Patents
Literature
70 results about "Link-state routing protocol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
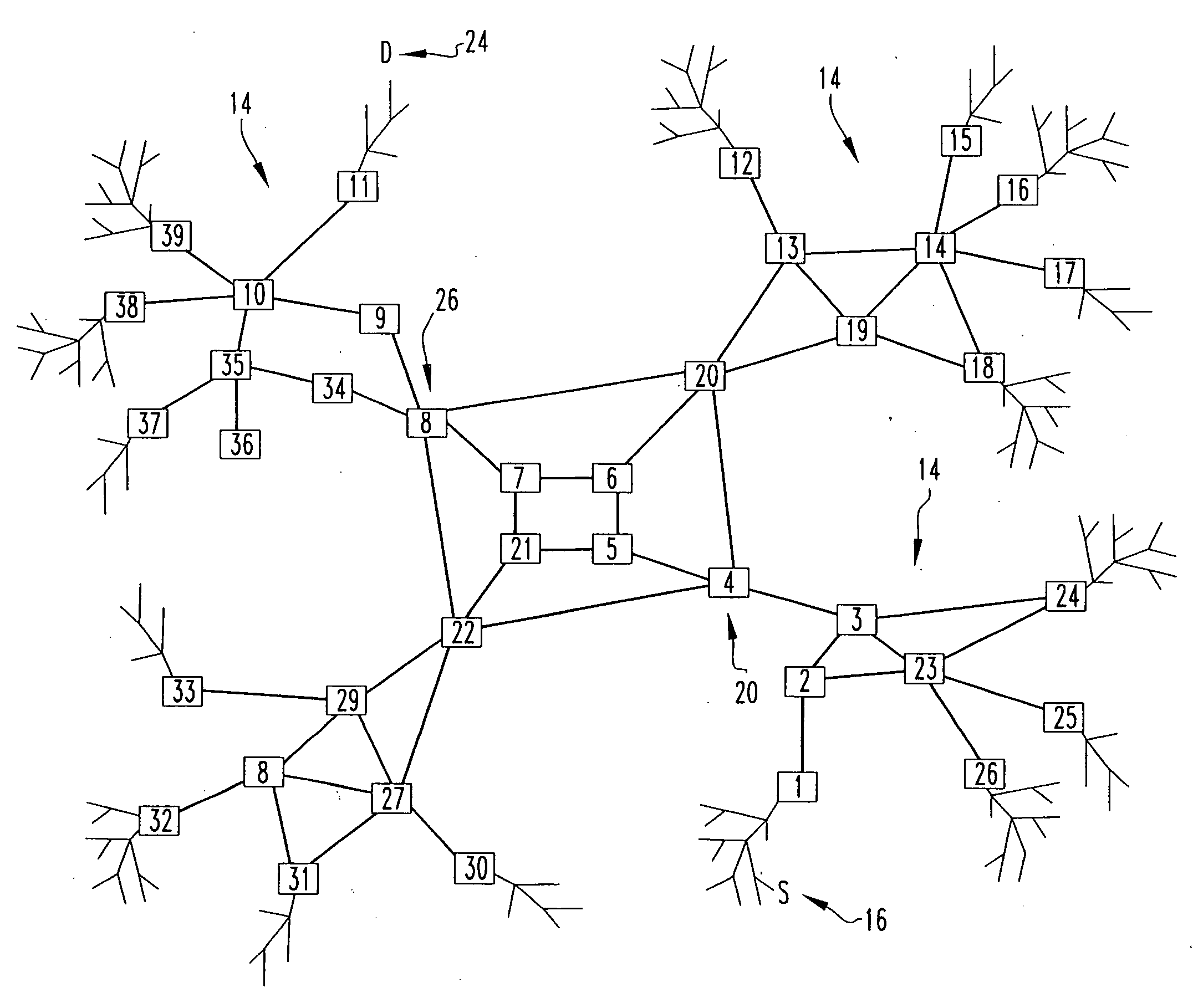
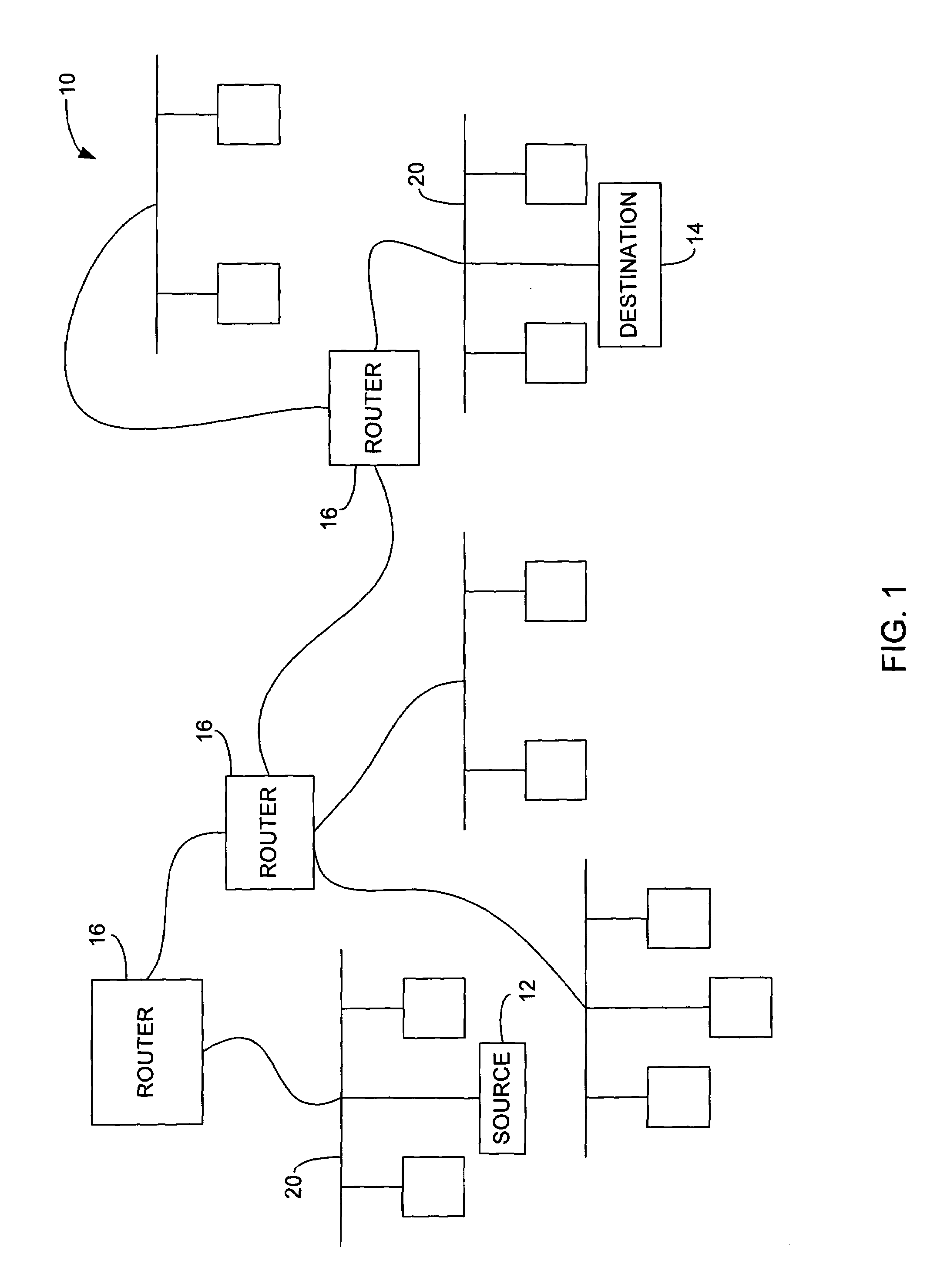
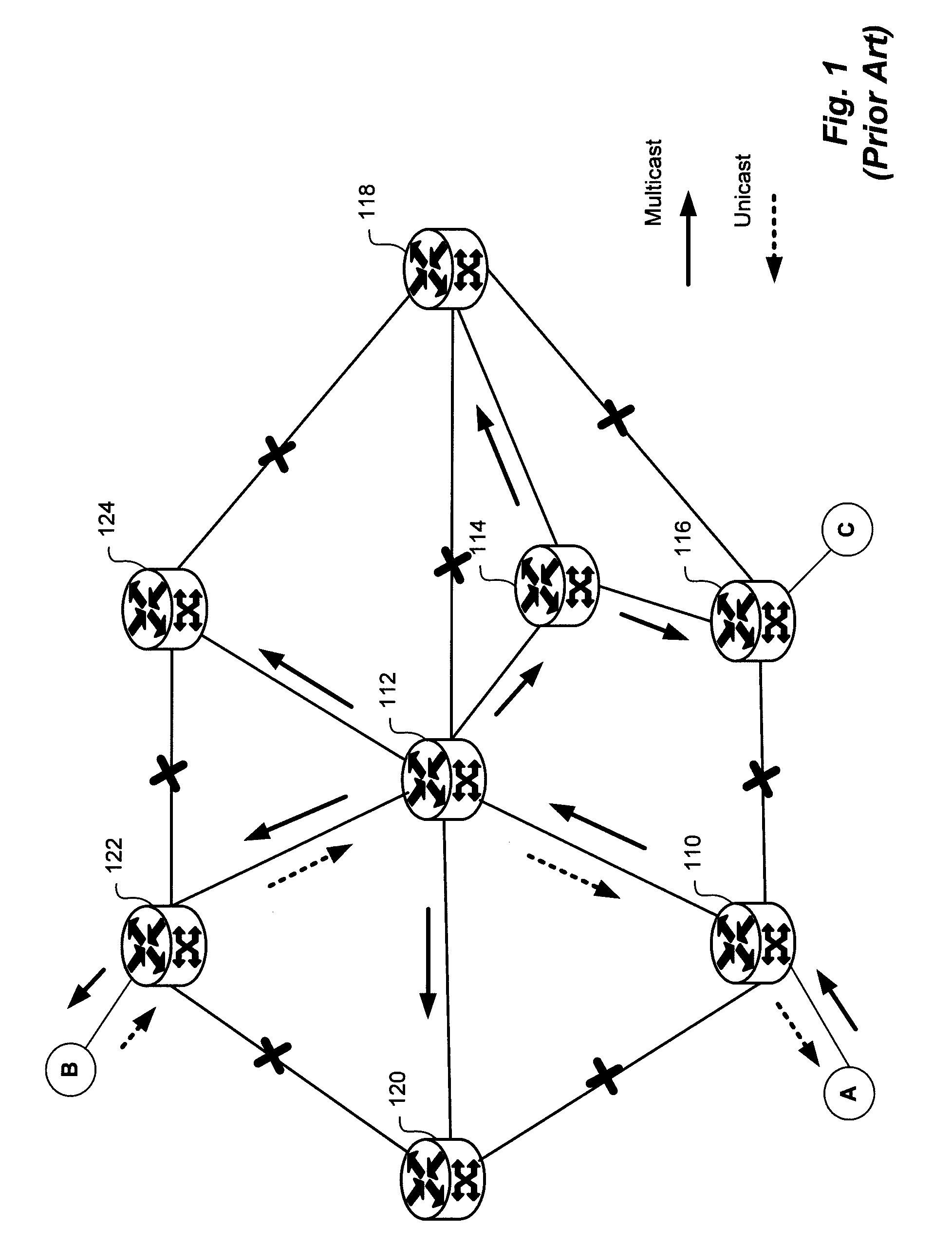
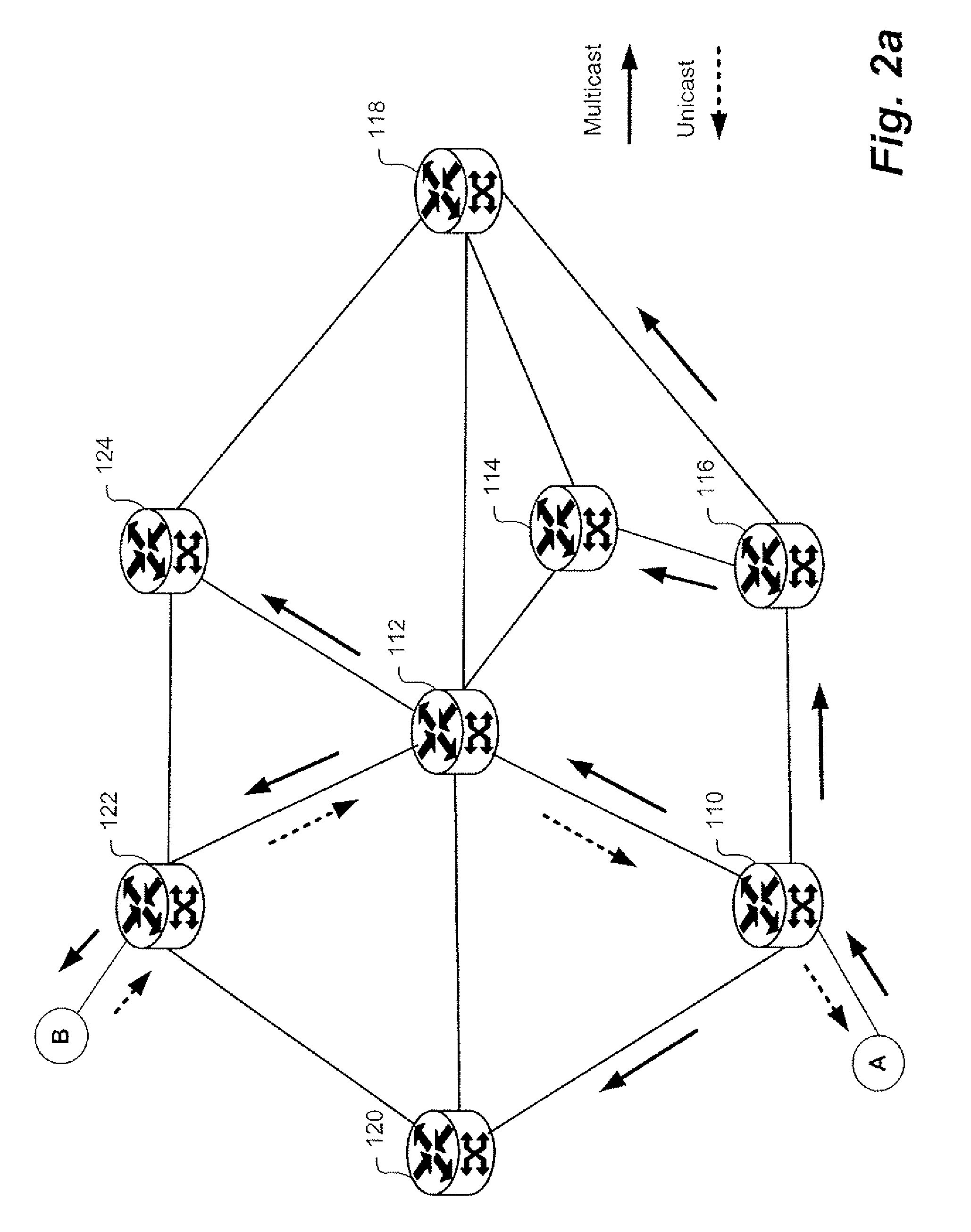
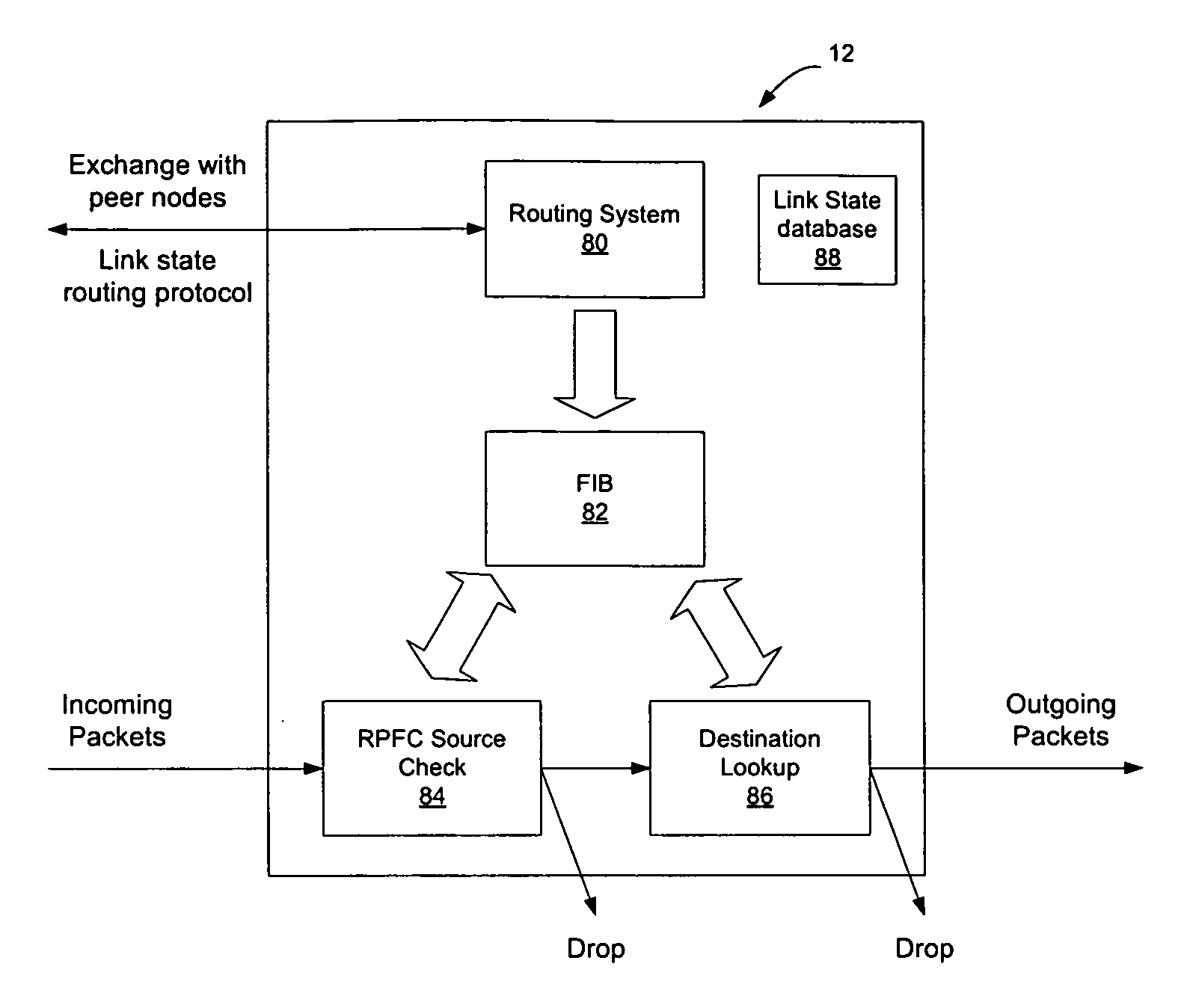
Link-state routing protocols are one of the two main classes of routing protocols used in packet switching networks for computer communications, the other being distance-vector routing protocols. Examples of link-state routing protocols include Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS).
Mobile ad hoc extensions for the internet
InactiveUS6845091B2Easy to addImprove robustnessError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTTEthernetNetwork measurement
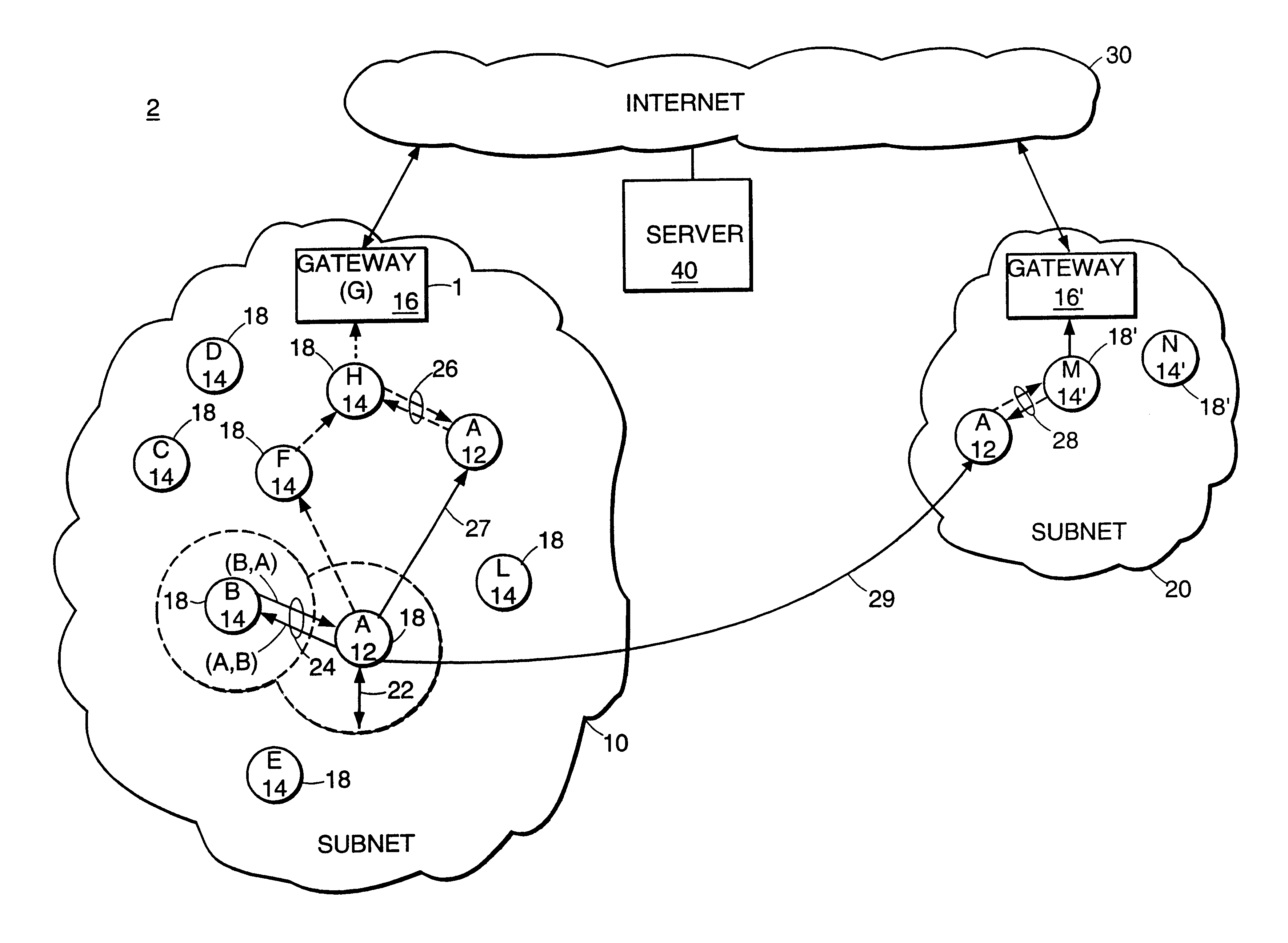
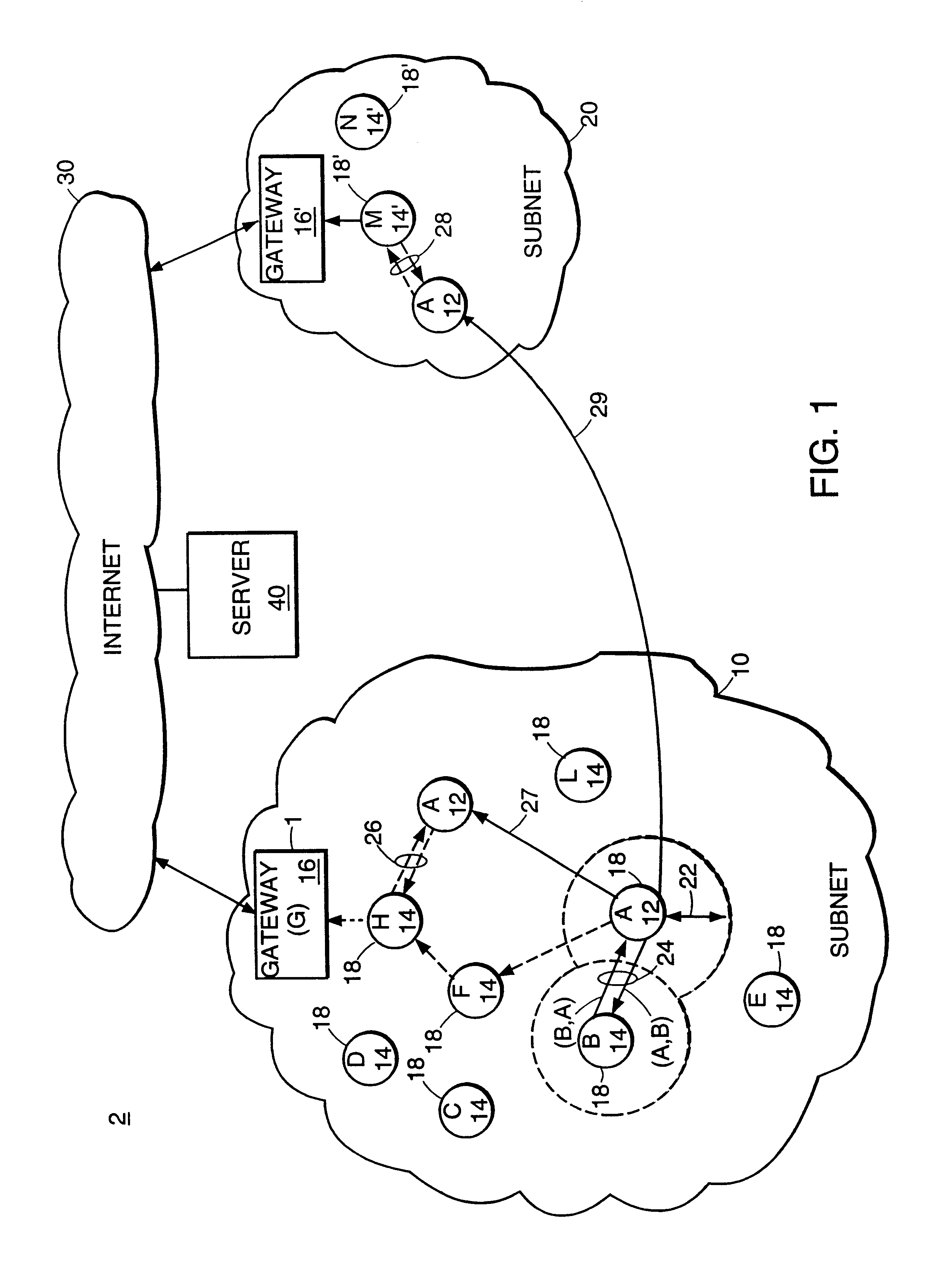
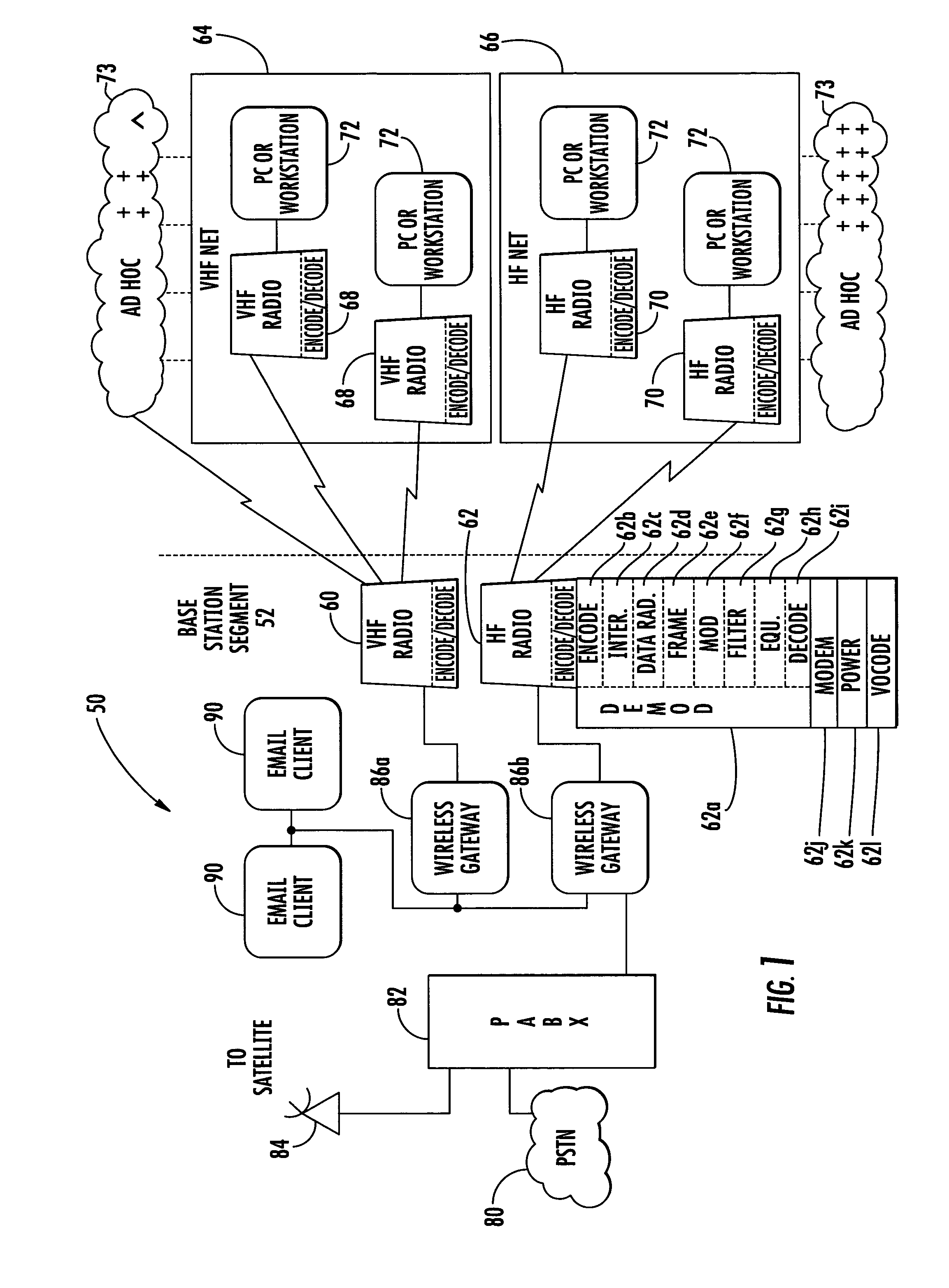
Described is an internetworking system having various mobile ad hoc extensions to the Internet that are particularly suited to the dynamic environment of mobile ad hoc networks. The internetworking system includes any combination of a link-state routing protocol for disseminating topology and link-state information over a multi-hop network comprised of nodes, a neighbor discovery protocol that can detect the appearance and disappearance of new neighbor nodes, an address format that facilitates deployment of IPv6 nodes in a predominantly IPv4 network infrastructure, a queuing mechanism that can update information upon resuming interrupted communications between nodes, and dynamic network measurement techniques for adaptively using wireless bandwidth when establishing and maintaining connections between nodes and a server.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Method and apparatus for disseminating topology information and for discovering new neighboring nodes
InactiveUS7327683B2Improve robustnessMinimize overheadError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsTopology informationLink-state routing protocol
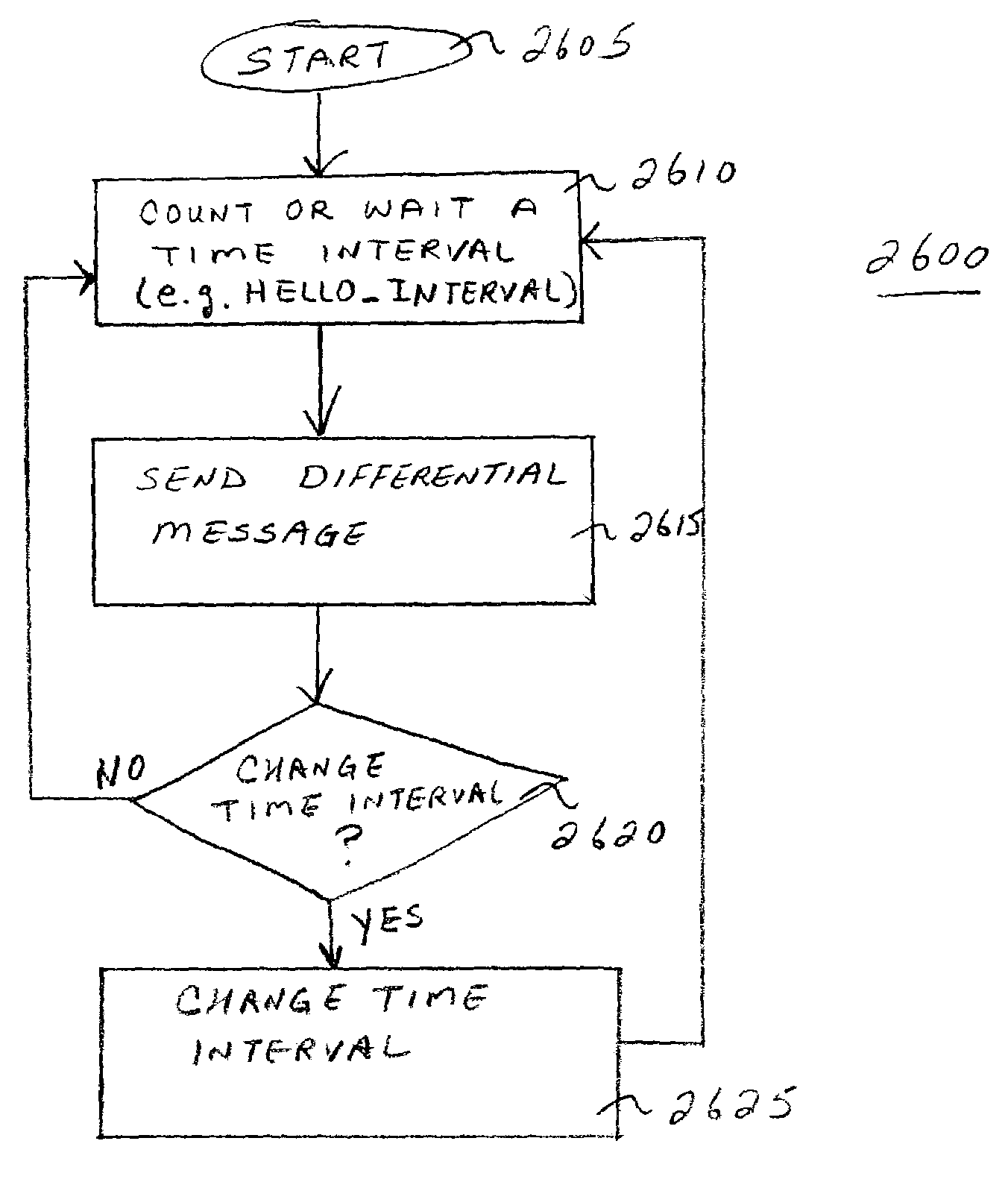
A proactive link-state routing protocol designed for mobile ad-hoc networks is disclosed, which provides hop-by-hop routing along shortest paths to each destination. Each node running the present protocol will compute a source tree (providing paths to all reachable nodes) based on partial topology information stored in its topology table. To minimize overhead, each node reports only “part” of its source tree to neighbors. The present invention employs a combination of periodic and differential updates to keep all neighbors informed of the reportable part of its source tree. The present invention performs neighbor discovery using “differential” HELLO messages that report only “changes” in the status of neighbors. This results in HELLO messages that are much smaller than those of other link-state routing protocols.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Methods and apparatus for routing in a mobile ad hoc network
InactiveUS6980524B1Telephonic communicationData switching by path configurationOverlap zoneLink-state routing protocol
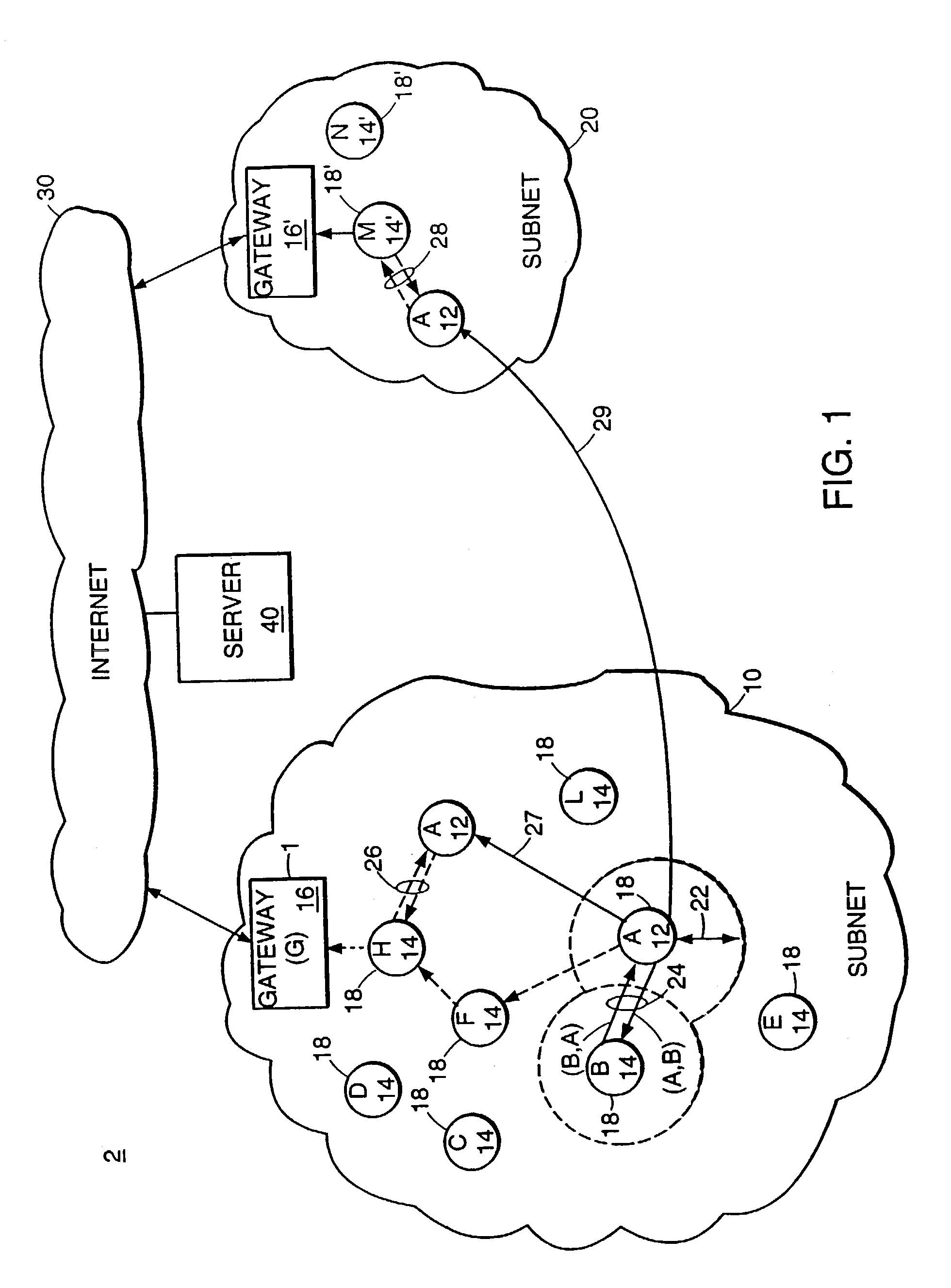
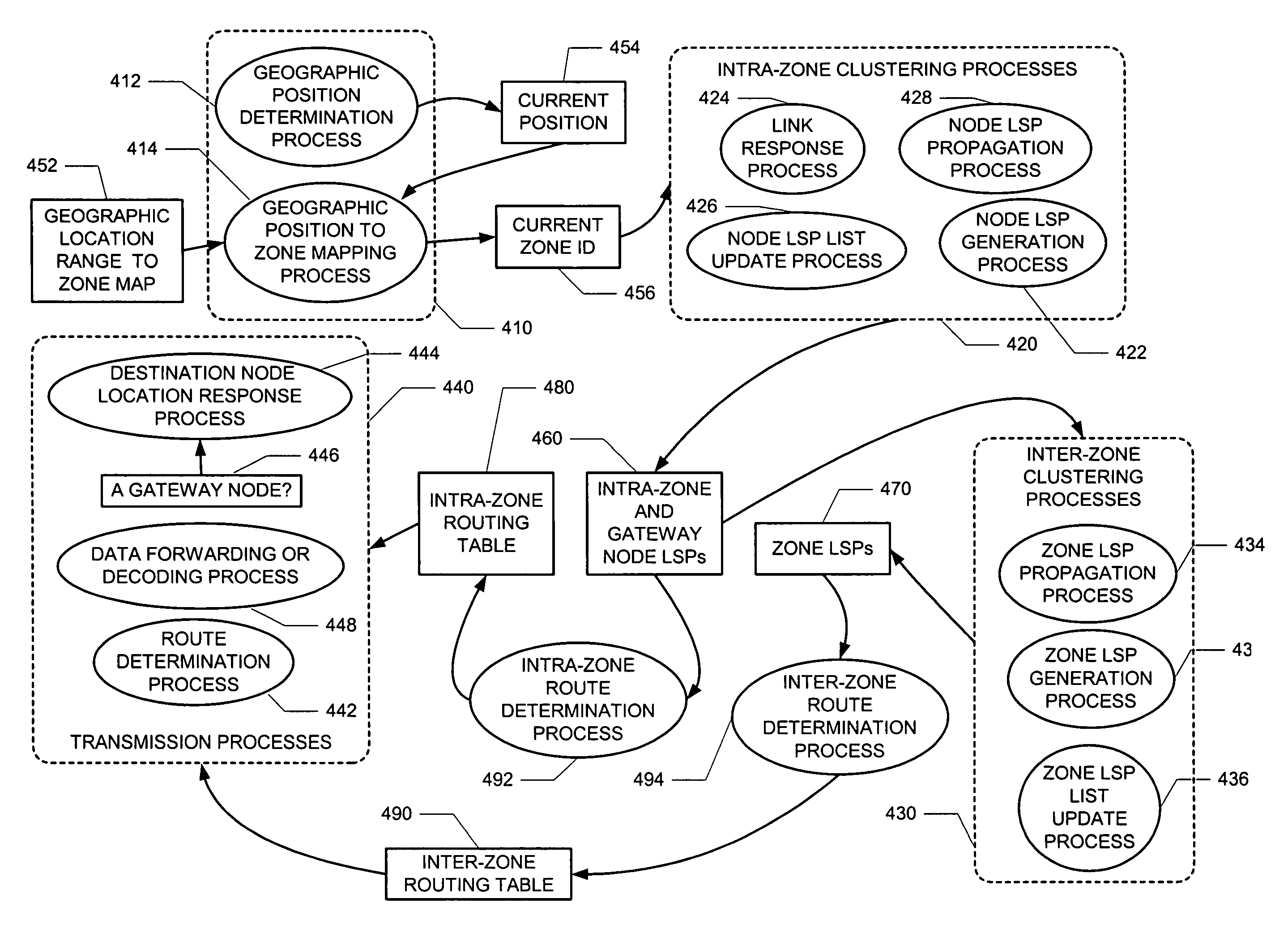
