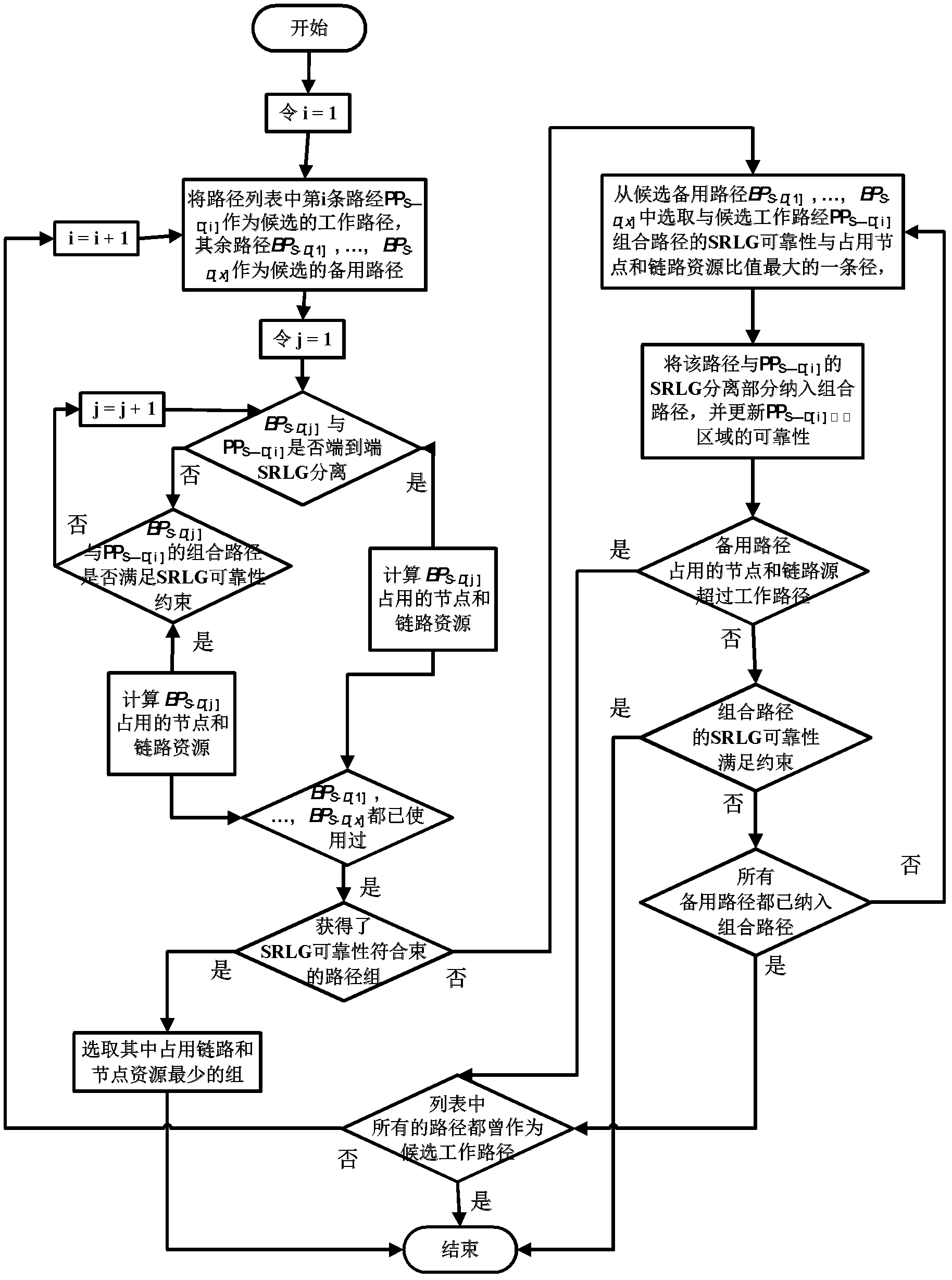
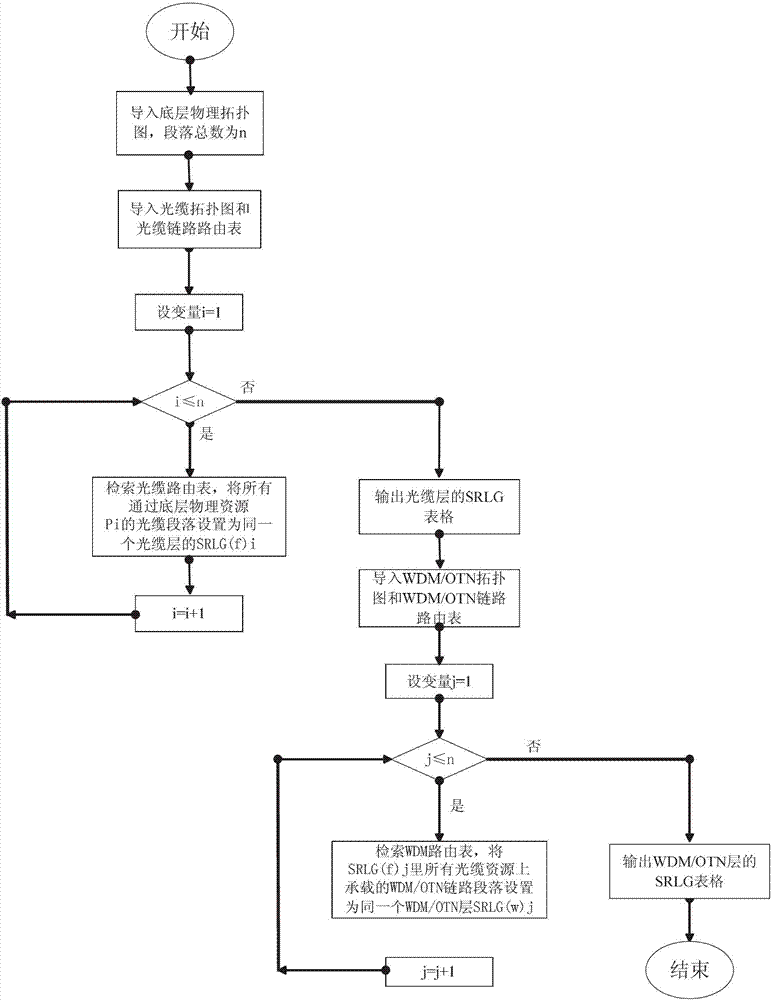
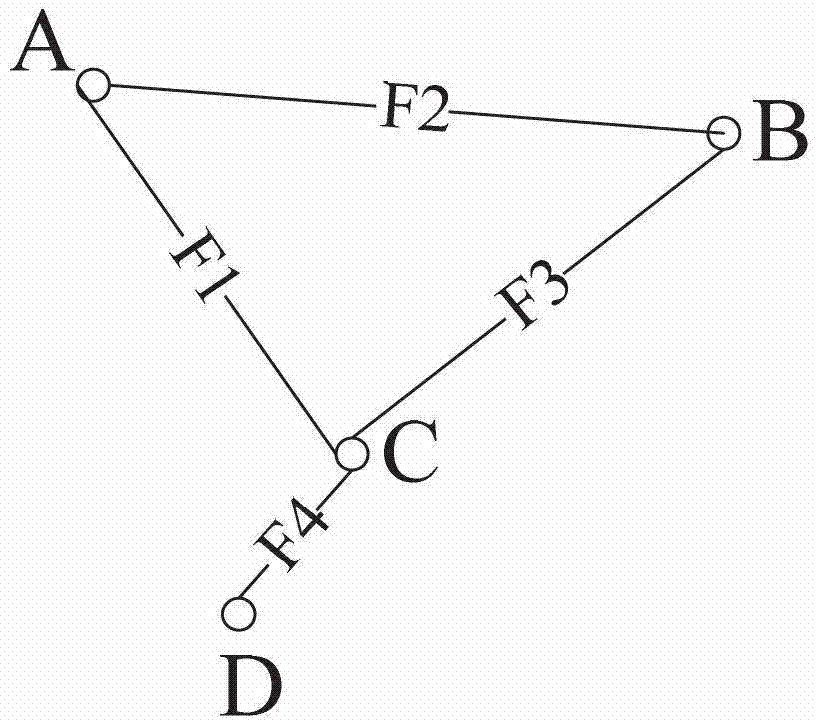
Patents
Literature
37 results about "Shared risk link group" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
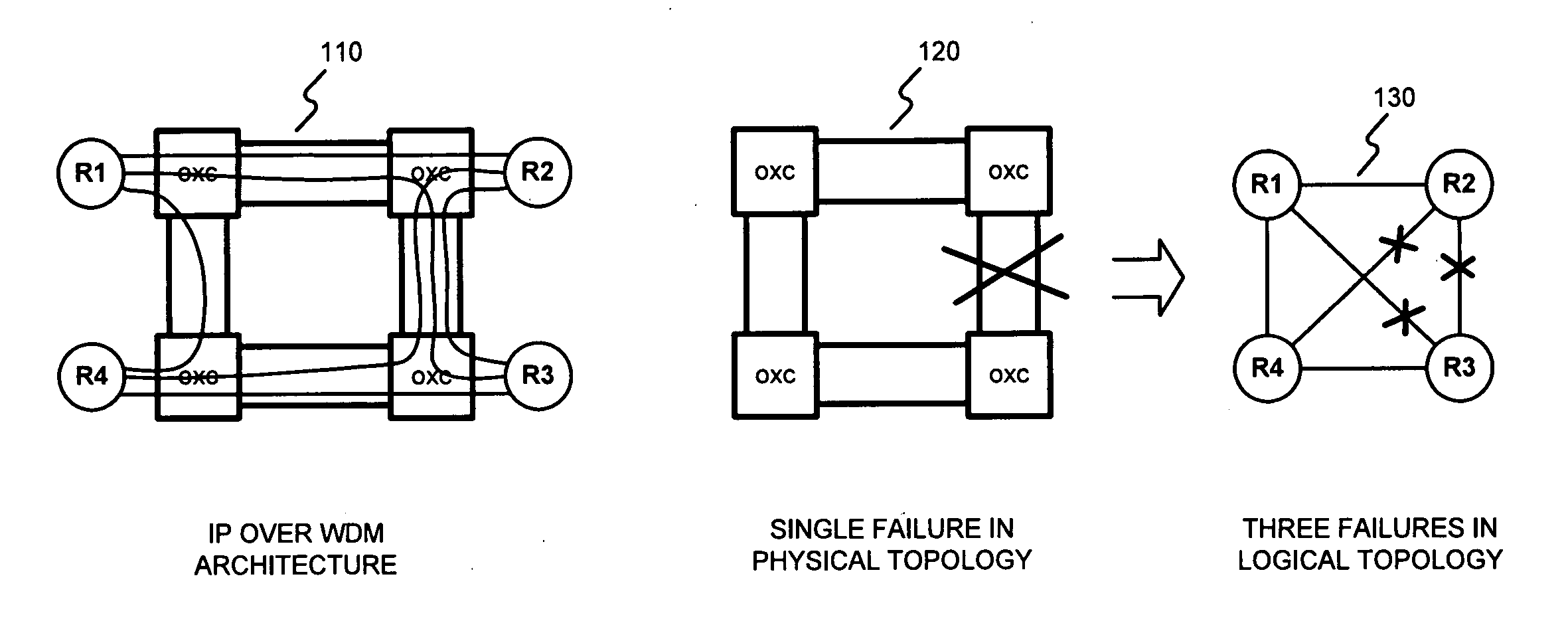
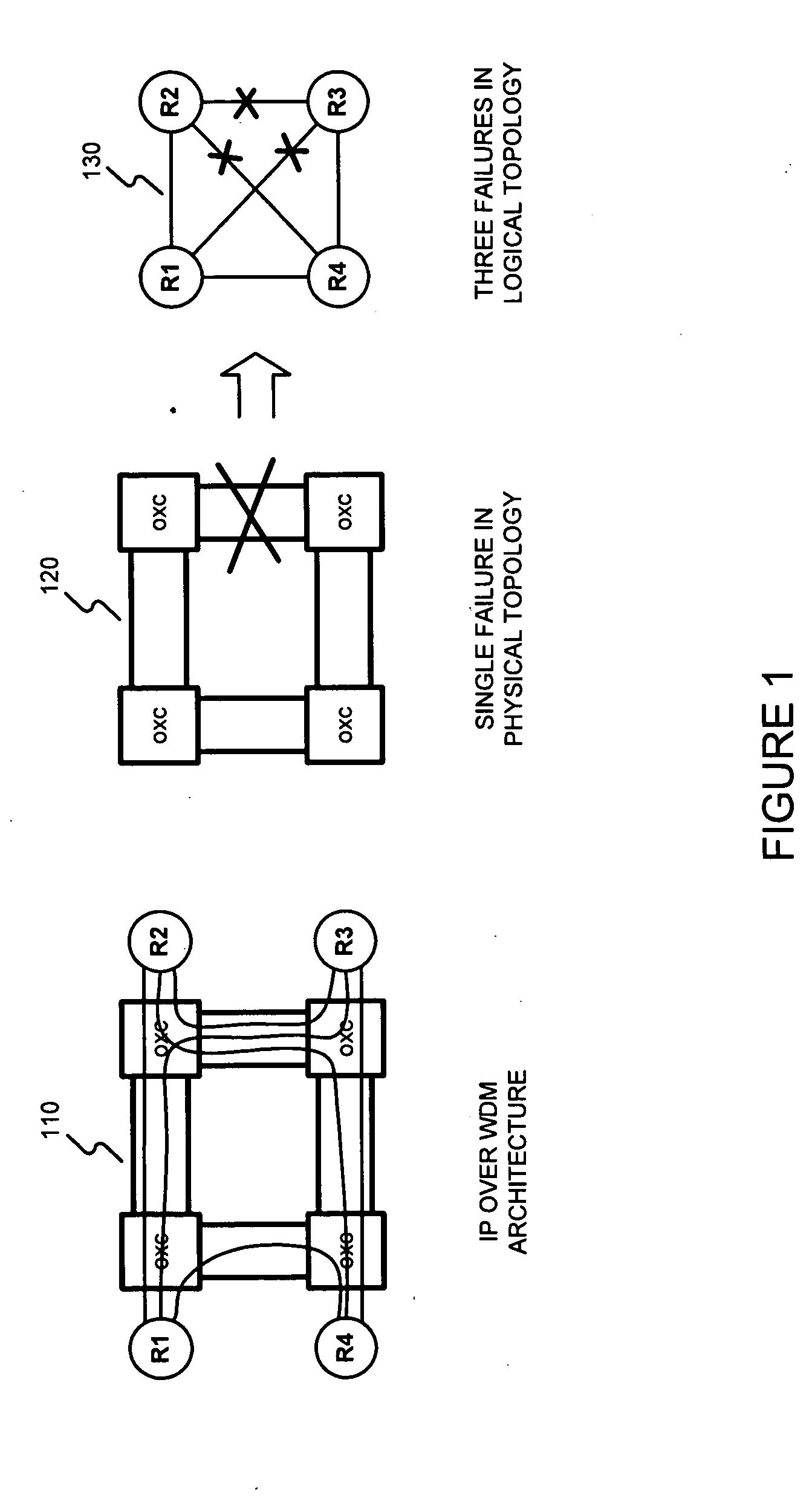
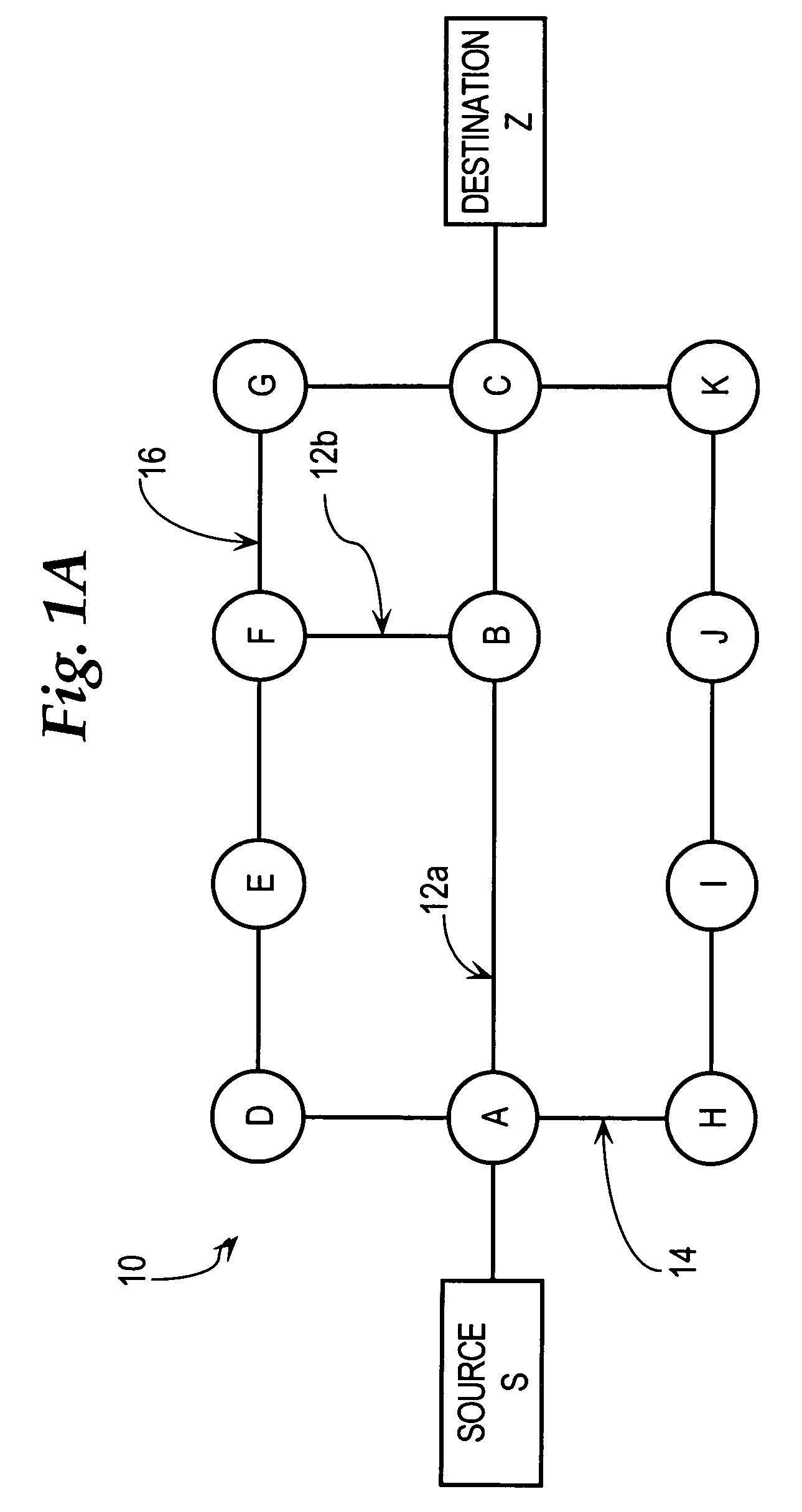
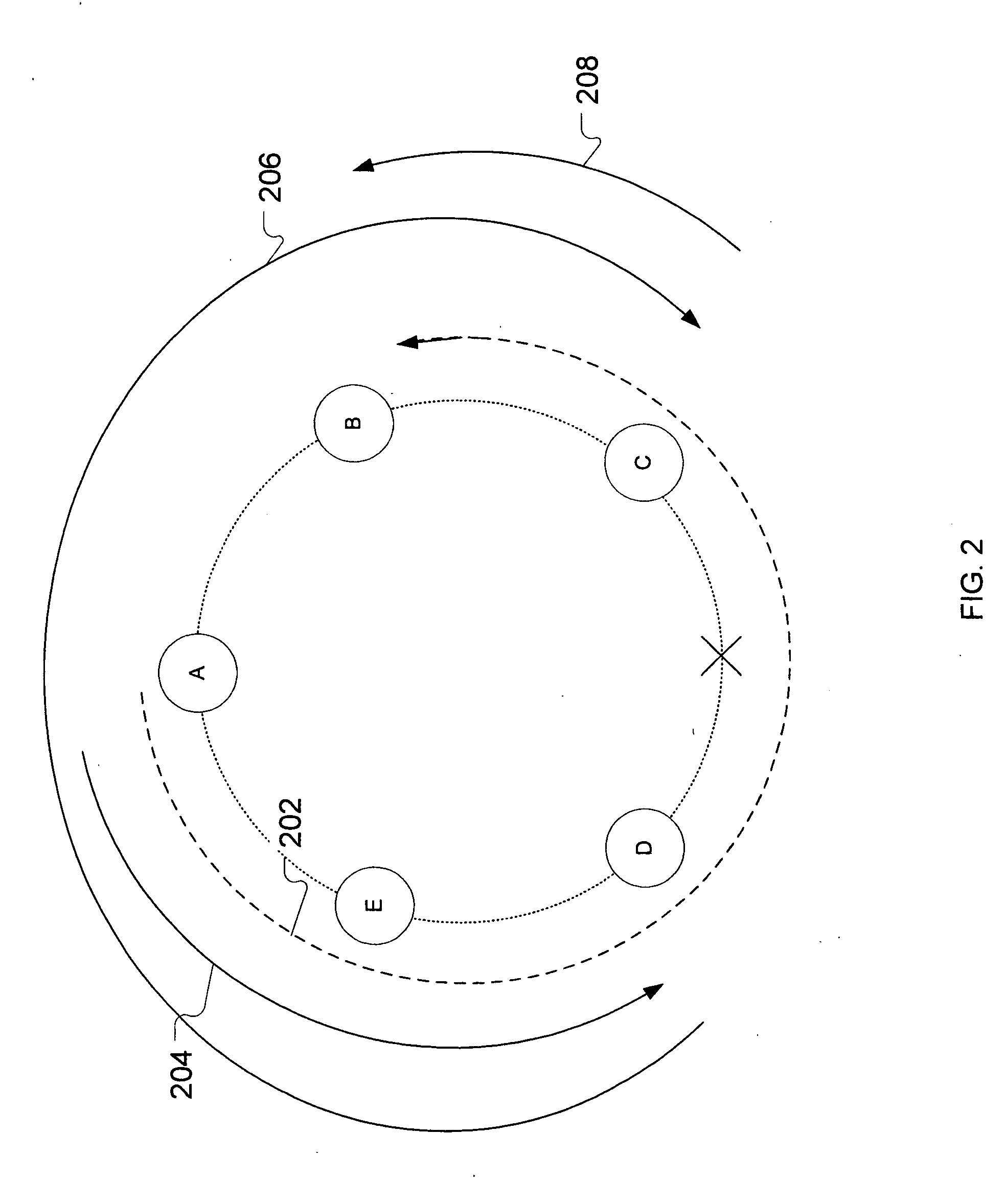
