Patents
Literature
110 results about "Source imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
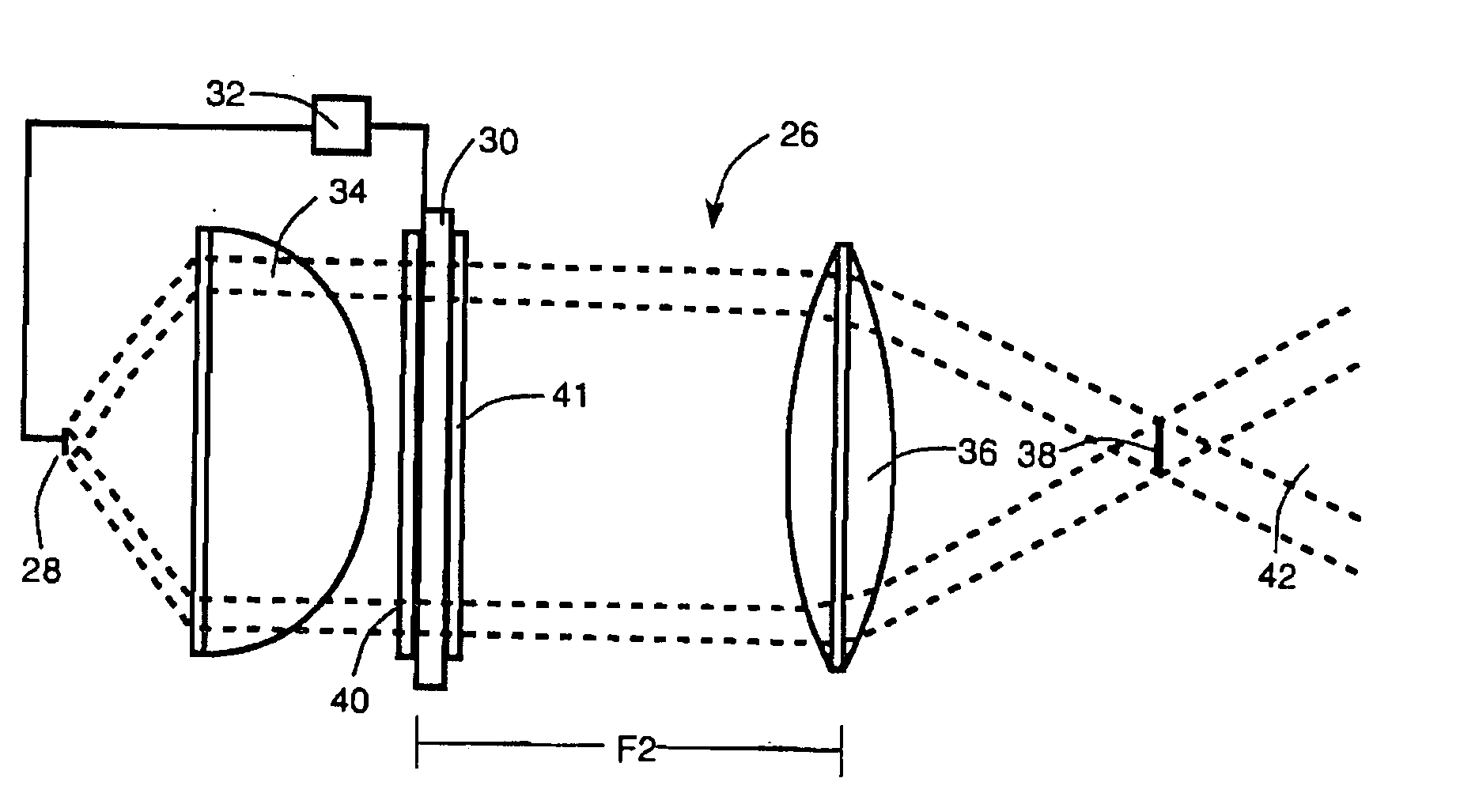
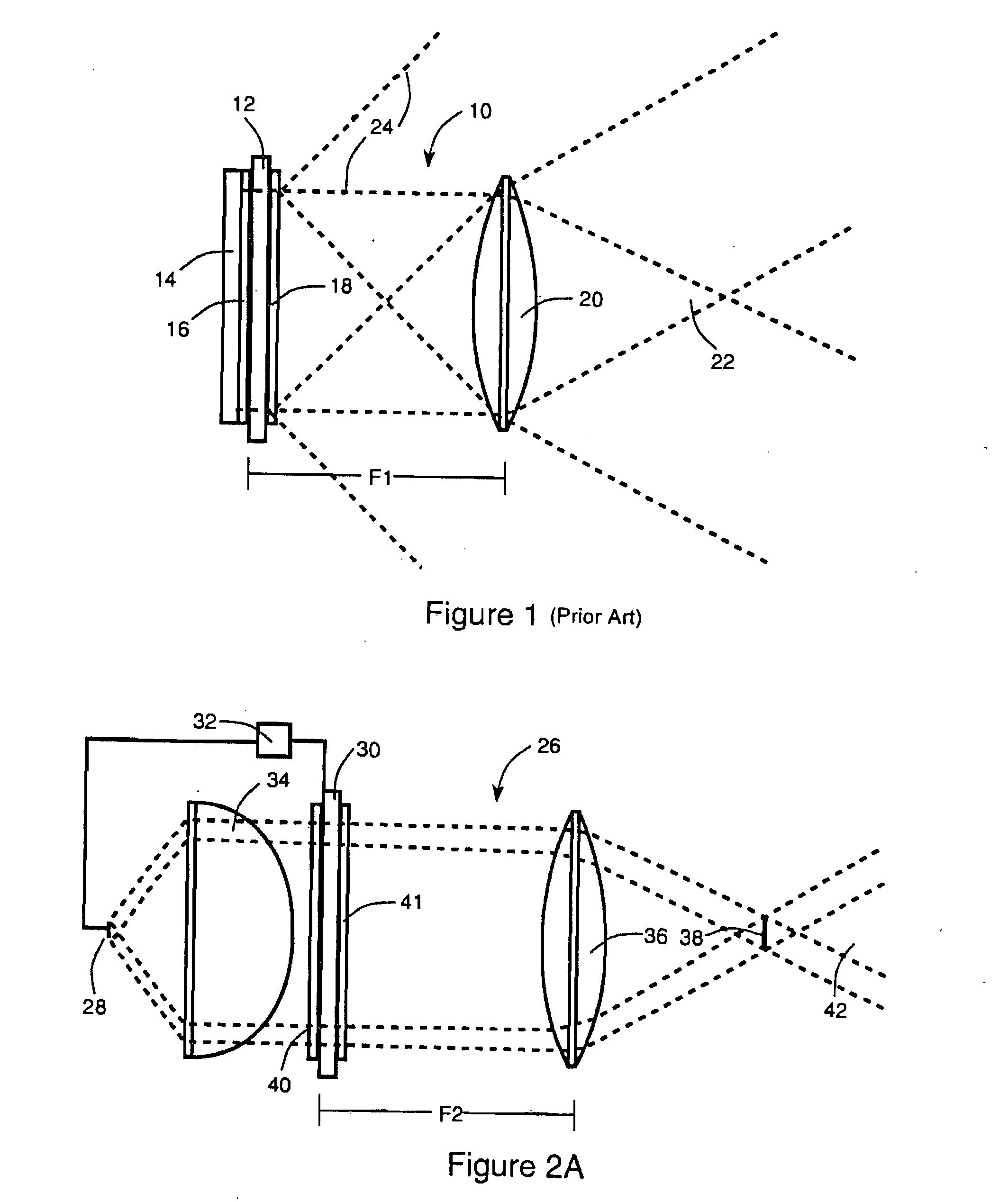
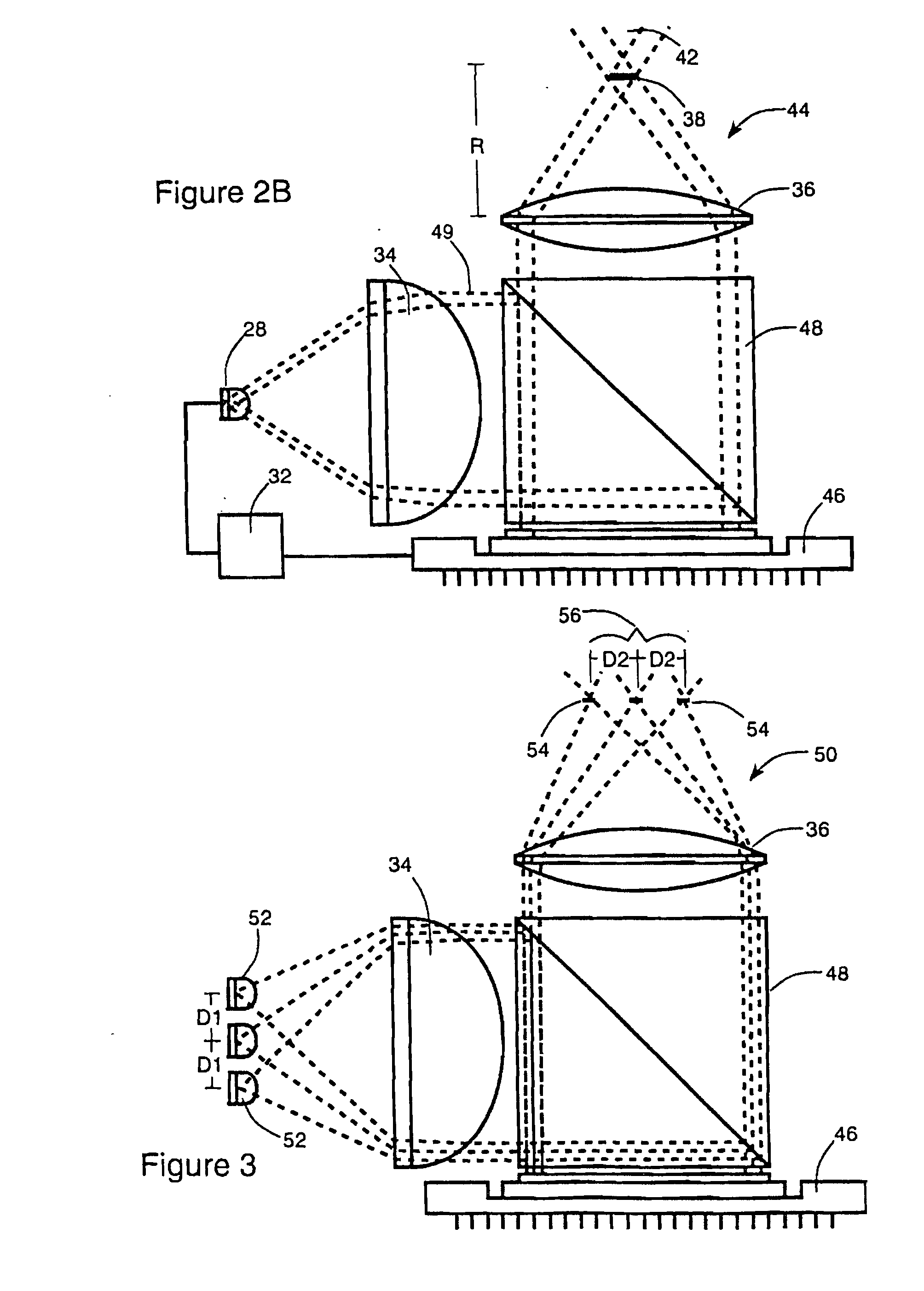
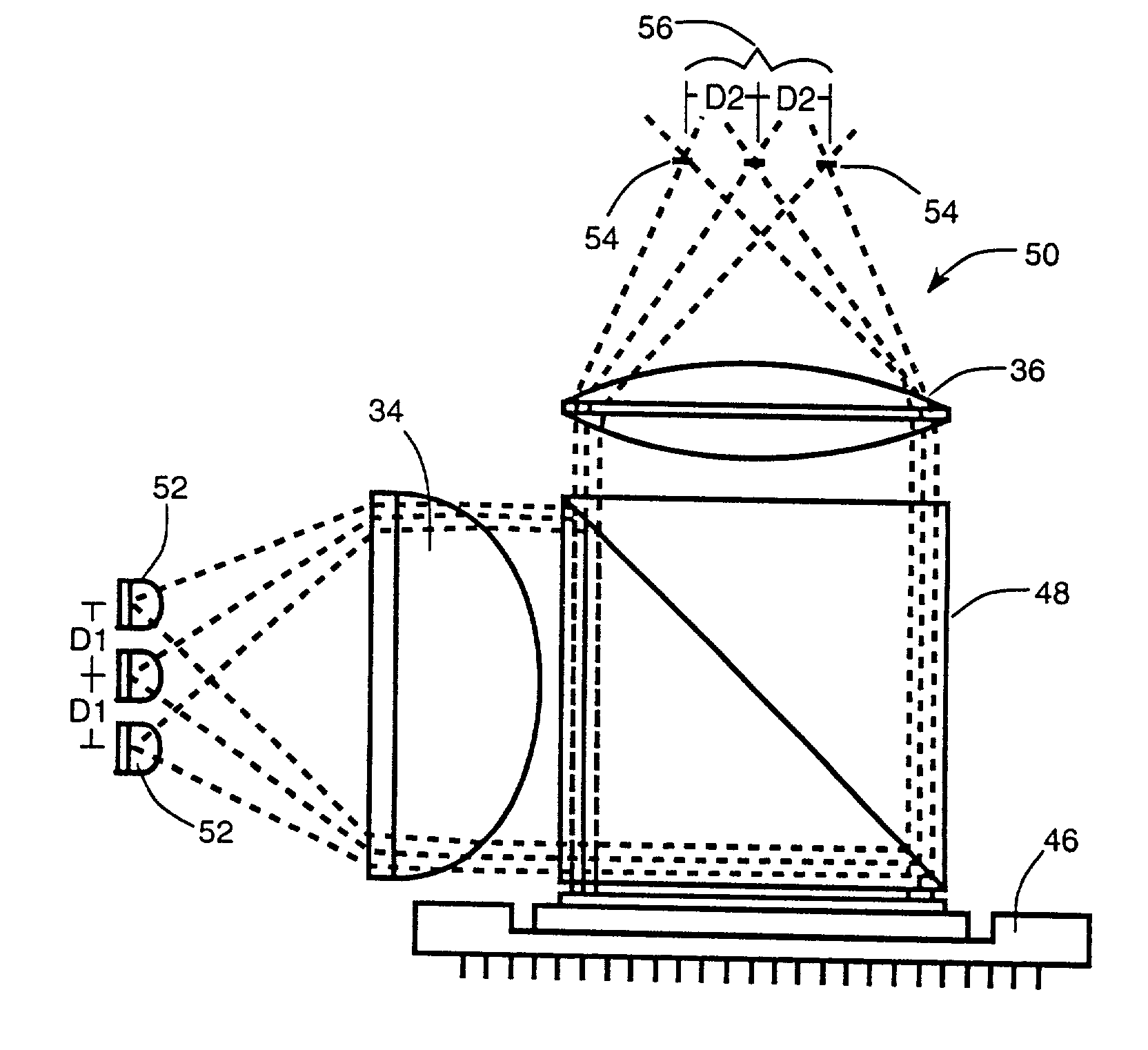
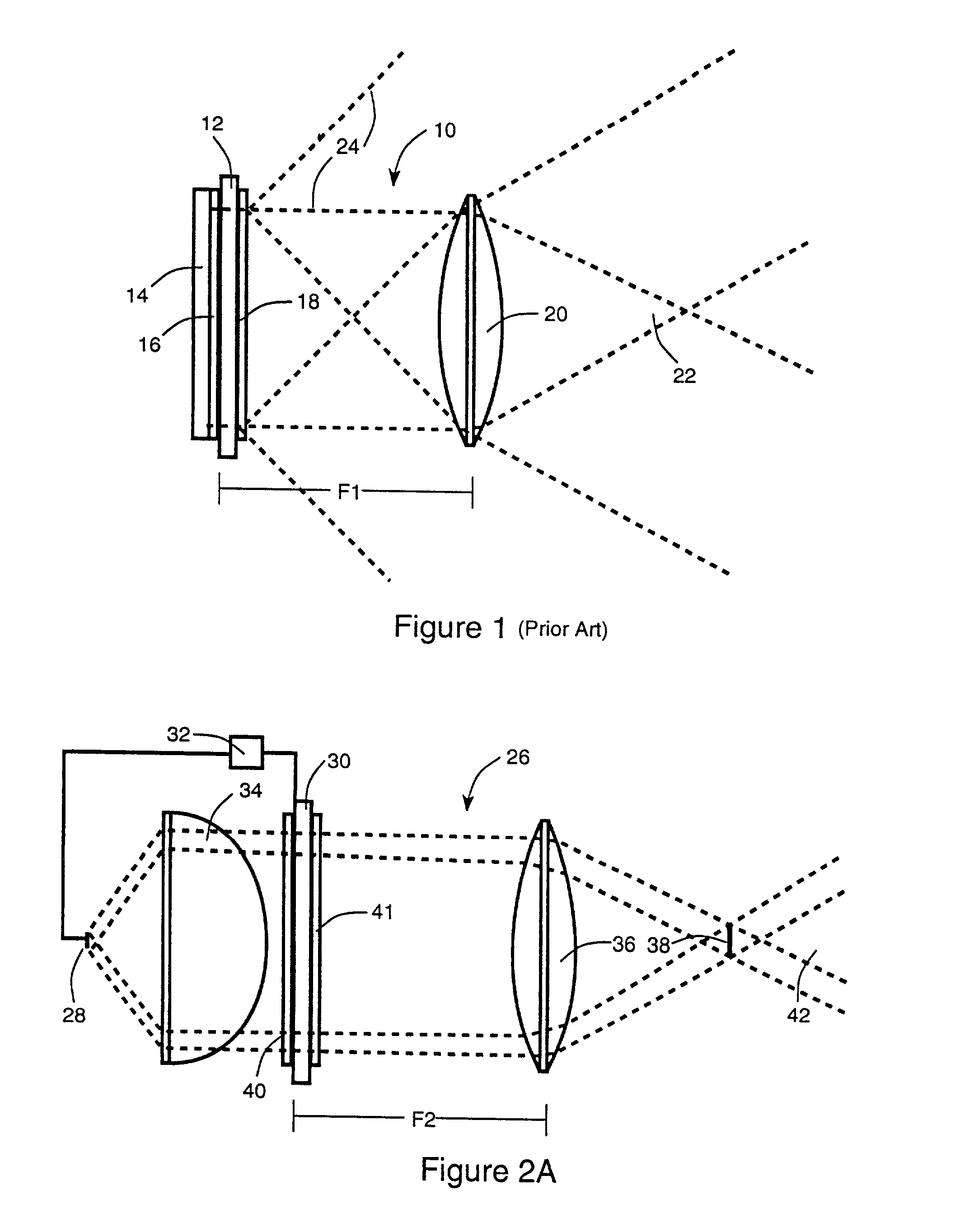
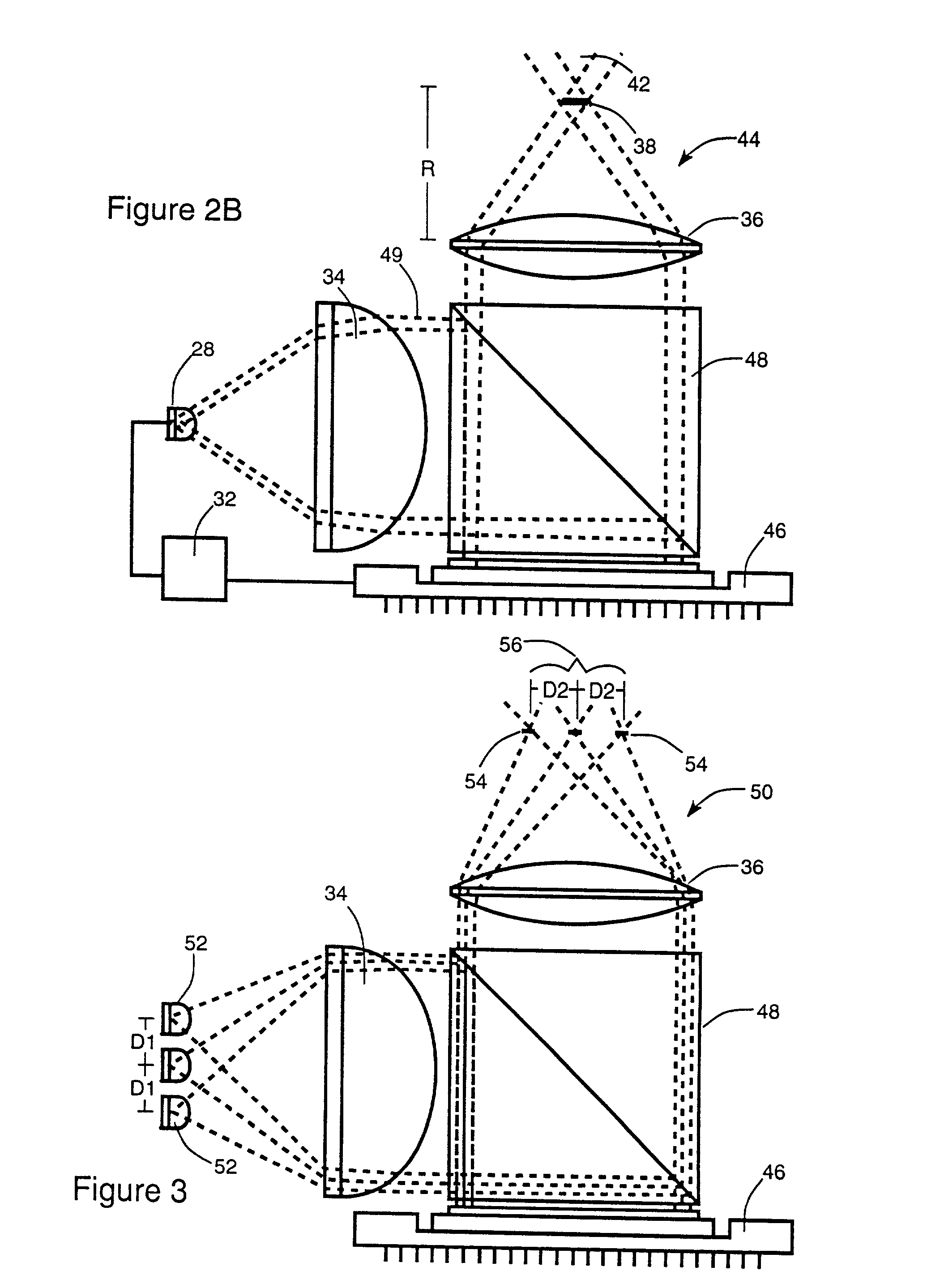
Optics arrangements including light source arrangements for an active matrix liquid crystal image generator
InactiveUS20060103913A1Precise positioningDisplay meansOptical light guidesBeam splitterSpatial light modulator
A system for producing modulated light is disclosed. The system comprises a spatial light modulator including a light modulating medium switchable between different states so as to act on light in ways which form overall patterns of modulated light. The system also includes an arrangement for switching the modulating medium between the different states in a controlled way and an illumination arrangement for producing a source of light. The system further includes an optics arrangement for directing light from the source of light into the spatial light modulator and for directing light from the spatial light modulator through a predetermined source imaging area. The optics arrangement cooperates with the illumination arrangement and the spatial light modulator so as to produce a real image of the source of light within the source imaging area such that an individual is able to view a virtual image of the overall patterns of modulated light from the source imaging area. A variety of novel optics arrangements are disclosed including specific combinations of different light sources, diffusing plates, polarizers, beam splitters, analyzers, lenses, mirrors, and holographic optical elements which allow the overall optical arrangement to be miniaturized to the same degree and in coordination with the spatial light modulator. The different light sources include using a plurality of light sources, such as LEDs, to form an array of light sources, each of the light sources providing light to a corresponding portion of the spatial light modulator.
