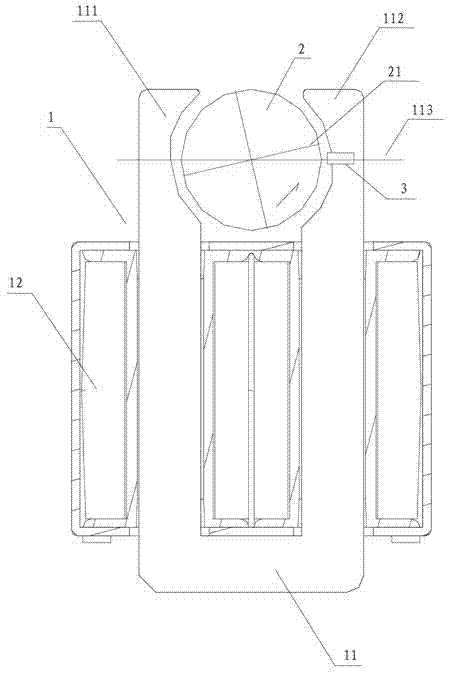
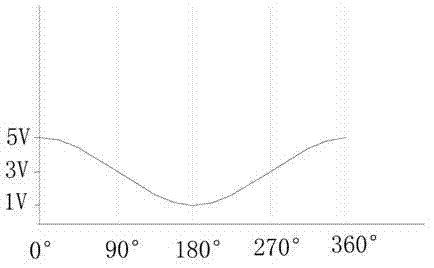
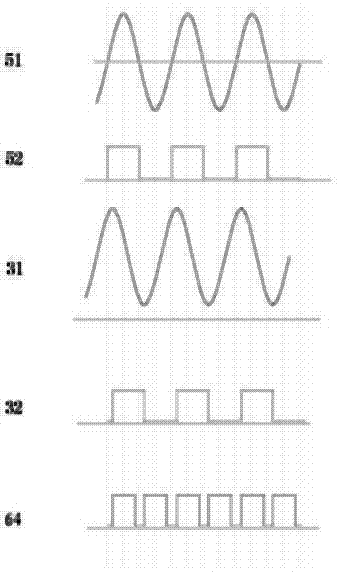
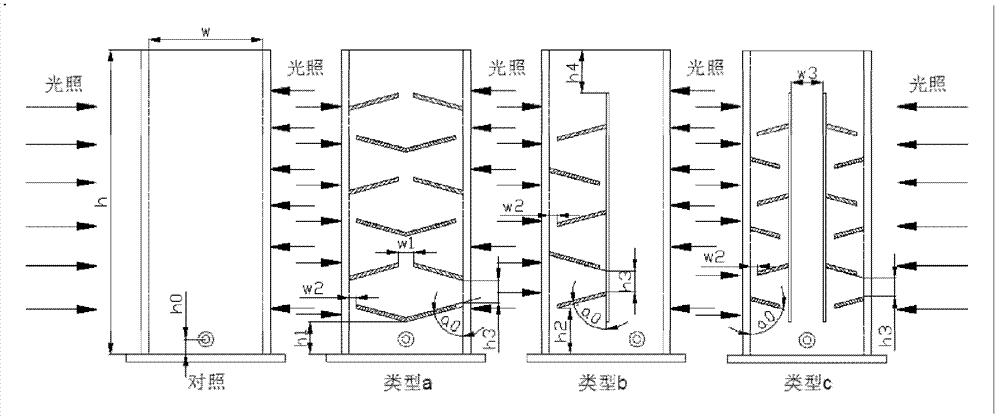
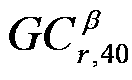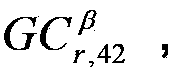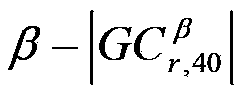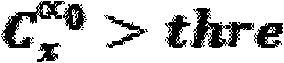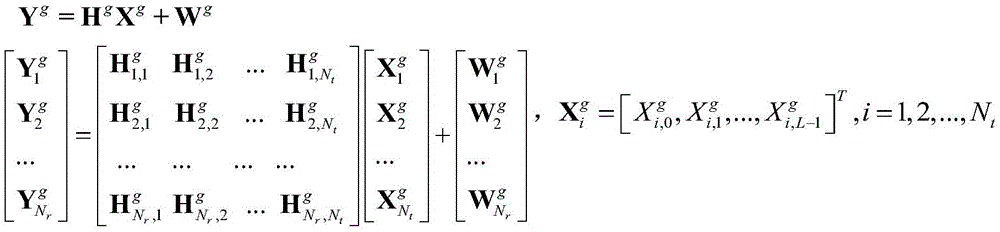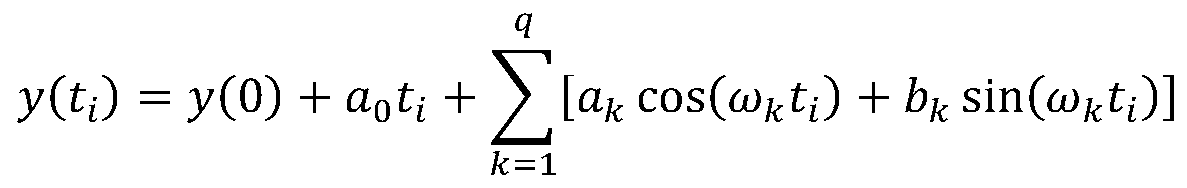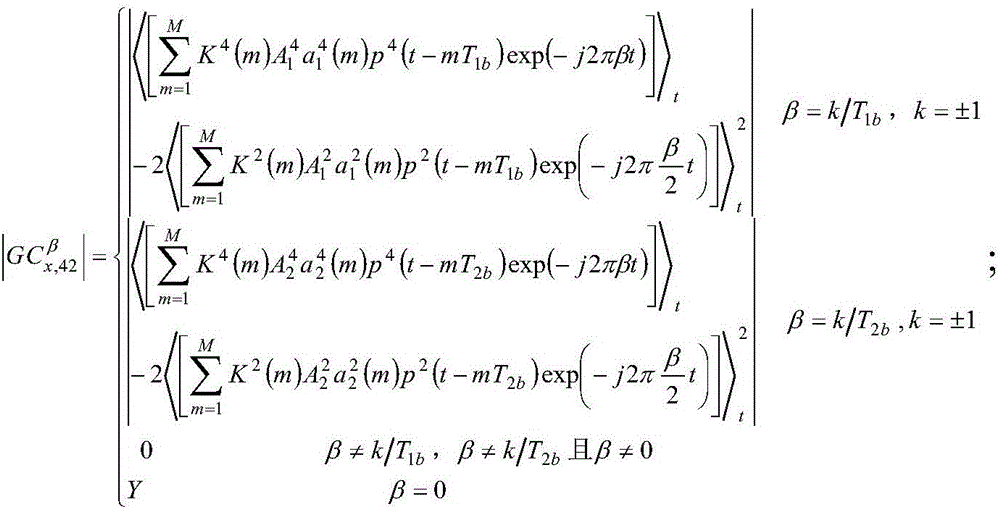Patents
Literature
219 results about "Cycle frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Frequency is the number of cycles in a unit of time. The "cycles" can be movements of anything with periodic motion, like a spring, a pendulum, something spinning, or a wave. Frequency is equal to 1 divided by the period, which is the time required for one cycle.
High frequency pressure swing adsorption
InactiveUS6176897B1High purityRecoverable expansion workNitrogen purification/separationGas treatmentSorbentEngineering
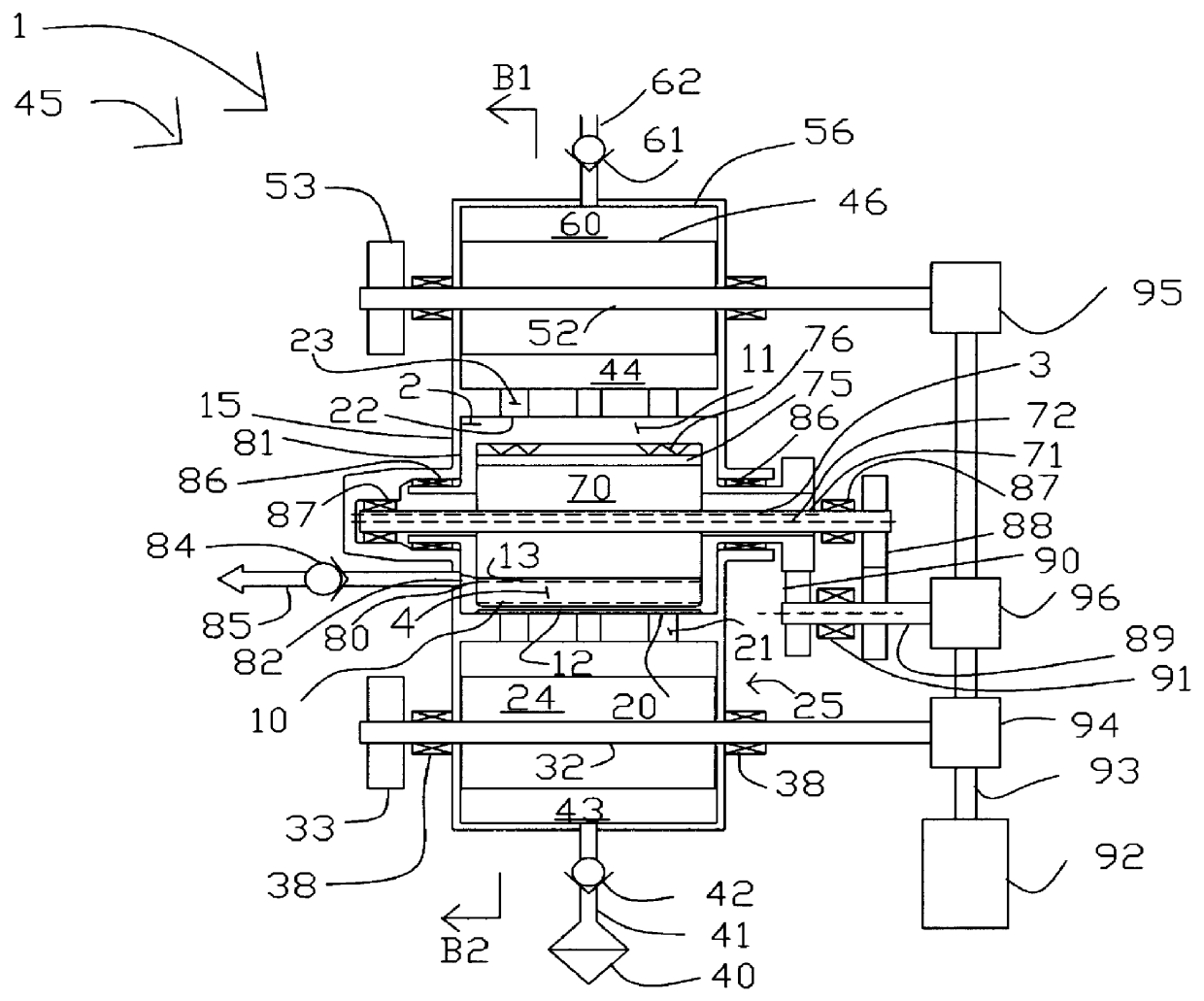
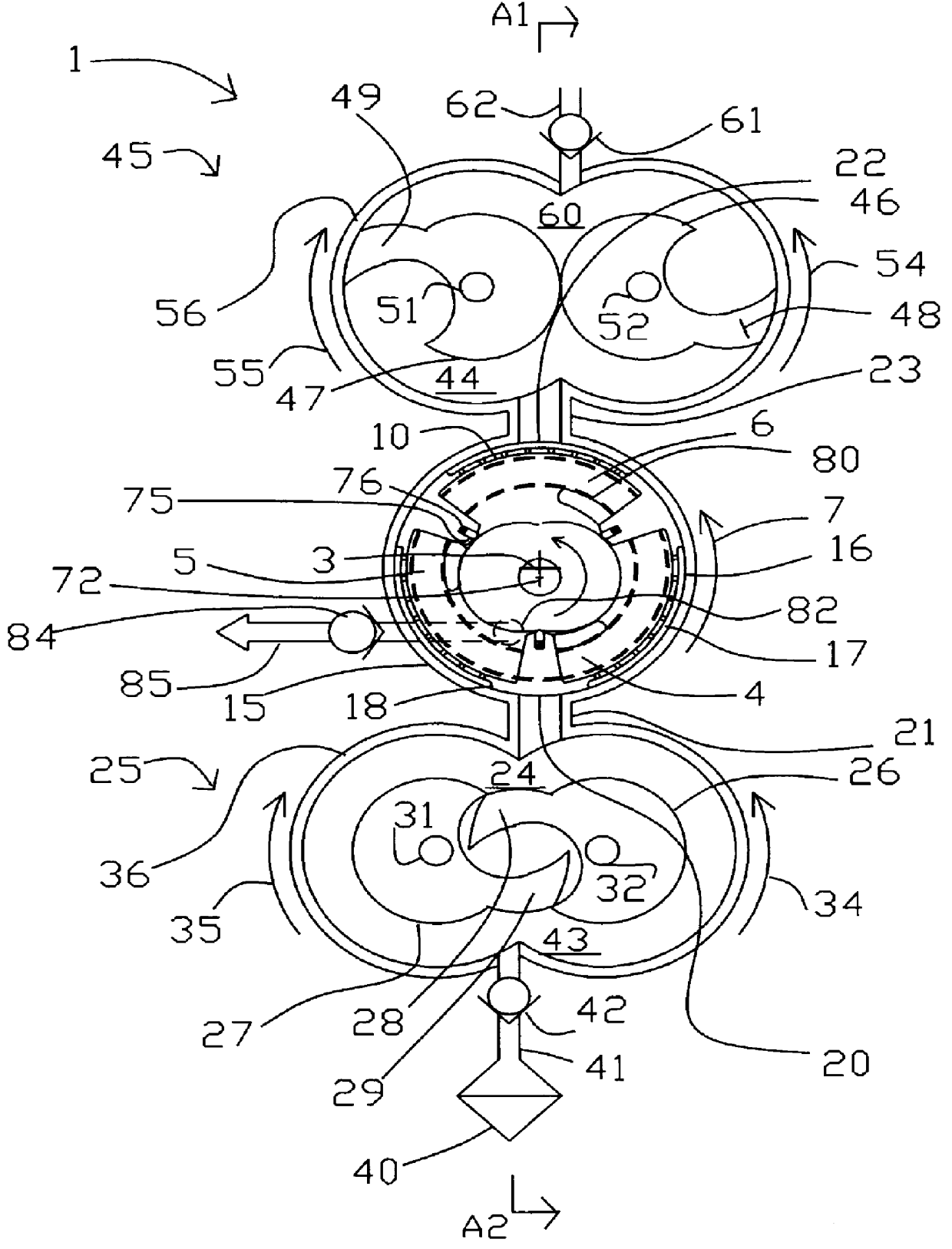
Pressure swing adsorption separation of a feed gas mixture, to obtain a purified product gas of the less strongly adsorbed fraction of the feed gas mixture, is performed in a plurality of preferably an even number of adsorbent beds, with each adsorbent bed communicating at its product end directly to a variable volume expansion chamber, and at its feed end by directional valves to a feed compressor and an exhaust vacuum pump. For high frequency operation of the pressure swing adsorption cycle, a high surface area layered support is used for the adsorbent. The compressor and vacuum pump pistons may be integrated with the cycle, reciprocating at twice the cycle frequency. Alternative configurations of the layered adsorbent beds are disclosed.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
High frequency rotary pressure swing adsorption apparatus
InactiveUS6056804AHigh-frequency operationCompact equipmentGas treatmentIsotope separationProduct gasDistributor
Pressure swing adsorption separation of a feed gas mixture, to obtain a purified product gas of the less strongly adsorbed fraction of the feed gas mixture, is performed with a cooperating set of "N" adsorbers in a rotary assembly, with each adsorber communicating at its product end directly to a rotary cyclic displacement chamber, and at its feed end by rotary distributor valve ports to a rotary piston feed compressor and a rotary piston exhaust vacuum pump. The compressor and vacuum pump are integrated with the cycle, and rotate at "N" times the cycle frequency. Alternative adsorber configurations for high frequency operation are disclosed.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC +1
Engineered adsorbent structures for kinetic separation
ActiveUS20060169142A1Easy to controlHigh selectivityGas treatmentMethane captureProduction rateSorbent
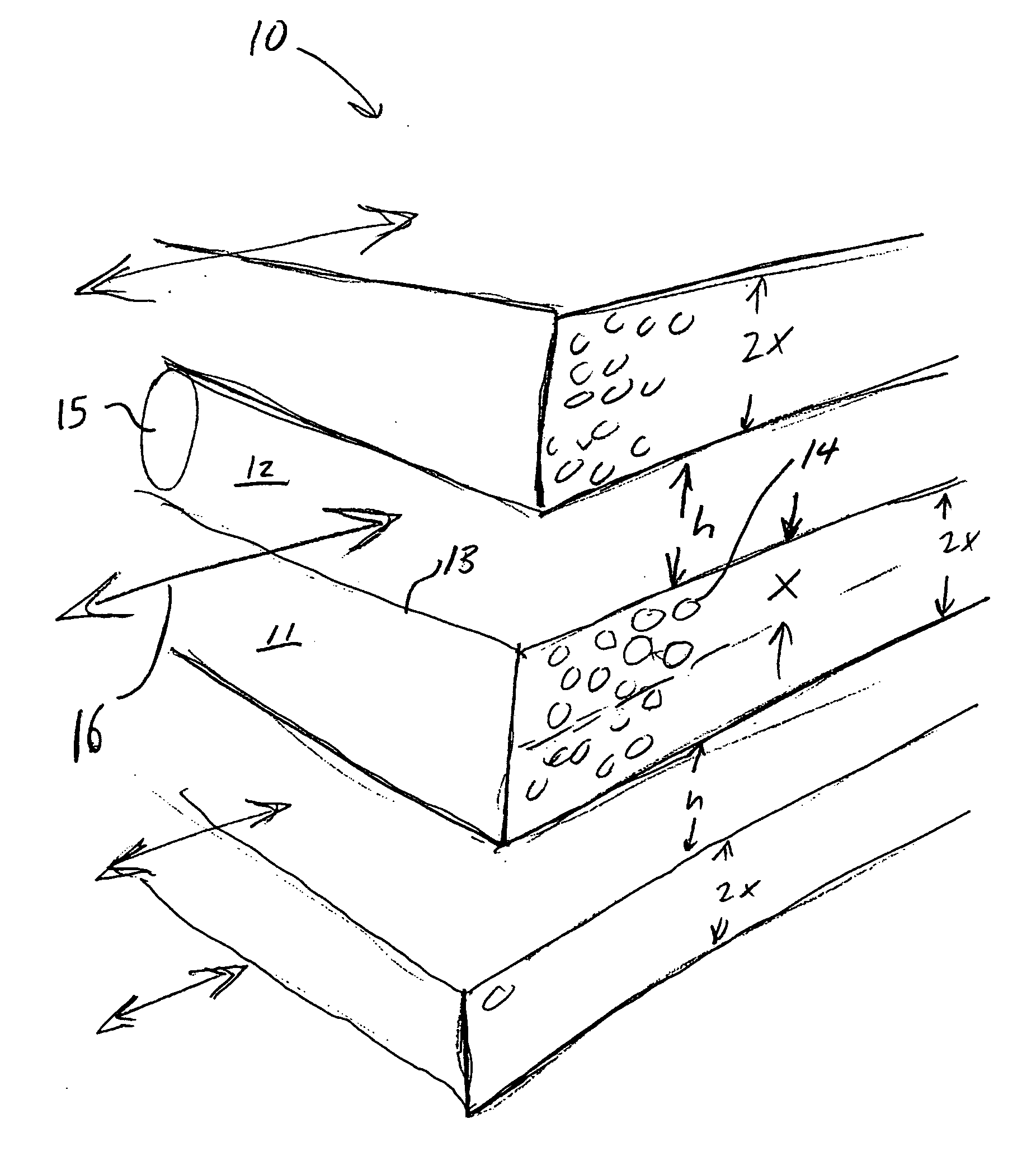
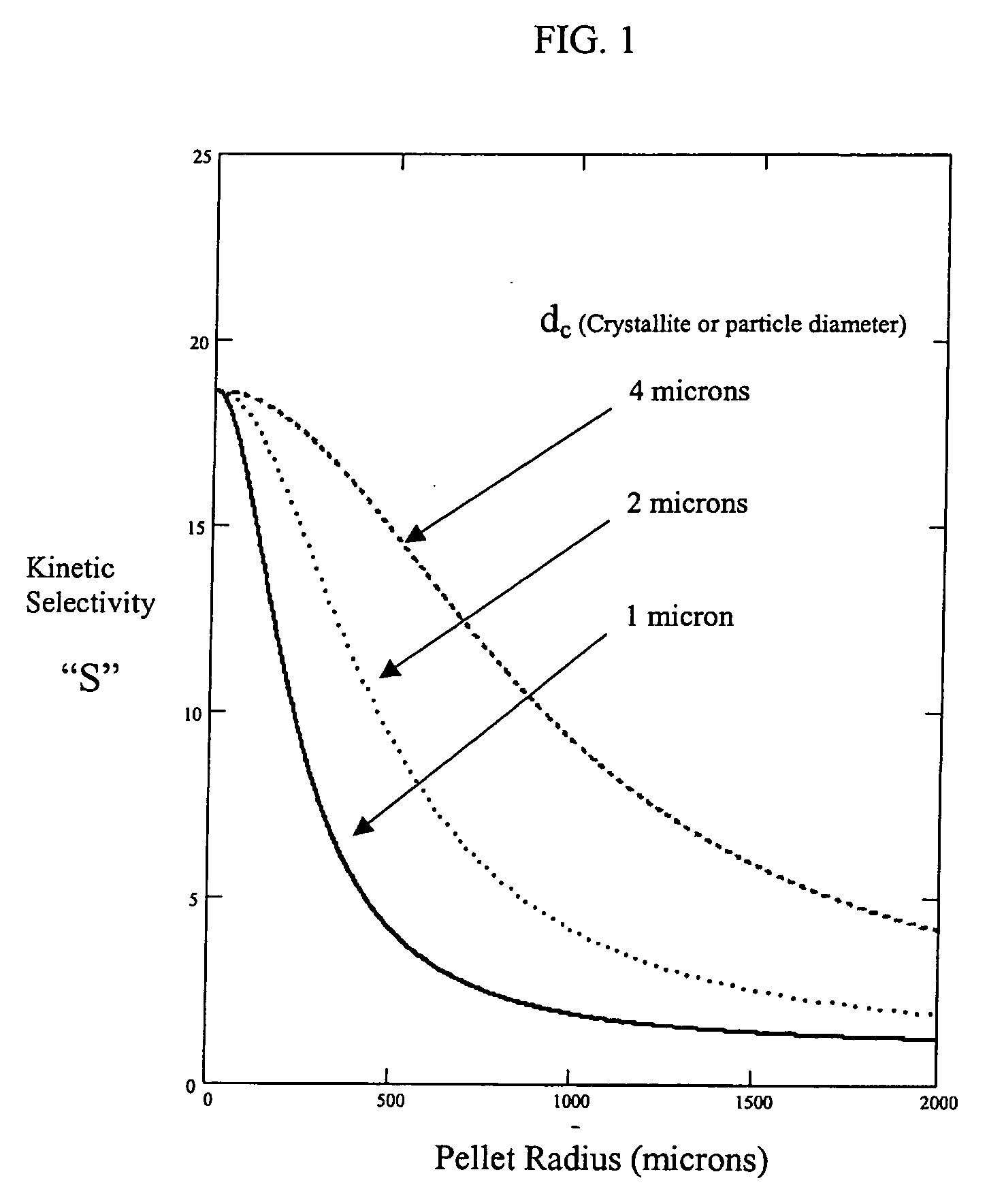
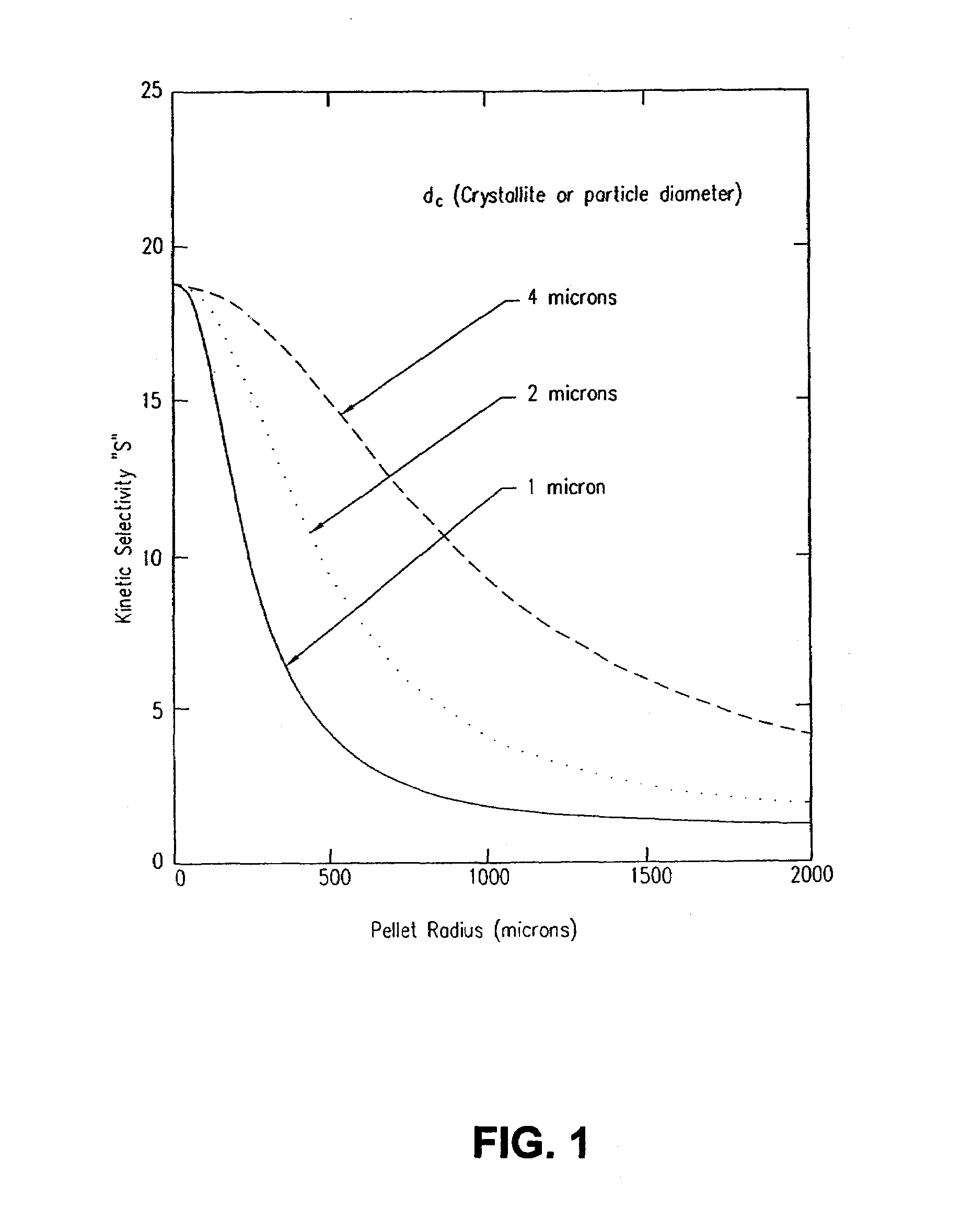
Improved adsorbent sheet based parallel passage adsorbent structures for enhancing the kinetic selectivity of certain kinetic-controlled adsorption processes, such as PSA, TSA and PPSA processes, and combinations thereof, are provided. The enhancements in kinetic selectivity made possible through the implementation of the present inventive improved adsorbent structures may unexpectedly enable significant intensification of selected kinetic adsorption processes relative to attainable performance with conventional adsorbent materials in beaded or extruded form. Such process intensification enabled by the present inventive adsorbent structures may provide for increased adsorption cycle frequencies, and increased gas flow velocities within the adsorbent beds, which may increase the productivity and / or recovery of a kinetic adsorption system incorporating the inventive adsorbent structures.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Liquid crystal display with color backlighting employing light emitting diodes
