Patents
Literature
21040 results about "Sorbent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A sorbent is a material used to absorb or adsorb liquids or gases.
Afinity domain for analyte sensor
InactiveUS20050176136A1Reduce impactBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteSorbent
Abstract of the DisclosureThe preferred embodiments provide a membrane system, particularly for use on an electrochemical sensor, wherein the membrane system includes an affinity domain that dampens the effects of target interferant(s) on the sensor. The affinity domain can be layer, surface, region, and / or portion of the membrane system formed using sorbents that have an affinity for the target interferant. The sorbents can be adapted to adsorb the interferants, for example using adsorbents such as chromatography packing materials. The sorbents can also be adapted to absorb the interferants by imprinting a molecular structure on the material that forms the affinity domain such that target interferants bind to the imprinted surfaces at the molecular level.
Owner:DEXCOM
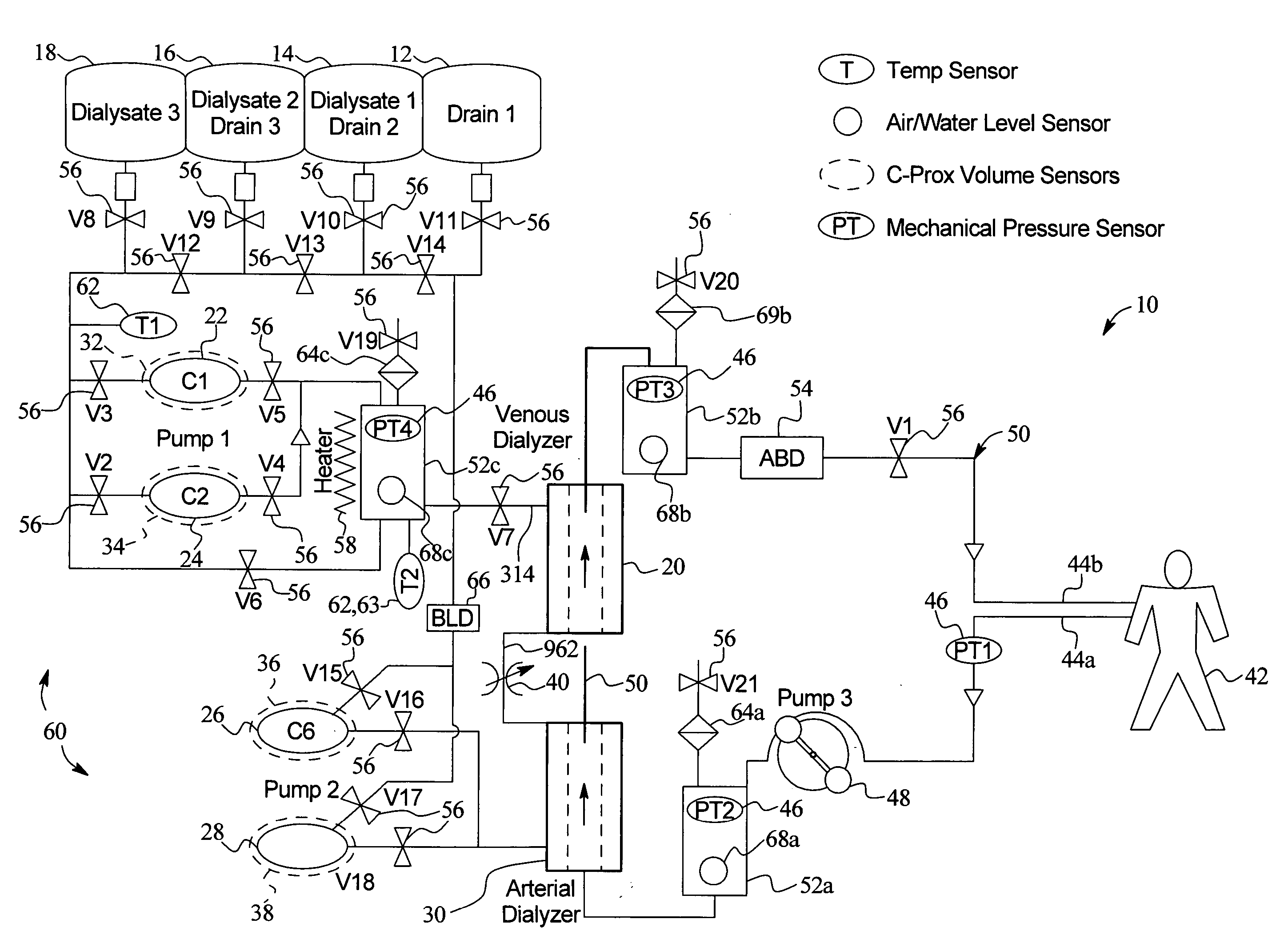
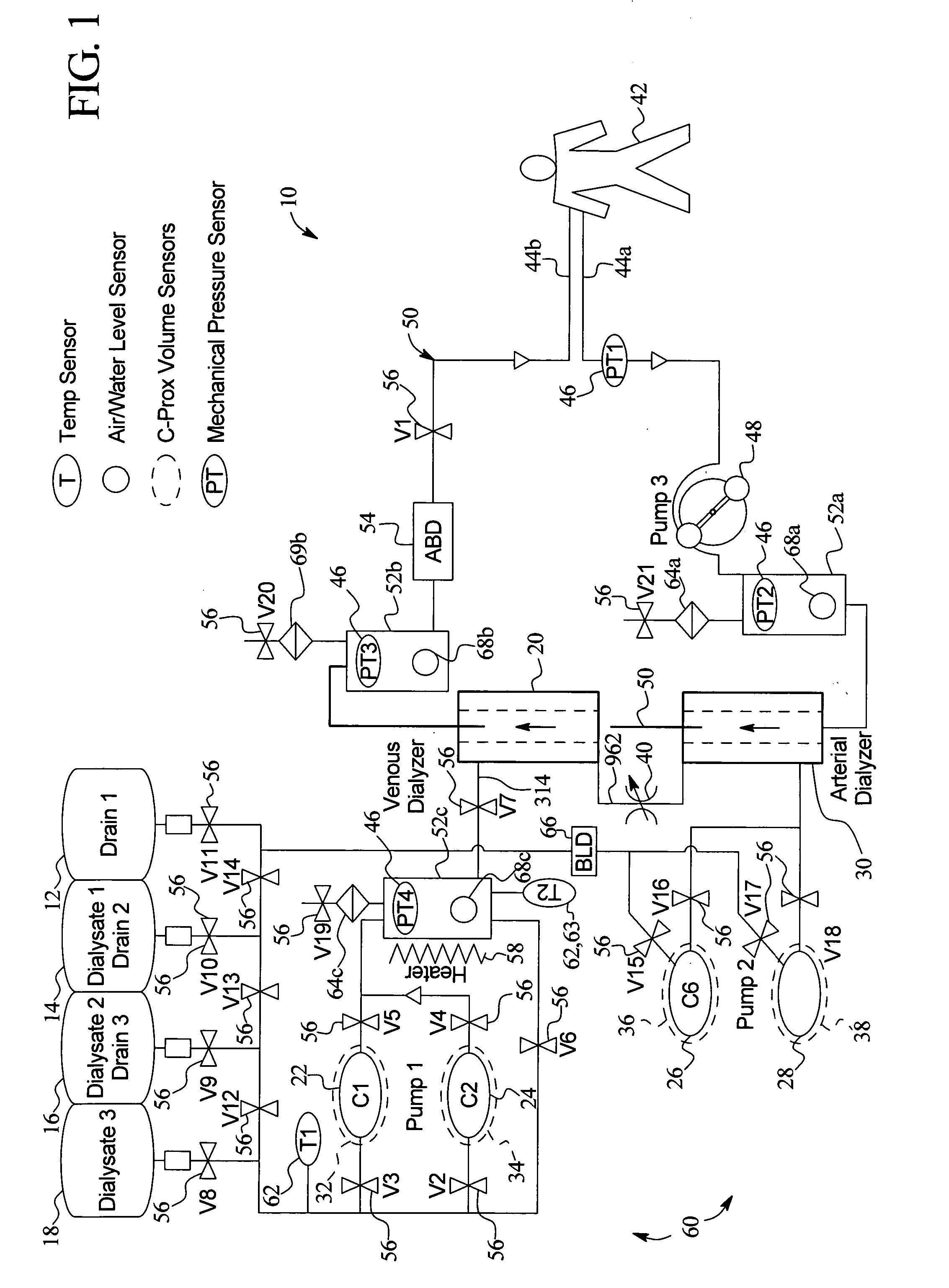
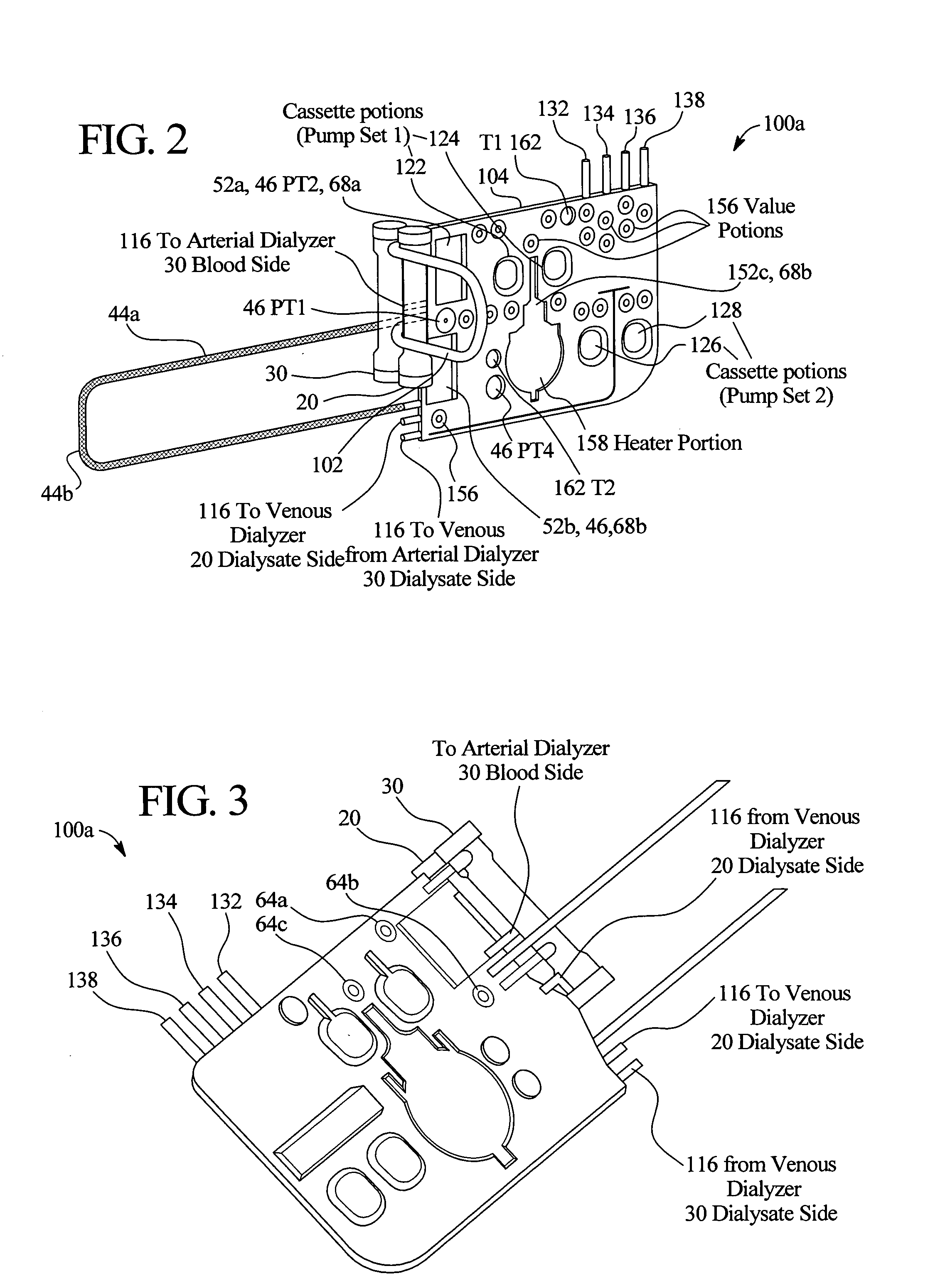
High convection home hemodialysis/hemofiltration and sorbent system
InactiveUS20050131332A1Easily set up sterile blood therapy systemImprove efficiencySemi-permeable membranesHaemofiltrationPositive pressureSorbent
A system, method and apparatus for performing a renal replacement therapy is provided. In one embodiment, two small high flux dialyzers are connected in series. A restriction is placed between the two dialyzers in the dialysate flow path. The restriction is variable and adjustable in one preferred embodiment. The restriction builds a positive pressure in the venous dialyzer, causing a high degree of intentional backfiltration. That backfiltration causes a significant flow of dialysate through the high flux venous membrane directly into the patient's blood. That backfiltered solution is subsequently ultrafiltered from the patient from the arterial dialyzer. The diffusion of dialysate into the venous filter and removal of dialysate from the arterial dialyzer causes a convective transport of toxins from the patient. Additionally, the dialysate that does not diffuse directly into the patient but instead flows across the membranes of both dialyzers provides a diffusive clearance of waste products.
Owner:BAXTER HEALTHCARE SA +1
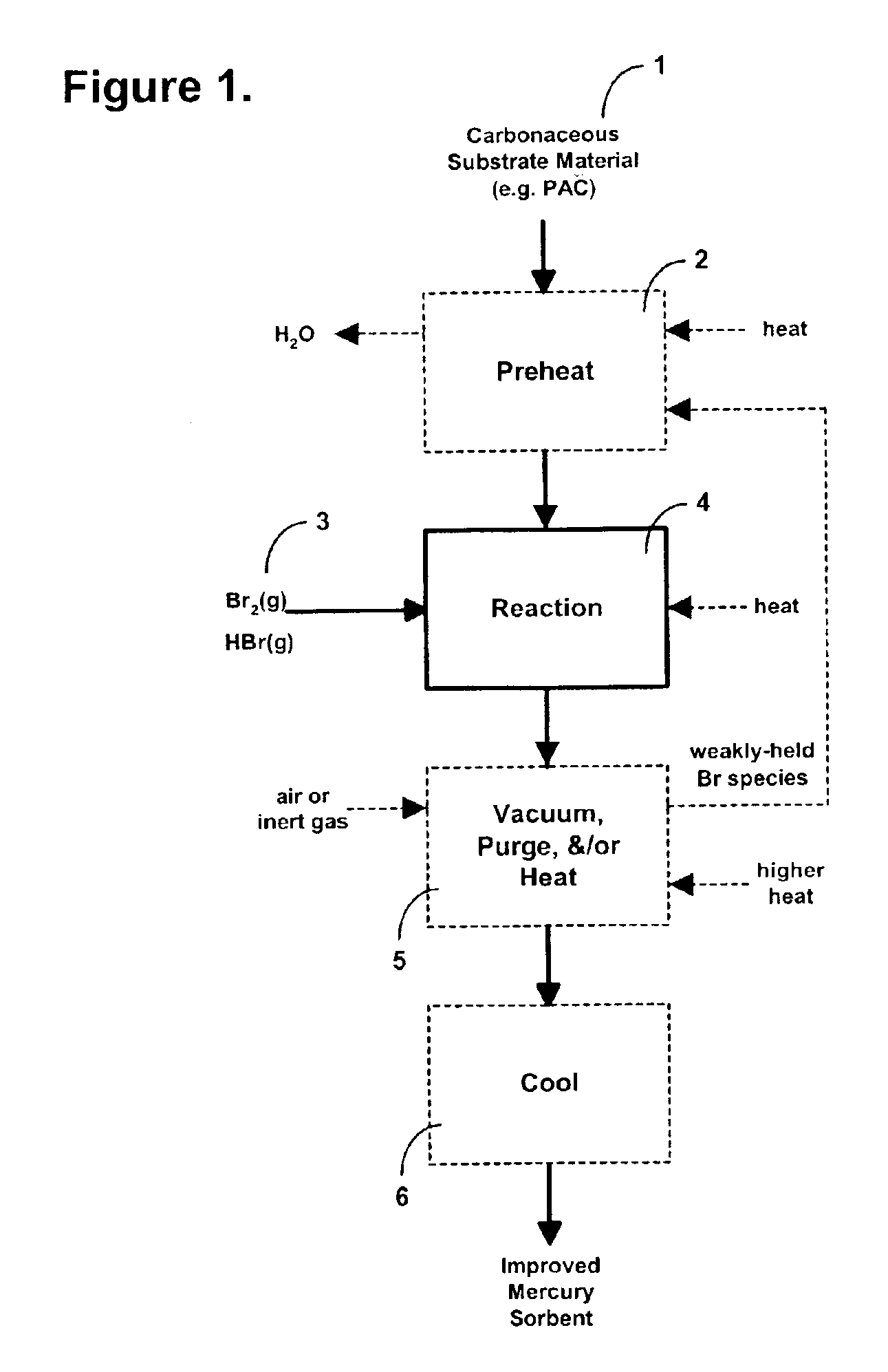
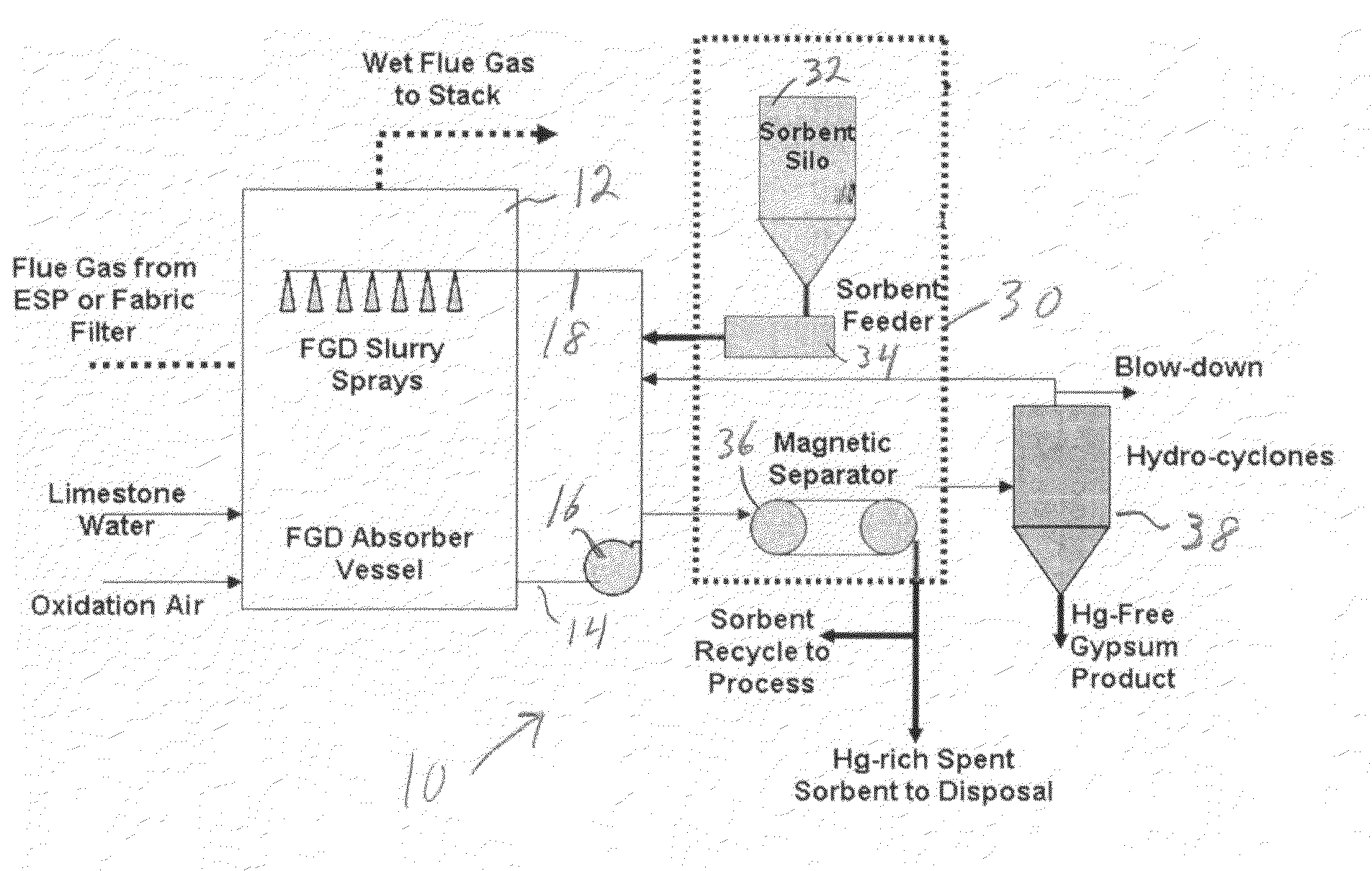
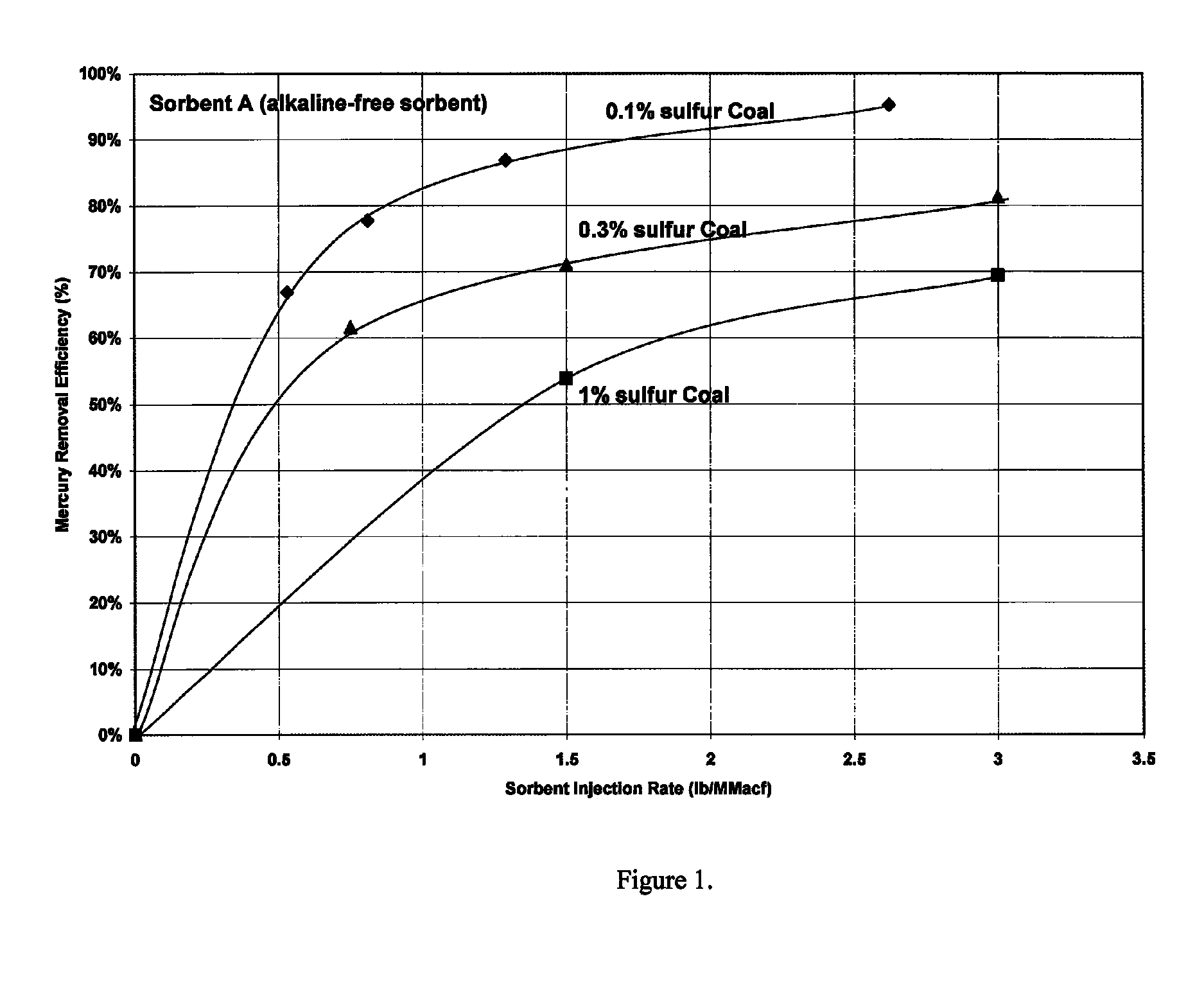
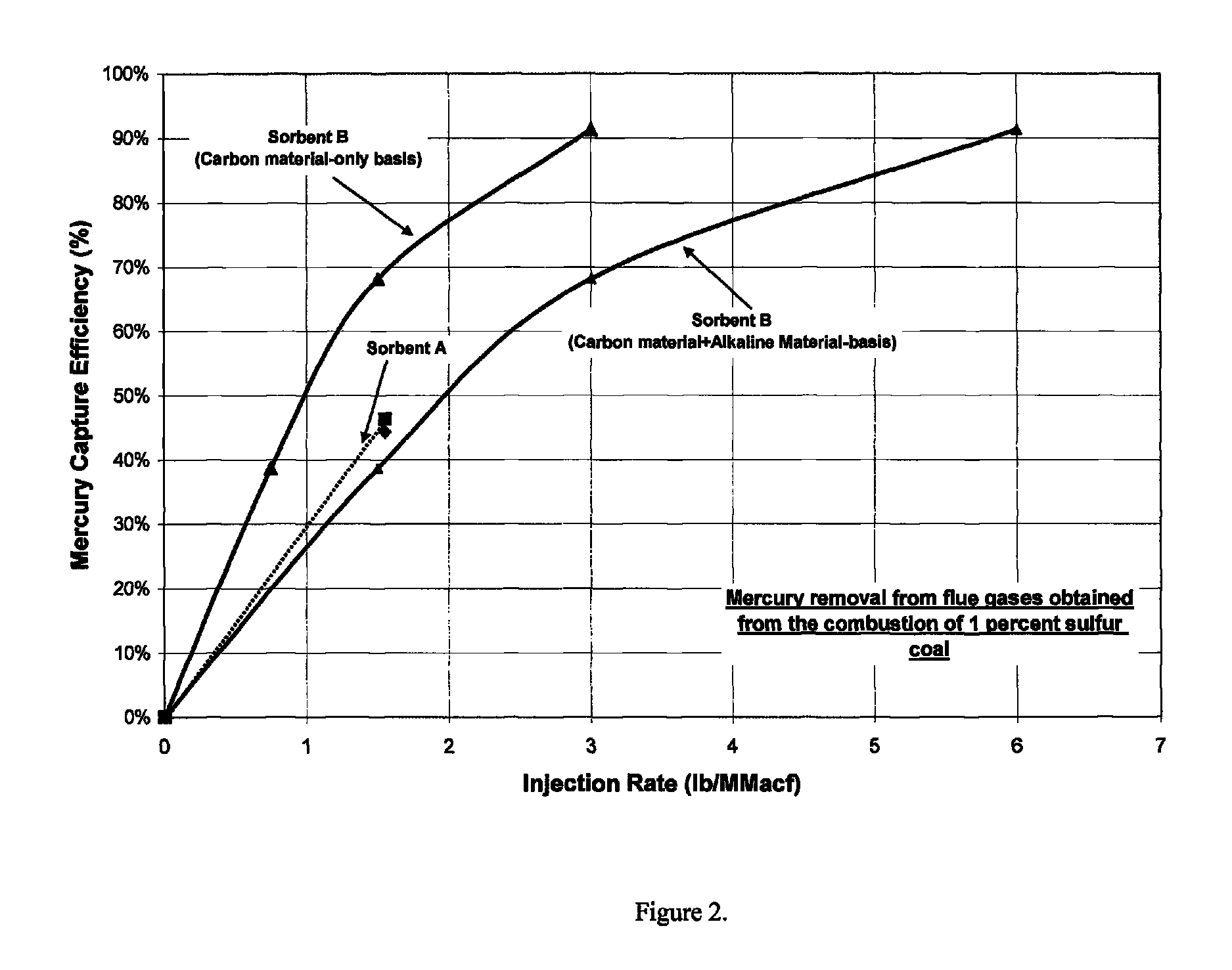
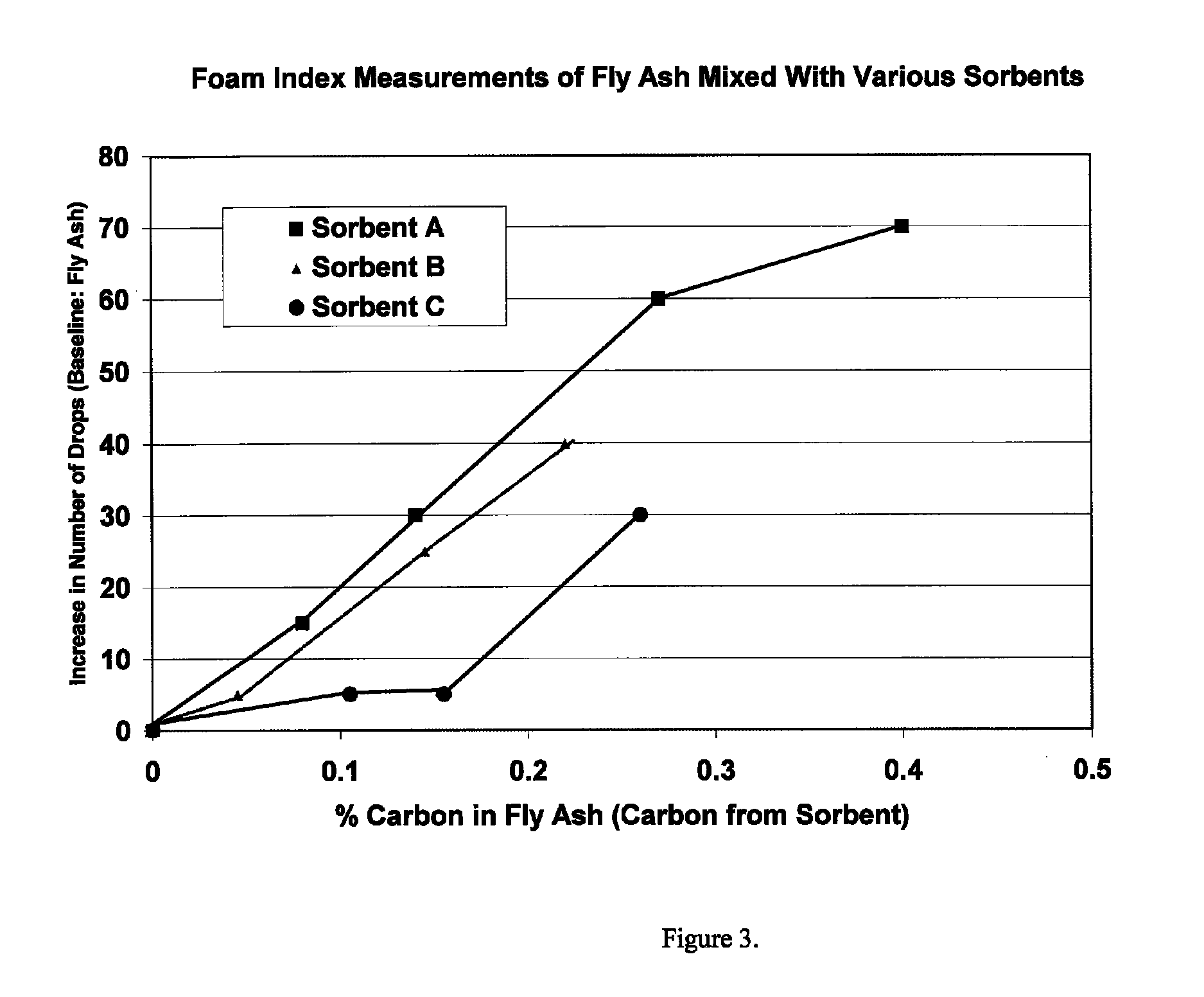
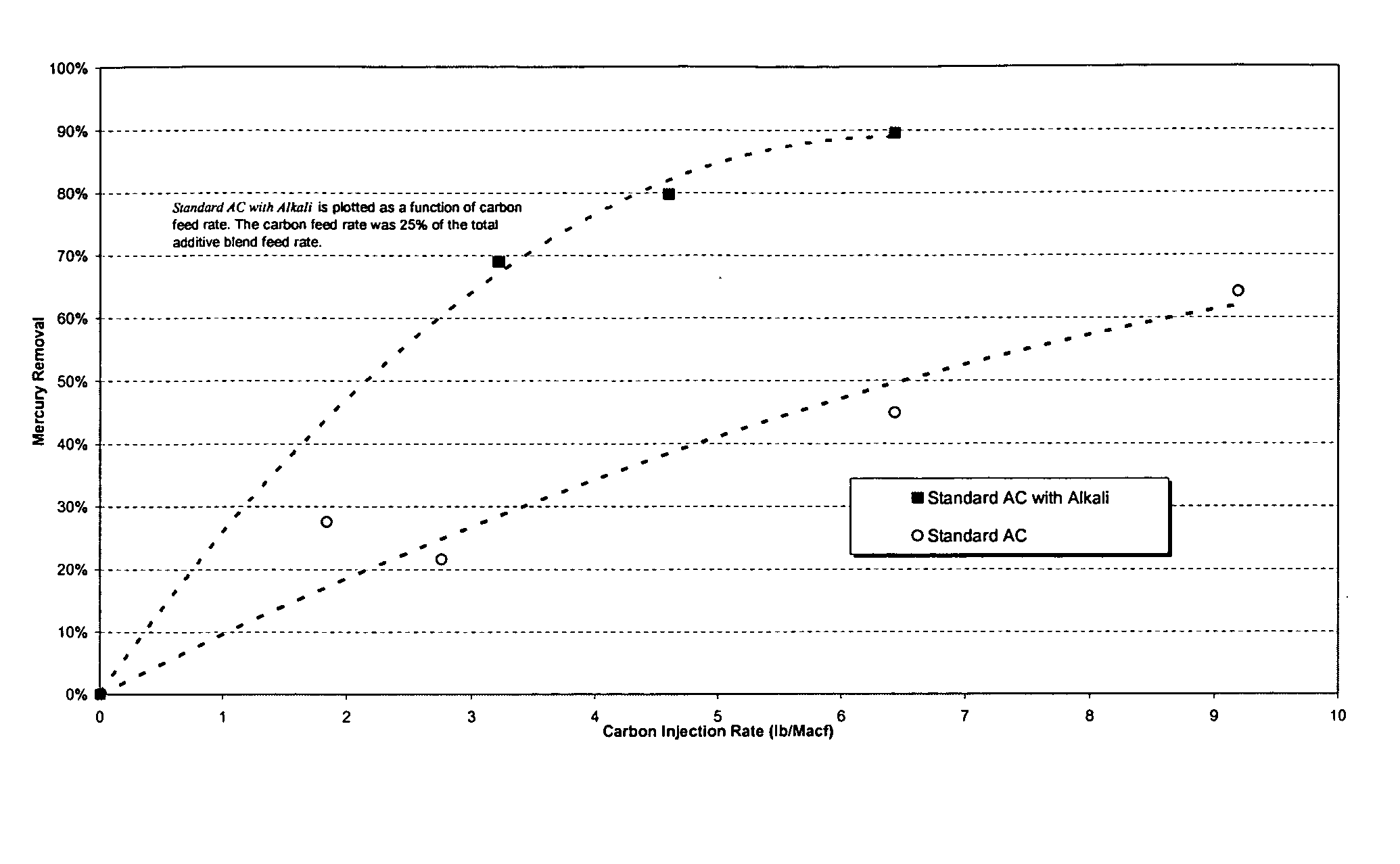
Sorbents and methods for the removal of mercury from combustion gases
InactiveUS6953494B2Improve abilitiesUnified processingGas treatmentOther chemical processesSufficient timeCombustion