Owner:DISPLAY TECHNOLOGIES INC
Magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging method and imaging system
ActiveCN102788836AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSource imagingAcoustic lens
The invention discloses a magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging method, comprising the steps of applying pulse excitation on a conductive target imaging body in a static magnetic field, generating an inductive vortex in the conductive target imaging body, and generating a Lorentz force by the interaction of the inductive vortex and the static magnetic field so as to cause the vibration of mass points in the imaging body to generate ultrasonic signals; receiving image signals of the ultrasonic signals of each mass point in the conductive target imaging body by using an array ultrasonic probe on a focal plane of an acoustic lens, imaging the received image signals of each mass point in the conductive target imaging body, so that each mass point image signal is proportional to the Lorentz force divergence of a corresponding point in the conductive target imaging body, and a Lorentz force divergence image of the conductive target imaging body or a reconstructed image according to current density rotation can be obtained according to the image signals of the ultrasonic signals detected by the array ultrasonic probe. A magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging system using the imaging method disclosed by the invention comprises a synchronous trigger and control module (1), an excitation source, an imaging system and a week signal detecting system.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High intensity focused ultrasound treatment head and system
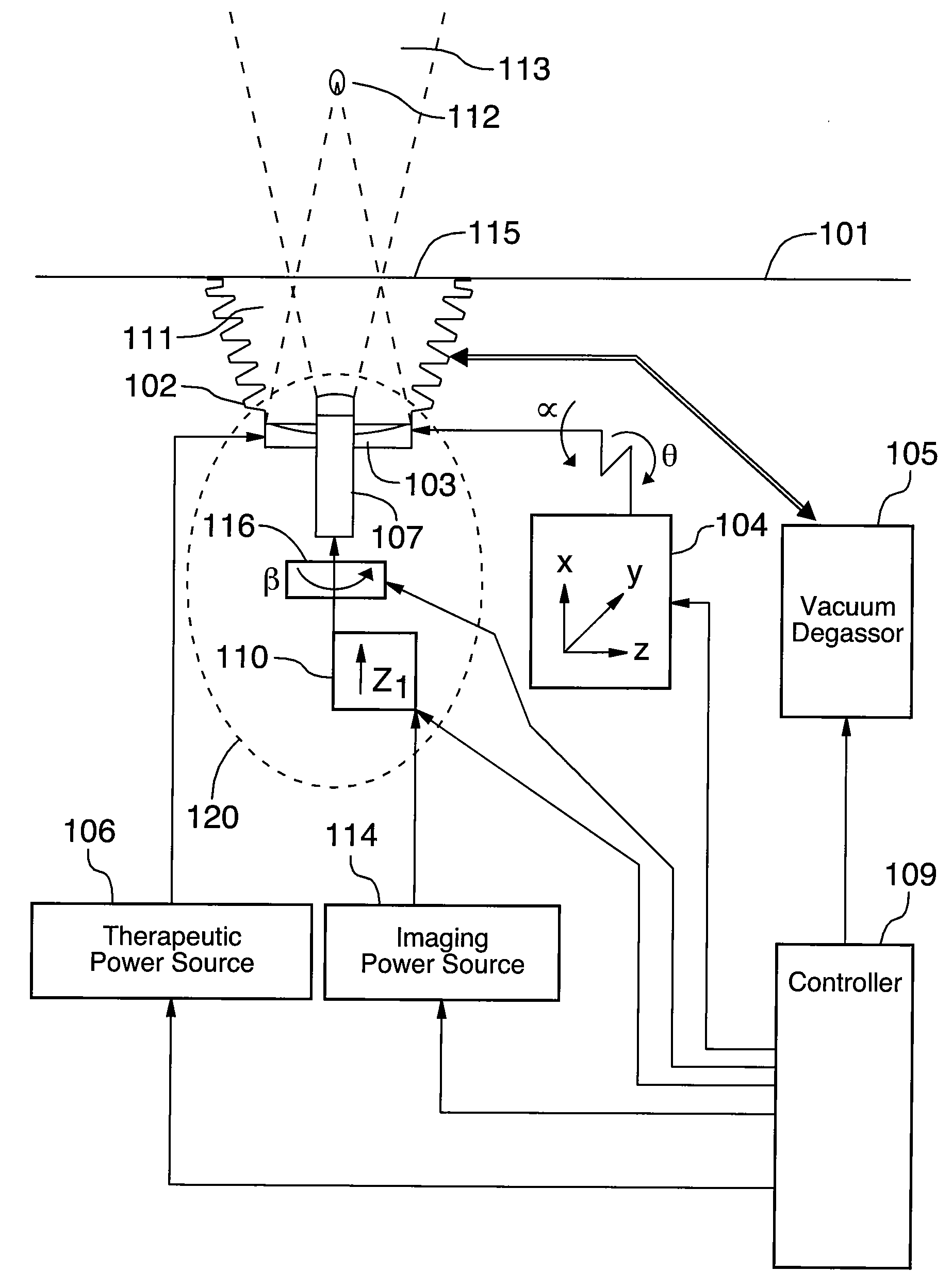
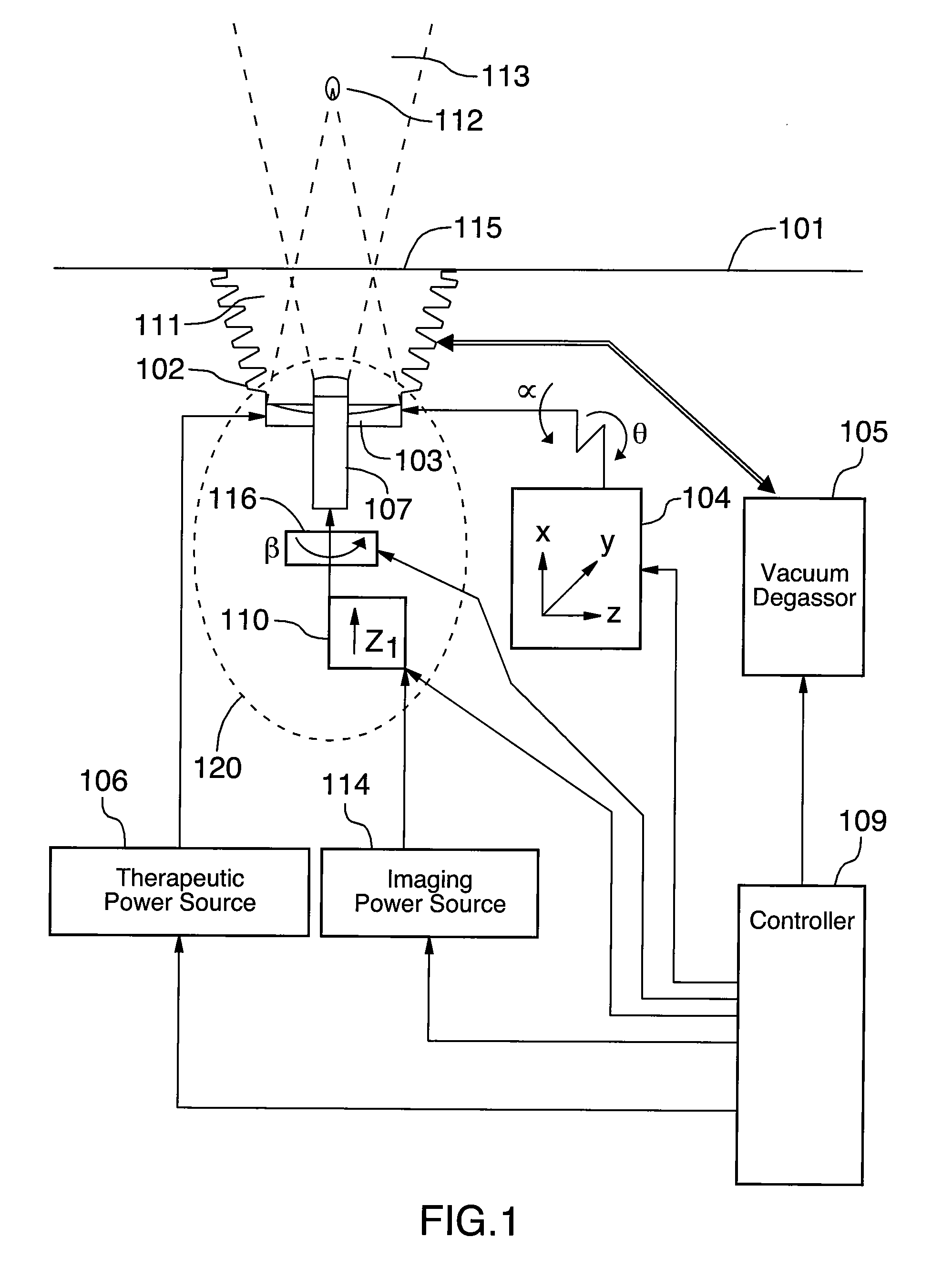
ActiveUS20080167555A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyTherapeutic bedRadiology
The system comprises a therapeutic bed, a chamber, a combined head, a motional apparatus, a therapeutic power source, an imaging power source, a vacuum degassor, and a controller. The therapeutic transducer, the imaging transducer, and a rotator, together form the combined head. The combined head may also include an actuator. The rotator and actuator move the imaging transducer relative to the therapeutic transducer. The therapeutic transducer produces high intensity focused ultrasound, and treats target tissue in the body.
Owner:ANGEL SCI & TECH CANADA
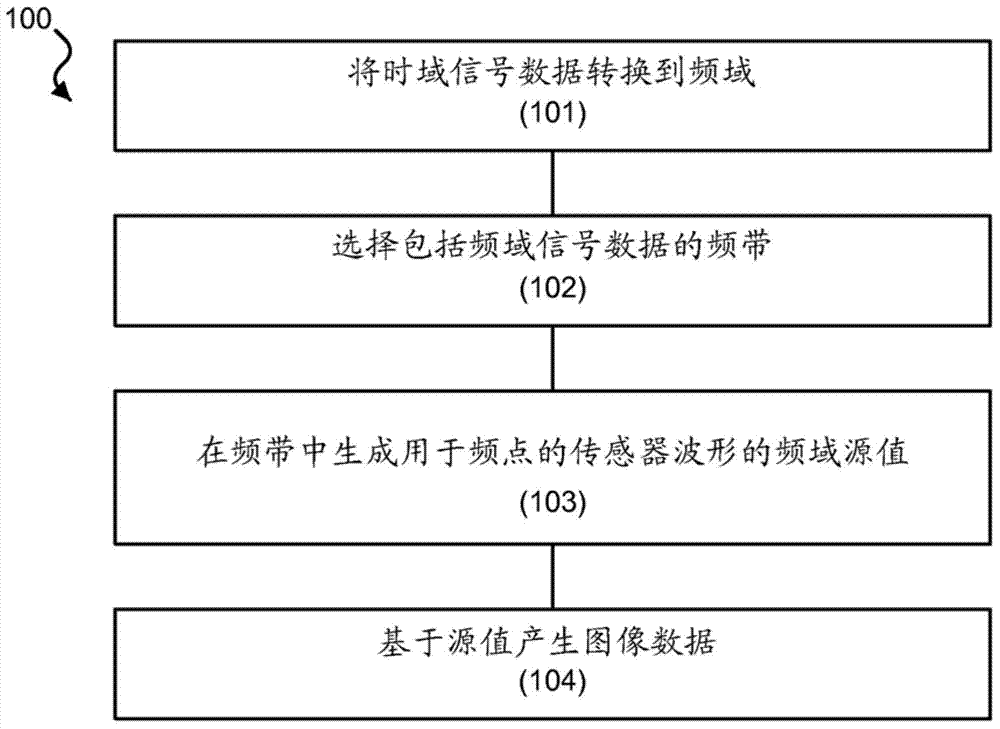
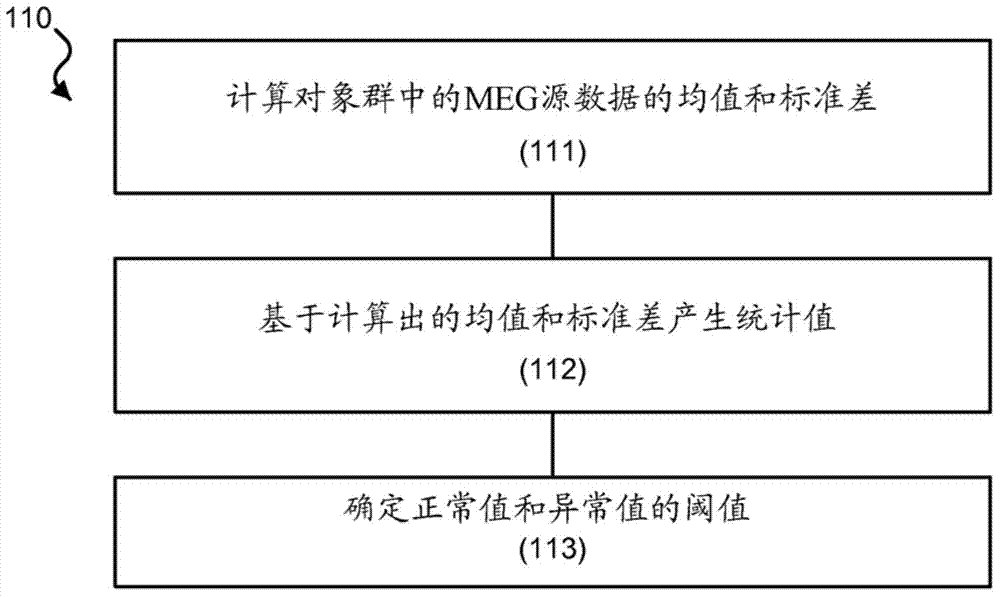
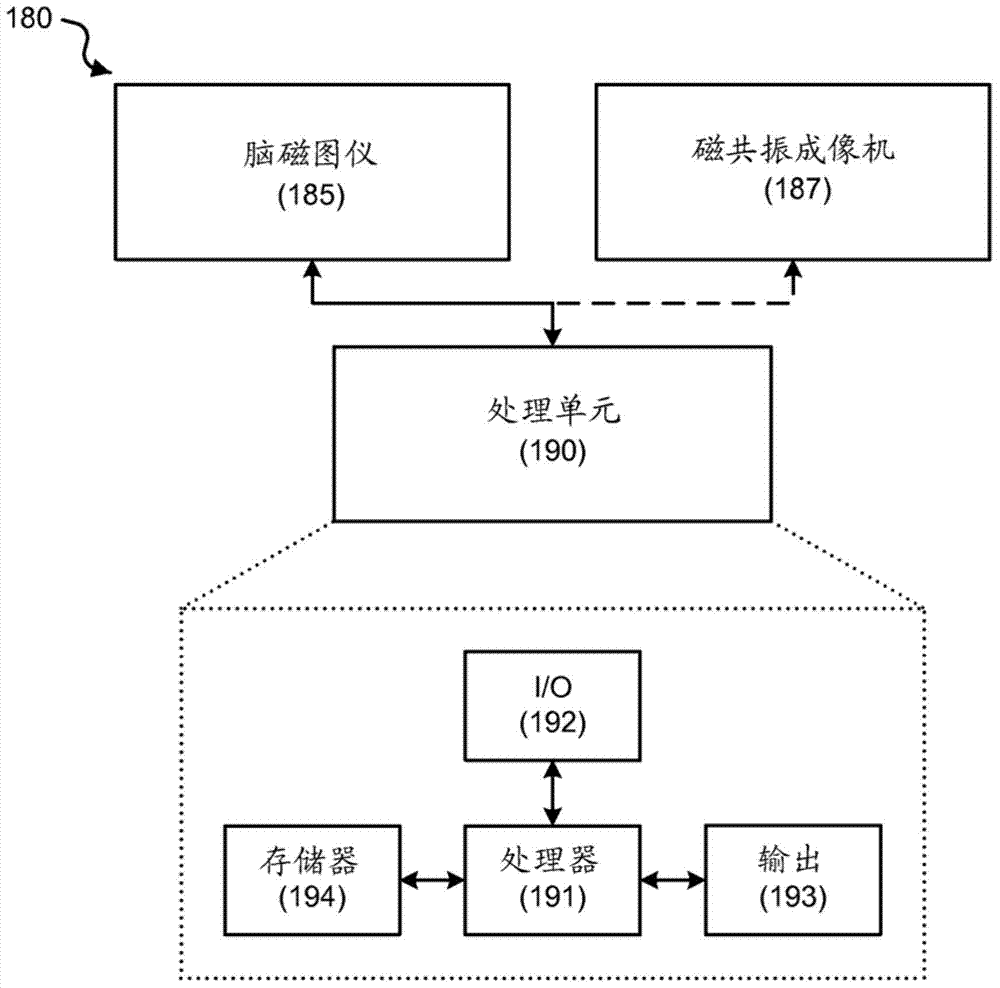
Magnetoencephalography source imaging
InactiveCN103717129AMagnetic measurementsMedical automated diagnosisMagnetoencephalographySource imaging
Techniques, devices and systems are disclosed for magnetoencephalography (MEG) source imaging. In one aspect, a method includes selecting signal data associated with one or more frequency bands from a spectrum of the signal data in the frequency domain, in which the signal data represents magnetic signals emitted by a brain of a subject and detected by a plurality of sensors outside the brain, defining locations of sources within the brain that generate the magnetic signals, in which the number of locations of the sources is selected to be greater than the number of sensors, and generating a source value of signal power based on the selected signal data corresponding to a respective location of the locations at the one or more frequencies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
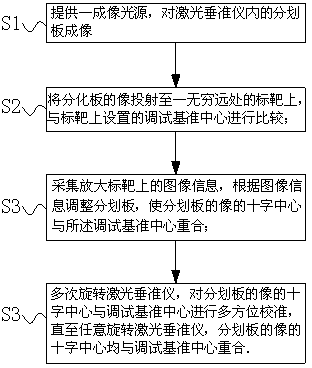
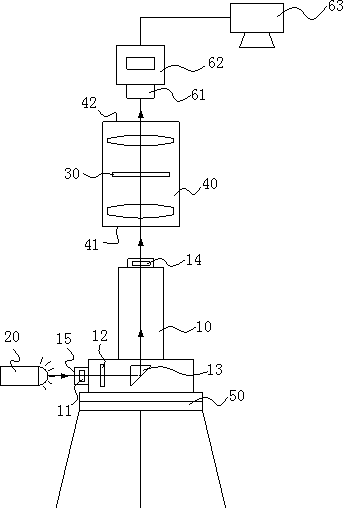
Source imaging-based laser plummet digital calibrating method and device
The invention discloses a source imaging-based laser plummet digital calibrating method and device. According to the method, a reticle is used as a projection entity, an imaging light source is used for reticle imaging so that the image of the reticle is projected to a target at the infinite point and an infinite projection state is simulated, the comparison between the projection state and a debugging reference center of the target is carried out, and according to an infinite offset state, the reticle is adjusted. Compared with the prior art utilizing a device for projecting the reference center at the infinite point to a reticle, the method provided by the invention has higher calibrating precision. The method realizes amplification of image information of the target by an image amplification processing system, is convenient for observation calibration by a user and further improves calibration accuracy.
Owner:武汉天宇光电仪器有限公司
Methods and apparatus for image fusion
ActiveUS9171219B2Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSource imagingComputer vision
Systems and methods configured to implement sliced source imaging to produce a plurality of overlapping in-focus images on the same location of a single imaging detector without using beamsplitters.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
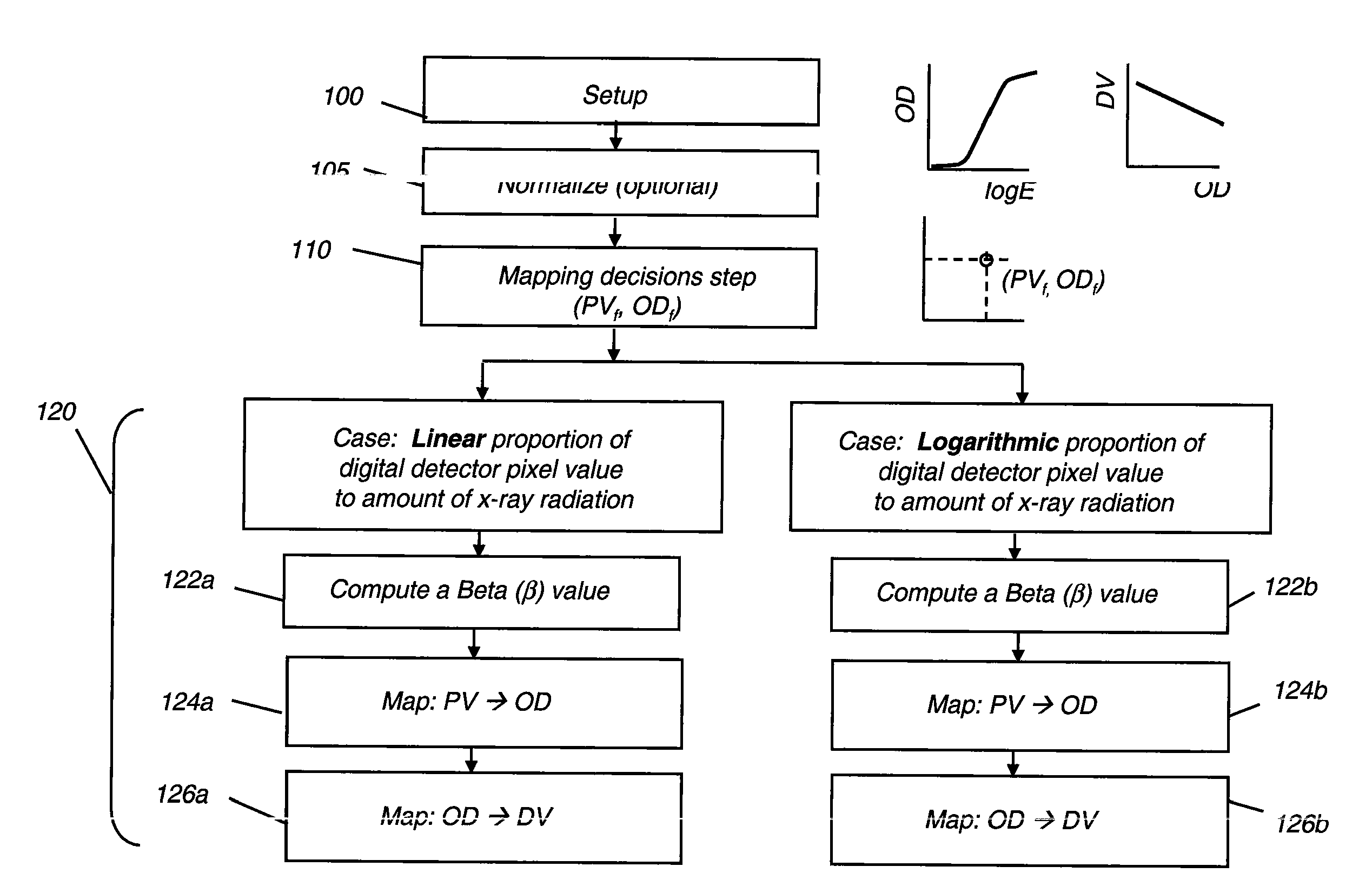
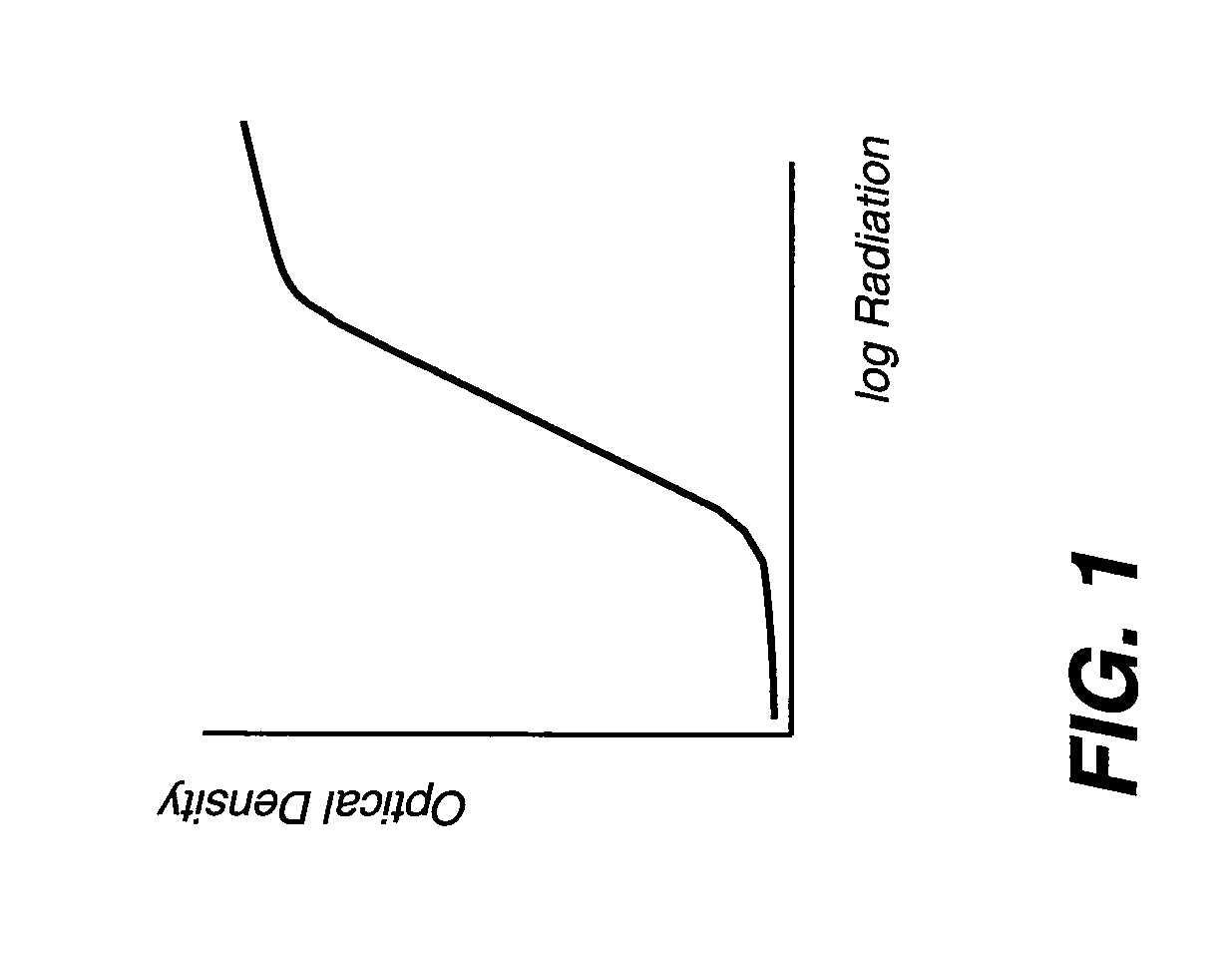
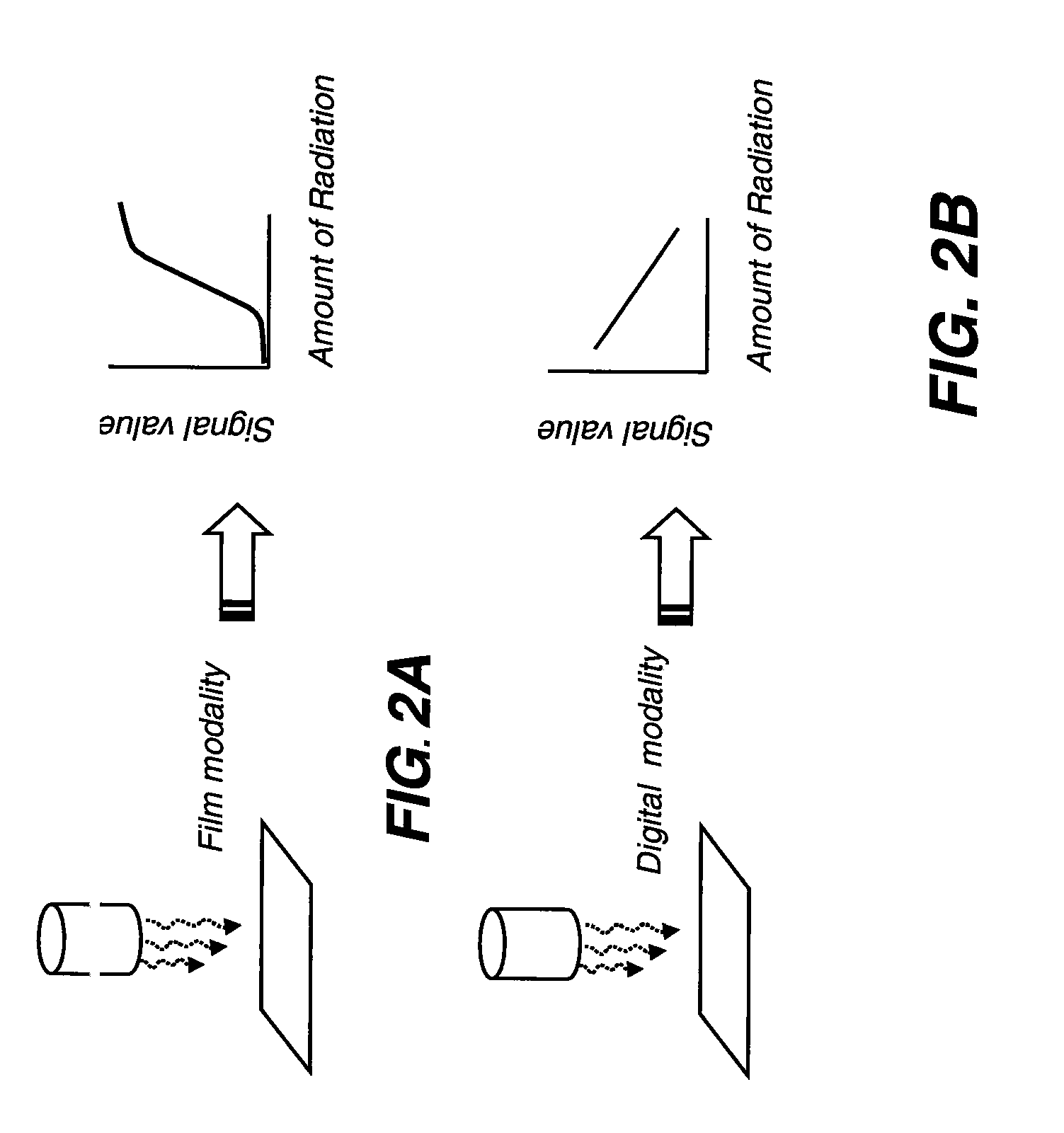
Sensitometric response mapping for radiological images
InactiveUS20090190716A1Character and pattern recognitionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationTarget signalSource imaging
A method for mapping radiological image data from a source imaging system to a target imaging system obtains sensitometric response data for both the source and the target imaging systems and identifies an anchor point that relates a specified source signal value to a specified target signal value. A transform is applied to map a range of source signal values to a corresponding range of target signal values, wherein the transform is defined according to the sensitometric response data obtained for both the source and the target imaging systems and according to the identified anchor point.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Optics arrangements including light source arrangements for an active matrix liquid crystal image generator
InactiveUS7012730B2Precise positioningProjectorsCathode-ray tube indicatorsSpatial light modulatorBeam splitter
A system for producing modulated light is disclosed. The system comprises a spatial light modulator including a light modulating medium switchable between different states so as to act on light in ways which form overall patterns of modulated light. The system also includes an arrangement for switching the modulating medium between the different states in a controlled way and an illumination arrangement for producing a source of light. The system further includes an optics arrangement for directing light from the source of light into the spatial light modulator and for directing light from the spatial light modulator through a predetermined source imaging area. The optics arrangement cooperates with the illumination arrangement and the spatial light modulator so as to produce a real image of the source of light within the source imaging area such that an individual is able to view a virtual image of the overall patterns of modulated light from the source imaging area. A variety of novel optics arrangements are disclosed including specific combinations of different light sources, diffusing plates, polarizers, beam splitters, analyzers, lenses, mirrors, and holographic optical elements which allow the overall optical arrangement to be miniaturized to the same degree and in coordination with the spatial light modulator. The different light sources include using a plurality of light sources, such as LEDs, to form an array of light sources, each of the light sources providing light to a corresponding portion of the spatial light modulator.
