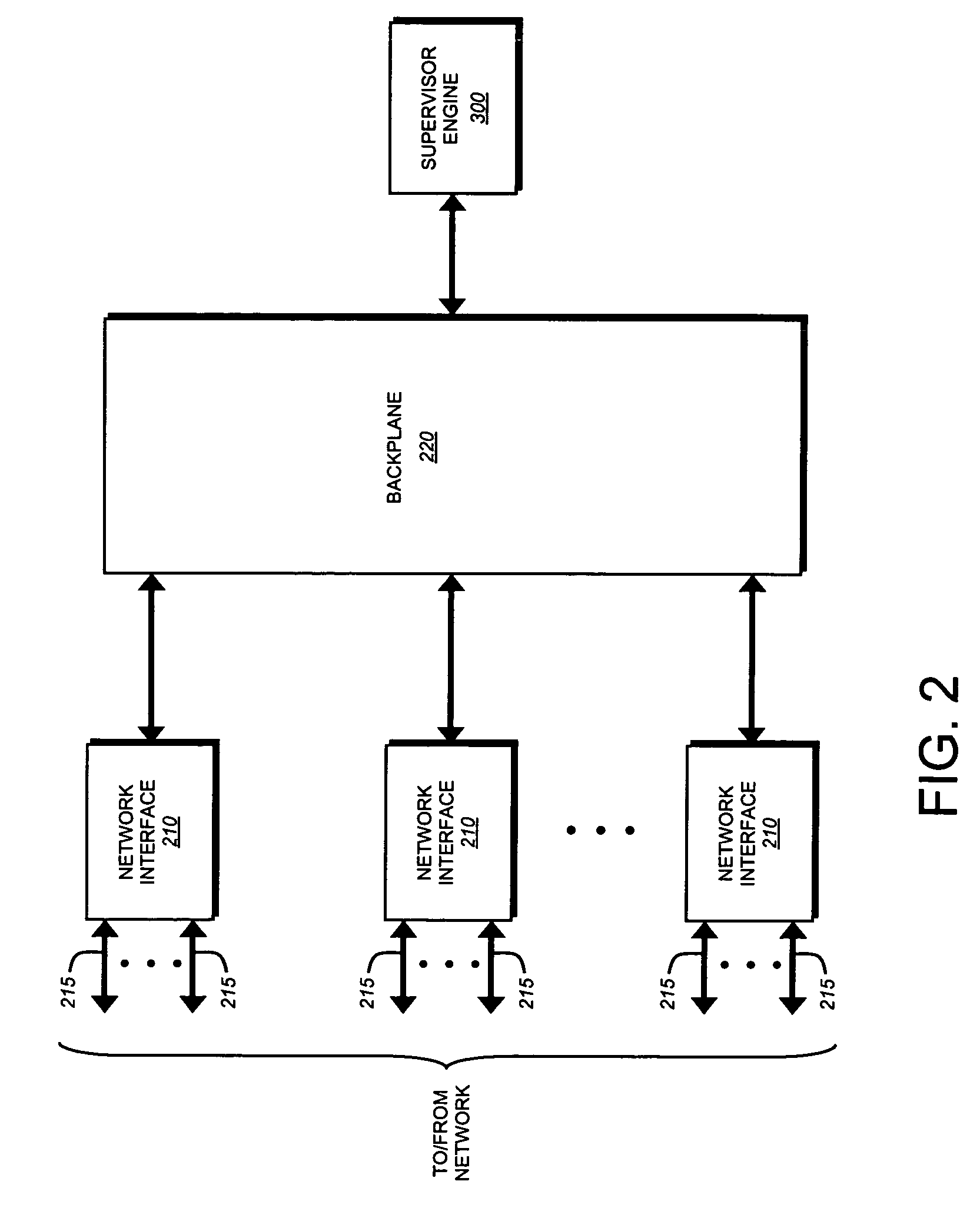
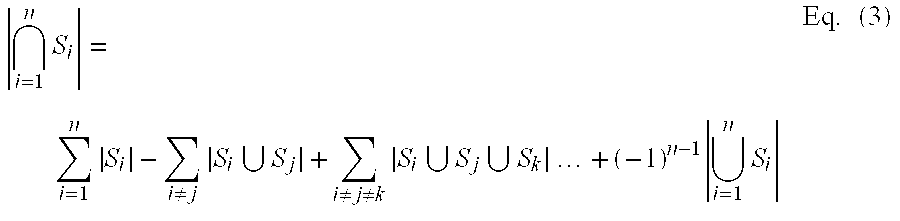Patents
Literature
60 results about "Link state packet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
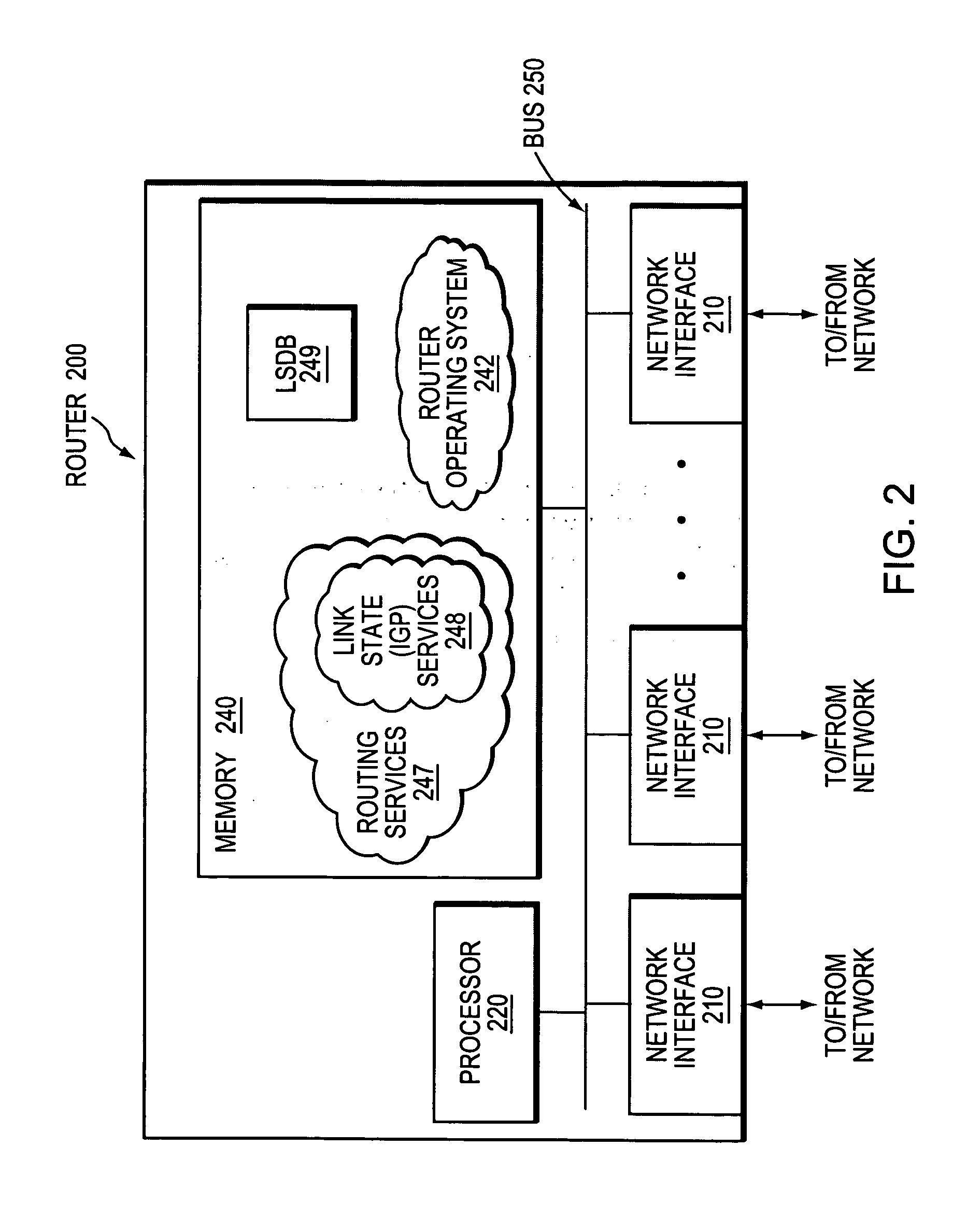
Link State Packet (LSP) is a packet of information generated by a network router in a link state routing protocol that lists the router's neighbors. Link state packet can also be further defined as special datagrams that determine the names of and the cost or distance to any neighboring routers and associated networks. They are used to efficiently determine what the new neighbor is, if a link failure occurs, and the cost of changing a link if the need arises. LSPs are queued for transmission, and must time out at about the same time. They must be acknowledged, and can be distributed throughout the network, but cannot use the routing database.
Methods and apparatus for requesting link state information
InactiveUS7174387B1Error detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer networkComplete sequence
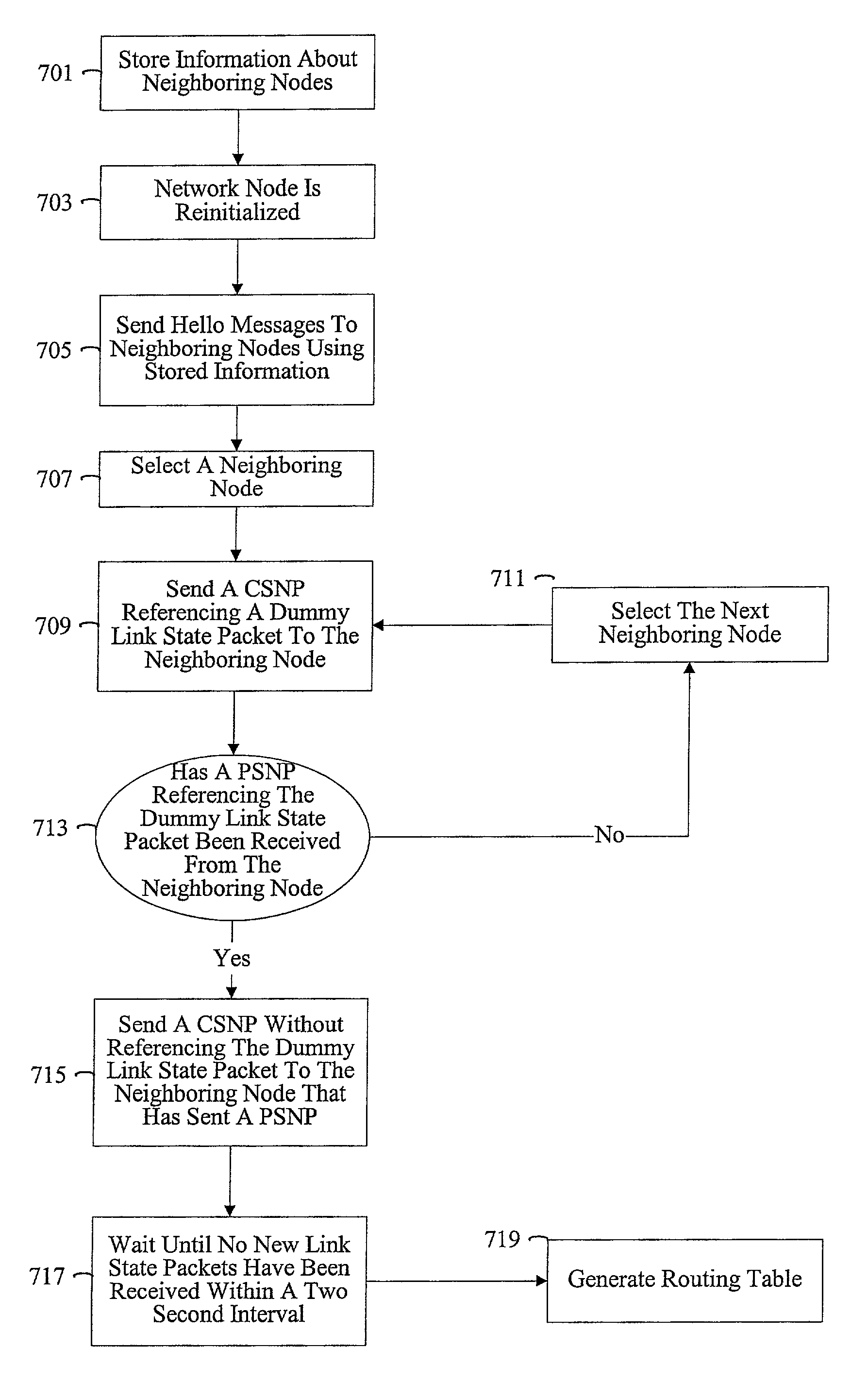
Methods and apparatus are provided for optimizing the reintroduction of a network node into a network. Information about neighboring nodes is stored in persistent memory. The network node can then be reinitialized and reintroduced into the network. Upon reintroduction, the network node can transmit heartbeat messages such as Hello messages to its neighboring nodes using information stored in persistent memory. A link state packet request message such as a Complete Sequence Numbers Packet referencing dummy link state information is transmitted to a neighboring node. A partial packet request message such as a Partial Sequence Numbers Packet referencing the dummy link state packet from the neighboring node can acknowledge that the Complete Sequence Numbers Packet has been received.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
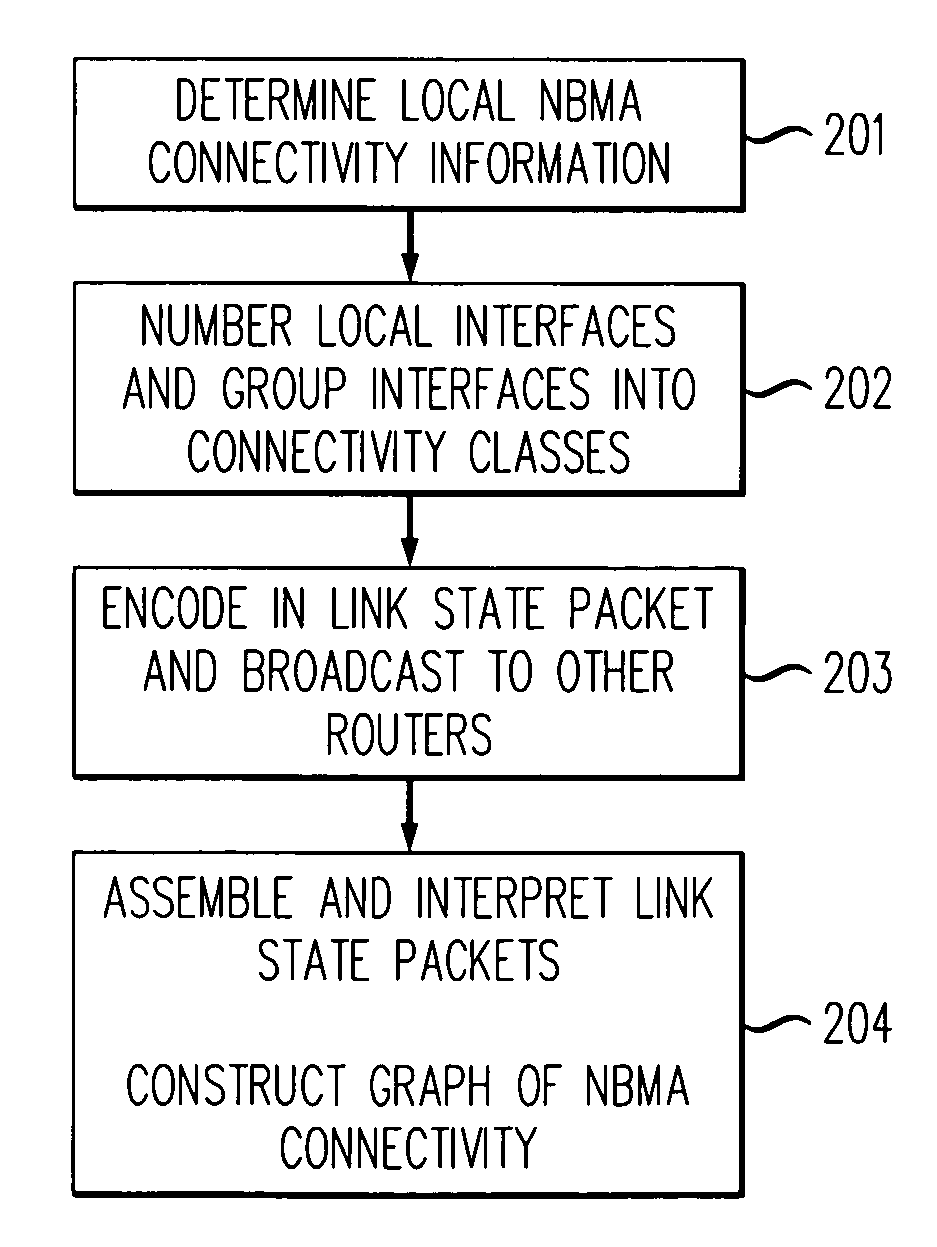
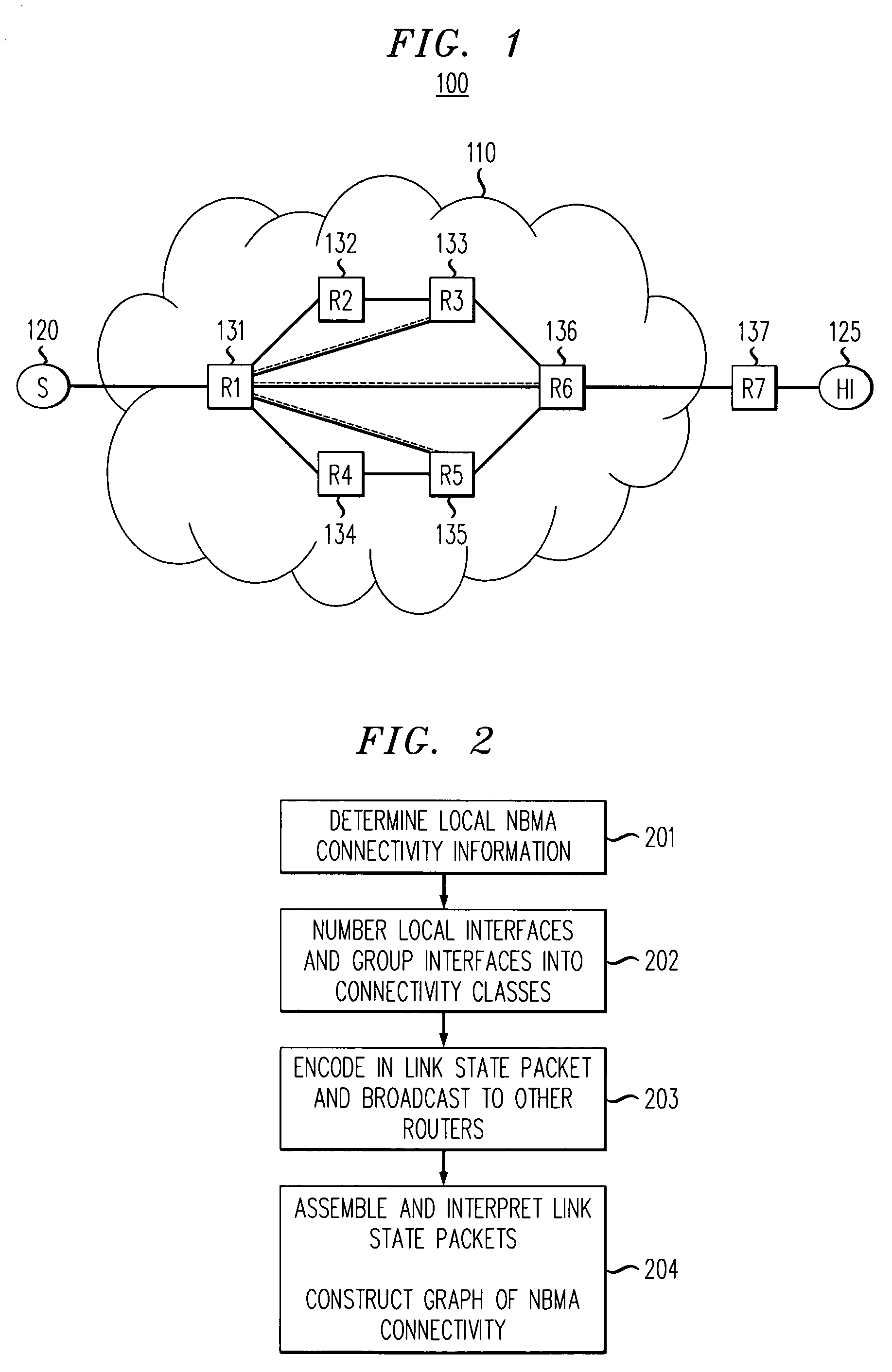
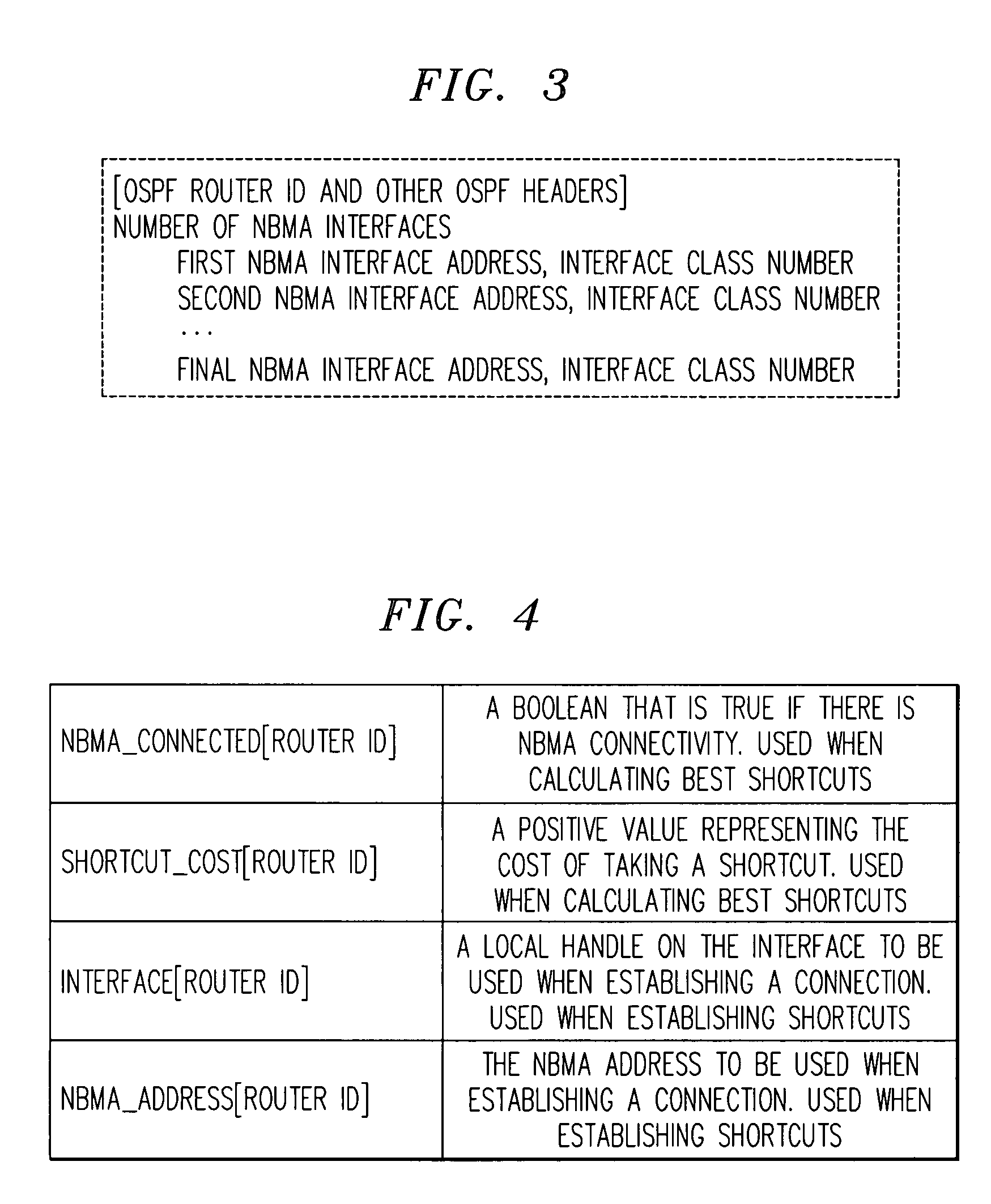
Method for determining non-broadcast multiple access (NBMA) connectivity for routers having multiple local NBMA interfaces
InactiveUS7808968B1Avoid overheadIntroduce latencyData switching by path configurationTier 2 networkLink state packet
The present invention discloses an efficient architecture for routing in a very large autonomous system where many of the layer 3 routers are attached to a common connection-oriented layer 2 subnetwork, such as an ATM network. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, a permanent topology of routers coupled to the subnetwork is connected by permanent virtual circuits. The routers can further take advantage of both intra-area and inter-area shortcuts through the layer 2 network to improve network performance. The routers pre-calculate shortcuts using information from link state packets broadcast by other routers and store the shortcuts to a given destination in a forwarding table, along with corresponding entries for a next hop along the permanent topology. The present invention allows the network to continue to operate correctly if layer 2 resource limitations preclude the setup of additional shortcuts.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Mechanism to improve concurrency in execution of routing computation and routing information dissemination
ActiveUS20060045024A1Efficient processingImprove concurrencyError preventionTransmission systemsInformation repositoryInformation Dissemination
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
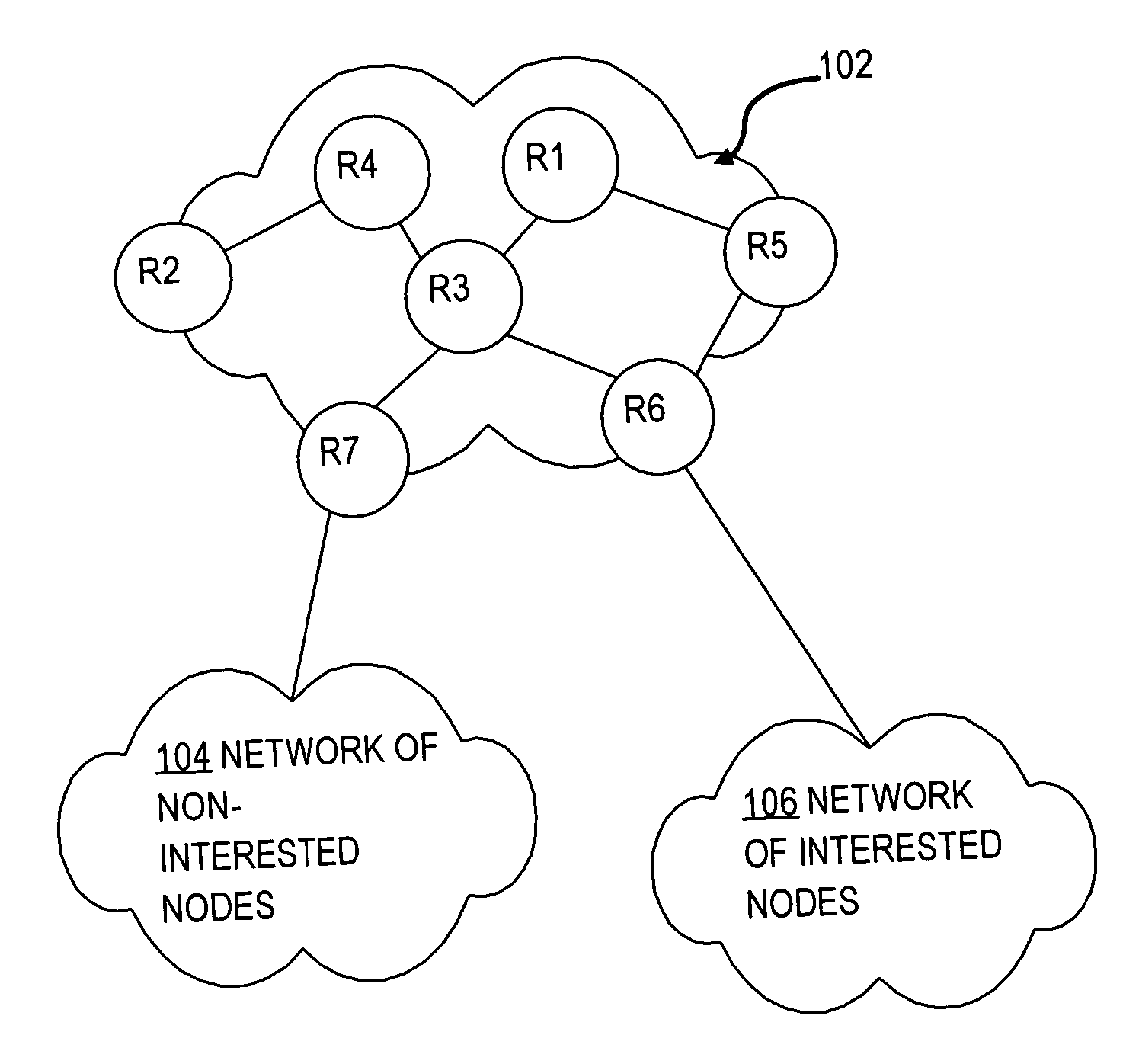
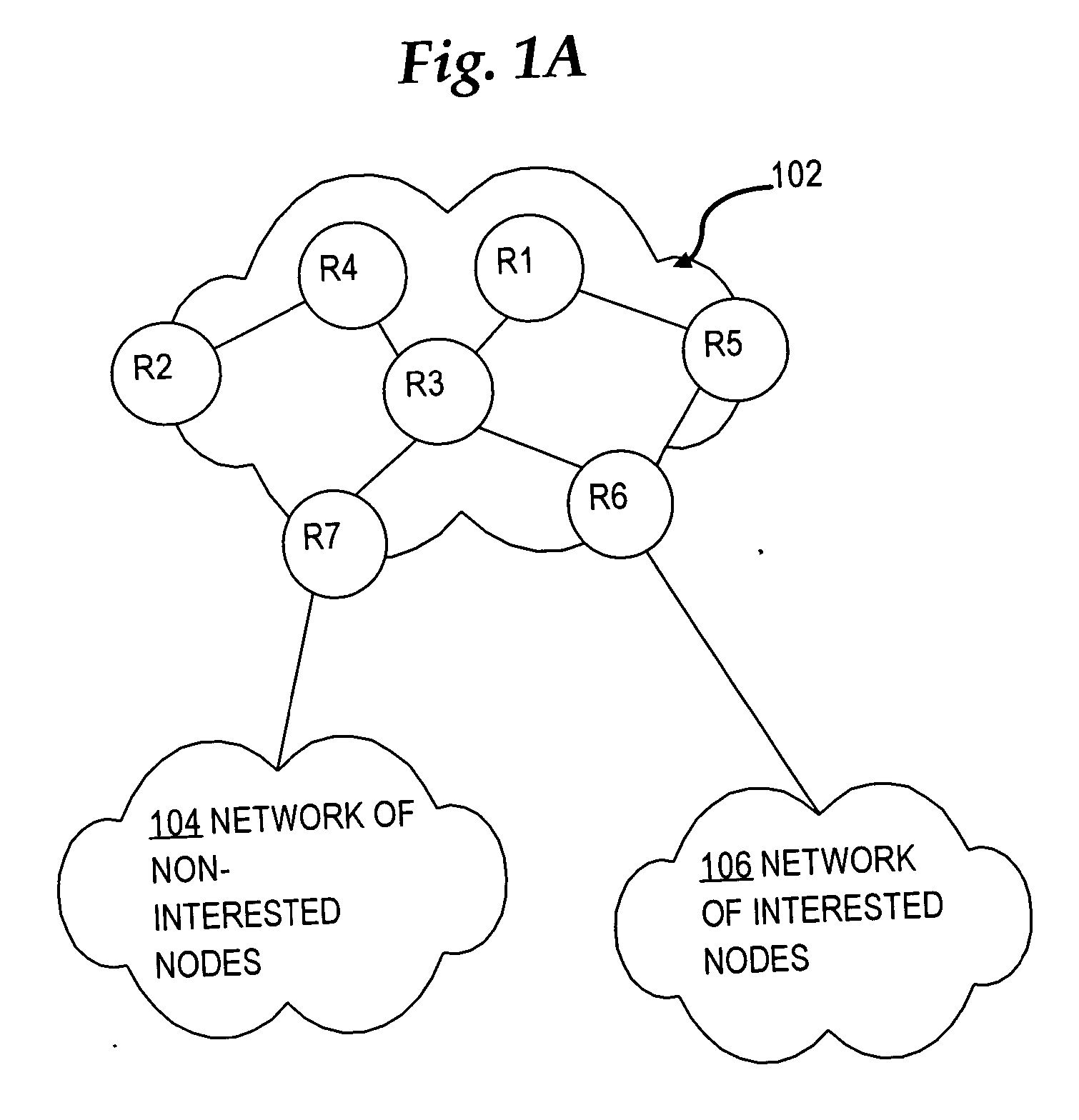
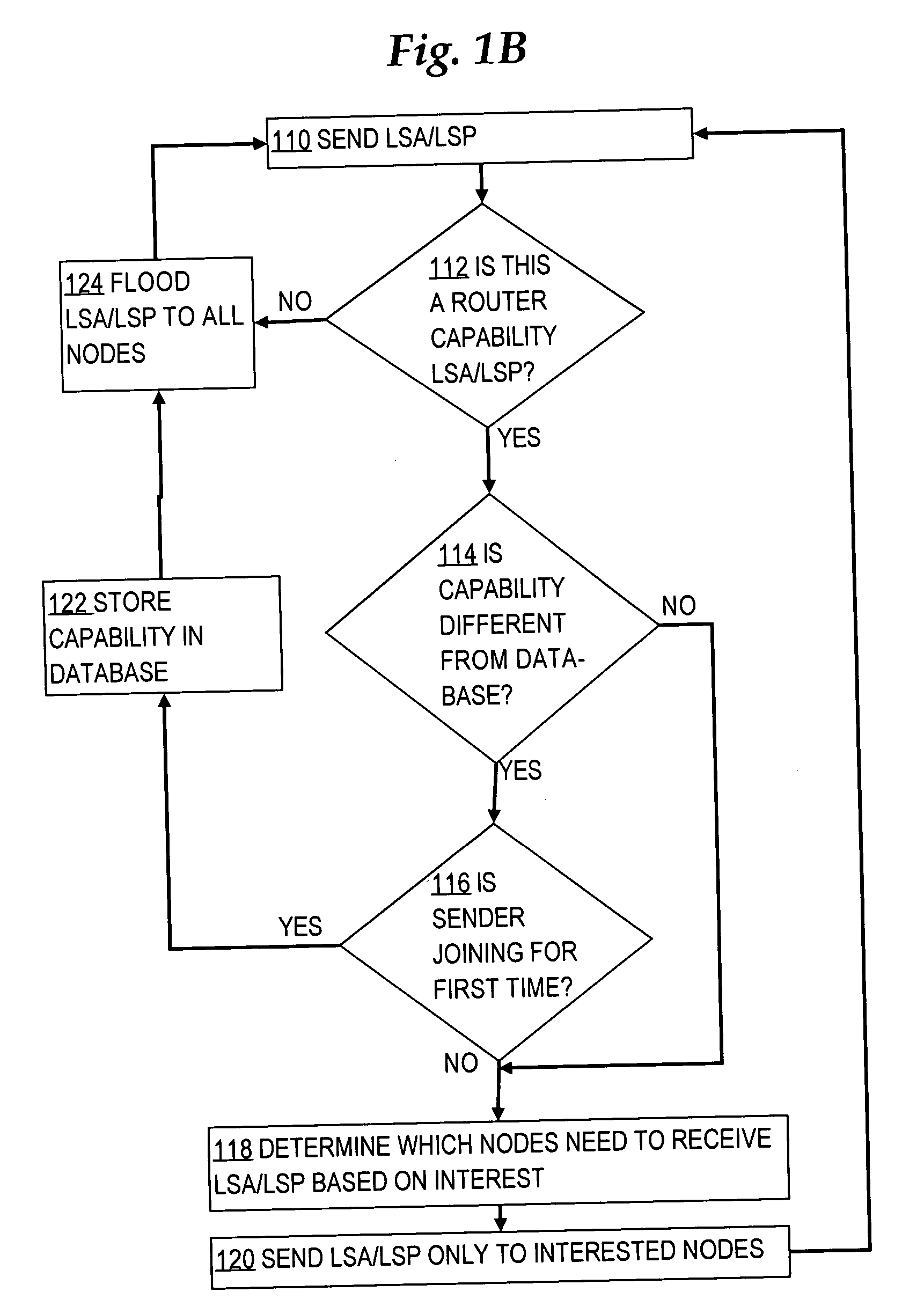
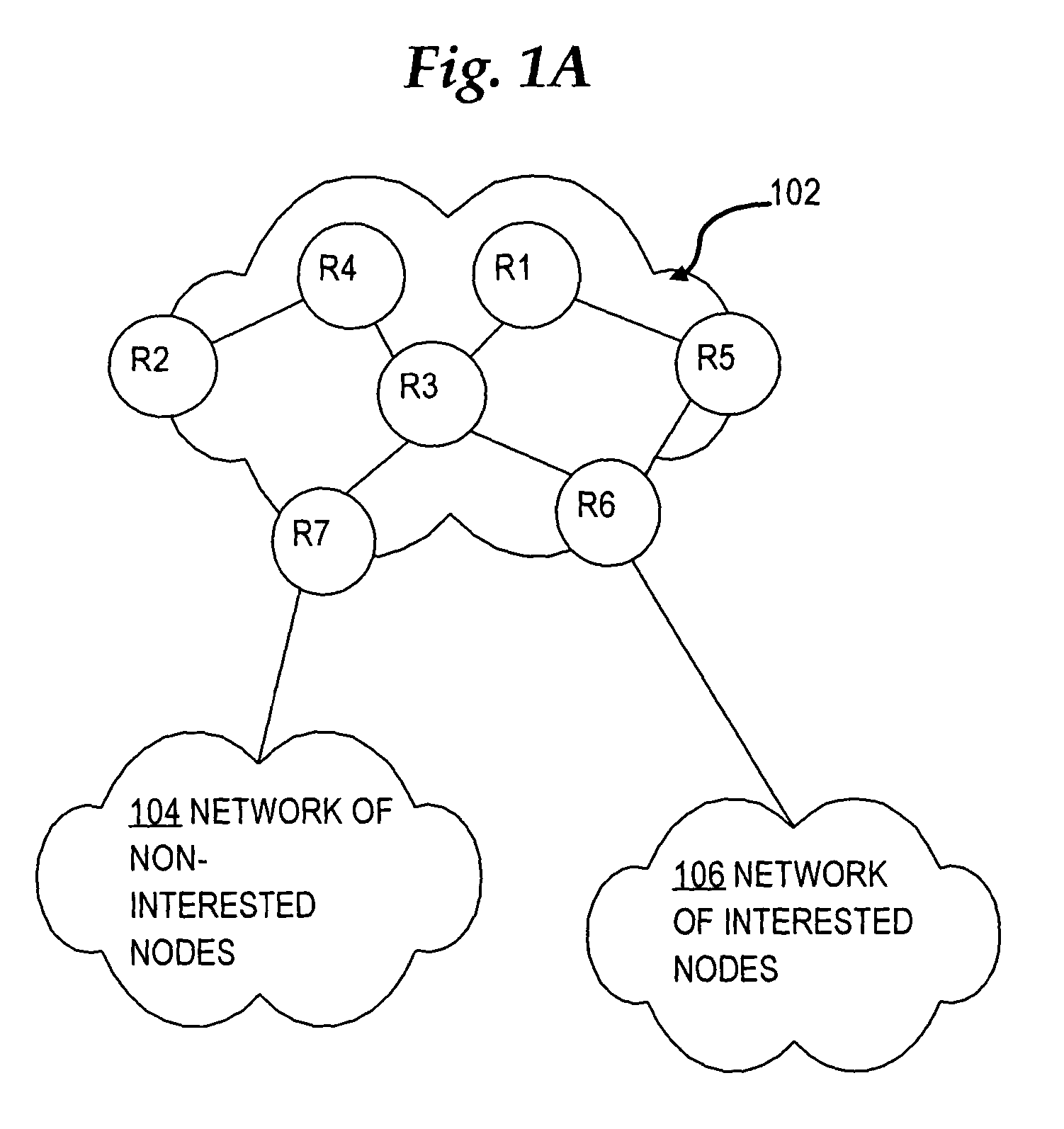
