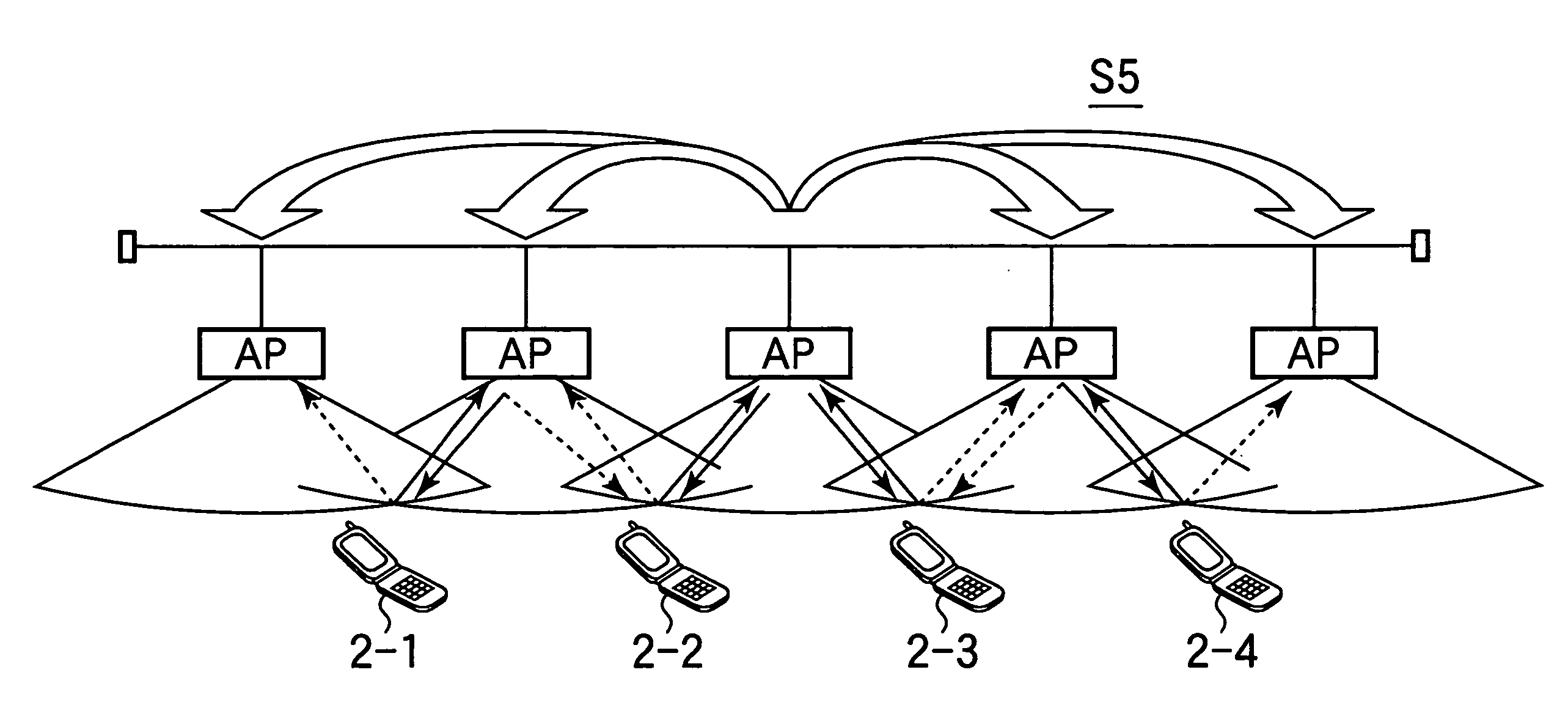
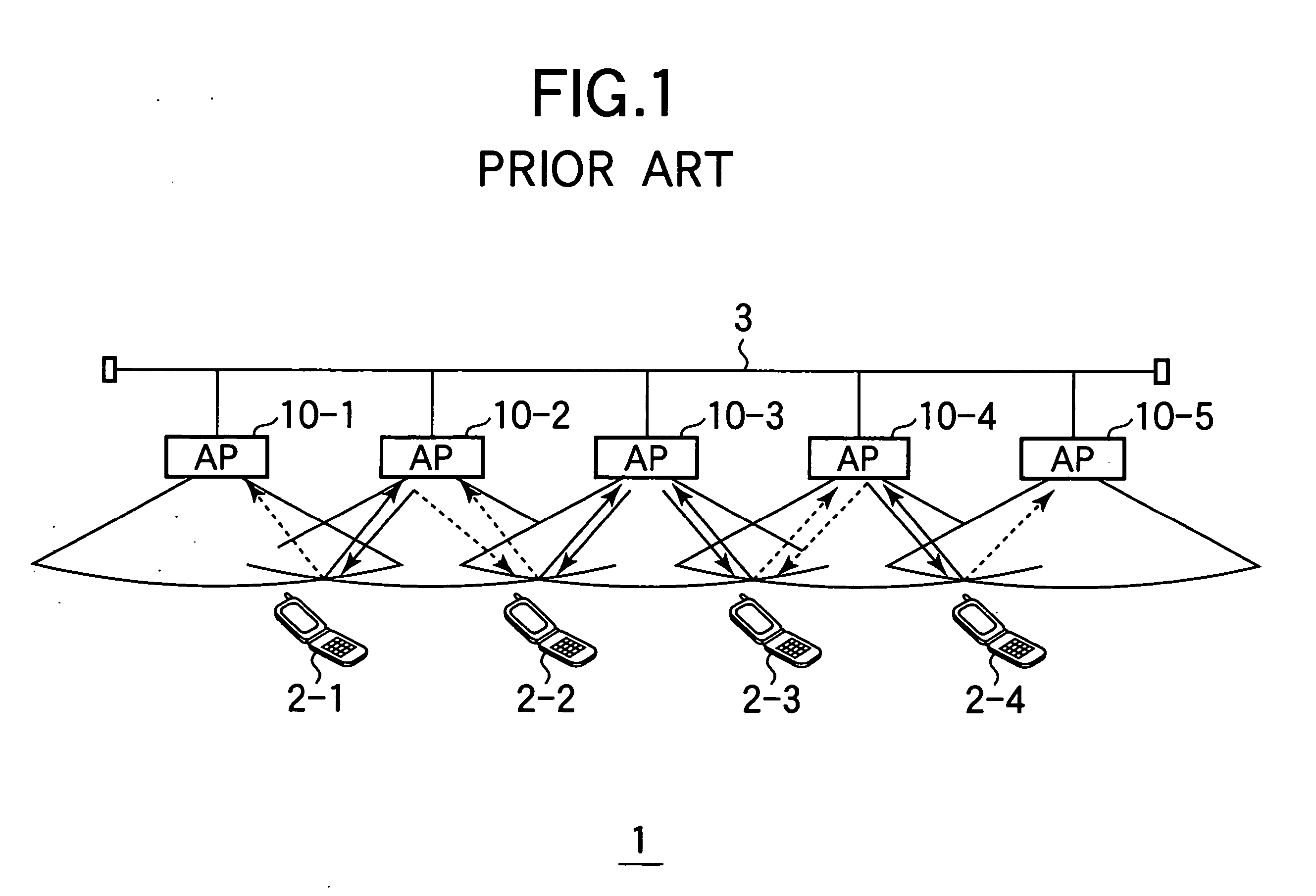
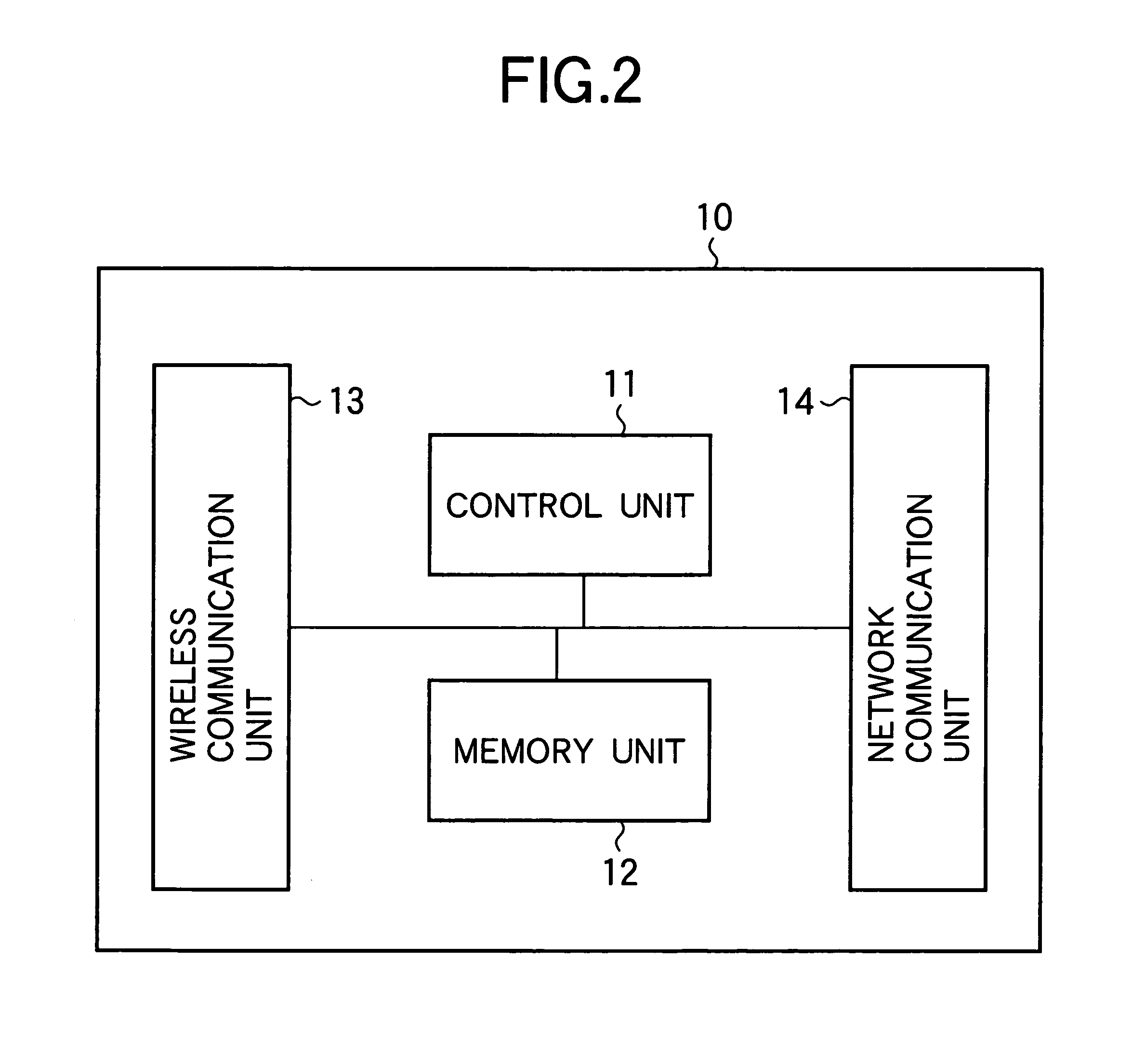
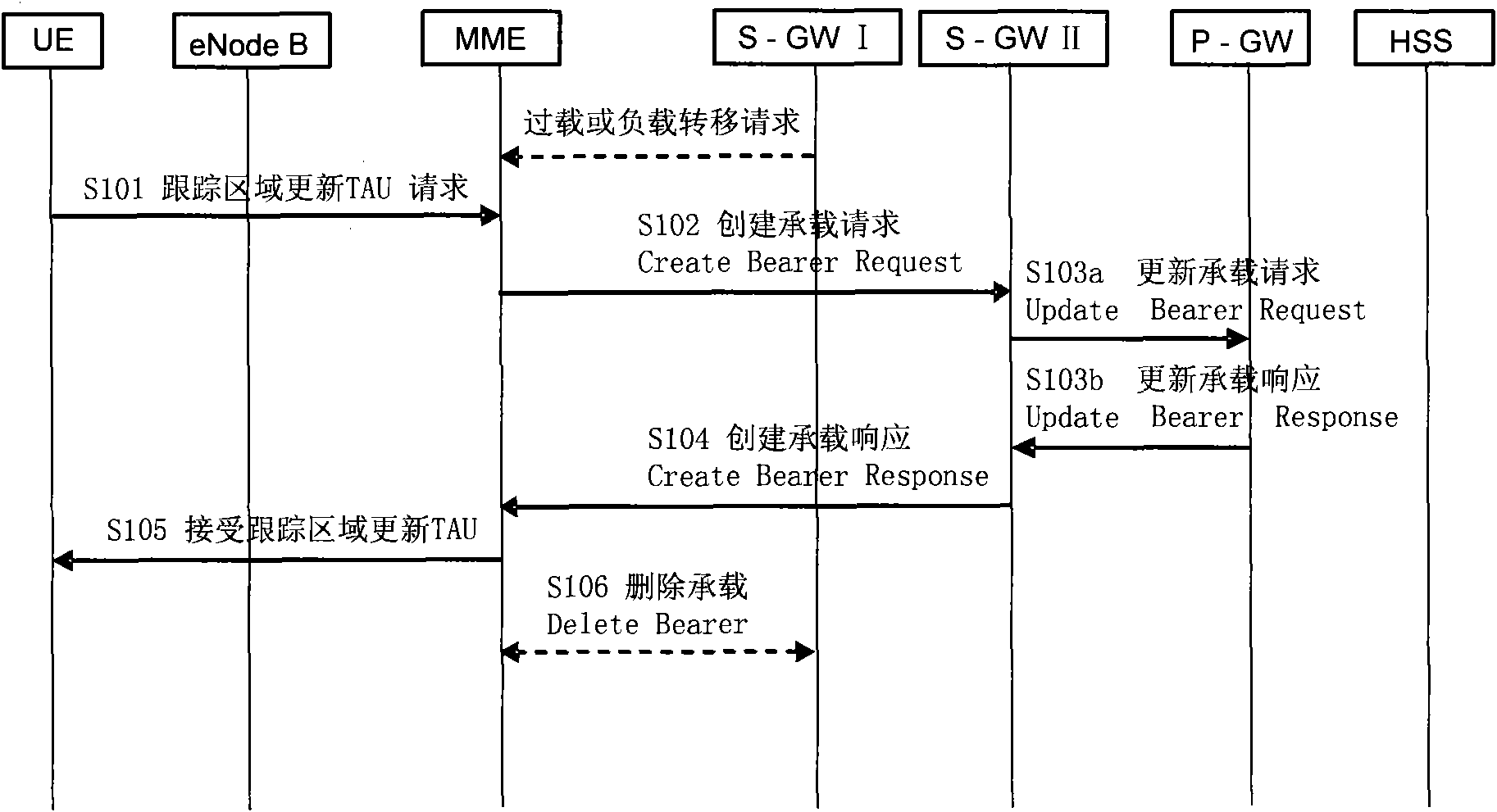
Patents
Literature
101 results about "Load redistribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
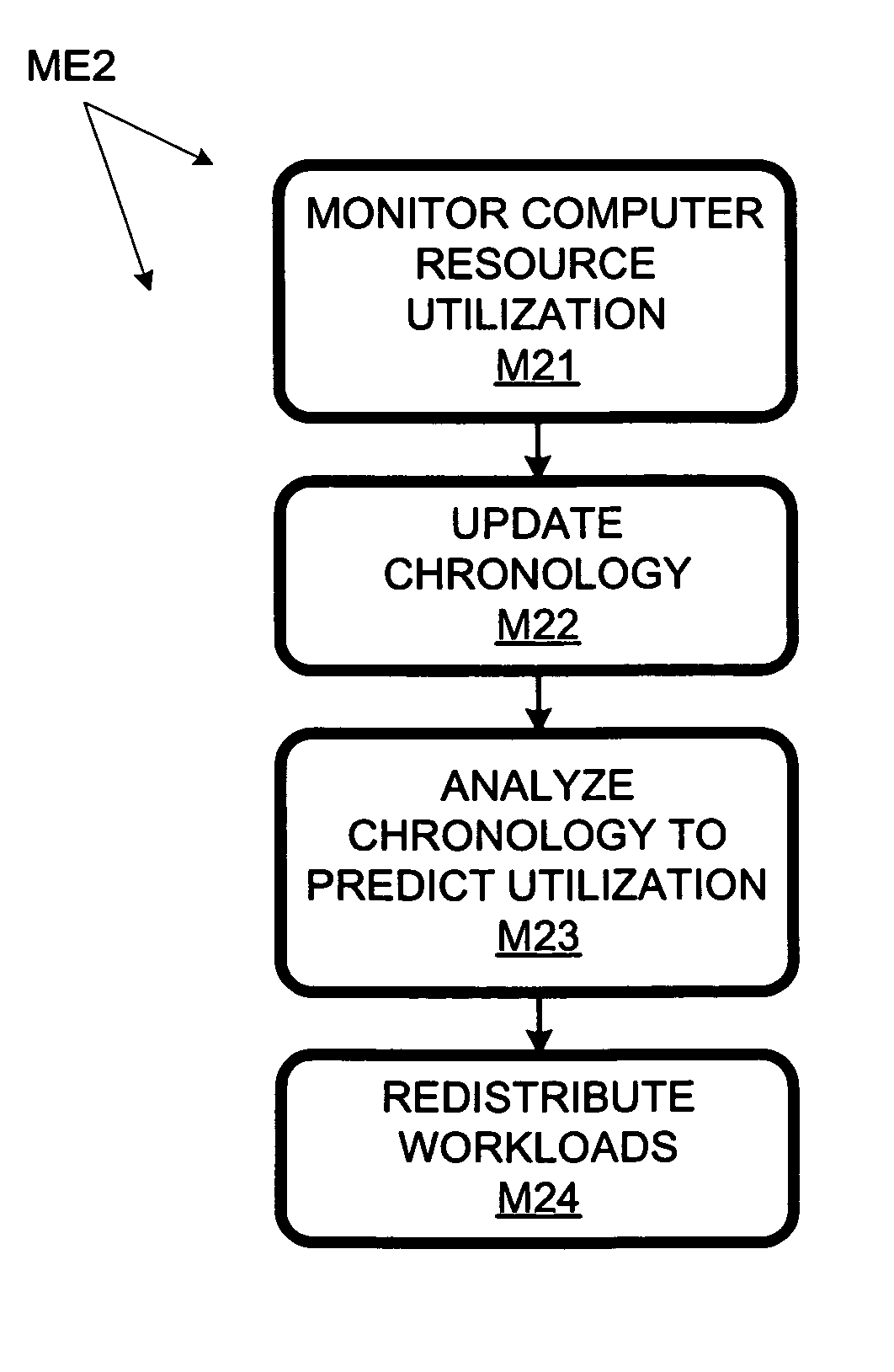
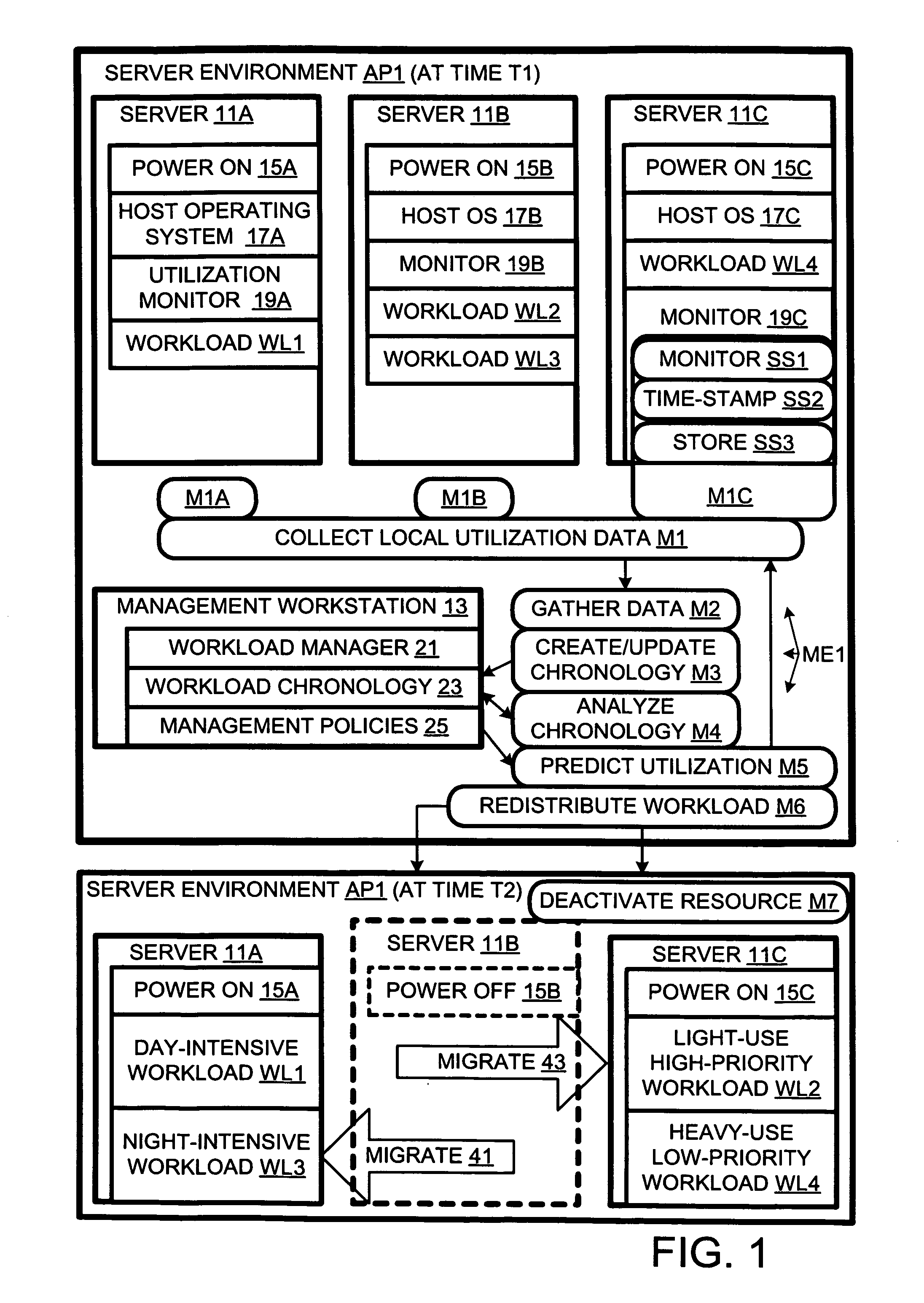
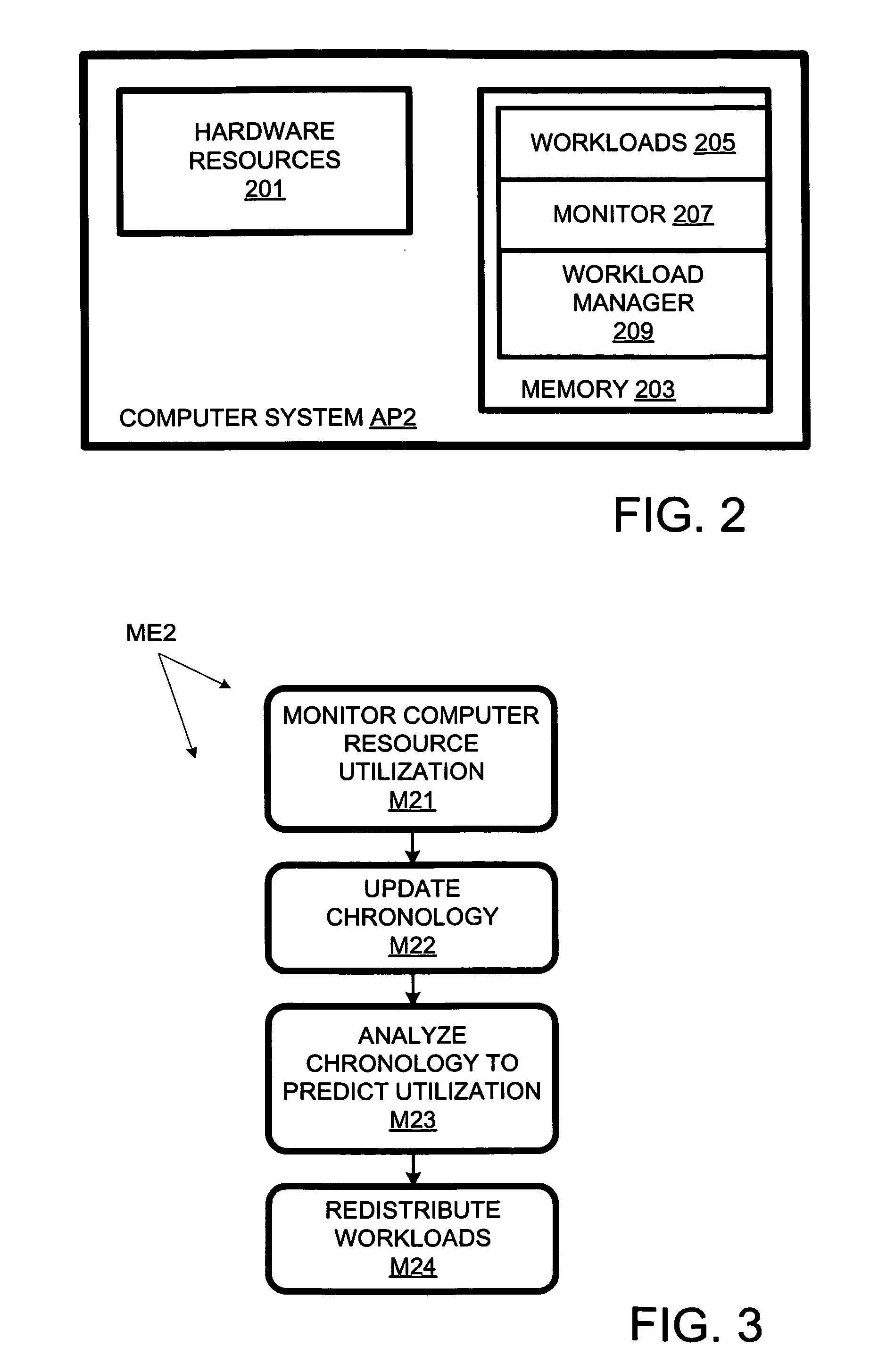
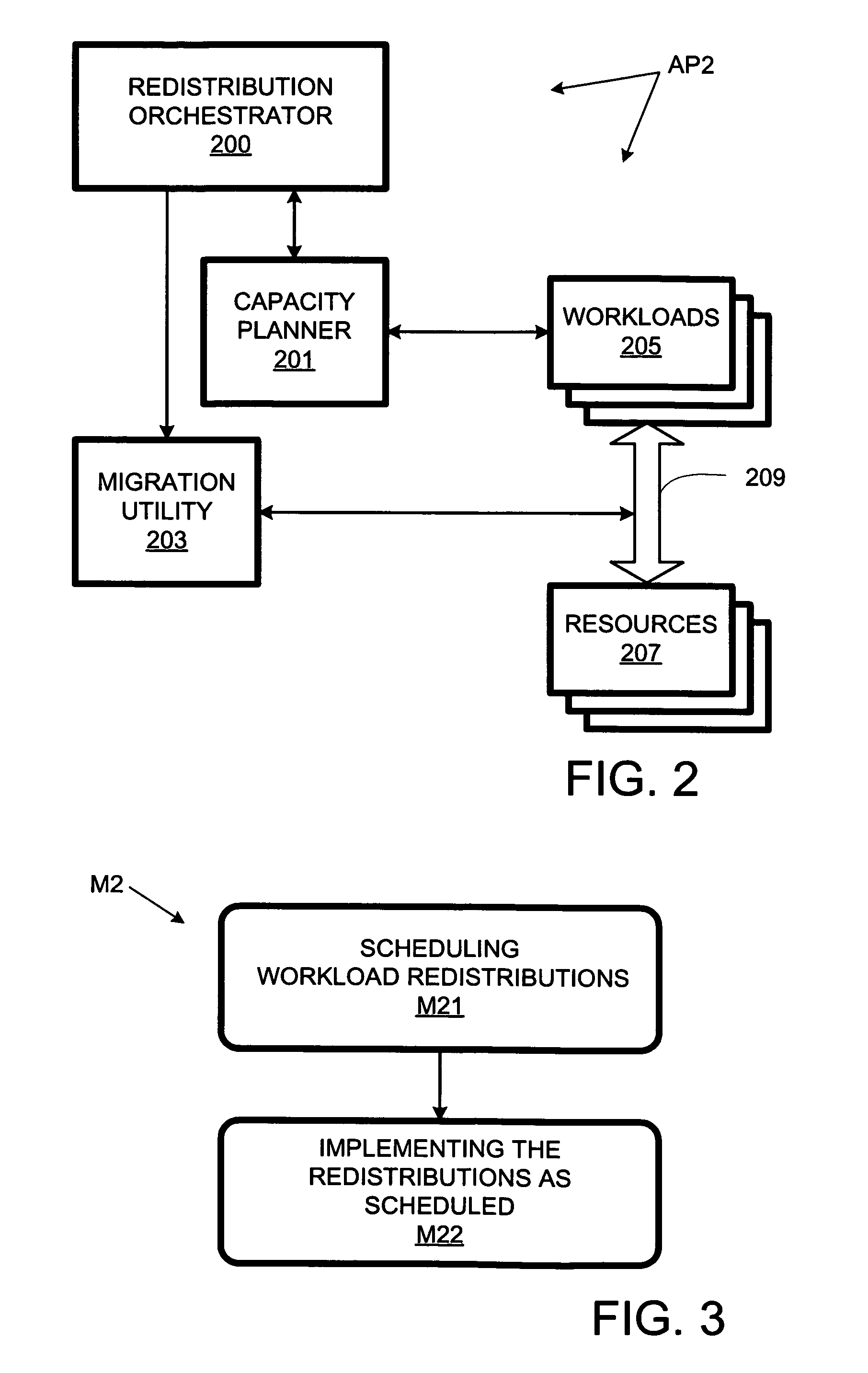
Computer workload redistribution
ActiveUS20070250838A1Error detection/correctionVolume/mass flow measurementComputer resourcesResource utilization
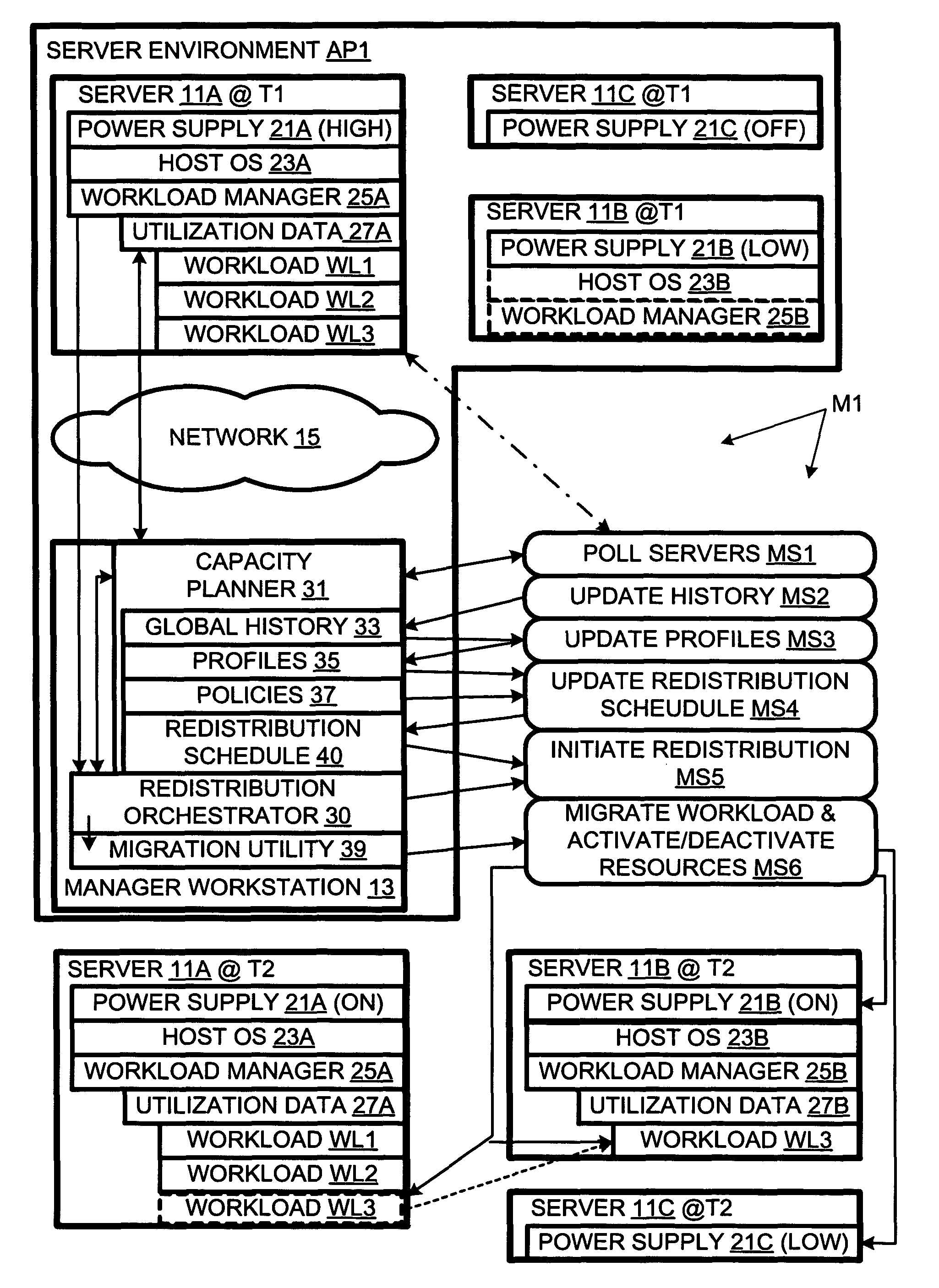
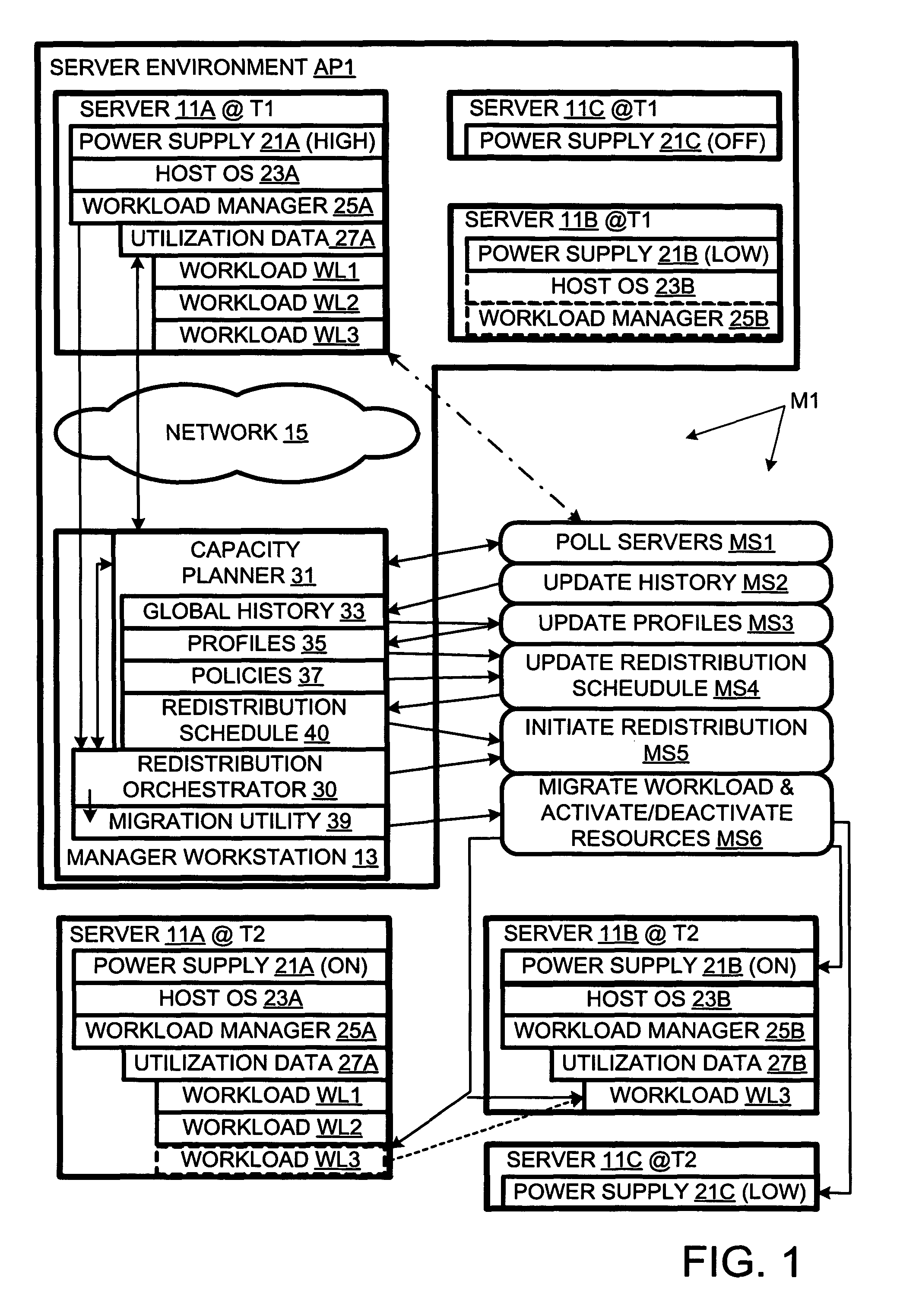
The present invention provides for redistributing workloads among computers to optimize resource utilization. Utilization by software workloads of computer resources is monitored to yield utilization data. A utilization chronology is updated using the utilization data. The chronology is analyzed to yield resource utilization predictions. The workloads are redistributed among the resources at least in part as function of said predictions.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
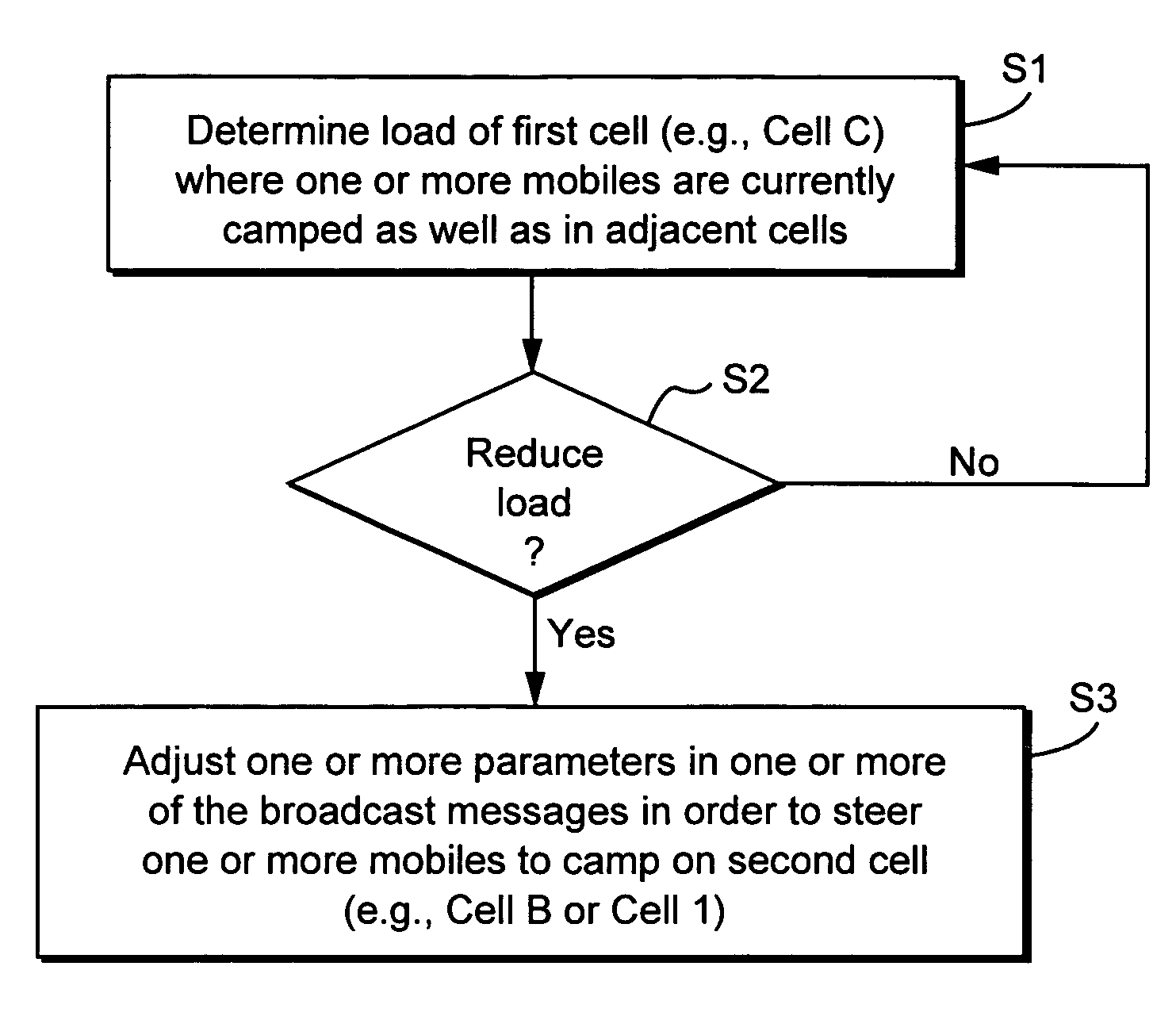
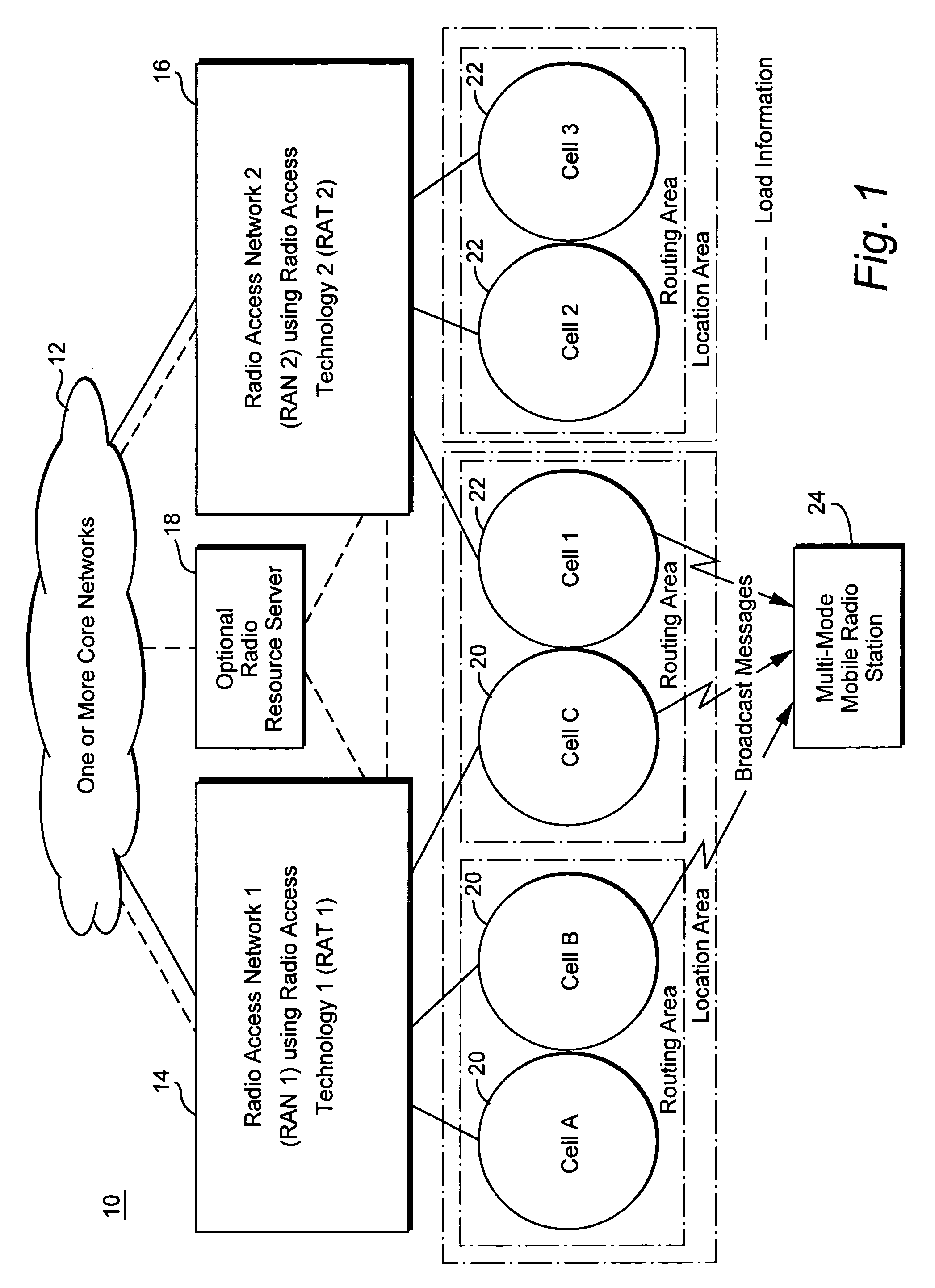
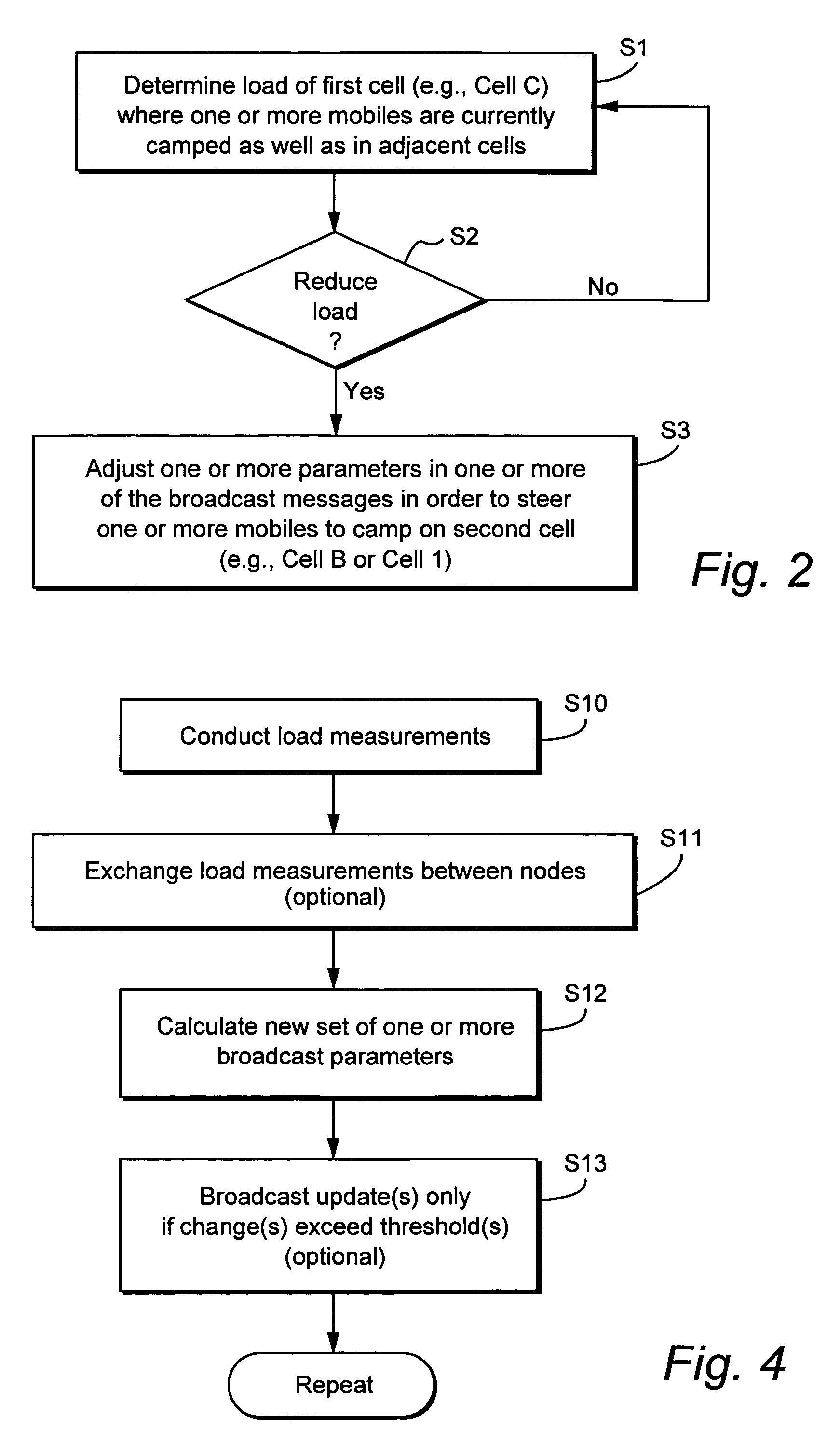
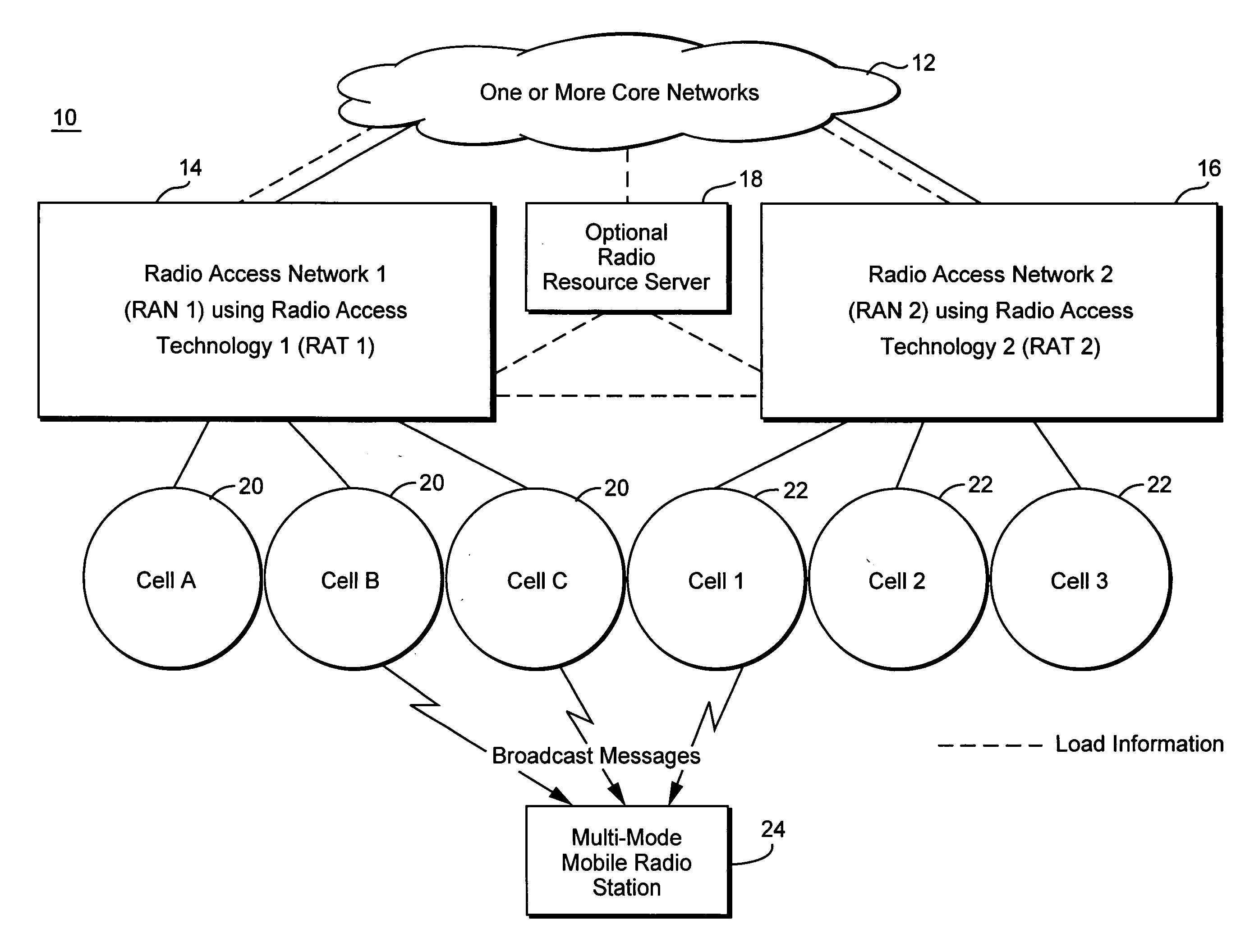
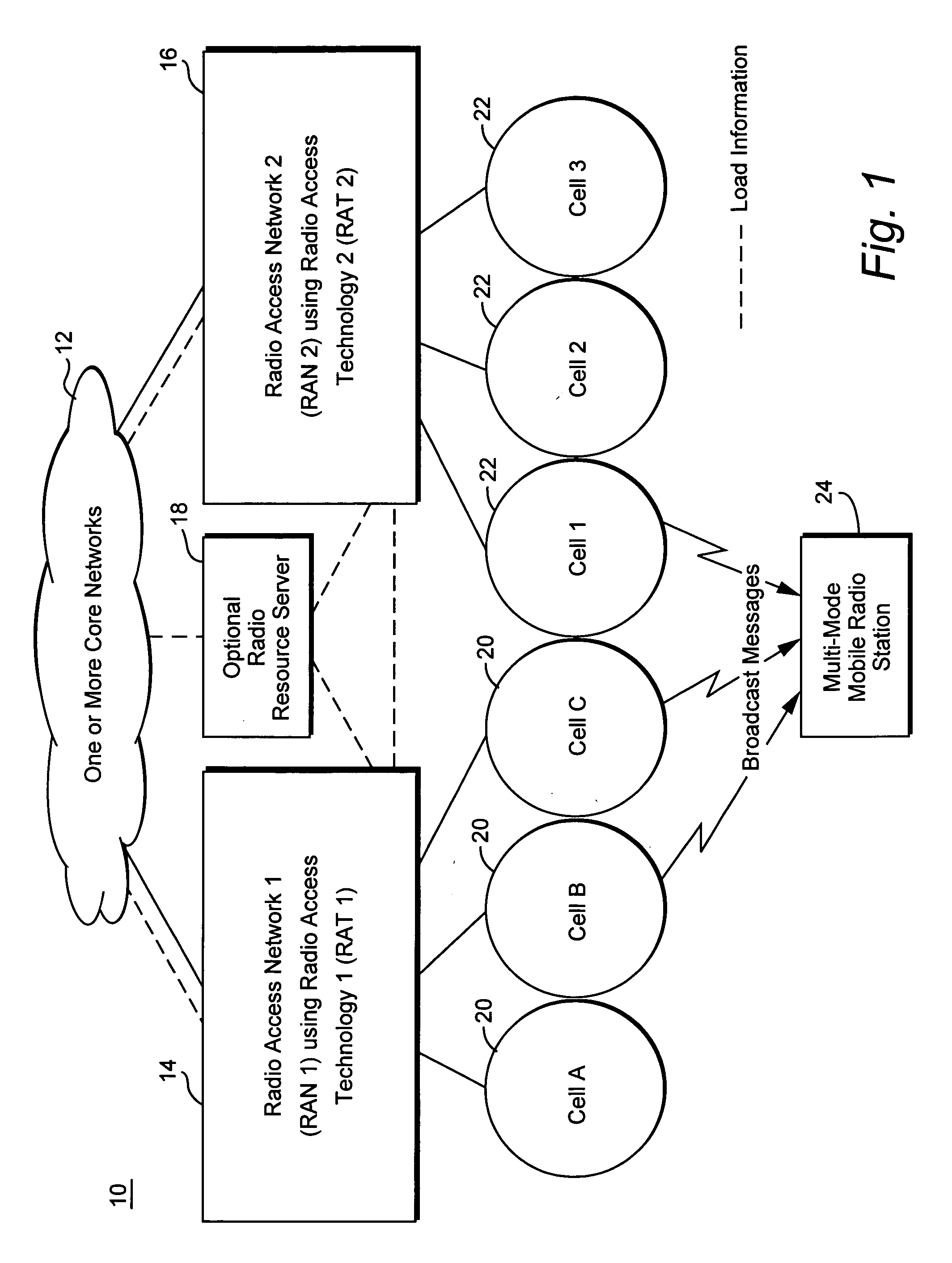
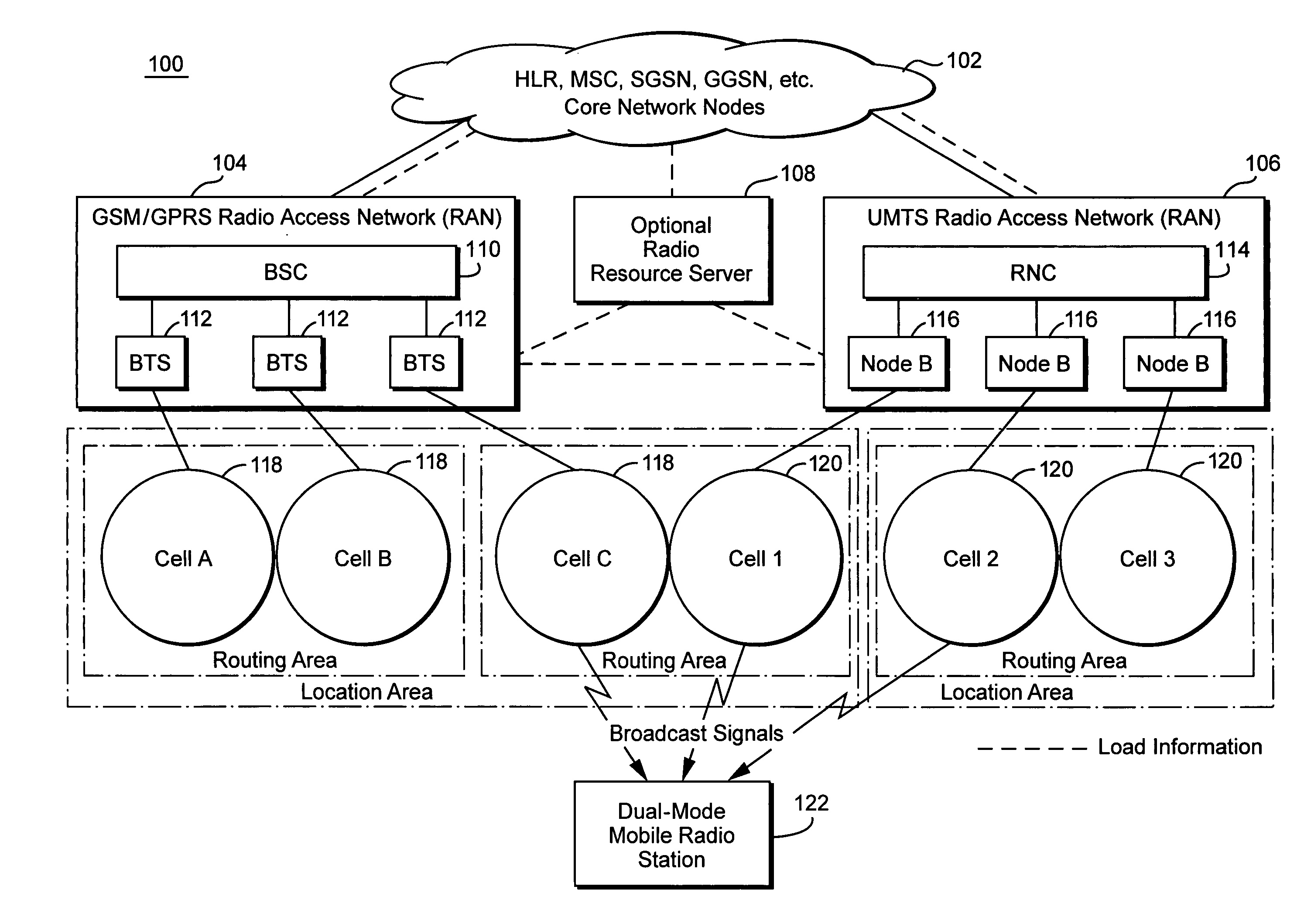
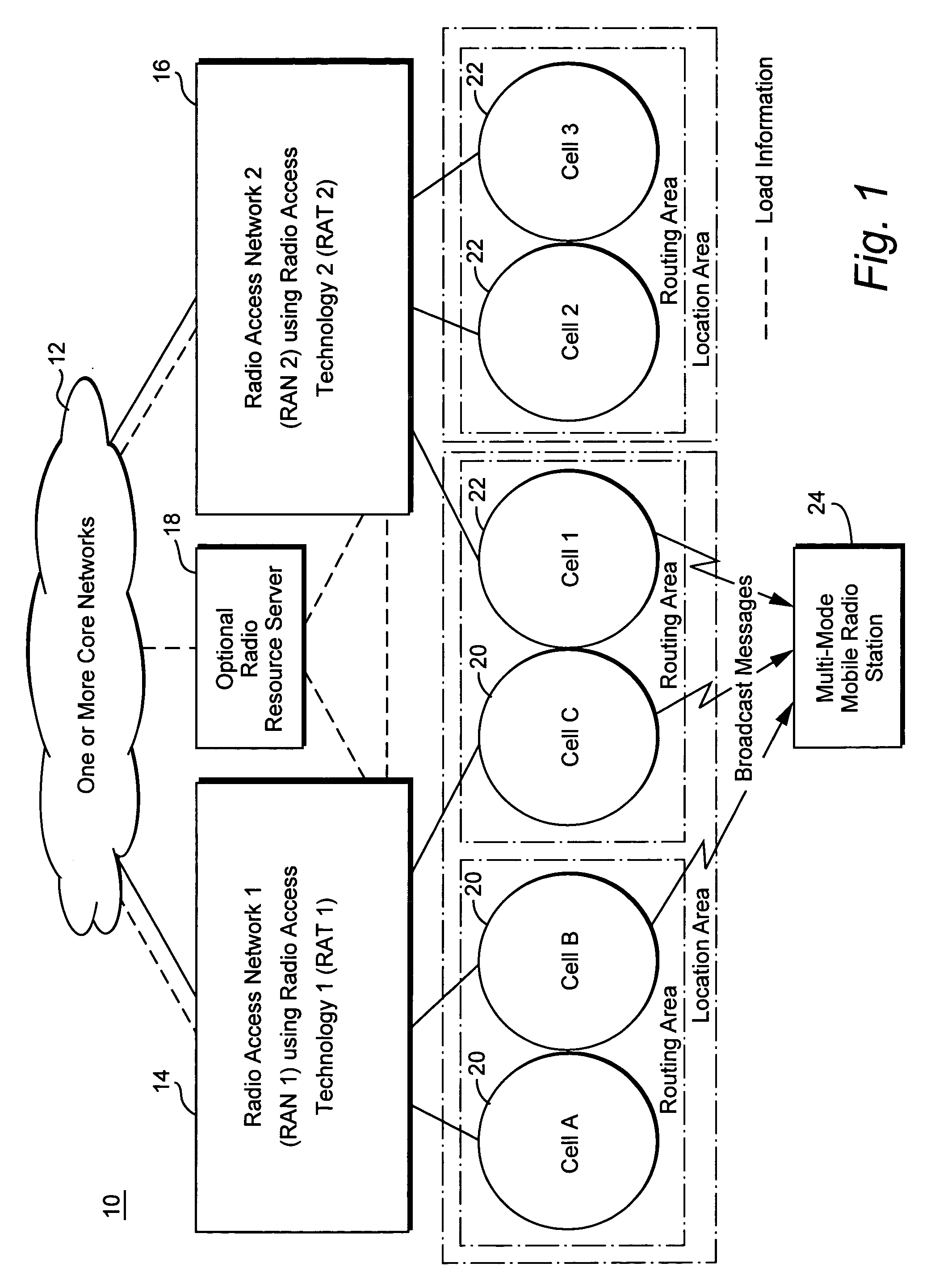