A “peer-to-peer” hierarchical routing protocol—also referred to as Zone-based Hierarchical Link State Routing protocol (or “ZHLS”)—which incorporates location information into a novel “peer-to-peer” hierarchical routing approach. The network may be divided into non-overlapping zones. Aggregating nodes into zones conceals the detail of the network topology. Initially, each node knows its own position and therefore zone ID through a position determination unit, such as a Global Positioning System (GPS). After the network is established, each node knows the low level (node level) topology about node connectivity within its zone and the high level (zone level) topology about zone connectivity of the whole network. A packet may be forwarded by specifying the hierarchical address—zone ID and node ID—of a destination node in the packet header.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INST OF NEW YORK
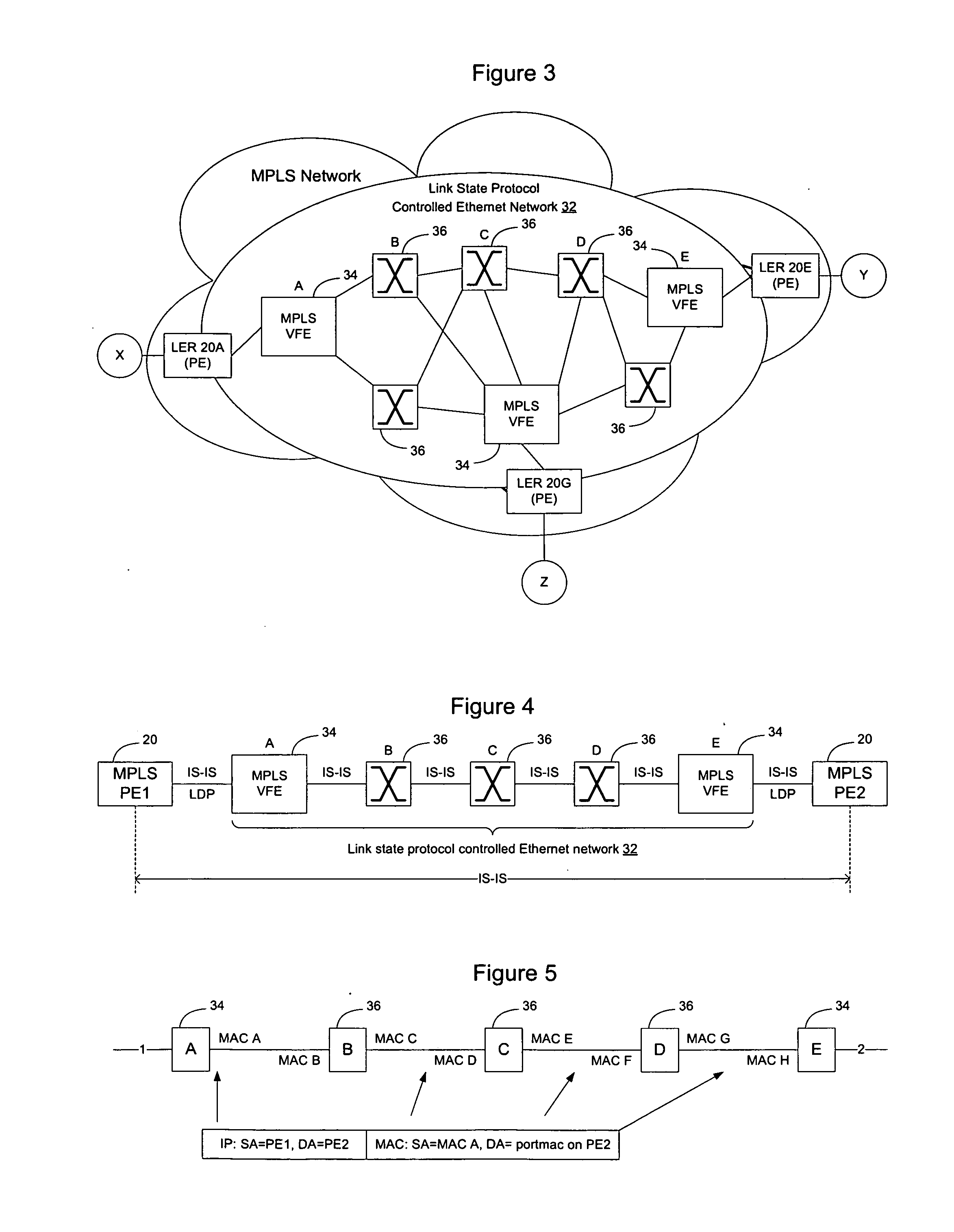
Multicast implementation in a link state protocol controlled Ethernet network
InactiveUS20070165657A1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationReliable multicastLink-state routing protocol
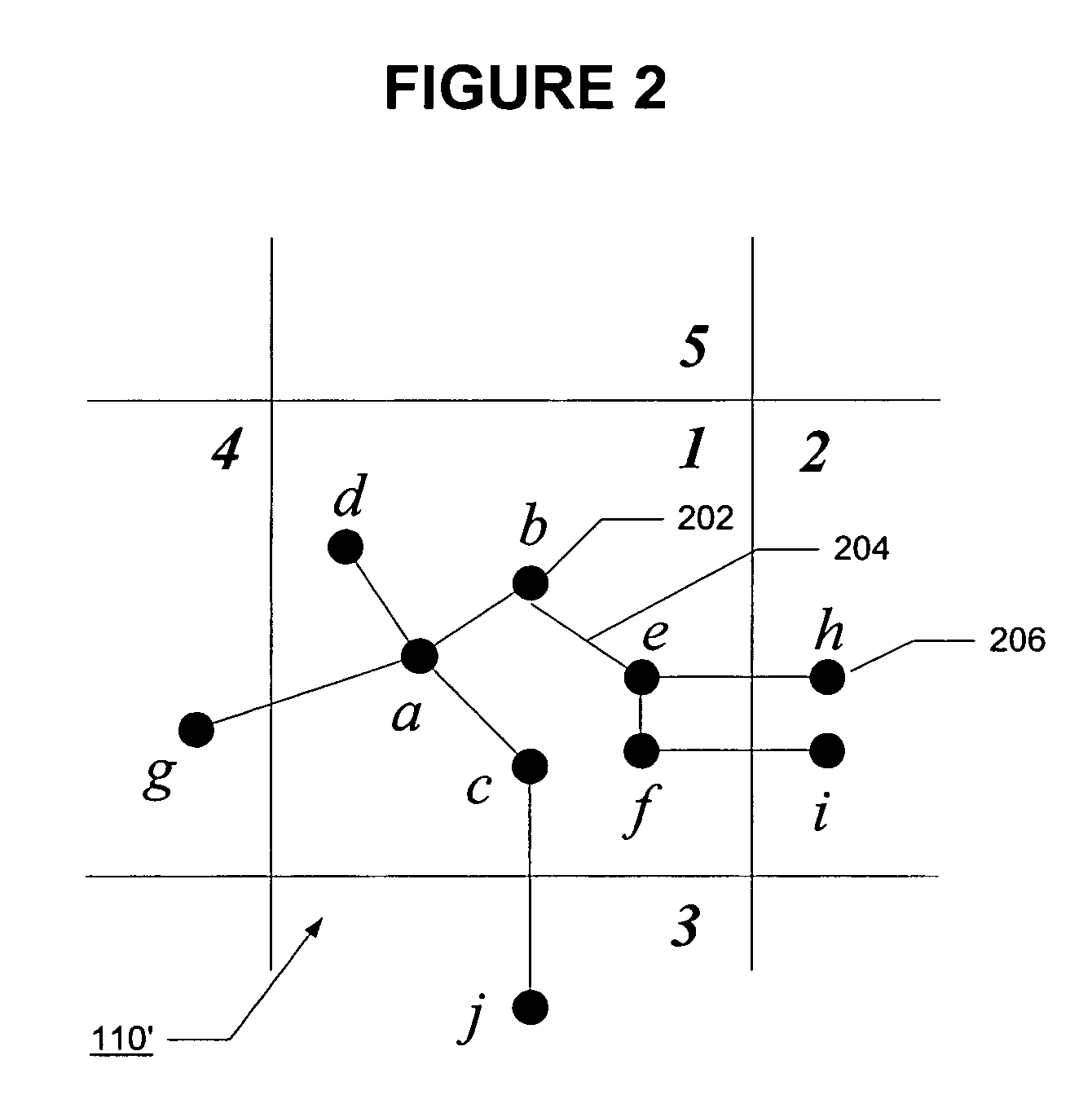
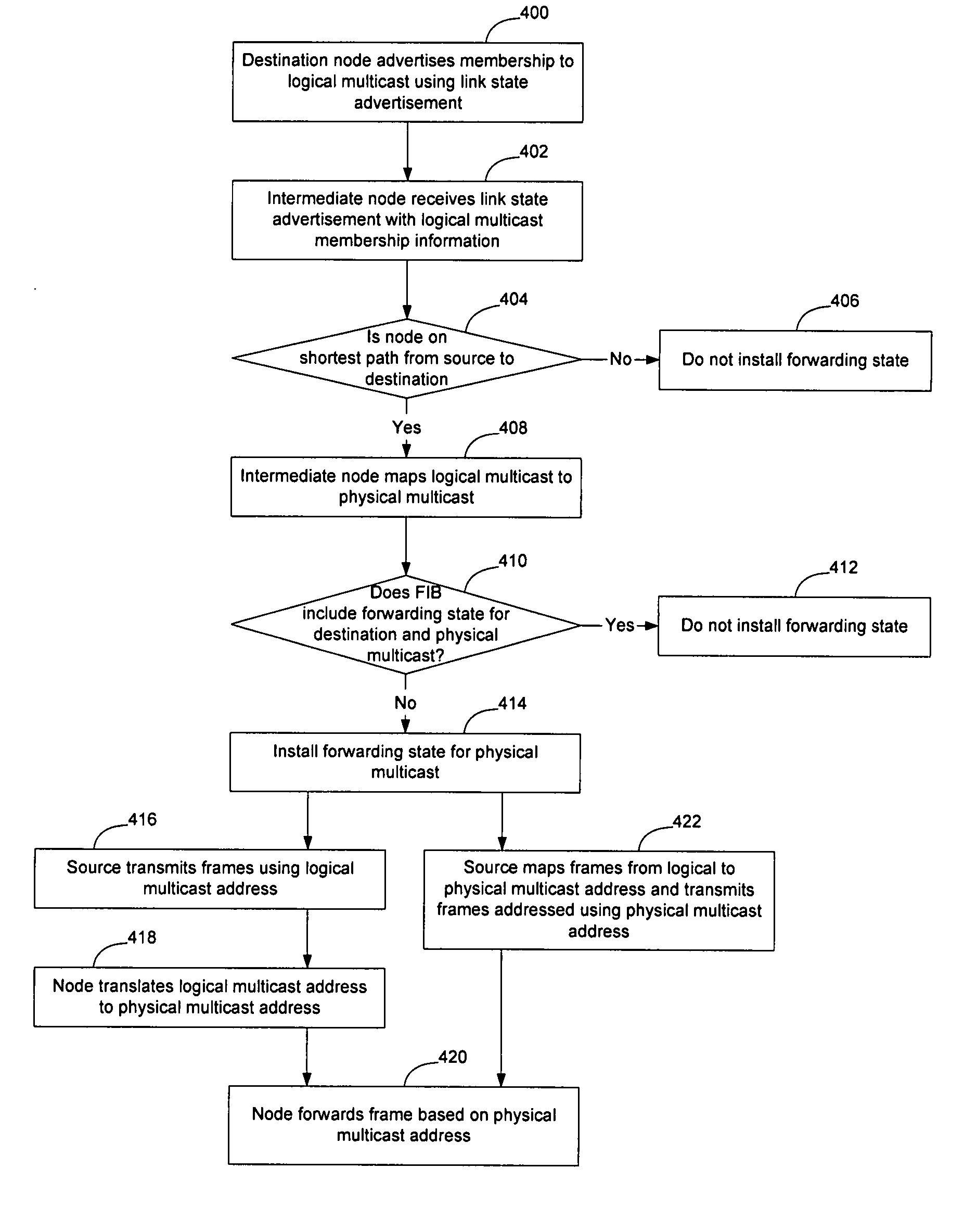
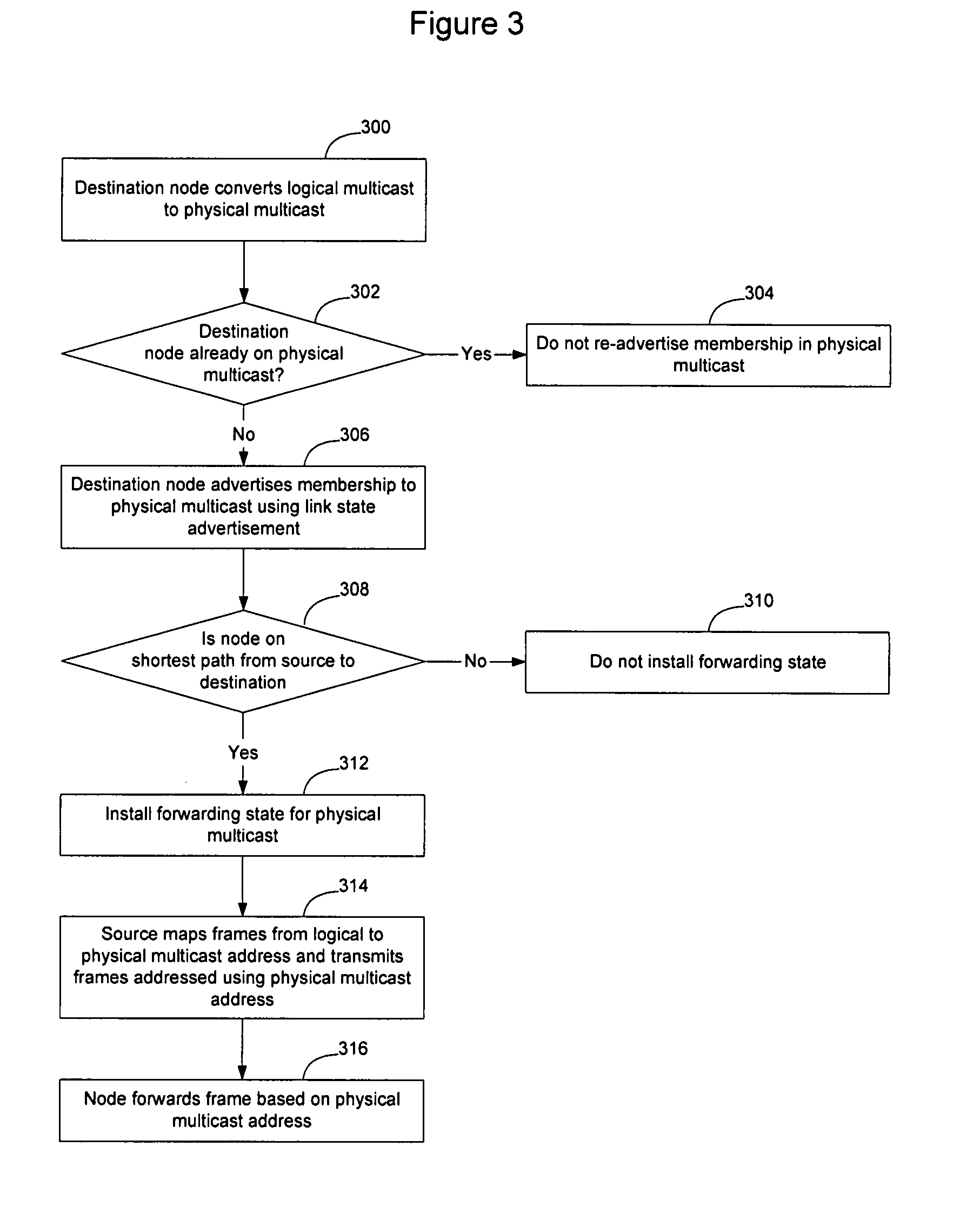
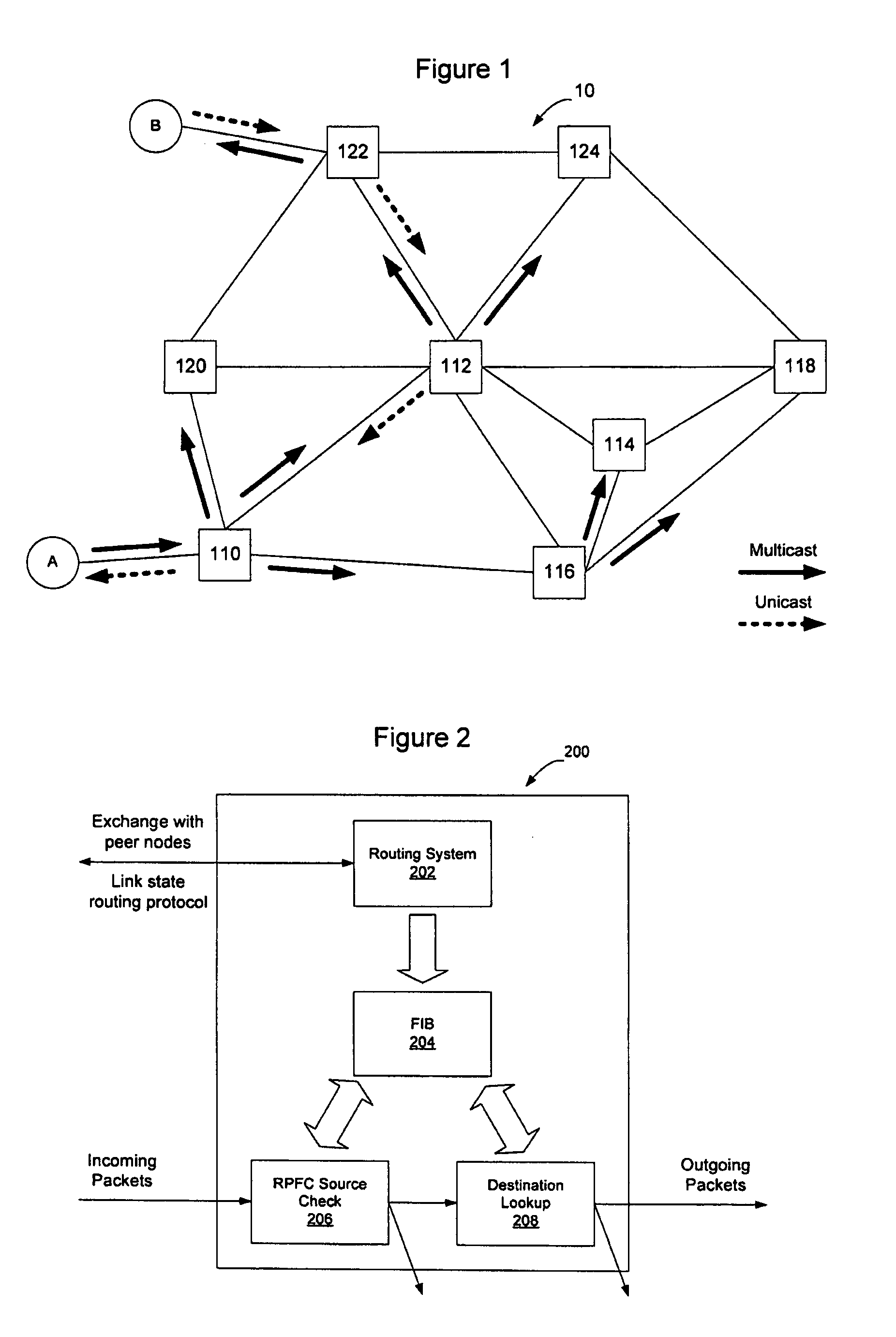
Forwarding state may be installed for sparse multicast trees in a link state protocol controlled Ethernet network by enabling intermediate nodes to install state for one or more physical multicast trees, each of which may have multiple logical multicast trees mapped to it. By mapping multiple logical multicasts to a particular physical multicast, and installing state for the physical multicast, fewer FIB entries are required to implement the multiple multicasts to reduce the amount of forwarding state in forwarding tables at the intermediate nodes. Mapping may be performed by destination nodes before advertising membership in the physical multicast, or may be performed by the intermediate nodes before installing state when a destination node advertises membership in a logical multicast. Intermediate nodes will install state for the physical multicast tree if they are on a shortest path between a source and at least one destination of one of the logical multicasts that has been mapped to the physical multicast.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and system for telecommunications including self-organizing scalable ethernet using is-is hierarchy
ActiveUS20100284418A1Data switching by path configurationLink-state routing protocolShortest path bridging
A first aggregation node in communication with the first network and the second network, the source node and internal nodes of the first network only having knowledge of each other and of the first aggregation node. The system includes a second aggregate node in communication with the second network and the third network, the internal nodes of the second network only having knowledge of each other and the first and second aggregate nodes, the destination node and the internal nodes of the third network only having knowledge of each other and the second aggregation node, the first and second aggregation nodes only having knowledge of each other, the destination node receiving the data from the source node using a link state routing protocol and shortest path bridging through the first second and third networks and the first and second aggregation nodes.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
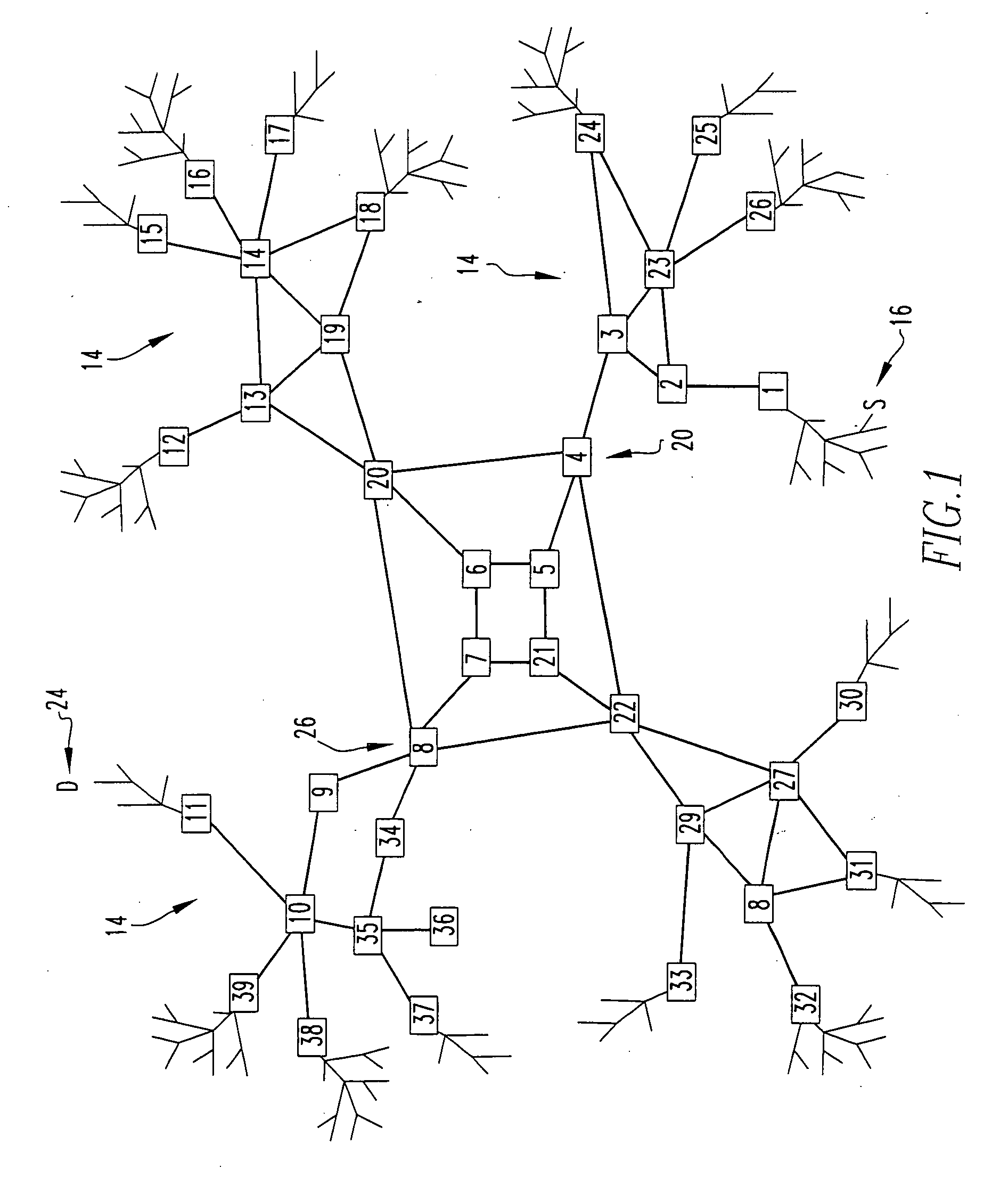
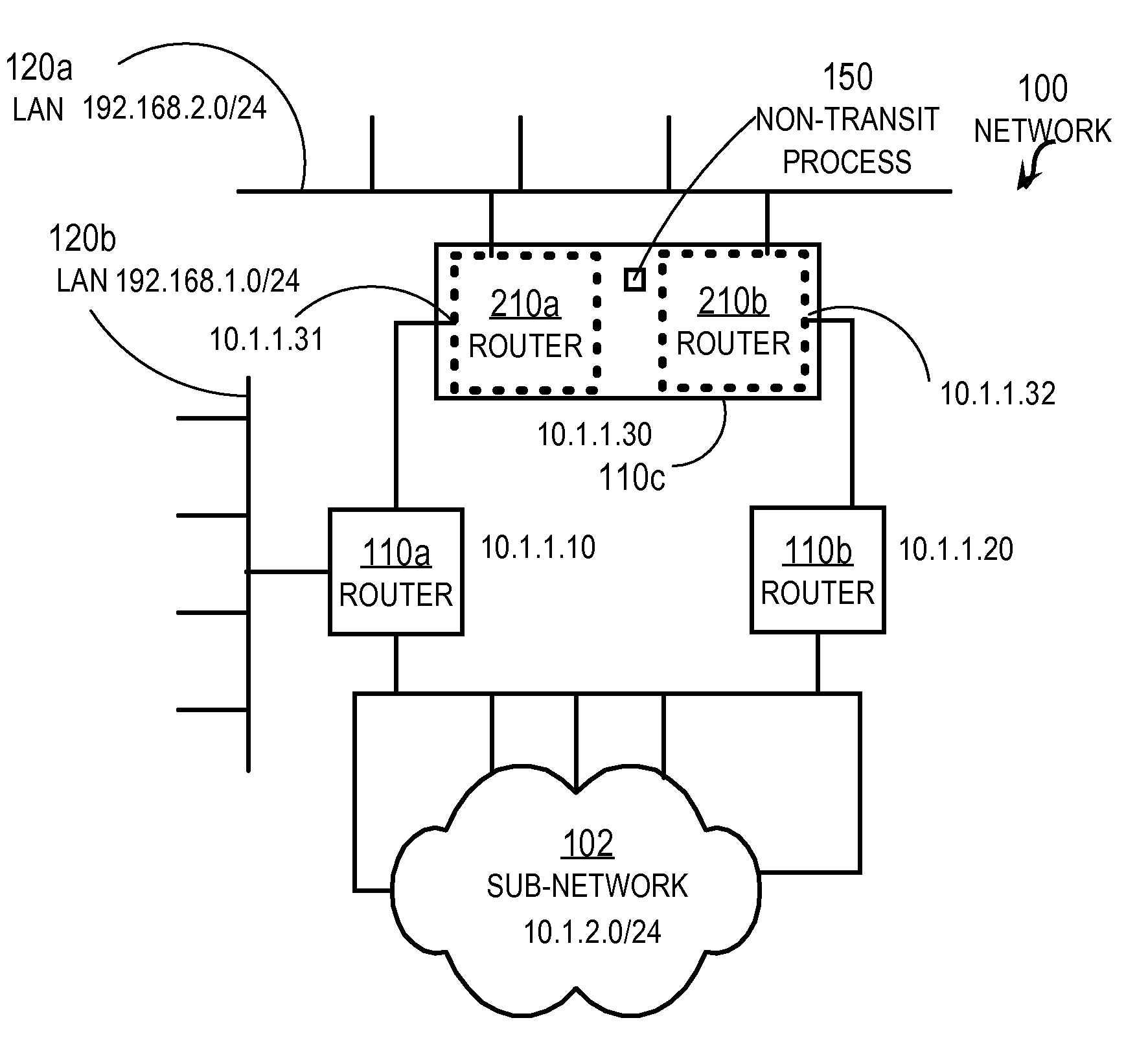
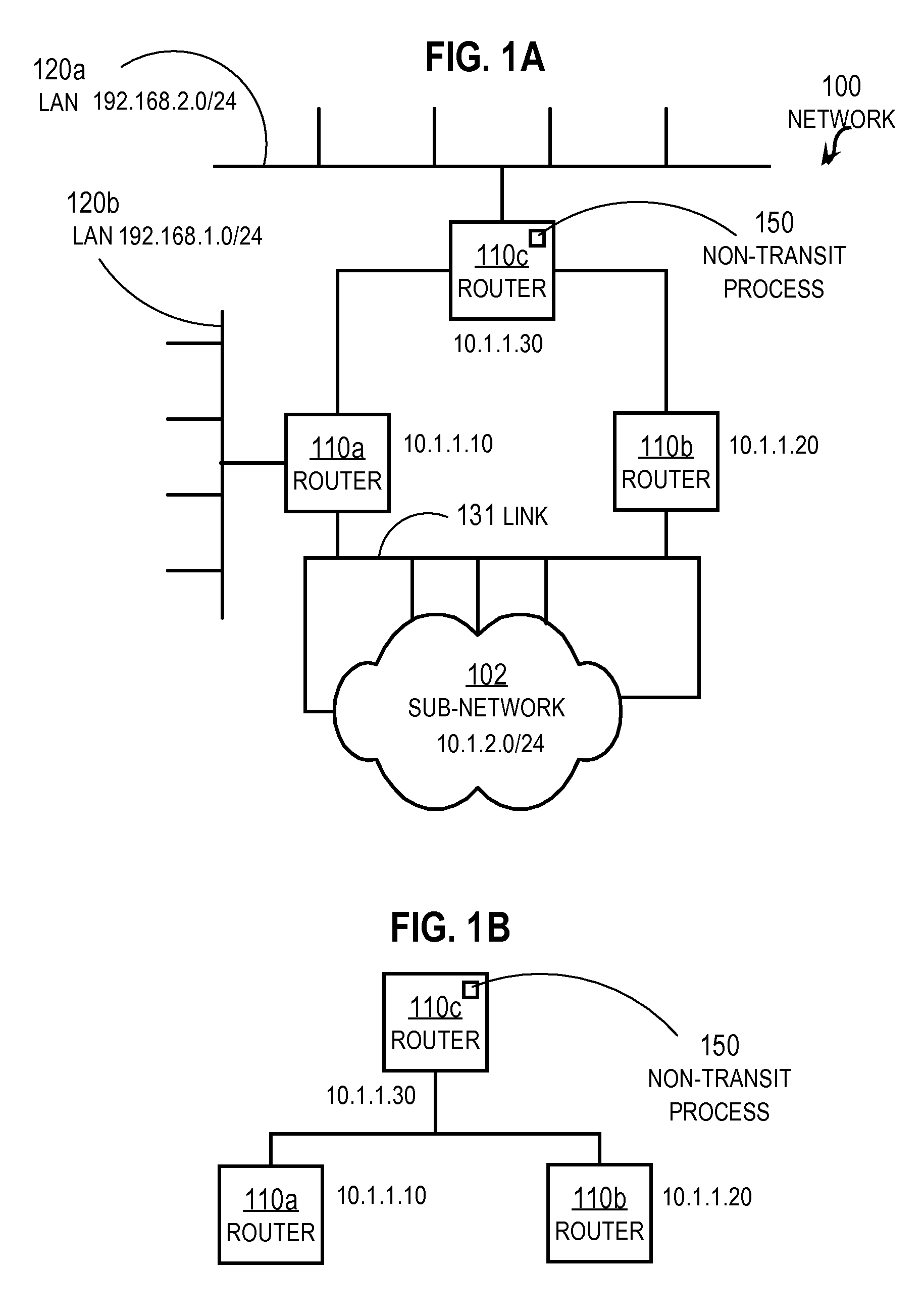
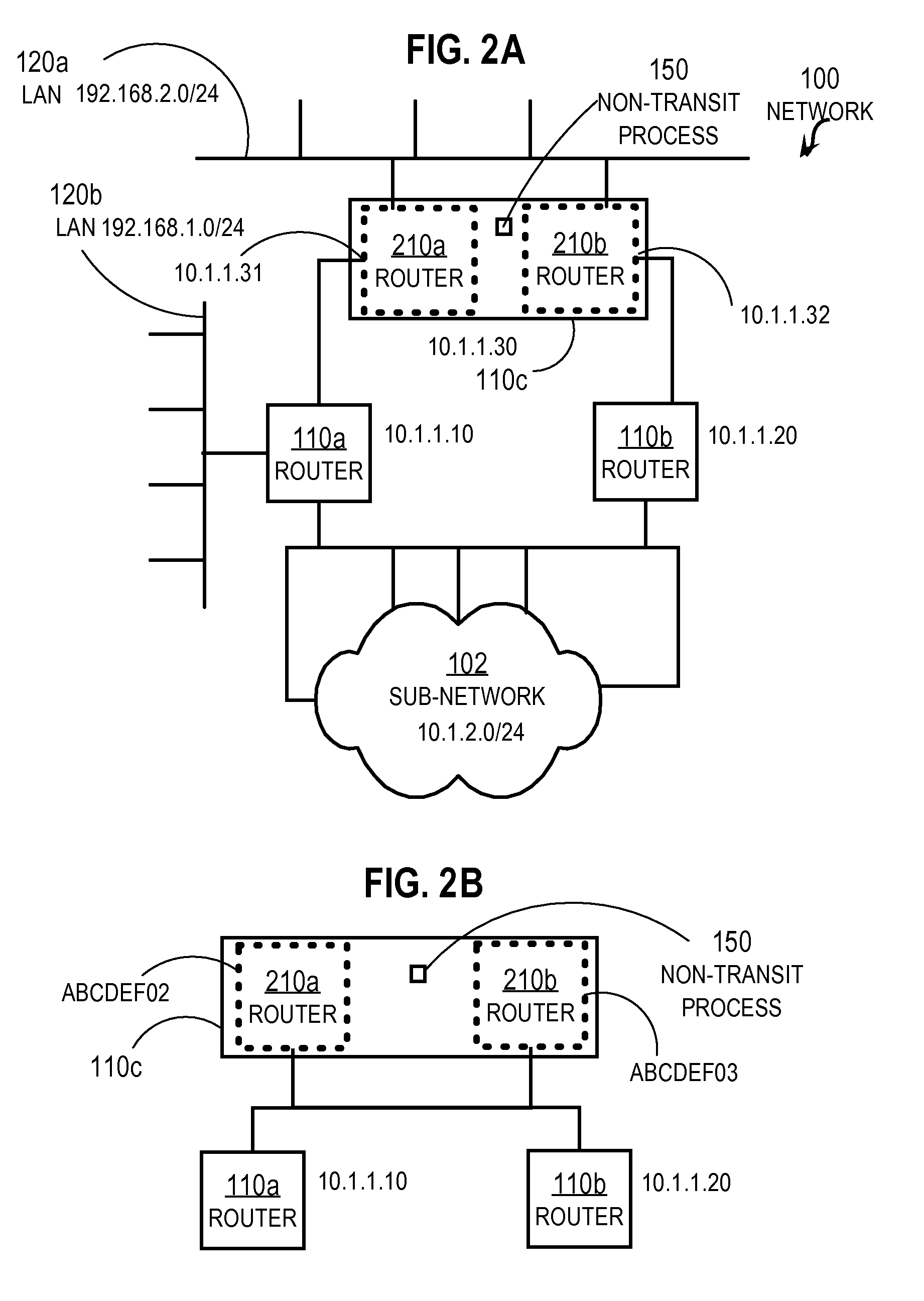
