Patents
Literature
297 results about "Market conditions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
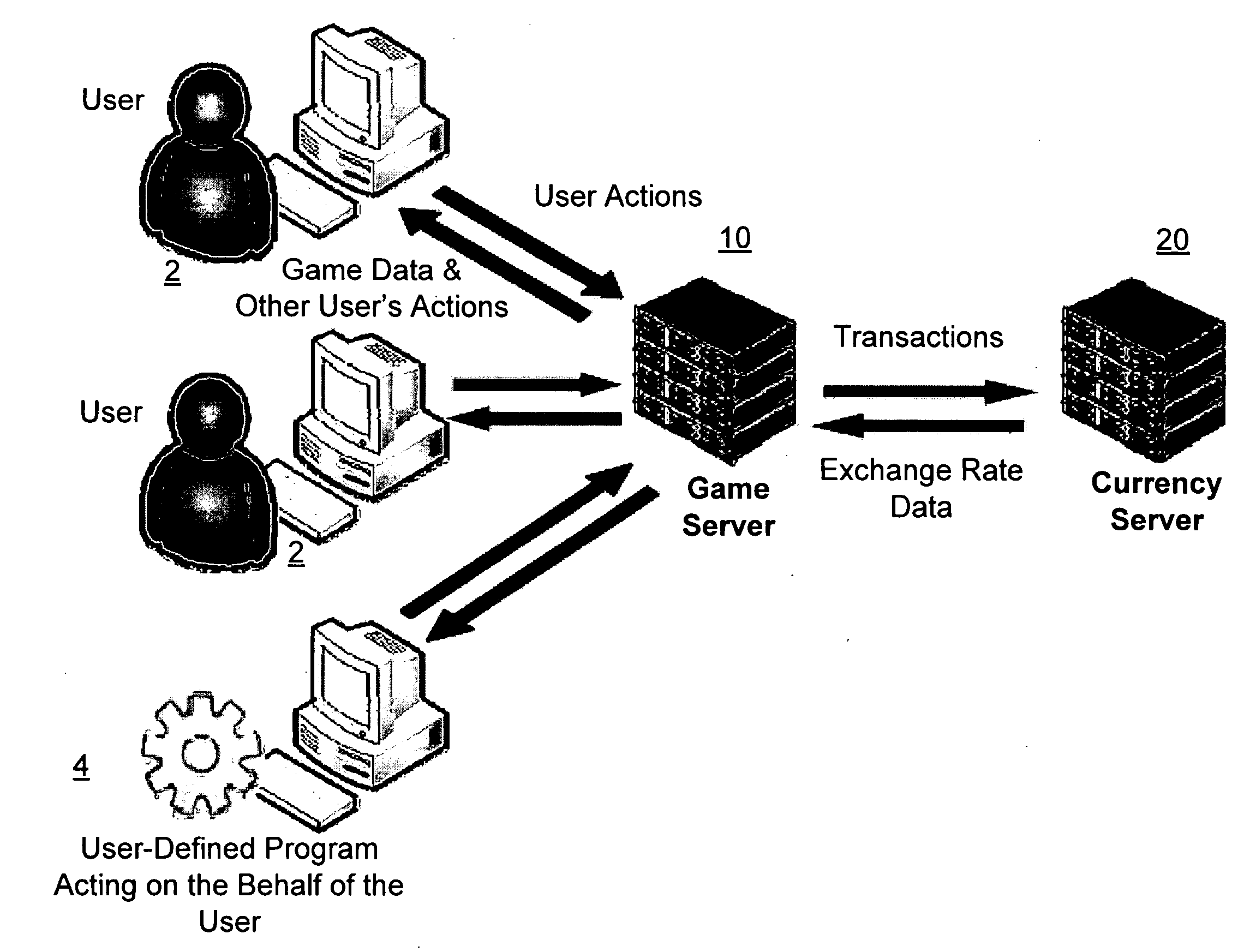
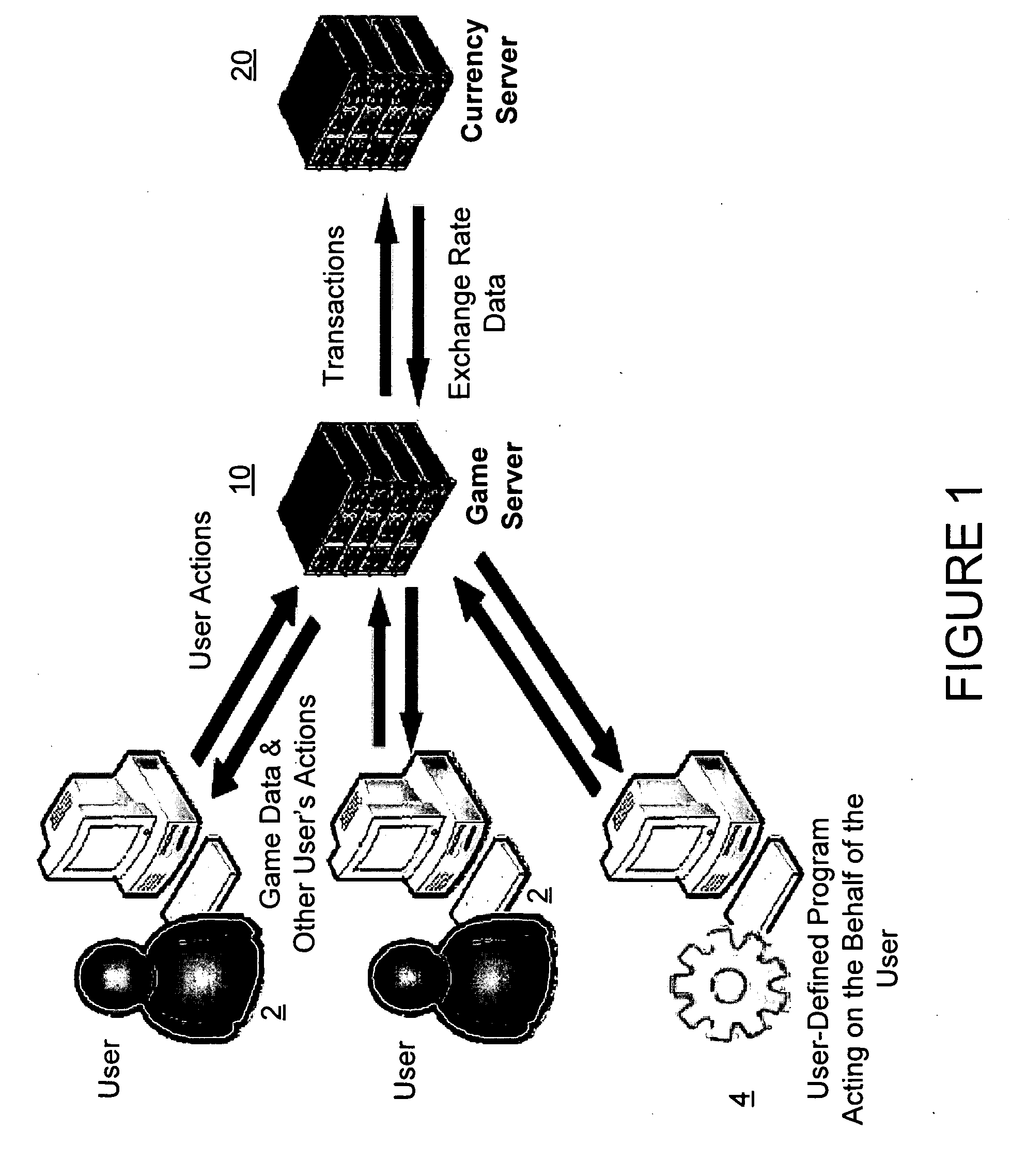
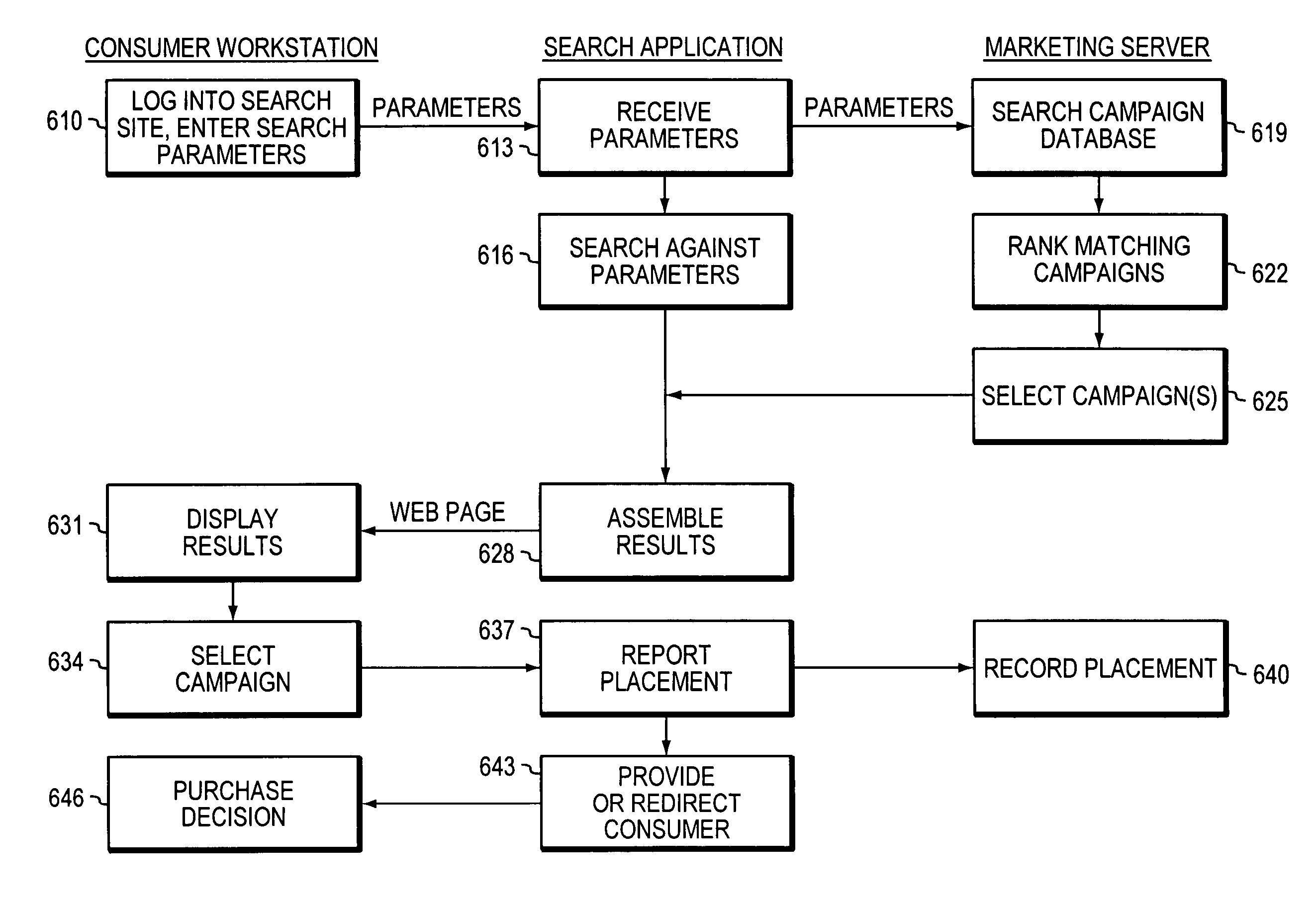
Network computer game linked to real-time financial data
InactiveUS20090181777A1Apparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesFinancial transactionMarket based
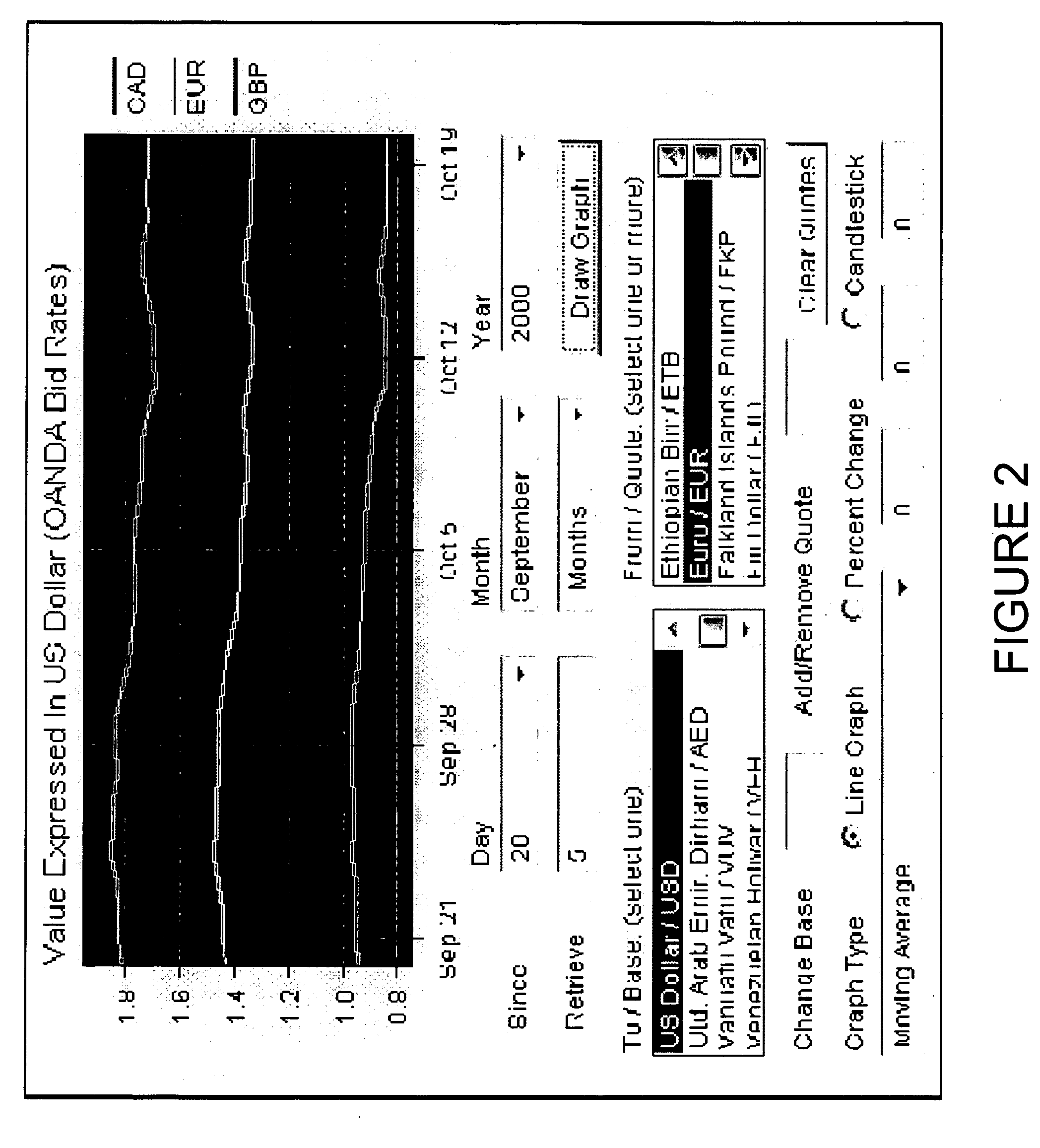
A network-based computer game that both uses real-time financial data to affect game state and uses participants' actions to determine and engage in financial transactions. A game server receives financial data on market conditions (such as currency markets) from a financial server and regularly synchronizes user's game environments to match the financial data. The game server propagates financial data to the game or games, coordinates communication (if any) between the games, and can initiate the opening and closing of positions in the financial market based on players' game behavior. The financial market can be a currency market, where one nation's currency can be exchanged for another currency at a certain exchange rate.
Owner:FINANCIAL DATA GAMES
Investment advice systems and methods
The present invention provides investment advice systems. One version of the present invention provides investment advice systems that allow a user to select one or more advisors from a list of investment advisors. According to this version of the invention, the end user can receive advice on a particular transaction either separately from each investment advisor or in consensus. The system offers advice in part on the user's portfolio, tax position and risk profile and in part on the advisors evaluation of current market conditions. Thus, when a user is considering making a transaction, the user can obtain advice that can take into portfolio information including a user's proposed transaction and / or user portfolio information. A user armed with the above-described customized advice can execute a specific transaction and have their portfolio updated to reflect execution of that (those) order(s). In an alternative embodiment, a user's desire to buy or sell a security and / or a need for rebalancing a user's portfolio can generate transaction(s). As a result, the system will generate a buy / sell list (including recommended alternatives) from which a user can select.
Owner:TEGRA118 WEALTH SOLUTIONS INC
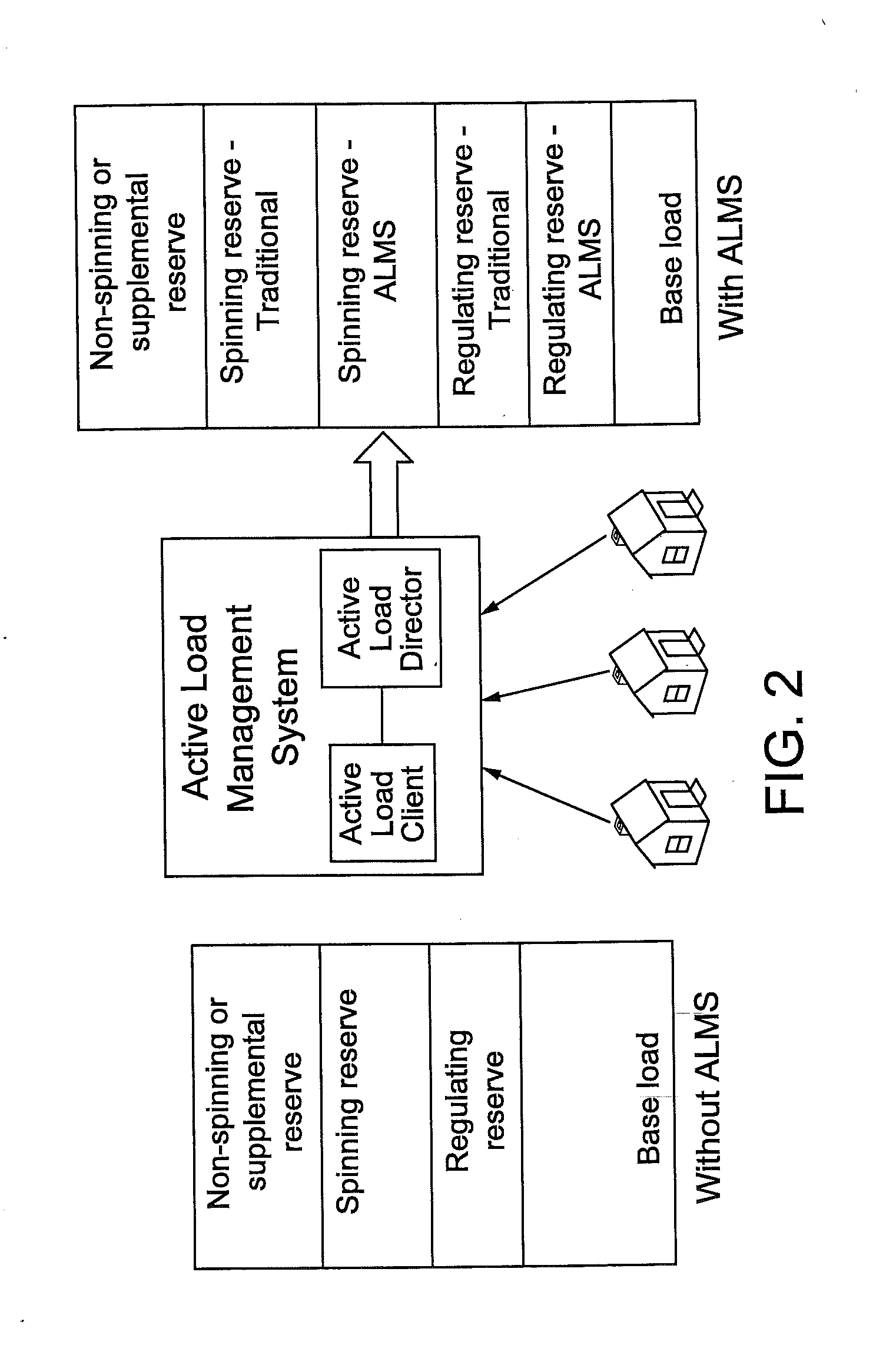
System and method for estimating and providing dispatchable operating reserve energy capacity through use of active load management
ActiveUS20110172837A1Generation forecast in ac networkLevel controlElectric vehicleActive Network Management
A utility employs an active load management system (ALMS) to estimate available operating reserve for possible dispatch to the utility or another requesting entity (e.g., an independent system operator). According to one embodiment, the ALMS determines amounts of electric power stored in power storage devices, such as electric or hybrid electric vehicles, distributed throughout the utility's service area. The ALMS stores the stored power data in a repository. Responsive to receiving a request for operating reserve, the ALMS determines whether the stored power data alone or in combination with projected energy savings from a control event is sufficient to meet the operating reserve requirement. If so, the ALMS dispatches power from the power storage devices to the power grid to meet the operating reserve need. The need for operating reserve may also be communicated to mobile power storage devices to allow them to provide operating reserve as market conditions require.
Owner:JOSEPH W FORBES JR +1
Multiple Trade Matching Algorithms
The disclosed embodiments relate to systems and methods which match / allocate an incoming order to trade with “resting,” i.e. previously received but not yet matched, orders, recognizing that the algorithm or rules by which the incoming order is matched may affect the operation of the market for the financial product being traded. In particular, the disclosed embodiments relate to an adaptive match engine which draws upon different matching algorithms, e.g. the rules which dictate how a given order should be allocated among qualifying resting orders, depending upon market conditions, to improve the operation of the market. Thereby, by conditionally switching among matching algorithms within the same financial product, as will be described, the disclosed match engine automatically adapts to the changing market conditions of a financial product, e.g. a limited life product, in a non-preferential manner, maintaining fair order allocation while improving market liquidity, e.g., over the life of the product.
