Patents
Literature
194 results about "Point spread" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interactive simulated baccarat side bet apparatus and method
A multi-player automated casino table card game platform enables play of casino table baccarat-type games according to rules effected through a processor. Rules may include games similar to Baccarat or Mini Baccarat with an optional side bet on a point spread between the player and bank hands.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
Interactive simulated baccarat side bet apparatus and method
A multi-player automated casino table card game platform enables play of casino table baccarat-type games according to rules effected through a processor. Rules may include games similar to Baccarat or Mini Baccarat with an optional side bet on a point spread between the player and bank hands.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
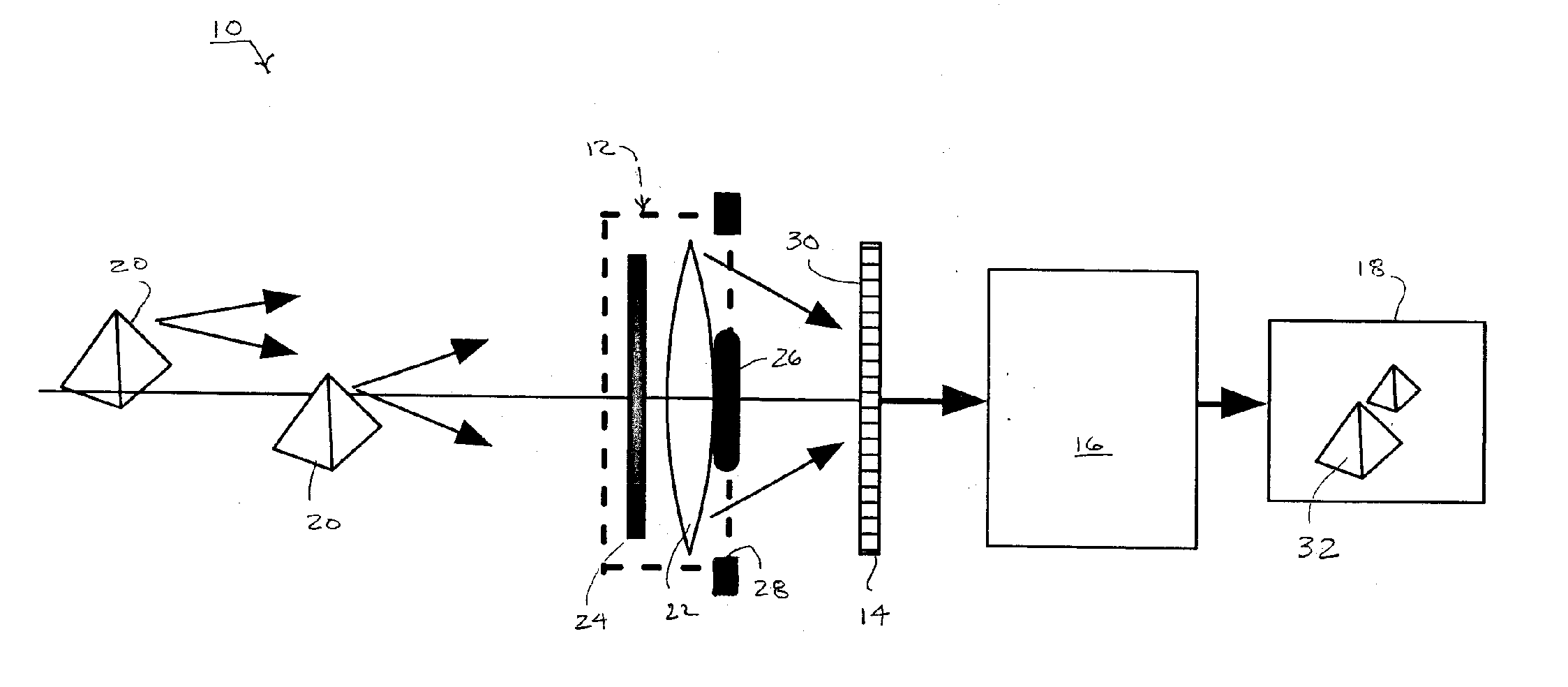
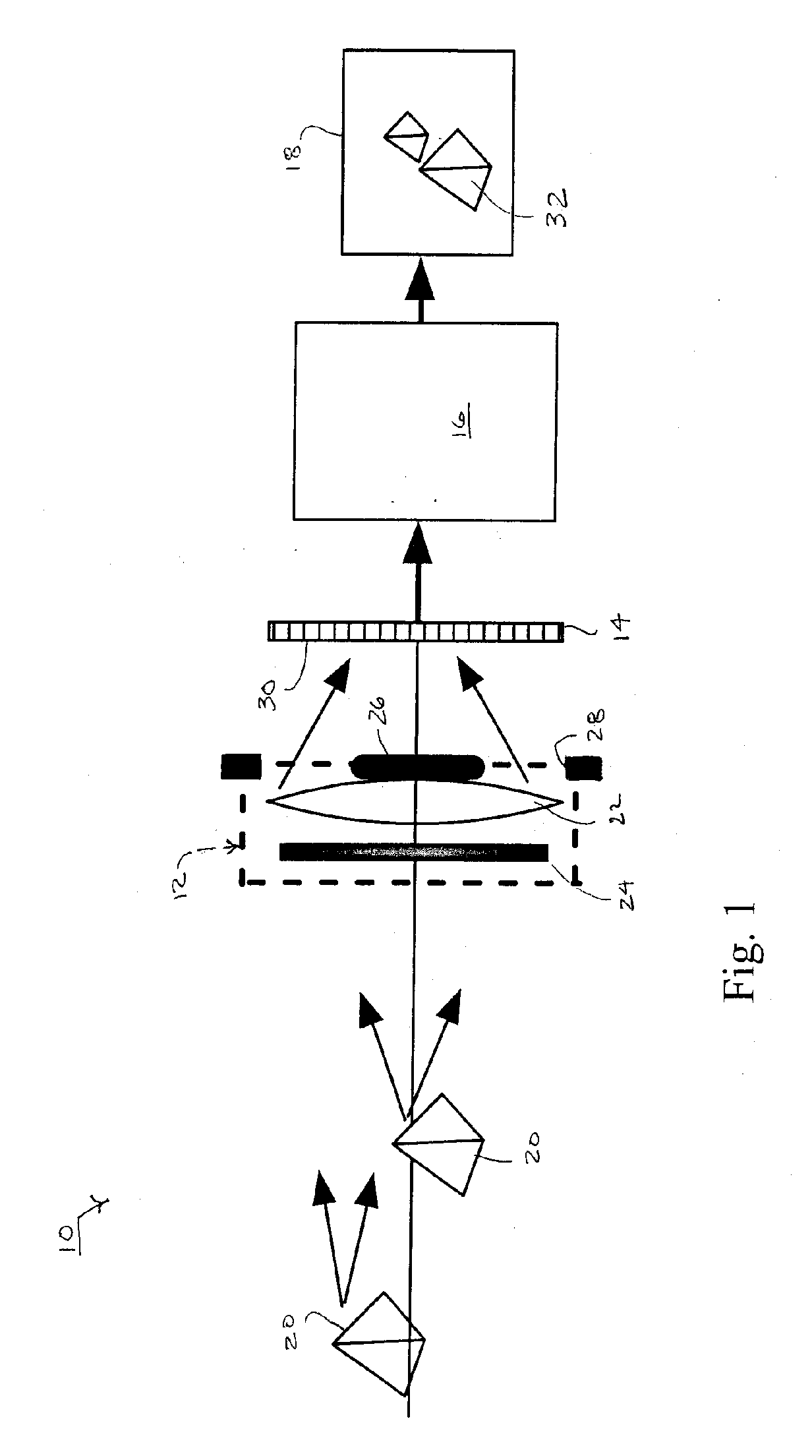
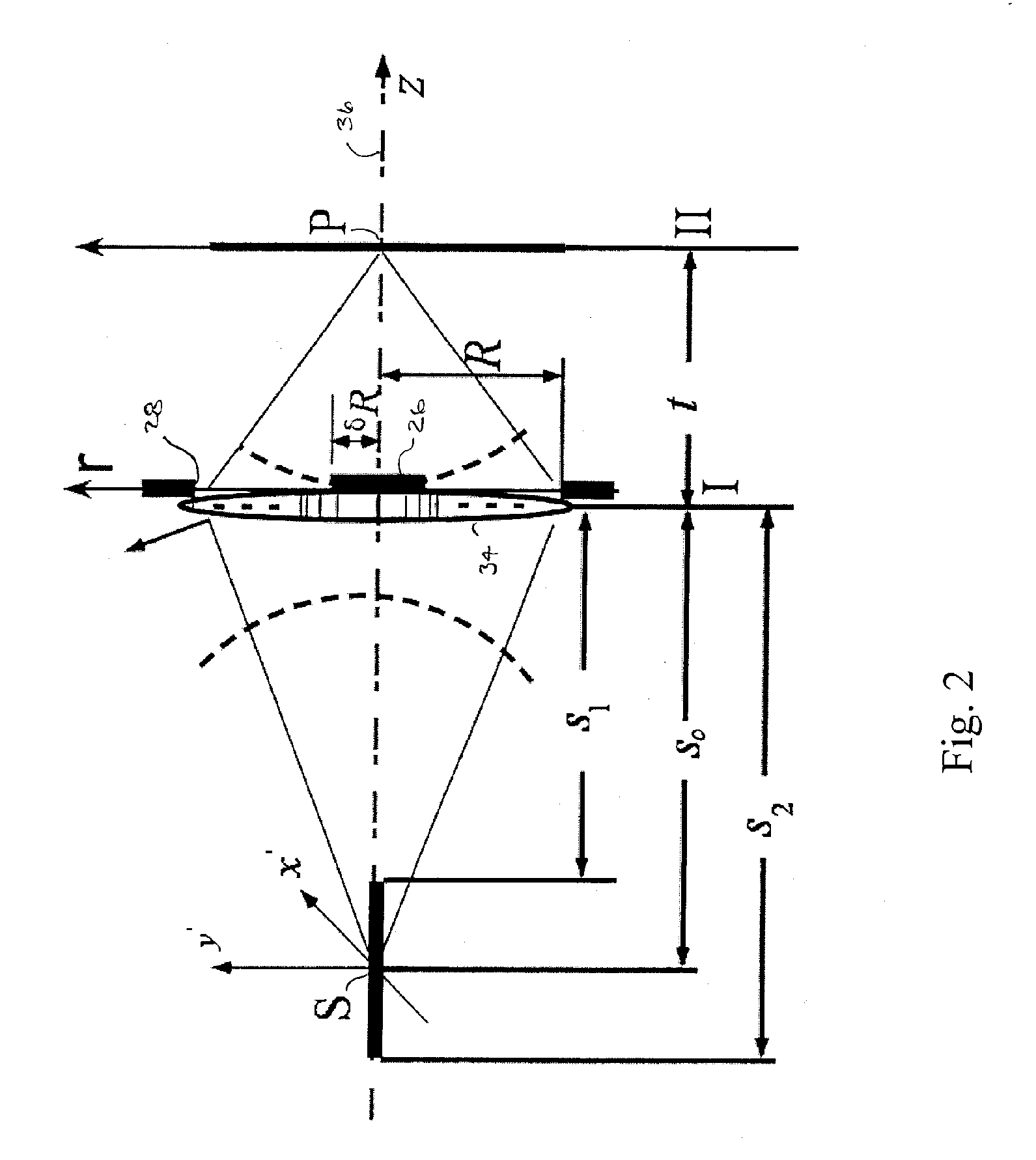
Methods and systems for measuring local scattering and aberration properties of optical media
Methods, systems, and media relating the display of scattering and / or absorption characteristics of an optical medium. For scattering measurements, a Hartmann-Shack calibration image of a measurement system is acquired to define a first plurality of point spread functions. A Hartmann-Shack test image of the medium is acquired to define a second plurality of point spread functions. A shift is determined between the test image and the calibration image. A point spread of each of the second plurality of point spread functions is measured, each of the second plurality of point spread functions including a component due to optical aberration of the medium and a component due to scatter. The component due to optical aberration is determined using the shift. The component due to optical aberration is deconvolved to determine the component due to scatter. A display of the local scattering characteristics is generated using the component due to scatter. For absorption measurements, a plurality of spot intensity measurements are acquired of a medium, each spot intensity measurement including a component due to reflectivity and a component due to absorption. The component due to reflectivity is determined, and the component due to absorption is determined.
Owner:ADVANCED RES TECH INST +1
Methods of calibrating an imaging system using calibration beads
InactiveUS6906792B2Improve liquidityEasy procedureImage analysisIndividual particle analysisPoint spreadSmall sample
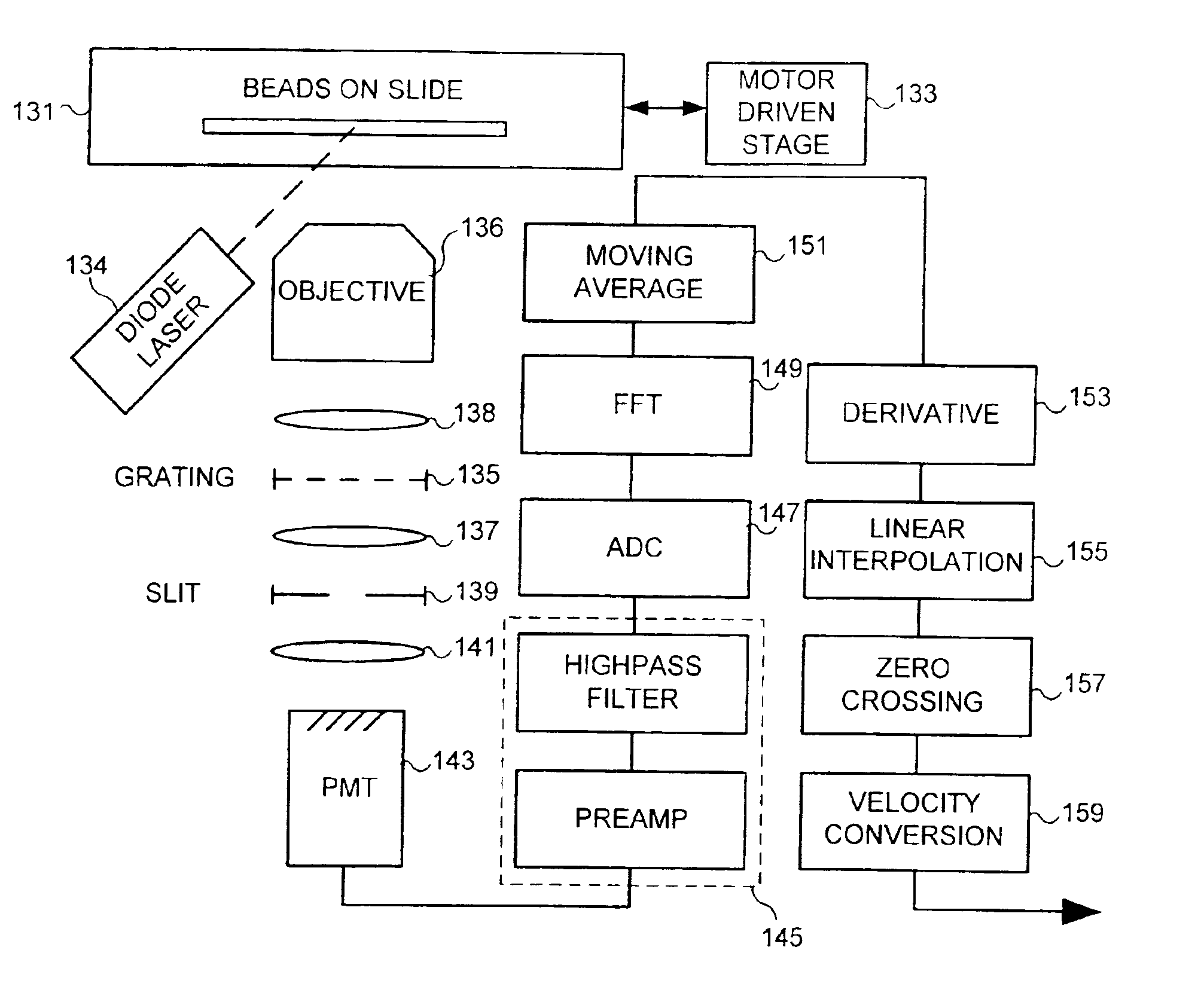
When utilized in a flow imaging instrument, calibration beads provide a known data source that can be employed in various self-diagnostic, calibration and quality metric applications for the both the optical system of the flow imaging instrument, as well as the flow cell of the flow imaging instrument. Such data can be used to determine point spread functions associated with an imaging system, to determine a sensitivity of an imaging system, and to determine a focal point of the imaging system. Imagery collected from calibration beads can be used to determine core size and stability and TDI / flow speed synchronization. Calibration beads can be beneficially employed to enable stable system operation, even when very low sample concentration, or very small sample sizes are to be analyzed.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
Extended depth of field using a multi-focal length lens with a controlled range of spherical aberration and a centrally obscured aperture
ActiveUS20060050409A1Increase contrastReduce image contrastImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint spreadIntermediate image
An extended depth of field is achieved by a computational imaging system that combines a multifocal imaging subsystem for producing a purposefully blurred intermediate image with a digital processing subsystem for producing a recovered image having an extended depth of field. The multifocal imaging system preferably exhibits spherical aberration as the dominant feature of the purposeful blur. A central obscuration of the multifocal imaging subsystem renders point-spread functions of object points more uniform over a range of object distances. An iterative digital deconvolution algorithm for converting the intermediate image into the recovered image contains a metric parameter that speeds convergence, avoids stagnations, and enhances image quality.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
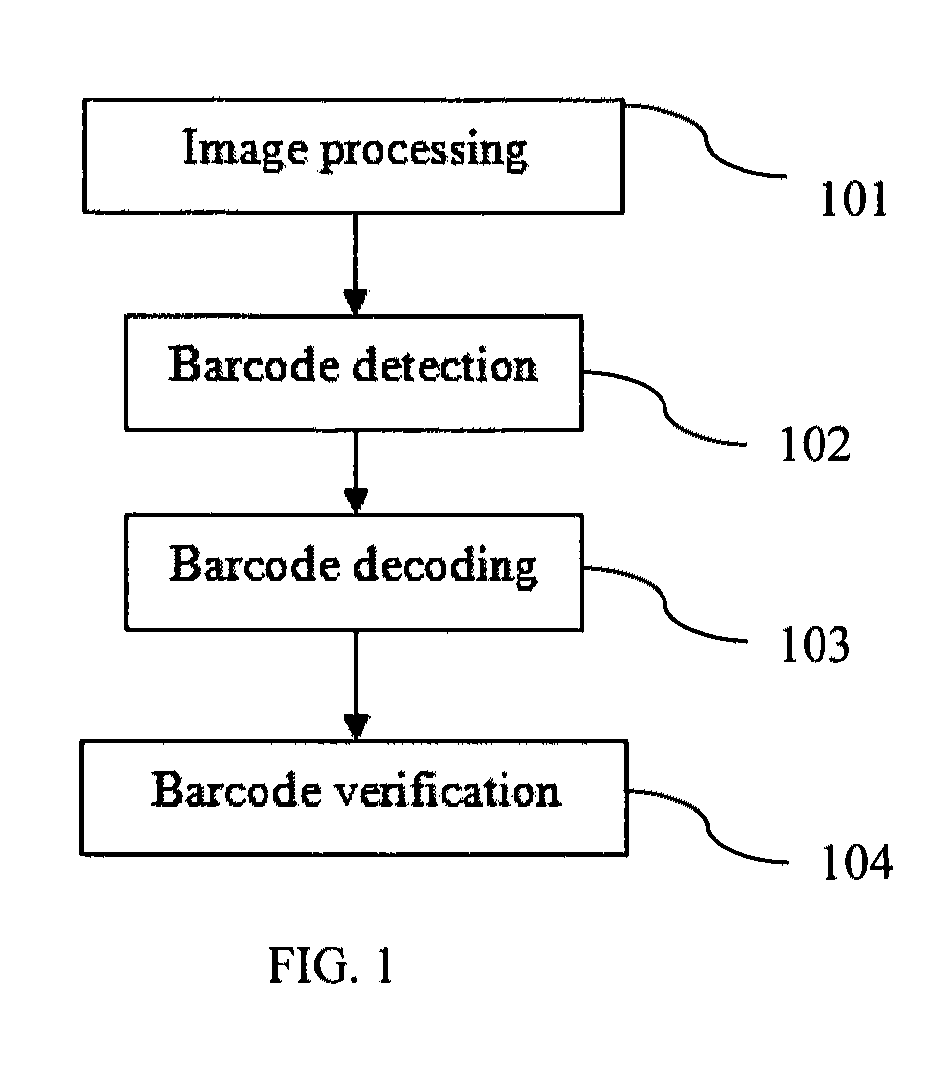
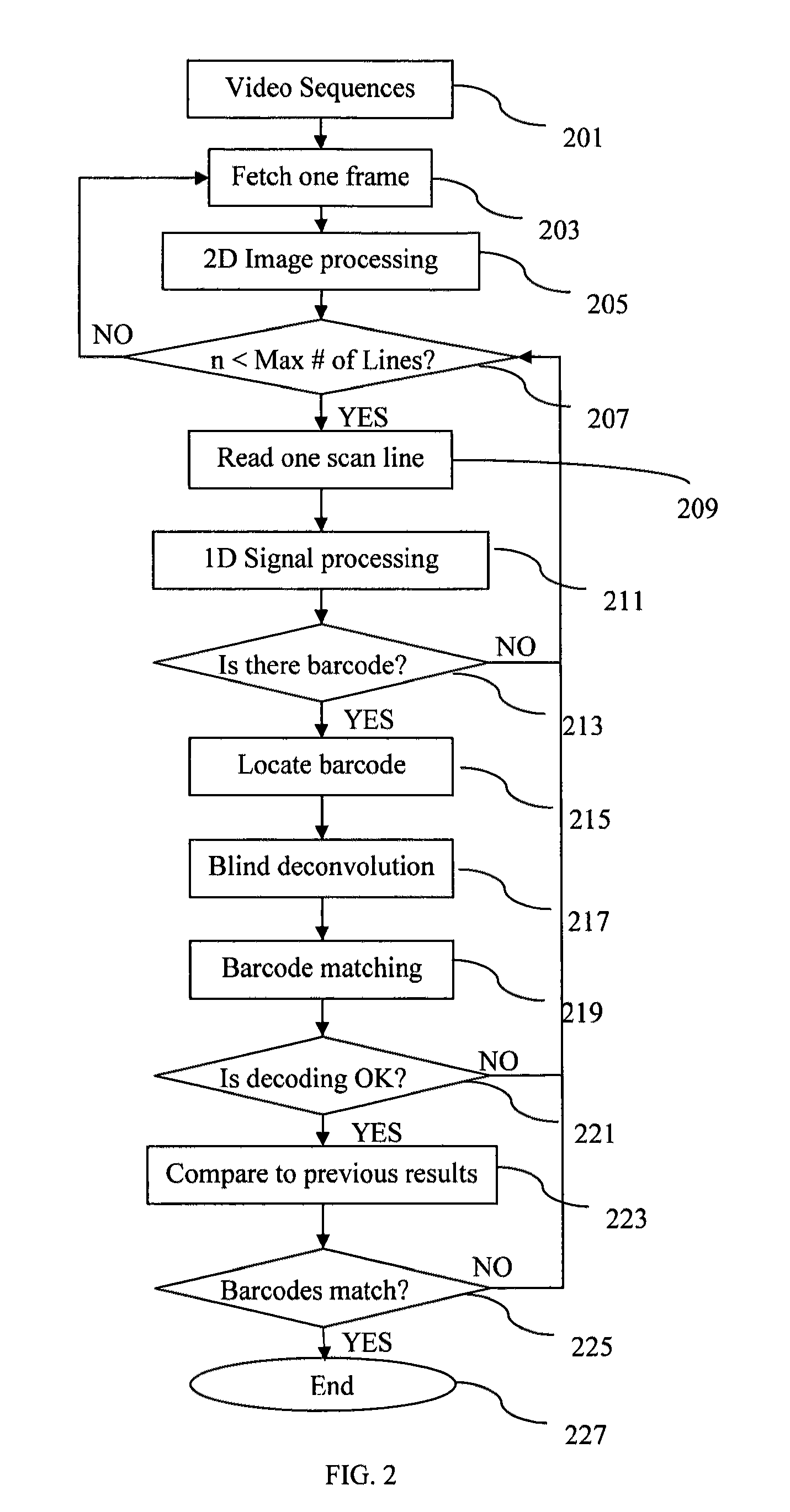
Real-time barcode recognition using general cameras
ActiveUS20120091204A1Reduce computing costEasy to measureSensing record carriersVerifying markings correctnessPattern recognitionPoint spread
A method, apparatus, and system for decoding and recognizing barcode information by using a general camera such as one in a mobile device is disclosed. The invention uses a set of compact point spread functions (PSF) with a squared-shape distribution to restore blurred barcode image for quick and efficient decoding and recognition. Image pre-processing methods are applied to reduce noise and normalize pixel grayscale. On each normalized image, the invention checks if the image contains barcode lines. If there is a barcode, the invention tries to identify the beginning and ending positions of the barcode. The invention selectively decodes multiple scan lines across the barcode and match against predefined barcode models. The best matched barcodes are saved in the history buffer.
