Patents
Literature
44 results about "Metrics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
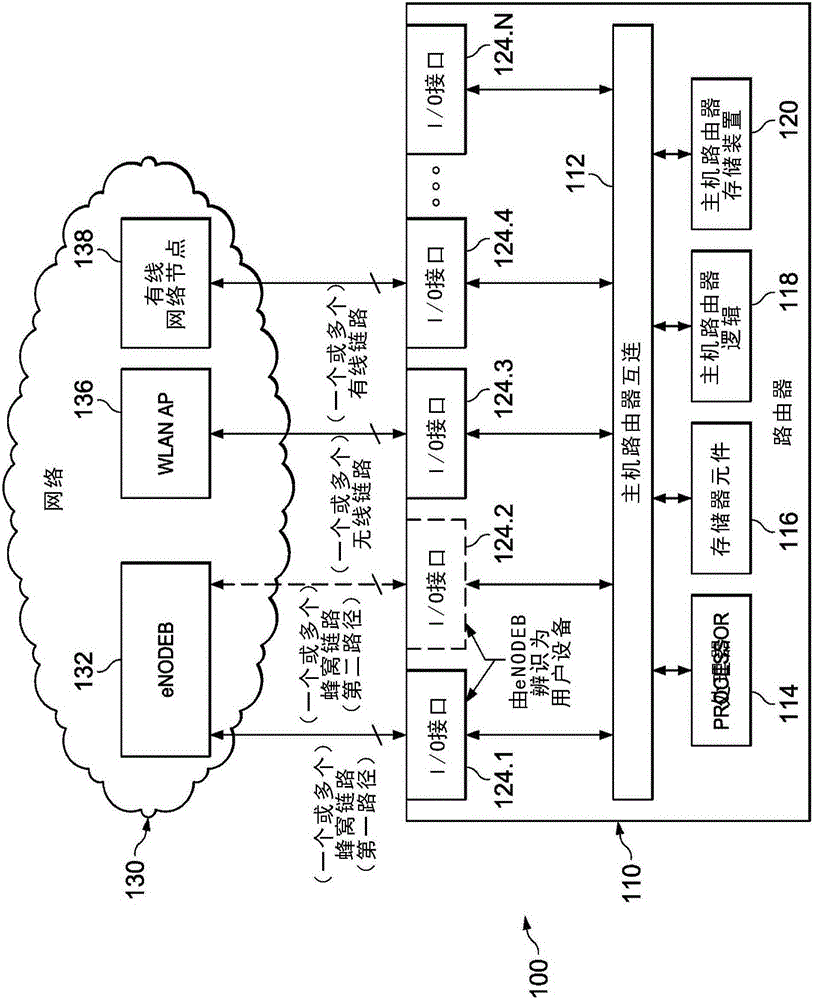
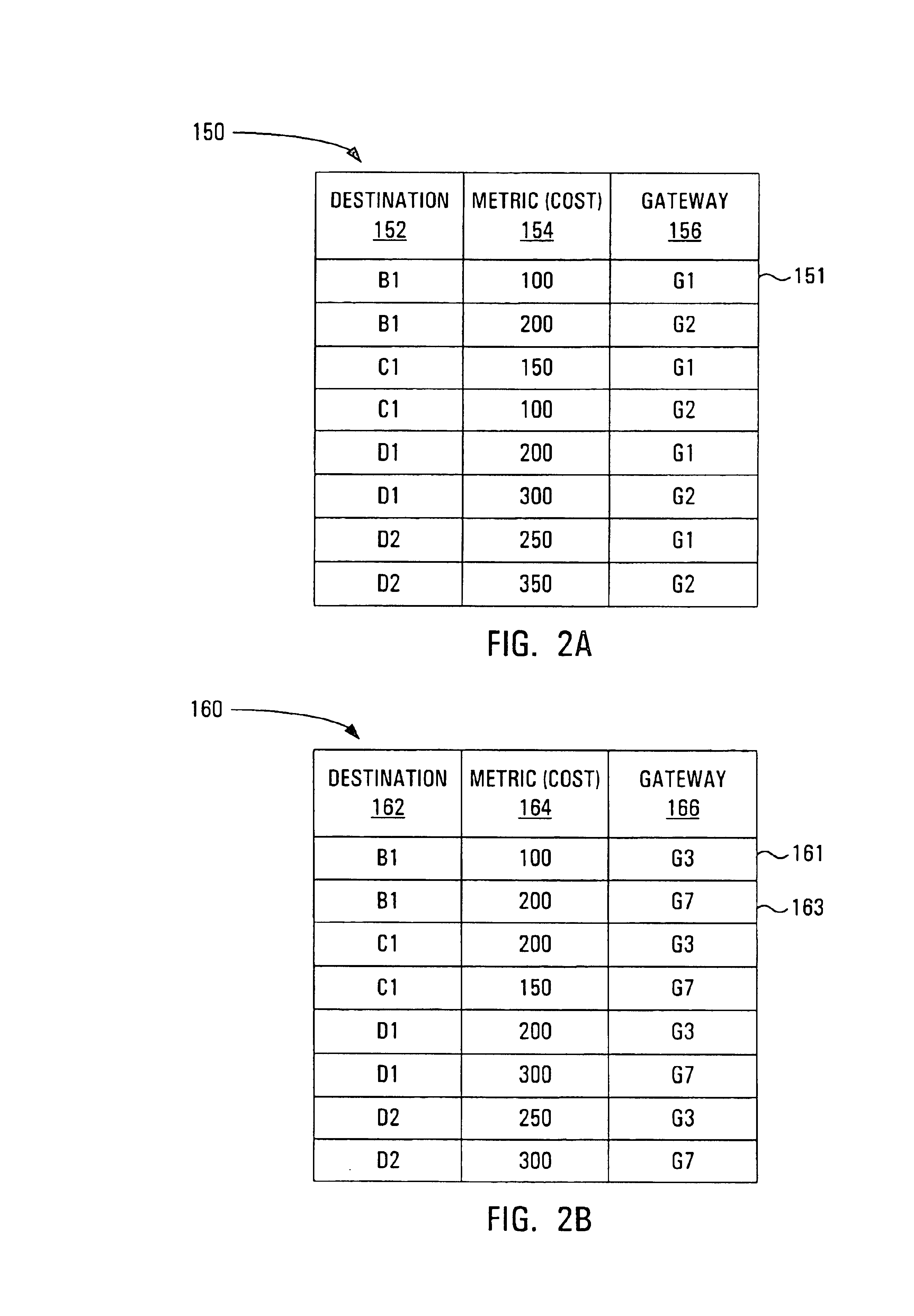
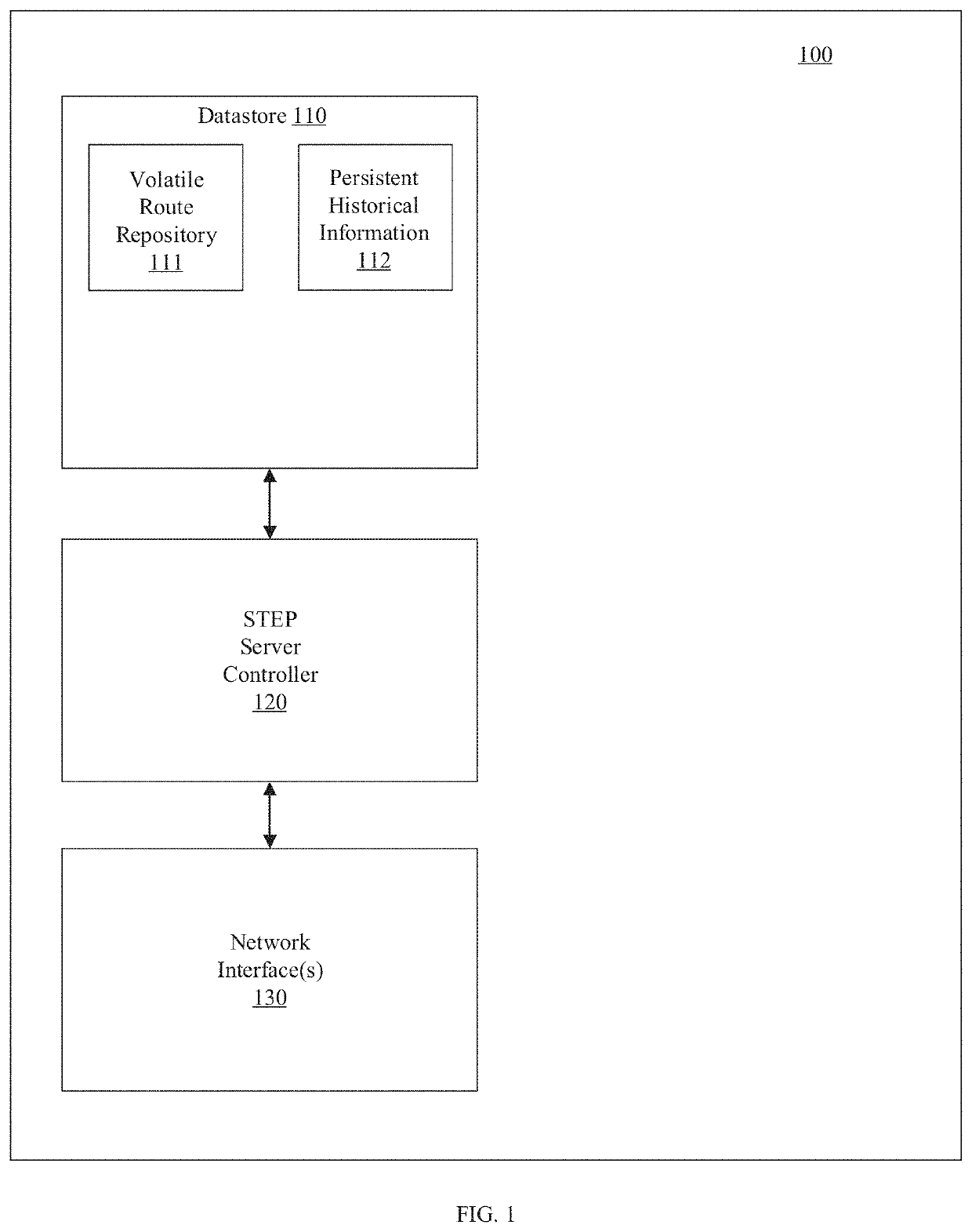
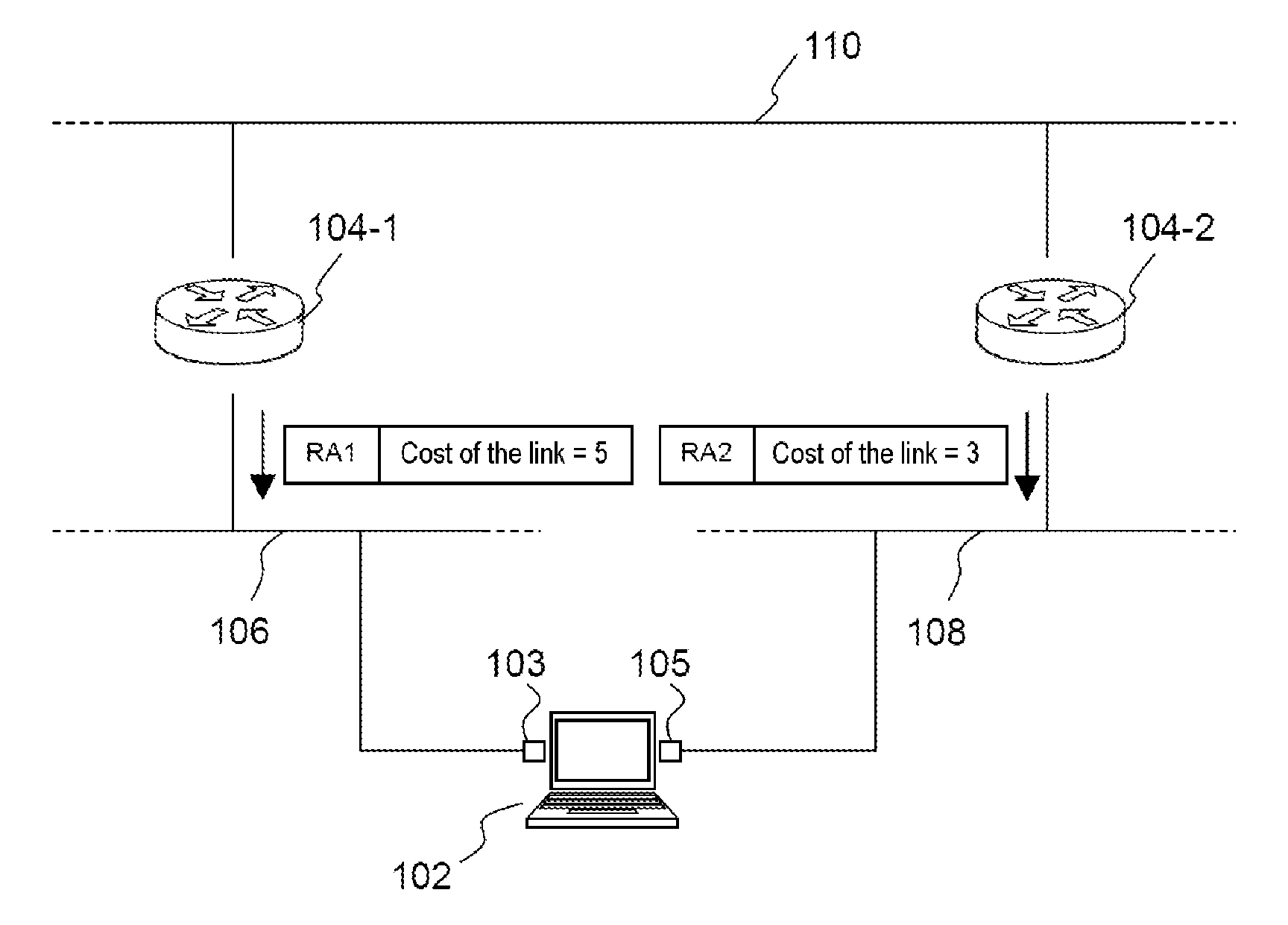
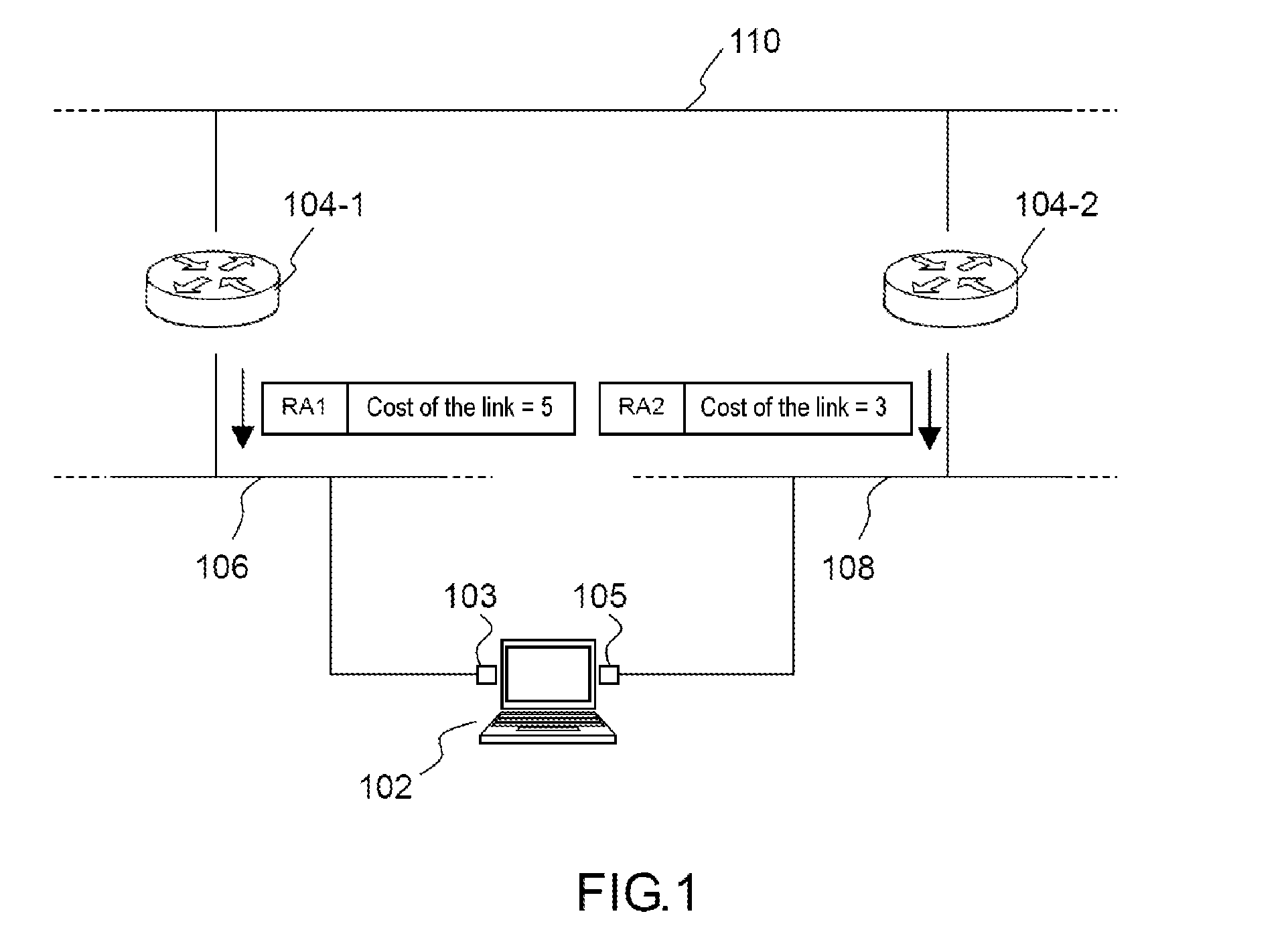
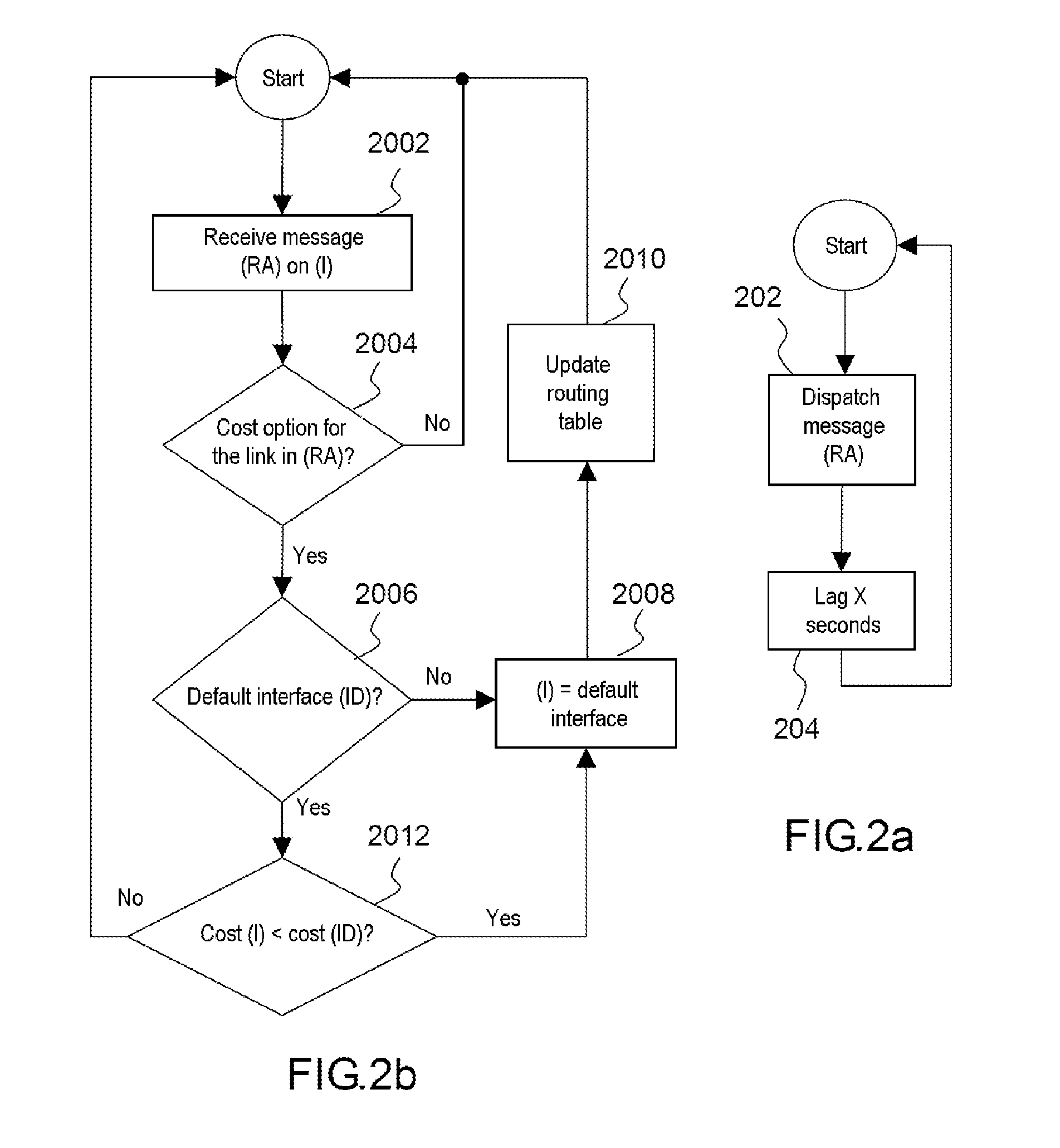
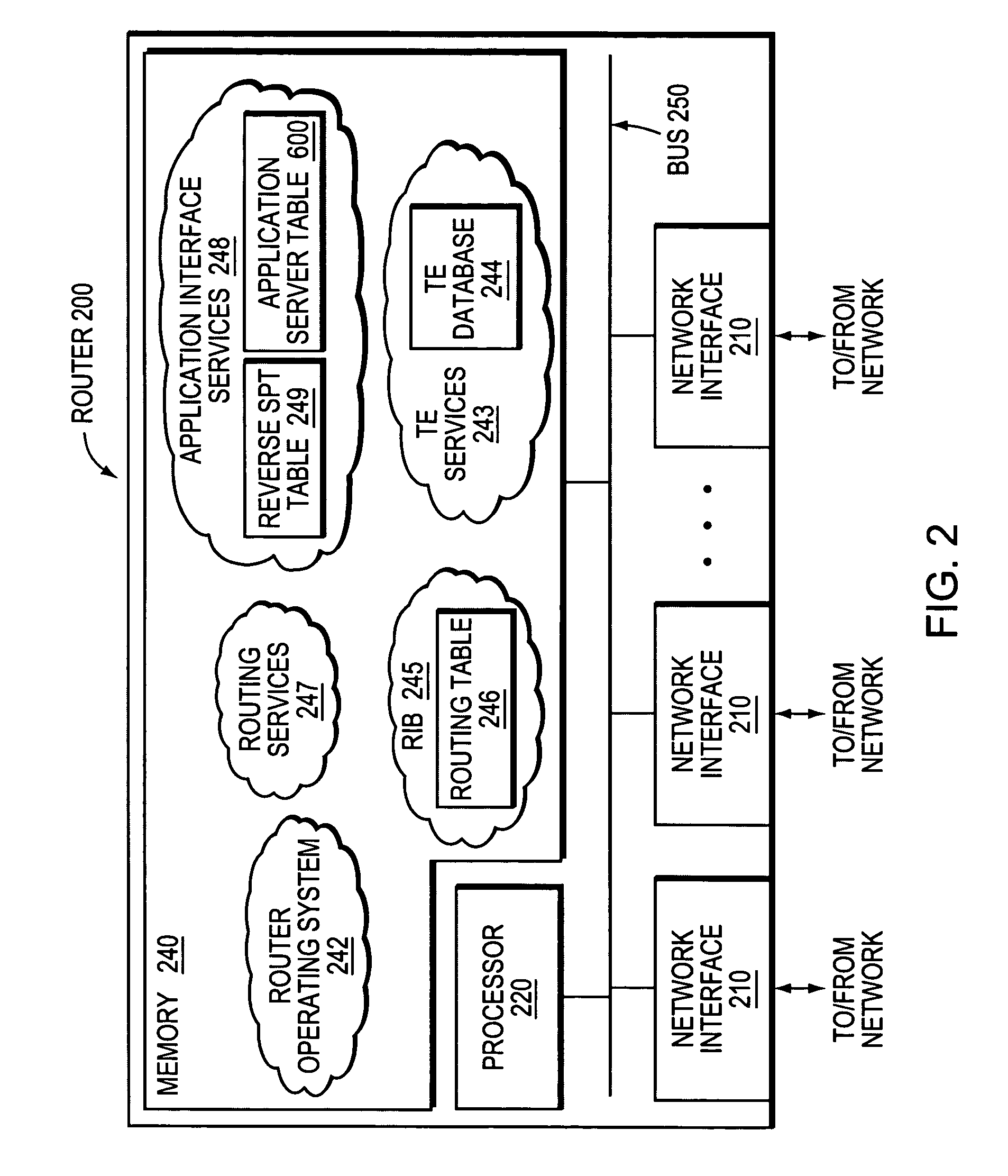
Router metrics are metrics used by a router to make routing decisions. A metric is typically one of many fields in a routing table. Router metrics help the router choose the best route among multiple feasible routes to a destination. The route will go in the direction of the gateway with the lowest metric.
