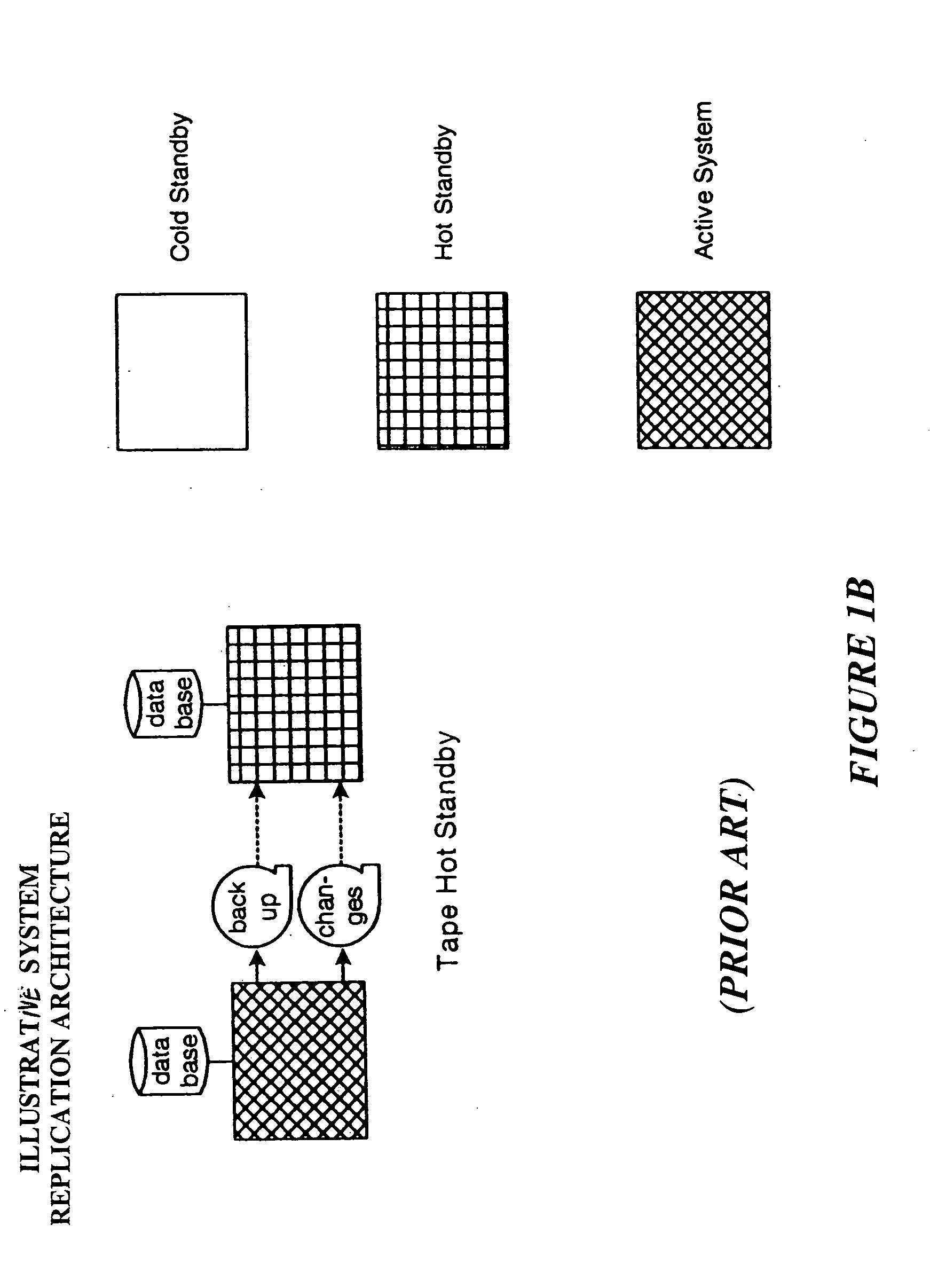
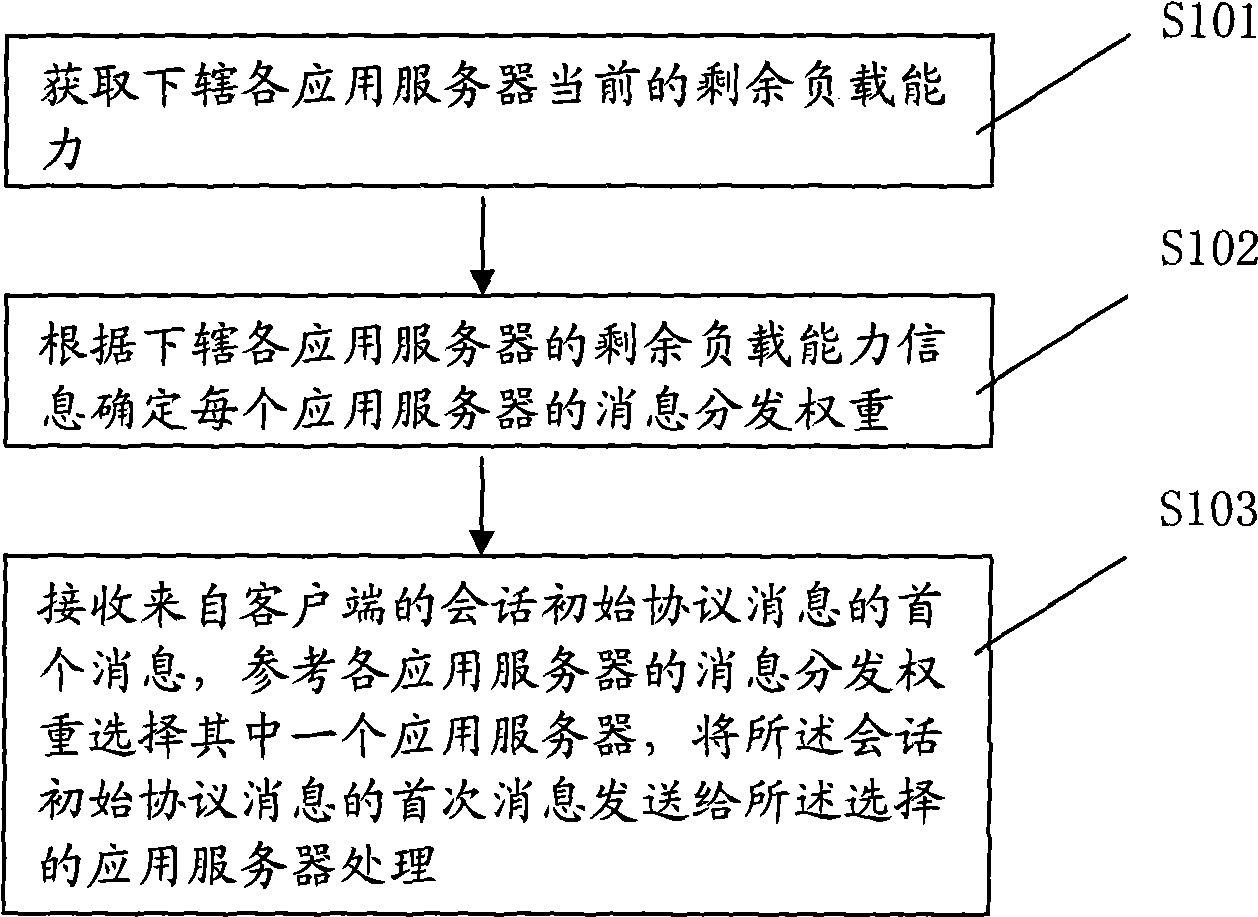
Patents
Literature
3153 results about "Load capacity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Warehouse Management & Equipment Glossary: Rated Load Capacity. Rated Load Capacity -The maximum load for which the equipment is designed by the manufacturer. Loading more product onto a rack than it is designed to handle could damage the structure and possibly lead to failure.
Single-chip microcomputer
InactiveUS20120023281A1Multiple functionsPerformance multiplePower managementEnergy efficient ICTMicrocontrollerMicrocomputer
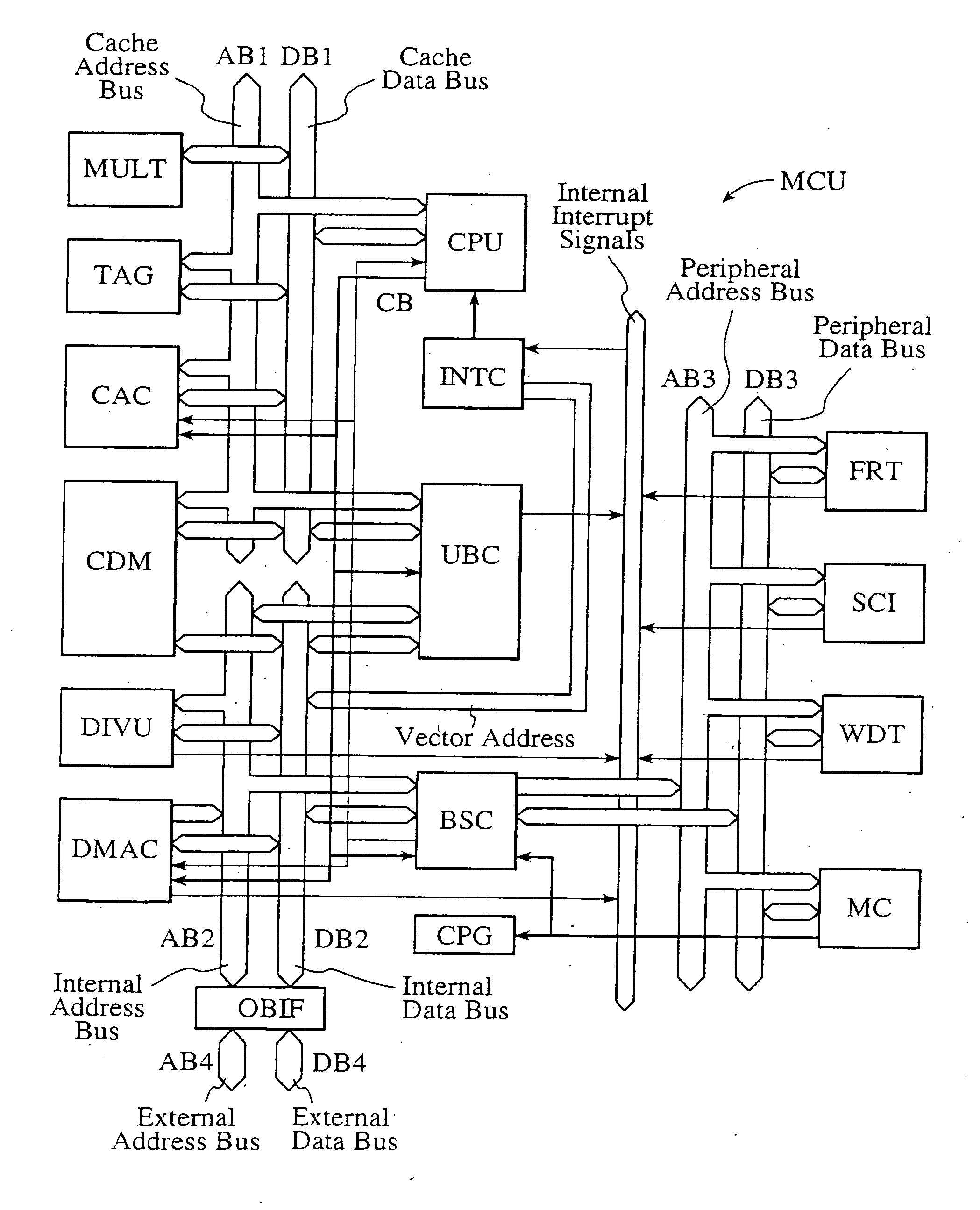
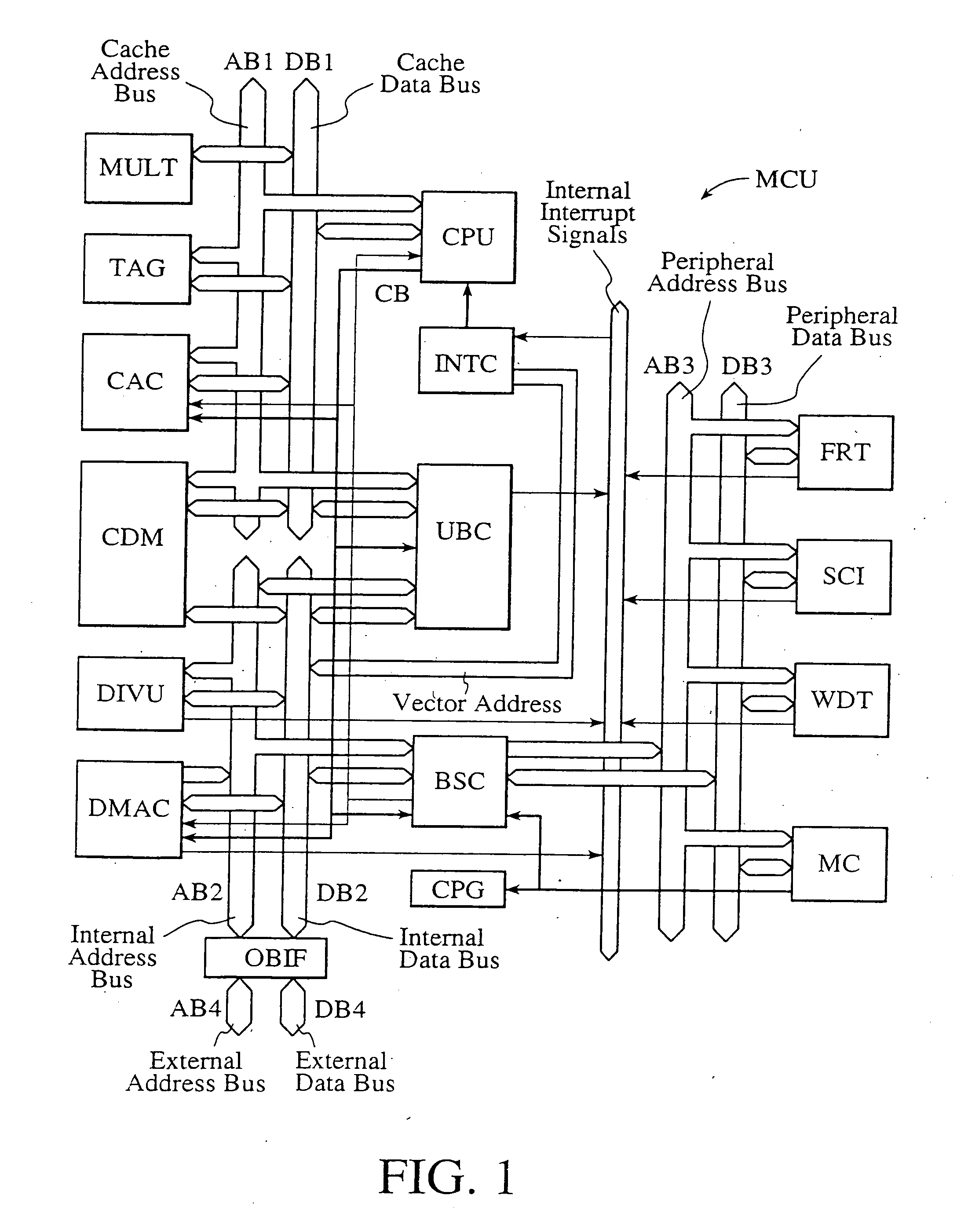
A single-chip microcomputer comprising: a first bus having a central processing unit and a cache memory connected therewith; a second bus having a dynamic memory access control circuit and an external bus interface connected therewith; a break controller for connecting the first bus and the second bus selectively; a third bus having a peripheral module connected therewith and having a lower-speed bus cycle than the bus cycles of the first and second buses; and a bus state controller for effecting a data transfer and a synchronization between the second bus and the third bus. The single-chip microcomputer has the three divided internal buses to reduce the load capacity upon the signal transmission paths so that the signal transmission can be accomplished at a high speed. Moreover, the peripheral module required to have no operation speed is isolated so that the power dissipation can be reduced.
Owner:KAWASAKI SHUMPEI +8
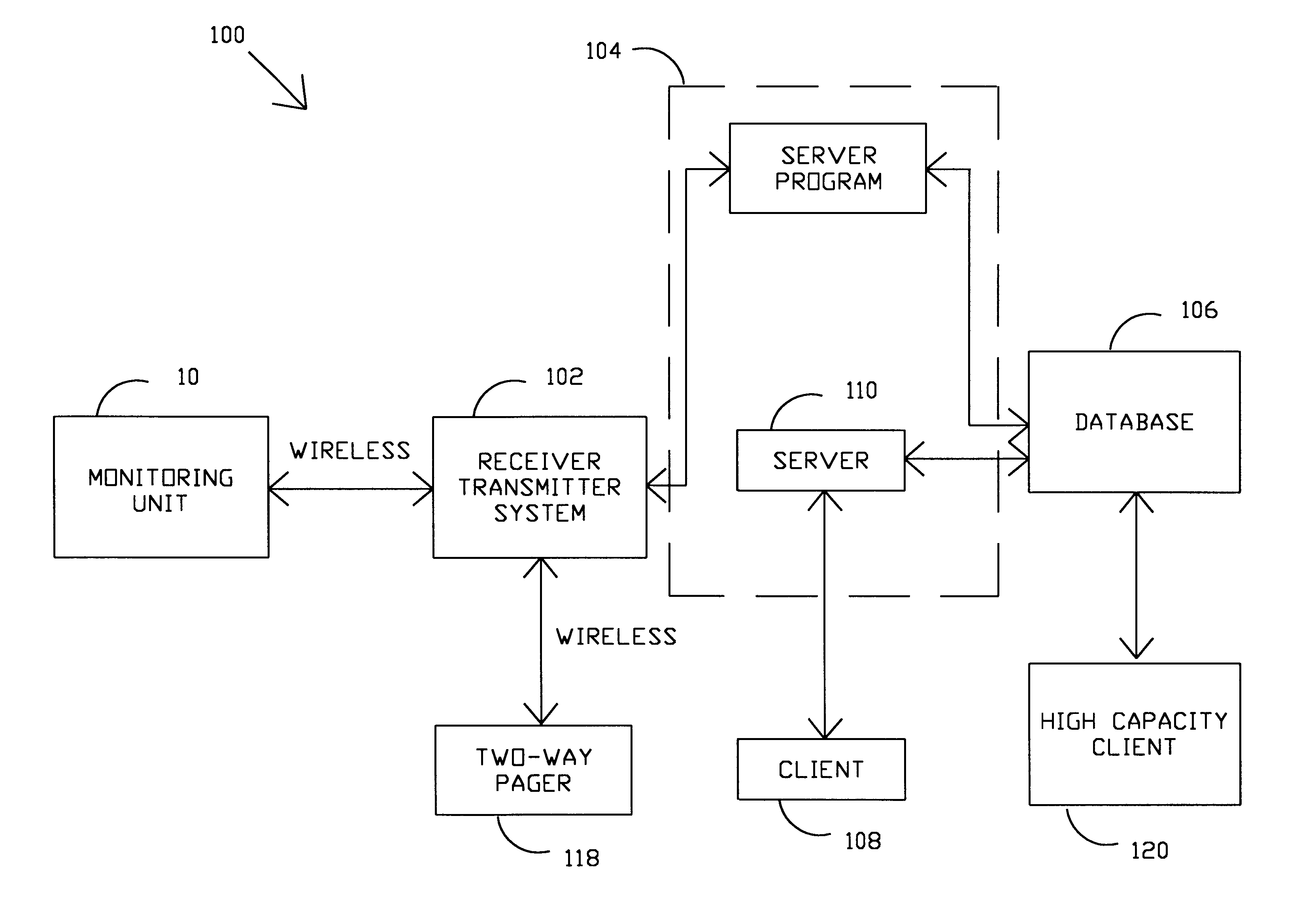
Logistics system and method
InactiveUS6879962B1Cost controlLow costHand manipulated computer devicesReservationsLogistics managementLeast cost
A logistics method is disclosed that provides logistics computer programming for controlling a plurality of transports to supply a plurality of delivery locations from one or more bases. Each of the bases and delivery locations are in communication with a central database, preferably an Internet server database, that contains updated logistics information. The central database is preferably automatically updated at selectable intervals as to transport location, destination, fuel level, speed, and heading. Manifests may be originated at the respective delivery location or at an associated base and are stored in the central database. Each material on the manifest is associated with information such as the authorized vendor, a description, storage preferences, units, hazardous designations and additional information if the material is hazardous. Given information about each transport such as load capacity, fuel level, location intelligence, and the like that is stored in the central database and information about the materials, manifest status, and other factors, potential least cost delivery routes using capable transports can be automatically produced for selection by an operator. The logistics computer programming automatically designates where each manifested material is stored on the transport. The computer programming associates a status designation with each manifest such as outstanding, staged, printed, loaded, unloaded, and cancelled. Each manifest is also associated with a priority which may range from emergency to routine. Updated logistics information concerning materials, manifests, vendors, transports, delivery locations, and operating companies is available from the central database.
