Patents
Literature
117 results about "Raman imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
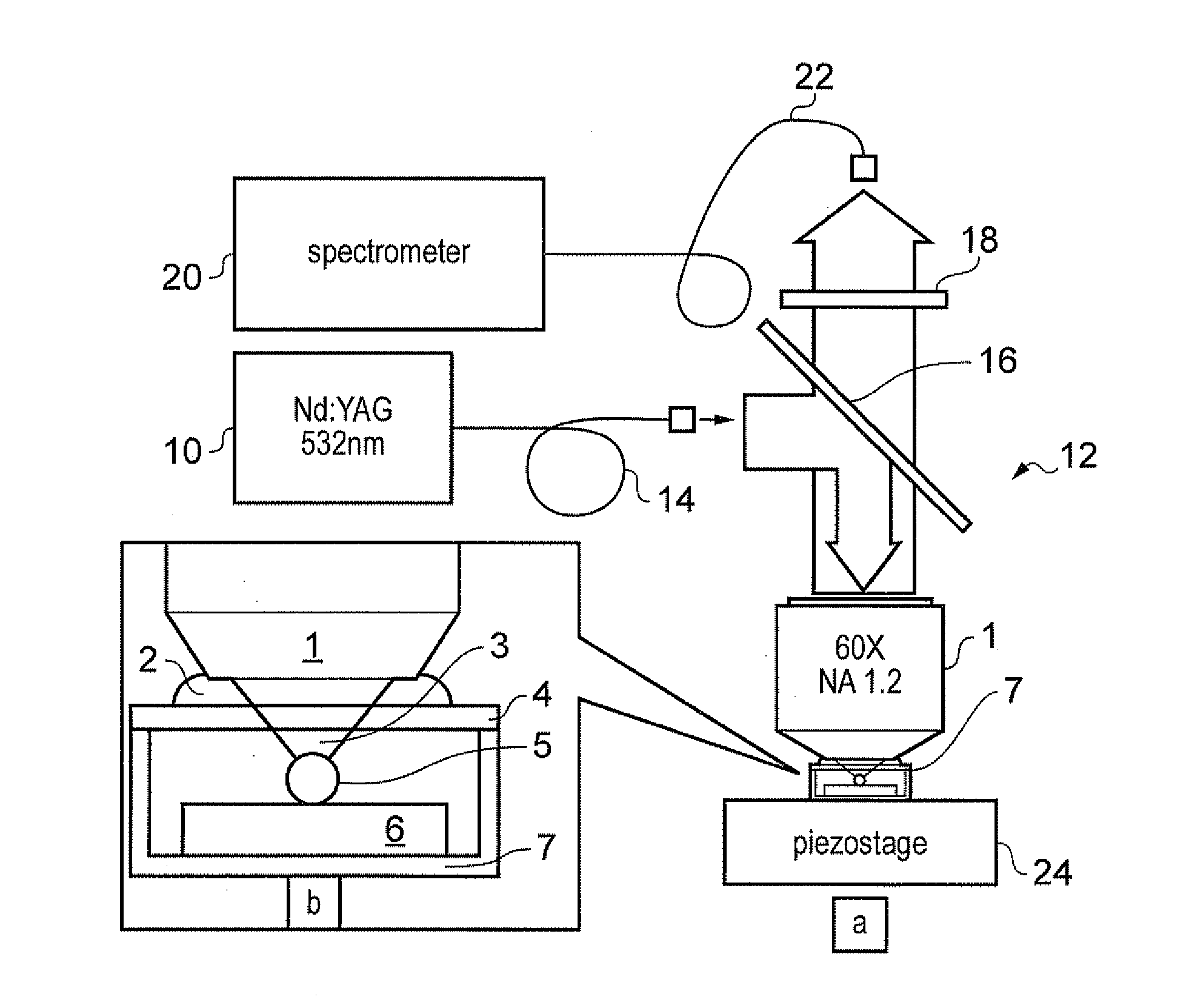
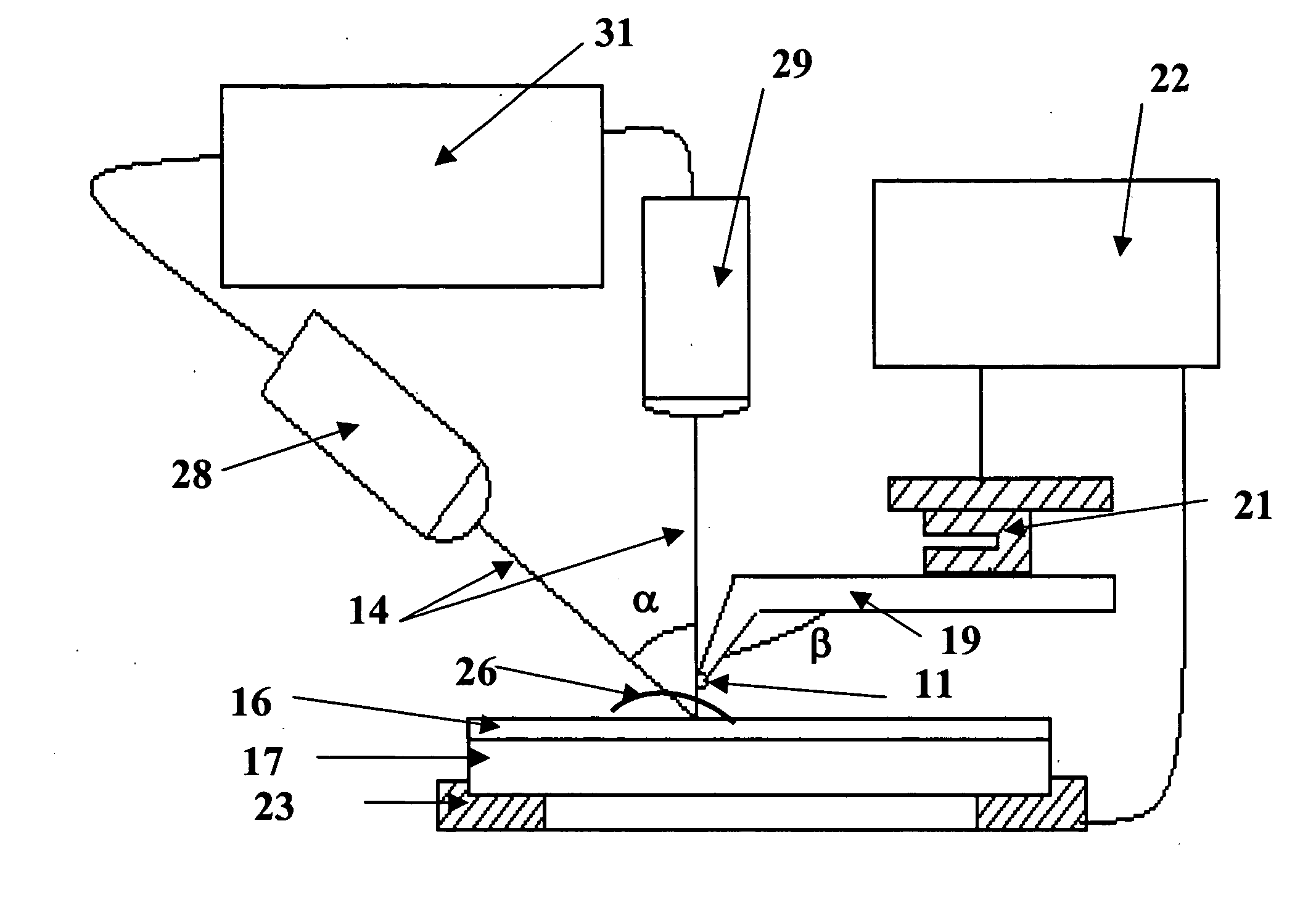
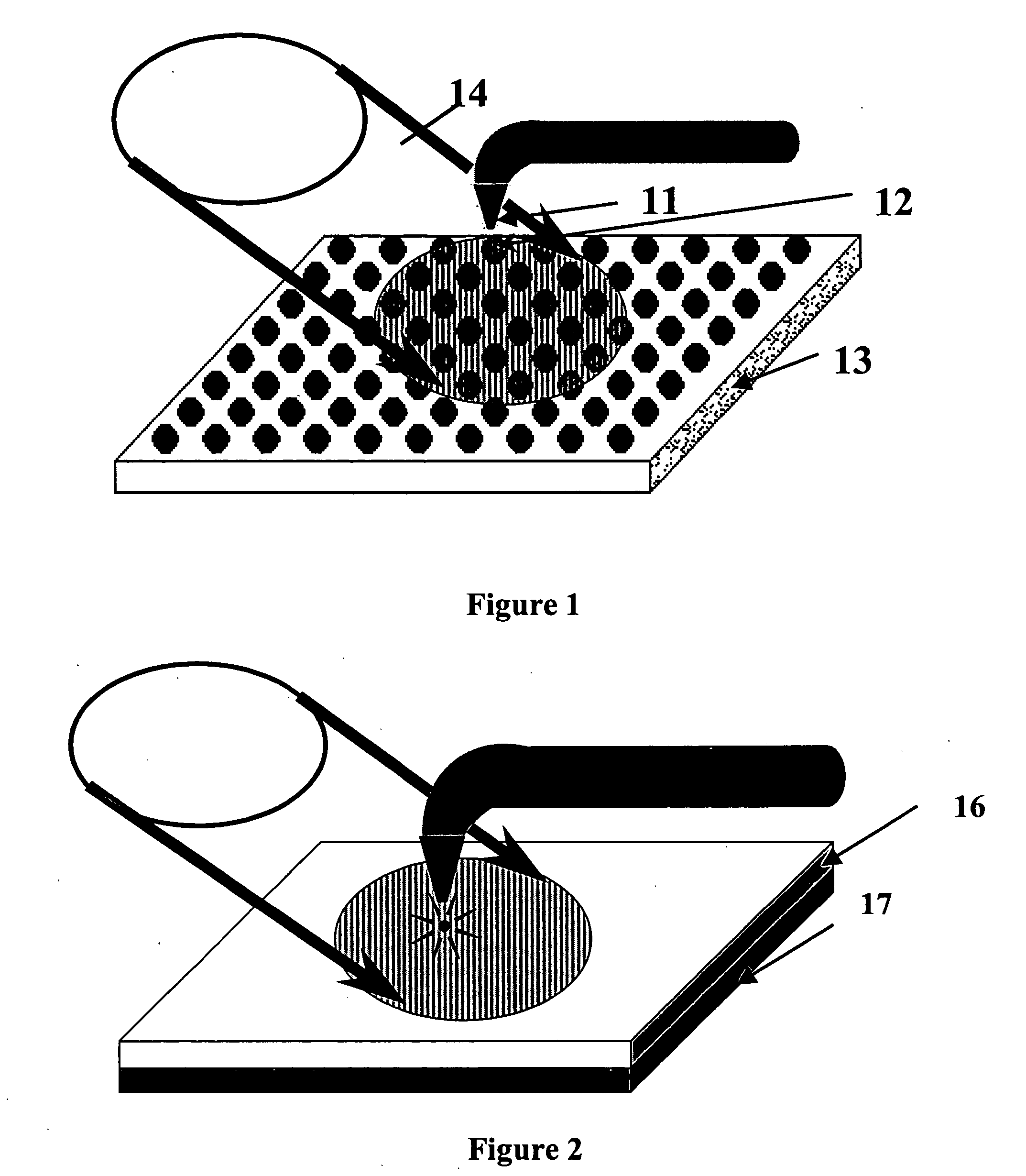
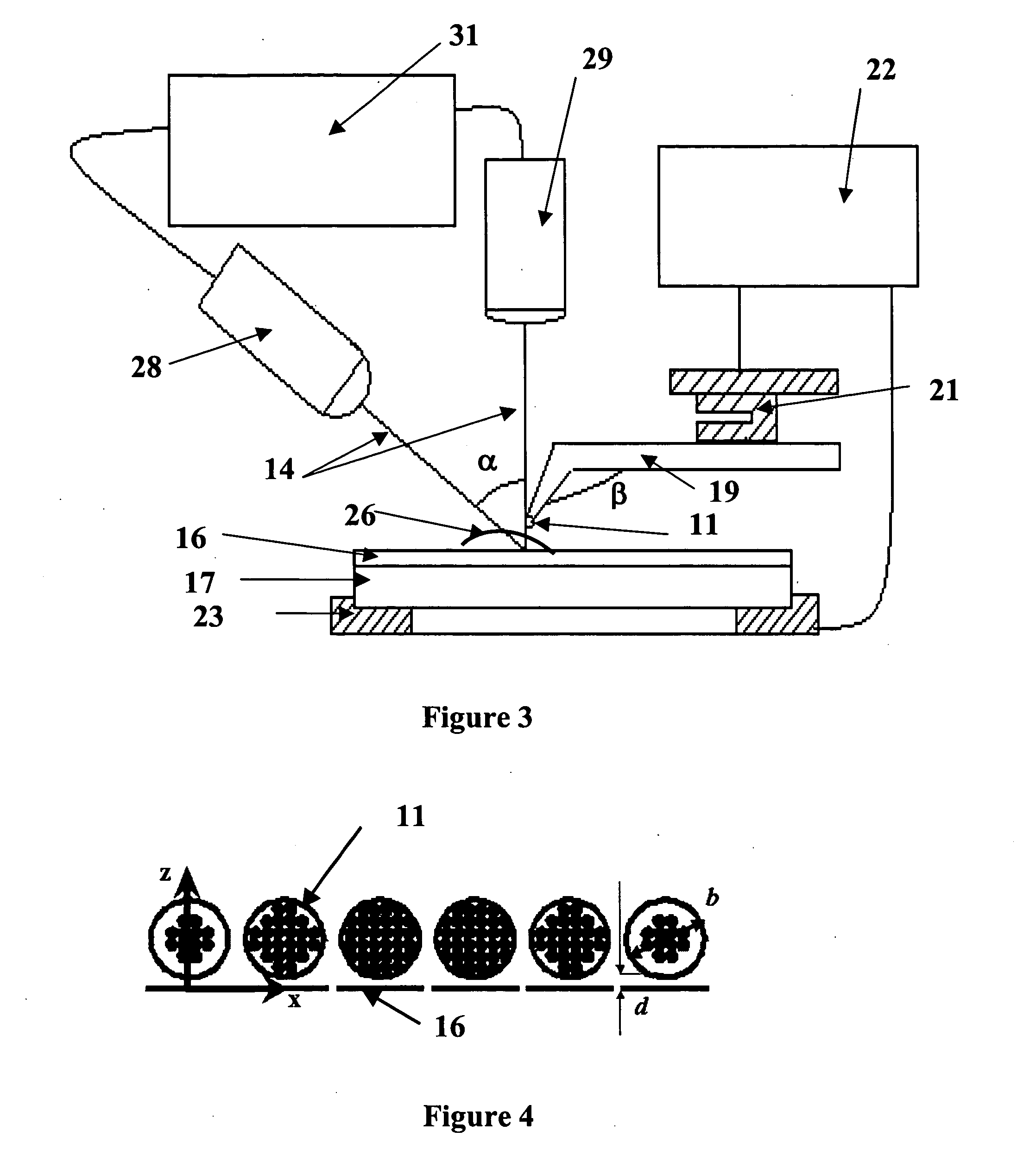
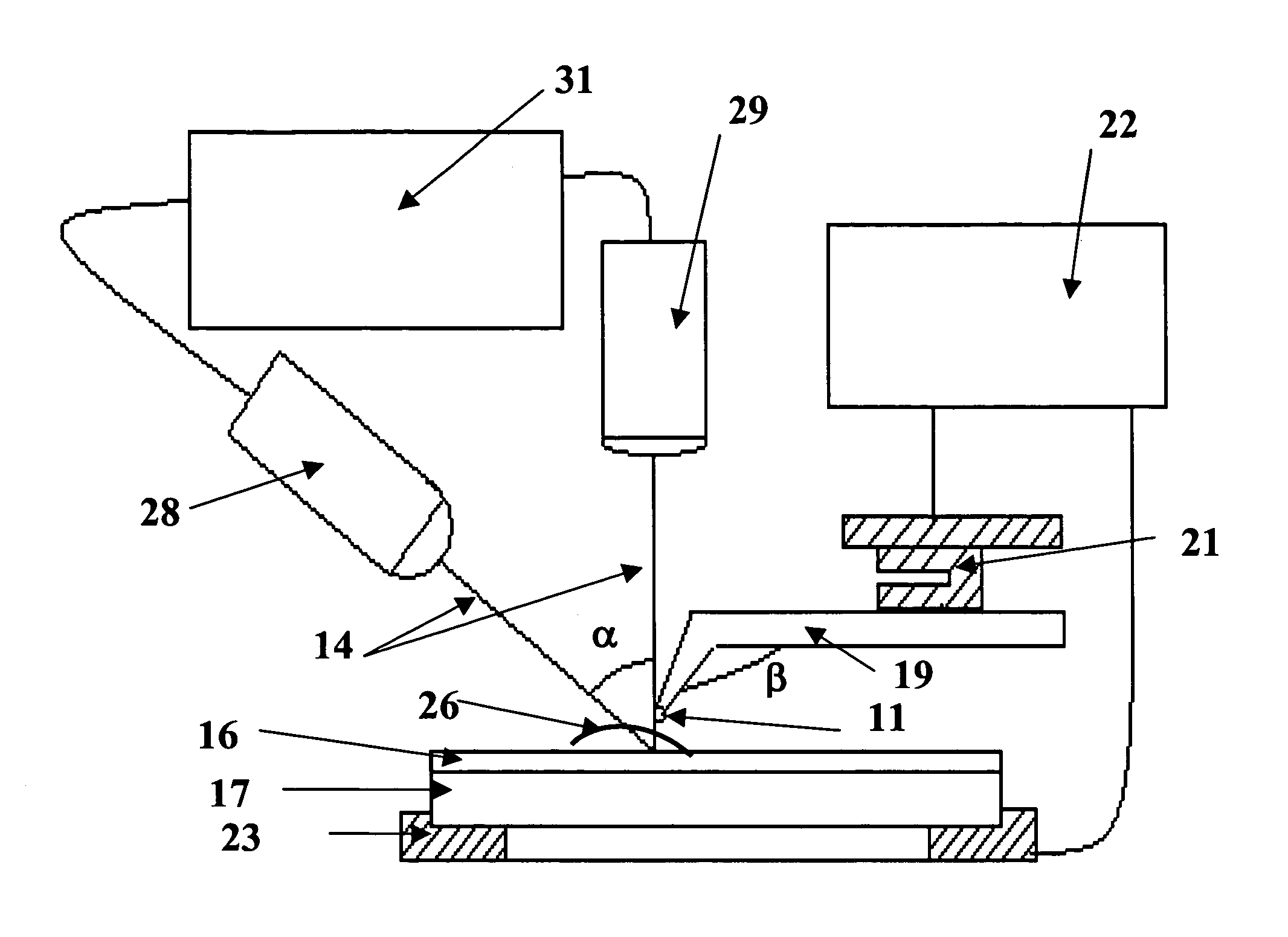
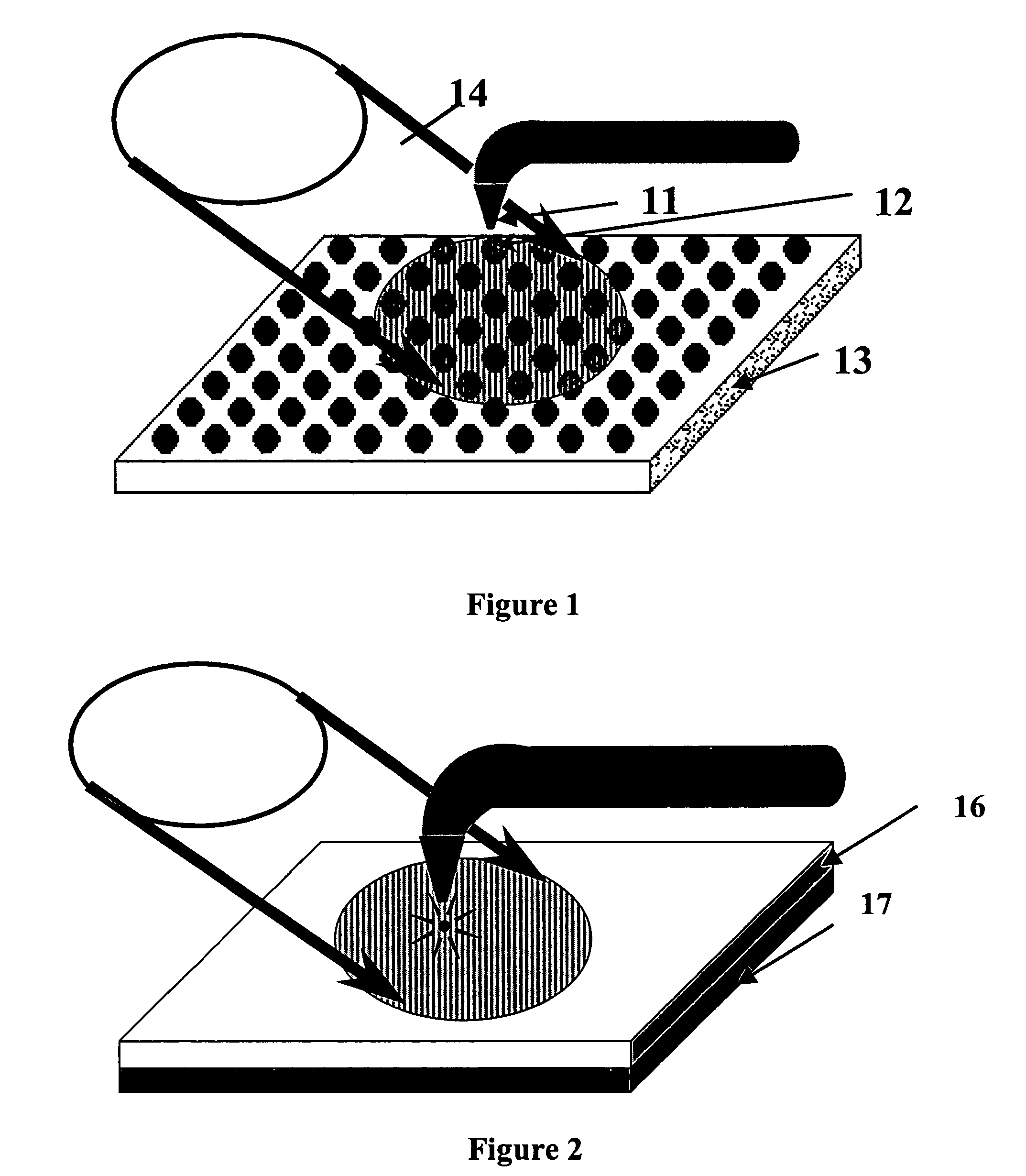
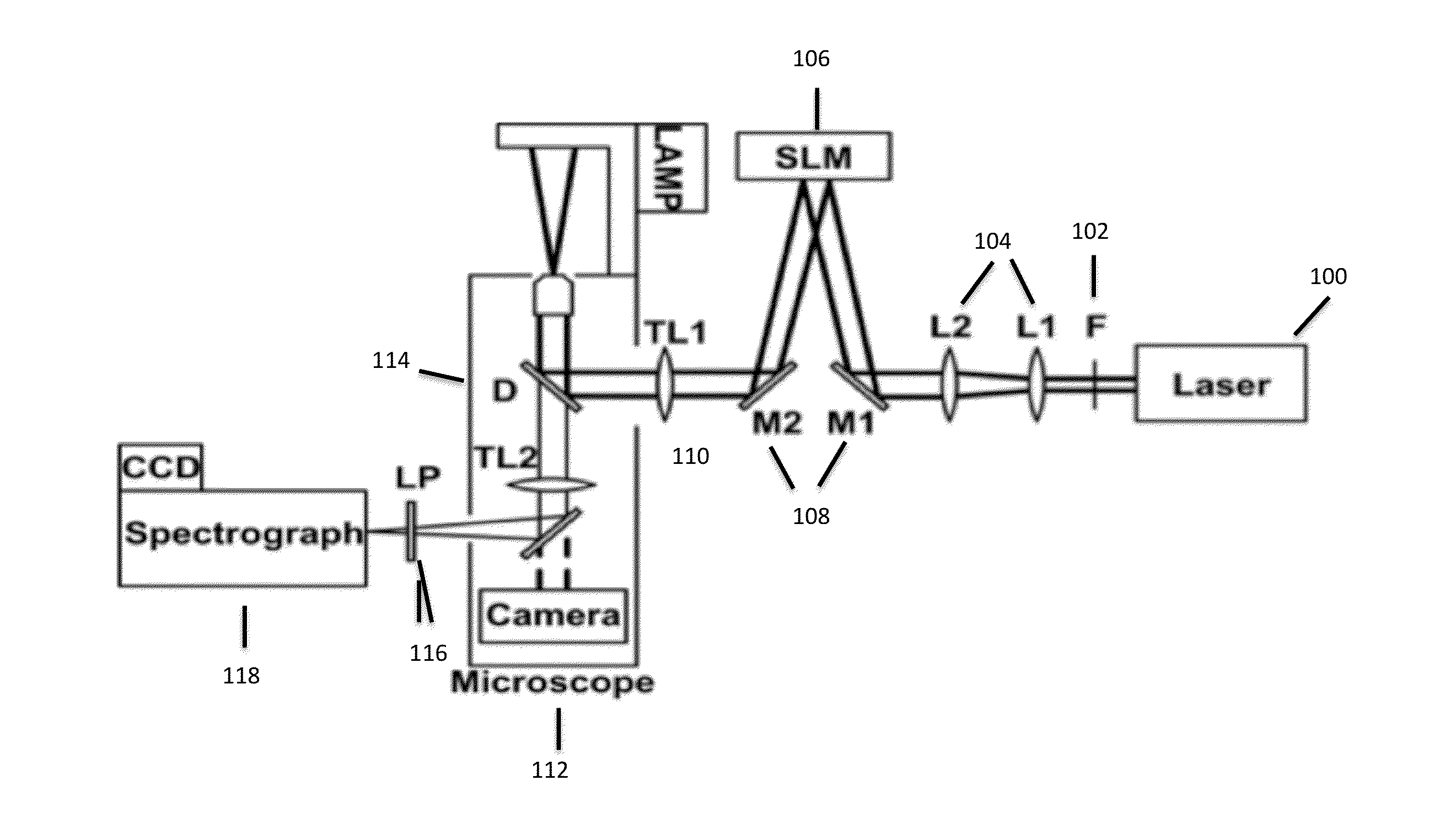
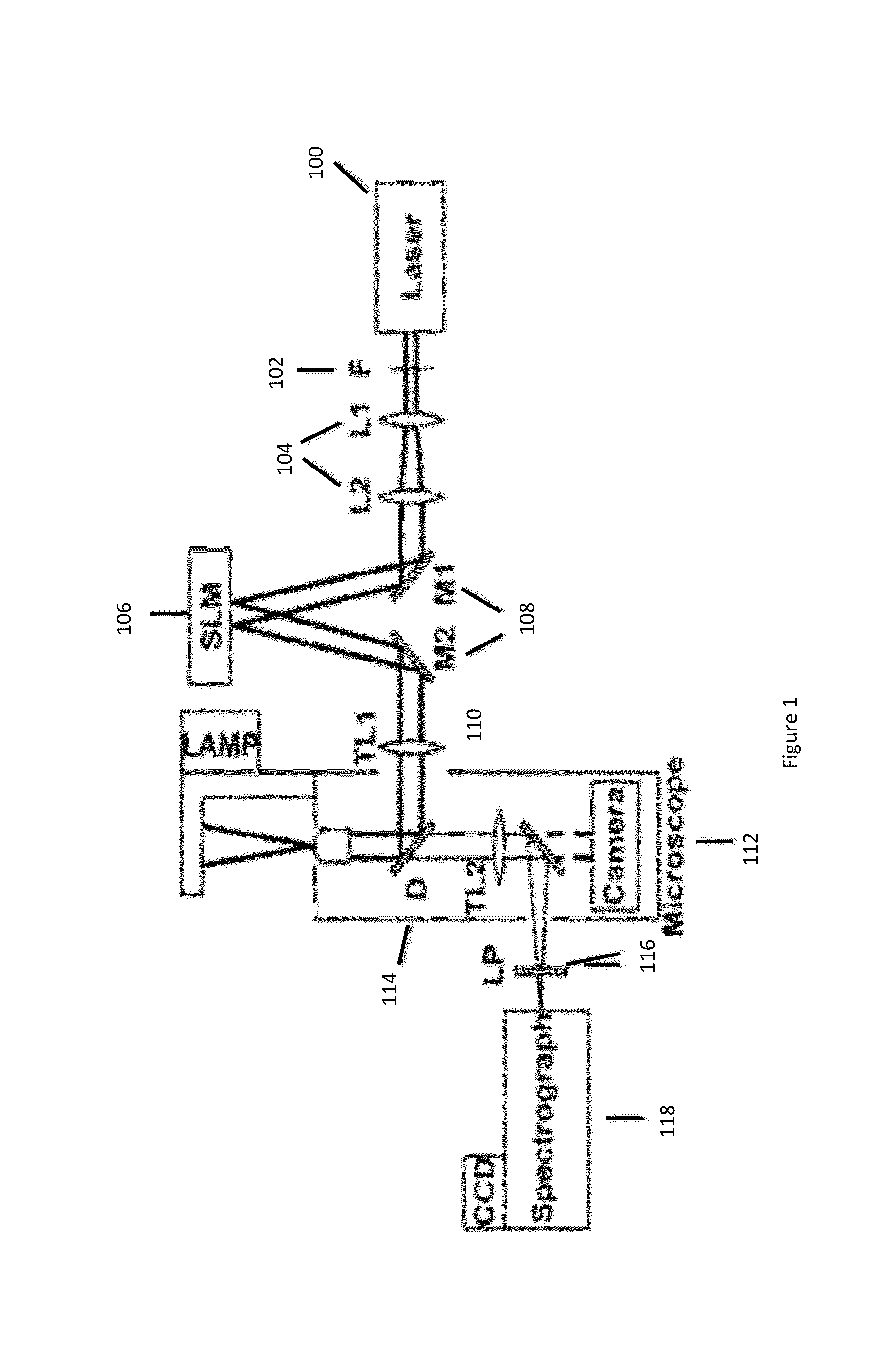
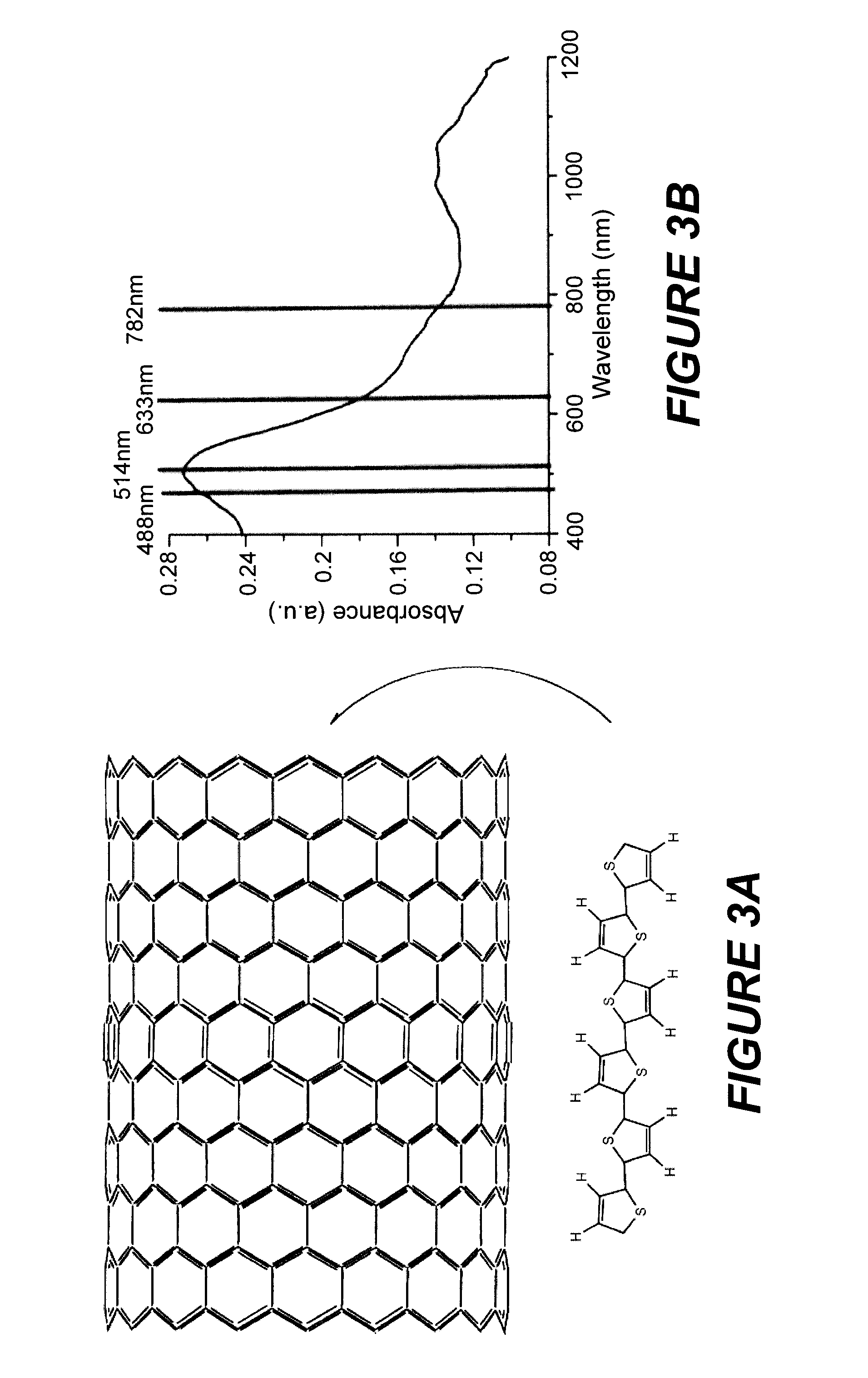
Raman spectral imaging (or mapping) is a method for generating detailed chemical images based on a sample’s Raman spectrum. A typical experiment uses sequential sample movement and spectrum acquisition, repeated hundreds, thousands or even millions of times, to collect data from the user defined image area.
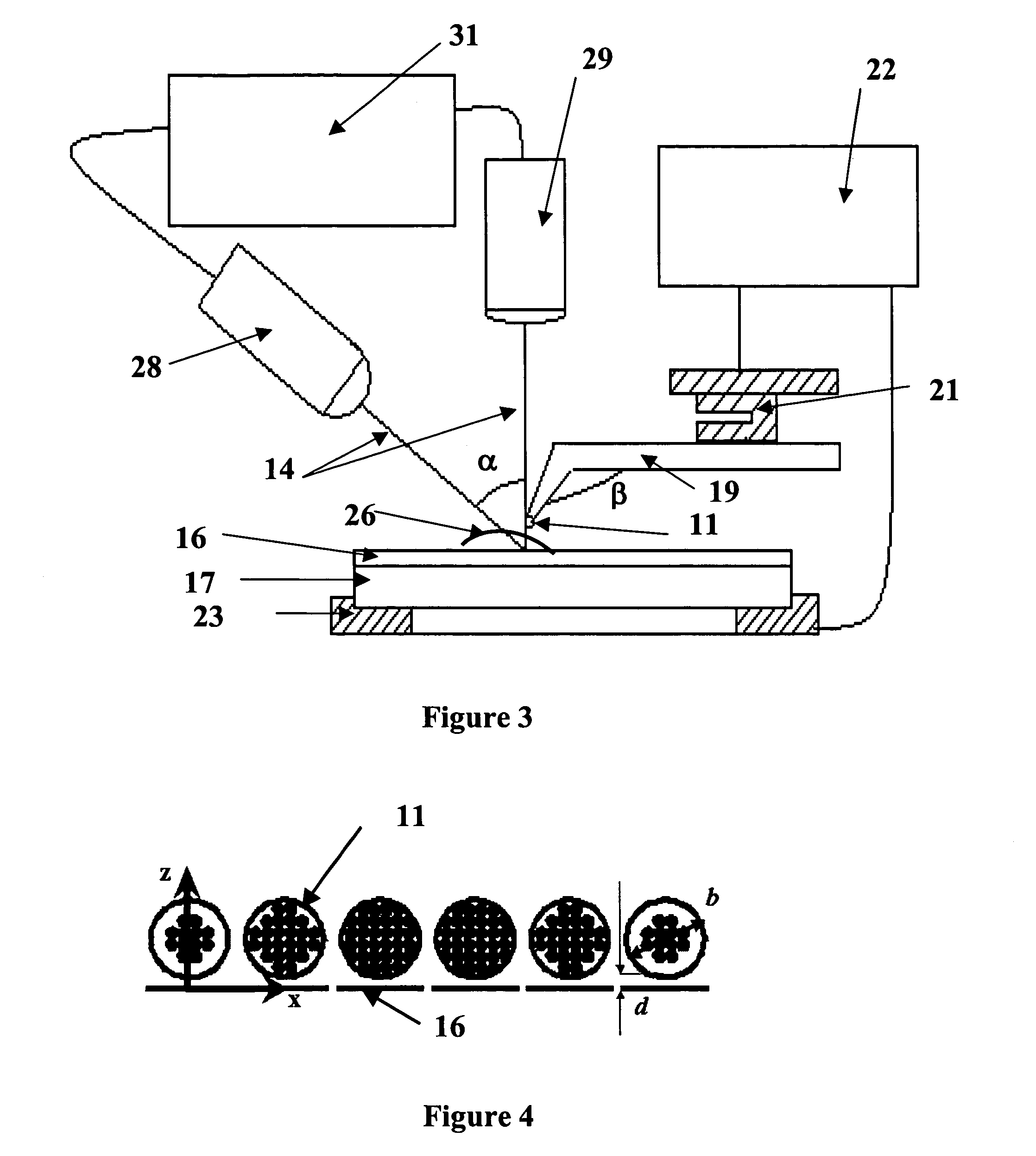
Near-field Raman spectroscopy
Near-field Raman imaging is performed by holding a dielectric microsphere (e.g. of polystyrene) on or just above the surface of a sample in a Raman microscope. An illuminating laser beam is focused by the microsphere so as to produce a near-field interaction with the sample. Raman scattered light at shifted wavelengths is collected and analysed. The microsphere may be mounted on a cantilever of an atomic force microscope or other scanning probe microscope, which provides feedback to hold it in position relative to the sample surface. Alternatively, the microsphere may be held on the sample surface by an optical tweezer effect of the illuminating laser beam.
Owner:RENISHAW PLC
Raman imaging and sensing apparatus employing nanoantennas
InactiveUS20040174521A1High sensitivityFacilitates nanoscale measurementRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringRaman imagingResonance
A Raman imaging and sensing apparatus is described. The apparatus employs a nanoantenna structure which includes a metal tip spaced from a metal surface or particle. A light beam impinges upon the nanoantenna and causes plasmon resonance. The plasmon resonance excites a sample resulting in dramatically enhanced Raman scattering of the sample. The Raman scatter is collected by a spectrophotometer which provides an output signal indicative of the composition of the sample.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Raman imaging and sensing apparatus employing nanoantennas
InactiveUS6985223B2High sensitivityFacilitates nanoscale measurementRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringRaman imagingResonance
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
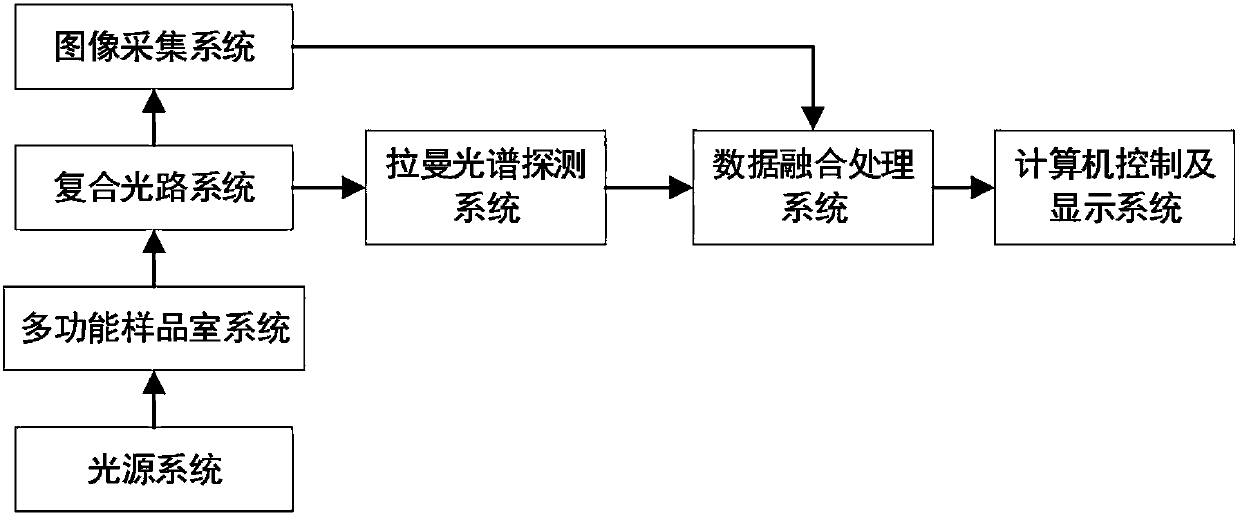
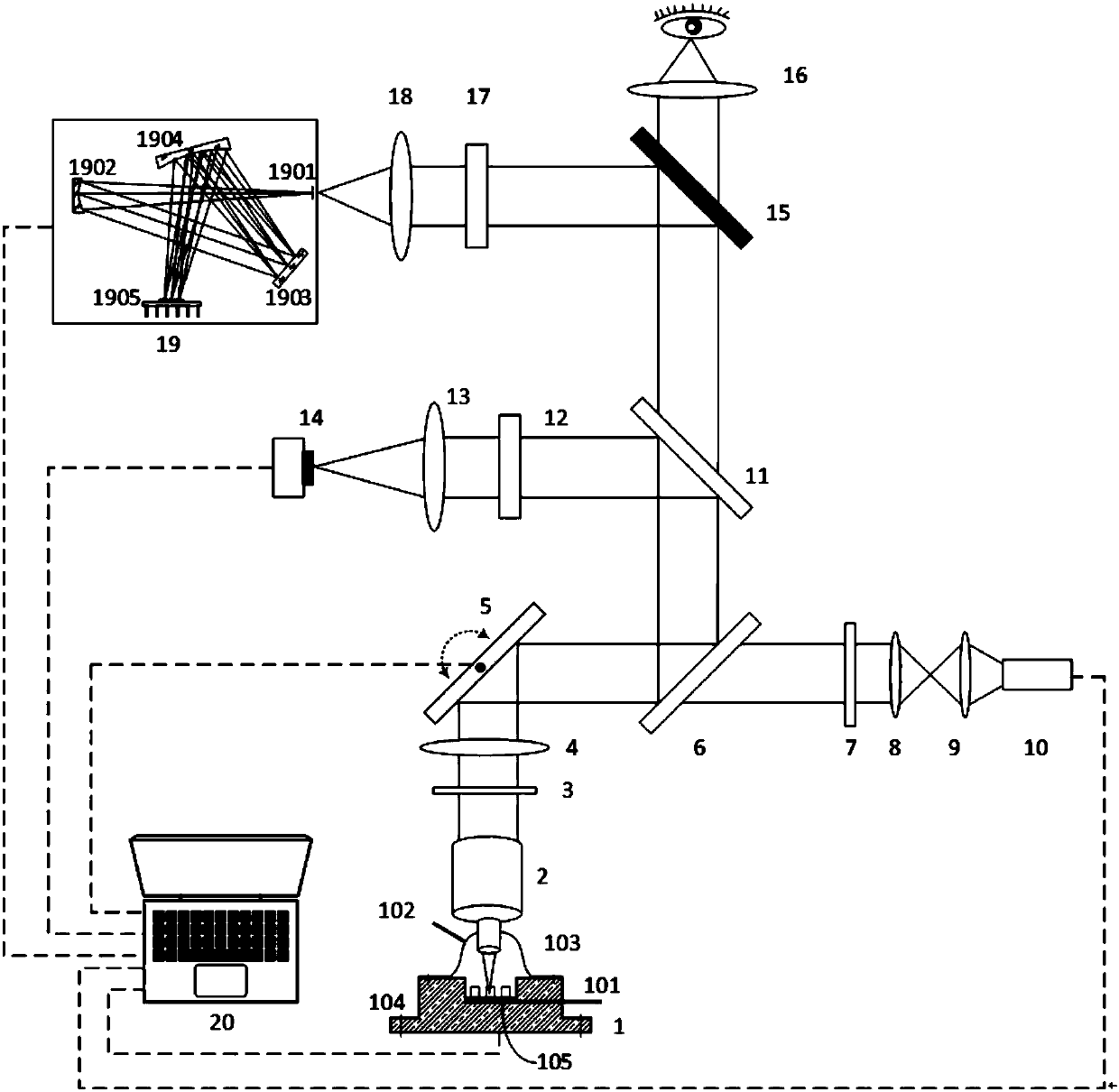
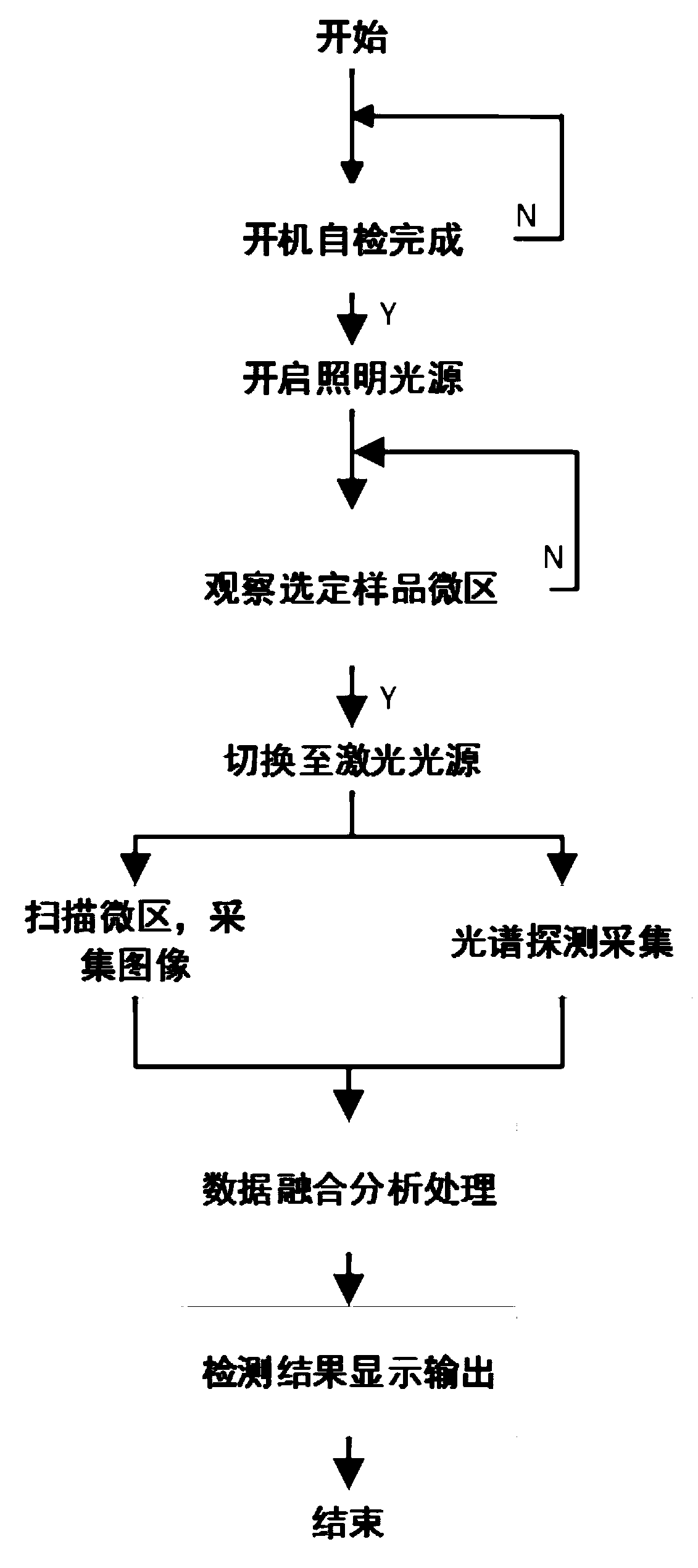
