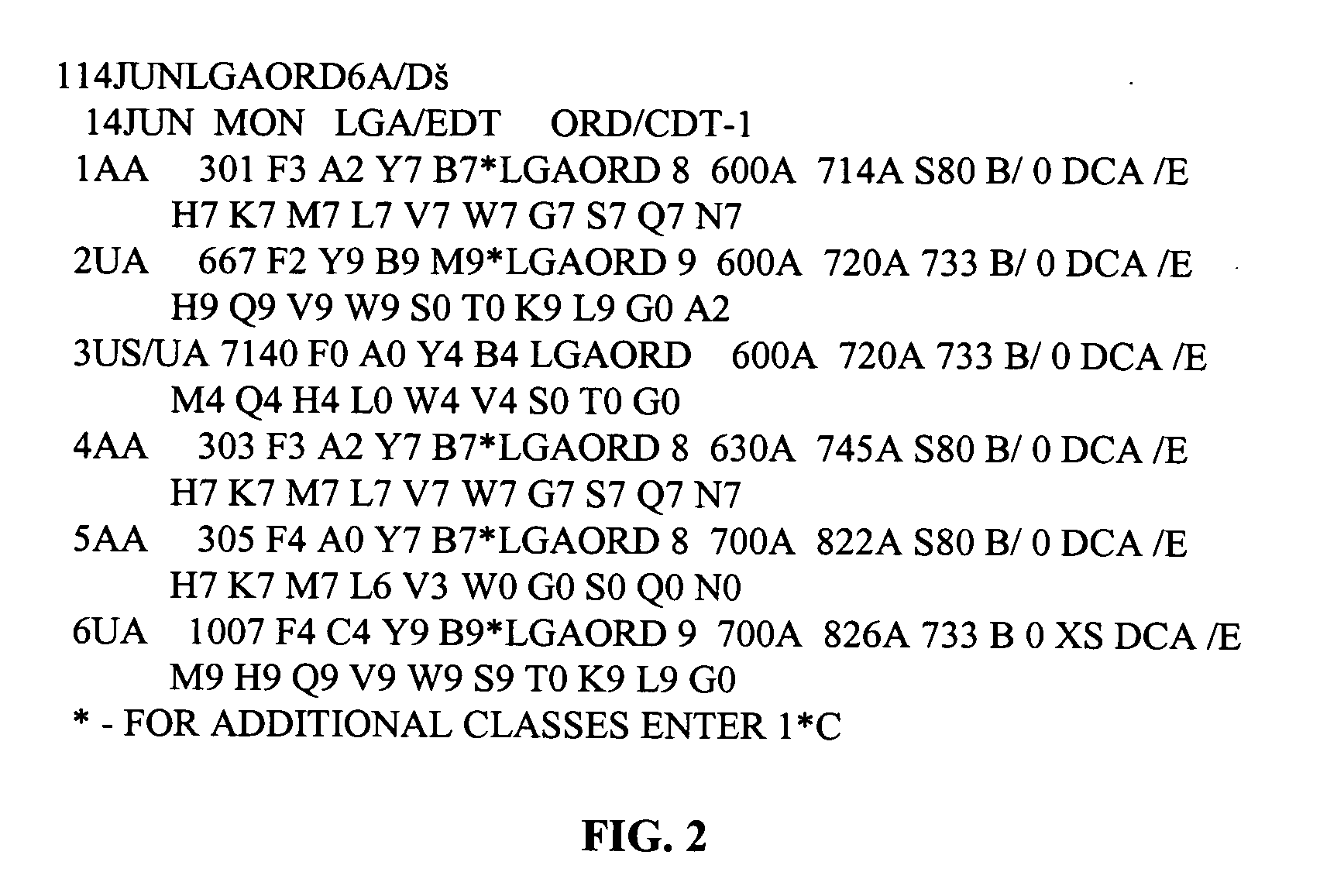
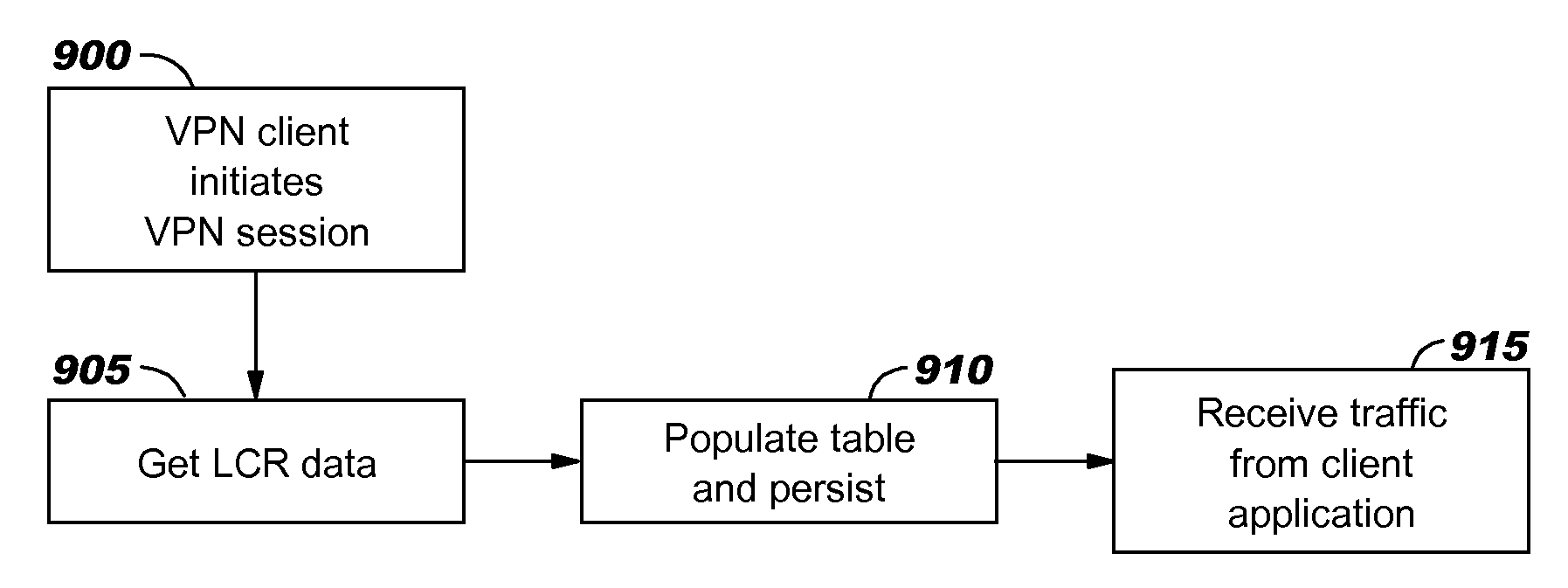
Patents
Literature
187 results about "Least cost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
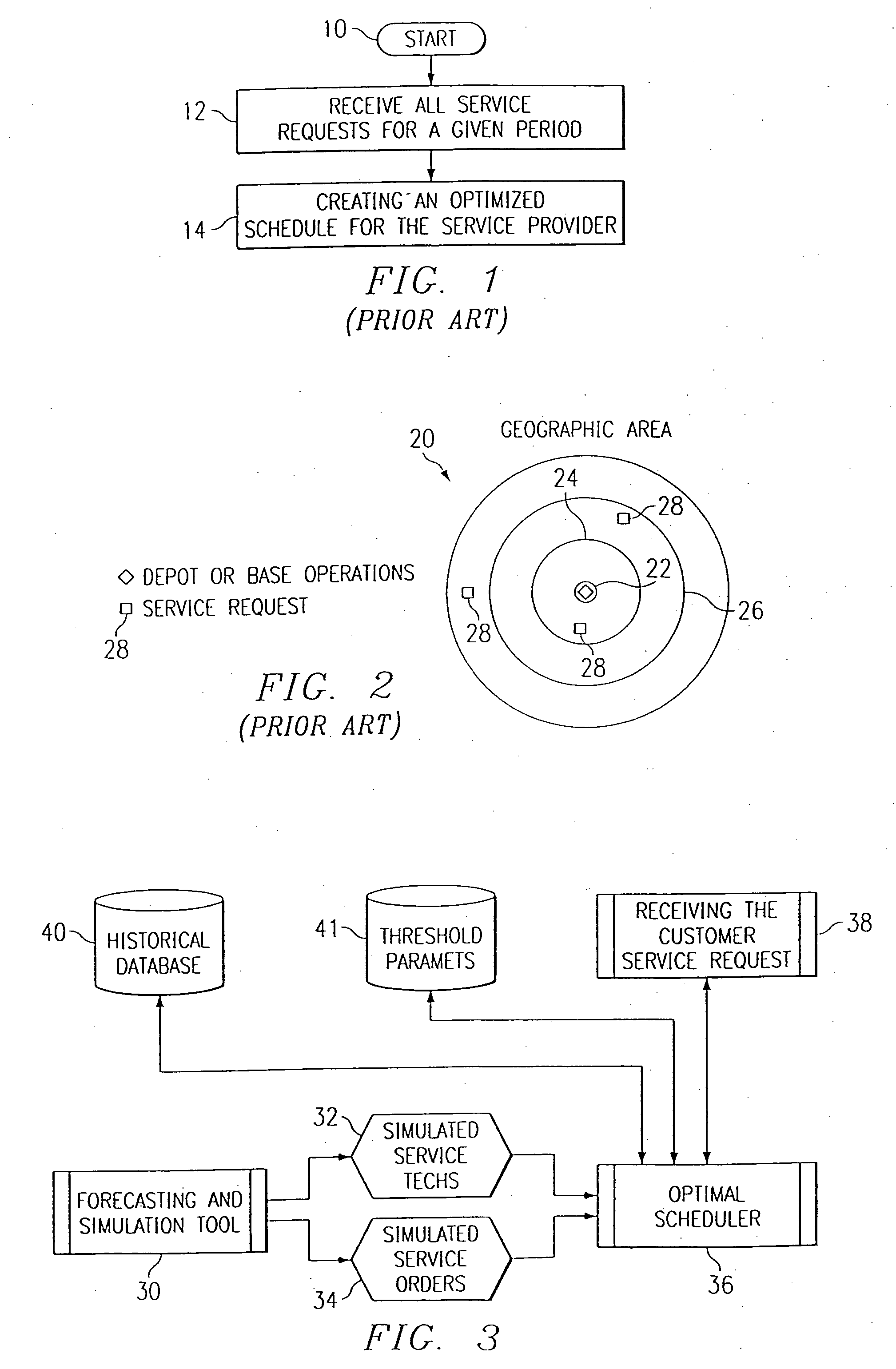
Least Cost Method. Definition: The Least Cost Method is another method used to obtain the initial feasible solution for the transportation problem. Here, the allocation begins with the cell which has the minimum cost. The lower cost cells are chosen over the higher-cost cell with the objective to have the least cost of transportation.
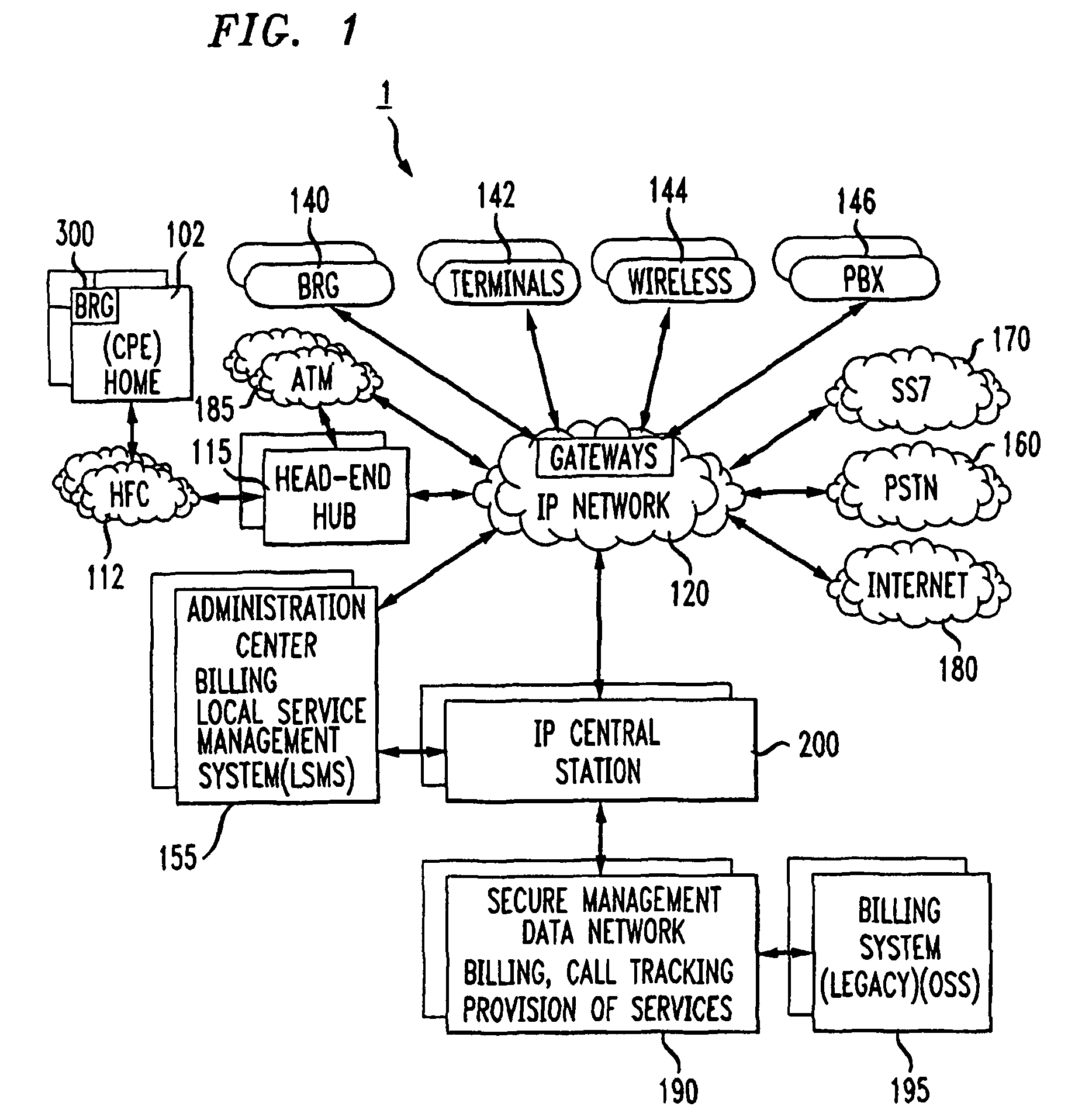
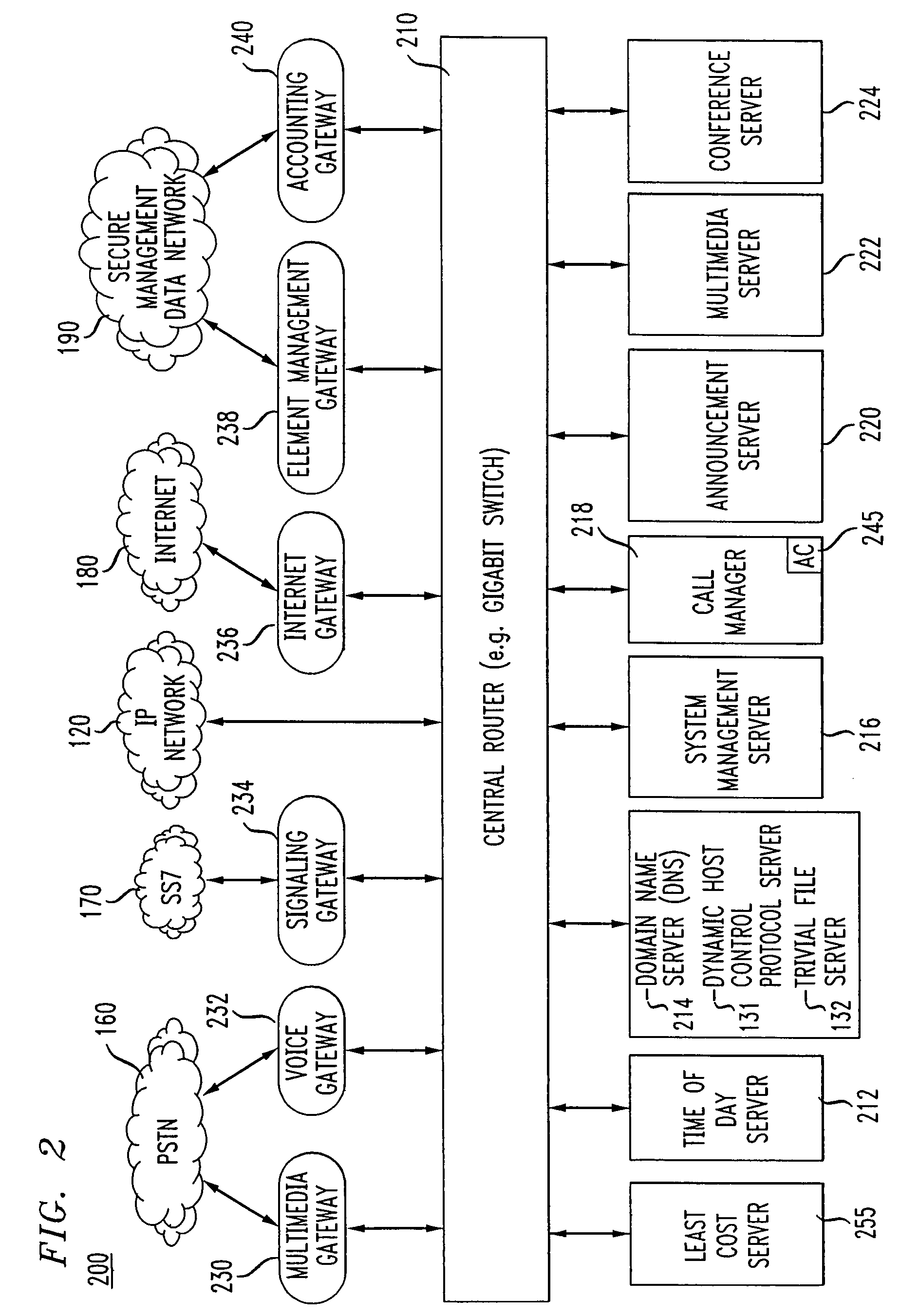
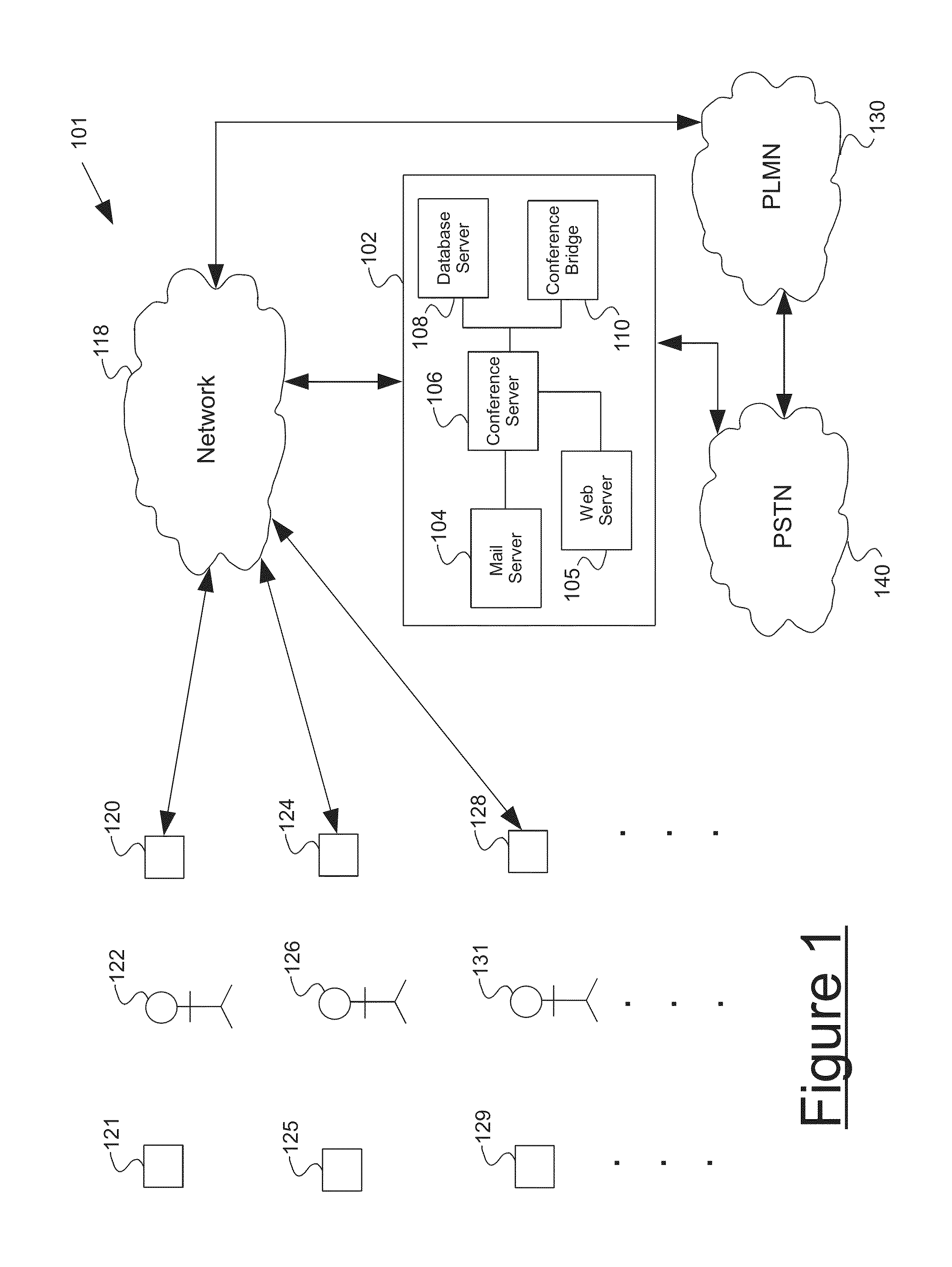
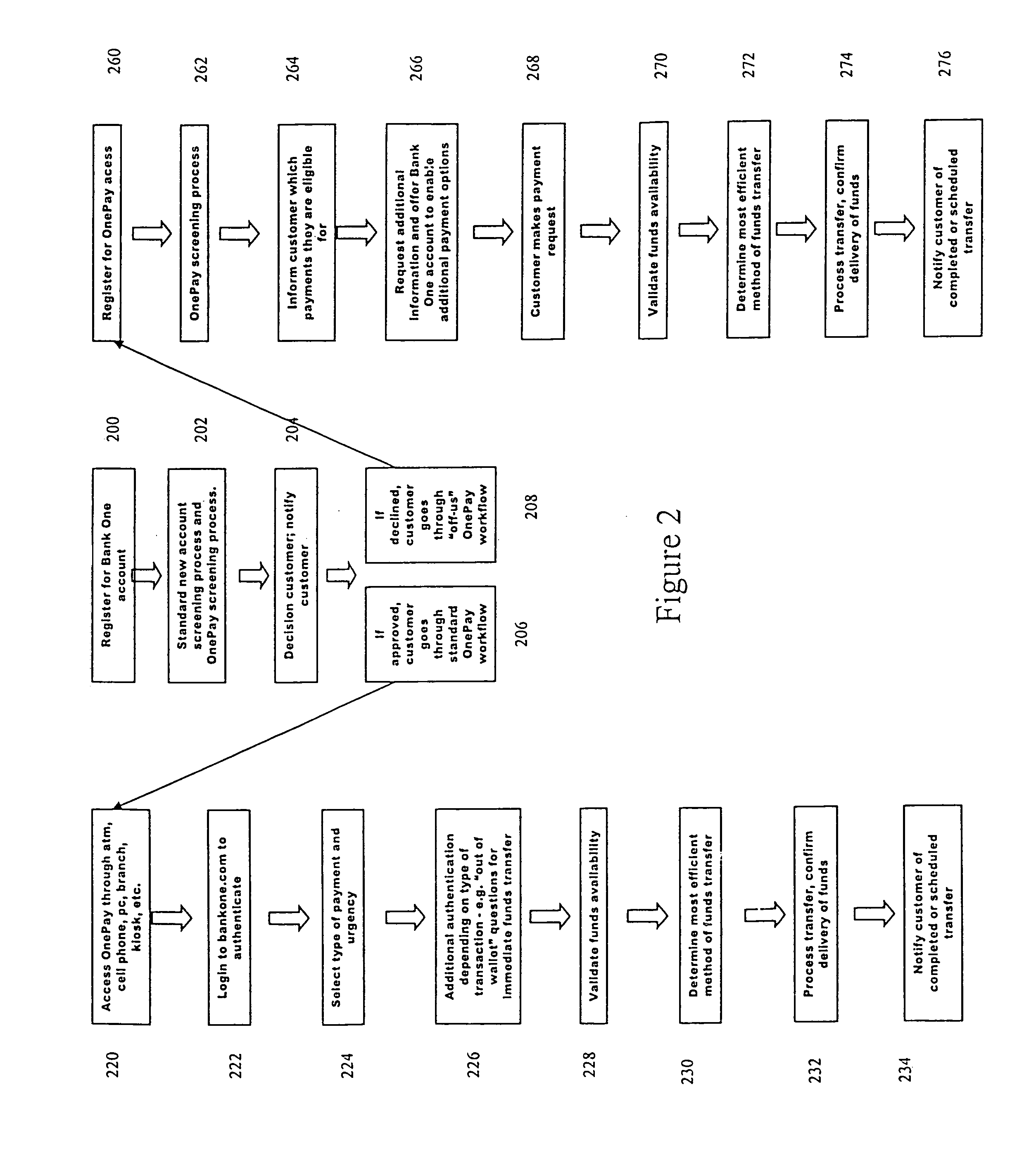
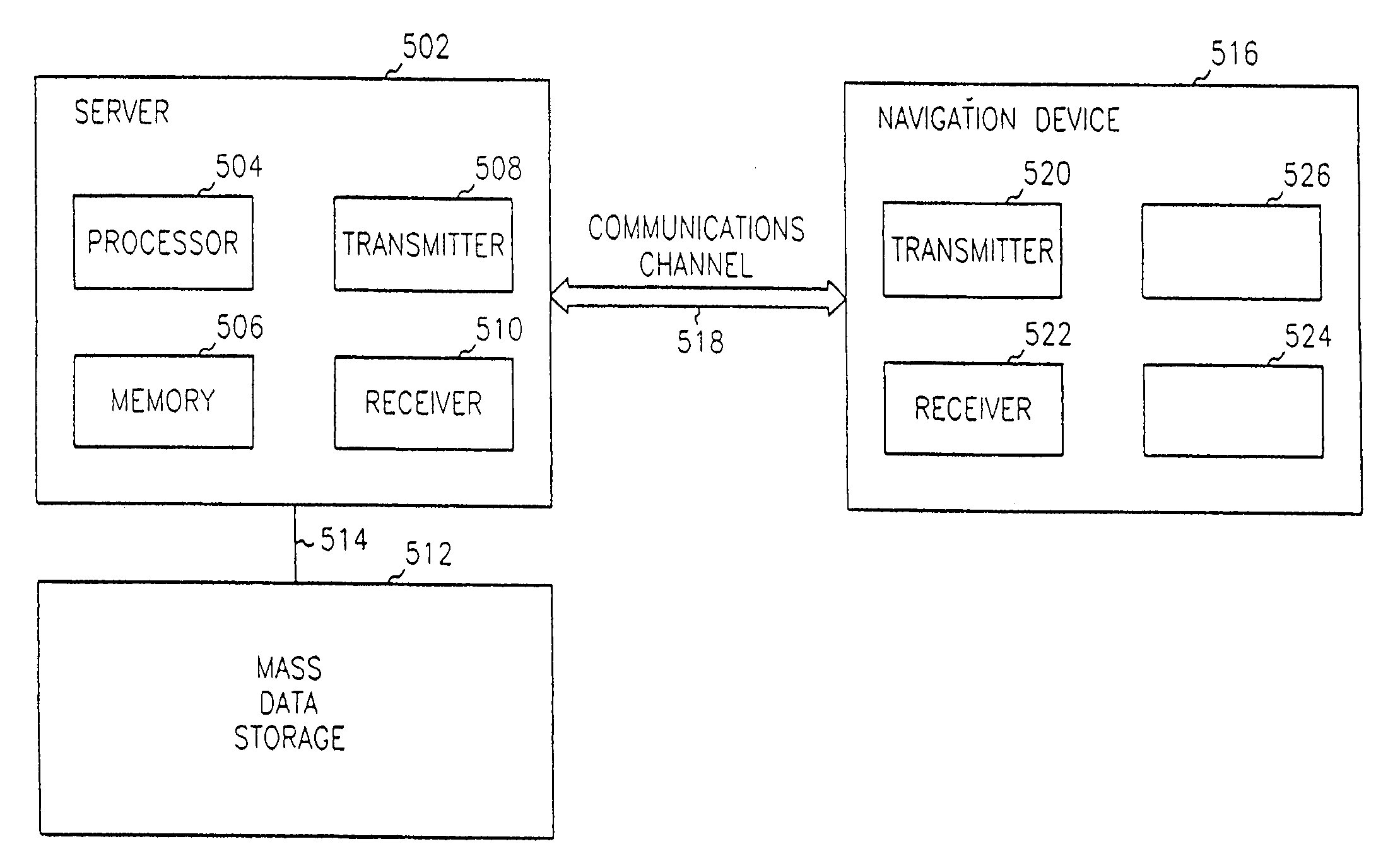
Method for billing IP broadband subscribers
InactiveUS7289489B1Least costMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsTelephonic communicationQuality of serviceLeast cost
A method of billing a variable bit rate communication between a first terminal and a distant terminal to a broadband subscriber permits changing billing parameters during a call in real time in response to user inputs including user requested changes in quality of service, changes in data rate and changes in preferred service provider. A variable bit rate communication to be billed has a variable quality of service related to the degree of utilization of a plurality of different networks. The billing method comprises the steps of i.) receiving user identification data at a first terminal and data representing a required bit rate and a default quality of service selected by the user, ii.) verifying the user identification data to be associated with the broadband service subscriber, iii.) determining least cost alternative network resources available for achieving the communication at the user selected default quality of service and the required bit rate, iv.) determining cost data associated with the network resources, v.) outputting to the user a least cost for the communication according to their selected default quality of service and alternative least cost network resources, vi.) coupling the first terminal and the distant terminal via the least cost determined network resources at the default quality of service and the required bit rate responsive to user authorization and vii.) billing for the communication at the default quality of service and according to the required bit rate after the termination of the communication.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method for billing IP broadband subscribers
InactiveUS7760711B1Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsTelephonic communicationQuality of serviceLeast cost
A method of billing a variable bit rate communication between a first terminal and a distant terminal to a broadband subscriber permits changing billing parameters during a call in real time in response to user inputs including user requested changes in quality of service, changes in data rate and changes in preferred service provider. A variable bit rate communication to be billed has a variable quality of service related to the degree of utilization of a plurality of different networks. The billing method comprises the steps of i.) receiving user identification data at a first terminal and data representing a required bit rate and a default quality of service selected by the user, ii.) verifying the user identification data to be associated with the broadband service subscriber, iii.) determining least cost alternative network resources available for achieving the communication at the user selected default quality of service and the required bit rate, iv.) determining cost data associated with the network resources, v.) outputting to the user a least cost for the communication according to their selected default quality of service and alternative least cost network resources, vi.) coupling the first terminal and the distant terminal via the least cost determined network resources at the default quality of service and the required bit rate responsive to user authorization and vii.) billing for the communication at the default quality of service and according to the required bit rate after the termination of the communication.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Logistics system and method
InactiveUS6879962B1Cost controlLow costHand manipulated computer devicesReservationsLogistics managementLeast cost
A logistics method is disclosed that provides logistics computer programming for controlling a plurality of transports to supply a plurality of delivery locations from one or more bases. Each of the bases and delivery locations are in communication with a central database, preferably an Internet server database, that contains updated logistics information. The central database is preferably automatically updated at selectable intervals as to transport location, destination, fuel level, speed, and heading. Manifests may be originated at the respective delivery location or at an associated base and are stored in the central database. Each material on the manifest is associated with information such as the authorized vendor, a description, storage preferences, units, hazardous designations and additional information if the material is hazardous. Given information about each transport such as load capacity, fuel level, location intelligence, and the like that is stored in the central database and information about the materials, manifest status, and other factors, potential least cost delivery routes using capable transports can be automatically produced for selection by an operator. The logistics computer programming automatically designates where each manifested material is stored on the transport. The computer programming associates a status designation with each manifest such as outstanding, staged, printed, loaded, unloaded, and cancelled. Each manifest is also associated with a priority which may range from emergency to routine. Updated logistics information concerning materials, manifests, vendors, transports, delivery locations, and operating companies is available from the central database.
