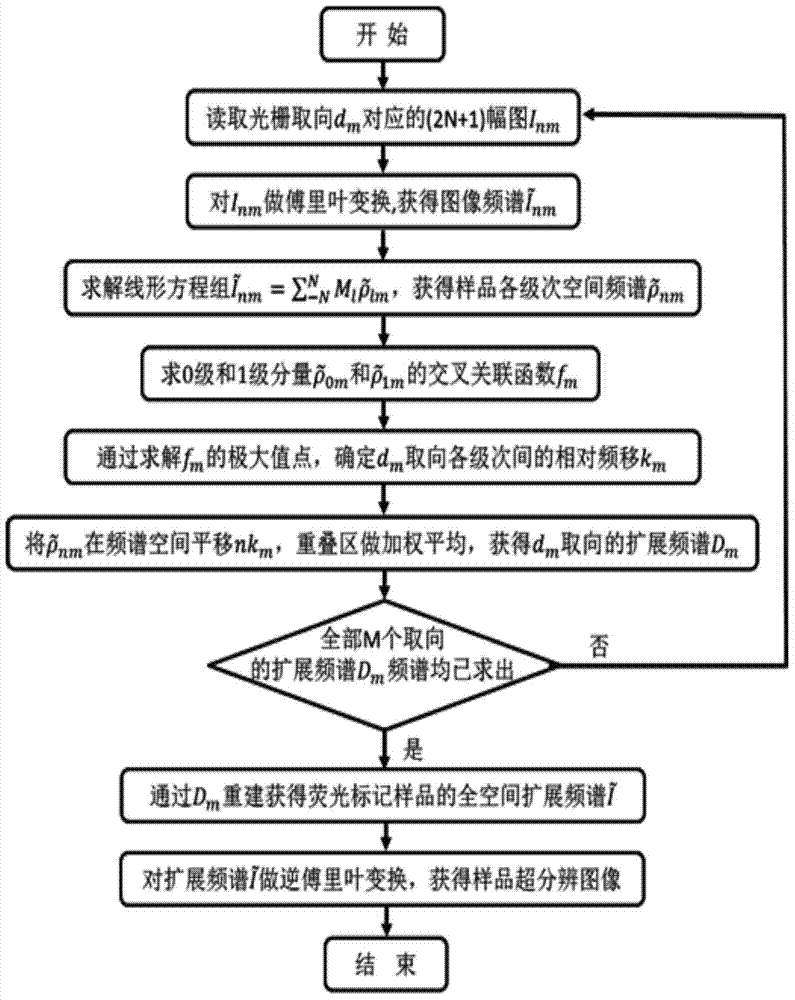
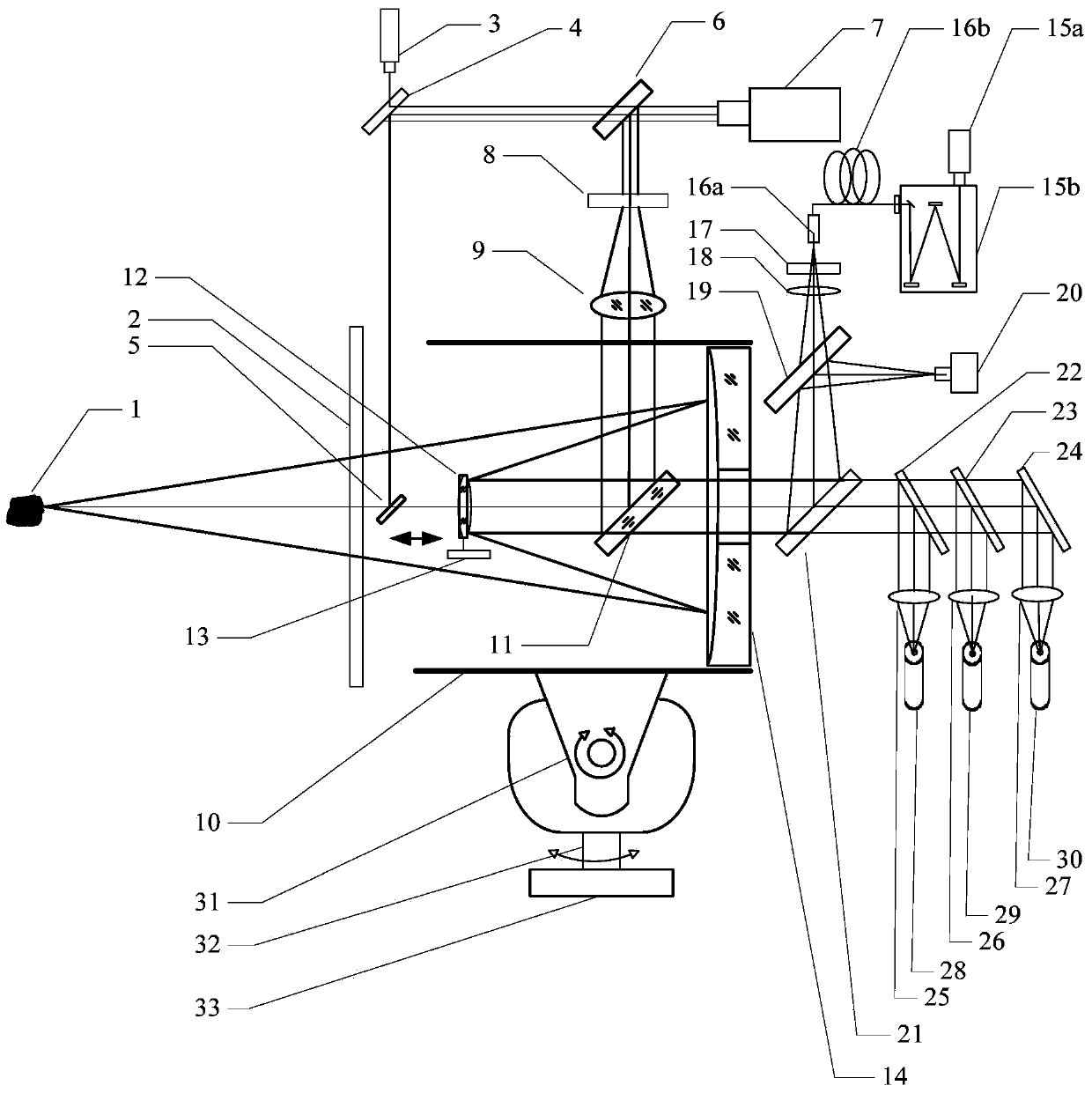
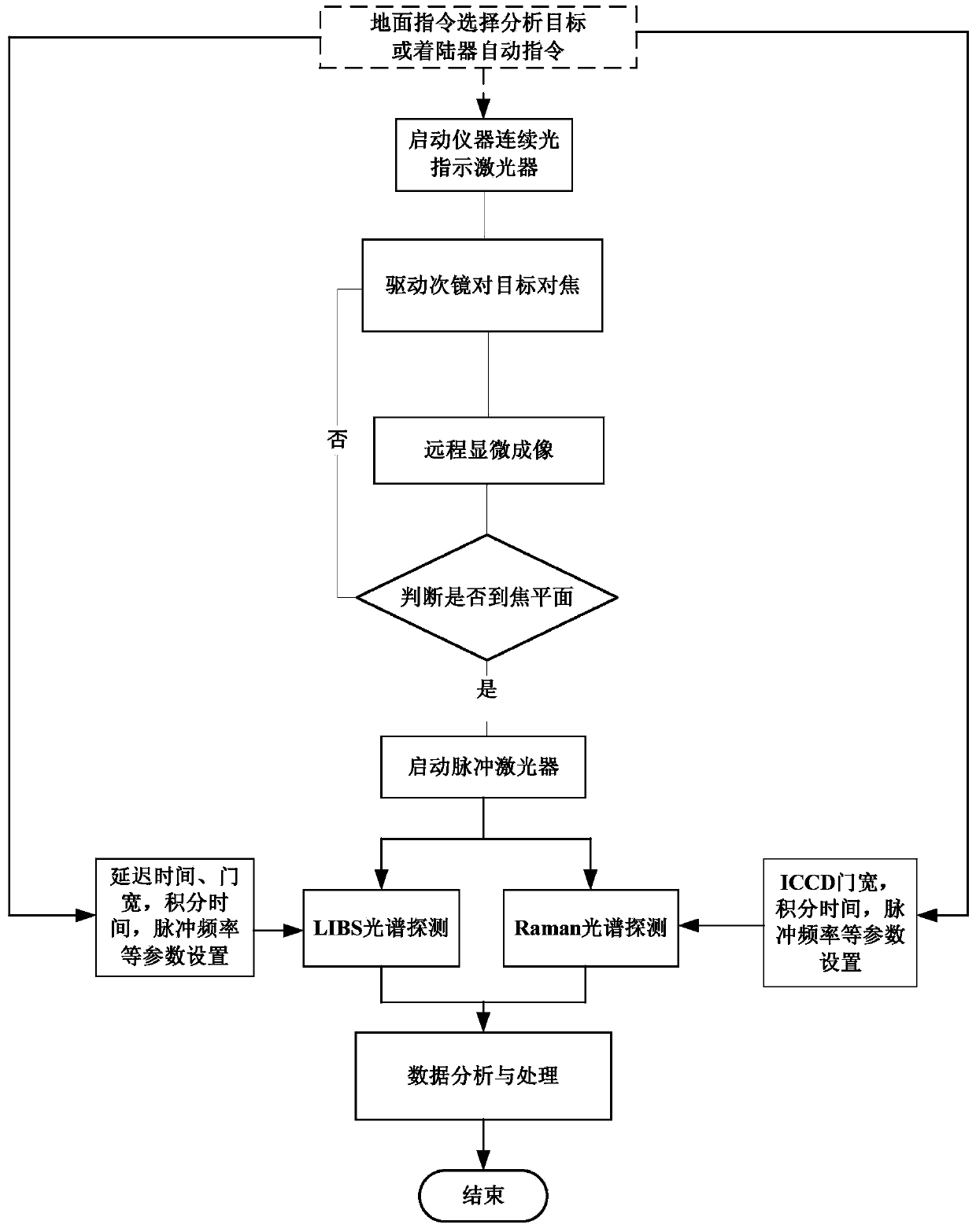
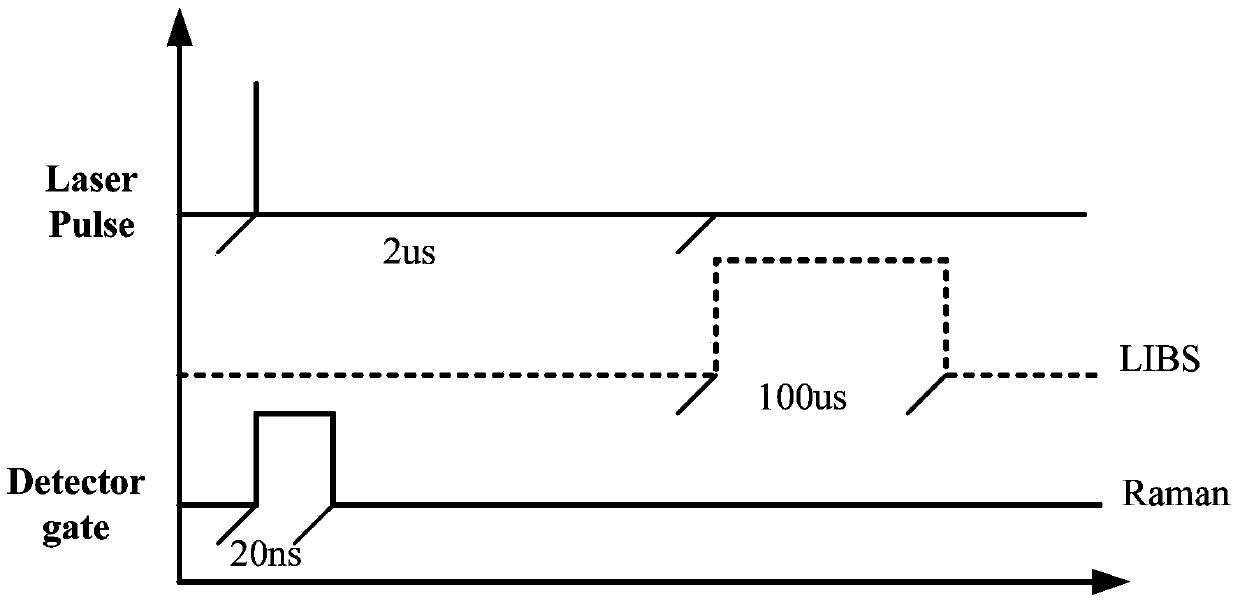
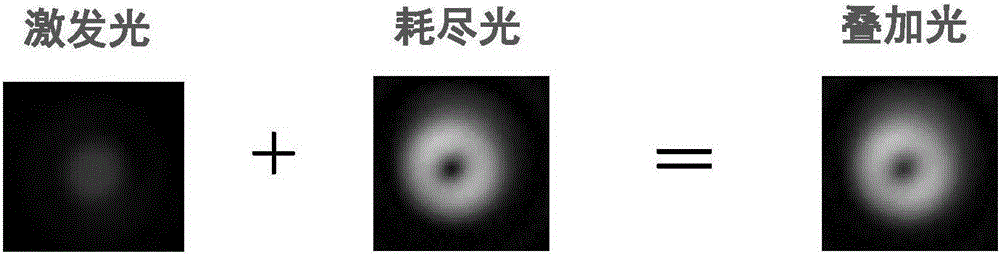
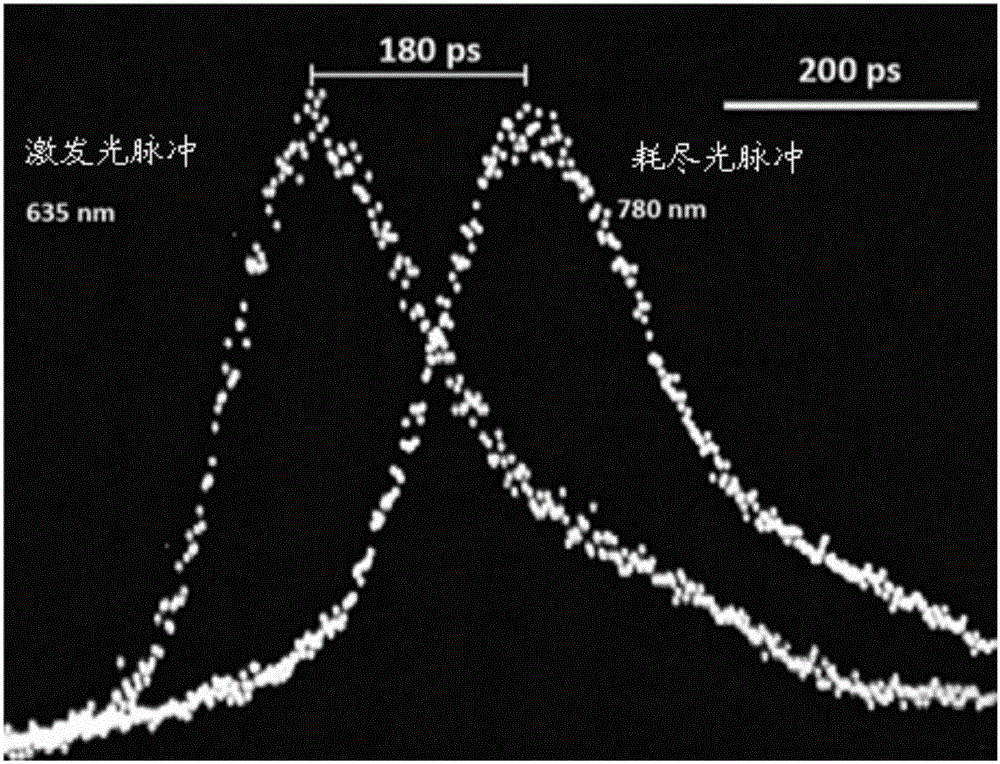
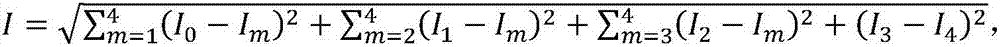Patents
Literature
2196 results about "Microscopic imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microscopy imaging techniques are employed by scientists and researcher to improve their ability to view the microscopic world. Advances in microscopy enable visualization of a broad range of biological processes and features in cell structure.