A color display device (210, 310, 410) includes a backlight (214, 414) that cyclically emits first, second, and third component color backlighting in turn over a cycle period. The cycle period repeats at a cycling frequency (f) that exceeds a maximum human visual response frequency. A liquid crystal display (LCD) (112, 312, 412) generates a first display during the first component color backlighting, a second display during the second component color backlighting, and a third display during the third component color backlighting.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Disinfection of dead-ended lines in medical instruments
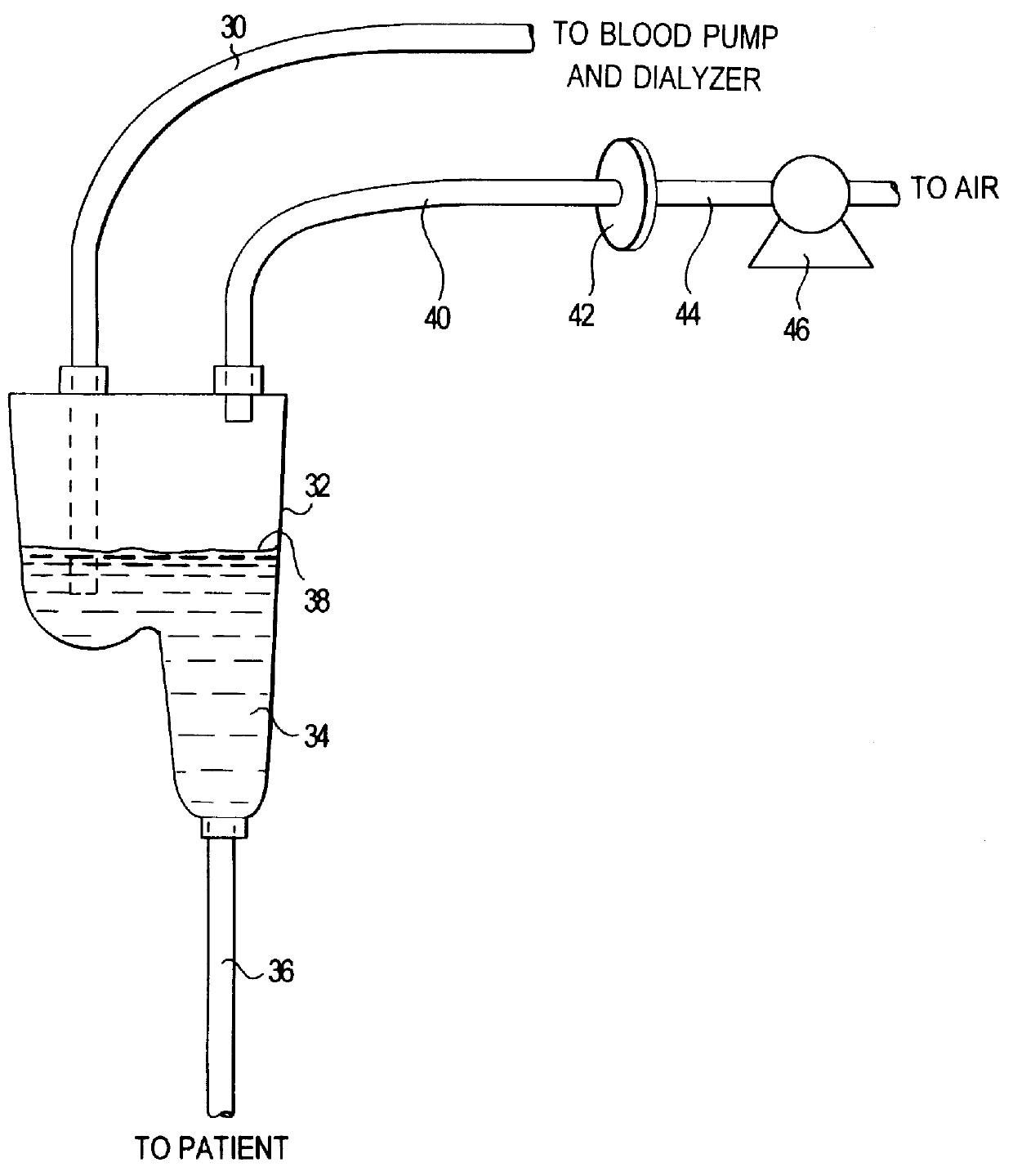
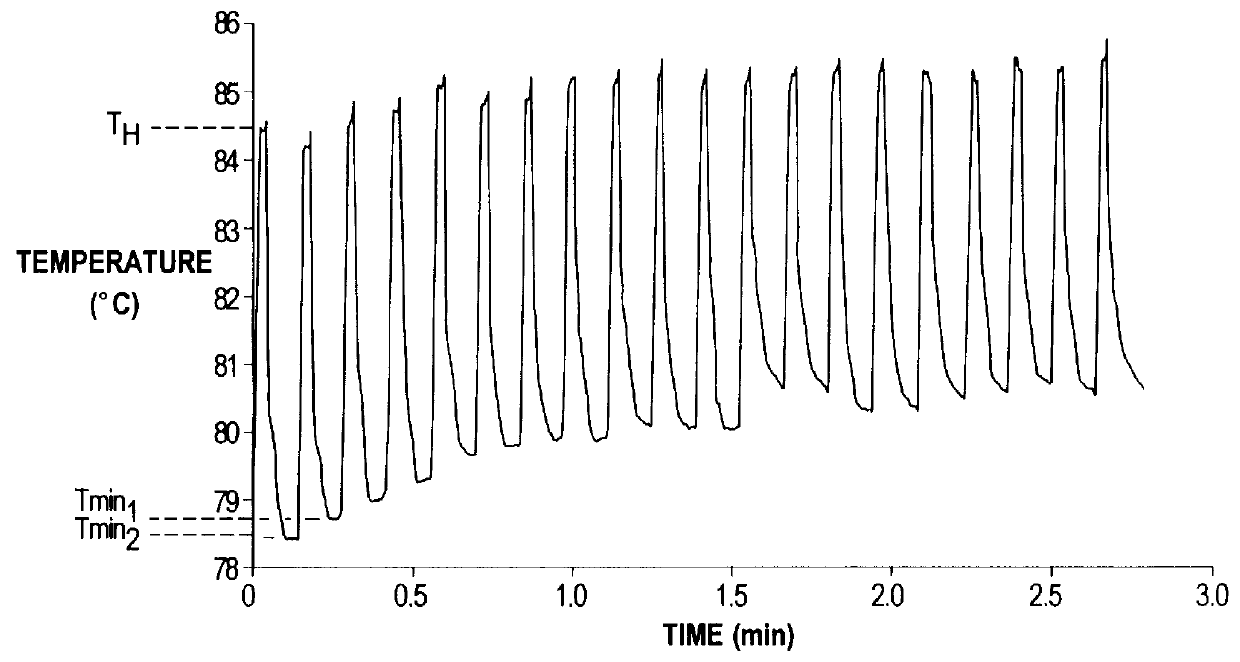
A method of disinfection of a dead-ended fluid line in a medical instrument such as a dialysis machine is described. The method comprises introducing a heated fluid into the fluid line, allowing the fluid to remain in the line for an experimentally determined optimal dwell period, removing the fluid from the fluid line, and then repeating the cycle for a time period sufficient to achieve a disinfection of the fluid line. The optimum dwell period and frequency for exchanging the heated fluid is determined so that the heated fluid is left resident in the line to exert a cidal effect but not so long that the it cools to the point of being ineffective, nor changed so frequently that that the time spent with no hot water resident in the line begins to detract (e.g., unduly prolong) the disinfection process. A representative cycle is introducing water at a temperature of about 85 degrees C, allowing it to reside in the fluid line for about 10 seconds, withdrawing the water, and then reintroducing water at 85 degrees C. The process continues for 1-2 hours. Variation from the representative cycle will be expected based on parameters such as the degree to which disinfection is to be achieved, the length and diameter of the fluid line, the temperature of the fluid, the ambient temperature, the presence of elements in the fluid line that contribute to heat loss, the material used for fluid line tubing, and whether the fluid comprises water or a disinfection solution such as a dilute citric acid solution. The optimum dwell period and frequency of the cycles can be determined experimentally from the teachings described herein.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +2
Engineered adsorbent structures for kinetic separation
ActiveUS7645324B2High selectivityIncrease cycle frequencyGas treatmentMethane captureProduction rateSorbent
Improved adsorbent sheet based parallel passage adsorbent structures for enhancing the kinetic selectivity of certain kinetic-controlled adsorption processes, such as PSA, TSA and PPSA processes, and combinations thereof, are provided. The enhancements in kinetic selectivity made possible through the implementation of the present inventive improved adsorbent structures may unexpectedly enable significant intensification of selected kinetic adsorption processes relative to attainable performance with conventional adsorbent materials in beaded or extruded form. Such process intensification enabled by the present inventive adsorbent structures may provide for increased adsorption cycle frequencies, and increased gas flow velocities within the adsorbent beds, which may increase the productivity and / or recovery of a kinetic adsorption system incorporating the inventive adsorbent structures.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
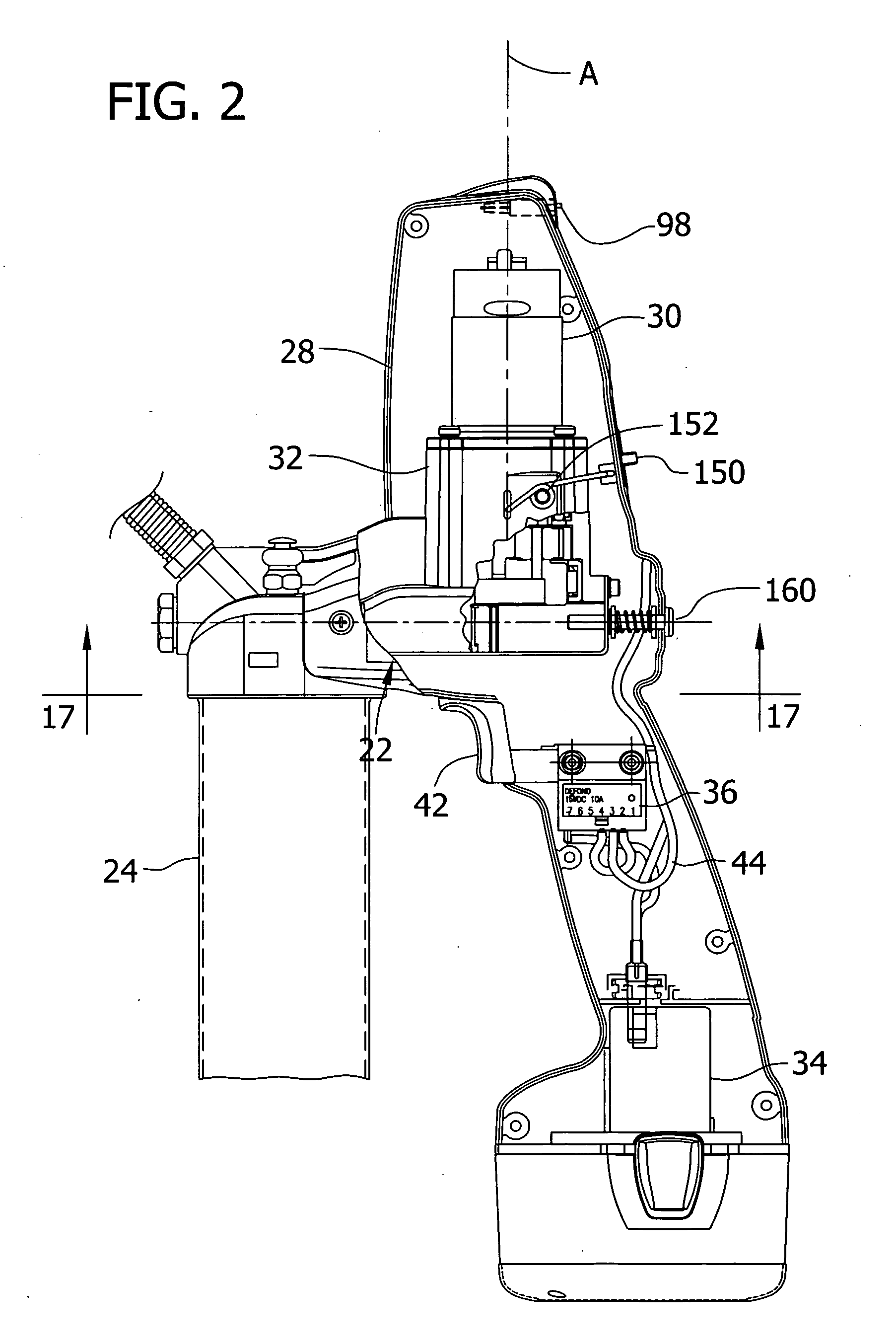
Grease gun
InactiveUS20060108180A1Avoid damageGuaranteed economic efficiencyManual lubricationMachines/enginesElectricityTransmitted power
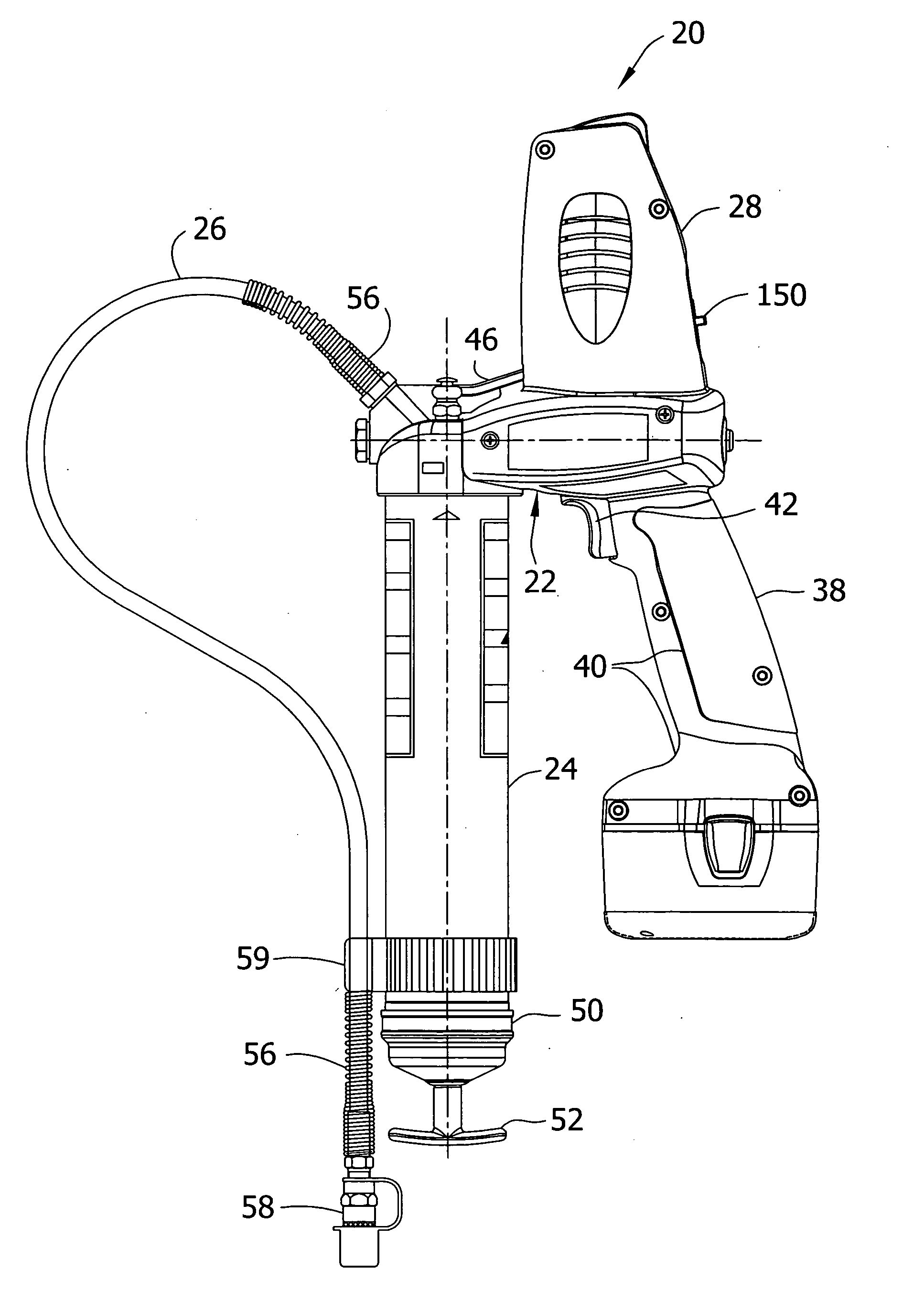
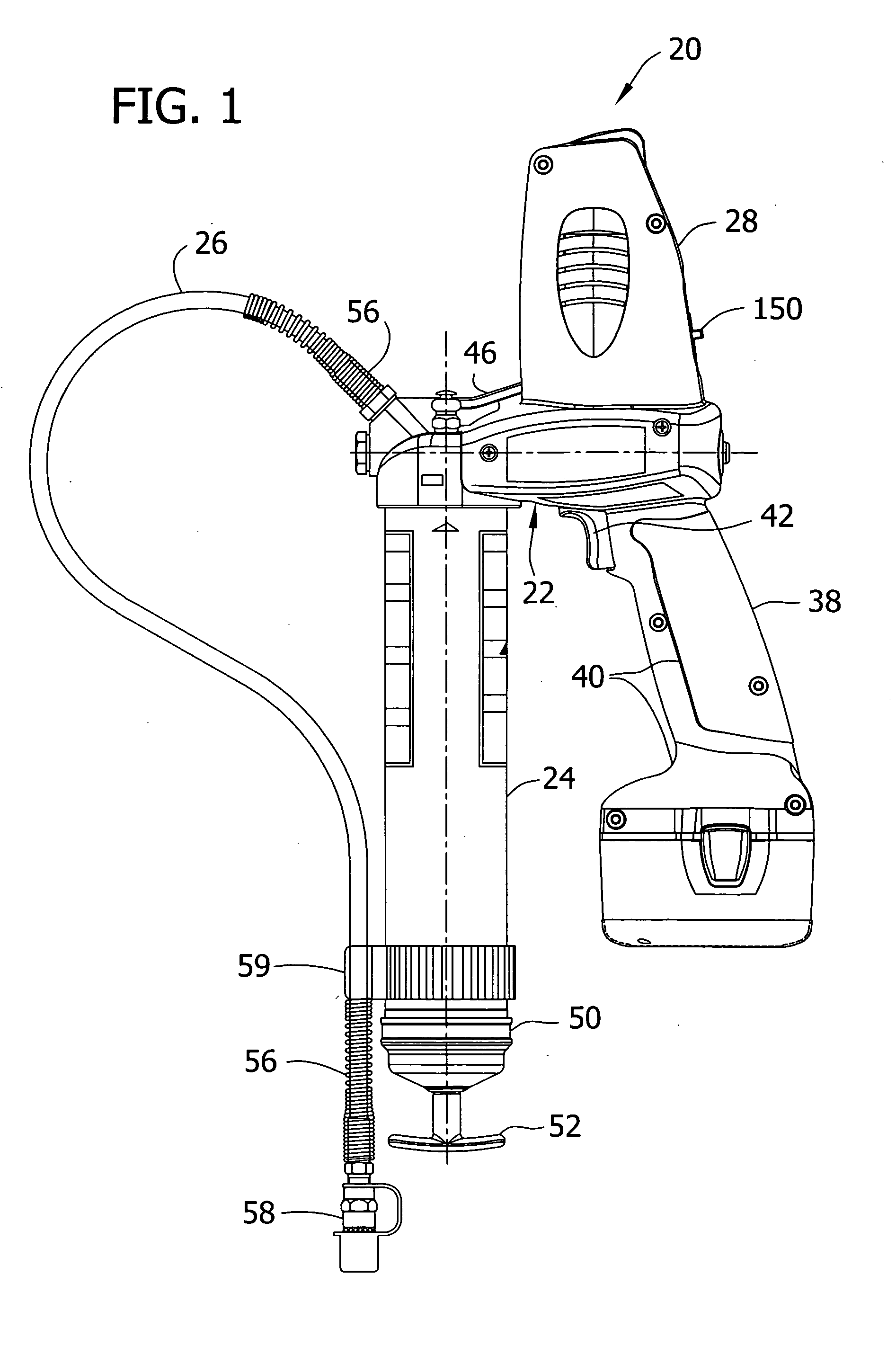
A device for dispensing a viscous fluid, such as grease gun for dispensing lubricant. The grease gun delivers lubricant with a selectable variation in pressure and / or output. It includes a reservoir, a pump having a reciprocating plunger, an electric motor driving the pump, and a variable speed transmission for transmitting power from the motor to the pump. The transmission has at least two different output speed settings adapted to be selected for reciprocating the plunger at different cyclical frequencies. A cycle indicator provides an indication corresponding to a quantity of lubricant dispensed. Embodiments of the grease gun include a pressure relief valve which inhibits damage due to an over-pressure condition, and a circuit breaker which inhibits damage due to electrical overload.