Owner:CITIZEN FINETECH MIYOTA CO LTD
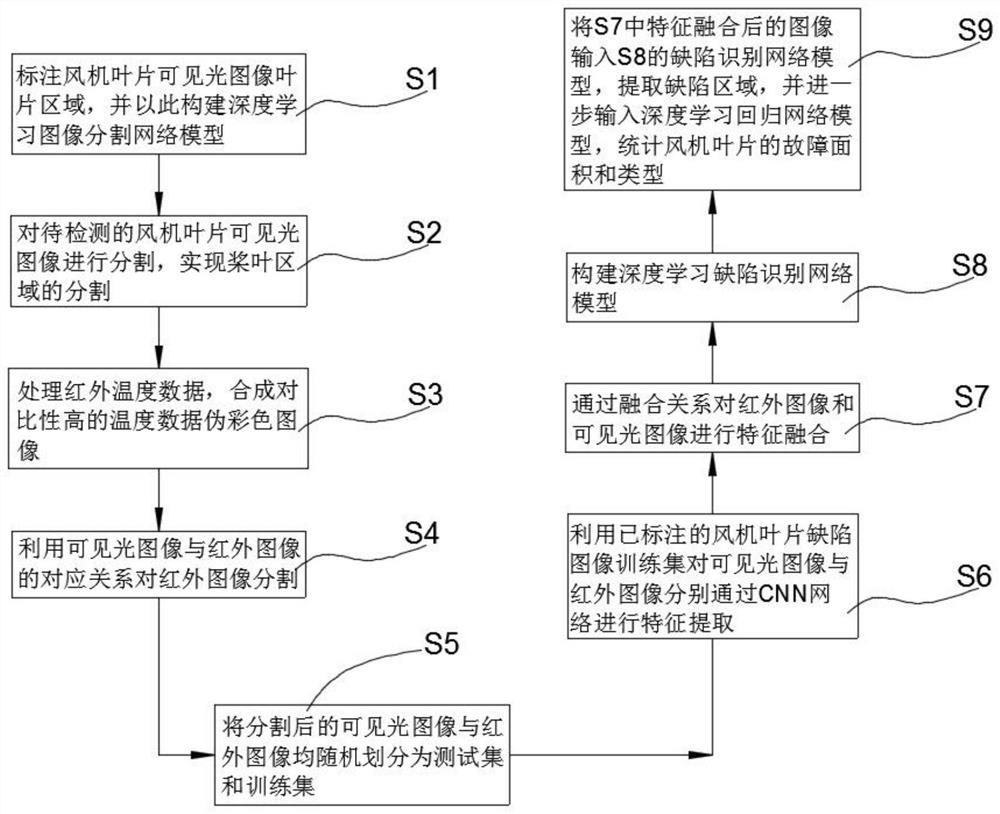
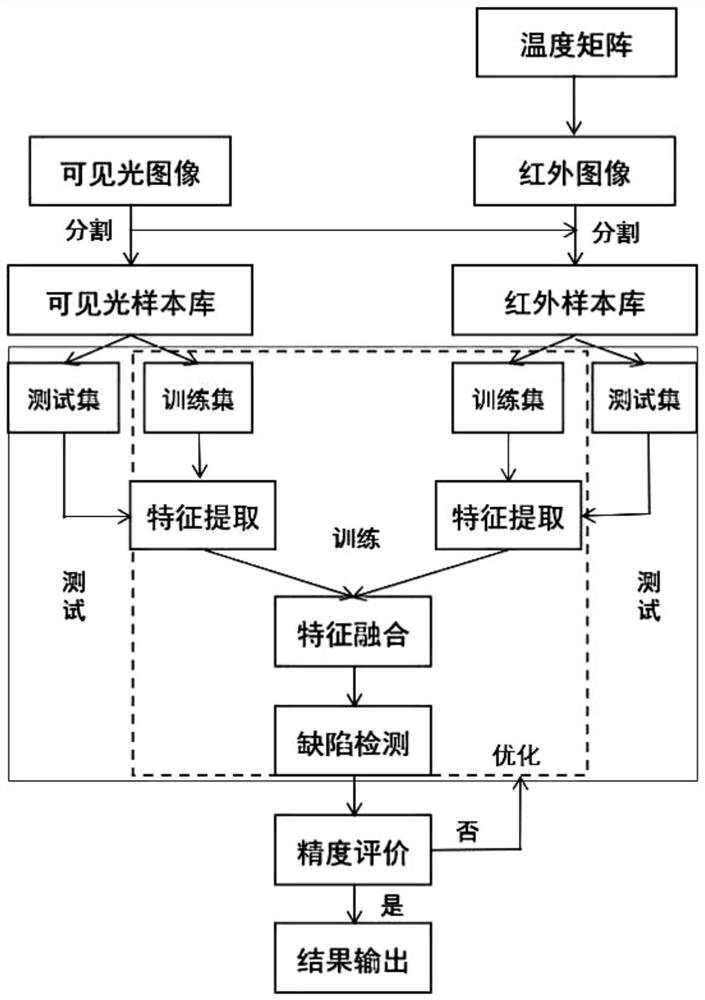
Fan blade defect intelligent detection method based on double-spectrum image
PendingCN111696075AAugmented realizationIncrease profitImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVisual technology
The invention relates to application of deep learning in the technical field of computer vision. The invention particularly relates to a fan blade defect intelligent detection method based on a double-spectrum image. According to the method, the image segmentation technology is utilized to realize segmentation of the blade area, background removal is realized, the identification efficiency and accuracy are improved, the infrared image and the visible light image are fused through the image processing technology, and then the deep learning technology is utilized to perform defect identificationon a large number of fan blade images. By accumulating a large amount of blade damage defect data and via techniques through big data, development rules of various damage defects in a large amount ofblade damage data are mined, a mathematical model is constructed, prediction and evaluation of the blade defects and the health state are finally achieved in combination with the machine automatic learning technology, the image processing technology and the double-light-source imaging technology are fused, the utilization rate of image information is effectively increased, and image feature information is obviously highlighted.
Owner:航天图景(北京)科技有限公司
Monocular vision sensor with triangulation ranging function
ActiveCN105004324ASolve the accuracy problemSolve positioningPicture interpretationOphthalmologyTriangulation
The invention provides a monocular vision sensor with a triangulation ranging function. The monocular vision sensor with the triangulation ranging function mainly comprises a shell, a socket, a circuit board, an imaging device, a laser device, a focus lens set, an illuminating light source, an imaging lens set, a measurement window and the like. A laser beam emitted by the laser device forms a collimated laser beam after passing through the focus lens set, and laser light spots are formed on the surface of a measured target. The imaging lens set images the measured target on the surface of the imaging device together with the laser light spots. Both the two-dimensional information and the distance information of the measured target can be obtained at the same time through calculation, and thus the three-dimensional information of the measured target is obtained by means of the monocular vision sensor. Compared with a conventional vision sensor, the monocular vision sensor with the triangulation ranging function has the advantages that a two-dimensional image of the measured target is obtained, meanwhile the value of the distance between the vision sensor and the measured target can be accurately obtained, and thus a three-dimensional vision sensor can be formed; in addition, the degree of integration is high, the size is small, cost is low, and measurement of a two-dimensional inclination angle can also be achieved.
Owner:上海钊晟传感技术有限公司
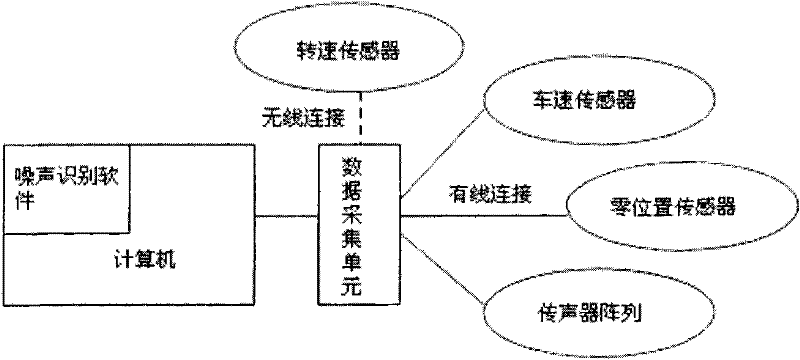
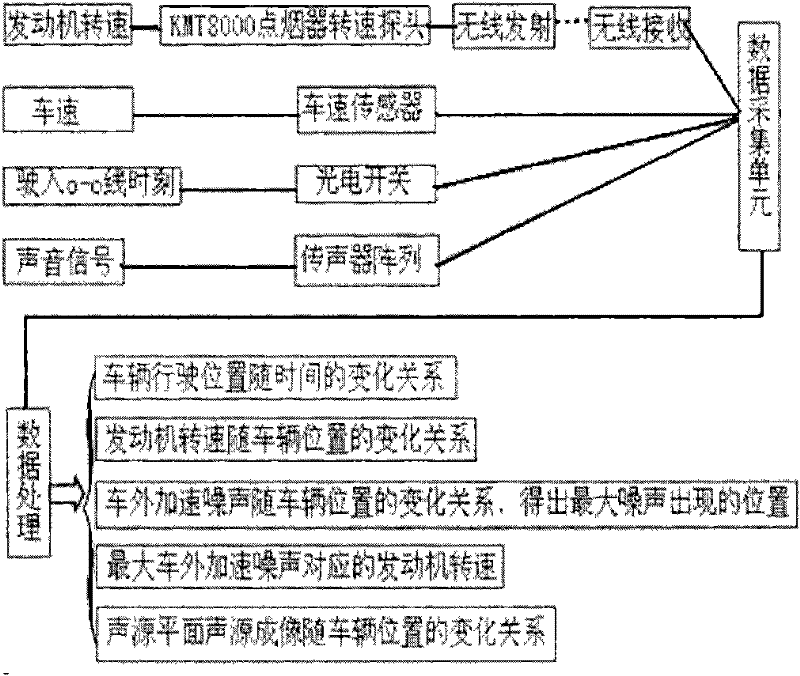
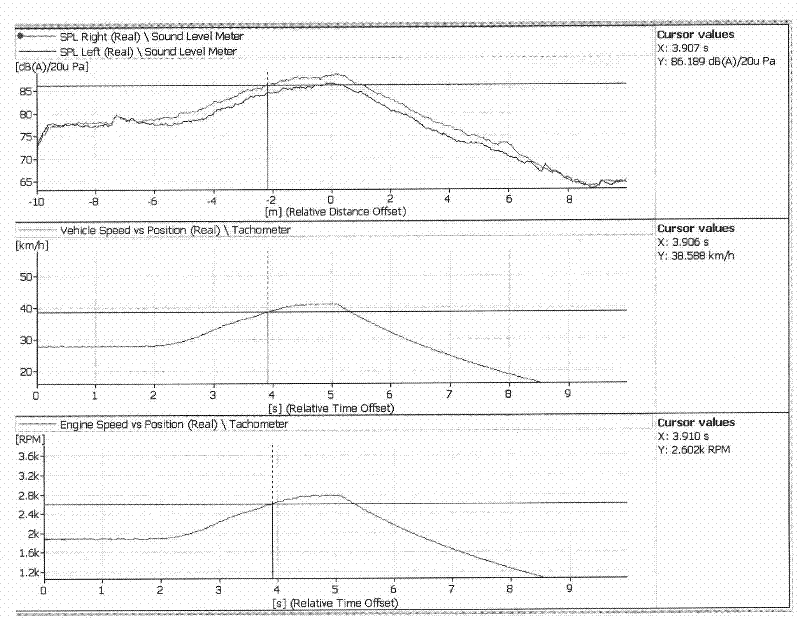
Automobile outfield pass-by-noise source recognition system and method
InactiveCN102445266ALower build costsReduce the numberSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementPosition fixationSound sourcesSource imaging