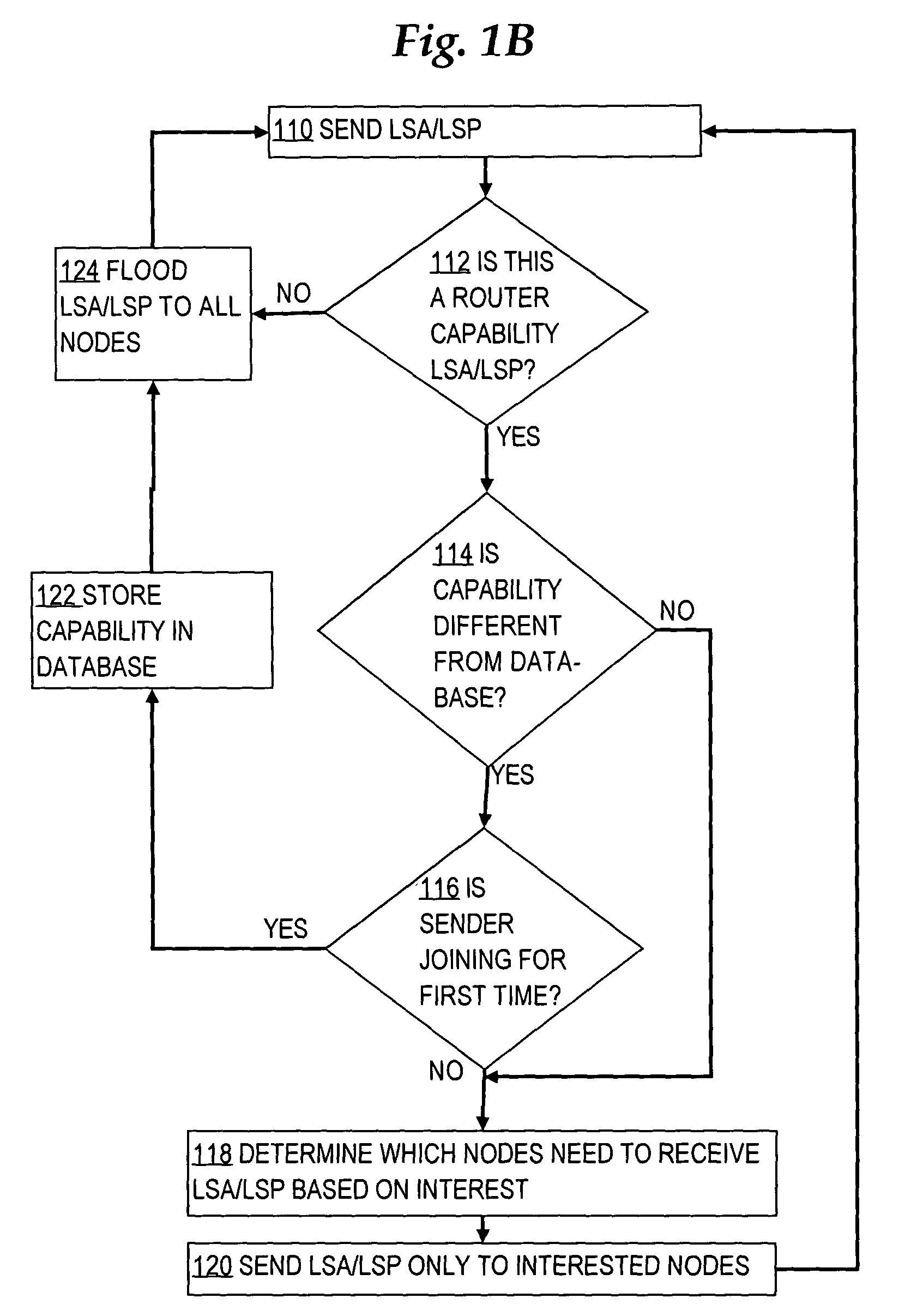
Selectively sending link state messages in a network link state protocol based on interest of network nodes
In a link state protocol such as an interior gateway protocol (IGP), link state advertisements or link state packets (LSA / LSPs) are sent only to network nodes that have expressed interest in them, rather than always flooding them.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Automatically configuring mesh groups in data networks
InactiveUS20100020726A1Prevent floodingReduce adverse effectsData switching by path configurationAuto-configurationTransfer mode
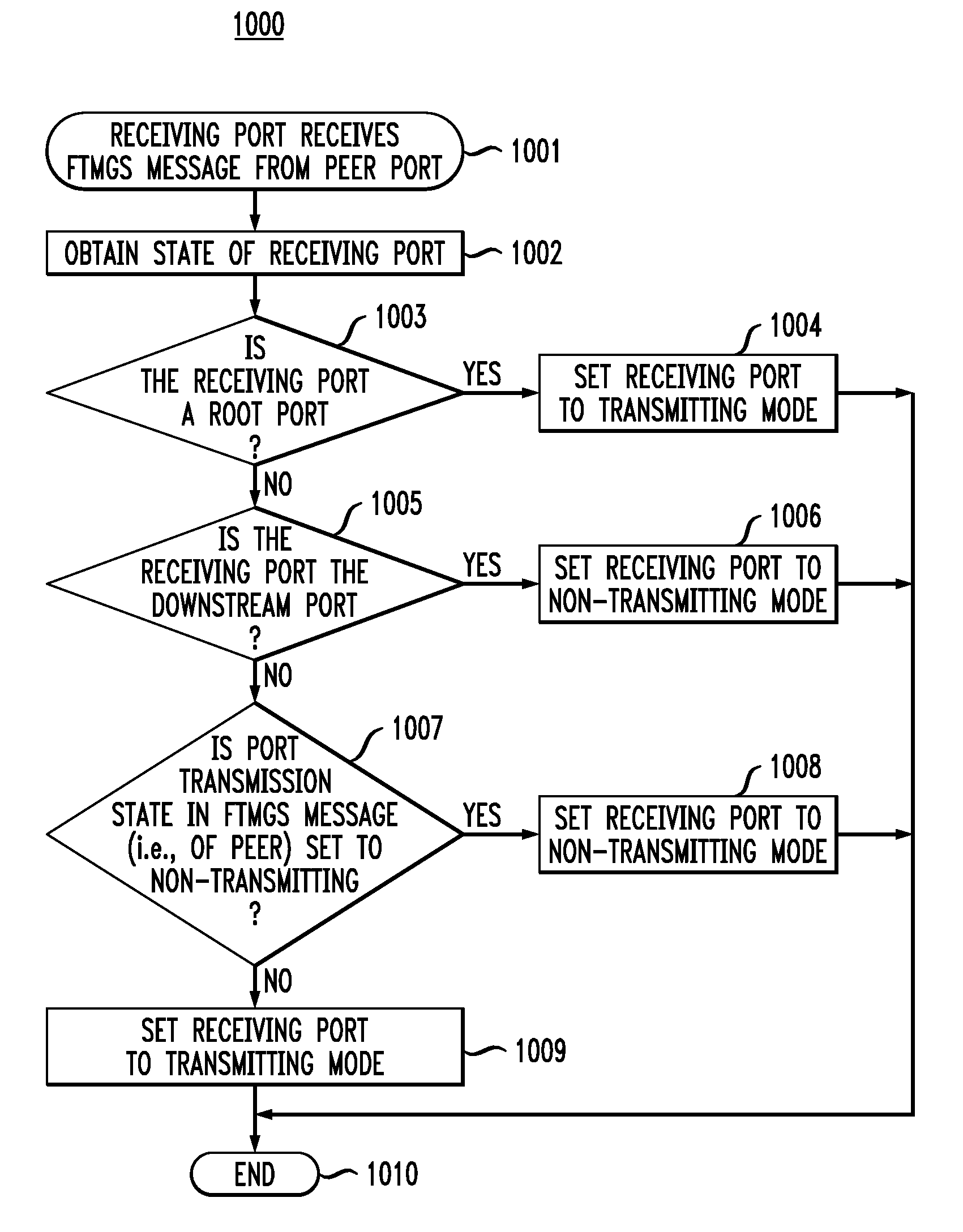
In one embodiment, a method for setting up a flow-through mesh group (FTMG) for transmitting link-state packets (LSPs) in a network having a plurality of nodes interconnected by links. The FTMG is a combination of multiple spanning trees for the network through which LSPs are forwarded. FTMG set-up messages are received at ports of each node of the network from peer ports of linked nodes. FTMG set-up messages identify root nodes of the multiple spanning trees and the transmission modes of the peer ports. The FTMG set-up messages are used to determine (1) a root node for each spanning tree, (2) a root port on each node for each spanning tree, and (3) directionality of ports of the nodes. FTMG set-up messages are then used to determine the transmission mode of ports of the nodes and, subsequently, to update the spanning trees and transmission modes, as needed.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Methods and apparatus for generating network topology information
ActiveUS7016313B1Frequency-division multiplex detailsDigital computer detailsLink state packetNetwork topology
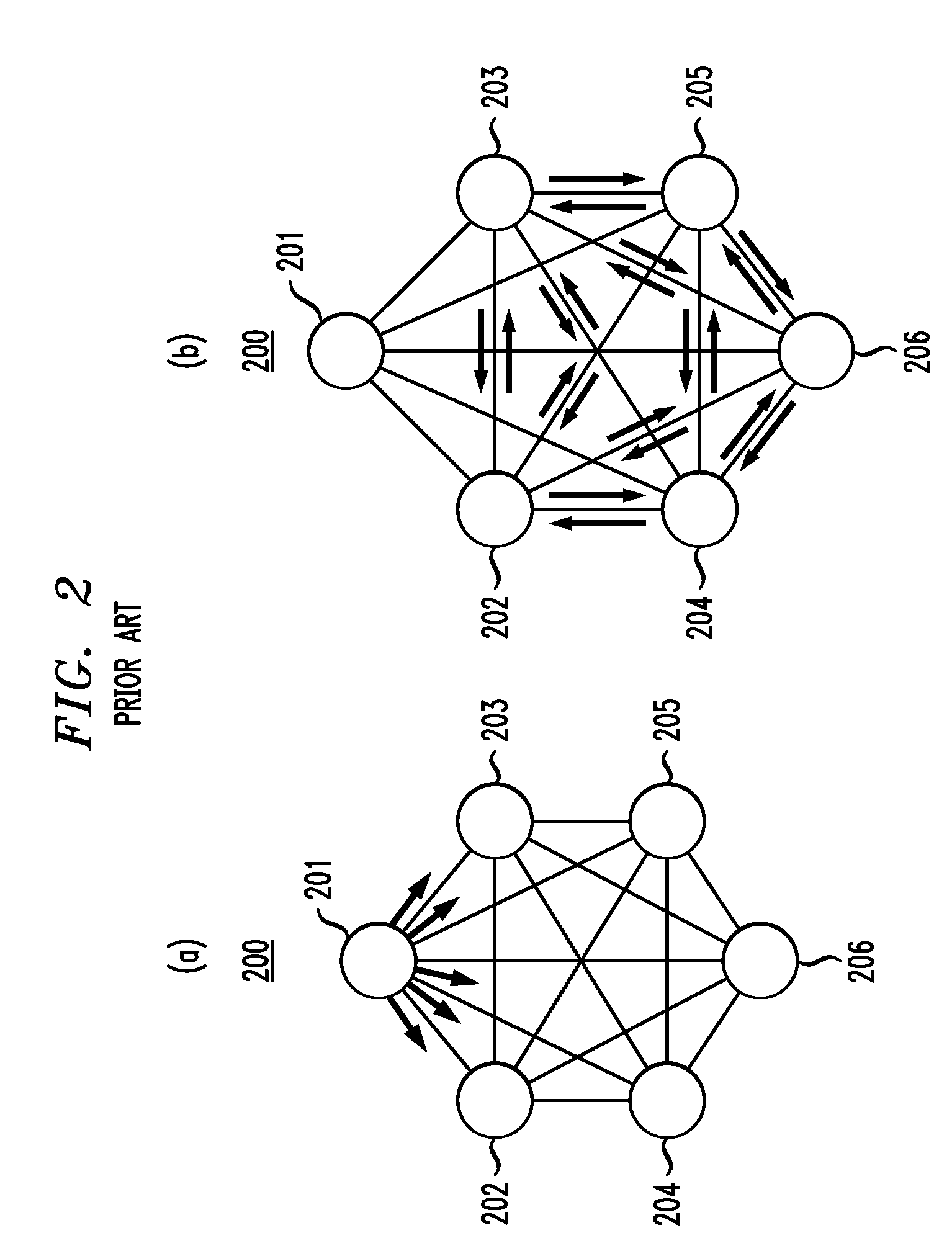
According to a specific embodiment of the present invention, methods and apparatus are disclosed for generating network topology information. A first link state packet associated with a first node is identified. A second link state packet associated with a second node is identified. Network topology information associated with the first node is generated using information from the first link state packet. Verification of two-way connectivity between the first node and the second node is deferred until analysis of the second link state packet is initiated for generating network topology information associated with the second node.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
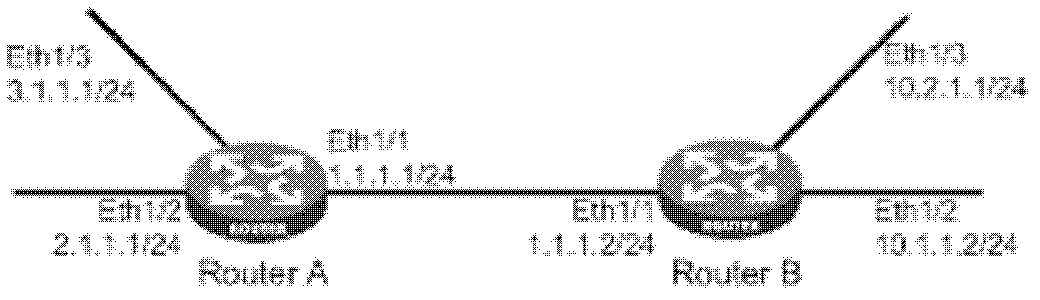
Method and apparatus for determining network routing information based on shared risk link group information
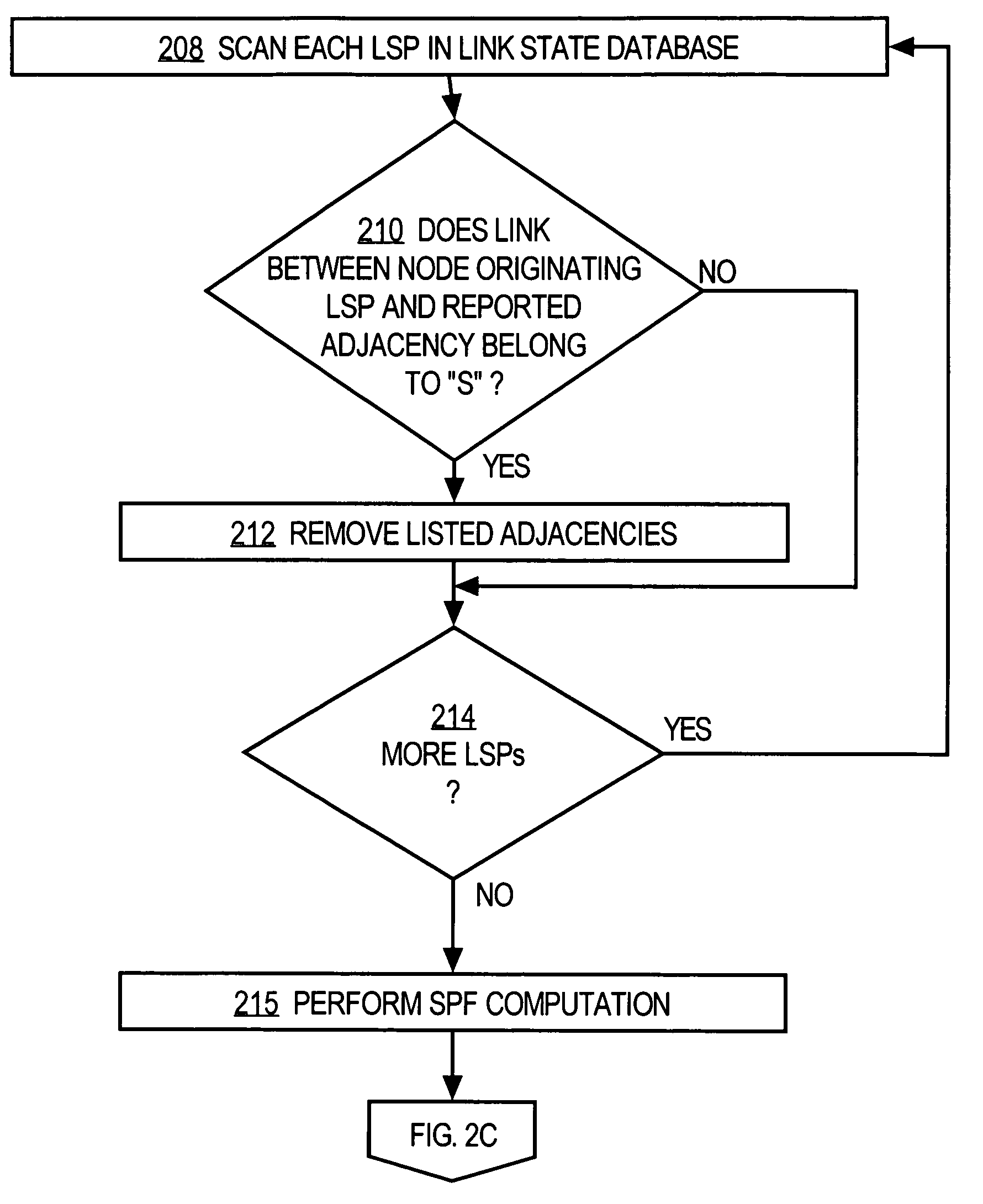
A method and apparatus are disclosed for performing a shortest path first network routing path determination in a data communications network based in part on information about links that are associated as shared risk link groups. Micro-loops are avoided in computing shortest path first trees by considering whether links are within shared risk link groups. In a first approach, for each link state packet in a link state database, listed adjacencies are removed if the link between the node originating the LSP and the reported adjacency belongs to a shared risk link group for which one component (local link) is known as down, and a shortest path first computation is then performed. In a second approach, during the SPT computation and after having added a first node to a path, each neighboring node is added to a tentative tree if and only if, a link between the first node and the neighboring node does not belong to a shared risk link group for which one component (local link) is known as down.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
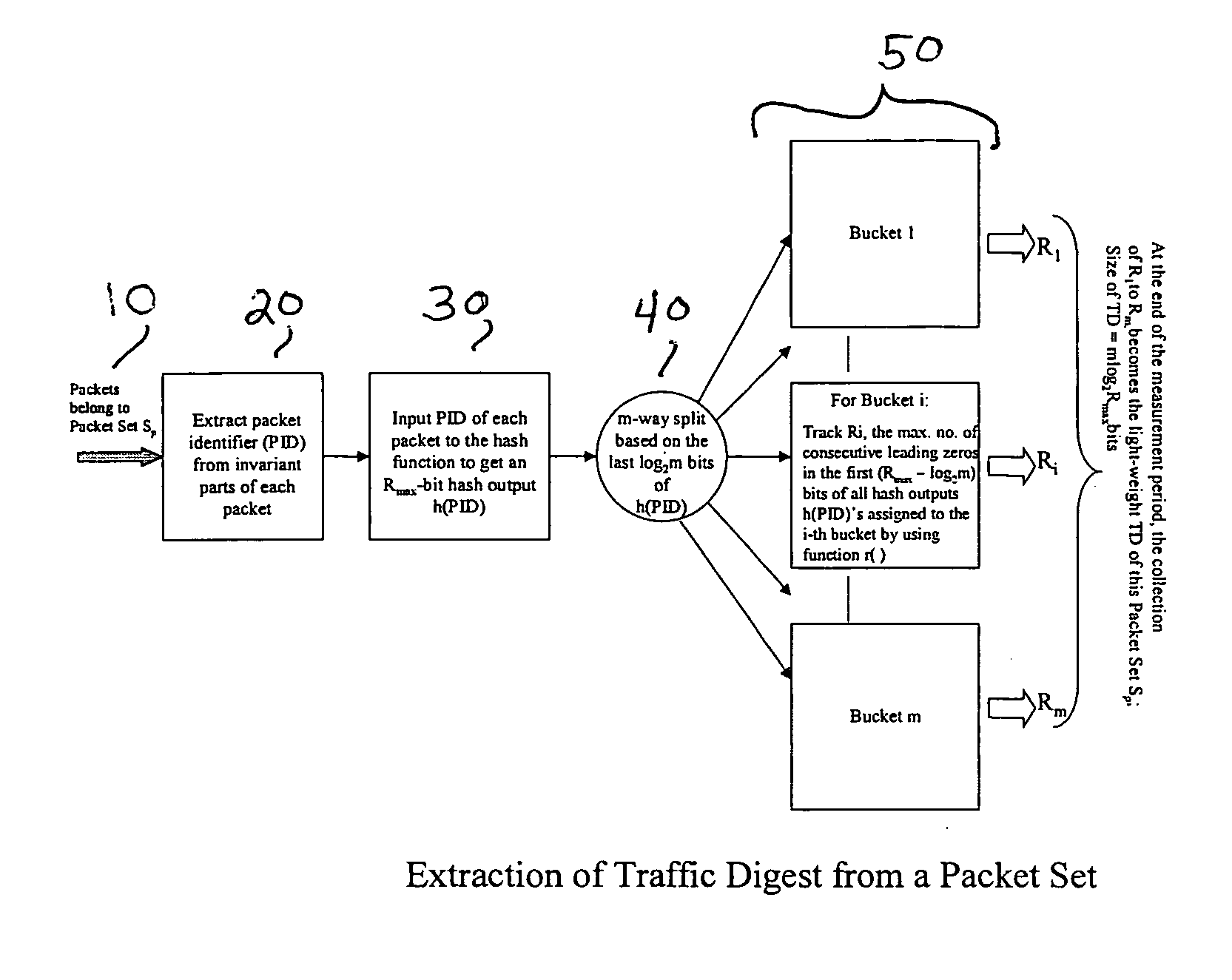