Owner:SMITH JOSEPH D
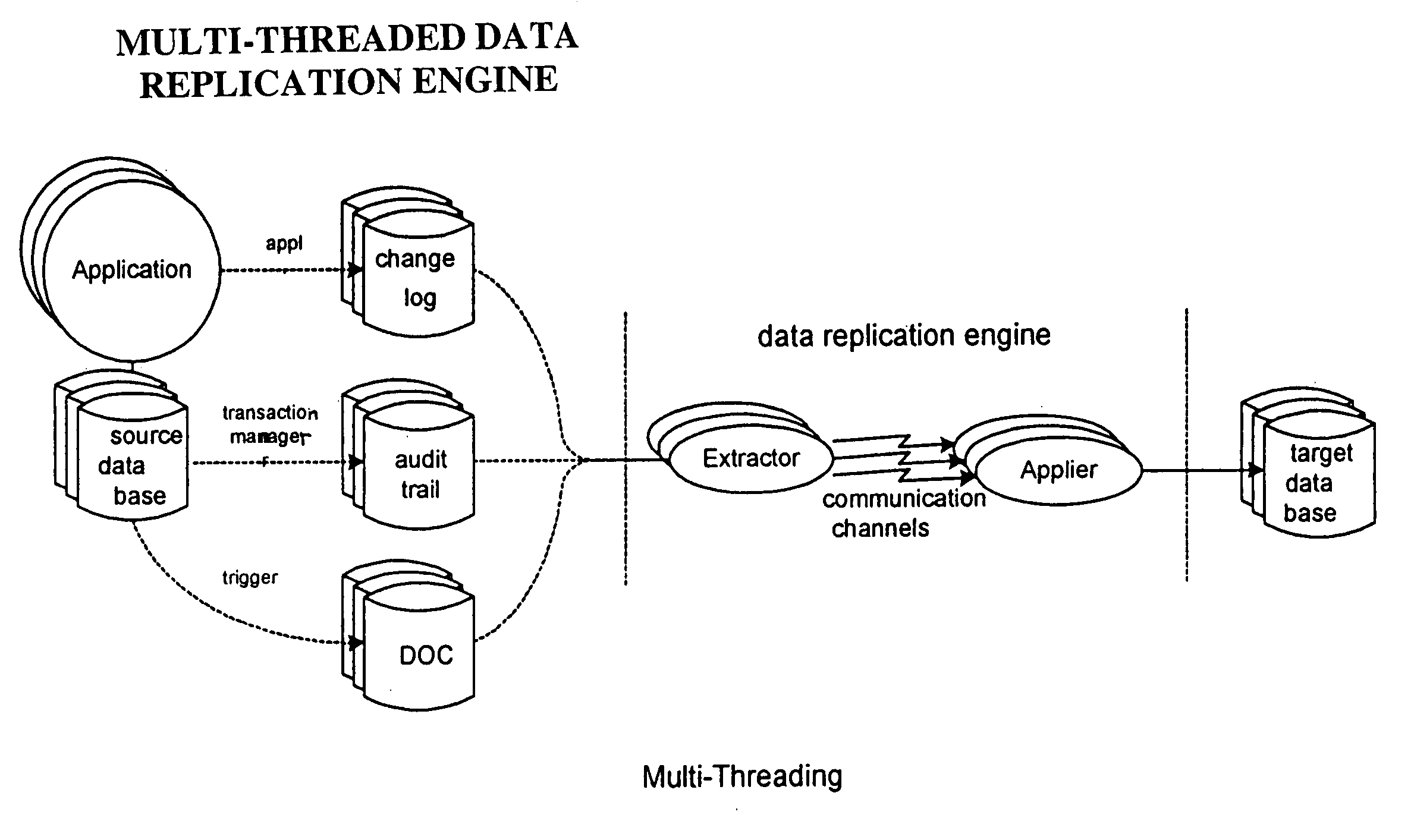
Method for ensuring referential integrity in multi-threaded replication engines
ActiveUS20050021567A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTransaction dataLoad capacity
During replication of transaction data from a source database to a target database via a change queue associated with the source database, one or more multiple paths are provided between the change queue and the target database. The one or more multiple paths cause at least some of the transaction data to become unserialized. At least some of the unserialized data is reserialized prior to or upon applying the originally unserialized transaction data to the target database. If the current transaction load is close or equal to the maximum transaction load capacity of a path between the change queue and the target database, another path is provided. If the maximum transaction threshold limit of an applier associated with the target database has been reached, open transactions may be prematurely committed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
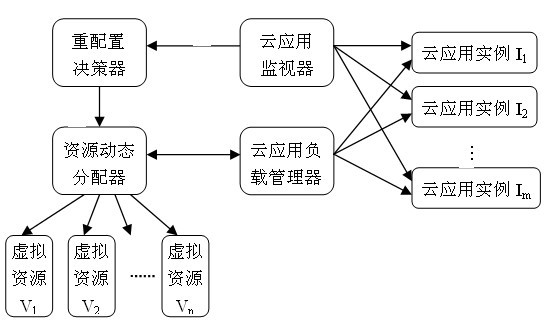
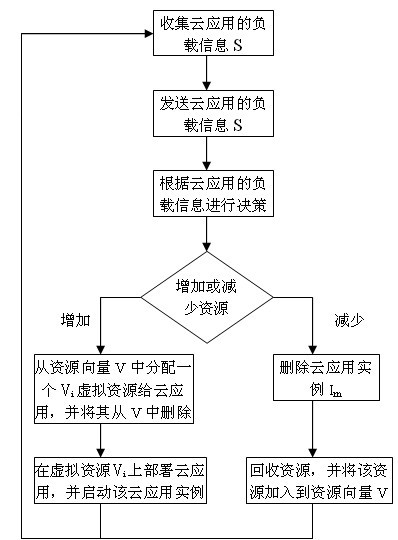
Cloud computing resource scheduling method based on dynamic reconfiguration virtual resources
InactiveCN101938416ADynamic Allocation OptimizationMeeting the Need for Dynamic ScalabilityData switching networksCurrent loadDecision taking
The invention relates to a cloud computing resource scheduling method based on dynamic reconfiguration virtual resources. The method comprises the steps of: using cloud application load information collected by a cloud application monitor as a basis; making a dynamic decision based on the load capacity of the virtual resources for running cloud application and the current load of the cloud application; and dynamically reconfiguring virtual resources for cloud application based on the decision result. Dynamic adjustment of resources is realized by a method for reconfiguring virtual resources for cloud application, without needing dynamic redistribution of physical resources or stopping executing cloud application. The method can dynamically reconfigure the virtual resources according to the load variation of the cloud application, optimize allocation of the cloud computing resources, realize effective use of the cloud computing resources, and meet the requirements on dynamic scalability of cloud application. In addition, the method can avoid waste of the cloud computing resources, and save the cost for using resources for cloud application users.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
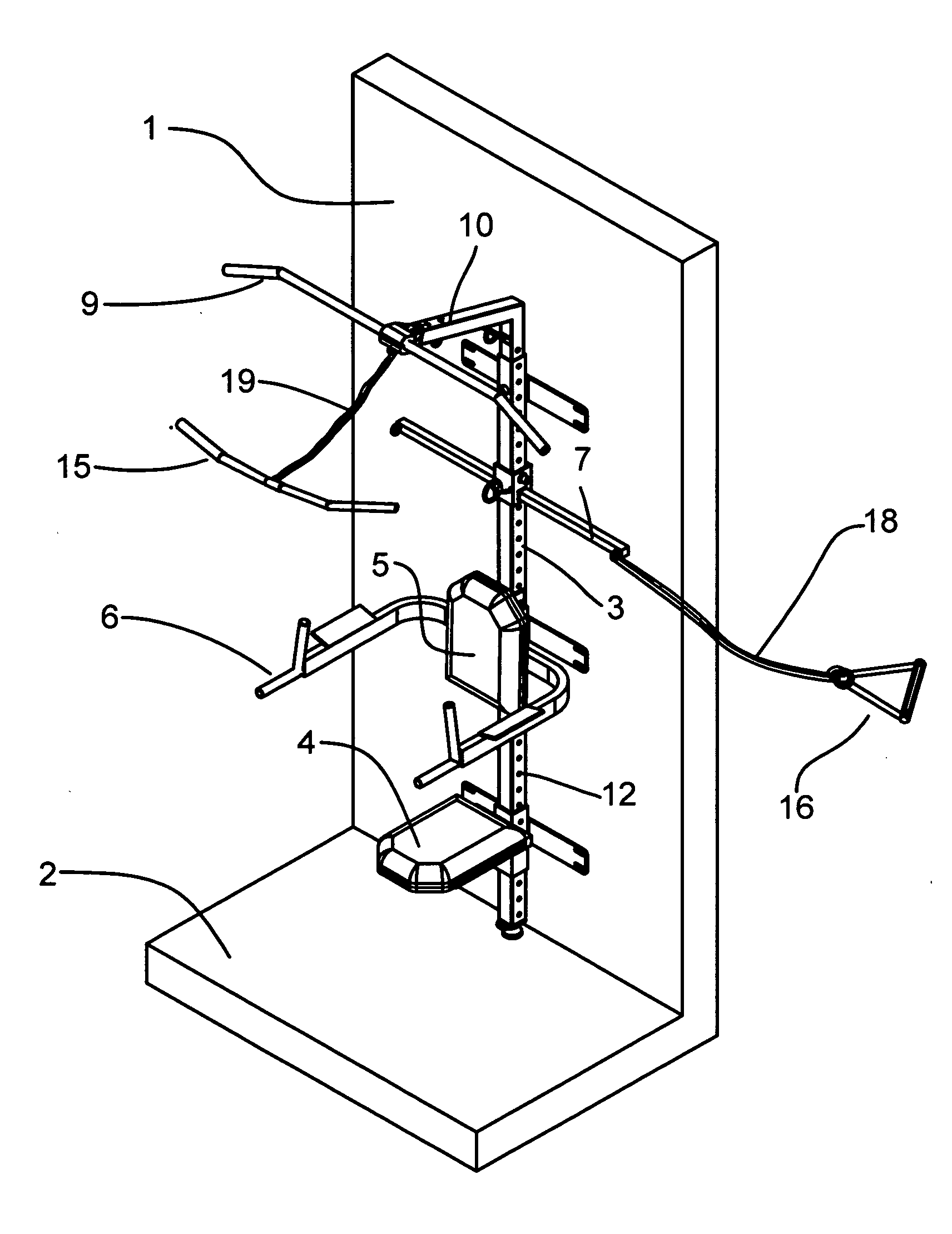
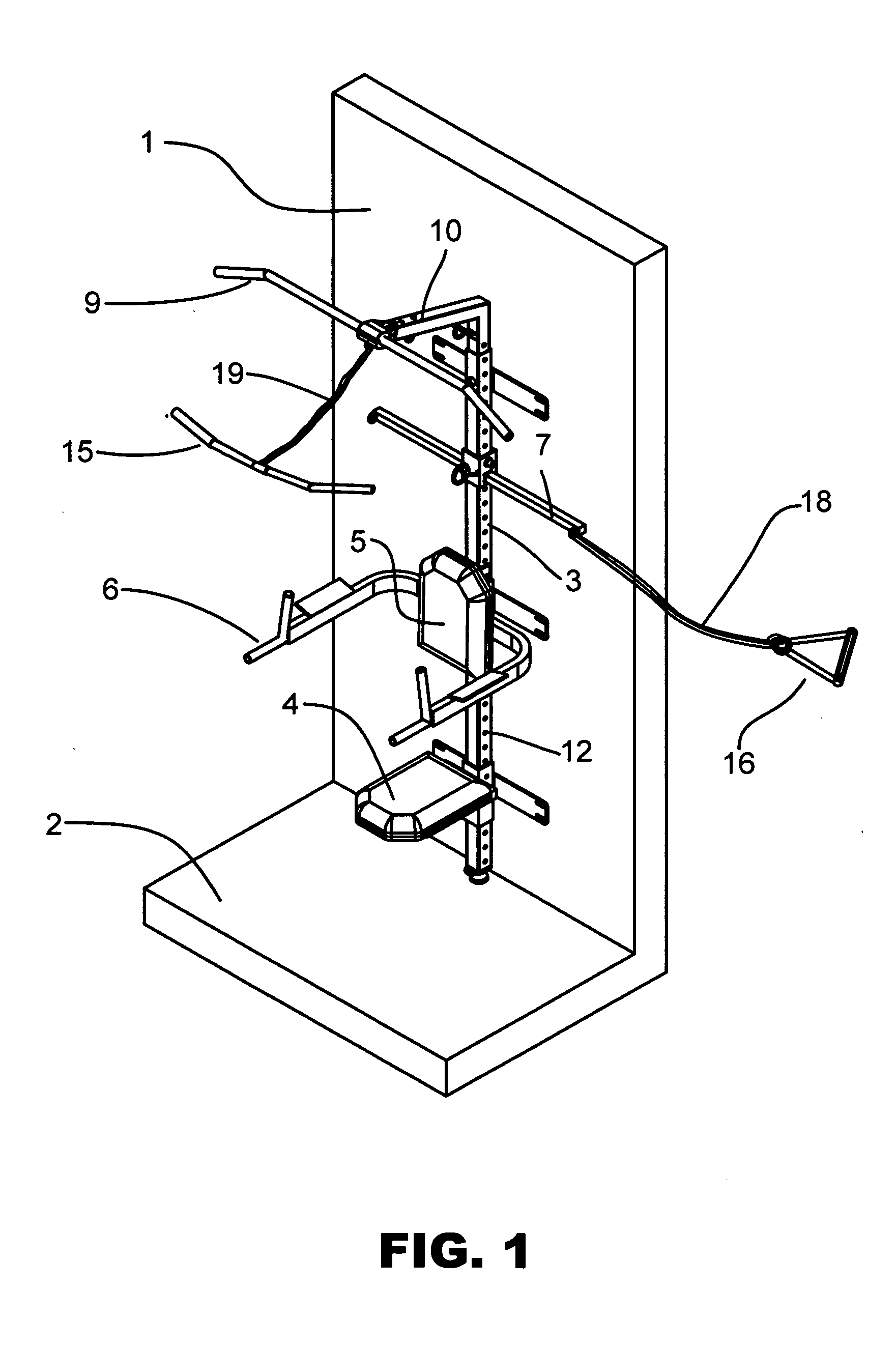
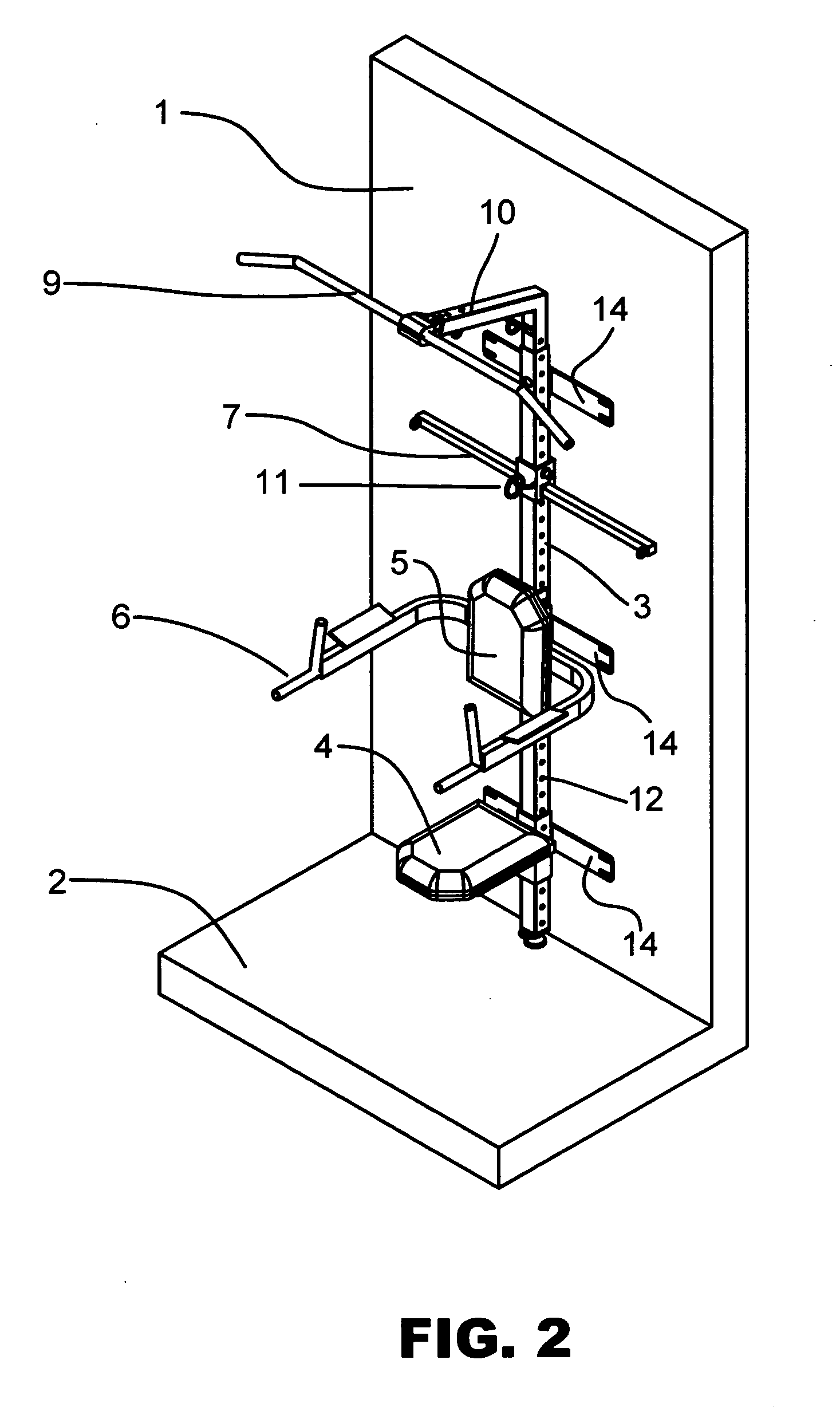
Wall-mounted home fitness training equipment
InactiveUS20100048368A1Easy to adjustIncrease the number ofStiltsHorizontal barsPull forceEngineering
An overall fitness trainer and can be a wall mounted unit that can utilize clip resistance bands as well as other techniques. These bands generally clip on the unit and onto different handles, bars and attachments to perform exercises. The unit can have a removable / adjustable pull up bar, dip bar and seat. It also includes a spring loaded, pull pin carriage that moves freely up and down a vertical spine. This allows for easy adjustment of the carriage and allows the user to attach the bands at multiple angles, widths and levels. This in turn increases the number of exercises the user can perform on the unit. The unit also typically has an o ring that attaches through the arm of the pull up attachment as well as a ½ O-ring at the bottom of the unit again increasing the number of exercises the user can perform. The unit can be attached to the wall with lag bolts into two or more studs. Some embodiments of the invention have an adjustable swivel foot that takes the stress off of the lag bolts and also adds to the overall load capacity of the unit. The apparatus typically has an optional telescoping central vertical spine that splits in two pieces to make the unit easier to ship. The central vertical spine allows attachments to be added and removed using spring loaded pins or plunger pins. Various embodiments of the invention can have an oscillating and telescopic bench, a dip bar, a seat, a knee stabilizer and a foot rest. All of these accessories can be attached and removed to the central spine adding to the versatility and scope of exercises that can be performed.
