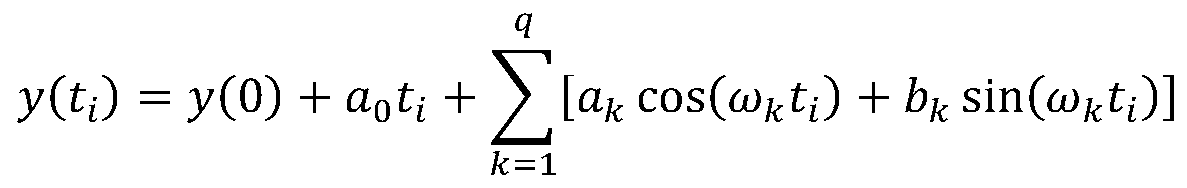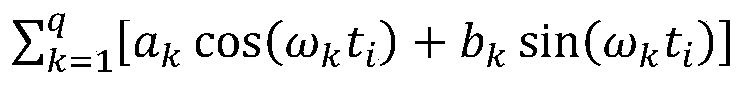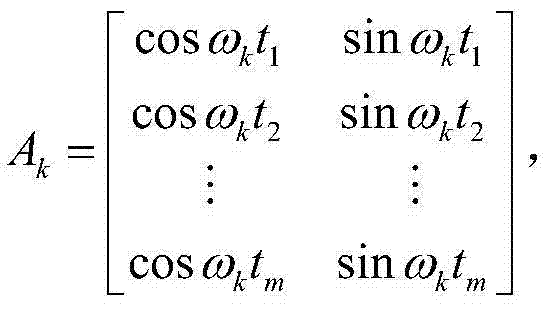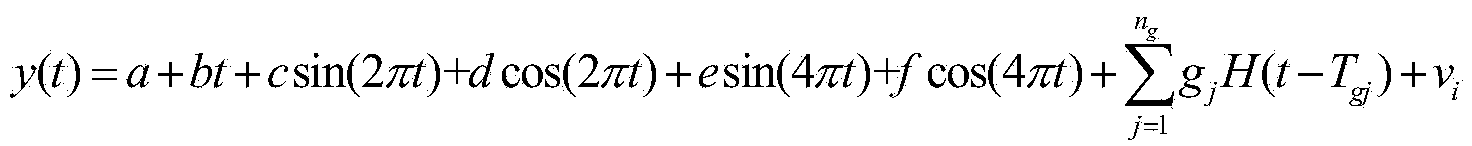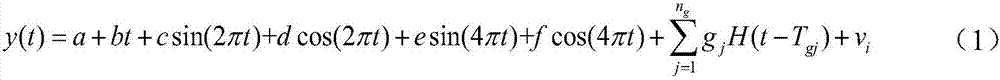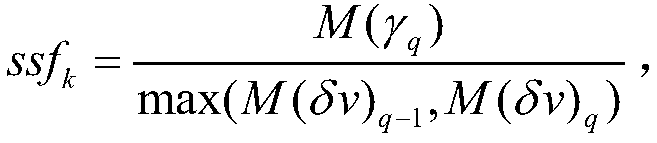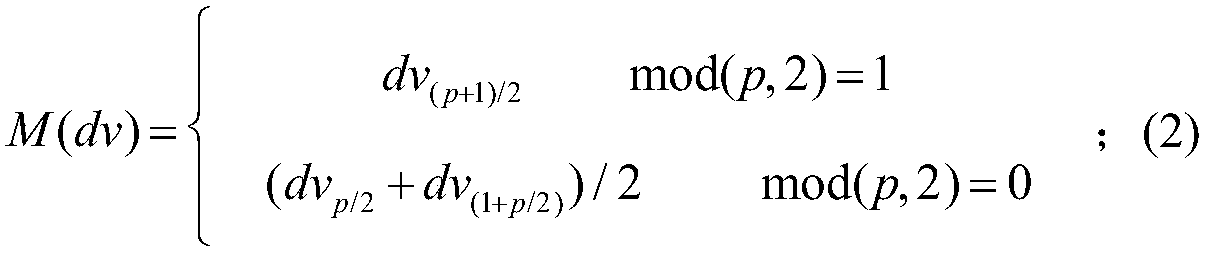Patents
Literature
77 results about "Coordinate time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the theory of relativity, it is convenient to express results in terms of a spacetime coordinate system relative to an implied observer. In many (but not all) coordinate systems, an event is specified by one time coordinate and three spatial coordinates. The time specified by the time coordinate is referred to as coordinate time to distinguish it from proper time.
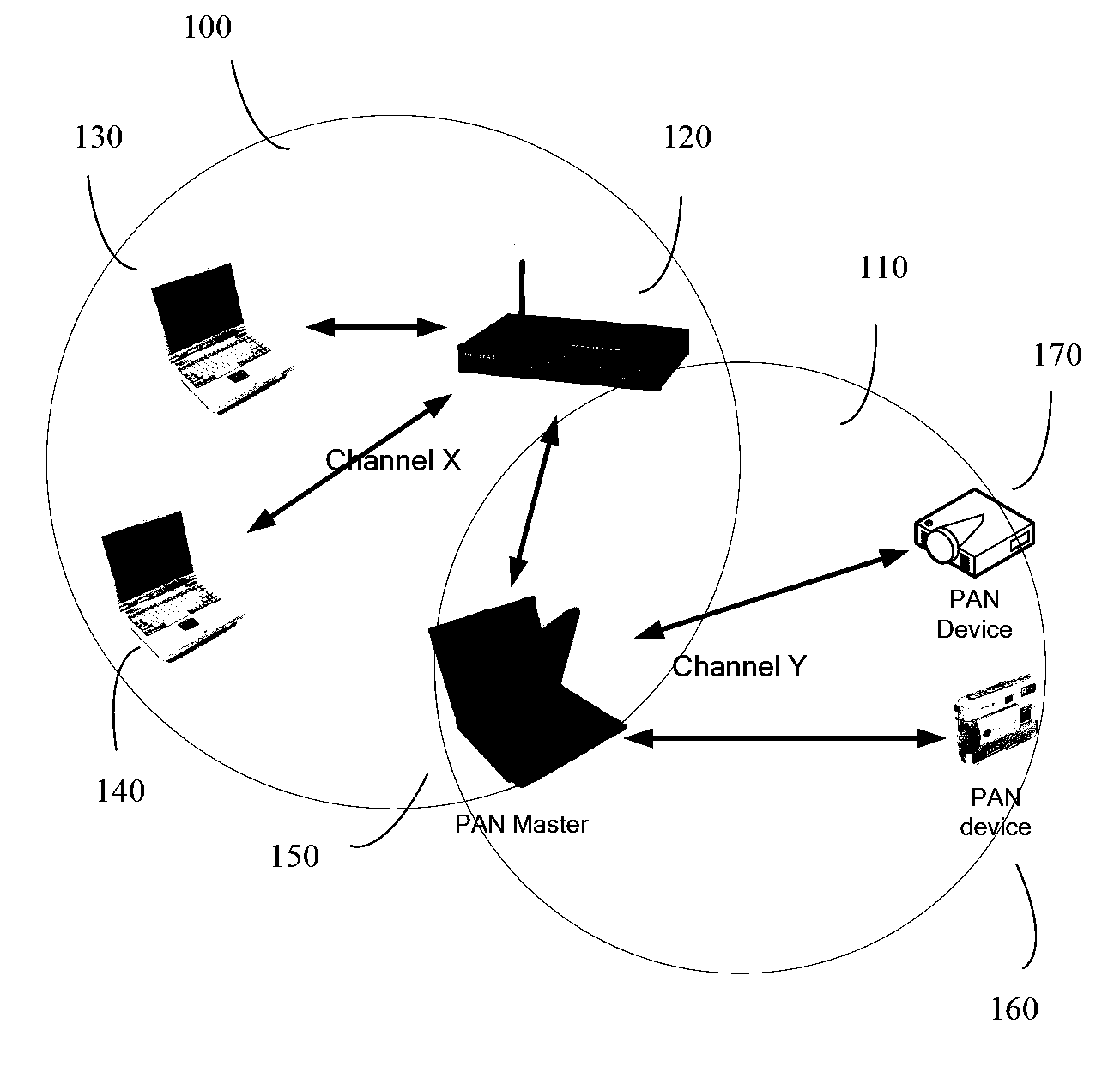
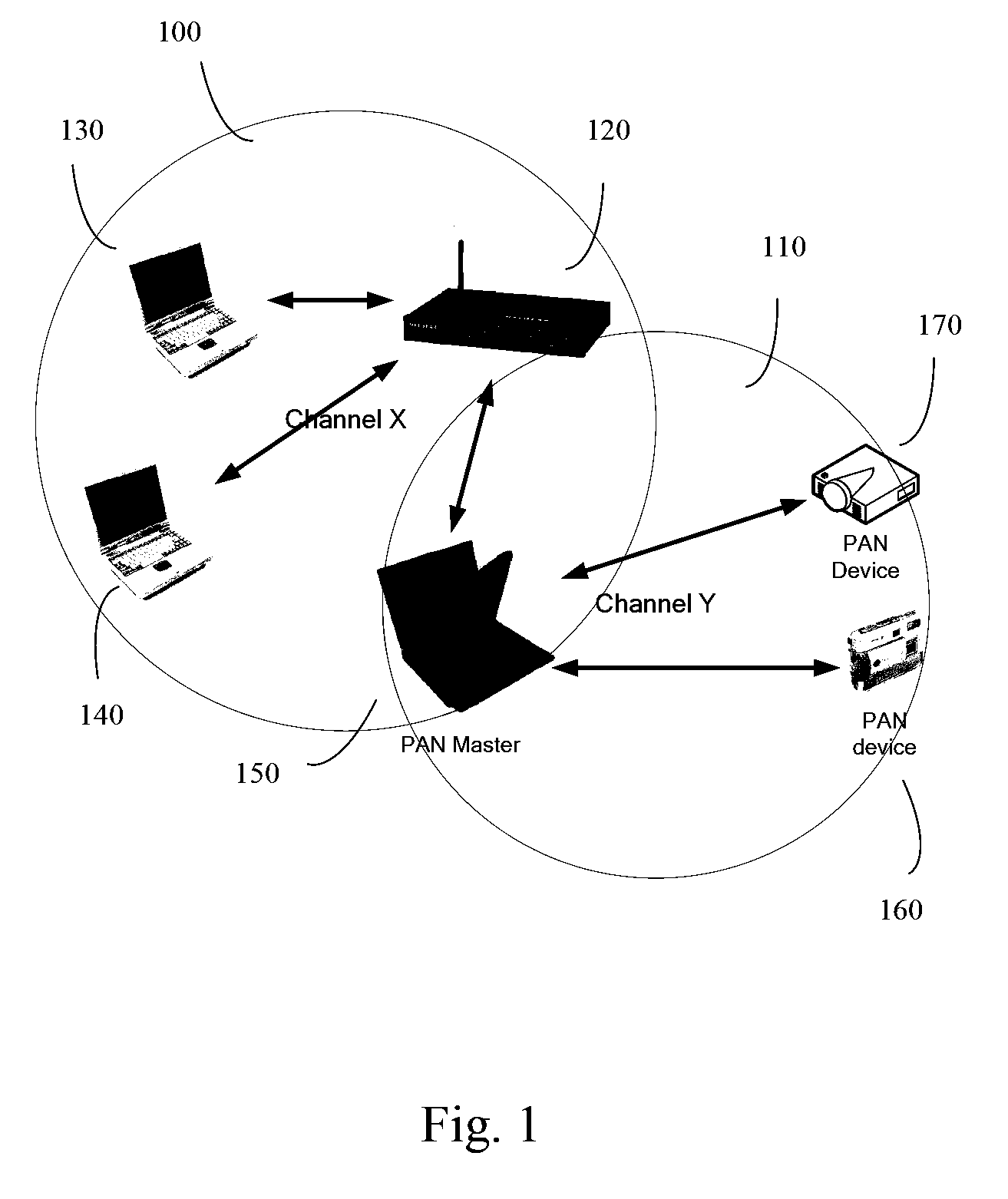
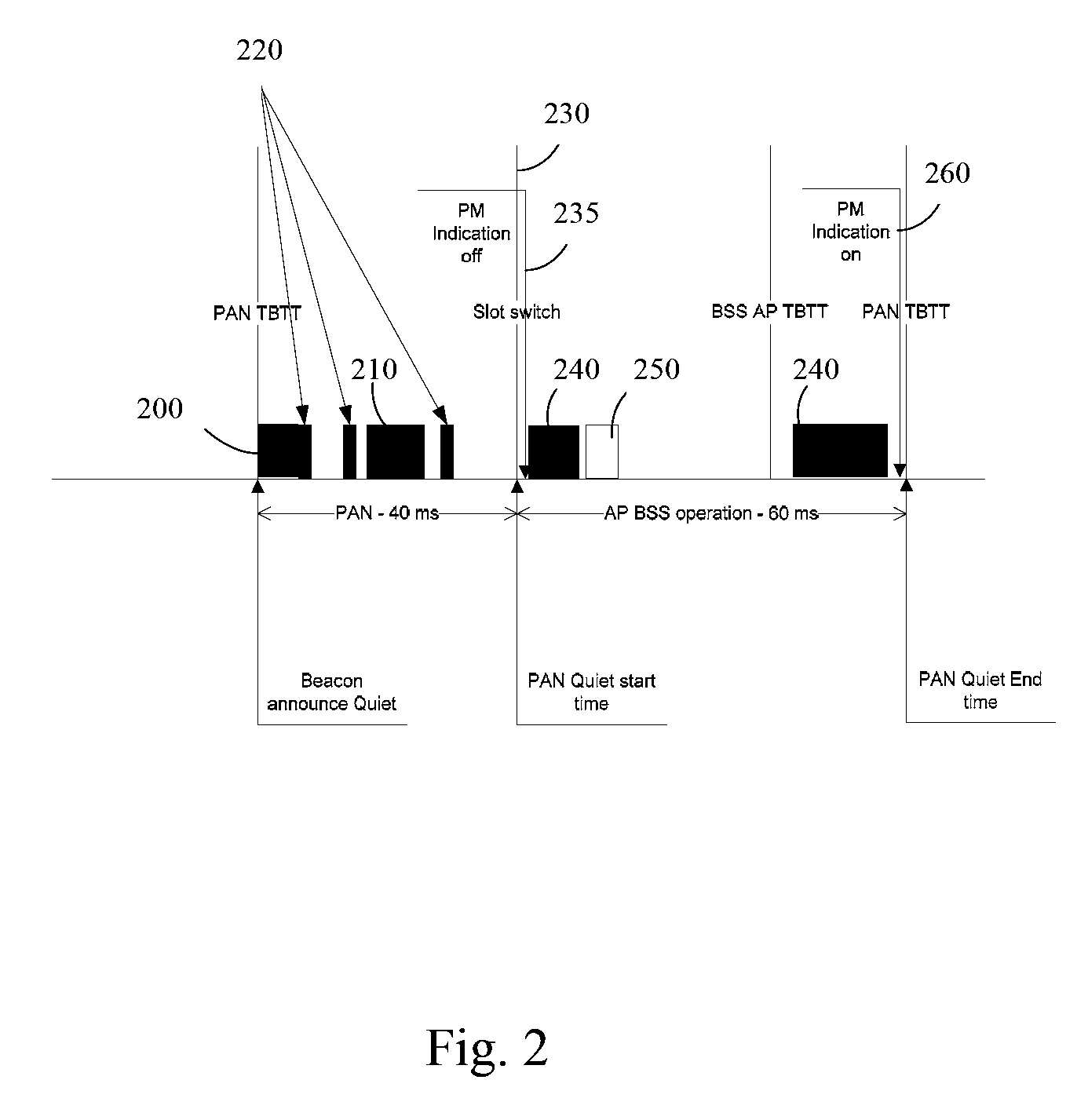
Method and apparatus for improved dual channel operation and access point discovery in wireless communication networks
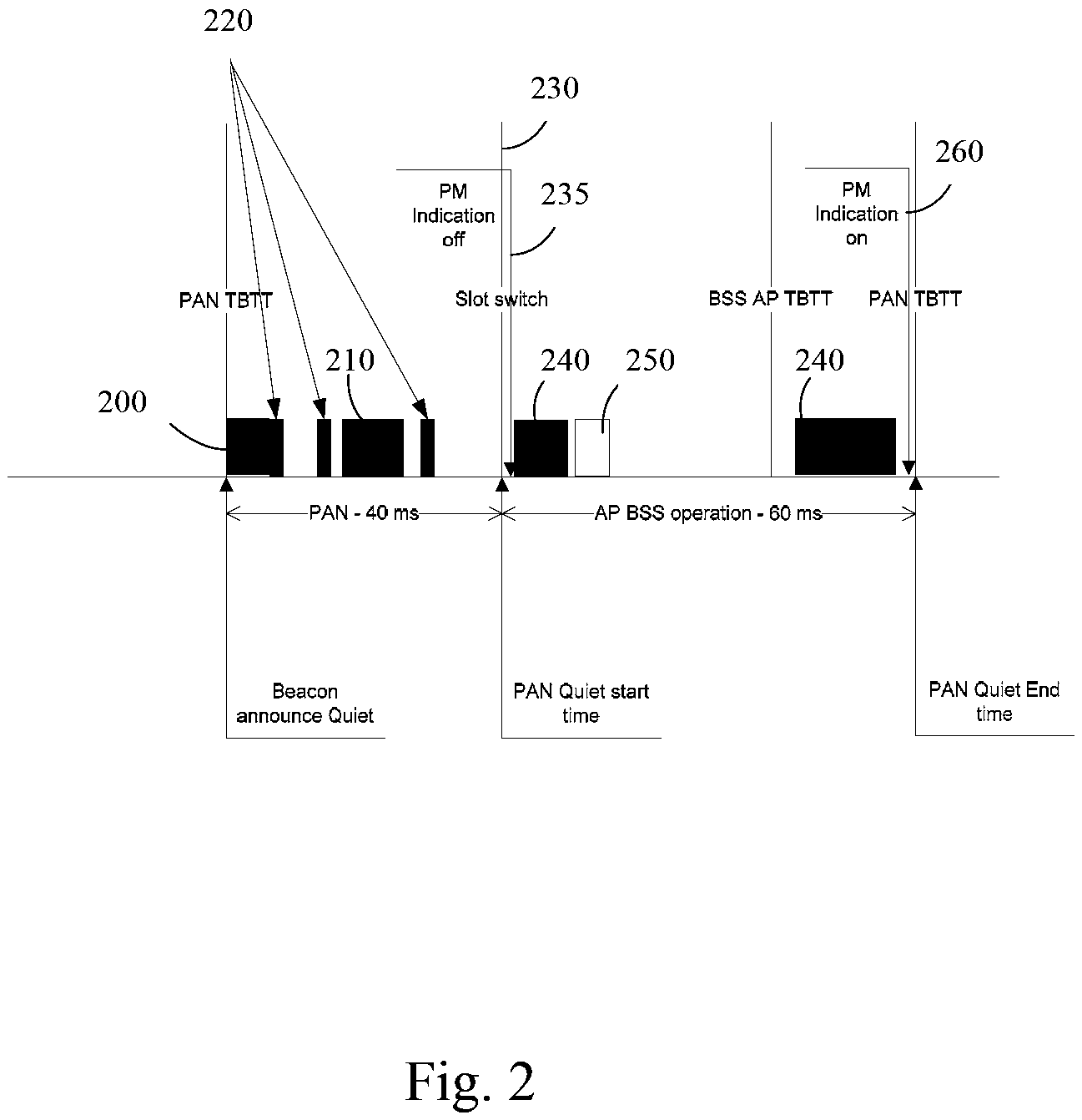
InactiveUS20090046673A1Reduction procedureEasy accessAssess restrictionTime-division multiplexTime division multiple accessCoordinate time
A method and apparatus of coordinating Time Division Multiple Access operation of wireless communication devices is disclosed. The method comprises an access point announcing a Quiet Period to one or more clients of the access point and transmitting as part of Target Beacons and probe responses an indication to the one or more clients that the access point will be absent from the communication channel for a period of time. The method also comprises the one or more clients establishing a connection with the access point after the Quiet Period when the access point is present on the communication channel on the basis of the indication.