Owner:SMITH JOSEPH D
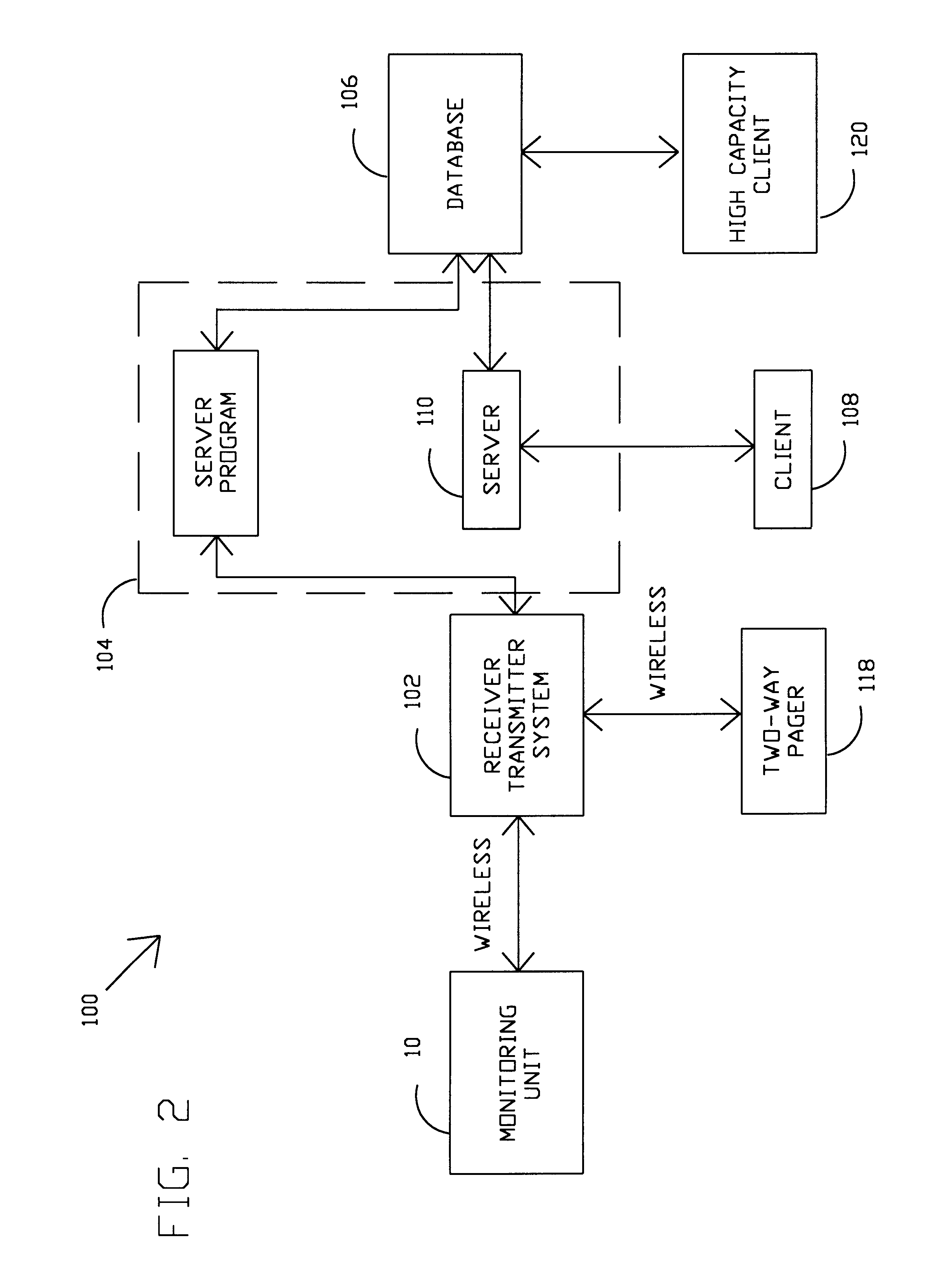
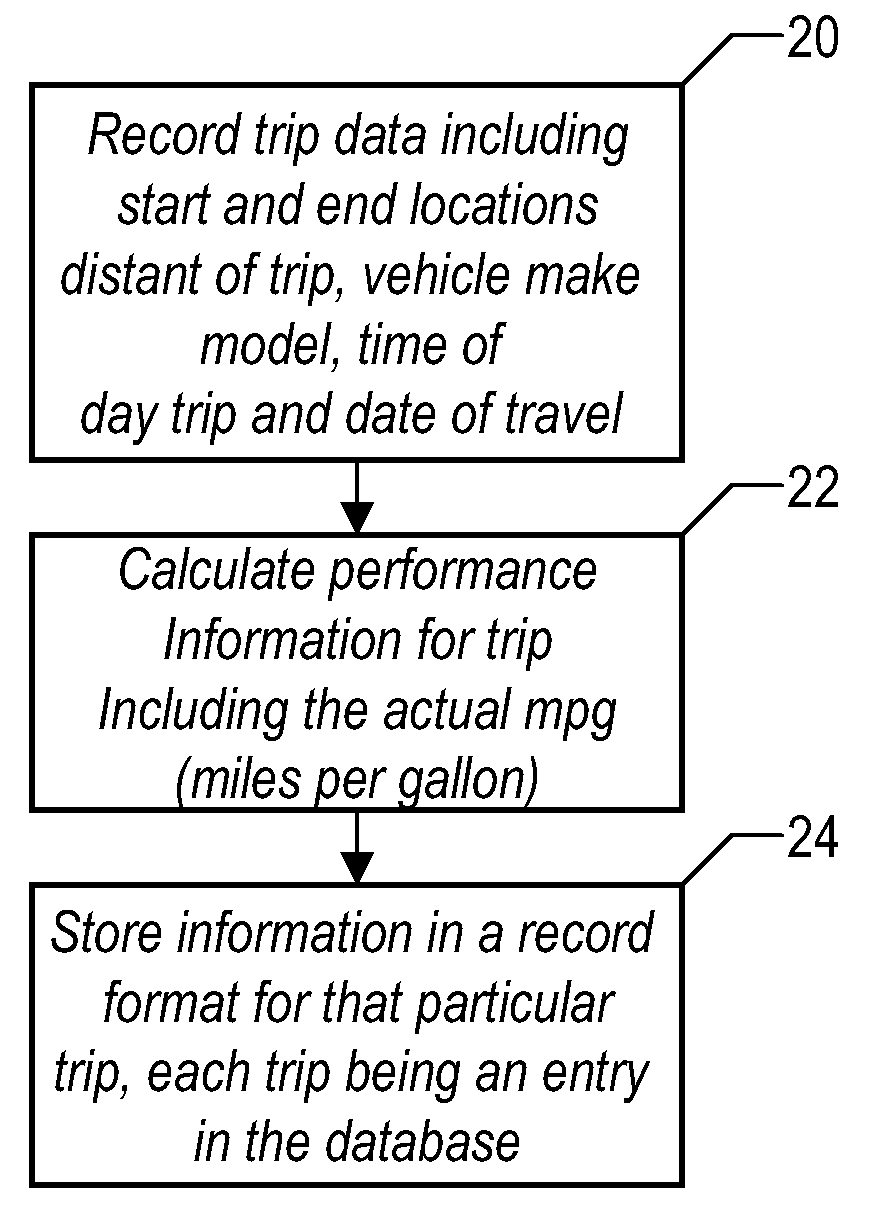
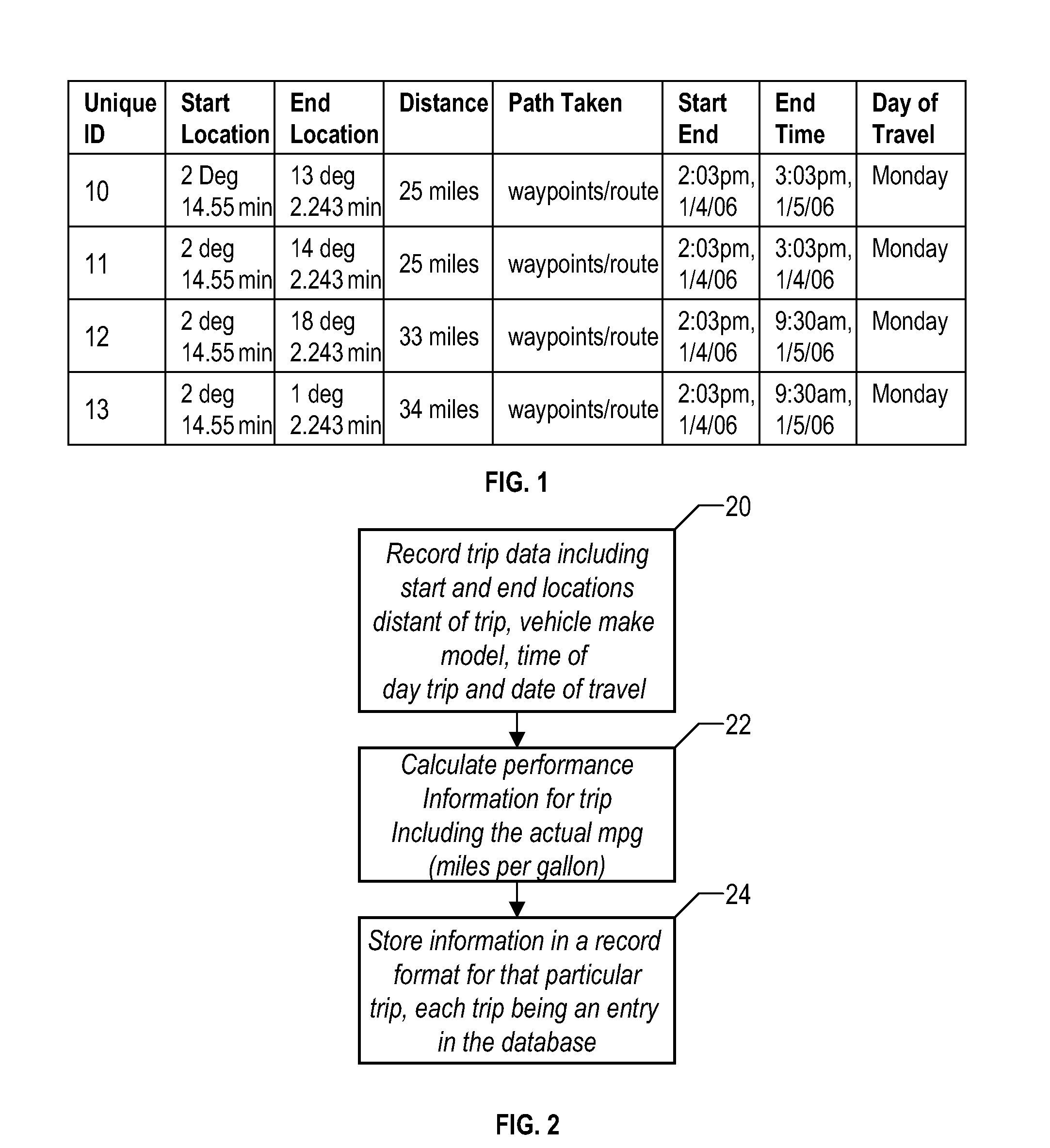
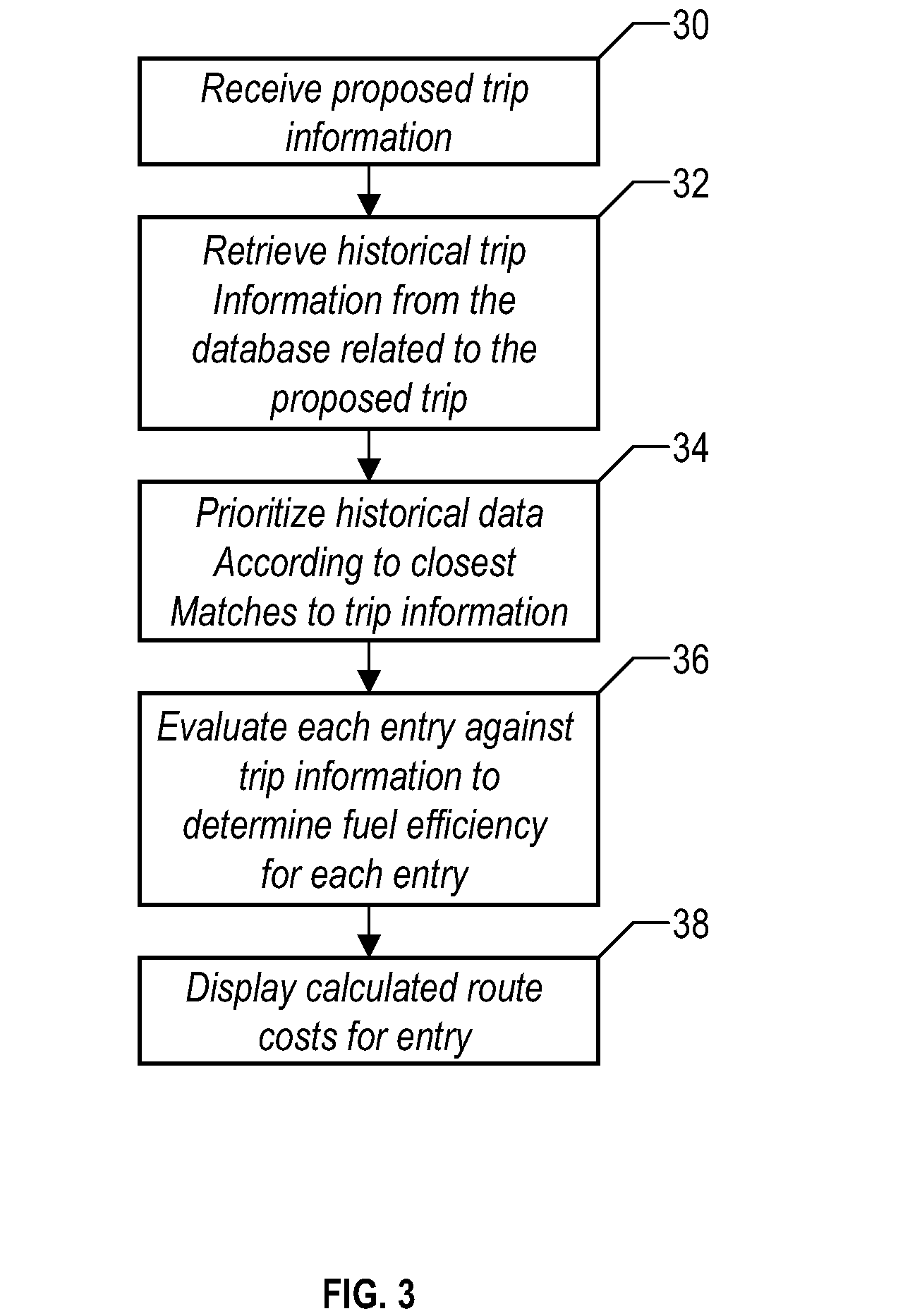
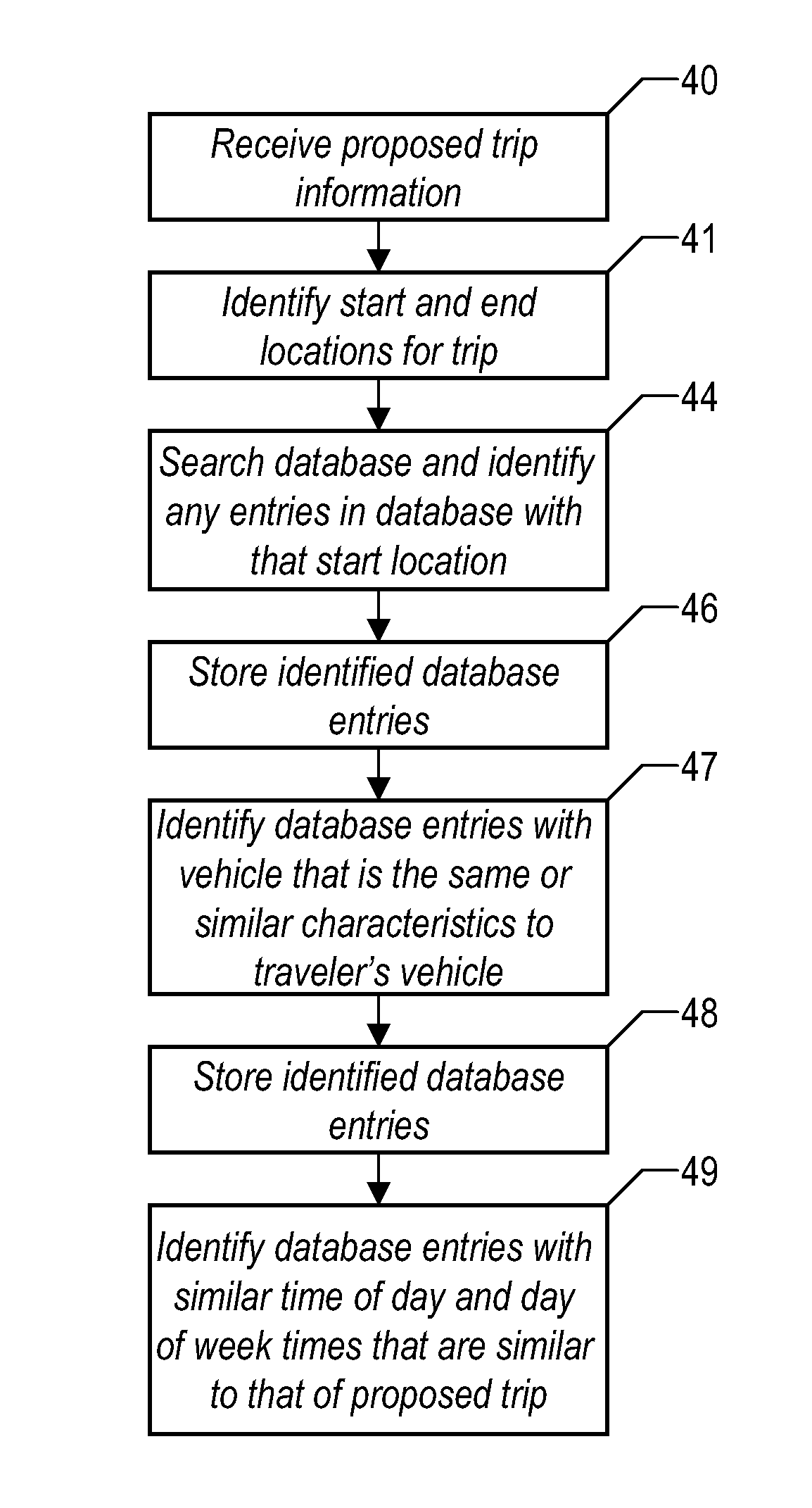
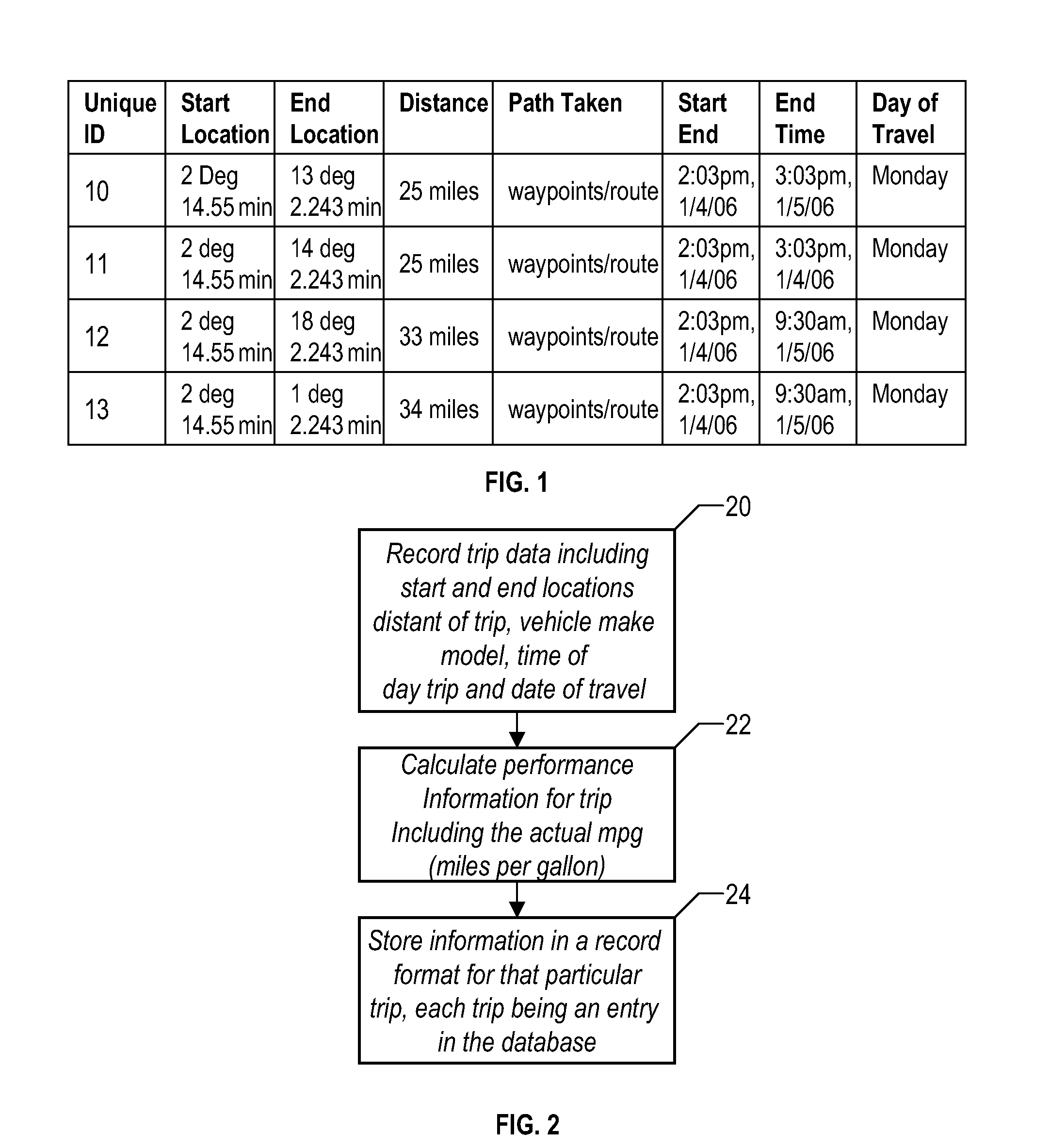
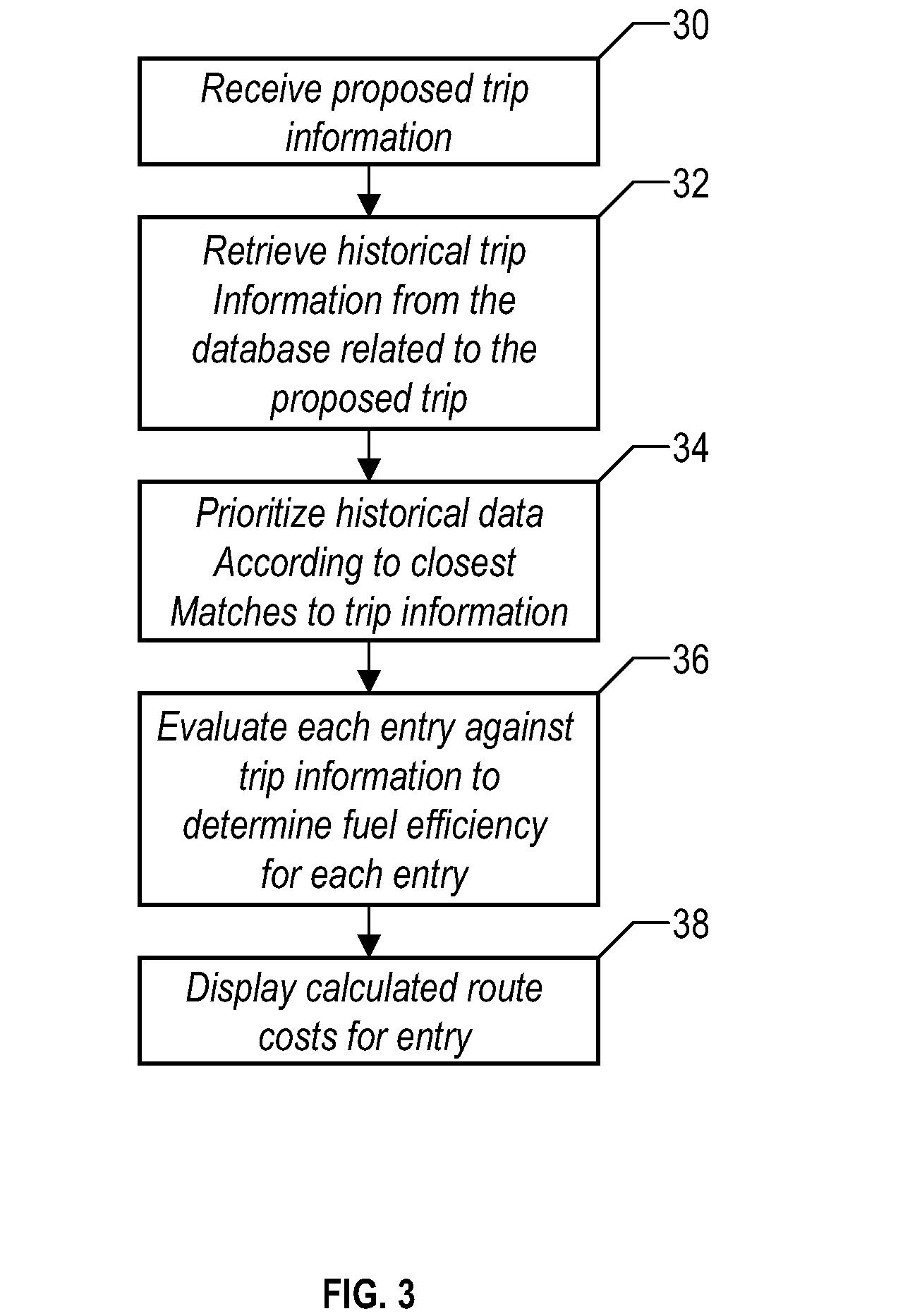
Method and system for calculating least-cost routes based on historical fuel efficiency, street mapping and location based services
ActiveUS20080125958A1Maximize fuel efficiencyLess fuelAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficTerrainDriver/operator
This disclosure outlines a method, which enables a vehicle driver to achieve increased fuel efficiency by implementing least-cost route planning based on terrain data and derived from advanced mapping, logging and location based services. Actual fuel efficiency is recorded and correlated by vehicle conditions, time of day and date, and then referenced to achieve the most accurate least-cost route plan for the intended destination.