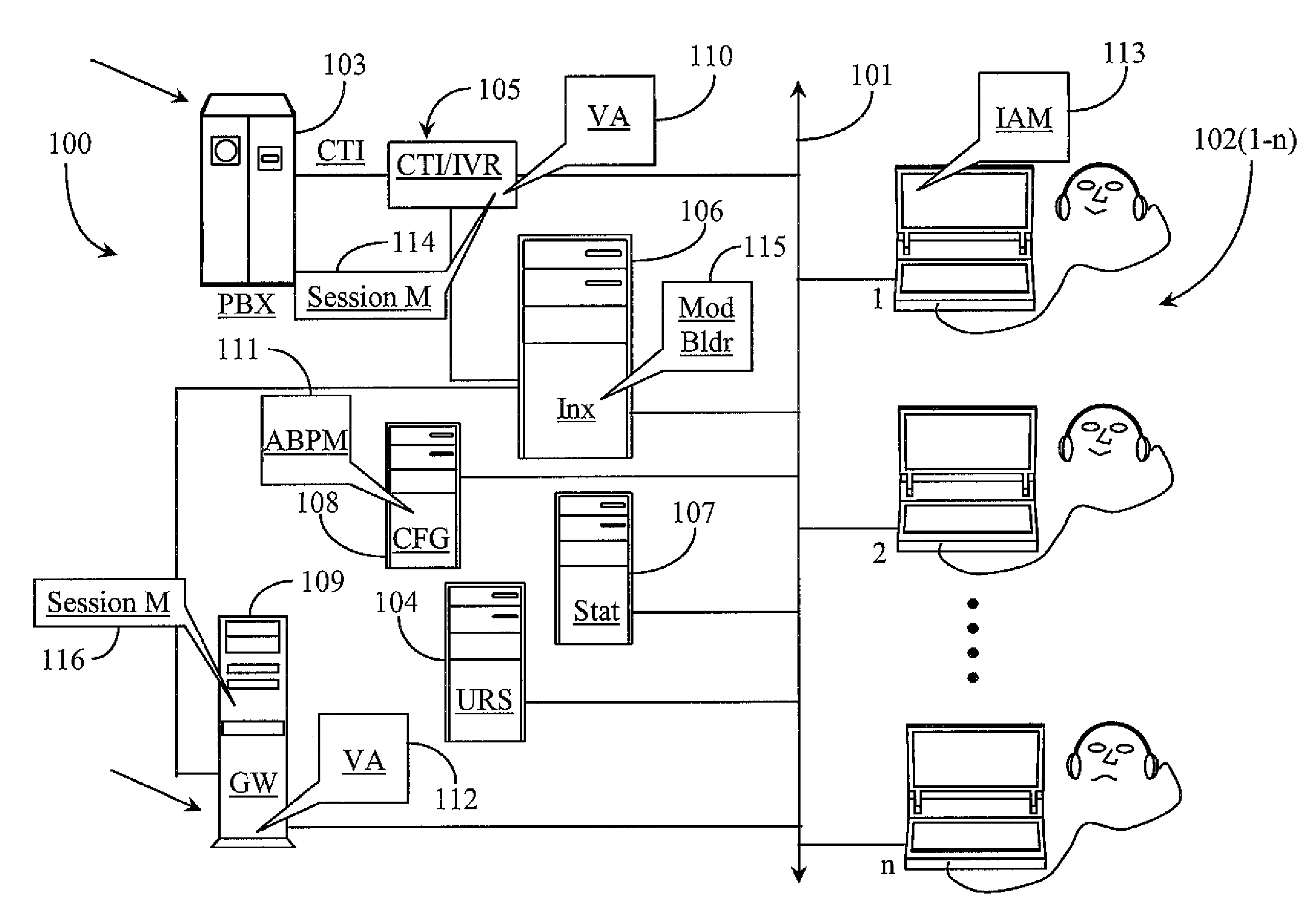
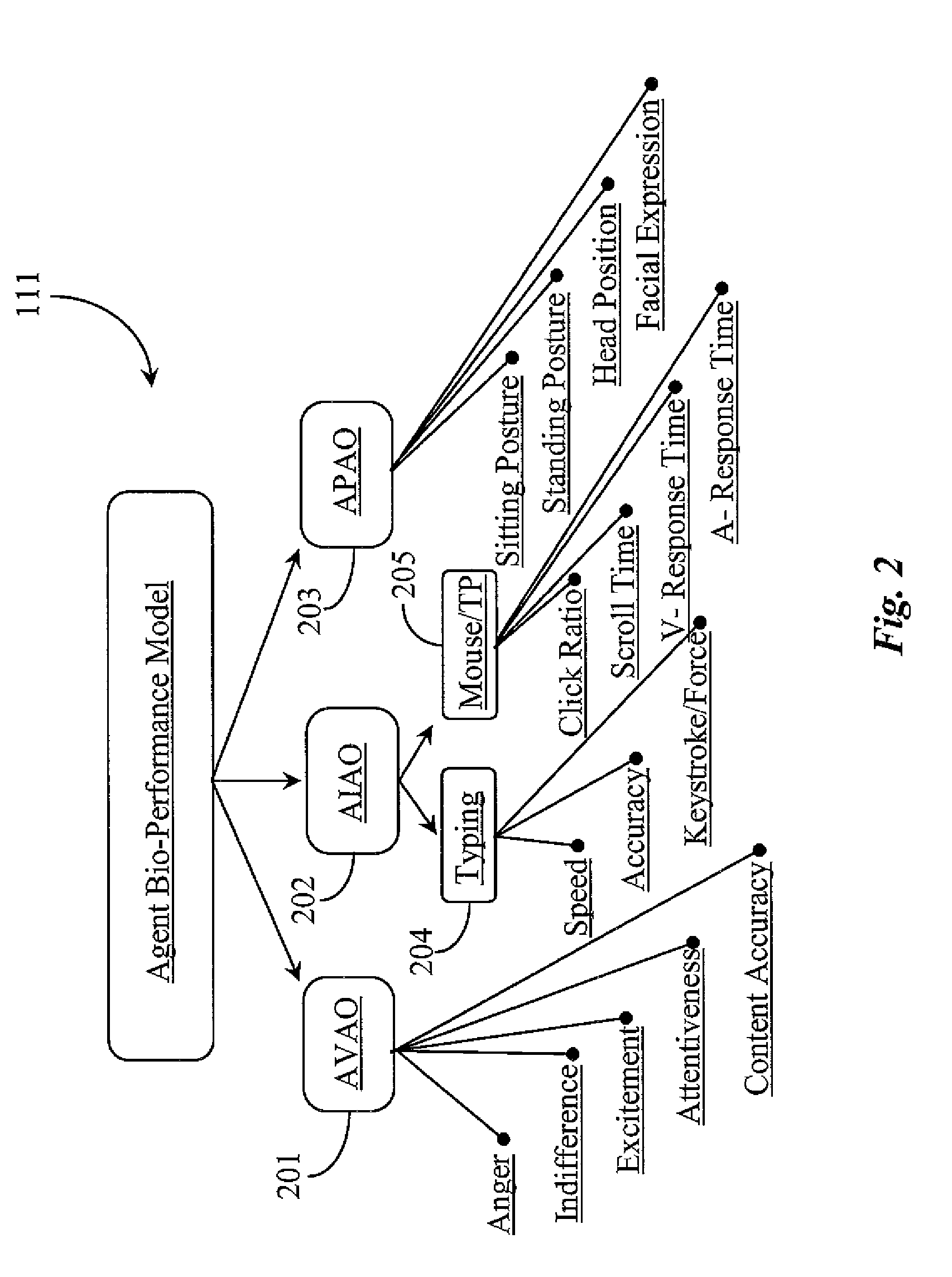
System for Routing Interactions Using Bio-Performance Attributes of Persons as Dynamic Input
ActiveUS20100158238A1Improve contact center efficiencyPreserve customer loyaltySpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSkill setsSpeech sound
A system for routing an interaction has a queue for staging the interaction, a router running a routing strategy for routing the interaction, and a number of object models maintained for a number of agents, the object models defining one or more agent skills, the values of the object models dynamically affected by real-time bio-metrics of the agents obtained through ongoing monitoring of voice and input actions of the agents. The routing strategy routes the interaction based on comparison of the dynamically-affected skill values of the agents, as evidenced in the object models.
Owner:GENESYS TELECOMMUNICATIONS LABORATORIES INC
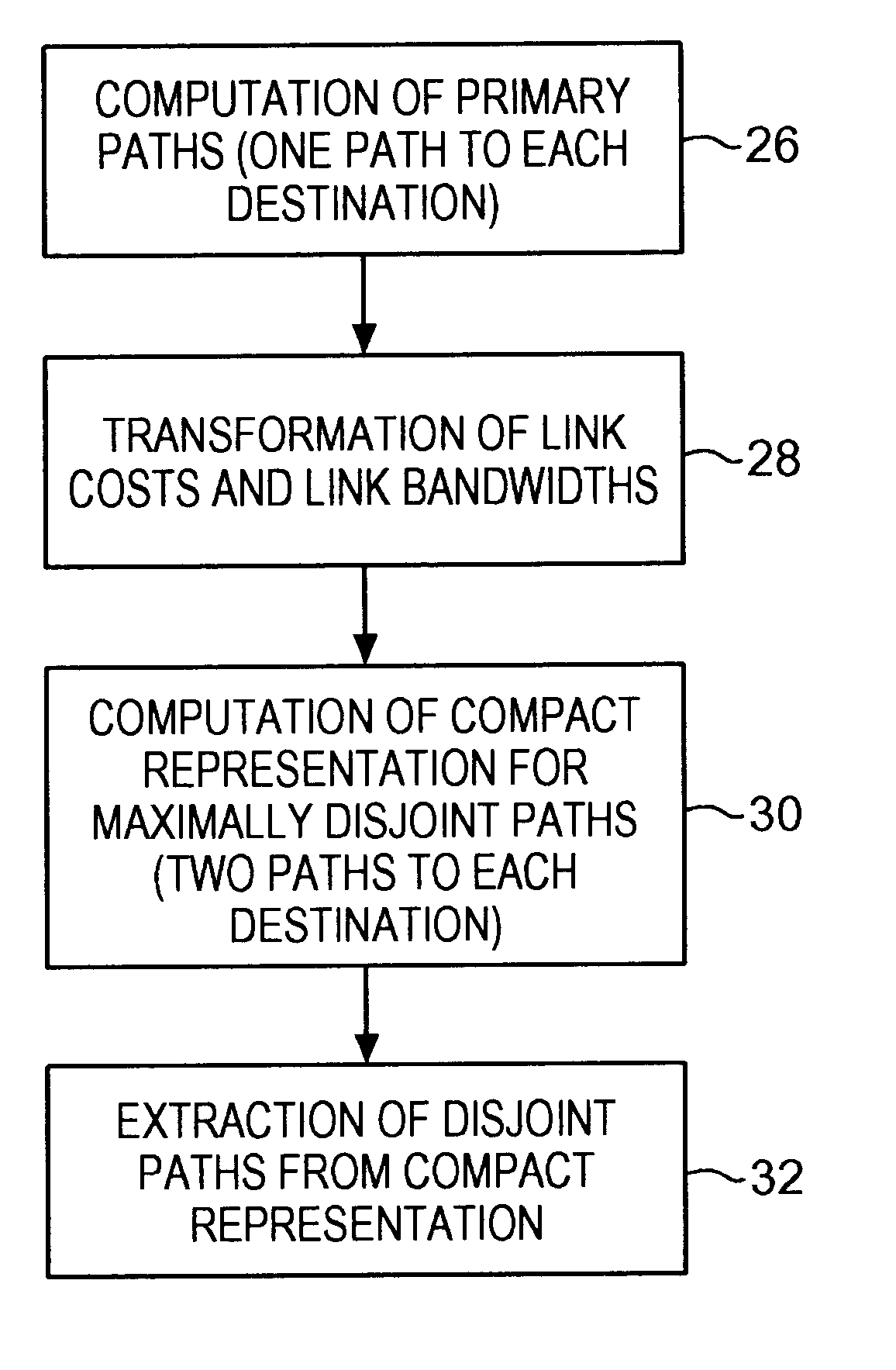
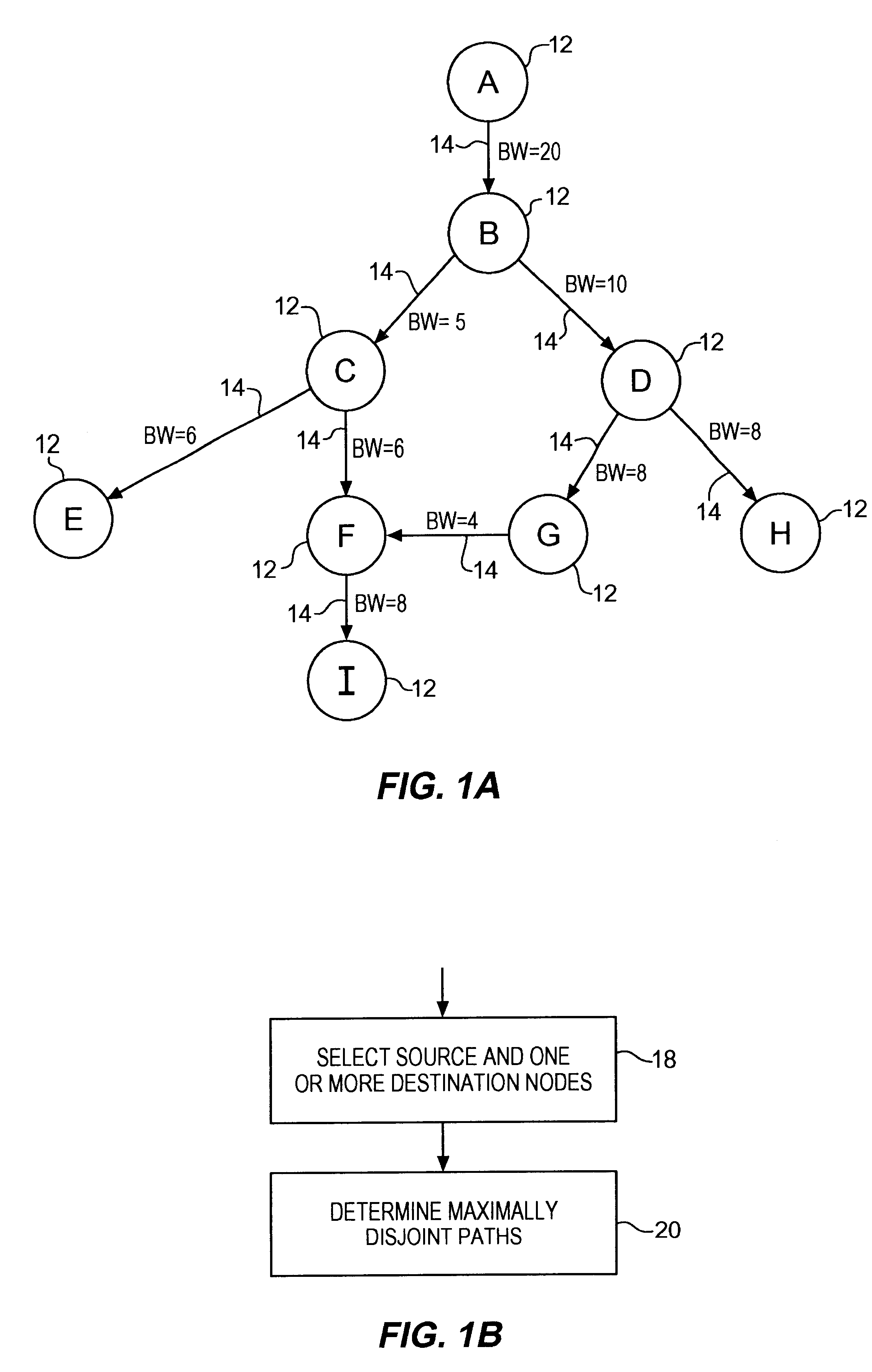
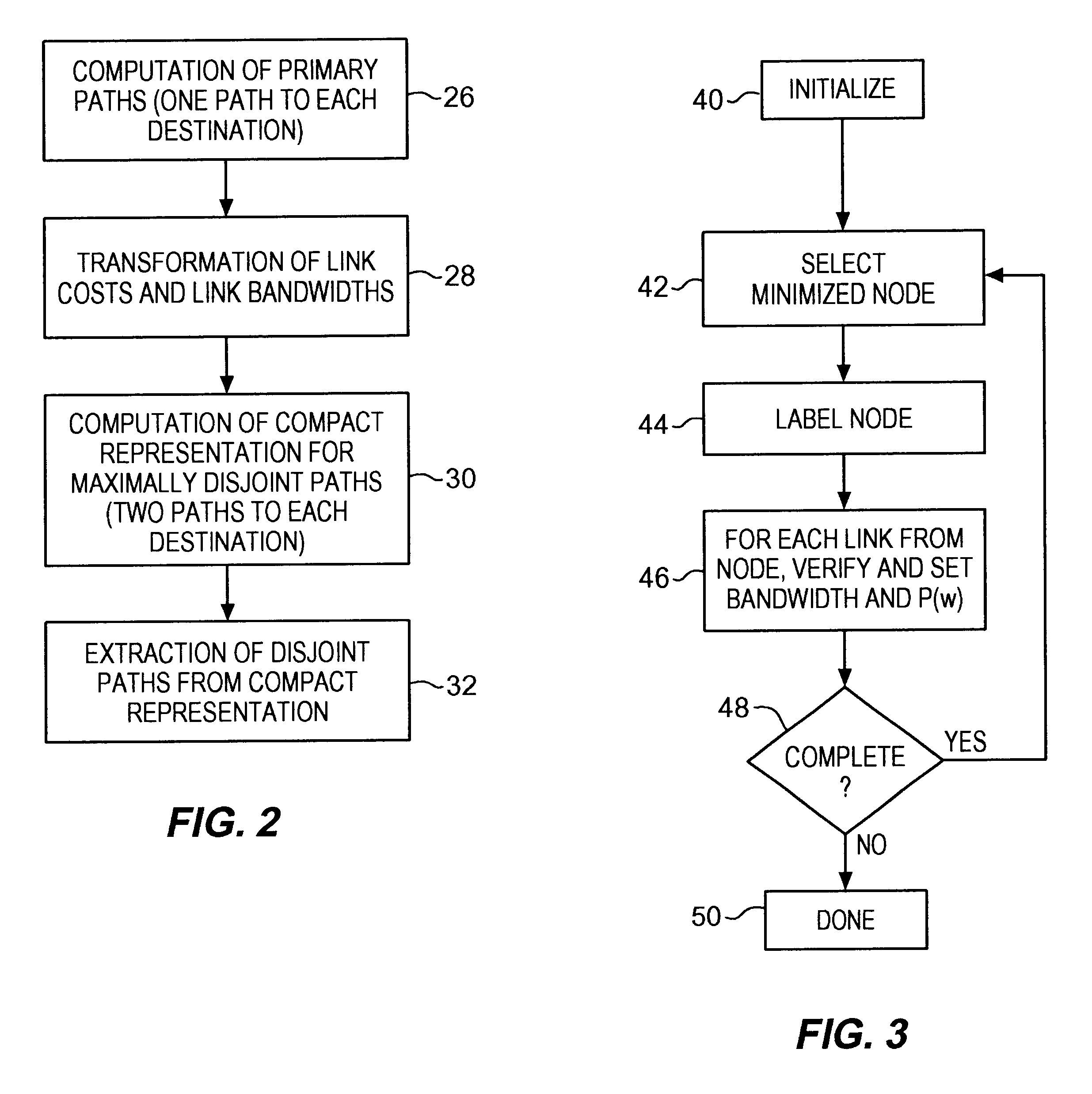
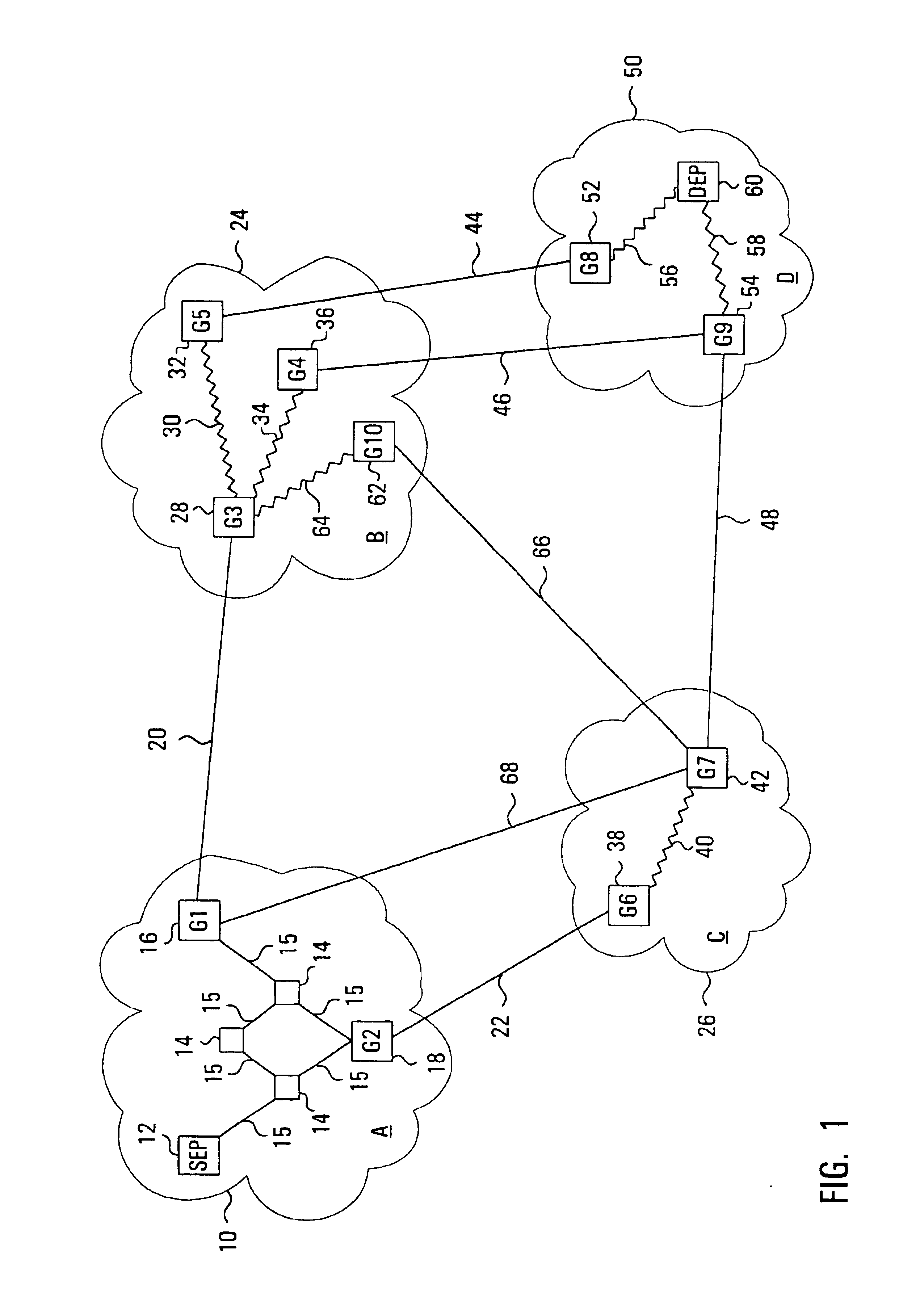
Communications network system and method for routing based on disjoint pairs of path
InactiveUS6542469B1Raise the possibilityMinimizes probabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPathPingHigh bandwidth
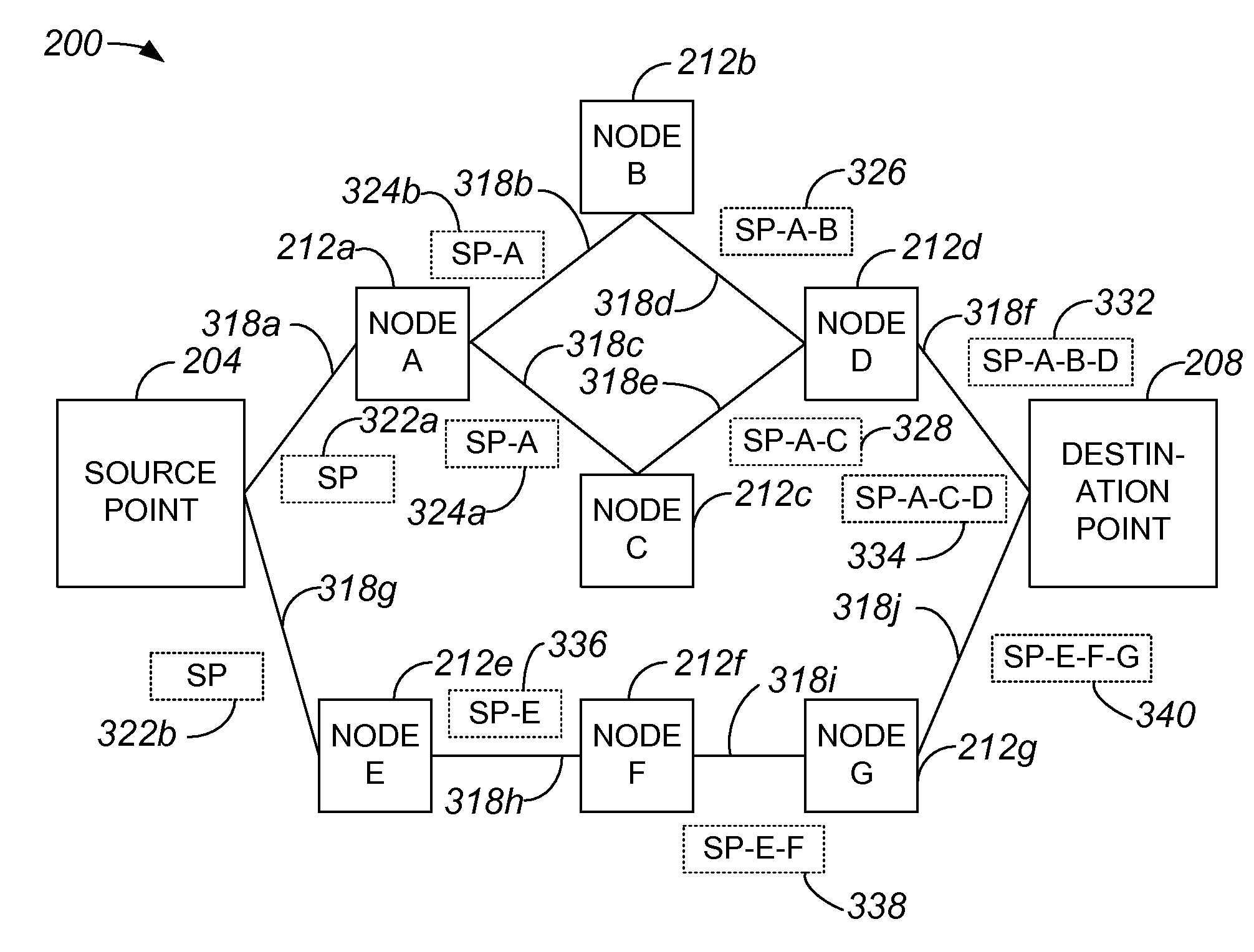
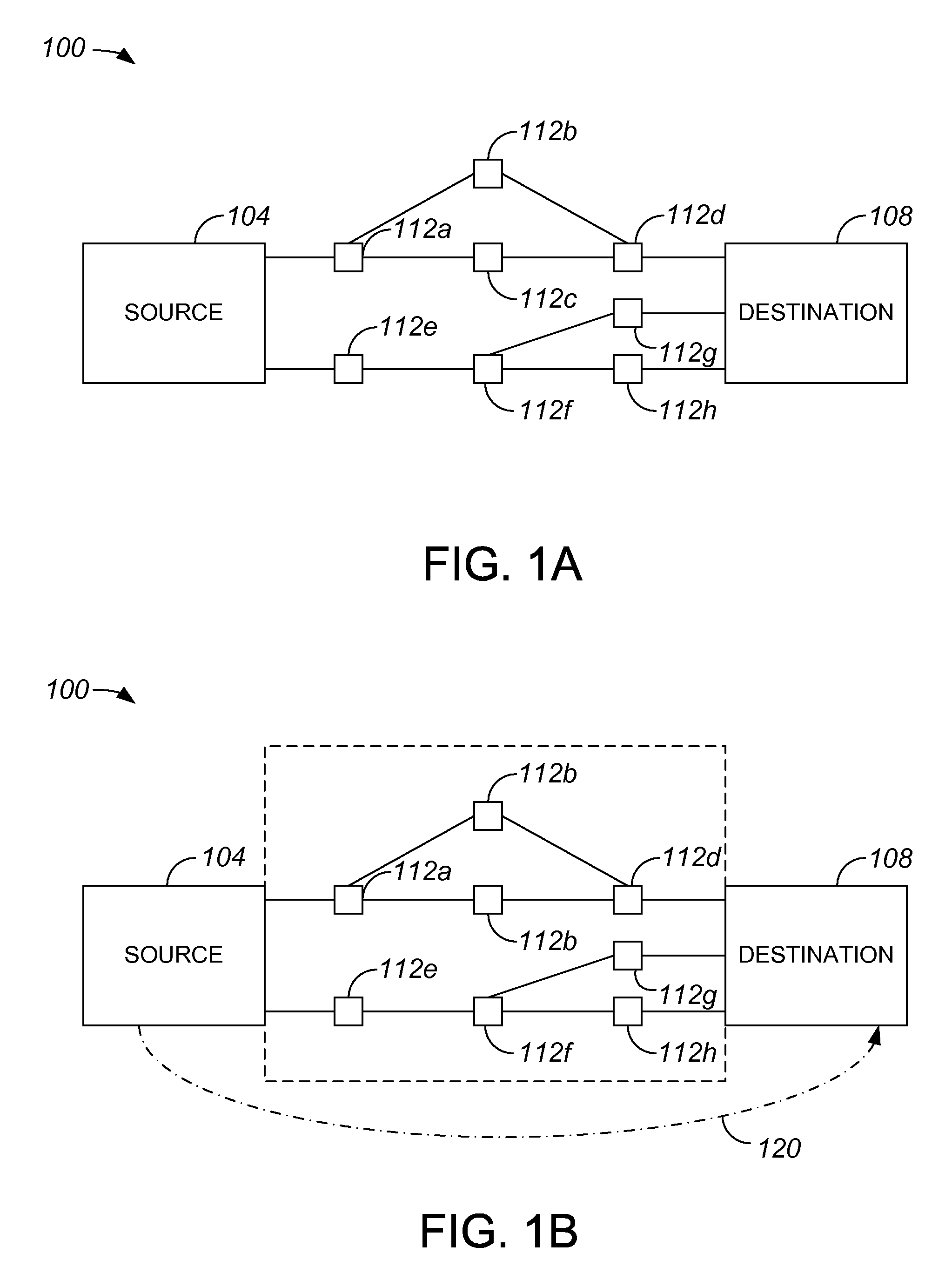
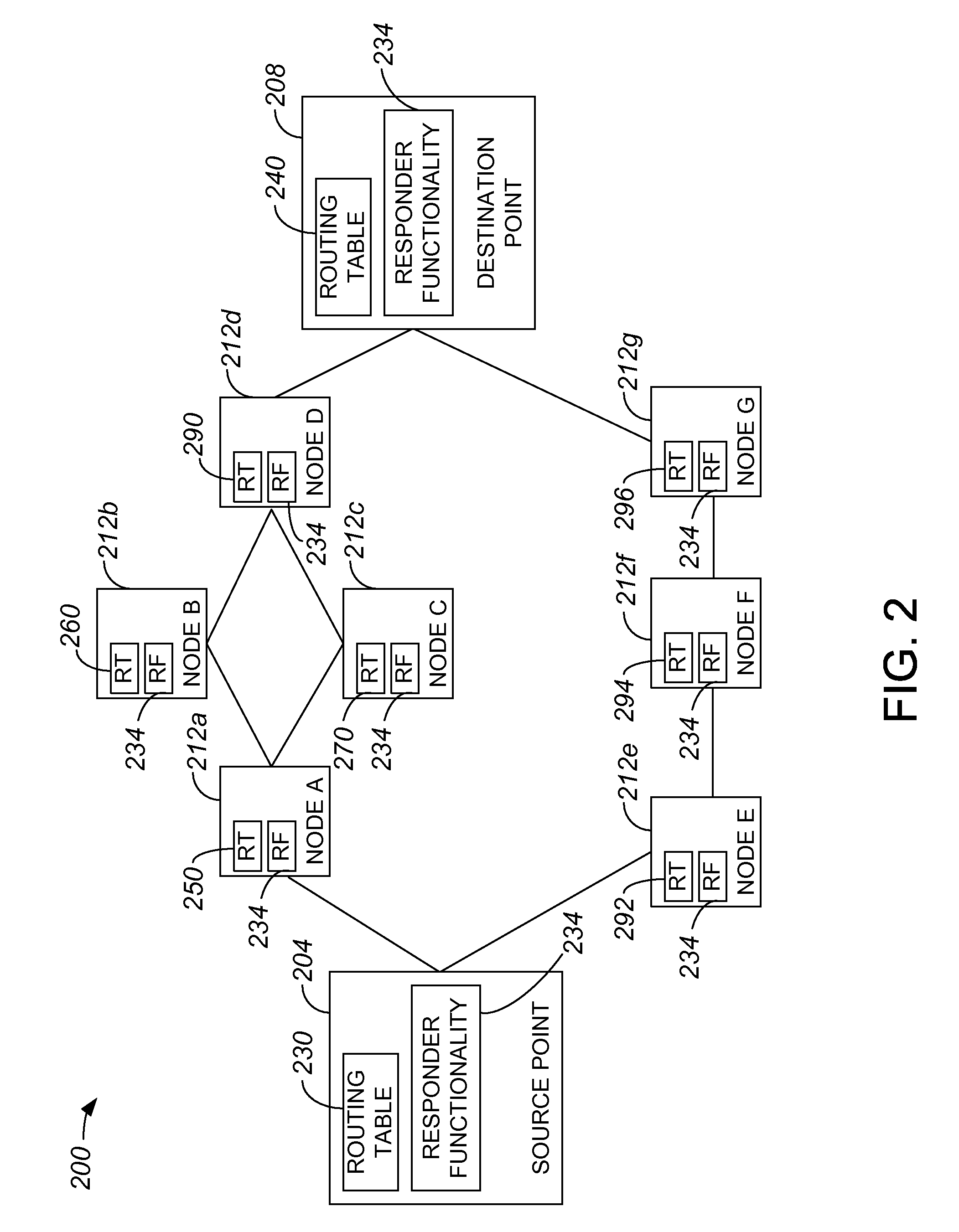
Methods for determining at least two pre-computed paths to a destination in a communications network are provided. The two paths are maximally disjoint. Maximally disjoint paths are paths where the number of links or nodes common to the two paths is minimized. This minimization is given a priority over other path considerations, such as bandwidth or cost metrics. By pre-computing a maximally disjoint pair of paths, the probability that an inoperable link or node is in both paths is minimized. The probability that the inoperable link or node blocks a transfer of data is minimized. Additionally, a pair of maximally disjoint paths is determined even if absolutely disjoint paths are not possible. The communications network may include at least four nodes, and maximally disjoint pairs of paths are pre-computed from each node to each other node. A third path from each node to each other node may also be computed as a function of bandwidth or a cost metric. Therefore, the advantages of the maximally disjoint pair of paths are provided as discussed above and a path associated with a higher bandwidth or lower cost is provided to more likely satisfy the user requirements of a data transfer.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
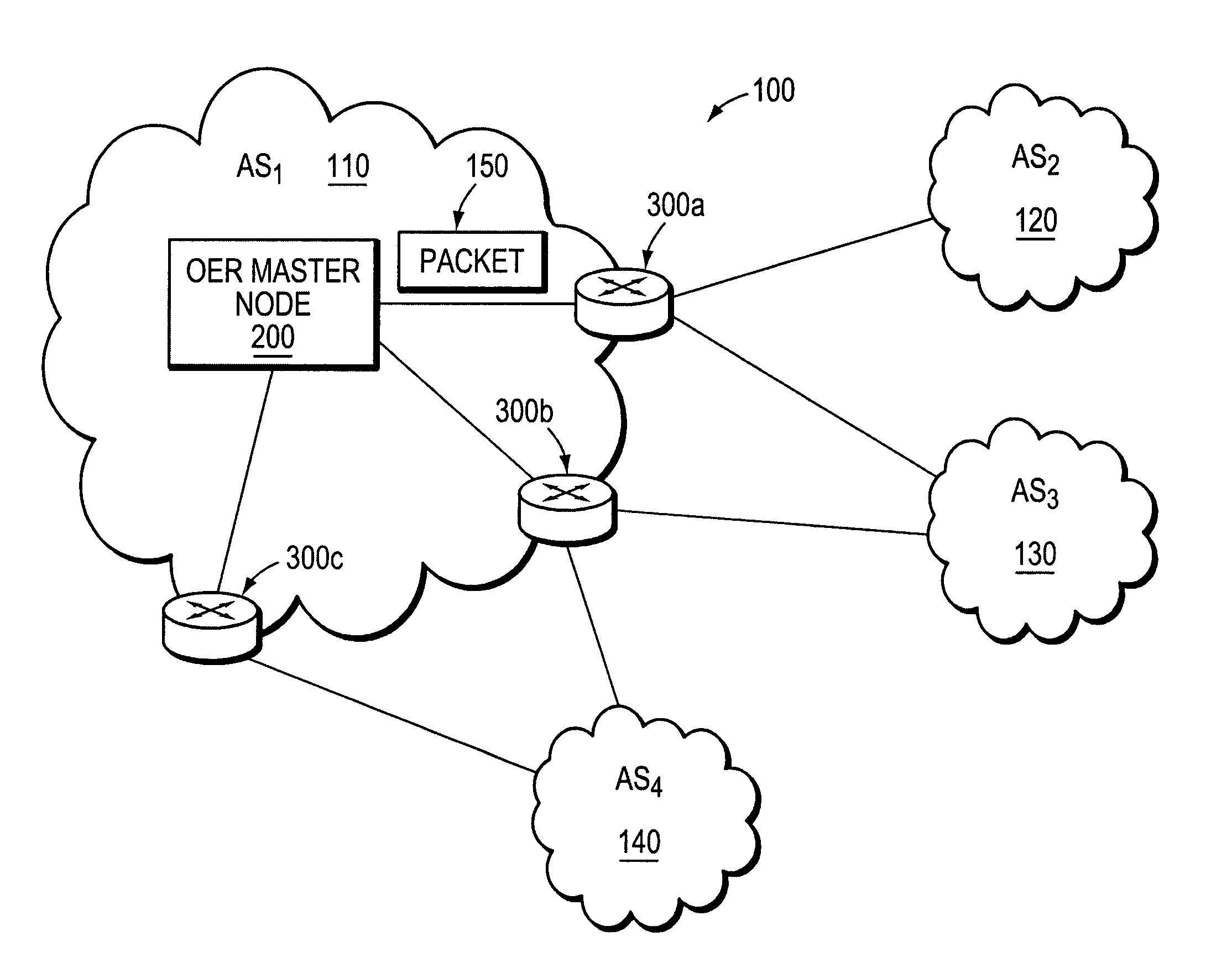
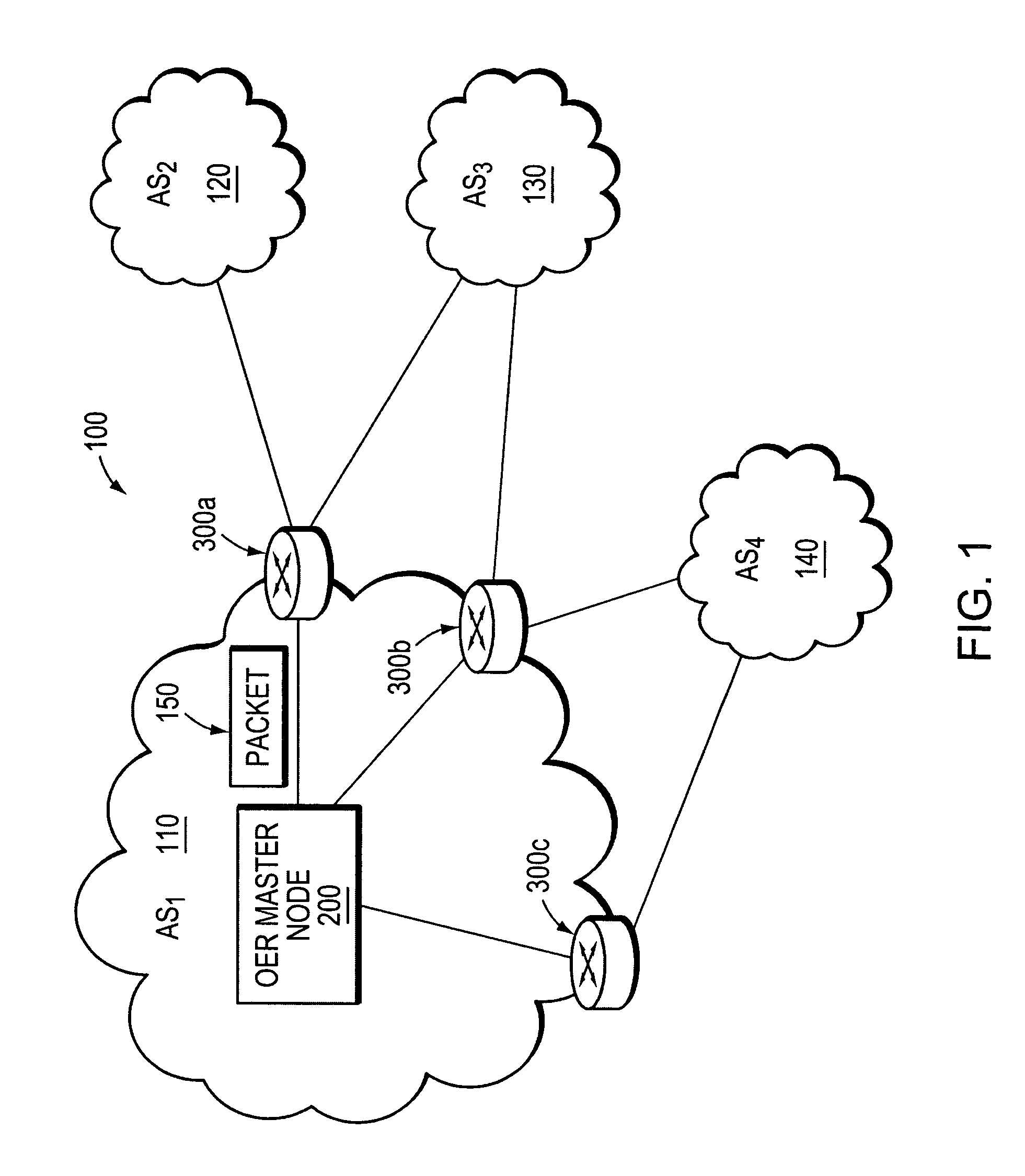
Method and apparatus for automatically optimizing routing operations at the edge of a network
ActiveUS8073968B1Consume resourceConsume timeMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTraffic capacityData stream
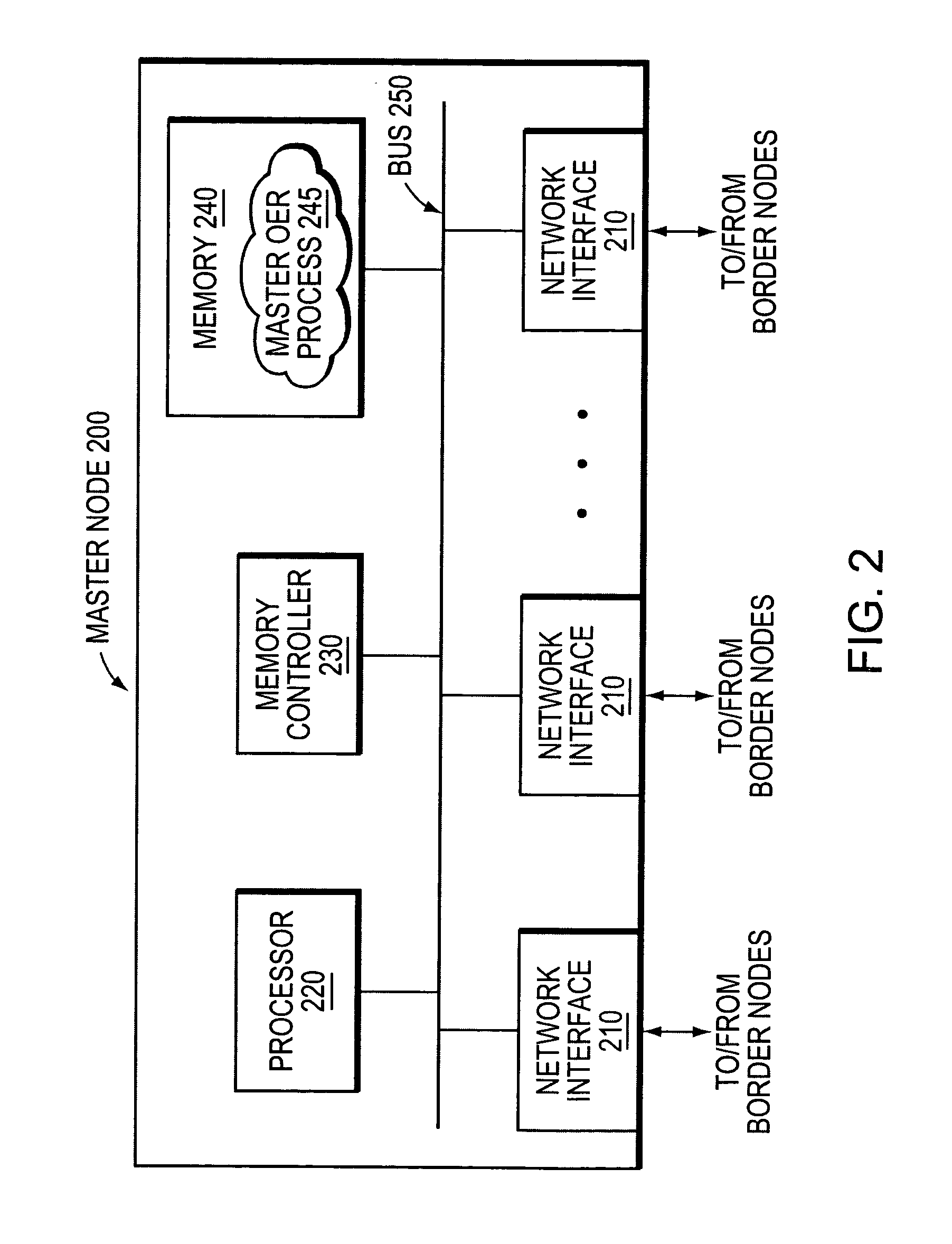