Aiming at a direct movement sound source recognition method and based on the combination of a beam forming sound source system and an integrated automobile outfield acceleration noise measurement system, the invention provides a automobile outfield pass-by-noise source recognition system which comprises a test computer, an ESS (engine speed sensor), a vehicle speed sensor, a zero position triggering sensor, a microphone array, a data acquisition unit and noise source recognition software. The system is simple in hardware connection, easy for algorithm implementation, low in cost and higher inmeasurement accuracy, and can be used for acquiring the relationship between the automobile running position and time, the relationship between the engine speed and the automobile position, the relationship between the automobile outfield acceleration noise and the automobile position, the engine speed corresponding to the maximal automobile outfield acceleration noise and the relationship between a noise source imaging plane and the automobile position during an automobile acceleration process.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
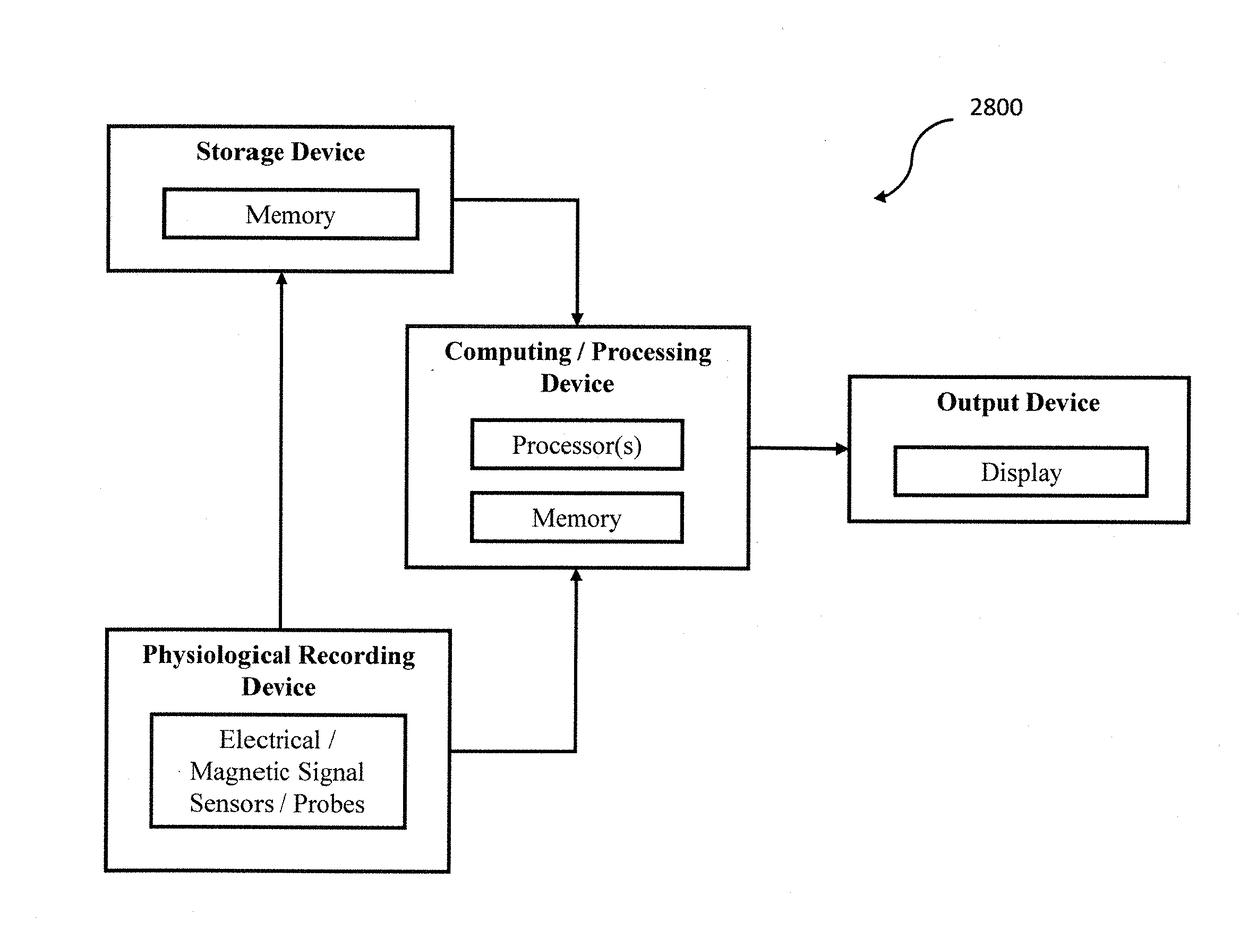
System and method for assessing electrical activity using an iterative sparse technique
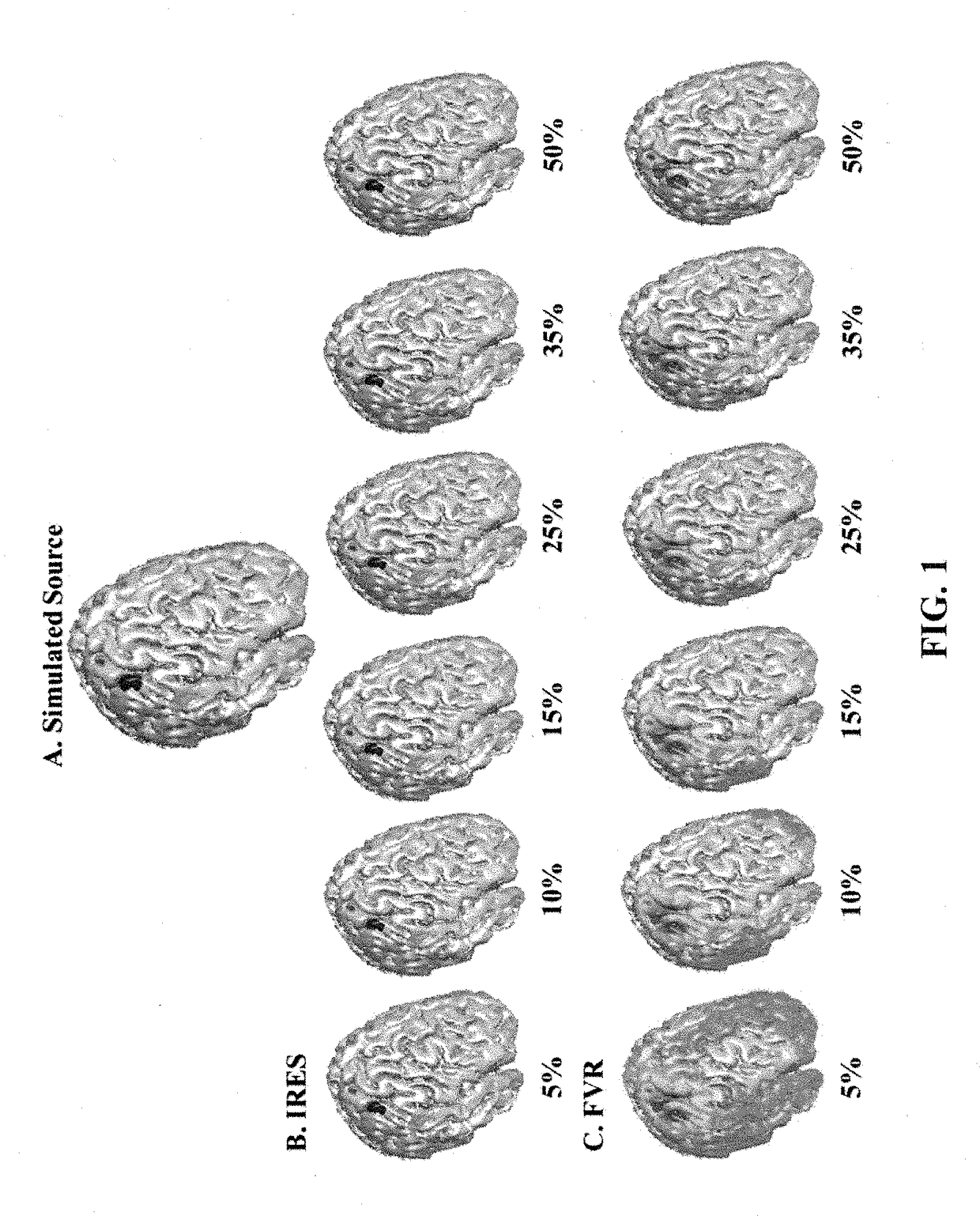
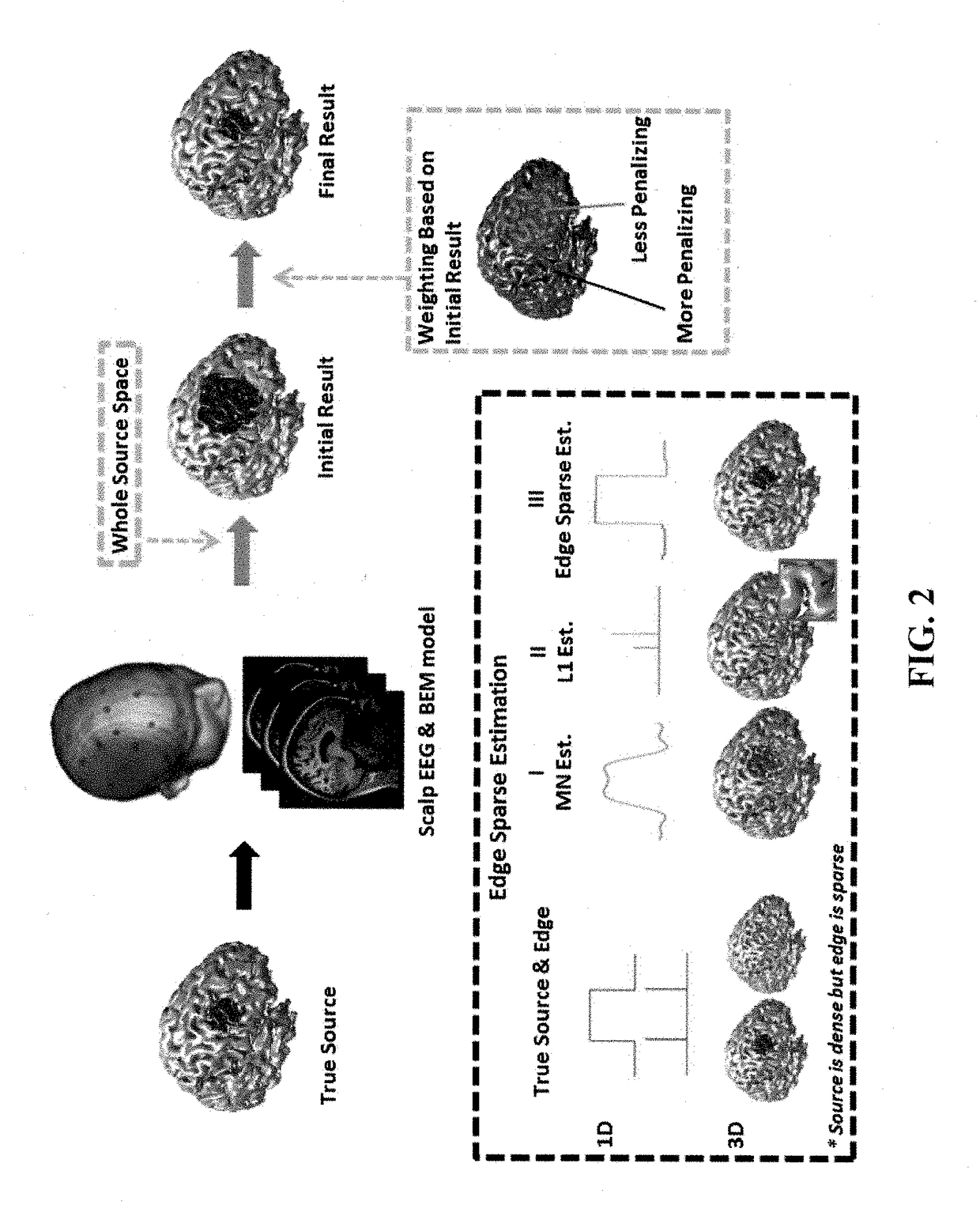
Three-dimensional electrical source imaging of electrical activity in a biological system (e.g., brain or heart) may involve sensor array recording, at multiple locations, of signals (e.g. electrical or magnetic signals) of electrical activity. An initial estimate of an underlying source is obtained. Edge sparsity is imposed on the estimated electrical activity to eliminate background activity and create clear edges between an active source and background activity. The initial estimate is iteratively reweighted and a series of subsequent optimization problems launched to converge to a more accurate estimation of the underlying source. Images depicting a spatial distribution of a source are generated based on the iteratively reweighted edge sparsity, and the time-course of activity for estimated sources generated. Iterative reweighting penalizes locations with smaller source amplitude based on solutions obtained in previous iterations, and continues until a desirable solution is obtained with clear edges. The objective approach does not require subjective thresholding.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Structured electron emitter for coded source imaging with an x-ray tube
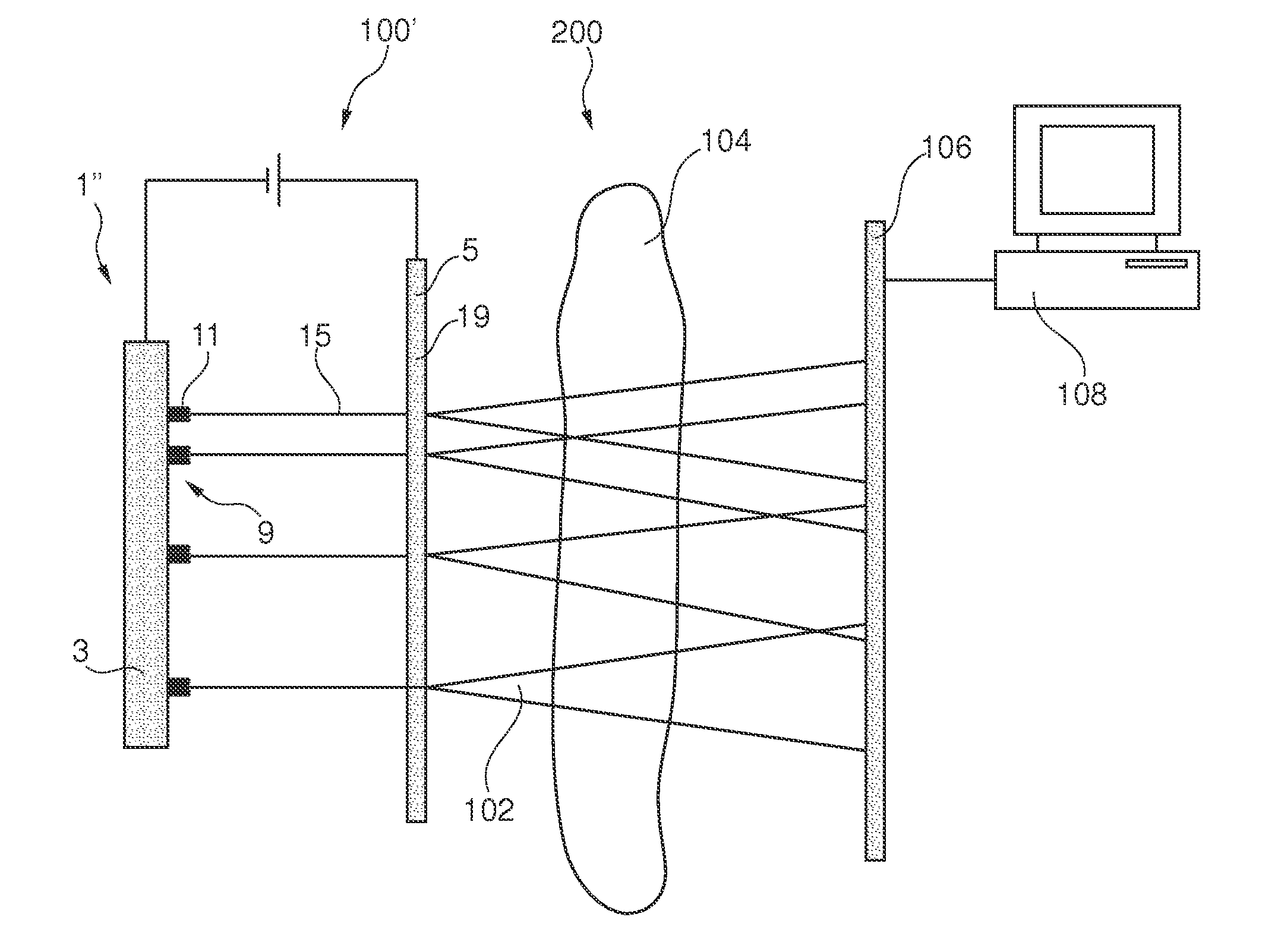
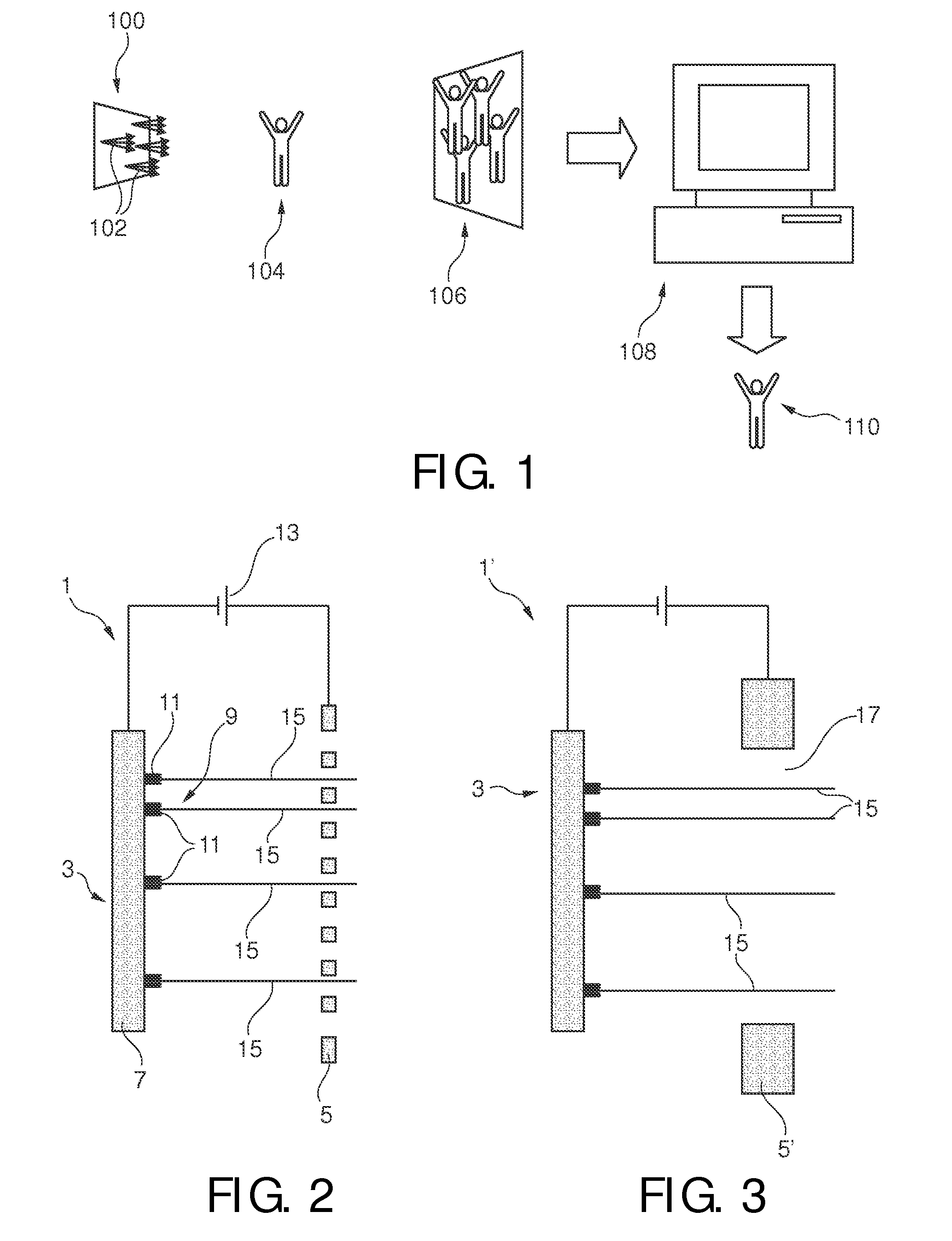
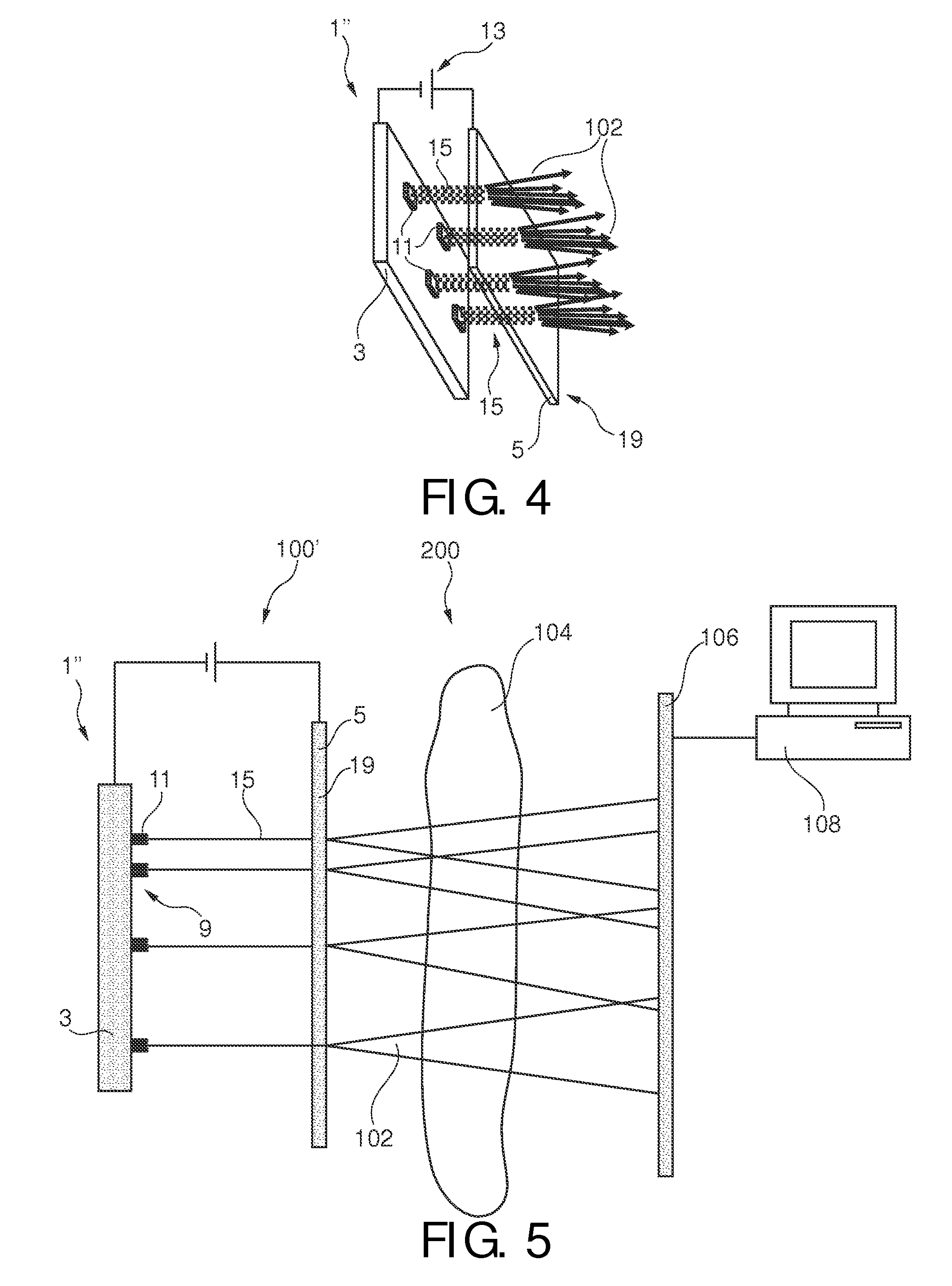
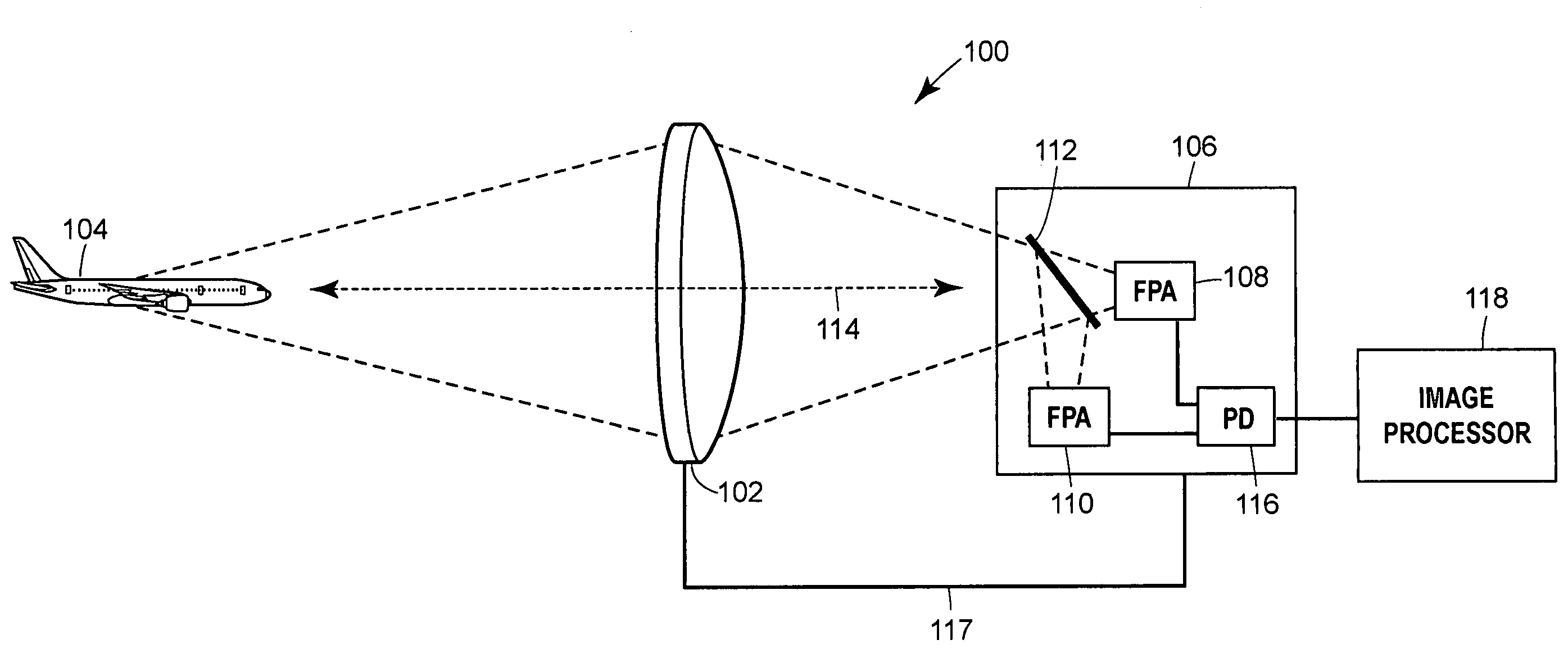
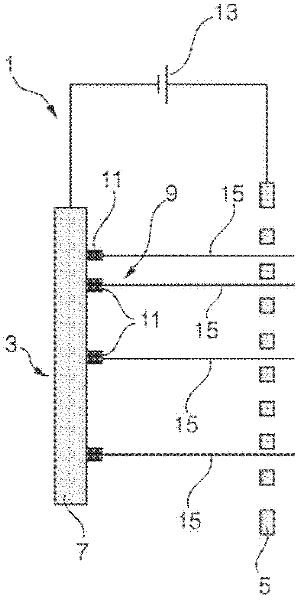
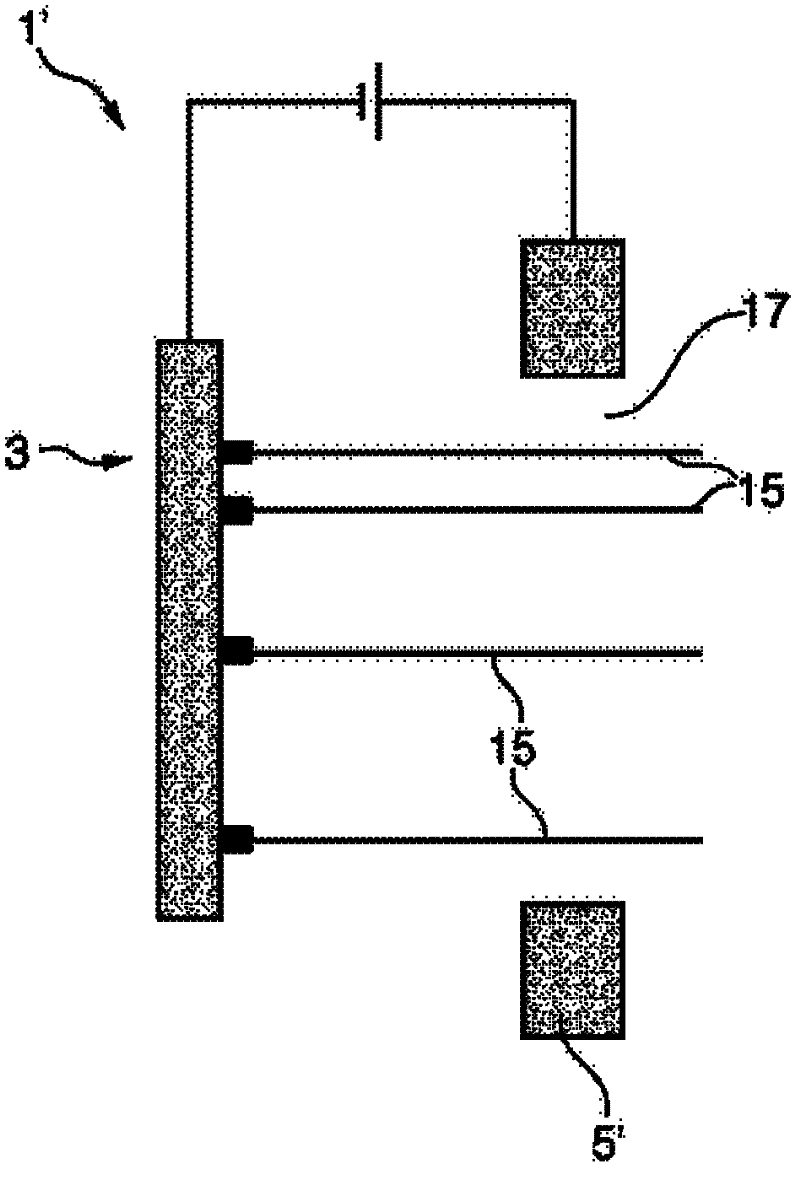
InactiveUS20120027173A1High mechanical strengthGood effectX-ray tube electrodesNanoopticsImage resolutionX-ray
An electron emitter (1) and an X-ray tube (100) comprising such electron emitter (1) are presented. The electron emitter (1) comprises a cathode (3) and an anode (5) wherein the cathode (3) comprises an electron emission pattern (9) of a plurality of local areas (11) spaced apart from each other, each area being adapted for locally emitting electrons via field emission upon application of an electrical field between the cathode (3) and the anode (5). Electron beams (15) emitted from the local areas (11) may generate several X-ray source intensity maxima in a specific geometric pattern. An apparent loss in spatial resolution due to overlapping images on a detector can be corrected by using specific intensity patterns for the X-ray source (100) and by applying dedicated decoding algorithms on the acquired image such as coded source imaging (CSI).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Closed-loop wavefront sensor using field programmable gate array
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Calibration device and method for transmitting and receiving optical axes of common-aperture telescope