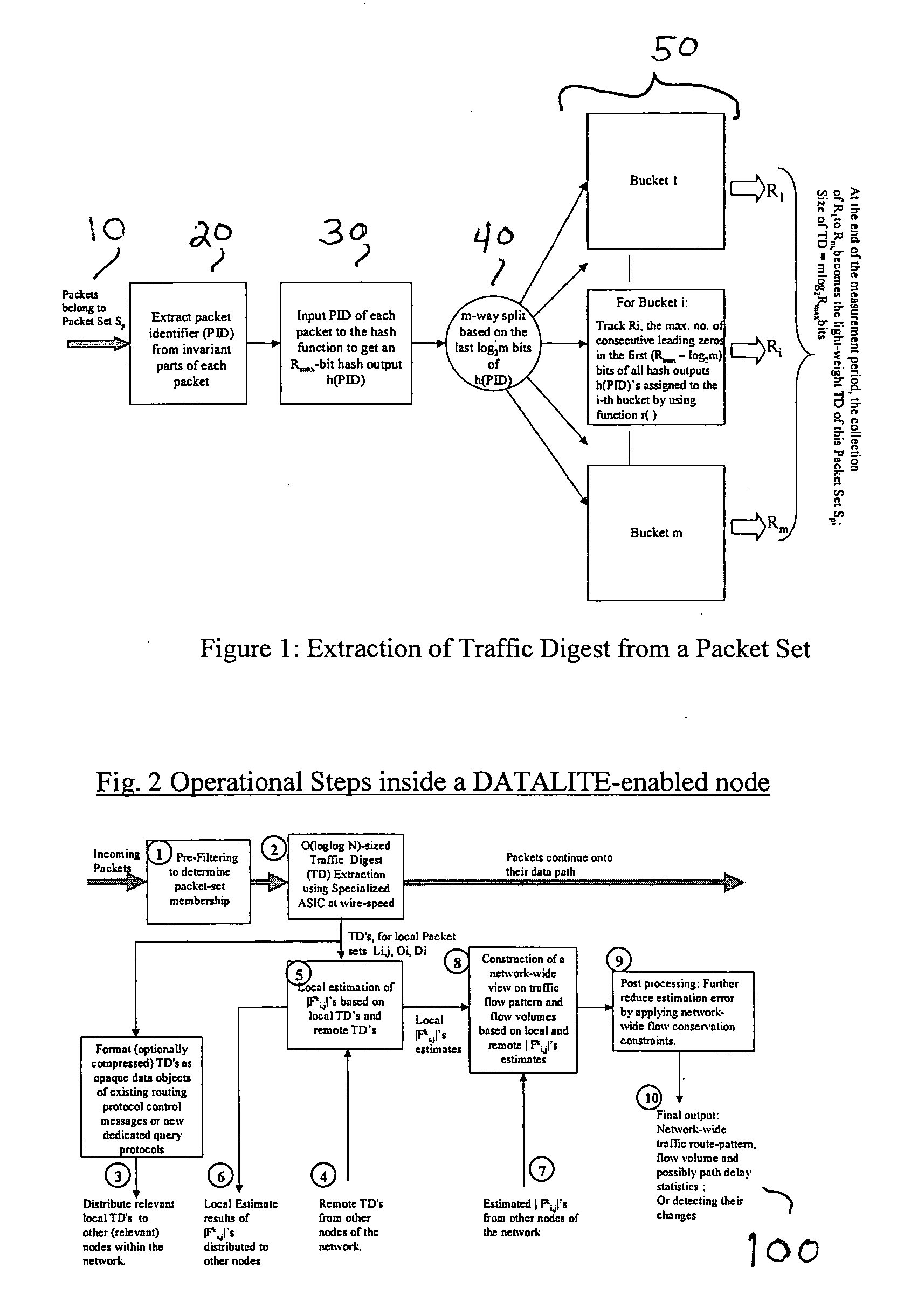
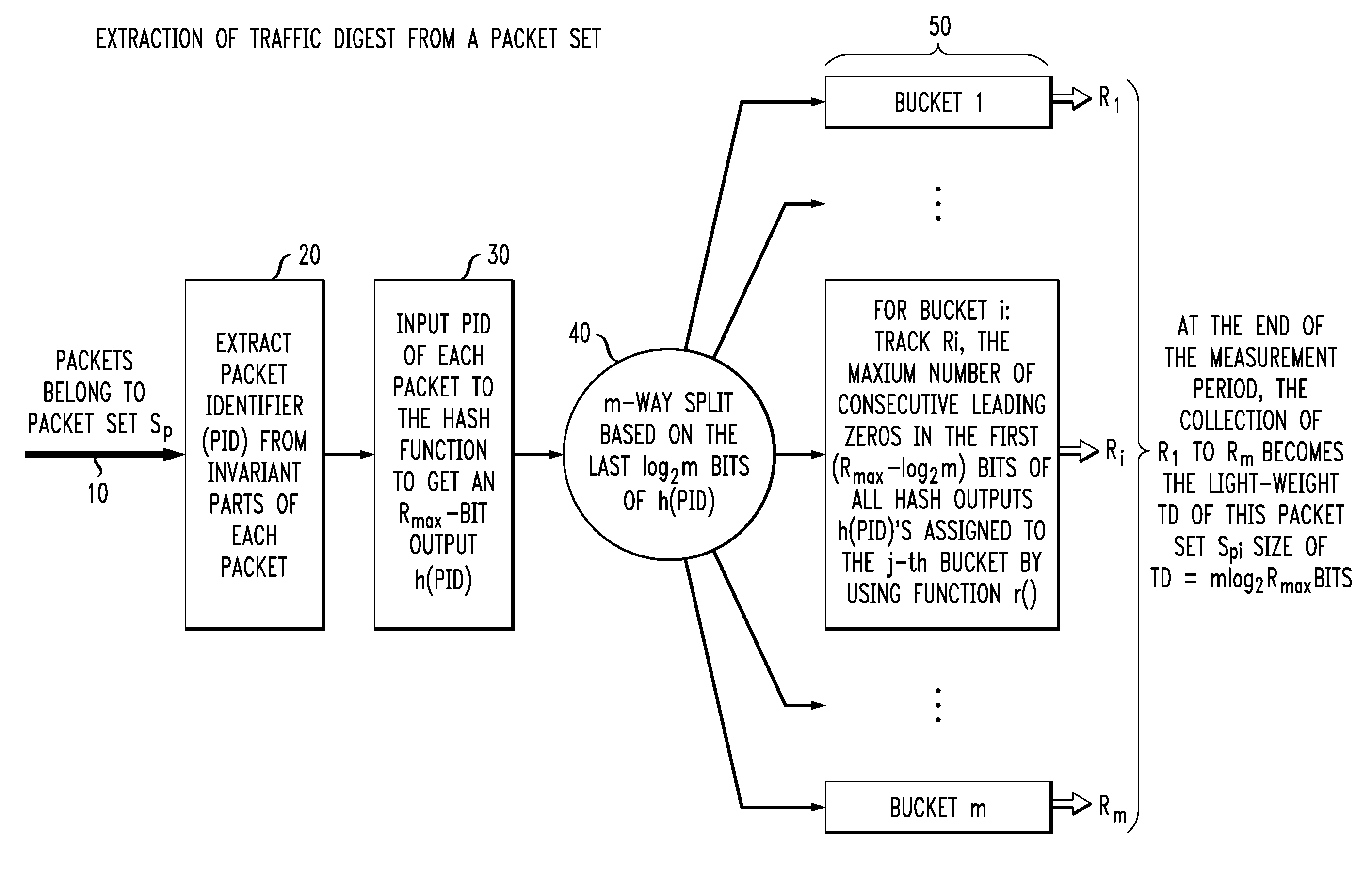
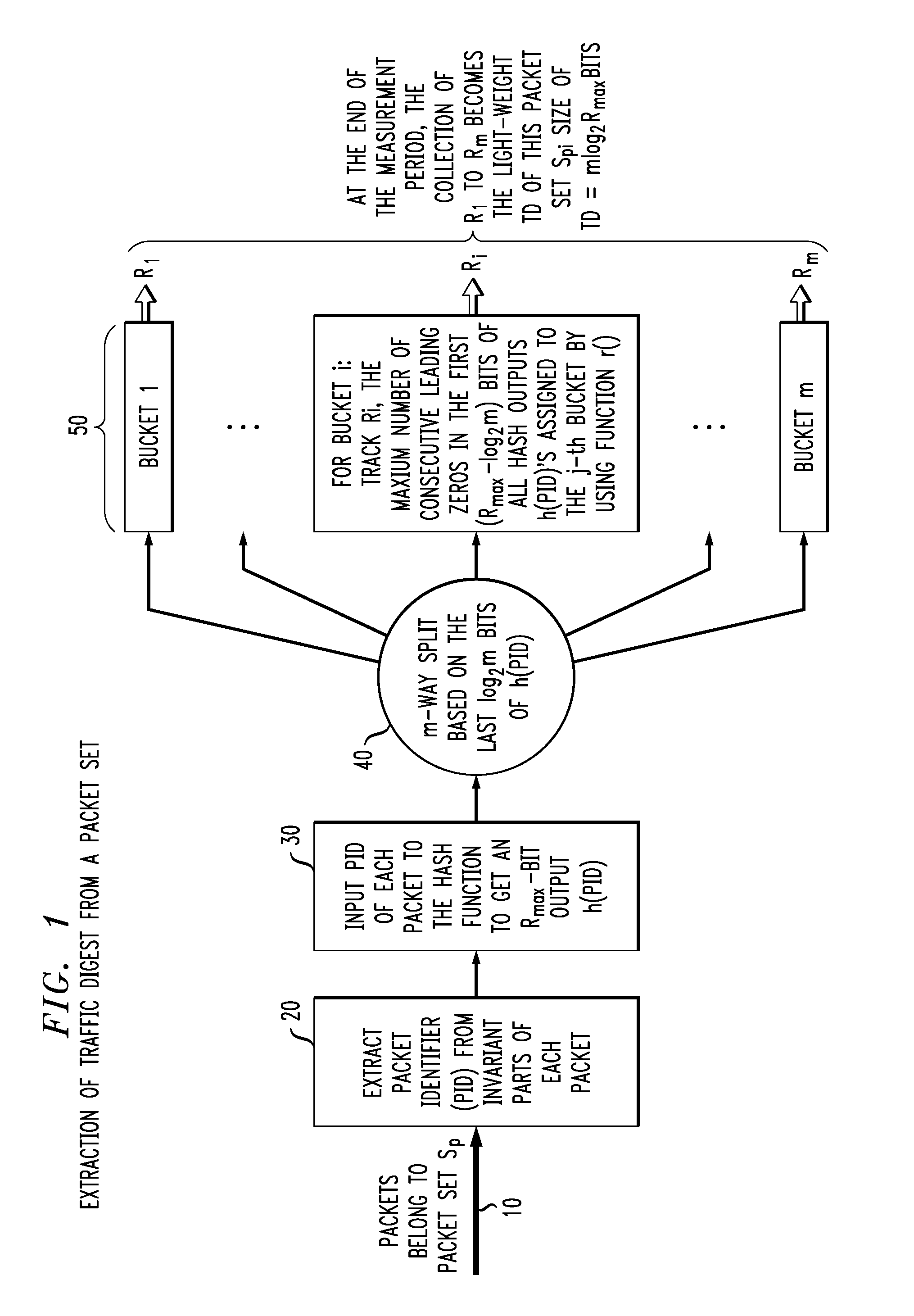
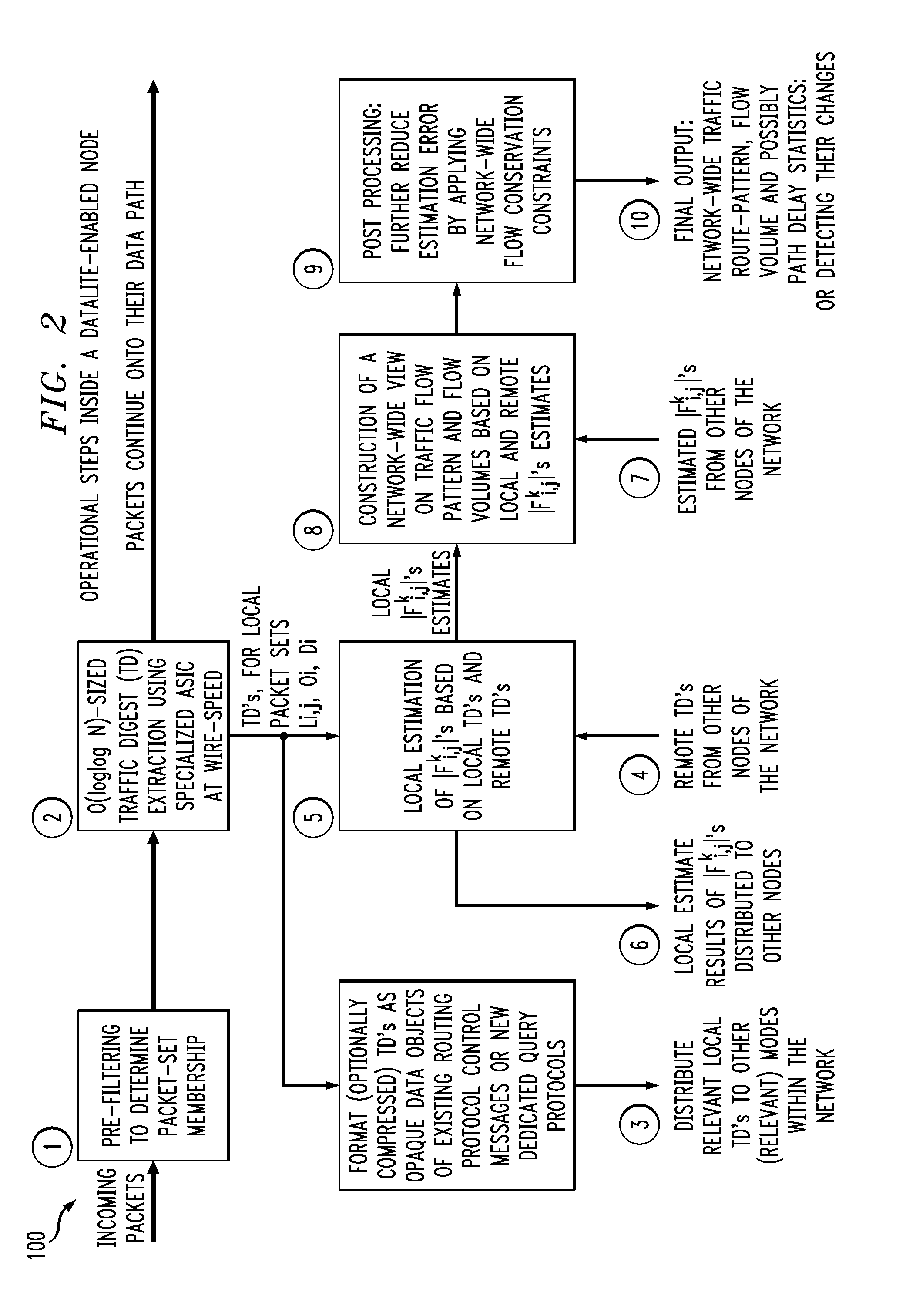
High-speed traffic measurement and analysis methodologies and protocols
InactiveUS20050220023A1Minimal communication overheadMore bandwidth is requiredError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNODALWire speed
We formulate the network-wide traffic measurement / analysis problem as a series of set-cardinality-determination (SCD) problems. By leveraging recent advances in probabilistic distinct sample counting techniques, the set-cardinalities, and thus, the network-wide traffic measurements of interest can be computed in a distributed manner via the exchange of extremely light-weight traffic digests (TD's) amongst the network nodes, i.e. the routers. A TD for N packets only requires O(loglog N) bits of memory storage. The computation of such O(loglog N)-sized TD is also amenable for efficient hardware implementation at wire-speed of 10 Gbps and beyond. Given the small size of the TD's, it is possible to distribute nodal TD's to all routers within a domain by piggybacking them as opaque data objects inside existing control messages, such as OSPF link-state packets (LSPs) or I-BGP control messages. Once the required TD's are received, a router can estimate the traffic measurements of interest for each of its local link by solving a series of set-cardinality-determination problems. The traffic measurements of interest are typically in form of per-link, per-traffic-aggregate packet counts (or flow counts) where an aggregate is defined by the group of packets sharing the same originating and / or destination nodes (or links) and / or some intermediate nodes (or links). The local measurement results are then distributed within the domain so that each router can construct a network-wide view of routes / flow patterns of different traffic commodities where a commodity is defined as a group of packets sharing the same origination and / or termination nodes or links. After the initial network-wide traffic measurements are received, each router can further reduce the associated measurement / estimation errors by locally conducting a minimum square error (MSE) optimization based on network-wide commodity-flow conservation constraints.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Automatic maintenance of a distributed source tree (DST) network
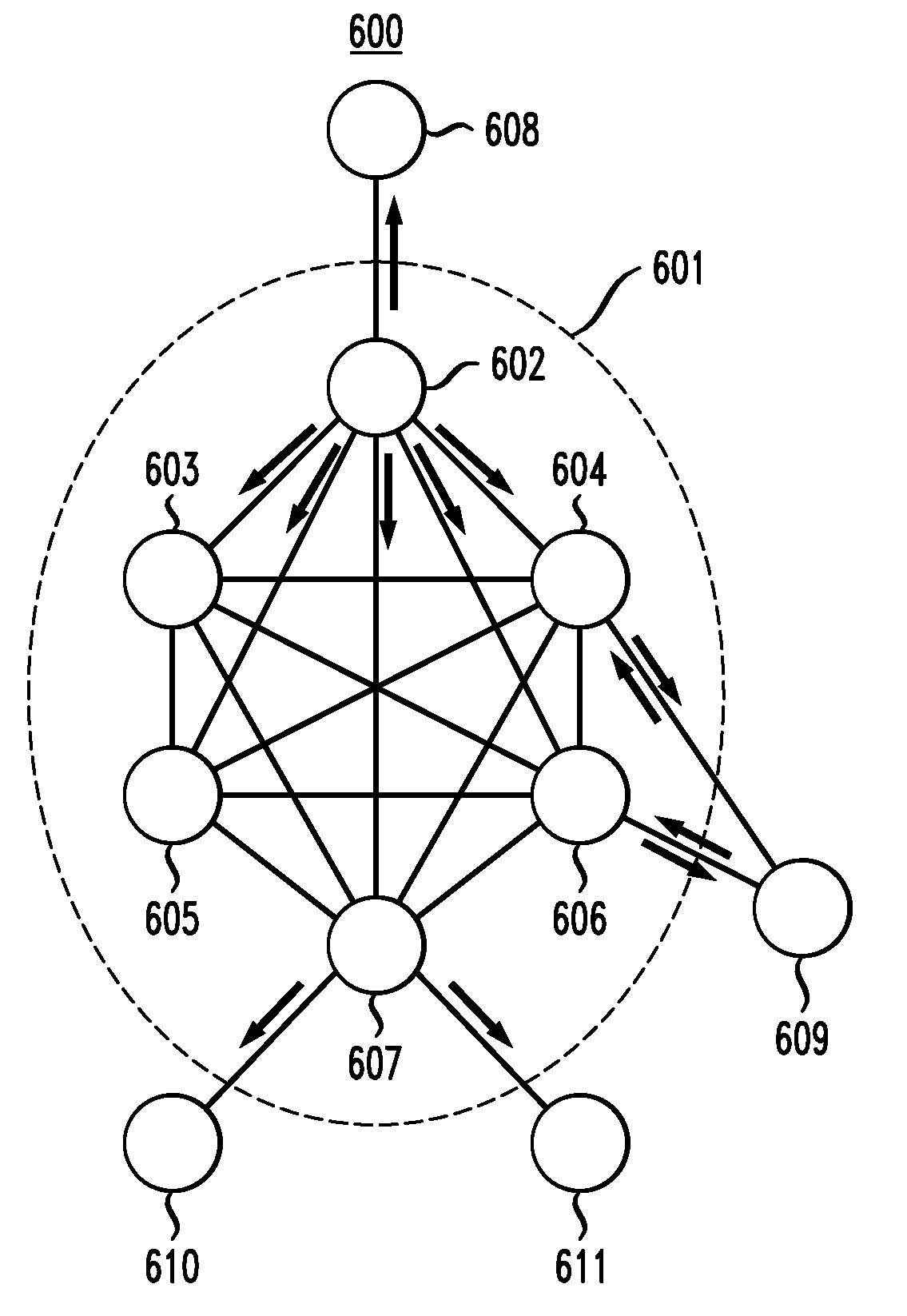
In one embodiment, an automatically maintained, distributed source tree (DST) network has a plurality of fully connected internal nodes. One or more internal nodes may be connected to one or more external nodes. A first internal node synchronizes its link-state database with another internal node by sending and receiving respective Reduced Sequence Number Packet-Data-Units (PDUs) (RSNPs). An RSNP includes summary information for link-state packets (LSPs) (1) originated by the first internal node, (2) received by the first internal node from the other internal node, and (3) received from and / or originated by external nodes. If an internal link fails, then the corresponding end-nodes may recover and maintain automatic DST operation by entering either relay-mode or switch-mode operation. In relay-mode operation, an end-node tunnels packets to the other end-node via an intermediary node. In switch-mode operation, an intermediary node is selected to forward packets from one end-node to the other end-node.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Method for avoiding neighbourhood oscillation of intermediate system and an intermediate system
ActiveCN101394354AAvoid shockRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsData switching networksLink state packetReal-time computing
