Patents
Literature
1217 results about "Network computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
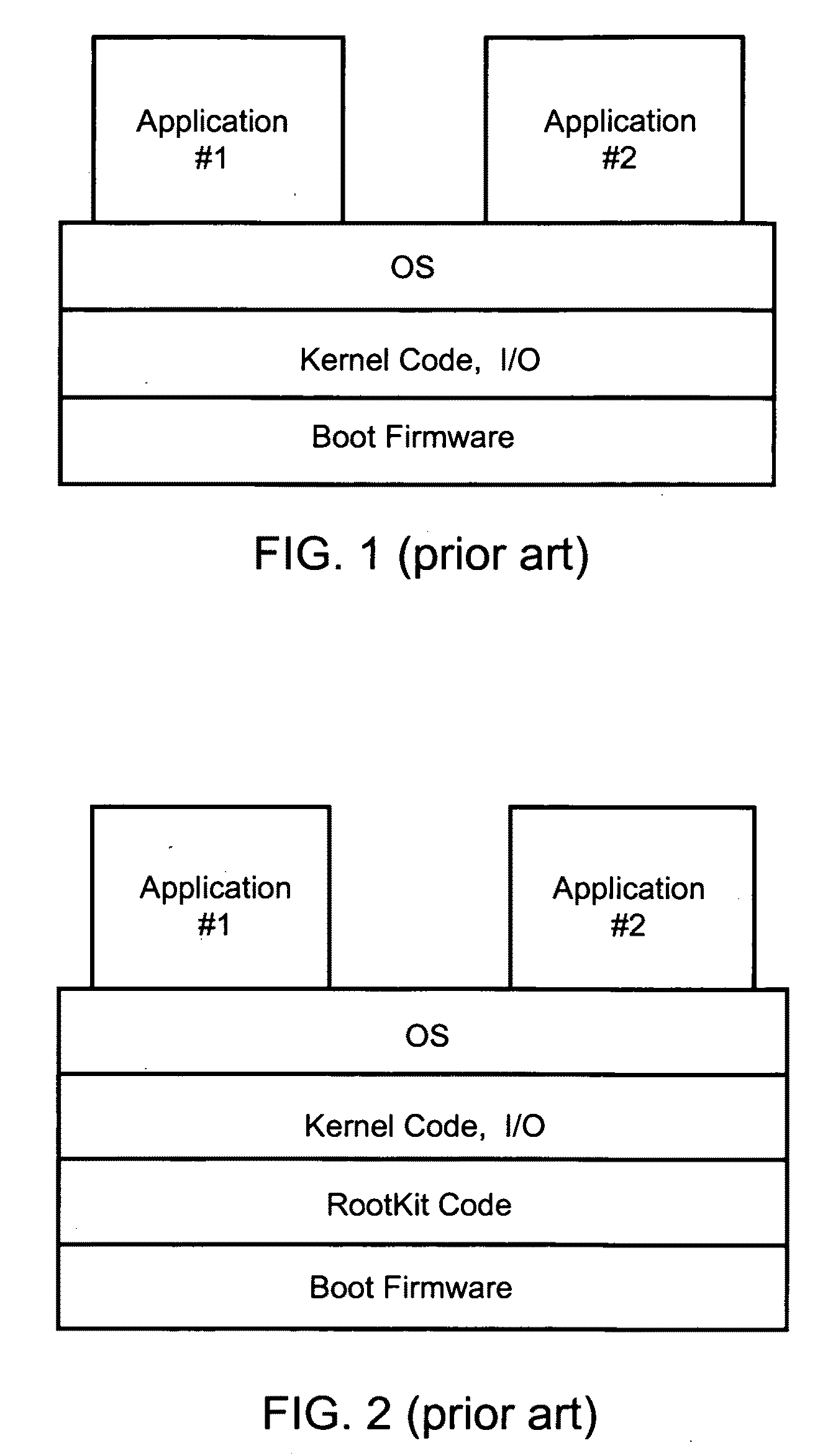
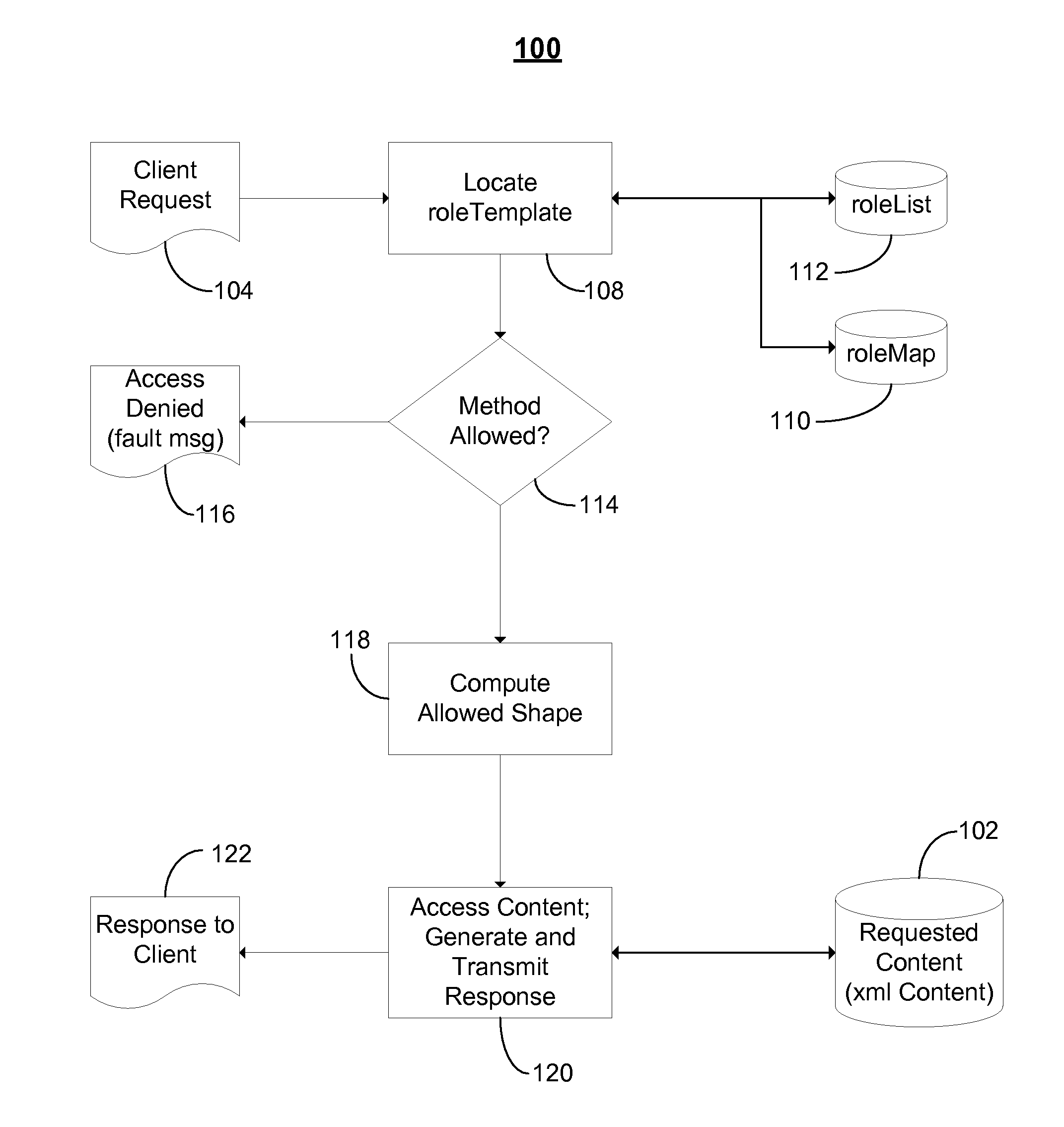
Hierarchical backup and retrieval system
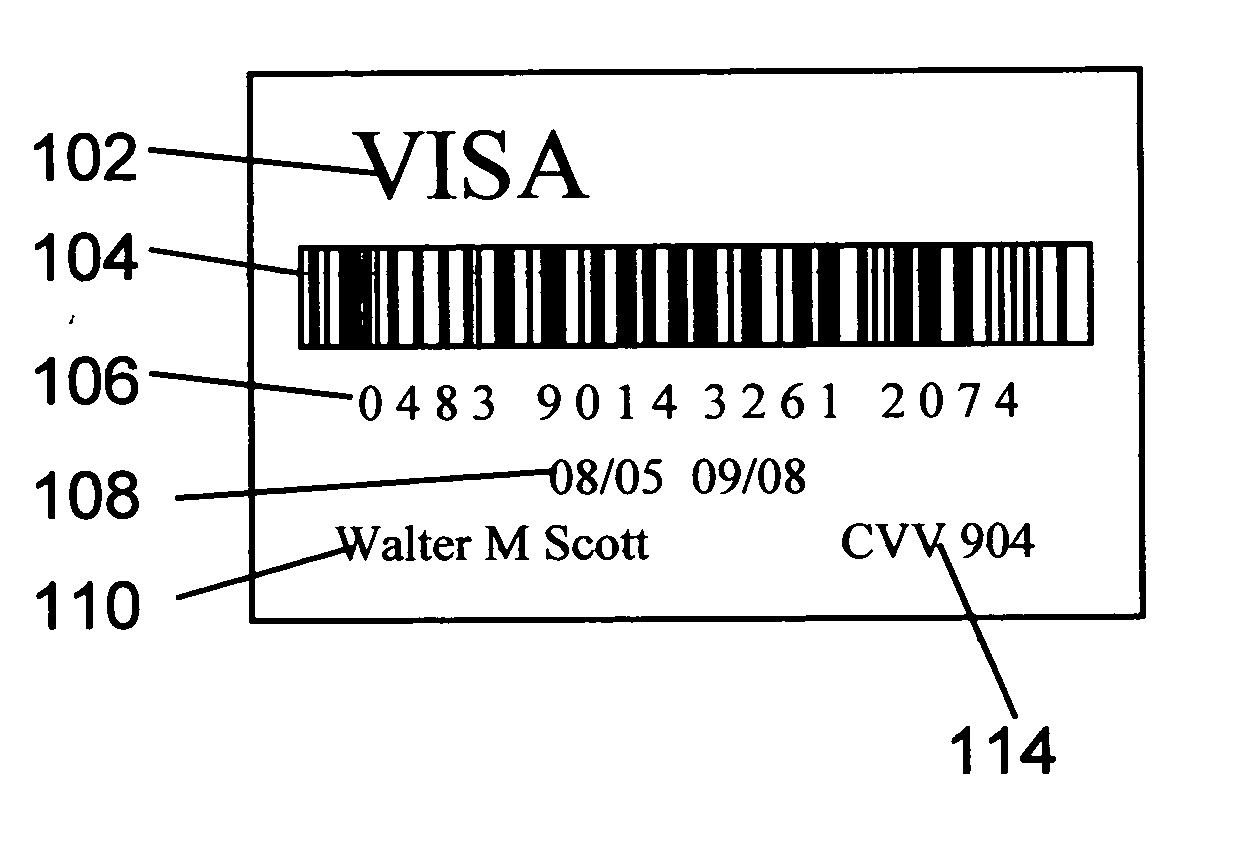
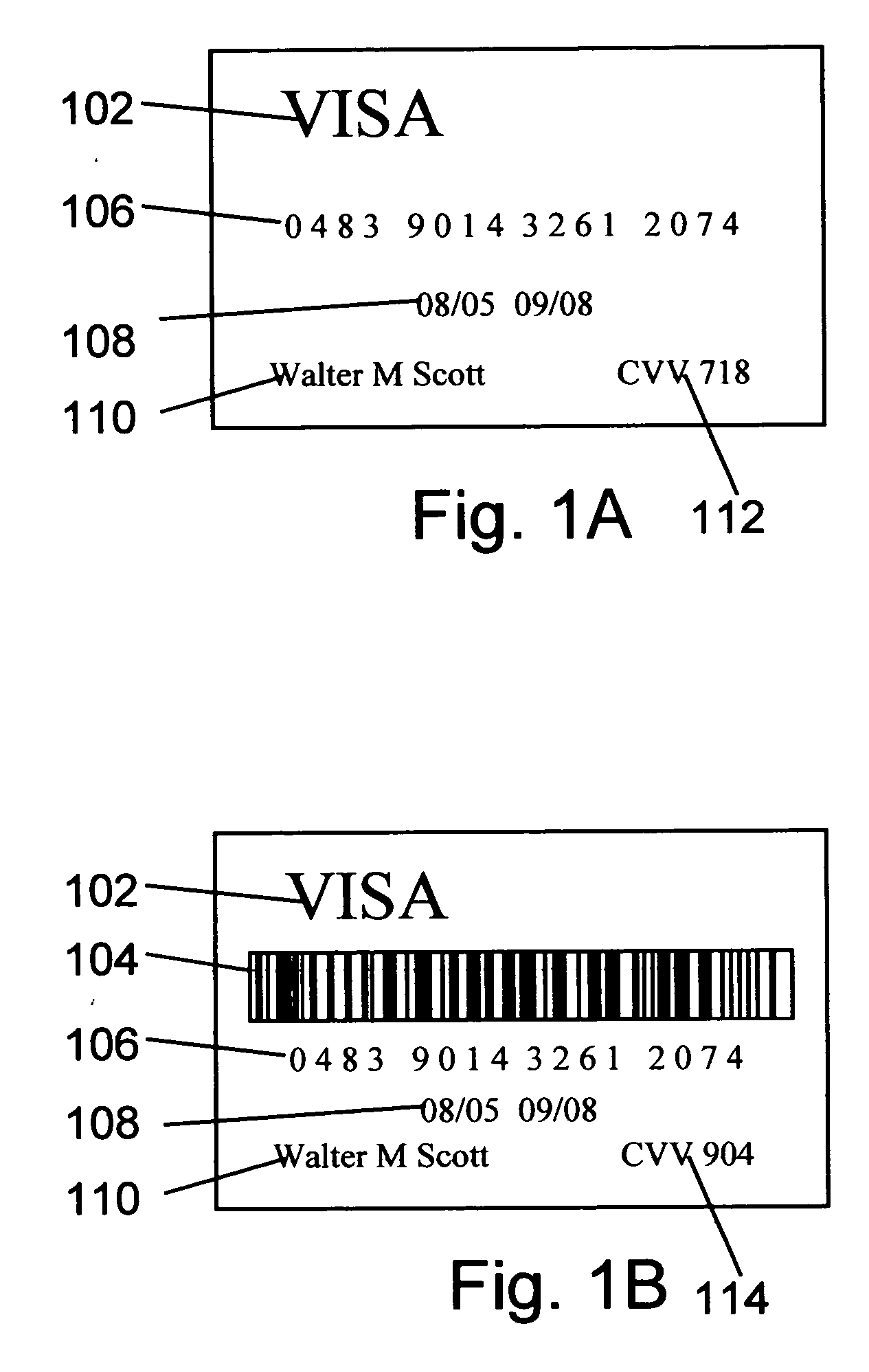
InactiveUS7395282B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSoftware agentAdministrative controls
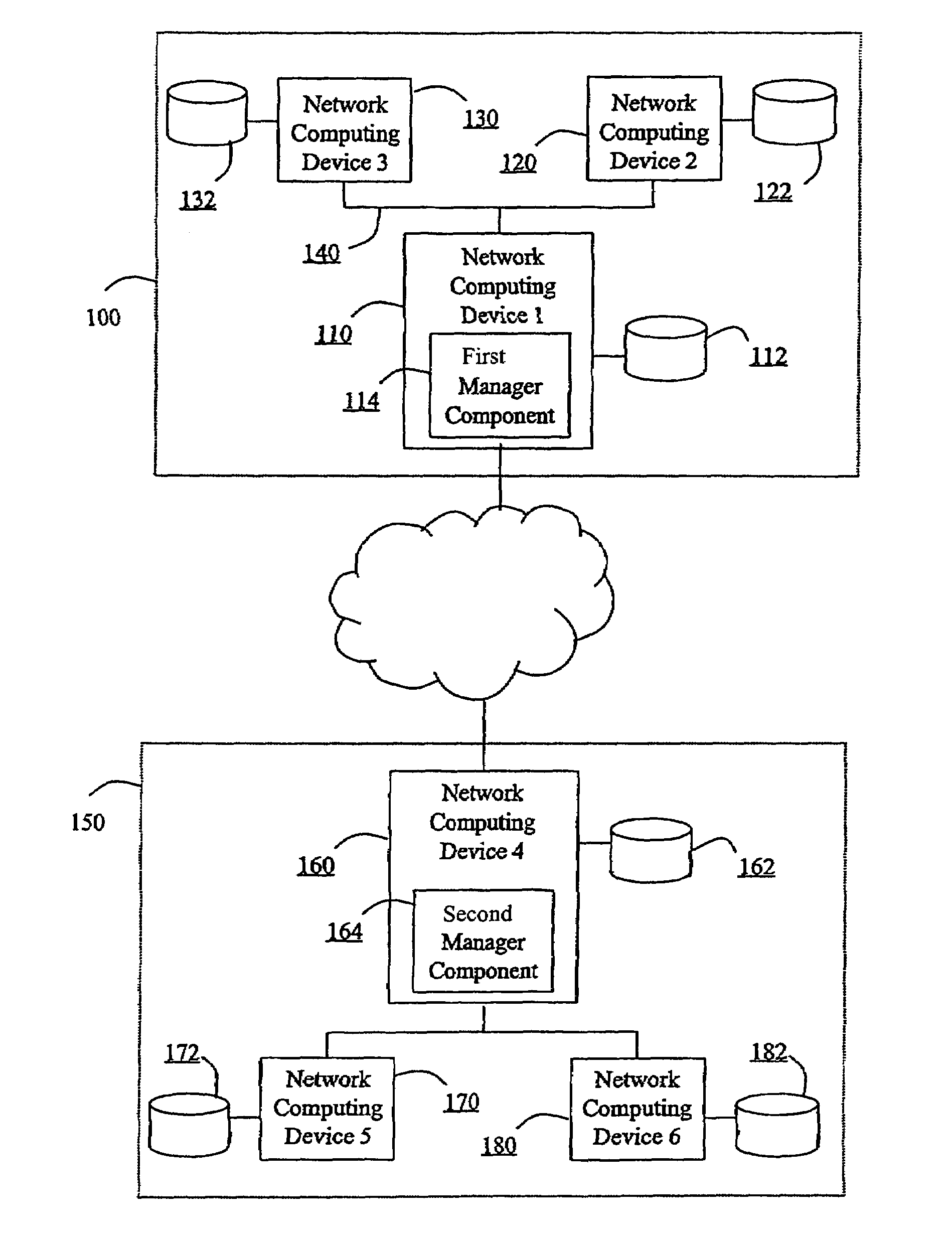
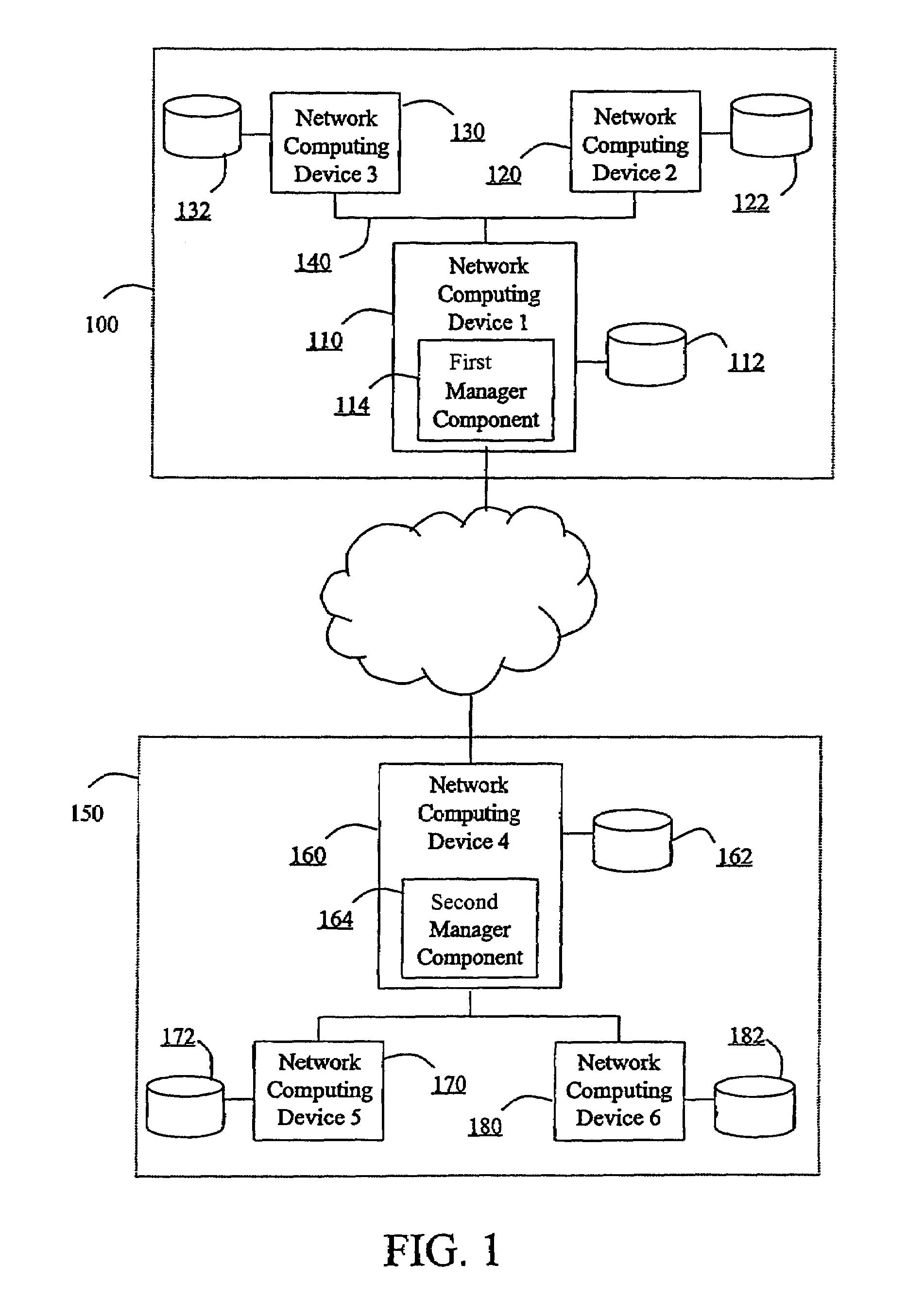
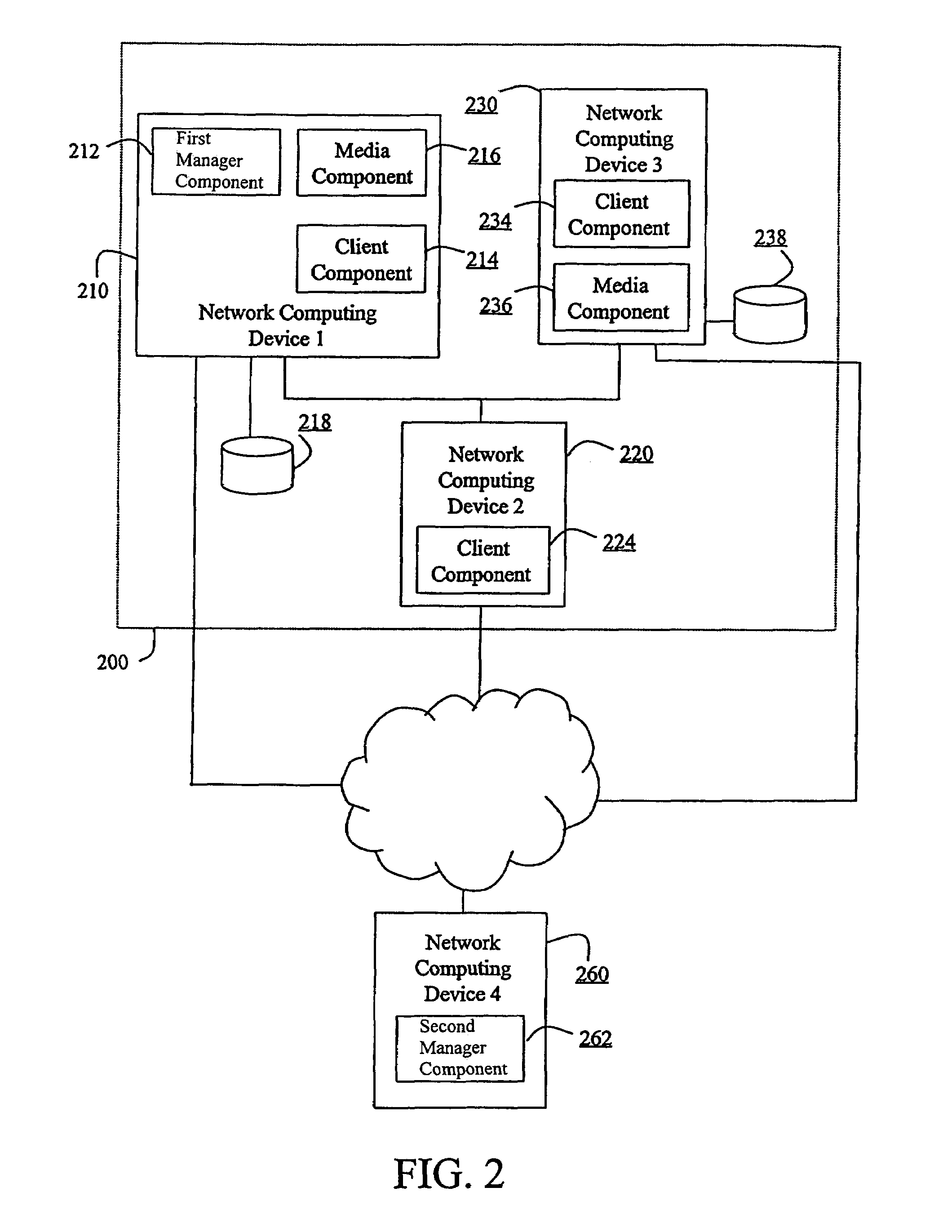
The invention is a hierarchical backup system. The interconnected network computing devices are put into groups of backup cells. A backup cell has a manager software agent responsible maintaining and initiating a backup regime for the network computing devices in the backup cell. The backups are directed to backup devices within the backup cell. Several backup cells can be defined. A manager software agent for a particular cell may be placed into contact with the manager software agent of another cell, by which information about the cells may be passed back and forth. Additionally, one of the software agents may be given administrative control over another software agent with which it is in communication.
Owner:COMMVAULT SYST INC
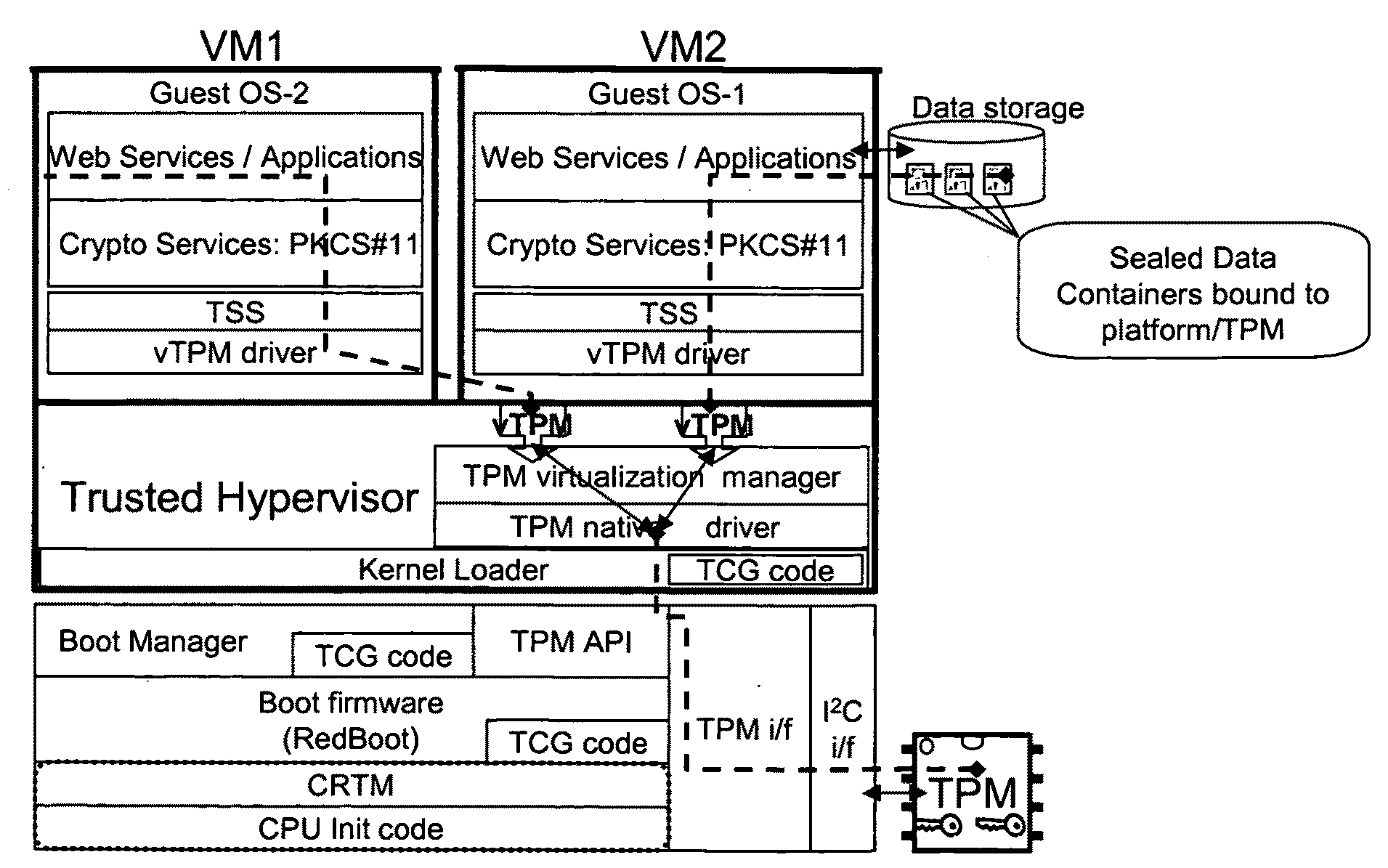
Distributed trusted virtualization platform
InactiveUS20090204964A1Key distribution for secure communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsVirtualizationEnd to end security
A platform architecture shifts the networked computing paradigm from PC+Network to a system using trusted mobile internet end-point (MIEP) devices and cooperative agents hosted on a trusted server. The MIEP device can participate in data flows, arbitrate authentication, and / or participate in implementing security mechanisms, all within the context of assured end-to-end security. The MIEP architecture improves platform-level capabilities by suitably (and even dynamically) partitioning what is done at the MIEP nodes, the network, and the server based infrastructure for delivering services.