Owner:SHI JIAZHENG +1
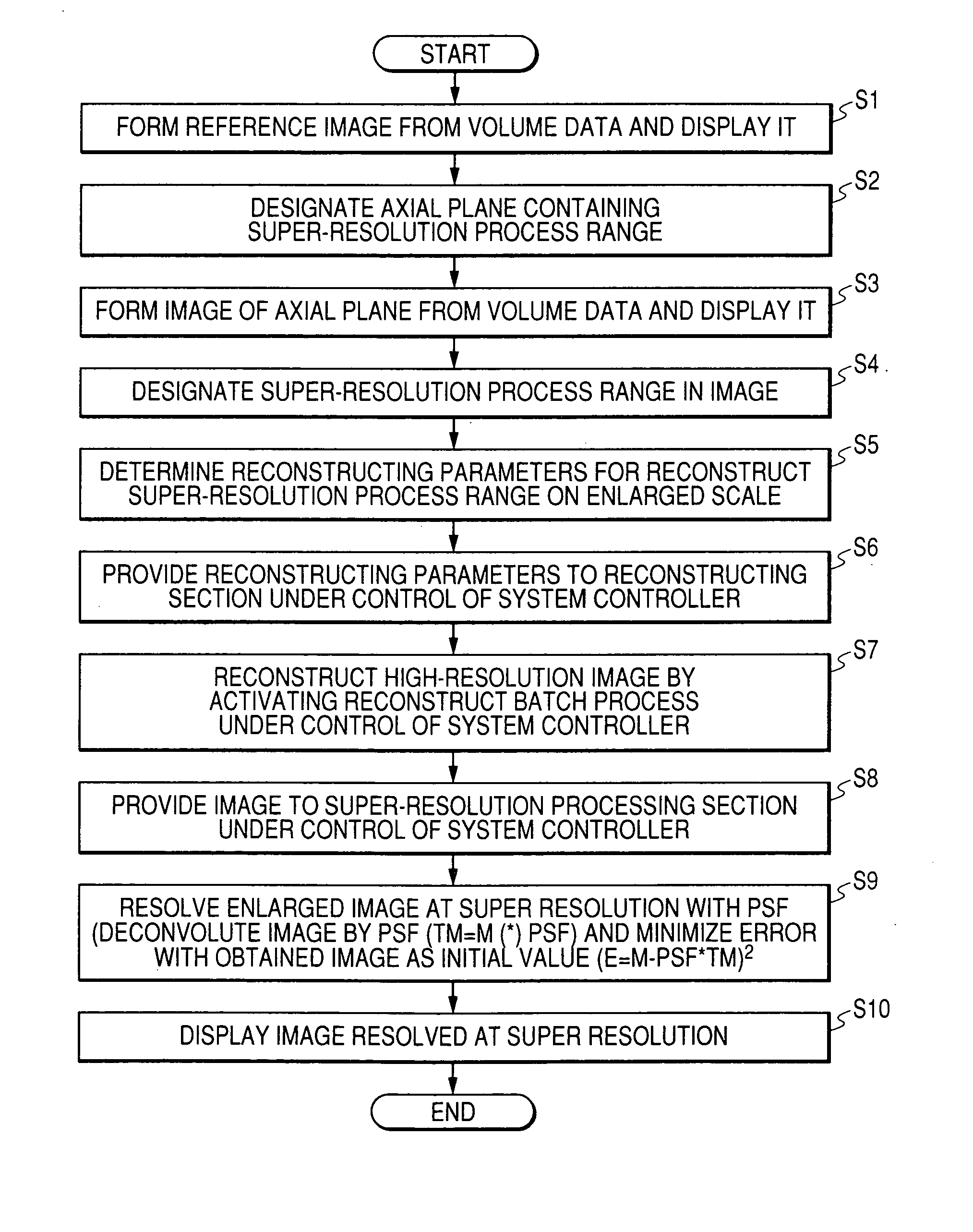
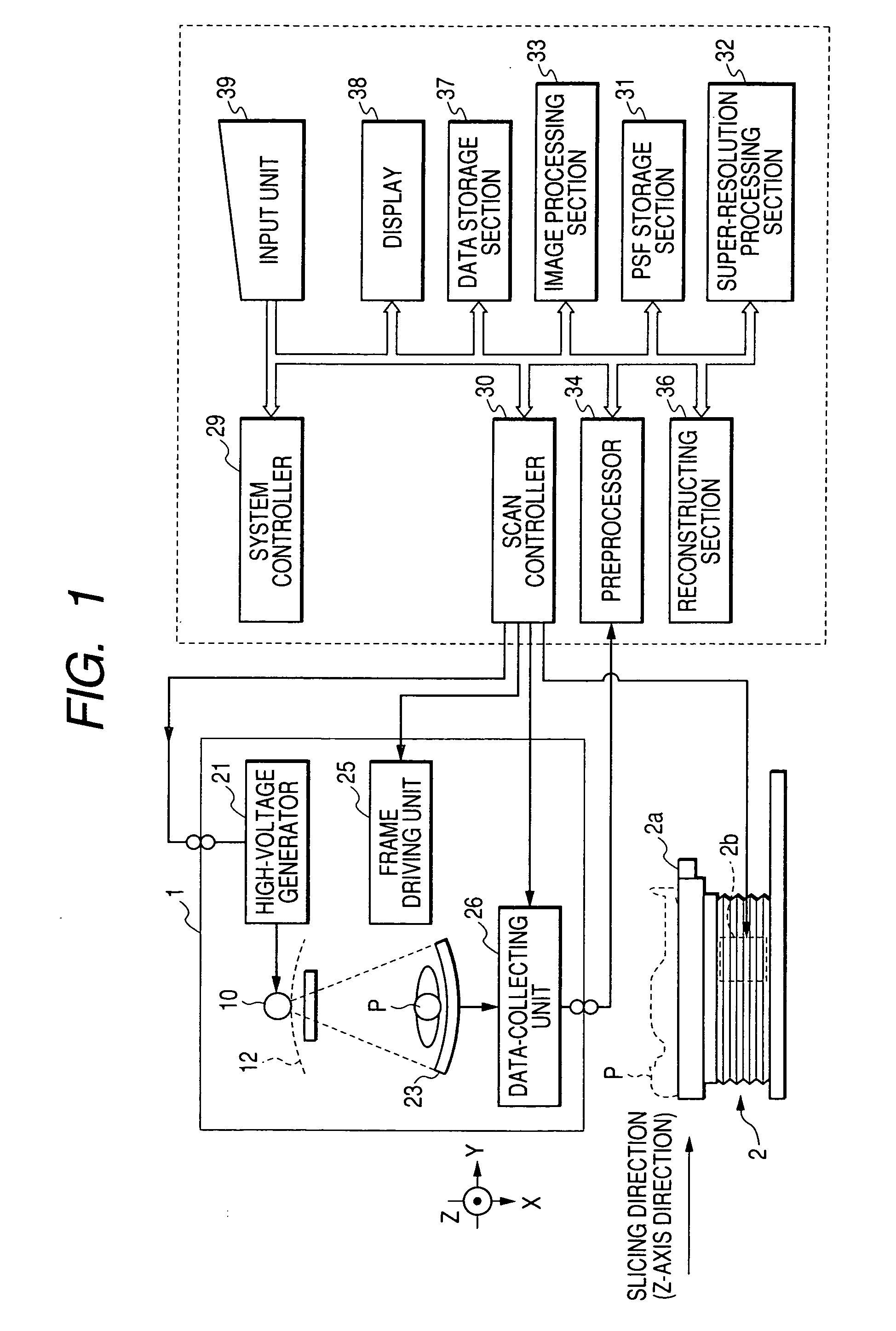
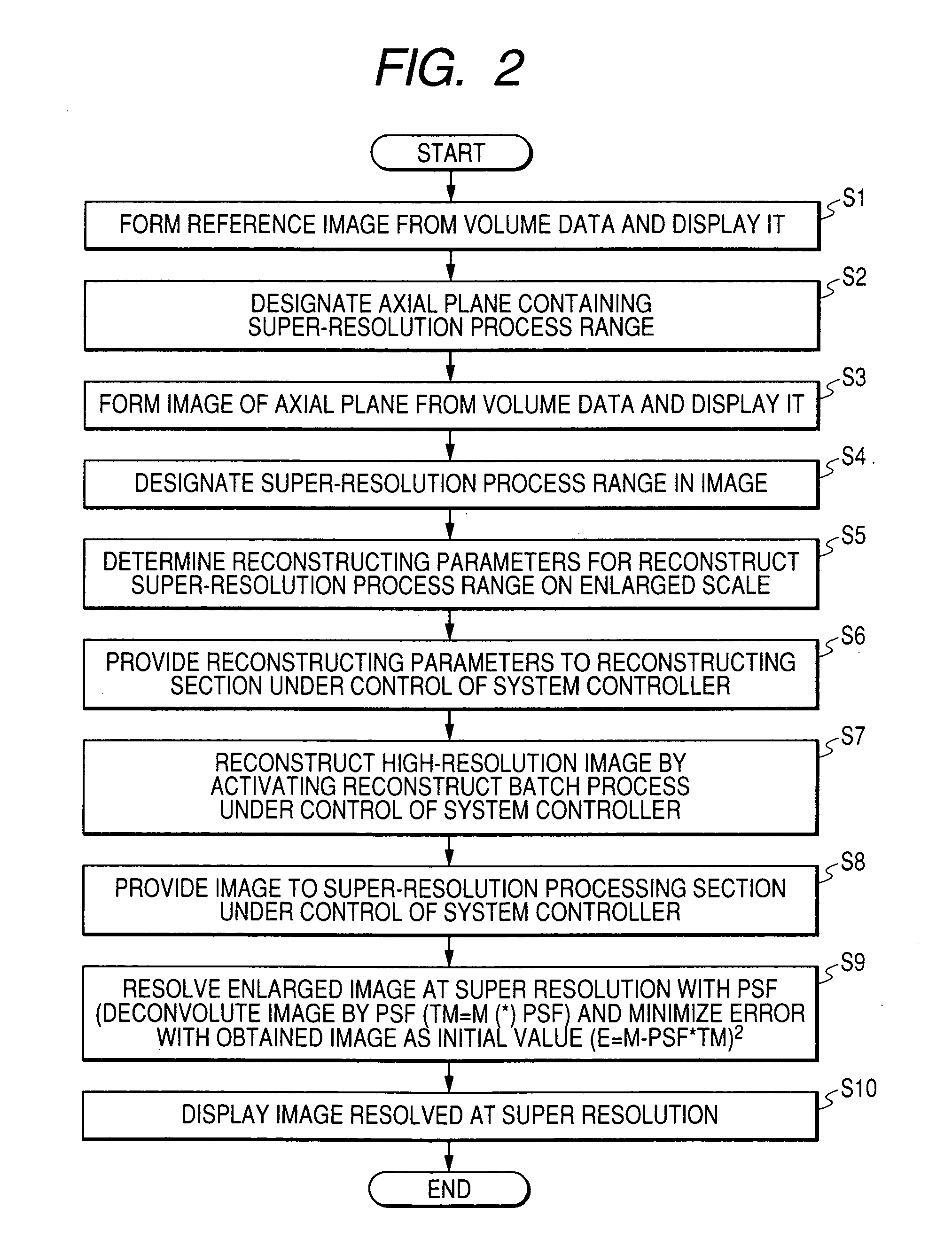
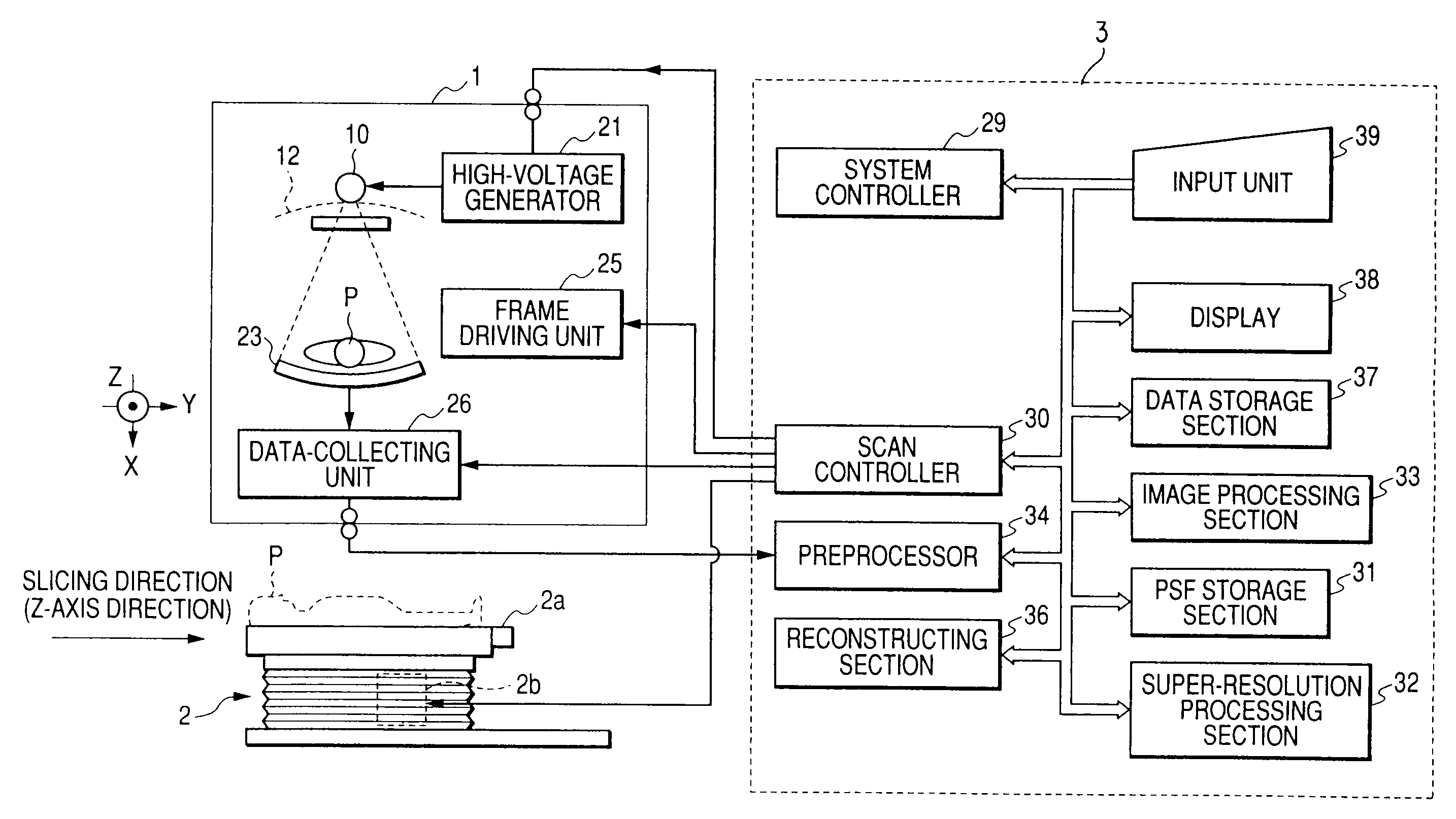
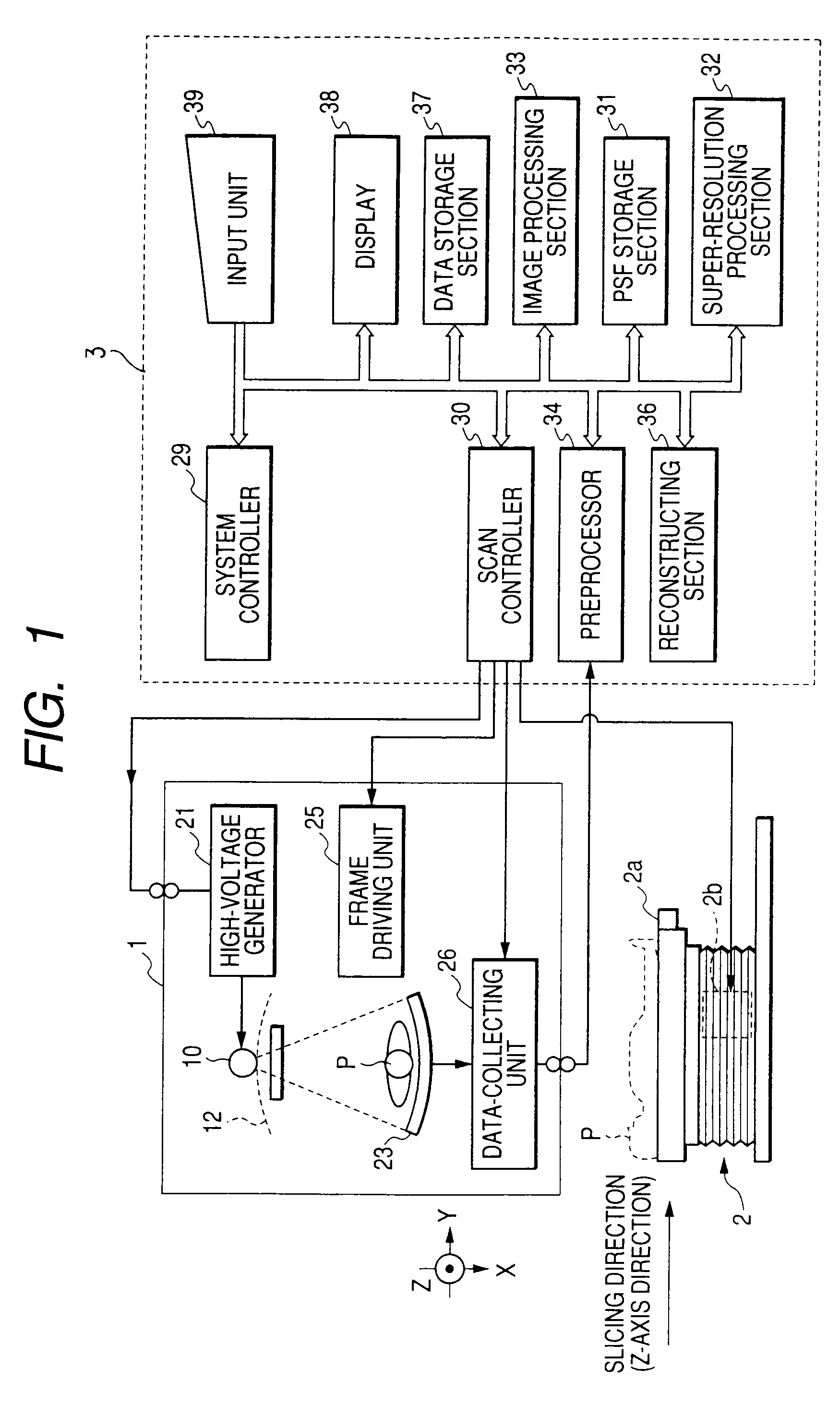
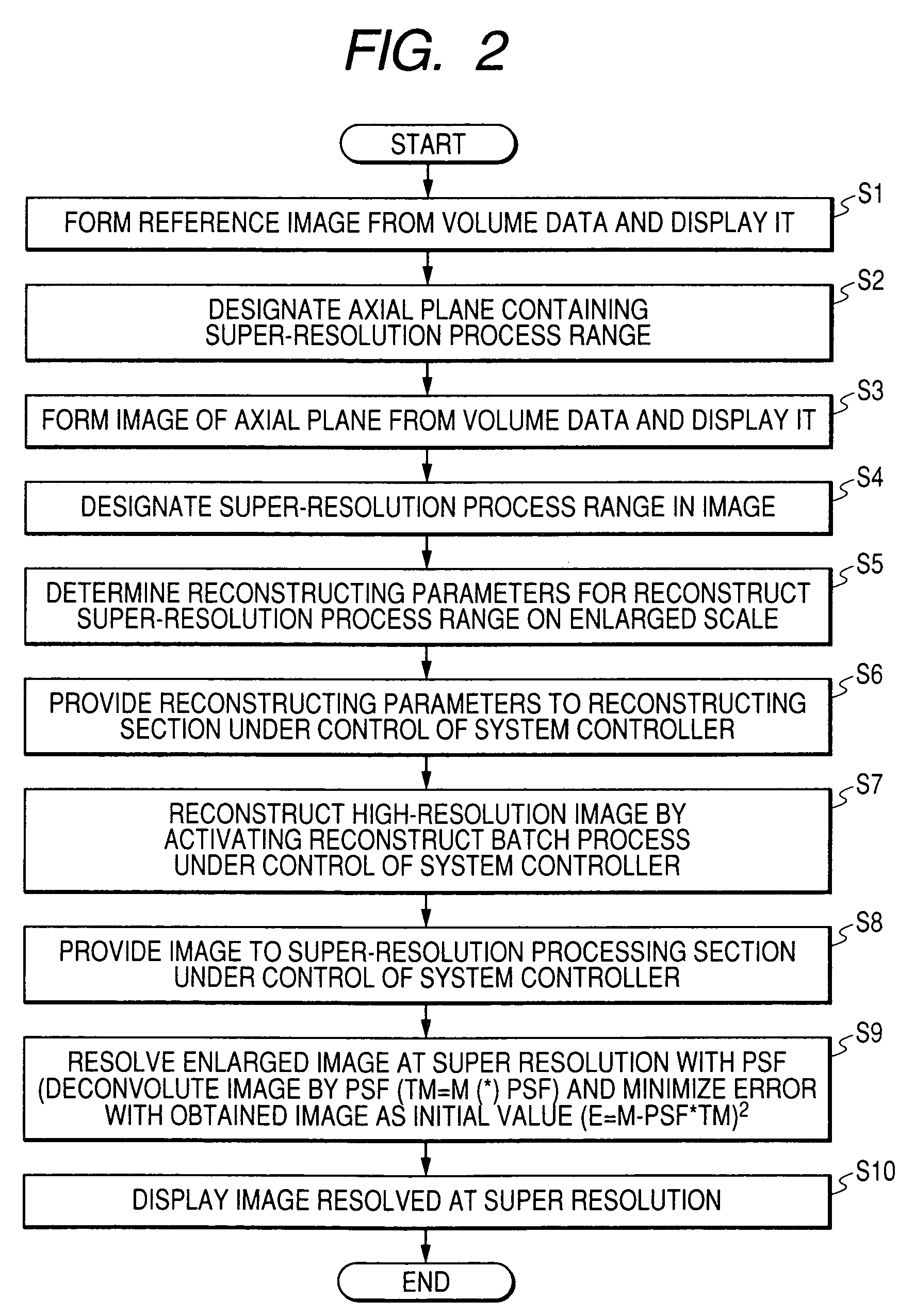
Super-resolution processor and medical diagnostic imaging apparatus
A super-resolution processor includes a storage section for storing data of point spread functions of an X-ray CT scanner which are acquired using a phantom and a super-resolution processing section performing super-resolution of image data of a sample generated by the X-ray CT scanner using the stored point spread functions.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
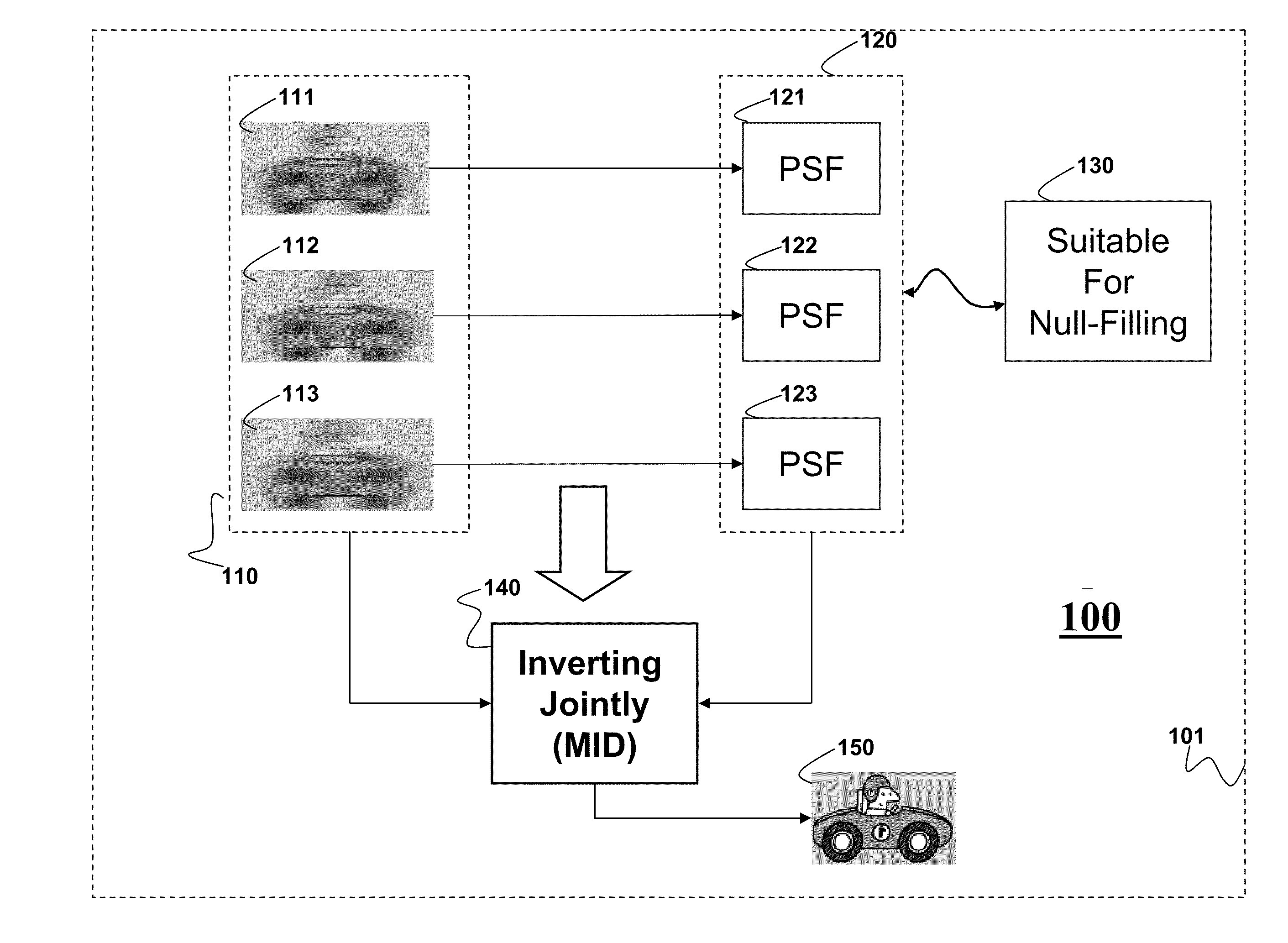
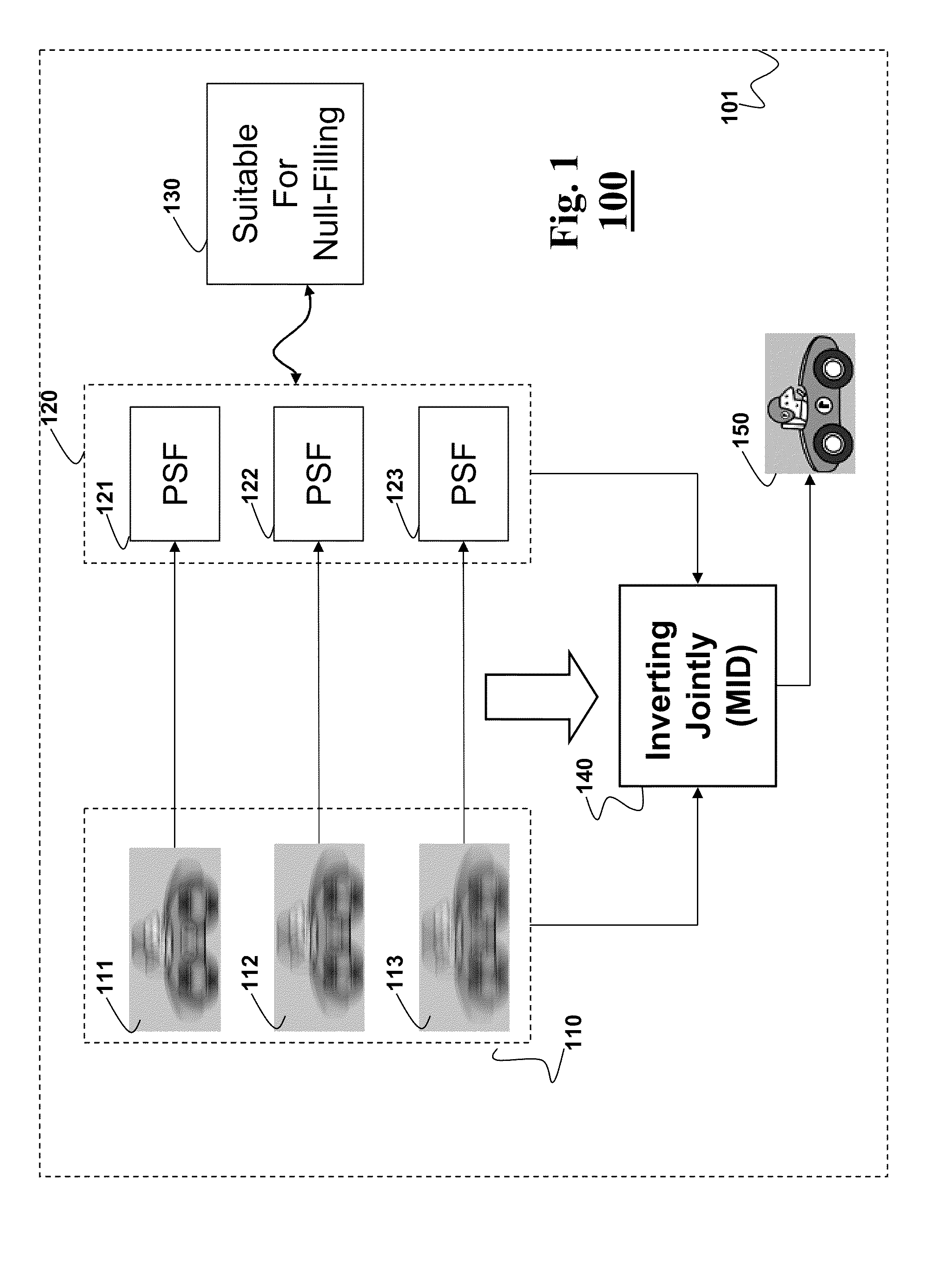
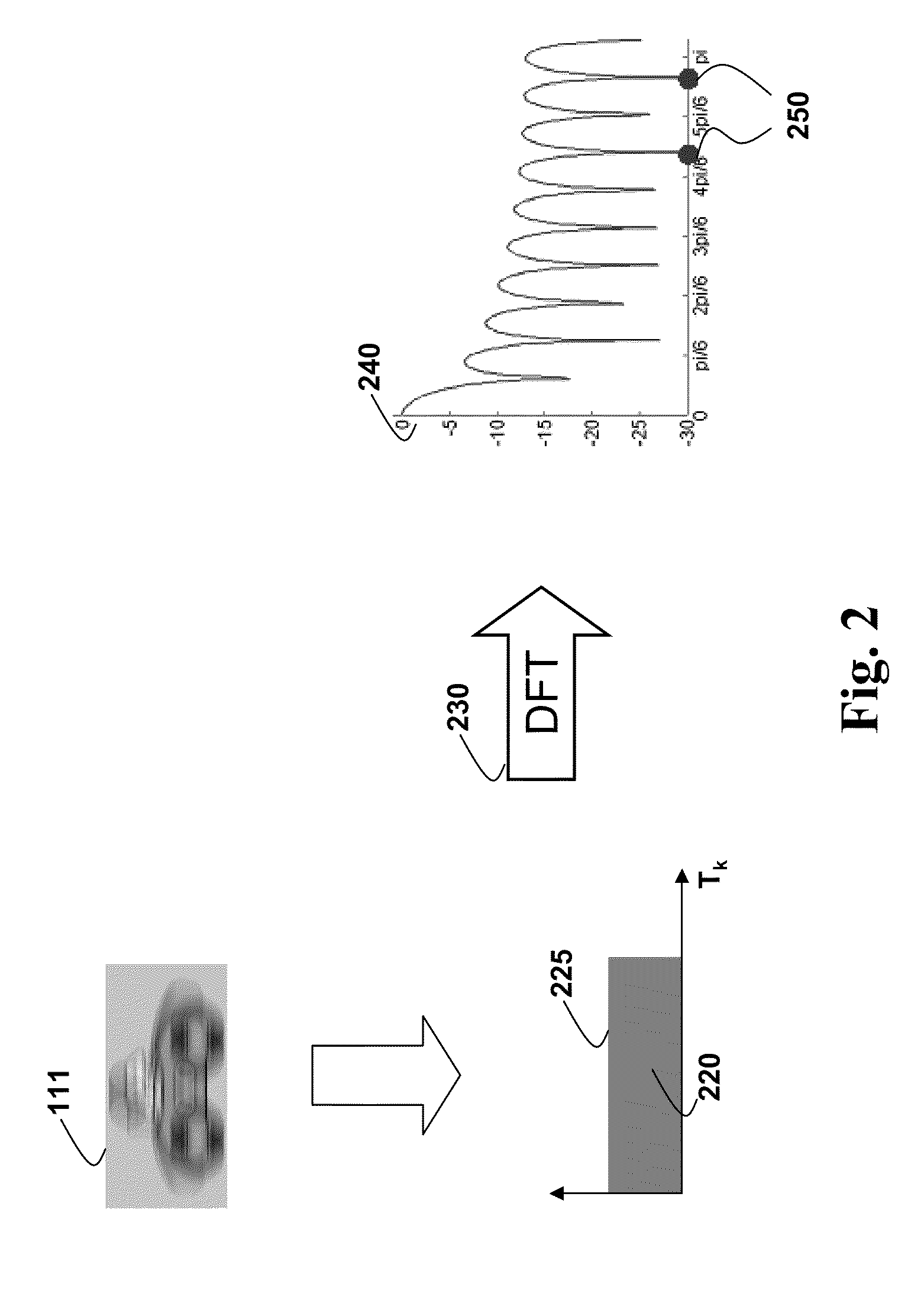
Multi-Image Deblurring
Embodiments of the invention describe a method for reducing a blur in an image of a scene. First, we acquire a set of images of the scene, wherein each image in the set of images includes an object having a blur associated with a point spread function (PSF) forming a set of point spread functions (PSFs), wherein the set of PSFs is suitable for null-filling operation. Next, we invert jointly the set of images and the set of PSFs to produce an output image having a reduced blur.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Indoor positioning method for receiving signal strength ordering fingerprint
InactiveCN103796163AAvoid Positioning ErrorsWireless commuication servicesPoint spreadComputer science
The invention, which belongs to the wireless positioning field, relates to an indoor positioning method for receiving a signal strength ordering fingerprint. The method comprises the following steps that: the number of sampling points spreading in a whole positioning area is determined; sampling point traversal is carried out, received signal strength indicator (RSSI) values of signal strengths of k wireless access points (AP) are obtained by detection at each sampling point, and arrangement is carried out to obtain an RSSI sequence, wherein each RSSI corresponds to one MAC address and the RSSI sequence ad the MAC addresses form sampling point position fingerprints jointly; the coordinates and the position fingerprints of the sampling points are stored into a fingerprint database; AP scanning is carried out at an unknown position to obtain a position fingerprint of an unknown position C and the MAC address sequence in the position fingerprint of the position C is matched with MAC address sequences of the position fingerprints of all sampling points in the fingerprint database; and a geographical coordinate corresponding to the sampling point with consistent matching is used as the current position of the unknown position C a. According to the invention, relative sequences of RSSIs of different APs are used as fingerprints and thus a positioning error caused by different RSSI absolute values by different wireless terminal scanning can be avoided.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Ultrasound imaging device
InactiveUS20110098565A1Enhanced isochronismDegree of reductionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringPoint spreadUltrasound imaging
A transmission / reception beamformer output provided with point spread functions having different wave number vector directions is used to obtain a compound image that is highly isochronous and sufficiently blurring-resistant.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
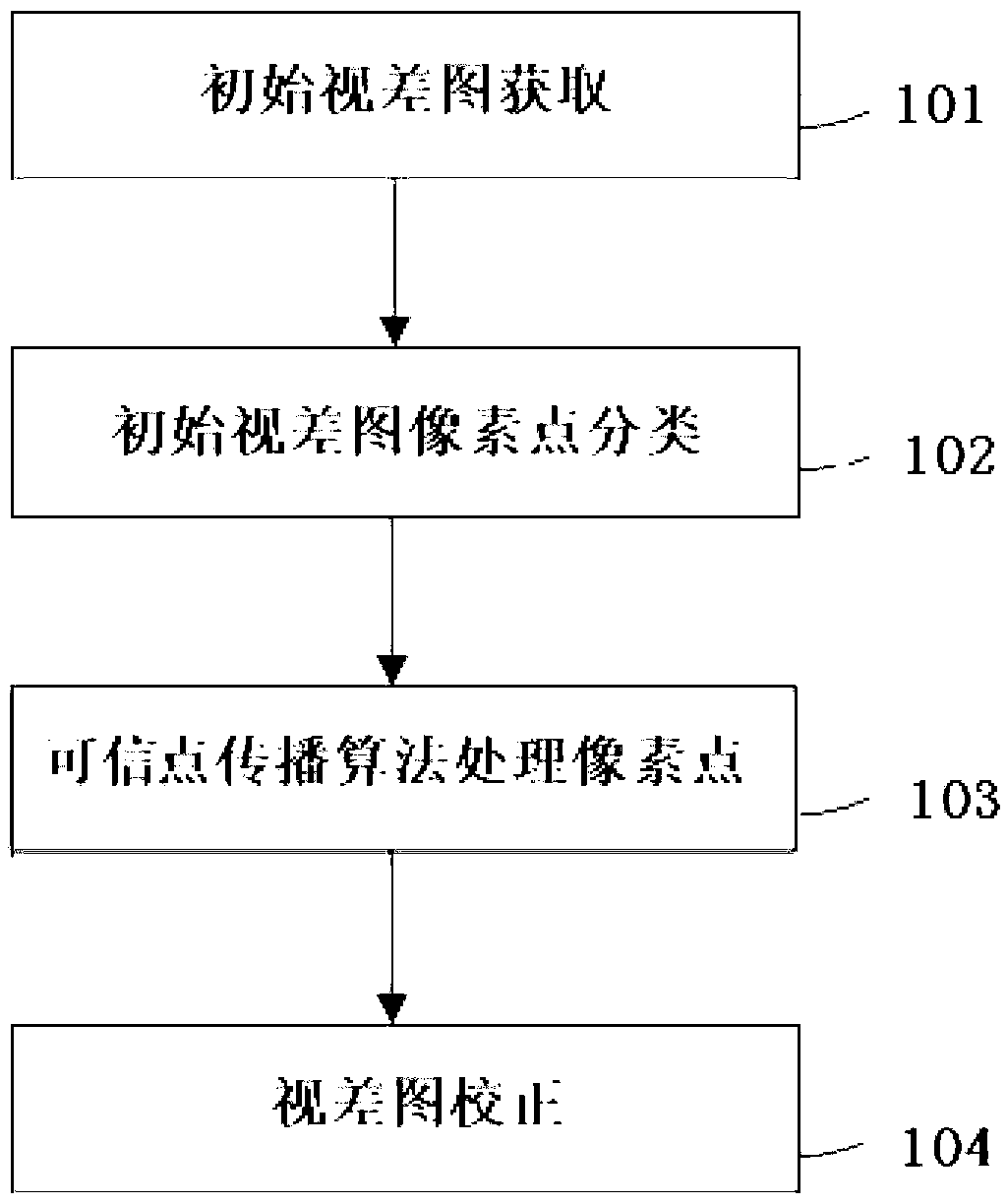
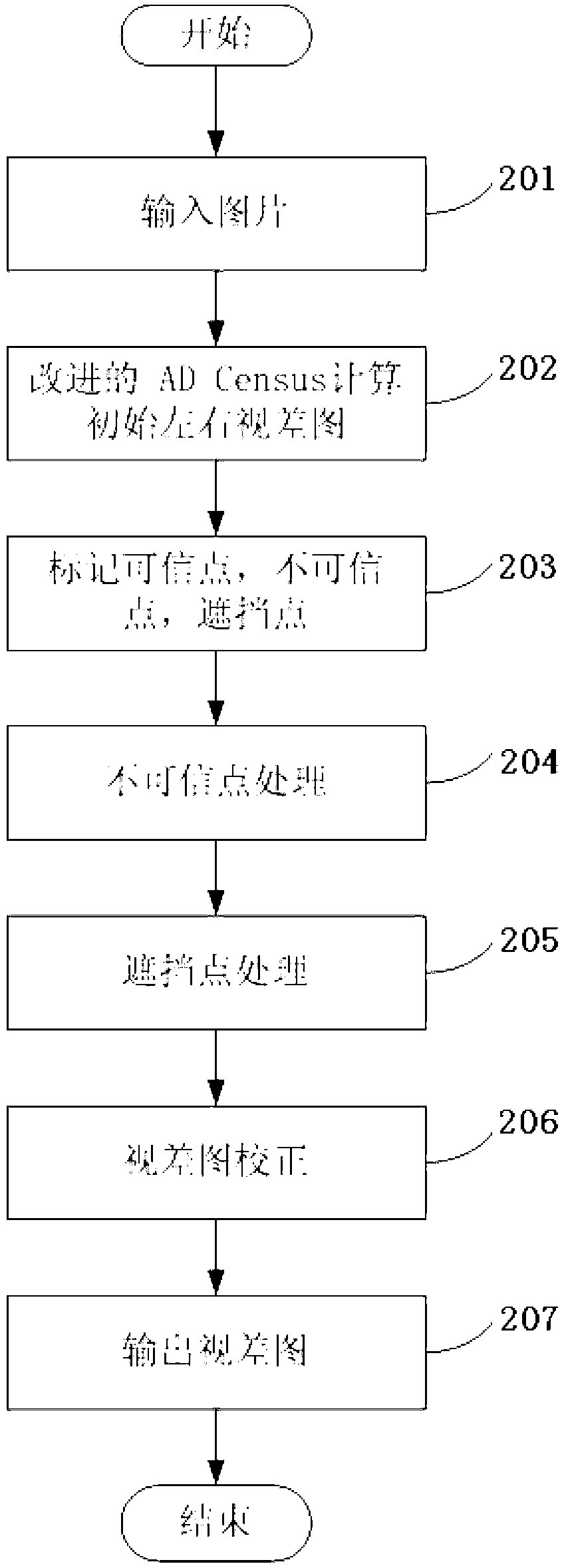
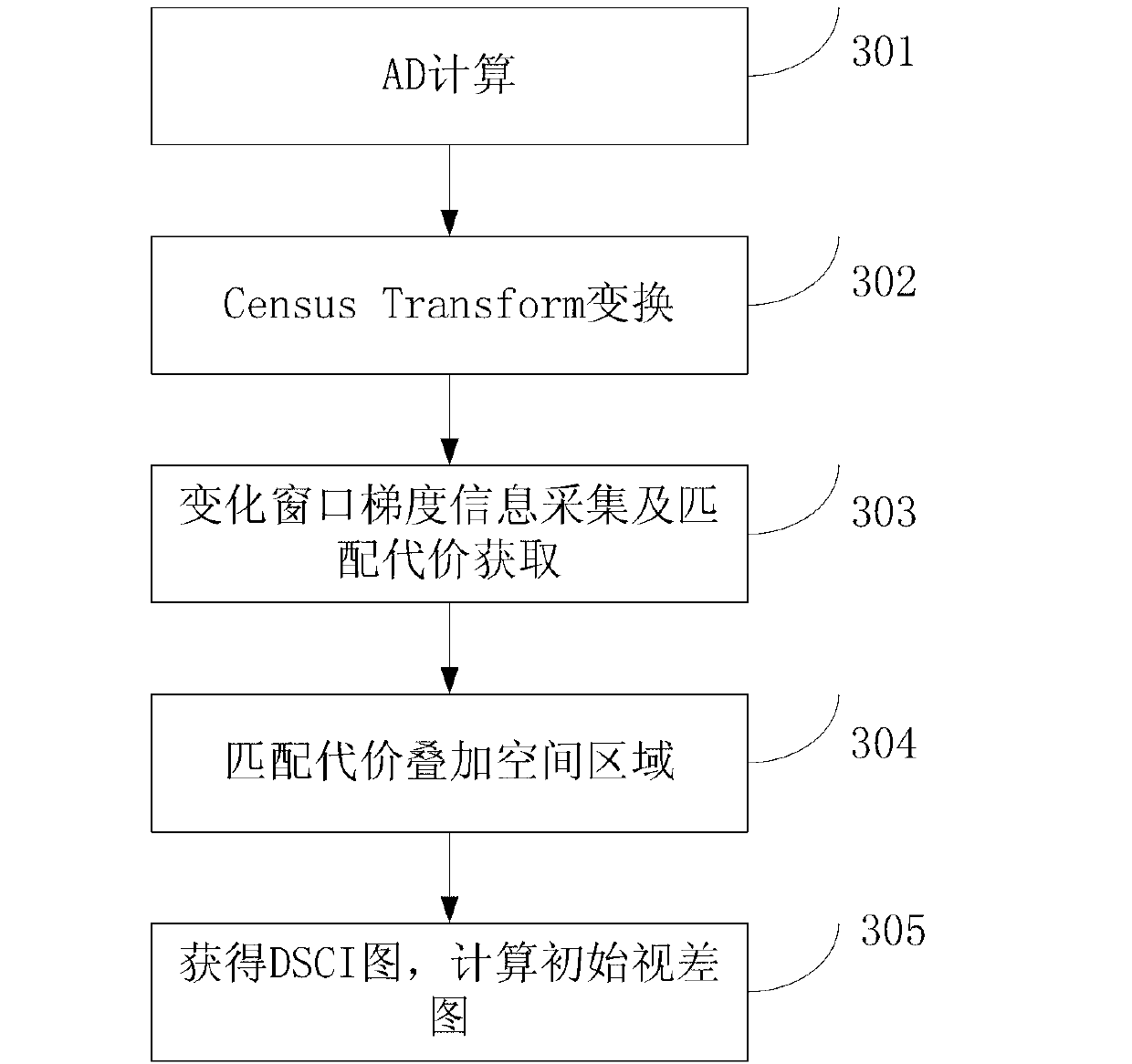
Local three-dimensional matching method based on credible point spreading