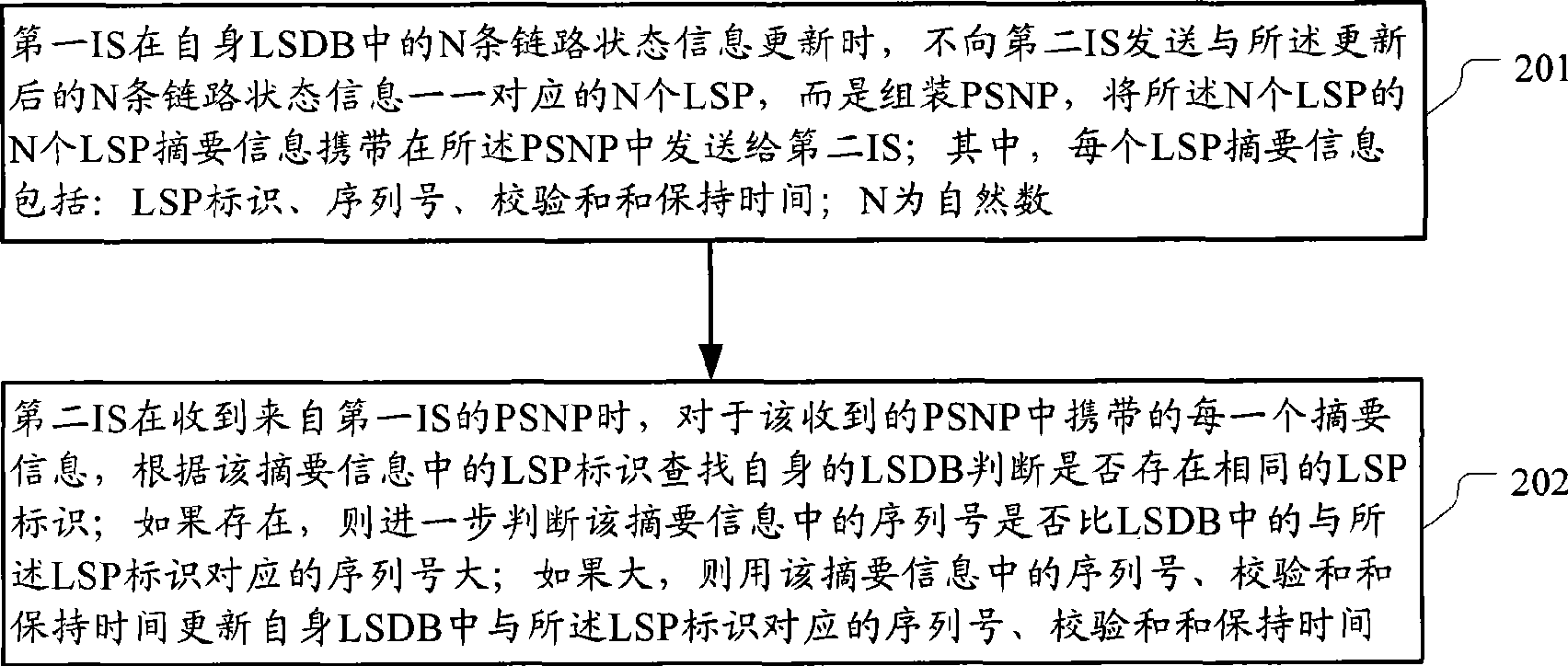
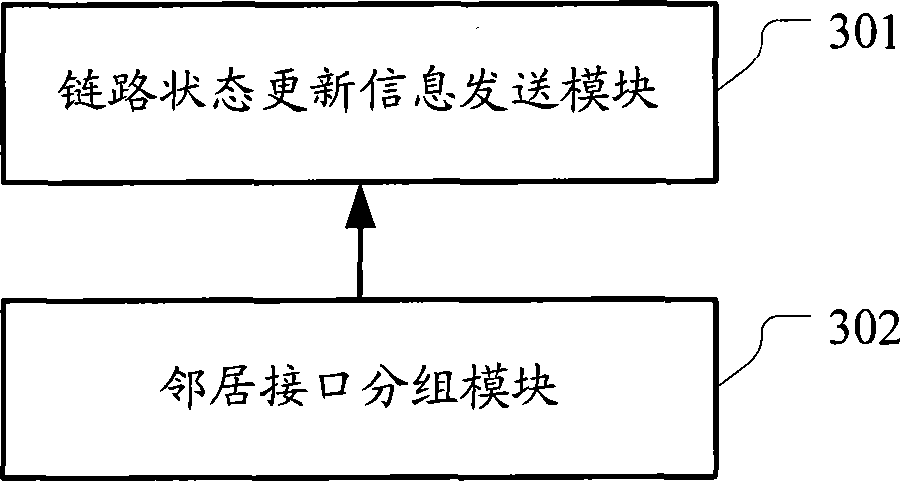
The invention discloses a method for avoiding neighborhood flap in an intermediate system (IS). When updating the state information of N links in the link state data base (LSDB) of an IS, the IS does not send a neighboring IS a partial sequence number packet (PSNP) carrying the summary information of the N link state packets (LSPs) one-to-one corresponding to the state information of the N links instead of the N LSPs, so that the neighboring IS can update the LSDB thereof according to the summary information of the N LSPs; wherein N is natural numbers. The invention also discloses an IS. The technical proposal provided in the invention remarkably reduces ISIS packet when updating the LSPs, so as to avoid ISIS neighborhood flap due to fullness of ISIS packet sending and receiving queues.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Method and equipment for announcing media access control (MAC) address information
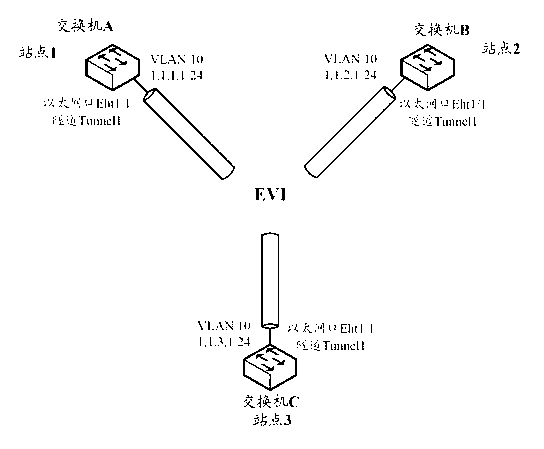
ActiveCN103078969AReduce the number of transfersSave network resourcesNetworks interconnectionVirtualizationInterconnection
The invention discloses a method and equipment for announcing media access control (MAC) address information. The method is applied to a virtualization network which consists of edge devices respectively in site networks of large two-layer interconnection. The method comprises the following steps of: competing for a primary device according to the priority by the edge devices respectively in the site networks in the same virtualization network case; sending a link-state packet (LSP) in which MAC address information required to be announced is packaged to the primary device when the edge devices respectively in the site networks need to announce the MAC address information if the device is a non-primary device; sending the LSP in which the MAC address information required to be announced is packaged to all neighbor devices of the device if the device is the primary device; and transmitting the received LSP to other neighbor devices except an LSP sender after the LSP in which the MAC address information is packaged is received by the edge devices respectively in the site networks if the device is the primary device. By adopting the method and equipment for announcing the MAC address information, network resources used during a process of announcing the MAC address information can be reduced.
Owner:XINHUASAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
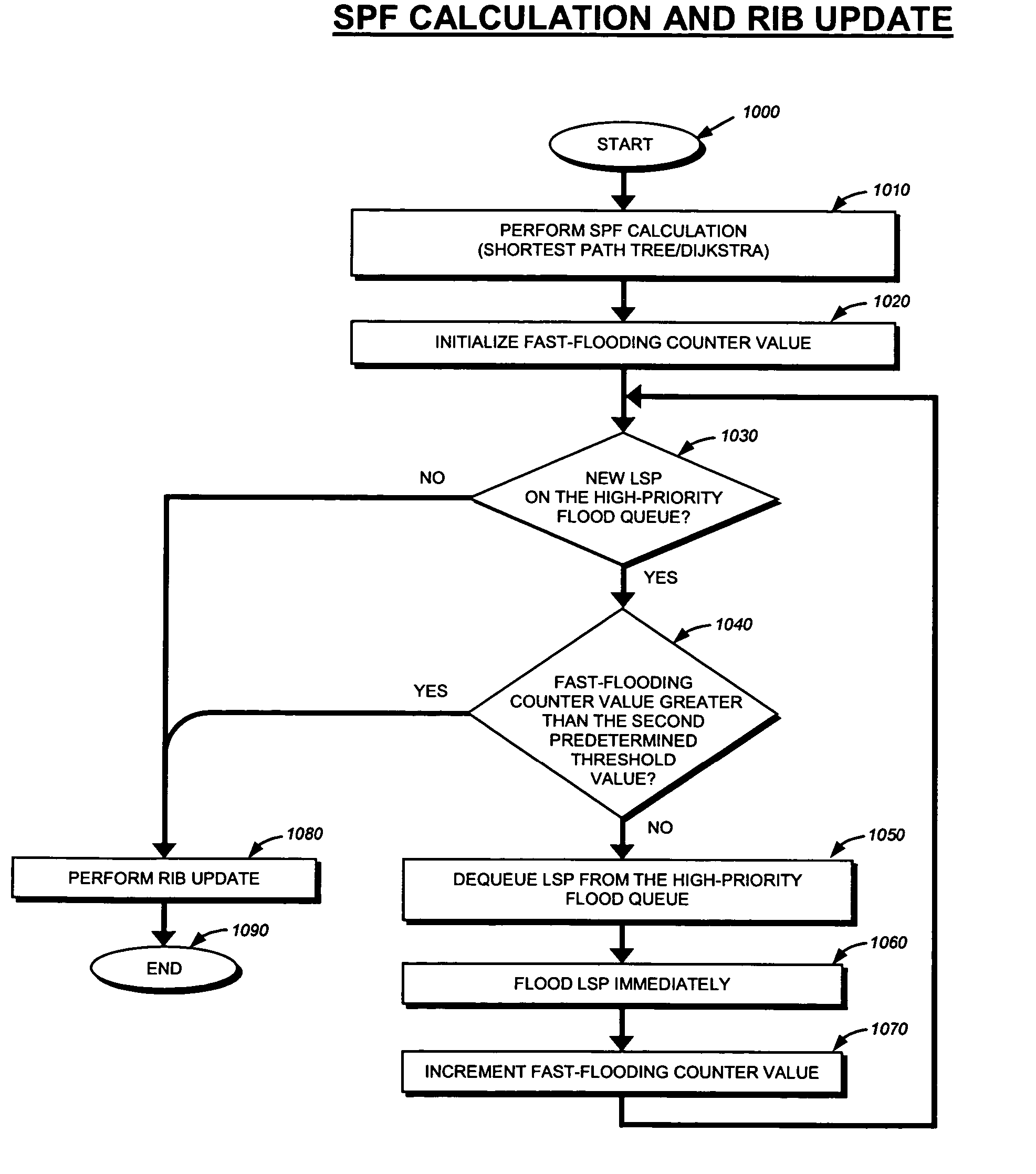
Method and apparatus for flooding link state packets to achieve faster convergence
ActiveUS20060072461A1Efficient floodingLow costError preventionTransmission systemsLink state packetDistributed computing
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for determining network routing information based on shared risk link group information
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Virtual routers for GMPLS networks
InactiveUS7995569B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationPhotonicsLink state packet
Virtual routers that abstract photonic sub-domains are provided for GMPLS networks. A virtual router uses a link viability matrix to keep track of the set of viable connections between inputs and outputs of a photonic sub-domain. A virtual router may receive RSVP-TE signaling messages and either allocate a working input to output link pair or, if explicitly signaled, verify that the requested link is currently viable. A virtual router also advertises, in its link state updates, the current set of possible outputs for any input link. Shortest path computations can be implemented utilizing virtual routers by modifying a topology graph in accordance with the link viability matrix of the virtual router.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