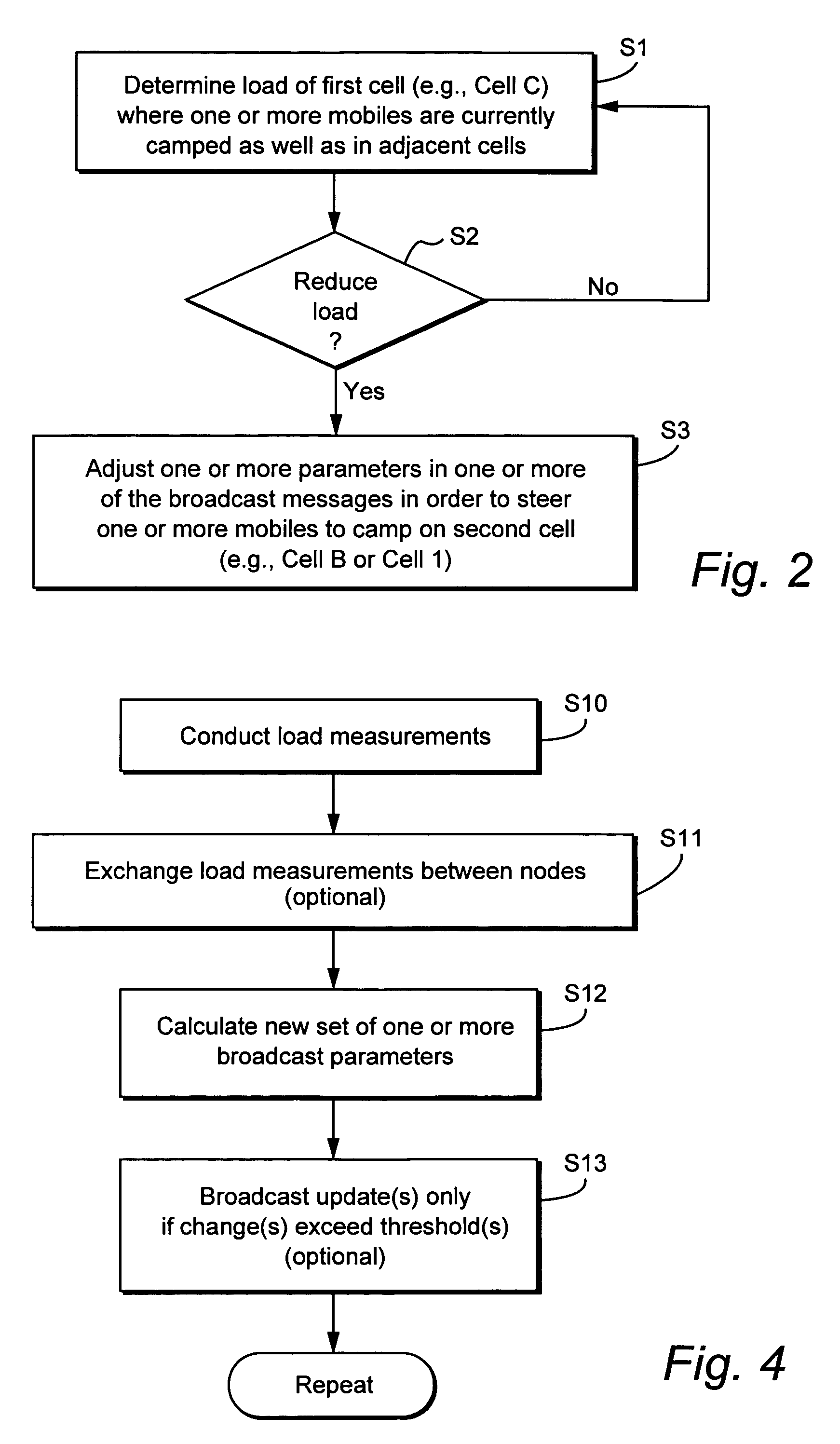
Method and apparatus for steering idle mobile stations
ActiveUS20060128394A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesTelecommunicationsMobile station
Load redistribution and other benefits may be achieved by dynamically distributing or “steering” idle mobile stations to a particular cell or area. For example, idle mobile stations may be steered from a loaded cell to less loaded cells by changing one or more cell broadcast parameters.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
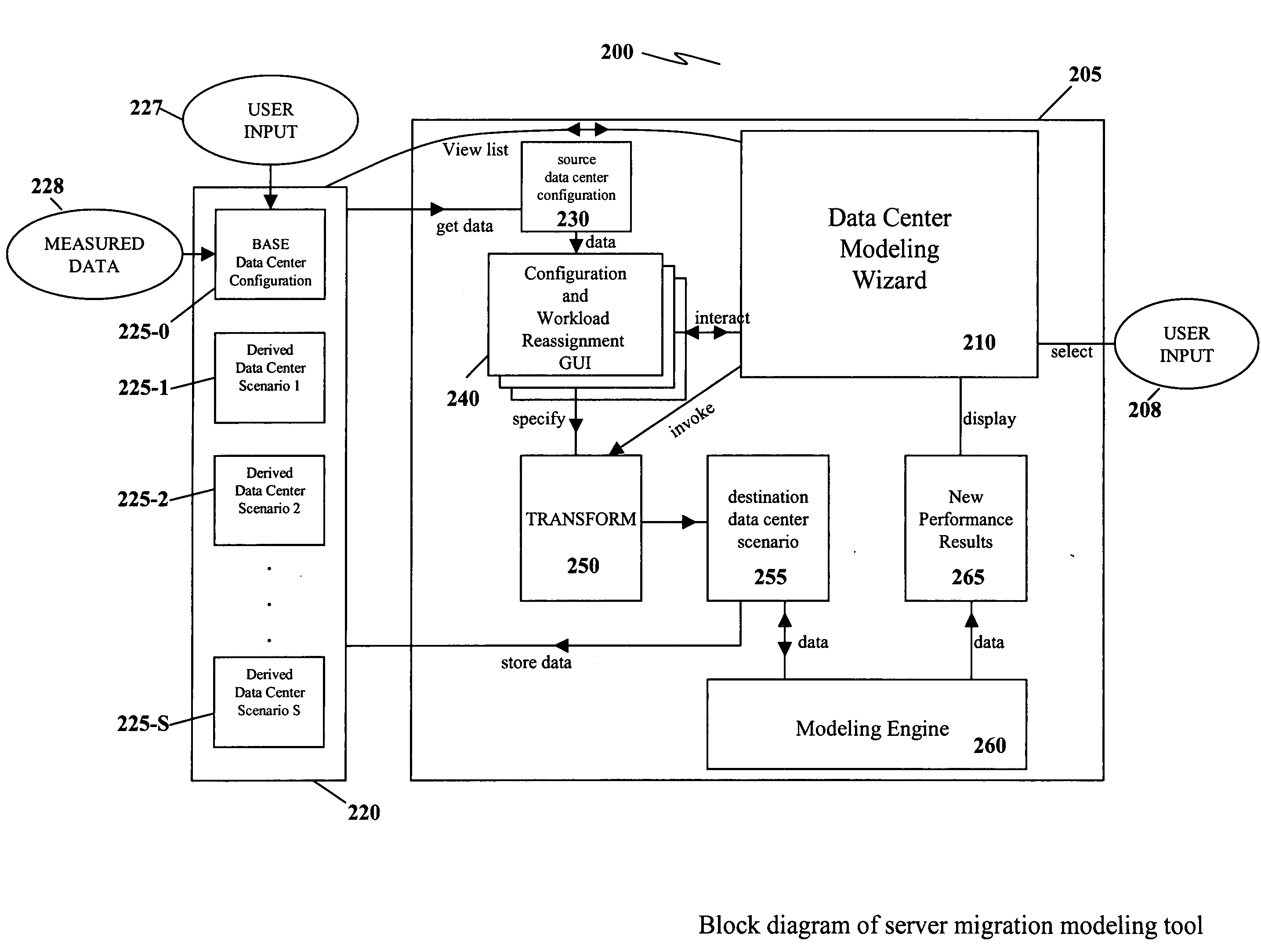
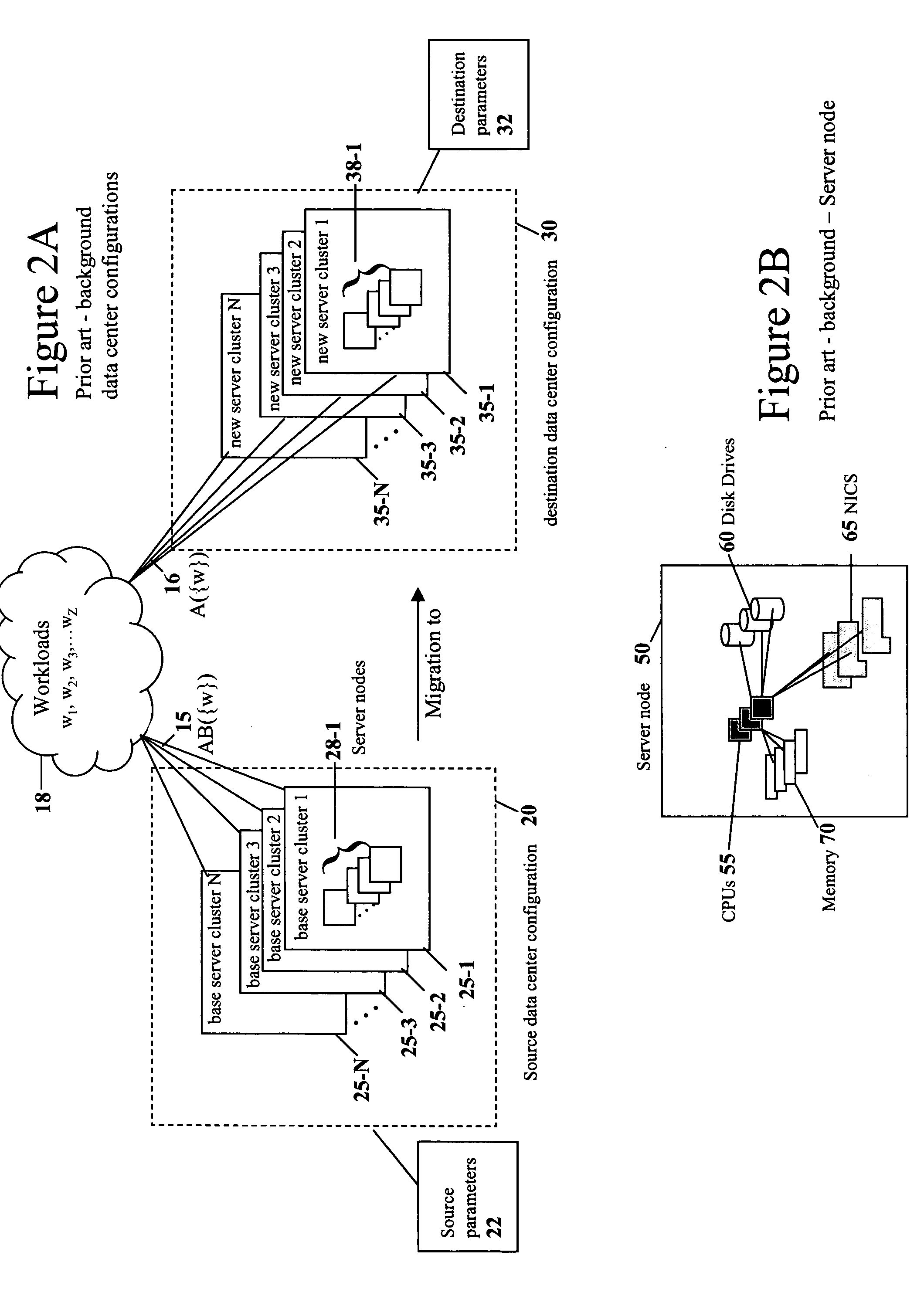
Apparatus and method for capacity planning for data center server consolidation and workload reassignment
InactiveUS20080077366A1Improve ease of useIncrease flexibilityAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDigital computer detailsCapacity planningWorkload
A server migration tool used to construct data center migration scenarios allowing for a user to rapidly manipulate a large number of input parameters required to describe a transformation from one data center configuration to a new data center configuration. The tool then performs the transformation and allows the user to interact with new data center configuration to understand its performance. A novel parameterization, speed independent service demand (SISD), greatly facilitates scaling performance metrics between different hardware platforms.