An Optimized Edge Routing (OER) technique provides efficiently data routing at the edge of a network or subnetwork. The technique employs a Master node that manages a set of border nodes located at the edge of the network or subnetwork. The Master node may be a stand-alone network management node or may be incorporated into a network node, such as a border node. Unlike prior implementations, the Master node instructs the border nodes to dynamically acquire (“learn”) prefixes of incoming and outgoing data flows and to selectively filter a set of learned address prefixes whose corresponding data flows match a predetermined set of criteria. The criteria may be based on routing metrics other than, or in addition to, conventional cost-based or distance-based metrics. Further, the criteria may include a set of filtering parameters that may be reconfigured, e.g., by the Master node, from time to time. Using the learned prefixes filtered by the border nodes, the Master node can distribute network traffic and utilize network bandwidth more efficiently than conventionally done.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for actively discovering internet protocol equal cost multiple paths and associate metrics
Methods and apparatus for identifying a best path from a plurality of equal cost paths while accounting for service level agreement (SLA) metrics are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a method for routing a packet that has a payload using a node includes obtaining the packet, and adding an address of the node to the payload. Adding the address of the node to the payload creates an augmented packet. The method also includes identifying at least one element to which the augmented packet is to be routed, and providing the augmented packet to that element. In one embodiment, the method also includes storing ingress and egress timestamps associated with the node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
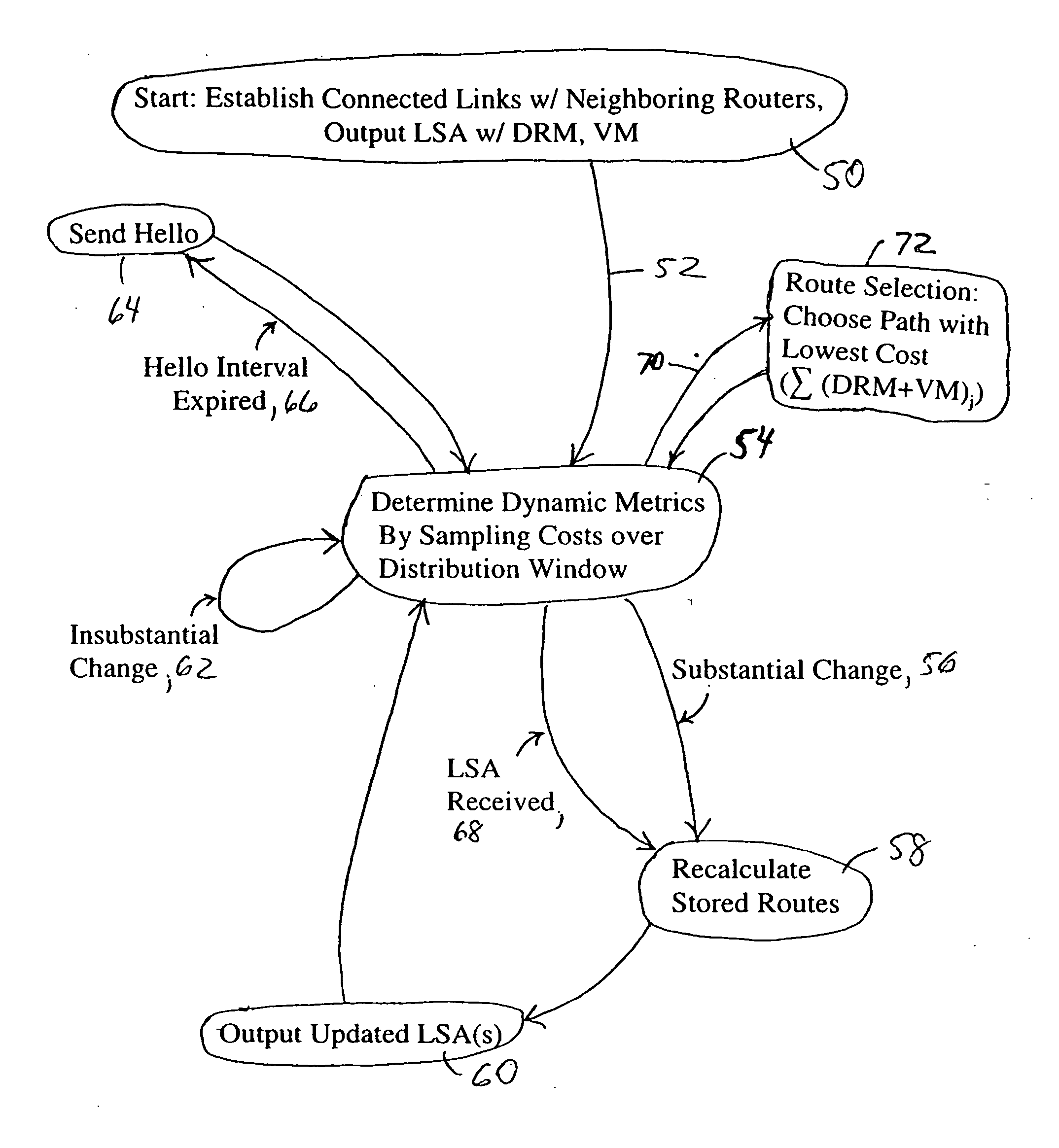
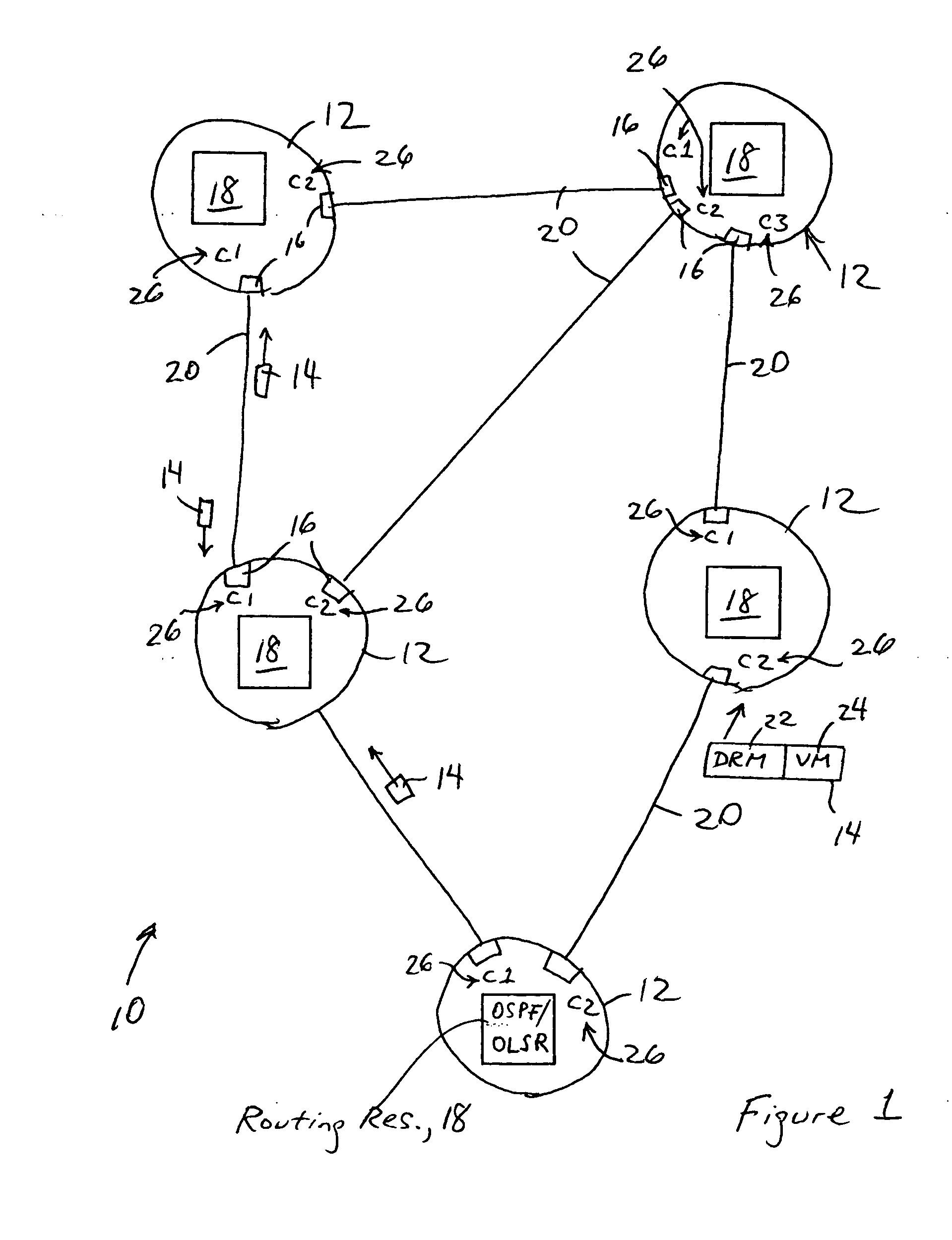
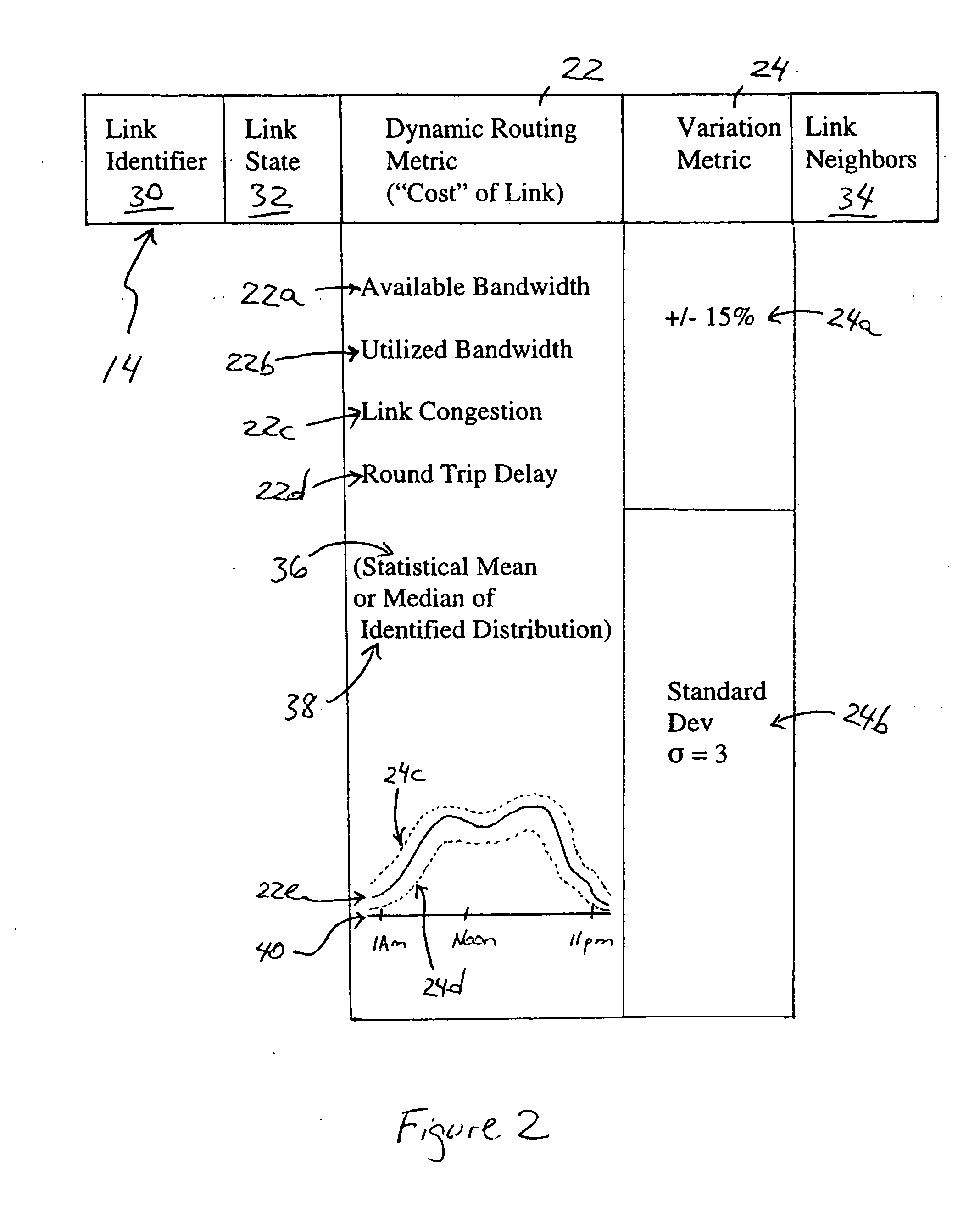
Link state advertisements specifying dynamic routing metrics and associated variation metrics and selective distribution thereof
InactiveUS20060291485A1Respond effectivelyIntroduce instabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLink-state advertisementAdaptive routing
Each router in a network is configured for executing a link state routing protocol based on outputting a corresponding first link state advertisement message describing a connected link of the router and that specifies a first dynamic routing metric identifying a first cost of the connected link, and a corresponding variation metric identifying a statistical variation of the dynamic routing metric. Each router also is configured for selectively outputting a corresponding second link state advertisement message describing the connected link and that specifies the corresponding variation metric and an updated dynamic routing metric identifying an updated cost of the connected link relative to the first cost, the second link state advertisement message selectively output based on the updated dynamic routing metric differing from the first dynamic routing metric by more than the variation metric, or the router having received another link state advertisement from another router in the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
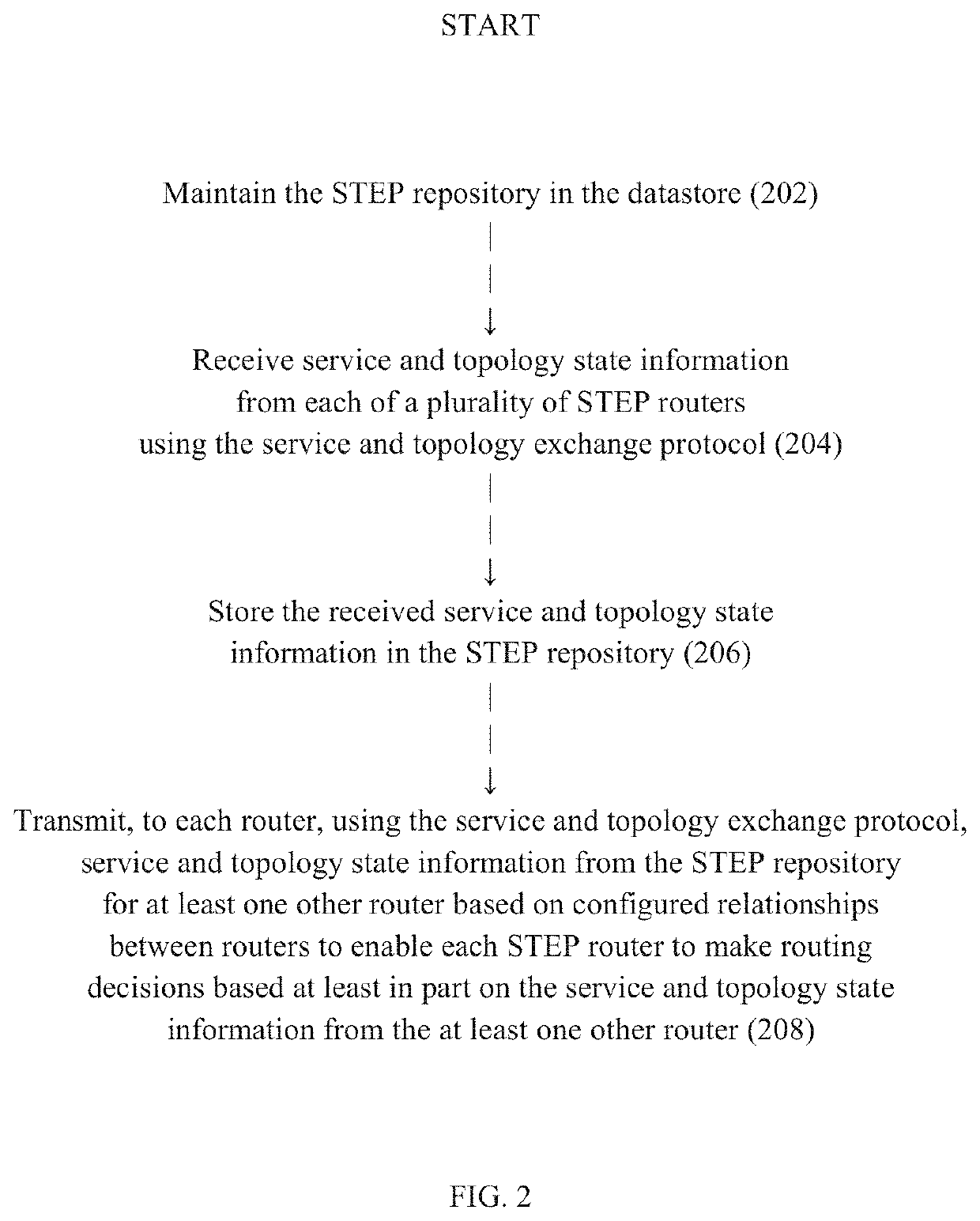
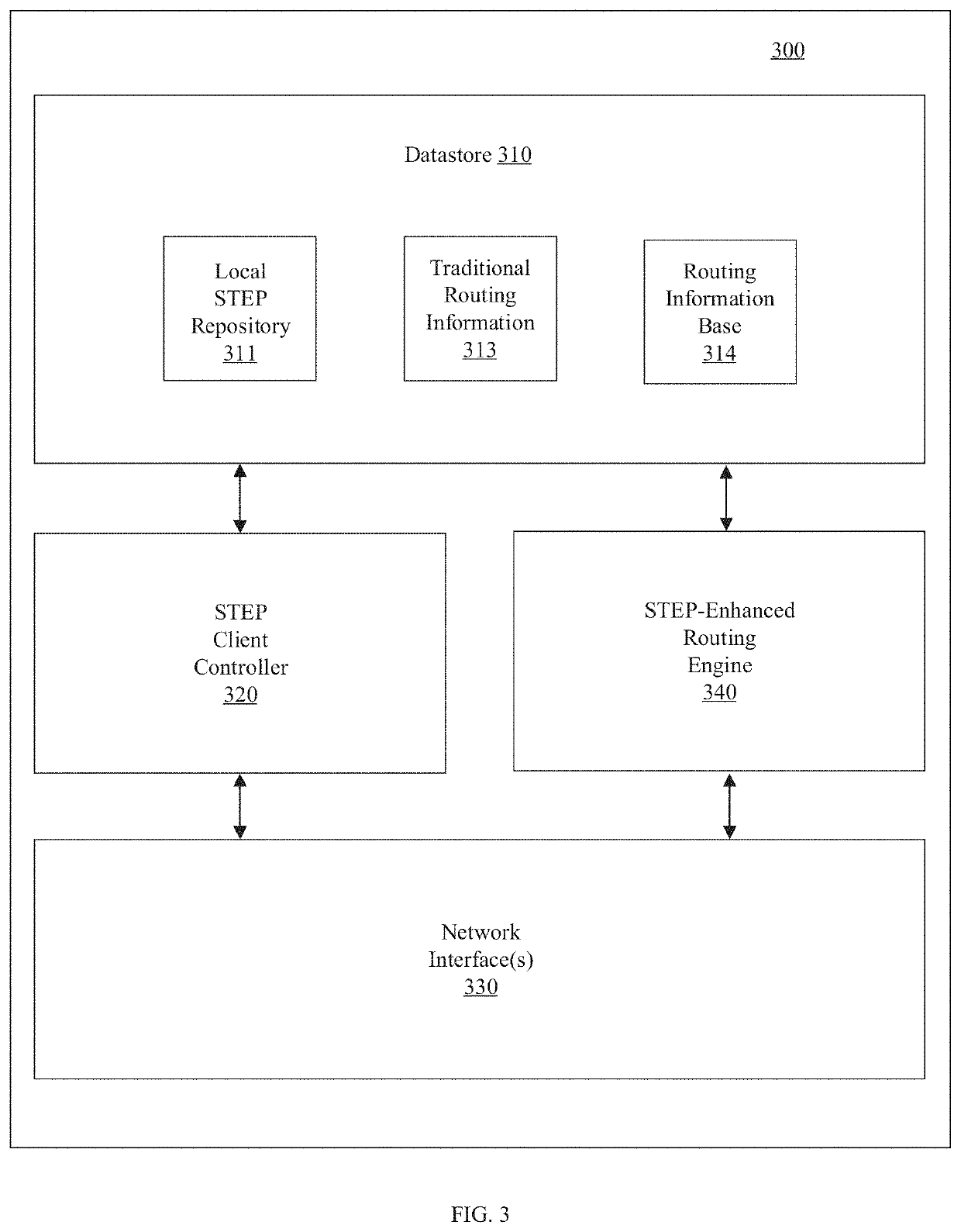
Routing using segment-based metrics
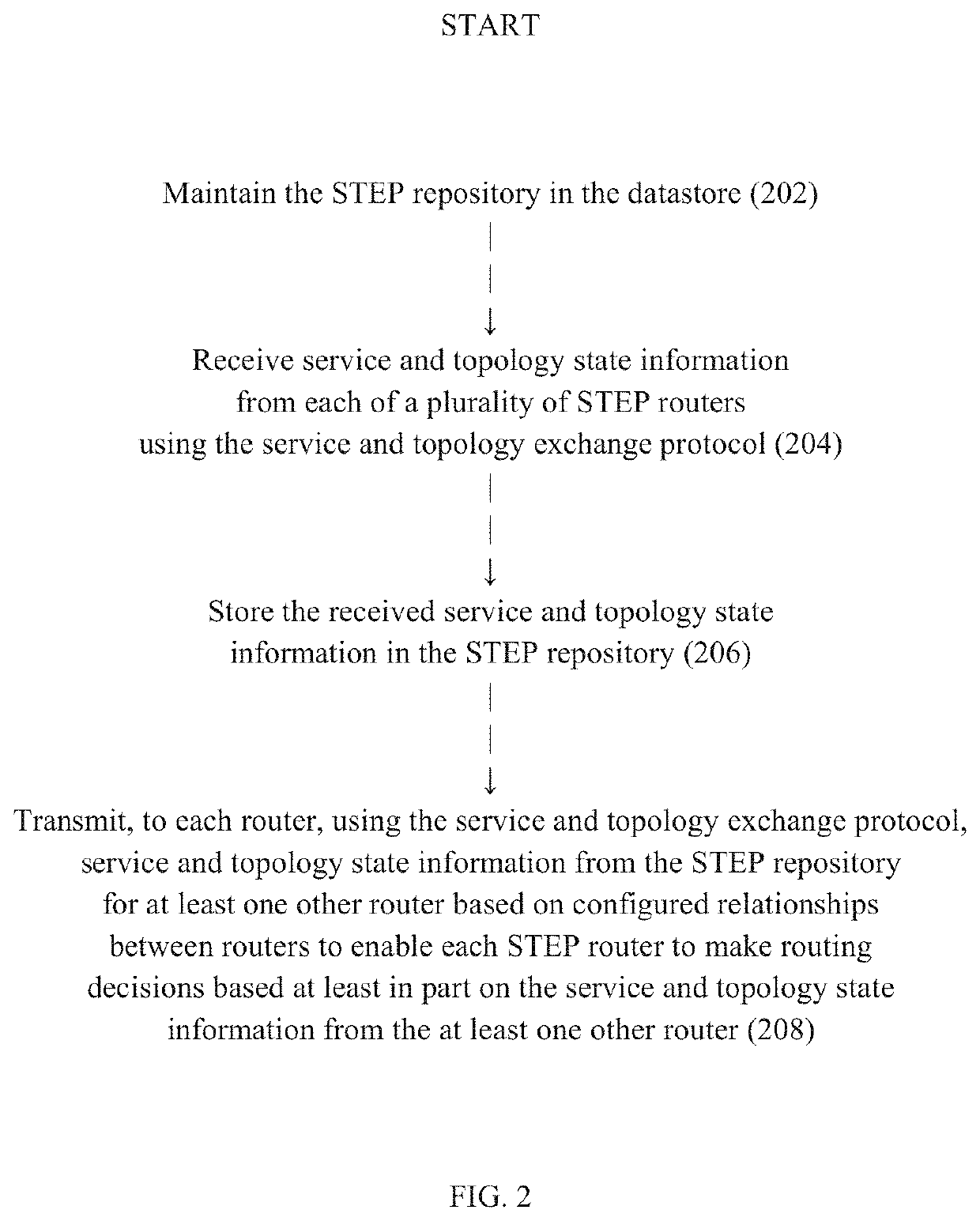
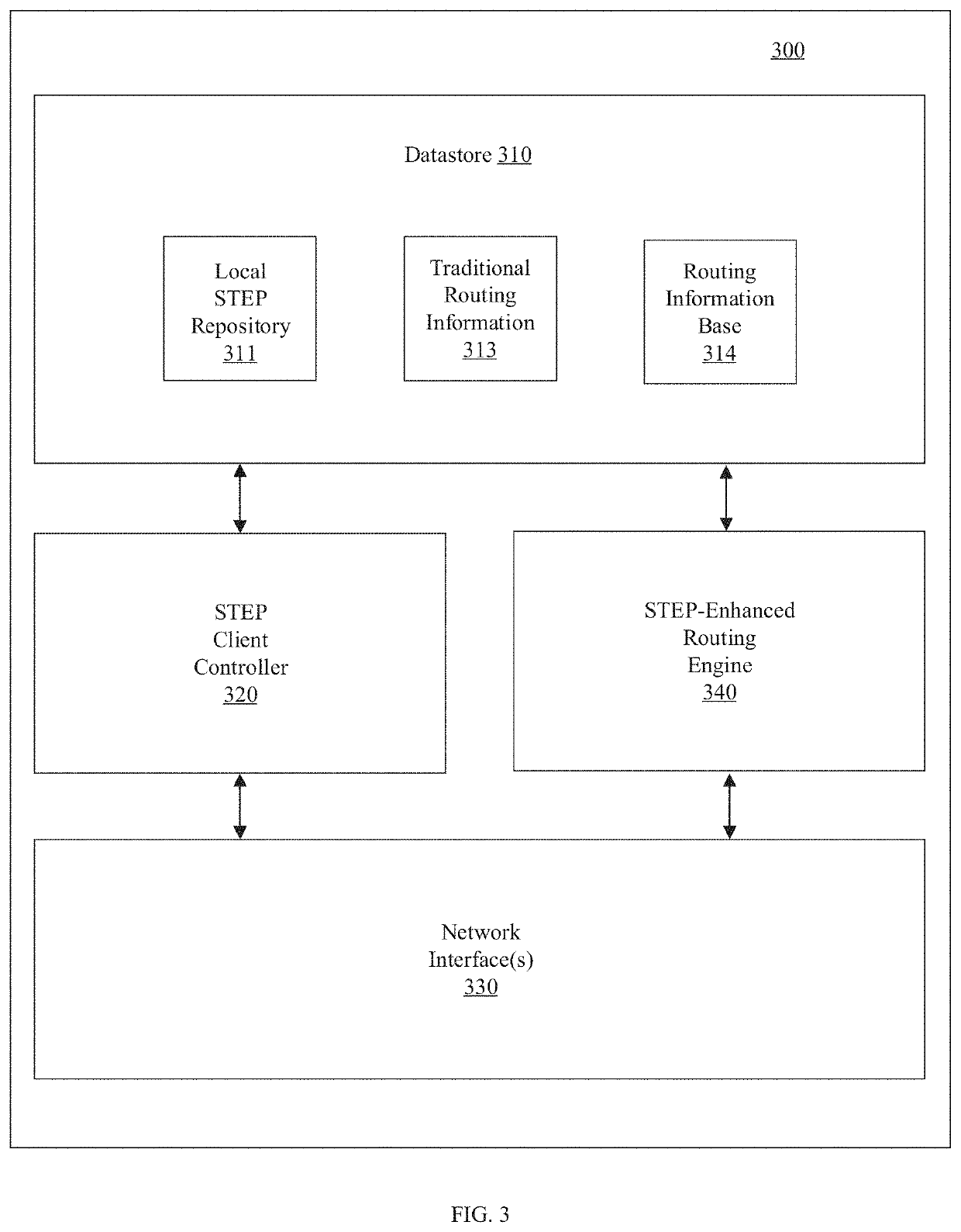