The invention discloses a local three-dimensional matching method based on credible point spreading. The local three-dimensional matching method includes: a, at least calculating minimum values and second minimum values of matching cost of pixel points under different parallax hypothesis by utilizing an AD (absolute intensity differences)-Census algorithm, and obtaining a DSCI image by combining with gradient information of images; b, obtaining initial disparity maps of the images according to the DSCI; c, dividing the pixel points into credible points, unlikelihood points and shielding points, wherein the credible points are determined by combining with the minimum values and the second minimum values to the matching cost; d, calculating the disparity values of the credible points and processing the unlikelihood points and the shielding points through the credible points to obtain the disparity values; and e, outputting a disparity image. The local three-dimensional matching method based on the credible point spreading effectively utilizes data in an initial disparity image, enables the credible points to be determined reasonably and accurately, further enables the following processing on the unlikelihood points and the shielding points to be accurate and finally ensures the accuracy of the matching method.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Complex index refraction tomography with sub lambda/6-resolution
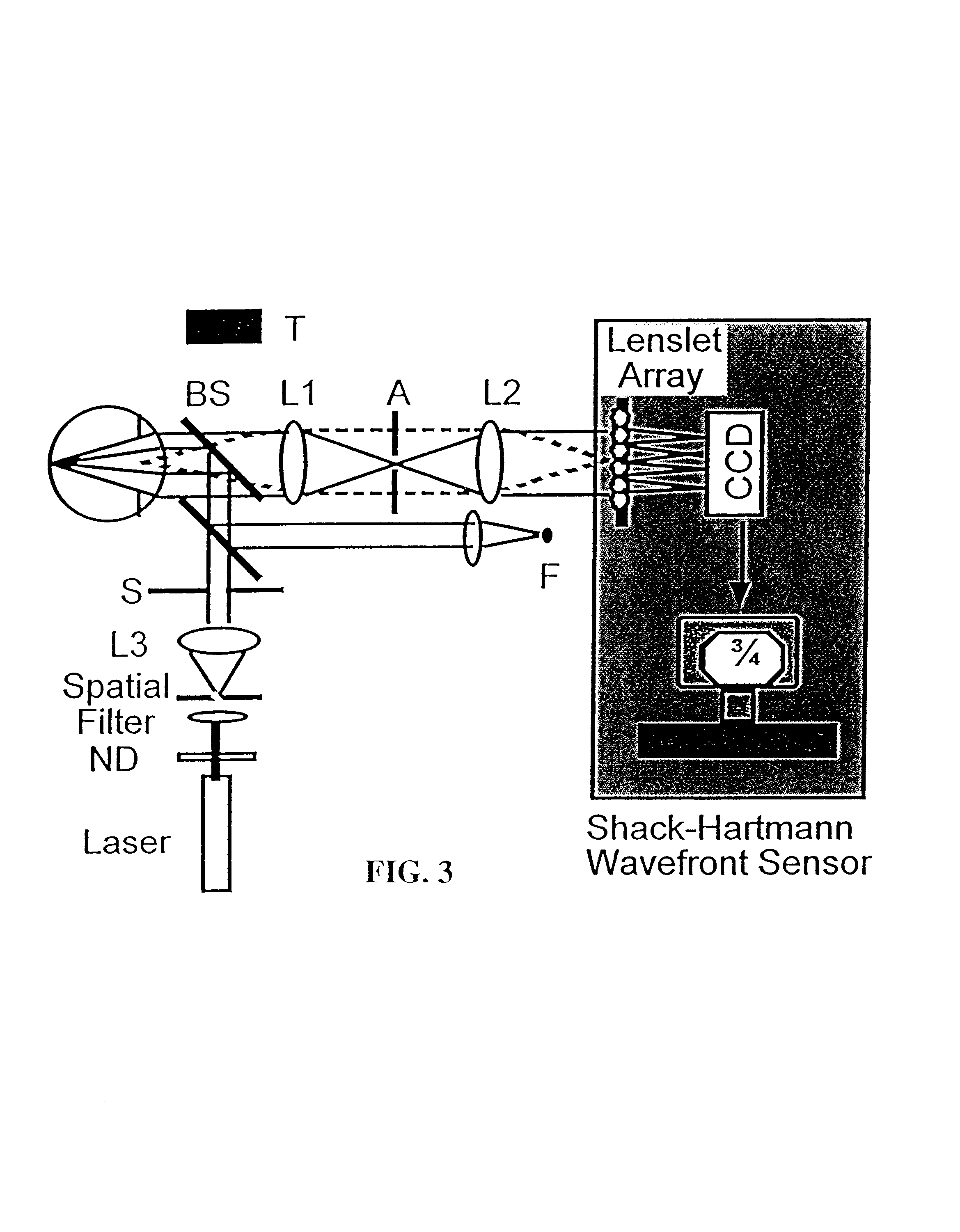
The present invention discloses a method to improve the image resolution of a microscope. This improvement is based on the mathematical processing of the complex field computed from the measurements with a microscope of the wave emitted or scattered by the specimen. This wave is, in a preferred embodiment, electromagnetic or optical for an optical microscope, but can be also of different kind like acoustical or matter waves. The disclosed invention makes use of the quantitative phase microscopy techniques known in the sate of the art or to be invented. In a preferred embodiment, the complex field provided by Digital Holographic Microscopy (DHM), but any kind of microscopy derived from quantitative phase microscopy: modified DIC, Shack-Hartmann wavefront analyzer or any analyzer derived from a similar principle, such as multi-level lateral shearing interferometers or common-path interferometers, or devices that convert stacks of intensity images (transport if intensity techniques: TIT) into quantitative phase image can be used, provided that they deliver a comprehensive measure of the complex scattered wavefield. The hereby-disclosed method delivers superresolution microscopic images of the specimen, i.e. images with a resolution beyond the Rayleigh limit of the microscope. It is shown that the limit of resolution with coherent illumination can be improved by a factor of 6 at least. It is taught that the gain in resolution arises from the mathematical digital processing of the phase as well as of the amplitude of the complex field scattered by the observed specimen. In a first embodiment, the invention teaches how the experimental observation of systematically occurring phase singularities in phase imaging of sub-Rayleigh distanced objects can be exploited to relate the locus of the phase singularities to the sub-Rayleigh distance of point sources, not resolved in usual diffraction limited microscopy. In a second, preferred embodiment, the disclosed method teaches how the image resolution is improved by complex deconvolution. Accessing the object's scattered complex field—containing the information coded in the phase—and deconvolving it with the reconstructed complex transfer function (CTF) is at the basis of the disclosed method. In a third, preferred embodiment, it is taught how the concept of “Synthetic Coherent Transfer Function” (SCTF), based on Debye scalar or Vector model includes experimental parameters of MO and how the experimental Amplitude Point Spread Functions (APSF) are used for the SCTF determination. It is also taught how to derive APSF from the measurement of the complex field scattered by a nanohole in a metallic film. In a fourth embodiment, the invention teaches how the limit of resolution can be extended to a limit of λ / 6 or smaller based angular scanning. In a fifth embodiment, the invention teaches how the presented method can generalized to a tomographic approach that ultimately results in super-resolved 3D refractive index reconstruction.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Method for establishing flood disaster geographical analysis and evaluation dynamic model
InactiveCN103927389AFunction increaseImprove performanceClimate change adaptationGeographical information databasesMathematical modelDynamic models
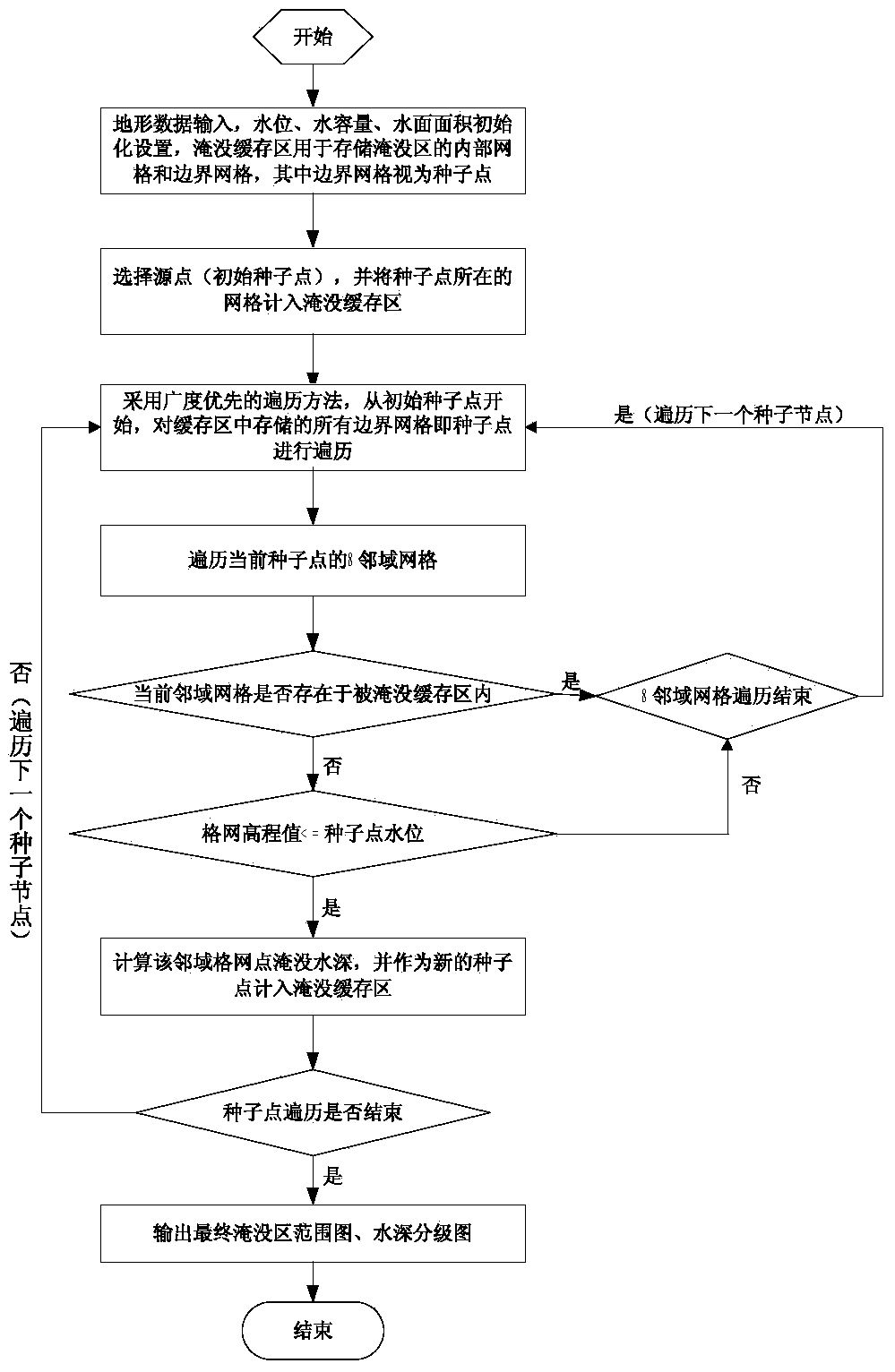