Owner:DONOFRIO DARREN
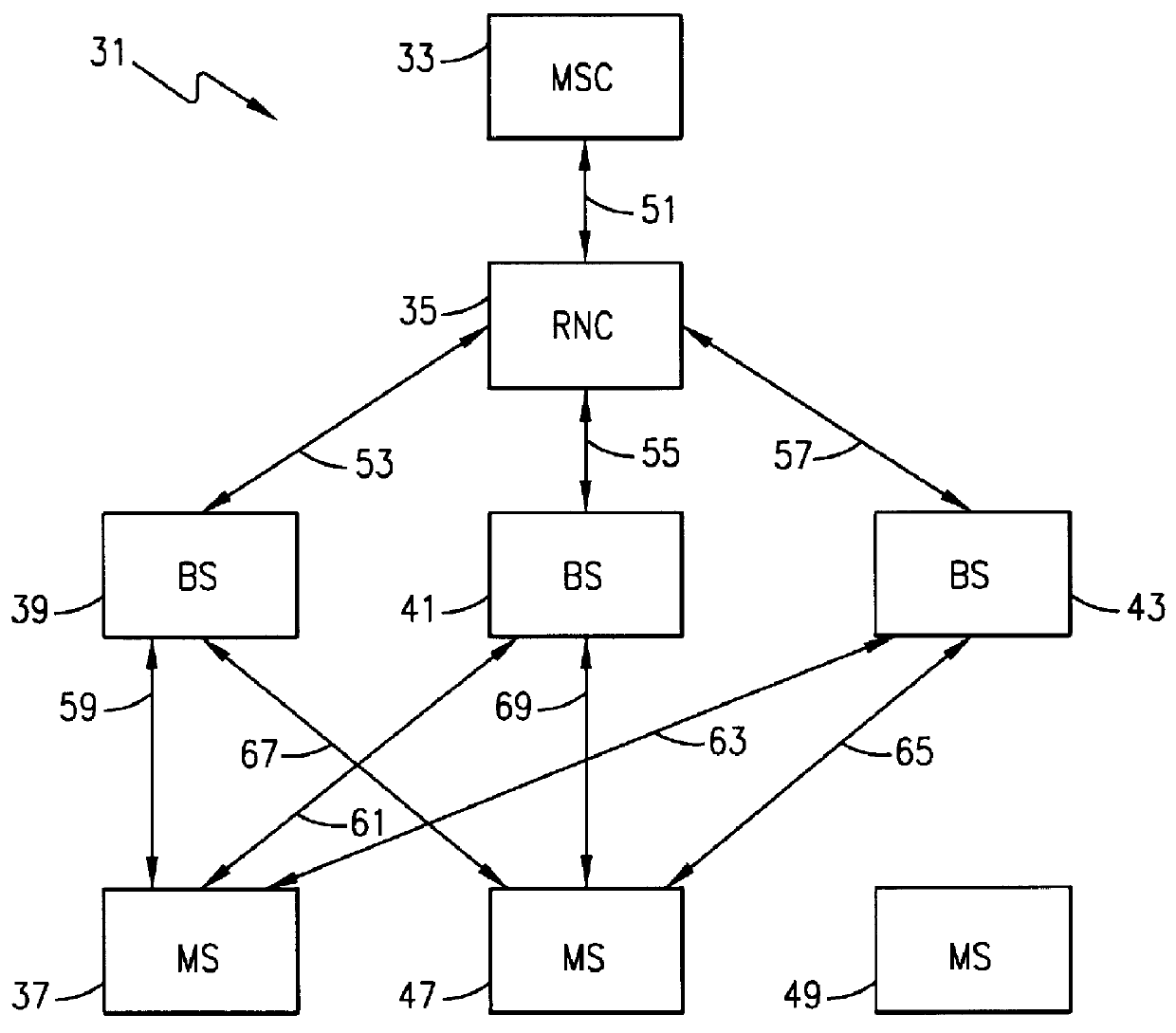
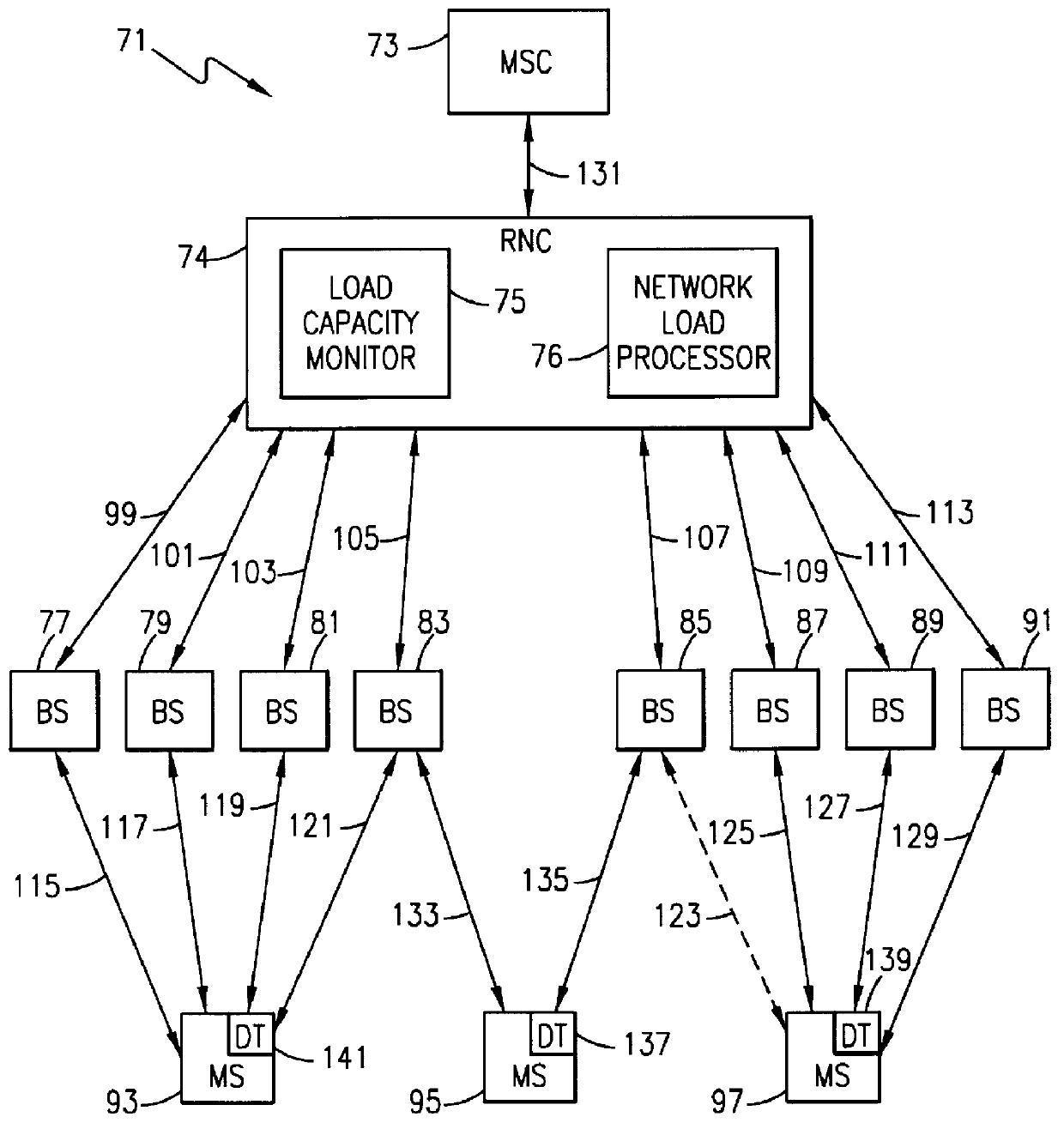
System and method of dynamically increasing the capacity of a code division multiple access radio telecommunications network
InactiveUS6078817ARadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationTelecommunications networkTransceiver
A method and system for dynamically increasing the capacity of a code division multiple access (CDMA) radio telecommunications network. The method begins by the radio telecommunications network receiving a request for access to the radio telecommunications network from an entering mobile station. Next, a load capacity monitor determines if the radio telecommunications network is fully loaded. When the radio telecommunications network is fully loaded, a network load processor releases one of a duplicate channel element (transceiver) used in the CDMA radio telecommunications network by one of the operating mobile stations. The network load processor then assigns the released channel element to the entering mobile station. The system includes a load capacity monitor to determine whether the radio telecommunications network is fully loaded. The system also includes a network load processor to reallocate duplicate channel elements from the operating mobile stations to the entering mobile station.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
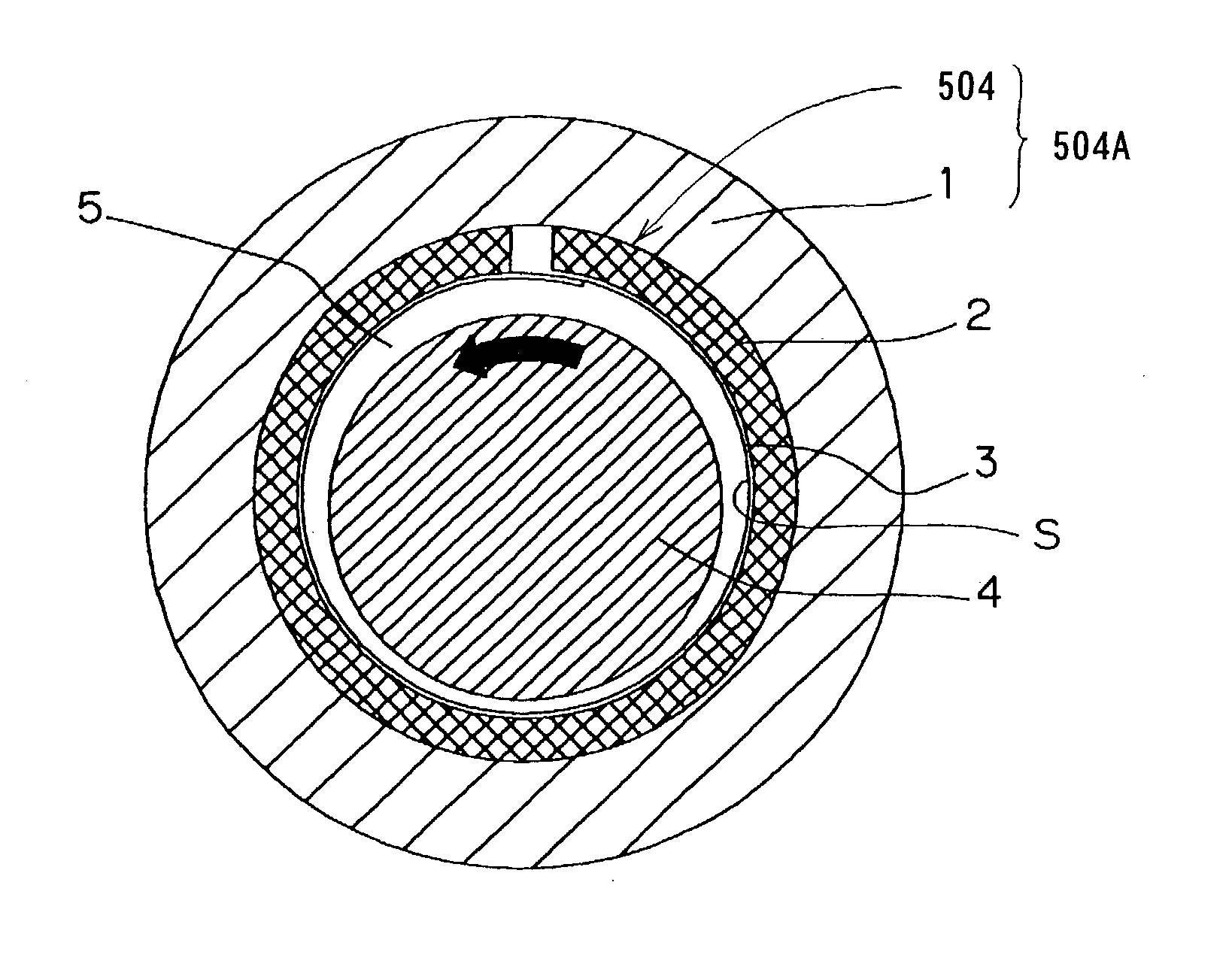
Foil bearing and spindle device using the same
InactiveUS20030169951A1Liquid spraying apparatusSliding contact bearingsThrust bearingBearing surface
A foil bearing is provided, which is simple in structure, has a large load capacity and a large damping capability and can therefore allow a rotary shaft having a large unbalance as compared with the conventional bearing to be driven stably at a high speed. A spindle device utilizing such foil bearing is also provided, which is designed to increase the permissible amount of unbalance and also to have a light-weight feature. Each of the foil bearings 504 and 505 includes an elastic member 2 prepared from a wire net formed by braiding wires, and a thin bearing foil 3 supported by the elastic member 2 and defining an elastic bearing surface S. The respective foil bearing 504 and 505 is used at least as a radial bearing 504 in the spindle device including a rotary shaft 4 having a head mount 501a, on which an atomizer head is mounted, and the radial and thrust bearings 504 and 505 for rotatably supporting the rotary shaft 4.
Owner:NTN CORP
Linear actuator
InactiveUS20050160846A1Smooth startIncrease load capacityToothed gearingsMechanical energy handlingBall bearingControl theory
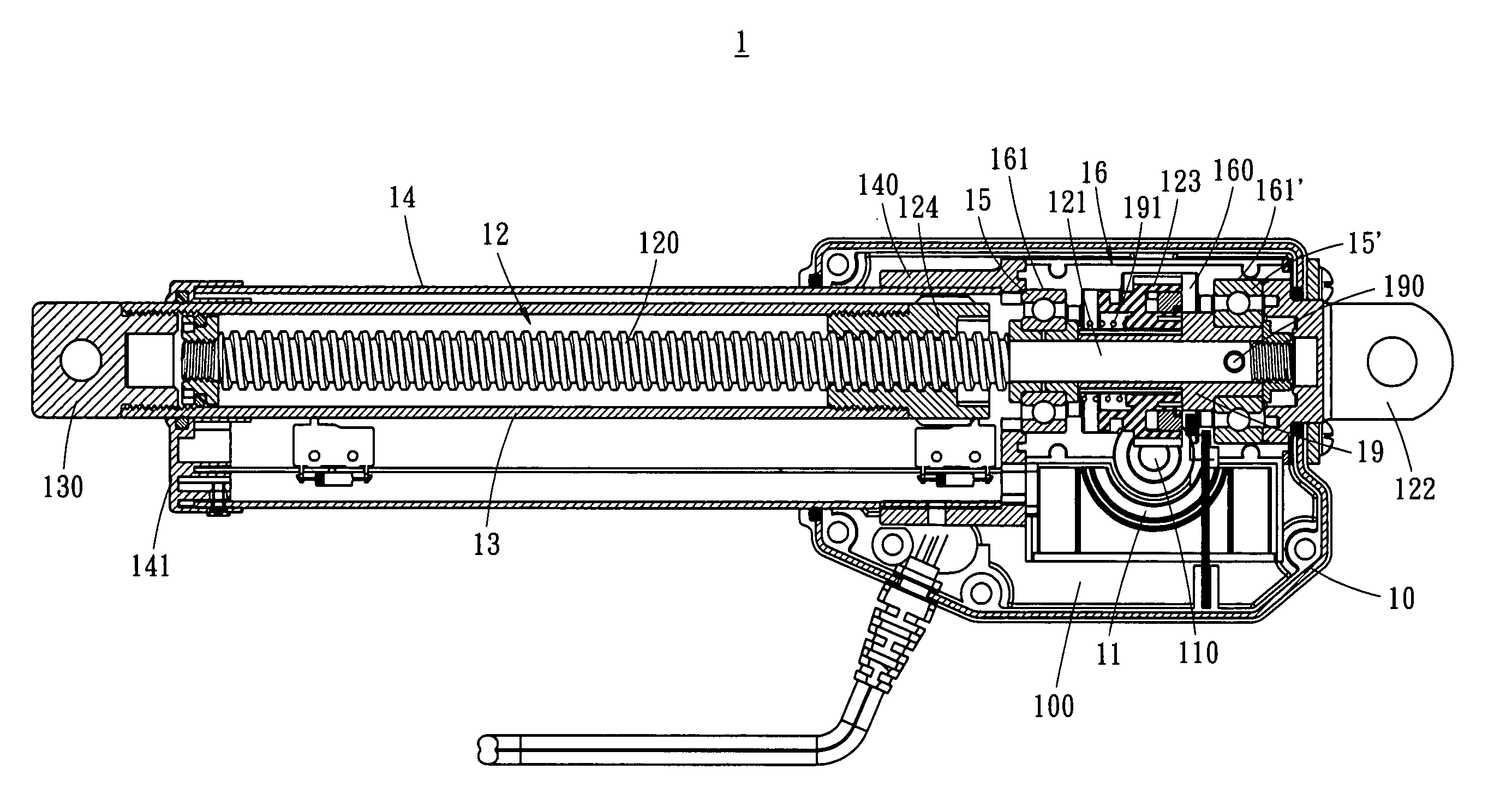
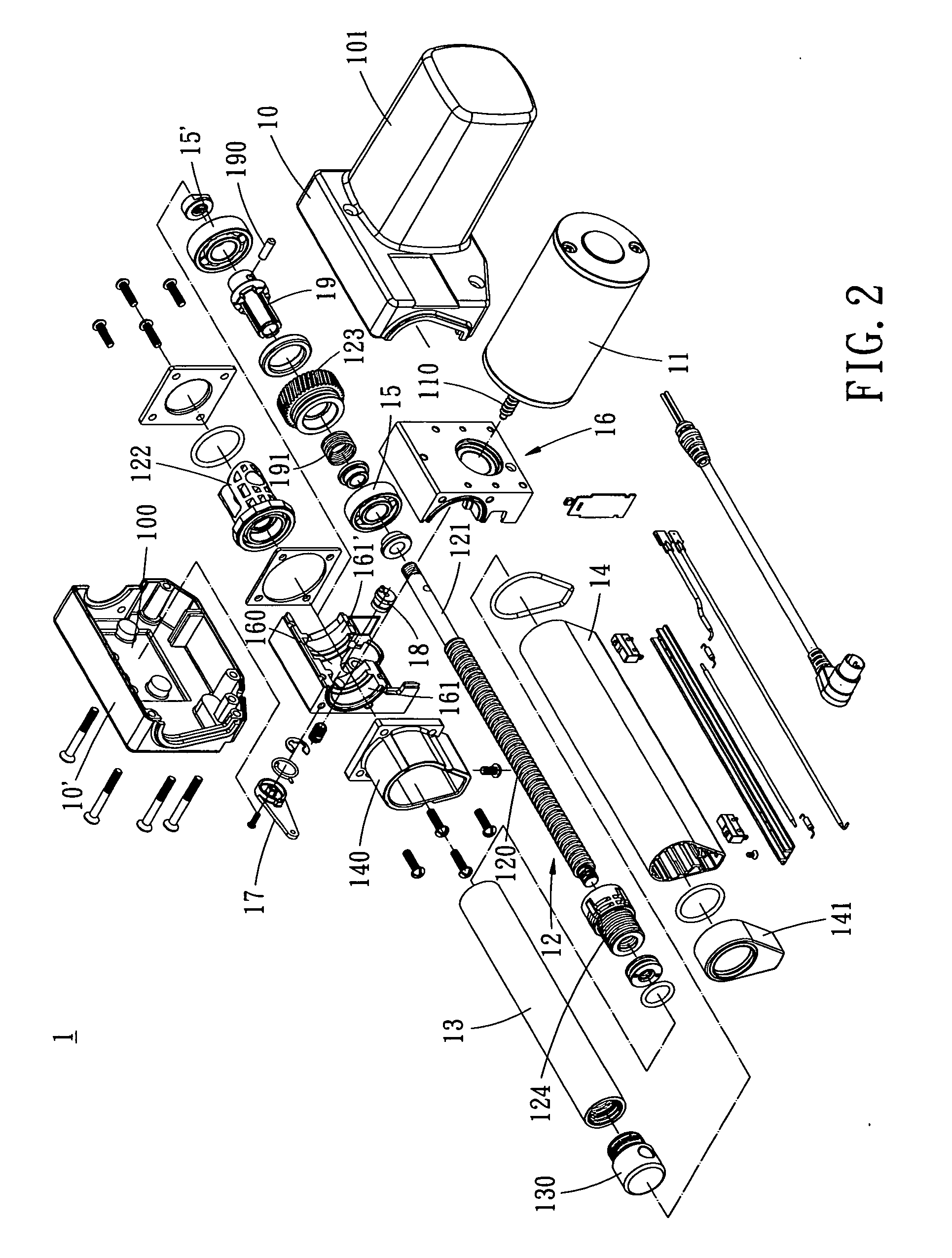
A linear actuator has two half-shells, a motor housing, a motor installed in the motor housing, a guiding screw driven by the motor, a screw nut engaged with the guiding screw, an interior tube encircling the guiding screw and connected with the screw nut at one end thereof, a moveable exterior tube telescoping the interior tube therein, at least two ball bearings subject to radial and axial load, and fitting seat installed in the half-shells. The fitting seat has to bearing seats for mounting the ball bearings, such that the load capacity of the linear actuator is increased, while the application safety is enhanced.
Owner:JAEGER INDAL
A kind of preparation method of efficient catalyst for synthesizing vinyl acetate by acetylene method
InactiveCN102284304ASimple processLow costOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSurface oxidationBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention provides a preparation method of a high-efficiency catalyst for synthesizing vinyl acetate by an acetylene method. The oxidant is used to oxidize the surface of activated carbon used as a catalyst carrier to change the oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of the activated carbon and improve its original pore structure, thereby effectively improving the loading capacity of the active component zinc acetate and significantly improving the catalyst efficiency. The invention has the advantages of cheap and easy-to-obtain raw materials, simple operation, high loading capacity of catalyst active components, good activity and long service life.
Owner:CHENGDU ORGANIC CHEM CO LTD CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Packaging system to provide fresh packed coffee
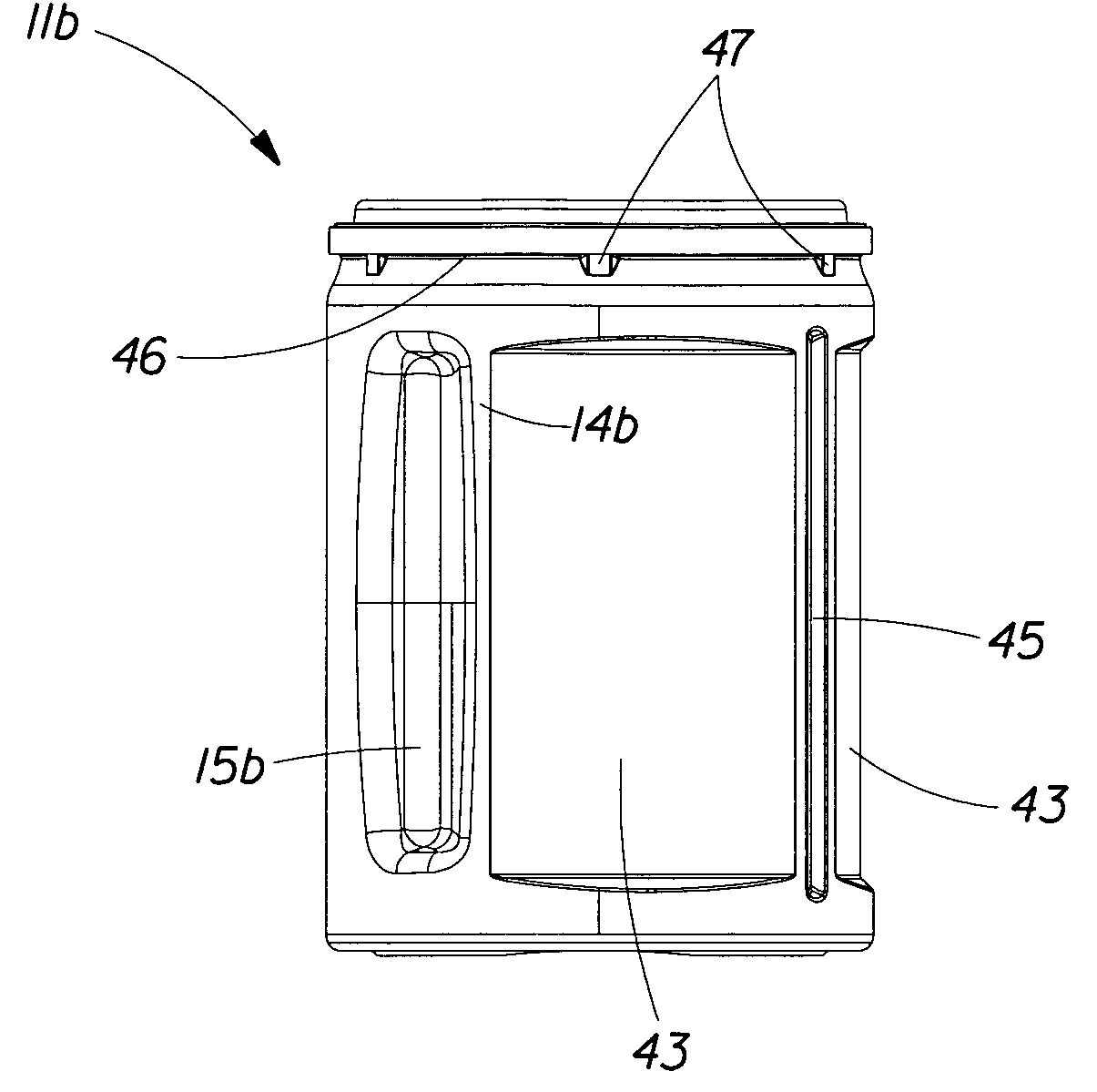
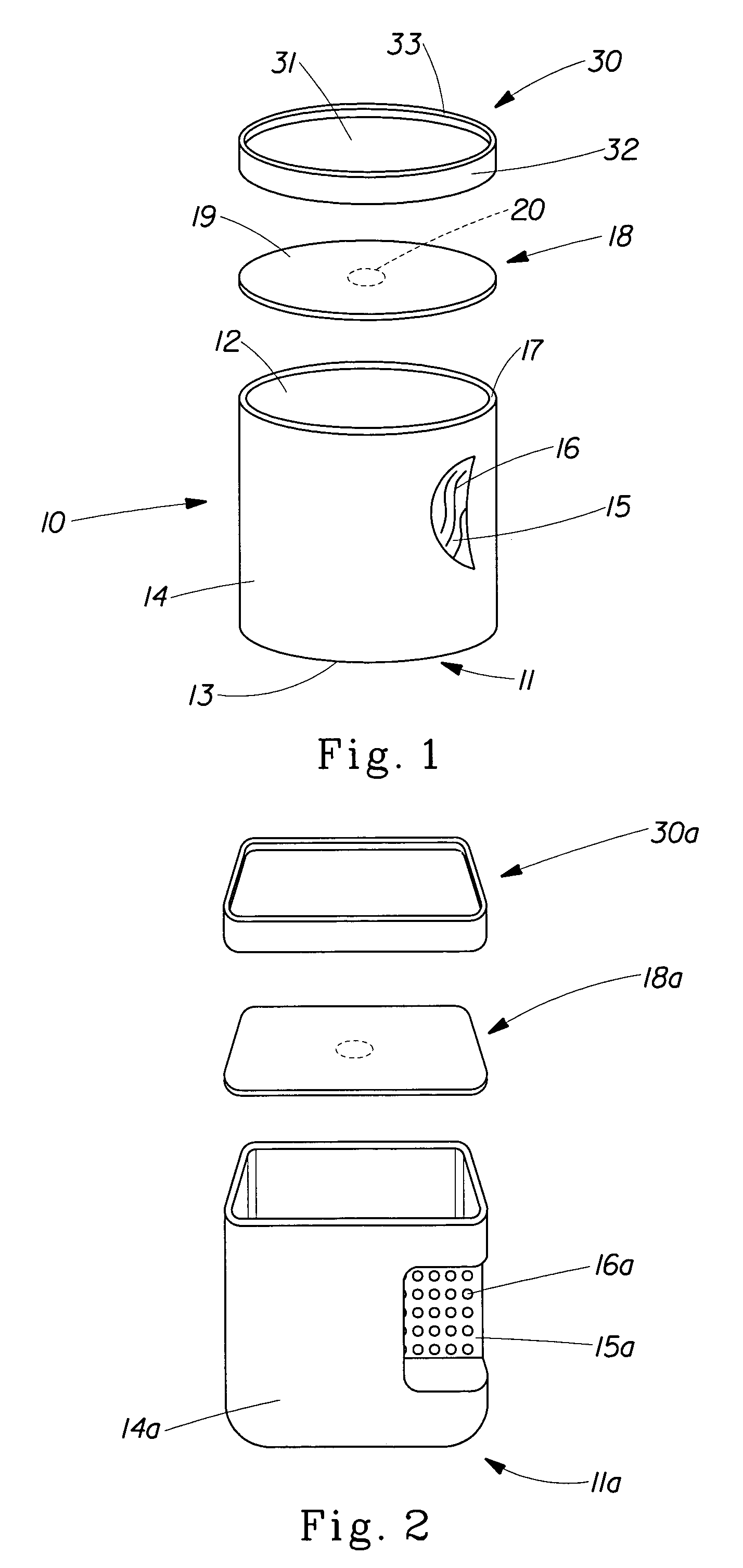
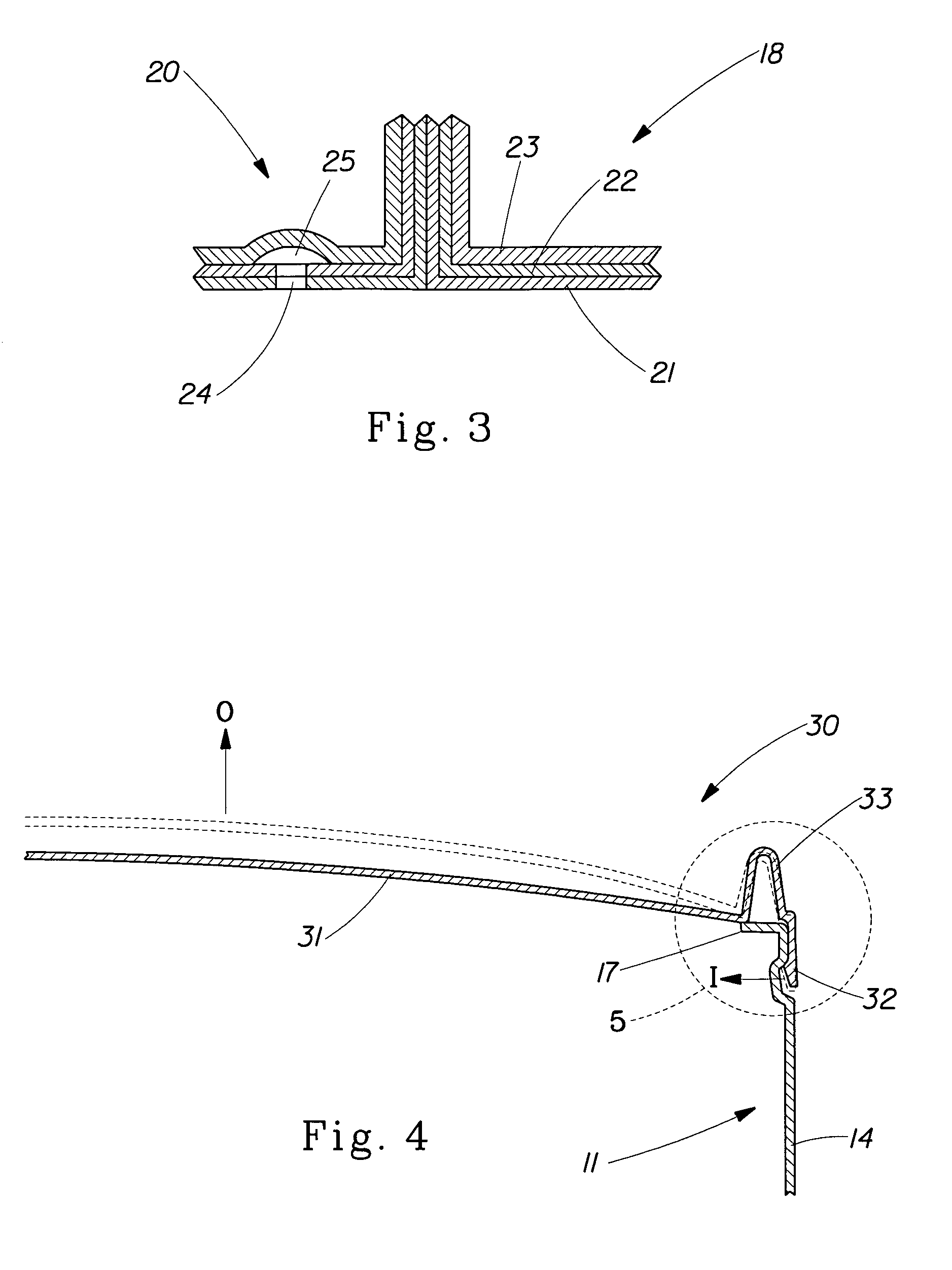
A fresh packaging system for roast and ground coffee having a top load capacity of at least about 16 pounds (7.3 Kg) comprising a container with a closed bottom, an open top, and a body enclosing a perimeter between the bottom and the top. A protuberance is continuously disposed around the perimeter of the body proximate to the top and forms a ridge external to the body. A flexible closure is removeably attached and sealed to the protuberance so that the closure seals the interior volume of the container. The container bottom and container body are constructed from a material having a tensile modulus number ranging from at least about 35,000 to at least about 650,000 pounds per square inch (at least about 2,381 to at least about 44,230 atm).