Owner:INTEL CORP
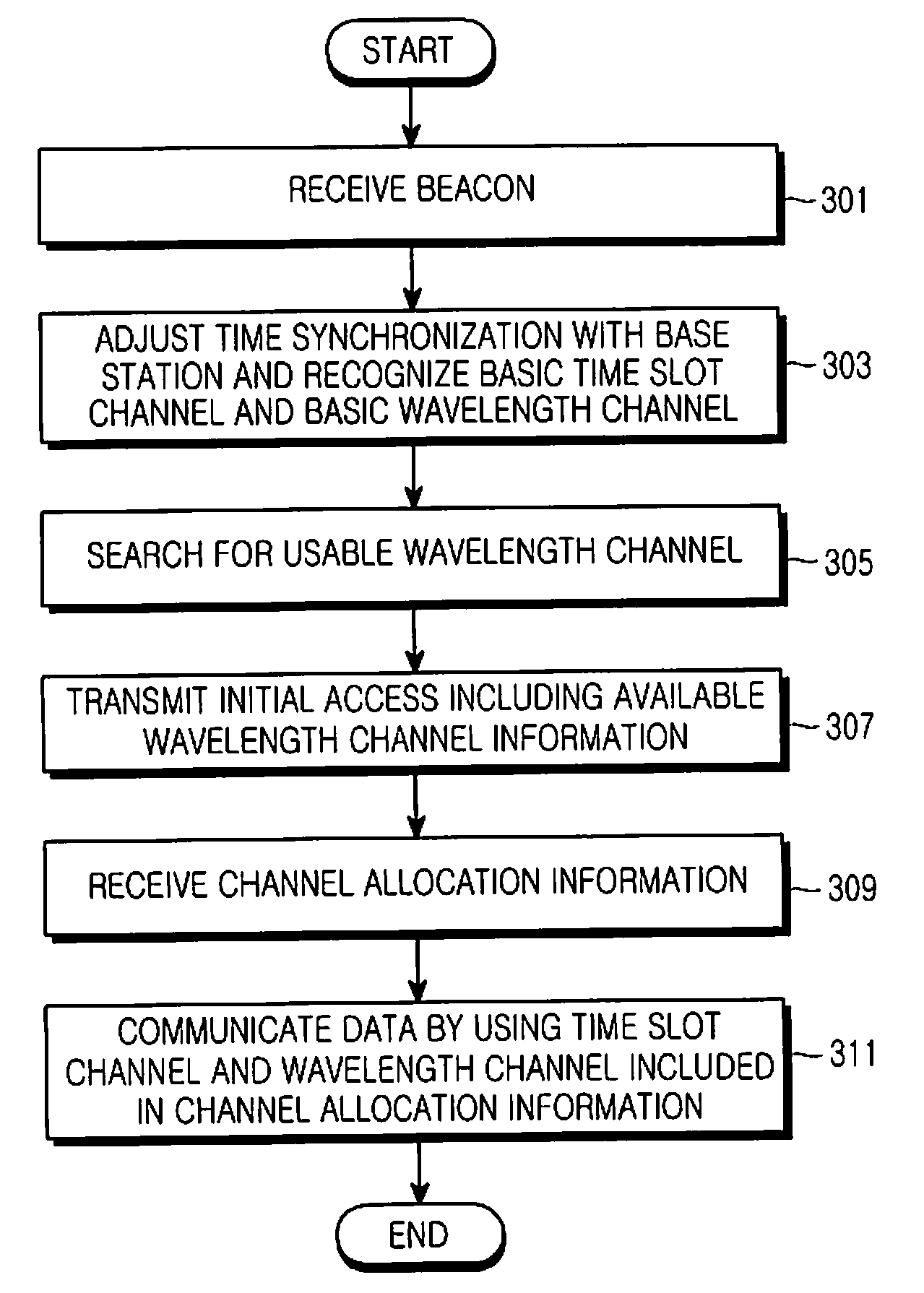
Method and apparatus for channel allocation in a visible light communication system
ActiveUS20110069957A1Easy to useWavelength-division multiplex systemsWireless systems/telephoneCurrent channelCoordinate time
A method and apparatus for allocating resources of a Visible Light Communication (VLC) terminal in a VLC system. The VLC terminal receives a beacon message from a base station, coordinates time synchronization with the base station, searches for an available wavelength channel, constructs available wavelength channel information, and transmits an initial access request using a basic time slot channel and a basic wavelength channel. The base station considers the available wavelength channel information and a current channel allocation condition, allocates an appropriate channel, and transmits channel allocation information to the VLC terminal. The VLC terminal and the base station communicate data with each other using an allocated time slot channel included in the channel allocation information and an allocated wavelength channel included in the channel allocation information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
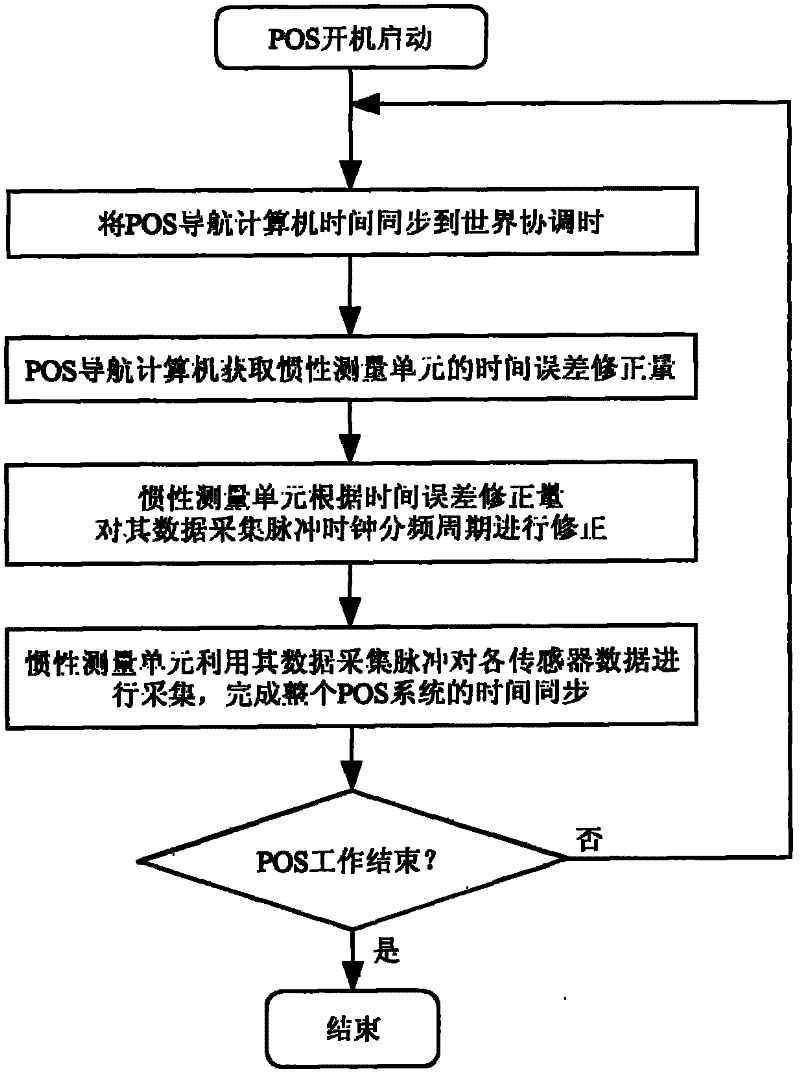
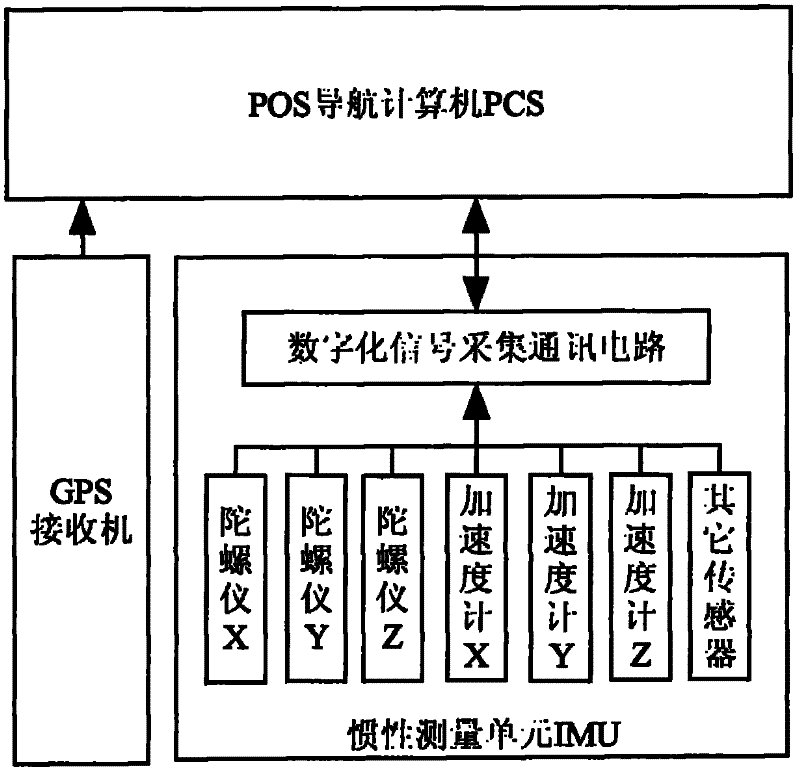
Software time synchronization method for position and orientation system
InactiveCN102183253AHigh precisionImprove time synchronization accuracySynchronous motors for clocksNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsClock driftCoordinate time
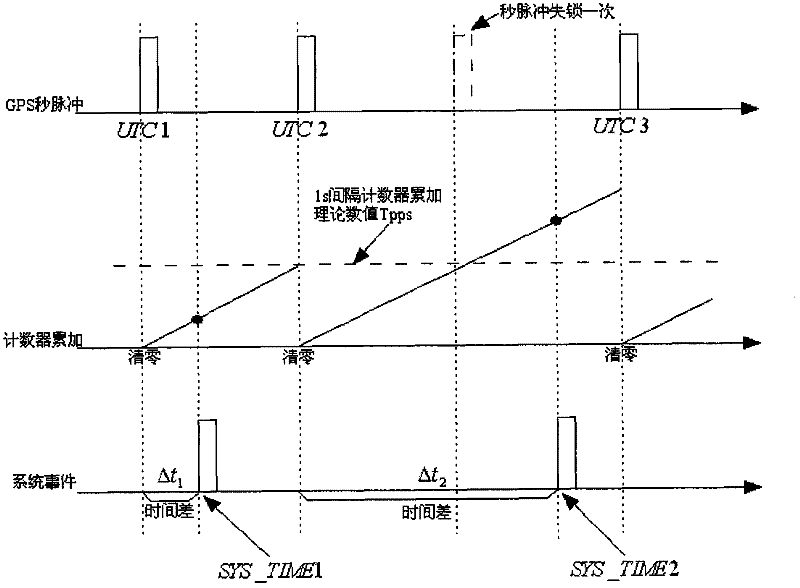
The invention provides a software time synchronization method for a position and orientation system (POS). The POS comprises an inertial measurement unit, a POS navigation computer, a GPS (Global Positioning System) receiver and the like. The time synchronization method comprises the following steps of: firstly synchronizing system time of the POS navigation computer to world coordinated time by using a GPS second pulse sent by the GPS receiver and a time counter; and synchronizing the data acquisition time of the inertial measurement unit with the world coordinated time through a method of correcting a frequency division period of a data acquisition pulse clock of the inertial measurement unit so as to complete the time synchronization of the POS. In the invention, the problem of reducing of synchronization accuracy of the POS in a short time due to the clock drift is solved through the method of changing the frequency division period of the data acquisition pulse clock, and the software time synchronization method has the characteristics of high accuracy and high anti-interference capacity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Medical kinematic analysis apparatus and a medical kinematic analysis method
InactiveUS20060058618A1Effective diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementKinematicsSystole
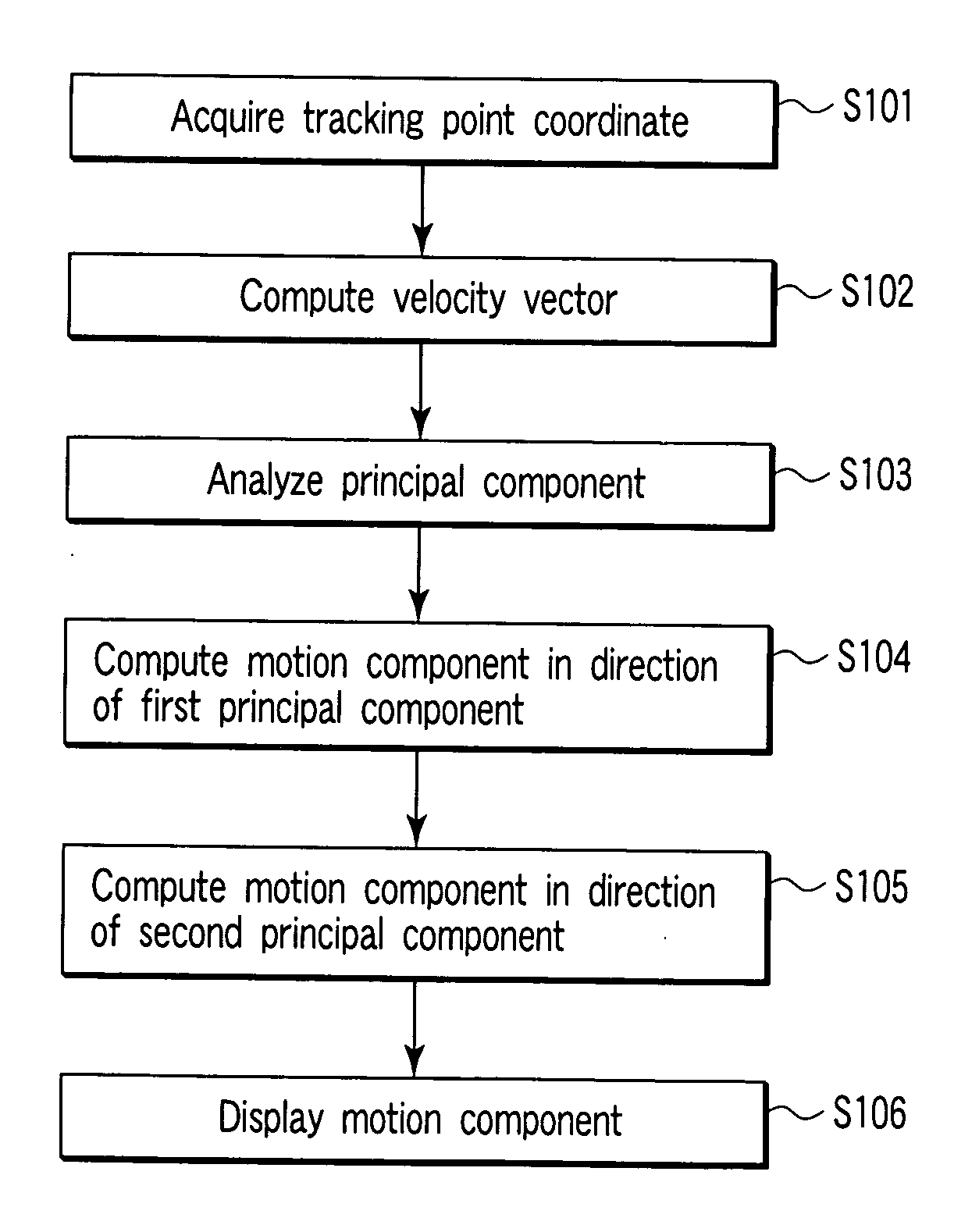
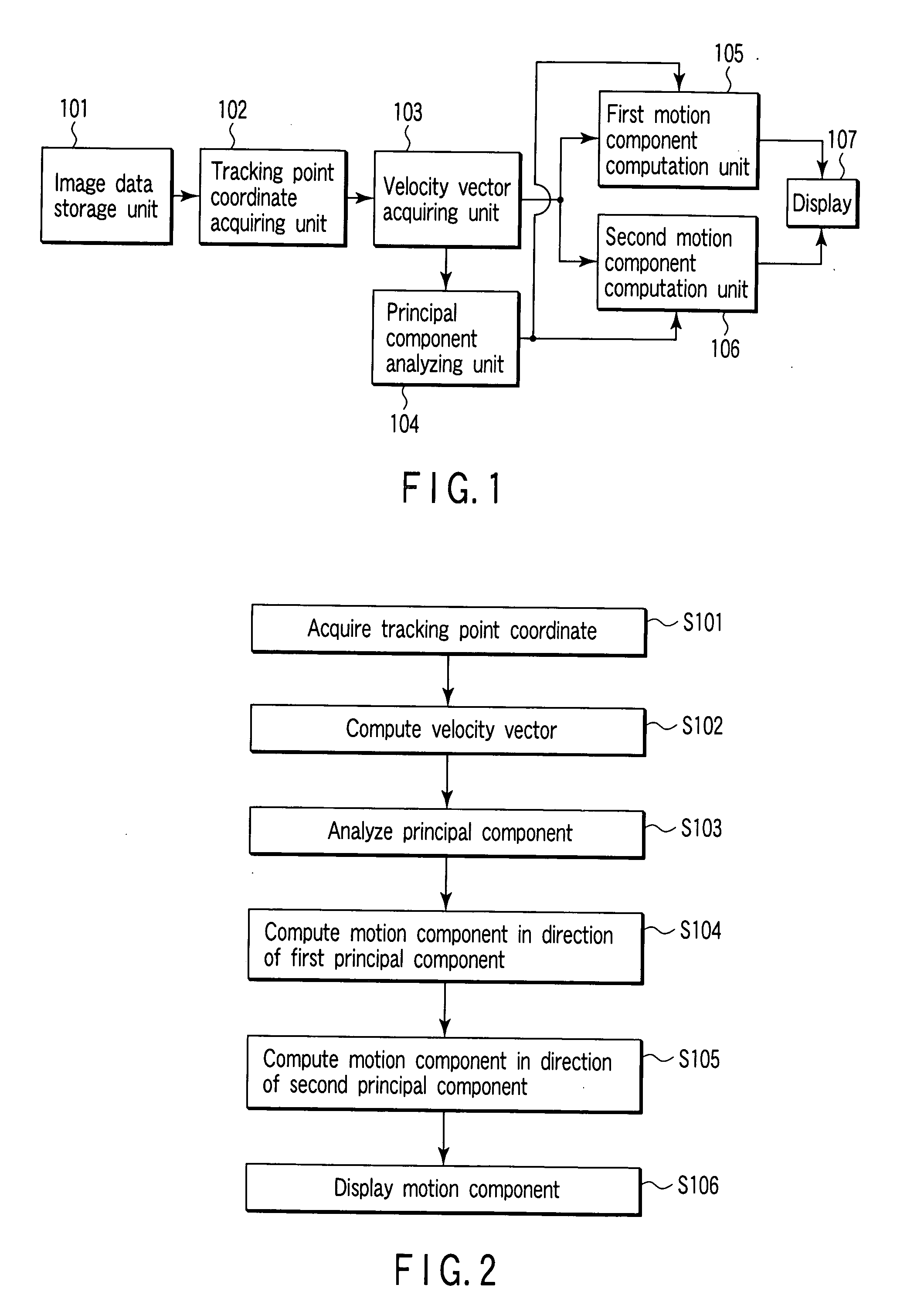
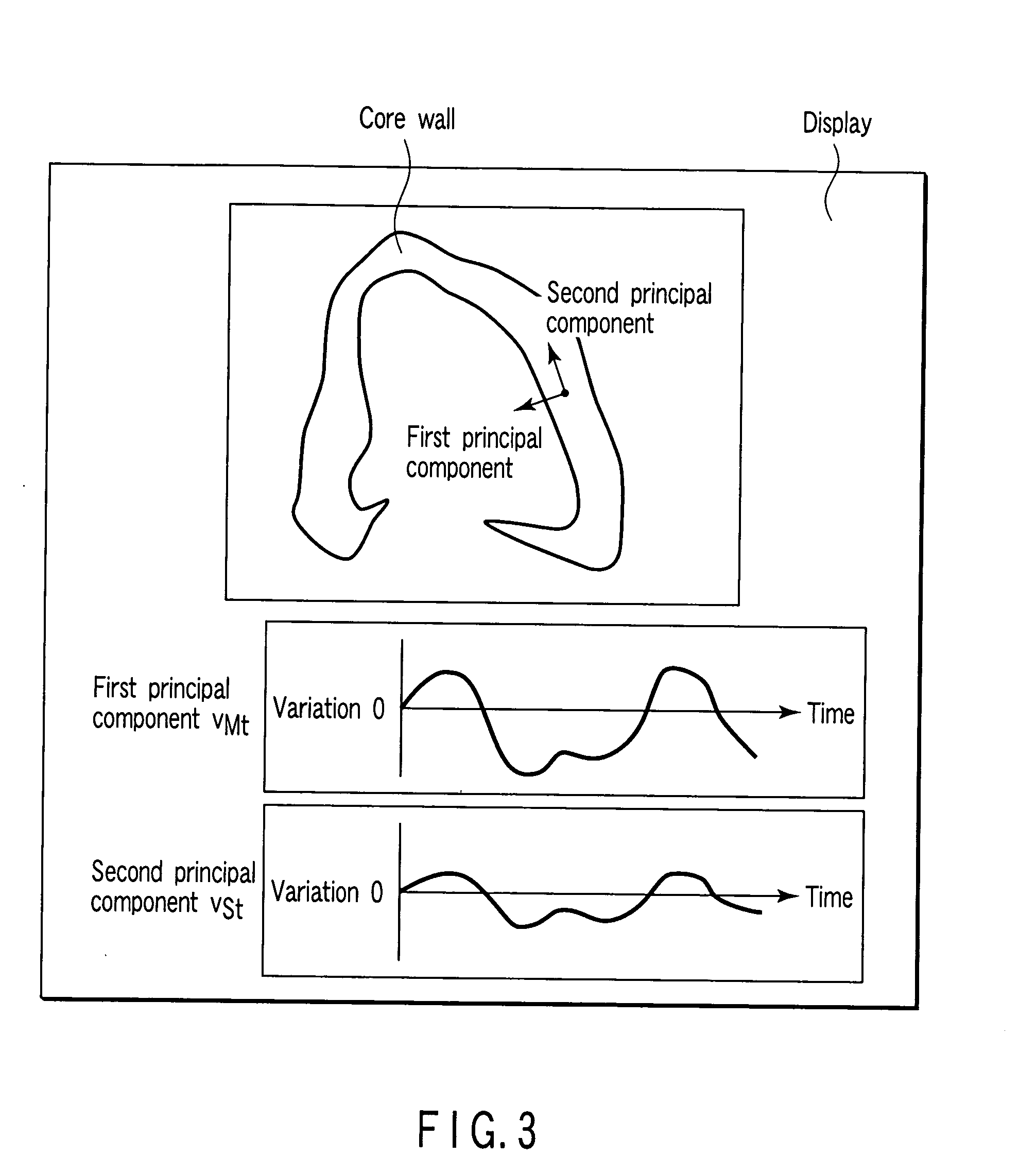
A medical kinematic analysis apparatuses includes a tracking point coordinate acquiring unit to generate coordinate time series data representing a coordinate of a tracking point on a heart from the time series image data, a motion information acquiring unit to generate time series motion information of the tracking point from the coordinate time series data, a first motion component computation unit to compute a motion component of a cardiac systole / diastolic direction from the time series motion information, and a second motion component computation unit to compute a motion component of a direction different from the cardiac systole / diastolic direction from the time series motion information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and device for coordinating interference
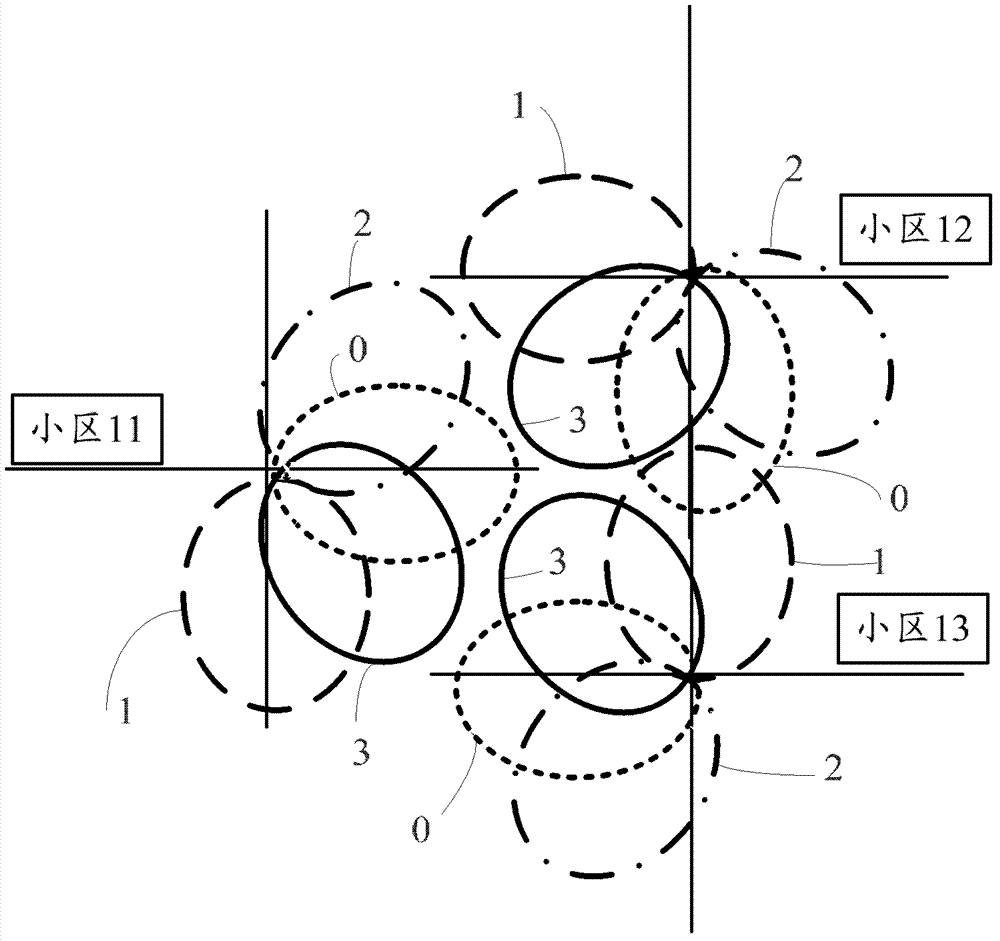
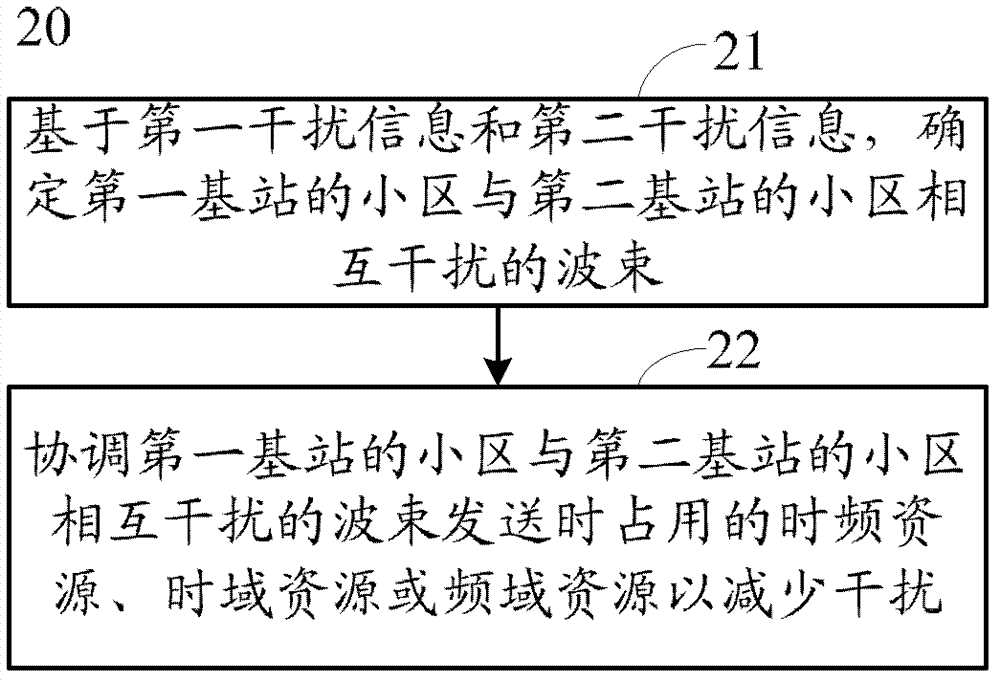
ActiveCN103369539AReduce mutual interferenceSite diversityNetwork planningTime domainCoordinate time
