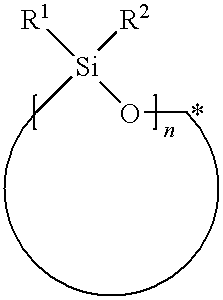
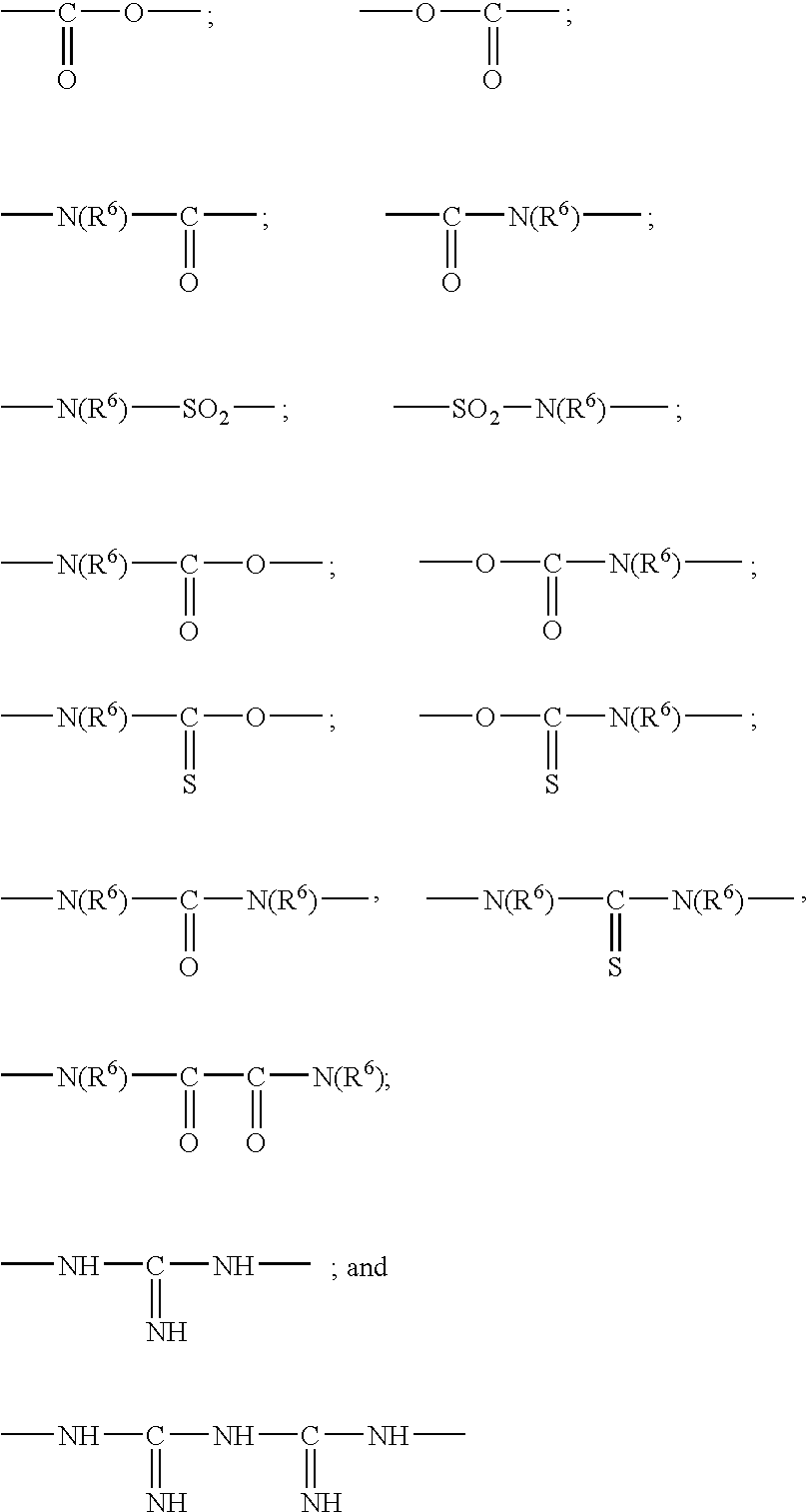Patents
Literature
859results about How to "Easy to disperse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminogly ycanases
PendingUS20060104968A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsSenses disorderNervous disorderHyaluronidaseRecombinant glycoprotein
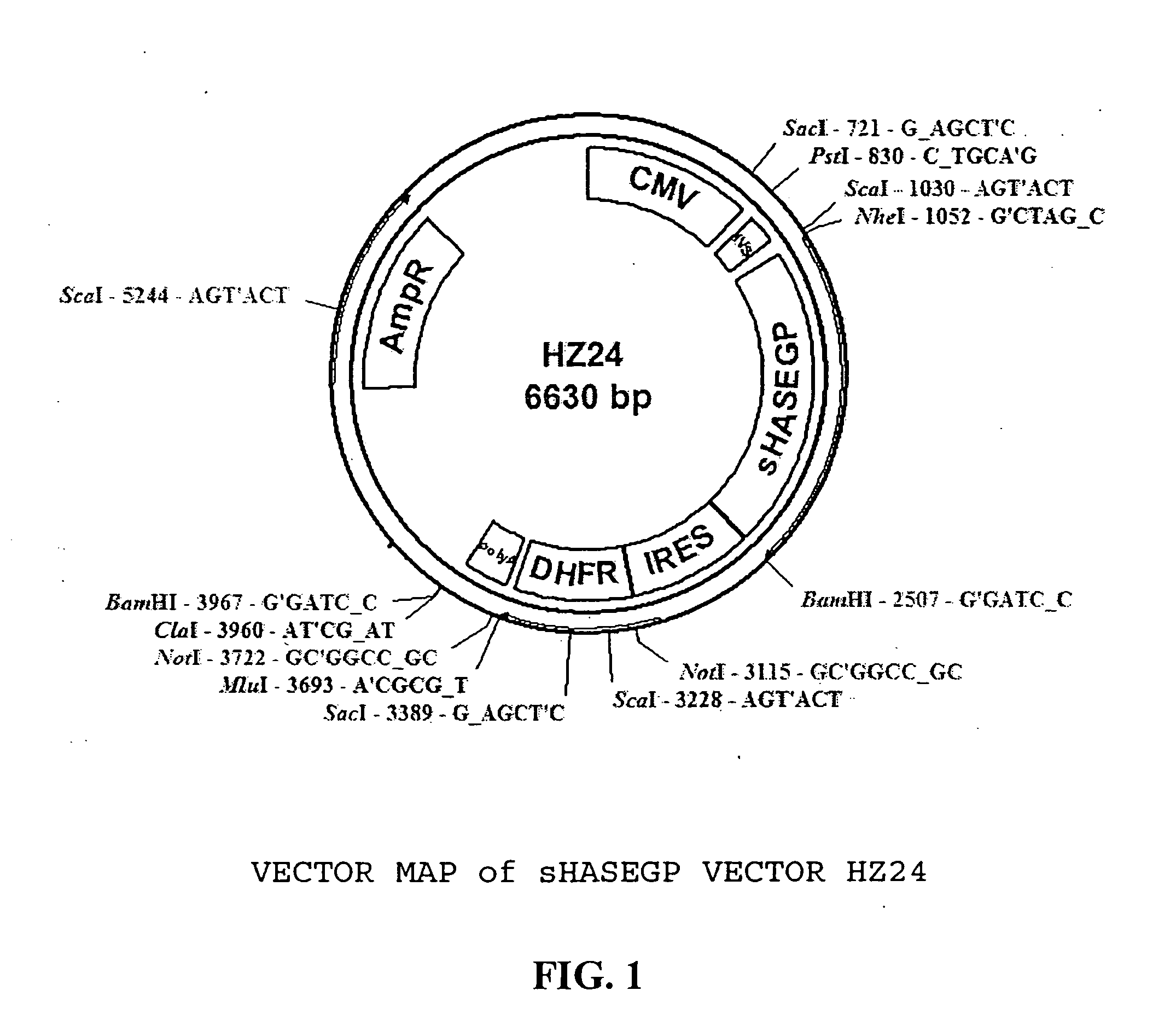
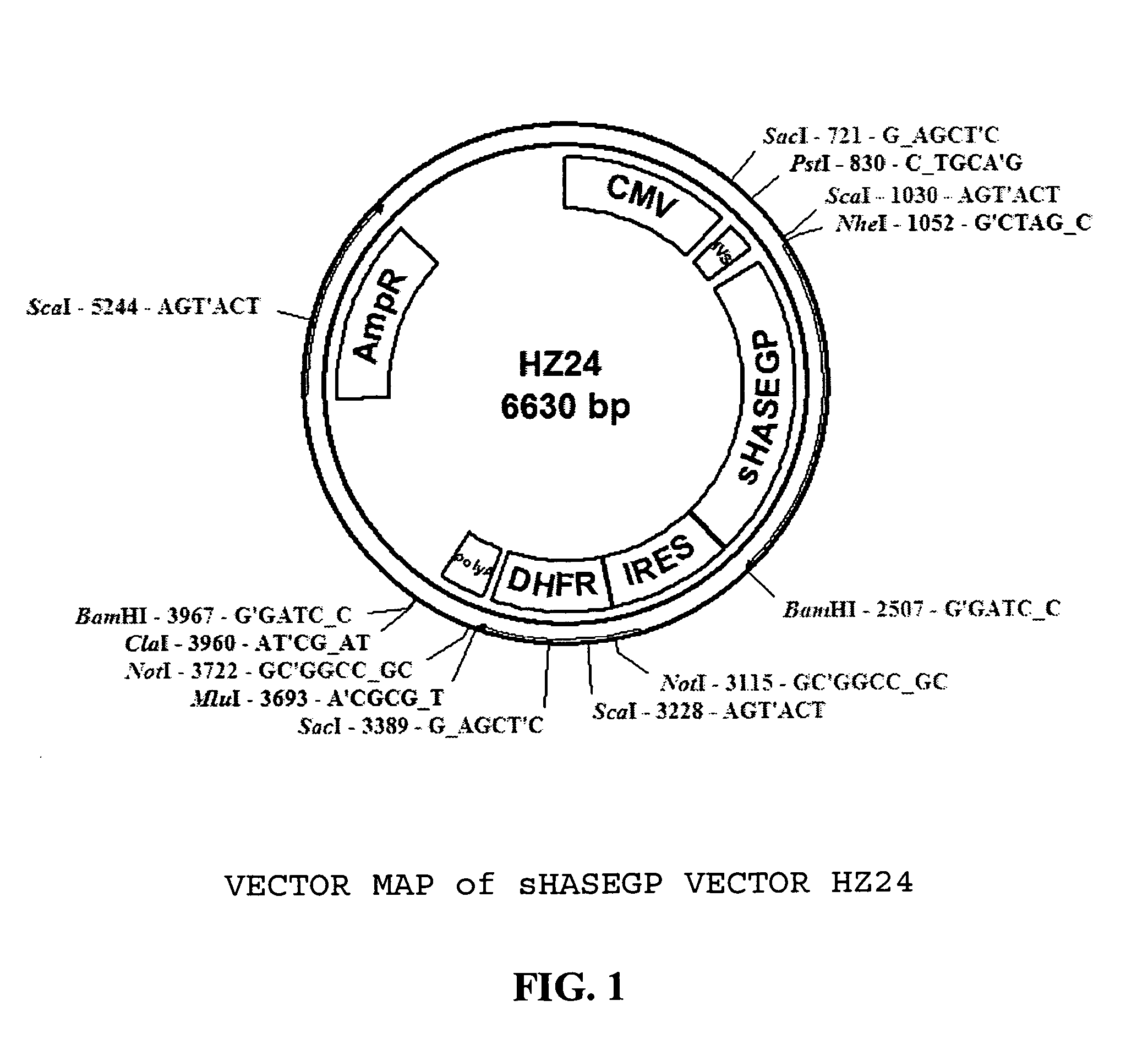
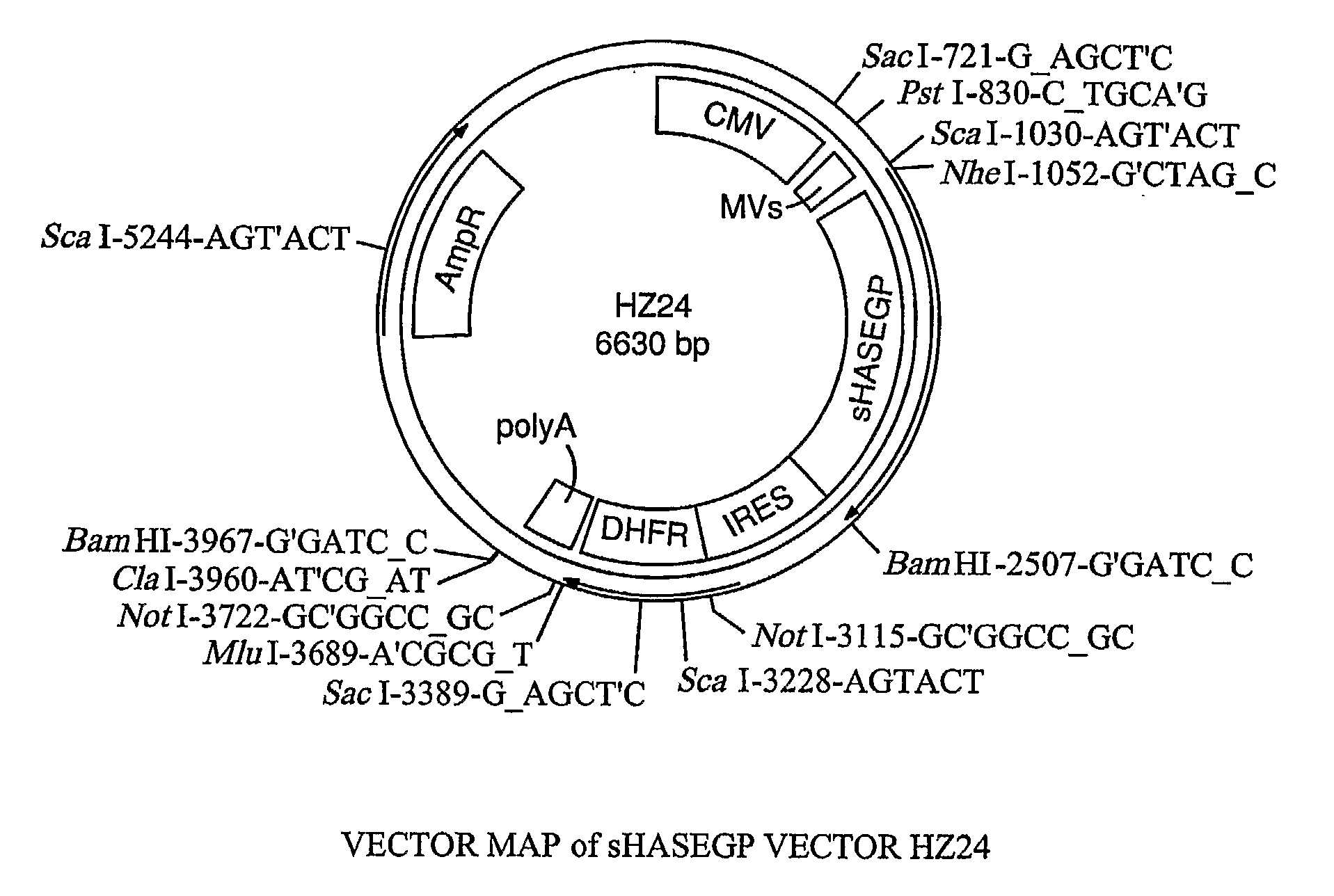
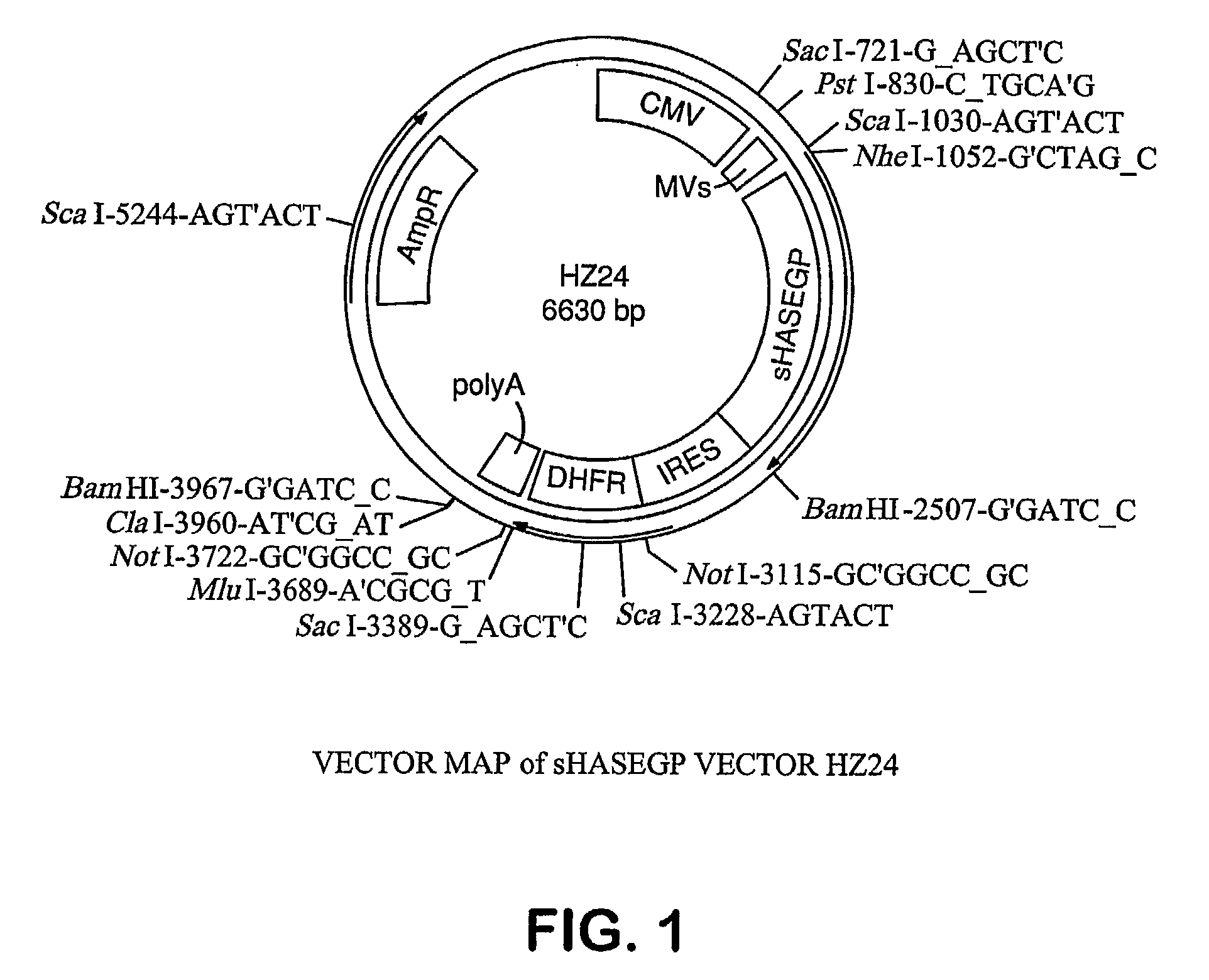
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20050260186A1Improve extentIncrease ratingsAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidasePathology diagnosis
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
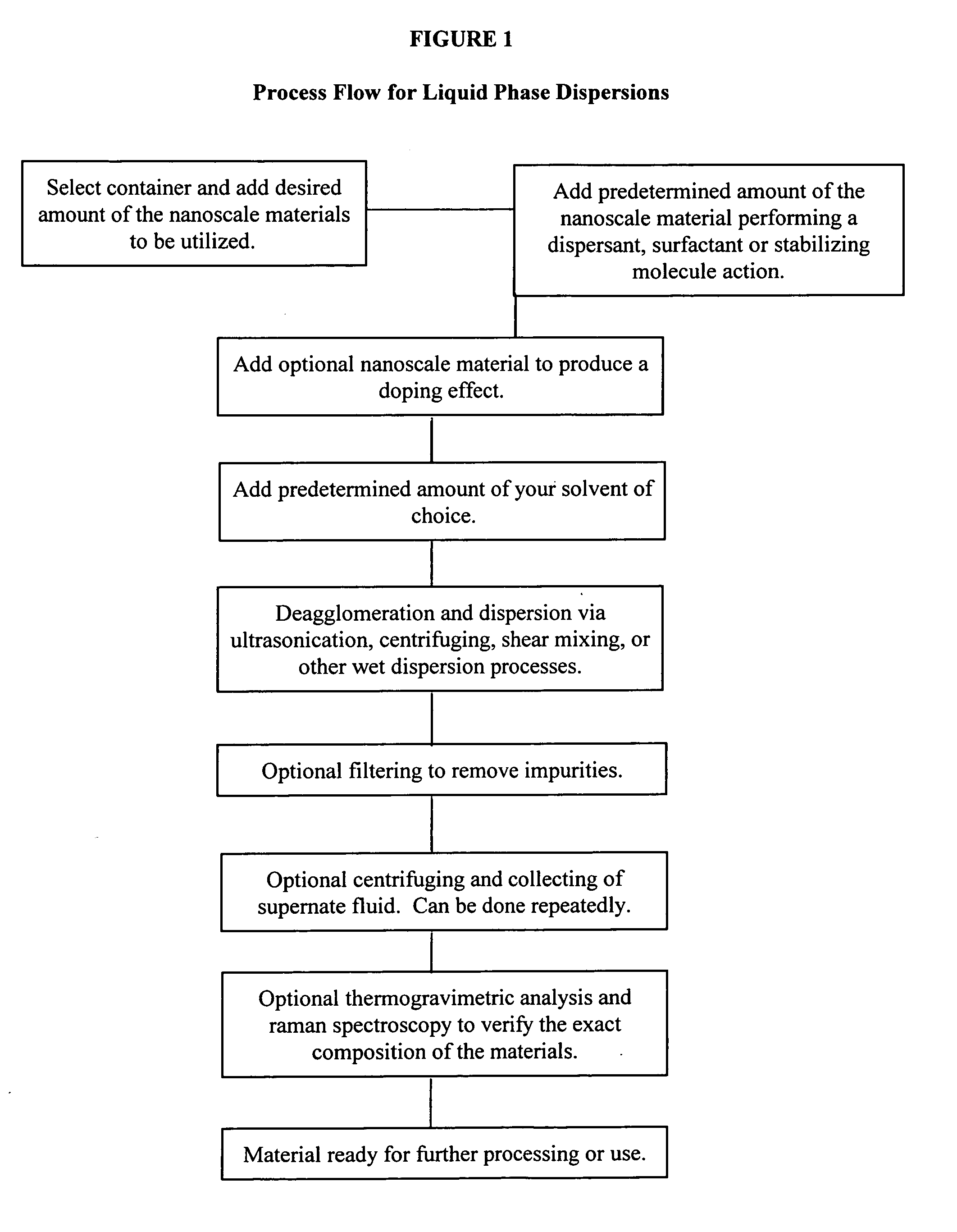
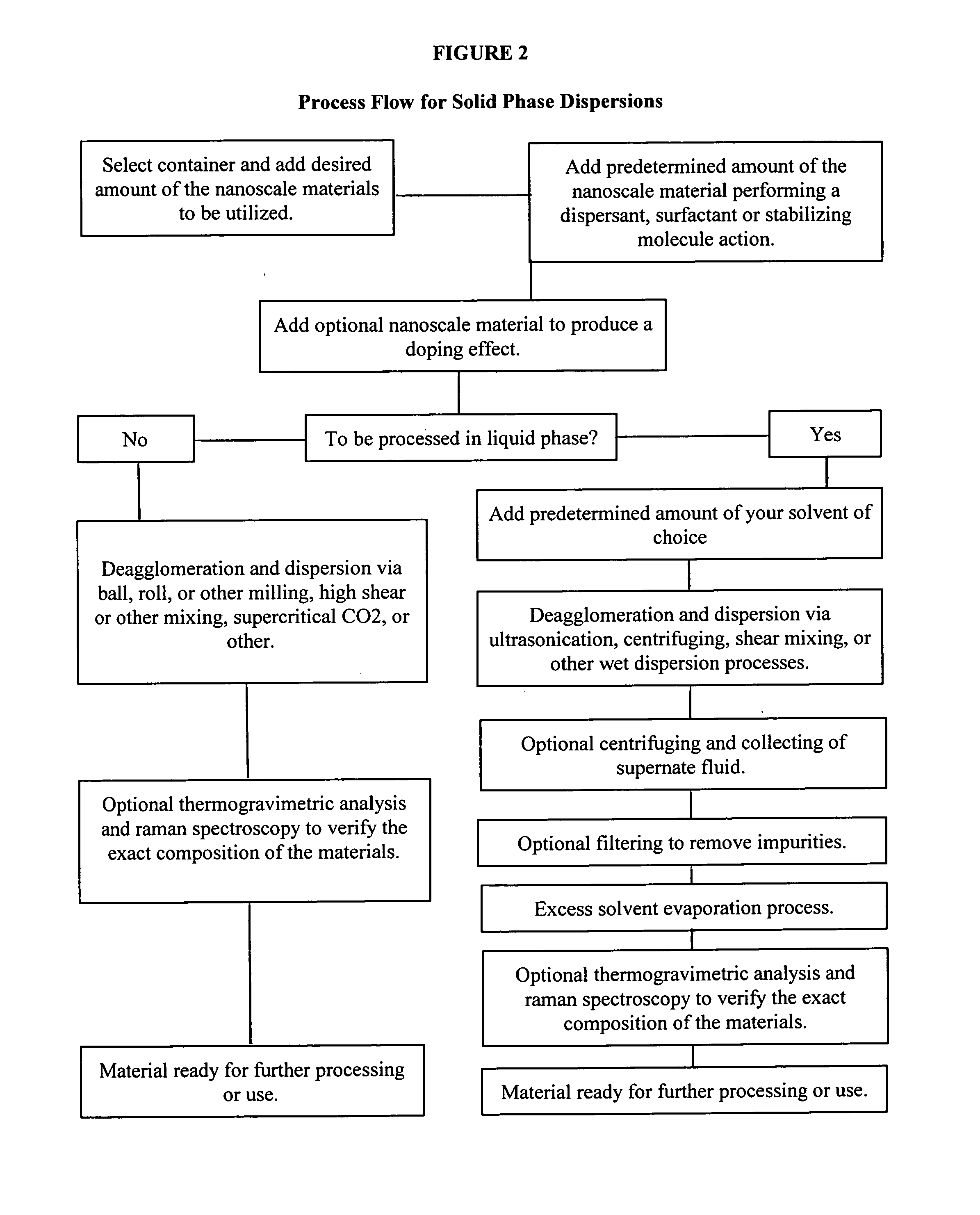
Utilizing nanoscale materials as dispersants, surfactants or stabilizing molecules, methods of making the same, and products produced therefrom
ActiveUS20110210282A1Good effectEasy to processMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismDielectricCapacitance
Novel dispersions of nanoparticles such as carbon nanotubes, carbon nanofibers, boron nanotubes, clay nanotubes, other nanotube species, buckminster fullerenes, graphene, graphene nanoplatelets, elements, oxides, nanoparticles, nanoclusters, nanopowders, nanocrystals, nanoscale molecules, other nanoscale materials, as well as products produced therefrom are described. These dispersions can then be further processed into a wide variety of products including but not limited to composite materials, polymers, resins, epoxies, emulsions, cements, coatings, clays, films, membranes, paper, fibers, inks, paints, pastes, electronics, spintronics, optics, biotechnology materials, electrodes, field emission or other displays, plating, capacitance, ceramics, catalysts, clays, ballistic materials, drug delivery, doping, magnetics, dielectrics, barrier layers, selective ion flow membranes, batteries, fuel cells, solar and other applications. The invention can also be used to protect electronics from electromagnetic interference, radio frequency interference or radio frequency identification. Most applications that utilize nanoparticles can benefit from this invention.