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY +3
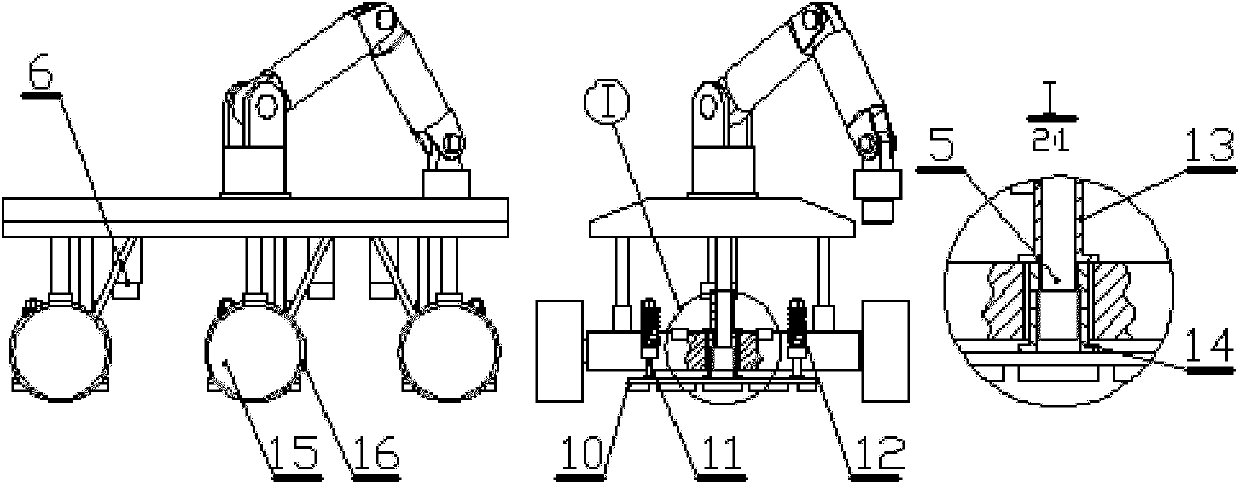
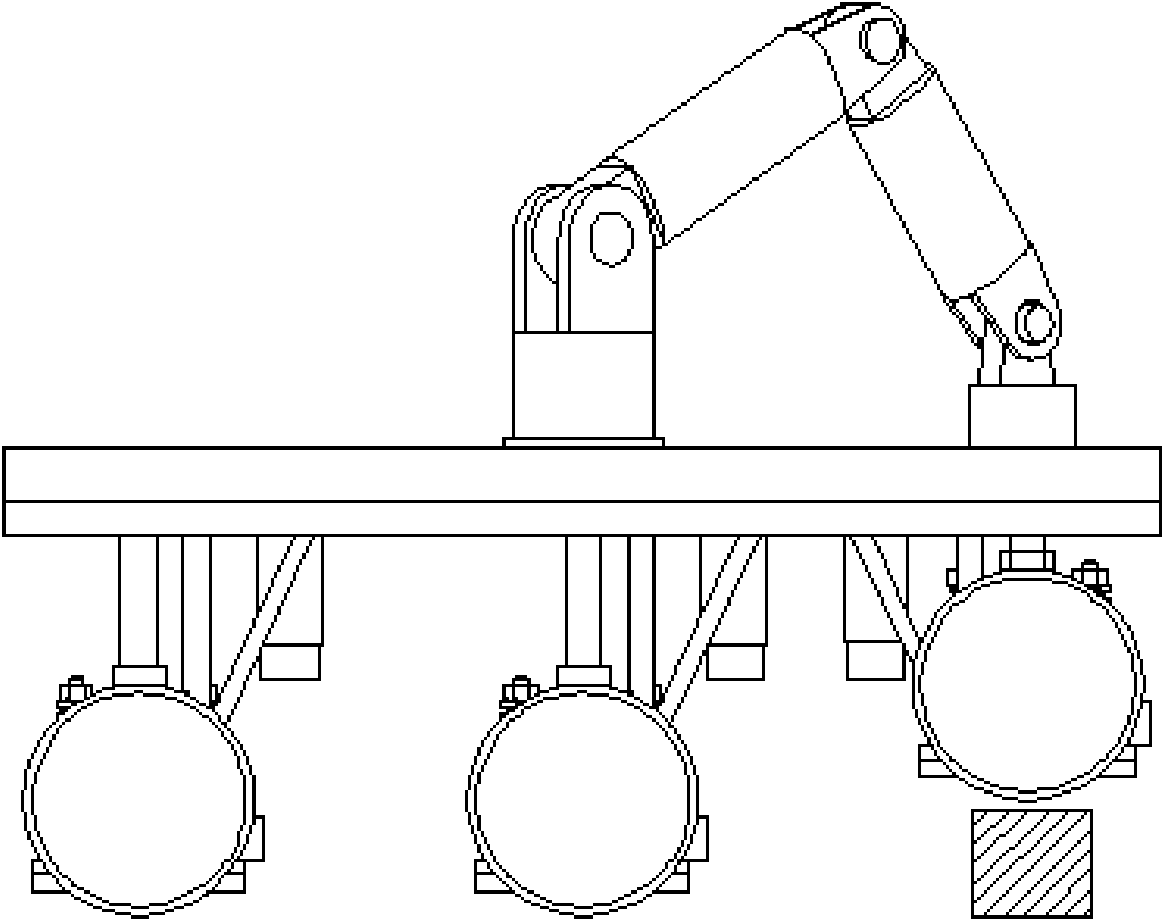
Wheel-foot combined obstacle detouring non-contact magnetic absorption type wall climbing robot system
InactiveCN101947777ASimple structureIncrease load capacityManipulatorVehiclesVehicle frameDrive motor
The invention discloses a wheel-foot combined obstacle detouring non-contact magnetic absorption type wall climbing robot system, belonging to the technical field of robots and comprising a robot frame, a 5-DOF (degree of freedom) robot arm, three groups of mobile absorption mechanisms, linear sliding rails, screws and drive motors, wherein the linear sliding rails, the screws and the drive motors respectively correspond to the three groups of mobile absorption mechanisms; the five-DOF robot arm is arranged above the robot frame; the three groups of linear sliding rails and screws are vertically arranged below the robot frame and two ends thereof are connected with the robot frame and the mobile absorption mechanism respectively; and the drive motor is fixedly connected with the mobile absorption mechanism. The invention solves the technical defects of the existing wall climbing robot in vertical wall surface operation, enables the robot to have the advantages of rapid speed and flexible steering of a wheeled mobile robot and have the characteristics of large magnetic absorption force and good load capacity as well as obstacle detouring capacity, and can satisfy the requirements of motion and operation in complicated environments.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
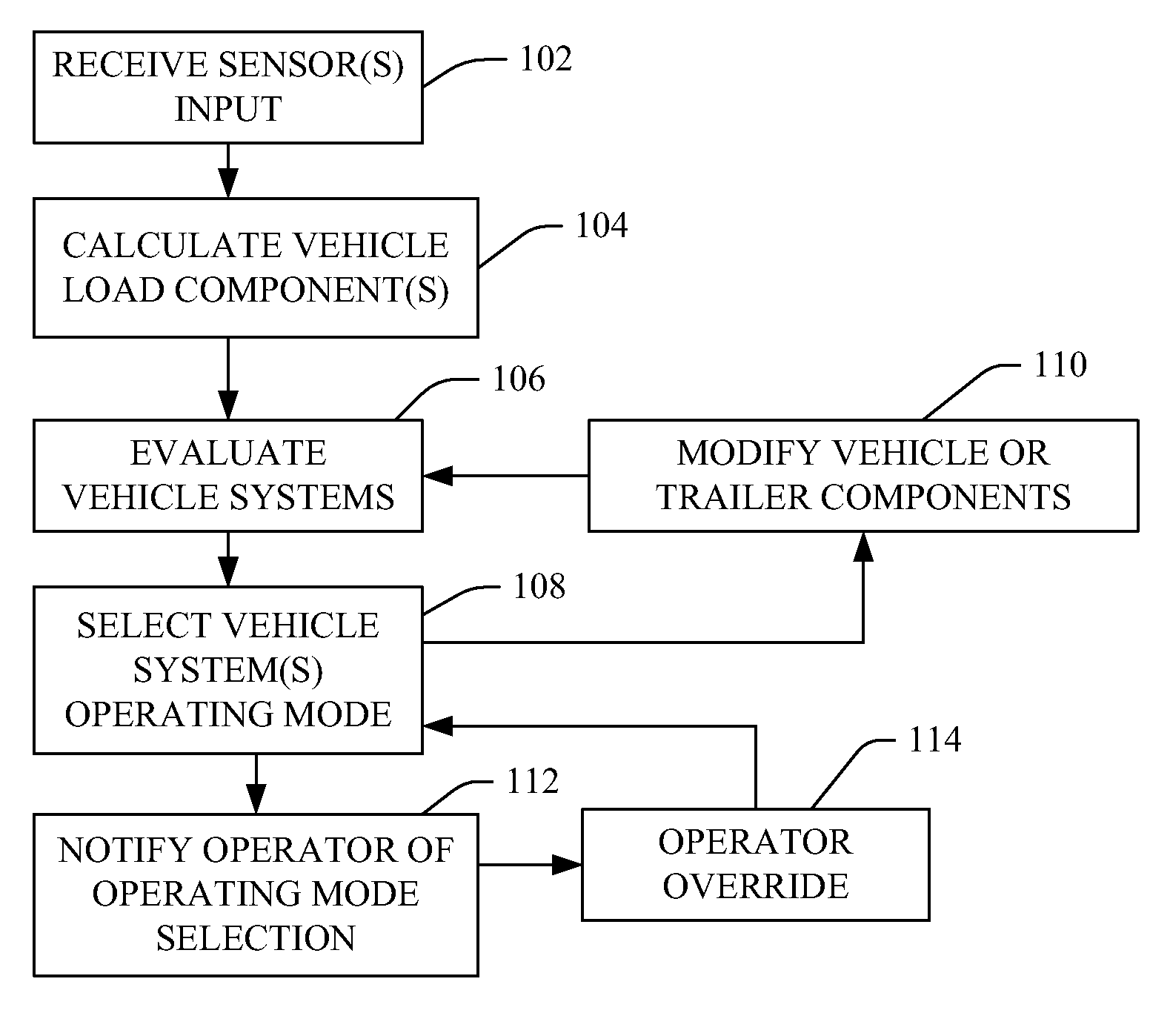
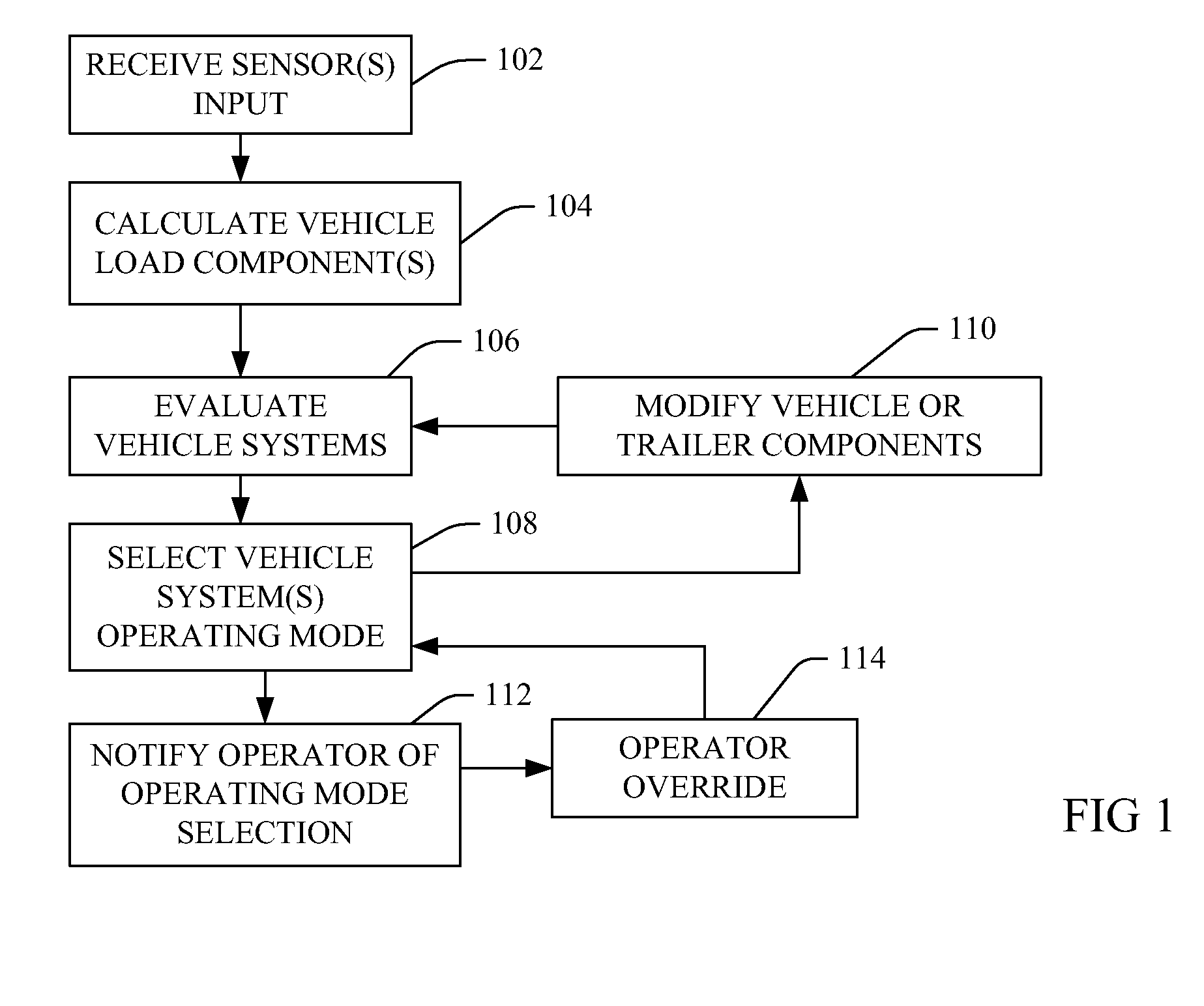
Adaptive vehicle configuration
InactiveUS20100114437A1Improve performanceImprove vehicle efficiencyDigital data processing detailsGearing controlOperation modeLoad distribution
Methods, including service methods, program products and systems are provided for sensing vehicle loads and responsively and automatically configuring a vehicle. Vehicle-mounted load sensors sense vehicle loads, a vehicle processing means calculating a load imparted to the vehicle and comparing imparted loads to load capacity ratings or thresholds and responsively adjusting a vehicle cooling, transmission, braking, suspension or engine system into a revised operating mode. Modifying a component may entail revising a load capacity rating or threshold and repeating sensing, calculating, comparing and adjusting until the revised rating or threshold is met, or progressively adjusting in proportion to a change in a historic sensed load. Adjusting of the vehicle system may be biased to a performance characteristic or a load distribution. A supervisory entity may override automatic adjustment.
