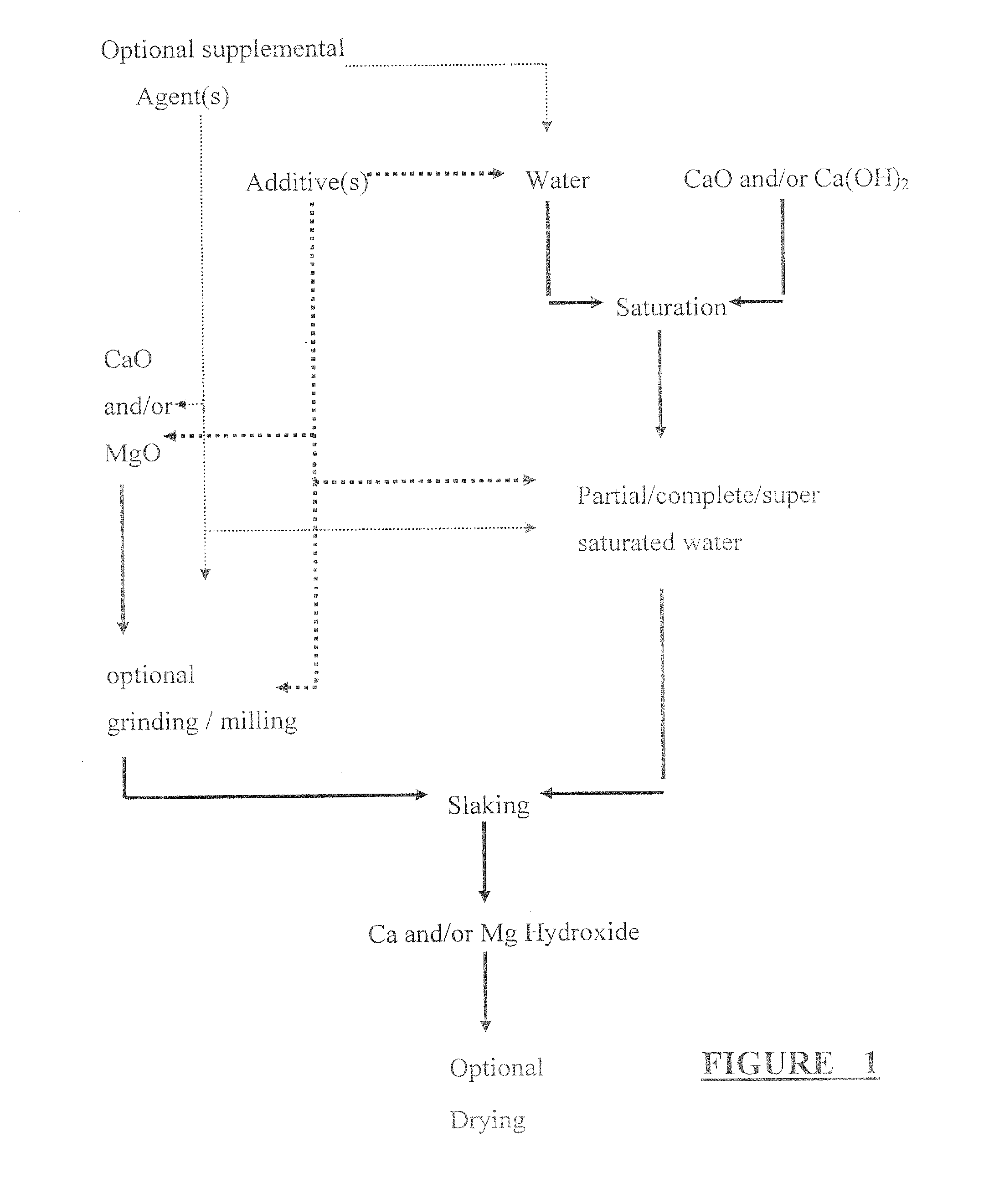
Calcium and/or magnesium hydroxide with very high reactivity, and preparation thereof
InactiveUS20100196239A1Reduce free water contentReduce and preventOther chemical processesUsing liquid separation agentDebyeCalcium hydroxide
Owner:LIME TECH CONSULTING
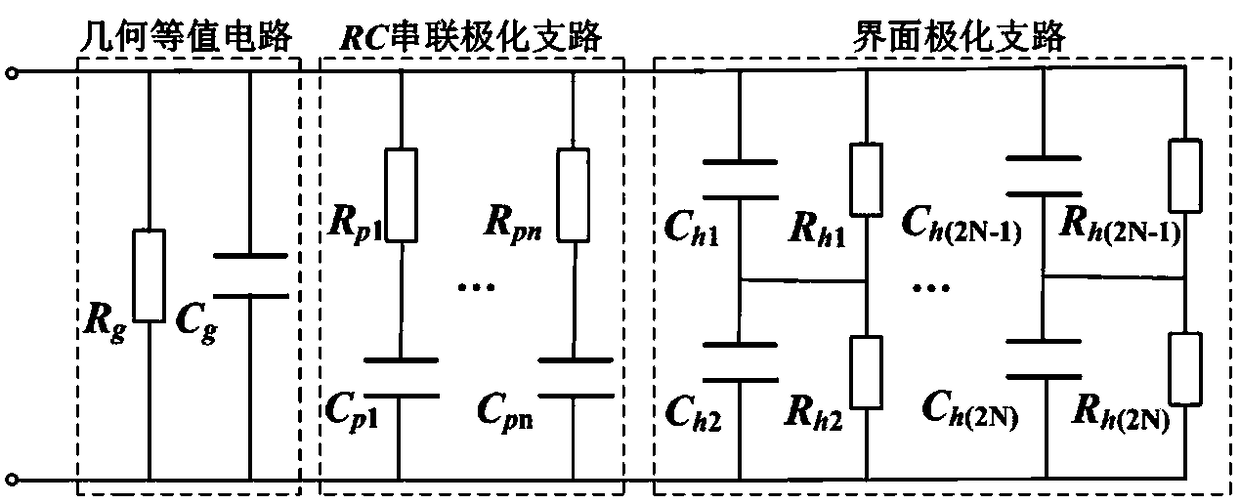
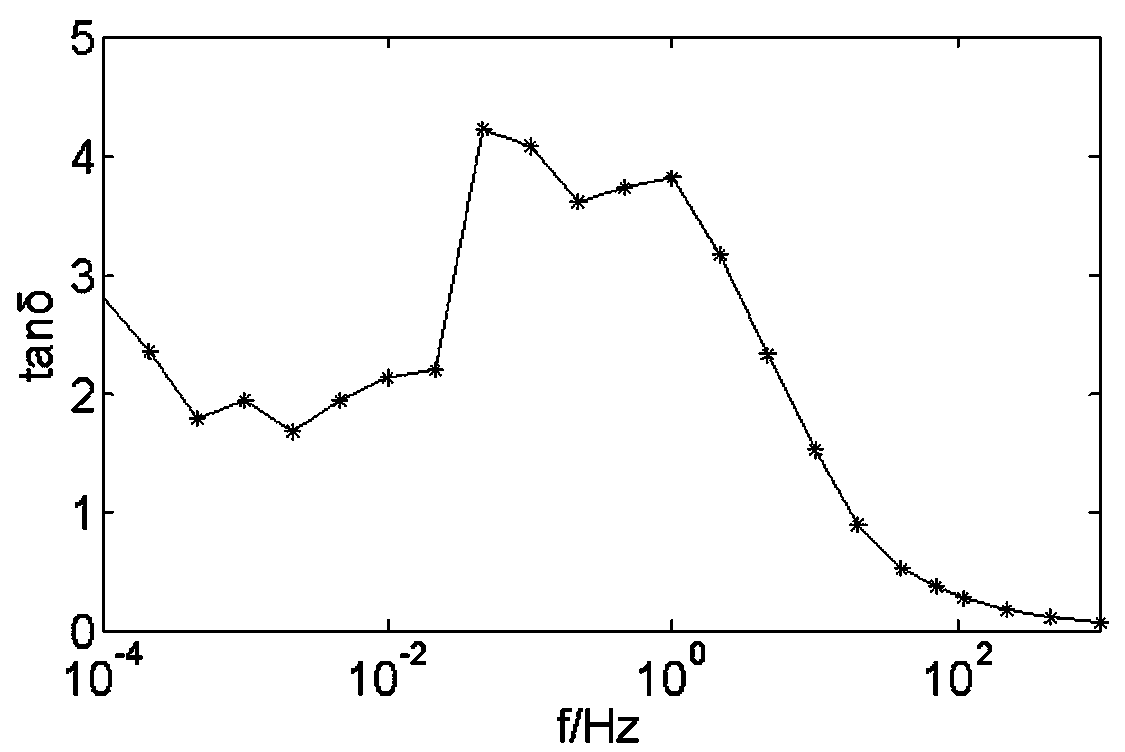
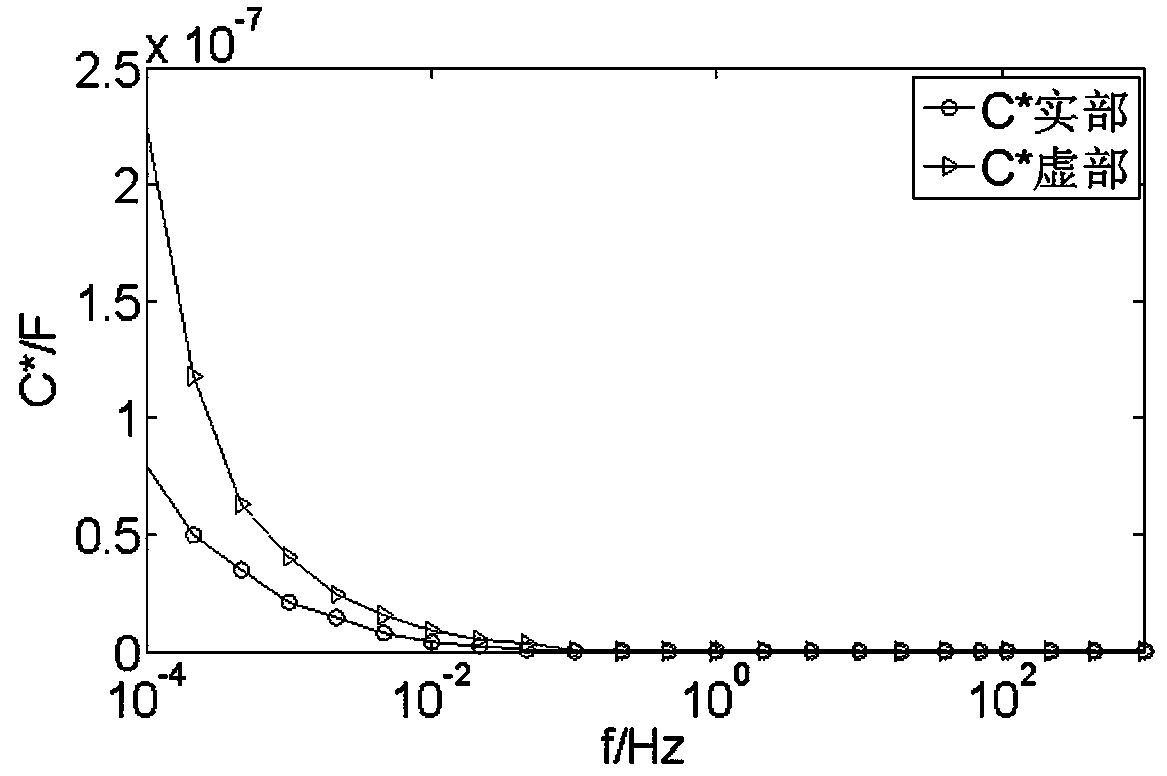
Frequency domain spectrum identification method considering parameters of oil-paper insulation interface polarization equivalent circuit
ActiveCN109142865AEasy to operateThe calculation result is accurateSpectral/fourier analysisDielectric property measurementsDebyeCircuit models
The invention relates to a frequency domain spectrum identification method considering the parameters of an oil-paper insulation interface polarization equivalent circuit. Oil-paper interface polarization is considered based on an extended Debye equivalent model, and an interface polarization branch is introduced. A multivariate equation set for calculating the parameters of circuit components isconstructed according