Microscopic Raman imaging spectrum rapid detection apparatus and method thereof
The invention discloses a microscopic Raman imaging spectrum rapid detection apparatus and a method thereof, which belong to the technical field of optical microscopic imaging and spectral measurement. The microscopic Raman imaging spectrum rapid detection apparatus comprises a light source, a multifunctional sample room, a composite optical system, an image acquisition system, a data fusion processing system, a Raman spectrum detection system, and a computer control and display system. According to white light or laser emitted by the light source, sample in-situ observation and microscopic Raman imaging spectrum real-time on-line detection are respectively realized, the data fusion processing system performs real-time analysis processing on images and spectrum information, and images andspectrum information are displayed and output in the computer control and display system. The microscopic Raman imaging spectrum rapid detection apparatus has the characteristics of compact structure,high spatial resolution, convenient usage, and stable performance, can be used in the fields of water quality detection, material analysis, petrochemical engineering, environment monitoring, and industrial precision detection, is convenient for field on-site investigation experiment and on-line test real-time analysis, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
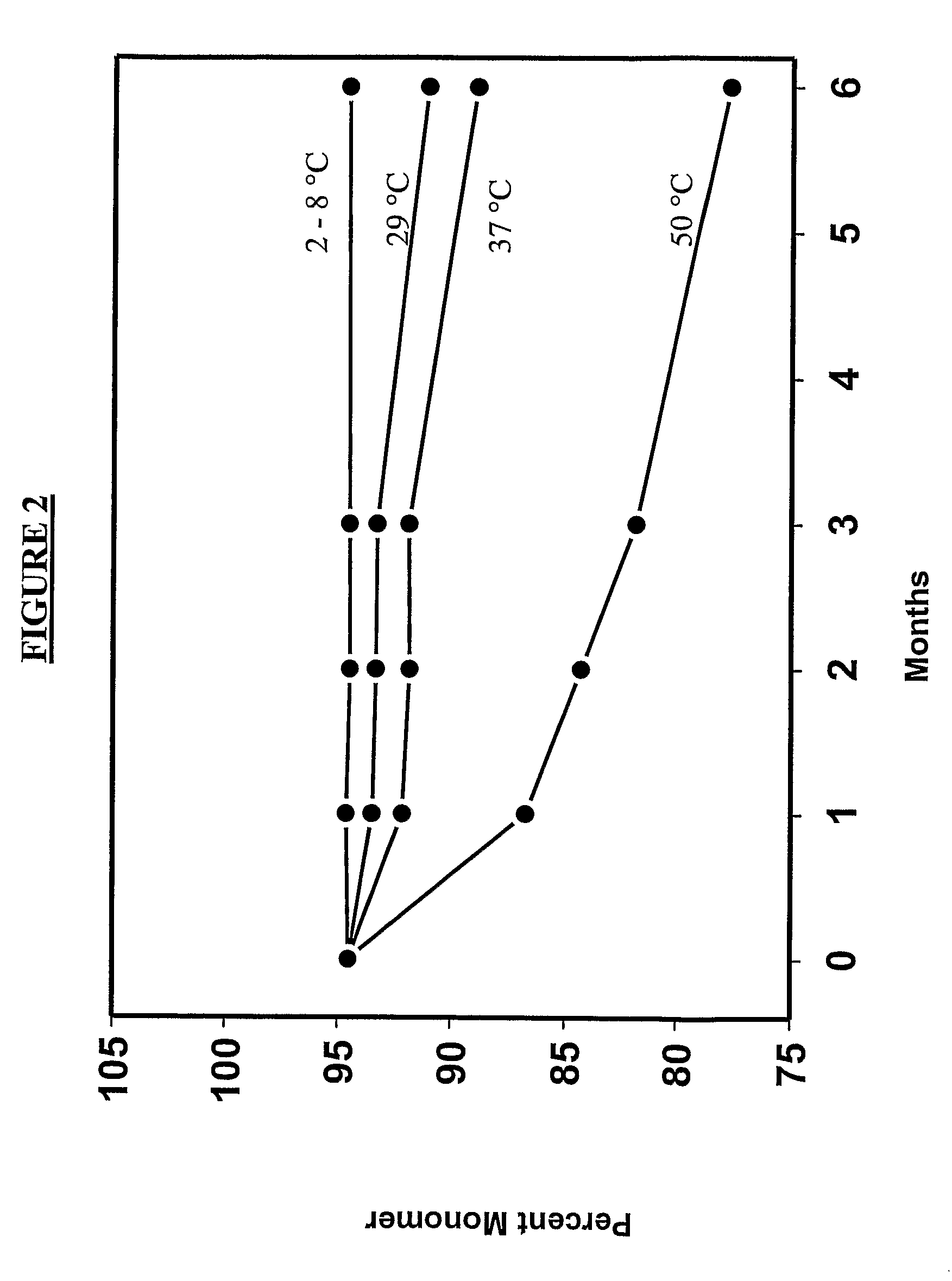
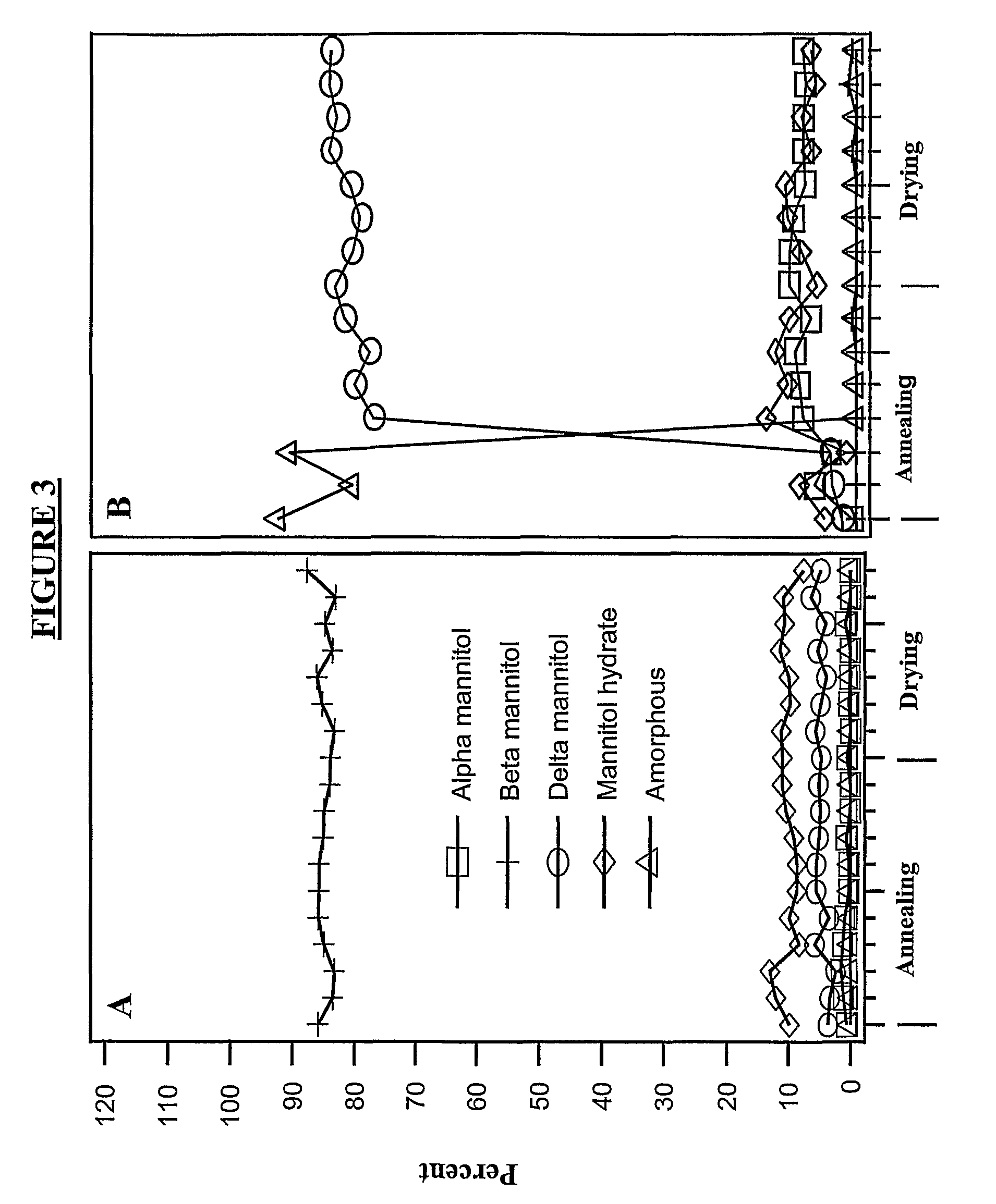
Concentrated Protein Lyophilates, Methods, and Uses
InactiveUS20080213215A1Reduce moisture contentSpeed up the flowRadiation pyrometryPeptide/protein ingredientsRaman imagingReal time analysis
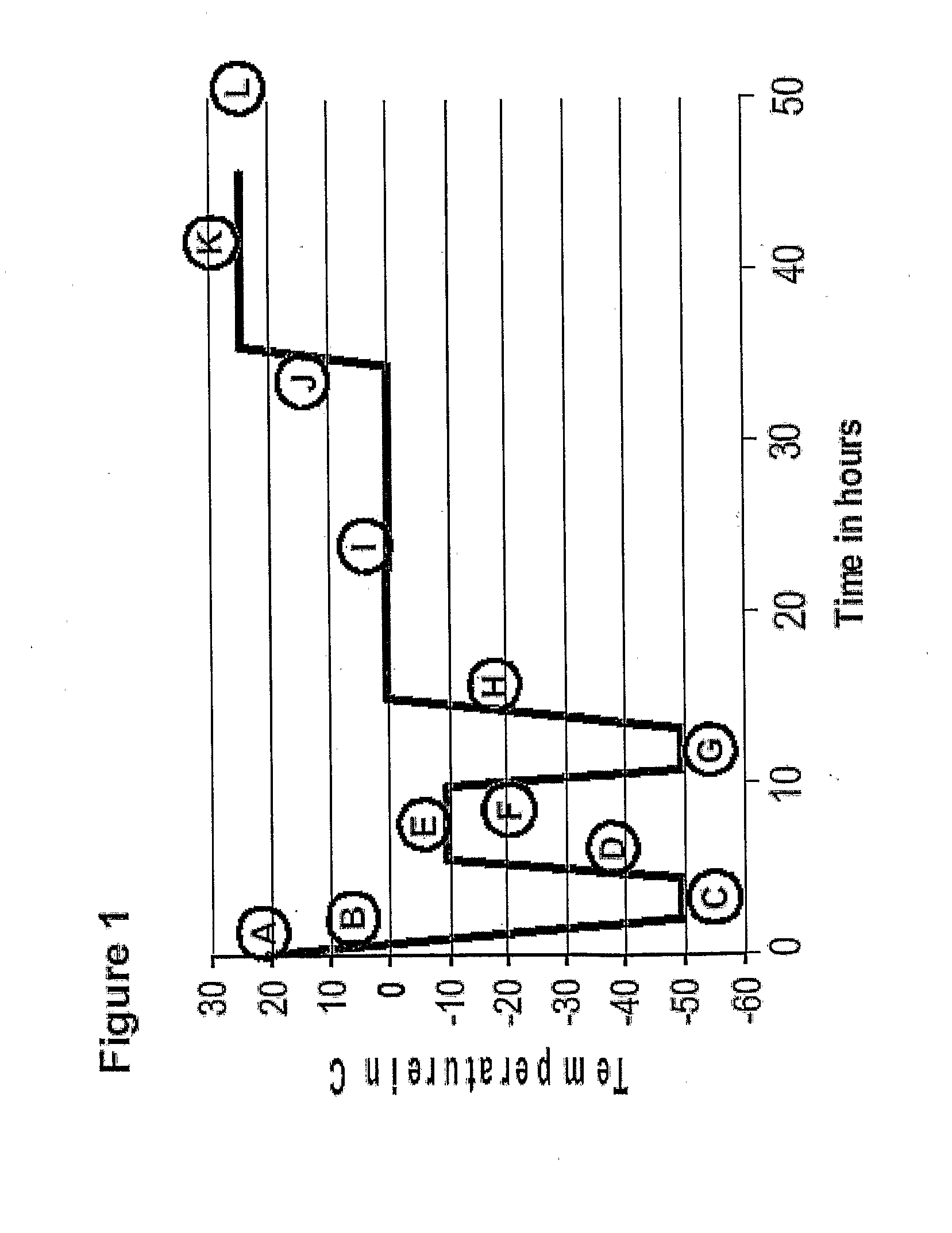
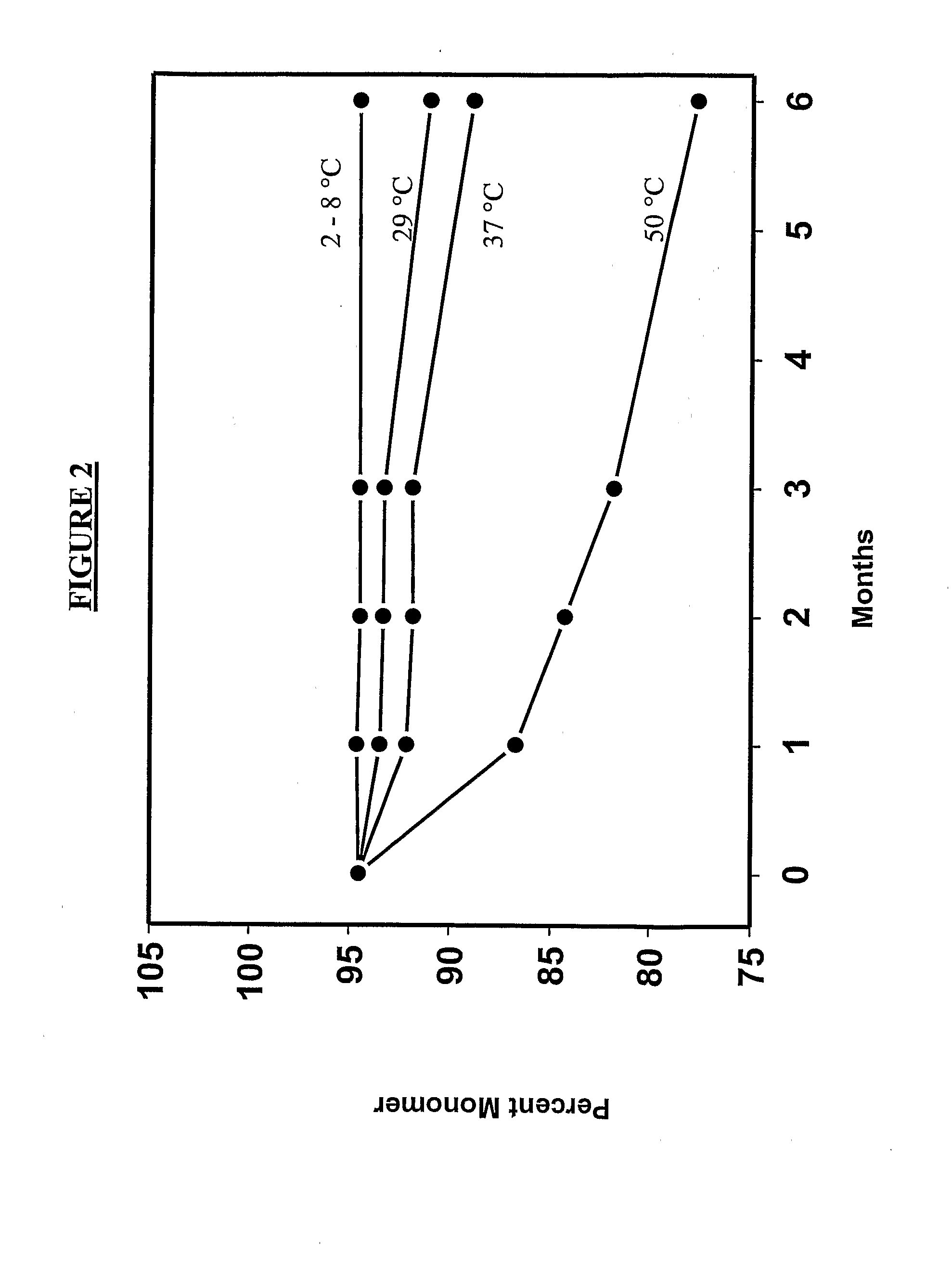
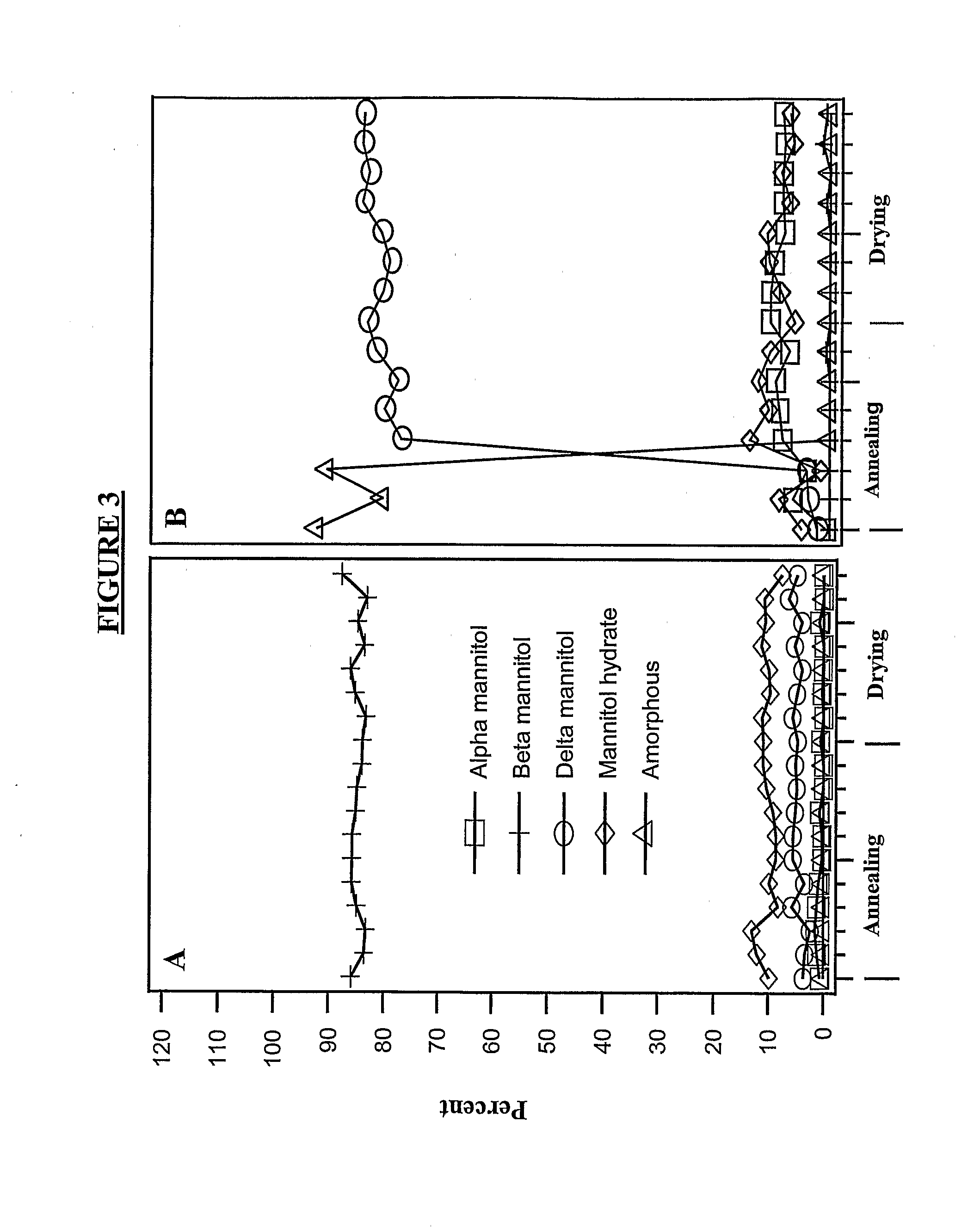
The invention provides, among other things, lyophilized compositions of high surface area that comprise a protein and that reconstitute quickly and efficiently to solution of high protein concentration with minimal formation, if any, of foam, effervescence, bubbles, turbidity, or particulates that might be deleterious. The invention also provides, among other things, methods for making the lyophilized compositions. The invention in additional aspects also provides Raman Imaging Spectrographic methods for real time analyses of polymorphs in a sample using PLS algorithms. By way of particular example, the use of the method for the analysis of mannitol polymorphs is described, and the use of the analysis to determine optimum compositions and lyophilization methods for producing lyophilates of pharmaceutical proteins having a predefined distribution of mannitol polymorphs and having the aforementioned reconstitution properties is also described.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Multifocal hyperspectral raman system and methods for imaging of materials