Owner:CHICAGO MERCANTILE EXCHANGE
Interactive method and apparatus for real-time financial planning
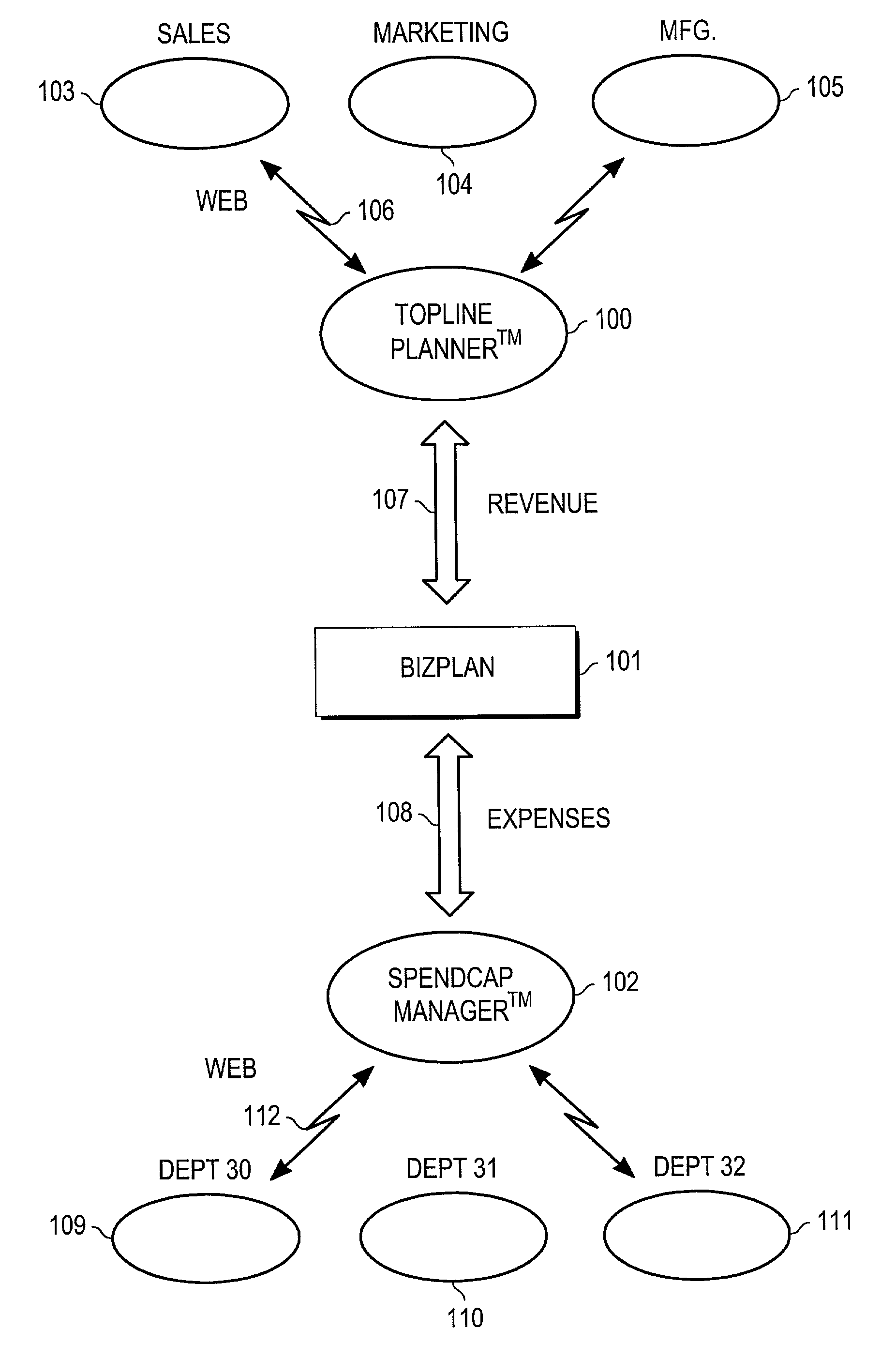
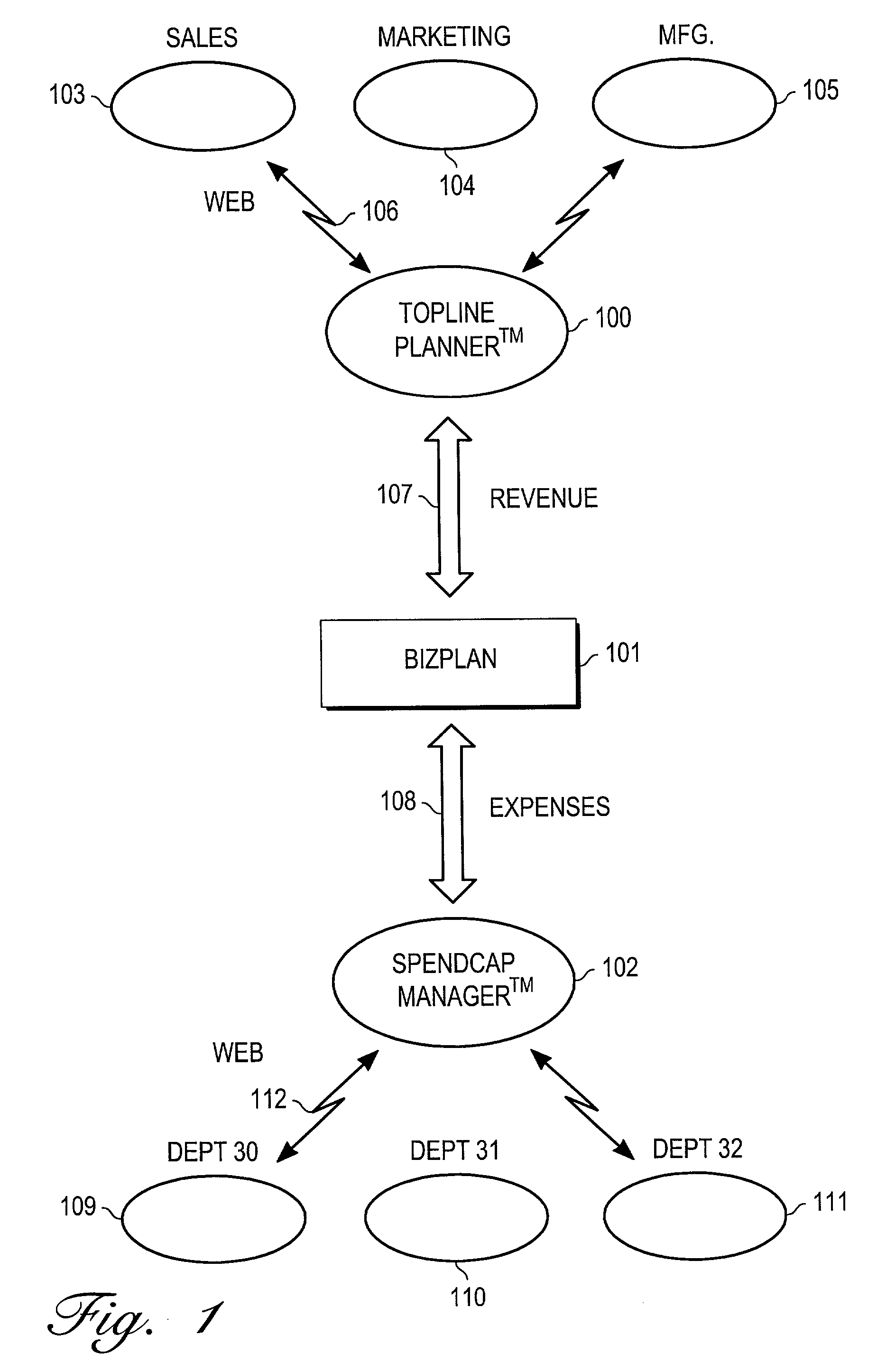
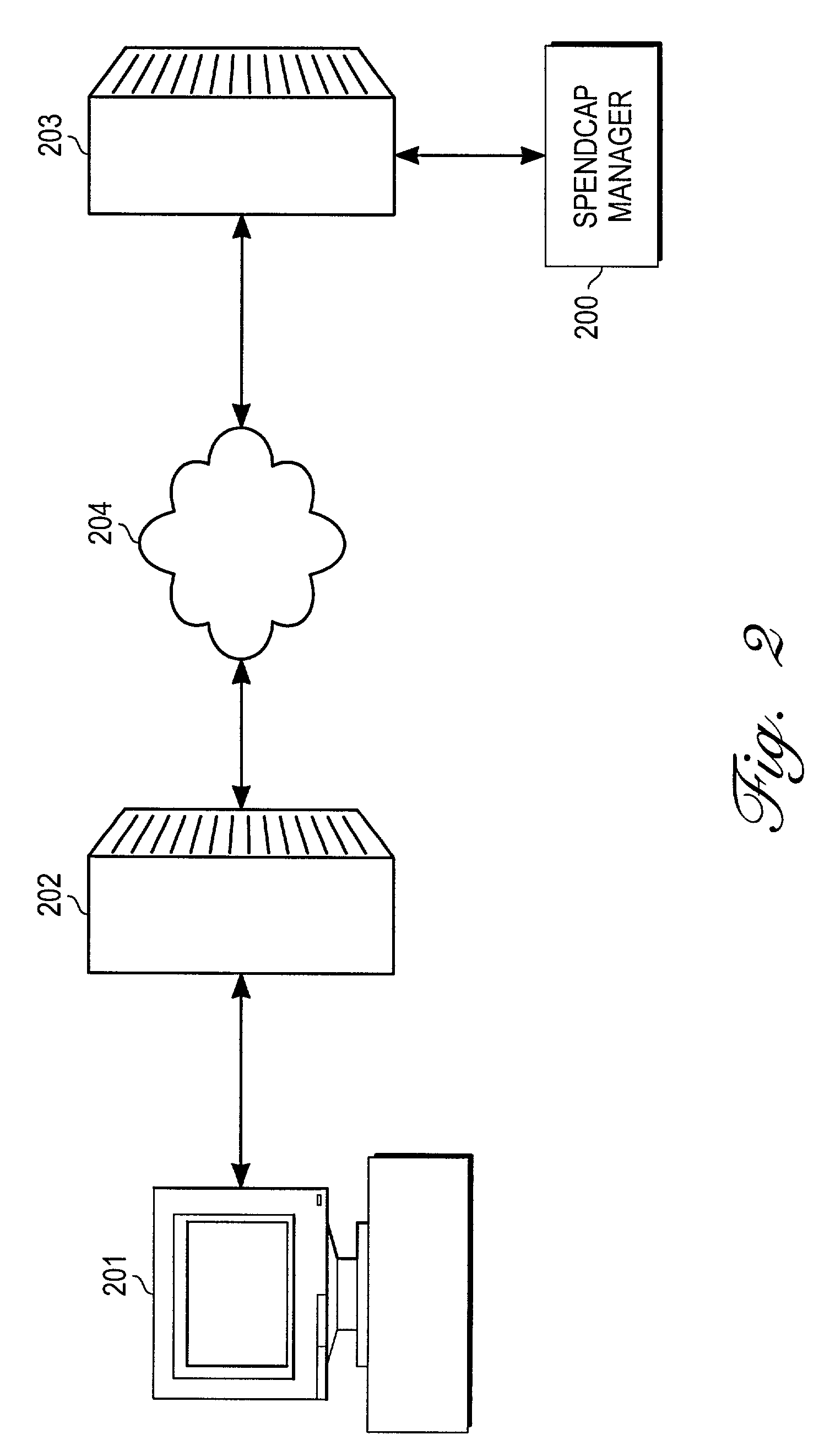
A method and apparatus for financial planning and control are disclosed that are capable of real-time response to changing market conditions. The disclosed method provides financial management and control tools that allow an organization to rapidly (on weekly or monthly frequencies, for example) realign financial resources throughout the organization in response to changing market and business conditions. The method links critical external information directly to company decision-making activities to allow a business to better align resources to capitalize upon opportunities or minimize the impact of adverse business conditions. The disclosed embodiment of the invention comprises several modules, including the TopLine Planner(TM) module, BizPlan(TM) module, and SpendCap Manager(TM) module. The TopLine Planner(TM) module receives inputs from and provides information to sales, marketing and manufacturing, and is coupled to the BizPlan(TM) module. The TopLine Planner(TM) module dynamically revises topline forecast information by capturing current outlook information from front line sources. Revenue information is passed between the TopLine Planner(TM) module and the BizPlan(TM) module. The BizPlan(TM) module rapidly refreshes expense plan information by using business rules and constraints. The BizPlan(TM) module is coupled to the SpendCap Manager(TM) module, and expense information is passed between the modules. The SpendCap Manager(TM) module distributes resources to all business managers and receives requests for increases in the allocation of resources.
Owner:INFOR US LLC
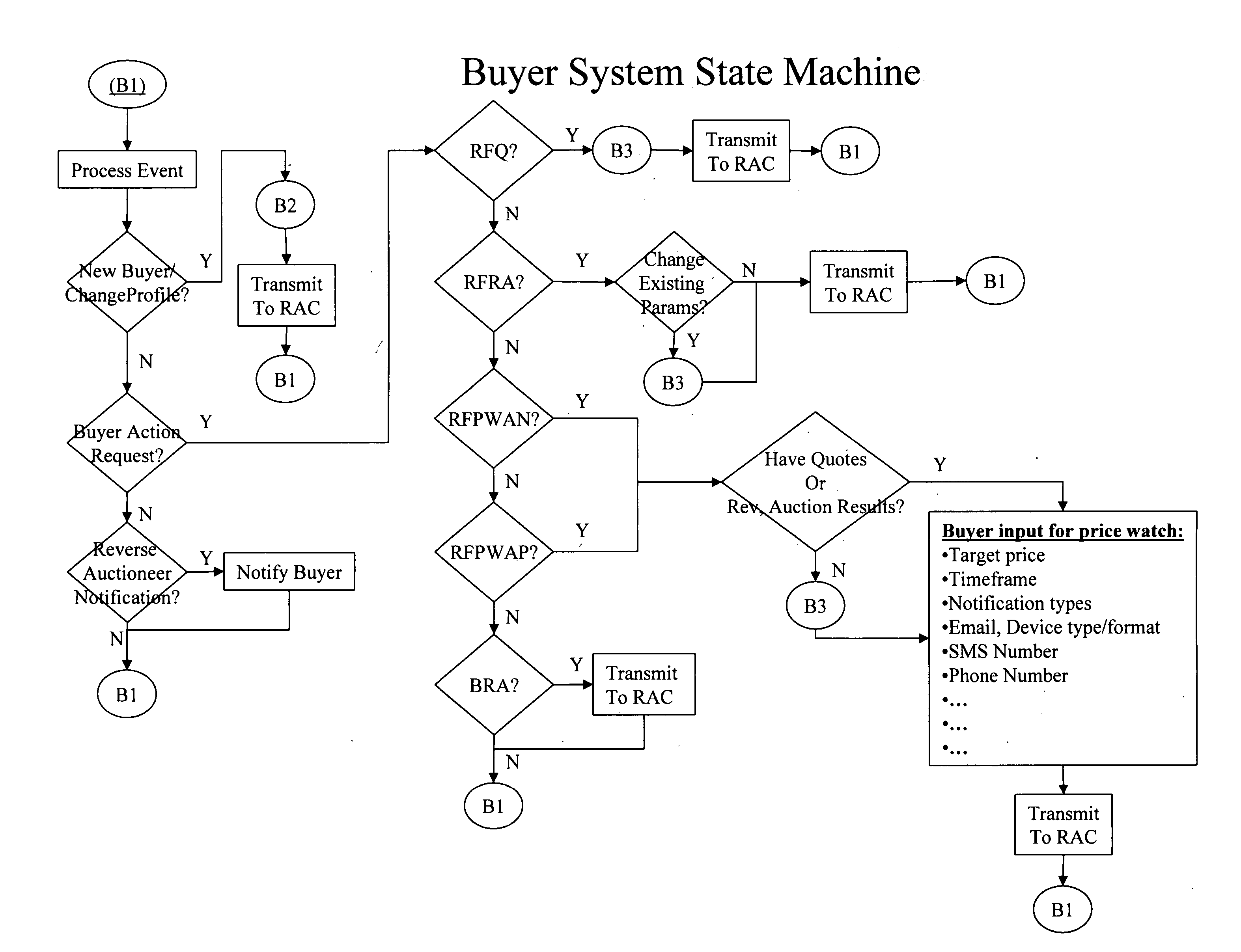
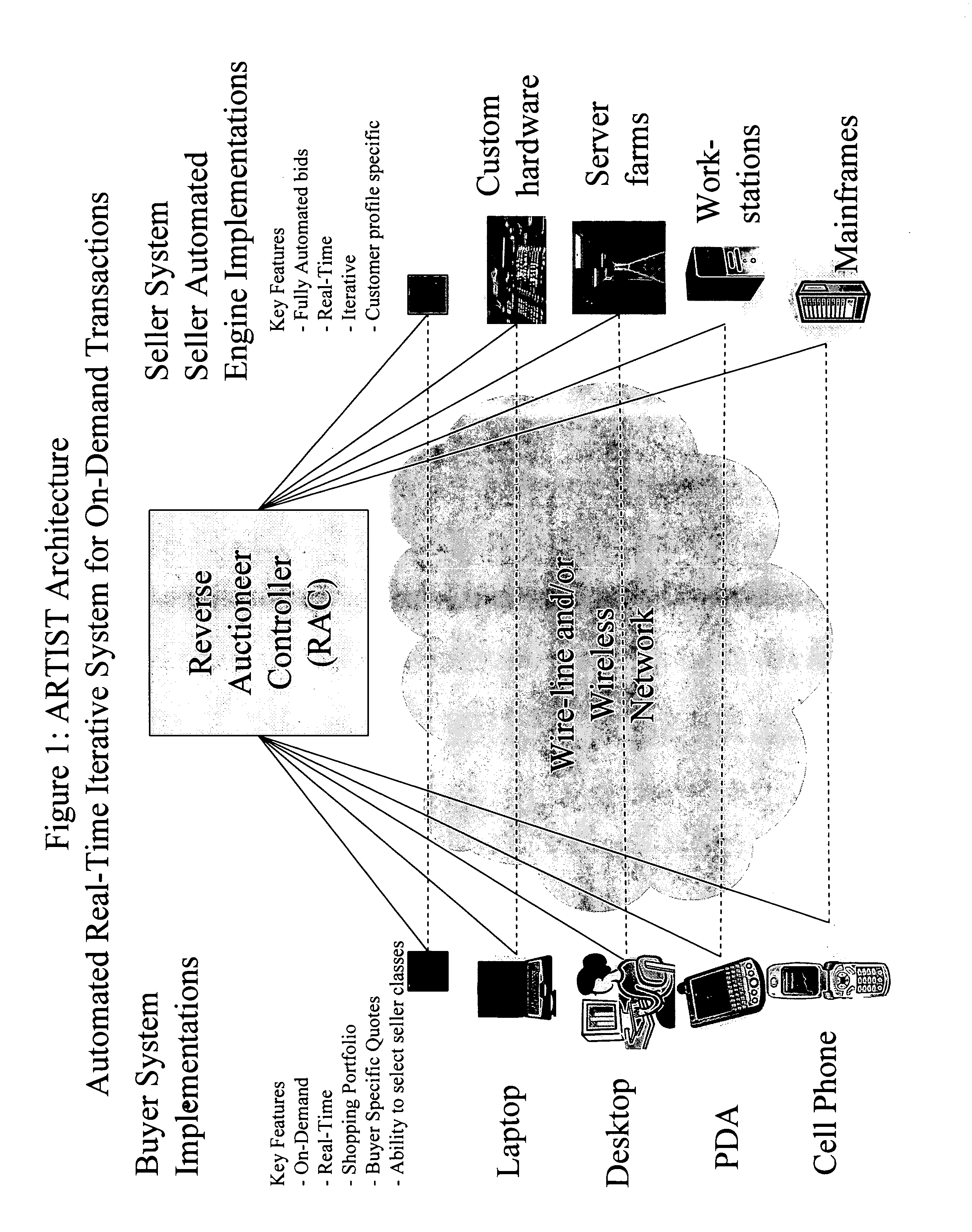
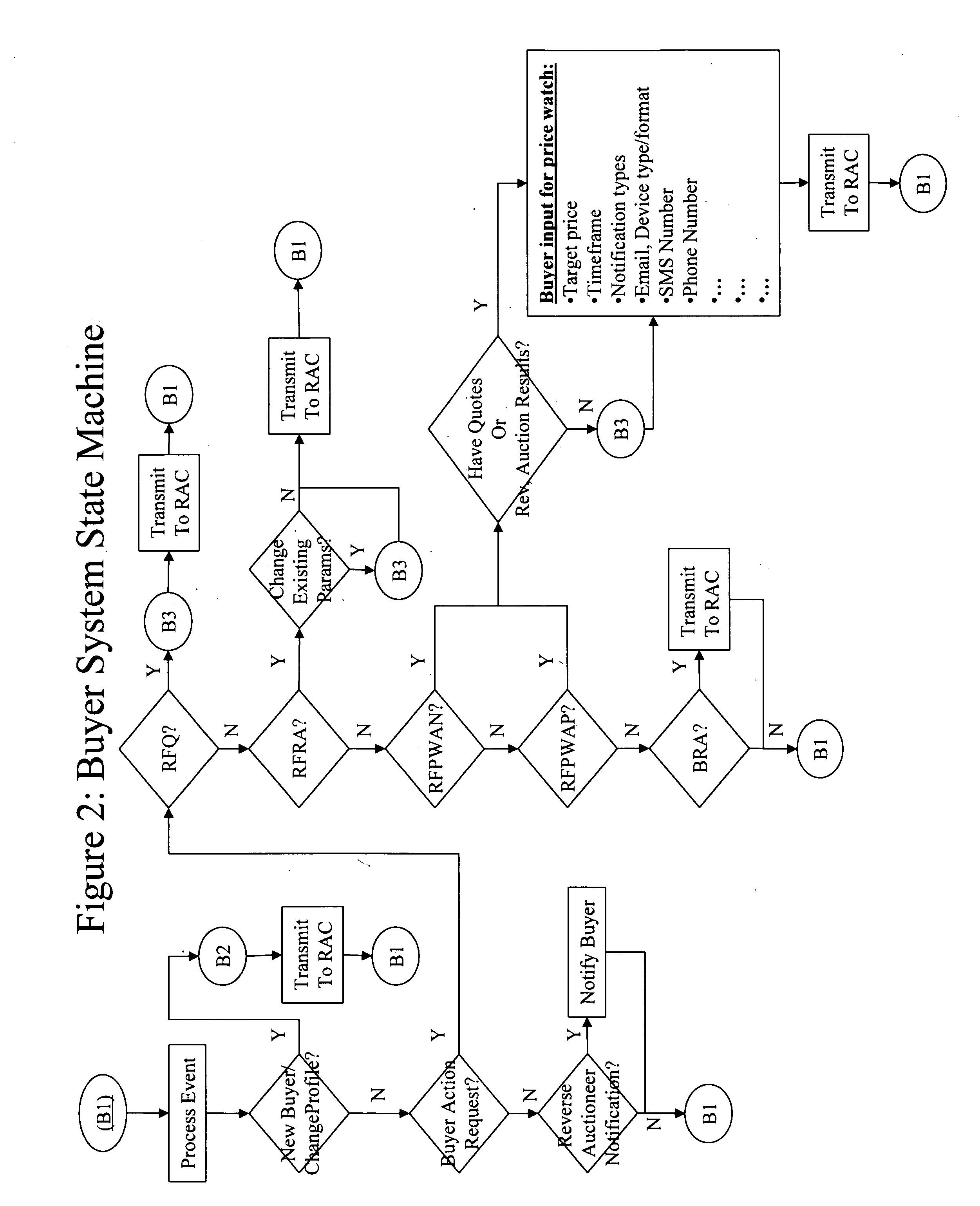
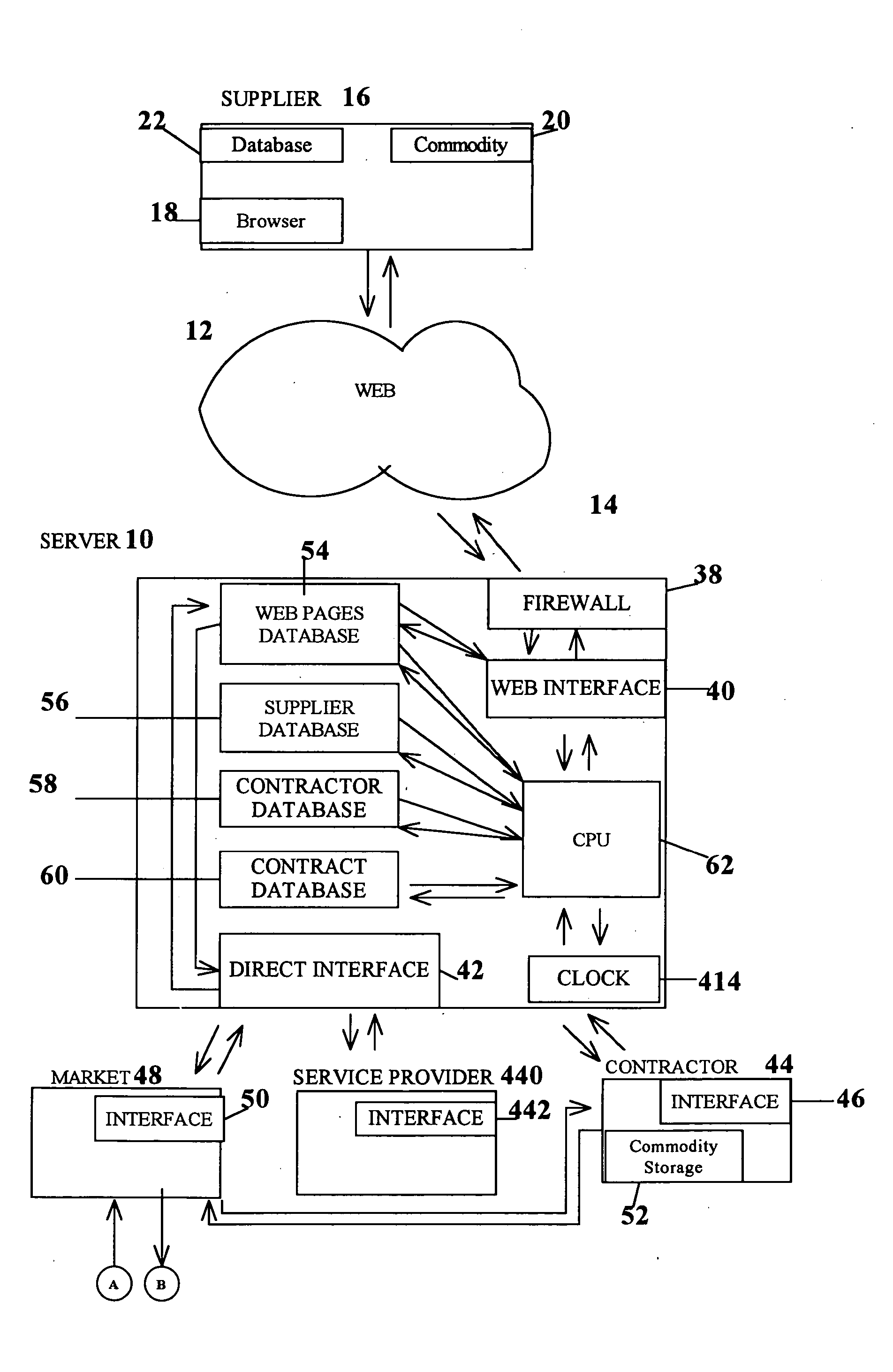
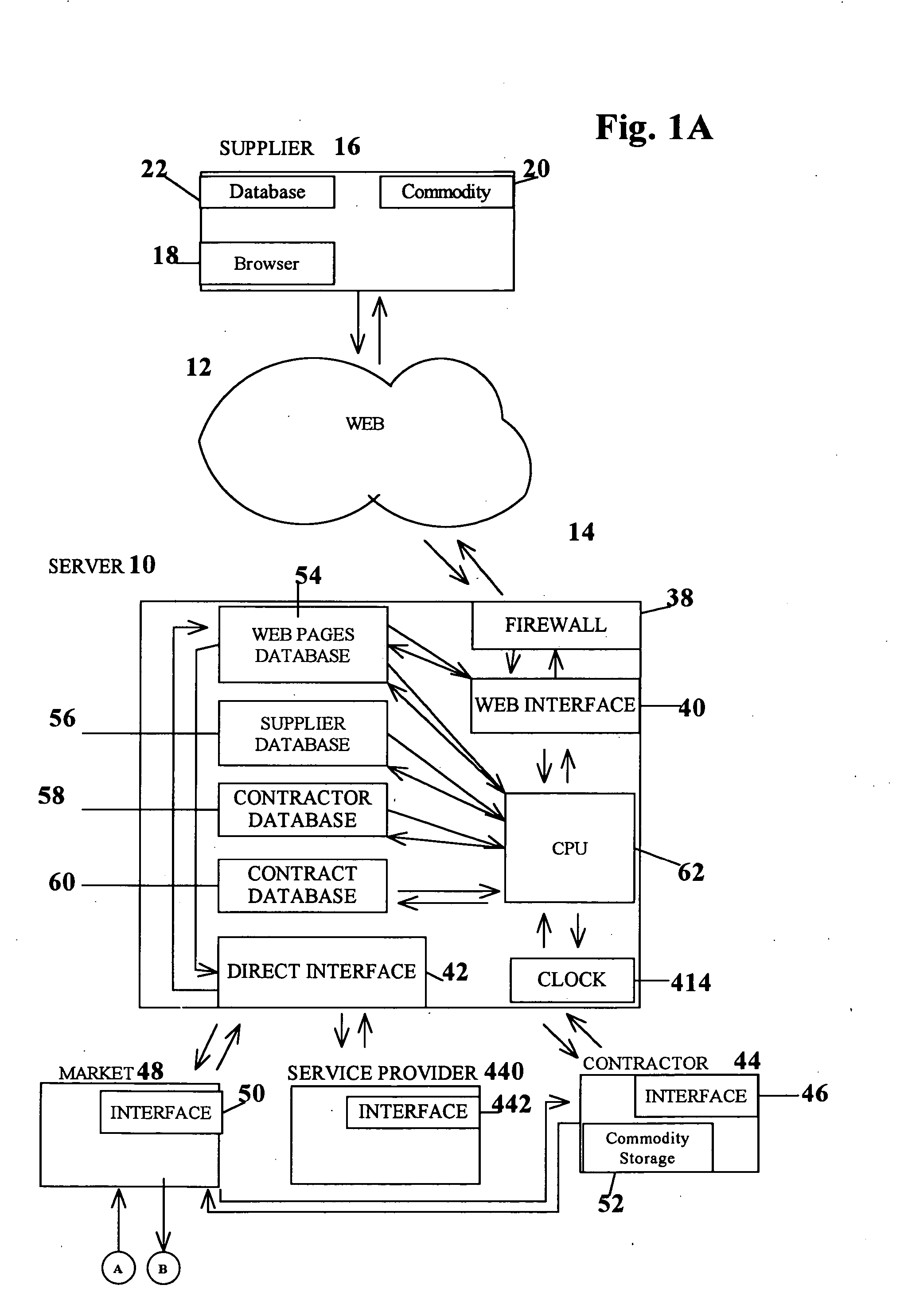
Method, system and apparatus for automatic real-time iterative commercial transactions over the internet in a multiple-buyer, multiple-seller marketplace, optimizing both buyer and seller needs based upon the dynamics of market conditions
ActiveUS20070208630A1Increasing overall reliability and dependabilityPromote recoveryFinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsMarket placeThe Internet
A method of communications network shopping by buyers of products and services for purchasing such from sellers in which buyers request an automatic reverse auctioneer or auction controller to initiate a reverse auction in real time amongst willing sellers and to solicit their automatic real-time iterative bidding price quotations for such products and services to be returned automatically over the network back to the controller under the iterative processing guidance of the controller to assure a best bid price quotation for the buyer; and automatically effecting buyer notification or purchase at such best price, all while the buyer may remain on-line, and without any manual intervention.