Owner:SLINGSHOT IOT LLC
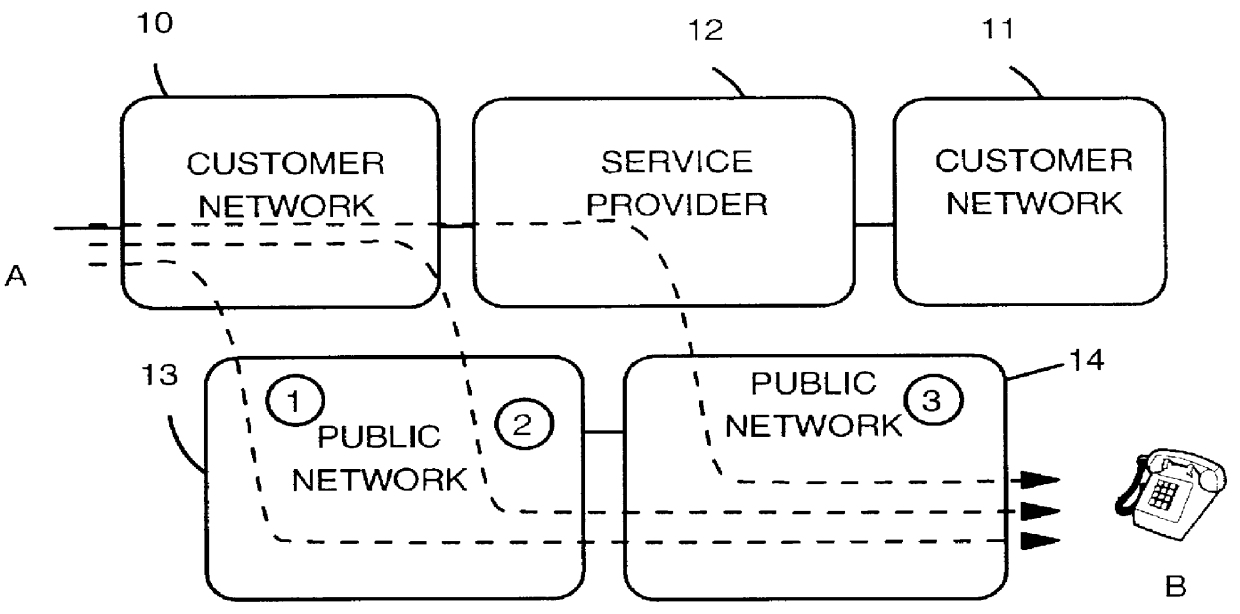
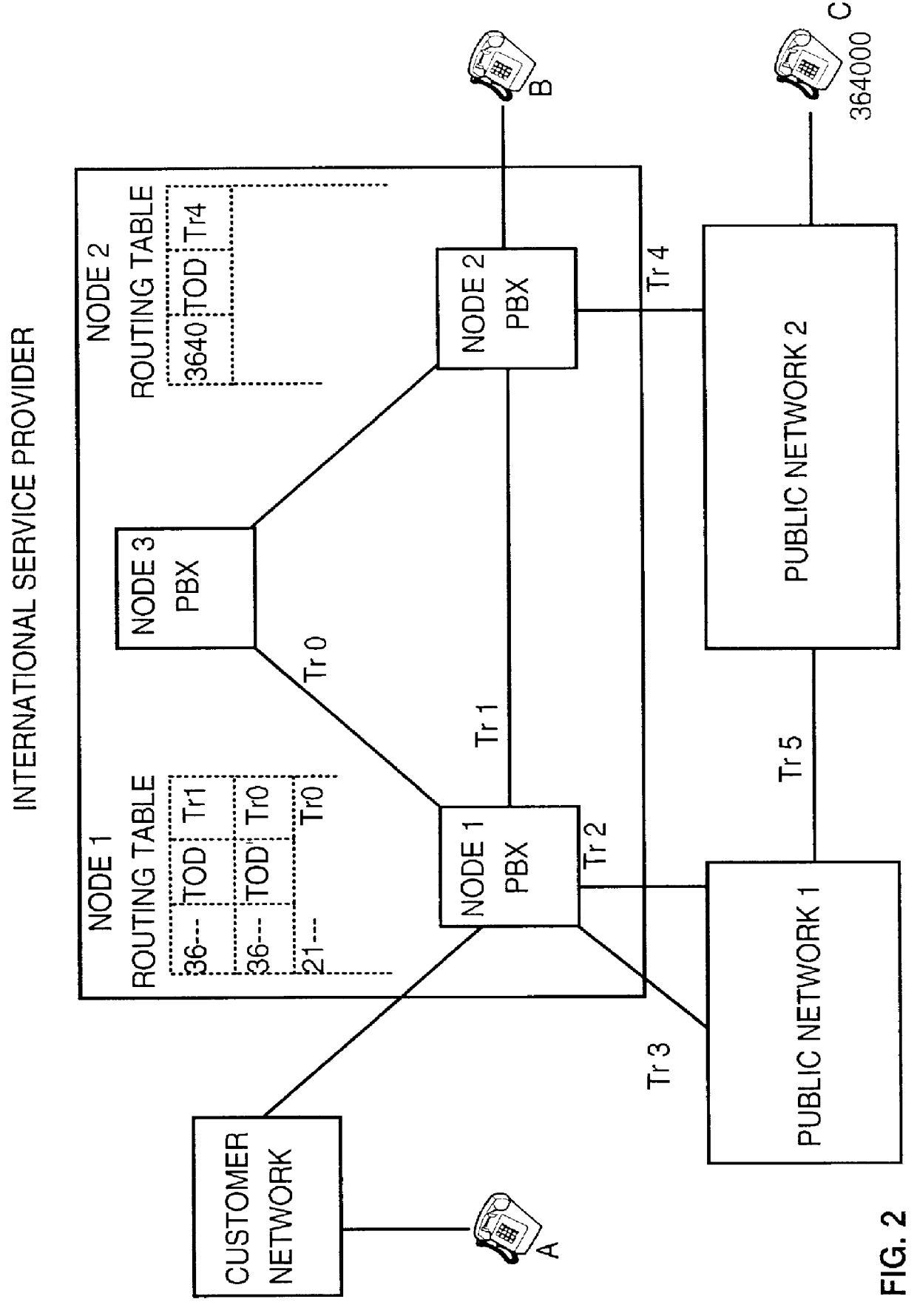
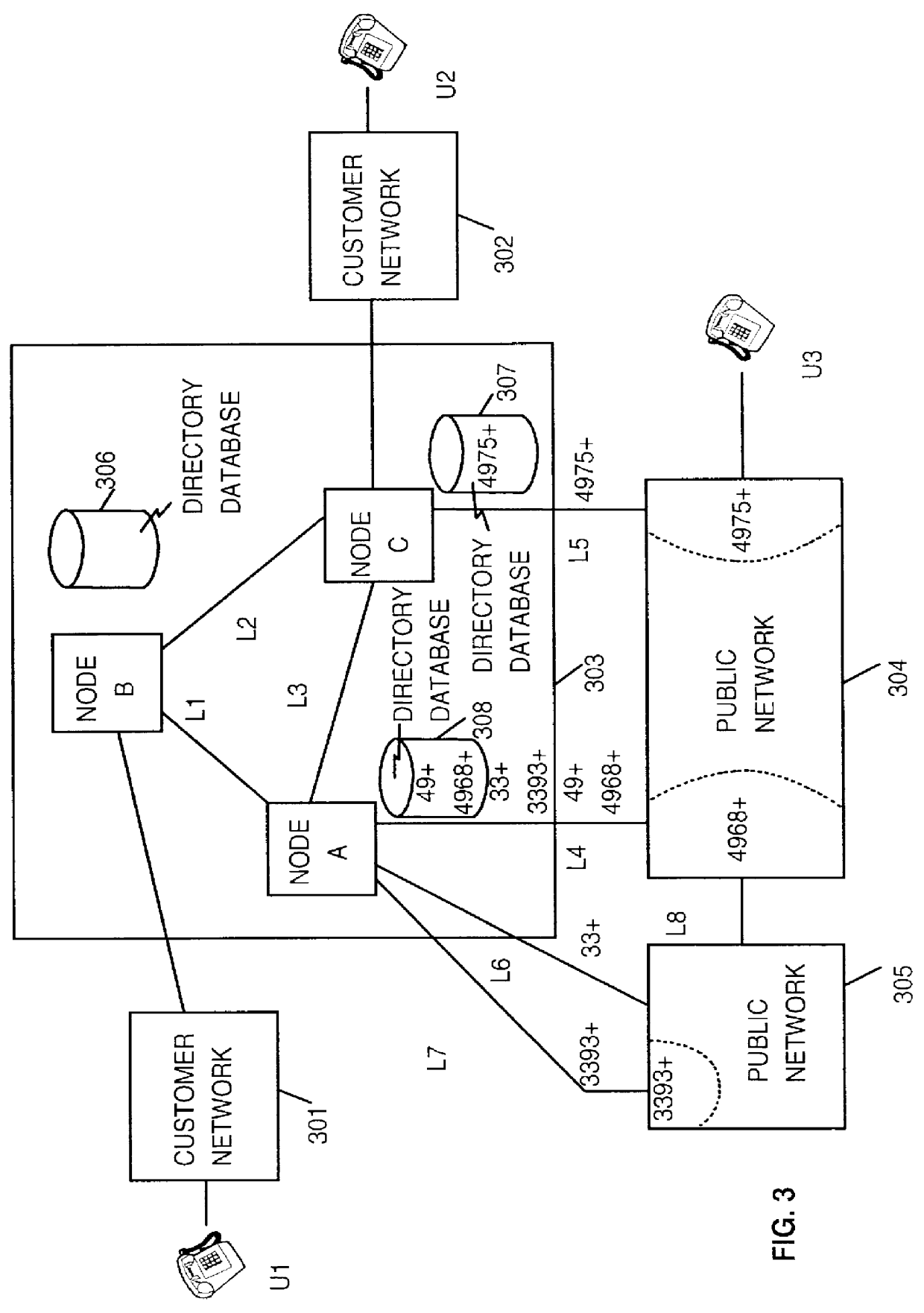
Method and system for performing a least cost routing function for data communications between end users in a multi-network environment
InactiveUS6104701ALow costLeast Cost RoutingInterconnection arrangementsError preventionPrivate networkLeast cost
A method and system for determining the best data path in a communication network is presented. A Least Cost Routing path between end users in a multi-network environment, including both public and private networks, is determined based upon a longest prefix match. At network activation time, the numbers or prefixes of numbers of end users attached to the public network (304, 305) are stored in entry node data bases A and C of the private network (303). Assuming an end user terminal U1 calls a target end user U3, an entry node B first checks for a longest prefix match between the called number and numbers already stored into its memory. If this is the first time U3 is called via node B, no match will occur and node B will then broadcast a Query to all nodes in the private network (i.e. Nodes A and C). Only those nodes providing possible access to U3 answer this Query. Node B then determines the longest prefix match with the called number amongst the various query answers, and sets the data path via that node having the longest prefix match.
Owner:IBM CORP
Static dense multicast path and bandwidth management
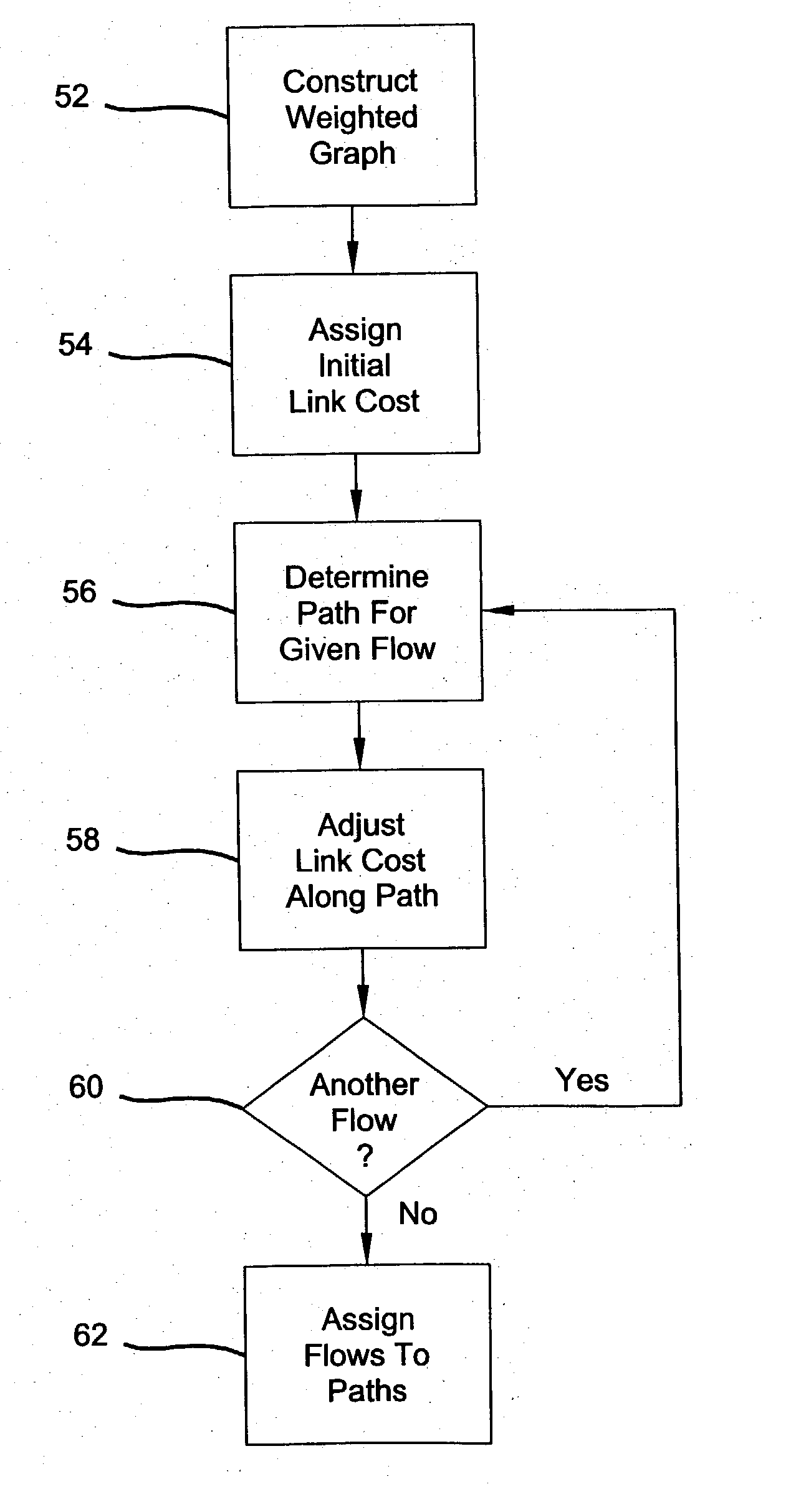
Improved algorithms are provided for performing path management for a plurality of select data transmission sessions in a multicast network. The algorithms include: constructing a weighted graph which represents topology of the network; assigning load correlated costs to network links; and computing least cost paths for each of the data transmission sessions which accounts for global bandwidth utilization.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
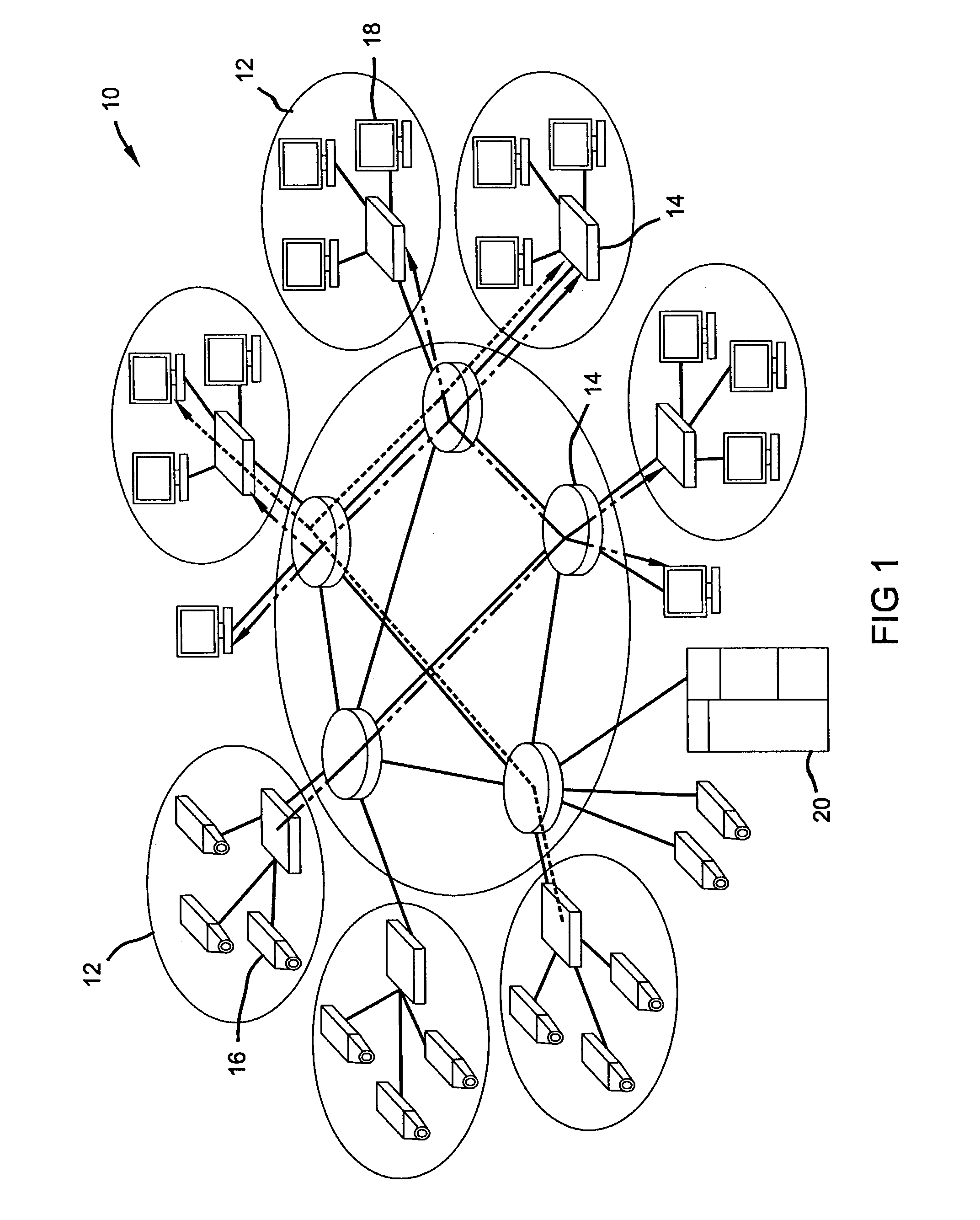
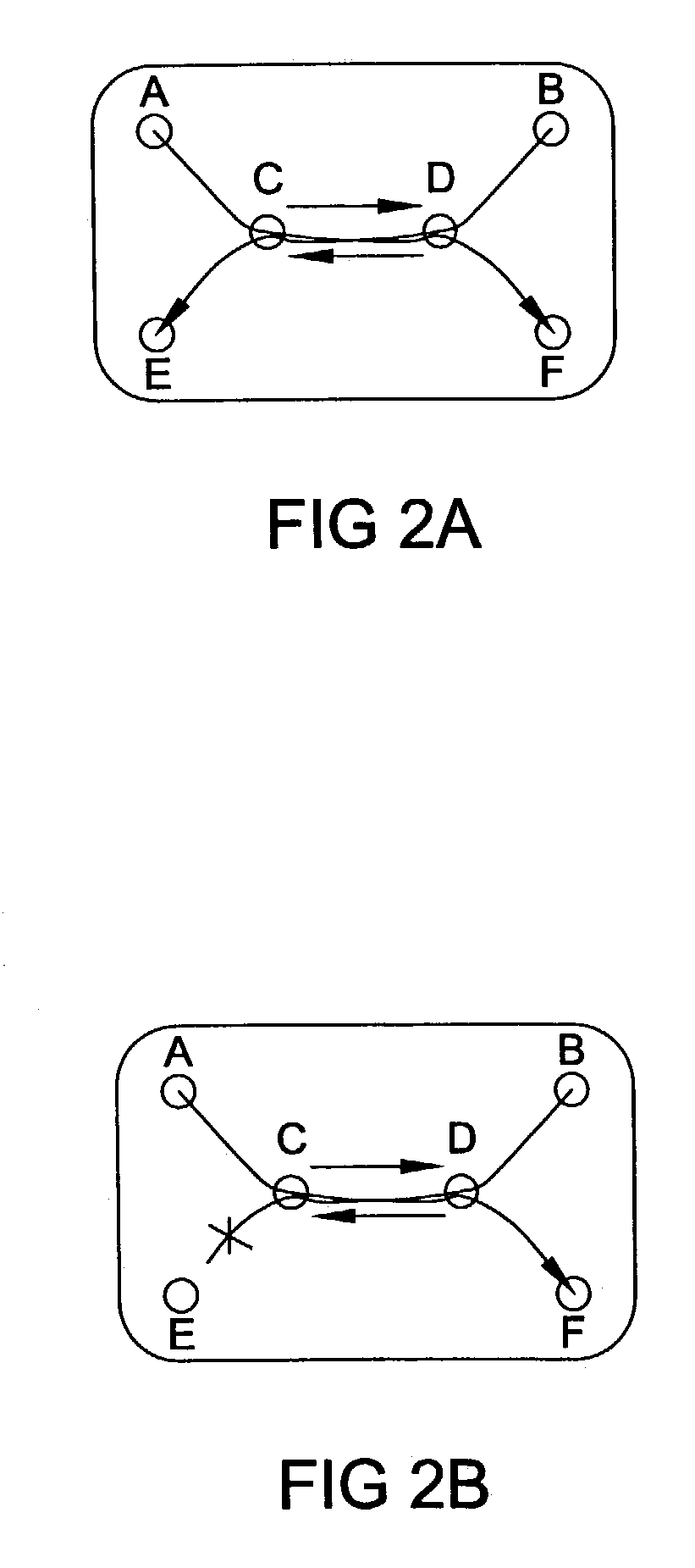
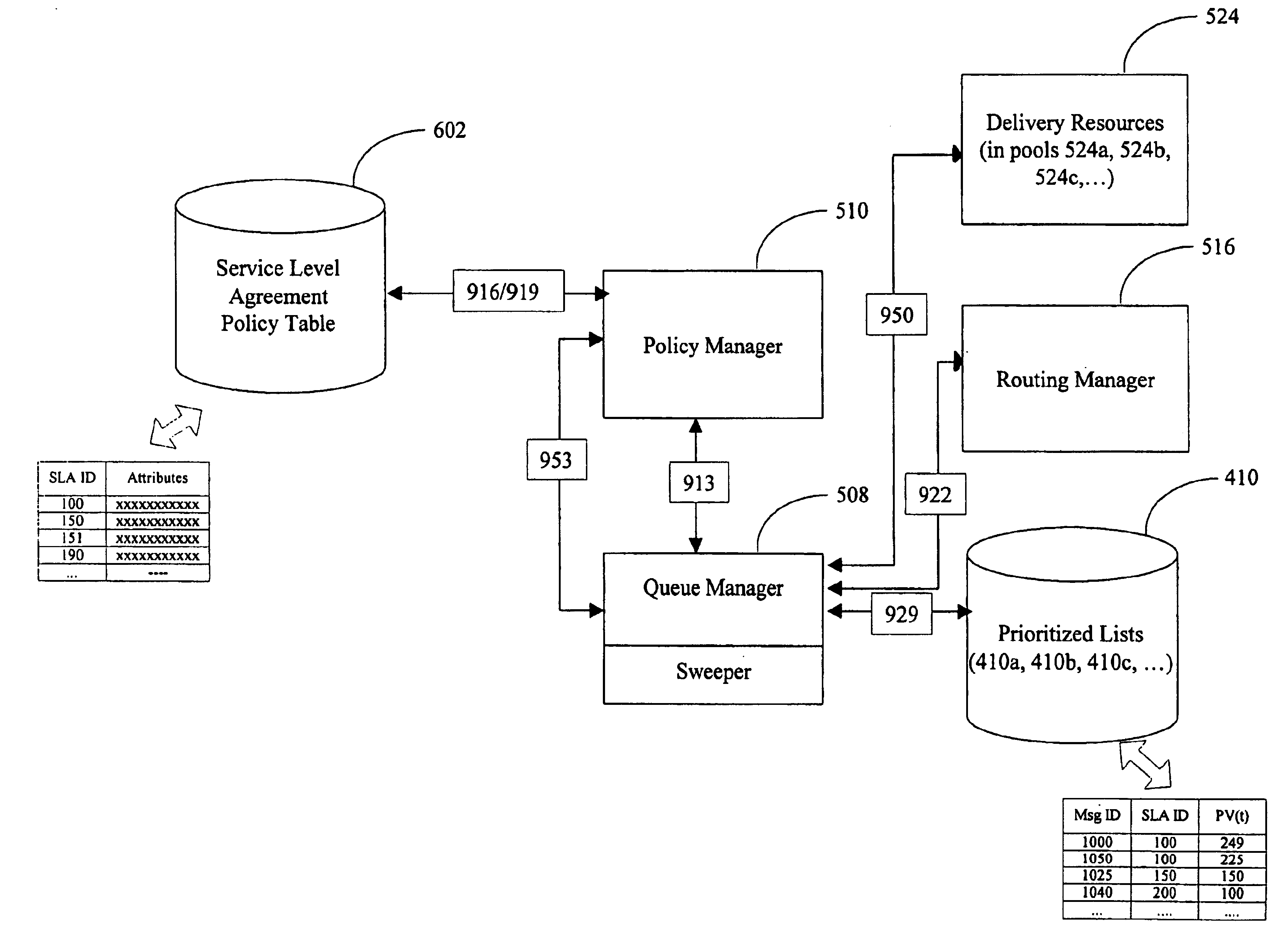
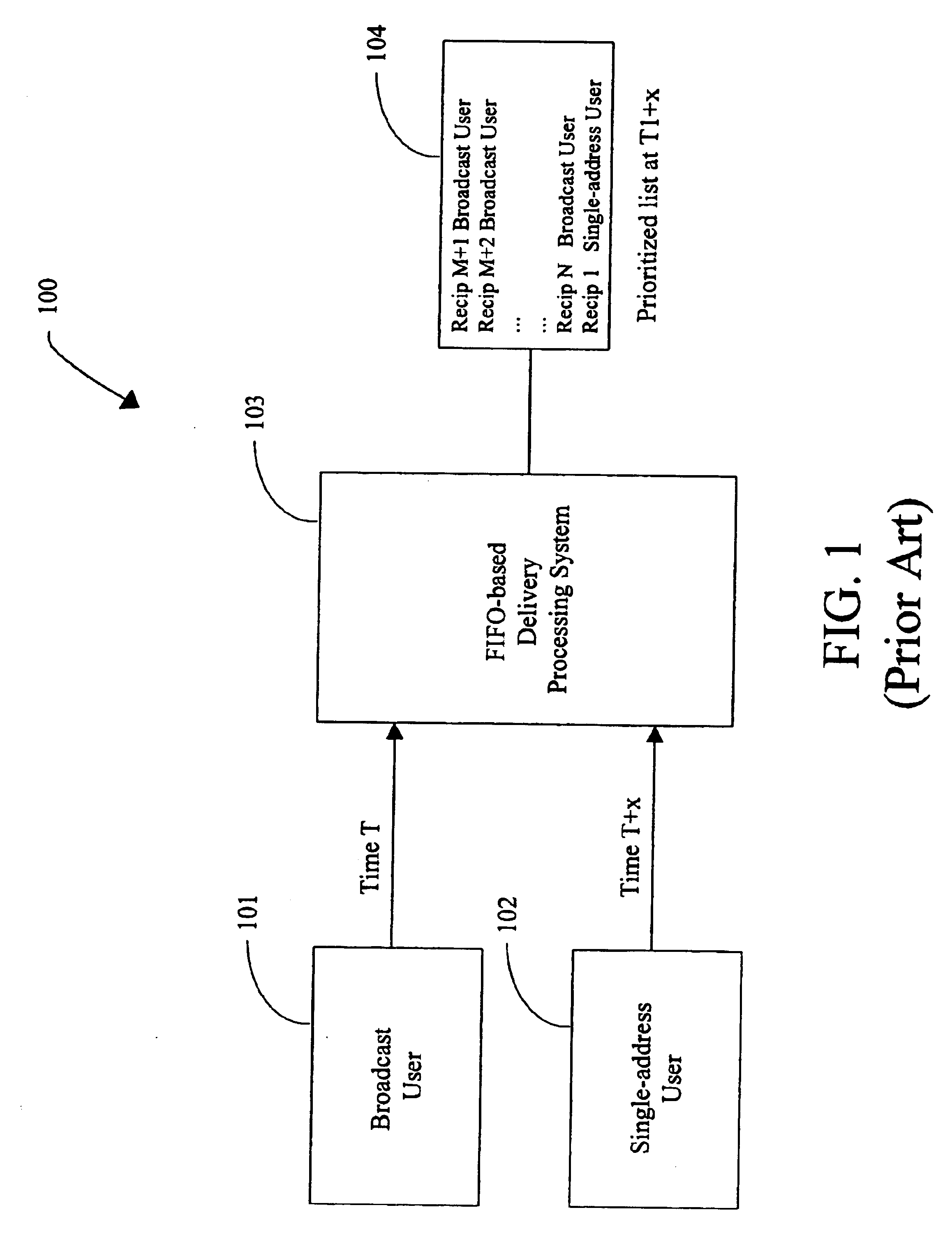
System and method for managing compliance with service level agreements
InactiveUS6917979B1Complete efficientlyGuaranteed levelMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksService-level agreementService level requirement
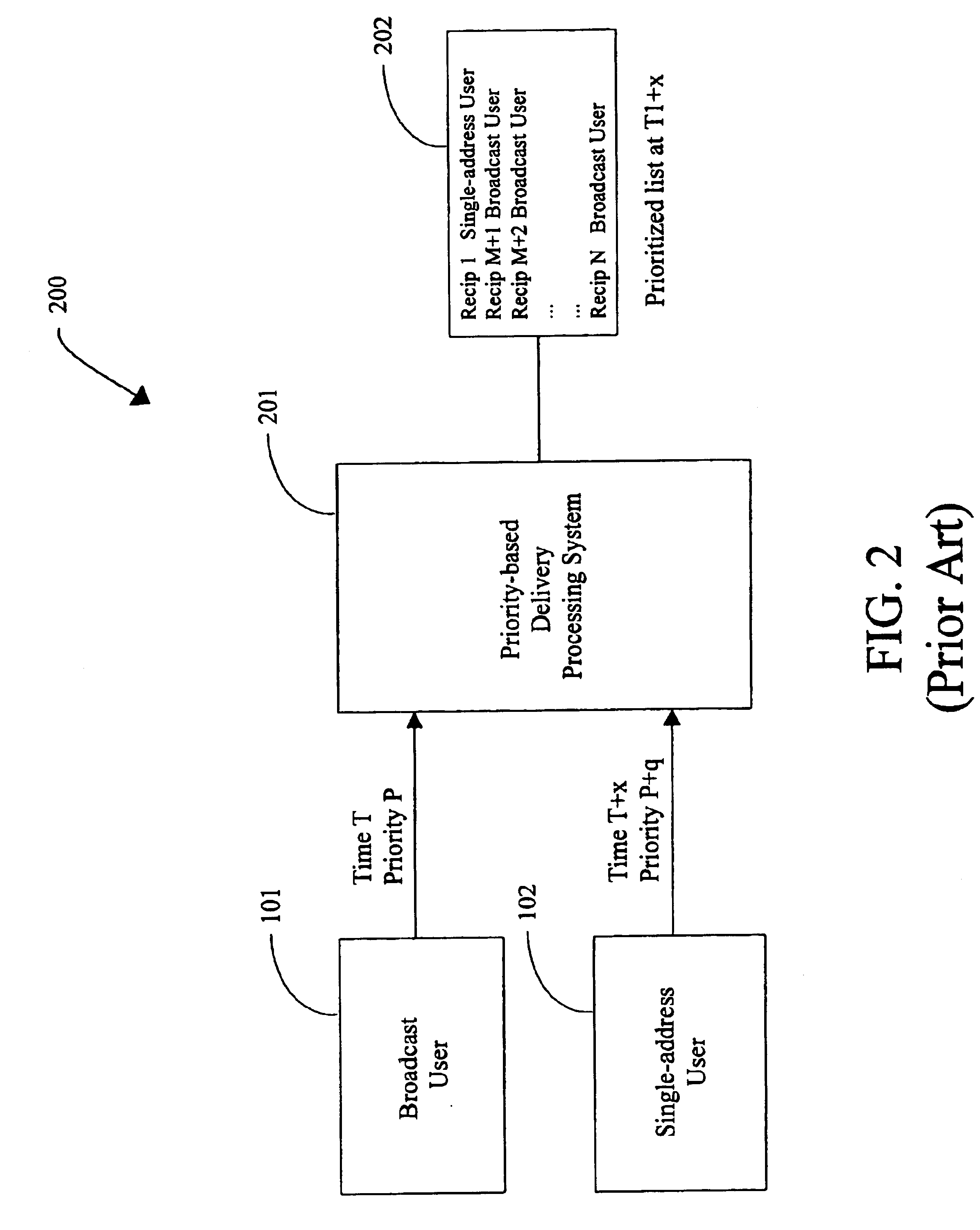
Compliance with subscriber job delivery requirements is managed and tracked. Job requirements set forth in service level agreements are stored electronically as delivery parameters. A queue manager creates a prioritized list of delivery jobs. A delivery manager delivers the jobs in accordance with the prioritized list. A routing manager determines optimal routes, e.g., least cost route for delivery of each job. Retries of jobs that are not successfully delivered can be performed. delivery job sources include broadcast subscribers, high- and low-priority single address subscribers, free subscribers and off-peak subscribers.