Owner:LINCOLN INDUSTRIES CORP
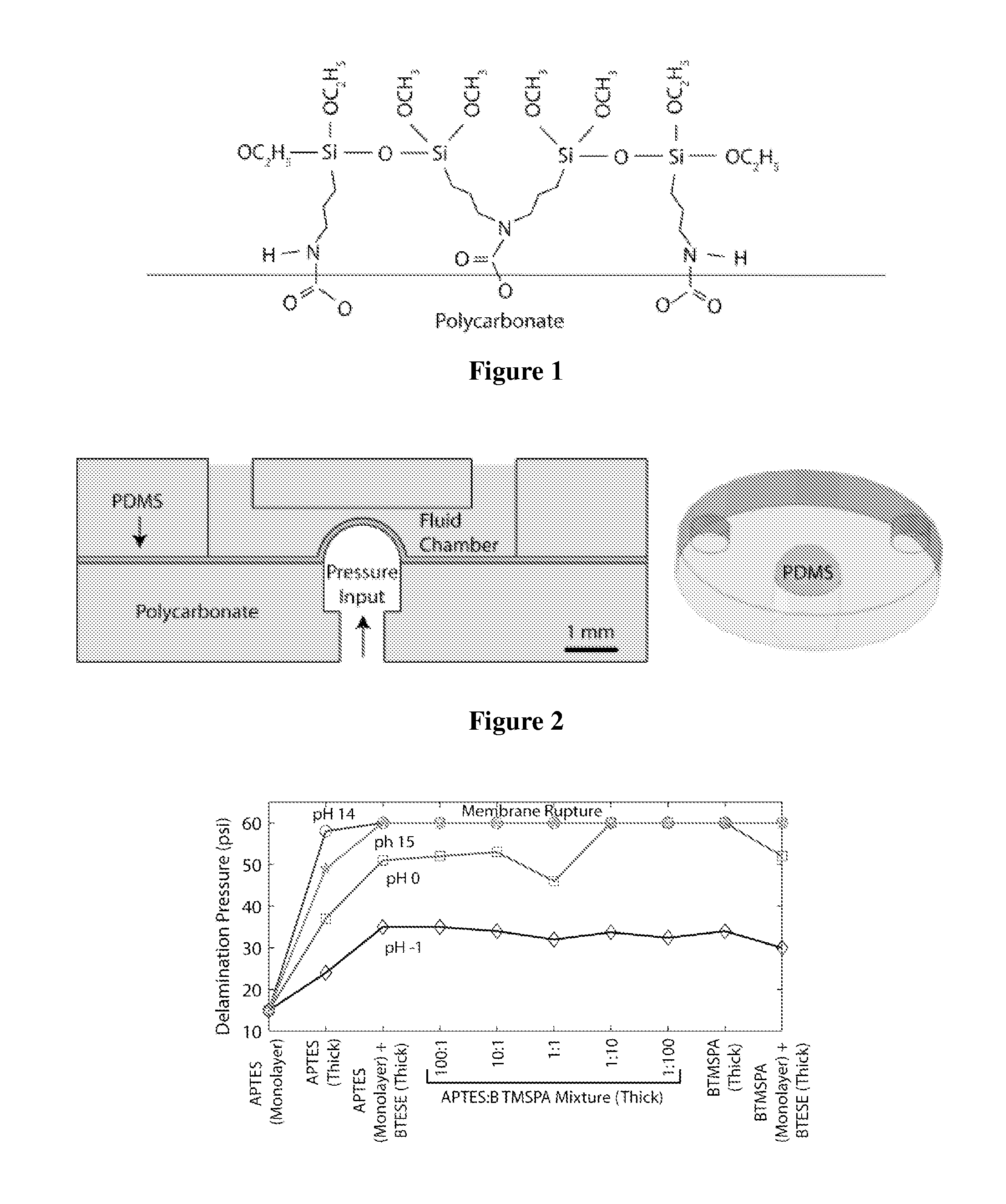
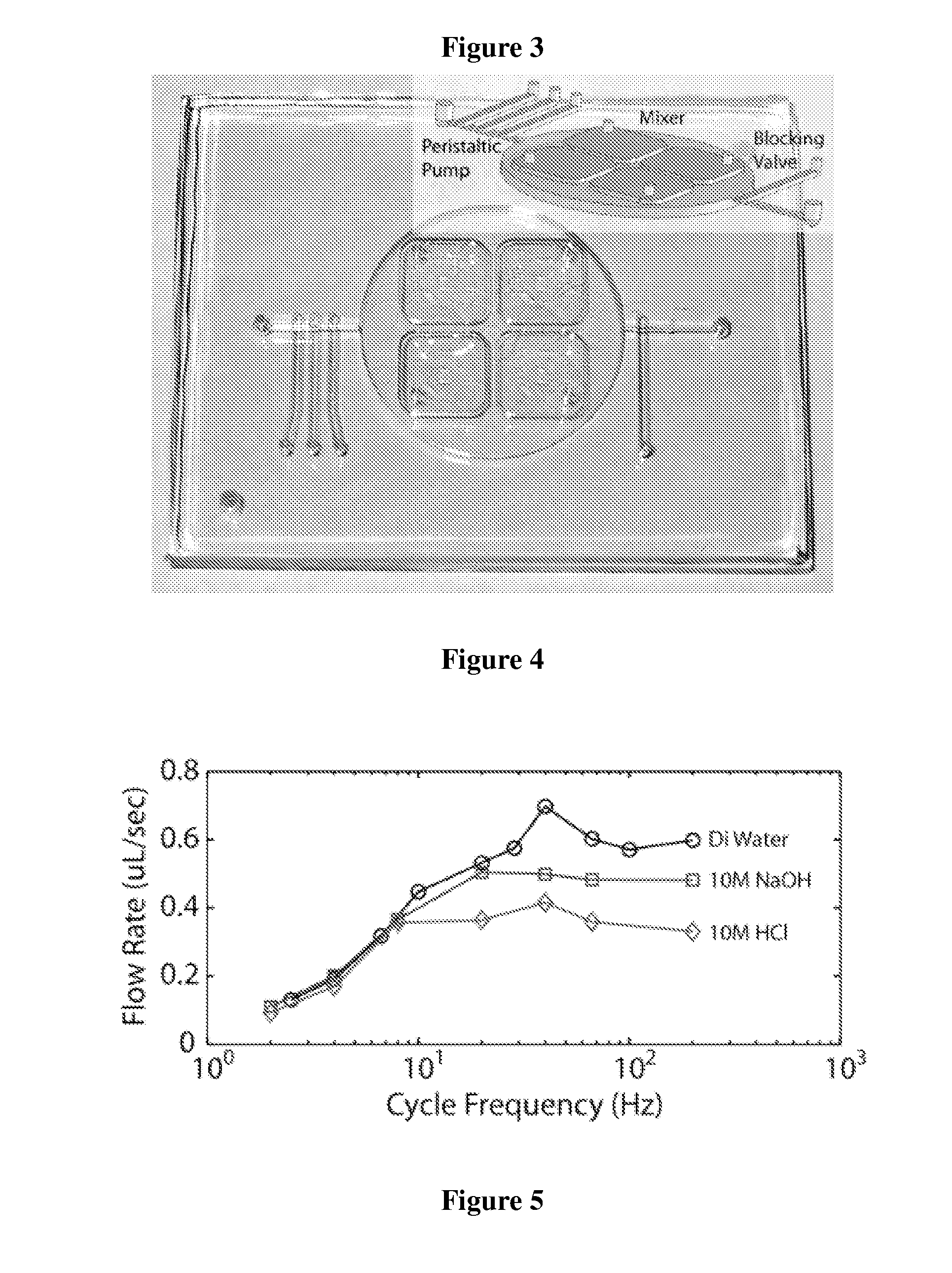
Method of hydrolytically stable bonding of elastomers to substrates
ActiveUS20110195260A1Hydrolytic stabilityAdhesive processesLaboratory glasswaresElastomerPeristaltic pump
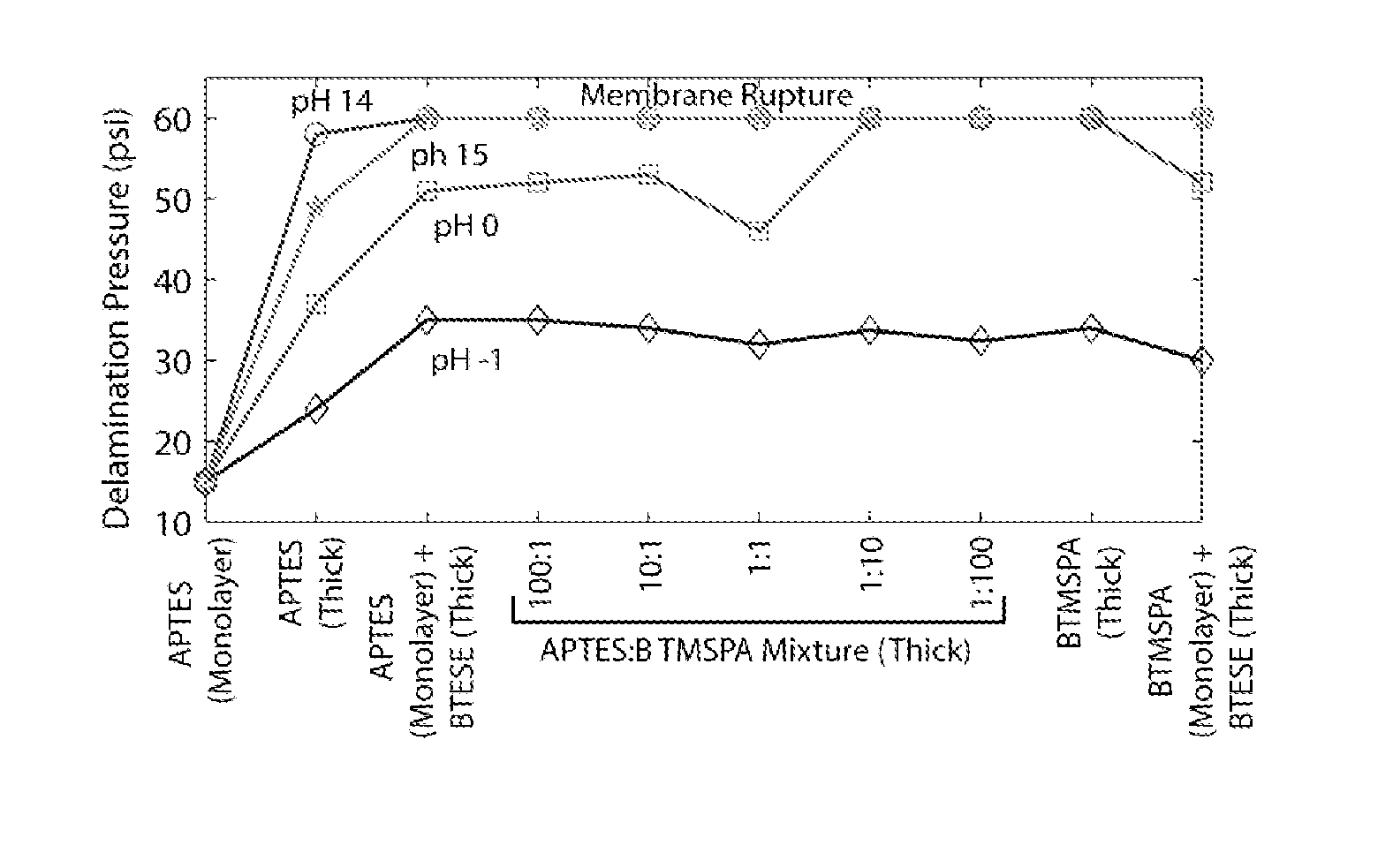
Active devices such as pumps and mixers have been fabricated in plastic-PDMS hybrid devices. By utilizing functionalized bis-silane primers, bond strength between Polycarbonate or PMMA and PDMS improved in dry and aqueous environments. Plastic-primer-PDMS layers exposed to acid and base solutions at 70° C. for 2 hours showed no signs of delamination at 30 psi for pH −1 to 15 and 60 psi for pH 0 to 15. A peristaltic pump fabricated in polycarbonate achieved consistent flow rates up to peristaltic cycle frequencies of 10 Hz in water, 1OM HCl, and 1OM NaOH solutions.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Joint spectrum detection method based on energy-cyclostationary characteristic
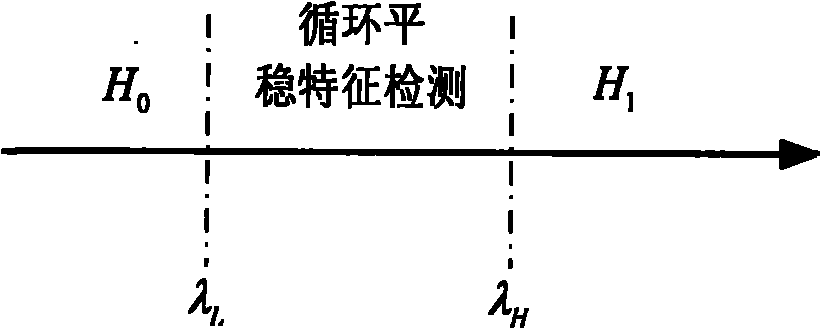
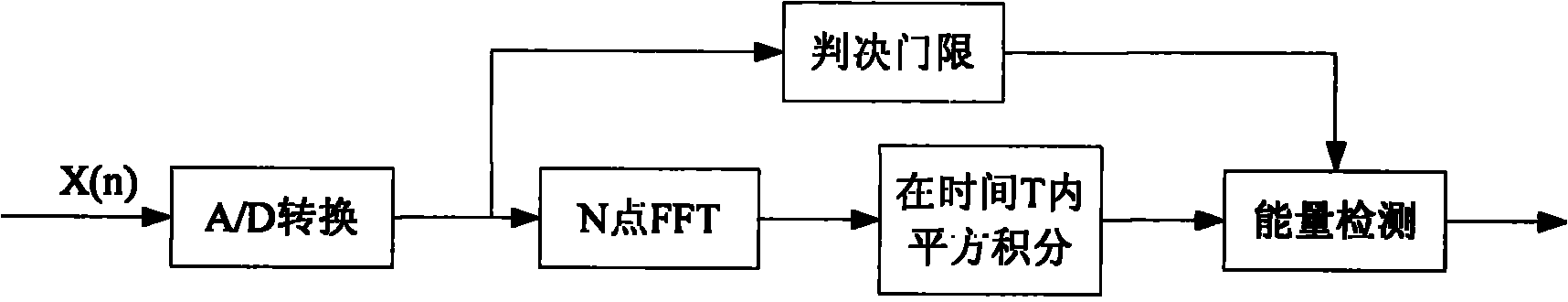
InactiveCN101834630AImprove detection rateEasy to detectTransmission monitoringWireless communicationFrequency spectrumEnergy based
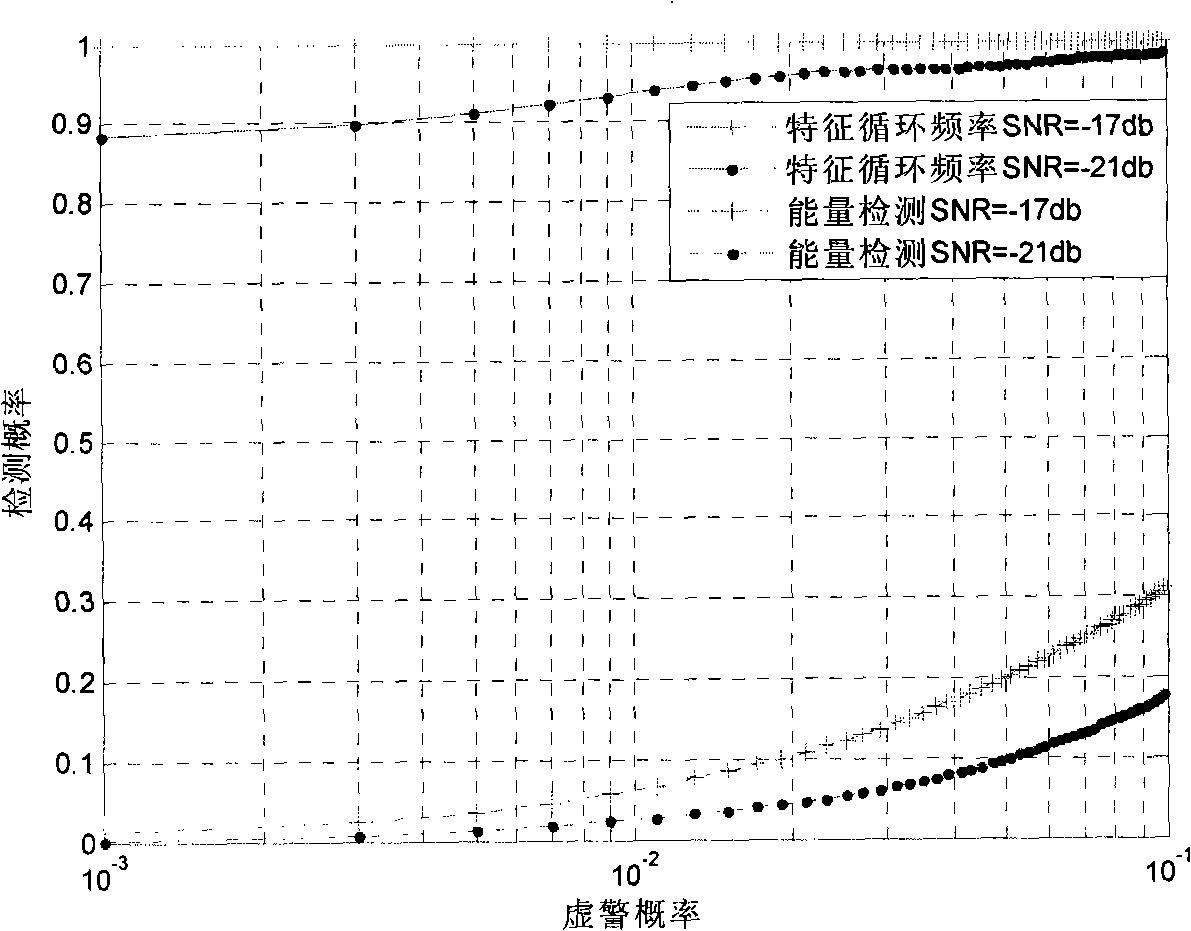
The invention relates to a joint spectrum detection method based on energy-cyclostationary characteristic for improving the detection probability and reducing the complexity as soon as possible at the same time. The invention utilizes the characteristics of energy detection and cyclostationary characteristic detection, and realizes spectrum joint detection in cognitive radio systems by utilizing two thresholds. In the invention, an energy detection method of the two thresholds is utilized for crude detection, if the energy is at both ends of the two thresholds, the energy of a signal to be detected is calculated, the energy obtained from the calculation is compared with the two predetermined thresholds, if the energy is no less than the high threshold, a primary user signal is determined to exist; if the energy is no more than the low threshold, the primary user signal is determined to not exist; and if the energy is between the two thresholds, the cyclostationary characteristic is utilized for detection, and the value of a specific cycle frequency is calculated and is compared with the cycle detection threshold, if the value is no less than the threshold, the primary user signal is determined to exist, and the primary user signal is determined to not exist if the value is no more than the threshold.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
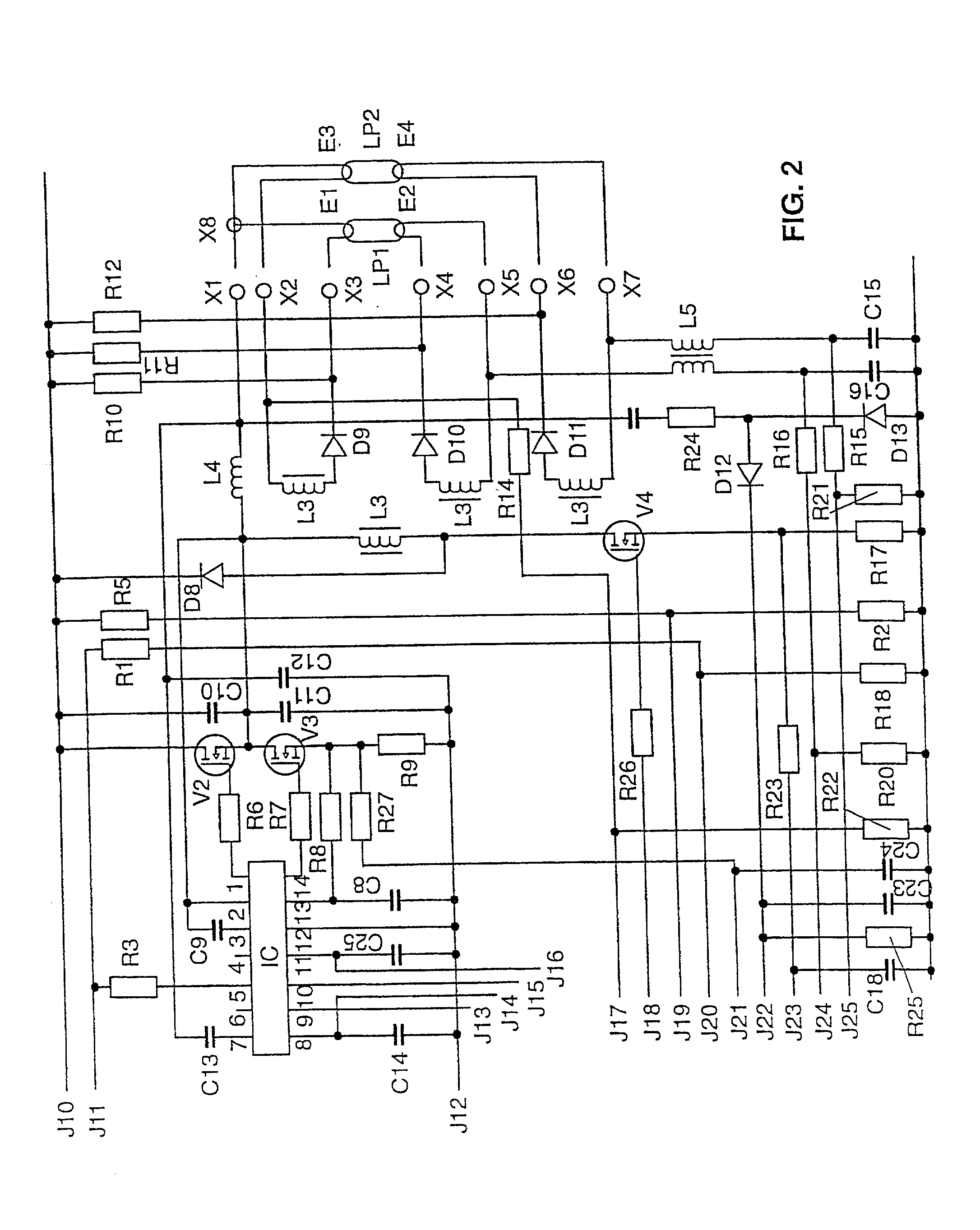
Microcontroller, switched-mode power supply, ballast for operating at least one electric lamp, and method of operating at least one electric lamp
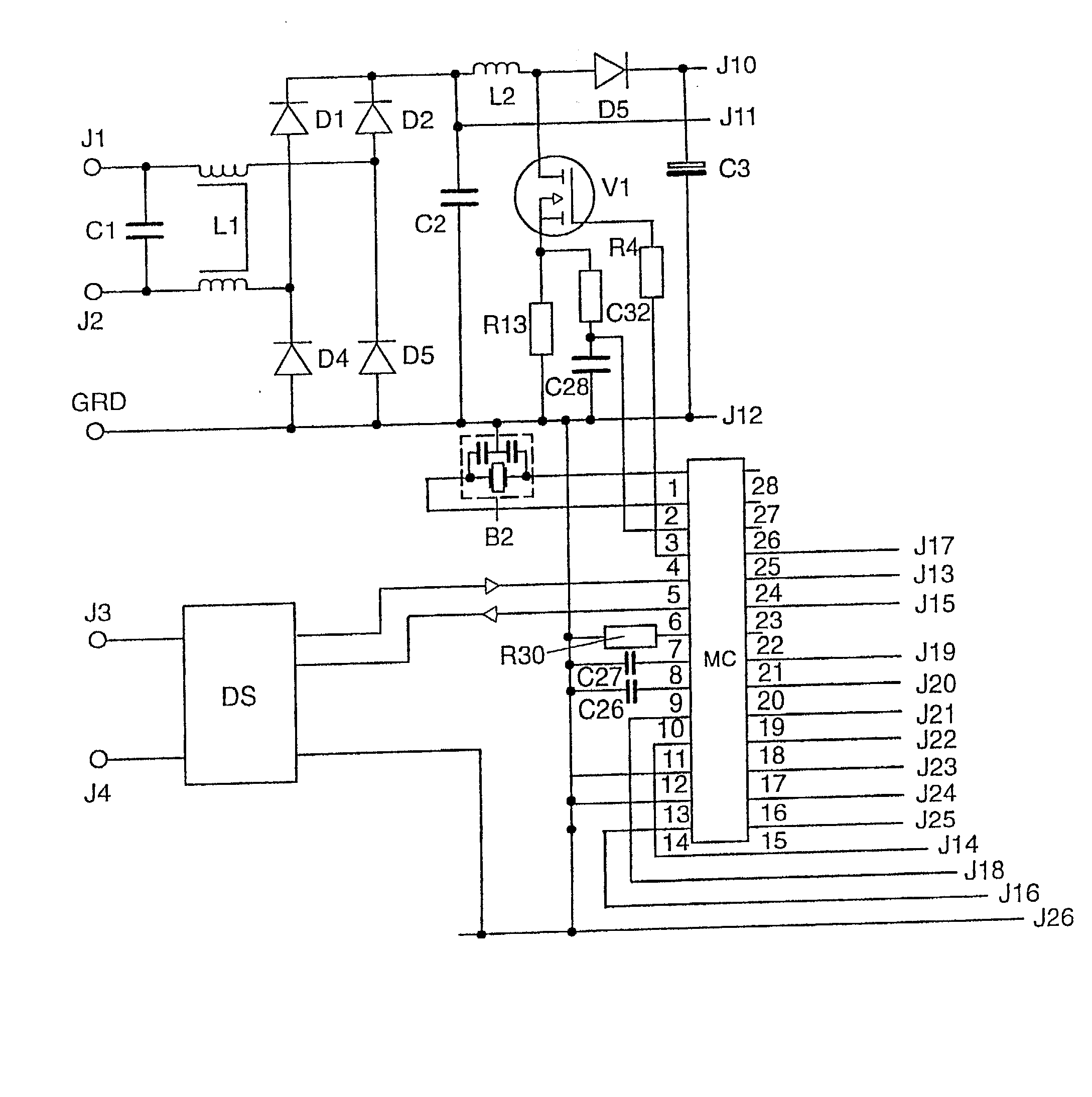
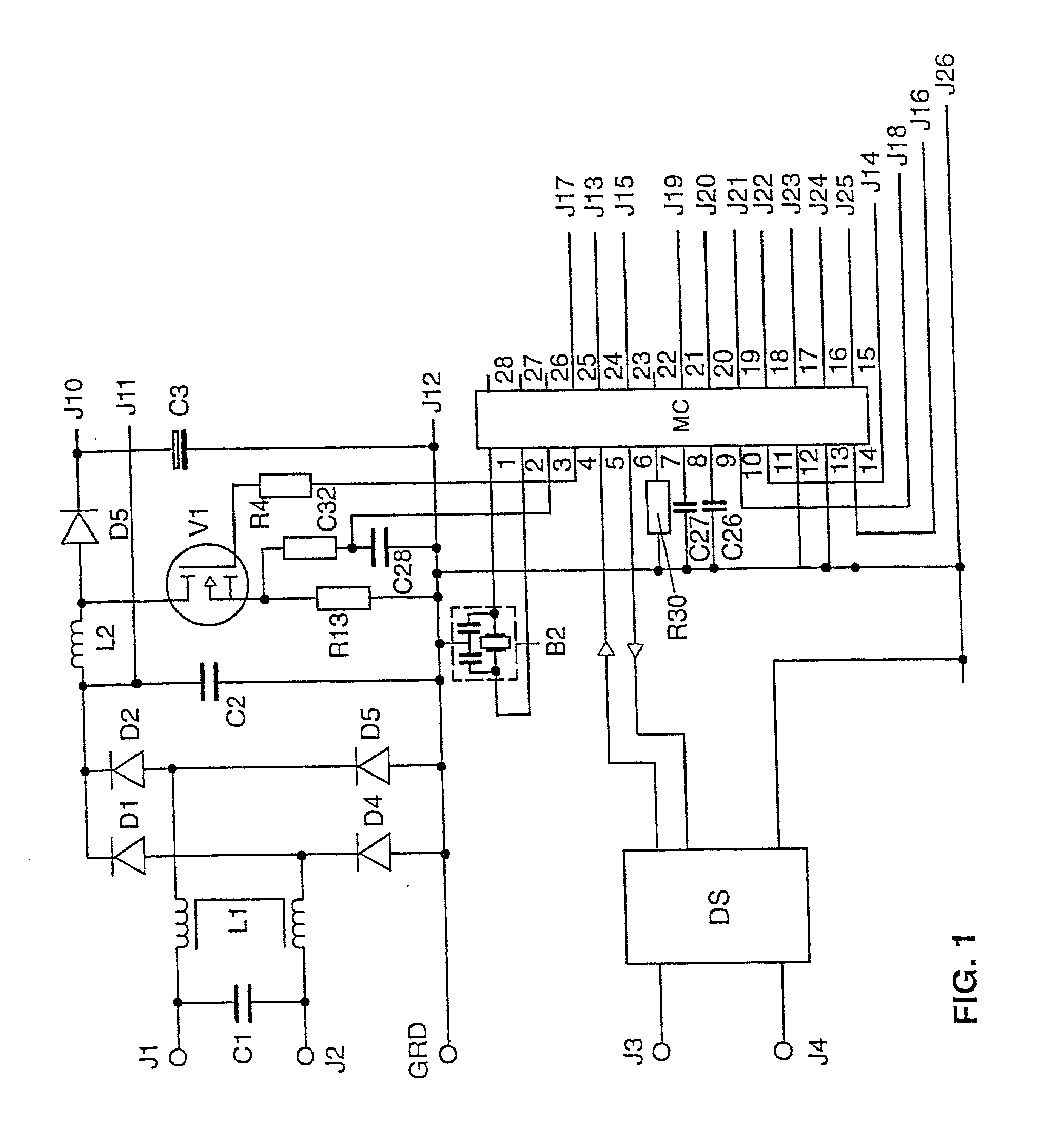
InactiveUS20020097008A1Save componentSimple meansElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementMicrocontrollerControl signal
The invention relates to a microcontroller (MC) having at least one device (G) for generating pulse-width modulated or frequency modulated control signals for a switched-mode power supply. According to the invention, this device (G) has a device (SQ1, SS1) for the alternate charging and discharging of an electric charge store (C27) that can be connected to the microcontroller (MC), control means for this device (SQ1, SS1) for controlling the charging and discharging operations, and evaluation means in order to evaluate the time periods which are needed for the individual charging and discharging operations; to generate pulse-width modulated or frequency modulated control signals. The microcontroller (MC) according to the invention generates finely graduated, frequency modulated or pulse-width modulated control signals which are independent of the operating cycle frequency of the microcontroller (MC). The invention further relates to a switched-mode power supply having such a microcontroller (MC) and an electronic ballast for operating at least one electric lamp, and also to an operating method for electric lamps. The frequency modulated or pulse-width modulated control signals for the inverter transistors (V2, V3), for the step-up converter transistor (V1) and for the transistor (V4) of the lamp electrode heating device of the ballast are generated directly by the microcontroller (MC).