Owner:PEAK SILVER ADVISORS
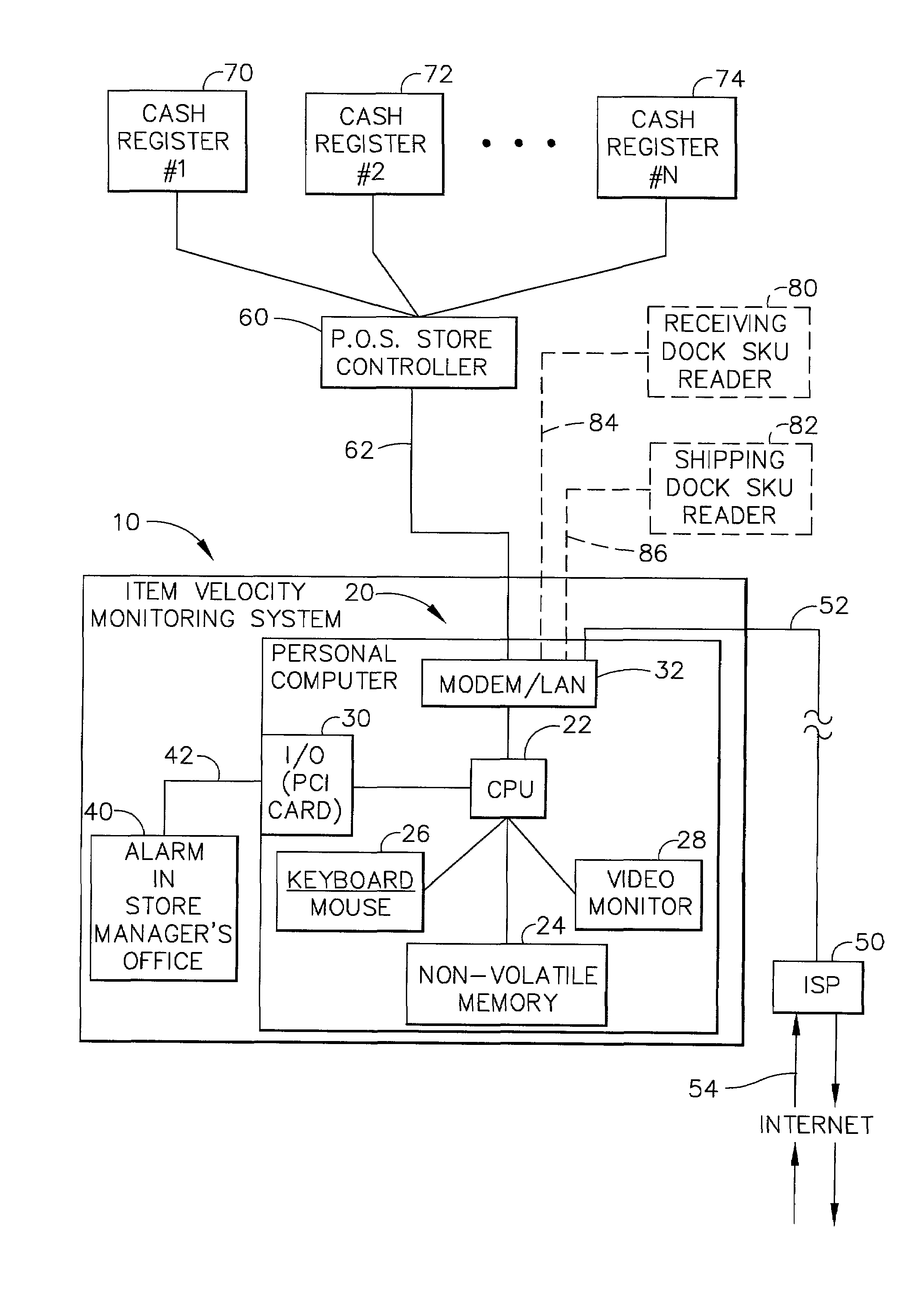
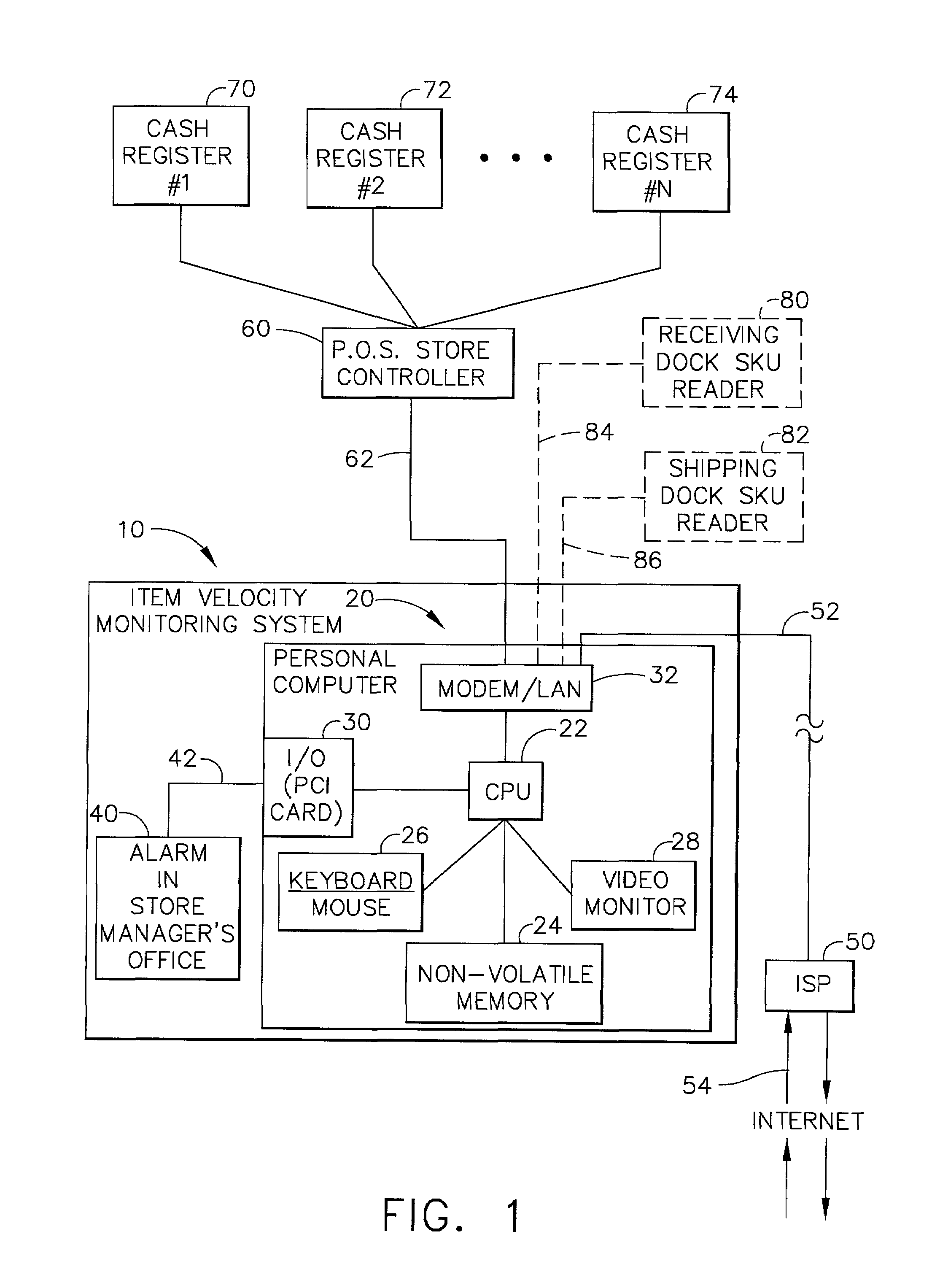
Method and apparatus for monitoring the flow of items through a store or warehouse
InactiveUS7240027B2Automatic detectionCoin-freed apparatus detailsCash registersThe InternetOperation mode
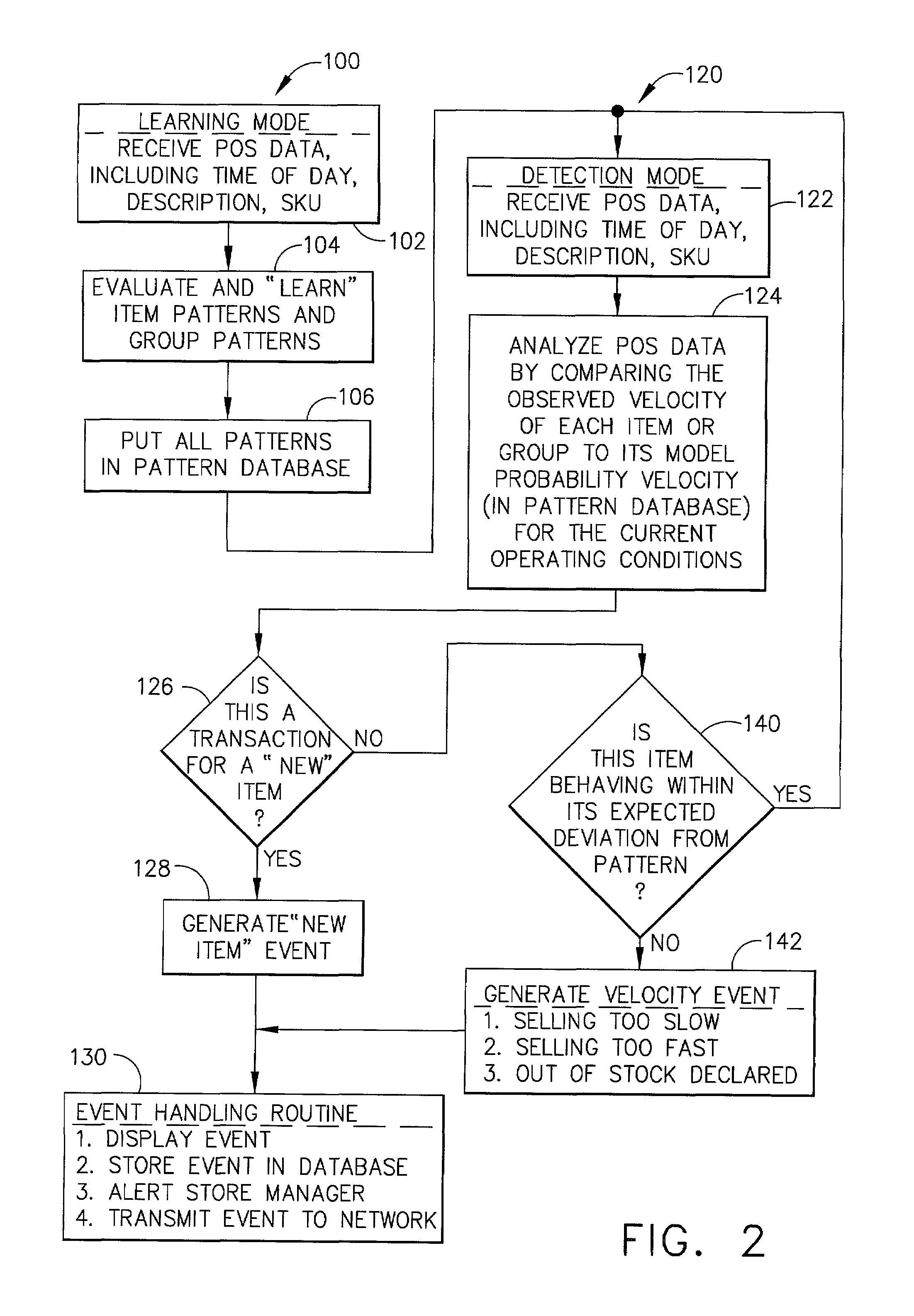
An item velocity monitoring system is provided which interfaces with a consumer retail store that has several cash registers that are tied into a “point of sale” store controller. The item velocity monitoring system is capable of detecting when sales (or other movement activities) of an item are occurring too quickly, or too slowly. The item velocity monitoring system is first “trained” in a learning mode of operations, during which item patterns and group patterns are evaluated and placed into a pattern database. The system then compares the observed item velocity to its model probability velocity, and if the observed item velocity deviates beyond the statistical model, a “velocity event” is generated, declaring one of the above selling “too quick” or “too slow” conditions. Once a velocity event is detected, an event handling routine displays the event, and can transmit the event information over a network (including the INTERNET) to a remote computer for additional analysis or record keeping. A “Loyalty Out-of-Stock System,” (LOSS) is incorporated in the above item velocity monitoring system which automatically detects when items for sale are out-of-stock (OOS), discovers the reasons for these “stock-outs,” and determines how customers react to these stock-outs. The LOSS operates on store data and models the expected item movement rate for each item under varying time-of-day, day-of-week, price, promotion, season, holiday, and market conditions; detects items that are moving abnormally slowly, thereby identifying items that may be improperly displayed; provides early warning that an item may go out-of-stock (OOS) by detecting items with abnormally high movement; detects and reports on items that are OOS at retail stores; summarizes OOS events for the store and retail chain management, and for suppliers, thereby identifying items that are over-stocked (too few OOS events), under-stocked (too many events), badly re-stocked (too long events); analyzes the OOS events to find patterns that explain why OOS's are occurring; and determines the impacts of these OOS events on store customers, thereby measuring losses to the retailer and supplier, and establishing the loyalty of consumers to the item, brand, and chain.