Owner:CTI NANOTECH
Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases and Methods of Preparing and Using Soluble Glycosaminoglycanases
InactiveUS20090123367A1Facilitated DiffusionEnhance convective transportBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHyaluronidaseNuclear chemistry
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated forms of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME +6
Dry Powder Drug Containment System Packages with Tabs, Inhalers and Associated Methods
InactiveUS20070221218A1Facilitate fluidic drug dispersionEasy to disperseRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsDrugInhaler
Dry powder drug containment packages with tab members and meted dose sealed drug compartments can be used in an inhaler having a flow chamber with a hook member that opens the drug compartments and / or a portion that flexes to vibrate the dry powder to facilitate fluidic active dispersion for inhalation.
Owner:ORIEL THERAPEUTICS INC
Mercury adsorbents compatible as cement additives
InactiveUS20080134888A1Efficient removalReduce distractionsGas treatmentOther chemical processesAluminateSorbent
Solid adsorbents, following their use for mercury removal from flue gas, that do not interfere with the ability of air-entraining additives (such as surfactants) to form stable bubbles when added to fly ash containing the adsorbents. The interference is overcome by heating the materials used in the manufacture of the adsorbent so that magnesium hydroxide and / or one or more alkali compounds containing one or more silicate, aluminate, and / or phosphate moiety, added or already present in the materials, binds multivalent cations present in the materials that could otherwise interfere with the surfactant activity.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Liquid atomizing device with reduced settling of atomized liquid droplets
ActiveUS20050279854A1Increase airflow rateIncrease evaporation rateMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzlesVena contracta diameterEvaporation
A liquid atomizing device for dispensing liquid droplets includes a container for holding a liquid, the container having a porous wick positioned to communicate the liquid from the container, and an orifice plate with apertures, the orifice plate being vibrated by a piezoelectric element to cause liquid communicated from the container to be atomized and dispensed as liquid droplets through the apertures. The device employs a unique placement and design of heaters or fans to promote evaporation and dispersion of the atomized liquid while the liquid is airborne.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
Lightning strike protection system for aircraft fuel tanks made of low electrical conductivity composite material
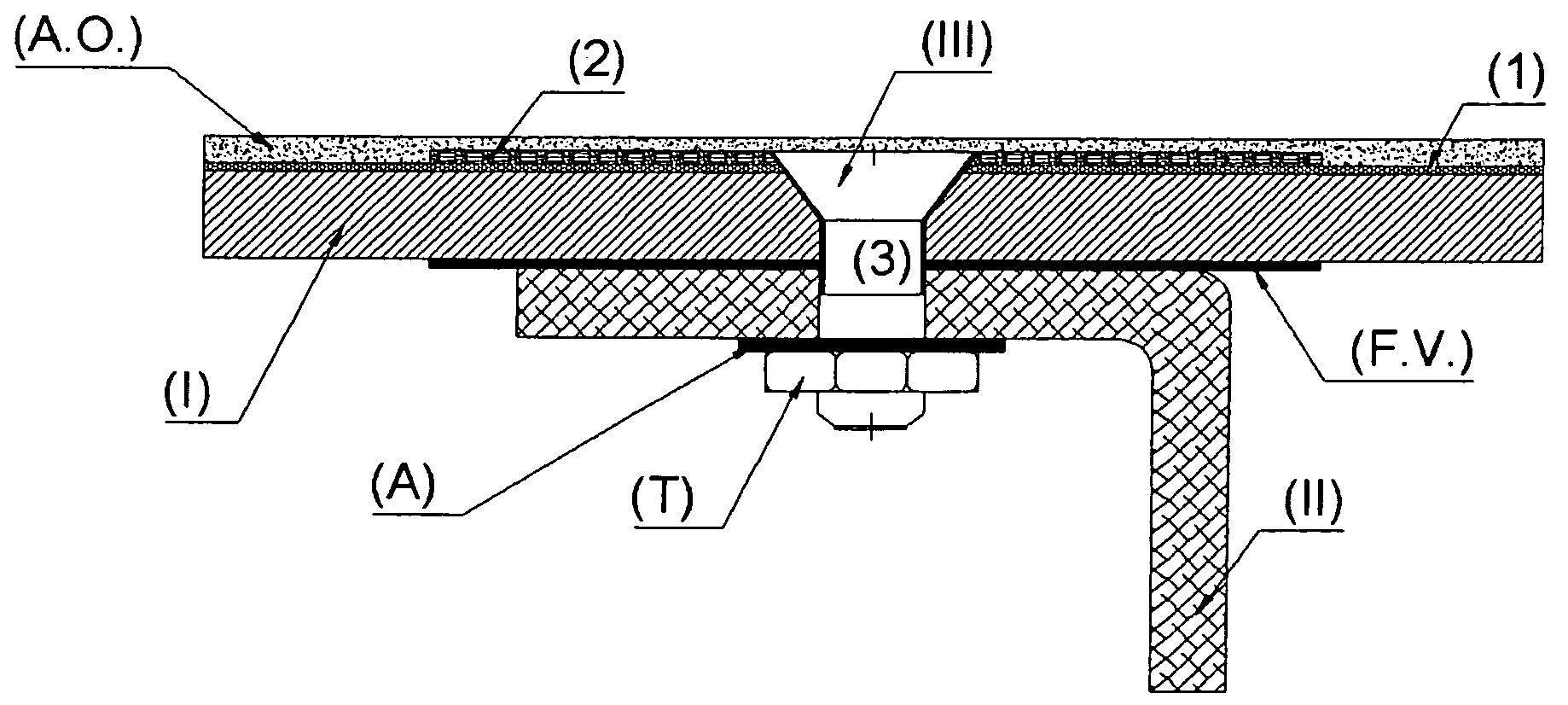
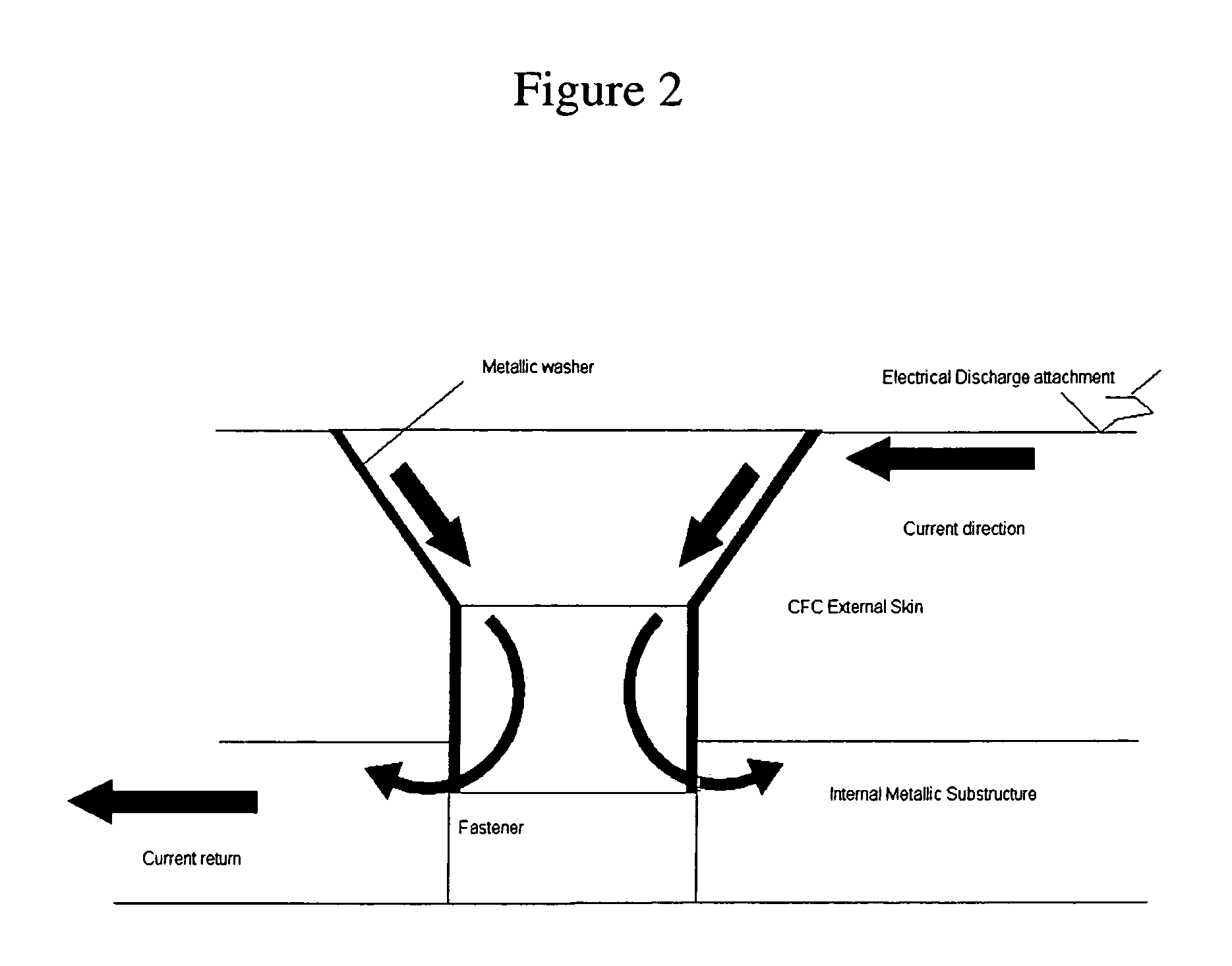
ActiveUS7307825B2Severe structural damage can be avoidedMinimize damageFuel tank safety measuresAircraft lighting protectorsLightning strikeFuel tank
Lightning strike protection system for aircraft fuel tanks made of low electrical conductivity composite material. The system comprises an electrical conductive thin wire mesh (1) that covers the whole external surface of the tank outer skin (I) made of composite and a thick wire metallic mesh (2) overlapping the mesh (1) at a minimum distance of 50 mm to both sides of a row of fasteners (III) joining the said outer skin (I) to one internal part (II) of either composite or metallic material. Both metallic meshes (1, 2) maintain electrical contact by their installation / assembly and by means of metallic countersunk head washers (3) connected to bonding points and set to the gap existing between the fastener (III) and the outer skin (I). The corresponding fabrication process is also described.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS SL
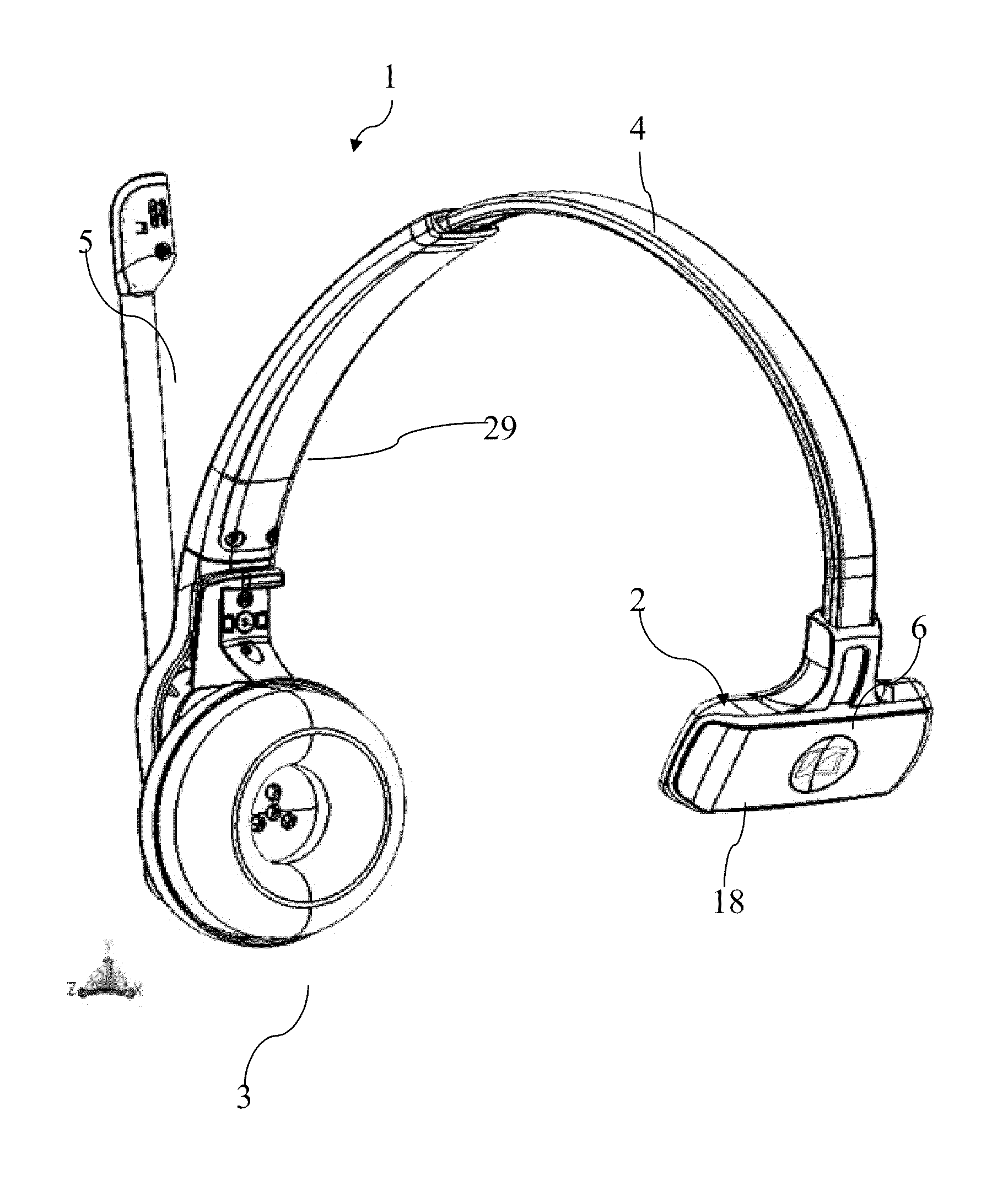
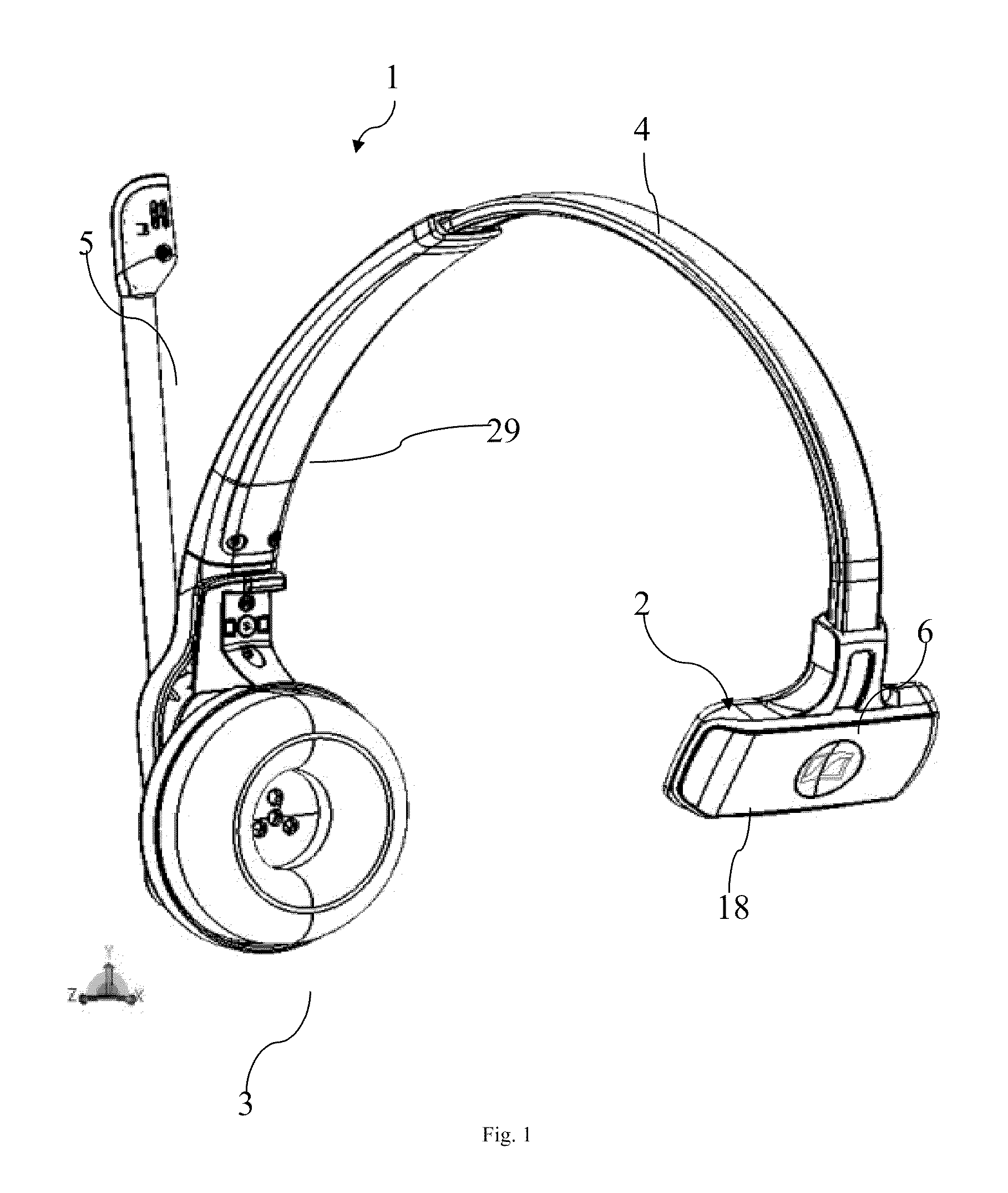
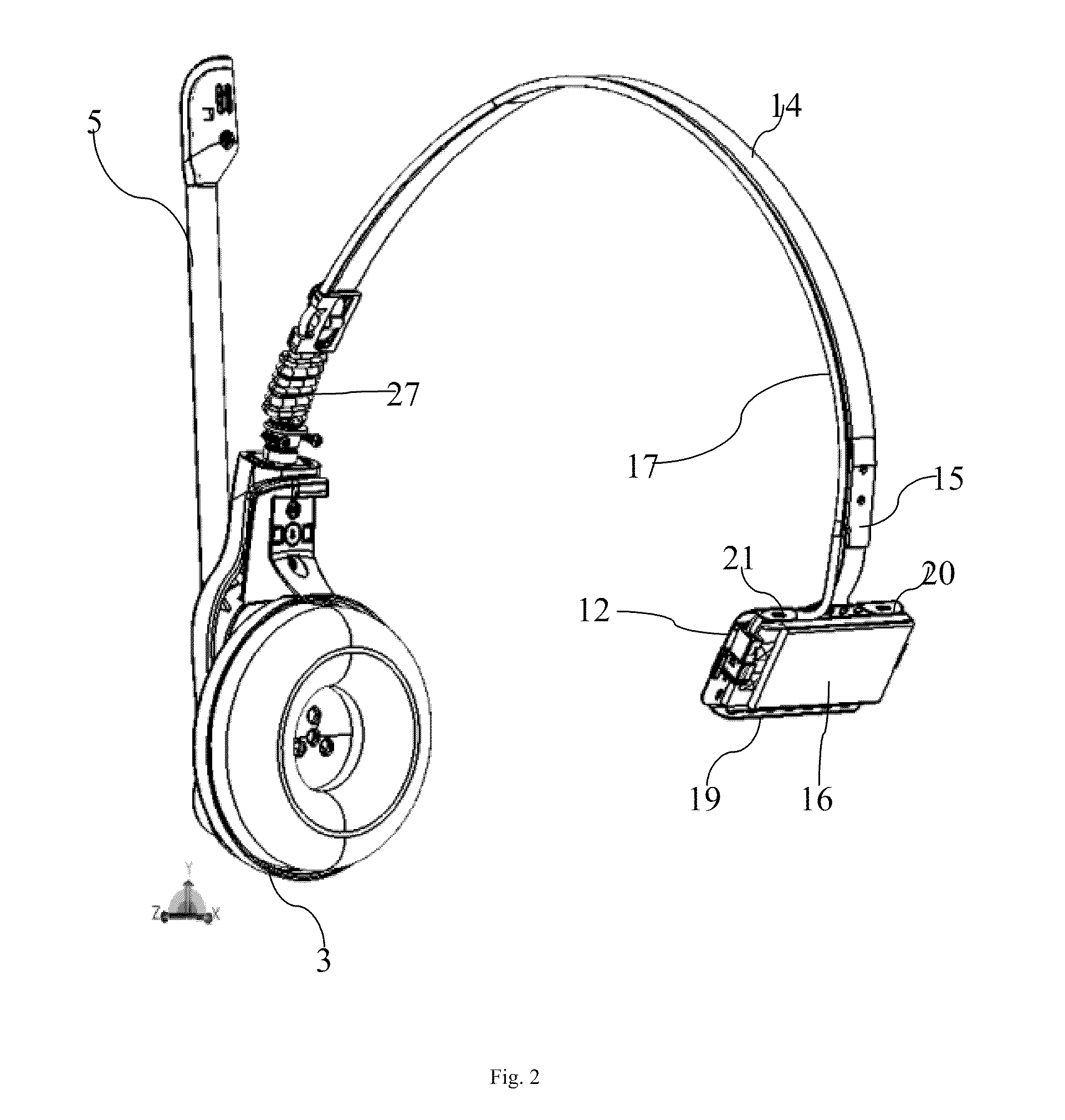
Headset with side support
A headset with side support is provided, where a speaker module is coupled to a side support by means of an elongate resilient spring such that the speaker module and the side support are placeable at each their side of a users head and where the spring provides a holding force which presses the speaker module and the side support in a direction towards each other wherein the spring comprises a metal core and this core comprises a re-enforcement at the side support which extends transversely to the length direction of the elongate spring.