Owner:NET2PHONE
Probabilistic scheduling
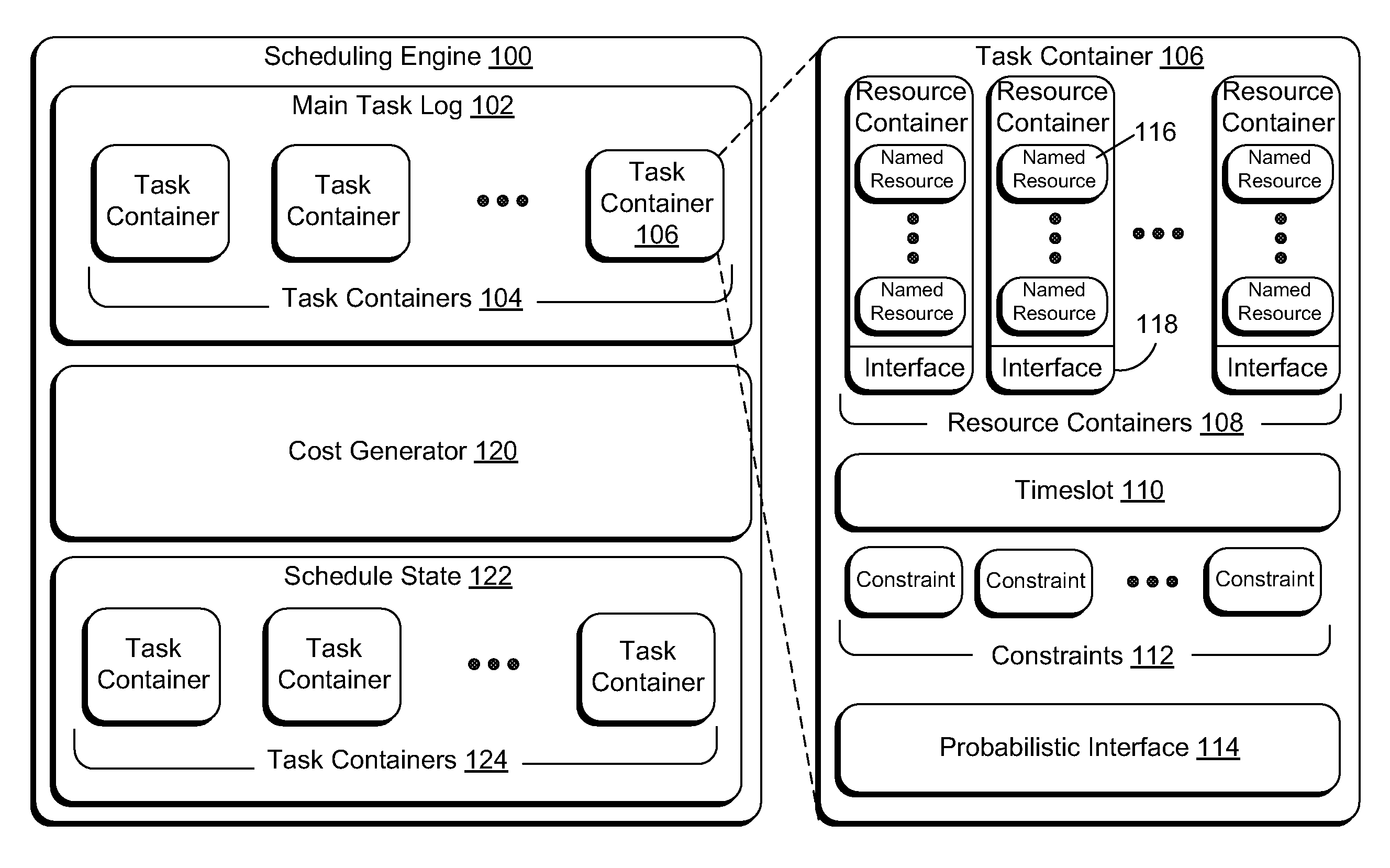
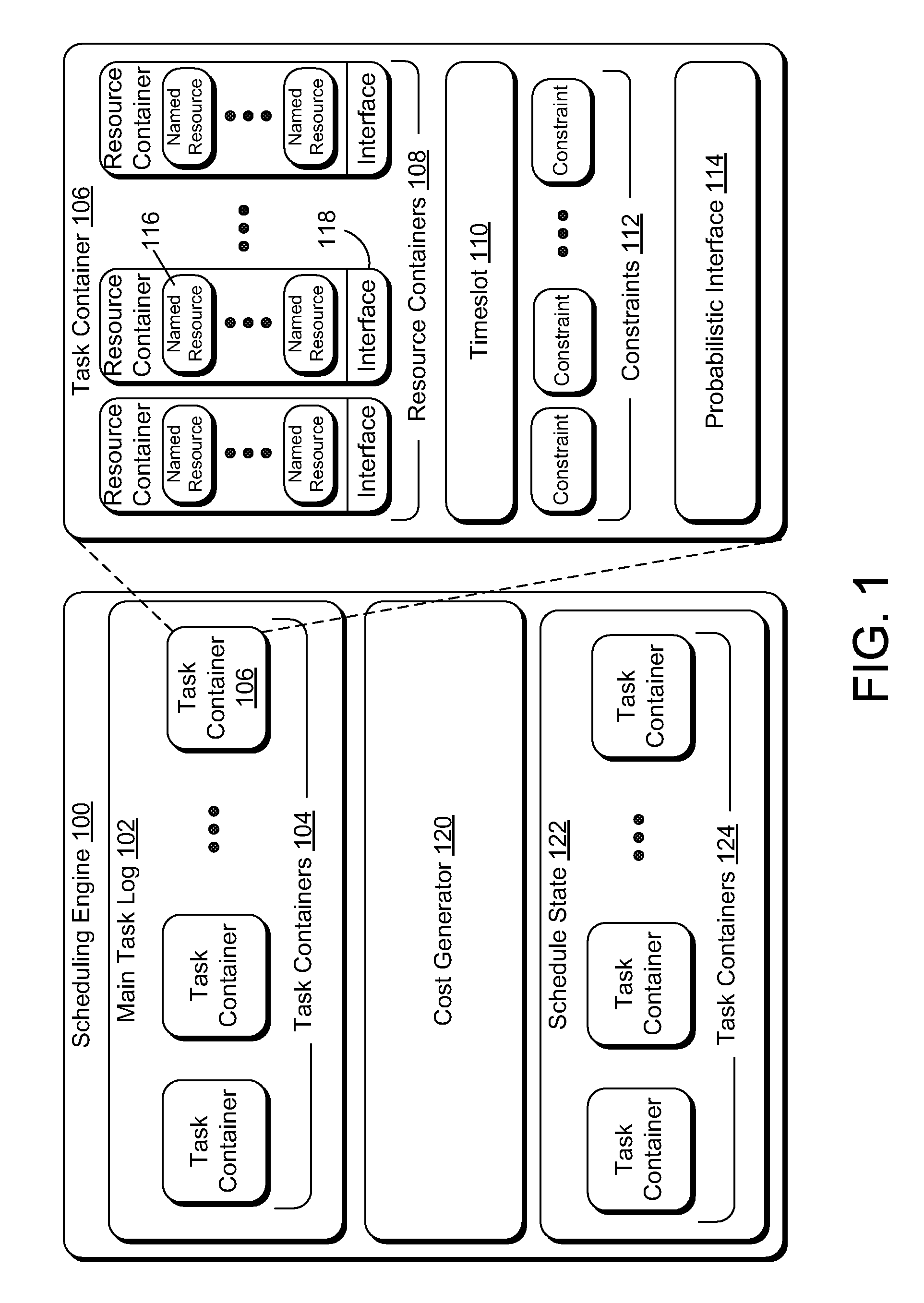
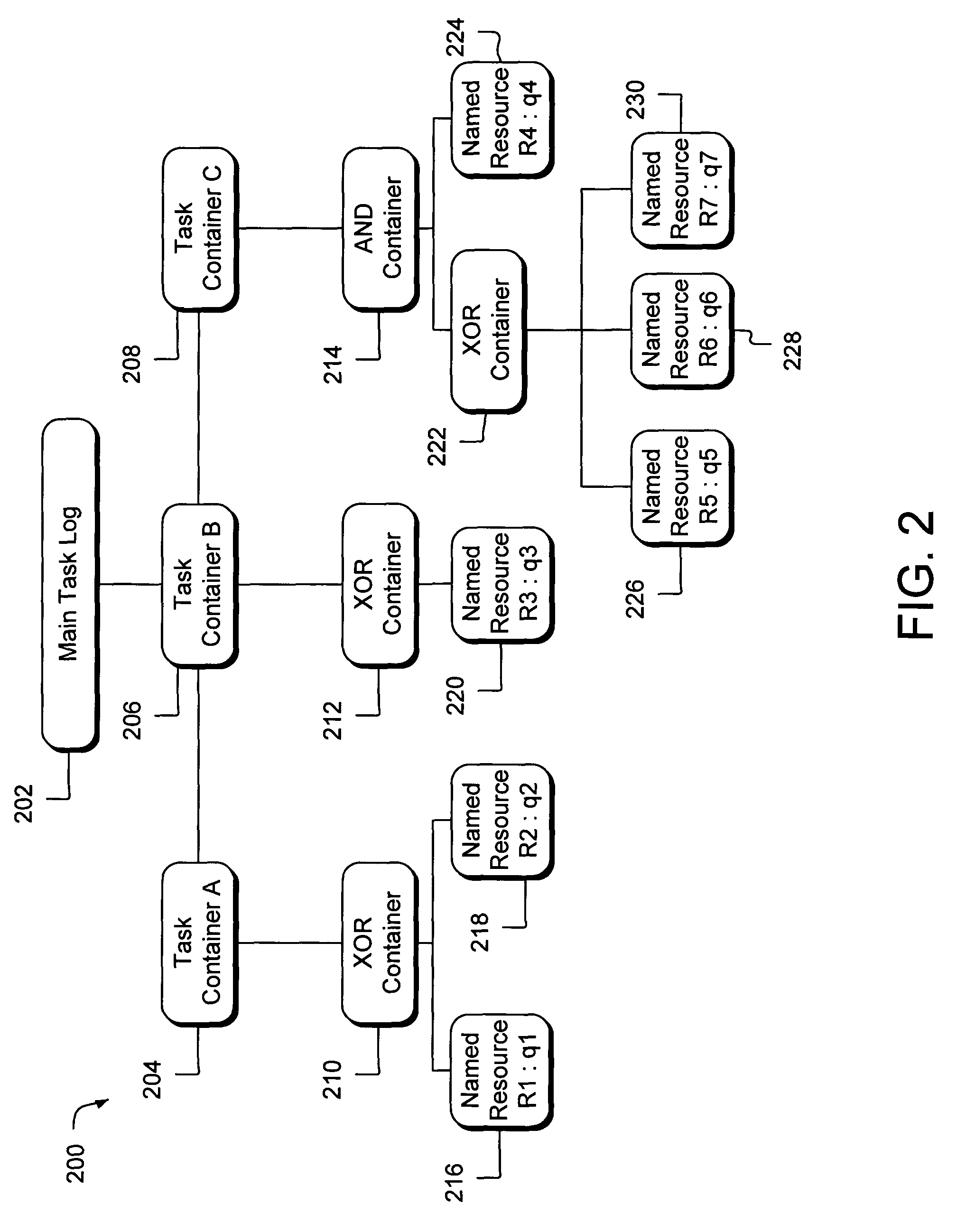
InactiveUS7516455B2Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsProbabilistic schedulingLeast cost
A method includes generating a cost associated with each of a plurality of tasks to be scheduled, and scheduling the minimum cost task if the minimum cost task successfully executes. Generating may include determining a pair-wise probability representing a probability that two tasks in the plurality of tasks conflict with each other. A system includes a cost generator generating costs associated with a plurality of tasks, the costs based on probabilities that each of the tasks influence the other tasks, and a scheduling engine operable to schedule the task with the least cost.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
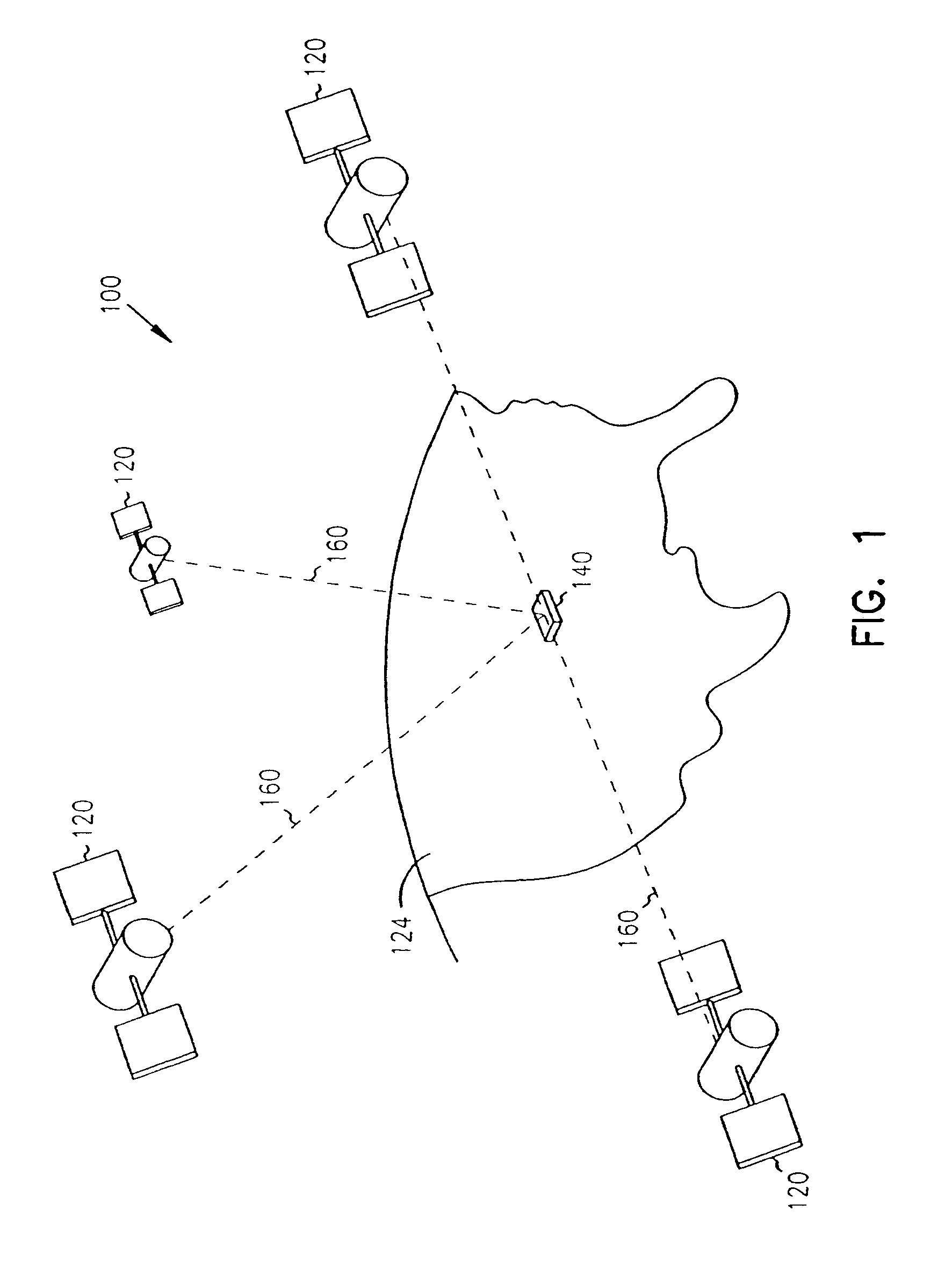
Route condition evaluation method and apparatus for navigation system
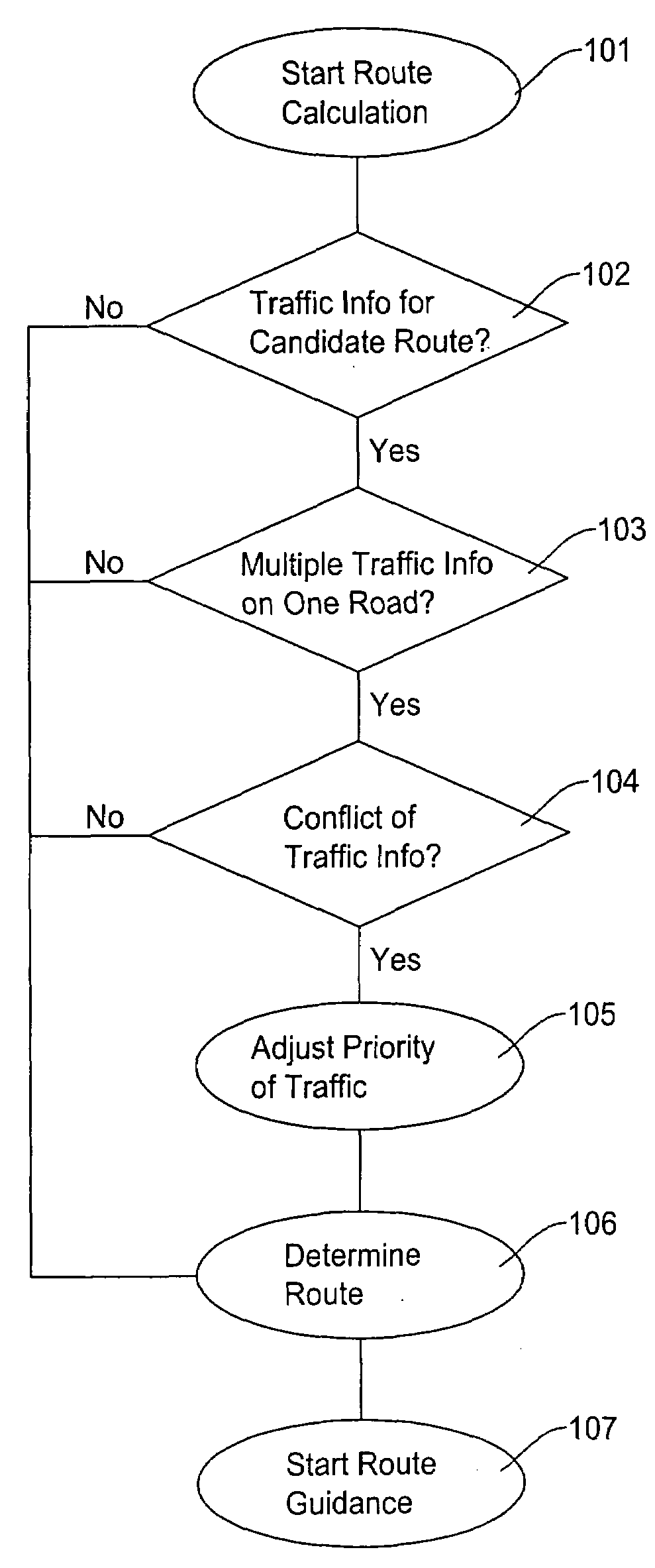
ActiveUS20080040031A1Low costAccurately determineInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlTraffic capacityEvent type
A method and apparatus for a navigation system evaluates an overall cost of each candidate route by incorporating traffic information such as traffic incident types and traffic flow speeds. An optimum route to the destination is determined by comparing the costs of two or more candidate routes and selecting a candidate route of the least cost. The method and apparatus determines relevancy and accuracy of the traffic information and adjusting the cost of the candidate route. When the traffic information on the candidate route shows a conflicting situation, the method and apparatus modifies the cost derived from the traffic information. When modifying the cost, the traffic speed information is prioritized over other type of traffic information.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
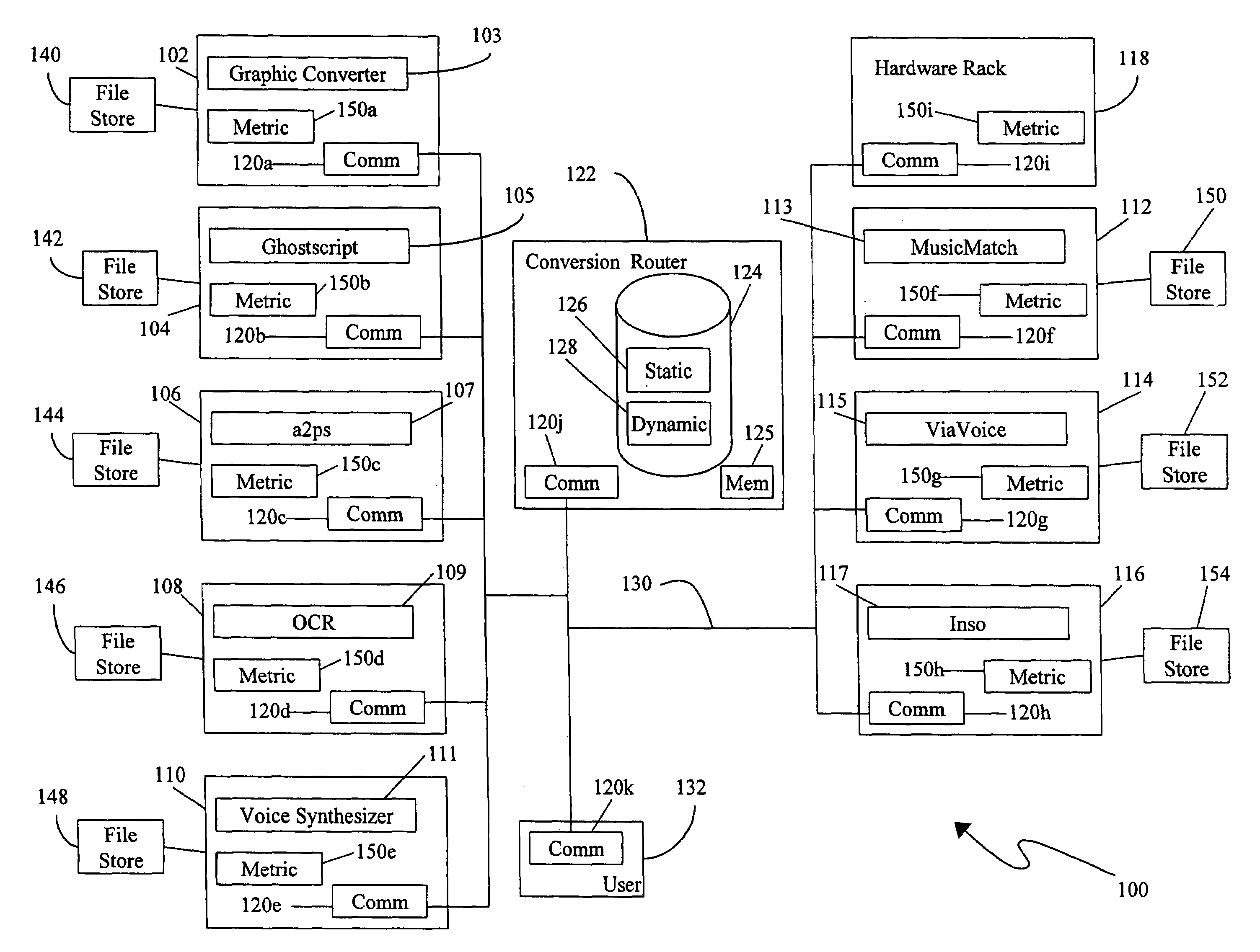
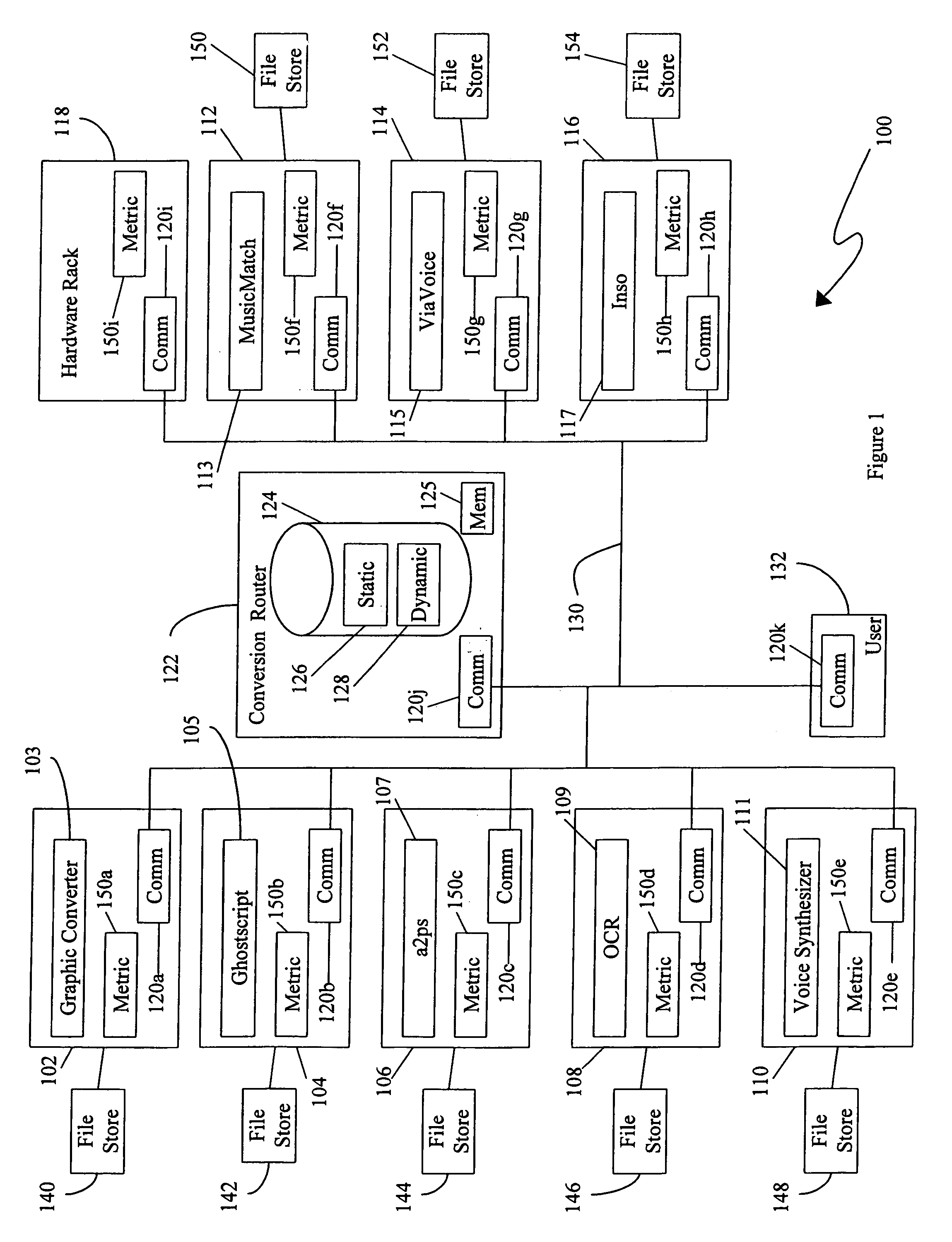
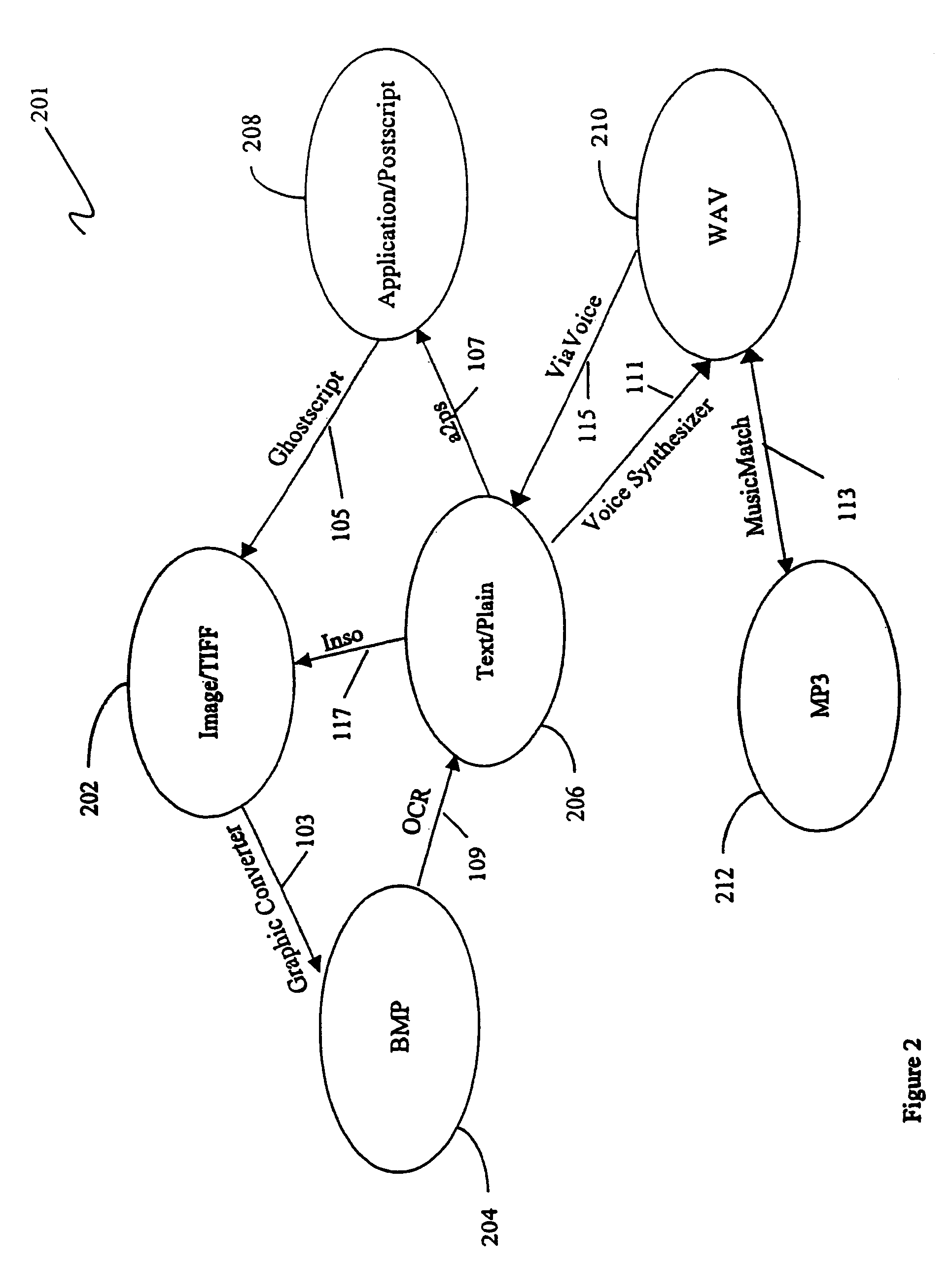
Flexible scalable file conversion system and method
A file conversion system provides a plurality of network computing platforms, each computing platform having one or more conversion engines executing thereon. When a file is to be transferred, a plurality of destination file types is determined. If all destination file types are different from the file's current type, the file is converted to a file having a type corresponding to one of the destination file type. If the file needs to be converted, then a conversion path, potentially passing through multiple conversion engines associated with a least conversion cost is chosen to perform the conversion. The file is sent to the computing platform on which the conversion engines associated with the least cost conversion are executing. Moreover, the least cost conversion can take into account the destination cost. Conversion costs are determined using a table of costs for performing various conversions. The table stores both static costs which remain constant during system operation and dynamic costs which vary with system operation.