Creating Non-transit Nodes in a Link State Network
InactiveUS20080259820A1Optimize networkData switching by path configurationUnique identifierLink-state routing protocol
In one embodiment, a method includes receiving a first link state initiation (HELLO) message from a first neighboring router. The HELLO message requests that a recipient node send a unique identifier for itself in a link state routing protocol. In response to receiving the first HELLO message, a first response message is sent that includes a first identifier from an identifier pool. The identifier pool contains for a local node a plurality of network identifiers that are unique among all nodes in the network that uses the link state routing protocol. A second HELLO message is received from a different second neighboring router. In response to receiving the second HELLO message, a second response message is sent that includes a different second identifier from the identifier pool.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
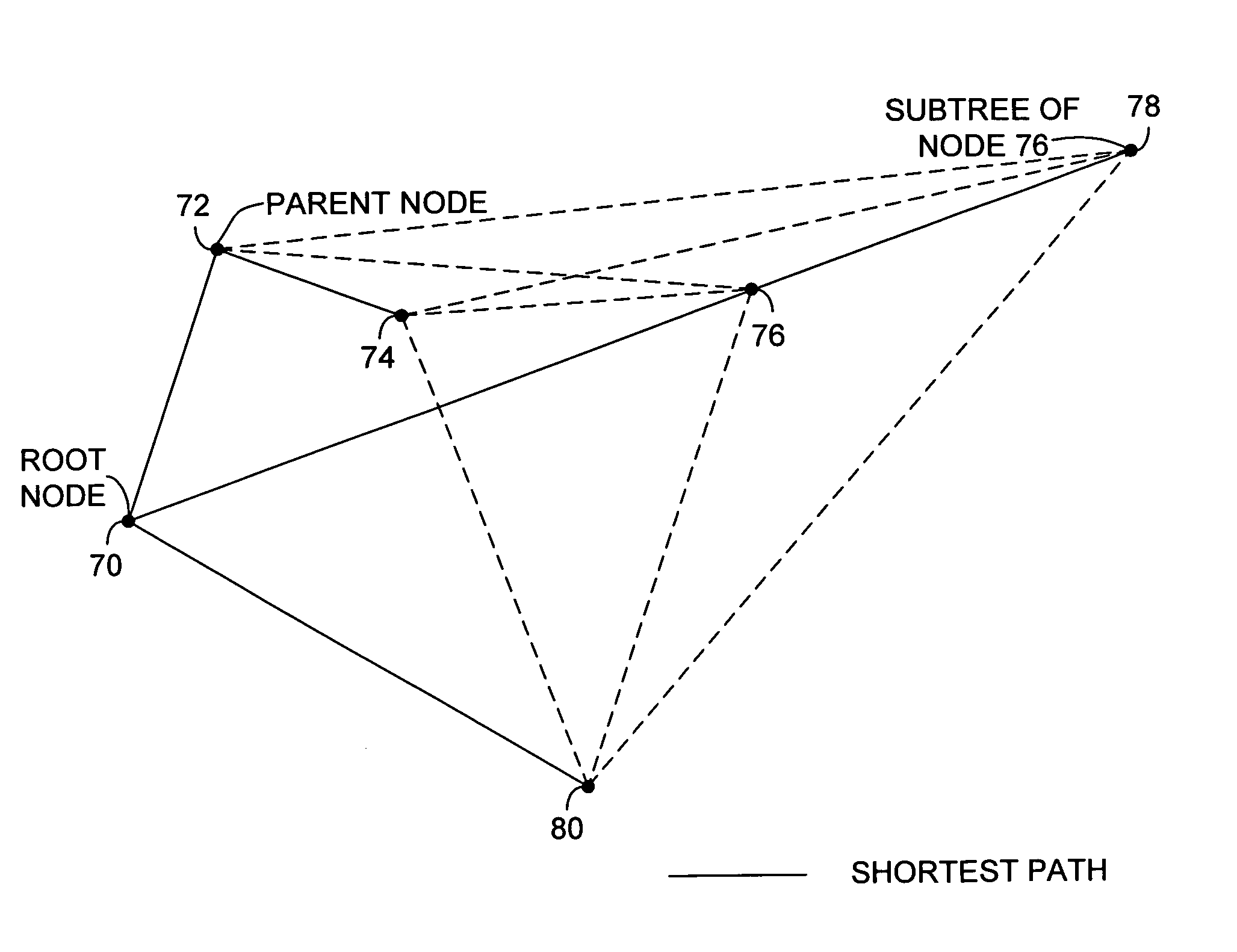
Method and system for accelerating route calculation in link state routing protocols
A method for performing route calculations in a link state routing protocol at a node within a computer network. The method includes evaluating existing routes of the node when new route information is received and recalculating routes for the node only when the new route information improves at least one of the existing routes or at least one of the existing routes is made worse or lost. A system for performing route calculations is also disclosed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and methods for improved network routing
ActiveUS20150236945A1Facilitate easy transitionData switching networksSelf adaptiveLink-state routing protocol
Known intra-domain routing methods (e.g., OSPF and IS-IS) are link-state routing protocols with hop-by-hop forwarding that sacrifice optimal traffic engineering for ease of implementation and management. Known optimal traffic engineering procedures are either not link-state methods or require source routing—characteristics that make them difficult to implement. Certain embodiments of the present invention include a fully distributed, adaptive, link-state routing protocol with hop-by-hop forwarding configured to achieve optimal traffic engineering. Such embodiments facilitate significant performance improvements relative to known intra-domain routing methods and decrease network infrastructure requirements.
Owner:CORNELL UNIV CENT FOR TECH LICENSING CTL AT CORNELL UNIV
System and methods for improved network routing
ActiveUS9521067B2Facilitate easy transitionData switching networksSelf adaptiveLink-state routing protocol
Known intra-domain routing methods (e.g., OSPF and IS-IS) are link-state routing protocols with hop-by-hop forwarding that sacrifice optimal traffic engineering for ease of implementation and management. Known optimal traffic engineering procedures are either not link-state methods or require source routing—characteristics that make them difficult to implement. Certain embodiments of the present invention include a fully distributed, adaptive, link-state routing protocol with hop-by-hop forwarding configured to achieve optimal traffic engineering. Such embodiments facilitate significant performance improvements relative to known intra-domain routing methods and decrease network infrastructure requirements.