to a circuit model and frequency domain dielectric spectrum test parameters; and the parameter values of all components in the equivalent circuit can be identified by establishing an objective function for solving the equation set and using an artificial intelligence algorithm. The frequency domain spectrum identification method considering the parameters of an oil-paper insulation interface polarization equivalent circuit presented by the invention has the advantages of simple operation process and accurate and reliable parameter calculation result.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Radiation curable coating composition
InactiveUS20060089450A1Improve adhesionFast curingPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsEmulsion paintsMethacrylateDebye
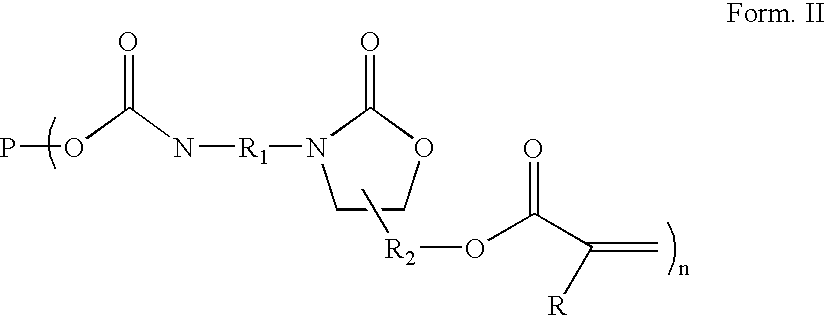
The present invention relates to a radiation curable coating composition comprising (A) a compound according to P-(D-(meth)acrylate)n having a number average molecular weight (Mn) of at least 500 kg / kmol, wherein n=240, P=oligomeric or polymeric backbone, and D comprises an urethane