Owner:PATENT TREUHAND GESELLSCHAFT FUR ELECTRIC GLUEHLAMPEN MBH
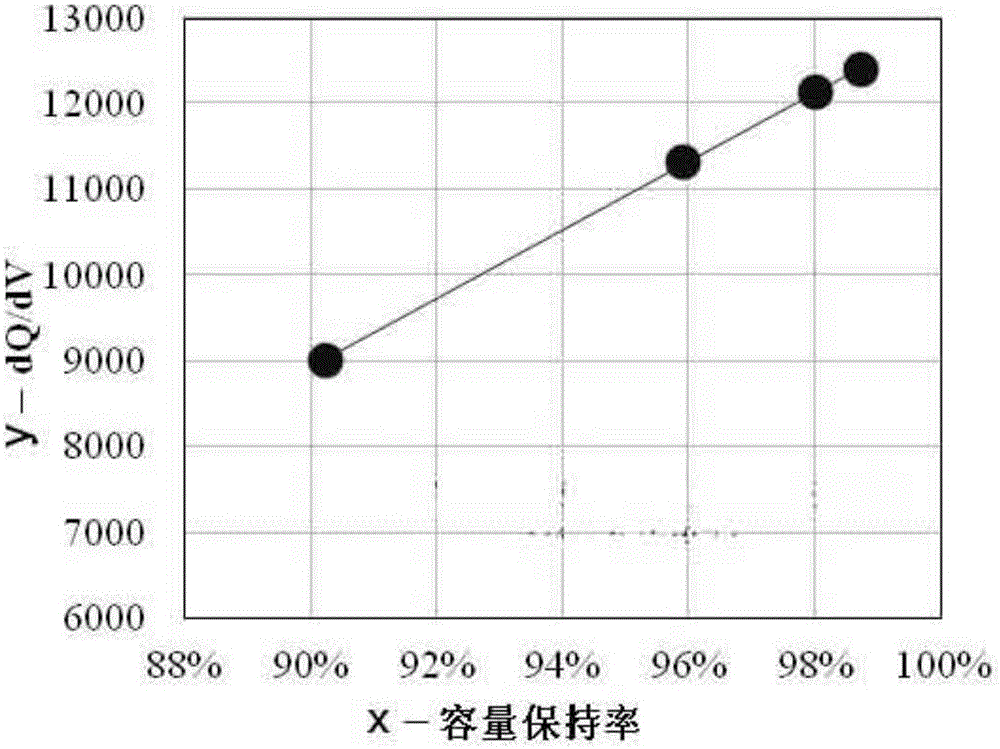
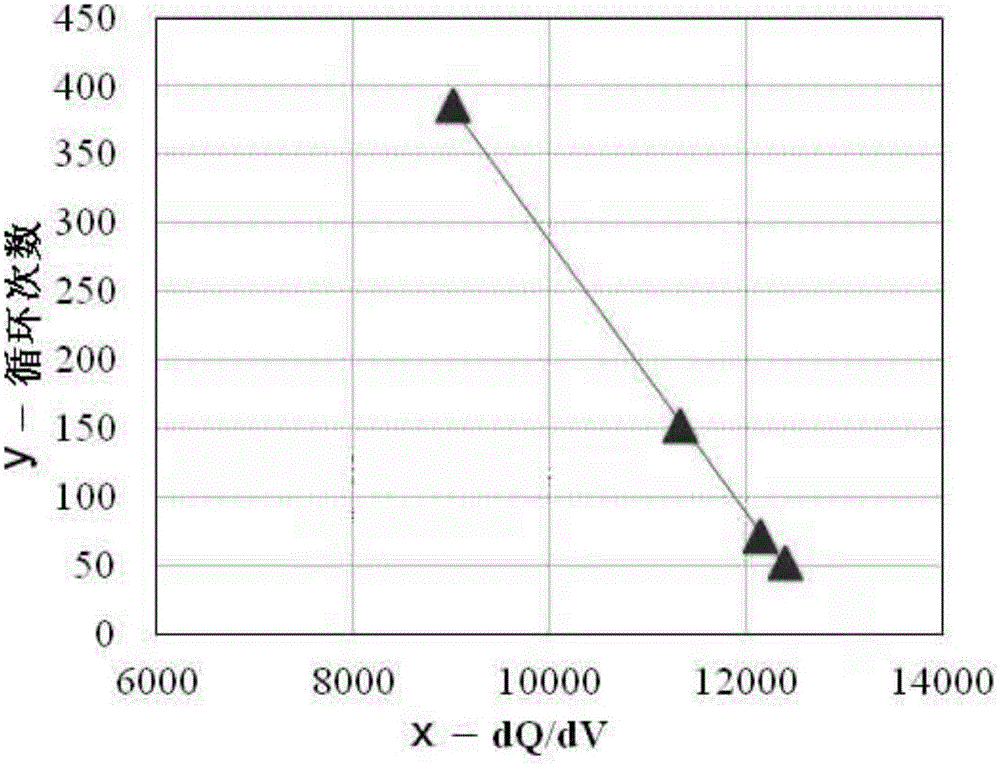
Battery cycle life prediction method
ActiveCN105068009ACycle Life PredictionRapid Evaluation ToolElectrical testingCapacity lossPower flow
The invention discloses a cycle system mode capable of achieving life prediction. The cycle system mode comprises the following steps: placing a to-be-evaluated battery in a cycling condition needing to be evaluated to perform a cycle test, recording an accumulated cycle frequency and the cycle capacity maintenance rate of the battery, performing small-current charging and discharging tests on the battery after each certain cycle frequency or capacity loss rate at the same time, recording voltage and capacity data of the battery in the charging and discharging process, and recording the corresponding cycle frequency and the corresponding capacity maintenance rate; and then performing data fitting and calculation according to the accumulated cycle frequency and the cycle capacity maintenance rate of the battery and differential data of the capacity on voltage, and performing prediction on the battery cycle life. Compared with a conventional cycle test, the cycle system mode greatly shortens the service life evaluation period and prevents energy consumption and resource waste which are generated by a long-term test; and, furthermore, because the data fitting is performed on the basis of short-term actually measured data, the cycle system mode has higher universality and high prediction accuracy compared with a pure theory calculation and experience model.
Owner:深圳一特科技有限公司
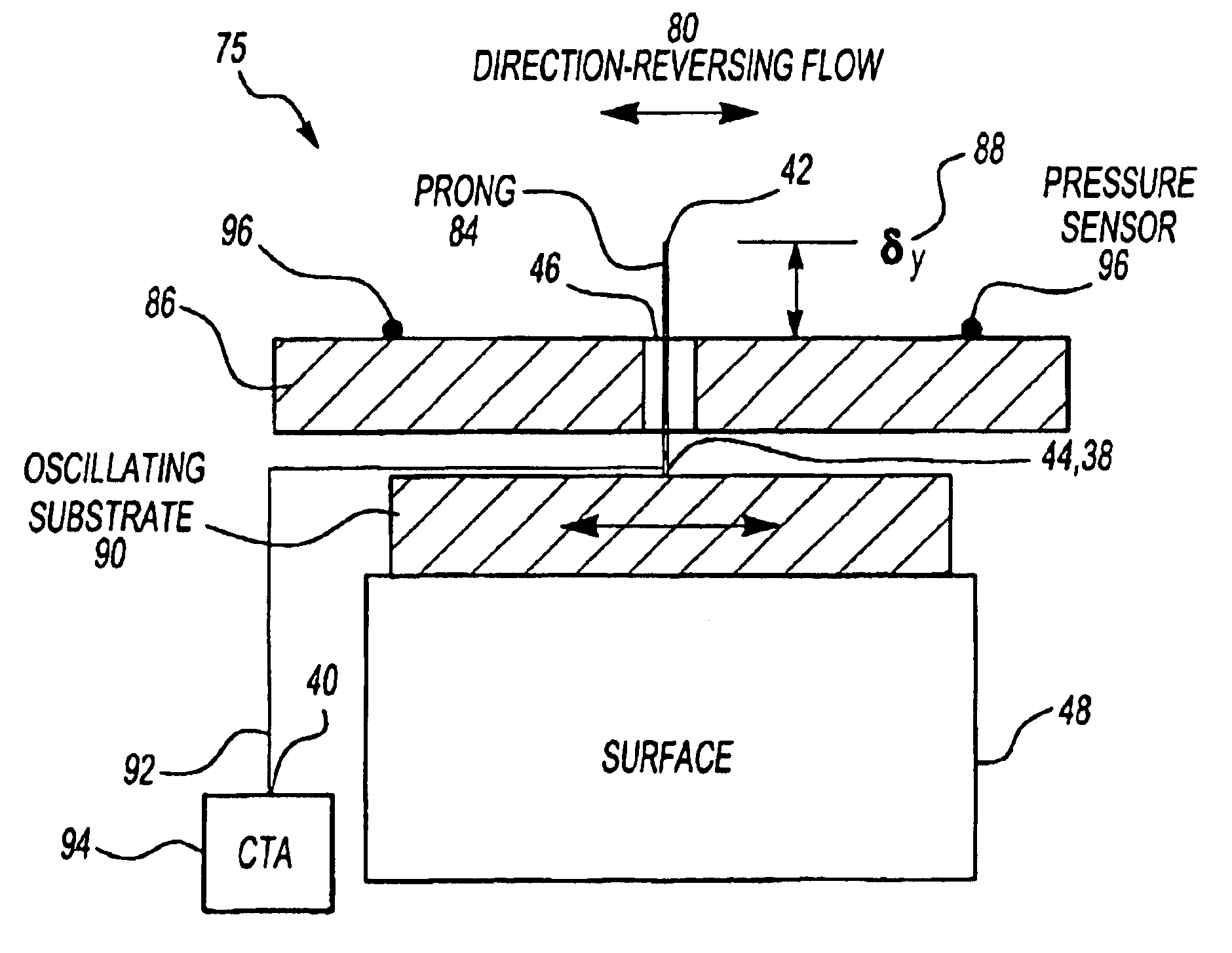
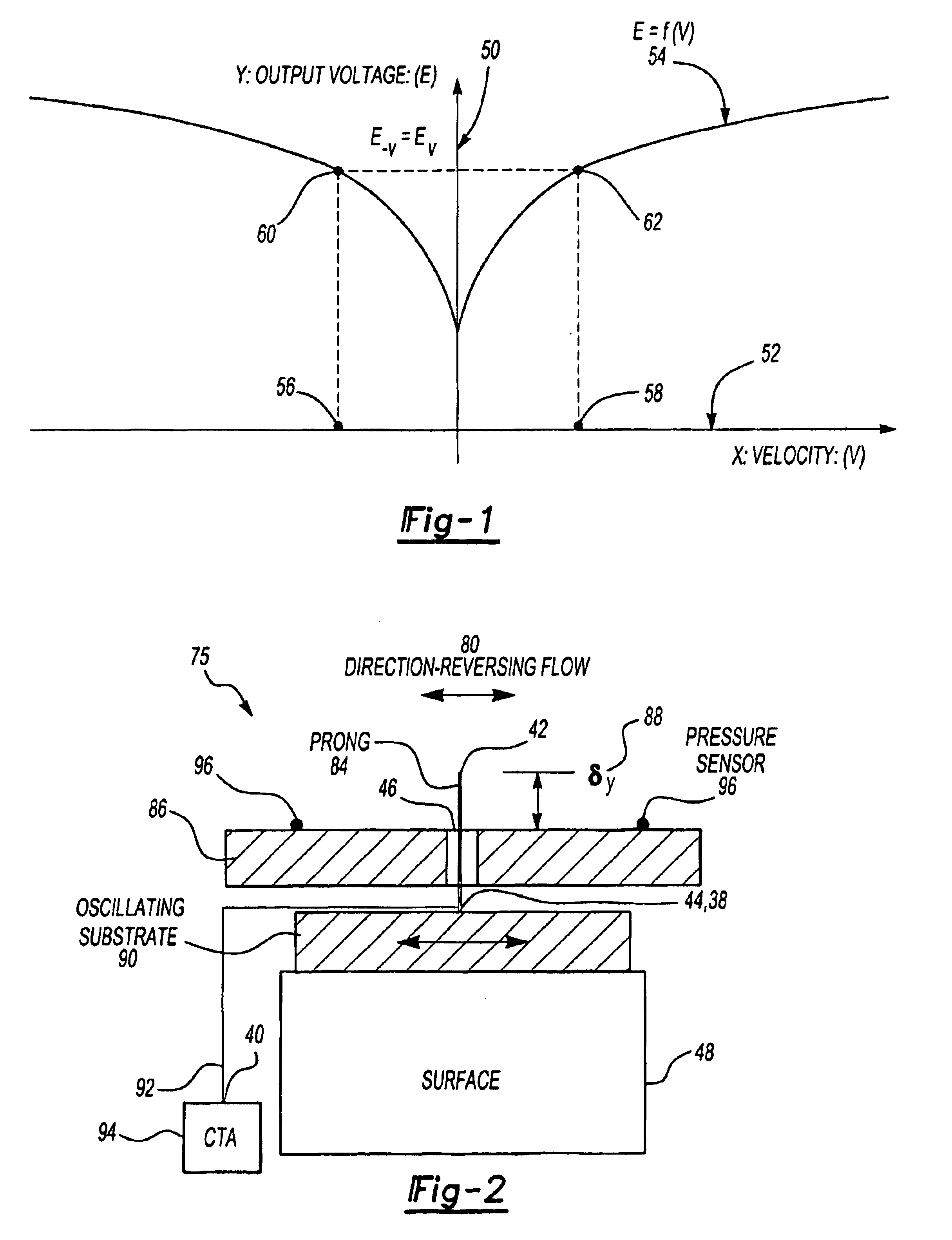
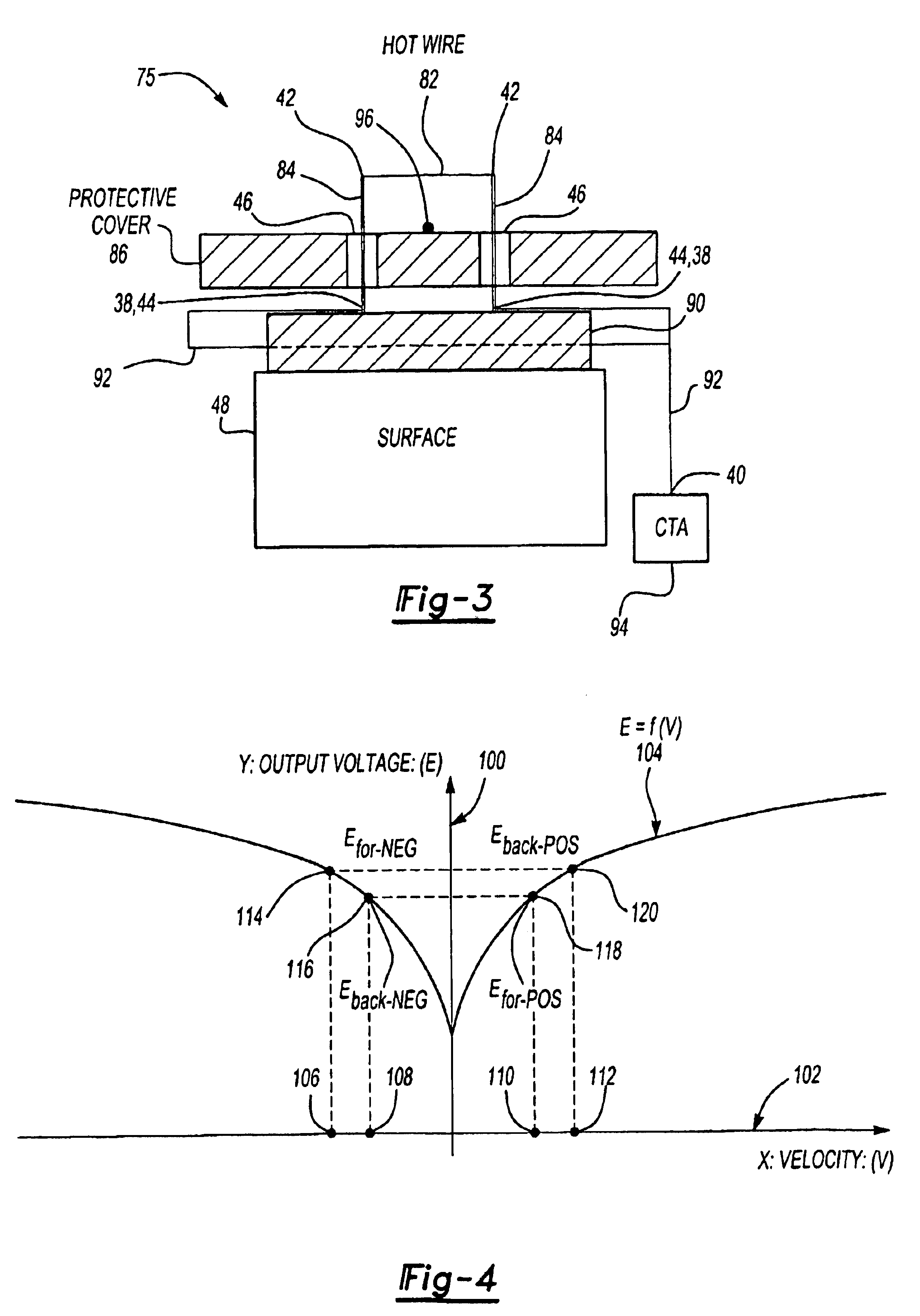
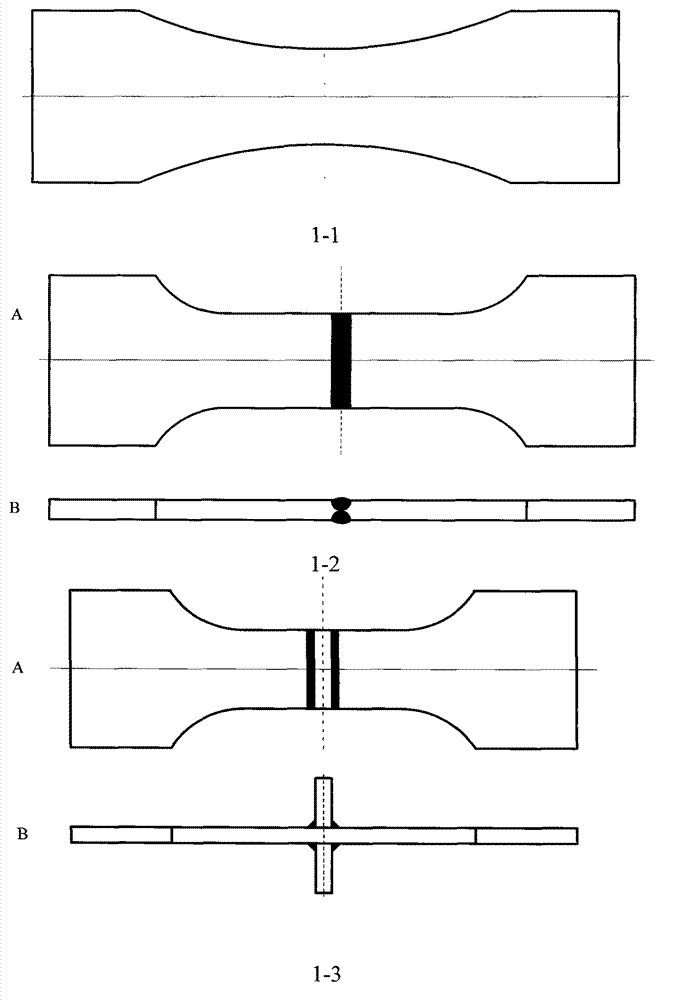
Oscillating hot wire of hot film flow sensor
InactiveUS6901795B2High spatial and temporal resolutionVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsFluid speed measurement using thermal variablesMeasurement deviceTemporal resolution
This invention is a flow measurement device that has high spatial (less than 1.0×1.0 mm2) and temporal resolution (greater than 10 s to 100 s kHz) to measure flow properties in unsteady and direction-reversing conditions. The present invention can have an oscillating substrate, hot wire prongs, a hot wire attached to the hot wire prong, sensor leads from the prongs to a constant temperature anemometry circuit (CTA), means for the oscillating substrate to oscillate the substrate at a frequency greater than a characteristic cycle frequency of the flow to be measured, at a frequency less than a CTA bandwidth frequency, and such that a frequency and amplitude (Aw) of oscillation are sufficiently large to be detected, and means to obtain two measurements during an oscillation cycle when the hot wire is at its maximum oscillation velocity. Alternatively, the prongs can be eliminated and a hot wire or hot film can be directly applied to the oscillating substrate.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
System for predicting fatigue limit of magnesium alloy member based on infrared thermal imaging, and method thereof
InactiveCN103076243ADetermining the fatigue limitAdvancedMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesControl systemFatigue testing