Owner:HYPERFORMIX
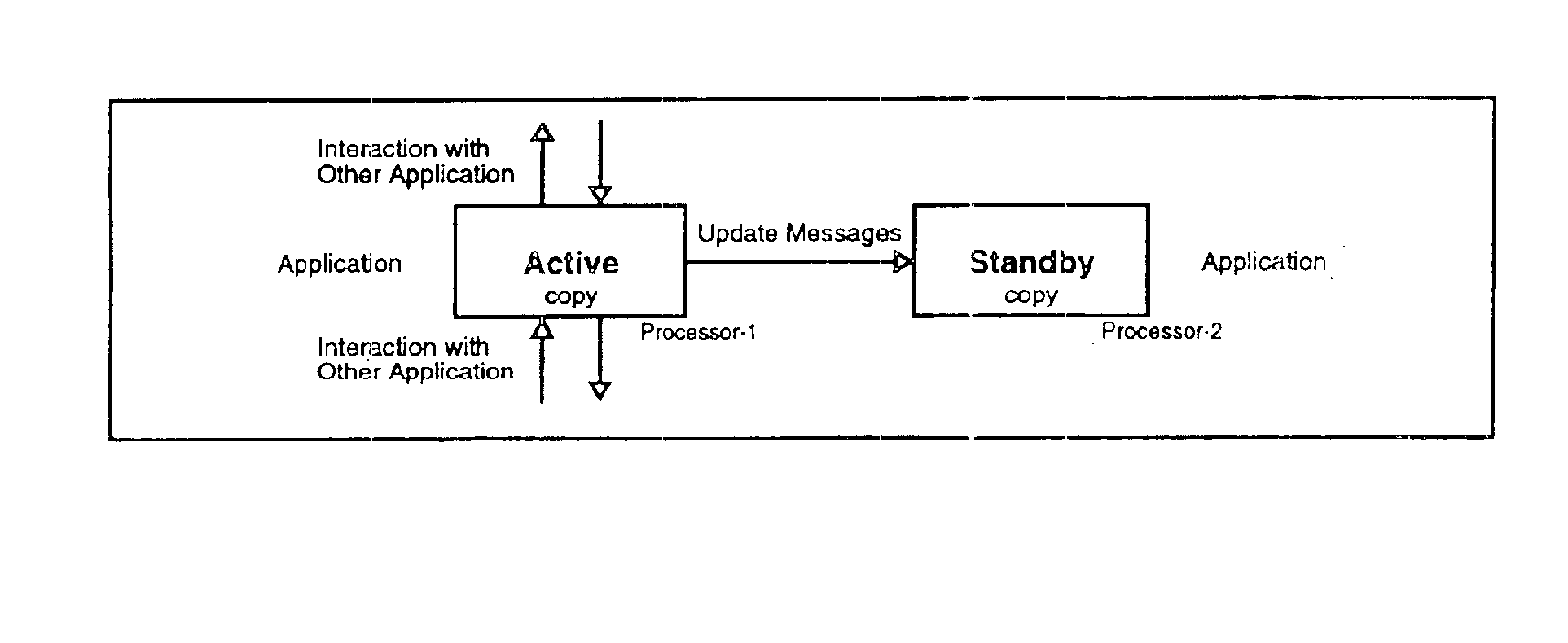
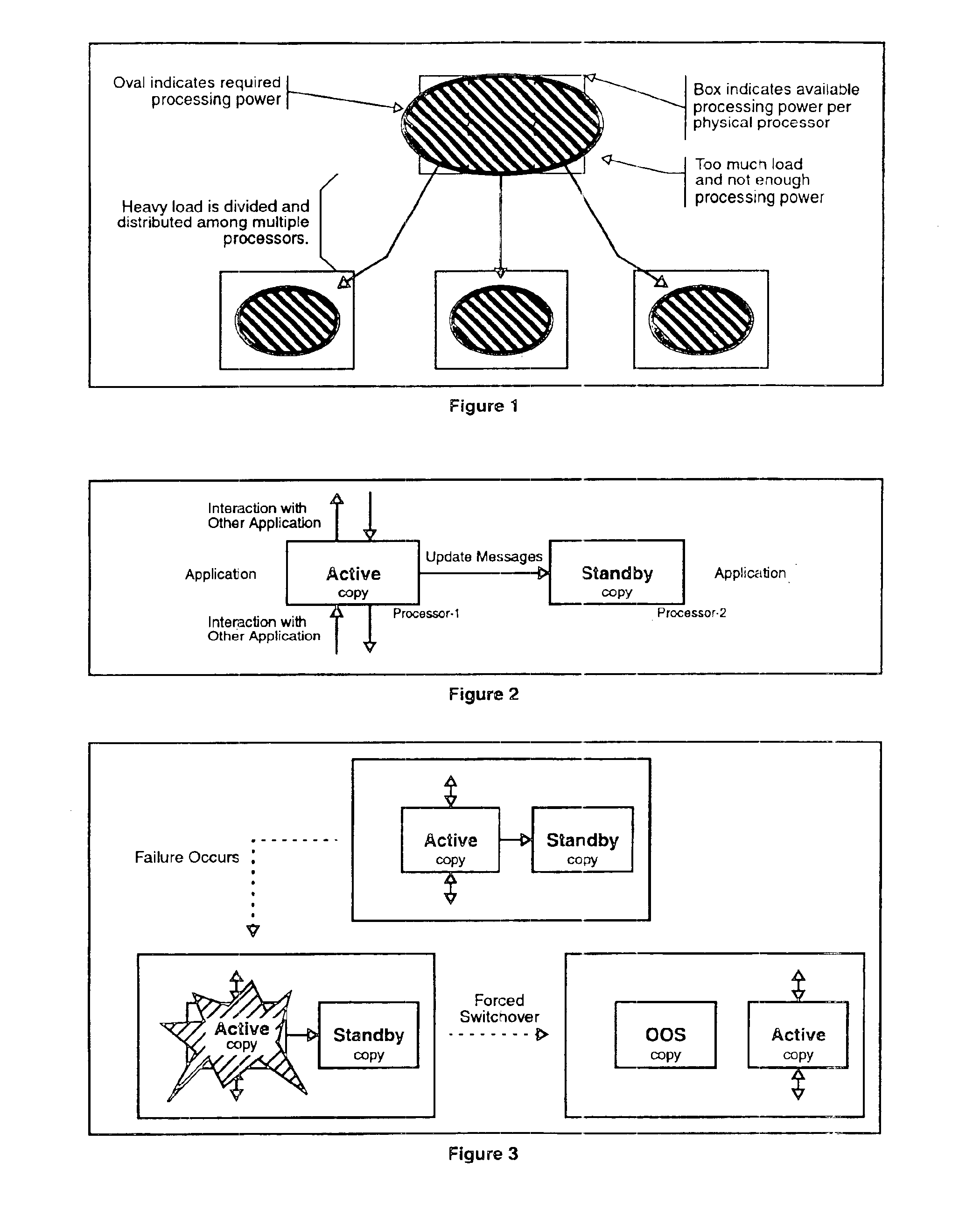
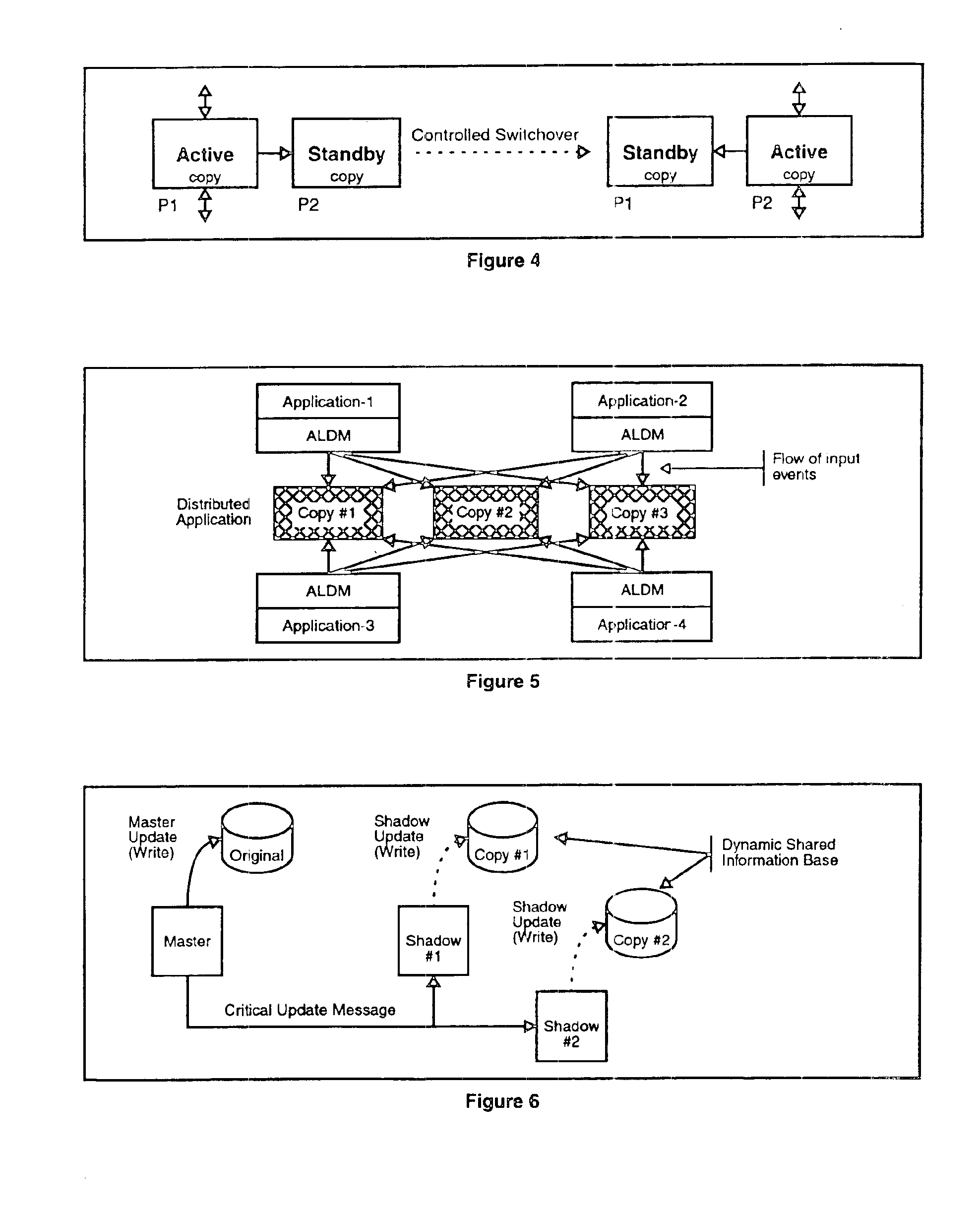
Apparatus and method for building distributed fault-tolerant/high-availability computed applications
InactiveUS6865591B1Multiple failureOptimal hardware utilizationMultiprogramming arrangementsTransmissionOperational systemSystem maintenance
Software architecture for developing distributed fault-tolerant systems independent of the underlying hardware architecture and operating system. Systems built using architecture components are scalable and allow a set of computer applications to operate in fault-tolerant / high-availability mode, distributed processing mode, or many possible combinations of distributed and fault-tolerant modes in the same system without any modification to the architecture components. The software architecture defines system components that are modular and address problems in present systems. The architecture uses a System Controller, which controls system activation, initial load distribution, fault recovery, load redistribution, and system topology, and implements system maintenance procedures. An Application Distributed Fault-Tolerant / High-Availability Support Module (ADSM) enables an applications( ) to operate in various distributed fault-tolerant modes. The System Controller uses ADSM's well-defined API to control the state of the application in these modes. The Router architecture component provides transparent communication between applications during fault recovery and topology changes. An Application Load Distribution Module (ALDM) component distributes incoming external events towards the distributed application. The architecture allows for a Load Manager, which monitors load on various copies of the application and maximizes the hardware usage by providing dynamic load balancing. The architecture also allows for a Fault Manager, which performs fault detection, fault location, and fault isolation, and uses the System Controller's API to initiate fault recovery. These architecture components can be used to achieve a variety of distributed processing high-availability system configurations, which results in a reduction of cost and development time.
Owner:TRILLIUM DIGITAL SYST
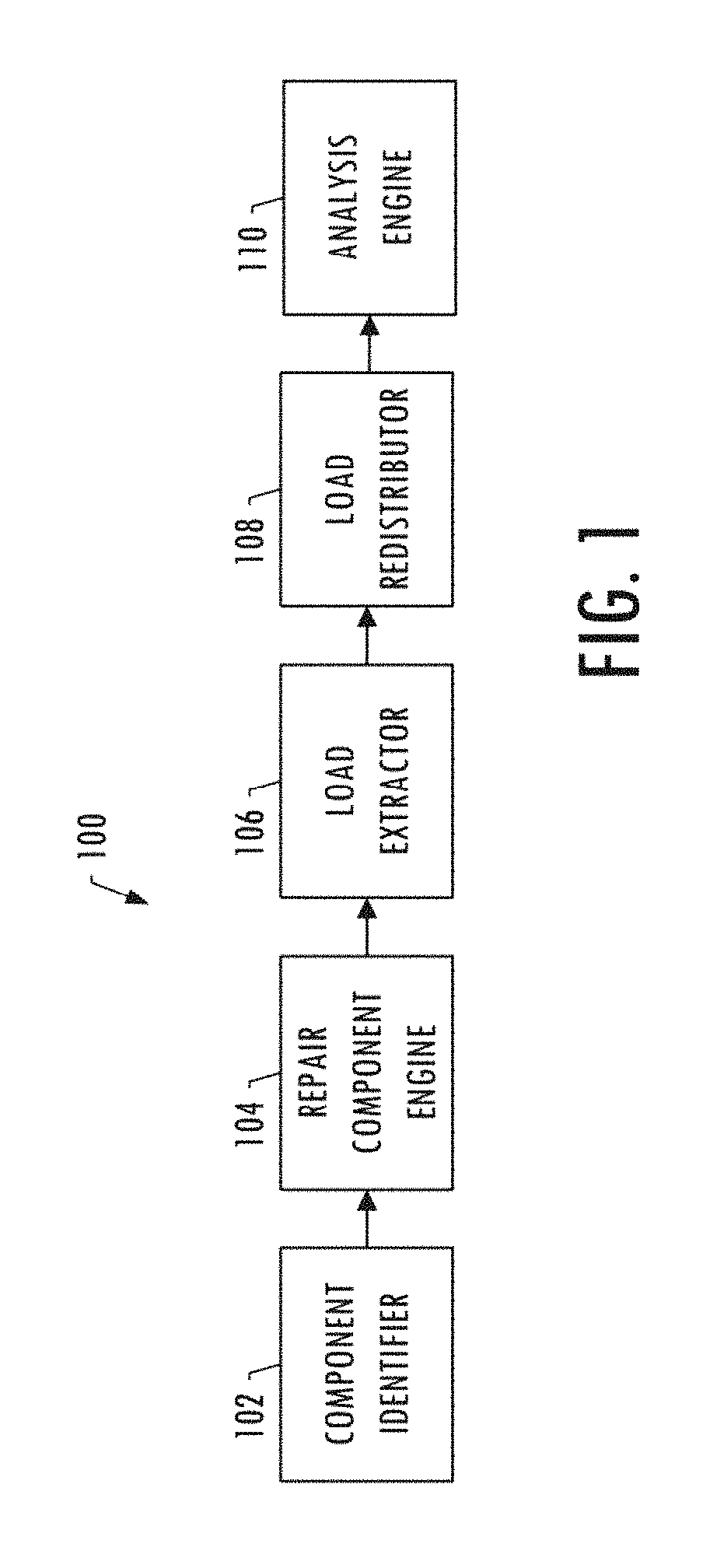
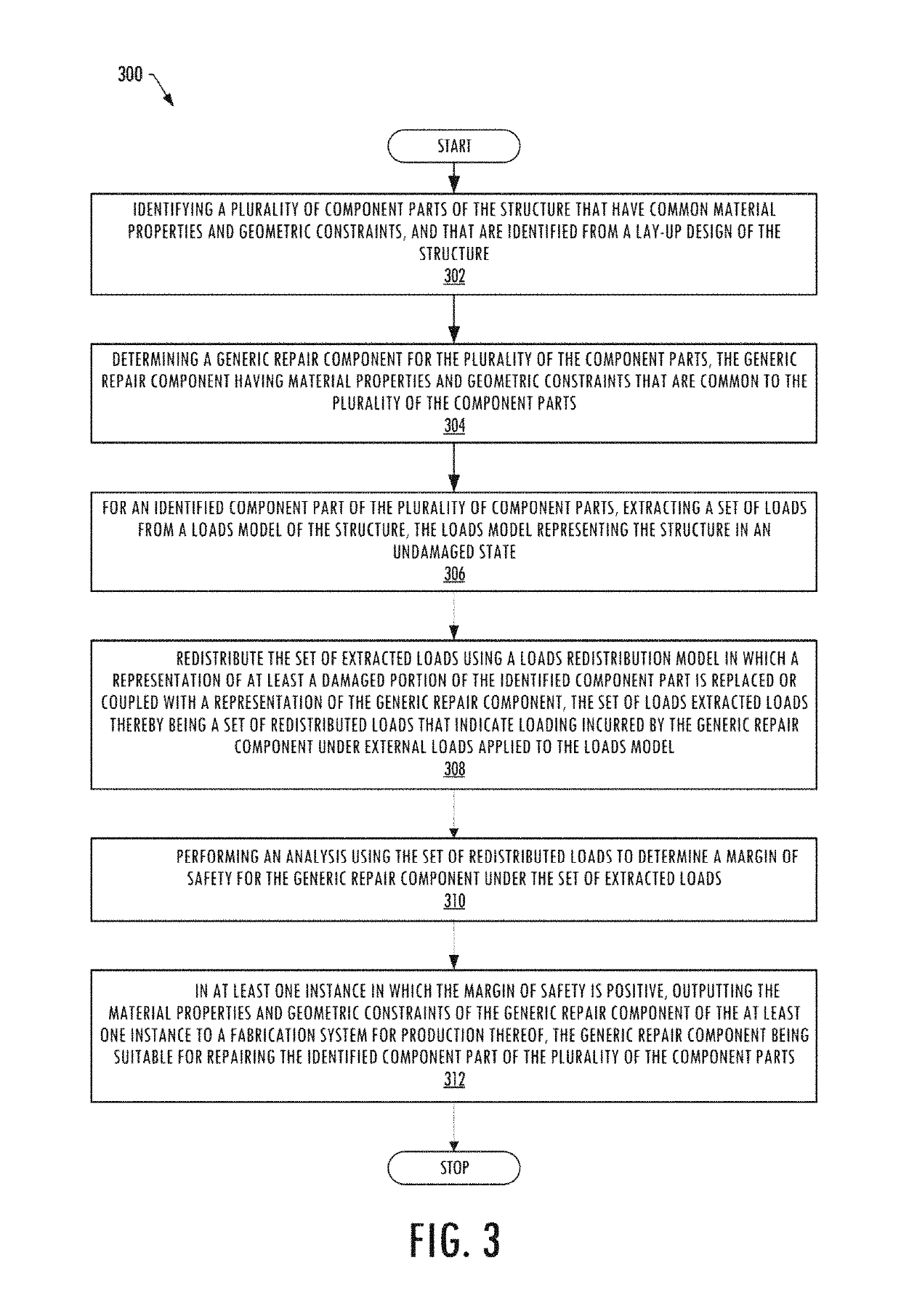
System for analysis of a repair for a structure
ActiveUS10275564B2Simple methodEffective timeGeometric CADCosmonautic vehiclesLoad modelLoad redistribution
An apparatus is provided for analysis of a repair for a structure by identifying component parts of the structure that have common material properties and geometric constraints, and based thereon determining a generic repair component for the component parts that also have the common material properties and the geometric constraints. A set of loads are extracted from a loads model of the undamaged structure and redistributed in a loads redistribution model at a damaged or defective portion of the component part. The set of redistributed loads indicate loading incurred by the generic repair component under an external load. The apparatus then uses the redistributed loads to perform an analysis to determine a margin of safety of the generic repair component and, in instances in which the margin of safety is positive, outputs the material properties and geometric constraints of the generic repair component to a fabrication system for production thereof.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
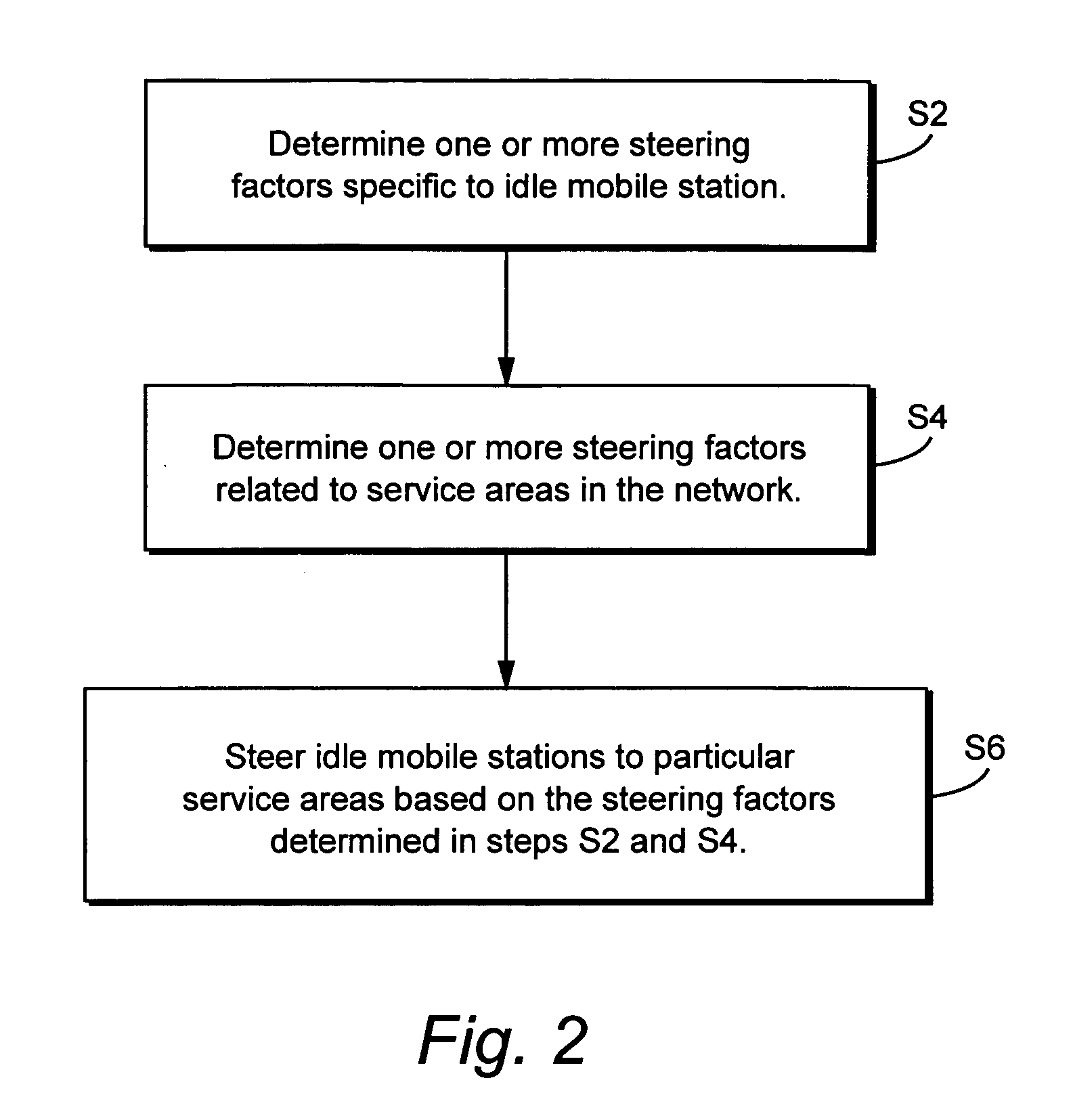
Method and apparatus for steering idle mobile stations
InactiveUS20060128392A1Simple processSimple mechanismNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionCyber operationsTelecommunications
Idle mobile stations are steered to a particular cell or service area to accommodate subscriber preferences or restrictions, subscription services, or network operator preferences or restrictions and / or to accomplish load redistribution or other network management functions. Multiple idle mobile station steering factors are considered. Steering may be accomplished using a variety of techniques such as rejecting registration attempts in certain cells and accepting those attempts in others and adjusting cell broadcast parameters.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System for and method of providing priority access service and cell load redistribution
InactiveUS6985740B2Emergency connection handlingNetwork traffic/resource managementCurrent cellCellular logic
Systems of and methods for providing cellular priority access and topological guidance information to cellular users are described, employing wireless ad hoc network and cellular logic. A centralized aspect of acquiring cell loading information and geographic coordinates is combine with a distributed scatternet forming aspect to enable guidance information to be computed and indicated to the user. The guidance information is reflective of cell loading and congestion status of neighboring cells, as well as the availability of alternative radio resources in the user's current cell or neighboring cells. The system may also be employed in re-distributing cell traffic among cells to optimally balance cell loads.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