Owner:MOTEGRITY +1
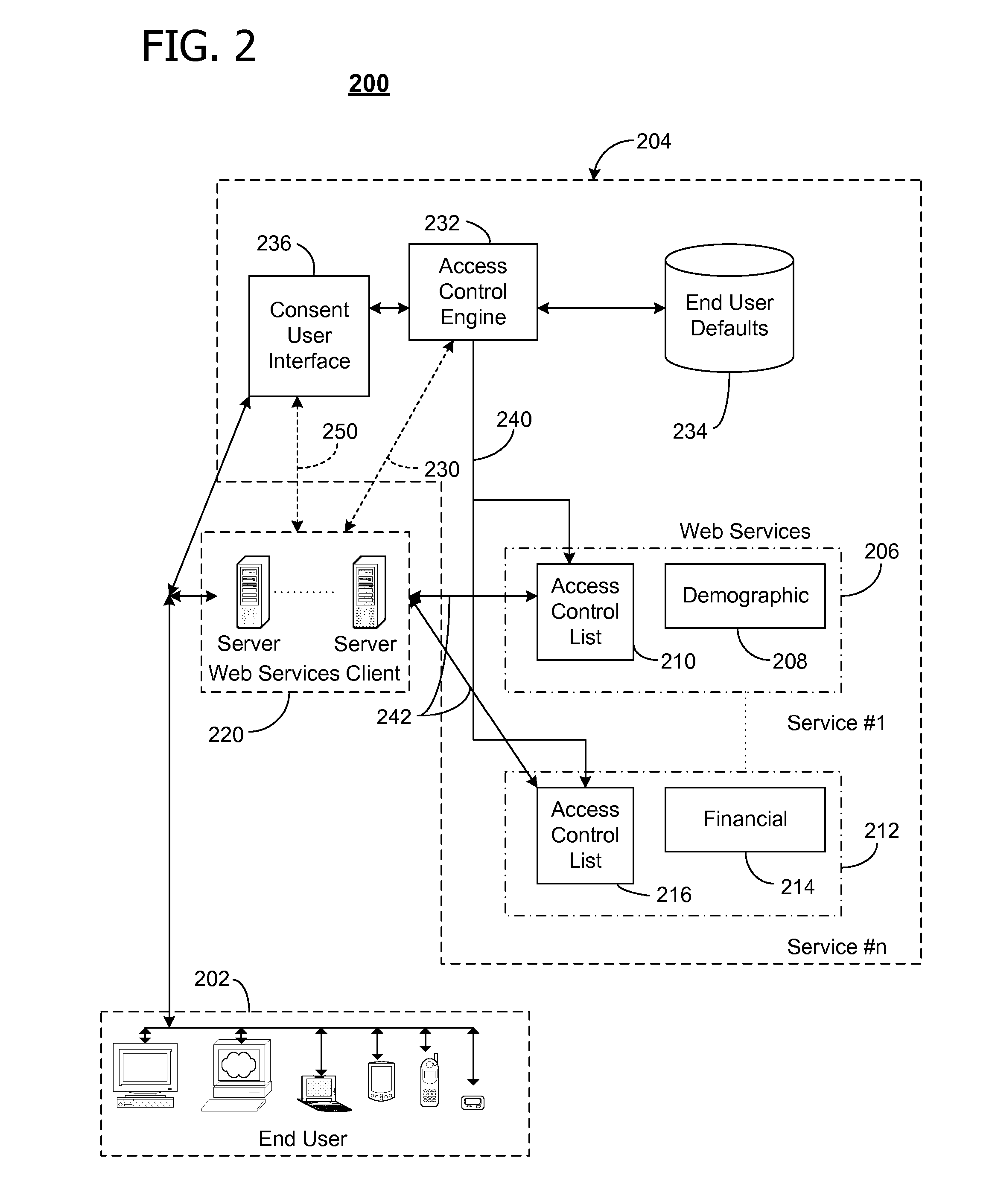
User-centric consent management system and method
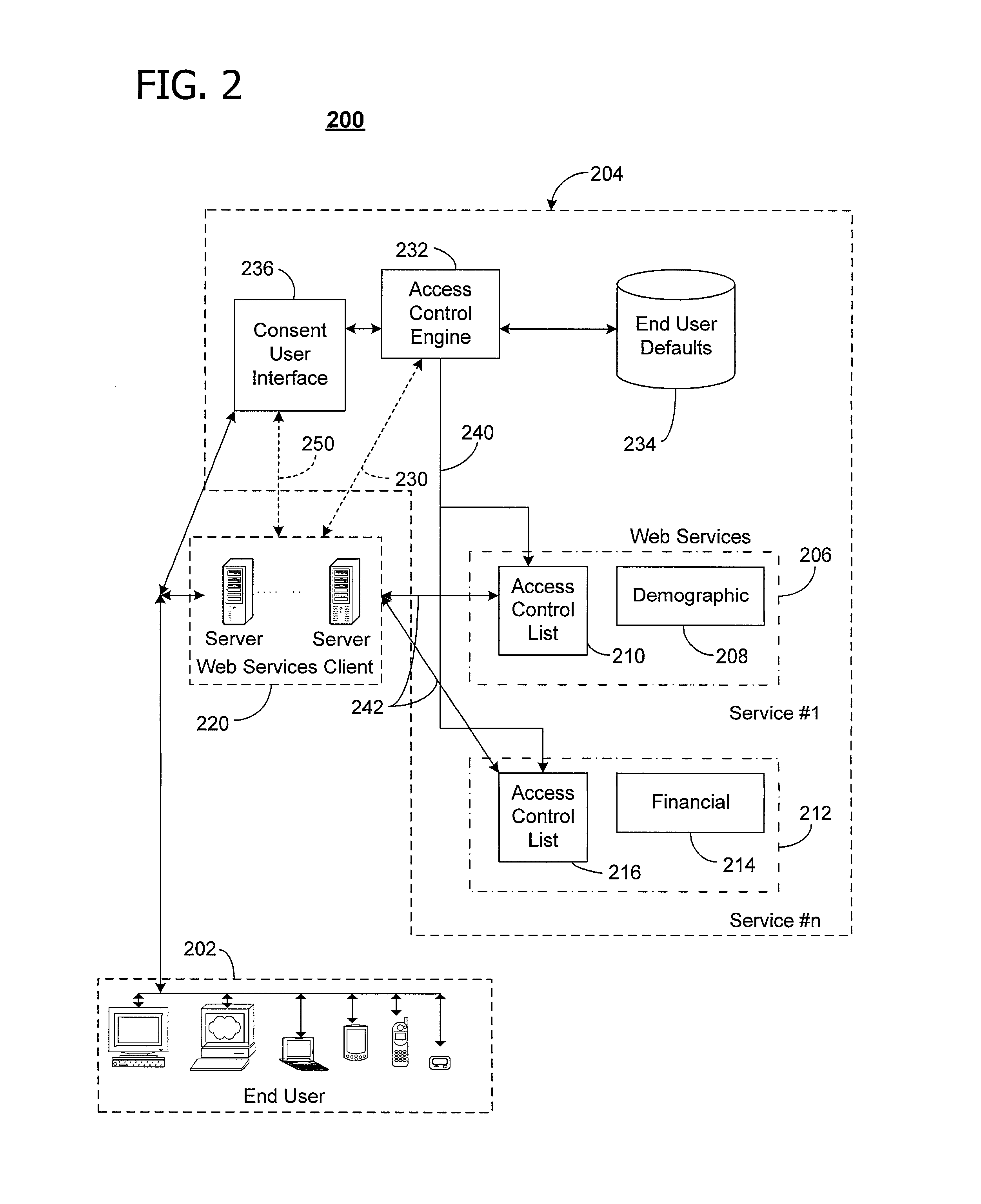
ActiveUS7076558B1Access controlDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsWeb serviceClient-side
In a network computing environment, a user-centric system and method for controlling access to user-specific information maintained in association with a web-services service. When a web-services client desires access to the user-specific information, the client sends a request. The request identifies the reasons / intentions for accessing the desired information. The request is compared to the user's existing access permissions. If there is no existing access permission, the request is compared to the user's default preferences. If the default preferences permit the requested access, an access rule is created dynamically and the client's request is filled, without interrupting the user. If the default preferences do not permit the request to be filled, a consent user interface may be invoked. The consent user interface presents one or more consent options to a party with authority to grant consent, thereby permitting the user to control whether the client's access will be filled.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
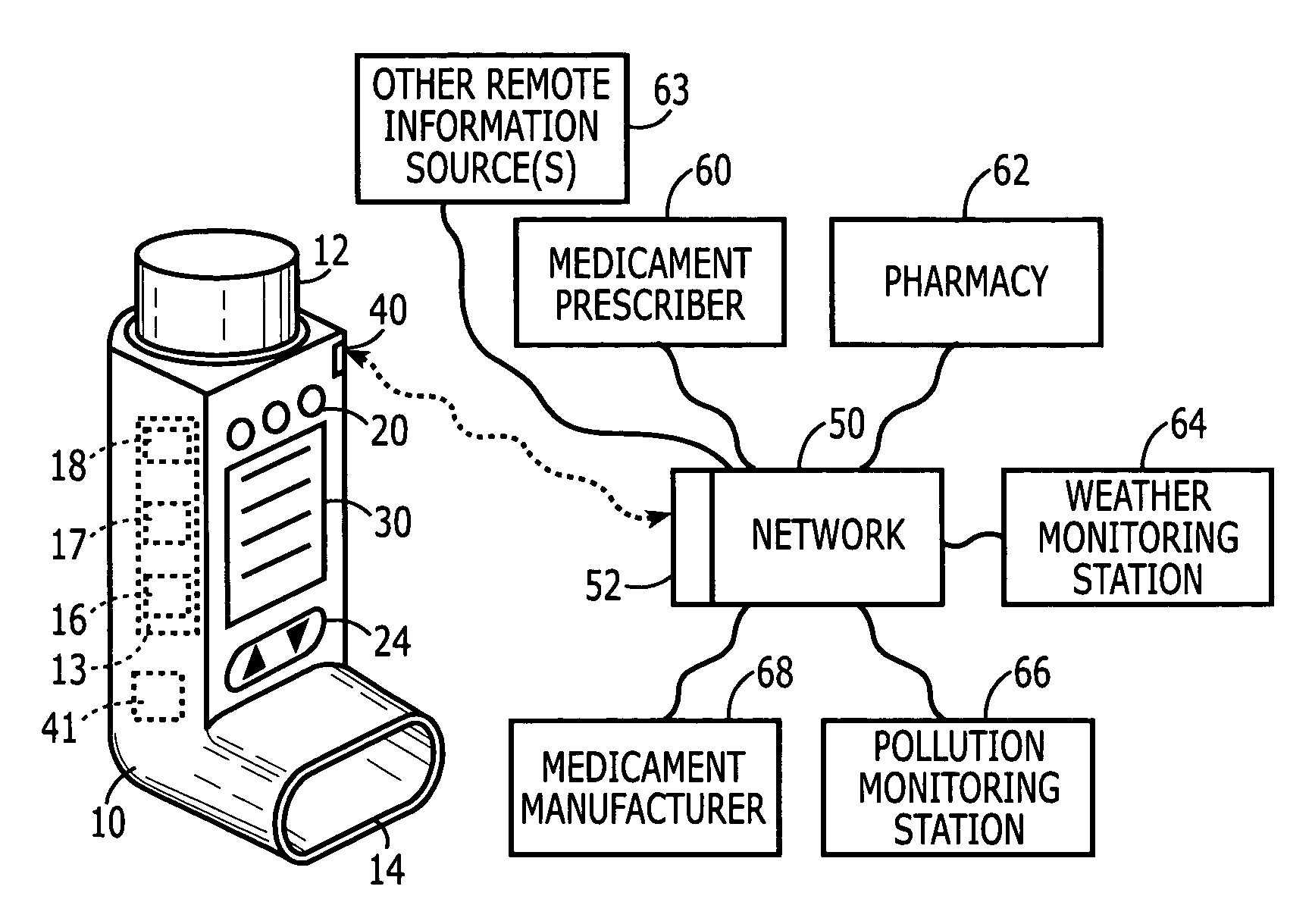
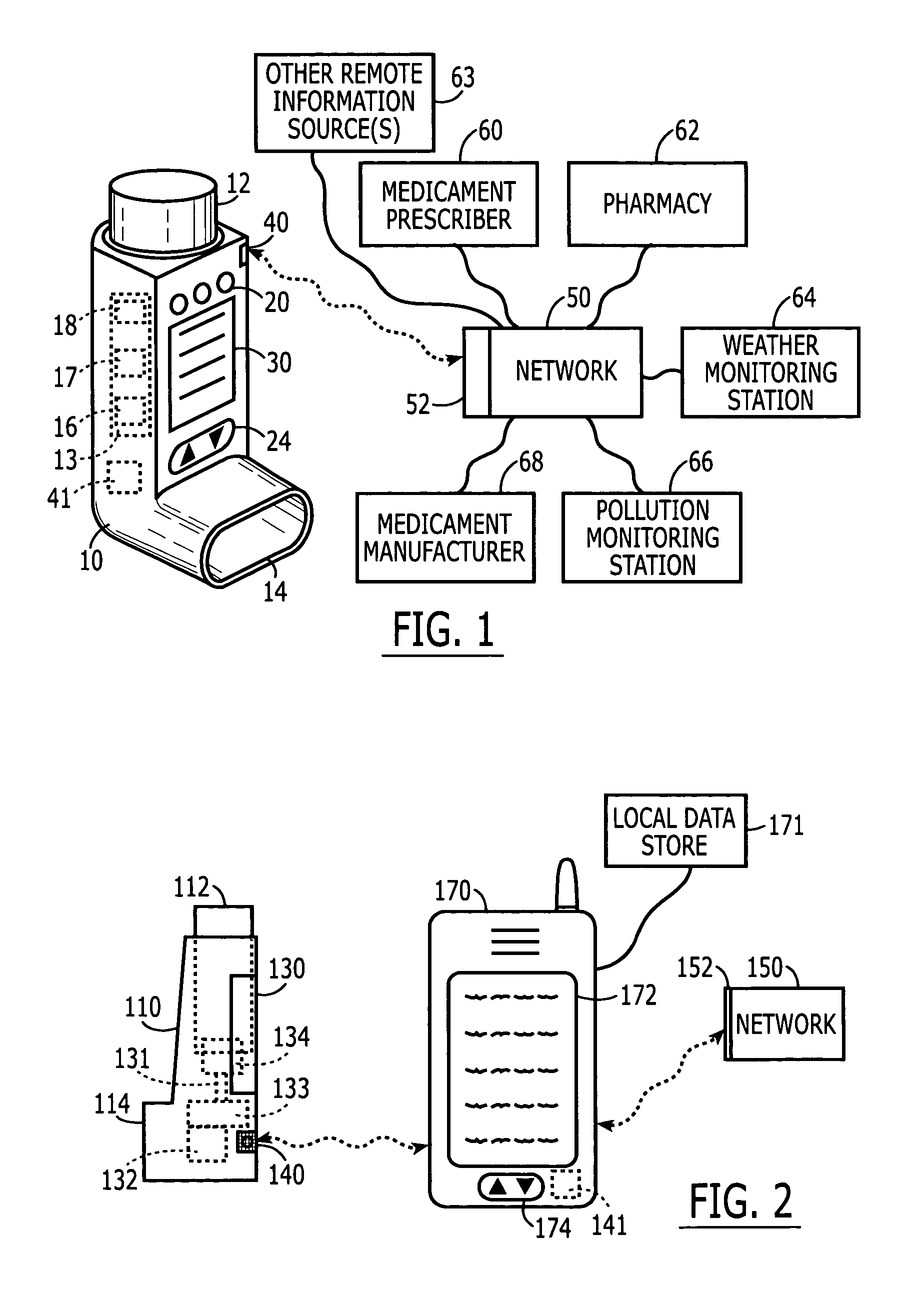
Medicament delivery system
InactiveUS6958691B1Simple systemEasy accessDigital data processing detailsDrug and medicationsComputer scienceDelivery system
There is provided a system for the delivery of medicament comprising a medicament container; a dispensing mechanism for dispensing medicament from the medicament container; an electronic data management system; and a communicator for wireless communication with a network computer system to enable communication of data between the network computer system and the electronic data management system. The electronic data management system comprises a memory for storage of data; a microprocessor for performing operations on the data; and a transmitter for transmitting a signal relating to the data or the outcome of an operation on the data.
Owner:GLAXO WELLCOME INC
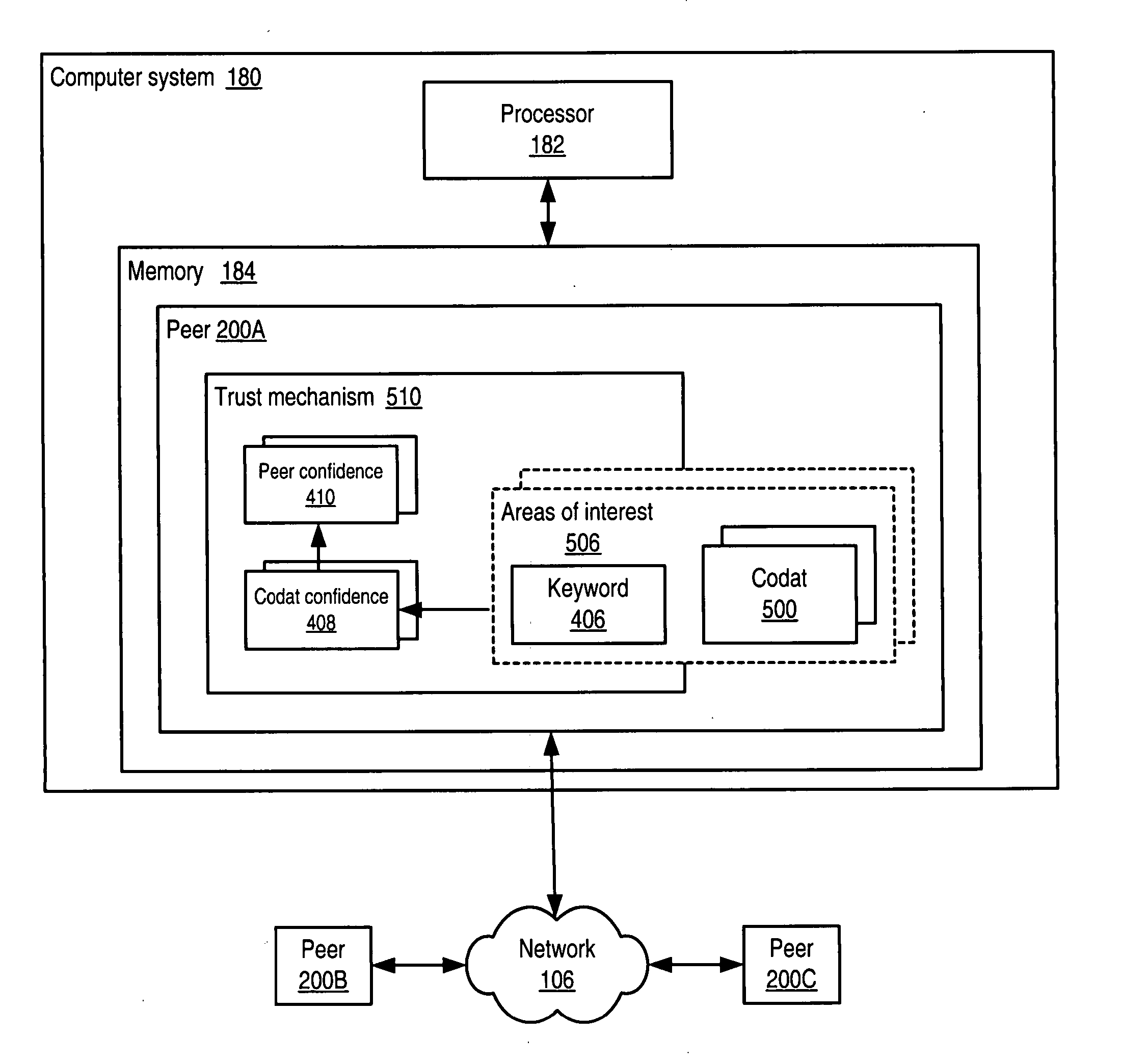
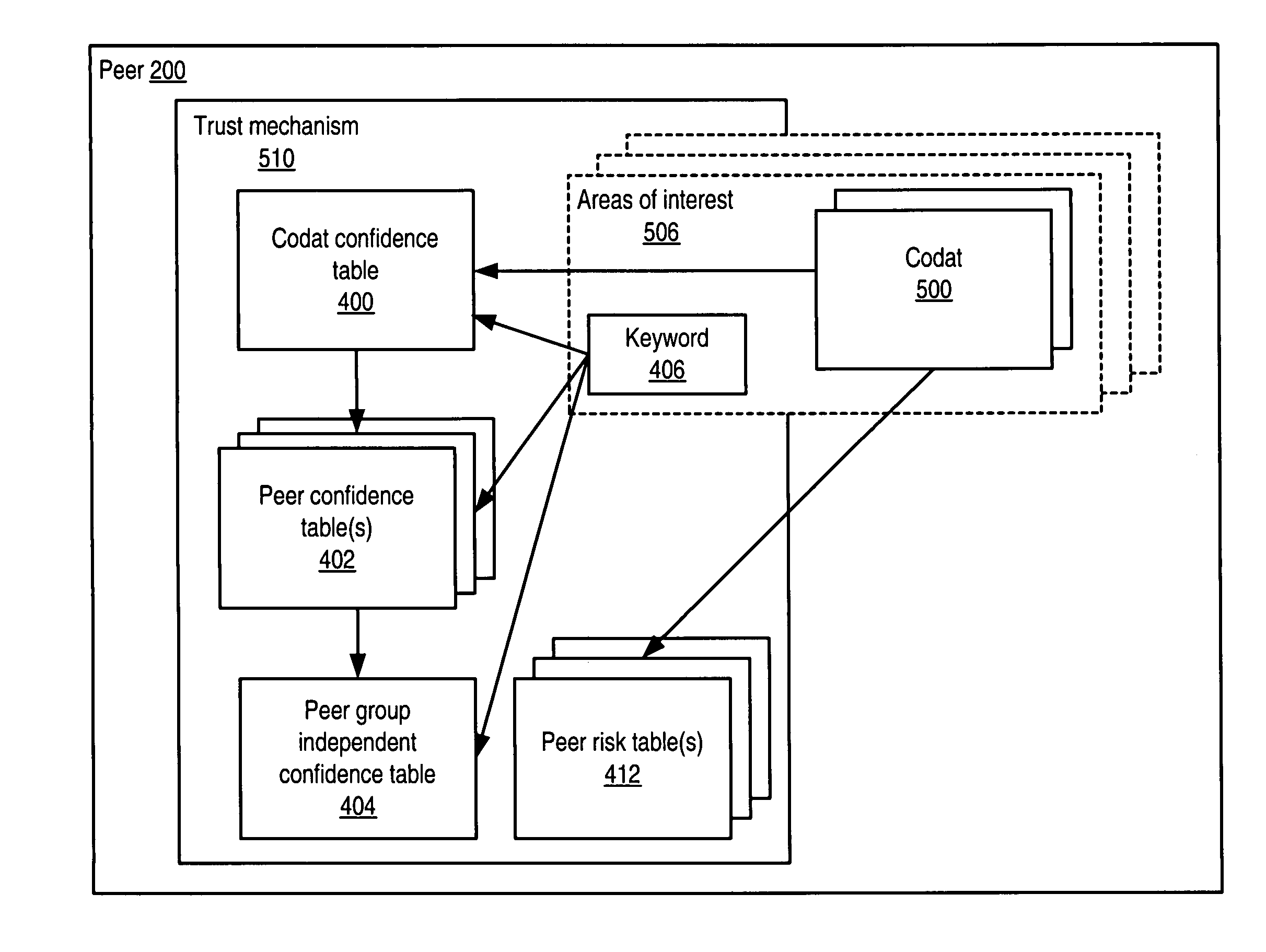
Trust mechanism for a peer-to-peer network computing platform
ActiveUS20050086300A1Generate and confidenceMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsTrust relationshipDatabase
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
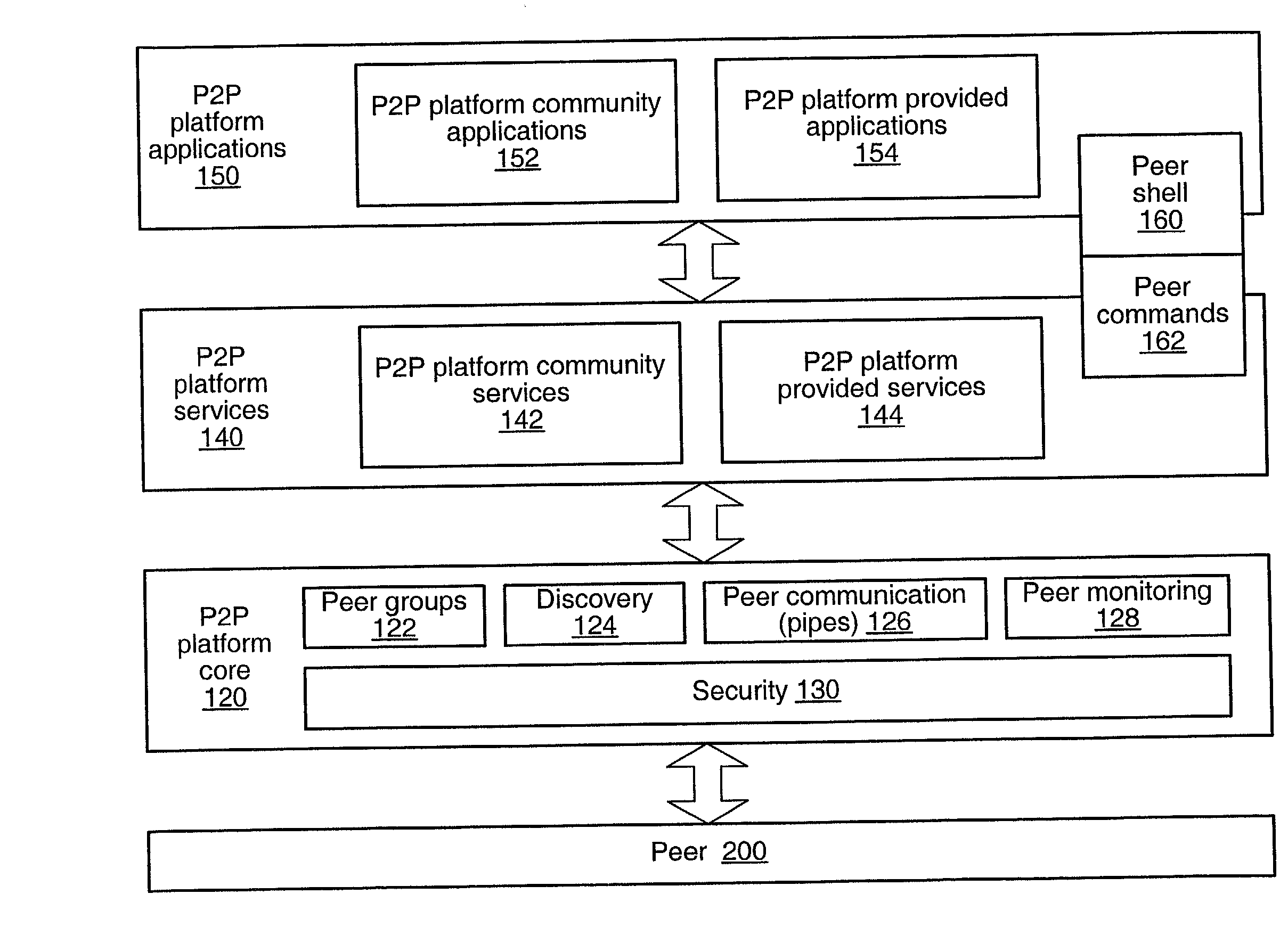
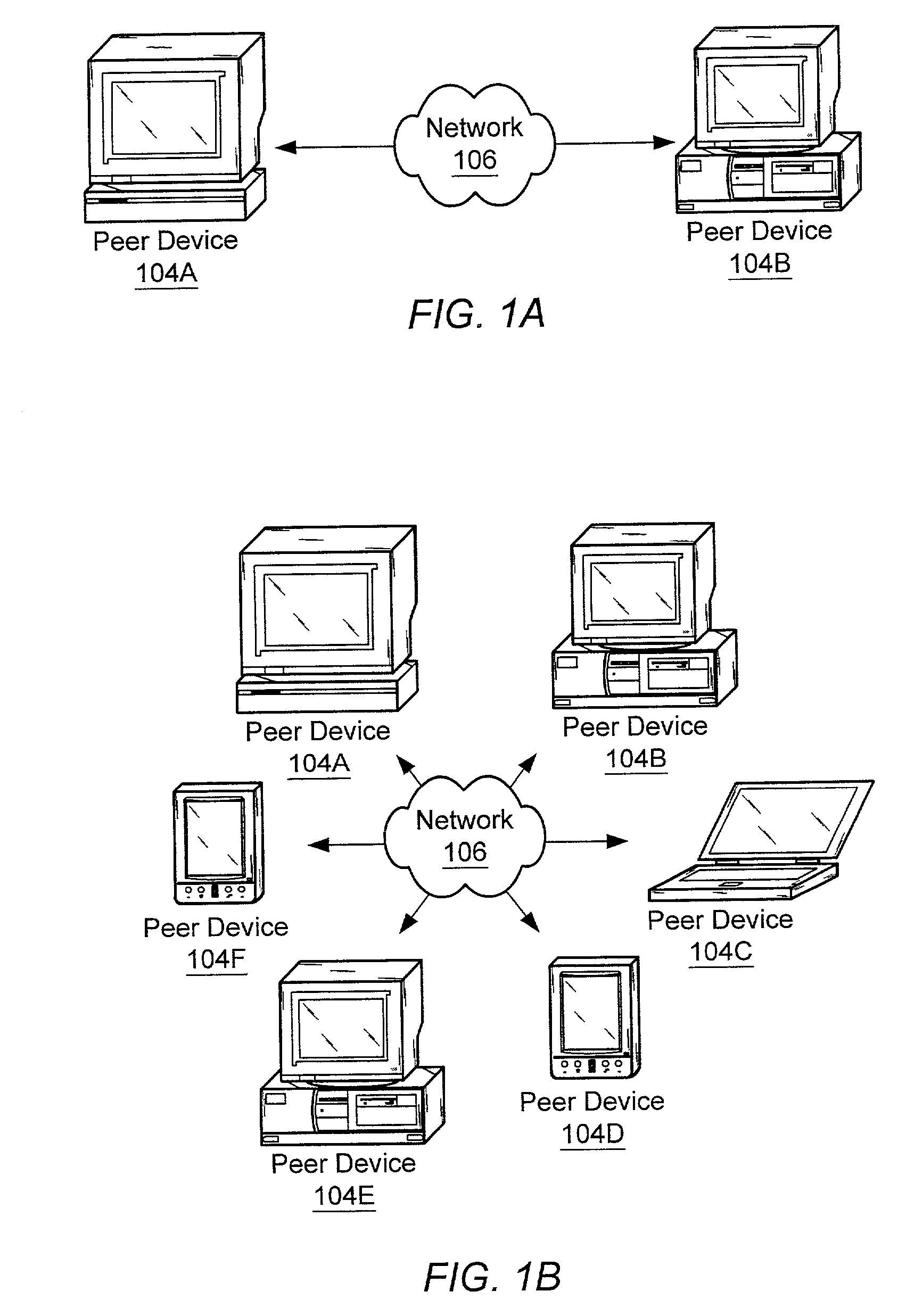
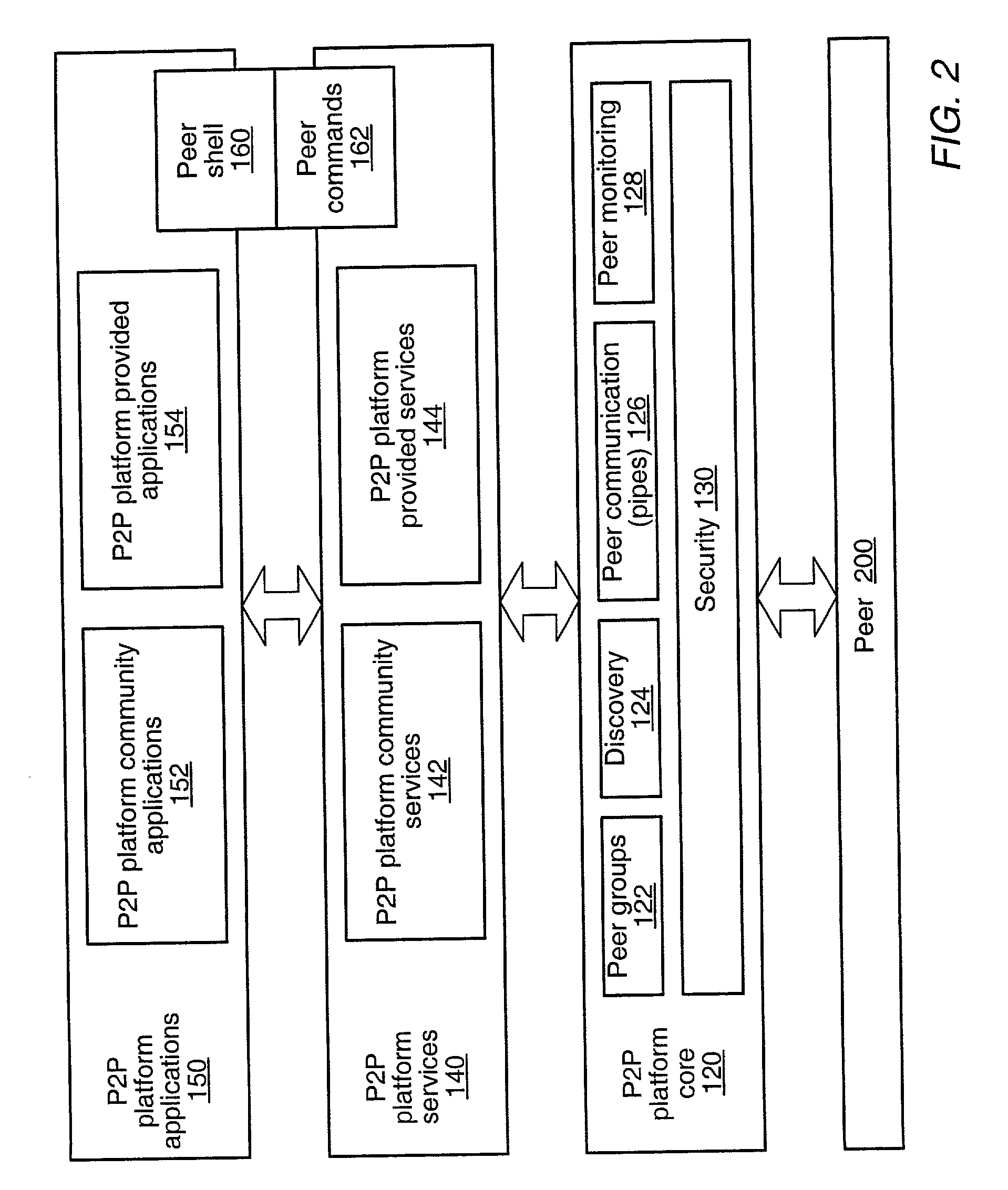
Peer-to-peer computing architecture
ActiveUS20020147771A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsPhysical addressProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
A system and method for providing an open network computing platform designed for peer-to-peer computing. The peer-to-peer platform may provide protocols for peer-to-peer services and applications that allow peers to discover each other, communicate with each other, and cooperate with each other to form peer groups. The protocols may include a peer membership protocol, a peer discovery protocol, a peer resolver protocol, a peer information protocol, a pipe binding protocol, and a peer endpoint protocol. Services and applications that participate in the protocols may be provided to deal with higher-level concepts. Advertisements may be used to publish peer resources. The peer-to-peer platform provides the ability to replicate information toward end users and may enable peers to find content that is closest to them. The peer-to-peer protocols and unique peer identifiers may allow peer nodes to move to different locations and access services and other content independent of network physical addresses.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Personal information security and exchange tool
InactiveUS7289971B1Facilitates formation and useEasy to useFinanceComputer security arrangementsCommand and controlElectricity market
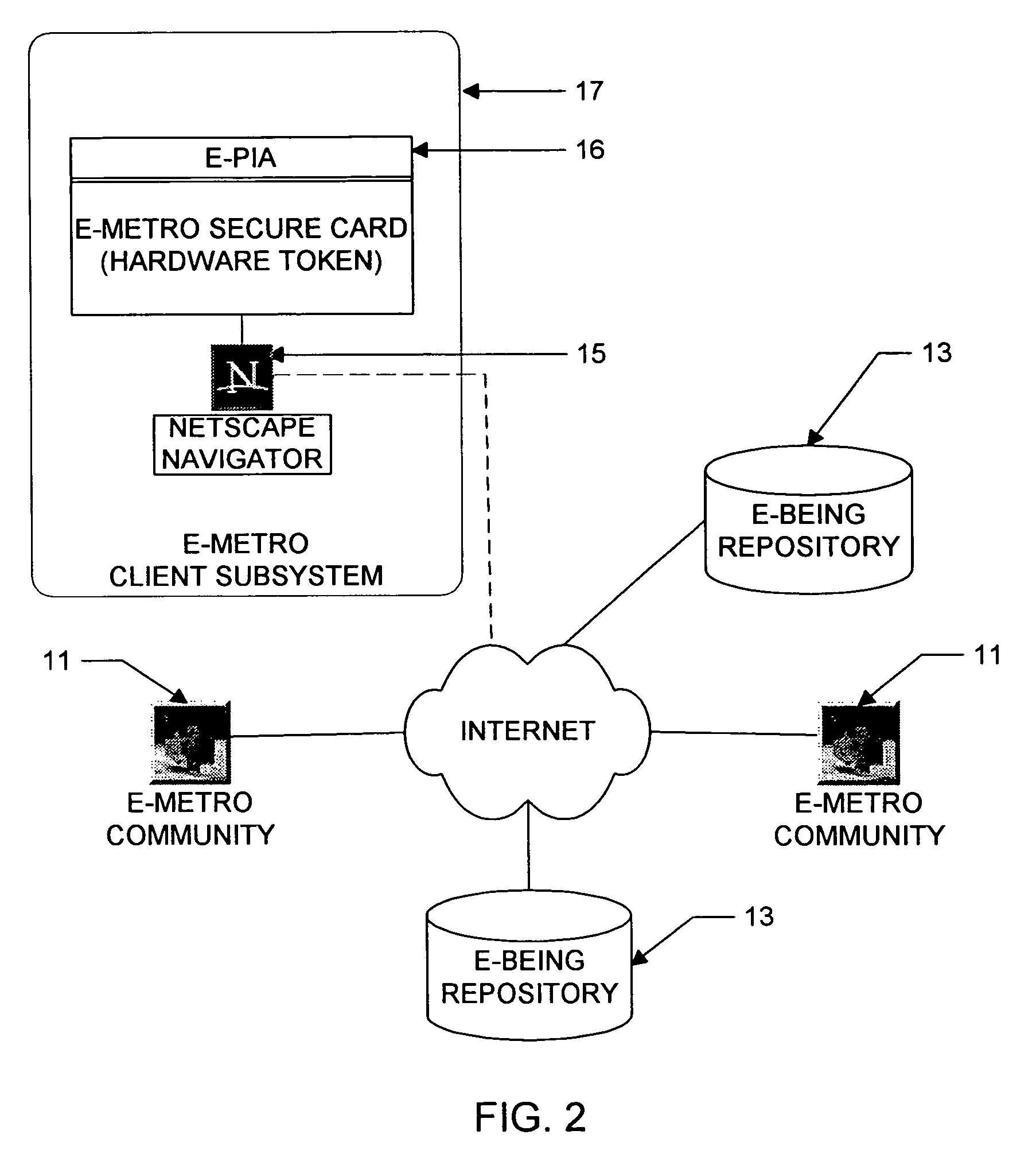
Utilization of the E-Metro Community and Personal Information Agents assure an effective and comprehensive agent-rule based command and control of informational assets in a networked computer environment. The concerns of informational privacy and informational self-determination are addressed squarely by the invention affording persons and entities a trusted means to author, secure, search, process, and exchange personal and / or confidential information in a networked computer environment. The formation of trusted electronic communities wherein members command and control their digital persona, exchanging or brokering for value the trusted utility of their informational assets is made possible by the invention. The present invention provides for the trusted utilization of personal data in electronic markets, providing both communities and individuals aggregate and individual rule-based control of the processing of their personal data.