A method for removing mercury and mercury-containing compounds from a combustion gas in an exhaust gas system has the steps of providing a mercury sorbent; injecting the mercury sorbent into a stream of the mercury-containing combustion gas for a sufficient time to allow at least an effective amount of the mercury and mercury-containing compounds in the combustion gas to adsorb onto the mercury sorbent, and collecting and removing the mercury sorbent from the combustion gas stream. The mercury sorbent is prepared by treating a carbonaceous substrate with an effective amount of a bromine-containing gas, especially one containing elemental bromine or hydrogen bromide, for a time sufficient to increase the ability of the carbonaceous substrate to adsorb mercury and mercury-containing compounds. The points of injecting and collecting and removing the mercury sorbent may be varied, depending upon the exact configuration of the exhaust gas system.
Owner:SORBENT TECH +1
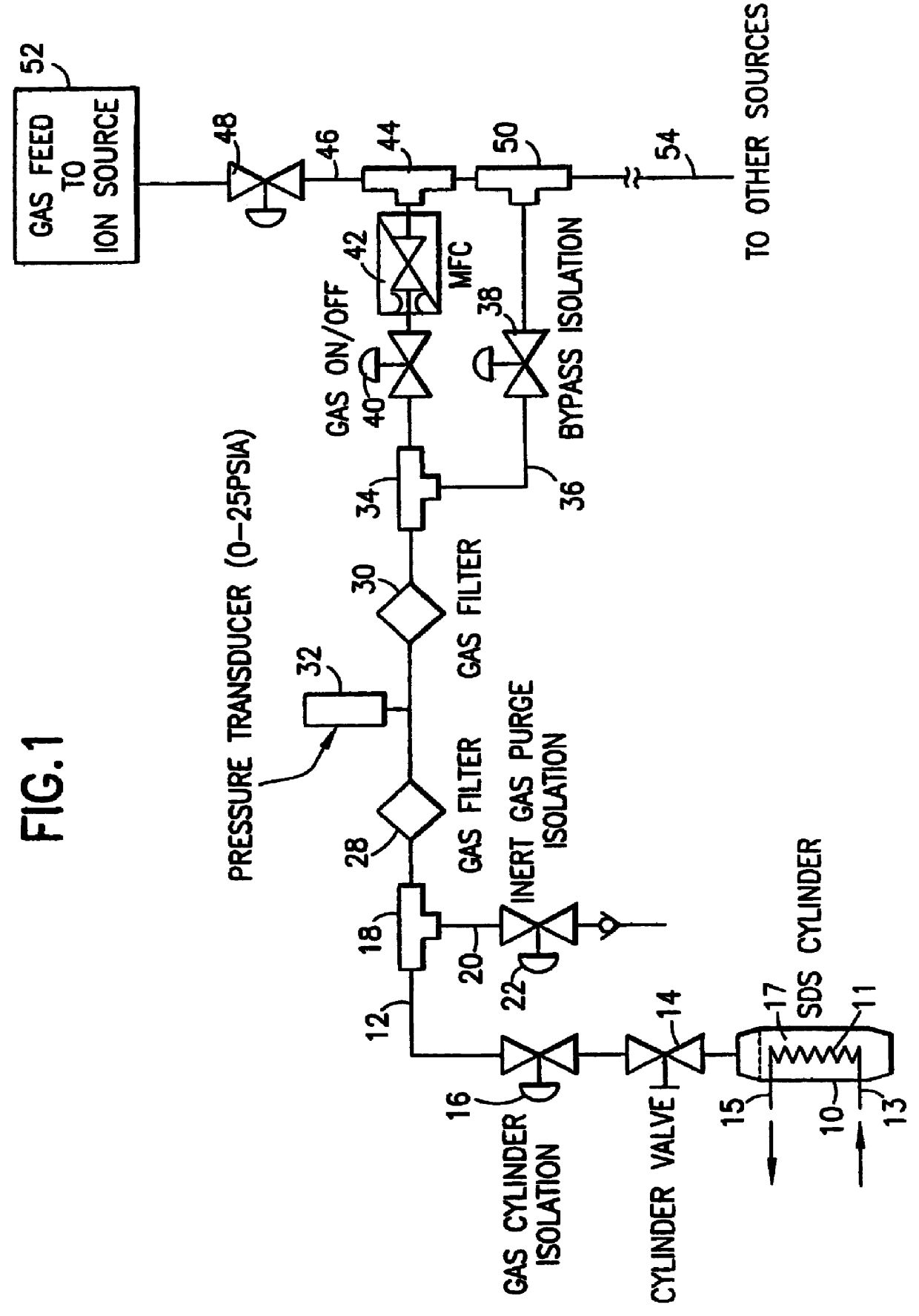
Fluid storage and dispensing system
InactiveUS6089027ACostPerformanceContainer filling methodsVacuum evaporation coatingSingle stageSorbent
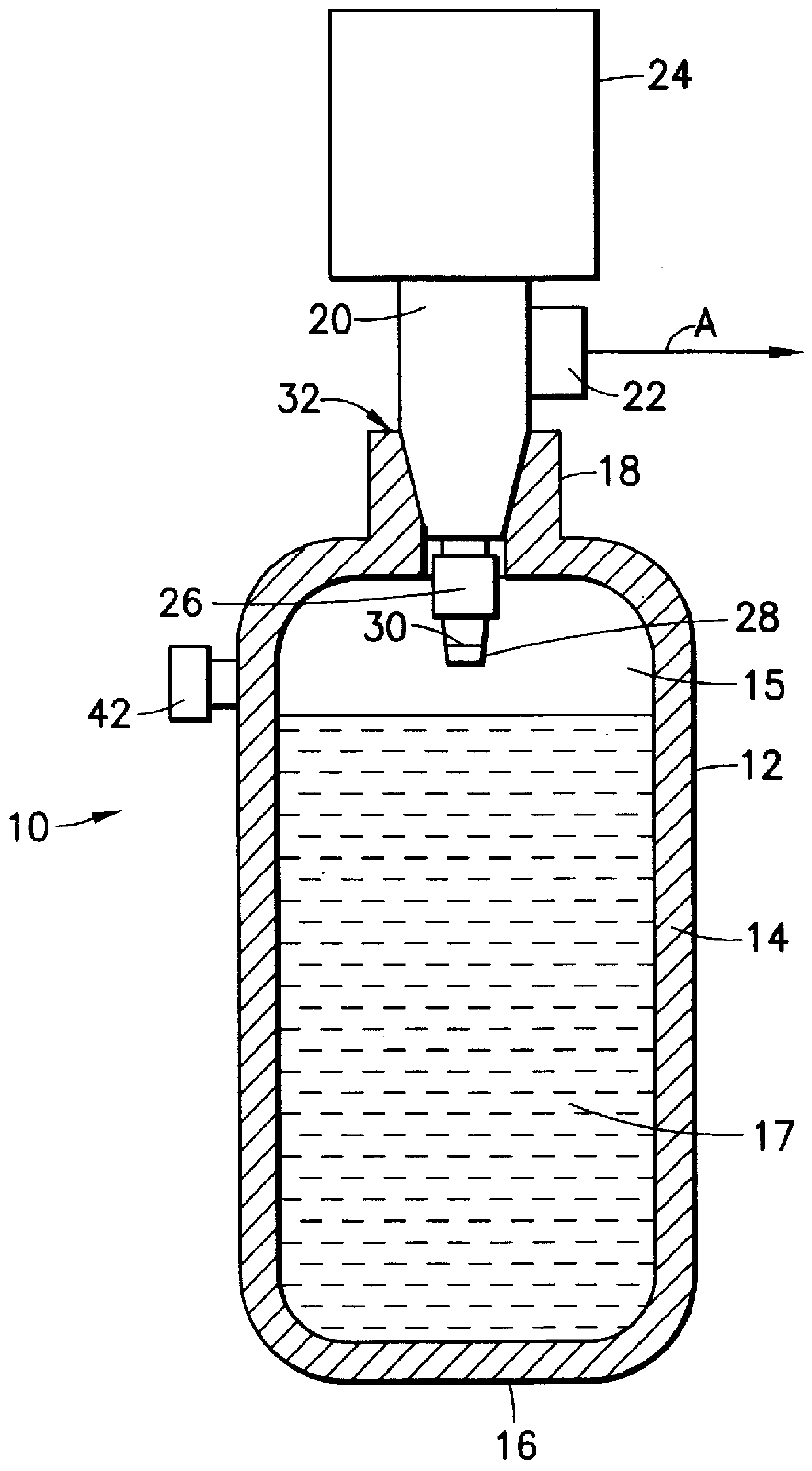
A fluid storage and dispensing system comprising a vessel for holding a fluid at a desired pressure. The vessel has a pressure regulator, e.g., a single-stage or multi-stage regulator, associated with a port of the vessel, and set at a predetermined pressure. A dispensing assembly, e.g., including a flow control means such as a valve, is arranged in gas / vapor flow communication with the regulator, whereby the opening of the valve effects dispensing of gas / vapor from the vessel. The fluid in the vessel may be constituted by a liquid that is confined in the vessel at a pressure in excess of its liquefaction pressure at prevailing temperature conditions, e.g., ambient (room) temperature. In another aspect, the vessel contains a solid-phase sorbent material having sorbable gas adsorbed thereon, at a pressure in excess of 50 psig. The vessel may have a >1 inch NGT threaded neck opening, to accommodate the installation of an interior regulator.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
High frequency pressure swing adsorption
InactiveUS6176897B1High purityRecoverable expansion workNitrogen purification/separationGas treatmentSorbentEngineering
Pressure swing adsorption separation of a feed gas mixture, to obtain a purified product gas of the less strongly adsorbed fraction of the feed gas mixture, is performed in a plurality of preferably an even number of adsorbent beds, with each adsorbent bed communicating at its product end directly to a variable volume expansion chamber, and at its feed end by directional valves to a feed compressor and an exhaust vacuum pump. For high frequency operation of the pressure swing adsorption cycle, a high surface area layered support is used for the adsorbent. The compressor and vacuum pump pistons may be integrated with the cycle, reciprocating at twice the cycle frequency. Alternative configurations of the layered adsorbent beds are disclosed.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Thief process for the removal of mercury from flue gas
InactiveUS6521021B1Low costQuench oxidationGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentParticulatesCombustion chamber