Owner:DUNNHUMBY LTD
Method and system for pricing financial derivatives
ActiveUS20050027634A1Accurately determineFair priceFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsPrice differenceComputer science
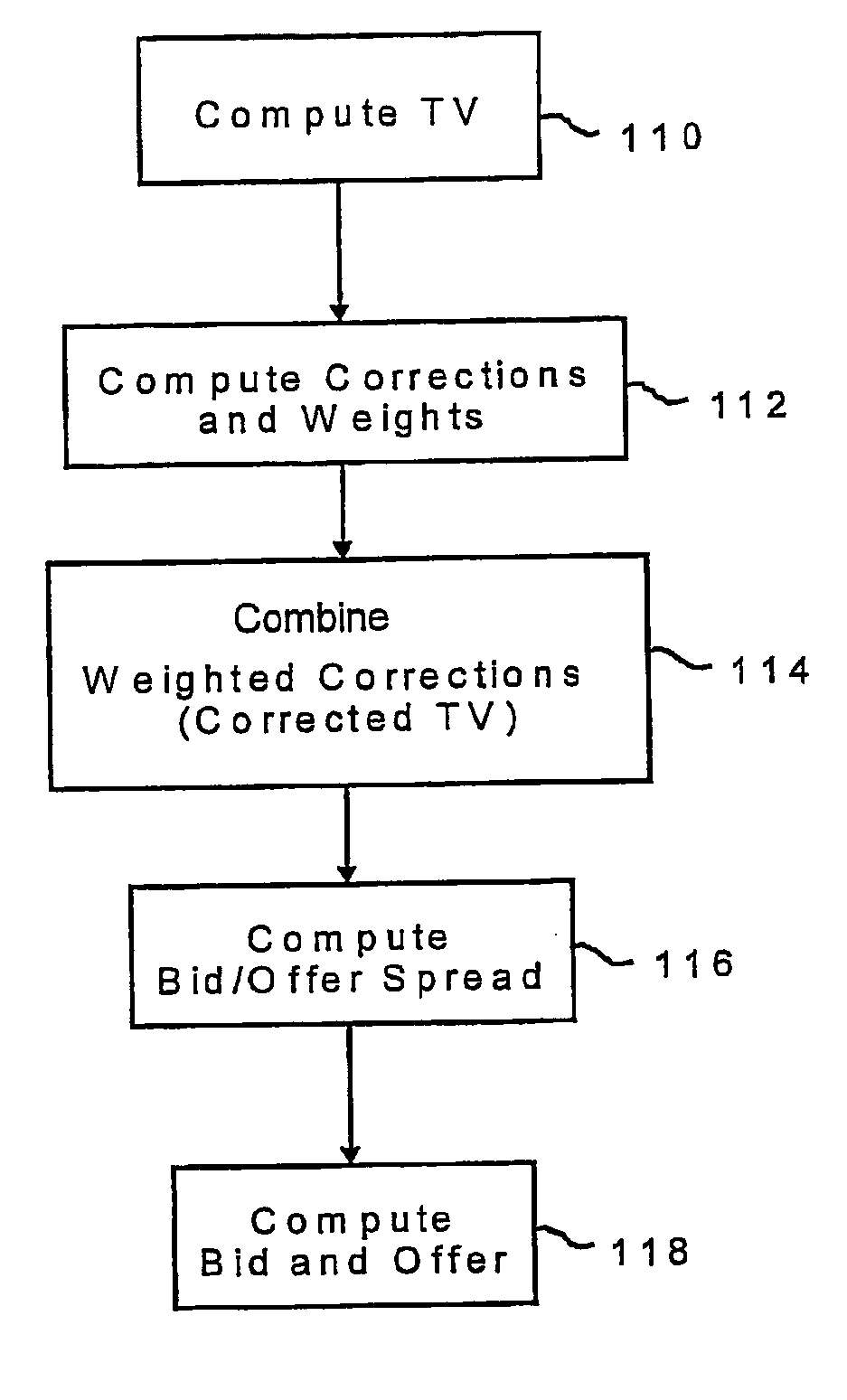
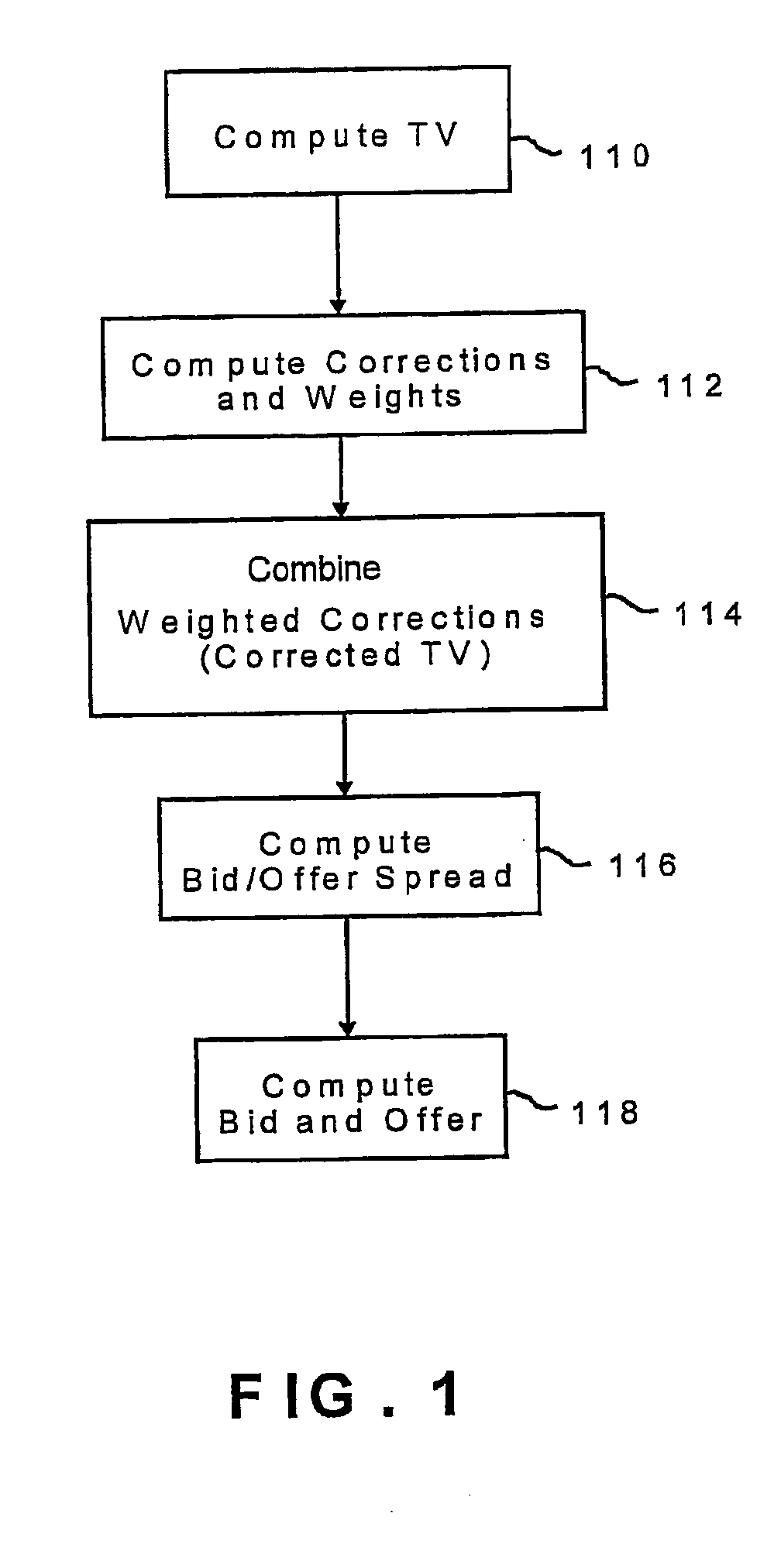
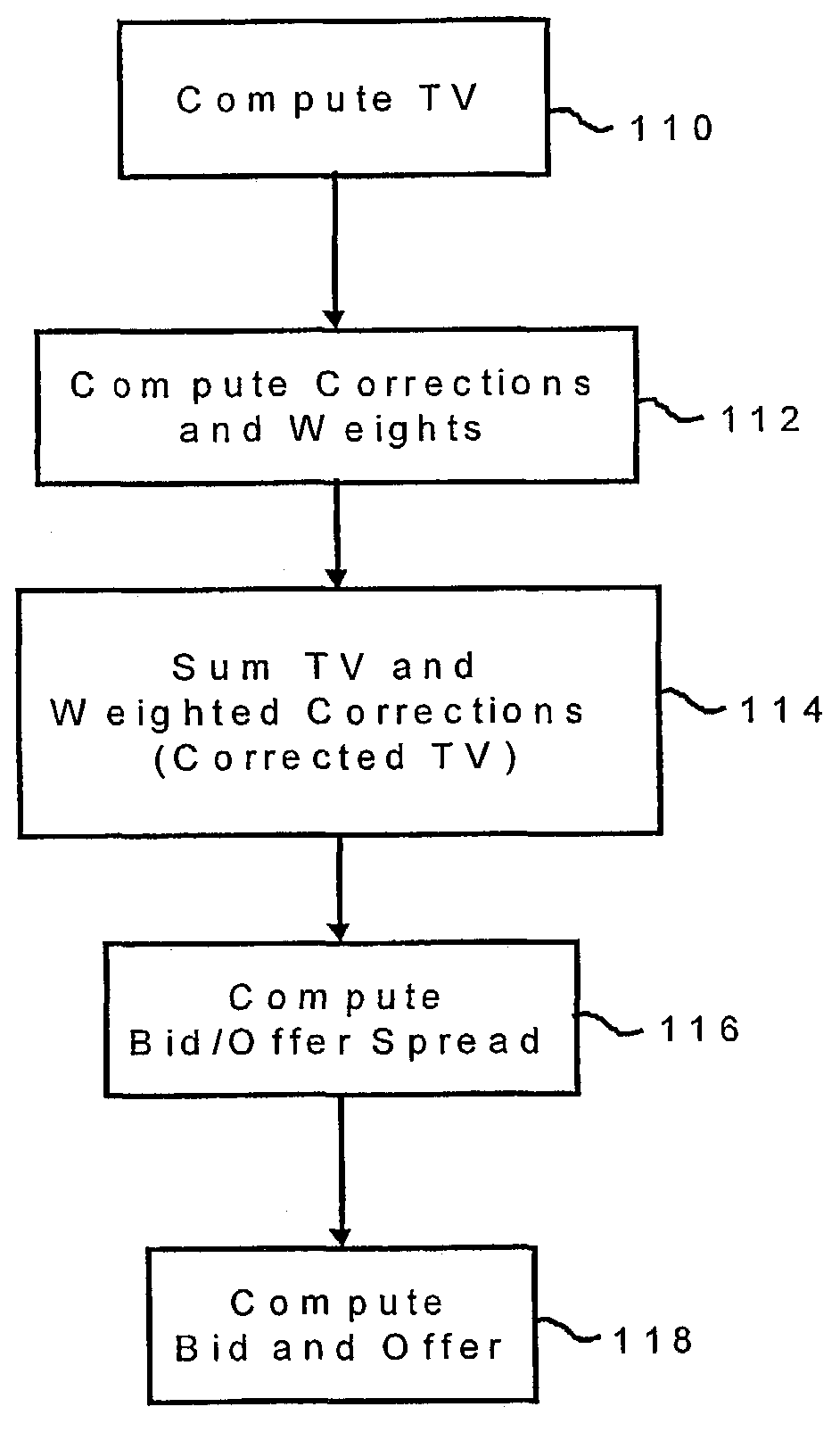
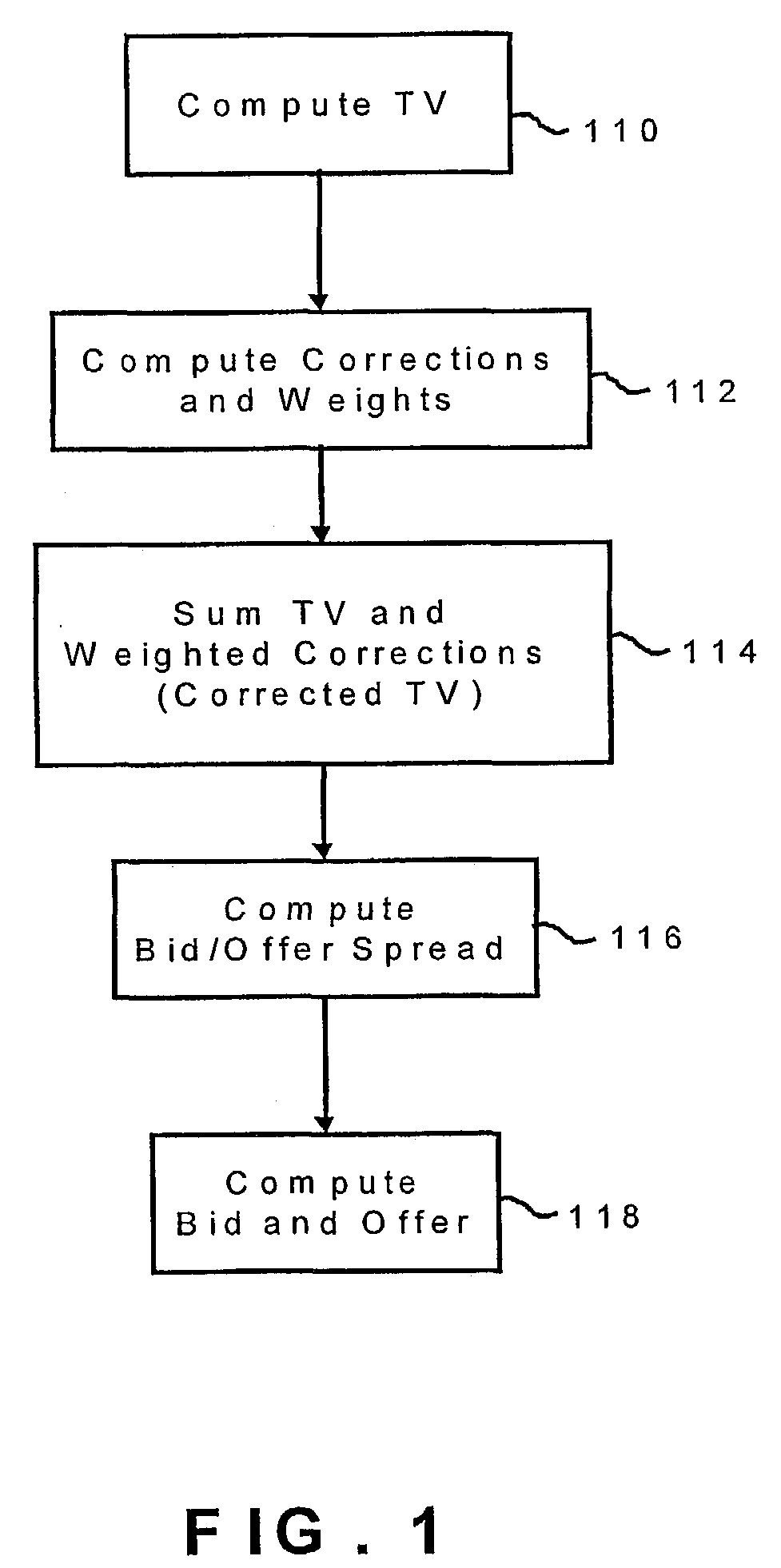
A method for providing a bid price and / or an offer price of an option relating to an underlying asset, the method including the steps of receiving first input data corresponding to a plurality of parameters defining the option, receiving second input data corresponding to a plurality of current market conditions relating to the underlying value, computing a corrected theoretical value (CTV) of the option based on the first and second input data, computing a bid / offer spread of the option based on the first and input data, computing a bid price and / or an offer price of the option based on the corrected TV and the bid / offer spread, and providing an output corresponding to the bid price and / or the offer price of said option.
Owner:SUPERDERIVATIVES INC
Method and system for pricing options
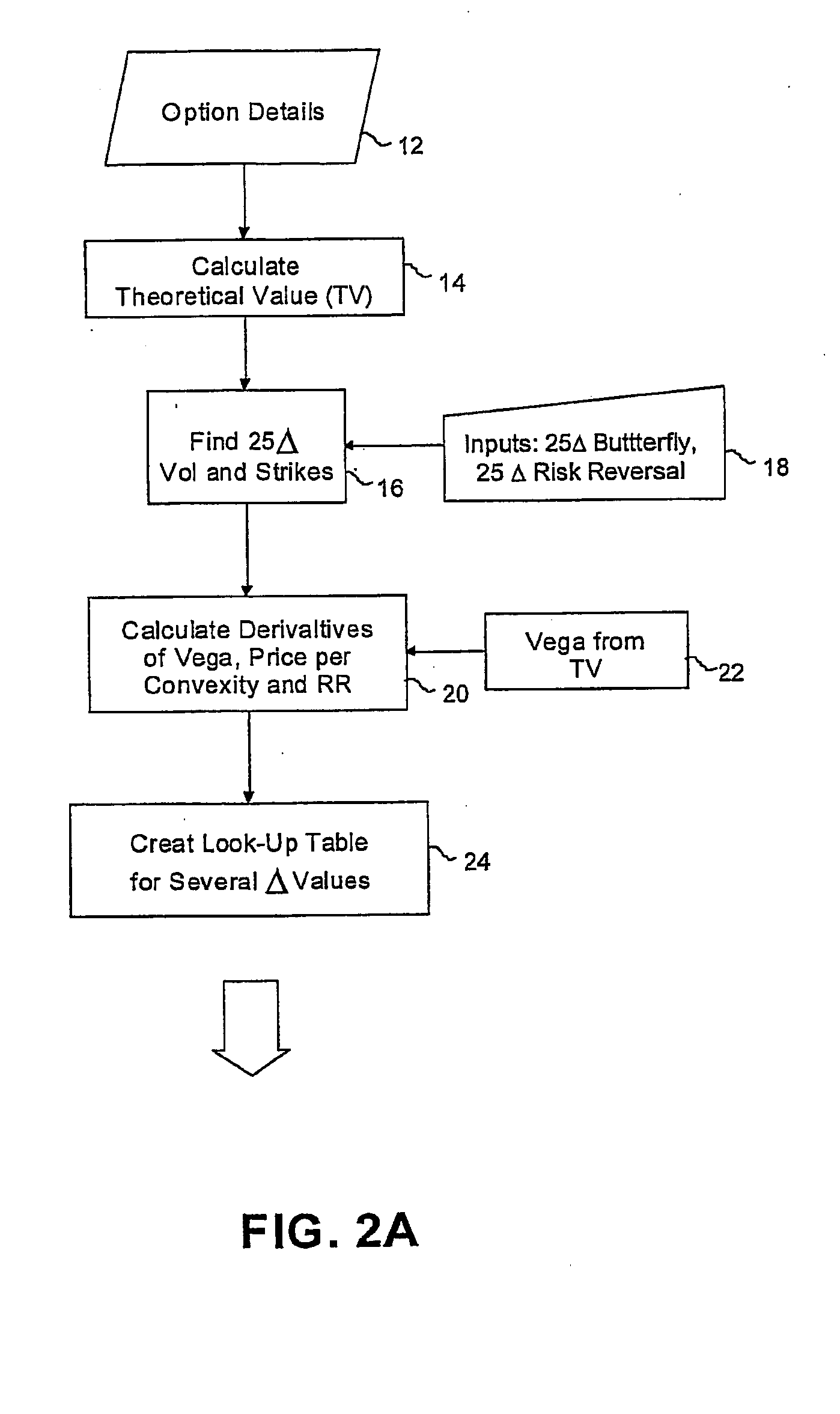
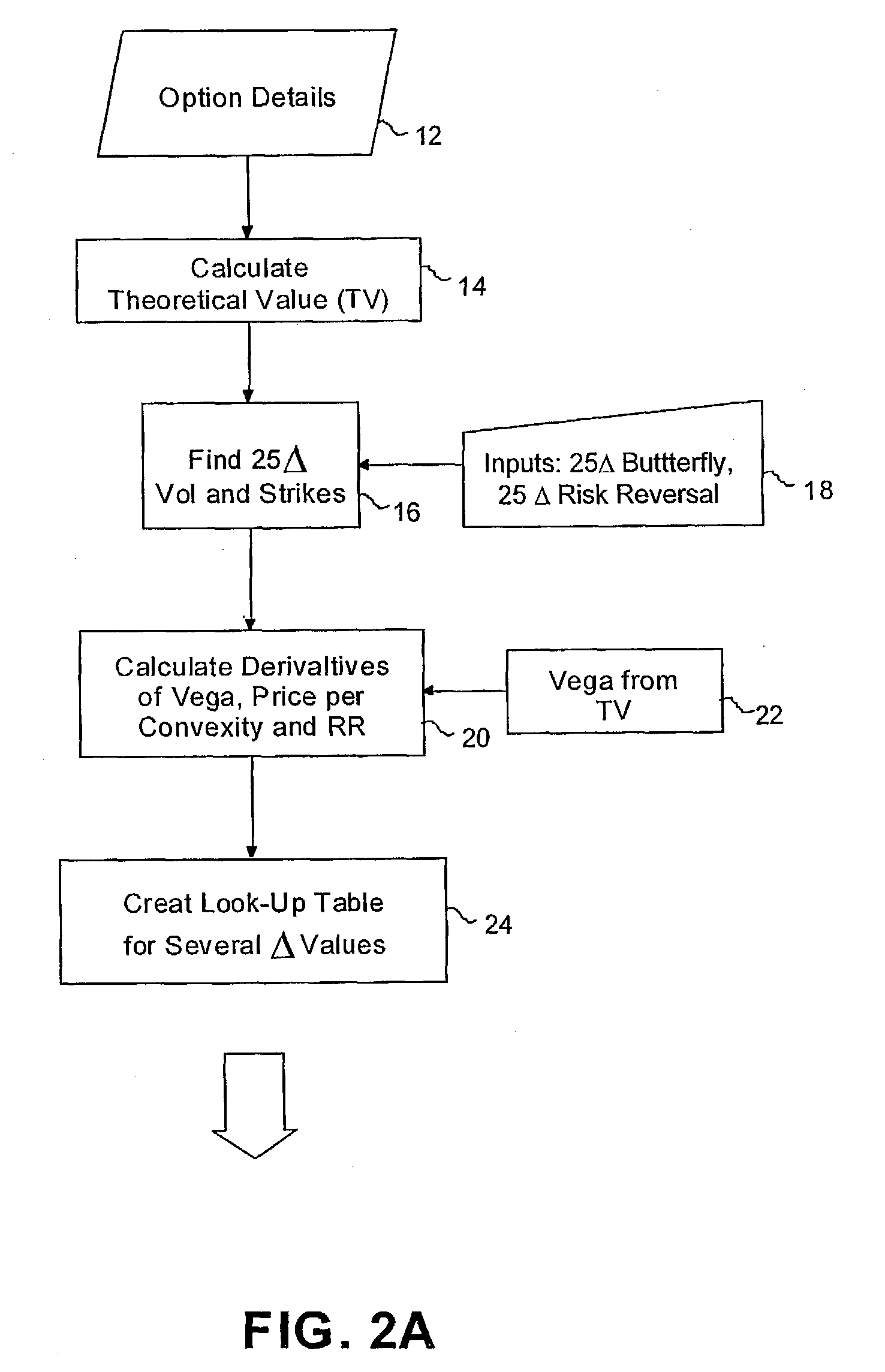
InactiveUS7315838B2Accurately determineFinanceMagnetic/electric field screeningSimulationMarket conditions
Owner:SUPERDERIVATIVES INC
Methods and apparatus for self-adaptive, learning data analysis
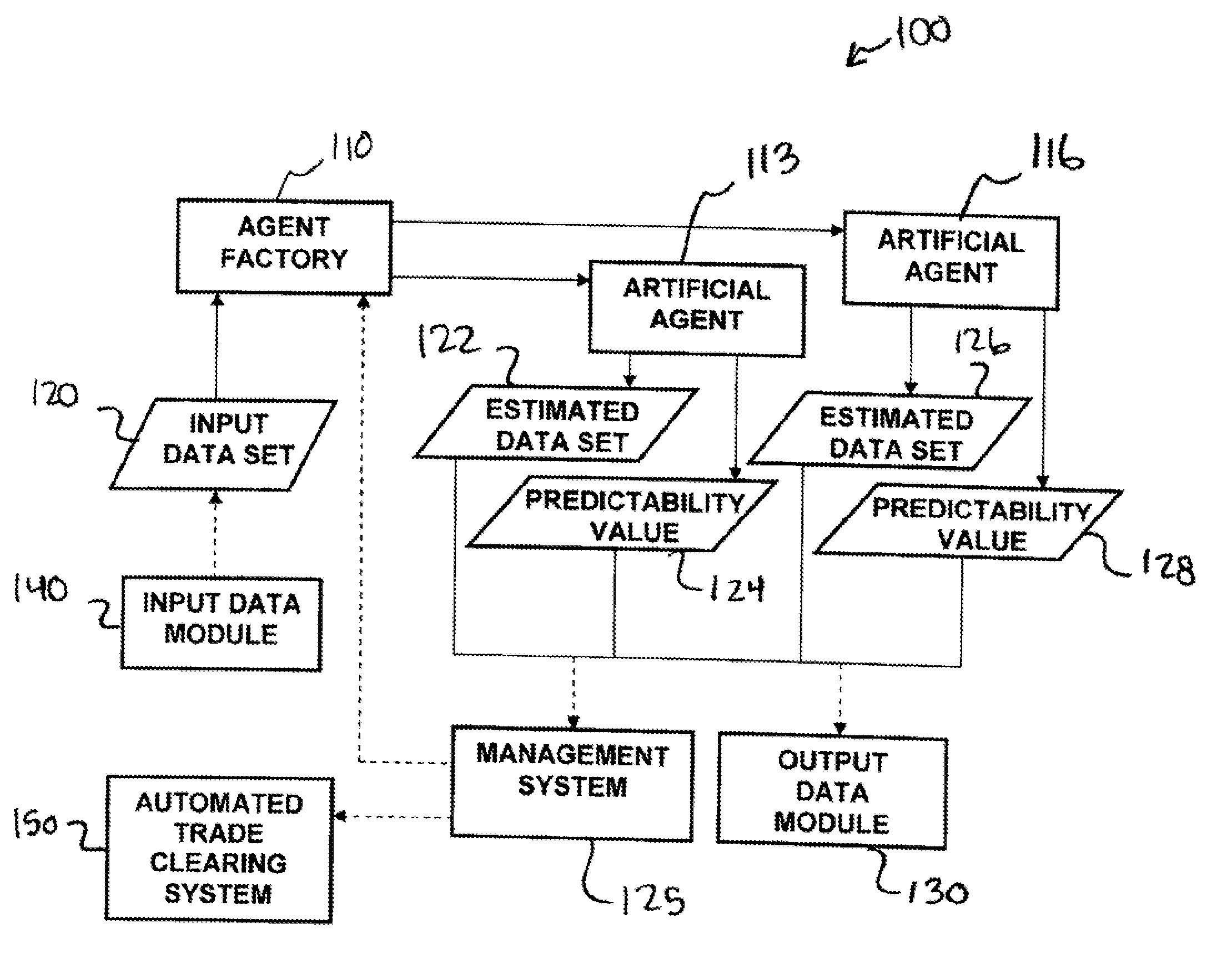
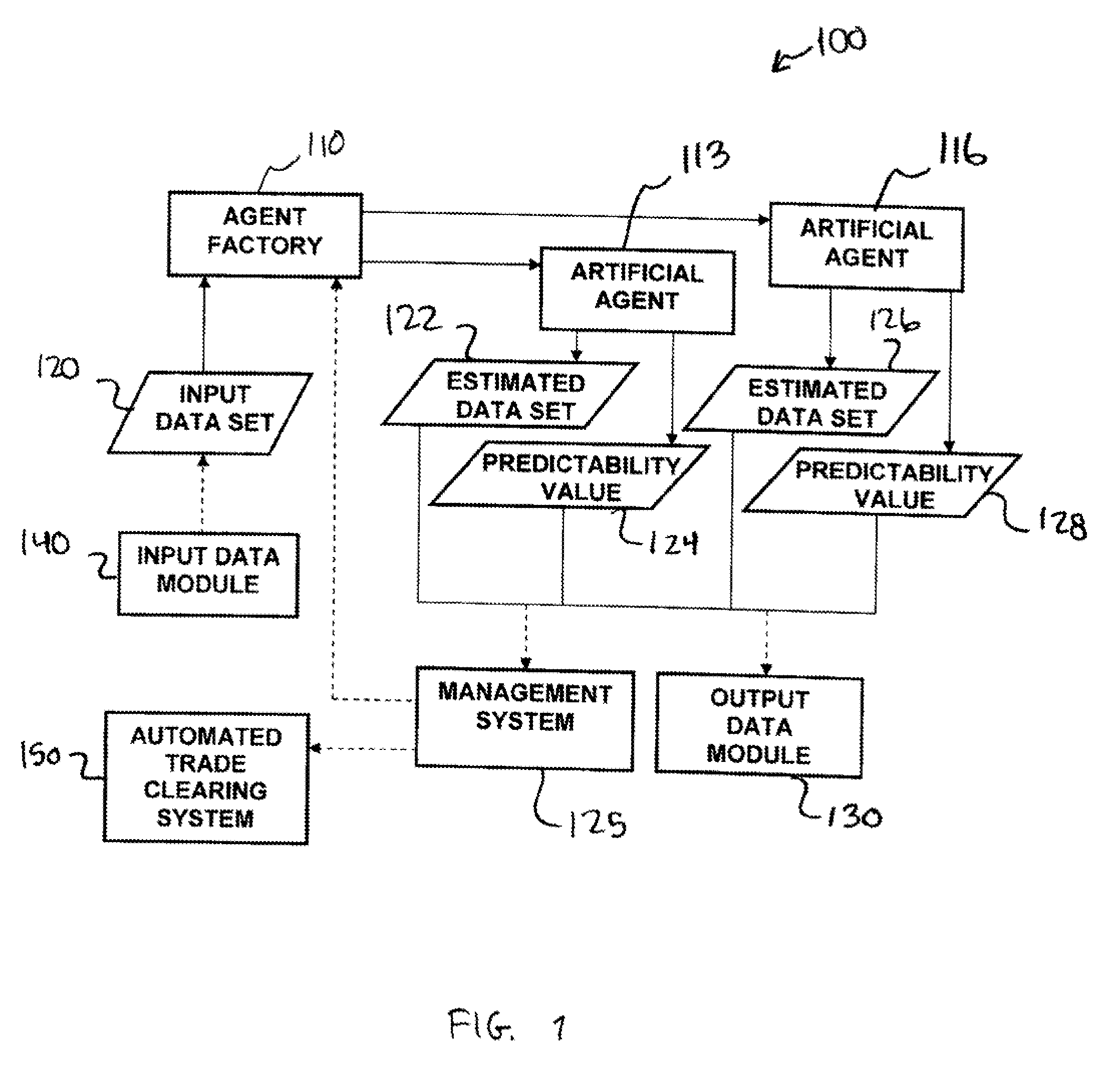
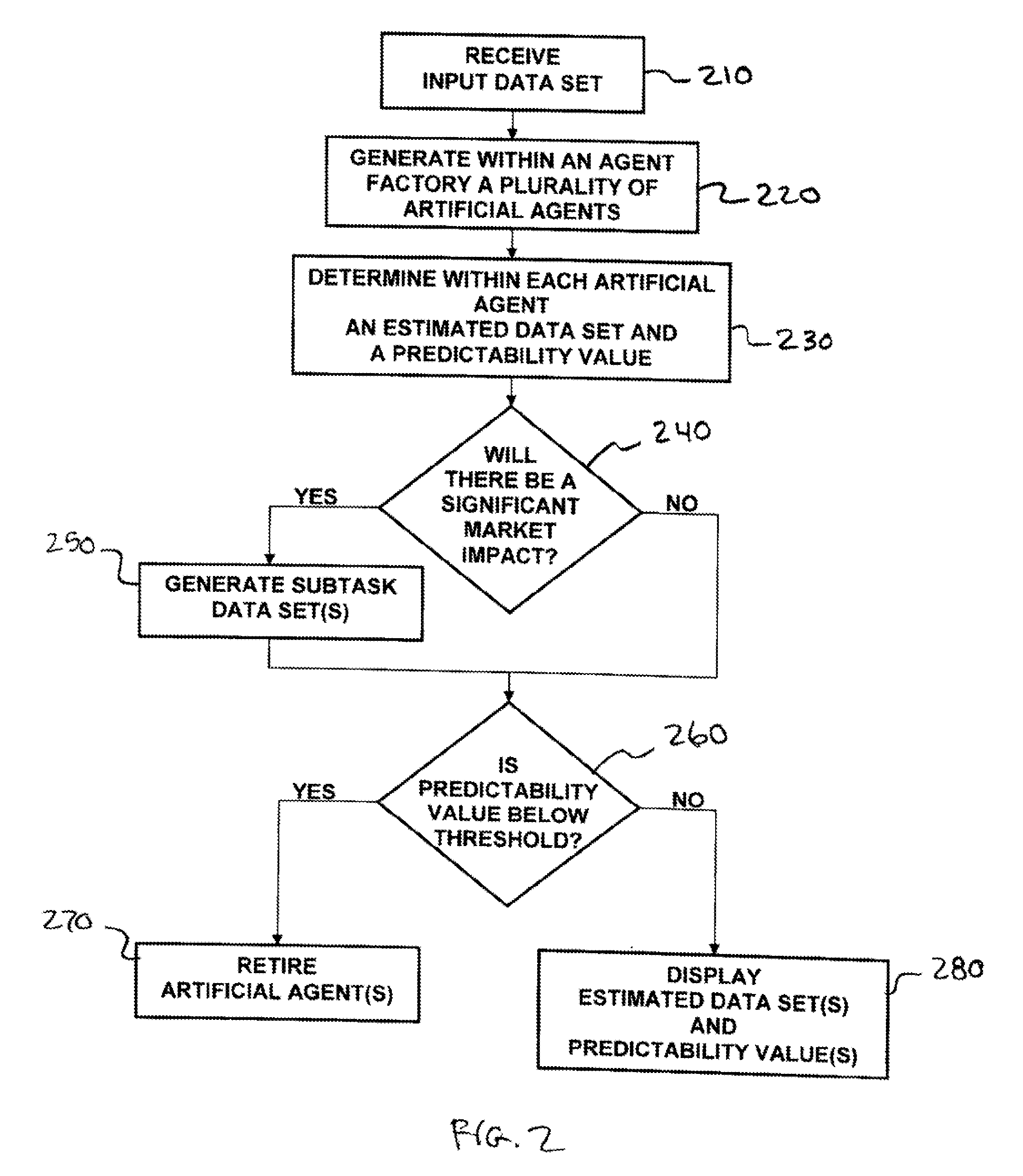
Methods and apparatus for analyzing financial data generally includes a predictive modeling system. The predictive modeling system may include an artificial agent responsive to an input data set. The artificial agent may produce an estimated data set including a market conditions data set. The market conditions data may include an estimate of at least one of liquidity of a market, strategy of a counterparty, and an effect of information leakage. The artificial agent may determine a predictability value for the estimated data set. The predictive modeling system may also include an agent factory responsive to the input data set. The agent factory may generate an artificial agent in response to the input data set.