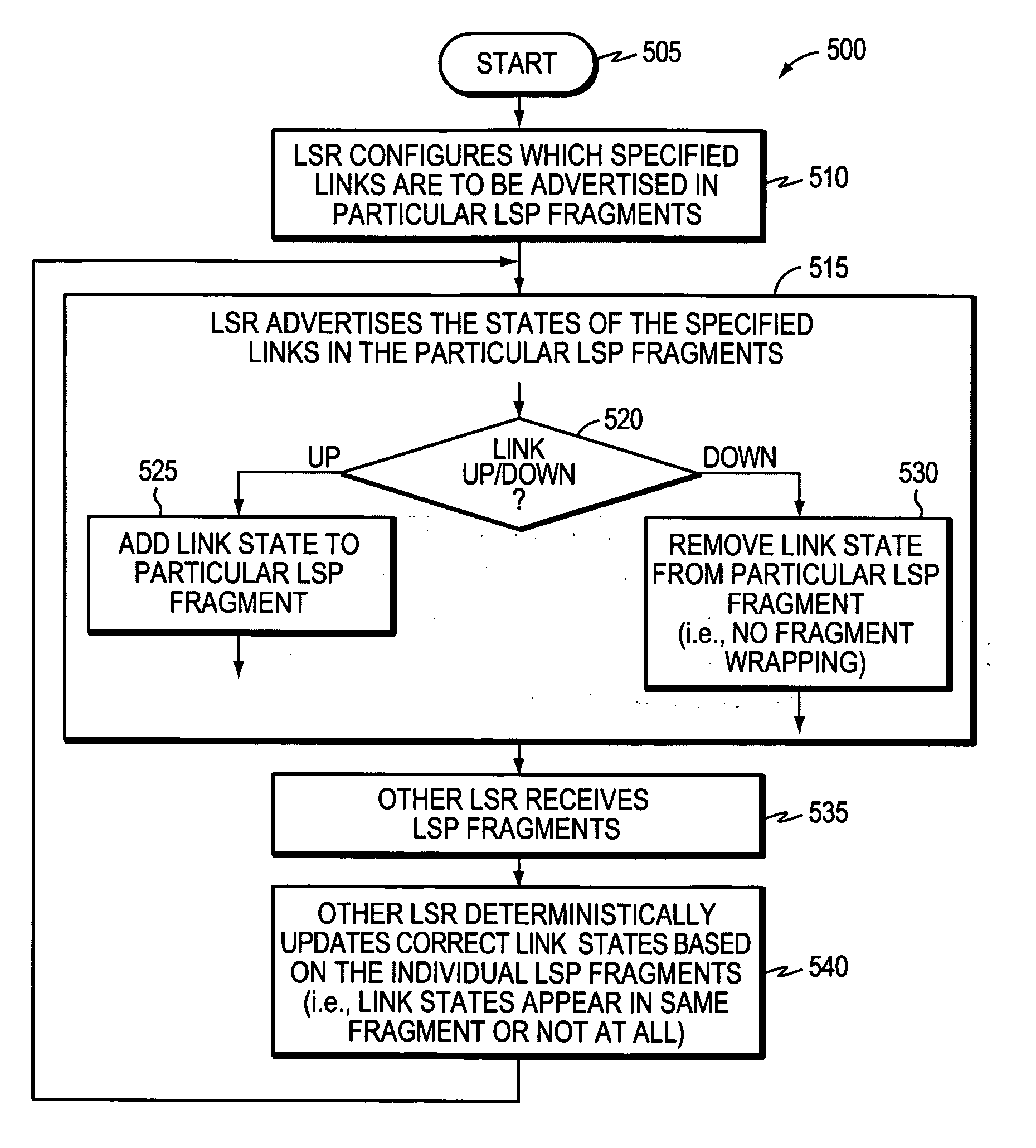
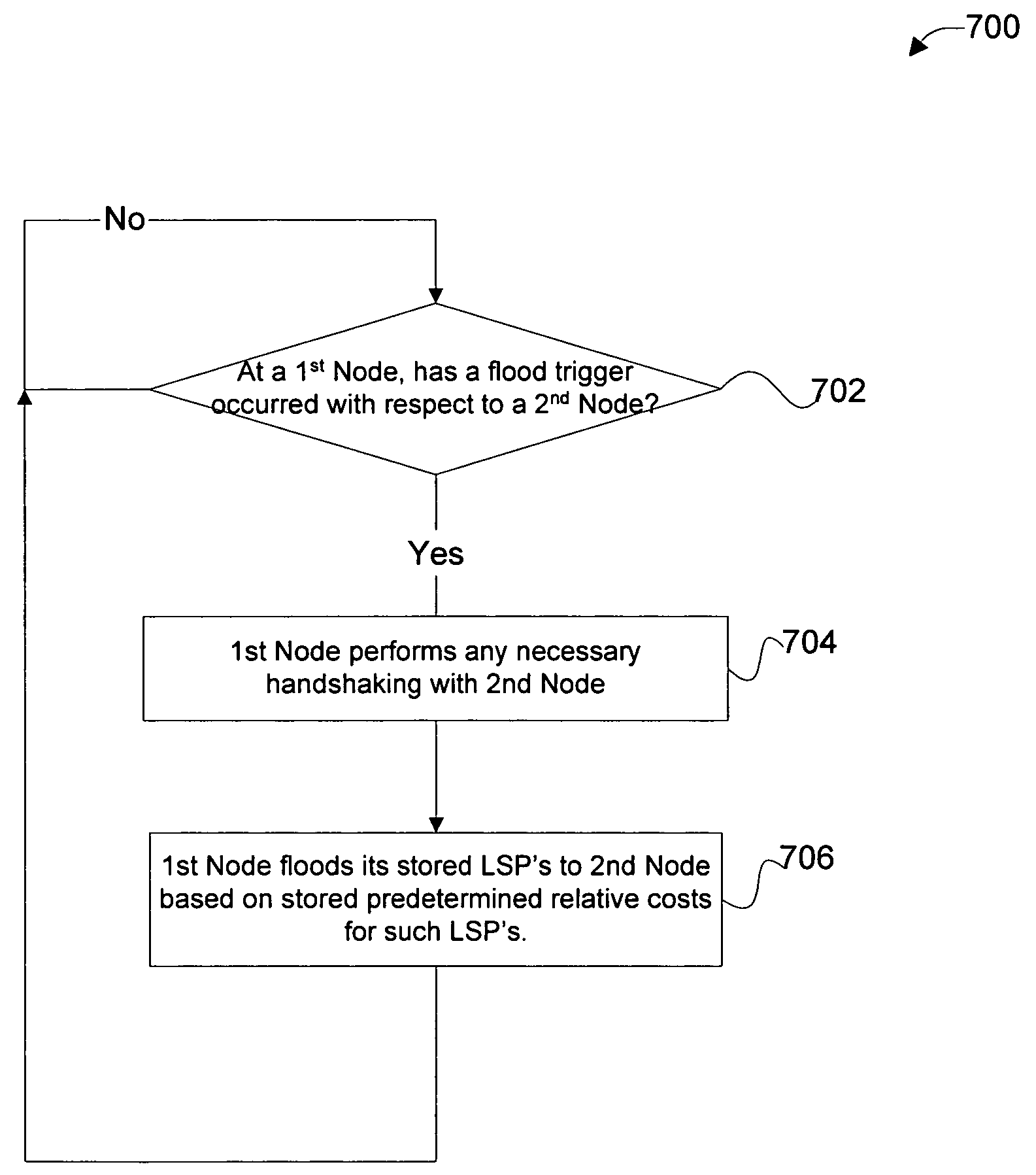
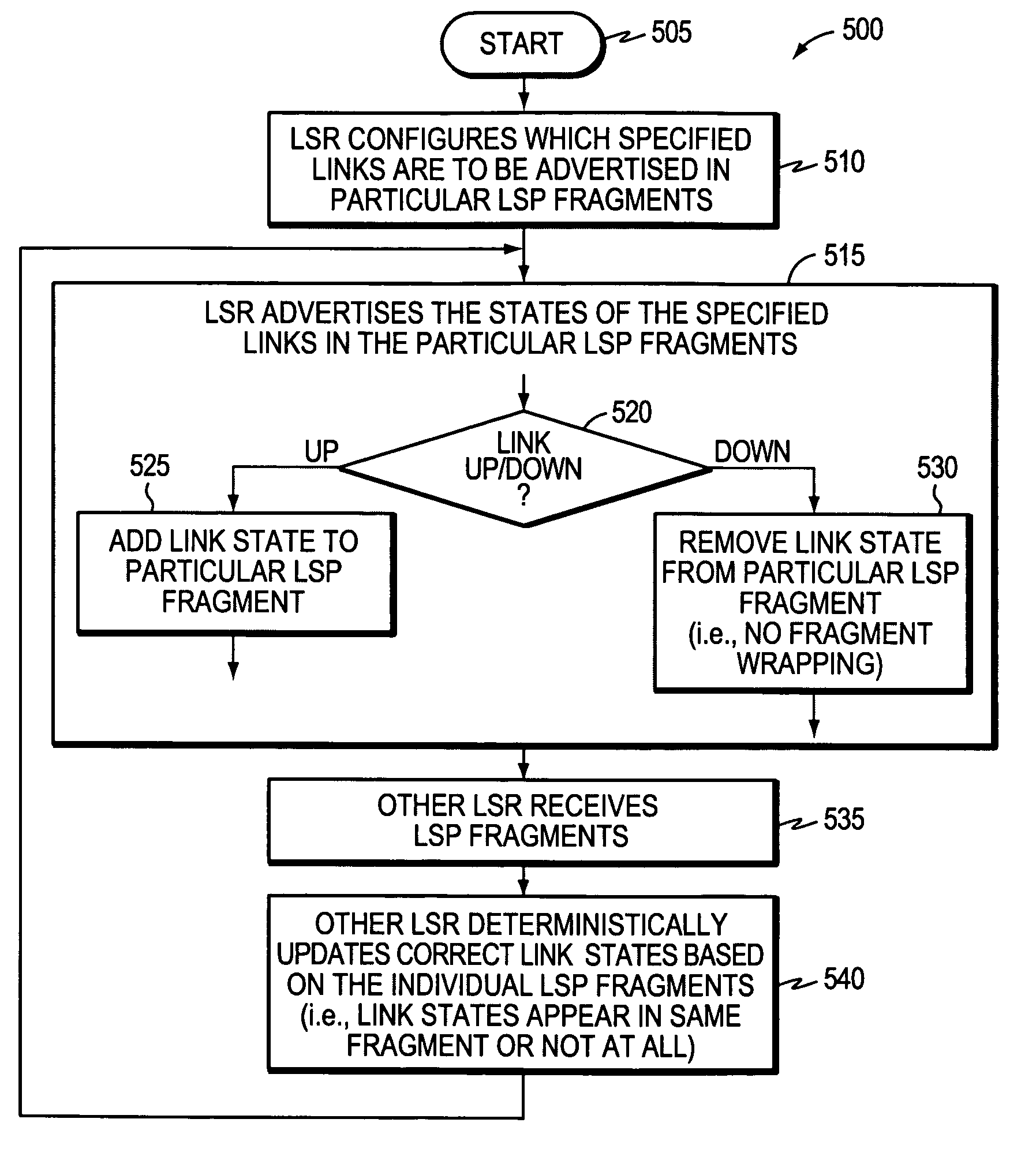
Technique for efficiently avoiding transient routing disturbances in link state routing protocols with link state packet fragmentation
InactiveUS20070286091A1Effective avoidanceAccurate updateError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsLink state packetRouting protocol
A technique efficiently avoids transient routing disturbances in link state routing protocols with fragmented link state packets (LSPs) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a link state router (LSR) specifies which of two or more links are to be advertised in each of two or more corresponding LSP fragments. The LSR advertises the states of the specified links in the corresponding LSP fragments to one or more other LSRs. In other words, each link of the LSR is assigned to a particular LSP fragment, and the state of the link is always to be advertised in that particular LSP fragment (i.e., no fragment wrapping). Upon receiving the LSP fragments, the other LSRs may update the correct link states based on the individual LSP fragments, i.e., without transient routing disturbances caused by fragment wrapping.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
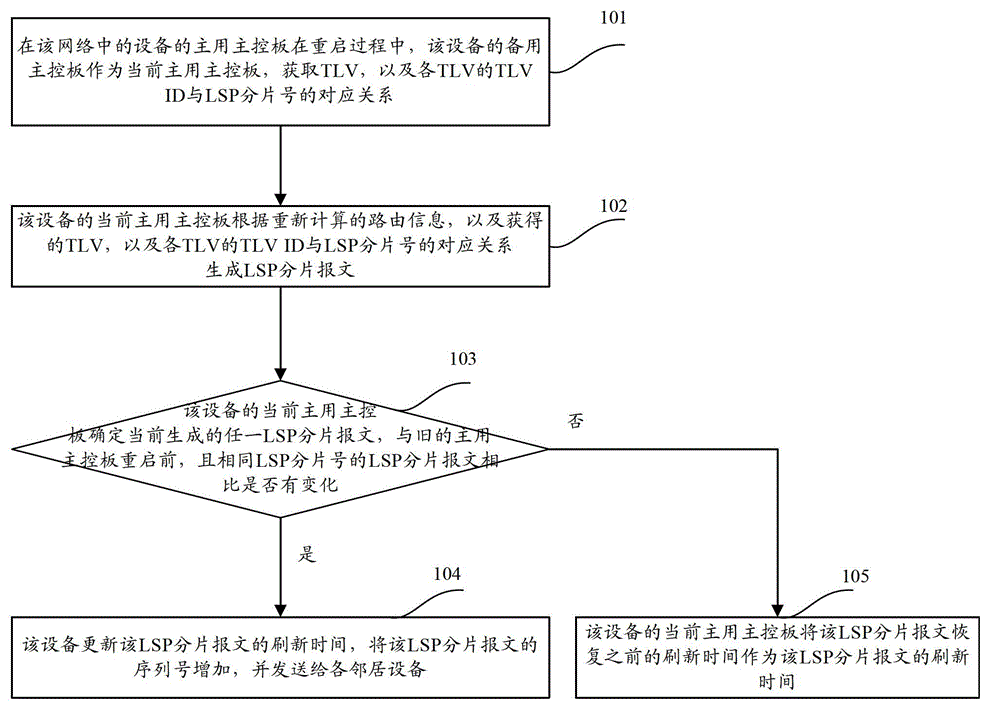
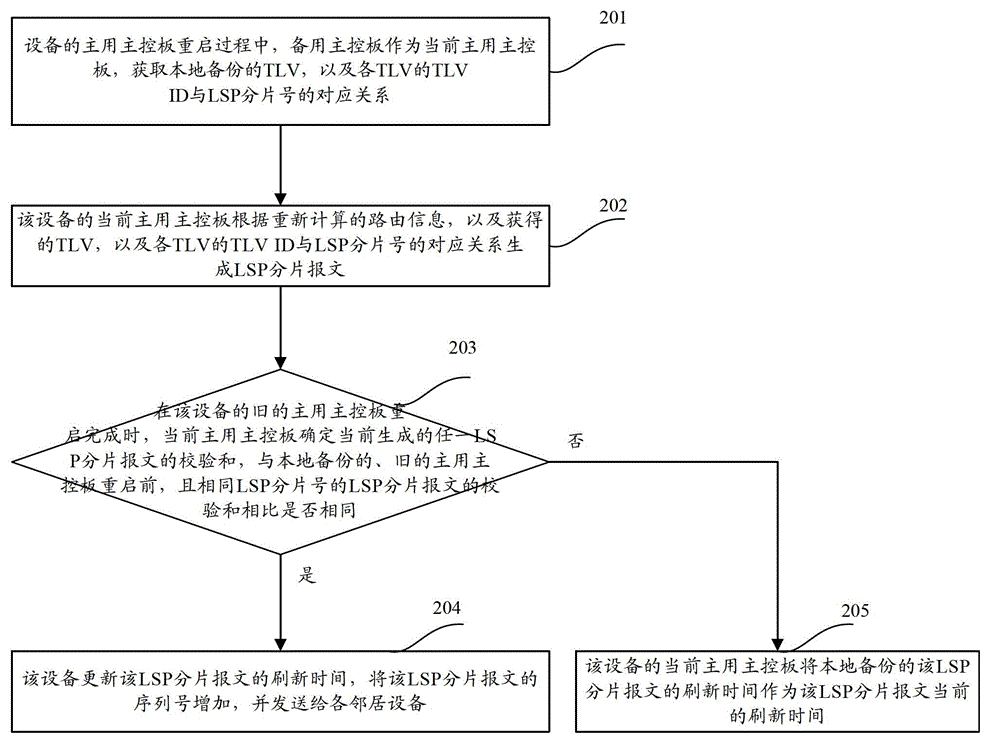
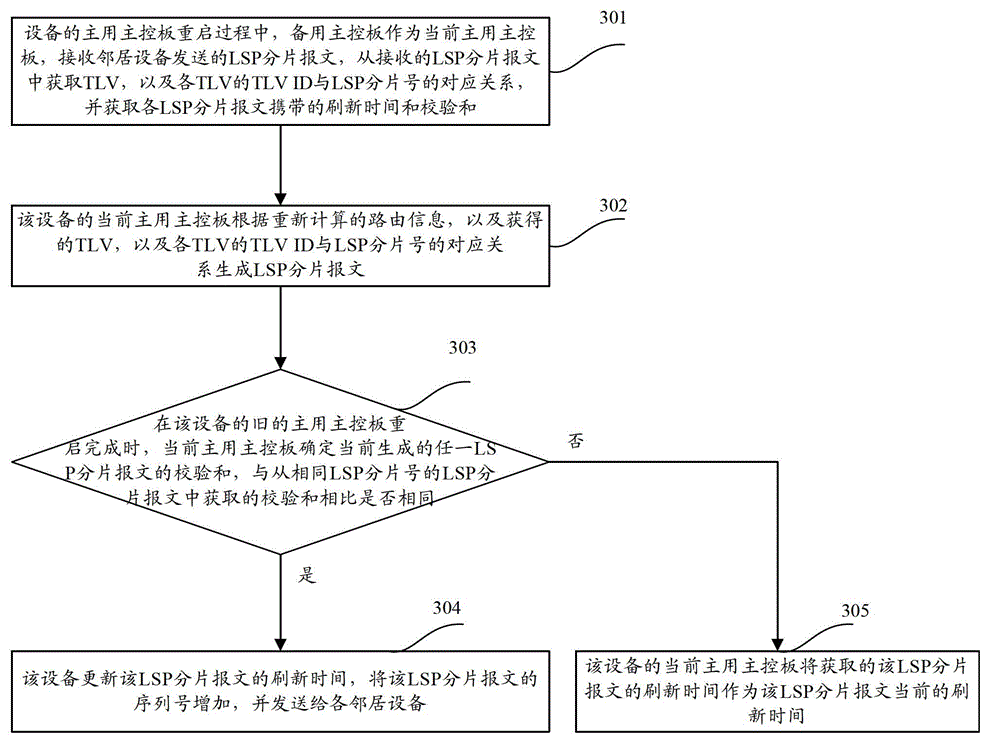
Method and equipment for generating and distributing link state protocol data unit fragment messages
The invention discloses a method for generating and distributing link state protocol data unit fragment messages, which comprises the following steps of: taking a standby main control board as a current active main control board in the restart process of an active main control board of equipment, generating the LSP (Link State Packet) fragment messages according to recalculated route information as well as a relation between TLV ID (Threshold Limit Value Identification) and LSP fragment numbers before the restart of the existing active main control board and only sending to neighbor equipment if compared with LSP fragment messages before the restart of the existing active main control board, the generated LSP fragment messages are changed. The invention also provides the equipment; and after the restart of the existing active main control board of the equipment is finished, the sending of the unnecessary LSP fragment messages is omitted.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
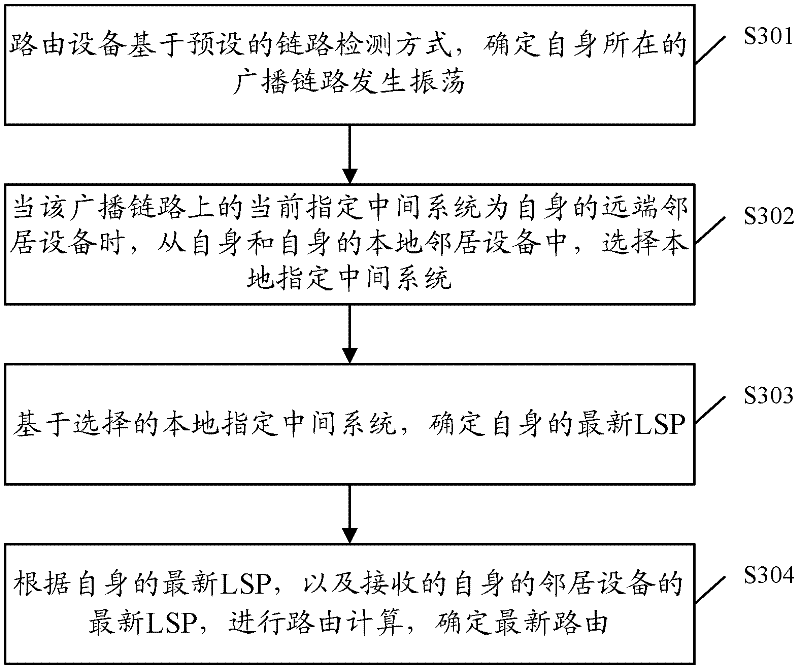
Routing determination method and routing device
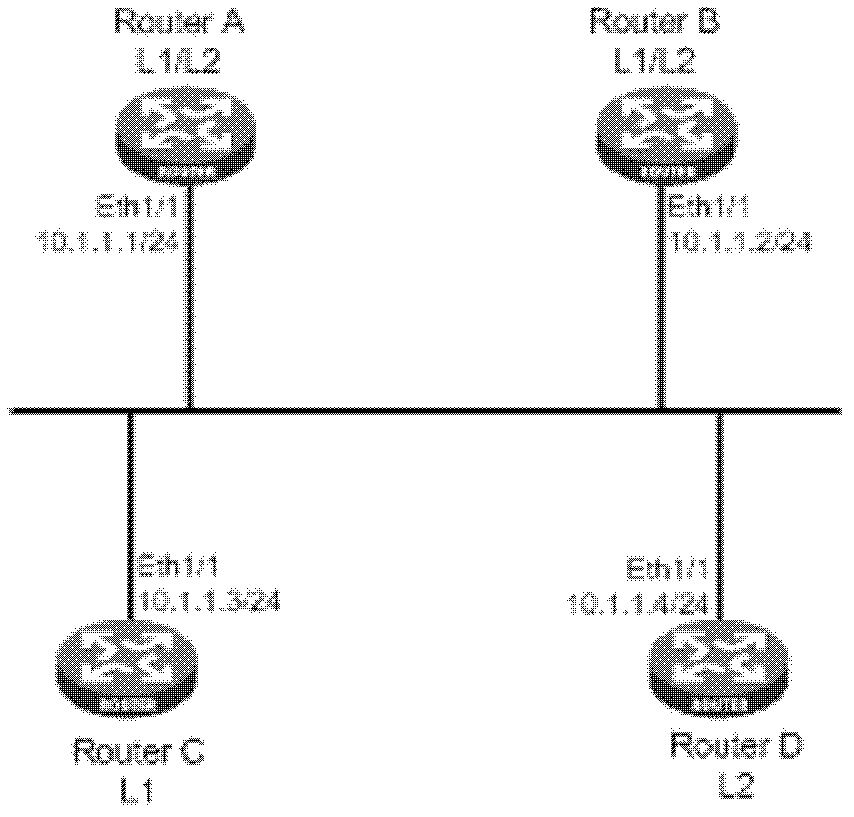
The invention discloses a routing determination method and a routing device. The method comprises the following steps: based on a preset link detection mode, the routing device determines that a broadcast link where the device is has oscillation; when a present assigned intermediate system at the broadcast link is a self distant end neighbor device, a local assigned intermediate system is selected from the device and a self local neighbor device; based on the selected local assigned intermediate system, a self latest LSP (link-state packet) is determined; according to the self latest LSP, and a received latest LSP of the neighbor device of the device, routing calculation is carried out, and a latest routing is determined. When the broadcast link has oscillation, one end of the broadcast link has a plurality of routing devices, and the assigned intermediate system is not included, by employing a scheme provided by an embodiment of the invention, the routing calculation is carried out, and routing convergence can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING XINWANG RUIJIE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Selectively sending link state messages in a network link state protocol based on interest of network nodes