The invention provides a calibration device and a calibration method for transmitting and receiving optical axes of a common-aperture telescope. The calibration device comprises a light source, an imaging detection system, a first reflector, a second reflector, a third reflector, a transmission sighting piece, an electric adjusting mirror, a spectroscope, a tracking quick reflector, an on-board laser transceiving device and a relay transmission optical path, wherein the light source, the imaging detection system, the third reflector, the transmission sighting piece and the electric adjusting mirror are arranged below the telescope; and the first reflector, the second reflector, the spectroscope, the tracking quick reflector, the on-board laser transceiving device and the relay transmission optical path are arranged above the telescope. The calibration device and the calibration method can realize efficient calibration of the transmitting and receiving optical axes of the common-aperture telescope, the optical path calibration method is simple, quick and high in precision (depending on resolution of the on-board laser transceiving device and the imaging detection system, generally can be up to mu rad magnitude order), manual operation is not needed, the optical path calibration time requires about a few minutes, and the optical path detection efficiency of the telescope system is significantly improved.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
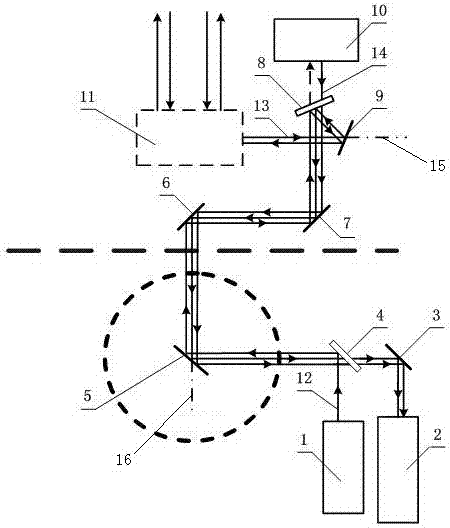
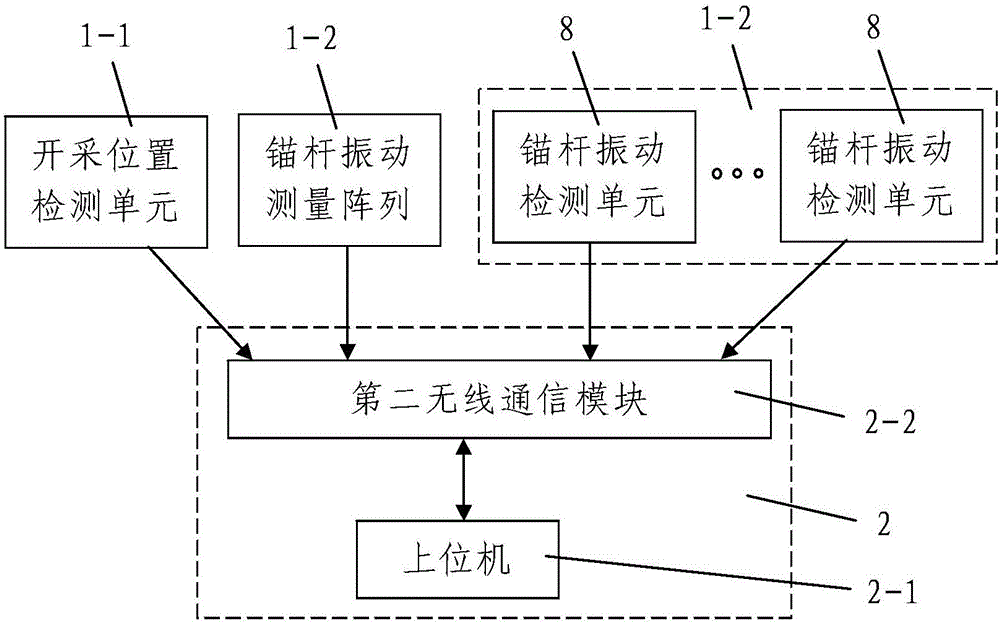
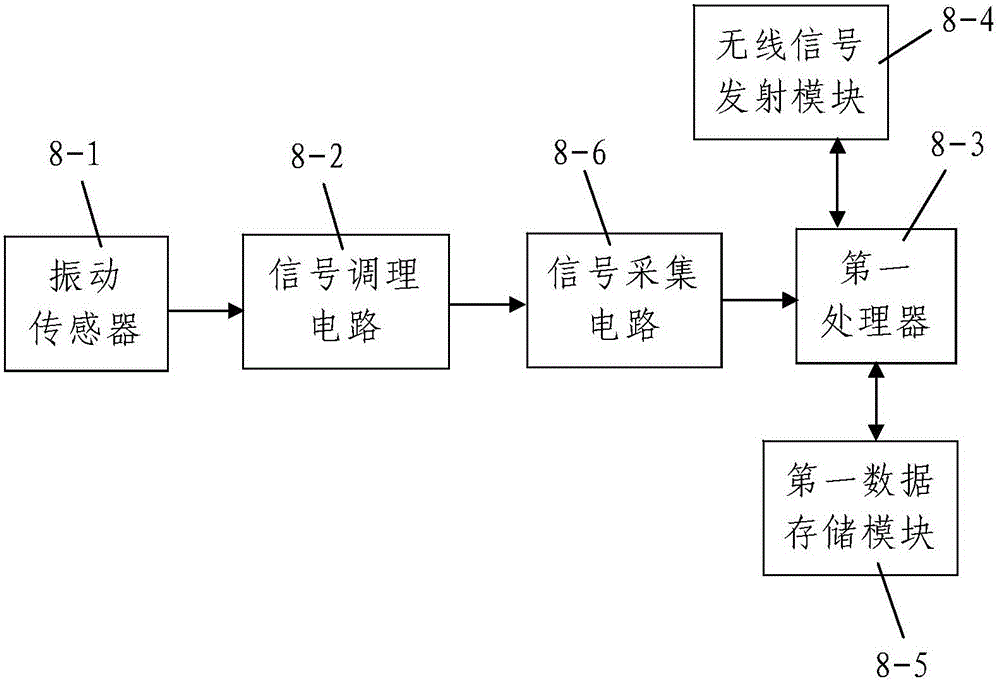
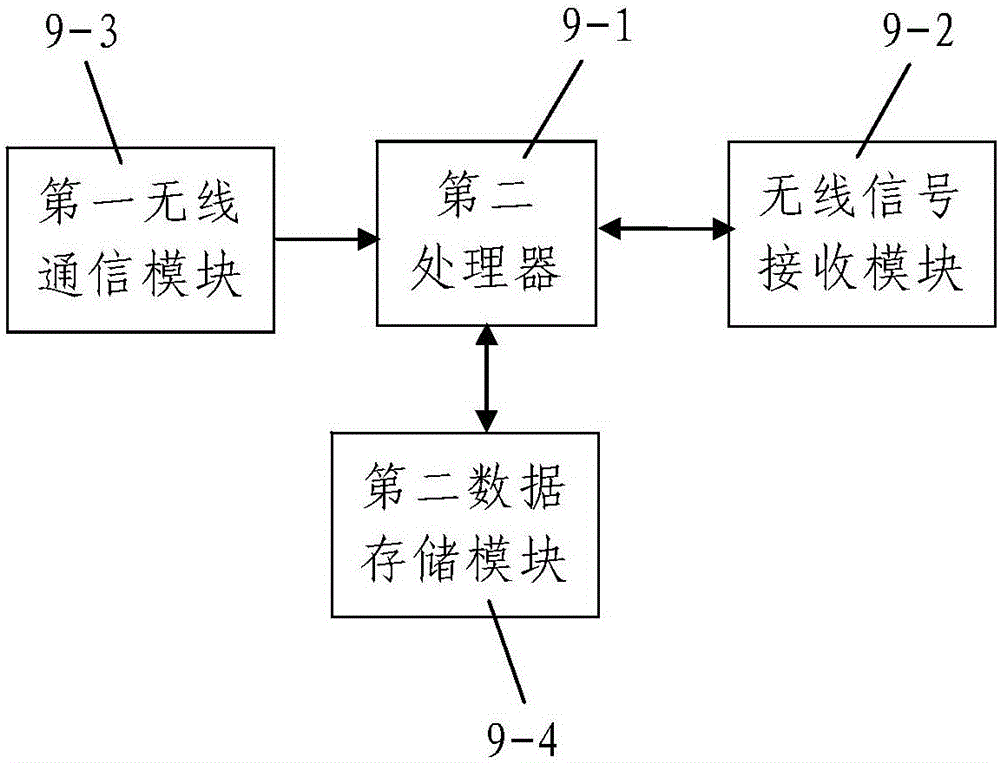
Dynamic tomography system and method for fully mechanized face near field coal rock under exploiting excitation of coal machine
ActiveCN105005081ASimple structureLow input costSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingTomographyVibration detection
The invention discloses a dynamic tomography system and method for a fully mechanized face near field coal rock under exploiting excitation of coal machine. The system comprises an array information synchronous acquisition device and a near-field coal rock tomography working station; the near-field coal rock tomography working station is connected to the array information synchronous acquisition device. The excitation source for vibration is a coal machine. The array information synchronous acquisition device comprises an exploiting position detection unit and two anchor rod vibration detection arrays that are uniformly arranged in a mining roadway. The system is simple in structure and reasonable in design. The system is also convenient to install and operate and is good in using effect. Taking a coal machine as an excitation source, the system makes good images. The invention further discloses a dynamic tomography method for a coal rock near a fully mechanized face under exploiting excitation of a coal machine; the method comprises following steps: 1) the anchor rod vibration detection units and the exploiting position detection units are deployed; 2) dynamic tomography for a coal rock near a fully mechanized face is done under an exploiting excitation of a coal machine. Such a method can be done with a few steps. Reasonably designed, the method can also be done very conveniently to provide dynamic chromatography imaging conveniently and quickly.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
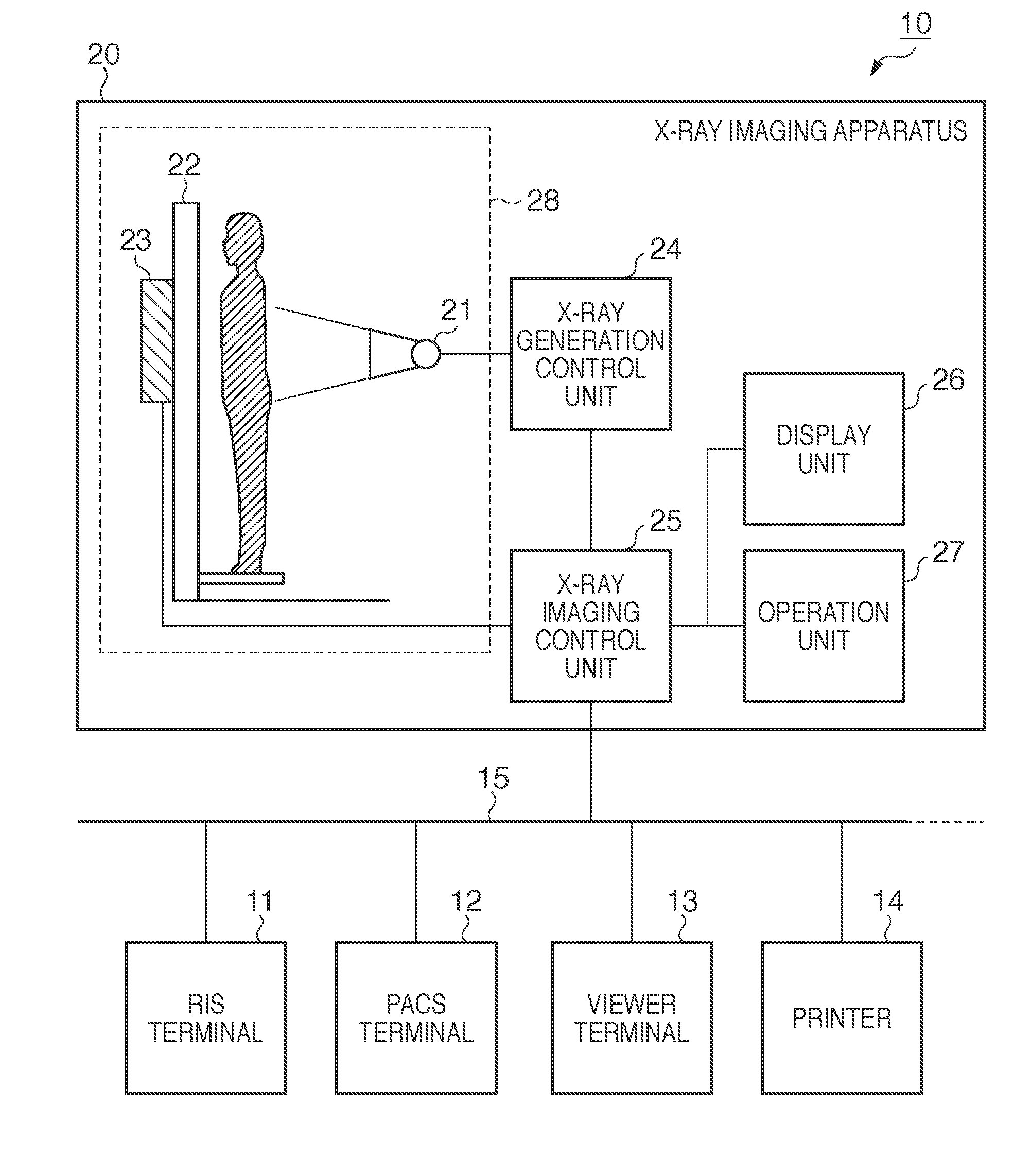
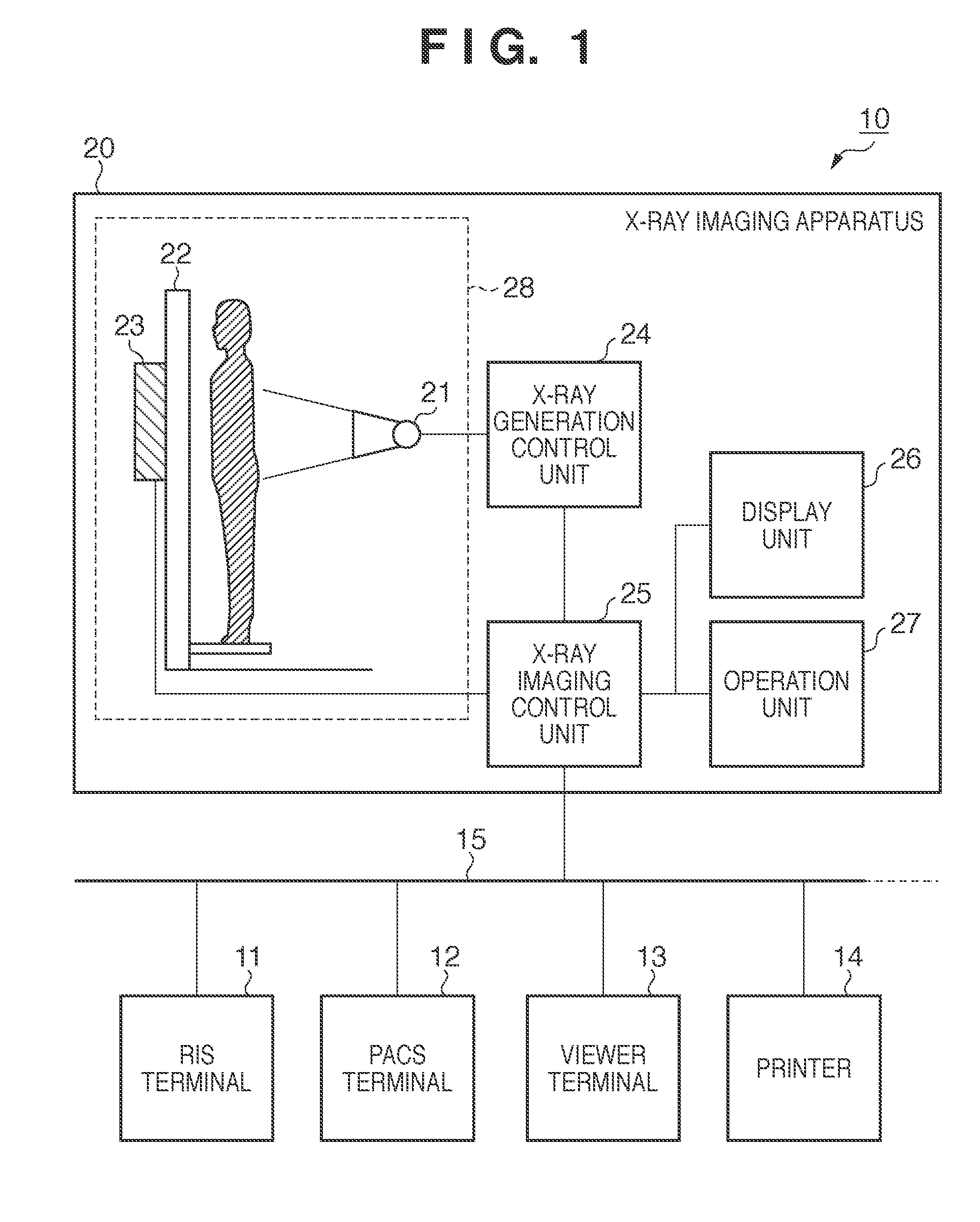
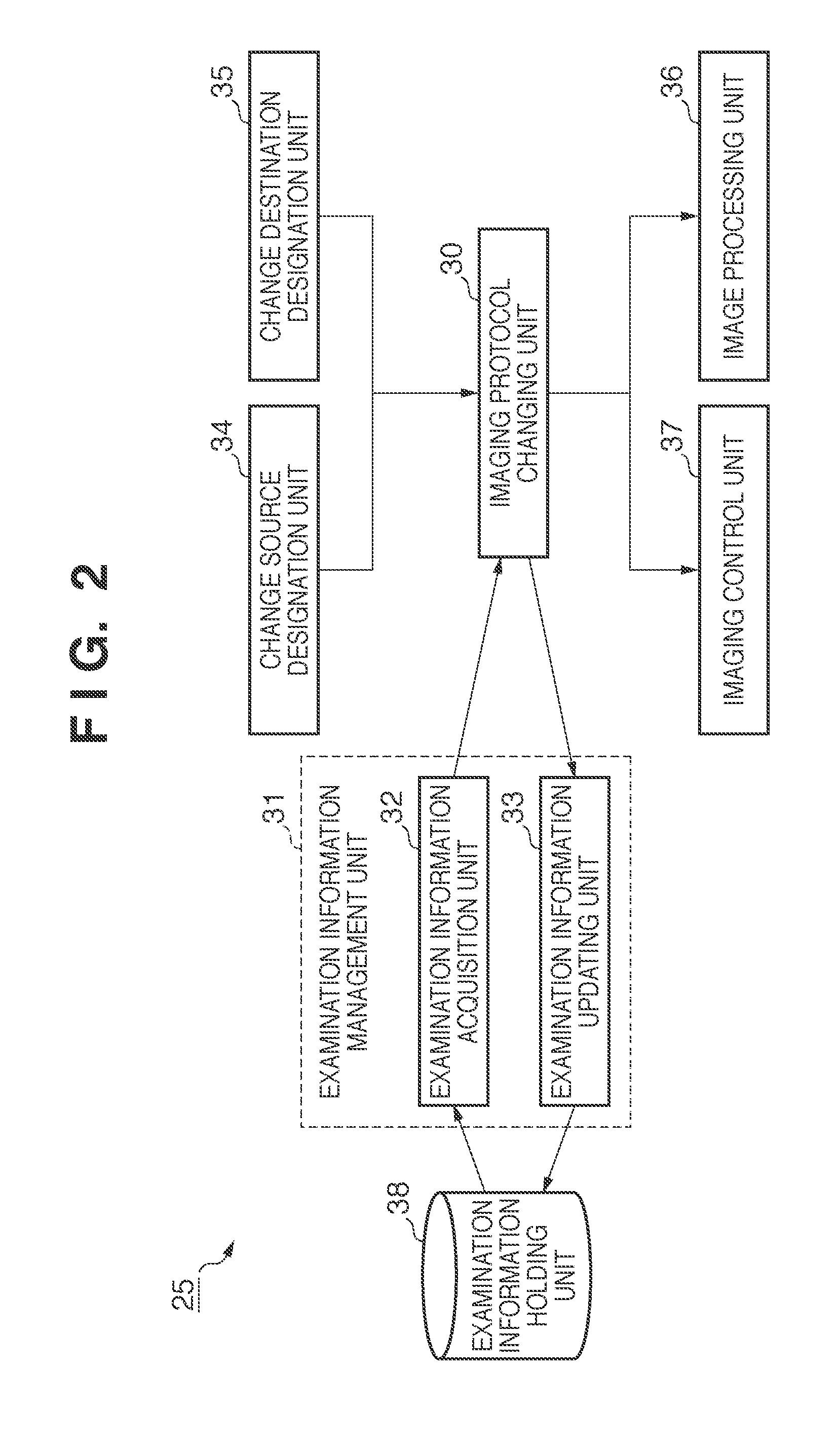
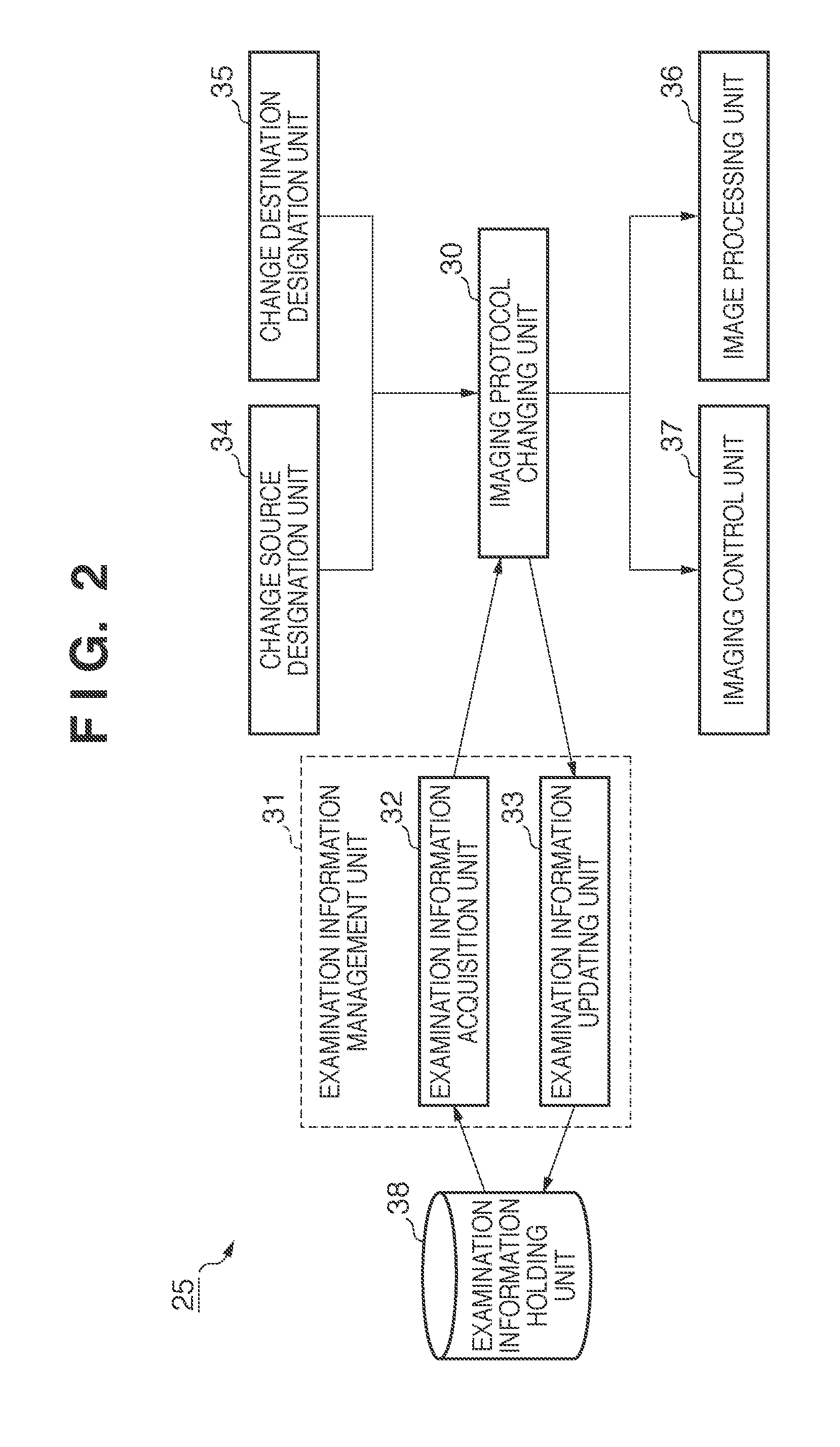
Radiographic imaging apparatus and processing method therefor
ActiveUS20110052034A1Easy to takeData processing applicationsImage analysisImaging processingSource imaging
A radiographic imaging apparatus performs imaging based on an examination order including a plurality of imaging protocols, executes image processing for the captured image based on the imaging protocol used at the time of the imaging, designates a change source imaging protocol and a change destination imaging protocol from the examination order based on an instruction of an operator, and changes the imaging protocol corresponding to the image captured based on the change source imaging protocol from the change source imaging protocol to the change destination imaging protocol. when the change of protocol is made, the apparatus executes image processing based on the change destination imaging protocol for the image before the image processing which is captured based on the change source imaging protocol.