A system and method for removing mercury from the flue gas of a coal-fired power plant is described. Mercury removal is by adsorption onto a thermally activated sorbent produced in-situ at the power plant. To obtain the thermally activated sorbent, a lance (thief) is inserted into a location within the combustion zone of the combustion chamber and extracts a mixture of semi-combusted coal and gas. The semi-combusted coal has adsorptive properties suitable for the removal of elemental and oxidized mercury. The mixture of semi-combusted coal and gas is separated into a stream of gas and semi-combusted coal that has been converted to a stream of thermally activated sorbent. The separated stream of gas is recycled to the combustion chamber. The thermally activated sorbent is injected into the duct work of the power plant at a location downstream from the exit port of the combustion chamber. Mercury within the flue gas contacts and adsorbs onto the thermally activated sorbent. The sorbent-mercury combination is removed from the plant by a particulate collection system.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Carbon Dioxide Capture and Mitigation of Carbon Dioxide Emissions
InactiveUS20080031801A1Pressure dropCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesLiquefactionSorbentSolid surface
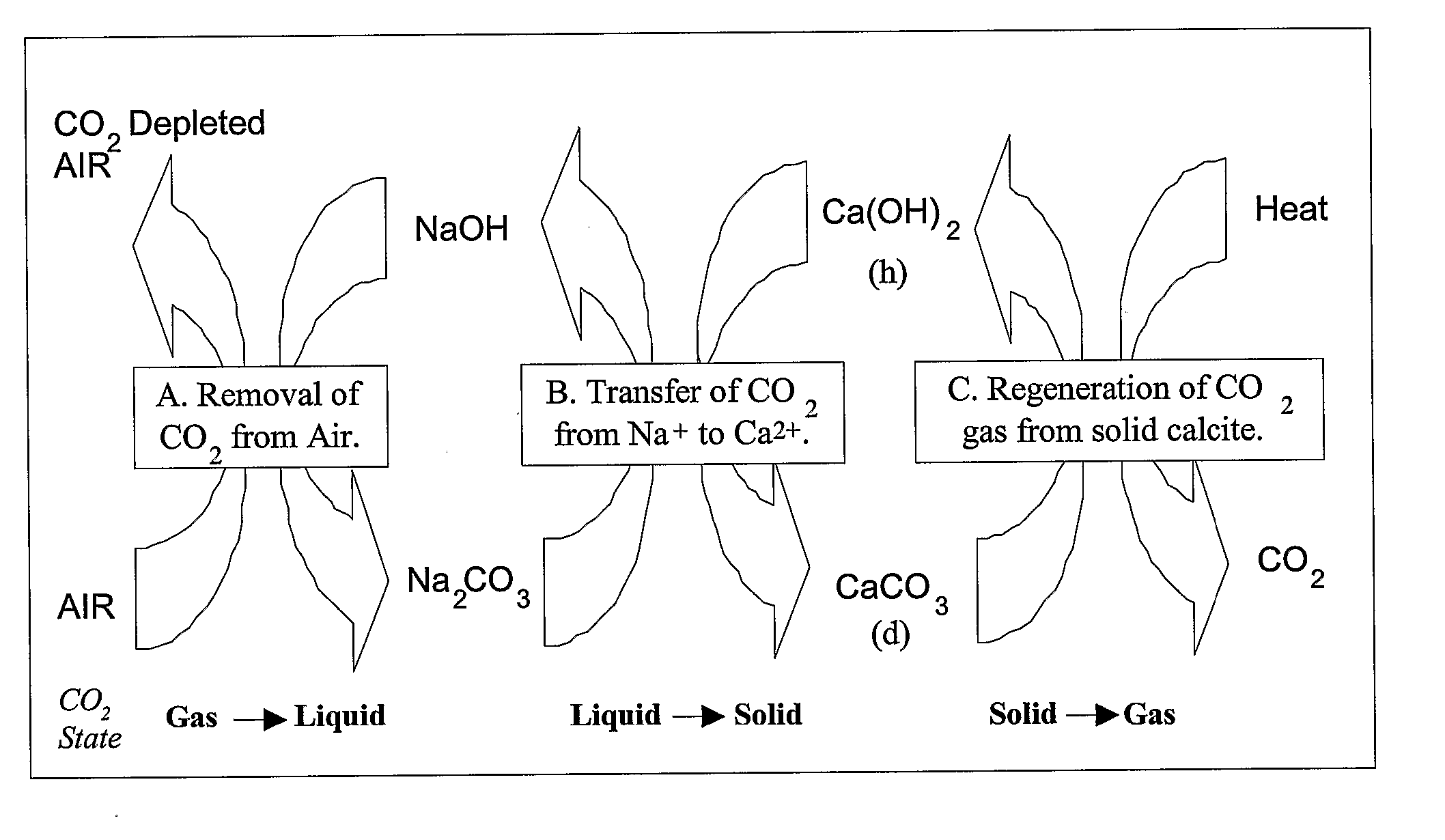
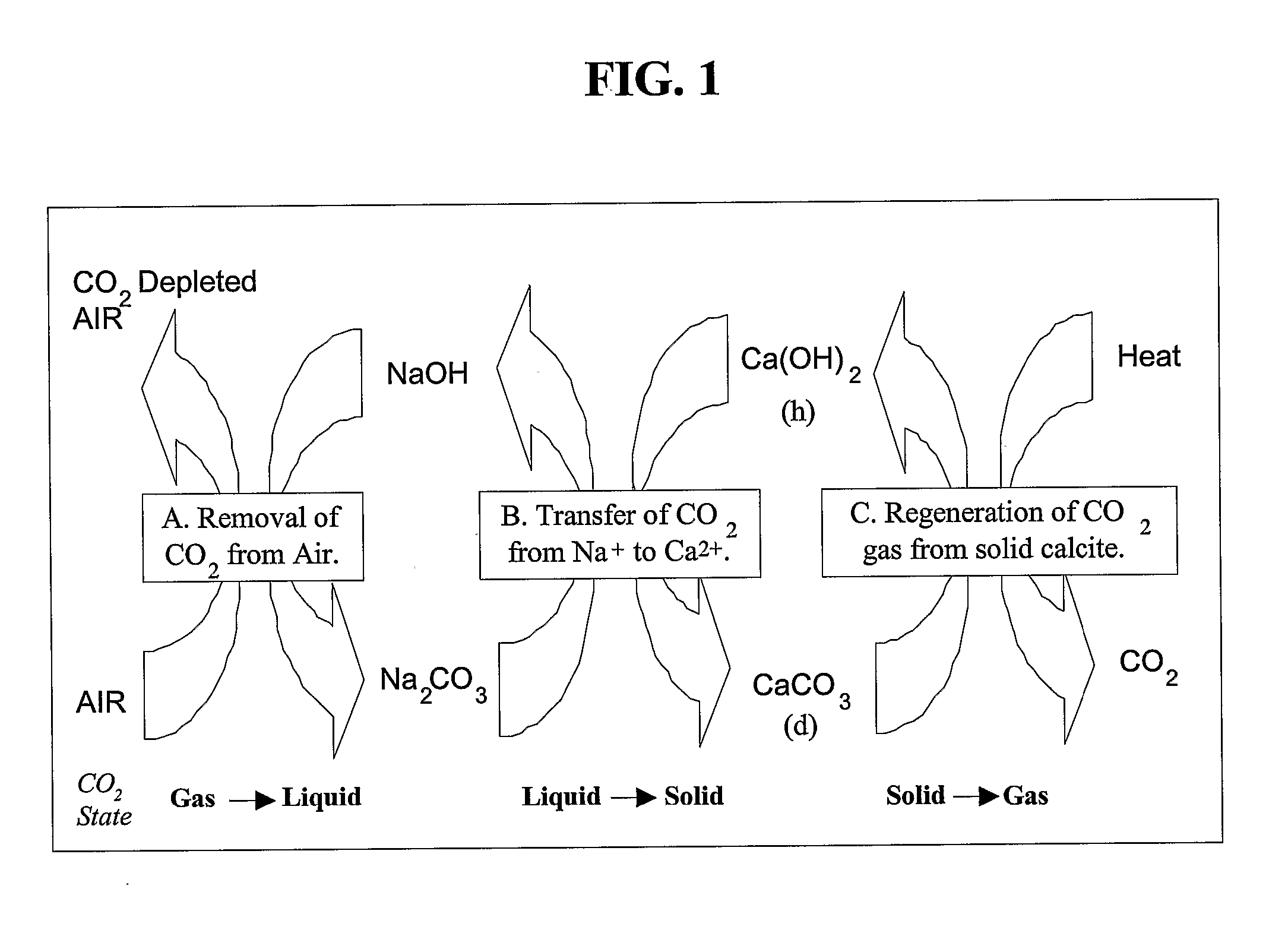
The present invention describes methods and systems for extracting, capturing, reducing, storing, sequestering, or disposing of carbon dioxide (CO2), particularly from the air. The CO2 extraction methods and systems involve the use of chemical processes, mineral sequestration, and solid and liquid sorbents. Methods are also described for extracting and / or capturing CO2 via condensation on solid surfaces at low temperature.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
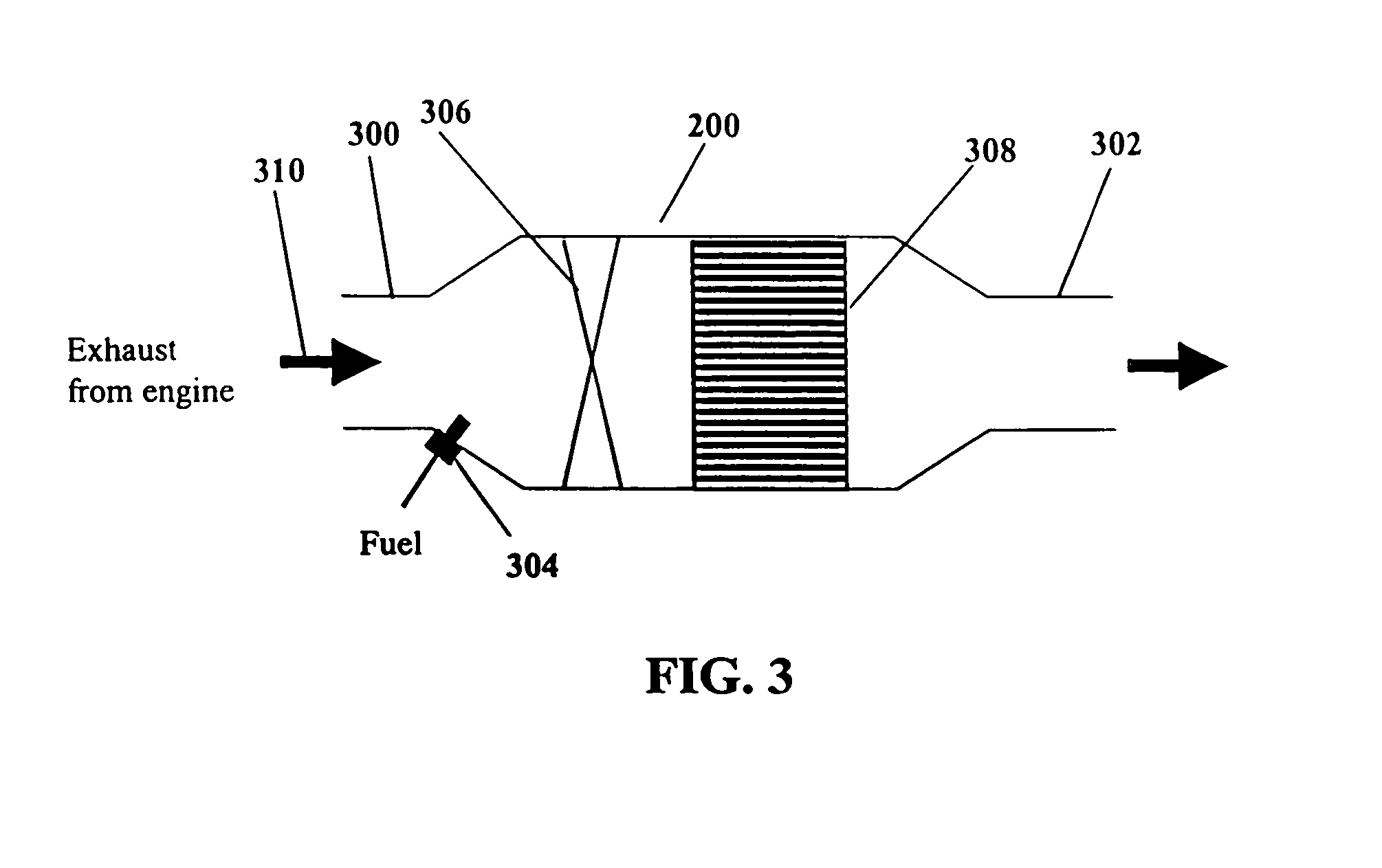
Fuel-cell engine stream conditioning system
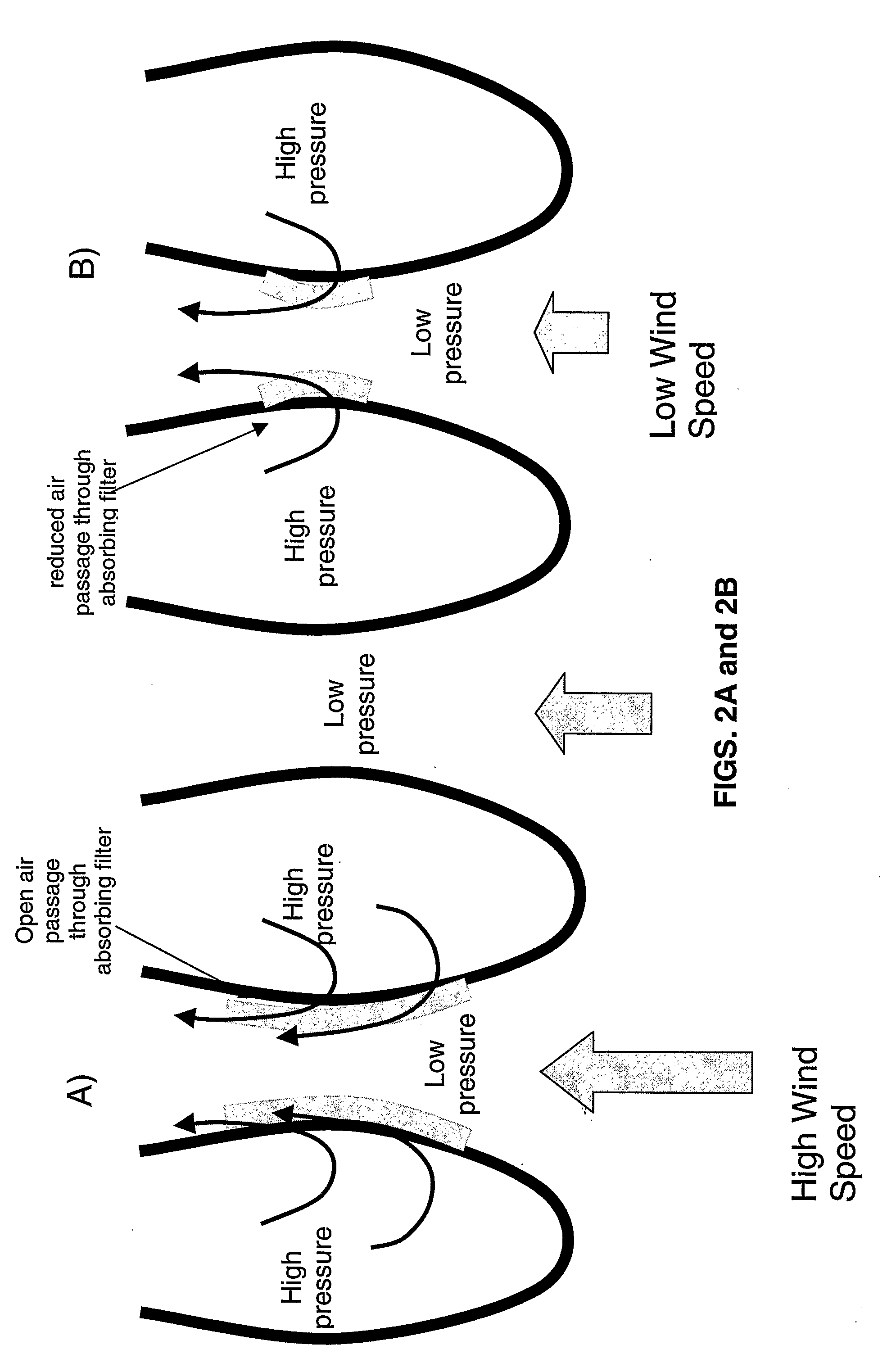
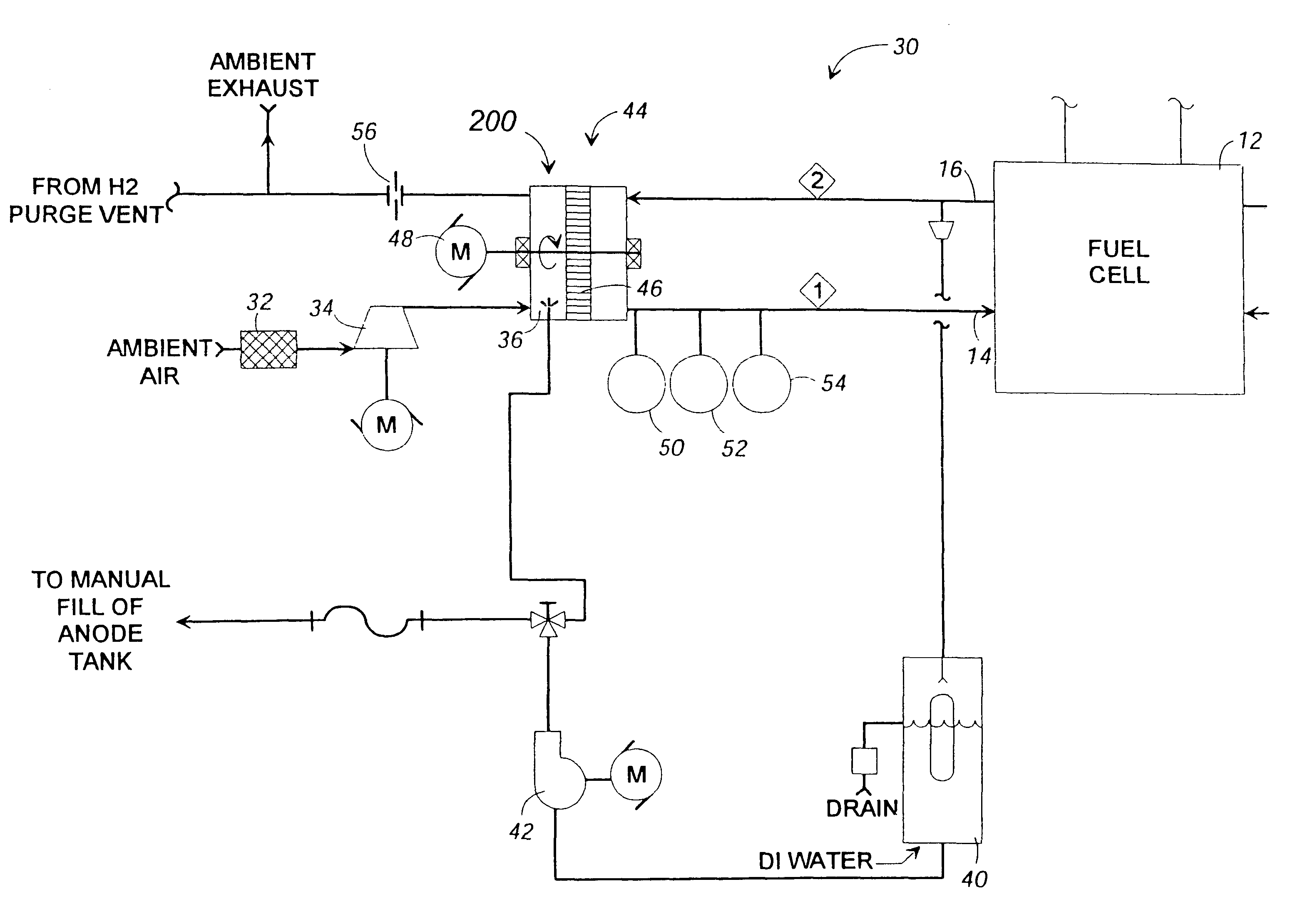
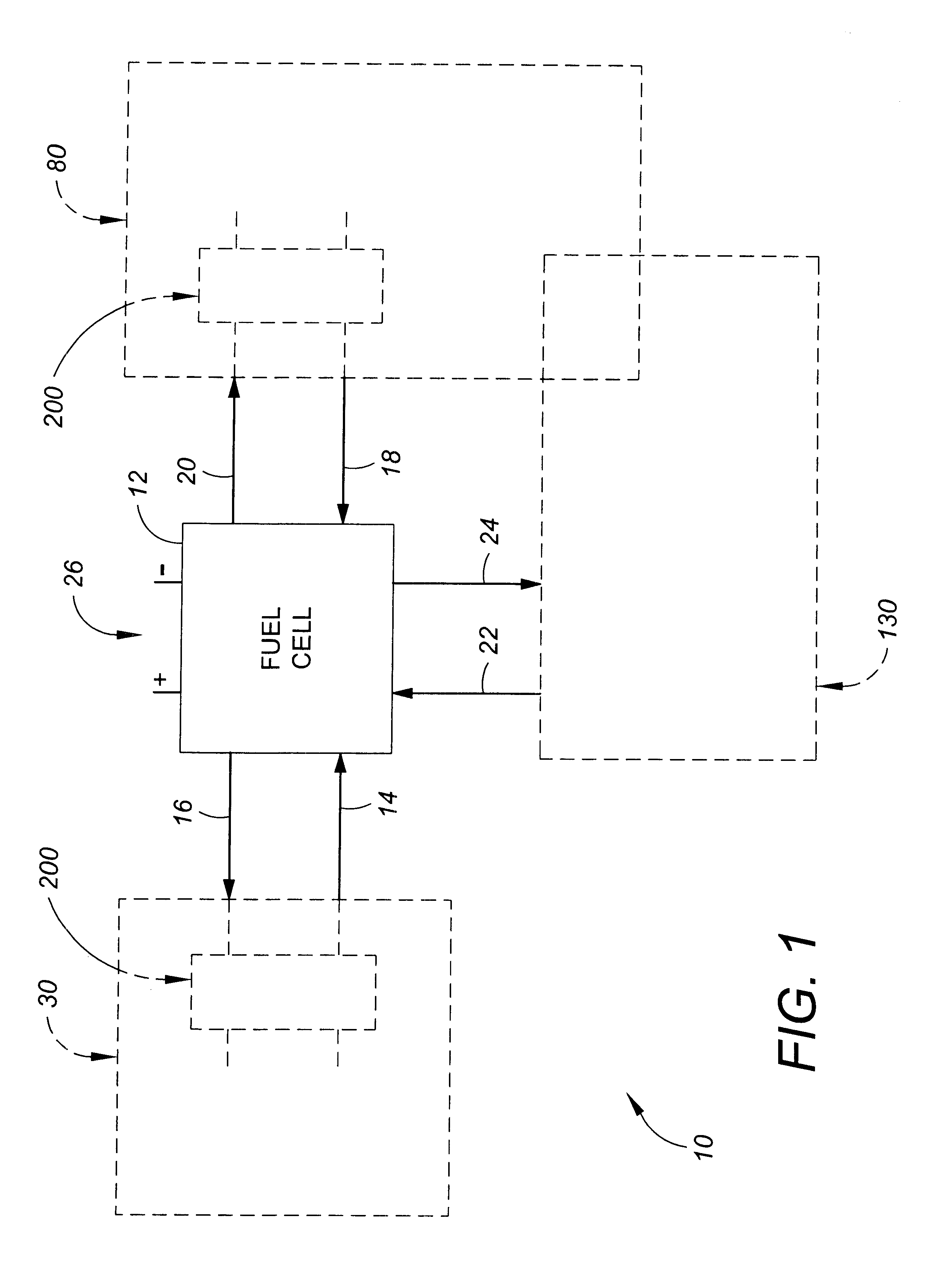
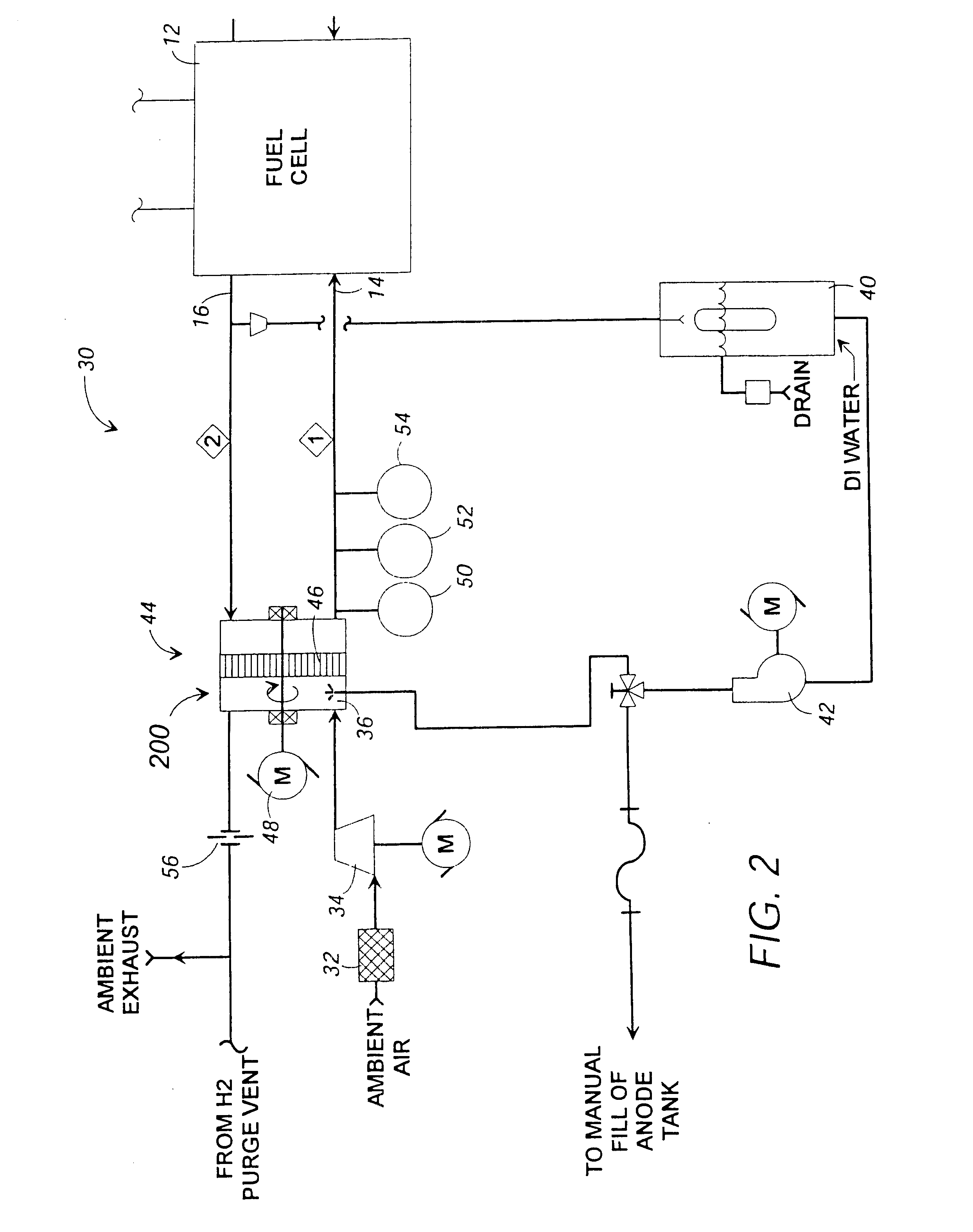
A stream conditioning system for a fuel cell gas management system or fuel cell engine. The stream conditioning system manages species potential in at least one fuel cell reactant stream. A species transfer device is located in the path of at least one reactant stream of a fuel cell's inlet or outlet, which transfer device conditions that stream to improve the efficiency of the fuel cell. The species transfer device incorporates an exchange media and a sorbent. The fuel cell gas management system can include a cathode loop with the stream conditioning system transferring latent and sensible heat from an exhaust stream to the cathode inlet stream of the fuel cell; an anode humidity retention system for maintaining the total enthalpy of the anode stream exiting the fuel cell related to the total enthalpy of the anode inlet stream; and a cooling water management system having segregated deionized water and cooling water loops interconnected by means of a brazed plate heat exchanger.