ActiveUS20150204789A1Large field of viewReduce acquisition timeRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyRaman imagingElectricity
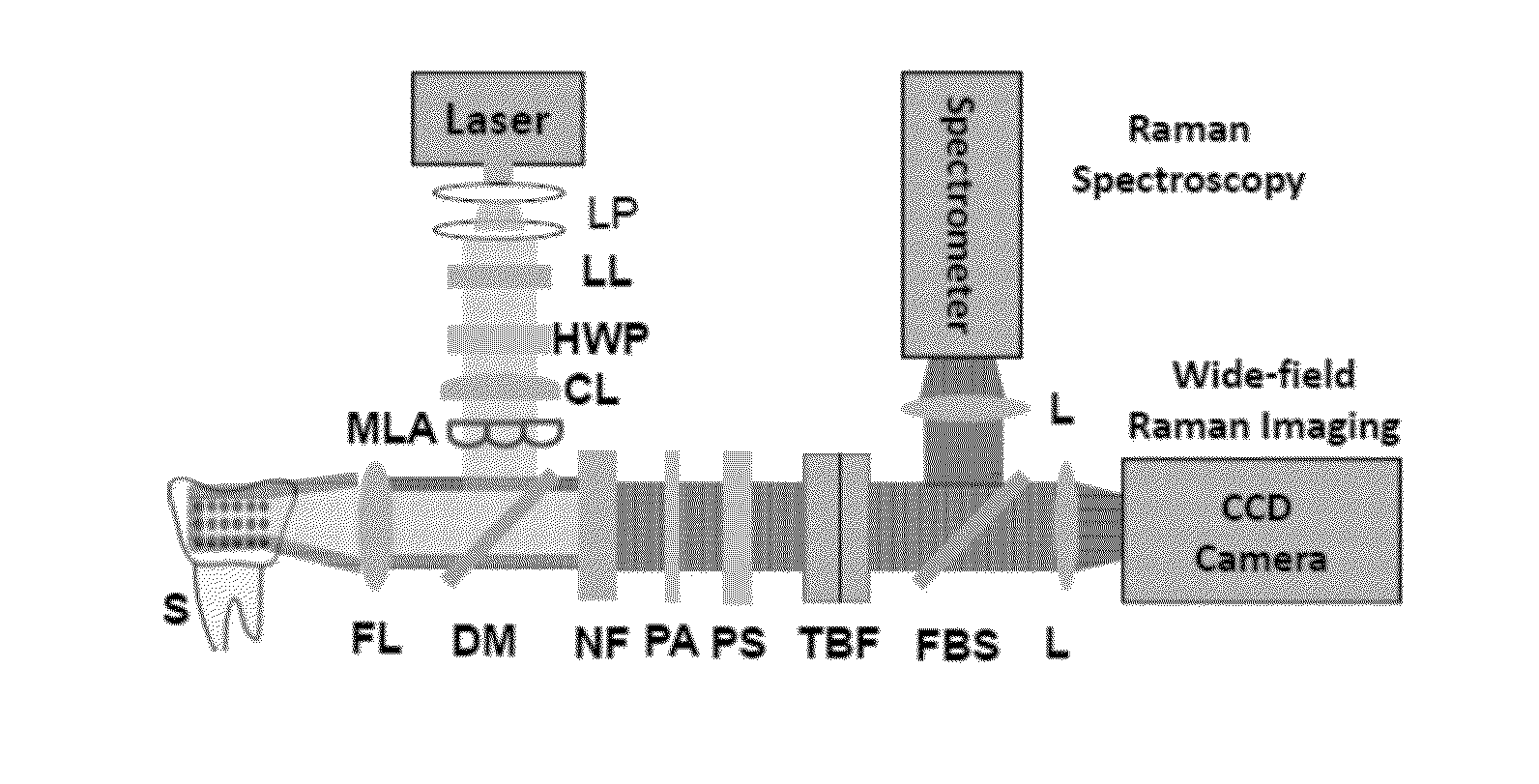
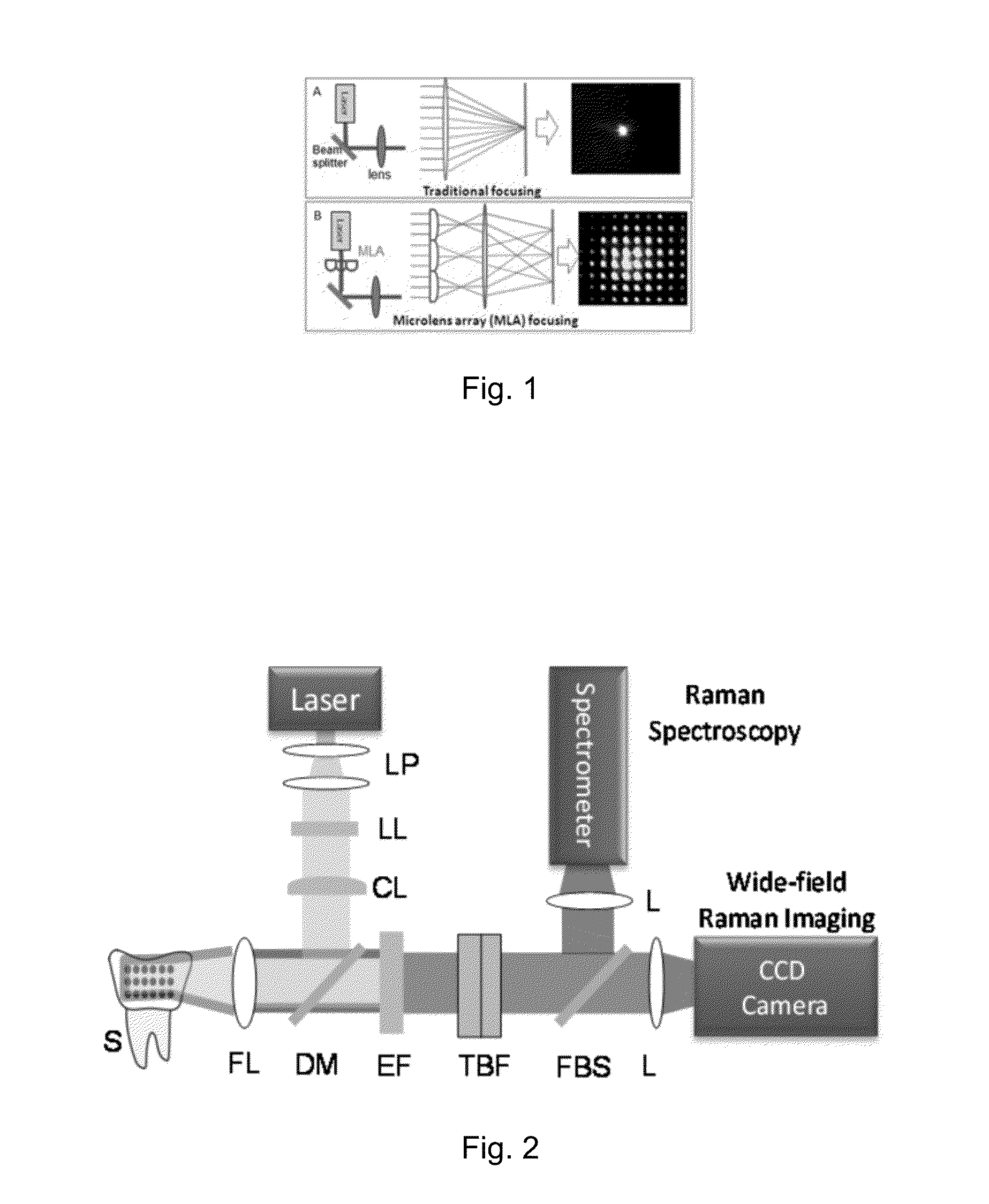
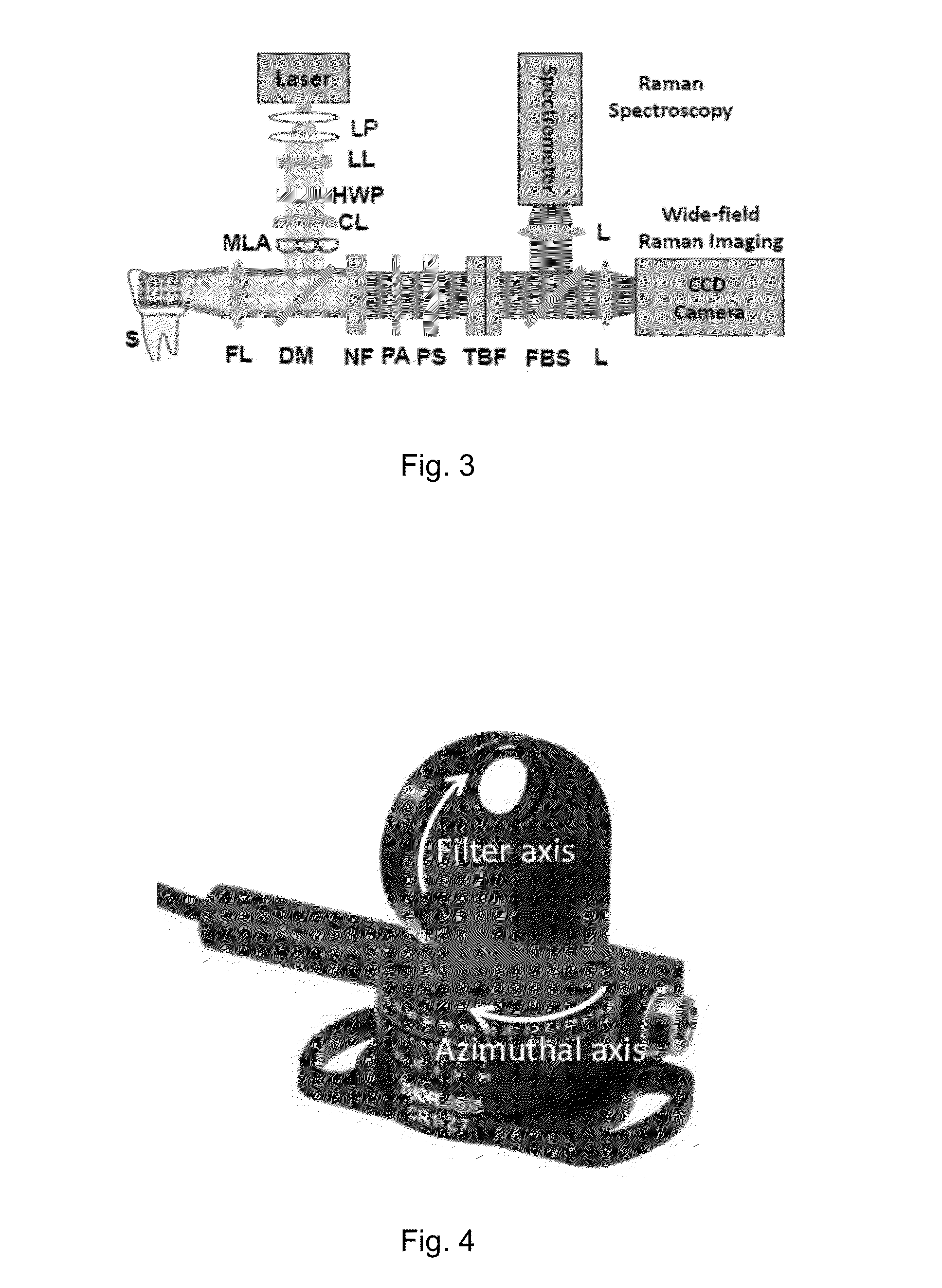
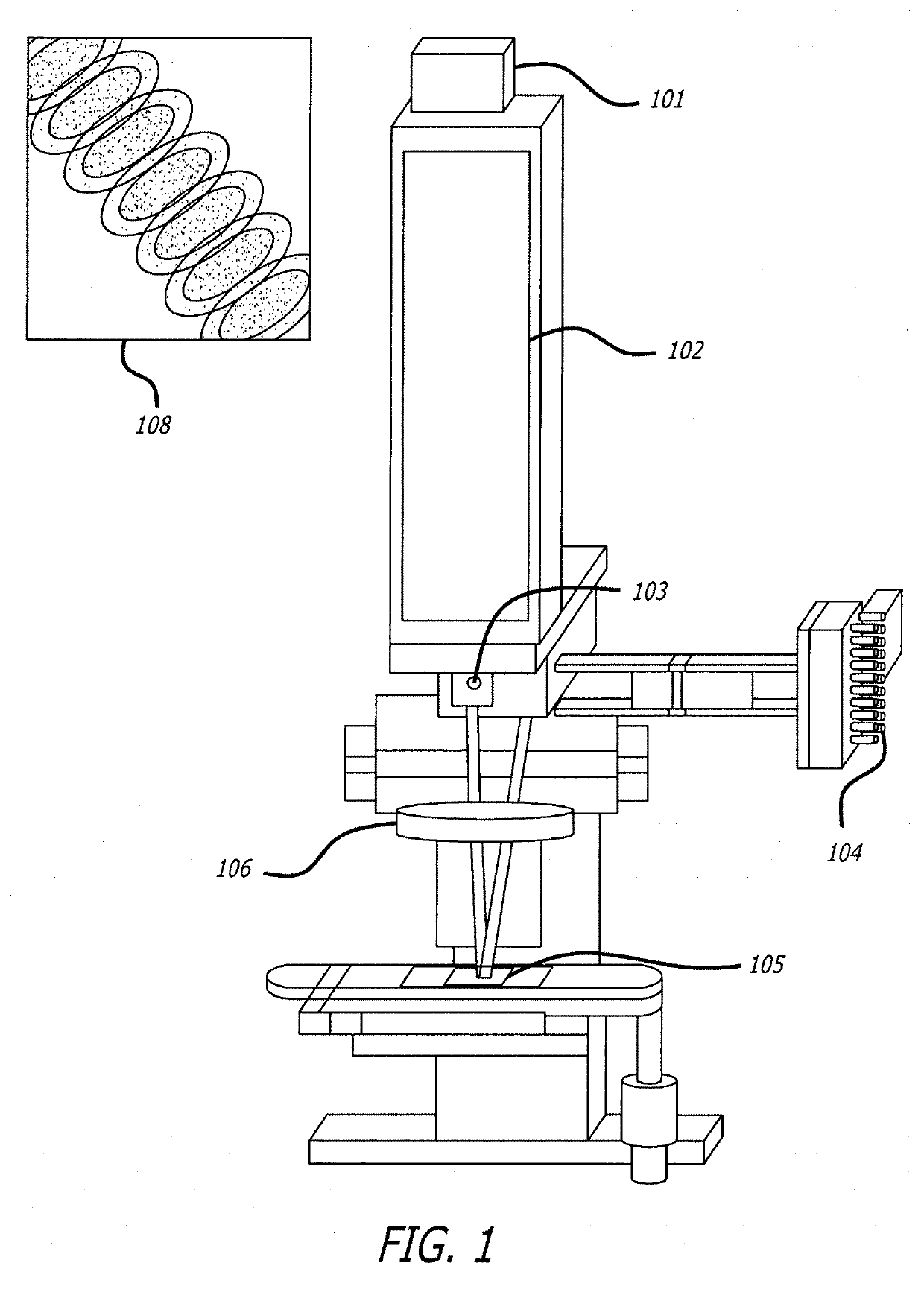
A hyperspectral Raman imaging system having the ability to focus on excitation laser beam over a relatively wide field of view due to the use of a lens array, in particular a microlens array. Hyperspectral selection is provided in one embodiment through the use of dual-axis controlled dielectric filtration. Methods for analyzing materials with the system are disclosed. The device or system can be used in generally any application where investigation of materials is required.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Apparatus and method for multimode analytical sensing of items such as food
ActiveUS20190293620A1Scattering properties measurementsRaman scatteringComputer hardwareRaman imaging
A multimode biological sample inspection apparatus and method is provided. The apparatus includes illumination hardware arrangement including transmission and sensing hardware, the illumination hardware arrangement configured to inspect a biological sample using at least two modes from a fluorescence imaging mode, a reflectance imaging mode, a scattering imaging mode, and a Raman imaging mode, and processing hardware configured to operate the illumination hardware arrangement according to a protocol including inspection settings of the at least two modes. The processing hardware receives scan results from the illumination hardware arrangement and identifies attributes of the biological sample. The processing hardware is configured to employ the attributes of at least one biological sample to alter the protocol.
Owner:SAFETYSPECT INC
Methodology of using raman imaging microscopy for evaluating drug action within living cells
InactiveUS6939686B2Convenient and cost-effective methodRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementStudy drugRaman imaging