Owner:CORNELL UNIV CENT FOR TECH LICENSING CTL AT CORNELL UNIV
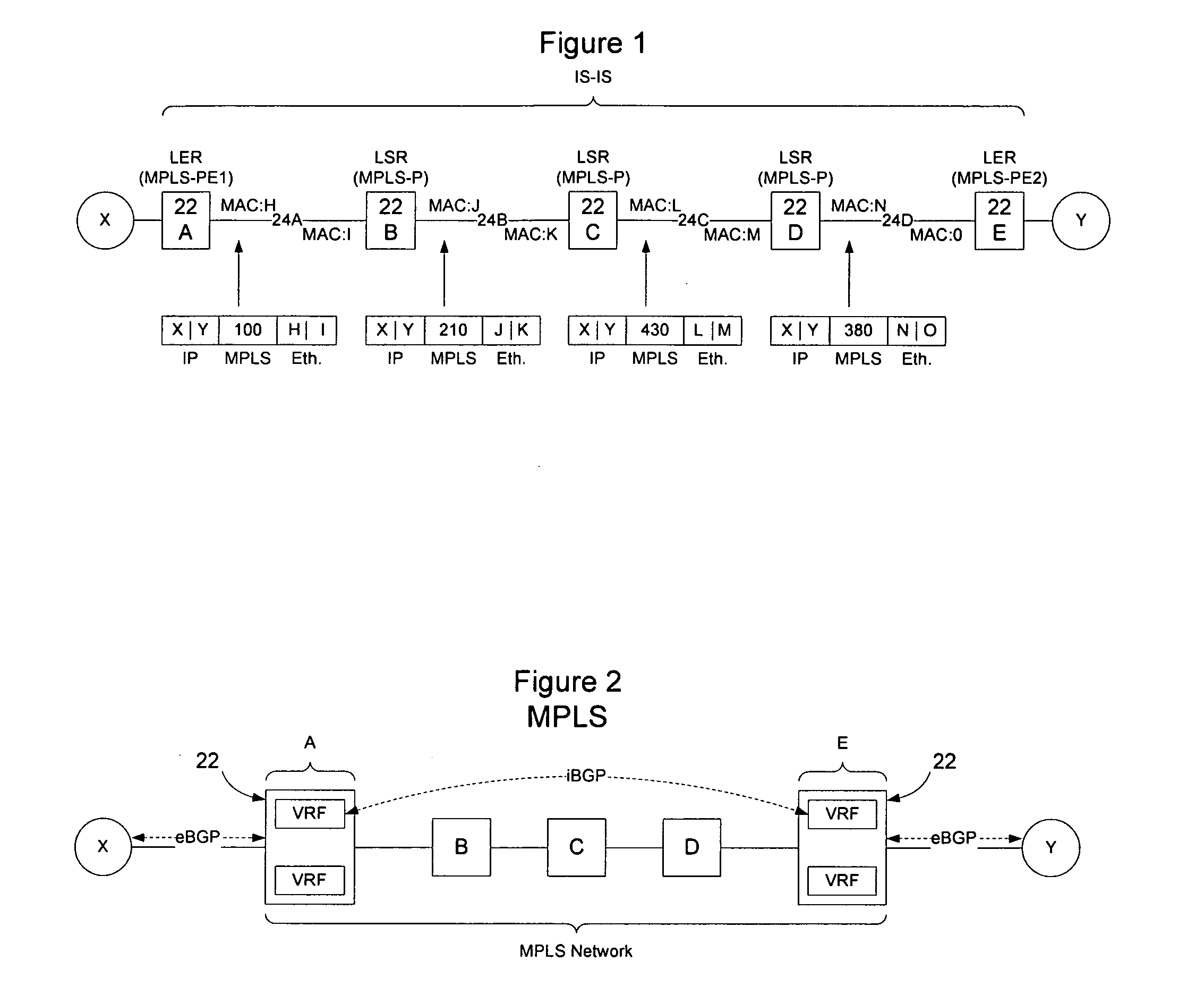
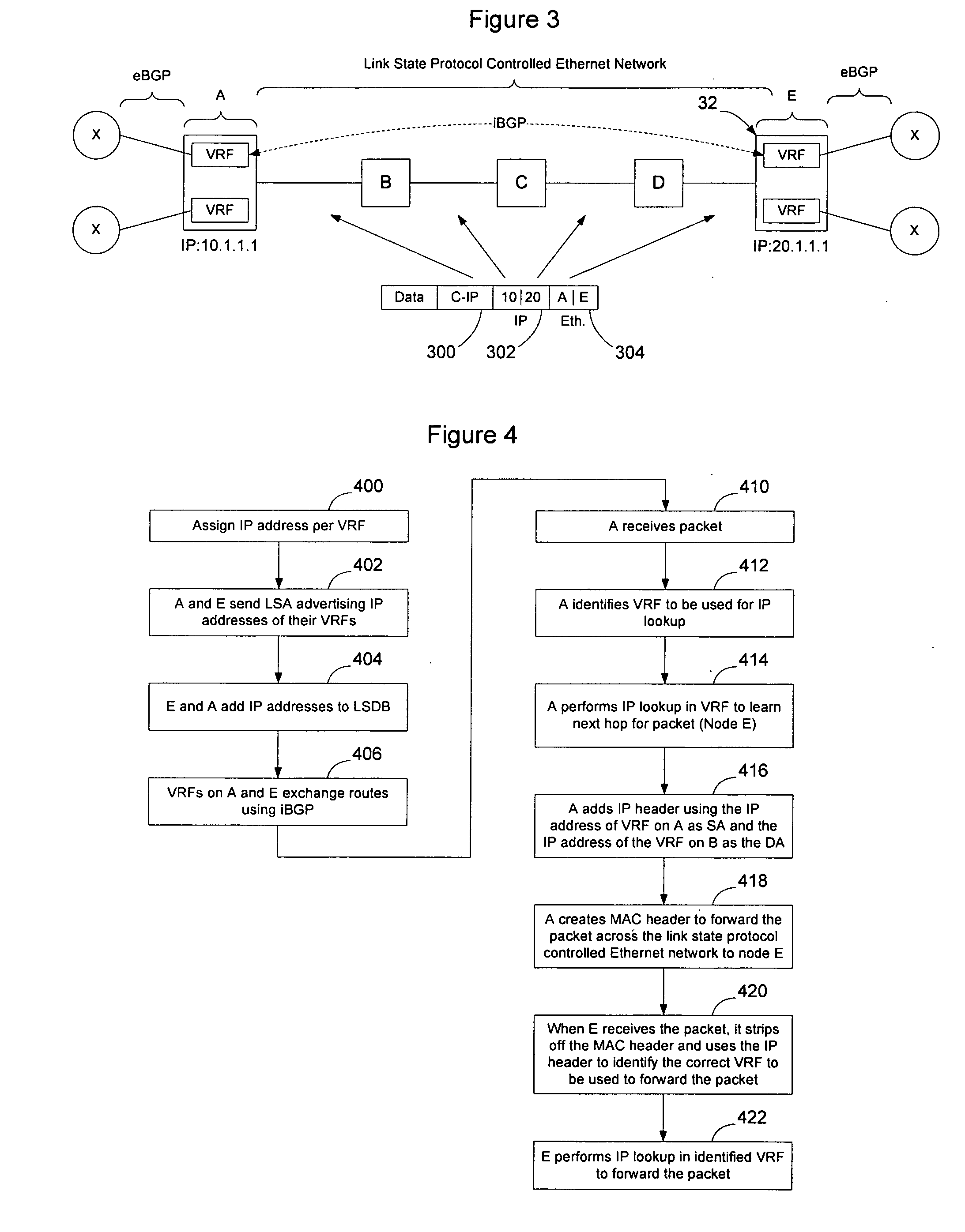
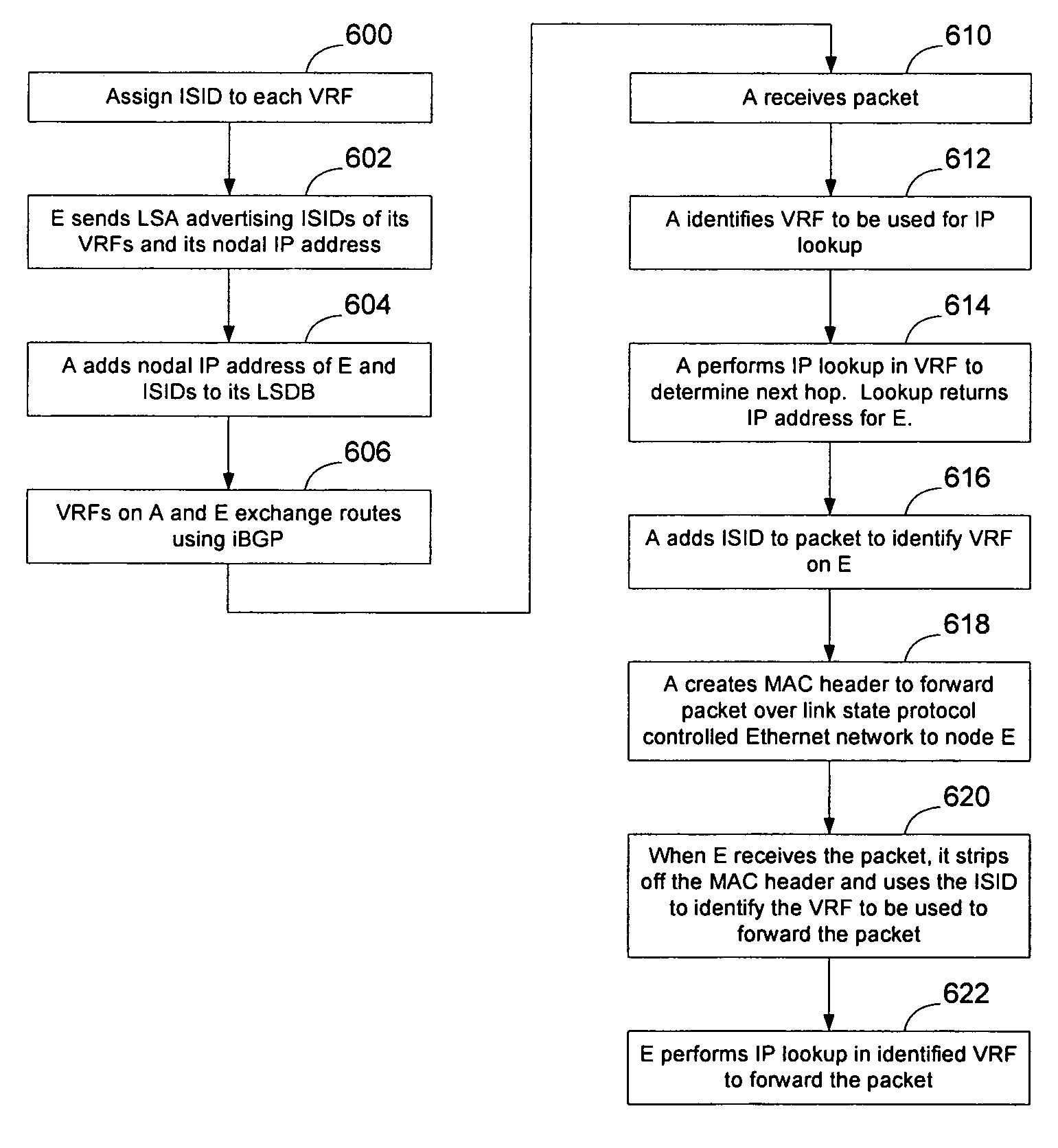
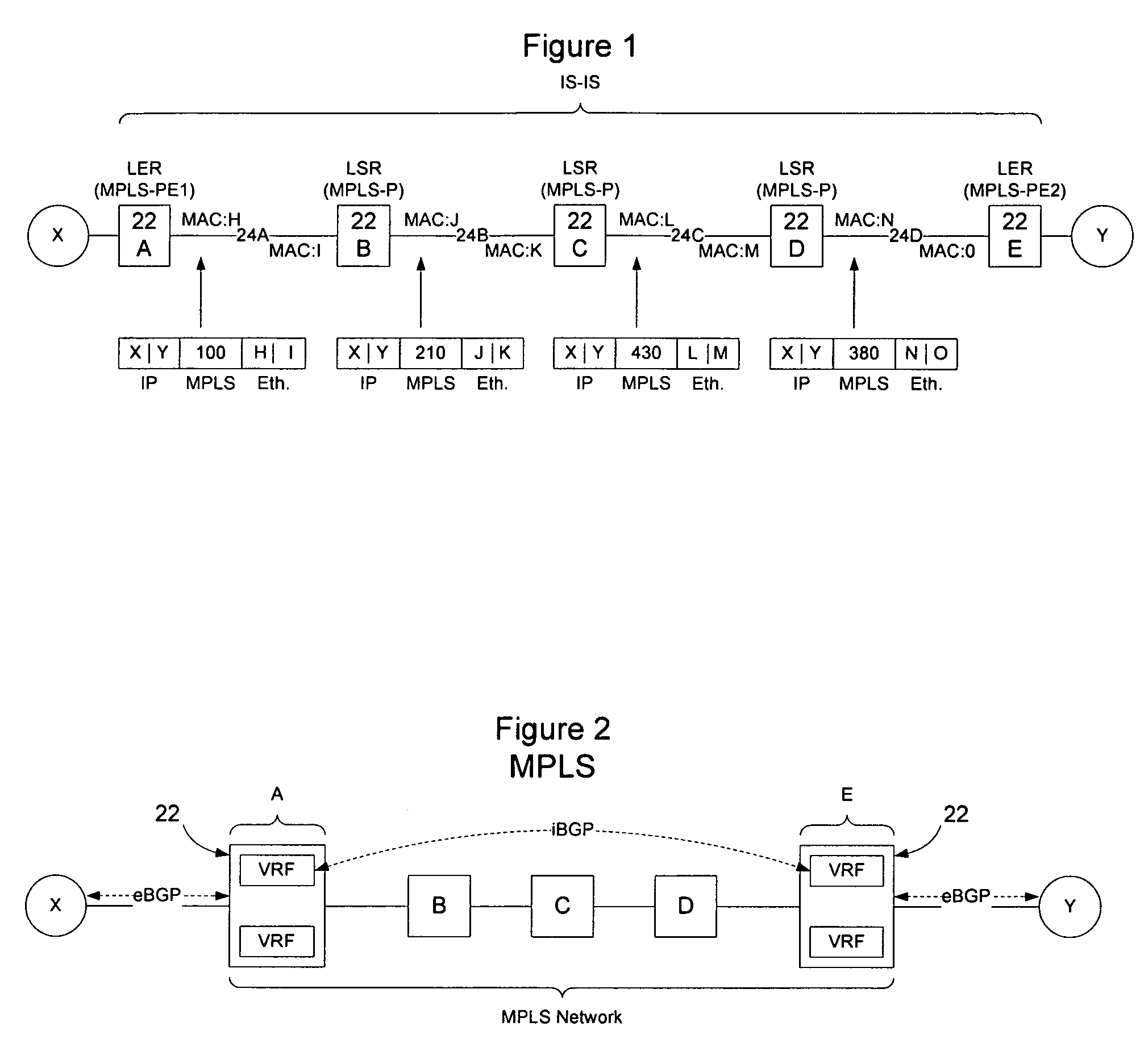
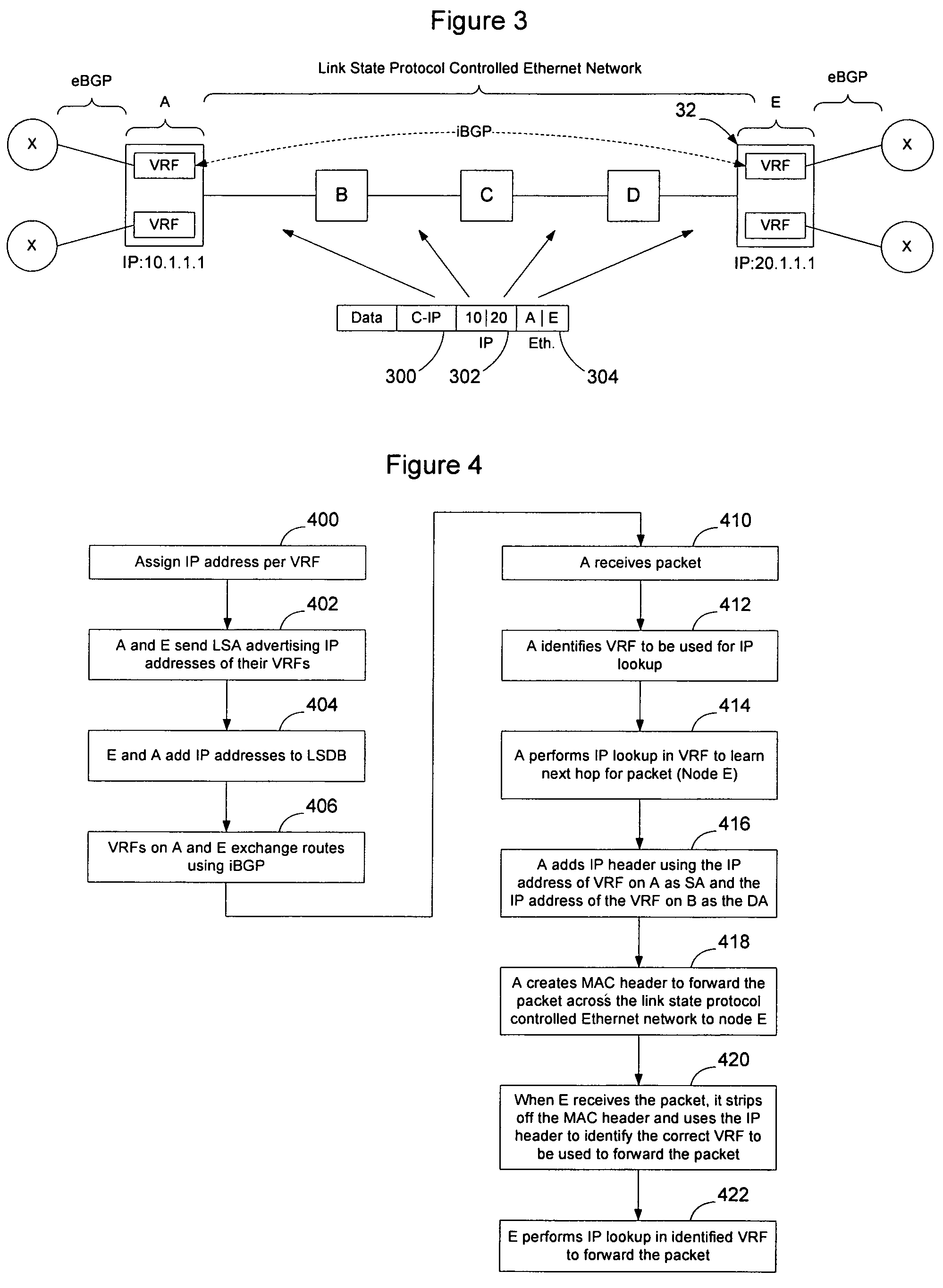
Implementation of VPNs over a link state protocol controlled Ethernet network
Nodes on a link state protocol controlled Ethernet network implement a link state routing protocol such as IS-IS. Nodes assign an IP address or I-SID value per VRF and then advertise the IP addresses or I-SID values in IS-IS LSAs. When a packet is to be forwarded on the VPN, the ingress node identifies the VRF for the packet and performs an IP lookup in customer address space in the VRF to determine the next hop and the IP address or I-SID value of the VRF on the egress node. The ingress node prepends an I-SID or IP header to identify the VRFs and then creates a MAC header to allow the packet to be forwarded to the egress node on the link state protocol controlled Ethernet network. When the packet is received at the egress node, the MAC header is stripped from the packet and the appended I-SID or IP header is used to identify the egress VRF. A customer address space IP lookup is then performed in the identified VRF on the egress node using the information in the client IP header to determine how to forward the packet. Customer reachability information within a VPN may be exchanged between VRFs using iBGP, or directly by using link state protocol LSAs tagged with the relevant I-SID.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
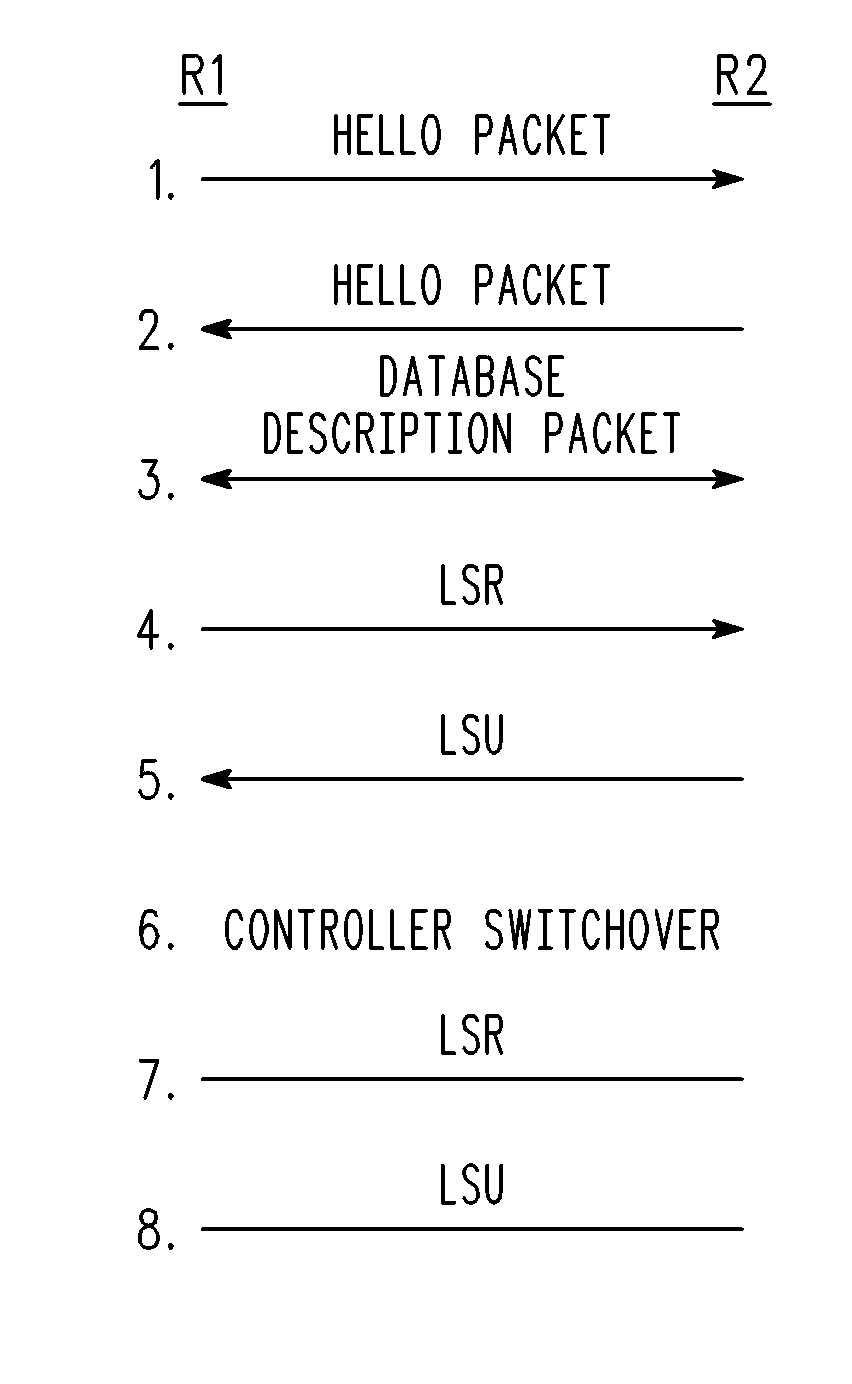
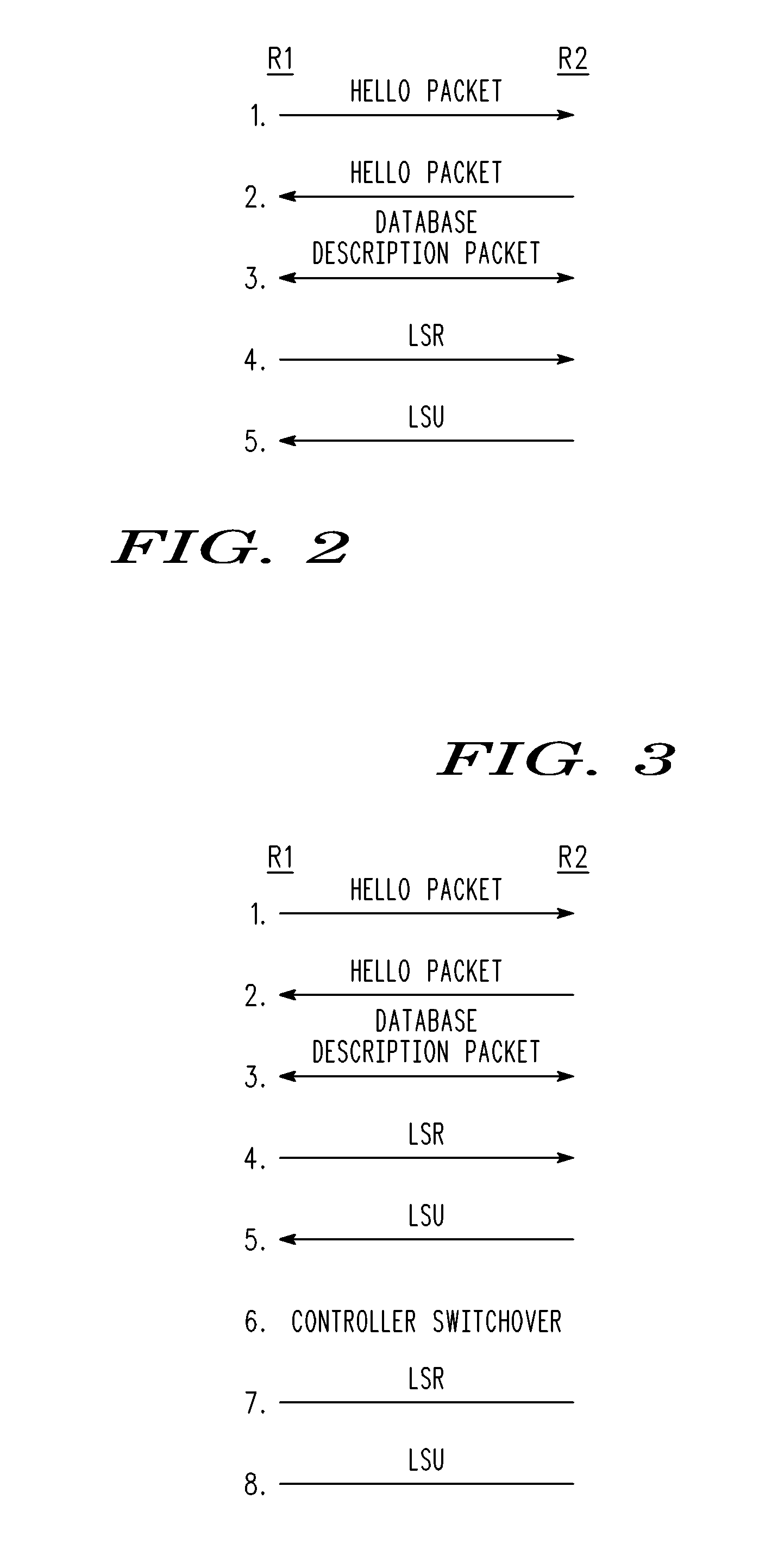
Method and Apparatus for Performing a Graceful Restart in a NSF-Capable Router Without Enhancing Link State Routing Protocols
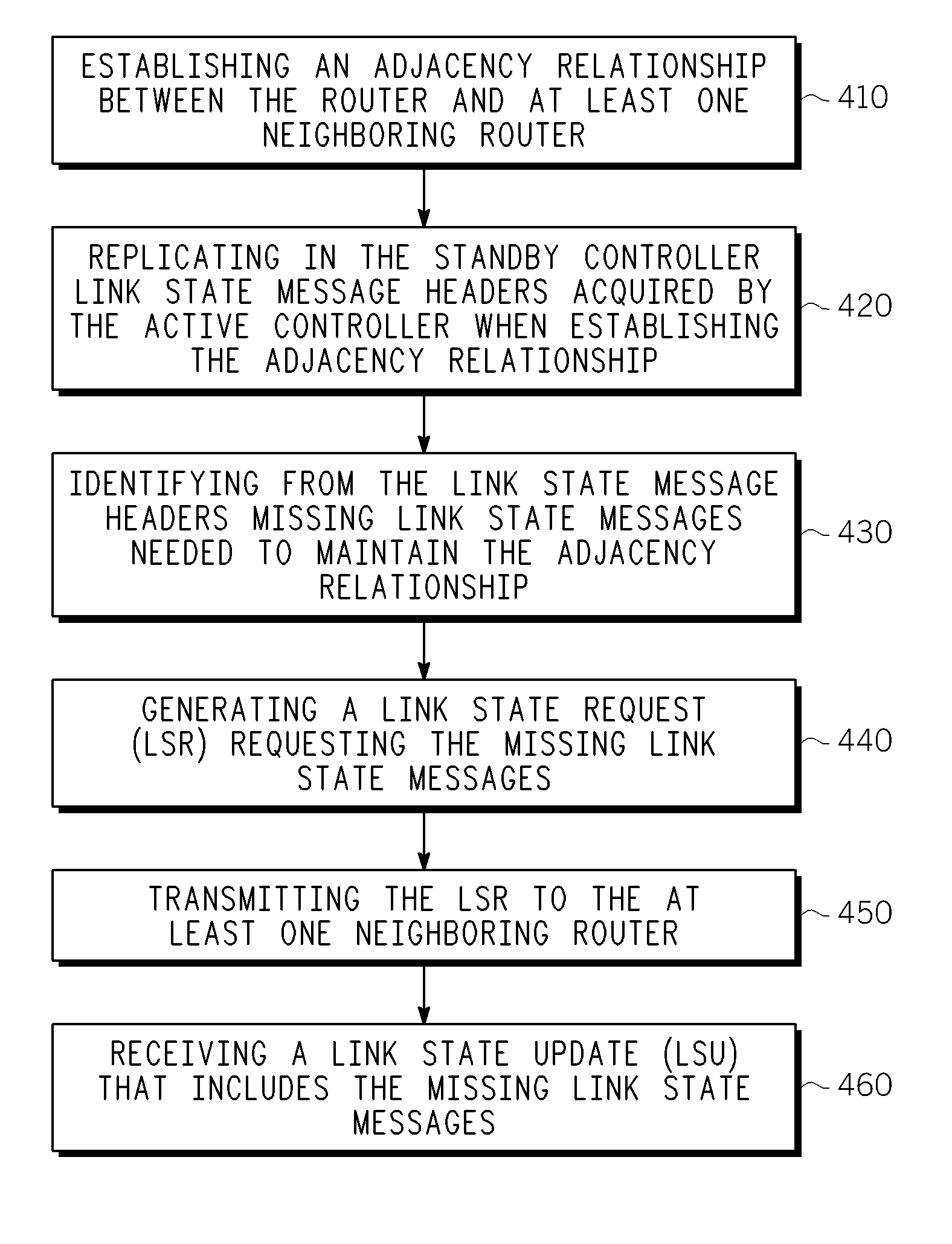
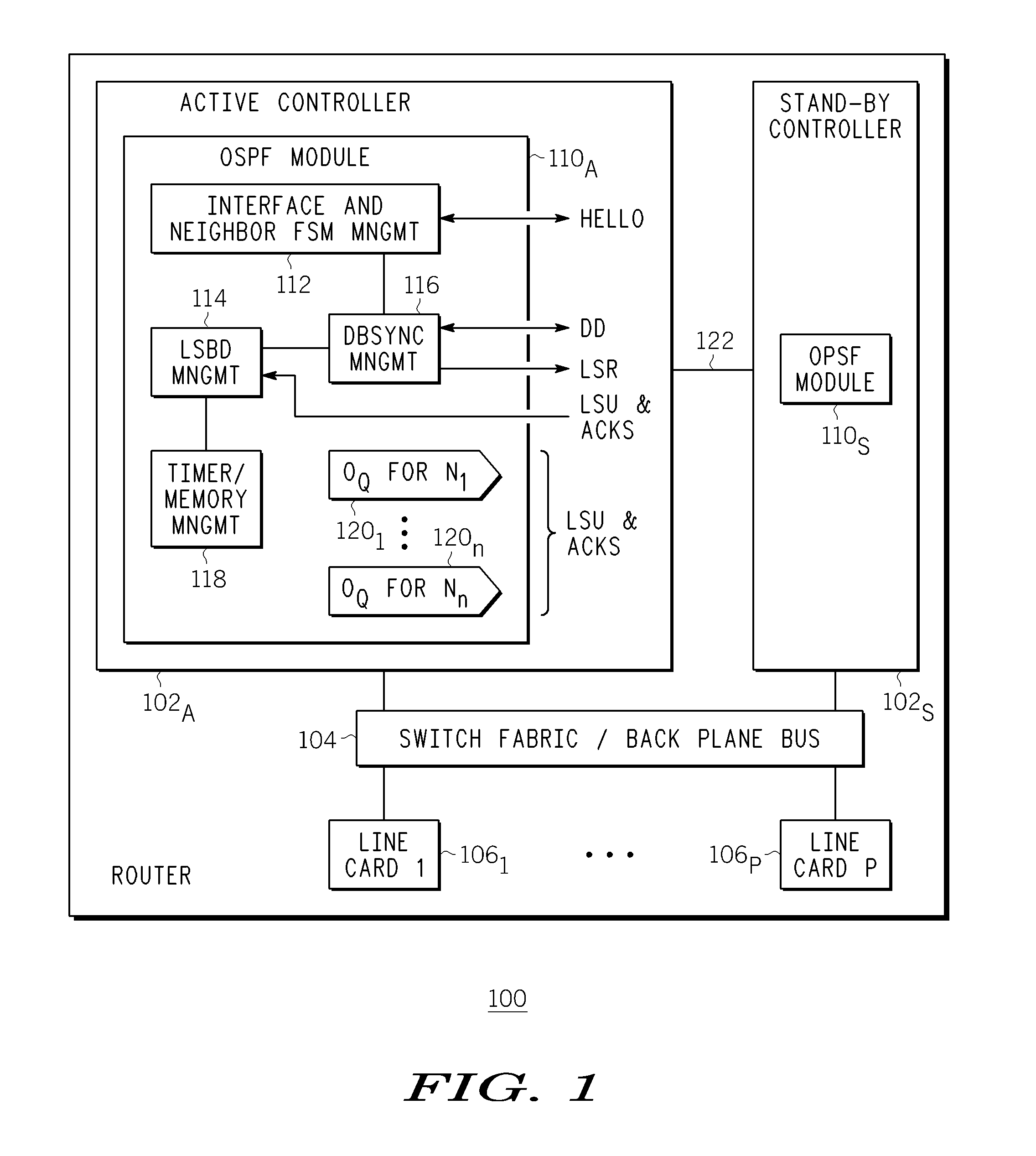
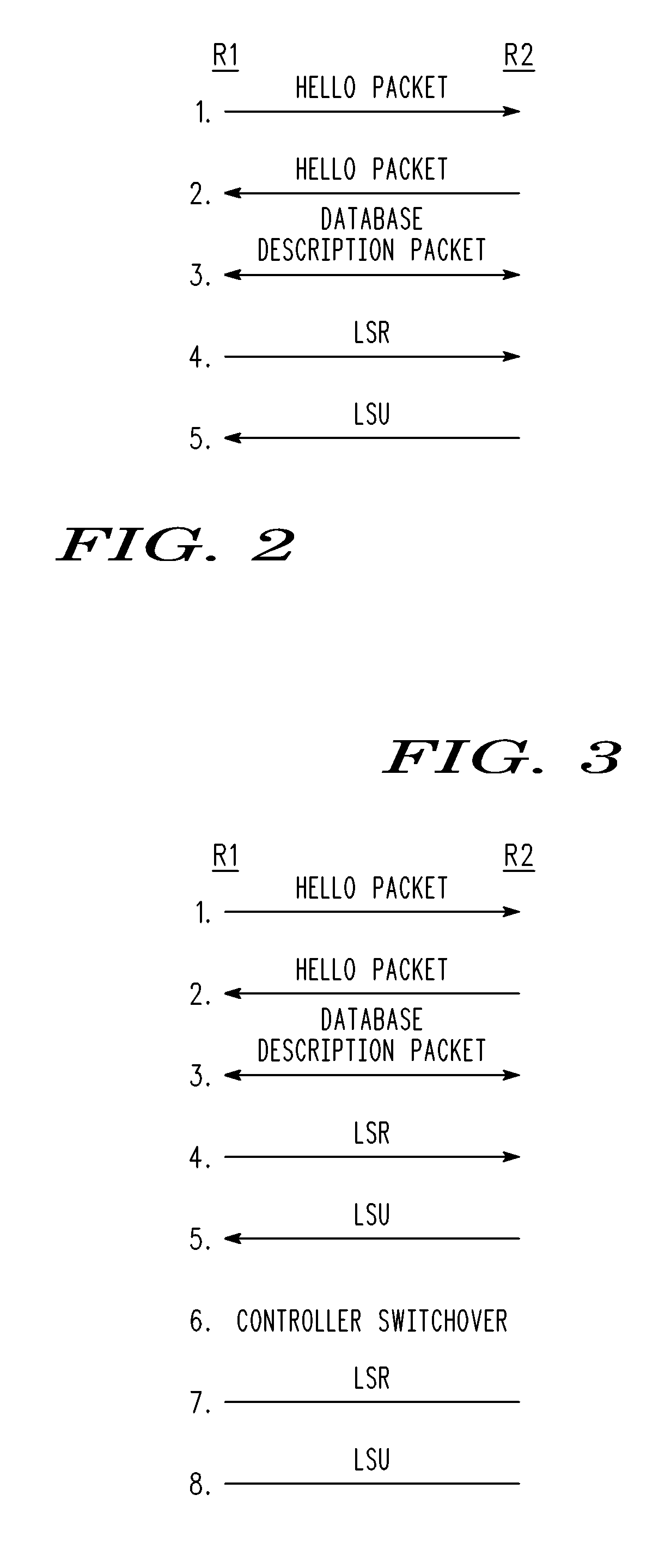