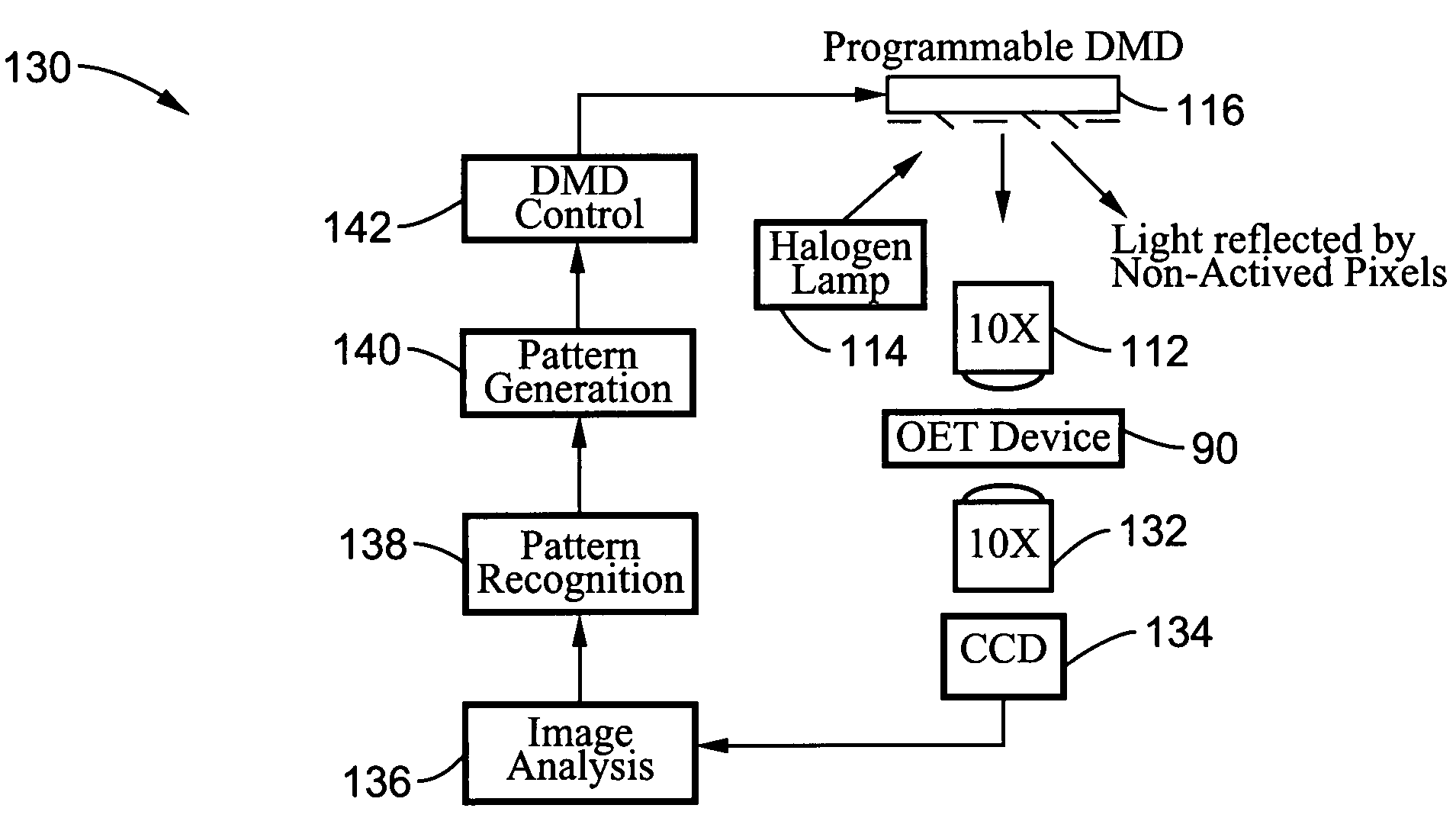
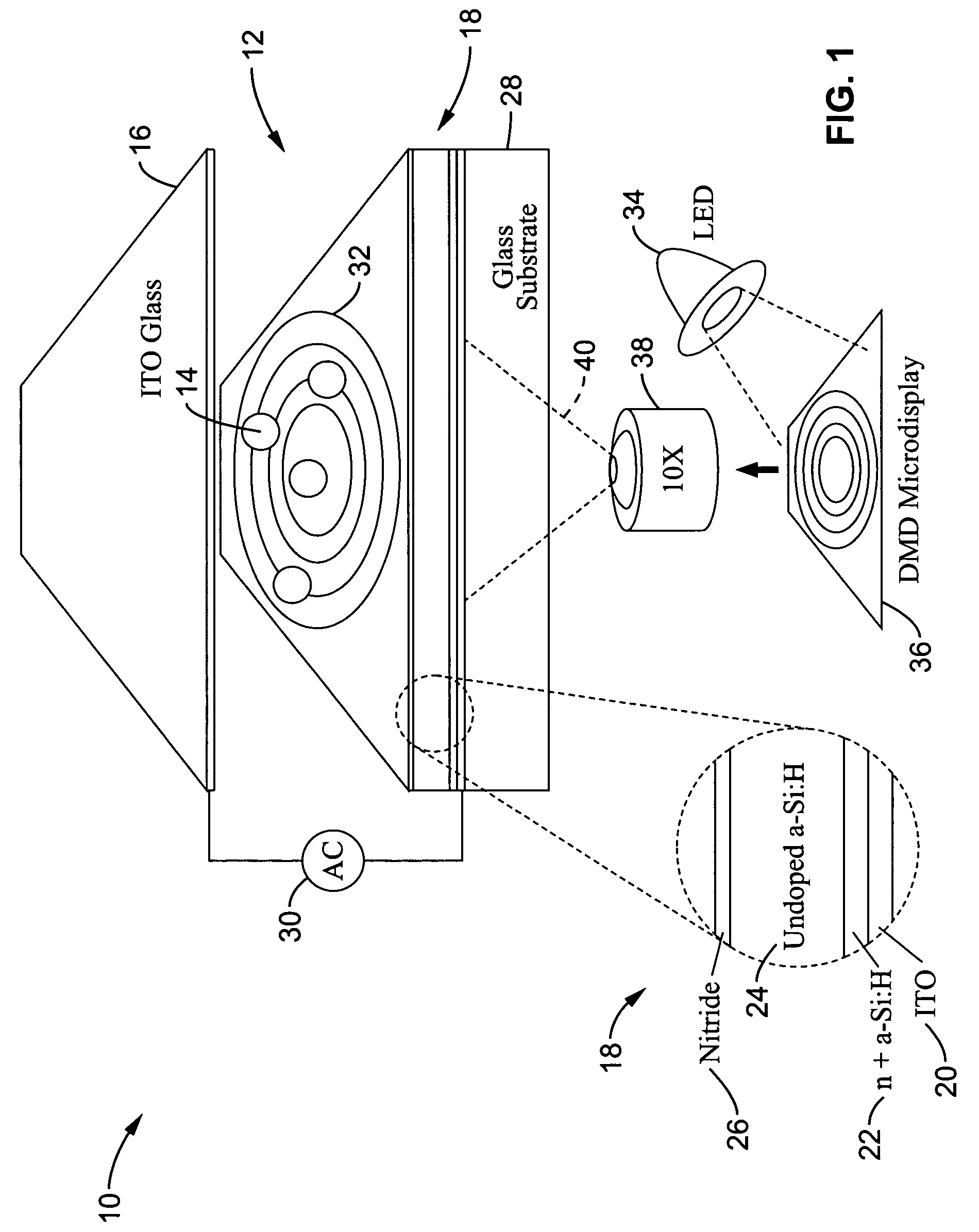
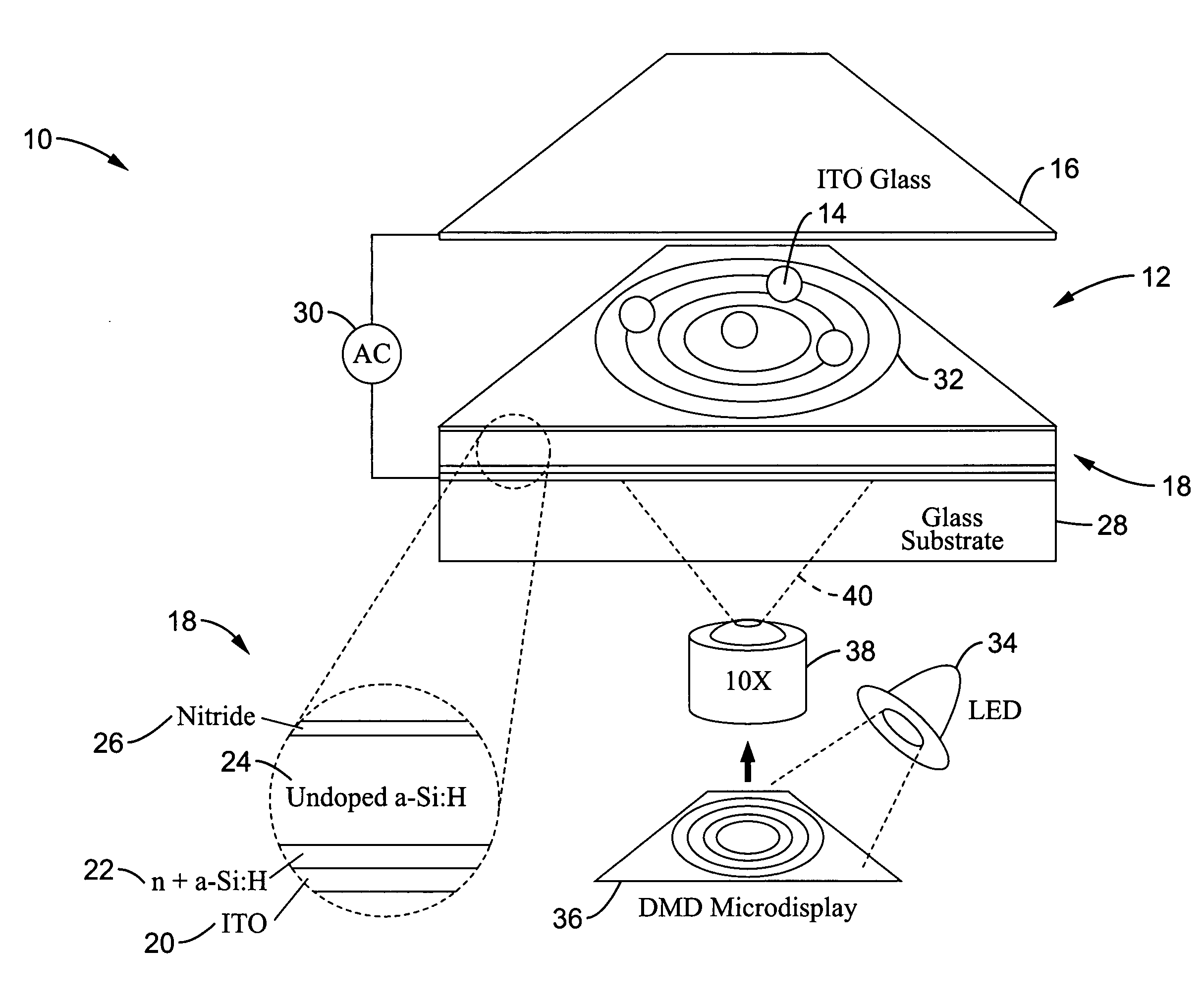
Optoelectronic tweezers for microparticle and cell manipulation
ActiveUS7612355B2Easy to operateEasy to createElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMicroparticleOpto electronic
An optical image-driven light induced dielectrophoresis (DEP) apparatus and method are described which provide for the manipulation of particles or cells with a diameter on the order of 100 μm or less. The apparatus is referred to as optoelectric tweezers (OET) and provides a number of advantages over conventional optical tweezers, in particular the ability to perform operations in parallel and over a large area without damage to living cells. The OET device generally comprises a planar liquid-filled structure having one or more portions which are photoconductive to convert incoming light to a change in the electric field pattern. The light patterns are dynamically generated to provide a number of manipulation structures that can manipulate single particles and cells or groups of particles / cells. The OET preferably includes a microscopic imaging means to provide feedback for the optical manipulation, such as detecting position and characteristics wherein the light patterns are modulated accordingly.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optoelectronic tweezers for microparticle and cell manipulation
ActiveUS20090170186A1Easy to operateEasy to createElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMicroparticleDielectrophoresis
An optical image-driven light induced dielectrophoresis (DEP) apparatus and method are described which provide for the manipulation of particles or cells with a diameter on the order of 100 μm or less. The apparatus is referred to as optoelectric tweezers (OET) and provides a number of advantages over conventional optical tweezers, in particular the ability to perform operations in parallel and over a large area without damage to living cells. The OET device generally comprises a planar liquid-filled structure having one or more portions which are photoconductive to convert incoming light to a change in the electric field pattern. The light patterns are dynamically generated to provide a number of manipulation structures that can manipulate single particles and cells or groups of particles / cells. The OET preferably includes a microscopic imaging means to provide feedback for the optical manipulation, such as detecting position and characteristics wherein the light patterns are modulated accordingly.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
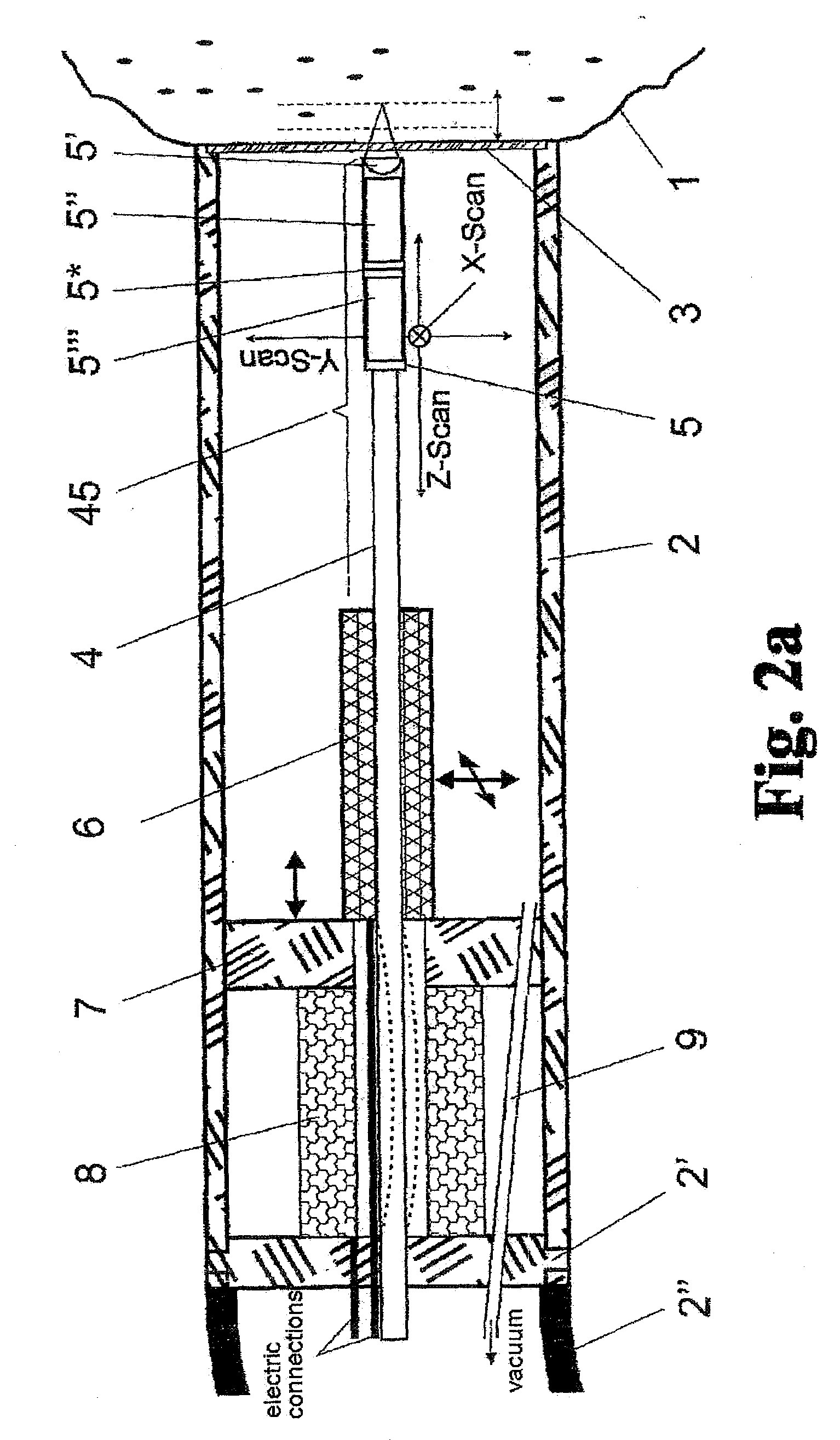
Method and arrangement for high-resolution microscope imaging or cutting in laser endoscopy
ActiveUS20080081950A1Accurate imagingPrecise microcuttingEndoscopesCatheterMicroscopic imageFlexible endoscope
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for high-resolution microscopic imaging in laser endoscopy based on laser-induced object reaction radiation and for performing microscopic cuts in biological tissue. In using multiphoton processes for endoscopic applications in biological materials with an accuracy of under one millimeter, radiation of a pulsed femtosecond laser is focused into an object by means of a transmission focusing optics unit comprising a transmission system and miniature focusing optics having a high numerical aperture greater than 0.55 to trigger a local object reaction radiation in the micrometer to nanometer range, and the distal end of the transmission focusing optics unit is moved in at least two dimensions for highly spatially resolved scanning of the object and for transmitting object reaction radiation which is scanned in a locally progressive manner to an image-generating system with a photon detector. In an other embodiment the femtosecond laser radiation is energy enhanced is applied to the same transmission focusing optics unit to perform microendoscopic surgery in biological tissue.
Owner:JENLAB
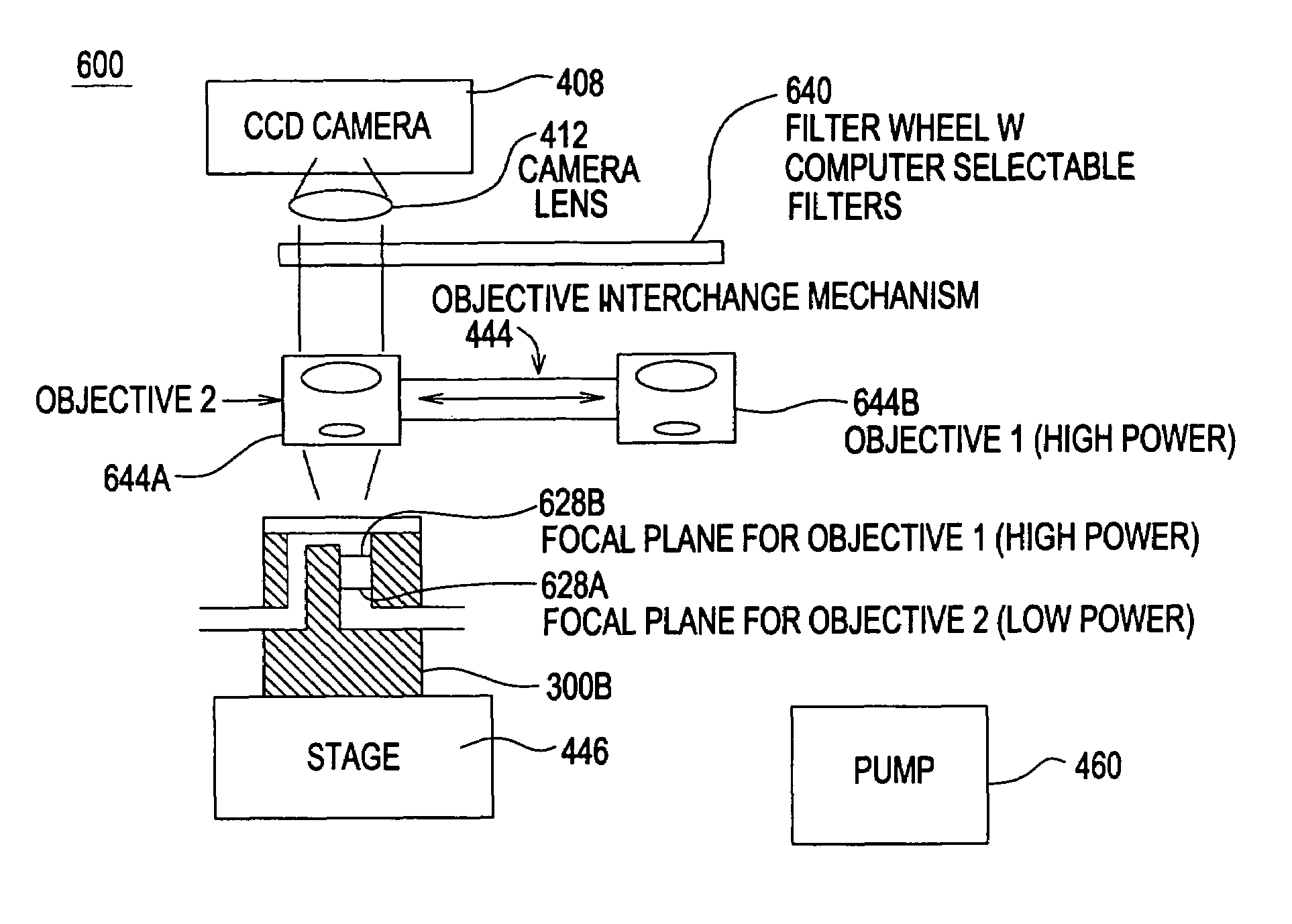
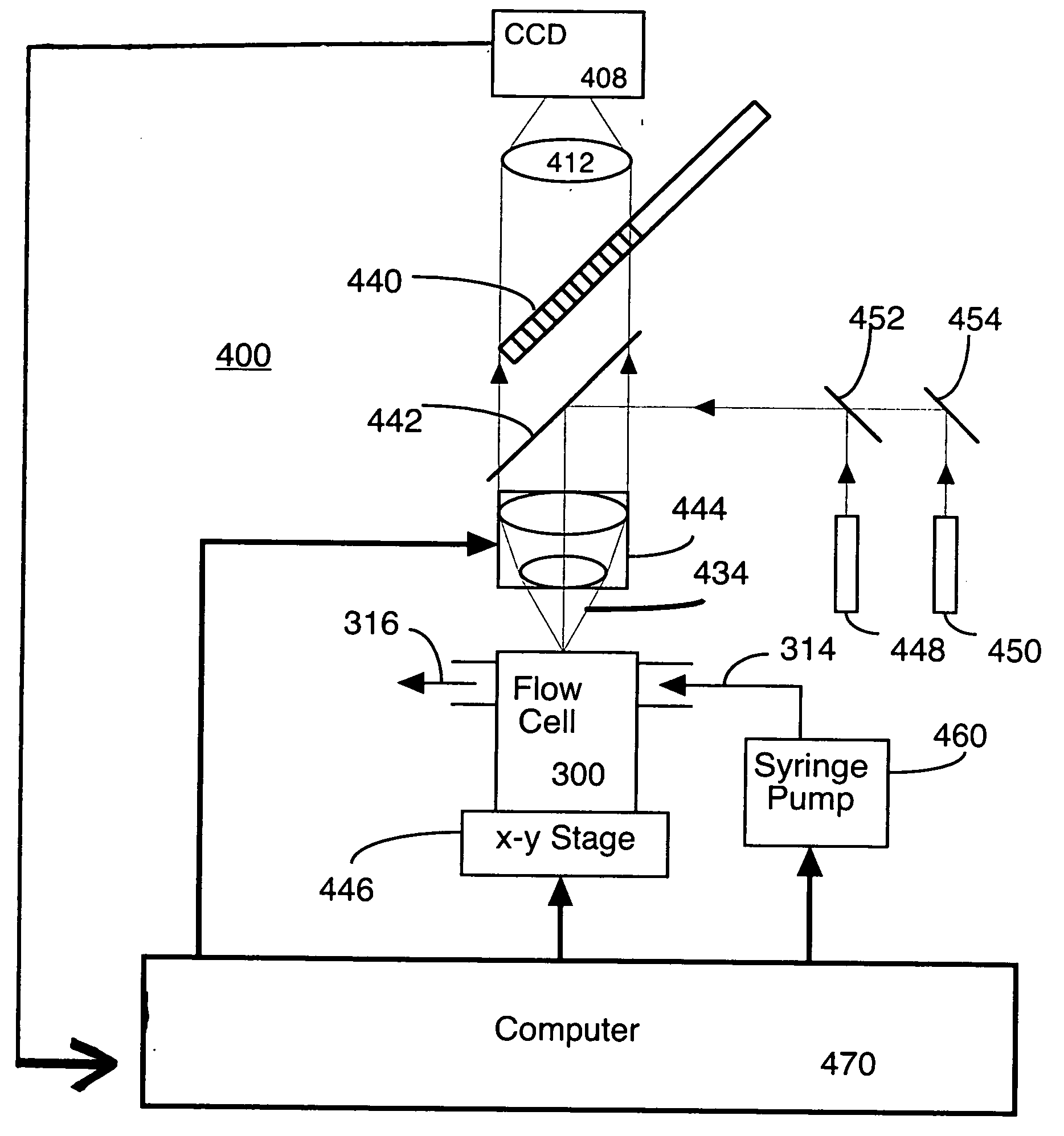
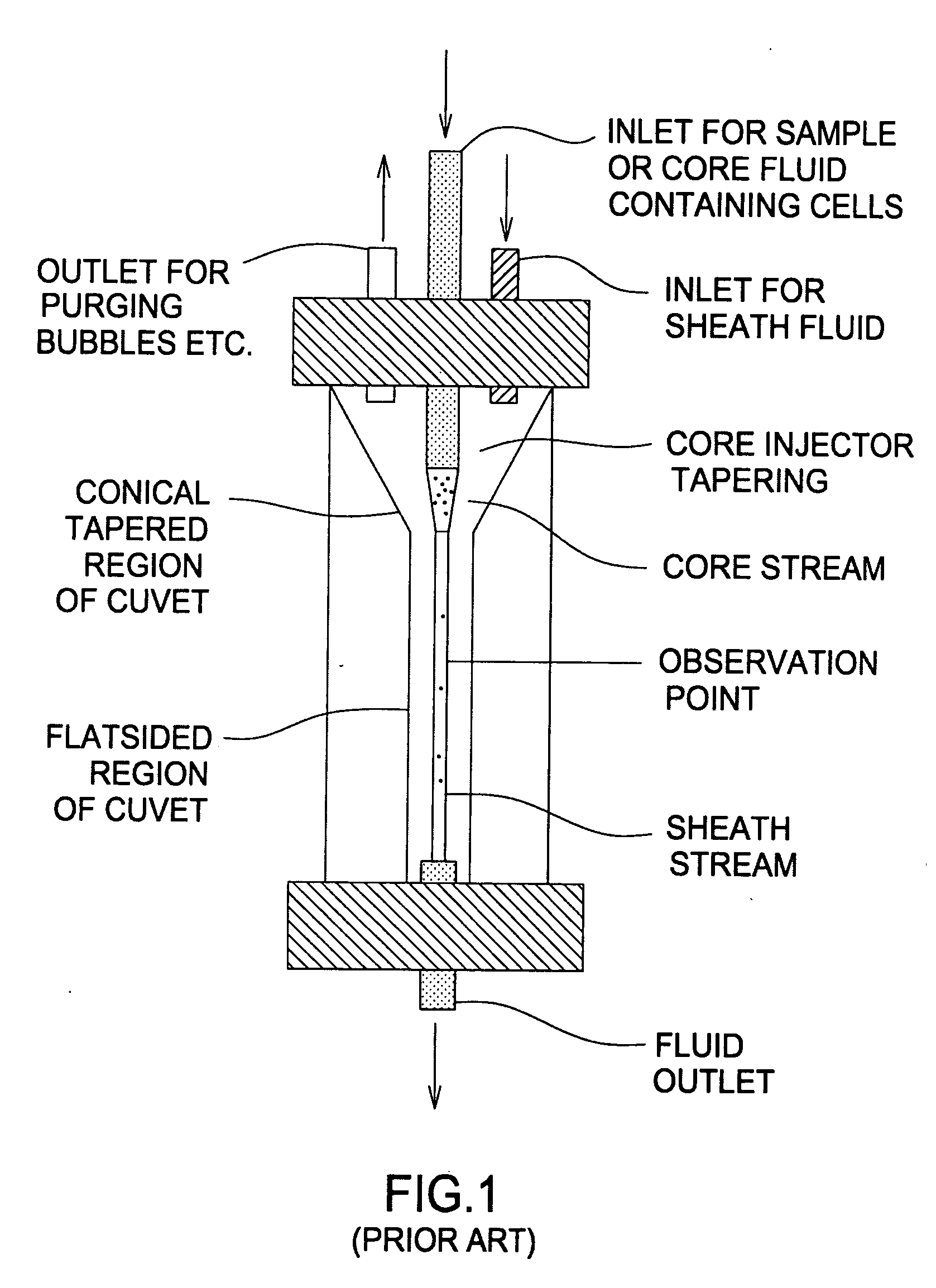
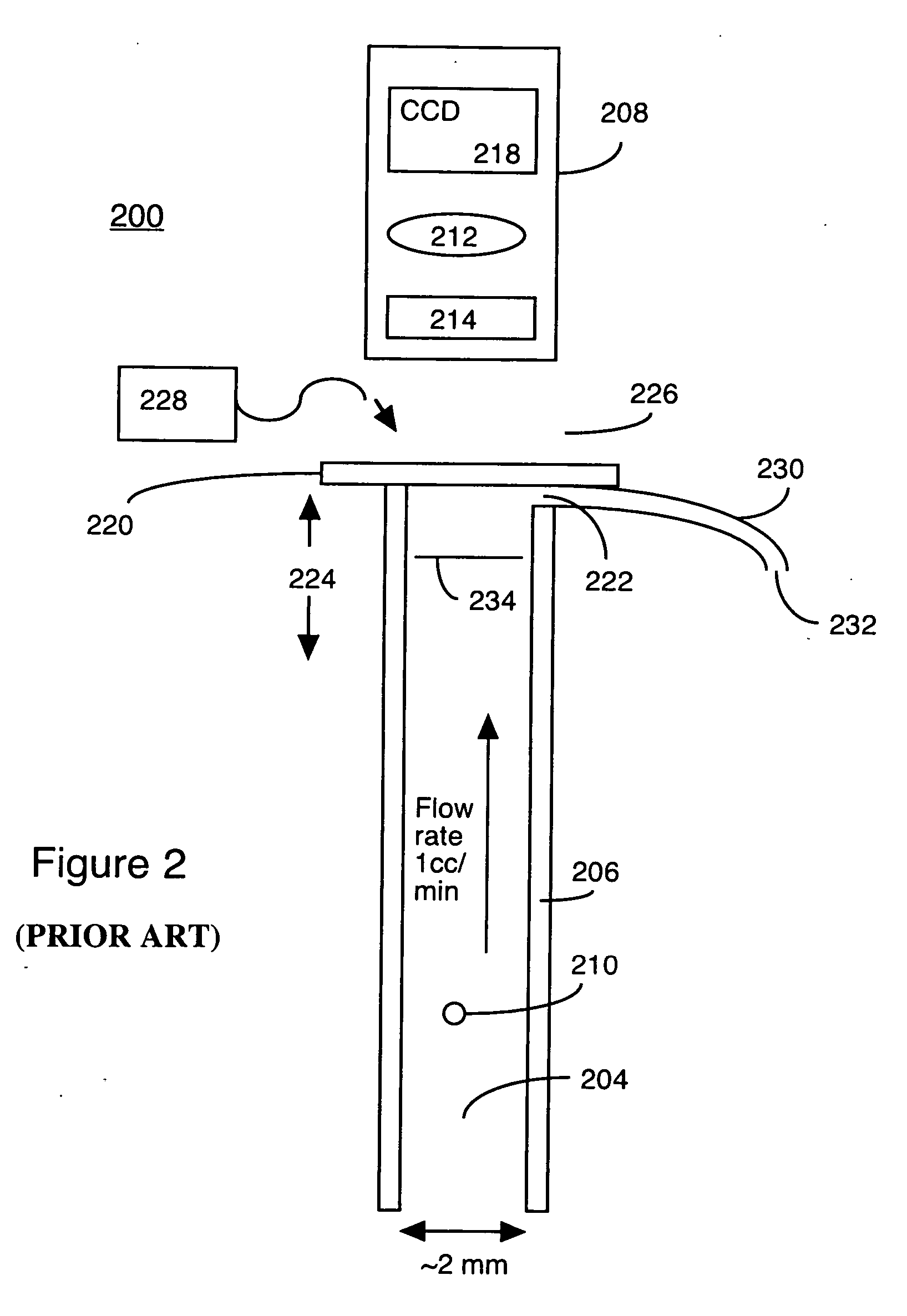
High resolution imaging fountain flow cytometry
InactiveUS7161665B2Improve throughputHigh resolutionWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh resolution imagingFlow cell
An imaging fountain flow cytometer allows high resolution microscopic imaging of a flowing sample in real time. Cells of interest are in a vertical stream of liquid flowing toward one or more illuminating elements at wavelengths which illuminate fluorescent dyes and cause the cells to fluoresce. A detector detects the fluorescence emission each time a marked cell passes through the focal plane of the detector. A bi-directional syringe pump allows the user to reverse the flow and locate the detected cell in the field of view. The flow cell is mounted on a computer controlled x-y stage, so the user can center a portion of the image on which to zoom or increase magnification. Several computer selectable parfocal objective lenses allow the user to image the entire field of view and then zoom in on the detected cell at substantially higher resolution. The magnified cell is then imaged at the various wavelengths.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Super-precision trans-scale in-situ nanometer indentation marking test system
ActiveCN101520389AThe test method is accurateAccurate and effective research and testing methodsUsing optical meansInvestigating material hardnessHead pressingImage resolution