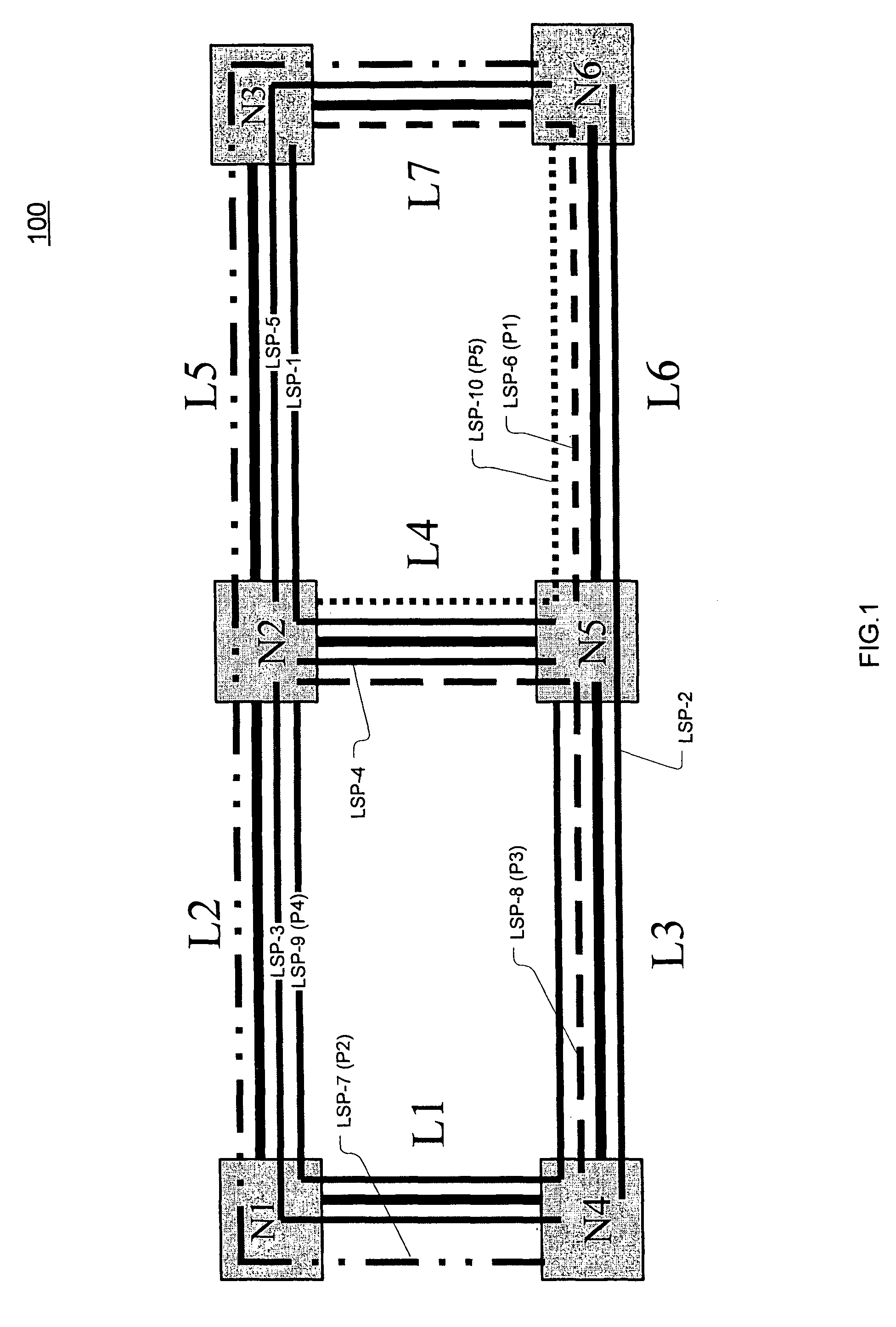
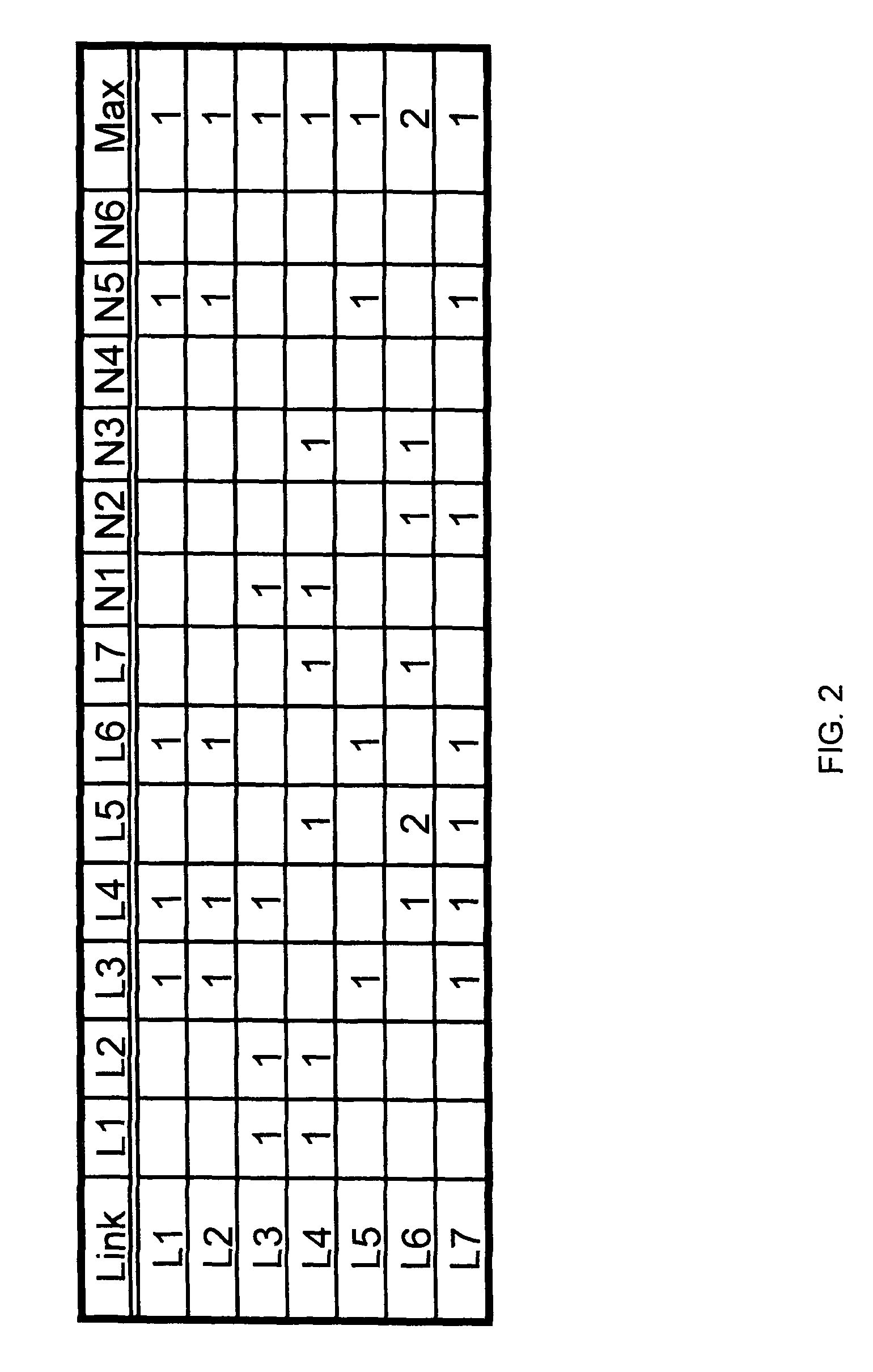
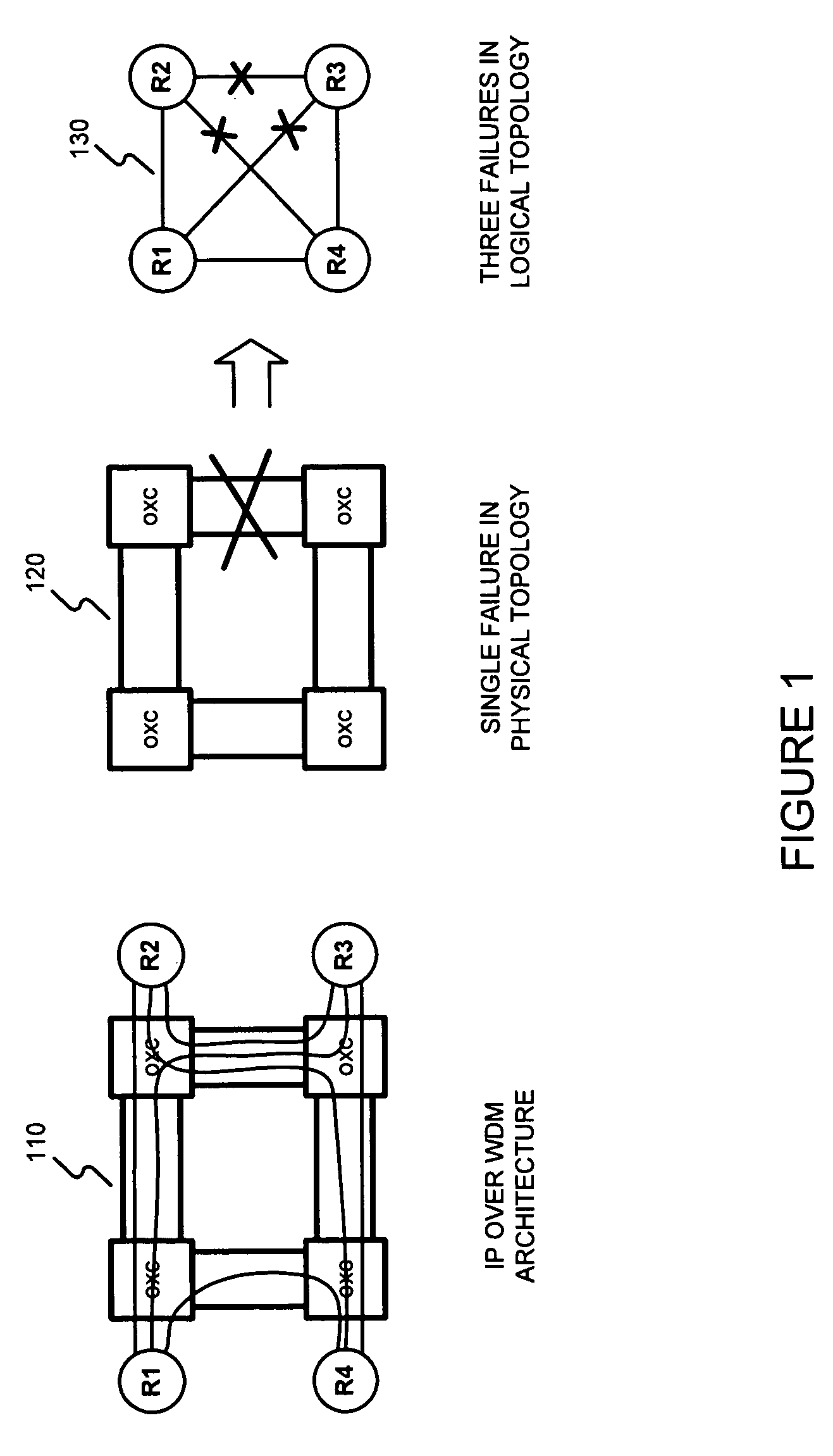
In MPLS traffic engineering, a Shared Risk Link Group (SRLG) is a set of links sharing a common resource, which affects all links in the set if the common resource fails. These links share the same risk of failure and are therefore considered to belong to the same SRLG.