The invention discloses a system for predicting the fatigue limit of a magnesium alloy member based on infrared thermal imaging, and a method thereof. The system comprises: fatigue tester jigs (1); a fatigue test piece (2) comprising a magnesium alloy base material and a welded joint test piece; a fatigue test control system (3); a fatigue test system (4) used for the fatigue test of the magnesium alloy base material and the welded joint test piece to obtain a magnesium alloy fatigue limit under a cycle frequency of 10<7 >; an infrared temperature measurement system (8) for obtaining the surface temperature change curve of the fatigue test piece (2) in the fatigue test process and recording the temperature change data of the fatigue test piece (2) in the fatigue process; and a comprehensive analysis system (5) applying origin software to compare the obtained magnesium alloy fatigue limit with a fatigue limit obtained through routine fatigue tests in order to judge the measurement accuracy. The system and the method can be used for estimating the dangerous point and the fatigue limit of a welding structure in service.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
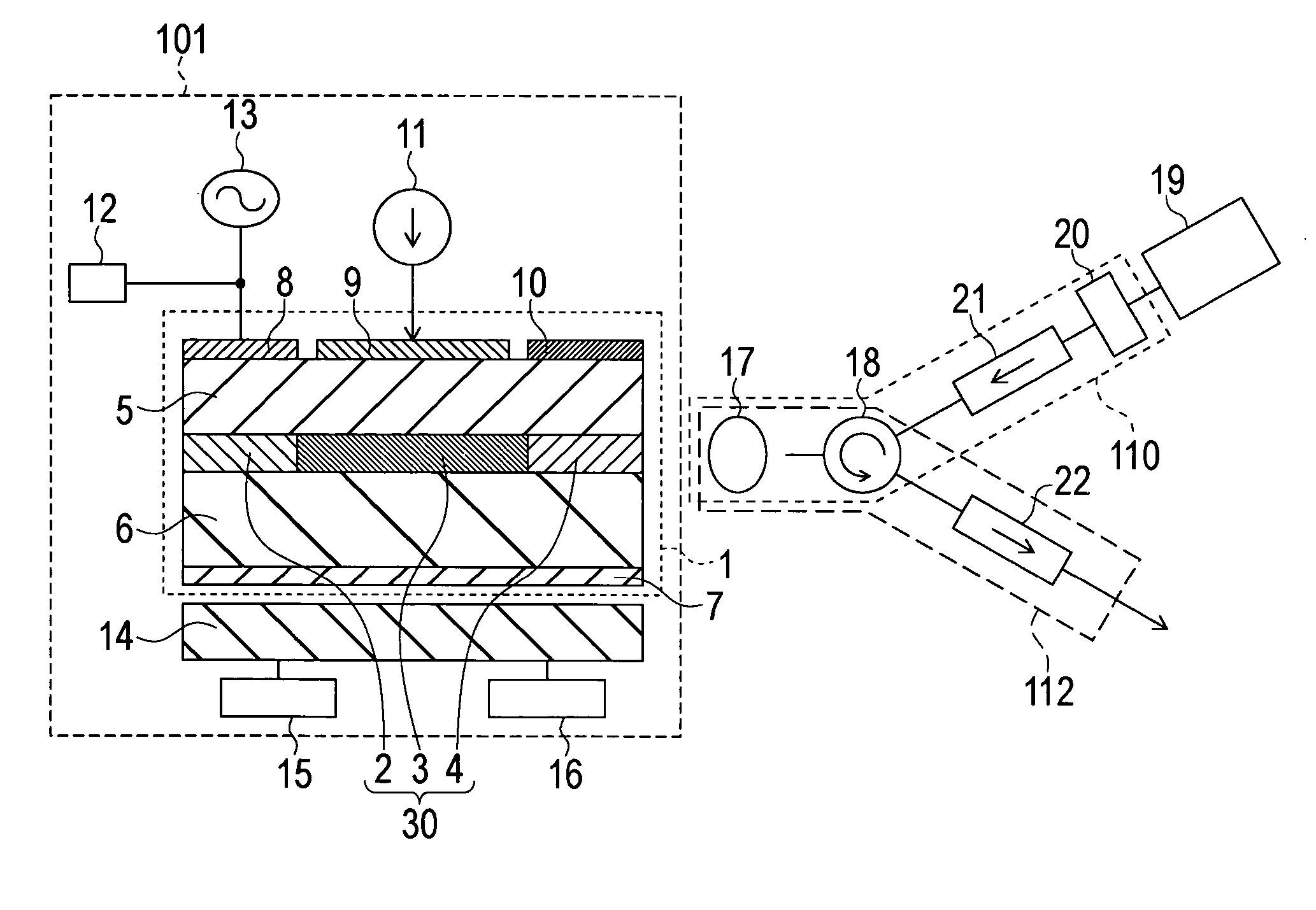
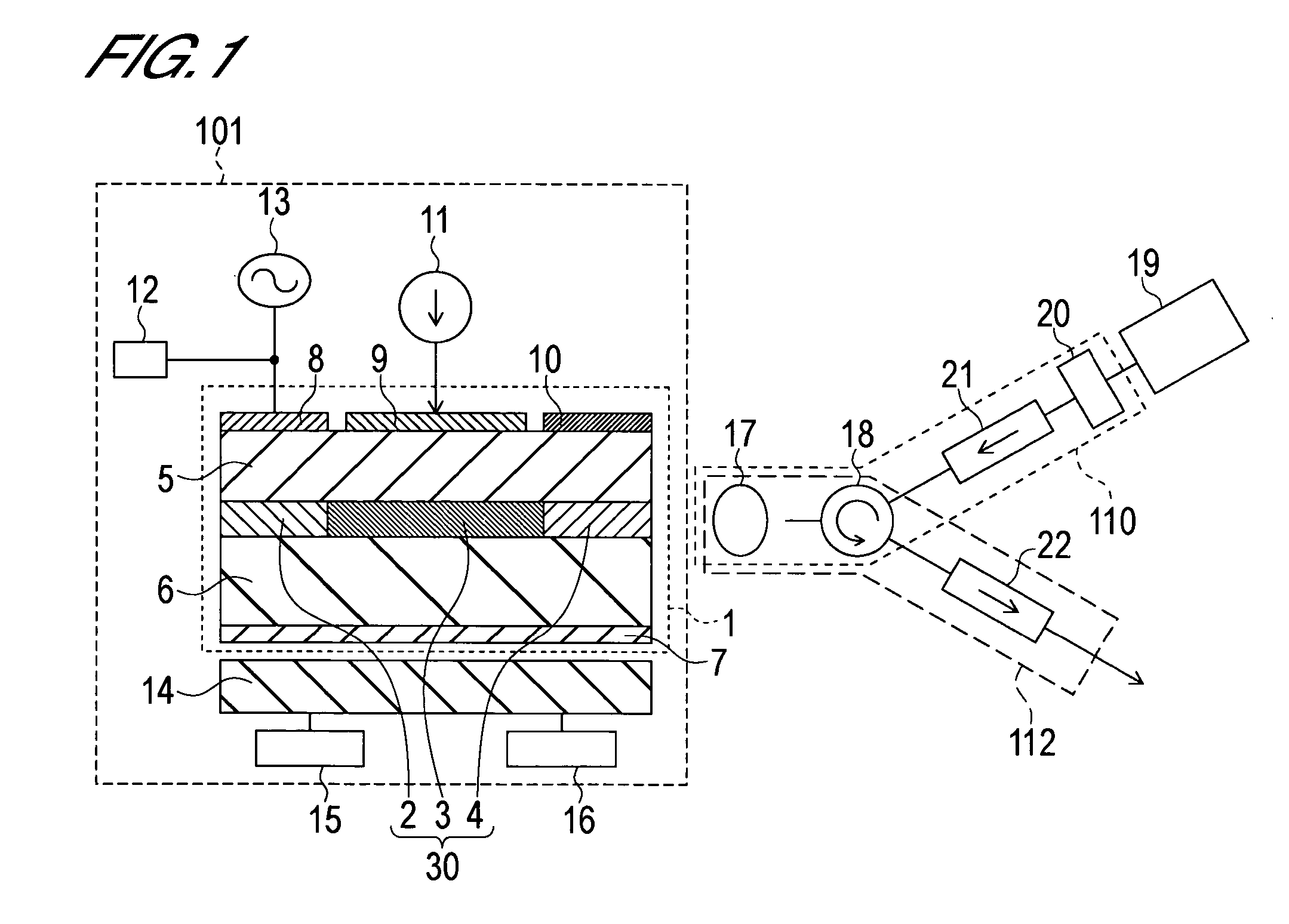
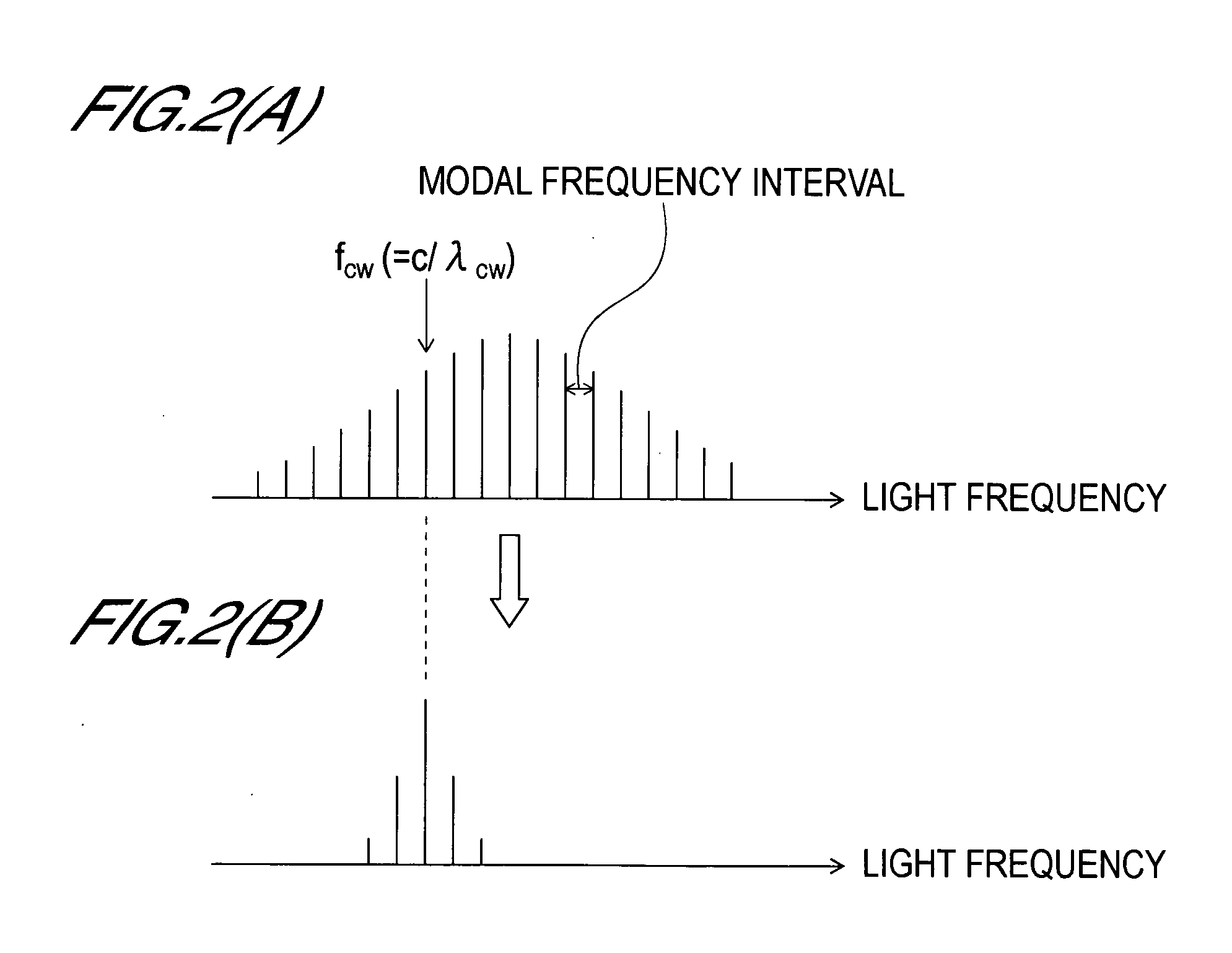
Mode-locked laser diode device and wavelength control method for mode-locked laser diode device
InactiveUS20060045145A1Compactness be sufficientlyOperation be sufficientlyLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceVoltage sourceOptical communication
The present invention generates optical pulses of which the wavelength width in the wavelength variable area is sufficiently wide and of which frequency chirping is suppressed enough to be used for optical communication systems. The present invention is constructed by an optical pulse generation section 101 including MLLD1, CW light source 19, first optical coupling means 110 and second optical coupling means 112. An optical wave guide 30 which includes an optical gain area 3, optical modulation area 2 and a passive wave-guiding area 4 is created in the MLLD. Constant current is injected into the optical gain area from the first current source 11 via the p-side electrode 9 and the n-side common electrode 7. Reverse bias voltage is applied to the optical modulation area 2 by a voltage source 12 via the p-side electrode 8 and the n-side common electrode. The modulation voltage with a frequency obtained by multiplying the cyclic frequency of the resonator of the MLLD by a natural number is applied to the optical modulation area by a modulation voltage source 13. The output light of the CW light source is input to the optical wave guide of the MLLD via the first optical coupling means, and the output light of the MLLD is output to the outside via the second optical coupling means.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
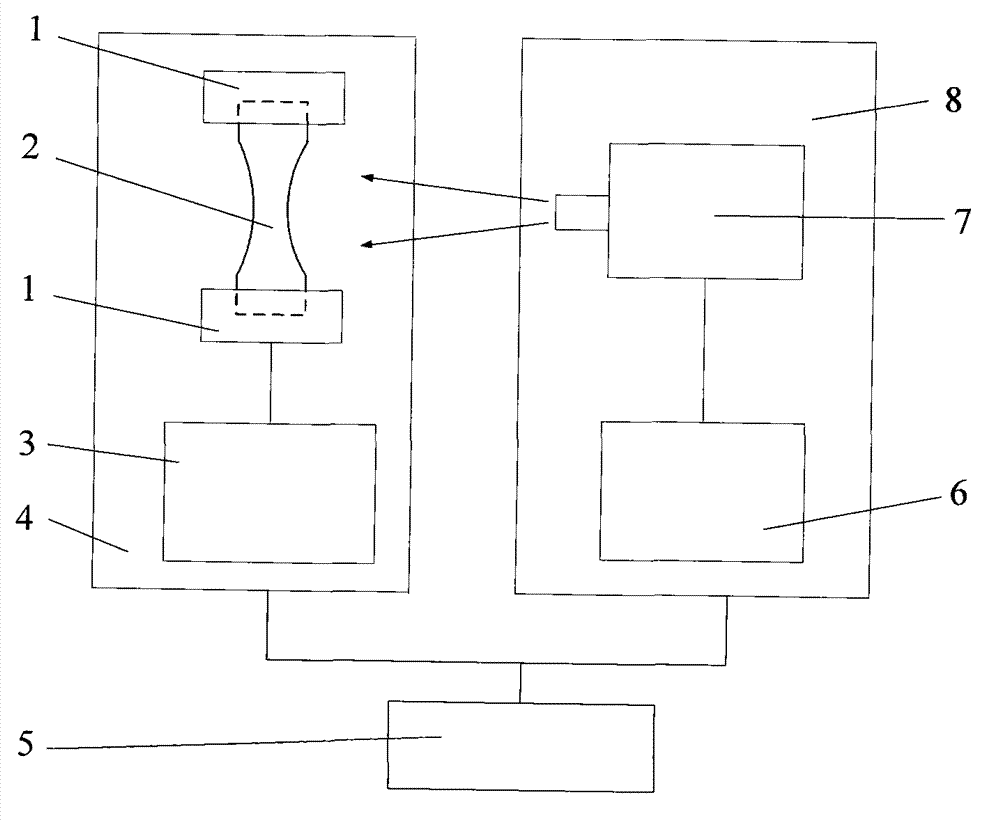
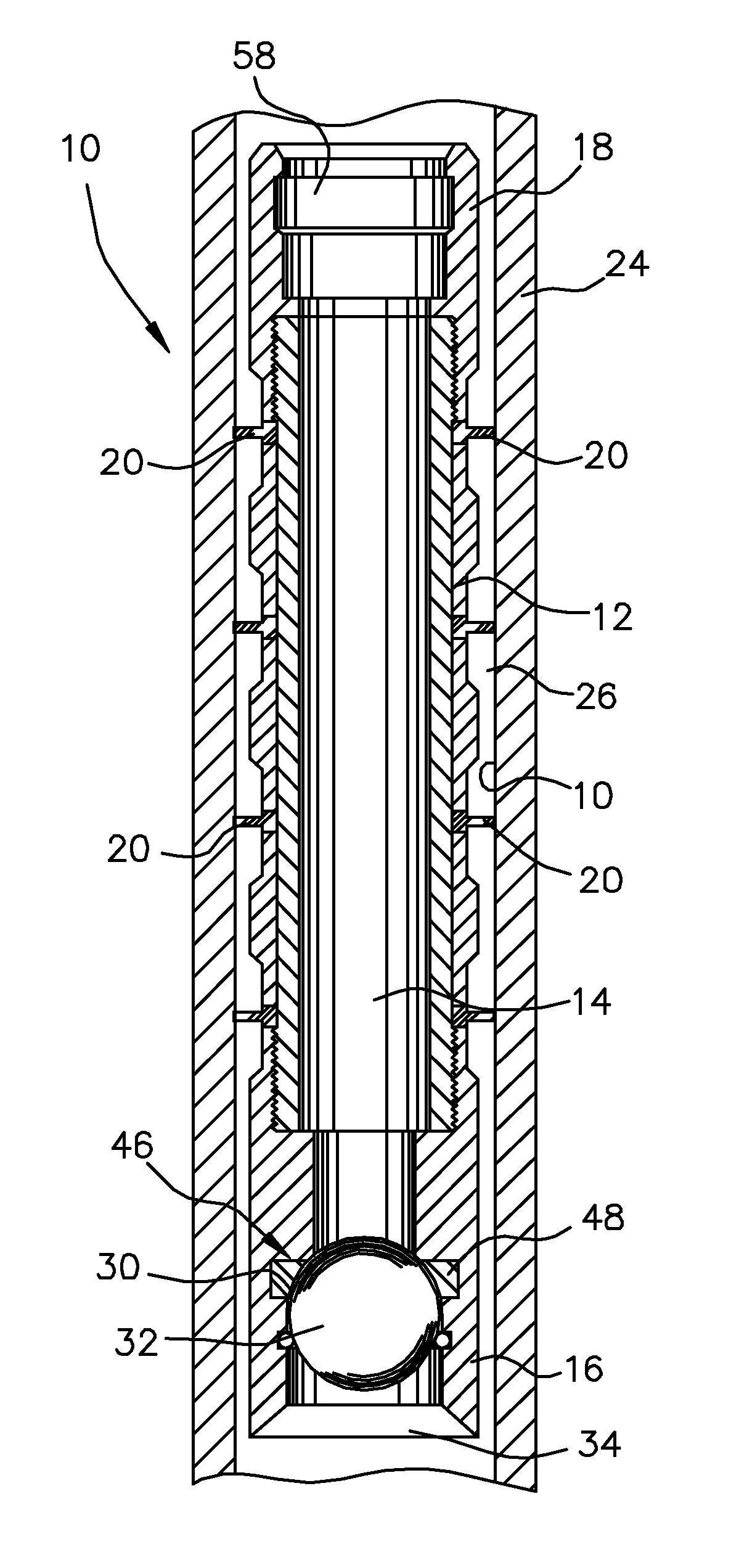
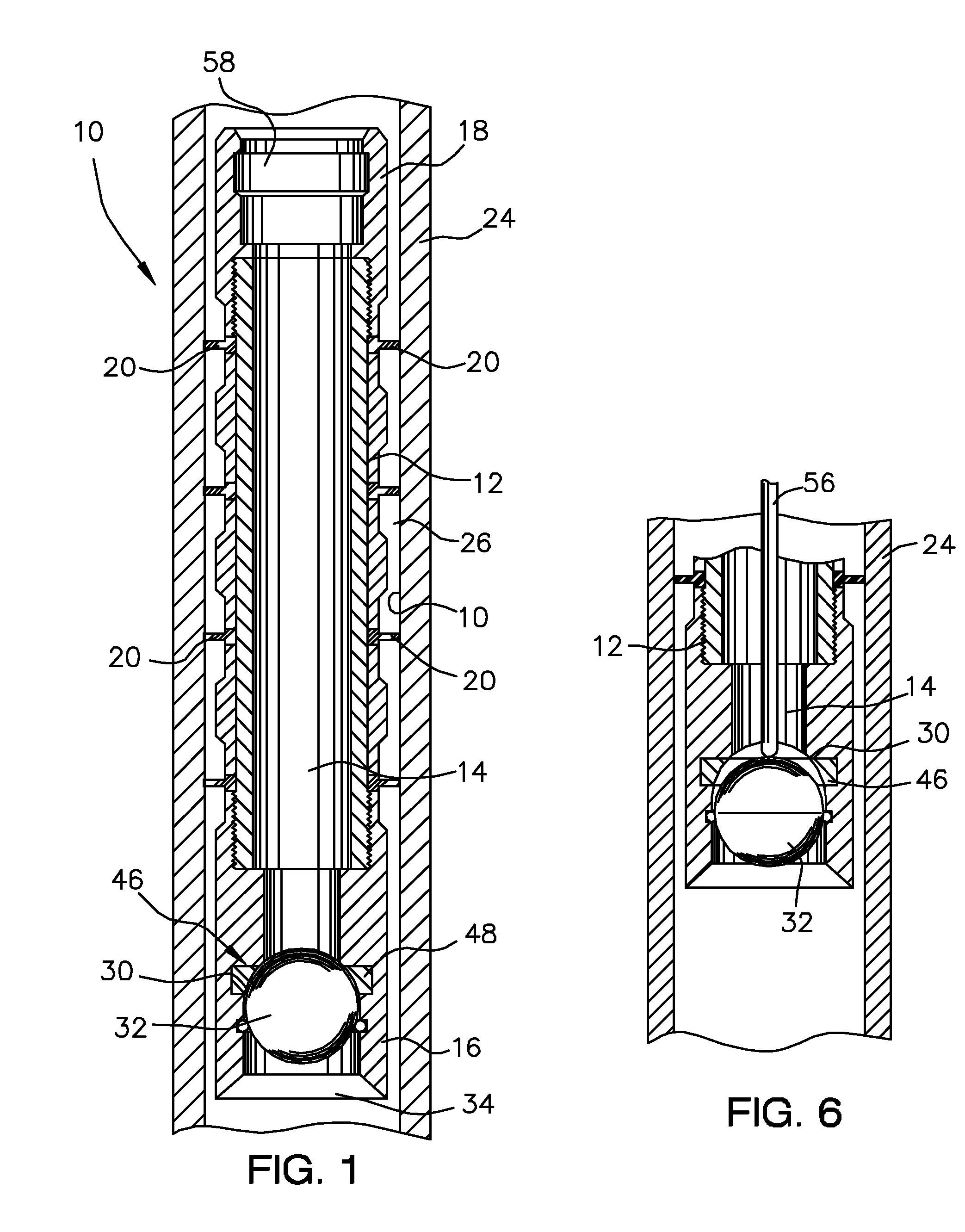
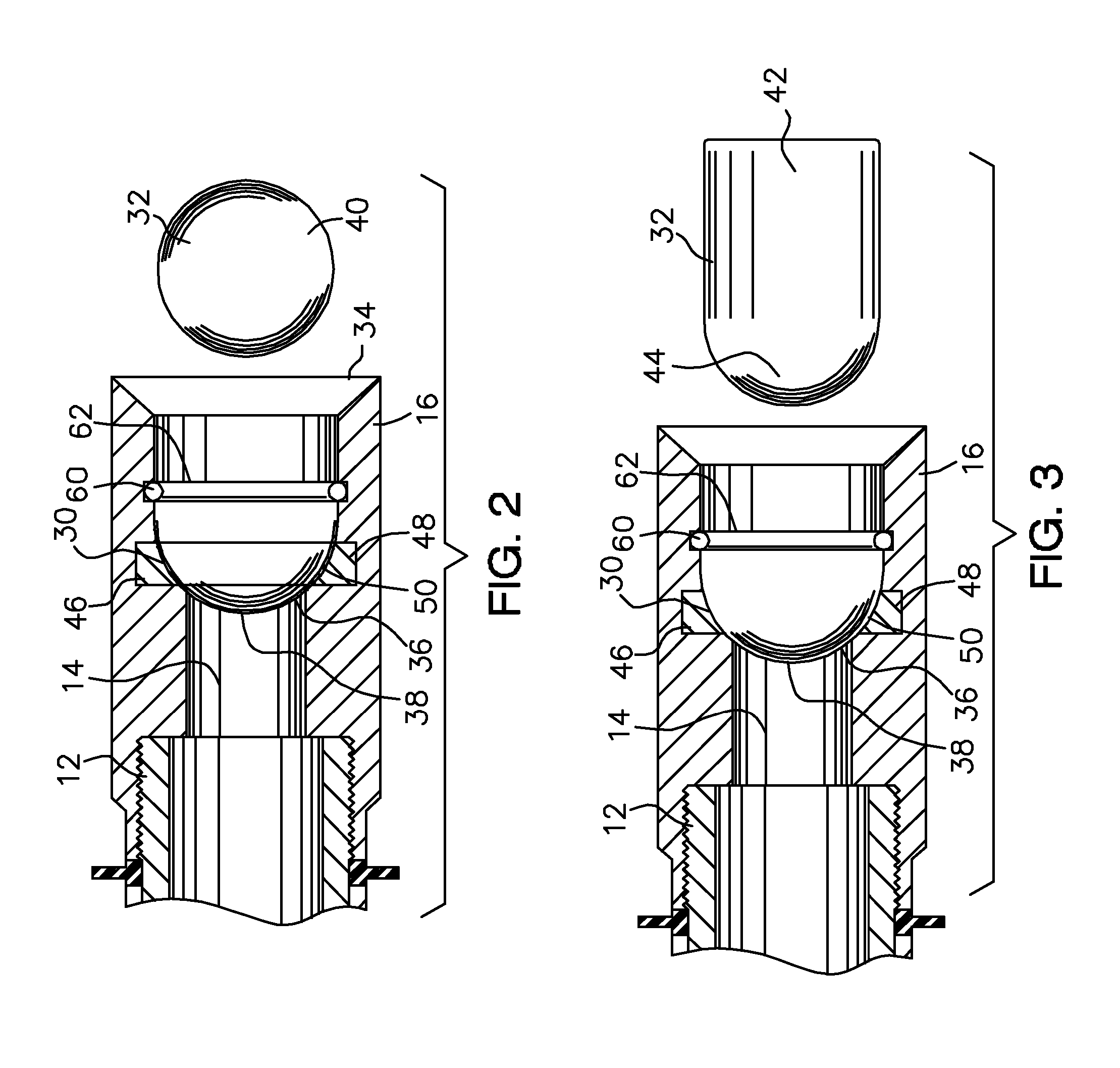
Plunger Lift Apparatus
A plunger of improved construction for reciprocating in a production string of a gas or oil well to remove fluid from the well. The plunger includes a sleeve having a through passage extending longitudinally from a first end to a second end, the second end forming a seat, a sealing means carried by the sleeve for engaging the inner surface of the production string, a detachable valve member releasably received by the seat to seal the through passage, and a catch positioned to releasably couple the detachable valve member to the sleeve within the seat. The catch retaining the detachable valve member until the detachable valve member is impacted at the surface of the well by a trip rod. The improved construction provides for the use of a heavier or more dense detachable valve member and a lighter or less dense sleeve than previously used in prior plungers, which results in a plunger having an increased efficiency and a greater cycle frequency.