Owner:ADAPTIV TECH
System and method for adaptive automated resource management and conservation
InactiveUS20140297001A1Accurately pattern of useEliminate needProgramme controlComputer controlElectricityResource Management System
Systems, methods, and devices to provide simple adaptive automated resource management of a resource system (such as but not limited to electricity, natural gas, water, data, bandwidth allocation, access to information, etc.) on a local basis, based on automatically detecting, measuring and combining time-varying resource provider preferences, resource market conditions, resource supply source conditions, environmental conditions and resource system impact on the environment, together with resource user locations, user priorities and preferences, and information about other conditions that may be relevant to the operation of the resource management system in order to optimize performance of the resource system to better meet or approach defined goals, and to measure and display the results achieved by the resource management system compared against those goals.
Owner:KASPAR LLC
Individualized marketing to improve capacity utilization
Suppliers of goods and / or services subject to shifts in capacity utilization design and implement marketing campaigns around utilization forecasts, targeting marketing expenditures on periods of excess capacity rather than periods without excess capacity, and in some embodiments also to alter variables such as pricing, consumer targeting, or even the intensity of the campaign itself on a dynamic basis in response to changing market conditions.
Owner:KAYAK SOFTWARE CORP
Investment advice systems and methods
The present invention provides investment advice systems. One version of the present invention provides investment advice systems that allow a user to select one or more advisors from a list of investment advisors. According to this version of the invention, the end user can receive advice on a particular transaction either separately from each investment advisor or in consensus. The system offers advice in part on the user's portfolio, tax position and risk profile and in part on the advisors evaluation of current market conditions. Thus, when a user is considering making a transaction, the user can obtain advice that can take into portfolio information including a user's proposed transaction and / or user portfolio information. A user armed with the above-described customized advice can execute a specific transaction and have their portfolio updated to reflect execution of that (those) order(s). In an alternative embodiment, a user's desire to buy or sell a security and / or a need for rebalancing a user's portfolio can generate transaction(s). As a result, the system will generate a buy / sell list (including recommended alternatives) from which a user can select.
Owner:CHECKFREE SERVICES CORP
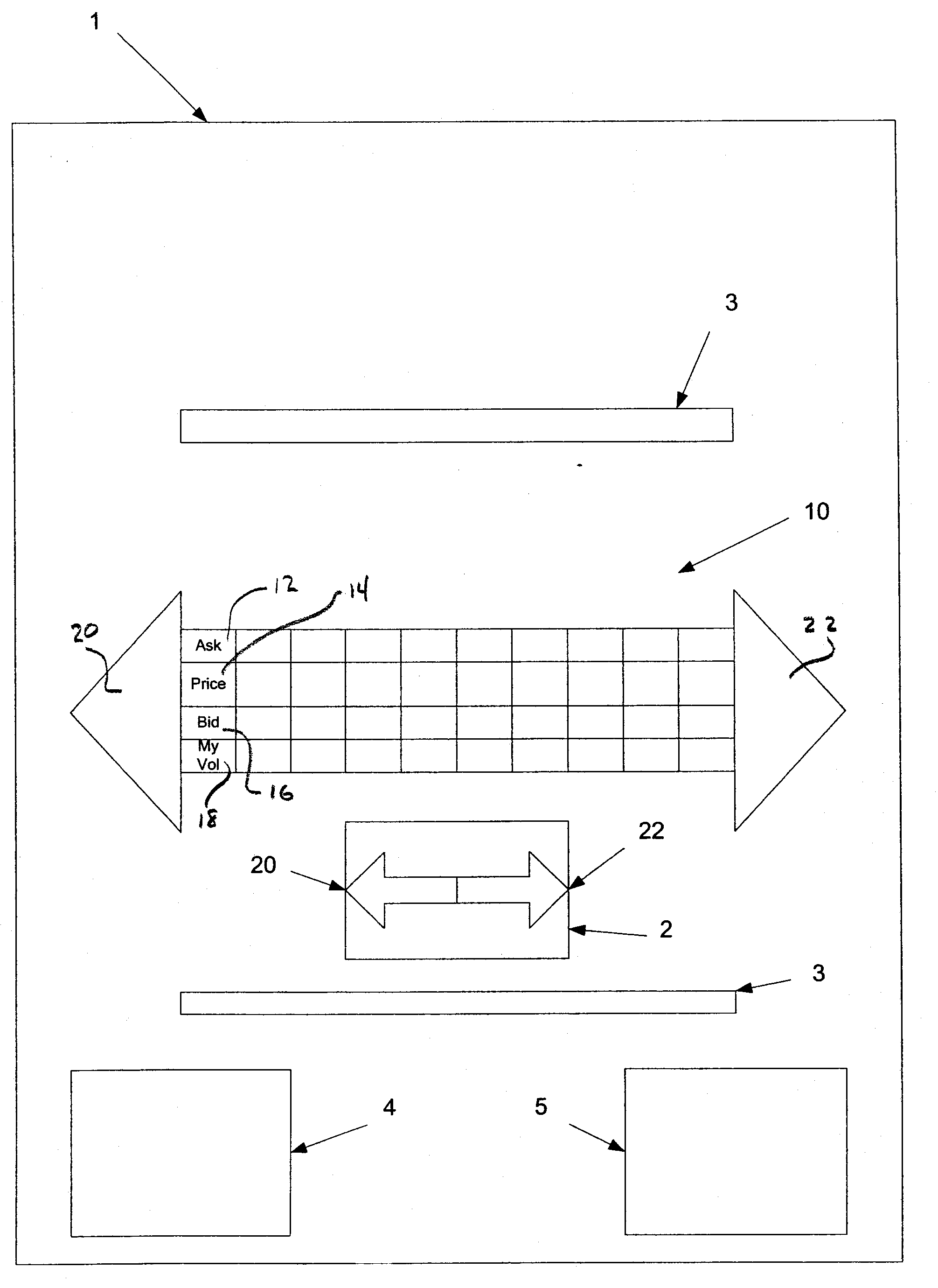
Trading system and method having a configurable market depth tool with dynamic price axis
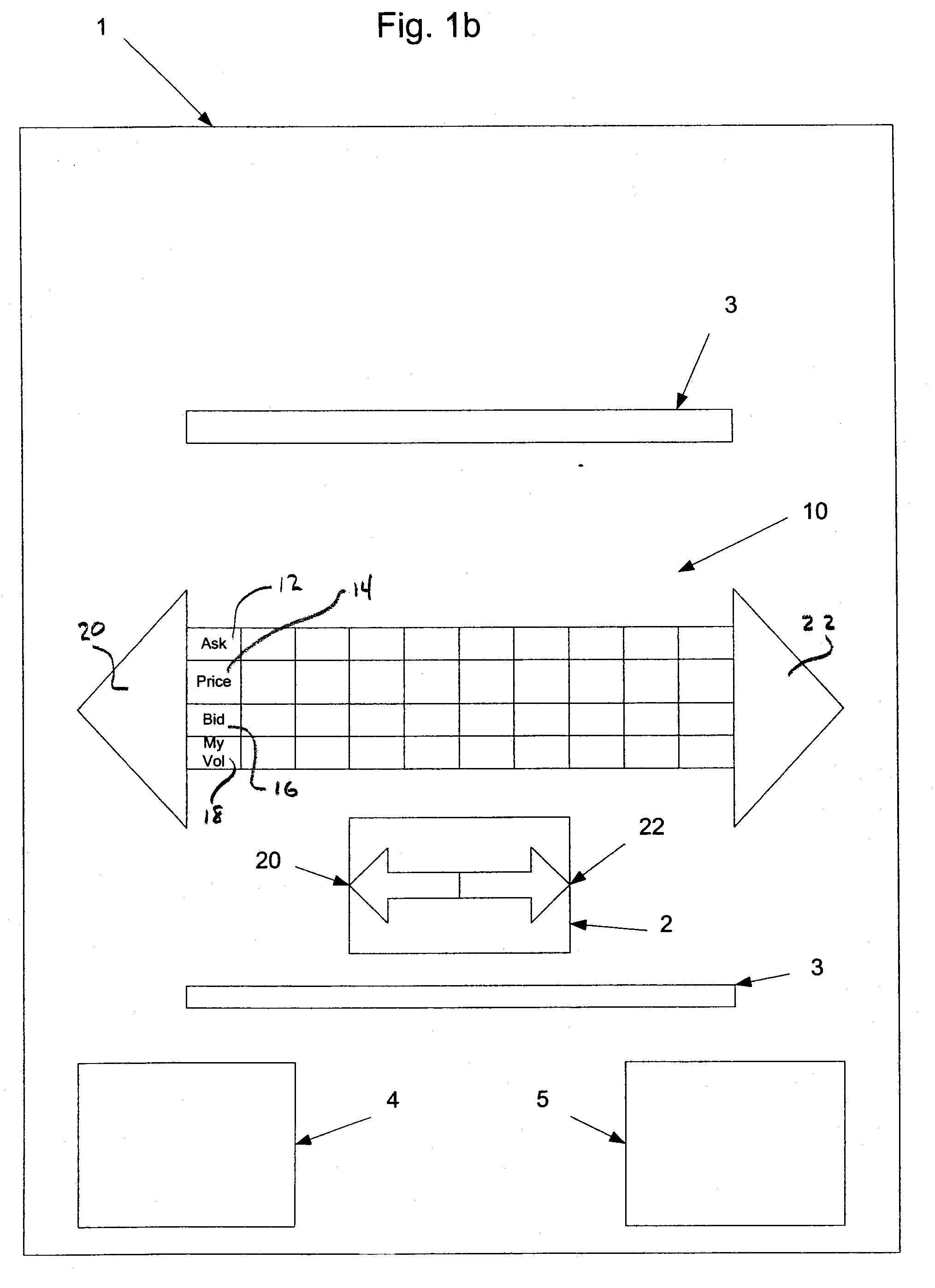
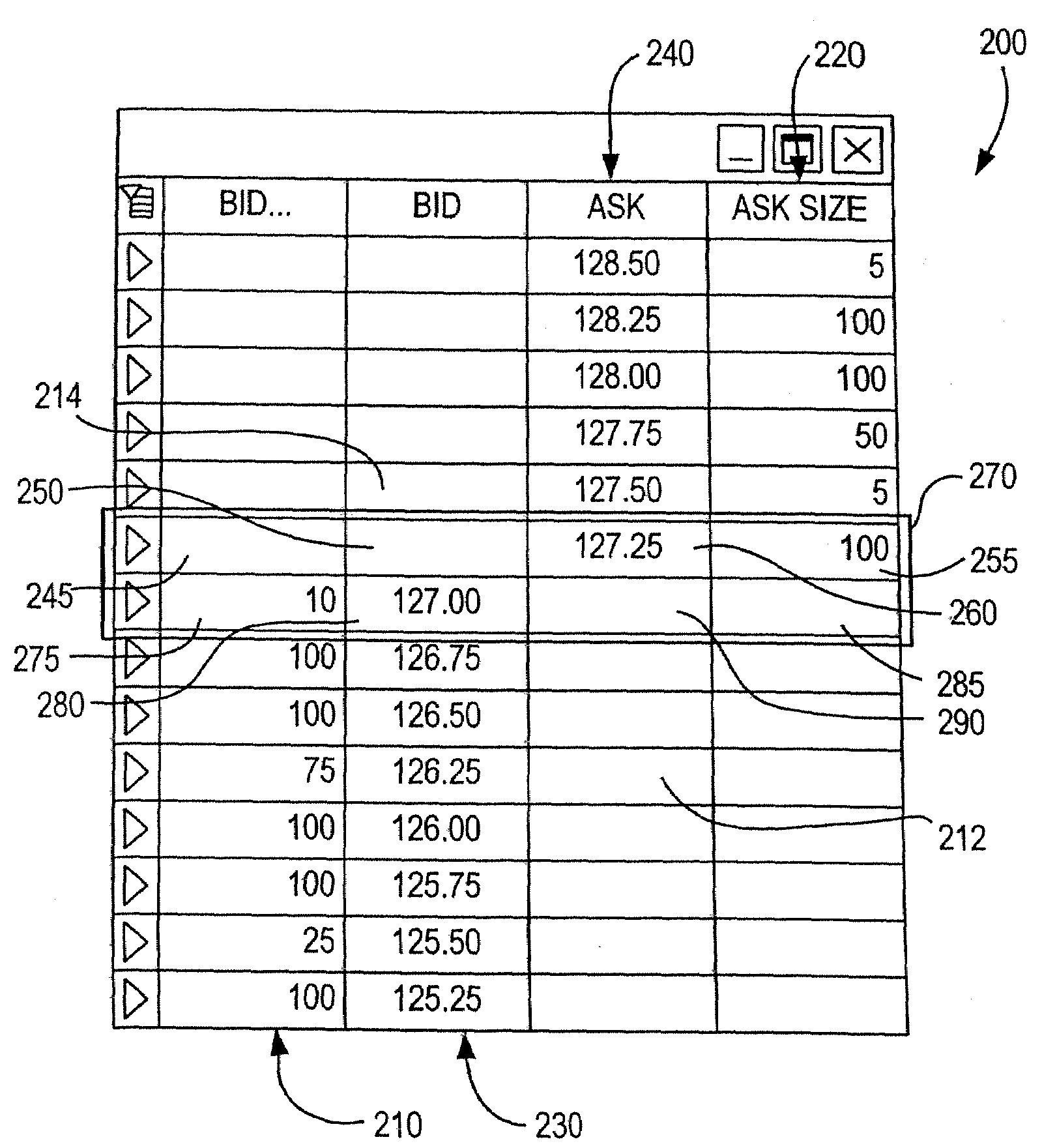
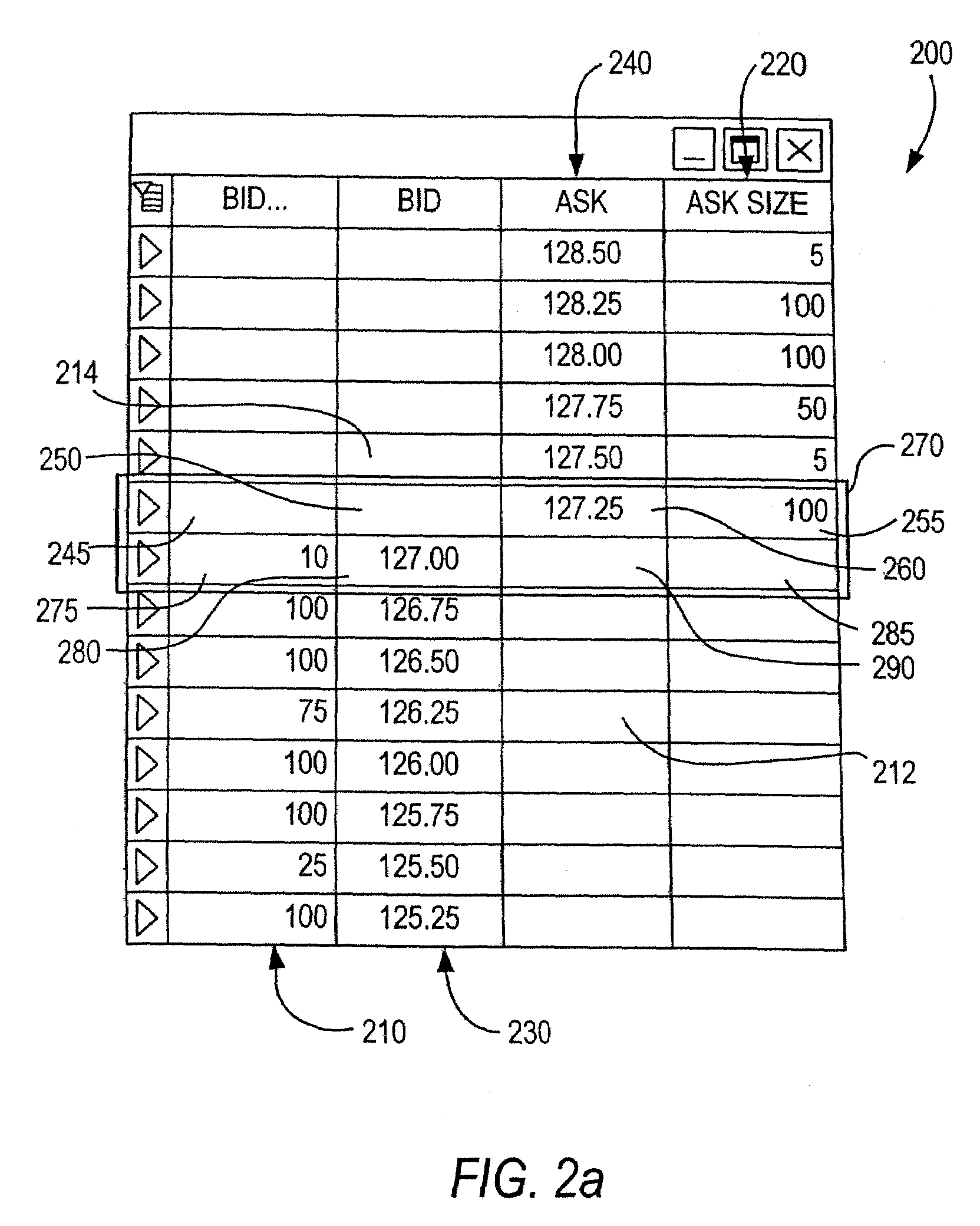
InactiveUS20070208654A1Comfort levelFinanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A system and method for the electronic trading of investment vehicles, such as stocks, bonds, options, commodities, stock and futures index contracts, and the like, is disclosed. The system and method provide a graphical user interface having a versatile and efficient market depth tool with a dynamic price axis for executing trades. The tool facilitates the display of and the rapid placement of trade orders within the market. The system provides for user initiated functionality to control, among other things, the manner in which the dynamic price axis moves in response to market conditions.
Owner:MF GLOBAL
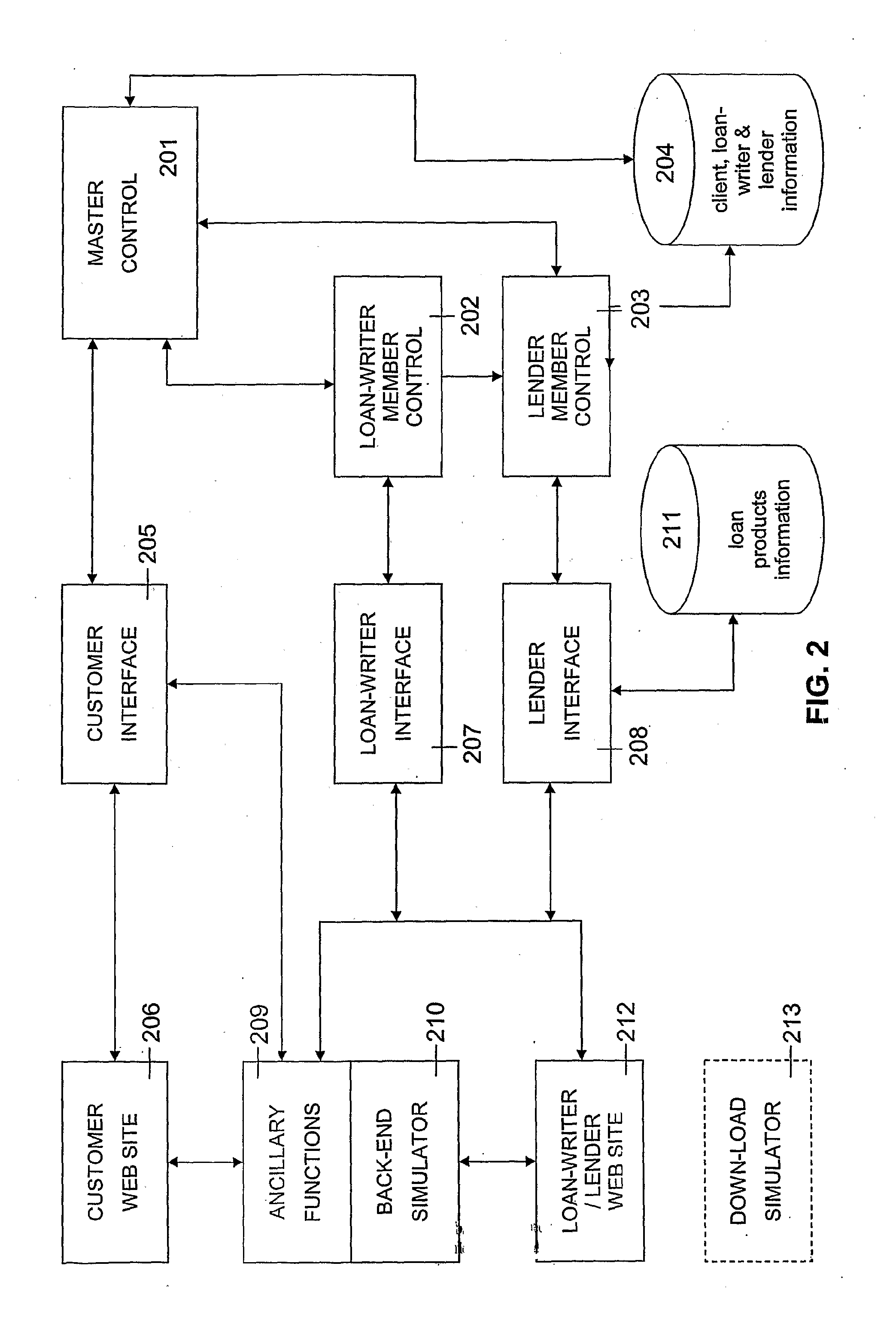
Loan Simulation Method And System
InactiveUS20070288357A1High simulationFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsApplication softwareComputer science
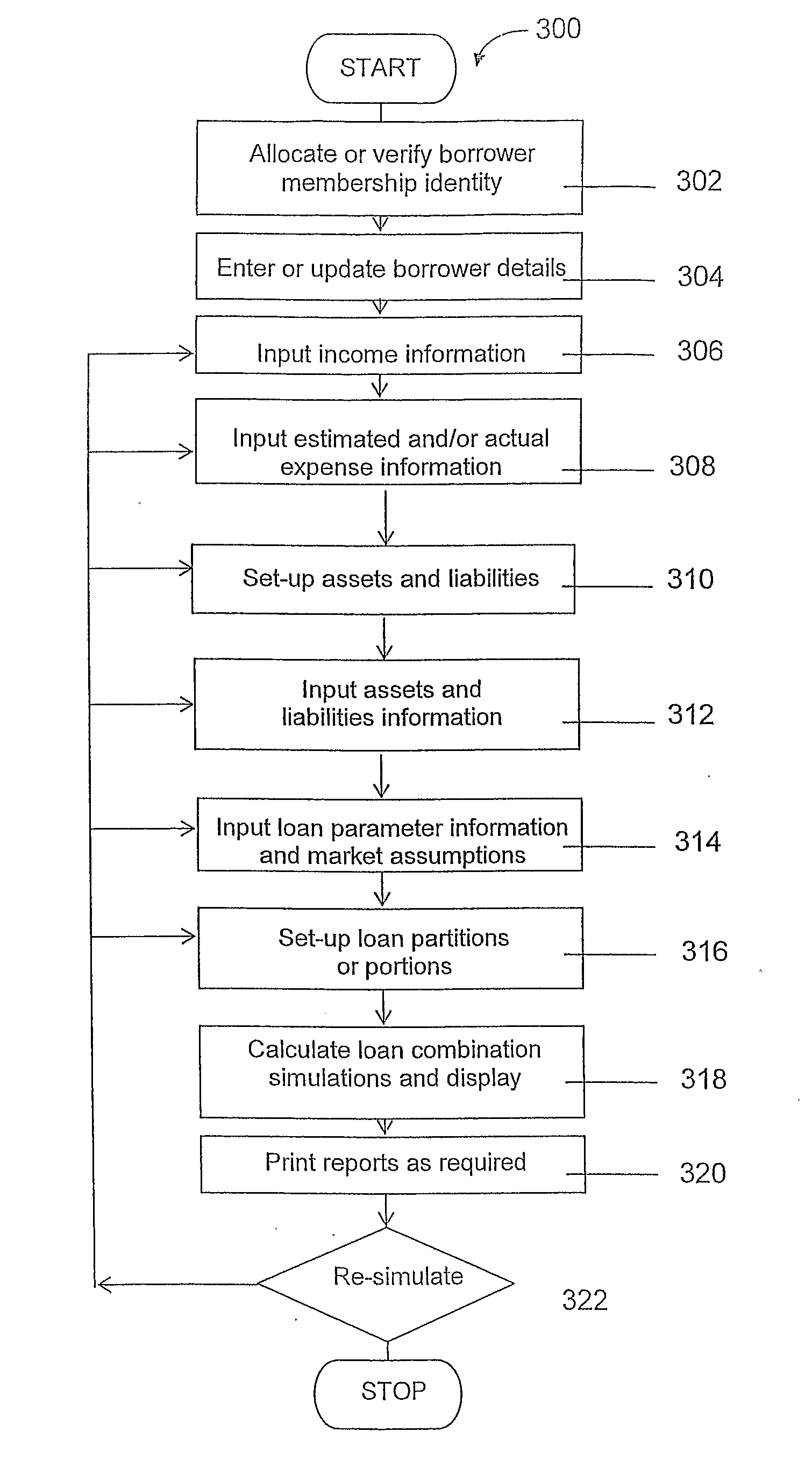
A method (300) of simulating for a borrower the performance of a loan, which loan contains a plurality of loan portions wherein each loan portion has different loan parameters, which borrower may verify their identity (302) and enter / update borrower details (304) as required. The method includes the steps of: inputting income information (306) about income of the borrower; inputting asset information and liability information (308) about assets and liabilities of the borrower; inputting expenditure information (310) about expenditure of the borrower; inputting loan parameter information (314) about the amount, interest rate, repayment mode and term of each of said plurality of portions of the loan; providing assumptions about future market conditions effecting the loan; calculating a flow of funds (318) available for repayment of each portion of the loan according to the borrower income, the borrower expenditure, the borrower assets and liabilities, and the loan parameter information and producing a simulation of loan balance according to the flow of funds and the assumptions about future market conditions, for display and / or printing (320). An on-line subscriber system (100) and application software (200) enabling users to conduct assessment and ongoing management of loans and similar finance products according to the method are also disclosed.