In a link state protocol such as an interior gateway protocol (IGP), link state advertisements or link state packets (LSA / LSPs) are sent only to network nodes that have expressed interest in them, rather than always flooding them.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
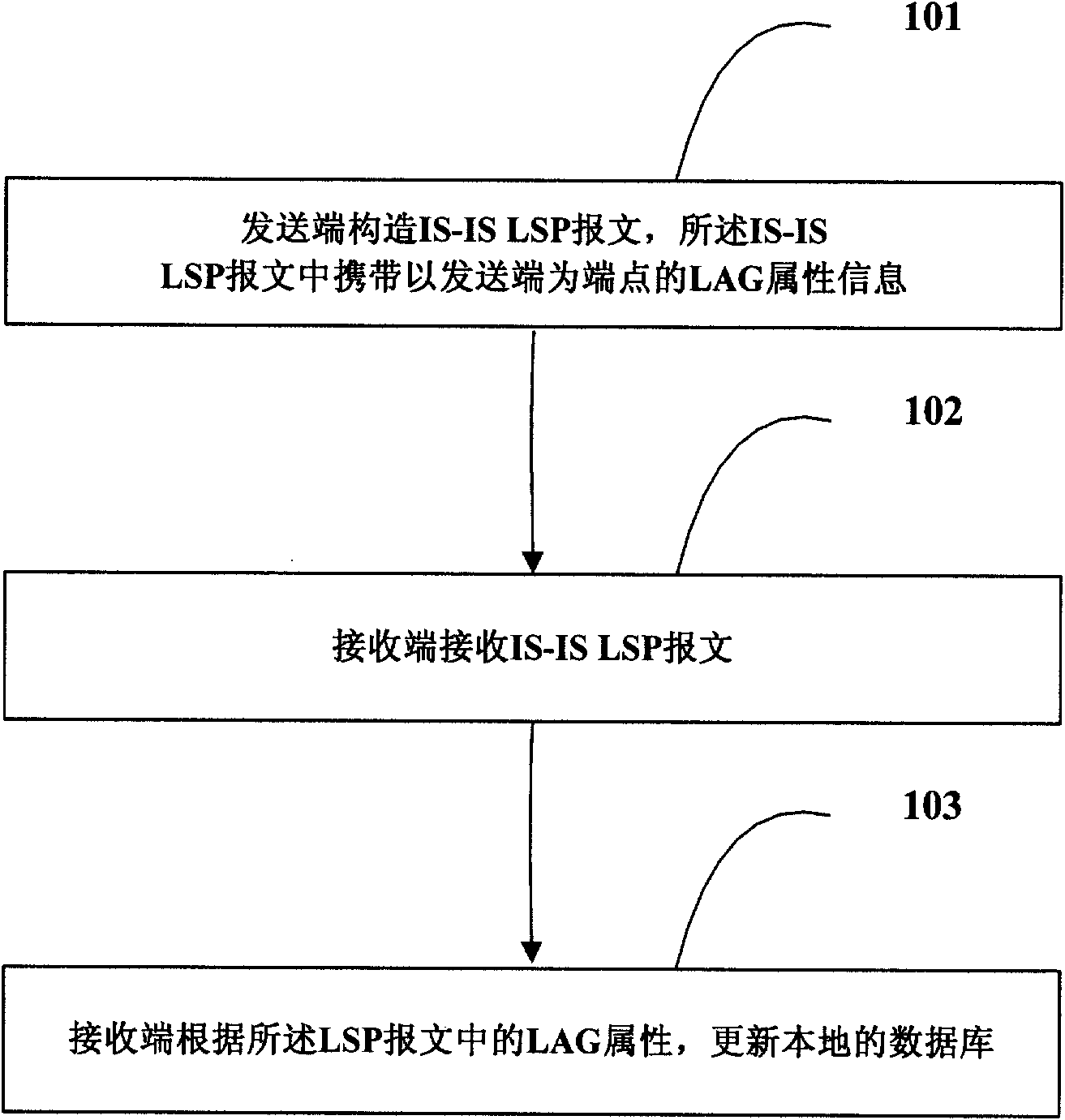
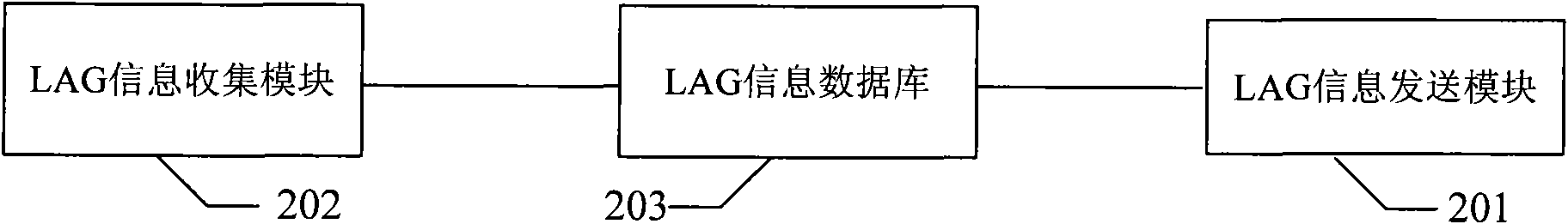
Information management method of link aggregation group and network node
InactiveCN101674229AImprove accuracyGuaranteed service qualityData switching networksLink aggregationLink state packet
The embodiment of the invention discloses an information management method of a link aggregation group (LAG), comprising the following steps: creating intermediate system-to-intermediate system (IS-IS) link state packet (LSP) messages containing LAG attribute information at a first network node and transmitting the messages to other nodes in a network; receiving a node of the IS-IS LSP messages containing LAG attribute information, and recording the LAG attribute information in the messages. The embodiment also discloses a network node. The embodiment can realize the management of the LAG attribute information.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
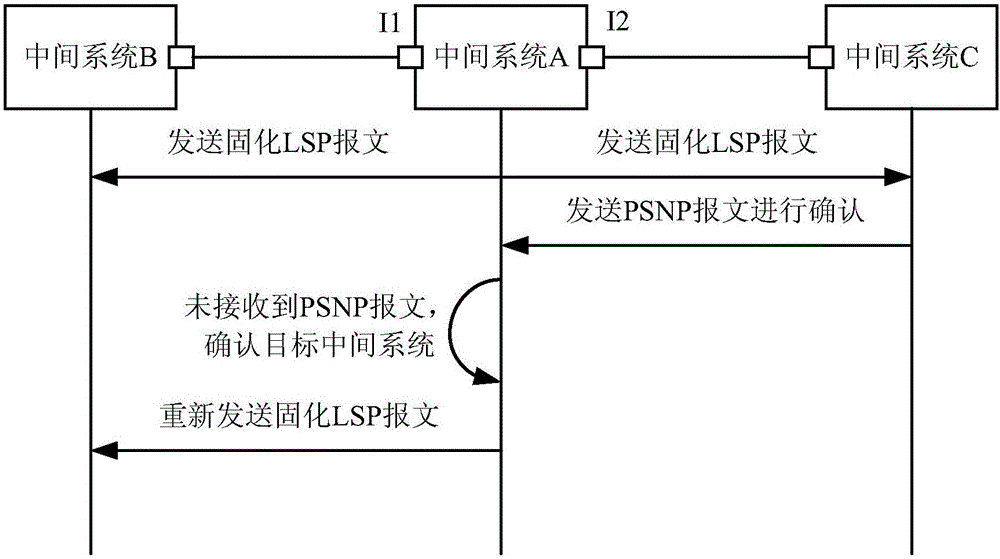
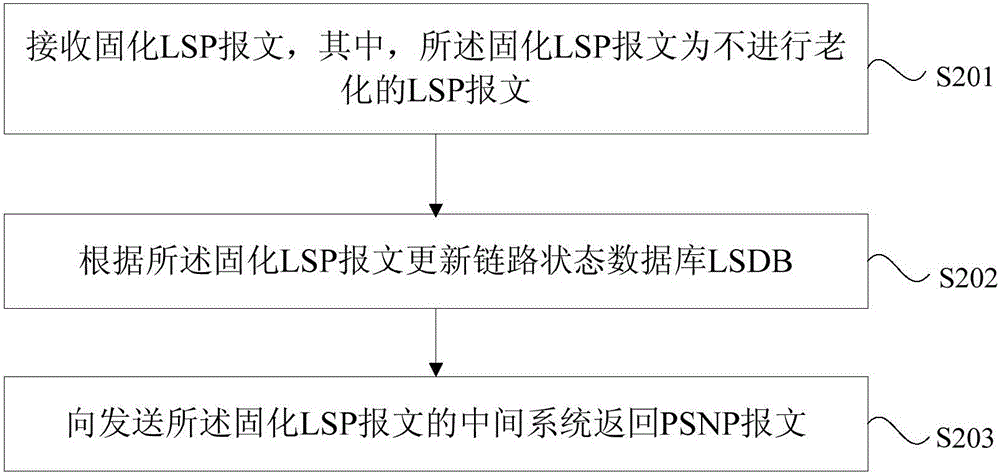
Link state synchronization method and device
The embodiments of the invention provide a link state synchronization method and a device which are applied to intermediate systems. The method comprises: sending solidified link state packets (LSP) to intermediate systems in neighboring relationship with itself wherein the solidified link state packets are link state packets (LSP) that are not subjected to aging; determining a targeted intermediate system wherein the targeted intermediate system is one that does not send partial sequence numbers packets (PSNP) to itself in a preset period; and sending the solidified link state packets (LSP) to the targeted intermediate system. The embodiments can avoid the periodical flooding LSP to all intermediate systems to maintain LSDB synchronization, therefore, saving network band width.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
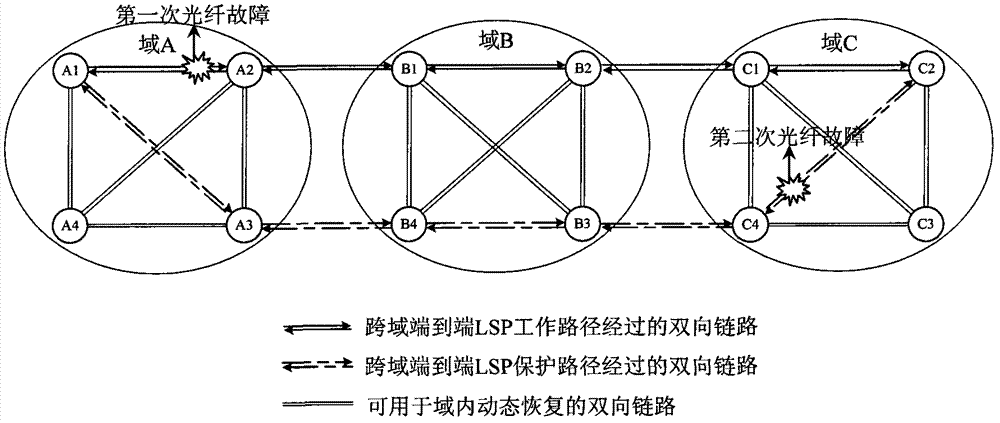
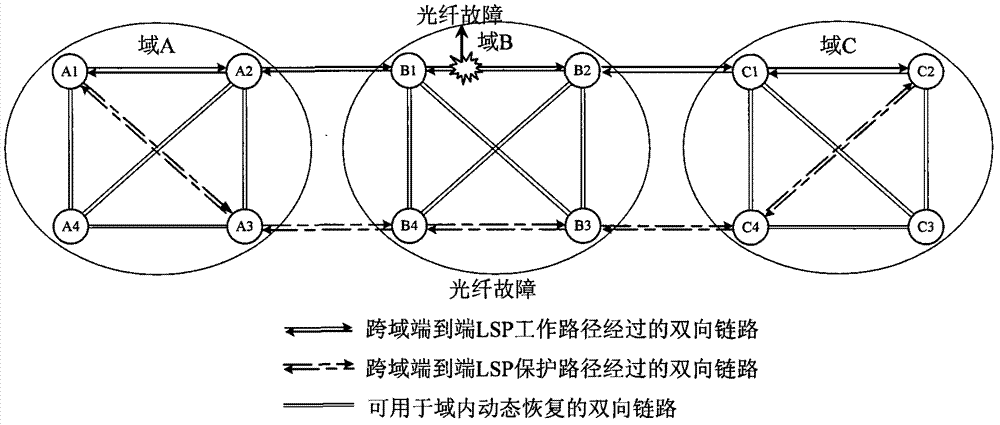
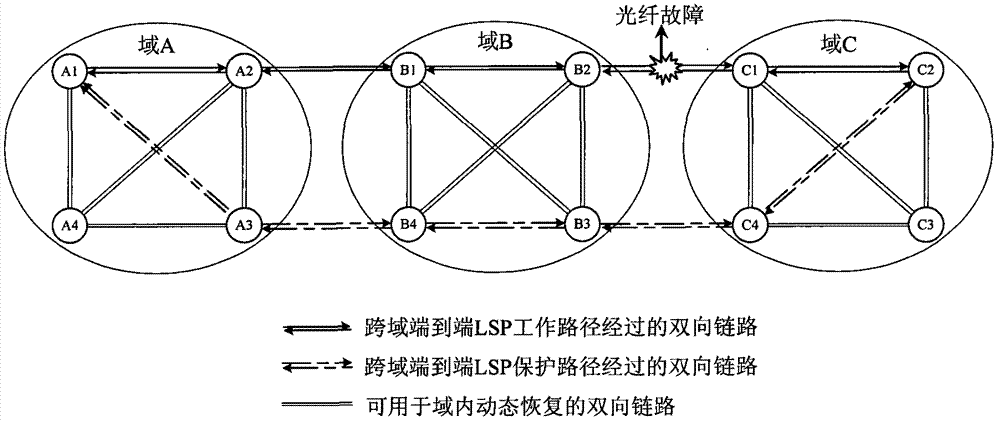
Method for protecting and recovering cross-domain end-to-end label switched path
ActiveCN102740175AImprove survivabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionLink state packetLabel switching
The invention discloses a method for protecting and recovering a cross-domain end-to-end label switched path and relates to the field of an automatic switched optical network. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, building a work path and N protection paths, wherein N is greater than or equal to 1; S2, judging the path in which a fault occurs, if the path is the work path, carrying out protection switching on business, and judging the position at which the fault is at the same time; if the position is in a source domain, a host domain or an intermediate domain, triggering one protection path bypassing a fault point in the domain in which the fault occurs; splicing the protection path with the protection paths without the fault in the other domains to form a new protection path; if the position is between the domains, performing no triggering on recovery of the work path with the fault; and if the fault is on the protection path, needing no protection switching on the business, triggering one new protection path in the domain, and splicing the protection path with the protection path without the fault in other domains to form another new protection path. According to the invention, by protecting, restoring and splicing an LSP (link state packet) of each segment, multipoint faults in the domains or between the domains are effectively resisted, and high reliability requirements of cross-domain business are met.