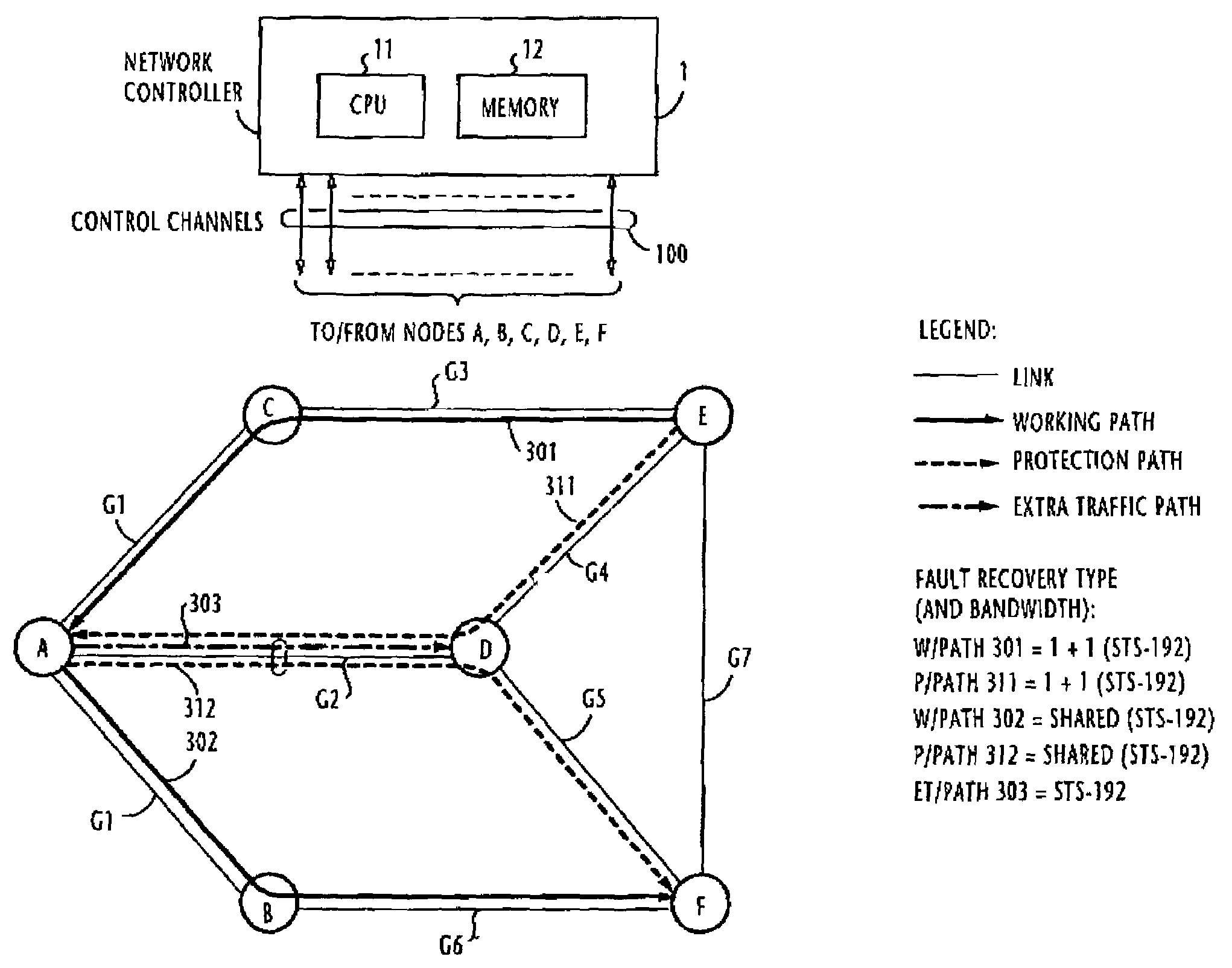
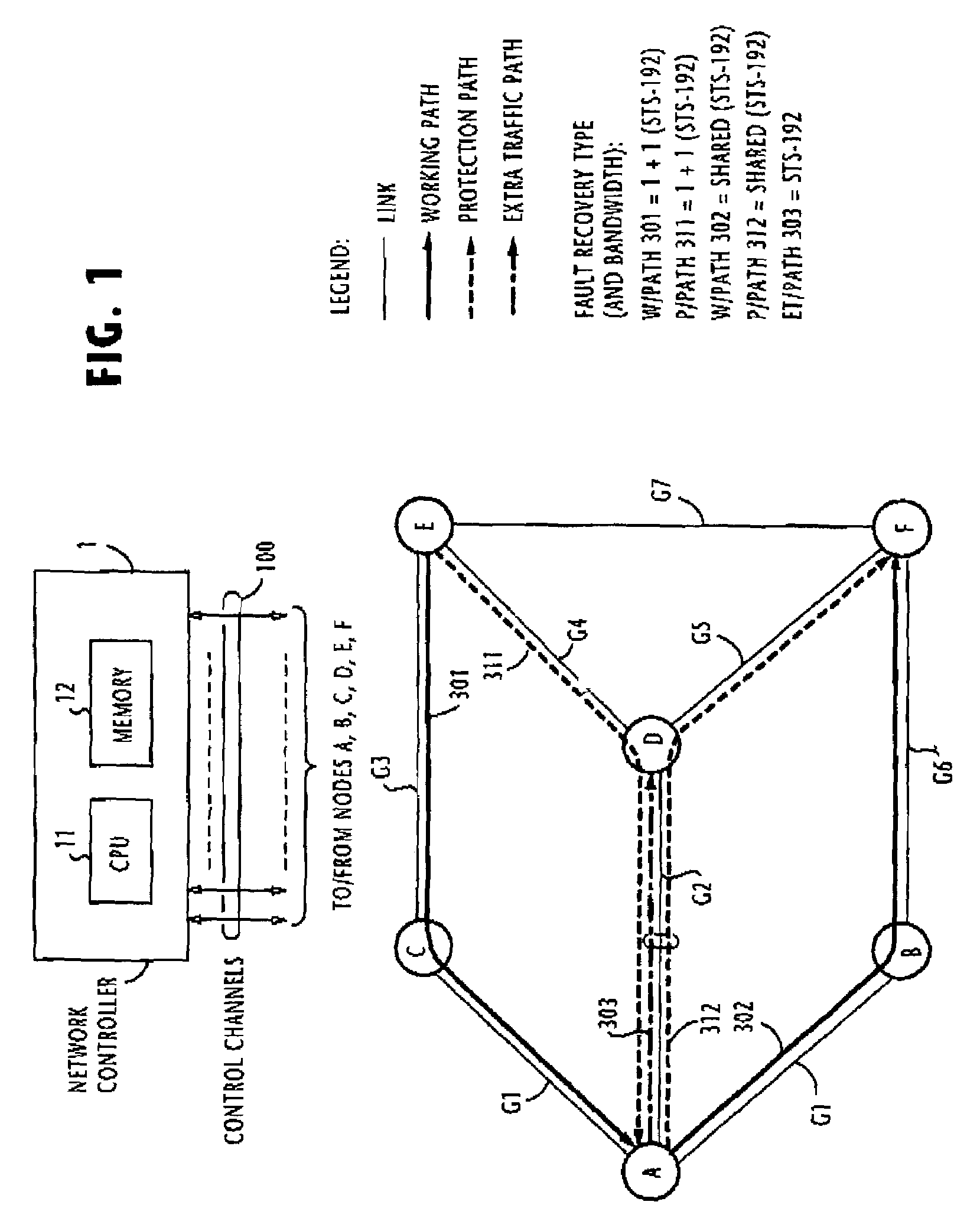
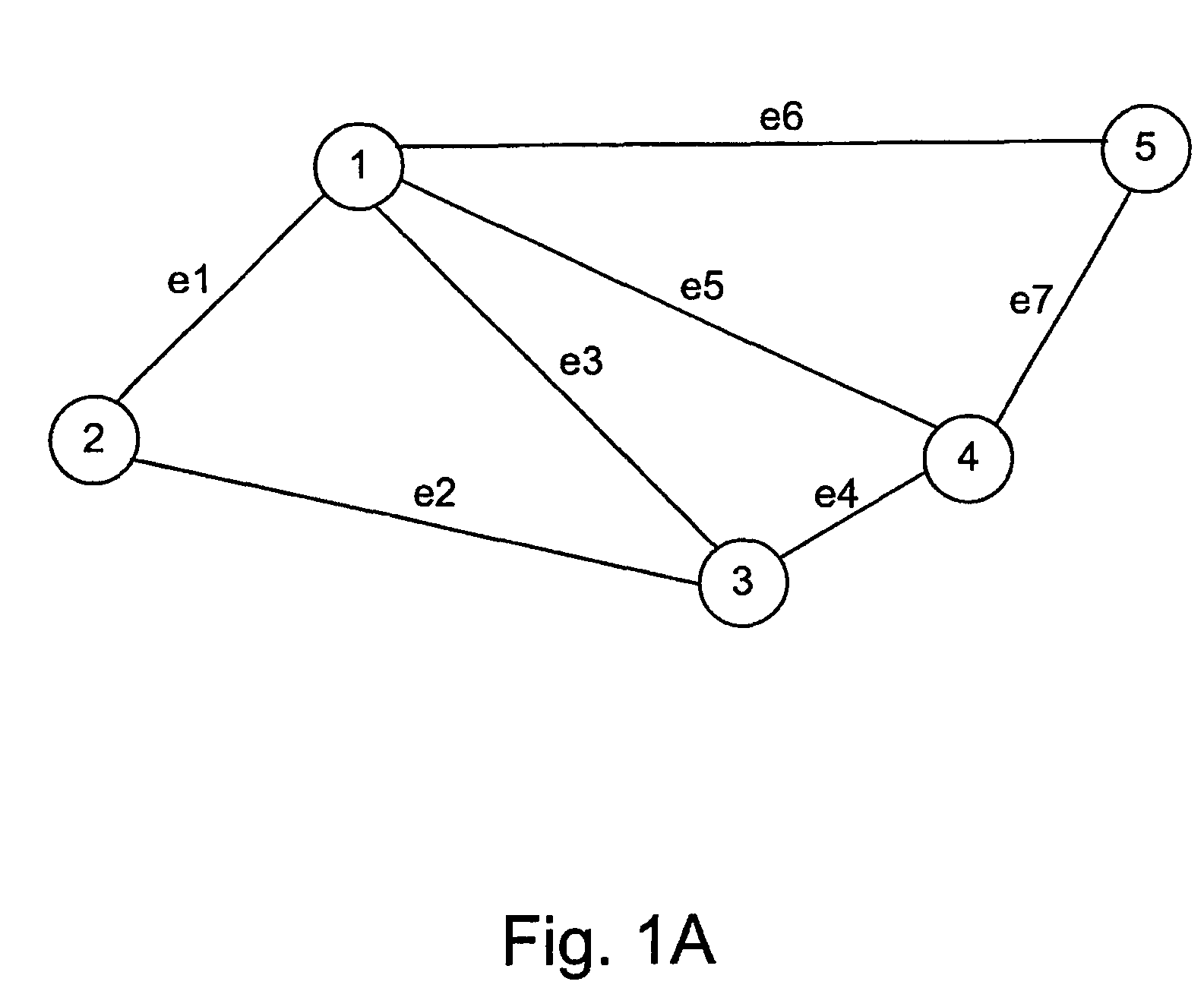
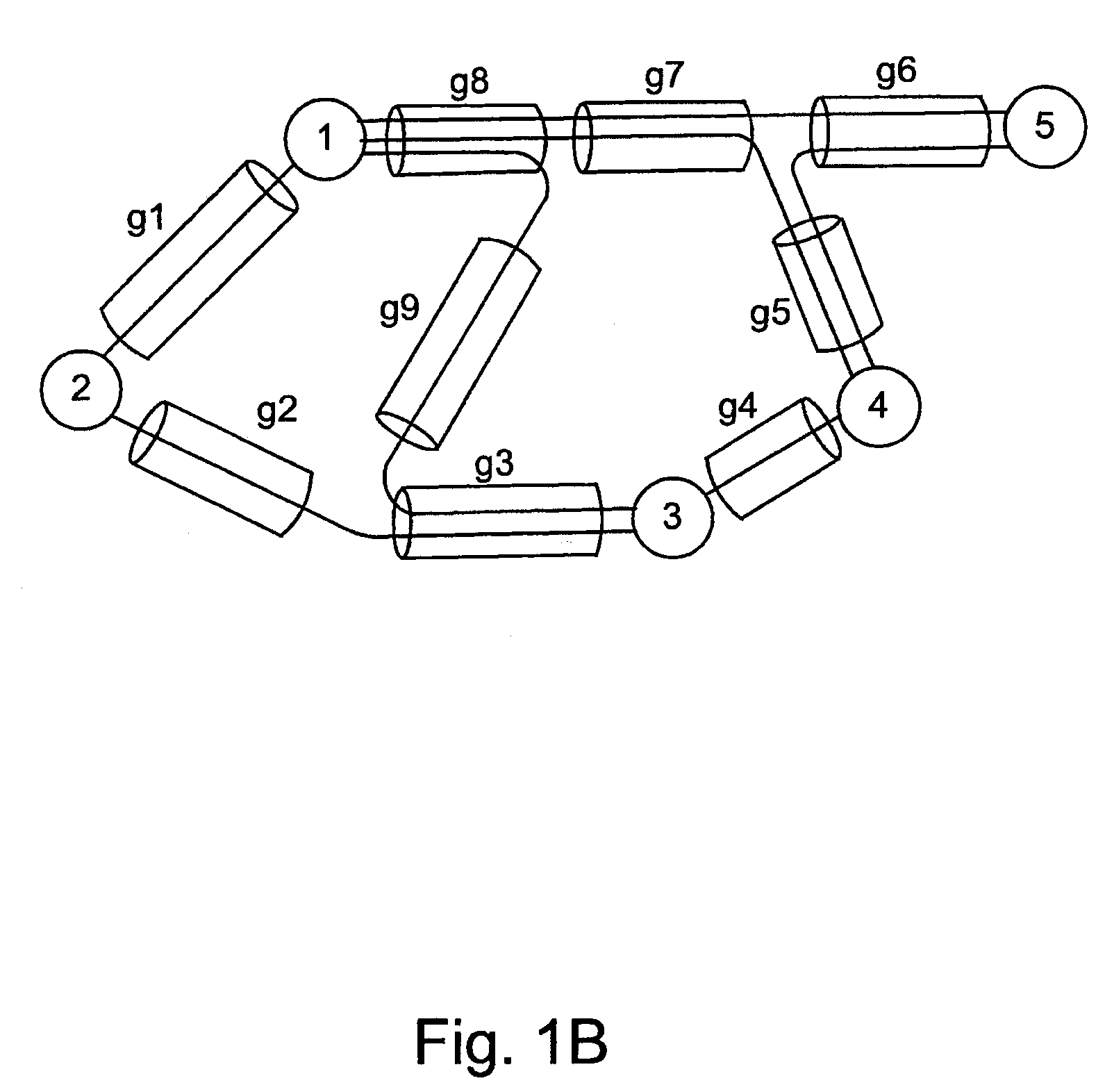
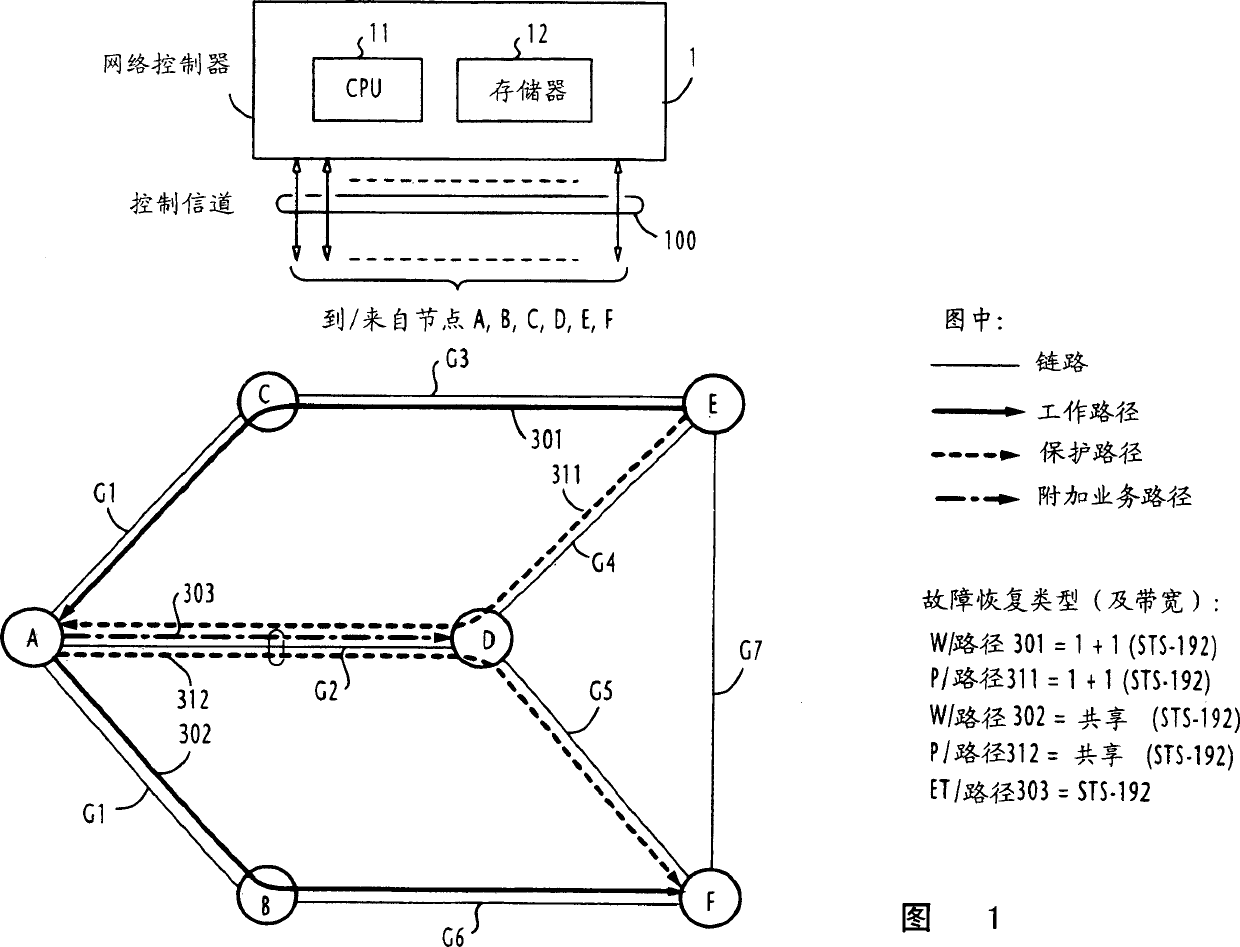
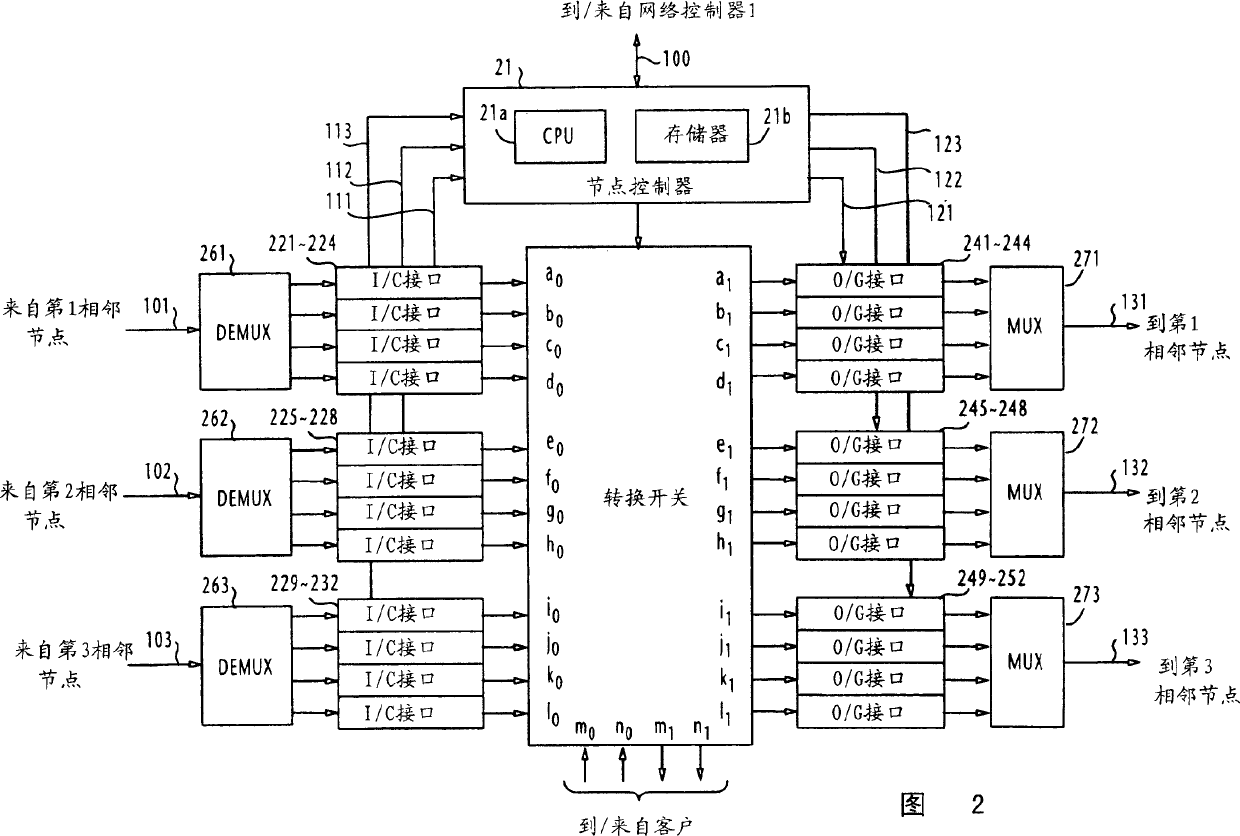
Path establishment method for establishing paths of different fault recovery types in a communications network
ActiveUS7248561B2Avoids unsuccessful fault-recoveryMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionShared risk link groupDistributed computing
In a communications network where multiple shared risk link groups are formed by links having a common risk, unreserved bandwidths are defined corresponding to all SRLG's and a maximum bandwidth of each link is set as an initial value of each of the defined unreserved bandwidths when a working path or a protection path of “1+1” or “1:1” recovery type is requested. When a protection path of “shared” recovery type is requested, unreserved bandwidths are defined corresponding to the SRLG's to which the links of its corresponding working path belong and a maximum bandwidth of each link is set as an initial value to each of the defined unreserved bandwidths. The bandwidth of the working or protection path is subtracted from each of the unreserved bandwidths. The request is rejected if a minimum of the subtracted values is smaller than a threshold.