Owner:EMPRISE TECH ASSOC
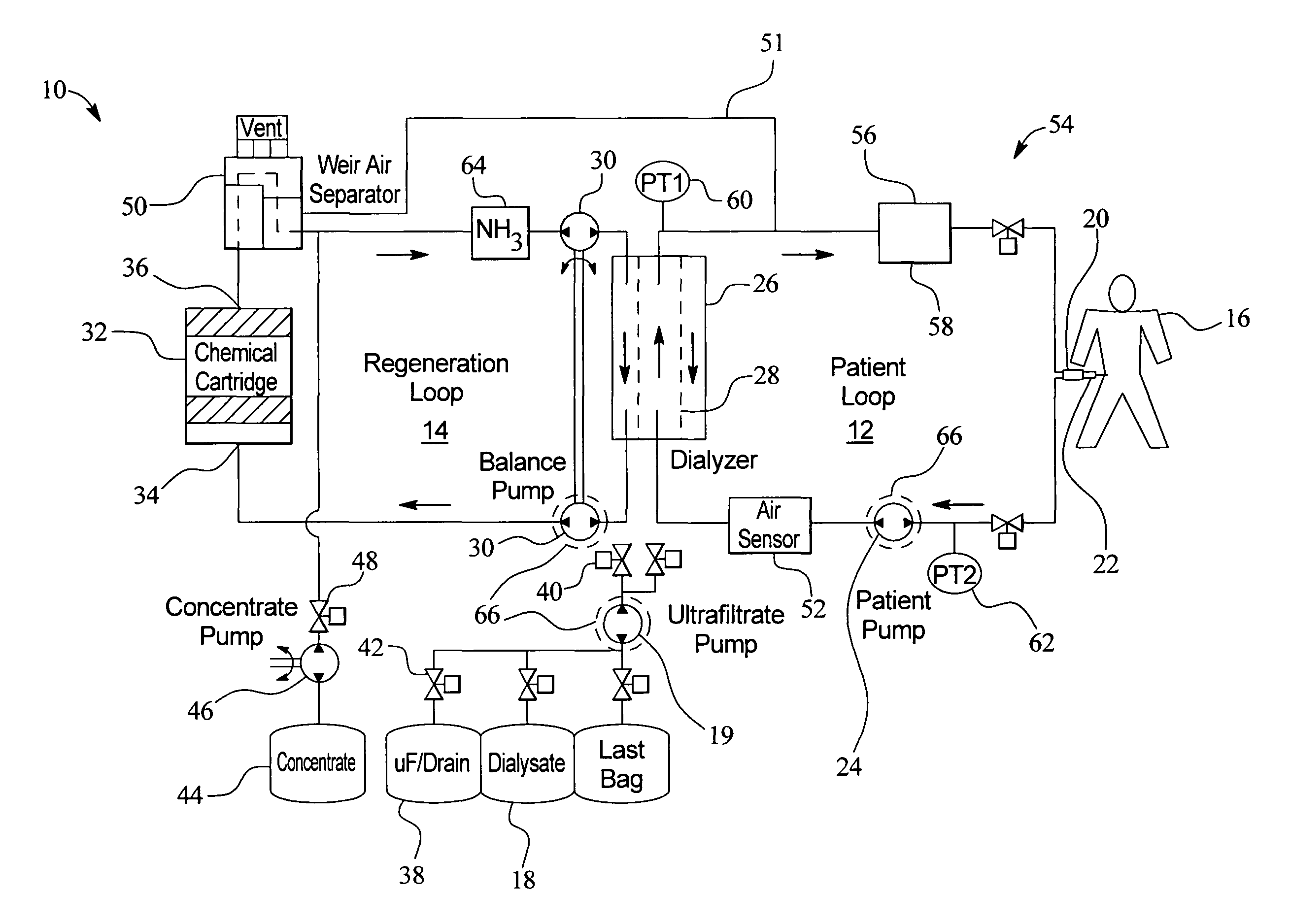
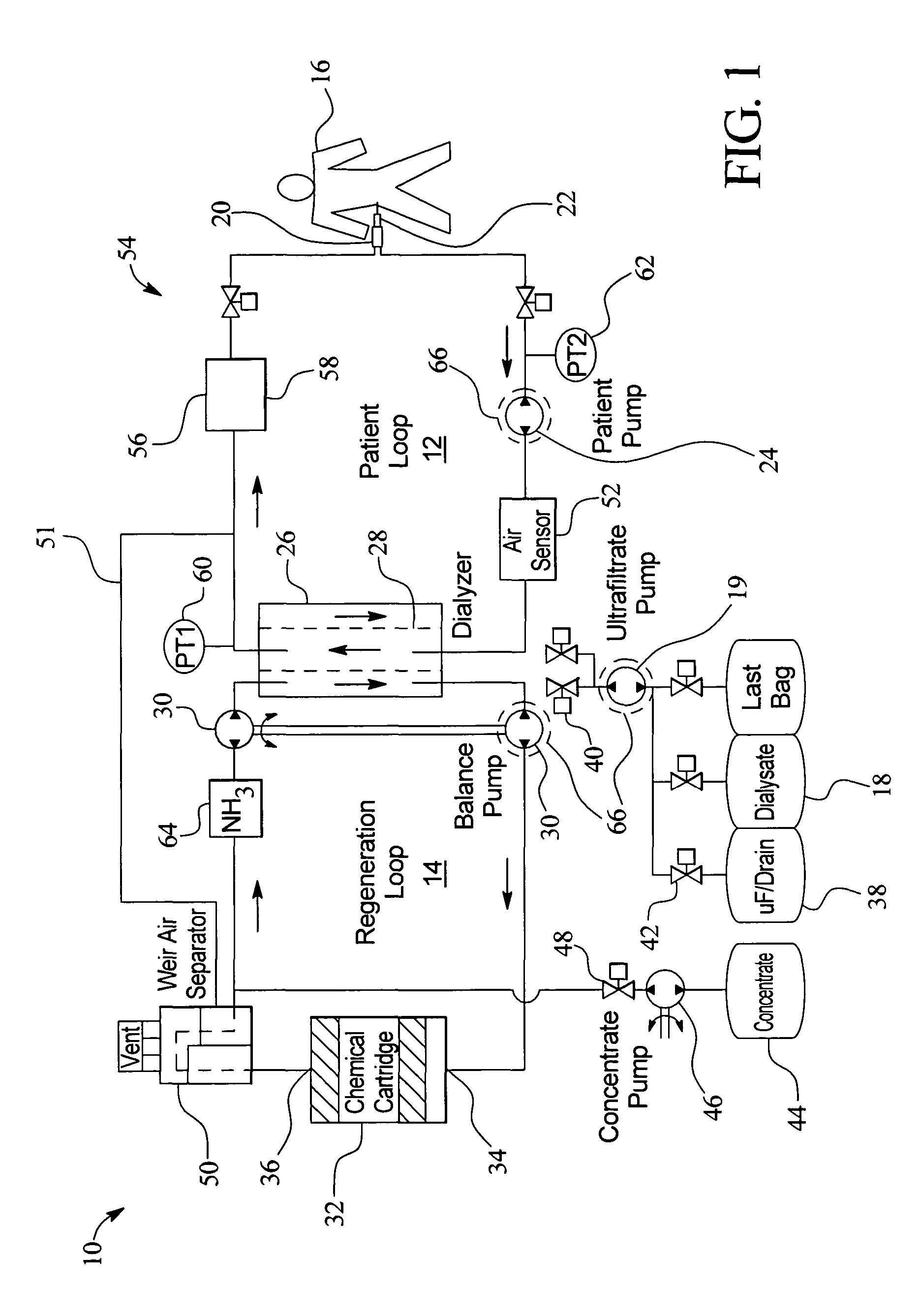
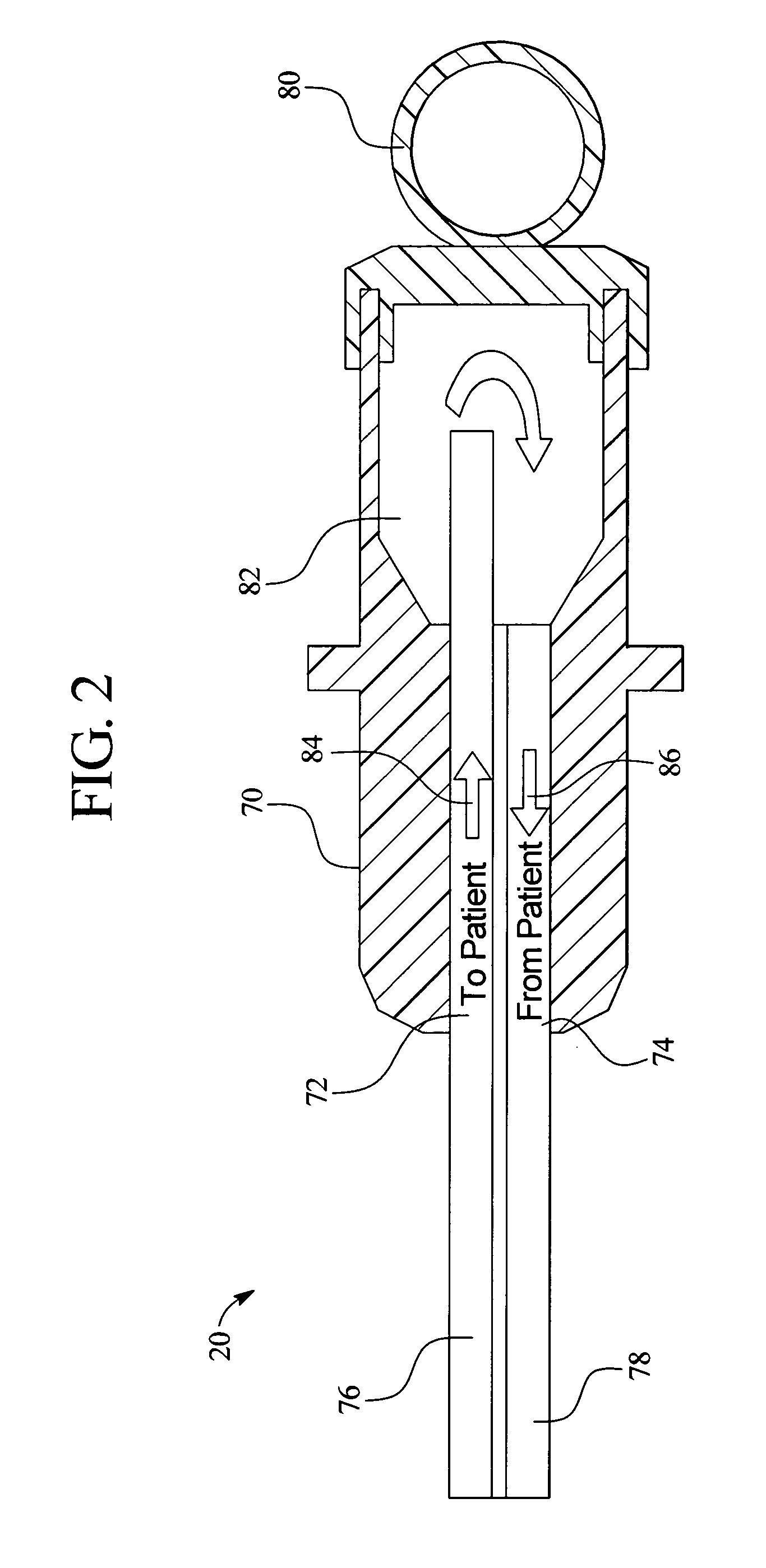
Systems and methods for performing peritoneal dialysis
ActiveUS7867214B2Strengthen the systemImprove methodSolvent extractionIon-exchanger regenerationMetabolic wasteSorbent
In a peritoneal dialysis embodiment of the present invention, spent dialysate from the patient's peritoneal cavity passes, along a patient loop, through a dialyzer having a membrane that separates waste components from the spent dialysate, wherein the patient loop returns fresh dialysate to the patient's peritoneal cavity. The waste components are carried away in a second regeneration loop to a regeneration unit or sorbent cartridge, which absorbs the waste components. The regeneration unit removes undesirable components in the dialysate that were removed from the patient loop by the dialyzer, for example, excess water (ultrafiltrate or UF), toxins and metabolic wastes. Desirable components can be added to the dialysate by the system, such as glucose and electrolytes. The additives assist in maintaining the proper osmotic gradients in the patient to perform dialysis and provide the necessary compounds to the patient.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
System and method for sequestration and separation of mercury in combustion exhaust gas aqueous scrubber systems
ActiveUS7722843B1Emission reductionMinimize re-emissionCombination devicesExhaust apparatusCombustionSorbent
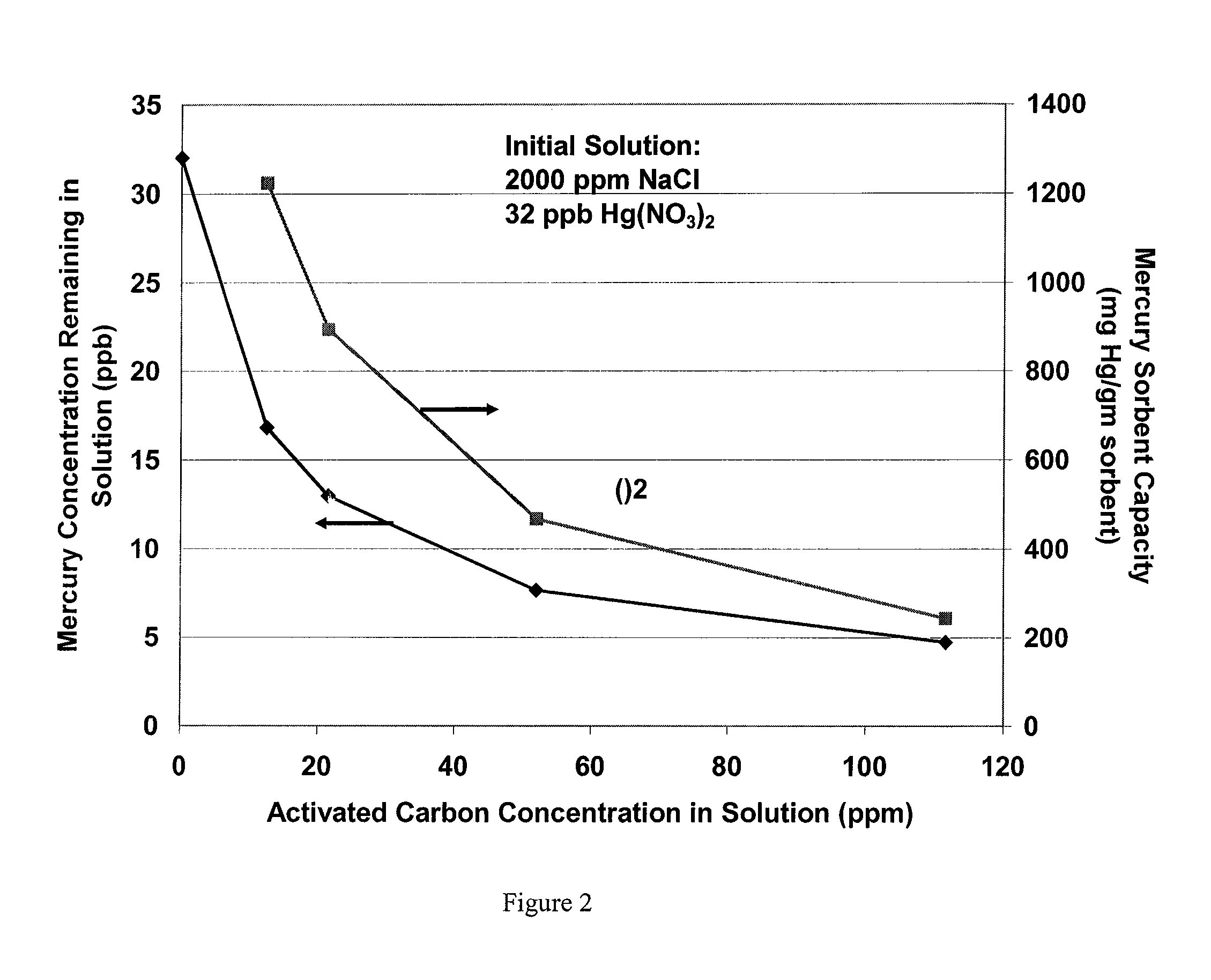
A process, system and sorbent for removal of mercury from a combustion exhaust gas stream in a combustion exhaust gas purification scheme that includes a combustion exhaust scrubber system that uses an aqueous liquid to remove acid gases from the combustion exhaust gas. A powdered mercury sorbent is used. The sorbent is introduced into the aqueous scrubber liquid in the scrubber system. After introduction of the mercury sorbent into the scrubber liquid, at least some of the mercury sorbent is separated from the scrubber liquid.