A graceful restart is provided in a NSF capable router. When a switchover to a standby controller is required, the standby controller receives replicated link state message headers from an active controller. The standby controller generates a link state request (LSR) message from the link state message headers and transmits the LSRs to neighboring routers. The standby controller receives a link state update that includes the link state messages. By using the LSRs, the standby controller can be quickly synchronized with its neighbors well within the grace period, thereby maintaining adjacency.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Node, routing control method, and routing control program
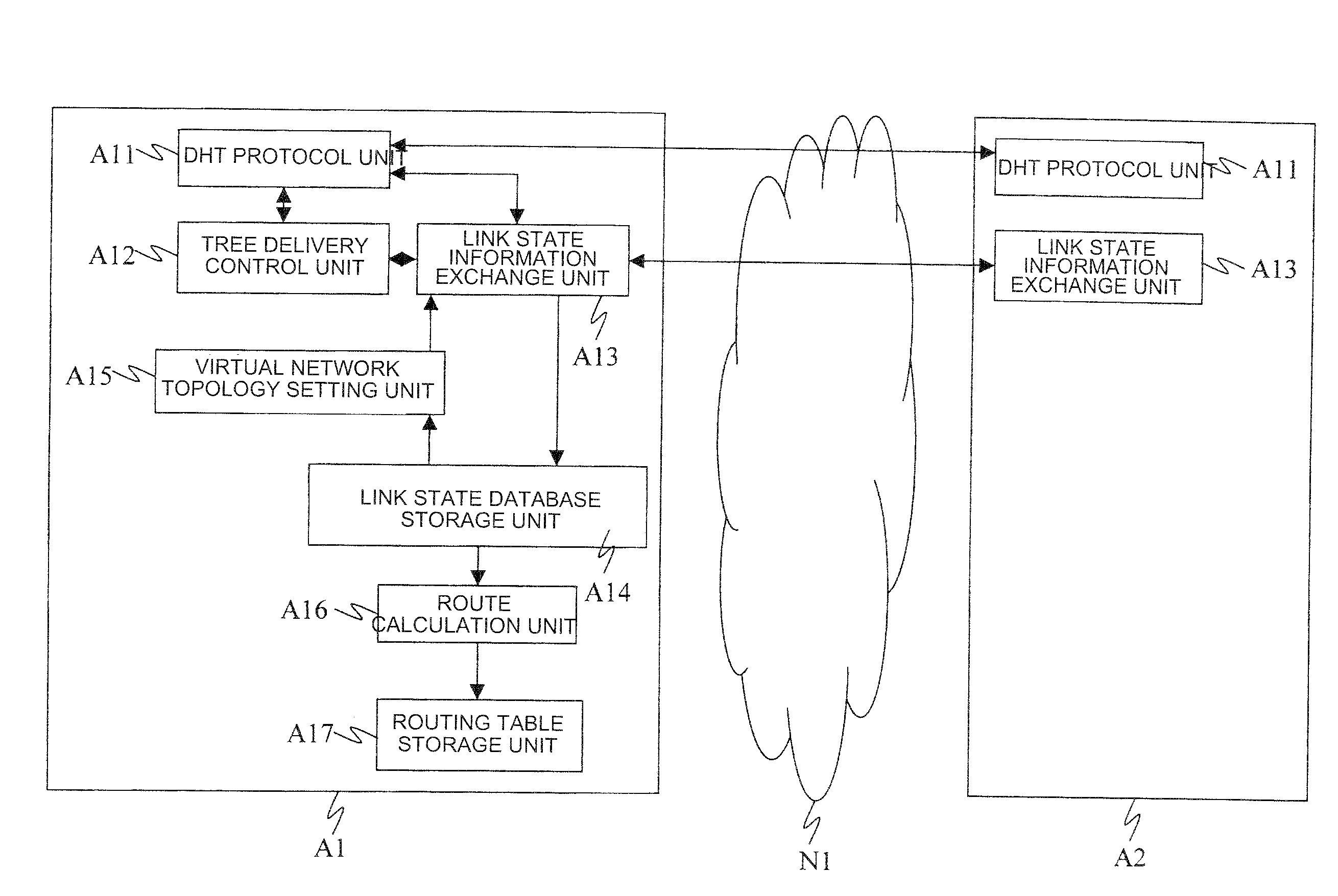
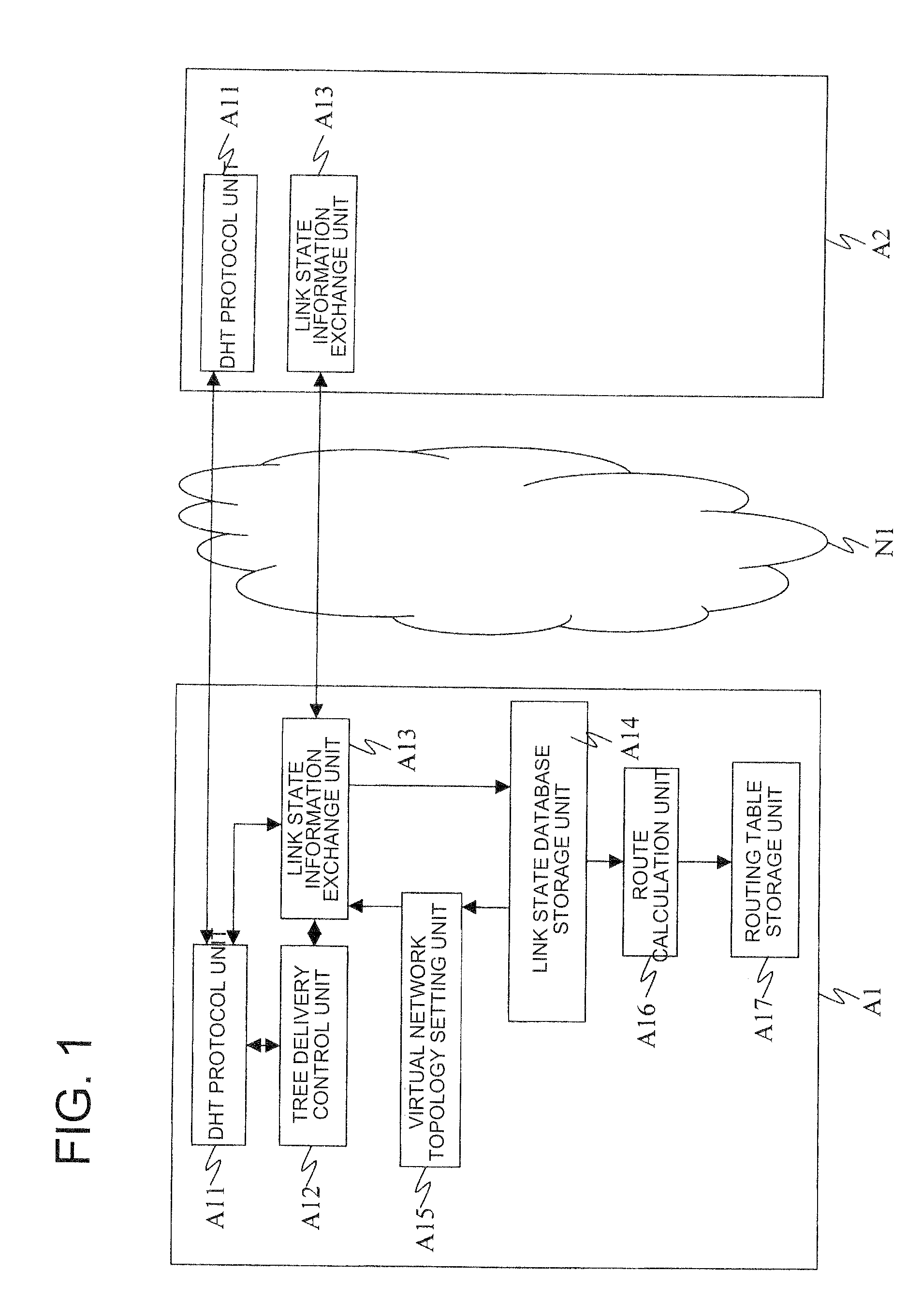
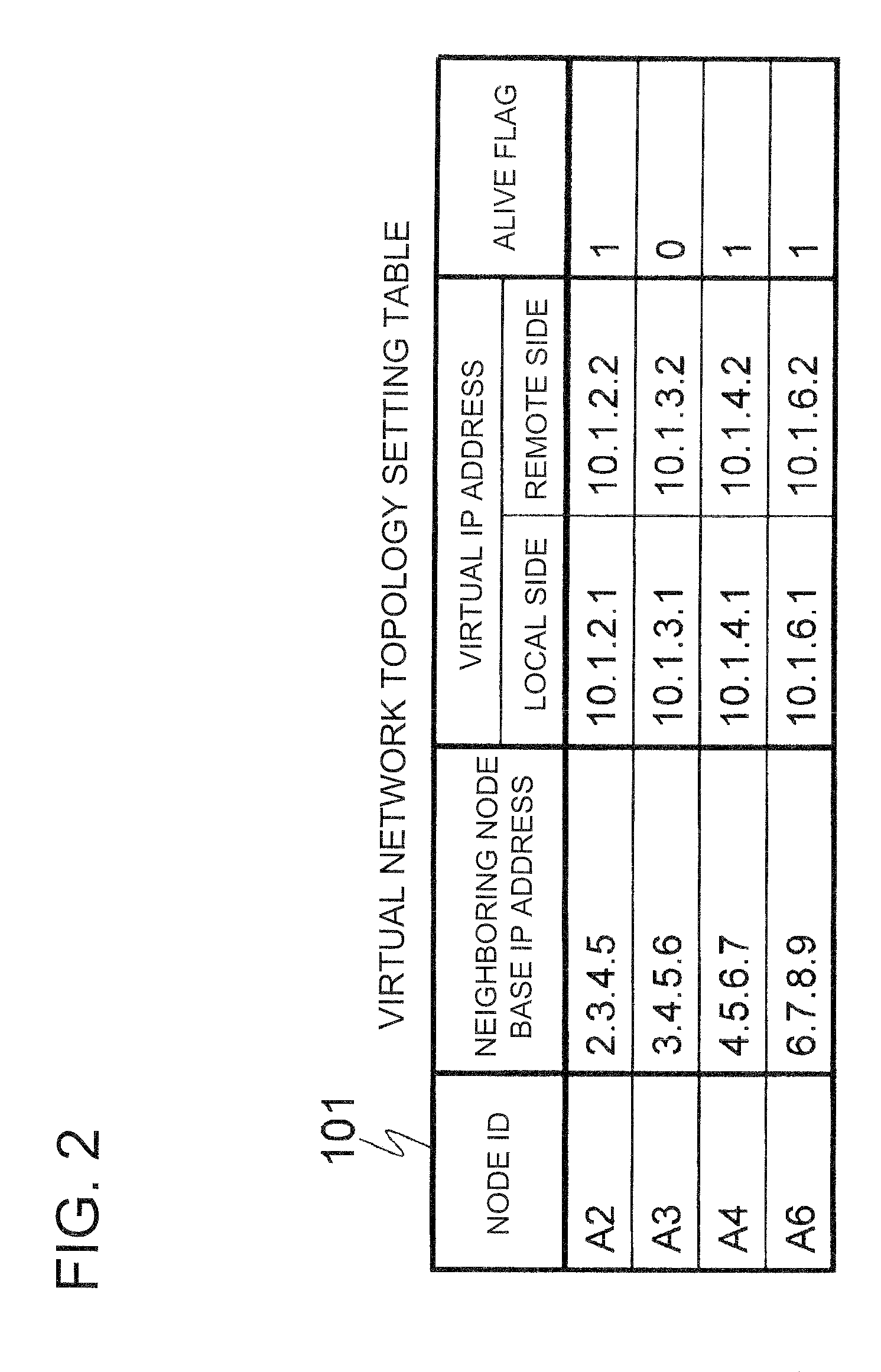
ActiveUS20090180489A1Reduce trafficData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsOptimized Link State Routing ProtocolLink-state routing protocol
Disclosed is a node that includes a distributed hash table generation means that generates a distributed hash table which indicates the next node to which a message is to be transferred, using a link state routing protocol, a link state information that exchange unit sends and receives link state information, and a tree delivery control unit that determines the transfer destination of the link state information so that the link state information is delivered along a tree where the source node of the link state information is a root.
Owner:NEC CORP
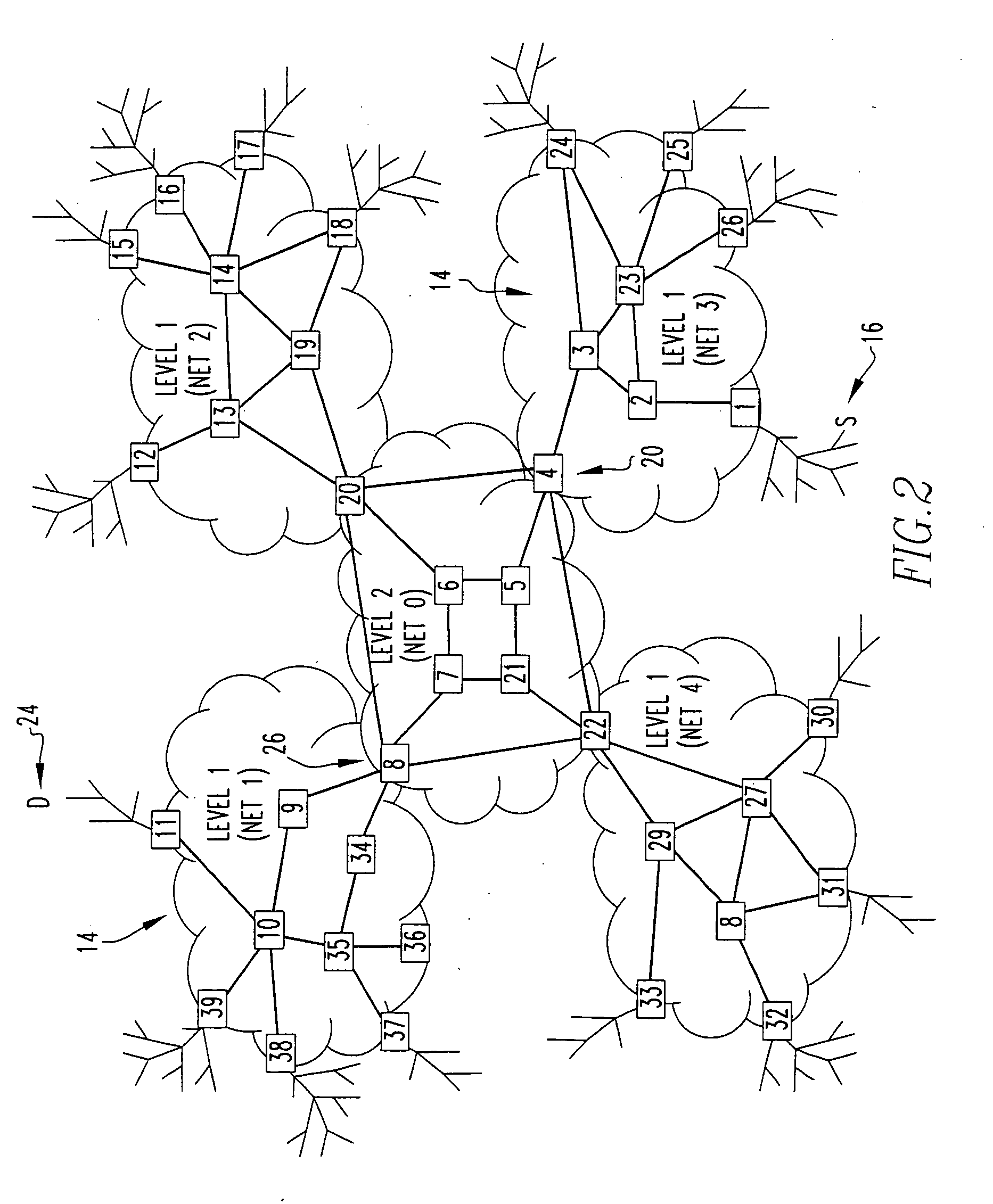
Method and system for topology construction and path identification in a two-level routing domain operated according to a simple link state routing protocol
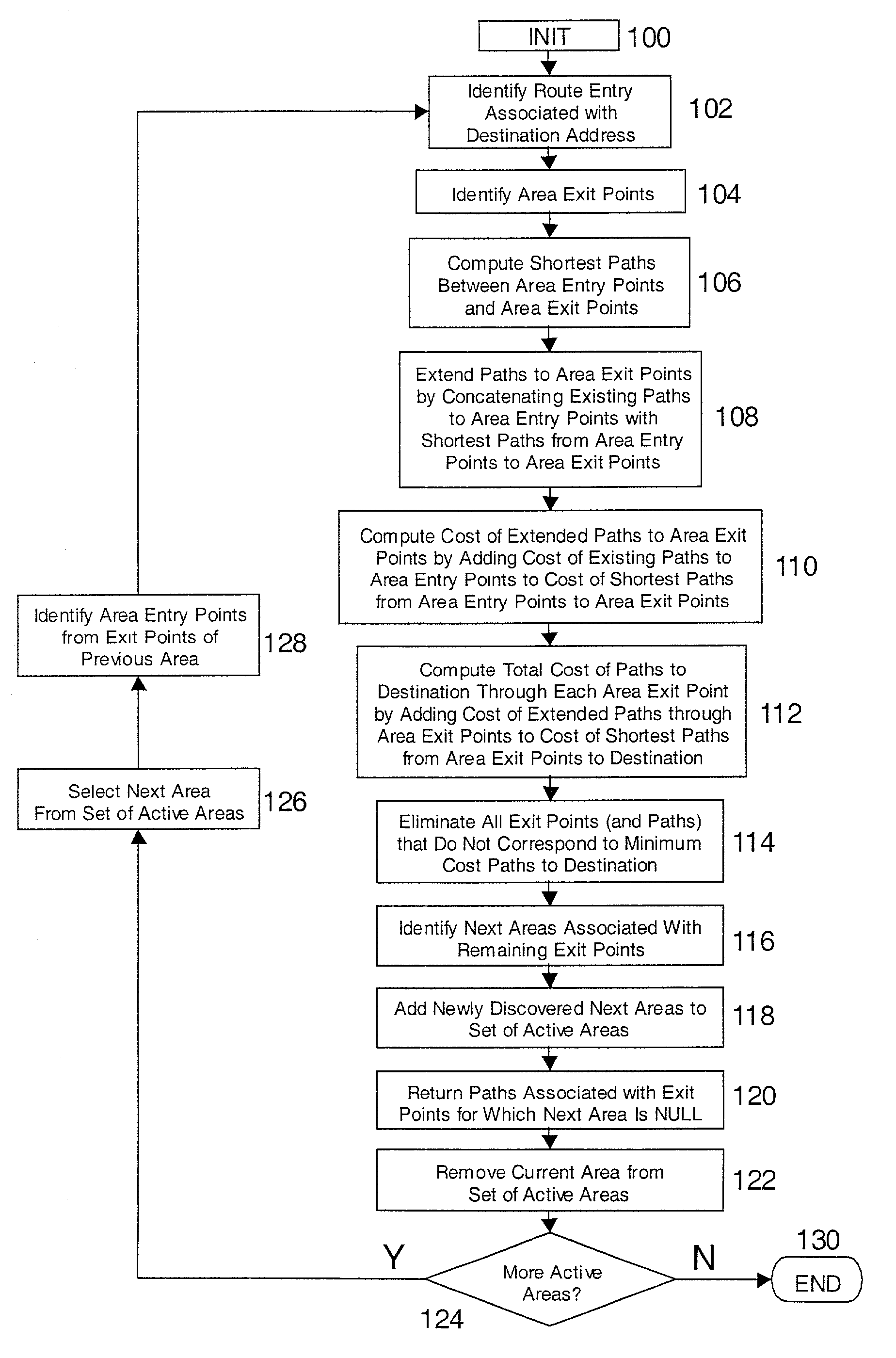
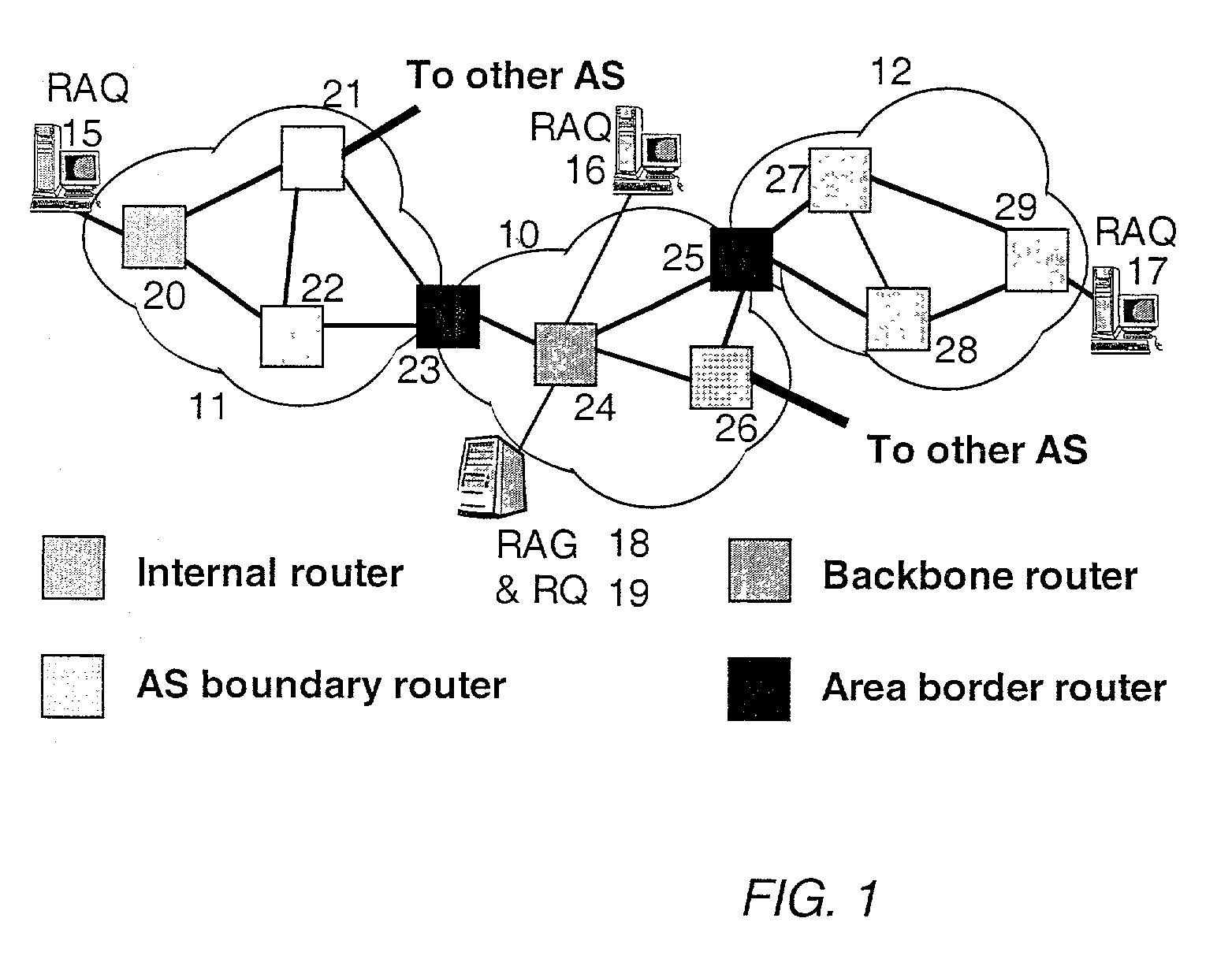
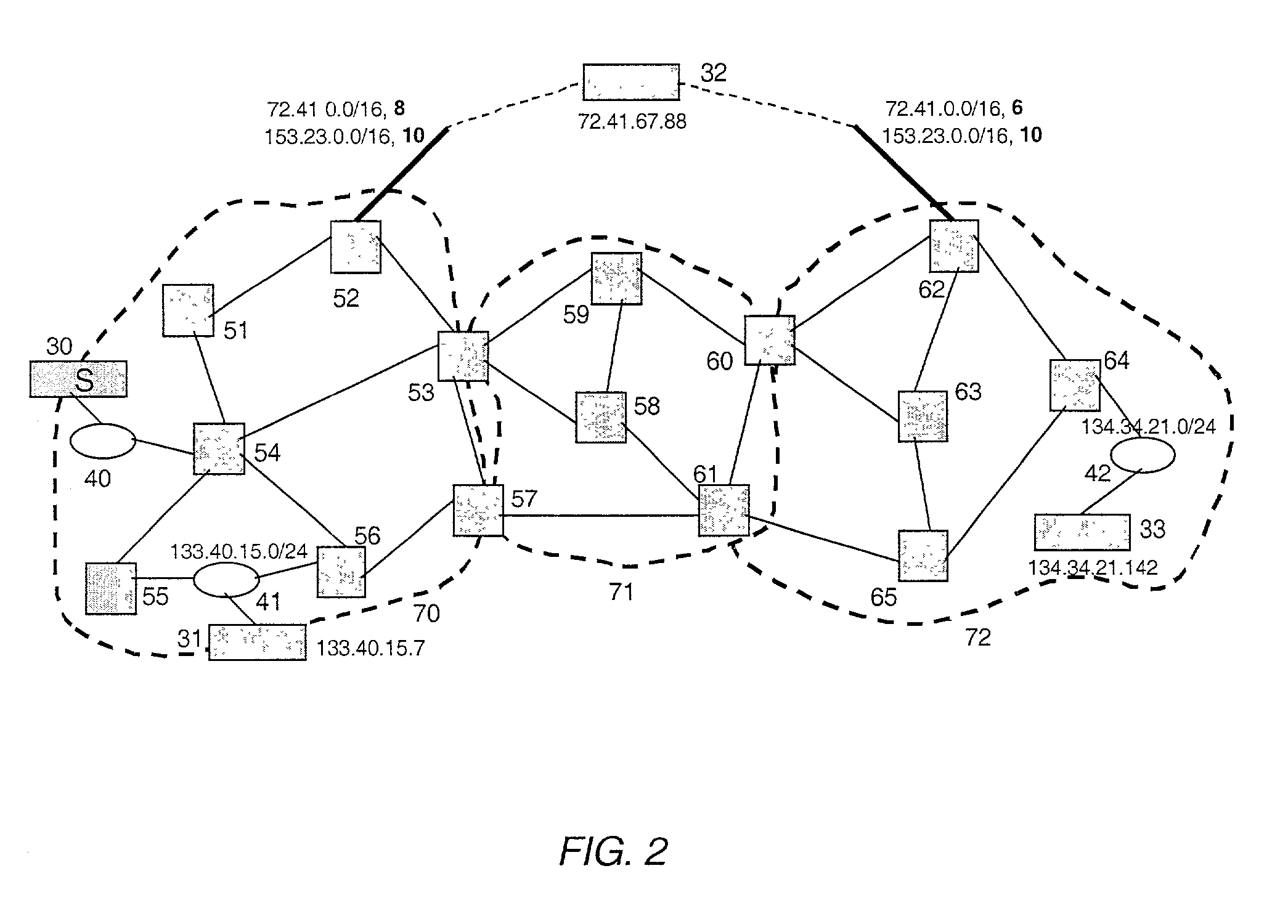
ActiveUS7120120B2Minimal costColor television with pulse code modulationError preventionEntry pointRouting domain
A method and system for extracting and building end-to-end route information in a two-level, multi-area Internet protocol (IP) autonomous system (AS) operated according to a simple link state routing protocol such as the Integrated System to Integrated System (IS-IS) protocol is disclosed. The method and system enables a user, such as a network administrator, to explicitly identify a full set of paths (links and routers) that a given IP packet would potentially traverse from its entry point in the area of the AS where it originates until its exit point in its intended destination or exit area.