The present invention provides a method and a device for interference coordination. The method comprises: determining mutually interfering wave beams between a cell of a first base station and a cell of a second base station based on first interference information and second interference information, the first interference information comprising a first cell set, the first cell set comprising a first interference cell to which the interference wave beam of a wave beam of the cell of the first base station belongs, the second interference information comprising a second cell set, and the second cell set comprising a second interference cell to which the interference wave beam of a wave beam of the cell of the second base station belongs; coordinating time-frequency resources, time domain resources or frequency domain resources occupied when the mutually interfering wave beams between the cell of the first base station and the cell of the second base station are sent, so as to reduce interference. The technical solution may provide a method for interference coordination. By coordinating, wave beams of the cells of the base stations are sent in a staggered manner in terms of the time-frequency resources, the time domain resources or the frequency domain resources, thereby reducing the mutual interference between the wave beams of the cells of the base stations without increasing uplink costs.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
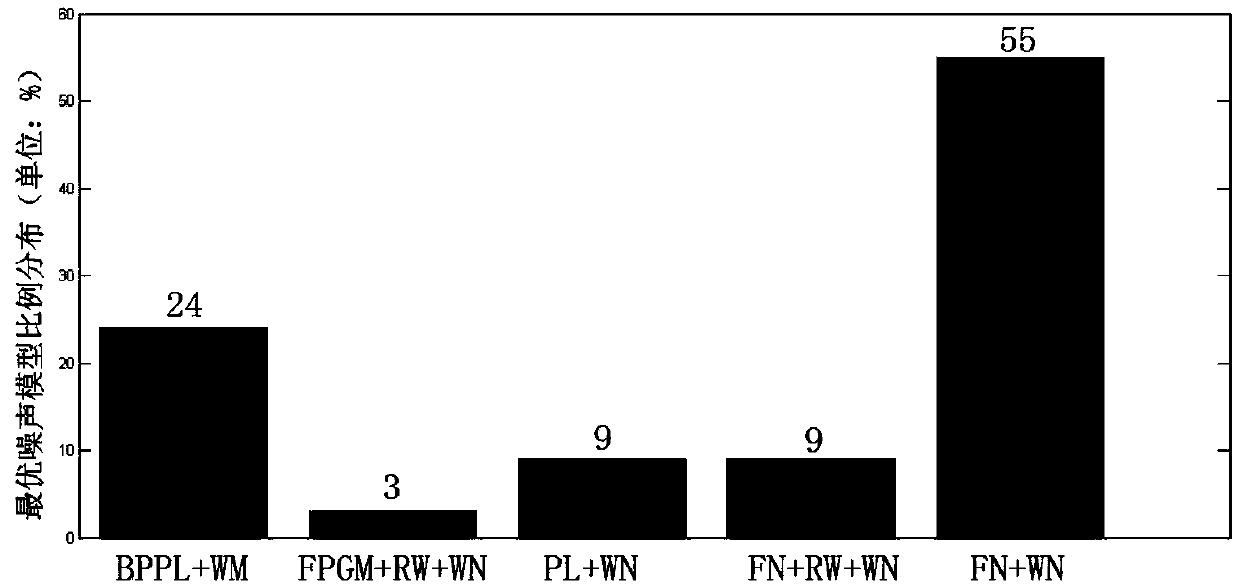
Establishing method of regional CORS coordinate time series noise model
InactiveCN104392414AExtract comprehensiveReliable extractionImage enhancementImage analysisTime domainPattern recognition
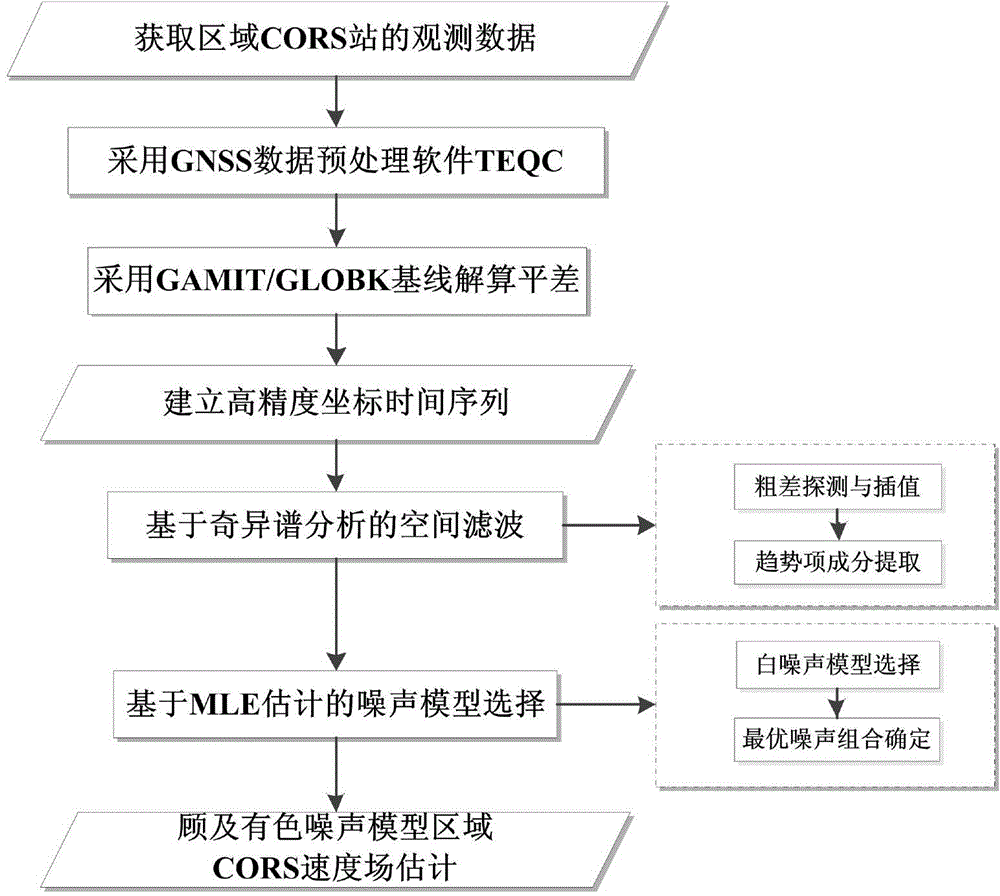
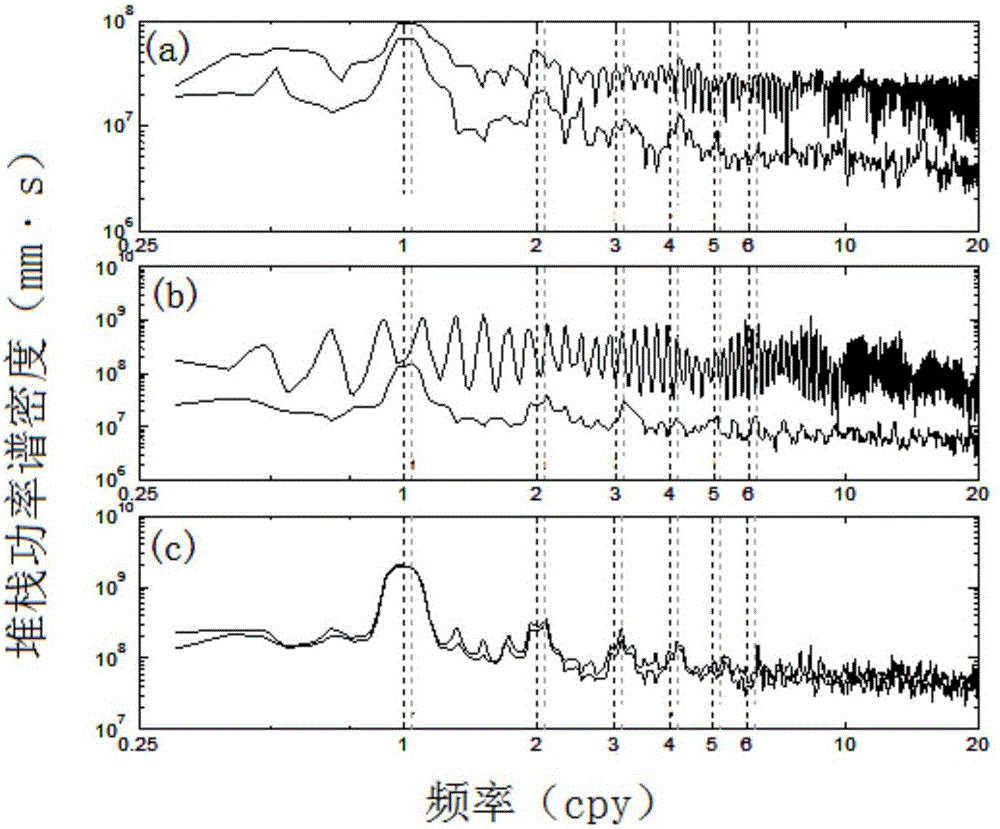
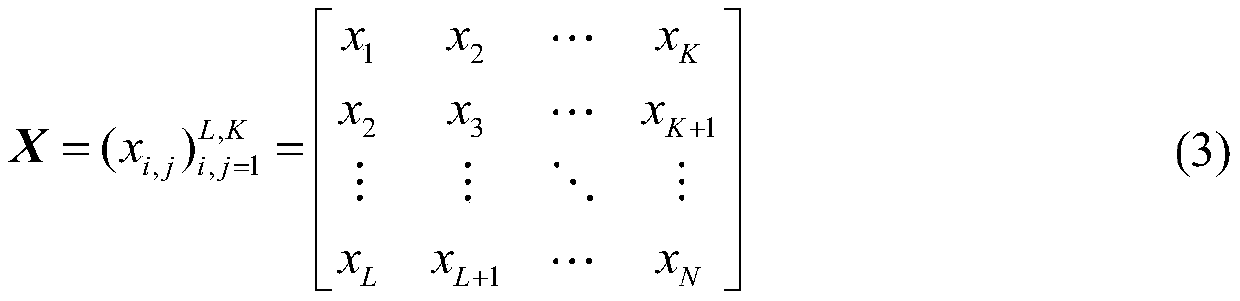
The invention relates to an establishing method of a regional CORS coordinate time series noise model. The establishing method is characterized by comprising the following steps that: step 1, observation data of a regional CORS station are obtained; step 2, GNSS data pre-processing software TEQC is adopted; step 3, GAMIT / GLOBK baselines are adopted to solve adjustment; step 4, a high-precision coordinate time series is established; step 5, singular spectrum analysis-based spatial filtering is performed; step 6, MLE estimation-based noise model selection is performed; and step 7, regional CORS velocity filed estimation is performed in view of colored noise models. According to the establishing method of the invention, time-domain frequency domain characteristic analysis is adopted to perform spatial filtering on the regional CORS time series; and maximum likelihood values are selected for different noise models of the regional CORS time series, so that judgment can be performed, and therefore, optimal noise models in the N (North), E (East) and U (altitude) are determined, and the regional CORS velocity filed can be estimated in view of the optimal noise models.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for acquiring noise models of coordinate time series of regional GPS (global positioning system) reference stations
ActiveCN104200036AImproving Observation AccuracyHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsCoordinate timeAlgorithm
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
GNSS base station crustal movement velocity estimation method in consideration of nonlinear change
InactiveCN109188466AOvercoming excessive punishmentReduce spurious motionSatellite radio beaconingSingular spectrum analysisEstimation methods
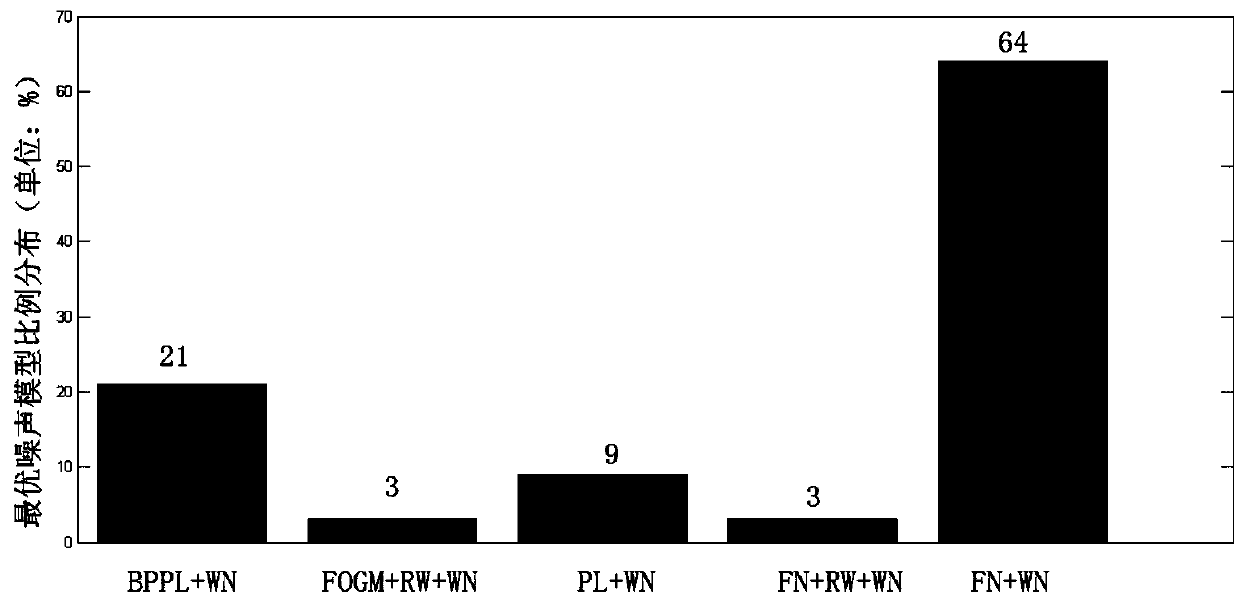
The invention discloses a GNSS base station crustal movement velocity estimation method in consideration of nonlinear change. In consideration of the influence on the base station velocity estimationby the GNSS base station nonlinear change, a random model and like, the latest resolving strategy is adopted to acquire a GNSS base station coordinate time sequence under an ITRF2014 framework, a timesequence model for performing separation on the nonlinear change of the base station coordinate time sequence is established by combining a real physical correction model, abnormal location gross error and step detection and like methods; and a GNSS base station coordinate time sequence background noise model determination technology based on the singular spectrum analysis method is adopted, andan improved Bayes information minimum criterion noise model estimation method is proposed base on above conditions, a GNSS base station crustal movement velocity field estimation method is provided, thereby providing accurate and reliable velocity field data basis for the crustal movement velocity field estimation.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Periodic detection method and system for GNSS observation station coordinate time sequence
ActiveCN110398753AAvoid blindnessImprove reliabilitySatellite radio beaconingFrequency spectrumHypothesis
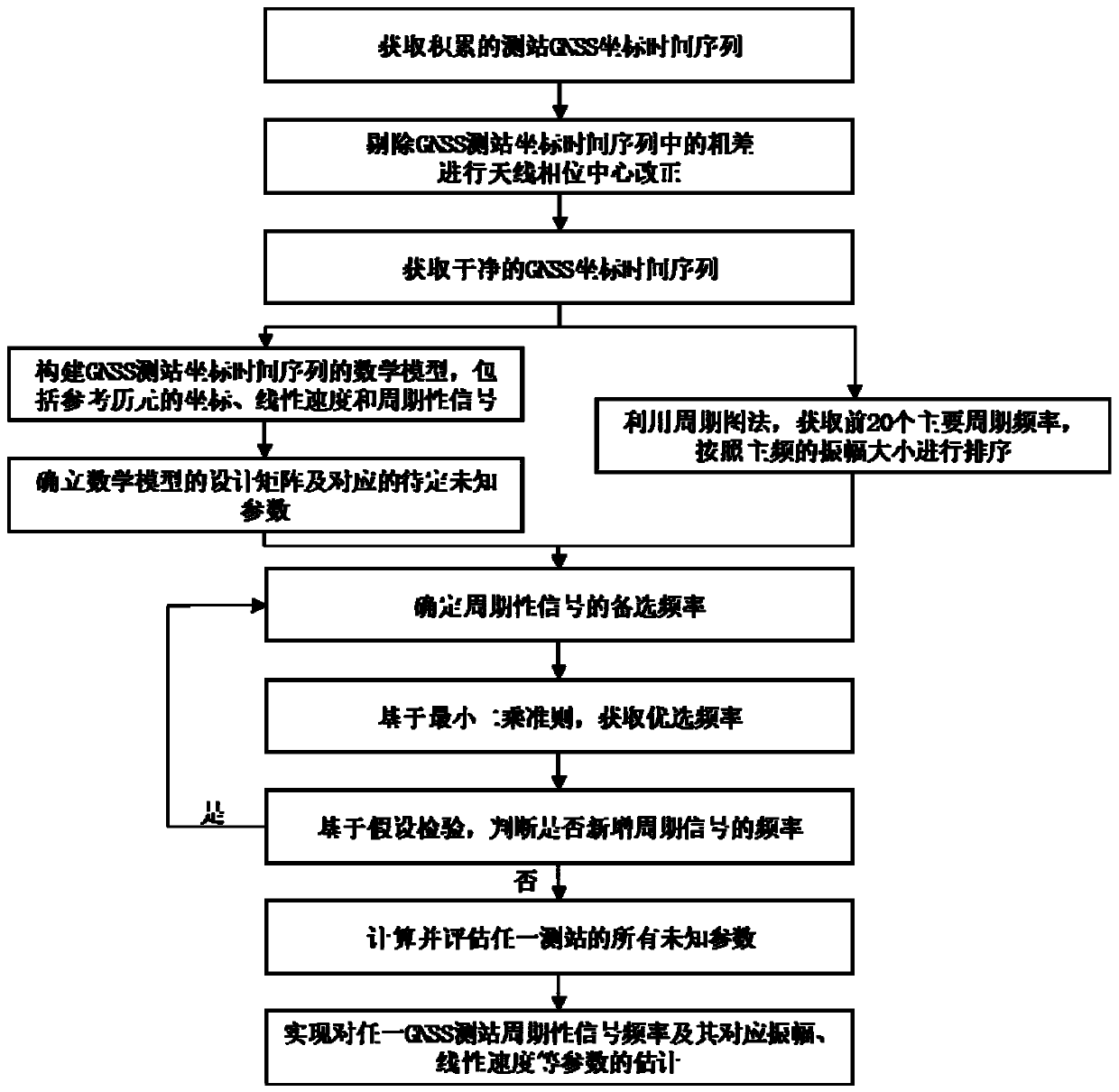
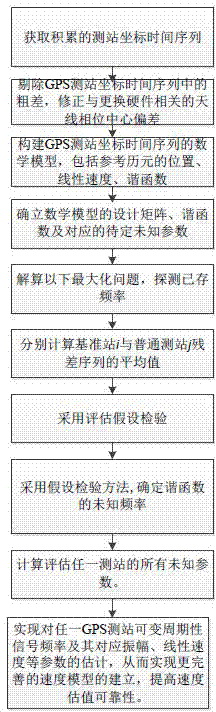