The invention relates to the field of disaster information management, in particular to a method for establishing a flood disaster geographical analysis and evaluation dynamic model. The method includes the steps that initial data of a region to be analyzed are collected, compressed and then stored in an established lightweight class spatial database; the initial data are retrieved, an established flood inundation analysis model is initialized, and a final flood inundated region areal map and a water depth classification map are acquired through a seed point spreading algorithm; integrated data of the final flood inundated region areal map and the water depth classification map are input to a flood disaster loss evaluation mathematical model and a flood risk evaluation mathematical model for calculation, and then the economic loss condition and the potential flood-hit risk degree of villages in a flood storage and detention region after flood inundation are acquired. A spatial database system and the flood inundation analysis model which are excellent in performance and stable and reliable in operation are established, the organization and management method of image raster data is optimized, the flood inundation condition of the flood storage and detention region under a given condition is visually displayed, and the consequential loss evaluation function is provided.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGYOULIAN TECH
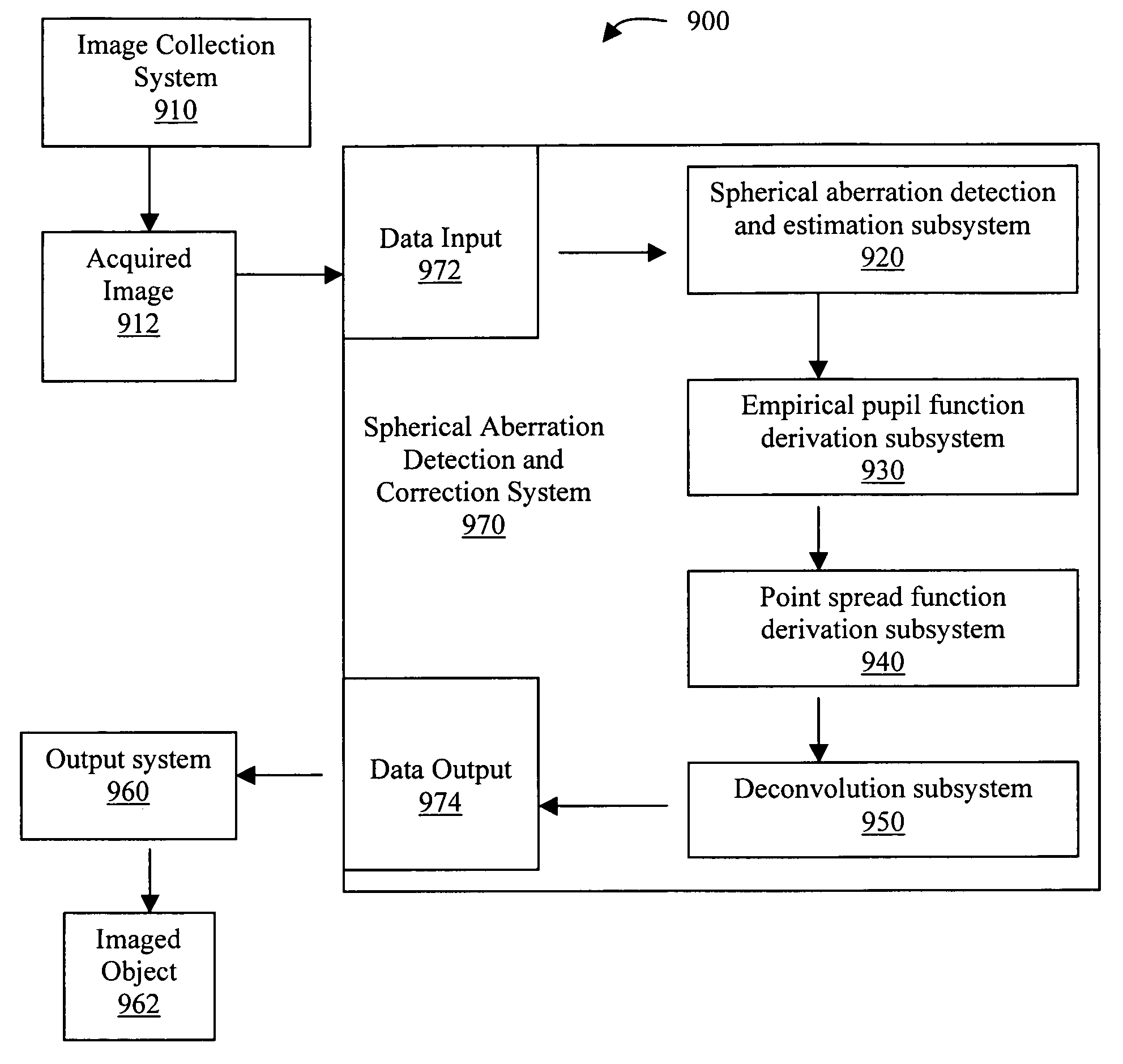
Methods, system, and program product for the detection and correction of spherical aberration
The present invention provides methods, a system, and a program product for the rapid detection and correction of spherical aberration in microscopy systems. More specifically, the present invention empirically derives a pupil function, adaptively corrects PSF parameters, and automatically detects the coefficient for spherical aberration. A first aspect of the invention provides a method for detecting and estimating spherical aberration in an acquired image obtained using an optical system, comprising the steps of deconvolving an image using each of a plurality of point spread functions, wherein each point spread function has a different spherical aberration value, calculating an image energy for each deconvolved image, and choosing as a spherical aberration coefficient the spherical aberration value corresponding to the deconvolved image having the lowest image energy, wherein a spherical aberration coefficient other than 0 indicates the presence of spherical aberration in the acquired image and its distance from 0 is an estimation of the degree and direction of spherical aberration.
Owner:MEDIA CYBERNETICS
Super-resolution processor and medical diagnostic imaging apparatus
A super-resolution processor includes a storage section for storing data of point spread functions of an X-ray CT scanner which are acquired using a phantom and a super-resolution processing section performing super-resolution of image data of a sample generated by the X-ray CT scanner using the stored point spread functions.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
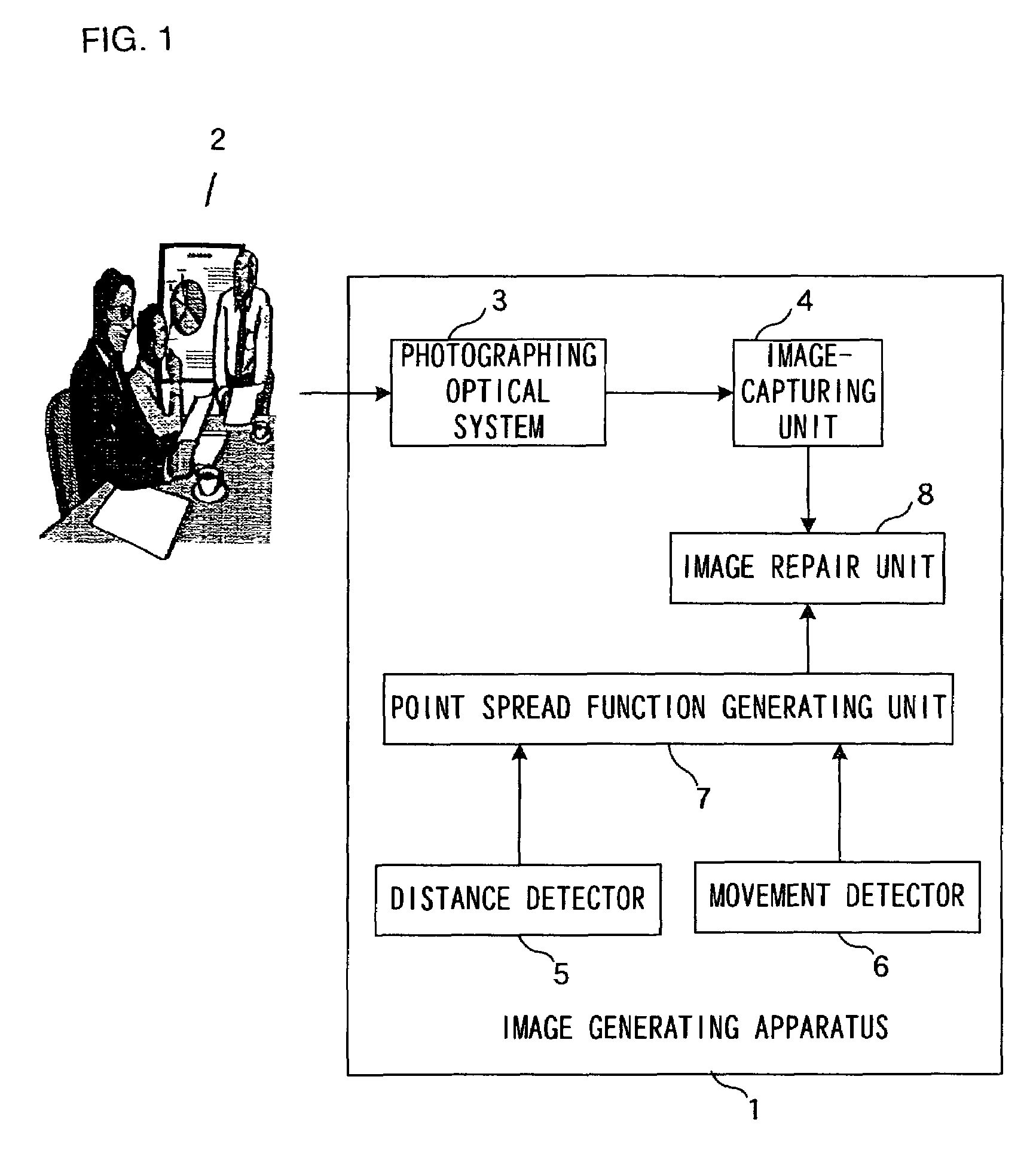
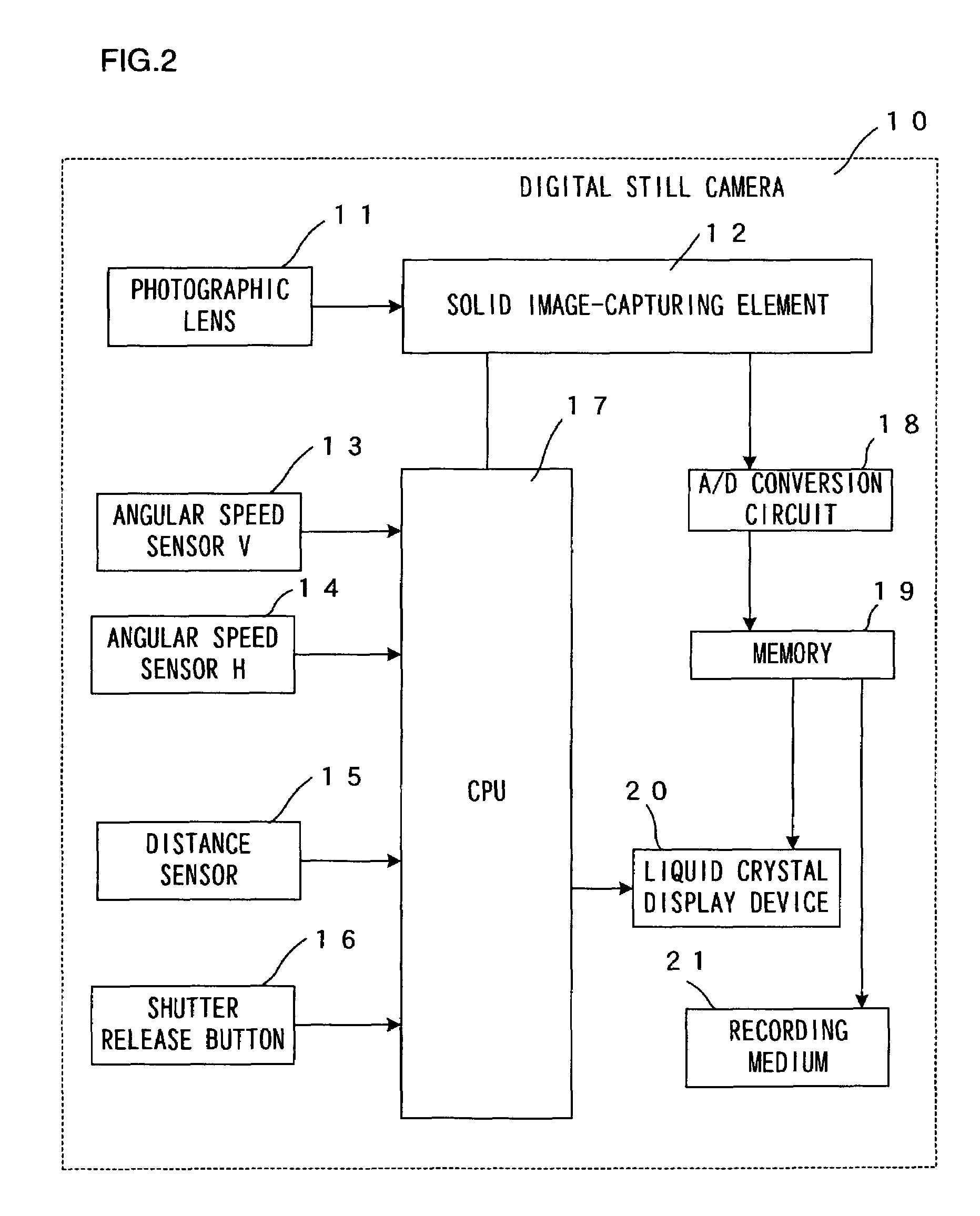
Image creating device and image creating method
InactiveUS7260270B2Efficient repairSuccessful repair on a blurred imageImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint spreadImaging processing
An image-capturing unit generates an image signal corresponding to an image of a subject formed by a photographing optical system. A point spread function generating unit generates varying point spread functions corresponding to various distances based upon two-dimensional distance distribution information indicating the two-dimensional distance distribution of the subject detected by a distance detection unit and an image blur signal indicating an image blur occurring during the exposure period which is detected by a blur detection unit. An image repair unit divides the image signal into partial images based upon the distance distribution information, executes image processing to repair the blur in the individual partial images by using the point spread functions corresponding to the various distances and creates a whole image by synthesizing the partial images in which the blur has been repaired.