A router advertises an aggregated service or route that can be evaluated by other routers as a unitary segment rather than as a group of individual links / paths associated with the aggregated service or route. The aggregated service or route can be based on service and topology state information received from one or more other routers and can be advertised with the router as the nexthop for the aggregated service or route. The router can advertise an aggregated metric for the aggregated service or route for use in such evaluation. An aggregated route can be associated with different aggregated metrics for different services.
Owner:128 TECH
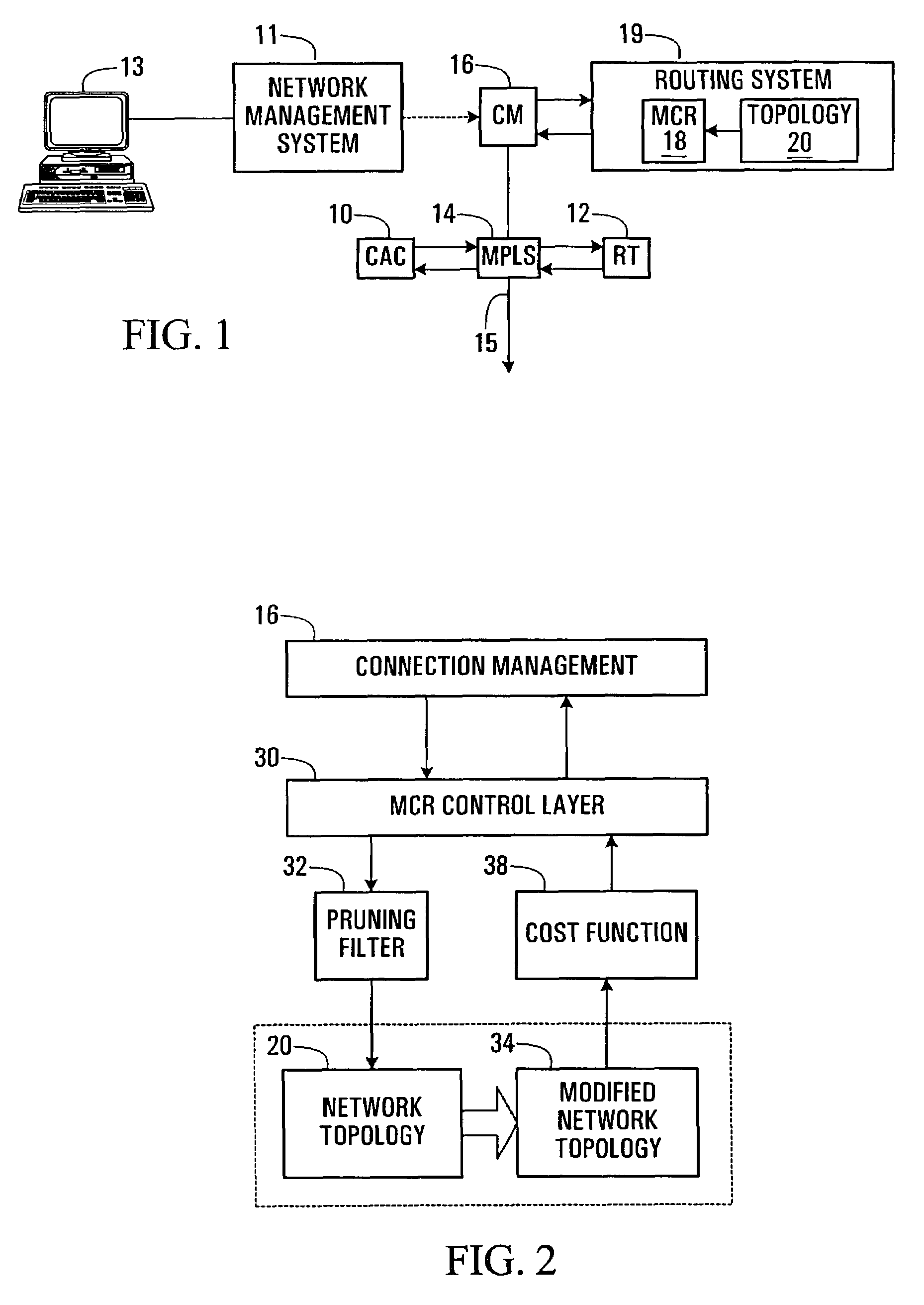
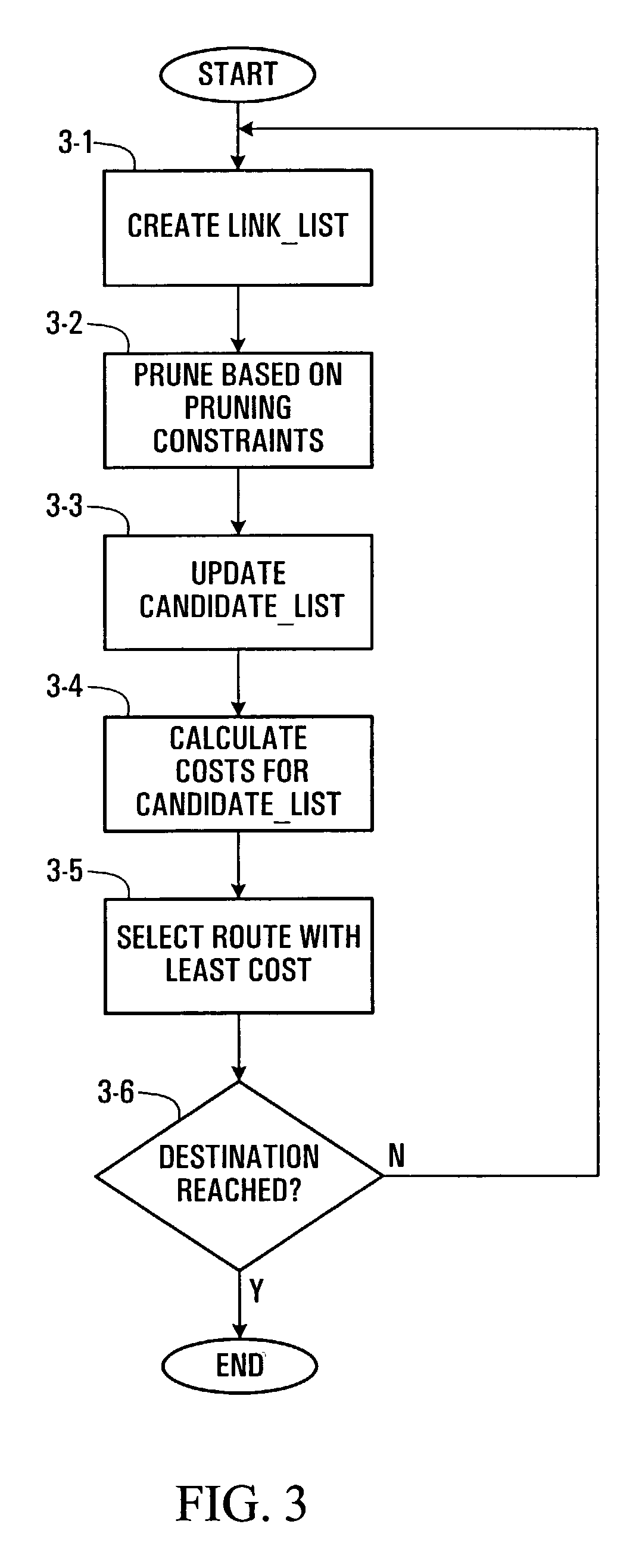
Multi-constraint routing system and method
ActiveUS7187652B2Good for load balancingIncrease costError preventionTransmission systemsLoad SheddingOptimum route
A routing system and method are provided which use a composite cost in identifying routes. This allows a simple way of identifying the best route taking multiple metrics into account for each link simultaneously. The system allows for the inclusion of pruning constraints, and allows for various objectives such as bin packing or load balancing to be achieved.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT CANADA
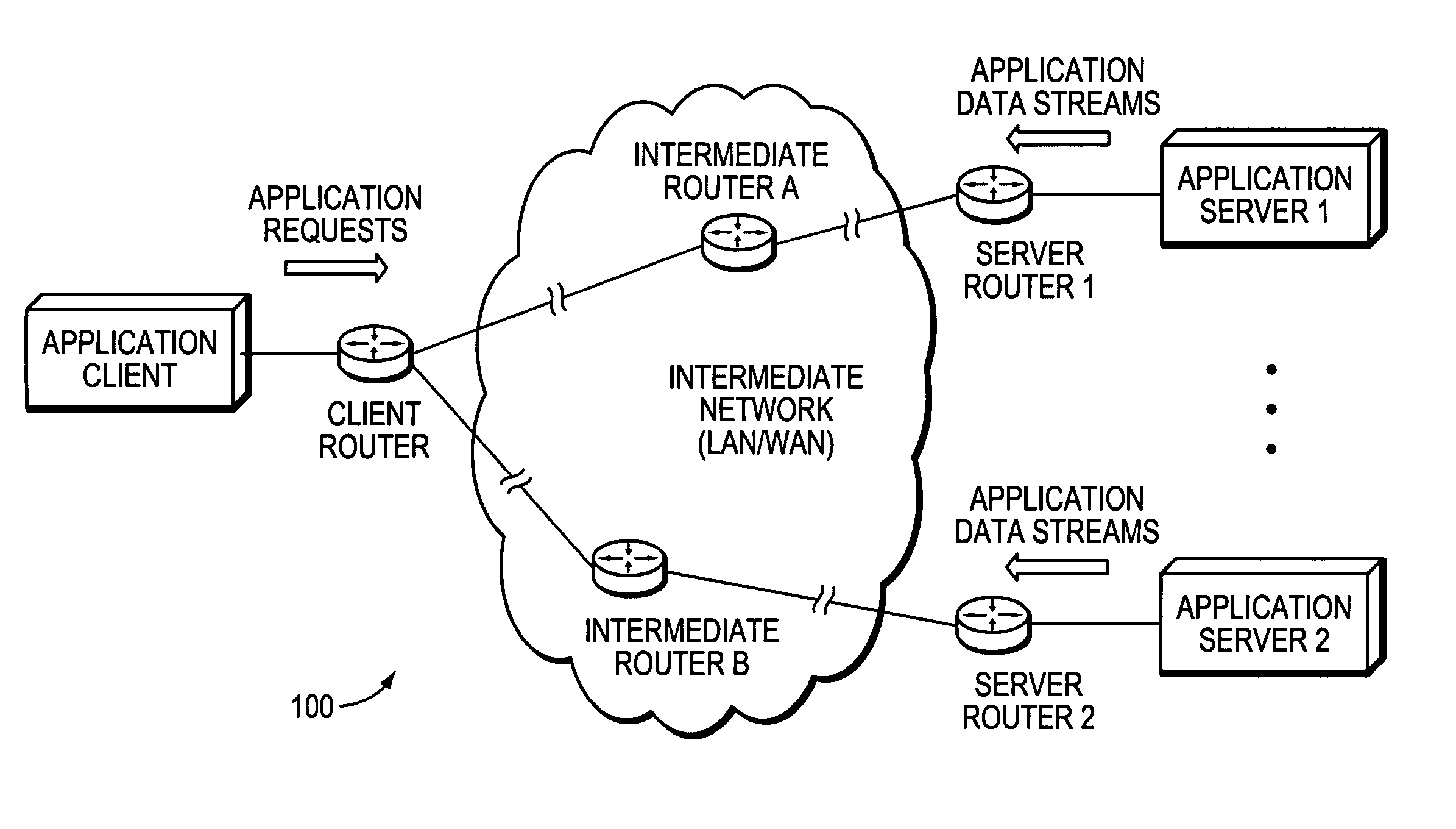
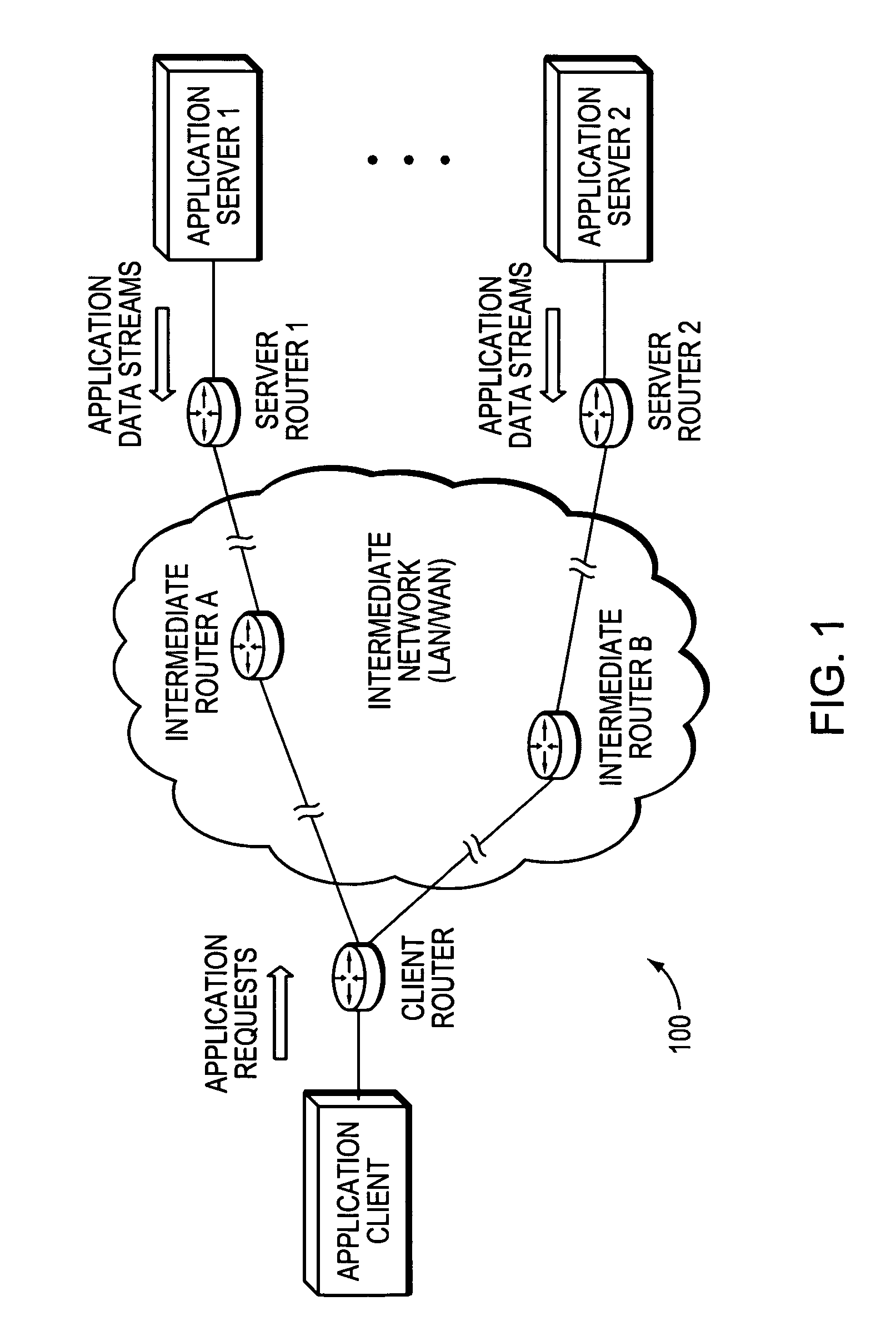
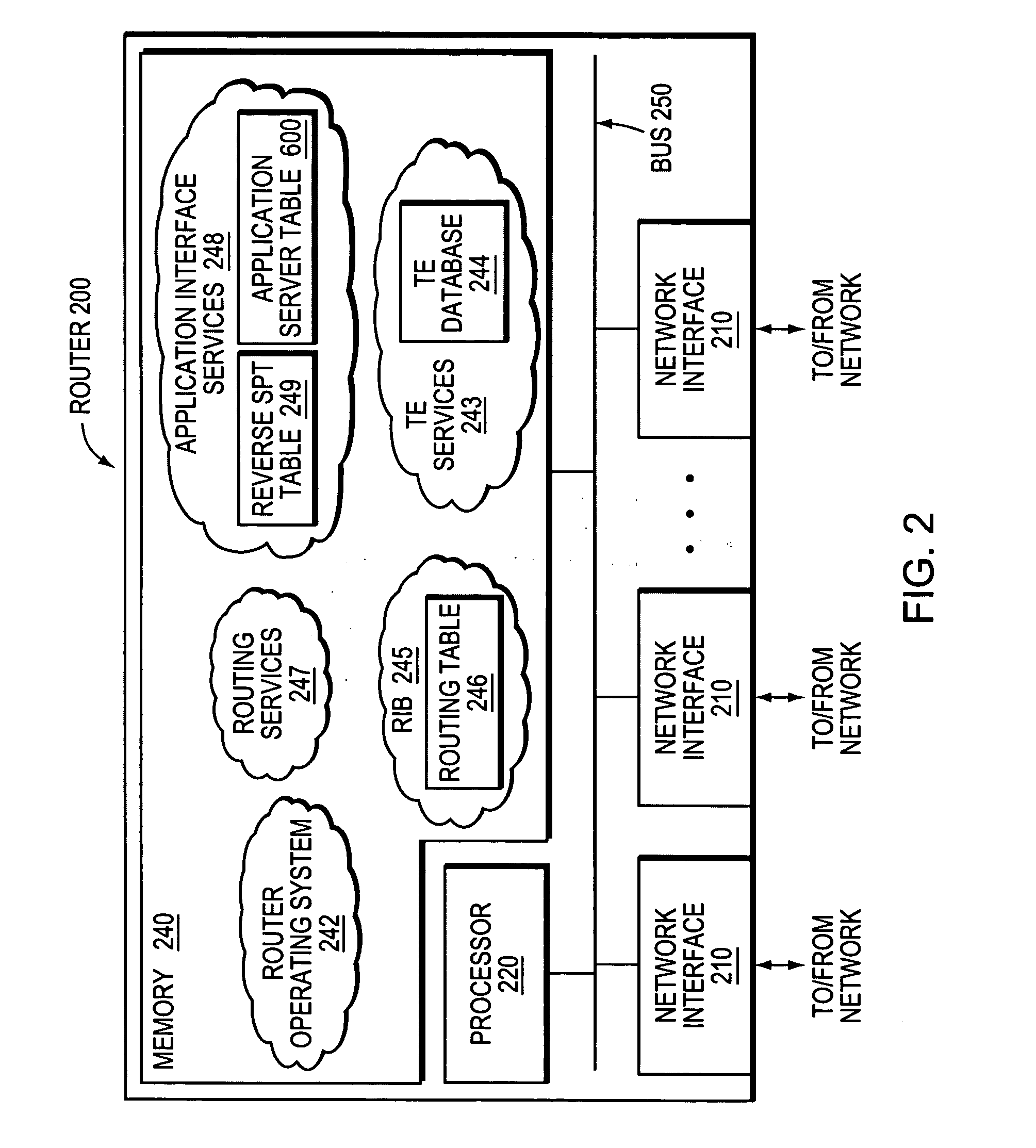
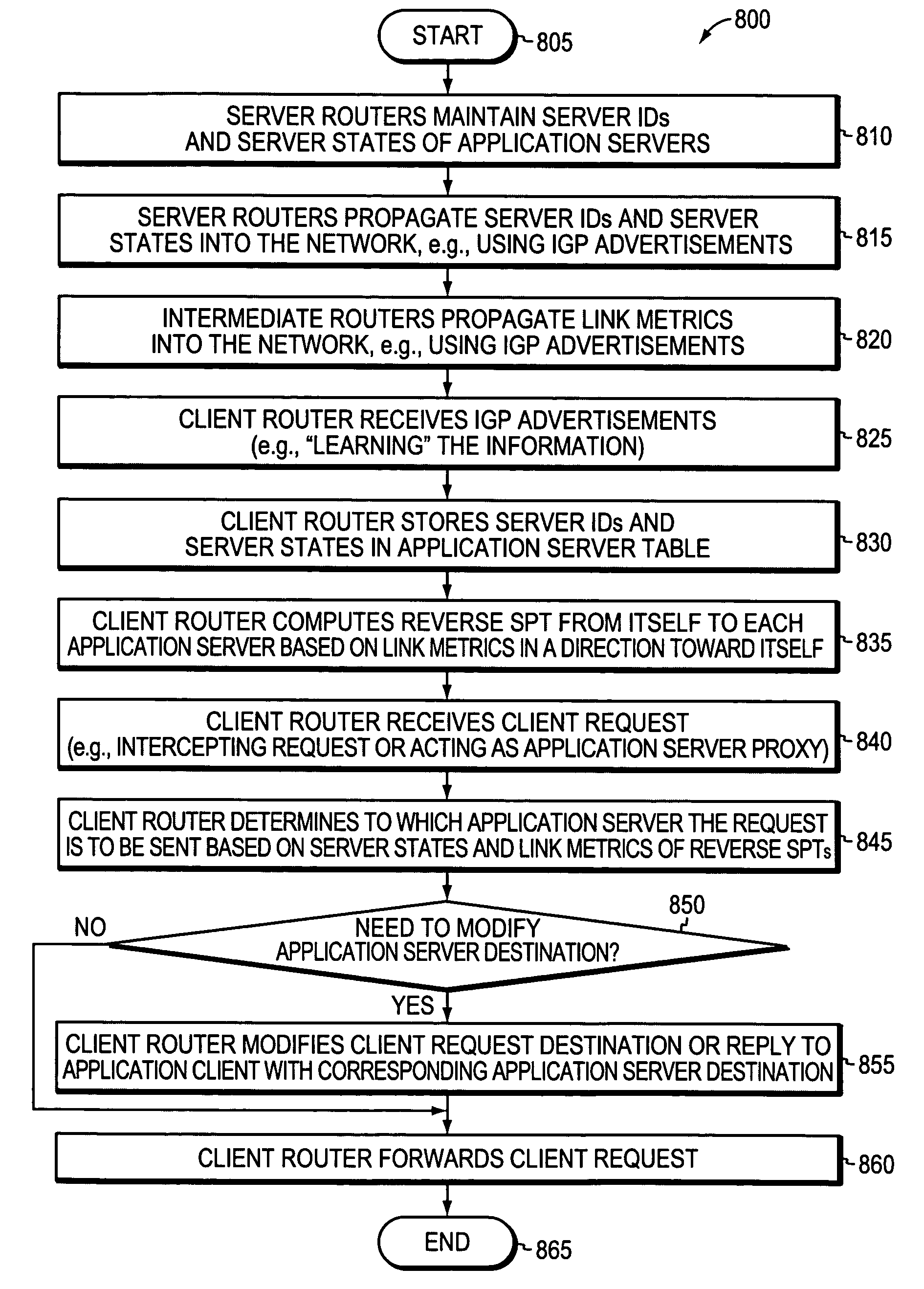
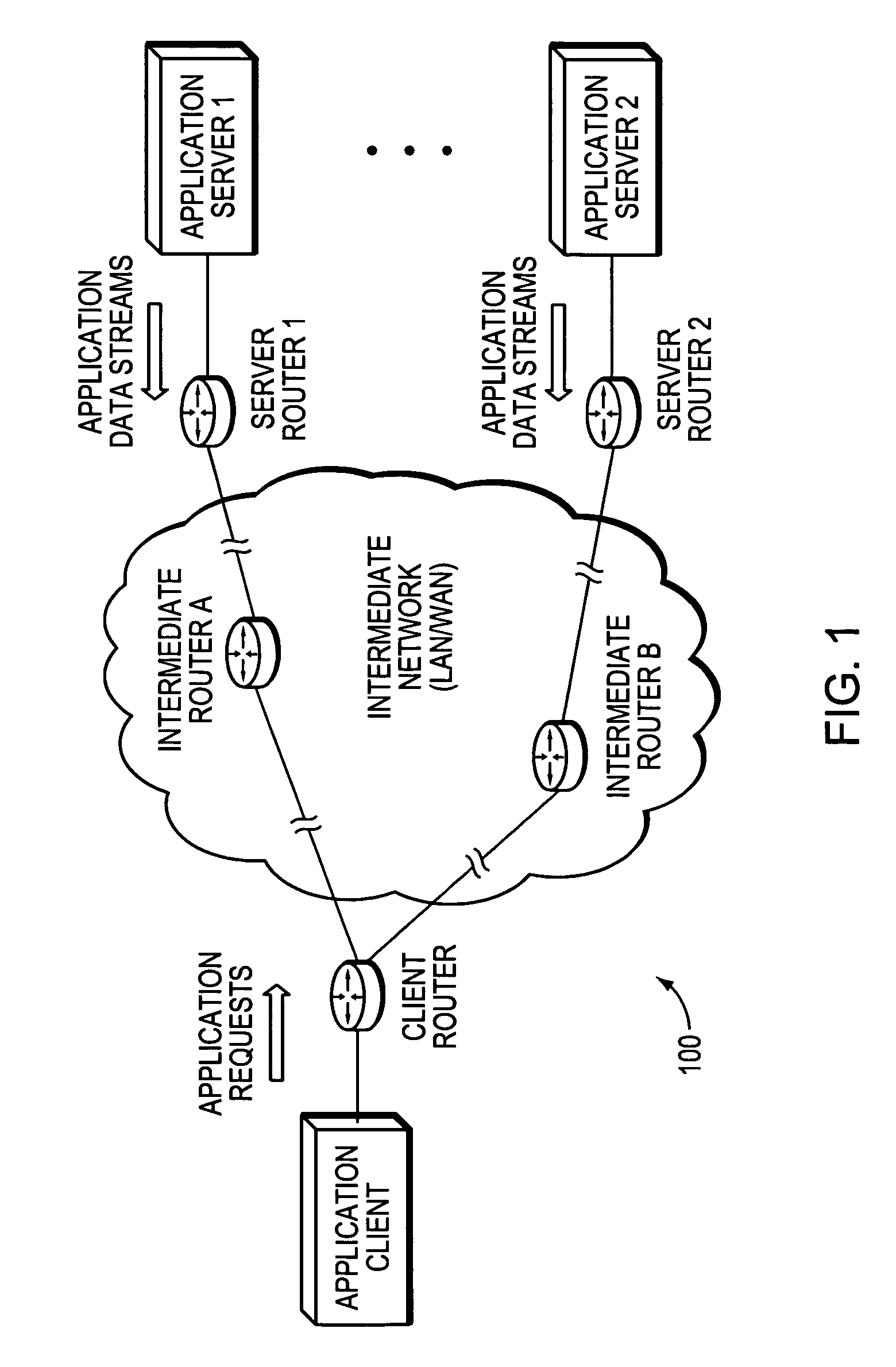
Technique for optimized routing of data streams on an IP backbone in a computer network
ActiveUS20070208874A1Easy to routeBroaden applicationDigital computer detailsTransmissionProtocol for Web Description ResourcesClient-side
A technique optimizes routing of application data streams on an Internet Protocol (IP) backbone in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a client router learns of server states (e.g., number of pending requests, etc.) of a plurality of application servers and also determines metrics of intermediate links between the application servers and the client router (intermediate link metrics), e.g., particularly link metrics in a direction from the application servers to the client router. Upon receiving an application request from an application client (“client request”), the client router determines to which of the application servers the client request is to be sent based on the server states and intermediate link metrics, and sends the client request accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Routing data packets in wireless networks with directional transmissions
ActiveUS20180020389A1Increase powerRaise the ratioSpatial transmit diversityNetwork topologiesWireless mesh networkTelecommunications
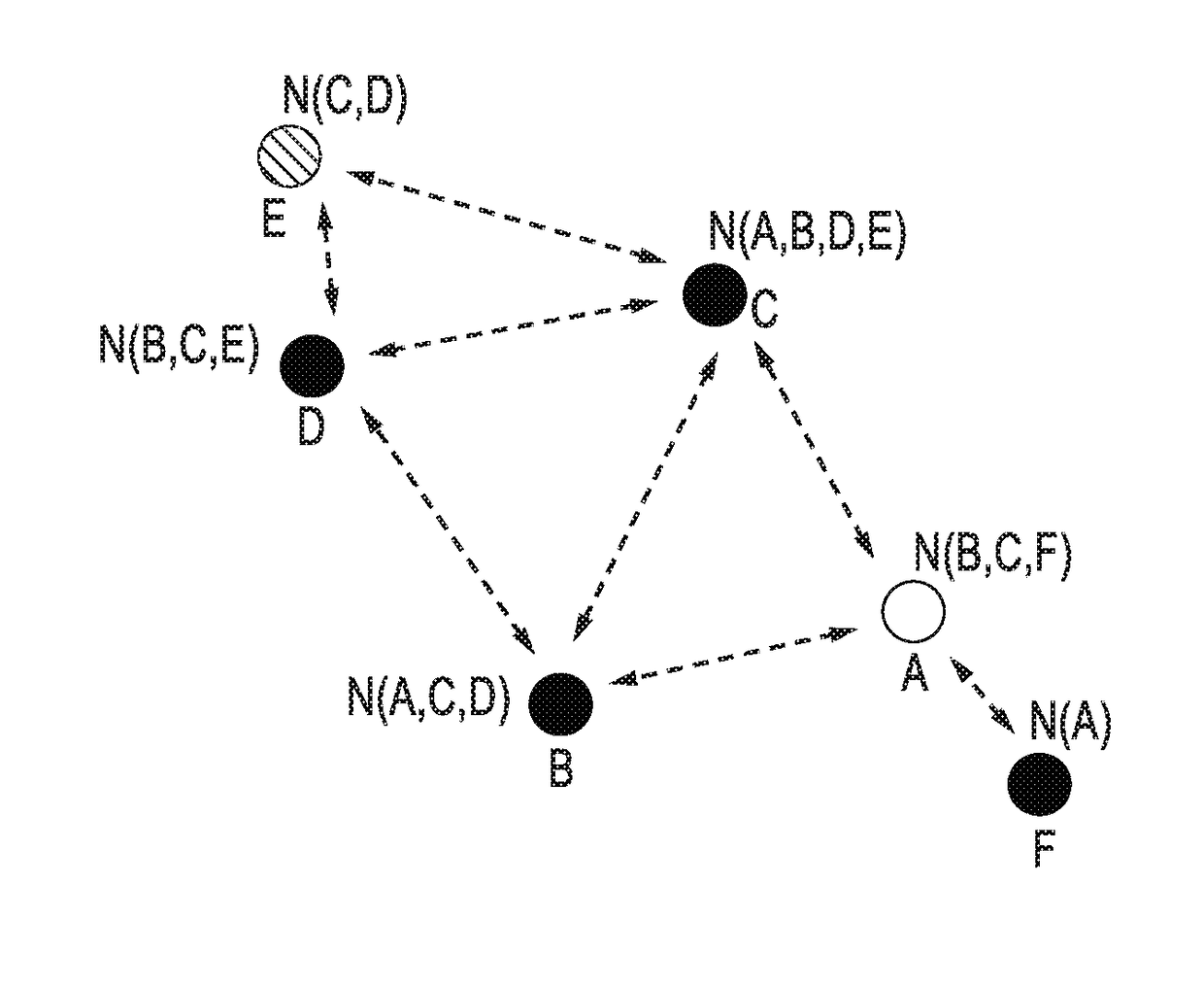
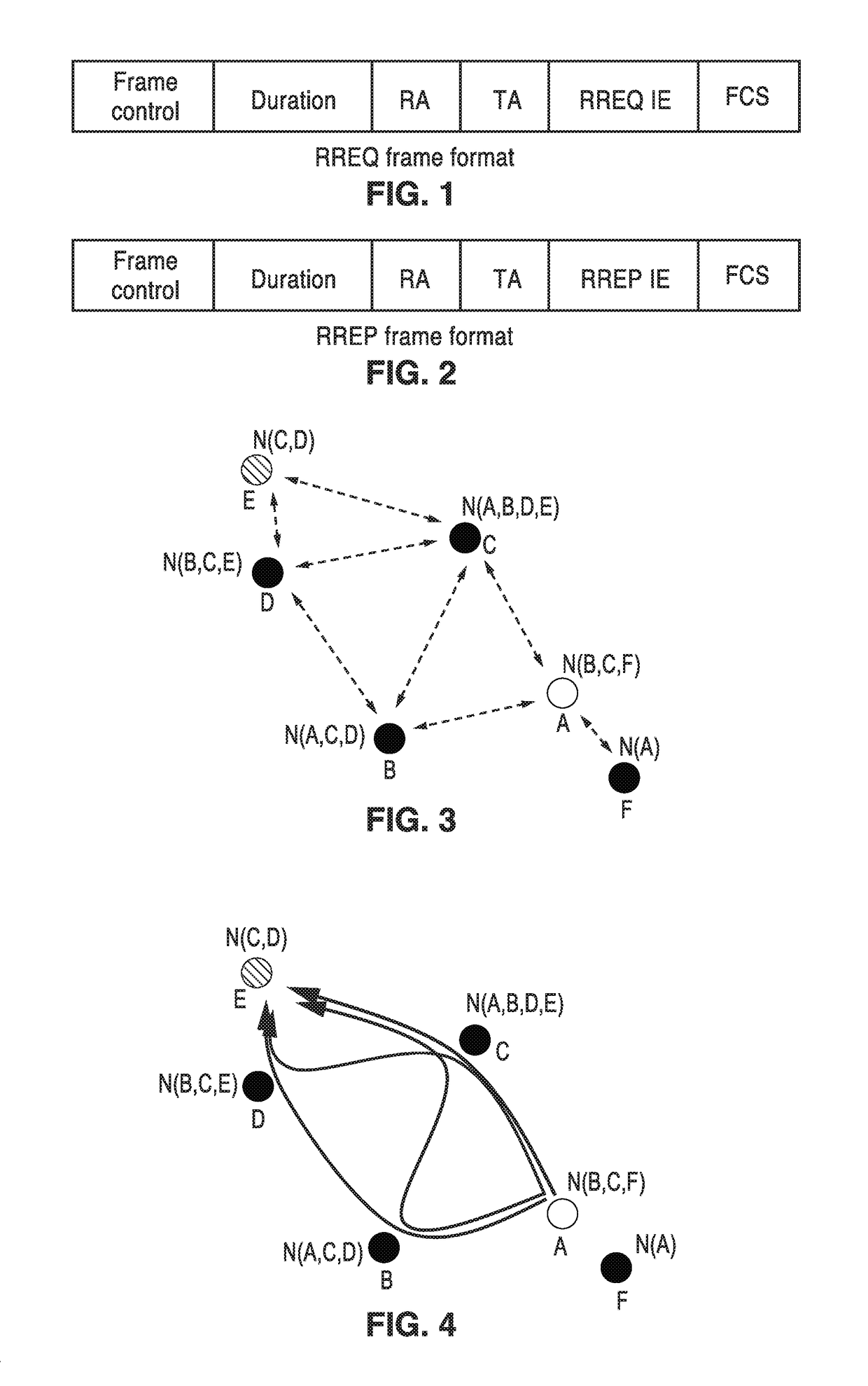
An apparatus and method for communicating via a routing protocol in a wireless network having directional transmission capabilities. Reliable peer stations are identified using Beamforming (BF) training feedback metrics. Routing discovery messages are transmitted by unicast to reliable peer stations, with neighborhood discovery lists disseminated among peer stations in a unicast mode. From the above information, routing tables are constructed with best routing between a source and a destination station, wherein messages can be routed using said routing table from a source peer station, through intermediate peer stations, to a destination peer station. In addition, other embodiments are described, including a simplified two-hop routing apparatus and method.