Owner:SENNHEISER COMM
High-efficiency environment-friendly antibacterial mould-proof inorganic composite nano paint and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102417748AEasy to disperseStorage stableAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesVolatile organic compoundEmulsion
The invention relates to a paint technology, an environment-friendly technology and an antibacterial mould-proof technology, in particular to high-efficiency environment-friendly antibacterial mould-proof inorganic composite nano paint and a preparation method thereof. The high-efficiency environment-friendly antibacterial mould-proof inorganic composite nano paint comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.5 to 5 percent of wetting dispersant, 0.01 to 20 percent of inorganic composite nano antibacterial agent concentrated pulp, 0.5 to 10 percent of hydrophobing agent, 0.5 to 10 percent of anionic powder, 0.5 to 8 percent of film-forming aid, 0.1 to 2 percent of anti-settling agent, 0.8 to 10 percent of antifreezing agent, 0.1 to 3 percent of defoaming agent, 4 to 30 percent of pigment, 0 to 30 percent of filler, 15 to 45 percent of emulsion, 0.1 to 4 percent of thickening agent, 0.1 to 3 percent of flatting agent, 0 to 3 percent of pH regulator and 0.5 to 45 percent of water. The high-efficiency environment-friendly antibacterial mould-proof inorganic composite nano paint is mainly prepared by adding the inorganic composite nano antibacterial agent into the basic materials, so that the paint has the coating characteristic of high performance, is low is cost, and has a function of purifying air, can eliminate harmful gas volatile organic compounds (VOC), formaldehyde and the like and also has a durable and high-efficiency antibacterial mould-proof function, so that the sterilizing rate within 6 hours reaches 100 percent and the mould-proof grade reaches the first grade. By the high-efficiency environment-friendly antibacterial mould-proof inorganic composite nano paint and the preparation method thereof, self-cleaning performance, hydrophobicity, scrubbing resistance, dirt resistance and weather resistance of the coating are improved; and the high-efficiency and durable antibacterial and mould-proof effect is achieved.
Owner:广东腐蚀科学与技术创新研究院
Urine dispersing urinal insert device
InactiveUS6920648B1Increase flexibilityEasy unit stackingUrinalsBathroom accessoriesUrineEngineering
A disposable, deodorant and splash proof urine dispersing device for placement in a urinal including a framework made of scented plastic material with a horizontal segmented supporting base and a central raised housing. The supporting base includes a plurality of perforated flexible segments and a central bottom frame with a central opening aligned with an outlet or drain in the urinal. The opening is surrounded by the multiple segments such that the device can flex and adapt to urinals of different sizes and designs. The central raised housing includes a horizontal or inclined top member and an upstanding peripheral wall connecting the top member with the central bottom frame in the supporting base. The peripheral wall includes flush relief openings and tapered for easy unit stacking. The top member includes a frame with a plurality of spaced parallel rods having a unique configuration for dispersing urine flow with reduced back splashing toward the user of the urinal.