Owner:IBM CORP
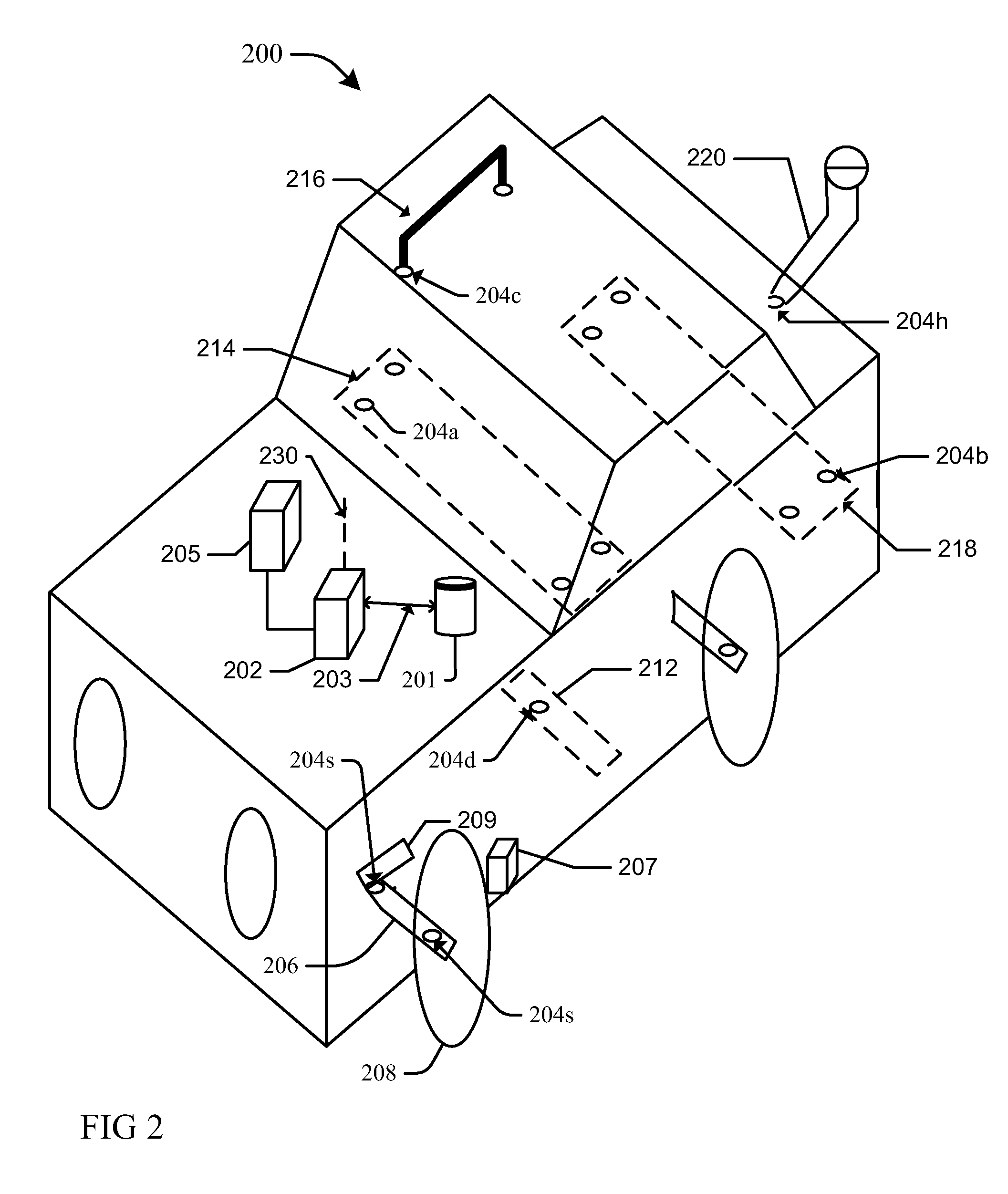
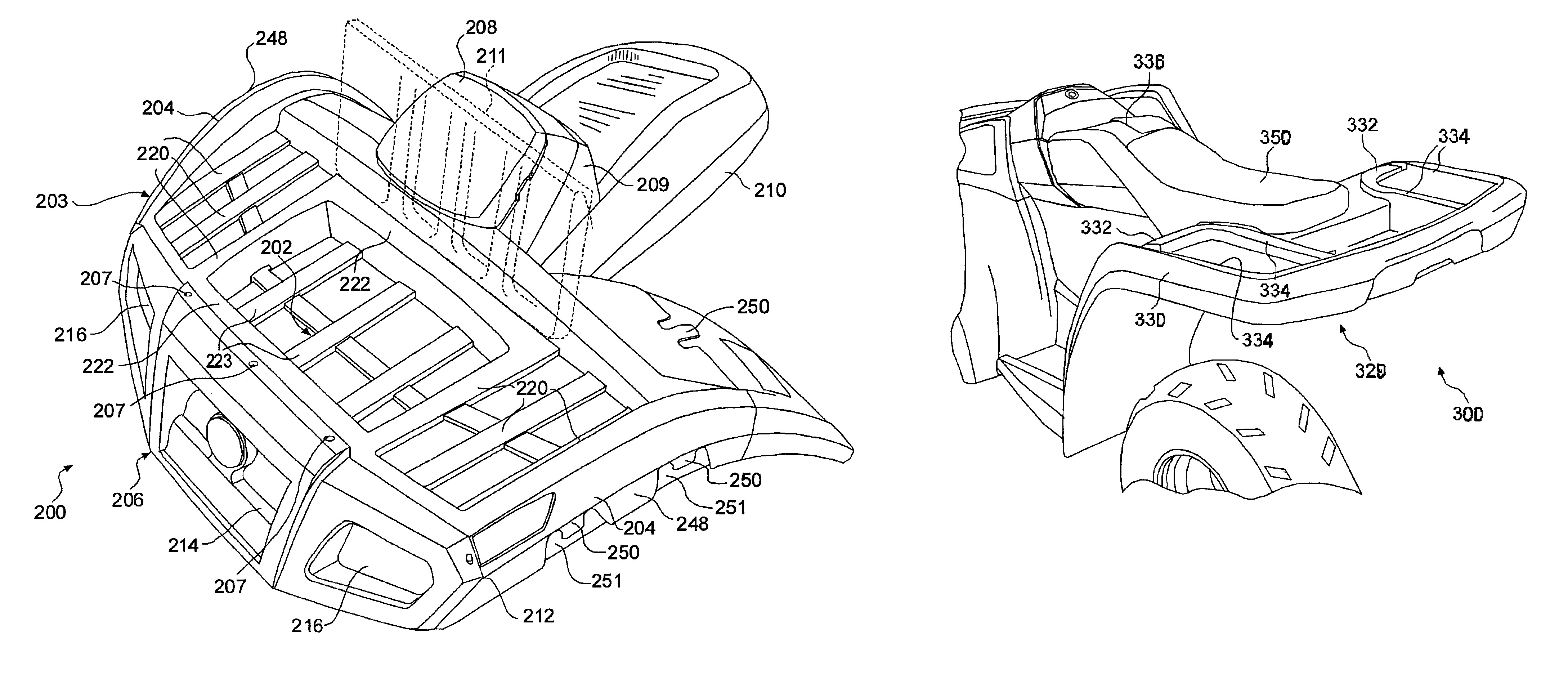
Fender structure for an all terrain vehicle
An all terrain vehicle (ATV) includes a plurality of wheels and a fender structure positioned over the wheels having a support portion designed as and defining a load-bearing surface. The fender structure may include a plurality of raised support portions that increase rigidity and load capacity. Additionally, it is not necessary to support either the fender structure or the support portion using the bumper of the ATV. The fender structure may be formed with plastic material, such as polyethylene, polypropylene or fiberglass-charged polyethylene, and may be manufactured using a blow-molding technique or an injection molding technique. The ATV may also include mud guards and a floor board that extends between the mud guards. The mud guards and the floor board may be formed as an integral or one piece unit with the fender structure. The mud guards can be injection molded or blow-molded while the fender structure can be blow-molded.
Owner:BOMBARDIER RECREATIONAL PROD INC
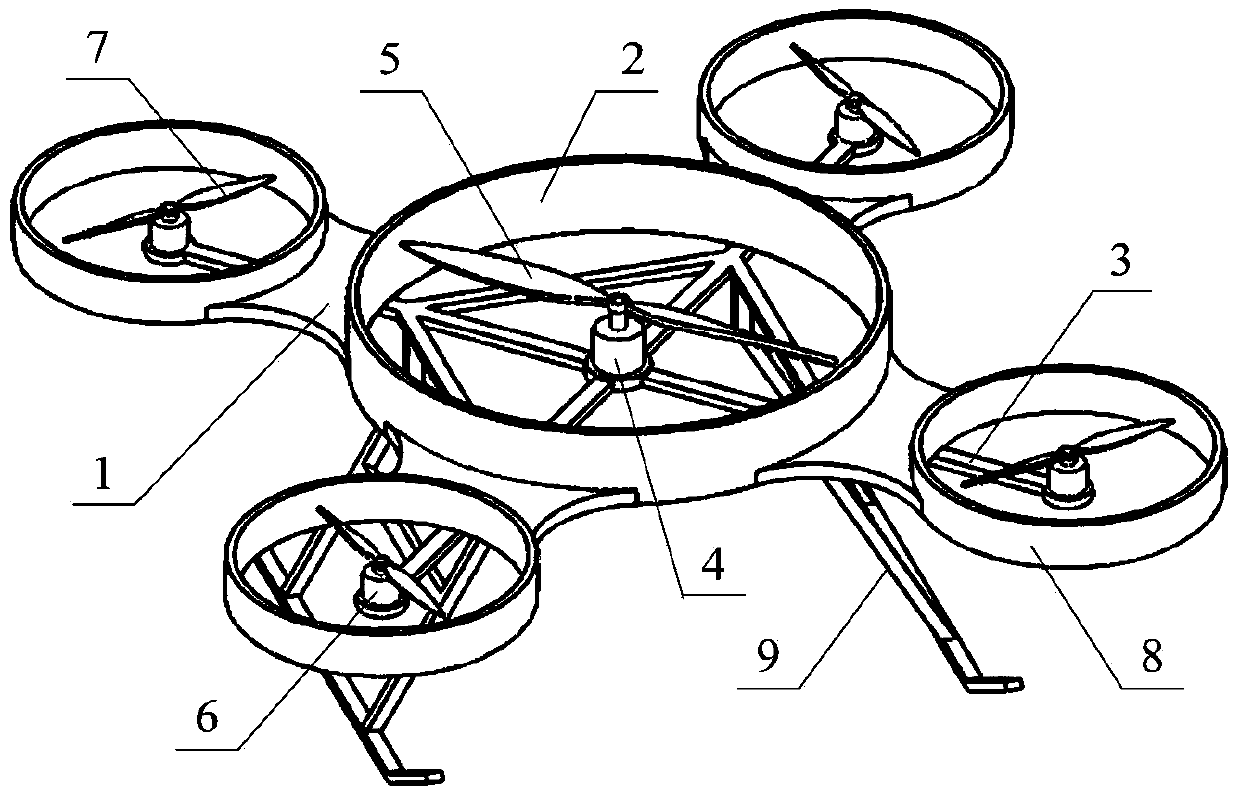
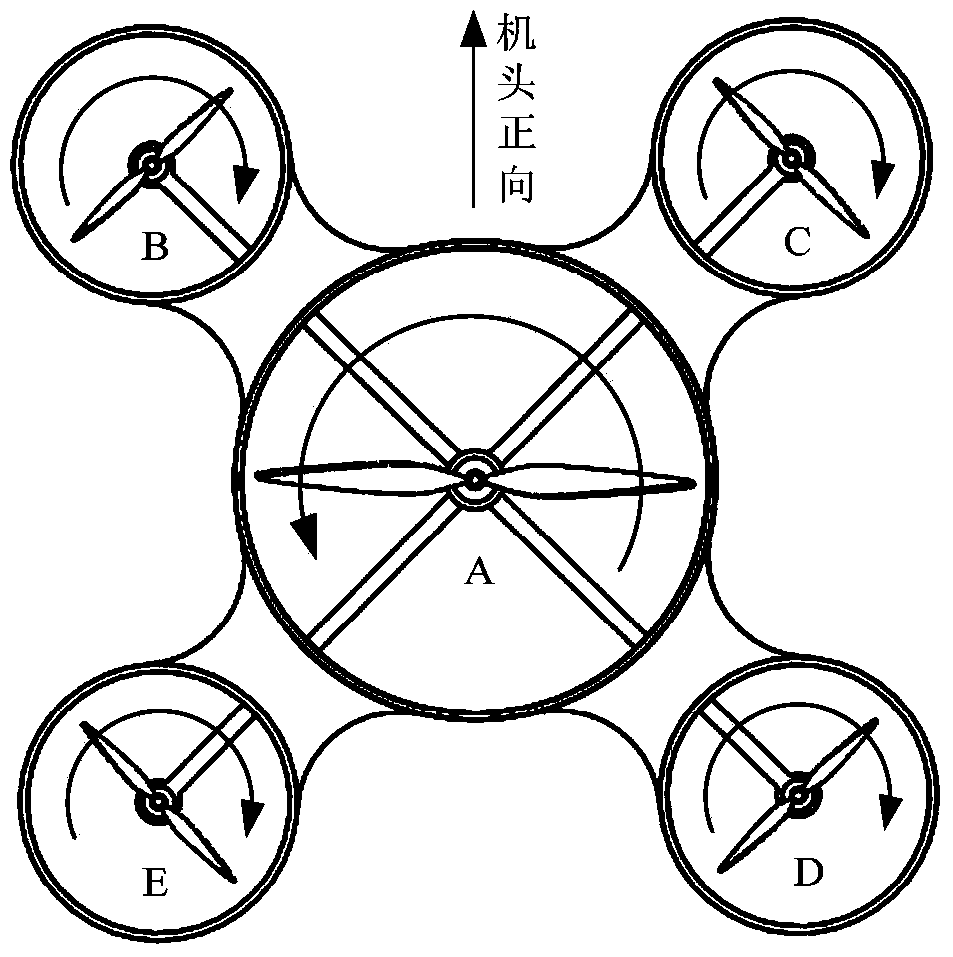
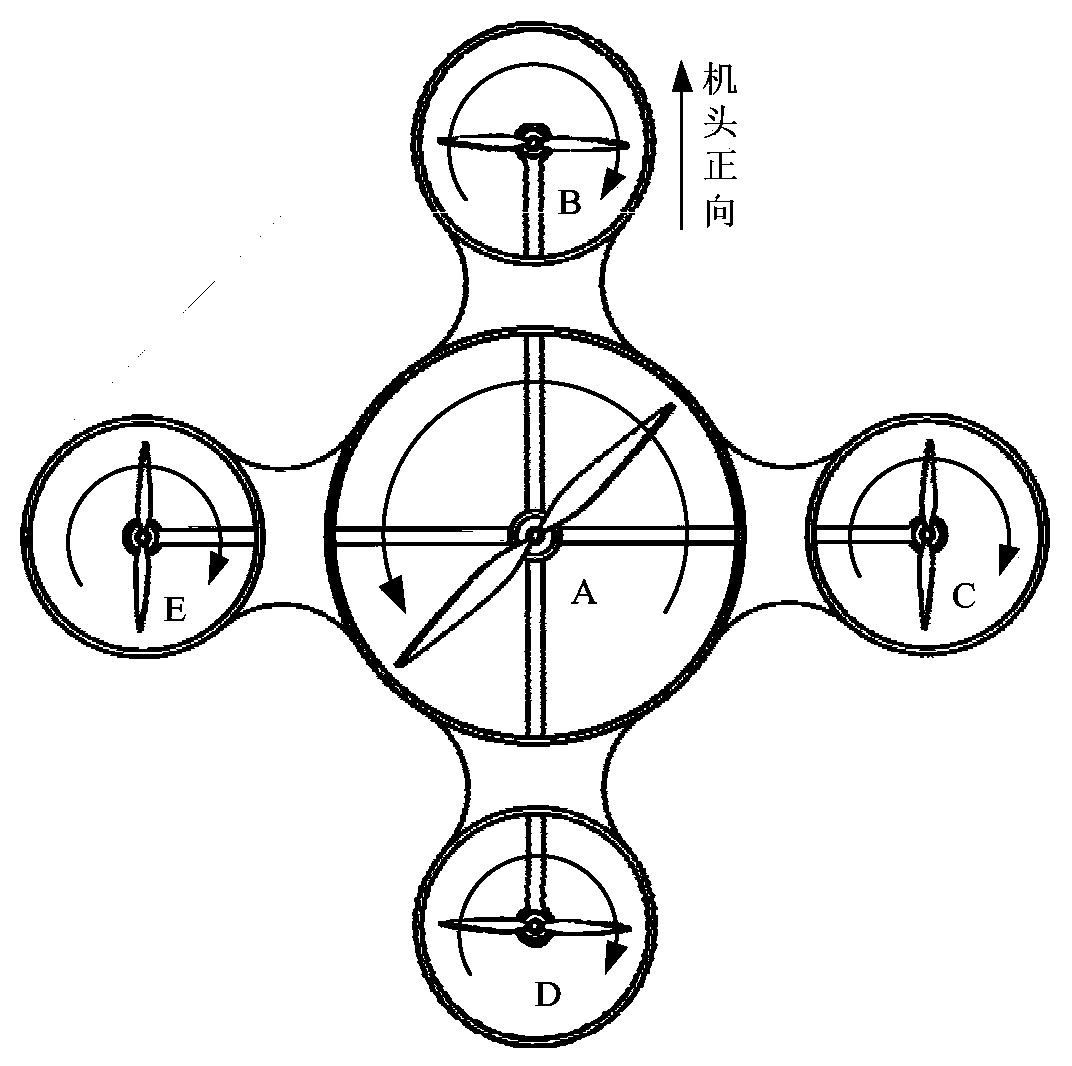
Multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle
The invention discloses a multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle which comprises a body, wherein a central duct is arranged at the center of the body; n rotor support arms are circumferentially and uniformly distributed in a radial manner on the periphery of the central duct, and n is greater than or equal to 3; a central rotor assembly is coaxially mounted in the central duct; the central rotor assembly comprises a central rotor motor and a central rotor connected with an output shaft of the central rotor motor; the central rotor motor is fixedly mounted at the center of the body; a peripheral rotor assembly is mounted on each rotor support arm; the peripheral rotor assembly comprises a peripheral rotor motor and a peripheral rotor connected with an output shaft of the peripheral rotor motor; the peripheral rotor motor is mounted on the rotor support arm; the size of the central rotor is greater than that of the peripheral rotor; the rotation direction of the central rotor is opposite to that of the peripheral rotor. Therefore, the multi-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle disclosed by the invention has the advantages of novel pneumatic layout, stable and reliable hovering and strong load capacity and is easy to realize in engineering.
Owner:NANJING CARVEDGE TECH
Variable-torque four-rotor aircraft with large load capacity
InactiveCN102490896AImprove maximum efficiencyStrong control abilityRotocraftJet aeroplaneWater level
The invention relates to a gyroplane and further relates to a variable-torque four-rotor aircraft with large load capacity. The variable-torque four-rotor aircraft with large load capacity contains a fuselage, four rotor arms which are connected with the fuselage and are symmetrically distributed, and rotors positioned on the rotor arms. Among the four rotors, two adjacent rotors rotate in opposite directions. The included angle of each rotor blade 1201 to the water level can be adjustable, thus making the lift force adjustable and further adjusting the attitude of the aircraft. According to the invention, operationality of the aircraft is substantially raised.
Owner:TIANJIN AURORA UAV TECH
Limiting requests by web crawlers to a web host
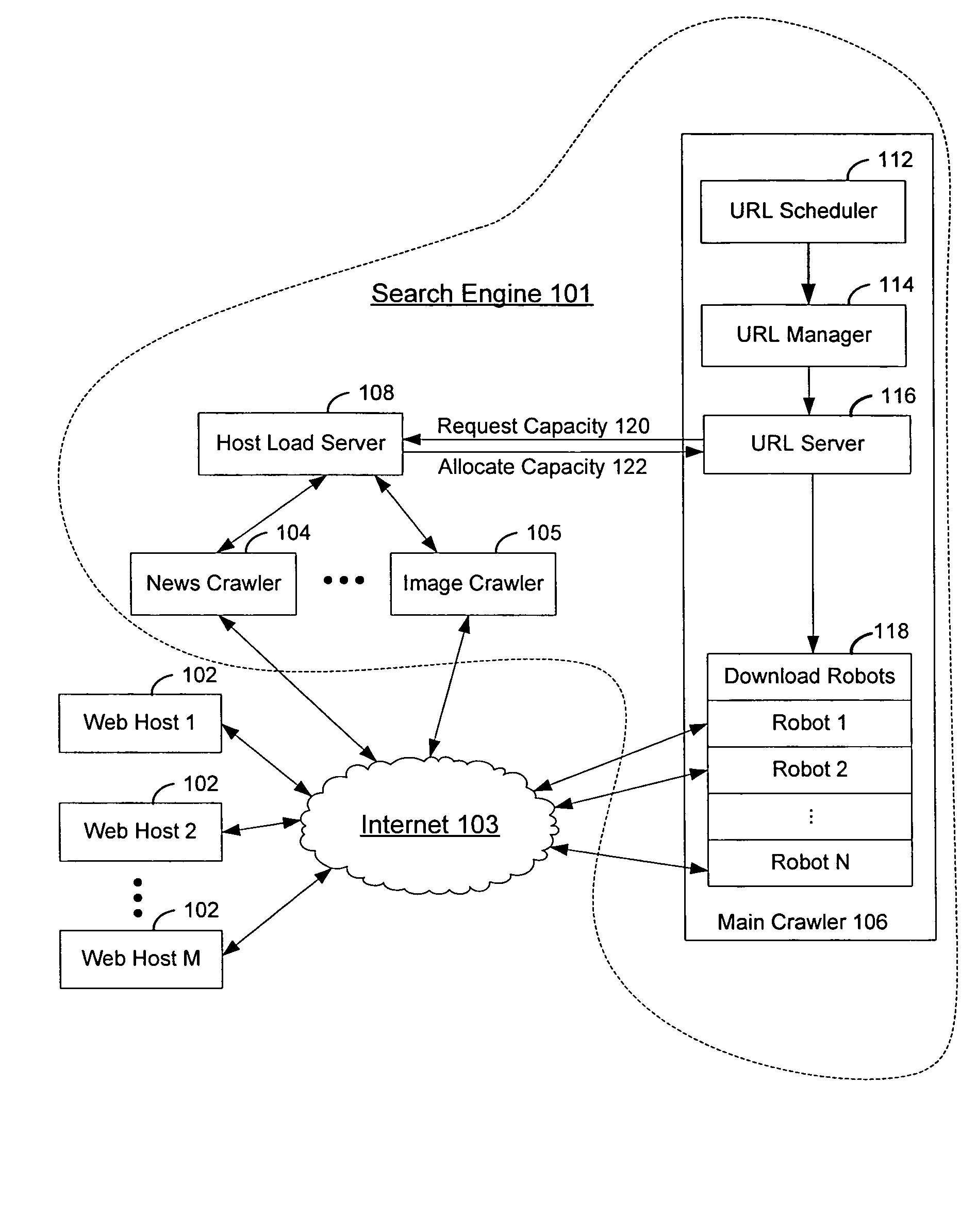
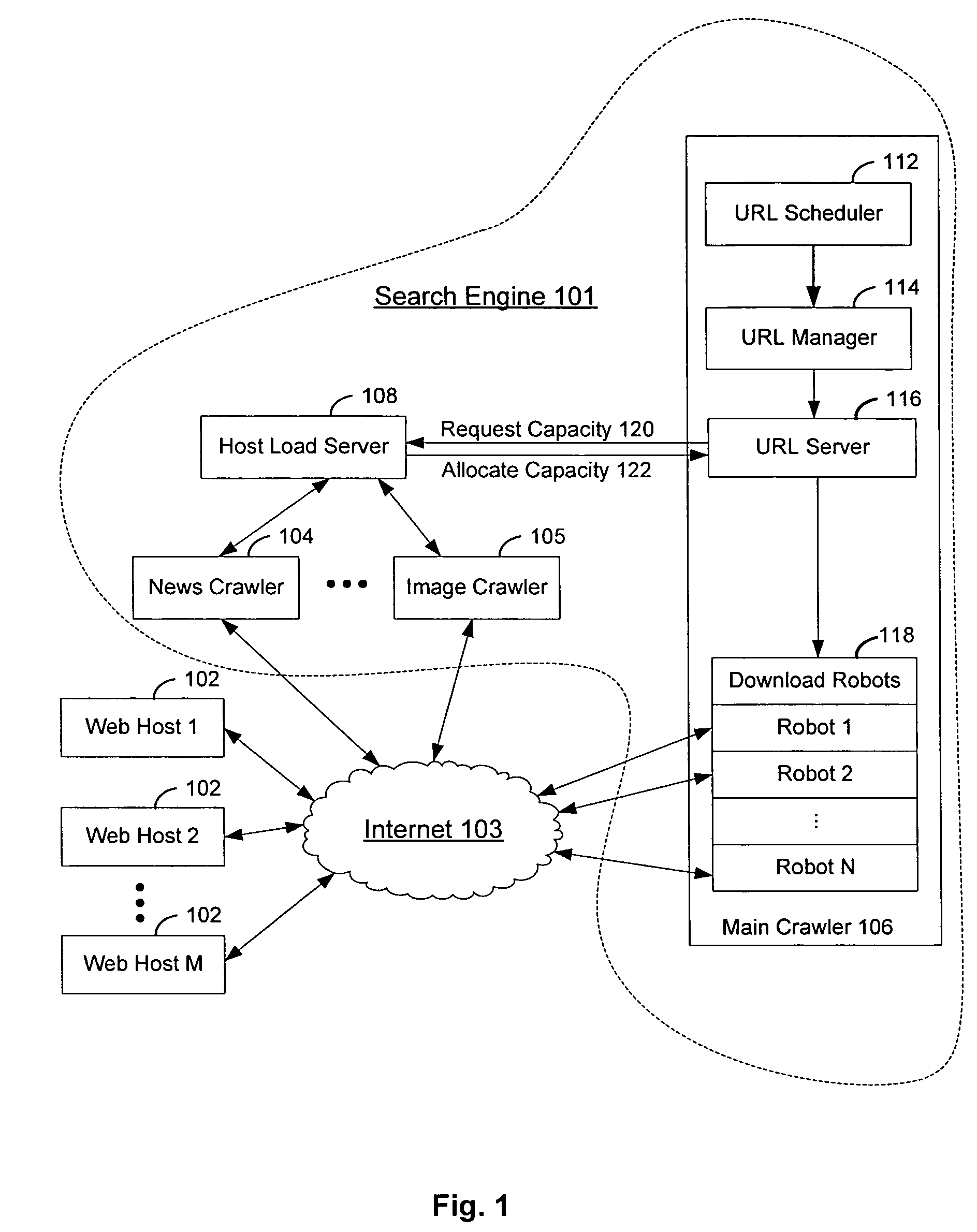
InactiveUS7774782B1Avoid losing its leaseReduce load capacityMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsLoad capacityWeb crawler
A host load server balances a web host's load capacity among multiple competing web crawlers of a search engine. The host load server establishes a lease for each pair of requesting web crawler and requested web host. The lease expires at a scheduled time. If the web crawler completes its mission of retrieving documents from the web host prior to the expiration of the lease, the host load server releases the load capacity allocated to the web crawler and makes it available for other competing web crawlers. If the web crawler submits a request for renewing its lease with the web host at the scheduled time, the host load server allocates another share of load capacity to the web crawler. If the web crawler does not submit any request at the scheduled time, the host load server terminates the lease and releases the load capacity for other web crawlers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Central air-conditioning self-optimization intelligent fuzzy control device and control method thereof
ActiveCN102721156AImprove cycle timeOptimize and adjust the running cycleSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusBusiness efficiencyHigh energy
The invention discloses a central air-conditioning self-optimization intelligent fuzzy control device and a control method thereof. Technological parameters and indoor and outdoor environmental parameters of all control points of a central air-conditioning system are collected, running efficiency of a circulating system and control ends are tracked in real time according to actual load capacity of the system and end cold and hot source requirements, operation cycle of a main machine is optimized and adjusted, operation energy efficiency of each link of the system is comprehensively controlled, so that the system can always run under working conditions of high energy efficiency ratio. Meanwhile, process data, energy consumption data and equipment running data of the central air-conditioning system are summarized to form an intelligent control base, technical process such as analysis and operation is performed through the a central air-conditioning self-optimization intelligent fuzzy controller, new control strategies are generated, on-line upgrading control algorithm and energy-saving potential mining are achieved, energy consumption of the system is optimized, the operation is simplified, so that the operating efficiency of each device of the system is adjusted, and the aims of high efficiency, energy saving and intelligent control are achieved.