Owner:SCHNEIDER GLENN +1
Digital modulation signal identifying method under non-gaussian noise in cognitive radio
InactiveCN102882820AHighlight the differenceEasy to identifyModulated-carrier systemsComputation complexityGreek letter epsilon
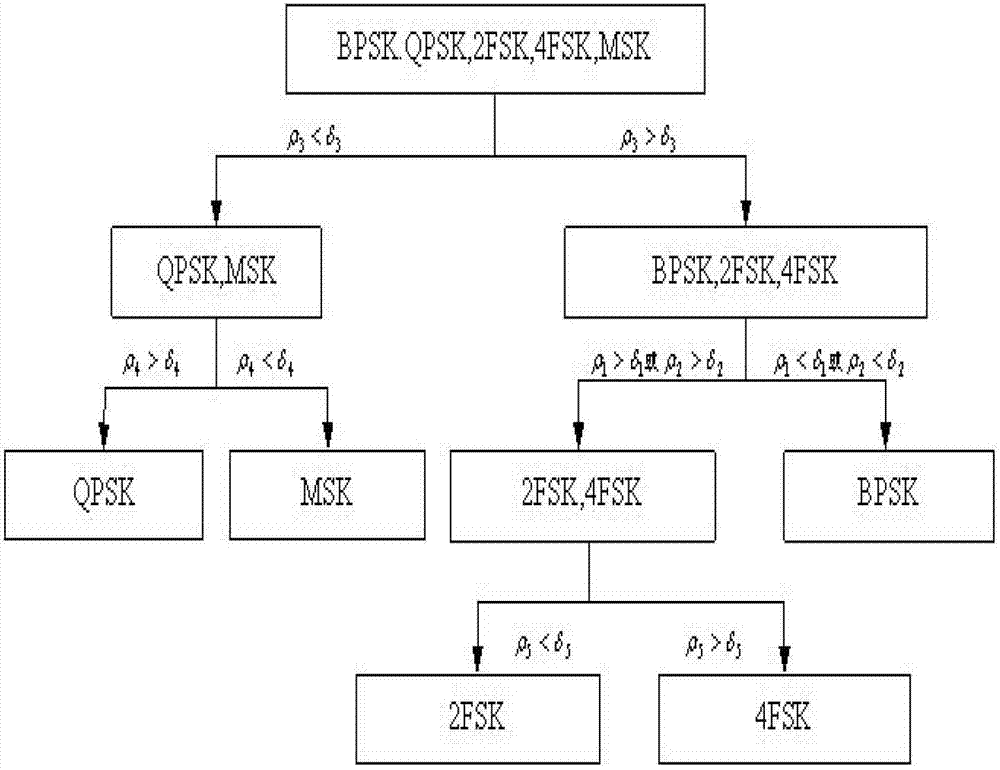
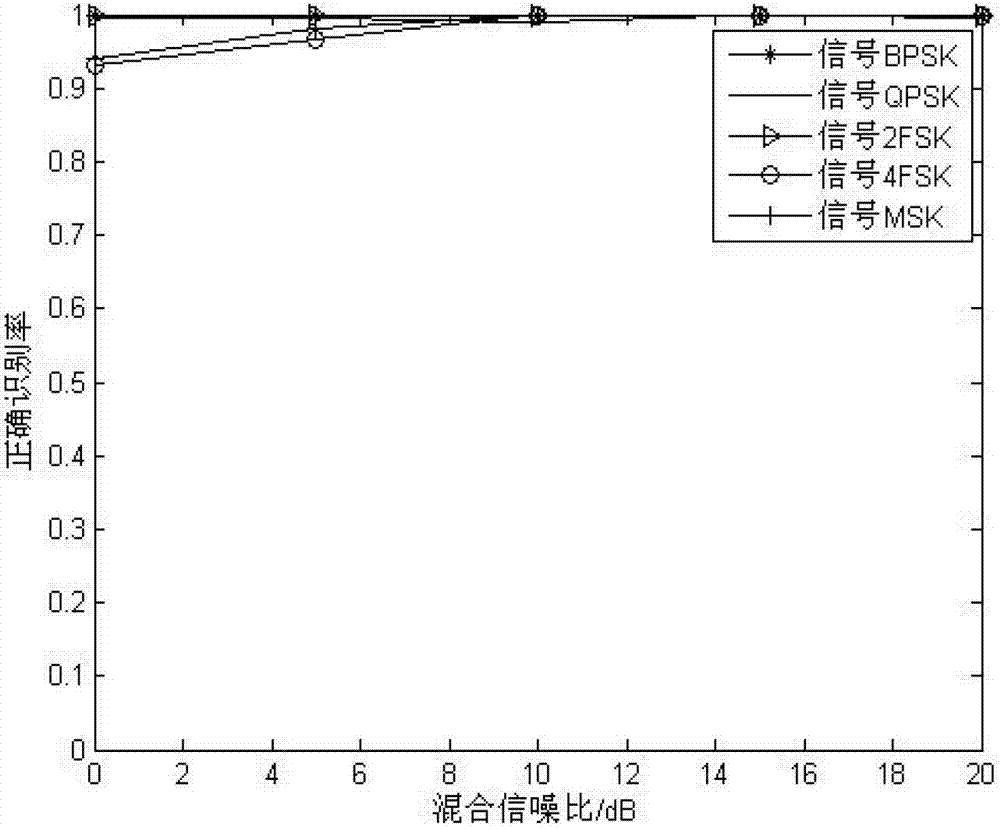
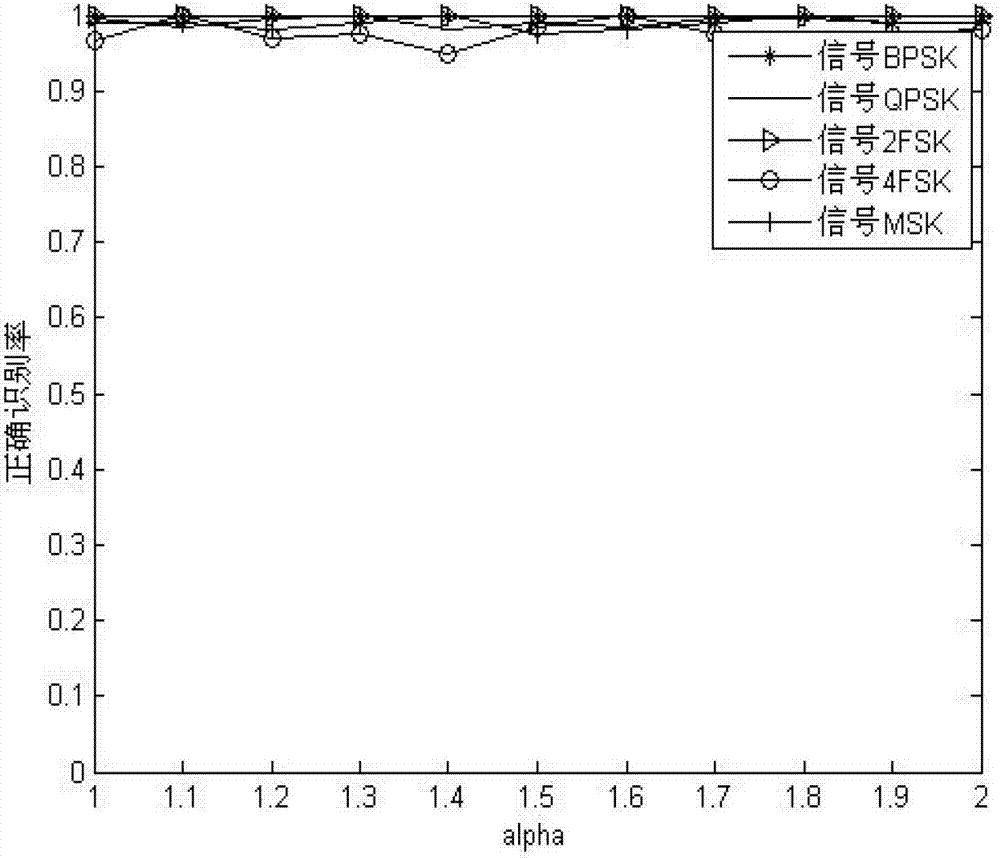
The invention discloses a digital modulation identifying method based on fractional lower order cyclic spectrum related coefficient under the non-gaussian noise in a cognitive radio, and the digital modulation identifying method is capable of solving the problems of bad modulation identifying performance and high calculating complexity under the background of the non-gaussian noise in the cognitive radio. The method comprises the following steps: sampling received signals; calculating relative coefficients rho 1, rho 2, rho 3, rho 4 and rho 5 of projections of fractional lower order cyclic spectrums of the fractional lower order cyclic spectrum calculating signals of the sampled signals at a section of the cycle frequency epsilon=0, a section of frequency f=0, and the cycle frequency epsilon face, and the projection at the frequency f face; and arranging a judgment threshold of a signal set, and identifying the signals in different modulating manners through a classifier based on a judging tree. Under a non-gaussian alpha stably distributed noise, the digital modulation identifying method is relatively high in identification rate, good in stability, and lower in calculation complexity, and is more suitable for a cognitive radio system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Time frequency overlap signal parameter estimation method under Alpha stable distribution noise
InactiveCN103607361AImprove robustnessEstimated performance is goodTransmitter/receiver shaping networksCarrier signalCoded element
The invention discloses a time frequency overlap signal parameter estimation method under Alpha stable distribution noise. The steps include: computing generalized fourth order circulation cumulants of the time frequency overlap signal under Alpha stable distribution noise and setting generalized fourth order circulation cumulant magnitude spectra beta-|GC<beta>(r, 40)| and beta-|GC<beta>(r, 42)| to zero in a small neighbourhood [0, delta0] in which the cycle frequency beta=0; detecting the highest spectrum lines P1 and P1* in beta-|GC<beta>(r, 40)| and beta-|GC<beta>(r, 42)| respectively according to a discrete spectrum line detection method, then setting the amplitude value GCmax of the spectrum line in beta-|GC<beta>(r, 40)| and the amplitude value GCmax* of the spectrum line in beta-|GC<beta>(r, 42)| to zero in small neighbourhoods [P1-delta0, P1+delta0] and [P1*-delta0, P1*+delta0], and thus cycle frequencies corresponding to P1 and P1* being a carrier wave velocity fc1 and a code element velocity fb1 of one of signal components of the time frequency overlap signal; and under the conditions that the code element velocities and the carrier wave frequencies of the overlap signal components are different, detecting the code element velocities of other signal components of the time frequency overlap signal in sequence according to the discrete spectrum line detection method, till the amplitude value GCk+1* of the (k+1)th spectrum line in beta-|GC<beta>(r, 42)| being smaller than GCmax* / 2, judging the number of mixed signals to be k at this time, and detecting the carrier wave frequencies of other signal components of the time frequency overlap signal in sequence according to the discrete spectrum line detection method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Network synchronization system and network synchronization method
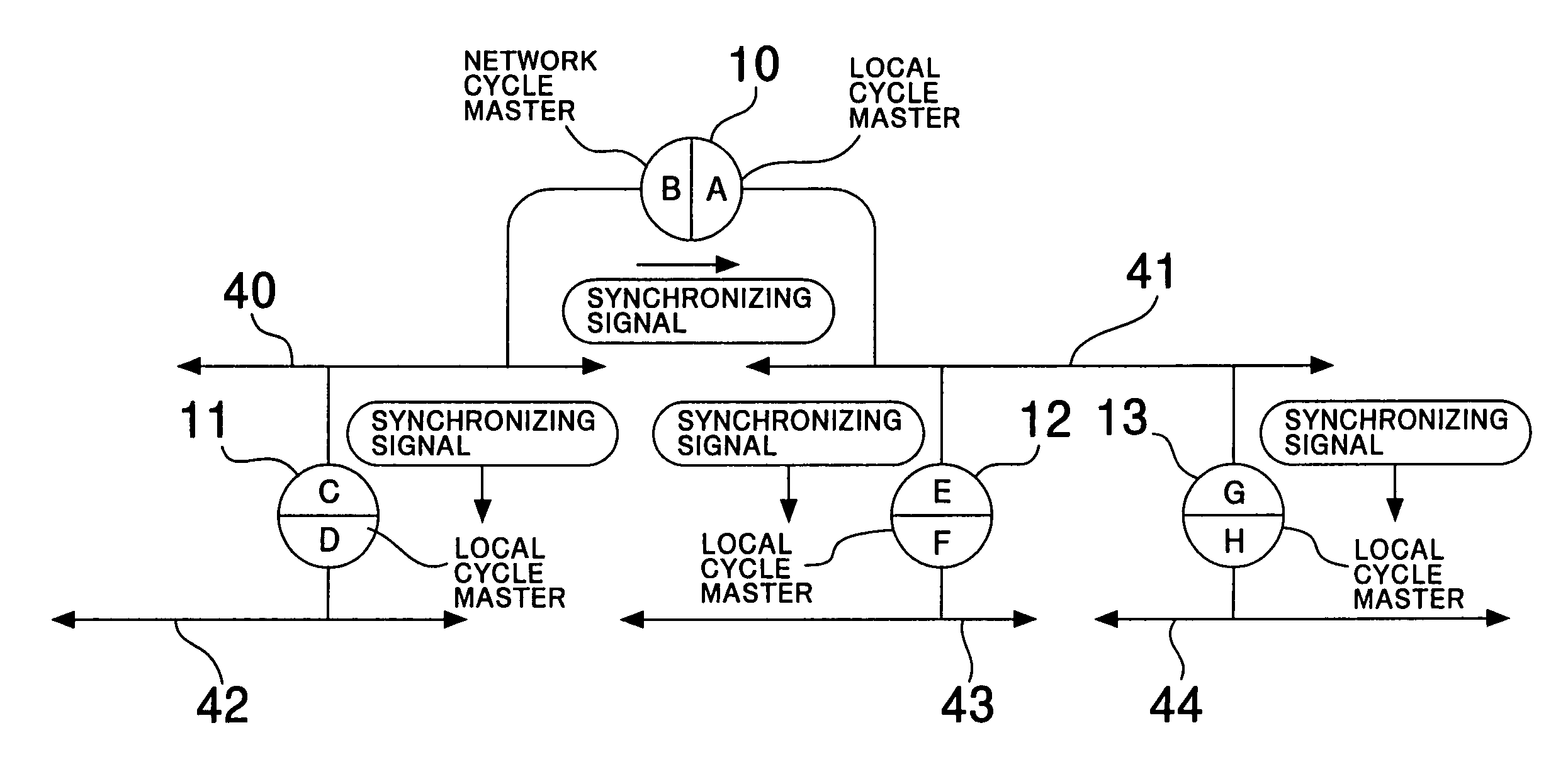
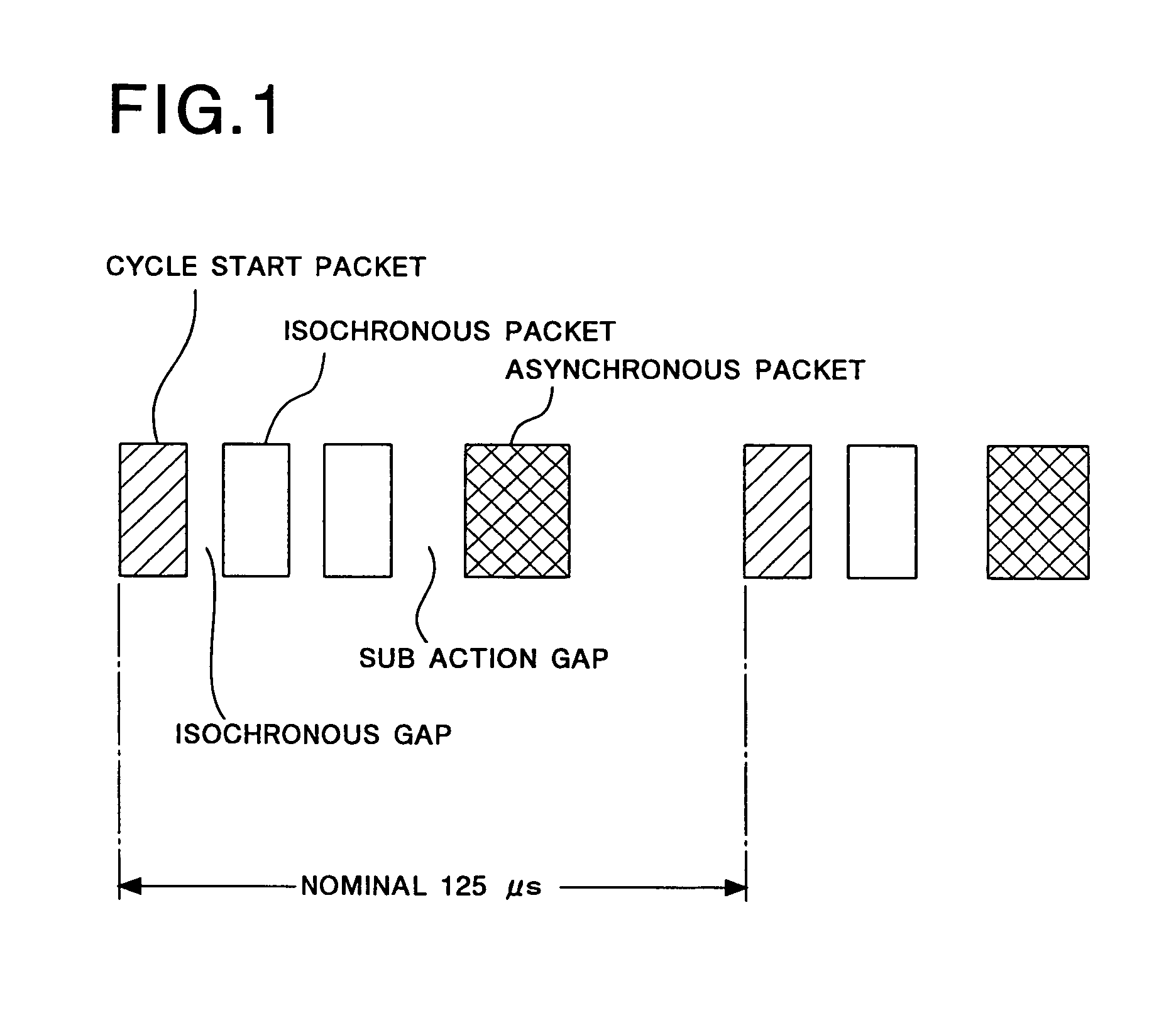
InactiveUS6975654B1Efficient use ofHybrid switching systemsTime-division multiplexPrimary stationExecution control
The invention provides, for an IEEE 1394 network wherein a plurality of IEEE 1394 serial buses are connected to each other by means of a bridge, a synchronization method between the buses wherein an existing 1394 apparatus operates even if it is connected to one of the buses and a band resource of the bus is not consumed. As a network cycle master which functions as a reference clock source of an entire network, an arbitrary one portal is selected. In each bus to which the network cycle master is not connected, a portal which has the least node hop number to the network cycle master is selected as a local cycle master. The other portals which are not selected are all set as a dependent portal. The network cycle master and the dependent portals transmit a synchronizing signal to the other portals in the same bridge. Each local cycle master receives the synchronizing signal transmitted from the network cycle master or the dependent portal in the same bridge and performs control of synchronizing the cycle frequency thereof with the cycle frequency of the portal which has transmitted the synchronizing signal. Each of the network cycle master and the local cycle masters operate as a cycle master in the bus to which it is connected.