Owner:NET2PHONE
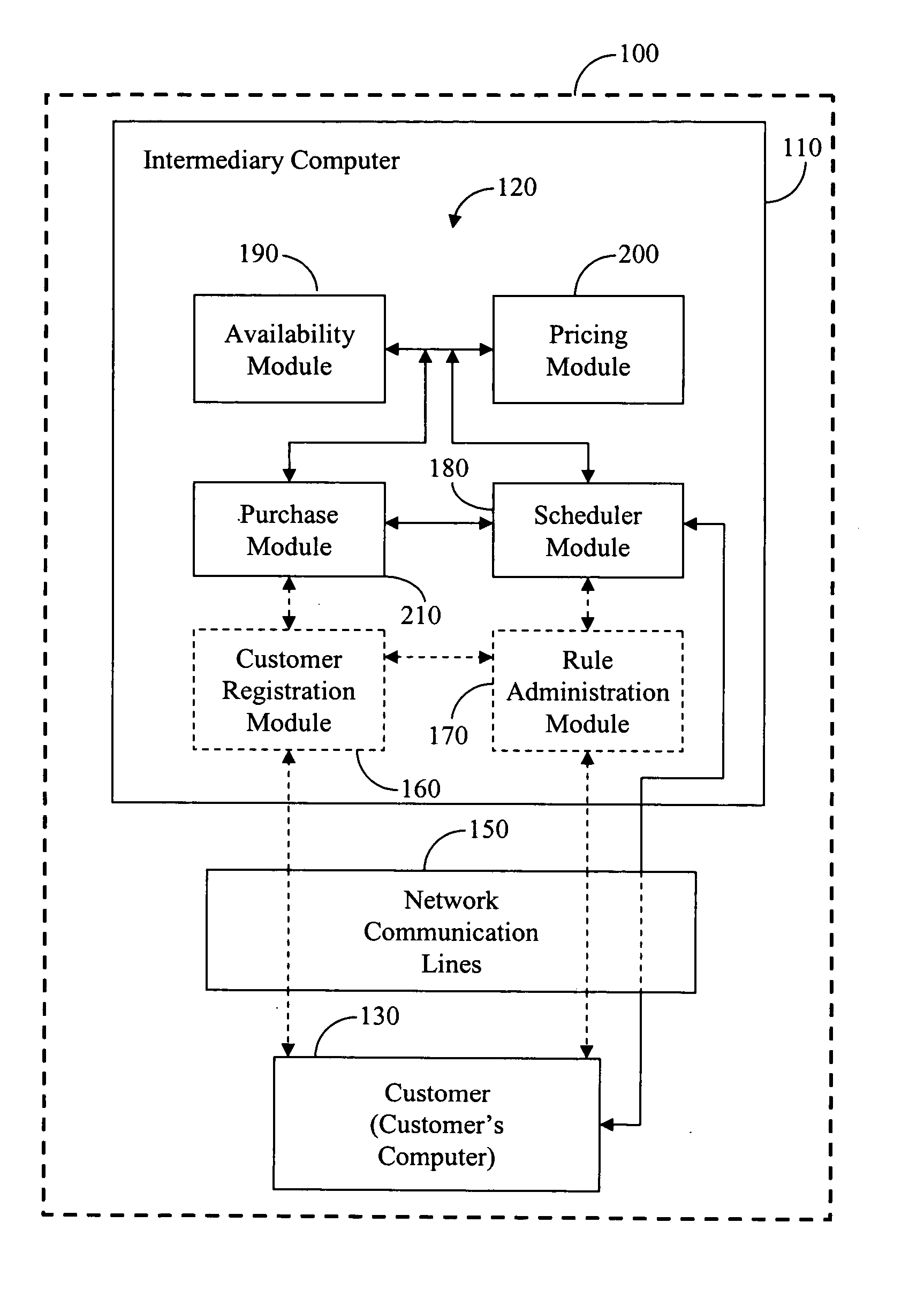
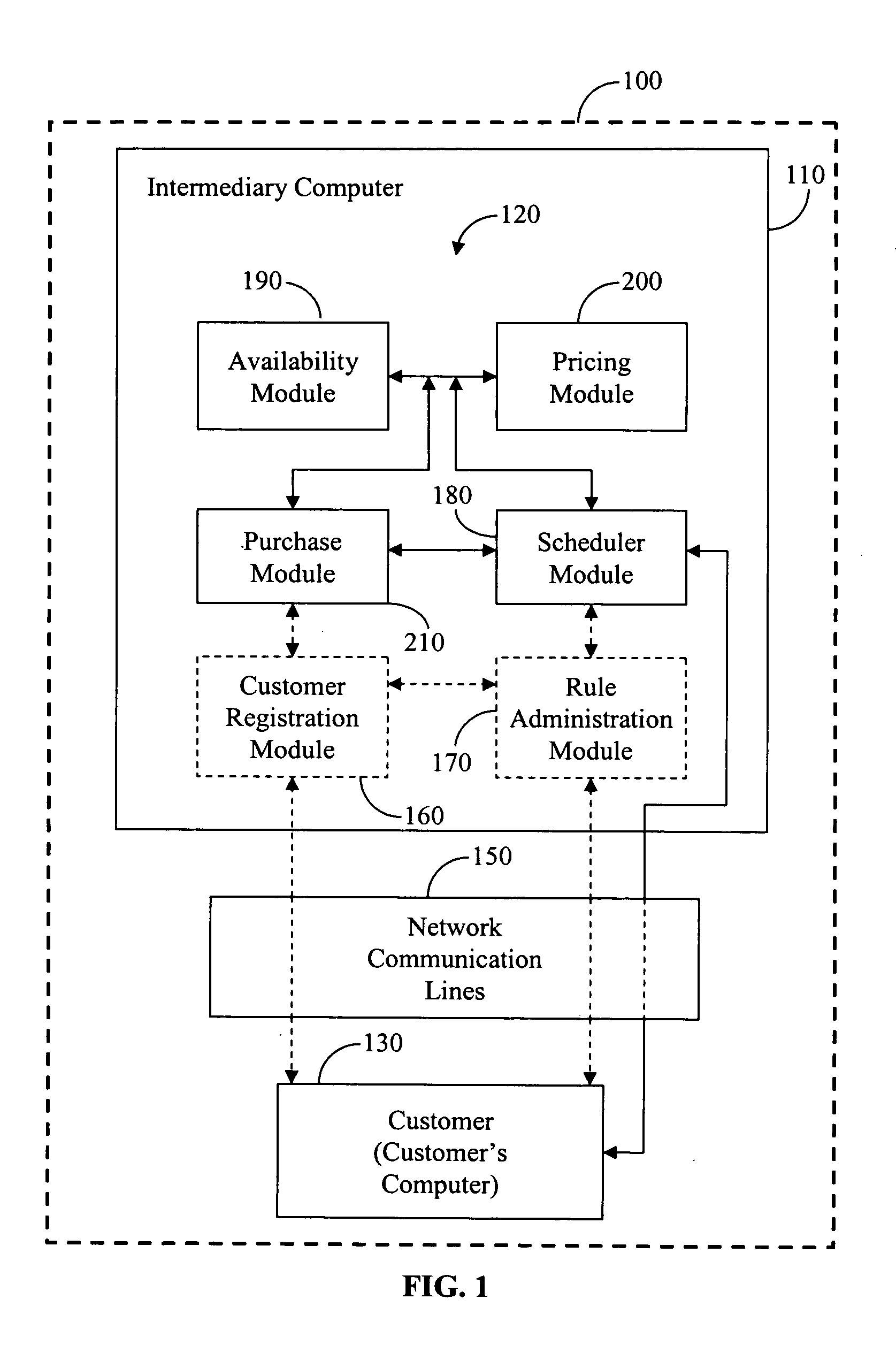
Devices, systems, and methods for providing remaining seat availability information in a booking class
InactiveUS20050228702A1Easy to judgeConservation valueReservationsForecastingTime scheduleLeast cost
A computer device is provided for determining remaining seats in a booking class having a maximum number of seats, which communicates with a user's computer device over a network to receive a user query, associated with travel parameters and including an amount of persons and at least two connect points, and obtains a schedule corresponding thereto. The schedule includes a cabin class with booking classes ranked by a criteria between a highest and a lowest booking class, the lowest booking class being a subset of the highest booking class. The computer device selects a least-cost-fare booking class from the ranked booking classes, which has an actual number of available seats at least equal to the amount of persons requesting seats and an applicable fare meeting the travel parameters, and provides an indicia thereof to the user, in direct response to the query. Associated systems and methods are also provided.
Owner:TRAVELOCITY COM LP
Method and system for calculating least-cost routes based on historical fuel efficiency, street mapping and location based services
ActiveUS7778769B2Maximize efficiencyLess fuelAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficTerrainDriver/operator
This disclosure outlines a method, which enables a vehicle driver to achieve increased fuel efficiency by implementing least-cost route planning based on terrain data and derived from advanced mapping, logging and location based services. Actual fuel efficiency is recorded and correlated by vehicle conditions, time of day and date, and then referenced to achieve the most accurate least-cost route plan for the intended destination.
Owner:SLINGSHOT IOT LLC
Static dense multicast path and bandwidth management
Improved algorithms are provided for performing path management for a plurality of select data transmission sessions in a multicast network. The algorithms include: constructing a weighted graph which represents topology of the network; assigning load correlated costs to network links; and computing least cost paths for each of the data transmission sessions which accounts for global bandwidth utilization.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Systems and methods for multipath routing
InactiveUS20060133282A1Provides redundancyError preventionTransmission systemsBalancing networkDatapath
A method and system for directing data packets from an origin node to a destination node in a multipath communication network having a plurality of nodes, where each node is connected to at least one other node by links. The apparatus includes a processor for obtaining cost information relating to each link in the network and for determining the least-cost route between the origin node and the destination node based on the cost information relating to each link. The processor establishes a cost margin representing a range of costs above the cost of the least cost route and identifies one or more alternate routes. A data storage device stores the cost information, and a network interface selectively routes the data packets through one or more of the least cost route and the one or more alternate routes falling within the established cost margin thus balancing the network load and providing alternate data paths in case the least-cost path is unavailable.
Owner:AVAYA INC
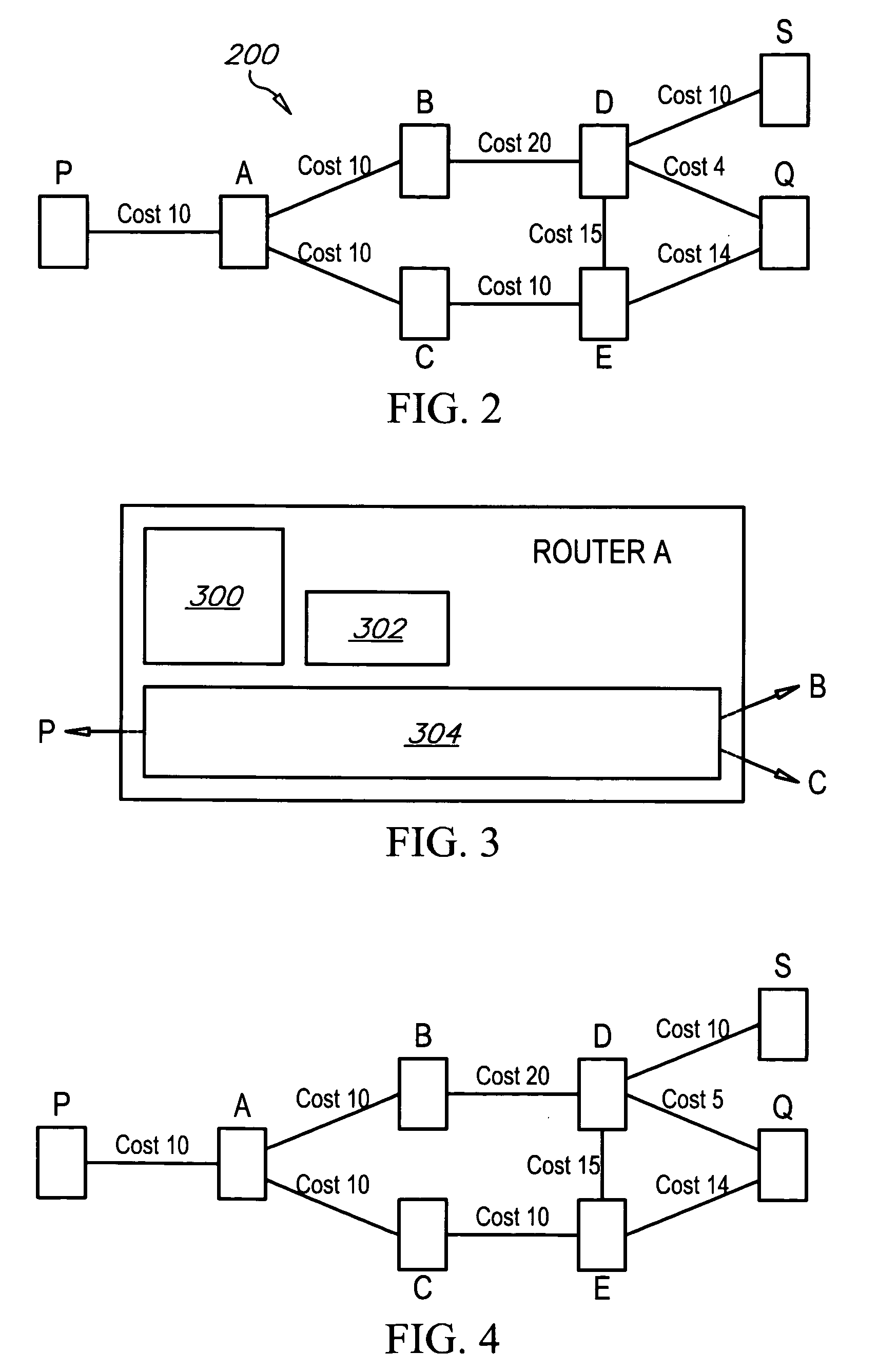
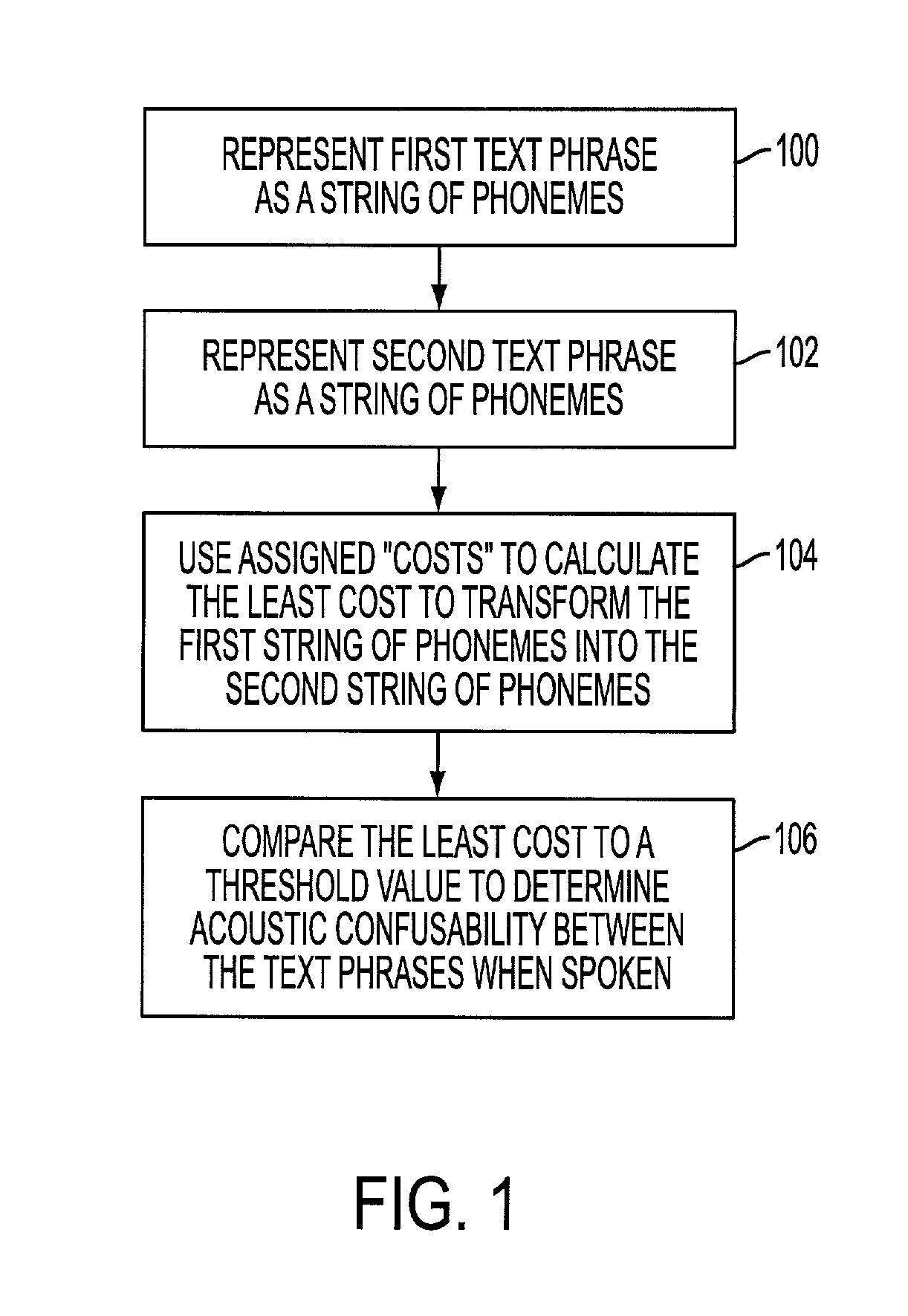
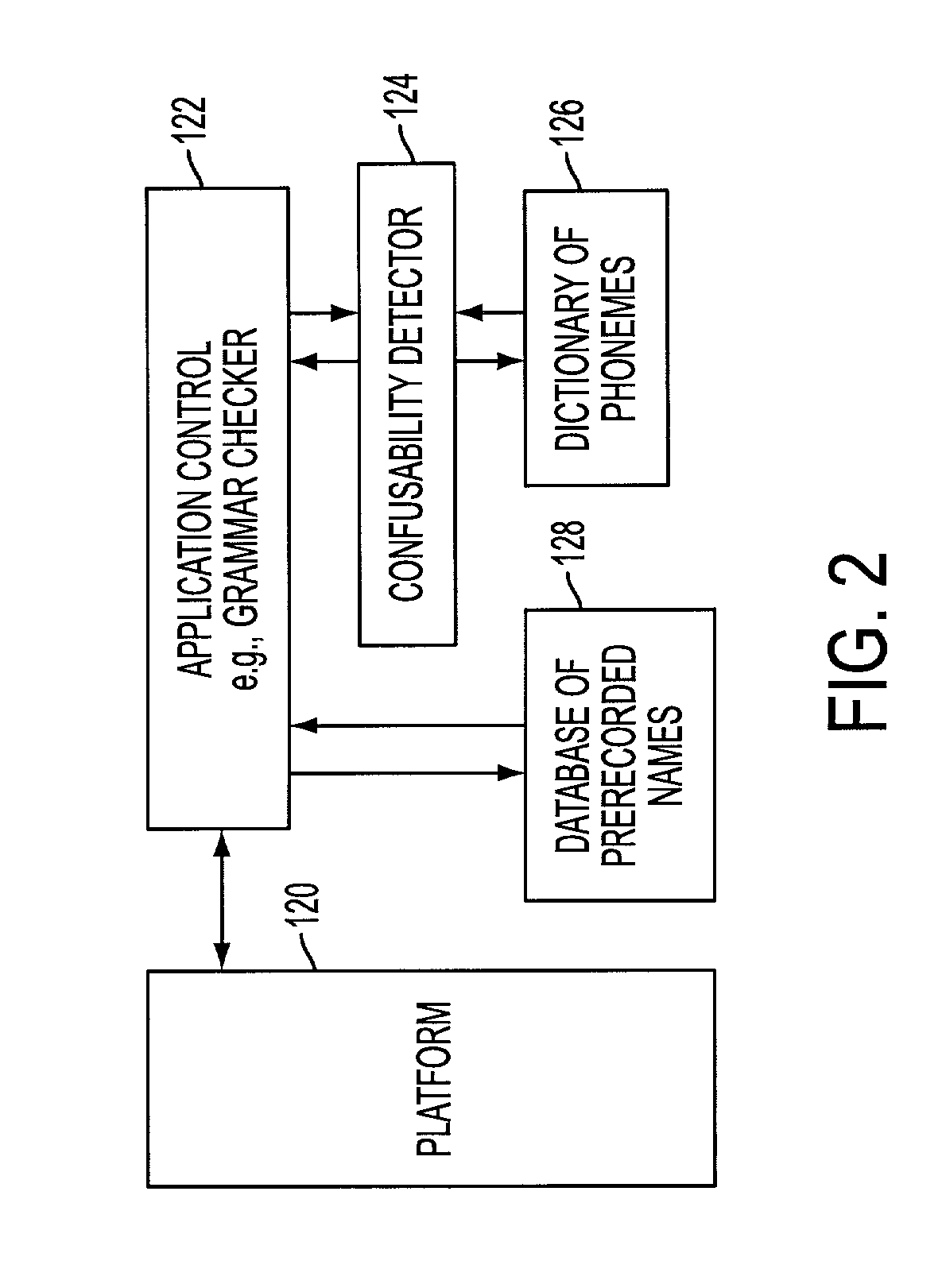
Method of assessing degree of acoustic confusability, and system therefor