Autonomous intelligent workload management
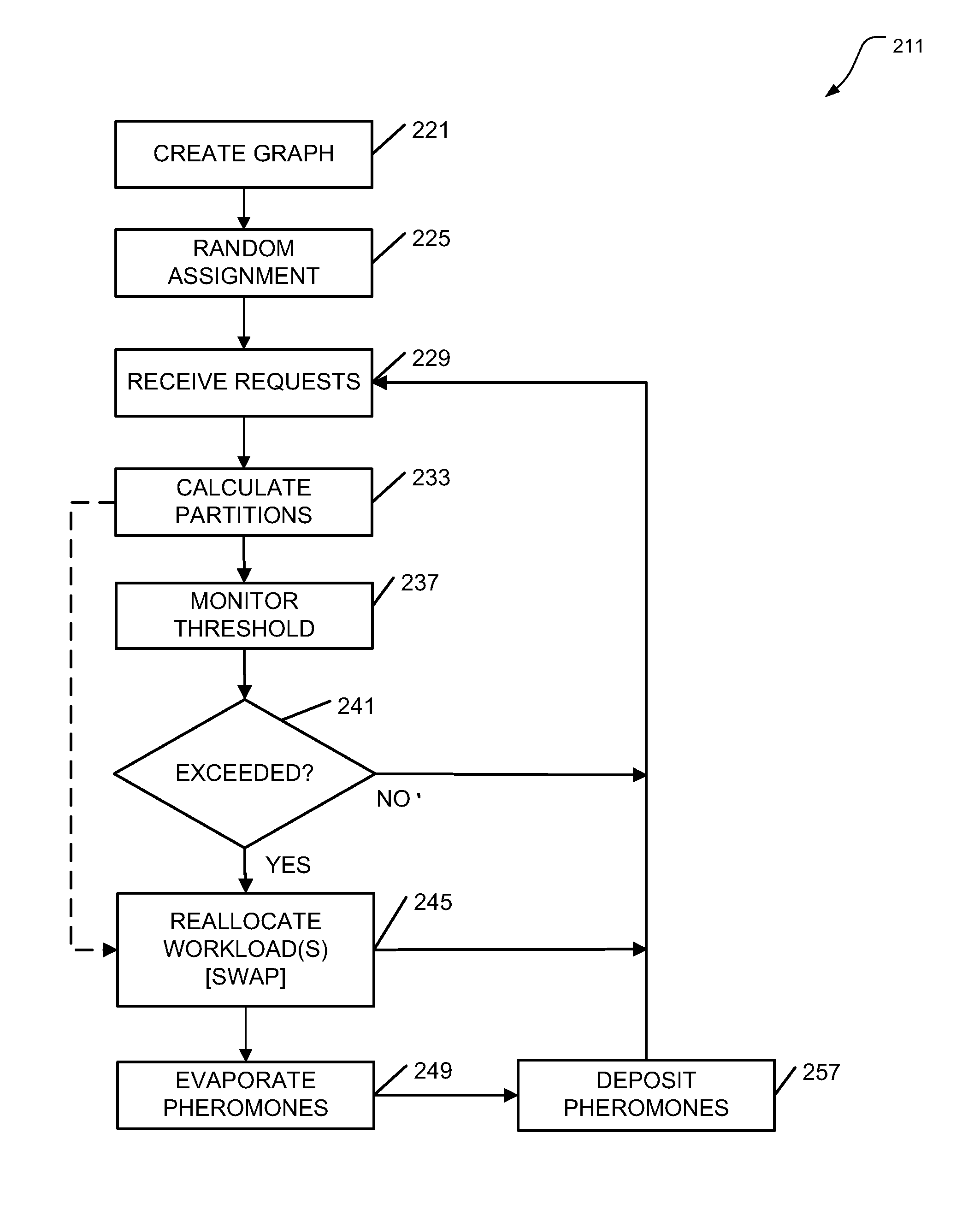
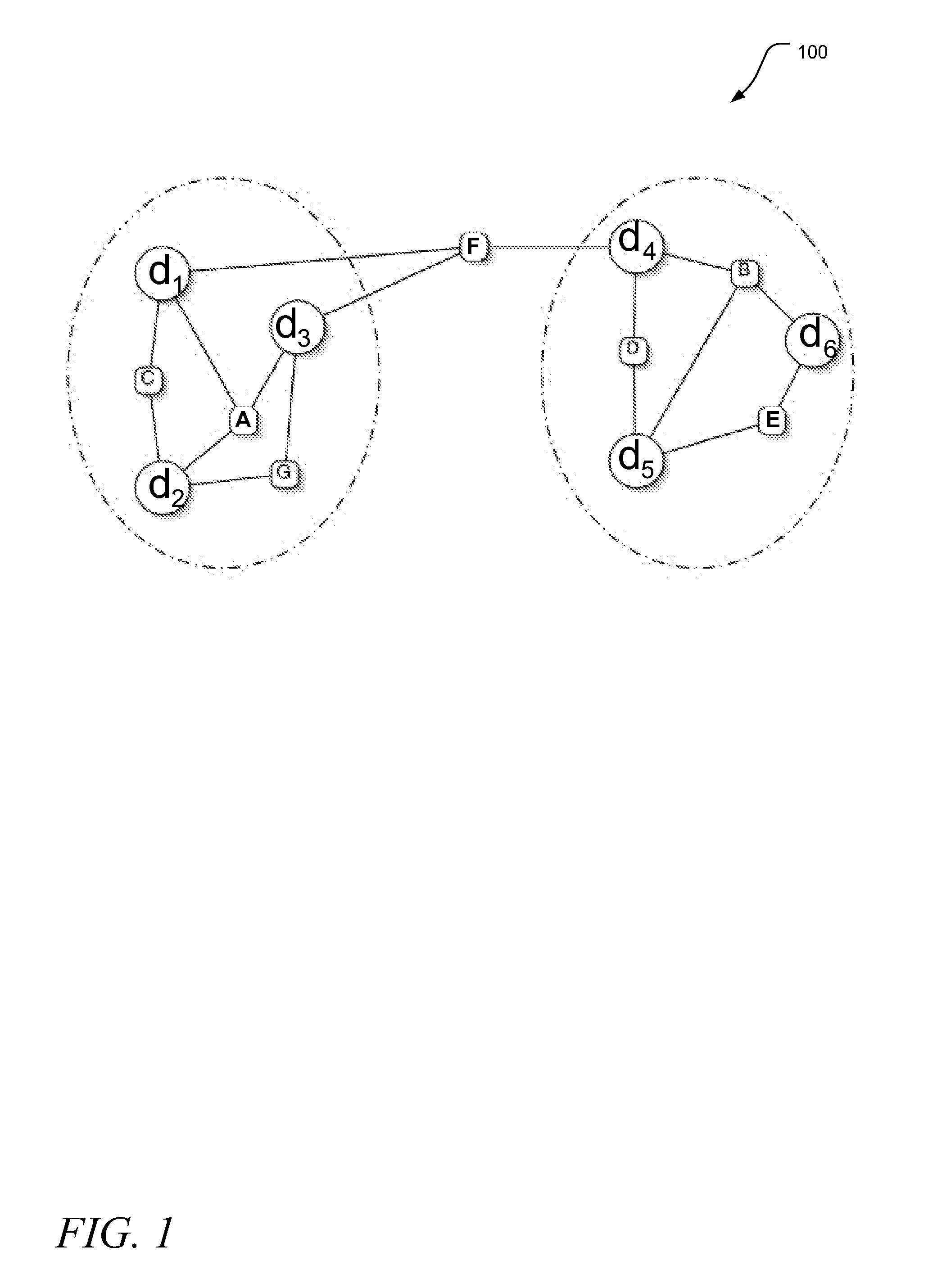
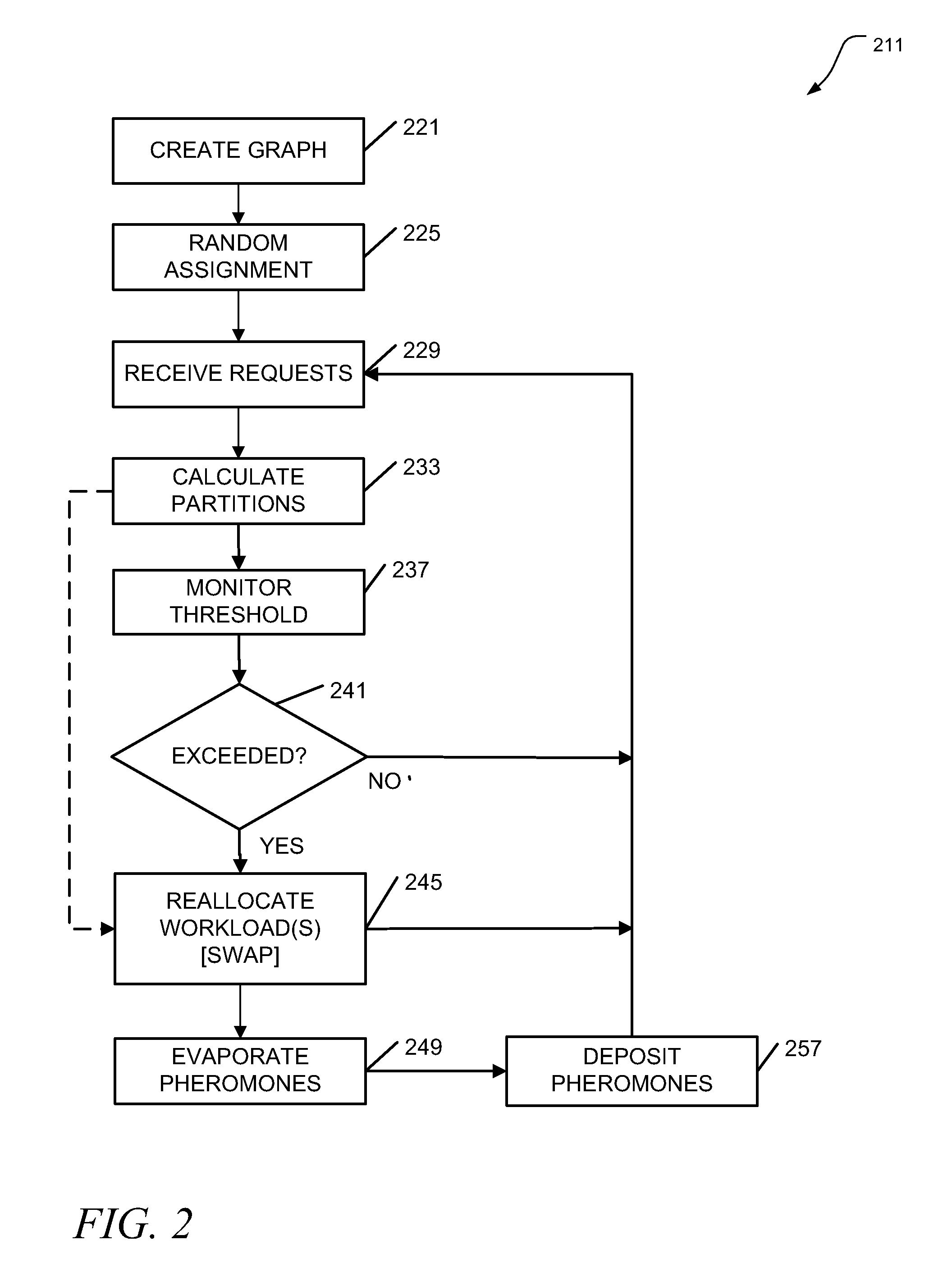
Apparatus, systems, and methods may operate to create a hypergraph of weighted vertices comprising computing resources and storage resources, and nets comprising workloads; to receive a plurality of requests to be addressed by a network associated with the hypergraph, at least some of the requests associated with data objects; to calculate partition schemes for the network based on the requests and the data objects according to an ant colony optimization heuristic; and to autonomously reallocate the workloads to the computing resources and / or the storage resources according to the partition schemes. The workloads may act as ants following a path defined by the vertices of the hypergraph. Further activities may thus include depositing pheromones along hyperedges of the hypergraph, wherein the hyperedges are used for swapping the vertices between the workloads. Additional apparatus, systems, and methods are disclosed.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
System for and method of providing priority access service and cell load redistribution
InactiveUS20050282554A1Improve performanceApply evenlyEmergency connection handlingNetwork traffic/resource managementCurrent cellCellular logic
Systems of and methods for providing cellular priority access and topological guidance information to cellular users are described, employing wireless ad hoc network and cellular logic. A centralized aspect of acquiring cell loading information and geographic coordinates is combine with a distributed scatternet forming aspect to enable guidance information to be computed and indicated to the user. The guidance information is reflective of cell loading and congestion status of neighboring cells, as well as the availability of alternative radio resources in the user's current cell or neighboring cells. The system may also be employed in redistributing cell traffic among cells to optimally balance cell loads.
Owner:F POSZAT HU
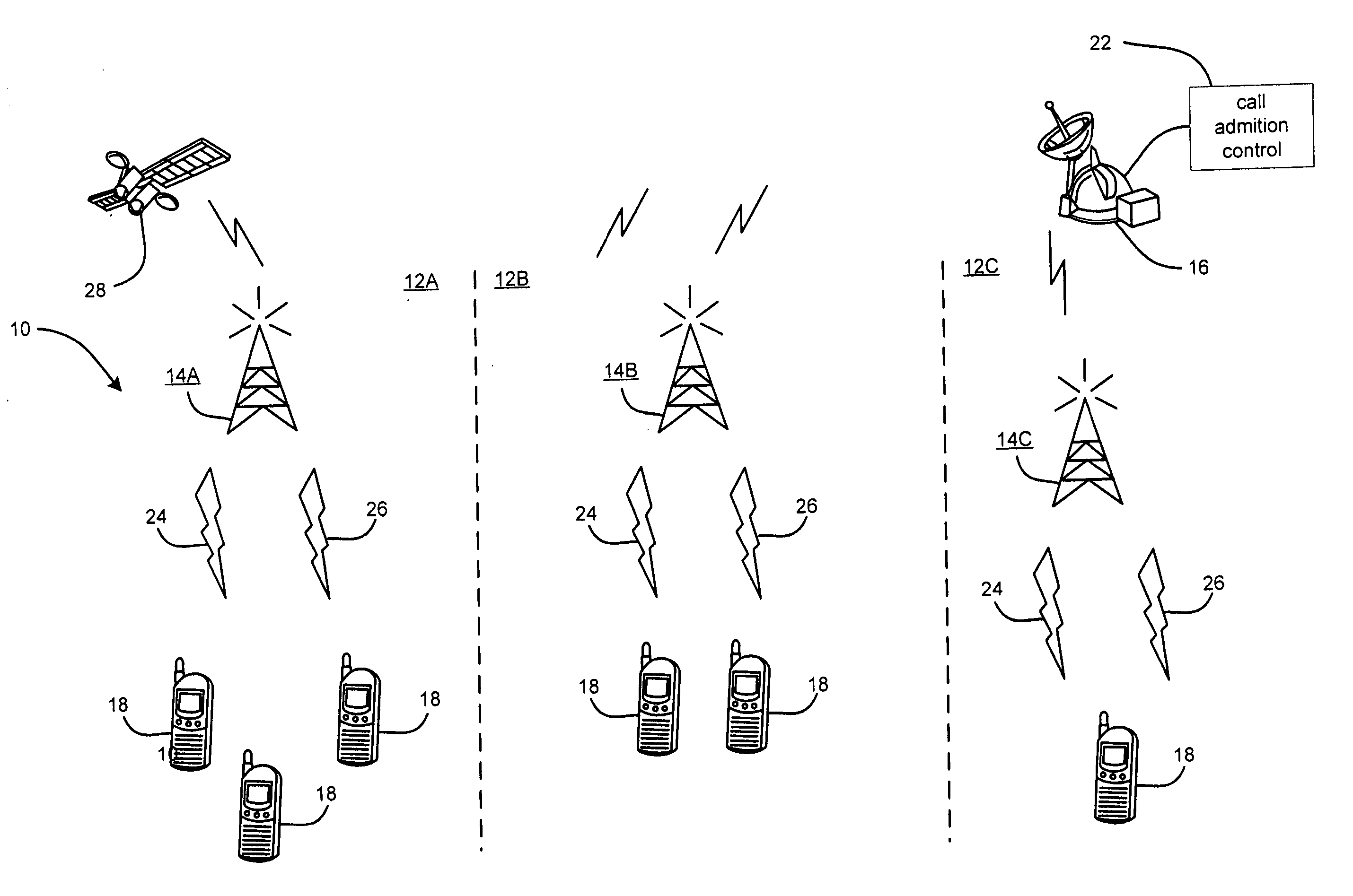
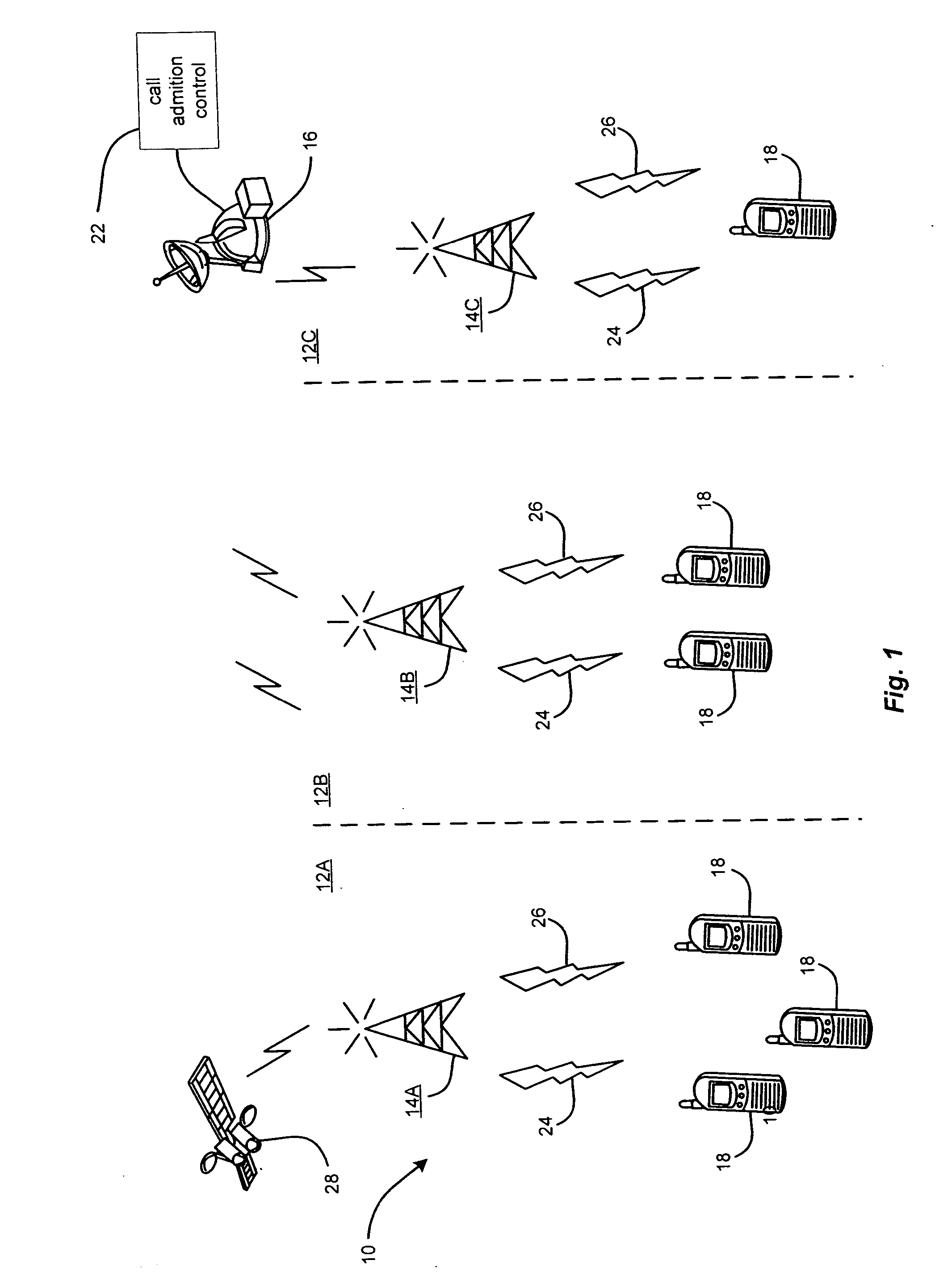
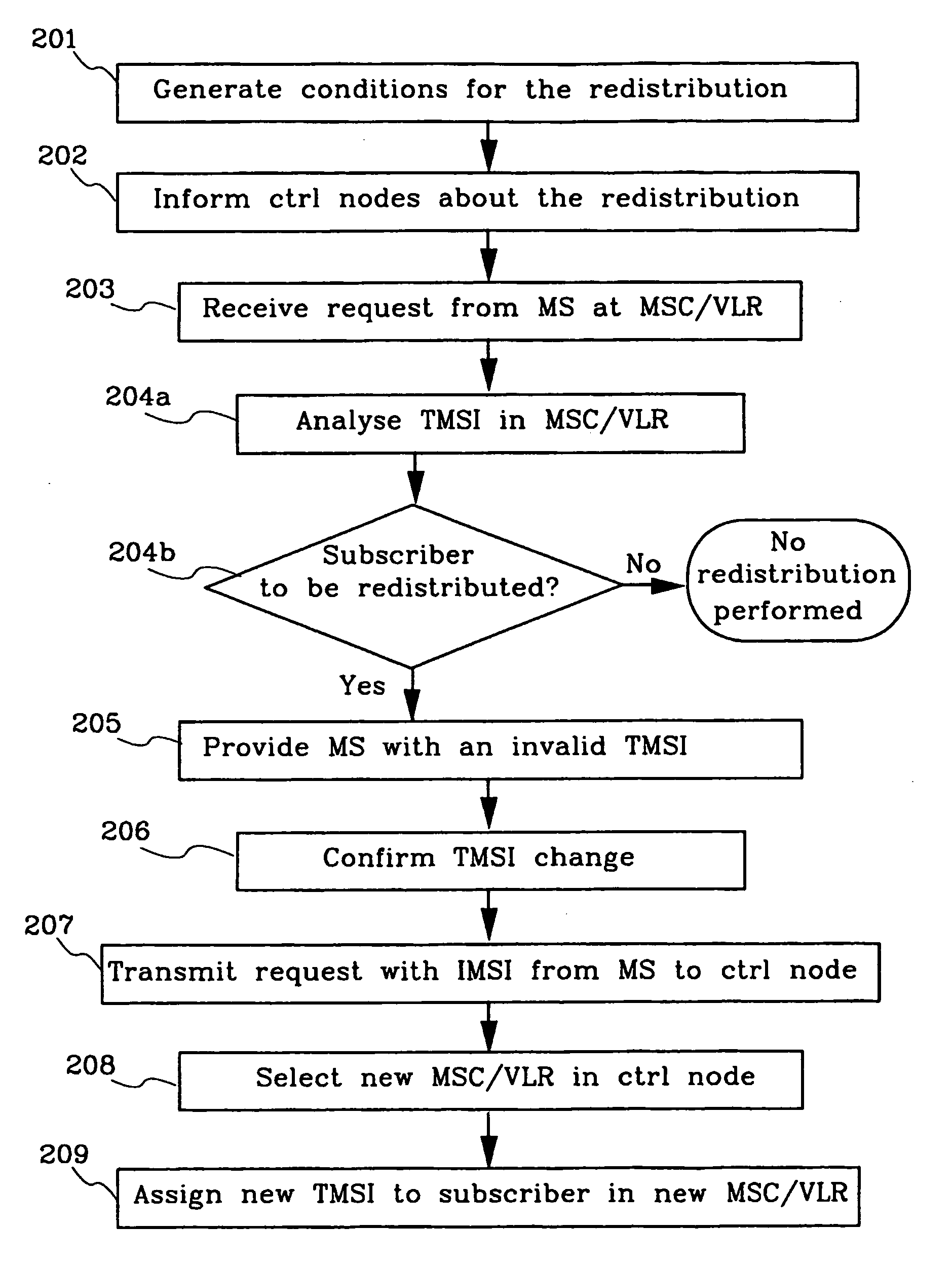
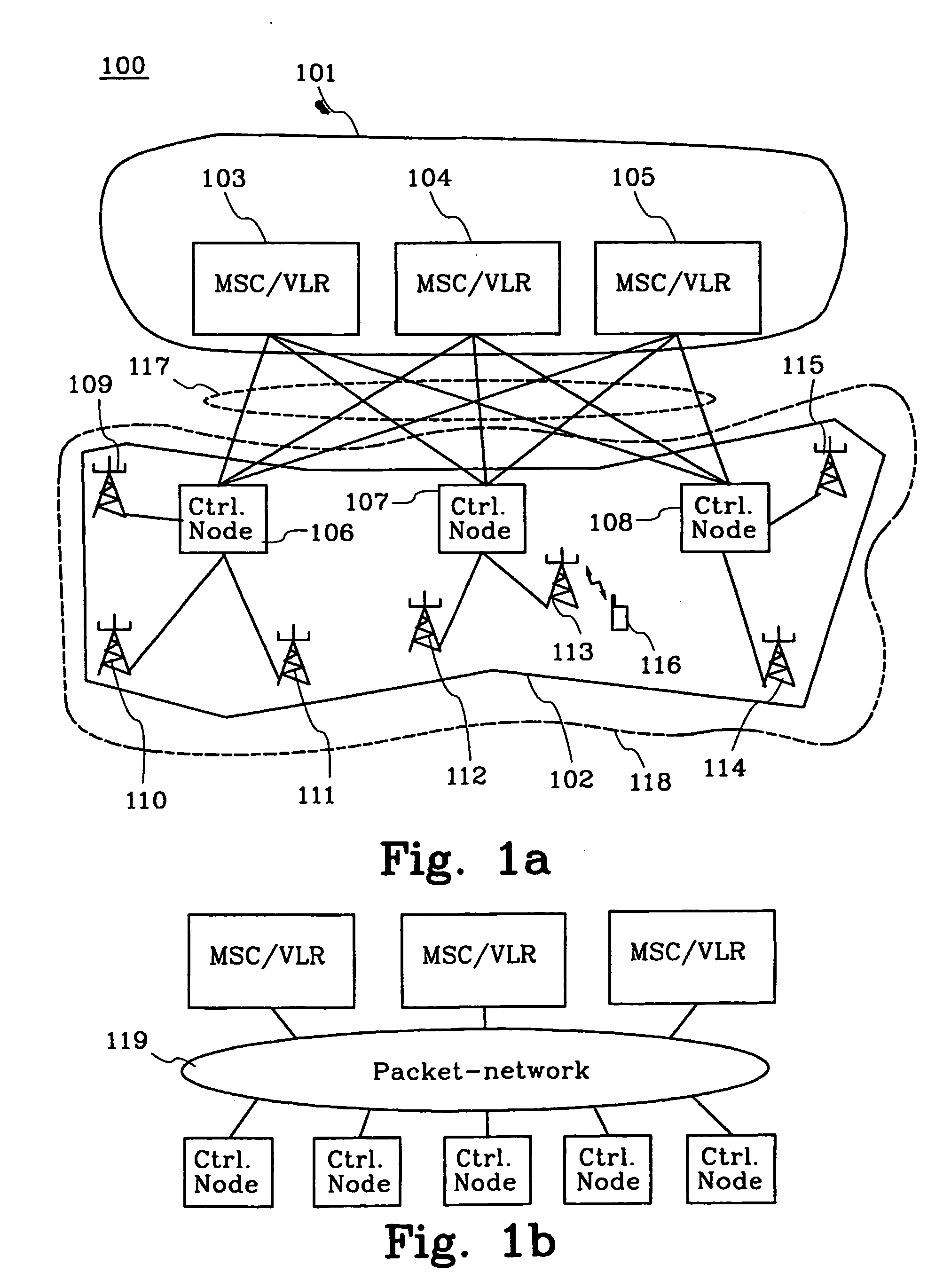
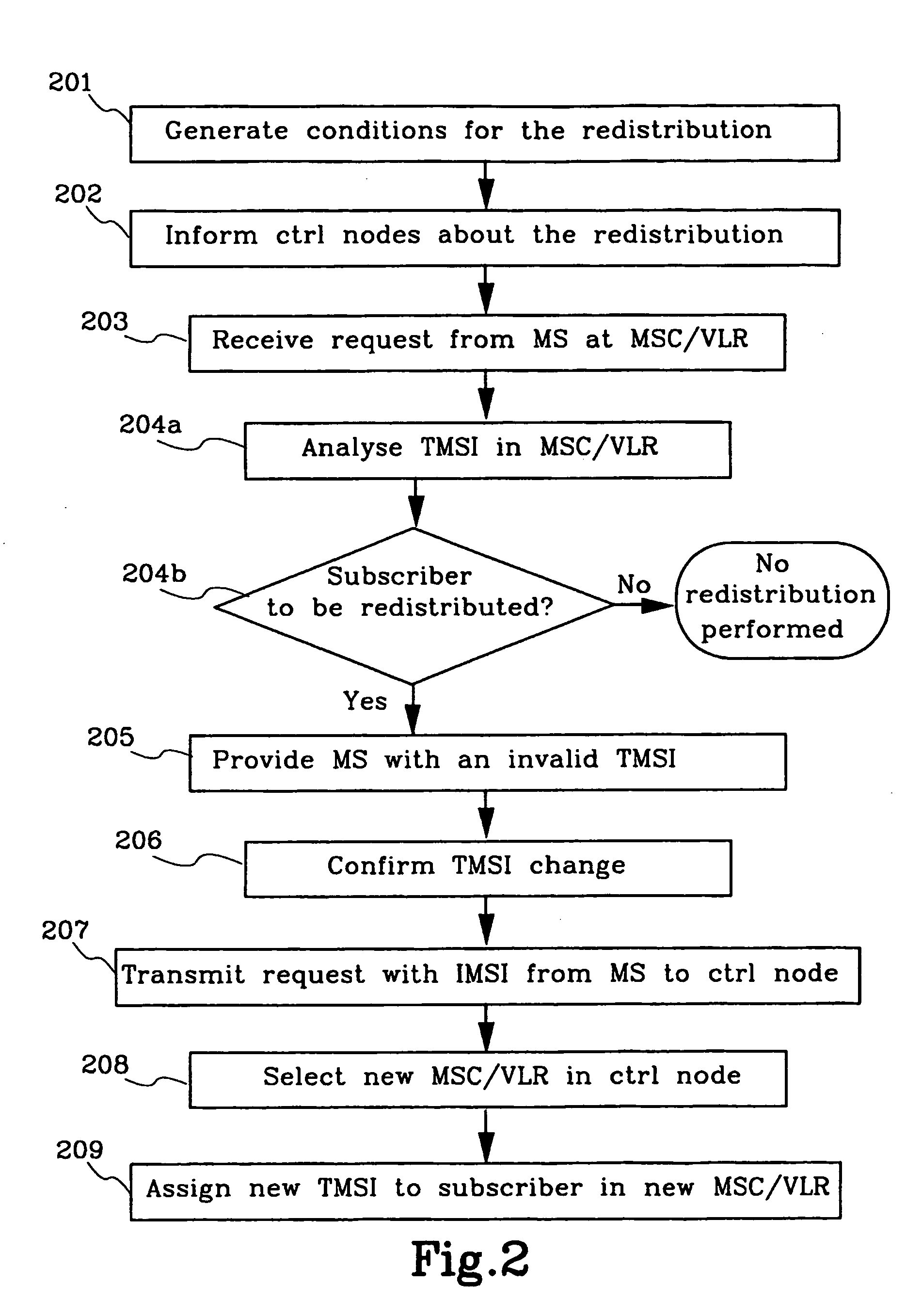
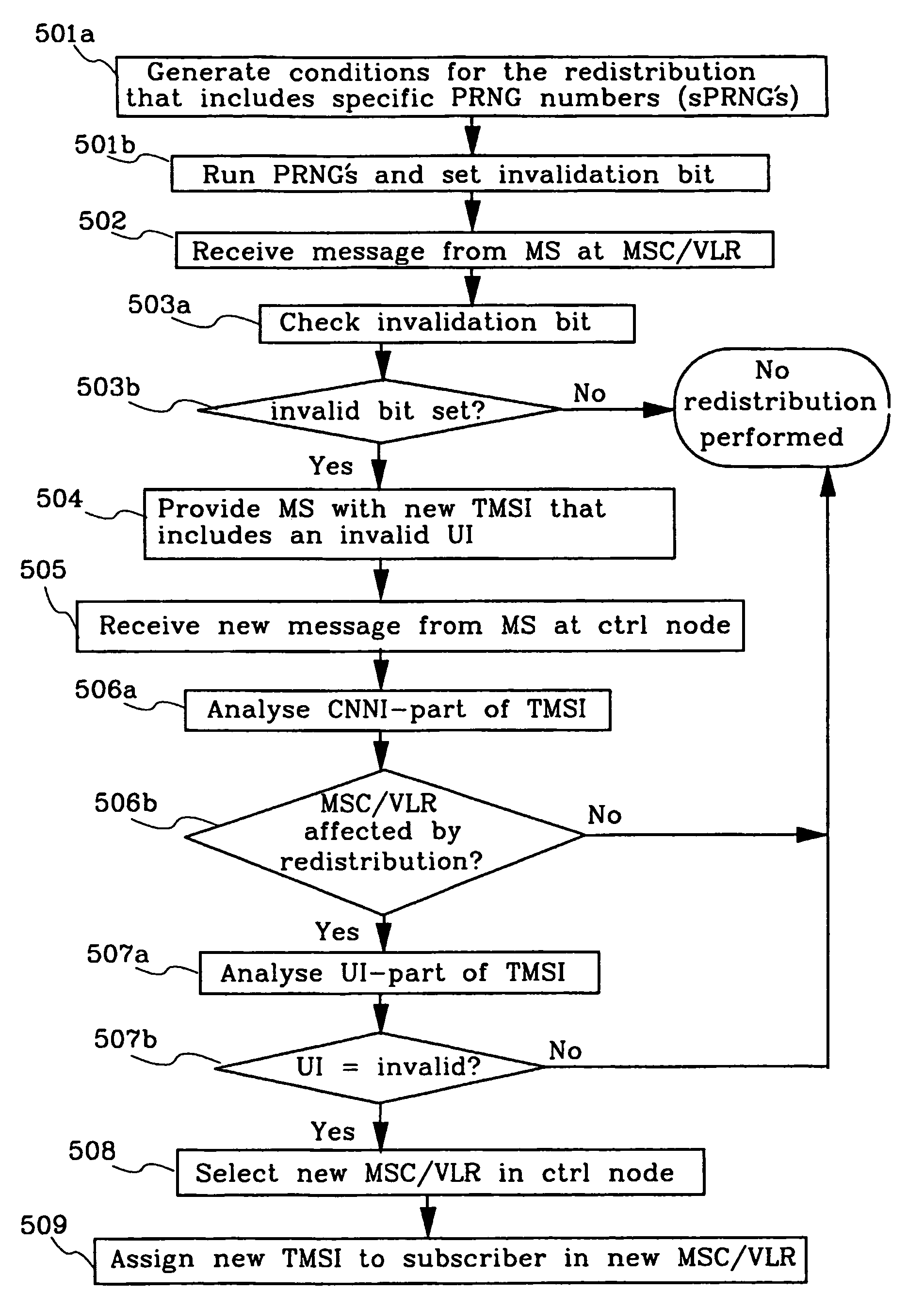
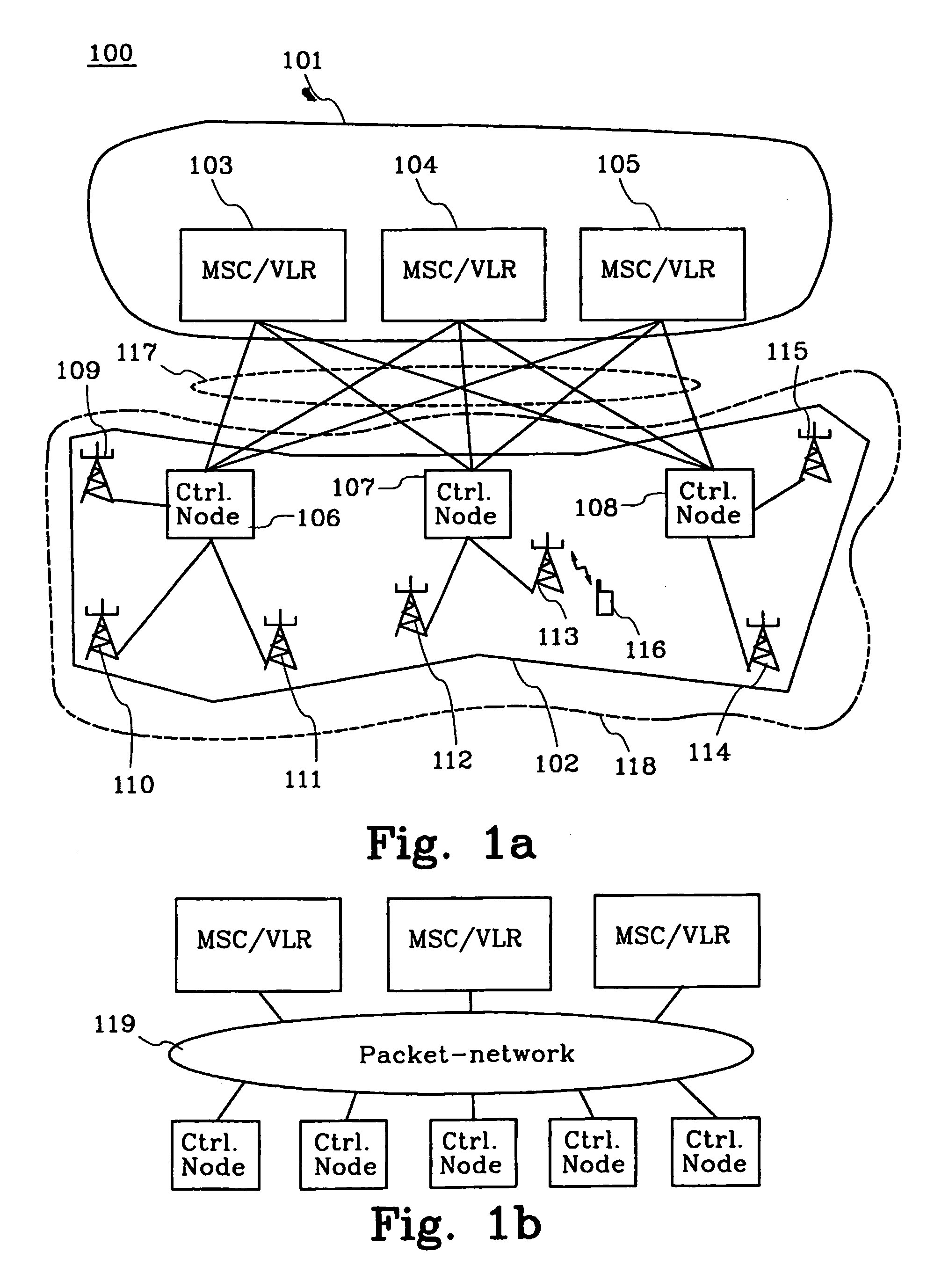
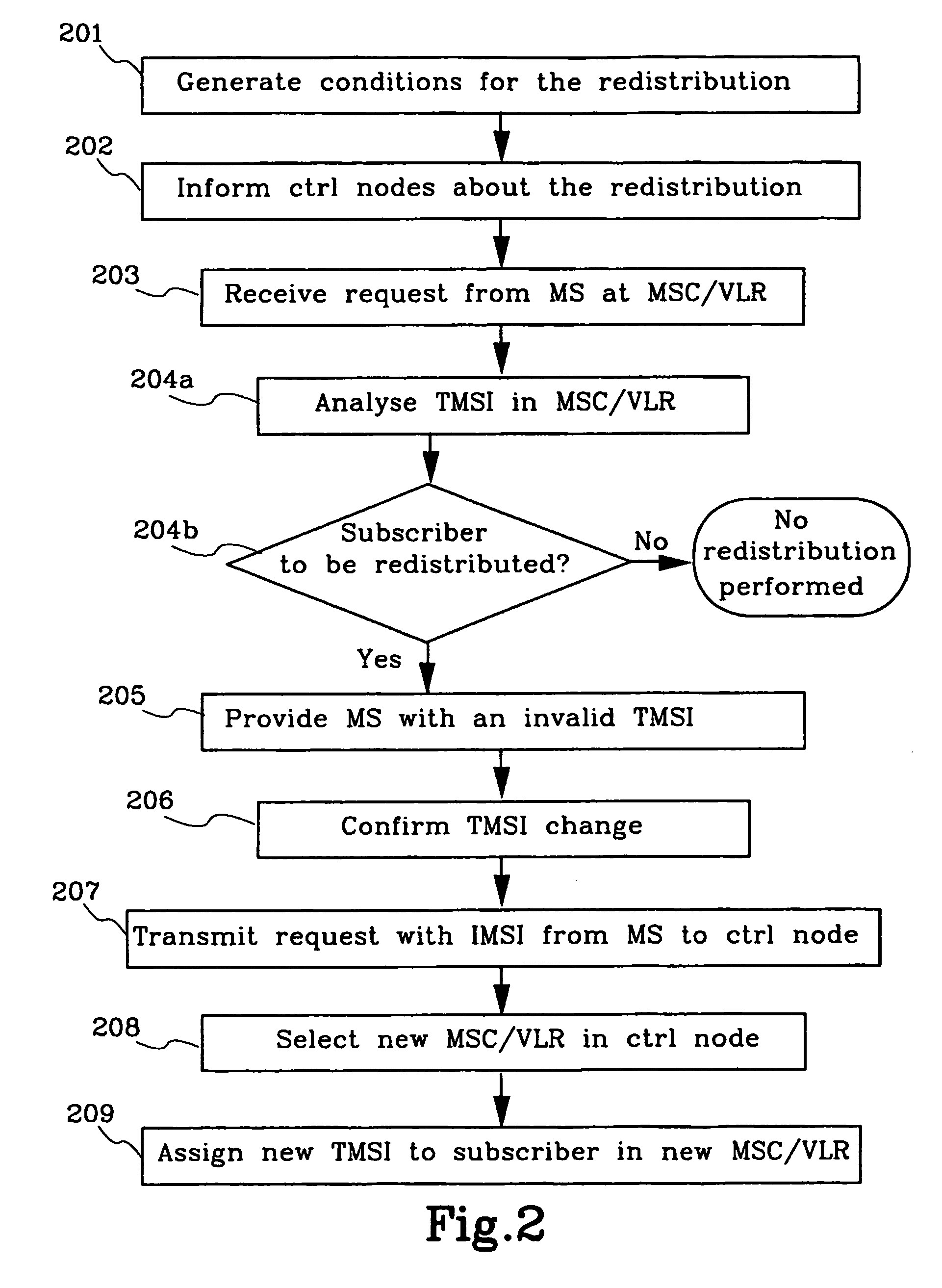
Method and means for redistribution of subscriber information in umts networks where the nodes are arranged in pools
InactiveUS20040248592A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsSubstation equipmentLoad redistributionCore network
The present invention relates to method and means for a system initiated subscriber information redistribution in order to achieve a load redistribution within a pool of core network nodes. The subscribers, that are affected by the redistribution, are determined by the bit values in their TMSI's. These specific TMSI's are then arranged to be treated as invalid by the cellular system. Messages etc. from subscribers with invalid TMSI's will be "trapped" in the cellular system and the subscriber information that belongs to these subscribers will be redistributed to new core network nodesn
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
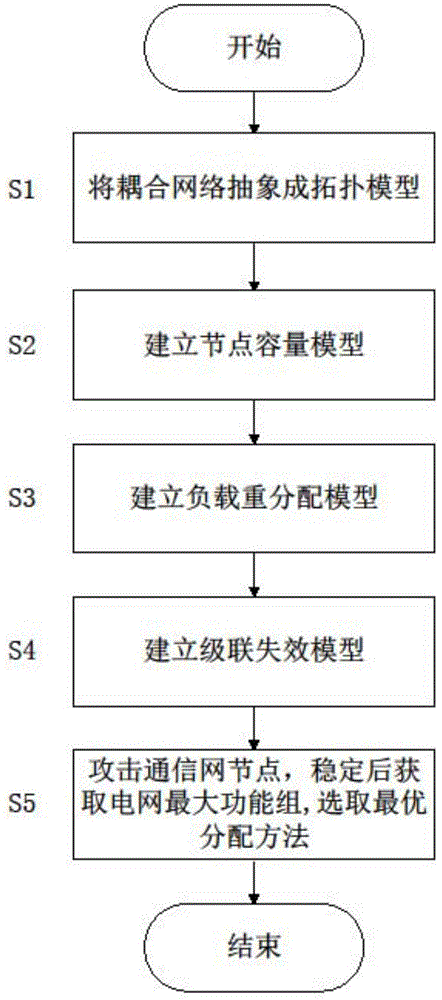
Load redistribution method for electric power coupling network to resist cascade failure
InactiveCN103957032AStrong invulnerabilityPower distribution line transmissionData switching networksCascading failureSocial benefits
The invention discloses a load redistribution method for an electric power coupling network to resist cascade failure. The load redistribution method for the electric power coupling network to resist the cascade failure comprises the steps of abstracting and simplifying equipment in a communication network and a power network as a coupling network topology model; establishing a node capacity model according to the characteristics of the coupling network; establishing a load redistribution model according to a distribution method of loads after node failure; establishing a cascade failure model according to the characteristics of node failure of the coupling network; attacking communications network nodes, obtaining the maximum function set of power grid nodes after the coupling network is stabilized, and selecting the optimal load redistribution method. The method improves the capacity of the electric power coupling network for resisting the cascade failure, is beneficial to reducing maintenance cost, and improves the economic benefits and the social benefits of an electrical power system.