The invention provides a periodic detection method and system for a GNSS observation station coordinate time sequence. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a GPS observation station coordinatetime sequence observed value, removing gross errors and correcting an antenna phase center deviation; performing preliminary spectrum analysis on the GPS observation station coordinate time sequence by using a periodogram method; acquiring a plurality of major cycle frequencies of a corresponding observation station, and sorting according to the amplitudes of main frequencies; describing the GPS observation station coordinate time sequence by using a harmonic function, acquiring a harmonic function model of the GPS observation station coordinate time sequence, and building a harmonic functionmodel matrix; using the main frequencies as prior constraints, and acquiring the standby frequencies of a plurality of periodic signals; resolving the harmonic function model based on a least squarescriterion, acquiring optimal frequencies and verifying the standby frequencies by using a hypothesis testing method, and building the harmonic function model including the plurality of optimal frequencies; and according to the standby frequency after hypothesis testing is performed, resolving the harmonic function model matrix based on the least squares criterion, and acquiring a detection resultof any GNSS observation station periodic signal.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for channel allocation in a visible light communication system
ActiveUS8380081B2Easy to useWavelength-division multiplex systemsWireless systems/telephoneCurrent channelCoordinate time
A method and apparatus for allocating resources of a Visible Light Communication (VLC) terminal in a VLC system. The VLC terminal receives a beacon message from a base station, coordinates time synchronization with the base station, searches for an available wavelength channel, constructs available wavelength channel information, and transmits an initial access request using a basic time slot channel and a basic wavelength channel. The base station considers the available wavelength channel information and a current channel allocation condition, allocates an appropriate channel, and transmits channel allocation information to the VLC terminal. The VLC terminal and the base station communicate data with each other using an allocated time slot channel included in the channel allocation information and an allocated wavelength channel included in the channel allocation information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-node coordinated time consistency management method
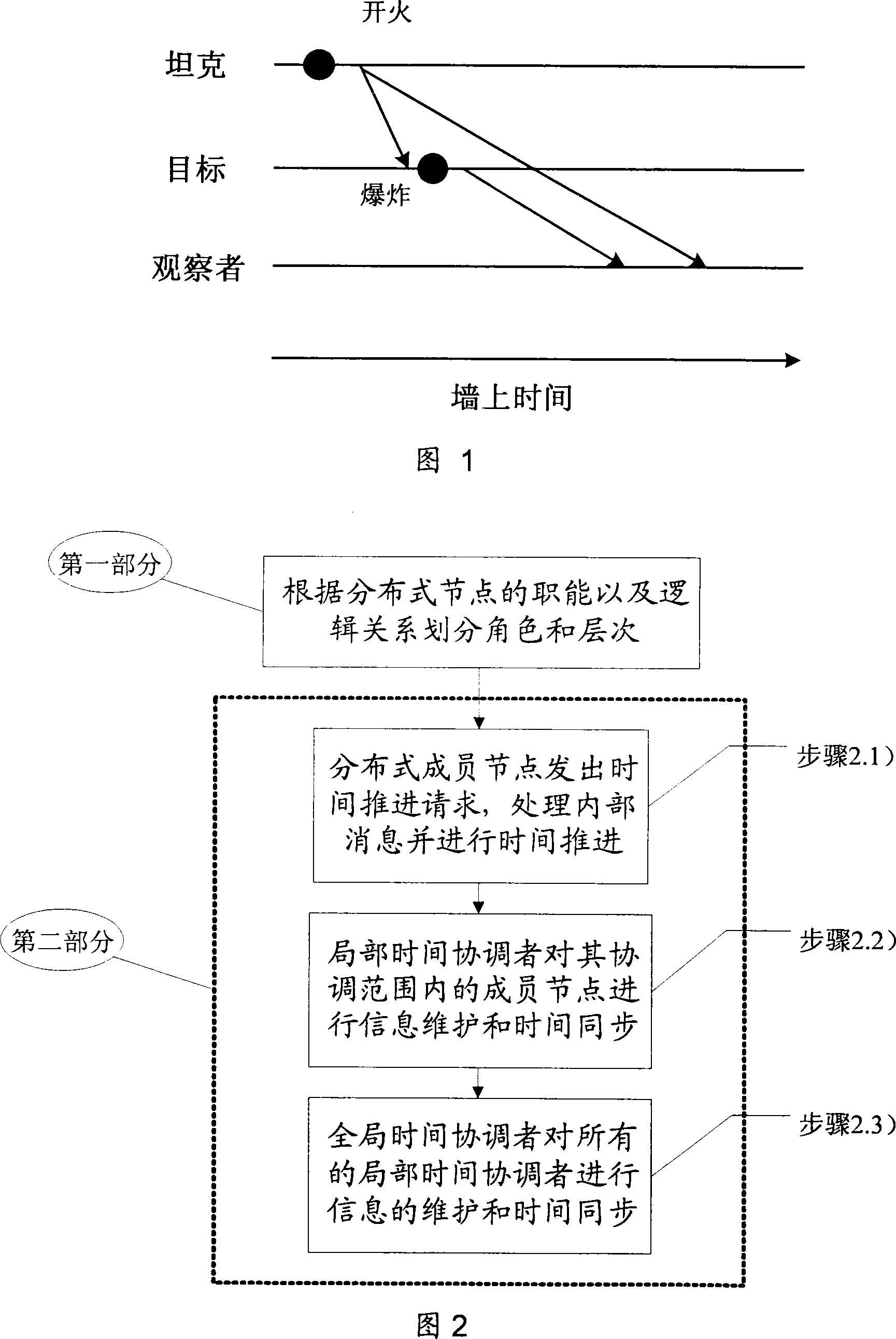
InactiveCN101132270AReduce the number of outputsReduce the number of timesData switching networksSynchronising arrangementCoordinate timeSystem time
This invention relates to a managing method for coordinating consistency of time by multiple nodes including two parts: 1, carrying out role and hierachical decomposion to nodes in a distributibve system according to functions and logic relations, 2, the time synchronized hierarchical association flow of the nodes includes the following steps: 2.1, the distributive member nodes send push time request to process internal messages and push the time, 2.2, a local time coordinator caries out information maintenance and time synchronization to member nodes in its coordinated sphere, 2.3, a global time coordinator maintains information and synchronizes time for all local time coordinators.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for calculating green wave effective coordinated time
InactiveCN102610108AImprove traffic capacityReal-time monitoring of running statusControlling traffic signalsCoordinate timeControl system
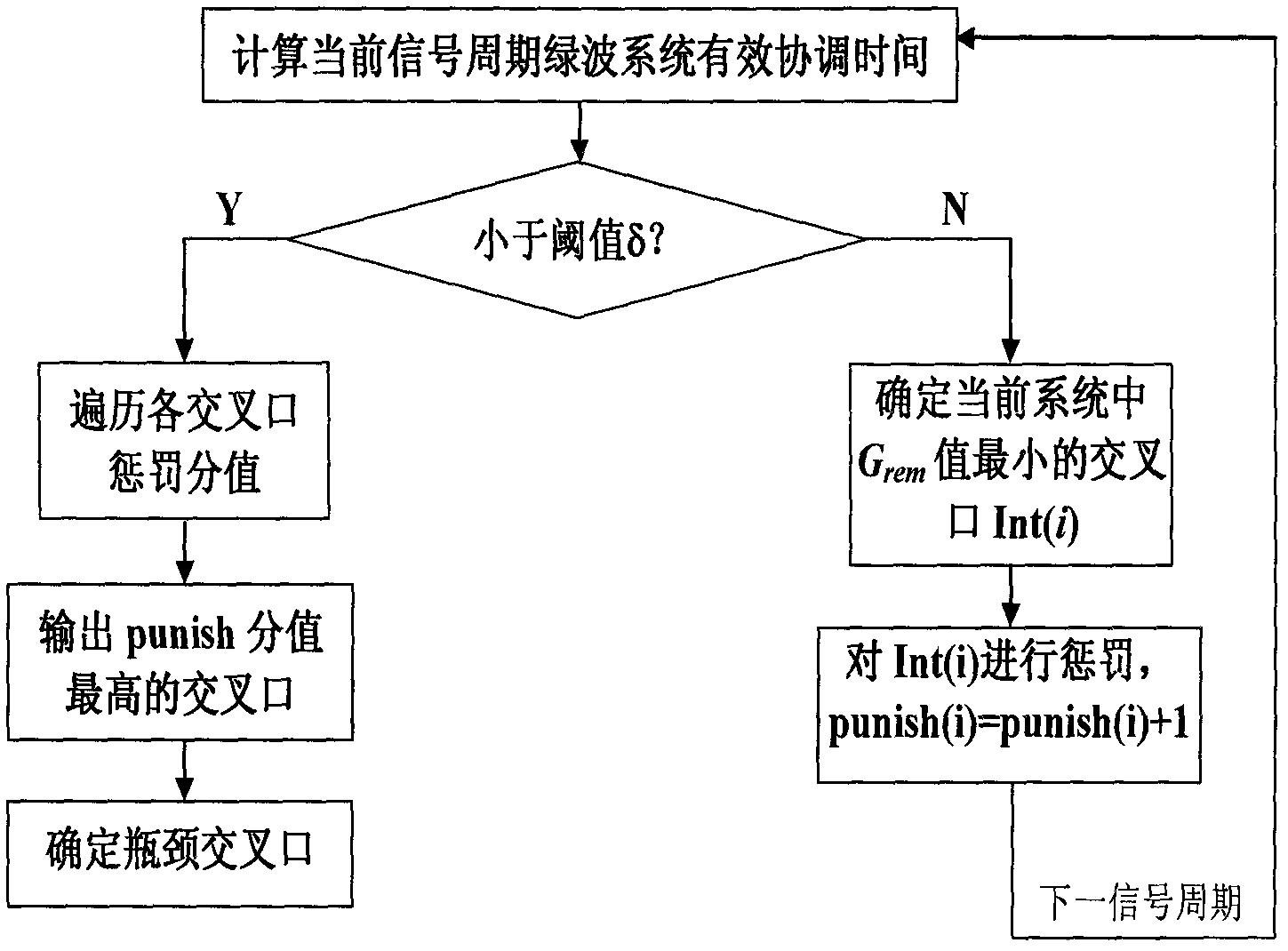
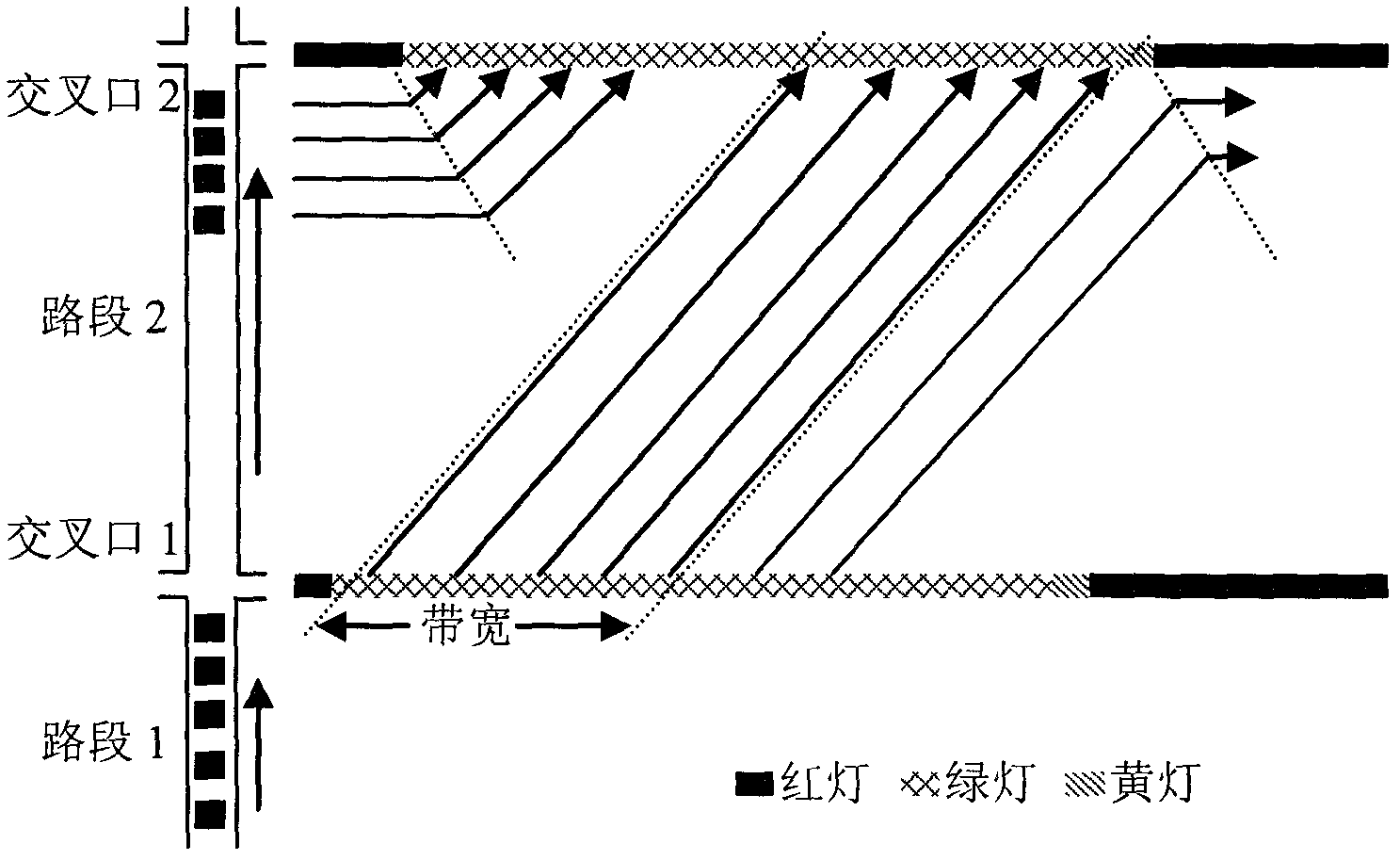
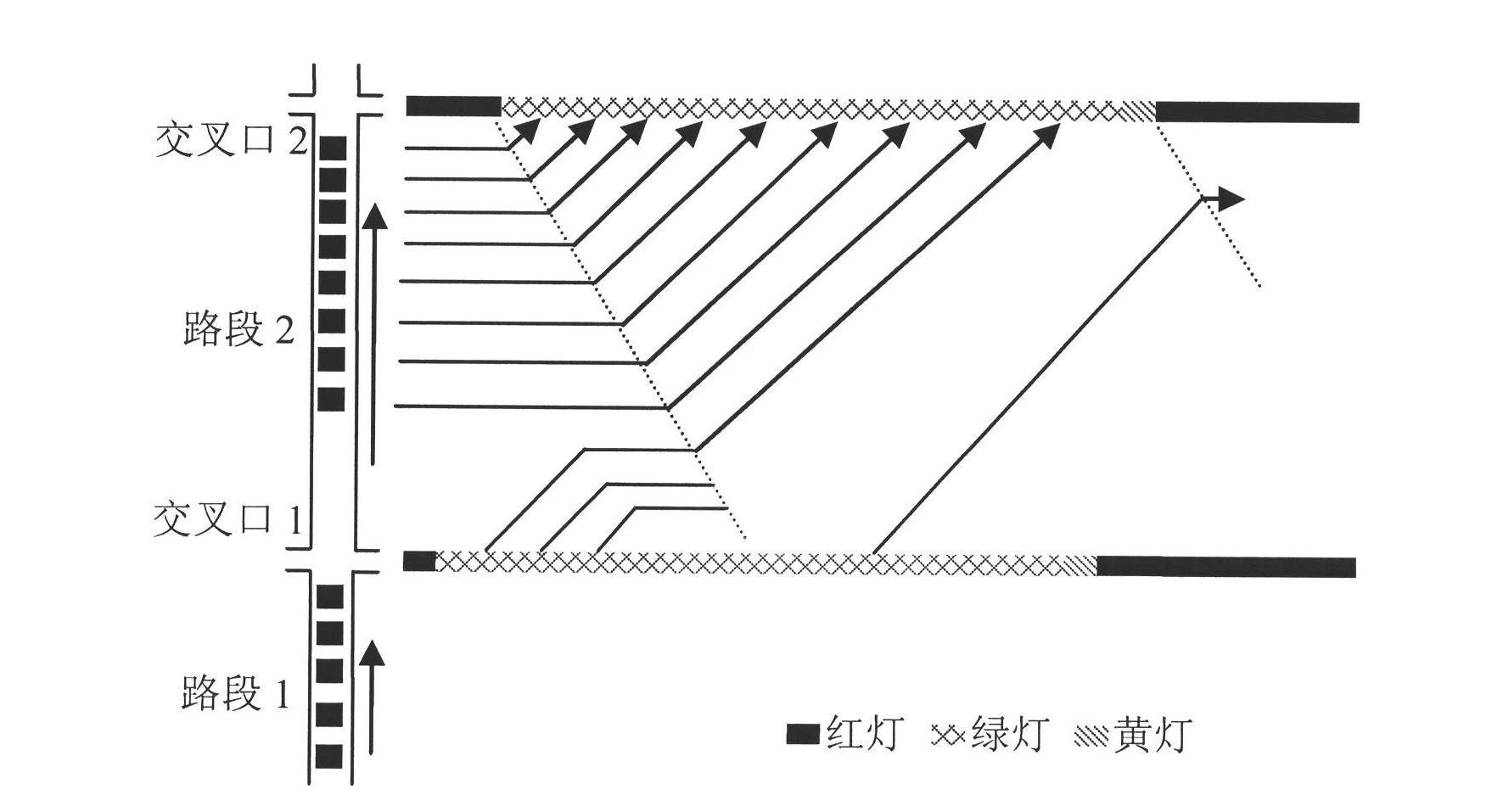
The invention discloses a method for calculating green wave effective coordinated time. For monitoring the running state and control effect of a trunk line green wave coordination control system to determine the switching time points of different trunk line traffic signal control schemes, a definition and a calculation method of effective coordinated time are firstly given, the running state of a current green wave coordination control system is dynamically monitored, a bottleneck intersection in a green wave coordination system is determined by accumulating punishment score values, and the influence of effective coordinated time on the switching time points of the signal control schemes is discussed lastly. As shown by a simulation test result, the running state of the green wave coordination control system can be effectively monitored by adopting the effective coordinated time, the bottleneck intersection in the system is discovered accurately, and technical support can be provided for improving a trunk line traffic organism and perfecting a trunk line control scheme.