Owner:NIKON CORP
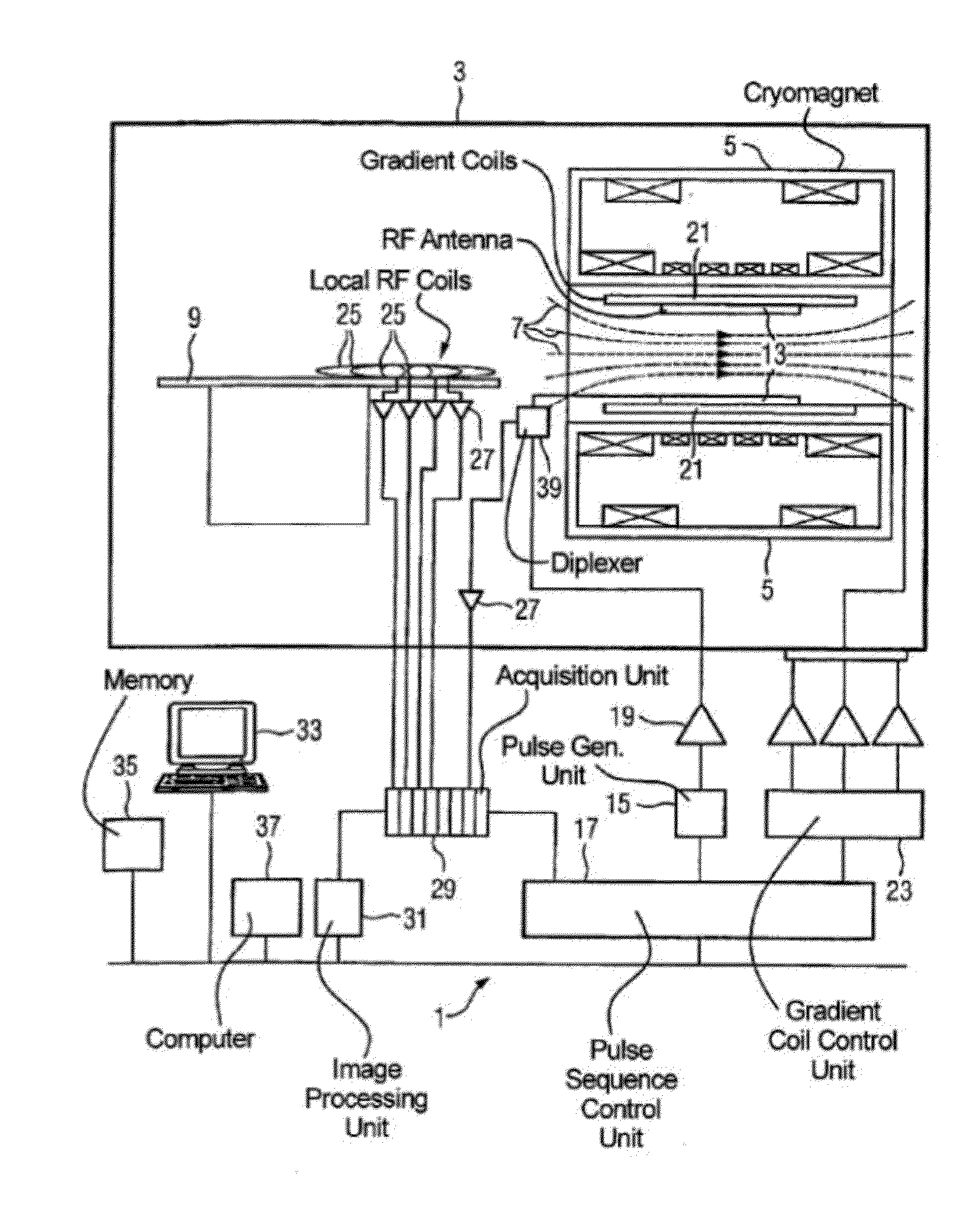
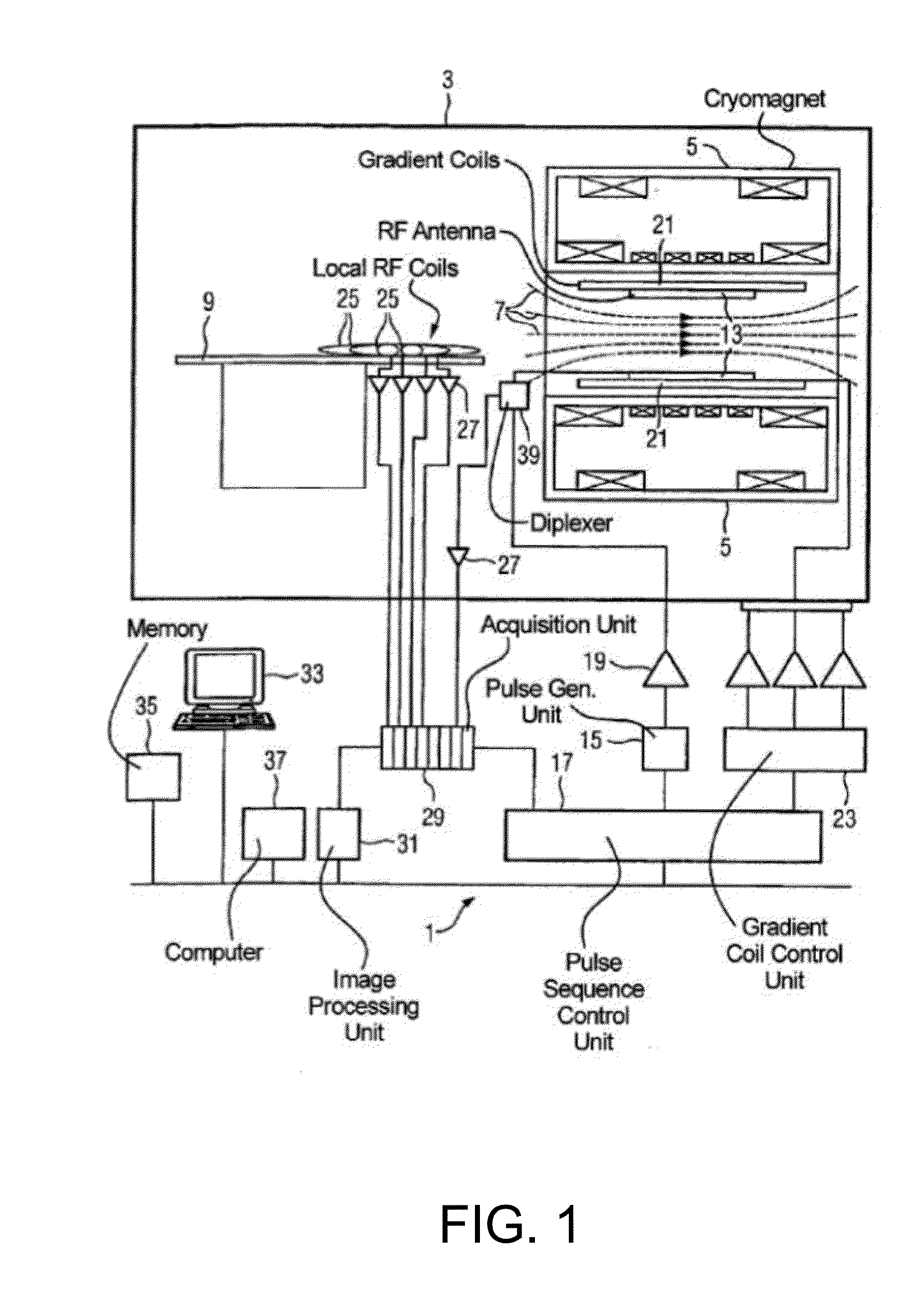
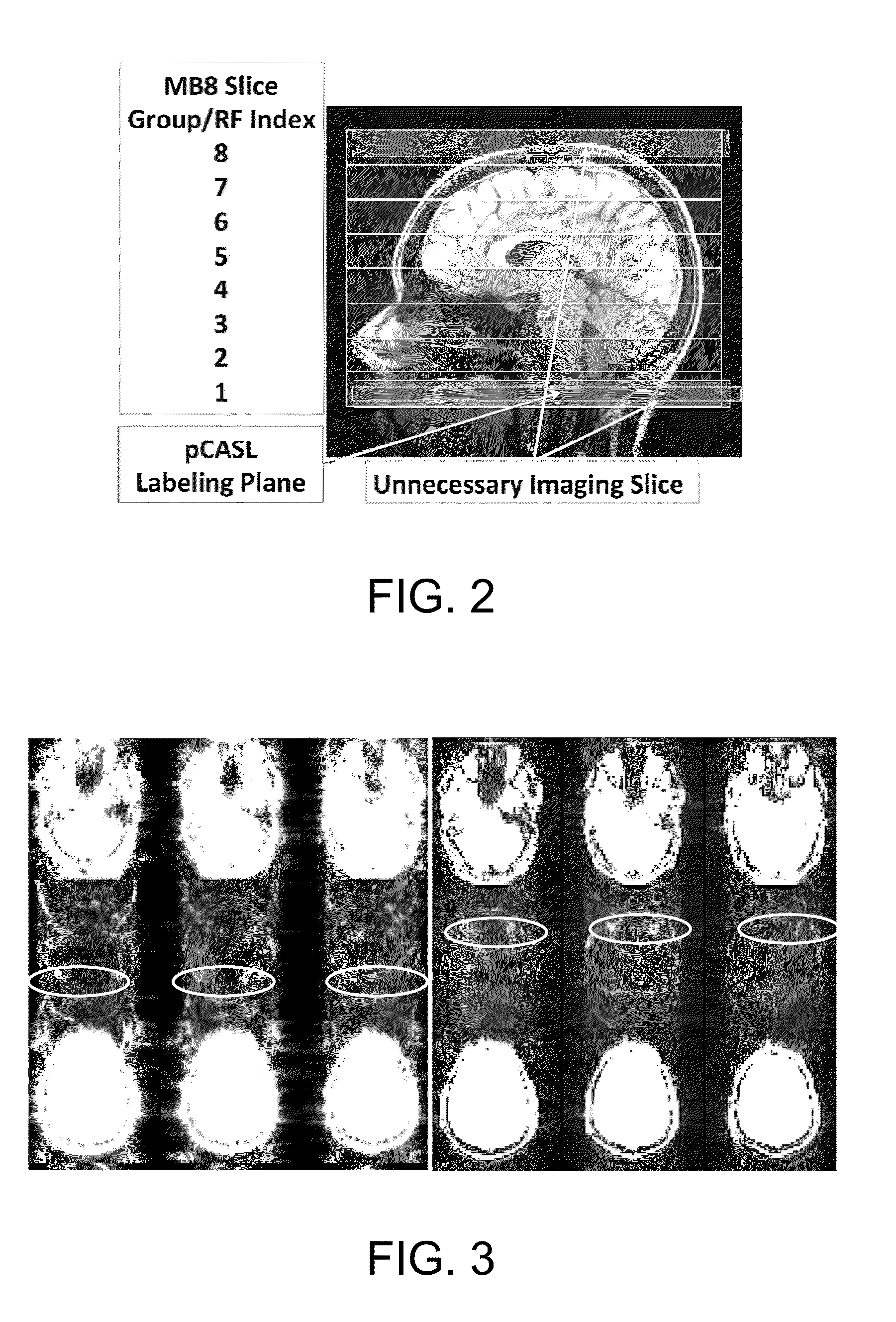
Apparatus And Method For Multi-Band MR Imaging
ActiveUS20150309142A1Enhance the imageMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPoint spreadMulti band
A magnetic resonance method and system are provided for providing improved multi-band (MB) magnetic resonance imaging. The adaptive MB imaging can be achieved by providing one or more modified multi-band excitation pulse sequences that include at least either one nullified “dummy” slice within a slab that is not excited simultaneously with the other slices during a single multislice acquisition sequence, or one excitation slice group that utilizes a non-uniform slice spacing between simultaneously excited slices. Adaptive GRAPPA or slice-GRAPPA kernel sizes can also be used during image reconstruction to improve speed without excessive point spread blurring or MB reconstruction failure. A total leakage factor (TLF) can also be determined based on test images using modified MB excitation sequences, and used to improve the adaptive MB procedure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
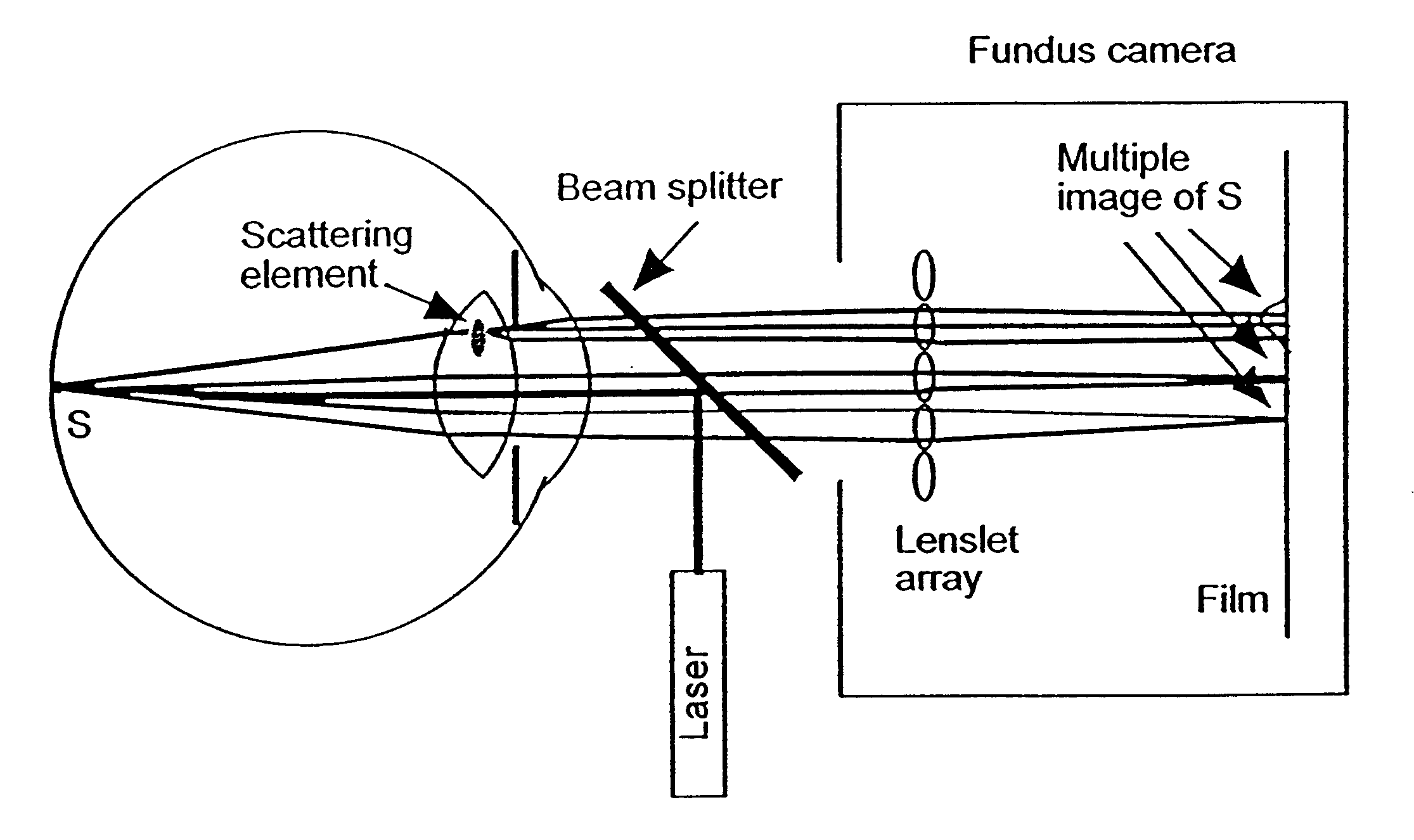
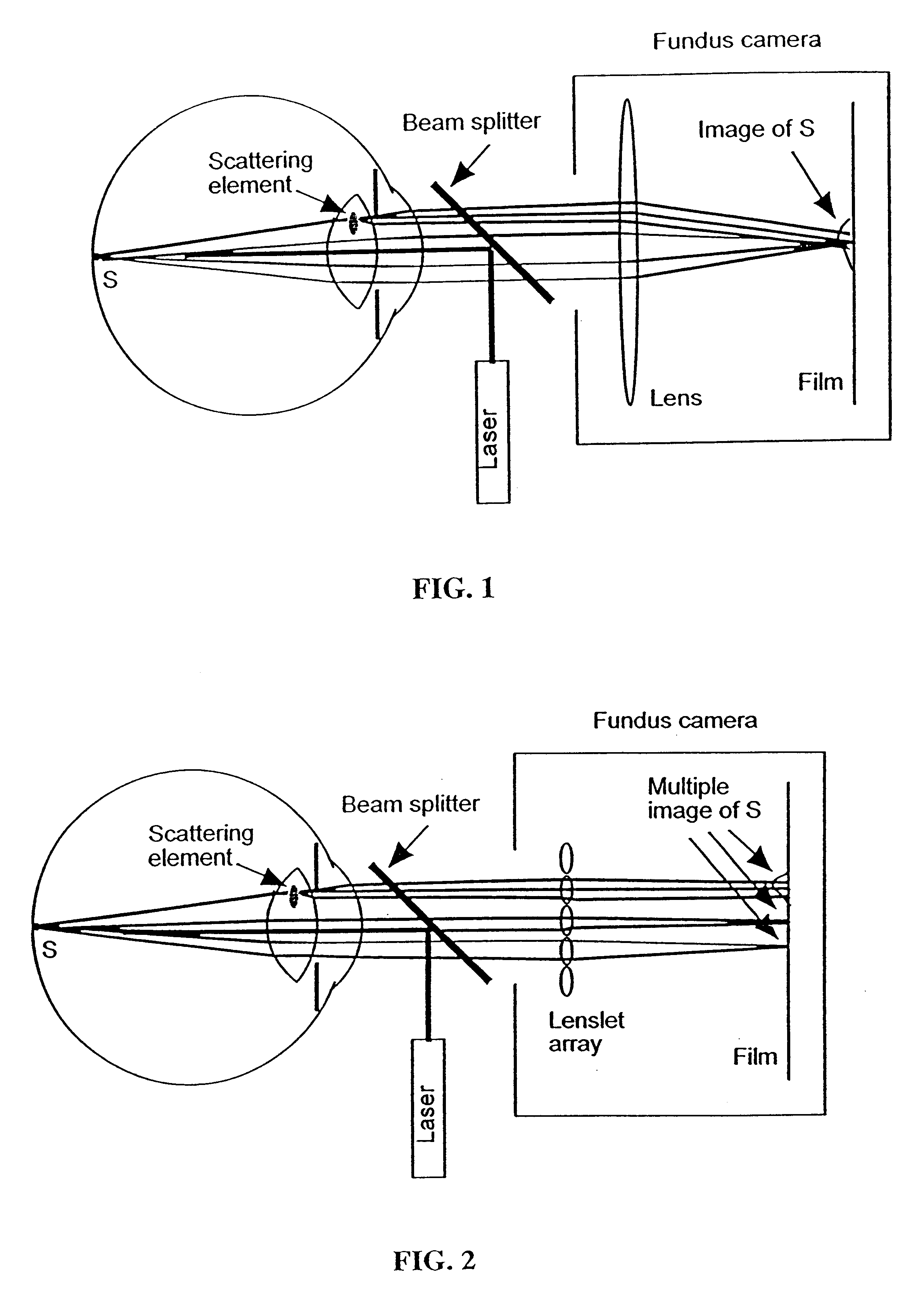
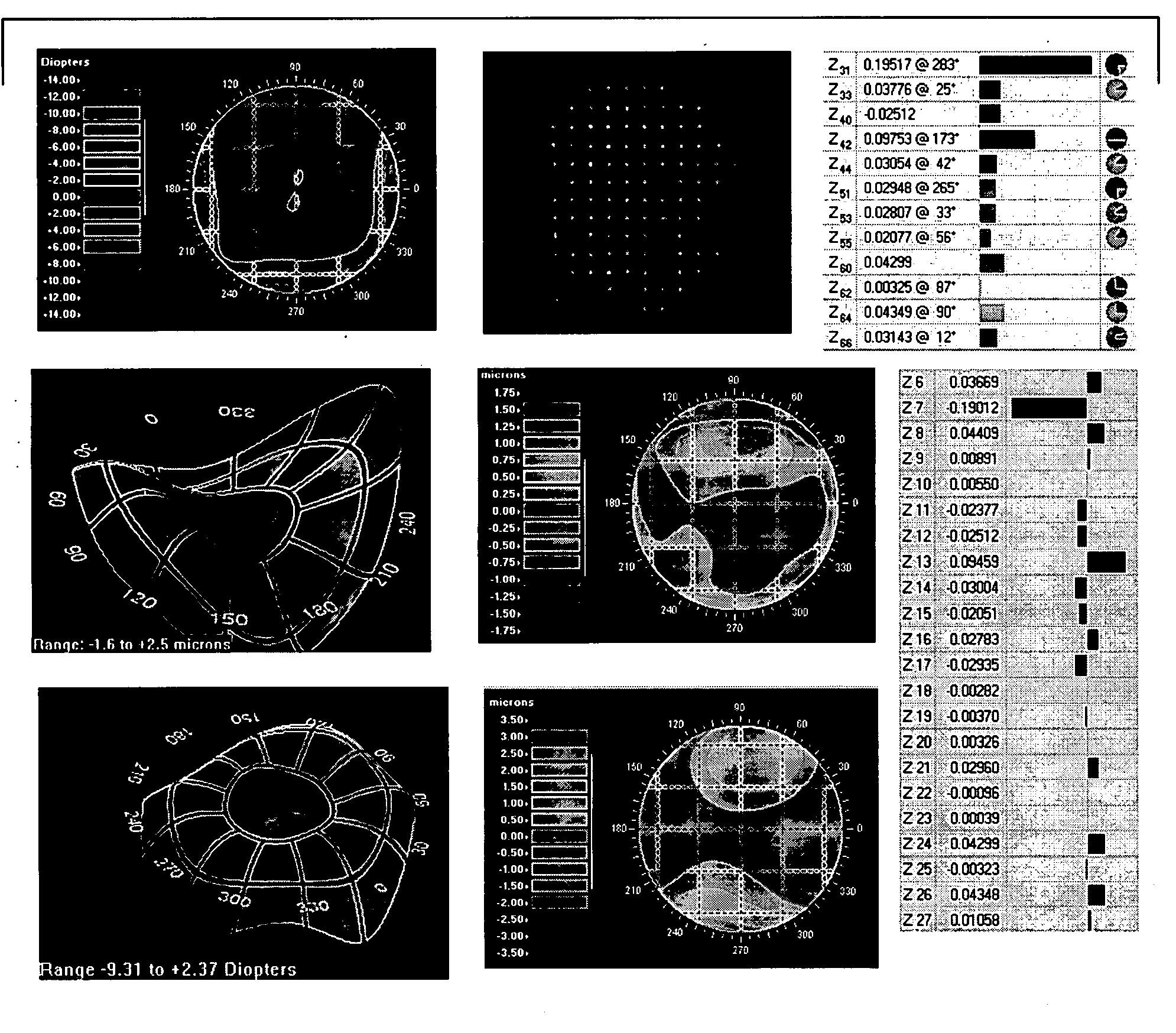
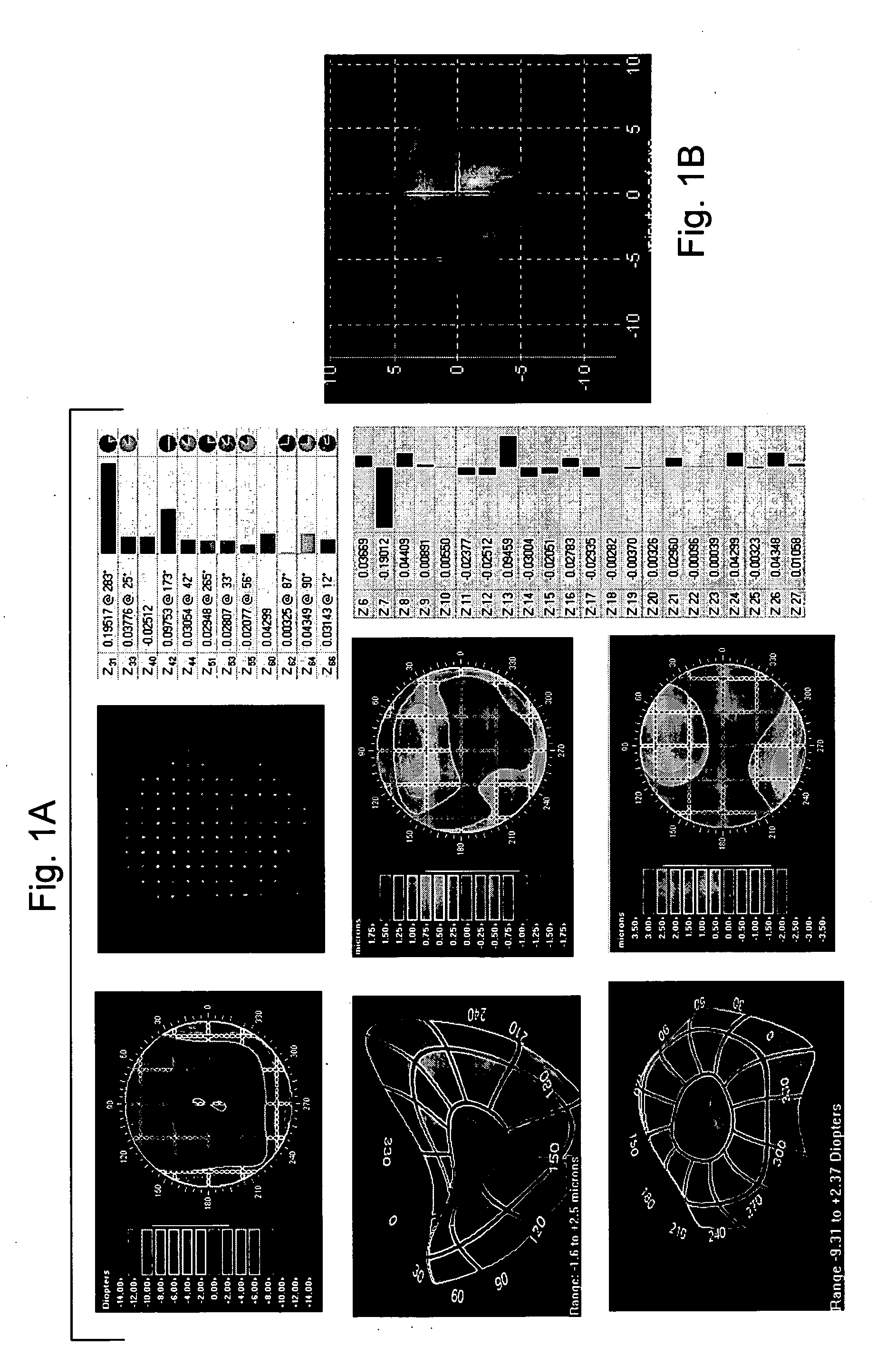
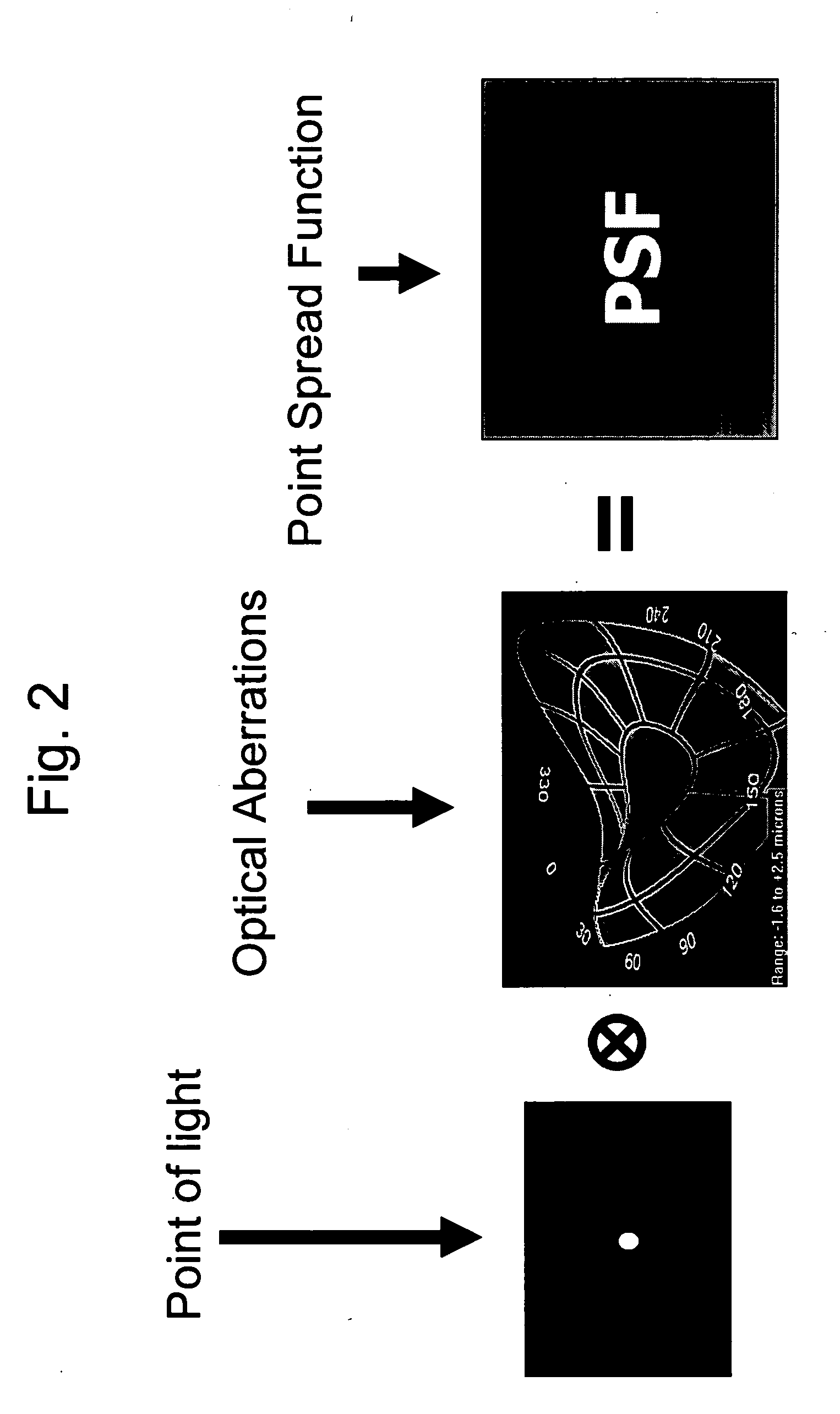
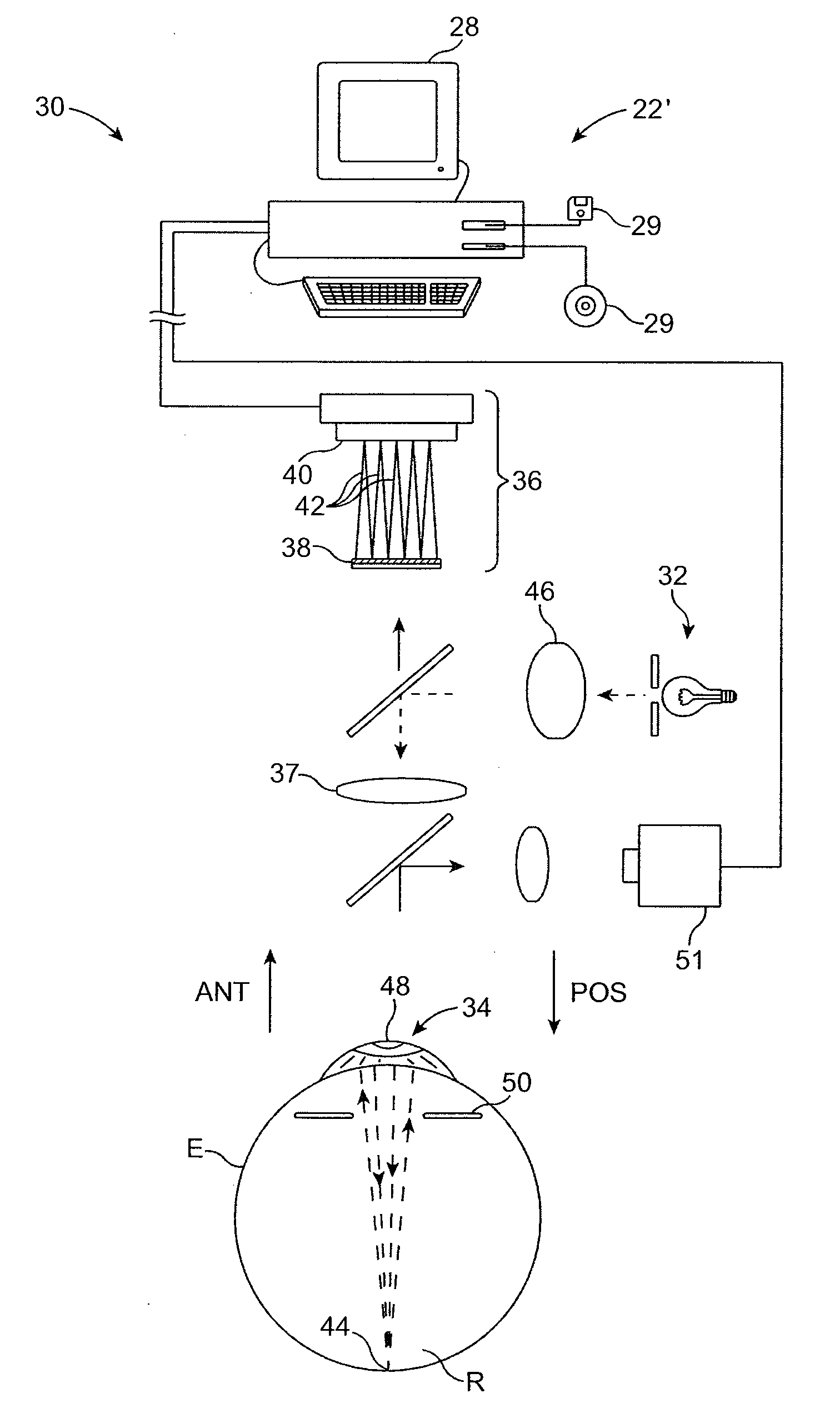
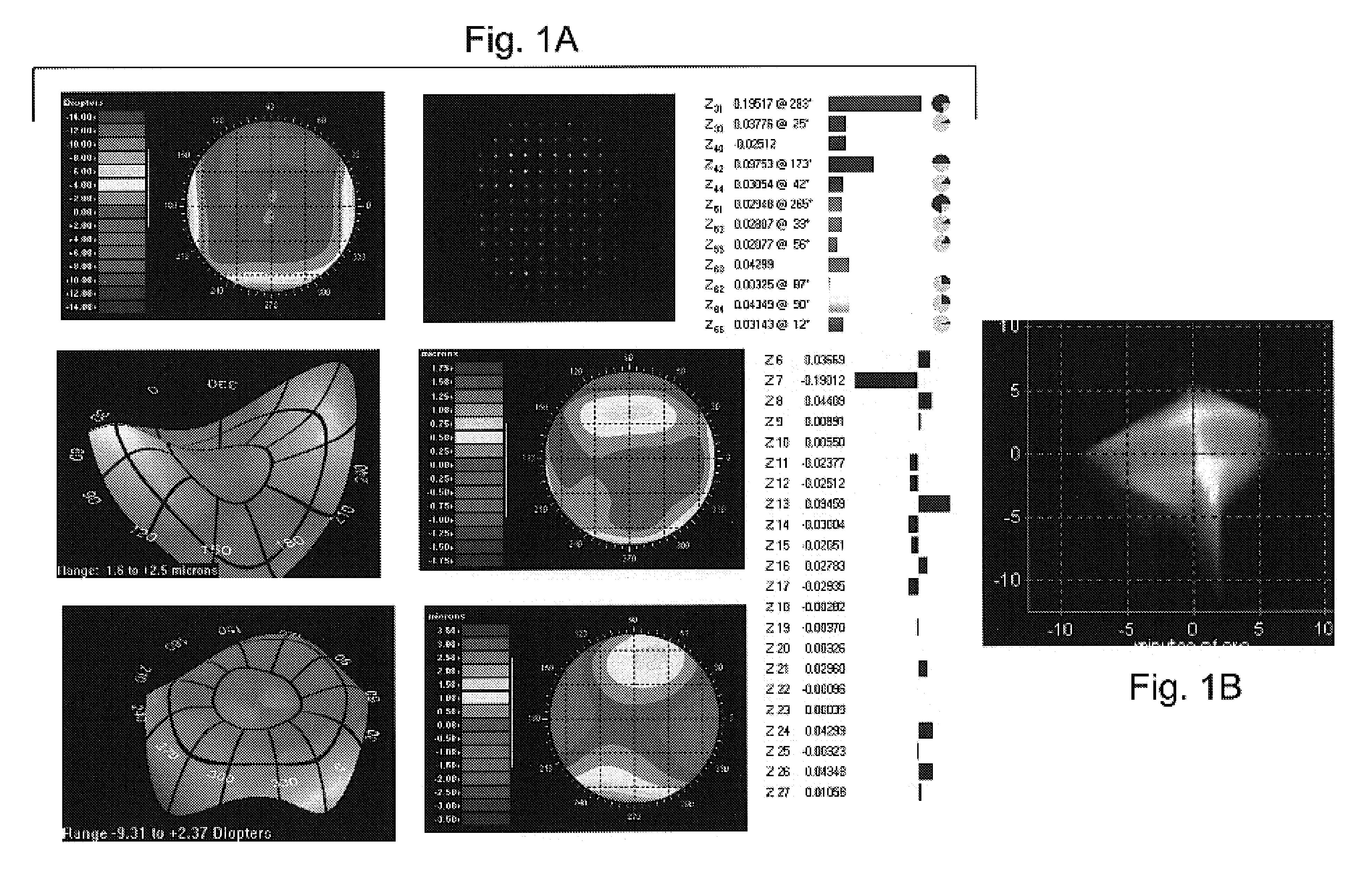
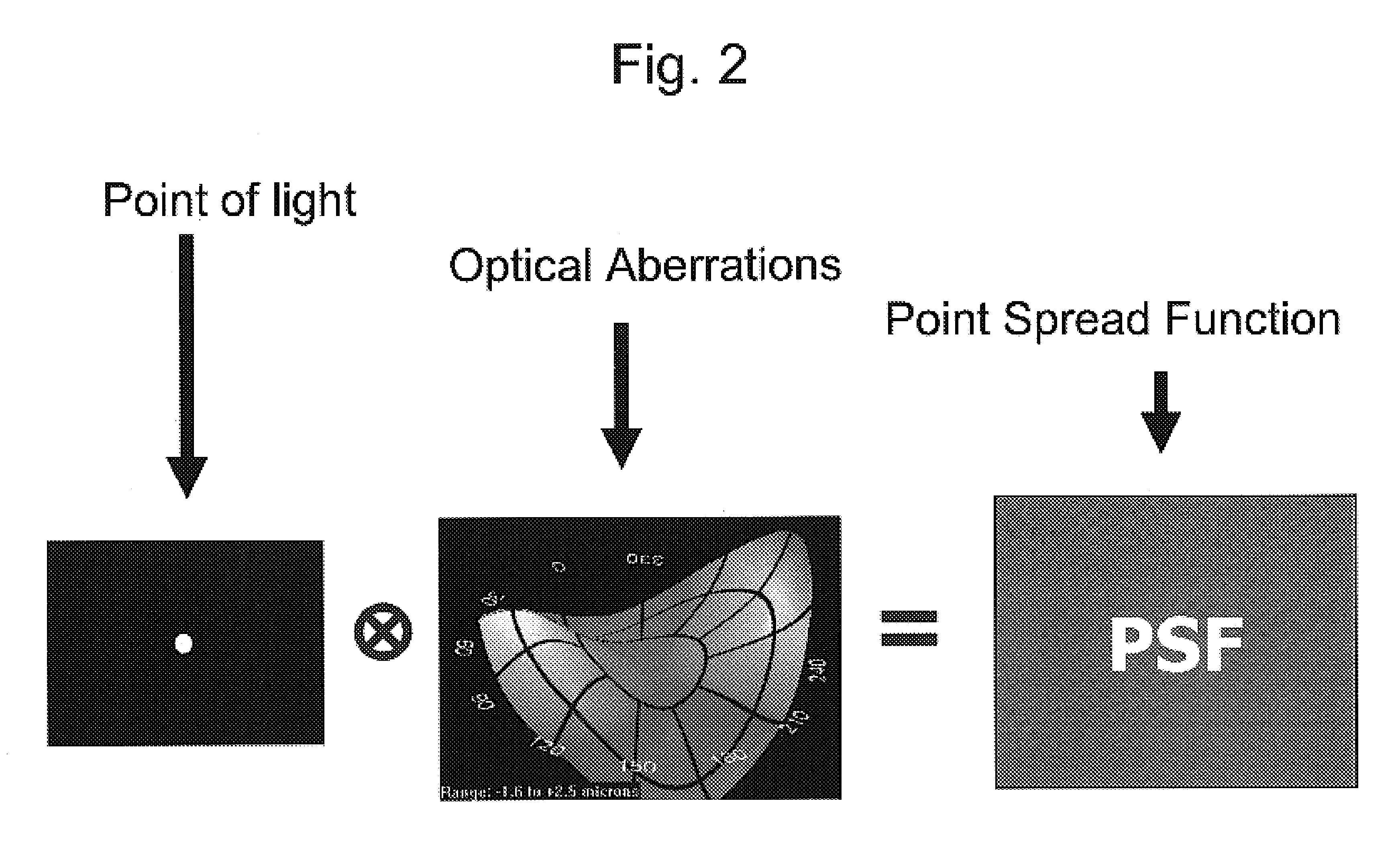
Volumetric point spread function for eye diagnosis and treatment
InactiveUS20050213040A1Improve refractive performanceLaser surgeryRefractometersDiffusion functionPattern perception
Systems and methods analyze, diagnose, and / or treat a patient's eye using modified forms of the point spread function (“PSF”) tailored to the vision system. Factors that alter perception of visual aberrations can be included and / or volumetric point spread functions calculated, often using point spread function calculations throughout a range of optical distances to more fully indicate the variation in visual perception of optics at different distances. A variety of visual affects of the human optical system can be simulated, analyzed, and modeled, including: single versus multiple wavelength sources, chromatic aberrations, retinal resolution, wavelength-dependent visual response, Stiles-Crawford effects, and / or non-linearity of retinal response. The perceived point spread function can offer objective confirmation of the patient's visual perception, allow a treating physician to see a closer approximation of what the patient sees, indicate the scale and significance of wavefront aberrations, and / or show which aberrations affect vision and which do not.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
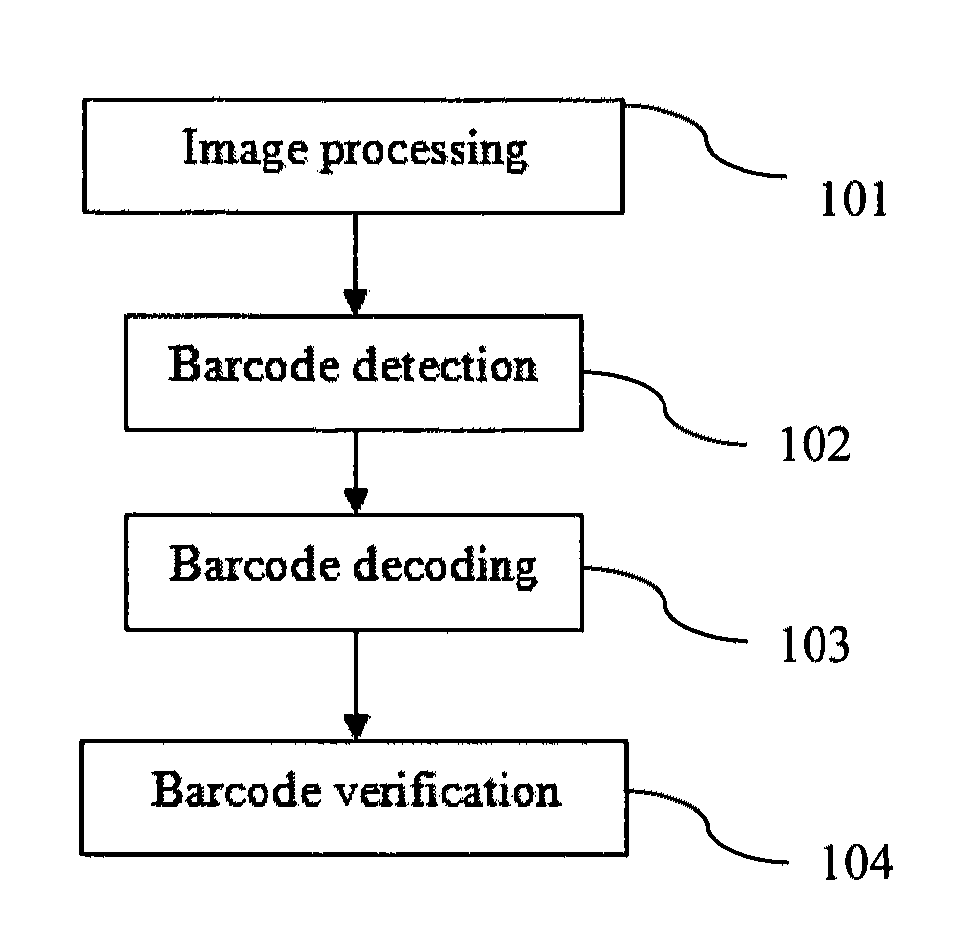
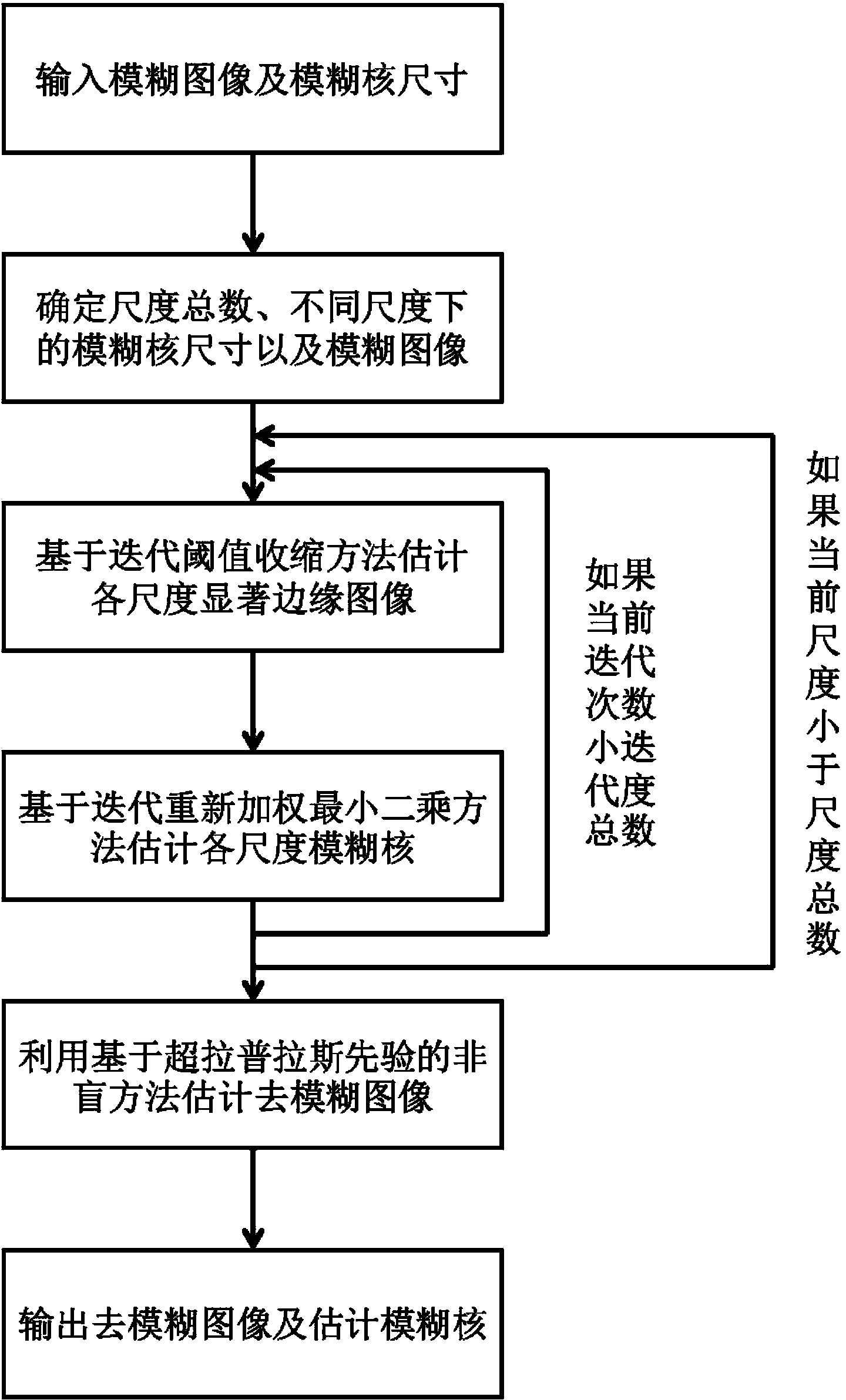
Blind camera shake deblurring method based on L0 sparse prior
ActiveCN103413277AQuick estimateEasy to implementImage enhancementImage analysisPoint spreadComputation complexity
The invention discloses a blind camera shake deblurring method based on the L0 sparse prior, and belongs to the technical field of digital image processing. The blind camera shake deblurring method is a method for deblurring blurred images caused by camera shaking, and various space-unchanged camera shaking blurred kernels, namely the point spread functions, can be estimated. The blind camera shake deblurring method solves the problem that a current variational bayes estimation method is high in computing complexity and solves the problem that a current maximum posteriori estimation method lacks strict optimization theory supports. The blind camera shake deblurring method comprises the steps of firstly, introducing remarkable edge sparse prior based on the L0 norm, and using the iterative hard threshold compressed method to achieve recessive automatic prediction of remarkable edge characteristics, secondly, introducing camera shake blurred kernel sparse prior, and using the iterative repeated weighted least square method to achieve rapid estimation of the blurred kernels, and finally, using the image non-blind deblurring method based on super-Laplacian prior to obtain a high-quality deblurred image. The flow diagram of the blind camera shake deblurring method is shown in the figure 1.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Spatial Frequency Wavefront Sensor System and Method