Owner:SONY CORP
Network routing process for regulating traffic through advantaged and disadvantaged nodes
ActiveUS7826372B1Without large amount of computational overheadImprove communication efficiencyError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityRouting table
A process for use in conjunction with a communications network routing protocol that automatically adjusts for congestion that may occur due to the presence of advantaged and partially disadvantaged nodes. The network nodes check to determine if they are advantaged or partially disadvantaged. Advantaged nodes may, for example, be airborne or satellite nodes having a high degree of network connectivity. Partially disadvantaged nodes may comprise nodes that are low on power. Advantaged nodes and partially disadvantaged nodes adjust the network metrics entered into the routing tables they use to advertise their routing information over the network to show longer pathways through such nodes. As a result the other nodes in the network reduce the amount of network traffic routed through advantaged and disadvantaged nodes.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Open service discovery and routing mechanism for configuring cross-domain telecommunication services
InactiveCN1957568AScalability issues are reduced or eliminatedAvoid bottlenecksData switching by path configurationService domainReachability
Apparatus and method are provided for distributing service domain reachability information across domain boundaries, thereby allowing domain management systems to determine routing for cross-domain services even when the domains have different technologies or administrators. A Service Domain Manager within each domain advertises to neighbouring domains which services it supports. A domain which receives such advertisements forwards the advertisement on to other domains. Each SDM builds a routing information table which specifies the service, the domain, the next hop, and optionally user defined metrics. The routing information table does not include end-point addresses, in order to keep the size of the table manageable. In this way, the NMS of each domain obtains an end-to-end view of service routes.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Routing system for internet traffic
ActiveUS20150103662A1Fine granularityMaximizes total sumError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsInternet trafficGlobal optimal
A deterministic approach for route selection in the Internet and other multi-homed networks is presented that is based upon a mathematical model that takes into consideration performance and costs while satisfying commitment constraints. The approach is expressed with a linear programming formulation that can be solved with conventional linear programming solver software. Performance metrics can be defined and combined in order to achieve the best route selection depending on requirements. Some of the potential benefits of the approach include: a global optimal solution for routing traffic (using metrics such as performance, cost, and other constraints), a dynamic weight assignment for performance metrics, and a flexible problem definition to add routing rules (e.g. static and restricted routes) to the model.