Owner:CANON KK
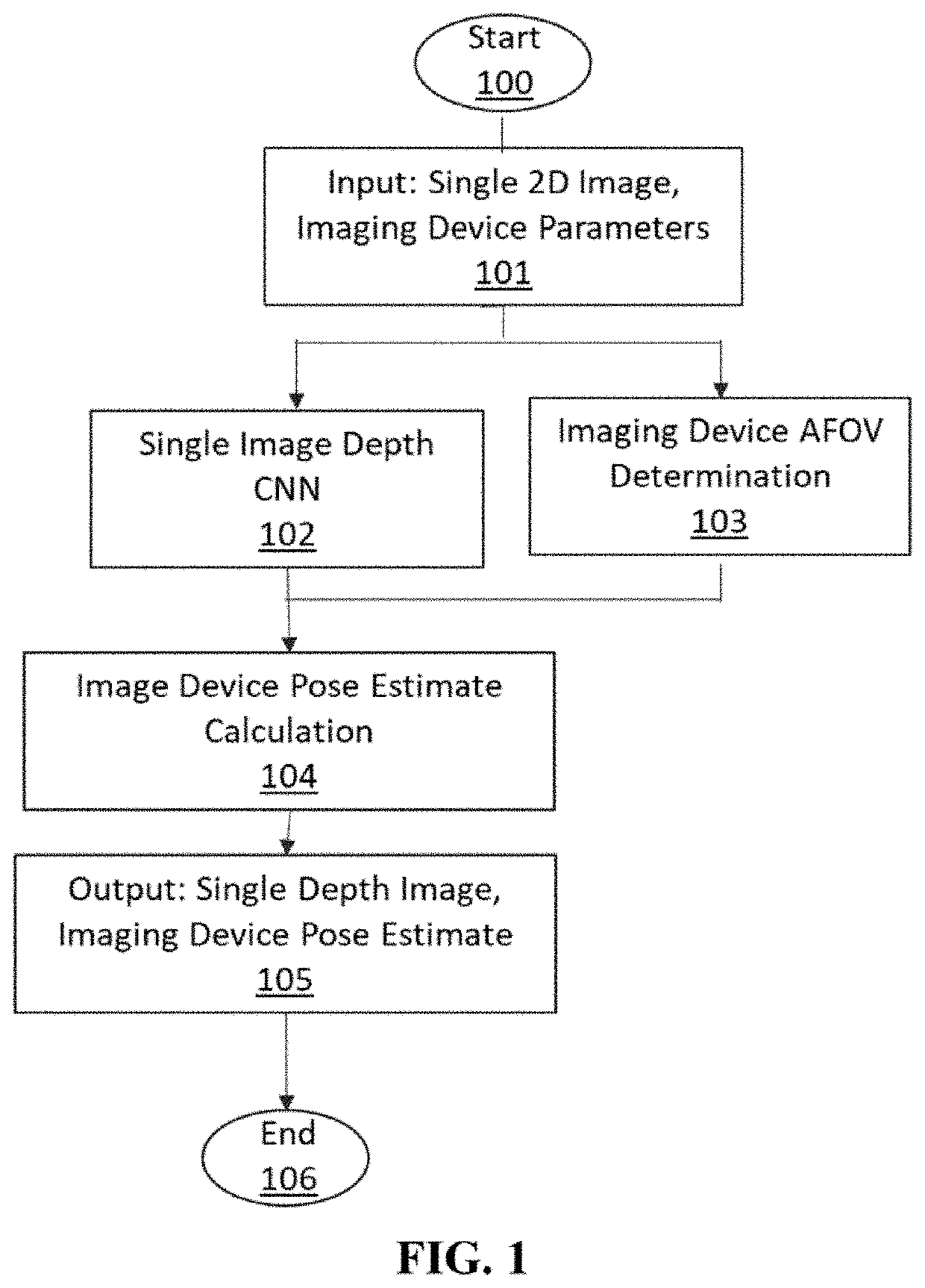
Machine learning based model localization system
ActiveUS10977818B2Qualitatively accurateExact matchImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionLocalization system
Owner:MANOR FINANCIAL INC
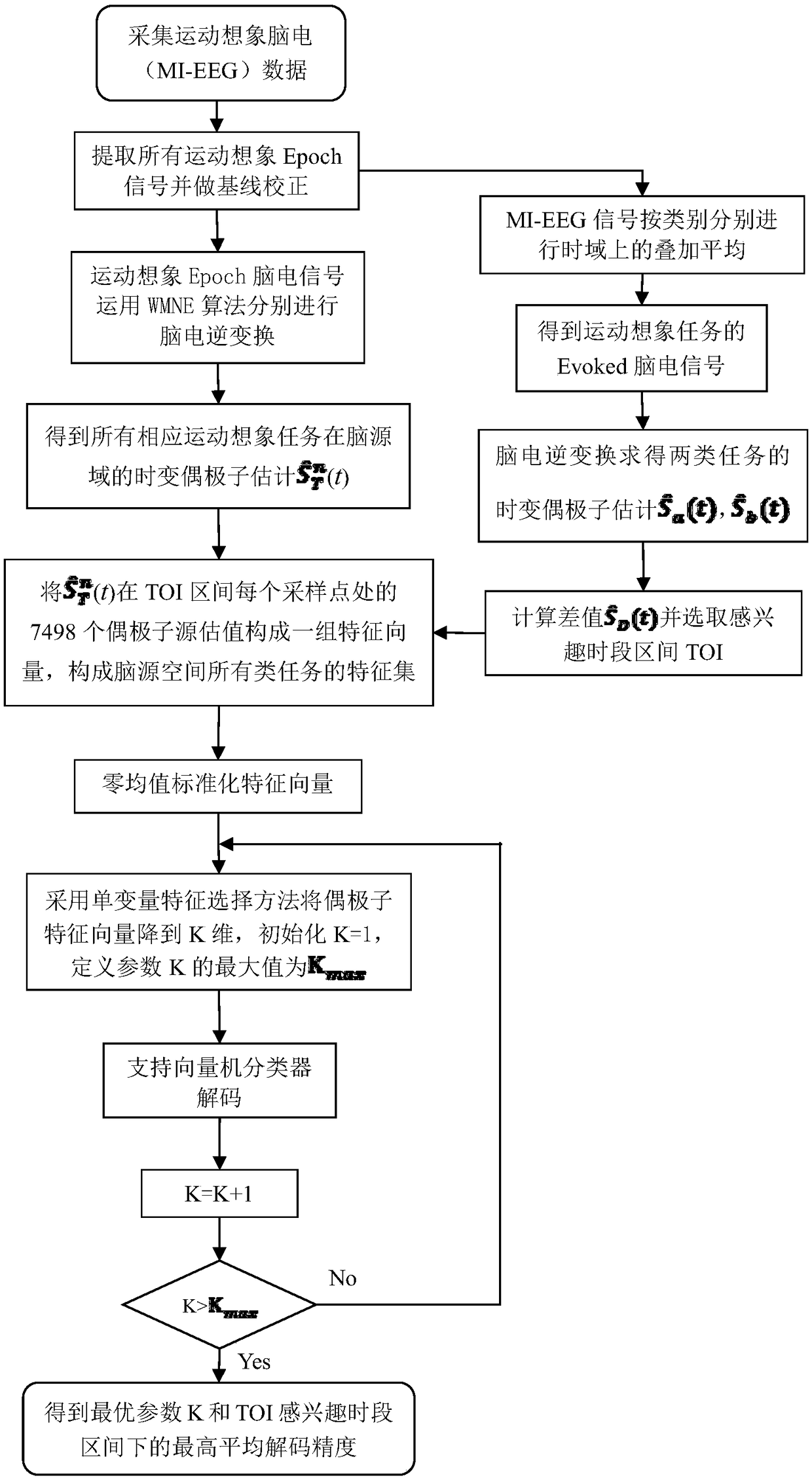
A decoding method of motor imaginary EEG signals based on OA-WMNE brain source imaging
ActiveCN109199376AExtended airspace feature informationReduce distractionsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTime domainFeature vector
A decoding method of motor imaginary EEG signals based on OA-WMNE brain source imaging is disclosed. The method includes firstly adopting baseline correction and superposition averaging in time domainto preprocess the EEG signals and then obtaining the superposition averaging signals of each motor imagery task; utilizing a WMNE algorithm to transform it into brain source space to obtain the dipole estimation; determining the time interval of interest (TOI) according to the difference of waveform between the two motion imagery dipoles; subjecting all single motion imaginary EEG signals to inverse transformation and forming all dipole amplitudes at each sampling point in TOI into eigenvectors to obtain a group of features at the sampling point; forming all the features on the sample pointsinto feature sample sets, which are normalized by zero-mean value, and reducing the feature dimension by using the univariate feature selection method; and finally, utilizing a support vector machineto classify the features so that the highest average decoding accuracy is obtained, the spatial resolution of EEG is improved, which is helpful to improve the decoding accuracy of motion imagination task.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Structured electron emitter for coded source imaging with an x-ray tube
InactiveCN102365703AHigh outputX-ray tube electrodesDischarge tube electron gunsImage resolutionX-ray
An electron emitter (1) and an X-ray tube (100) comprising such electron emitter (1) are presented. The electron emitter (1) comprises a cathode (3) and an anode (5) wherein the cathode (3) comprises an electron emission pattern (9) of a plurality of local areas (11) spaced apart from each other, each area being adapted for locally emitting electrons via field emission upon application of an electrical field between the cathode (3) and the anode (5). Electron beams (15) emitted from the local areas (11) may generate several X-ray source intensity maxima in a specific geometric pattern. An apparent loss in spatial resolution due to overlapping images on a detector can be corrected by using specific intensity patterns for the X-ray source (100) and by applying dedicated decoding algorithms on the acquired image such as coded source imaging (CSI).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
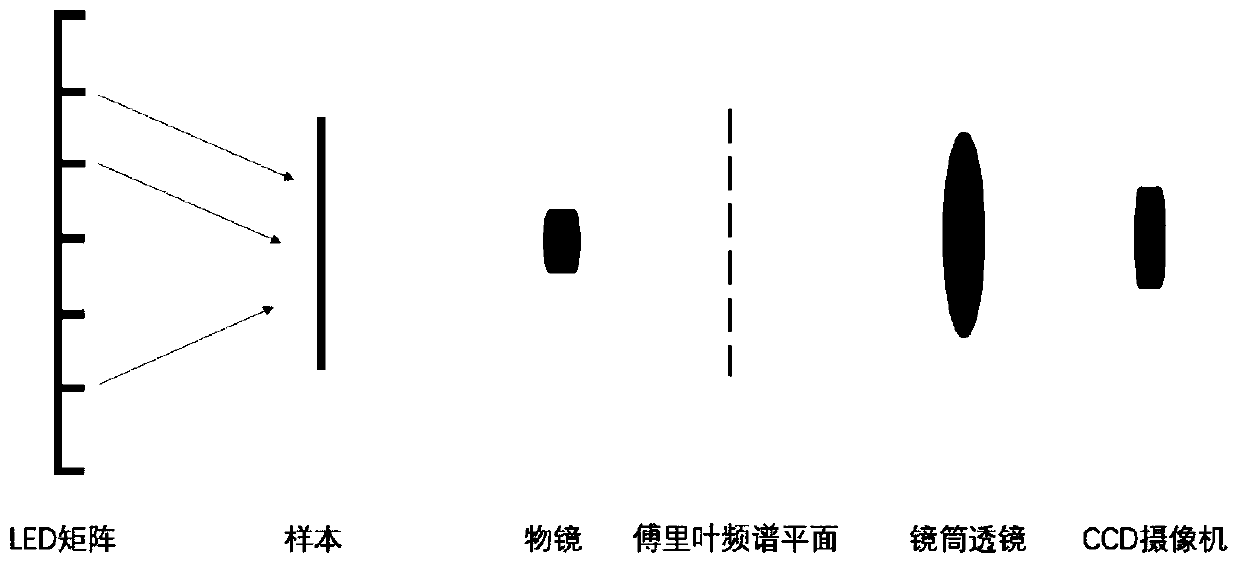
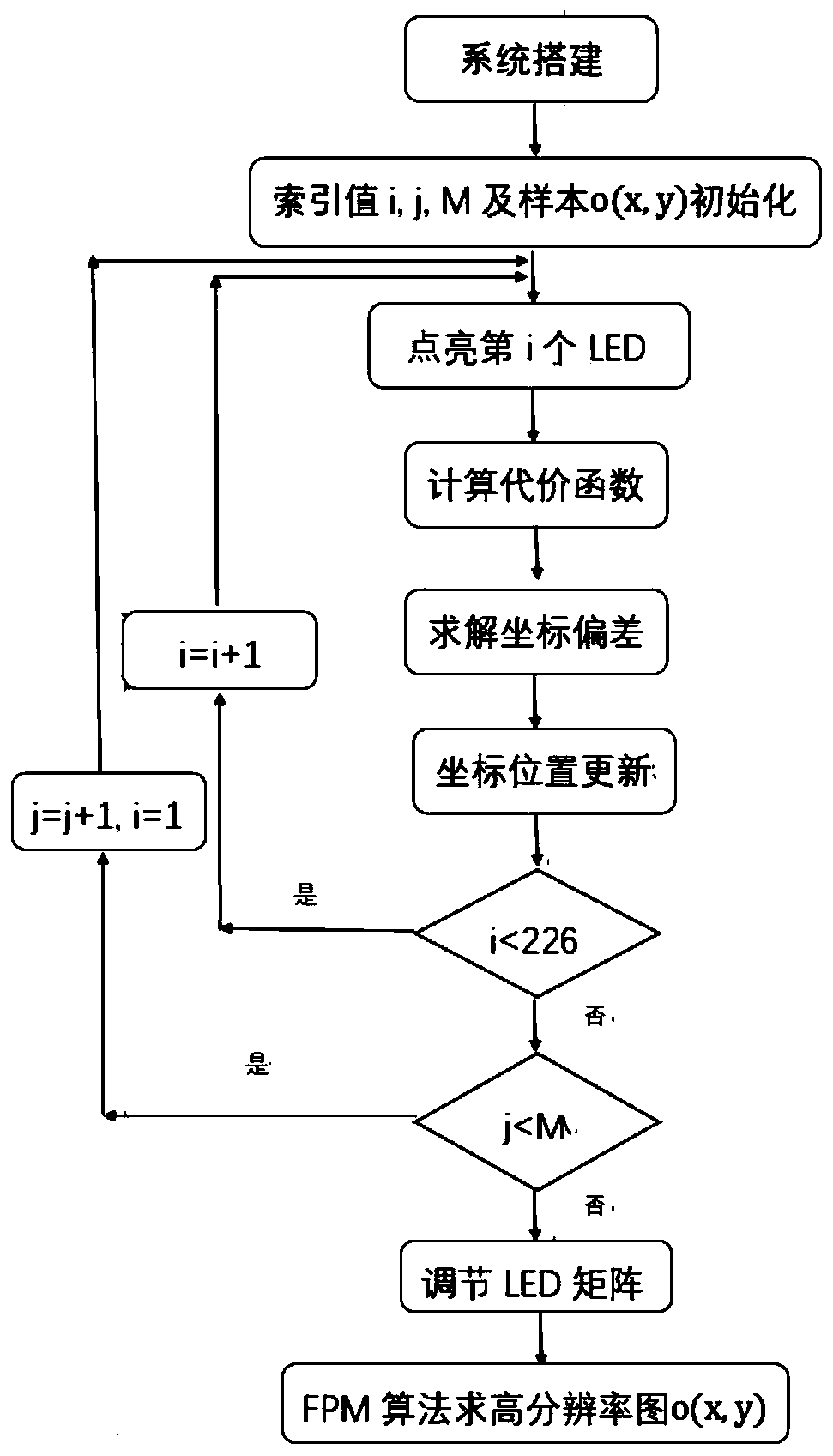
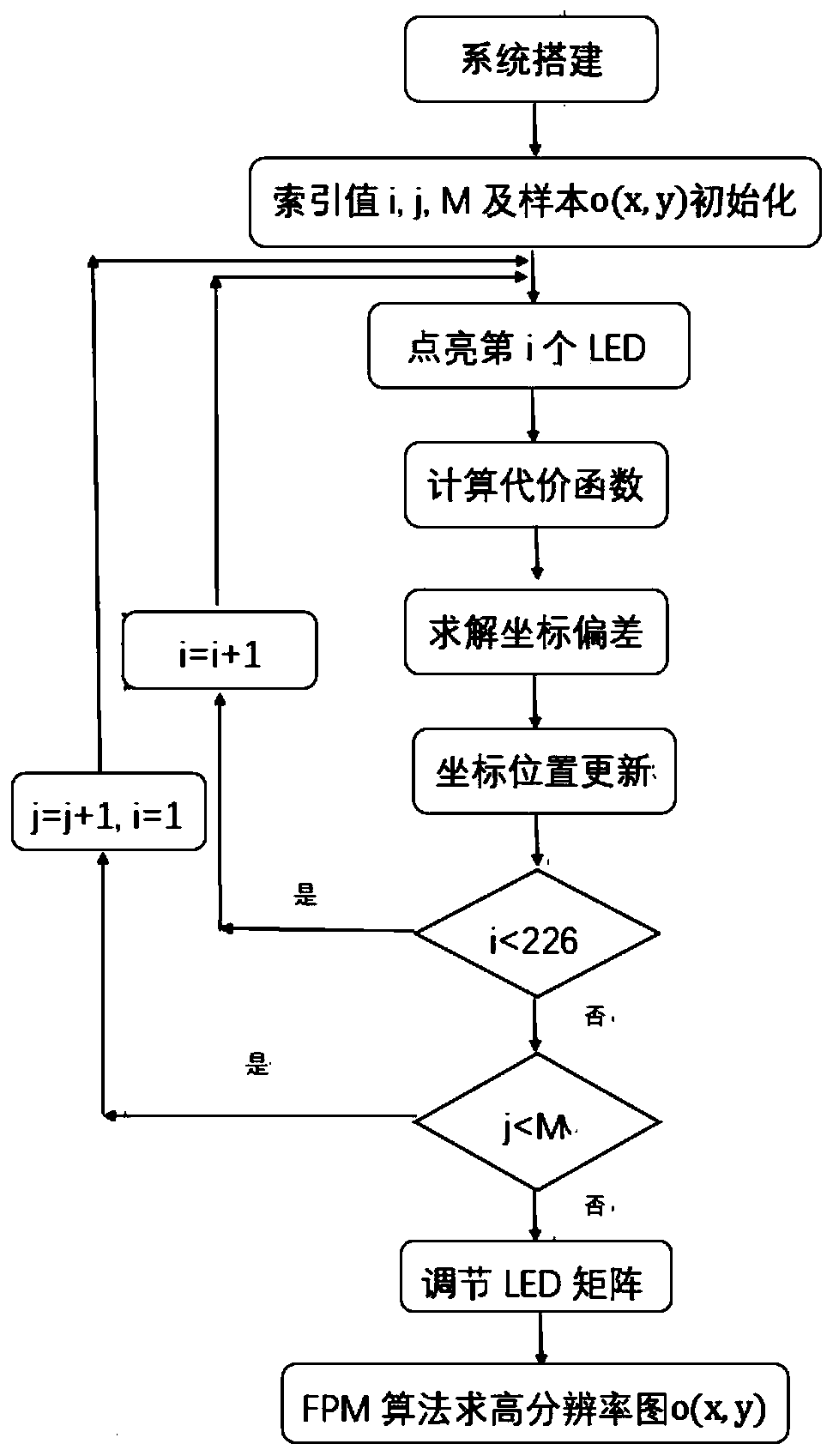
LED matrix correction method based on Fourier laminated imaging
The invention relates to an LED matrix correction method based on Fourier laminated imaging. The method comprises the following steps: modeling an imaging system and an LED matrix, and defining an initial position vector of each LED; calculating a cost function according to the captured low-resolution image; correcting the position deviation of each LED by taking solving the global optimal solution of the cost function as a target; and reconstructing a high-resolution image of the target sample after correcting the position deviation of the LED illumination matrix according to a Fourier laminated imaging method. According to the invention, position correction of the illumination light source is completed according to the optical calculation imaging theory and data collected by the opticalimaging system. For a multi-light-source imaging system, if the position arrangement of the lighting elements is not reasonable, many adverse effects such as imaging quality reduction can be caused tothe imaging system; by correcting the positions of the light sources using the method of the invention, the imaging definition of the system can be well improved, and artifacts generated by the lightsource arrangement structure on images can be weakened.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
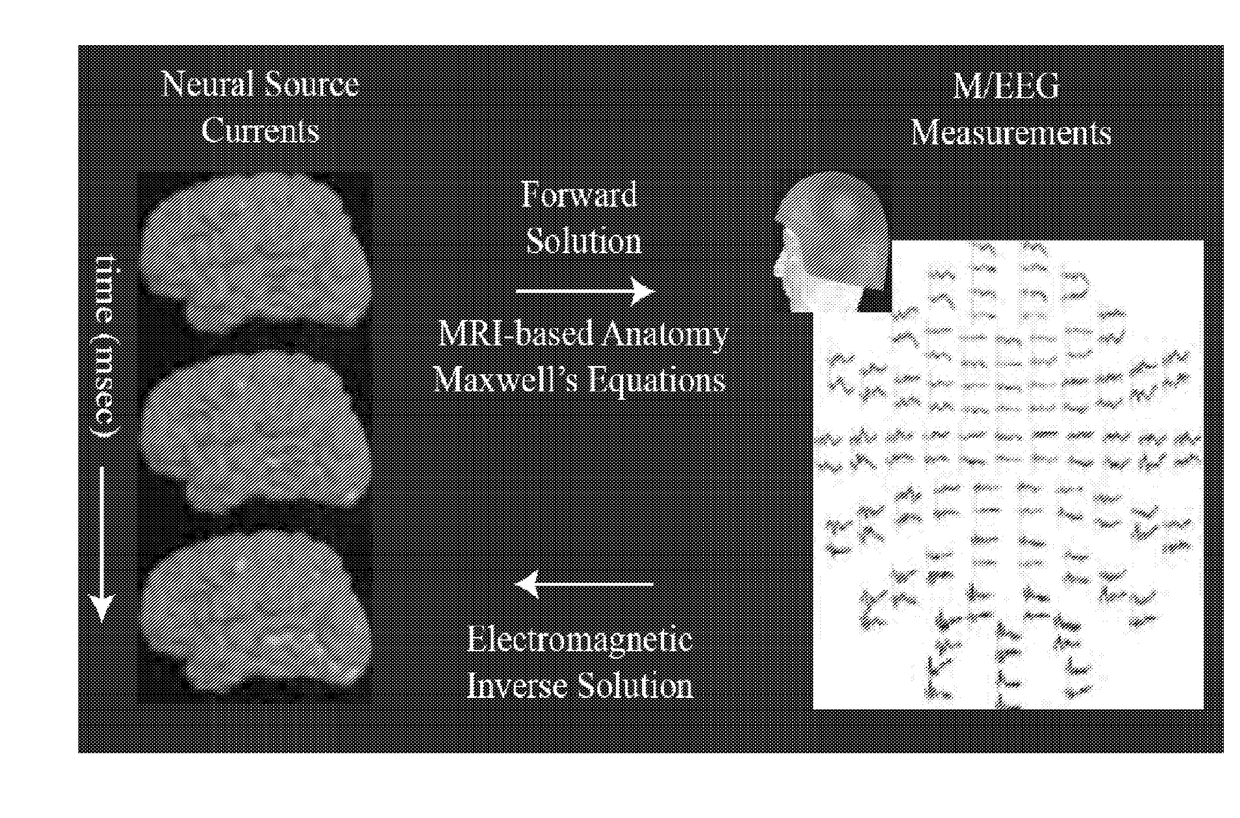
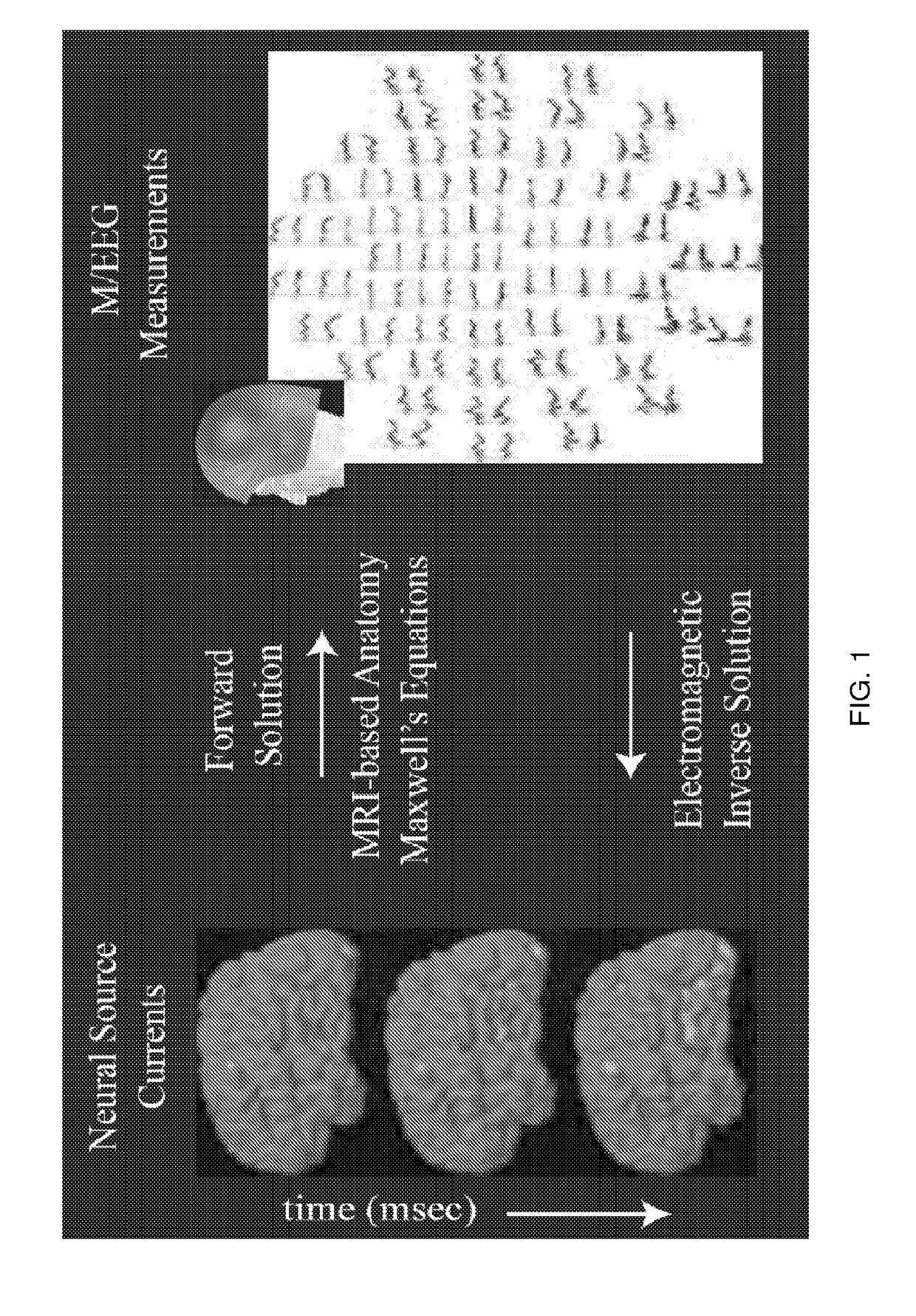
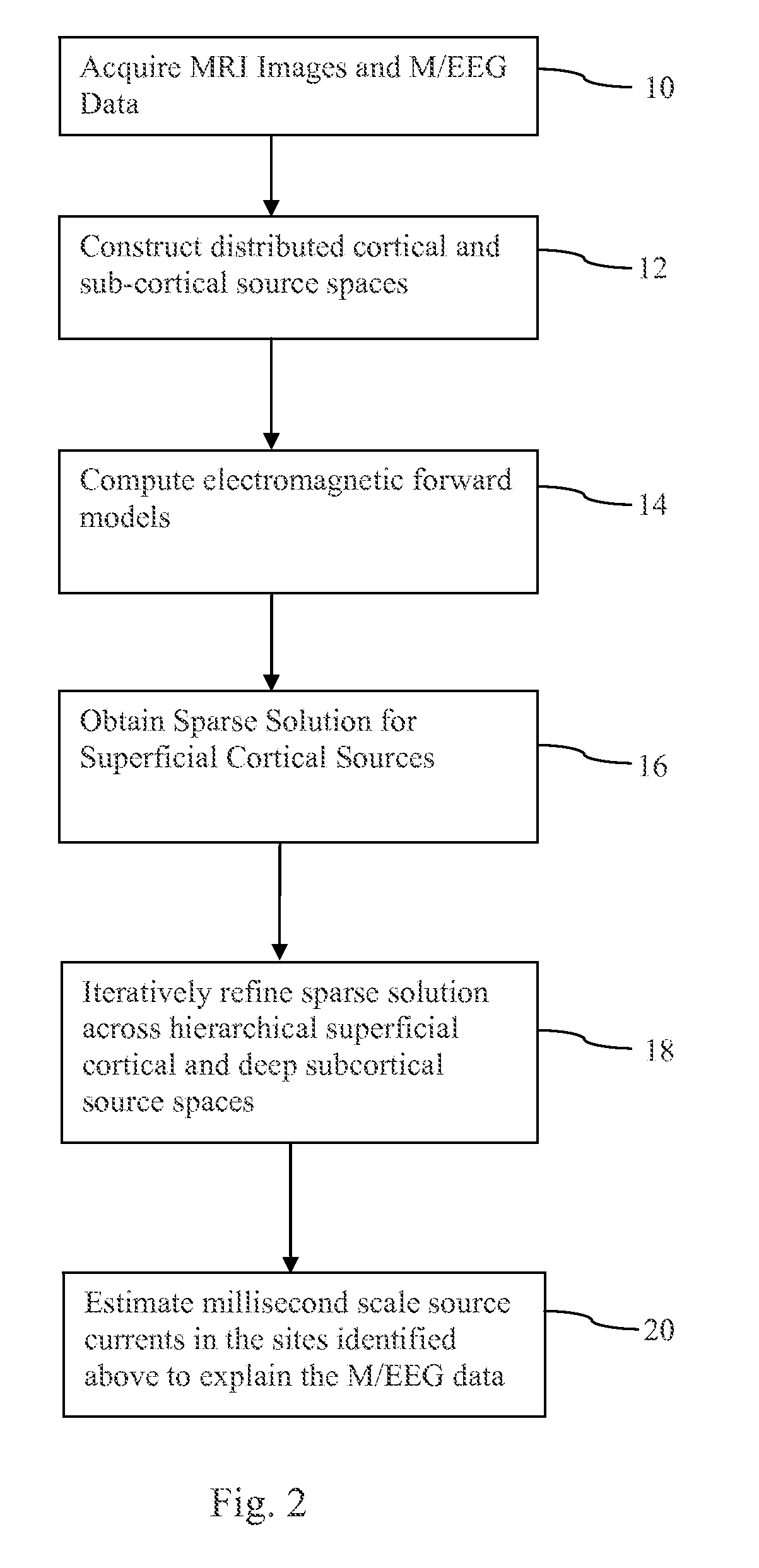
Deep brain source imaging with m/eeg and anatomical MRI
ActiveUS20170332933A1High resolutionReduce resolutionElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyEeg dataSource modeling
A method for non-invasively resolving electrophysiological activity in sub-cortical structures located deep in the brain by comparing amplitude-insensitive M / EEG field patterns arising from activity in subcortical and cortical sources under physiologically relevant sparse constraints is disclosed. The method includes a sparse inverse solution for M / EEG subcortical source modeling. Specifically, the method employs a subspace-pursuit algorithm rooted in compressive sampling theory, performs a hierarchical search for sparse subcortical and cortical sources underlying the measurement, and estimates millisecond-scale currents in these sources to explain the data. The method can be used to recover thalamic and brainstem contributions to non-invasive M / EEG data, and to enable non-invasive study of fast timescale dynamical and network phenomena involving widespread regions across the human brain.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Radiographic imaging apparatus and processing method therefor