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD +1
High-speed traffic measurement and analysis methodologies and protocols
InactiveUS7397766B2Reduce errorsMinimal communications overheadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNODALTraffic capacity
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method and device for preventing traffic from interrupting
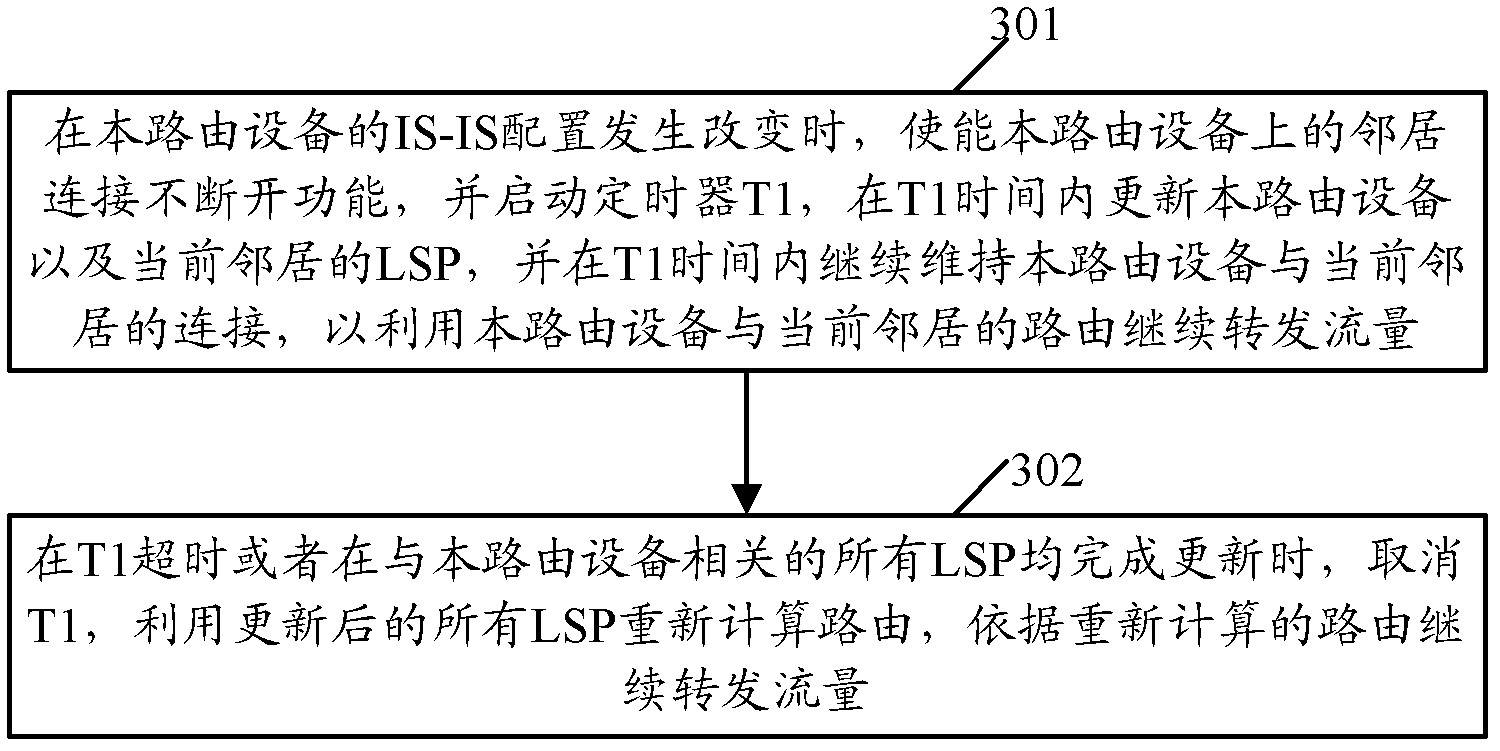
ActiveCN102571605AForwarding is normalAvoid interruptionData switching networksTraffic capacityCurrent neighbor
The invention provides a method and a device for preventing traffic from interrupting. According to the method and the device, a timer T1 and a function of keeping neighbor connection continuous are configured on routing equipment, when the configuration of an intermediate system to intermediate system routing protocol (IS-IS) of the routing equipment is changed, the connection between the routing equipment and current neighbors can be continuously maintained in a T1 time, and the update of link-state packets (LSPs) of the routing equipment and the current neighbors can also be ensured in the T1 time, and the traffic is continually to be forwarded for preventing the traffic from interrupting by utilizing the routing equipment and routers of the current neighbors.
Owner:XINHUASAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Route selection method and route selection device in content center network
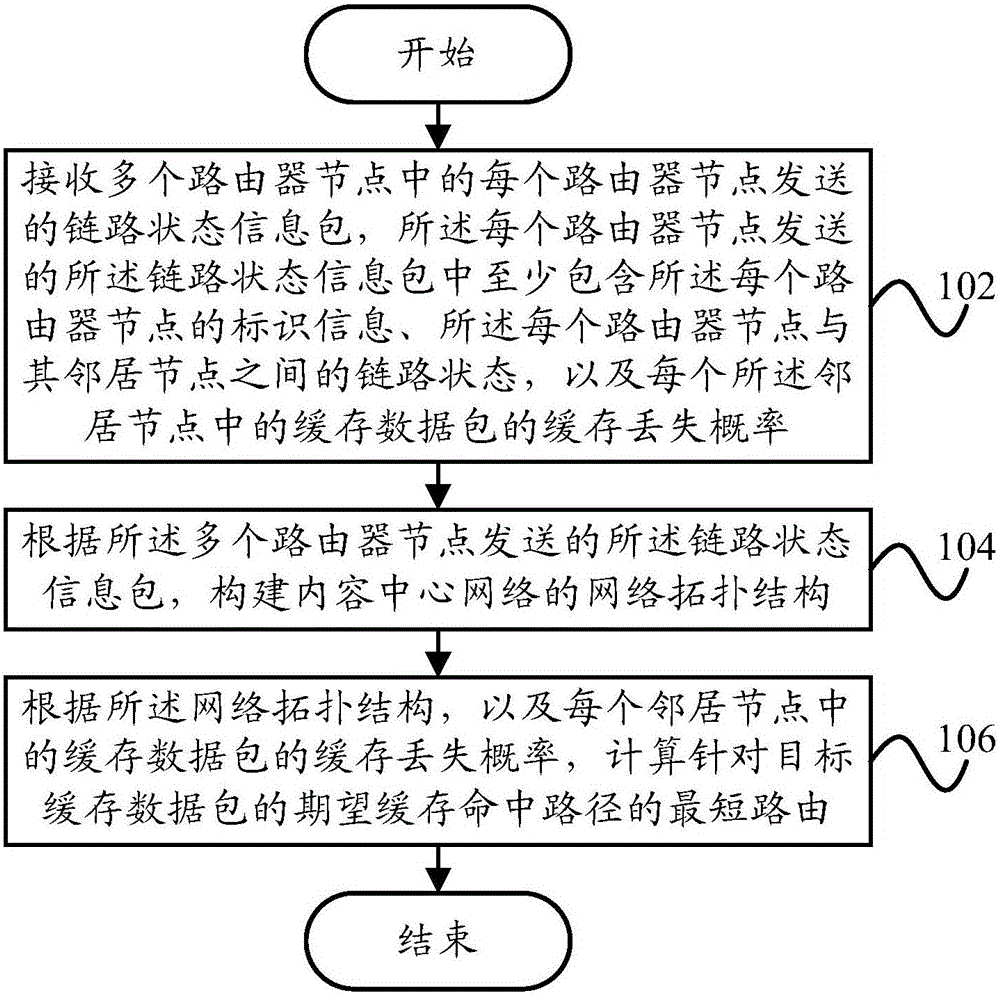
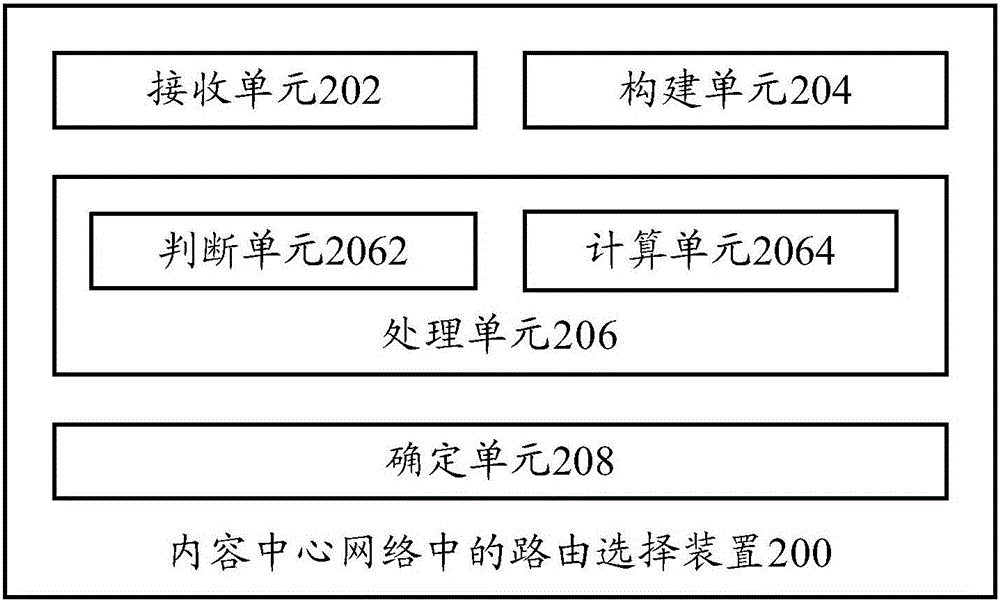
ActiveCN107181775AEasy accessImprove fetch rateData switching networksNetwork packetStructure of Management Information
The invention provides a route selection method and route selection device in a content center network. The route selection method comprises: a link state packet sent by each of a plurality of router nodes is received, wherein the link state packet sent by each router node at least includes identifier information of each router node, a link state between each router node and a neighbor node, and a cache loss probability of a cache packet in each neighbor node; a network topology structure of a content center network is constructed according to the link state information packets sent by the plurality of router nodes; and a shortest route for an expected cache hit path of a target cache data packet is calculated based on the network topology structure and the cache loss probability of the cache data packet of each neighbor node. Therefore, the user can obtain a request data packet rapidly.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Automatically configuring mesh groups in data networks
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method and apparatus for flooding link state packets to achieve faster convergence
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Technique for efficiently avoiding transient routing disturbances in link state routing protocols with link state packet fragmentation
InactiveUS7751336B2Effectively avoidAccurate updateError preventionTransmission systemsLink state packetRouting protocol