Owner:GO FIGURE CALCULATORS
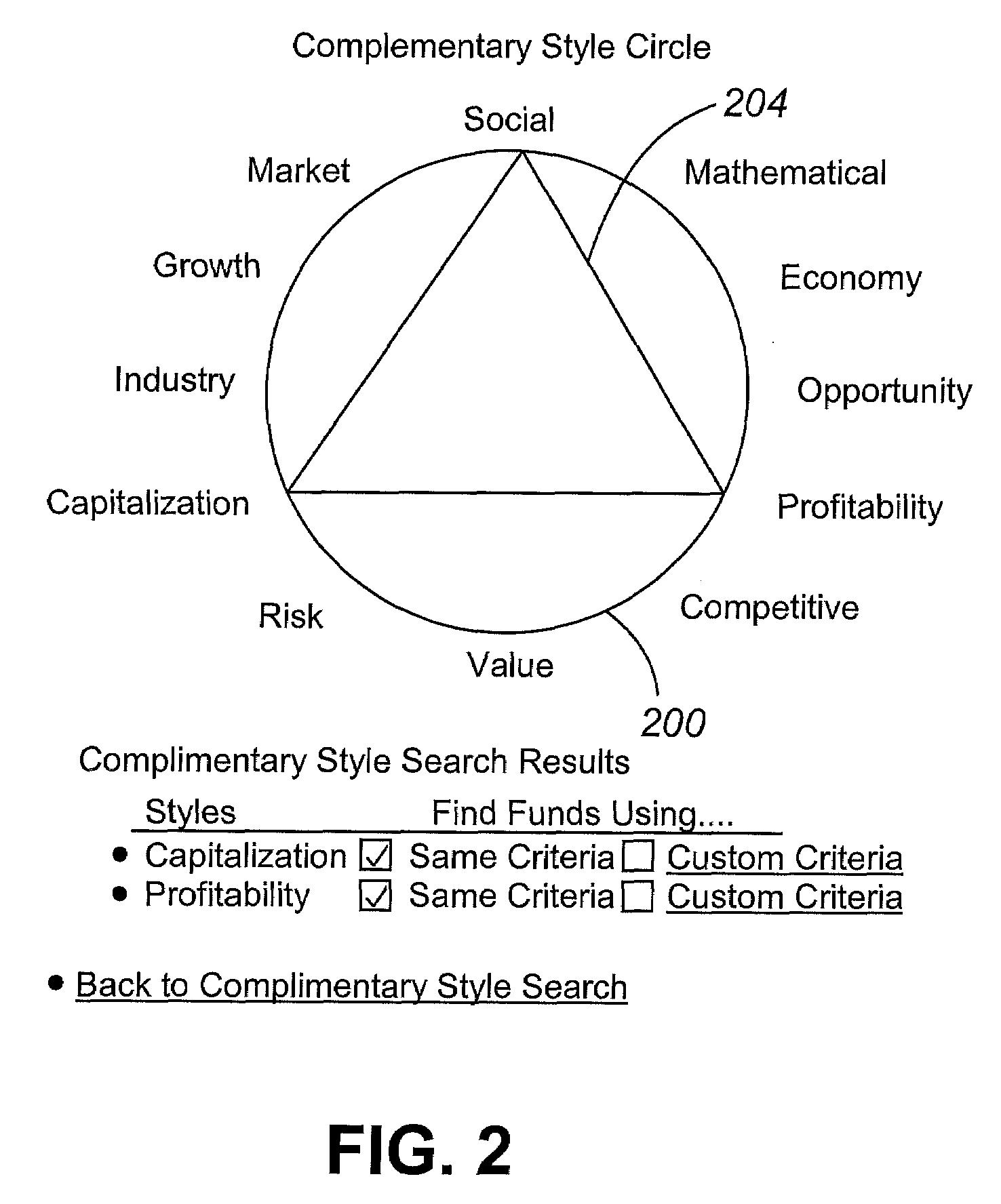
Investment classification and tracking system
ActiveUS20080071702A1Effectively and efficiently configureIncreased riskFinanceForecastingKnowledge managementTracking system
The present invention is directed to an asset classification system based on investment strategy. The investment strategies include capitalization strategy, competitive position strategy, economic conditions strategy, future growth investment strategy, market condition strategy, opportunity strategy, profitability strategy, risk strategy, social considerations strategy, and valuation strategy.
Owner:ATHENAINVEST
Individualized marketing to improve capacity utilization
Suppliers of goods and / or services subject to shifts in capacity utilization design and implement marketing campaigns around utilization forecasts, targeting marketing expenditures on periods of excess capacity rather than periods without excess capacity, and in some embodiments also to alter variables such as pricing, consumer targeting, or even the intensity of the campaign itself on a dynamic basis in response to changing market conditions.
Owner:KAYAK SOFTWARE CORP
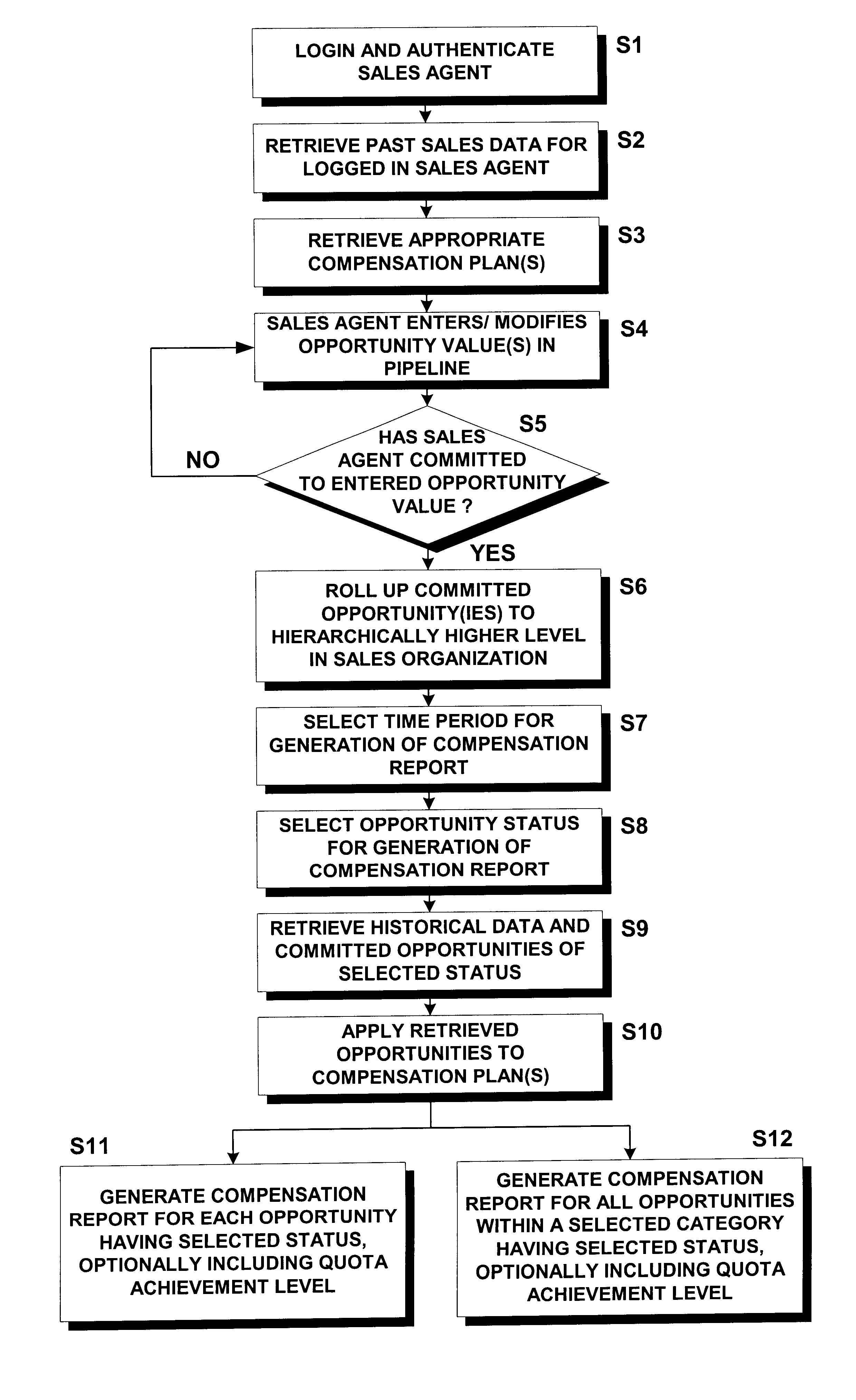
Income planner for corporate sales agents
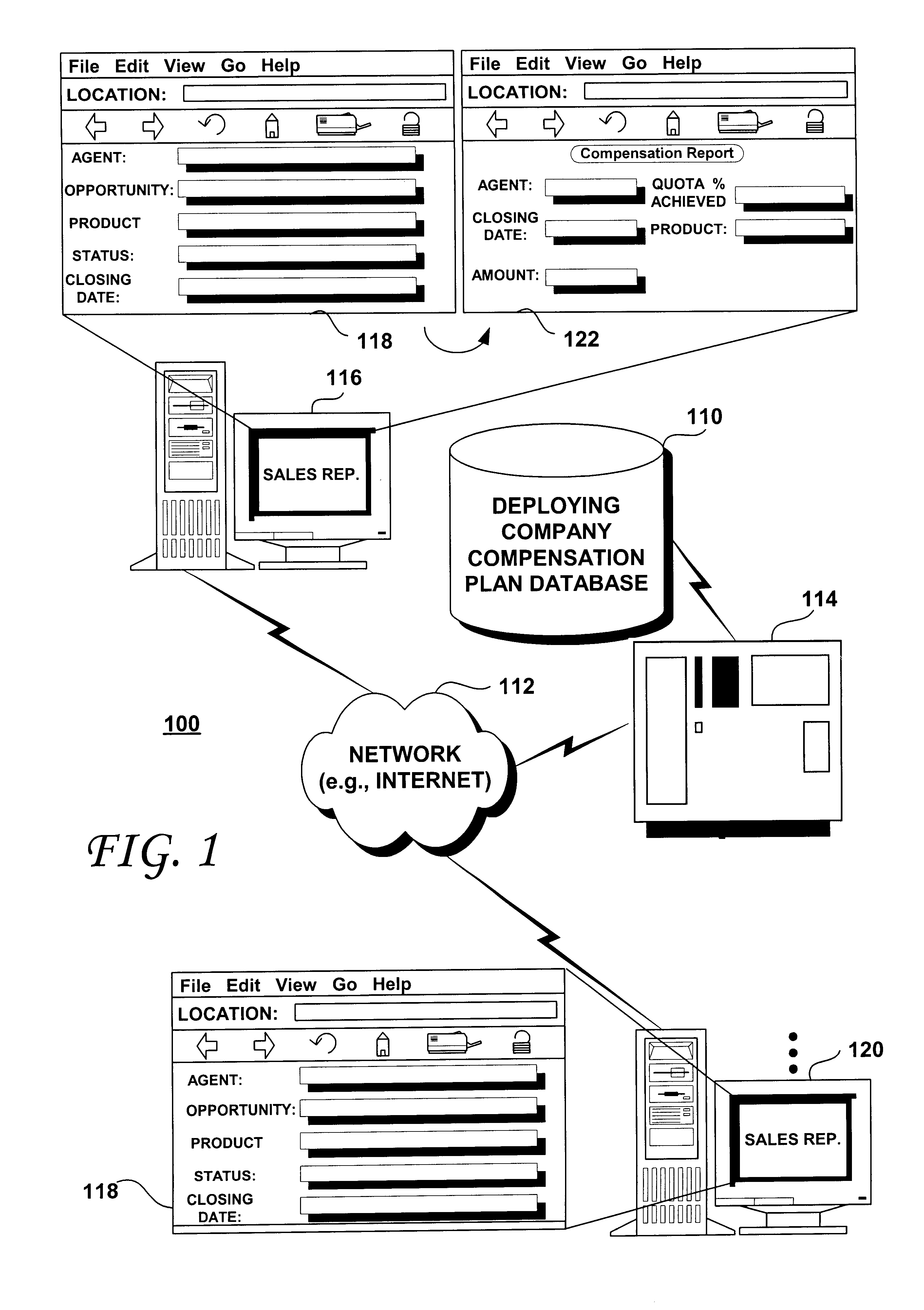
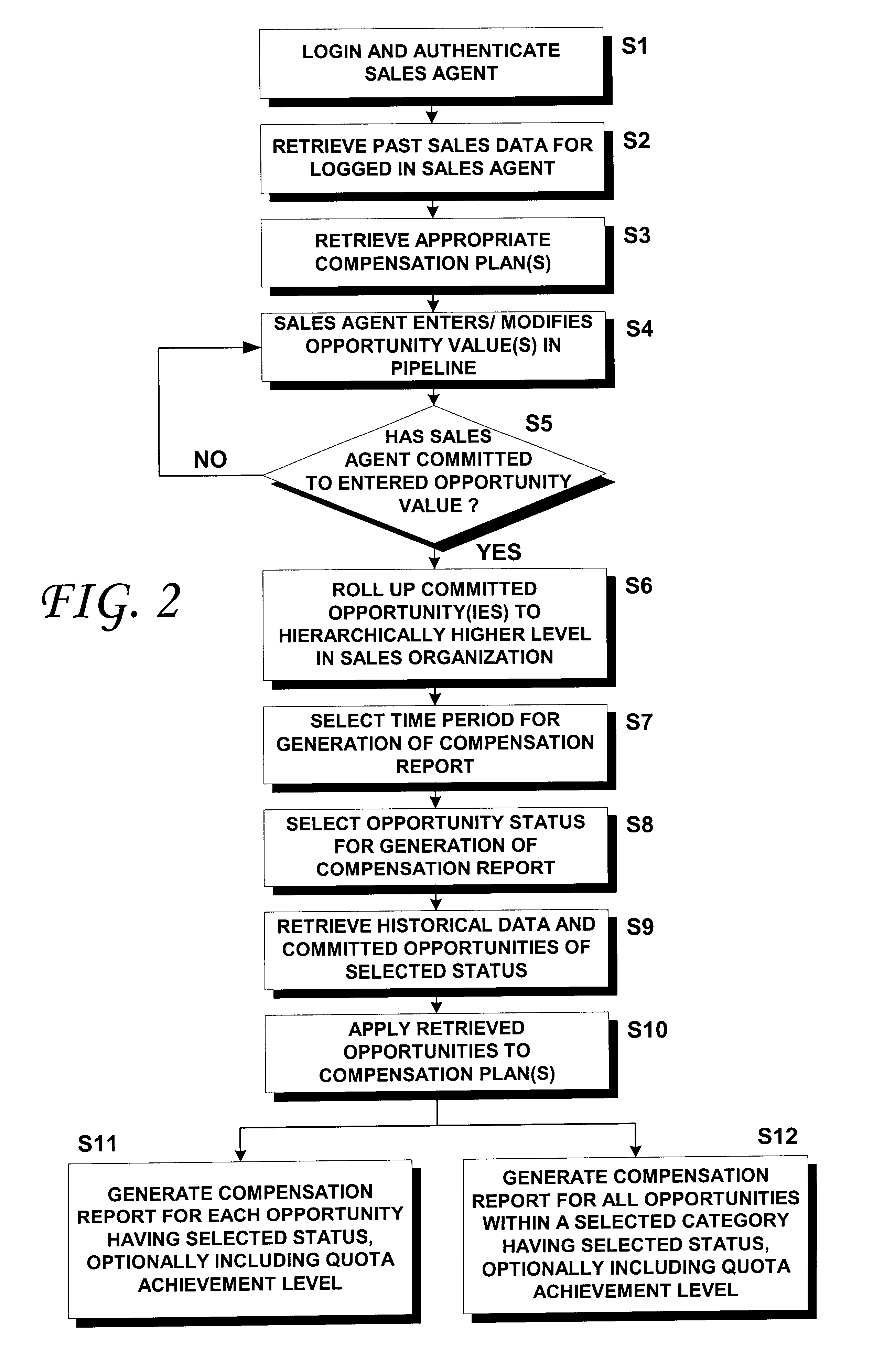
A computer-implemented method for computing the compensation for sales agents within a corporate sales force of a deploying company includes steps of creating one or more sales agent compensation plans tailored to provide an incentive for the sales agents to sell goods and / or services according to a corporate sales strategy. The compensation plan(s) are then stored within a database. Sales agents are then provided with remote access to the database via a computer network, such as the Internet. The sales agents may then input past sales into the database and may input, qualify, modify and / or store future sales opportunities into the database. The past sales and future sales opportunities may then be applied to one or more of the stored compensation plan(s) to calculate the sales agents' compensation. Quota achievement levels may be included in the calculated compensation and graphically or textually displayed for the sales agents. The sales agents may enter hypothetical sales opportunities and determine, in real time, how those hypothetical sales opportunities would affect their compensation, should the sales underlying the hypothetical opportunities close. The compensation plans may be updated and / or replaced as needed to enable the sales force to easily respond to changing market conditions and / or as new products, services and / or promotions are offered by the deploying company.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
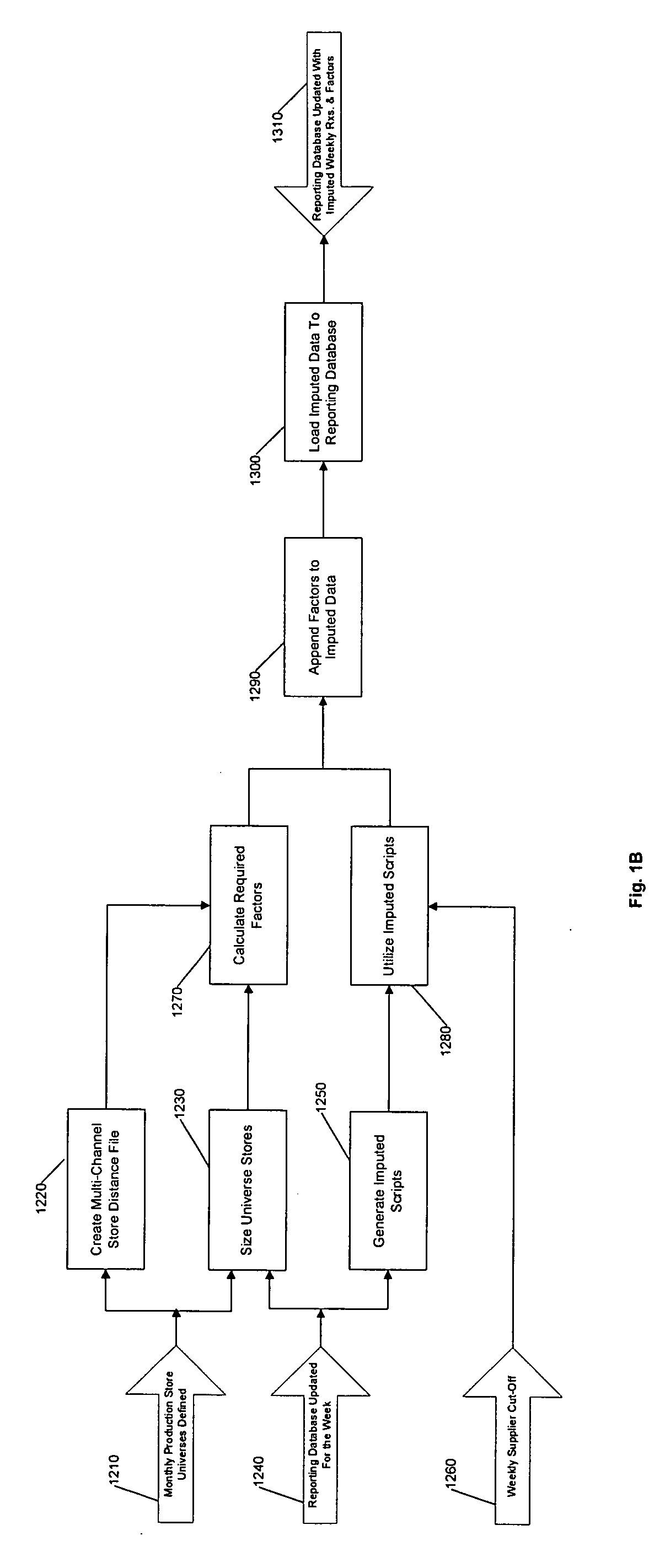
Projection factors for forecasting product demand
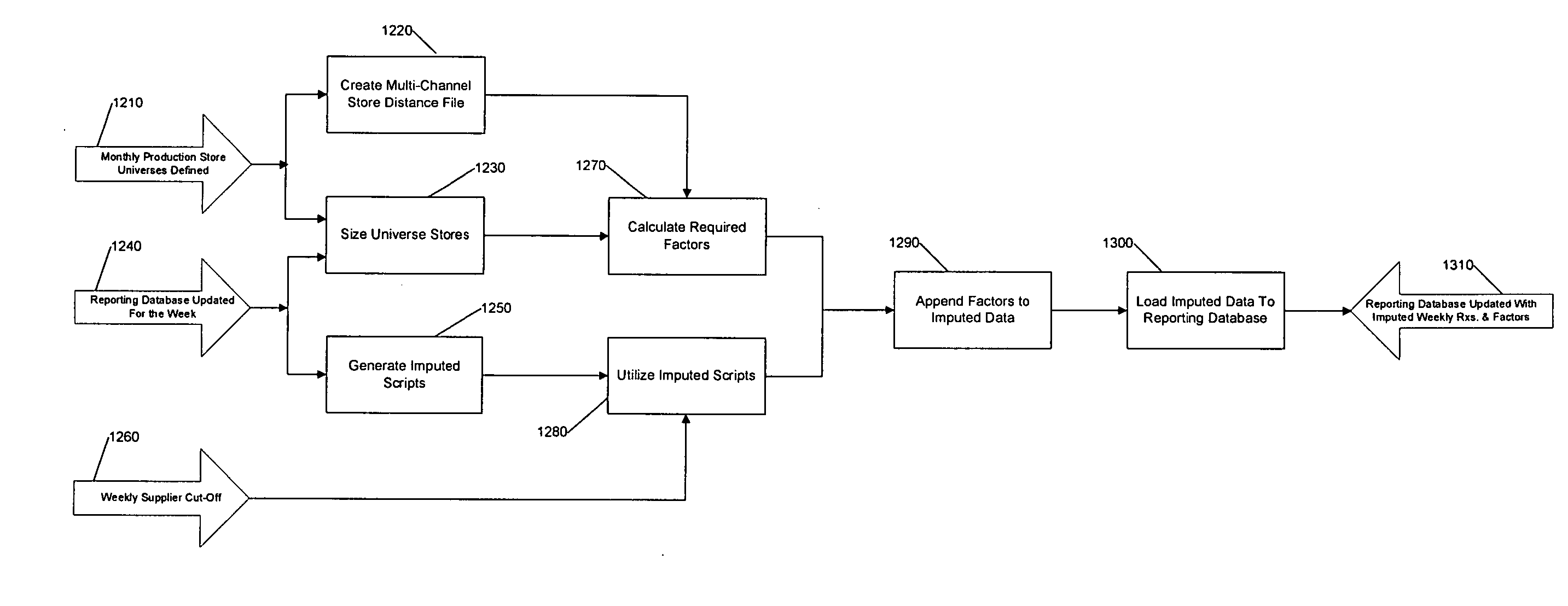
Projection factors are used to project product sales data from sample retail outlets to the universe of outlets. Weekly forecasts of market conditions and product demand are generated based on the projected product sales data. The projection factors and the weekly forecasts are updated during the course of the forecasted week, for example, daily, as data on actual product sales during the forecasted week is received.