Owner:NEC CORP
Efficient trap avoidance and shared protection method in survivable networks with shared risk link groups and a survivable network
InactiveUS20050031339A1Improve bandwidth efficiencyMany timesLaser detailsOptical multiplexHigh bandwidthShared risk link group
An efficient trap avoidance and shared protection method in a survivable network with shared risk link groups. The invention includes a fast and efficient heuristic algorithm for avoiding traps, an algorithm, which may also be applied effectively to shared SRLG protection. Compared to other existing algorithms, the algorithm embodied in the present invention runs much faster, and yet falls into few traps, and achieves a much higher bandwidth efficiency. This technology can be applied to MPLS, ATM, SONET, WDM, and other high-speed survivable network designs.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method and apparatus for determining network routing information based on shared risk link group information
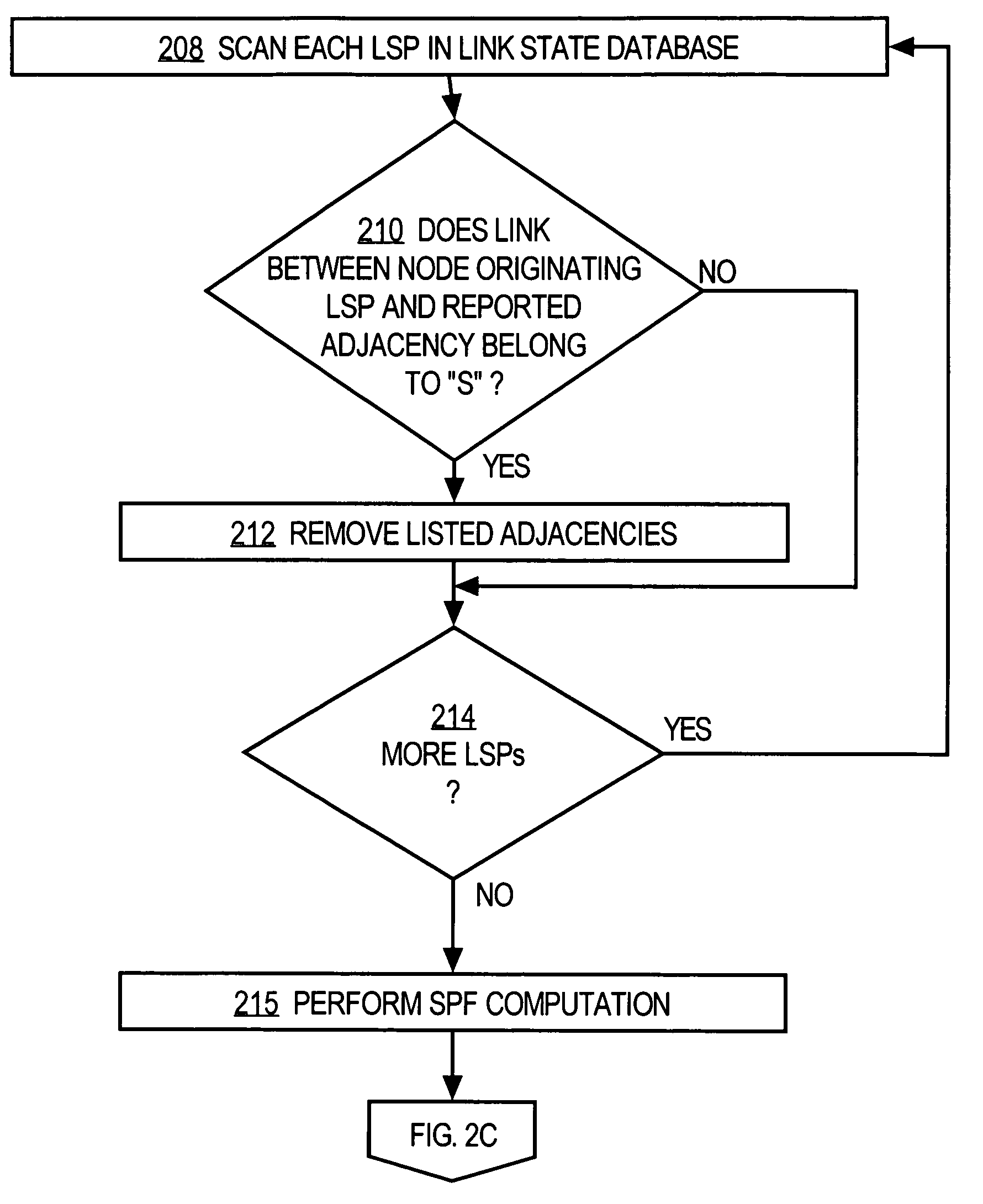
A method and apparatus are disclosed for performing a shortest path first network routing path determination in a data communications network based in part on information about links that are associated as shared risk link groups. Micro-loops are avoided in computing shortest path first trees by considering whether links are within shared risk link groups. In a first approach, for each link state packet in a link state database, listed adjacencies are removed if the link between the node originating the LSP and the reported adjacency belongs to a shared risk link group for which one component (local link) is known as down, and a shortest path first computation is then performed. In a second approach, during the SPT computation and after having added a first node to a path, each neighboring node is added to a tentative tree if and only if, a link between the first node and the neighboring node does not belong to a shared risk link group for which one component (local link) is known as down.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
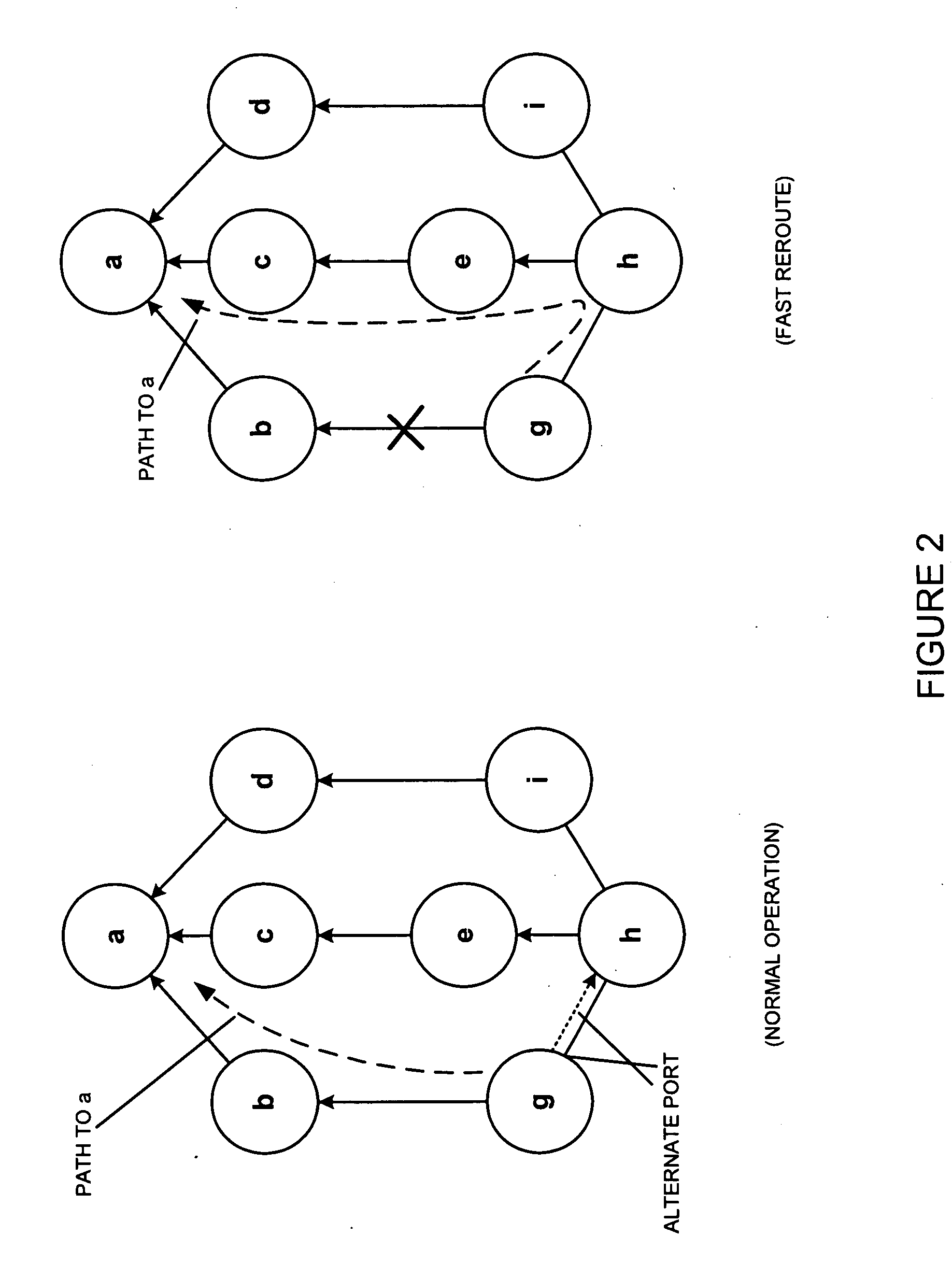
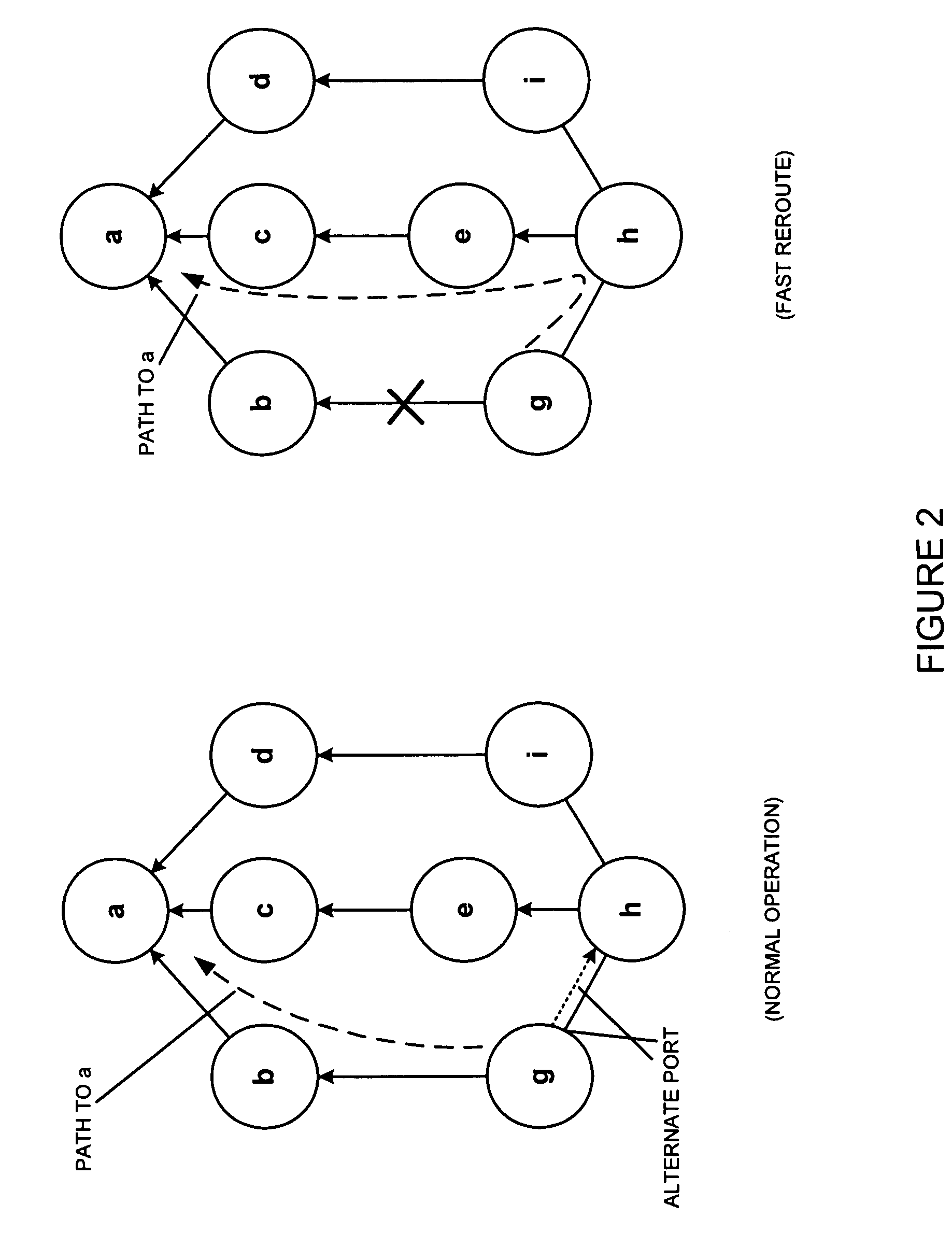
Internet protocol fast reroute for shared risk link group failure recovery
InactiveUS20100315943A1Promote recoveryReduce decreaseError preventionTransmission systemsInternet protocol suiteShared risk link group