A method of using Raman imaging microscopy to evaluate drug actions in living cells is disclosed. Specifically the invention describes the methods of using Raman imaging microscopy to detect drug uptake, distribution, binding, and metabolism in a single cell, and to study drug pharmacokinetics at the cellular level. The method involves measuring the Raman image of both the drug and the cell. Control images and post-treatment images of the cell were studied. Ratio images were calculated and the requisite information was obtained from a study of the intensity of the bright areas in the ratio images.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Laser system for photonic excitation investigation
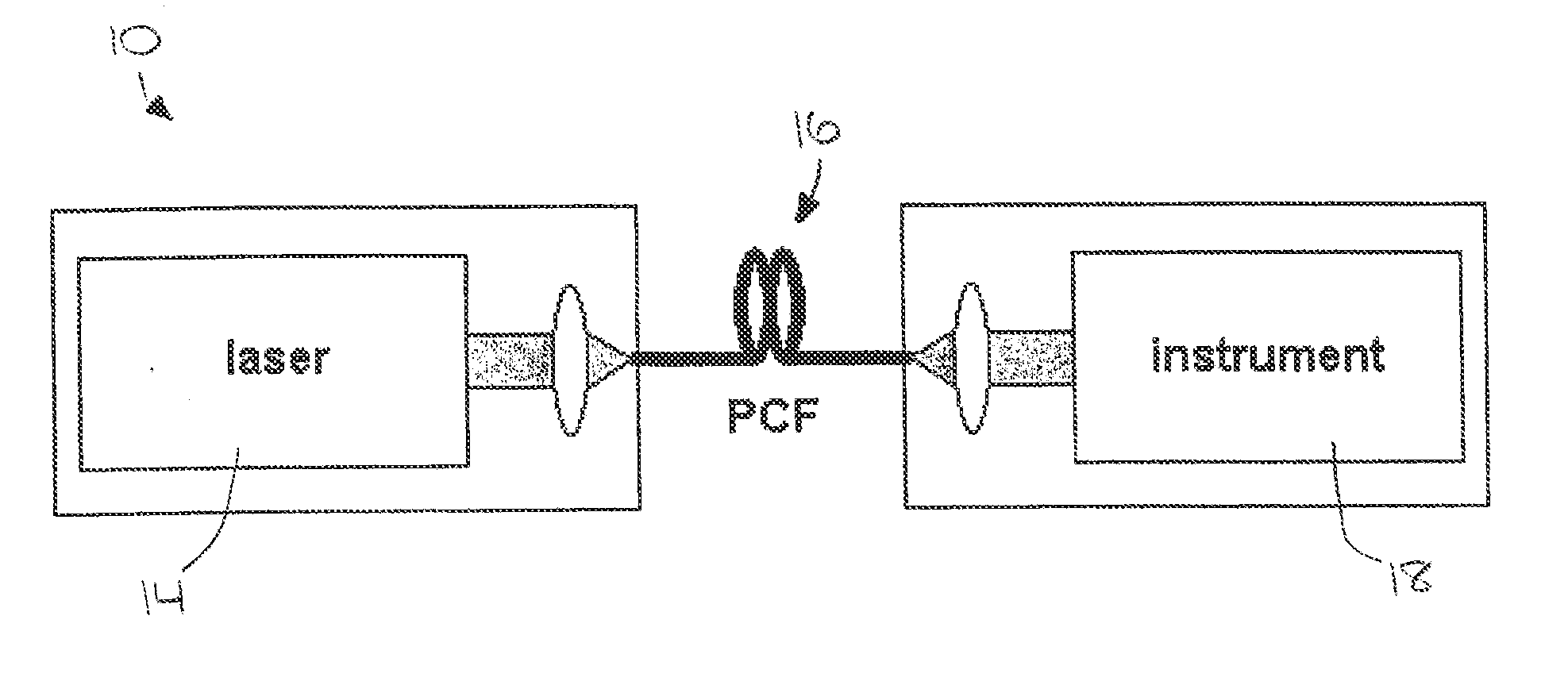
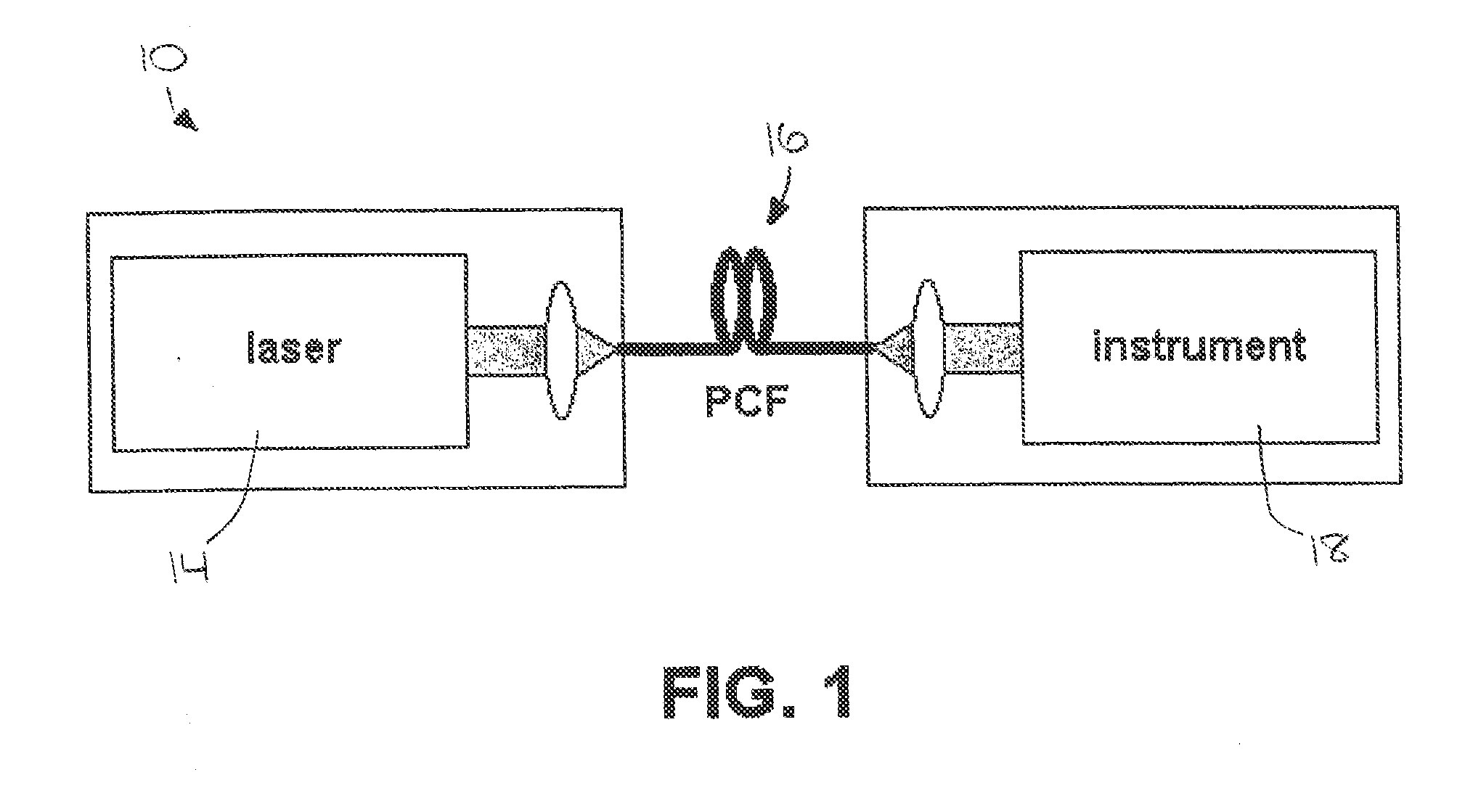
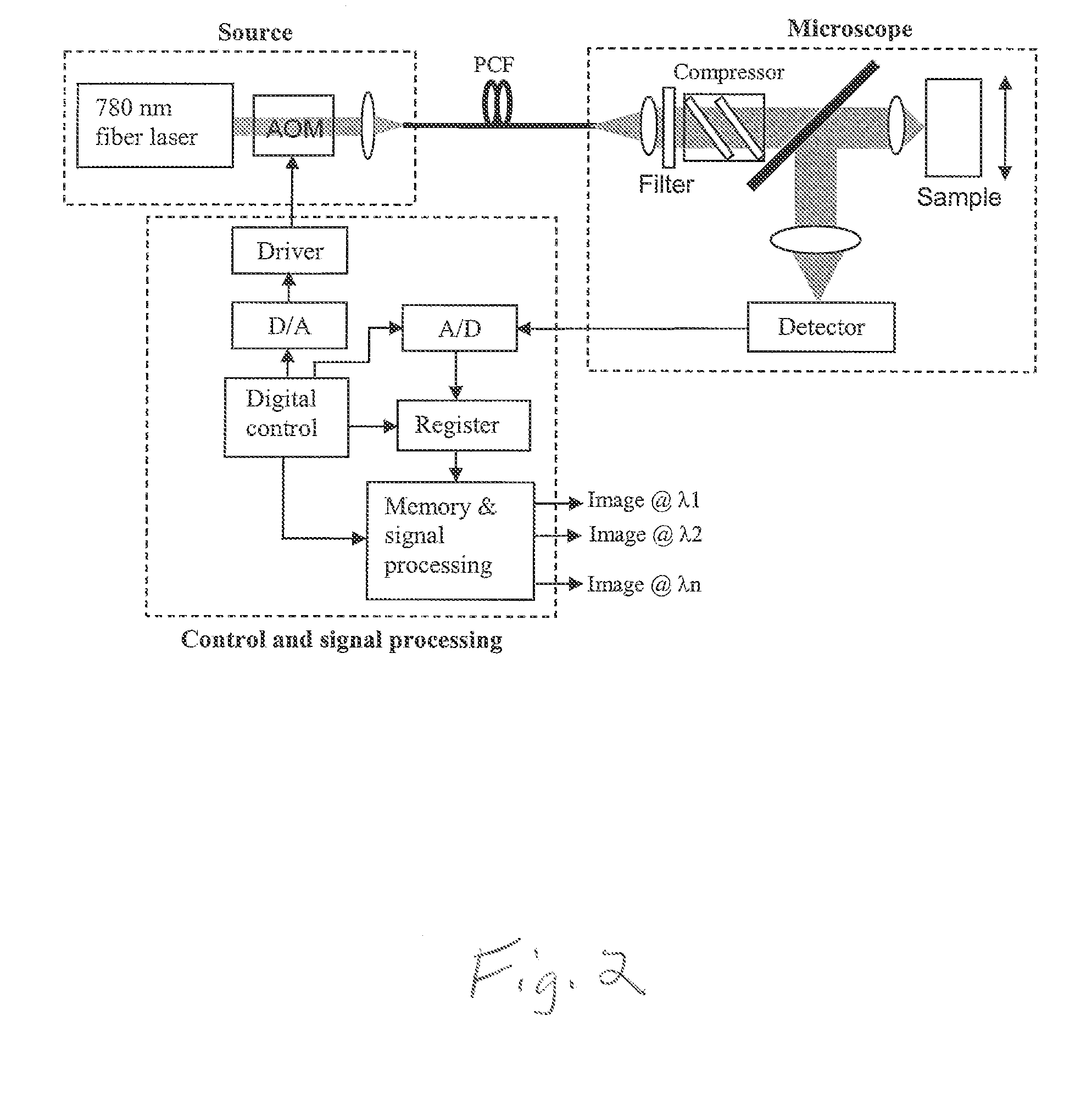
A laser system (10) for use in photonic excitation investigation of a target object, in which the target object interacts with incident photons and emits a corresponding photon which is detected and used to generate an image of the target object. The laser system (10) includes a pulsed fiber laser (14) for producing a laser beam, and a non-linear photonic crystal fiber (16) for carrying the laser beam from the laser (14) to an instrument (18) for photonically exciting the target object. The photonic crystal fiber (16) allows for switching, or tuning, the wavelength of the laser beam. In two-photon microscopy, the laser system (10) allows for providing multiple wavelengths for exciting a plurality of different fluorophores simultaneously. In coherent Raman imaging and spectroscopy, the laser system (110) allows for using a single laser to provide two laser beams of different wavelengths.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Concentrated protein lyophilates, methods, and uses
InactiveUS7956160B2Speed up the flowReduce moisture contentBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsRaman imagingParticulates
The invention provides, among other things, lyophilized compositions of high surface area that comprise a protein and that reconstitute quickly and efficiently to solution of high protein concentration with minimal formation, if any, of foam, effervescence, bubbles, turbidity, or particulates that might be deleterious. The invention also provides, among other things, methods for making the lyophilized compositions. The invention in additional aspects also provides Raman Imaging Spectrographic methods for real time analyses of polymorphs in a sample using PLS algorithms. By way of particular example, the use of the method for the analysis of mannitol polymorphs is described, and the use of the analysis to determine optimum compositions and lyophilization methods for producing lyophilates of pharmaceutical proteins having a predefined distribution of mannitol polymorphs and having the aforementioned reconstitution properties is also described.