A technique efficiently avoids transient routing disturbances in link state routing protocols with fragmented link state packets (LSPs) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a link state router (LSR) specifies which of two or more links are to be advertised in each of two or more corresponding LSP fragments. The LSR advertises the states of the specified links in the corresponding LSP fragments to one or more other LSRs. In other words, each link of the LSR is assigned to a particular LSP fragment, and the state of the link is always to be advertised in that particular LSP fragment (i.e., no fragment wrapping). Upon receiving the LSP fragments, the other LSRs may update the correct link states based on the individual LSP fragments, i.e., without transient routing disturbances caused by fragment wrapping.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Mechanism to improve concurrency in execution of routing computation and routing information dissemination
ActiveUS7558214B2Efficient processingImprove concurrencyData switching by path configurationInformation repositoryInformation Dissemination
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Variable translucency no-sight routing for AD-HOC networks
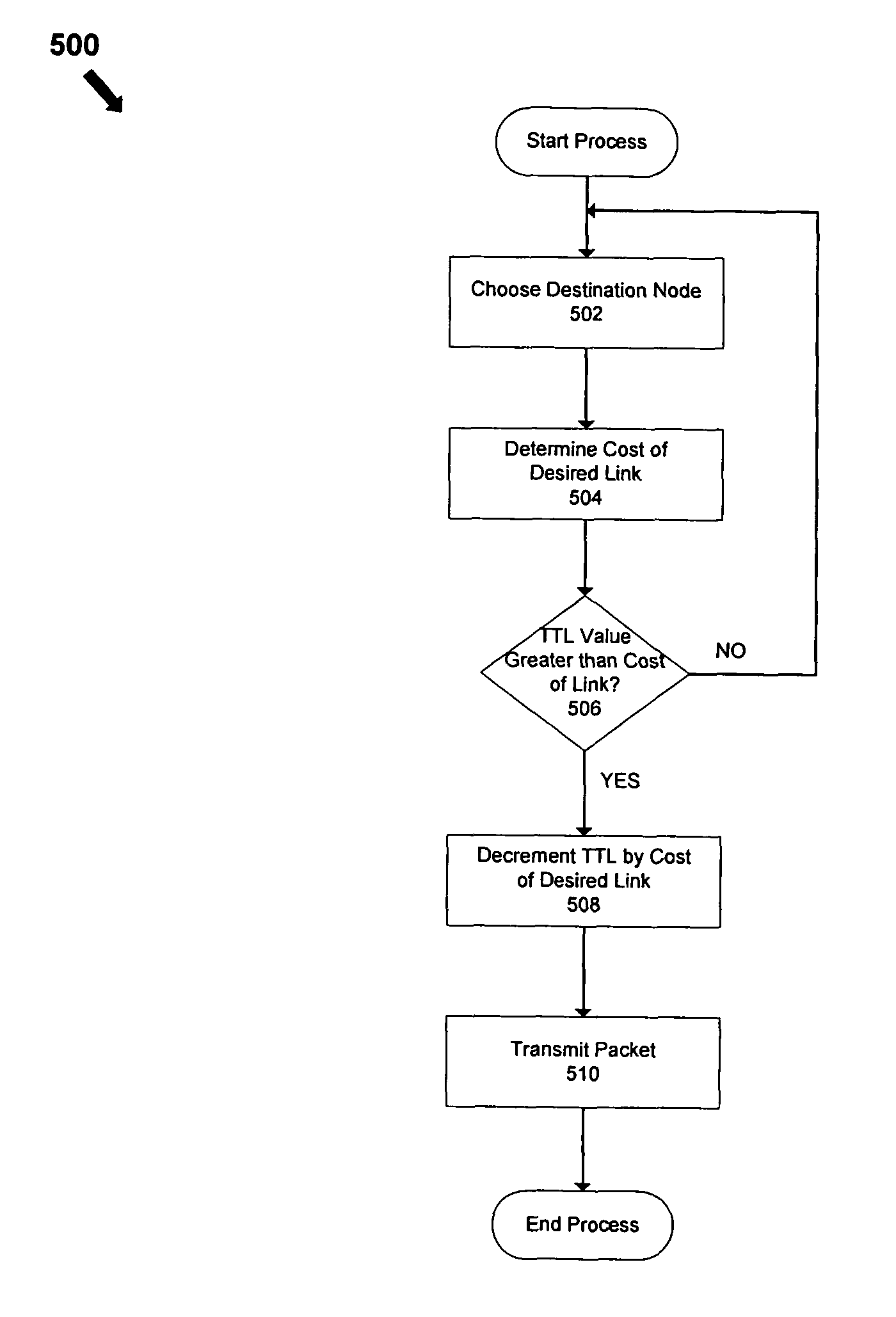
InactiveUS8144595B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A system comprising a plurality of nodes forming a network and a link-state packet capable of being transmitted by a source node in the network to a destination node in the network over a communication link; wherein the source node subtracts a transmission cost associated with the communication link from a time-to-live value associated with the link-state packet prior to transmitting the link-state packet to the destination node. Each node in the network may be configured to use a routing protocol, such as a no-sight routing protocol, to assign the transmission cost to the communication link.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP +1
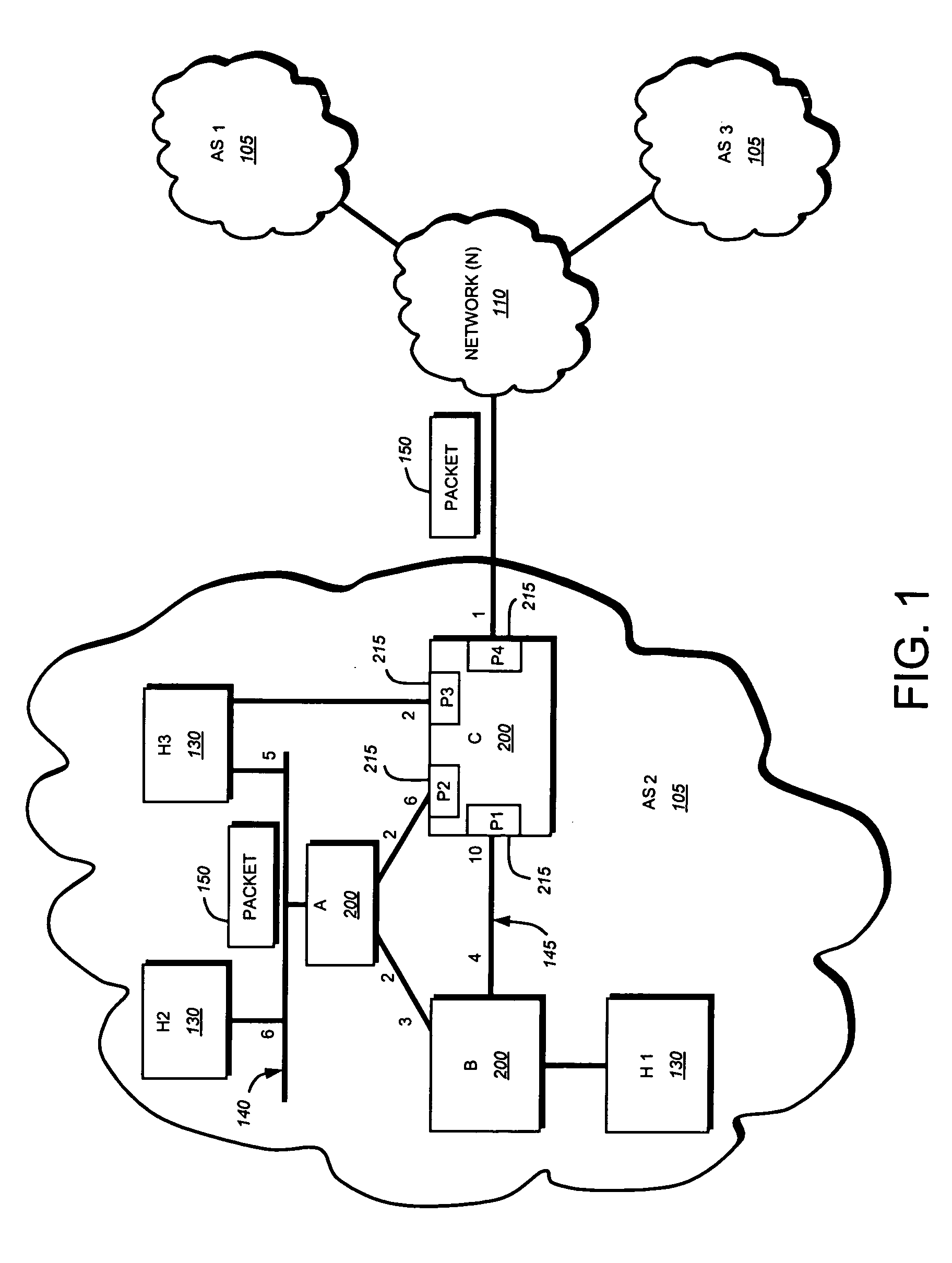
Packet network routing
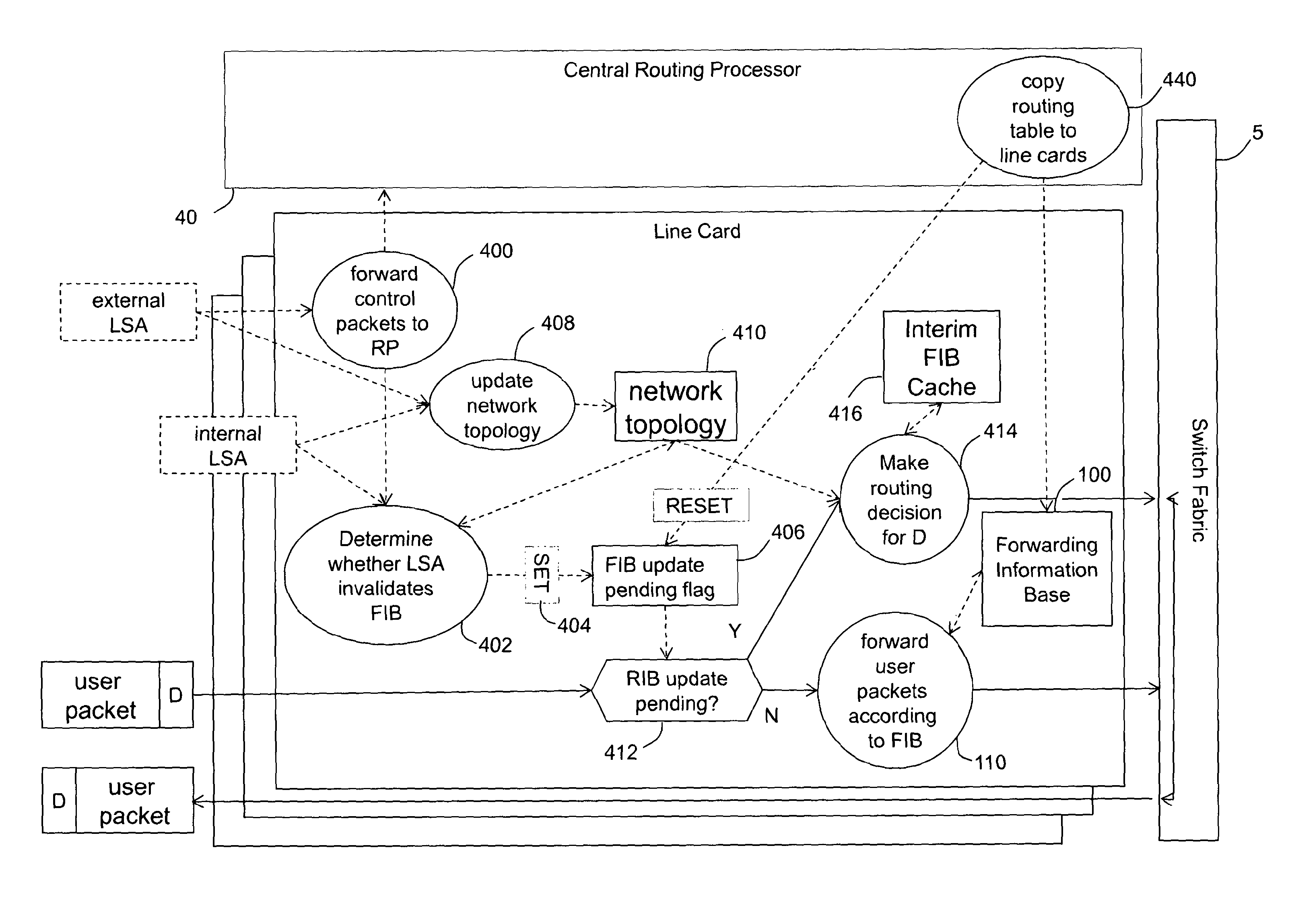
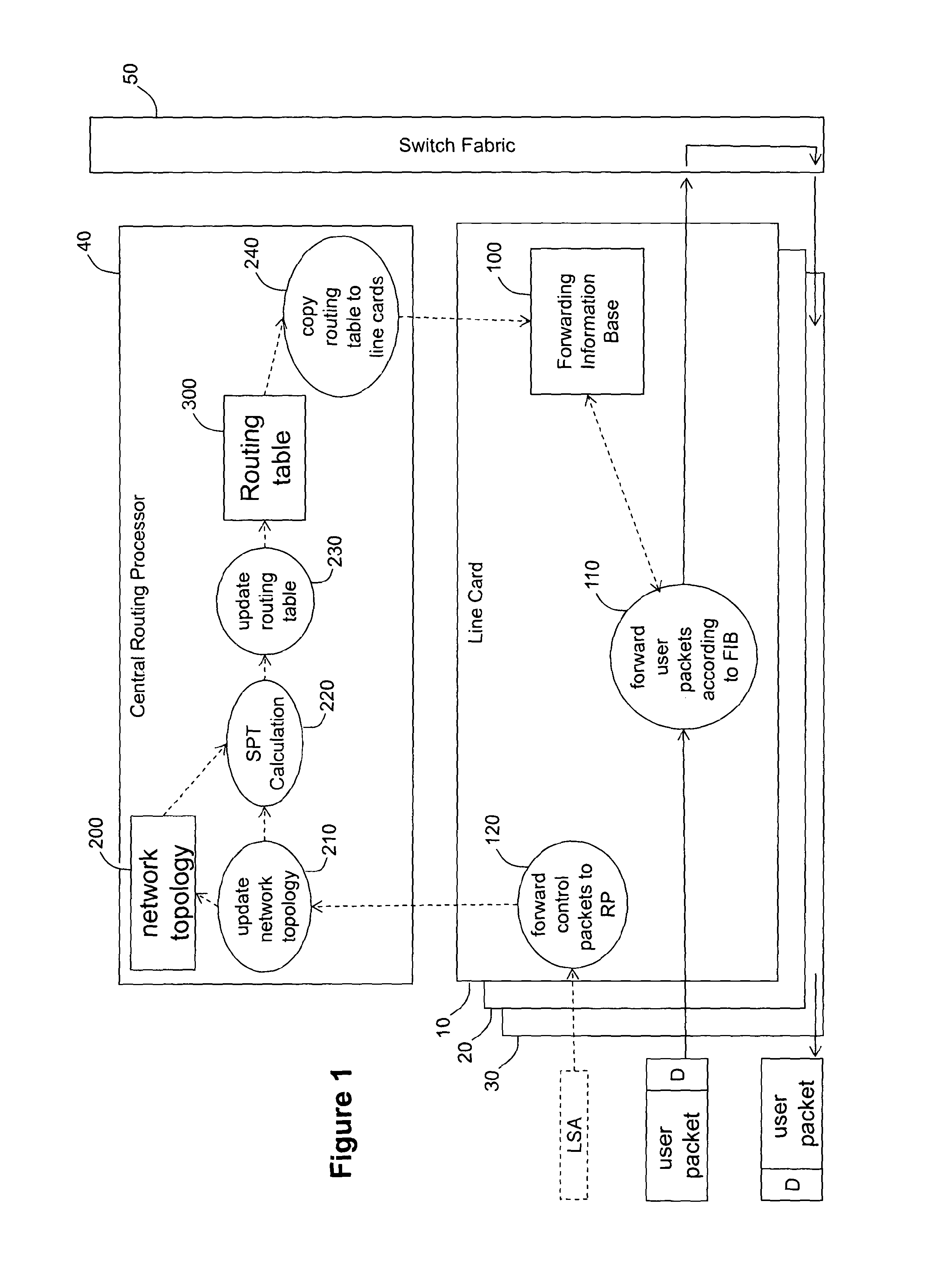
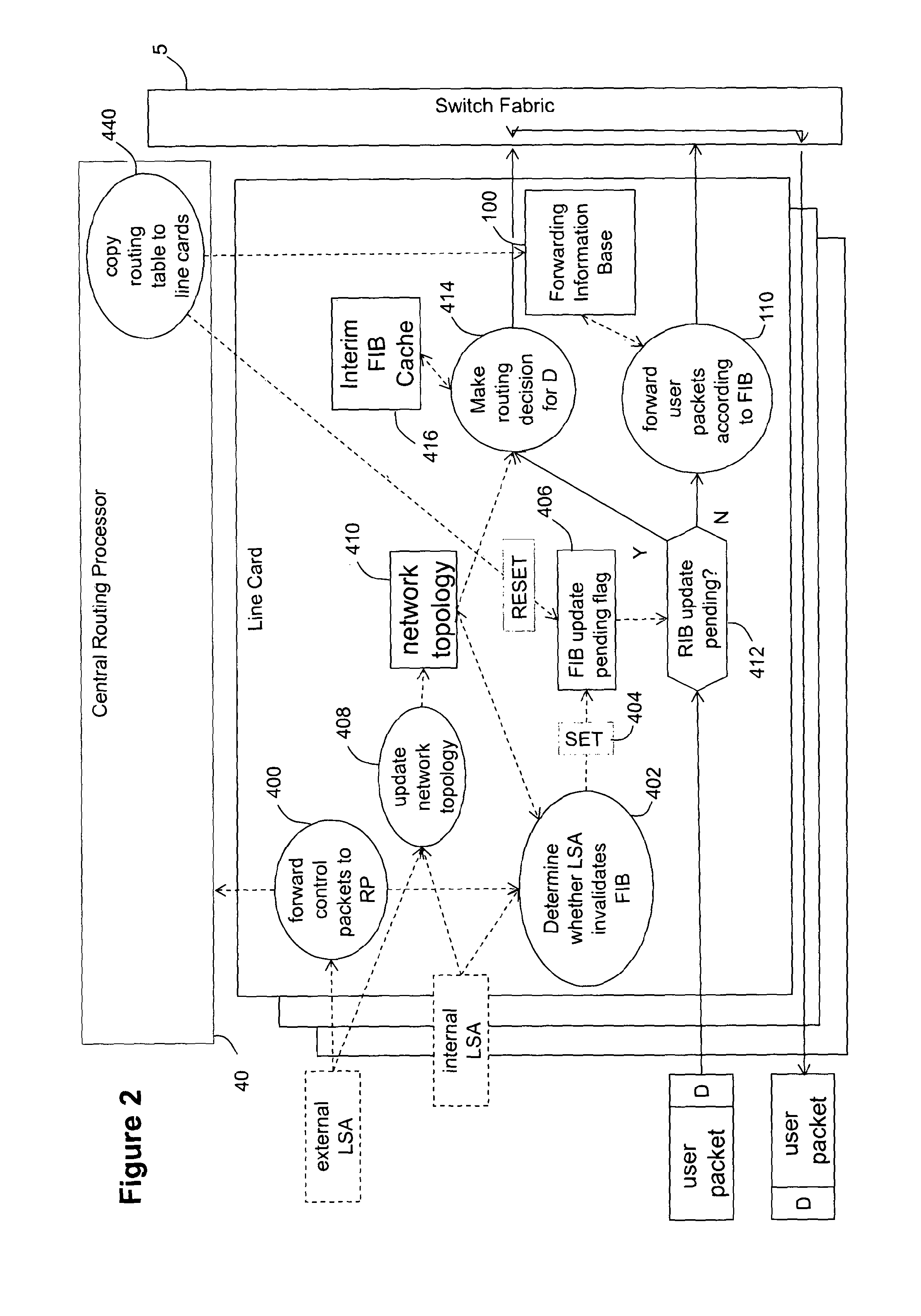
A line card for use in a router or packet switch is disclosed. A problem with conventional routers or packet switches is that they can take over a second to fully react to a network state update from another router or packet switch. Such network state packets are used in dynamic routing protocols intended to route packets around a failed or overloaded router. In operating in according with dynamic routing protocols, conventional routers or packet switches react to such network state packets by updating the routing tables used by the line cards to send packets, or data extracted from packets, to the egress port (often on a different line card in the router or network switch) appropriate for the destination address found in the packet. Any packets which arrive between the network state packet's arrival and the completion of the ensuing routing table update on the line cards, can be misrouted—which can cause them to be delayed or dropped by the network. The described embodiments address this problem by operating the line card to react to a network state update packet by running a restricted routing algorithm to provide interim routes while a conventional comprehensive routing algorithm runs in parallel to provide a comprehensive set of routes. In this way, a faster, if less thorough, reaction to the arrival of a network state update packet is provided, which reduces the risk of packets being misrouted while the network converges. The technique has application to any packet networks, but is especially useful in Internet Protocol packet networks or Multi-Protocol Label Switching networks.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com