Owner:郭海锋
GPS observation station coordinate time sequence periodic-detection method and system
InactiveCN104765055AImprove reliabilityGuaranteed accuracySatellite radio beaconingCoordinate timeLeast squares
The invention provides a GPS observation station coordinate time sequence periodic-detection method and system. The GPS observation station coordinate time sequence periodic-detection method comprises the steps of 1 obtaining an observed value of a GPS observation station coordinate time sequence, 2 removing a gross error of the observed value of the GPS observation station coordinate time sequence and rectifying an antenna phase center deviation, 3 adopting a harmonic function to describe the GPS observation station coordinate time sequence so as to obtain a harmonic function model of the GPS observation station coordinate time sequence and designing a harmonic function model matrix, 4 adopting a least square method to resolve the harmonic function model matrix and detecting the periodicity of the GPS observation station coordinate time sequence. The GPS observation station coordinate time sequence periodic-detection method and system can process GPS observation station coordinate time sequences including time-variant periodic signals and ensure detection accuracy.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
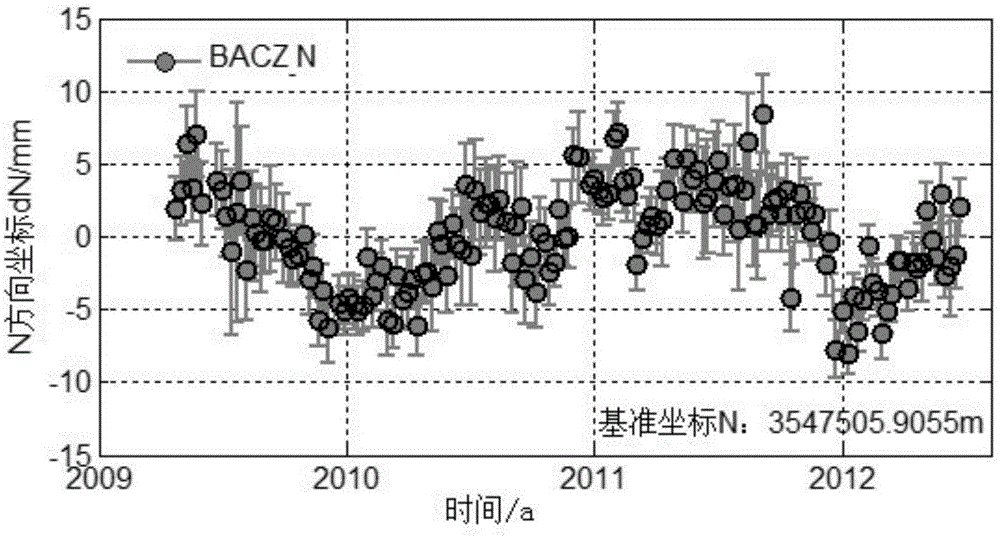
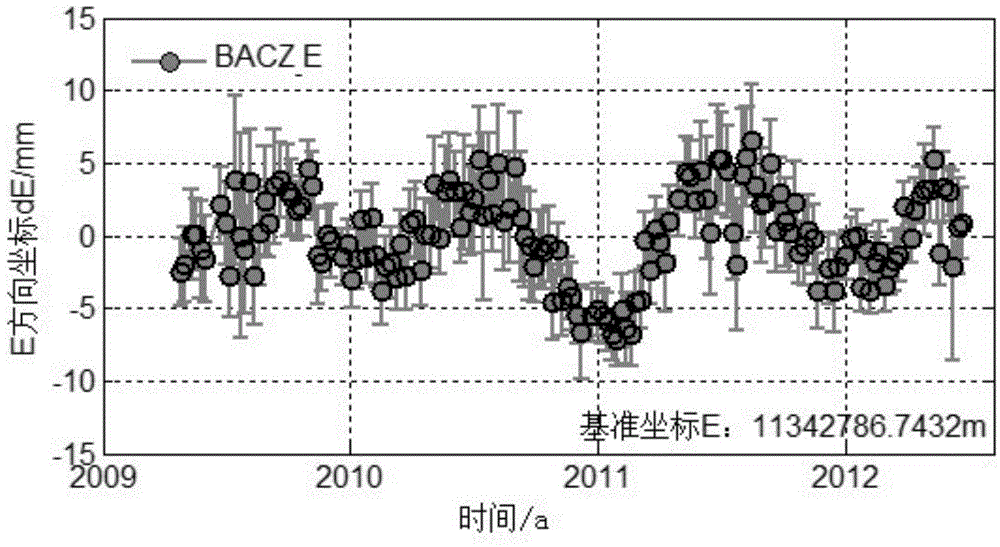
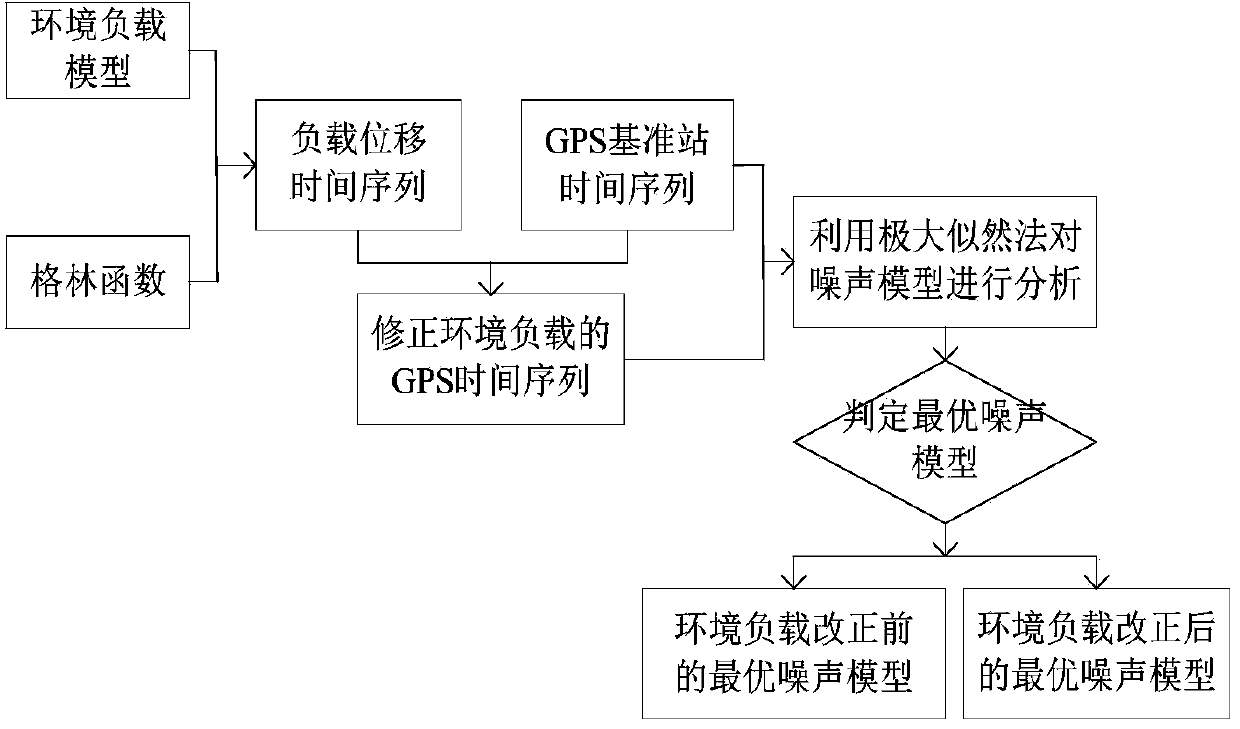
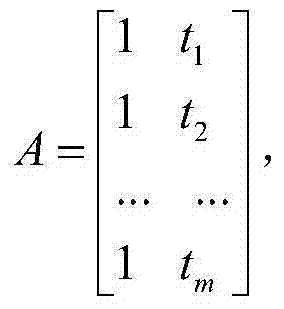
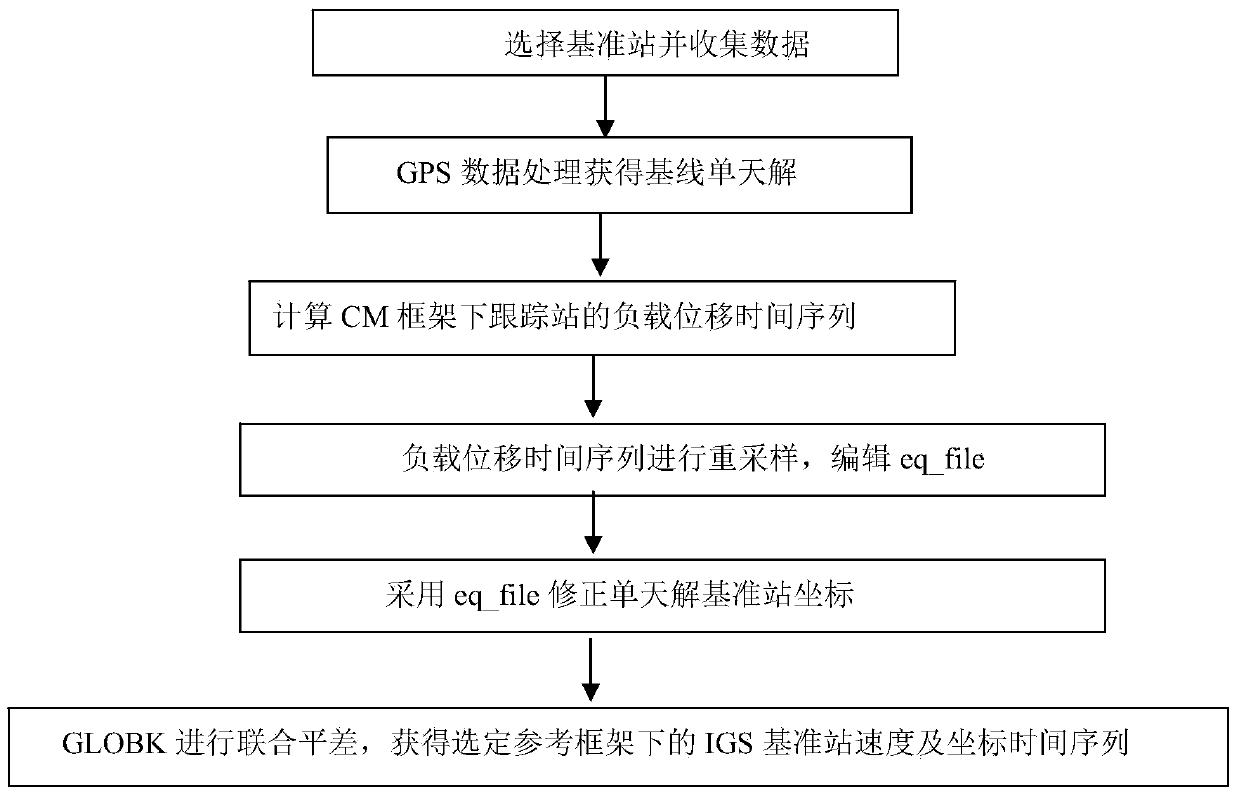
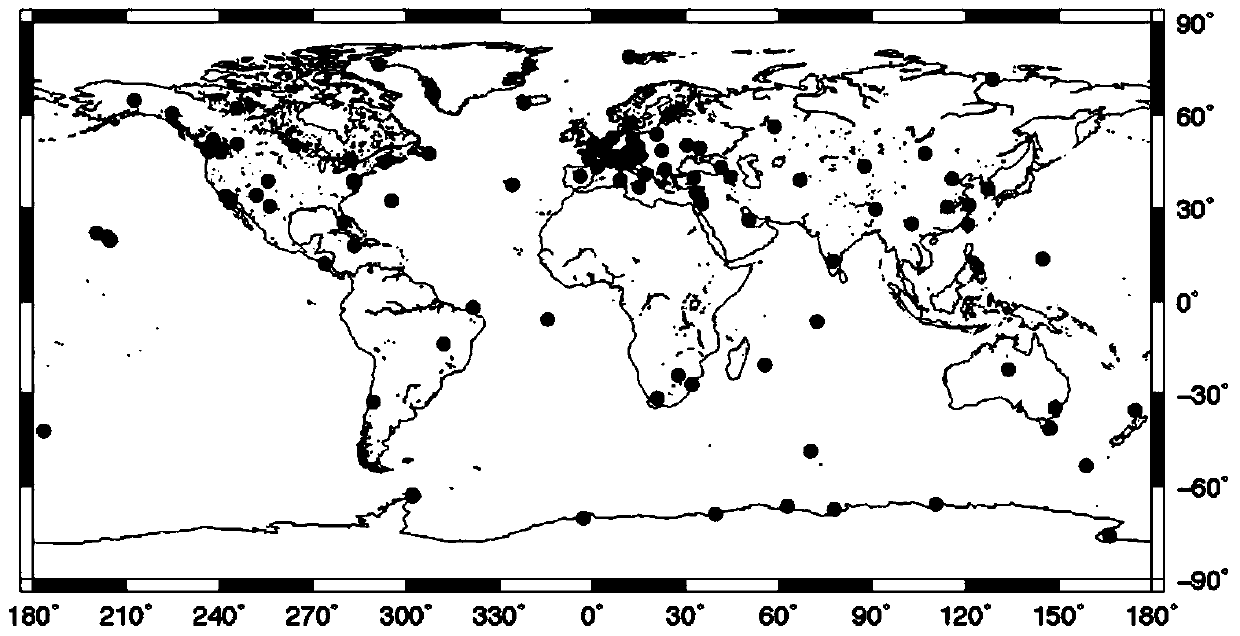
Correction method and system of environmental load of GPS (global positioning system) coordinate time series
The invention discloses a correction method and system of environmental load of a GPS (global positioning system) coordinate time series. The method includes the steps of 1, acquiring observation data of IGS (international GPS service) reference stations, and processing the observation data by an optimal data processing model to obtain a reference line one-day solution of each IGS reference station; 2, according to the theory of elastic deformation of earth, acquiring an environmental load displacement time series of each IGS reference station under a CM (center of mass) frame; 3, correcting reference station coordinates of the reference line one-day solutions through the environmental load displacement time series of the IGS reference stations; 4, subjecting the corrected reference line one-day solutions to combined adjustment by Kalman filtering to obtain velocity and coordinate time series of the IGS reference stations. The correction method and system has the advantages that actually running GPS coordinate time series of the reference stations can be better indicated, and more reliable reference station positions and velocities can be obtained.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for stability analysis of reference point for GNSS automatic deformation monitoring
ActiveCN106066901AAccurate removalImprove signal-to-noise ratioMeasurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsMissing dataSlope stability analysis
The invention discloses a method for stability analysis of reference point for GNSS automatic deformation monitoring, which comprises the following steps: calculating the GNSS observation data to obtain the coordinate residual time series of the reference point; detecting and removing rough errors in the coordinate residual time series of the reference point; extracting and removing the linear trend and the cyclical term in the series; conducting interpolation to the time series if there exist missing data in the coordinate residual time series after the removal of the trend and the cyclical term; extracting the common-mode error of the residual time series and removing the common-mode error from each residual series; and finally, using a quantification calculating method to determine whether the remaining residual series follows a normal distribution or not. If it is, then the reference point is regarded as stable; otherwise, instable. According to the invention, it can effectively eliminate the common error of a station, improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the coordinate time series, and finally make the main error of the coordinate time series of the station limited to observed random noise to judge whether the station is stable or not.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
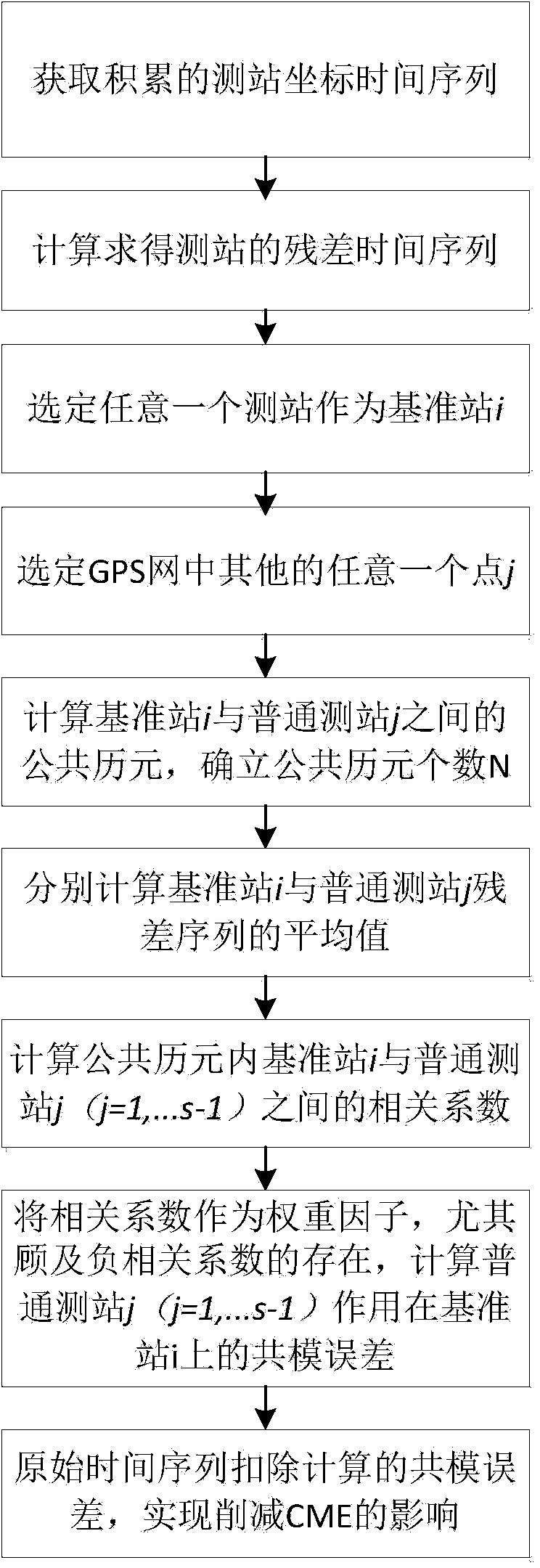