A scheme to achieve fast recovery from SRLG failures in the IP layer is described. An exemplary scheme, called multi-section shortest path first (“MSSPF”), builds on the idea of IP Fast Reroute (“IPFRR”), guarantees 100% recovery of SRLG failures and causes no dead loops. Given a source node, a destination node, and a shared risk group failure on a next hop from the source node to the destination node, failure recovery information may be determined by (1) accepting a graph representing network topology information including the source node and the destination node, (2) determining a node which is able to reach the destination node using a route which does not include the source node, wherein a path from the source node to the determined node is not affected by the shared risk group failure, and (3) storing, in association with the shared risk group failure, both (i) a network address associated with the determined node and (ii) an alternative output port of the source node using the shortest path from the source node to the determined node.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
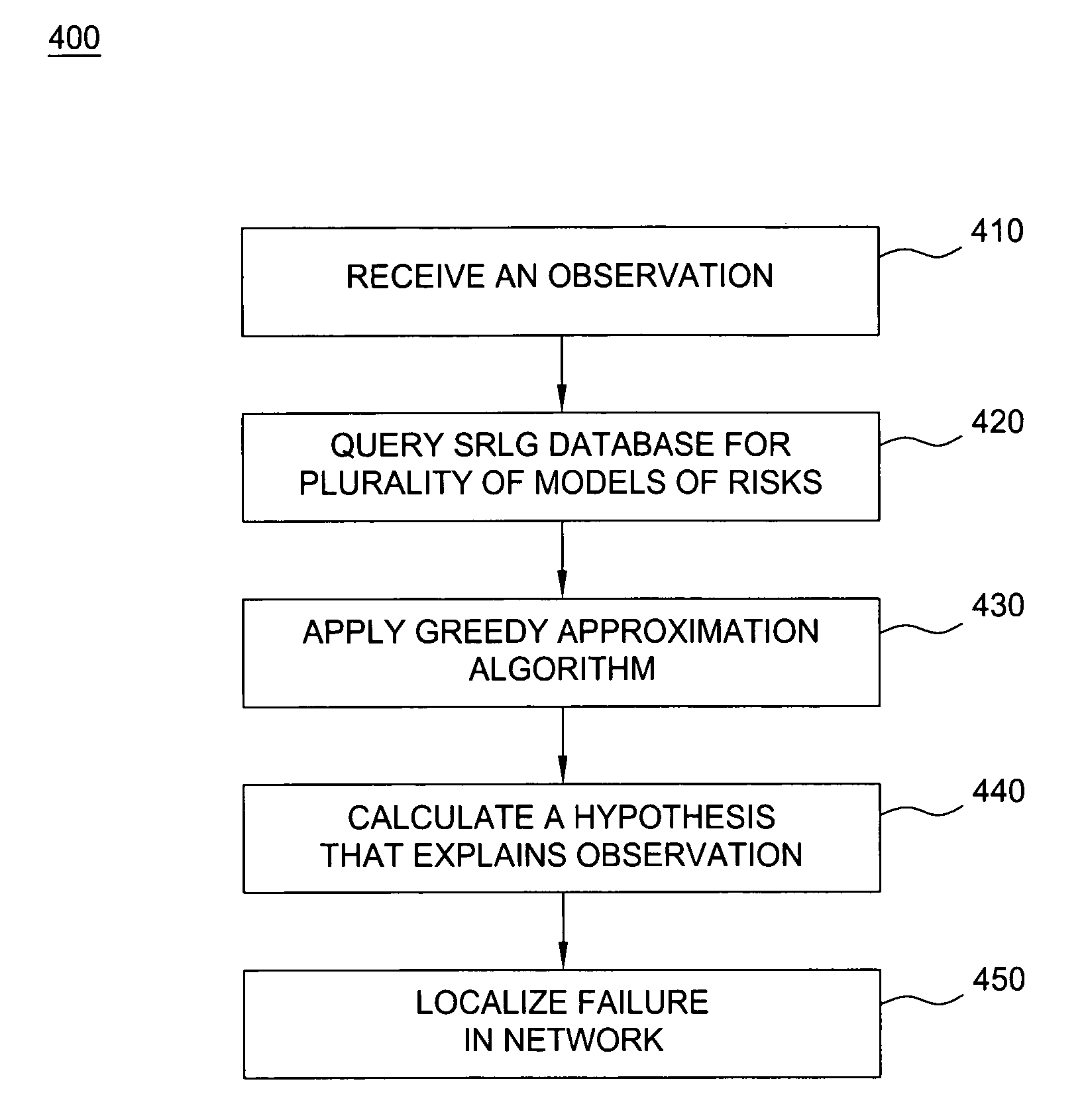
Method and apparatus for fault localization in a network
InactiveUS7577099B1Special service provision for substationError preventionSpatial correlationHypothesis
A method and apparatus for automatically localizing failures in a network. Failures can be localized by receiving an observation, querying a database for a plurality of models of risks and calculating a hypothesis from the plurality of models of risks that explains the observation. The observation comprises link failures reported by a plurality of data sources. The plurality of models or risks represents links that would likely be impacted by the failure of each component within the network stored in a Shared Risk Link Group (SRLG) database. A Spatial Correlation Engine (SCORE) applies an algorithm to calculate a hypothesis from the plurality of models of risks that explains the observation, thereby, automatically localizing failures in a network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method and apparatus for determining network routing information based on shared risk link group information
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
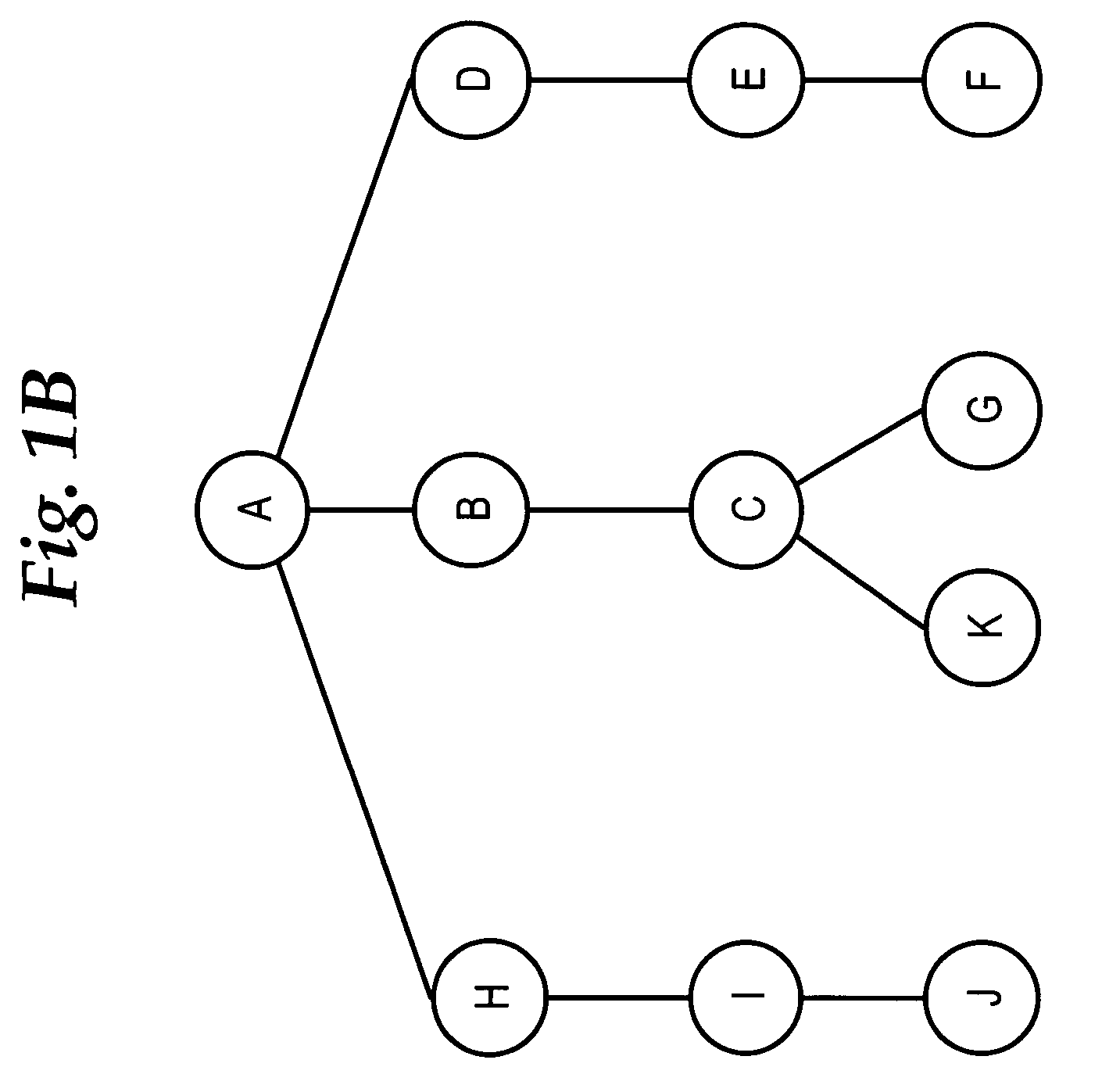
Method for graphically representing network topological objects and network topological object relationships in network planning