group and an heterocyclic group, said heterocyclic group having a Boltzmann average dipole moment of at least 2.5 Debye, and (B) a reactive diluent. The heteorocylic group is preferably an oxazolidone group. The invention further relates to a method for making a resin composition comprising a compound comprising an oxazolidone group and an (meth)acrylate group, said method comprising a reaction step introducing the (meth)acrylate group into the compound, wherein said reaction step is carried out in the presence of an antioxidant.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
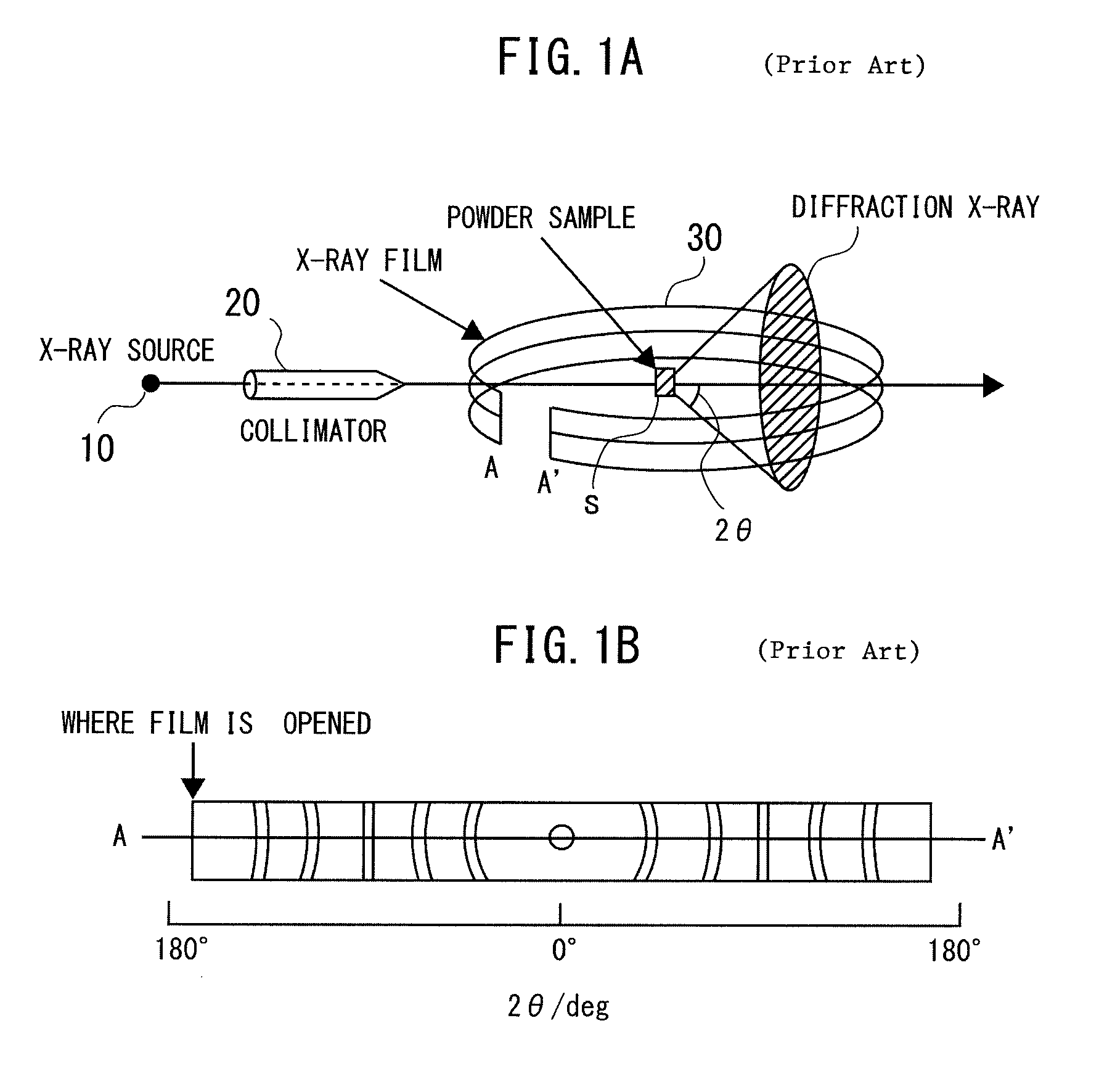
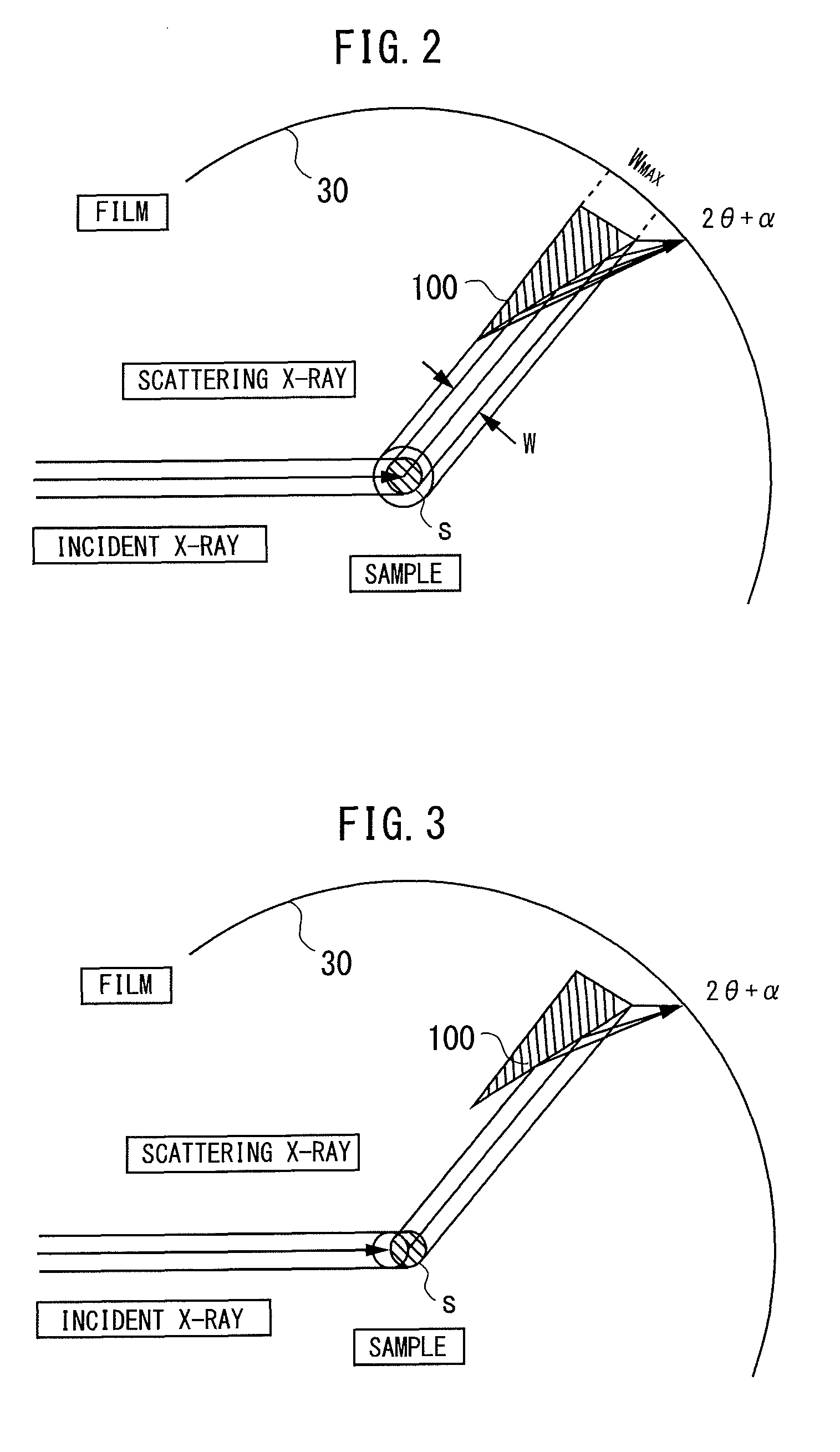
Quantitative measuring method and apparatus of metal phase using x-ray diffraction method, and method for making plated steel sheet using them
InactiveUS6821361B2Increase diffracted X-ray intensityHigh measurement accuracyHot-dipping/immersion processesHeat treatment process controlX-rayX-ray scattering techniques