Owner:山东金洲科瑞节能科技有限公司
Electromagnetic repulsion force system and permanent magnetic system coupled self-adapting control mechanism
InactiveCN101315836AMaintain mechanical strengthMaintain output capacitySwitch power arrangementsHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesKinematicsRepulsion force
The invention discloses a self-adaptive control mechanism which couples an electromagnetic repulsion system with a permanent magnetism system. The invention adopts an electromagnetic repulsion device spinning disk of circular table structure, relatively to the circular disk spinning disk, which maintains the mechanical strength and output capacity of the spinning disk, simultaneously greatly reduces the increase of kinematic scheme mass of the control mechanism, and greatly enhances the driving load capacity of the control mechanism. The control mechanism of the invention adopts the self-adaptive motion proposal, which avoids the frequent high speed motion of a breaker, reduces the mechanical strength request for the breaker, and prolongs the motion life of the breaker effectively.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
High-precision laser photocuring 3D (three dimensional) printer
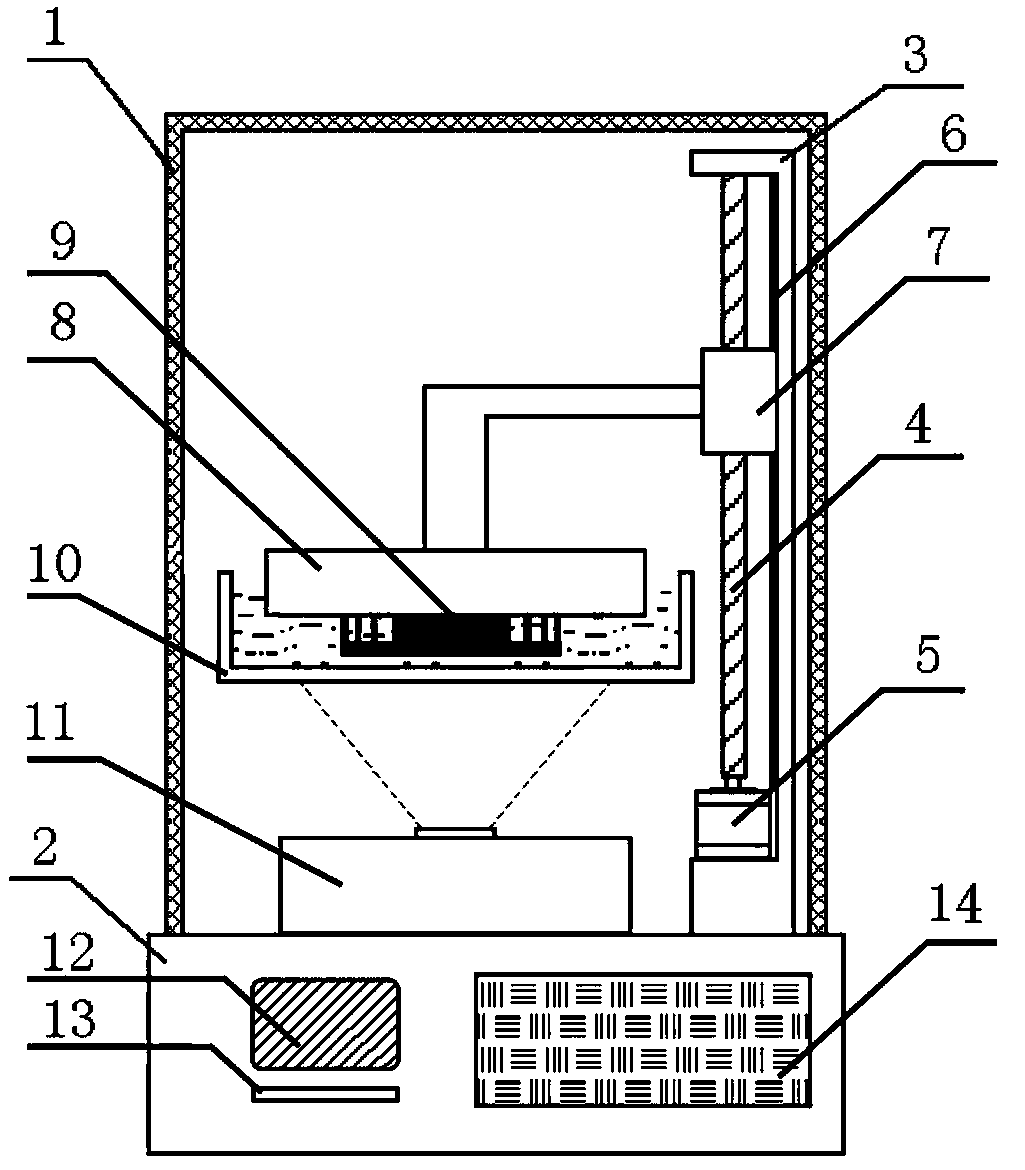
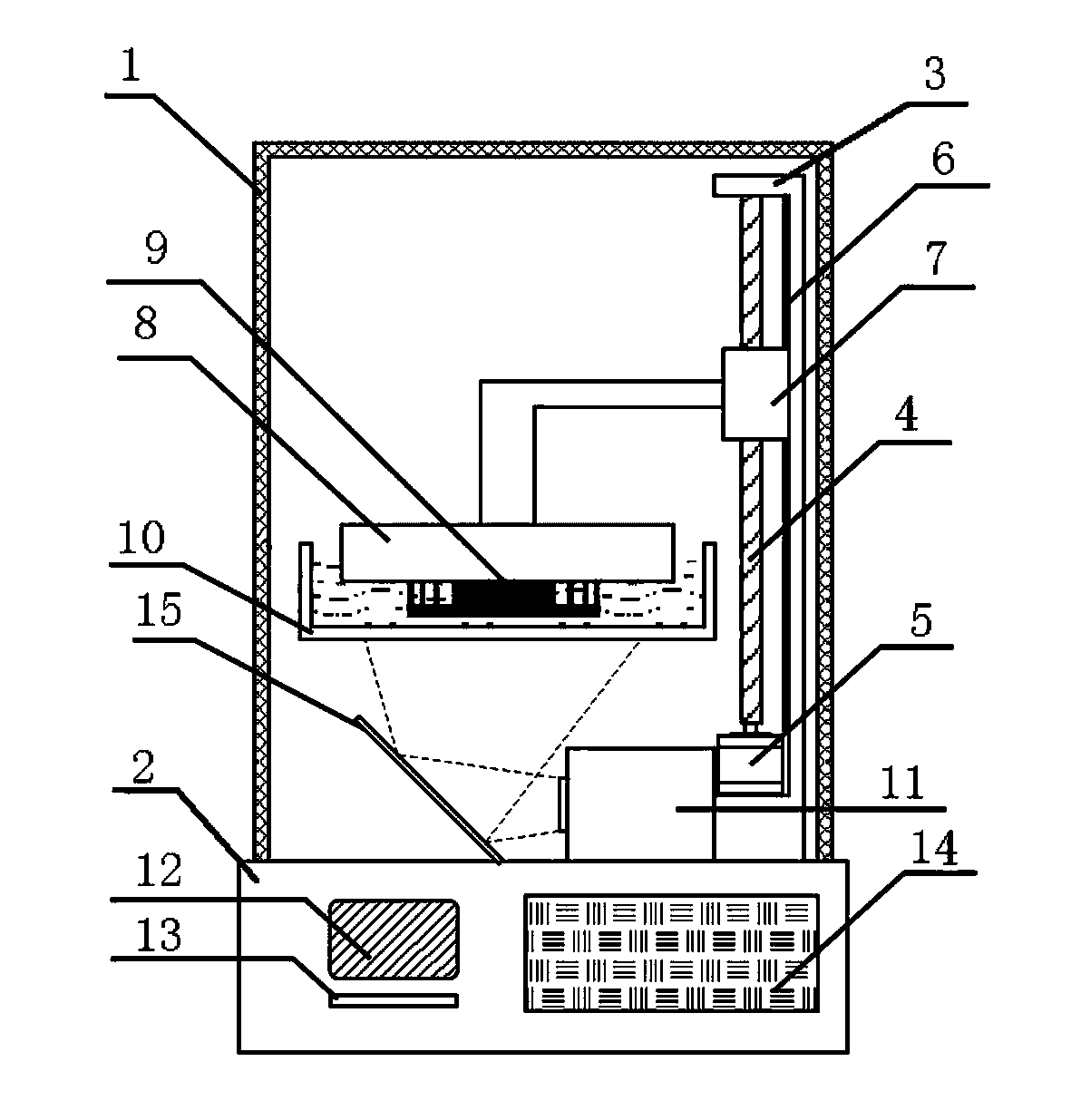
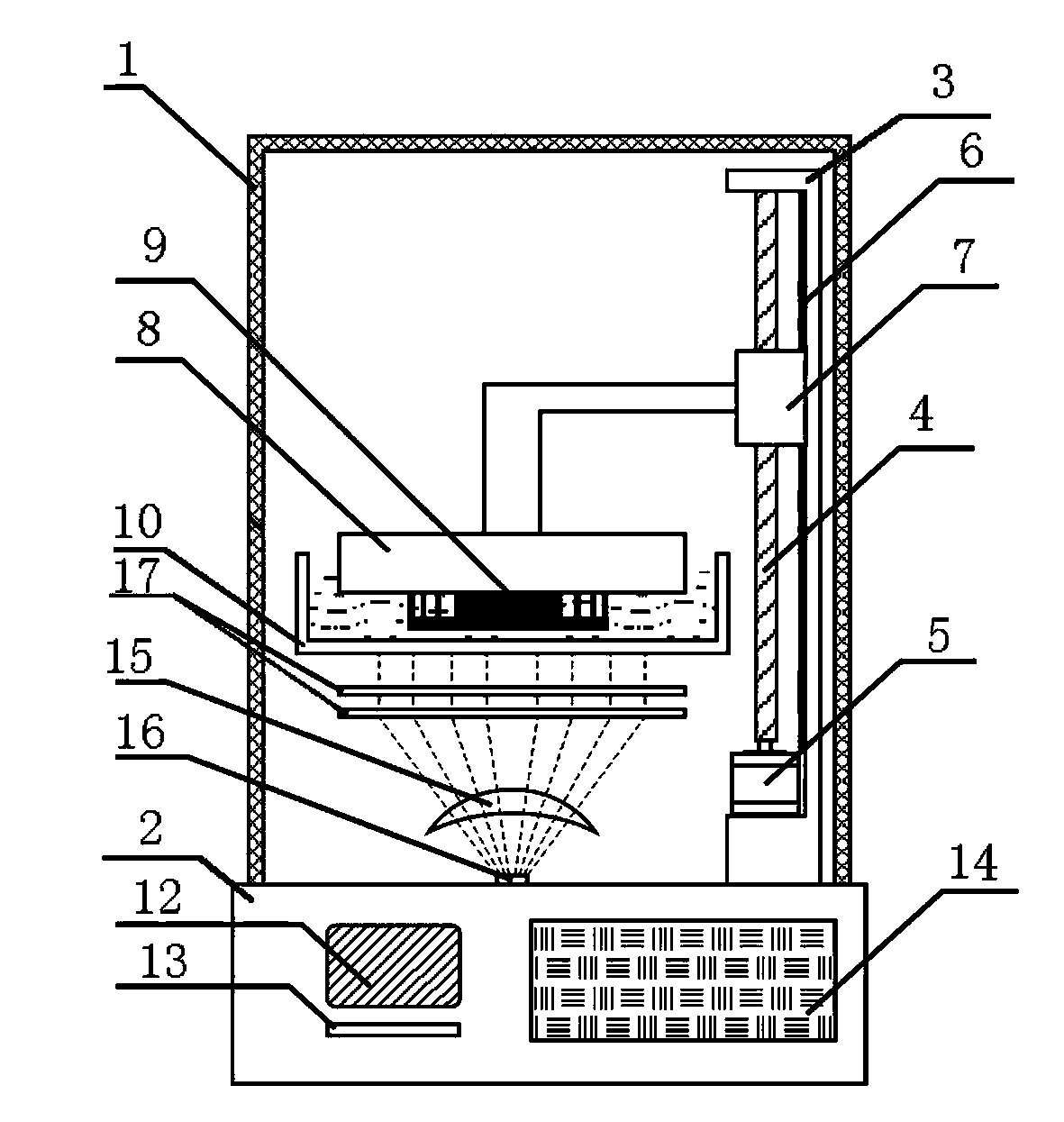
The invention relates to a high-precision laser photocuring 3D (three dimensional) printer. The high-precision laser photocuring 3D printer comprises a shell and a pedestal. The high-precision laser photocuring 3D printer has the beneficial effects that one end of a high-precision ball screw is connected with a servo motor, the control precision of the servo motor is guaranteed by a rotary encoder at the rear end of a motor shaft and is accurate, and the high-precision laser photocuring 3D printer utilizes the servo motor, so that the printer is stable, and the energy consumption is reduced; as the ball screw has the characteristics of high positioning precision, small friction force, high rigidity and strong load capacity, the molding precision of the printer is high; a circuit control module is connected with a touch screen and a power supply switch respectively through data wires to intelligently control the printer, so that the control precision and processing efficiency are increased; a digital projection device comprises a digital projector horizontally fixed on the upper side of the pedestal, and a plane mirror, so that the structure of the printer is compact; the digital projection device comprises an ultraviolet source and a focusing lens, and the focusing lens is arranged above the ultraviolet source, so that the realizing theory is simple, and the cost performance is high.