InactiveCN101916320AGraphical way is intuitive and conciseGraphics are clear and comprehensiveData switching networksSpecial data processing applicationsNODALGraphics
The invention relates to a method for graphically representing network topological objects and network topological object relationships in network planning. The logical topological structure of a physical network is represented in a topological graph drawing area in planning software by the following operation steps: 1, drawing a station and nodes; 2, drawing an optical cable between two nodes; 3, drawing an optical fiber pair on the optical fiber; 4, drawing end-to-end service connection between the two nodes; 5, drawing a shared risk link group; 6, creating linear multiplex section protection; 7, creating a ring; and 8, creating service route. In the method for graphically representing the network topological objects and network topological object relationships in network planning, the graphical representation mode is direct, simple, clear and complete, all network topological objects in an SDH / ASON network are covered basically, and thus, it is relatively easy to define a mathematic model required by the operation of the planning software on this basis, and a mathematic foundation is provided for the operation of the software.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
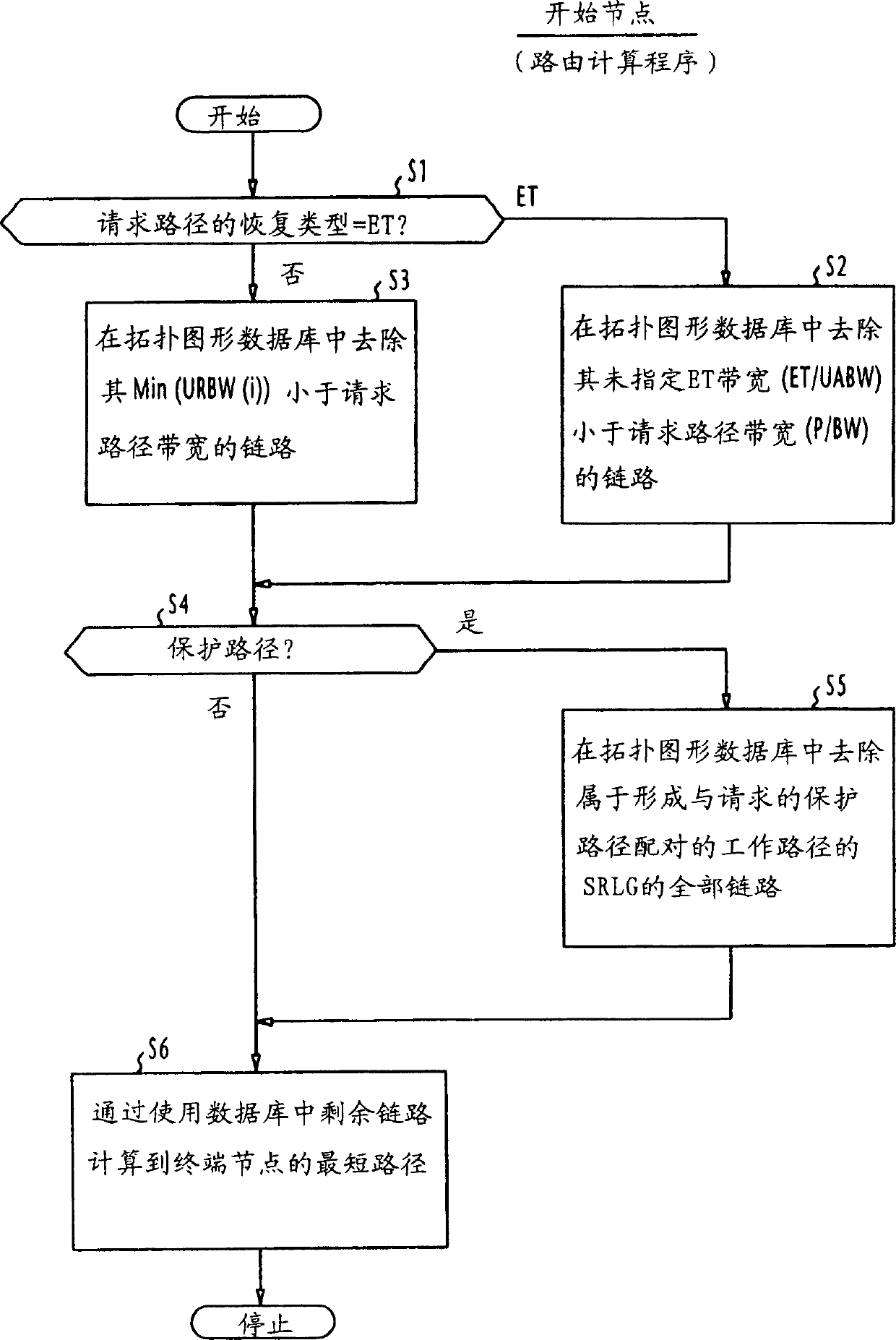
Link Property Setting Method, Route Calculating Method And System Using The Same
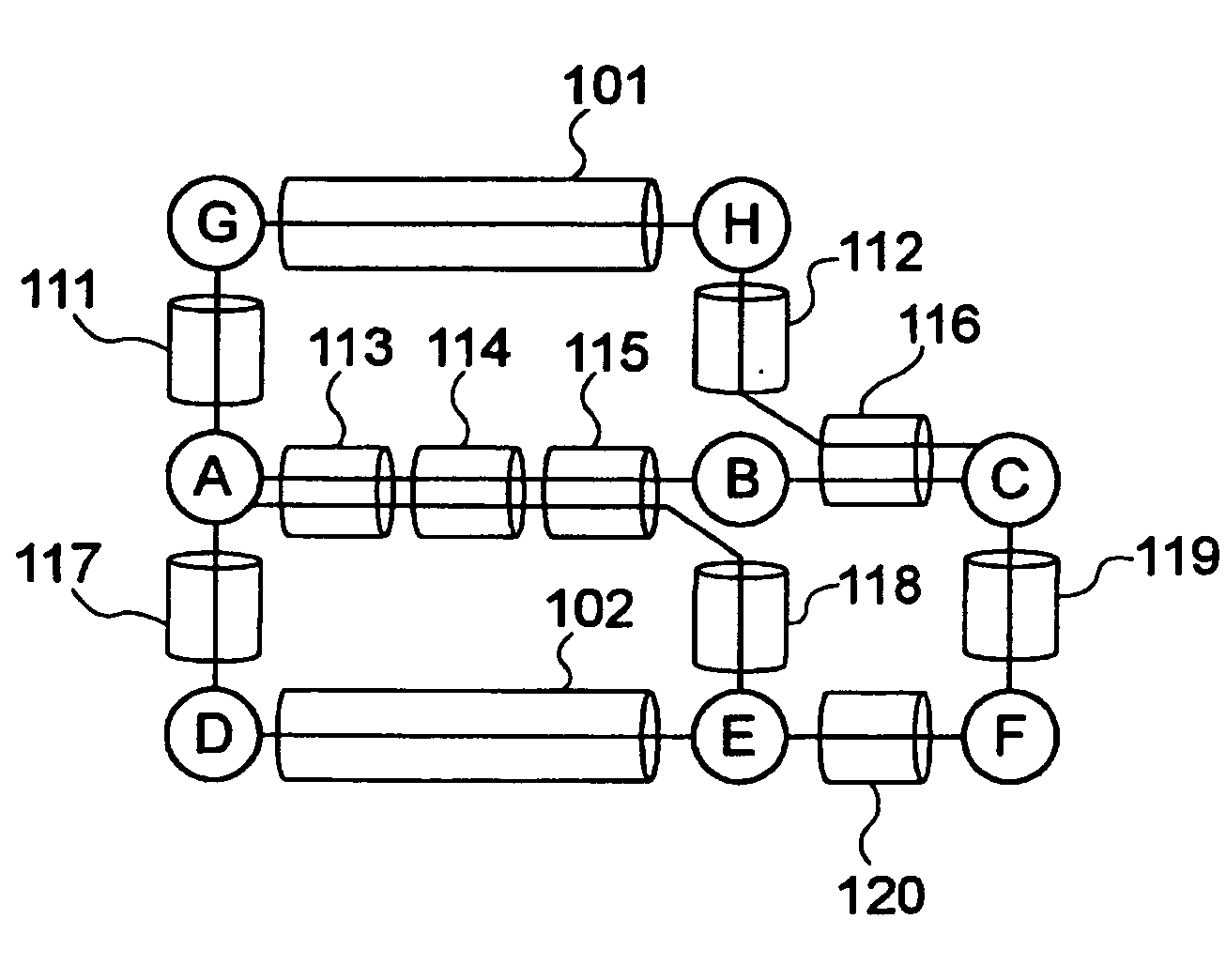
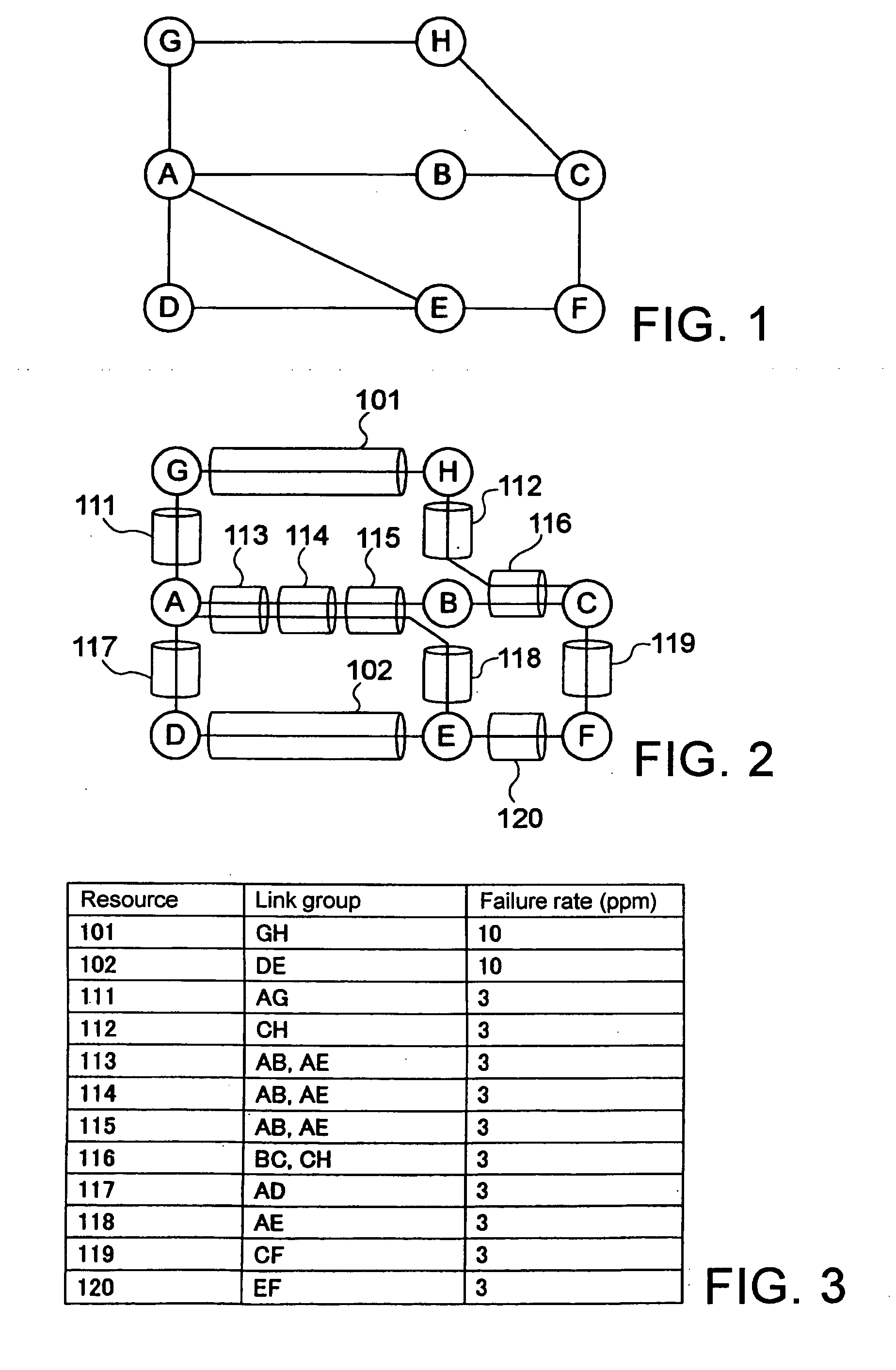
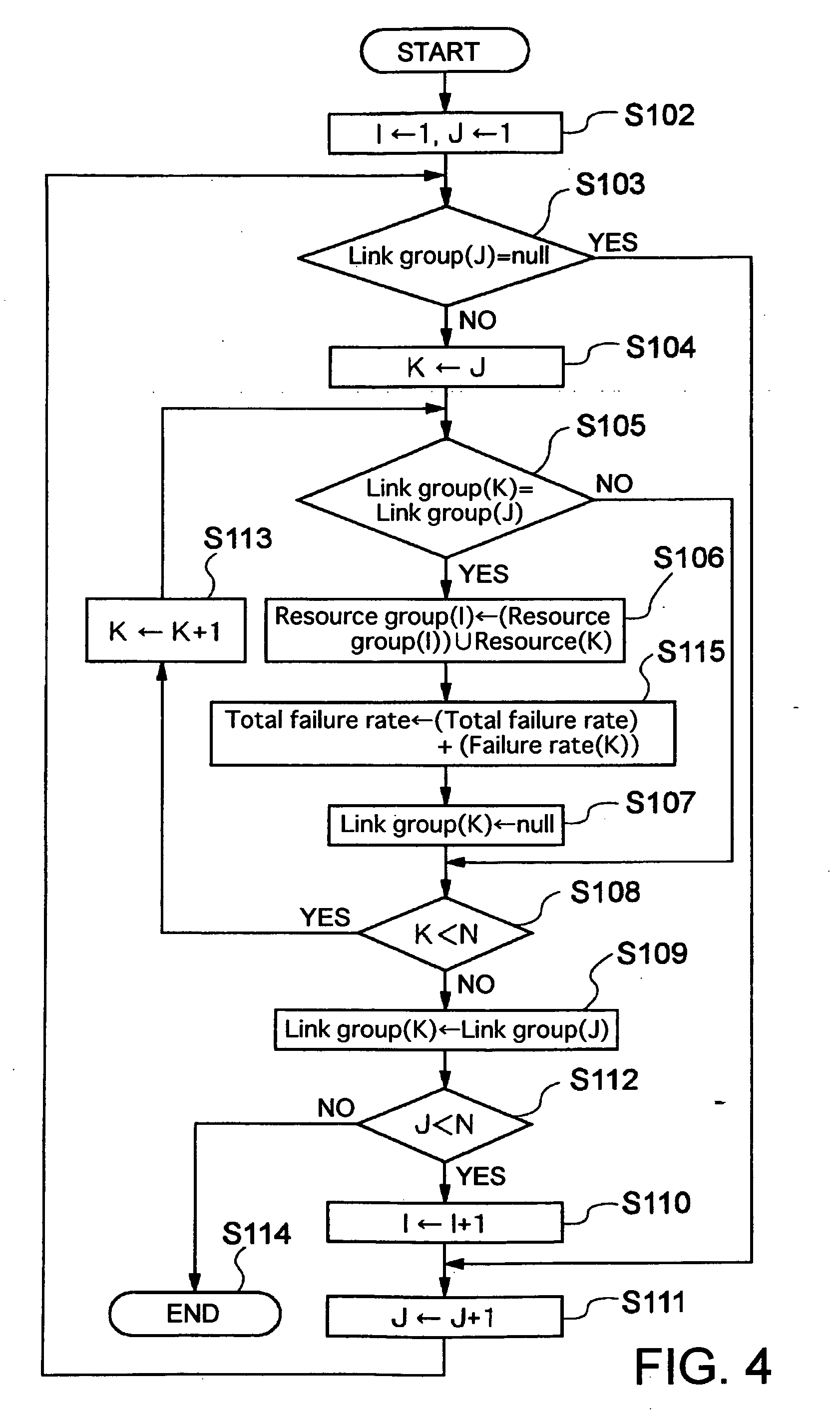
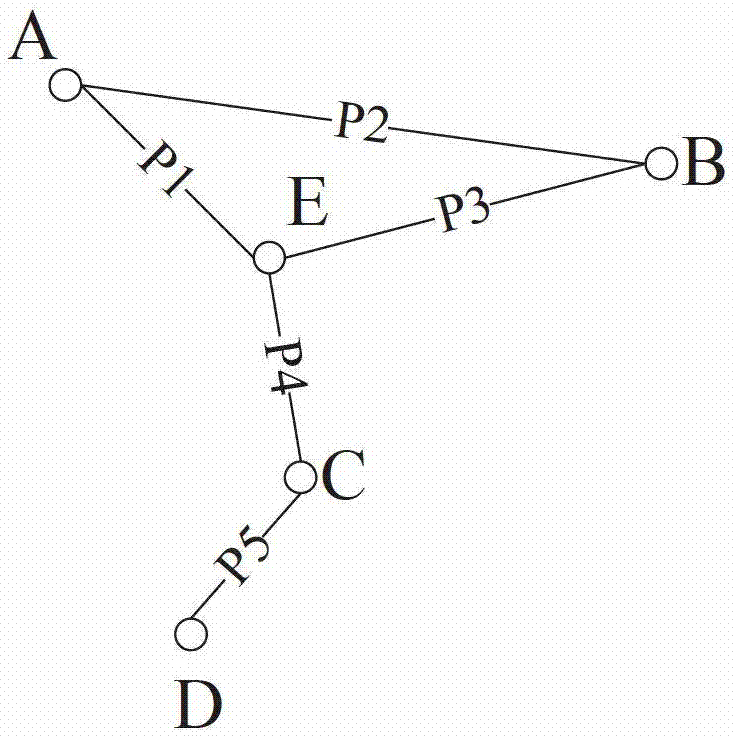
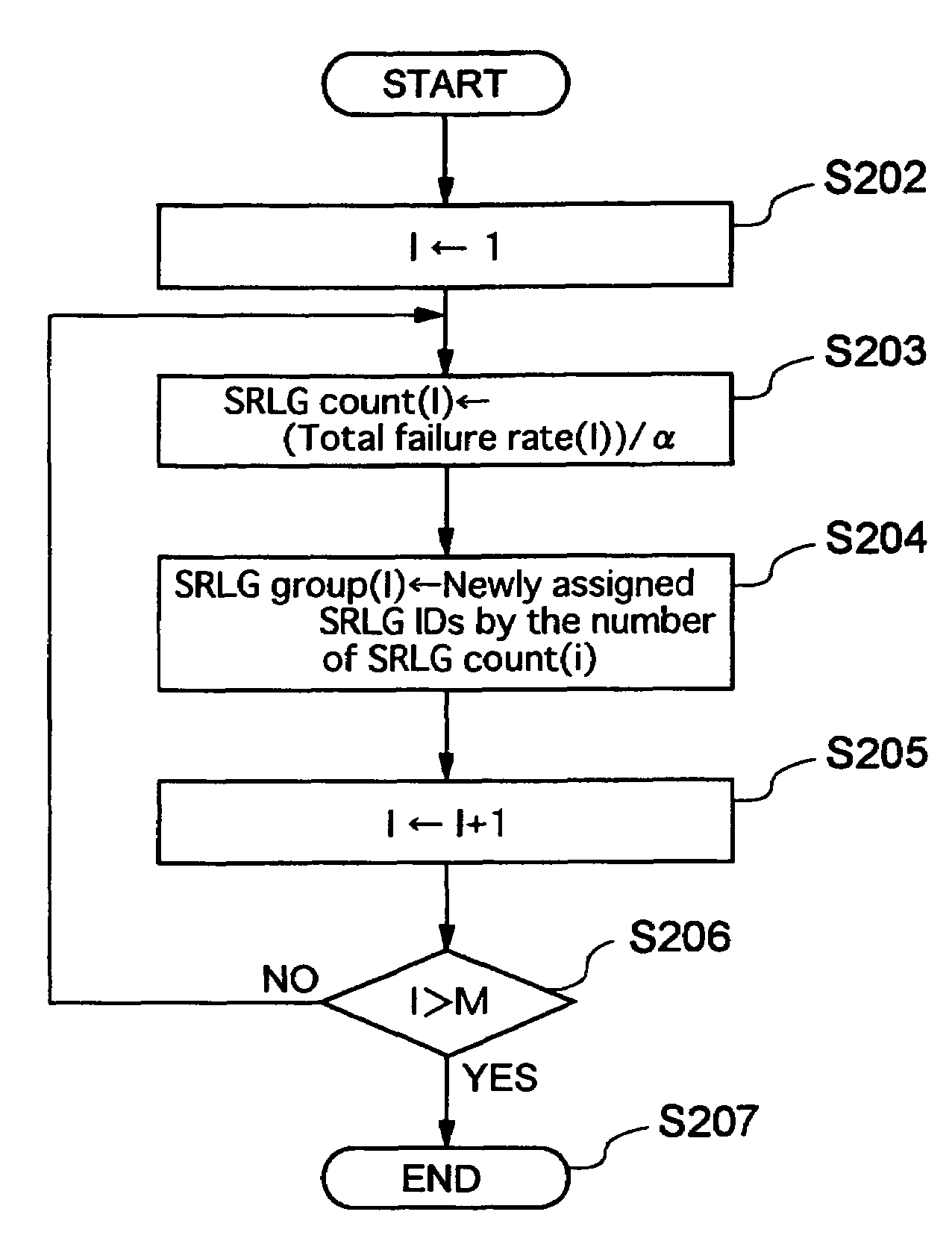
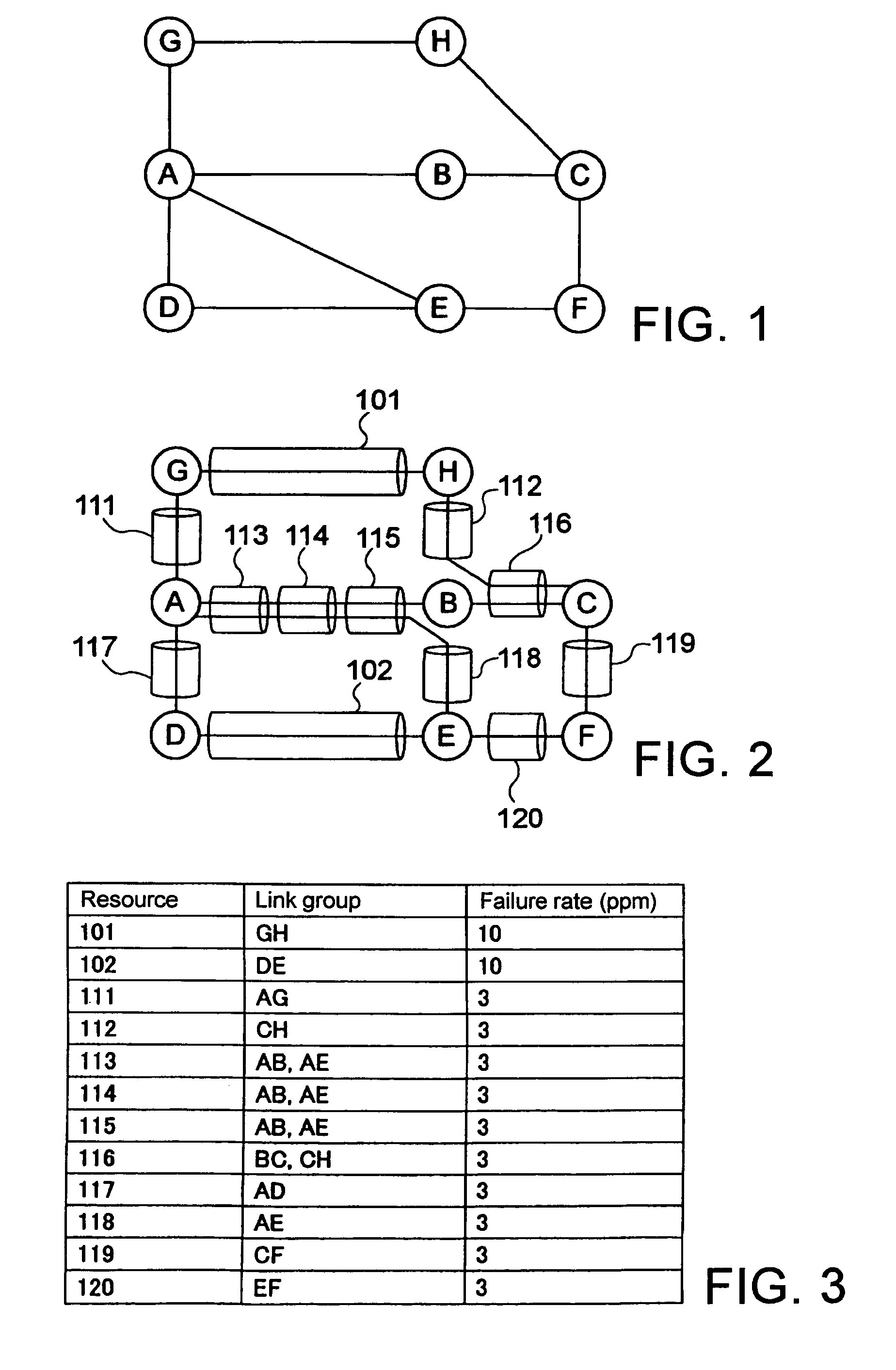
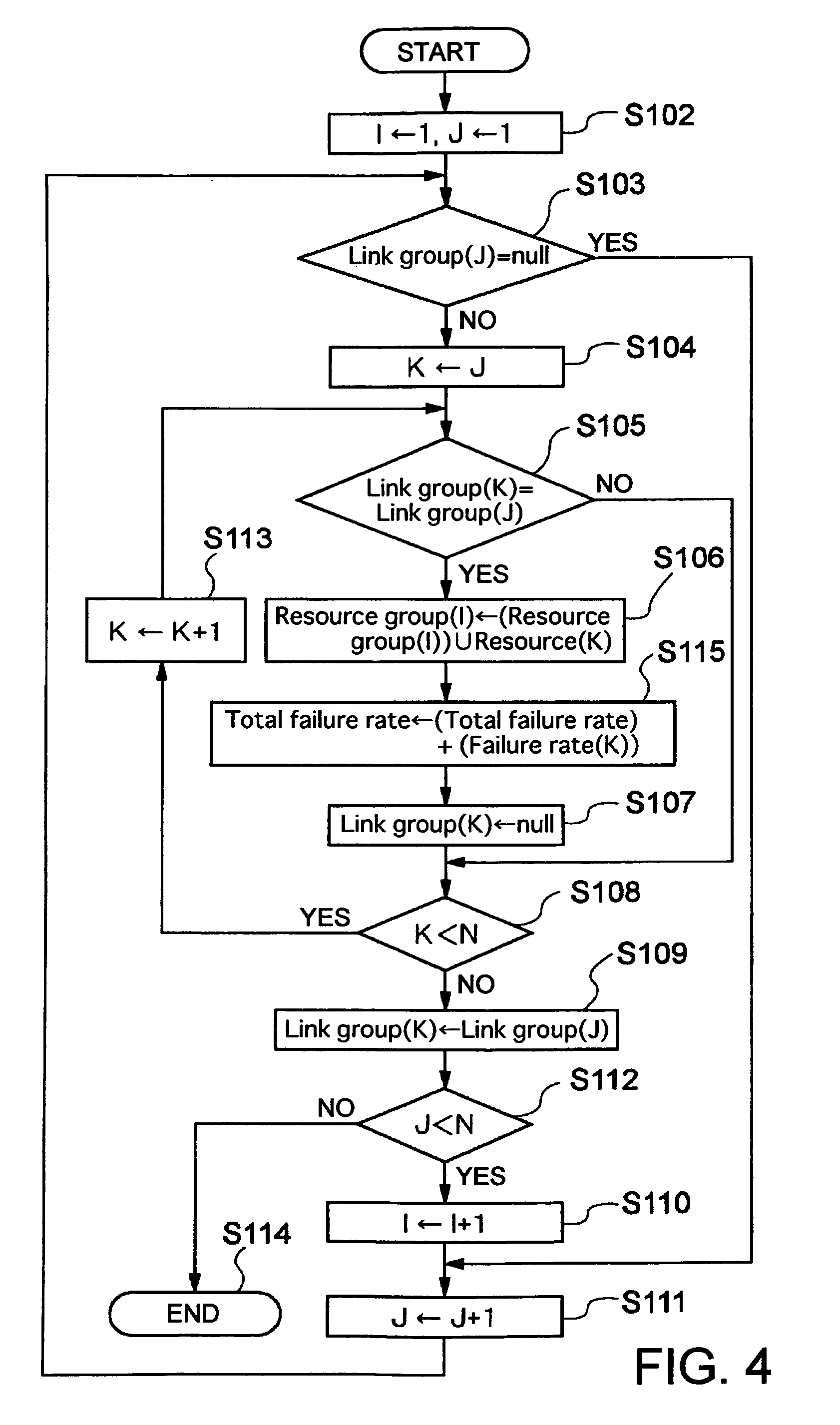
A method of setting shared risk link group identification information (SRLG ID) which is one of link properties employed for calculating a route for a path in a communications network including nodes and links for interconnecting the nodes, and indicates a link group which shares resources, comprises the step of assigning a number of SRLG IDs to the link group in accordance with a failure rate of resources shared by that link group. A route calculating method for calculating routes for a working path and a standby path comprises the step of calculating the routes such that a minimum number of SRLG IDs duplicate between all links on the route of the working path and all links on the route of the standby path.