Correlation coefficient-based method for weakening CME (common mode error) influence in coordinate time sequence
ActiveCN103823993AGuaranteed accuracySolve the distance problemSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientCoordinate time
The invention provides a correlation coefficient-based method for weakening the CME (common mode error) influence in a coordinate time sequence. The correlation degree of the GPS (global positioning system) measuring interstation coordinate time sequence is represented by adopting correlation coefficients between a reference station and common measuring stations, and the correlation coefficient is used as the weight for calculating the GPS measuring interstation common-mode error. Meanwhile, the GPS measuring interstation negative correlation is not omitted, a positive correlation and a negative correlation are substituted into the CME calculation system at the same time, positive and negative correlation are equally treated as the weight factor for measuring the GPS measuring interstation CME influence. According to the correlation coefficient-based method, the technical problems that the existing method for weakening the CME influence in the coordinate time sequence is limited in interstation distance, low in space accuracy and the like are solved, and the method can process the measuring interstation CME influence of a GPS network being more than 2000km and can ensure the space response accuracy.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
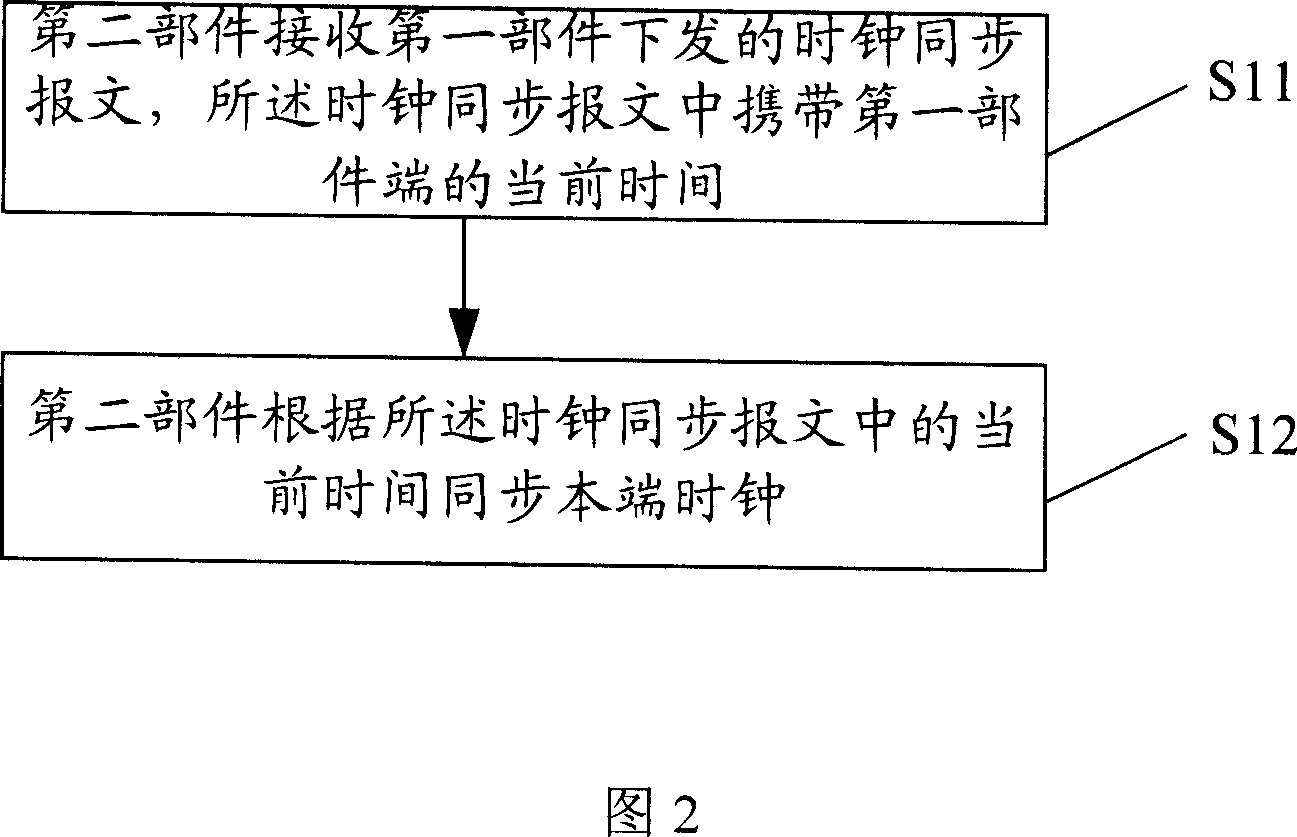
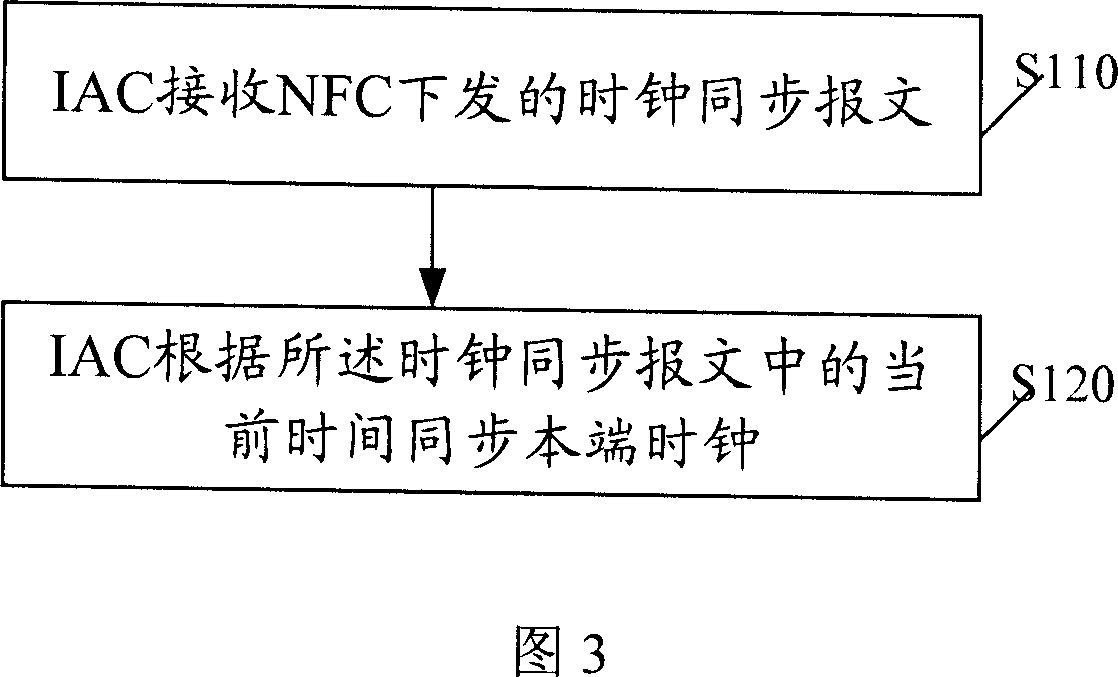
Clock synchronizing method and first part and second part using this method
InactiveCN1925386AAchieving Clock SynchronizationAchieve synchronizationData switching networksSynchronising arrangementCoordinate timeComputer science
This invention relates to clock synchronous method to fulfill synchronous clock between first and second parts, which comprises the following steps: a, second part receives clock message from first part with current time in the message; b, the second part coordinates time according to second part. This invention also discloses one first and second part of this method.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for improved dual channel operation and access point discovery in wireless communication networks
InactiveUS7885220B2Reduction procedureEasy accessAssess restrictionRadio transmissionTime division multiple accessCoordinate time
Owner:INTEL CORP
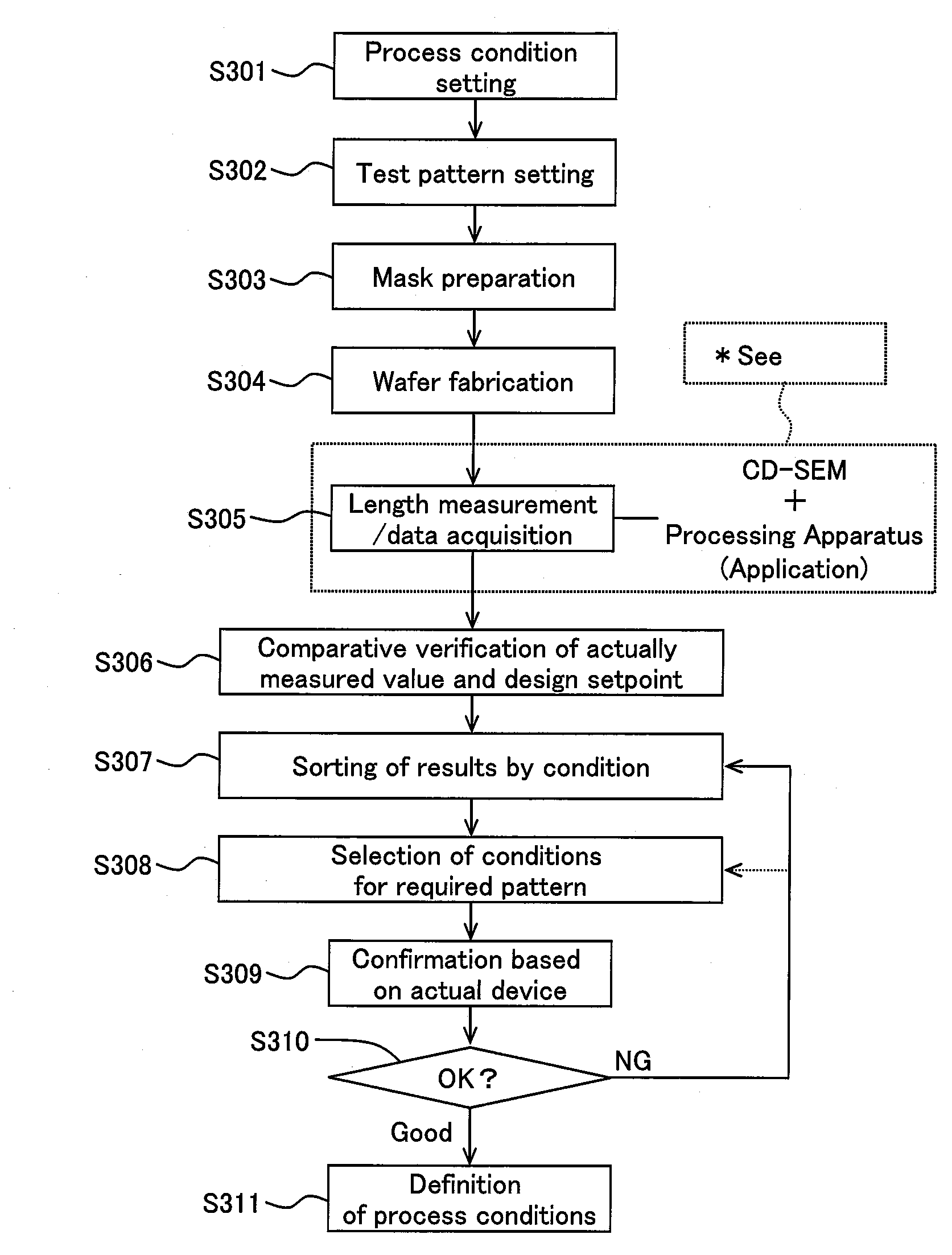
Method of OPC Model Building, Information-Processing Apparatus, and Method of Determining Process Conditions of Semiconductor Device
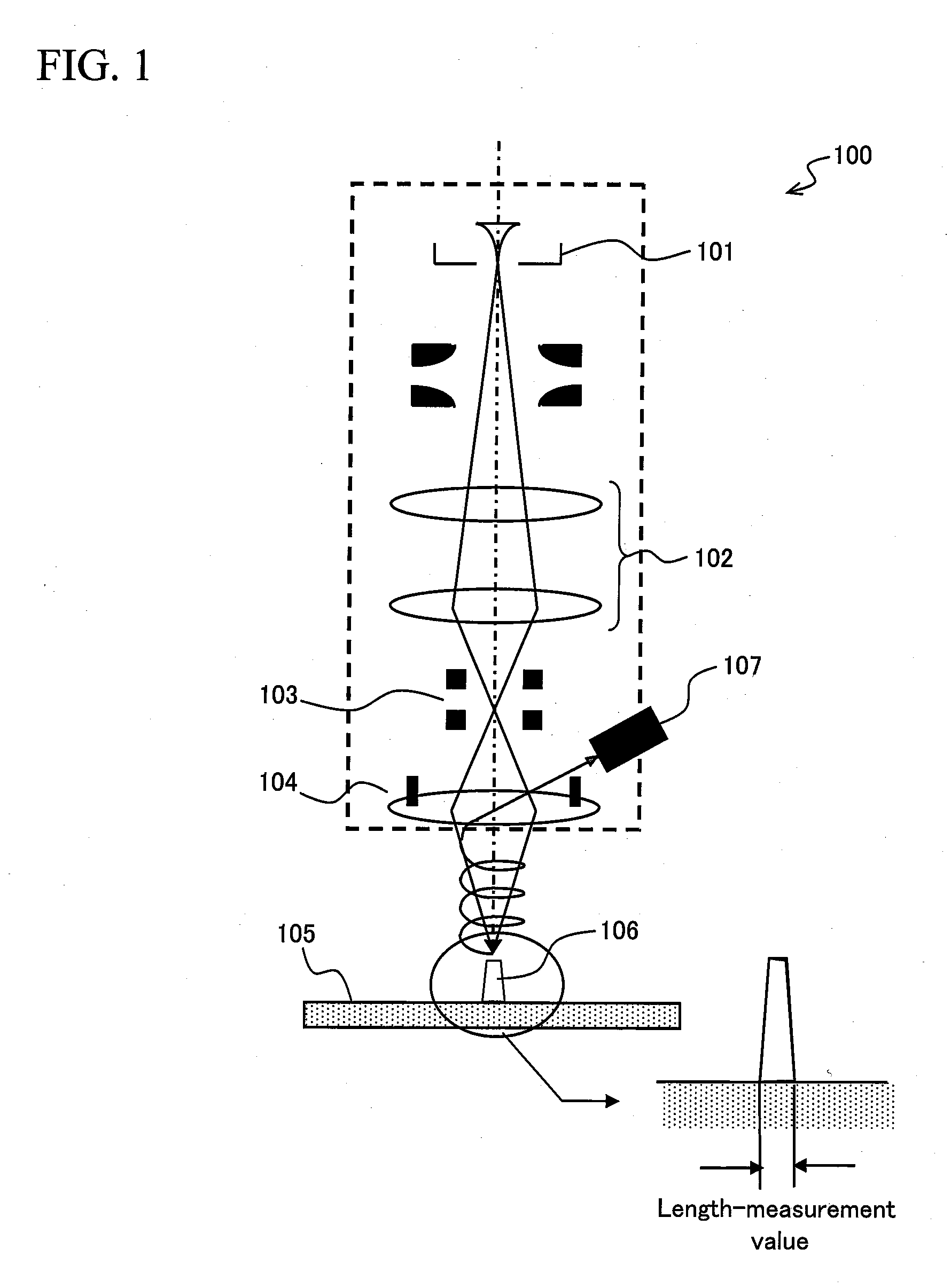
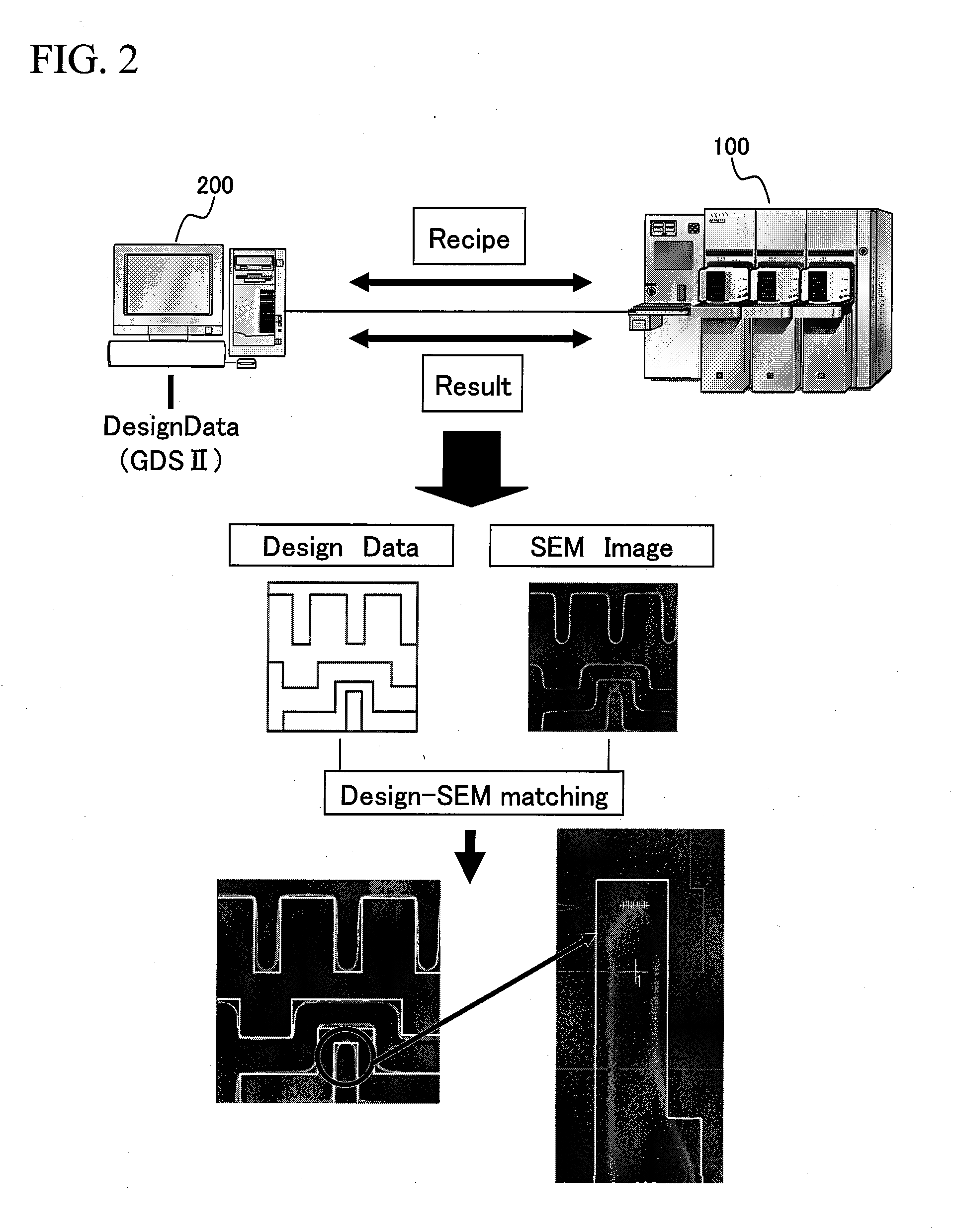
InactiveUS20080250380A1Solid-state devicesPhotomechanical apparatusInformation processingCoordinate time
A method capable of quantitatively evaluating two-dimensional patterns and a system to which the method is applied are provided. In the present invention, a reference coordinate system is set in order to convert pattern edge information (one-dimensional data) acquired by measurement using an existing critical dimension machine into coordinate data. Thus, a pattern is converted into coordinate information. Next, a function formula is determined from this coordinate information by approximate calculation and a pattern is represented by the mathematical expression y=f(x). Integrating y=f(x) in the reference coordinate used when calculating the coordinate data gives the area of the pattern, whereby it is possible to convert the coordinate data to two-dimensional data.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
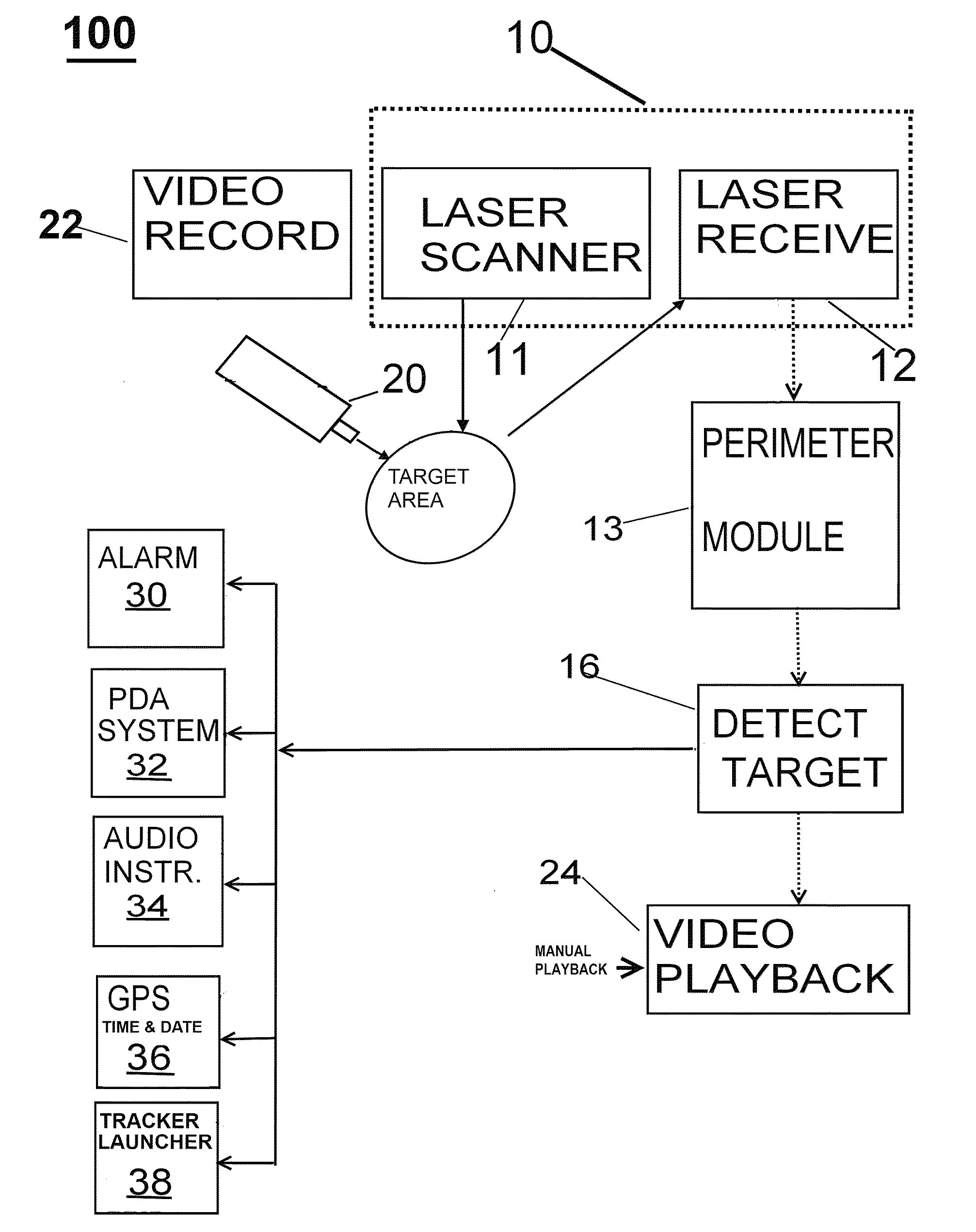
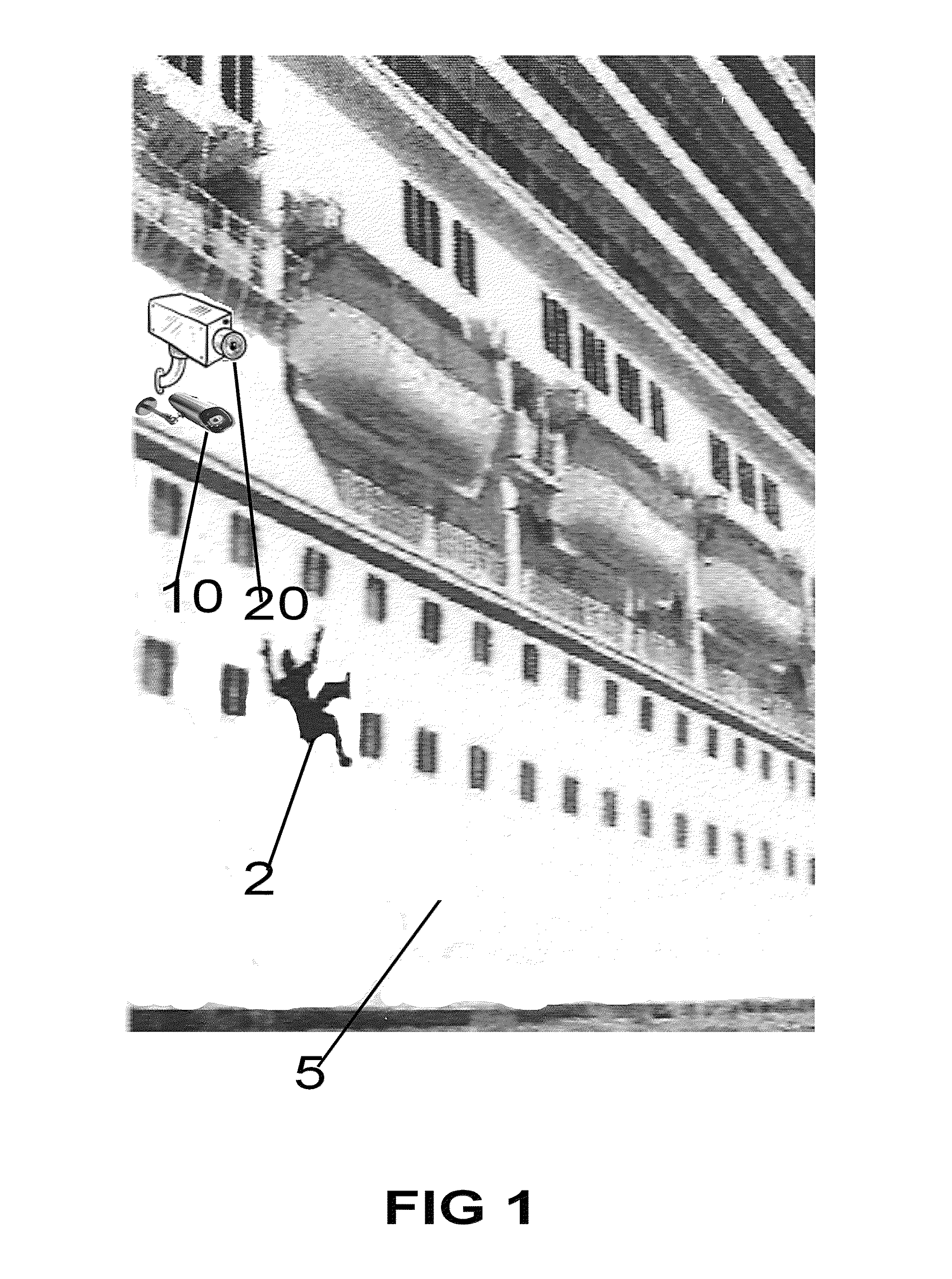
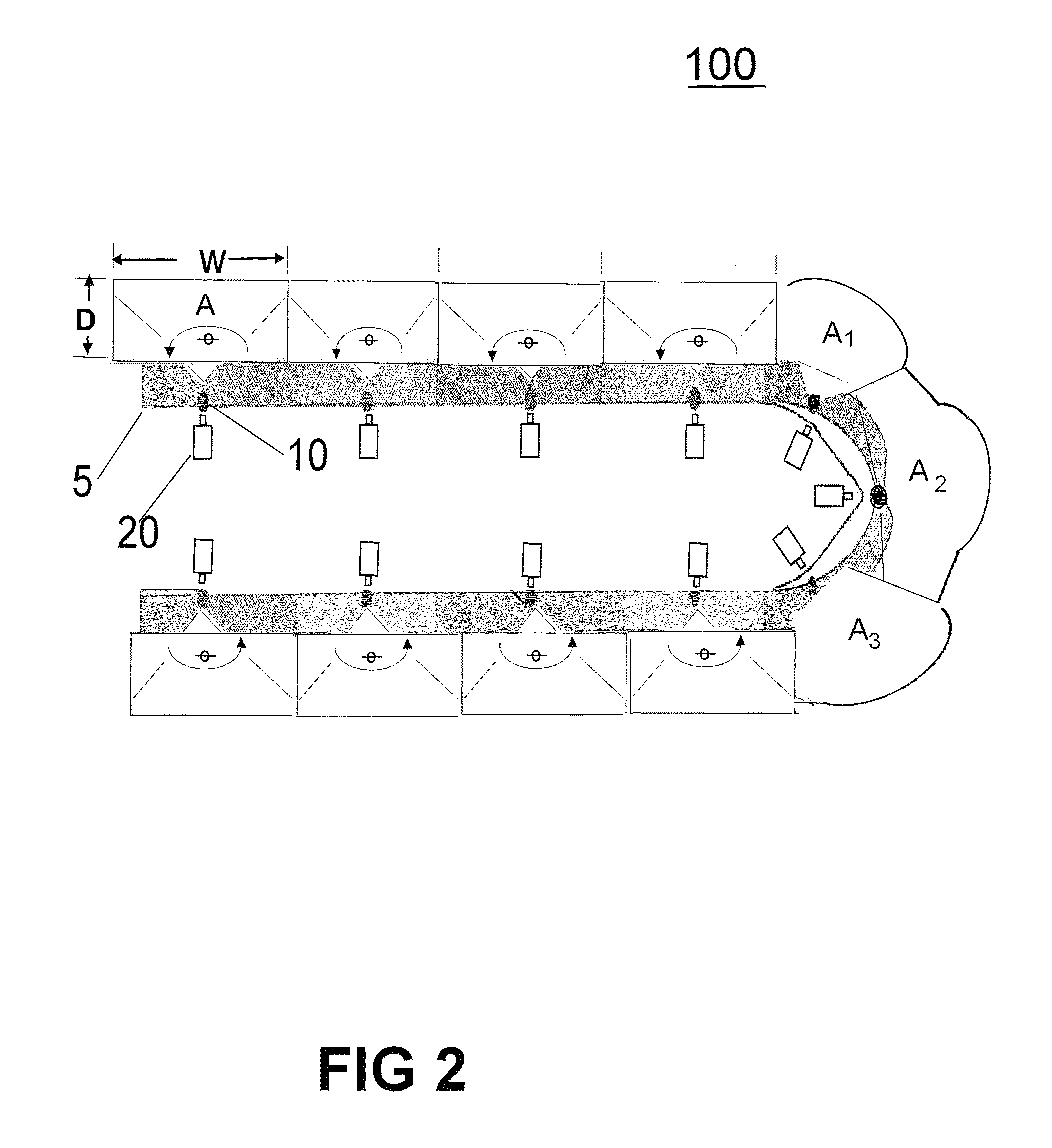
Maritime overboard detection and tracking system
A process and system for detecting the presence of a person overboard including: setting the perimeter of an area to scan, scanning the area 180 degrees in azimuth utilizing a laser beam for receiving a reflection of the laser beam off the person, detecting the reflection and playing back a video recording of the trajectory of the person, wherein the area above and below the perimeter of an area to scan is continuously video recorded and wherein upon detecting the target, one or more of audio and visual alarms alert that crew, and wherein an alarm with location is sent to PDA system with GPS coordinates time and date. Additionally a launcher deploys a device to track the person overboard, and allows persons on the ship or in a control center to ascertain the location of the person overboard.