Owner:SUSKI MICHAEL R +1
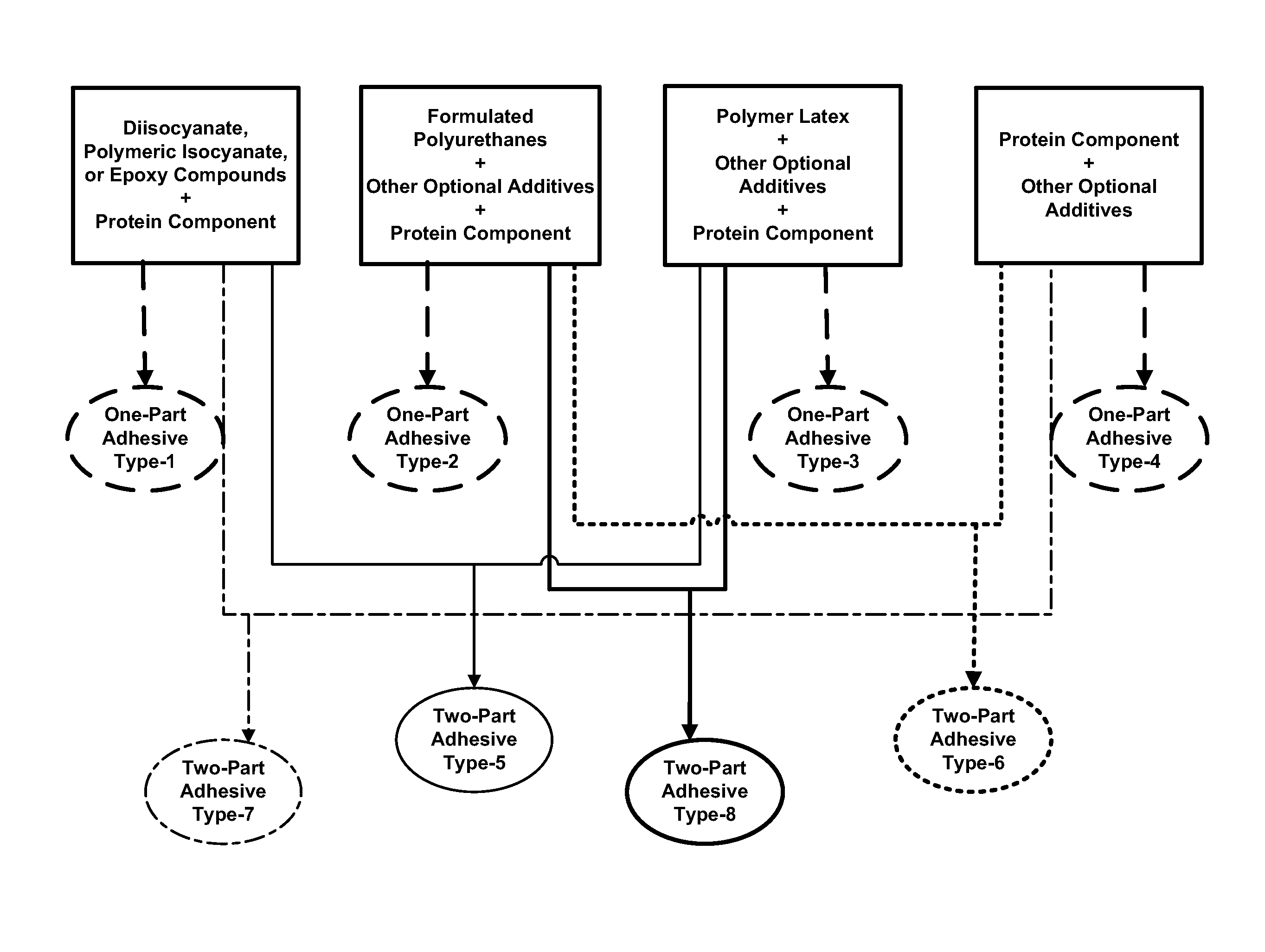
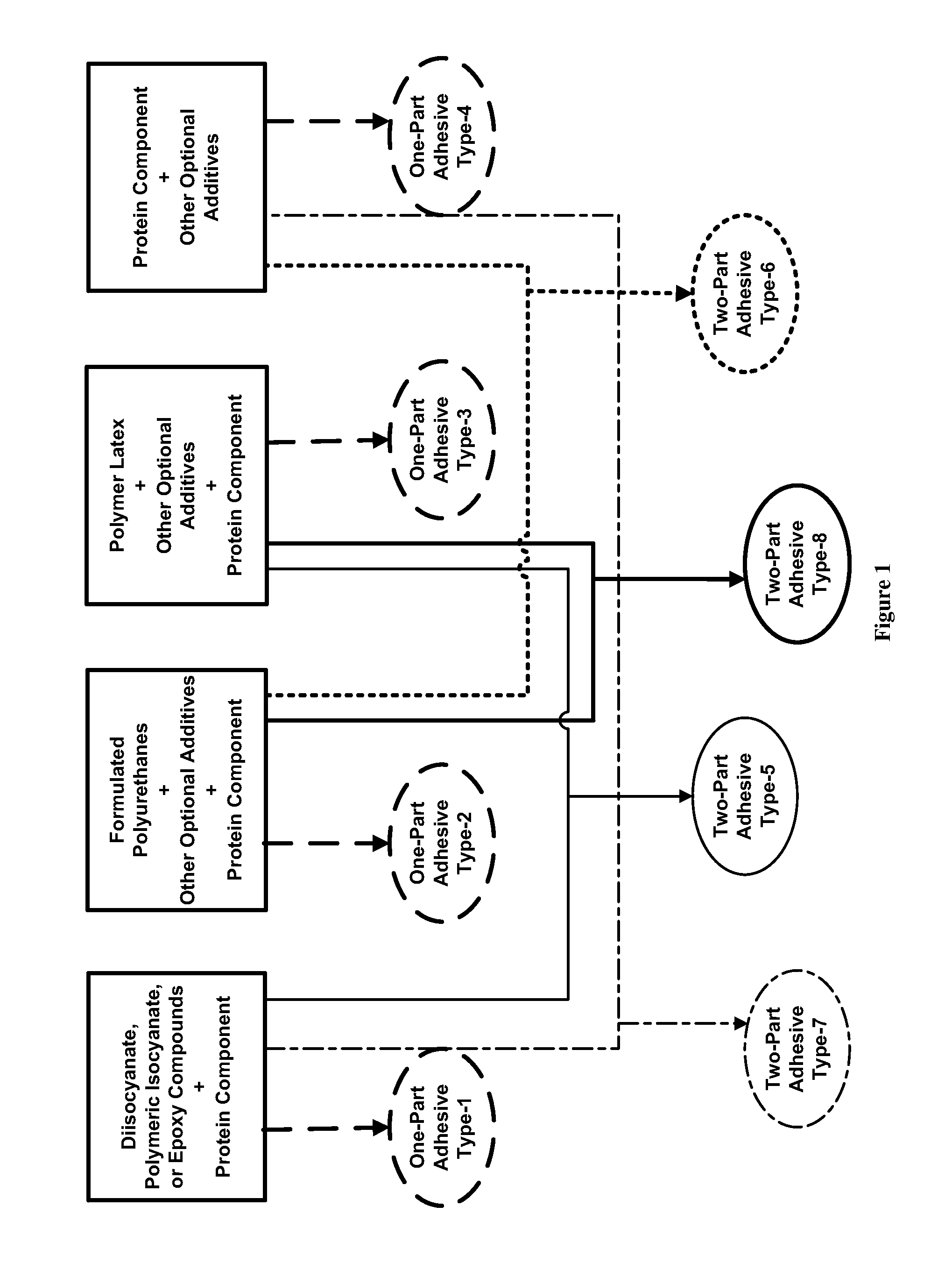
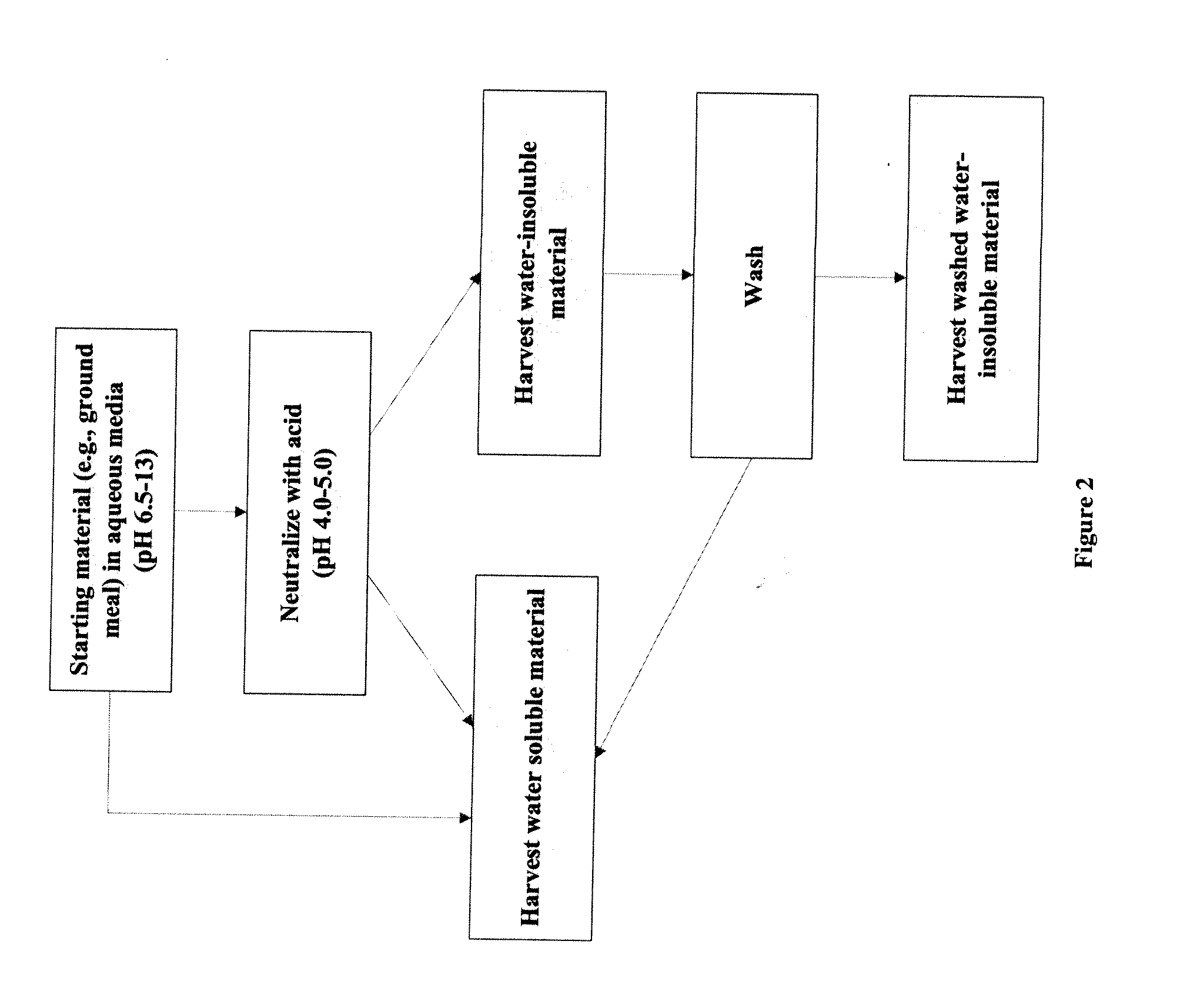
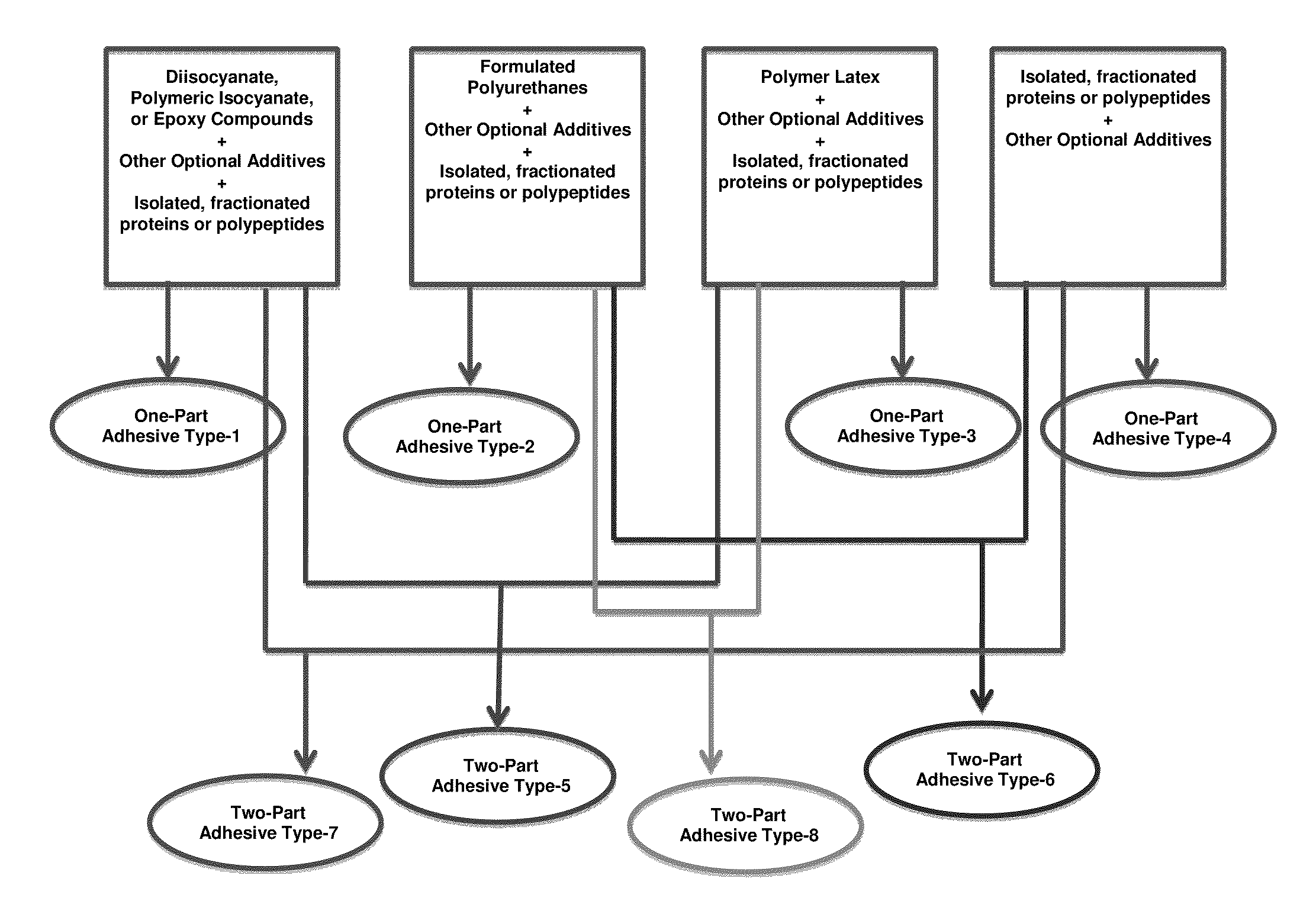
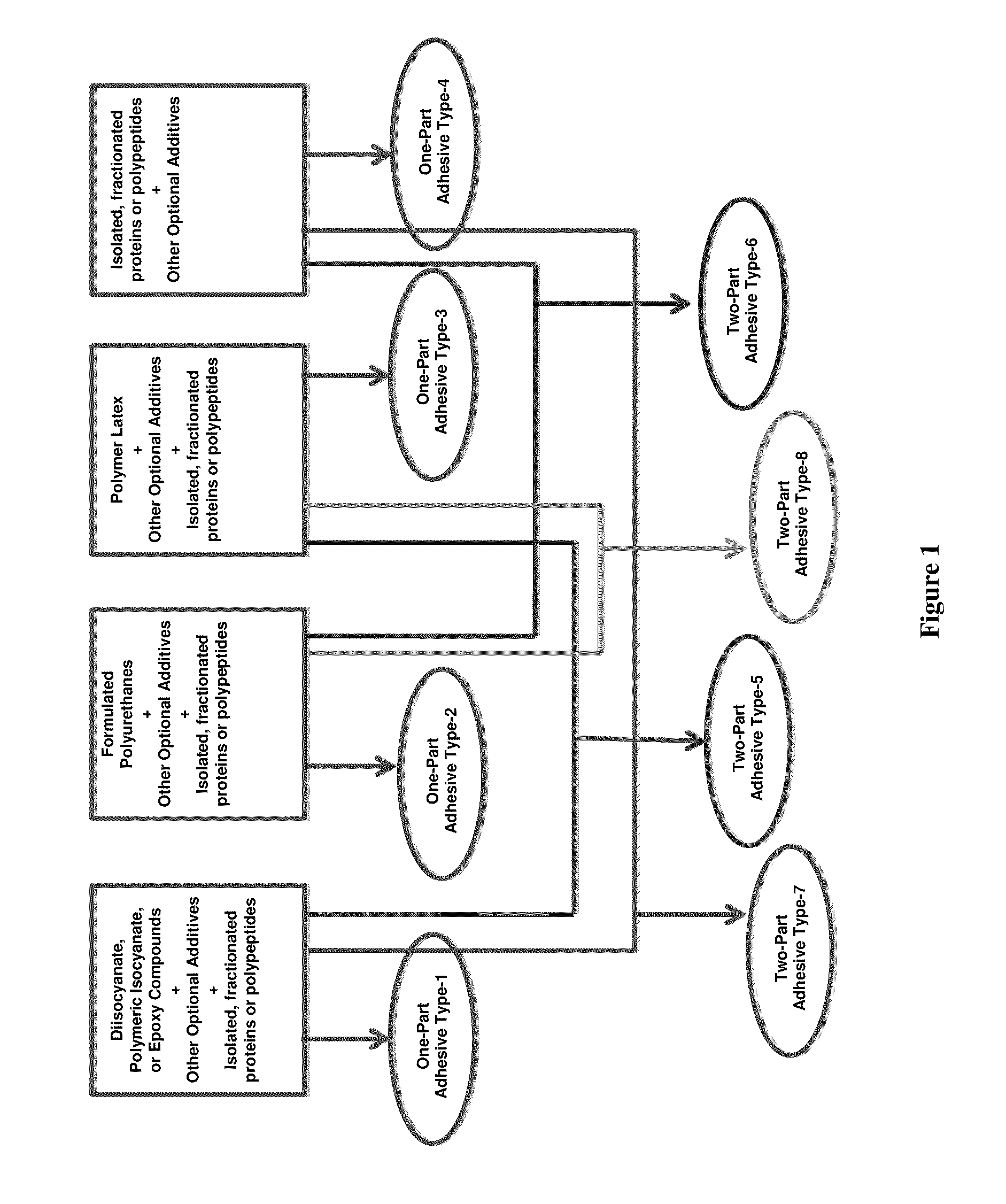
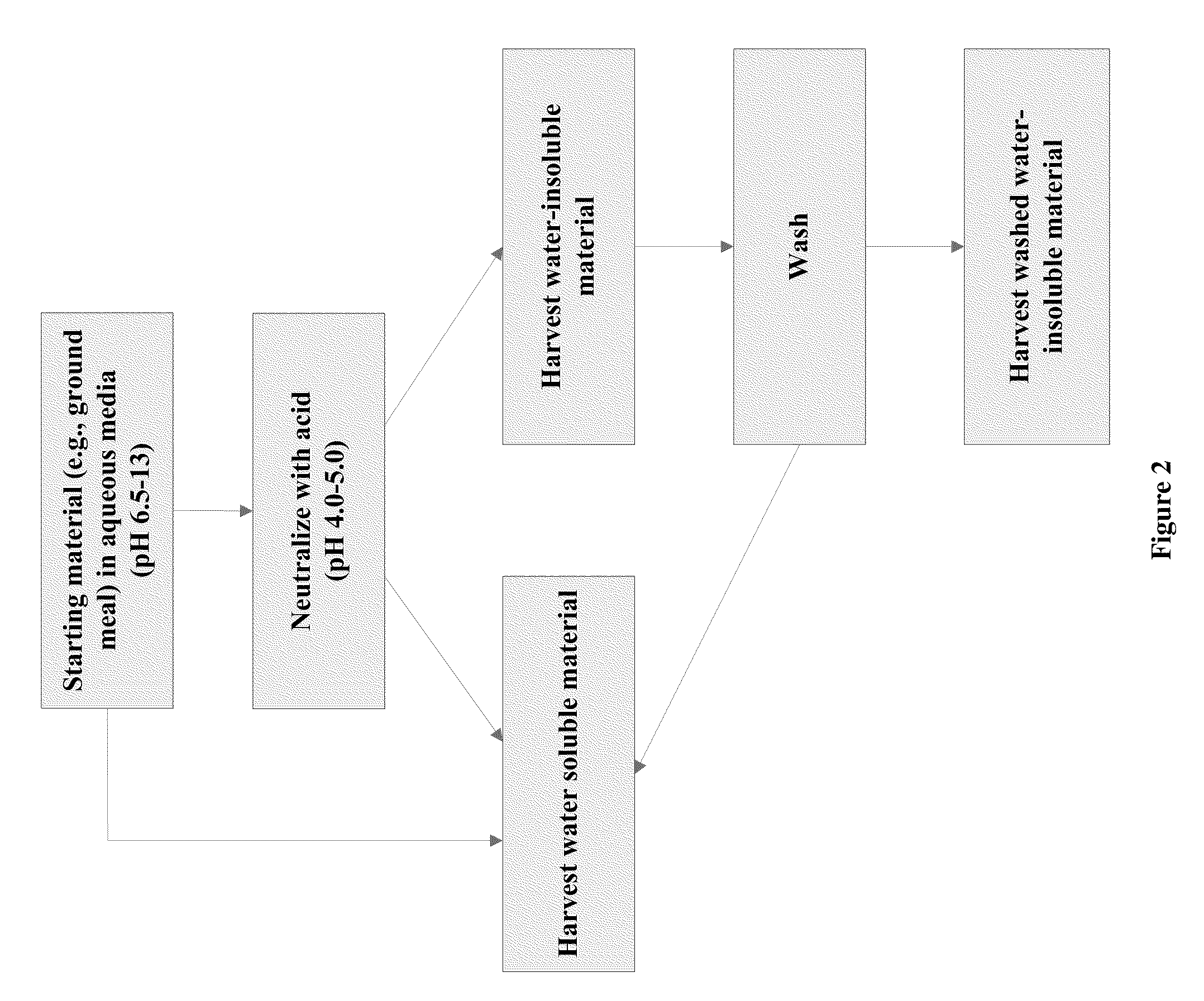
Protein-Containing Adhesives, and Manufacture and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20110311833A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove performanceAdhesive processesPaper coatingAdhesiveProtein
Owner:EVERTREE
Protein-Containing Emulsions and Adhesives, and Manufacture and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20100310877A1Process environmental protectionEasy to disperseAdhesive processesPeptide/protein ingredientsEmulsionAdhesive
Owner:EVERTREE
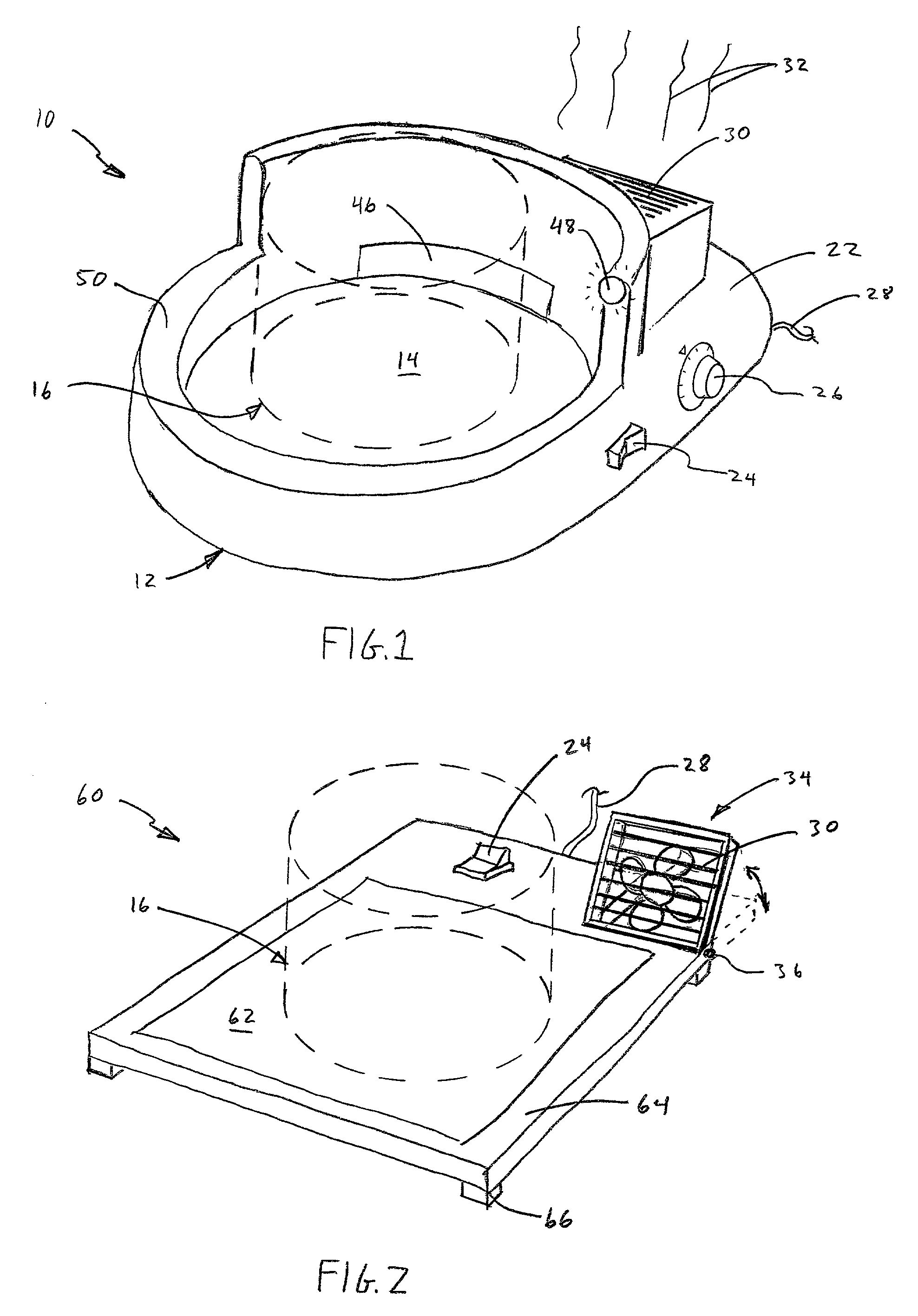
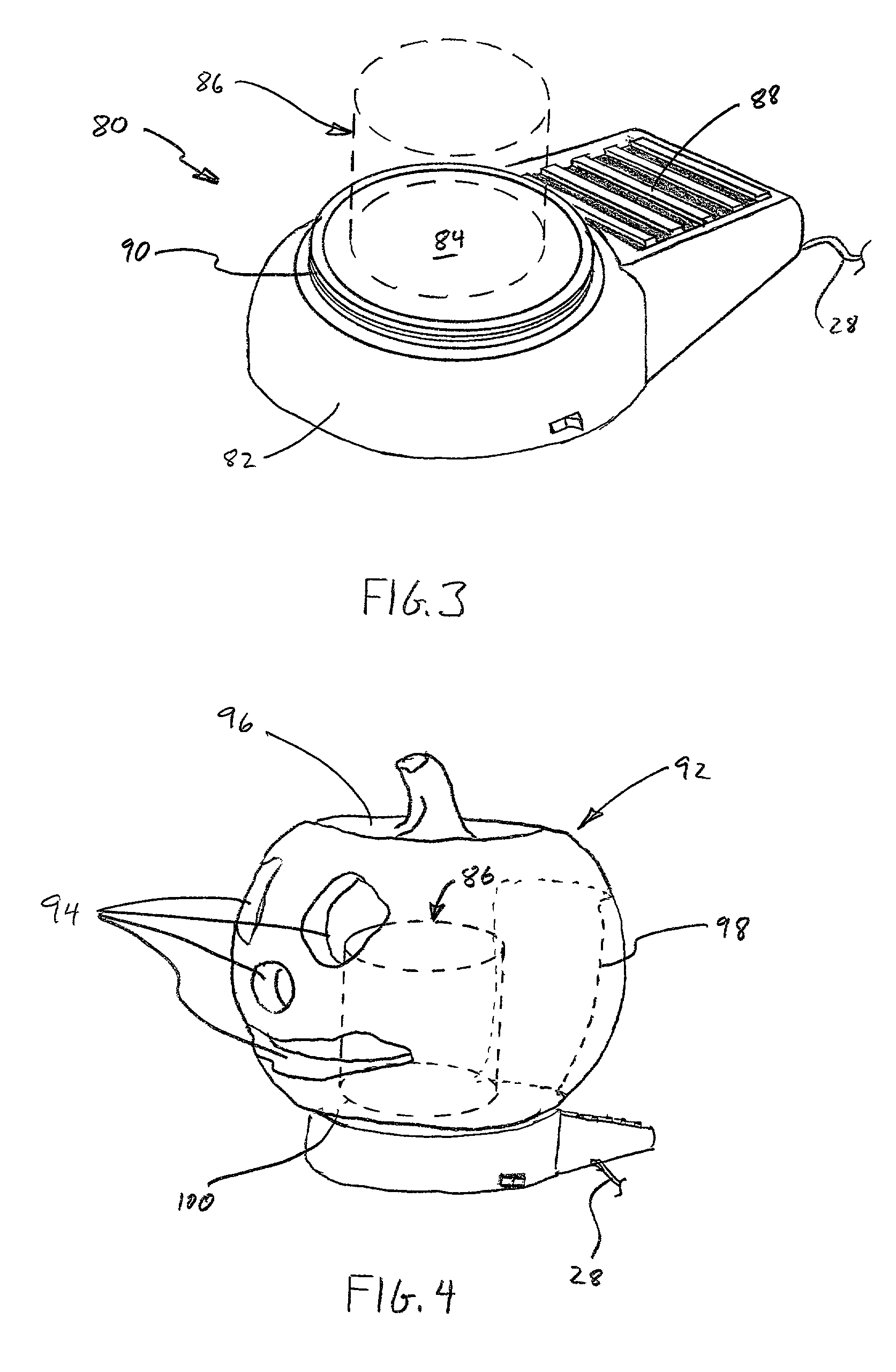
Candle warmer
InactiveUS7132084B1Good dispersionSurrounding environmentPropellersSpace heating and ventilationWaxAir cycle
A scent dispersion system, comprising a heating device having a top surface, and a container of scented wax disposed upon the top surface of the heating device. Upon heating, scent from the wax is caused to disperse into the surrounding environment. The system may further comprise an air circulating fan associated with the heating device, for circulating air around the container of scented wax, to help disperse the scent.
Owner:B&B ACQUISITION INC (DBA CANDLE WARMERS ETC)
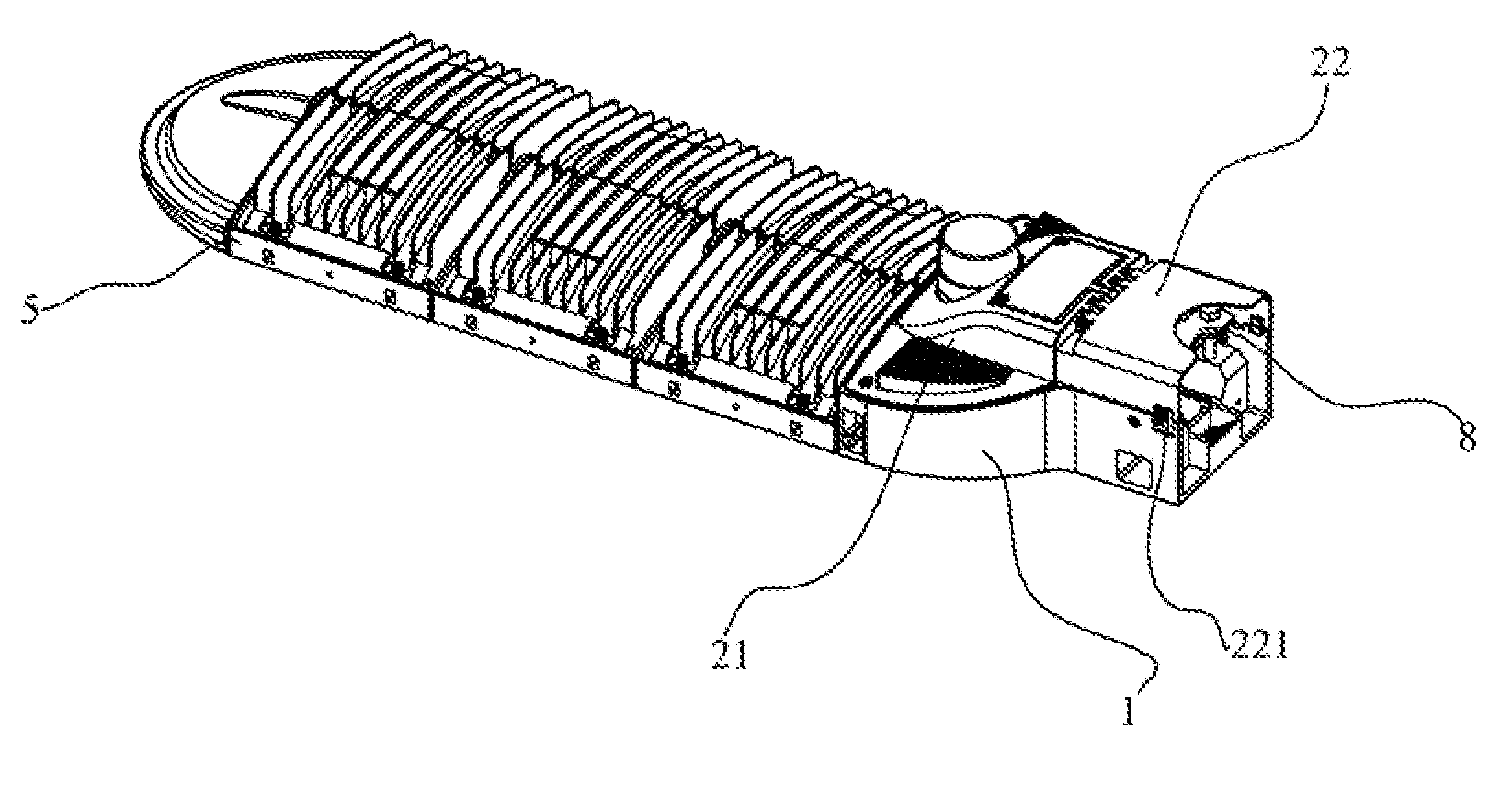
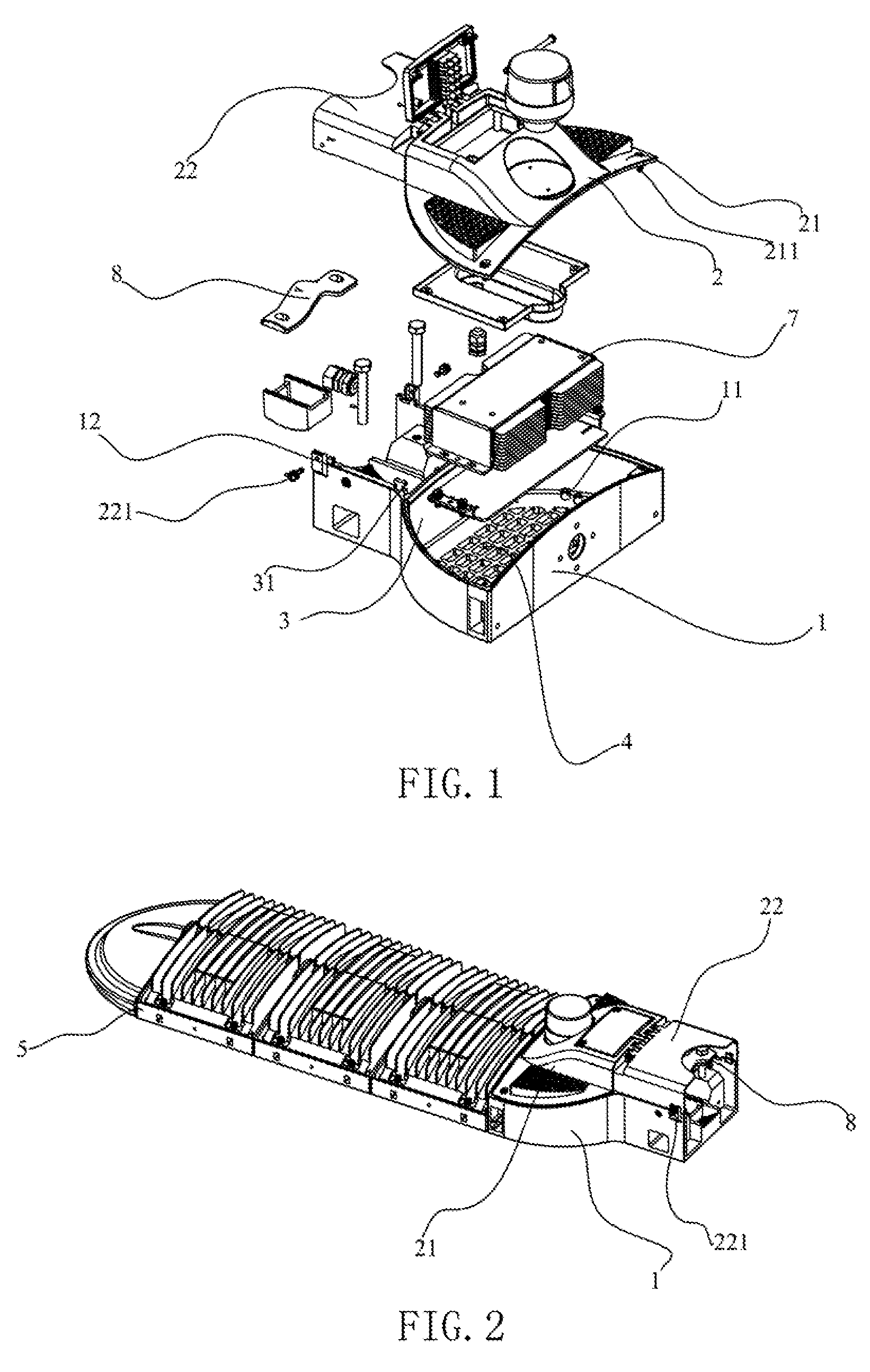
LED streetlamp installation seat and LED streetlamp
InactiveUS20120287654A1Improve working efficiencyLow costNon-electric lightingMechanical apparatusLED lamp
An exemplary LED streetlamp installation seat and an LED lamp both has a seat body (1), which has a first accommodating chamber (11) and a second accommodating chamber (12) the first accommodating chamber (11) being used to accommodate a control device (7) for controlling the LED streetlamp and the second accommodating chamber (12) being used to accommodate a fixing device (8) for installing the LED lamp to a lamp-post; and a cover cap, corresponding to the first and the second accommodating chambers (11, 12), which has a first cap (21) and a second cap (22), the first cap (21) and the second cap (22) being hinge-joined. The first cap (21), corresponding to the first accommodating chamber (11), is detachably connected to the first accommodating chamber (11). The second cap (22), corresponding to the second accommodating chamber (21), is detachably connected to the second accommodating chamber (21).