ActiveUS20080073525A1Easy searchMore accuratePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPoint spreadWavefront sensor
Devices systems, and methods can characterize an optical surface of an object. A wavefront sensor system focuses light energy propagating from the object to form a pattern on a detector. The system maps the pattern to an array with a transform function such as a Fourier transform. The values of array correspond to characteristic locations and signals in a transform space, for example an intensity of spatial frequency signals in frequency space. The characteristic location and intensity of these signals in transform space are used to measure the optical surface. For example, a characteristic frequency of a spatial frequency intensity peak in Fourier transform space can be used to estimate the location of spots on the detector. Alternatively, the characteristics can be used to the measure sphere, cylinder and axis of a wavefront, wavefront elevation maps and point spread functions, often without locating positions of individual spots on the detector.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
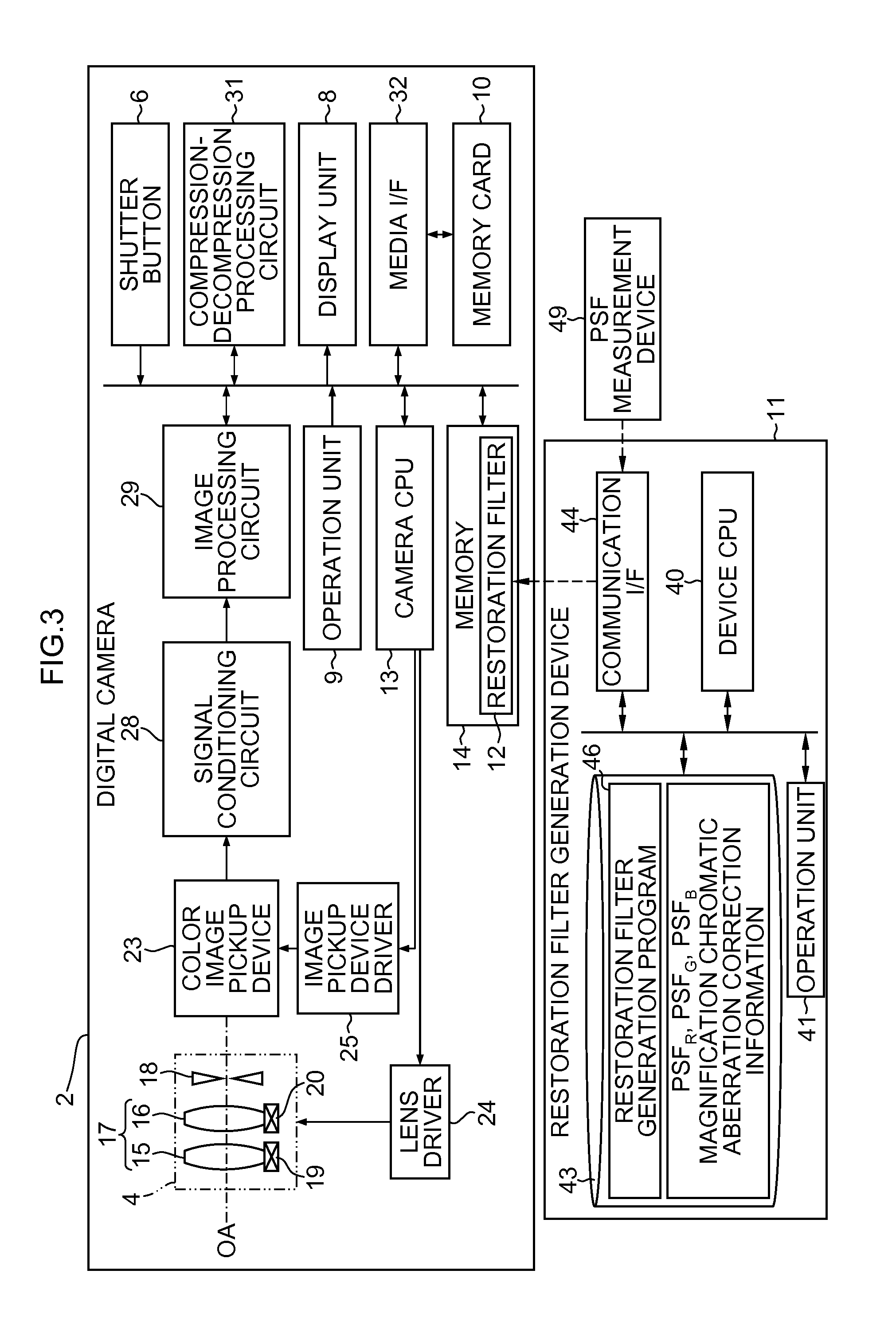
Restoration filter generation device and method, image processing device, imaging device, and non-transitory computer-readable medium
ActiveUS20160027155A1Reducing arithmetic loadReduce loadImage enhancementImage analysisPoint spreadImaging processing
A restoration filter generation device that generates a restoration filter for a restoration process on the basis of a point spread in an optical system, the restoration process being performed on luminance system image data as image data concerning a luminance which is generated on the basis of image data for each color of plural colors acquired by an image pickup device having the optical system, the restoration filter generation device includes a first transfer function acquisition device, a correction information acquisition device, a second transfer function acquisition device, a third transfer function calculation device, and a restoration filter generation device that generates the restoration filter for the restoration process on the basis of the third transfer function calculated by the third transfer function calculation device.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
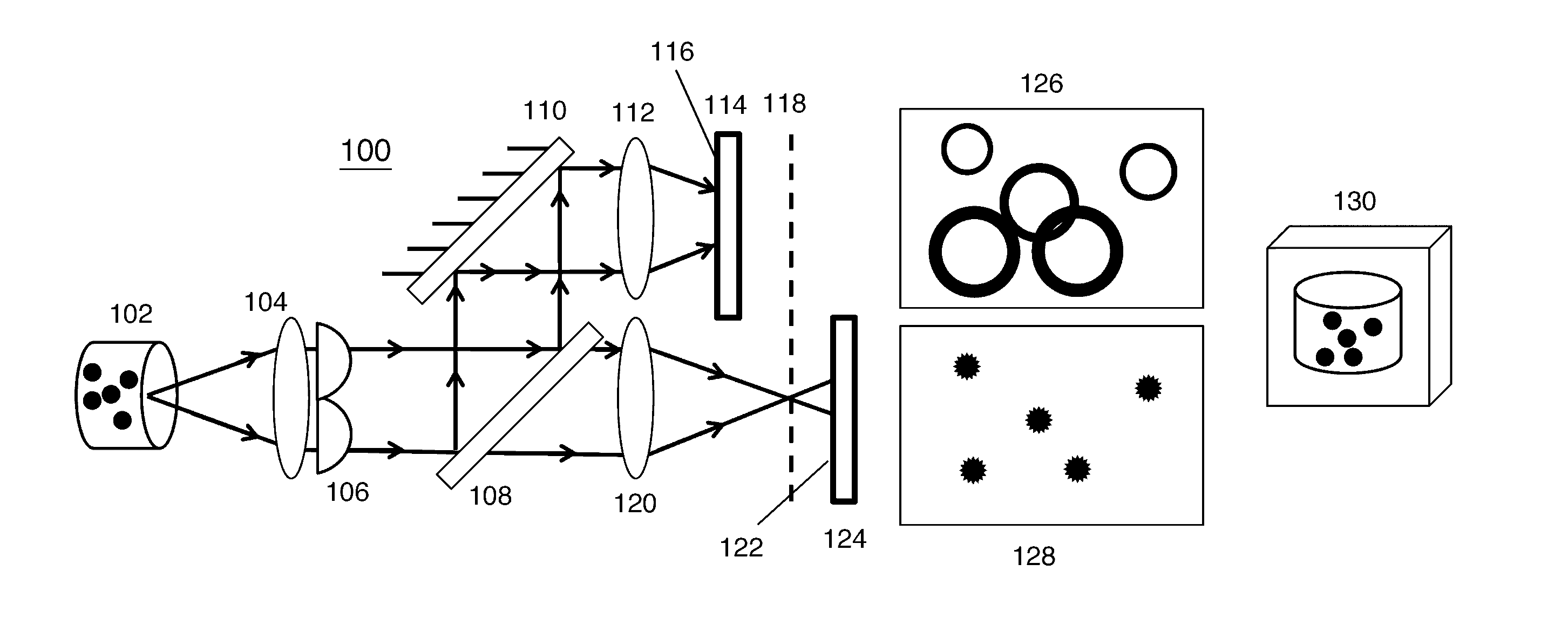
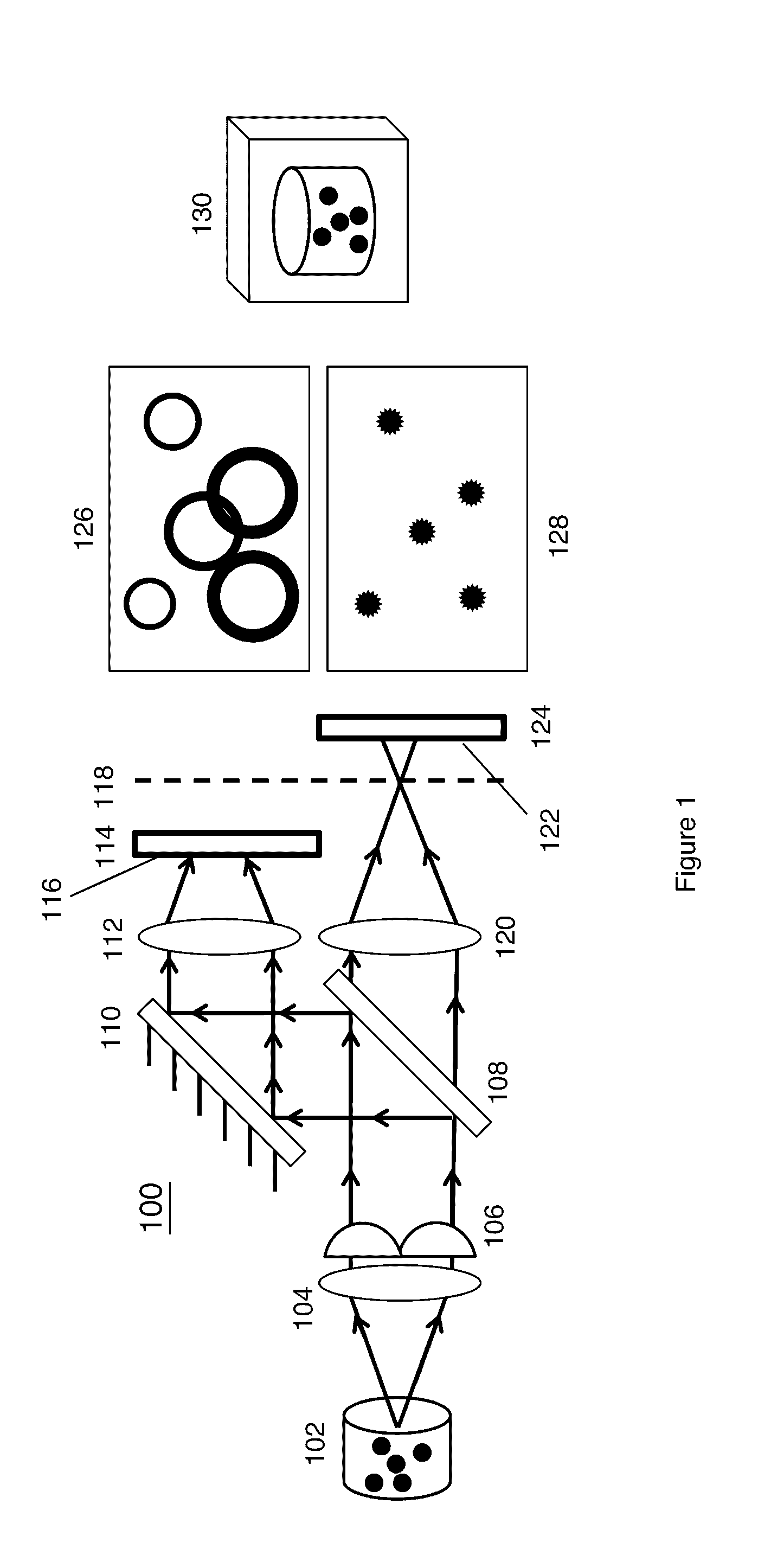
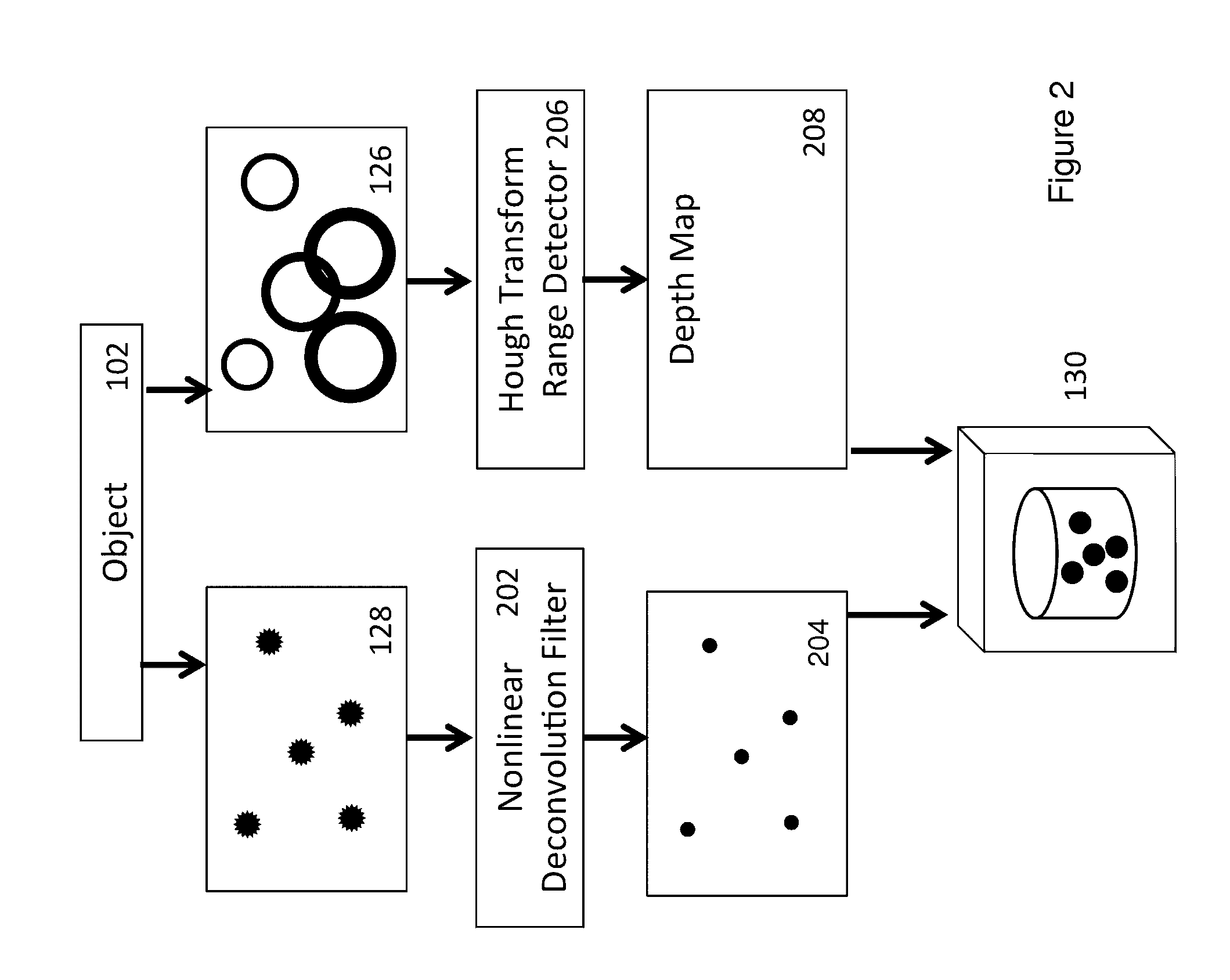
Engineered Point Spread Function for Simultaneous Extended Depth of Field and 3D Ranging
InactiveUS20140192166A1Reduce impactRestore fine detailImage enhancementImage analysisPoint spreadWavefront
Optical systems utilize waveplates to simultaneously encode information for increasing image depth of field and for providing a depth map of the imaged object or sample. These waveplates are configured to result in a focus-invariant point spread function in one focal region, and to result in point spread functions that vary as a function of range within the imaged object in a different focal region. For example, a basic compound microscope might have a specially shaped waveplate inserted at the back aperture plane of the microscope objective to manipulate the phase of the wavefront. An image formed on one side of the plane of best focus is focus invariant, and is brought into focus by a restoring algorithm. An image formed on the other side of the plane of best focus captures point spread functions comprising rings that vary with depth within the imaged object.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Systems and methods for color defringing
ActiveUS8477394B2Character and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationPoint spreadDiffusion function
A system and method for defringing chromatic aberrations that occur in imaging devices such as scanners. The system comprises shift filters to shift lines in the various color planes together. In addition in each color plane, a spread filter is used to compensate for the unequal point spread functions of each color. Furthermore, the results can be enhanced by filtering in the luminance-chrominance space.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Volumetric point spread function for eye diagnosis and treatment
InactiveUS7377648B2Improve refractive performanceLaser surgeryRefractometersDiffusion functionPattern perception
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
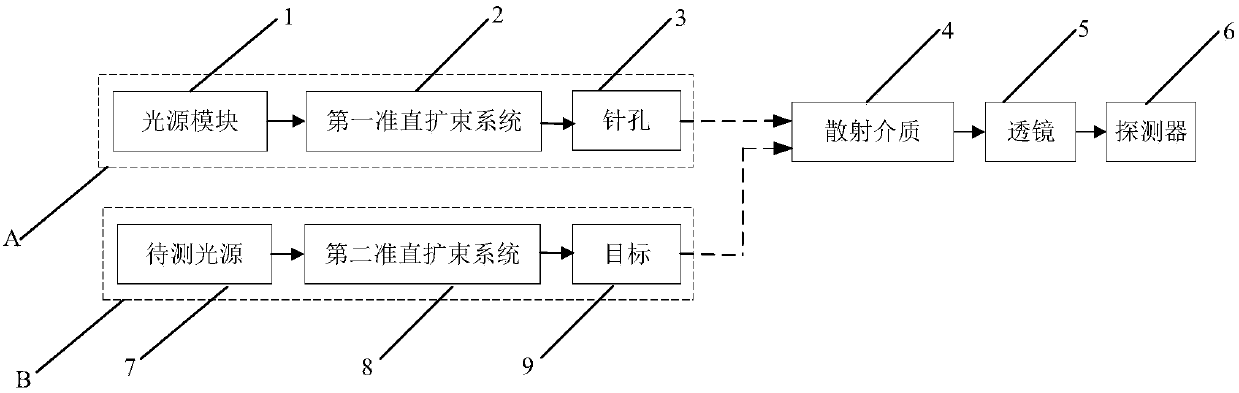