Owner:北京华泽云通网络科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for steering idle mobile stations
ActiveUS7187934B2Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesTelecommunicationsMobile station
Load redistribution and other benefits may be achieved by dynamically distributing or “steering” idle mobile stations to a particular cell or area. For example, idle mobile stations may be steered from a loaded cell to less loaded cells by changing one or more cell broadcast parameters.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
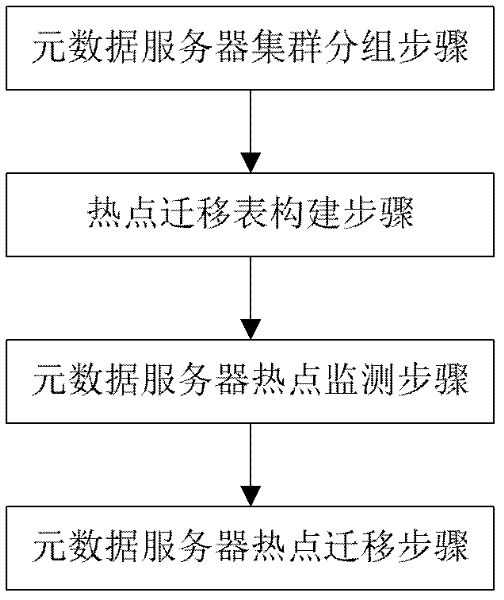
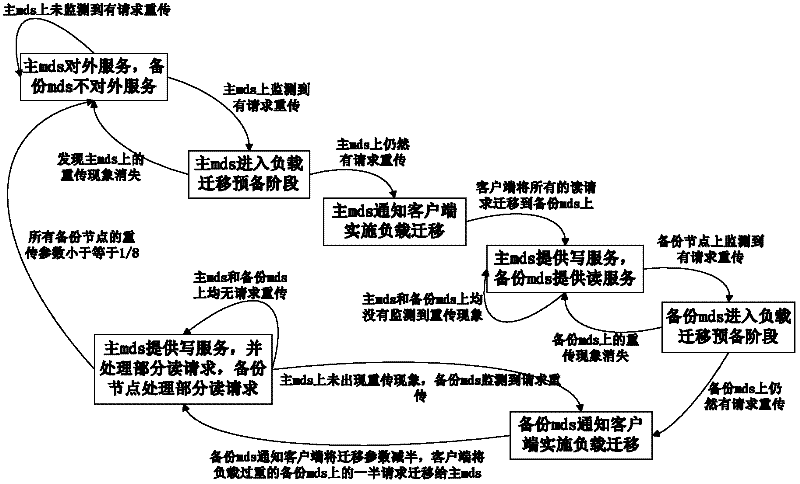
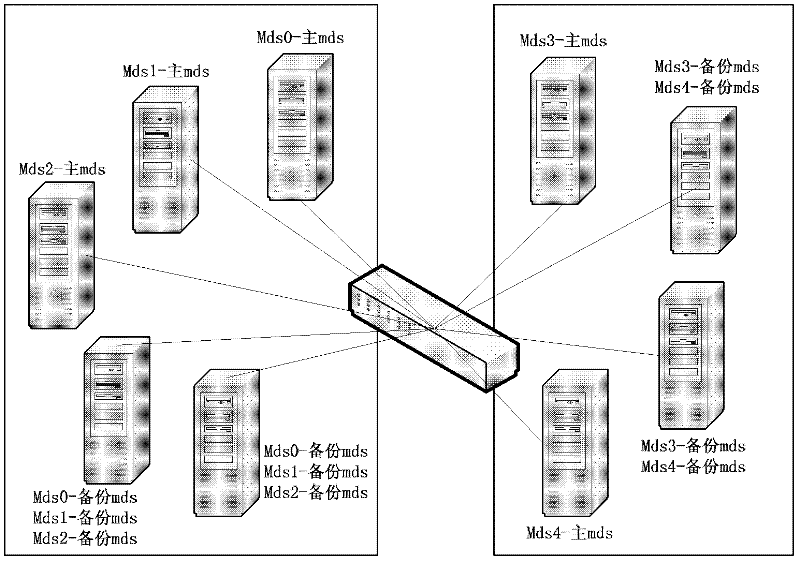
Hot spot balancing method for metadata server
The invention discloses a hot spot balancing method for a metadata server, which is applied in a metadata server cluster. The hot spot balancing method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: (1) dividing the metadata server cluster into a plurality of groups, each of which comprises a plurality of main metadata servers and a plurality of backup metadata servers; (2) constituting a hot spot shifting table on a client to record the information of the main metadata servers and the backup metadata servers when the client is mounted on the main metadata server; (3) monitoring the loading condition of each metadata server to judge whether the metadata server is a query hot spot; (4) and performing hot spot shifting on the corresponding metadata server, namely changing the hot spot shifting table and adjusting the hot spot shifting parameters in the table to lead the client to redistribute request load if the monitored metadata server is the hot spot. With the adoption of the hot spot balancing method provided by the invention, the hot spot problem in the metadata server cluster can be effectively solved, and the hot spot balancing for the whole metadata server cluster can be realized.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
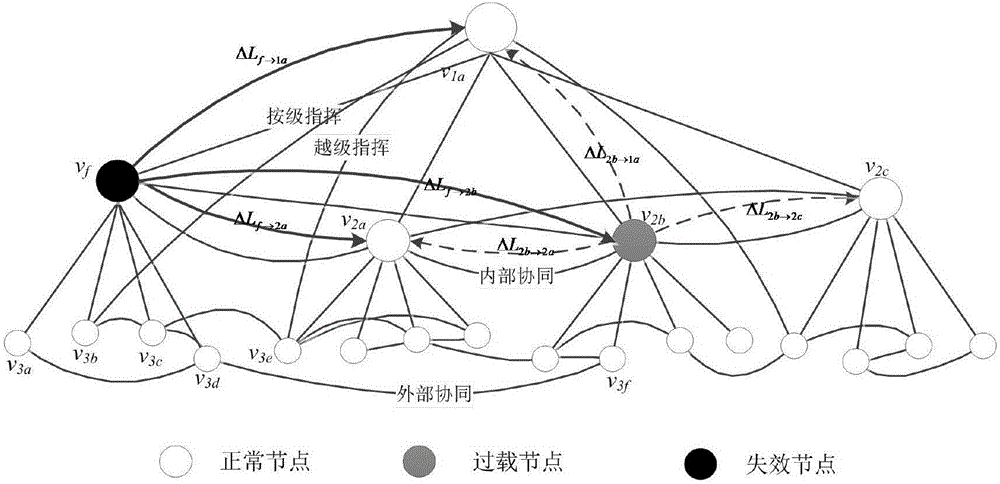
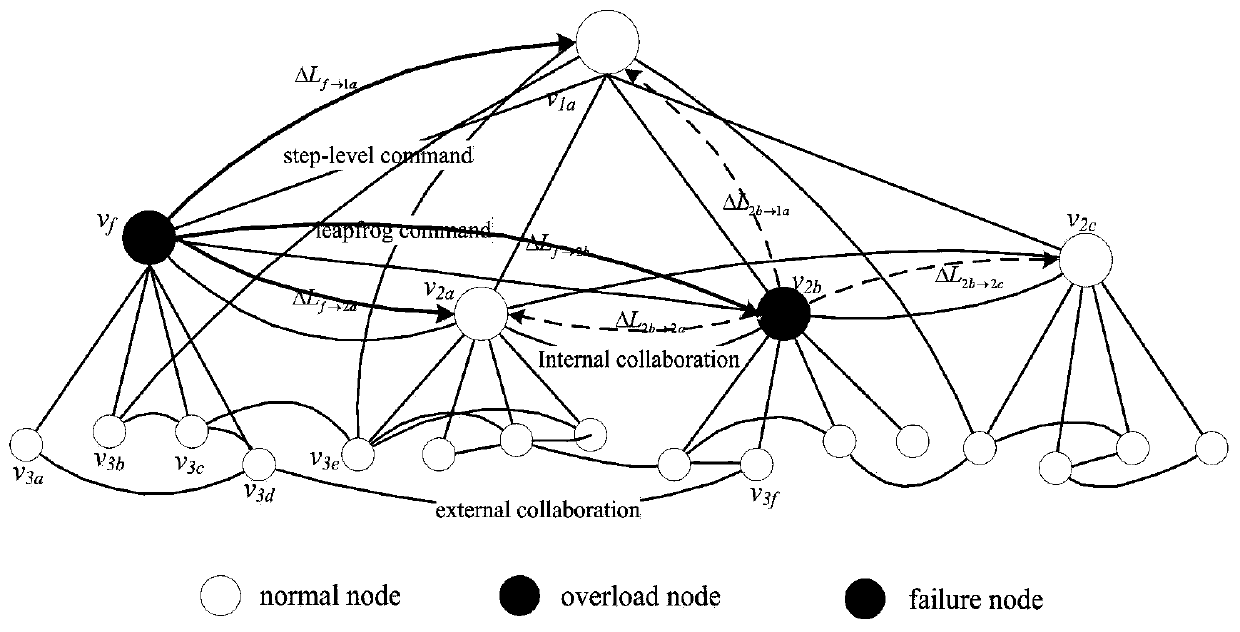
Establishment method of command network cascading failure model having hierarchical structure
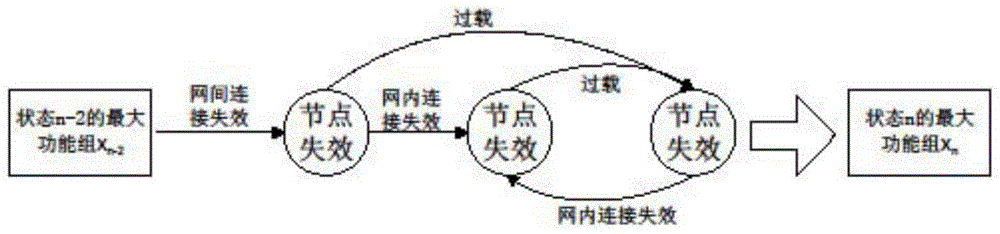
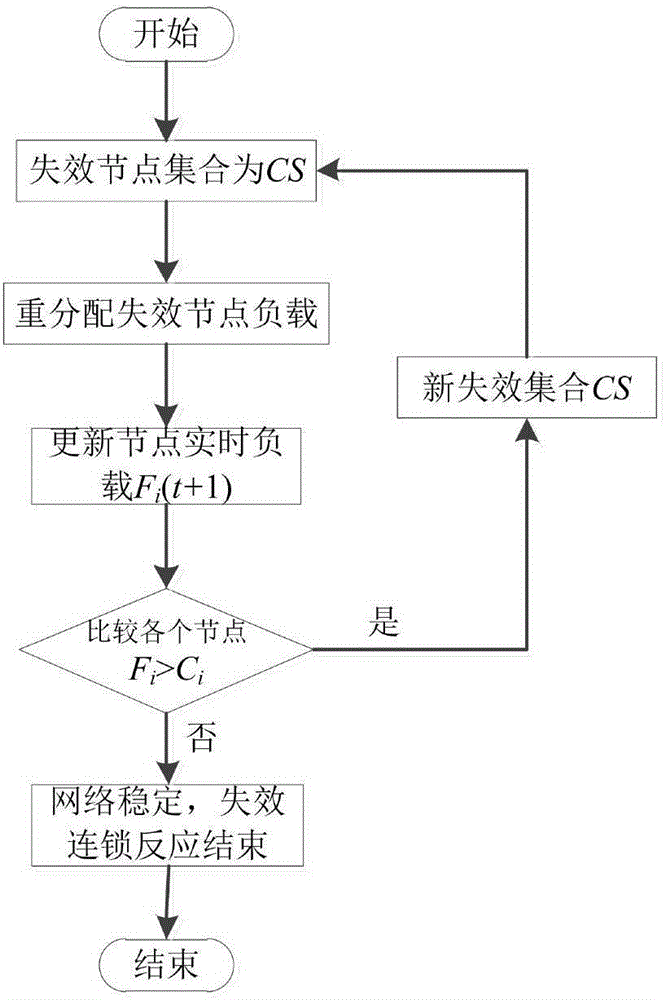
ActiveCN106789376AEffectively analyze the problem of invulnerabilityImprove survivabilityData switching networksCascading failureLoad redistribution
The invention relates to an establishment method of a command network cascading failure model having a hierarchical structure. The method concretely comprises the following steps: S1, defining the initial load and capacity of nodes in a command network; S2, using a command network failure node load redistribution method to update the loads of all the intact nodes in the network for once; S3, evaluating the cascading anti-destruction performance of the command network; S4, establishing the command network cascading failure model; S5, adjusting parameters in the model according to the established cascading failure model, using the provided cascading anti-destruction performance evaluation to estimate the anti-destruction performance of the command network, and enabling the cascading anti-destruction performance of the command network to be optimal. The method combines the hierarchical structure of the command network and takes the strict affiliation in the command network into account, thus being capable of better reflecting the internal mechanism and extrinsic behavior of command network cascading failure effectively and accurately.
Owner:DALIAN UNIVERSITY
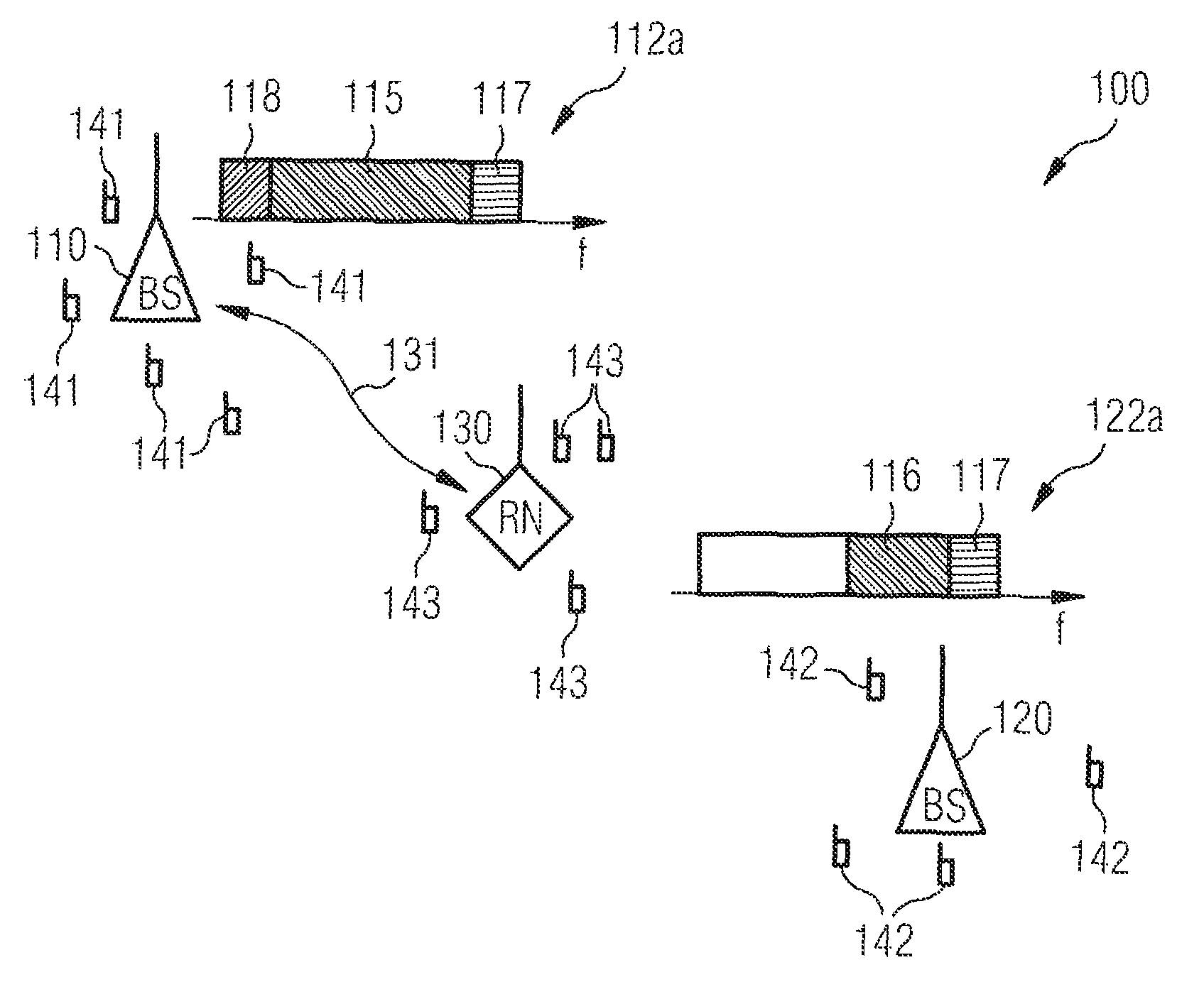
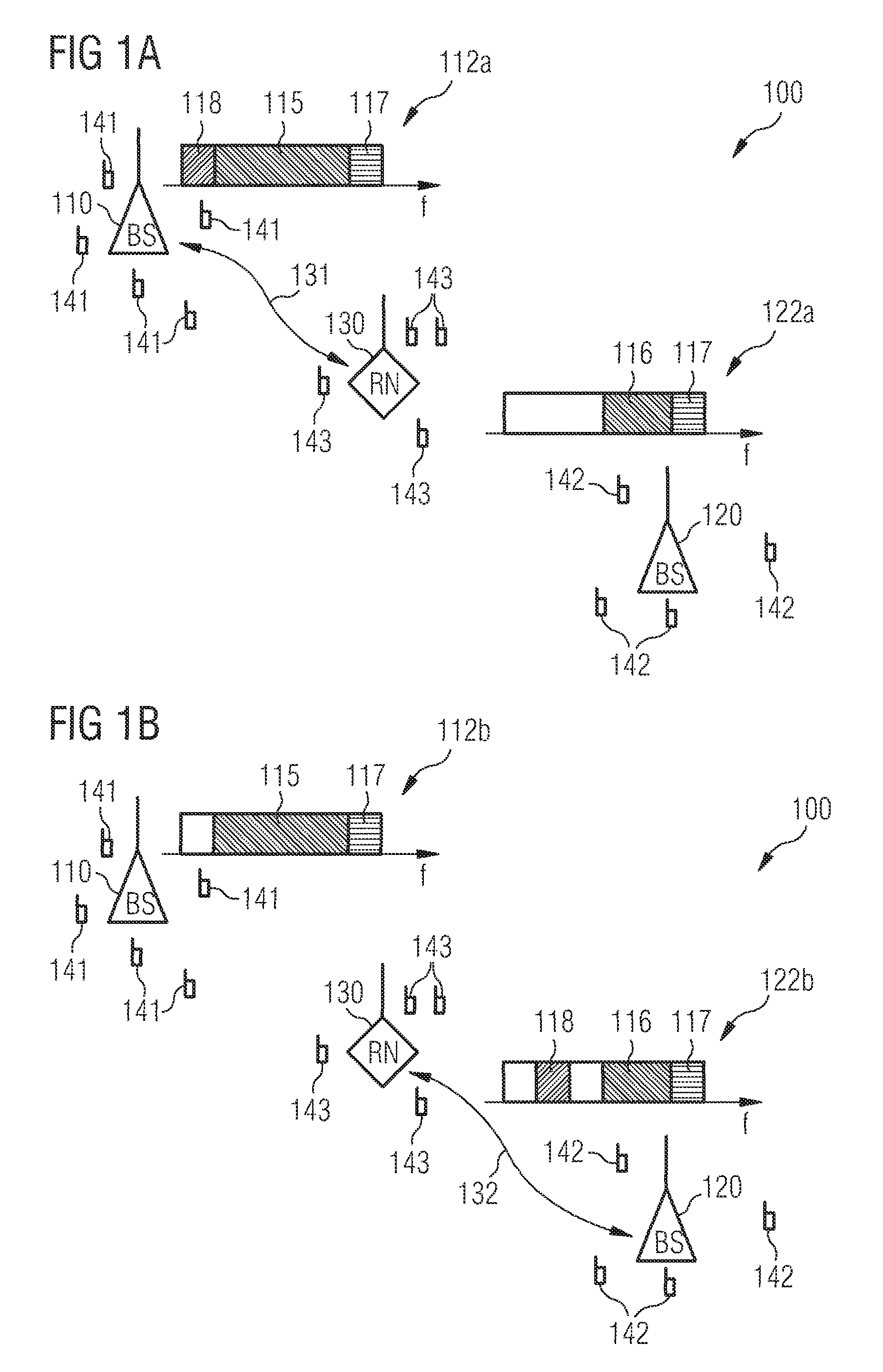
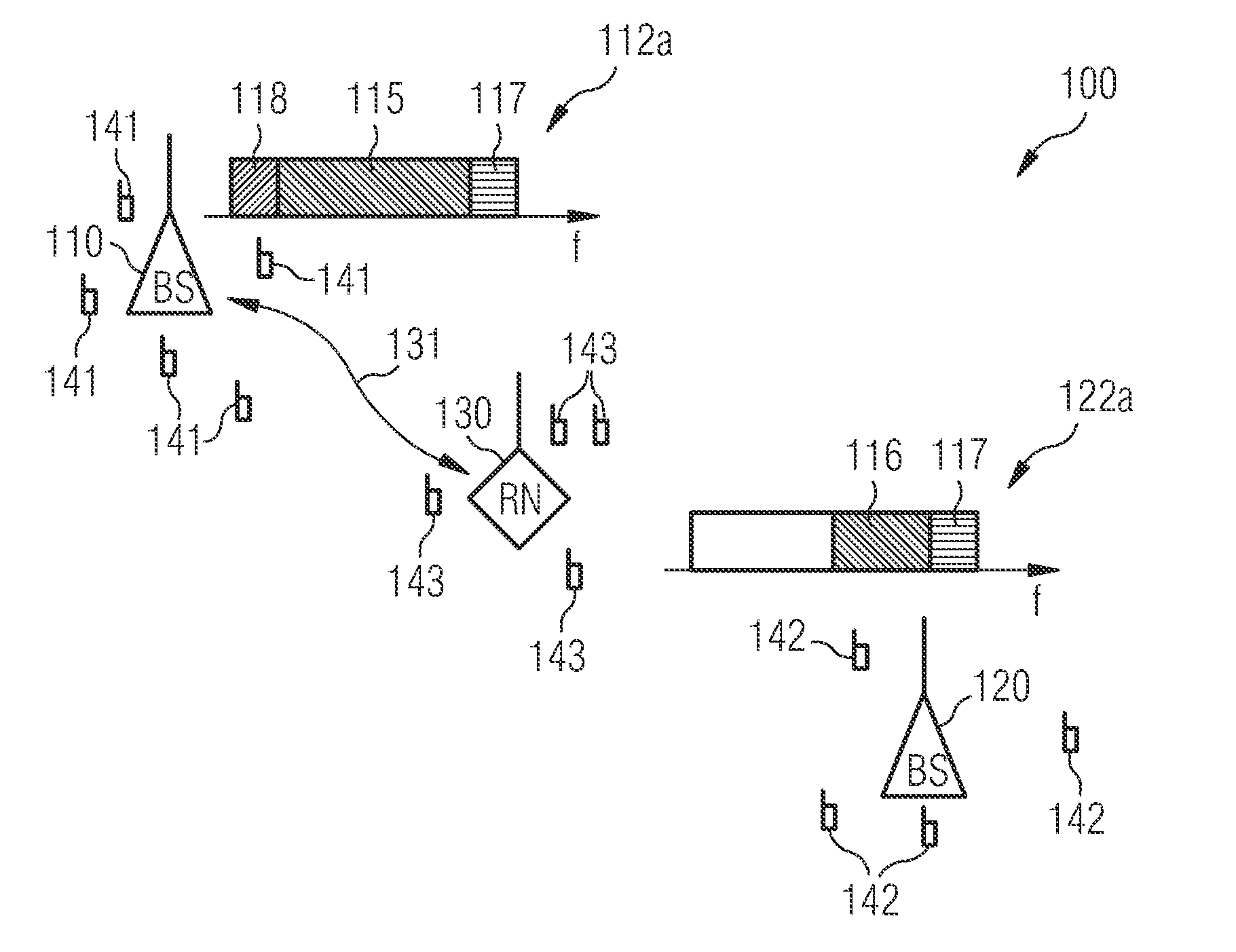
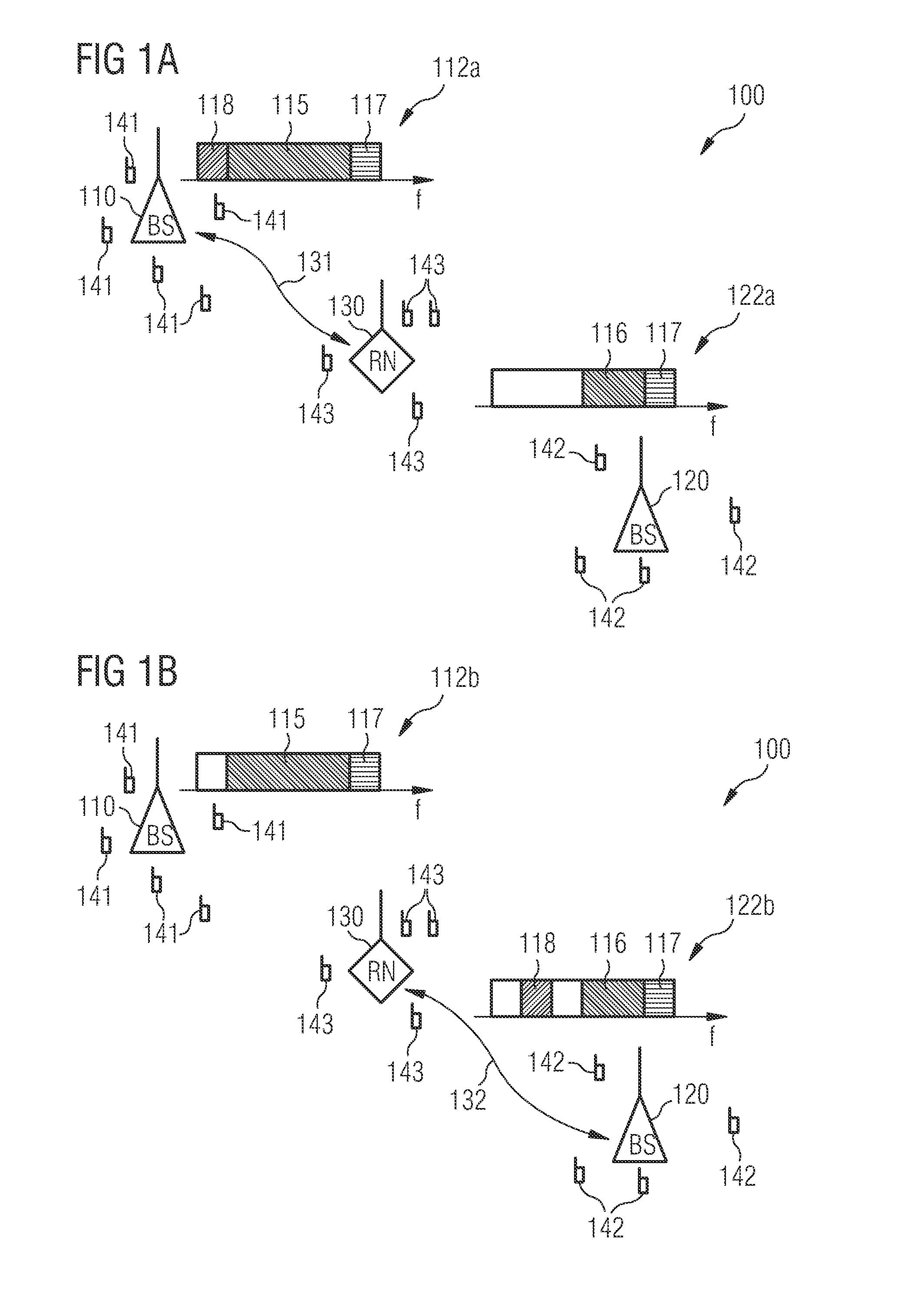
Data load redistribution within a relay enhanced telecommunication network
InactiveUS8811887B2Guaranteed interference effectEasily contributeFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunications networkLoad distribution
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Load redistribution method and system for reducing interference in a wireless network
ActiveUS20060239230A1High bandwidthBalance network loadNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTelecommunicationsDistribution method
A wireless network in which wireless terminals associate with particular access points maintains information about the positions and associations of the terminals and calculates loads on access points. To provide increased bandwidth at a heavily loaded access point, terminals associated with adjacent access points are handed over to more distant access points, so that the adjacent access points become less active and generate less interference. The hand-over is initiated and carried out by the access points concerned, rather than by the terminal that is handed off. Loads can accordingly be balanced promptly and interference can be reduced.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