Owner:SHENZHEN BANG BELL ELECTRONICS
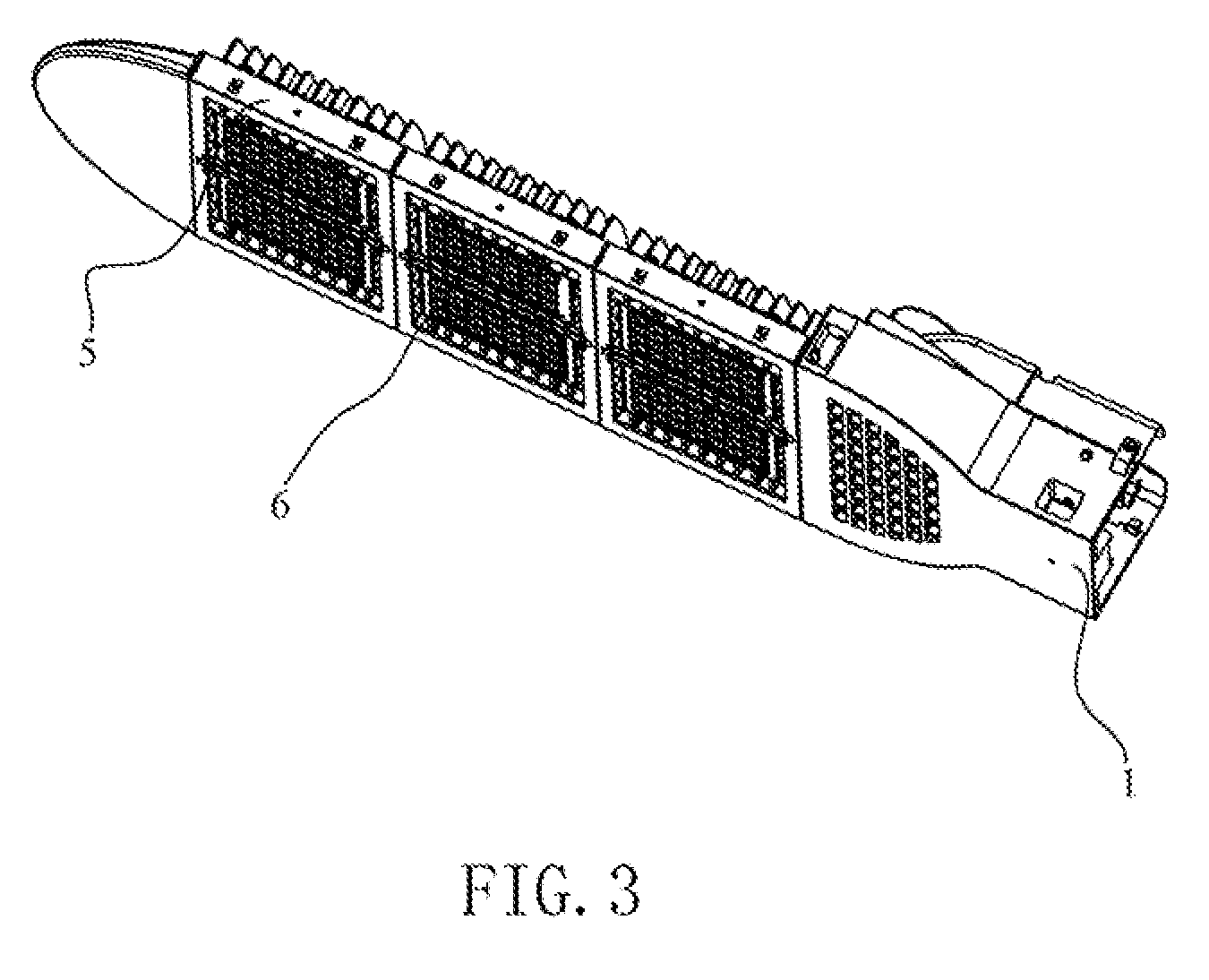
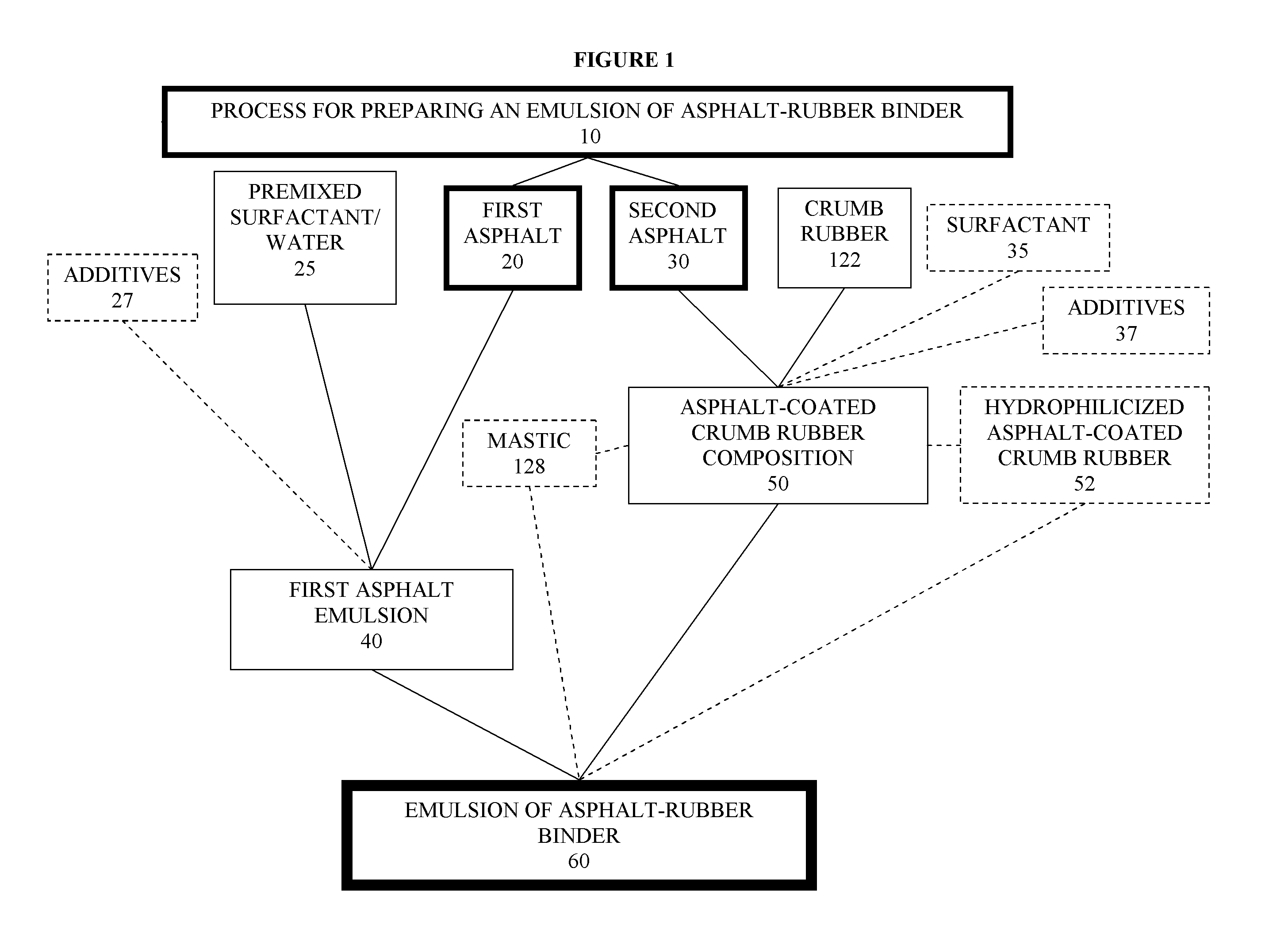
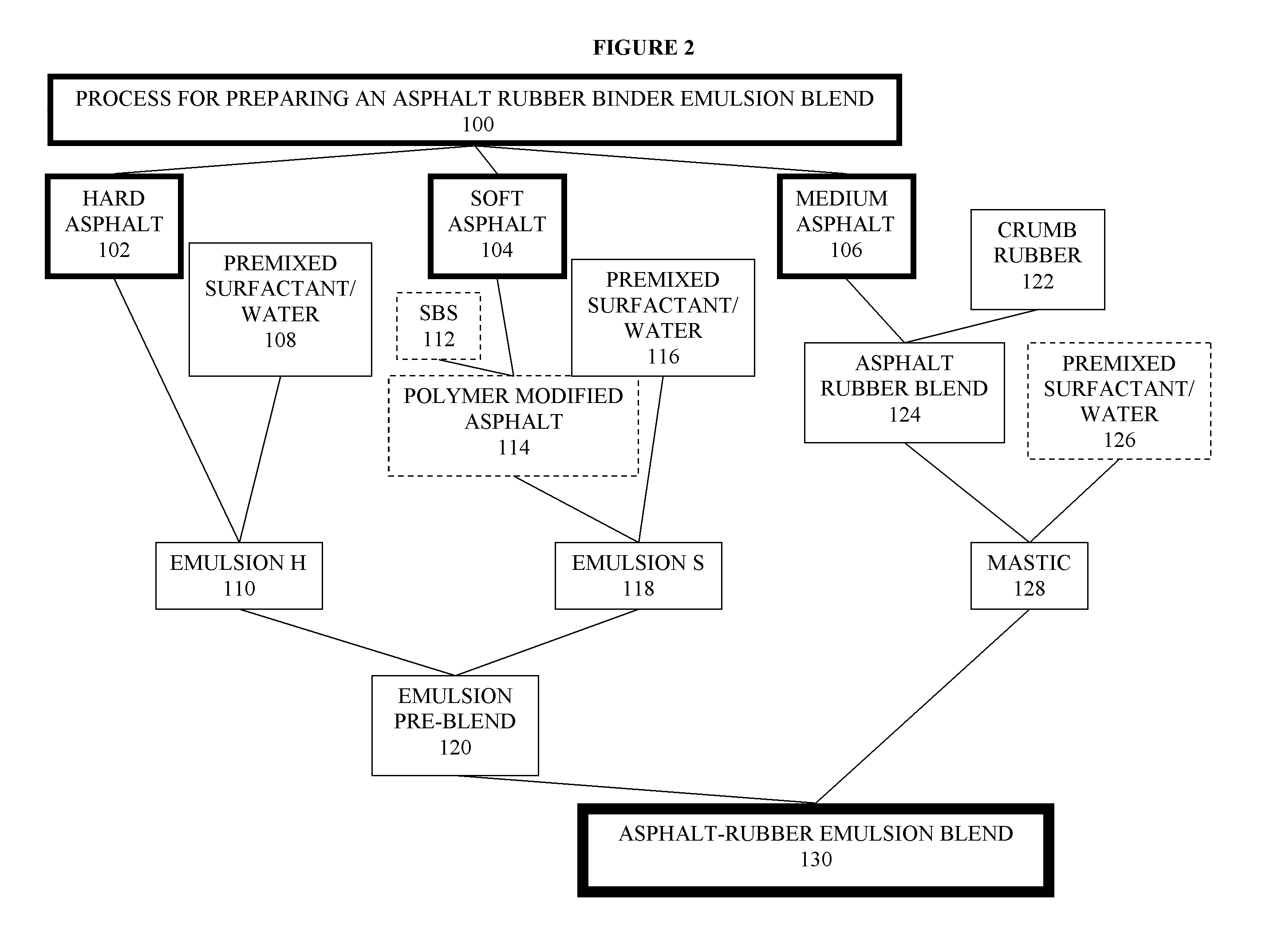
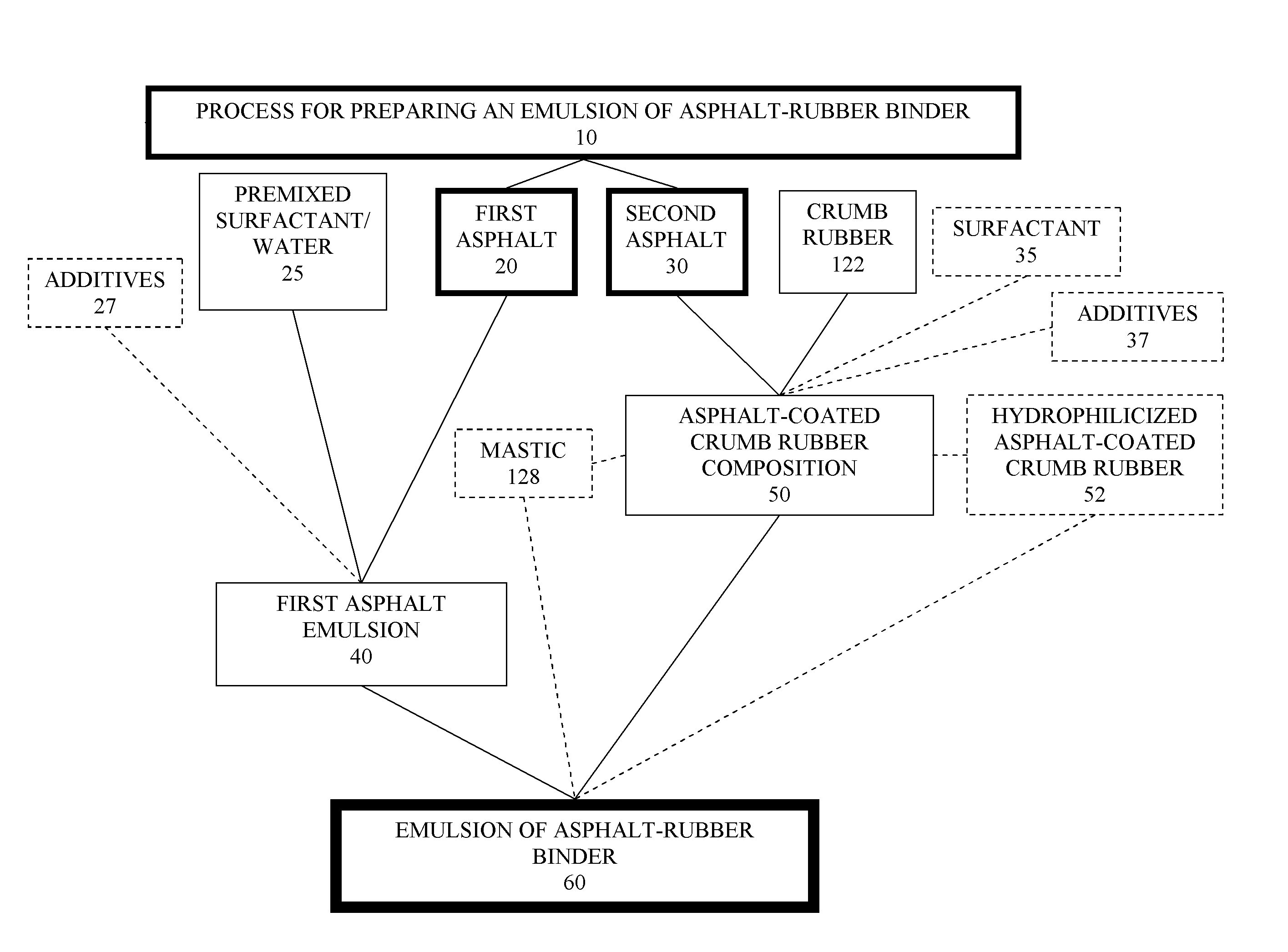
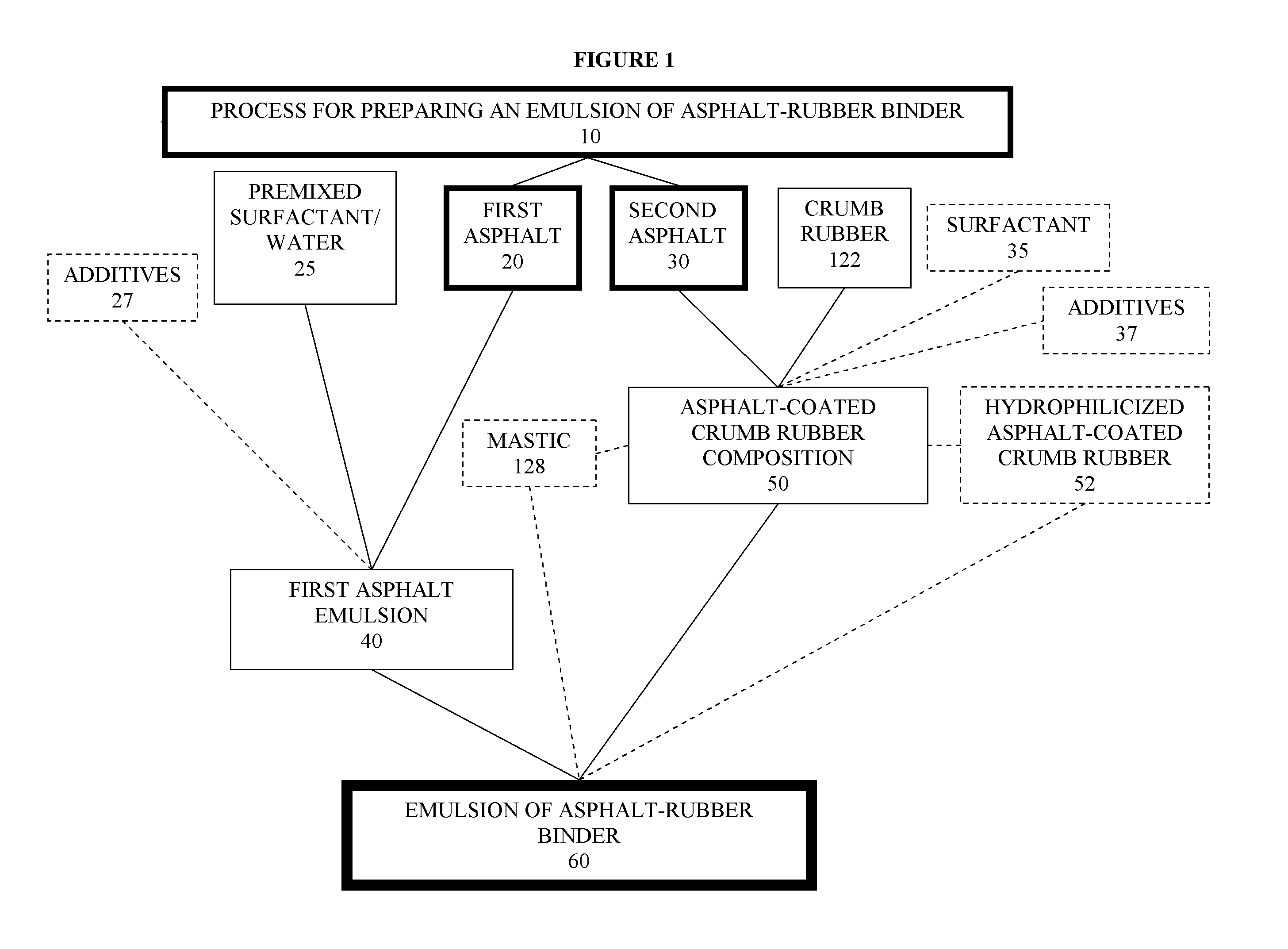
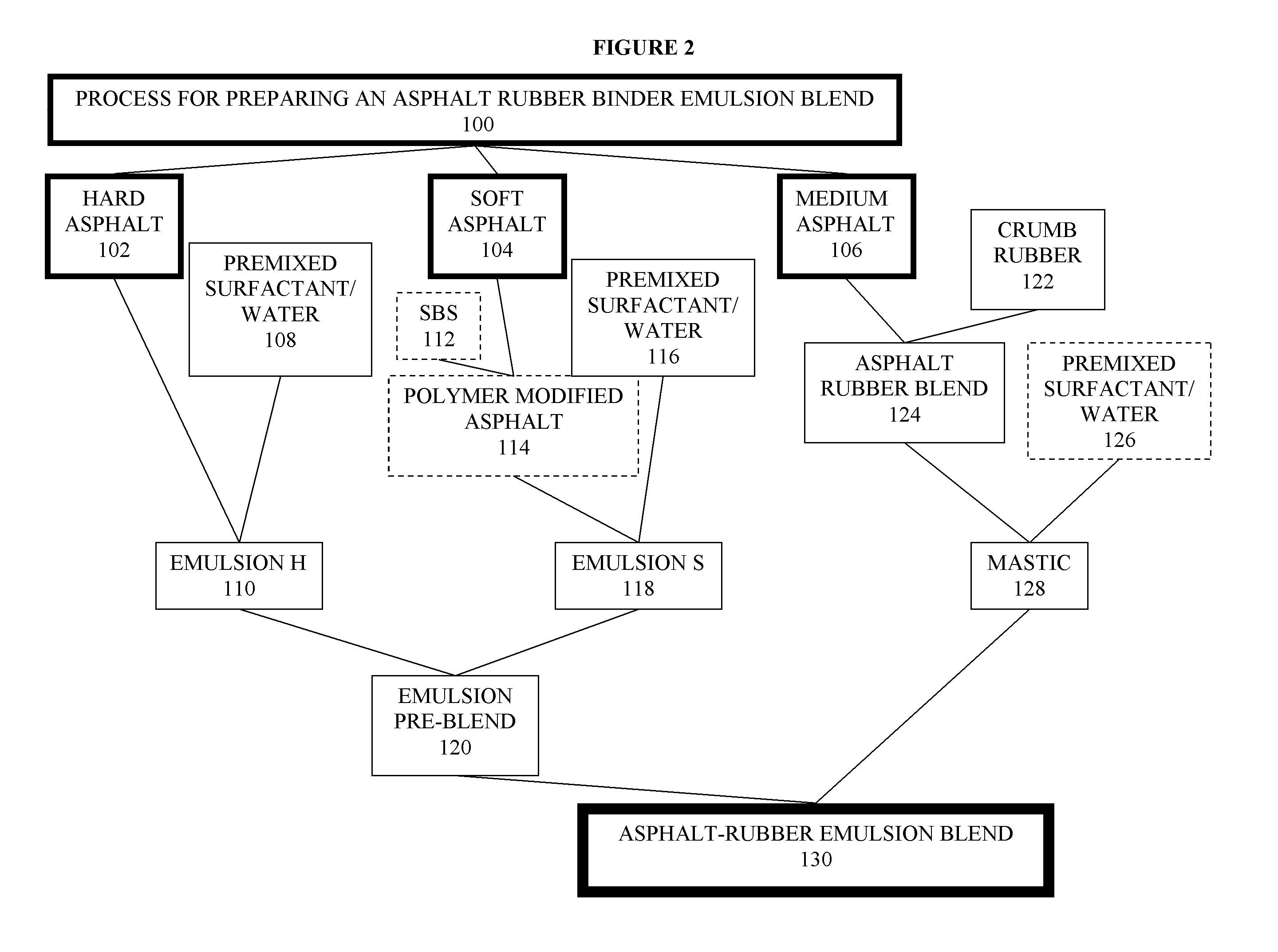
Asphalt-rubber compositions and systems and methods for preparing same
ActiveUS8808445B2Temperature insensitiveEasily applied to road surfaceBituminous material adhesivesBuilding insulationsEngineeringCrumb rubber
Owner:COE WILLIAM B
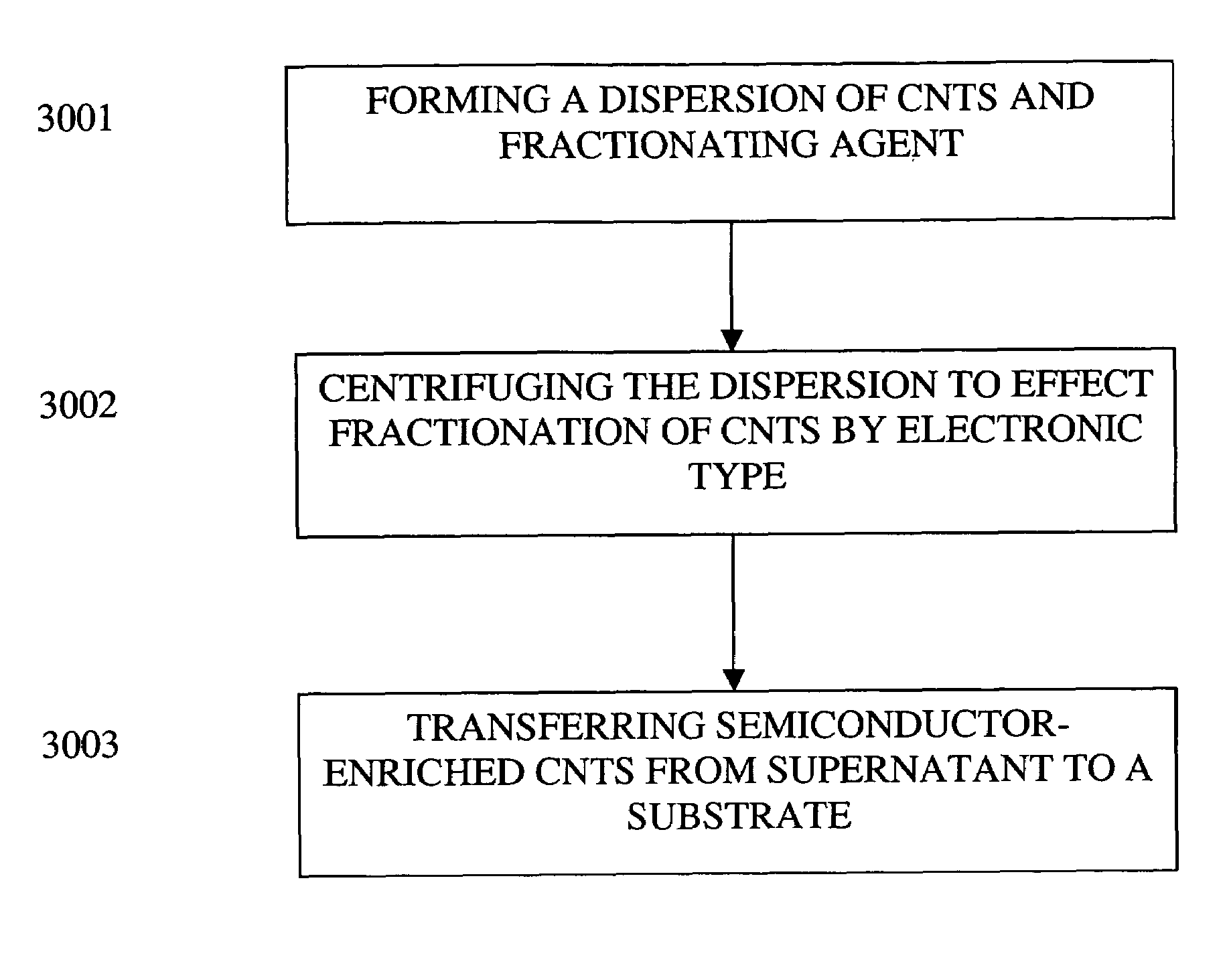
High performance field effect transistors comprising carbon nanotubes fabricated using solution based processing
InactiveUS7226818B2Easy to disperseFacilitate such dispersalMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotubeField-effect transistor
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Care and/or make-up cosmetic composition structured with silicone polymers and organogelling agents, in rigid form
InactiveUS20050245673A1Easy to disperseImprove staminaCosmetic preparationsMake-upHydrogenRoom temperature
The invention relates to a care and / or make-up cosmetic composition comprising a liquid fatty phase comprising at least one silicone oil, structured with a gelling system comprising 1) at least one polymer having a weight-average molecular mass ranging from 500 to 500 000, containing at least one moiety comprising: at least one polyorganosiloxane group consisting of 1 to 1 000 organosiloxane units in the chain of the moiety or in the form of a graft, and at least two groups capable of establishing hydrogen interactions, the polymer being solid at room temperature and soluble in the liquid fatty phase at a temperature of 25 to 250° C., and 2) at least one non-polymeric organogelling agent.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Silicone gel-based compositions for wound healing and scar reduction
ActiveUS20090143333A1Reduce formationGood lookingBiocideSilicon compound active ingredientsWound healingSilicone Gels
This invention is a composition comprising a cyclic siloxane, a silicone occlusive fluid, a silicone occlusive gel, and a silicone resin powder. The composition is useful for wound healing.
Owner:VALEANT PHARMA INT