The invention relates to a super-precision trans-scale in-situ nanometer indentation marking test system which integrates driving, loading, detecting and micro-nanometer dynamic performance tests, super-precision marking processing and in-situ observation into a whole. The system mainly comprises an objective table, a regulation mechanism, a detection unit, a precise pressed-into driving unit, a detection unit of load signals and displacement signals and a high-resolution digital microscopic imaging system, wherein the objective table is precisely positioned along the directions of the X axis and the Y axis; the regulation mechanism and the precise pressed-into driving unit are in the direction of the Z axis and are assembled on a base; the high-resolution digital microscopic imaging system is used for observing the deforming and damaging conditions of the material in the storing and testing process; the objective table as well as the regulation mechanism and the precise pressed-into driving unit in the direction of the Z axis are assembled on a base; the high-resolution digital microscopic imaging system is arranged on the objective table; a precise dynamic sensor detecting the pressure of a diamond tool head pressed into a material and a sensor I detecting the precise displacement of the objective table in the directions of the X axis and the Y axis are arranged on the objective table; and a sensor II used for detecting the precise displacement of a diamond tool head in the direction of the Z axis of pressed-into depth is arranged on the base by a support I.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Automatic focusing microscope based on eccentric beam method and focusing method thereof
ActiveCN104932092AImprove noise immunityHigh precisionMicroscopesMicroscopic imageLinear relationship
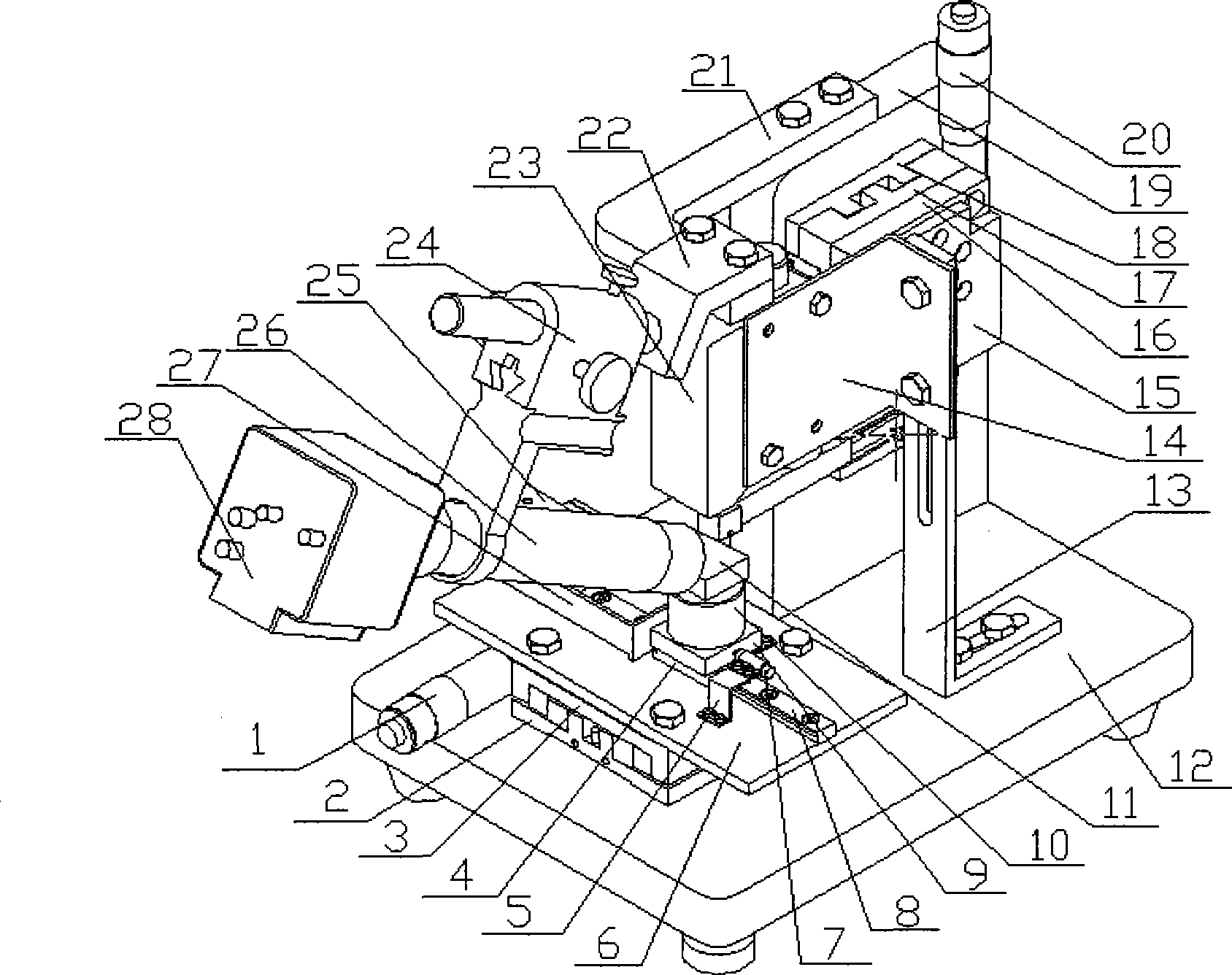
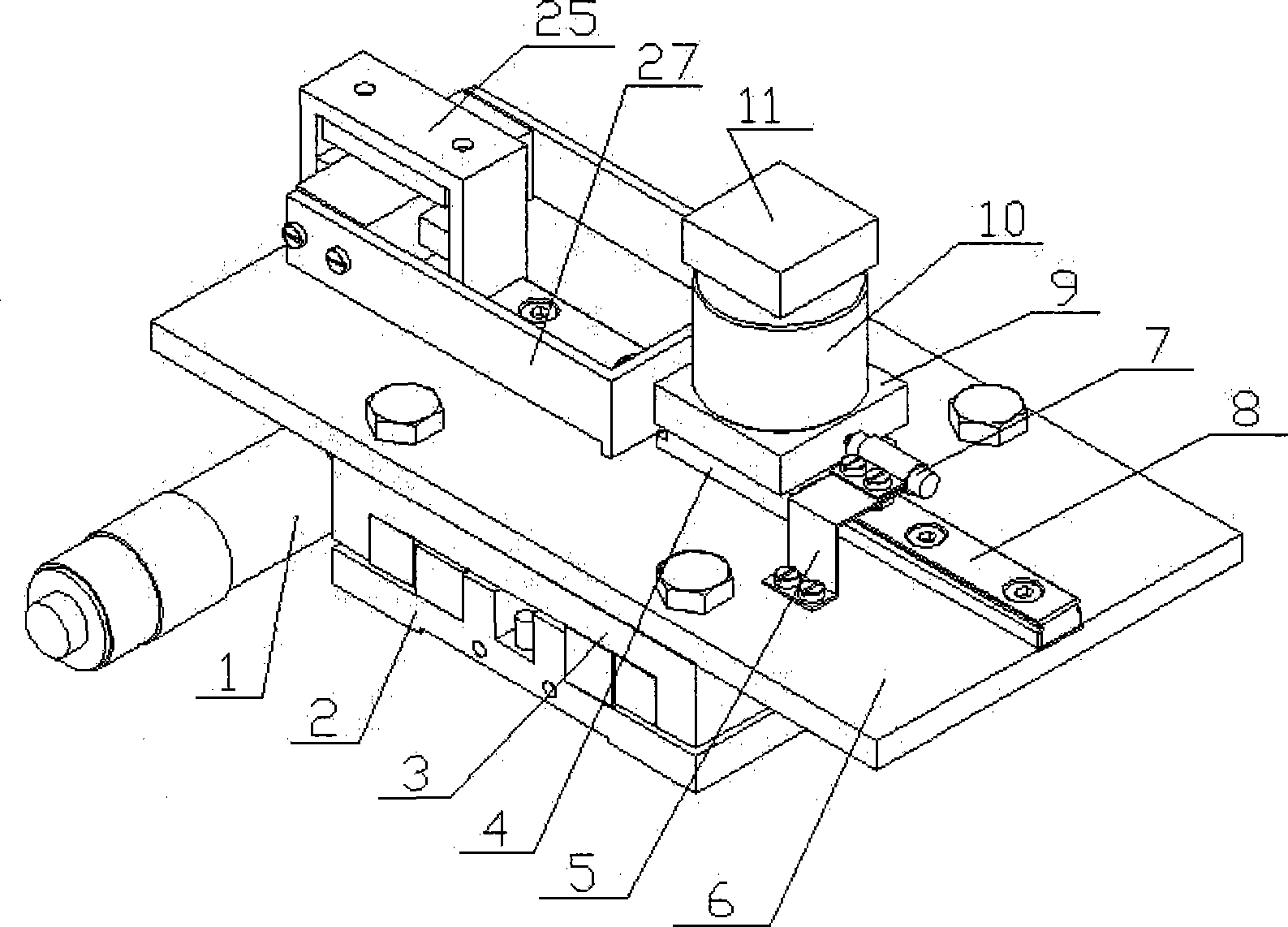
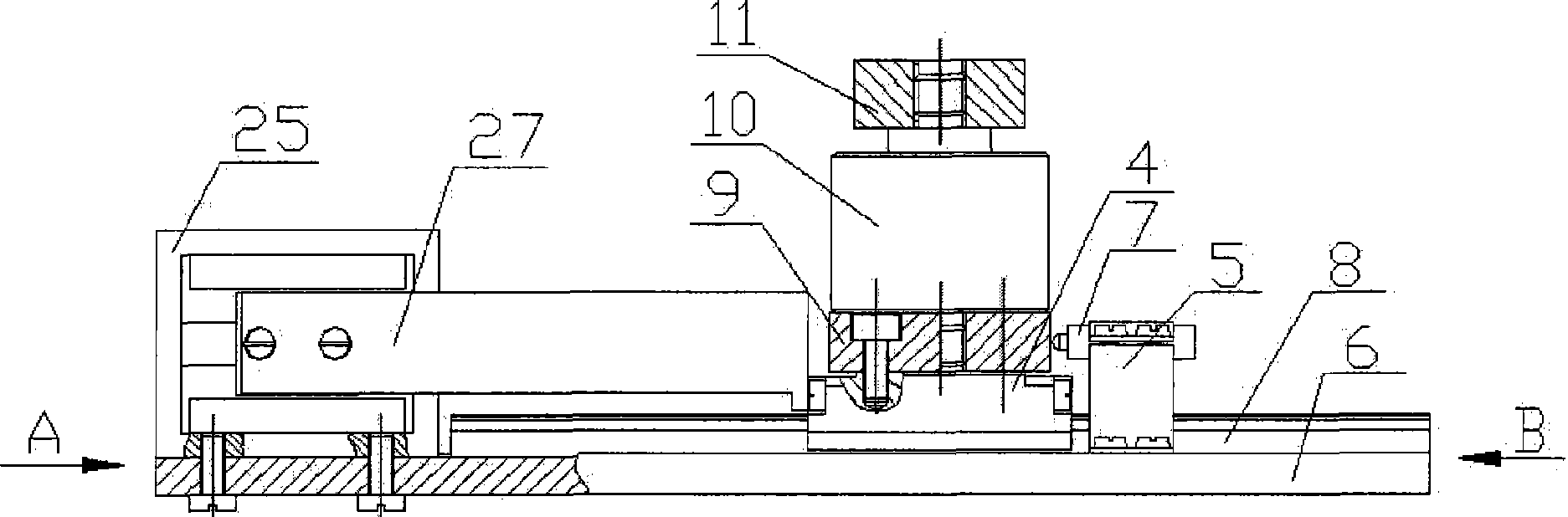
The invention discloses an automatic focusing microscope based on an eccentric beam method and a focusing method thereof. The hardware comprises an eccentric beam defocus amount detection module, a microscopic imaging module, a piezo lens drive, an XY stage and a computer processing system. The defocus amount detection module transmits a semicircular laser beam to irradiate the surface of a sample and acquire a semicircular spot image formed by sample reflection. The computer processing system uses self-adaptive median filtering, Canny edge detection based on OSTU, the least square fitting and other algorithms to process the grayscaled spot image to acquire spot radius. According to a radius-defocus amount linear relationship model, the sample defocus amount in a field of vision can be calculated. The piezo lens drive drives a lens to compensate the defocus amount. After focusing, the microscopic imaging module acquires a clear sample image. The automatic focusing microscope based on the eccentric beam method and the focusing method thereof, which are provided by the invention, have the advantages of fast focusing speed, high focusing accuracy and large linear range, and can meet the requirement of fast and precise focusing of the microscope under a high power lens.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device
ActiveCN103439254AImproving the Detection Capability of Micro-area Raman SpectroscopyHigh detection sensitivityRaman scatteringRayleigh scatteringHigh resolution imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of microscopic spectrum imaging, and relates to a spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device, wherein a confocal microscopic technology and a Raman spectrum detecting technology are combined. A spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system is constructed by using rayleigh scattering light discarded in confocal Raman spectrum detection, high-resolution imaging and detection of a three-dimensional geometric position of a sample are realized; and a spectrum detection system is controlled by using an extreme point of the spectroscopic pupil confocal microscopic imaging system to be capable of accurately capturing Raman spectrum information excited by a focusing point of an objective lens, and further spectroscopic pupil confocal Raman spectrum high-space-resolution imaging and detection of image and spectrum integration are realized. The spectroscopic pupil laser confocal Raman spectrum testing method and device provide a new technical approach for high-space-resolution detection of the three-dimensional geometrical position and spectrum in a microcell, can be widely applied to the fields such as physics, chemistry, biomedicine, material science, environmental sciences, petrochemical engineering, geology, medicines, foods, criminal investigation and jewelry verification, and are capable of carrying out nondestructive identification and deep spectrum analysis of a sample.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Micron-nano scale in-situ nano indentation and scratching test system
InactiveCN101876609AThe test method is accuratePrecision equipmentUsing optical meansInvestigating material hardnessImage resolutionEngineering
The invention relates to a micron-nano scale in-situ nano indentation and scratching test system which integrates driving, precise loading and signal detection, micron-nano scale mechanics performance testing, ultraprecise scratching processing and high resolution in-situ observing as one. The system is mainly composed of a precise positioning platform at X-axis and Y-axis directions, a precise linear positioning platform at Z-axis direction, a precise indentation driving unit, a load signal and displacement signal detection unit and a high resolution digital microscopic imaging system for observing and storing material deformation and damage conditions in the test process. The precise positioning platform at the X-axis and Y-axis directions is assembled on a base, the precise linear positioning platform at the Z-axis direction is assembled on a side plate, the precise indentation driving unit, a precise mechanical sensor for detecting the indentation material pressure of a diamond tool head and a precise displacement sensor for detecting the indentation depth of the diamond tool head to along the Z-axis direction are assembled on the precise linear positioning platform at the Z-axis direction, and the high resolution digital microscopic imaging system is assembled on a beam.