Owner:AMGEN INC
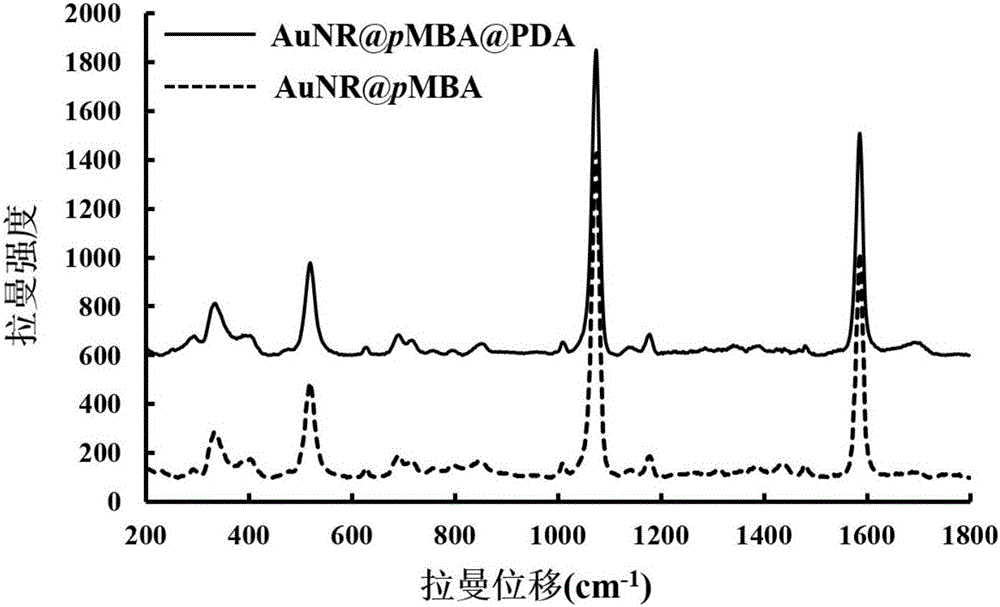
Polydopamine coated gold nanorod material as well as preparation method and application of polydopamine coated gold nanorod material
InactiveCN106692995AAchieve specific labelingGood biocompatibilityEnergy modified materialsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsRaman imagingTumor target
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and in particular relates to a polydopamine coated gold nanorod material as well as a preparation method and application of the polydopamine coated gold nanorod material. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: by taking CTAB (cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide) as a template agent, synthesizing a polydopamine coated gold nanorod material; modifying an antibody onto the surface of the material, thereby obtaining a multifunctional polydopamine coated gold nanorod material. Thus, a tumor cell Raman imaging detection and real-time photothermal therapy platform is constructed. The experiments prove that the gold nanorod material is capable of realizing specific effective tumor target cell marking and performing rapid surface-enhanced Raman spectral imaging scanning on the tumor cells under excitation of near-infrared light; and the tumor target cells are accurately identified by the imaging results, and after the target cells are identified, the infrared light can be focused onto the tumor target cells, the irradiation time is prolonged, and the material is heated by utilizing the photo-thermal conversion effect of the gold nanorod material so as to kill the tumor cells in real time. The polydopamine coated gold nanorod material disclosed by the invention is novel, convenient, practical and efficient and has huge clinical application potential.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Raman spectrum imaging resolution target and preparation method thereof
The invention is applicable to an imaging system, and provides a Raman spectrum imaging resolution target. The Raman spectrum imaging resolution target comprises a substrate and a molecular layer formed on the substrate, wherein the molecular layer forms a preset grating structure by a nano-processing technology. The Raman spectrum imaging resolution target can be used as a universal Raman spectrum microscopic imaging resolution calibration standard part, which is applicable to Raman microscopic imaging systems with various resolution ratios, including surface Raman enhanced microscopic imaging, confocal Raman imaging, wide field Raman imaging and other various novel Raman imaging systems. The Raman spectrum imaging resolution target has the characteristics of simple processing, stable process, repeated bulk manufacture, convenience in use, repeated utilization, high transportation convenience and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Gold-as-core silver-as-shell ''Raman silent zone'' substrate and preparation method and application thereof
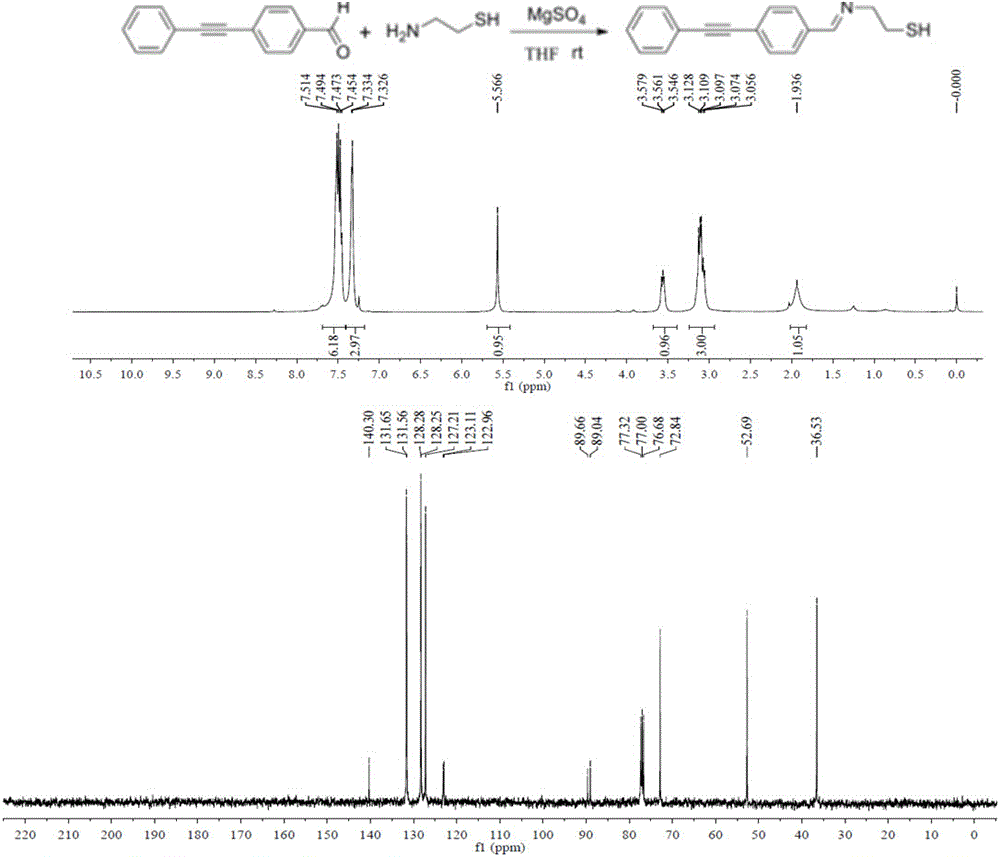
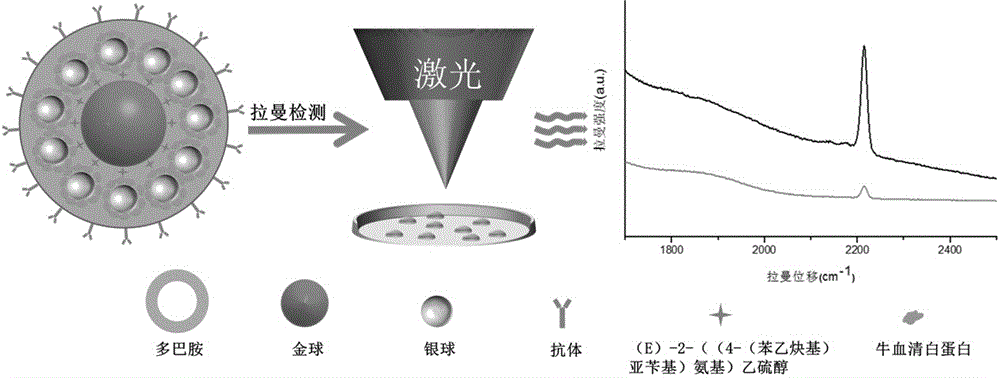
ActiveCN106248648AEnhancement effect is goodKeep aliveRaman scatteringRaman imagingBovine serum albumin
The invention belongs to the technical field of separation and analysis of biological macromolecules, and particularly relates to a gold-as-core silver-as-shell ''Raman silent zone'' surface enhancement Raman scattering substrate and a preparation method and application thereof in Raman imaging in living cells. The preparation process is as follows: gold nanoparticles containing ''Raman silent zone'' probe molecules are in situ synthesized by hydrothermal method, the gold nanoparticles are re-dissolved in a borax solution, and ''Raman silent zone'' molecules (E) 2 ((4 (phenyl ethynyl) benzylidene) amino) ethyl mercaptan are added; ascorbic acid and silver nitrate are added for in situ reduction of silver nanoparticles; bovine serum albumin is added, and finally through dopamine self polymerization, an antibody is connected to the material for preparing the ''Raman silent zone'' surface enhancement Raman scattering substrate capable of specifically recognizing tumor cells. Experiments show that the ''Raman silent zone'' surface enhancement Raman scattering substrate has a prominent enhancing effect on a probe signal, the ''Raman silent zone'' surface enhancement Raman scattering substrate material is free of template, low-cost and low-toxicity, is used in imaging in living cells, and is novel, convenient, practical and efficient.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Wide field raman imaging apparatus and associated methods
ActiveCN105377108AAccurate removalMedical imagingScattering properties measurementsTumor targetRaman imaging
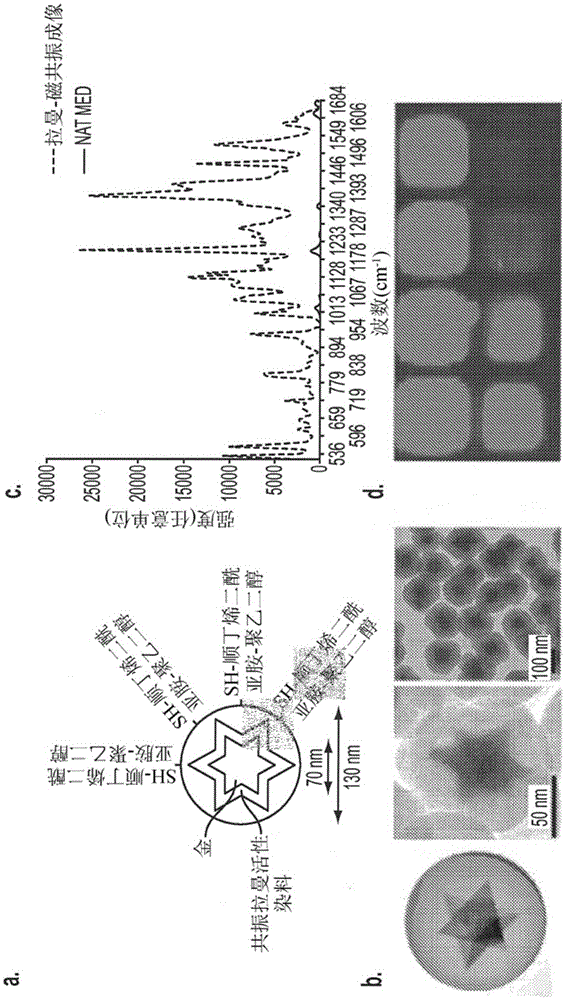
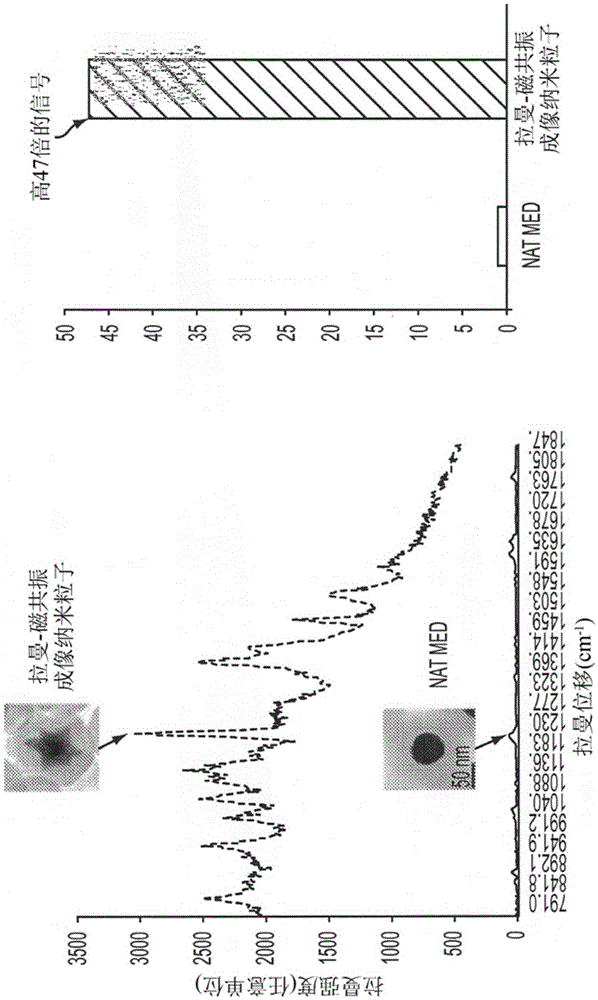
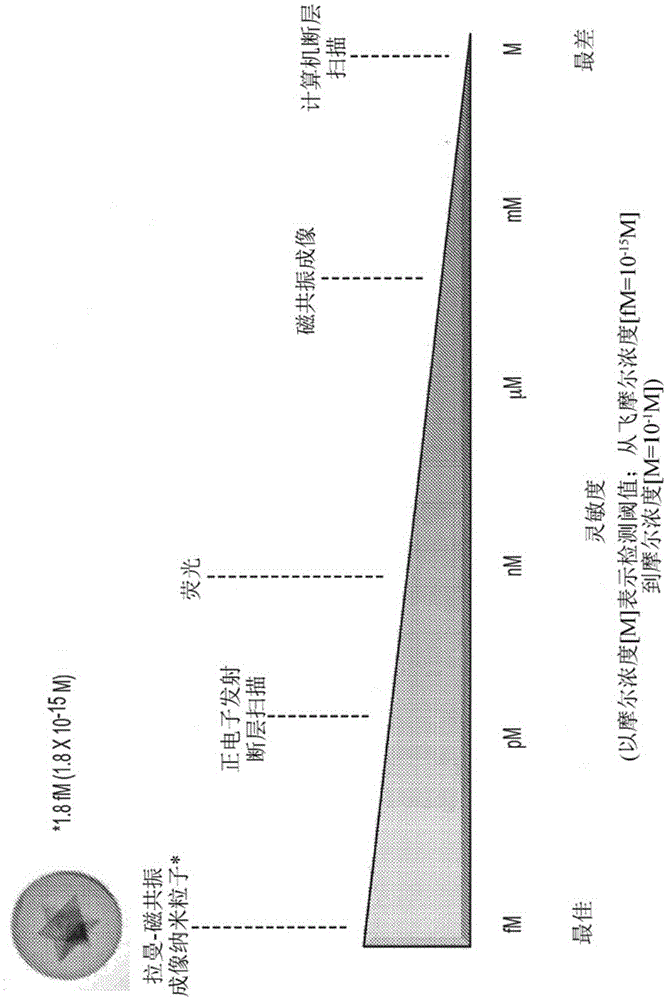
Apparatus and methods are presented herein that permit real-time, accurate detection of residual tumor in the operating room. The Raman-based wide-field imaging apparatus and methods described herein permit real-time imaging of tumor-targeted R-MR nanoparticles over a wide field.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES
Method for large-area representation of graphite/silicon/amorphous carbon composite structure silicon-carbon cathode powder body
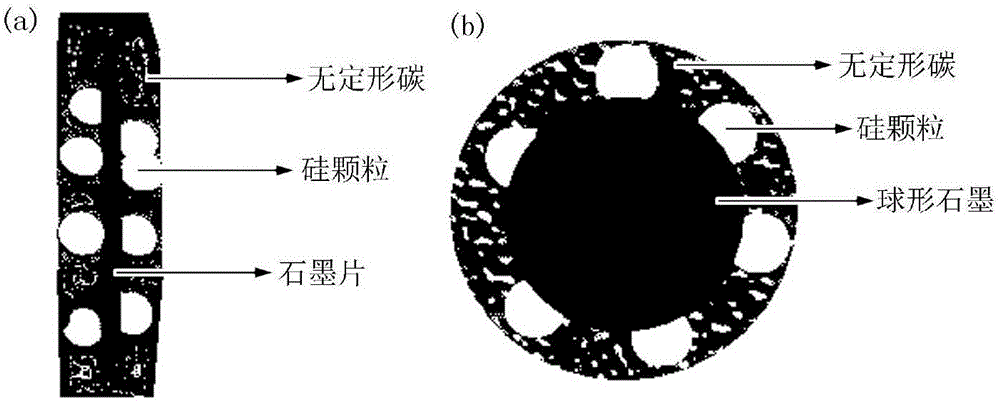
InactiveCN106229486ARapid assessment of structural homogeneityRapid Quality AssessmentCell electrodesRaman imagingGlass sheet
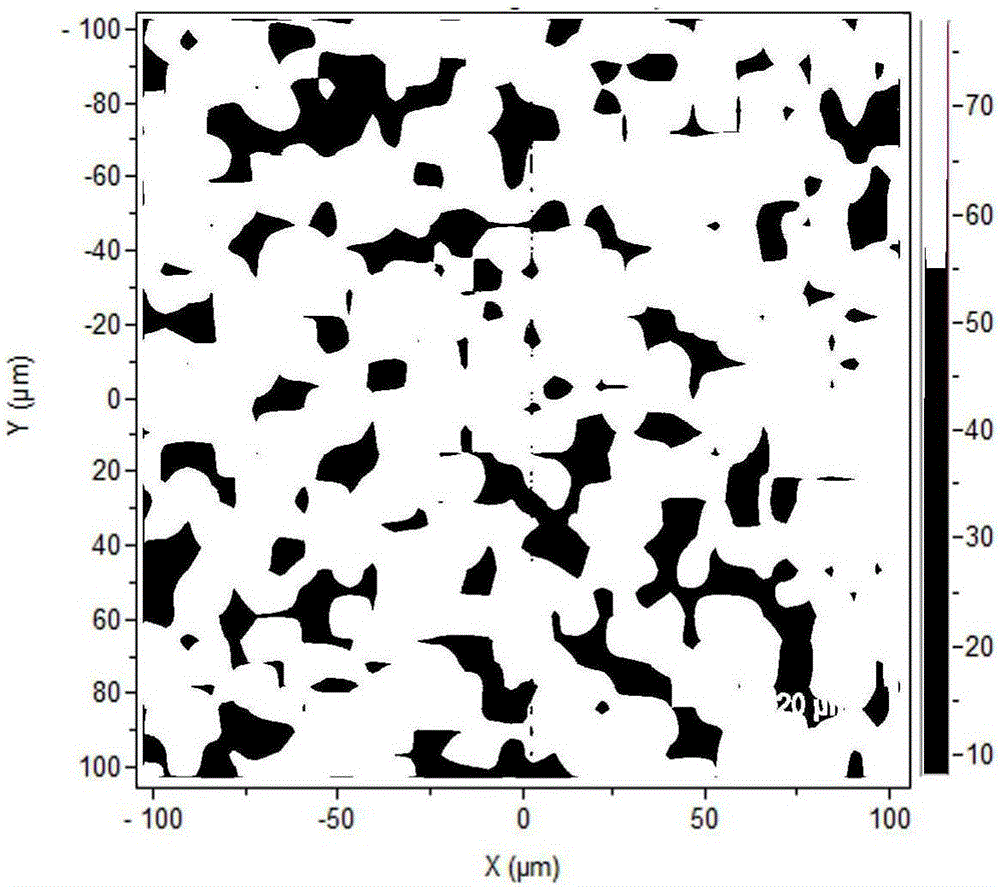
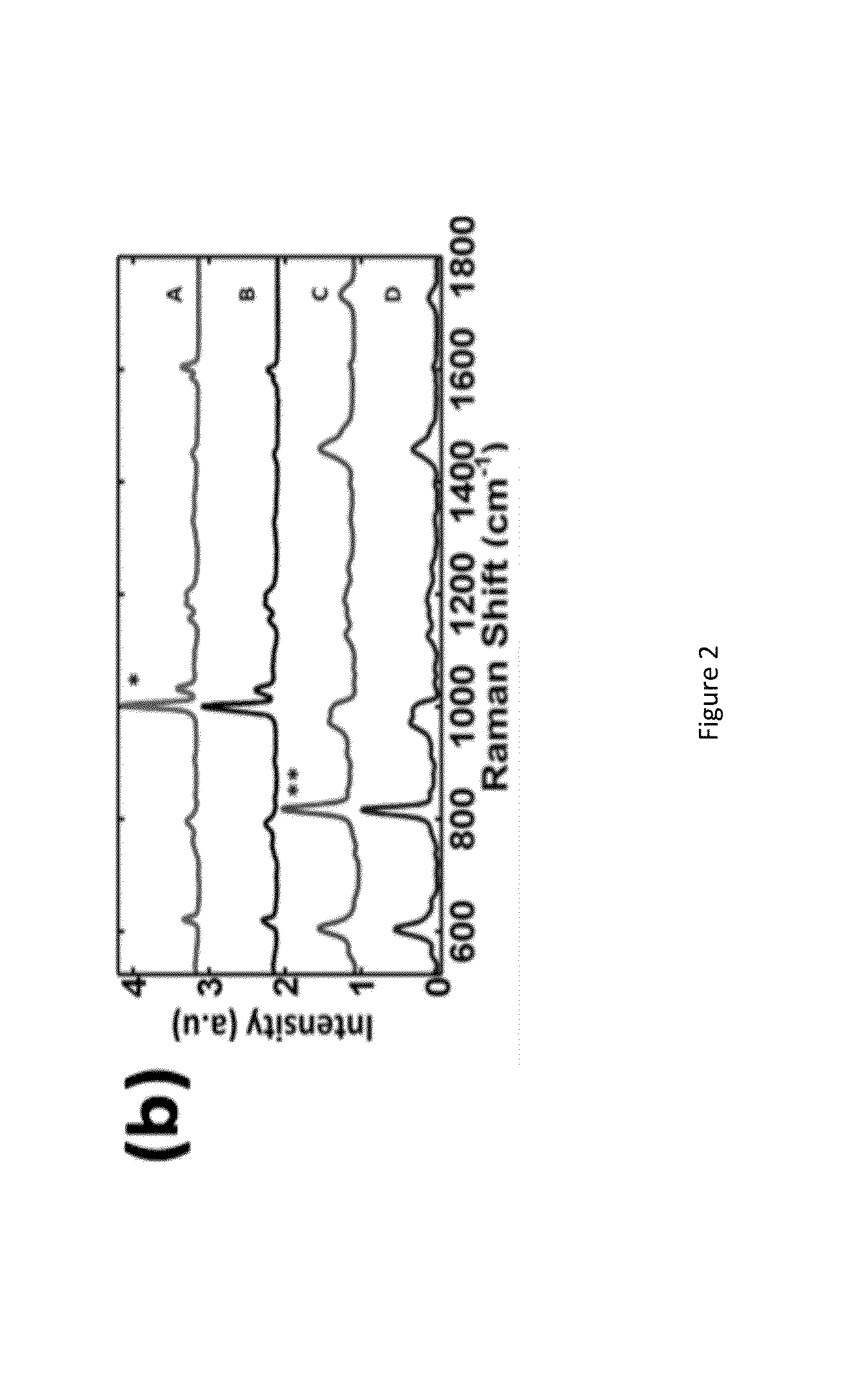
The invention discloses a method for large-area representation of a graphite / silicon / amorphous carbon composite structure silicon-carbon cathode powder body. The method comprises the following steps: placing the graphite / silicon / amorphous carbon composite structure silicon-carbon cathode powder body in the middle of a glass sheet with two flat surfaces, and compacting and flattening the powder body; testing the powder body with a laser Raman spectrometer, adjusting the peak of an obtained common Raman single spectrum to appear at positions near to 520 cm<-1>, 1,350 cm<-1> and 1,590 cm<-1>, and obtaining a test condition; obtaining a Raman imaging spectrum according to the test condition; respectively forming Raman imaged pictures for the intensities of a silicon peak, a carbon D peak and a carbon G peak, respectively imaging a ratio of the carbon D peak to the carbon G peak and a ratio of the carbon G peak to the carbon D peak, and judging whether the components and the structures in the powder body are consistent. The representation method disclosed by the invention is simple and quick, and can realize large-area representation of the distribution of silicon-carbon cathode components and research the structure consistency, so that the method has extremely high application prospect.