Production of upgraded petroleum by supercritical water
ActiveUS20160312129A1Long residence timeLong exposureSolvent extractionHydrocarbon oil crackingPetroleumPetroleum engineering
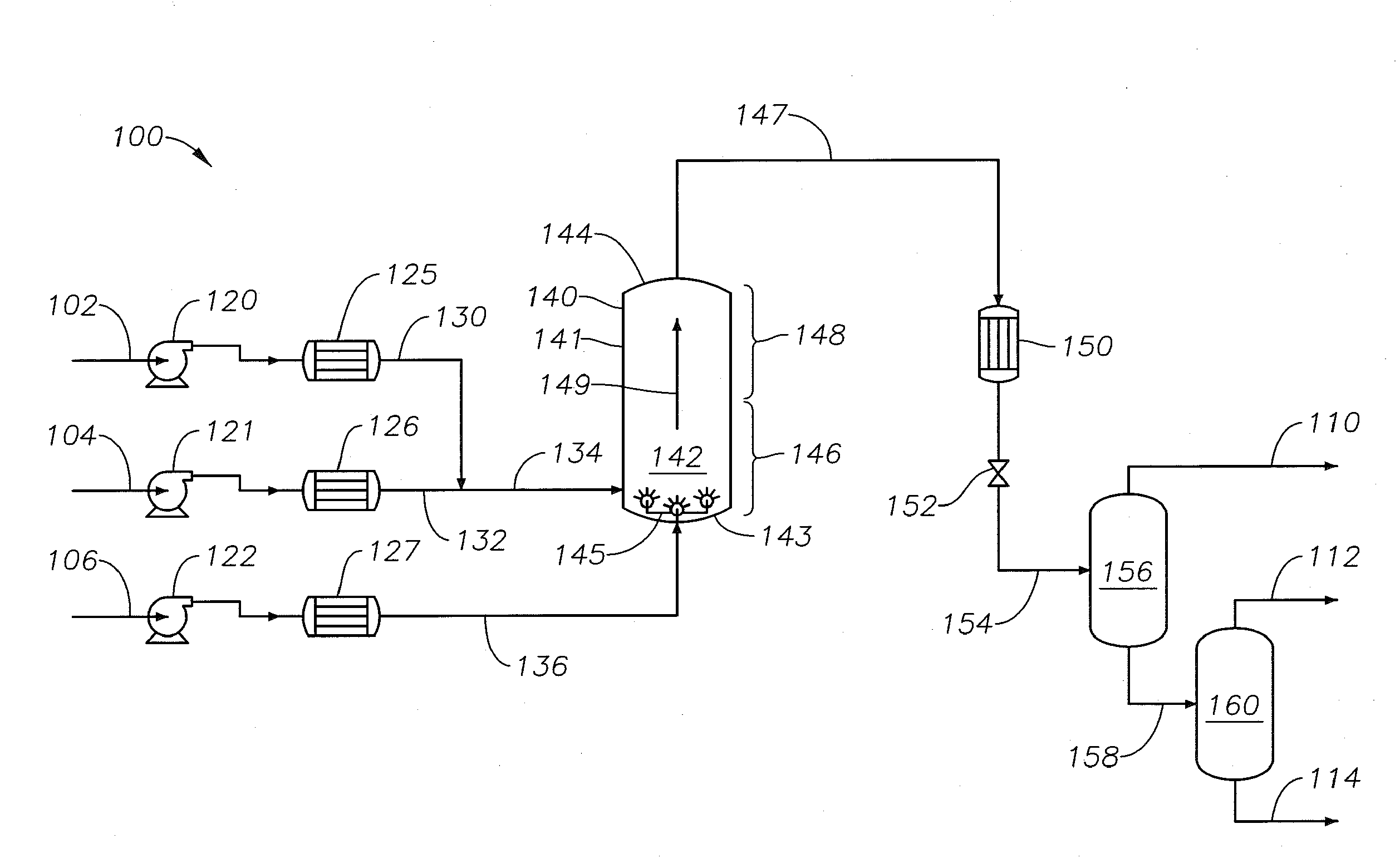
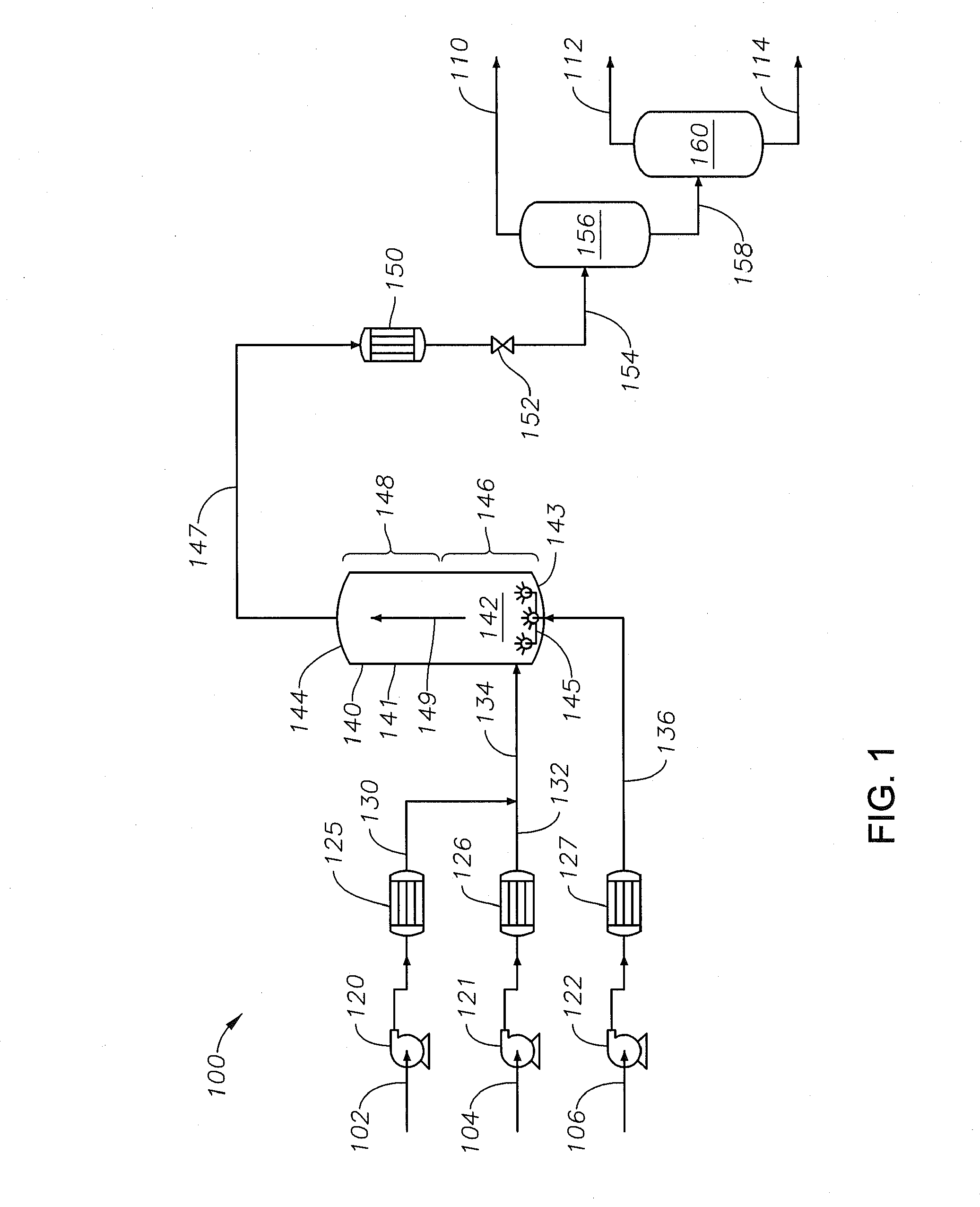
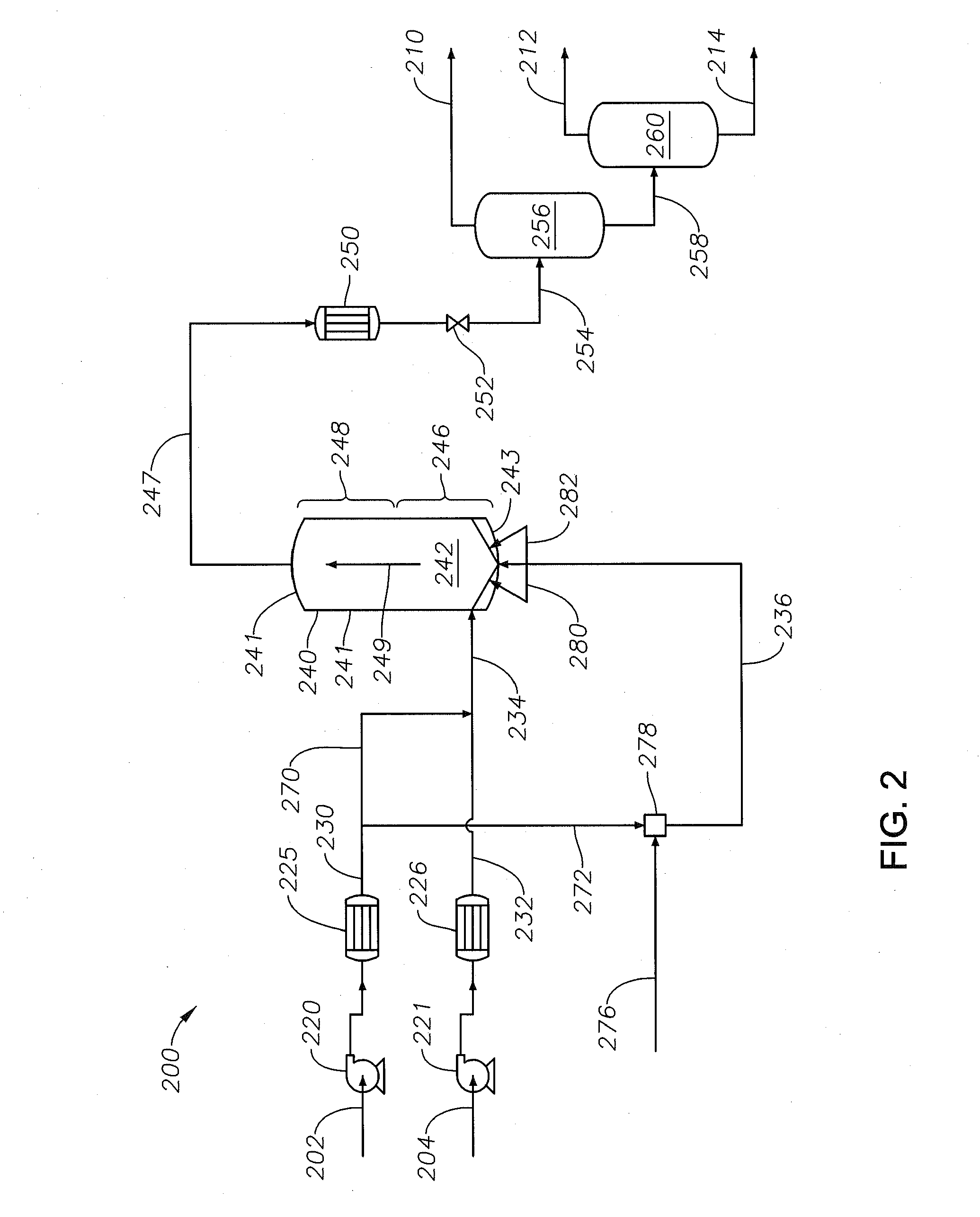
A method for upgrading a petroleum feedstock using a supercritical water petroleum upgrading system includes introducing the petroleum feedstock, water and an auxiliary feedstock. The method includes operating the system to combine the petroleum feedstock and the water to form a mixed petroleum feedstock and introducing separately and simultaneously into a lower portion of an upflowing supercritical water reactor. The auxiliary feedstock is introduced such that a portion of a fluid contained within the upflowing reactor located proximate to the bottom does not lack fluid momentum. An embodiment of the method includes operating the supercritical water petroleum upgrading system such that the upflowing reactor product fluid is introduced into an upper portion of a downflowing supercritical water reactor. The supercritical water petroleum upgrading system includes the upflowing supercritical water reactor and optionally a downflowing supercritical water reactor.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Apparatus for injecting fluid into meat products
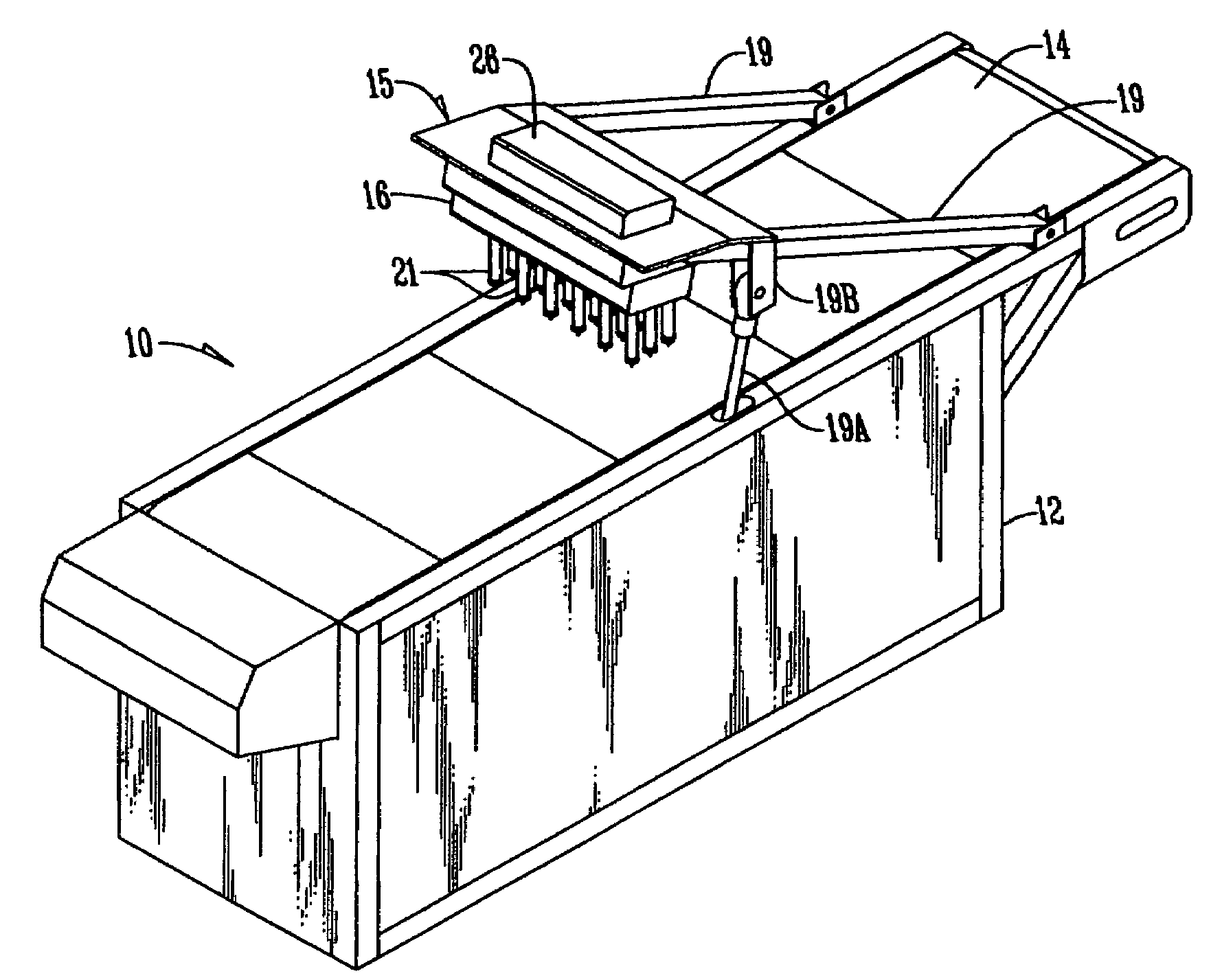
InactiveUS7302885B2Easy to disperseIncrease in sizeGrain huskingGrain polishingSyringe needleBiomedical engineering
A method for injecting fluid into meat products comprises taking a plurality of hollow fluid injection needles having sharpened discharge ends, and connecting the needles to a source of pressurized liquid; penetrating the sharpened ends of the needles into the product and thence withdrawing the same while discharging fluid into the product and vibrating the needles for a period of time while they are within the product to enlarge the size of a penetration hole within the product caused by the penetration of the needles to a size greater than the size of the needles to create at least a partial space around the needles to permit fluid from the needles to migrate into the spaces around the needles. The needles have a roughened outside surface.