Owner:INTERNAP HLDG LLC
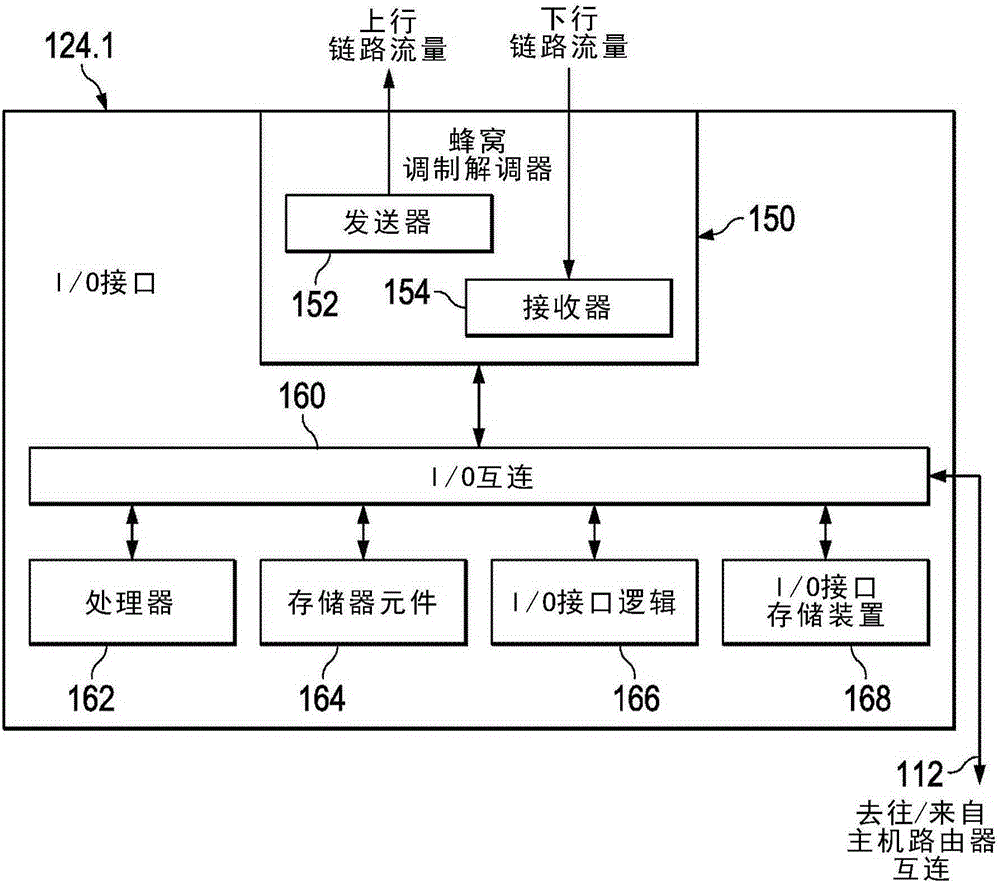
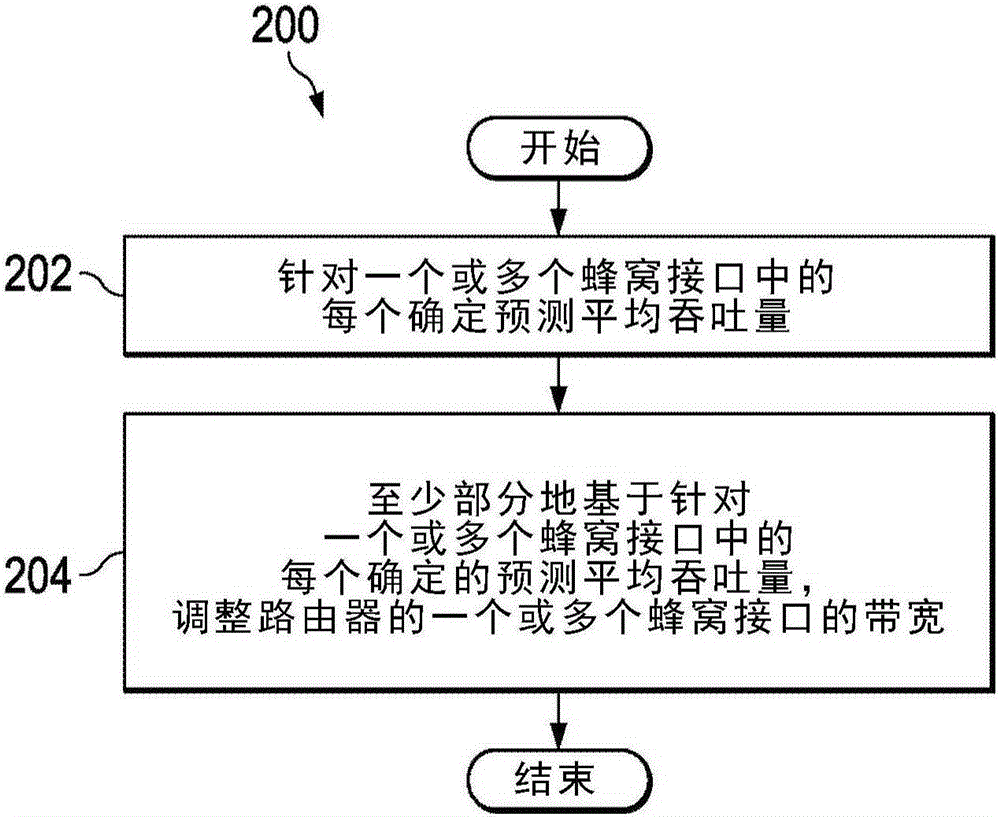
System and method for dynamic bandwidth adjustments for cellular interfaces in a network environment
A method for managing cellular interfaces for routing equipment in a network environment is provided that includes determining a predicted average throughput for each of one or more cellular interfacesof a router and adjusting bandwidth for each of the one or more of the cellular interfaces based, at least in part, on the predicted average throughput determined for each of the one or more cellular interfaces. Another method is provided which includes determining a variance in path metrics for multiple cellular interfaces and updating a routing table for the cellular interfaces using the determined variance if there is a difference between the determined variance and a previous variance determined for the cellular interfaces. Another method is provided which includes monitoring watermark thresholds for a MAC buffer of a cellular interface; generating an interrupt when a particular watermark threshold for the MAC buffer is reached; and adjusting enqueueing of uplink packets into the MAC buffer based on the interrupt.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Quasi-deterministic gateway selection algorithm for multi-domain source routed networks
InactiveUS6873616B1Reduced gateway overloadingReduce the likelihood of failureMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationDistributed computingMulti domain
A system and a method of selecting gateways using stored metrics associated with each route out of the domain and with each destination is presented. The metrics represent some measure to be minimized by the routing system, such as cost or delay. The route is selected quasi-deterministically. A first selection is made deterministically based on the stored metrics in order to attempt to use the optimum path. If a connection can not be established through the deterministically selected gateway, an alternate gateway is selected randomly from among the remaining gateways capable of reaching the destination at a reasonable cost.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Load sharing method of non-equivalent route and equipment
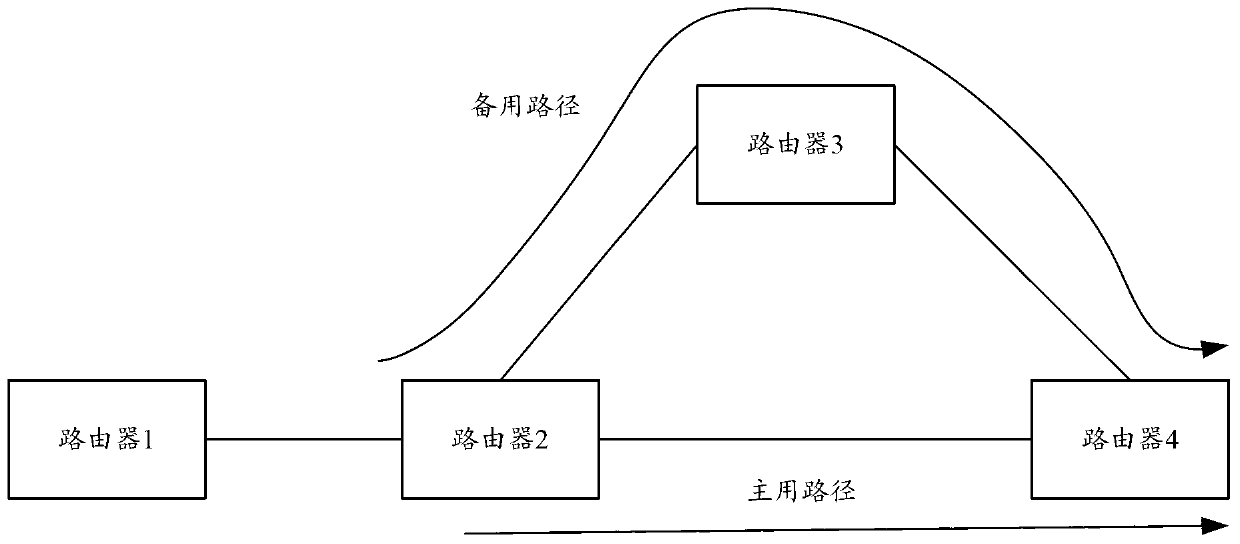
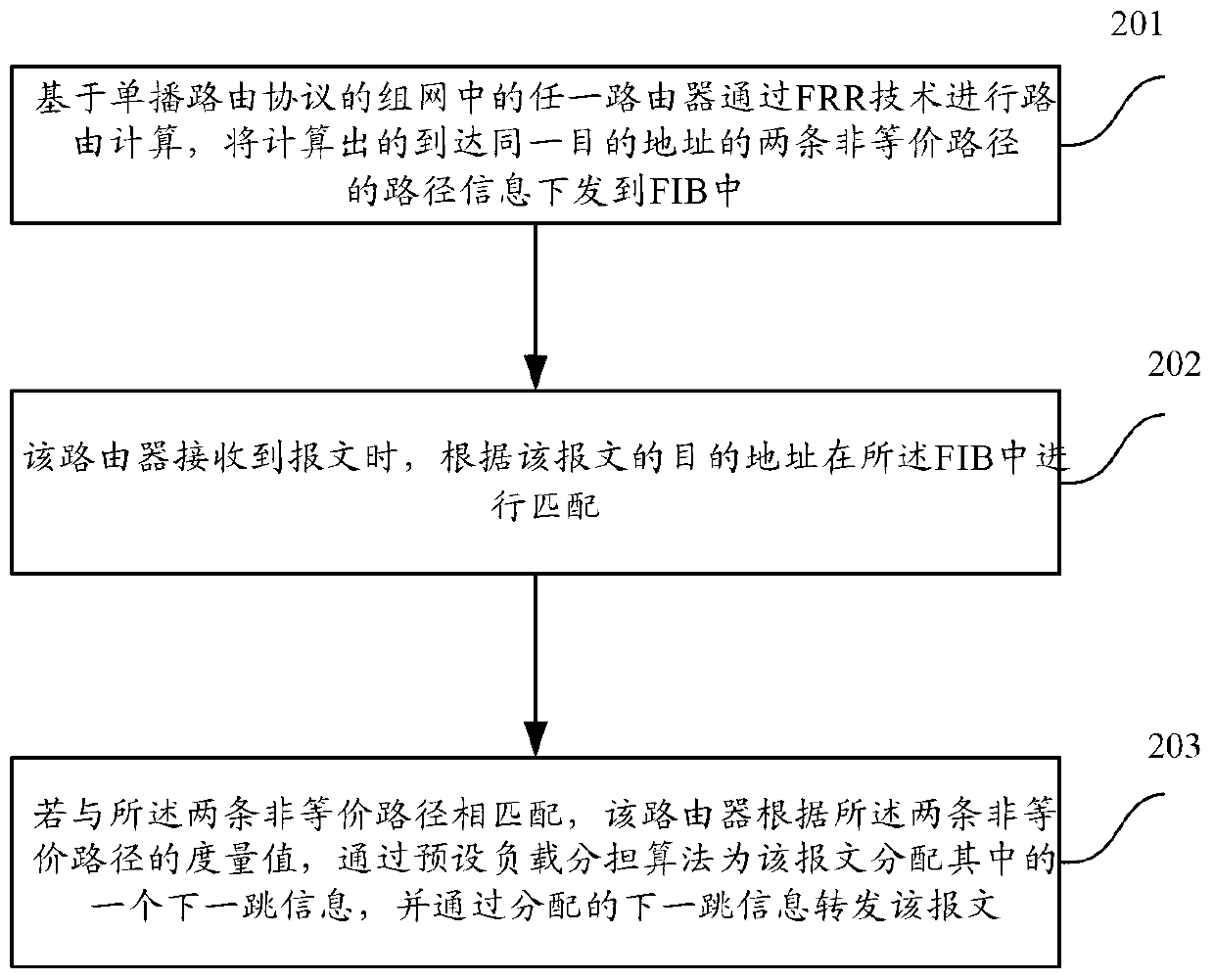
The invention discloses a load sharing method of non-equivalent route. The method comprises the following steps: performing route calculation through an FRR (Fast Reroute) technology based on any router in a network of a unicast routing protocol; issuing calculated route information of two non-equivalent paths to an FIB (Forwarding Information Base); and enabling the traffic in proportion pass through two non-equivalent paths according to the metrics included in the path information. Based on the same inventive conception, the invention also provide equipment, which can support the load sharing of the non-equivalent route on the unicast routing protocol, so that the utilization rate of bandwidth is improved and the network bandwidth is increased.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Multi-path dynamic routing algorithm
Disclosed is a routing algorithm that uses a new concept of node metric system for optimizing the throughput of a network, in particular, a shared medium network. The measure of congestion of a path in the network is represented by a path metric which is computed by summing the node metrics of the intermediate nodes on the path. Factors used in computing node metrics include the following: 1. future traffic load from neighboring nodes to the node; and 2. future traffic load from the node to the neighboring nodes.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Routing using segment-based metrics
A router advertises an aggregated service or route that can be evaluated by other routers as a unitary segment rather than as a group of individual links / paths associated with the aggregated service or route. The aggregated service or route can be based on service and topology state information received from one or more other routers and can be advertised with the router as the nexthop for the aggregated service or route. The router can advertise an aggregated metric for the aggregated service or route for use in such evaluation. An aggregated route can be associated with different aggregated metrics for different services.
Owner:128 TECH
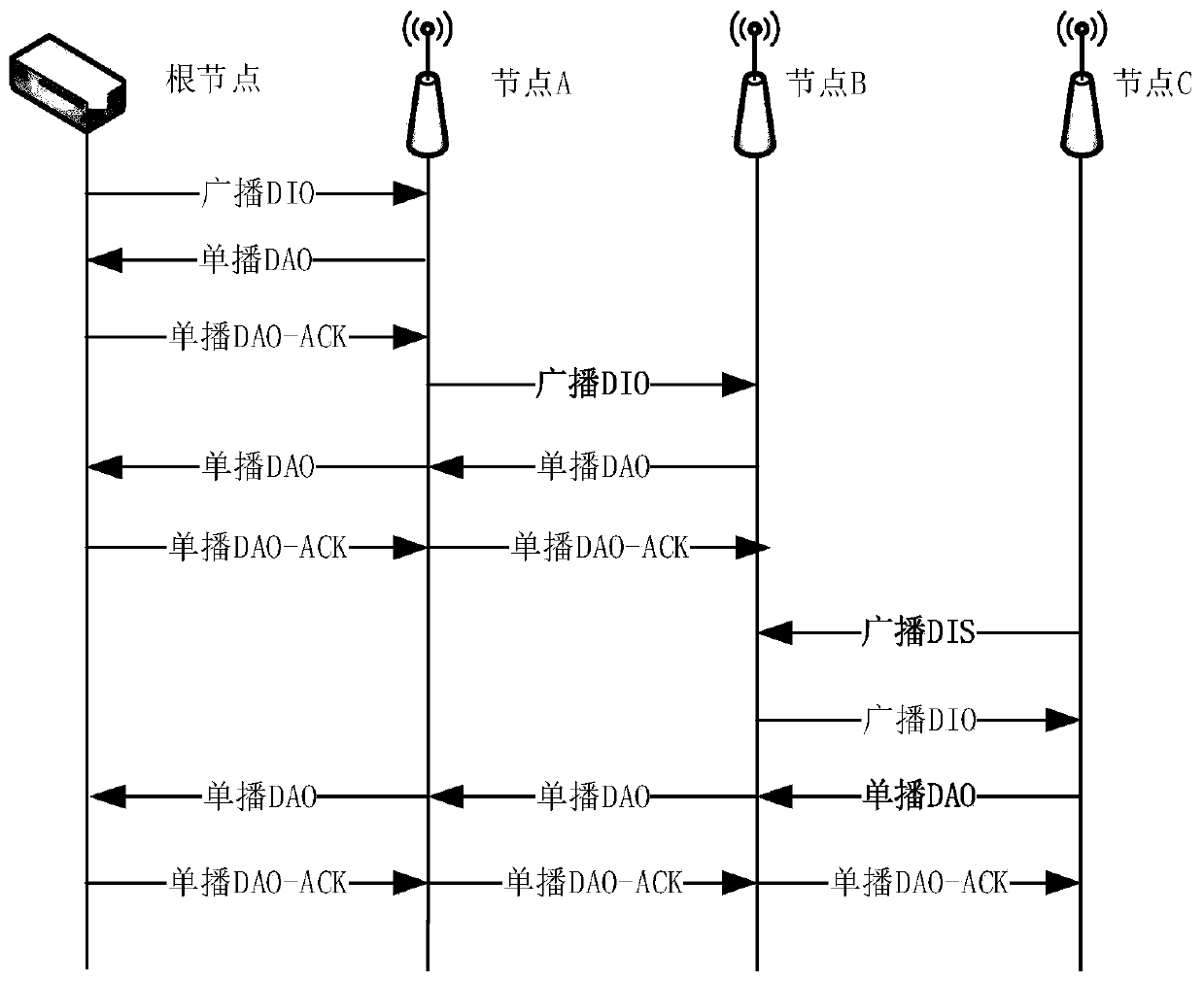
RPL routing method based on bidirectional father node decision
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless sensor network communication, and provides an RPL routing method based on bidirectional father node decision. The RPL routing method comprisesthe following steps of: selecting an optimal father node according to routing metrics of all candidate father nodes by a child node; after consulting information is carried through an M-DAO message and the optimal father node receives the M-DAO message transmitted by the child node, judging whether to establish connection with the child node or not according to the information carried in the M-DAOmessage and the current network condition of the optimal father node; and finally, completing networking. According to the RPL routing method, the optimal father node is selected through an optimal father node selection mechanism, so that the probability that the node with heavy link load is selected as the father node is avoided, and meanwhile, a large number of child nodes are prevented from being connected to the node; and secondly, through adopting the bidirectional father node decision mechanism, the data processing capacity of the father node is considered, and the thunder effect causedby the fact that DIO messages cannot finally reflect the connection condition of the node is relieved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
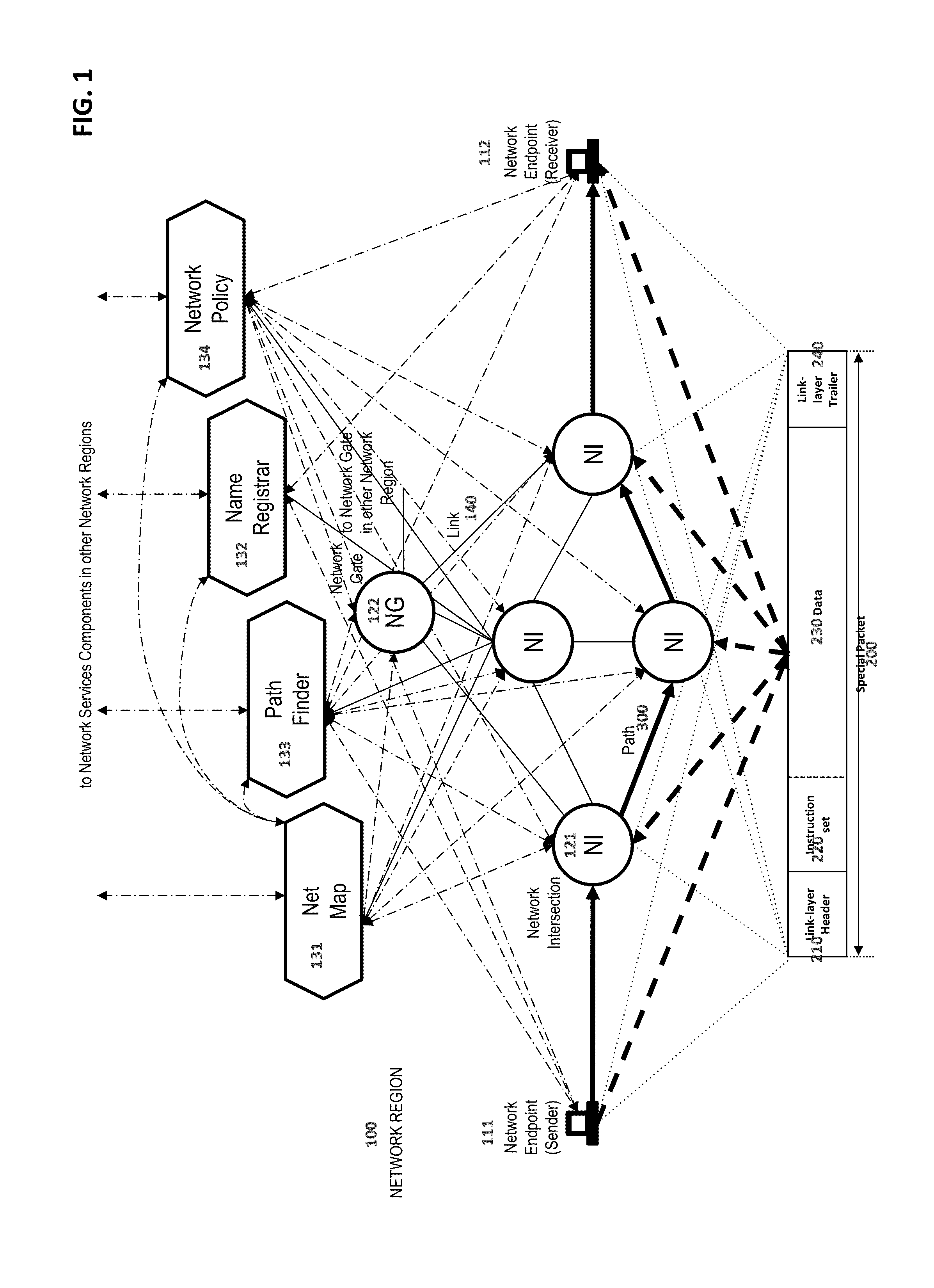
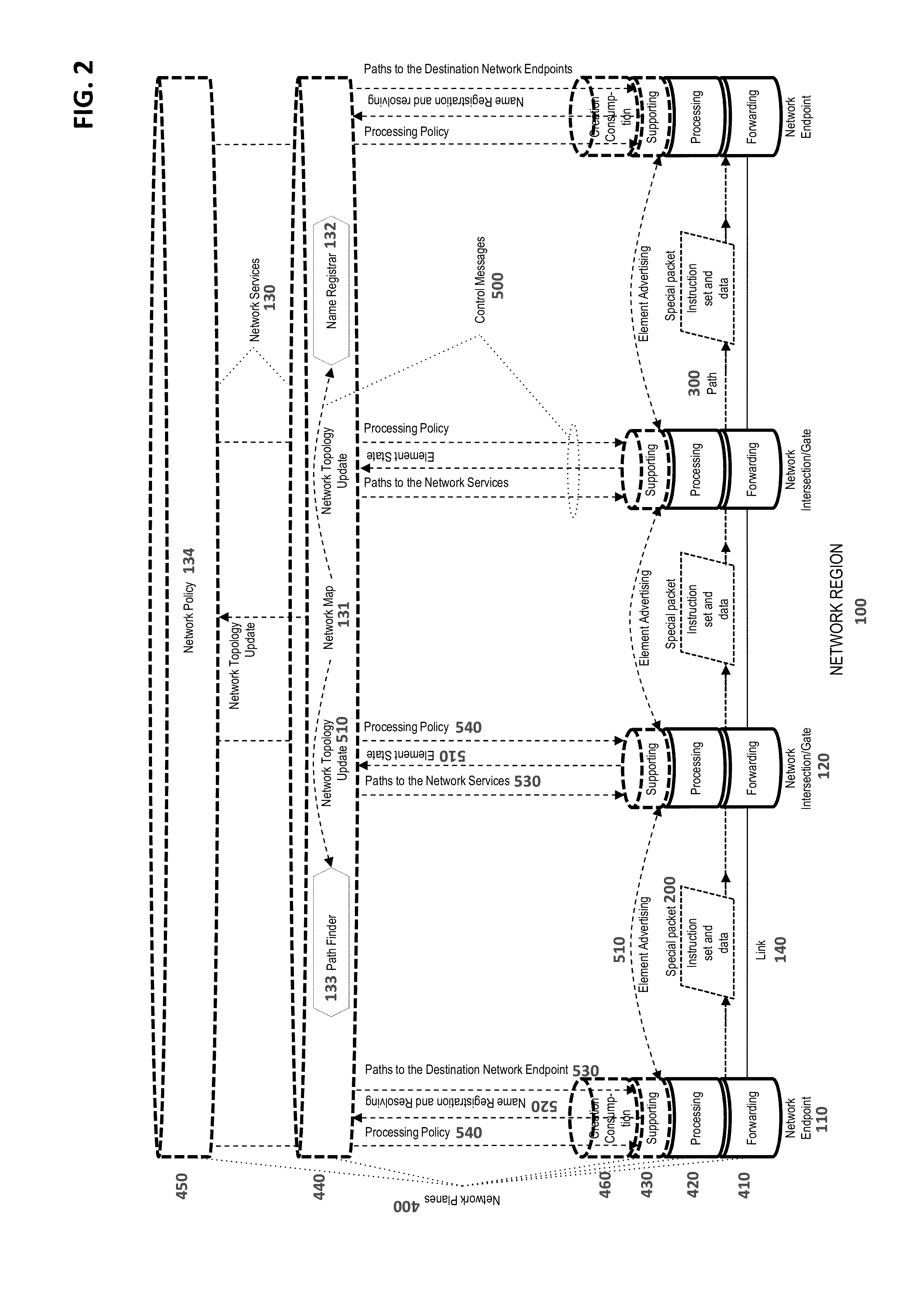
Methods and Systems for Packet Delivery Based Upon Embedded Instructions
ActiveUS20150071109A1New efficiencyEfficient deliveryData switching by path configurationPathPingData pack
New communication system with packet's retransmission elements that do not use and do not depend on any routing protocol provides definite mechanisms to deliver packets from sender to receiver. Packet's retransmission elements are no longer in charge for calculating and maintaining routing tables in order to make decision regarding packet forwarding from ingress port to egress port. Each packet besides data contains set of instructions that presents complete path description from sender to receiver and rules of packet's processing on its way depending on various network metrics. The set of instructions is devised to be executed or interpreted by each network element that packet passing through. The outcome of instructions execution provides decision regarding packet forwarding and transformation. In order to provide information for path calculation and rules of packet processing there are centralized services—Network map, Pathfinder, Name registrar and Network policy.
Owner:DZEKON GRIGORI +1
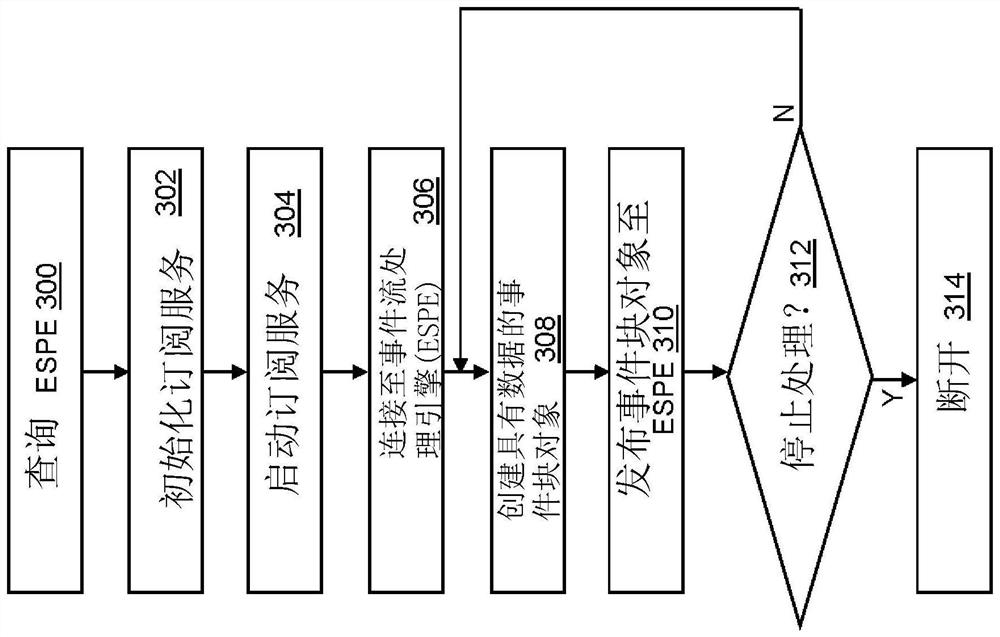
Routing management through event stream processing cluster manager
The invention relates to routing management by an event stream processing cluster manager. The routing management is characterized by computing a device management router; defining an instantiation manager engine based on the manager engine, and instantiating a manager ESPE based on the created manager ESP model; creating a router profile based on the mapping information read from the manager profile, the mapping information describing a connection between the event publish source and a source window of the manager ESPE; instantiating a router engine based on the created router profile; and initiating a connector to receive an event based on a router profile. The event is received in a source window of a manager ESPE processed based on a manager ESP model. A third computing device is selected by the router engine based on usage metrics received from each of a plurality of windows defined by a remote ESP model configured to further process a processed event upon receiving the processedevent.