Owner:赵宏伟
High resolution imaging fountain flow cytometry
InactiveUS20050036139A1Improve throughputHigh sensitivityWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh resolution imagingFlow cell
An imaging fountain flow cytometer allows high resolution microscopic imaging of a flowing sample in real time. Cells of interest are in a vertical stream of liquid flowing toward one or more illuminating elements at wavelengths which illuminate fluorescent dyes and cause the cells to fluoresce. A detector detects the fluorescence emission each time a marked cell passes through the focal plane of the detector. A bi-directional syringe pump allows the user to reverse the flow and locate the detected cell in the field of view. The flow cell is mounted on a computer controlled x-y stage, so the user can center a portion of the image on which to zoom or increase magnification. Several computer selectable parfocal objective lenses allow the user to image the entire field of view and then zoom in on the detected cell at substantially higher resolution. The magnified cell is then imaged at the various wavelengths.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Incoherent digital holography three-dimensional dynamic microscopic imaging system and method
ActiveCN103257441ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical diffractionSpatial light modulator
The invention provides an incoherent digital holography three-dimensional dynamic microscopic imaging system and method and belongs to the field of an optical diffraction imaging and incoherent digital holography technology. Three-dimensional microscopic imaging of dynamic samples is achieved through adoption of a single exposure phase shift technology based on a phase spatial light modulator on the condition of incoherent light illumination. In a hologram shooting light path, incident light is incoherent light transmitted or reflected by the samples, is subjected to convergence of a collimation lens and modulation of the spatial light modulator, and is received by an image sensor. The image sensor and the spatial light modulator are respectively connected with a computer. Diffraction spectroscopic phase mask patterns which are made and generated in the computer are loaded on the spatial light modulator. In order to enable a plurality of phase holograms to be recorded by the system through one-time exposure, a phase loading method on the spatial light modulator needs to be adjusted to a regional phase shift loading method. The incoherent digital holography three-dimensional dynamic microscopic imaging system and method can be used for simultaneously recording the plurality of incoherent digital holograms through one-time exposure, and can be used for carrying out real-time three-dimensional imaging with low requirements for coherence of light sources. Moreover, any moving components or scanning components are not needed in the system.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging method and system
ActiveCN104515759AImprove imaging resolutionReduce bleaching effectFluorescence/phosphorescenceRapid imagingFluorescence
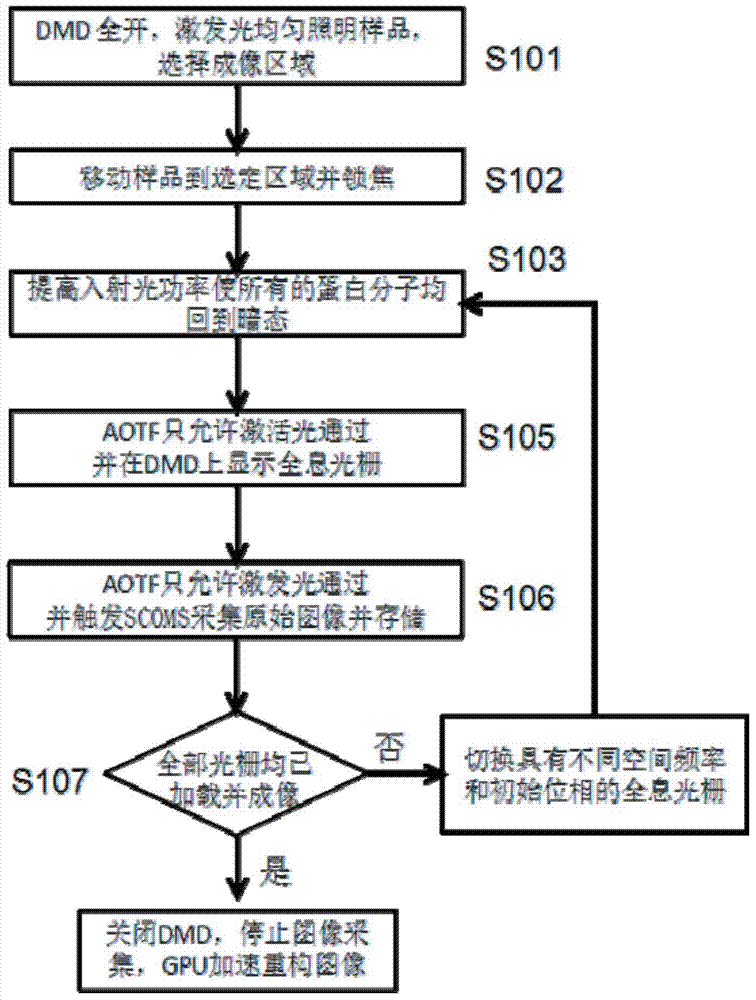
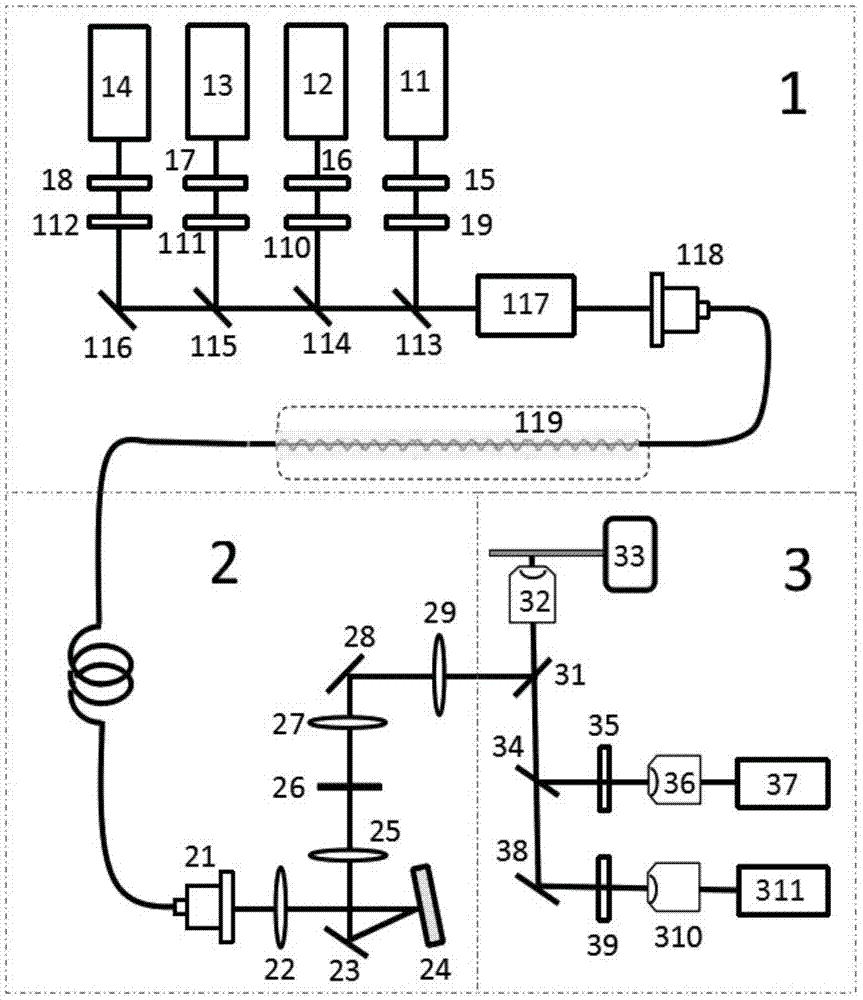
The invention discloses a non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging method which comprises the following steps: 1) loading a computed hologram on a digital microscopic array; 2) generating a first spatial structure light field which meets sine distribution and is used for activating fluorescent protein, and radiating the first spatial structure light field to the surface of a sample, so as to convert a part of protein to be in an illuminated state from a dark state; 3) radiating the sample in a second spatial structure light field so as to enable fluorescent protein in the bright state to emit fluorescent light, collecting the fluorescent light, and imaging in a photoelectric detector; 4) repeating the step 2) and the step 3), acquiring a plurality of spatial frequencies, acquiring a plurality of initial phases in each direction to obtain a plurality of original images, and reestablishing a super-resolution image according to a GPU acceleration algorithm. The invention further discloses a non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging system. The non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging method has the advantages of relatively high system imaging resolution, high fluorescent drifting resistance, low phototoxicity and rapid imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Remote in-situ integrated test system for planet surface substances and atmosphere
ActiveCN103743719ARapid positioningReduce volumeRaman scatteringElectromagnetic wave reradiationContinuous lightElement analysis
The invention discloses a remote in-situ integrated test system for planet surface substances and atmosphere. The whole system comprises: a miniature pulse solid state laser, a Cassegrain telescope system, a one-dimensional precise mobile platform, a continuous light indicating positioning laser, various optical elements and echelle spectrographs, ICCD, a high-resolution camera and a photomultiplier. According to the system and method of the invention, the combination of technologies of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), Raman spectroscopy (Raman), and laser radar is realized in the same system; the system of the invention adopts modular design, is high in integration level, small in size, and light in weight, and can realize long-distance surface microimaging, long-distance substance element analysis, long-distance substance composition analysis, and planet boundary layer atmosphere detection.
Owner:东莞市中科原子精密制造科技有限公司
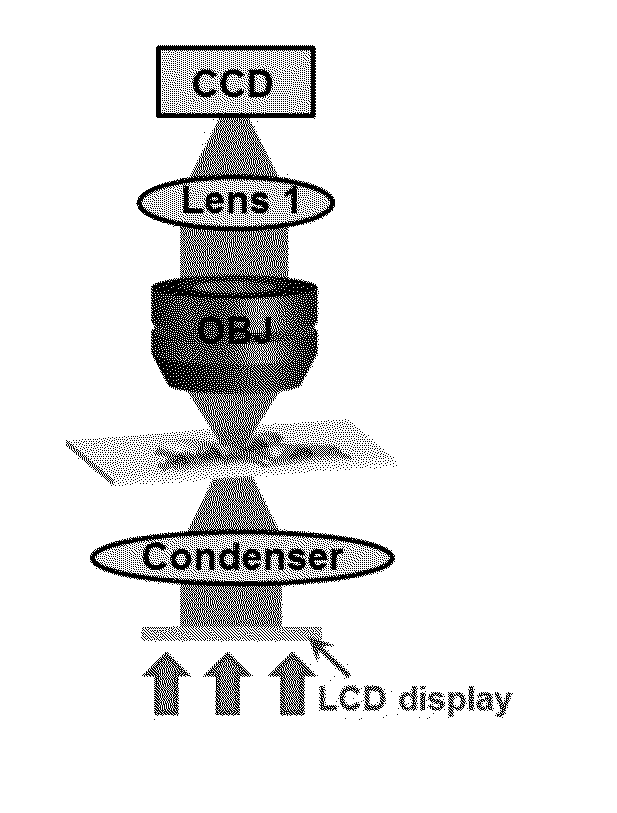
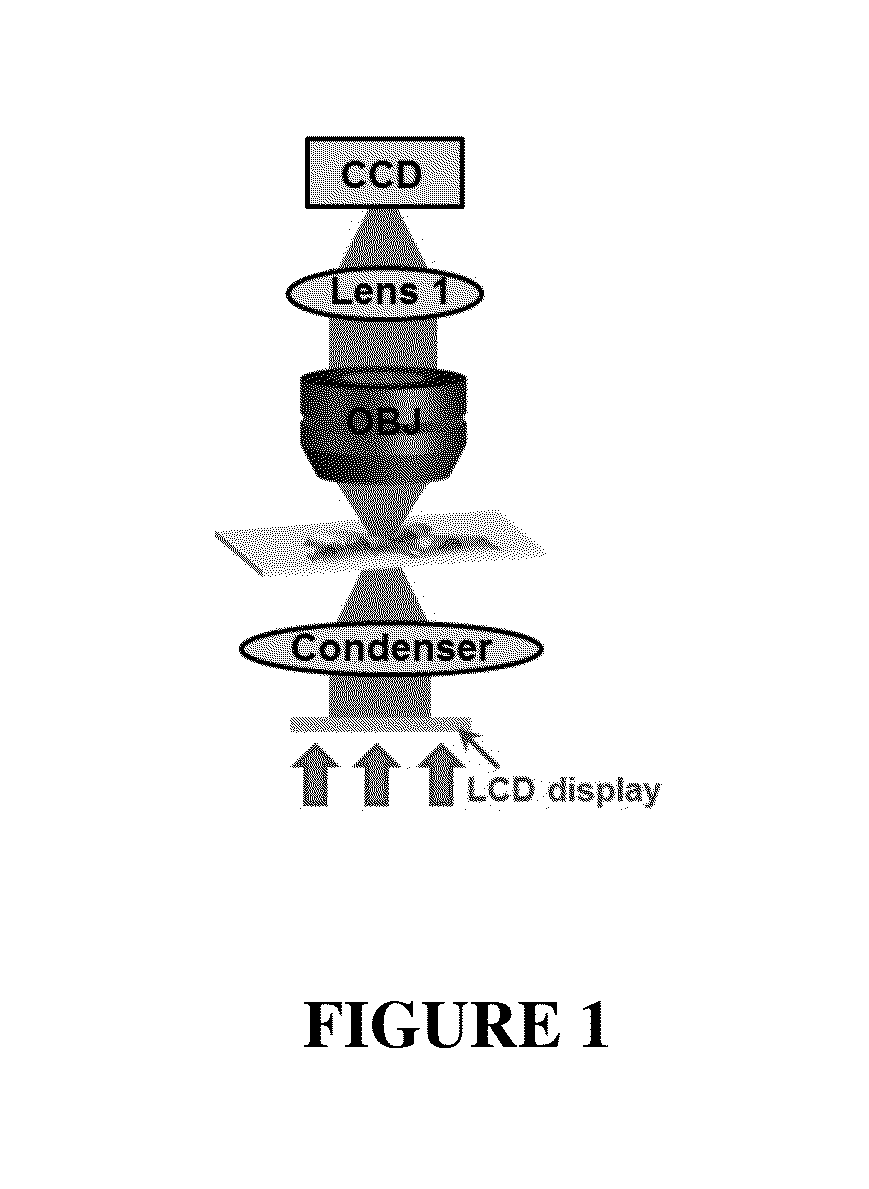
Method and Arrangement for Collimated Microscopic Imaging
InactiveUS20090250632A1Technology is easy to implementHigh-resolution imagePhotometryLuminescent dosimetersSpatially resolvedFluorescence
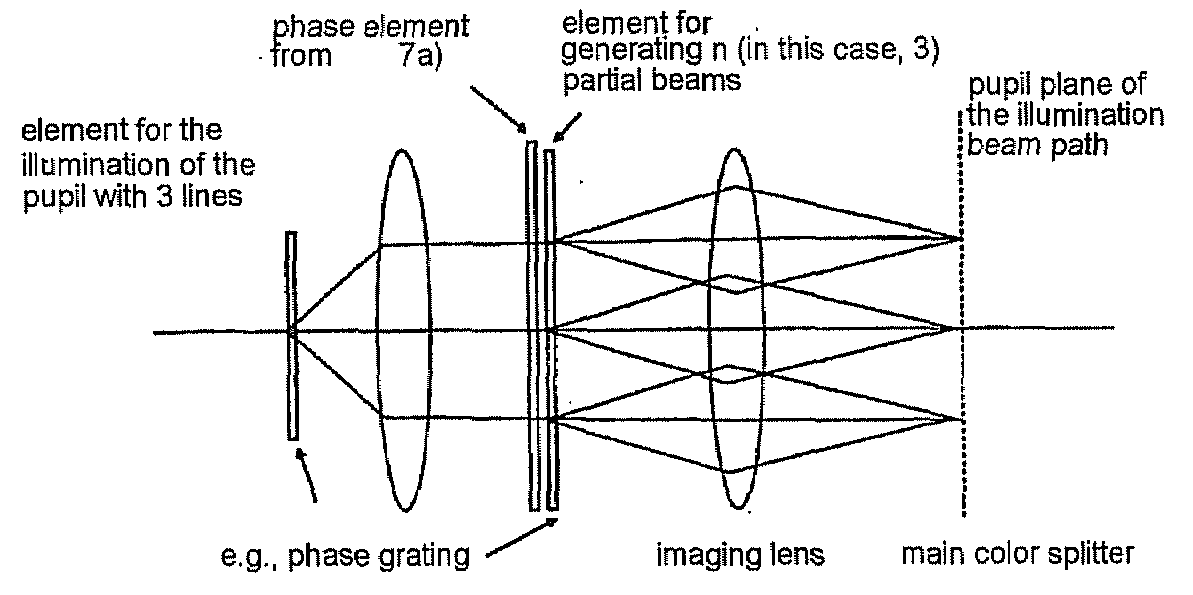
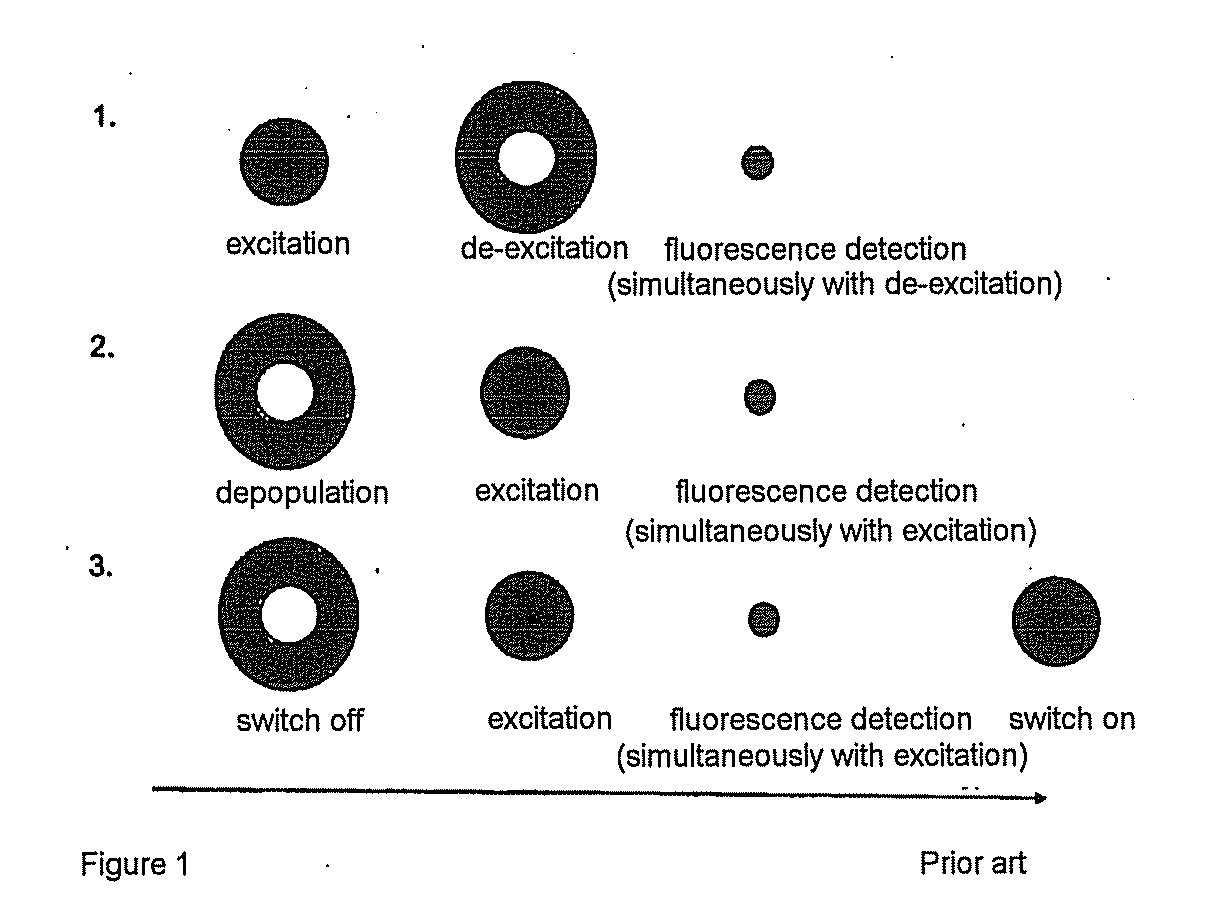
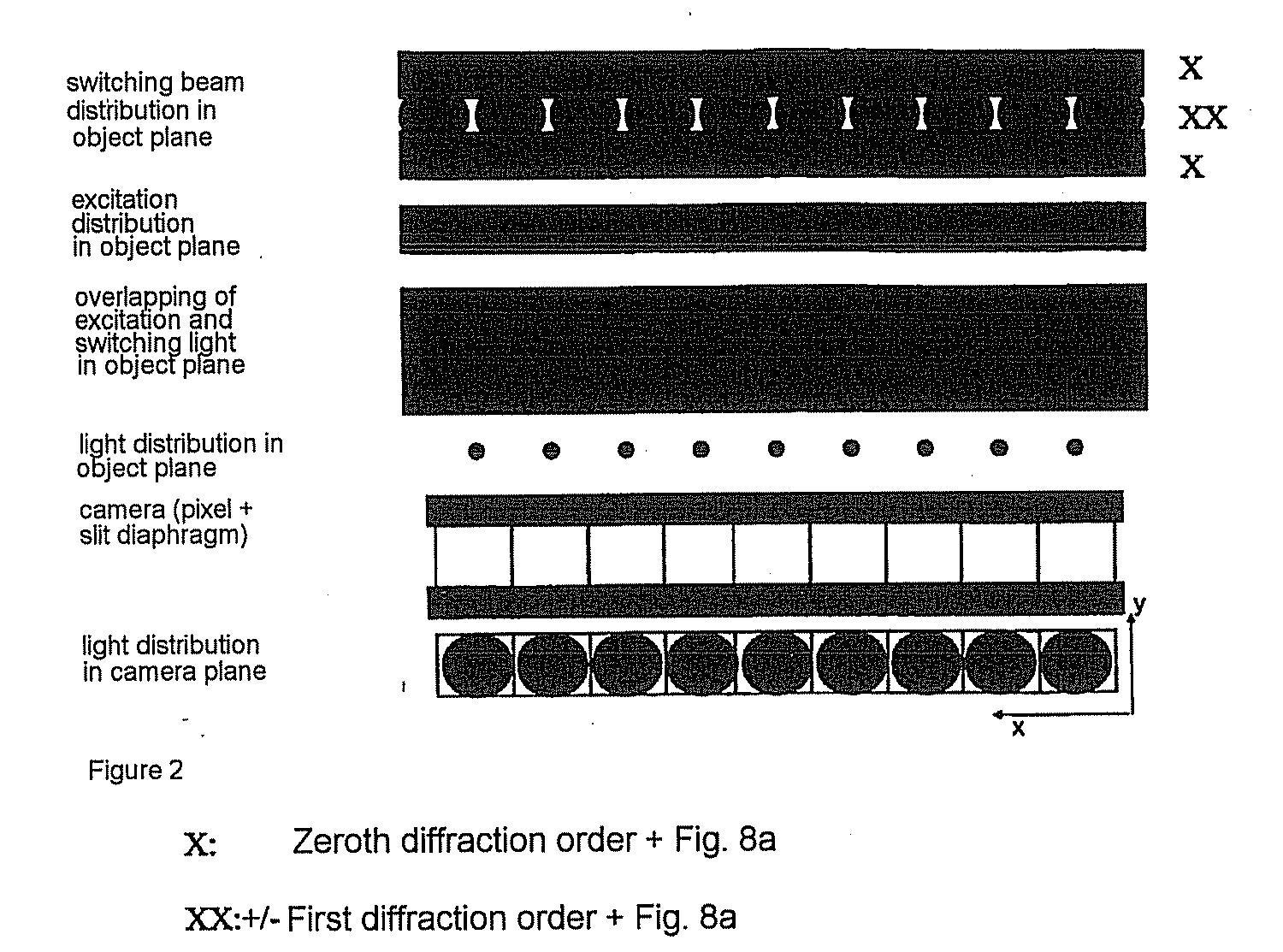