Owner:SONS OF INNOVATION LLC
Provider link state bridging
InactiveUS7688756B2Efficient comprehensive utilizationMinimize impactSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationReverse path forwardingNetwork packet
Provider Link State Bridging (PLSB) expands static configuration of Ethernet MAC forwarding tables by the control plane and utilizes direct manipulation of Ethernet forwarding by a link state routing system. At least one media-access-control (MAC) address for unicast forwarding to the bridge and at least one MAC address for multicast forwarding from the bridge are assigned. Bridges exchange state information by a link state bridging protocol so that a synchronized configured view of the network is shared between nodes. Each node can calculate shortest path connective between peer bridging nodes and populated the appropriate forwarding tables. A reverse path forwarding check is performed on incoming packets to provide loop suppression. During times of network instability the loop suppression can be disabled for unicast packets as identified by the destination MAC address to buffer packets and minimize the impact on traffic flow.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
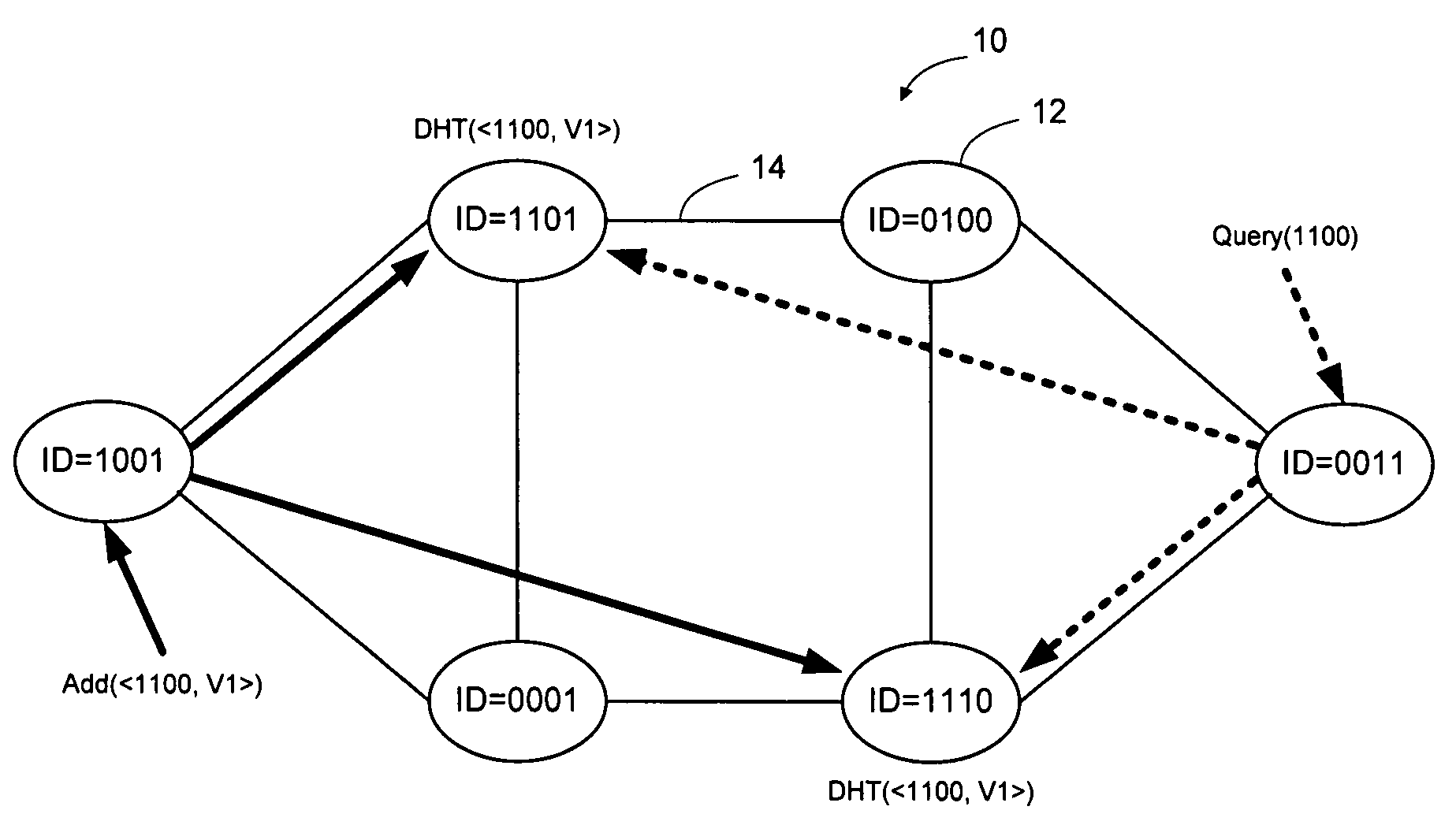
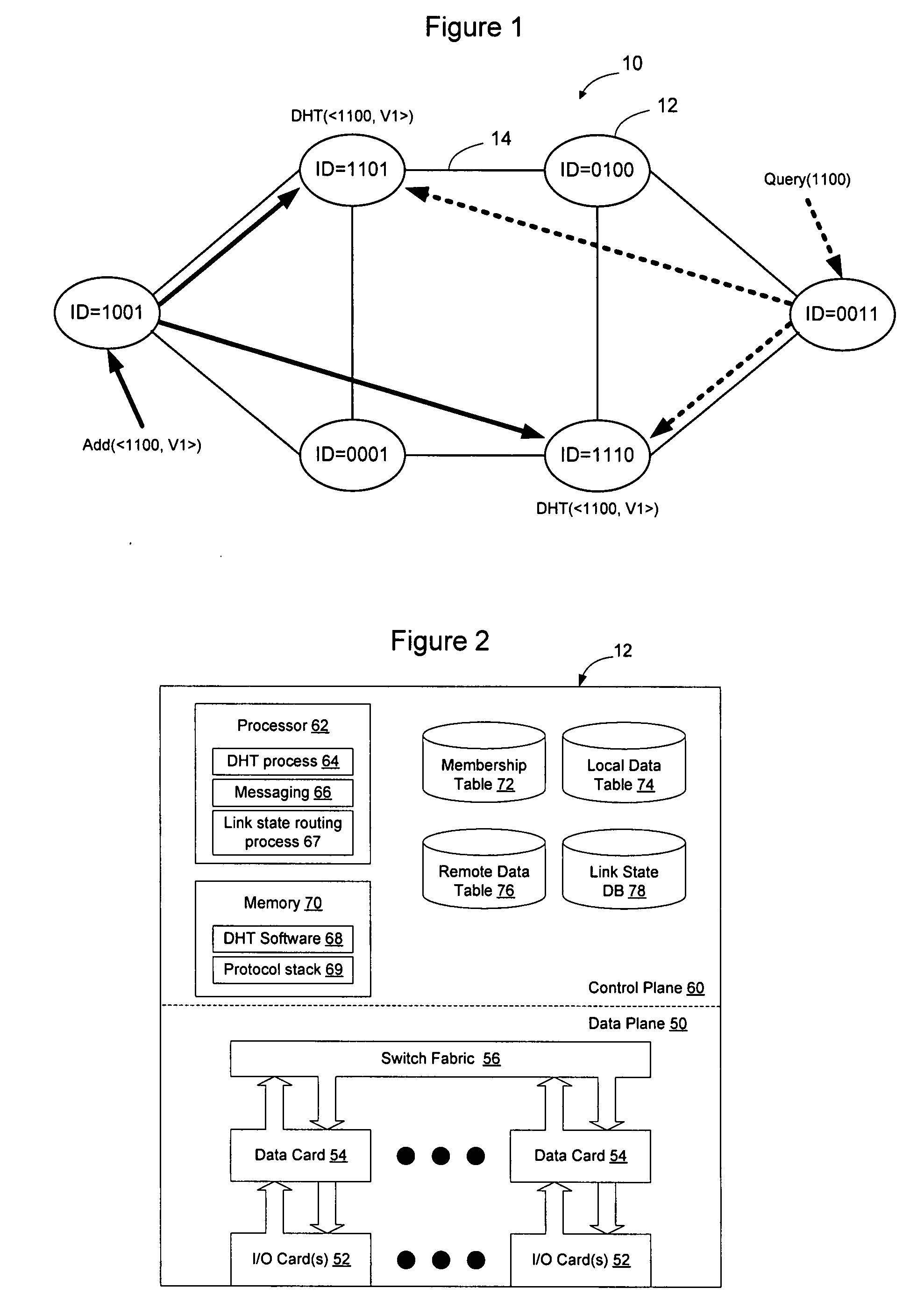
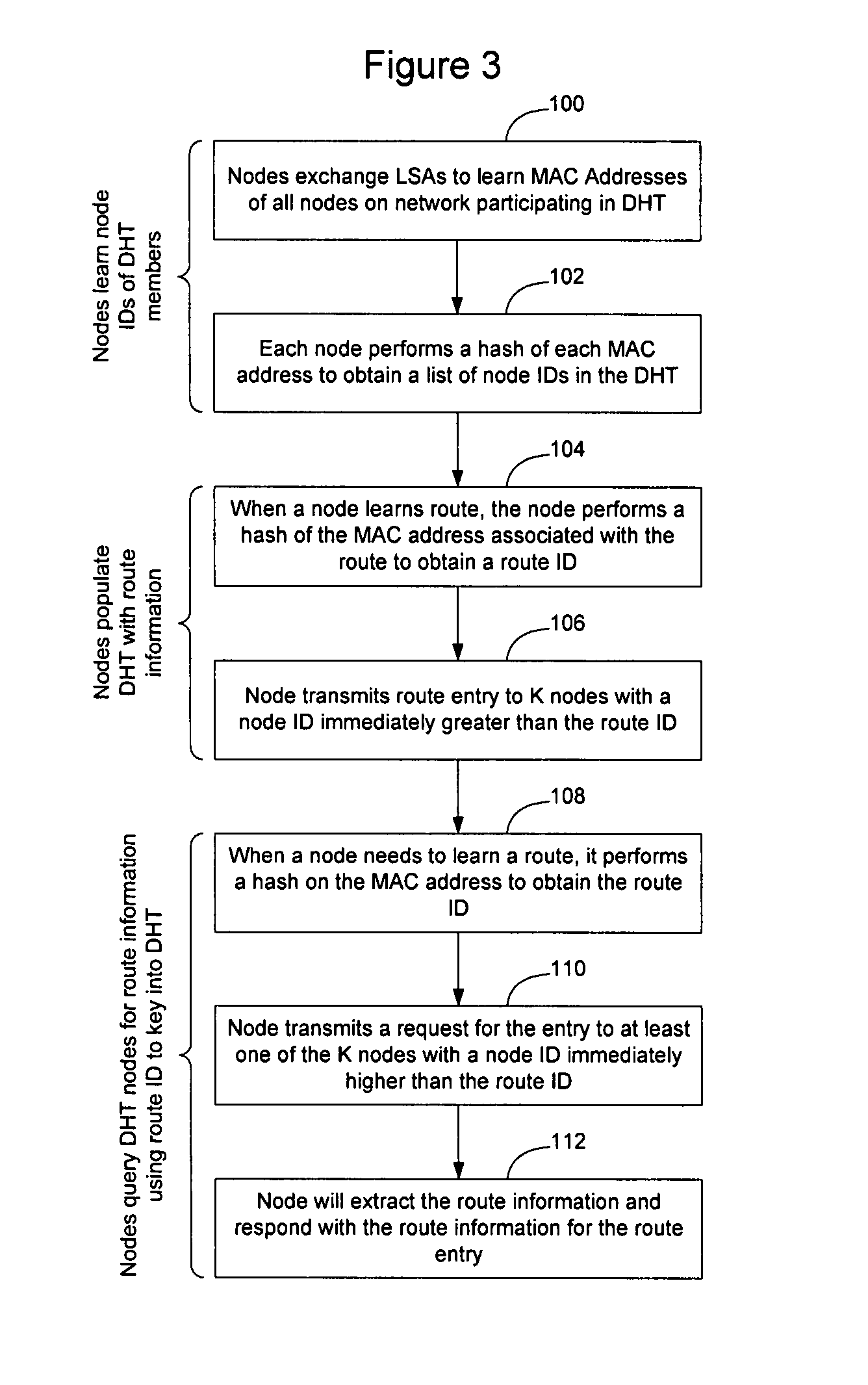
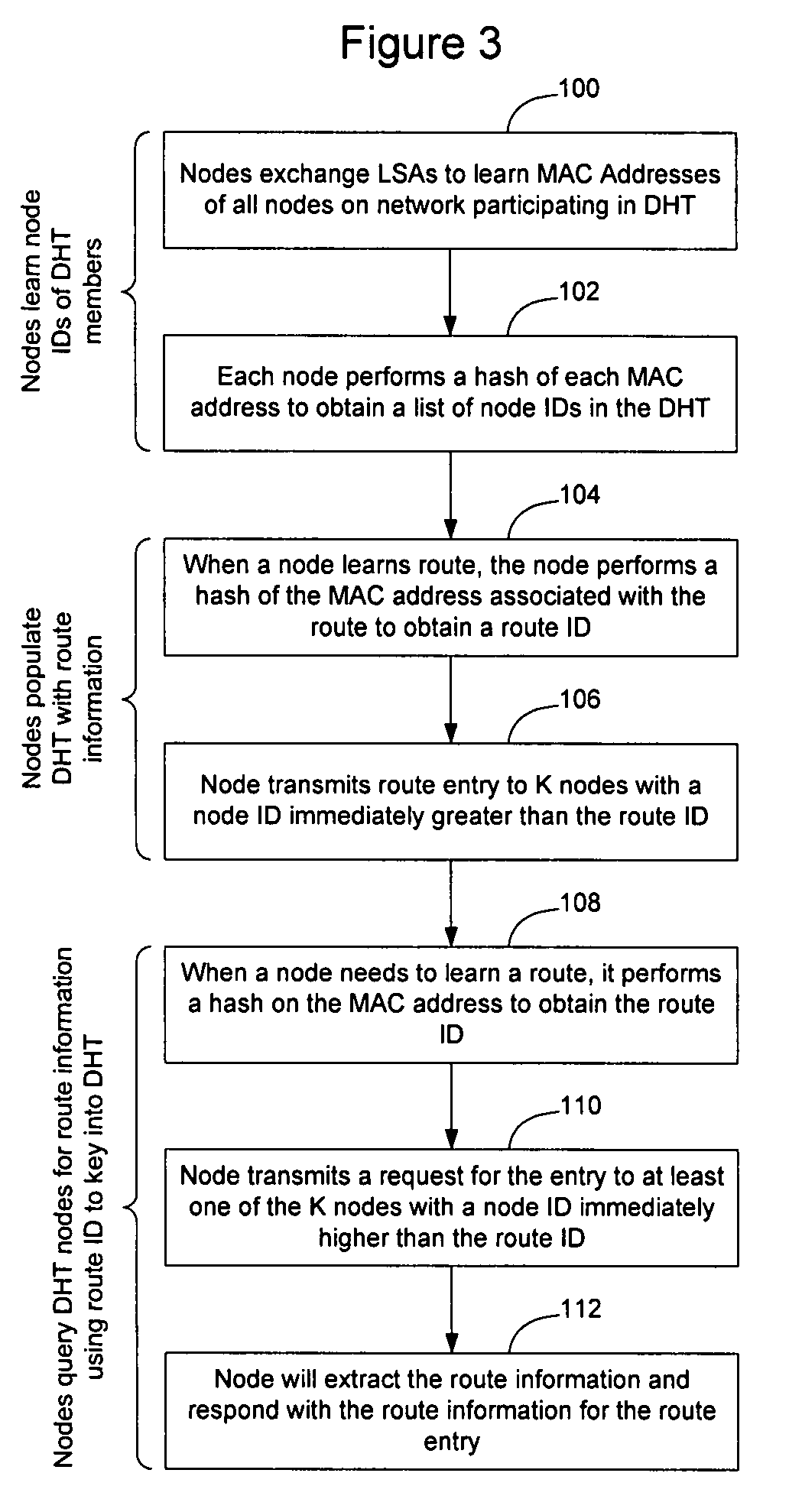
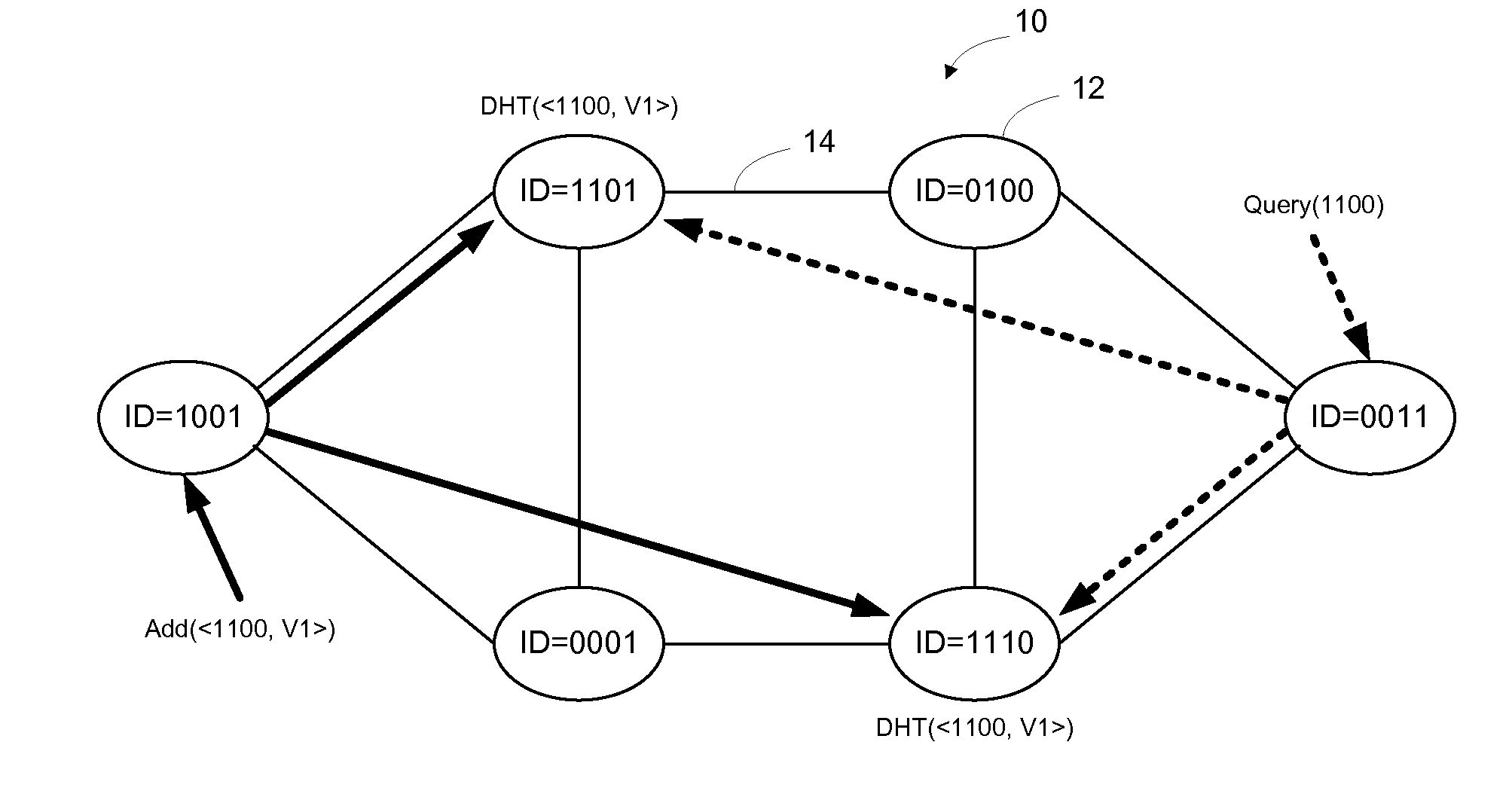
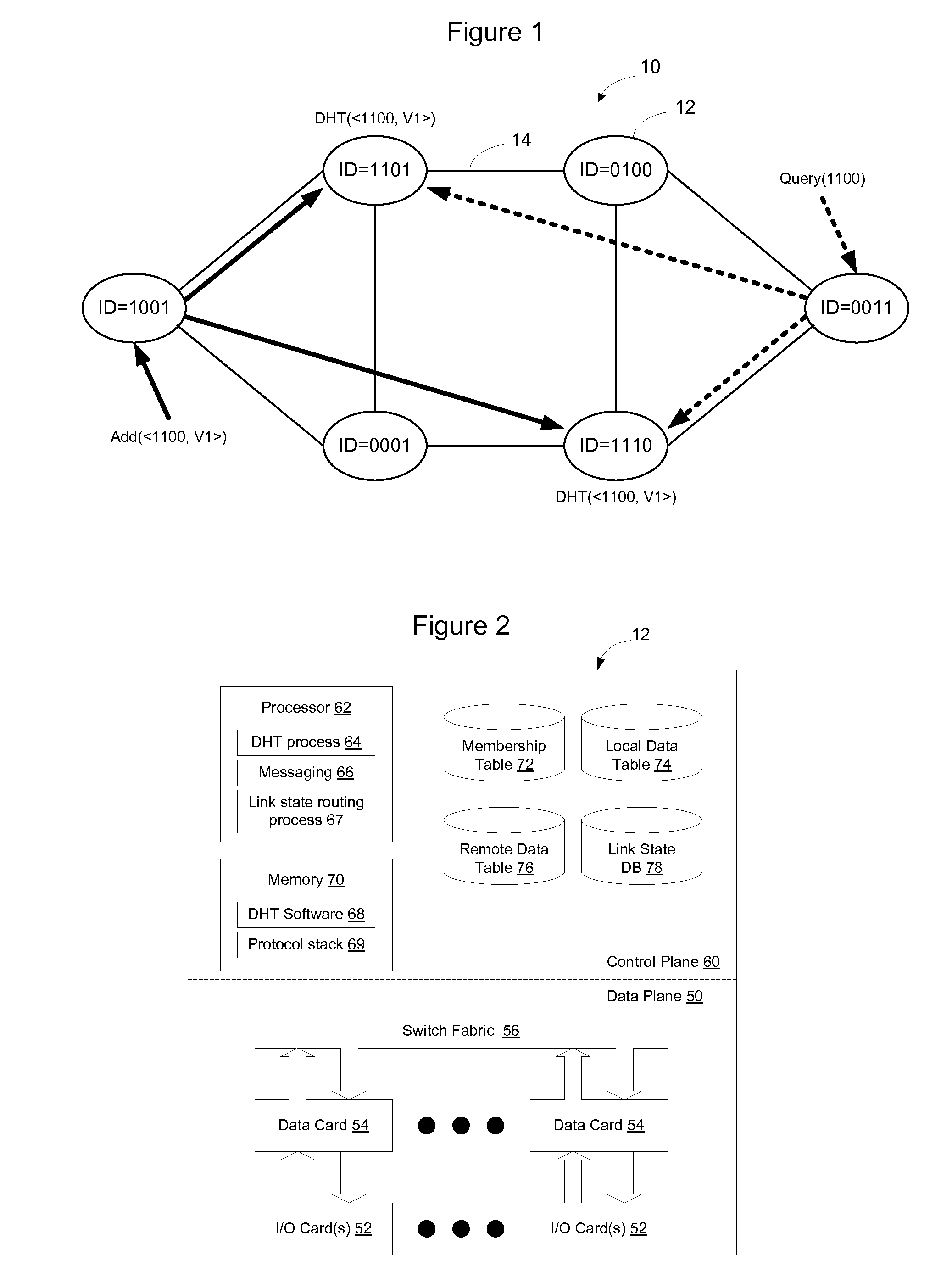
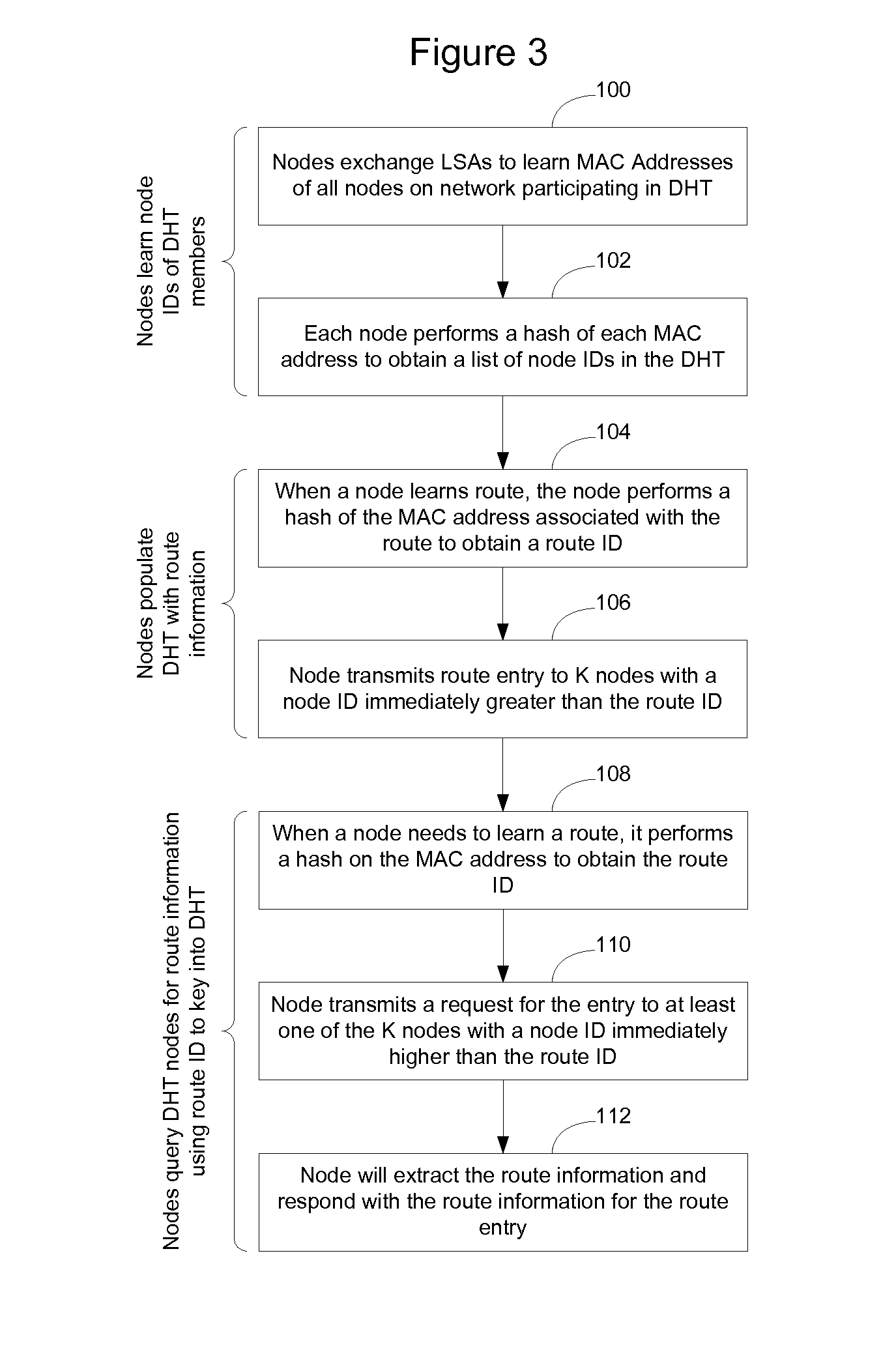
Distributed storage of routing information in a link state protocol controlled network
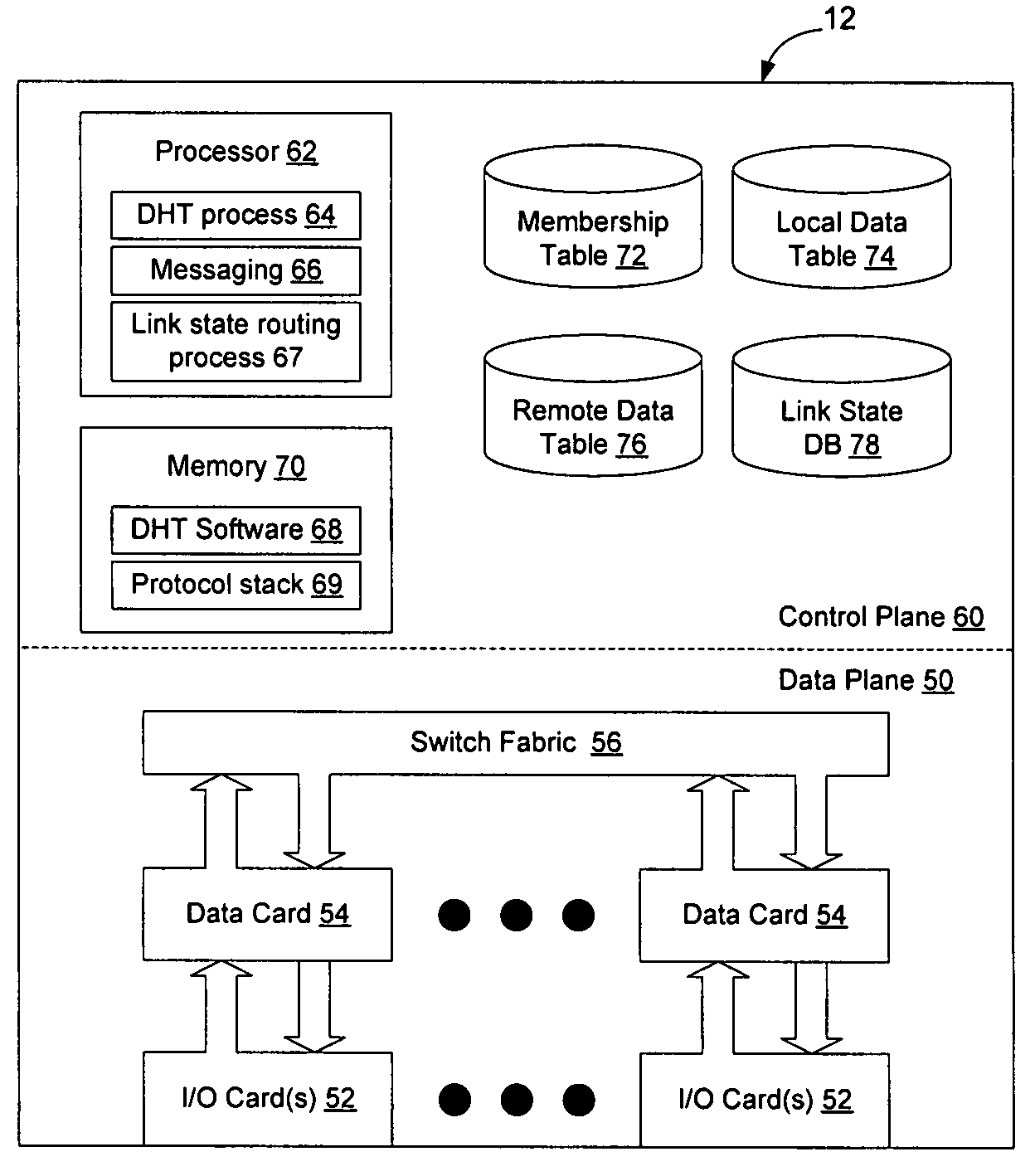
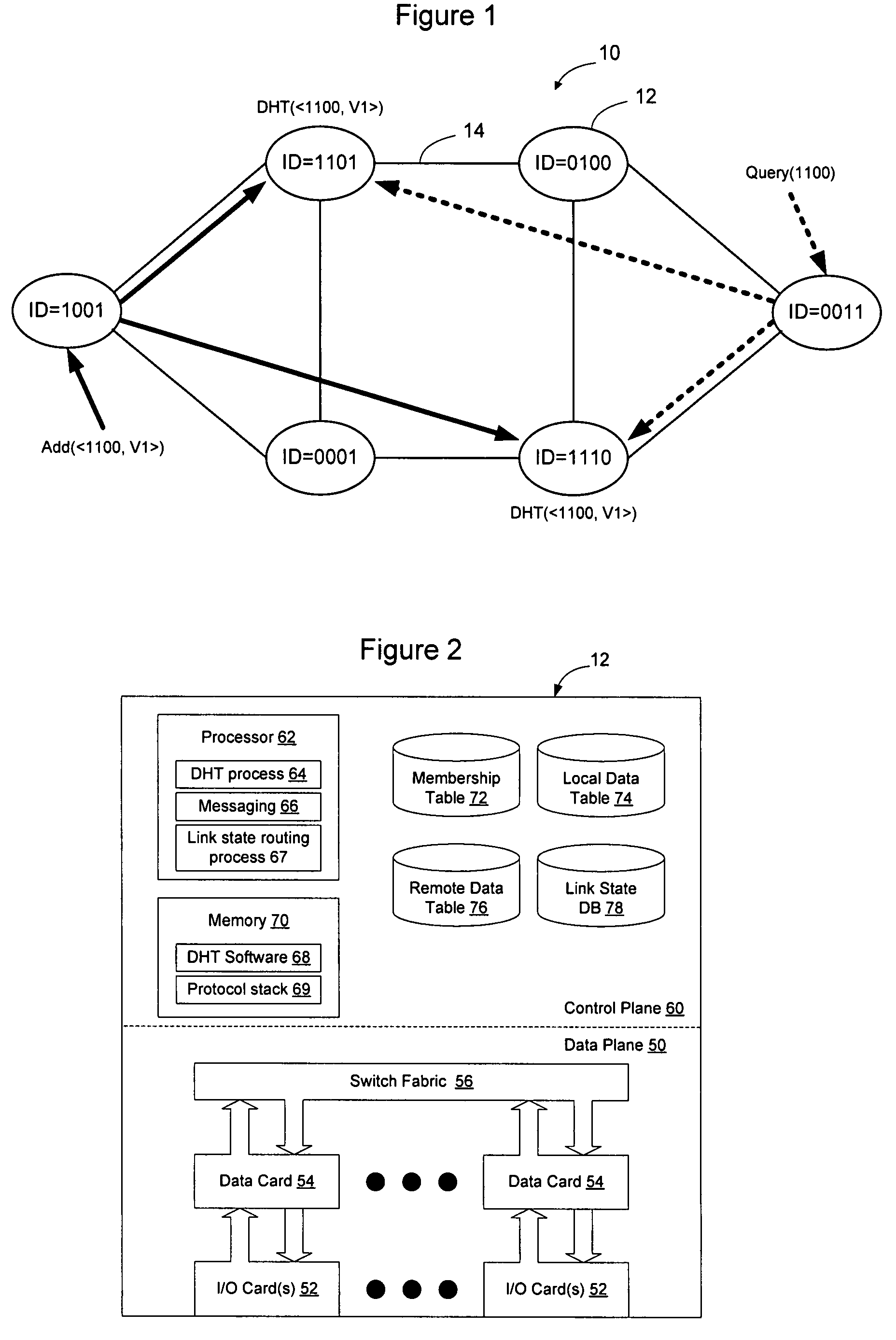
A distributed hash table is implemented to store routing information on a network. Node IDs exchanged in connection with implementation of a link state routing protocol are used as keys in the distributed hash table, and routes are stored at one or more nodes on the network. When a route is learned, the route is processed against the set of keys to determine which nodes should store the route. When a route is needed, the route is processed against the set of keys to determine which nodes should have the route information. The manner in which the route is processed against the set of keys is the same in both instances, so that the DHT may be used to store and retrieve route information on the network. The DHT may be implemented to store MAC addresses, IP addresses, MPLS labels, or other information of interest to enable routes to be stored and learned by network elements on the network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
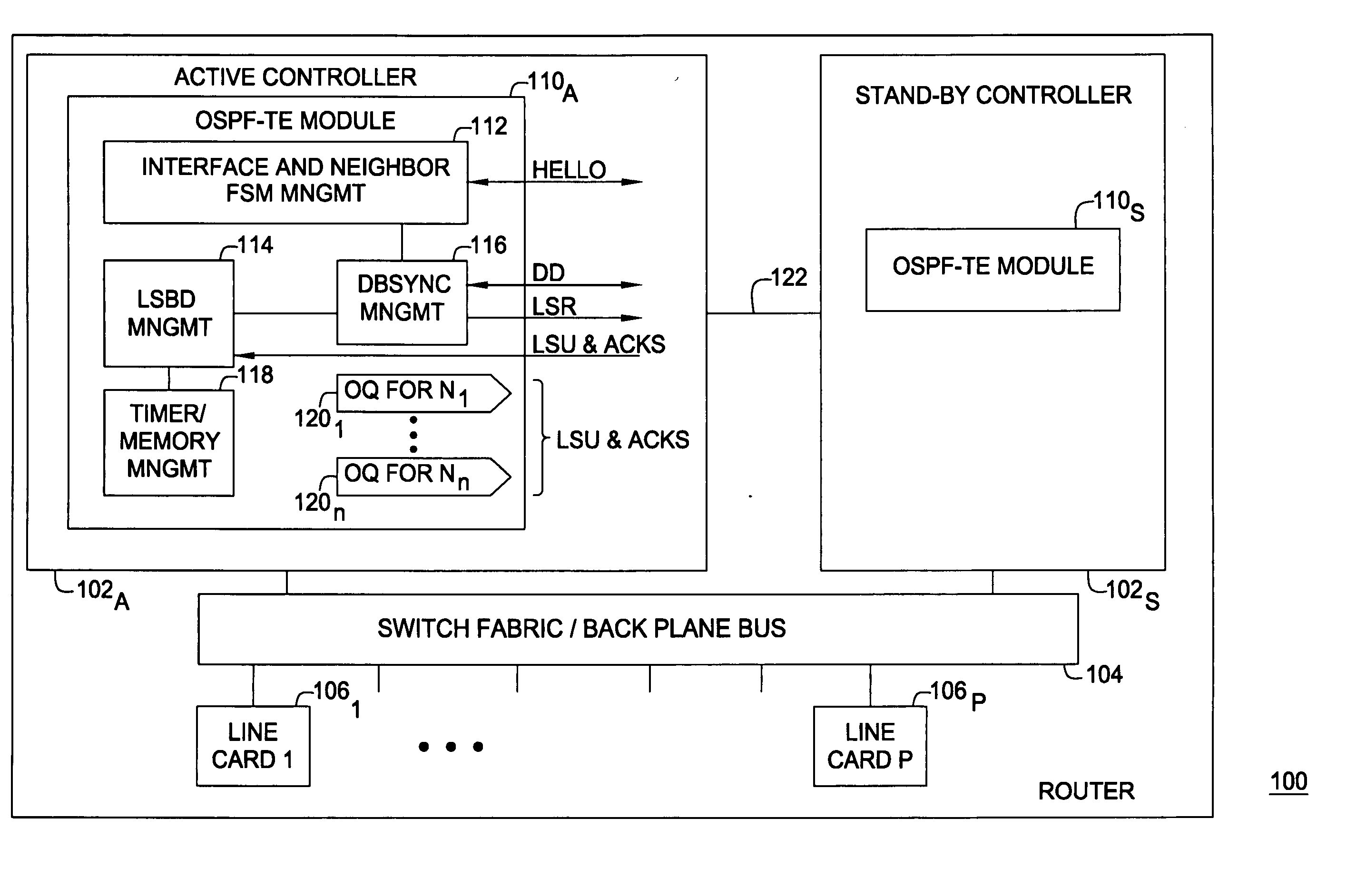
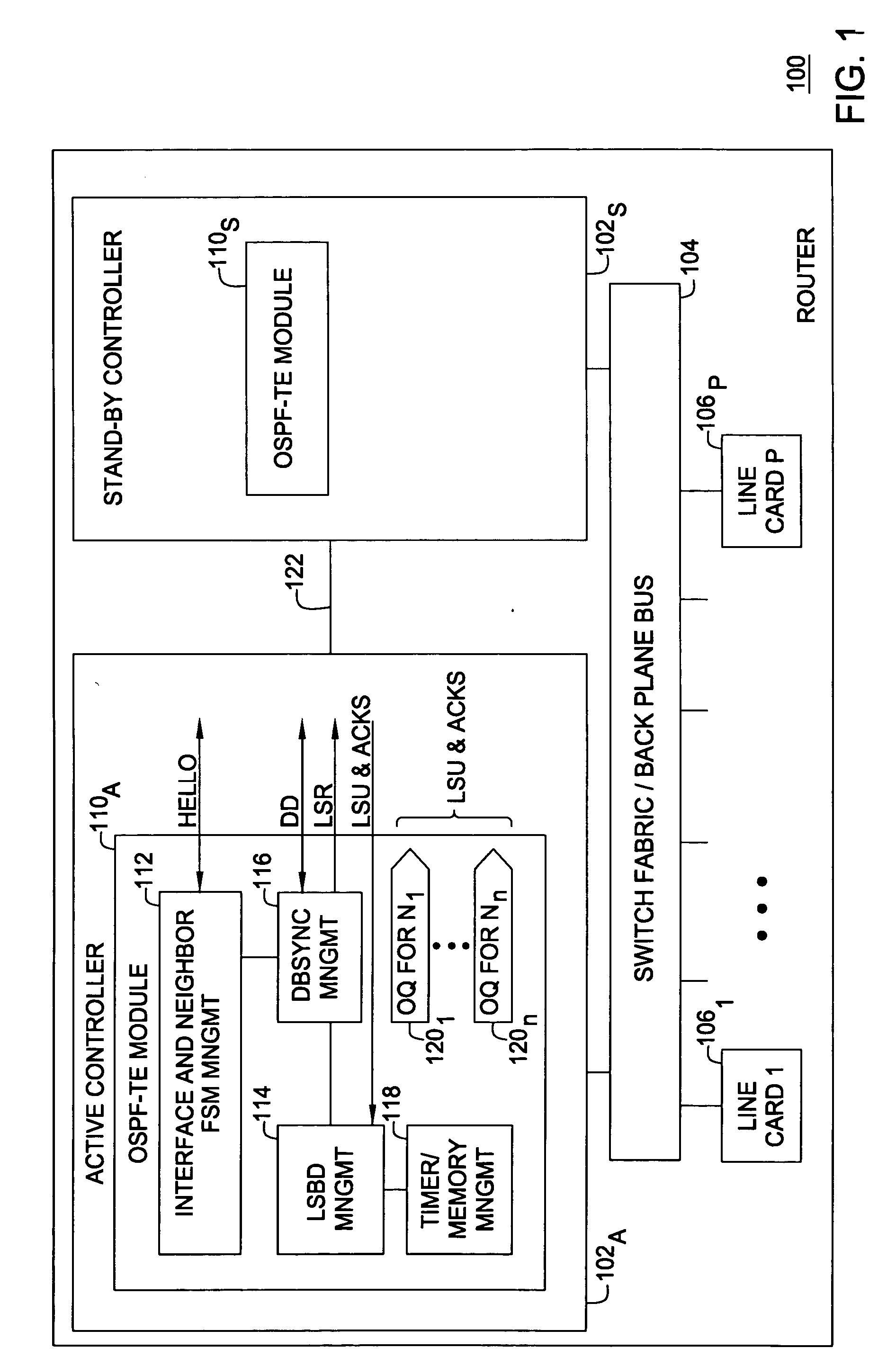
Network transparent OSPF-TE failover
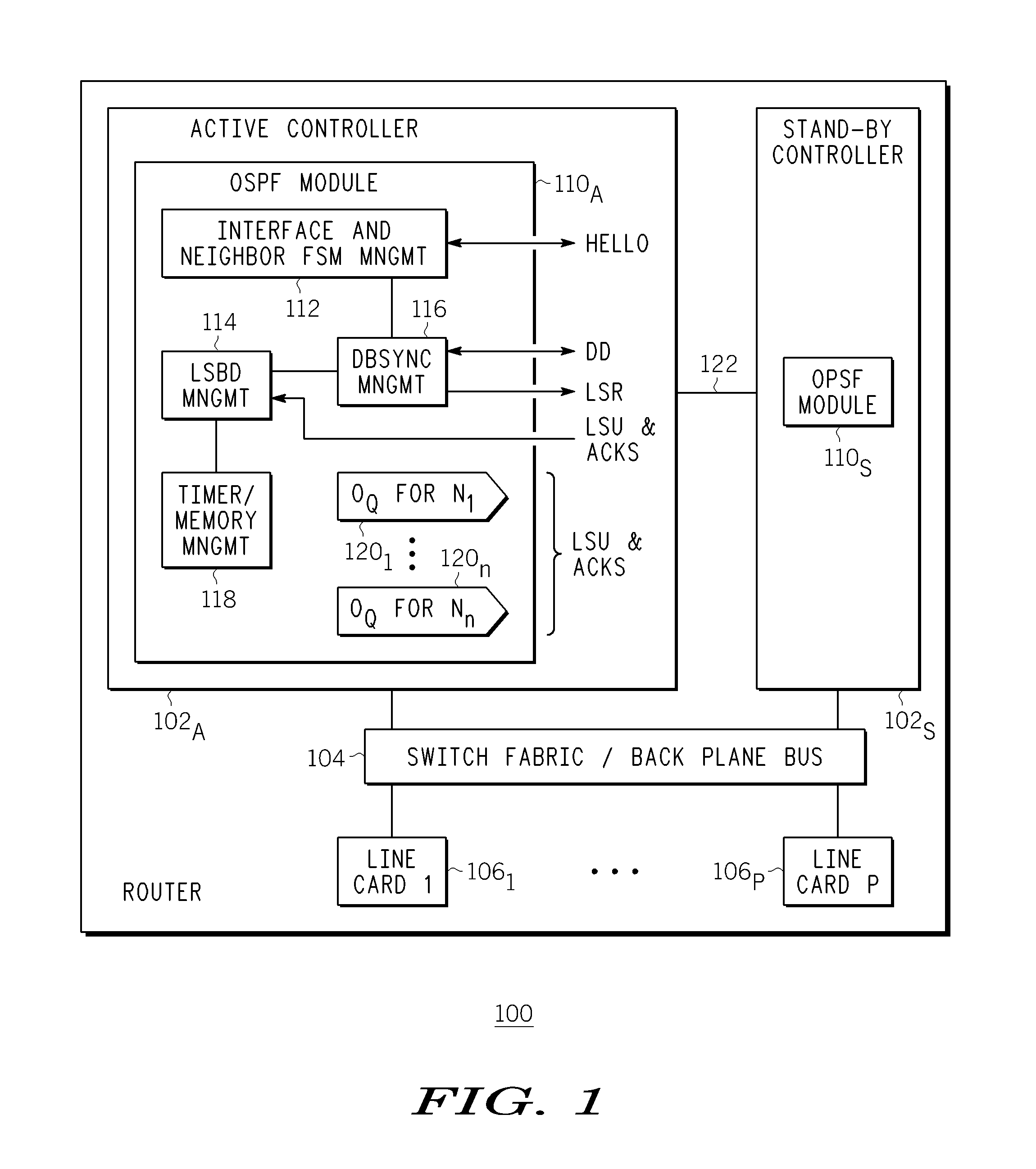
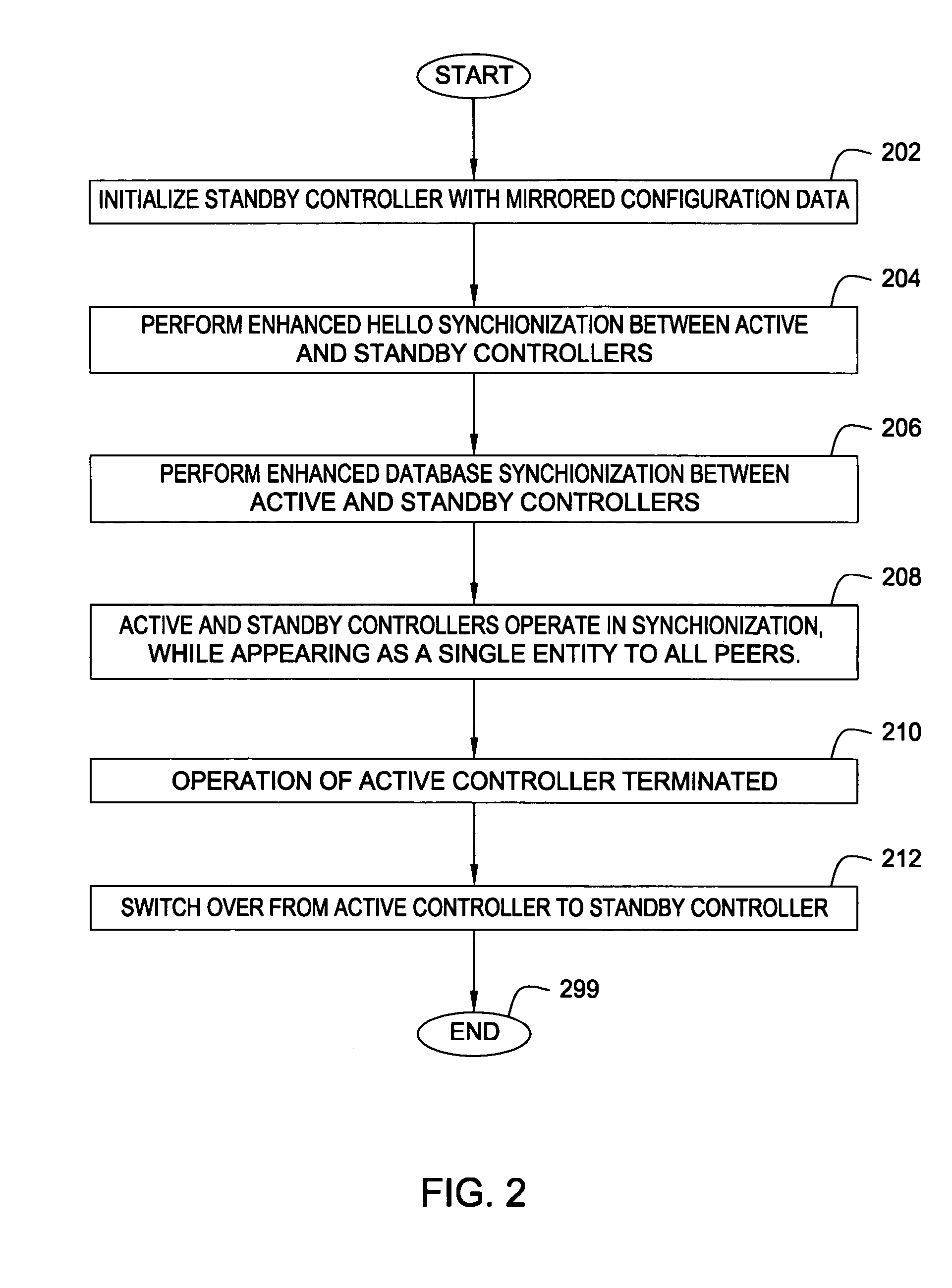
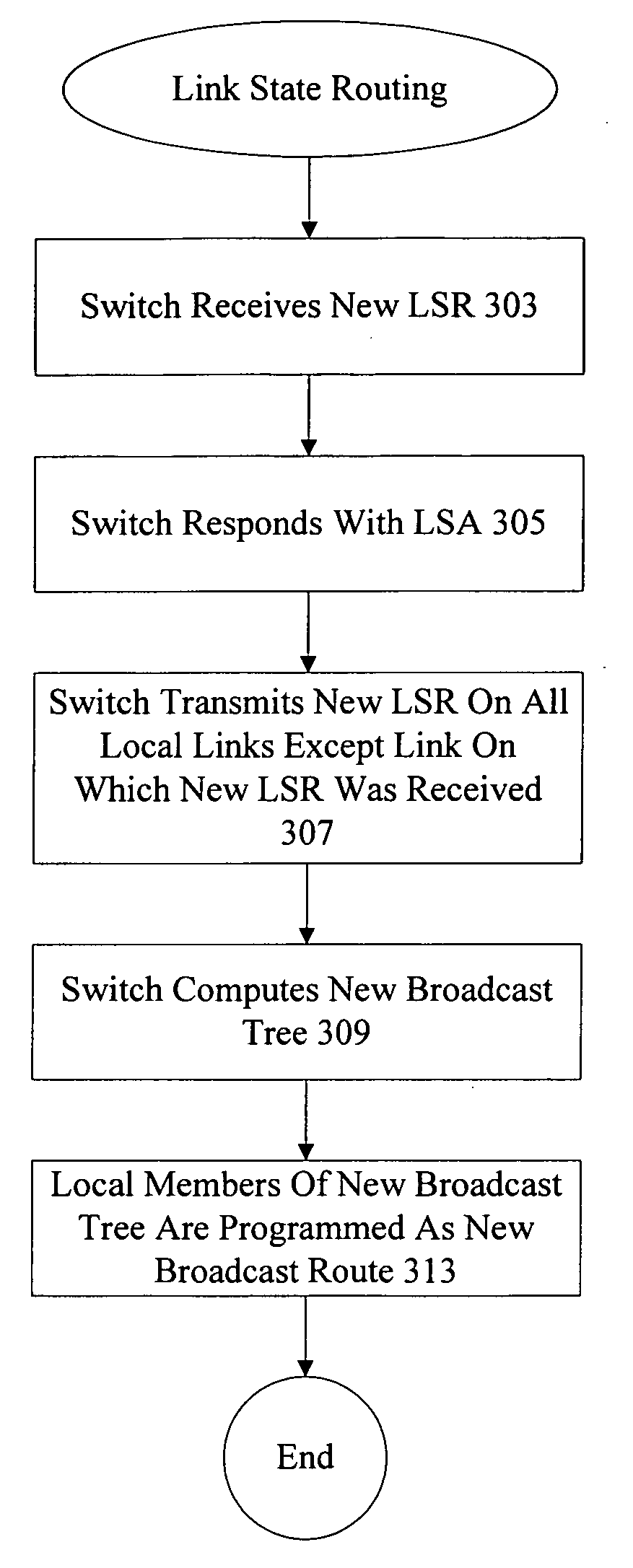
ActiveUS20060215547A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFailoverData synchronization
A method and apparatus for providing link state routing protocol redundancy in a router. A router includes an active controller and at least one standby controller. An internal adjacency relationship is established between the active controller and the standby controller to enable automatic switchover upon disablement of said active controller. The adjacency relationship is established by mirroring configuration data on a standby controller from an active controller, synchronizing Hello information between the active and standby controllers, and synchronizing database information between the active and standby controllers.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and apparatus for performing a graceful restart in a NSF-capable router without enhancing link state routing protocols
InactiveUS7804770B2Error preventionTransmission systemsOptimized Link State Routing ProtocolLink-state routing protocol
A graceful restart is provided in a NSF capable router. When a switchover to a standby controller is required, the standby controller receives replicated link state message headers from an active controller. The standby controller generates a link state request (LSR) message from the link state message headers and transmits the LSRs to neighboring routers. The standby controller receives a link state update that includes the link state messages. By using the LSRs, the standby controller can be quickly synchronized with its neighbors well within the grace period, thereby maintaining adjacency.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Multicast implementation in a link state protocol controlled ethernet network
InactiveUS20110032936A1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationIP multicastReliable multicast
Forwarding state may be installed for sparse multicast trees in a link state protocol controlled Ethernet network by enabling intermediate nodes to install state for one or more physical multicast trees, each of which may have multiple logical multicast trees mapped to it. By mapping multiple logical multicasts to a particular physical multicast, and installing state for the physical multicast, fewer FIB entries are required to implement the multiple multicasts to reduce the amount of forwarding state in forwarding tables at the intermediate nodes. Mapping may be performed by destination nodes before advertising membership in the physical multicast, or may be performed by the intermediate nodes before installing state when a destination node advertises membership in a logical multicast. Intermediate nodes will install state for the physical multicast tree if they are on a shortest path between a source and at least one destination of one of the logical multicasts that has been mapped to the physical multicast.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Distributed storage of routing information in a link state protocol controlled network