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
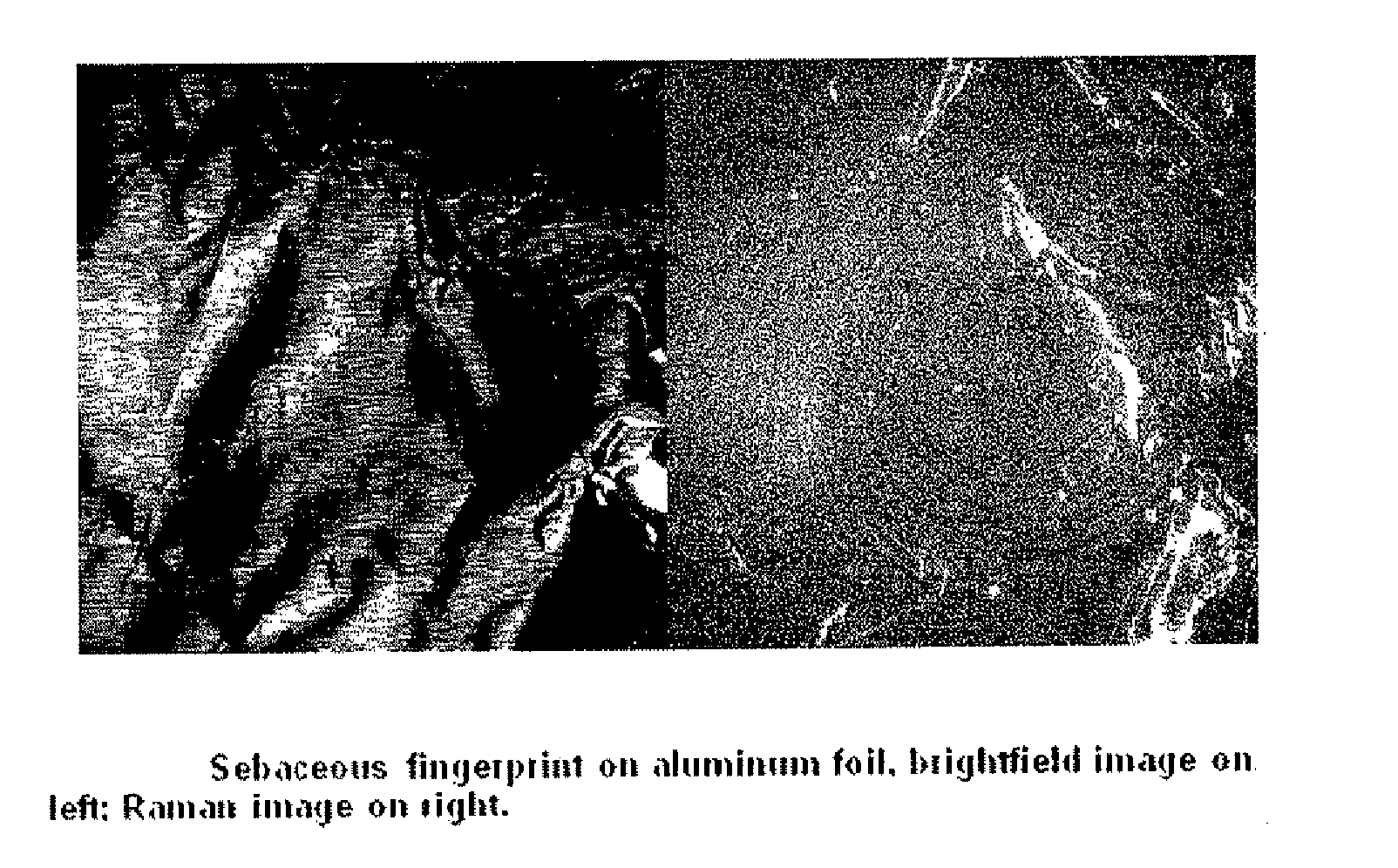
Detection of latent prints by raman imaging
InactiveUS20100021023A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansRaman imagingLatent fingerprint
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
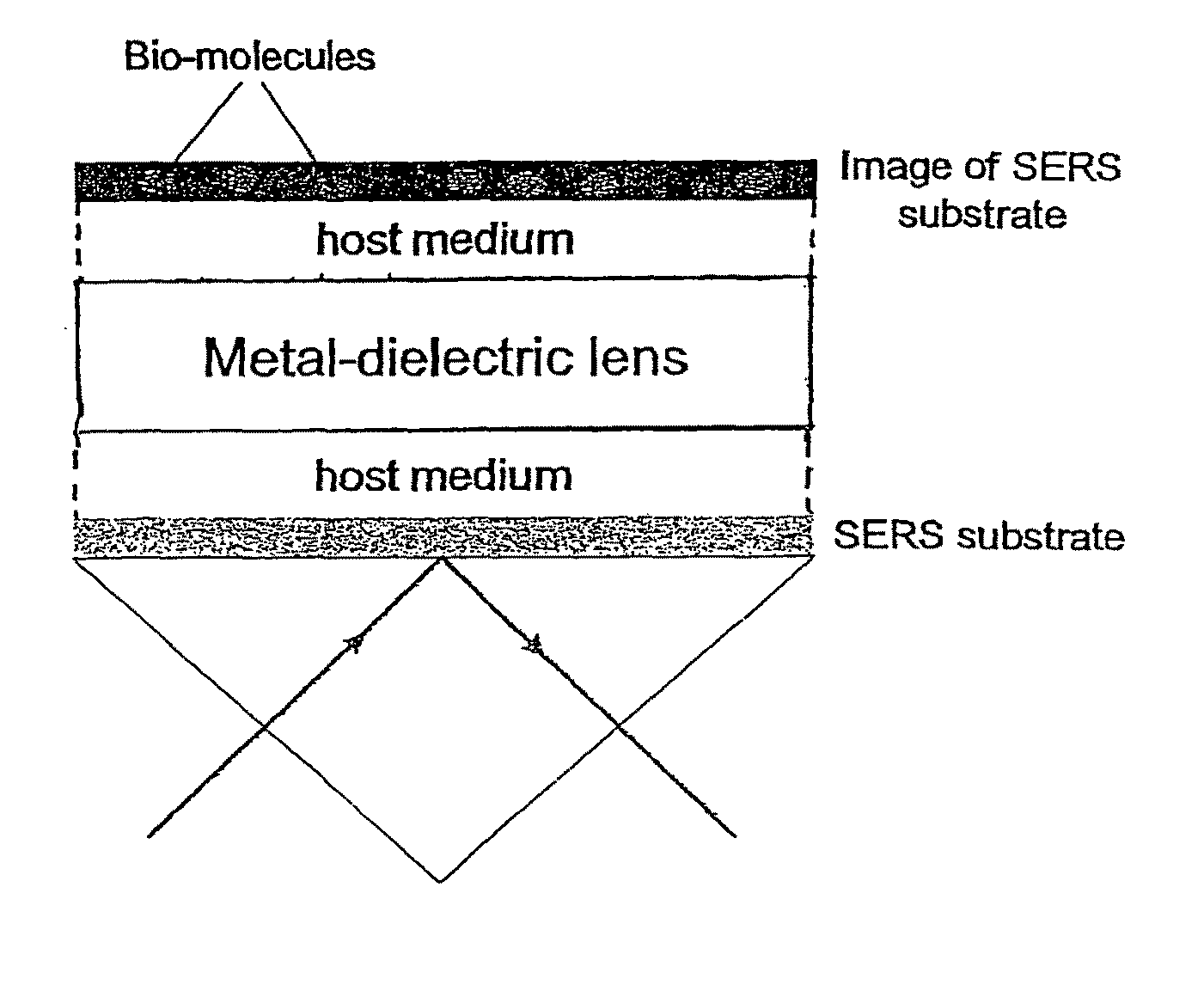
Near field raman imaging
ActiveUS8599489B2High resolutionFast and accurate calculationNanoopticsMicroscopesRaman imagingBio molecules
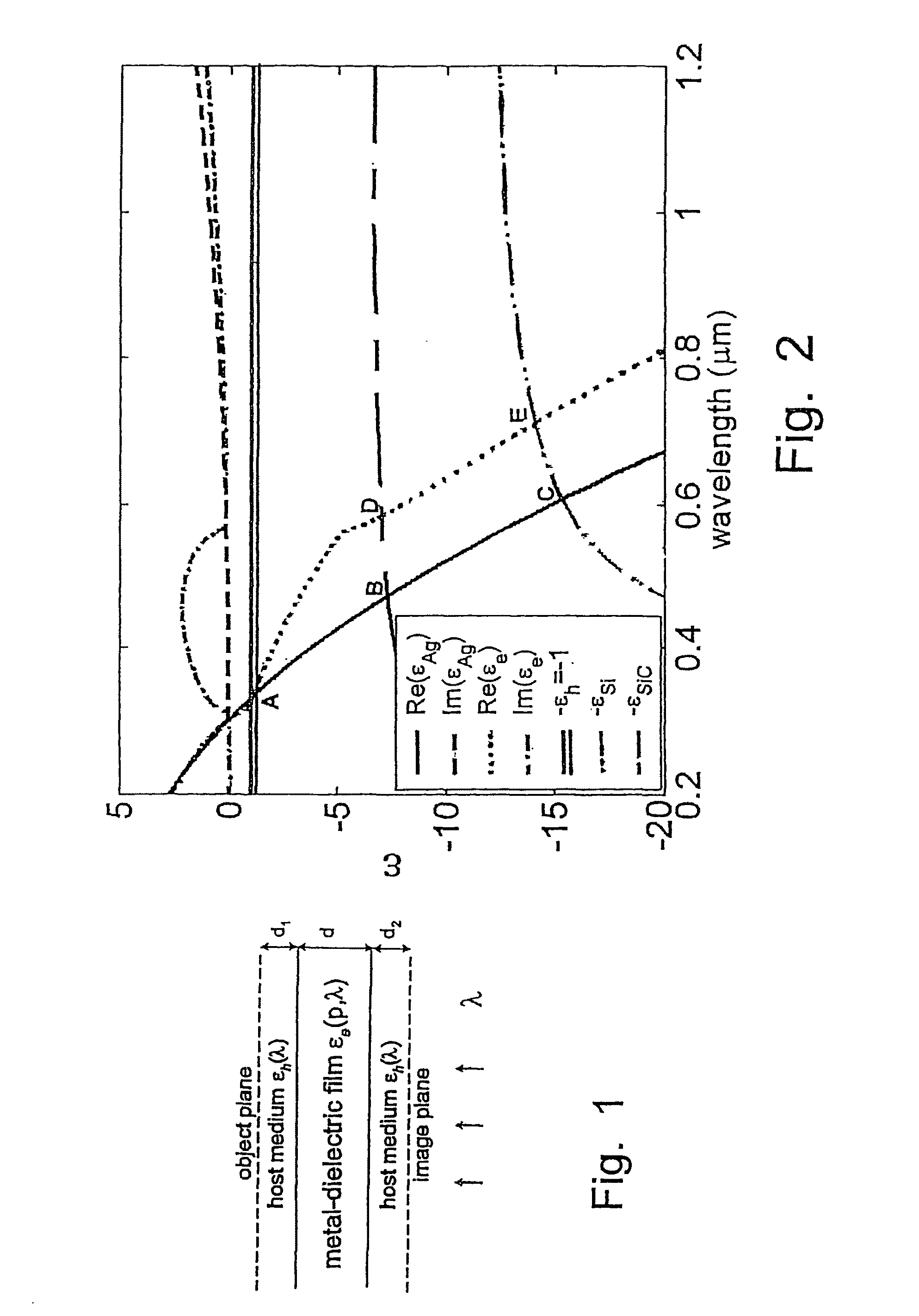
A tunable super-lens (TSL) for nanoscale optical sensing and imaging of bio-molecules and nano-manufacturing utilizes negative-index materials (NIMs) that operate in the visible or near infrared light. The NIMs can create a lens that will perform sub-wavelength imaging, enhanced resolution imaging, or flat lens imaging. This new TSL covers two different operation scales. For short distances between the object and its image, a near-field super-lens (NFSL) can create or enhance images of objects located at distances much less than the wavelength of light. For the far-zone, negative values are necessary for both the permittivity ∈ a permeability μ. While well-structured periodic meta-materials, which require delicate design and precise fabrication, can be used, metal-dielectric composites are also candidates for NIMs in the optical range. The negative-refraction in the composite films can be made by using frequency-selective photomodification.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method for quantitative and homogenous analysis of gluing diaphragm material in lithium ion battery
InactiveCN107167463AQuick Qualitative AnalysisAccurate qualitative analysisRaman scatteringRaman imagingElectrical battery
The invention discloses a method for quantitative and homogenous analysis of a gluing diaphragm material in a lithium ion battery. The method comprises the following steps: using a Raman spectrometer to perform a Raman spectroscopy detection on standard samples of all known components in the diaphragm material respectively, acquiring Raman characteristic peak position data in each Raman spectrum, and then establishing a database; performing Raman spectroscopy detection on a to-be-detected gluing diaphragm sample under same conditions to acquire a Raman spectrogram and a Raman image respectively; comparing to obtain composition of the to-be-detected gluing diaphragm sample; performing a Raman spectroscopy imaging test on a gluing region of the to-be-detected gluing diaphragm sample; and utilizing strength distribution of a characteristic peak position in the Raman spectrogram of a gluing substance to judge the gluing homogeneity in the to-be-detected gluing diaphragm sample. The method can rapidly perform quantitative analysis on components of a gluing diaphragm, and can reflect coating distribution of the gluing diaphragm by a Raman imaging technology, thereby indirectly inspecting the stability and homogeneity of a production process.
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
Optical path structure of spatial heterodyne Raman imaging spectrometer
The invention provides an optical path structure of a spatial heterodyne Raman imaging spectrometer. The optical path structure mainly comprises a collimating lens, a focusing lens, a first Raman light filter, a beam splitting prism, two wedged prisms, two blazed gratings, a second Raman light filter, an aspherical lens, an imaging lens set, an area array detector, an object stage, a beam expanderand a laser. Raman light emitted by a sample is focused on the blazed gratings on two arms of an interferometer after passing through the collimating lens, the focusing lens and the first Raman lightfilter, then combined again by the beam splitting prism to obtain spatial heterodyne Raman interference light, and finally received by the area array detector after passing through the second Raman light filter, the aspherical lens and the imaging lens set. Through adoption of the aspherical lens, the acquisition speed of each frame of the heterodyne Raman interference light acquired by the areaarray detector is effectively increased; through the optical path structure, rapid measurement of a Raman spectrum at each position on the surface of the sample to be detected is achieved; meanwhile,the optical path structure has the advantages of high resolution, large light flux, a wide measured waveband range and the like.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
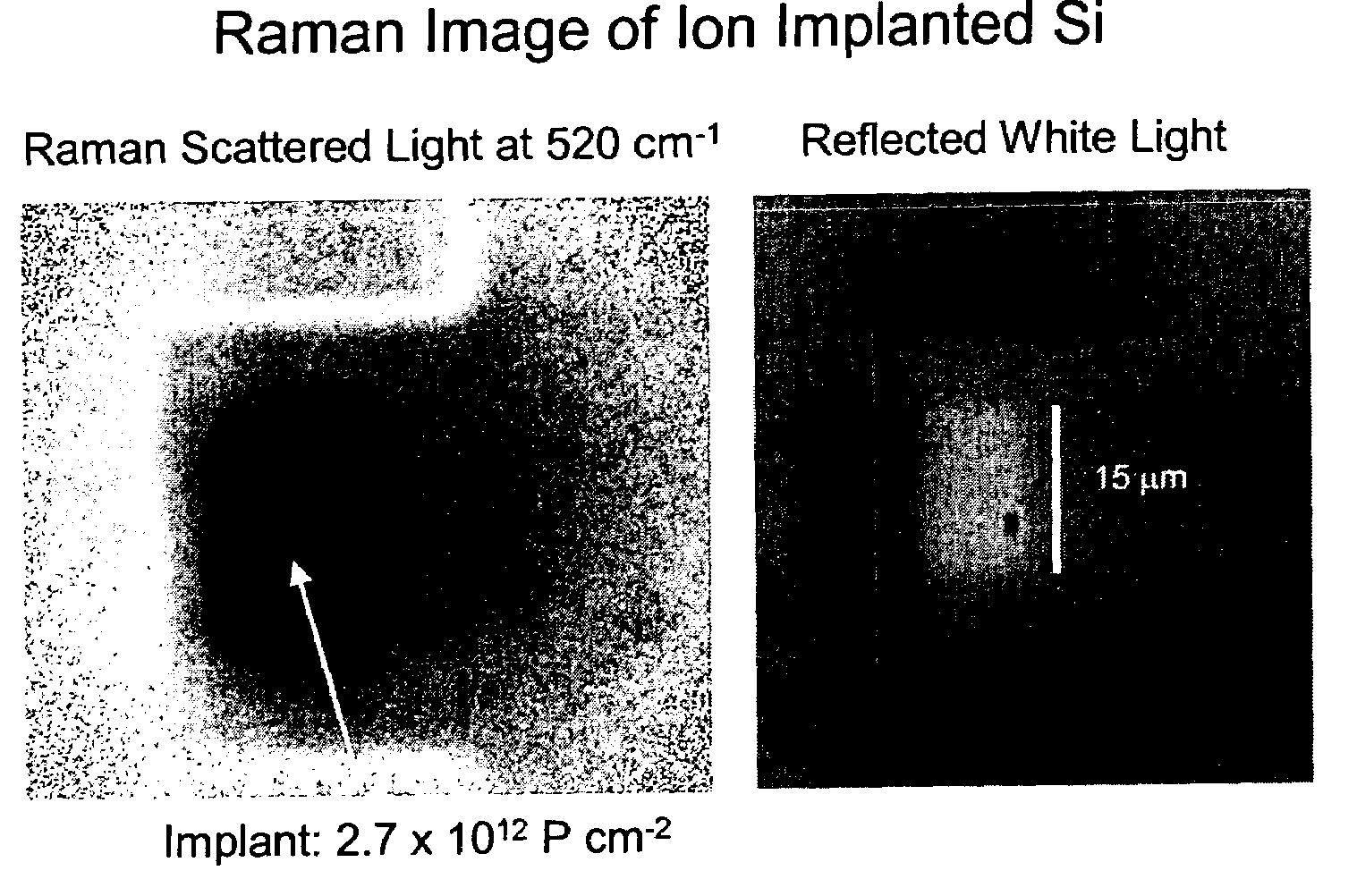
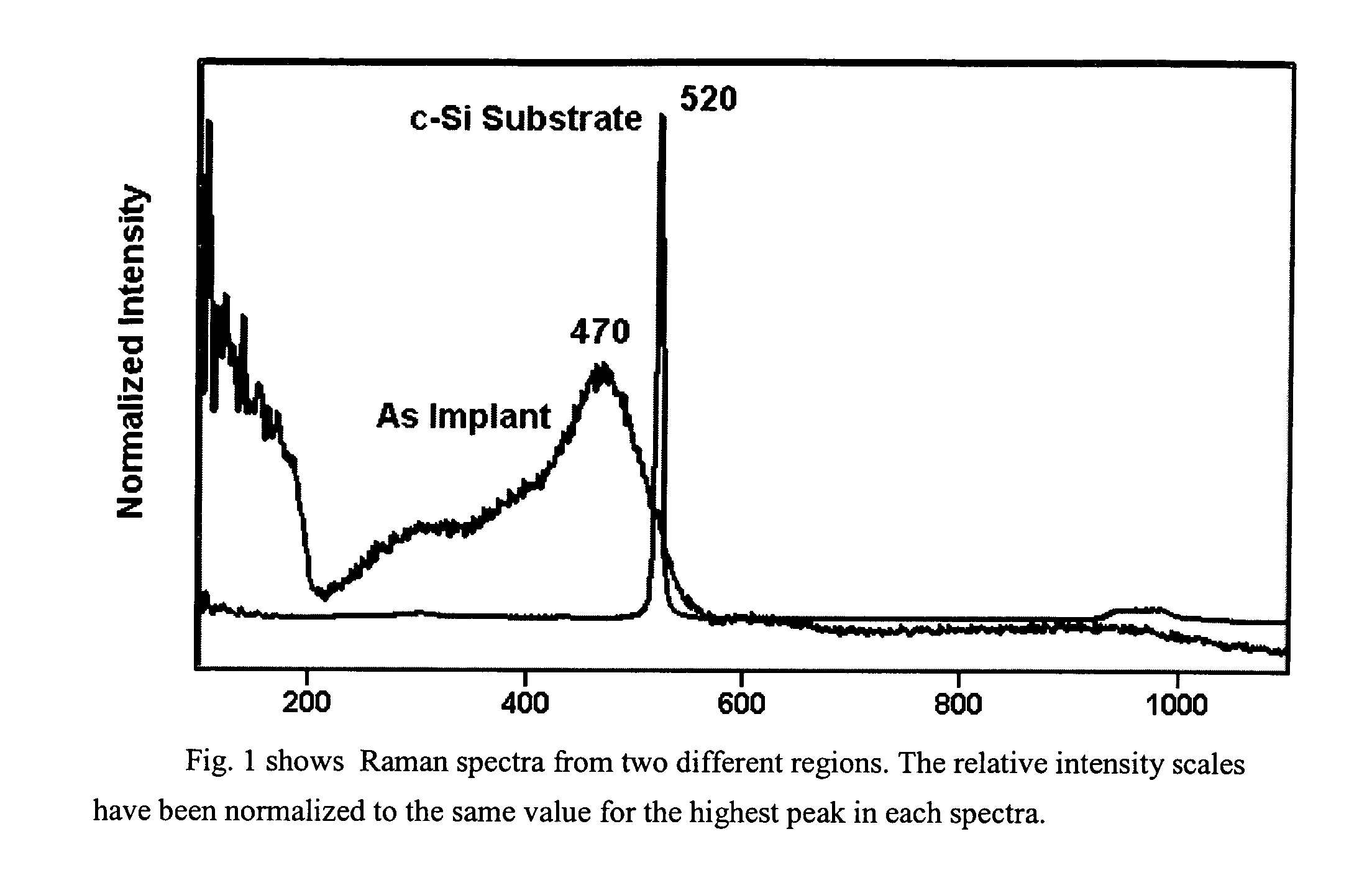
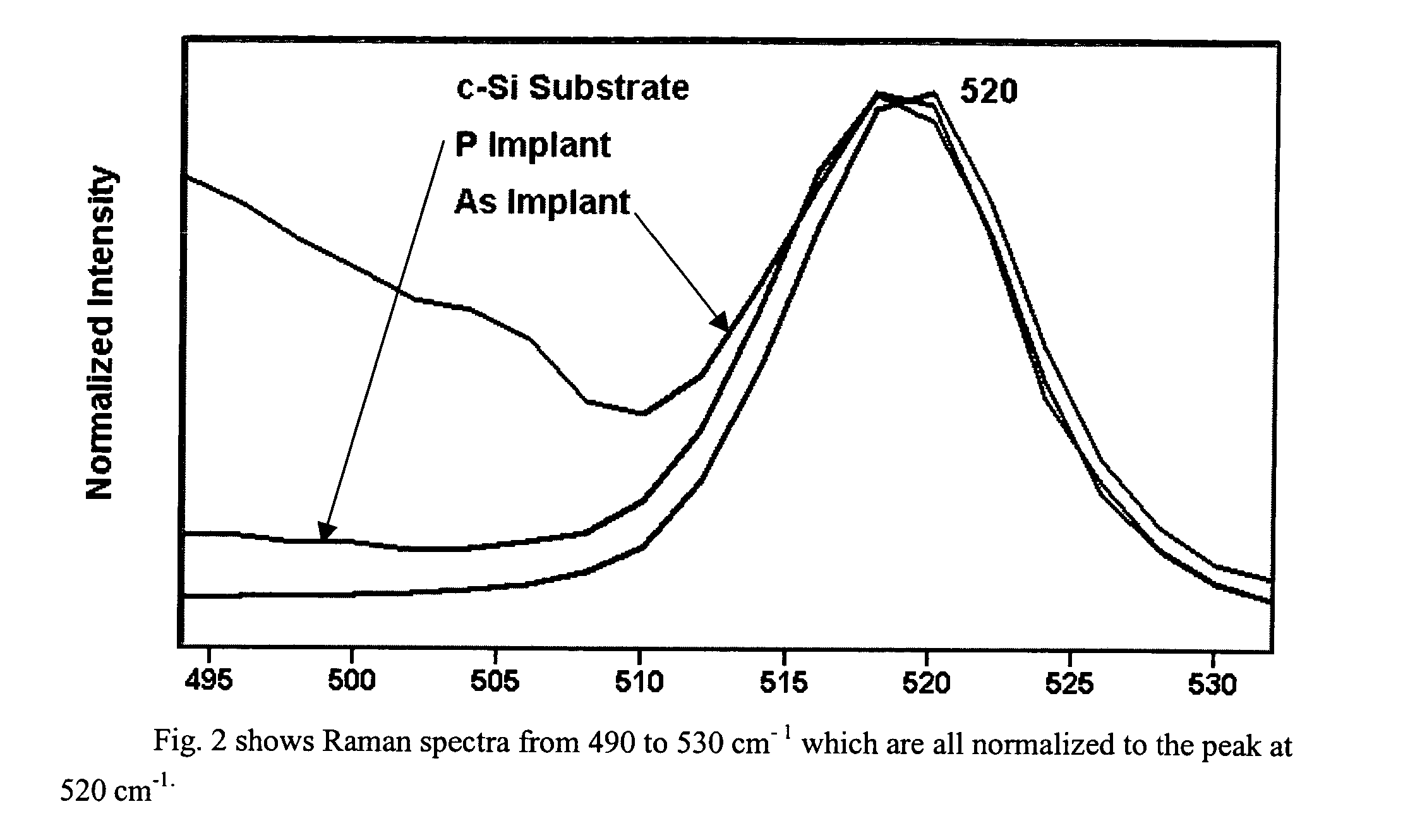
Method for Raman imaging of semiconductor materials
InactiveUS7123358B2Material becomes quickHigh spatialImage enhancementRadiation pyrometryRaman imagingSemiconductor materials
An ion implanted semiconductor surface is illuminated with a flood illumination of monochromatic radiation, and an image of the surface is taken using light which has been Raman scattered. The illumination and imaging system are calibrated by flood illuminating a uniformly Raman scattering surface.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