Owner:SAS INSTITUTE
Method and device for selecting a communication interface
InactiveUS20160112300A1Port to become blockedSolution value is not highData switching by path configurationCommunication interfaceDistributed computing
A method and a device for selecting a communication interface of a source host so as to transmit data to a destination host in an optimal manner. The method allows the source host to calculate the total route cost to the destination host from each of its interfaces, as a function of the routing metrics, and to select the interface corresponding to the lowest value of total route cost.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Configuring traffic allocations in a router
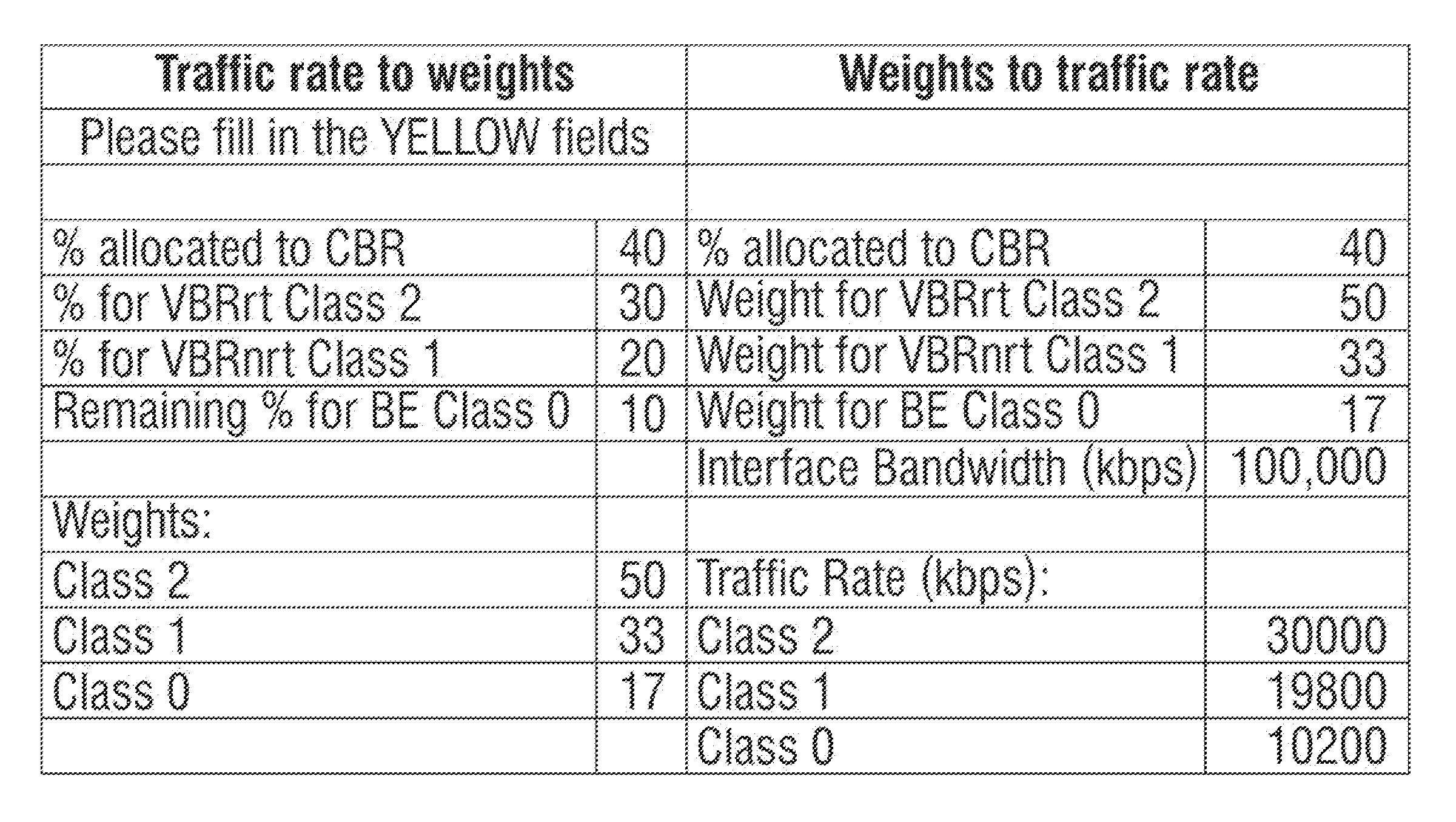
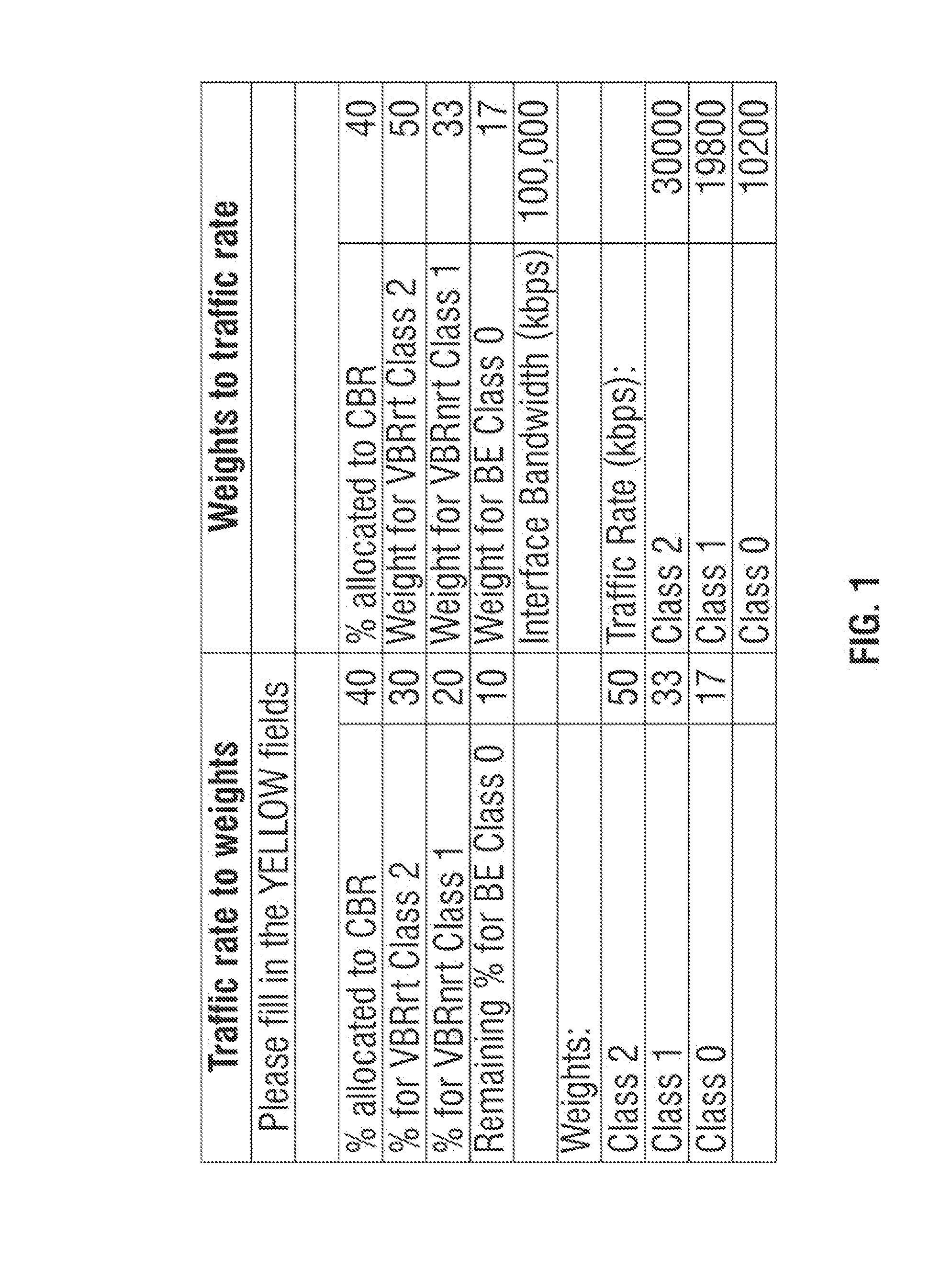
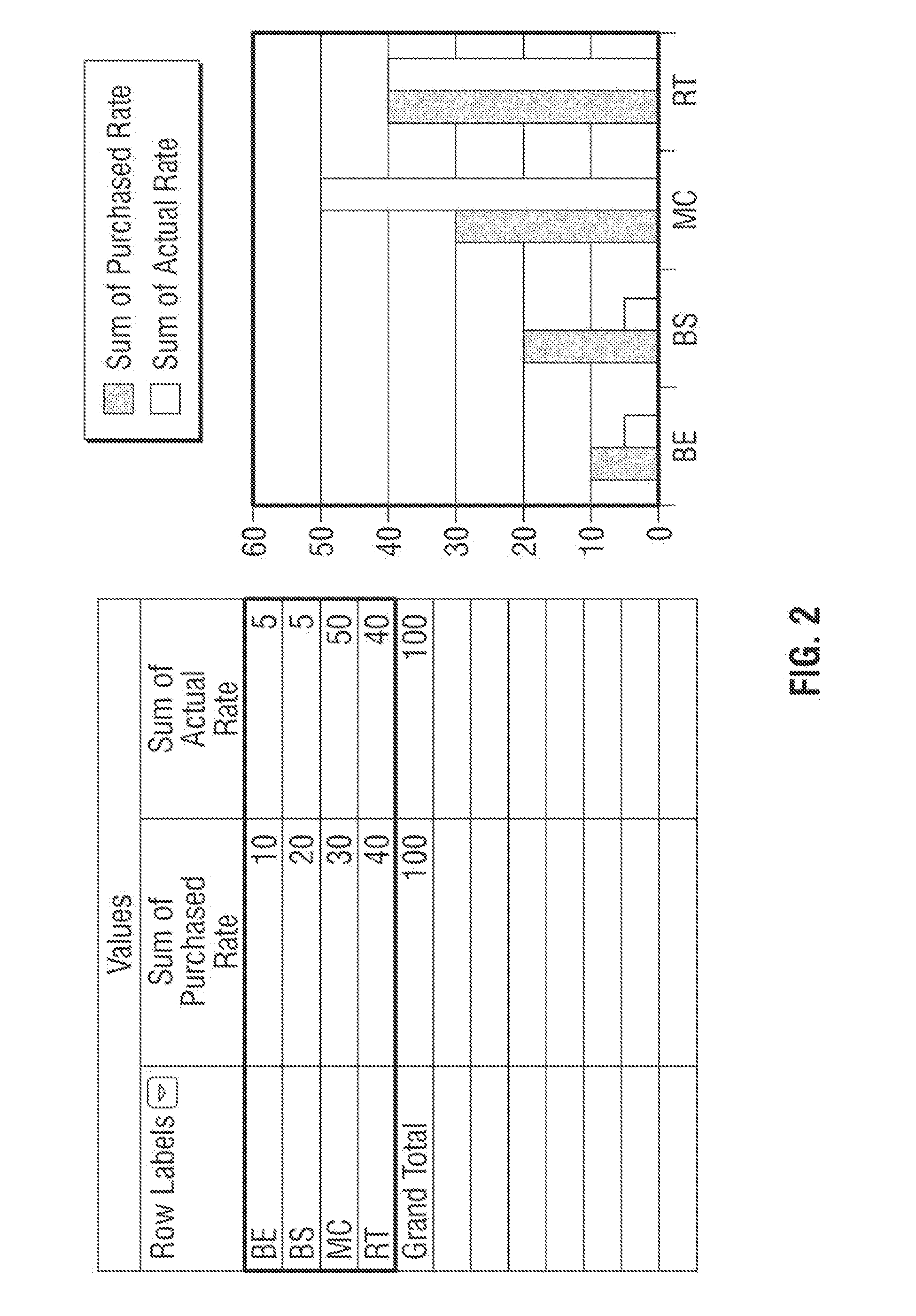
Disclosed herein are methods and calculators for configuring traffic allocations for service classes with different Quality of Service (QoS) in a router. Example embodiments involve setting allocations at a router based on traffic rate values and / or traffic weight values provided by a user. The router may monitor actual traffic rates to ensure that traffic is not being dropped due to improper rate allocations and to provide historical data for optimizing traffic allocations. In addition, the router may automatically adjust traffic allocations to avoid dropping high(er) priority traffic. The router may also transmit alarms to the user and / or to other network devices to prompt traffic re-routing and / or re-allocation of traffic rates. Example methods and apparatus ensure appropriate traffic allocation to meet certain QoS metrics.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Communications system
ActiveUS8503448B2Reduce bandwidth requirementsIncrease delayData switching by path configurationCommunications systemMetrics
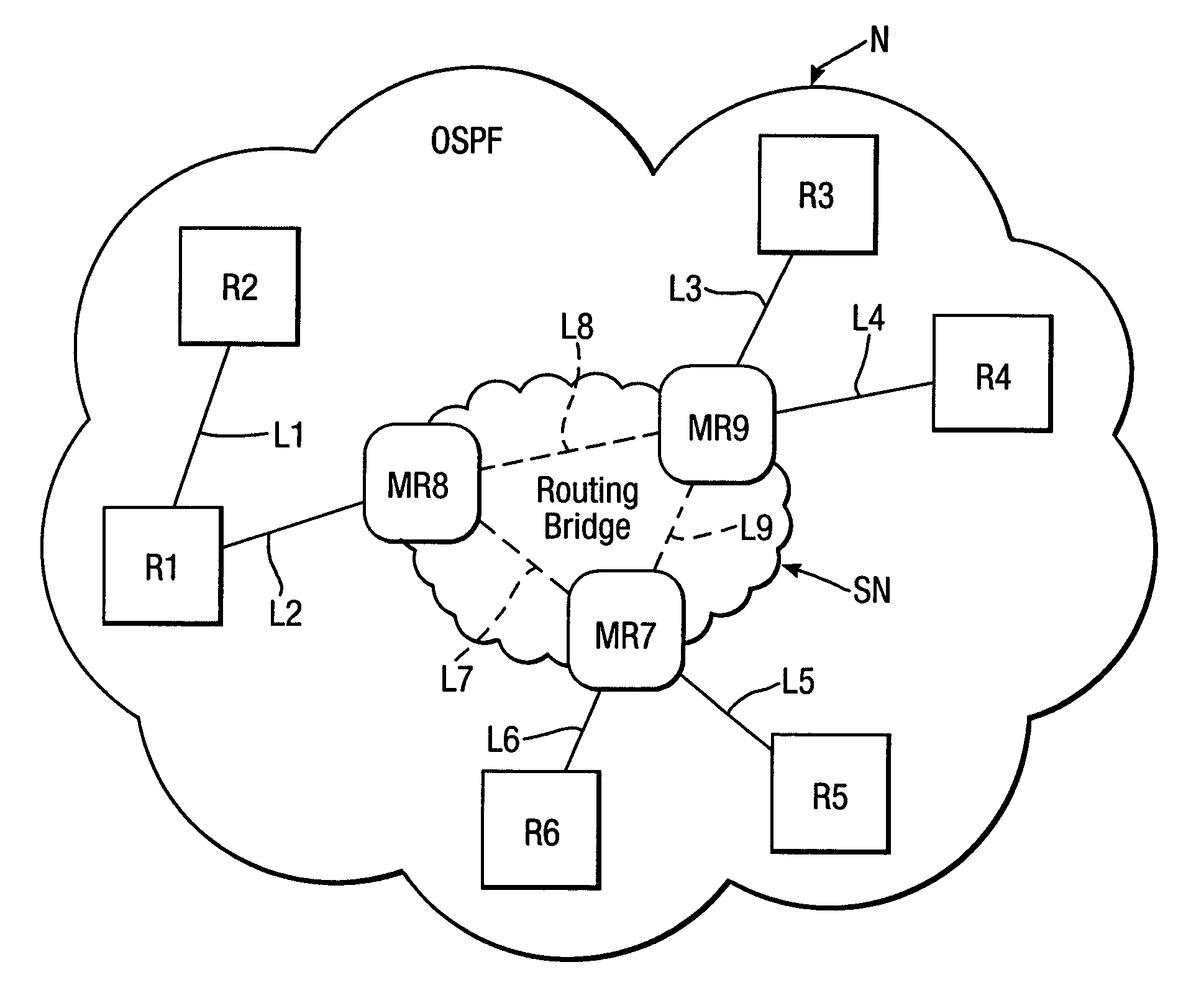
A Communications system for communicating over low bandwidth or high latency links incorporates a router MR7 configured to route a message to any like-configured router MR8, MR9 linked to it. Communications are implemented at network layer with UDP IP message packets. There are no hello messages. The message format 20 includes routing information but not designated and backup routers, which avoids loss of service from designated router changes and reduces bandwidth requirements. Configured routers MR7 to MR9 have different message formats 20, 40 for communicating with configured routers MR7 to MR9 and with unconfigured routers R1 to R6 respectively, and can link different protocols. A configured router MR7 deletes routes to like-configured routers MR8, MR9 with route metrics not superior to other routes with like destination. It also deletes routes with inferior metrics to related routes in an incoming message, and retains received route information regarding a new route or a route with superior metric. Some routes are not advertised, e.g. loop-back routes, multicast or broadcast routes, experimental destinations, unconfigured or zero-configured addresses, and routes matching a summary route and any user configured routes / networks.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
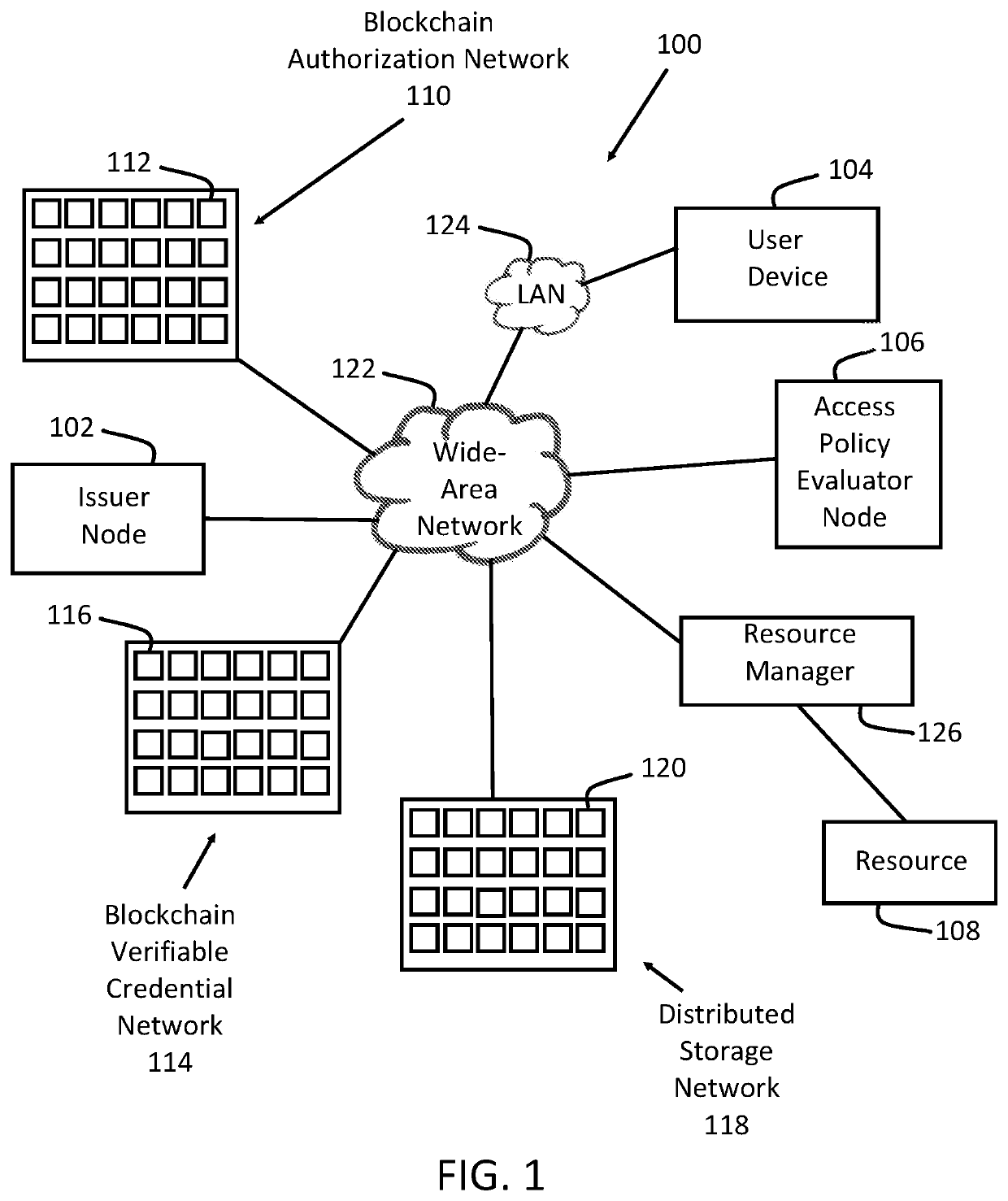
Distributed ledger-based ad-hoc system, apparatus and method
A system, method and apparatus for routing traffic in ad-hoc networks. A routing blockchain network processes routing node information proposals received from manager nodes of network clusters. Performance metrics of one or more nodes in the system are verified using distributed ledger techniques and provided to the manager nodes as updates to each manager node's routing information. The manager nodes further determine routing paths for ad-hoc communication requests based on an authentication event that defines conditions necessary to route traffic streams in association with a particular resource.
Owner:BEYOND AEROSPACE LTD
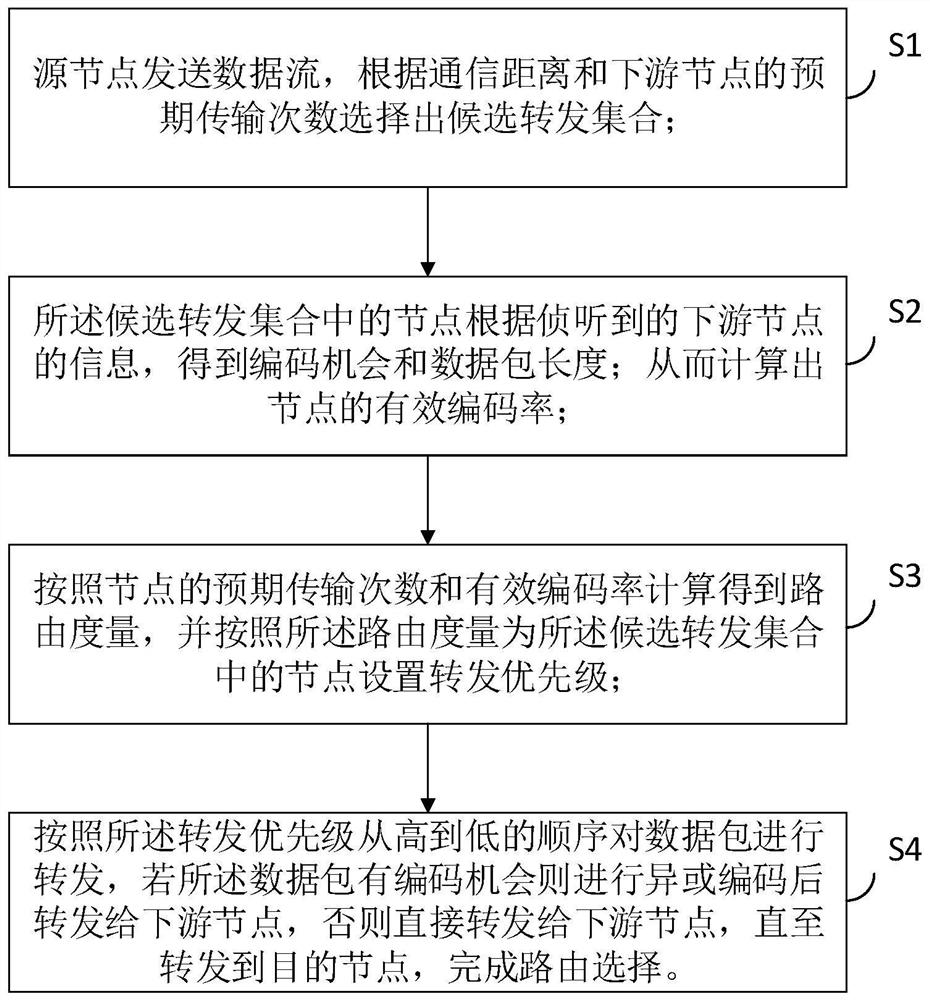
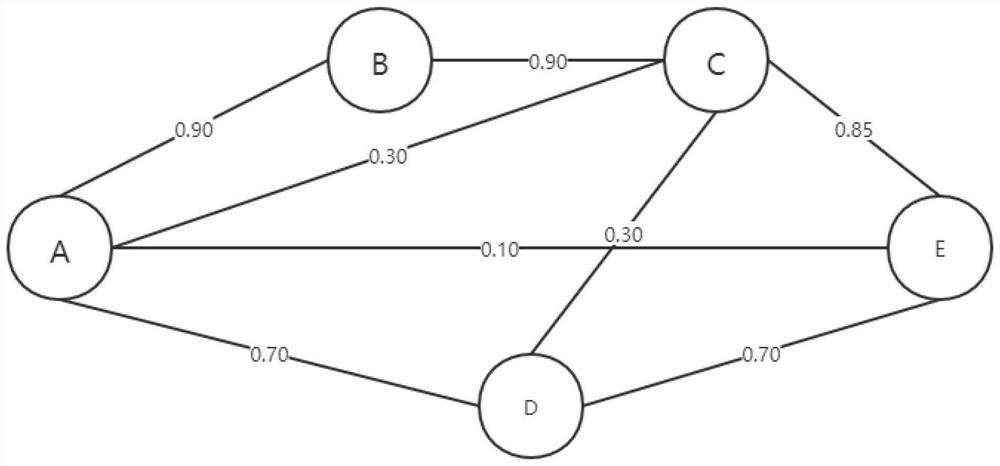
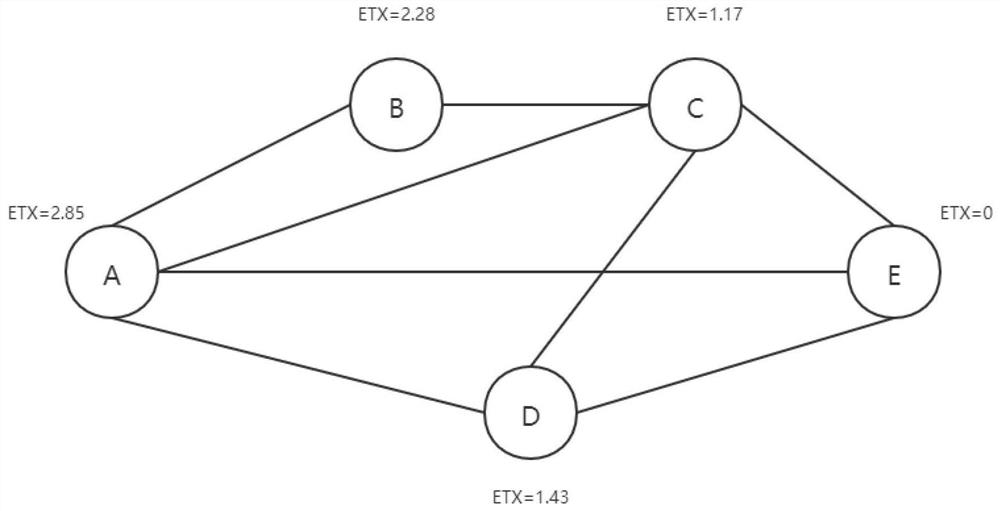
Opportunistic routing method based on network coding in wireless network
ActiveCN112584460AReduce the number of expected transfersImprove throughputHigh level techniquesWireless communicationComputer networkData stream
The invention relates to the field of opportunistic routing selection in a wireless communication network, in particular to an opportunistic routing selection method based on network coding in a wireless network, which comprises the following steps that: a source node sends a data stream and selects a candidate forwarding set; the node in the candidate forwarding set obtains a coding opportunity and a data packet length according to the monitored information of the downstream node; the candidate node calculates a routing metric according to the node storage information and the information in the candidate forwarding set of the node; and the nodes in the candidate forwarding set set set forwarding priorities according to the routing metrics of the nodes so as to coordinately forward the data packets. When code forwarding is carried out, effective data transmission can be further increased through matching of the length of the data packet and searching of the coding opportunity, and therefore the network throughput and the transmission stability are improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
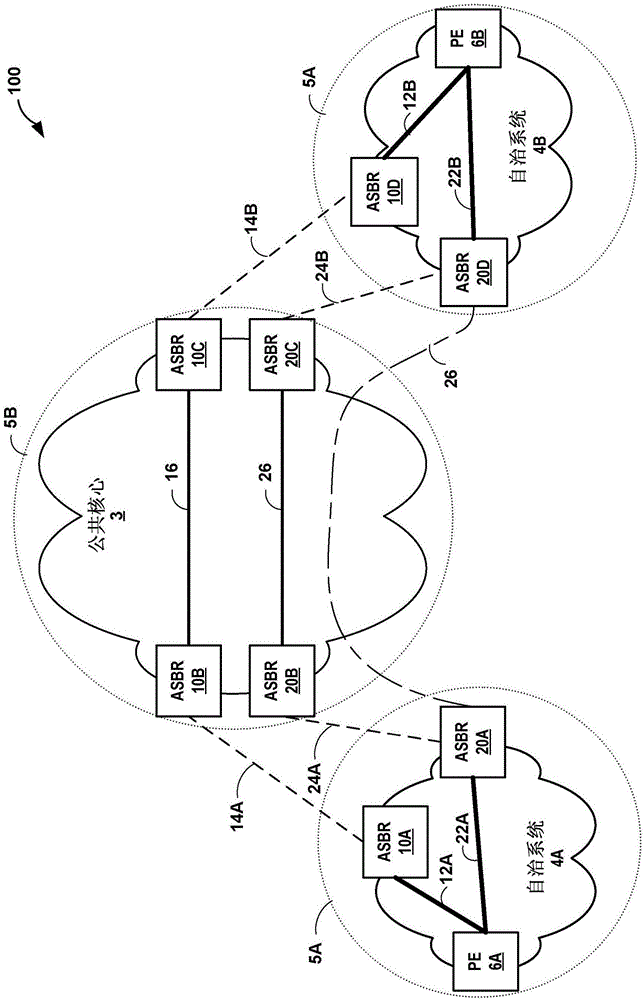
Scaled inter-domain metrics for link state protocols