A method and apparatus for quantitatively measuring a metal phase contained in a galvanized layer by X-ray diffractometry, and a method of producing a galvanized steel sheet by using the method and apparatus. The diffracted X-ray intensity from a metal phase contained in the galvanized layer is increased to improve measurement accuracy, thereby permitting application to on-line measurement. The diffracted X-rays from the metal phase are measured over a predetermined range on a Debye ring, or measured at a plurality of positions on the Debye ring to increase the diffracted X-ray intensity, thereby improving measurement accuracy. The X-ray beam produced by an X-ray source is compressed and made parallel and monochromatic by a multilayer film mirror to increase diffracted X-ray intensity, improving measurement accuracy. Particularly, the present invention is applied to measurement of the degree of alloying of hot-dip galvanization.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
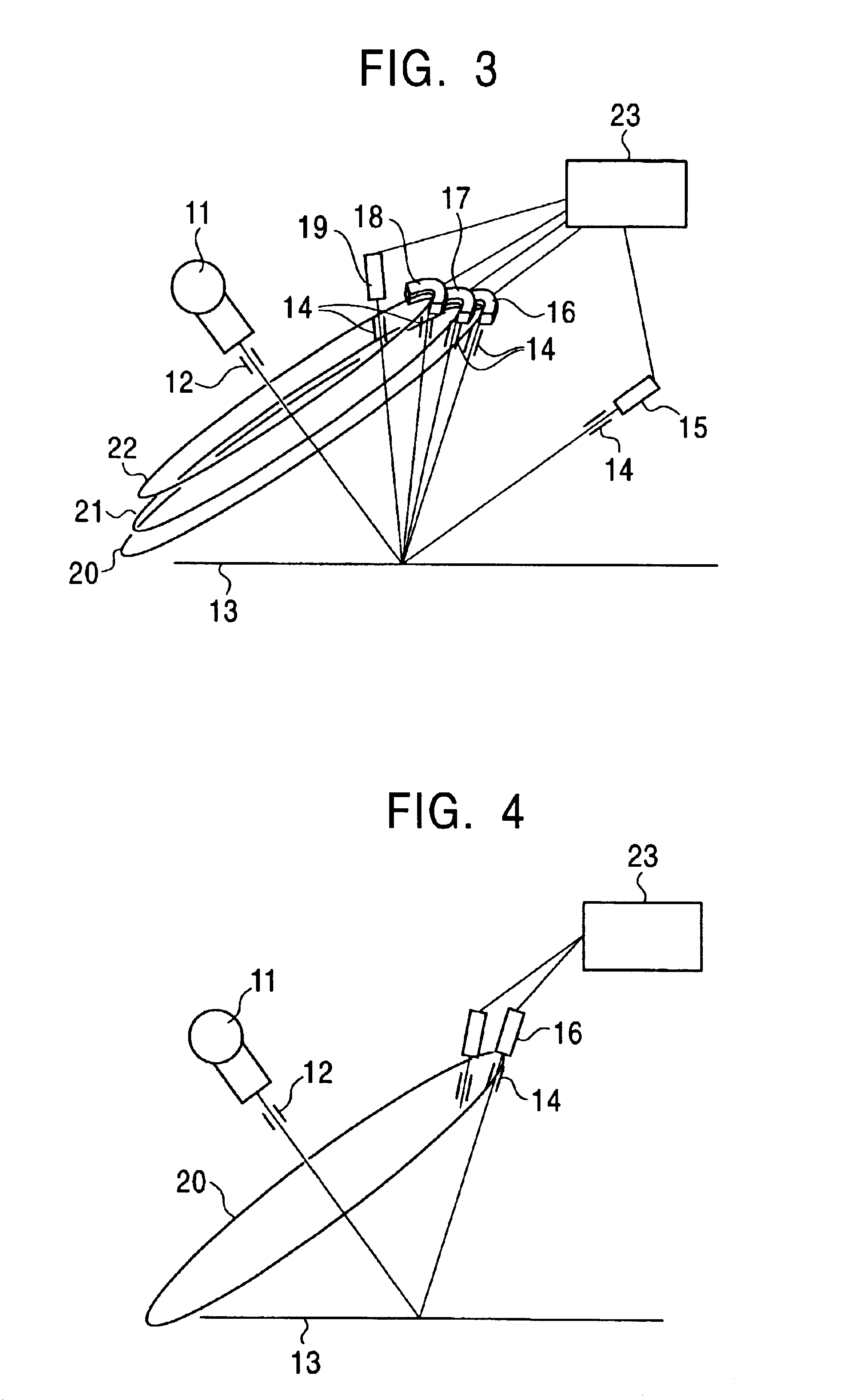
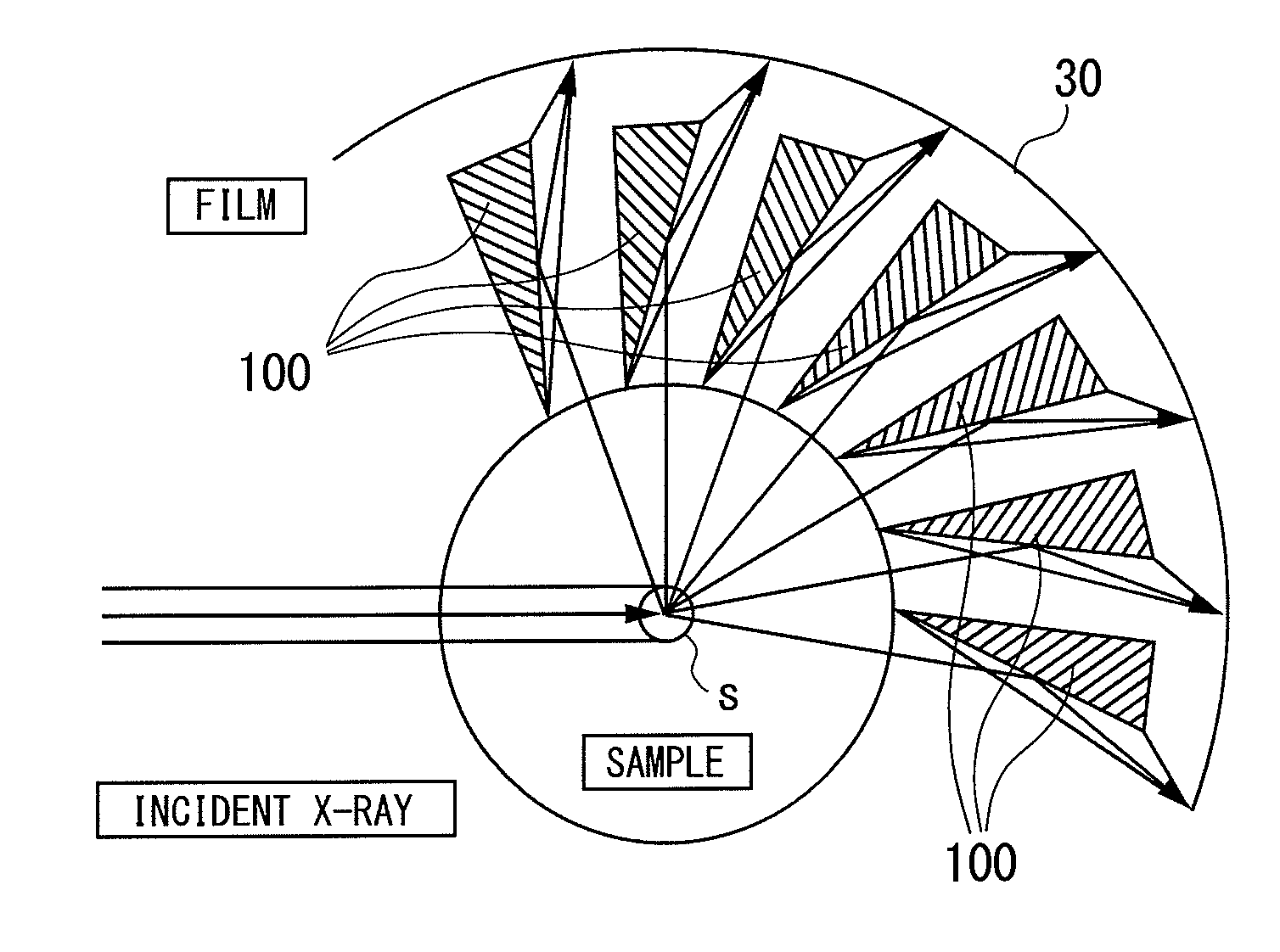
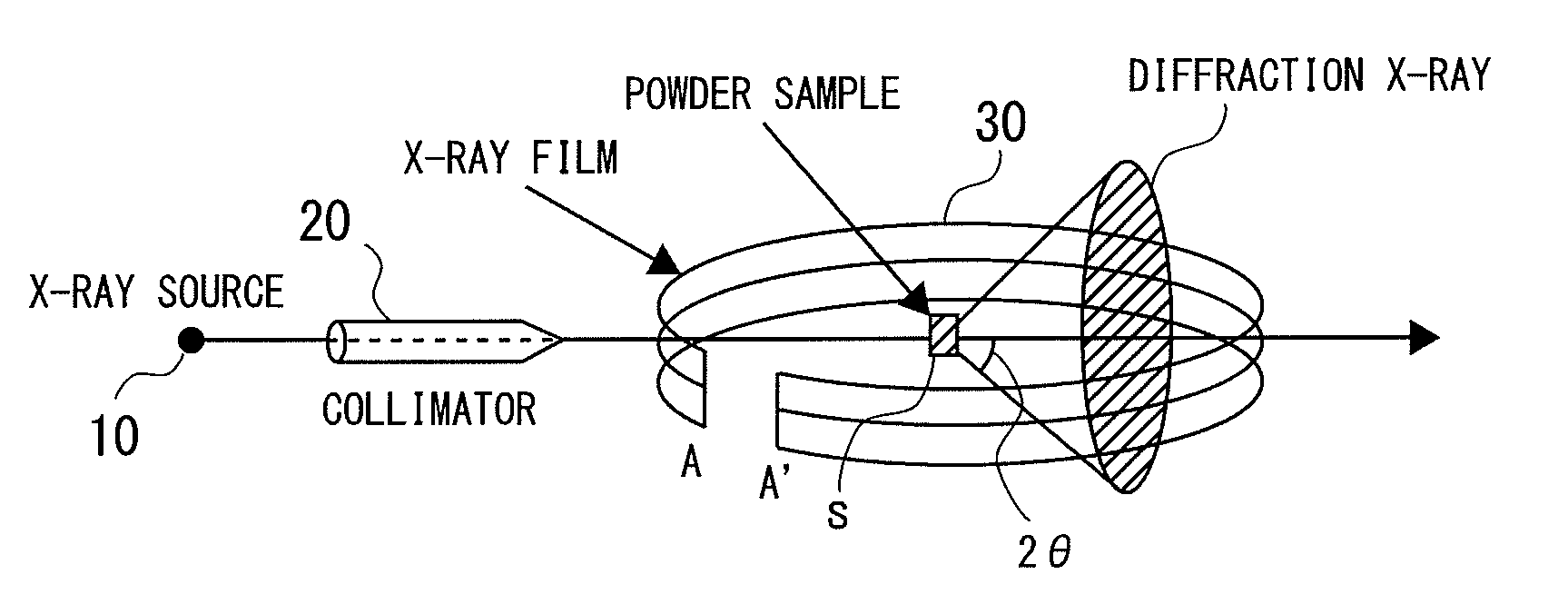
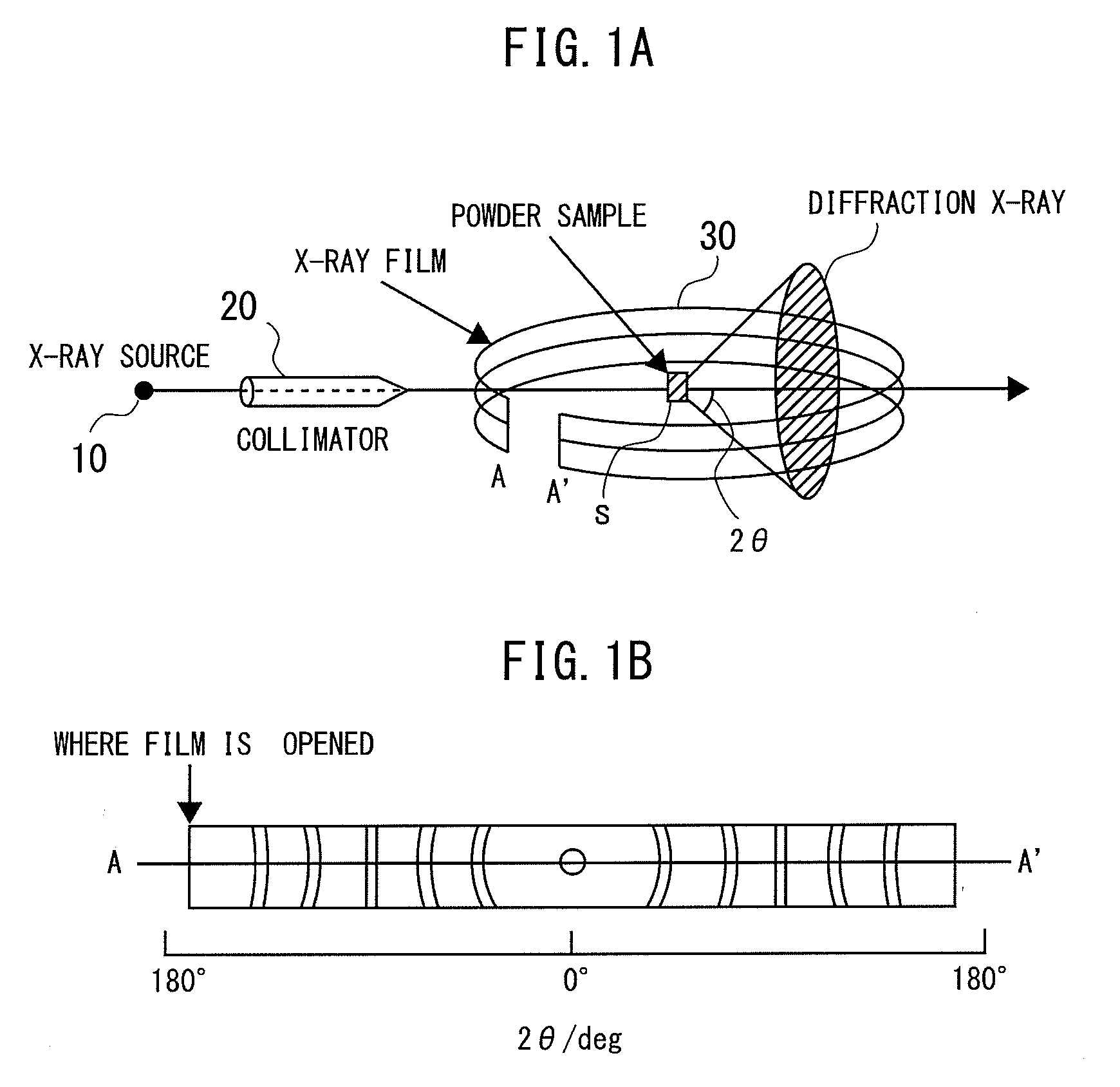
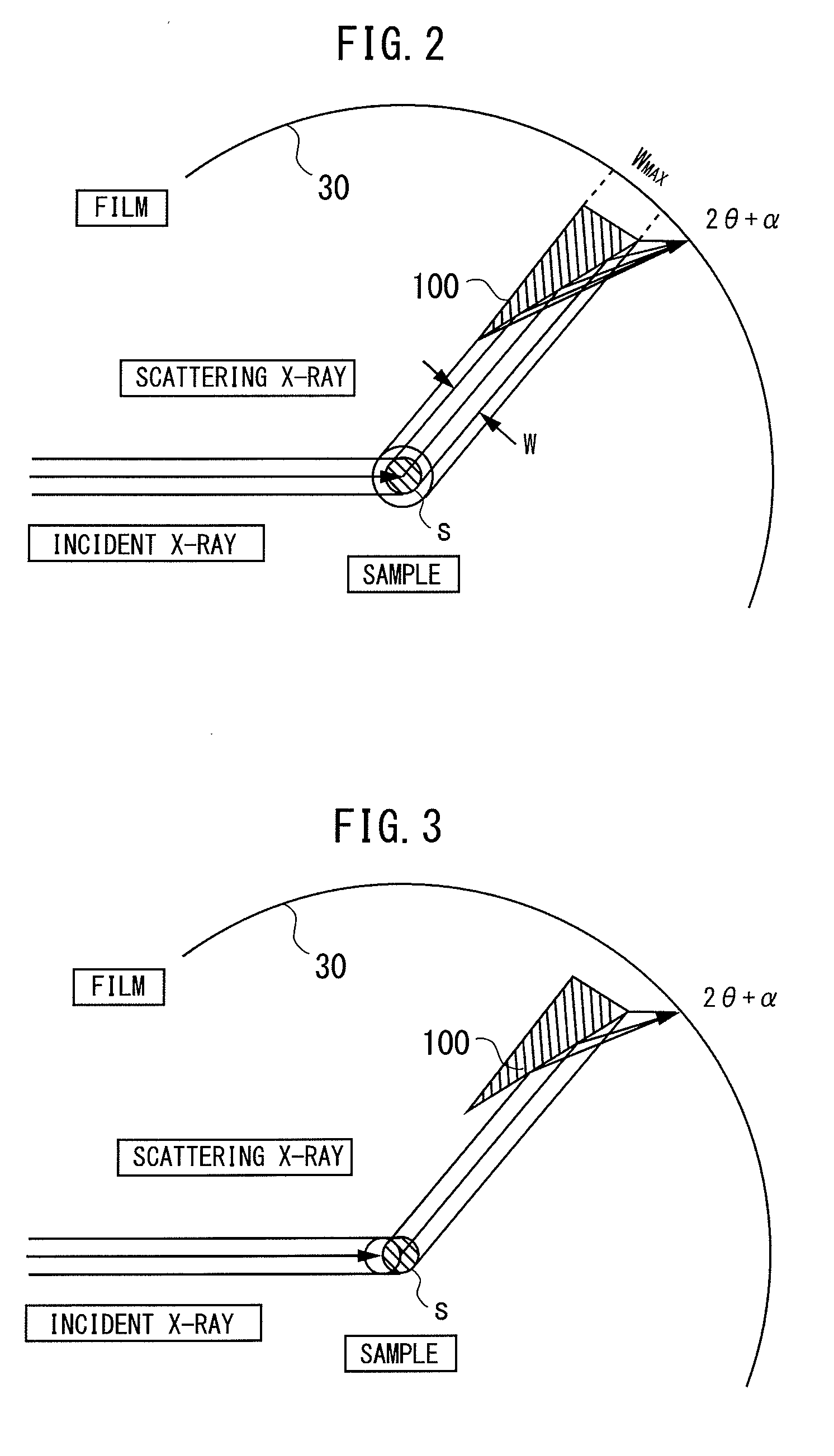