Owner:NEC CORP
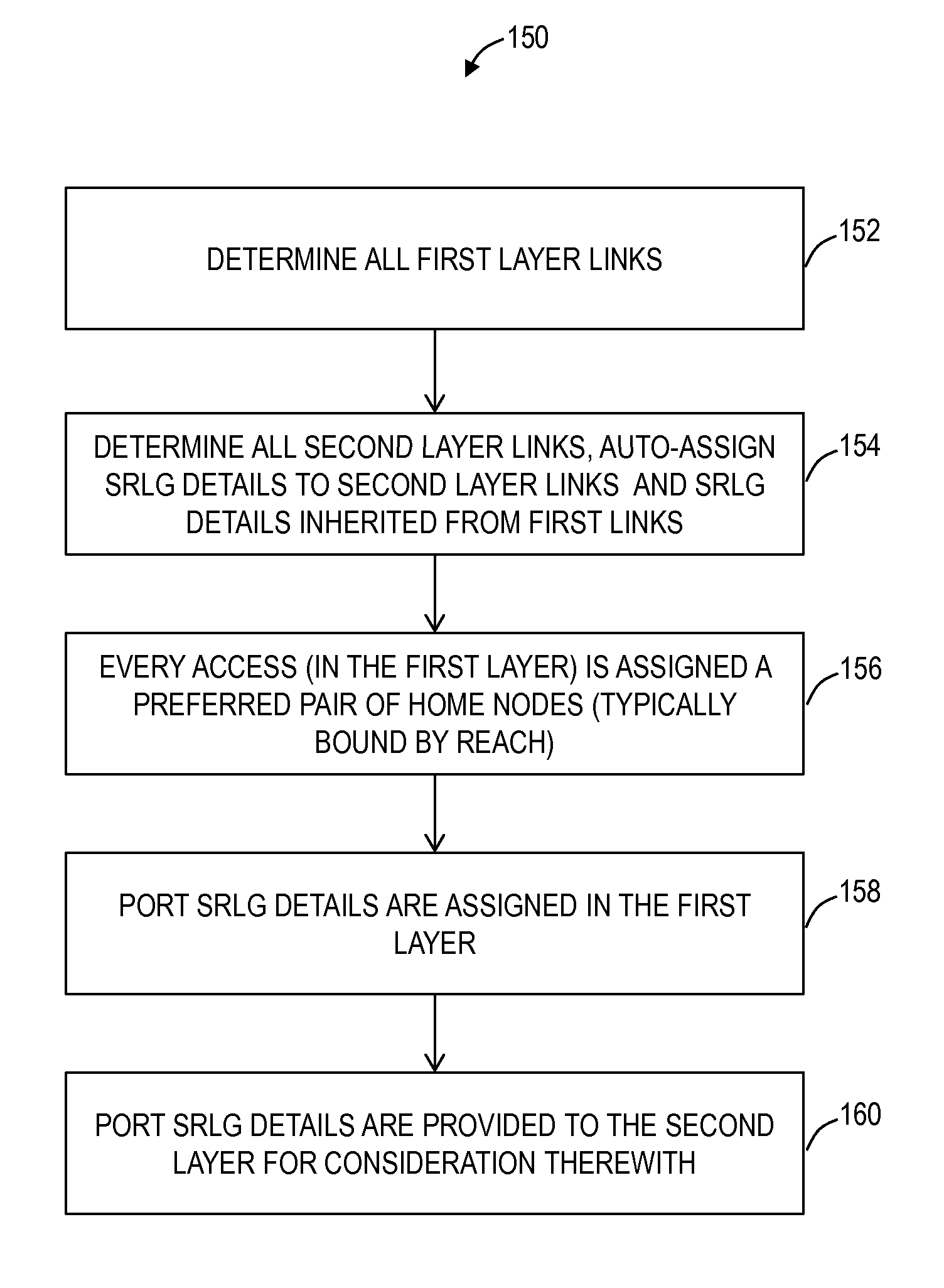
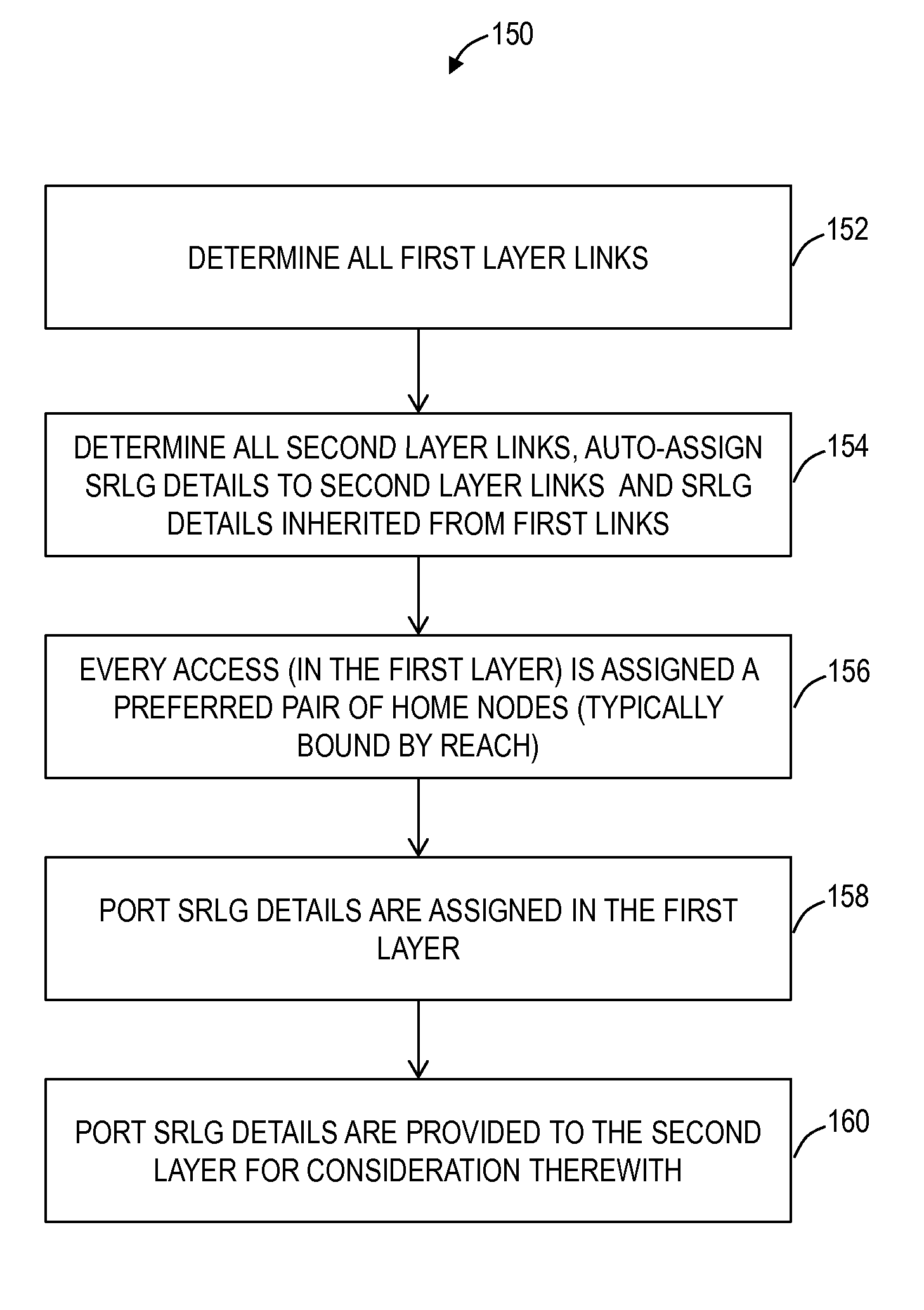
Drop port based shared risk link group systems and methods
ActiveUS20140147107A1Transmission monitoringOptical multiplexShared risk link groupSingle point of failure
Drop port based shared risk link group (SRLG) systems and methods assign SRLG information to drop ports in another level or layer of a network. Thus, drop side SRLG information can be shared between different networks or layers enabling a combination with line side SRLG information within a network to identify and prevent single points of failure across the networks. Typically, SRLG details are assigned to line ports (NNI ports) within a network and this information is not shared with external networks or network layers for routing a connection through the network and the external networks. By assigning SRLG details to a drop port, this information can be relayed between the network and the external networks and considered when planning a route through all of the networks.
Owner:CIENA
Efficient trap avoidance and shared protection method in survivable networks with shared risk link groups and a survivable network
InactiveUS7701848B2Improve bandwidth efficiencyMany timesError preventionTransmission systemsHigh bandwidthShared risk link group
An efficient trap avoidance and shared protection method in a survivable network with shared risk link groups. The invention includes a fast and efficient heuristic algorithm for avoiding traps, an algorithm, which may also be applied effectively to shared SRLG protection. Compared to other existing algorithms, the algorithm embodied in the present invention runs much faster, and yet falls into few traps, and achieves a much higher bandwidth efficiency. This technology can be applied to MPLS, ATM, SONET, WDM, and other high-speed survivable network designs.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for establishing recovery type path of different faults in one communication network
InactiveCN1437356AMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionShared risk link groupDistributed computing