Owner:IMS SOFTWARE SERVICES
Method and apparatus for pricing a commodity
Owner:CONSTELLATION SOFTWARE UK
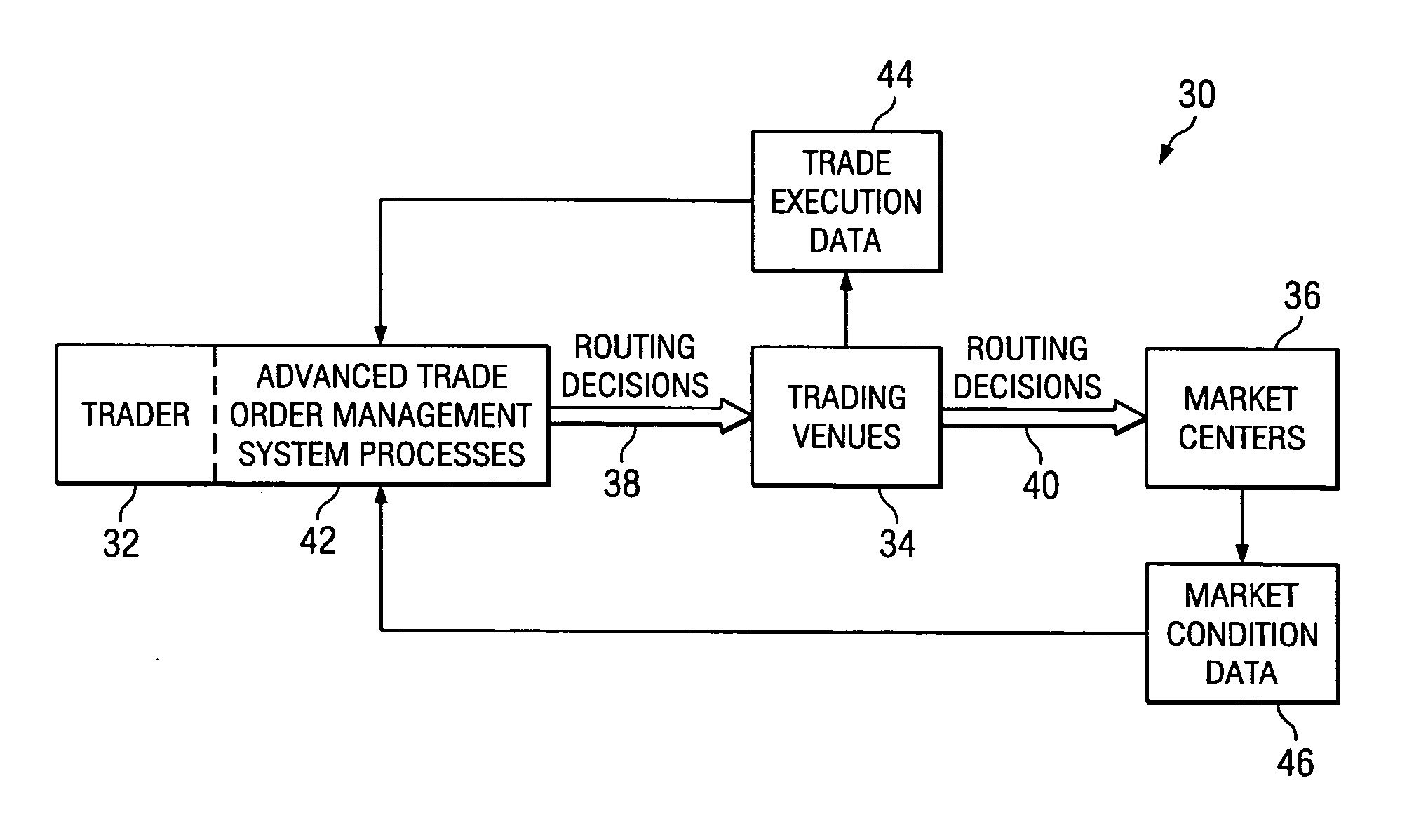
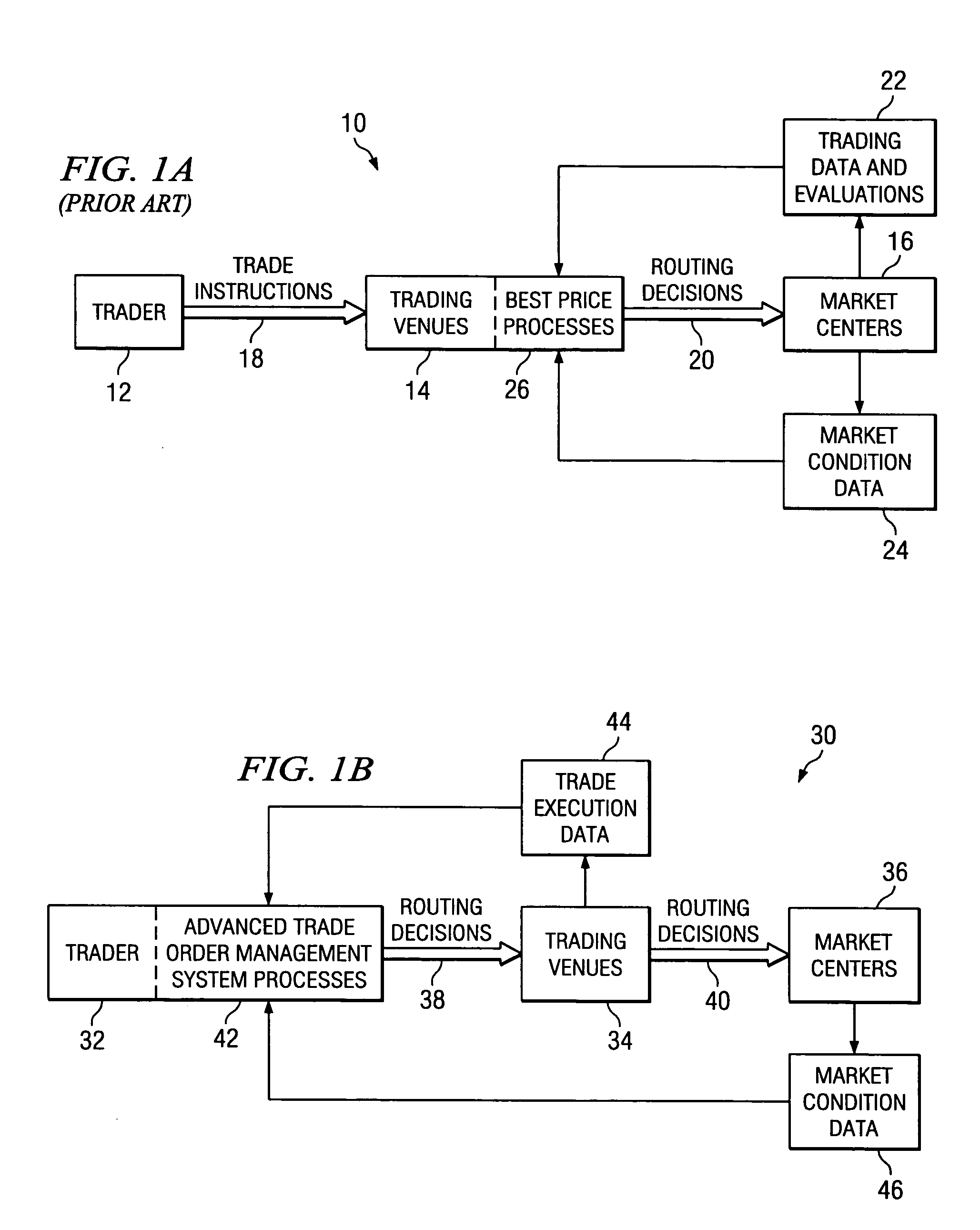
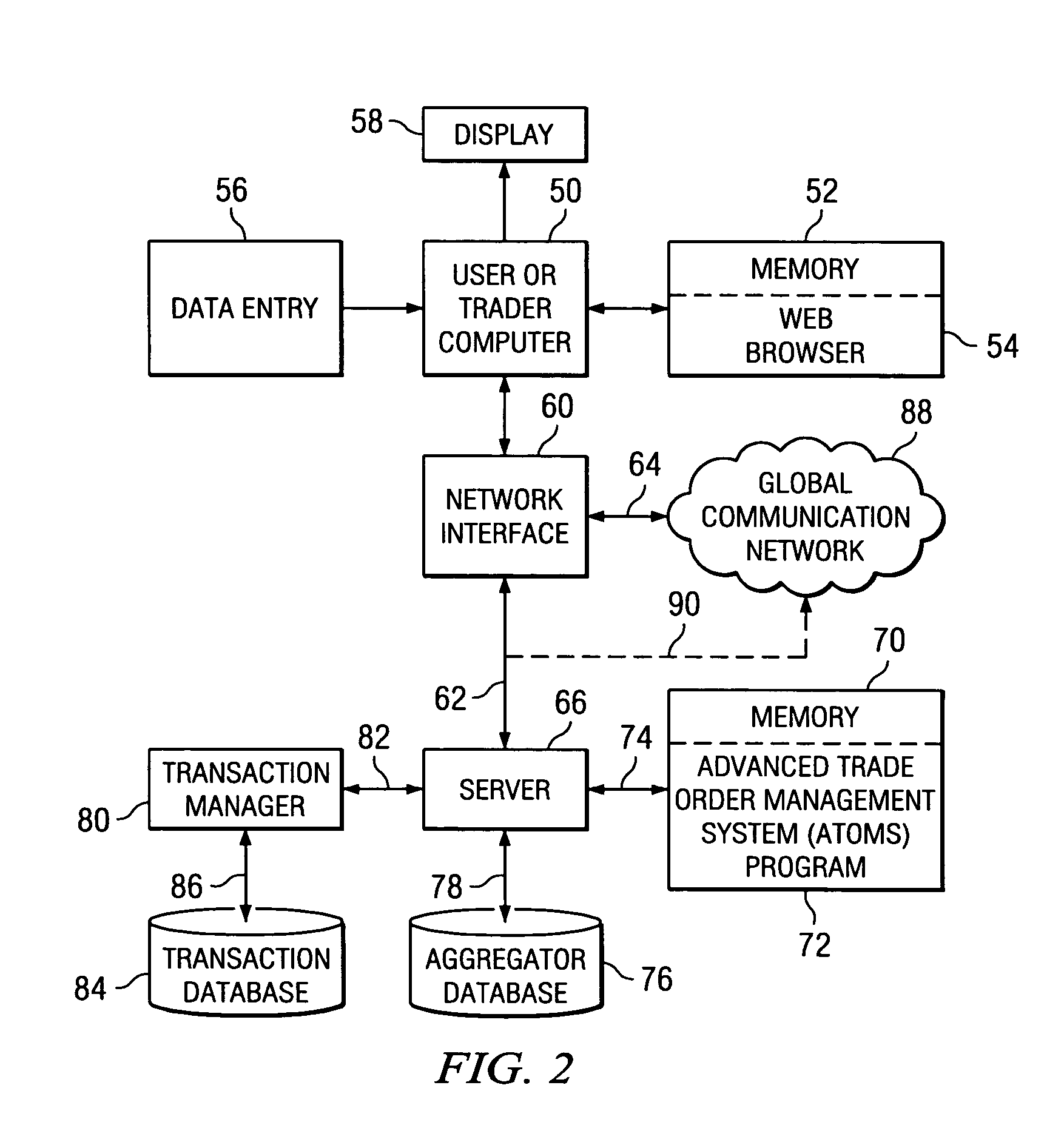
Method and system for investment trading venue selection
There is disclosed a method and system for scoring and selecting investment security trading venues using a computer-based advanced trade order management (ATOM) system. An ATOM program is launched on a user computer. Trading venue execution data and market condition data are processed post-trade at the trader location to compile or update a trade report for the plurality of the trading venues dealing in a particular security. In a pre-trade analysis conducted by the ATOM system prior to executing a trade order, trading venues are ranked according to their trading performance. The rankings are displayed in order of the highest performing venues, to enable the user / trader to select an optimum trading venue for an investment trade.
Owner:STACKPOLE DOWELL
Reduction of financial instrument volatility
InactiveUS20050131796A1Reducing earnings volatilityComplete banking machinesFinanceReduction procedureQualitative property
An earnings volatility reduction procedure includes determining a first sensitivity value of a portfolio to underlying market conditions, trading in an immunizing instrument having a second sensitivity value substantially equal in magnitude and opposite in value of the first sensitivity value, and trading in a qualifying instrument having a third sensitivity value substantially equal to the first sensitivity value. A derivative portfolio (in particular, one that includes a financial instrument for which changes in value are characterized as earnings pursuant to FAS 133) is structured by determining a sensitivity of the derivative portfolio with respect to financial conditions in a trading market, executing an immunizing purchase of a second trading instrument in an amount equal to the magnitude of the current sensitivity and opposite in value, and executing a qualifying sale of a third trading instrument in an amount equal to amount of the current sensitivity.
Owner:GOLDMAN SACHS & CO LLC
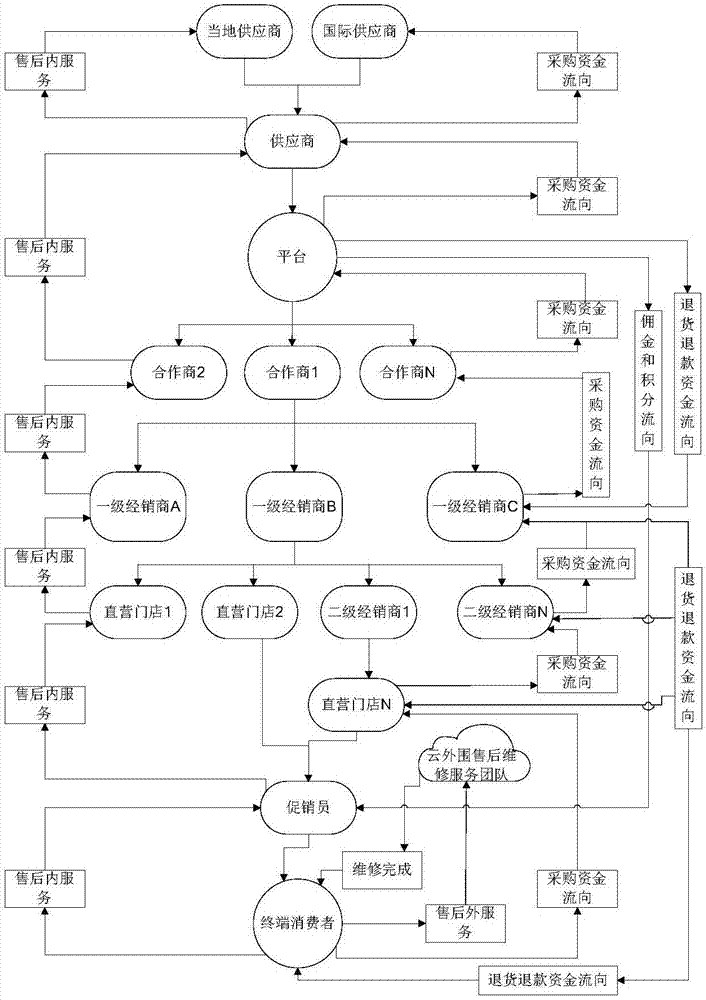
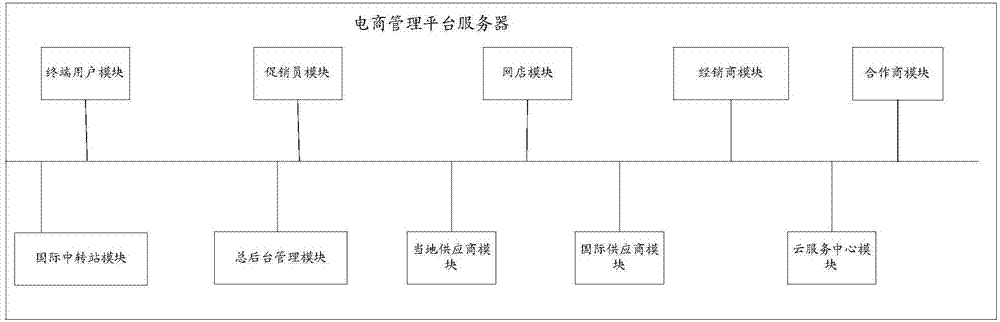
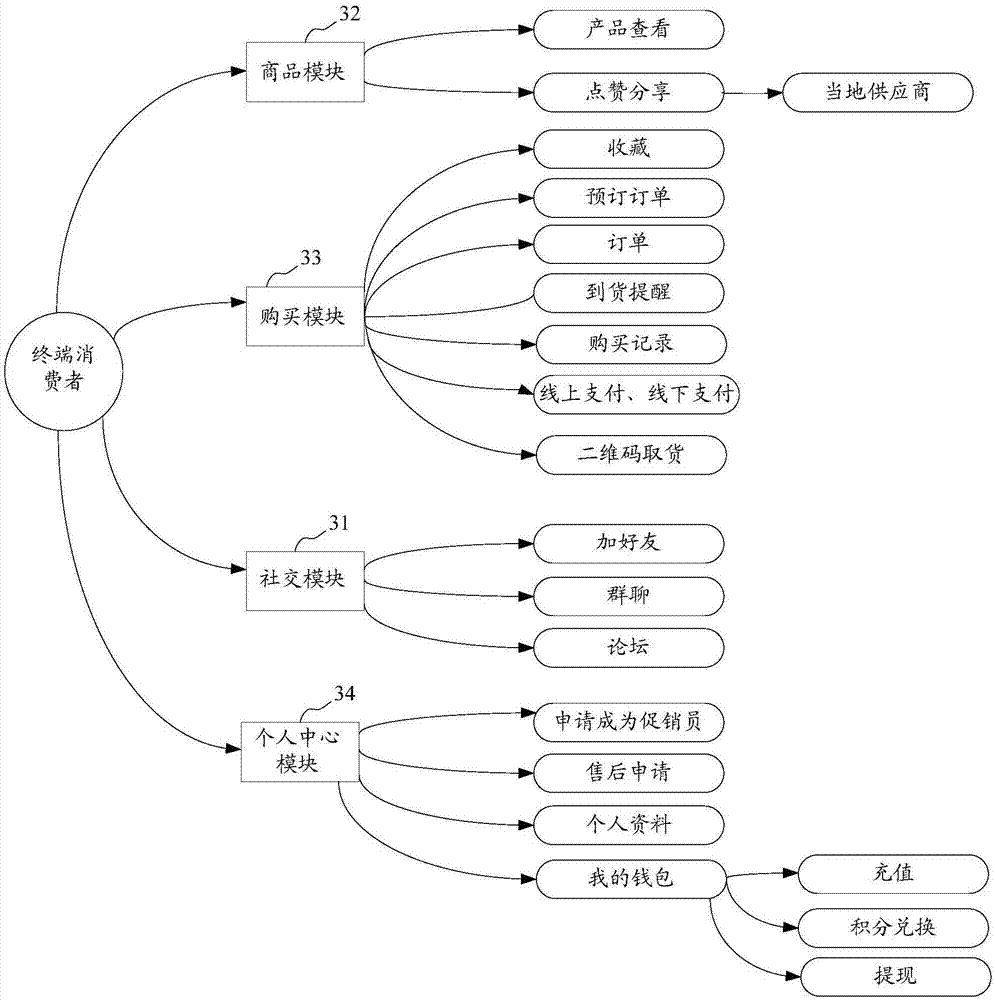
Cross-border vertical e-commerce management method
ActiveCN107886391AImprove user experienceEasy to manage centrallyBuying/selling/leasing transactionsPaymentSystem integration
The invention discloses a cross-border vertical e-commerce management method, and the method is based on an industrial e-commerce management platform which integrates a supplier, an importer, a dealer, a second-level dealer, a direct-sales store, a sales promoter, a terminal consumer, and an aftersales cloud service center. The method achieves the system integration of the industrial resources ina mode of Internet + conventional channels, facilitates the central management, and can provide more and more scientific data for each role or provide parameters for each role so as to help the rolesmake decisions. Moreover, all parties participating in the transaction can complete the transaction through the e-commerce management platform built through the cross-border vertical e-commerce management method. For example, the method can achieve the information transmission, quick ordering, payment, sales promotion, aftersales and cloud maintenance services, greatly reduces the time cost and manpower and material cost of transaction for all parties, and improves the success rate of trades. The method also provides corresponding data and analyses of market conditions for each role, providesreference for each role for each decision making, and improves the user experience.
Owner:兰世德
Systems and methods for providing dynamic price axes in featured user interfaces
ActiveUS20090043664A1Quick and accurate and efficient executionFinancePayment architectureDisplay deviceMarket change
The invention relates to systems and methods that provide a user interface for use with an electronic trading system. The interface includes a display that shows a bid price axis and an ask price axis, as well as corresponding sizes, and a visual indicator of the inside market. When the inside market changes in response to changing market conditions, the display of the inside market clearly shows a spatial movement of the inside market as well as the representative price(s) associated therewith, thereby rendering the two price axis dynamic axis. The user interface is easy to use, intuitive as well as customizable, and contains features that facilitate efficient electronic trading and shows trading activity pertaining to the user as well as the market in general.
Owner:BGC PARTNERS LP
Systems and methods for providing dynamic price axes
InactiveUS20070240053A1Quick and accurate and efficient executionPrice fluctuationFinanceInput/output processes for data processingMarket changeComputer science
The invention relates to systems and methods that provide a user interface for use with an electronic trading system. The interface displays a bid price axis and an ask price axis, as well as corresponding sizes, and an indication of the inside market. When the inside market changes in response to changing market conditions, the indication of the inside market changes locations before being restored to its original location by shifting the bid and ask prices in a direction parallel to the bid or ask price axis. The user may enter trade commands at different price levels using an input device. In order to help prevent such trade commands from being entered at erroneous price levels, the system locks a pointer associated with the input device to a price the user points to during the shifting process, unless the pointer is moved away from that price.