X-ray diffraction measuring apparatus having debye-scherrer optical system therein, and an X-ray diffraction measuring method for the same
An X-ray diffraction measuring apparatus equipped with Debye-Scherrer optical system therein, comprises a generator for generating a characteristic X-ray to be irradiated upon a sample to be measured; an X-ray detector being disposed to surround that sample around; and a focusing arrangement, being disposed between the sample and the X-ray detector, for collecting an X-ray scattering from the sample covering over a predetermined angle, in a peripheral direction, around the sample, and for focusing and irradiating it upon the X-ray detector.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
X-Ray Diffraction Measuring Apparatus Having Debye-Scherrer Optical System Therein, and an X-ray Diffraction Measuring Method for the Same
An X-ray diffraction measuring apparatus equipped with Debye-Scherrer optical system therein, comprises a means for generating a characteristic X-ray to be irradiated upon a sample to be measured; an X-ray detector means being disposed to surround that sample around; and a focusing means, being disposed between the sample and the X-ray detector means, for collecting an X-ray scattering from the sample covering over a predetermined angle, in a peripheral direction, around the sample, and thereby irradiating it upon the X-ray detector means.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
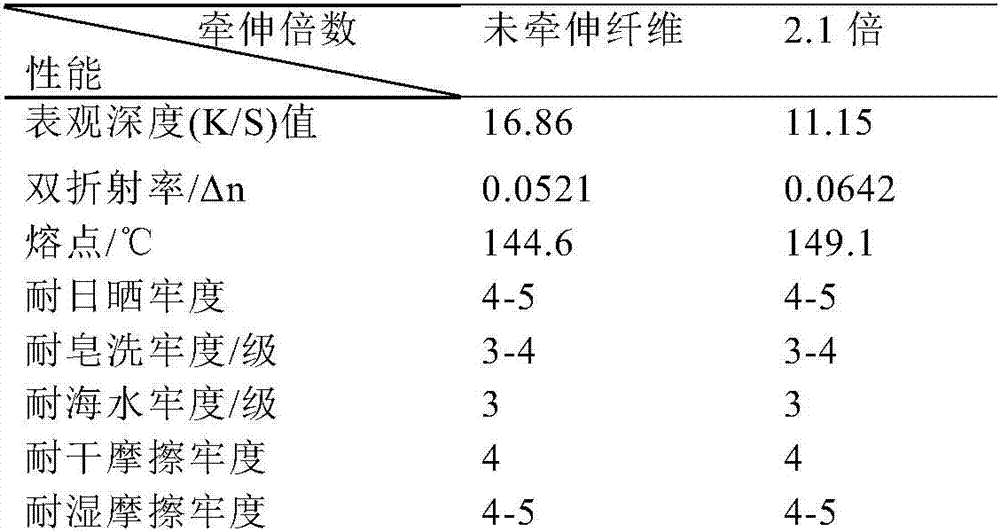
Colored ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers and preparation method thereof
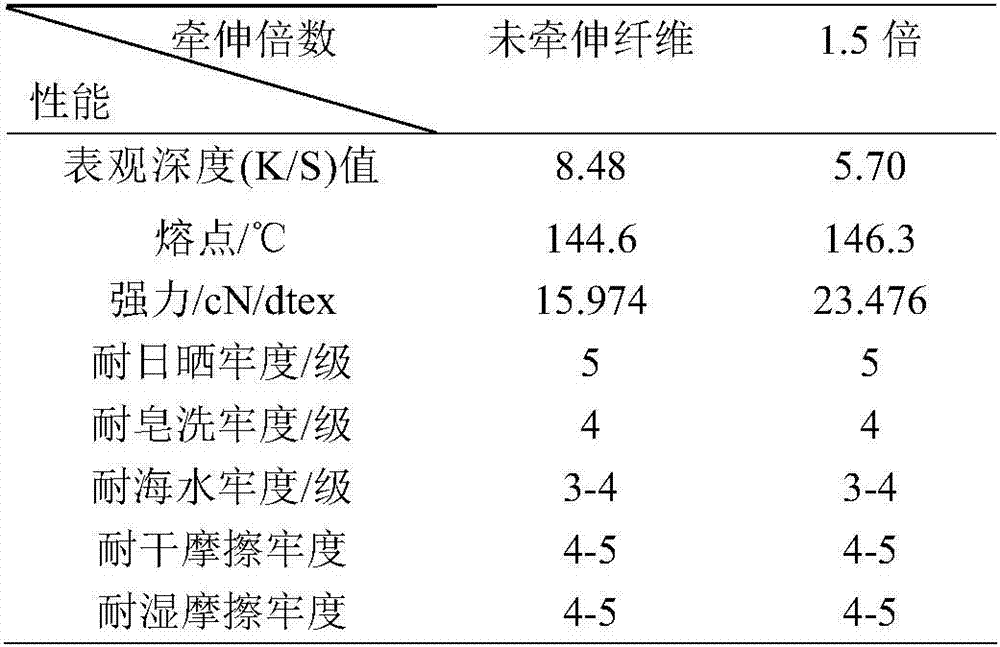
The invention relates to colored ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing dyeing liquor in an ultrasonic way, wherein the amount of a dispersing agent accounts for 0.05-0.5% of the mass of the dyeing liquor, the amount of a dye accounts for 0.5-10% of the mass of the fibers, the bath ratio is 1 to (10 to 100), and the dye is selected from highly hydrophobic azo disperse dyes or anthraquinone disperse dyes which have dipole moments of less than 5.0 Debye; (2) putting the dyeing liquor and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene extract fibers into a dyeing machine, wherein the dyeing