InactiveUS7684352B2Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationIp addressLink-state routing protocol
A distributed hash table is implemented to store routing information on a network. Node IDs exchanged in connection with implementation of a link state routing protocol are used as keys in the distributed hash table, and routes are stored at one or more nodes on the network. When a route is learned, the route is processed against the set of keys to determine which nodes should store the route. When a route is needed, the route is processed against the set of keys to determine which nodes should have the route information. The manner in which the route is processed against the set of keys is the same in both instances, so that the DHT may be used to store and retrieve route information on the network. The DHT may be implemented to store MAC addresses, IP addresses, MPLS labels, or other information of interest to enable routes to be stored and learned by network elements on the network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Preventing transient loops in broadcast/multicast trees during distribution of link state information
ActiveUS20070127396A1Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsTraffic capacityOptimized Link State Routing Protocol
According to the present invention, methods and apparatus are provided to improve the link state routing protocol (LSRP) to prevent transient loops during topology changes. Broadcast and shared multicast traffic may be dropped on particular ports upon detecting link state change until neighboring nodes have computed routes using updated link state information. An acknowledgment is sent upon receiving a link state record. Sync and sync-ack packets are used to determine when link state information is synchronized with that of peer nodes.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for detecting unreliable or compromised router/switches in link state routing
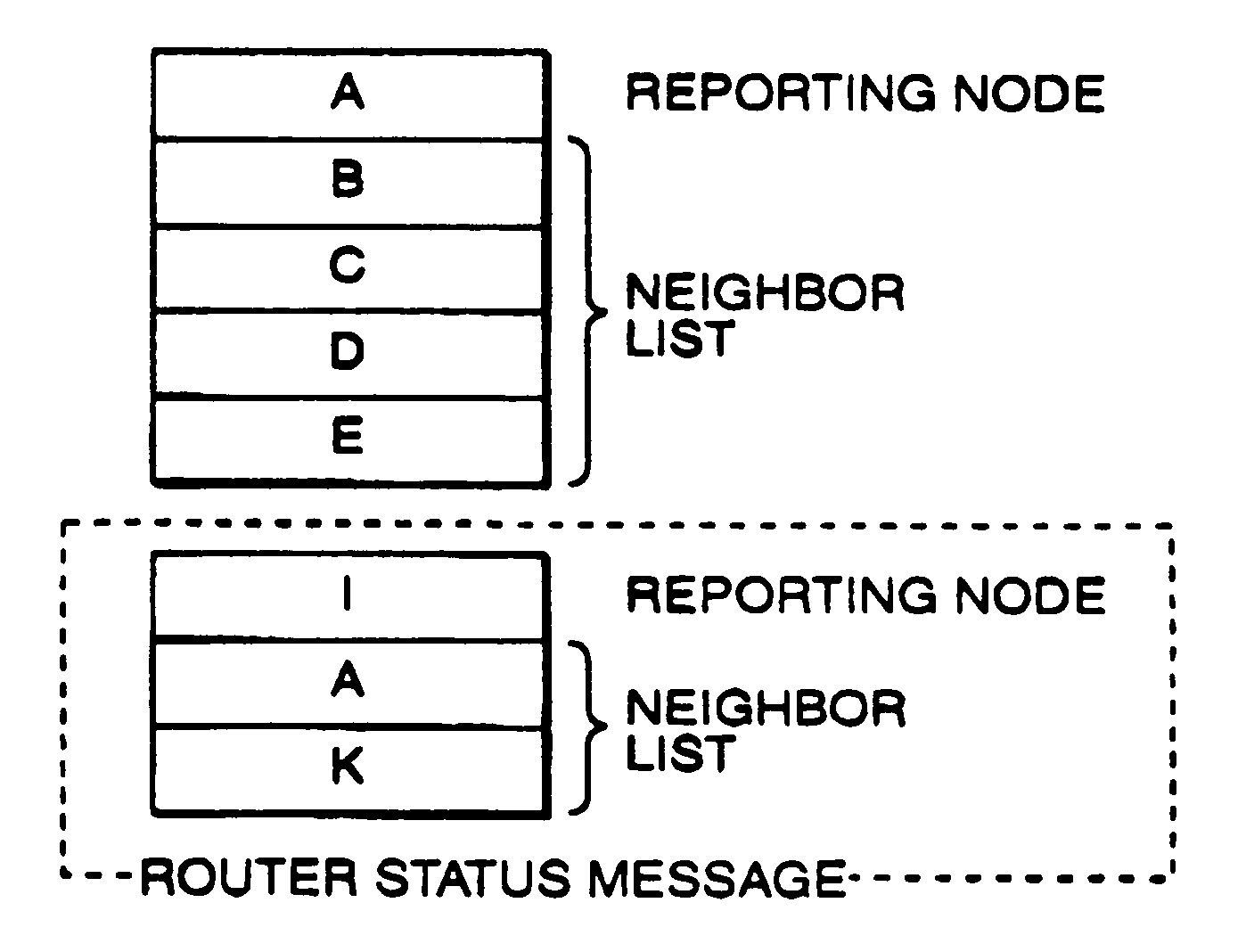
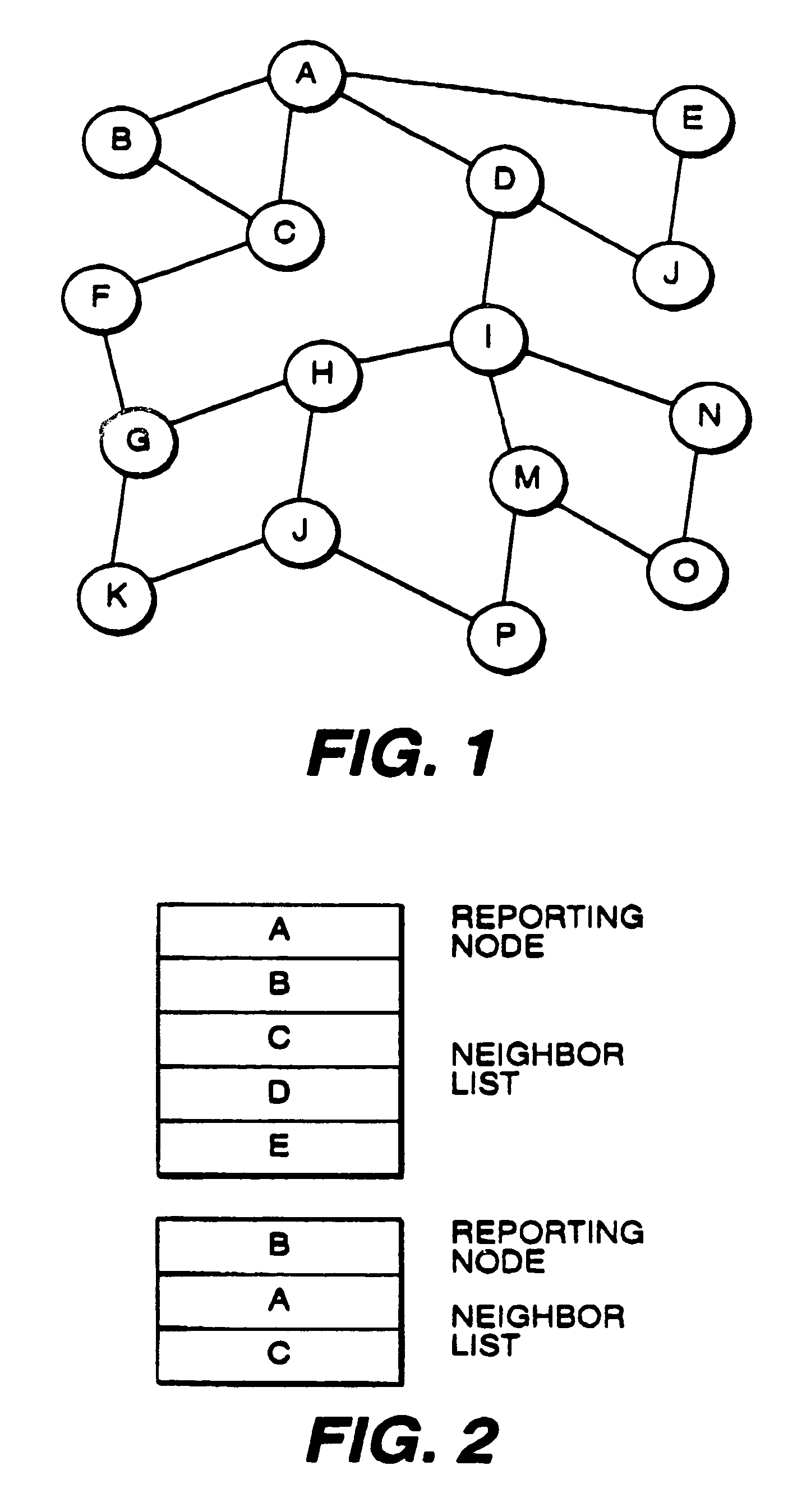
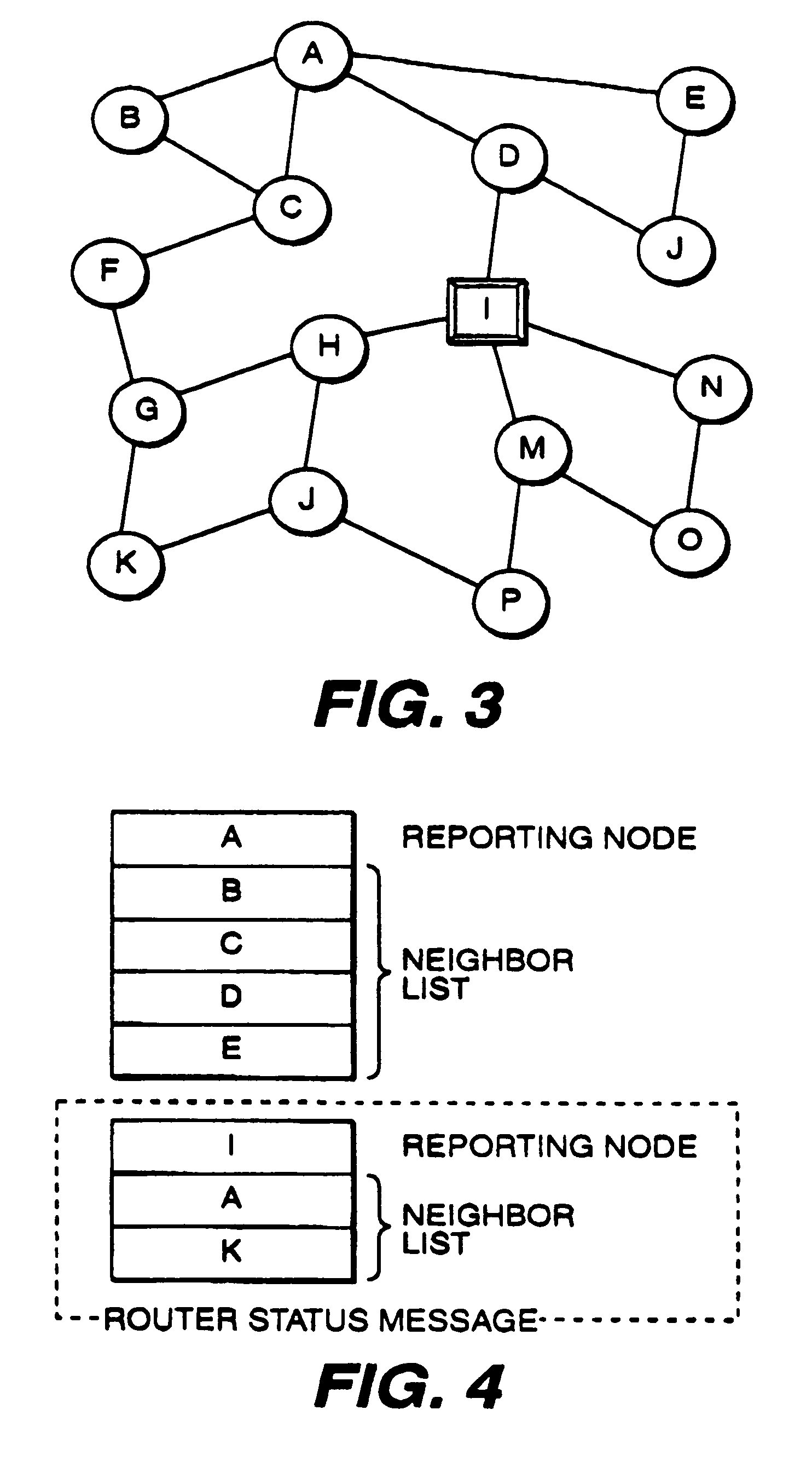
InactiveUS7035223B1Quick identificationError preventionTransmission systemsComputer networkStructure of Management Information
Method and apparatus for detecting whether router status information sent from a first router is unreliable, includes structure and / or steps for storing a router status database. Structure and / or steps are provided for receiving a first signal corresponding to a first router status message sent by the first router, the first router status message containing router status information indicative of the status of communication between the first router and a second router. Further, structure and / or steps are provided for issuing an alarm signal if the signal comparison reveals that the first and second router status messages contain non-complementary router status information. Such information can be flooded through the network to isolate the unreliable / compromised router.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
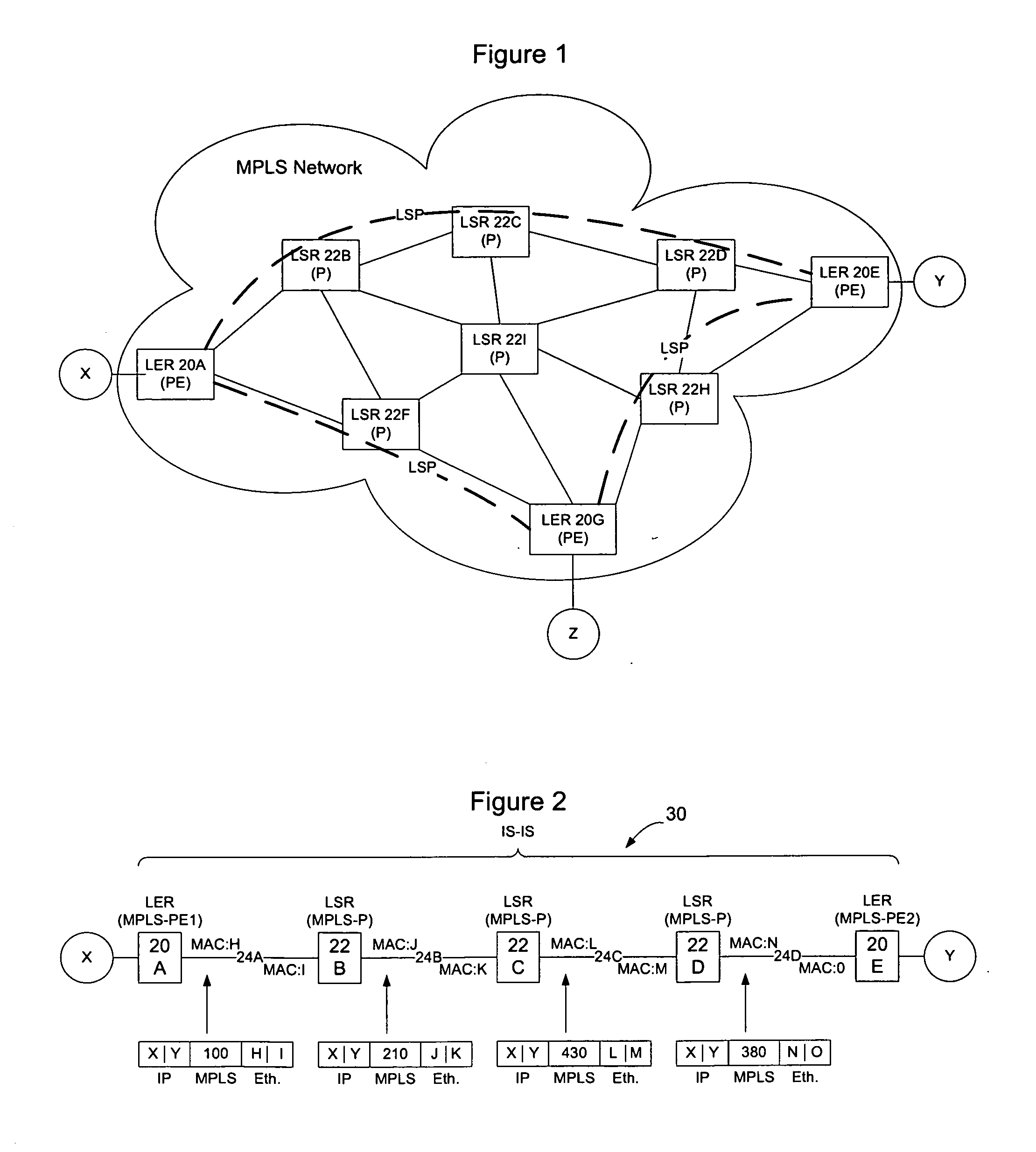
MPLS P node replacement using a link state protocol controlled ethernet network
When a MPLS Virtual Forwarding Entity (VFE) on a Link State Protocol Controlled Ethernet Network learns a forwarding equivalency class (FEC) to label binding from an attached MPLS-LER, it will determine an associated MAC address for the FEC, and advertise the FEC / label binding along with the MAC address. Nodes in the Ethernet network will install shortest path forwarding state for the MAC to the MPLS-VFE advertising the FEC / label binding. Each MPLS-VFEs on the Ethernet network that receive the advertisement will update its database and generate a label that is distributed to attached MPLS LERs using LDP. When the MPLS-LER needs to transmit traffic to the FEC, it will use the label provided by the MPLS-VFE. The MPLS-VFE maintains a mapping between the label and the MAC address so that it may use the MAC address to forward the packet across the Ethernet network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
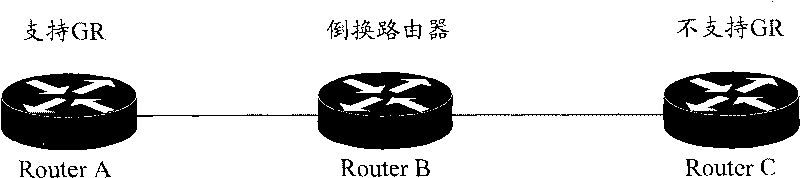
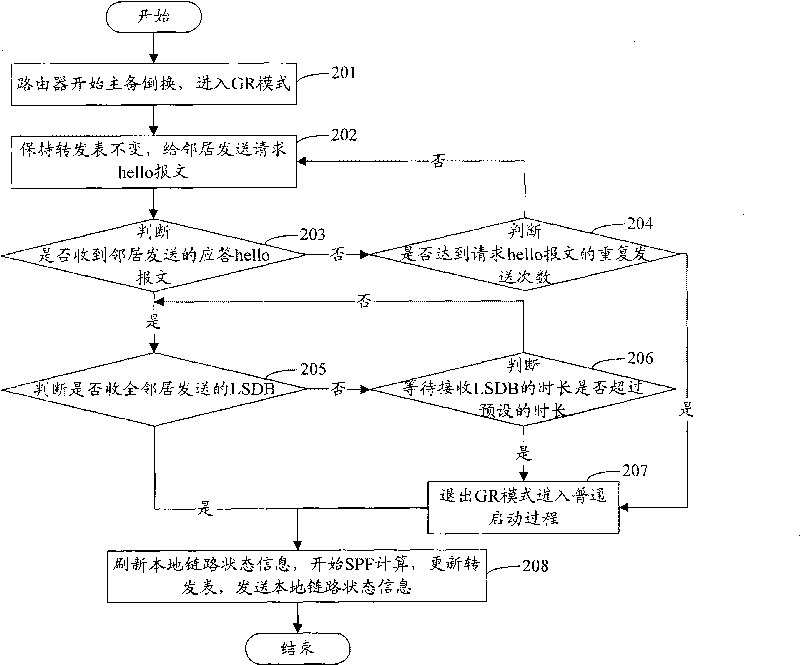
Method and device for realizing graceful restart of link state routing protocol
InactiveCN101741738AImprove stabilityImprove performanceData switching networksOptimized Link State Routing ProtocolCurrent neighbor
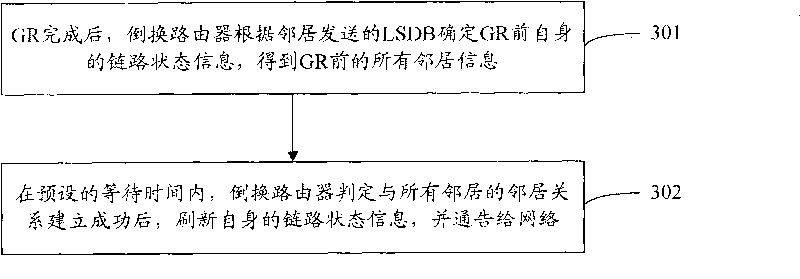
The invention discloses a method for realizing graceful restart of a link state routing protocol, comprising the following steps: after graceful restart (GR) is completed, a switching router determines current self link state information of GR according to link state data base (LSDB) transmitted by a neighbor supporting GR function and obtains all current neighbor information of the GR; the neighbors comprise neighbors supporting GR function and neighbors not supporting GR function; in preset waiting time, the switching router judges the neighbourhoods of all neighbors are successfully established, refreshes self link state information and informs the network; the invention also provides a device for realizing graceful restart of a link state routing protocol; with the device and method of the invention adopted, routing oscillation can be resolved in the application environment where the switching router is in coexistence with a part of neighboring routers not supporting GR function.