Super-resolution spectral imaging system and super-resolution spectral imaging method based on scattering medium
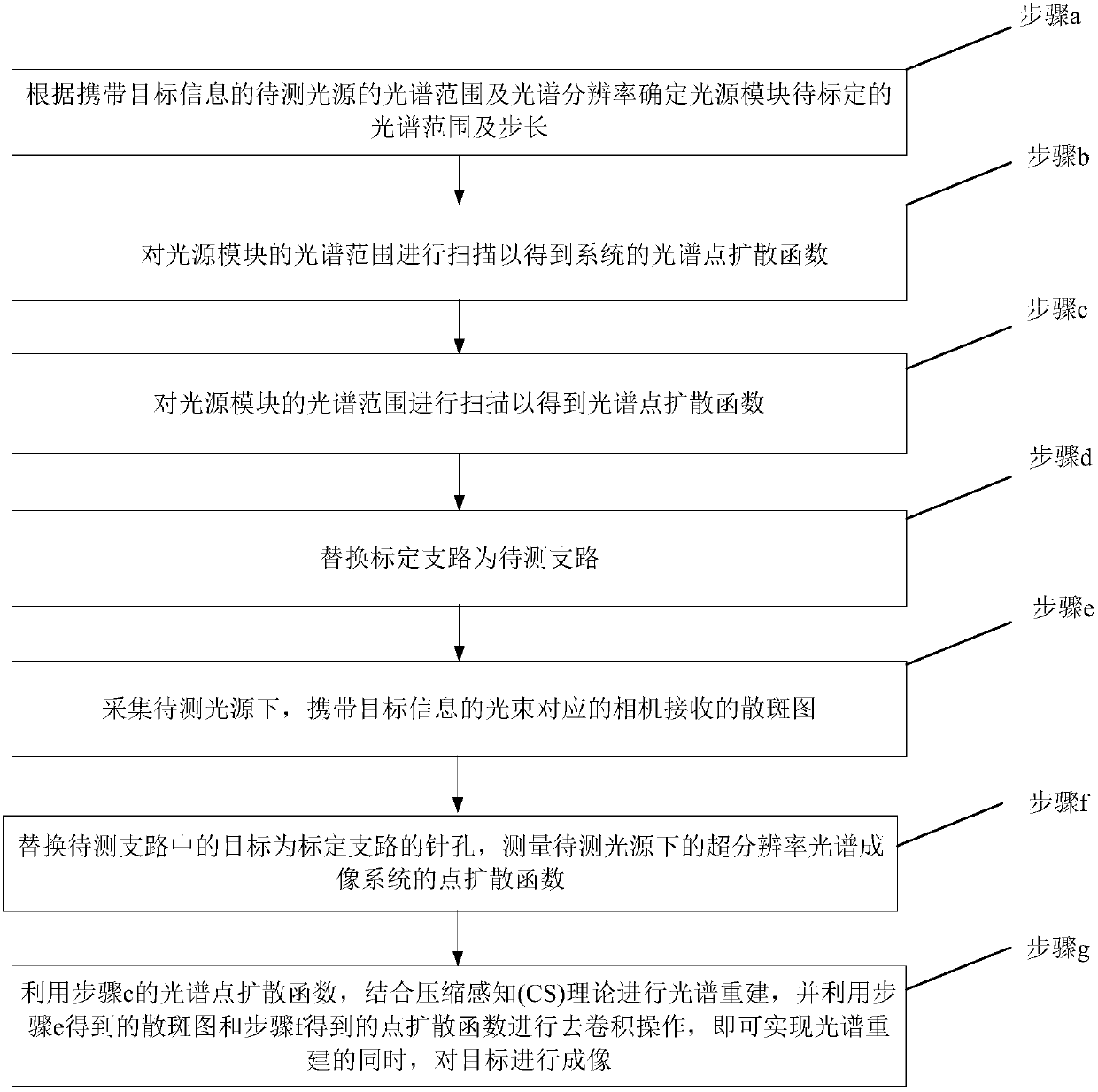
ActiveCN107907483AEnable Spectral MeasurementsAchieve target imagingColor/spectral properties measurementsPoint spreadMean free path
The present invention relates to a super-resolution spectral imaging system and a super-resolution spectral imaging method based on a scattering medium. The super-resolution spectral imaging system comprises a calibration branch A, a scattering medium 4, a lens 5, a detector 6 and a branch B to be detected, wherein the calibration branch A comprises a light source module 1, a first collimation beam expansion system 2 and a pinhole 3, and the branch B to be detected comprises a light source 7 to be detected, a second collimation beam expansion system 8 and a target 9. According to the embodiments of the present invention, the point spread functions of the system are measured when the light source module outputs different wavelengths so as to construct the spectral point spread function (SPSF), the spectral reconstruction is achieved by using the compressed sensing (CS) method while the scattering medium with the appropriate scattering mean free path is matched, and the speckle receivedby the camera is subjected to convolution removing by using the point spread function corresponding to the wavelength of the light source to be detected, such that the maximum super-resolution imagingcan be achieved without the increase of the complexity of the system; and the super-resolution spectral imaging system has advantages of simple structure, easy control, low component cost, strong anti-disturbance capability and wide application field.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Pixel frequency based star sensor high accuracy calibration method
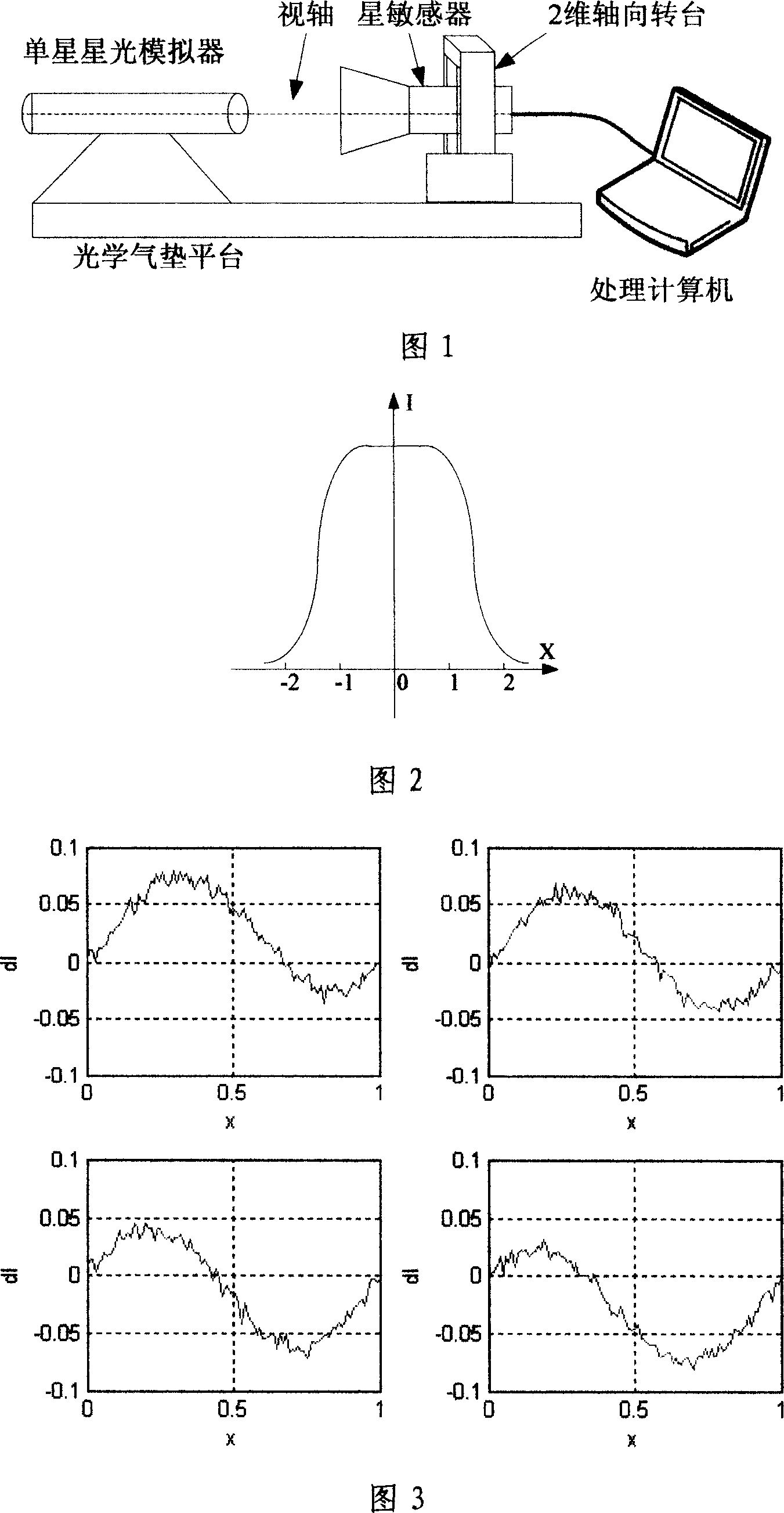
InactiveCN101013065AImprove calibration accuracyEasy to calculateStructural/machines measurementCosmonautic vehicle trackingPoint spreadStar tracker
The invention relates to the space technology, and to the improvement of the star sensor calibration method. The invention uses the calibration system which including air cushion platform, single-star starlight simulator, star tracker, two-dimensional axial turntable platform and data-processing computer, its steps being: establishing point spread function model, establishing a centroid algorithm formula, establishing a centroid algorithm pixel frequency error model, and data acquisition. The invention provides a more practical point spread model; improving satellite sensor calibration precision; the calibration model is simple and easy to calculate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
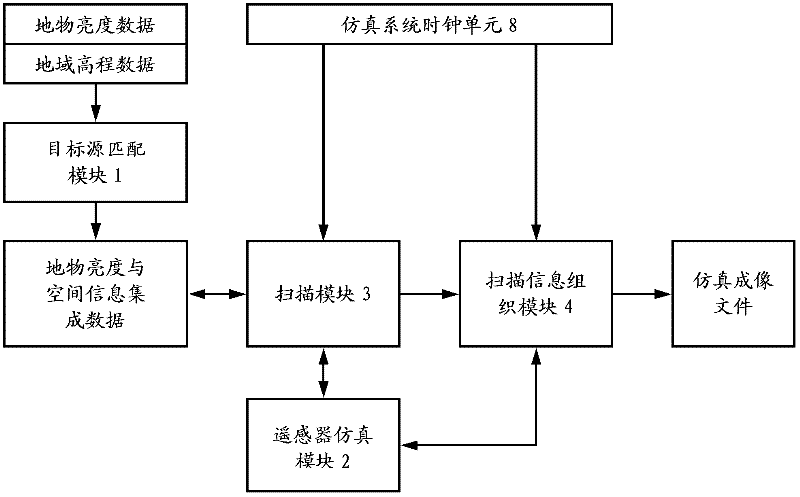
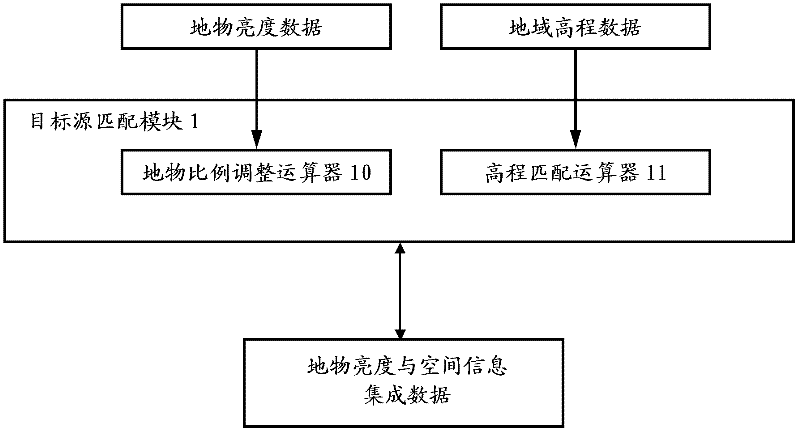
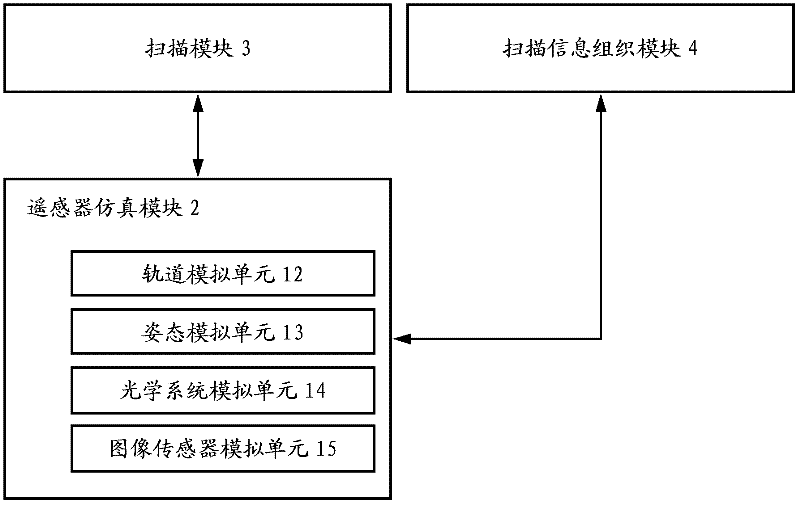
Computer emulation system for actual ground object imaging by space optical remote sensor
The invention relates to a computer emulation system for actual ground object imaging by a space optical remote sensor. A target source matching module of the system is used for supplying ground object brightness and space information integrating data to a scanning module; a remote scanner emulation module is used for supplying remote sensor track parameters, posture parameters, optical system focal distances, point spread functions of all sub-fields of an optical system and physical parameters of an image sensor to the scanning module and a scanning information organization module; a clock unit of the emulation system is used for supplying time synchronization information to the scanning information organization module; the scanning module is used for receiving an image coordinate gray level time sequence of each image element according to the received information and supplying the image coordinate gray level time sequence to the scanning information organization module; and the scanning information organization module is used for obtaining a brightness matrix of a ground imaging emulation image according to the received information. According to the computer emulation system for the actual ground object imaging by the space optical remote sensor, provided by the invention, the ground imaging process can be emulated by the space optical remote sensor with any posture on any track; and the computer emulation system is compact in structure and is easy to update according to actual scientific research requirements.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-resolution rapid deconvolution sound source imaging algorithm