Owner:STORK TOWNSEND BV
Soluble glycosaminoglycanases and methods of preparing and using soluble glycosaminoglycanases
ActiveUS20100196423A1Reduce sensitivityGreater serum half-livesAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHyaluronidaseNuclear chemistry
The invention relates to the discovery of novel soluble neutral active Hyaluronidase Glycoproteins (sHASEGPs), methods of manufacture, and their use to facilitate administration of other molecules or to alleviate glycosaminoglycan associated pathologies. Minimally active polypeptide domains of the soluble, neutral active sHASEGP domains are described that include asparagine-linked sugar moieties required for a functional neutral active hyaluronidase domain. Included are modified amino-terminal leader peptides that enhance secretion of sHASEGP. The invention further comprises sialated and pegylated form of a recombinant sHASEGP to enhance stability and serum pharmacokinetics over naturally occurring slaughterhouse enzymes. Further described are suitable formulations of a substantially purified recombinant sHASEGP glycoprotein derived from a eukaryotic cell that generate the proper glycosylation required for its optimal activity.
Owner:HALOZYME
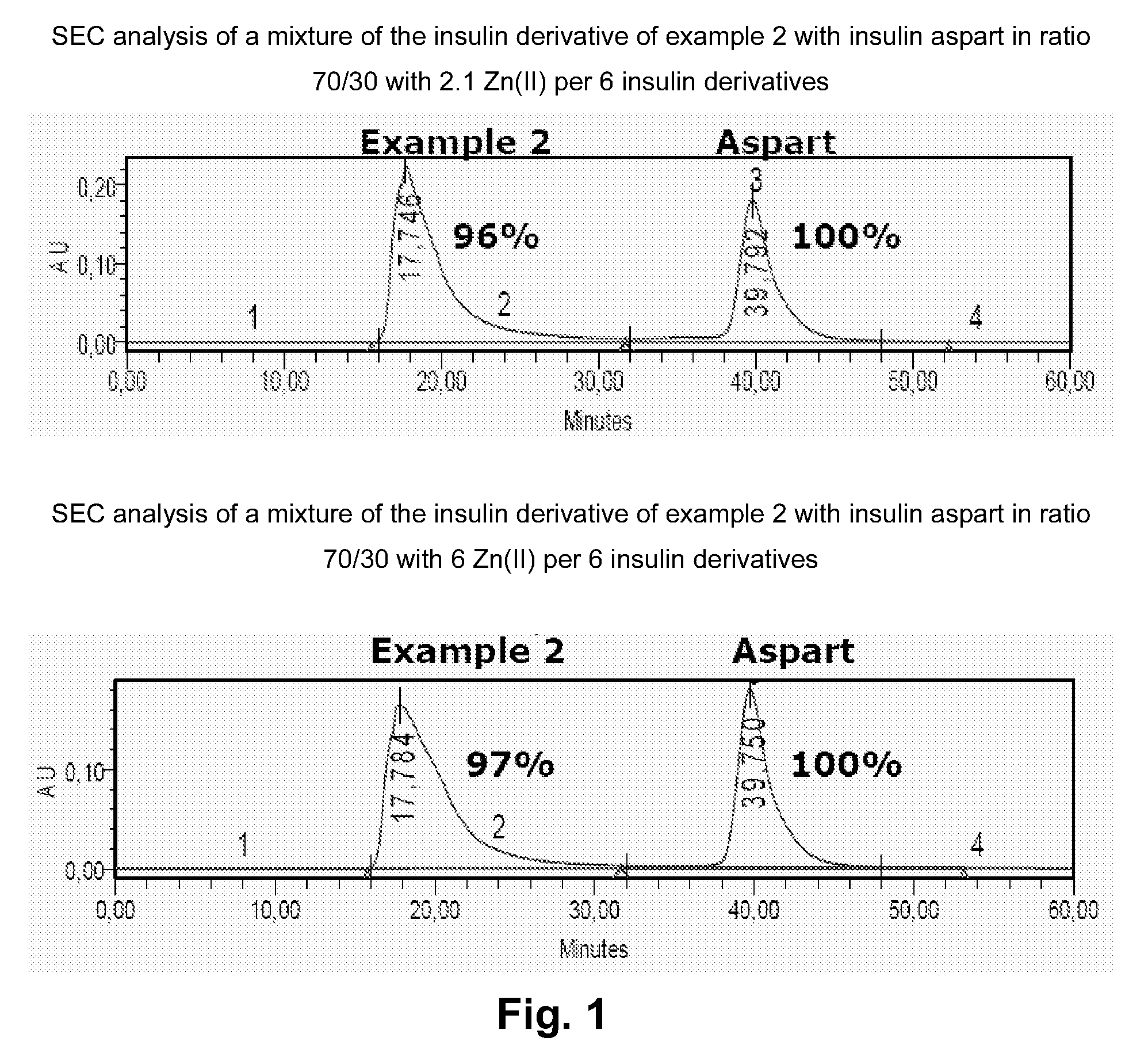
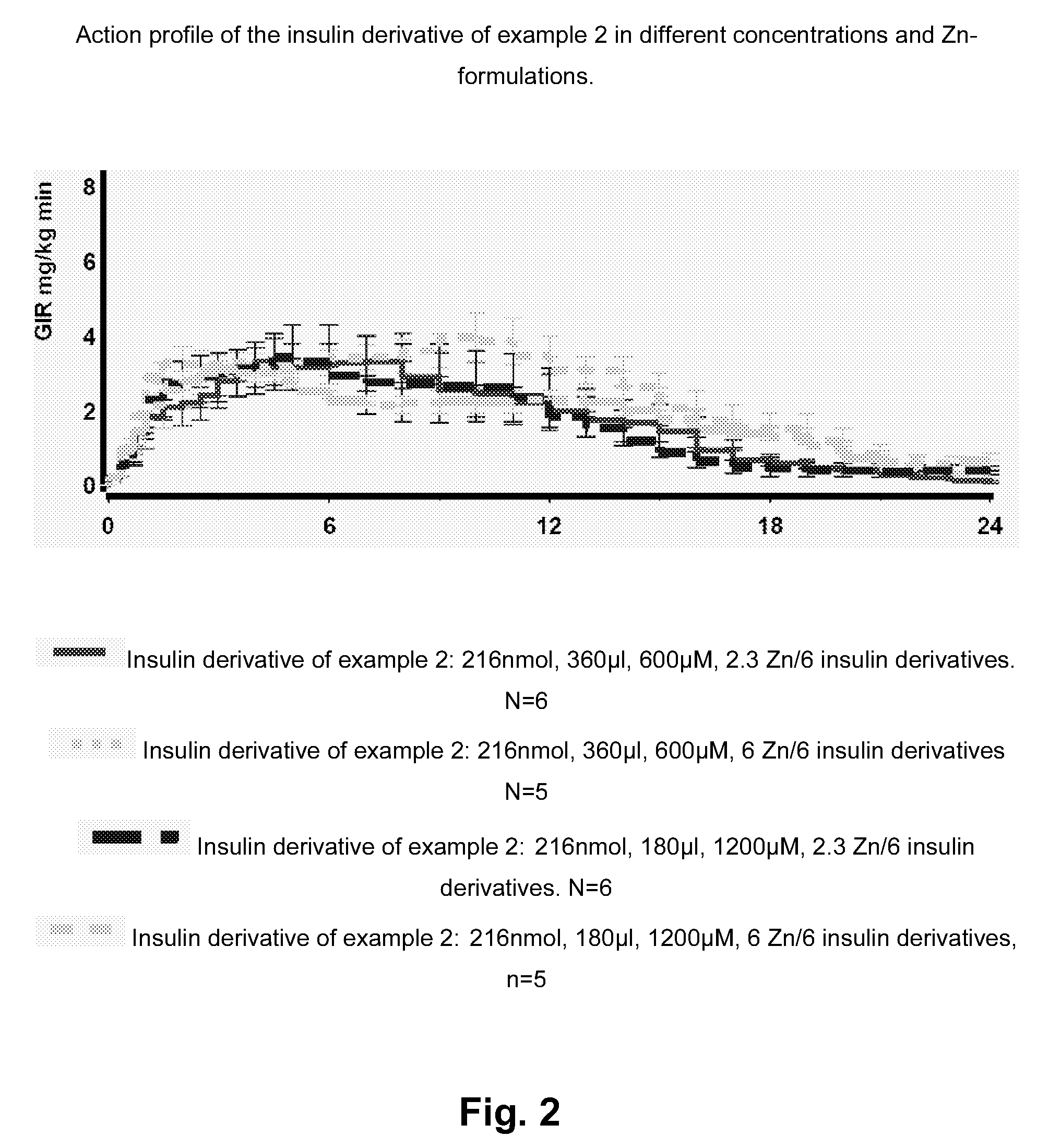
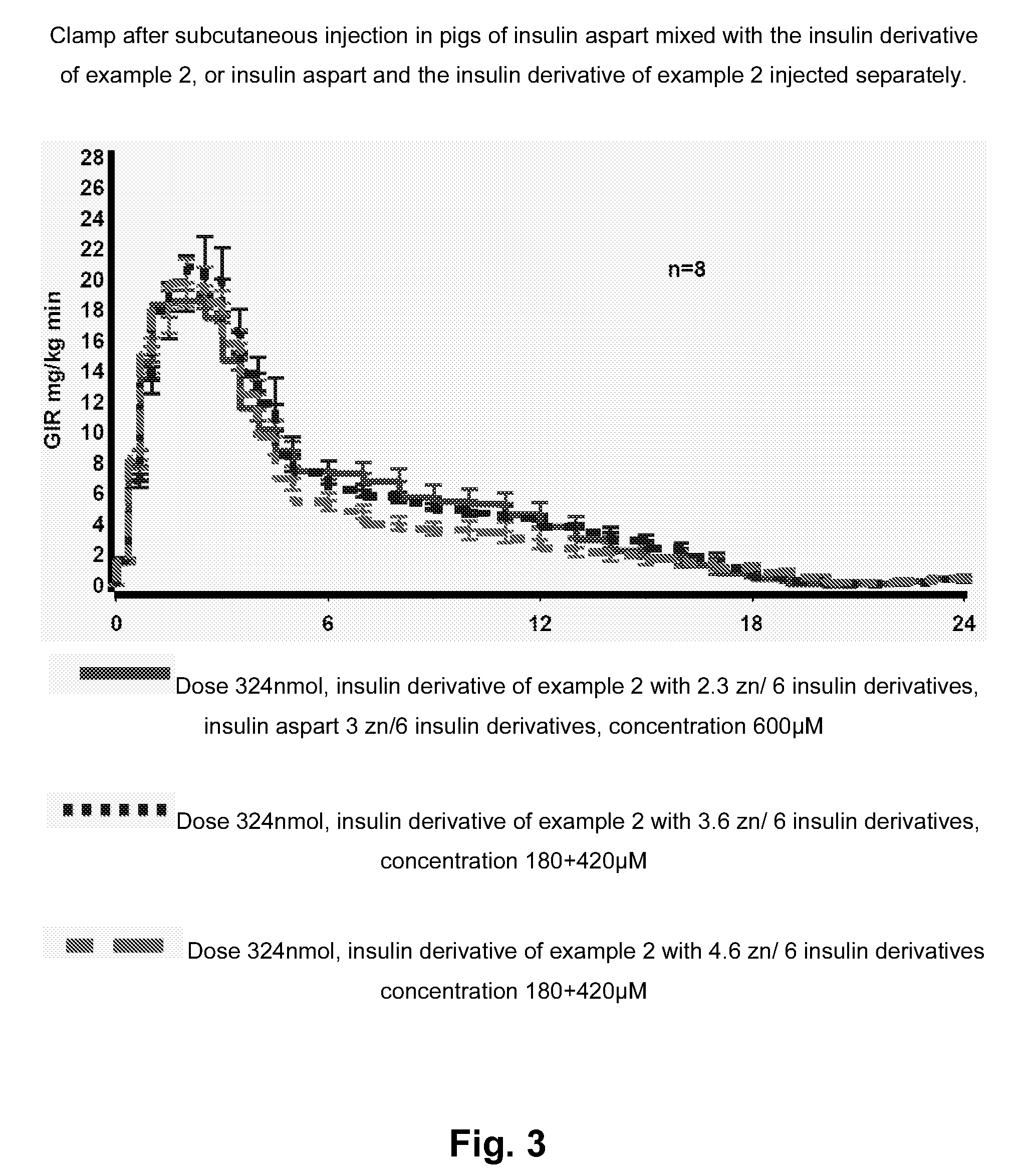
Insulin Derivative
InactiveUS20090239785A1Prolonged profile of actionNo bluntingPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDrugHuman insulin
The present invention relates to novel human insulin derivatives which are soluble at physiological pH values and have a prolonged profile of action. The invention also relates to methods of providing such derivatives, to pharmaceutical compositions containing them, to methods of treating diabetes and hyperglycaemia using the insulin derivatives of the invention and to the use of such insulin derivatives in the treatment of diabetes and hyperglycaemia.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
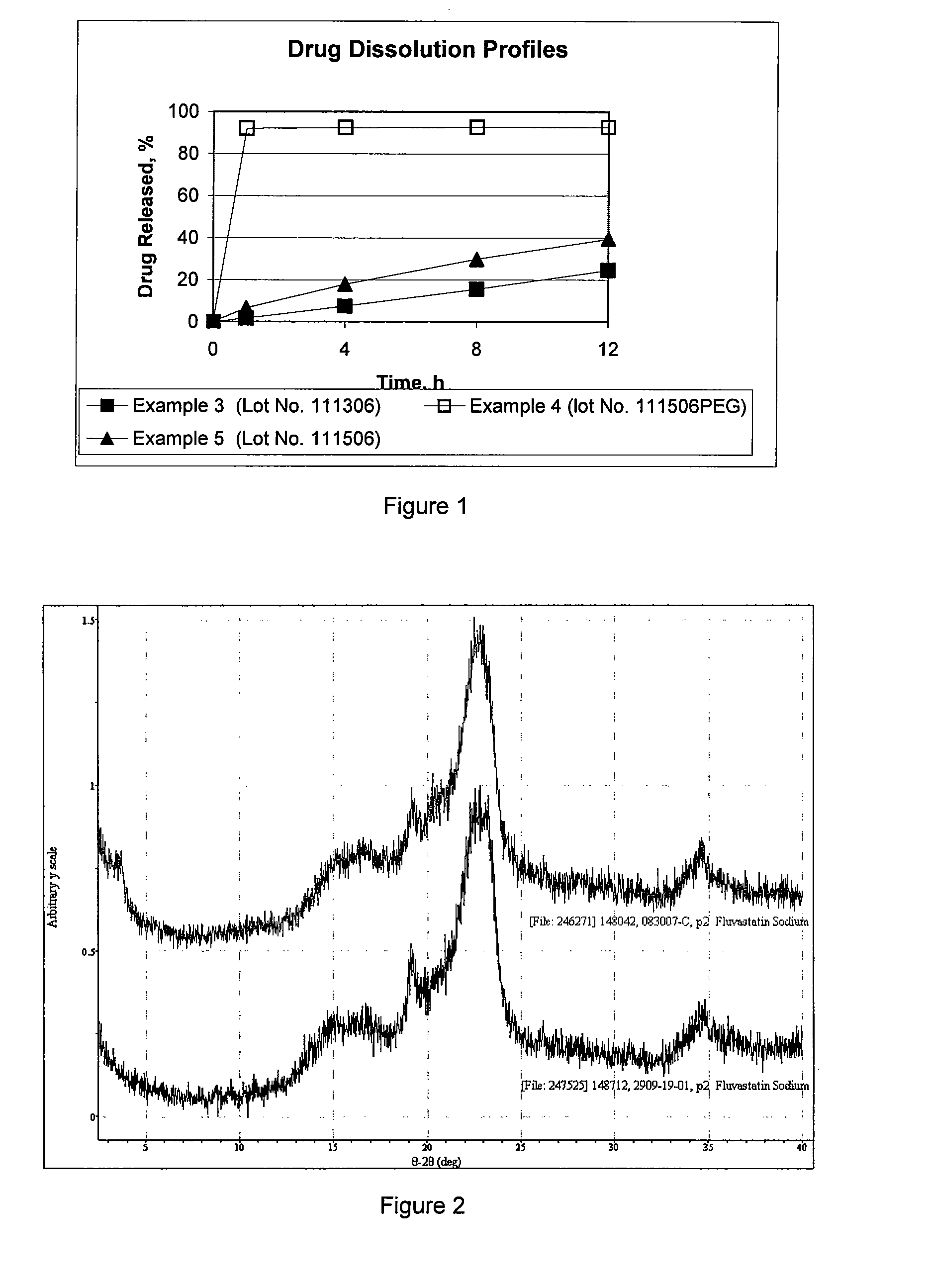
Solid dispersion composition
A solid dispersion composition containing fluvastatin and a polymer is provided. Optionally, a surfactant is included. The fluvastatin appears to be amorphous and the solid dispersion composition enables fluvastatin to be constantly released over a time period.