Owner:CYVA RES HLDG
Network computer game linked to real-time financial data
InactiveUS20090181777A1Apparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesFinancial transactionMarket based
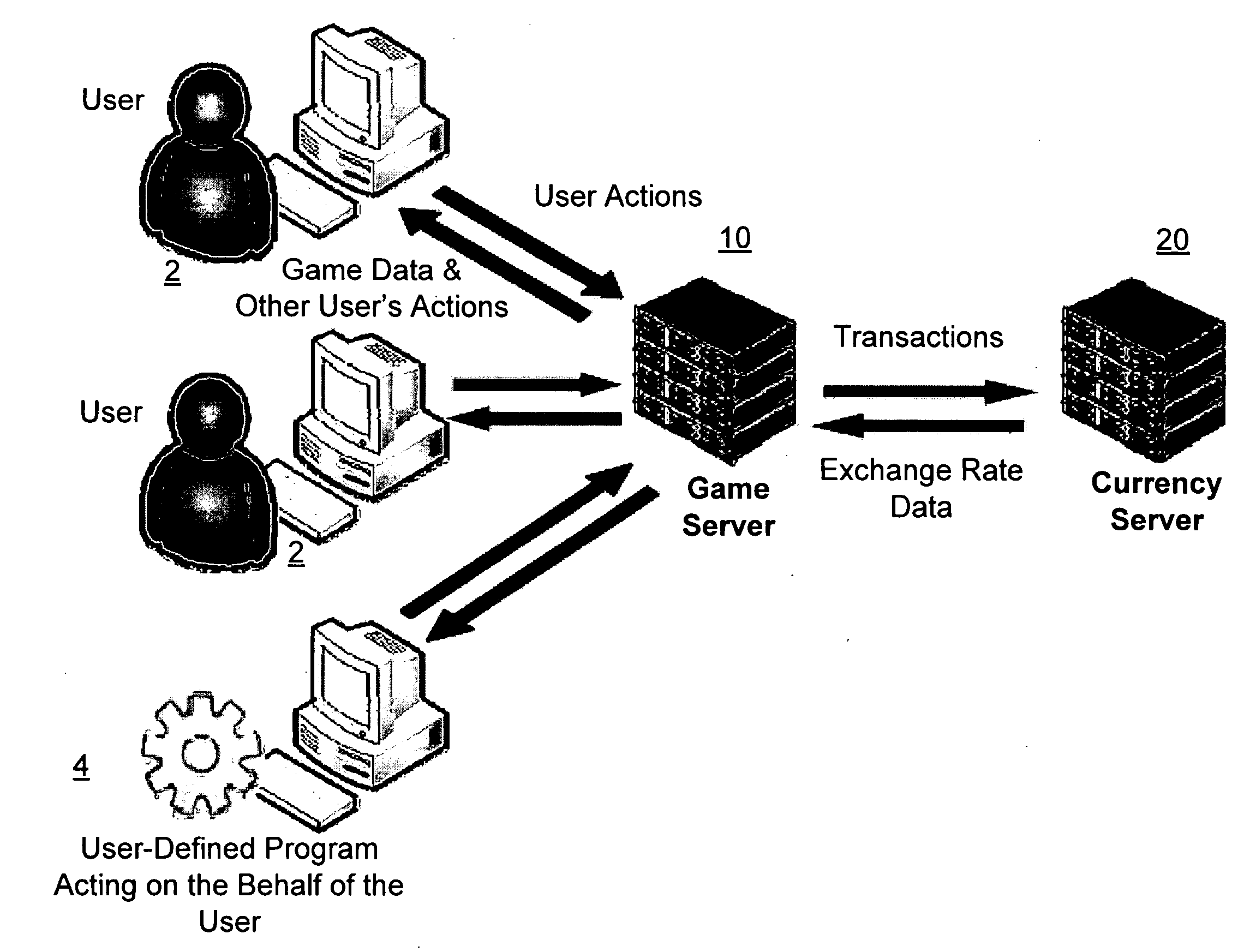
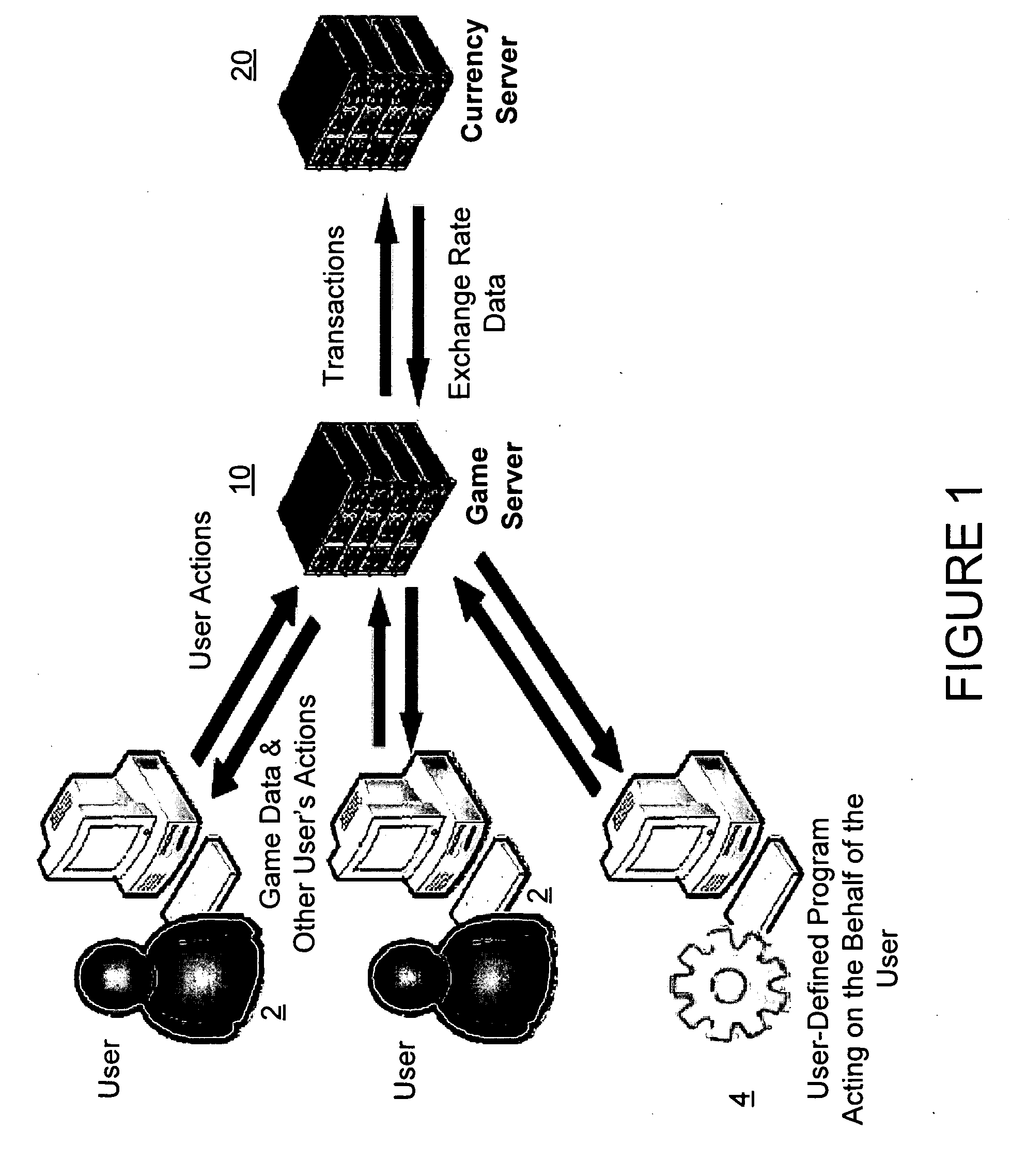
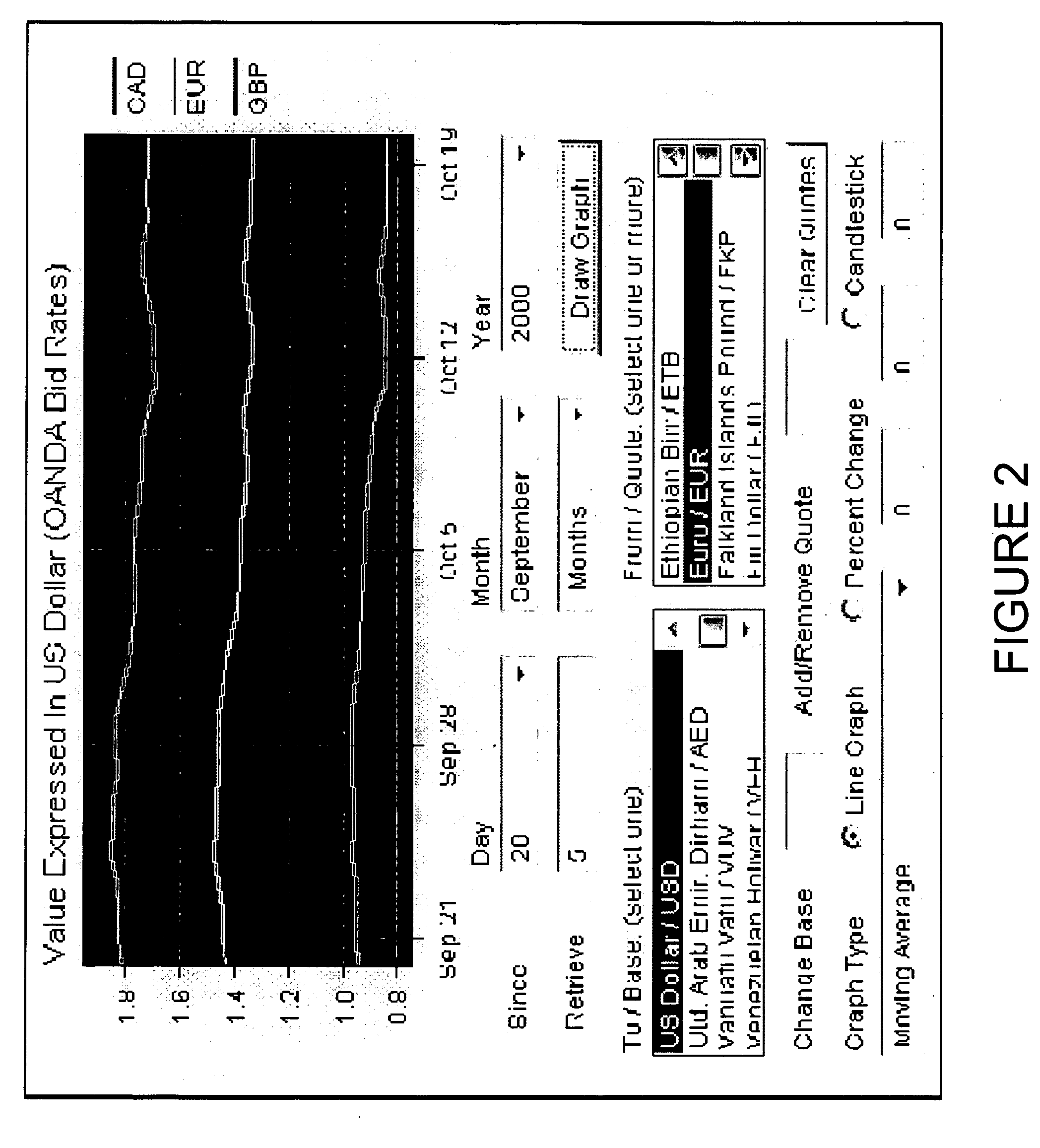
A network-based computer game that both uses real-time financial data to affect game state and uses participants' actions to determine and engage in financial transactions. A game server receives financial data on market conditions (such as currency markets) from a financial server and regularly synchronizes user's game environments to match the financial data. The game server propagates financial data to the game or games, coordinates communication (if any) between the games, and can initiate the opening and closing of positions in the financial market based on players' game behavior. The financial market can be a currency market, where one nation's currency can be exchanged for another currency at a certain exchange rate.
Owner:FINANCIAL DATA GAMES
Modular entertainment and gaming system configured for network boot, network application load and selective network computation farming
InactiveUS6908391B2Overcomes technical lagOvercomes security limitationApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesModularityThe Internet
A secure and modular architecture for monitoring and controlling clusters of pay entertainment and gaming devices. The architecture allows flexible and secure use of state-of-the-art multimedia and Internet technologies to attract the younger player generation used to flashy and networked games. Cash or cash-less entertainment and gaming devices are supported.
Owner:MUDALLA TECH INC THOITS LOVE HERSHBERGER & MCLEAN
Universal client and consumer
InactiveUS7287252B2Error detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsGraphicsGraphical user interface
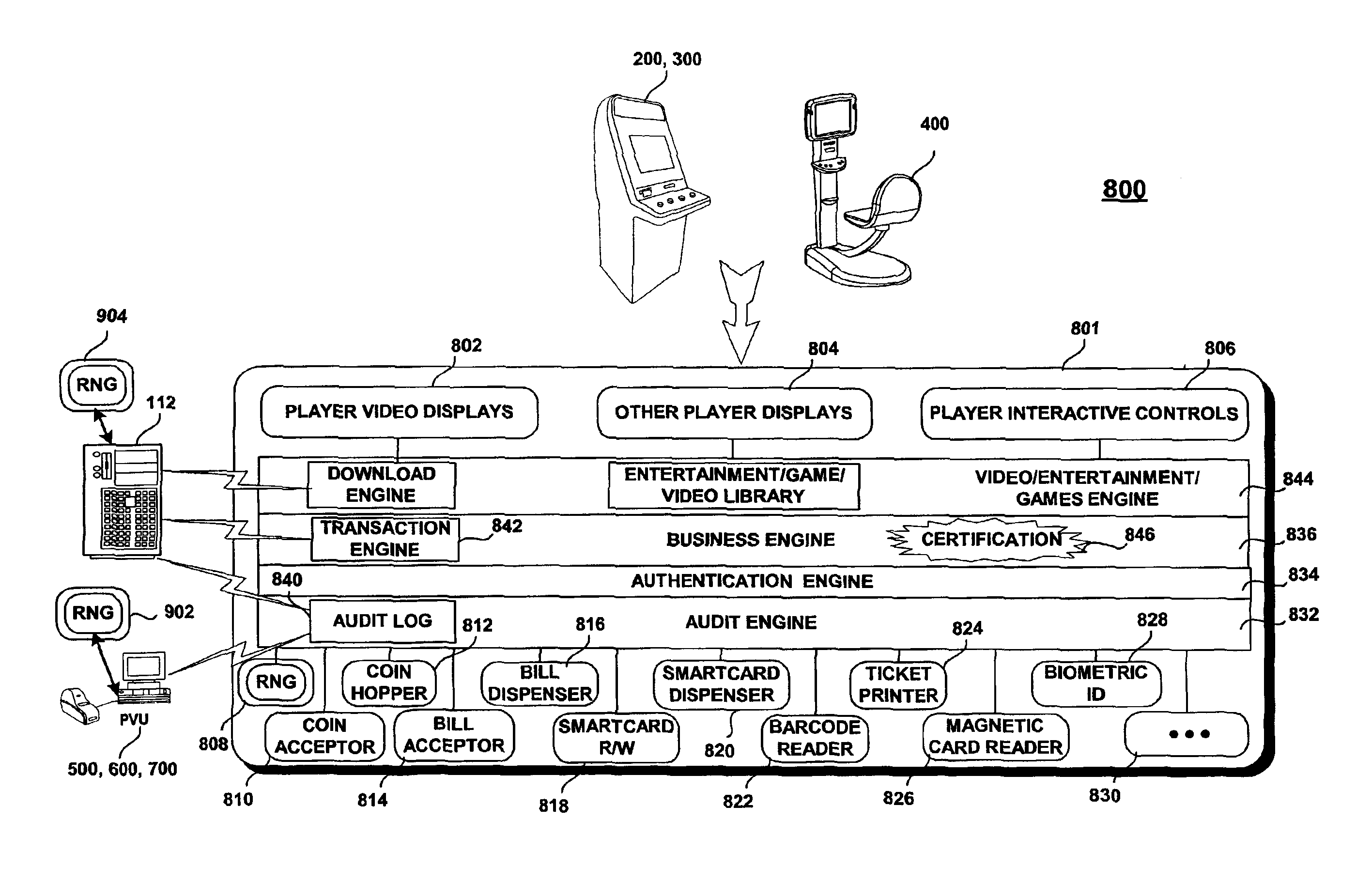
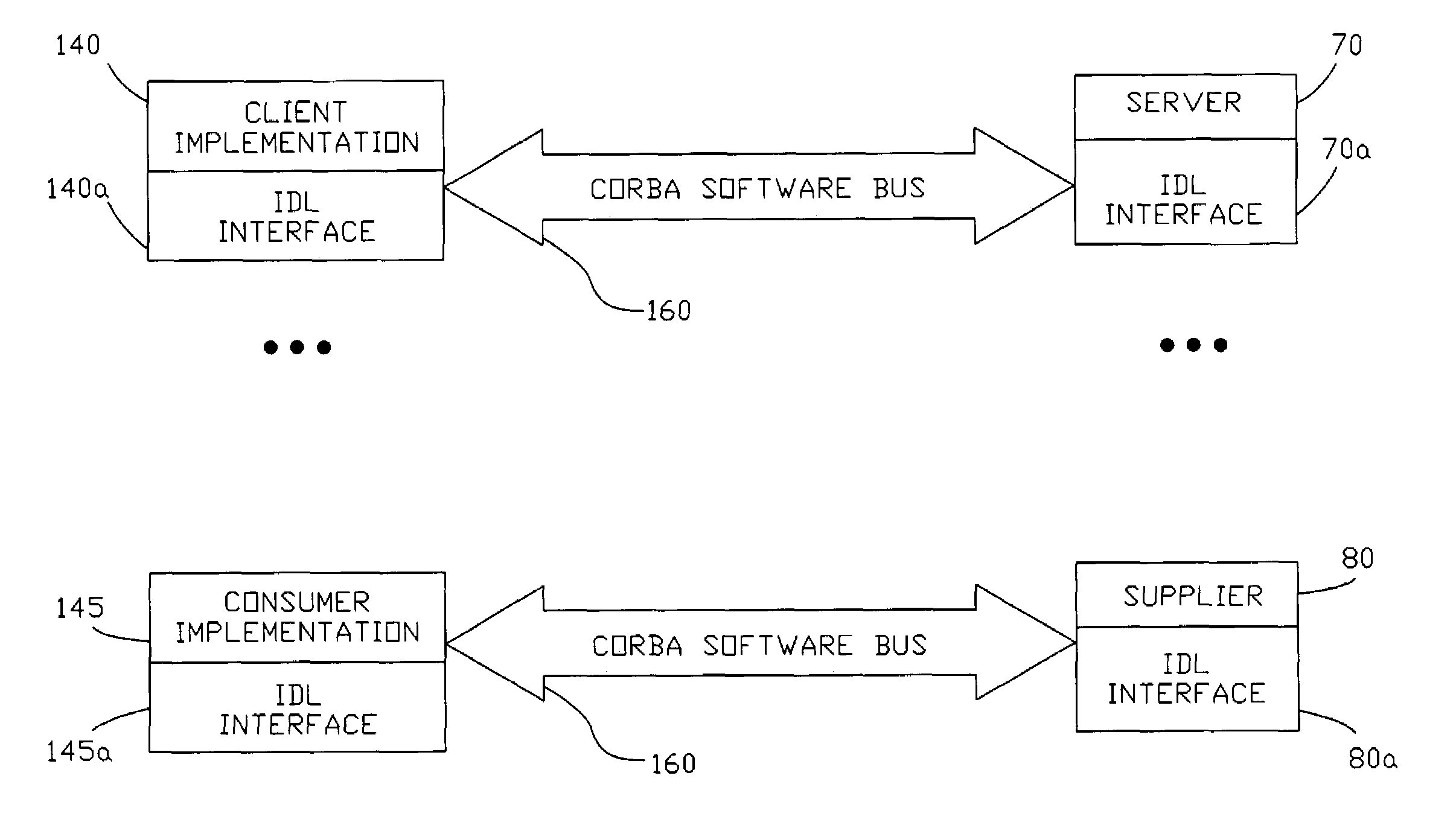
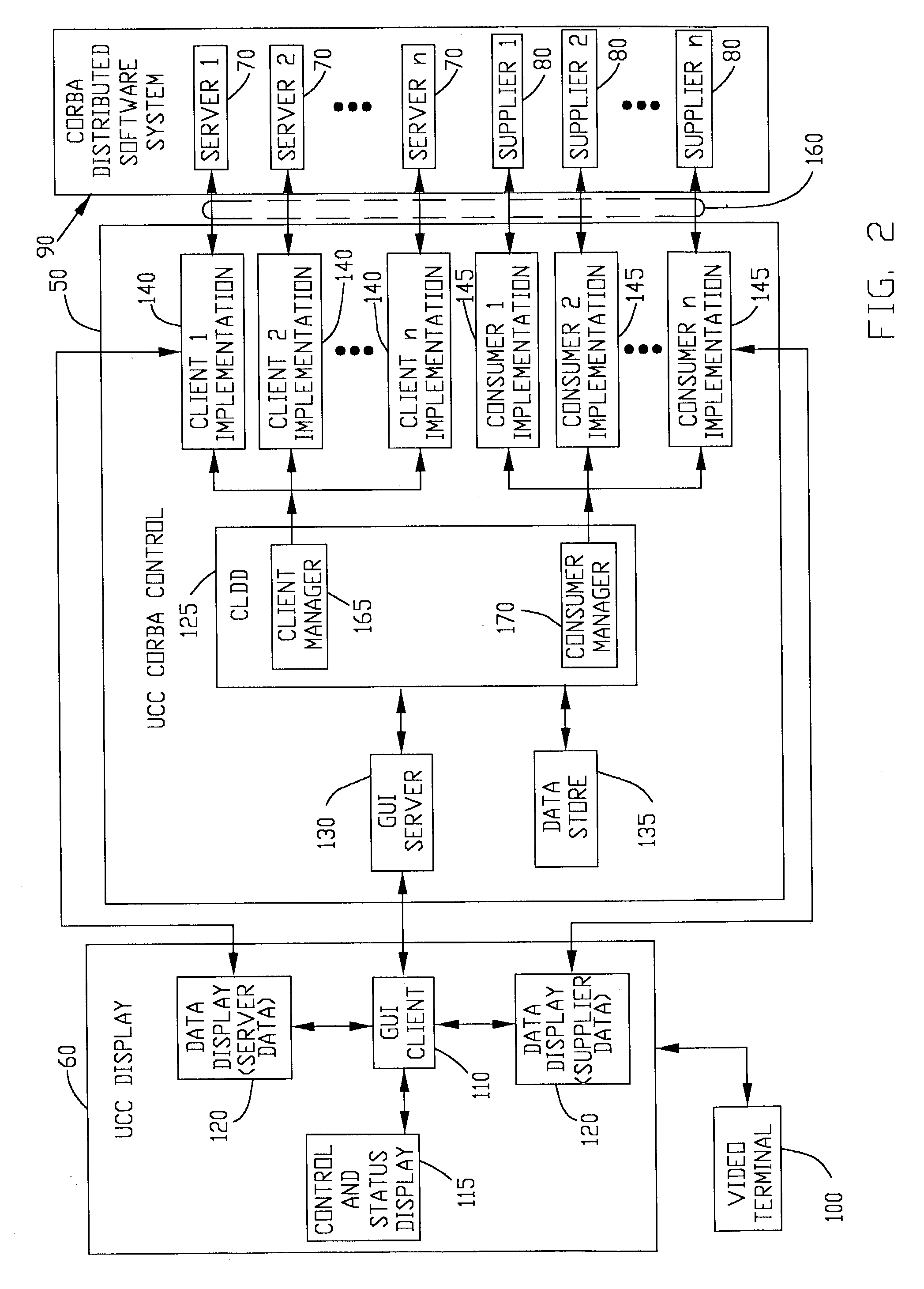
In a network computing environment with a distributed software system utilizing Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA), a Universal Client and Consumer tool that creates Client and Consumer implementations for use in interacting with any existing Servers and / or Suppliers in the system, and displaying the data resulting from the interactions for the purpose of validating the operation, functionality and performance of the Servers and Suppliers. The tool creates a graphical user interface for the user to select Servers or Suppliers to evaluate. The tool identifies the Server or Supplier IDL interface, and then creates either a Client or Consumer Implementation that uses the same corresponding IDL interface. The tool then attempts to connect to the Server or Supplier and where appropriate allow the user to invoke methods. Data received from the Servers and / or Suppliers is displayed on a video device and logged for later analysis.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
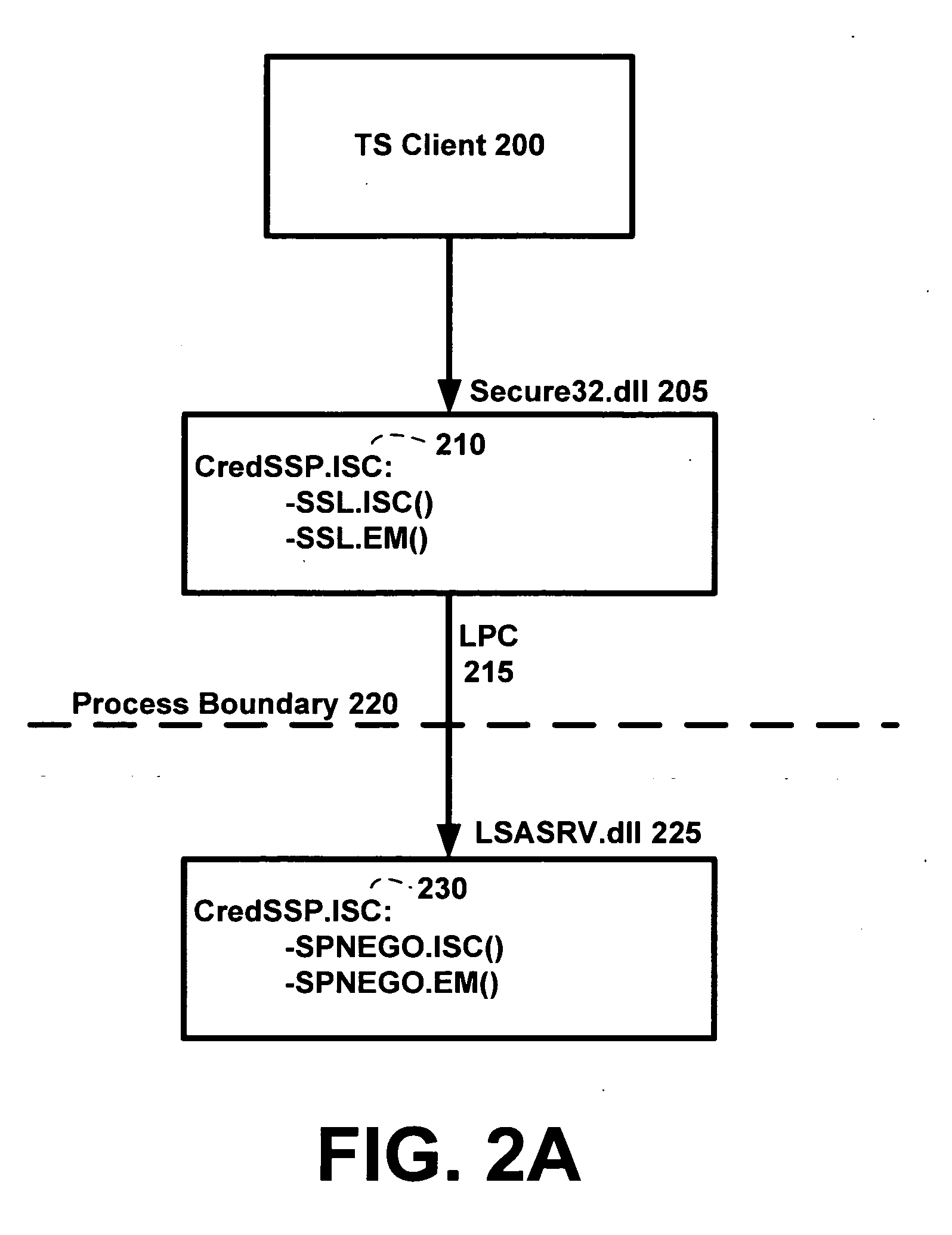
Policy driven, credential delegation for single sign on and secure access to network resources
ActiveUS20070277231A1Wide rangeMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionNetwork conditionsTrust level
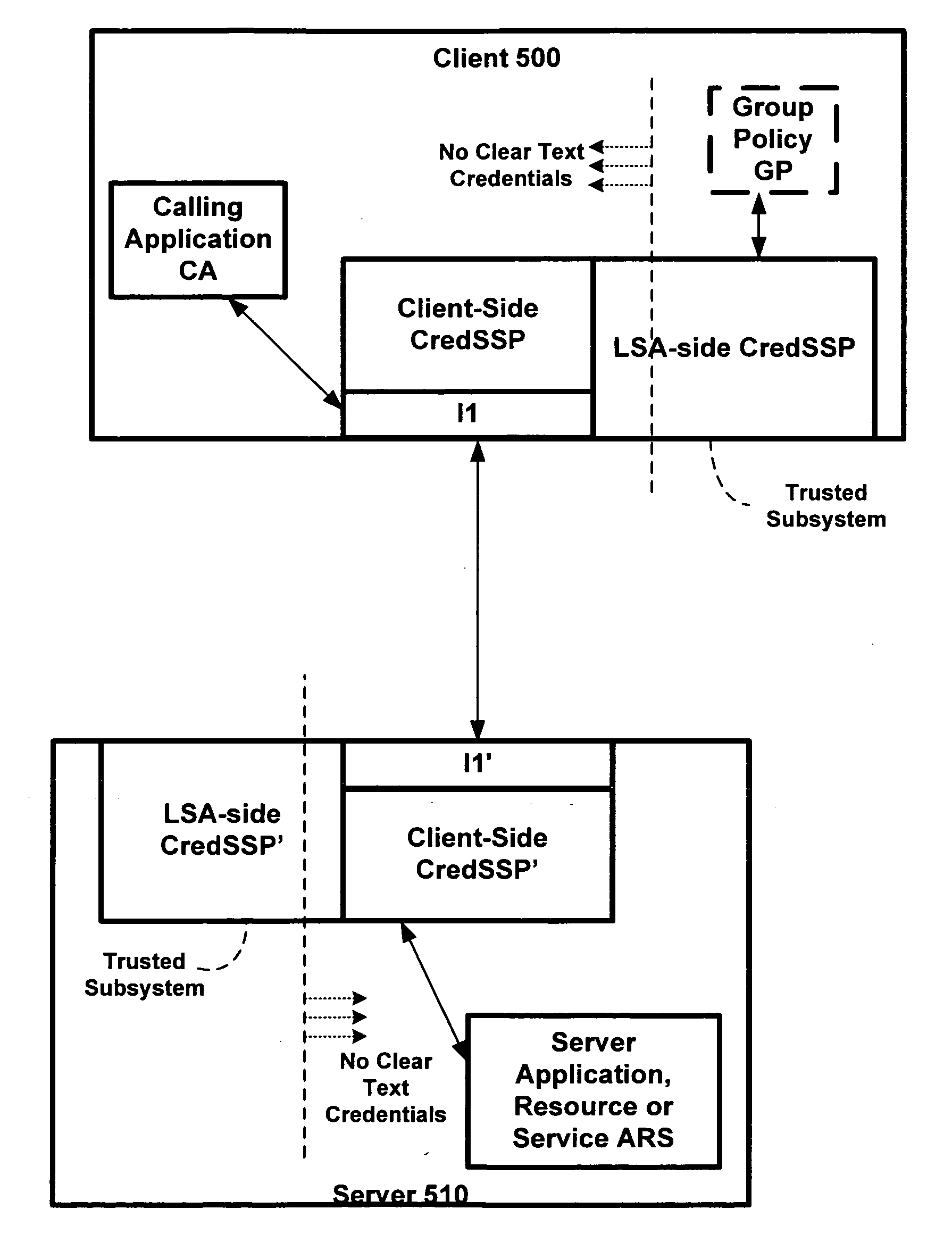
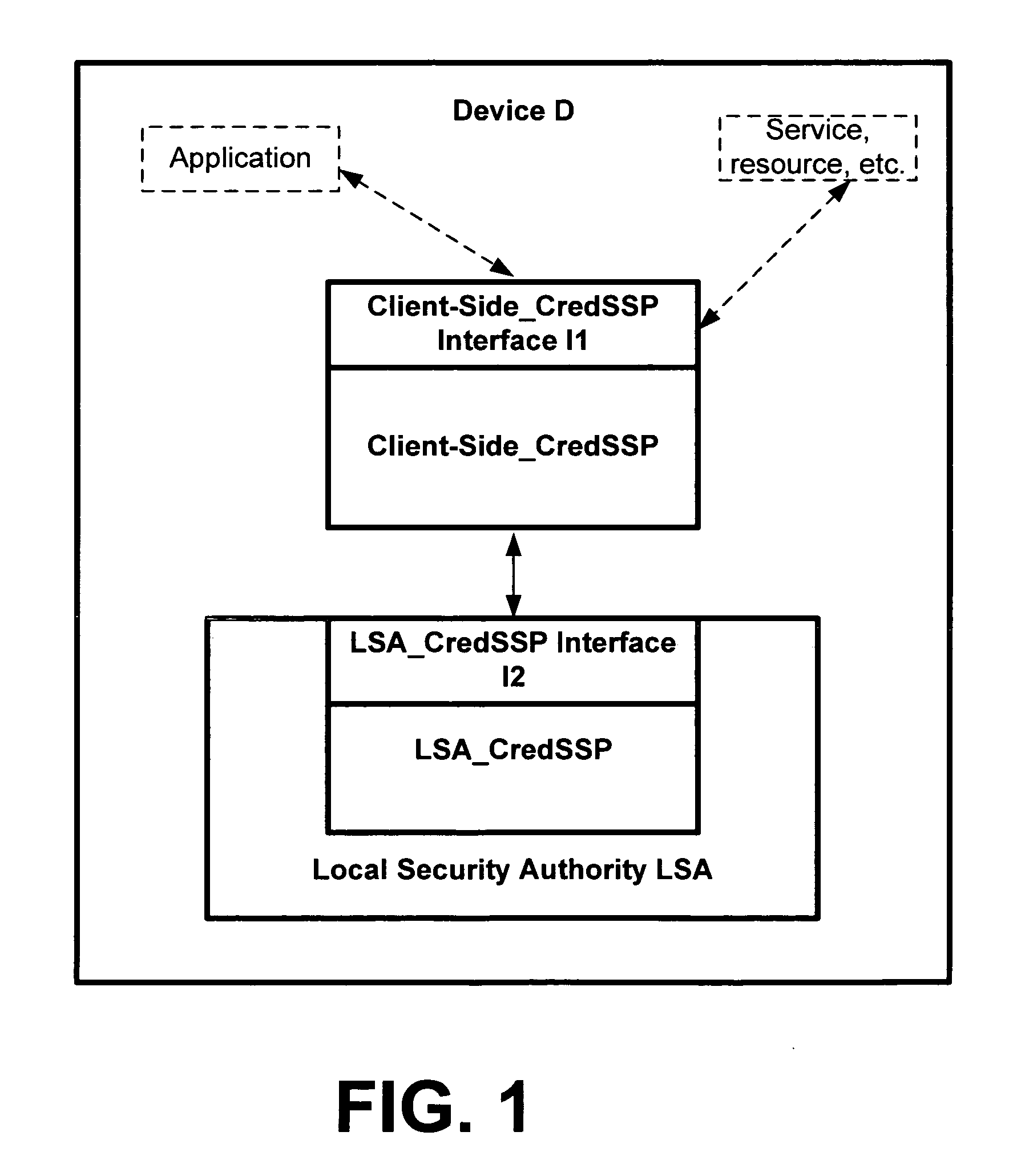
A credential security support provider (Cred SSP) is provided that enables any application to securely delegate a user's credentials from the client, via client side Security Support Provider (SSP) software, to a target server, via server side SSP software in a networked computing environment. The Cred SSP of the invention provides a secure solution that is based in part upon a set of policies, including a default policy that is secure against a broad range of attacks, which are used to control and restrict the delegation of user credentials from a client to a server. The policies can be for any type of user credentials and the different policies are designed to mitigate a broad range of attacks so that appropriate delegation can occur for given delegation circumstances, network conditions, trust levels, etc. Additionally, only a trusted subsystem, e.g., a trusted subsystem of the Local Security Authority (LSA), has access to the clear text credentials such that neither the calling application of the Cred SSP APIs on the server side nor the calling application of the Cred SSP APIs on the client side have access to clear text credentials.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
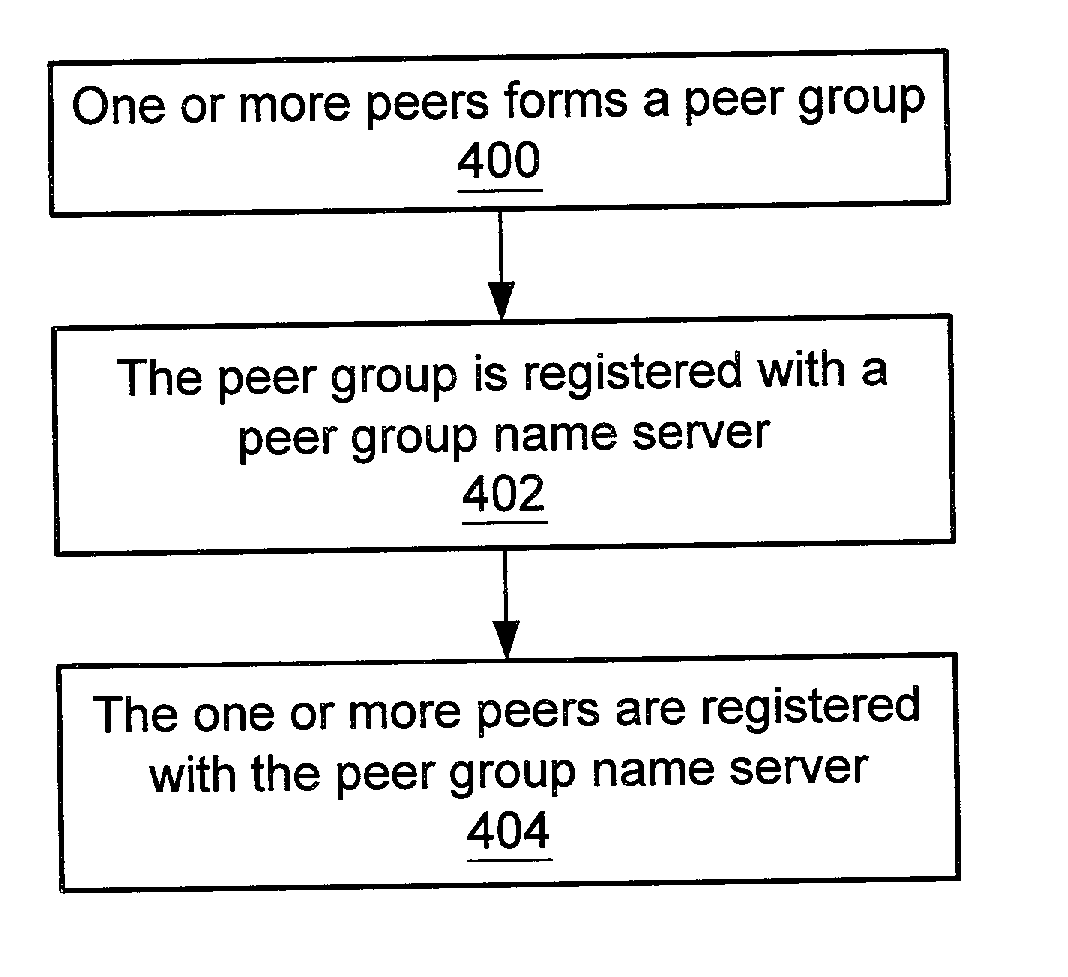
Peer group name server