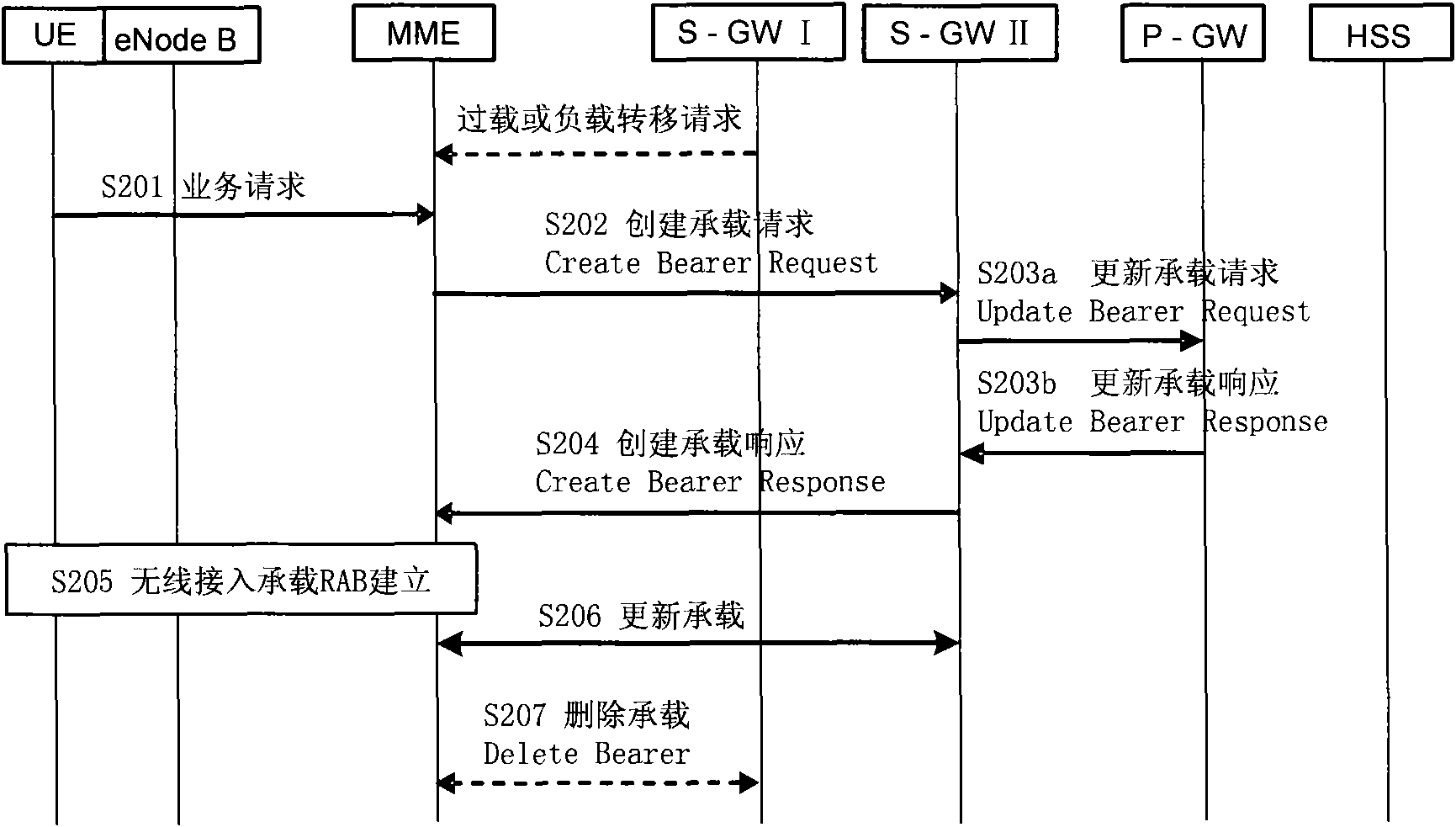
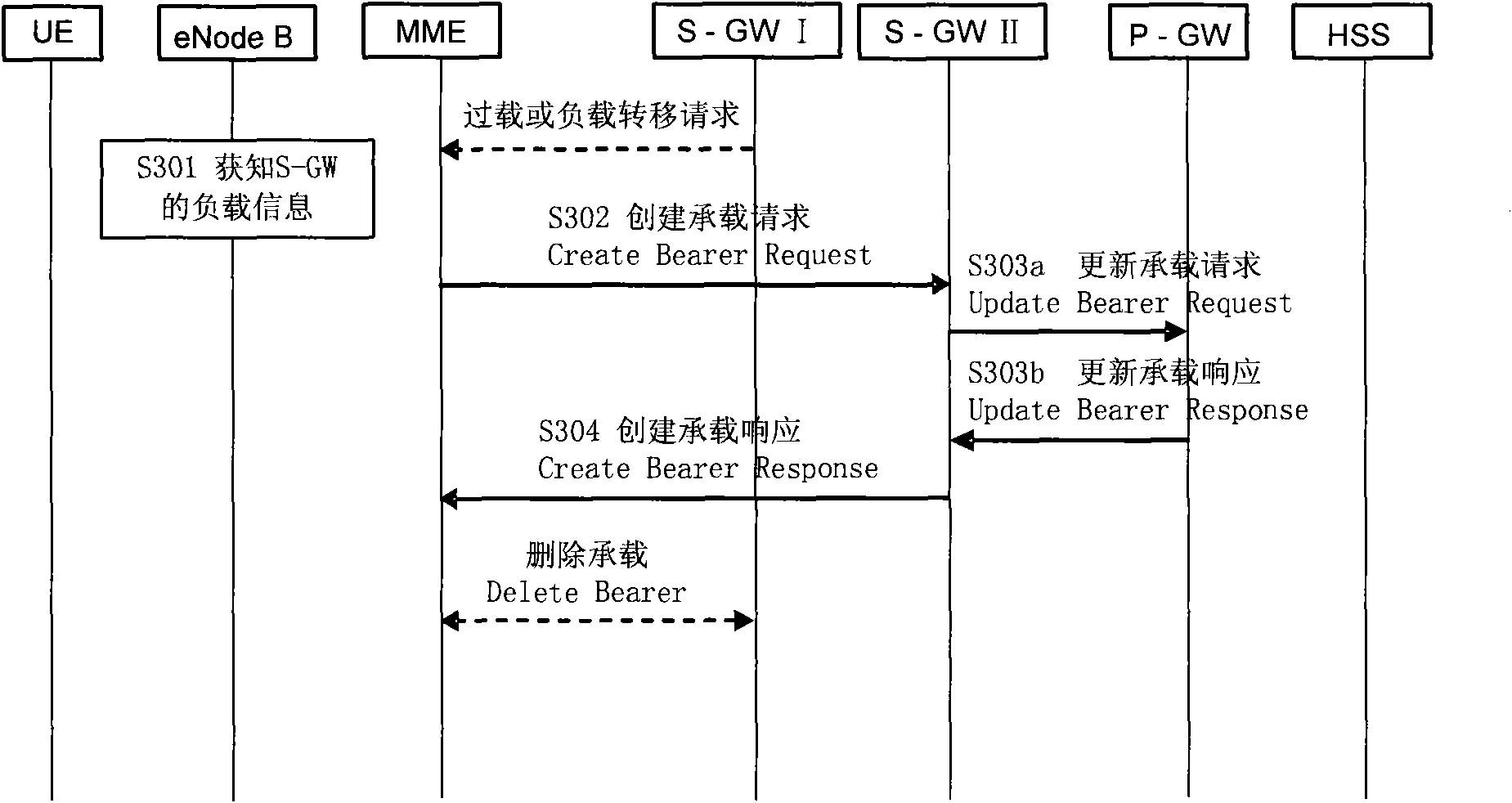
Method and device for realizing load transfer
ActiveCN101686498APrevent overloadEasy to operateNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksComputer networkService gateway
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for realizing load transfer, which comprises the following steps: receiving the overload information or a load transfer request of a first service gateway; transferring user equipment (UE) to a second service gateway which is not overloaded, and establishing bearing between the UE and the second service gateway; and updating the corresponding bearing information between the second service gateway and a corresponding packet data network gateway. According to the embodiment of the invention, a novel service gateway is selected to the UE to be transferred when a condition that the load of the service gateway needs to be transferred is judged, and the corresponding bearing of the novel service gateway is established so as to complete transferring. Thus, by the load redistribution of user face nodes, the load transfer on the service gateway is realized, the overload of the service gateway is avoided, and the maintenance operation and the management are convenient.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for reducing power dissipation in a multi-processor system
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
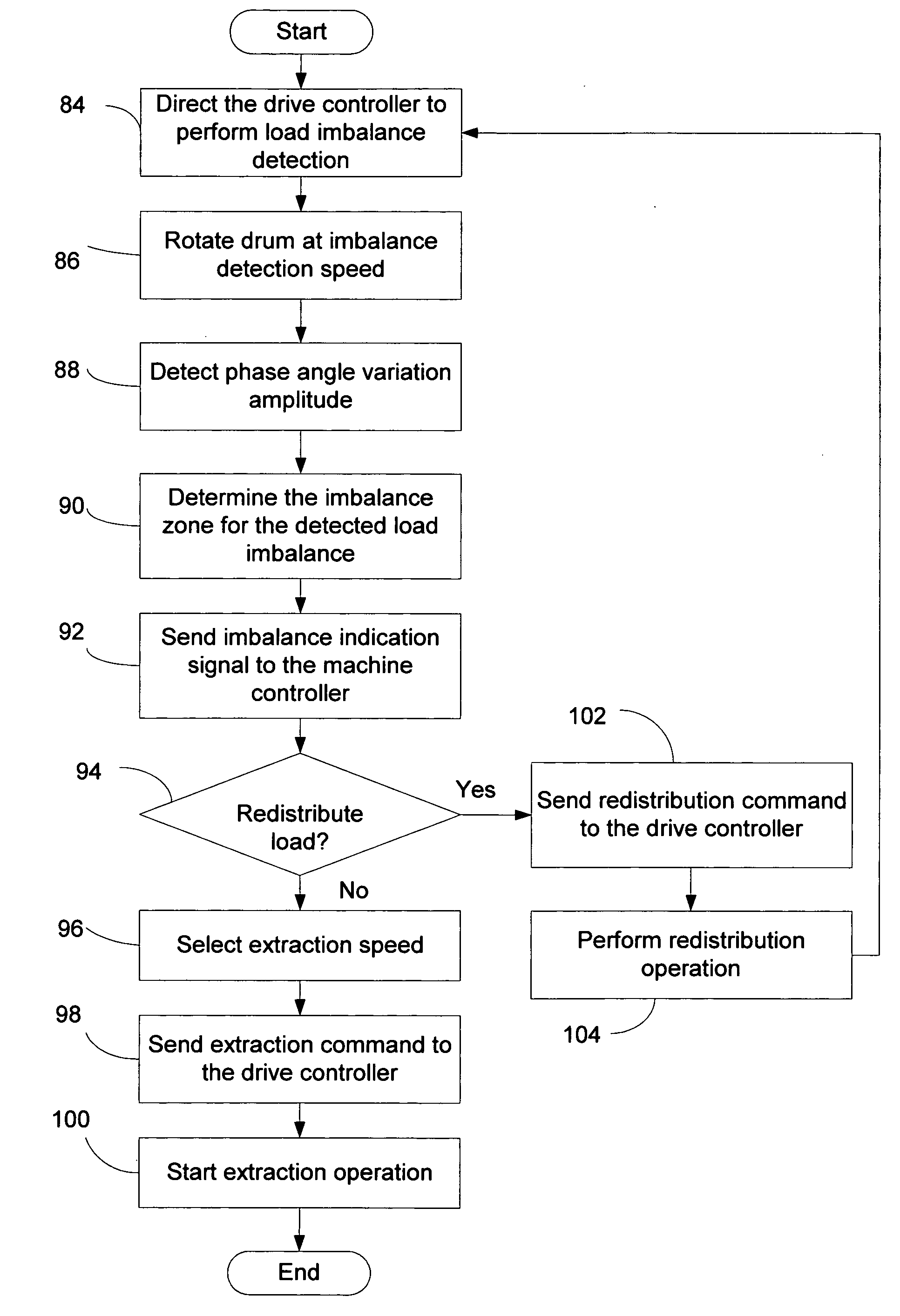
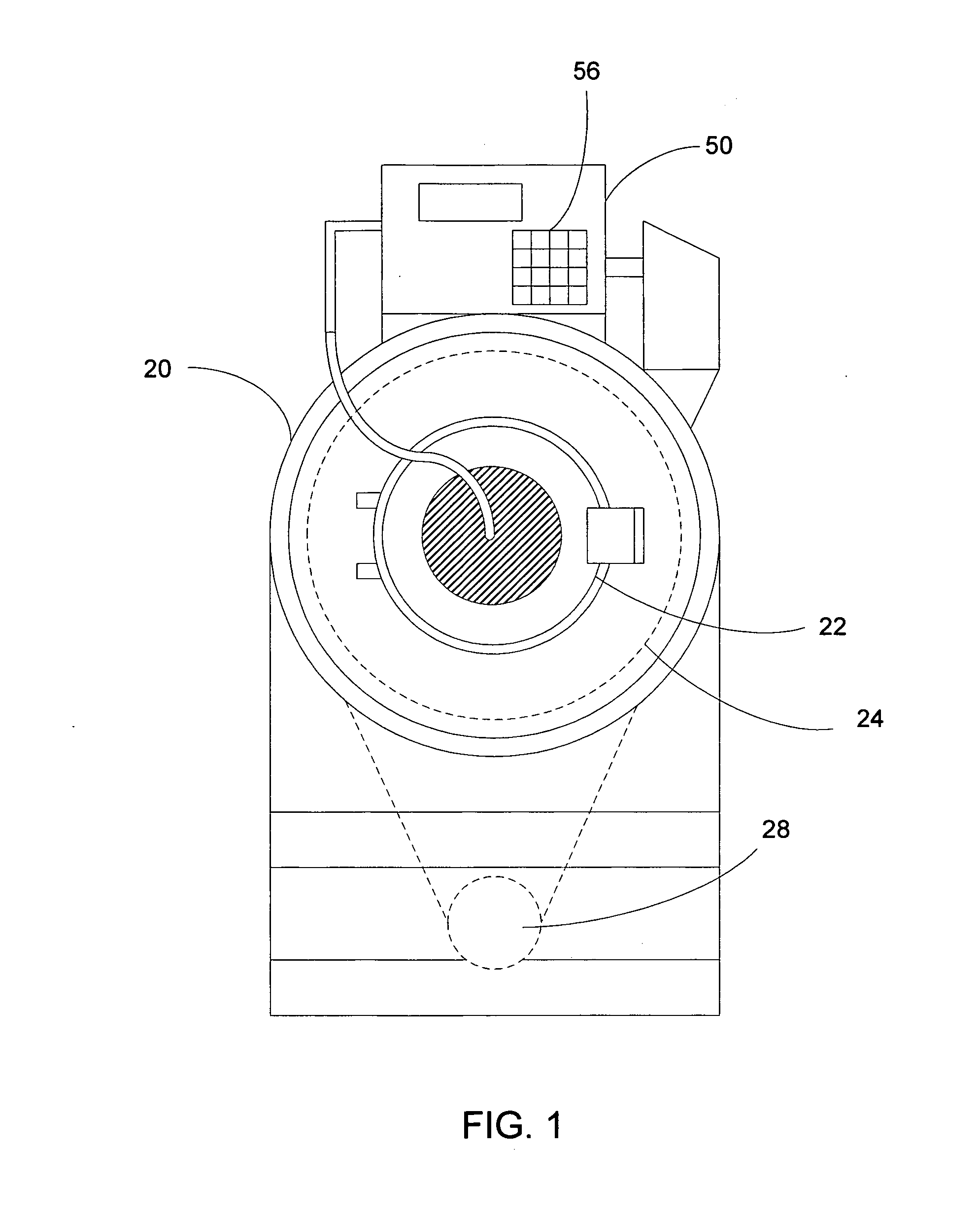
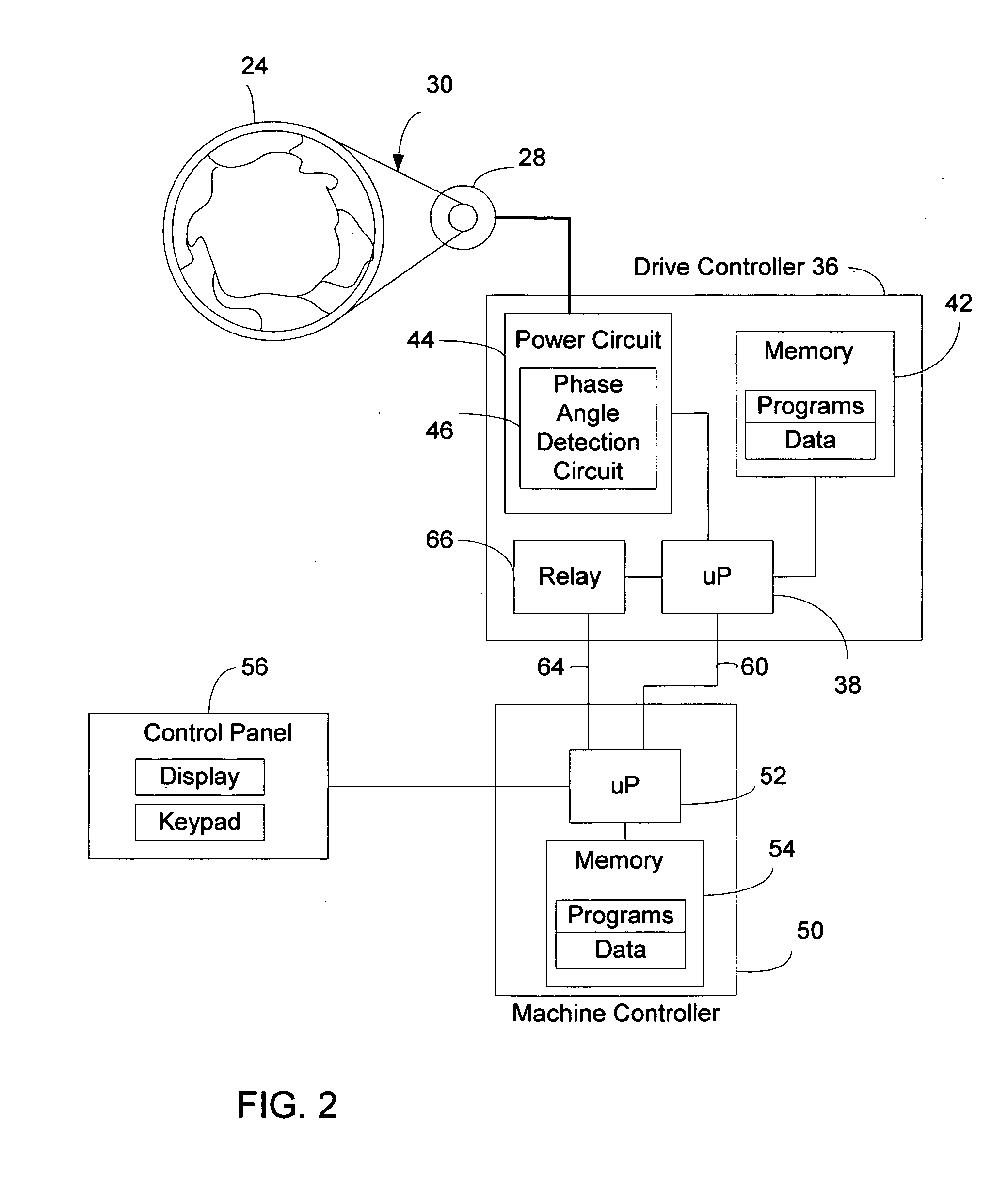
Laundry machine control system for load imbalance detection and extraction speed selection
ActiveUS20070294838A1Avoid severe damageSevere mechanical stressOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusDriving currentLaundry washing machine
A control system for a laundry washing machine with a horizontal wash drum detects load imbalance in the drum and selects a proper rotation speed for the drum in a water extraction operation. A drive controller for the motor turning the drum detects a phase angle variation in the drive voltage and drive current applied to the motor as an indication of the load imbalance in the drum, and determines whether the detected load imbalance falls in one of a plurality of pre-defined load-imbalance zones. The drive controller then provides a signal indicating the detected imbalance zone to a machine controller of the washing machine. The machine controller selects a proper rotation speed for the extraction operation based on the detected imbalance zone, or alternatively initiates a load-redistribution operation to reduce the load imbalance.
Owner:ALLIANCE LAUNDRY SYSTEMS
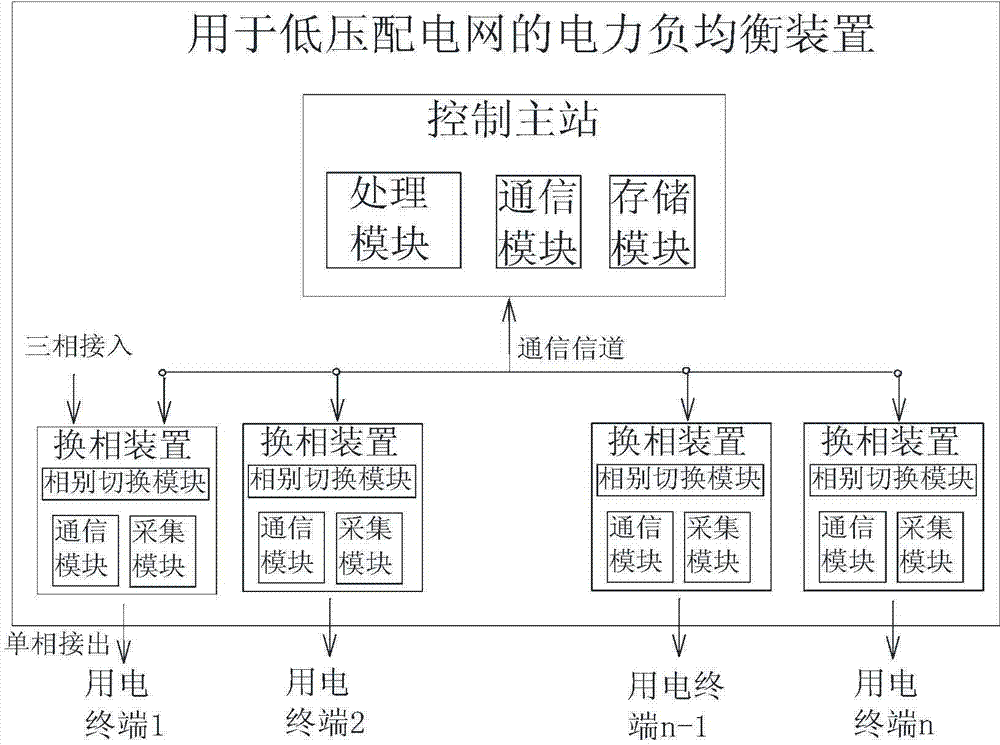
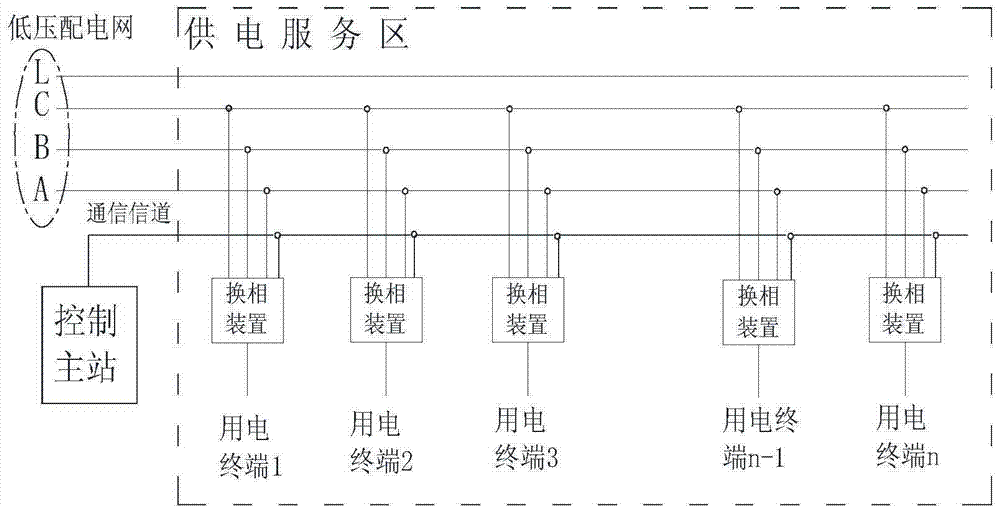
Power load balancing method and device for low-voltage power distribution network
InactiveCN104852396AAchieve three-phase load balancingImprove the quality of power supplyPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionPolyphase network asymmetry reductionPhase conversionElectricity
The invention discloses a power load balancing method and device for a low-voltage power distribution network. According to the method, the distribution condition of the load of electricity utilization terminals on three-phase lines of the low-voltage power distribution network is monitored in real time; when the distribution of the load of the electricity utilization terminals on the three-phase lines is uneven, and three-phase load unbalance is brought about; and the distribution of the load of the electricity utilization terminals between three phases of the low-voltage power distribution network is automatically adjusted, so that the load of the electricity utilization terminals can be evenly distributed on the three-phase lines, and therefore, three-phase load balance of the low-voltage power distribution network can be realized. The device includes phase conversion devices and a control master station; the phase conversion devices are arranged user ends; the electricity utilization terminals are connected into the low-voltage power distribution network through the phase conversion devices; and the control master station is used for dynamically controlling phase connection of the phase conversion devices, so that the load of the electricity utilization terminals can be evenly distributed on the three-phase lines of the low-voltage power distribution network. With the power load balancing method and device of the invention adopted, the load connected into the low-voltage power distribution network can be re-distributed on each phase with continuous power supply ensured, and the three-phase load balance of the low-voltage power distribution network can be realized, and line loss can be reduced, and power supply quality can be improved.