Owner:SRINIVASACHAR SRIVATS
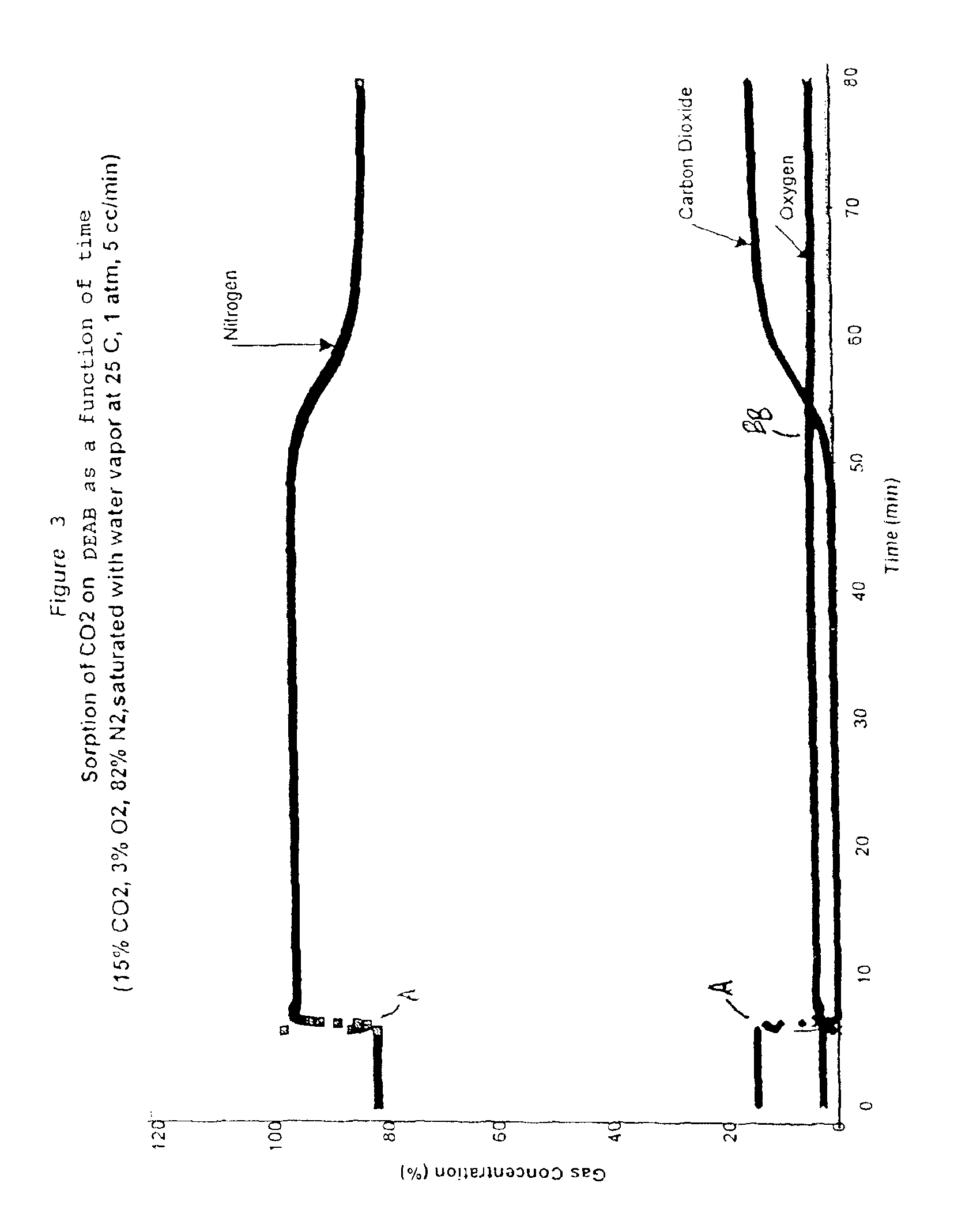
Solid sorbents for removal of carbon dioxide from gas streams at low temperatures
InactiveUS6908497B1Promote regenerationRegeneration process is inexpensiveGas treatmentOther chemical processesGas solidSorbent
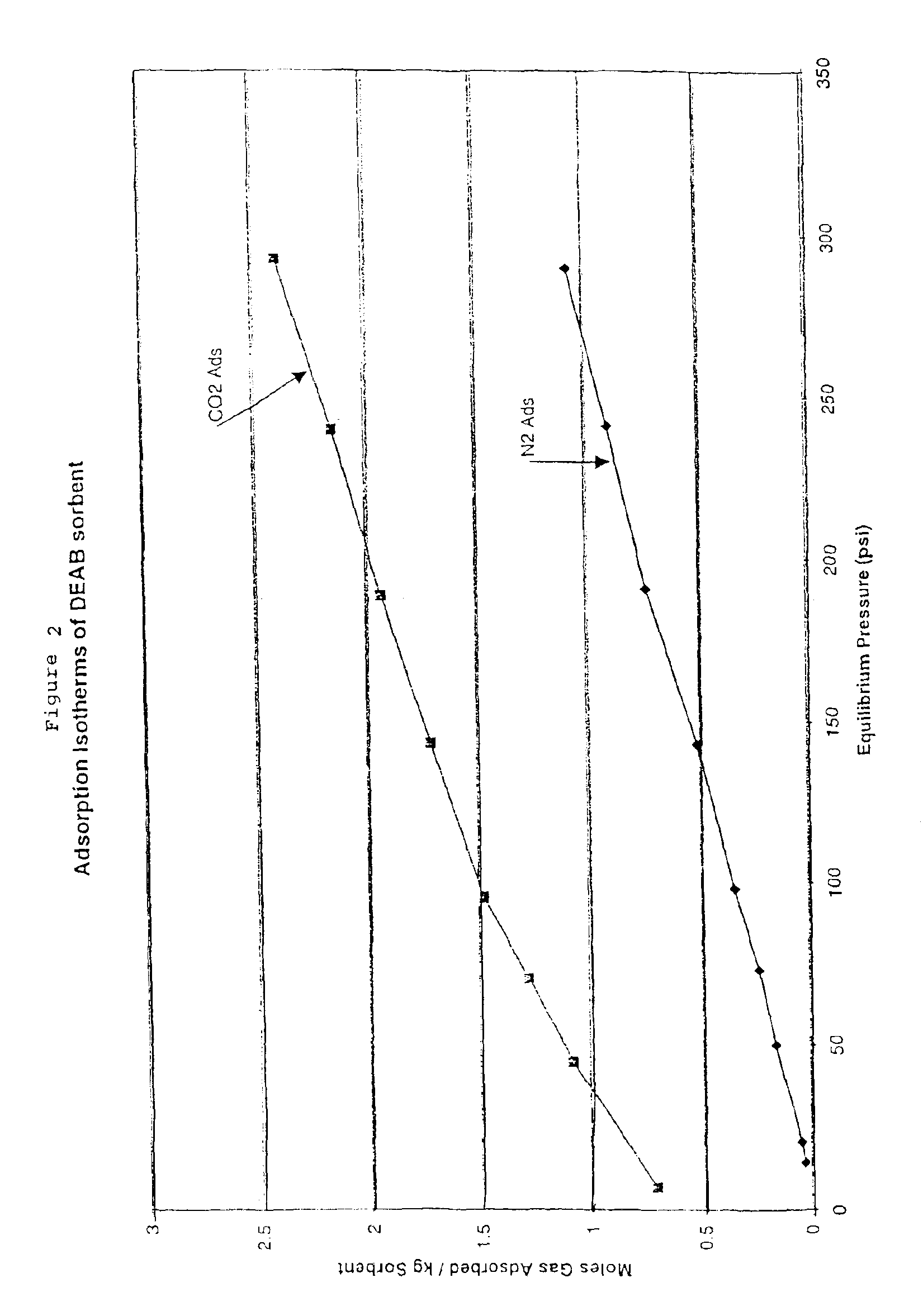
New low-cost CO2 sorbents are provided that can be used in large-scale gas-solid processes. A new method is provided for making these sorbents that involves treating substrates with an amine and / or an ether so that the amine and / or ether comprise at least 50 wt. percent of the sorbent. The sorbent acts by capturing compounds contained in gaseous fluids via chemisorption and / or physisorption between the unit layers of the substrate's lattice where the polar amine liquids and solids and / or polar ether liquids and solids are located. The method eliminates the need for high surface area supports and polymeric materials for the preparation of CO2 capture systems, and provides sorbents with absorption capabilities that are independent of the sorbents' surface areas. The sorbents can be regenerated by heating at temperatures in excess of 35° C.
Owner:ENERGY U S DEPARMENT OF
Modified adsorbent for dry scrubbing and use thereof
The present invention provides an amine functionalised adsorbent for use in dry scrubbing process. The adsorbent comprises amine functionalised mesoporous silica in which the amine groups are present at or near the surface of the silica, including within the pore walls and channels of the silica. The present invention further provides methods of preparing the adsorbent and of using the adsorbent for the adsorption of CO2 and / or other acid gases.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OTTAWA
Removal of CO2, N2, or H2S from gas mixtures by swing adsorption with low mesoporosity adsorbent contactors
The present invention relates to the separation of one or more of CO2, N2, and H2S gas components from a gas mixture containing at least a second gas using a swing adsorption process unit. The adsorbent contactors of the swing adsorption process unit are engineered structured adsorbent contactors having a plurality of flow channels wherein 20 volume percent or less of the open pore volume of the contactors is in the mesopore and macropore range.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Removal of heavy hydrocarbons from gas mixtures containing heavy hydrocarbons and methane
A process for the separation of one or more heavy hydrocarbon gases from a gas mixture containing heavy hydrocarbon gas components and methane. The process is conducted in swing adsorption apparatus containing adsorbent contactor having a plurality of flow channels and wherein 20 volume percent or less of the open pore volume of the contactors, is in the mesopore and macropore range.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Method for reducing emissions from evaporative emissions control systems
InactiveUS6540815B1Loss in working capacityEmission reductionGas treatmentNon-fuel substance addition to fuelHigh concentrationSorbent
Disclosed is a method for sharply reducing diurnal breathing loss emissions from automotive evaporative emissions control systems by providing multiple layers, or stages, of adsorbents. On the fuel source-side of an emissions control system canister, high working capacity carbons are preferred in a first canister (adsorb) region. In subsequent canister region(s) on the vent-side, the preferred adsorbent should exhibit a flat or flattened adsorption isotherm on a volumetric basis and relatively lower capacity for high concentration vapors as compared with the fuel source-side adsorbent. Multiple approaches are described for attaining the preferred properties for the vent-side canister region. One approach is to use a filler and / or voidages as a volumetric diluent for flattening an adsorption isotherm. Another approach is to employ an adsorbent with the desired adsorption isotherm properties and to process it into an appropriate shape or form without necessarily requiring any special provision for dilution. The improved combination of high working capacity carbons on the fuel source-side and preferred lower working capacity adsorbent on the vent-side provides substantially lower diurnal breathing emissions without a significant loss in working capacity or increase in flow restriction compared with known adsorbents used in canister configurations for automotive emissions control systems.
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
Encapsulation of organic electronic devices using adsorbent loaded adhesives
InactiveUS20030143423A1Effective and easy-to-applyImprove abilitiesDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDesiccantSorbent
Disclosed herein are organic electronic devices that are encapsulated at least in part by adsorbent-loaded transfer adhesives. The adsorbent material may be a dessicant and / or a getterer. The adsorbent-loaded transfer adhesive may form a gasket around the periphery of the device, or may cover the entire device and its periphery. An encapsulating lid covers the device.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Flue gas mercury control
ActiveUS8080088B1Enhance particulate collectionReducing fly ash resistivityGas treatmentIsotope separationActivated carbonHalogen
An adsorbent composition for removing mercury from a flue gas stream, and a method of its use. The composition is a powdered activated carbon having at least one of a halogen-containing component and an alkaline component dispersed thereon. A flow agent can be composited with the material to maintain flowability in situ.
Owner:SRINIVASACHAR SRIVATS
Engineered adsorbent structures for kinetic separation
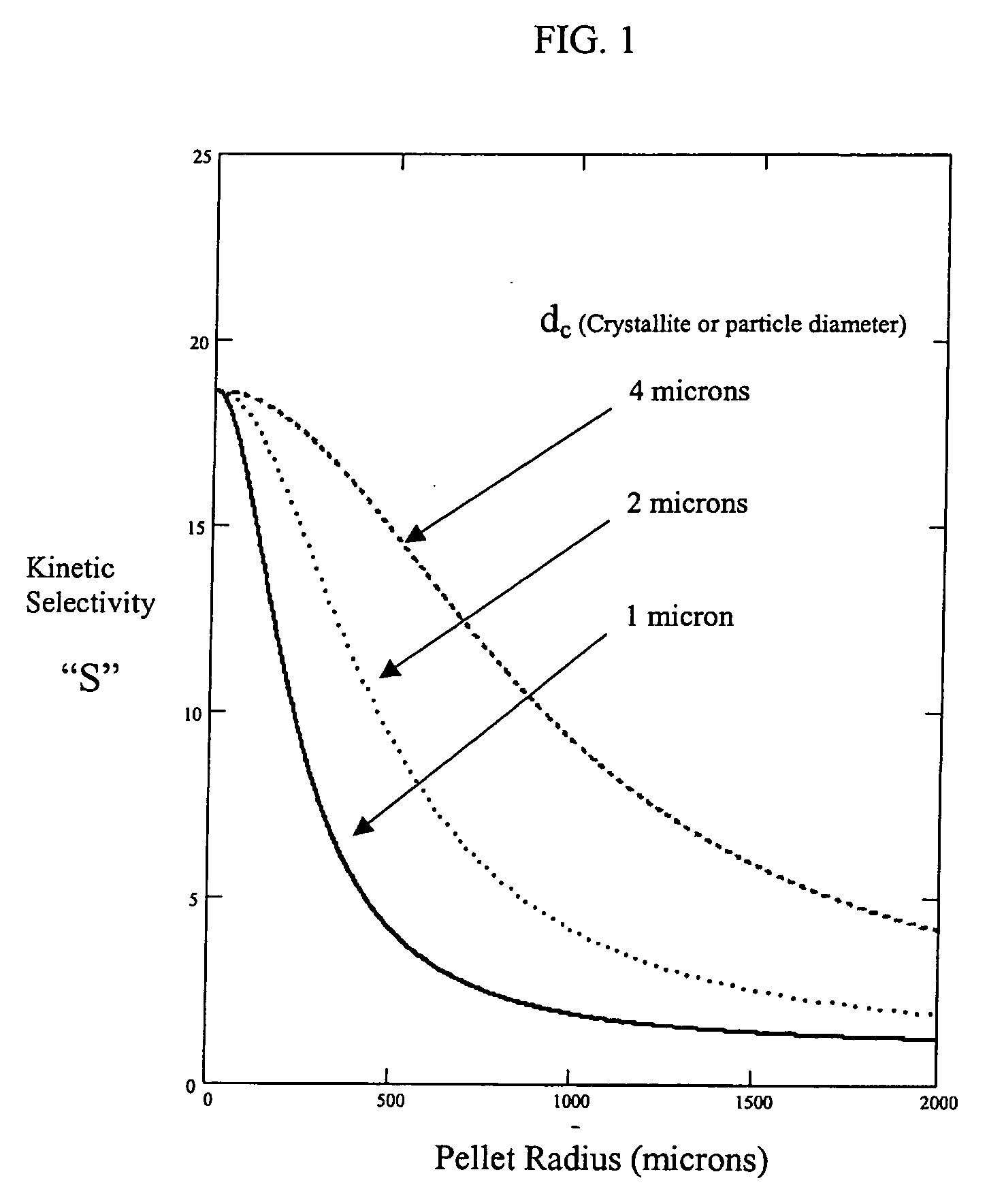
ActiveUS20060169142A1Easy to controlHigh selectivityGas treatmentMethane captureProduction rateSorbent
Improved adsorbent sheet based parallel passage adsorbent structures for enhancing the kinetic selectivity of certain kinetic-controlled adsorption processes, such as PSA, TSA and PPSA processes, and combinations thereof, are provided. The enhancements in kinetic selectivity made possible through the implementation of the present inventive improved adsorbent structures may unexpectedly enable significant intensification of selected kinetic adsorption processes relative to attainable performance with conventional adsorbent materials in beaded or extruded form. Such process intensification enabled by the present inventive adsorbent structures may provide for increased adsorption cycle frequencies, and increased gas flow velocities within the adsorbent beds, which may increase the productivity and / or recovery of a kinetic adsorption system incorporating the inventive adsorbent structures.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Particle-containing fibrous web
InactiveUS20060096911A1Lower overall pressure dropLow carbon shedding tendencyBreathing filtersDispersed particle separationPolymer scienceSorbent
A porous sheet article comprising a self-supporting nonwoven web of polymeric fibers and at least 80 weight percent sorbent particles enmeshed in the web, the fibers having sufficiently greater elasticity or sufficiently greater crystallization shrinkage than similar caliper polypropylene fibers and the sorbent particles being sufficiently evenly distributed in the web so that the web has an Adsorption Factor A of at least 1.6×104 / mm water. The articles have low pressure drop and can provide filter elements having long service life and an Adsorption Factor approaching and in some instances exceeding that of a packed carbon bed.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Sorbent composition, process for producing same and use in desulfurization
A particulate adsorbent composition comprising a mixture of zinc oxide, silica, alumina and substantially reduced valence cobalt for use in desulfurizing a cracked gasoline or diesel fuel feed stream in a desulfurization zone by: The desulfurization zone contacts the feed stream, then separates the resulting low sulfur content stream and the sulfurized adsorbent, regenerates and activates the separated adsorbent, and then returns to the desulfurization zone.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
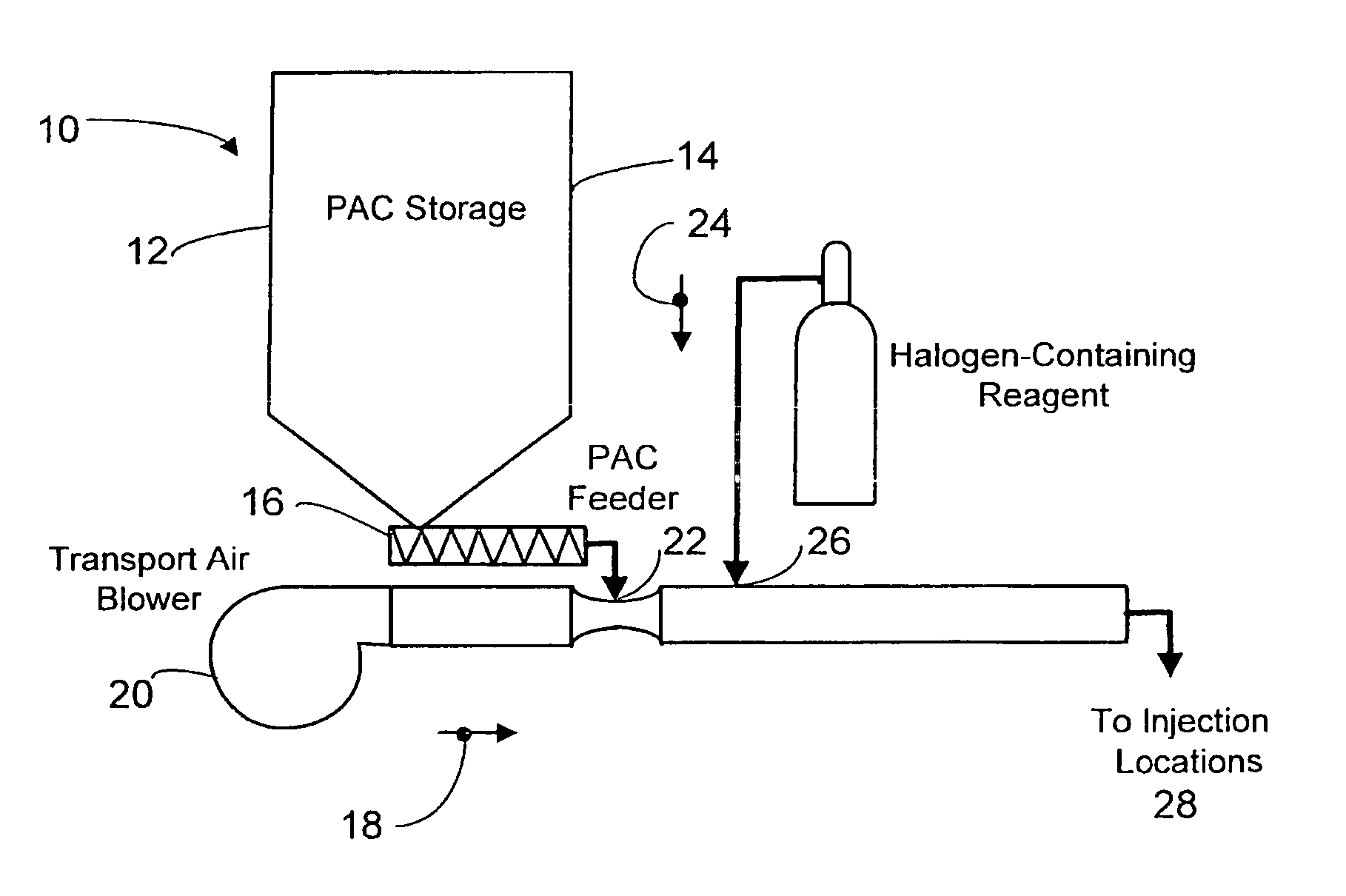
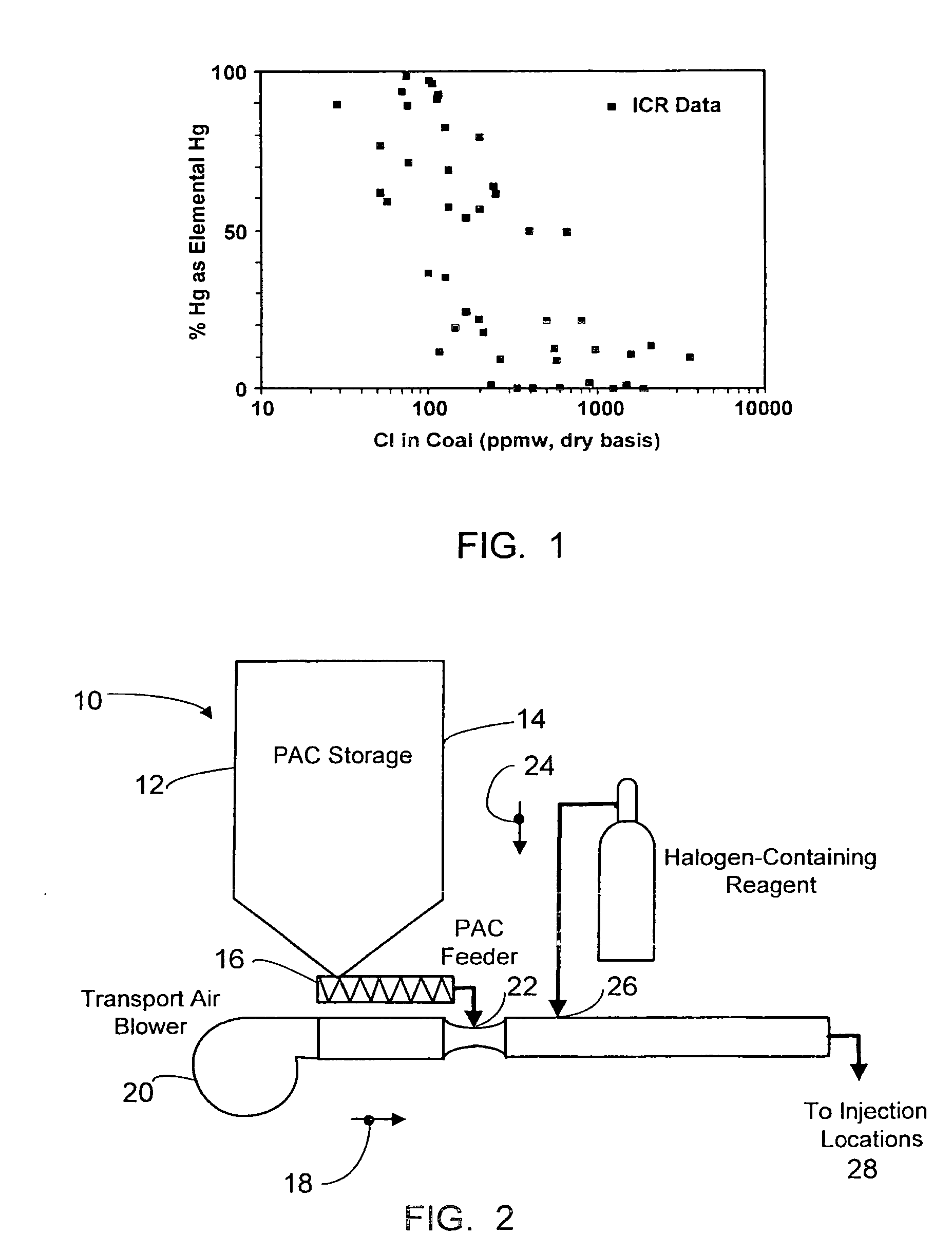
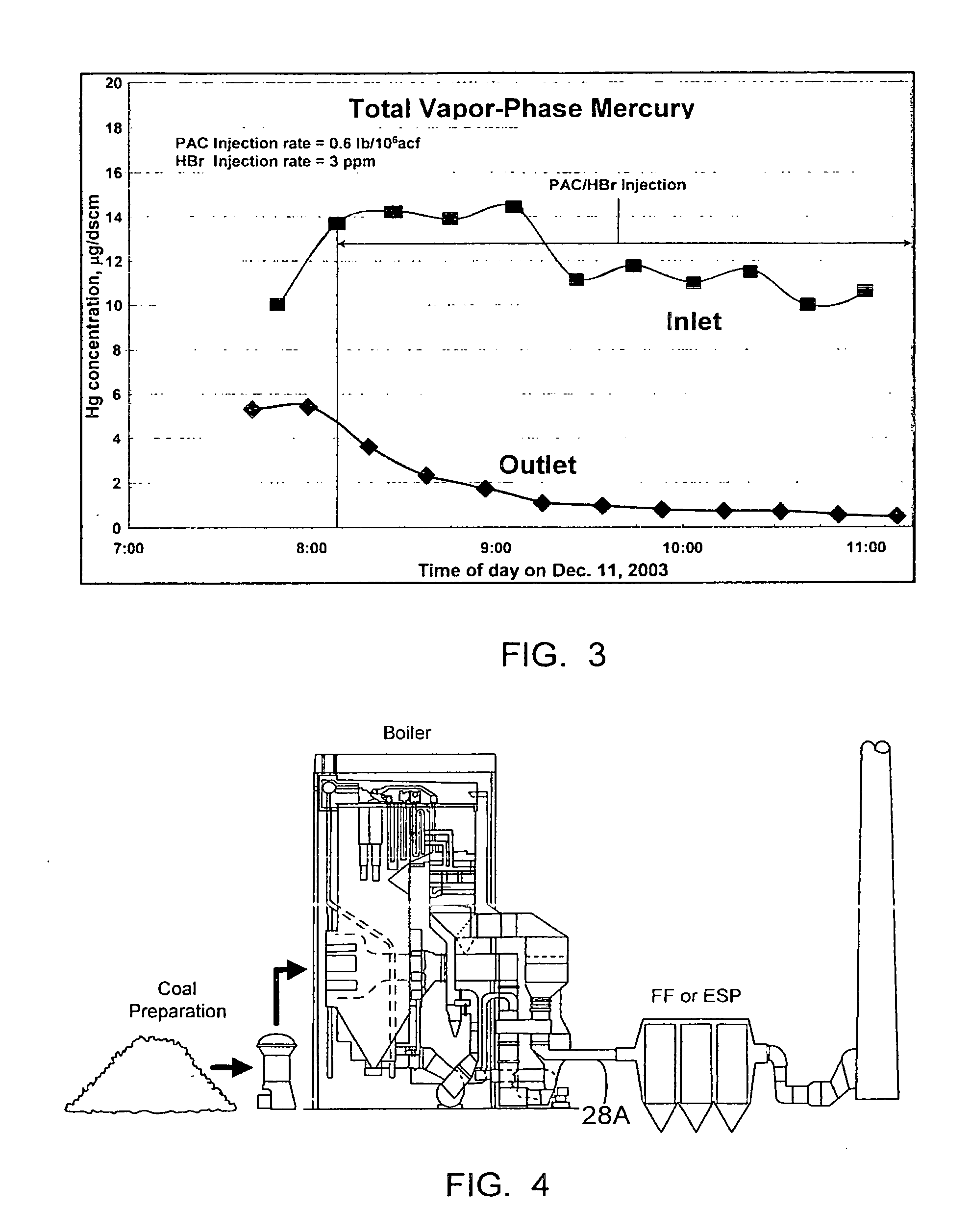
Dynamic halogenation of sorbents for the removal of mercury from flue gases
InactiveUS20070180990A1Efficient ConcentrationEasy to captureGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentHalogenSorbent
A halogen-containing gas is injected into a flowing transport air / sorbent stream at a point close to the point where the sorbent and transport air first mix to maximize the residence time available for the halogen-containing compound to be adsorbed onto the sorbent surface prior to the sorbent being injected into a flue gas containing mercury. This process maximizes the benefit and utilization of the halogen-containing reagent by placing it exactly where it is needed to facilitate elemental mercury removal—on the surface of the sorbent. The sorbent particles with their loading of adsorbed halogen-containing reagent enter the flue gas with a high reactivity for the removal of elemental mercury.