In general, techniques are described by which to provide a scaled end-to-end view of link metrics to integrate multiple non-uniform Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) domains. For example, an Accumulated Interior Gateway Protocol (AIGP) attribute, a non-transitive BGP attribute, which includes a link metric assigned to a link within a first IGP domain, is scaled to conform to a metric scale of the second IGP domain. The AIGP attribute may also add link metric assigned to a link within the second IGP domain and may add static metrics of non-IGP links connecting the IGP domains. An IGP domain may set its IGP to the scaled AIGP attribute such that the link metric may include a uniformly scaled end-to-end view of link metrics across the IGP domains. Additionally, a sham-link is assigned a metric value in accordance with the scaling techniques.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Technique for optimized routing of data streams on an IP backbone in a computer network
ActiveUS8825898B2Easy to routeReduce needMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication serverData stream
A technique optimizes routing of application data streams on an Internet Protocol (IP) backbone in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a client router learns of server states (e.g., number of pending requests, etc.) of a plurality of application servers and also determines metrics of intermediate links between the application servers and the client router (intermediate link metrics), e.g., particularly link metrics in a direction from the application servers to the client router. Upon receiving an application request from an application client (“client request”), the client router determines to which of the application servers the client request is to be sent based on the server states and intermediate link metrics, and sends the client request accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
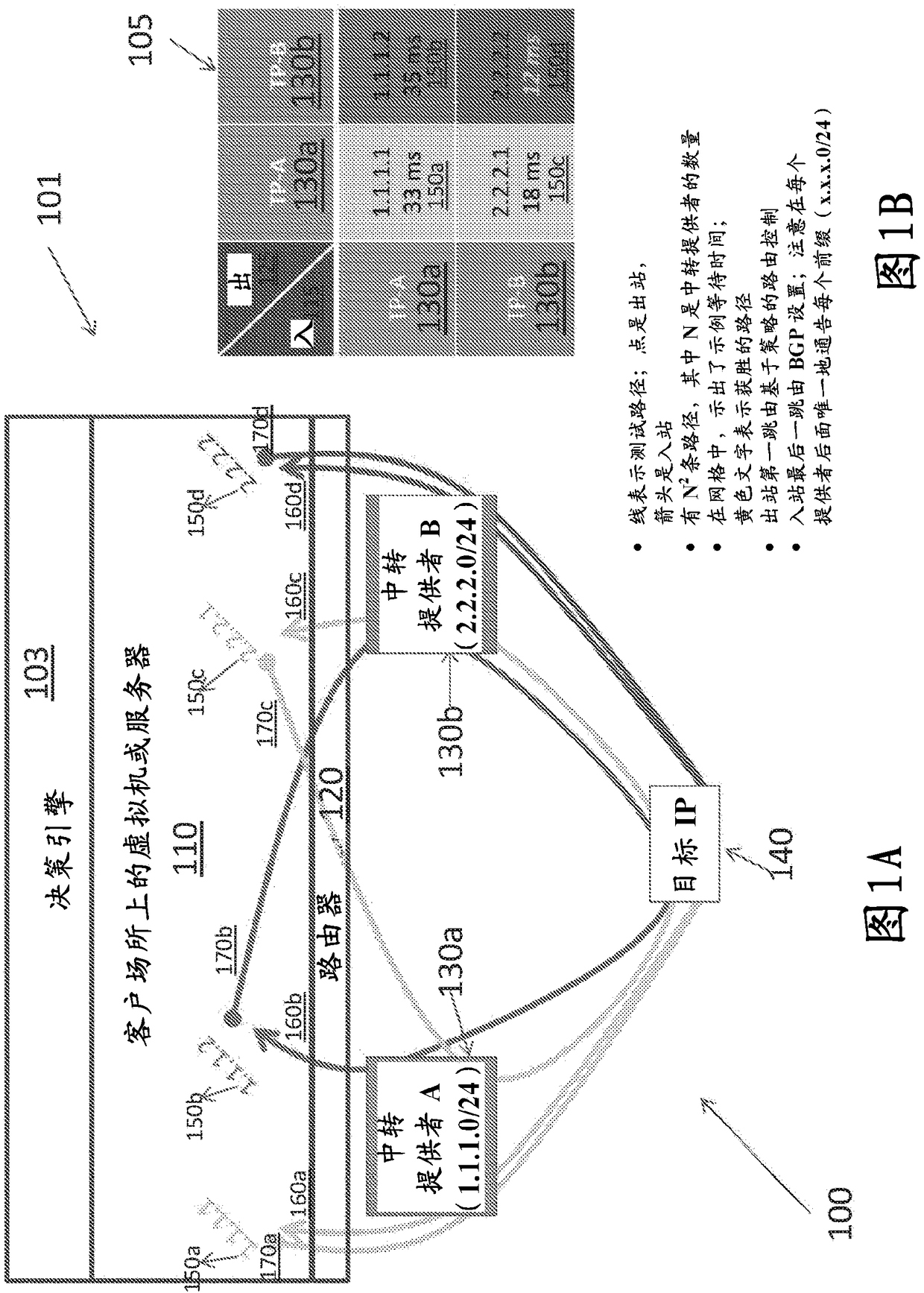
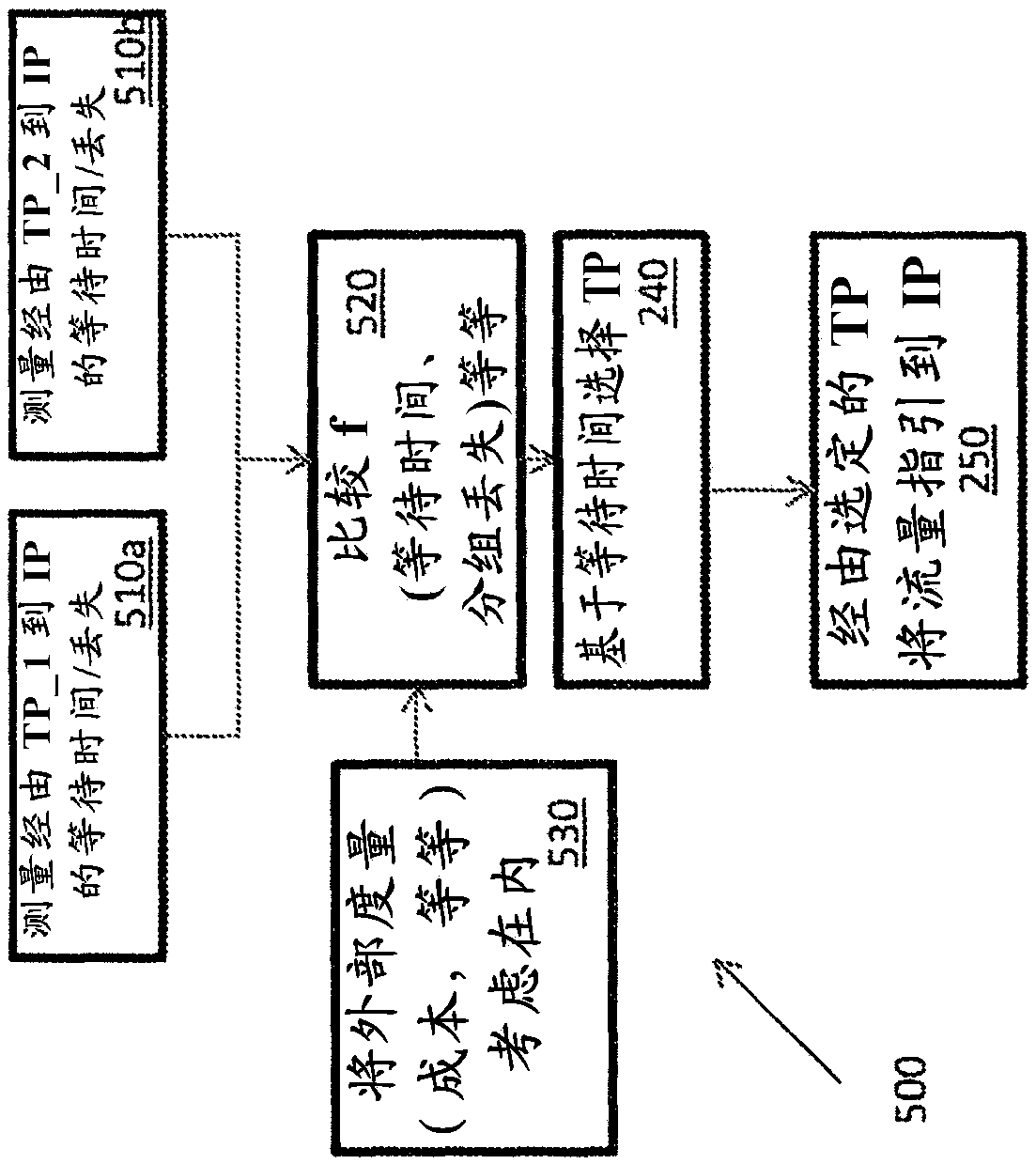
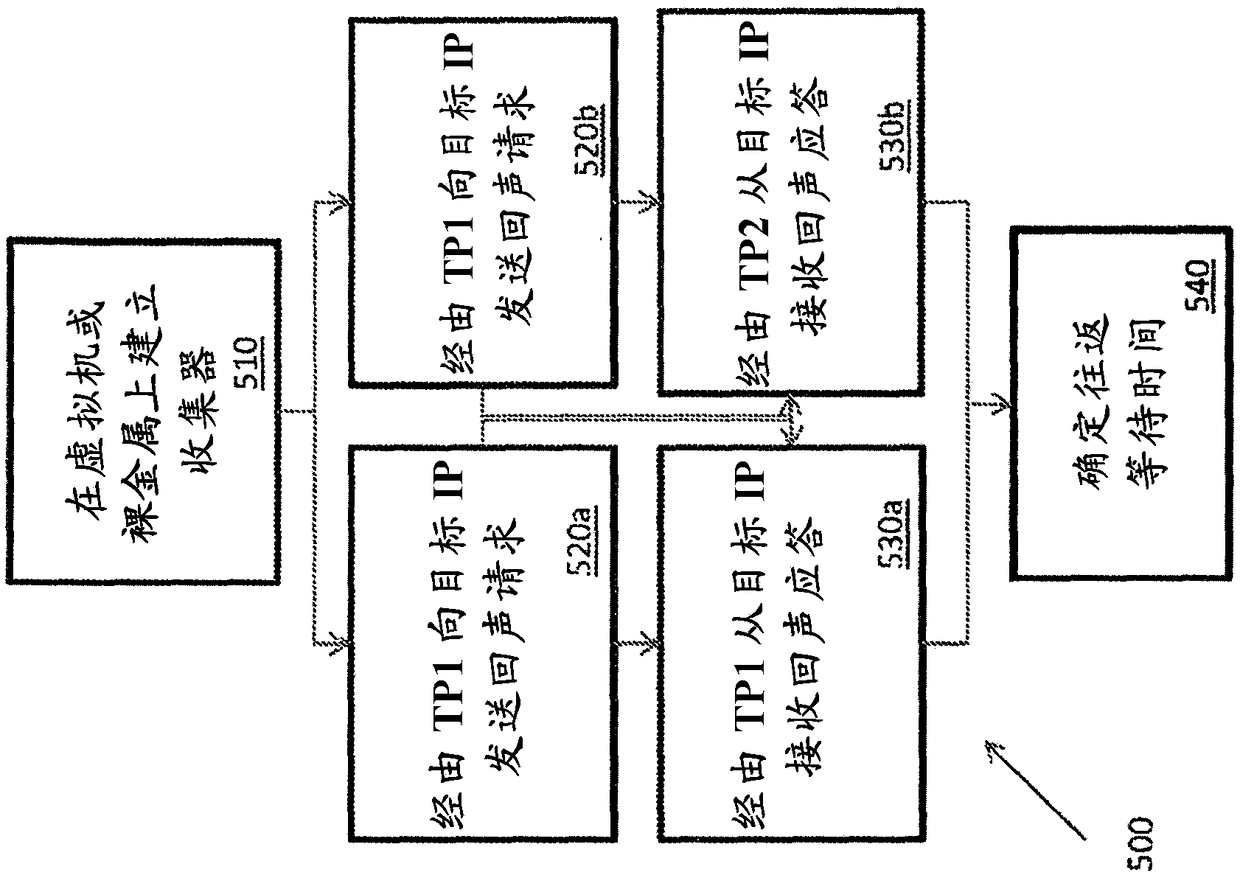
Methods and apparatus for real-time traffic steering using real-time user monitoring data
Conventional internet routing is handled using routing protocols such as the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). However, simple BGP does not account for latency, packet loss, or cost. To address this problem, smart routing systems that route traffic fast and in a cost-effective manner are implemented. In one approach, smart routing systems measure, compare, and analyze round-trip latencies and other metrics between a customer premises and one or more endpoints. Optimal inbound and outbound transit providers are selected for each endpoint based on these measurements. Other smart routing systems collect and analyze Real User Monitoring (RUM) data to predict latency performance of different content origins for serving data to a particular client based on the client's IP address and the content origins' IP addresses, which are ranked by performance. These rankings are used to steer traffic along lower latency paths by resolving Domain Name System (DNS) queries based on the performance associated with the IP addresses.
Owner:DYNAMIC NETWORK SERVICES
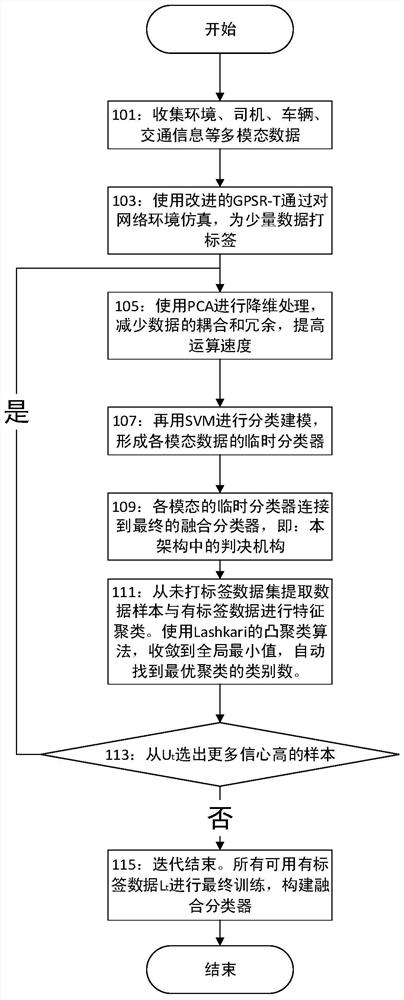
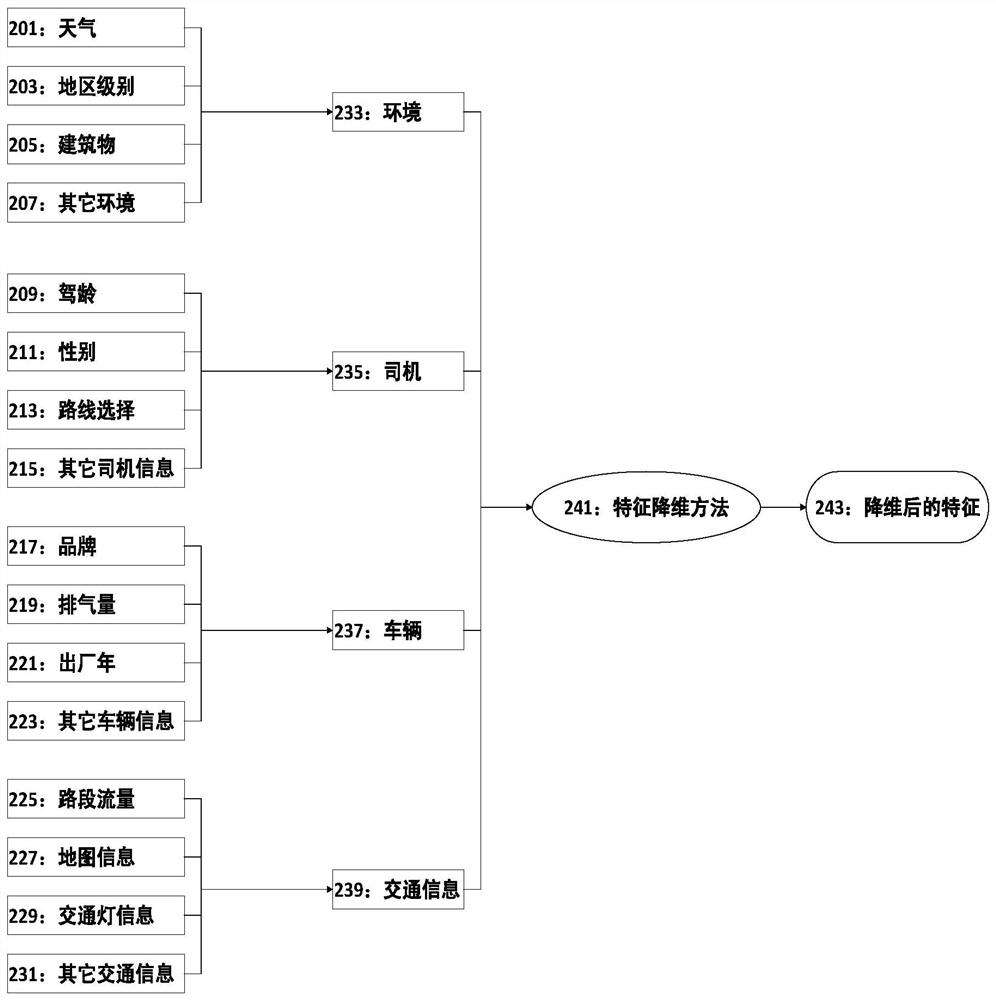
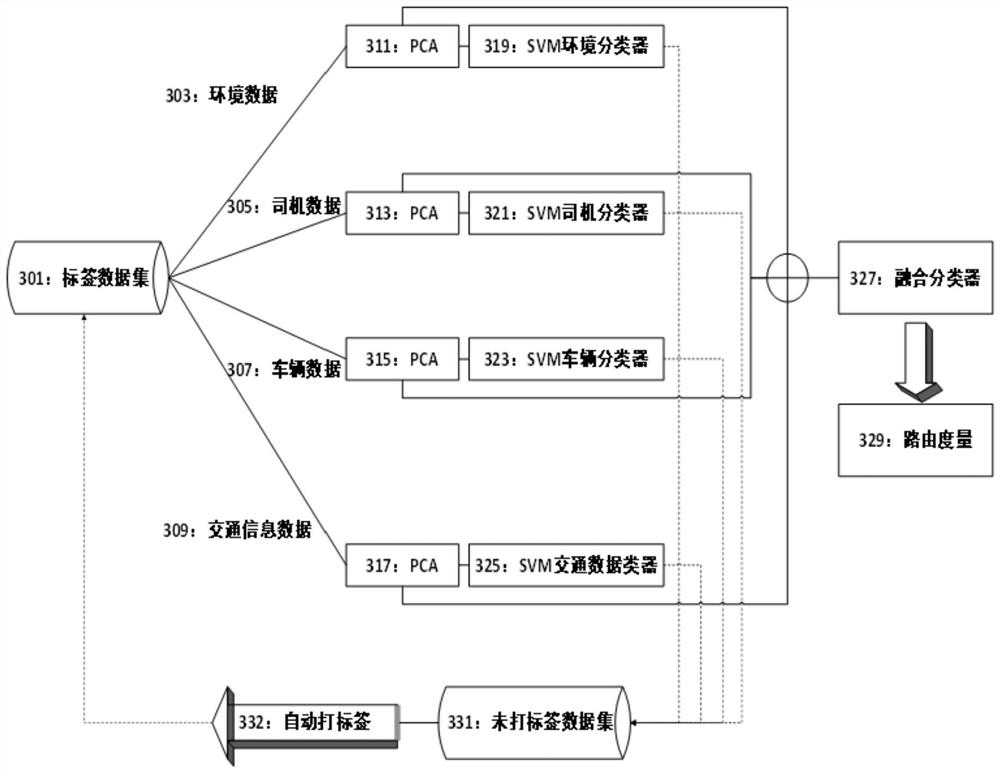
A Generation Method of Routing Metrics Based on Multimodal Data
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless networks, especially the technical field of network layer routing search in a vehicular ad-hoc network, and particularly provides a multimodal data-based routing metric generation method. By analyzing multiple types of modal data representing environment, driver, vehicle and traffic information, traffic-data based routing metric (TDR) is established, so that the judgment precision of reliability of an intermediate node is improved; a small amount of labeled data is learned and cooperatively trained by using a semi-supervised multimodal machine learning architecture; the cooperative training process is divided into two iterative processes including positive training and label upgrading; and the routing metric is constructed. A mechanism for generating the routing metric based on a machine learning algorithm is proposed; massive routing constraint points are considered; the influence of related data on routing is analyzed from the data mining perspective; and the routing metric for accurately judging the routing reliability is generated. Massive unlabeled data and a small amount of the labeled data are analyzed by utilizing the semi-supervised multimodal architecture, and a training modeling process is finished with the minimum cost.
Owner:辽宁数联达科技有限公司
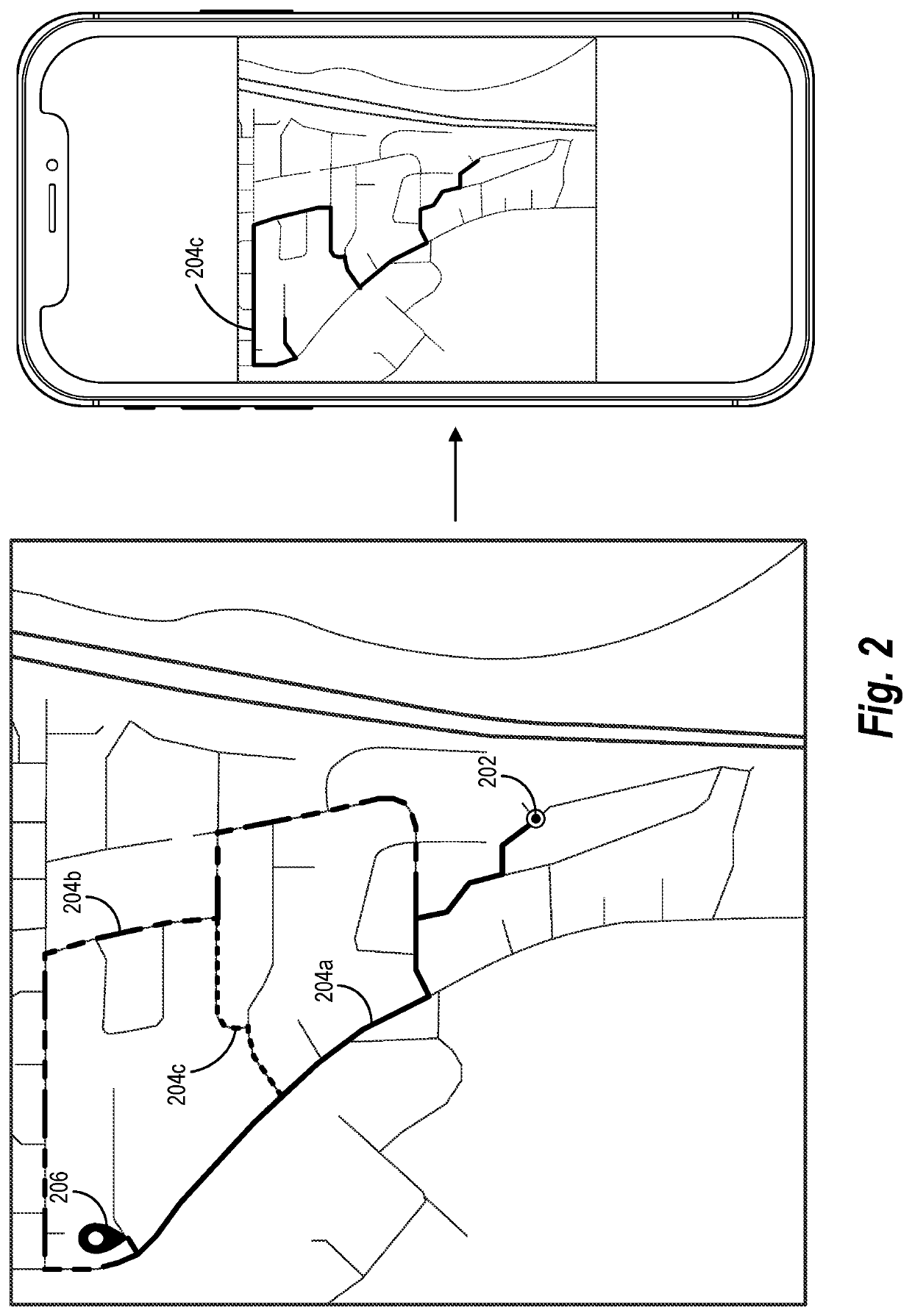
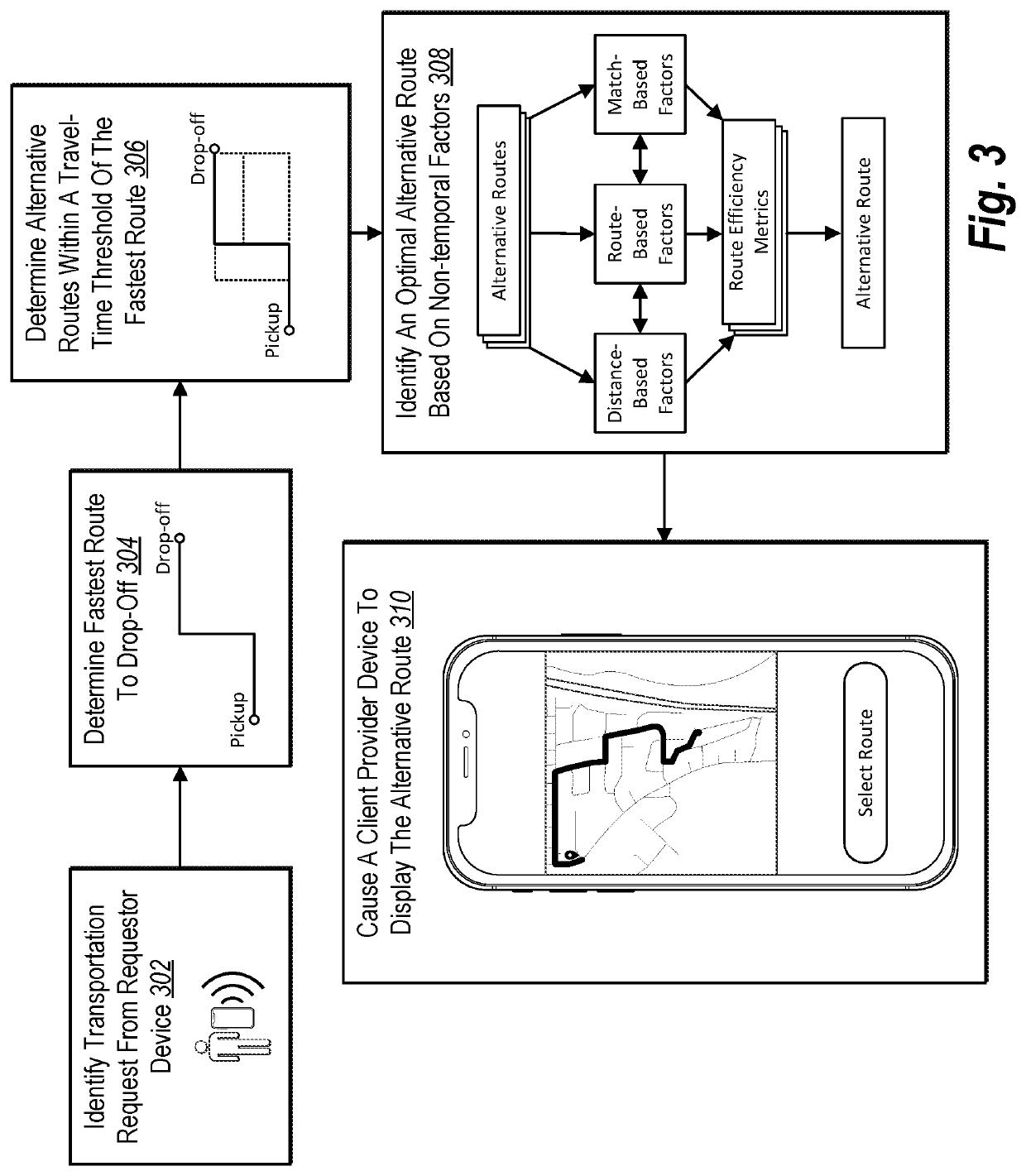
Providing improved, real-time transportation route interfaces utilizing route efficiency metrics based on non-temporal factors
PendingUS20220307845A1Improve efficiencyIncrease flexibilityInstruments for road network navigationMetricsSimulation
The present disclosure relates to systems, non-transitory computer-readable media, and methods that improve efficiency and flexibility of implementing computer devices by providing efficient user interfaces to provider devices that include optimal digital routes selected based on dynamic route efficiency metrics. In particular, the disclosed systems can identify and surface an optimal alternative route from a pickup location to a drop-off location associated with a transportation match based on a variety of dynamic non-temporal factors. The disclosed systems can utilize a variety of computer implemented models to determine non-temporal factors, such as distance efficiency metrics, route-segment access efficiency metrics, congestion efficiency metrics, risk efficiency metrics, and match-based efficiency metrics. The disclosed systems can then combine these non-temporal factors utilizing a common efficiency framework to determine and surface an optimal alternative route.
Owner:LYFT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com