ActiveCN106443587AAvoid winding errorsReduce the number of iterationsPosition fixationSound sourcesCompressed sensing
The invention discloses a high-resolution rapid deconvolution sound source imaging algorithm which is characterized by comprising the following steps: calculating a point spread function of a sound source at the central position of a sound source calculation plane by utilizing approximation space translation invariance of the point spread function in the process of constructing a point spread function matrix of the deconvolution sound source imaging algorithm; constructing the point spread function matrix through a method for circularly shifting the point spread function at the central position upwards and downwards, so that calculation of the total point spread functions is avoided, the calculated amount, and the calculation speed and efficiency are improved; realizing rapid sparse deconvolution reconstruction of sound source intensity energy distribution through an orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm by utilizing space sparse prior of the sound source and combining compressed sensing in the deconvolution reconstruction process of the sound source intensity energy distribution, so that the iterations are reduced, and the calculation efficiency and resolution ratio are improved. The algorithm disclosed by the invention has high calculation efficiency and spatial resolution and is capable of well rapidly identifying and locating the position of the sound source in the space.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for obtaining panorama by using code aperture camera
ActiveCN103177432AReduce stitching errorsAvoid blurImage enhancementGeometric image transformationPoint spreadDiffusion function
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a panorama by using a code aperture camera. Distant-view panoramas that all parts are clear can be obtained by utilizing the method. The method comprises the following steps of: shooting a view by using the code aperture camera; calculating so as to obtain the sizes of point spread functions of points in shot images; clarifying the images by utilizing the corresponding relationship between the sizes and the depths of the point spread functions and utilizing a deconvolution algorithm; and splicing the clarified images so as to obtain the panorama. By utilizing the method, the splicing mistakes caused by shielding articles in the view are reduced when the images are spliced, and the problem of image blurring caused by the inconsistency of field depths in shooting when the panorama is spliced is avoided. According to the method, the code camera is adopted to acquire the view, so that the requirement on equipment is relatively low, and no extra depth acquiring equipment is used when obtaining an optimal panorama; and the method is simple and convenient in shooting process and easy to implement and popularize.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
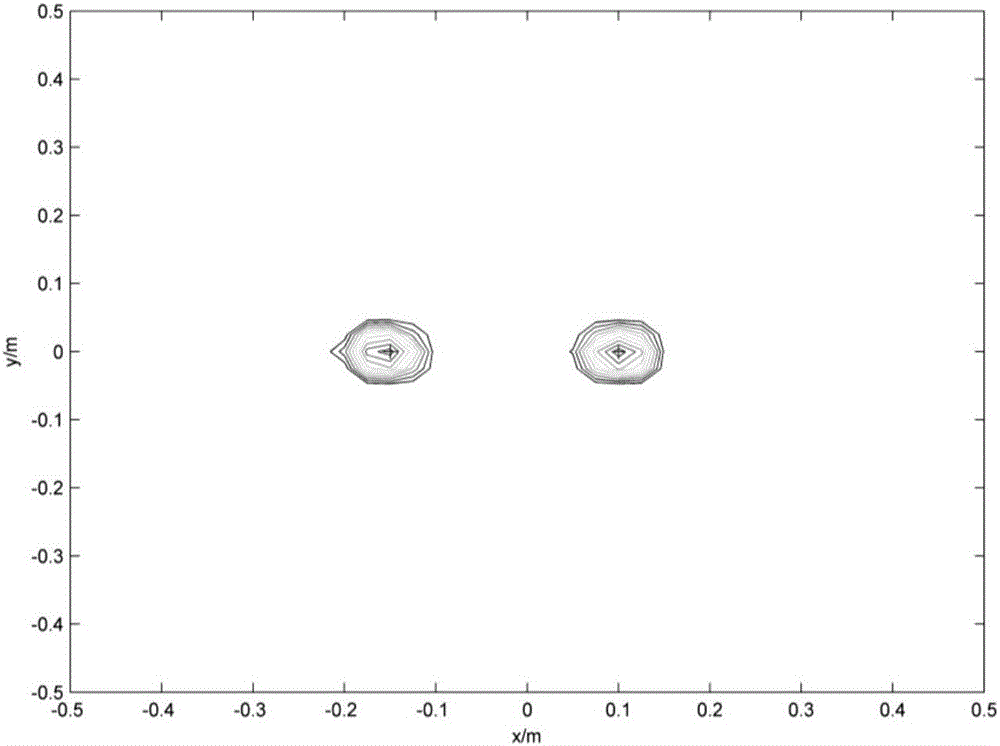
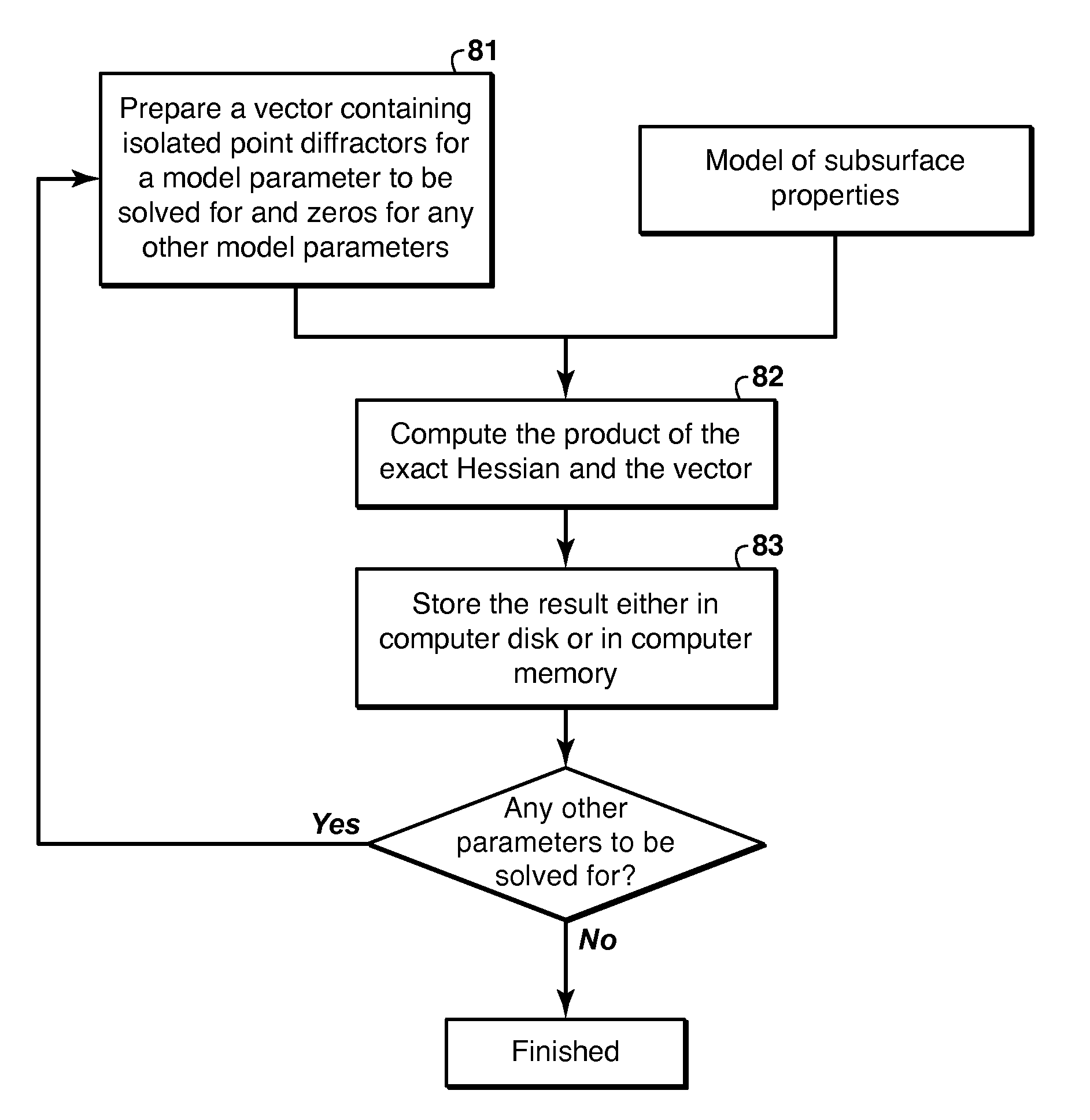
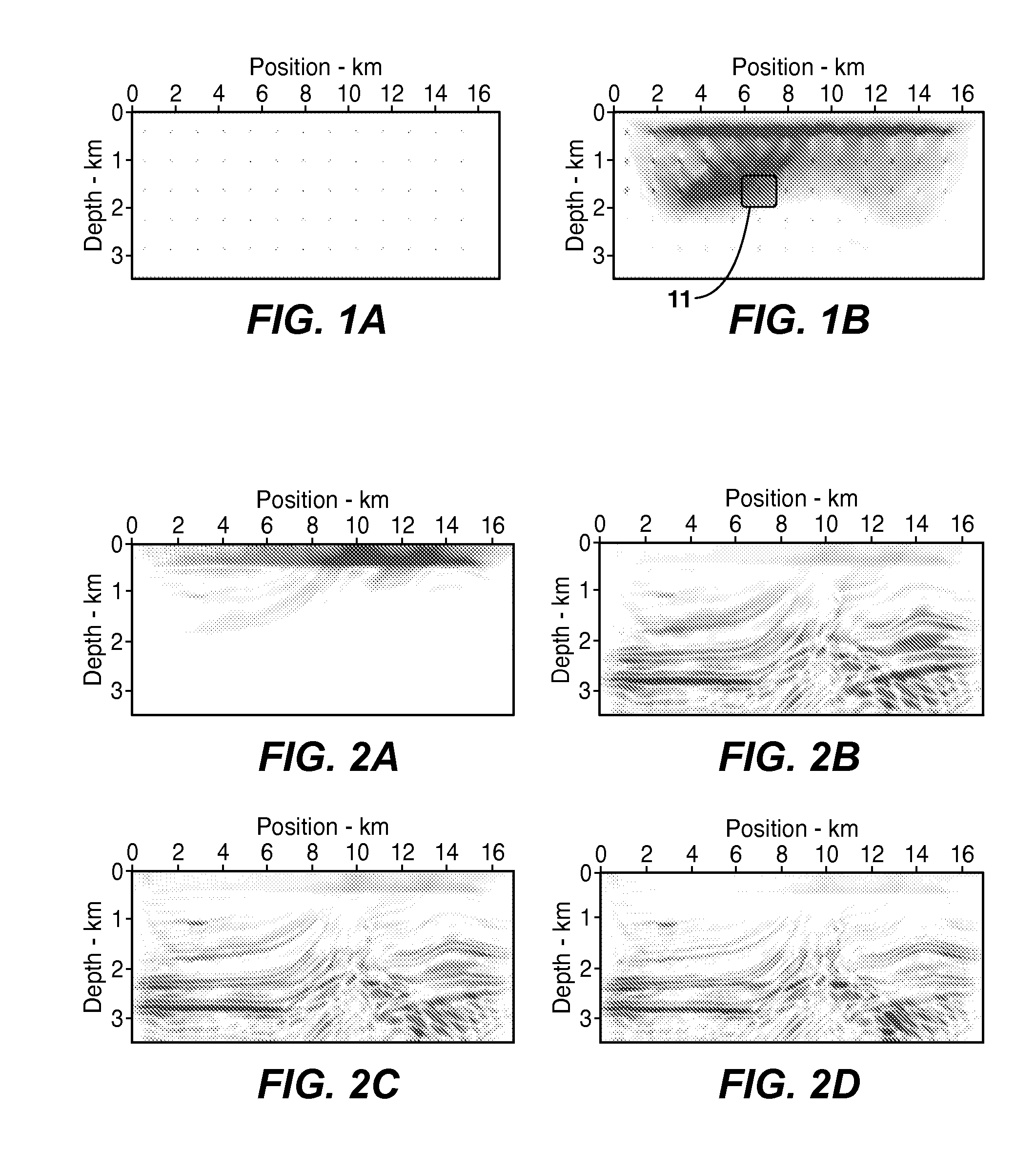
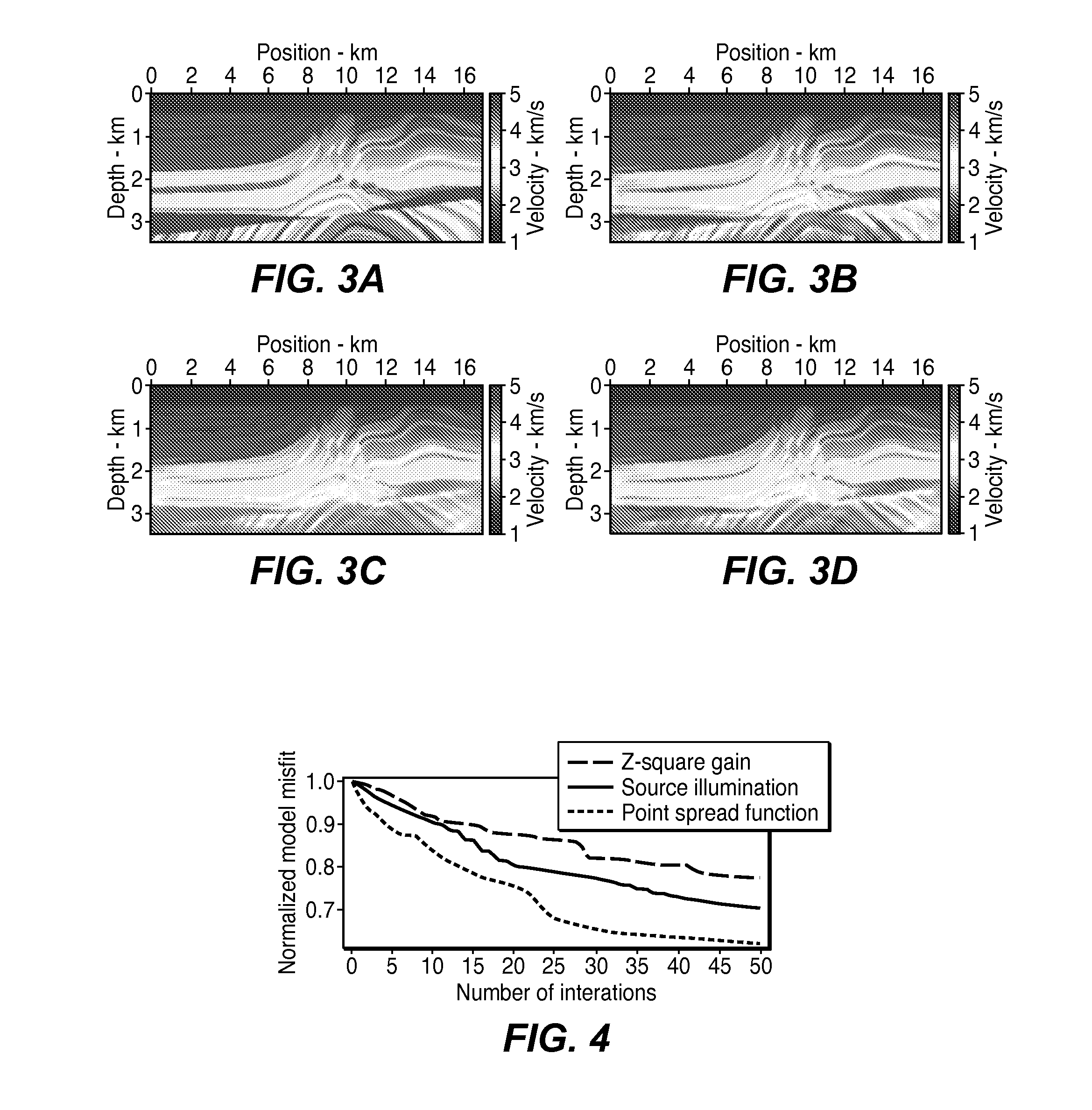
Accelerating Full Wavefield Inversion with Nonstationary Point-Spread Functions
ActiveUS20150073755A1GeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationDiffusion functionPoint spread
Method for reducing computational time in inversion of geophysical data to infer a physical property model (91), especially advantageous in full wavefield inversion of seismic data. An approximate Hessian is pre-calculated by computing the product of the exact Hessian and a sampling vector composed of isolated point diffractors (82), and the approximate Hessian is stored in computer hard disk or memory (83). The approximate Hessian is then retrieved when needed (99) for computing its product with the gradient (93) of an objective function or other vector. Since the approximate Hessian is very sparse (diagonally dominant), its product with a vector may therefore be approximated very efficiently with good accuracy. Once the approximate Hessian is computed and stored, computing its product with a vector requires no simulator calls (wavefield propagations) at all. The pre-calculated approximate Hessian can also be reused in the subsequent steps whenever necessary.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com