Owner:THE BABCOCK & WILCOX CO
Process for removing a target gas from a mixture of gases by swing adsorption
The present invention relates the separation of a target gas from a mixture of gases through the use of engineered structured adsorbent contactors in pressure swing adsorption and thermal swing adsorption processes. Preferably, the contactors contain engineered and substantially parallel flow channels wherein 20 volume percent or less of the open pore volume of the contactor, excluding the flow channels, is in the mesopore and macropore range.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Encapsulation of organic electronic devices using adsorbent loaded adhesives
InactiveUS6936131B2Improve abilitiesSimplify the packaging processSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDesiccantSorbent
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
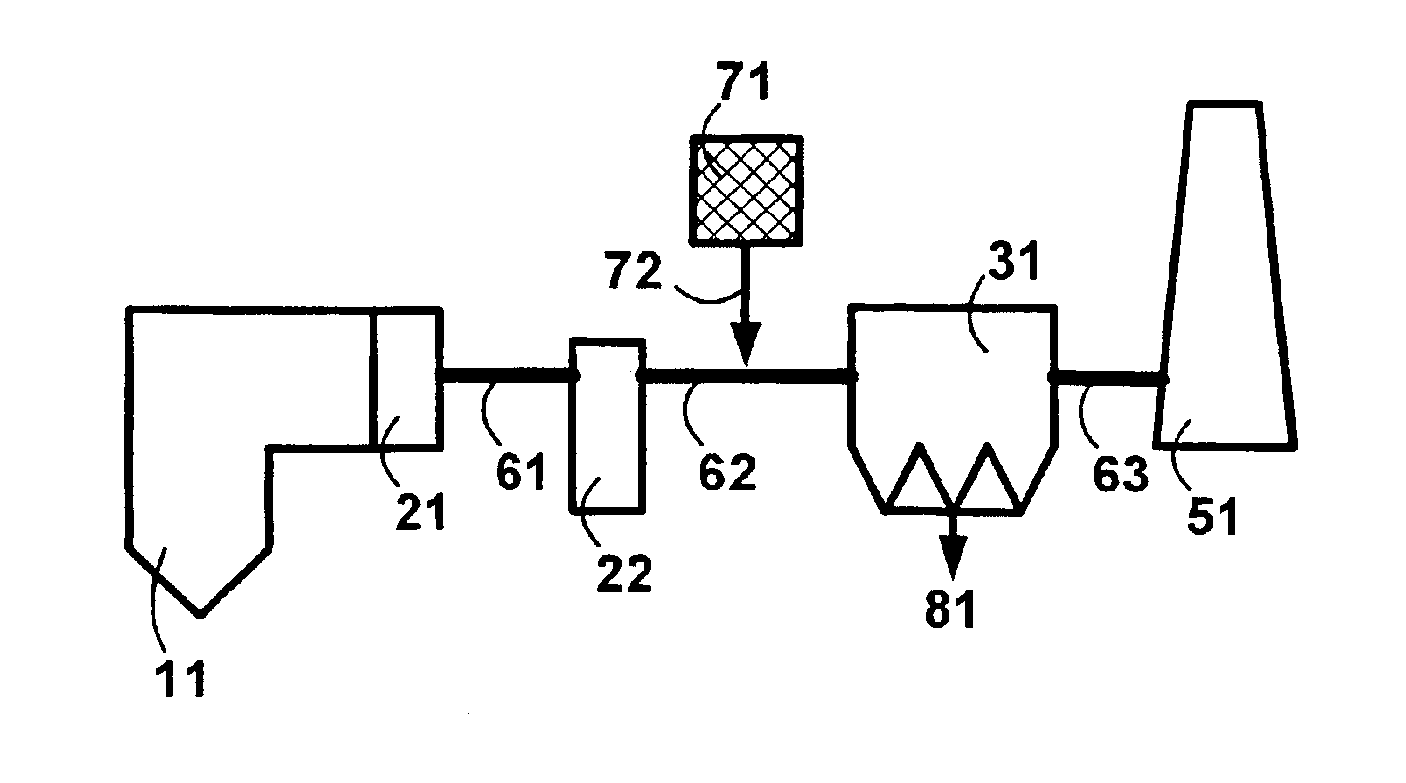
Control of mercury emissions from solid fuel combustion
InactiveUS6848374B2Remove pollutantsEasy to captureCombination devicesGas treatmentSorbentSolid fuel
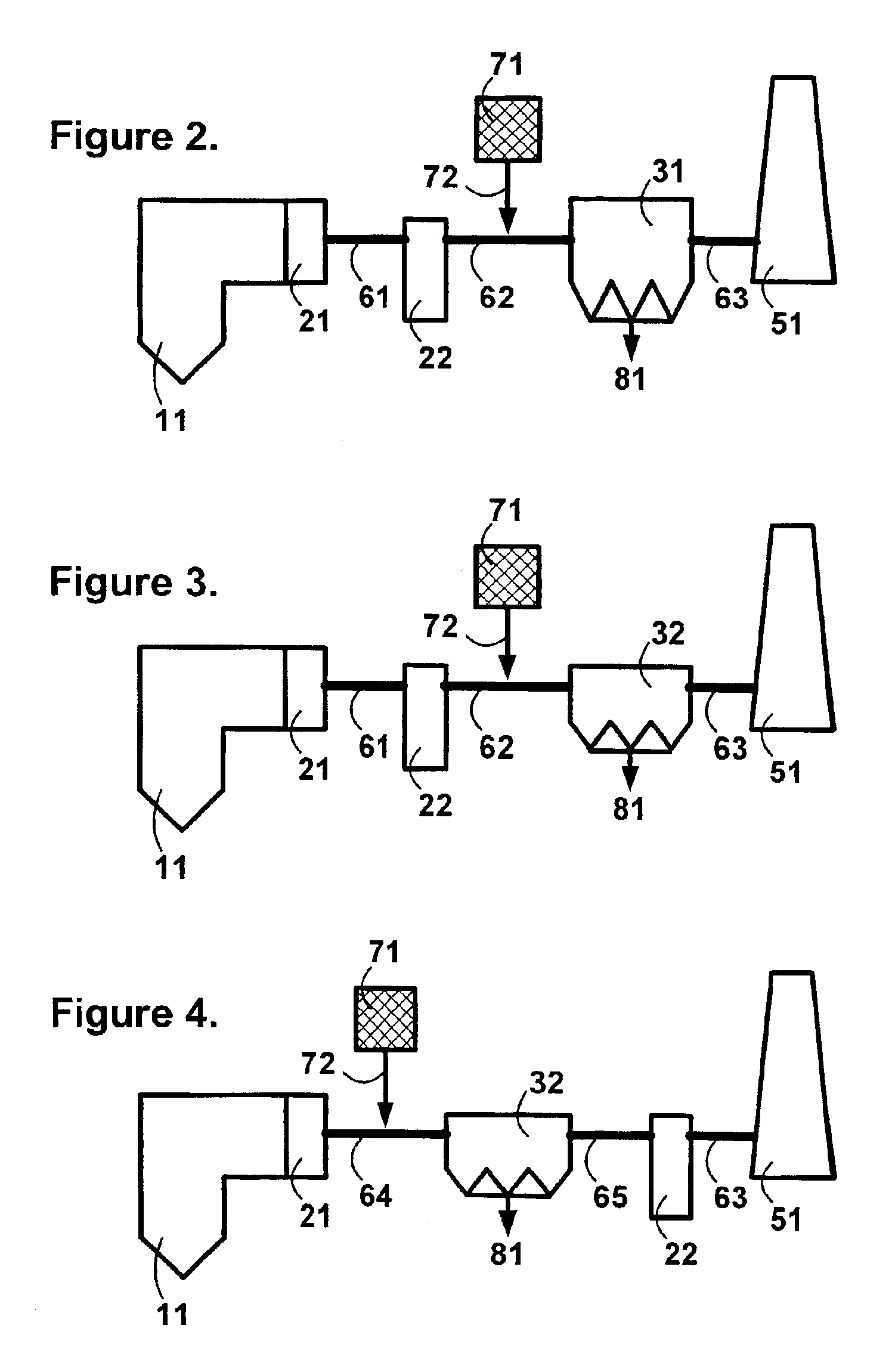
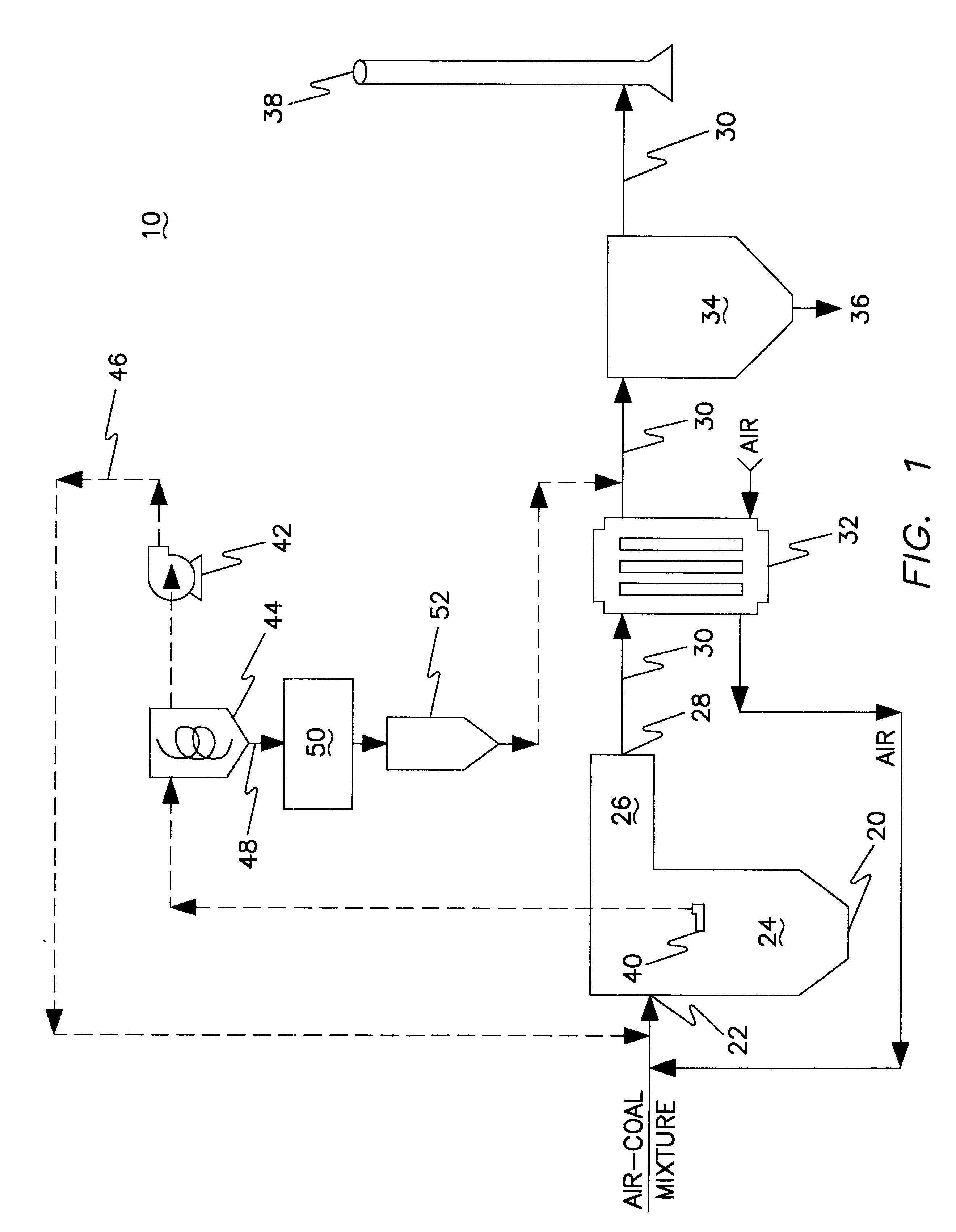
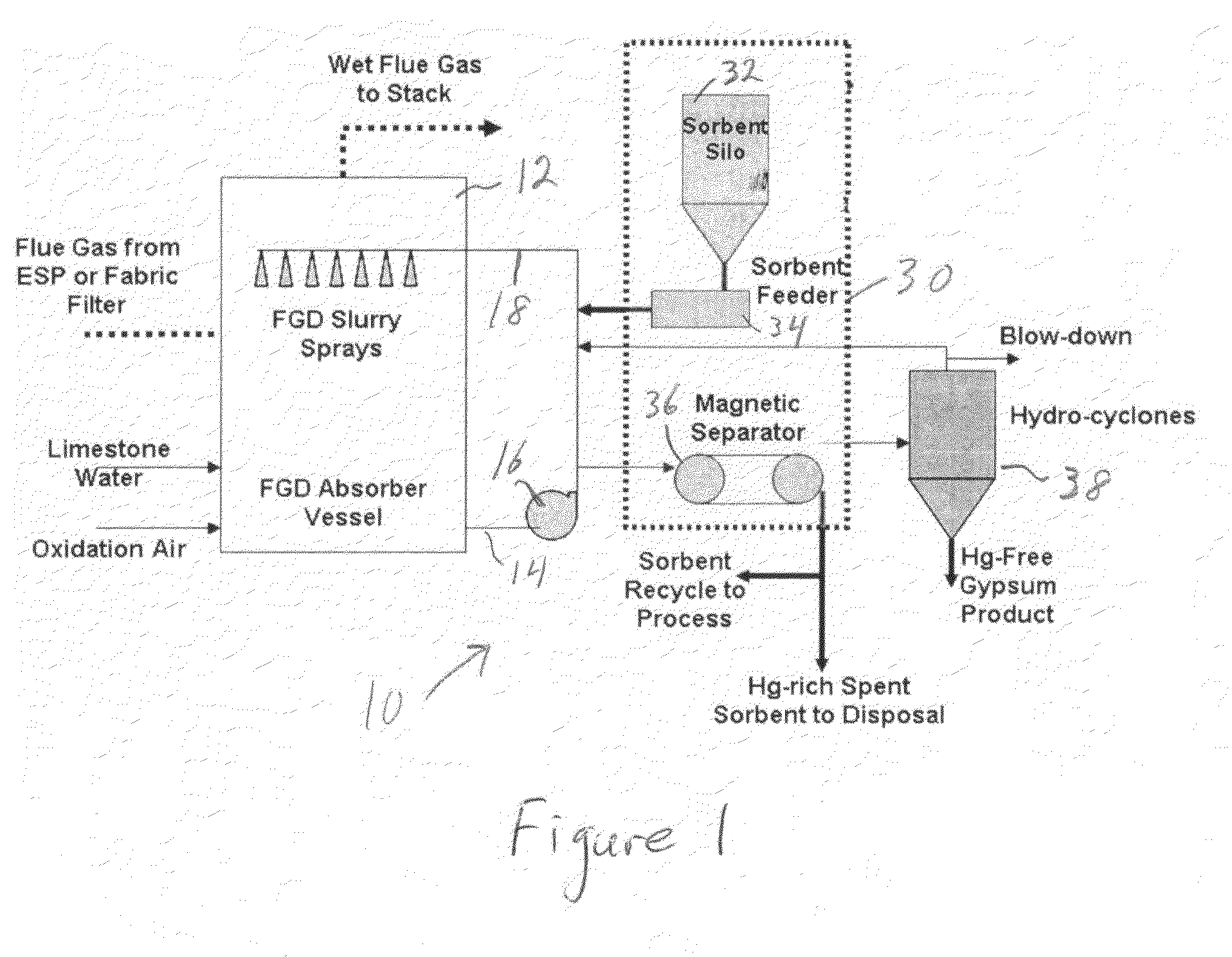
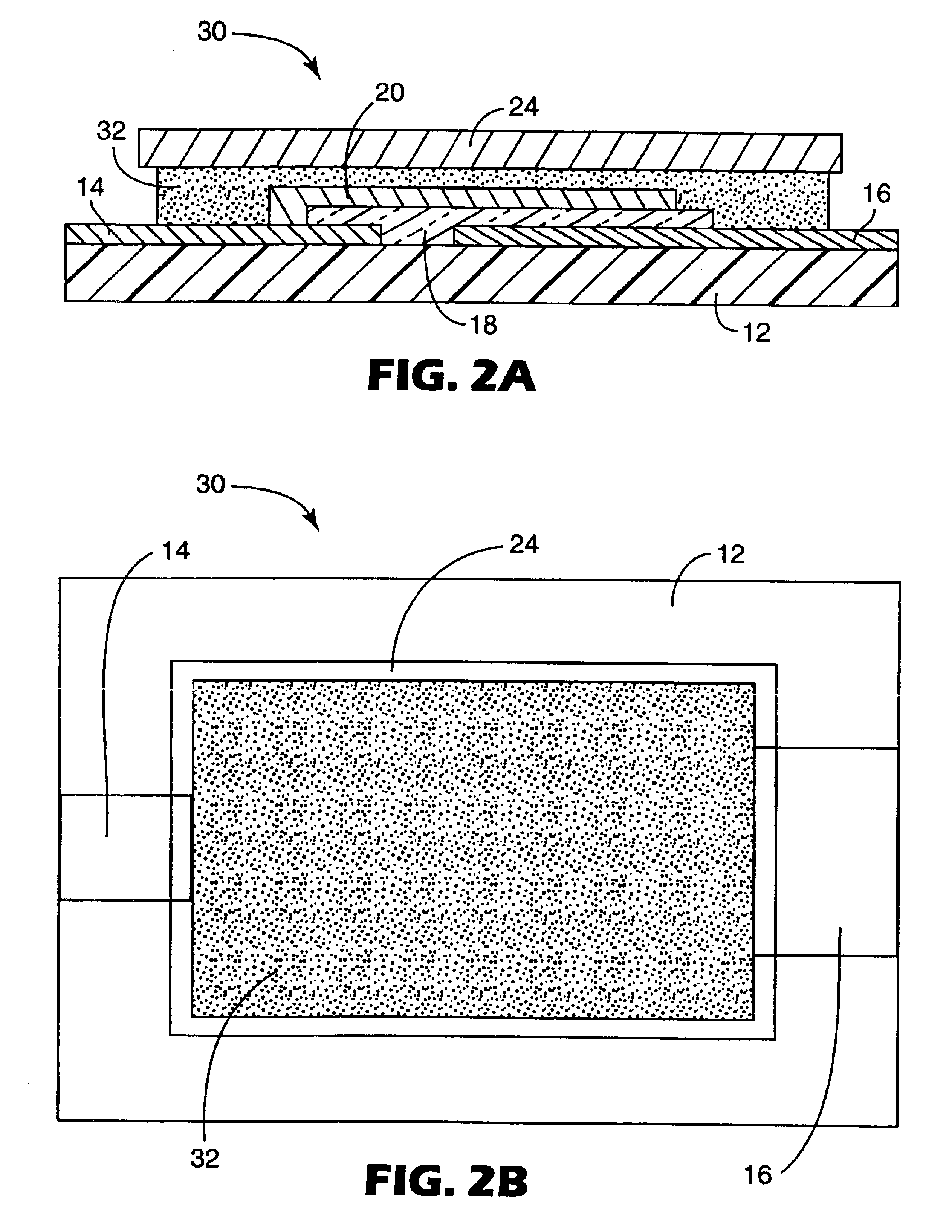
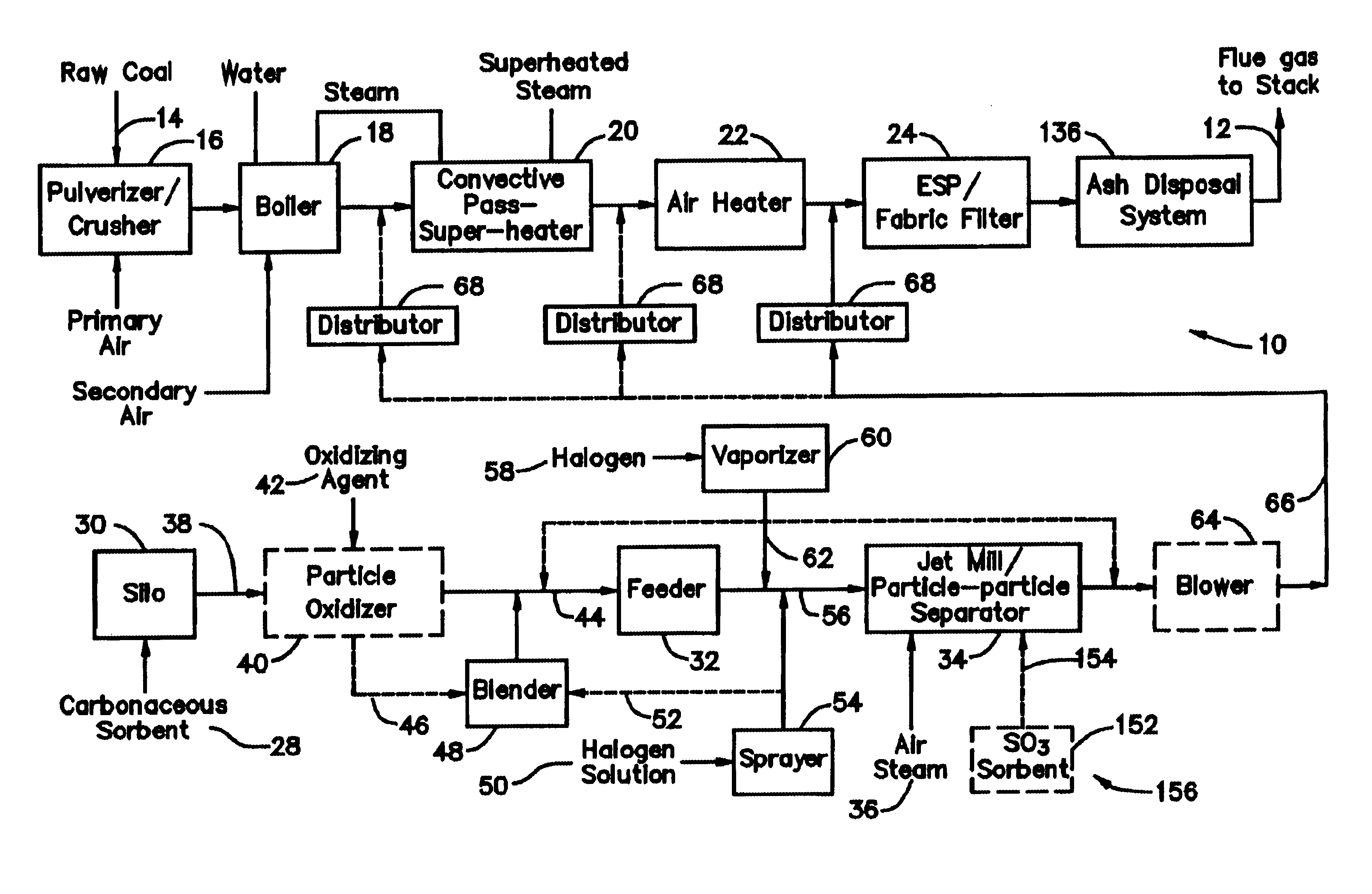
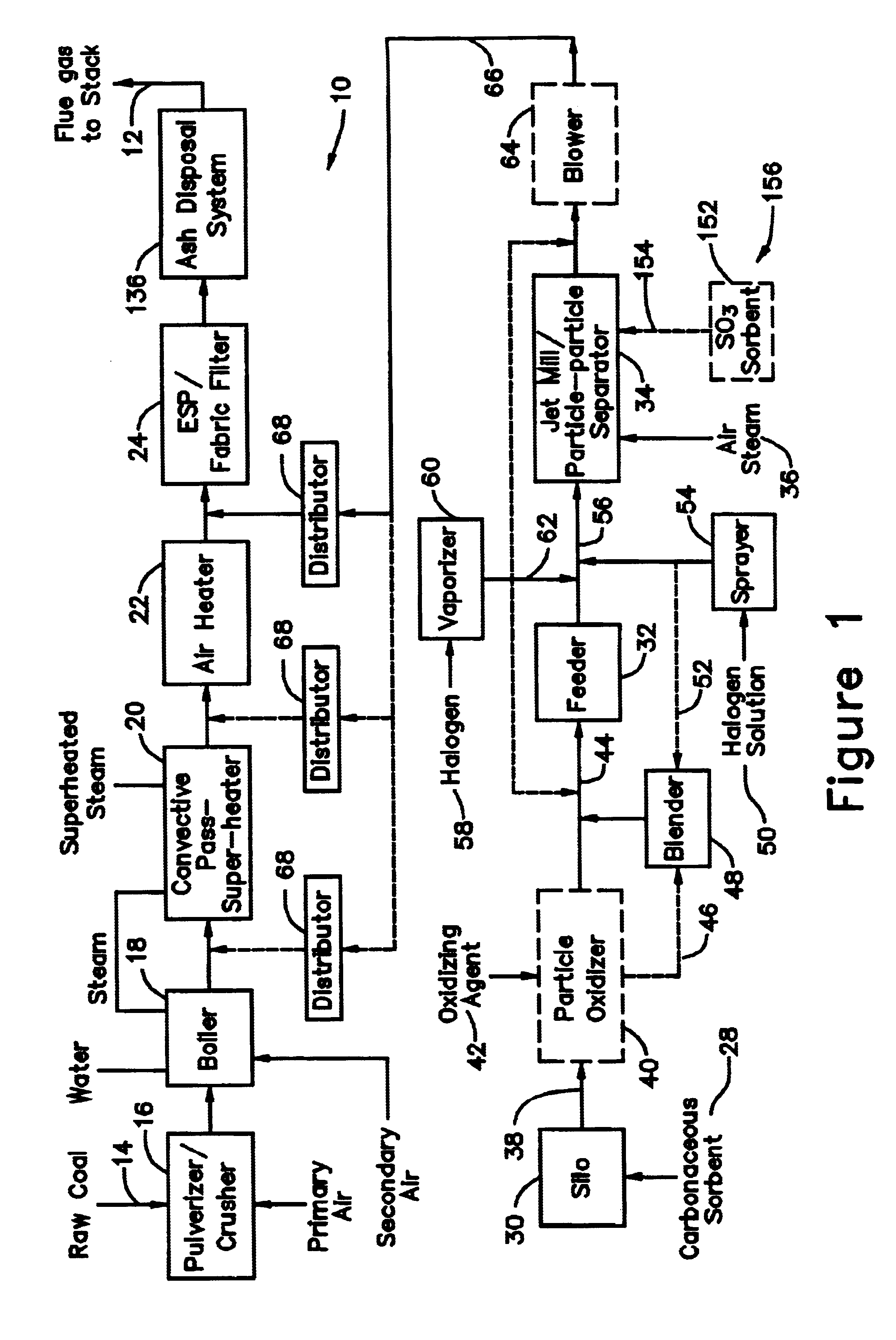
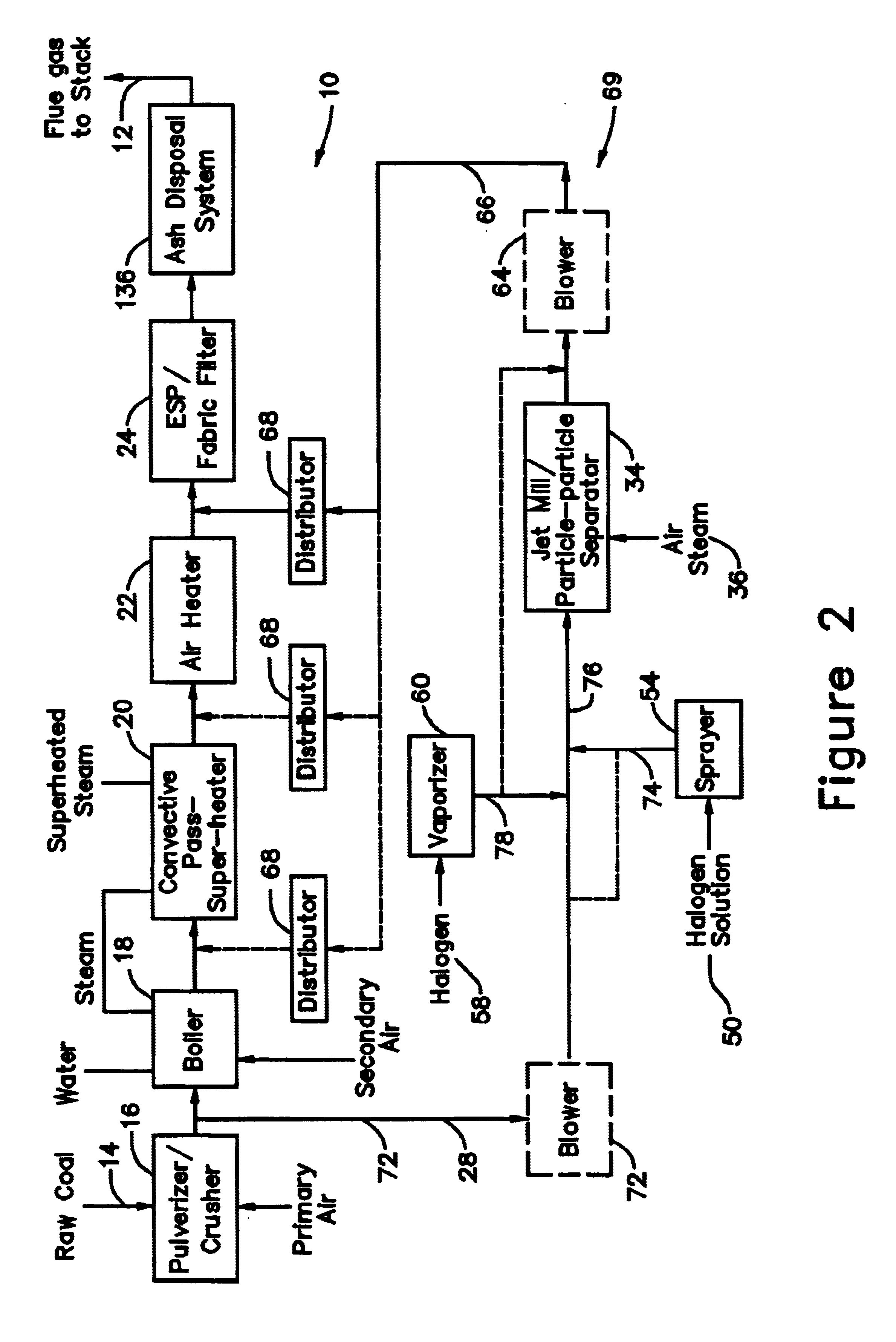
A system 26 for removing elemental mercury or mercury compounds handles carbonaceous sorbent 28 of a starter batch stored in a silo 30 in an agglomerated state. The sorbent 28 is fed by a feeder 32 to a separation device 34, which comminutes (if necessary) and de-agglomerates the sorbent particles 28 to their primary size distribution. This device 34 may be a particle-particle separator or a jet mill, where compressed air or high-pressure steam is the energy source. The de-agglomerated sorbent 28 of a contact batch created from the starter batch is conveyed by an airsteam for injection at a contact location 66 in a flue gas duct whereat carbonaceous sorbent of the contact batch adsorbs mercury from the flue gas.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