Owner:SECURITY IDENTIFICATION SYST
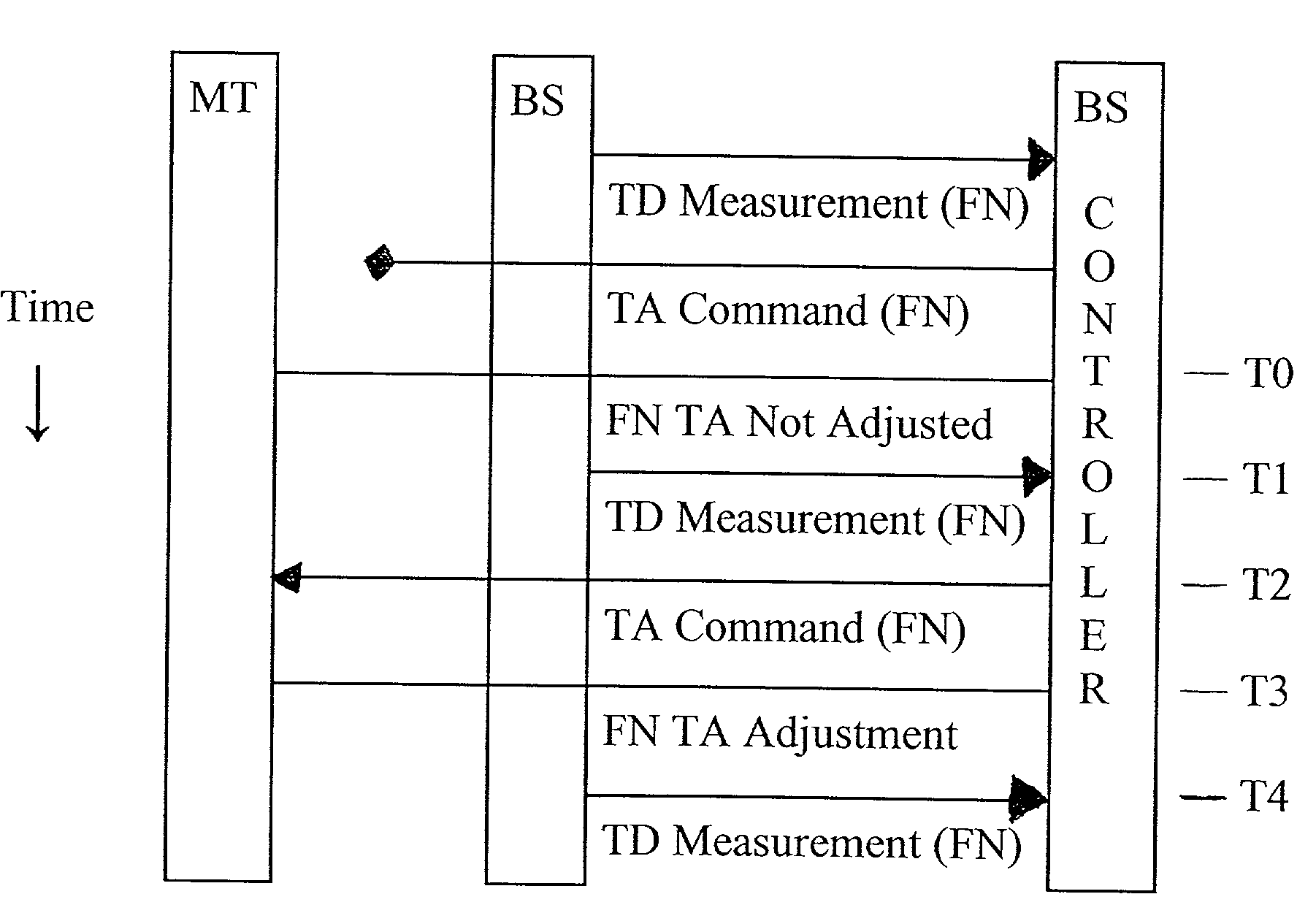
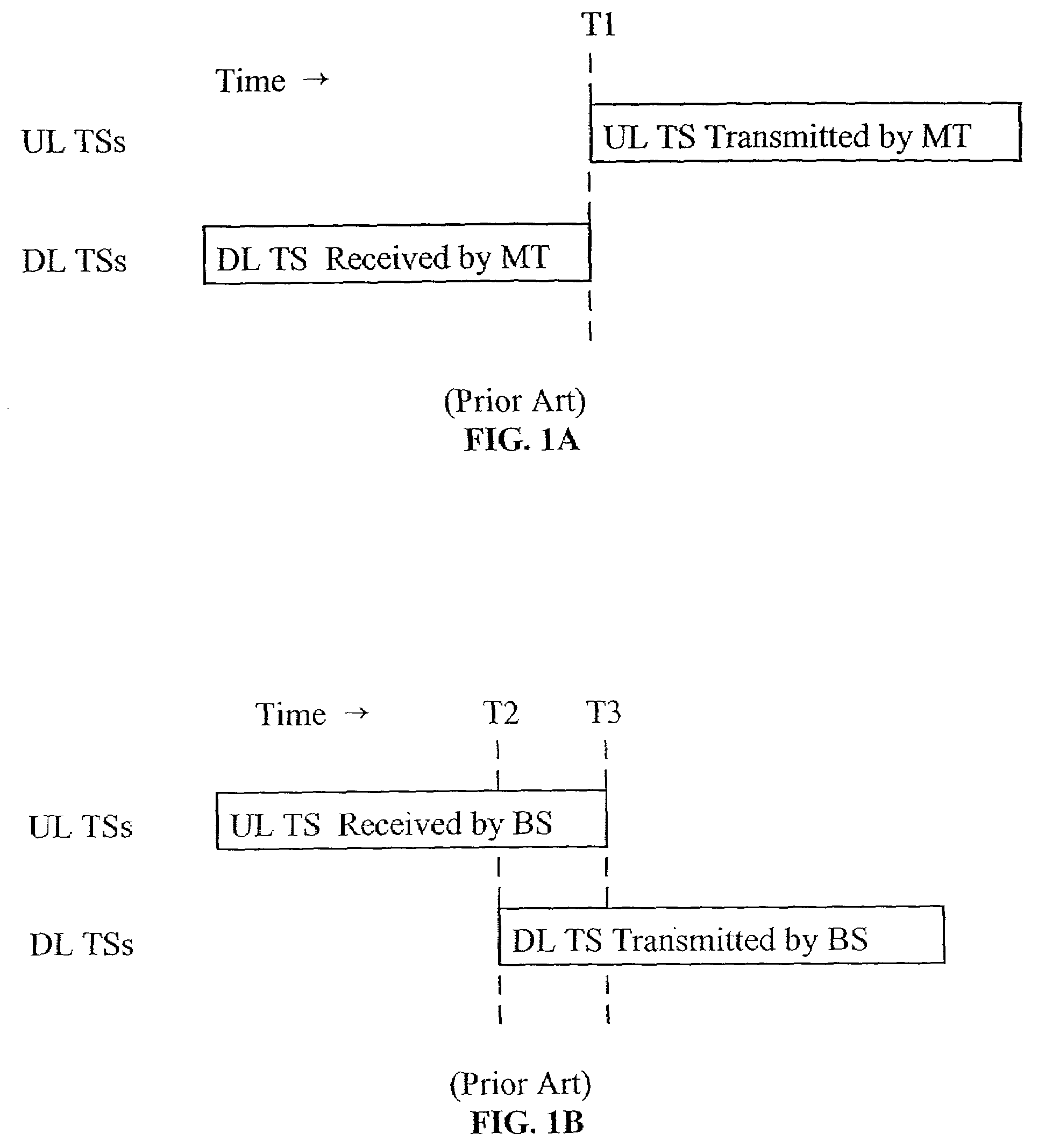
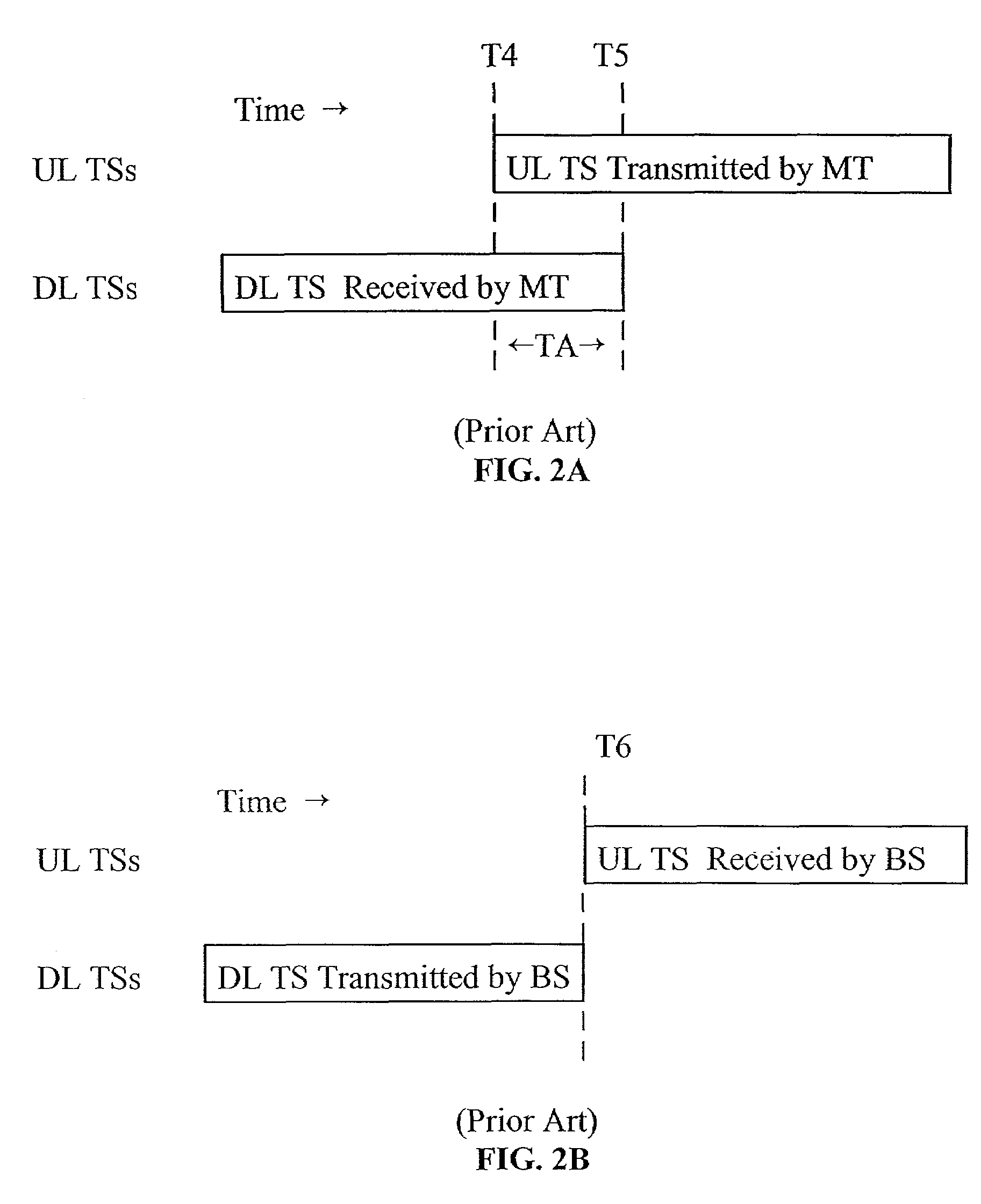
Synchronization of timing advance and deviation
InactiveUS7573913B2Facilitate methodReducing the latency from timing deviation (TDSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexTime deviationCoordinate time
A system and method for reducing the latency from timing deviation (TD) measurement to time advance (TA) adjustment. The invention uses a deterministic procedure to coordinate time advance (TA) commands and timing deviation (TD) measurements so that failed transmissions or mobile terminals signal propagation changes can be recognized and corrected much more rapidly. Radio resource efficiency is maximized by minimizing signaling overhead through effectively reducing the frequency of time advance commands. This is accomplished by using TA command signals which include a Connect Frame Number (CFN) to specify particular radio frames for time advance (TA) adjustment. The potential for timing deviation (TD) measurements to be incorrectly processed in conjunction with adjusting a physical reception window and calculating mobile termination location is minimized, without excessive command signaling requirements.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
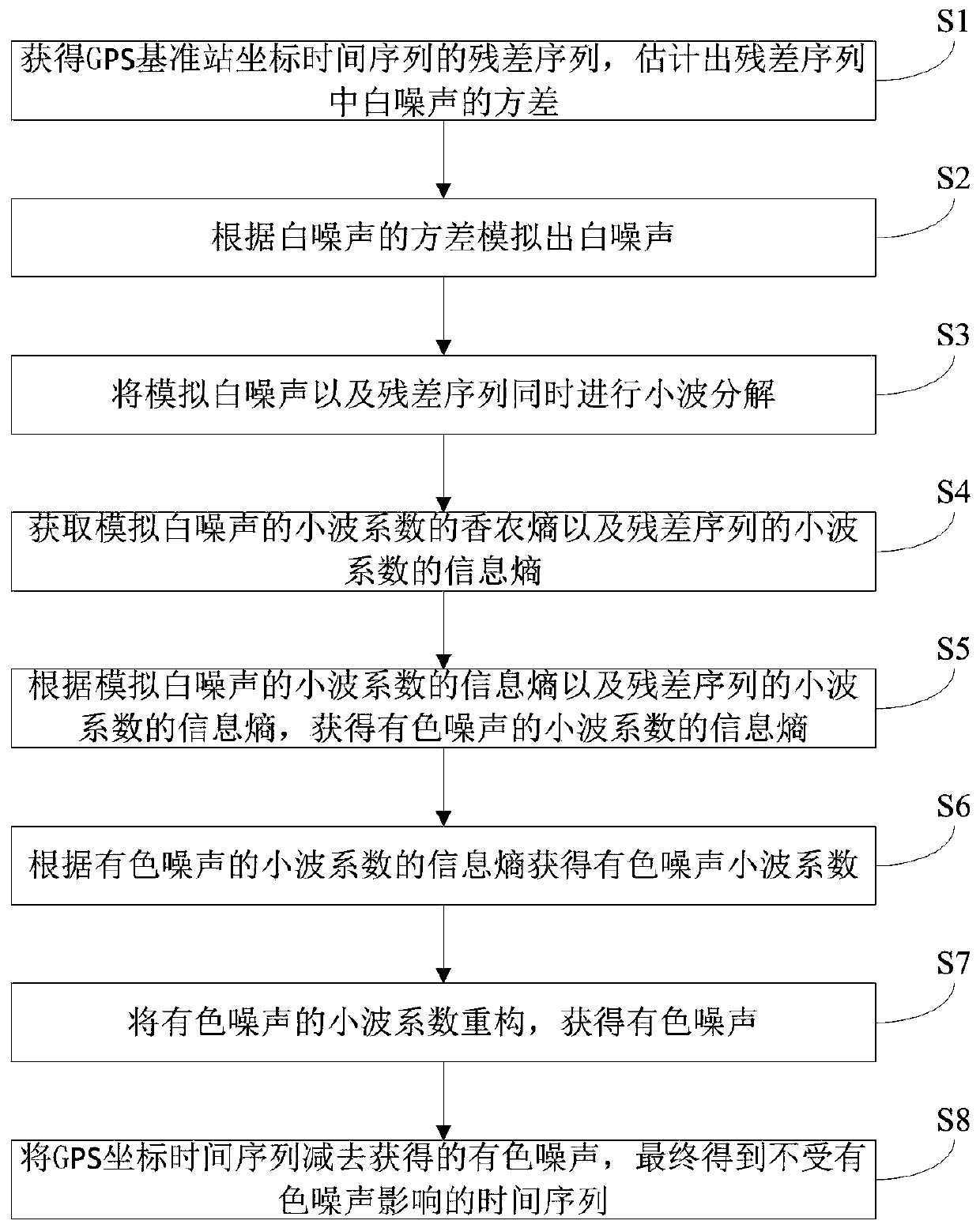
Method for removing colored noise in GPS coordinate time sequence
ActiveCN109709585APreserve nonlinear motion characteristicsAccurate measurement of station motion parametersSatellite radio beaconingLinear motionCoordinate time
The invention provides a method for removing colored noise in the GPS coordinate time sequence. The method comprises steps that S1, a residual sequence of the GPS base station coordinate time sequenceis obtained, and the variance of white noise in the residual sequence is estimated; S2, the white noise is simulated according to the variance of the white noise; S3, the simulated white noise and the residual sequence are simultaneously subjected to wavelet decomposition; S4, an information entropy of wavelet coefficients of the simulated white noise and the information entropy of wavelet coefficients of the residual sequence are obtained; S5, the information entropy of the wavelet coefficients of the colored noise is obtained; S6, wavelet coefficients of the colored noise are obtained according to the information entropy of the wavelet coefficients of the colored noise; S7, the wavelet coefficients of the colored noise are reconstructed to obtain the colored noise; and S8, the obtainedcolored noise is subtracted from the GPS coordinate time sequence, and the time sequence that is unaffected by the colored noise is finally obtained. The method is advantaged in that influence of thecolored noise in the GPS coordinate time sequence can be effectively removed, and non-linear motion characteristics of the GPS coordinate time sequence are preserved.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY SIYUAN SURVEY & DESIGN GRP
Method for accurately quantifying influence of thermal expansion effect on GPS coordinate time series
The invention discloses a method for accurately quantifying influence of a thermal expansion effect on a GPS coordinate time series. The method includes collecting a surface temperature time series of an IGS reference station, and collecting observation station information; calculating the total influence of the thermal expansion effect on an IGS reference station coordinate time series, i.e., Sequence A; adopting a surface mass load redistribution model to calculate a vertical direction displacement time series of the IGS reference station caused by environmental loads, i.e., Sequence B; adopting a GPS precise data processing model to obtain a coordinate time sequence of the IGS reference station, i.e., Sequence C; deducting Sequence B from Sequence C to obtain Sequence C-B; deducting Sequence A from Sequence C-B to obtain Sequence C-B-A; and based on the Sequence C-B and Sequence C-B-A, proposing that numerical value indexes are utilized to qualify the influence of the thermal expansion effect on the GPS coordinate time series. The method for accurately quantifying the influence of the thermal expansion effect on the GPS coordinate time series can obtain actual motion in the vertical direction of the IGS reference station caused by temperature variation, and adopts the numerical value indexes to accurately quantify the influence of the thermal expansion effect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
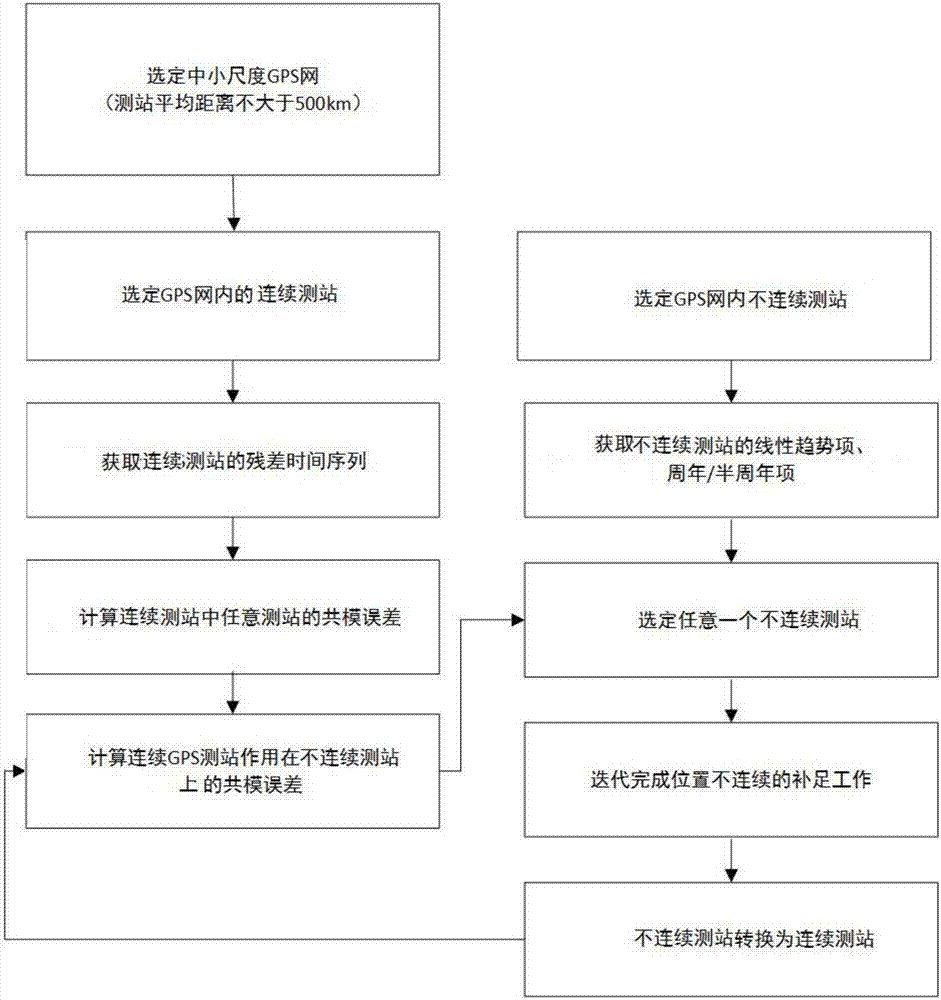
GPS coordinate time sequence discontinuity complementing method based on common-mode error
The invention discloses a GPS coordinate time sequence discontinuity complementing method based on a common-mode error, and the method comprises the steps: S1, selecting a medium- and small-scale GPS network, and selecting a plurality of continuity measurement stations from the continuity measurement stations in the medium- and small-scale GPS network; S2, obtaining the residual error coordinate time sequence of the continuity measurement stations according to the coordinate time sequence observation data of the continuity measurement stations; S3, selecting any one measurement station from the plurality of selected continuity measurement stations as a reference base station, and determining the common epoch of the reference station and the common continuity measurement stations in the medium- and small-scale GPS network; S4, obtaining the common-mode error that all common continuity measurement stations in the medium- and small-scale GPS network jointly act on the reference station; S5, complementing the GPS coordinate time sequence of a discontinuity measurement station in the medium- and small-scale GPS network through the common-mode error. According to the invention, the method achieves the complementing of the discontinuous data through employing the similarity of the continuous data residual error time sequence of the spatial distribution in the medium- and small-scale range, and improves the derivative quality based on the GPS coordinate time sequence.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
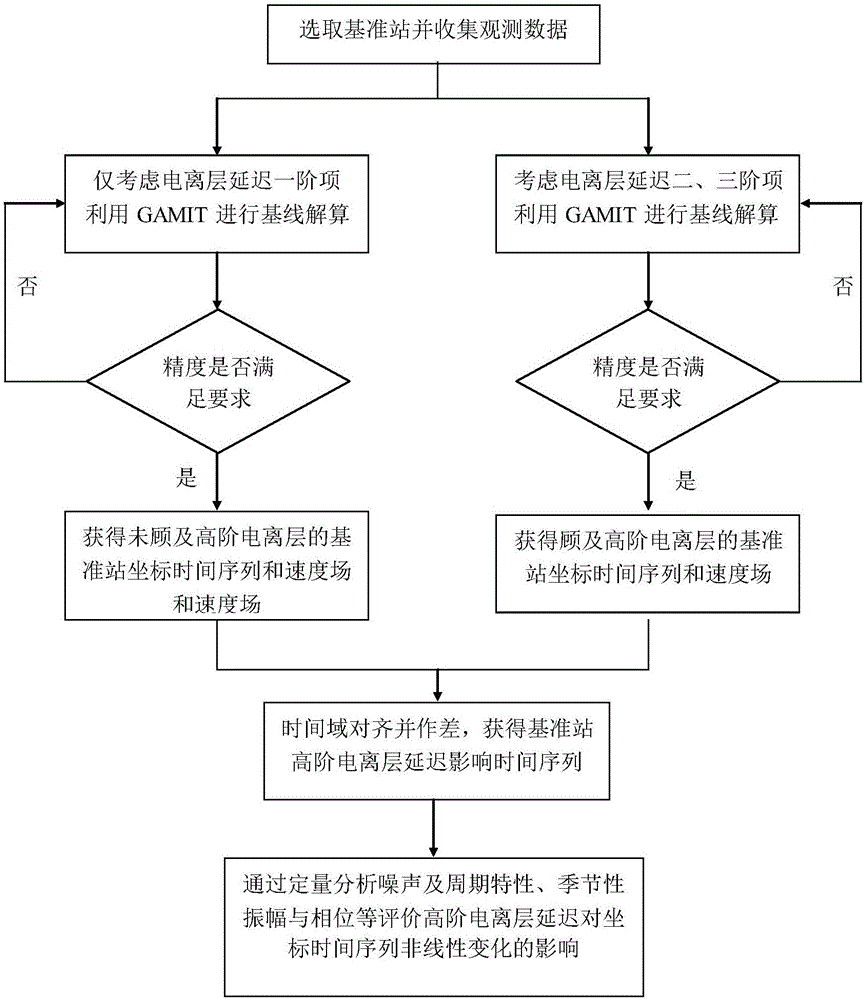
A quantitative method for influences on a GPS coordinate time series by a higher-order item ionospheric delay
The invention discloses a quantitative method for influences on a GPS coordinate time series by a higher-order item ionospheric delay. The method comprises the steps of collecting original observation data of a GPS base station; obtaining a GPS coordinate time series considering only the first order term of the ionospheric delay based on the historical observation data and recording the GPS coordinate series as sequence A; calculating the GPS coordinate time series corrected by the ionospheric high order term based on the historical observation data and recording the series as sequence B; aligning the series A and the series B in a time domain and subtracting the series A and the series B to obtain a high-order term ionospheric delay influence time series of the GPS base station and recording the series as sequence C; and separately subjecting the sequence A, sequence B and sequence C to noise analysis to obtain the observation station speed, noise characteristics and seasonal information corresponding to each sequence so as to quantify the influence of the high-order term ionospheric delay. The quantitative method of the invention can quantitatively determine the influence of the high-order ionospheric delay on the observation station coordinate time series, and can better explain the non-linear variation source presented in the GPS coordinate time series.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
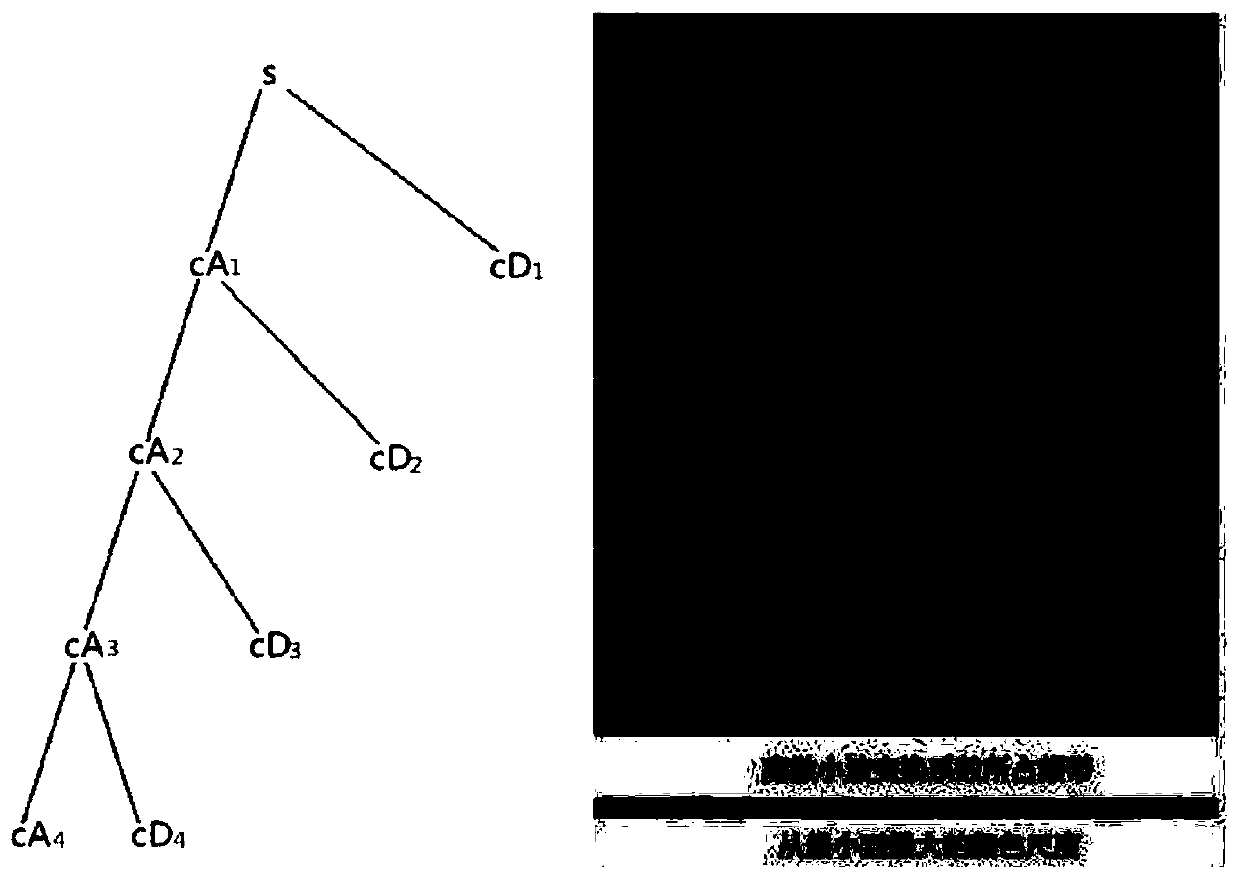
GNSS observation station nonlinear motion modeling method and device
PendingCN110069868AHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmDecomposition
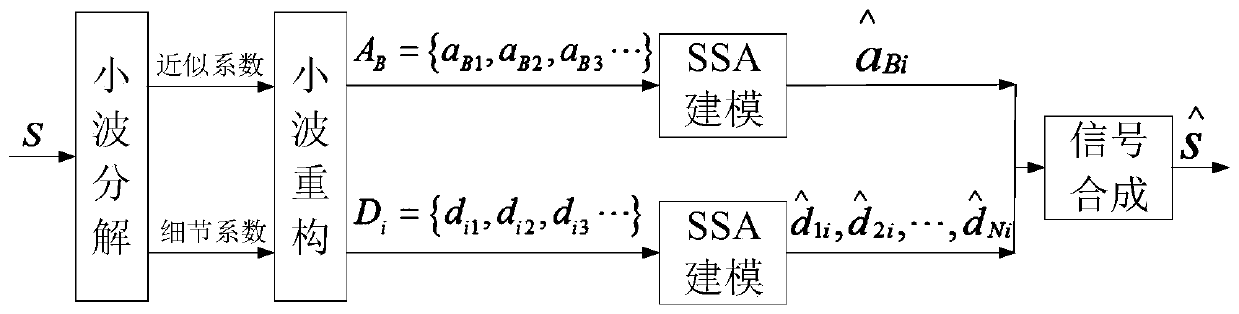