ActiveUS8494247B2Easy to takeImage analysisData processing applicationsImaging processingSource imaging
Owner:CANON KK
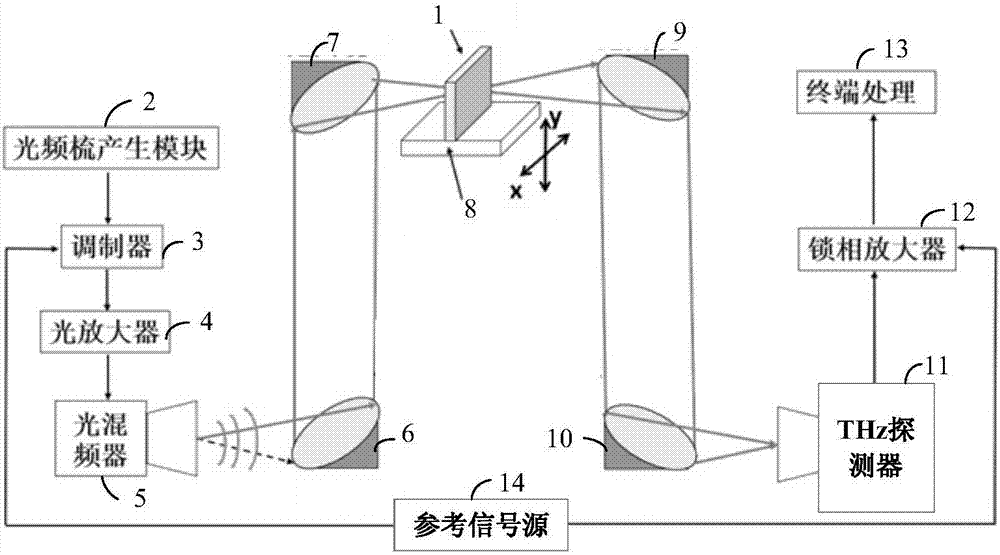
Terahertz imaging system based on photonics technology
ActiveCN106996918AEliminate interferenceNot easy to damageMaterial analysis by optical meansImaging qualitySignal on
The invention provides a terahertz imaging system based on a photonics technology. The terahertz imaging system comprises an optical frequency comb generation module, an optical mixer module, a scanning module, a mobile platform, a focusing module, a terahertz detector module and a terminal processing module, wherein the optical frequency comb generation module can generate optical beat frequency signals, the optical mixer module can convert the optical beat frequency signals into terahertz signals, the scanning module can collimate the terahertz signals and gather the terahertz signals on an article to be measured, the mobile platform can drive the article to be measured to move, the focusing module can gather terahertz signals scattered from the article to be measured, the terahertz detector module can convert the terahertz signals into electrical signals, and the terminal processing module can obtain a two-dimensional image of the article to be measured according to the electric signals. As the terahertz imaging system disclosed by the invention utilizes the optical frequency comb generation module as a light source, and the interference phenomenon in the image is eliminated, imaging quality is obviously improved; meanwhile, required luminous power is smaller than 30 percent of an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier source imaging system, so that cost of the system is greatly reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Defect detection device and method
ActiveCN112697800AEasy and fast customizationImprove detection accuracyOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPhotovoltaic energy generationMirror reflectionControl cell
The invention provides a defect detection device and method, the defect detection device comprises a dark field illumination light source, an imaging lens, a full Stokes polarization integral camera, a motion table and a control unit, the dark field illumination light source is used for providing a linearly polarized light beam, and the motion table is used for bearing a to-be-detected sample; the linearly polarized light beam is obliquely projected to a to-be-detected sample and forms a signal light beam after being reflected and scattered by the to-be-detected sample, and the signal light beam is projected to the full Stokes polarization integral camera after passing through the imaging lens; the control unit drives the motion platform to move, so that the full-Stokes polarization integral camera completes scanning and shooting of the to-be-detected sample to form a full-Stokes polarization picture at the same time, defect detection is carried out after mirror reflection signals in the data are filtered out through data processing of the full-Stokes polarization picture, and the defect information of the to-be-detected sample is obtained. According to the invention, the defect detection and identification speed and accuracy are improved.
Owner:上海御微半导体技术有限公司
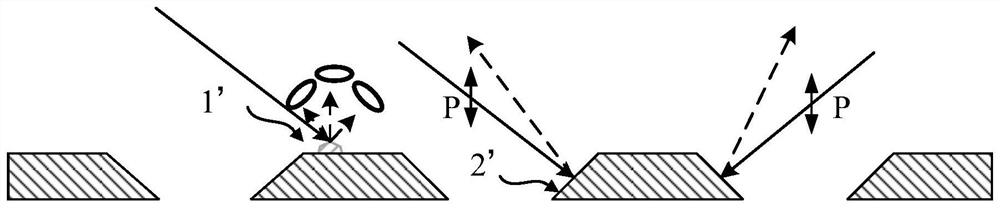
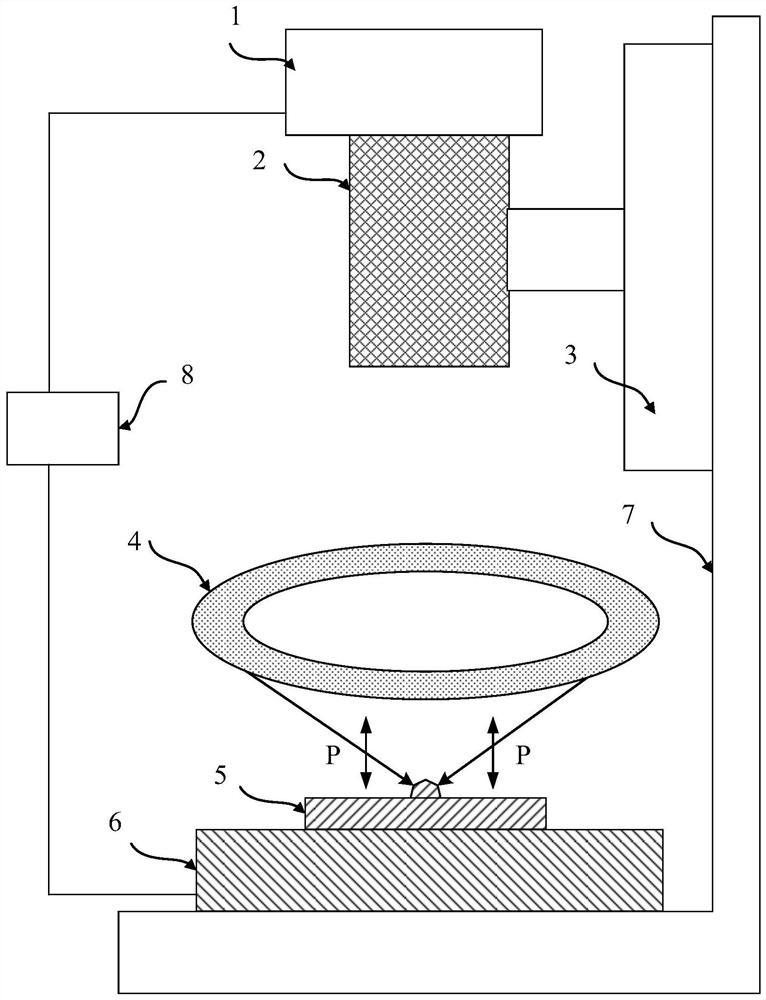
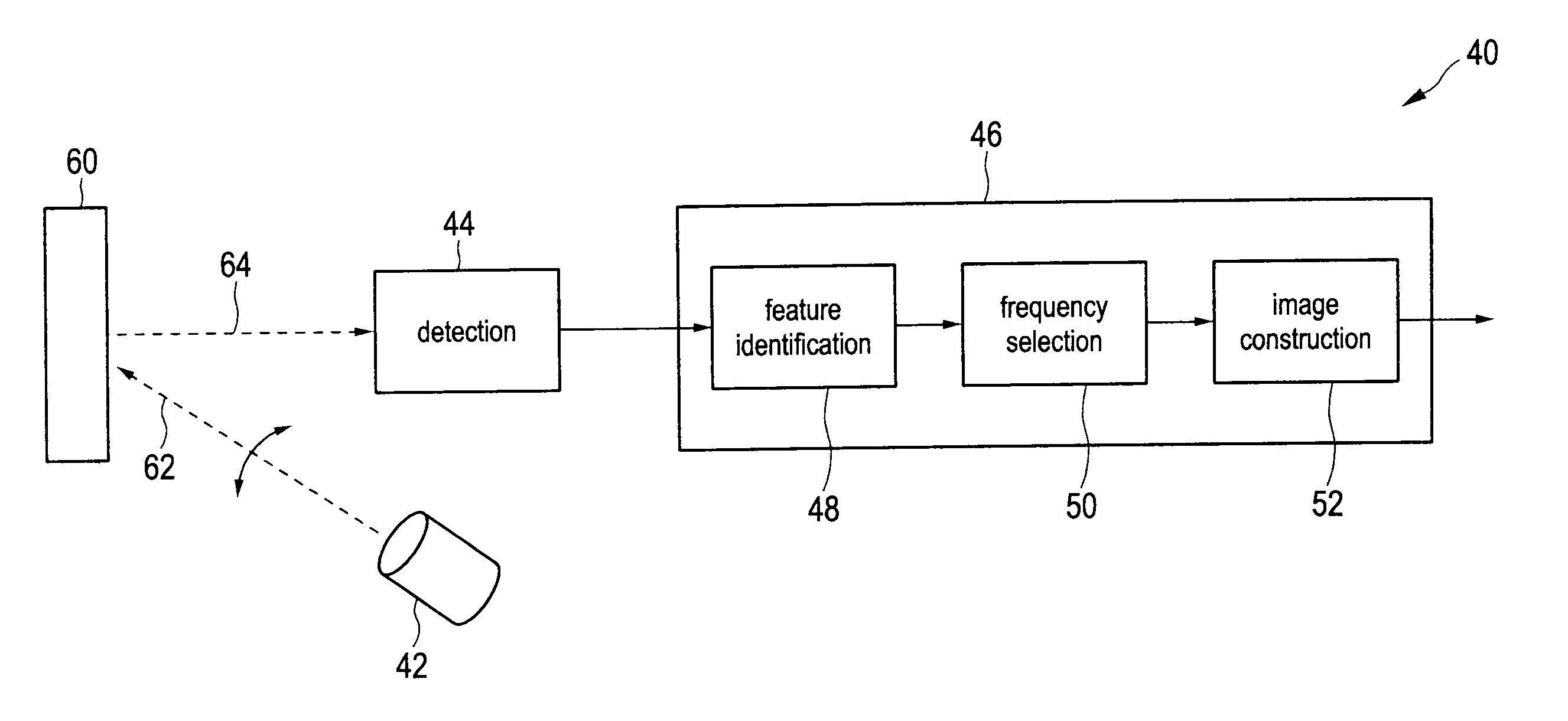
Active imaging device and method for speckle noise reduction
ActiveUS20110273585A1Reduce speckle noiseLittle effortImage enhancementImage analysisFluenceFeature selection
The present invention relates to an active imaging device for imaging a scene, comprising a scene illuminator that illuminates said scene with radiation at multiple illumination frequencies or an illumination frequency range covering multiple illumination frequencies, a radiation detector that detects radiation received from said scene in response to said illumination and that generates detection data from said detected radiation, a feature identifier that analyses said detection data and identifies different features in said scene, a frequency selector that separately selects for the identified features one or more selected illumination frequencies resulting in the minimum speckle noise in an image of the respective feature constructed from the detection data, which have been generated from radiation received in response to the illumination of the scene with radiation at said one or more selected illumination frequencies, and an image constructor that constructs a final image from the detection data, wherein the image portions of the identified features are constructed from the detection data, which have been generated from radiation received in response to the illumination of the scene with radiation at said one or more selected illumination frequencies, and wherein said image portions are combined into the final image.
Owner:SONY CORP
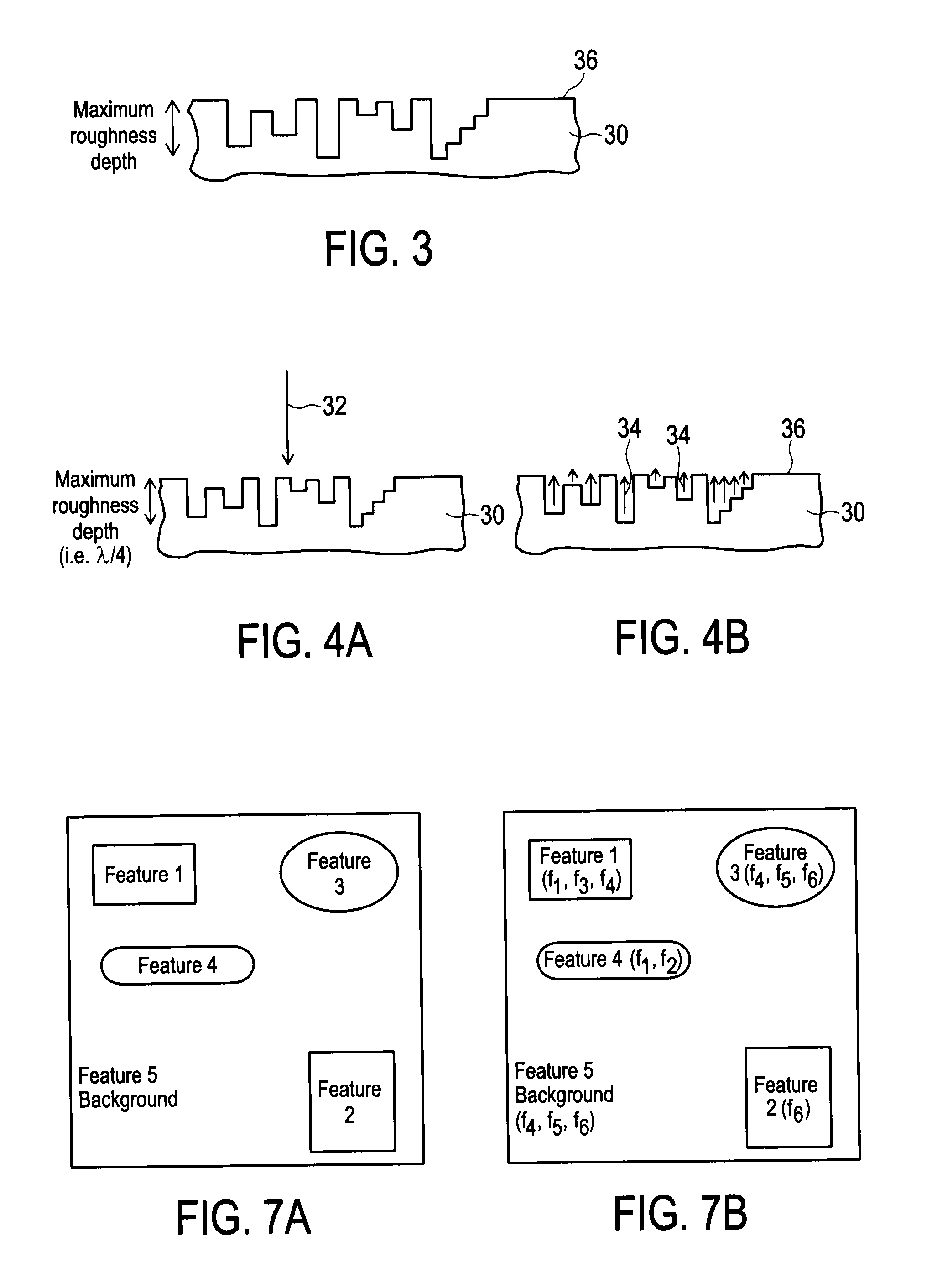
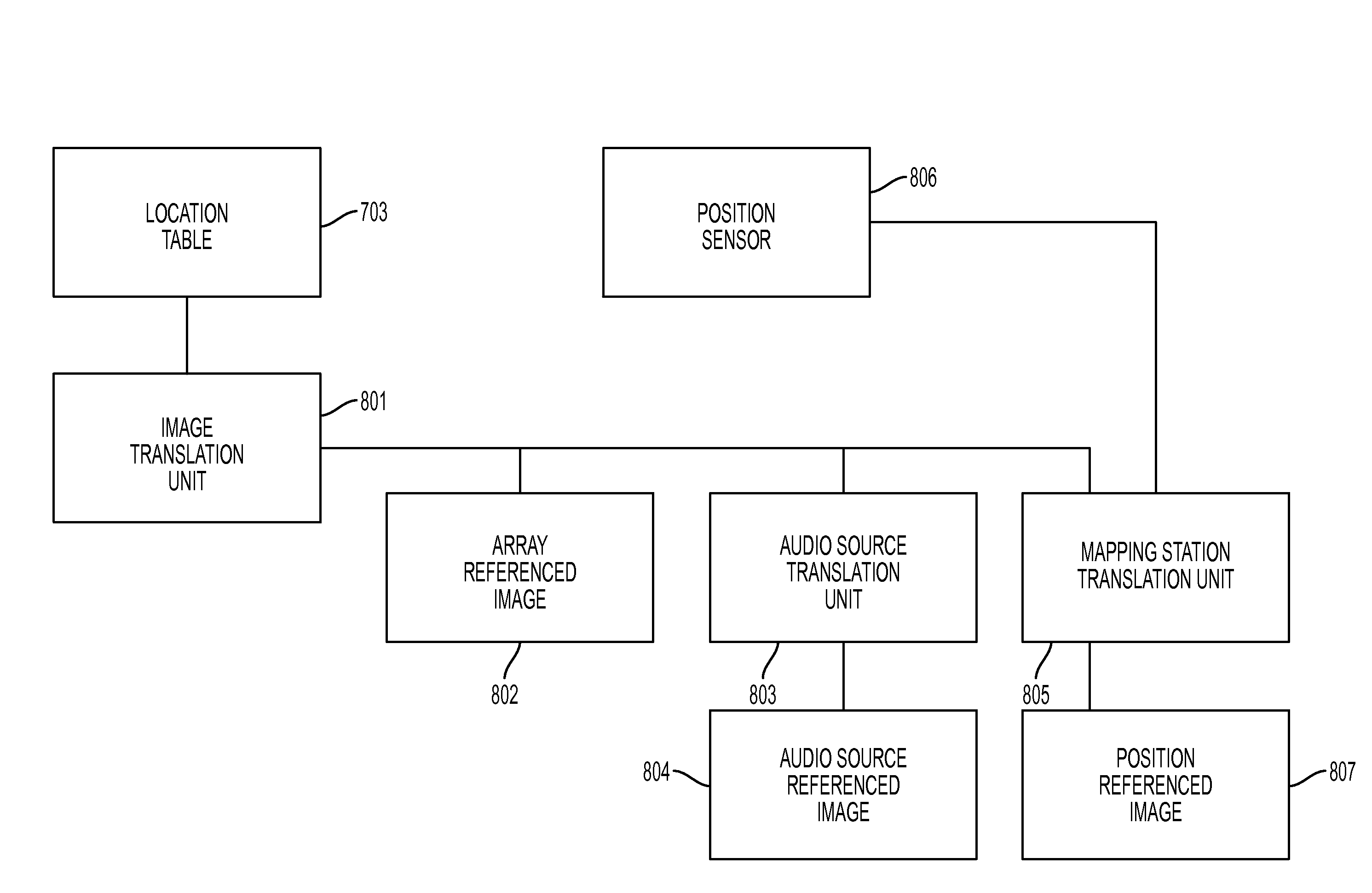
Audio source imaging system
InactiveUS20160161589A1Enhance audio environmentImprove the environmentDirection/deviation determination systemsSensor arraySource imaging
An audio source imaging system translates audio source location information from a format suitable for an audio source location and isolation system to a format suitable for a user display. The transformation may be to an image referenced to the position of a sensor array, the position of one of the tracked audio sources, or a position with a known displacement from the sensor array.