temperature is 90-120 DEG C, the dyeing time is 15-150min, and the pH value of the dyeing liquor is 4-9; carrying out reductive cleaning and drying on the dyed extract fibers; (3) carrying out stretch orientation on the dried ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene colored extract fibers to obtain the finished product of the ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers. The method provided by the invention is simple and convenient as well as easy to control; the prepared colored ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fibers have high apparent depth, color fastness and strong retention rate.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CLOTHING TECH
Catalyst for Olefin Polymerization and Polymerization Method Using the Same
Disclosed is a catalyst for olefin polymerization, comprising: Component [A]: a prepolymer obtained by olefin prepolymerization on solid titanium catalyst component having an average particle size of 25 to 70 μm produced by contacting of a solid component (i) having an average particle size of 26 to 75 μm, containing magnesium, titanium, halogen, and an electron donor (c3), and being free from detachment of titanium by washing with hexane at 25° C., a polar compound (ii) having a dipole moment of 0.50 to 4.00 Debye, and at least one compound (iii) selected from liquid titanium (d) and an electron donor (e), in which the content of titanium in the solid component (i) is reduced by ≧25% by weight, and the weight ratio of the sum of the electron donor (c3) and the electron donor (e) to titanium [electron donor (c3+e) / titanium atoms] is ≧7;Component [B]: an organometallic compound; andComponent [C]: an organosilicon compound represented by the following formula (I):Si(OR1)3(NR2R3) (I)(wherein R1 is a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 8 carbon atoms, R2 is a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 12 carbon atoms or hydrogen atom, R3 is a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 12 carbon atoms).According to the catalyst, an olefin polymer having high stereoregularity and low molecular weight (high fluidity) can be efficiently provided.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com