A method and arrangement for collimated microscopic imaging, including a first illumination of a sample in at least one region for exciting fluorescence, and a spatially resolving detection of the sample light by detector elements, the detection being associated with the region, wherein by means of a second illumination a sub-division of the region into separate fluorescent partial regions occurs, which are associated with the detector elements. The separation of the partial regions is carried out by the spatial separation of the fluorescent regions by means of intermediate regions having reduced fluorescence or no fluorescence, and / or by means of different spectral properties of the fluorescence from the partial regions.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MIKROLMAGING
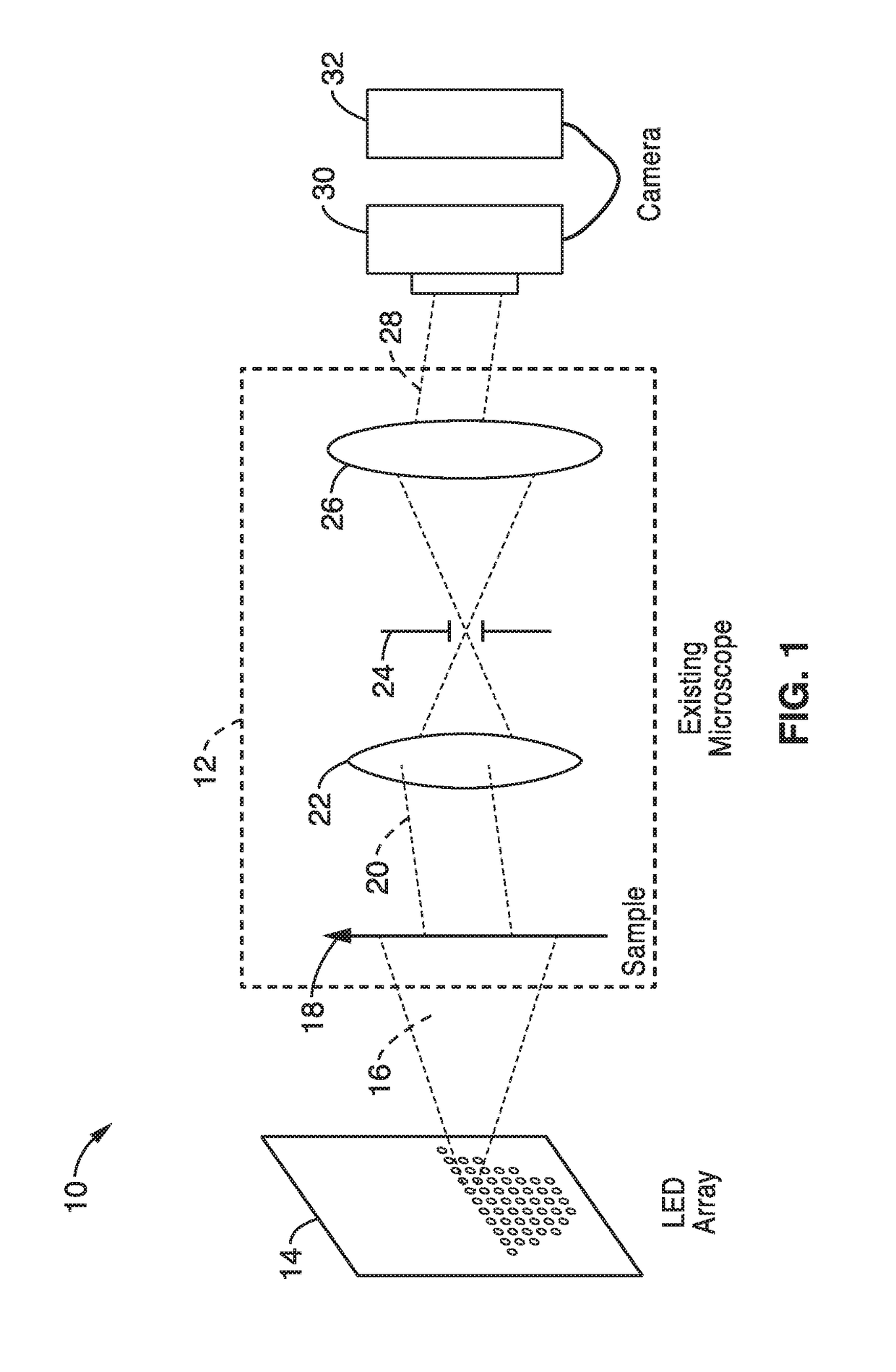
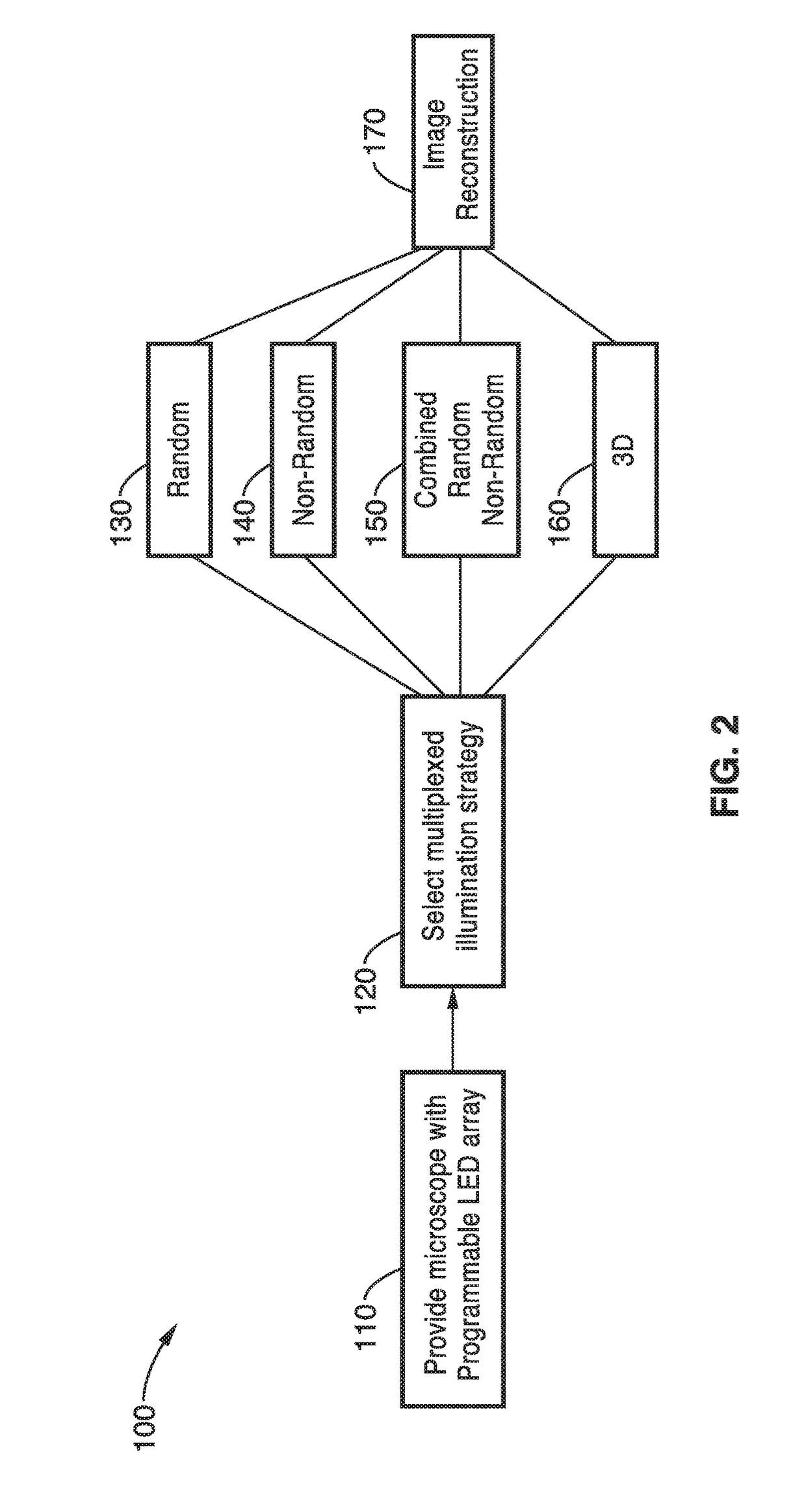
Fourier ptychographic microscopy with multiplexed illumination
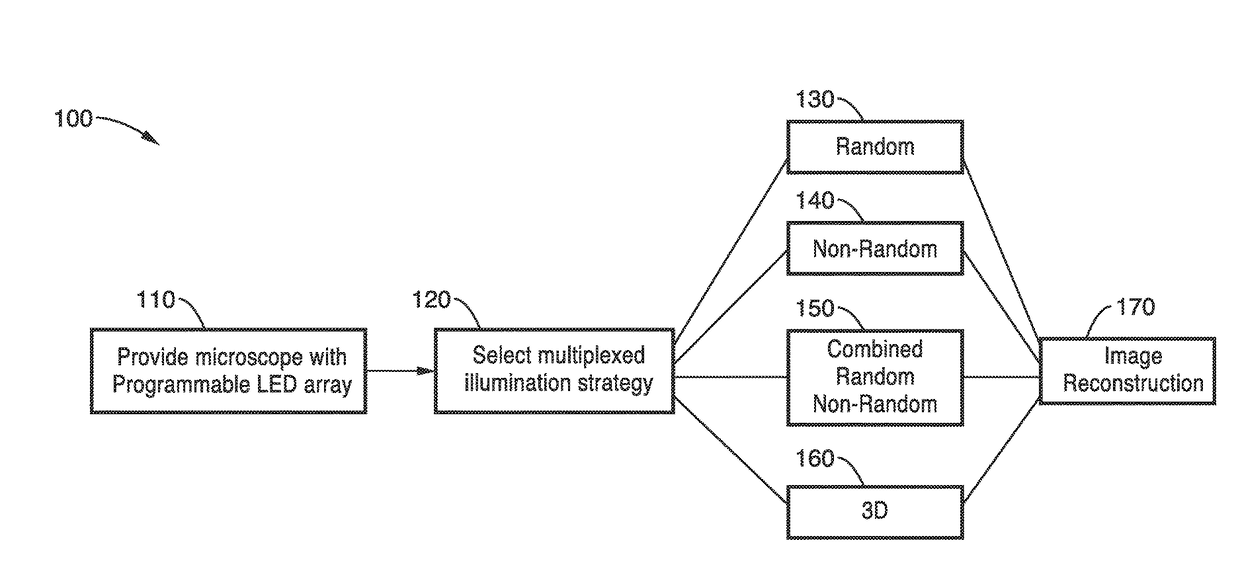
InactiveUS20170146788A1Exploits redundancyFaster sample dynamicImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMicroscopic imageWide field
A system and methods for wide field of view, high resolution Fourier ptychographic microscopic imaging with a programmable LED array light source. The individual lights in the LED array can be actuated according to random, non-random and hybrid random and non-random illumination strategies to produce high resolution images with fast acquisition speeds. The methods greatly reduce the acquisition time and number of images captured compared to conventional sequential scans. The methods also provide for fast, wide field 3D imaging of thick biological samples.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Three-dimensional laser washing device
InactiveCN103056517ASimple structureImprove stabilityLaser beam welding apparatusCleaning processes and apparatusFocal positionDisplacement control
The utility model discloses a three-dimensional laser washing device. The three-dimensional laser washing device comprises a pulsed laser with indicating red light and a control system of the same pulsed laser, a beam spread collimation optical system, a two-dimensional optical scanning galvanometer and a controller of the same two-dimensional optical scanning galvanometer, a focusing position regulator and a displacement controller. The focusing position regulator consists of a focusing lens, a filter, a microscopic imaging lens, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) and a processor, wherein the focusing lens is fixed with the microscopic imaging lens, the indicating red light of the pulsed laser reflects on the sample and images on the CCD (Charge Coupled Device), the microscopic imaging lens moves longitudinally to find a position where the contrast ratio is the highest and the image edge is the clearest, the position is a focus position of the focusing lens, and the three-dimensional laser washing device consists of the two-dimensional scanning galvanometer and the focusing lens. The three-dimensional laser washing device makes full use of the two-dimensional laser washing device which is based on the optical galvanometer scanning system, presetting the surface shape of the washing material is not required before cleaning, thereby having the advantages of being wide in application, simple in structure, good in stability, easy to debug, and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
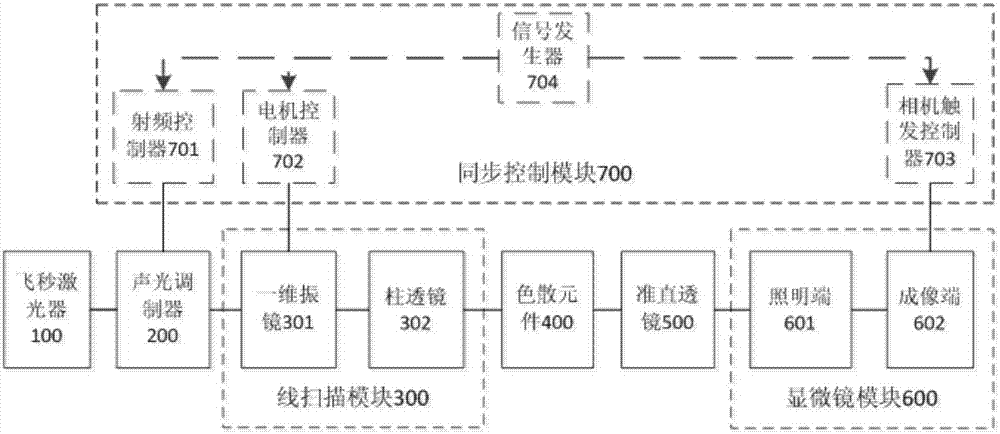
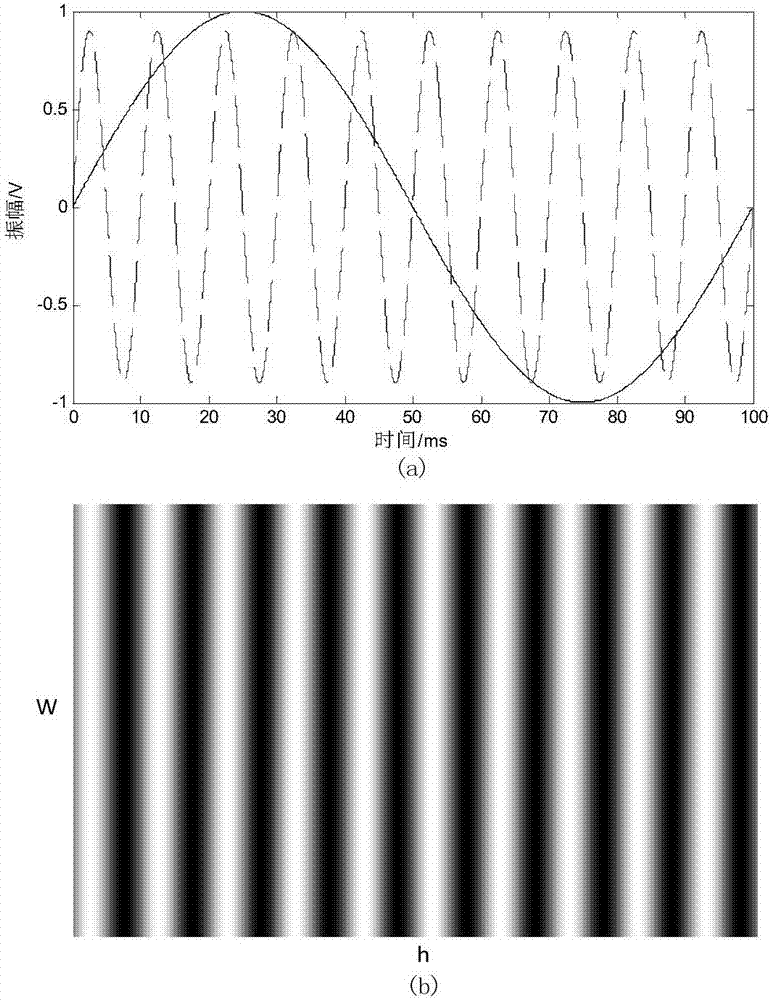
Structural light microscopic imaging system based on line scanning time-space focusing
InactiveCN107144955AHigh resolutionIncrease contrastMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesGratingLight spot
The invention discloses a structural light microscopic imaging system based on line scanning time-space focusing. The system comprises the components of a femto second laser device; an acousto-optical modulator which is used for periodically modulating light source strength according to a sine function; a line scanning module which is used for scanning in a linear focusing light spot direction and a vertical linear light spot function; a dispersion element which is used for generating a spatial chirp; a collimating lens which is used for focusing different frequency components after grating dispersion to a parallel transmission direction; a microscope module; and a synchronous control module which is used for performing synchronous controlling on the acousto-optical modulator, the line scanning module and the microscope module, thereby obtaining a reconstructed image. According to the structural light microscopic imaging system, the reconstructed image can be obtained through strength-modulated line scanning structural light illumination in a line scanning time-space focused scanning mode and strength change of synchronously modulated excited light, thereby improving resolution and contrast in line scanning time-space focusing and reducing excitation outside a focal plane caused by medium scattering.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Disposable microscope and portable display
ActiveUS20100208054A1Minimal set-upFull connectivityCannulasEndoscopesImage manipulationDisplay device
Various embodiments for providing removable, pluggable and disposable opto-electronic modules for illumination and microscopic imaging are provided, for use with portable display devices. Generally, various medical or industrial miniature microscopes can include one or more solid state or other compact electro-optic illuminating elements, electronic vision systems and means of scanning located thereon. Additionally, such opto-electronic modules may include illuminating optics, imaging optics, and / or image manipulation and processing elements. The illuminating elements may have different wavelengths and can be time-synchronized with an image sensor to illuminate an object for imaging or detecting purpose or other conditioning purpose. All control and power functions of such disposable microscope units can be made in the control unit that the disposable microscopes are plugged into.