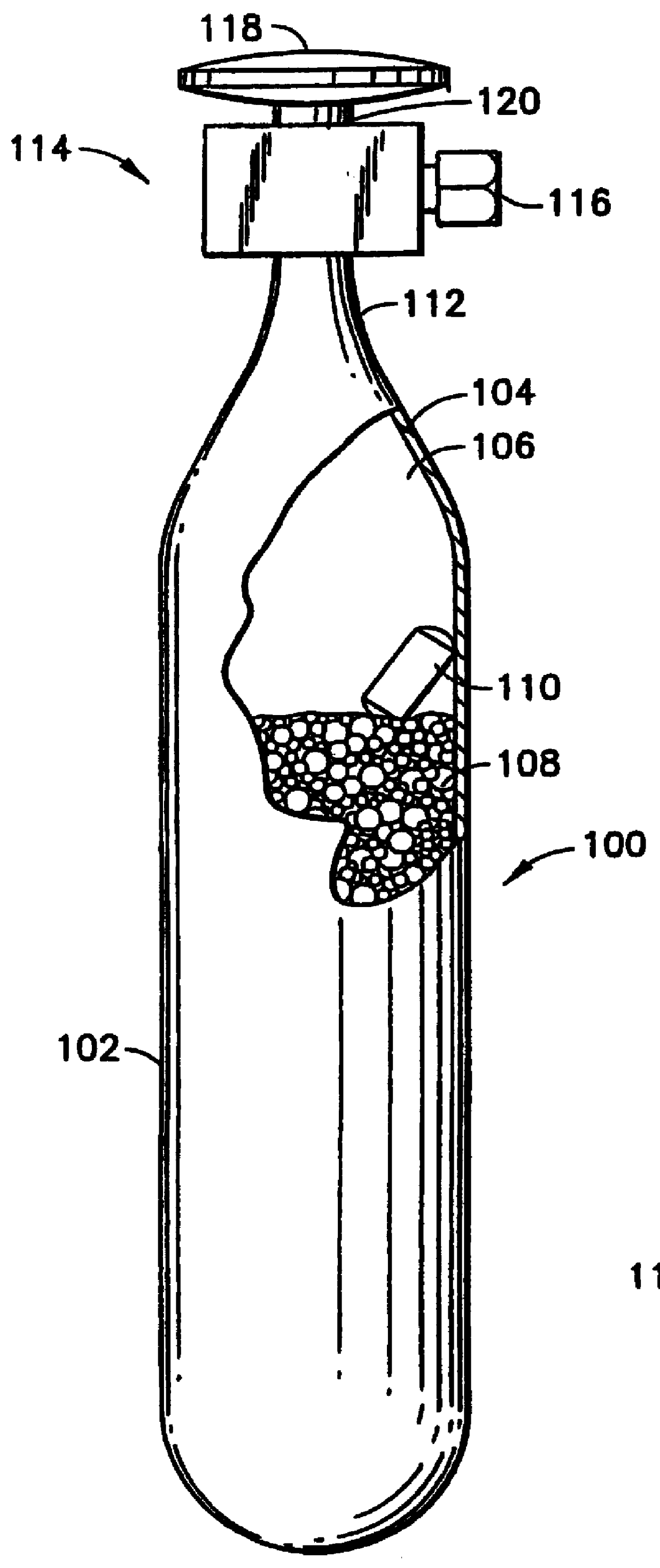
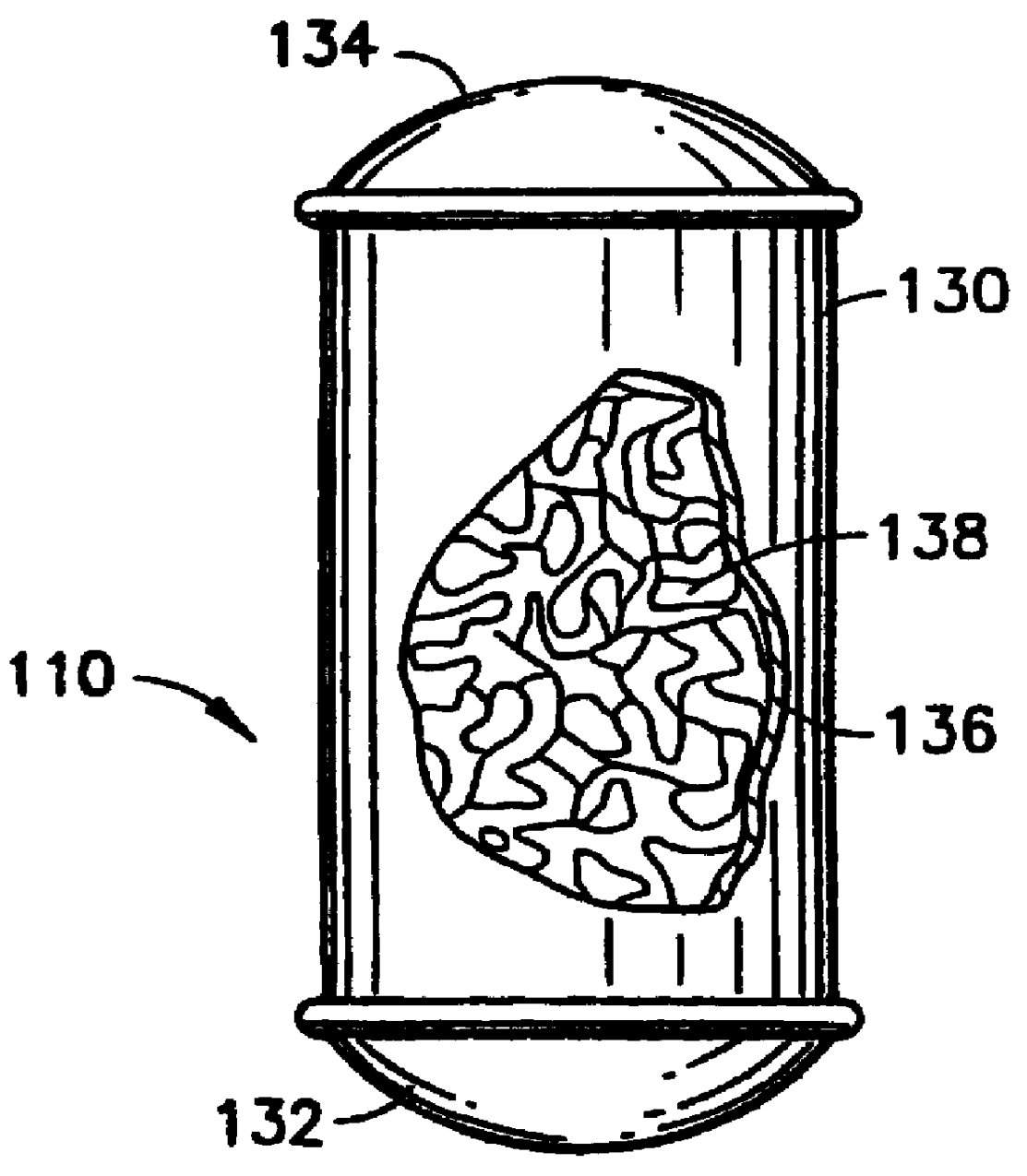
Sorbent-based gas storage and delivery system for dispensing of high-purity gas, and apparatus and process for manufacturing semiconductor devices, products and precursor structures utilizing same
A sorbent-based gas storage and dispensing system, including a storage and dispensing vessel containing a solid-phase physical sorbent medium having a sorbate gas physically adsorbed thereon. A chemisorbent material is provided in the vessel to chemisorb the impurities for gas phase removal thereof in the storage and dispensing vessel. Desorbed sorbate gas is discharged from the storage and dispensing vessel by a dispensing assembly coupled to the vessel. The chemisorbent may be provided in a capsule including an impurity-permeable, but sorbate gas-impermeable membrane, and installed in the vessel at the time of sorbent material loading. Semiconductor manufacturing processes and products manufactured by such processes are described.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
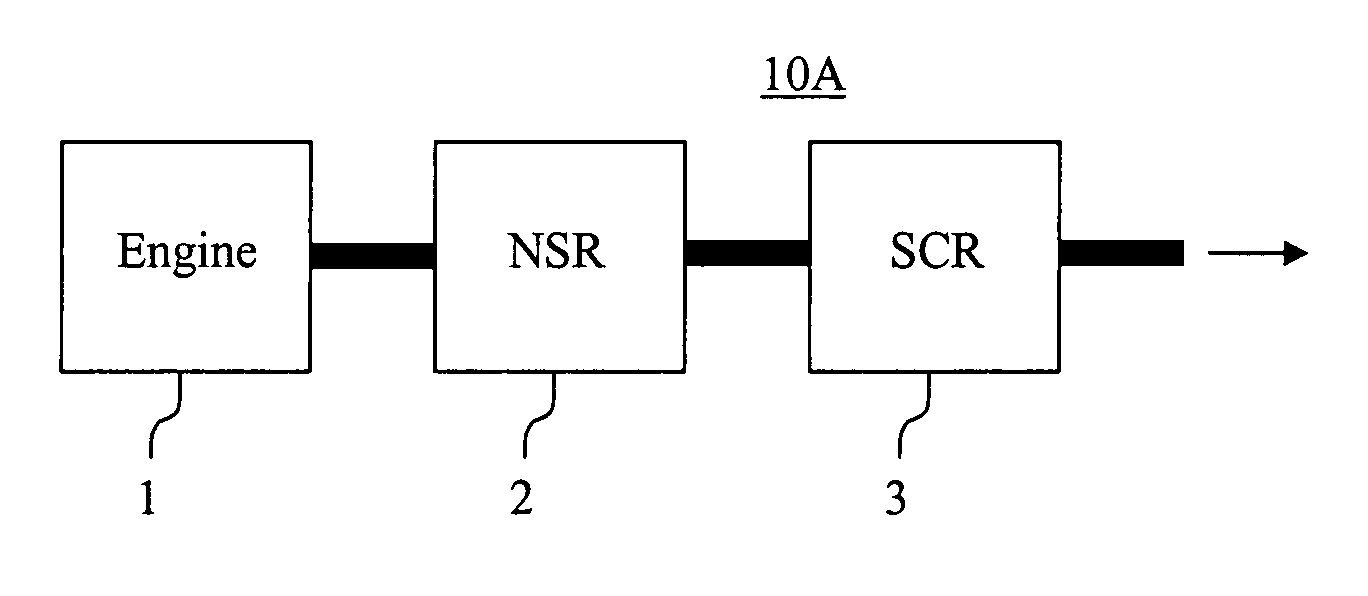
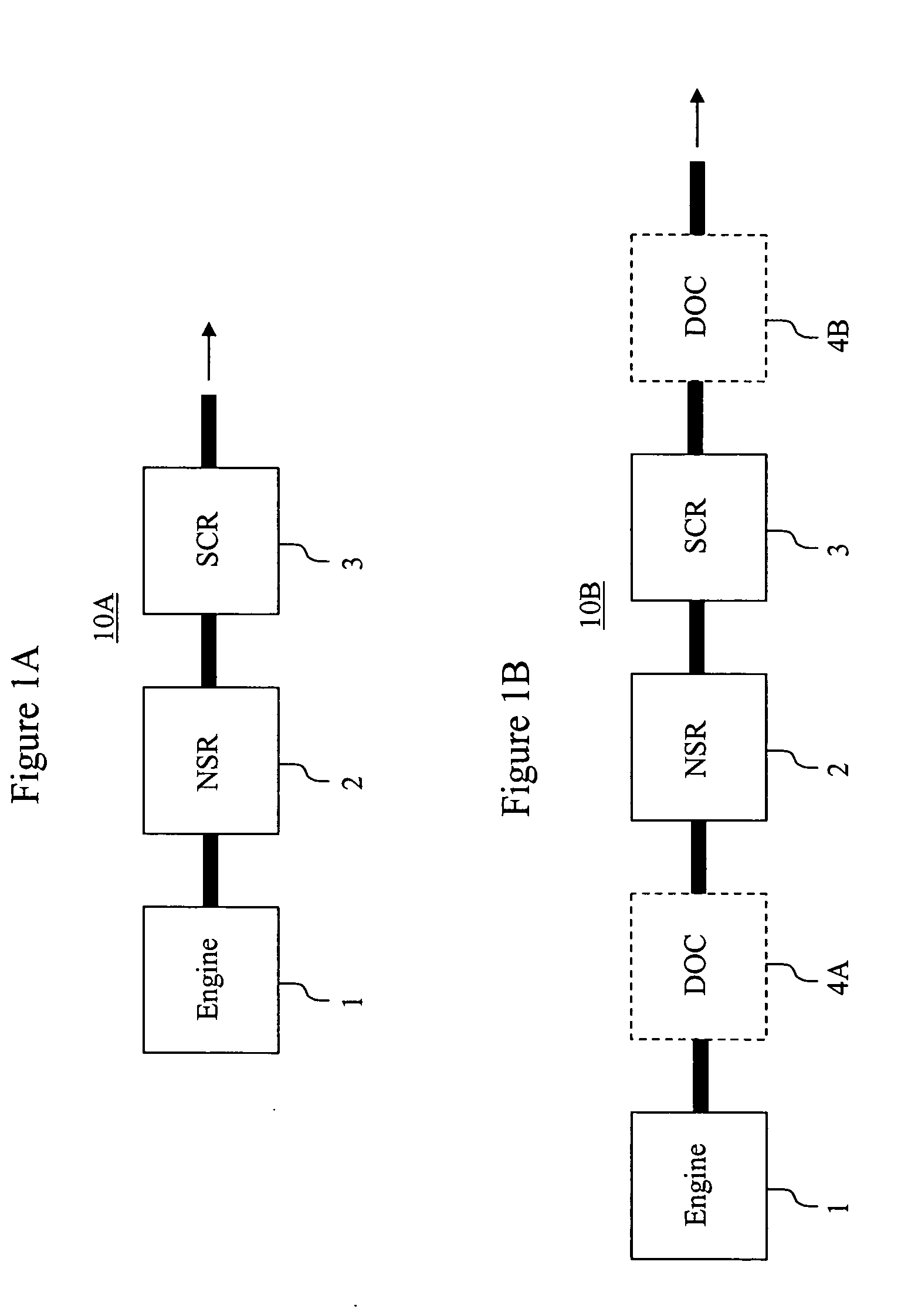
Emissions treatment system with NSR and SCR catalysts
ActiveUS20050129601A1Small sizeReduce amount particulate matterGas treatmentNitrogen compoundsSorbentGasoline
Provided is an emissions treatment system for an exhaust stream, having a NOx storage reduction (NSR) catalyst with a NOx sorbent at a concentration of at least 0.1 g / in3 and a platinum group metal component dispersed on a refractory metal oxide support; and, an SCR catalyst disposed downstream of the NSR catalyst. The emissions treatment system is advantageously used for the treatment of exhaust streams from diesel engines and lean burn gasoline engines.