A system and method for providing a name service in a peer-to-peer environment is described. A peer group name server may be a standalone name server that may be used in peer-to-peer applications and environments. A network computing platform may be used as a basis for establishing and operating a peer-to-peer network. A peer group name server may cache information about peers, peer groups and other entities. Peers may discover other peers, peer groups and other entities through the peer group name server. A peer group name server may serve as a reverse lookup provider. A peer group name server may act as a registrar for named entities (e.g. peers) in the peer-to-peer networking environment. In one embodiment, peer group name servers may maintain information about other peer group name servers, thus making a network of decentralized peer group name servers.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
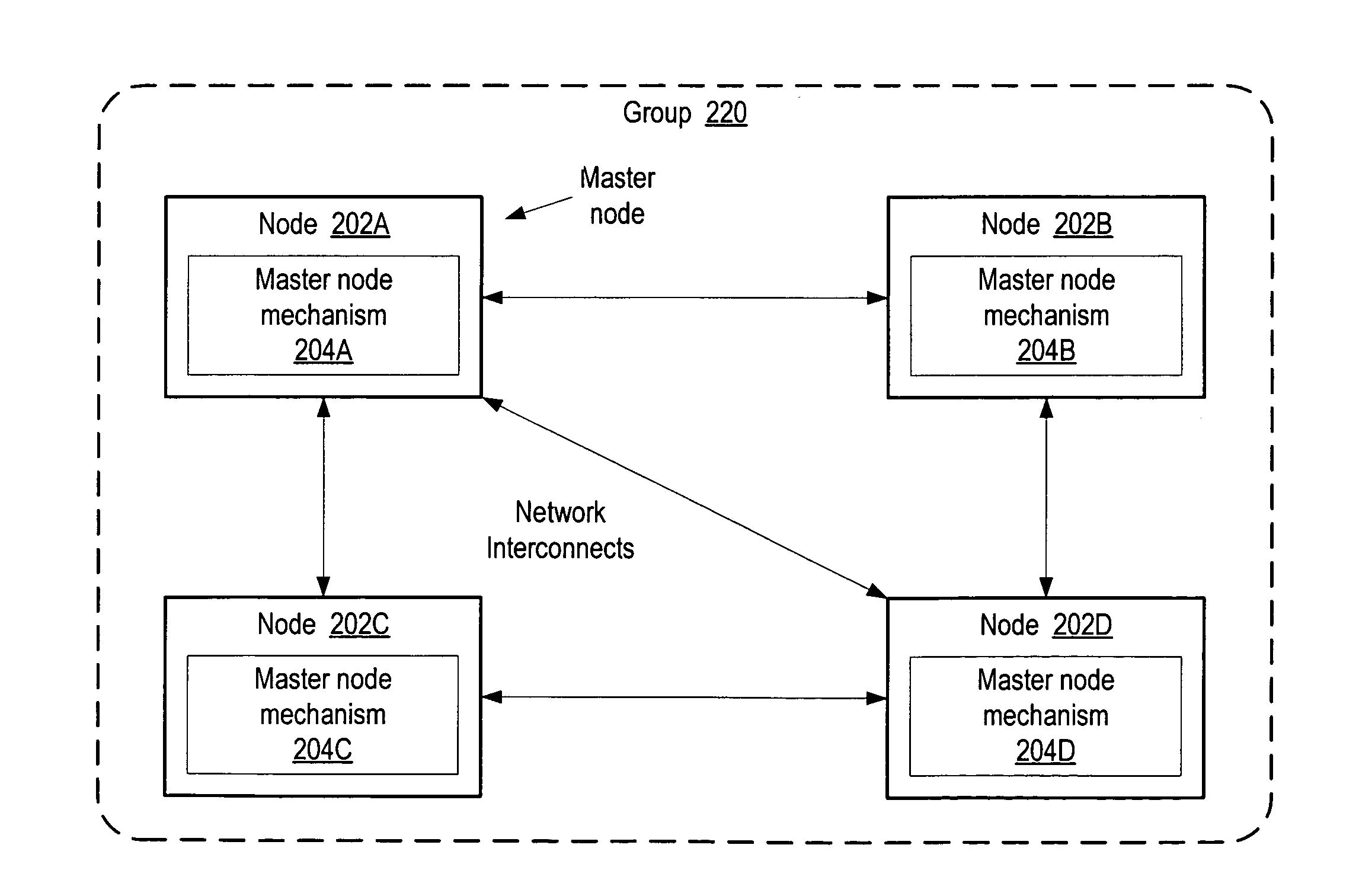
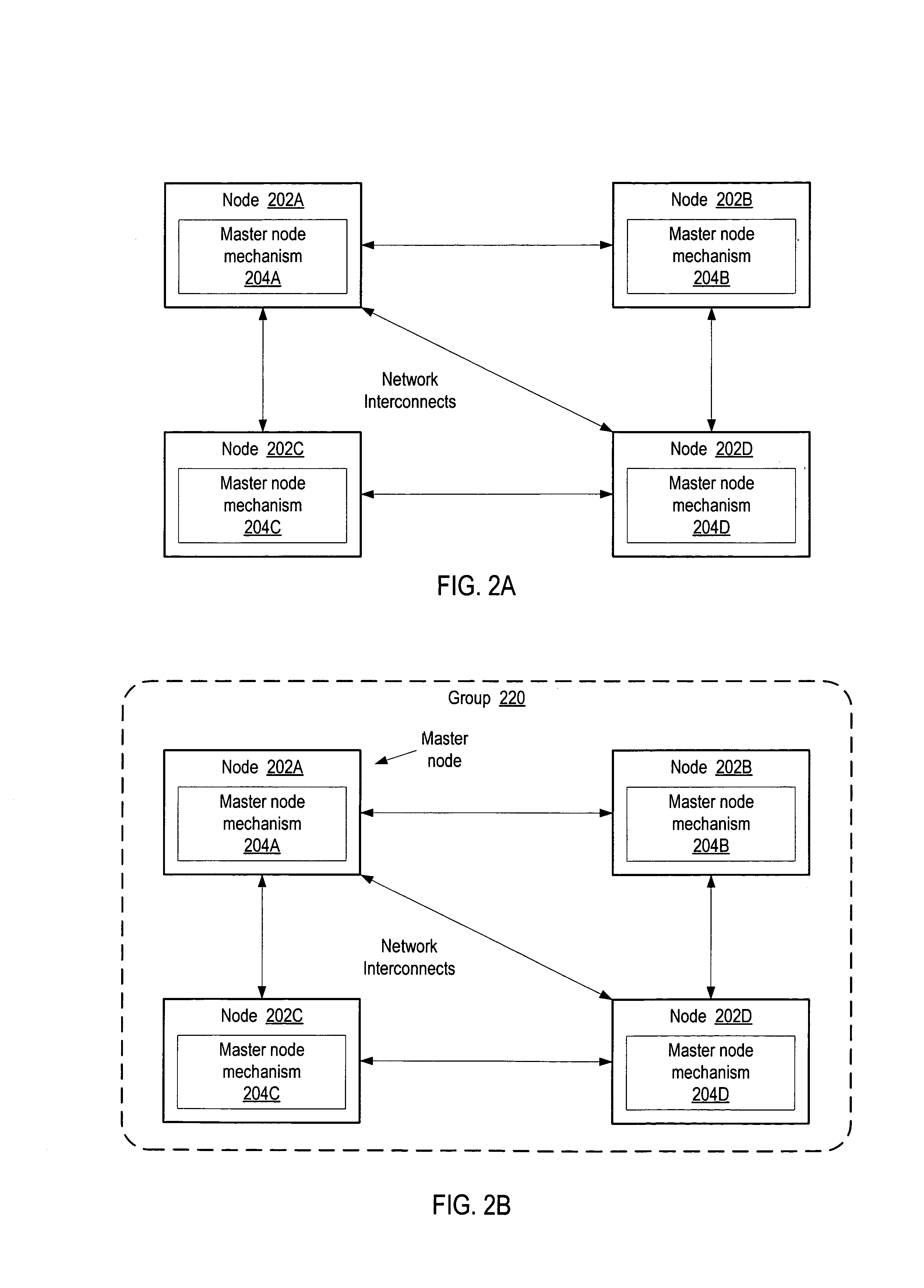
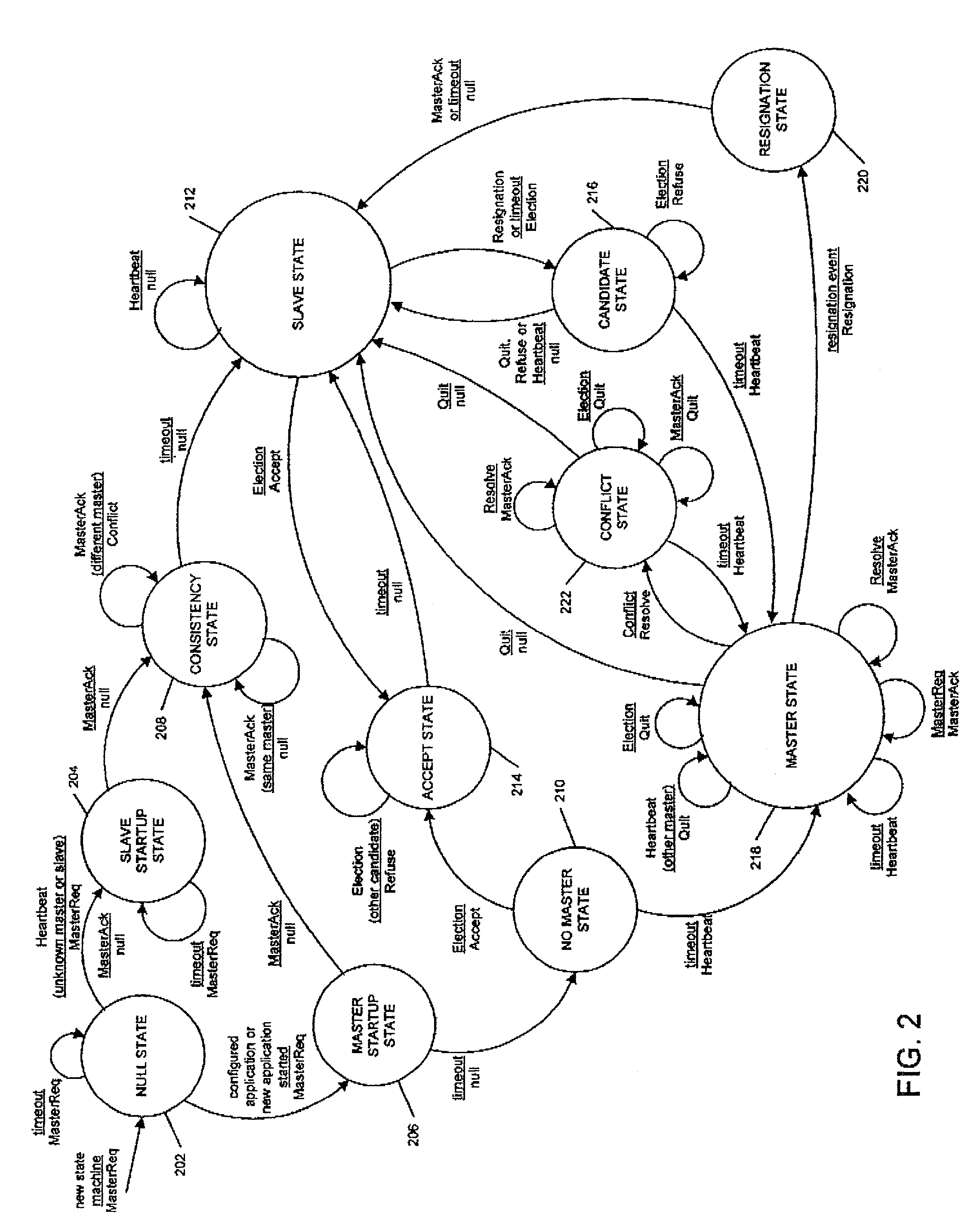
Method and apparatus for self-organizing node groups on a network
Method and apparatus for the self-organization of nodes into groups in network computing environments. Embodiments may provide the ability to deploy nodes on a network, and to allow the nodes to organize into groups without human intervention. In one embodiment, a node may broadcast a query looking for a master node for the group. If the query produces no responses, the node may self-elect as the master node for the group and the node may broadcast its presence as the master node. If two or more nodes self-elect as master nodes, the nodes may negotiate to determine which node will be the master node. If the master node becomes unavailable, the remaining nodes in the group may elect a new master node. Some embodiments may be implemented on a peer-to-peer platform, such as the JXTA peer-to-peer platform, which may allow the scope of the group to span subnetworks and networks.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
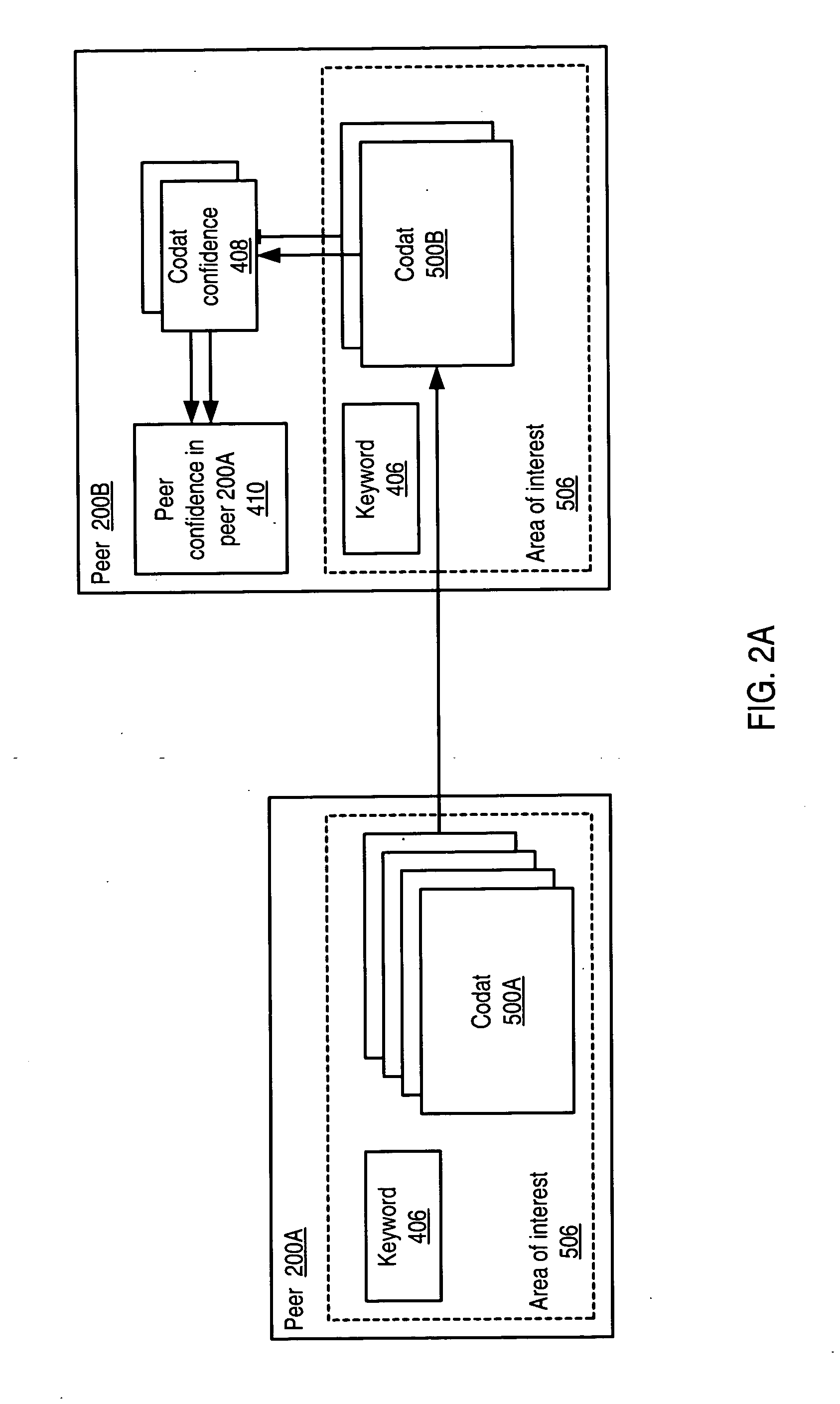
Trust mechanisms for a peer-to-peer network computing platform
ActiveUS7275102B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsTrust relationshipDatabase
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
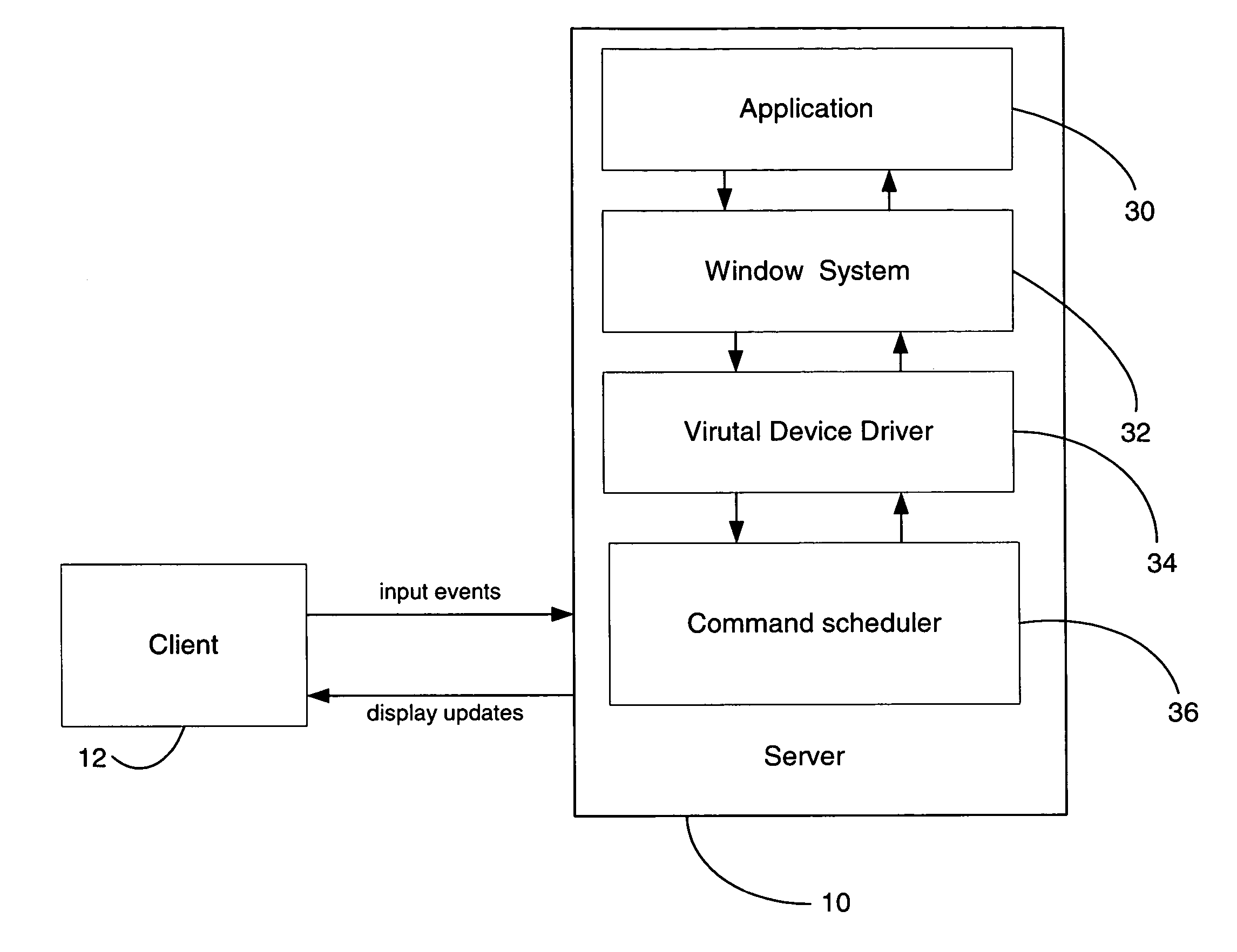
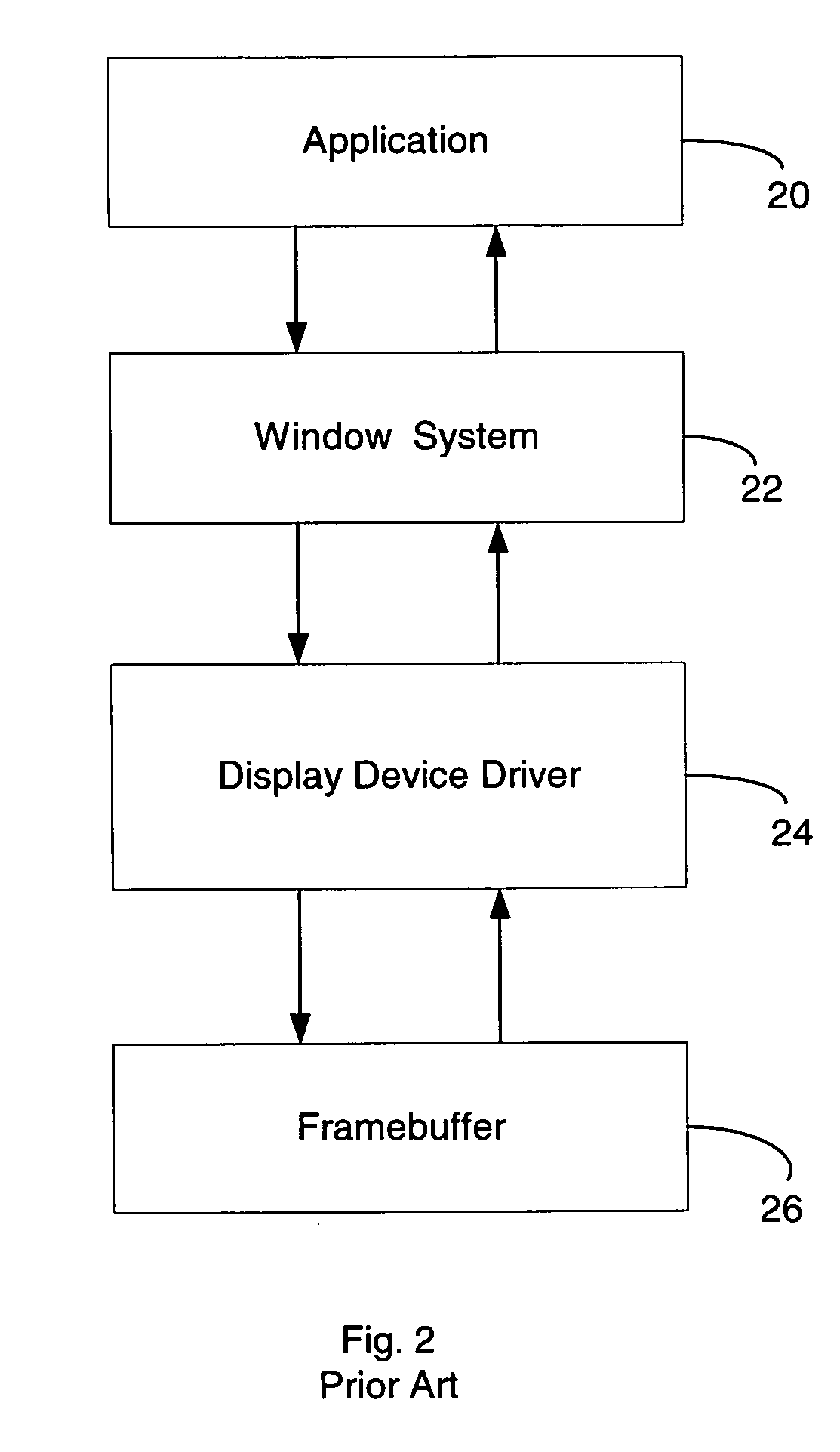
Thin-client network computing method and system
InactiveUS20060184614A1Multiple digital computer combinationsImage data processing detailsComputer hardwareUser input
A method and system are provided for executing an application remotely on a server computer for a client computer in a computer network. The server receives at user input from the client computer associated with the application, and executes the application. The server processes display commands of the application to generate display primitives, and translates the display primitives into lower level display commands defining display updates using semantic information of the display primitives. The lower level display commands are selected from a predetermined set of lower level display commands. The lower level display commands are aggregated and ordered into one or more command queues. Each command queue is associated with a given display region. The server computer transmits the lower level display commands in the one or more command queues over the network to the client computer. The client computer is capable of translating the lower level display commands into hardware calls for causing the client computer to display the display updates.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
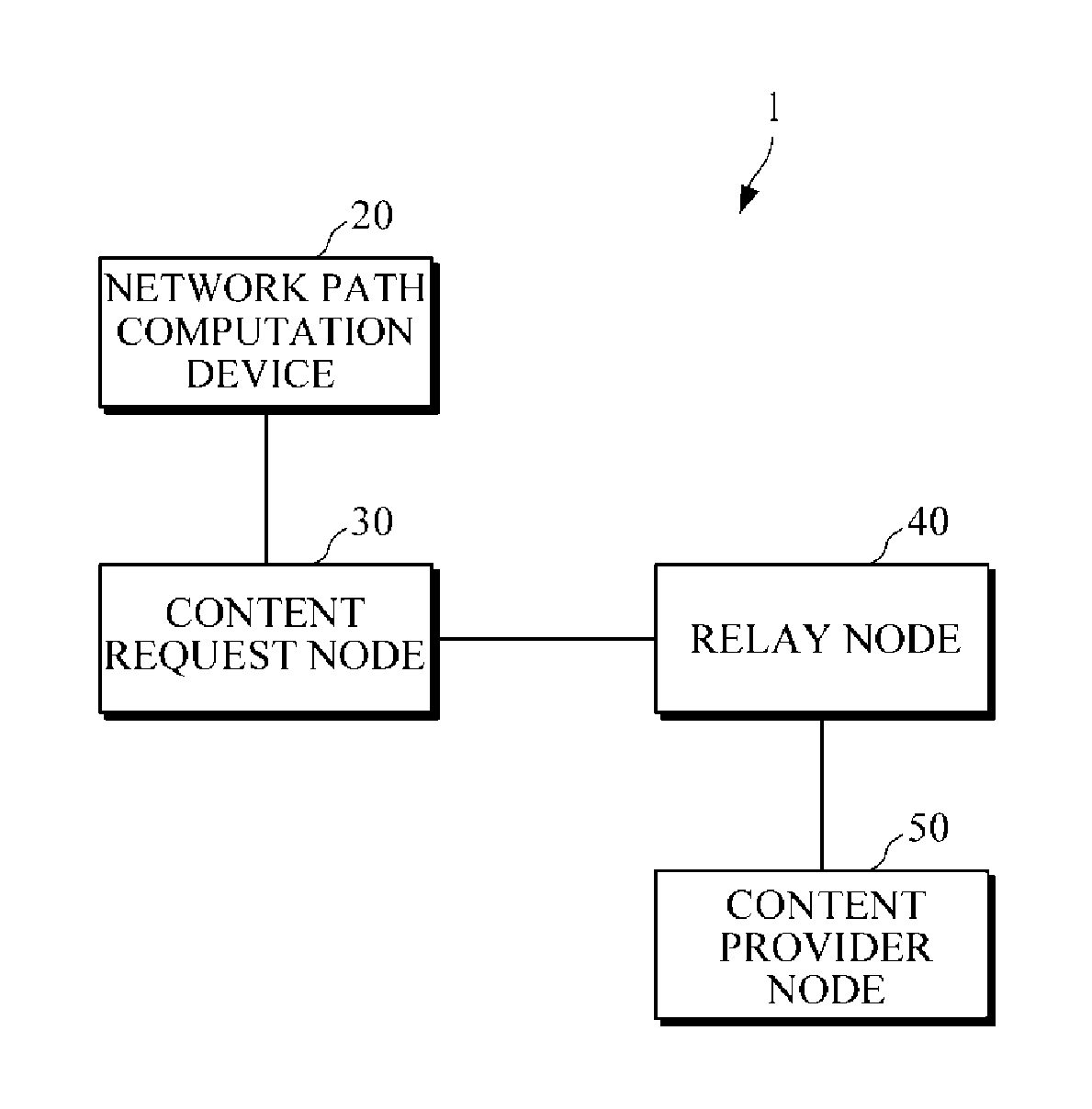
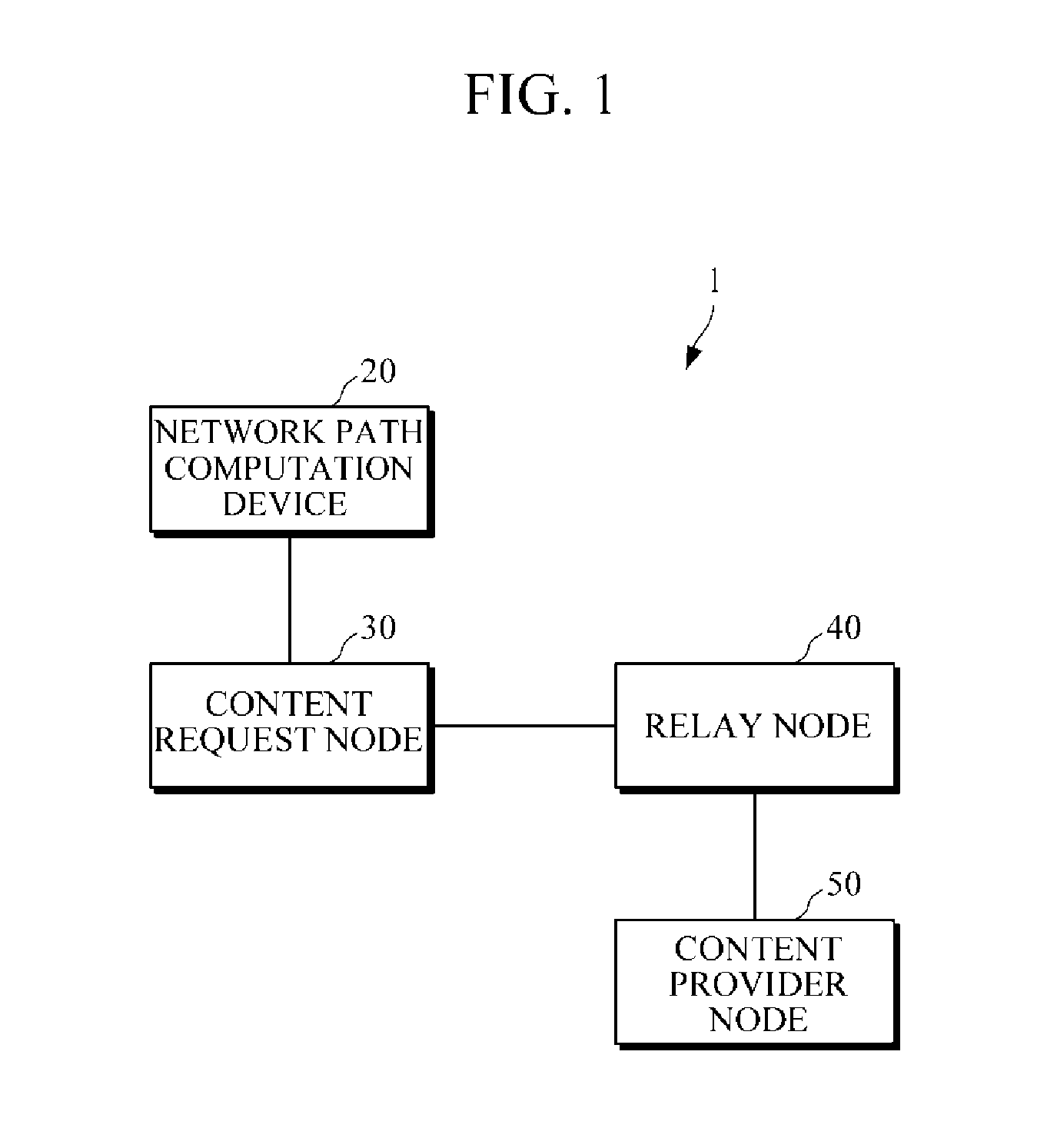
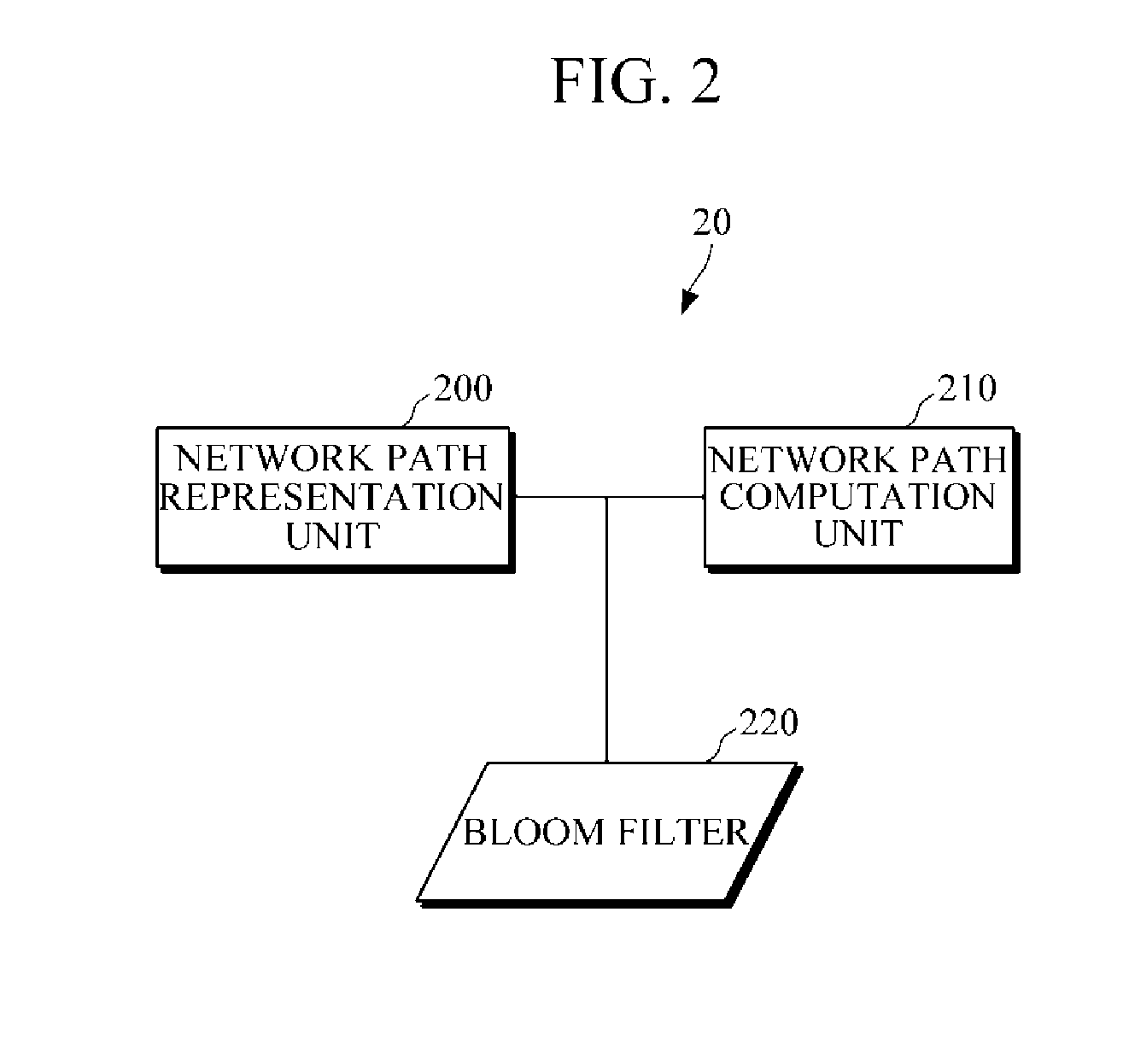
Information centric network system including network path computation device, content request node, and relay node and method of computing network path using information centric network
InactiveUS20130304937A1Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationNetworked systemNetwork computing
An information centric network system and a method of computing a network path using the information centric network system. The network path computation device includes: a network path representation unit configured to represent a network path using a BF; and a network path computation unit configured to, in response to a request from a content request node, compute the network path from the content request node to a content provider node, and, in response to the network path representation unit representing the network path using the BF, transmit the BF to the content request node.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Language model adaptation via network of similar users
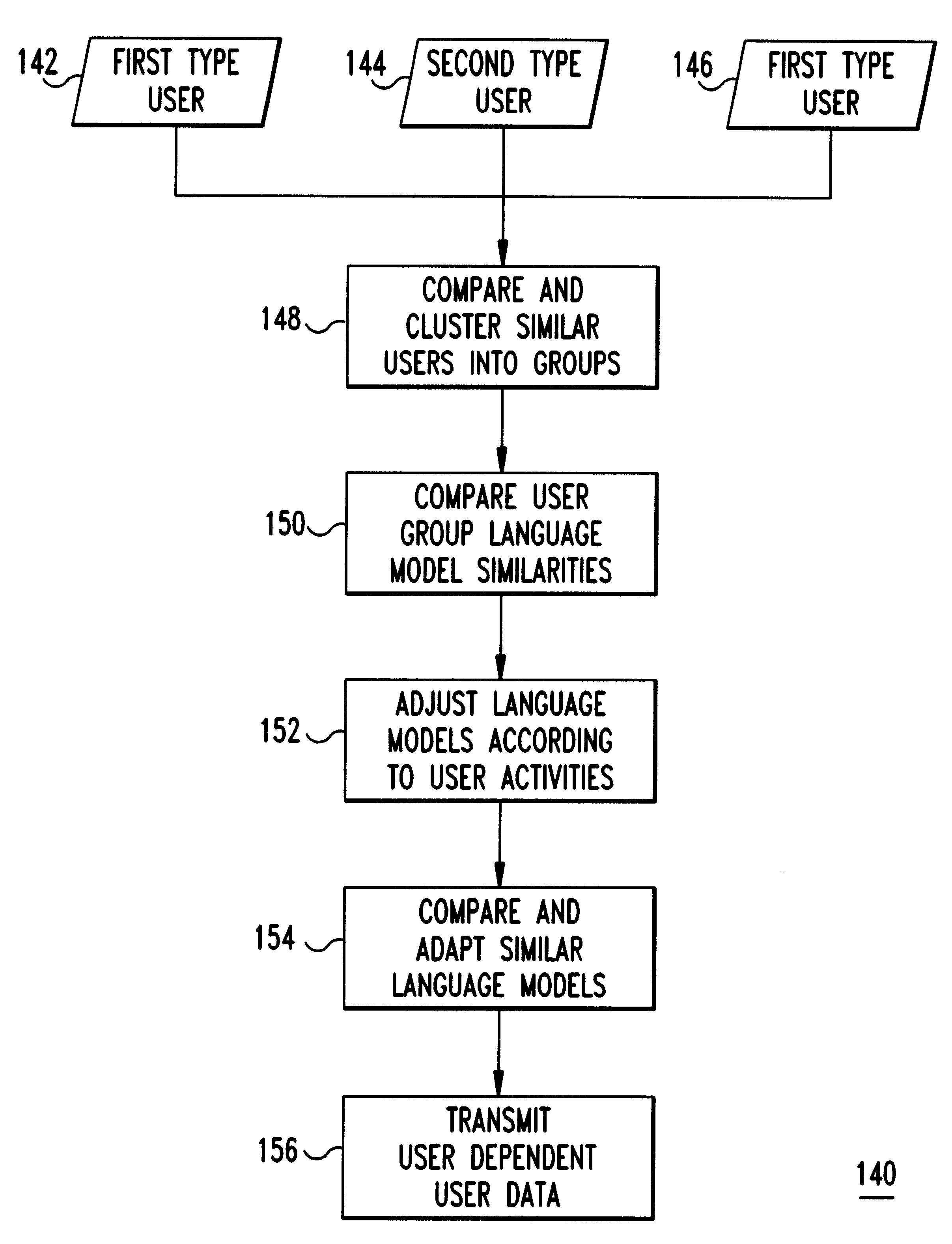
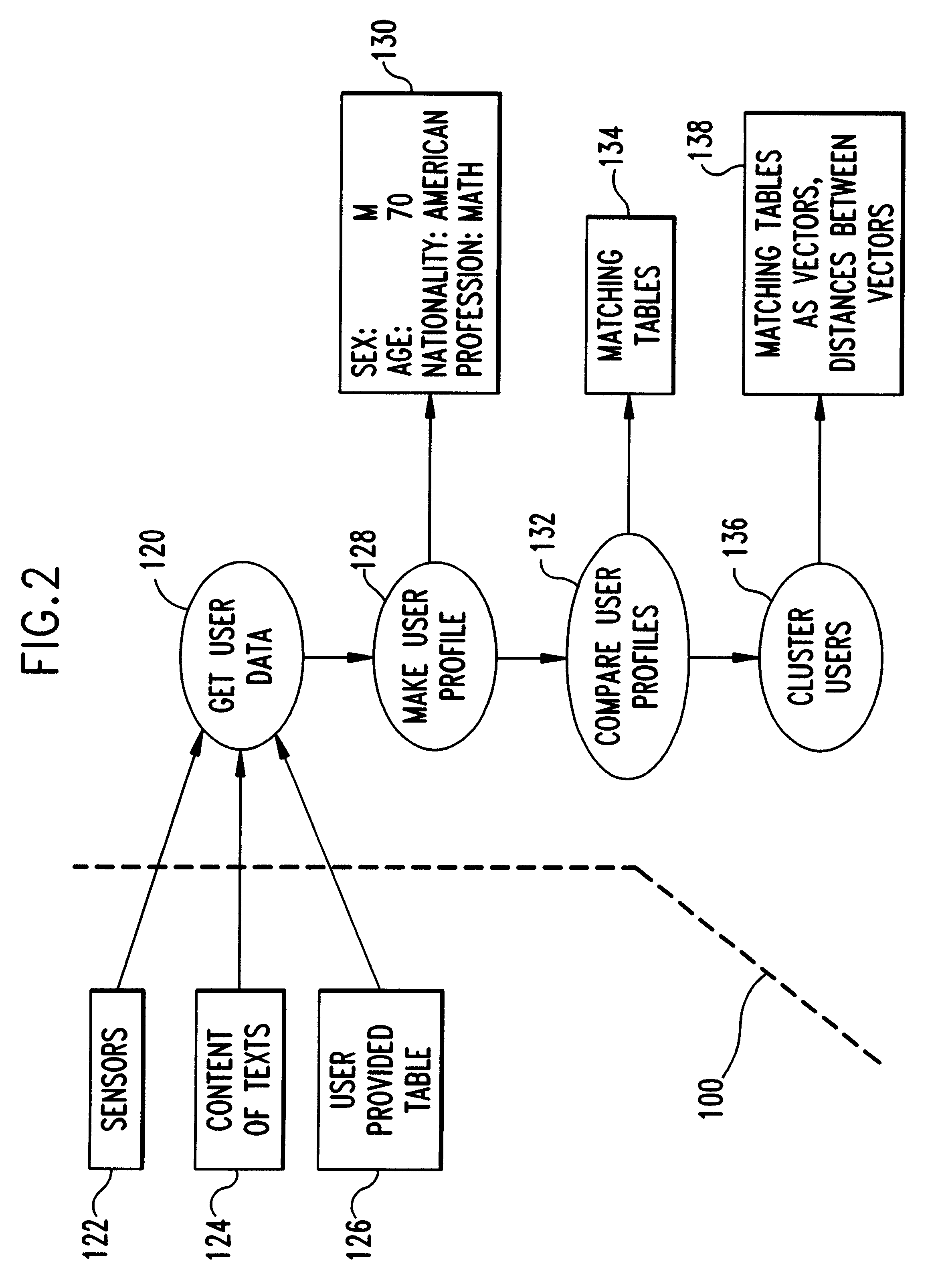