Owner:VIVID MEDICAL
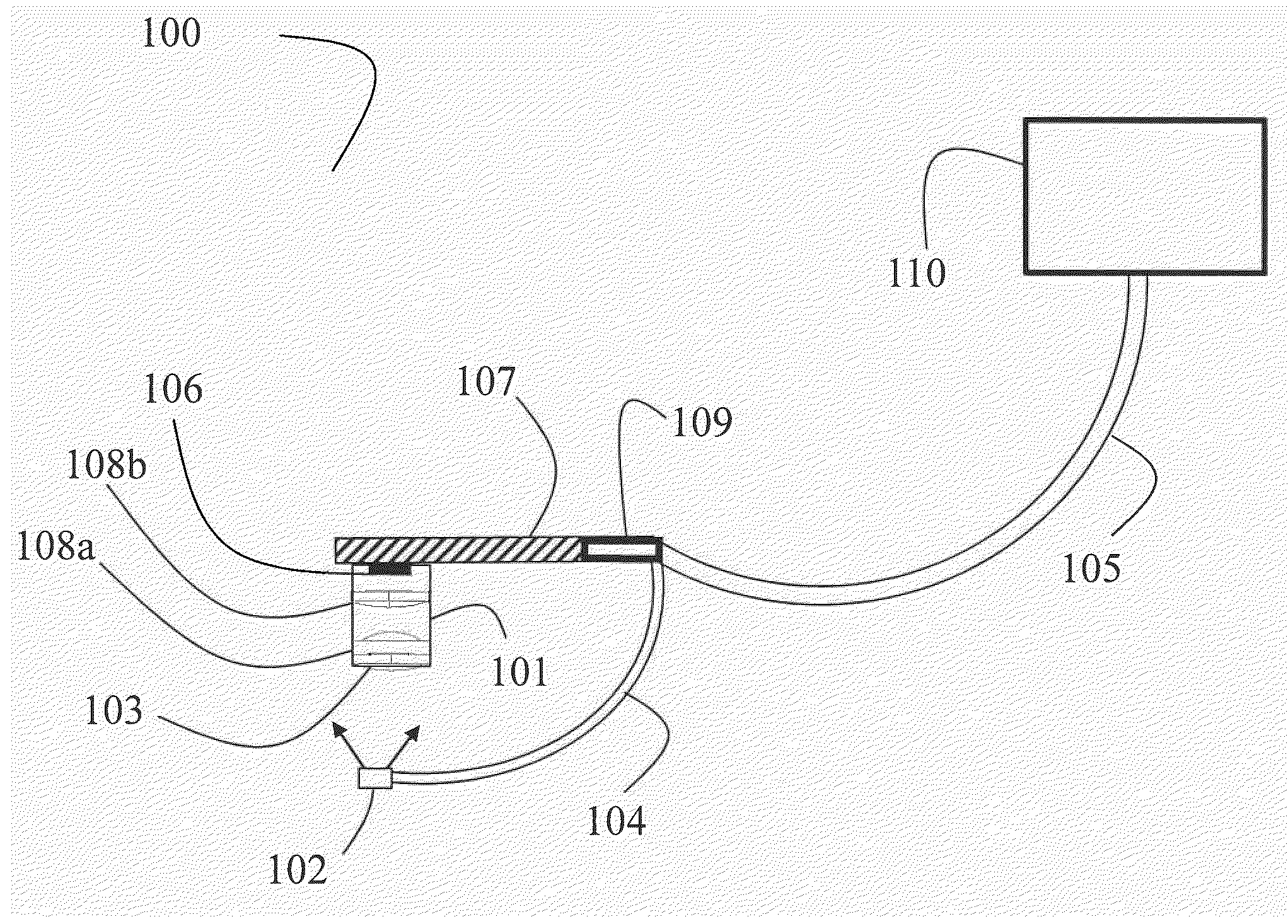
Magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging method and imaging system
ActiveCN102788836AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSource imagingAcoustic lens
The invention discloses a magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging method, comprising the steps of applying pulse excitation on a conductive target imaging body in a static magnetic field, generating an inductive vortex in the conductive target imaging body, and generating a Lorentz force by the interaction of the inductive vortex and the static magnetic field so as to cause the vibration of mass points in the imaging body to generate ultrasonic signals; receiving image signals of the ultrasonic signals of each mass point in the conductive target imaging body by using an array ultrasonic probe on a focal plane of an acoustic lens, imaging the received image signals of each mass point in the conductive target imaging body, so that each mass point image signal is proportional to the Lorentz force divergence of a corresponding point in the conductive target imaging body, and a Lorentz force divergence image of the conductive target imaging body or a reconstructed image according to current density rotation can be obtained according to the image signals of the ultrasonic signals detected by the array ultrasonic probe. A magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging system using the imaging method disclosed by the invention comprises a synchronous trigger and control module (1), an excitation source, an imaging system and a week signal detecting system.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Super-resolution confocal microimaging method and device based on column polarization vortex beam
The invention provides a super-resolution confocal microimaging device based on a column polarization vortex beam. The super-resolution confocal microimaging device comprises a pinhole filter, a collimating lens, a polarization and phase transformation system, a pupil filter, an optical filter, a detector and a three-dimensional translational platform, wherein a beam emitted from a laser passes the pinhole filter to obtain a Gauss basic mode beam, the collimating lens collimates the Gauss basic mode beam into the parallel beam, the polarization and phase transformation system allows the parallel beam to pass and obtain the column polarization vortex beam with preset polarization and phase distribution, the pupil filter allows the column polarization vortex beam to pass and to be reflected through a beam splitter and focused on a to-be-detected sample through a collecting lens, light signals reflected from the sample pass the collecting lens and the beam splitter to be incident on the optical filter, and the optical filter only allows a fluorescence signal of the light signals to be transmitted, the fluorescence signal is focused on a detecting pinhole through the collecting lens and is detected and converted, through the detector, into an electrical signal to be output, the sample is placed on the three-dimensional translational platform, detection of the sample at different positions can be realized by moving the three-dimensional translational platform, and accordingly three-dimensional scanning imaging of the sample can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
Total internal reflection holographic microscope
ActiveUS7812959B1Fast imagingEasy accessUsing optical meansOptical elementsTotal internal reflectionPhase shifted
The present invention provides for a digital holographic microscope using a holographic interferometer and incorporating a TIR sample mount and microscopic imaging optics. The microscope uses phase shifting from frustrated internal reflection within a prism to measure nanometric distances. The invention also provides for a numerical reconstruction algorithm of an inclined surface of the object / prism.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Multi-beam laser interference cross-scale 3D (three dimension) printing system and method
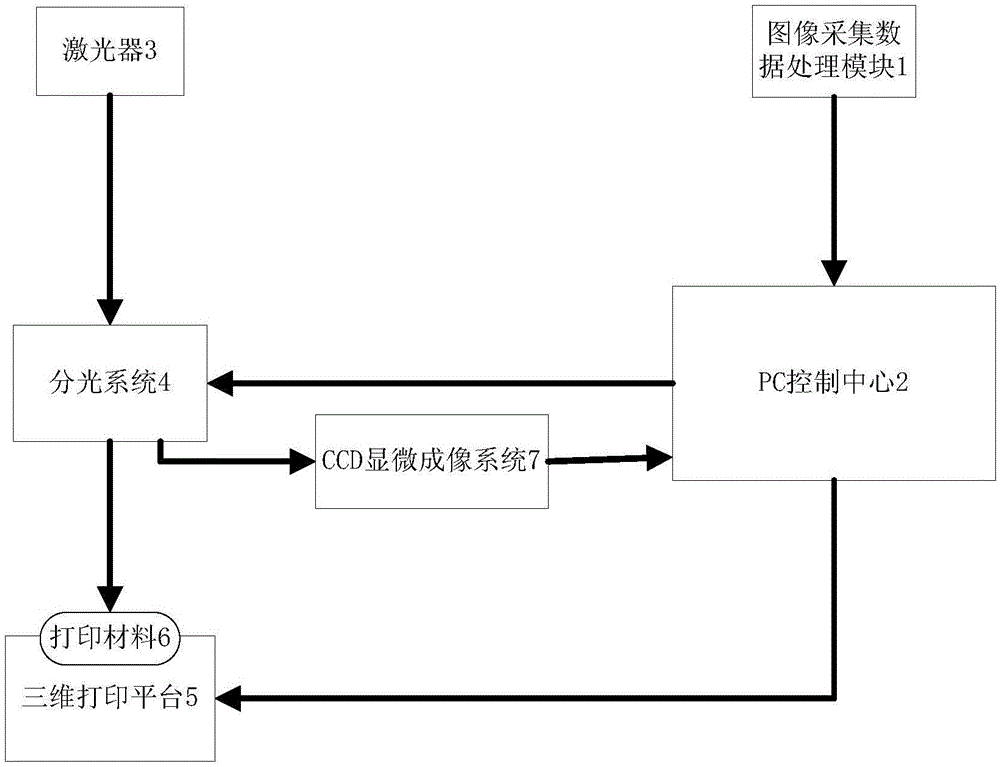
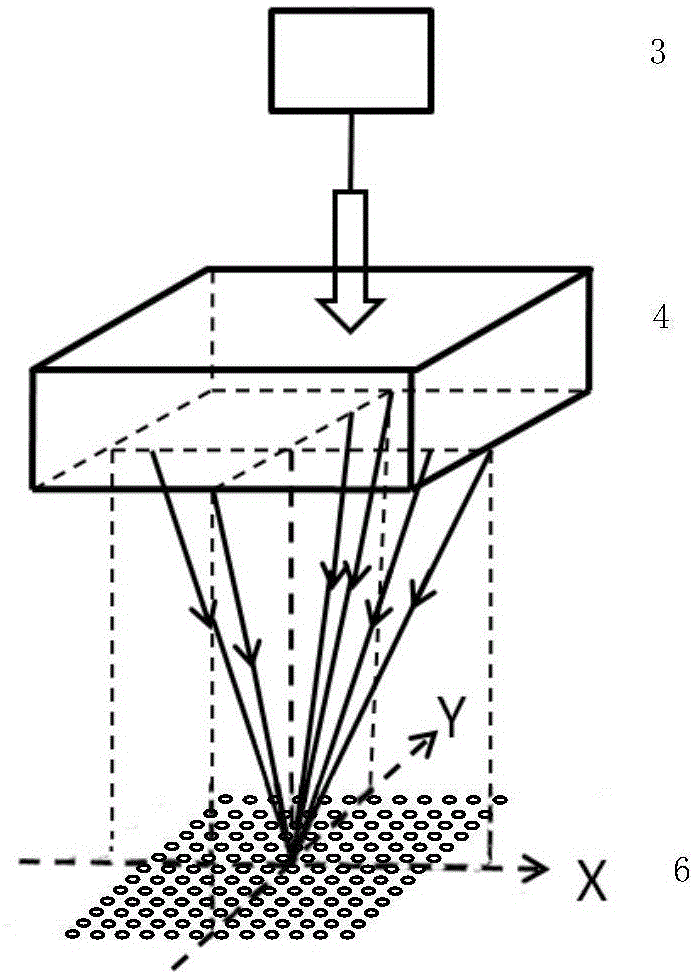
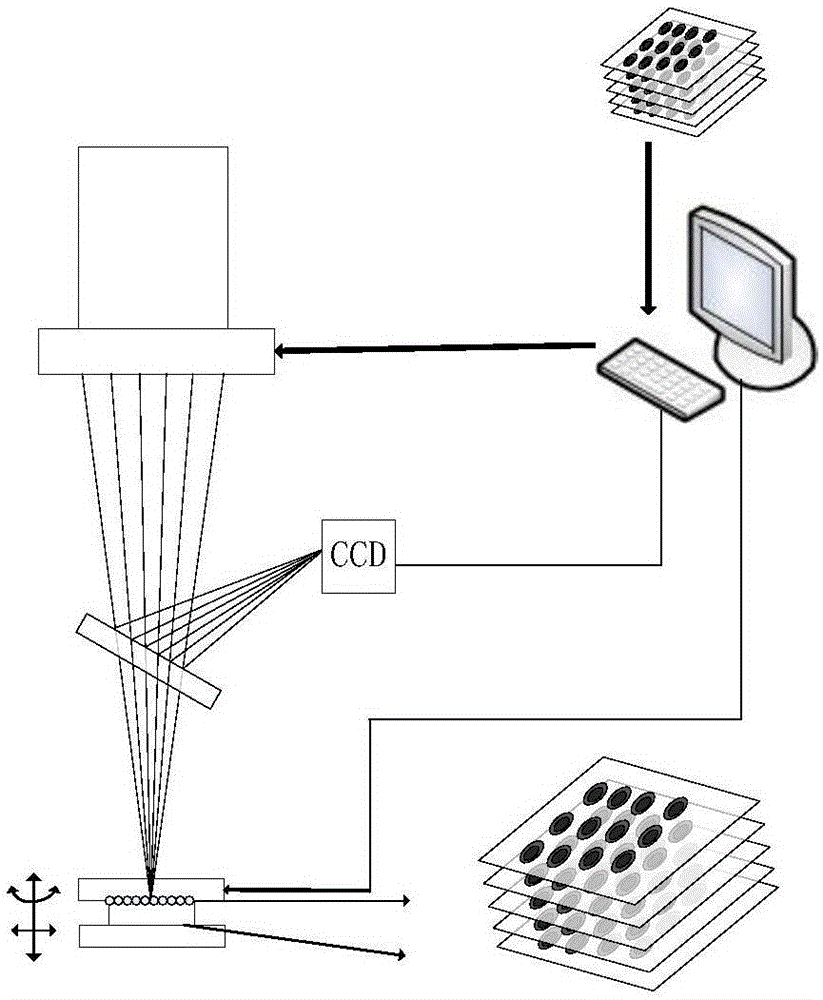
ActiveCN104999670ALarge exposure field areaImprove efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusBeam splittingEngineering
The invention relates to a system and a method for achieving cross-scale 3D (three dimension) printing by adopting a micro-nano composite periodic structure interference light source generated by a multi-beam laser interference technology, belonging to improvement on the existing 3D printing method. The system comprises an image acquisition data processing module (1), a PC control center (2), a laser (3), a beam splitting system (4), a 3D printing platform (5), a printing material (6) and a CCD microscopic imaging system (7). Original 3D printing speed and resolution are improved, a micro-nano composite structure material of a printed object is directly formed, and the system and the method belong to a high-speed large-area efficient micro-nano composite structure 3D printing technology.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
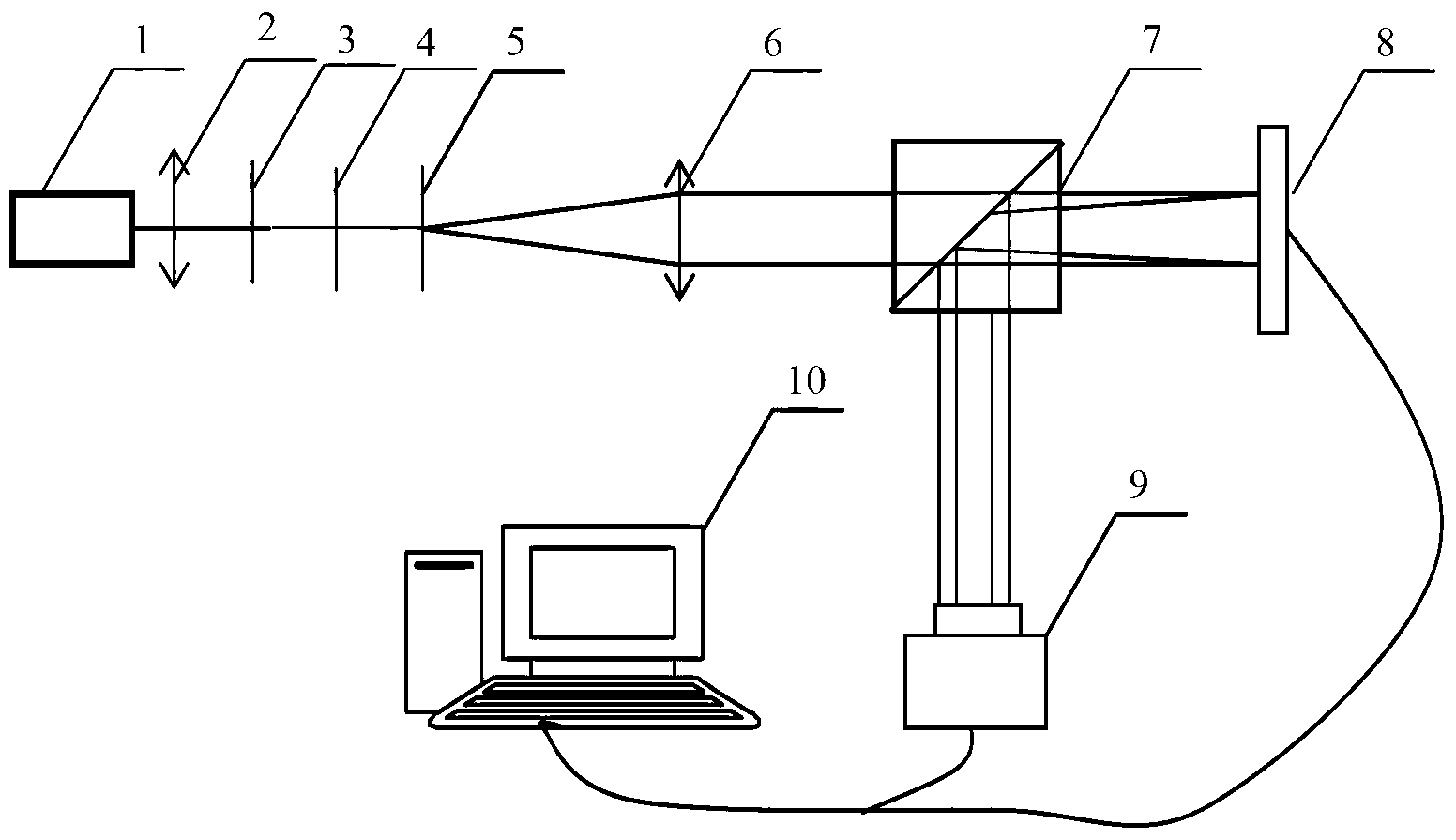
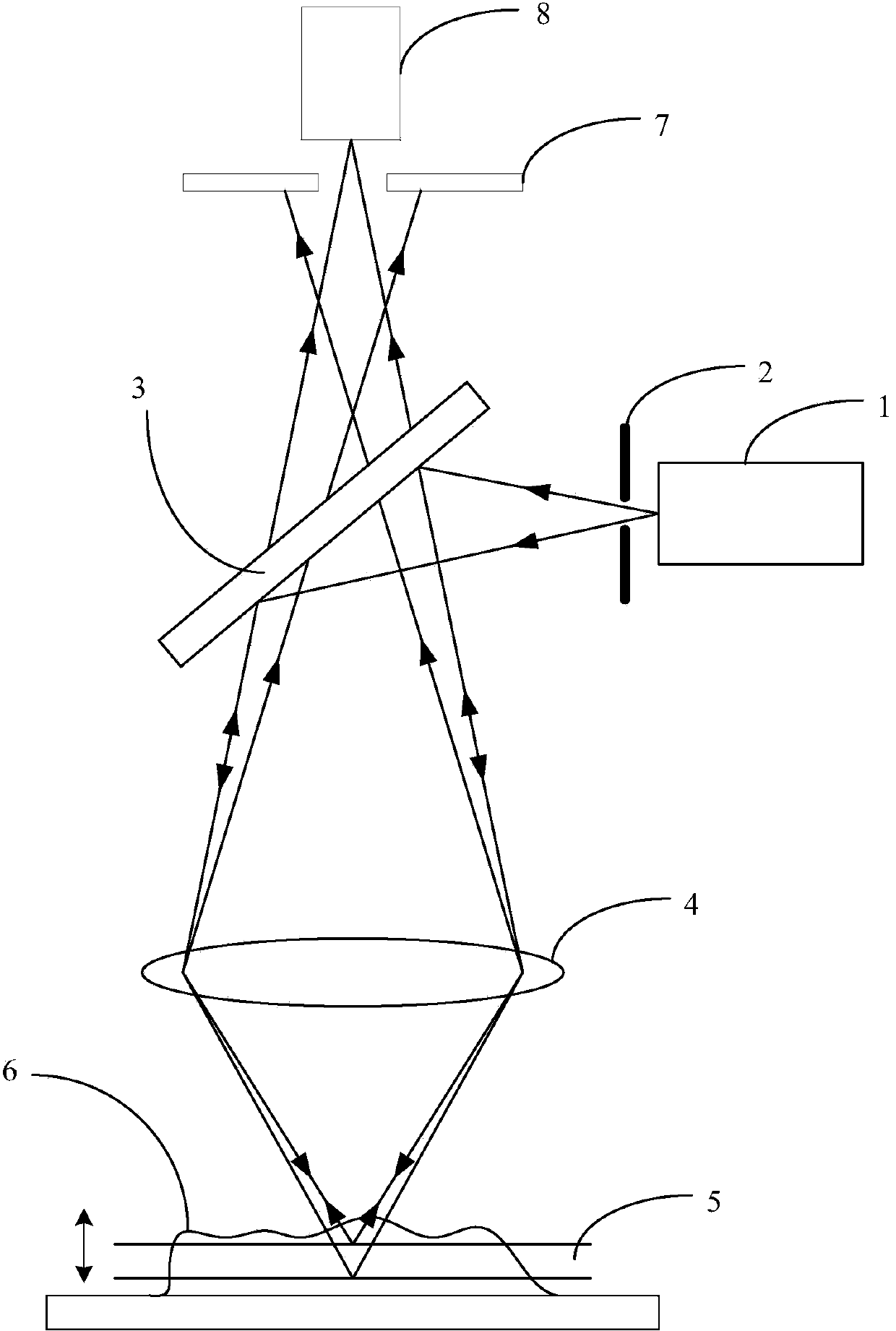
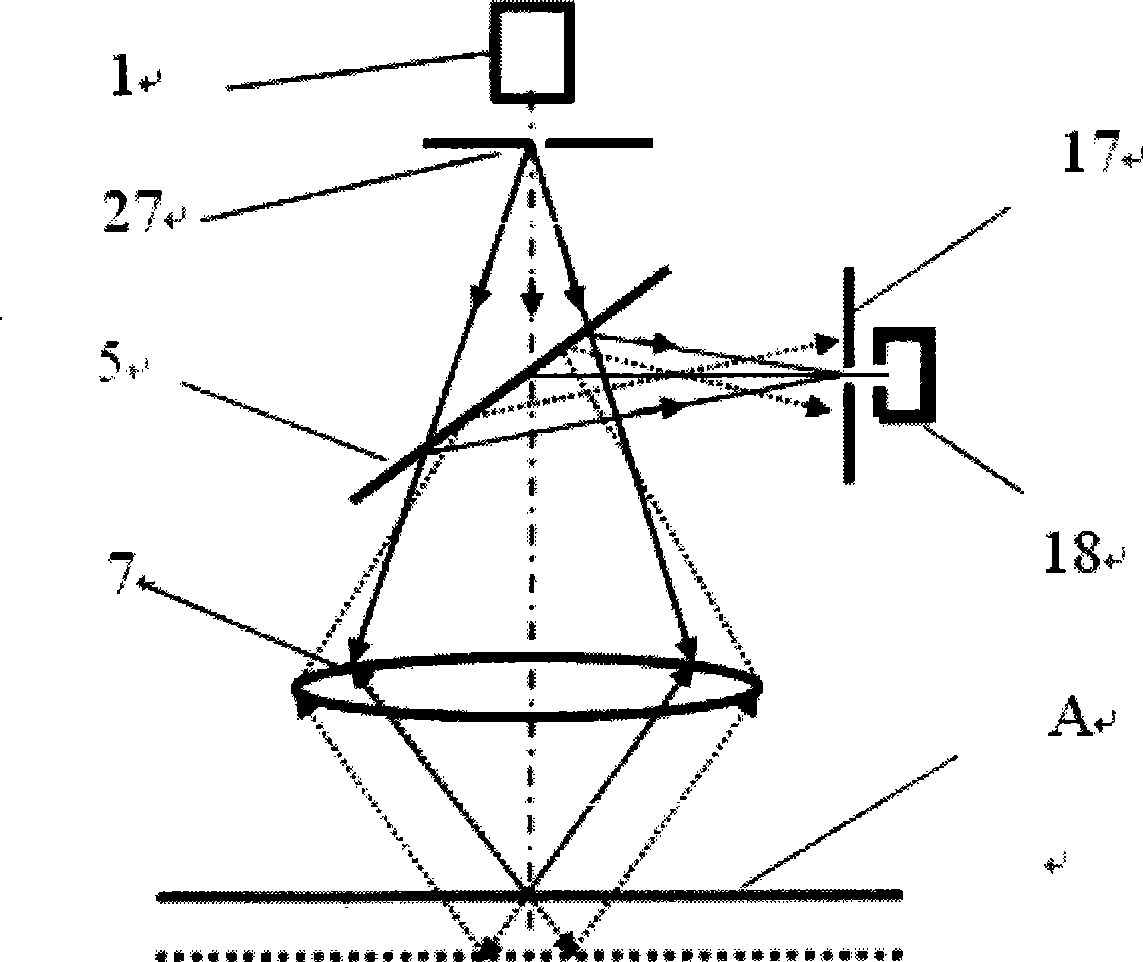
Ultra-discrimination differential confocal microscope with macro-micro view field observation
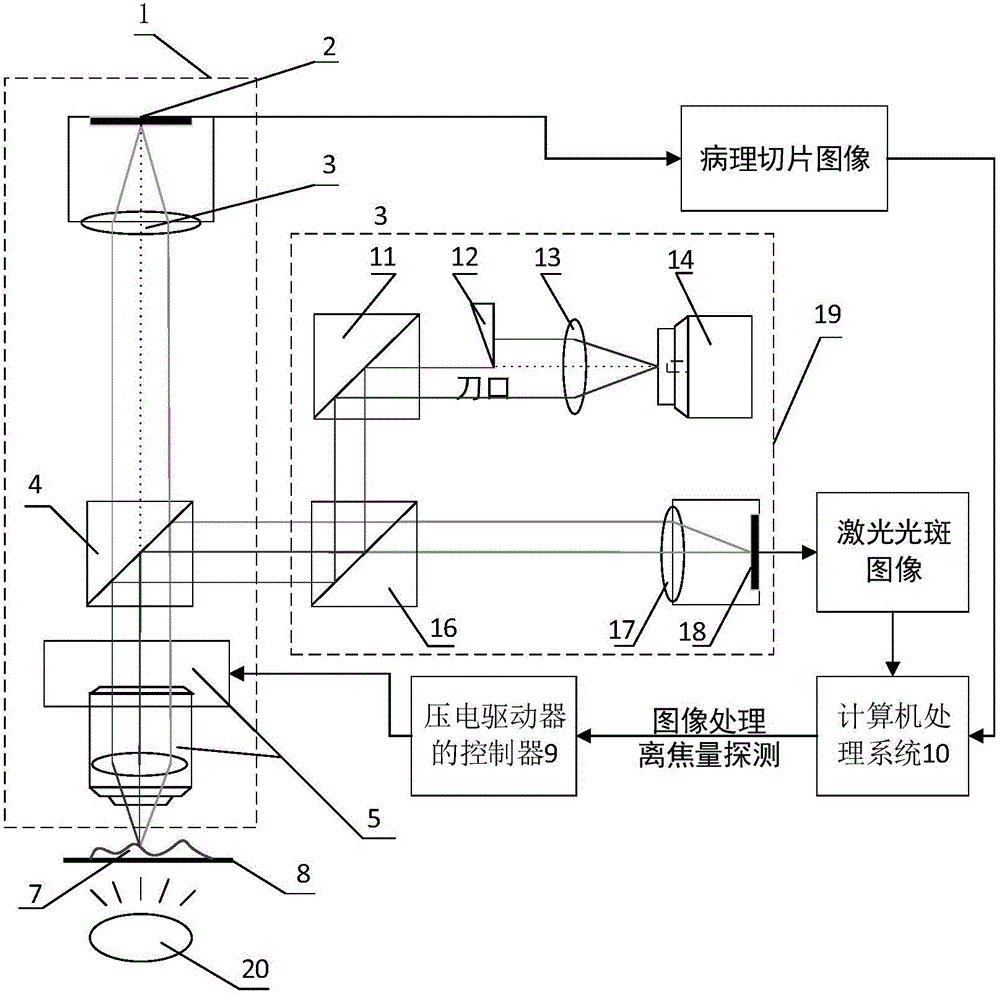