Owner:BASF CATALYSTS LLC
System and methods for improved emission control of internal combustion engines using pulsed fuel flow
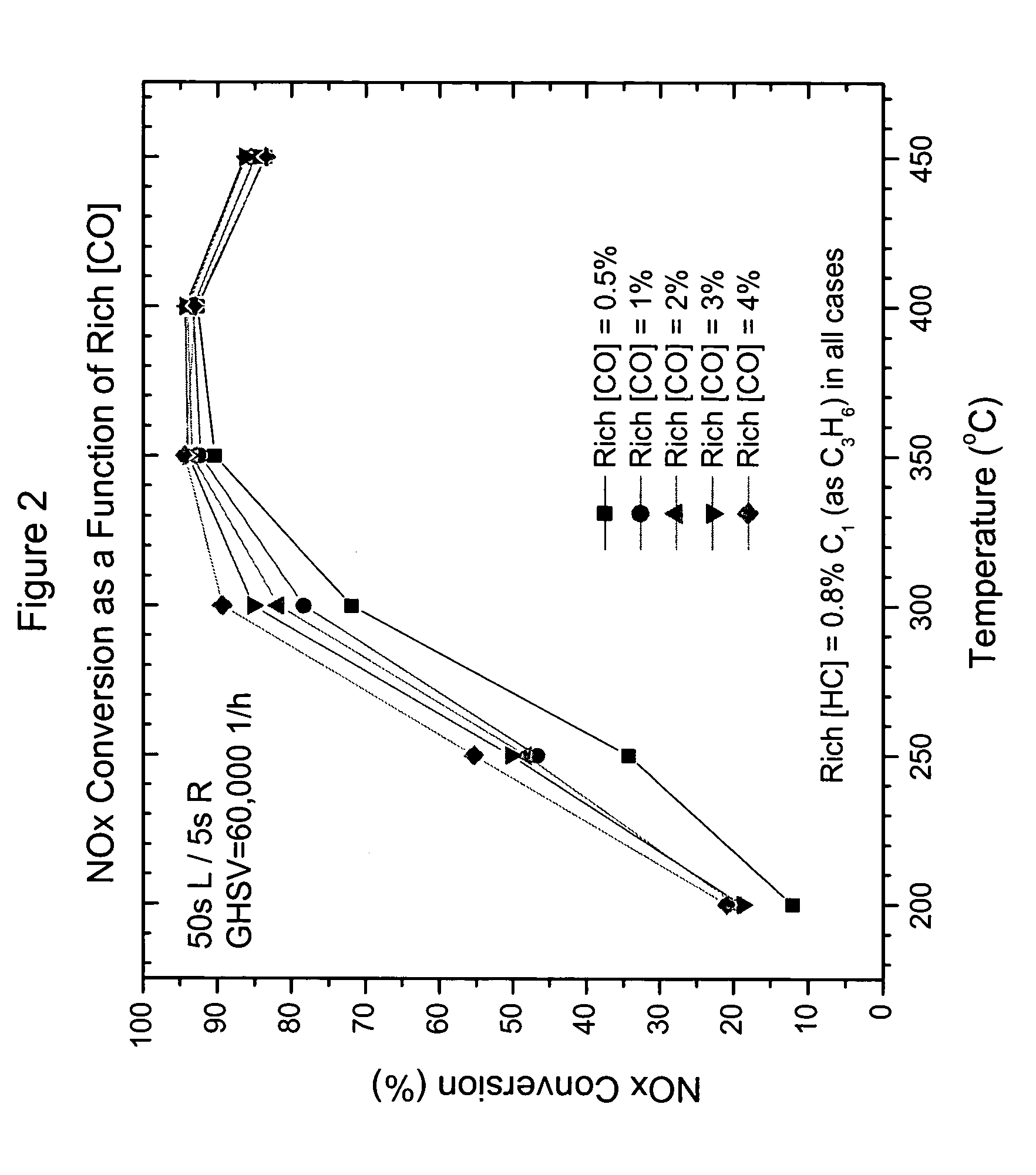
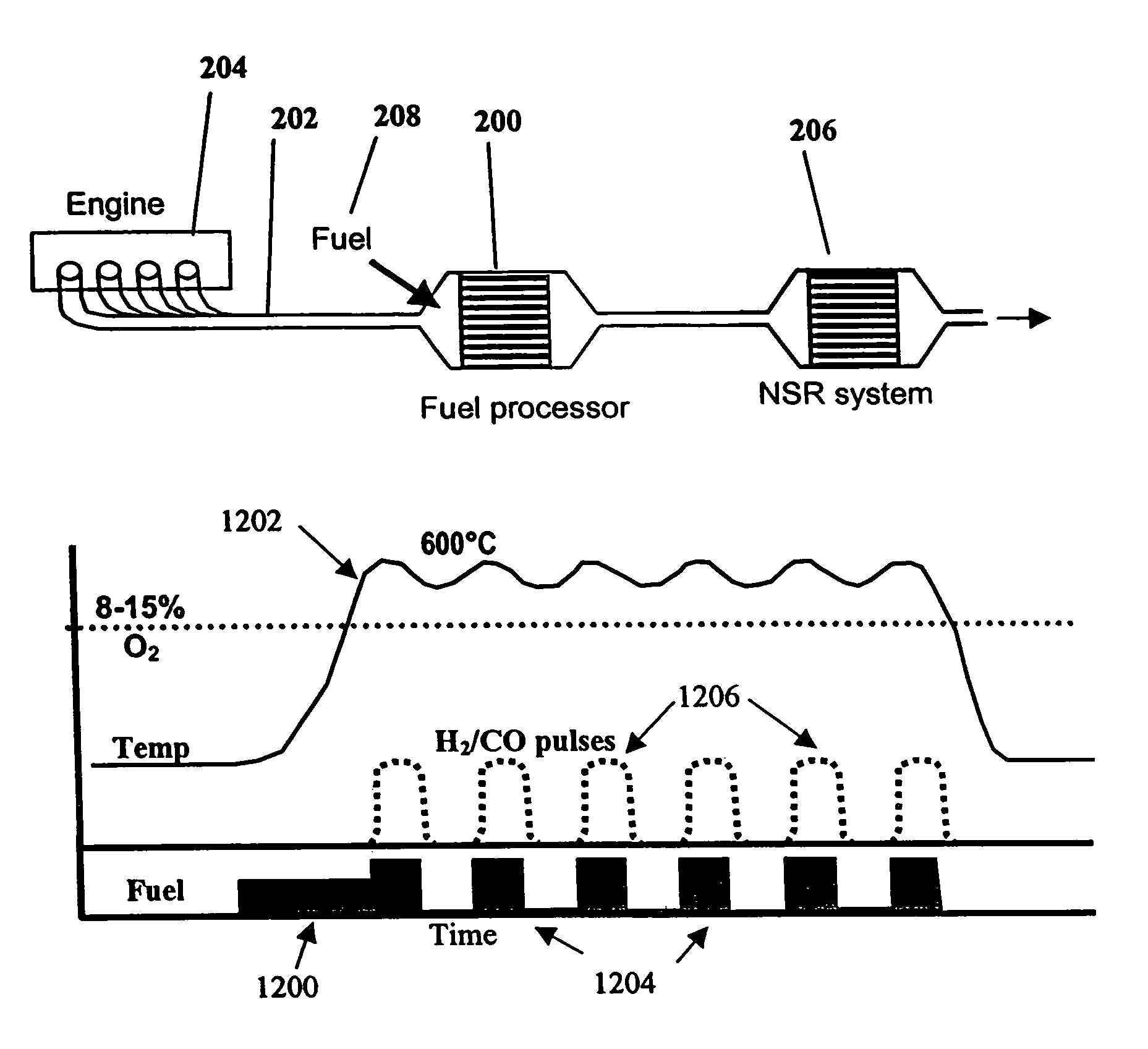
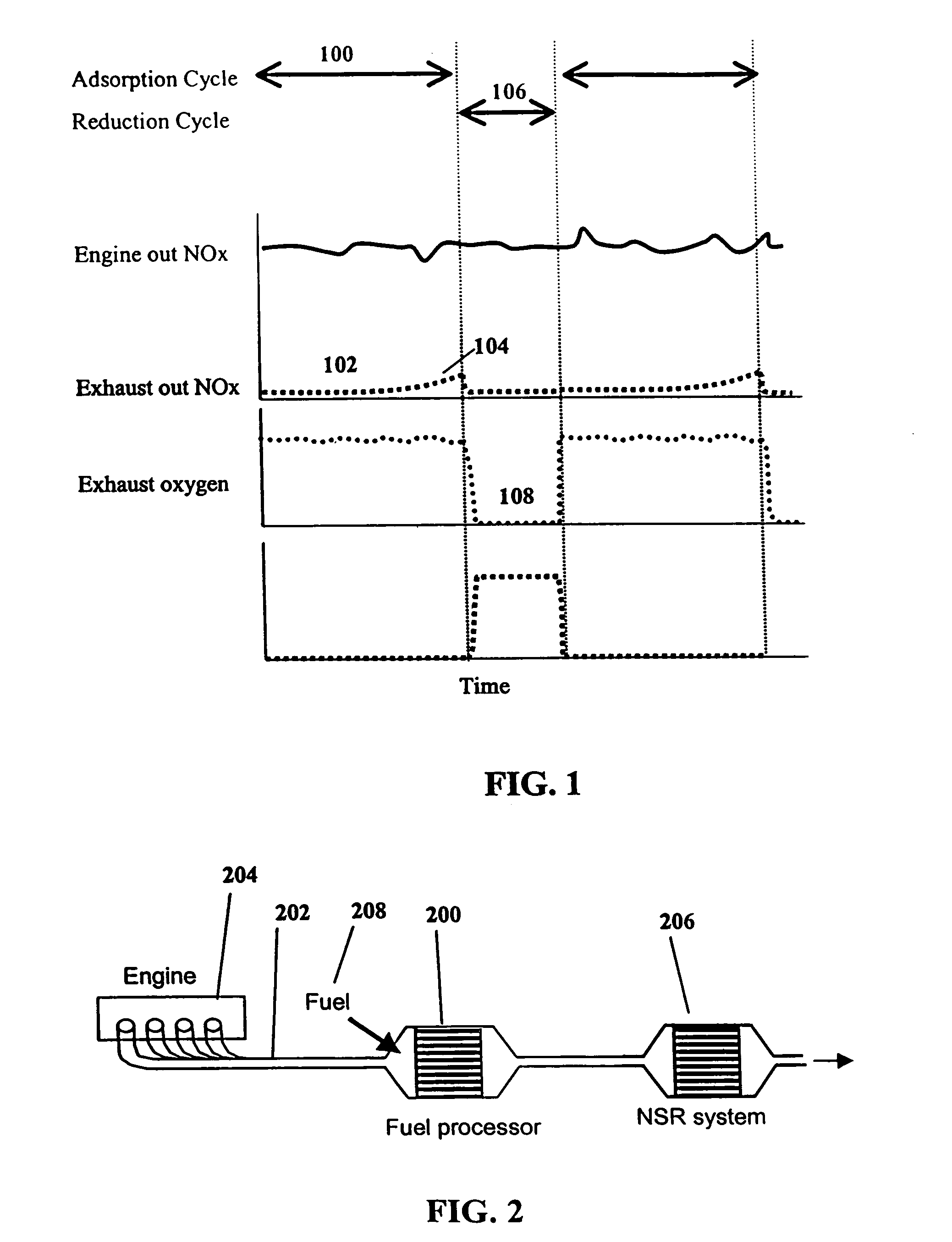
InactiveUS7082753B2Save oilReducing greenhouse gas emissionExhaust apparatusCombustion enginesPartial oxidationExternal combustion engine
The present invention provides systems and methods to improve the performance and emission control of internal combustion engines equipped with nitrogen oxides storage-reduction (“NSR”) emission control systems. The system generally includes a NSR catalyst, a fuel processor located upstream of the NSR catalyst, and at least one fuel injection port. The fuel processor converts a fuel into a reducing gas mixture comprising CO and H2. The reducing gas mixture is then fed into the NSR catalyst, where it regenerates the NSR adsorbent, reduces the NOx to nitrogen, and optionally periodically desulfates the NSR catalyst. The fuel processor generally includes one or more catalysts, which facilitate reactions such as combustion, partial oxidation, and / or reforming and help consume excess oxygen present in an engine exhaust stream. The methods of the present invention provide for NSR catalyst adsorbent regeneration using pulsed fuel flow. Control strategies are also provided.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Carbon Dioxide Recovery
Disclosed herein is a method and system for separating carbon dioxide (CO2) from a CO2 containing gas stream containing water vapor and additional impurities, for example, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and mercury. The CO2 is captured by subjecting the CO2 gas feed stream to a temperature swing adsorption step. The temperature swing adsorption step comprises an adsorption step for producing a substantially dry carbon dioxide-depleted stream, and an adsorbent regeneration step comprising heating the adsorbent bed to produce a substantially water vapor-free carbon dioxide stream. Moisture from the gas stream containing CO2 is optionally removed by pressure swing adsorption, temperature swing adsorption, membrane separation, or absorption prior to CO2 capture.
Owner:INNOSEPRA LLC
Sorbents for the oxidation and removal of mercury
ActiveUS20060048646A1Reduce the amount requiredHigh activityGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentActivated carbonHalogen
A promoted activated carbon sorbent is described that is highly effective for the removal of mercury from flue gas streams. The sorbent comprises a new modified carbon form containing reactive forms of halogen and halides. Optional components may be added to increase reactivity and mercury capacity. These may be added directly with the sorbent, or to the flue gas to enhance sorbent performance and / or mercury capture. Mercury removal efficiencies obtained exceed conventional methods. The sorbent can be regenerated and reused. Sorbent treatment and preparation methods are also described. New methods for in-flight preparation, introduction, and control of the active sorbent into the mercury contaminated gas stream are described.
Owner:MIDWEST ENERGY EMISSIONS CORP
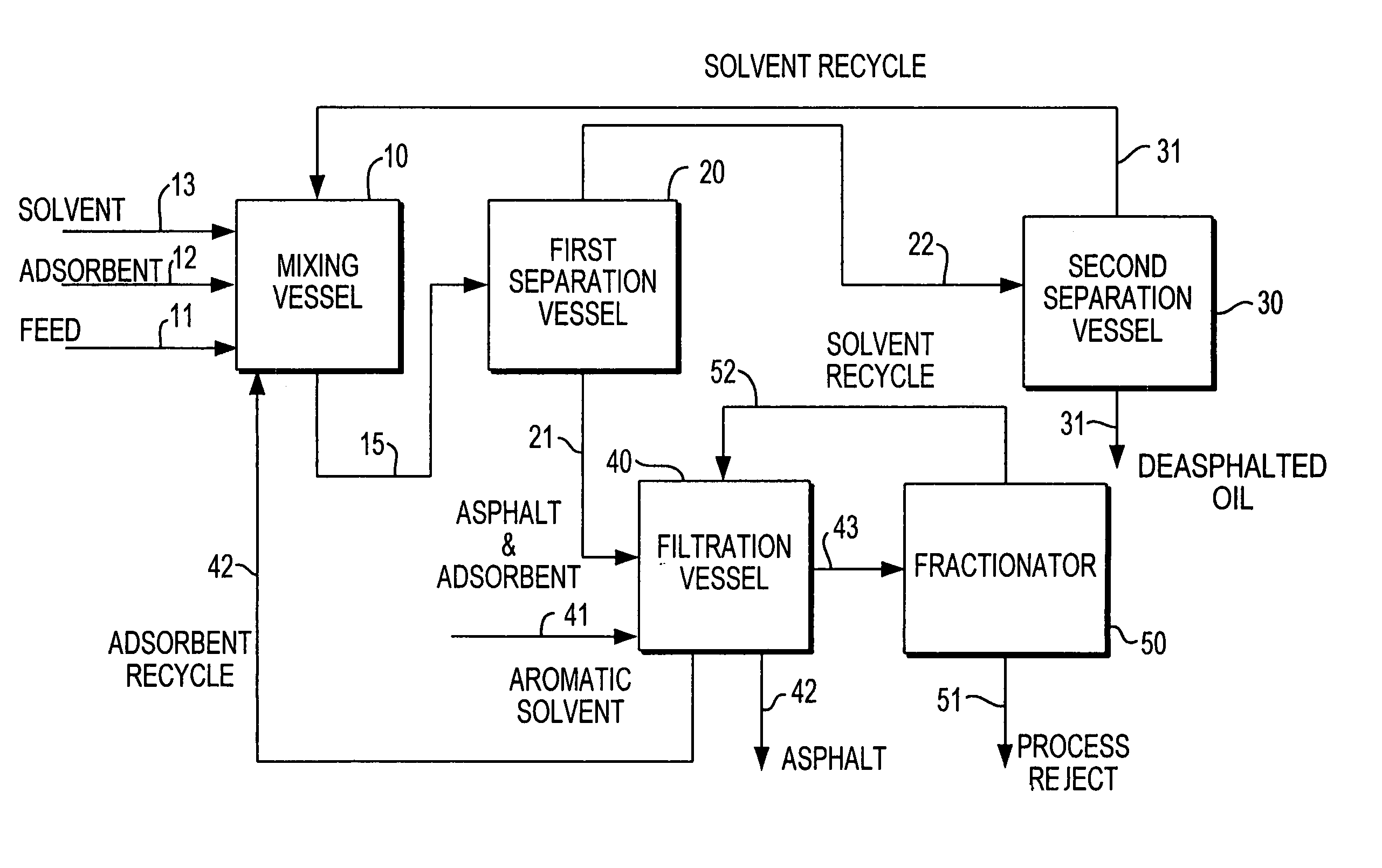
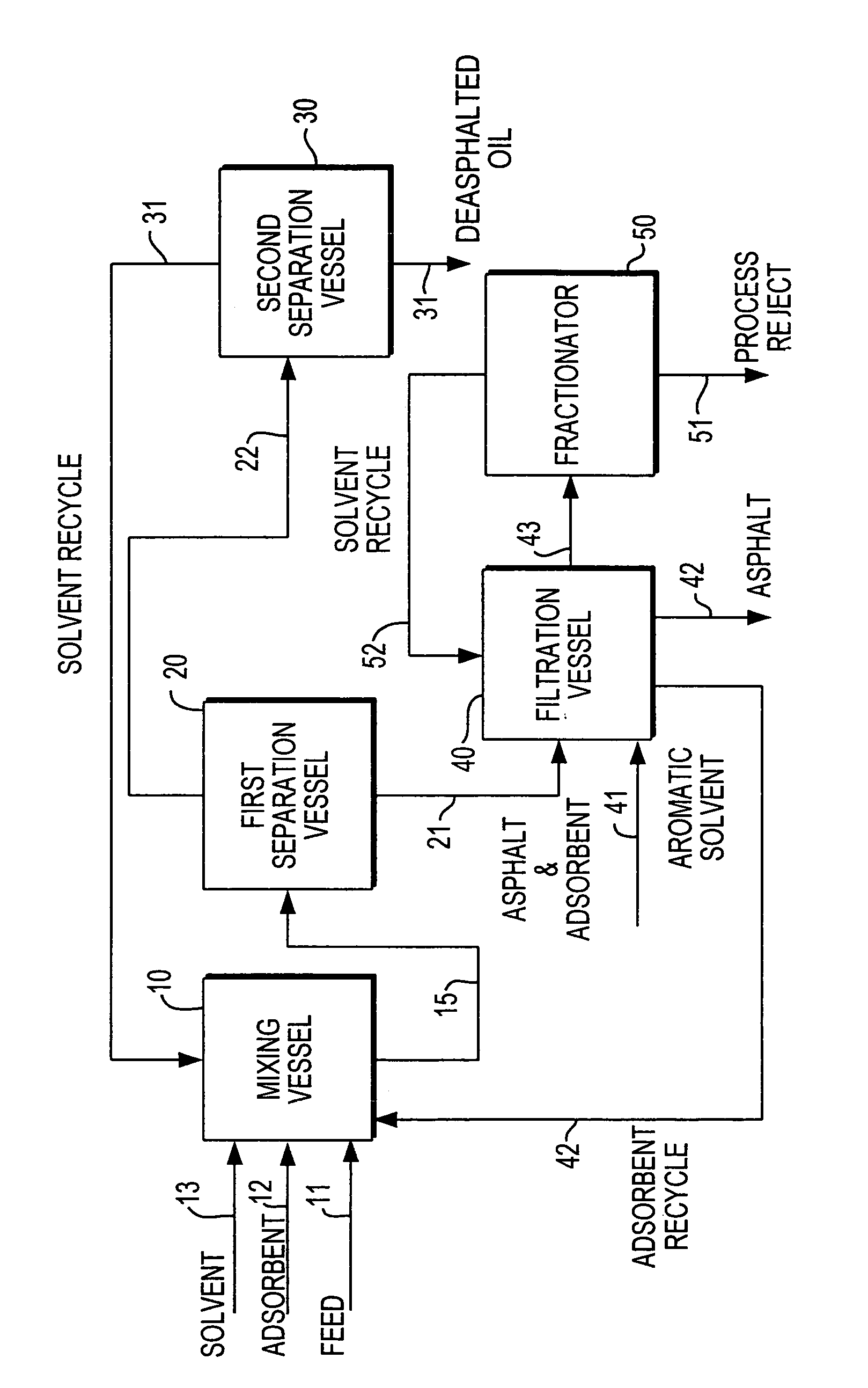
Enhanced solvent deasphalting process for heavy hydrocarbon feedstocks utilizing solid adsorbent
ActiveUS7566394B2Improve performanceImprove current efficiencyWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionHydrocarbon distillationBenzeneActivated carbon
A solvent deasphalting of crude oil or petroleum heavy fractions and residues is carried out in the presence of a solid adsorbent, such as clay, silica, alumina and activated carbon, which adsorbs the contaminants and permits the solvent and oil fraction to be removed as a separate stream from which the solvent is recovered for recycling; the adsorbent with contaminants and the asphalt bottoms is mixed with aromatic and / or polar solvents to desorb the contaminants and washed as necessary, e.g., with benzene, toluene, xylenes and tetrahydrofuran, to clean adsorbant which is recovered and recycled; the solvent-asphalt mixture is sent to a fractionator for recovery and recycling of the aromatic or polar solvent. The bottoms from the fractionator include the concentrated PNA and contaminants and are further processes as appropriate.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com