Owner:RUIAN MAITIAN NETWORK TECH
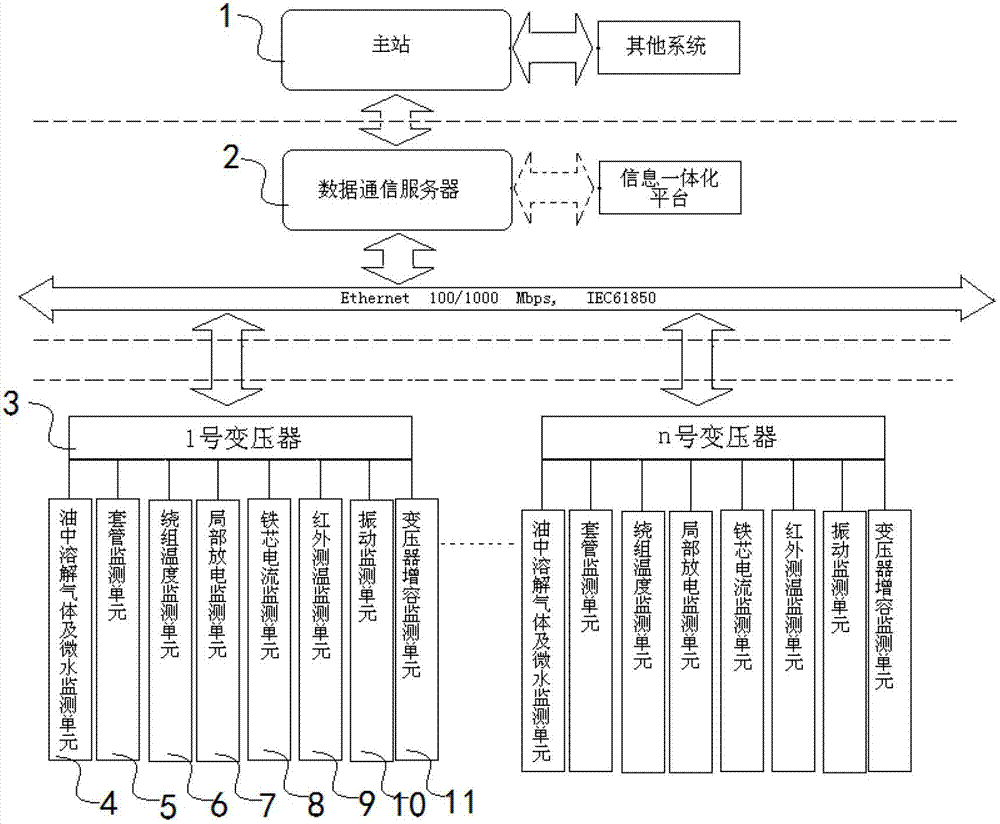
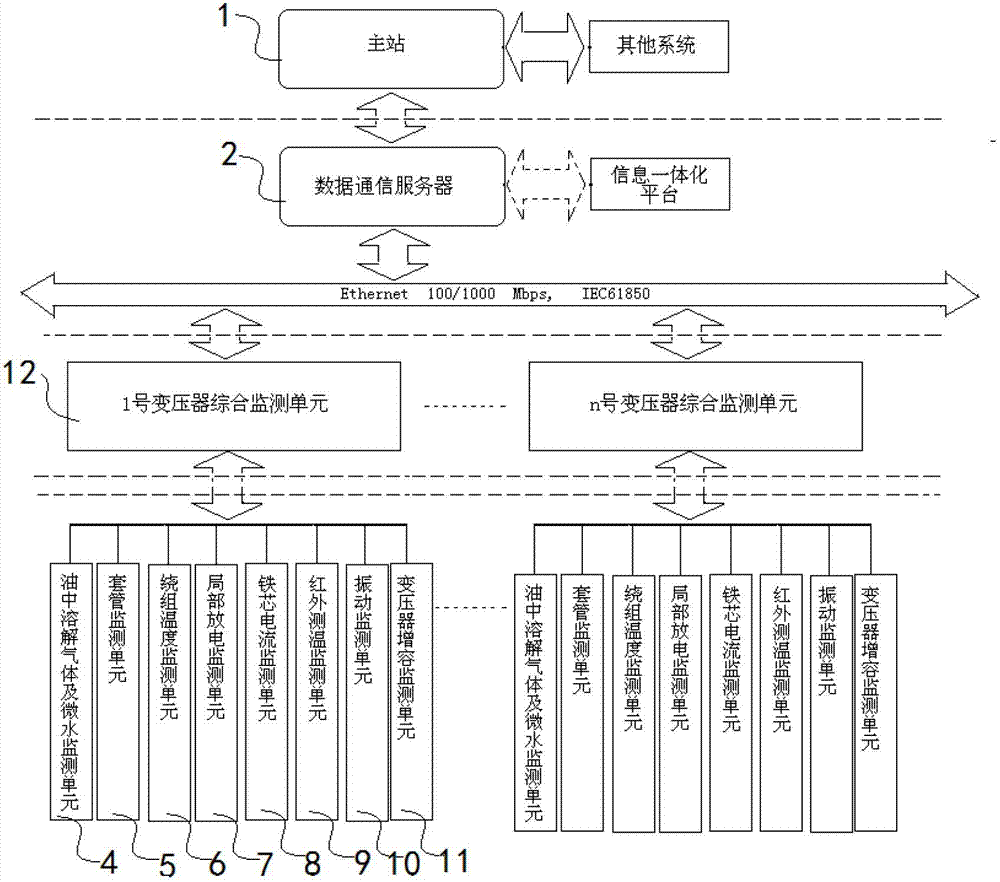
On-line monitoring networking of power transformer of intelligent substation
ActiveCN103199621AScalableFunctionalCircuit arrangementsSustainable buildingsPower flowSmart substation
The invention discloses on-line monitoring networking of a power transformer of an intelligent substation. The on-line monitoring networking synthetically considers all on-line monitoring projects of a current power transformer, namely on-line monitoring of gas dissolved in oil and micro water, on-line monitoring of casing pipes, on-line monitoring of winding fiber temperature detection, on-line monitoring of partial discharging, on-line monitoring of iron core grounding currents, on-line monitoring of infrared temperature detection, on-line monitoring of vibration, on-line monitoring of transformer load capacity and the like. Basic configuration, technical parameters and the like of each monitoring project are comprehensively studied and ruled. According to the on-line monitoring networking of the power transformer of the intelligent substation, on-line monitoring technology of the power transformer of the intelligent substation is studied in detail, and all the monitoring principles and monitoring technology indexes of on-line monitoring units of all current and national transformers are studied in an omnibearing mode. A monitoring unit of the load capacity of the transformer is firstly raised and applied, and detailed study is performed on software functions of an on-line monitoring system. A set of complete and formal technical standards of the on-line monitoring system of the power transformer are set up for the intelligent substation.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
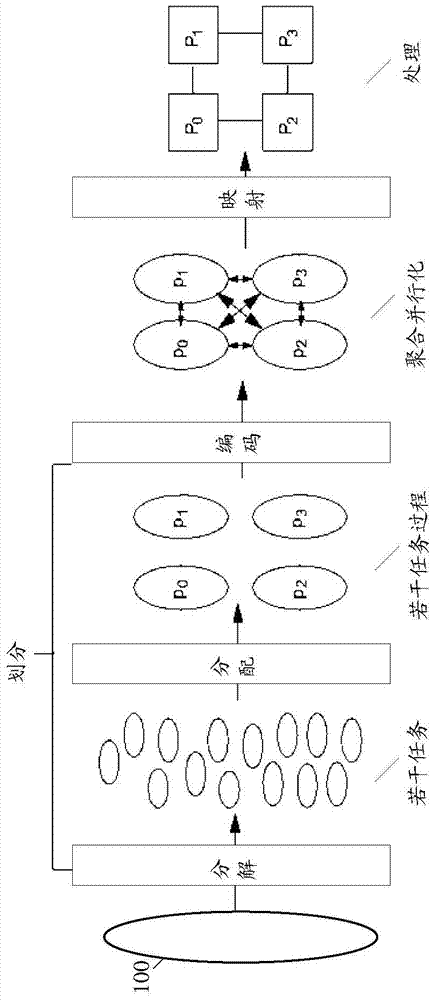
Parallel computation method and system
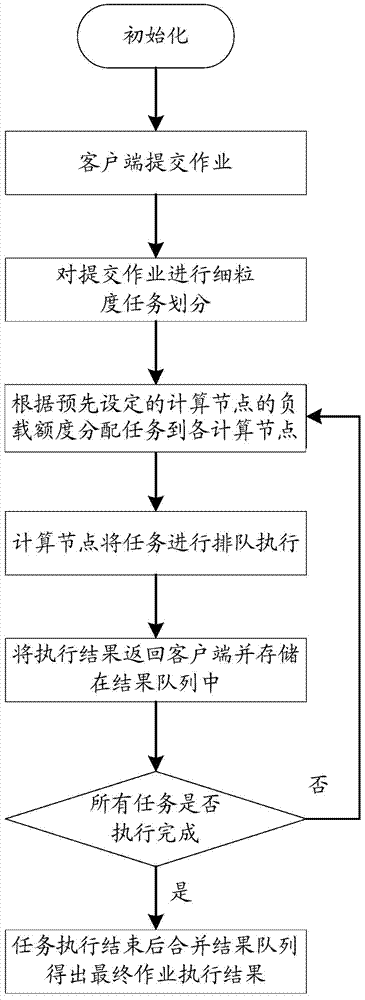
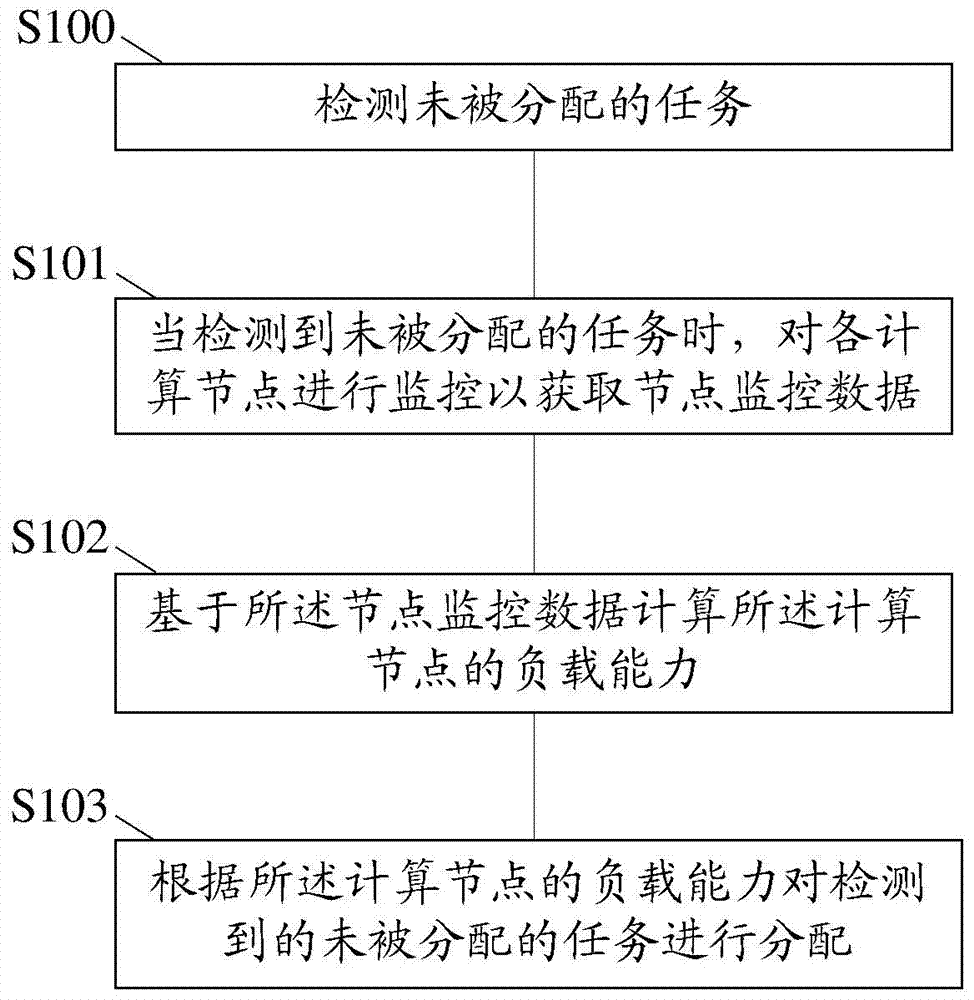
InactiveCN103617086ARealize a reasonable distributionImplement resource monitoringResource allocationParallel computingComputing systems
The invention relates to a parallel computation method and system. The method includes: monitoring each computing node to acquire node monitoring data; calculating load capacity of each computing node according to the node monitoring data; assigning tasks to be assigned according to the load capacities of the computing nodes. Correspondingly, the system comprises a node monitoring unit, a task load management unit and a task scheduling unit. Through the application of the technical scheme, task can be reasonably assigned during parallel computation and parallel computation can be executed more efficiently.
Owner:NEUSOFT CORP
Anti-knock container
ActiveCN1632445AOpen and close flexible and convenientNot easy to wearAmmunition storageDetonatorEngineering
The invention belongs to storage and transportation equipment for detonating materials (detonators), in particular to an anti-explosion container. The anti-explosion container includes an upper cover, a cylinder and a fixed bracket. It is characterized in that the cylinder is composed of an outer cylinder and an inner cylinder, wherein the outer cylinder is a cylinder with an open upper end and a closed lower end. The lower part of the inner cylinder is provided with a lower wave breaking plate. , the upper cover is composed of a top cover plate and a cover wall, wherein the lower end of the cover wall is provided with an upper wave dissipation plate, the cover wall and the upper port of the outer cylinder are connected by splines, and the top cover plate is provided with explosion-venting bolts. The invention can not only ensure safety when the detonating equipment and explosives are transported in the same vehicle, but also can seal the harmful gas generated by the explosion in the container in case of an explosion in the container, and discharge the harmful gas after it is transported to a suitable place. In order to avoid polluting the environment and causing casualties and damage to surrounding personnel and facilities. It has the advantages of flexible and convenient opening and closing, large loading capacity, long service life, and good anti-explosion and explosion-proof performance.
Owner:蒋友明
Method and apparatus for making foam blocks and for building structures therewith
InactiveUS6848228B1Easy to handleEasy to transportStrutsConstruction materialFoaming agentLoad capacity
Foam blocks may be manufactured using a two part urethane foaming agent or the like at the construction site using a mold that may be disassembled into a plurality of component pieces for ease of transportation and to facilitate removal of a block. Preferably, the blocks are formed in the mold in which a facing is placed such that the facing is bonded to the foam of the block. A wall constructed from successive courses of blocks will have intersecting horizontal and vertical channels which may be filled with concrete and reinforcing rod to produce a wall with high horizontal and vertical load capacity as well as superior insulating properties.
Owner:WILLIAMS CHESTER W
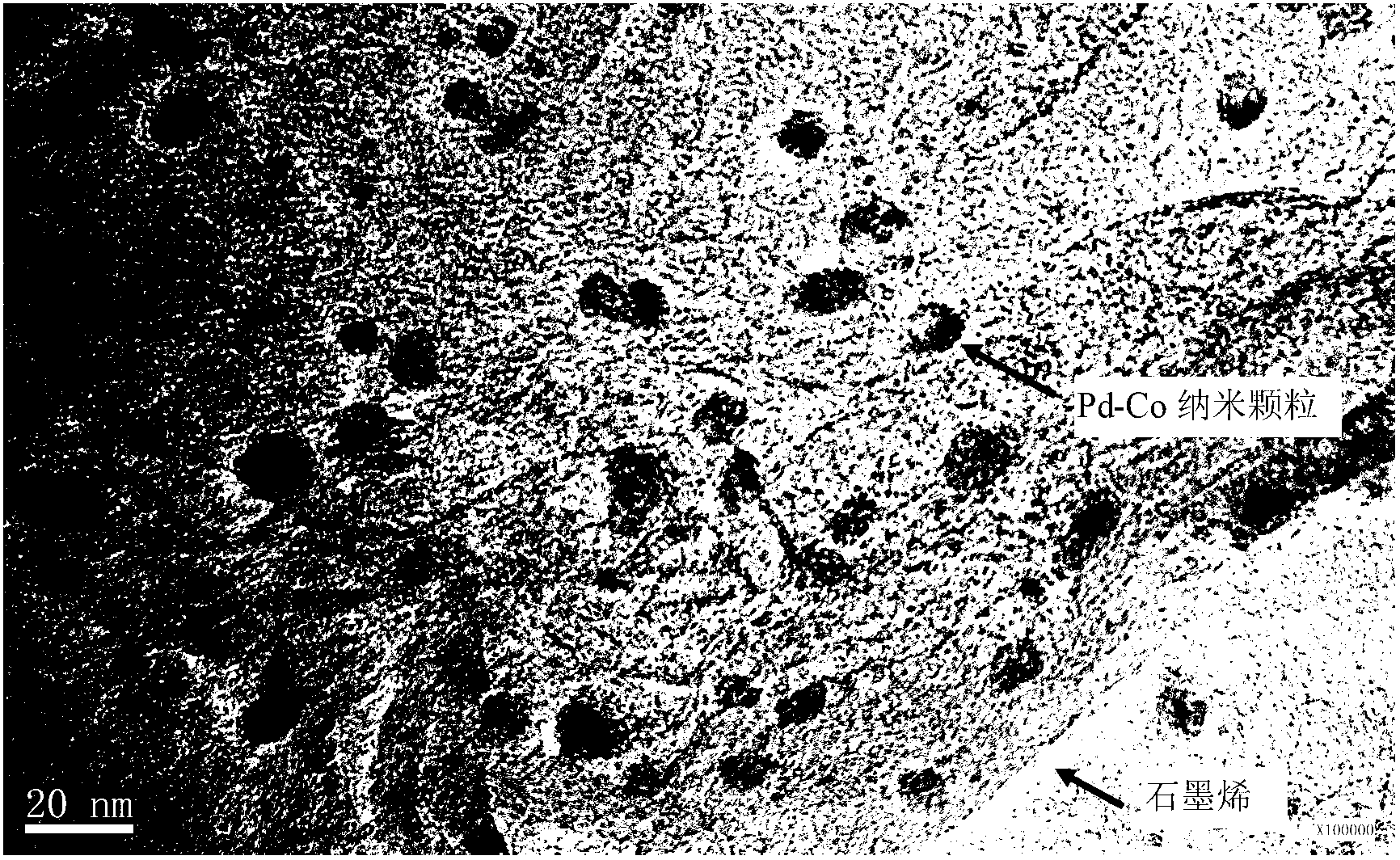
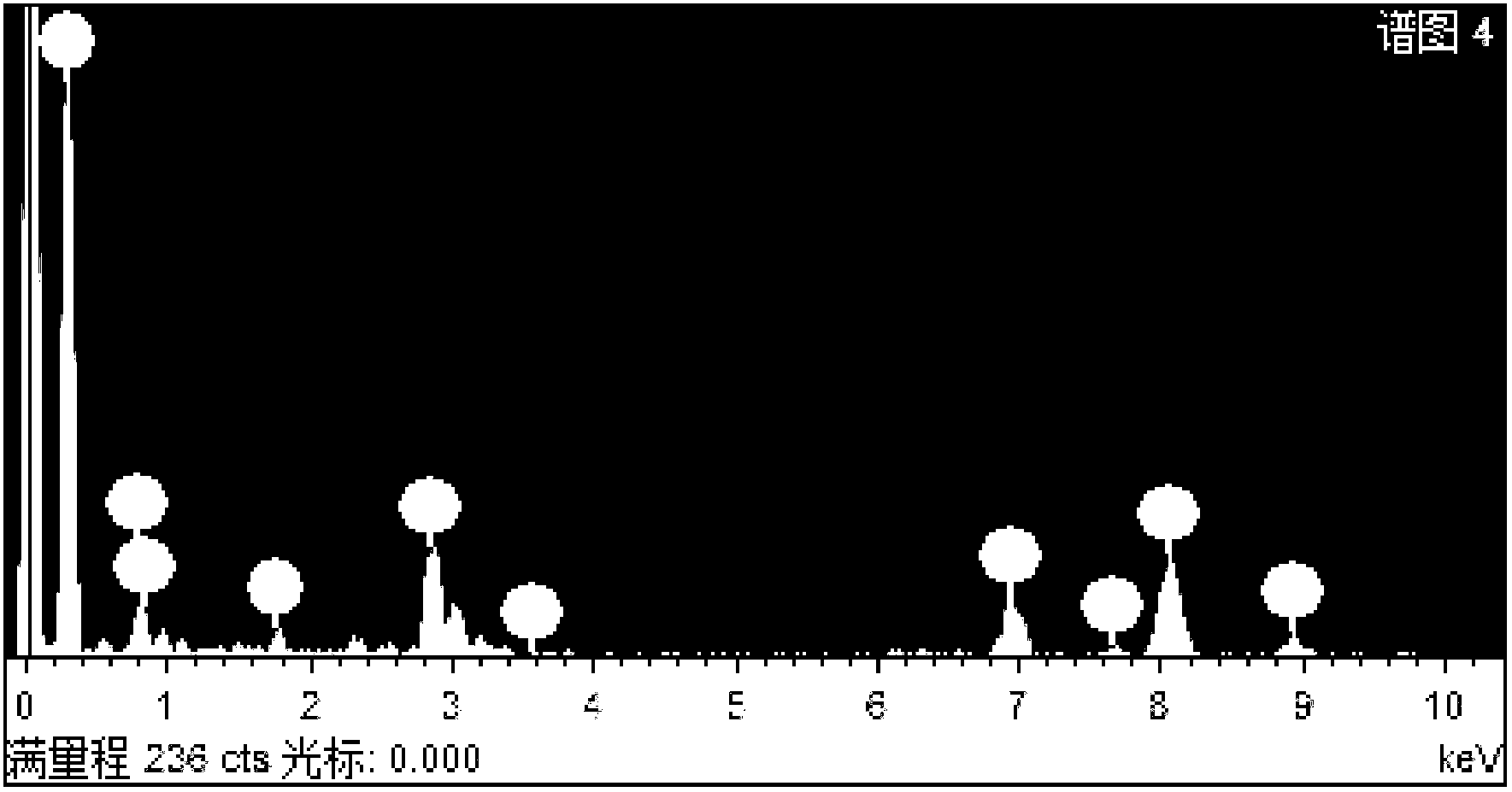
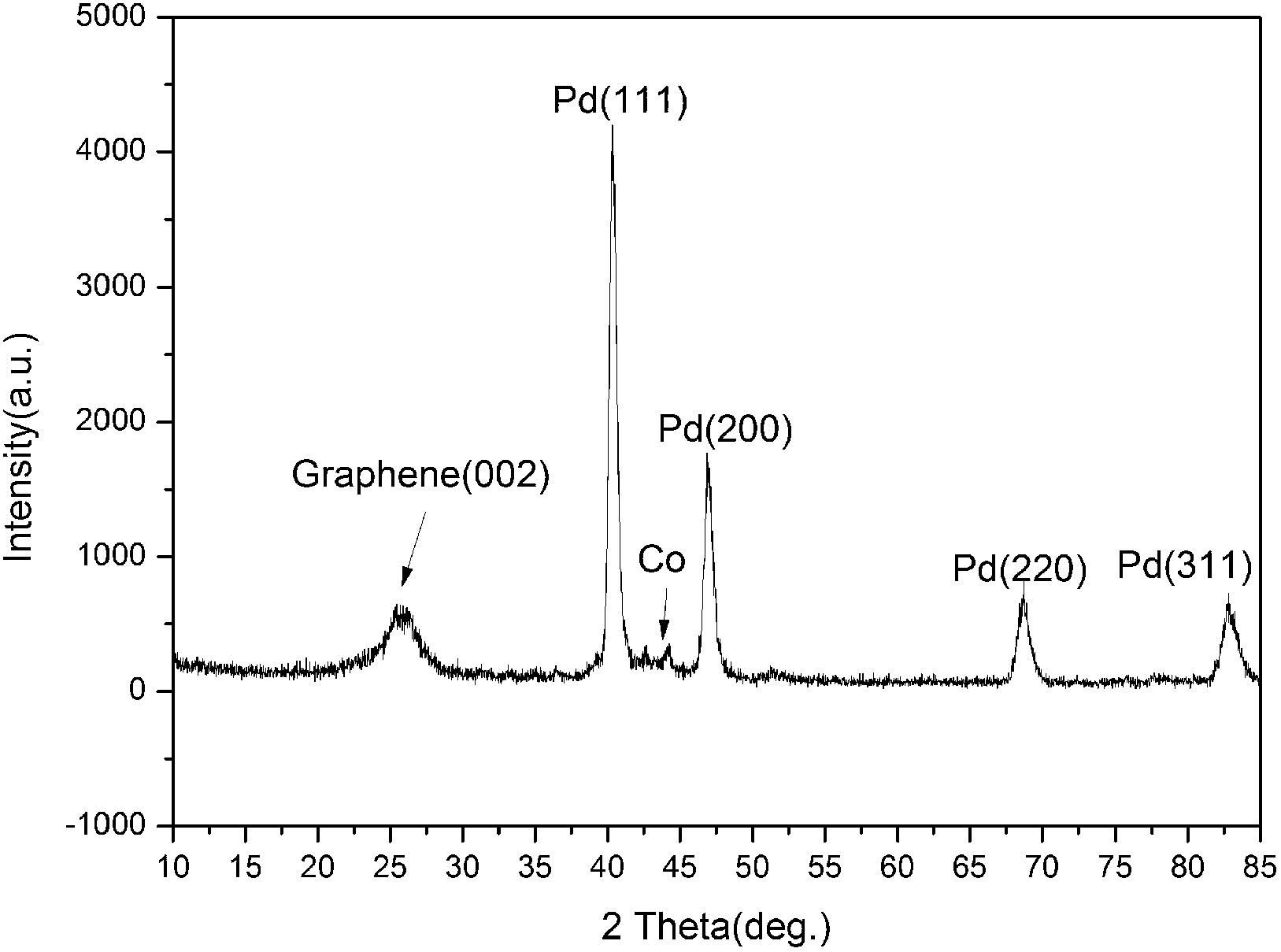
Method for preparing bimetallic nanometer alloy composite material by taking graphene as carrier
ActiveCN103007963AEvenly dispersedLow impurity contentMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectromagnetic shieldingAlloy composite
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bimetallic nanometer alloy composite material by taking graphene as a carrier. The method comprises the following steps of: by taking a precious metal N salt (N=Pd, Pt) and a transition metal M salt (M=Co, Ni and Cu) as precursors and taking graphene oxide as a matrix, reducing the components by employing a reducing agent; and finally, washing, filtering, drying, grinding and roasting to obtain the high-purity graphene bimetallic nanometer composite material. The composite material has high nanoparticle load capacity, stable structure, high uniformity and high dispersing property, has high binding force with the graphene and is high-efficiency in preparation method, low in cost, simple in process and suitable for industrial production. The composite material can be widely applied to the fields of magnetic targeting materials, various catalysts, electromagnetic shielding wave-absorbing materials, super-capacitor electrode materials and other related function materials.