Owner:中能合湖南科技有限公司
Method and means for redistribution of subscriber information in UMTS networks where the nodes are arranged in pools
InactiveUS7054629B2Limited amountRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesLoad redistributionCore network
The present invention relates to method and means for a system initiated subscriber information redistribution in order to achieve a load redistribution within a pool of core network nodes. The subscribers, that are affected by the redistribution, are determined by the bit values in their TMSI's. These specific TMSI's are then arranged to be treated as invalid by the cellular system. Messages etc. from subscribers with invalid TMSI's will be “trapped” in the cellular system and the subscriber information that belongs to these subscribers will be redistributed to new core network nodes.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Overload processing method and system for mobility management entity
InactiveCN102811462ANormal service accessNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionLoad redistributionMobility management
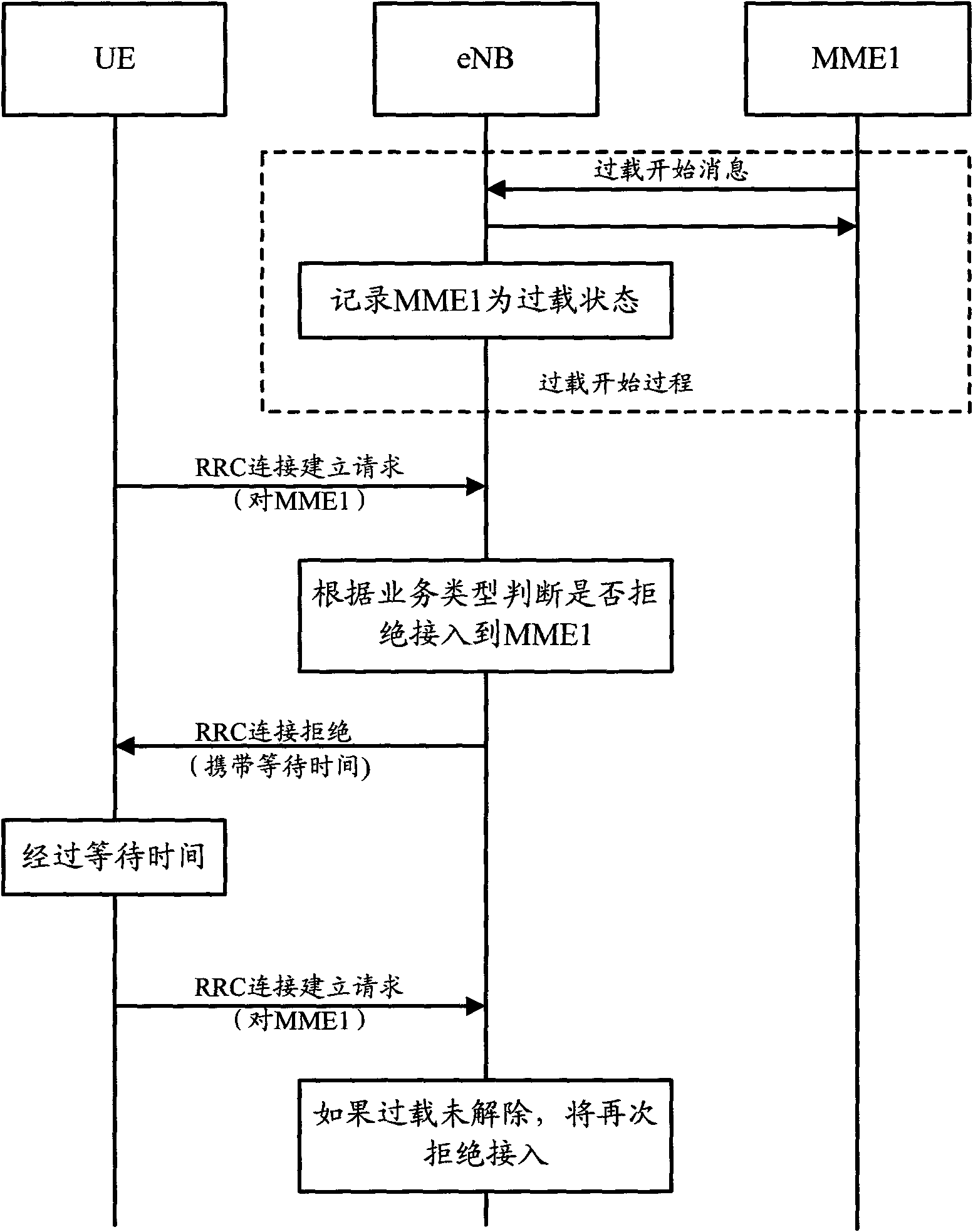
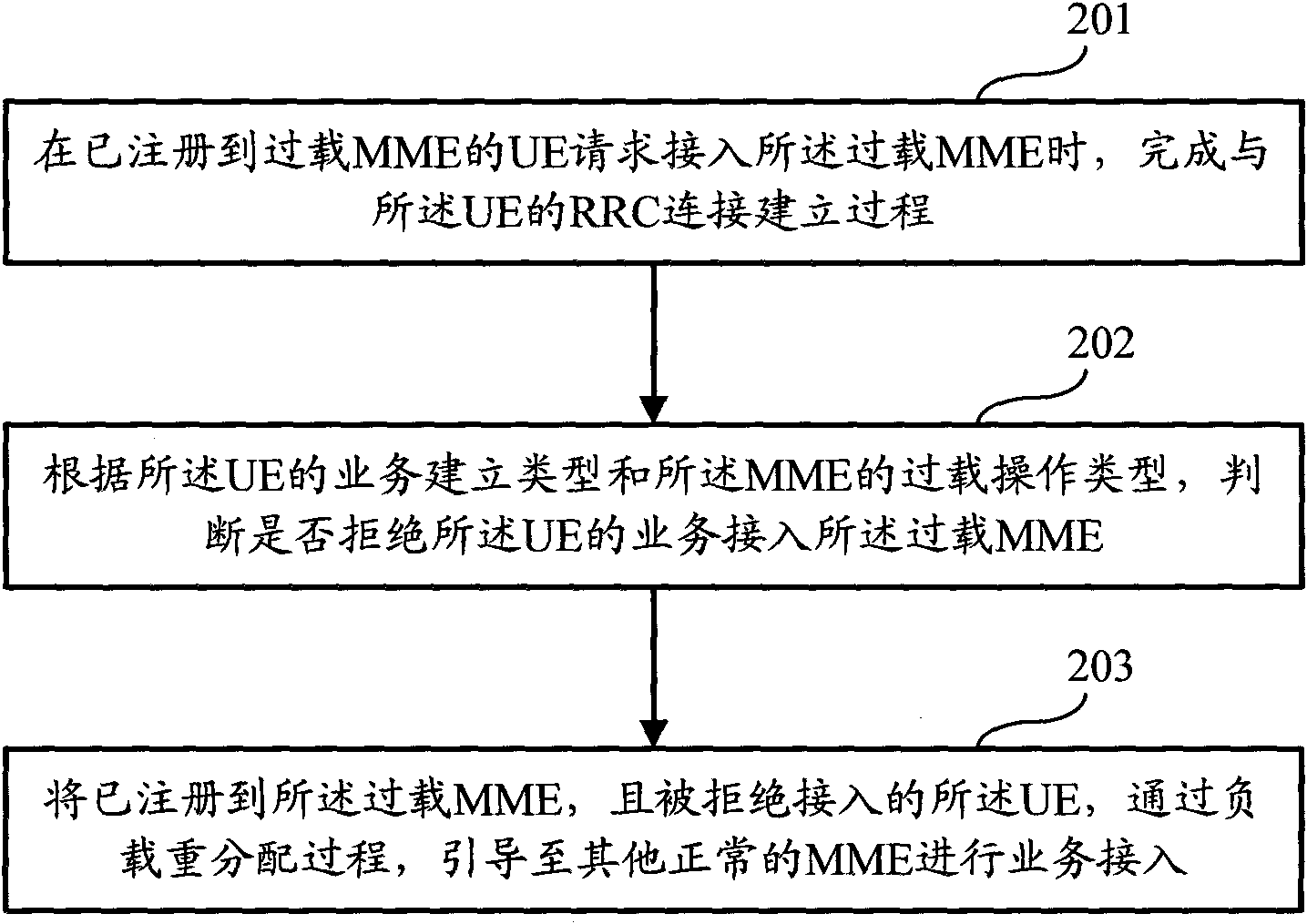
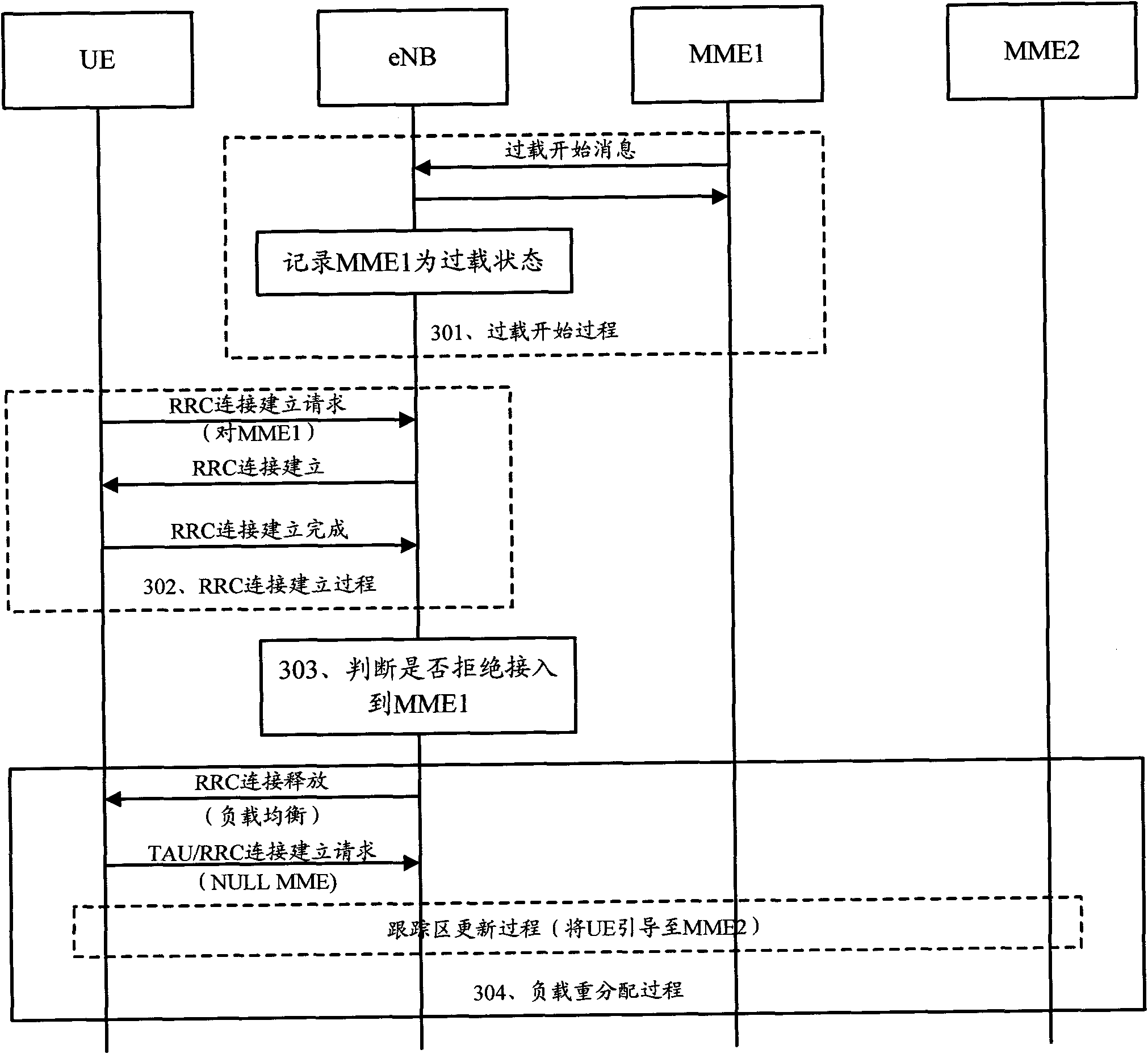
The invention discloses an overload processing method for a mobility management entity, the method comprises the following steps: when UE (user equipment) registered in the overload MME (mobility management entity ) requests to access the overload MME, completing an establishing process of RRC (radio resource control) with the UE; establishing types and overload operation types of the MME according to business of the UE, and judging whether to reject the business of the UE accessing the overload MME or not; guiding the UE which has registered in the overload MME and is rejected accessing the UE to other normal MMEs to carry out business access by a process of load redistribution. The invention further discloses an evolution base station, by adopting the method and the base station, the UE registered in the overload MME can still carry out normal business access when the MME is overloaded.
Owner:POTEVIO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
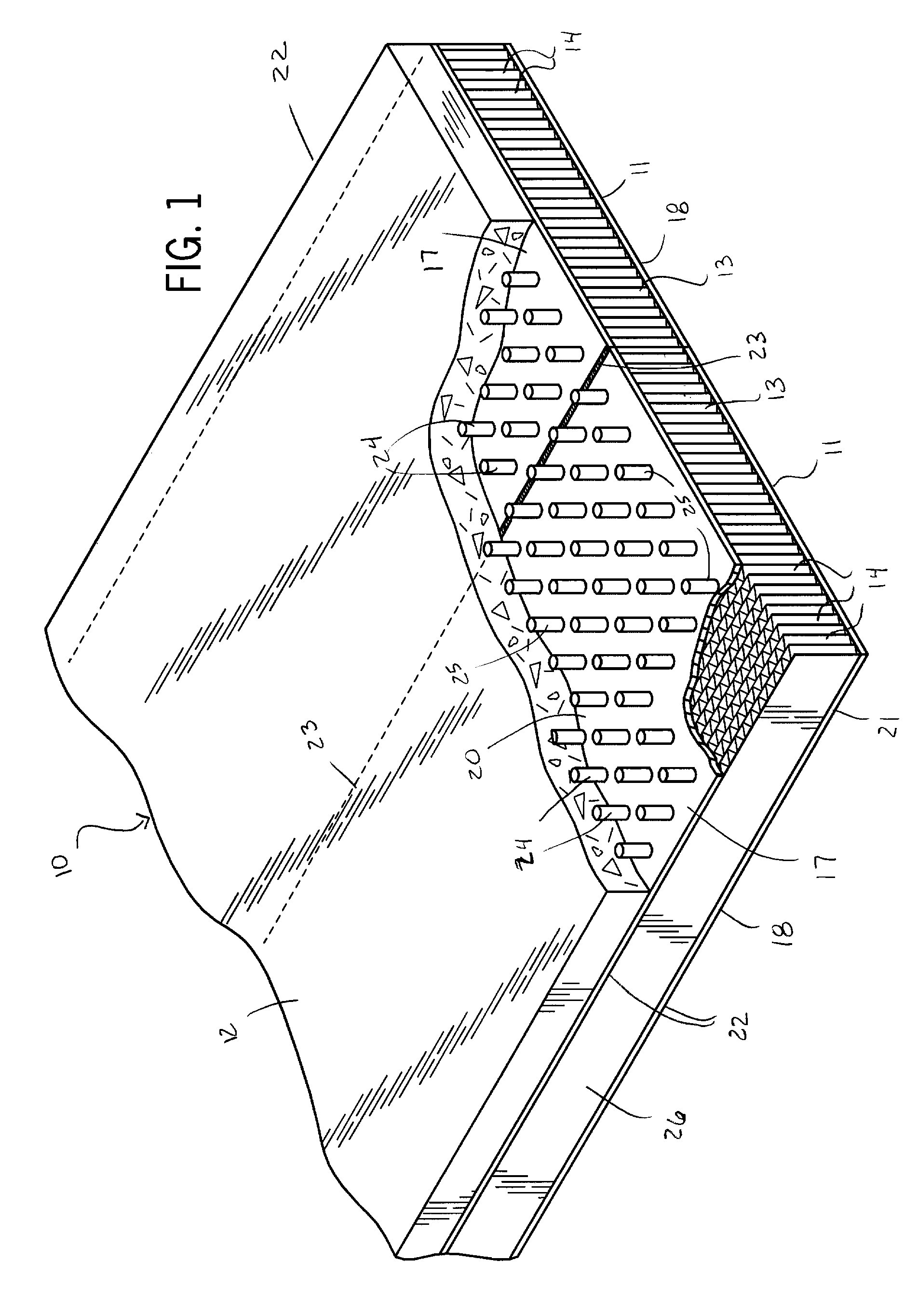
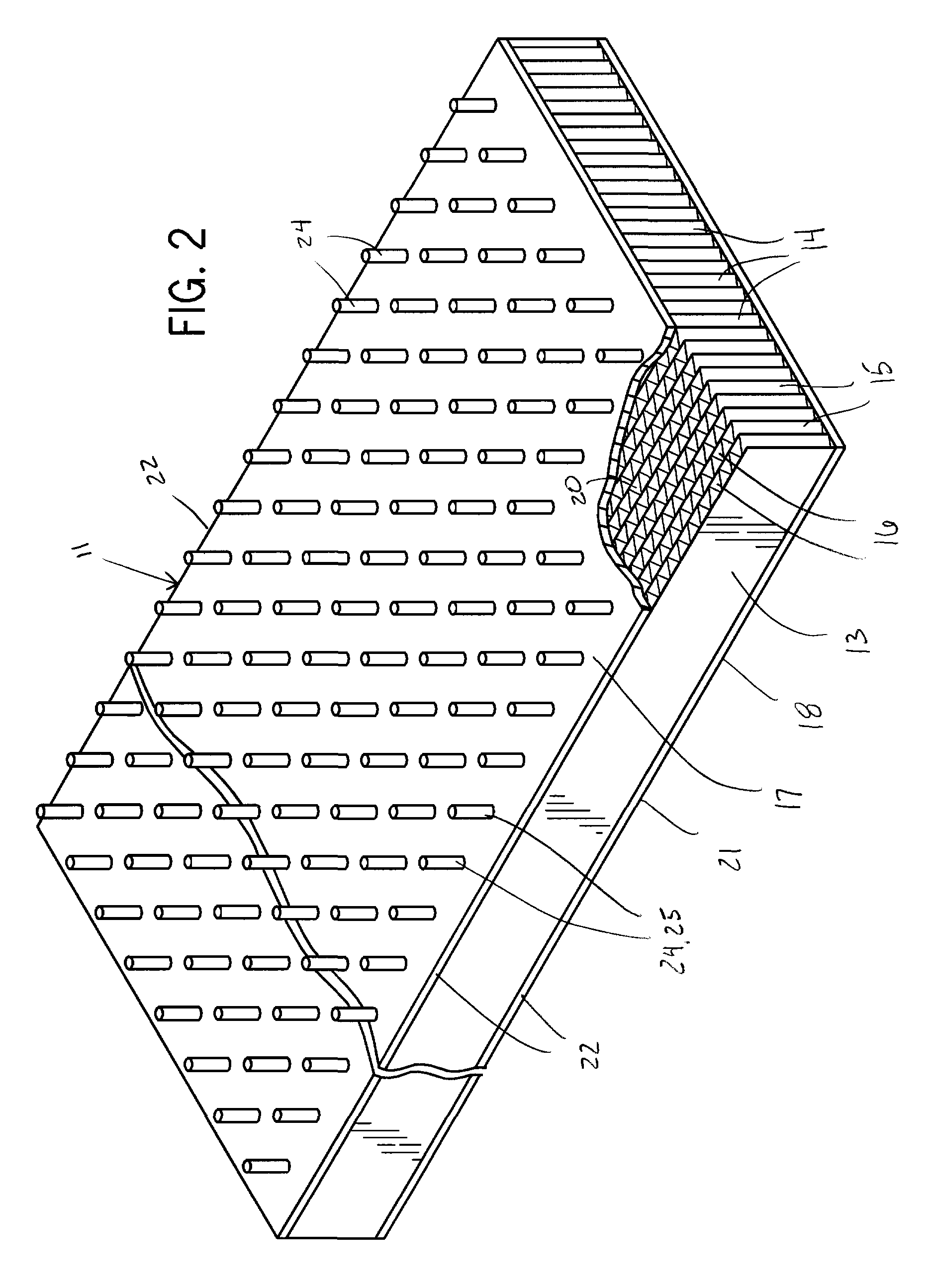
Hollow Core Floor and Deck Element
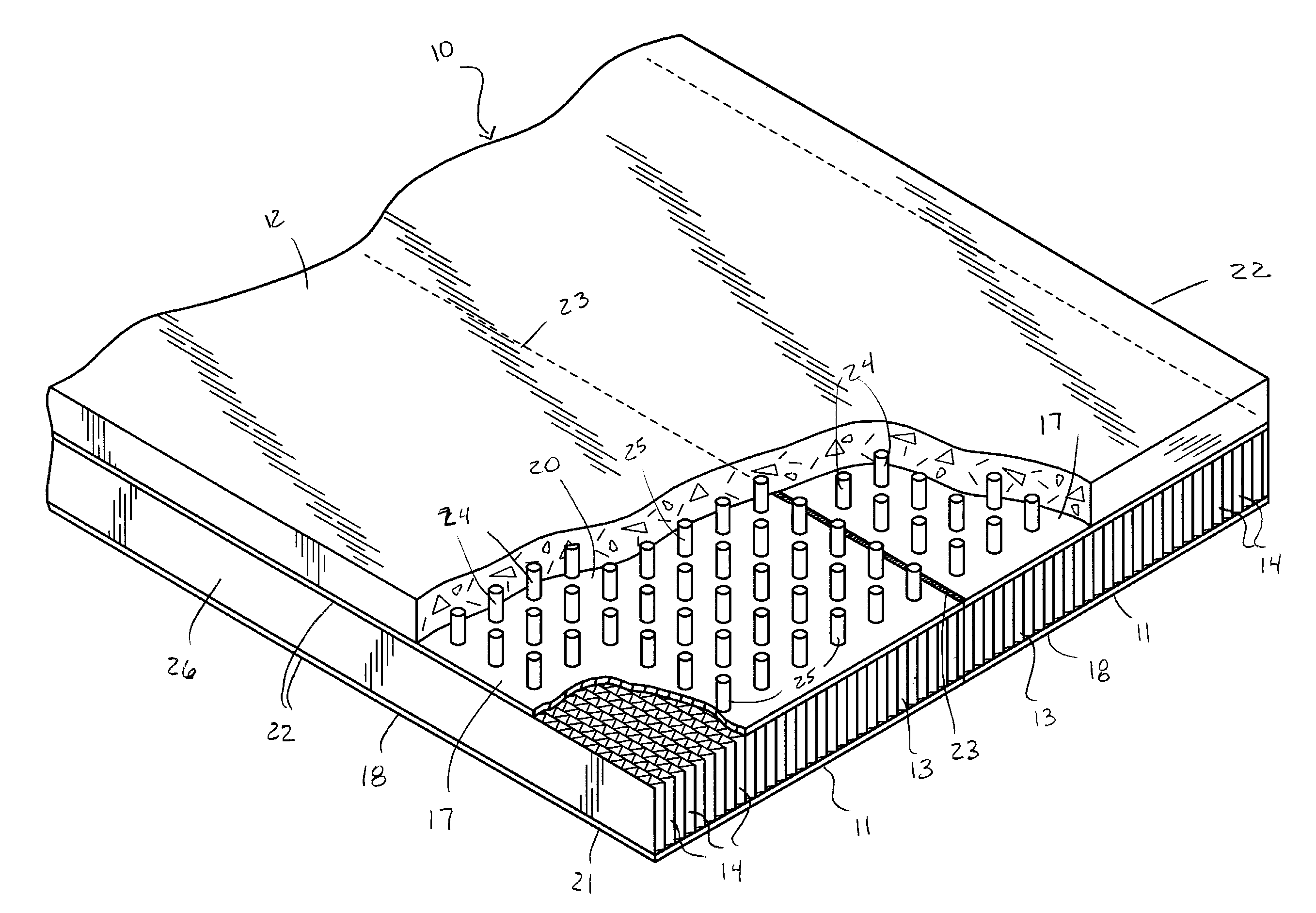
InactiveUS20080010943A1Improve carrying capacityOvercome biasConstruction materialFloorsHorizontal stressFloor slab
A stress-optimized structural support which may be utilized as a beam or assembled with similar supports to form a building floor or roof panel or a bridge deck utilizes an open core element, made preferably of suitably treated fluted paper, upper and lower thin skin sheets, preferably steel skins, and a layer of concrete poured over the top skin. Modules comprising the hollow core element and the upper and lower skin sheets are fabricated to lengths required for building floor, roof or bridge spans and, when joined by welding or otherwise joining the upper and lower skin sheets of adjacent elements along their full lengths, provide a floor or roof deck structure of a large span with horizontal stresses distributed omnidirectionally. A post-stressing tensile system redistributes and reduces the load on the roof deck by about one-half. Small building decks utilizing the stress redistribution system can be combined to build a large span roof in which multiple tensioning systems are coordinated to simultaneously effect the load redistribution.
Owner:MARSCHKE CARL R
Data Load Redistribution Within a Relay Enhanced Telecommunication Network
InactiveUS20110223854A1Guaranteed interference effectEasily contributeNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTelecommunications networkLoad distribution
It is described a method for changing the data load distribution within a telecommunication network comprising including a first base station, a second base station and a relay node being connected to the first base station and / or to the second base station. The described method includes (a) establishing for each of a plurality of user equipments a first indirect connection to the first base station via the relay node, (b) establishing in a collective manner for each of the plurality of user equipments a second indirect connection to the second base station via the relay node, and (c) terminating in a collective manner for each of the plurality of user equipments the first indirect connection. It is further described a network element, which is adapted to carry out the above described data load redistribution method, and a computer program, which is adapted for controlling the above described data load redistribution method.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
A method for reallocating load
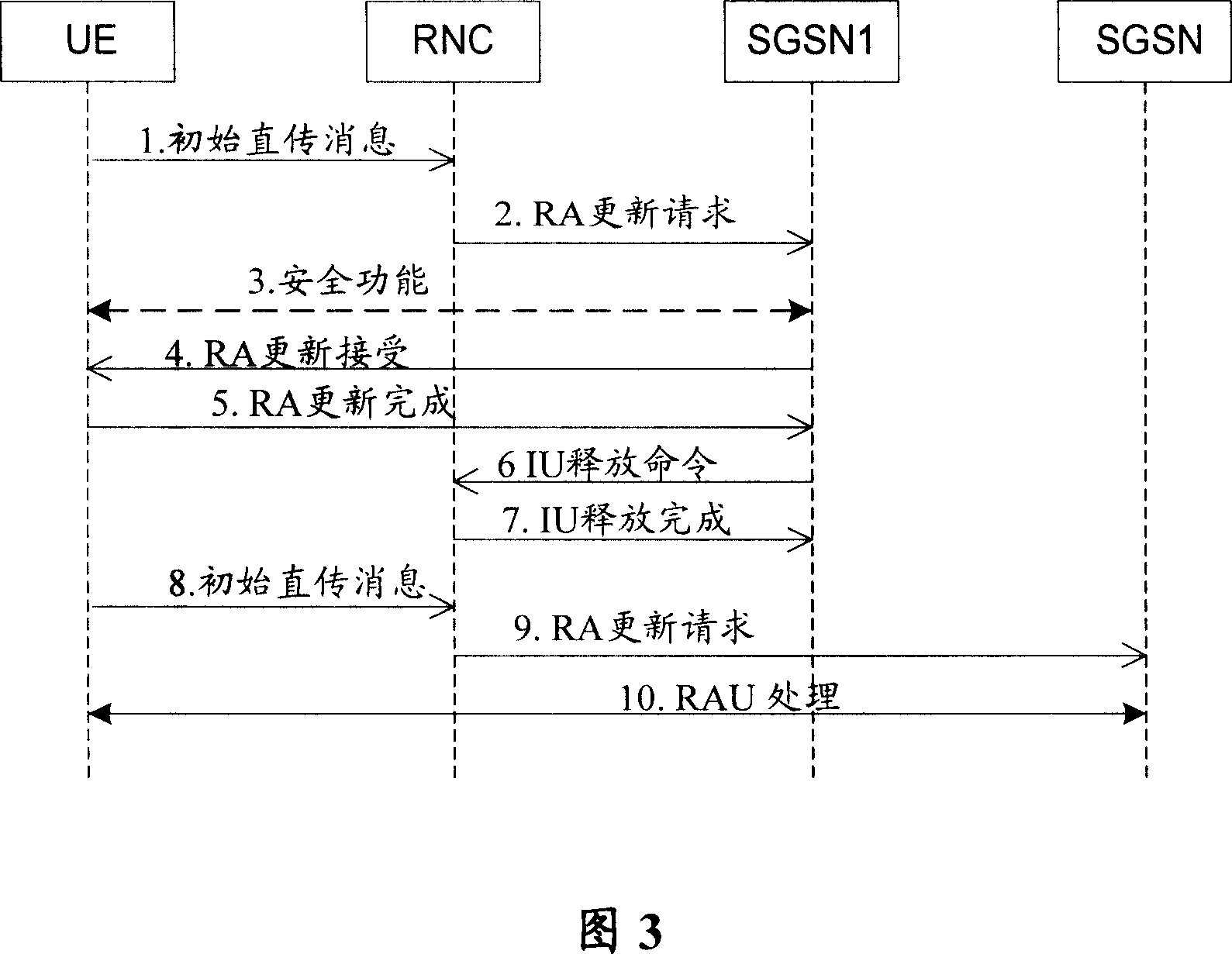
ActiveCN101146316ASave resourcesImprove the efficiency of load redistributionNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsLoad redistributionParameter Type
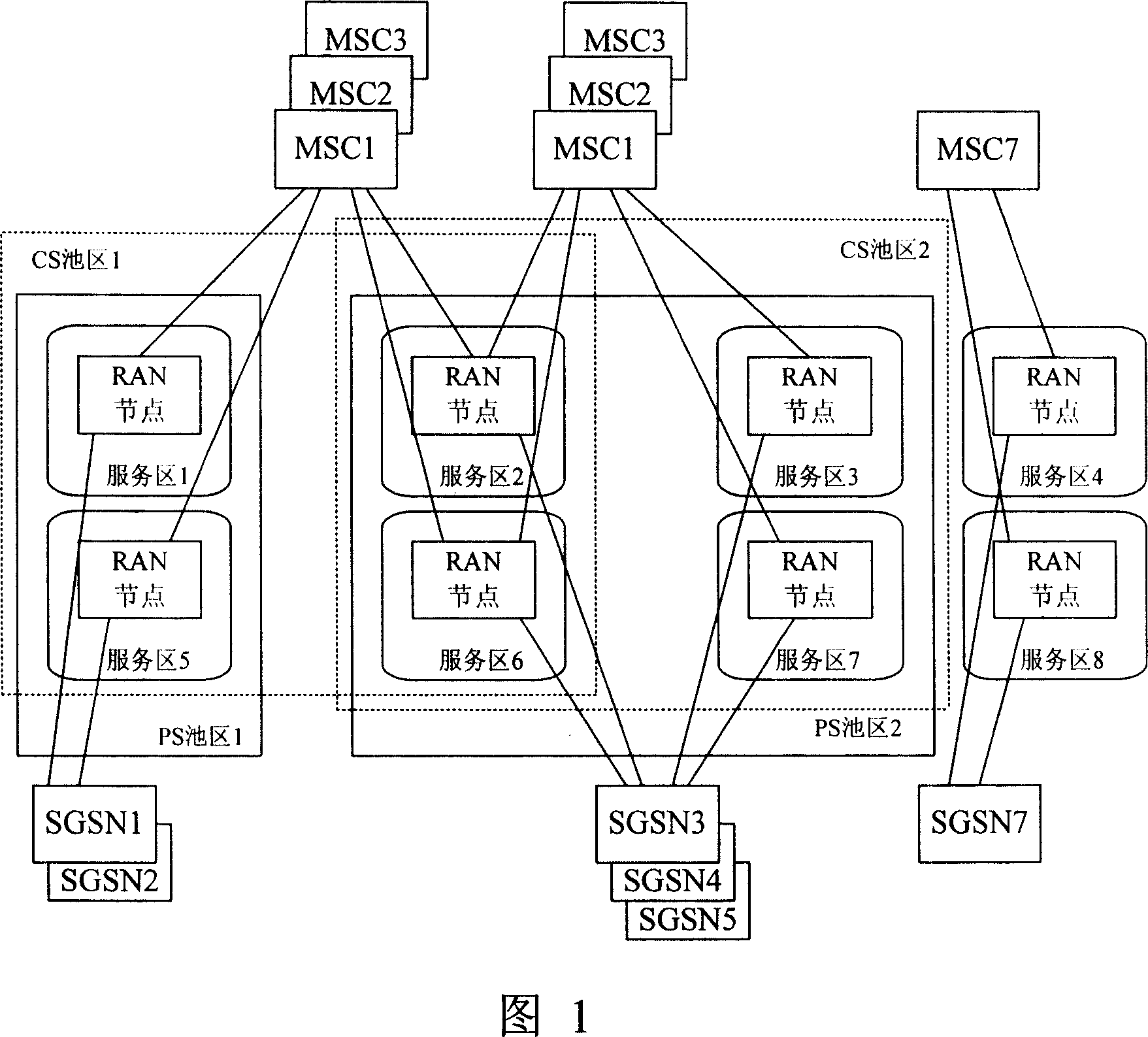
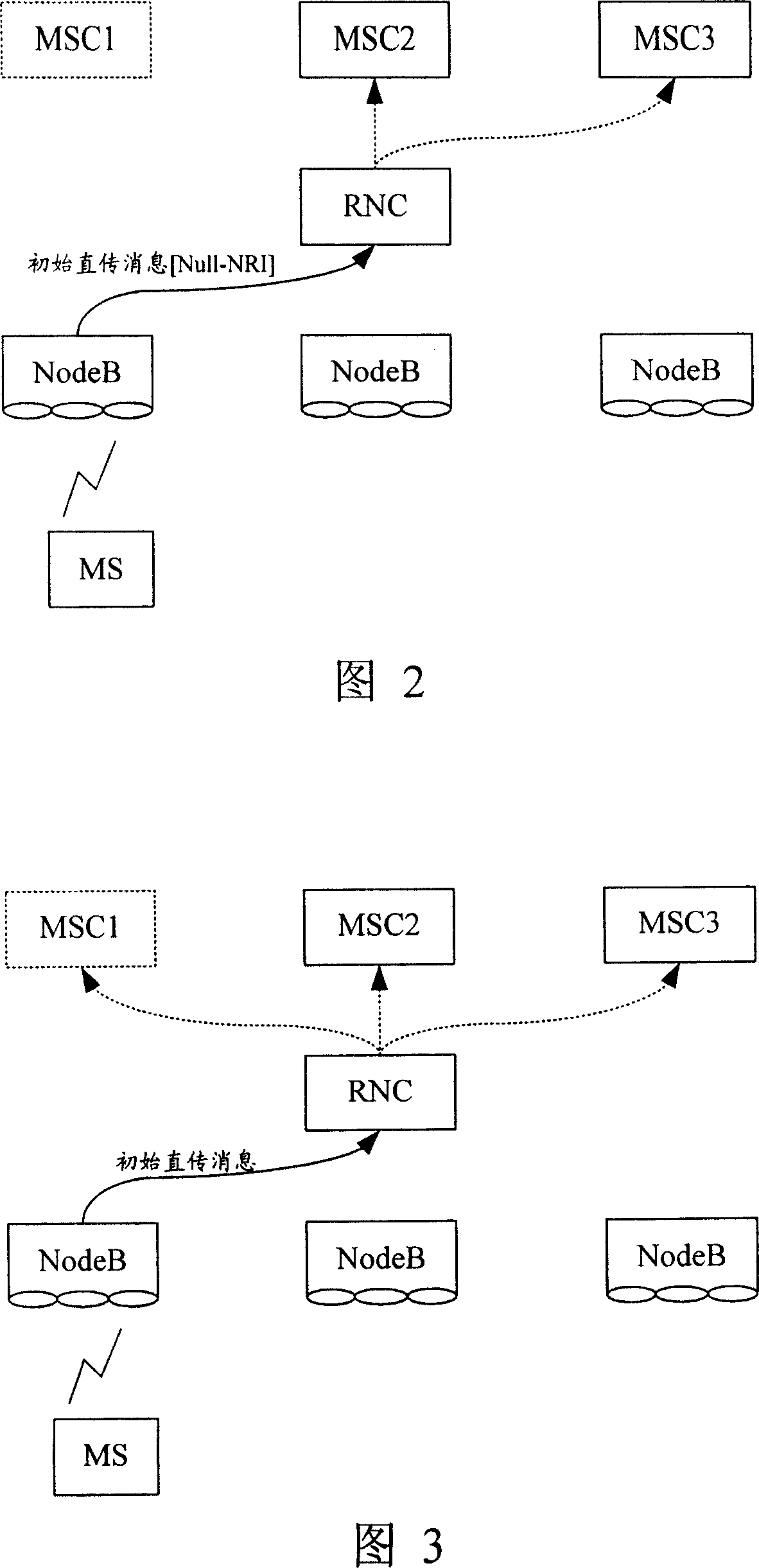
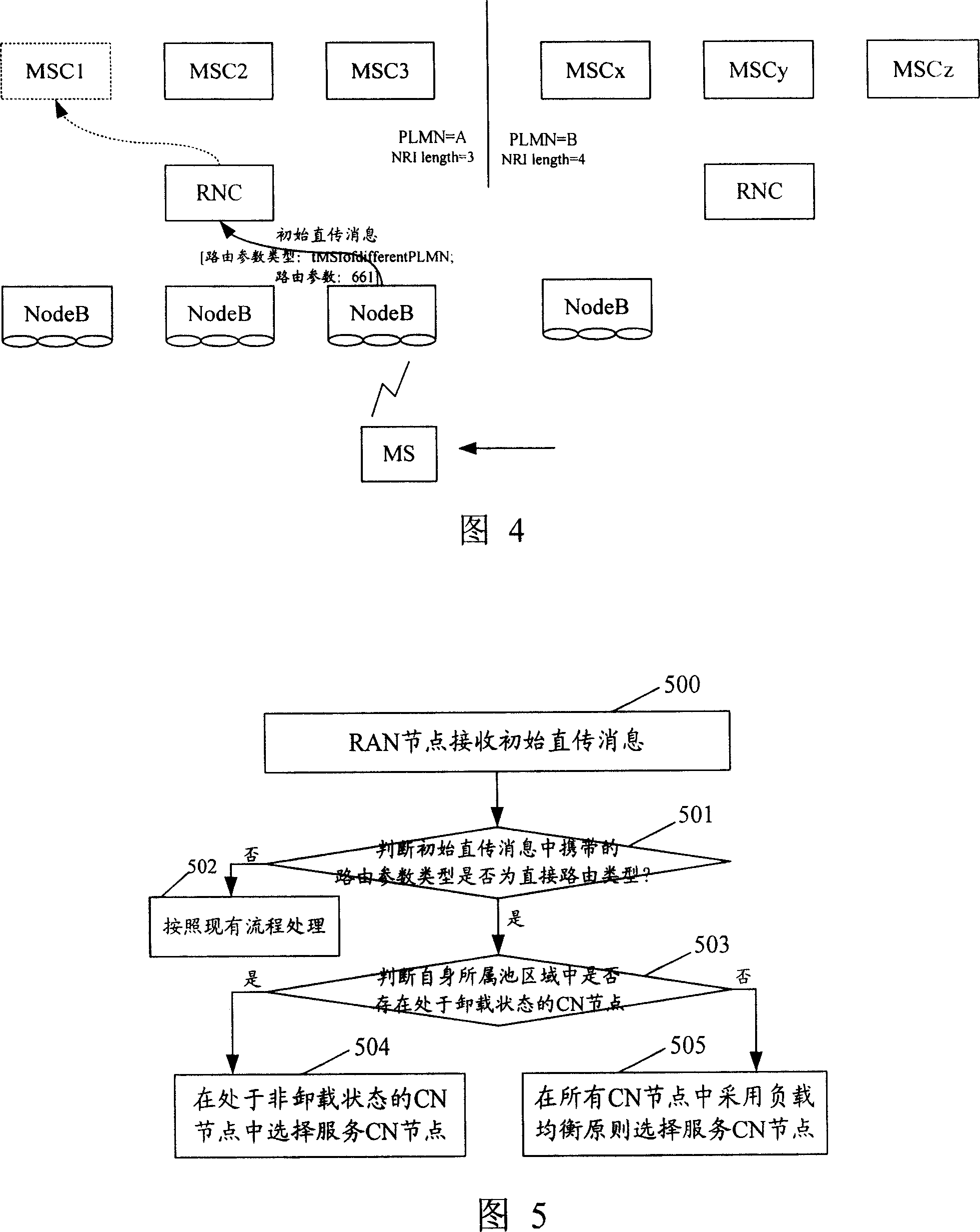