Owner:NEC CORP
Frequency spectrum detection method based on characteristic cyclic frequency
InactiveCN101494508AImprove performanceTroubleshoot Spectrum Detection ProblemsTransmission monitoringWireless communicationFrequency spectrumSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
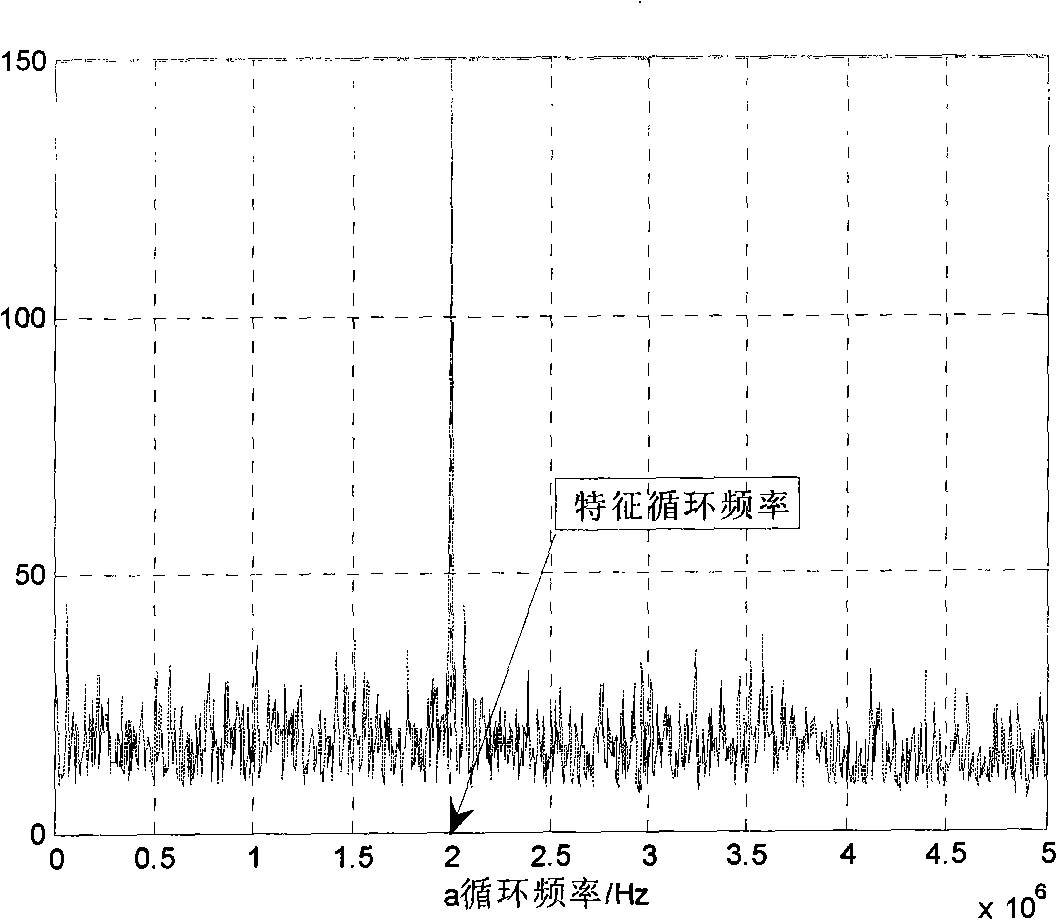
The invention relates to a frequency spectrum detection method based on characteristic cycle frequency, belonging to the technical field of wireless communication. When carrying out cycle spectrum processing of finite length to signals, the invention only carries out processing to cycle spectrum value at the characteristic cycle frequency of signals; simultaneously, the purpose of controlling detection probability and false-alarm probability of the signals is achieved by the adjustment of decision threshold. Based on the basic theory of cycle spectrum detection, the invention adopts finite signal length and selects the characteristic cycle frequency of signals to carry out frequency spectrum detection; when the cycle spectrum value at the characteristic cycle frequency is larger than preset threshold, the frequency spectrum is considered to be occupied or is considered to not be occupied. The proposal greatly improves the frequency spectrum detection performance and solves the problem that frequency detection is carried out under very low signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
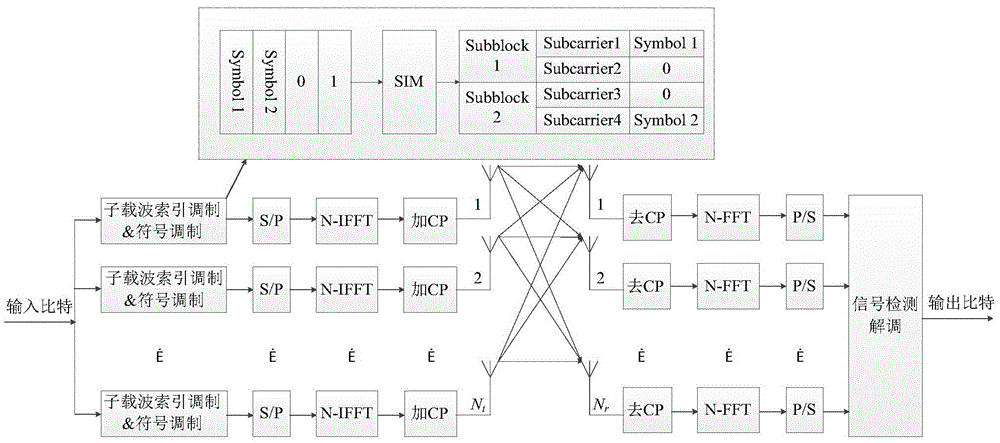
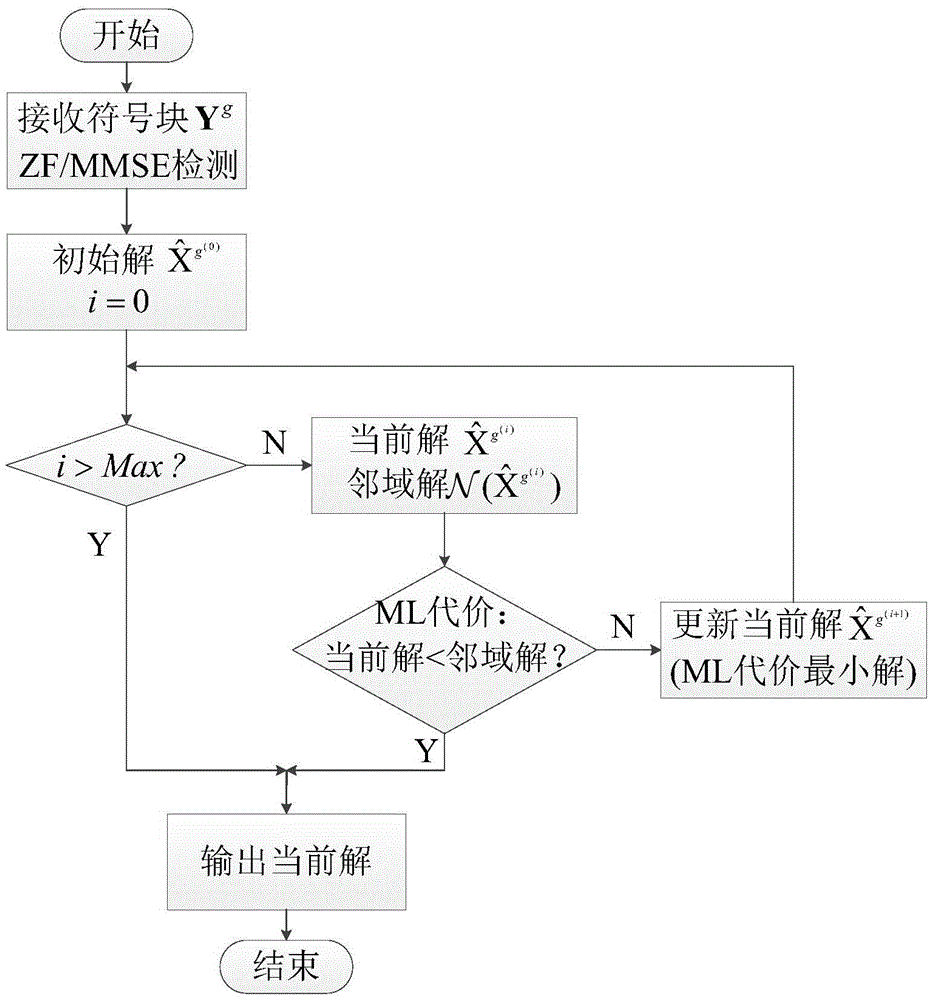
Low-complexity detection method for MIMO-OFDM system with subcarrier index modulation
InactiveCN105591717AReduce complexityError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsMulti inputRound complexity
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and relates to technologies of multi-input multi-output (MIMO), orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), and subcarrier index modulation (SIM) and related signal detection technology. The method includes: firstly, ZF / MMSE equalization of a reception symbol vector corresponding to a sub-carrier block is performed to obtain an initial solution (current solution) vector, then neighborhood space search is performed based on the current solution vector, the neighborhood space is defined as a vector set of all solutions different from the current solution vector only via a modulation symbol or a sub-carrier index, and finally, ML costs of the current solution and a neighborhood solution thereof are compared, and the solution with the minimum ML cost is reserved as the current solution of the next cycle. The process is circulated and searched for many times until the ML cost of the current solution is smaller than the ML cost of all the neighborhood space solutions or the cycle is above the upper limit of the cycle frequency, the finally obtained current solution is outputted, and original information bits are recovered via demodulation. The method is advantageous in that the BER performance close to ML is obtained, and the calculation complexity is effectively reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
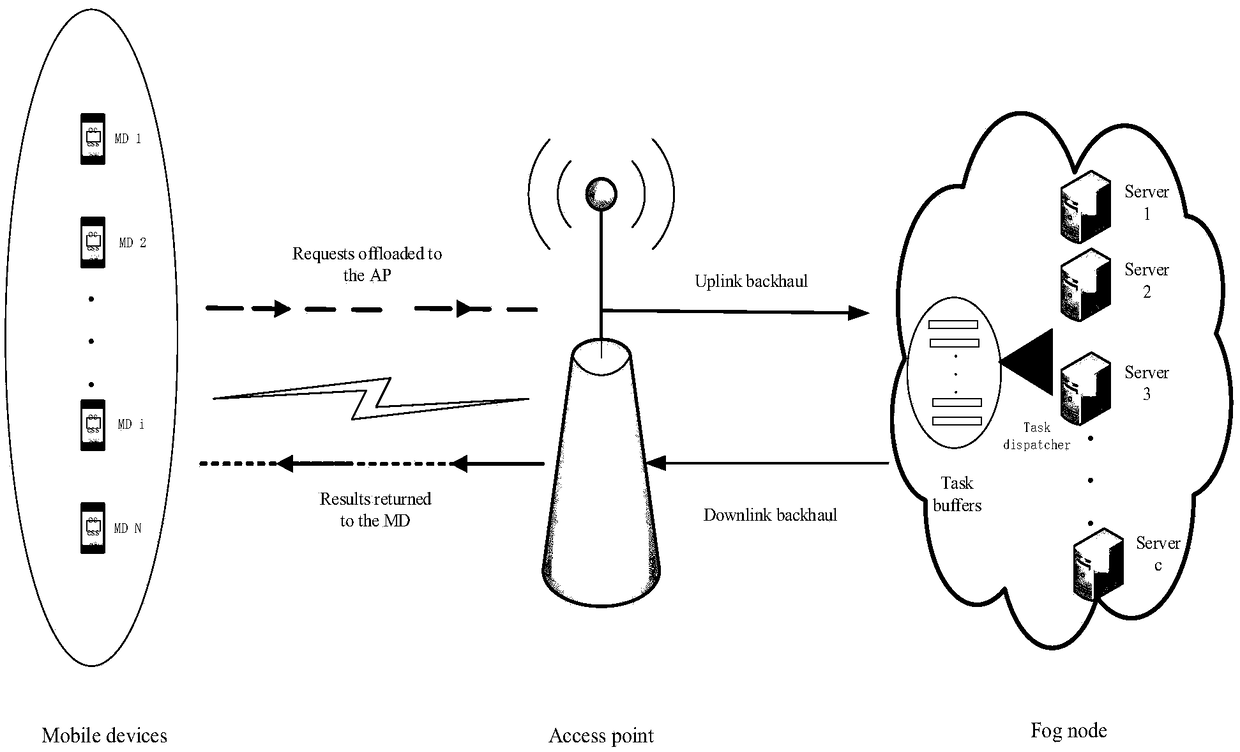
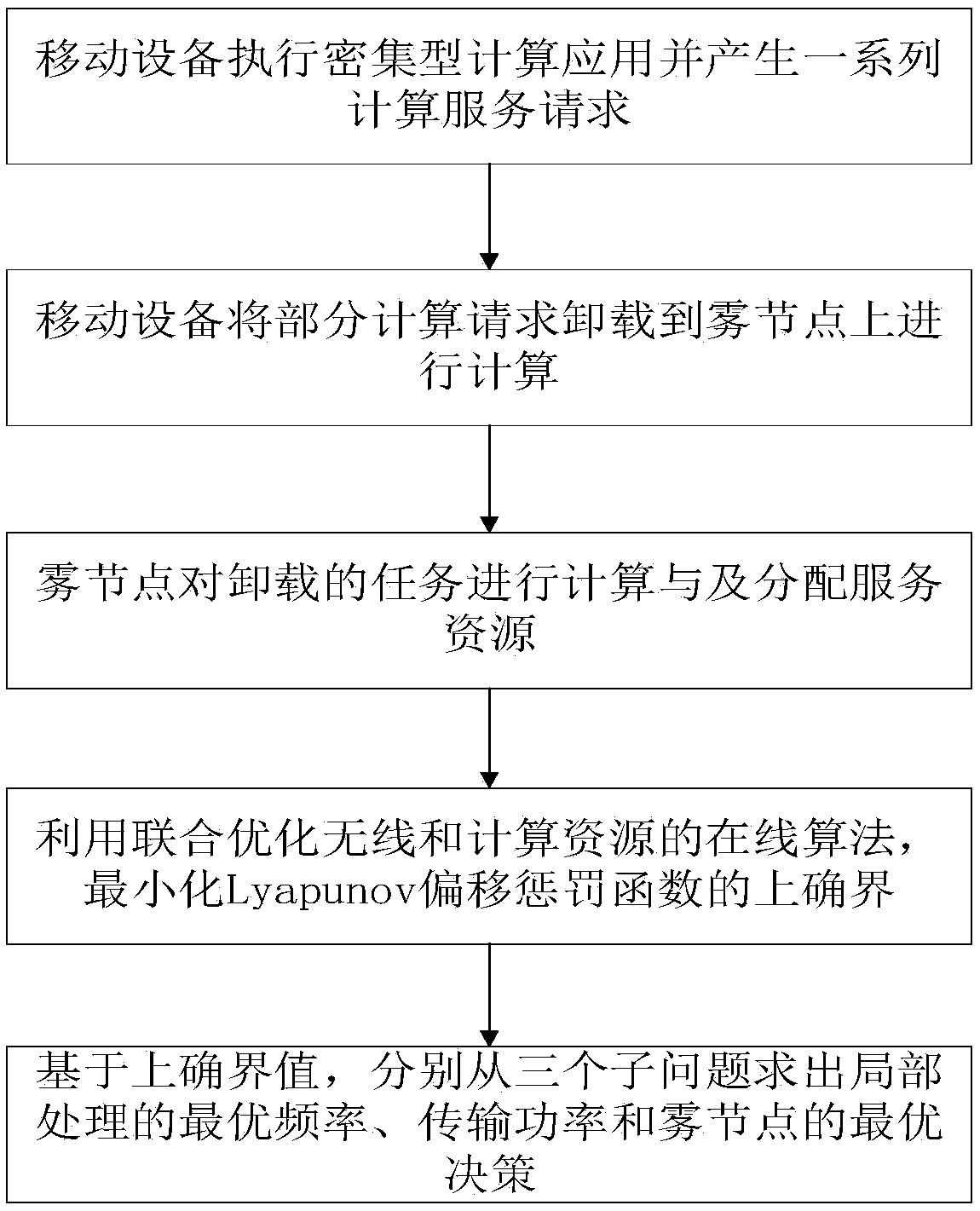
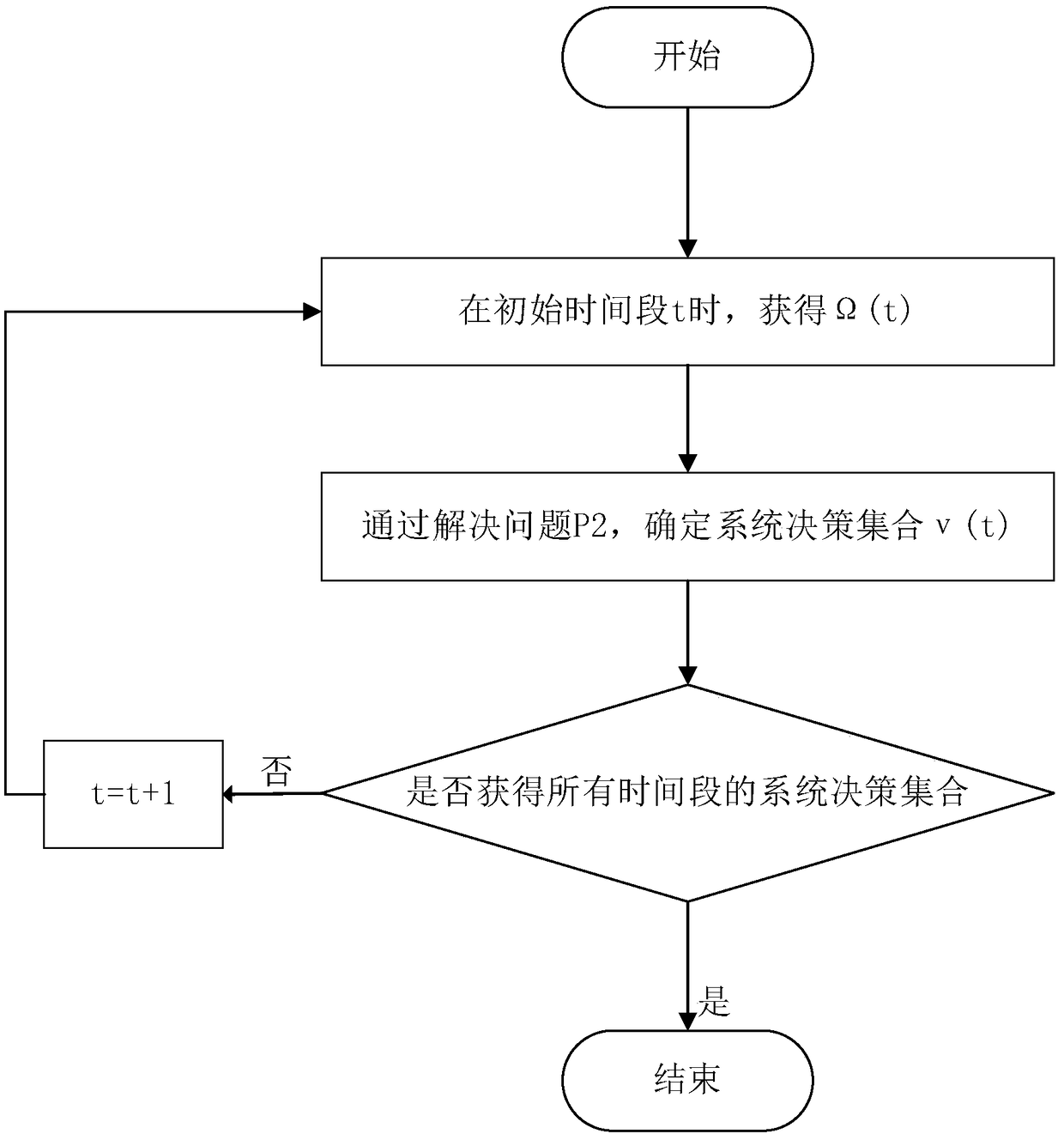
A dynamic unloading method of fog computation based on Lyapunov optimization
ActiveCN109343904AImprove performanceOptimum CPU cycle frequencyResource allocationProgram loading/initiatingLyapunov optimizationFog computing
The invention provides a dynamic unloading method of fog calculation based on optimization, belonging to the field of wireless network communication. The present invention divides the calculation request into a local calculation portion and a fog calculation portion. By offloading computationally intensive requests to fog nodes, application performance can be significantly improved. An online joint radio and computational resource algorithm based on Lyapunov optimization is used to derive the upper bound of Lyapunov migration penalty function. By minimizing the upper bound from the perspectiveof different decision variables, , the optimal CPU cycle frequency of local processor is obtained with a convex optimization method. By using the predefined offload priority function, the optimal transmission power of the optimal subchannel is obtained. On the fog node, the optimal request scheduling decision is obtained by absurdity proof.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
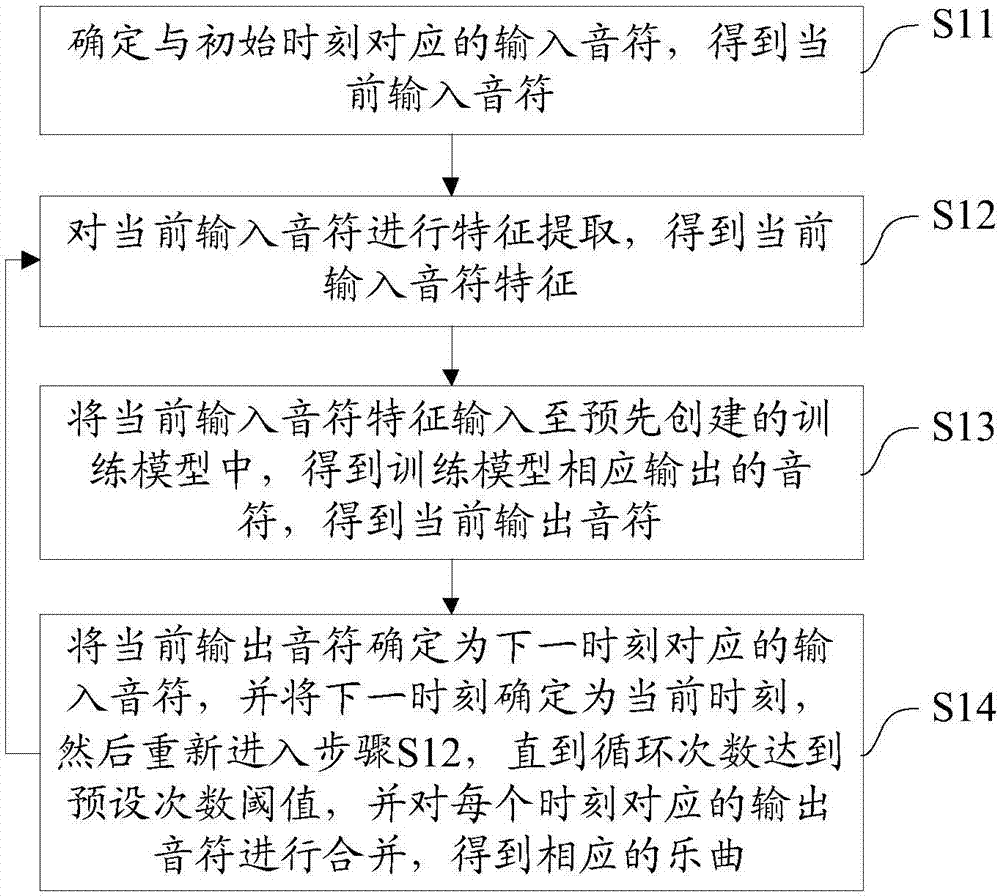
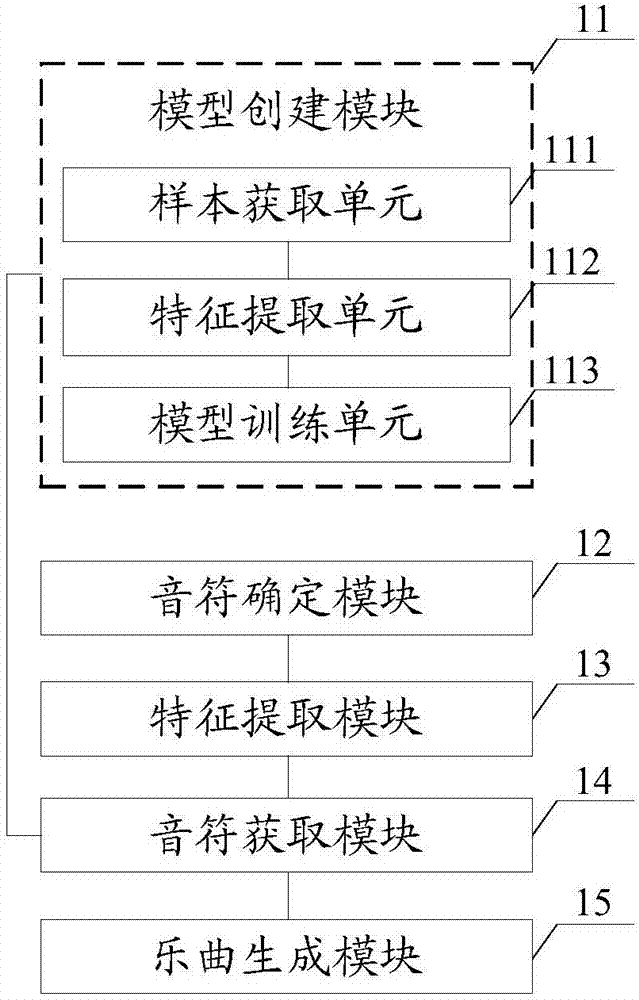
Automatic arrangement method and system
InactiveCN107123415AImprove creation efficiencyReduce creative costsElectrophonic musical instrumentsFeature extractionData mining
The invention discloses an automatic arrangement method and system. The method comprises steps that step S11, an input note corresponding to the initial time is determined, and a present input note is acquired; step S12, characteristic extraction of the present input node is carried out to acquire characteristics of the present input note; step S13, the characteristics of the present input note are inputted to a pre-established training model to acquire a note correspondingly outputted by the training model, and a present output note is acquired; step S14, the present output note is determined to be an input note corresponding to the next time, the next time is determined to the present time, the process re-enters into the step S12 till cycle frequency reaches a preset frequency threshold, and the output notes of the corresponding time are merged to acquire a corresponding music. The method is advantaged in that music creation efficiency is substantially improved, moreover, music creation cost is reduced, and the music creation threshold is reduced.