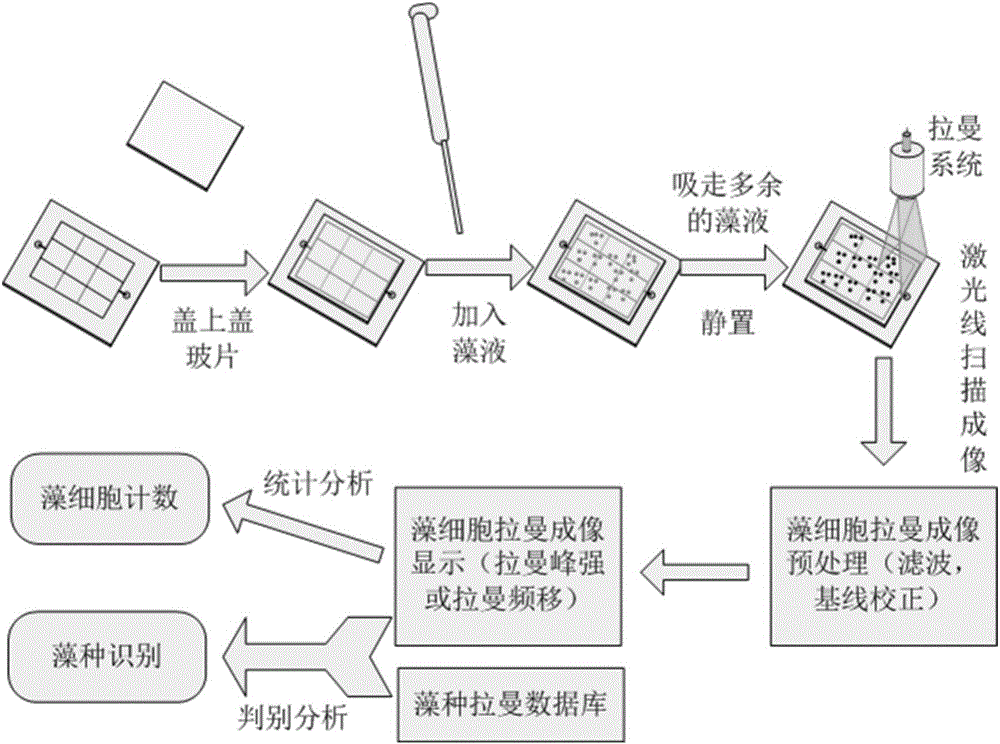
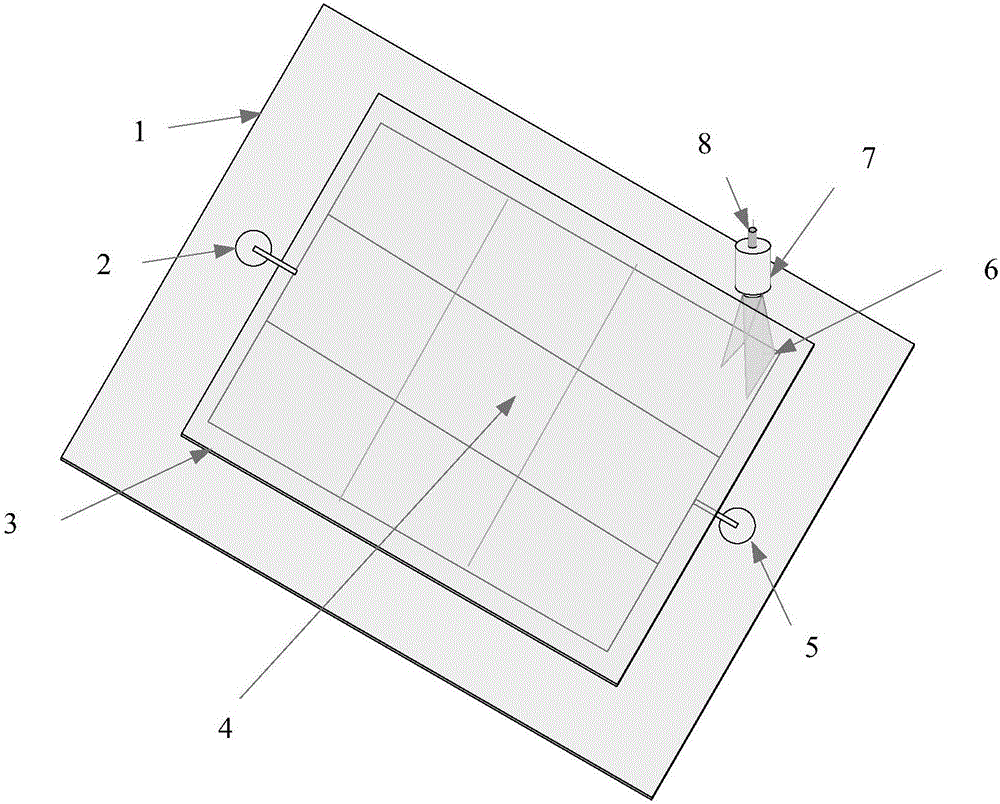
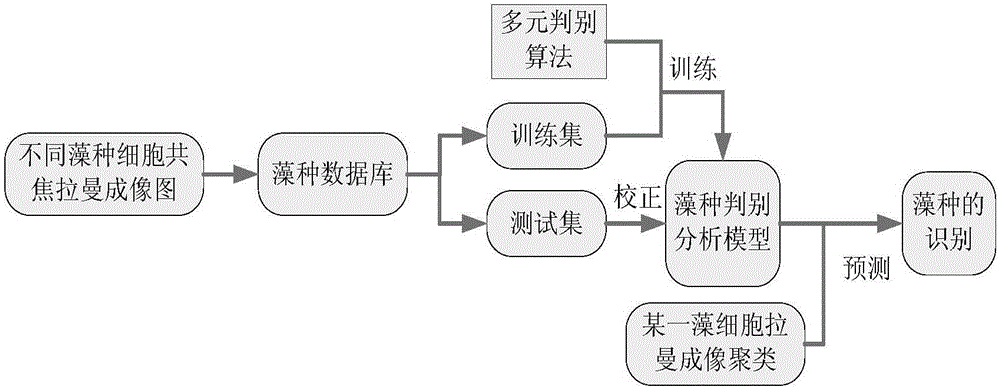
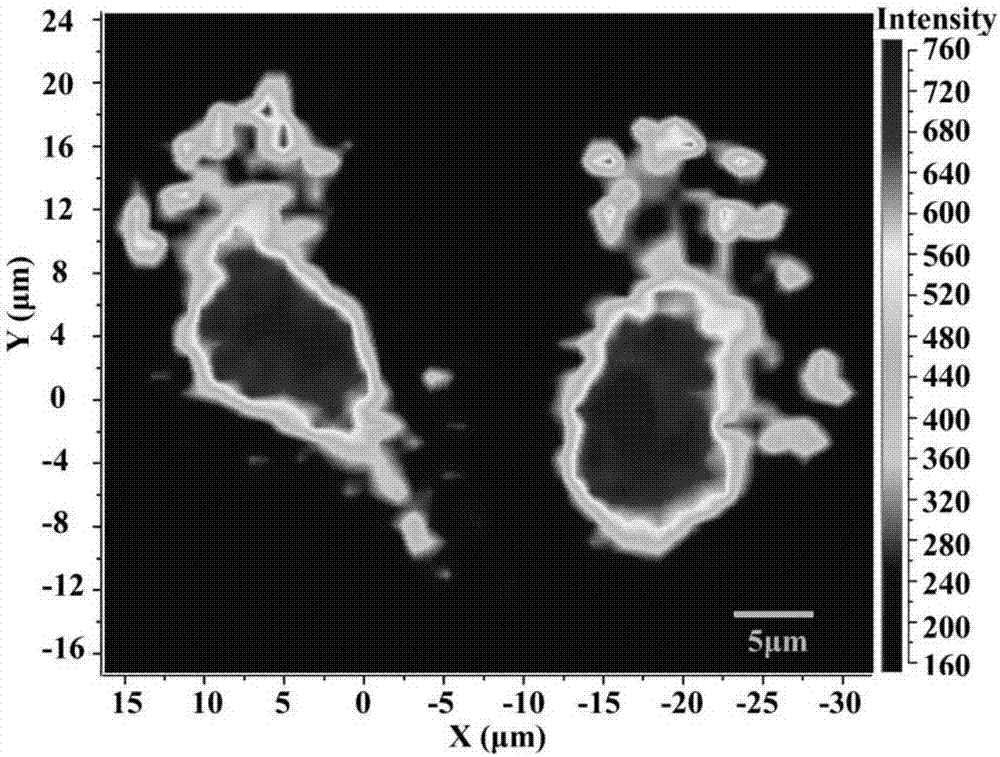
Method for counting algae cells and determining algae species on basis of line scanning Raman microscopy imaging
ActiveCN106442463ADiscriminant Analysis FastDiscriminant analysis is accurateRaman scatteringRaman imagingAlgae
The invention discloses a method for counting algae cells and determining algae species on basis of line scanning Raman microscopy imaging. The method comprises steps as follows: preparation of an algae cell detection counting board, pretreatment of algae cell samples, algae cell imaging and algae cell counting and algae specie determination based on algae cell Raman imaging. According to the method for counting the algae cells and determining the algae species on the basis of line scanning Raman microscopy imaging and multivariate data mining, algae cell counting and rapid determination and analysis of the algae species in an algae solution can be realized, and accurate counting of the algae cells and synchronous rapid recognition of the algae species are easy to realize.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
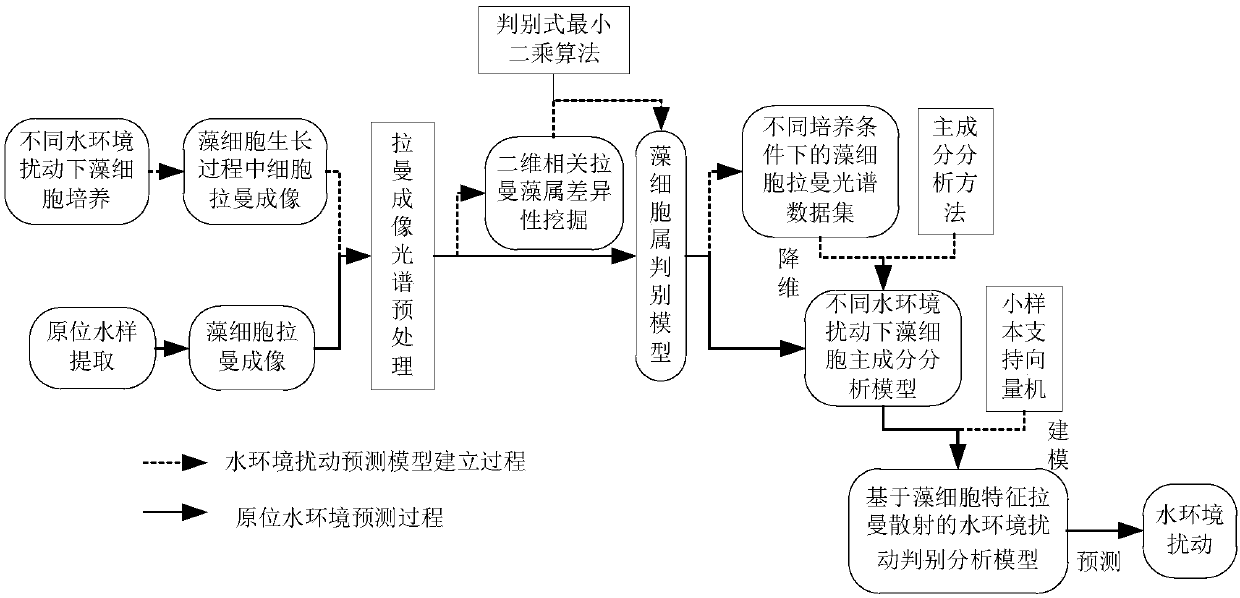
Method for evaluating water environment disturbance based on characteristic Raman scattering of alga cells
InactiveCN107941783ARapid assessmentRaman scatteringCharacter and pattern recognitionRaman imagingBiology
The invention relates to a method for evaluating the water environment disturbance based on characteristic Raman scattering of alga cells, belonging to the technical field of water environment evaluation. The method comprises the following steps: (S1) culturing alga cells under different simulated water environment disturbance factors; (S2) carrying out sampling representation on alga liquid in aculturing period, carrying out Raman imaging on the alga cells by virtue of a confocal microscope Raman spectrometer, and carrying out pretreatment on a Raman spectrum of the alga cells; (S3) analyzing characteristic Raman spectrums of the alga cells under different culturing conditions, so as to obtain the Raman difference of characteristic fingerprints of the alga cells, and determining the category of the alga cells; (S4) establishing a water environment disturbance evaluation model based on the characteristic Raman scattering of the alga cells; and (S5) evaluating and predicting a water environment according to the water environment disturbance evaluation model established in the steps (S4). According to the method, the characteristic Raman spectrum of the alga cells is established andis utilized for predicting the disturbances of different environments, so that the rapid evaluation of the water environment disturbance is realized.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
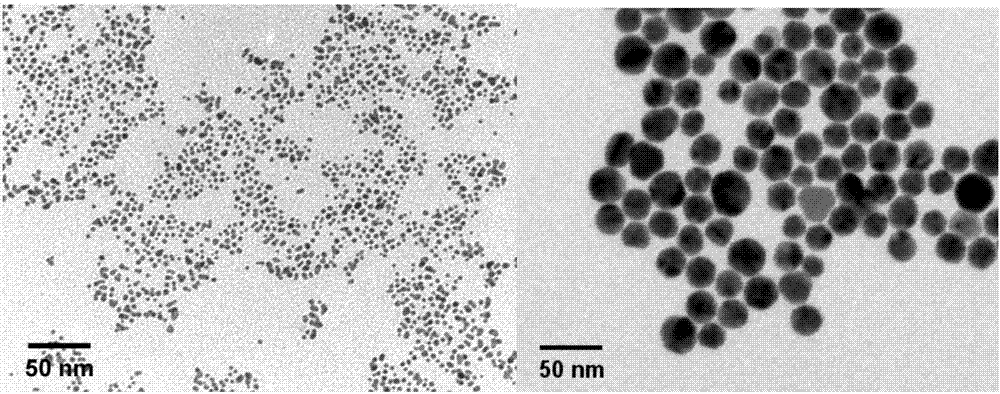
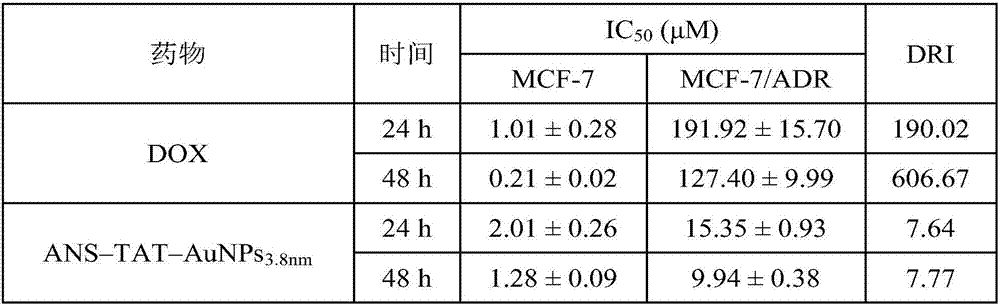
2-(9-methylene anthracene) thiosemicarbazide and TAT modified gold nanoparticle drug delivery system and application
InactiveCN106983732AGood biocompatibilityLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsRaman scatteringRaman imagingThiourea
The invention provides a 2-(9-methylene anthracene) thiosemicarbazide and TAT modified gold nanoparticle drug delivery system. The 2-(9-methylene anthracene) thiosemicarbazide and TAT modified gold nanoparticle drug delivery system has the advantages that a gold nanosphere drug delivery system with the particle size being 3.8nm (sodium borohydride reduction method) and a gold nanosphere drug delivery system with the particle size being 22.1nm (sodium citrate reduction method) are built, the surfaces of the systems are modified with polypeptide TAT, the systems modified by the polypeptide TAT are used as the carriers of 2-(9-methylene anthracene) thiosemicarbazide, the fact that the drug-resistance index of large-particle-size gold nanospheres to drug-resistance cells is smaller is discovered through the antitumor activity evaluation of MCF-7 sensitive cells and MCF-7 / ADR drug-resistance cells, and the fact shows that large-particle-size carriers are more suitable for tumor drug resistance treatment and the 22.1nm gold nanospheres have an enhancing effect on the Raman signal of the 2-(9-methylene anthracene) thiosemicarbazide and can be used for cellular-level Raman imaging.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Method and system for active-illumination parallel raman microspectroscopy
ActiveUS20140029003A1Improved sampling flexibilityHigh laser power duty cycleRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsRaman imagingWide field
An active-illumination parallel Raman microspectroscopy scheme for simultaneously collecting Raman spectra from multiple points in a full-spectra range. A combination of multi-point laser illumination with wide-field Raman imaging is employed in order to allow for simultaneous imaging of multiple points not aligned on a single line.