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical microscopic imaging and optical precision measurement and relates to a super-resolution differential con-focal microscope with both macro field coverage observation and micro field coverage observation. The invention mainly comprises a laser (1), a beam expander (2), a spectroscope (4), a polarization spectroscope (5), a range extension tracking and measuring system (6), a measuring objective lens (7), two optical collectors (16) and (19), pinholes (17) and (20), detectors (18) and (21), an LED light emitting diode (12) which is arranged in a direction opposite to the reflection direction of the spectroscope and a CCD detector (11) which is arranged in a direction opposite to the reflection direction of a spectroscope (9). The LED light emitting diode and the CCD detector are used for realizing macro-field coverage observation of a con-focal microscope through imaging the surface type of the detected samples, and the axial resolution power of the con-focal microscope can be raised through deploying the optical path of the differential con-focal microscope.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
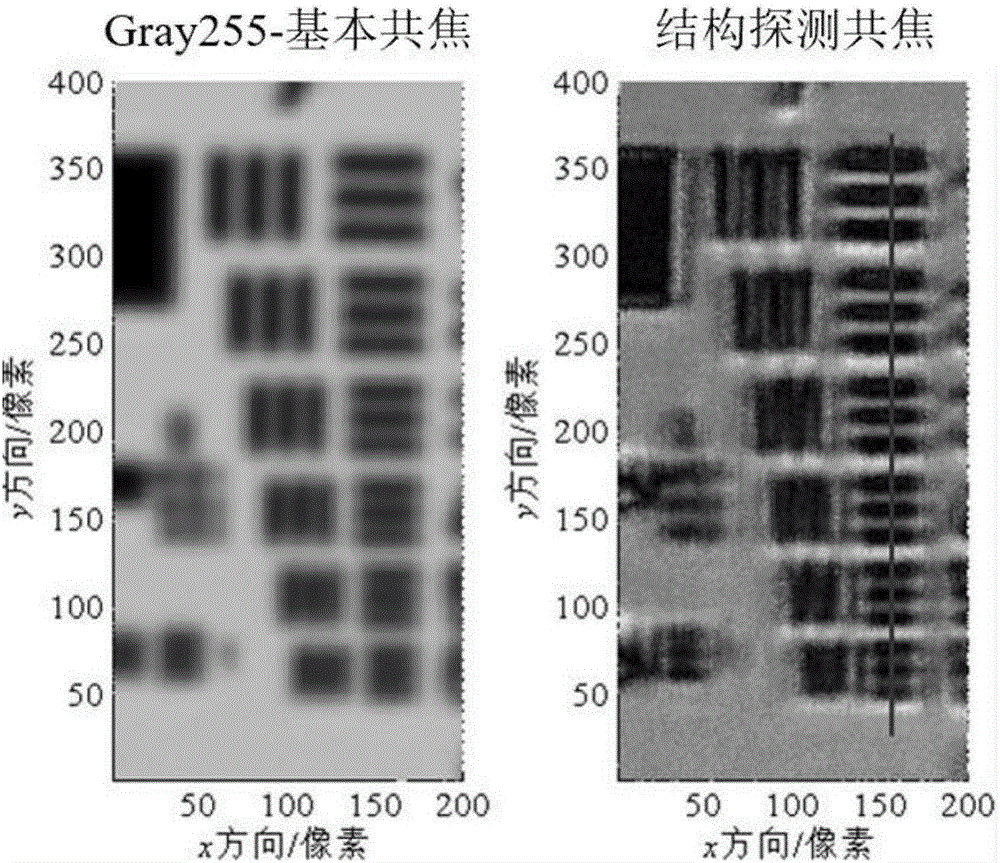
Structure detection confocal microscopy imaging method and apparatus based on spatial light modulator
ActiveCN106767400ARealize 3D ImagingStructure detection implementationUsing optical meansSpatial light modulatorPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention provides a structure detection confocal microscopy imaging method and apparatus based on a spatial light modulator, and mainly solves problems of low image acquisition rate and long image processing time of conventional confocal microscopy imaging. According to the method, a structure detection method is introduced to a confocal scanning microscopic system, a structure detection function is simulated by employing the spatial light modulator, detection light spots are modulated, the light intensity after modulation is measured by employing a photoelectric detector, a light intensity value corresponding to a sampling point of a to-be-measured sample is obtained, and three-dimensional imaging of the to-be-measured sample can be realized with the combination of a scanning mechanism of the confocal microscopy system. The invention also provides a measuring device applicable to the method, structure detection is realized through the transmission type spatial light modulator and the photoelectric detector, the resolution is high, and the imaging speed is high.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
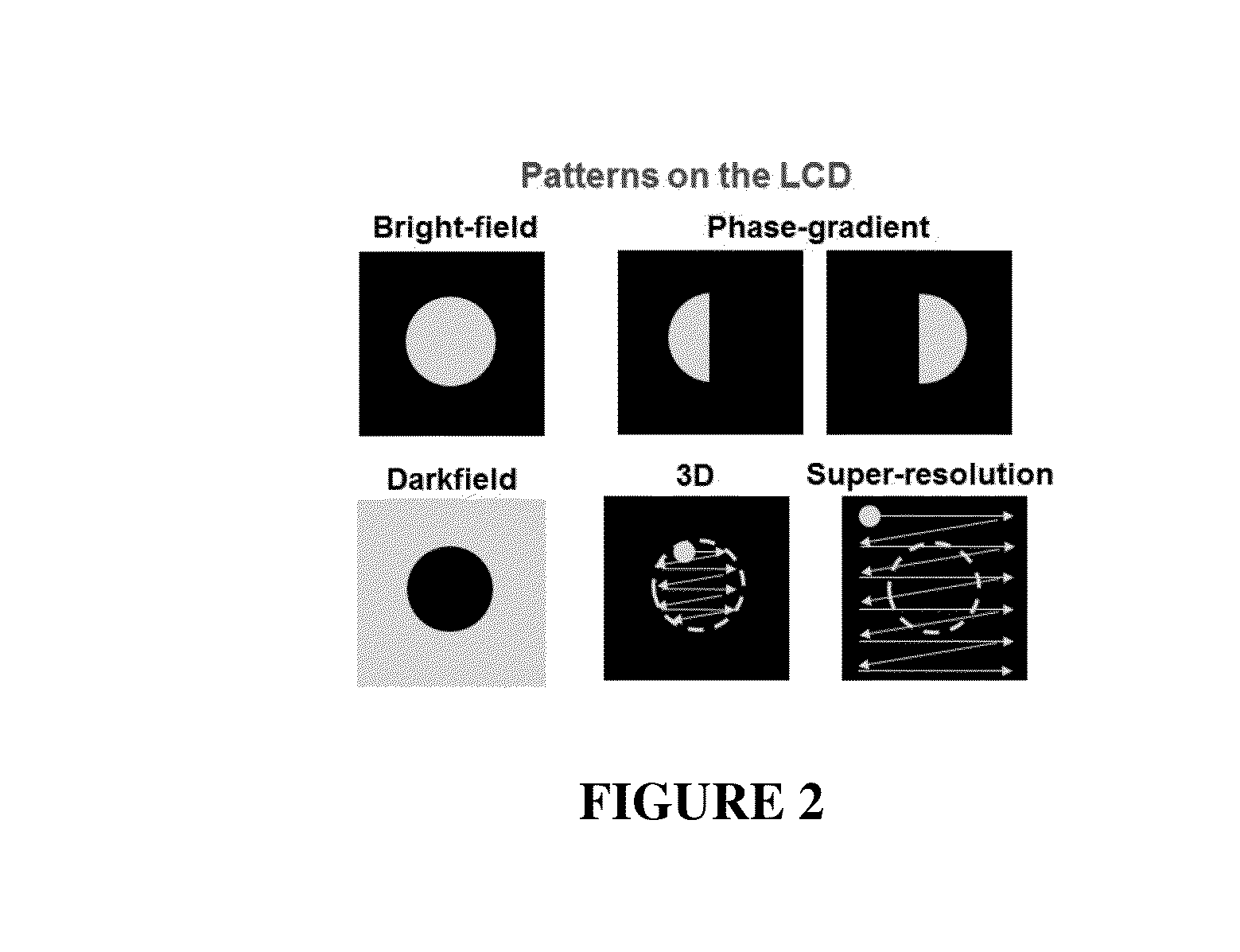
3D Microscopy With Illumination Engineering
InactiveUS20160202460A1Television system detailsColor television detailsSpatial light modulatorFluorescence
The present disclosure provides improved microscopic imaging techniques, equipment and systems. More particularly, the present disclosure provides advantageous microscopy assemblies with illumination engineering (e.g., 3D microscopy assemblies with illumination engineering), and related methods of use. Disclosed herein is an imaging technique / assembly that uses a spatial light modulator (“SLM”) for 3D tomographic imaging with brightfield or fluorescence illumination that can also be utilized for bright-field, dark-field, phase-contrast, and super-resolution microscopy. Disclosed herein are methods and instrumentation / assemblies having preferred uses for 3D tomographic imaging, and phase-contrast and super-resolution imaging. The present disclosure advantageously provides for assemblies and methods configured to create 3D tomographic images by way of acquiring a series of images with varied angle illumination using a SLM and computational reconstruction that substantially eliminates the need to move the sample. The disclosed assemblies and methods are also able to acquire bright-field, dark-field, various contrast, and super-resolution images.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
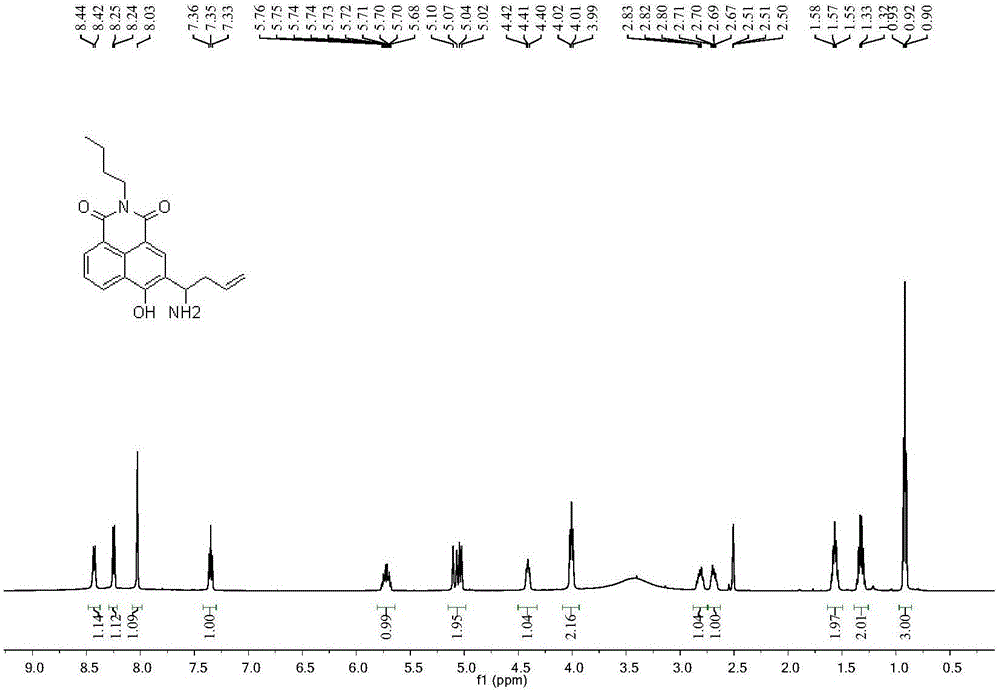
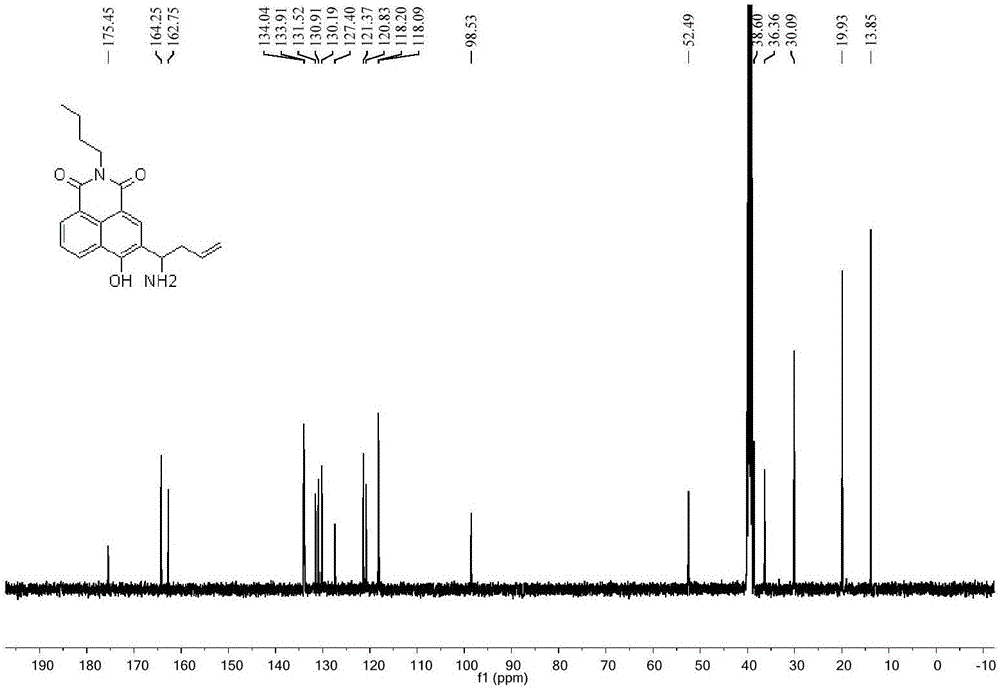
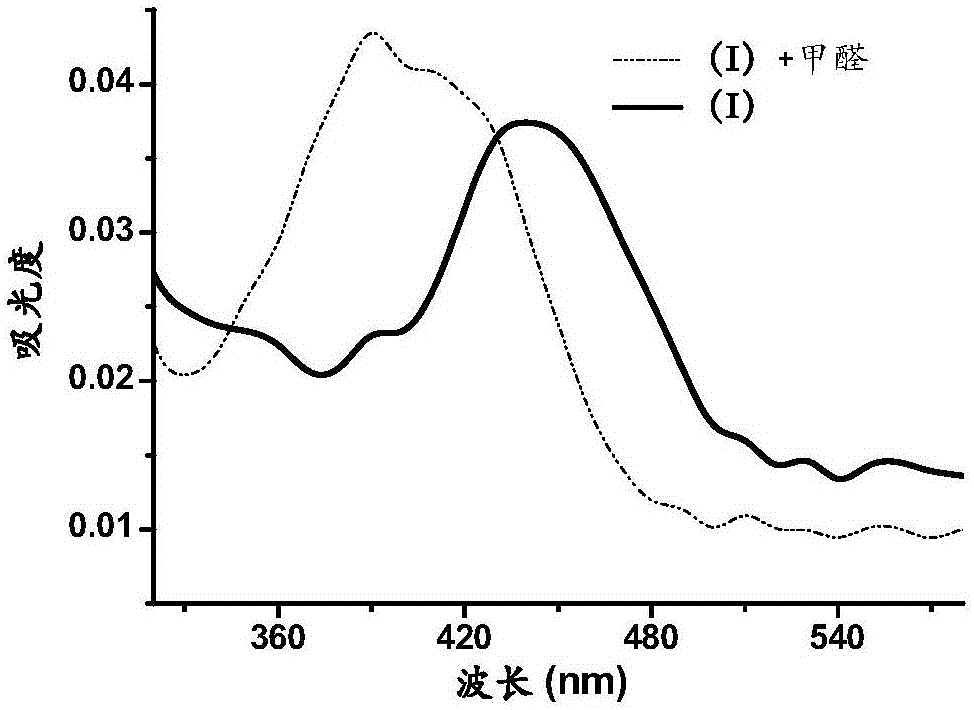
Two-photon formaldehyde fluorescent probe and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN105924394AStrong specificityReduce autofluorescence backgroundOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceCell membrane
The invention discloses a two-photon formaldehyde fluorescent probe and preparation and application thereof. The probe is a novel formaldehyde probe taking 1,8-naphthalimide as a two-photon fluorogen on the basis of an intramolecular charge transfer mechanism. Probe molecules have good light stability and a large Stoke's shift, the probe can well detect the formaldehyde concentration in a neutral buffer solution, and meanwhile compared with other aldehyde compounds, the probe has good specificity on formaldehyde. It is well proved through two-photon confocal fluorescence microscopic imaging experiments that the probe can permeate through a cell membrane to enter cells and can detect a change of the formaldehyde concentration in the cells, and an effective research tool for researching the physiological action of formaldehyde in the cells is provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
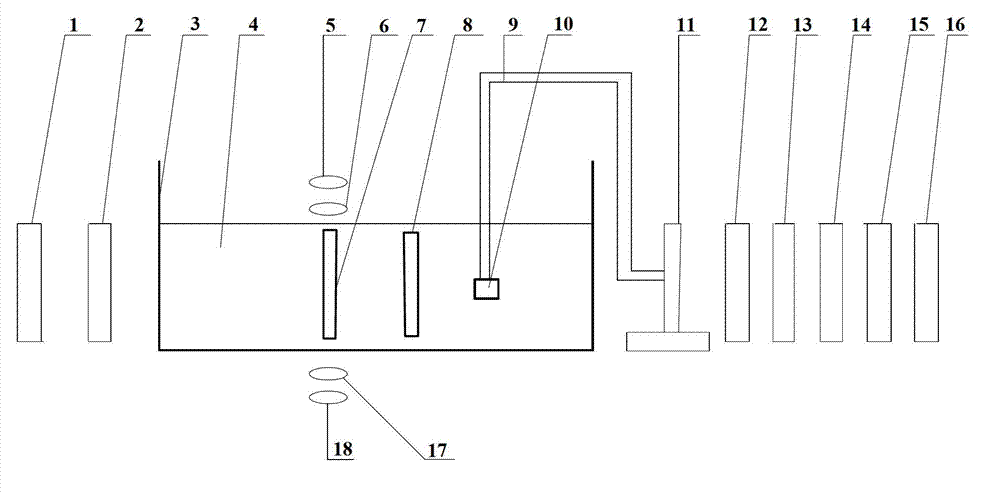
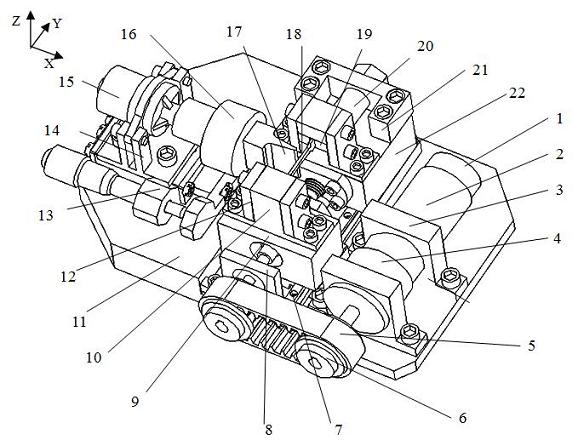
Stretching, compression and bending combined load mode material mechanics performance test device under microscope
ActiveCN102384875AGood structural compatibilityRich test contentMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady bending forcesElectromechanicsEngineering
The invention relates to a stretching, compression and bending combined load mode material mechanics performance test device under a microscope, and belongs to the electromechanics. A test platform includes a precision stretching / compression load driving unit, a precision bending load driving unit, a clamping unit, a detecting unit and the like. The test platform can be used for the sole stretching / compression test, sole three-point bending test, and the stretching / compression-bending combined load test. The invention has the advantages that the structure is small and compact, and the tests can be performed under the real-time observation of the optical microscope; the loading mode of the combined load is in conformity with the stress state of material and members under the actual workingcondition, and combined with the optical microscopic imaging system, deepgoing study on the micromechanics behavior and denaturing impairment mechanism of the material under the action of combined load can be carried out.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Super-resolution imaging system