Owner:BIOKEY
Substrate, device, method of manufacturing device, method of manufacturing active matrix substrate, electro-optical apparatus and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20080132009A1Avoid defectsEasy to disperseSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive matrixEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
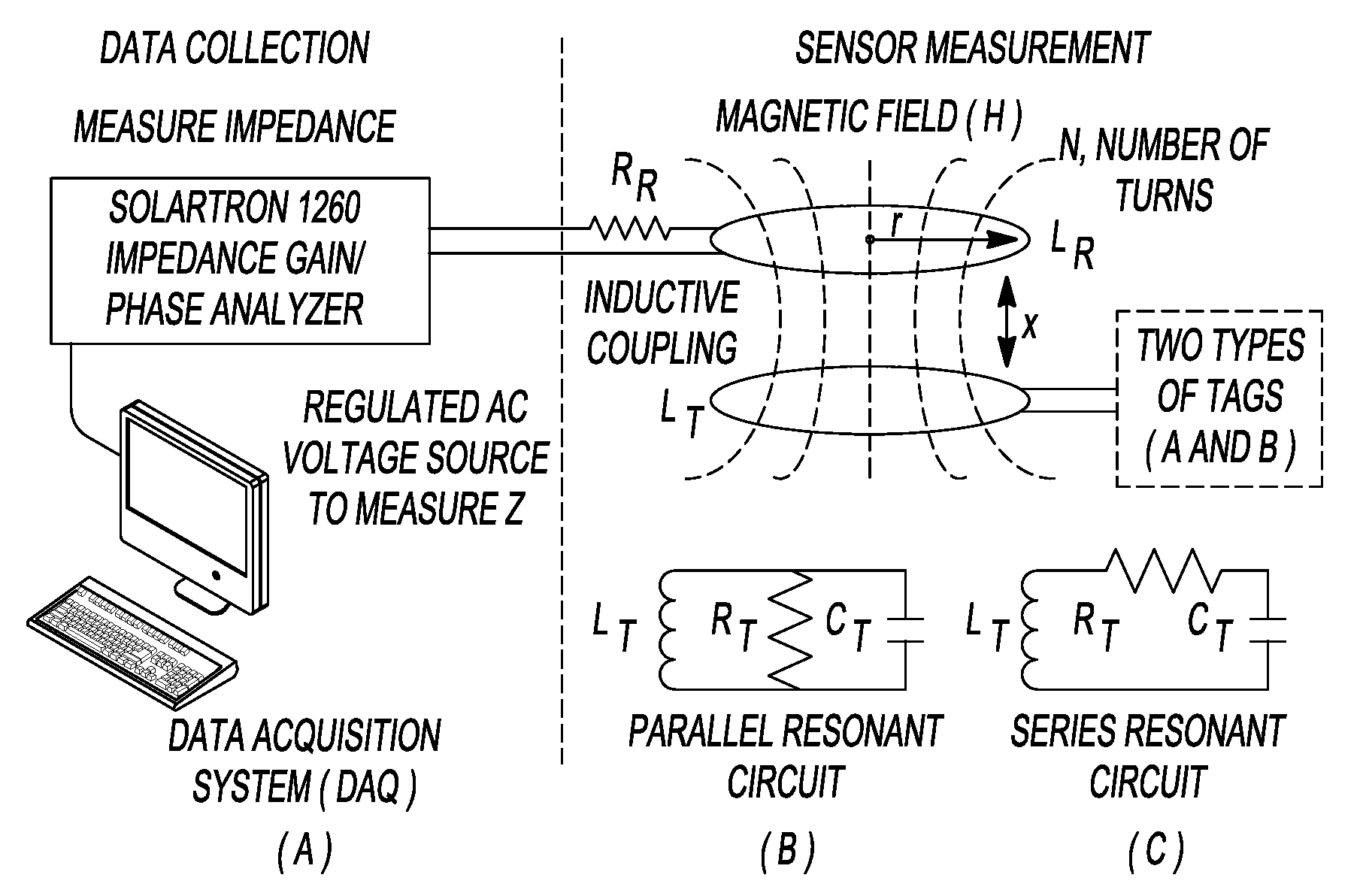
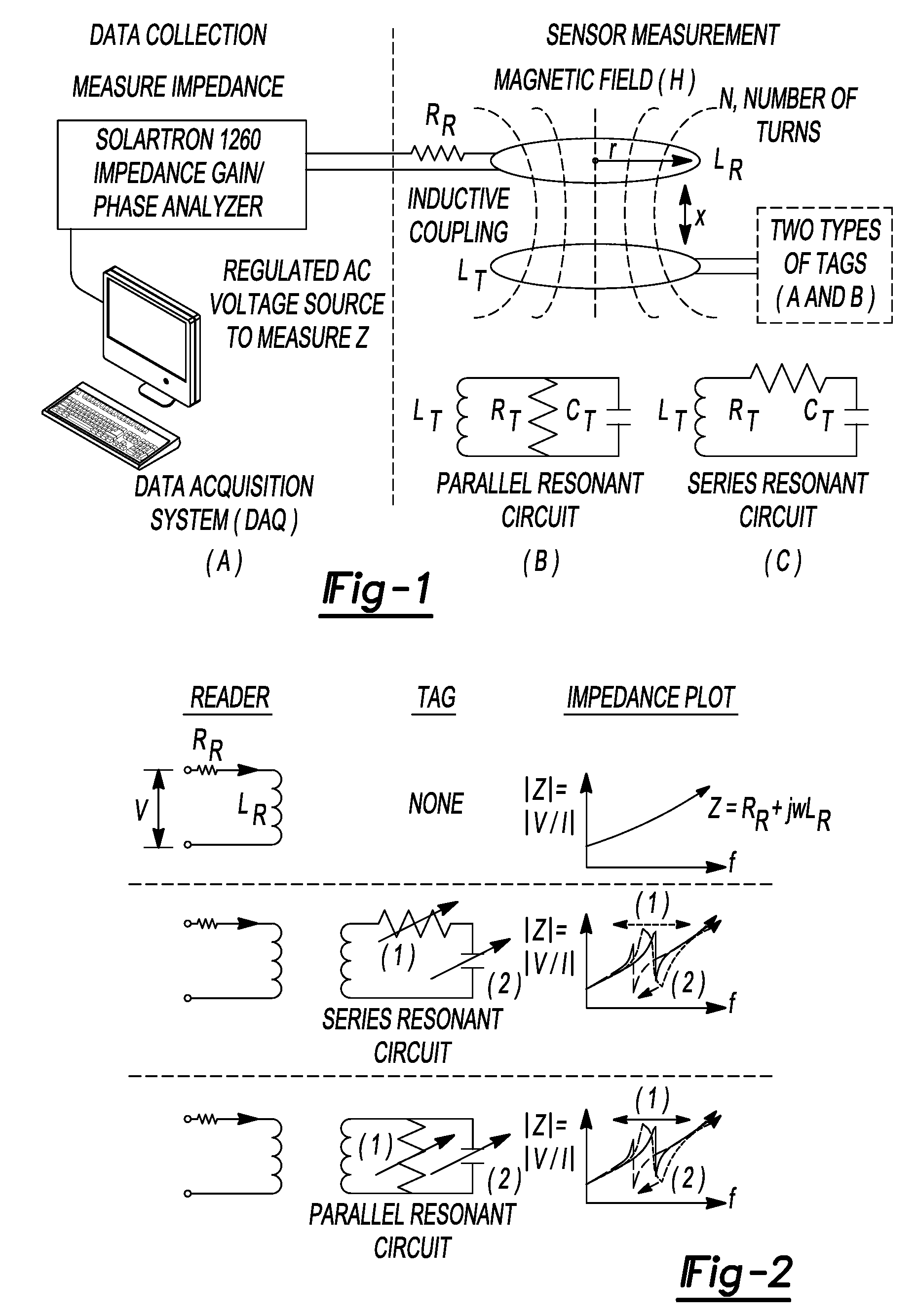
Passive wireless readout mechanisms for nanocomposite thin film sensors
ActiveUS20090121872A1Increase in bulk film conductivityImprove conductivityMemory record carrier reading problemsRecord carriers used with machinesNanocomposite thin filmsElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method for sensing a stimulus comprising providing a sensing assembly having a first structure and a second structure, wherein the first structure is made of a material different than the second structure and each of the first structure and the second structure is nanoscale. The method further includes providing an inductive antenna operably coupled to the sensing assembly, disposing the sensing assembly upon a spatial area, exposing the sensing assembly to the stimulus thereby producing a detectable change in the sensing assembly, and wirelessly coupling a reader with the inductive antenna to obtain a signal representative of the detectable change in the sensing assembly.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Asphalt-rubber compositions and systems and methods for preparing same
ActiveUS20100168274A1Temperature insensitiveEasily applied to road surfaceBituminous material adhesivesBuilding insulationsEngineeringCrumb rubber
One embodiment provides a process for preparing an asphalt-coated crumb rubber composition that meets the specification set forth in ASTM D80-02 or deviations thereof which may be established by the specifying agency from time to time. The process generally comprises obtaining asphalt of different penetration grades, combining the asphalt of each grade with preselected chemicals to form separate premixed components, blending the premixed components together under predetermined conditions to form, upon curing, an asphalt-coated crumb rubber composition that meets certain physical requirements for asphalt-rubber binder (ARB), such as those set forth in ASTM D8-02. Advantageously, the resulting asphalt-coated crumb rubber composition not only meets the physical requirements of ARB used in road paving but also has improved dispersion of the rubber, such as dispersion of the rubber in an oil-in-water emulsion of an asphalt.
Owner:COE WILLIAM B
Masterbatch Composition, Rubber Composition Containing The Same, And Valucanizate
InactiveUS20070197688A1Easy to disperseImprove mechanical propertiesGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSpecial tyresFiberMasterbatch
The main object of the invention is to provide a masterbatch composition capable of increasing the dispersibility of short fibers in a rubber composition. According to the invention, this object is to solve the above-described problems by providing a masterbatch composition comprising 5 to 78 parts by weight of α,β-ethylenically unsaturated nitrile monomer unit-containing copolymer rubber (A), 5 to 78 parts by weight of a multifunctional compound (B) and / or a plasticizer (B′) having a molecular weight of 400 or more, and 17 to 90 parts by weight of short fibers (C) of 0.1 to 12 mm in length, provided that the sum of (A), (B) and / or (B′), and (C) is 100 parts by weight.
Owner:ZEON CORP
Surfboard protective shoulder bag
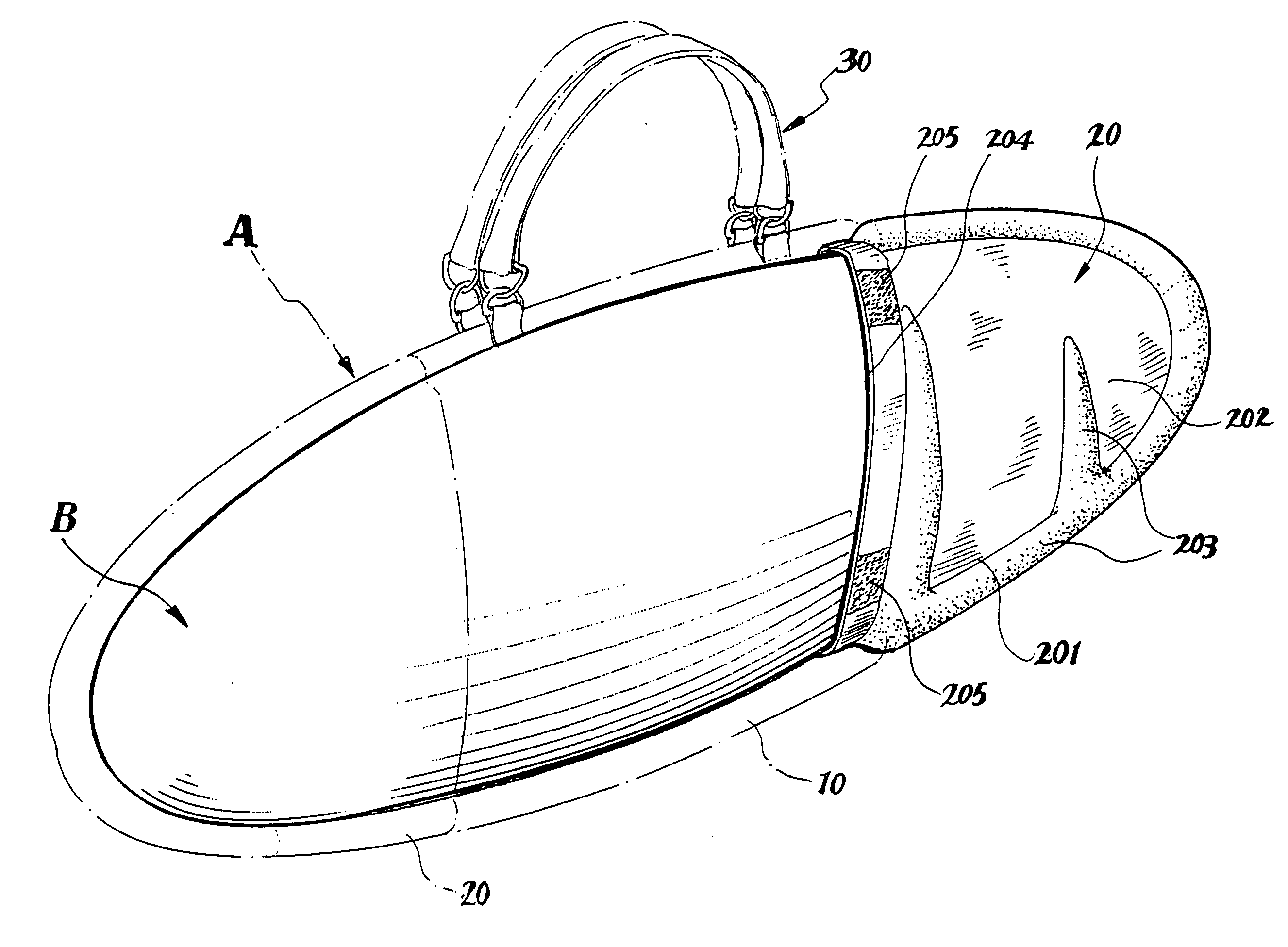
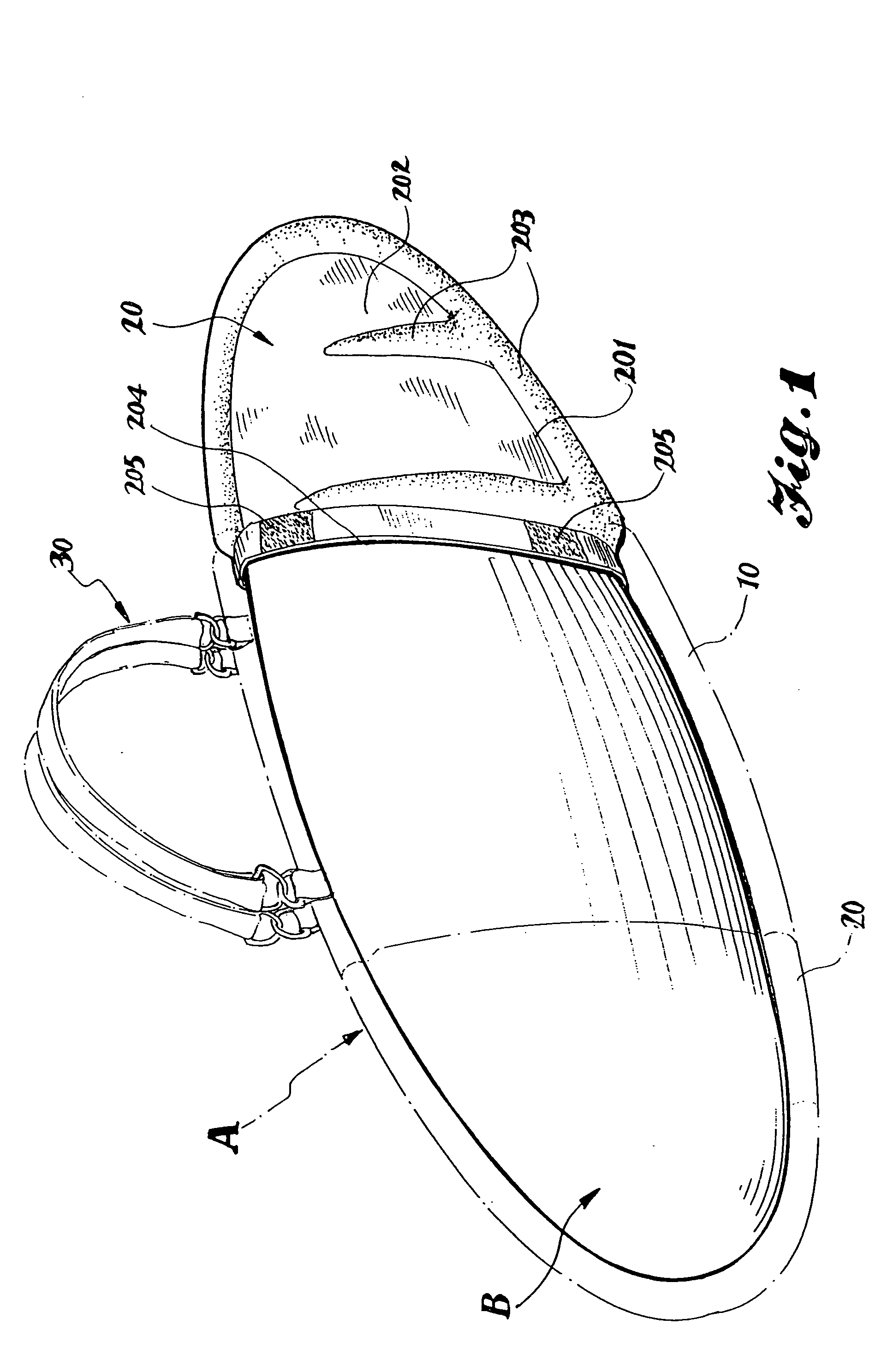
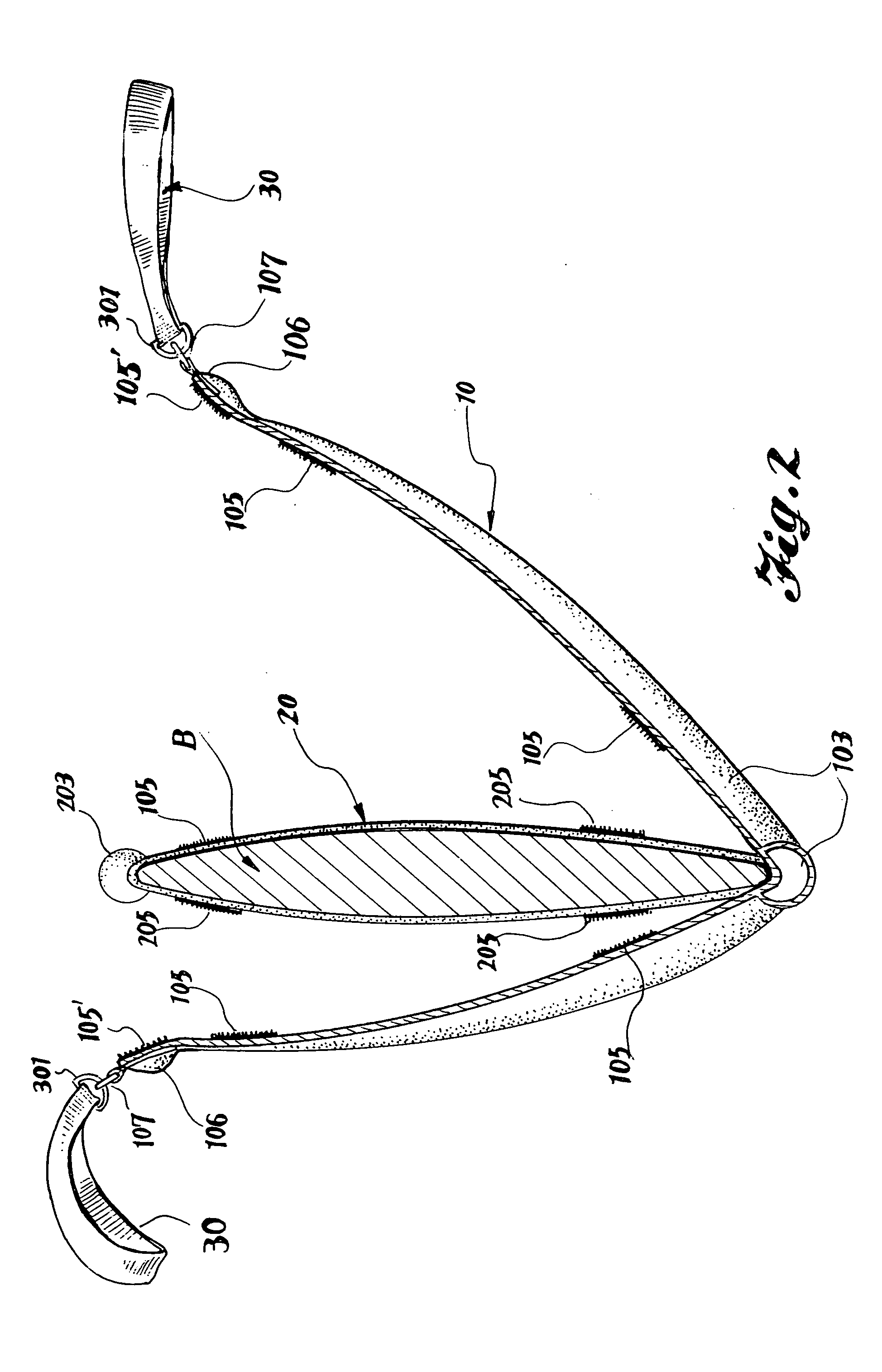
InactiveUS20060016842A1Easily packed intoEasy retrievalTravelling sacksWater sport boardsFolded formEngineering
Owner:LU CHENG LUN
Package structure
ActiveCN102194804AEasy to disperseReduce breakageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSiliconElectrical and Electronics engineering
A package structure includes a first die, and a second die over and bonded to the first die. The second die has a size smaller than a size of the first die. A dummy chip is over and bonded onto the first die. The dummy chip includes a portion encircling the second die. The dummy chip includes a material selected from the group consisting essentially of silicon and a metal. the heat generated in bottom chip and top die may be easily dissipated to form a low stress and reduce the possibility of the breakage of the bottom chip.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com