A language recognition system, method and program product for recognizing language based input from computer users on a network of connected computers. Each computer includes at least one user based language model trained for a corresponding user for automatic speech recognition, handwriting recognition, machine translation, gesture recognition or other similar actions that require interpretation of user activities. Network computer users are clustered into classes of similar users according to user similarities such as, nationality, profession, sex, age, etc. User characteristics are collected by sensors and from databases and, then, distributed over the network during user activities. Language models with similarities among similar users on the network are identified. The language models include a language model domain, with similar language models being clustered according to their domains. Language models identified as similar are modified in response to user production activities. After modification of one language model, other identified similar language models are compared and adapted. Also, user data, including information about user activities and language model data, is transmitted over the network to other similar users. Language models are adapted only in response to similar user activities, when these activities are recorded and transmitted over the network. Language models are given a global context based on similar users that are connected together over the network.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
Licensed application installer
InactiveUS6948168B1Data processing applicationsSoftware engineeringComputer terminalApplication software
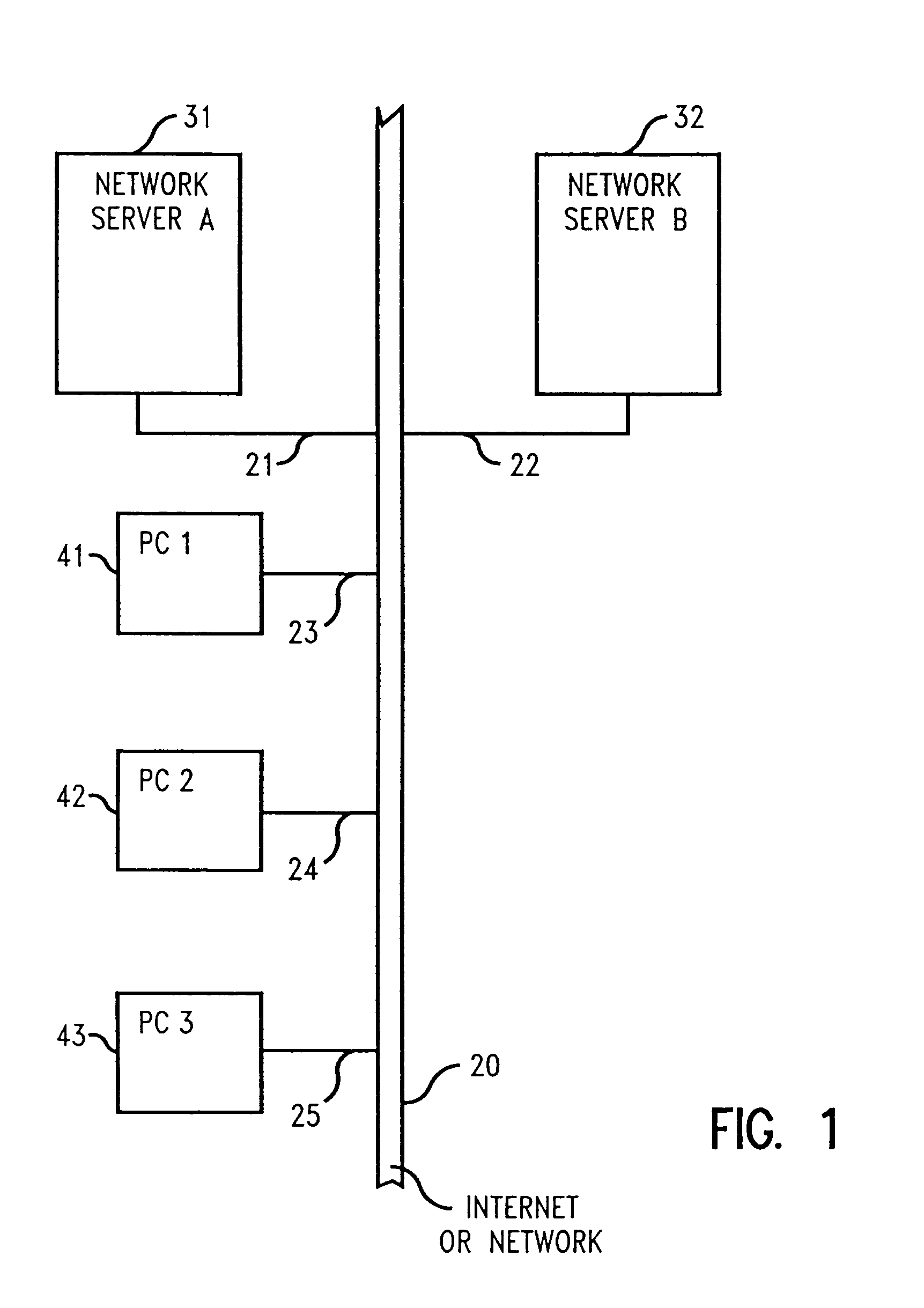
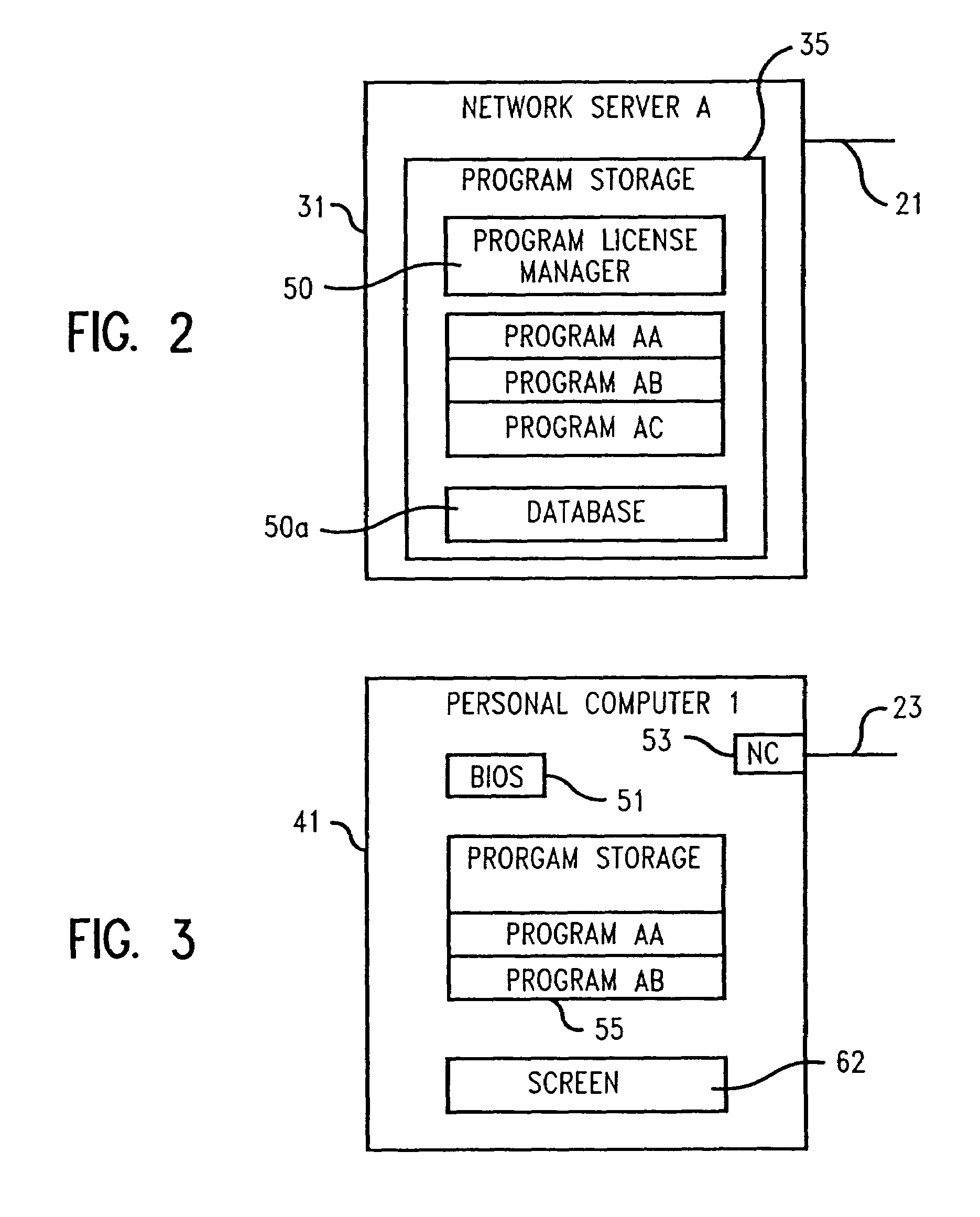
A method and system of installing licensed software on an end user's computer comprising having a program storage device and a unique computer identifier distinguishing the end user computer from other computers, e.g., a BIOS serial number or a network adapter address. The network computer contains a plurality of different software for license to end users and a database listing computer identifiers licensed to run the software. The end user computer sends to the network computer a command to run a program identifying to the end user computer the software listed as licensed by the computer identifier of the end user computer. The network computer contacts the end user computer and determine its end user computer identifier, verifies listing of the end user computer identifier in the network computer database, and identifies to the end user computer all of the software on the network computer program storage device listed as licensed by the computer identifier of the end user computer using an executable program on the network computer. The end user computer sends to the network computer a selection of the software to be downloaded. The network computer downloads the selected software and installs it on the end user computer program storage device.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
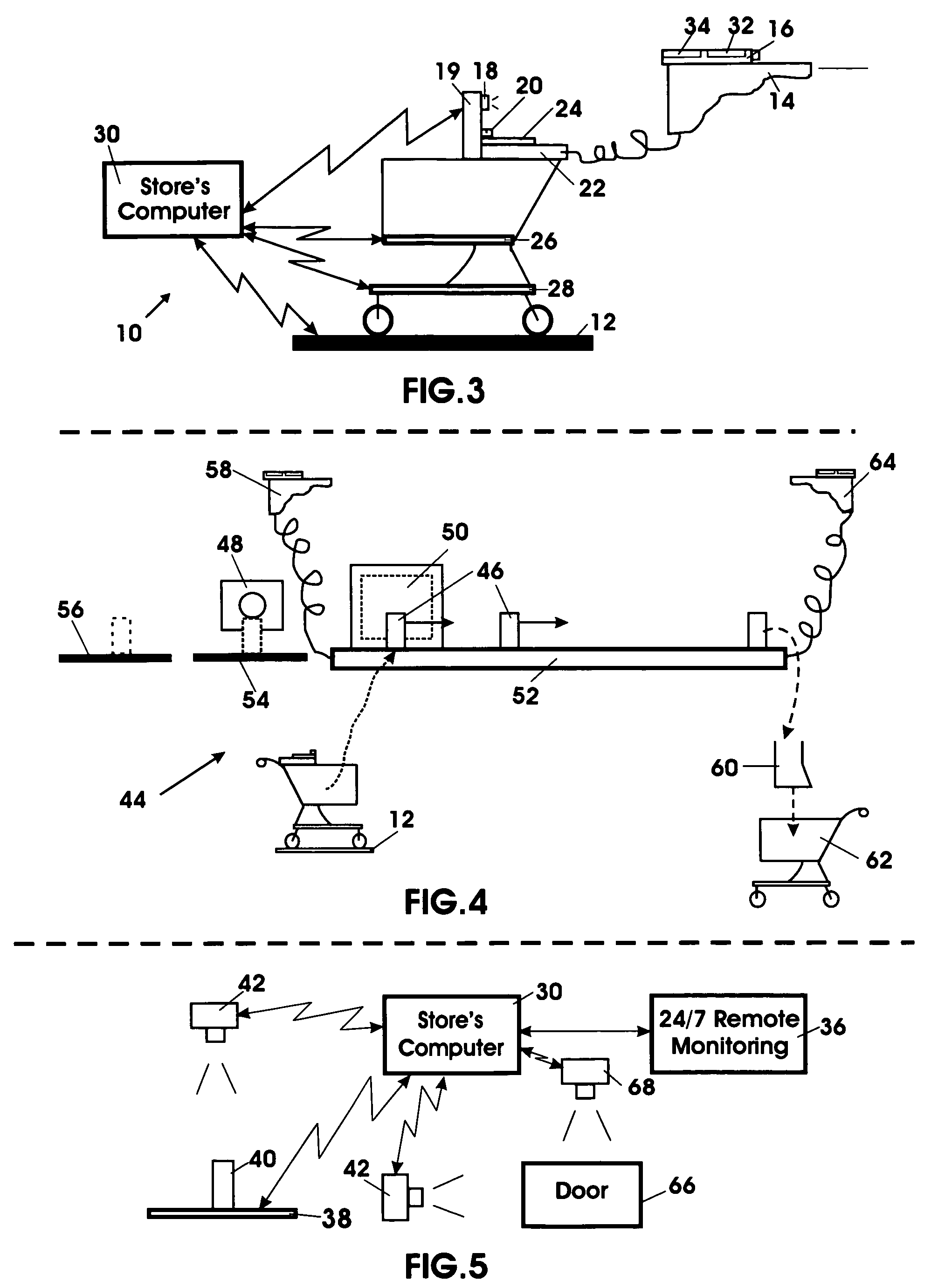
System and method for security protection, inventory tracking and automated shopping cart checkout
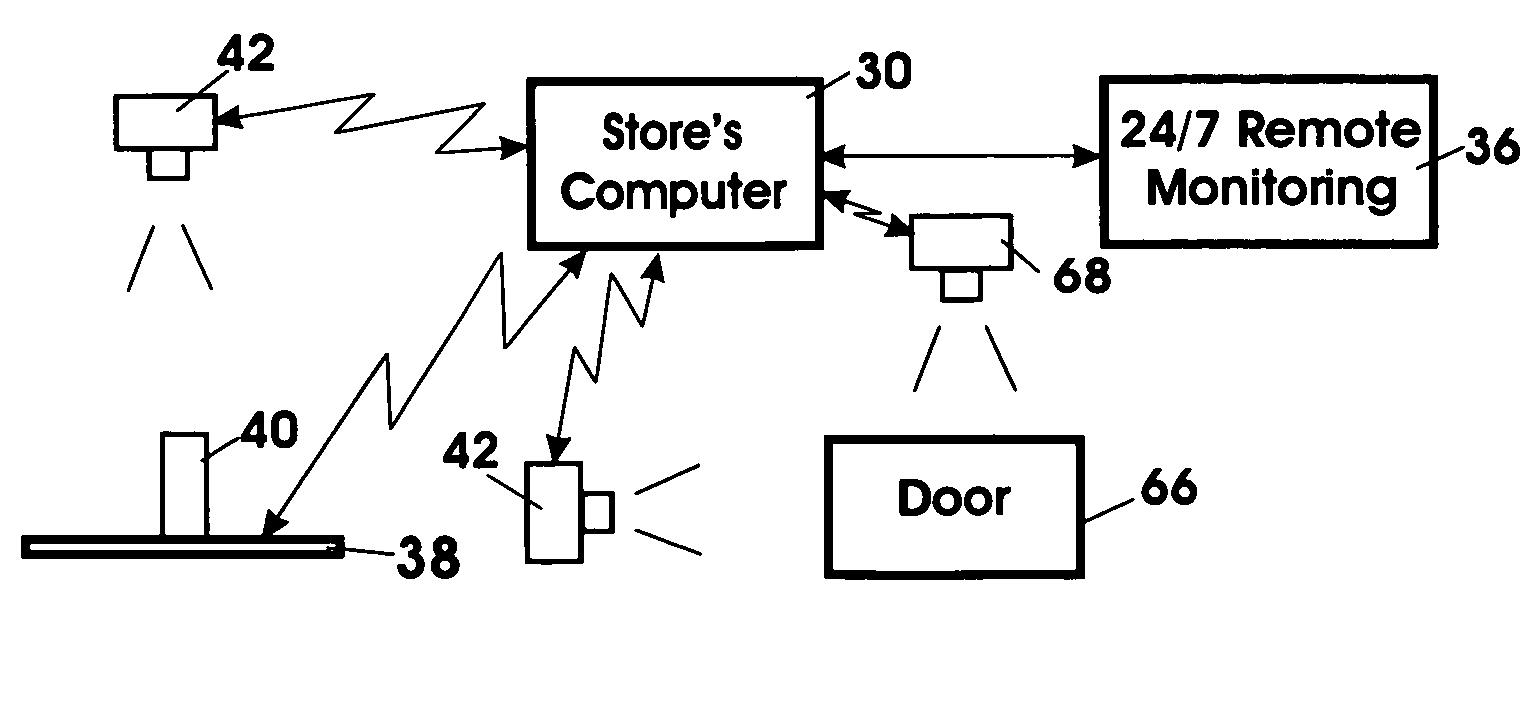
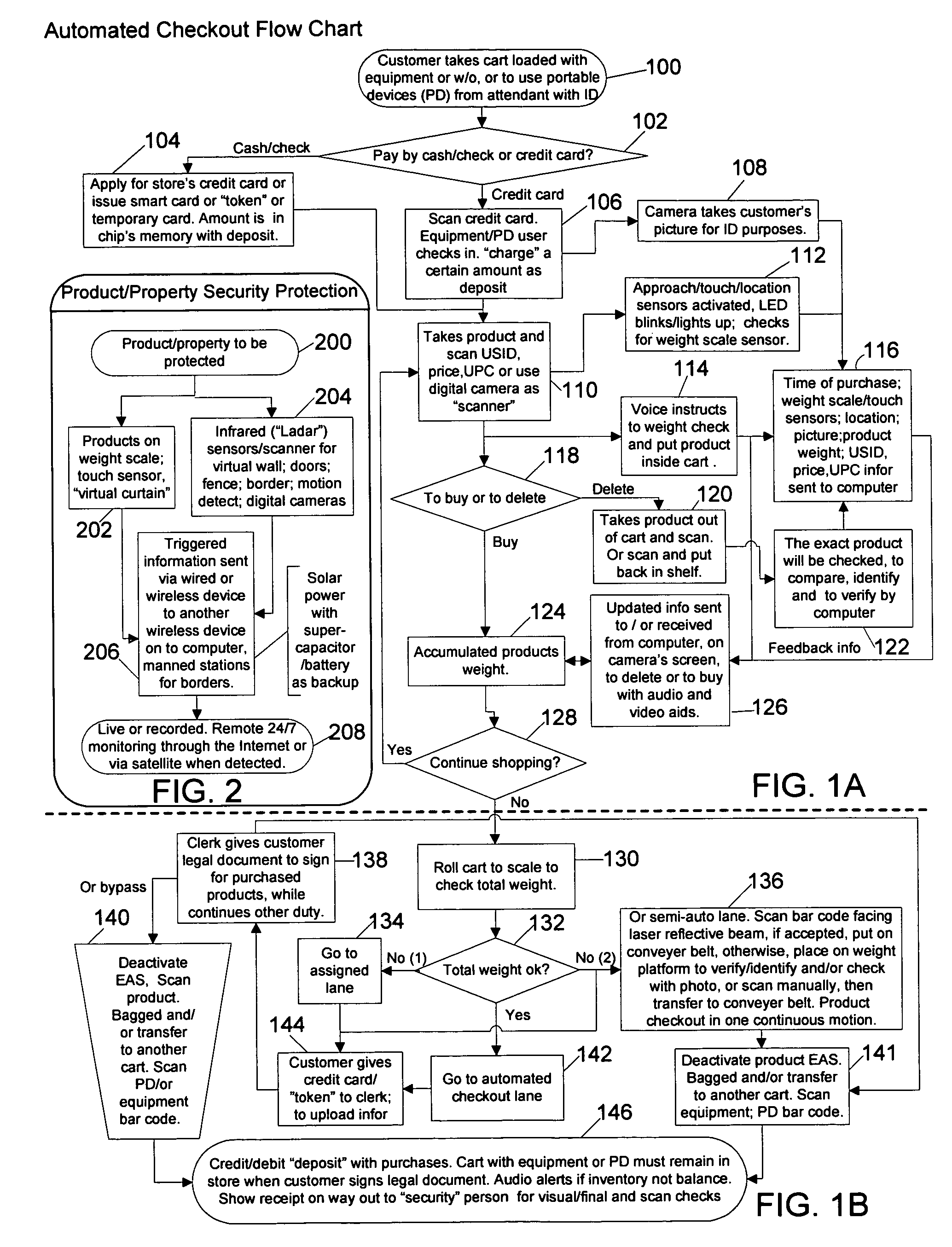
The three major problems of retail / wholesale industry, i.e. Security, Inventory, Self CheckOut (SISCO) are achieved by “virtual salesperson” and provided by synergism techniques of 5W's (Weight, Who, What, Where and When). A system that includes combination of steps and / or means for uniquely identifying each and every product (UPC / USID indicium), at a vendor retail premises; steps and / or means for protecting the product / property (brain-like recognition); steps and / or means for detecting / registering a product at a vendor retail premises that has been taken from its storage or display location; steps and / or means for registering that the product has been put into a customer's shopping cart; steps and / or means for tracking customer's location with a unique ID tagging wireless device to a shopping cart; steps and / or means for automatically transacting a purchase of the product, steps and / or means for paying for the product at the vicinity of the products location with laptop / net computers at both ends of exit aisle and / or more computers at convenient places with attached scanner and card payment device; steps and / or means for notifying the customer to pay if the product has not been properly or timely paid for; any missed / unwanted items will be accounted for at reduced manned checkout stations, to received itemized purchases receipt and to sign signature, and steps and / or means for customer ID checking in and checking out by “security guard” wirelessly scans customer's receipt for inventory / security tracking.