Owner:UNIV HOUSTON SYST
Hollow SiO2 wrapped hollow Au cage nanometer bell and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN105290393AGuaranteed stabilityImprove drug loading capacityMaterial nanotechnologyRaman imagingSignalling molecules
The invention discloses a hollow SiO2 wrapped hollow Au cage nanometer bell and a preparing method and application thereof. The nanometer bell comprises a hollow SiO2 micro ball and a hollow Au cage movably arranged in an inner cavity of the hollow SiO2 micro ball. The preparing method of the nanometer bell comprises the steps that an Ag cuboid and the like are utilized as a template, the hollow Au cage is manufactured, Raman signal molecule modification and SiO2 shell layer wrapping are carried out on the surface of the Au cage, and an SiO2 wrapped hollow Au cage core-shell structure nanometer particle is formed; and in addition, the selective surface etching is carried out on the core-shell structure nanometer particle, and the nanometer bell is prepared. The nanometer bell has high stability and biocompatibility and can serve as a good medicine carrier, the absorption in a near-infrared area can be adjusted, the light energy of near-infrared lasers is converted into heat energy, meanwhile, the Raman signal can be enhanced, and huge application prospects are achieved in the medical fields such as medicine carrying, photo-thermal treatment and Raman imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Gold-silver nanoflower particle with core-shell structure, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110227816AThe synthesis method is simpleSynthetic method is fastMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingRaman imagingPetal
The invention discloses a gold-silver nanoflower particle with a core-shell structure, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The gold-silver nanoflower particle is quickly synthesized by adopting tea polyphenol as a reducing agent and a stabilizing agent, and no extra surface active agent and seed crystal needs to be used, so that low energy consumption and environment protection are realized. Dense multi-branched gold petals are distributed on the surface of the obtained gold-silver nanoflower particle, so that the gold-silver nanoflower particle has a remarkable near-infrared light absorption property and a favorable photo-thermal heating performance, and can be applied to photo-thermal therapy based on a near-infrared light; and meanwhile, the obtained gold-silver nanoflower particle further has an excellent surface enhanced Raman performance with good stability and is hopefully applied to Raman imaging of cells so as to have a favorable application prospects in cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
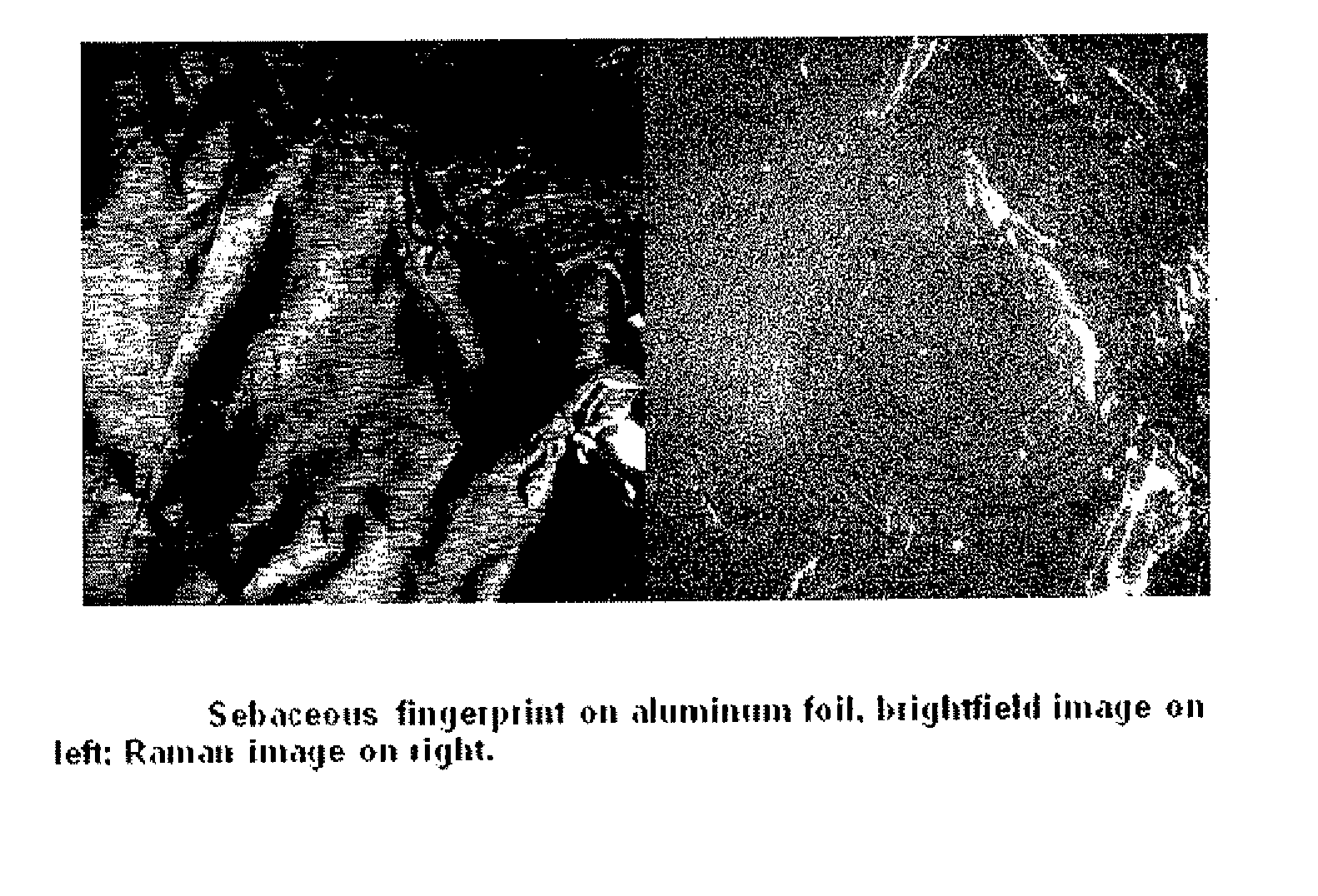
Detection of latent prints by Raman imaging
InactiveUS7869031B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansRaman imagingLatent fingerprint
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Raman super-resolution microimaging system based on structured light illumination and imaging method
The invention discloses a Raman super-resolution microimaging system based on structured light illumination and an imaging method and solves the technical problems in the prior art that the structuredlight super-resolution fluorescence microscopy relies on a fluorescent marker and thus has poor specificity, fluorescence bleaching and light injury often happen after long-time observation of the sample, and the Raman super-resolution microimaging technology is implemented based on a near field scanning way and thus has relatively low stability and cannot perform panoramic fast imaging of the sample. The imaging system disclosed by the invention comprises a structured light generation device, a Raman signal excitation device and a one-time Raman imaging device. Through combination of the structured light super-resolution fluorescence microscopy and the Raman super-resolution microimaging technology, the imaging system realizes non-marked, panoramic and fast super-resolution imaging, andcan be applied to the research directions such as cell membranes, artificial phospholipid membranes, artificial nano pores, endocytosis / transfer single molecule and particle system, mechanism of virusentering cells, dynamic process of molecules in living cell, interaction of nano cells and biological effect.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Raman scattering nanoprobes
ActiveUS20130323856A1Promote dispersion and solubilityEasy to disperseComponent separationLaminationRaman imagingLight beam
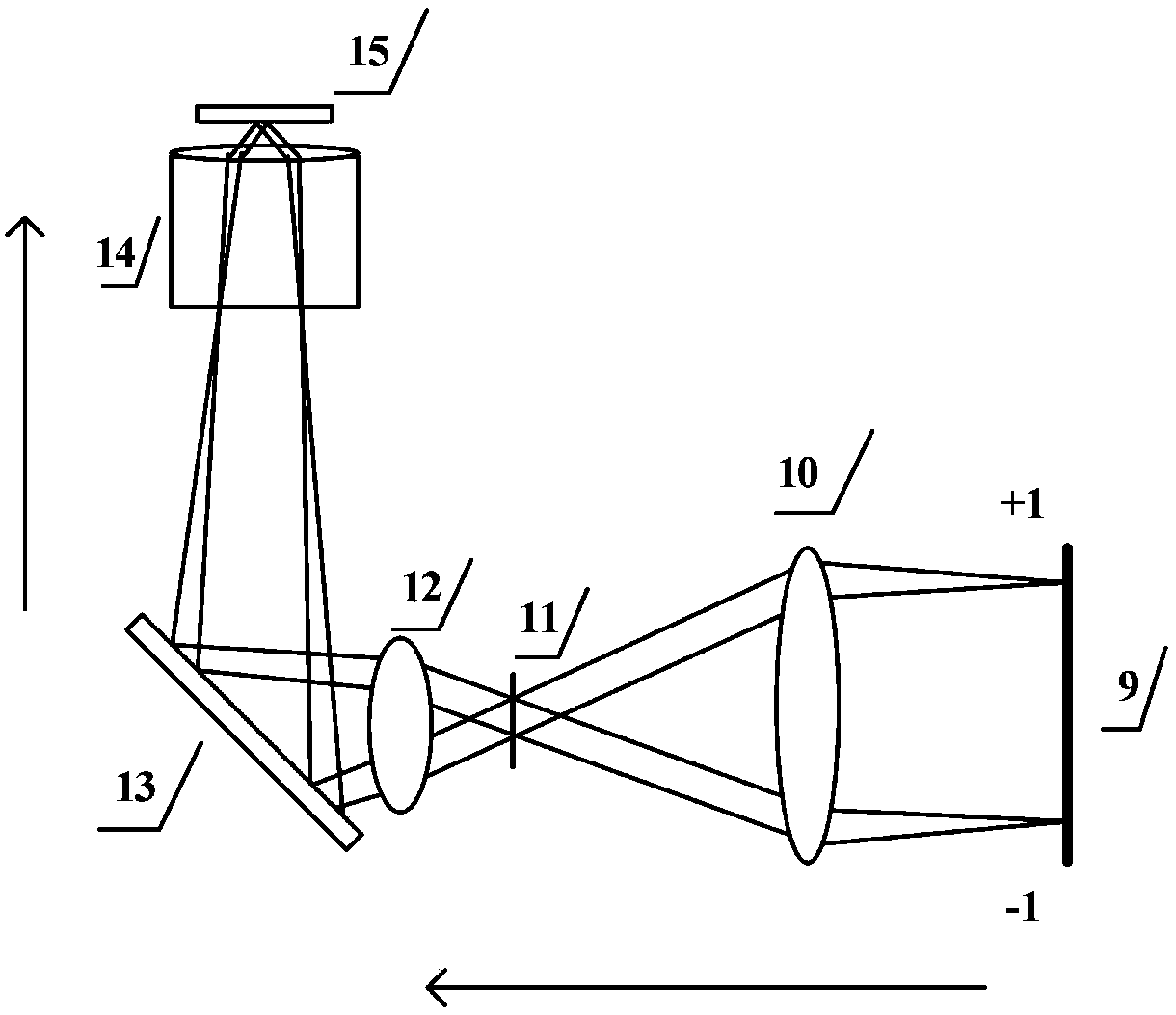
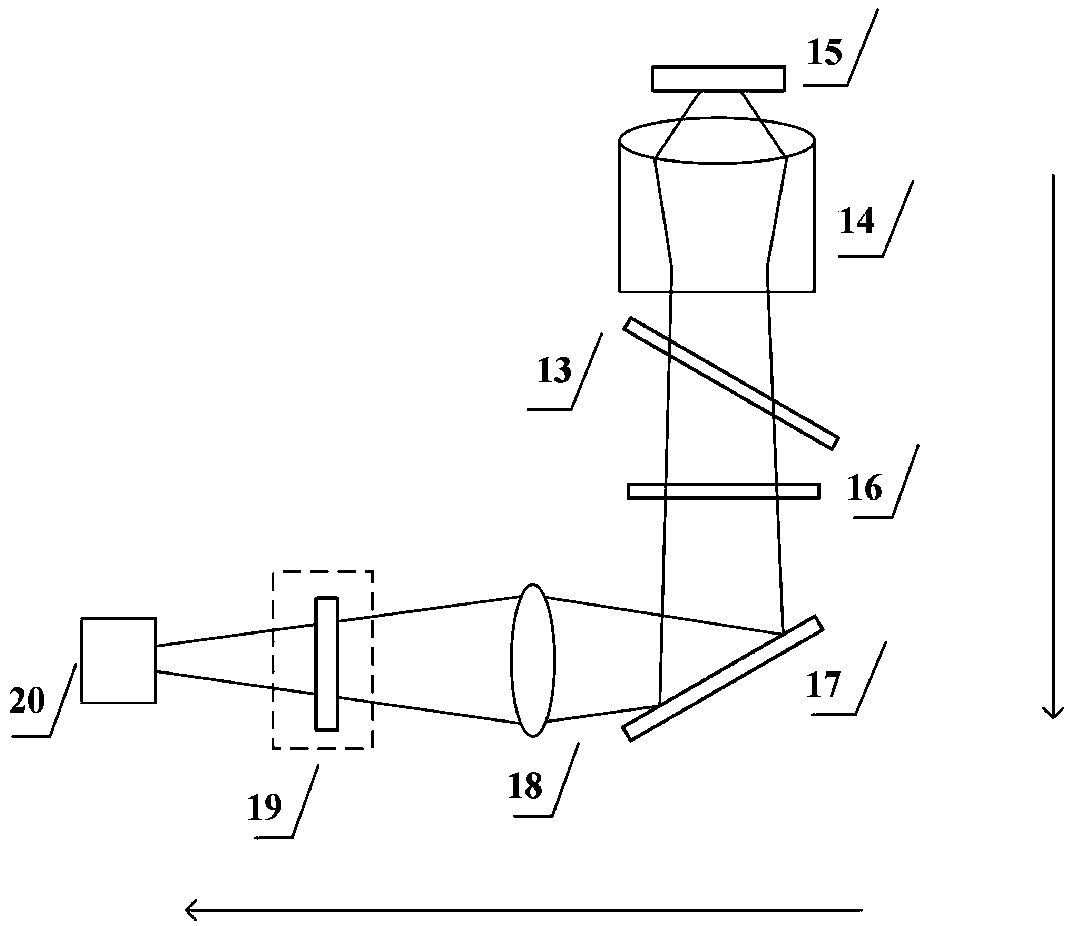
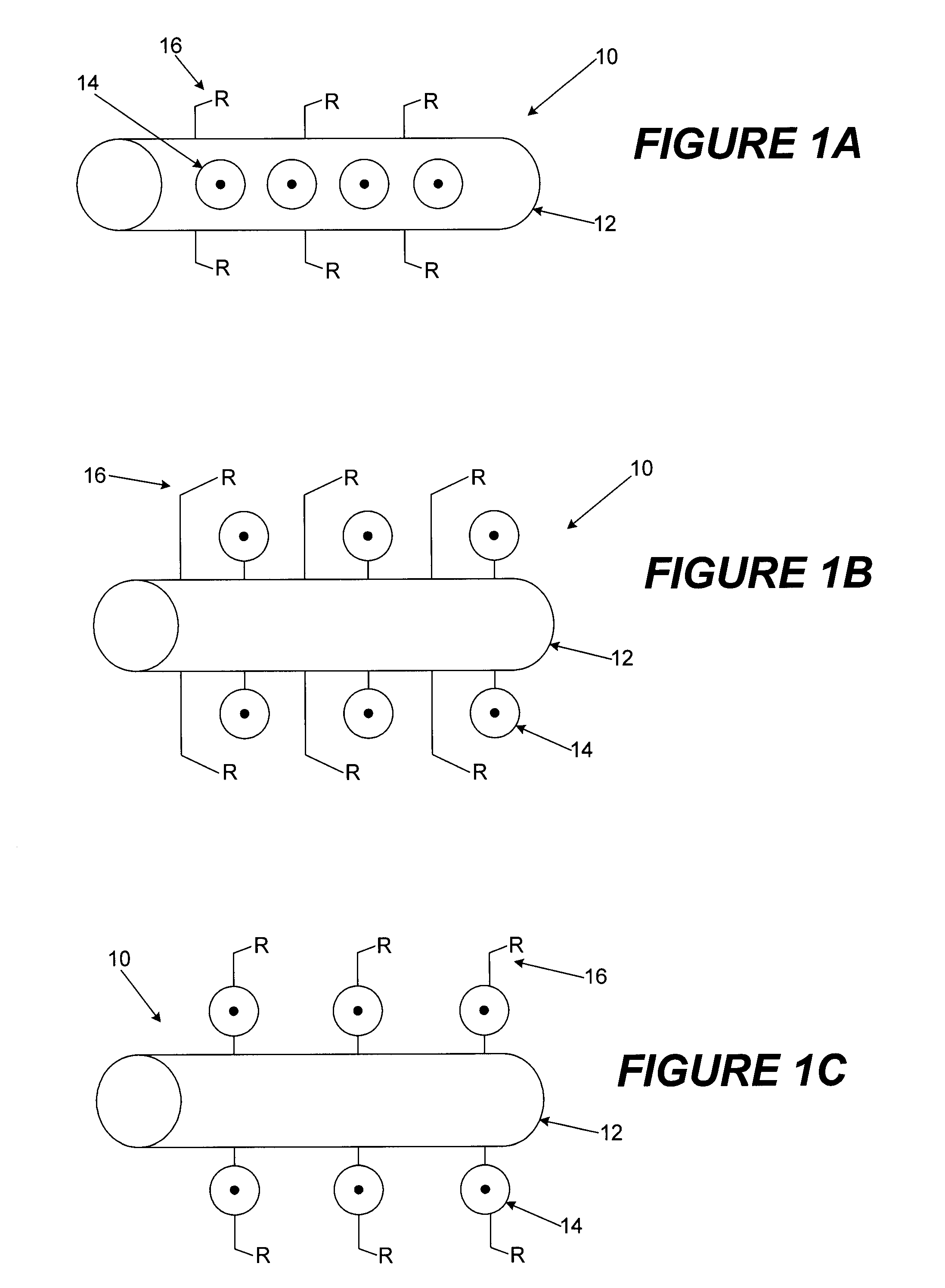
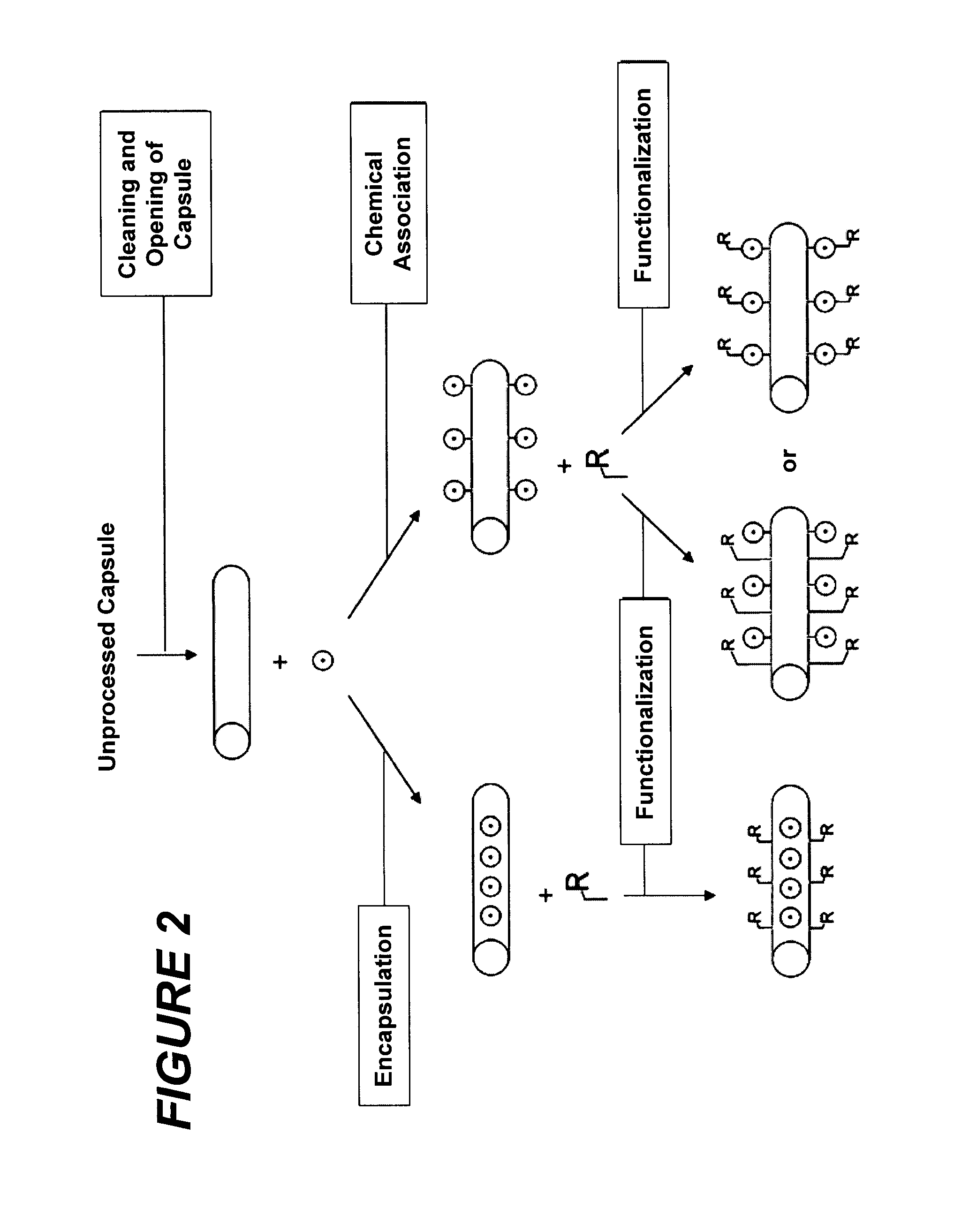
A Raman scattering probe, and a method of making such a probe, uses a capsule of nanometric size, such as a nanotube, to which is coupled at least one Raman-active molecule. The Raman-active molecule may be encapsulated in, or attached on the exterior of the capsule, and exhibits a Raman scattering response when the probe is illuminated by an excitation light beam. A functionalization chemical group that is attached to an exterior of the capsule provides a connection between the capsule and a target material. This functionalization may include a generic chemical functionalization that bonds with any of a plurality of secondary chemical groups each of which bonds directly with a different target. A method of using the probe for Raman spectroscopy or Raman imaging is also provided.
Owner:VALORISATION RECH LLP
Optical-interference-free Raman labeling probe and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105823770AEliminate interfering peaksGuaranteed Narrowband Single Peak Output ModeRaman scatteringBandpass filteringRaman imaging
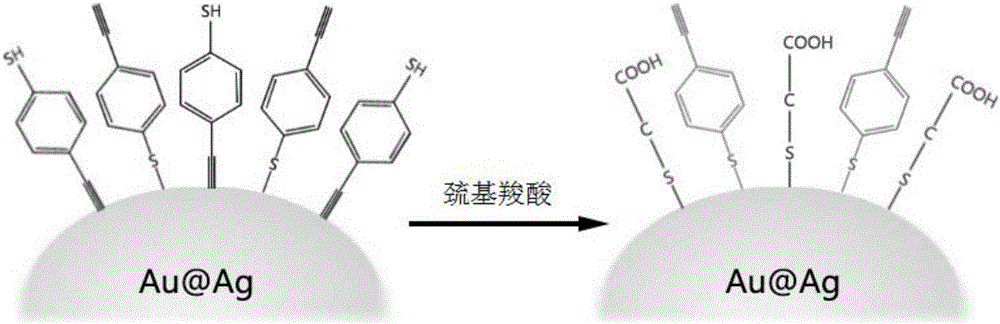
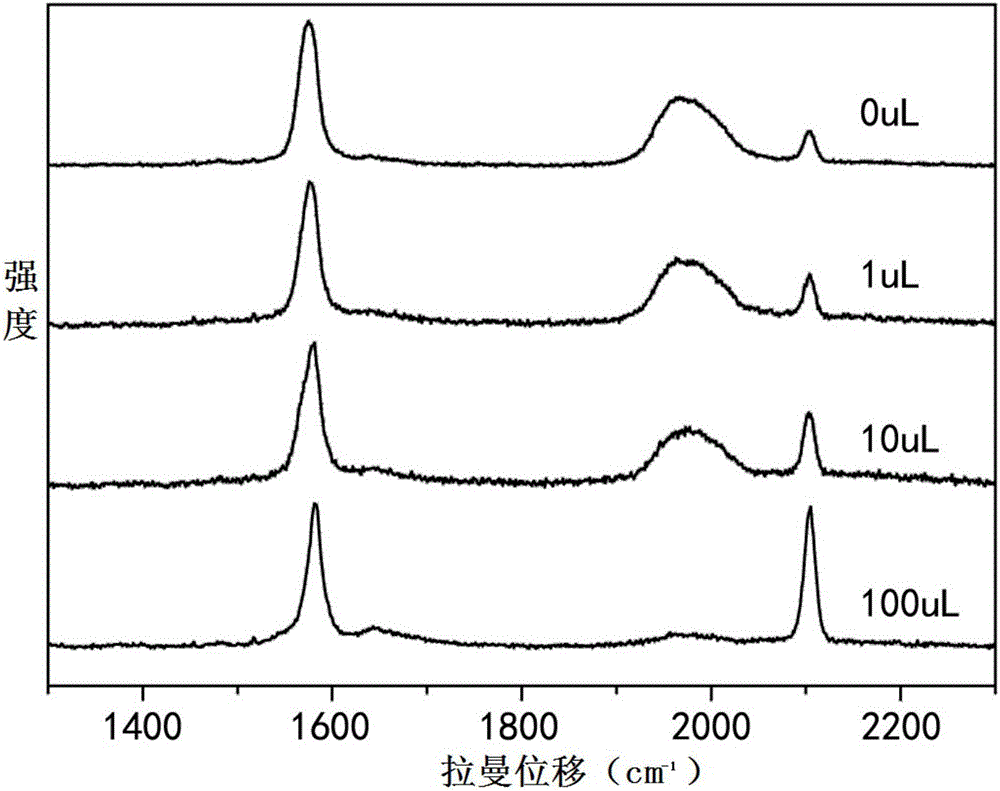
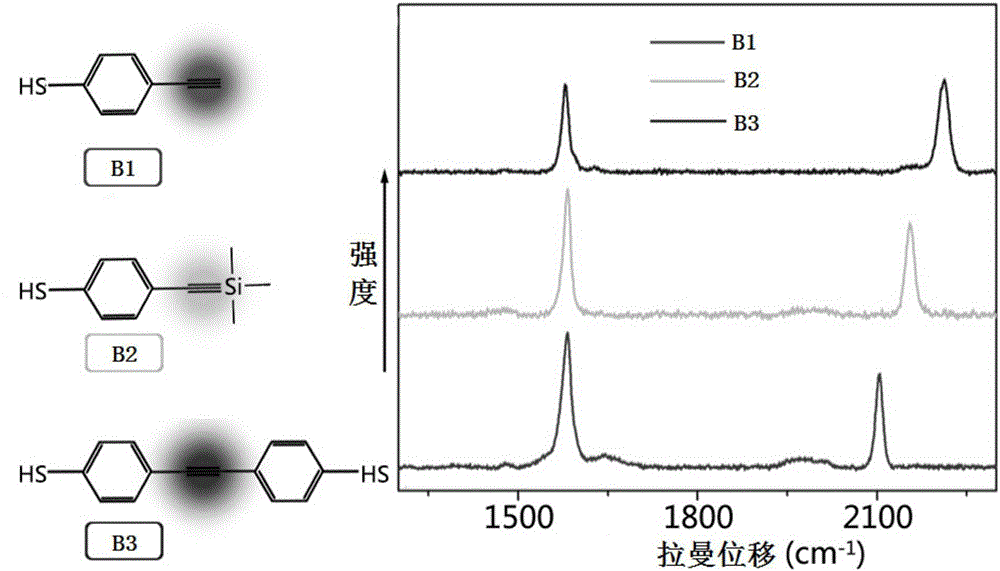
The invention designs a series of signal molecules with Raman scattering peaks in the wave number area of 1800-2400 cm<-1> by using a sulfydryl phenylacetylene as a body structure, selects gold and silver nano-particles as reinforcing substrates of Raman signals, enables alkyne signal molecules with sulfydryls to be self-assembled on the surfaces of the reinforcing substrates, uses mercaptoacetic acid to optimize SERS signals, then selects a light-transmitting and hydrophilic package material rich in active reaction groups for probe package and finally grafts specific biological targeting functional molecules to an outer layer of the package material .A probe has strong optical response to Raman scattering, adopts narrow-band unimodal transmission, is free of optical background interferences and has the great significance in the biological imaging field of simultaneous marking of multiple components .The technology can extend to design and development of a no-raster ultra-fast Raman imager using a bandpass filter as a beam splitting device and using a photomultiplier tube (PMT) or an avalanche photodiode (APD) as a detecting device, overcome the technical bottlenecks of Raman imaging point-by-point scanning and slow imaging and fills the blank in the market of optical imaging instruments .
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com