Owner:BGC PARTNERS LP
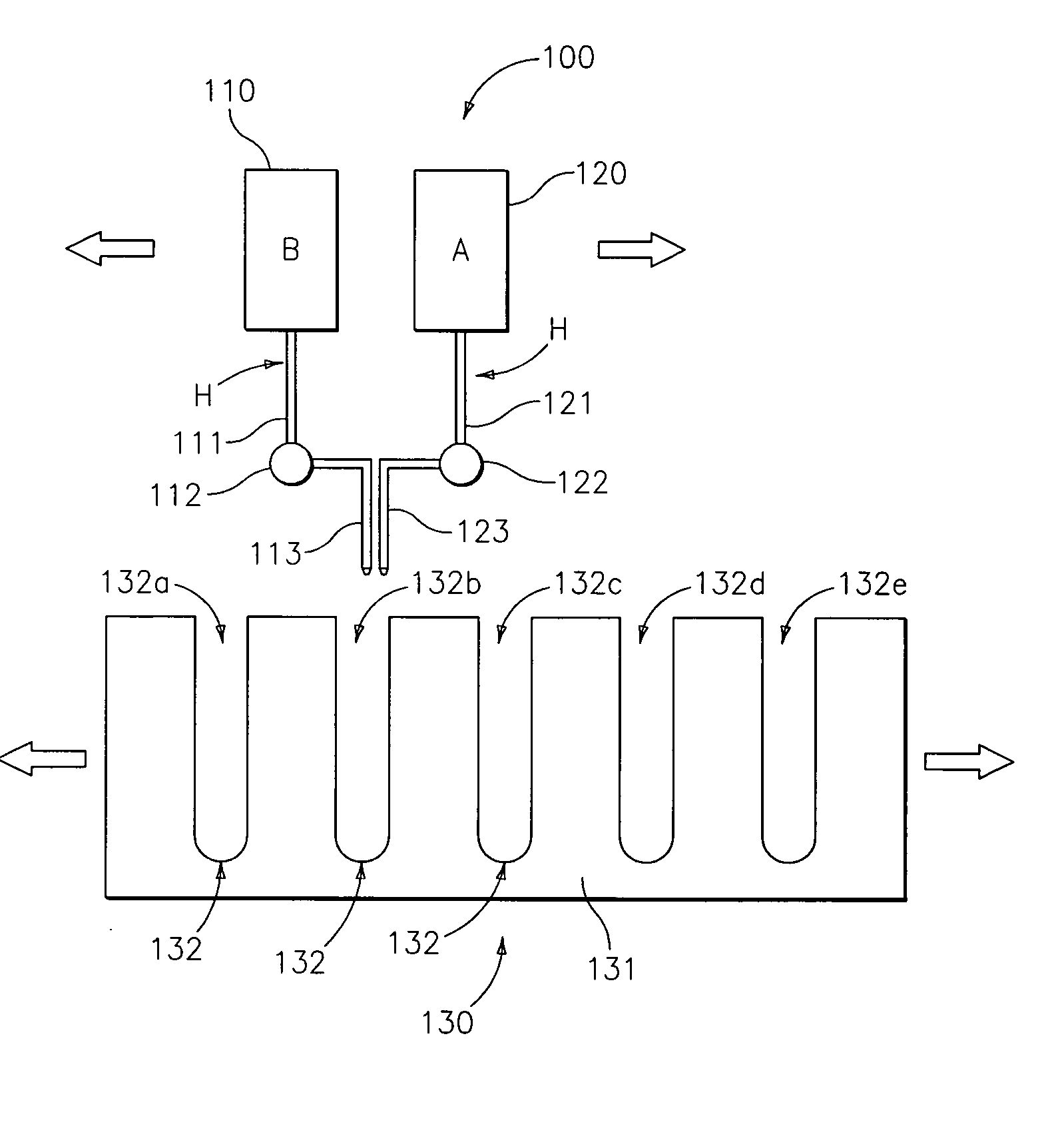
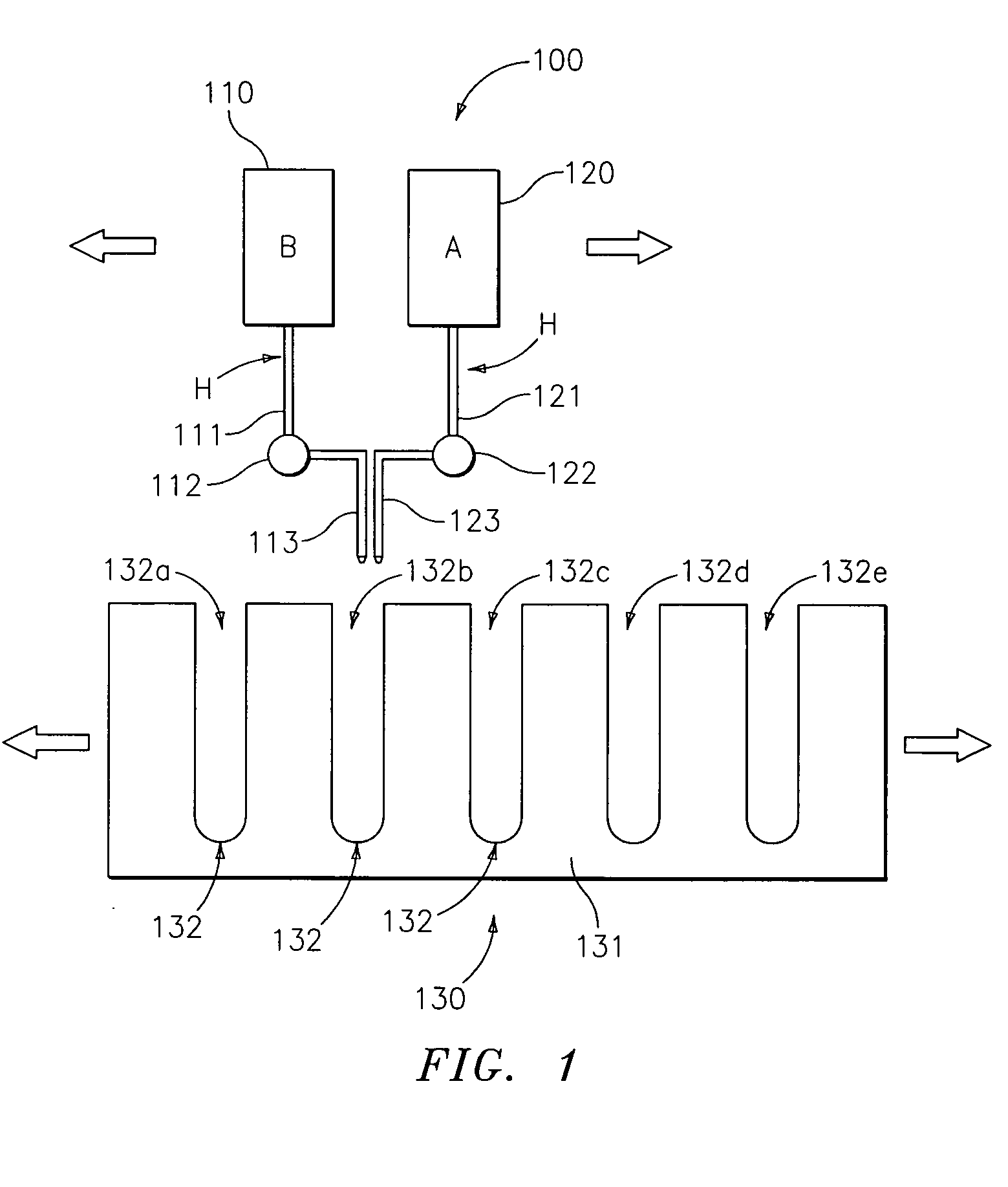
High throughput preparation of lubricating oil compositions for combinatorial libraries
InactiveUS20050095714A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsMaterial analysis by optical meansDowntimeHigh flux
A high throughput preparation of a plurality of different lubricating oil compositions for combinatorial libraries and subsequent high throughput screening for lubricant performance is provided. The methods can advantageously be optimized using combinatorial chemistry, in which a database of combinations of lubricating oil compositions are generated. As market conditions vary and / or product requirements or customer specifications change, conditions suitable for forming desired products can be identified with little or no downtime.
Owner:CHEVRON ORONITE CO LLC
Systems and Methods for Providing Dynamic Price Axes
ActiveUS20070271171A1Quick and accurate and efficient executionRegulation stabilityFinanceCommerceMarket changeComputer science
The invention relates to systems and methods that provide a user interface for use with an electronic trading system. The interface displays a bid price axis and an ask price axis, as well as corresponding sizes, and an indication of the inside market. When the inside market changes in response to changing market conditions, the indication of the inside market changes locations before being restored to its original location by shifting the bid and ask prices in a direction parallel to the bid or ask price axis. The user may enter trade commands at different price levels using an input device. In order to help prevent such trade commands from being entered at erroneous price levels, the system locks a pointer associated with the input device to a price the user points to during the shifting process, unless the pointer is moved away from that price.
Owner:BGC PARTNERS LP
High throughput screening methods for lubricating oil compositions
InactiveUS20050092072A1Improve throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial testing goodsFood additiveChemical composition
A method for determining storage stability for a plurality of fluid lubricant samples of different lubricating oil compositions is provided. Each sample includes a combination of one or more base oils and one or more lubricating oil additives. The methods can advantageously be optimized using combinatorial chemistry, in which a database of combinations of lubricating oil additives or lubricating oil compositions containing such additives is generated. As market conditions vary and / or product requirements or customer specifications change, conditions suitable for forming desired products can be identified with little or no downtime.
Owner:CHEVRON ORONITE CO LLC
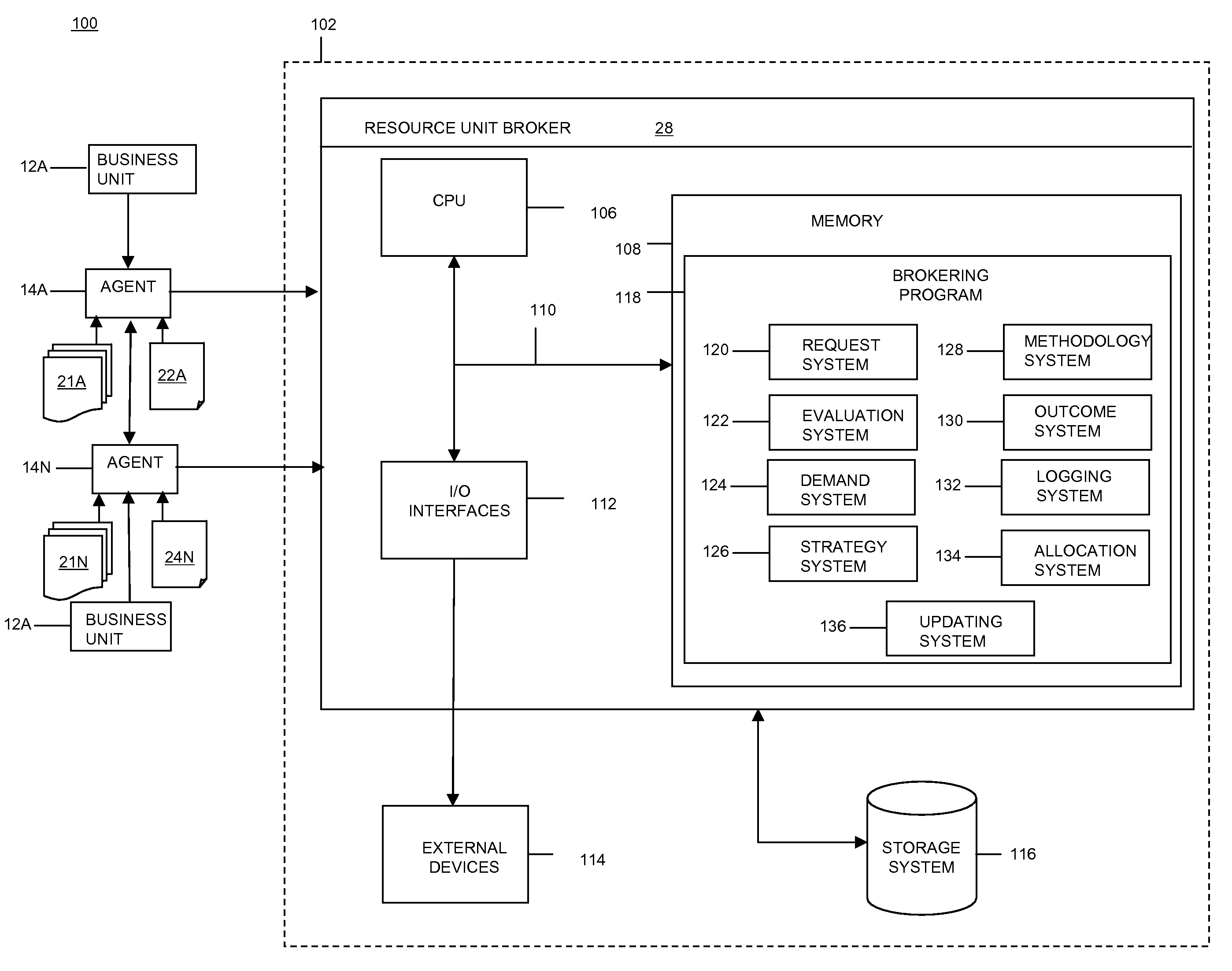
Method, system, and program product for selecting a brokering method for obtaining desired service level characteristics
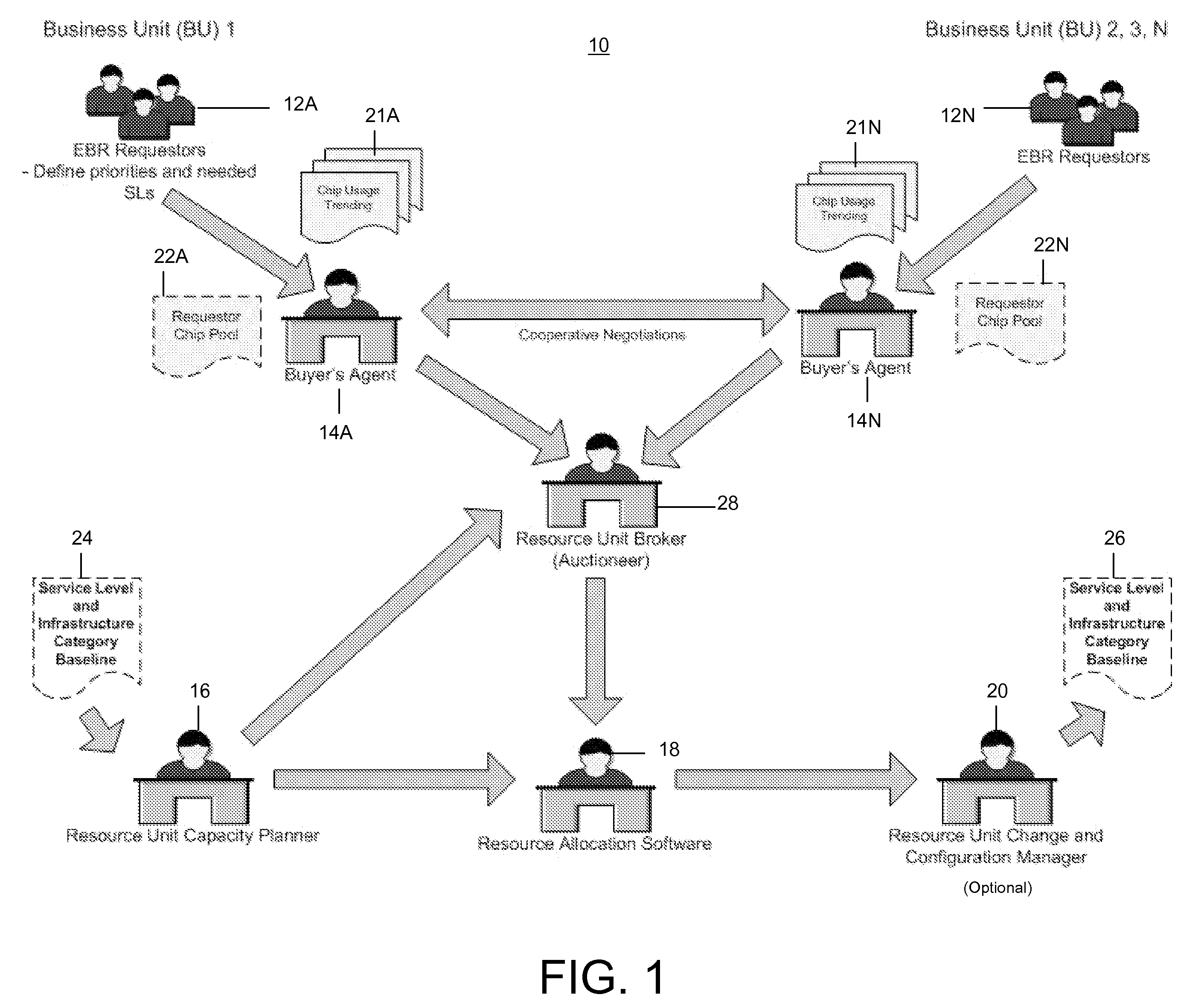
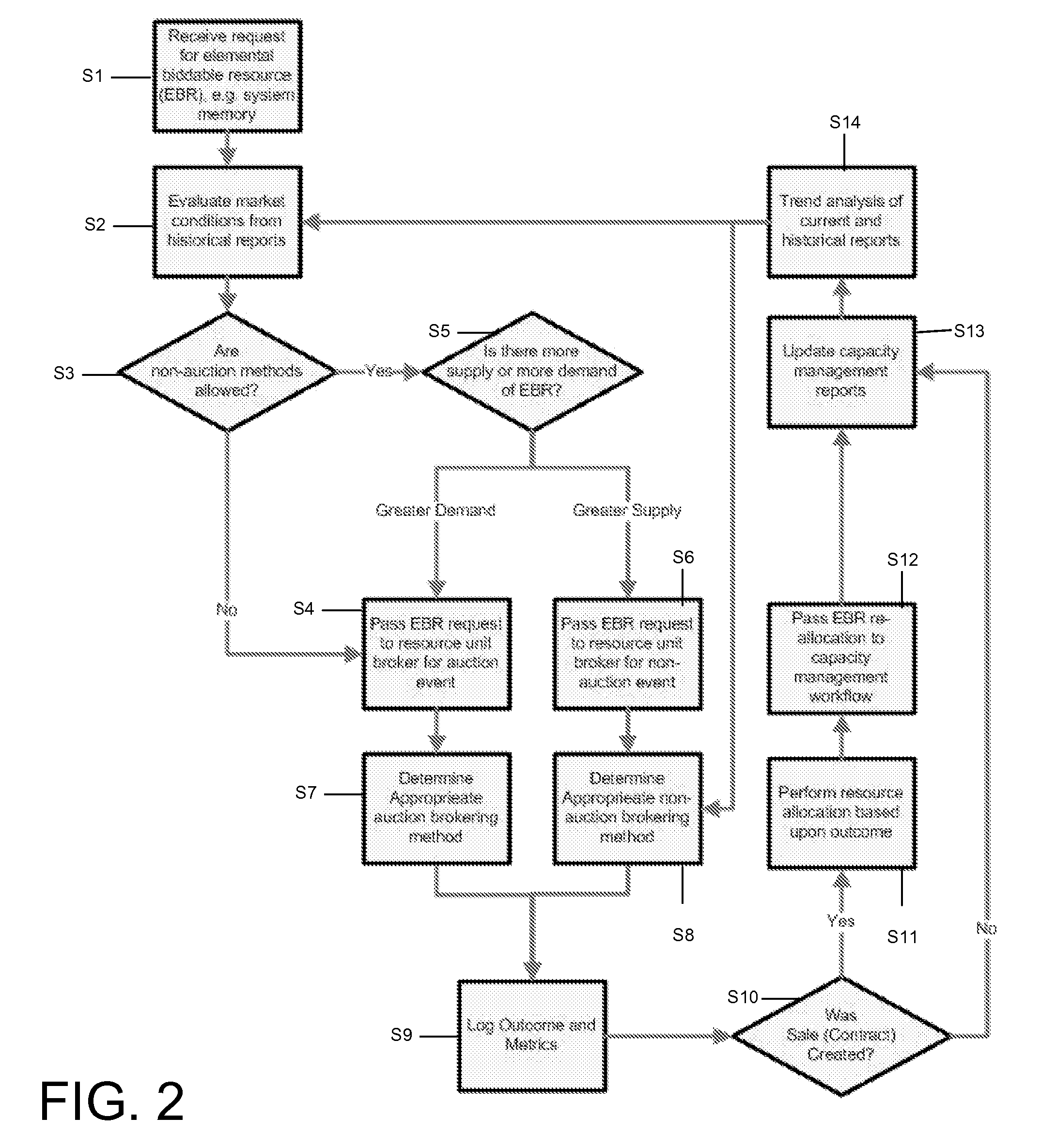
Under the present invention, a set (e.g., one or more) of requests (e.g., from a single bidder or multiple bidders) for an elemental bidding resource (EBR) is received. Market conditions for the EBR are evaluated from historical data. It is then determined whether a demand for the desired EBR exceeds a supply of the EBR. Based on the market conditions, the supply, and the demand, a brokering strategy (e.g., auction versus non-auction) and associated method are selected to allocate the EBR. A resource unit broker (RUB) will then determine an outcome of the brokering method to fulfill at least one of the set of requests. The outcome and associated metrics can then be logged, it can be determined whether a sales contract was created, the EBR can be allocated, and reports / data can be updated accordingly.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for automating proposals involving direct and indirect sales
InactiveUS20060041496A1Generate efficientlyCreate efficientlyFinanceMarketingThird partyIndividual item
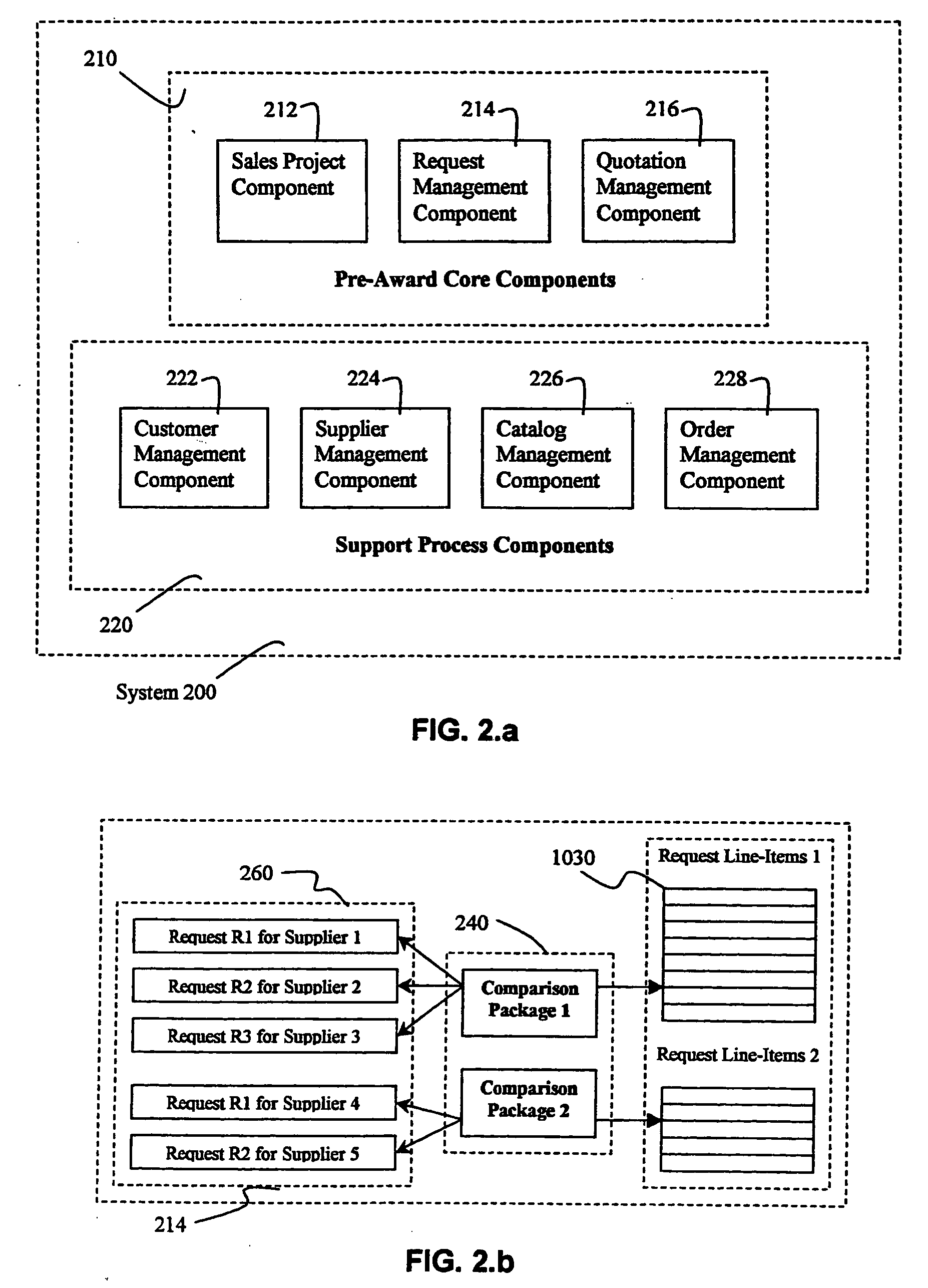
A sales automation system is described. The system can be customized to generate complex proposals involving direct and indirect sales. The system allows users to manage sales projects comprising complete solutions. Proposals are generated by integrating third party products and services offering and by using a pool of products stored in the system catalog. Requests to third party suppliers and service providers are managed by the system and integrated after evaluation in the final proposal to the customer. Search and allocation of products allows users to quickly identify products from a large data pool. Proposal items are structured in a way that enable flexible calculations of resale values based on market conditions and specific variables related to third party suppliers. The system is structured to enable proposals offering to multiple customers for a single project. This structure is extended beyond the proposal preparation cycle until the order phase.
Owner:AMIN MAGED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com