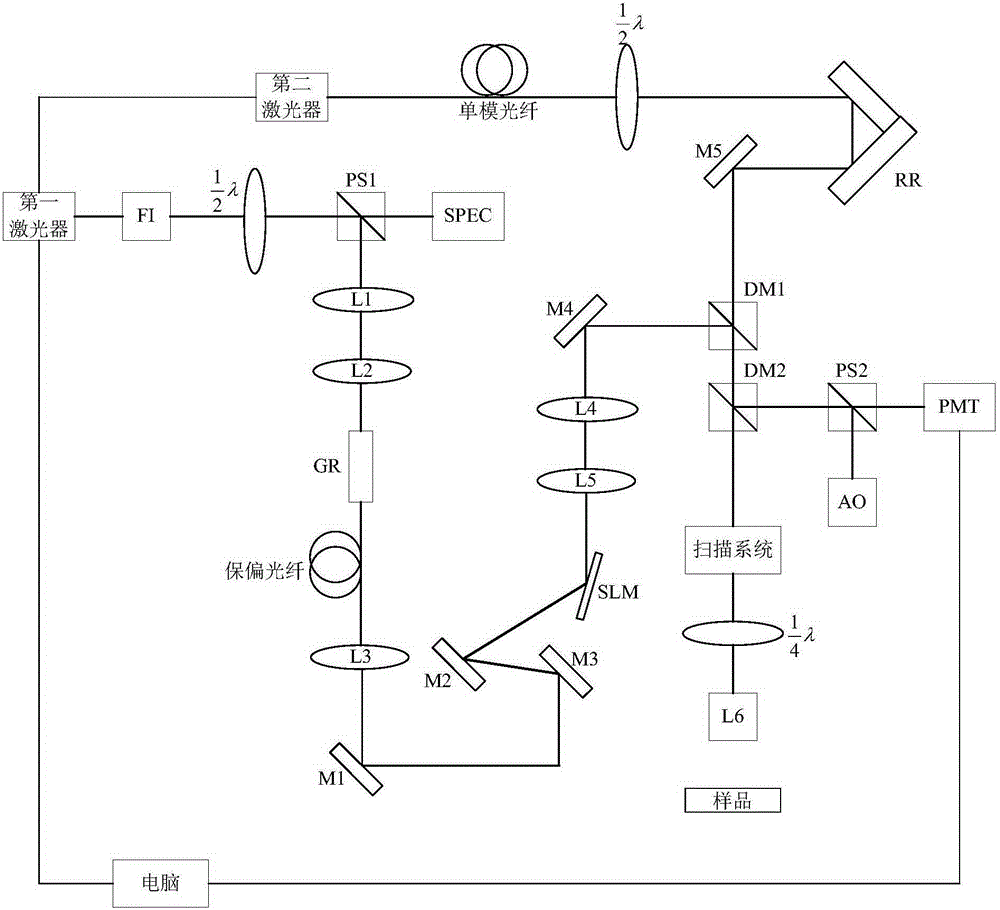
InactiveCN105241857ARealize aberration correctionImprove spatial resolutionFluorescence/phosphorescencePulse beamSpatial light modulator
The invention discloses a super-resolution imaging system. The imaging system comprises a first laser, a second laser, a first half-wave plate, a first pulse beam splitter, a spectrometer, a first battery of lens, a glass rod, polarization maintaining optical fibers, a spatial light modulator, a first object lens, a battery of reflectors, a second battery of lens, a reflector, single mode fibers, a second half-wave plate, a retroreflector, a reflector, a first dichroic mirror, a second dichroic mirror, a scanning system, a one fourth slide, a spacial object lens, a second pulse beam splitter, and a photomultiplier. A coherent optical adaptive technique is adopted to carry out aberration correction so as to increase the spatial resolution of a STED super-resolution microscopic imaging system, thus the aberration caused by uneven surface of a biological sample and uneven distribution of inner refractive index of a sample is eliminated, and the spacial resolution is increased.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
A method for pattern recognition of cancer cells using soft x-ray microscopic imaging
InactiveCN102297873APreparing sample for investigationBiological neural network modelsMicroscopic imageSoft x ray
This invention discloses a method for utilizing soft X-ray microimaging for cancer cell image recognition. The method comprises the steps of 1) sample preparation; 2) pathological examination; 3) soft X-ray imaging; and 4) analysis and recognition. This invention applies soft X-ray microimaging for cancer cell image recognition, successfully obtains the soft X-ray microscopic image of a cancer cell by scanning the cancer cell with synchrotron radiation soft X-ray microimaging, provides recognition steps and experimental data, and establishes a method for utilizing soft X-ray microimaging for cancer cell image recognition. This invention creates a method for analyzing soft X-ray microscopic images, provides a novel synchrotron radiation soft X-ray pathological diagnosis method for cancer diagnosis, and provides an extremely valuable basis for the creation and clinical application of soft X-ray pathology in the 21st century.
Owner:NO 128 HOSPITAL OF HANGZHOU
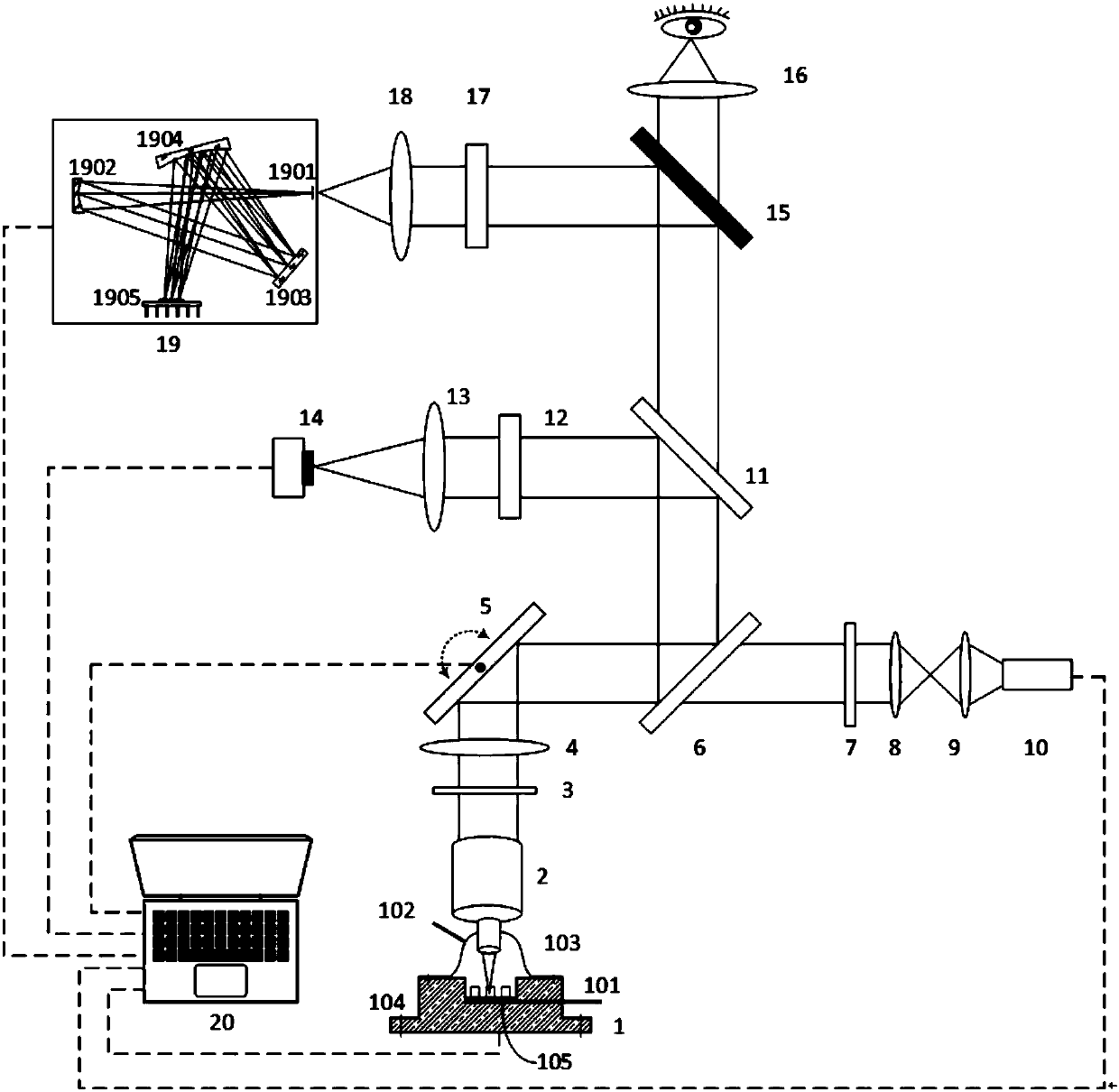
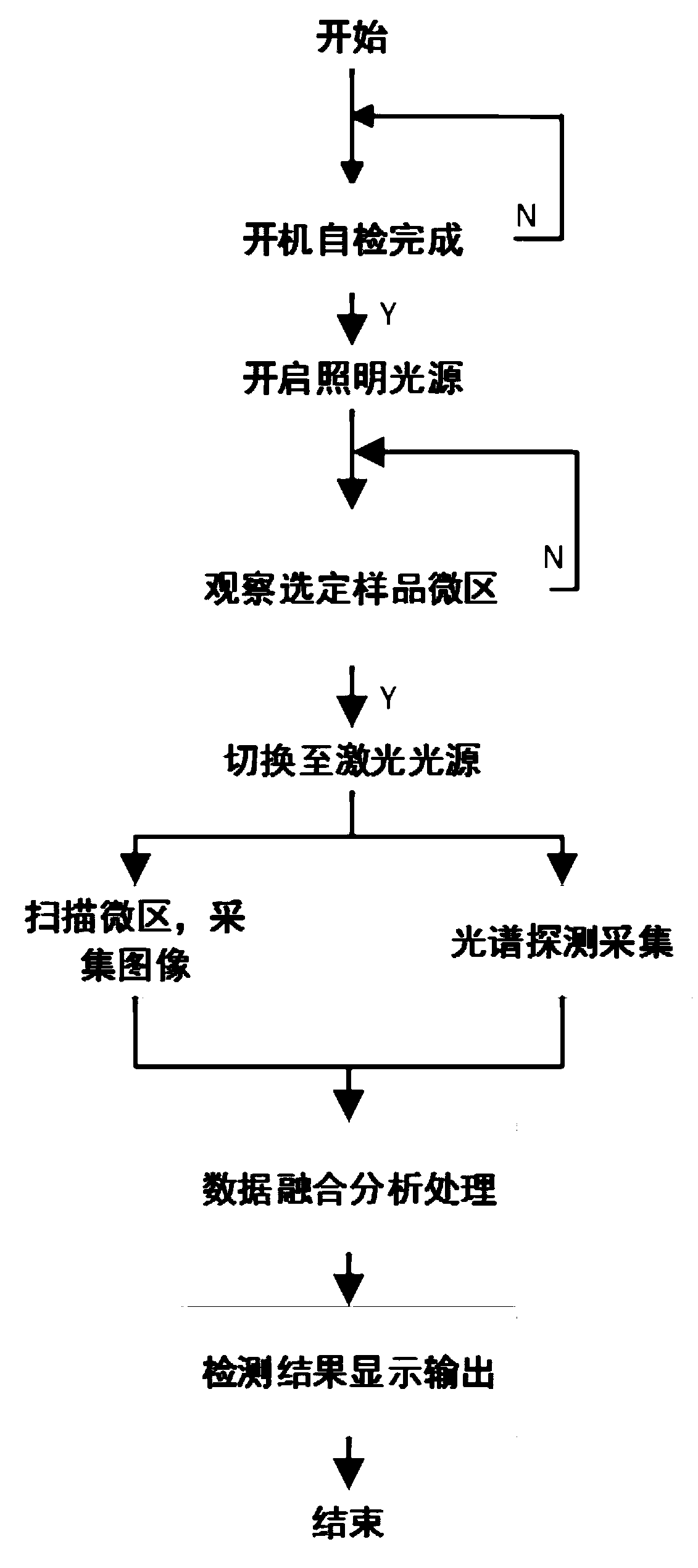
Microscopic Raman imaging spectrum rapid detection apparatus and method thereof
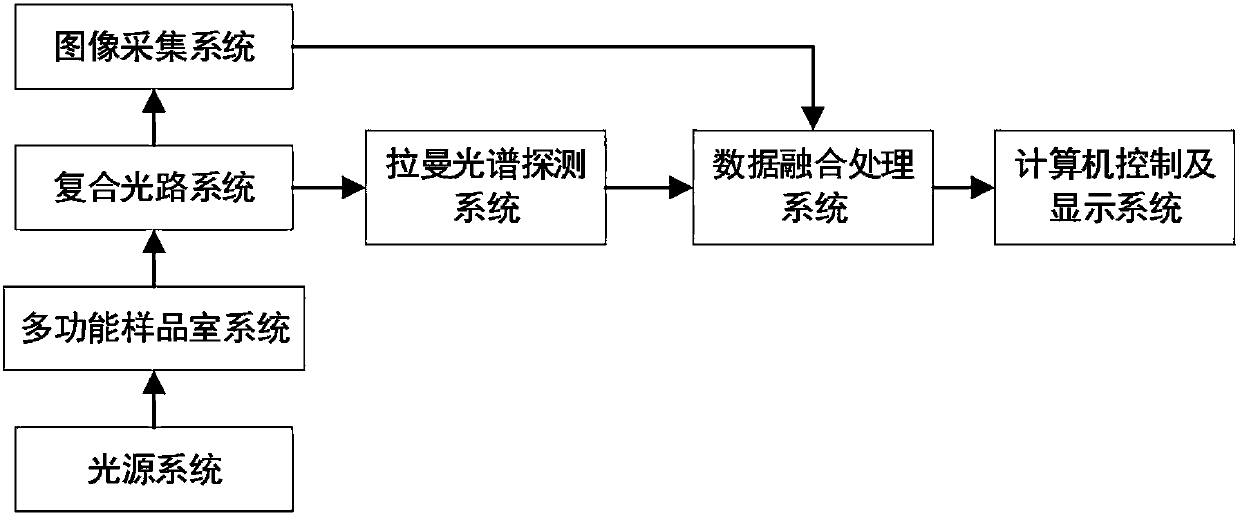
The invention discloses a microscopic Raman imaging spectrum rapid detection apparatus and a method thereof, which belong to the technical field of optical microscopic imaging and spectral measurement. The microscopic Raman imaging spectrum rapid detection apparatus comprises a light source, a multifunctional sample room, a composite optical system, an image acquisition system, a data fusion processing system, a Raman spectrum detection system, and a computer control and display system. According to white light or laser emitted by the light source, sample in-situ observation and microscopic Raman imaging spectrum real-time on-line detection are respectively realized, the data fusion processing system performs real-time analysis processing on images and spectrum information, and images andspectrum information are displayed and output in the computer control and display system. The microscopic Raman imaging spectrum rapid detection apparatus has the characteristics of compact structure,high spatial resolution, convenient usage, and stable performance, can be used in the fields of water quality detection, material analysis, petrochemical engineering, environment monitoring, and industrial precision detection, is convenient for field on-site investigation experiment and on-line test real-time analysis, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
High dynamic image acquisition device based on microscopic imaging detection and method thereof
InactiveCN101441320AImprove detection accuracyImprove clarityMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesCircular discMicroscopic image
The invention relates to a high dynamic image acquisition process based on micro-imaging detection and its device, comprising a microscope and a computer system. A digital CCD image sensor is equipped on the microscope. A circular disc type optical gradient attenuator and a controller are arranged at the lower part of the object lens. Under the condition of invariant exposure time for CCD, the computer controls the rotary location for the circular disc type optical gradient attenuator sheet to take the multi-frame microscopic image with different light exposure in the same visual field and further obtain the high dynamic range image information in the scene. The invention utilizes the computer image processing technique to perform a preprocessing and blocking treatment to the sequence frame of the microscopic image with different light exposure, selects the corresponding block of different frames of the sequence microscopic image in the same position to take part in the synthesis of the high dynamic microscopic image, and finally performs the smooth and amalgamation process to the synthesis image to realize the output of the high dynamic microscopic image. The invention effectively represents the scene information in light region and dark region and improves the detecting precision of the micro-imaging detecting system.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com