Owner:RCL PRODS
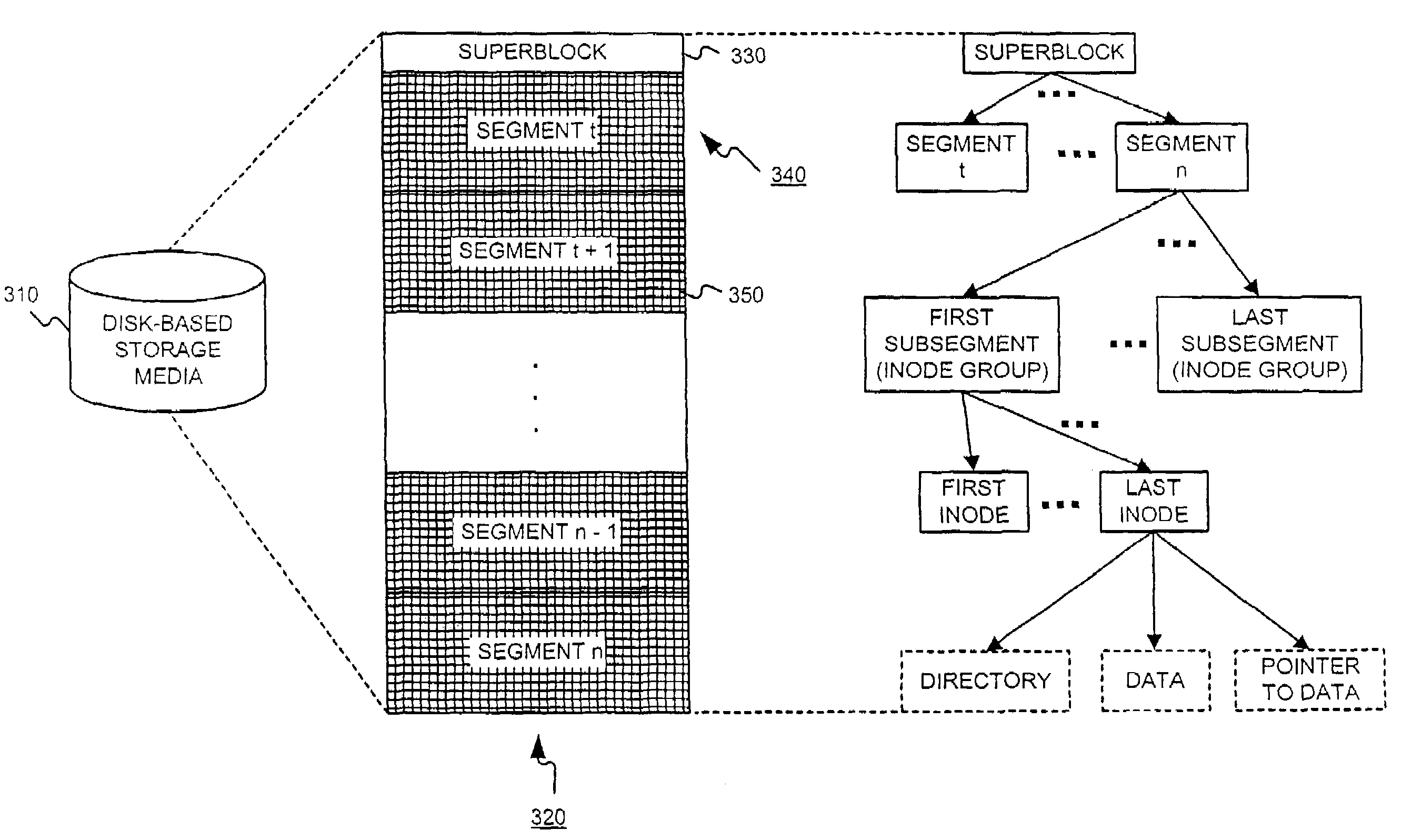
Distributing files across multiple, permissibly heterogeneous, storage devices
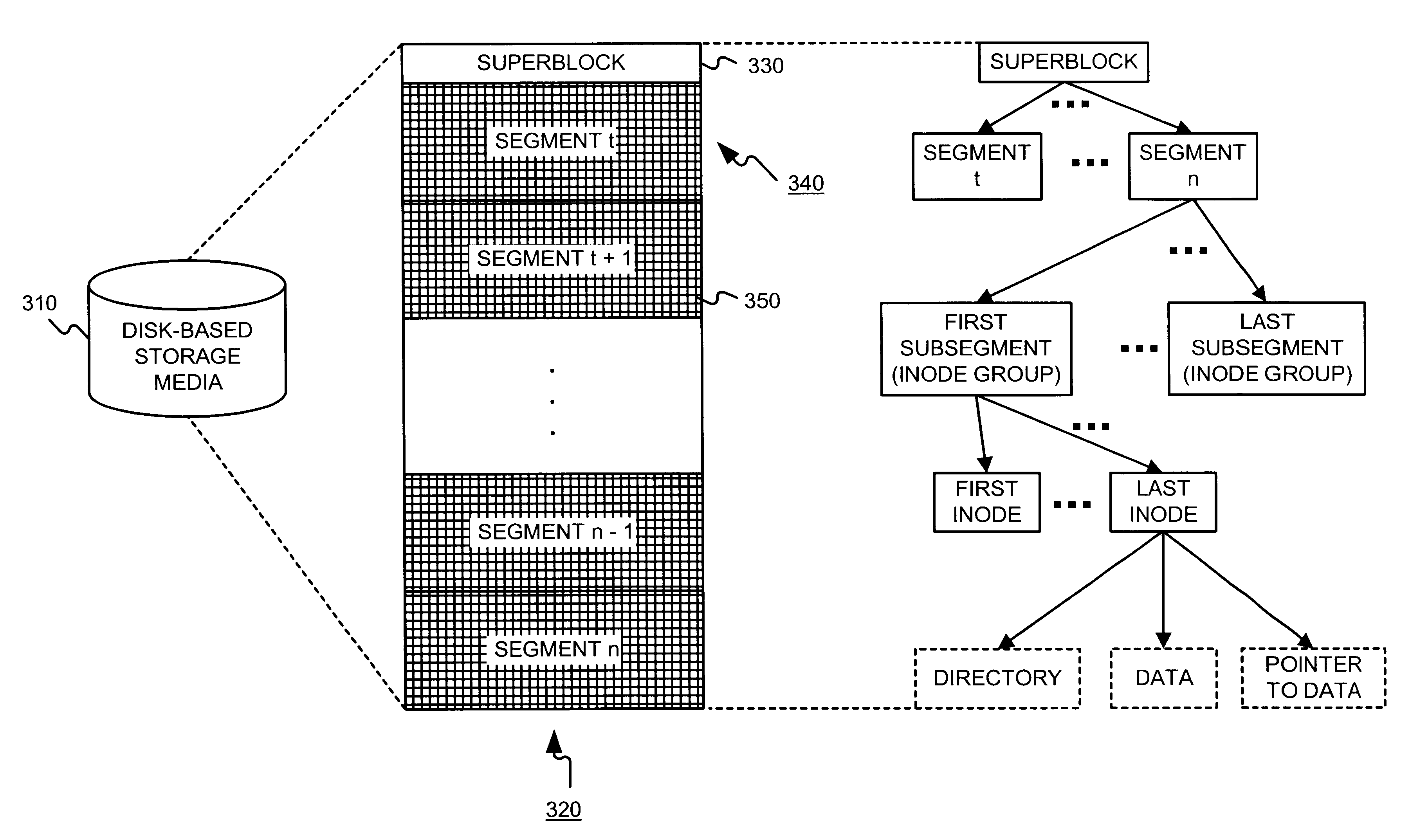
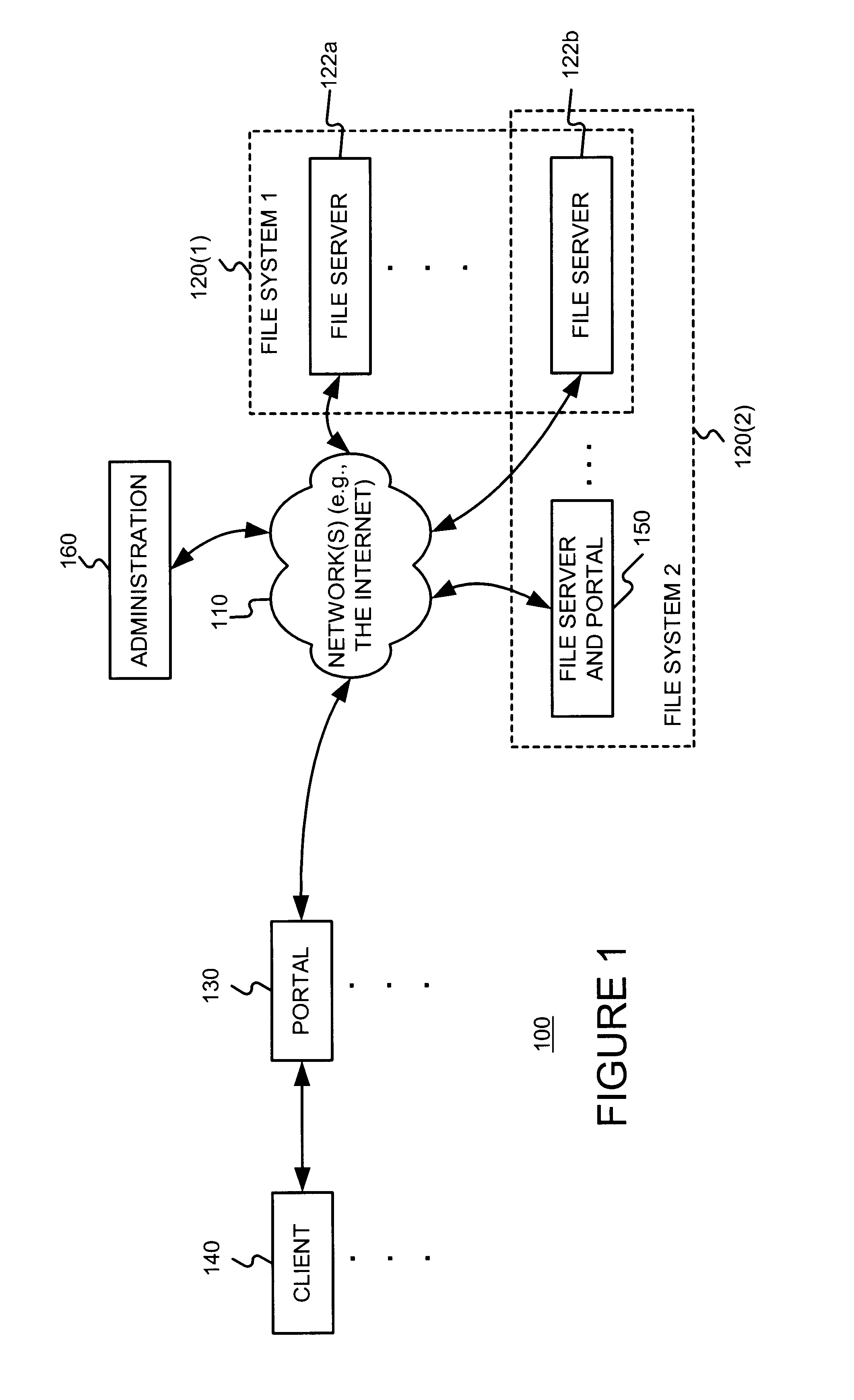
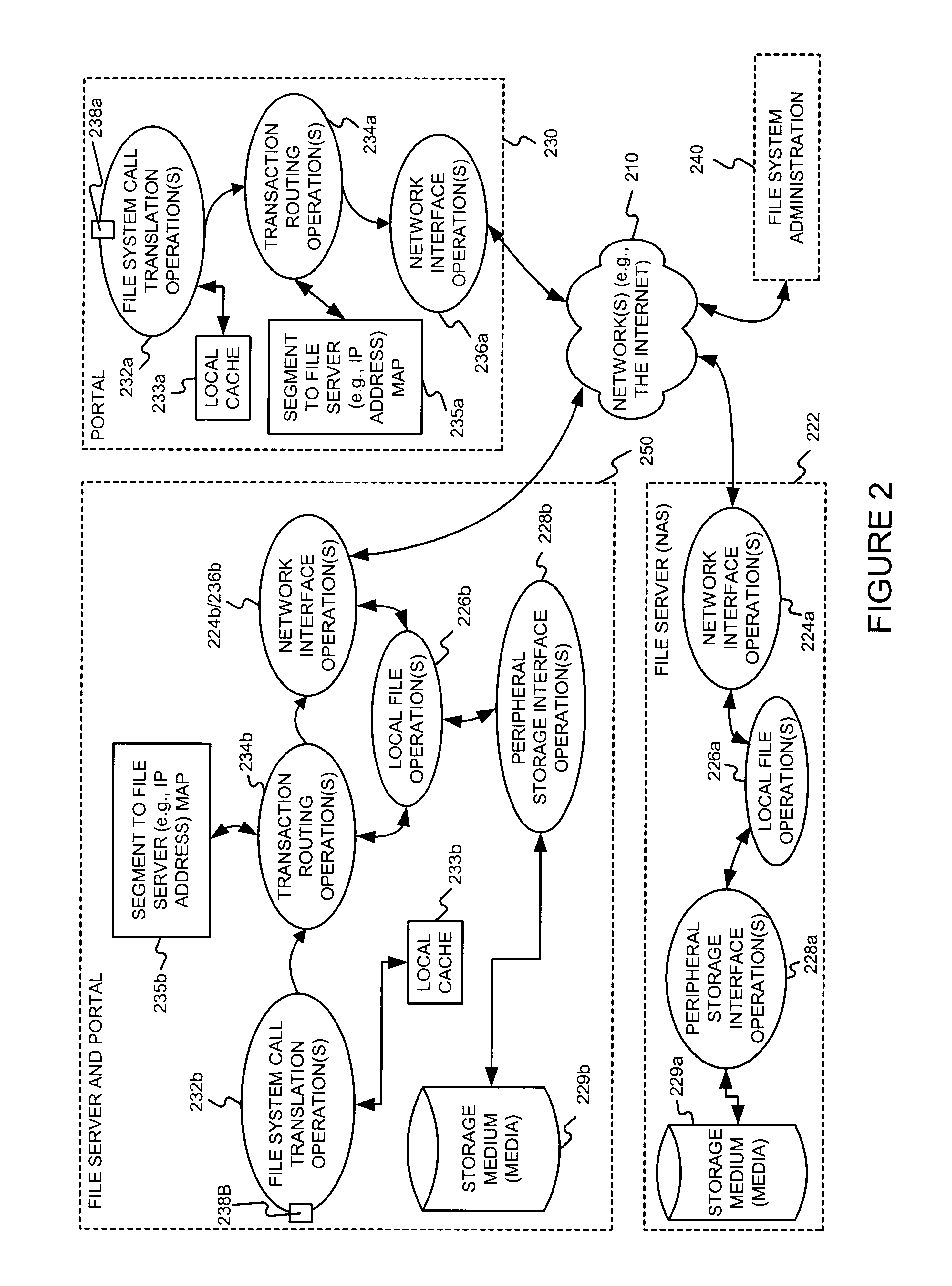
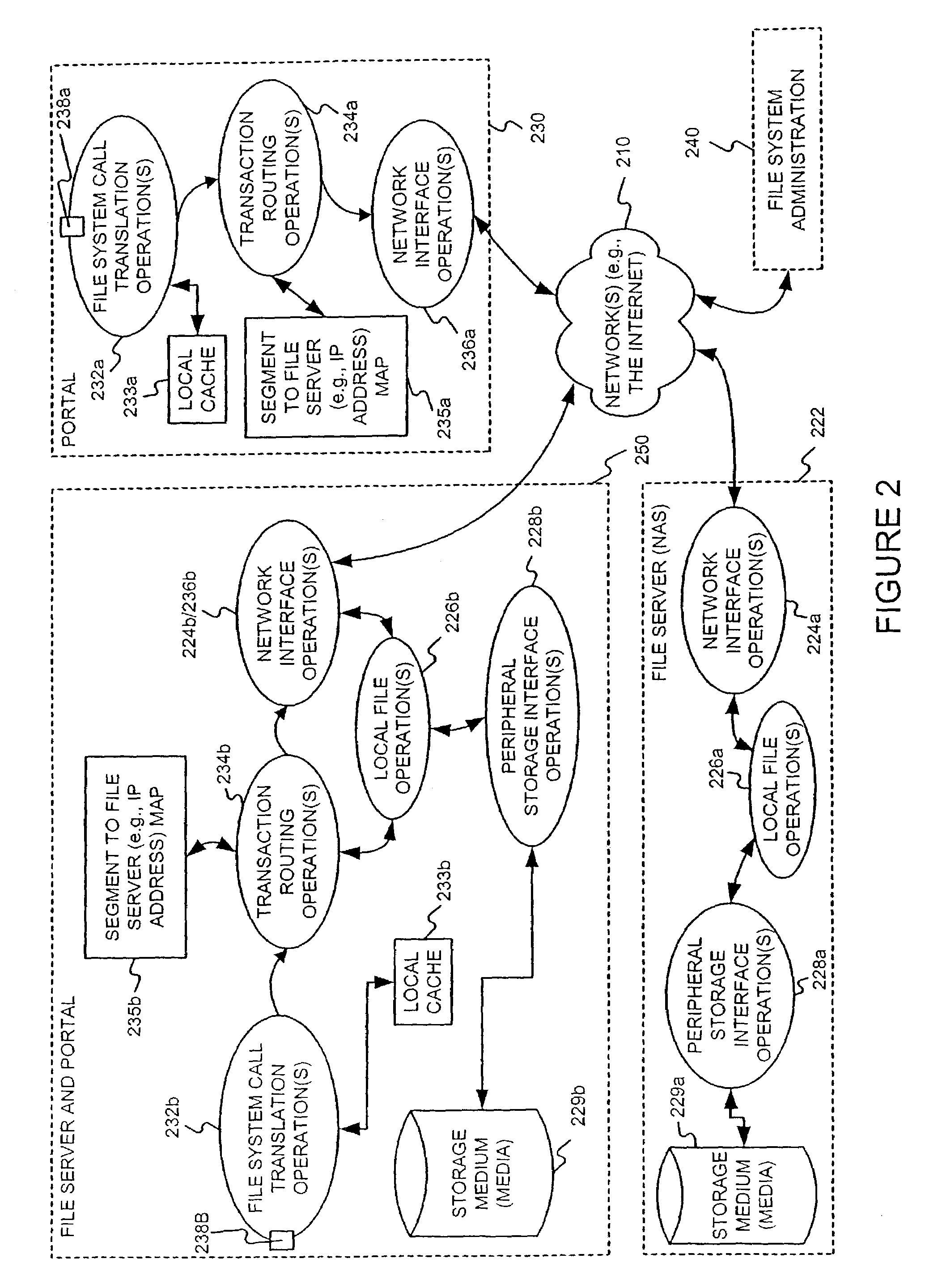
A file system (i) permits storage capacity to be added easily, (ii) can be expanded beyond a given unit, (iii) is easy to administer and manage, (iv) permits data sharing, and (v) is able to perform effectively with very large storage capacity and client loads. State information from a newly added unit is communicated (e.g., automatically and transparently) to central administration and management operations. Configuration and control information from such operations is communicated (e.g., automatically) back down to the newly added units, as well as existing units. In this way, a file system can span both local storage devices (like disk drives) and networked computational devices transparently to clients. Such state and configuration and control information can include globally managed segments as the building blocks of the file system, and a fixed mapping of globally unique file identifiers (e.g., Inode numbers) and / or ranges thereof, to such segments.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
System, method and program product for account transaction validation
A system, method and program product for account transaction validation which may be downloaded or otherwise installed on a networked computing device such as a cell phone or other networked computing device. The networked computing device provides an encrypted validation code to a merchant for each transaction. The validation code is uniquely computed for each transaction and may be based on transaction time and / or other transaction data. The code algorithm is unique for each cardholder. Only the bank transaction center has knowledge of the particular algorithm for each cardholder. When transaction details such as transaction dollar amount are included in the generation of the code, the code may be used to validate the reported transaction dollar amount. An algorithm is disclosed for generating a unique code based on time and / or transaction dollar amount.
Owner:LOVETT ROBERT
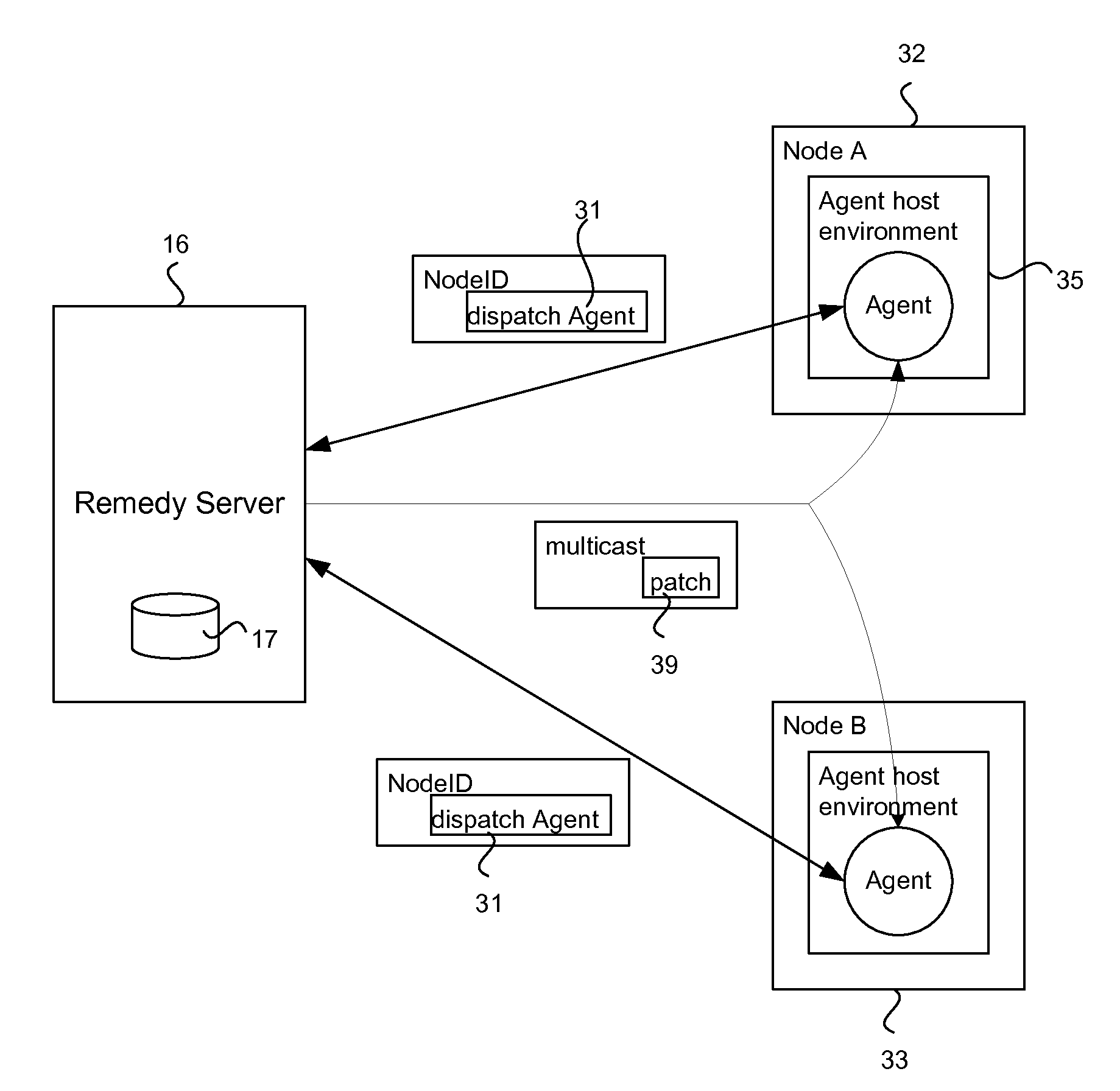
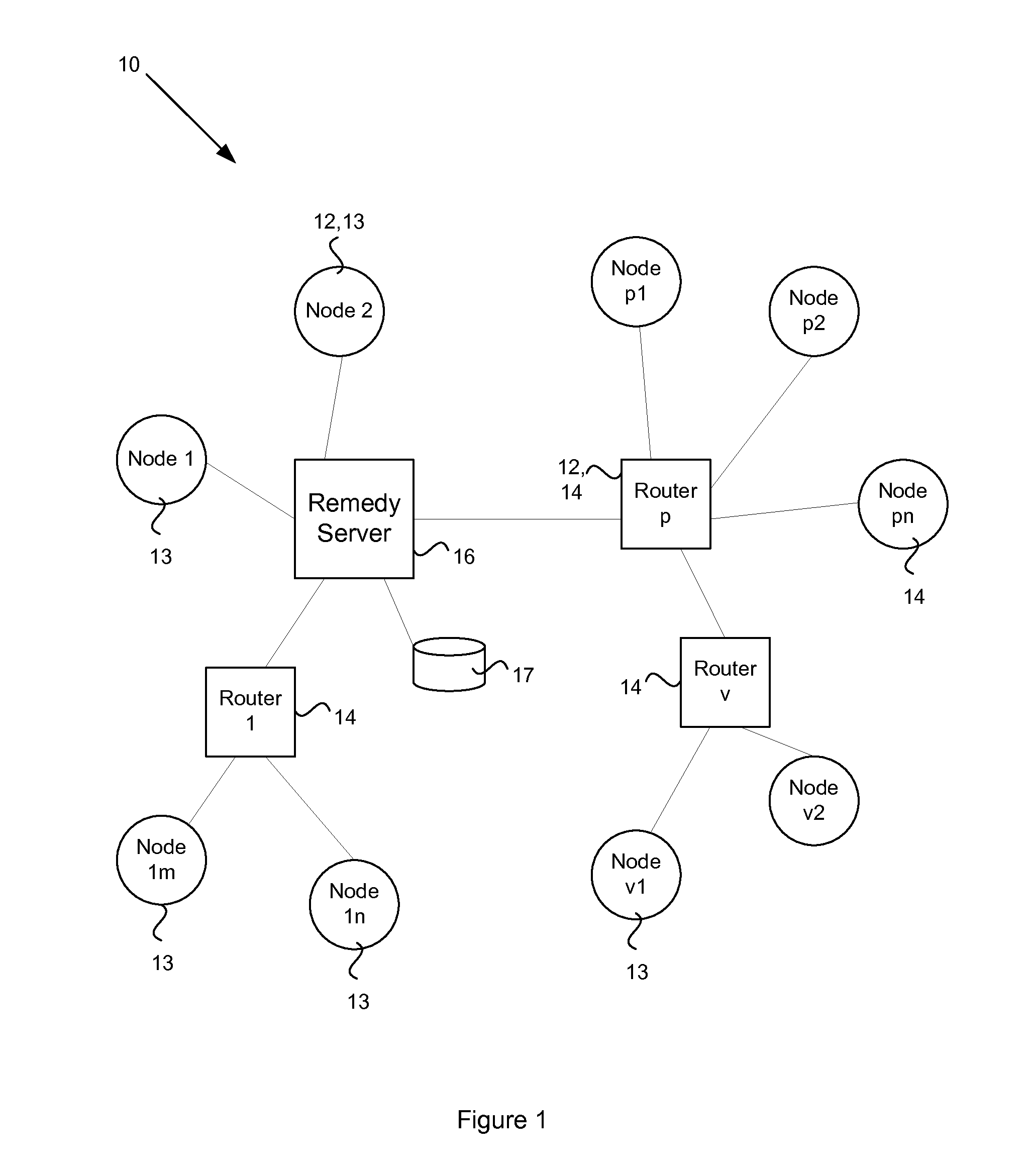
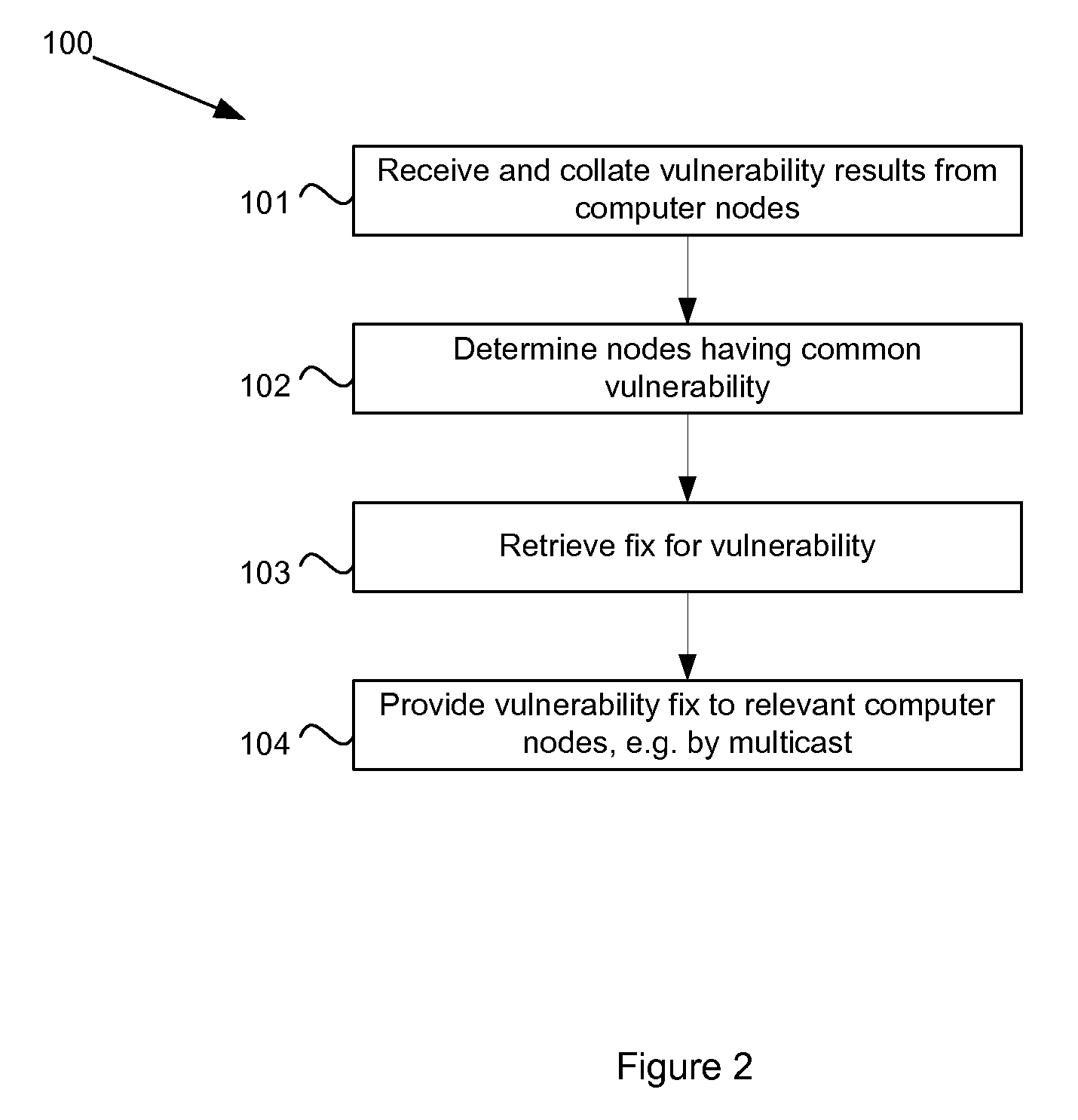
System and method for resolving vulnerabilities in a computer network
InactiveUS20110138469A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionSecurity levelComputer science
In a computer network, a remedy server may be provided that controls vulnerability scans of the computer nodes. The remedy server determines a security level of a computer node and dispatches an agent to the node with a scan matching the security level. The agent executes the scan and reports the scan results to the remedy server. The remedy server collates scan results from a plurality of the network computers and determines which computers have a common vulnerability. A fix for the vulnerability, such as an executable patch file, is retrieved and multicast to those relevant computers.