Owner:安徽皖瑞能源科技有限公司
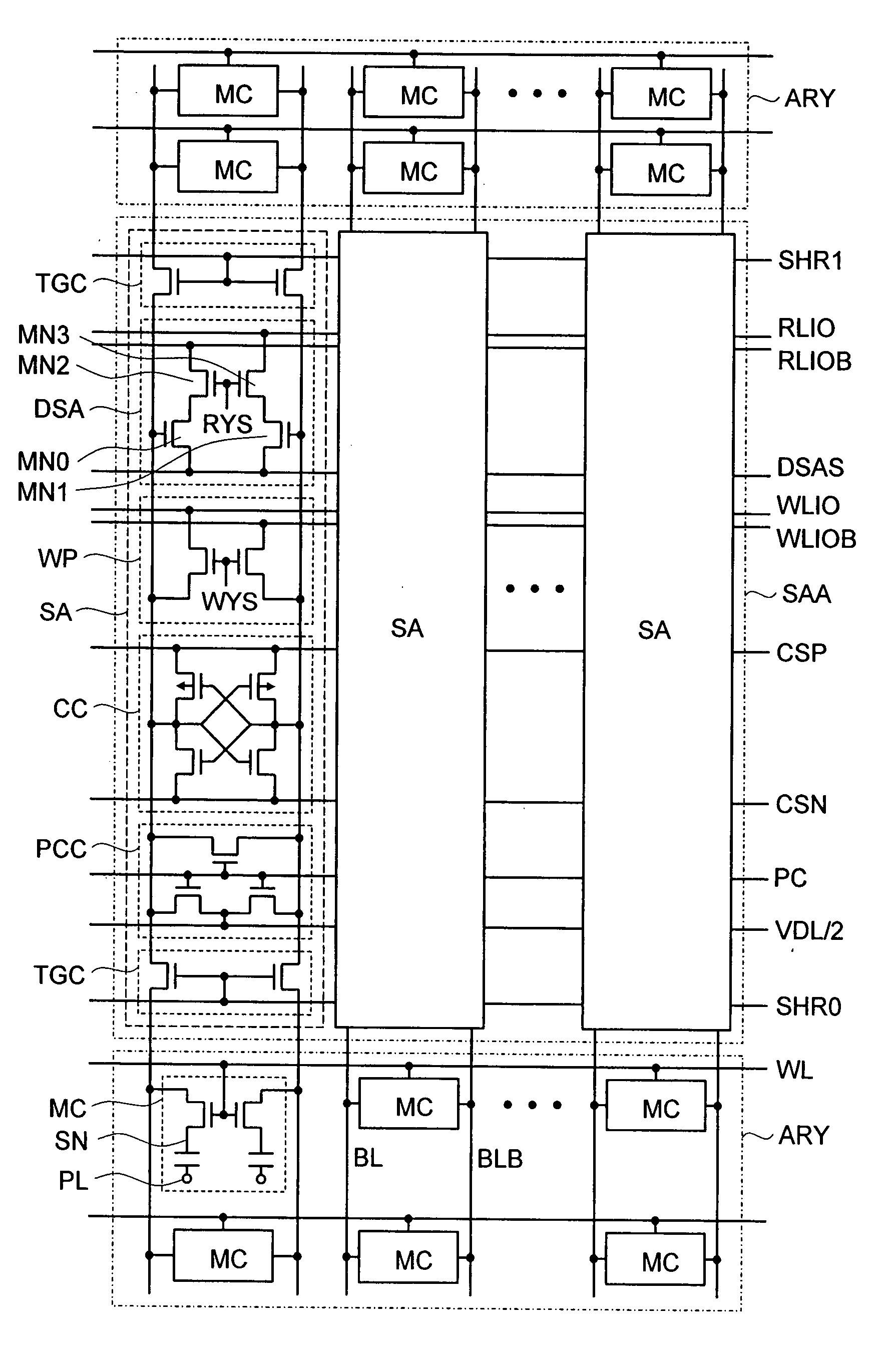
Sense amplifier for semiconductor memory device
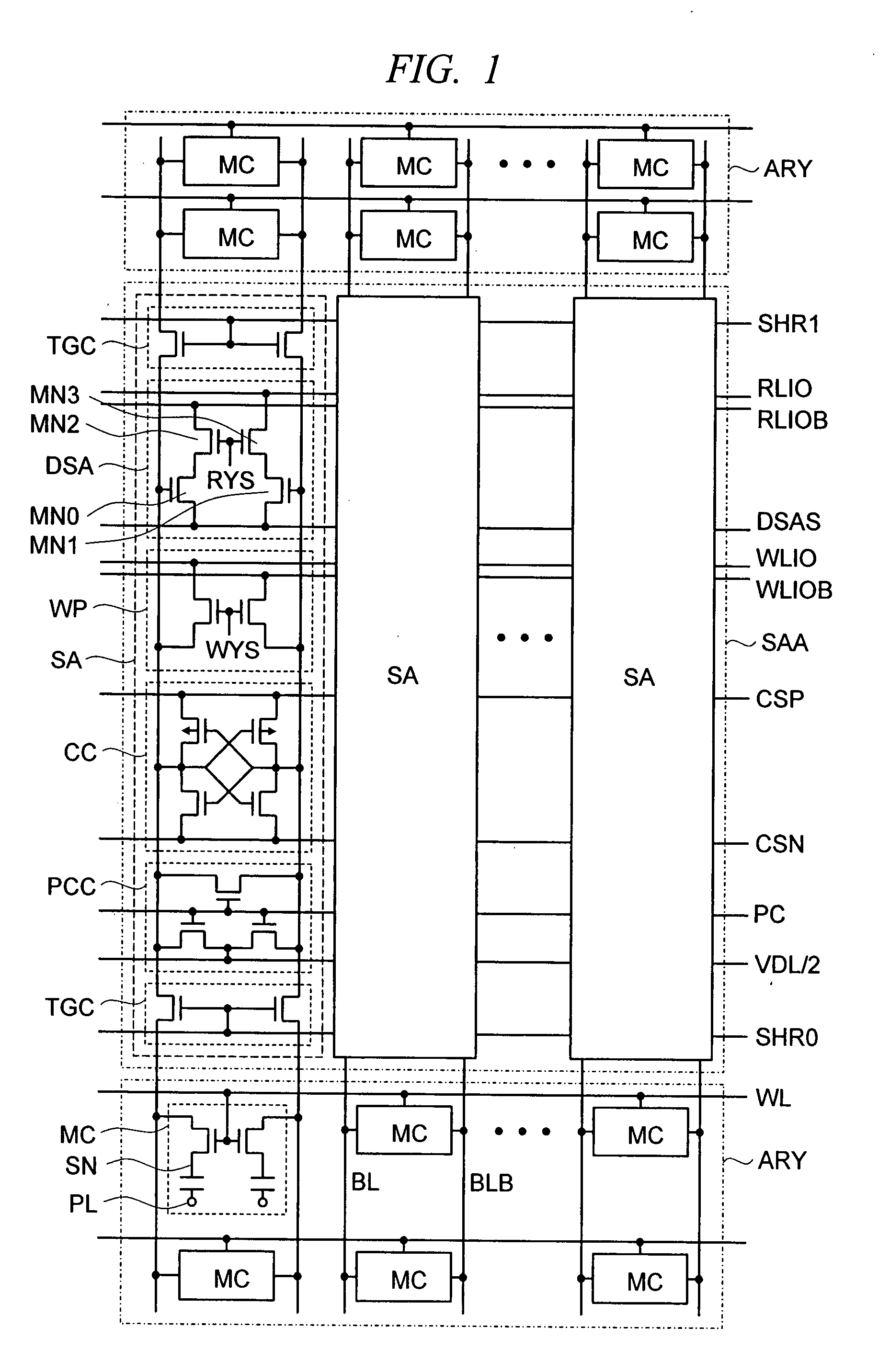
A direct sense amplifier of the present invention incorporates and isolates: an MOS transistor serving as a differential pair and having a gate connected to a bit line; and an MOS transistor controlled by a column select line wired between RLIO lines in a bit-line direction, and further connects a source of the MOS transistor serving as the differential pair to a common source line wired in the word-line direction. Since the direct sense amplifier only in a select map is activated by the column select line and the common source line during an read operation, power consumption is significantly reduced during the read operation. Also, since a parasitic capacitance of the MOS transistor serving as the differential pair is separated from the local IO line, a load capacity of the local IO line is reduced and the read operation is speeded up. In addition, during the read operation, a data pattern dependency of the load capacity of the local IO line is reduced and a post-manufacture test is easily made.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
Rapidly-deployable lightweight load resisting arch system
ActiveUS20060174549A1Requires minimizationAdditional strength and stiffnessArched structuresVaulted structuresFiberVertical plane
A rapidly-erectable lightweight load resisting system for the construction of buried arched bridges, tunnels or underground bunkers, has a plurality of lightweight arched tubular support members which are formed of a fiber reinforced polymer material and are substantially oriented in a vertical plane. The lightweight tubular support members are connected by at least one or more lateral force resisting members which are positioned in a direction perpendicular to the vertical plane of the tubular support members, and which are capable of transferring vertical loads to the tubular support members and of providing lateral-load capacity to the load resisting system. The tubular support members are fitted with one or more holes near the top which allows them to be filled with a suitable material to provide additional strength or stiffness.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MAINE
Device for sealing and inflating an inflatable object
InactiveUS7021348B2Quick to useEasy and quick sealTyresLiquid transferring devicesSealantLoad capacity
A device for inflating a tire having gone flat to a wanted pressure and for sealing and inflating a puncture tire. The device includes a compressed-air source, a tubular container filled with a sealing agent, and a first conduit having an adapter at its second end for connecting the conduit to a valve on the tire. The container furthermore has an inlet opening for passage of compressed air from the compressed-air source and an outlet opening for passage of sealing agent. The container is enclosed by a tubular cylinder having at one end an aperture closed by a cover. The cover is mounted displaceable on the cylinder between a first operative position and a second operative position. Thereby, it is obtained that the device is quick and easy to operate. Sealing and inflating of a puncture tire are done in between one and three minutes. Packed up, the device takes up practically no space whereby the heavy and bulky spare wheel is made unnecessary. Thereby, the space and load capacity previously occupied by the spare wheel is utilized.
Owner:ACTIVE TOOLS INTERNATIONAL (HK) LIMITED
Method, device and system for load distribution
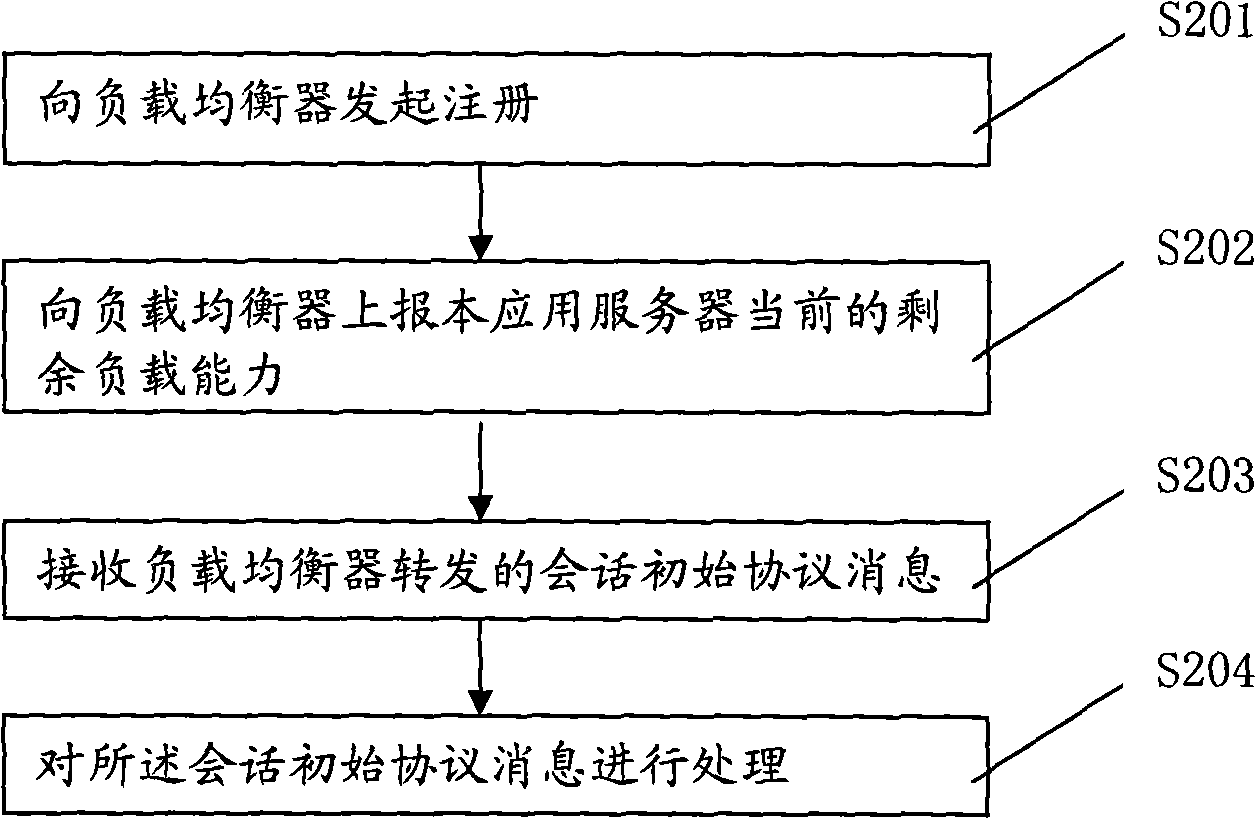
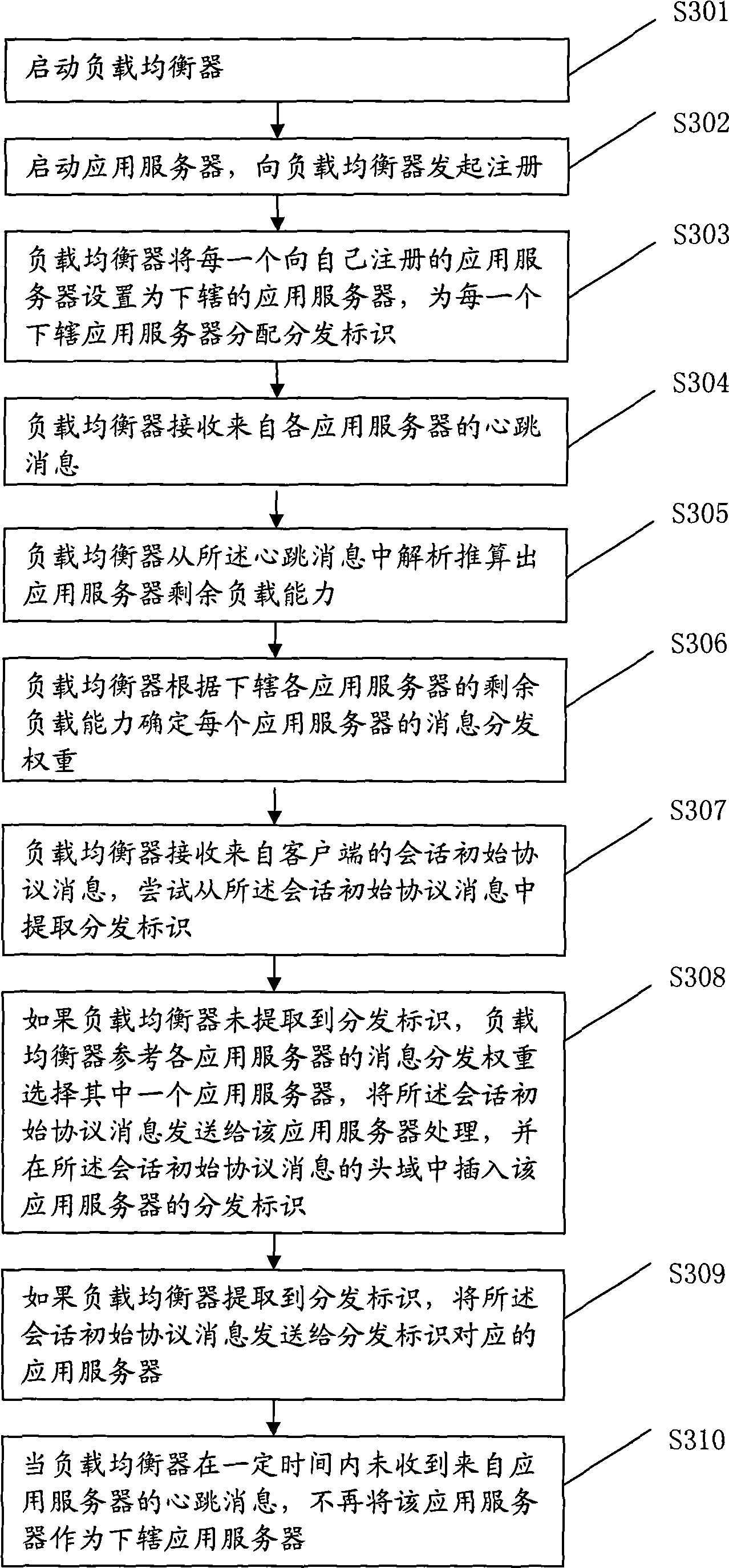
InactiveCN101534244ALoad balancingAllocate resources effectivelyData switching networksApplication serverClient-side
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method, a device and a system for load distribution. The method for lateral load distribution of a load equalizer comprises the steps of: acquiring current remaining load capacities of various affiliated application servers; determining the message distribution weight of each application server according to the remaining load capacities of the affiliated application servers; and receiving a first message of initial session protocol messages which come from a client, referring the message distribution weights of the application servers, selecting one of the application servers, and sending the first message of the initial session protocol messages to the application server for processing. Through the embodiment of the invention, system resources can be effectively configured.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Production method of high-power precision alloy SMD (surface mount device) resistor
InactiveCN104051099AImprove cooling effectHigh precisionResistors adapted for applying terminalsAlloyThermal transmittance
The invention provides a production method of a high-power precision alloy SMD (surface mount device) resistor. The production method comprises the steps: respectively combining two oxygen-free copper strips with two sides of a resistor alloy strip to form an integrated strip-shaped resistor strip, and wrapping a high-heat-conductivity substrate with the integrated strip-shaped resistor strip; etching a basic resistor structure on a wrapping body; precisely adjusting the resistance value of the basic resistance structure; coating, terminal electroplating and printing a resistor body to form a high-power precision alloy SMD resistor. The material with high heat radiation capability and high heat conductivity such as a metal substrate, a high-heat-conductivity ceramic substrate is used as the substrate, so that the actual load capacity of the resistor is greatly increased; the oxygen-free copper strip is partially arranged on the side surface and below the substrate and used as an electrode lead, so that the contact area is increased, and the heat conductivity of the resistor body is also increased on the other hand.
Owner:SHENZHEN YEZHAN ELECTRONICS
Load-prediction-based control system and method for heating ventilation air-conditioning system
InactiveCN106403207ARealize energy savingOptimal control methodMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsControl systemAir conditioning
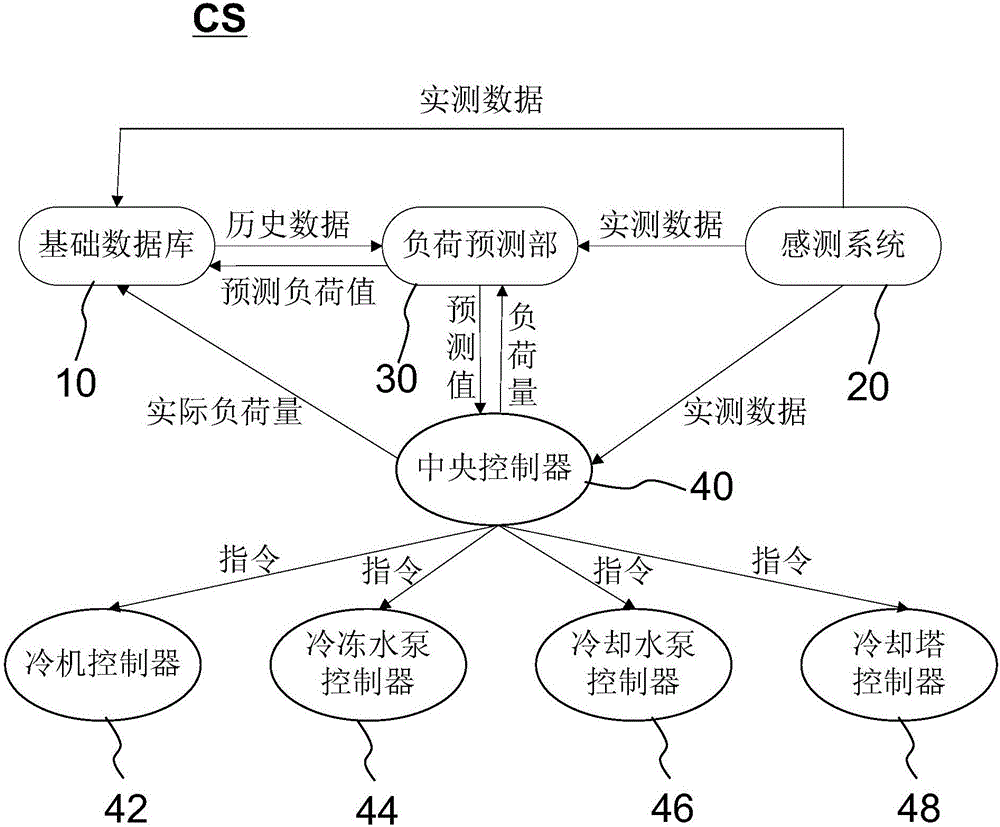
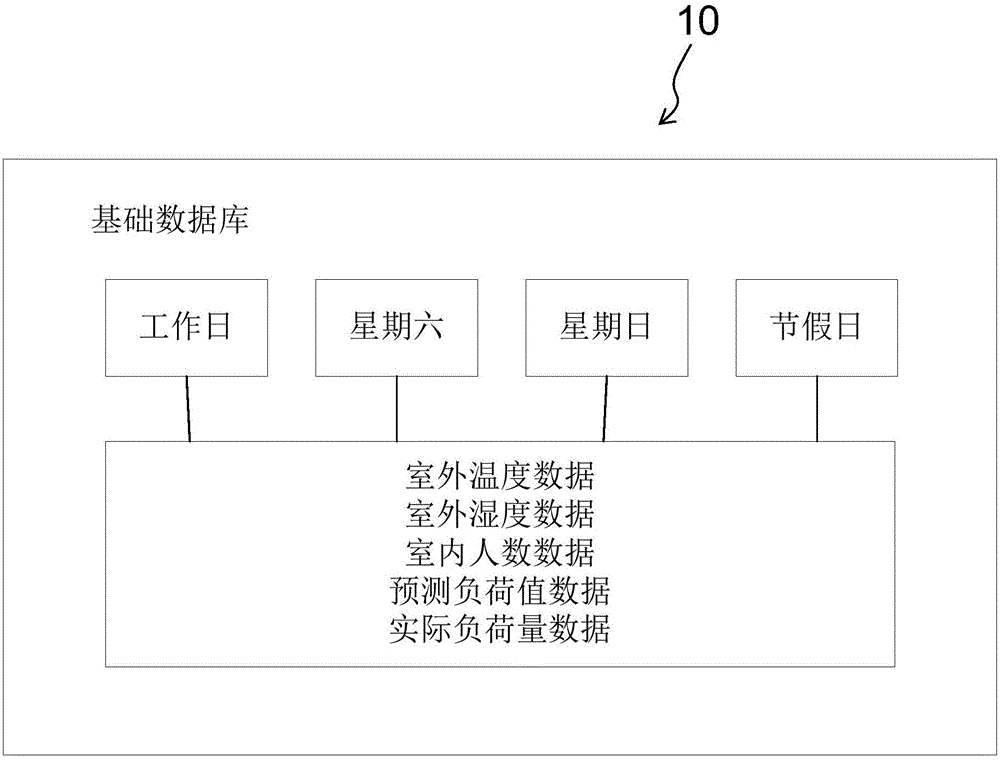
The invention relates to a load-prediction-based control system and method for a heating ventilation air-conditioning system. On the one hand, the load-prediction-based control system (CS) for the heating ventilation air-conditioning system is provided. The control system comprises a foundation database (10), a sensing system (20), a load predication part (30) and a central controller (40), wherein the foundation database is used for storing data related to the heating ventilation air-conditioning system, the sensing system is used for providing measured data related to the heating ventilation air-conditioning system, the load predication part is used for calculating a predicted load value of the heating ventilation air-conditioning system, and the central controller is used for calculating actual load capacity of the heating ventilation air-conditioning system on the basis of the measured data. The central controller sends out a control command for controlling operation of the heating ventilation air-conditioning system on the basis of the difference value of the predicted load value and the actual load capacity. According to the load-prediction-based control system and method, stable and optimized energy saving control over the heating ventilation air-conditioning system can be achieved.
Owner:珠海横琴能源发展有限公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com