The invention provides a GNSS observation station nonlinear motion modeling method and device, and belongs to the technical field of global positioning navigation systems. The method comprises the steps of obtaining an original coordinate time sequence of a GNSS observation station; performing wavelet decomposition and reconstruction on the original coordinate time sequence to obtain a low-frequency part and a multi-layer high-frequency part; performing singular spectrum decomposition and reconstruction on the low-frequency part and each layer of high-frequency part; synthesizing the low-frequency part after singular spectrum decomposition and reconstruction and the high-frequency part of each layer to obtain a fitting sequence of an original coordinate time sequence; and modeling the fitting sequence. The method comprises the following steps: an original coordinate time sequence is decomposed into relatively single and smooth low-frequency parts and high-frequency parts of all layersby utilizing wavelet decomposition and reconstruction; and then singular spectrum decomposition and reconstruction are performed on each part, so that the probability that part of periodic items suchas seasonal periodic items and monthly periodic items are rejected as noise is reduced to a certain extent, and the modeling precision is improved.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
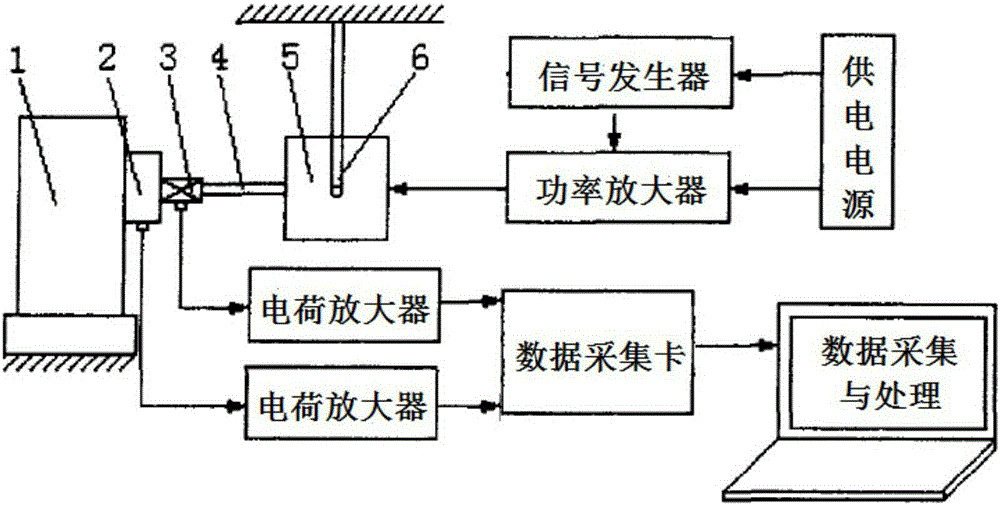
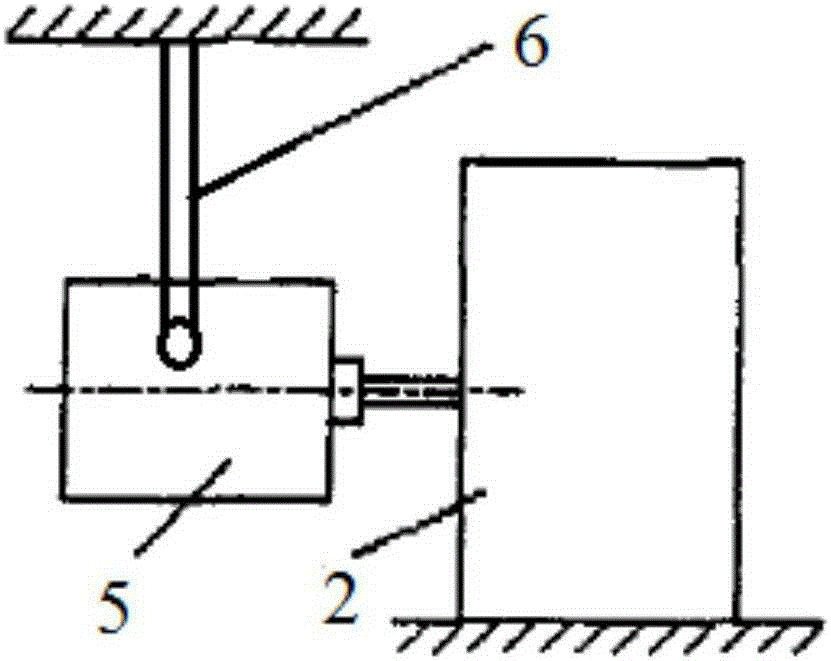
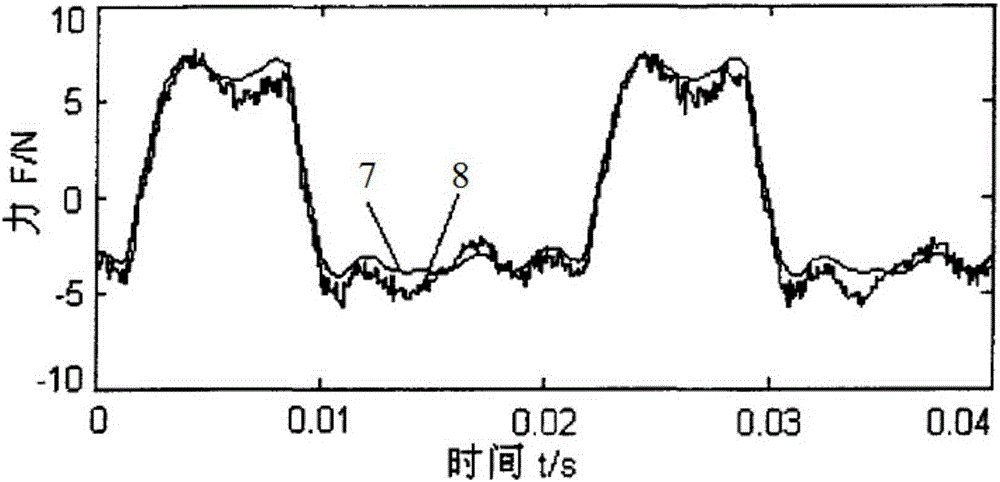
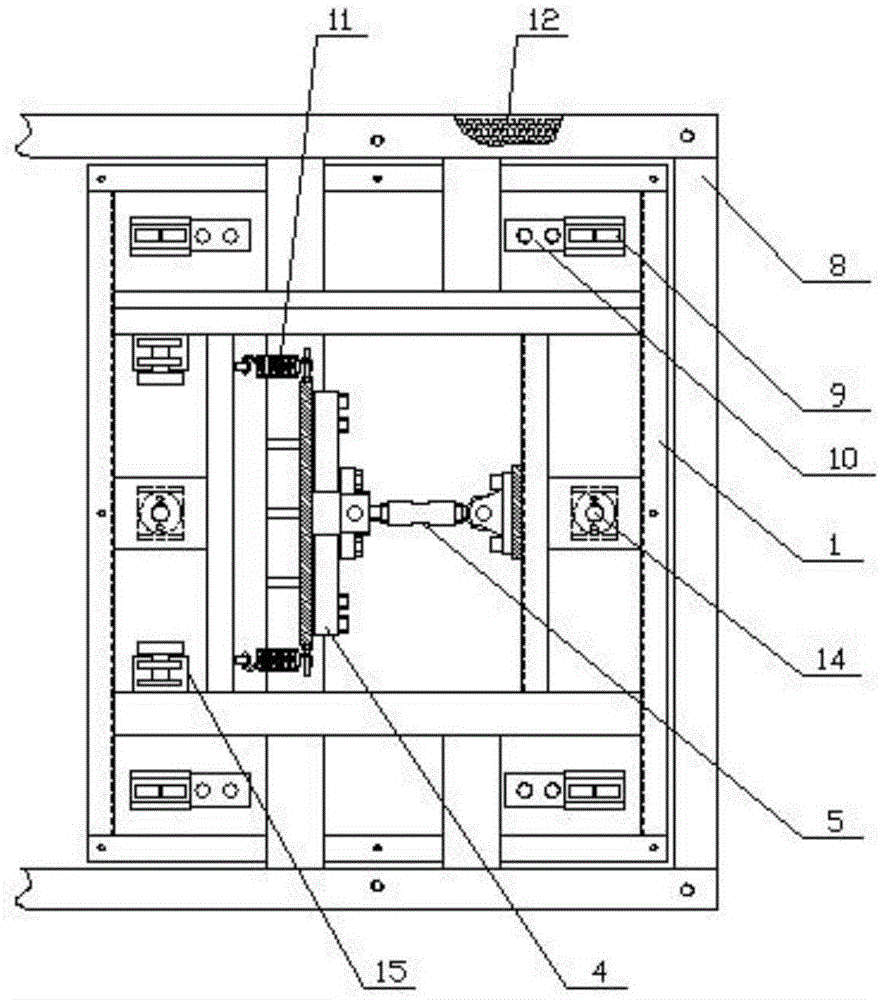
Test platform dynamic performance evaluation method with input and output signal waveform comparison
InactiveCN105181239AEasy to operateThe evaluation method is intuitiveForce/torque/work measurement apparatus calibration/testingCoordinate timeData acquisition
The invention provides a test platform dynamic performance evaluation method with input and output signal waveform comparison, belonging to the field of dynamic performance testing. The method can be applied to the fields of mechanical engineering, aerospace and the like to evaluate the dynamic performance of a test platform. An experimental device is formed by a signal generator, a power amplifier, a rubber rope, a vibration exciter, a jack, an impedance head, a test bench, a test platform, a charge amplifier, a data acquisition card and a computer. The evaluation method comprises the following steps that the ratio of an output waveform vertical coordinate absolute value to a horizontal coordinate time integral and an input waveform vertical coordinate absolute value to the horizontal coordinate time integral in the same cycle are compared, the dynamic performance of the test platform is good if the ratio is close to 1. The test device is simple, the operation is easy, the evaluation method is intuitive and easy to understand, the dynamic performance of the test platform can be quickly determined, and the method has broad application space.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
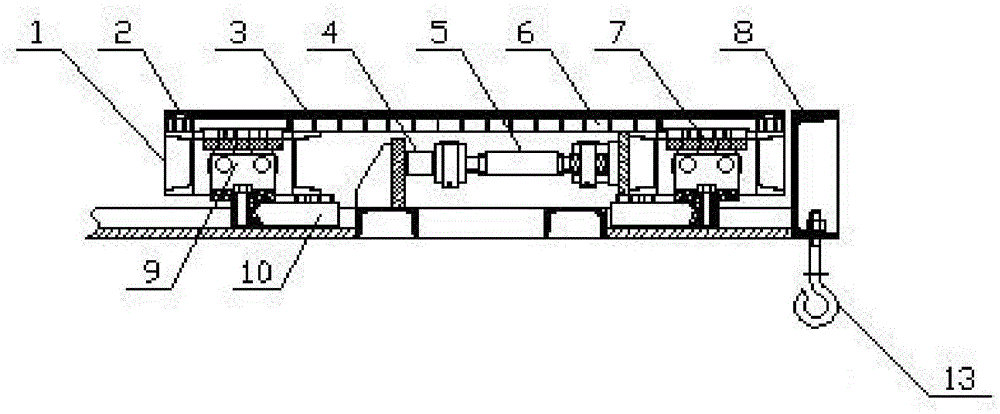
Test bed for braking performance of automobile/train
ActiveCN105606378AReduce testing labor intensityImprove detection efficiencyVehicle testingData processing systemElectricity
The invention discloses a test bed for the braking performance of an automobile / a train. The test bed is characterized in that a signal acquisition part of a sensor is composed of a left detection unit group and a right detection unit group which are formed by linearly arranging a plurality of detection units, and the left detection unit group and the right detection unit group are in symmetric distribution. A braking detection unit comprises a braking sand-adhering plate; the braking sand-adhering plates on the left detection unit group and the right detection unit group are independent, with a distance of 8 mm; each braking detection unit and each weighing detection unit work independently to respectively realize acquisition of braking data and weight data and are independently connected with a signal acquisition processing device; and the signal acquisition processing device is electrically connected with a data processing system. The automobile / train is subjected to multi-axial overall online detection, so that the braking time sequence of the vehicle, the dynamic braking power of the entire vehicle, the poor braking process, the coordinate time and the like of the entire vehicle can be detected in one braking process, therefore, the labor intensity of detection is alleviated, the detection efficiency is improved, and the braking performance of the vehicle can be reflected more truly.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANCHE TECH
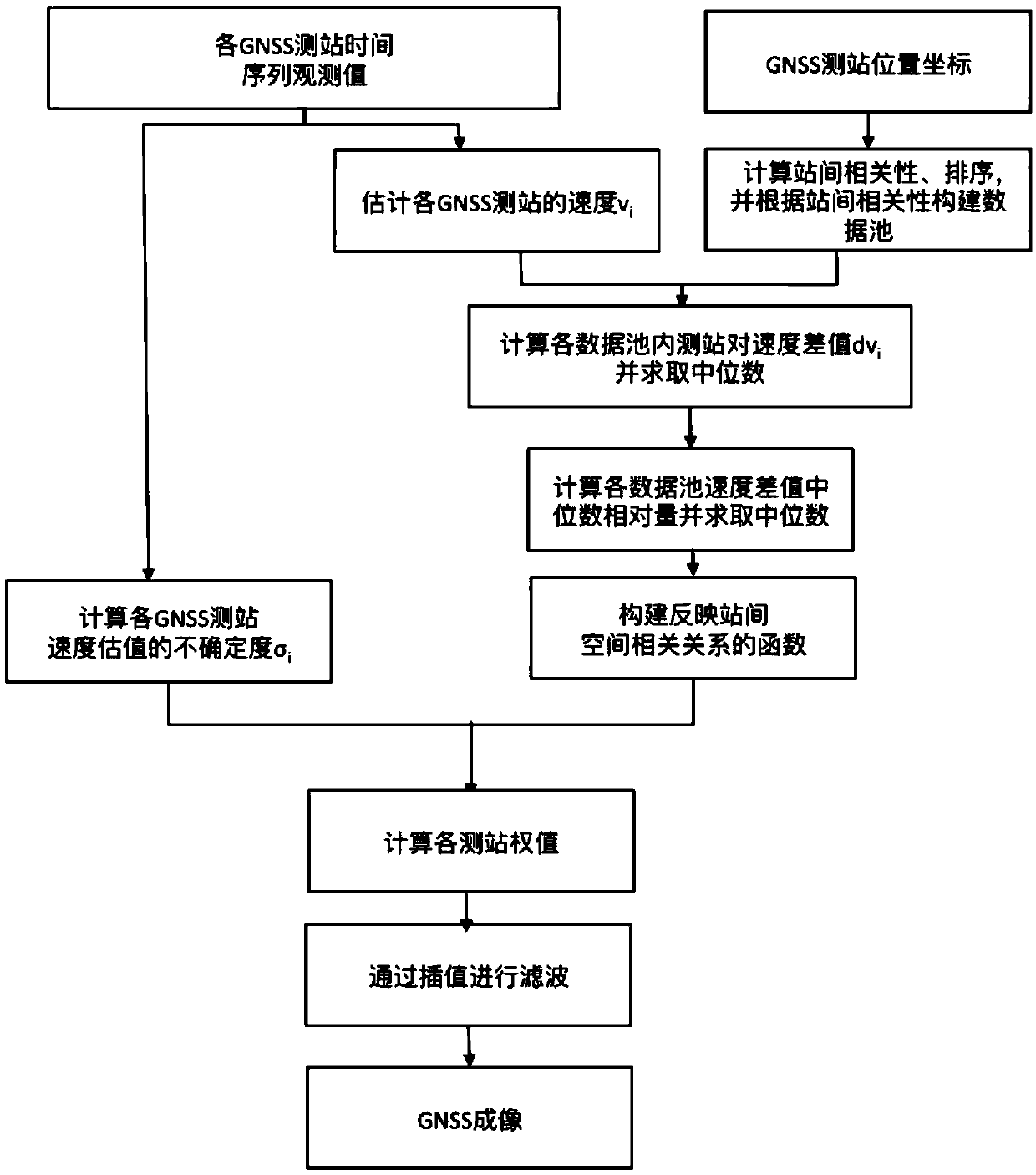
GNSS imaging method based on inter-station correlation spatial structure function construction
ActiveCN109581441AOvercoming the lack of time resolutionTake advantage ofCharacter and pattern recognitionSatellite radio beaconingCorrelation coefficientGeodesics on an ellipsoid
The invention provides a GNSS imaging method based on inter-station correlation spatial structure function construction. The method comprises the steps that coordinate time sequence observation valuesof GNSS observation stations and the velocity and velocity uncertainty of each GNSS observation station are input; in combination with geologic and geodetic results of a research region, clustering is performed on the observation stations in a GNSS network to obtain cluster regions; the correlation coefficient of an observation station pair formed by two arbitrary observation stations in each cluster region is calculated, data pool division is performed according to the correlation coefficients of the observation stations, and a plurality of data pools in each cluster region and the GNSS observation station pairs in each data pool are acquired; in each cluster region, the mid-value and absolute median deviation of the correlation coefficients of all the observation station pairs in each data pool are calculated, a spatial structure function of each cluster region is constructed, and a final spatial structure function of the whole GNSS network is formed according to a standard; and according to the velocity uncertainty and the spatial structure function, the weights of all the observation stations within the research range are determined, a spatial interpolation method is utilizedto perform spatial interpolation, and then an image is formed.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Beidou coordinate time sequence prediction method and device, equipment and storage medium
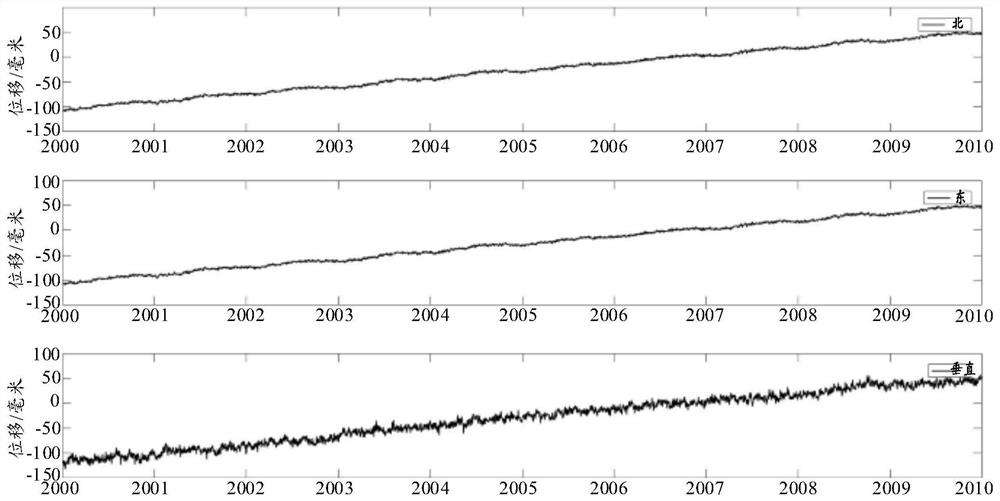
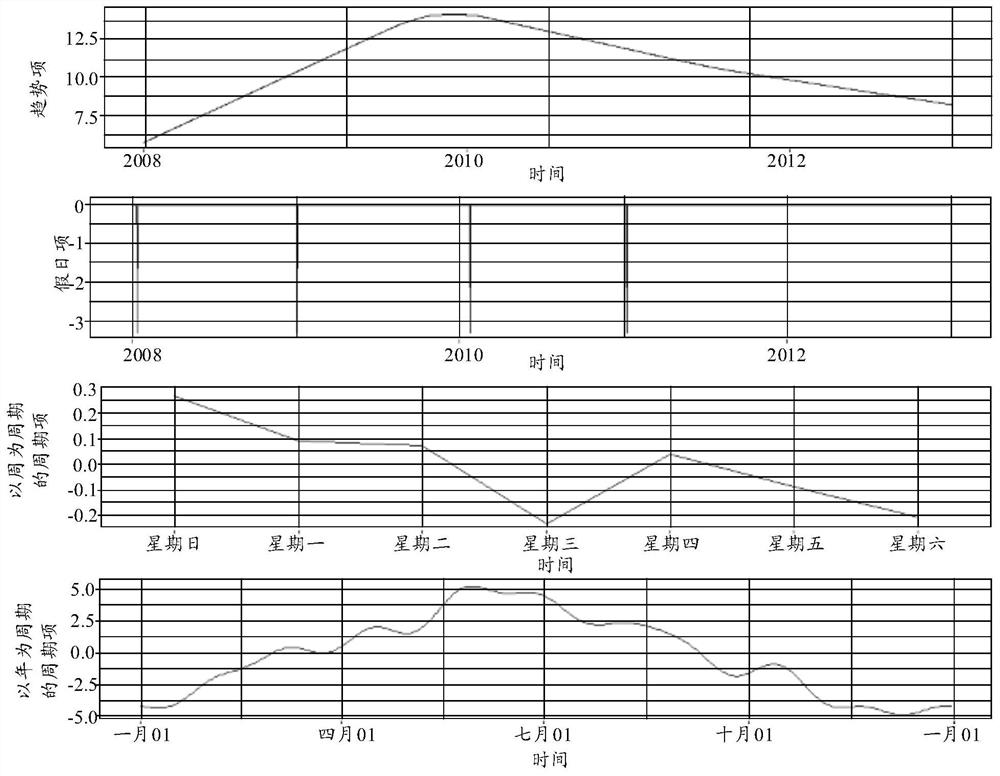
ActiveCN112612822ABiological neural network modelsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmCoordinate time
The invention discloses a Beidou coordinate time sequence prediction method, device and equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the interpolation processing of original data of a Beidou coordinate time sequence, and obtaining initial data; decomposing the initial data to obtain first data, second data, third data and fourth data; performing fitting prediction on the first data, the second data, the third data and the fourth data; obtaining first fitting data and first prediction data of the first data, second fitting data and second prediction data of the second data, third fitting data and third prediction data of the third data, and fourth fitting data and fourth prediction data of the fourth data; determining a fitting parameter and a prediction parameter of the coordinate time sequence according to the first fitting data, the second fitting data, the third fitting data, the fourth fitting data, the first prediction data, the second prediction data, the third prediction data and the fourth prediction data; and evaluating the precision of fitting prediction based on the fitting parameters and / or the prediction parameters.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY SIYUAN SURVEY & DESIGN GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com