Owner:OSOCAD REMOTE LIABILITY
Storage allocation in a distributed segmented file system
InactiveUS7406484B1Efficient executionStorage capacity can be easilyData processing applicationsTransmissionInodeData sharing
A file system (i) permits storage capacity to be added easily, (ii) can be expanded beyond a given unit, (iii) is easy to administer and manage, (iv) permits data sharing, and (v) is able to perform effectively with very large storage capacity and client loads. State information from a newly added unit is communicated (e.g., automatically and transparently) to central administration and management operations. Configuration and control information from such operations is communicated (e.g., automatically) back down to the newly added units, as well as existing units. In this way, a file system can span both local storage devices (like disk drives) and networked computational devices transparently to clients. Such state and configuration and control information can include globally managed segments as the building blocks of the file system, and a fixed mapping of globally unique file identifiers (e.g., Inode numbers) and / or ranges thereof, to such segments.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and apparatus for exchanging heartbeat messages and configuration information between nodes operating in a master-slave configuration
InactiveUS7421478B1Multiple digital computer combinationsNon-redundant fault processingMultiple applicationsComputer science
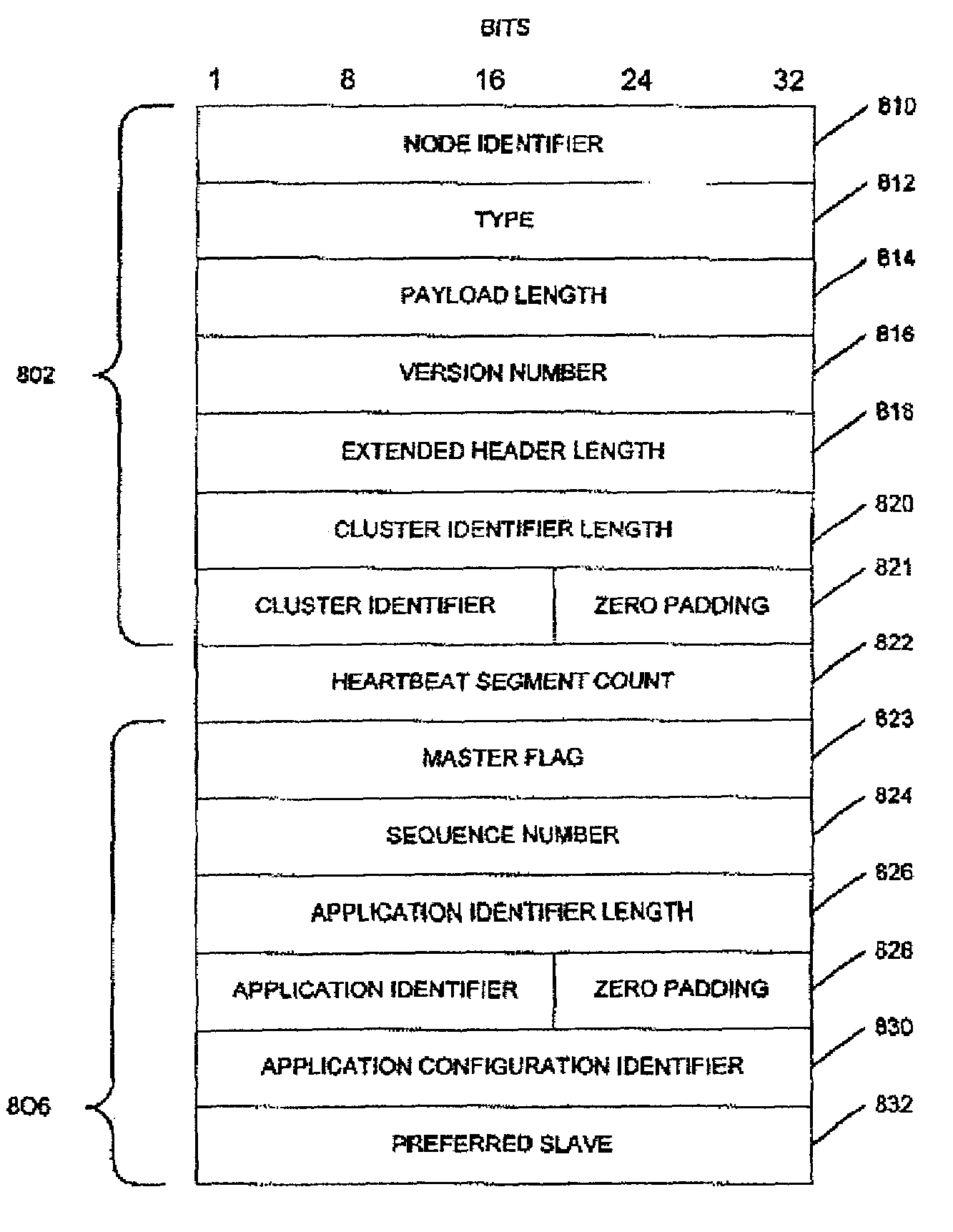
A node (101, FIG. 1), within a networked computer system (100), is capable of supporting communications with other nodes relating to operating multiple application instances in a master-slave configuration. Each node periodically generates and sends (520, 526, FIG. 5) a Heartbeat message (FIG. 8) that indicates the operational status for one or more application instances being managed by the node. When a node receives a Heartbeat message from a remote node, it evaluates (FIG. 10) the Heartbeat information for each application instance reported in the message, and takes any appropriate actions. The node also determines (1206, FIG. 12) whether new configuration information should be obtained for each of the application instances the node is managing, and requests (1210, FIG. 12) that new configuration information, when necessary.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
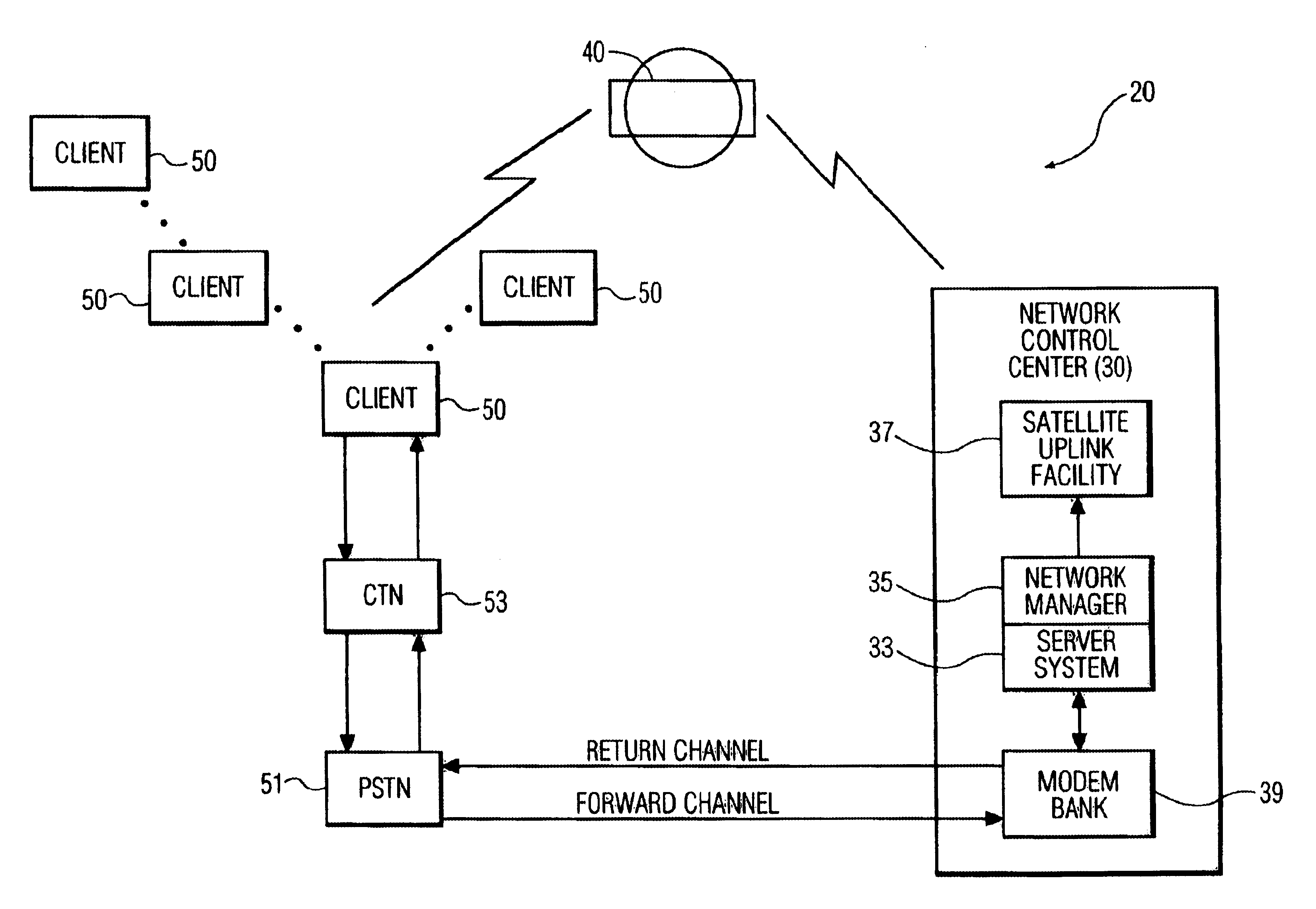
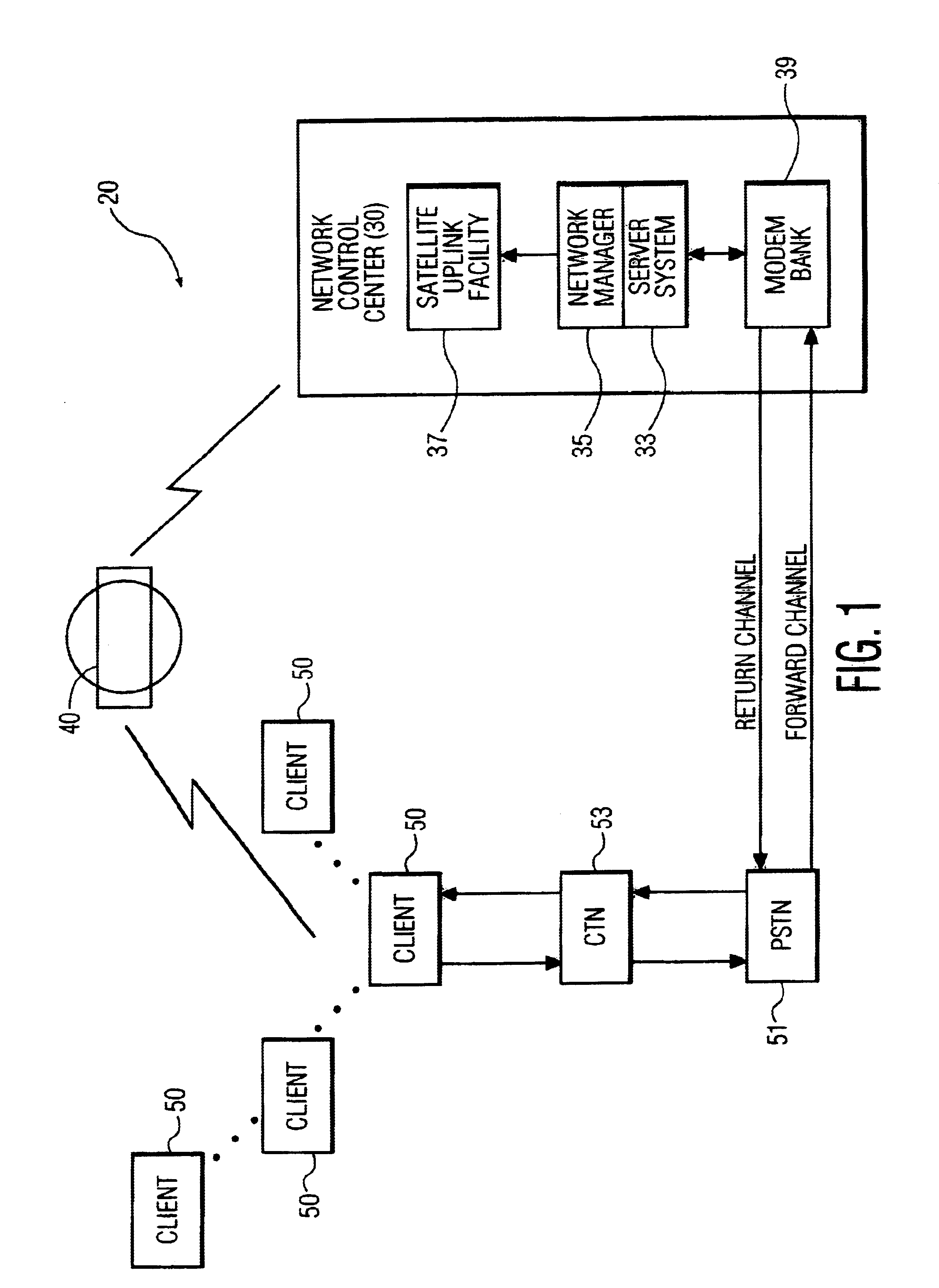
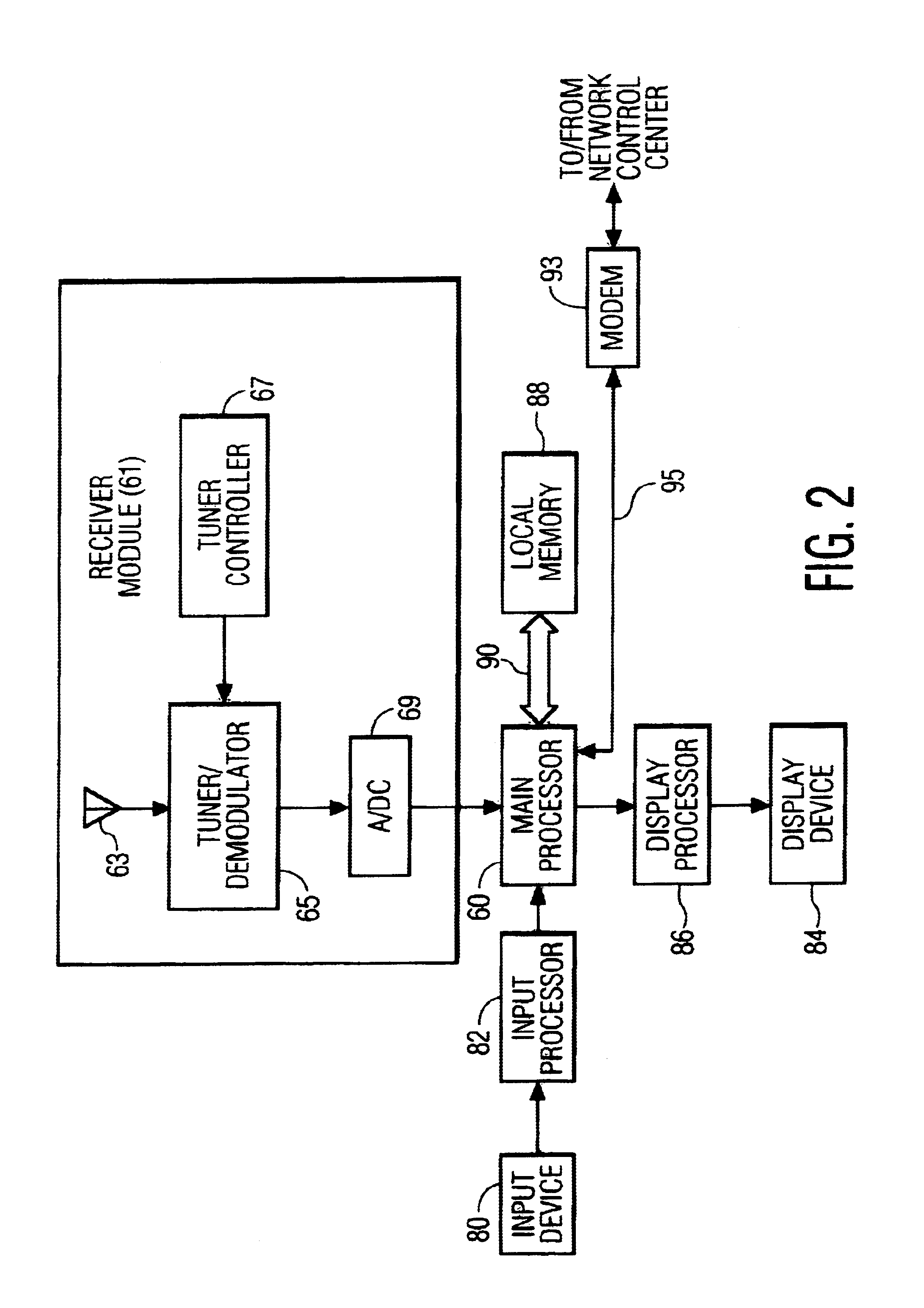
System for broadcasting software applications and portable data communications device for use in such a system
InactiveUS6928468B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsModem deviceApplication software
A communications system consisting of a server system that stores software applications, a broadcast system that broadcasts the software applications, and a multiplicity of portable clients that each include a receiver having a tuner that is selectively tunable to receive a selected one of the software applications broadcasted by the broadcast system. The portable clients can be any type of portable data communications device, such as a hand-held, palm-top, or notebook computing device, a PDA, an intelligent cellular phone, or any other personal multimedia appliance or Network Computer (NC). The broadcast system can be any suitable satellite or terrestrial air or cable broadcast system. The software applications can consist of a broad spectrum of different software applications, such as word processing, video games, spreadsheets, address books, calendars, and the like. Each of the portable data communications devices includes a receiver that has a tuner that is selectively tunable to receive a selected one of a plurality of software applications broadcasted by a broadcast system, a user-interface that enables a user to select one of the broadcasted software applications for downloading, a processor for executing the downloaded software applications, and a modem for establishing a two-way communications link with a network control system. The two-way communications link includes a forward channel over which the portable data communication device can transmit client data to the network control system, and a return channel over which the network control system can transmit system data to the portable data communication device. The client data can include requests for unrecoverable software application data and client software download request data.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
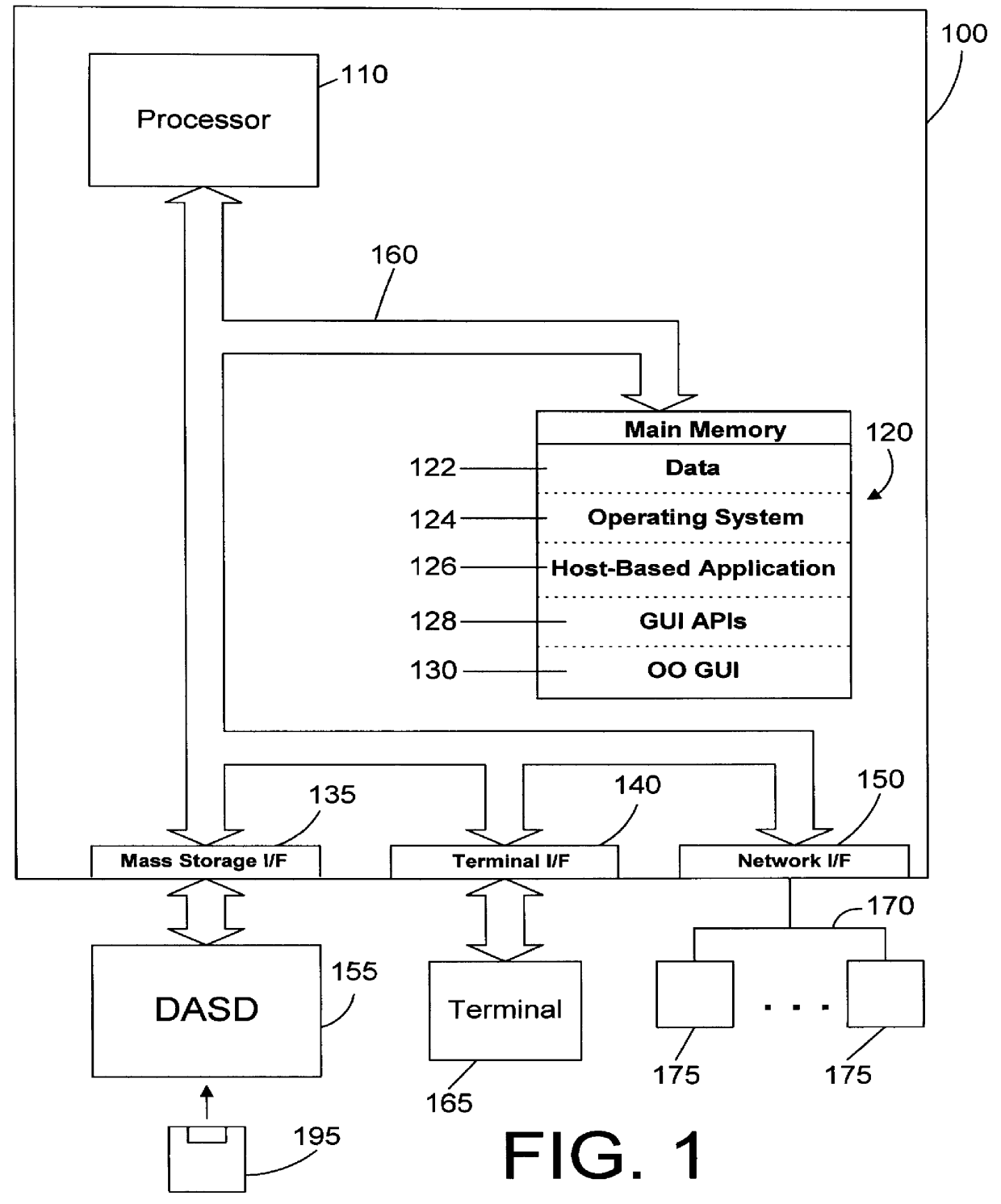
Object oriented apparatus and method for providing a graphical user interface for host-based software applications
InactiveUS6064382ANot affectQuickly and easily combined and re-usedMultiple digital computer combinationsExecution for user interfacesGraphicsGraphical user interface
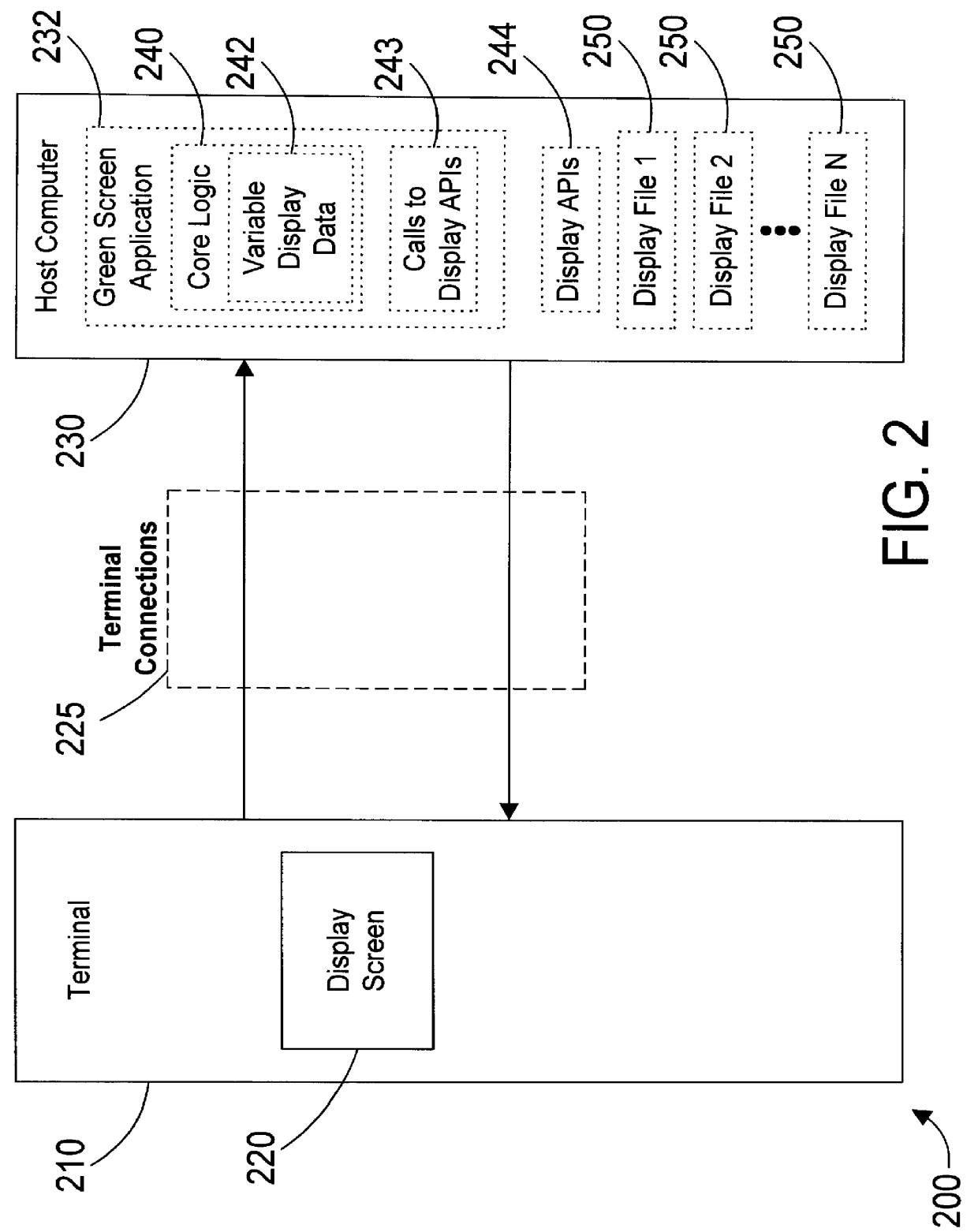
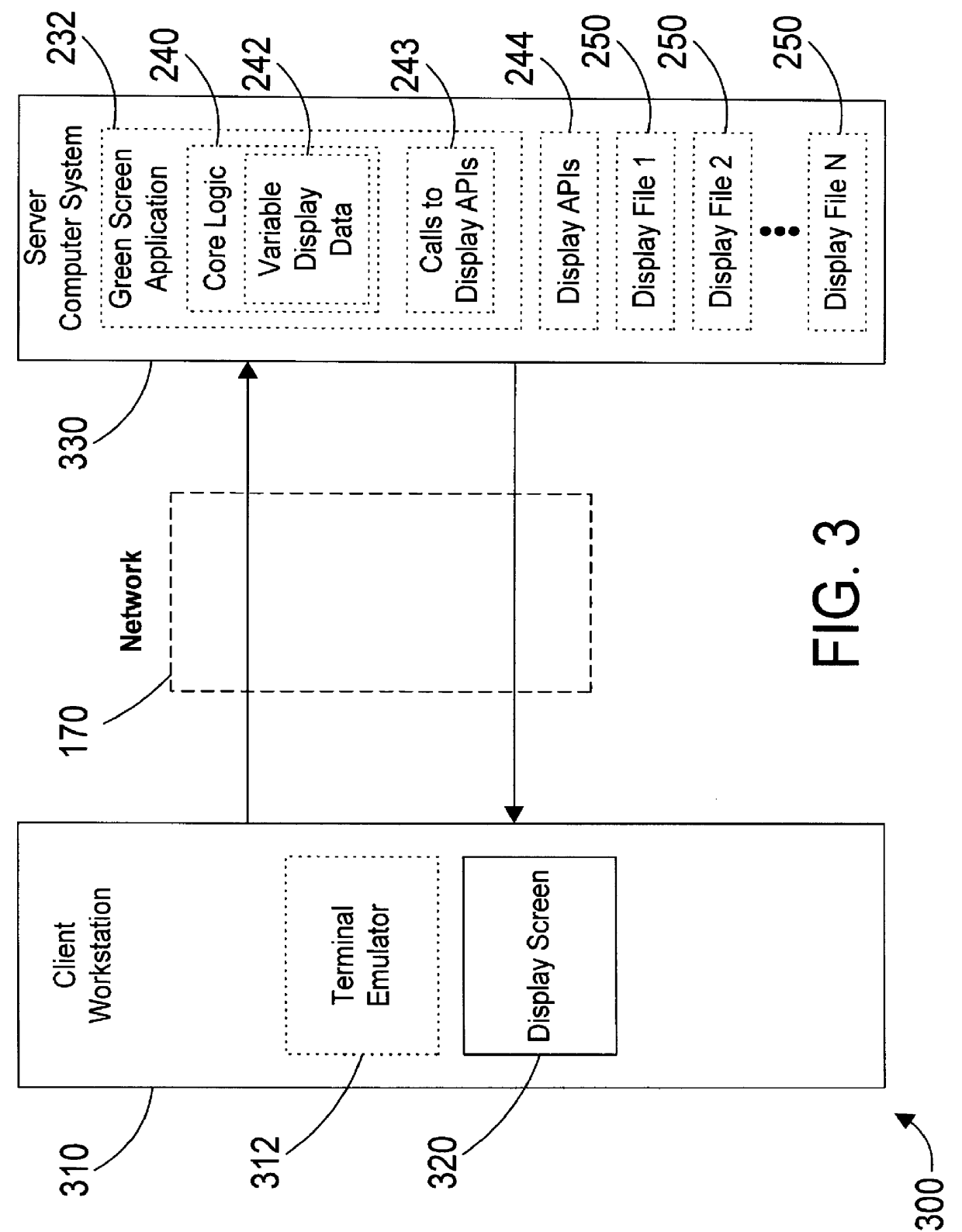
An object oriented computer apparatus and method provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for existing host-based (i.e., green screen) applications by defining some object oriented classes that reside on the client workstation, and by substituting function calls for display data in the green screen application with function calls that interface with the object oriented GUI defined by the classes. In this manner the present invention takes advantage of the processing power of client workstations in a network computing environment by having the client run the GUI. The underlying green screen application is modified to replace all display function calls with new function calls to the GUI, but this change is relatively minor and does not affect the underlying core logic of the application. In addition, the new function calls access the GUI screens directly without having to determine which screen is being displayed.