Owner:ZTE CORP
System and method for communicating over mesh networks using waveform-enhanced, link-state routing
ActiveUS8213409B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexTelecommunications linkCommunications system
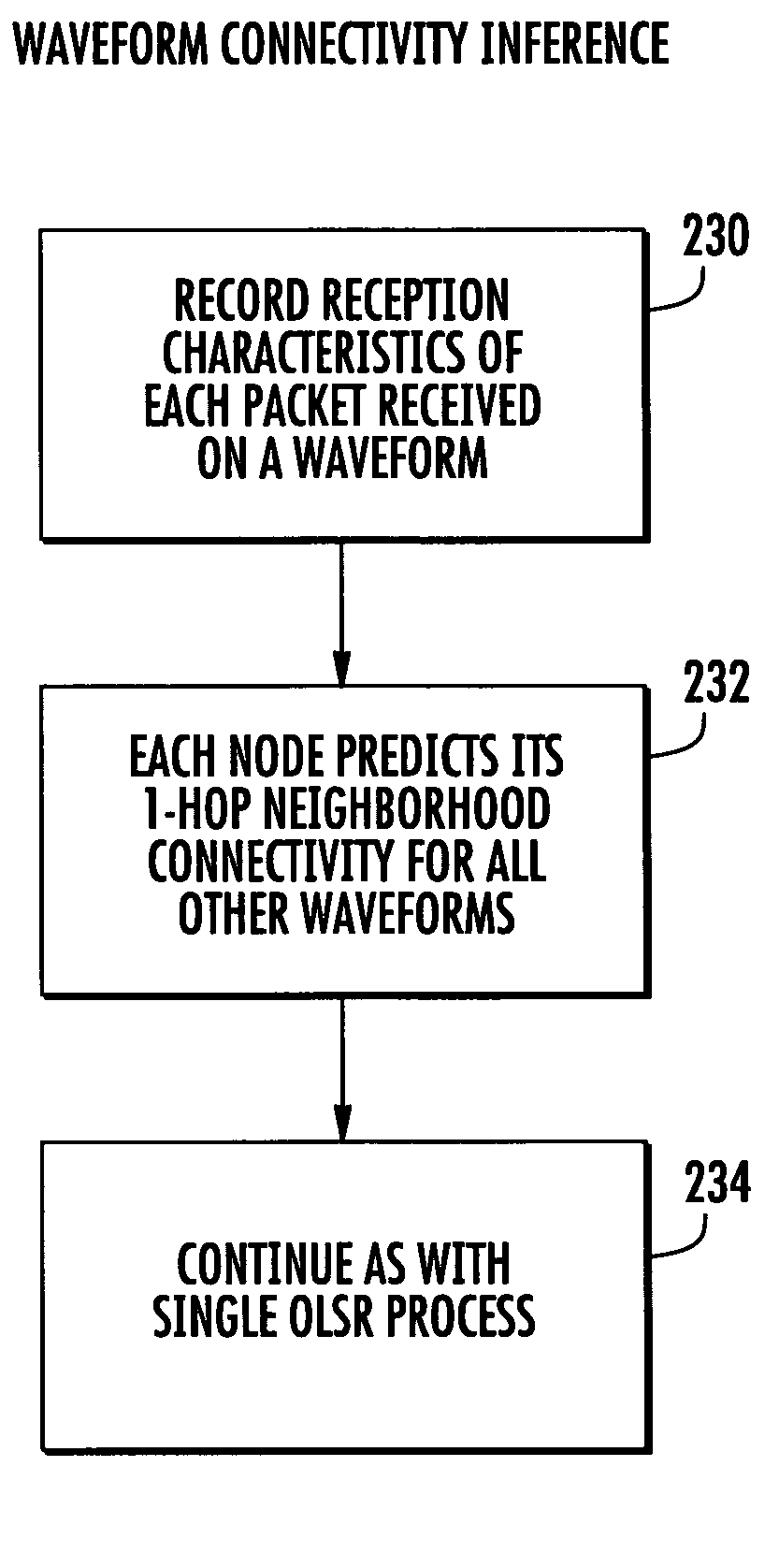
A communication system includes a plurality of mobile nodes forming a mesh network. A plurality of wireless communication links connect the mobile nodes together. Each mobile node is formed as a communications device and operative for transmitting data packets wirelessly to other mobile nodes via the wireless communications link from a source mobile node through intermediate neighboring mobile nodes to a destination mobile node using a link state routing protocol and multiple waveforms.
Owner:STINGRAY IP SOLUTIONS LLC
Preventing transient loops in broadcast/multicast trees during distribution of link state information
InactiveUS20070127395A1Data switching by path configurationOptimized Link State Routing ProtocolTraffic capacity
According to the present invention, methods and apparatus are provided to improve the link state routing protocol (LSRP) to prevent transient loops during topology changes. Broadcast and shared multicast traffic is dropped upon detecting link state change until neighboring nodes have computed routes using updated link state information. An acknowledgment for a link state record is sent only after route computation is complete using updated link state information.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Technique for efficiently avoiding transient routing disturbances in link state routing protocols with link state packet fragmentation
InactiveUS20070286091A1Effective avoidanceAccurate updateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLink state packetRouting protocol
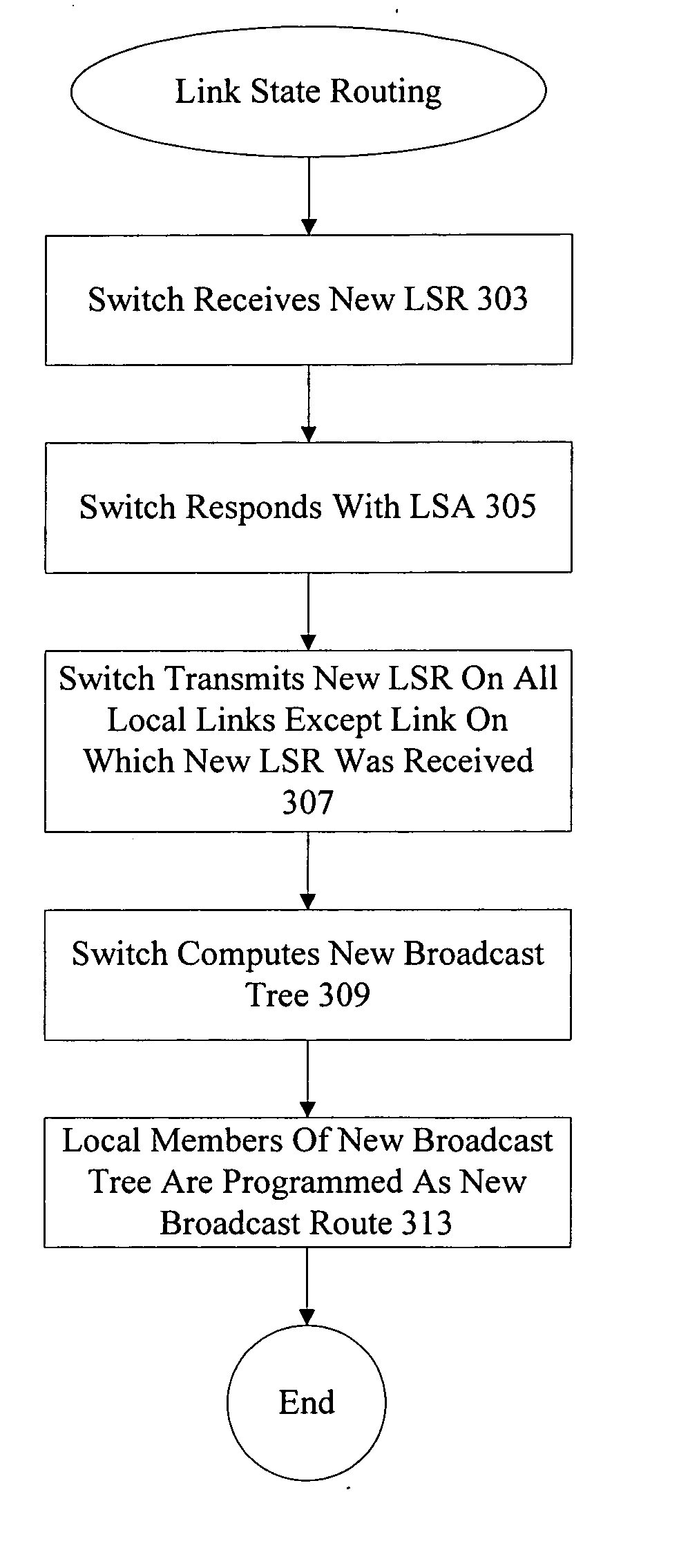
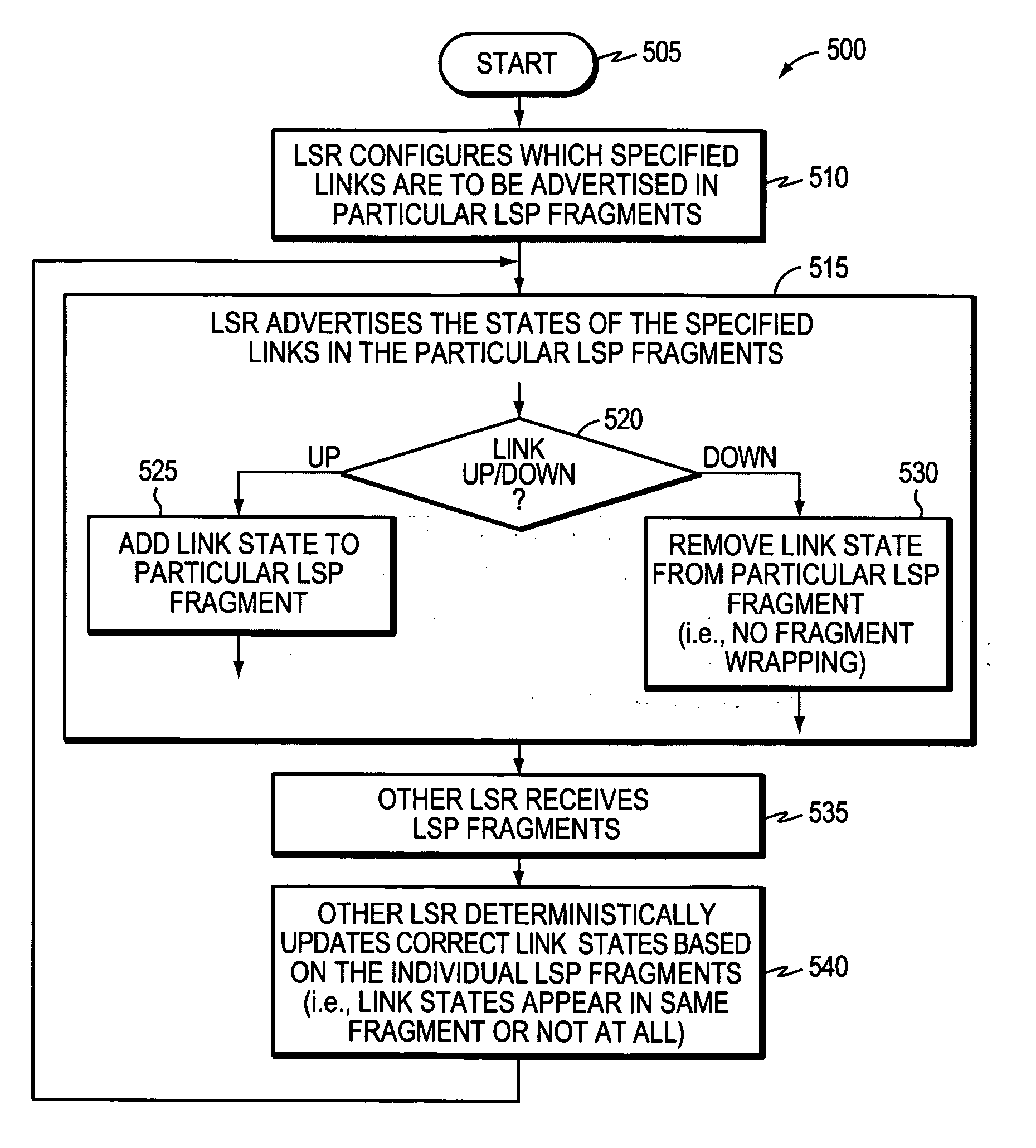
A technique efficiently avoids transient routing disturbances in link state routing protocols with fragmented link state packets (LSPs) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a link state router (LSR) specifies which of two or more links are to be advertised in each of two or more corresponding LSP fragments. The LSR advertises the states of the specified links in the corresponding LSP fragments to one or more other LSRs. In other words, each link of the LSR is assigned to a particular LSP fragment, and the state of the link is always to be advertised in that particular LSP fragment (i.e., no fragment wrapping). Upon receiving the LSP fragments, the other LSRs may update the correct link states based on the individual LSP fragments, i.e., without transient routing disturbances caused by fragment wrapping.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Route processing method, routing processor and router
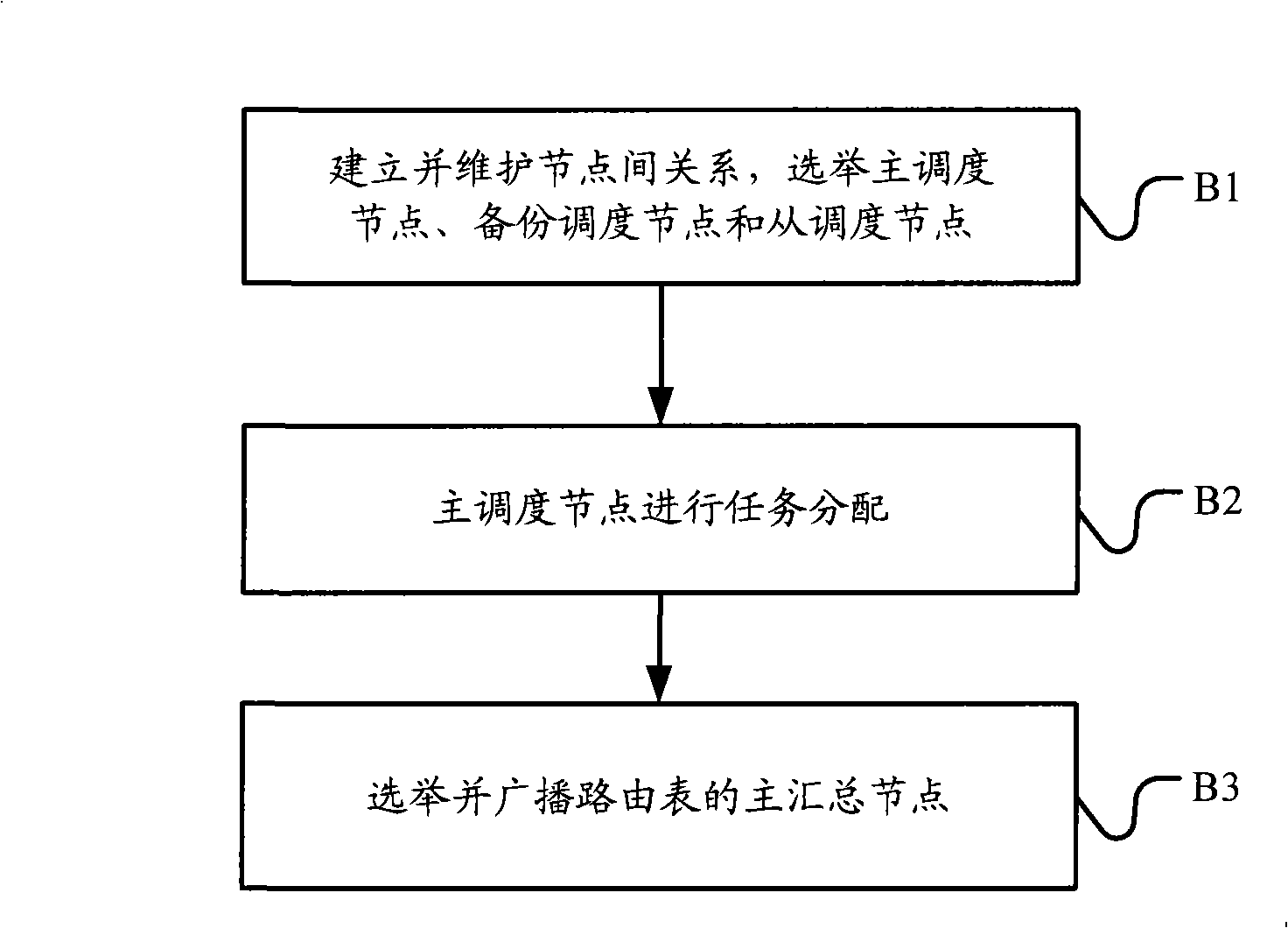
InactiveCN101309201AImprove scalabilityMake full use of resourcesNetworks interconnectionExtensibilityLink-state routing protocol
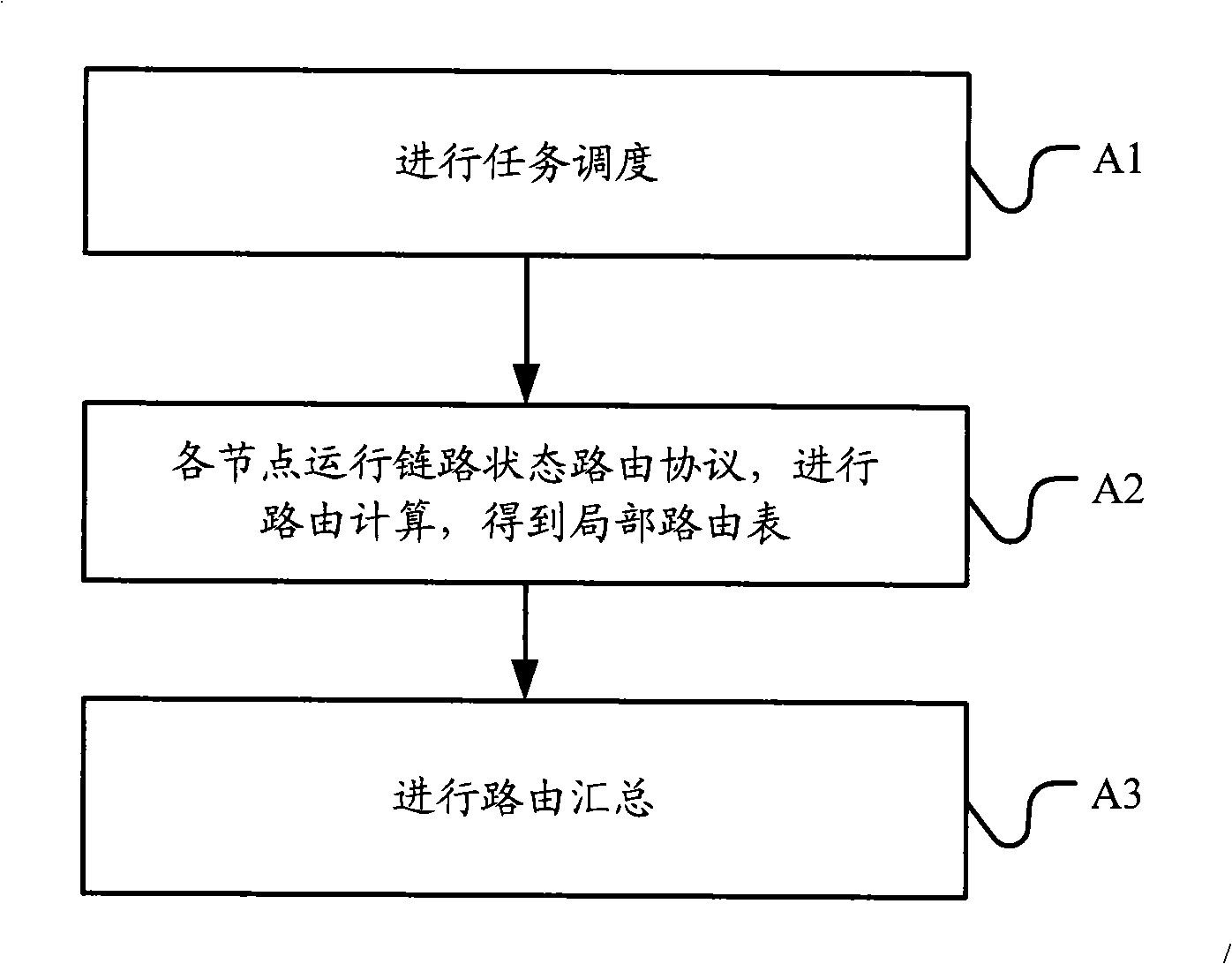
The invention embodiment discloses a route processing method which includes that the connections among the nodes in the network are established; the nodes are processed with task scheduling; the nodes operate the link-state routing protocol, process route computation and obtain the route results according to the scheduled tasks; the route computation results of the nodes are acquired and the route summarization is processed. The invention embodiment also provides a route processor which includes a task scheduling module used for the task scheduling, a protocol operation module used for operating the link-state routing protocol according to the scheduled tasks, computing the routes and obtaining the route computation results and a route summarization module used for summarizing the route computation results. The invention embodiment also provides a router which has multi-route processor frame. The technical proposal provided by the route processing method can realize the extensibility of the link-state routing protocol.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Method and system for topology construction and path identification in a routing domain operated according to a link state routing protocol
ActiveUS7330435B2Simple methodColor television with pulse code modulationError preventionEntry pointRouting domain
A method and system for extracting and building end-to-end route information in a multi-area Internet protocol (IP) autonomous system (AS) operated according to a link state routing protocol such as the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol is disclosed. The method and system enables a user, such as a network administrator, to explicitly identify a full set of paths (links and routers) that a given IP packet would potentially traverse from its entry point in the area of the AS where it originates until its exit point in its intended destination or exit area.
Owner:SONS OF INNOVATION LLC
Distributed Storage of Routing Information In a Link State Protocol Controlled Network
A distributed hash table is implemented to store routing information on a network. Node IDs exchanged in connection with implementation of a link state routing protocol are used as keys in the distributed hash table, and routes are stored at one or more nodes on the network. When a route is learned, the route is processed against the set of keys to determine which nodes should store the route. When a route is needed, the route is processed against the set of keys to determine which nodes should have the route information. The manner in which the route is processed against the set of keys is the same in both instances, so that the DHT may be used to store and retrieve route information on the network. The DHT may be implemented to store MAC addresses, IP addresses, MPLS labels, or other information of interest to enable routes to be stored and learned by network elements on the network.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Implementation of VPNs over a link state protocol controlled ethernet network
Nodes on a link state protocol controlled Ethernet network implement a link state routing protocol such as IS-IS. Nodes assign an IP address or I-SID value per VRF and then advertise the IP addresses or I-SID values in IS-IS LSAs. When a packet is to be forwarded on the VPN, the ingress node identifies the VRF for the packet and performs an IP lookup in customer address space in the VRF to determine the next hop and the IP address or I-SID value of the VRF on the egress node. The ingress node prepends an I-SID or IP header to identify the VRFs and then creates a MAC header to allow the packet to be forwarded to the egress node on the link state protocol controlled Ethernet network. When the packet is received at the egress node, the MAC header is stripped from the packet and the appended I-SID or IP header is used to identify the egress VRF. A customer address space IP lookup is then performed in the identified VRF on the egress node using the information in the client IP header to determine how to forward the packet. Customer reachability information within a VPN may be exchanged between VRFs using iBGP, or directly by using link state protocol LSAs tagged with the relevant I-SID.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com