Predicting speech recognizer confusion where utterances can be represented by any combination of text form and audio file. The utterances are represented with an intermediate representation that directly reflects the acoustic characteristics of the utterances. Text representations of the utterances can be directly used for predicting confusability without access to audio file examples of the utterances. First embodiment: two text utterances are represented with strings of phonemes and one of the strings of phonemes is transformed into the other strings of phonemes for a least cost as a confusability measure. Second embodiment: two utterances are represented with an intermediate representation of sequences of acoustic events based on phonetic capabilities of speakers obtained from acoustic signals of the utterances and the acoustic events are compared. Predicting confusability of the utterances according to a formula 2K / (T), K is a number of matched acoustic events and T is a total number of acoustic events.
Owner:MAVENIR INC
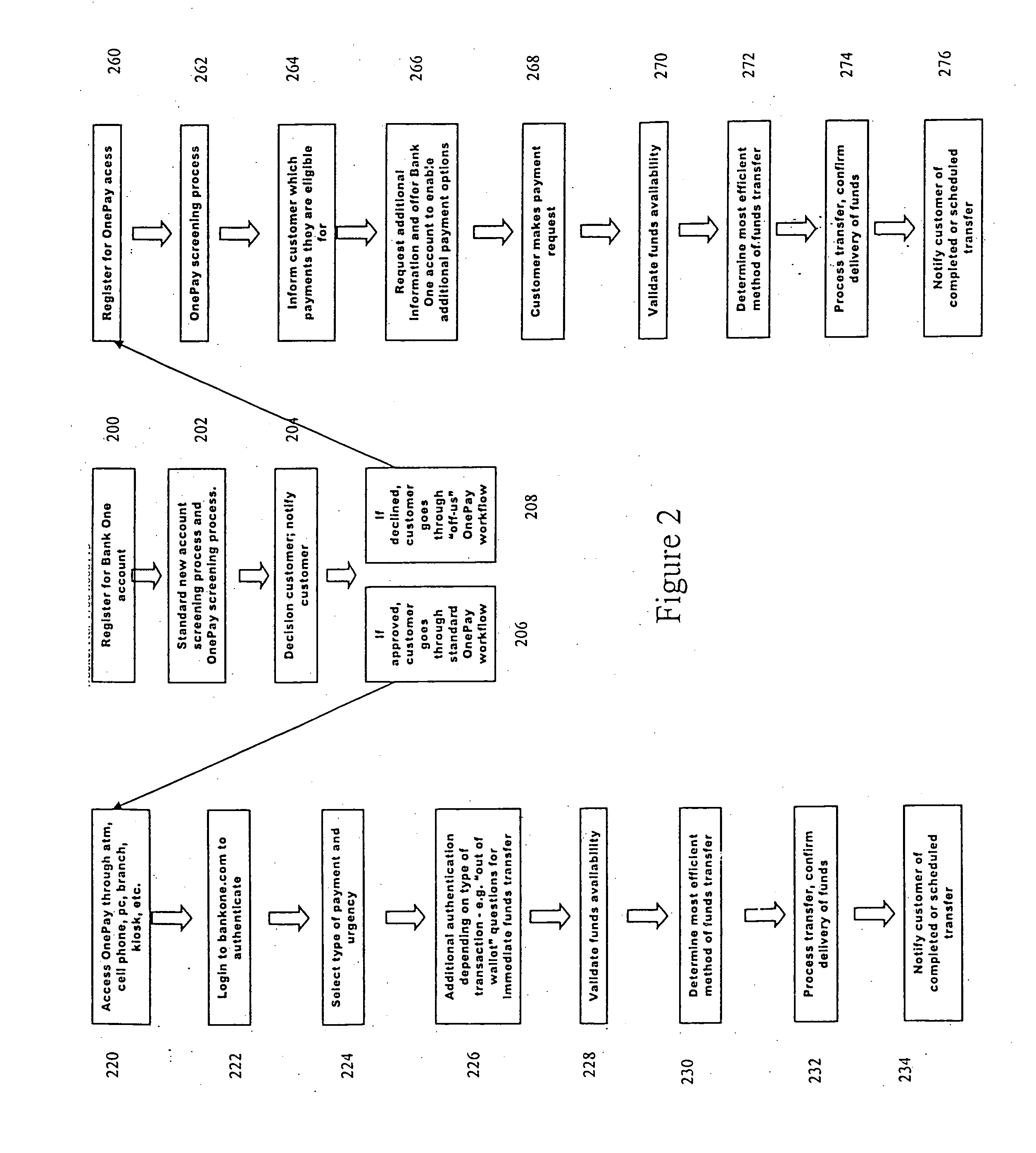
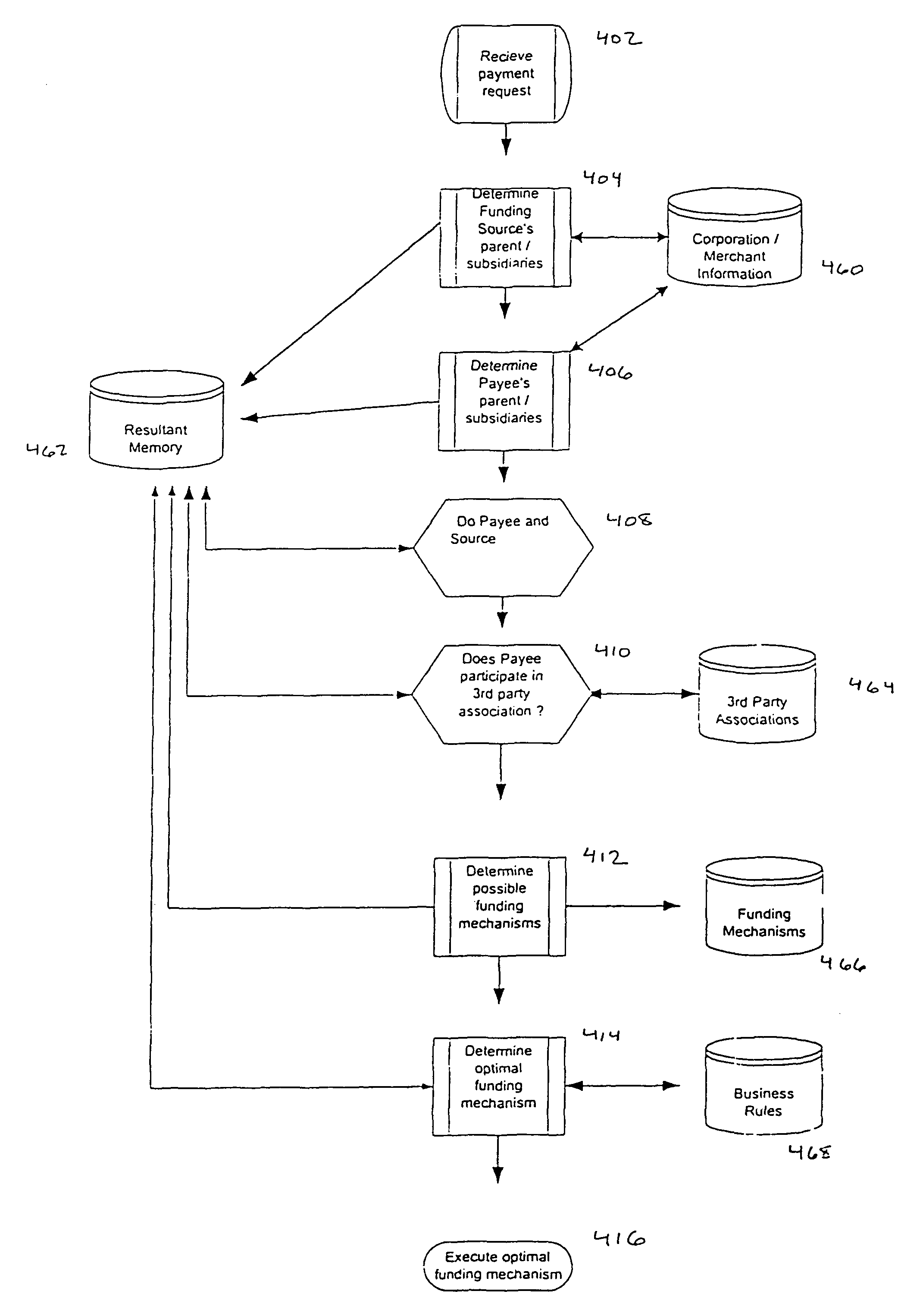
System and method for selectable funding of electronic transactions
InactiveUS20070005496A1Increase rangeIncrease flexibilityFinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPaymentLeast cost
A system for transferring funds to pay bills and to and from selected accounts on an optimized is provided. A mediation engine may manage the payments made to selected payees, including by scheduling the payments and selecting sources for funds. A rules-based optimizer may automatically select the least-cost or other most efficient or desirable transaction, given the customer's available funds, types of funds and payment date. All payment providers and payees may manipulated using one seamless view. A customer service representative may also view the transfers.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
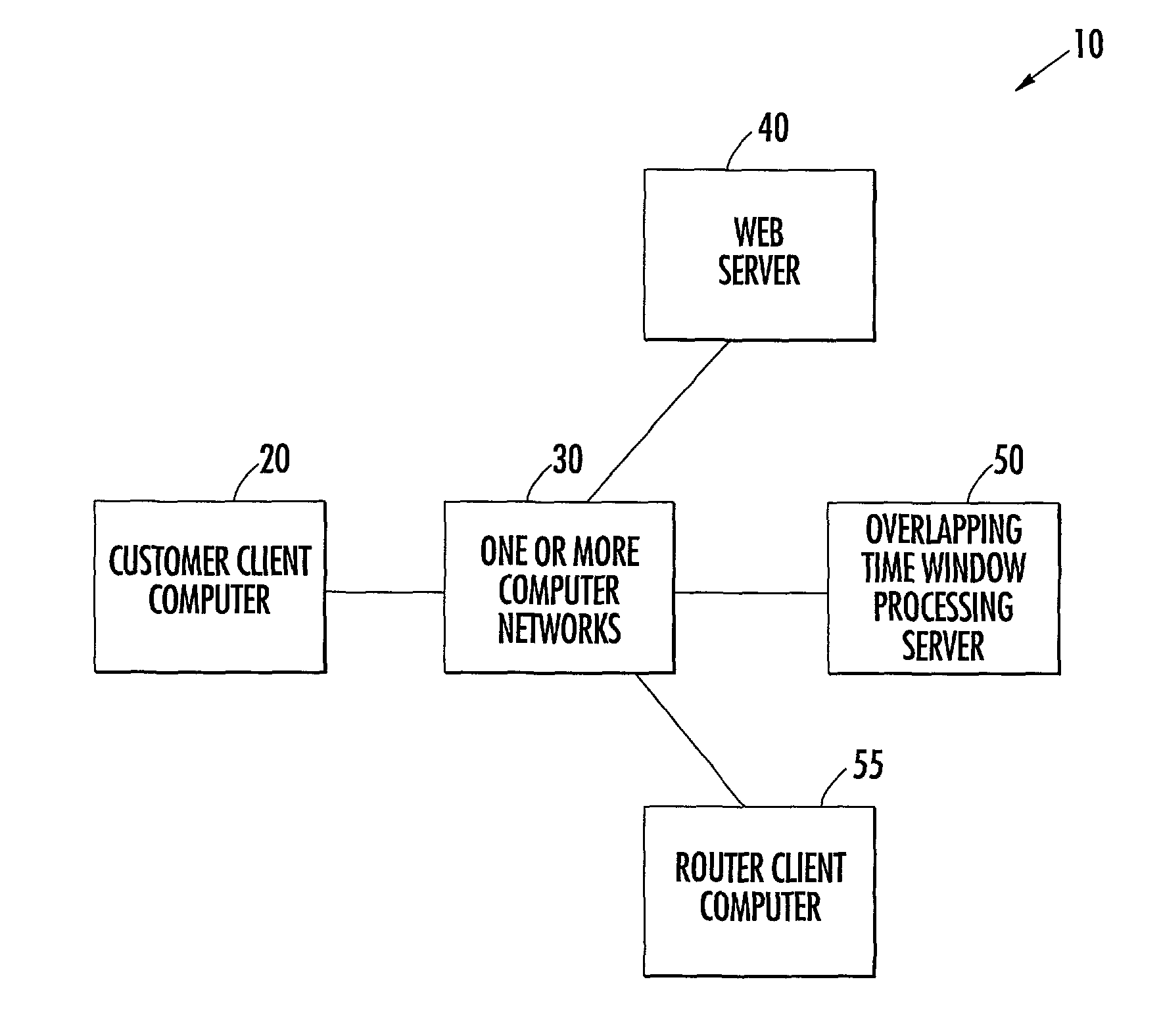
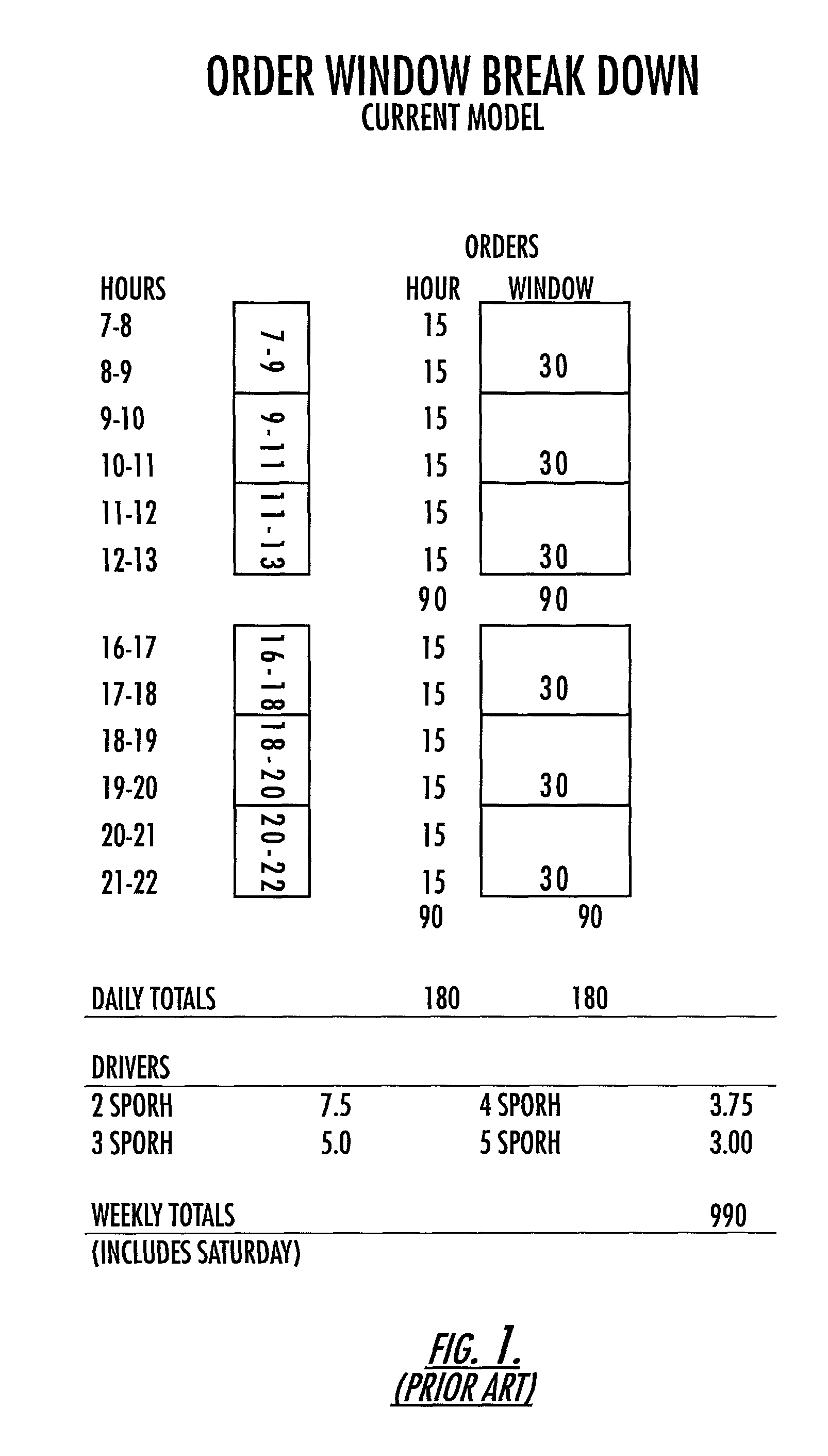
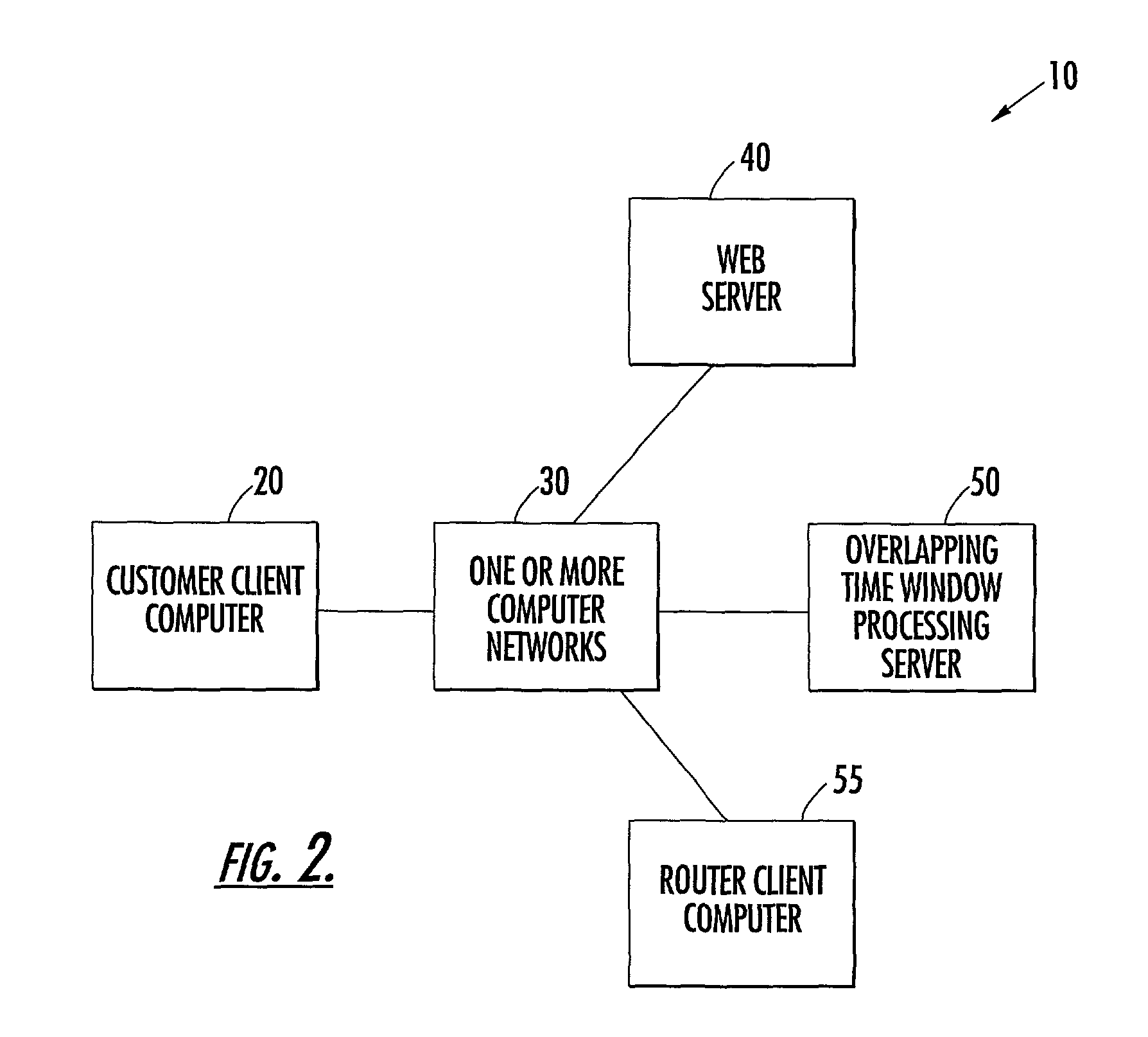
Method and system of delivering items using overlapping delivery windows
ActiveUS7925524B2Easy to useVehicle position indicationBuying/selling/leasing transactionsLeast costTime windows
A method and system for obtaining desired times from intended recipients of items is provided. The method provides each recipient with a plurality of time windows that overlap with one another in time from which the recipient may choose a time for delivery of an item and receives choices made by recipients from the plurality of overlapping windows. One aspect of the invention includes applying predetermined parameters to the time windows to determine which time windows to offer to the recipients as available times from which the recipient may choose a time for delivery. Such parameters may include, among others, which time windows have associated with them the least cost of service in making the delivery, whether the cost of delivering within a time window is less than a monetary threshold, and whether a maximum number of orders to be delivered within one time window has been reached.
Owner:UNITED PARCEL SERVICE OF AMERICAN INC
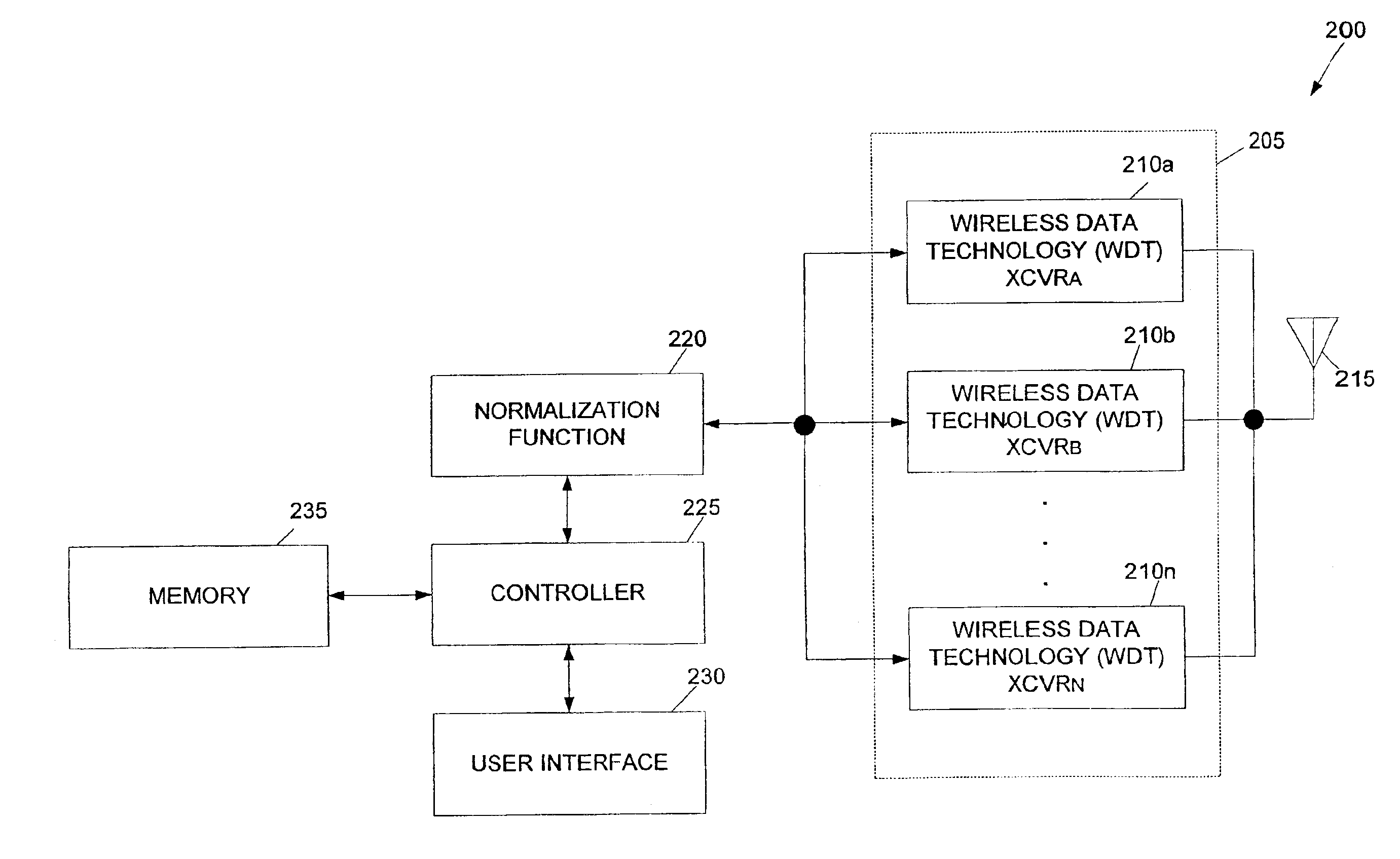
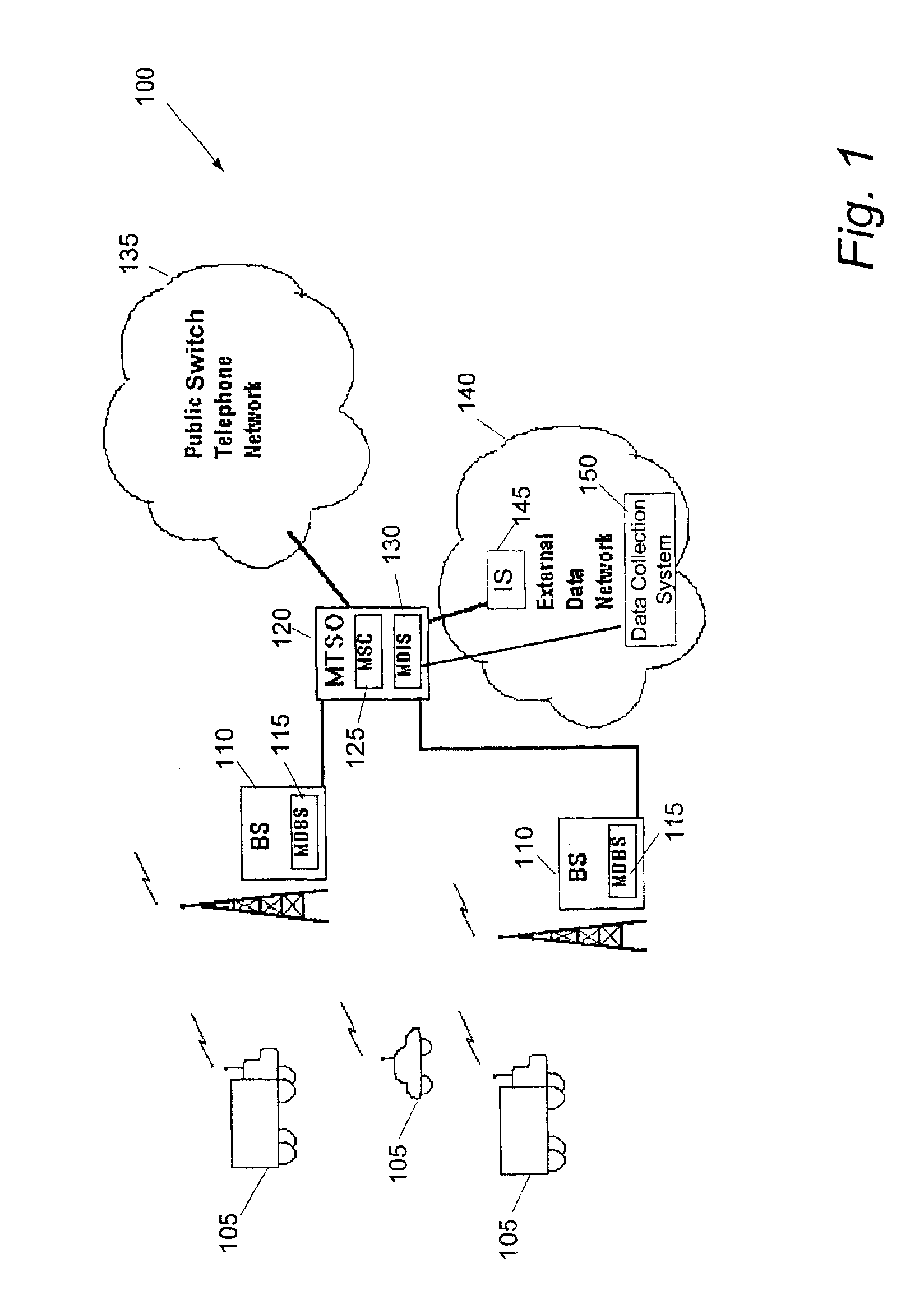
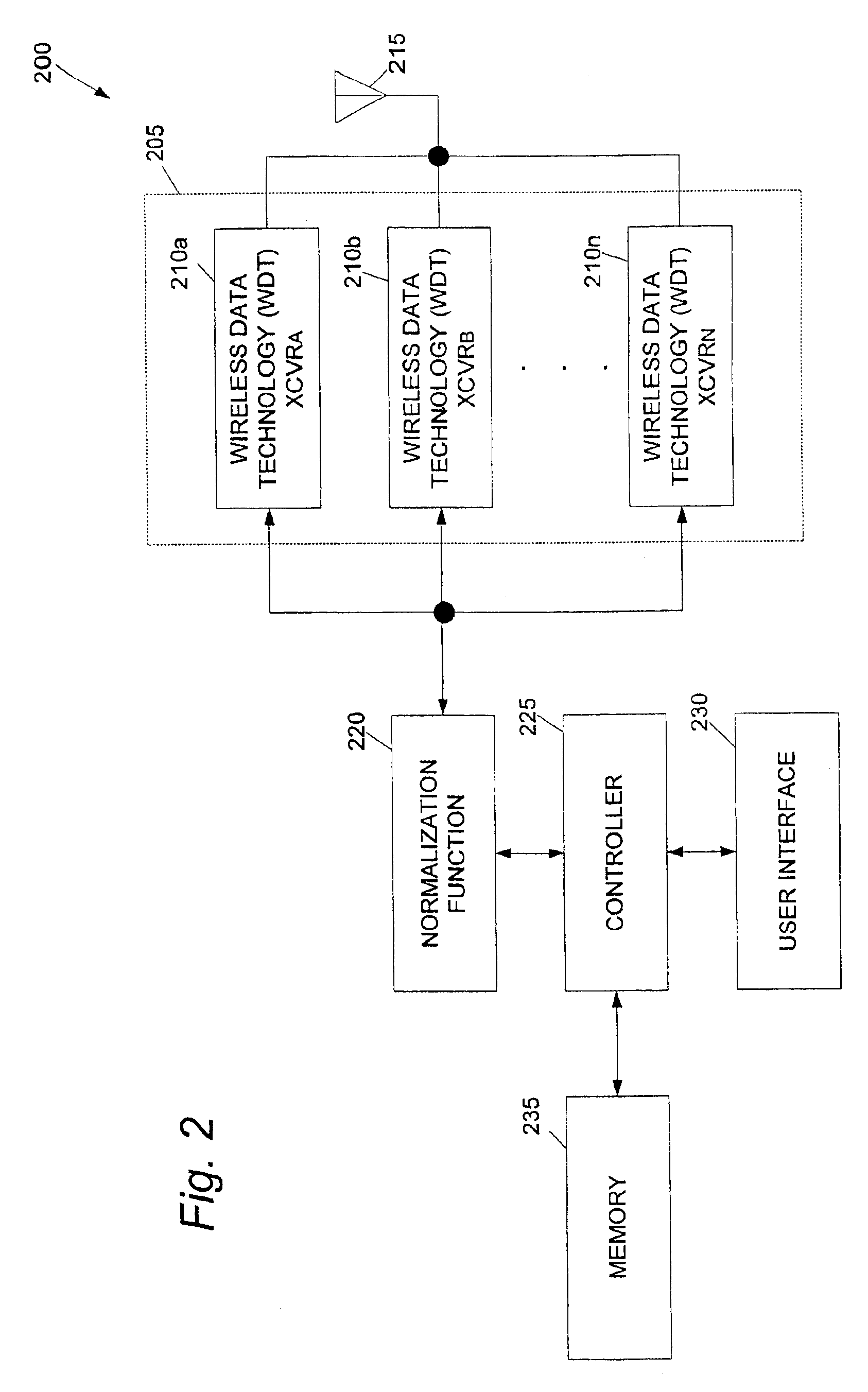
Multiple wireless data transport transceiver system
InactiveUS6882843B1Least costEfficient and cost-effectiveError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsModem deviceTransceiver
A wireless communications device that can support the communication of a data message via a selected one of multiple wireless data transport (WDT) technologies. A wireless communications device can support CDPD, control channel data transport technologies, such as the “CELLEMETRY” data communications service, and voice-channel modem operations by combining these WDT technologies within a single radio device. In the radio-to-base system direction, the appropriate WDT technology can be chosen based upon the data volume for the communication application. A control channel data transport technology can be used for very low volume; CDPD can be used for medium volume; and voice-channel modem operation can be used for large volume. The appropriate WDT technology can be automatically selected for use with the present data application to achieve an effective communication of the data content via the cellular system while also accomplishing a least cost distribution of the data content. The wireless communications device can be implemented by a single monolithic component for efficient manufacture and convenient use.