Owner:IBM CORP
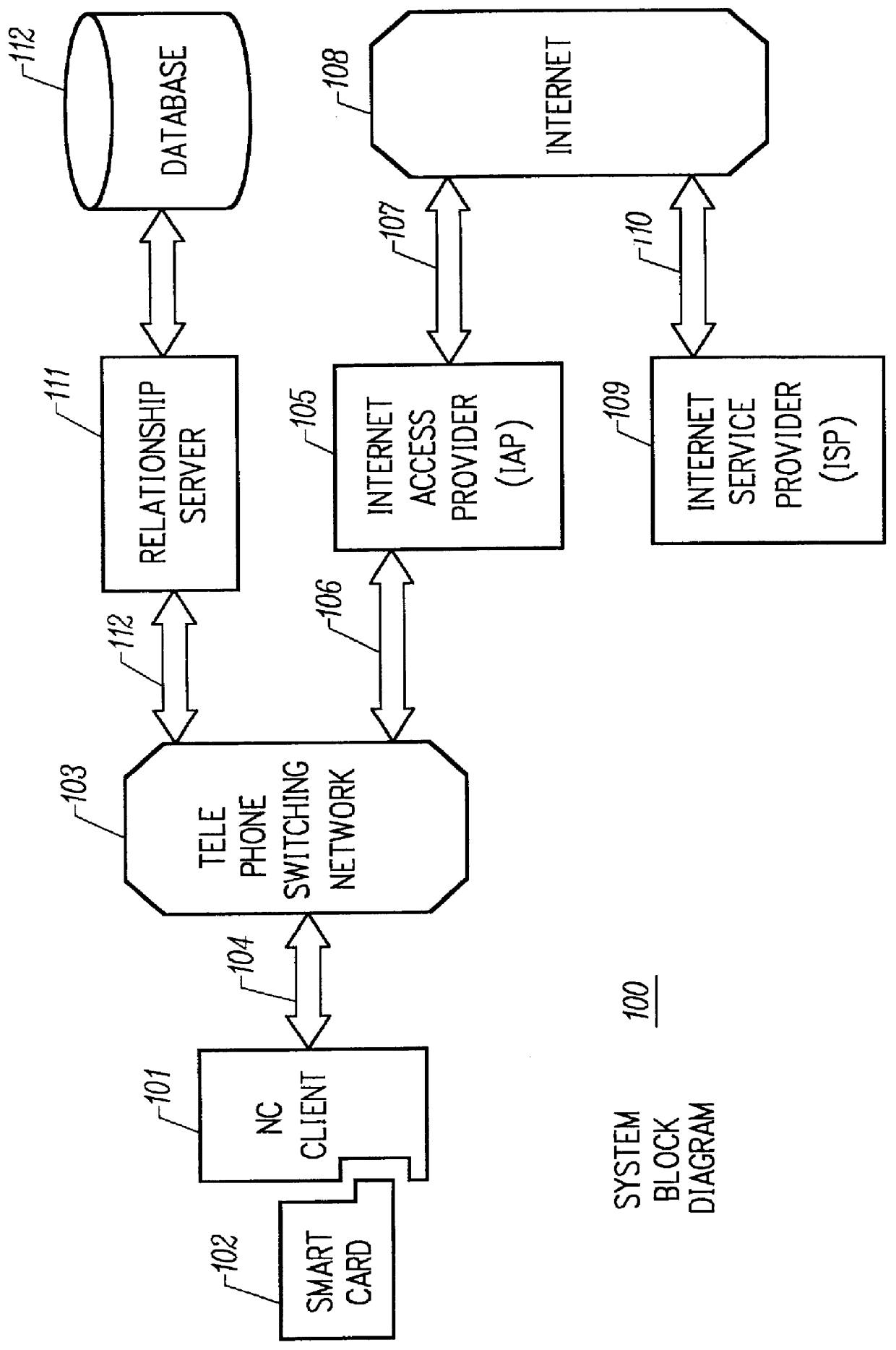
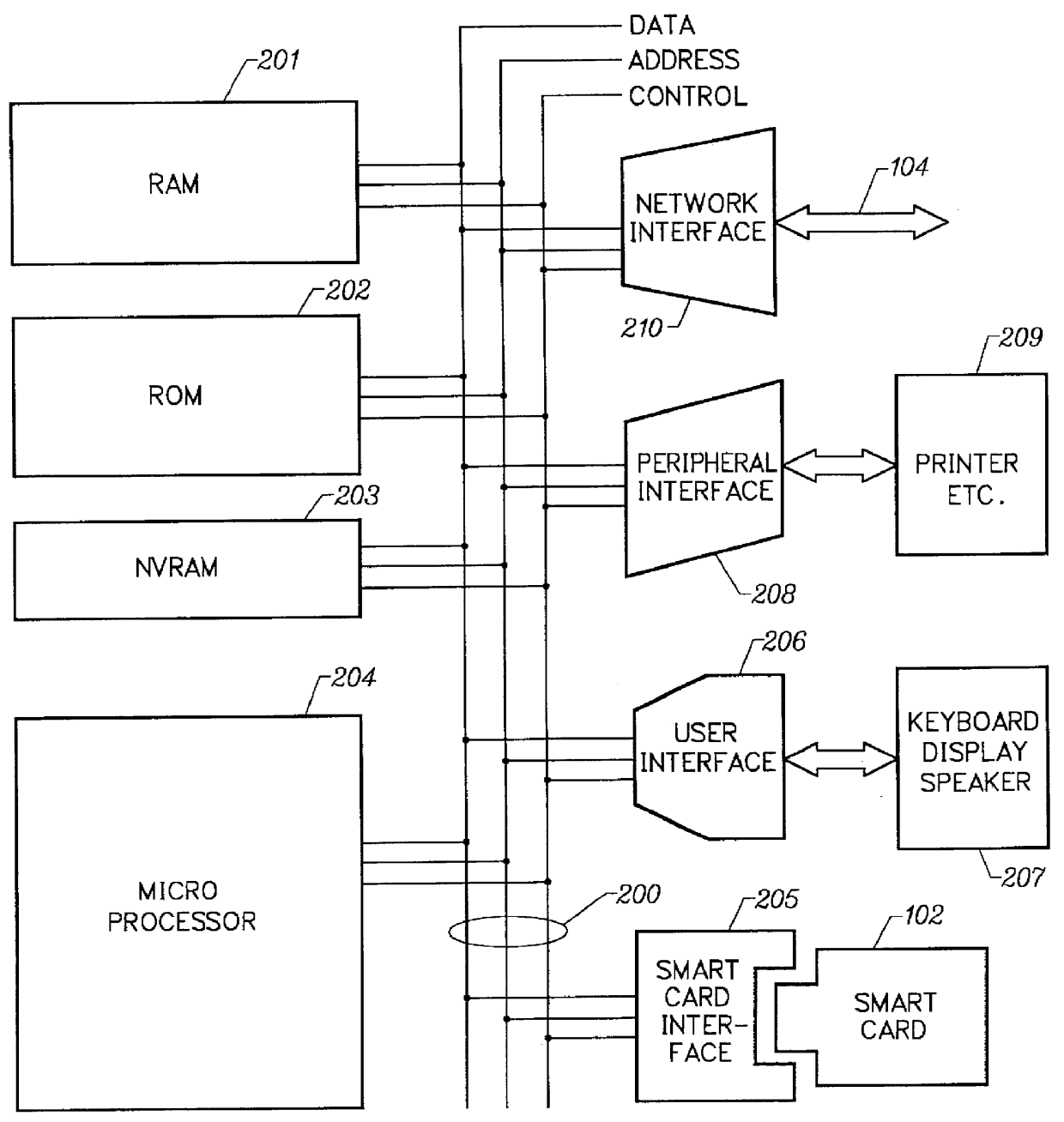
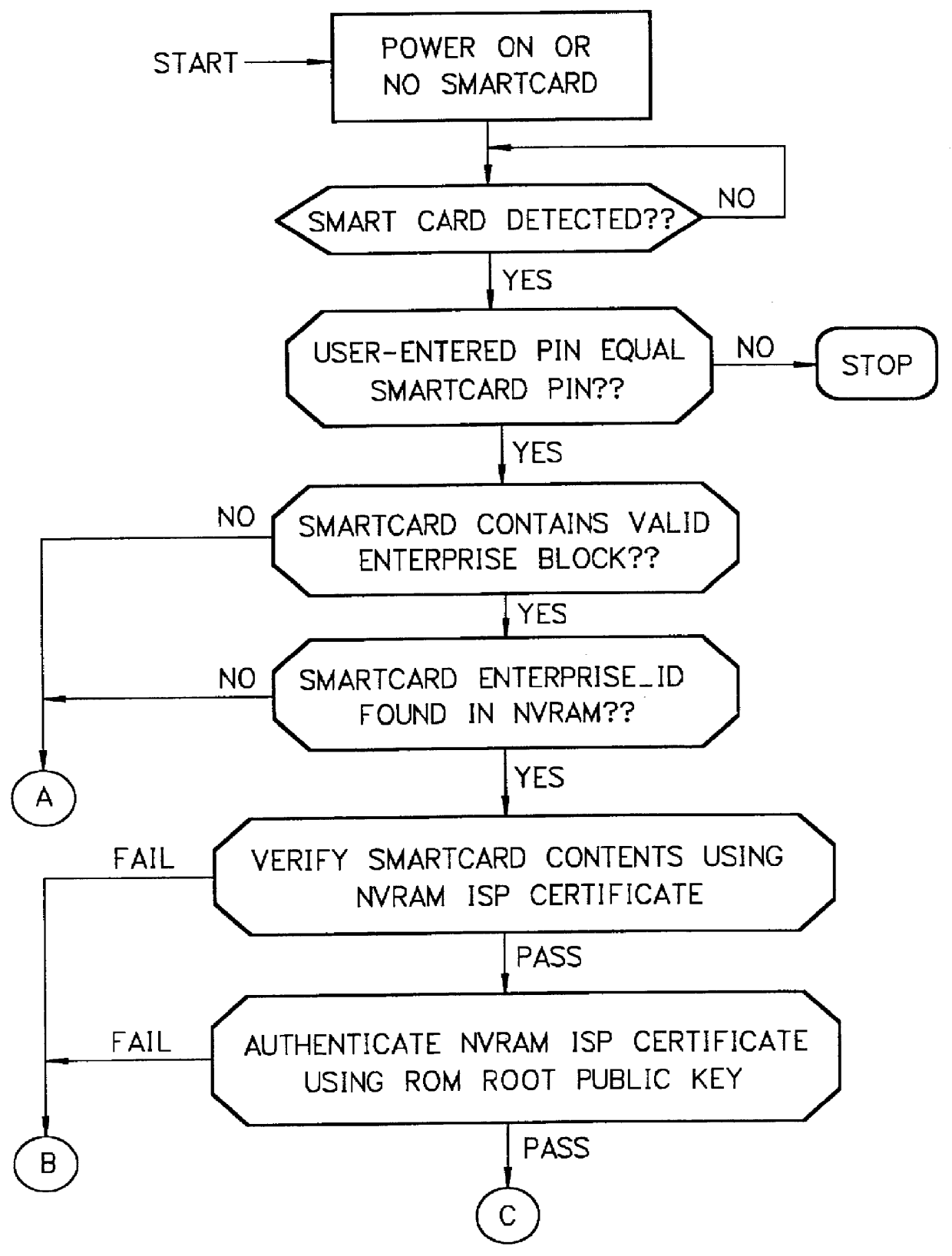
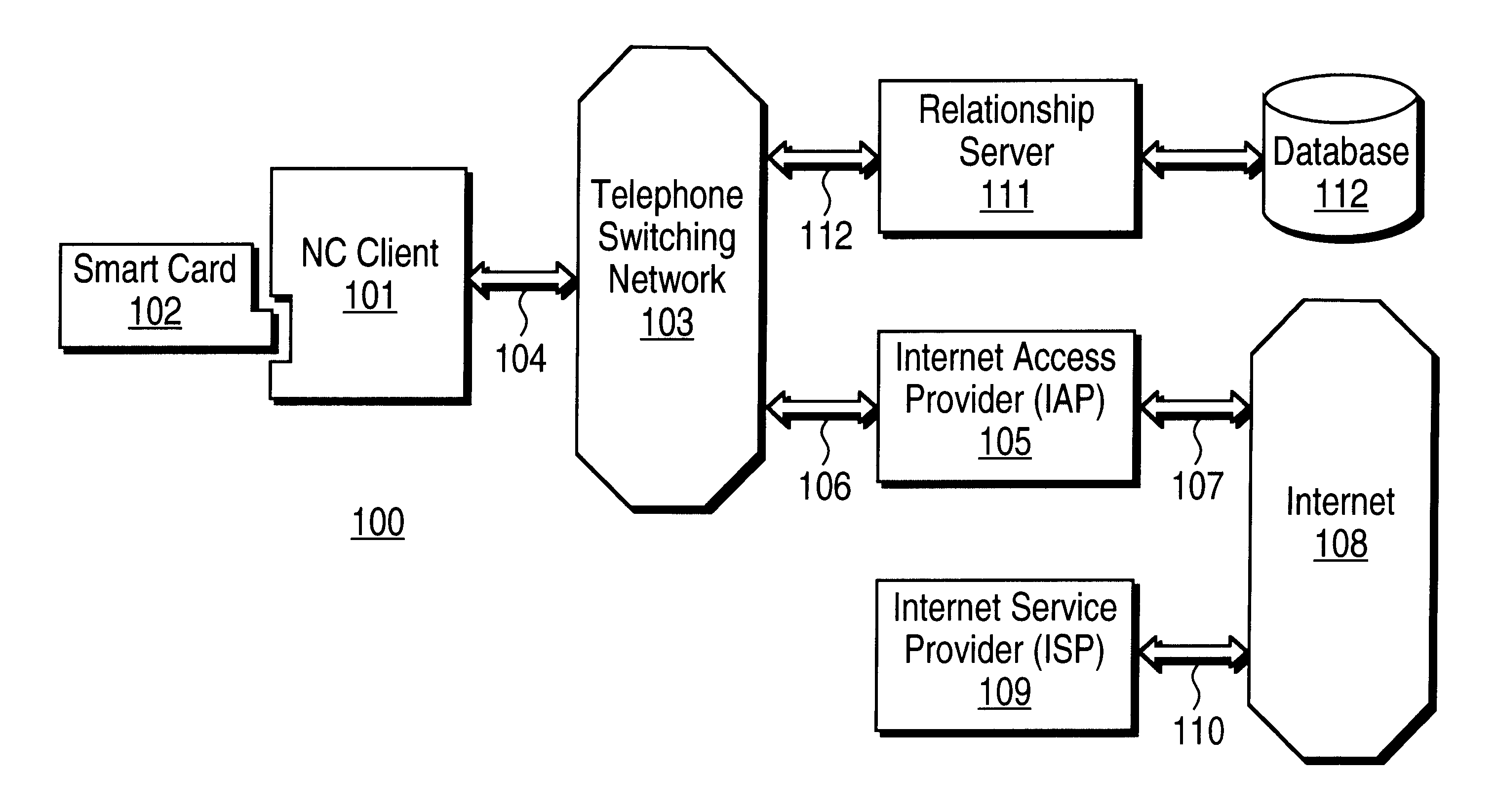
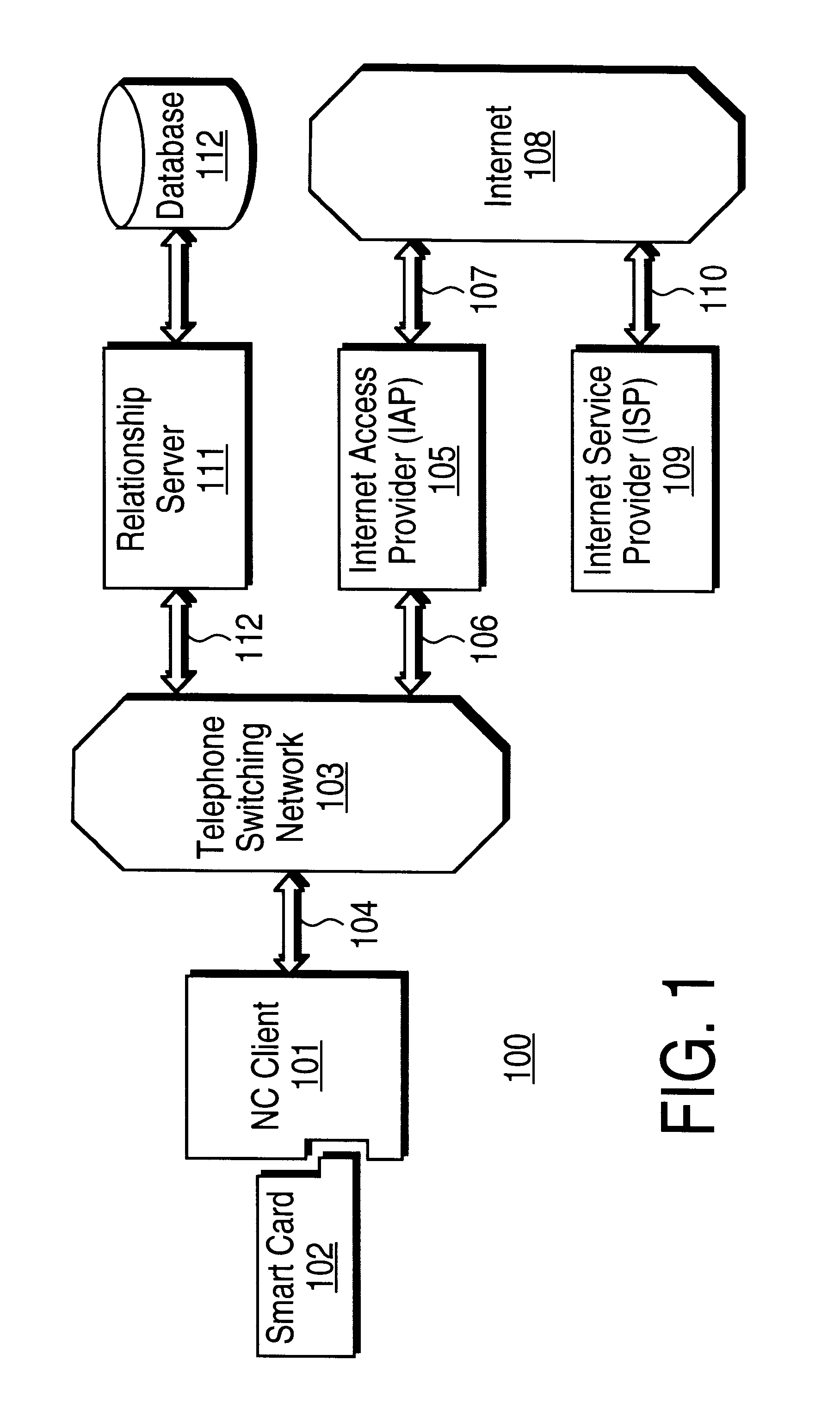
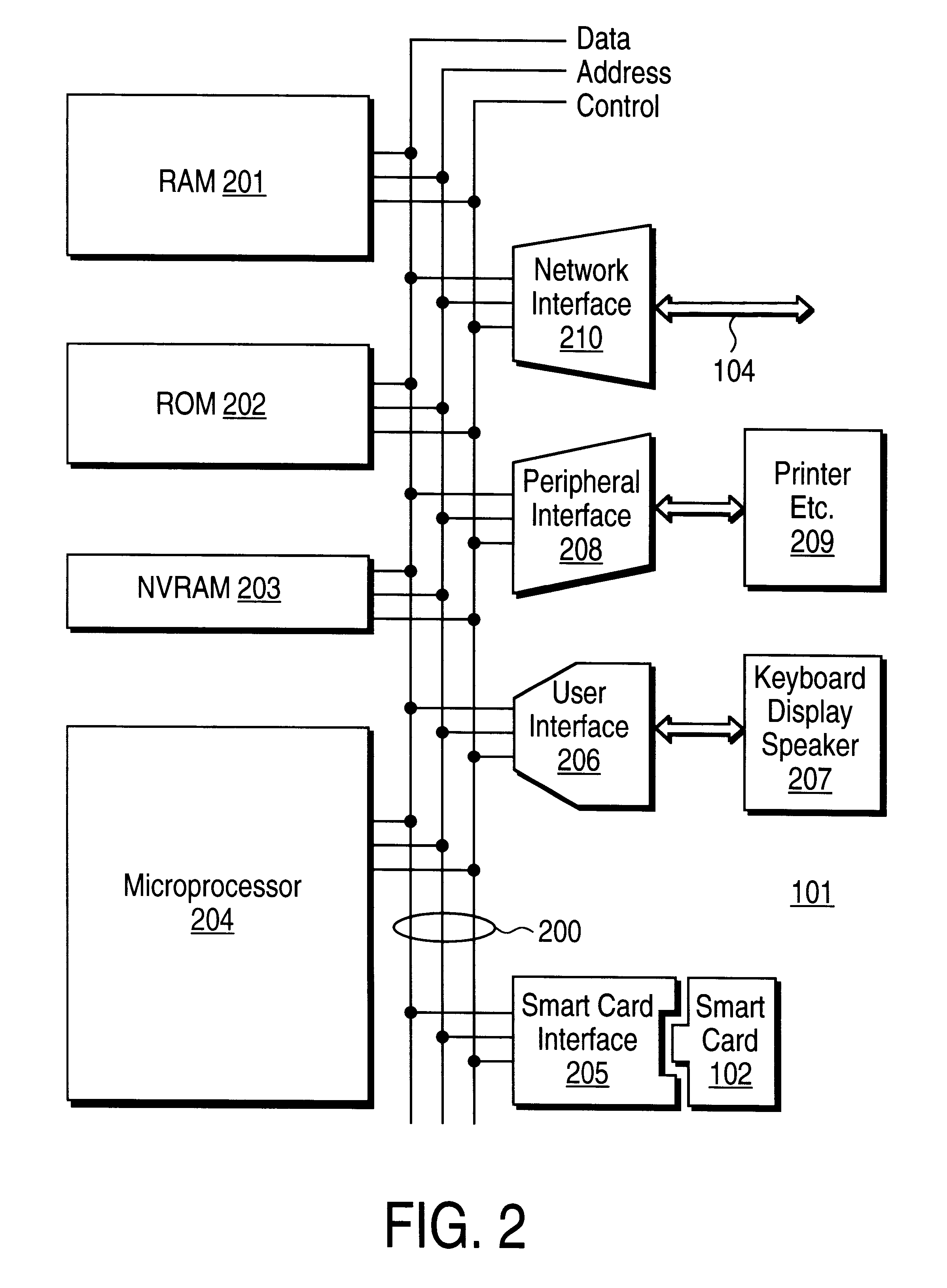
Mechanism for users with internet service provider smart cards to roam among geographically disparate authorized network computer client devices without mediation of a central authority
InactiveUS6108789ADigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureServer allocation
User specific internet service provider (ISP) account information is stored on the user's smart card, but the ISP specific connection information is stored within a network computer client device (NC). When the NC is first powered on and used, it calls the relationship server to receive connection information corresponding to the ISP that is either specified on the first user's smart card or is otherwise chosen by the first user. This connection information is preferably stored in non-volatile memory within the NC, so that even if the NC is powered down, it maintains the ability to connect to the ISP designated by its previous user. Each ISP is designated by a unique enterprise identification number assigned by the relationship server. When a subsequent user inserts his smart card into an NC, the NC compares the enterprise identification number on the smart card to the enterprise identification number within the NC. If the enterprise identification numbers match, the NC connects to the IAP already stored in the NC without dialing the relationship server. Only if the enterprise identification numbers do not match must the NC then dial the relationship server to download connection information for the ISP designated by the smart card enterprise identification number. In the preferred embodiment, the ISP contents of the smart card are digitally signed by the ISP. If the enterprise identification numbers match, then the ISP contents of the smart card are cryptographically authenticated using the public key within the authorized usage certificate for the ISP. If the cryptographic authentication fails, then the NC reprograms the smart card.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM MANAGEMENT LLC
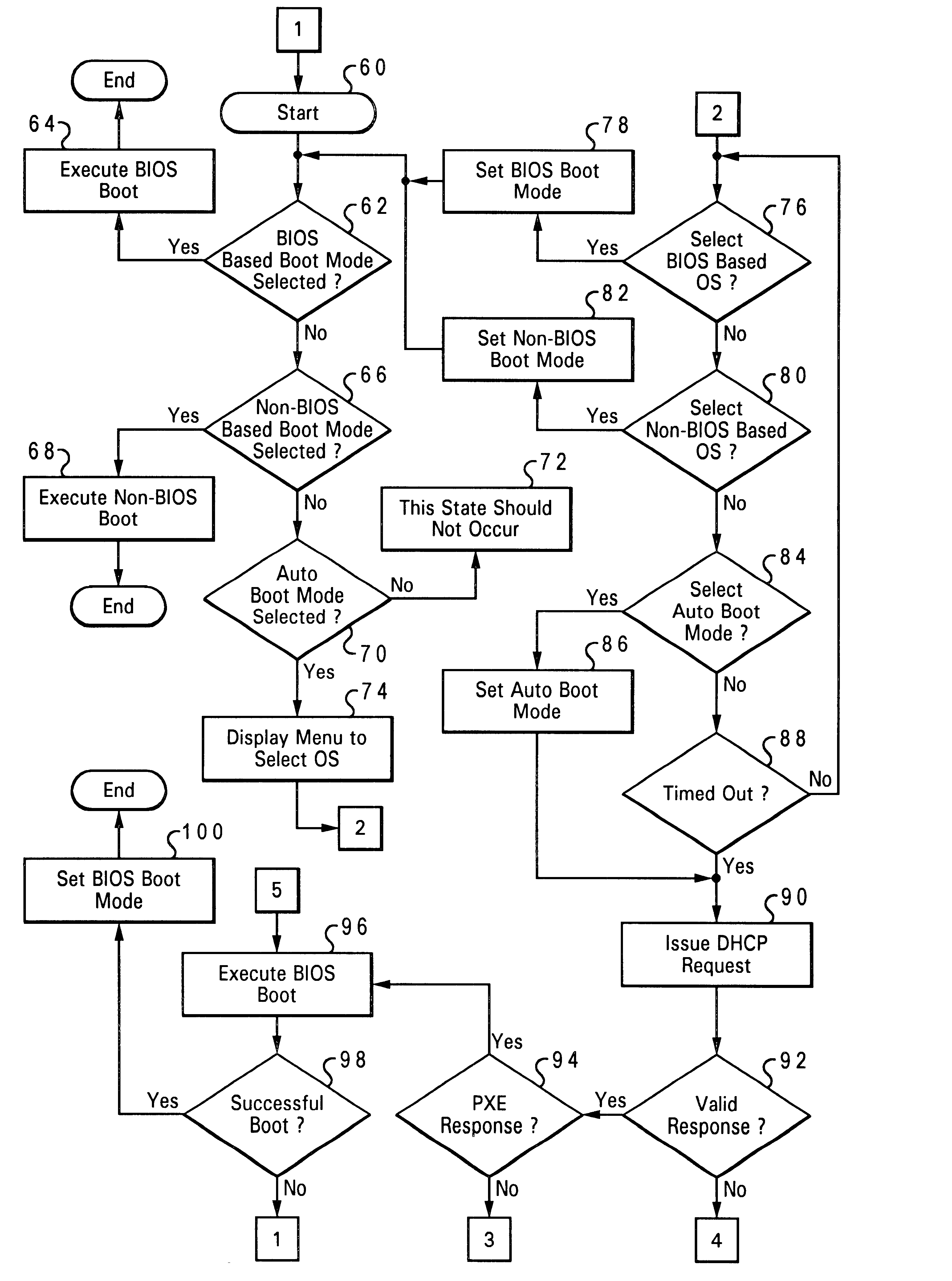
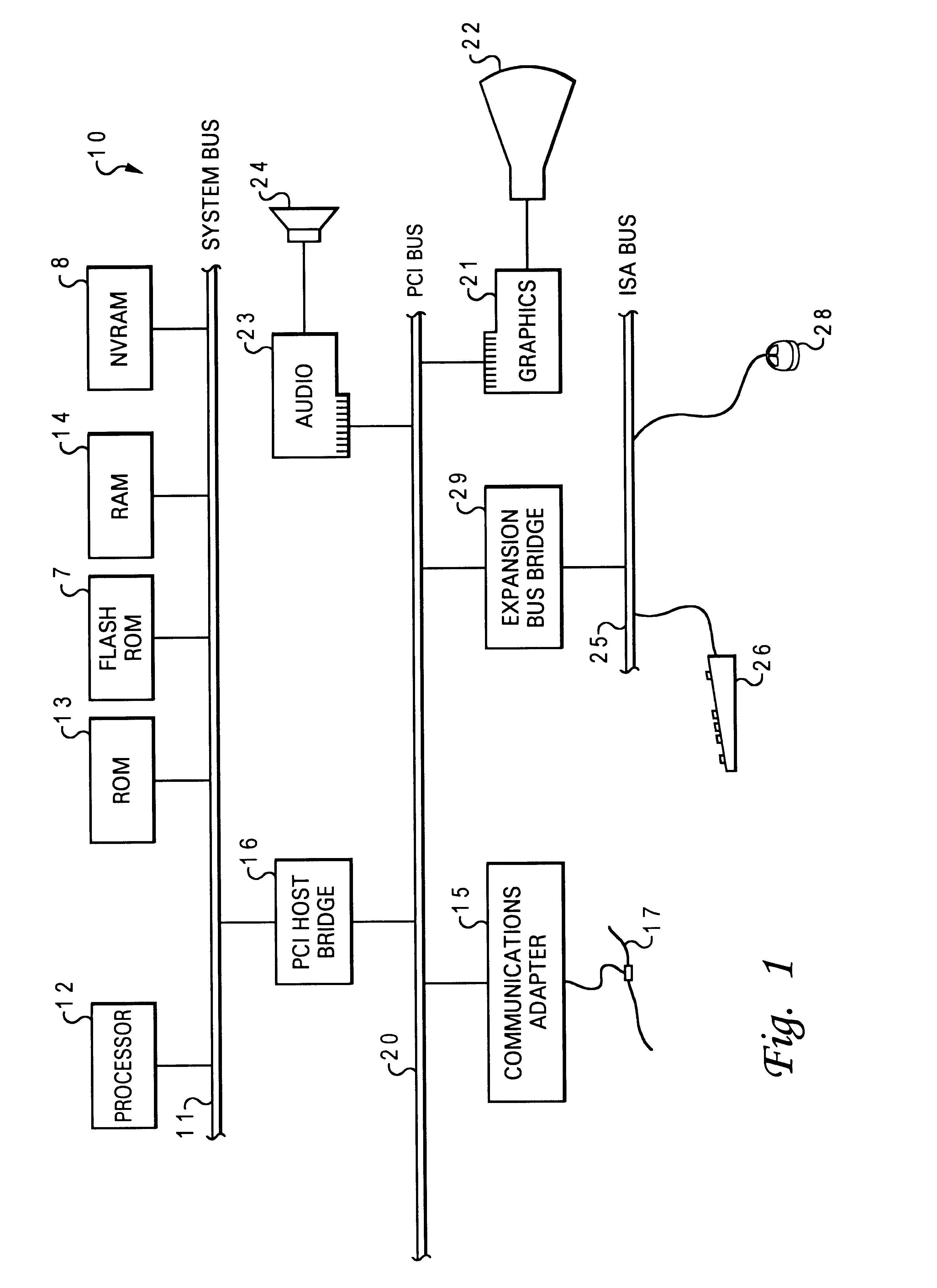
Method and system for automatically configuring the boot process of a computer having multiple bootstrap programs within a network computer system
InactiveUS6490677B1Automatically configuring the boot process of a network computerDigital computer detailsProgram loading/initiatingAuto-configurationProcess configuration
A method and system for automatically configuring a boot process of a network computer initially connected within a network comprising at least one server. A request is broadcast from a network computer to a network for an available server, upon a first initiation of the network computer within the network. Responses from the broadcast are gathered which indicate whether a server is available. A selected boot program is then executed from among multiple boot programs available in the network computer. The selected boot program and the identity of an available server are stored as boot process configuration settings in a nonvolatile storage of the network computer, in response to successful execution of the boot program, such that a subsequent boot process of a network computer is automatically configured.
Owner:LENOVO PC INT
User-centric consent management system and method
InactiveUS20070038765A1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsWeb serviceClient-side
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Internet service provider preliminary user registration mechanism provided by centralized authority
InactiveUS6385651B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsRelational databaseDigital signature
User and network computer client device (NC) registration with an internet service provider (ISP) occurs in two phases: the first phase with the relationship server and the second phase with the ISP. In the first phase, the NC sends the relationship server a unique identifier of the NC manufacturer, such as the manufacturer identification number. In the preferred embodiment, the NC also transmits an enterprise identification number from a smart card uniquely specifying the ISP to which the user wishes to connect. The relationship server queries a relationship database using the manufacturer and enterprise identification numbers. In the preferred embodiment, the relationship server determines whether the specified manufacturer has authorized connection to the specified ISP; if no authorization exists in the relationship server database, then the relationship server disconnects from the NC. Otherwise, the relationship server transmits NC connection information and initial registration contents for the ISP to the NC. The NC preferably writes the initial registration contents to the user's smart card. In the preferred embodiment, the initial registration contents is identical for all users of the same ISP and is digitally signed by the ISP. The second phase of the user registration is entirely governed by the ISP. Upon authentication of the ISP using the authorized usage certificate for the ISP within the NC, the ISP is free to overwrite the user's initial registration contents user specific ISP account information that the ISP digitally signs. In the preferred embodiment, although the initial registration contents for the ISP on the user's smart card is overwritten during the second phase of user registration, the NC connection information remains the same after registration with the ISP. Although the ISP is allowed to overwrite this data (either the smart card contents or the NVRAM contents) at anytime.
Owner:TVWORKS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com