Owner:STAGES LLC
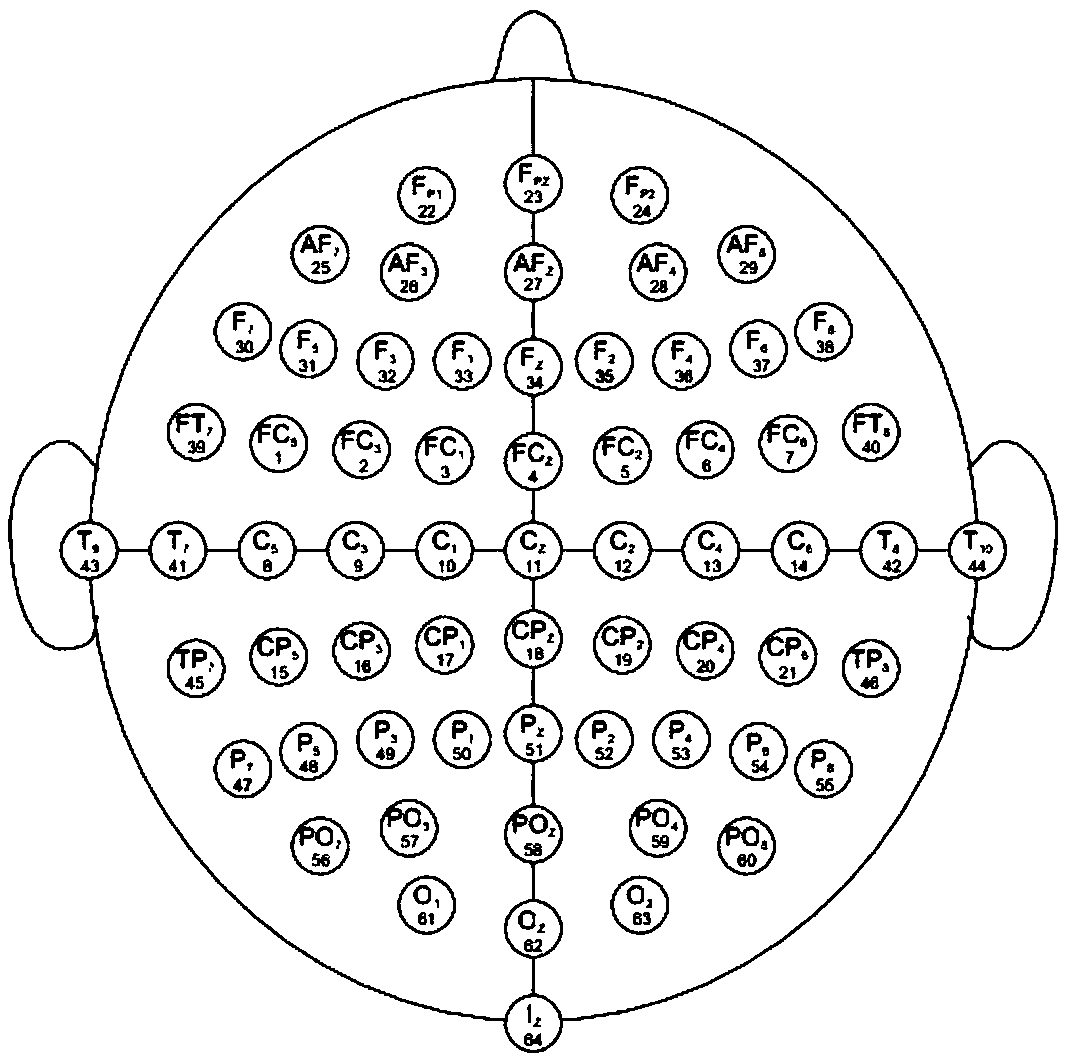
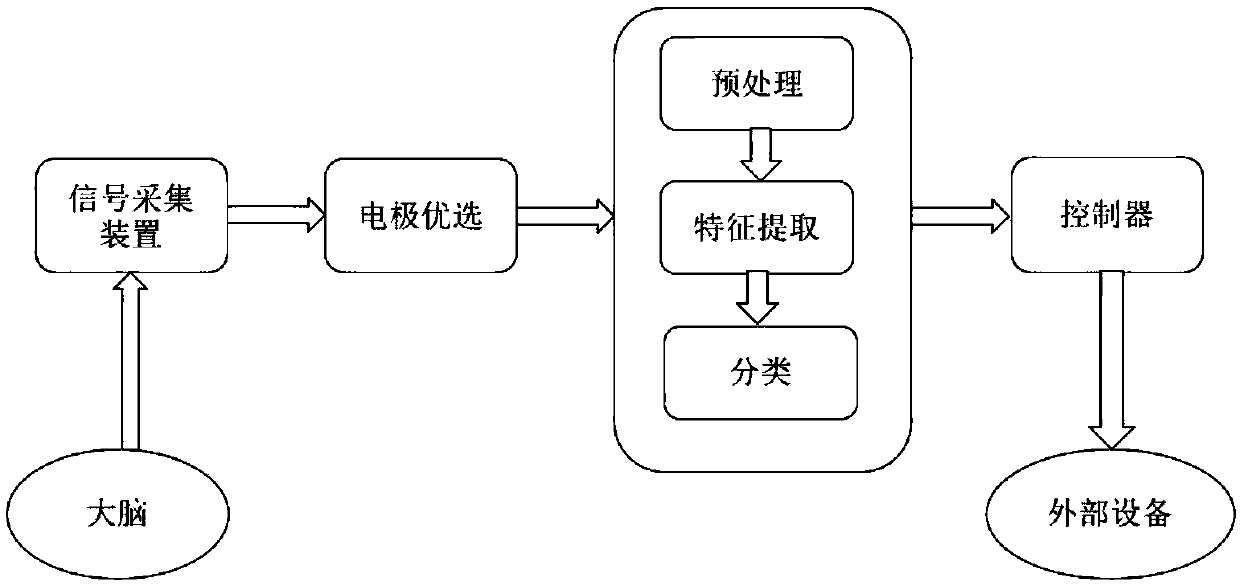
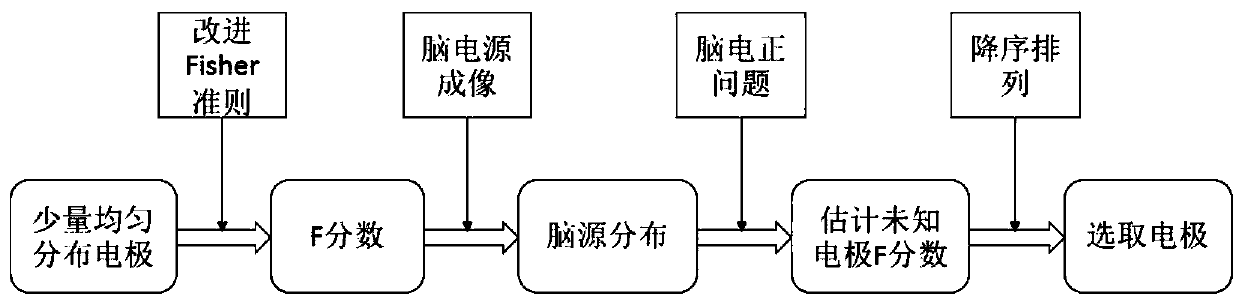
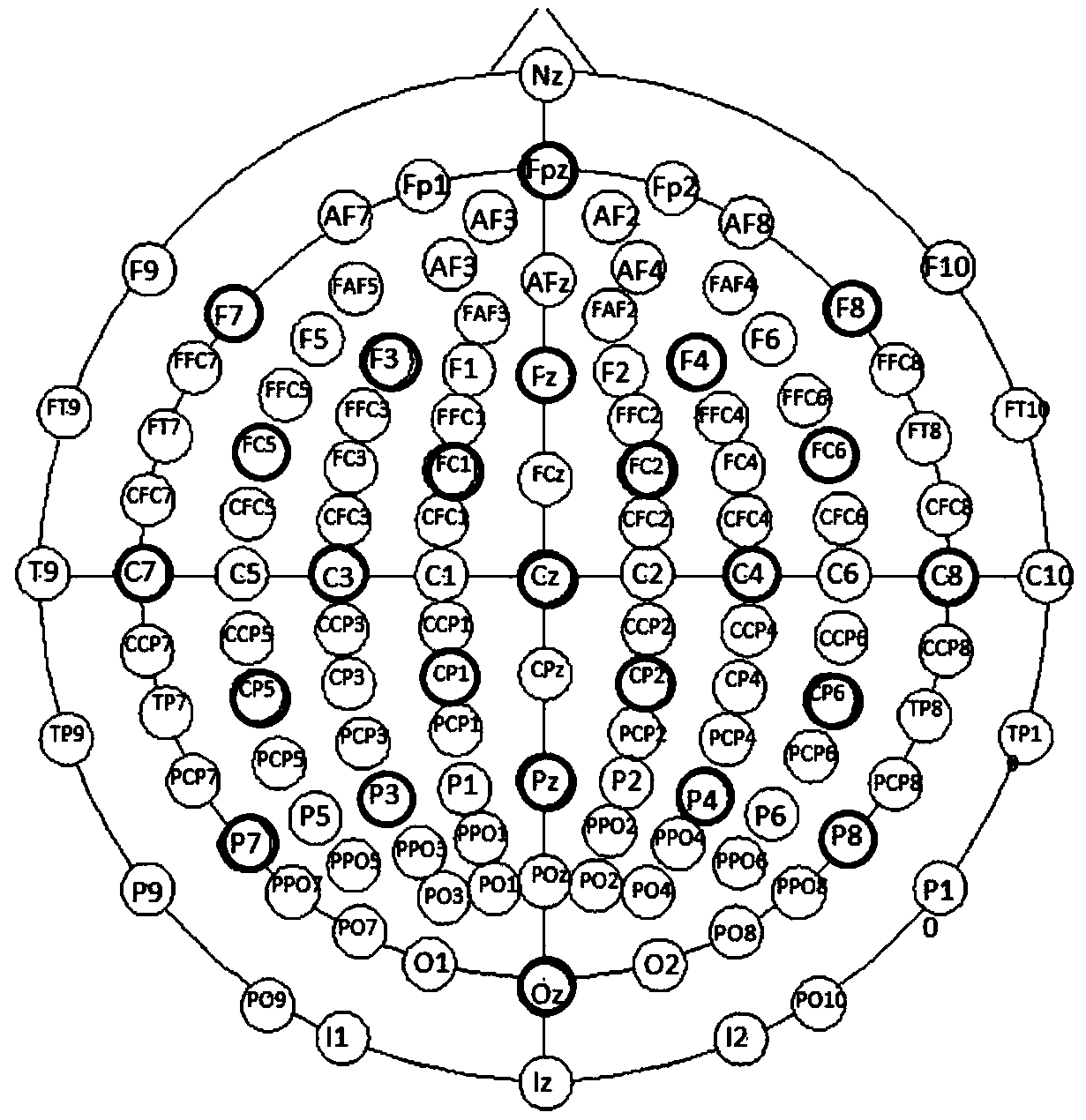
Electrode optimization method based on brain source imaging technology
ActiveCN108681394AReflect the differenceF score achievedInput/output for user-computer interactionCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmTransfer matrix
The invention discloses an electrode optimization method based on a brain source imaging technology. An improved Fisher criterion is used for solving the F score of each collected electrode which is evenly distributed; a brain source imaging technology is used for carrying out inverse transformation on the obtained F score to the cortex to obtain corresponding brain source distribution; an electroencephalogram forward problem is solved, i.e., on a premise that a transfer matrix between the cortex and dandruff is known, and the estimation value of the F score of an unknown electrode is solved;and finally, the estimation value of the F score is subjected to descending sorting, and parts of electrodes with a highest score value are selected as an optimal electrode. By use of the method, theproblems that electrode optimization depends on experiences or an amount of experiment collection electrodes in a motor imagery task is large can be solved, and the functions that a small quantity ofelectrodes is used for pre-estimating the contribution degree of the unknown electrode and the electrode optimization is carried out can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
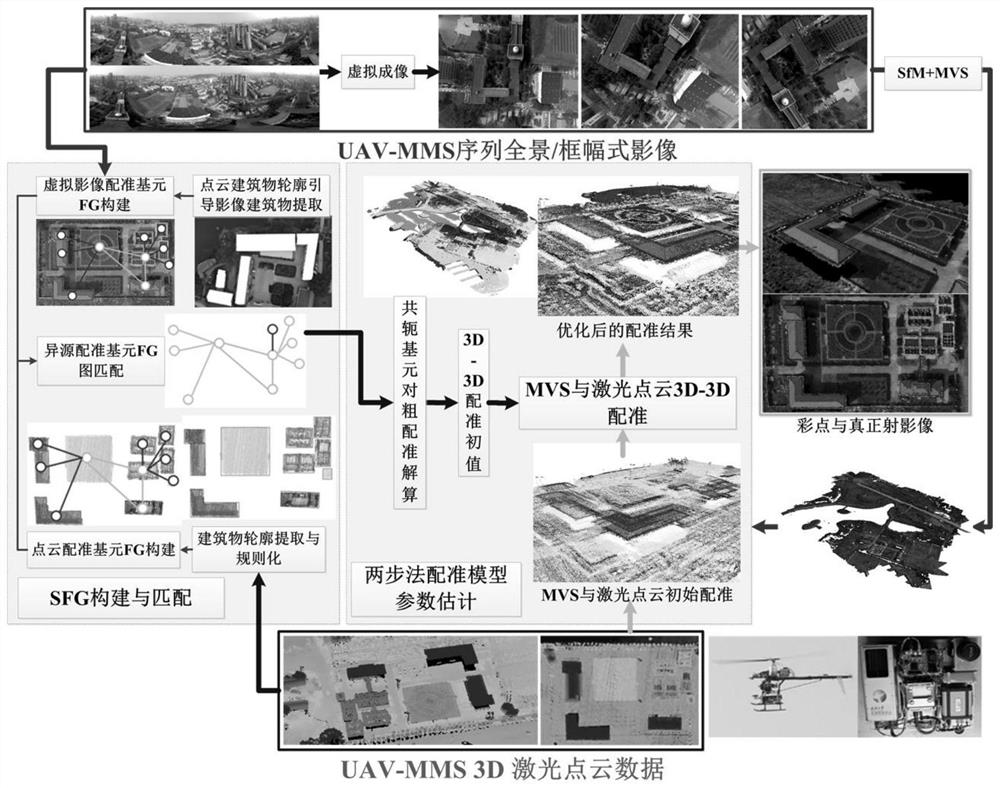
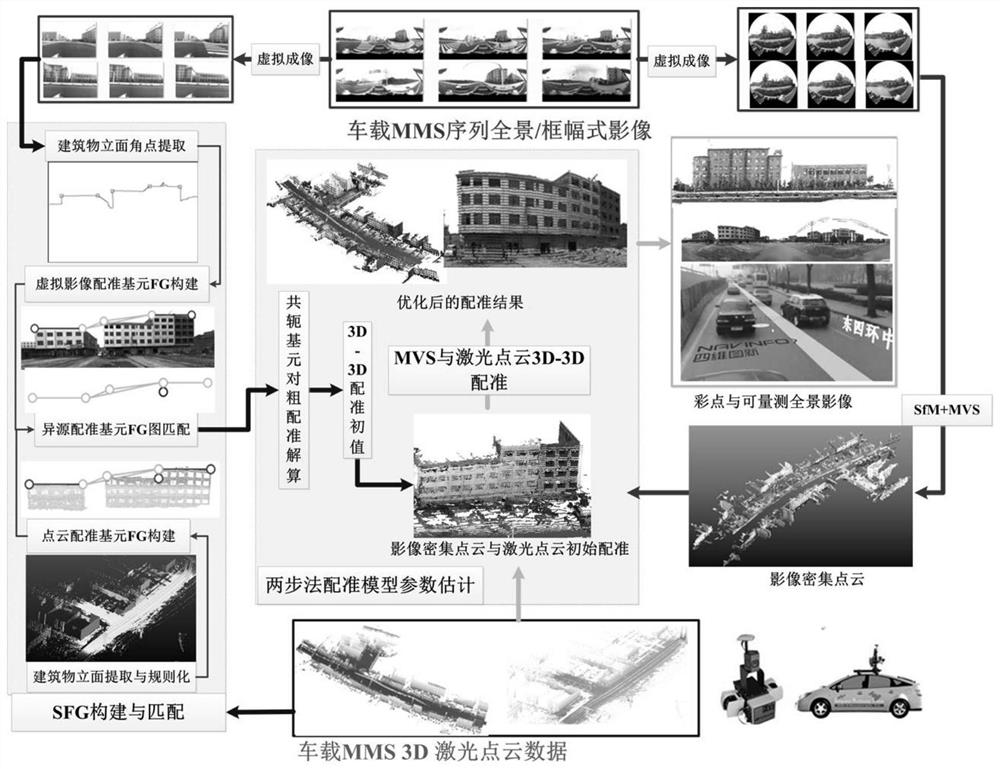
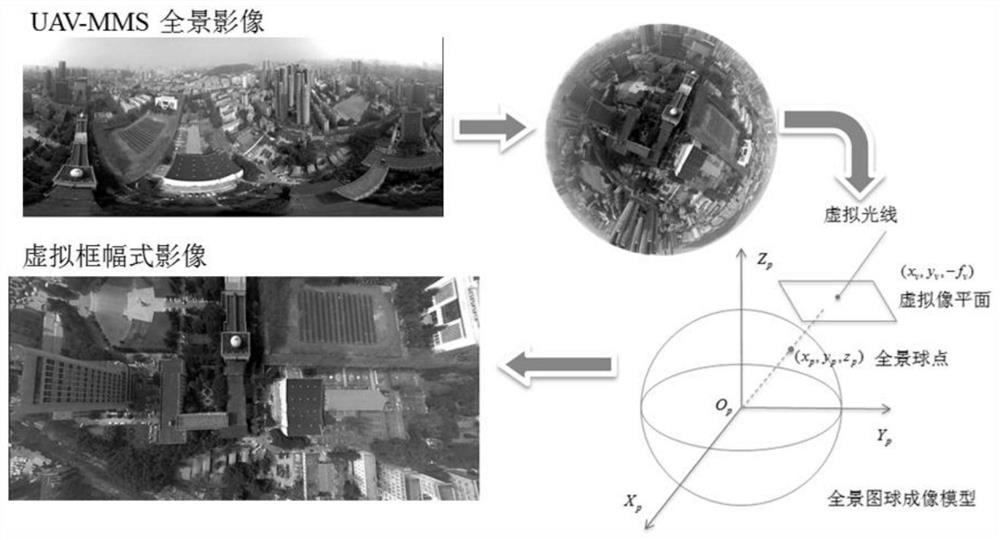
Automatic registration method for laser point cloud and sequence panoramic image
Aiming at the problems that the quality, the precision and the spatial data reference of unmanned aerial vehicle / vehicle-mounted mobile measurement laser point cloud and the sequence panoramic image data are not uniform, and registration errors exist among multi-source imaging data, the invention provides an automatic registration method for realizing the automatic registration of the laser point cloud and the sequence panoramic image based on the SFGM (Space Fingerprint Graph Matching). On the basis of registration primitive extraction, homonymy matching is achieved through a space fingerprint map method, then robust registration is achieved from coarse to fine, and the technical bottleneck of point cloud and image automatic data registration is broken through. The result of the invention lays a solid data foundation for the joint analysis and processing of multi-source spatial data, and serves the fields of basic surveying and mapping, smart cities, navigation, location services and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
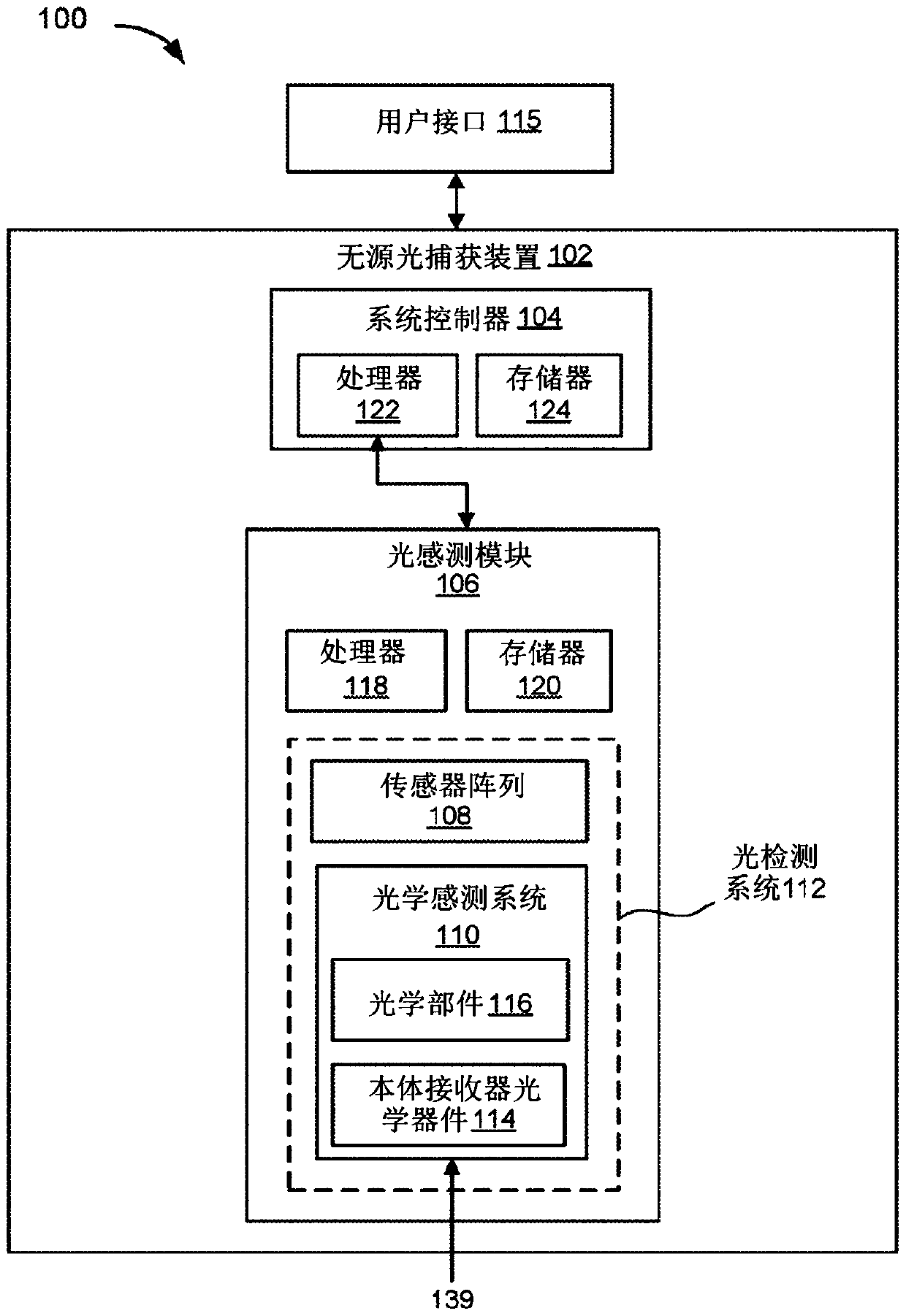
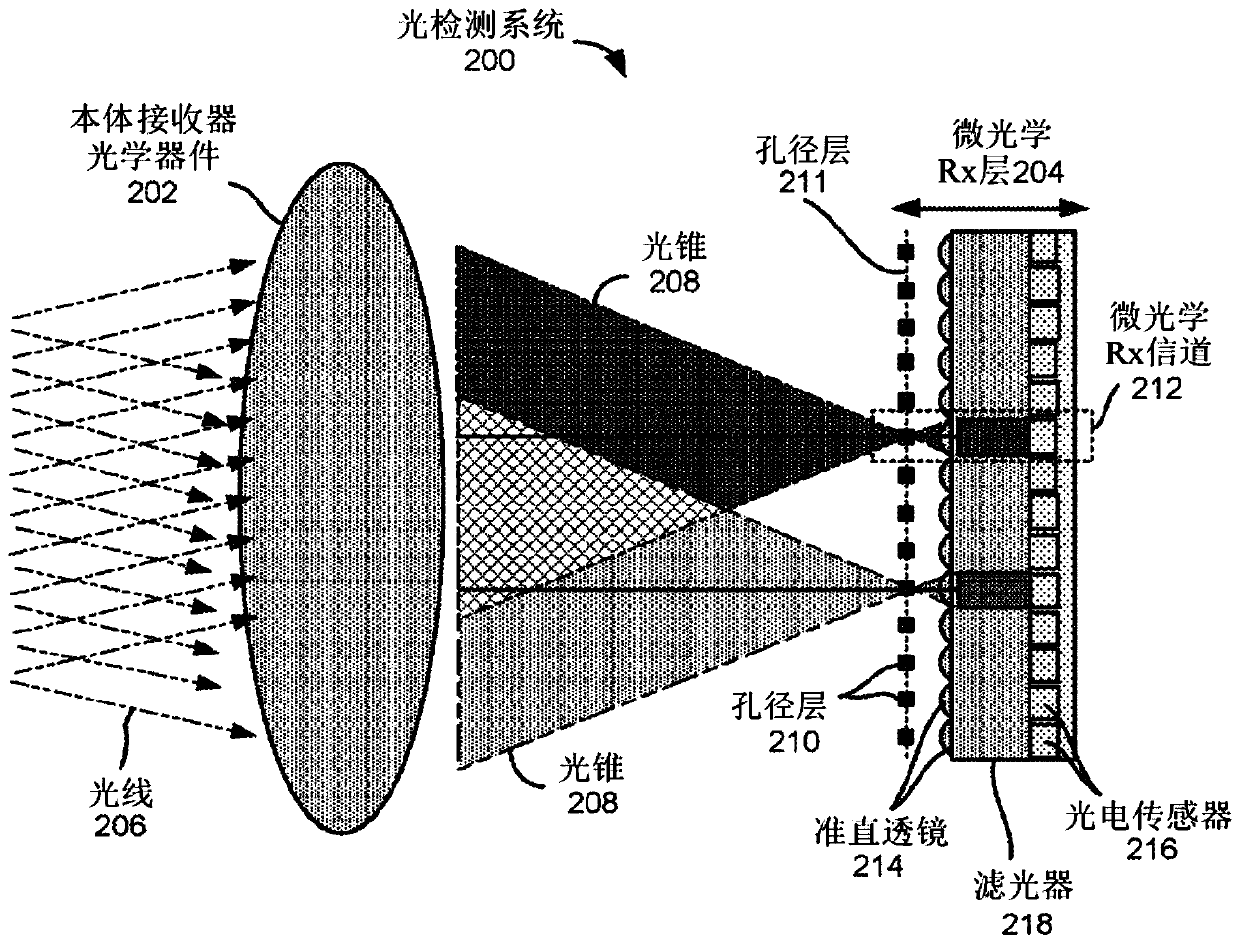
Optical imaging transmitter with brightness enhancement
Embodiments describe optical imagers that include one or more micro-optic components. Some imagers can be passive imagers that include a light detection system for receiving ambient light from a field. Some imagers can be active imagers that include a light emission system in addition to the light detection system. The light emission system can be configured to emit light into the field such thatemitted light is reflected off surfaces of an object in the field and received by the light detection system. In some embodiments, the light detection system and / or the light emission system includesmicro-optic components for improving operational performance.
Owner:OUSTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com