Owner:SIERRA WIRELESS AMERICA
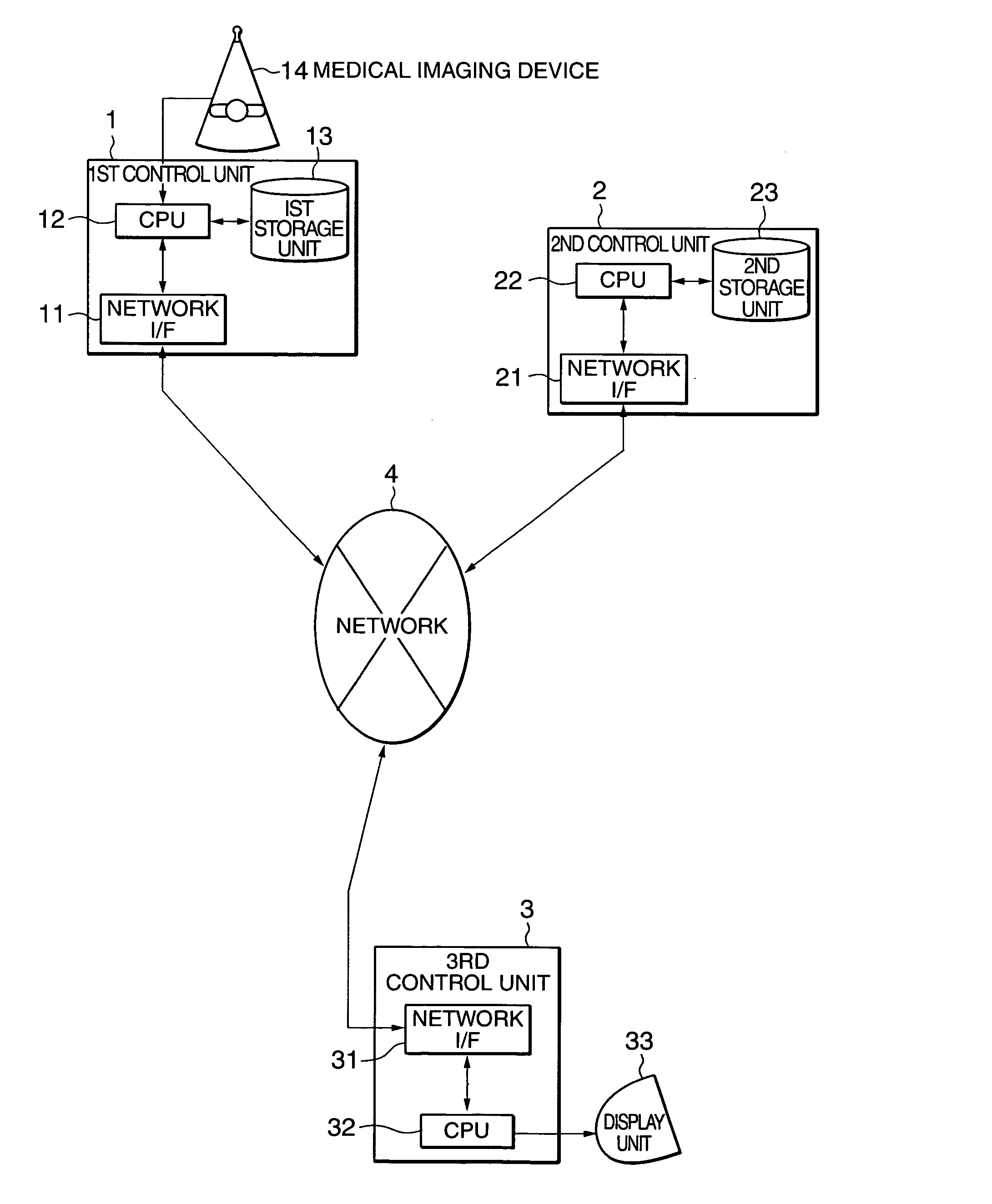
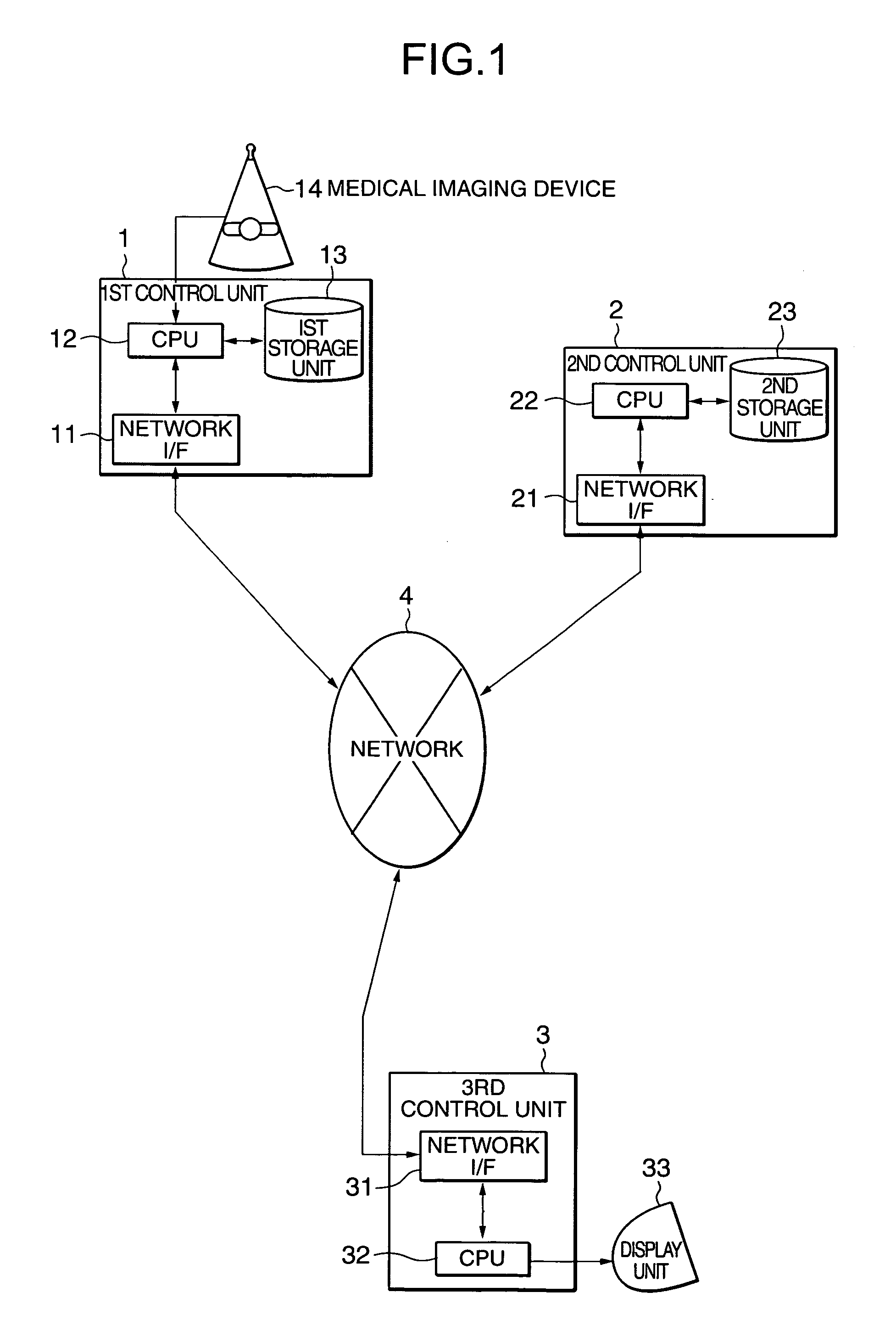
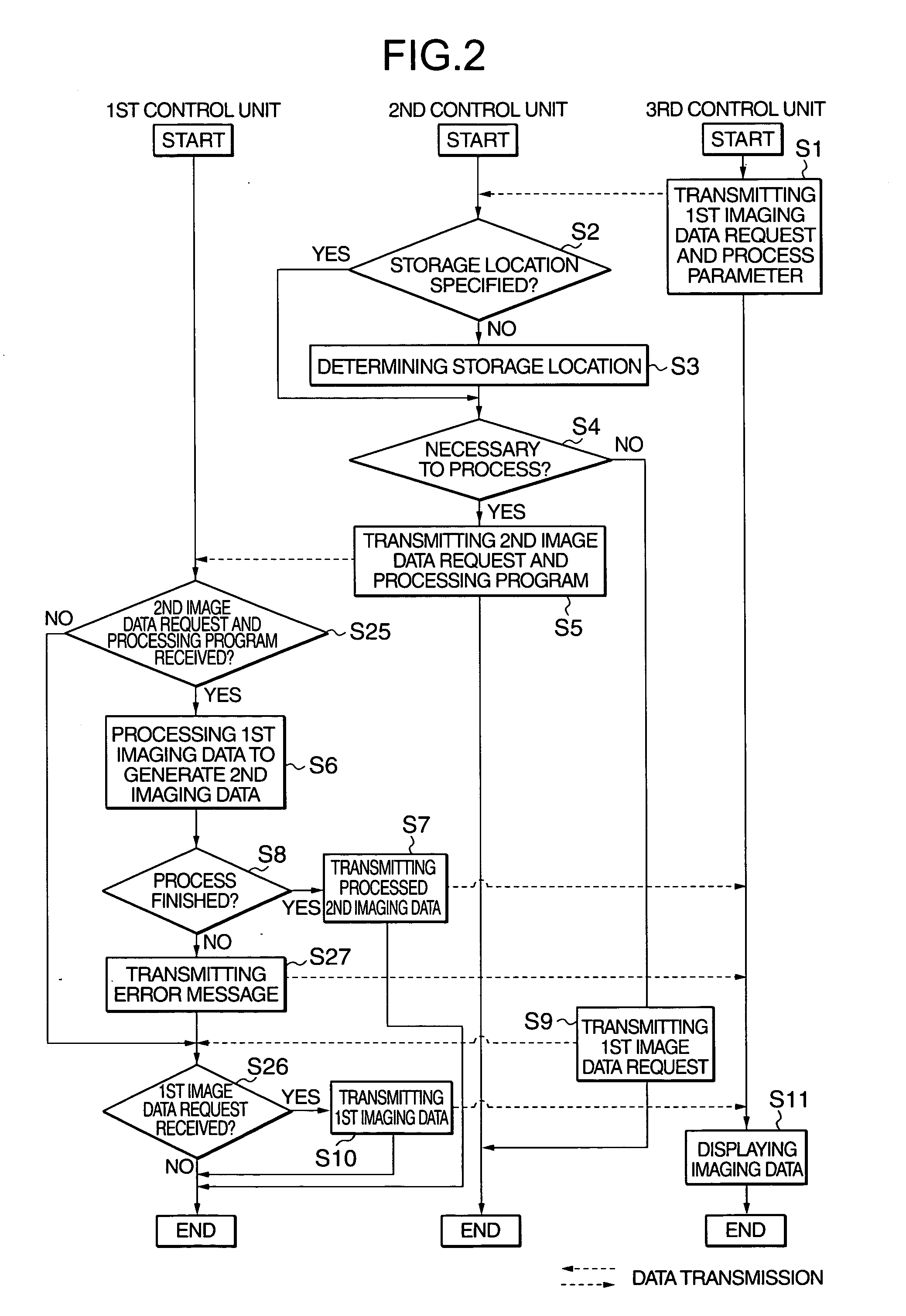
Medical imaging communication system, method and software
InactiveUS20050080330A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData setImaging data
The picture archiving and communication system (PACS) substantially optimizes a post-scanning command process in accordance with a user-specified priority for further processing a selected set of imaging data that has been collected by medical imaging devices such as a CT scanner and a MRI scanner and stored in distributed storage units on the network. The user-specified priority includes the least response time, the least costs and the least network traffic. The user-specified priority is optionally fixed in some preferred embodiments.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
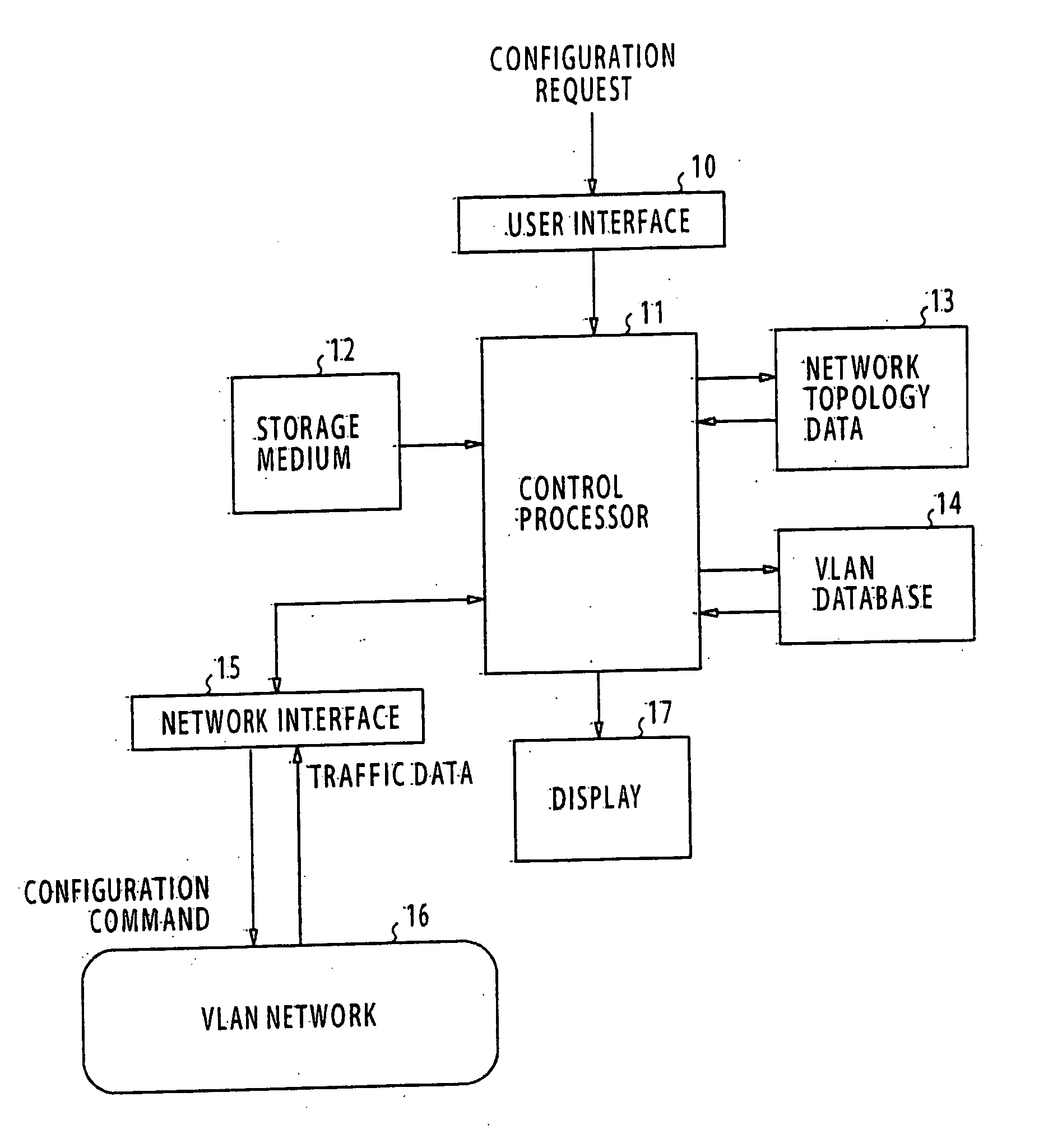
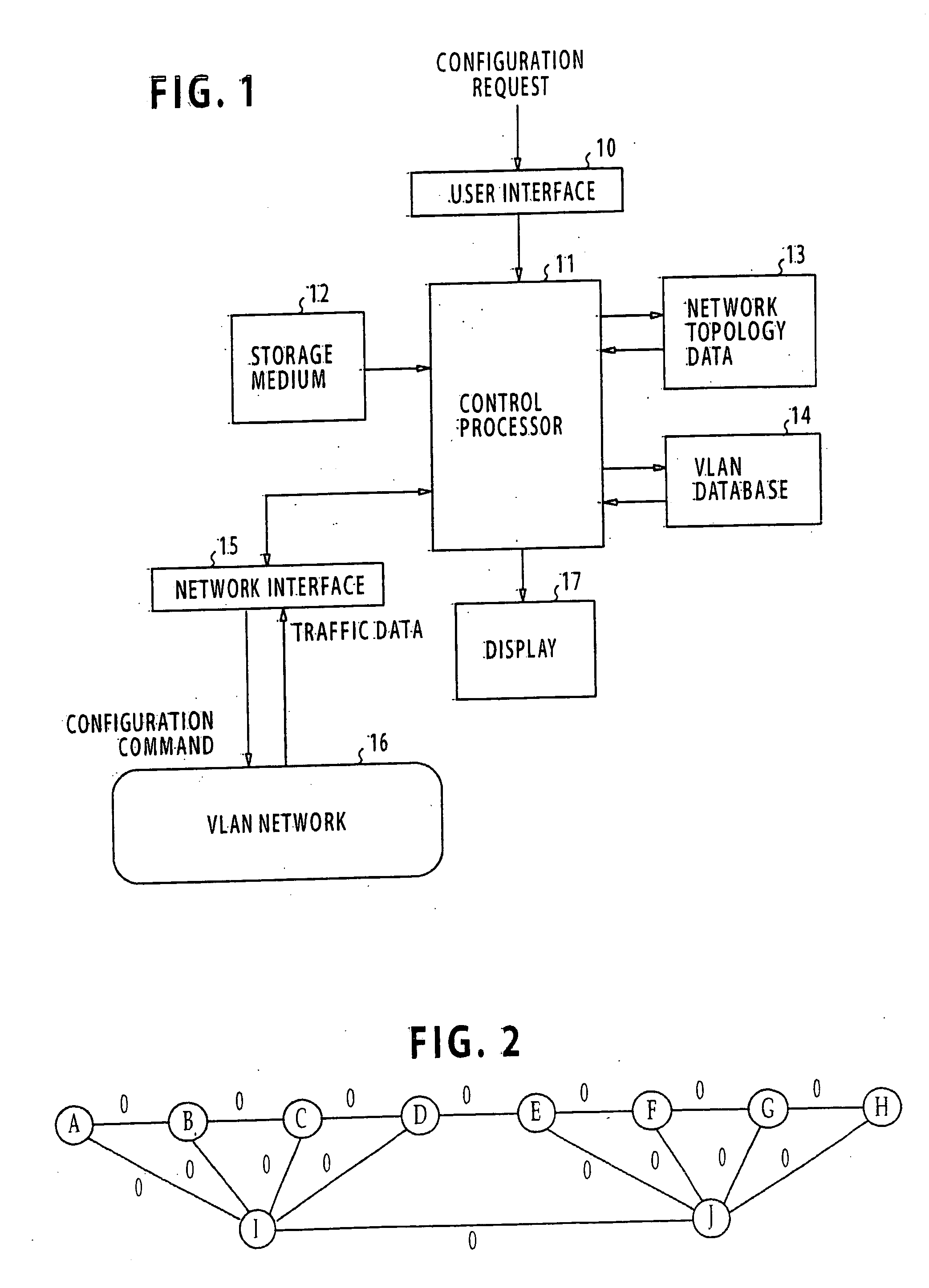
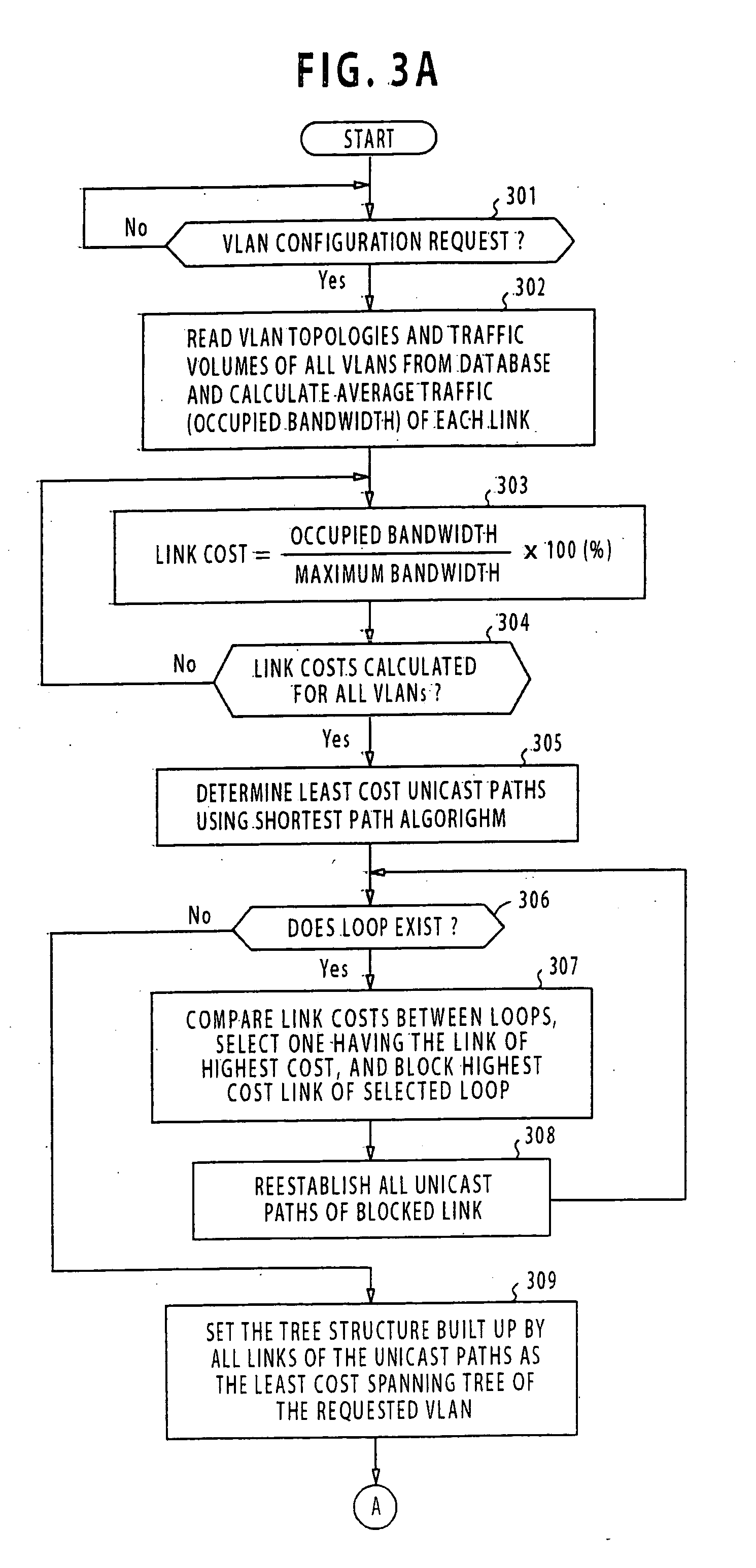
Method and apparatus for designing a spanning tree virtual network
ActiveUS20050063321A1Reduce varianceEvenly dispersedStar/tree networksNetworks interconnectionShort path algorithmLeast cost
An apparatus for designing a virtual VLAN network includes a database containing data representing a plurality of VLAN networks in a spanning tree topology, each of the VLAN networks being formed of a plurality of VLAN member nodes interconnected by links. In response to a network configuration request from a communications network, control circuitry determines the costs of the links, and then determines least cost unicast paths by using a shortest path algorithm. A search is made through the least cost unicast paths for detecting a loop. If at least one loop is detected, a link of highest cost of the loop is blocked. All unicast paths of the blocked link are reestablished through links that circumvent the blocked link. A spanning tree built up with all the links accommodating the least cost unicast paths is established. Configuration command is sent to the network for configuring it according to the established spanning tree.
Owner:NEC CORP
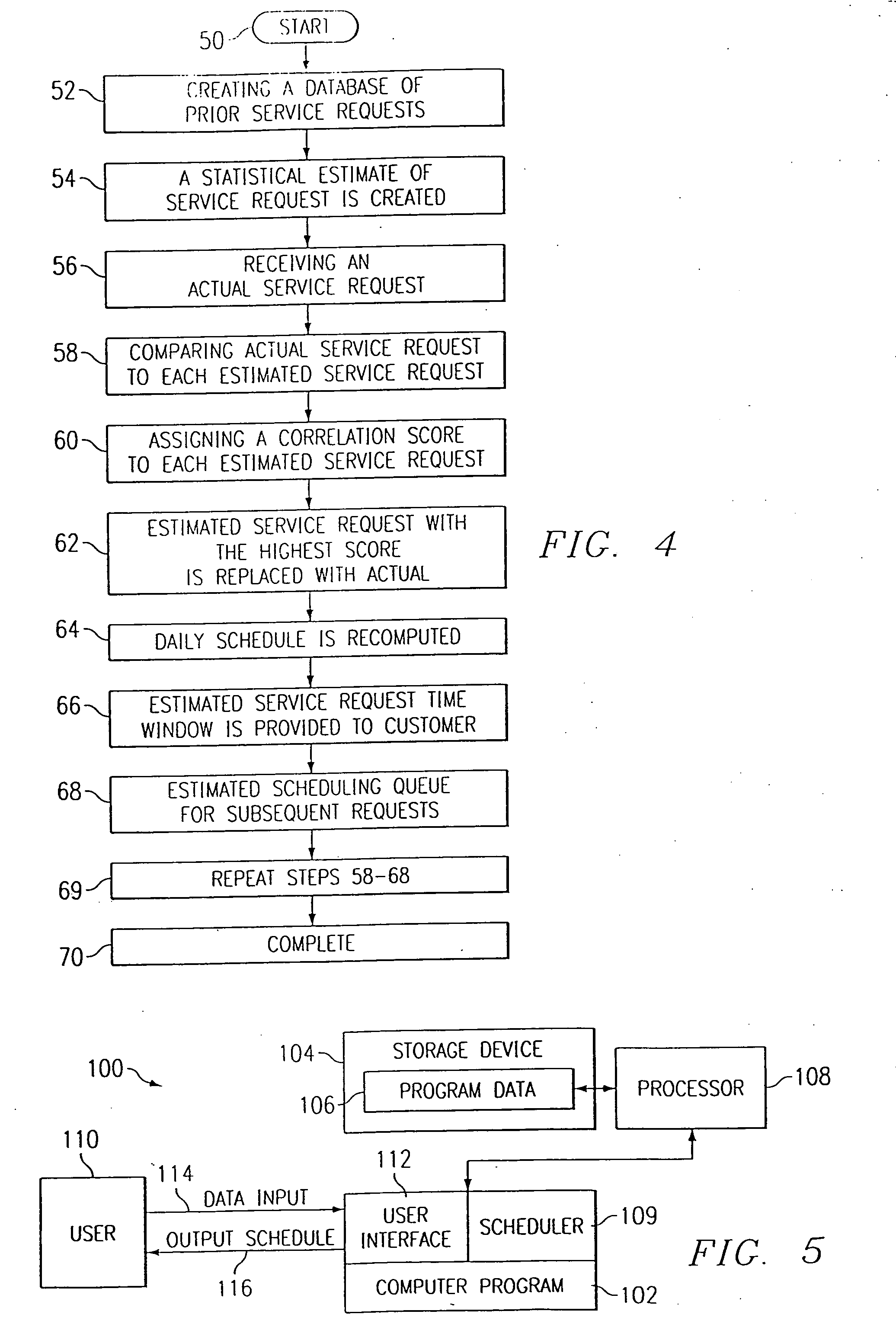
Method and system for allocating specific appointment time windows in a service industry
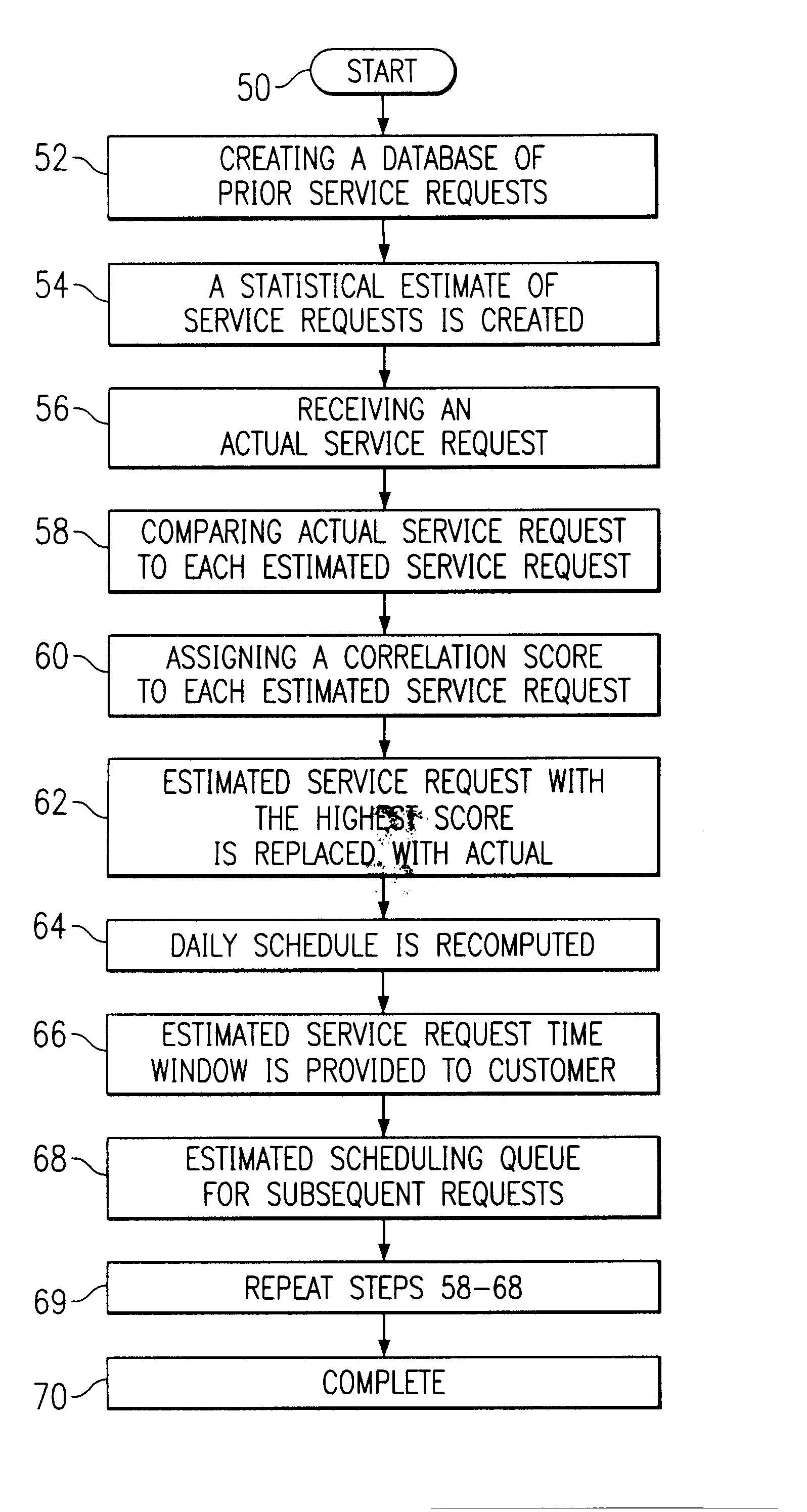
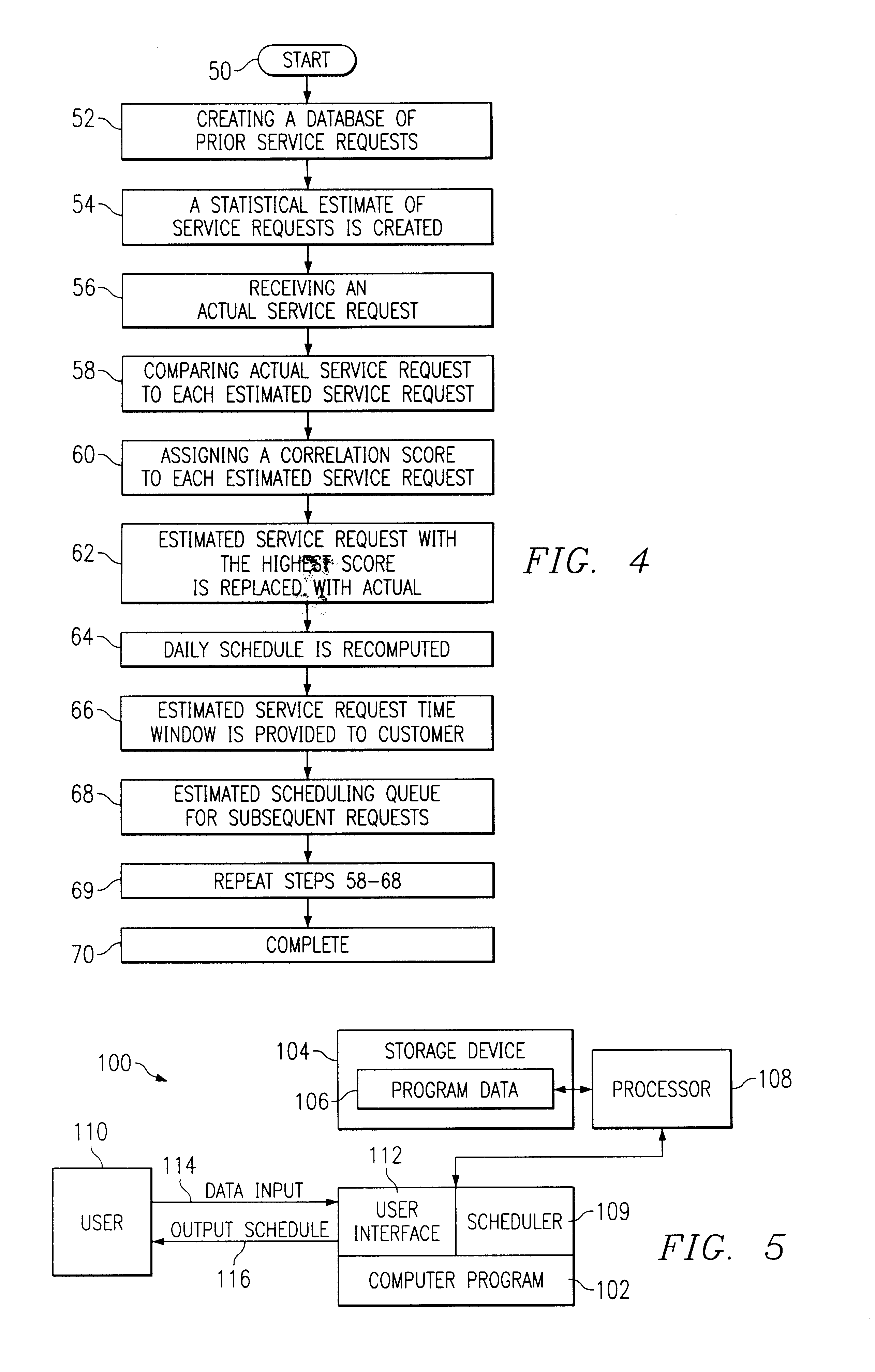
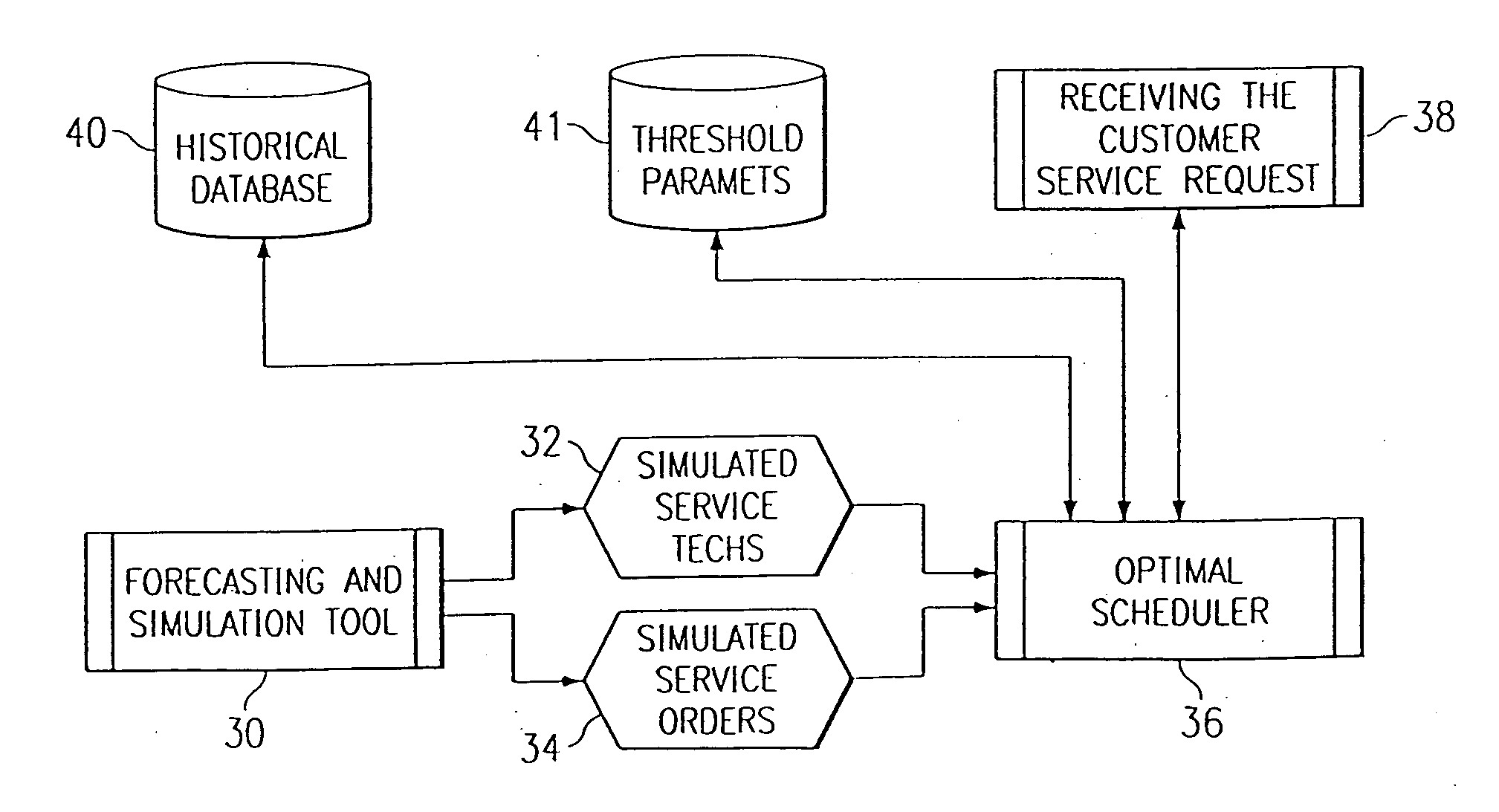
InactiveUS7127412B2Improved customer serviceImprove satisfactionDigital computer detailsTechnology managementTime scheduleLeast cost
The present invention provides a method for allocating appointment time windows. The steps of this method include creating a statistical estimate of a daily schedule comprising a series of estimated service orders. An actual service order is then received. This actual service order is inserted into the daily schedule by using a set of scheduling instructions for determining the least cost to employ the available service resources. At this point, this actual service order does not have a system imposed time window. The set of scheduling instructions is used to determine a time window surrounding this insertion point. If the customer accepts this time window, then the closest estimated service order is replaced by this actual service order, and the daily schedule is recomputed based upon the revised set of service orders to yield a revised daily schedule. This process may be repeated for any number of days or time periods from which the customer may choose the time window best meeting the customer's availability.