Owner:吴振国 +1
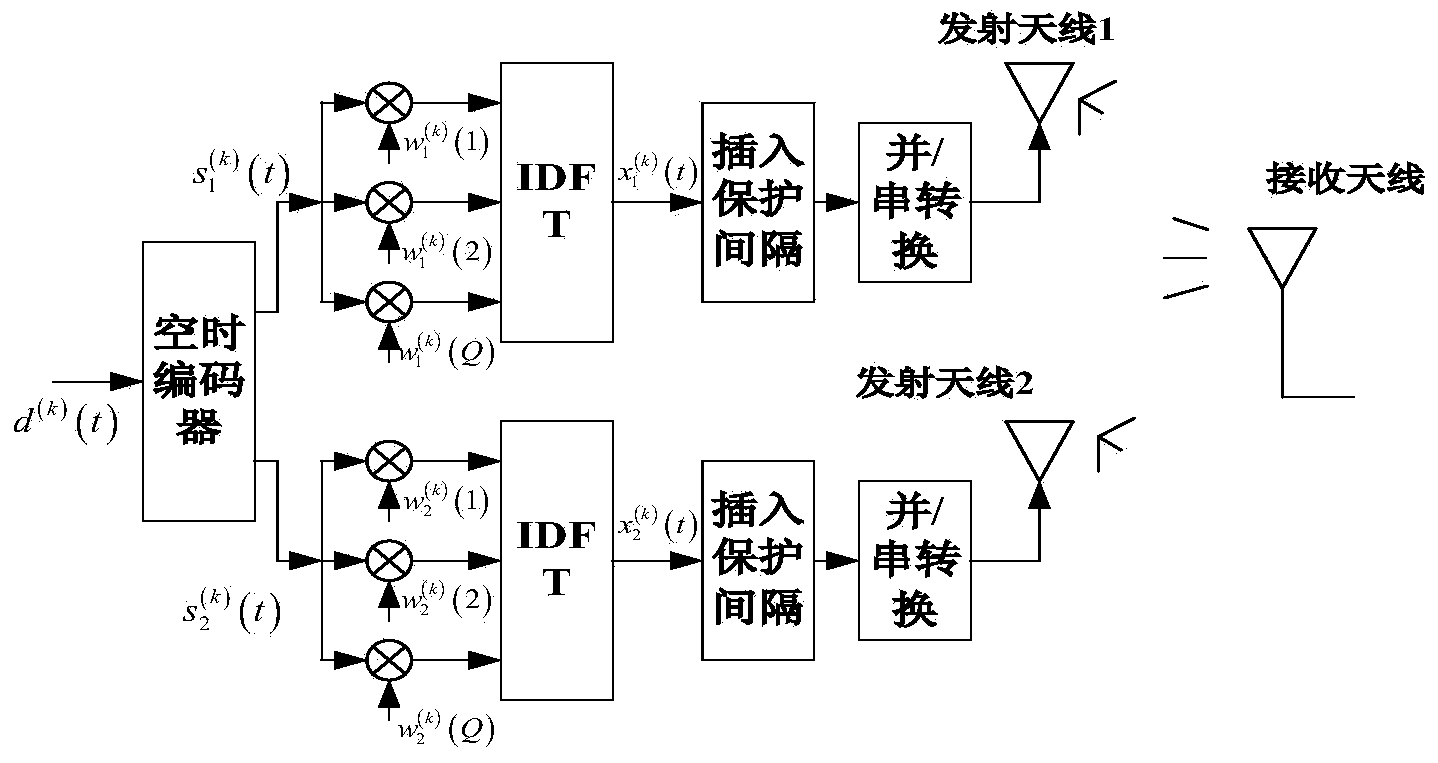
Space time block coding (STBC) MC-CDMA (Multicarrier Code Division Multiple Access) signal blind identification method based on cyclostationarity
ActiveCN104393963AEasy to identifyEfficient identificationReceiver specific arrangementsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionCdma signalPhysical model
The invention claims to protect a space time block coding (STBC) MC-CDMA (Multicarrier Code Division Multiple Access) signal blind identification method based on the cyclostationarity, and belongs to the technical field of signal processing. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a selection standard of signal correlation functions according to the baseband physical model, signal construction and matrix representation of an STBC MC-CDMA system, and estimating corresponding fourth-order cumulants of the correlation functions; combining a fourth-order cyclic cumulant with the parameter of a channel to establish a cyclic statistic; and extracting a detection threshold according to the detection of cycle frequency, and making a judgment by comparing the detection threshold with the cyclic statistic to realize identification. As indicated by computer simulation, STBCMC-CDMA signals can be effectively identified with low complexity by adopting an algorithm adopted in the invention, and working under the condition of low input signal to noise ratio is feasible. Meanwhile, compared with a conventional identification algorithm, the algorithm adopted in the invention has the advantage that the influence of random noise is reduced by using the advantage of the fourth-order cyclic cumulant, so that the system performance is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
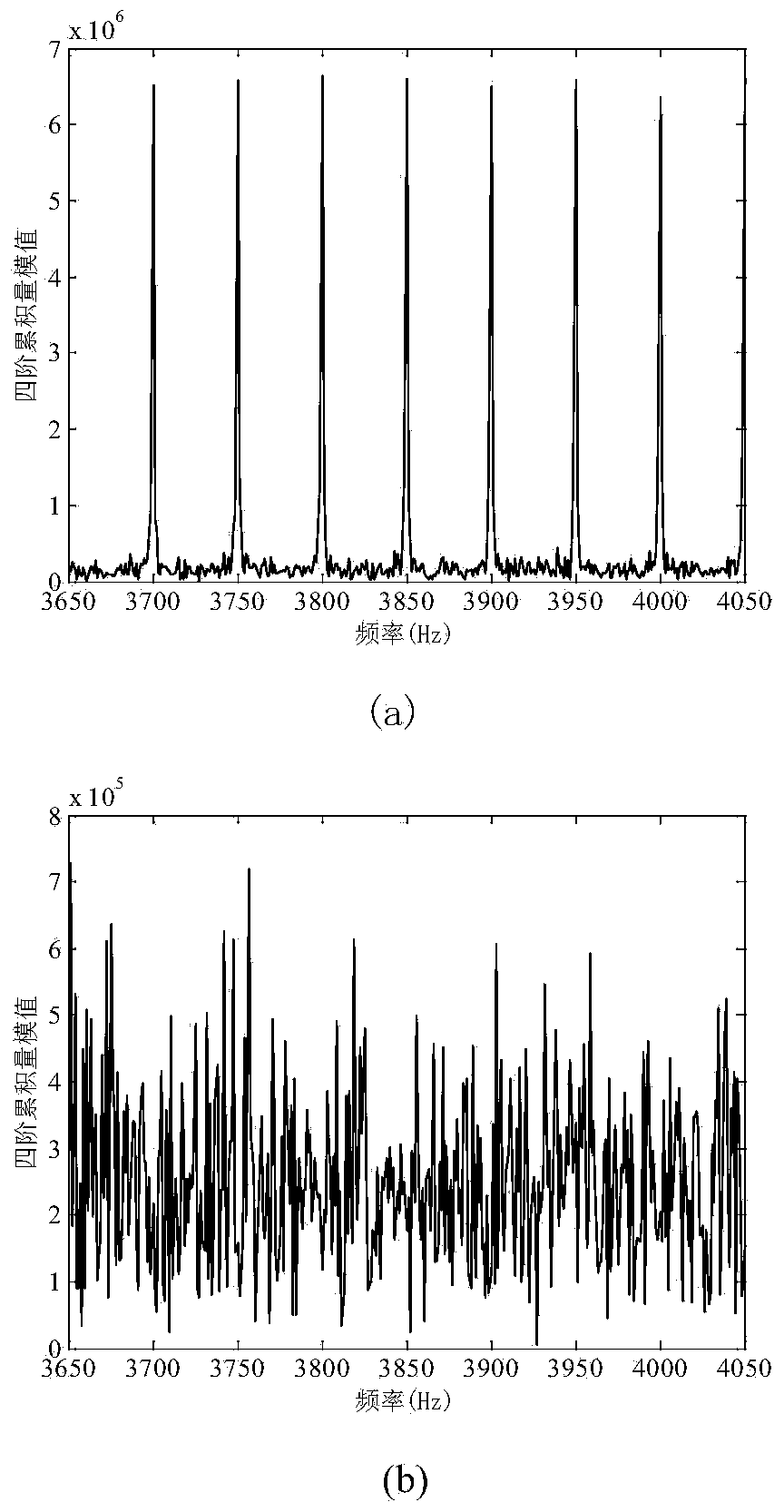
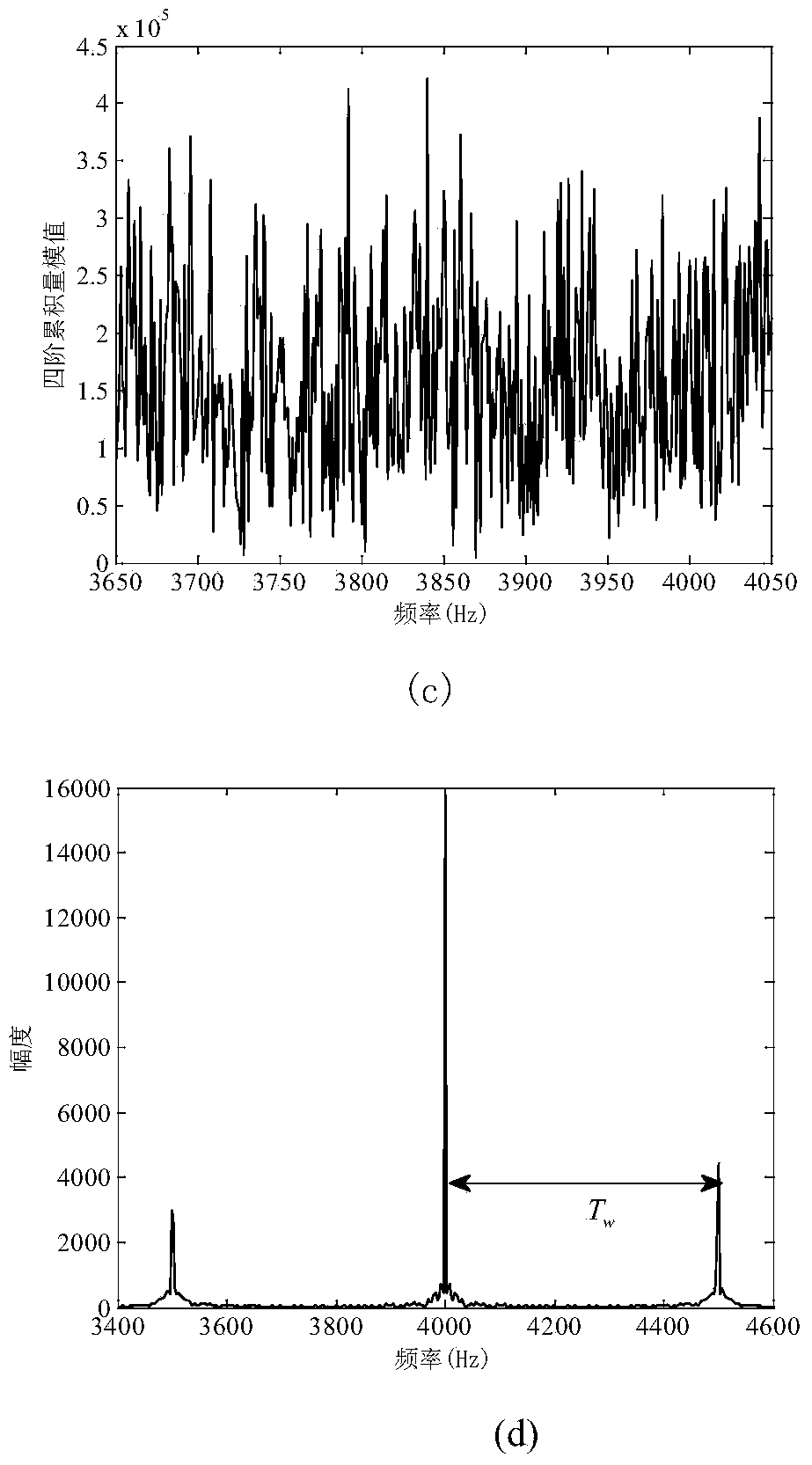
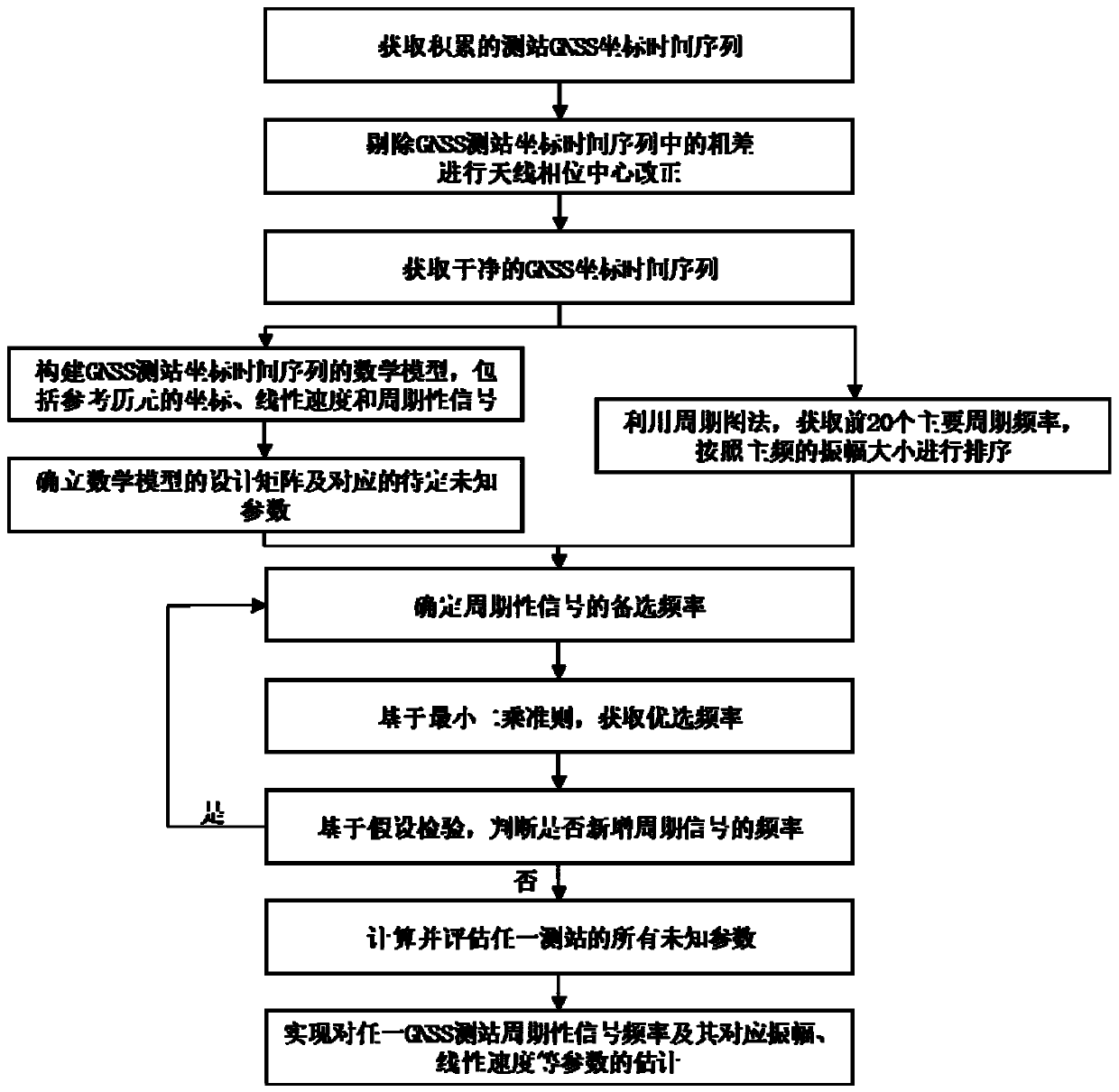
Periodic detection method and system for GNSS observation station coordinate time sequence
ActiveCN110398753AAvoid blindnessImprove reliabilitySatellite radio beaconingFrequency spectrumHypothesis
The invention provides a periodic detection method and system for a GNSS observation station coordinate time sequence. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a GPS observation station coordinatetime sequence observed value, removing gross errors and correcting an antenna phase center deviation; performing preliminary spectrum analysis on the GPS observation station coordinate time sequence by using a periodogram method; acquiring a plurality of major cycle frequencies of a corresponding observation station, and sorting according to the amplitudes of main frequencies; describing the GPS observation station coordinate time sequence by using a harmonic function, acquiring a harmonic function model of the GPS observation station coordinate time sequence, and building a harmonic functionmodel matrix; using the main frequencies as prior constraints, and acquiring the standby frequencies of a plurality of periodic signals; resolving the harmonic function model based on a least squarescriterion, acquiring optimal frequencies and verifying the standby frequencies by using a hypothesis testing method, and building the harmonic function model including the plurality of optimal frequencies; and according to the standby frequency after hypothesis testing is performed, resolving the harmonic function model matrix based on the least squares criterion, and acquiring a detection resultof any GNSS observation station periodic signal.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Estimation method for signal interference noise ratio in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system
InactiveCN102790744AEfficient separationQuality improvementMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFrequency spectrumComputation complexity
The invention discloses an estimation method for a signal interference noise ratio in an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) system. Through obtaining a period self-correlation function of a received signal on a receiving end of the OFDM system, the energy distribution rule of a transmission signal, a radio frequency interference signal and the period self-correlation function of Gauss white noise is analyzed, the signal power can be effectively separated from the noise-added interference power by selecting an appropriate delay variable and a circulating frequency, and then according to the definition of the signal interference noise ratio, a signal interference noise ratio value during a signal transmission process is effectively estimated. By the adoption of the estimation method, the calculation complexity is low, the estimation precision is high, aiming to the situation that current frequency spectrum resource is gradually deficient, the utilization rate of a frequency band can be well increased, and under the environment of more serious radio frequency interference, performance of the communication system can be effectively improved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Electronically controlled directionally rotating single-phase self-starting permanent-magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN102790565AGood for eliminating influenceImprove stabilitySingle motor speed/torque controlElectronic commutatorsPermanent magnet rotorSynchronous motor
An electronically controlled directionally rotating single-phase self-starting permanent-magnet synchronous motor comprises a stator, a permanent-magnet rotor, a power electronic circuit and a control circuit; and an alternating-current power supply outputs voltage to the stator via the power electronic circuit. The control circuit comprises a detection circuit and a position sensor; the detection circuit is used for detecting the state of the alternating-current power supply; the position sensor is mounted nearby the periphery of the rotor to detect the state of the permanent-magnet rotor; and according to the output of the detection circuit and the output of the position sensor, the power electronic circuit is controlled. The output of the detection circuit includes the transient cycle time of the alternating-current power supply; the output of the position sensor includes the frequency of the magnetic poles of the rotor passing by the position sensor; and when the frequency of the magnetic poles of the rotor passing by the position sensor in a cycle of specified frequency is two times higher than the cycle frequency, the power electronic circuit decreases the voltage outputted to the stator and keeps the voltage at a specified value. The motor can keep optimal performance, however, no-load running vibration, noise and temperature rise are remarkably improved, and the structure is simpler and more reliable.
Owner:HANYU GRP CO LTD
Light direction hybrid reinforcement-based novel internal component and photobioreactor
InactiveCN103361257AIncrease mixing intensityIncrease light intensityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhotobioreactorEngineering
The present invention provides a novel photobioreactor and an internal component thereof. The photobioreactor comprises a transparent housing and multiple regularly arranged transparent baffle plates. The baffle plates are axially placed in the housing and tilt horizontally. A trapezoidal partial space is formed between the baffle plates. The photobioreactor enables fluid in a central area (dark area) of the reactor and fluid in a surface area (light area) of the reactor to rapidly and periodically circulate, thereby enhancing mixing of fluid along a radial direction (light direction) of the reactor.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +2
Airplane suspension joint structure fatigue test design method
ActiveCN105975704ASolving the Difficulty of Designing Structural Fatigue TestsAnalysis steps are clearGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationTest designElement model
The invention relates to an airplane suspension joint structure fatigue test design method comprising the following steps: 1, building a whole-aircraft finite element model and carrying out whole-aircraft solution; 2, carrying out load distribution according to each flange rigidity proportion so as to obtain the load of each flange, and simplifying a testpiece structure form; 3, building a local detail model and carrying out calculation solution; 4, obtaining fatigue margin of a test zone and a transition segment; 5, enhancing the rigidity of the transition segment structure according to the obtained fatigue margin; 6, determining transition segment length L1 and L2; 7, loading according to a preset cycle sequence and cycle frequency so as to carry out fatigue tests. The airplane suspension joint structure fatigue test design method is based on the features that the airplane suspension joint structure is complex in jointing, more in transfer lines, and hard to design tests; the airplane suspension joint structure fatigue test design method can provide loads and load distribution rules of joints and each bolt, thus finally determining a testpiece structure form and loading scheme.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Signal-to-noise ration estimating method of time frequency overlapping signals under frequency spectrum sharing mode
ActiveCN105933257AEasy to measureImprove estimation performanceTransmission monitoringMulti-frequency code systemsLow noiseFrequency spectrum
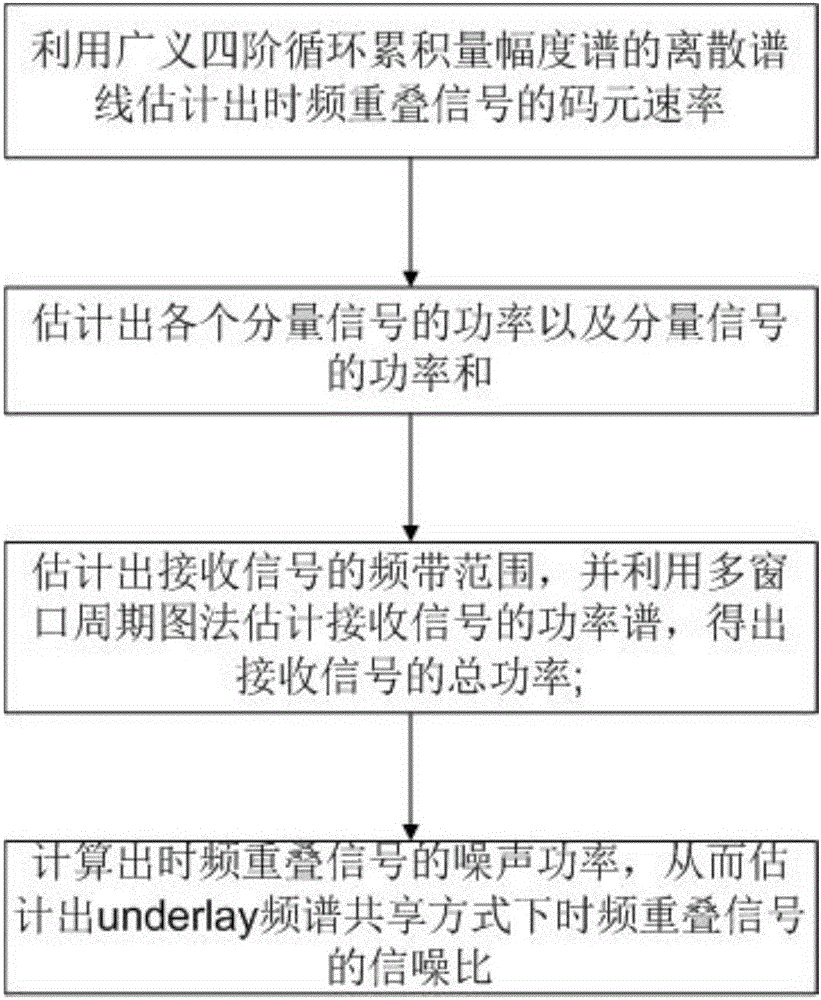
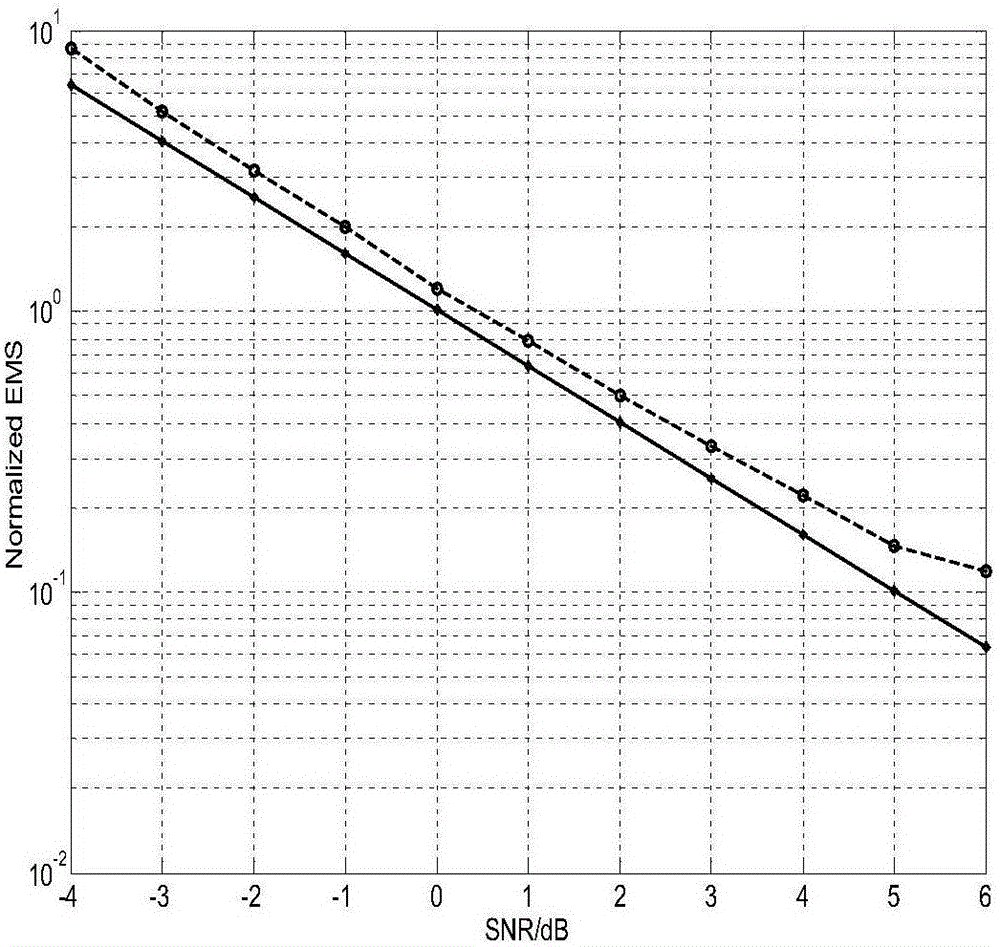
The invention discloses a signal-to-noise ration estimating method of time frequency overlapping signals under a frequency spectrum sharing mode. According to the method, a code element rate of time frequency overlapping signals is estimated according to a cyclic frequency corresponding to a discrete spectral line of an amplitude spectrum of a generalized fourth-order cyclic cumulant of receiving signals; power of each component signal and a power sum of the component signals are estimated; a frequency band scope of the receiving signals is estimated, and total power of the receiving signals is obtained by estimating a power spectrum of the receiving signals by use of a multi-window periodogram method; and noise power of the time frequency overlapping signals is calculated, and accordingly, a signal-to-noise ratio of the time frequency overlapping signals under the underlay frequency spectrum sharing mode is estimated. According to the invention, under the conditions of a low noise-to-signal ratio and a high frequency spectrum overlapping rate, the estimation performance for the signal-to-noise ratio of the time frequency overlapping signals under the underlay frequency spectrum sharing mode is excellent.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Prediction method for life of secondary battery based on particle filter and mechanism model
ActiveCN106055775ALife expectancyReduce forecast errorSpecial data processing applicationsLower limitState variable
Provided is a prediction method for life of a secondary battery based on particle filter and a mechanism model. The invention is aimed at solving the problem in the prior art that the prediction for life of a secondary battery is totally based on data drive and does not take the defect of an object mechanism so that a prediction result for the life of an electrochemical power source has poor accuracy.In a training stage, a particle filter method is utilized for tracking the actual value of internal state variables for the battery such that a regression equation of state variables varying with charge-discharge cycle frequency changes is obtained as a new state equation. In a prediction stage, the new state equation is utilized for calculating estimation values of state variables during unknown charge-discharge circulation in order to generate multiple particles. Multiple estimation values for capacity observation values are taken into an observation equation such that medians of estimation values for multiple capacity observation value are utilized for predicting the battery capacity in the future during the charge-discharge circulation. When the pre-set battery capacity reaches the lower limit, difference value between cycle numbers corresponding to the capacity observation value and cycle numbers used in the training stage is used as the residual number of cycles available for the battery.
Owner:珠海中力新能源科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com