The invention discloses a method for implementing load redistribution. The method comprises: a RAN node receives an initial direct transfer message, wherein the routing parameter type carried by the initial direct transfer message is of direct routing type; and the RAN node selects a servicing CN node from CN nodes in non-unloaded state when CN nodes in unloaded state exist in the belonging domain. In the inventive method, when the routing parameter type carried by the initial direct transfer message is of direct routing type, the RAN excludes the CN nodes in unloaded state and selects the servicing CN node from the CN nodes in non-unloaded state only. Therefore, on one hand, the invention can increase the efficiency of load redistribution and save network resources, on the other hand, the invention can reasonably realize the load redistribution and the selected servicing CN node is valid. Additionally, the servicing CN node is selected based on the load balance principle with regard of the five situations when the routing parameter type is of direct routing type, thereby ensuring the load balance between the CN nodes.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for reallocating core network service
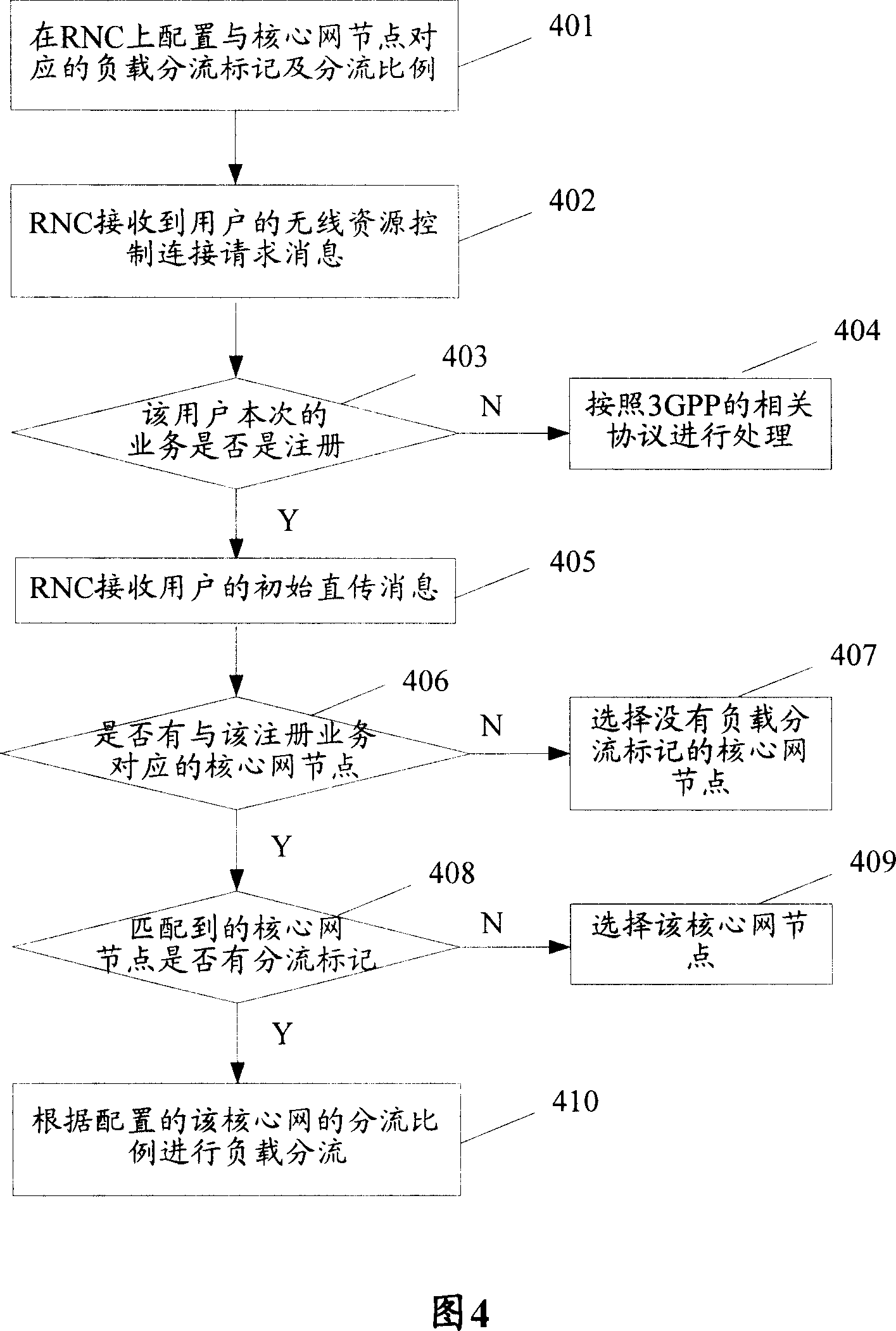
ActiveCN101128047AEasy to implementReduce shockNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio Network ControllerLoad redistribution
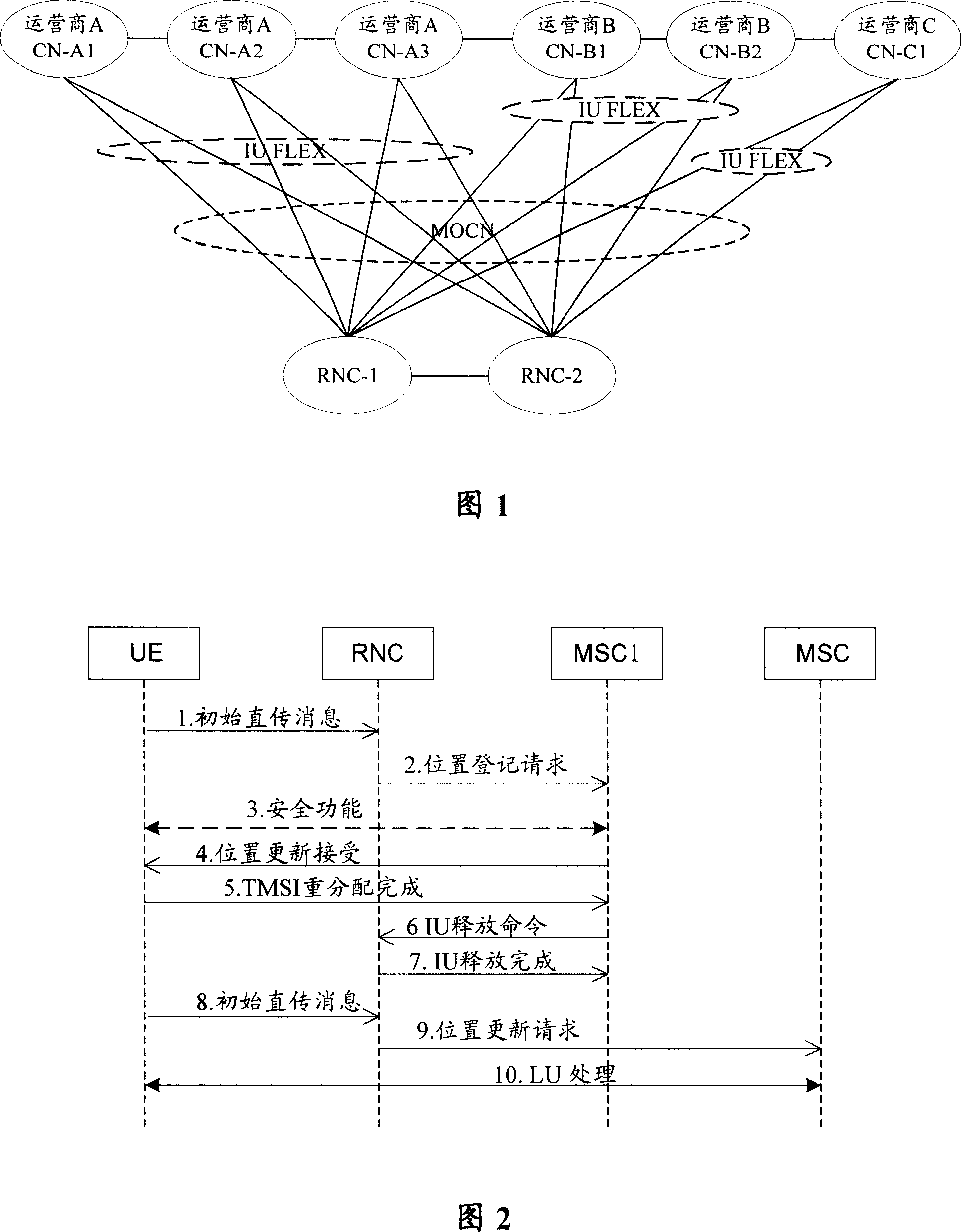
The utility model discloses a method for realizing reassignment of core network business, comprising the following steps: a load shunt marker and a shunt proportion corresponding to the core network node is allocated at the radio network controller RNC; when receiving the message from the user and judging the request business of the user as the registration business, the RNC acquires the core network node corresponding to the registration business; if the core network node carries no load shunt marker, the RNC selects the core network node; if the core network node carries the load shunt marker, the RNC conducts load shunt according to the allocated shunt proportion of the core network. The utility model enables to realize the load redistribution at any scene simply and conveniently.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Command and control network cascade failure model construction method based on node importance
InactiveCN110290006AImprove cascade invulnerabilityImprove accuracyData switching networksCascading failureCommand and control
The invention discloses a command and control network cascading failure model construction method based on node importance. The cascading failure resistance of a command and control network can be remarkably improved by reasonably adjusting corresponding parameters in a model, and the cascading destruction resistance of the command and control network is optimal due to the existence of optimal model parameters. According to the OODA combat theory and in combination with the concept of combat link betweenness, a new initial load definition method, a nonlinear load capacity model and a load redistribution strategy are given, and the internal mechanism and the external behavior of command and control network cascade failure can be reflected more effectively and accurately.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
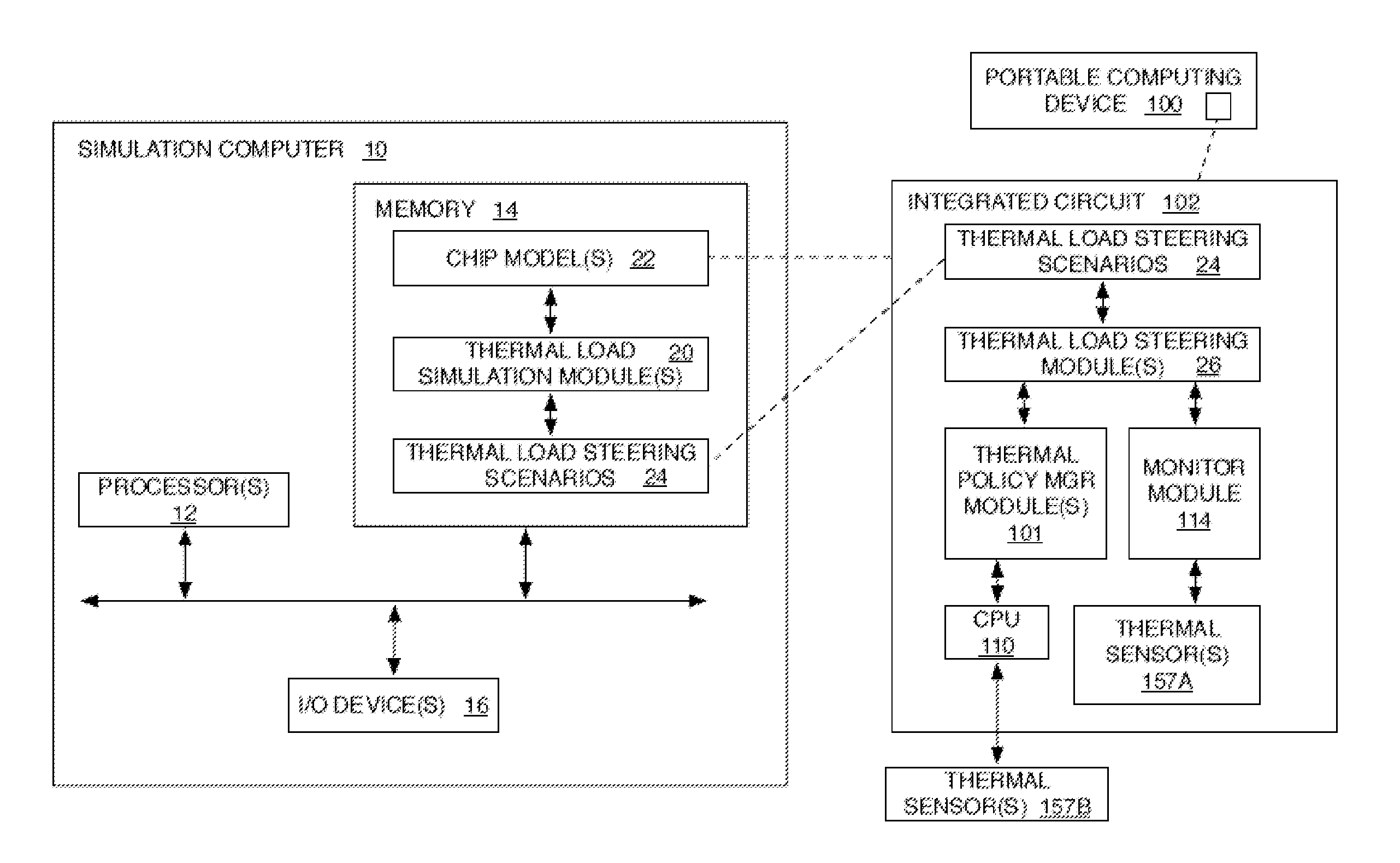
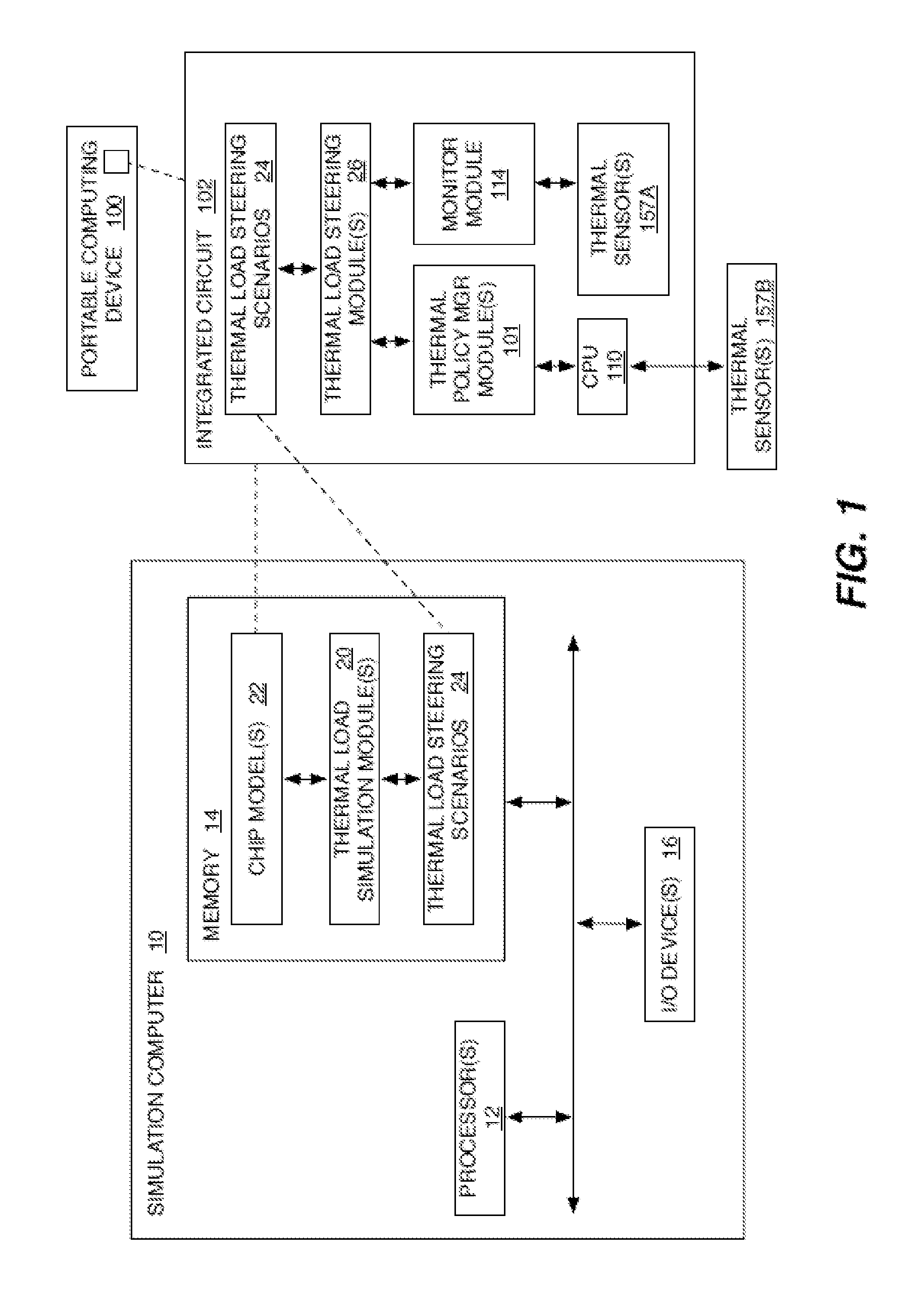
Method and system for thermal load management in a portable computing device
ActiveUS8942857B2Reduce power densityLower quality of serviceMultiprogramming arrangementsPower supply for data processingThermal energyEngineering
Methods and systems for leveraging temperature sensors in a portable computing device (“PCD”) are disclosed. The sensors may be placed within the PCD near known thermal energy producing components such as a central processing unit (“CPU”) core, graphical processing unit (“GPU”) core, power management integrated circuit (“PMIC”), power amplifier, etc. The signals generated by the sensors may be monitored and used to trigger drivers running on the processing units. The drivers are operable to cause the reallocation of processing loads associated with a given component's generation of thermal energy, as measured by the sensors. In some embodiments, the processing load reallocation is mapped according to parameters associated with pre-identified thermal load scenarios. In other embodiments, the reallocation occurs in real time, or near real time, according to thermal management solutions generated by a thermal management algorithm that may consider CPU and / or GPU performance specifications along with monitored sensor data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
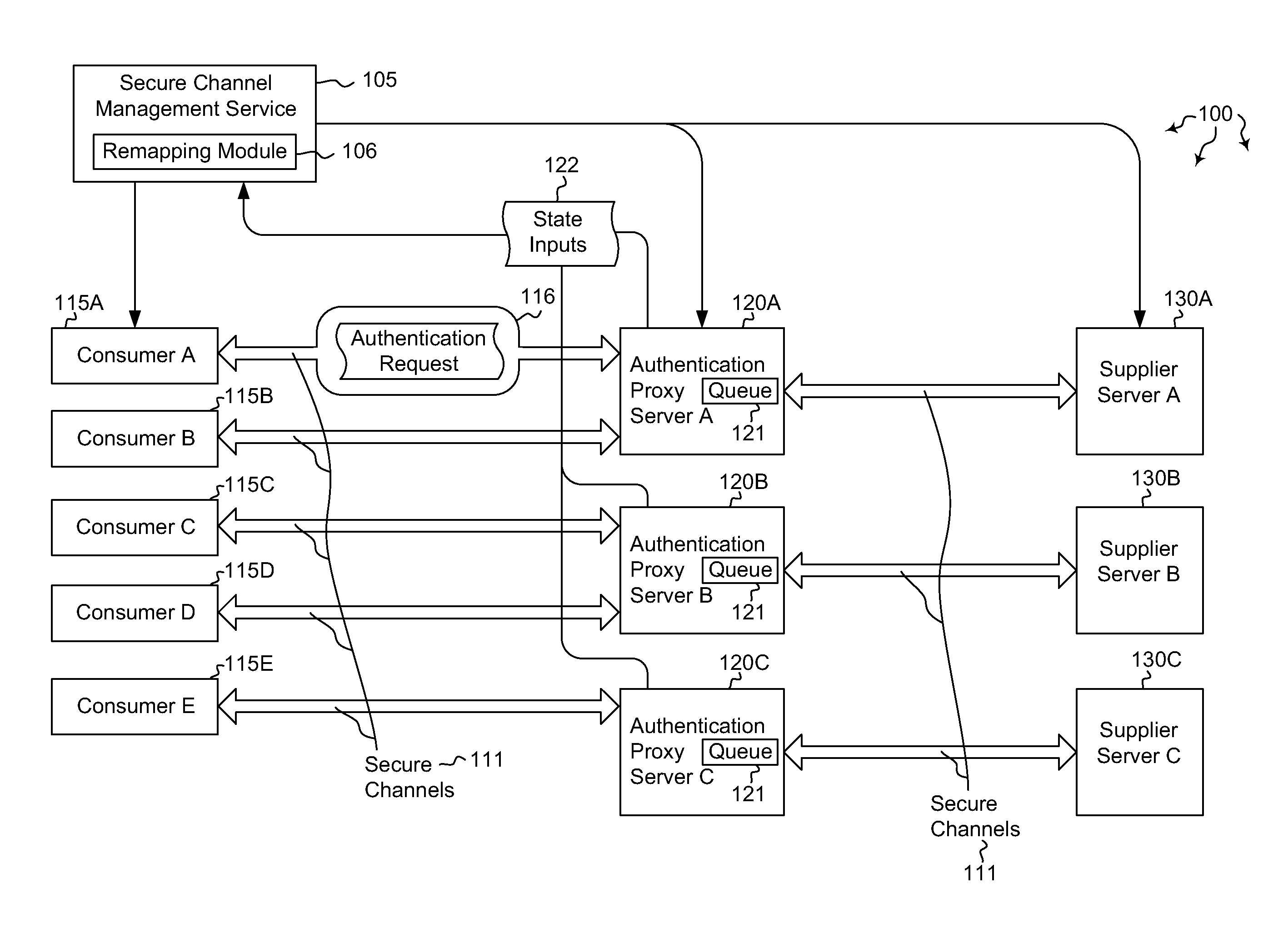
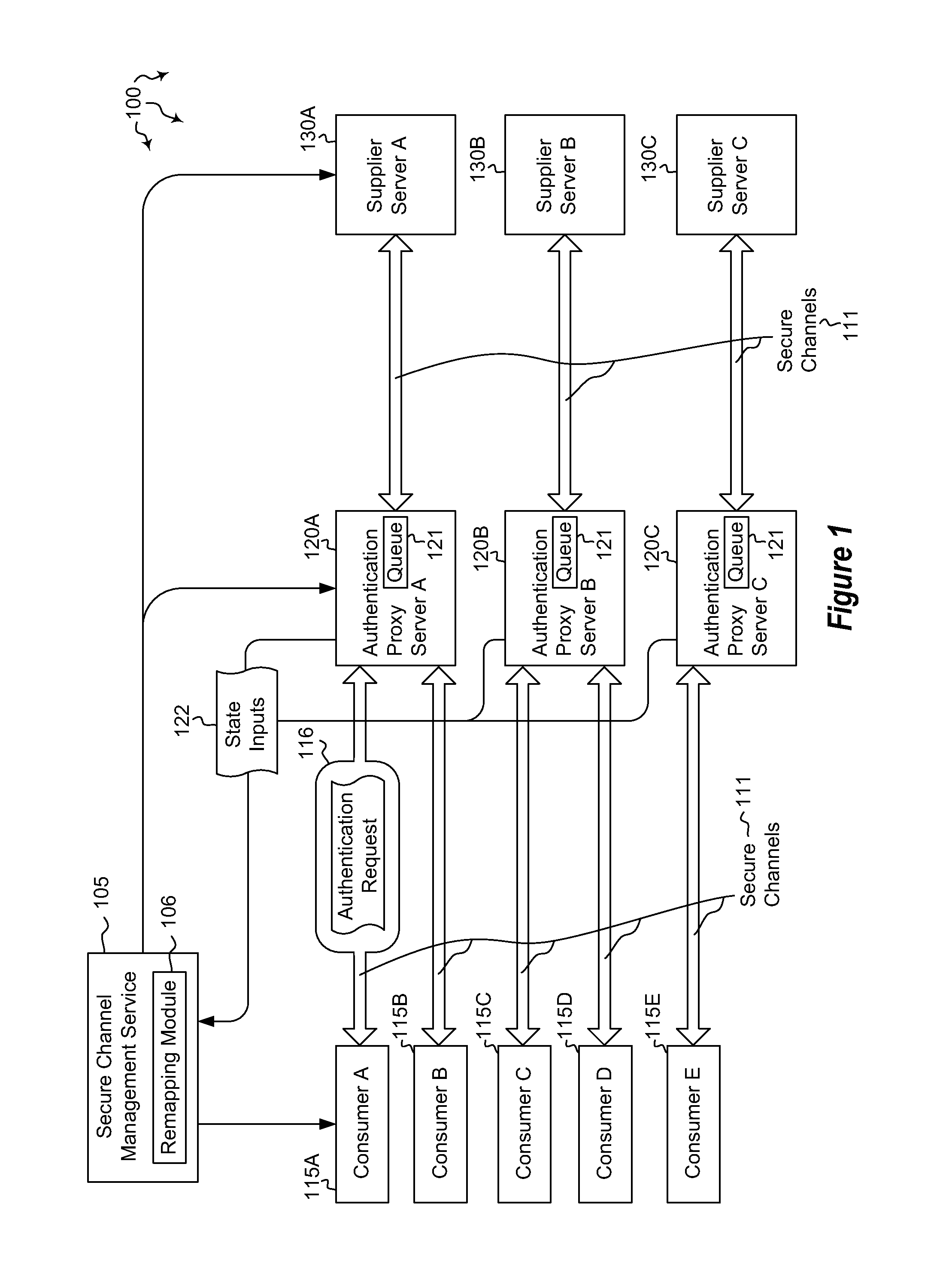
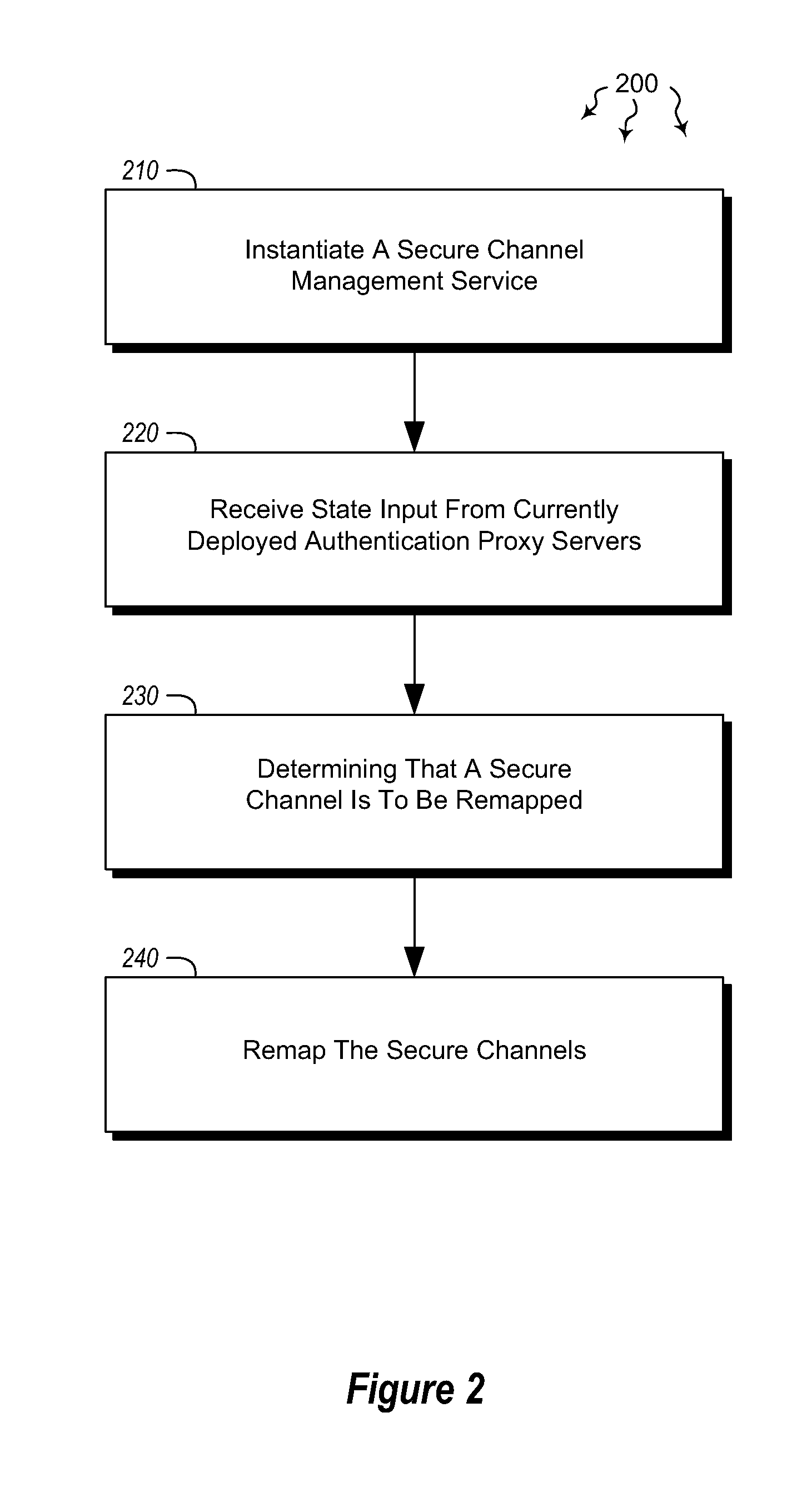
Dynamic load redistribution among distributed servers
ActiveUS20120030749A1Well formedMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputerized systemAuthentication server
Embodiments are directed to redistributing authentication requests among a plurality of authentication servers and to centrally managing authentication affinities among distributed servers using a secure channels affinity service. A computer system instantiates a secure channel management service configured to manage secure channel connections. The secure channel management service receives state inputs from currently deployed authentication servers. The authentication servers may be configured to queue authentication requests for transmission to authentication servers. The computer system determines that, based on the received state input, at least one of the secure channels is to be remapped to a different authentication server. The computer system also remaps the determined secure channels to distribute future authentication requests among the authentication servers. In some cases, the current state of an authentication proxy server is embedded in communications transmitted by the authentication server, such that the secure channel connections are managed using the embedded state information.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com