Owner:GEOTAB
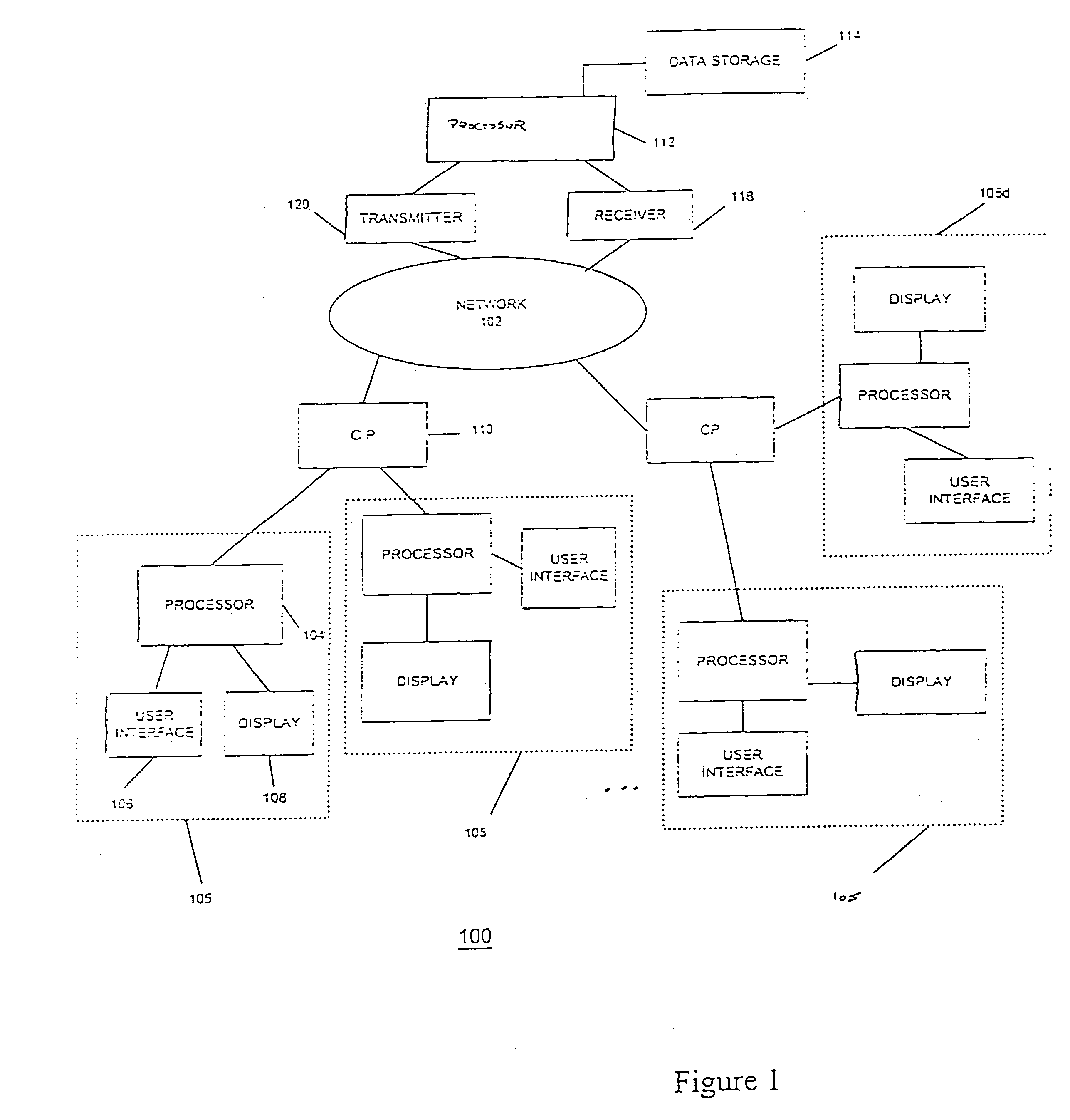
System and Method of Routing Conference Call Participants
InactiveUS20140051383A1Least costLeast connection costSpecial service provision for substationAccounting/billing servicesLeast costTeleconference
A system and method of routing a conference call participant to a conference call is disclosed. Participant location data is requested from an electronic device of the conference call participant. The participant location data is received on a system server from the electronic device of the conference call participant. A least cost connection conference call access phone number is determined from an access number group of one or more available conference call access phone numbers based on the location data from the electronic device of the conference call participant. The conference call participant is provided with the least cost connection conference call access phone number.
Owner:DOERR GREGORY JOSEPH +1
System and method for selectable funding of electronic transactions
InactiveUS7801814B2Increase rangeIncrease flexibilityFinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPaymentLeast cost
A system for transferring funds to pay bills and to and from selected accounts on an optimized is provided. A mediation engine may manage the payments made to selected payees, including by scheduling the payments and selecting sources for funds. A rules-based optimizer may automatically select the least-cost or other most efficient or desirable transaction, given the customer's available funds, types of funds and payment date. All payment providers and payees may manipulated using one seamless view. A customer service representative may also view the transfers.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Alternate routes generation
InactiveUS20020143464A1Reduce the amount of solutionSpeed controllerInstruments for road network navigationLeast costRoad networks
An improved method to automatically generate one or more useful alternatives to the least-cost point-to-point route on a road network. The method discourages reuse of road sections that have been previously used by inflating the costs associated with these road sections before the recalculation of the search algorithm.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
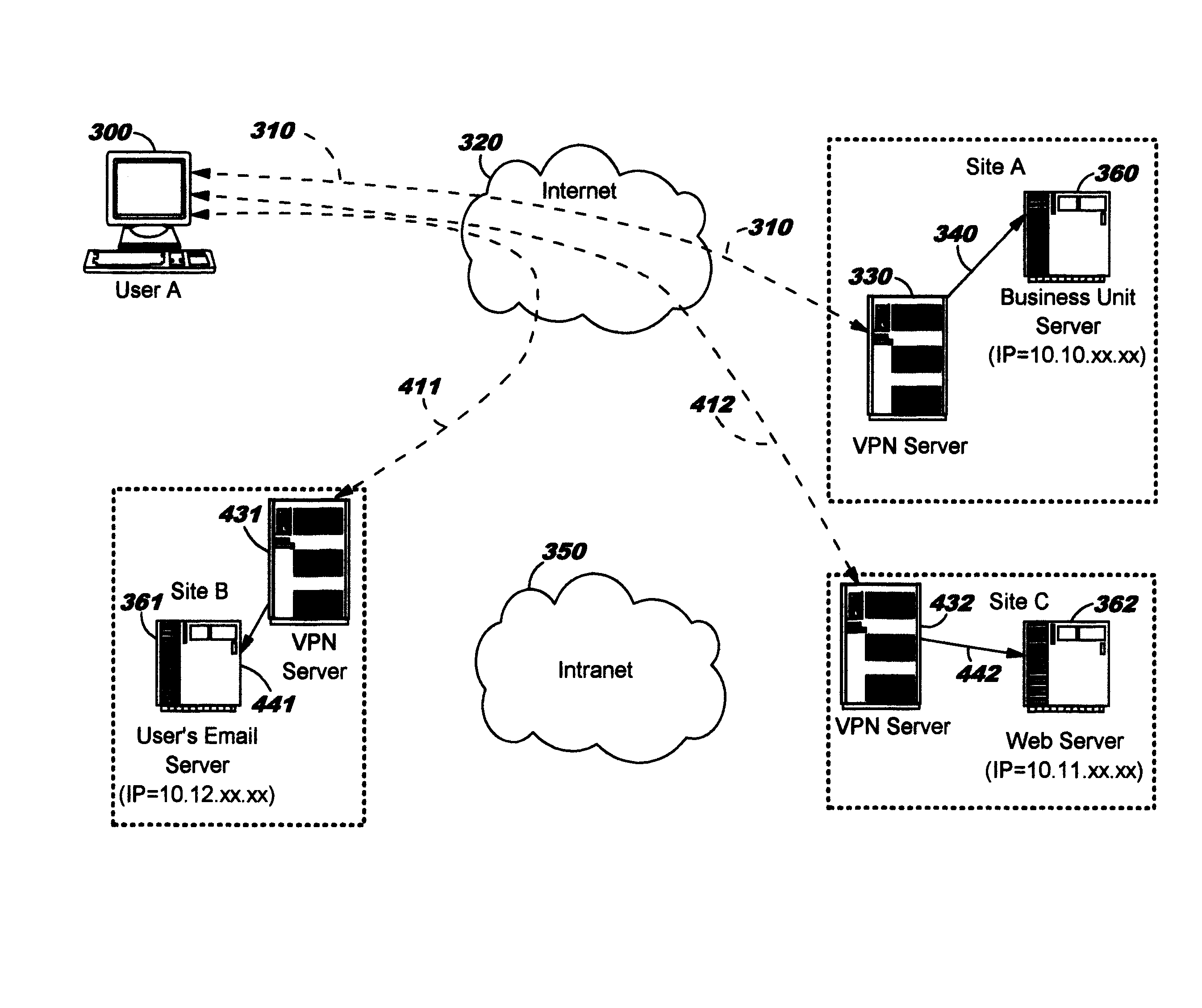
Dynamic Network Tunnel Endpoint Selection
ActiveUS20110083174A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsLeast costEnterprise computing
Dynamically selecting an endpoint for a tunnel into an enterprise computing infrastructure. A client dynamically selects a gateway (which may alternatively be referred to as a boundary device or server) as a tunnel endpoint for connecting over a public network (or, more generally, an untrusted network) into an enterprise computing infrastructure. The selection is made, in preferred embodiments, according to least-cost routing metrics pertaining to paths through the enterprise network from the selected gateway to a destination host. The least-cost routing metrics may be computed using factors such as the proximity of selectable tunnel endpoints to the destination host; stability or redundancy of network resources for this gateway; monetary costs of transmitting data over a path between the selectable tunnel endpoints and destination host; congestion on that path; hop count for that path; and / or latency or transmit time for data on that path.
Owner:A10 NETWORKS
Dynamic network tunnel endpoint selection
ActiveUS7992201B2Facilitate communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlLeast costEnterprise computing
Dynamically selecting an endpoint for a tunnel into an enterprise computing infrastructure. A client dynamically selects a gateway (which may alternatively be referred to as a boundary device or server) as a tunnel endpoint for connecting over a public network (or, more generally, an untrusted network) into an enterprise computing infrastructure. The selection is made, in preferred embodiments, according to least-cost routing metrics pertaining to paths through the enterprise network from the selected gateway to a destination host. The least-cost routing metrics may be computed using factors such as the proximity of selectable tunnel endpoints to the destination host; stability or redundancy of network resources for this gateway; monetary costs of transmitting data over a path between the selectable tunnel endpoints and destination host; congestion on that path; hop count for that path; and / or latency or transmit time for data on that path.
Owner:A10 NETWORKS
Method and system for allocating specific appointment time windows in a service industry
InactiveUS20070038498A1Increase their customer-responsivenessImprove satisfactionDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsTime scheduleAppointment time
The present invention provides a method for allocating appointment time windows. The steps of this method include creating a statistical estimate of a daily schedule comprising a series of estimated service orders. An actual service order is then received. This actual service order is inserted into the daily schedule by using a set of scheduling instructions for determining the least cost to employ the available service resources. At this point, this actual service order does not have a system imposed time window. The set of scheduling instructions is used to determine a time window surrounding this insertion point. If the customer accepts this time window, then the closest estimated service order is replaced by this actual service order, and the daily schedule is recomputed based upon the revised set of service orders to yield a revised daily schedule. This process may be repeated for any number of days or time periods from which the customer may choose the time window best meeting the customer's availability.
Owner:GEOTAB
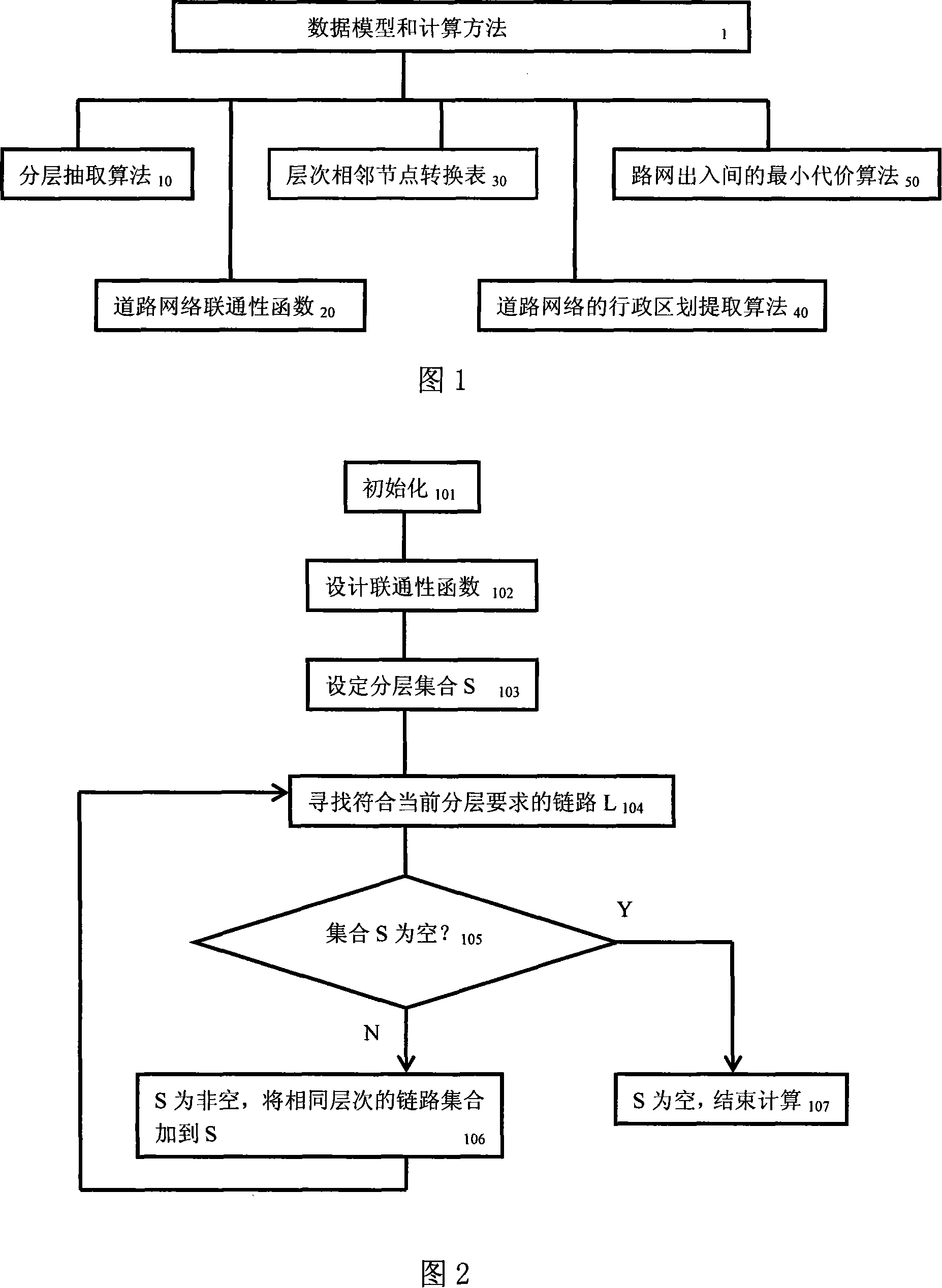
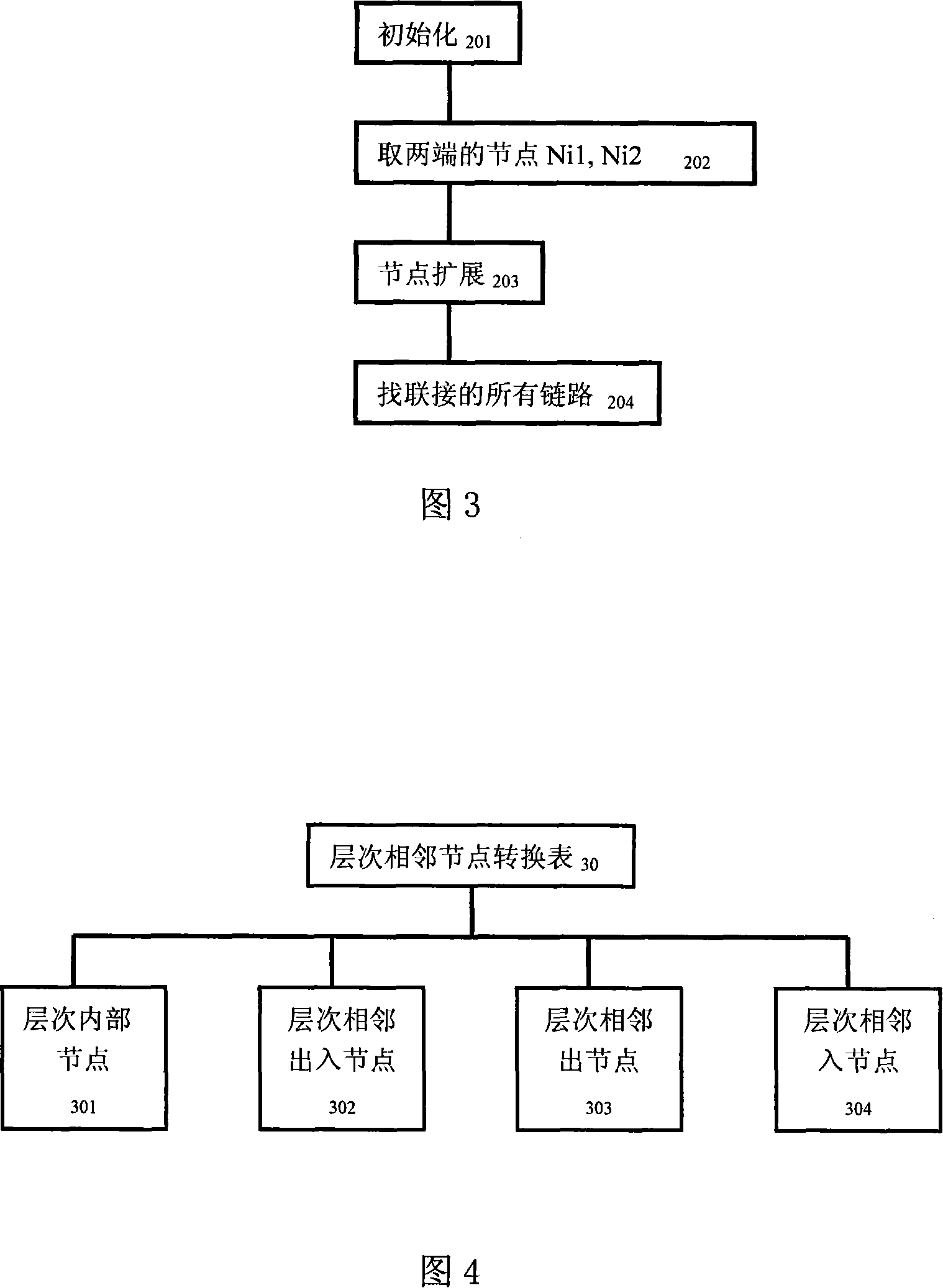
Road topology data model for navigation and calculation method
InactiveCN101149268AGuaranteed connectivityRetain heuristic dataInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsLeast costLogical analysis
An application technology field relates to the navigation, especially the analysis and picking method of the road topological data used in the navigation and setting the data model, which is a road topological data model and computing method used in navigation to treat the road with big area and long distance in navigation map data. The method includes the stratified extracting arithmetic, the road connection calculation function, the hierarchical adjacent node transition table, the road web canton extracting arithmetic and the least cost arithmetic of road net in-out; it mainly solves the technology problem of route calculation of long distance and big area. The invention can insure the connection of whole road web; it can store the starting data of route calculation and improves the route calculation efficient; so it can get the logical analysis result in the logical time and cost range.
Owner:上海上大鼎正软件股份有限公司
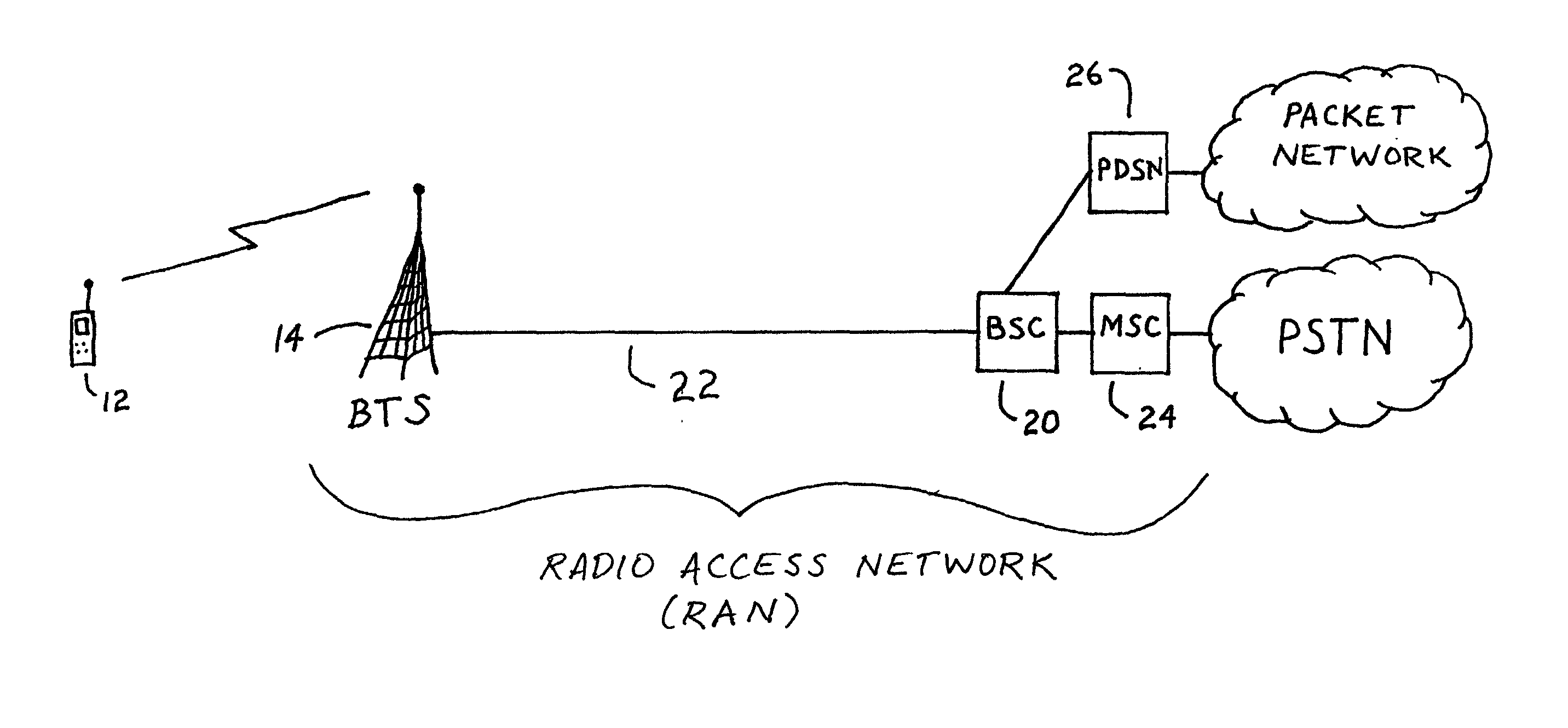
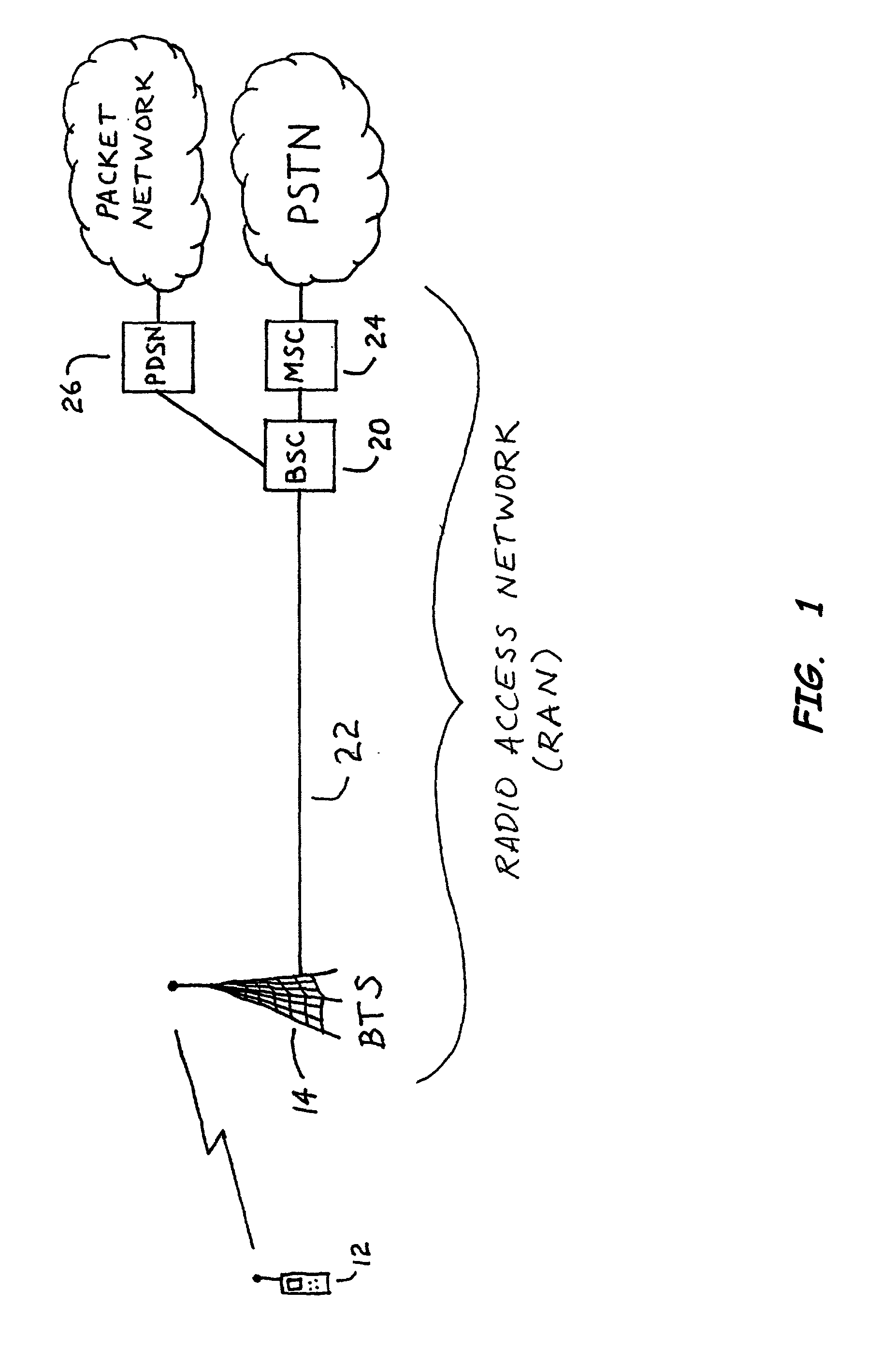
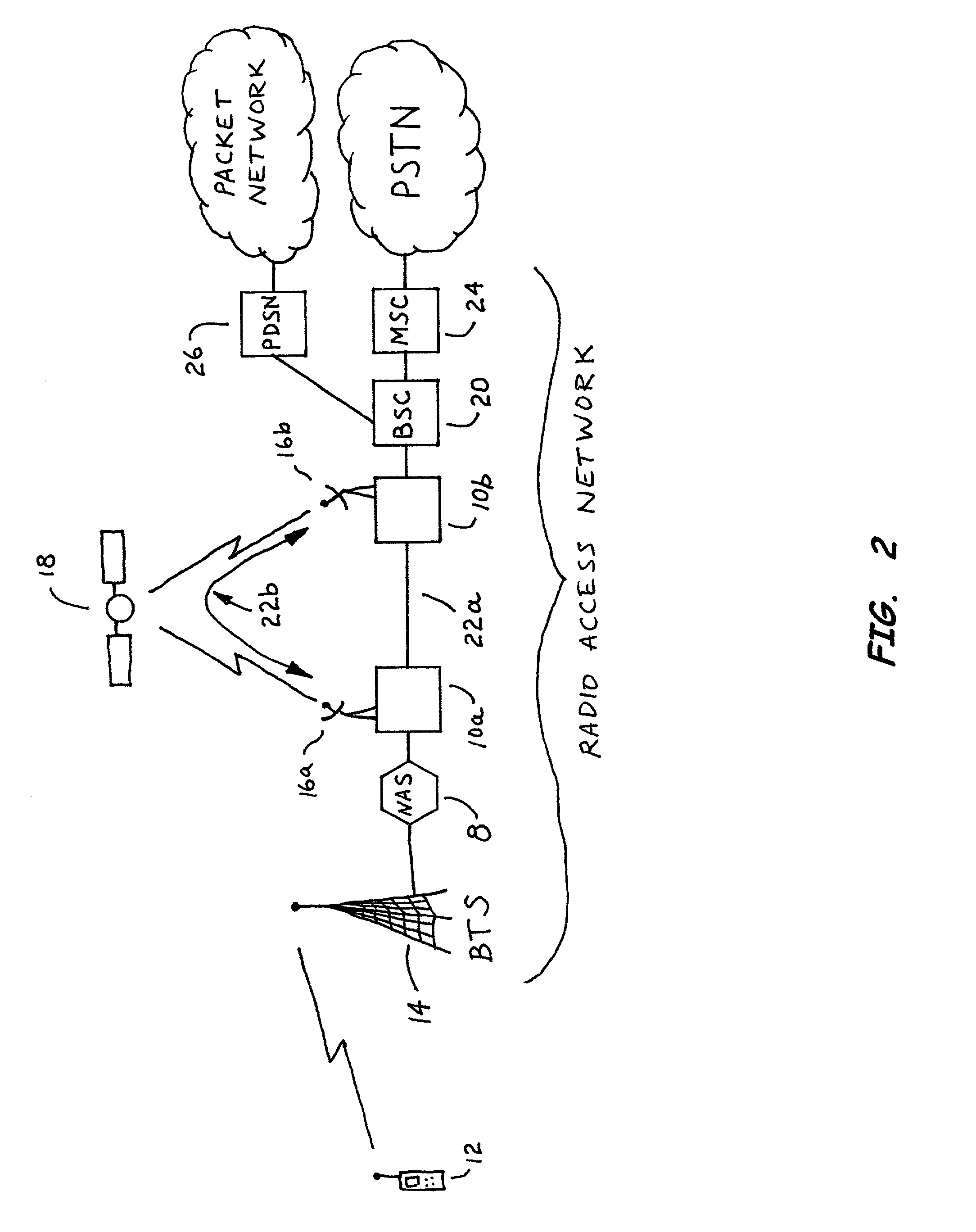
System and method for data routing for fixed cell sites
InactiveUS20040001439A1Improve real-time medium qualityImprove latencyError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunications linkLeast cost
An intelligent switching system and method provides an alternate, least-cost telecommunications link (which may be a wireless link) between a base transceiver station (BTS) and a base station controller (BSC) in a radio access network (RAN). Signals may be routed via the alternate telecommunications link or via an existing telecommunications link based on the sensitivity of the signals to transmission latency. The switching system may determine the sensitivity of the signals to transmission latency.
Owner:SPRING SPECTRUM LP
Systems, functional data, and methods for generating a route
InactiveUS6975940B1Increased RAM capacityRapidly and efficiently generatesInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsLeast costComputer science
Devices, systems, functional data and methods are provided for an improved route generation in navigational enabled devices. In generating the route, the available locations are inspected repetitively and locations adjacent to a last selected location are inserted into a first data structure such that the first location of the first data structure is always a least cost location associated with all adjacent locations comprising the first data structure. The first location is then optionally inserted into a second data structure. The generated route includes the current location, one or more first locations, and the destination.
Owner:GARMIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com