In a communications network where multiple shared risk link groups are formed by links having a common risk, unreserved bandwidths are defined corresponding to all SRLG's and a maximum bandwidth of each link is set as an initial value of each of the defined unreserved bandwidths when a working path or a protection path of "1+1" or "1:1" recovery type is requested. When a protection path of "shared" recovery type is requested, unreserved bandwidths are defined corresponding to the SRLG's to which the links of its corresponding working path belong and a maximum bandwidth of each link is set as an initial value to each of the defined unreserved bandwidths. The bandwidth of the working or protection path is subtracted from each of the unreserved bandwidths. The request is rejected if a minimum of the subtracted values is smaller than a threshold.
Owner:NEC CORP
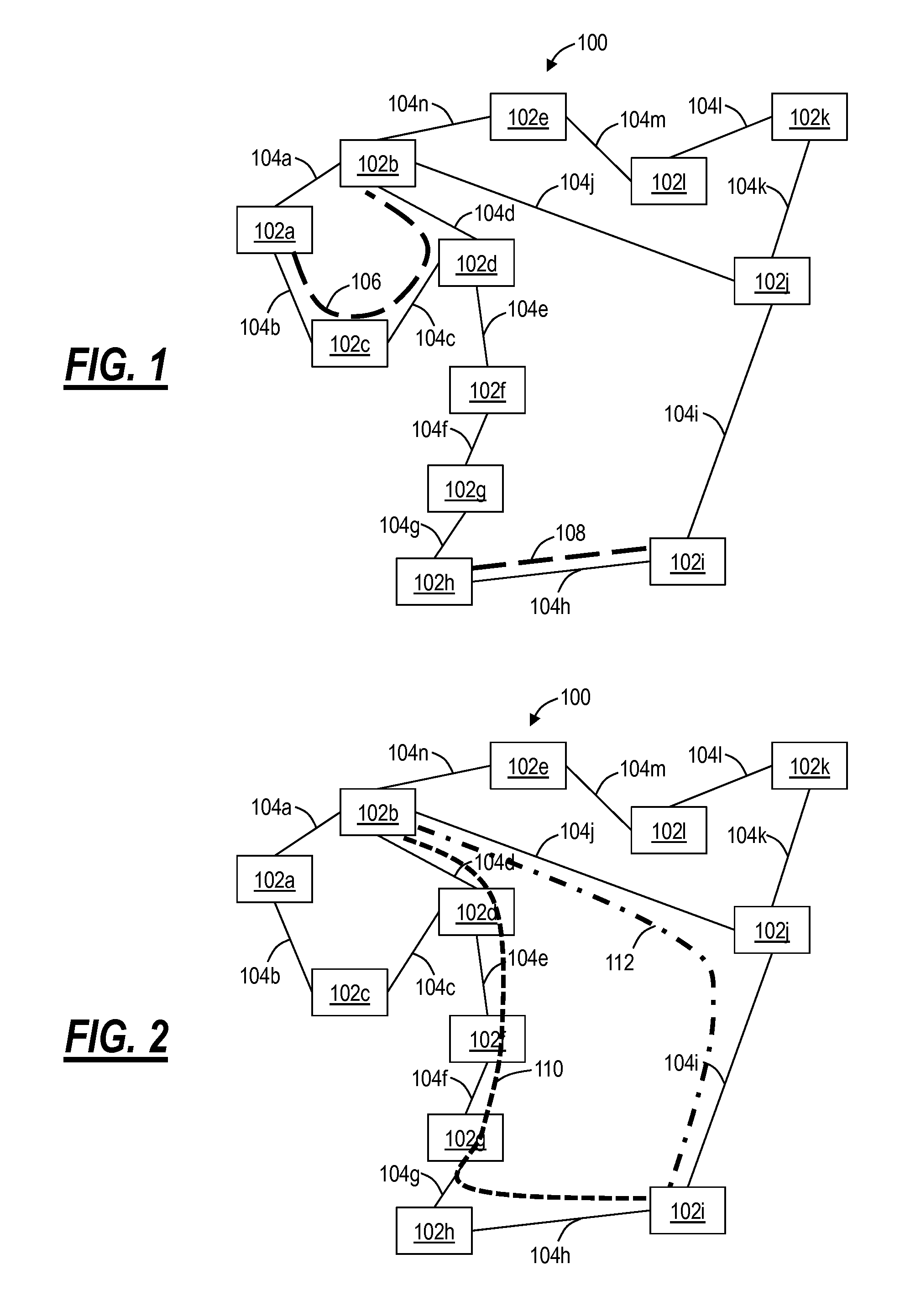
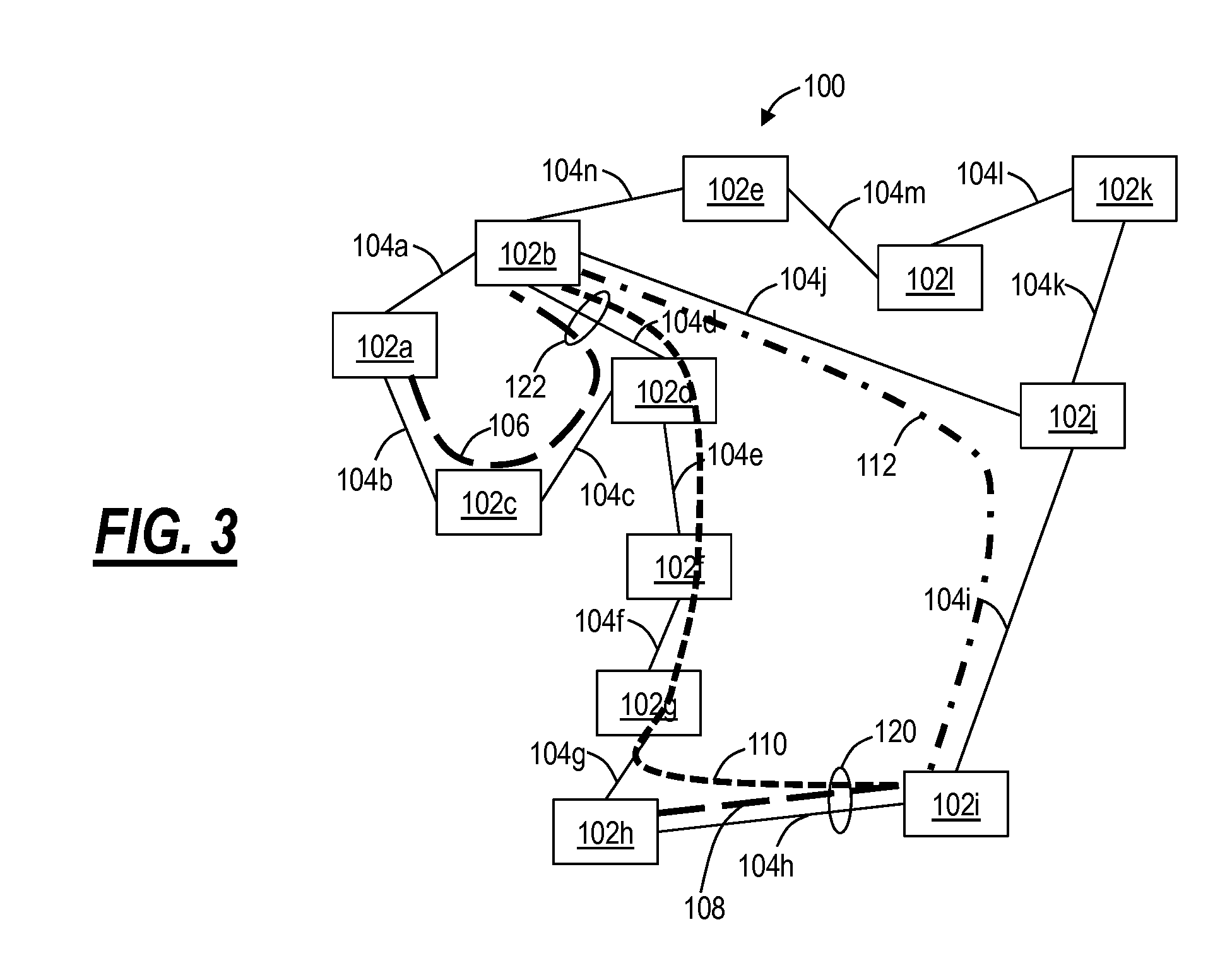
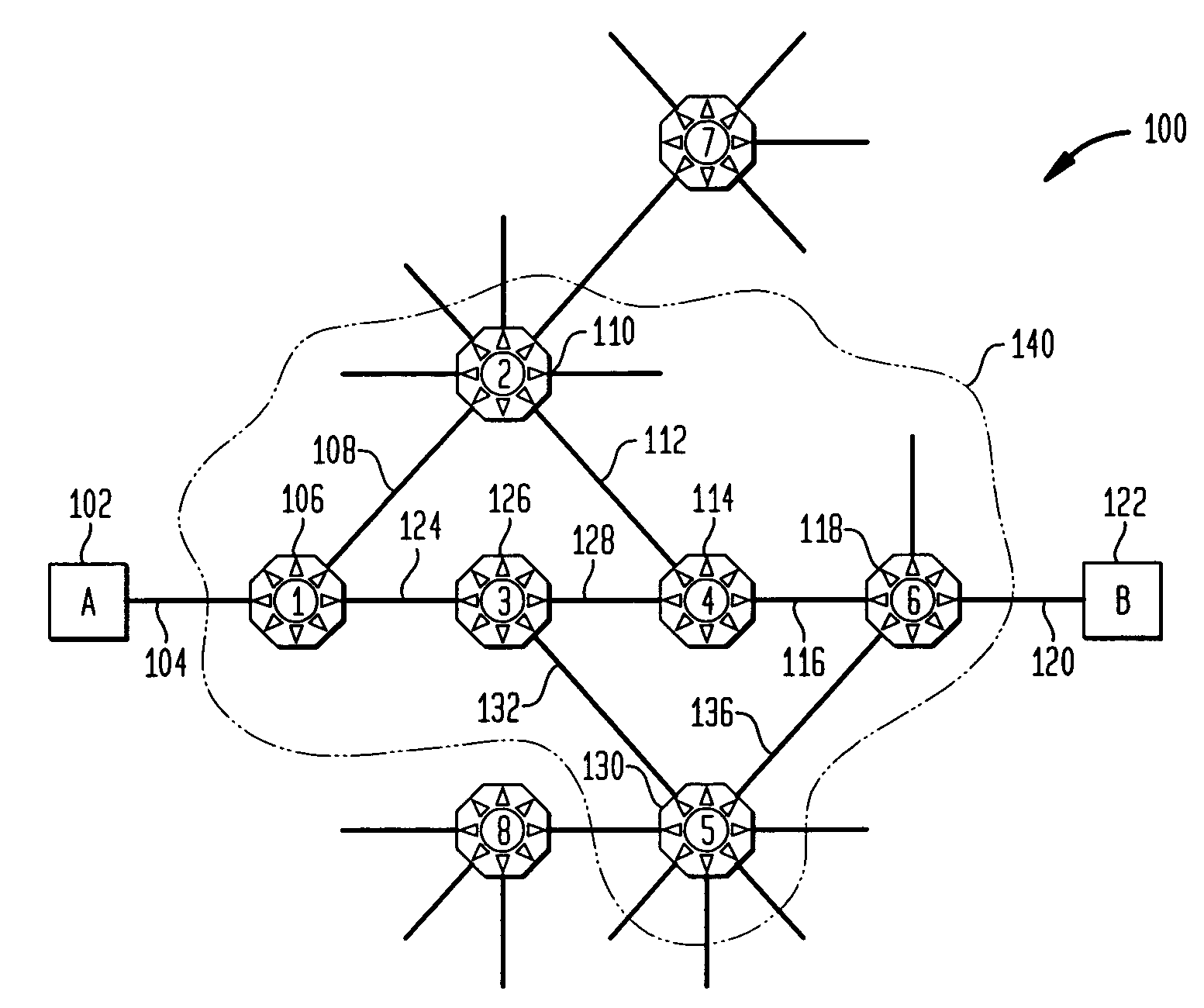
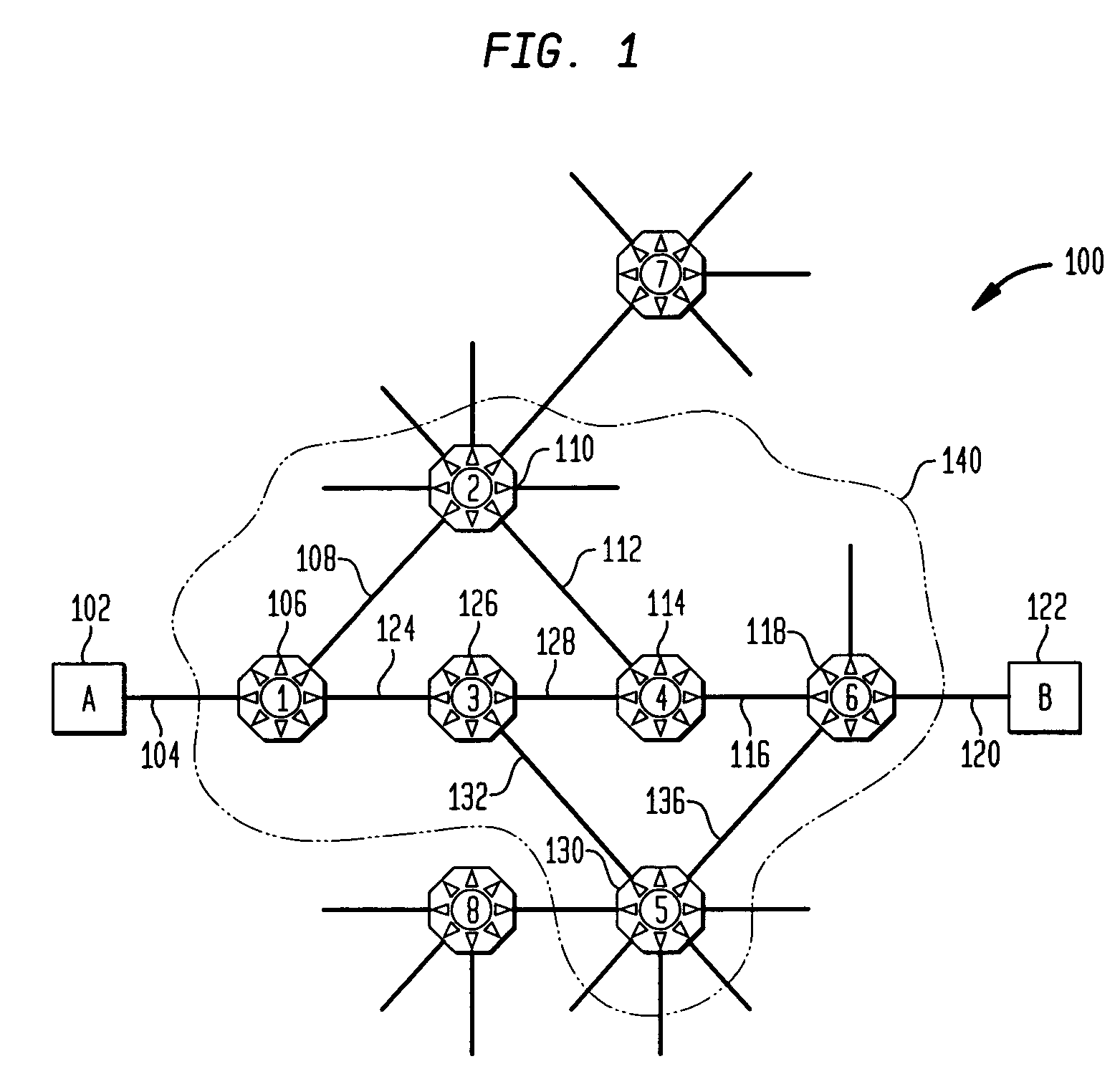
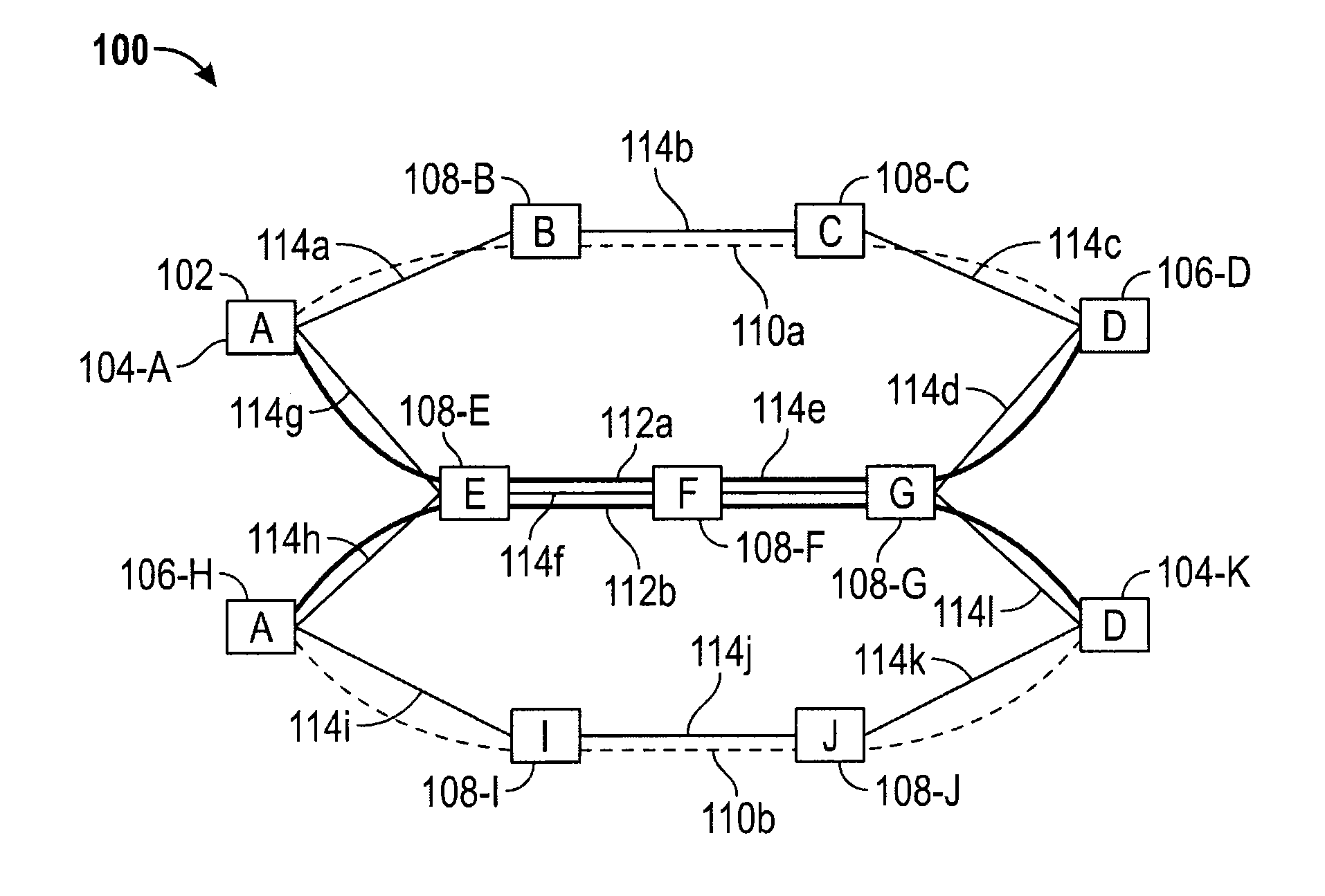
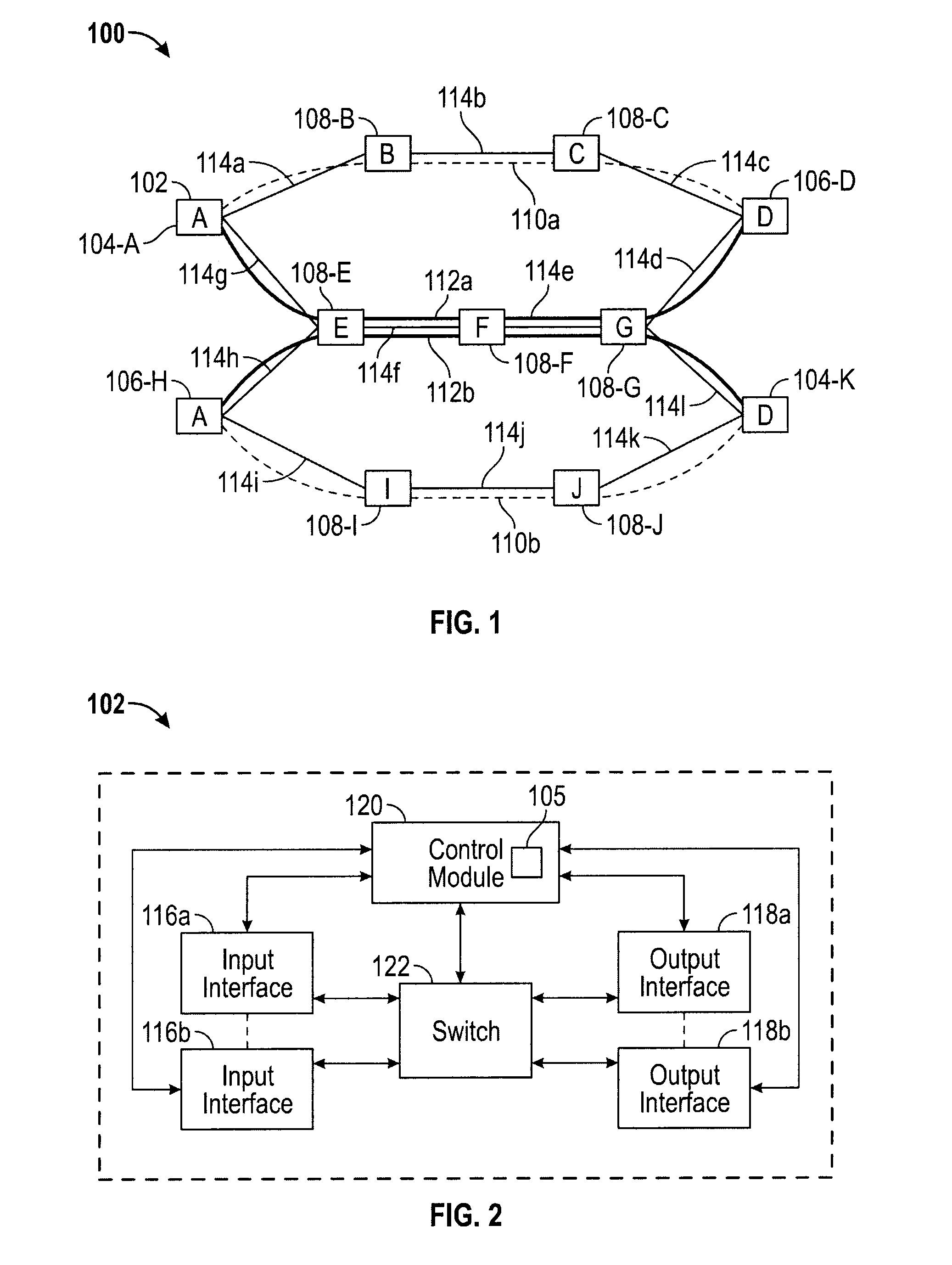
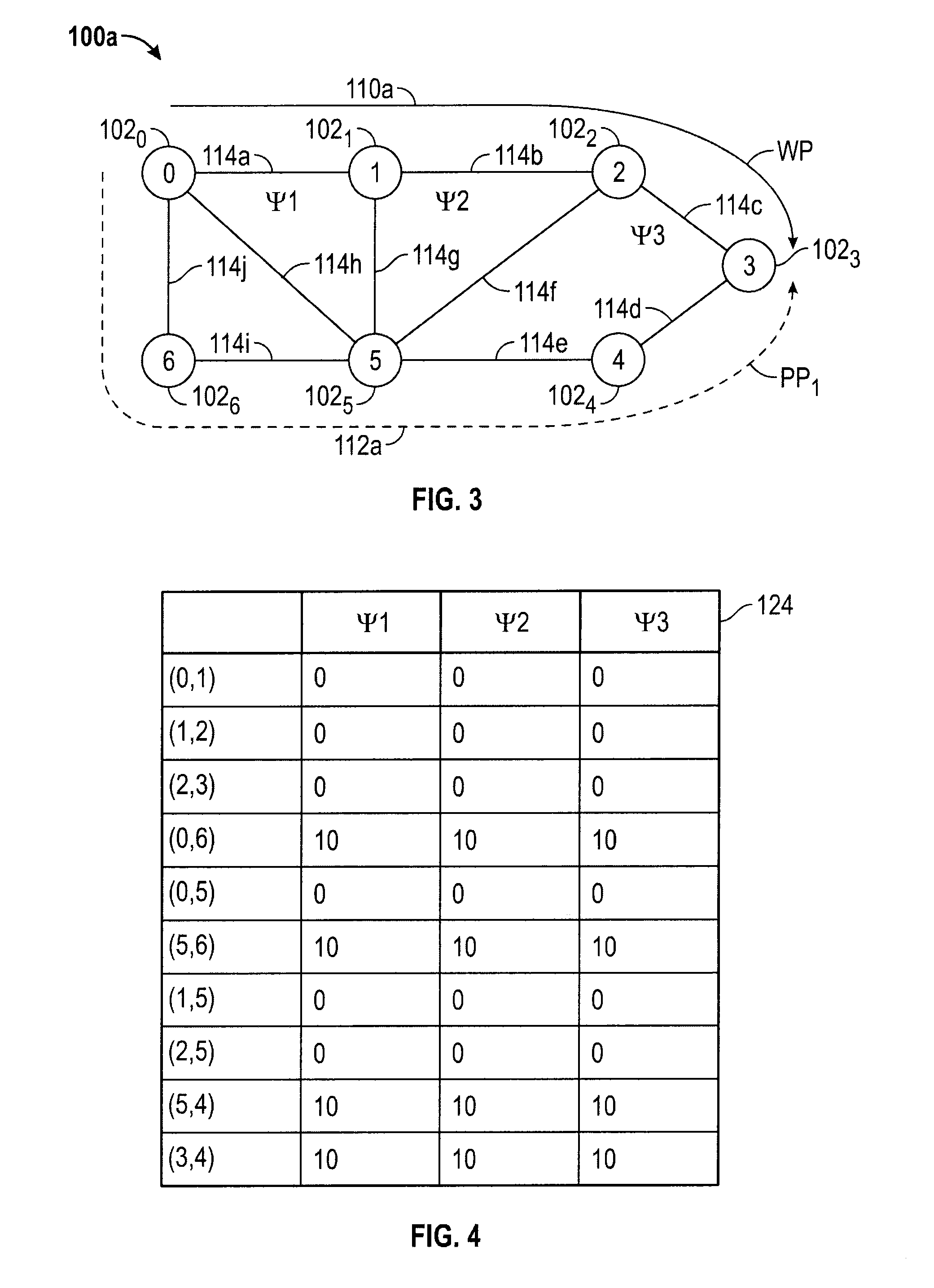
Methods of network routing having improved resistance to faults affecting groups of links subject to common risks
A number of techniques are described for routing methods that improve resistance to faults affecting groups of links subject to common risks. One of these techniques accounts for failure potentials in physical networks by considering shared risk link groups separately from performance and costs metrics in determining a primary routing path and a backup path. A shared risk link group (SRLG) is an attribute attached to a link to identify edges that have physical links in common and can therefore be simultaneously disrupted due to a single fault. Another technique considers node disjointness and provides a solution of two paths that are as node disjoint as possible and minimizes administrative costs. The techniques may further be combined in a priority order thereby providing a solution of at least two paths that are strictly SRLG disjoint, as node-disjoint as possible, and have minimum administrative costs. Due to the priority order of evaluation and typical network physical configurations of links, with the links associated common fault SRLGs, the priority ordering technique is very efficient in determining at least two paths for routing between a source and destination node.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and system for network routing selection
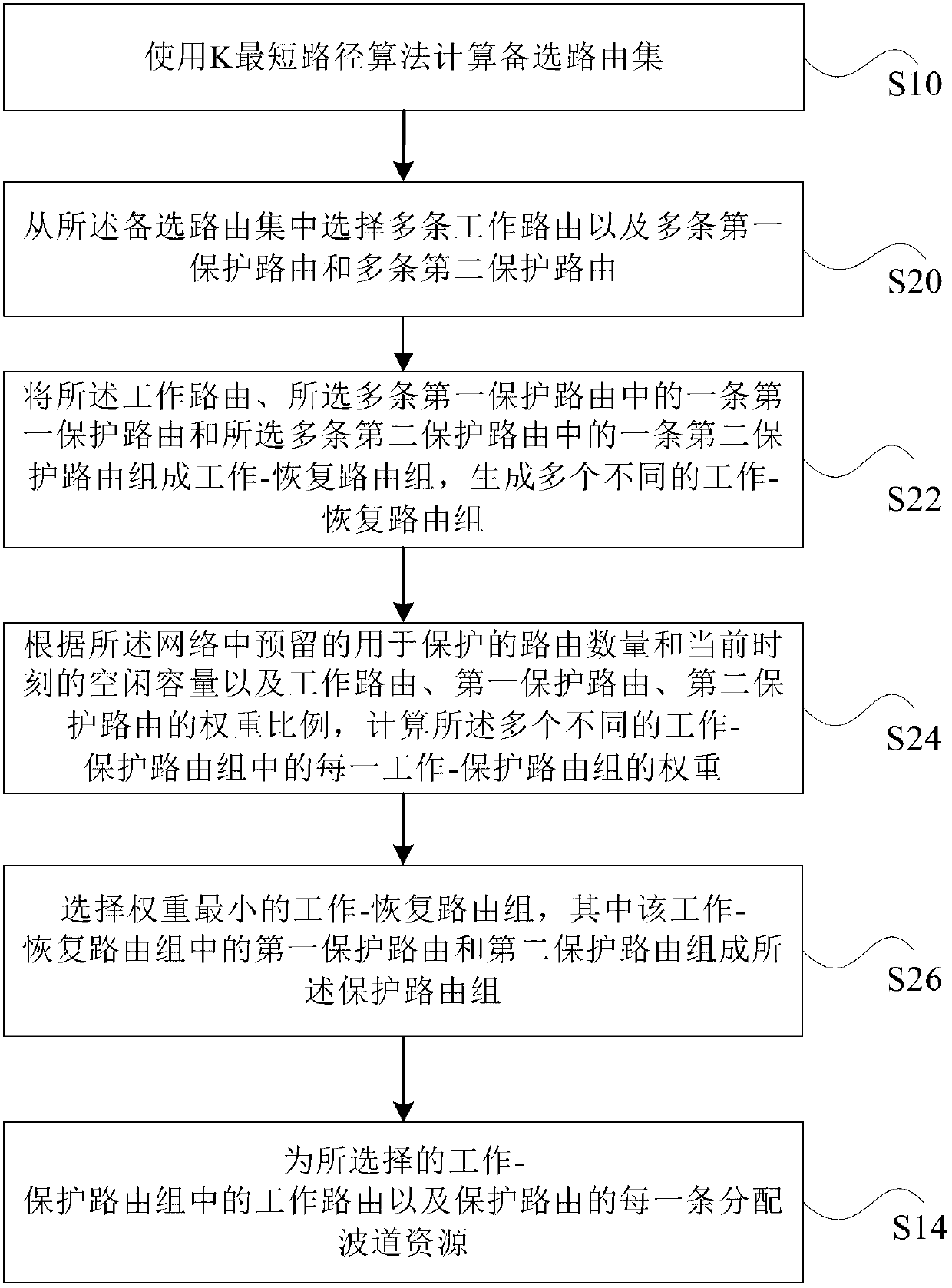
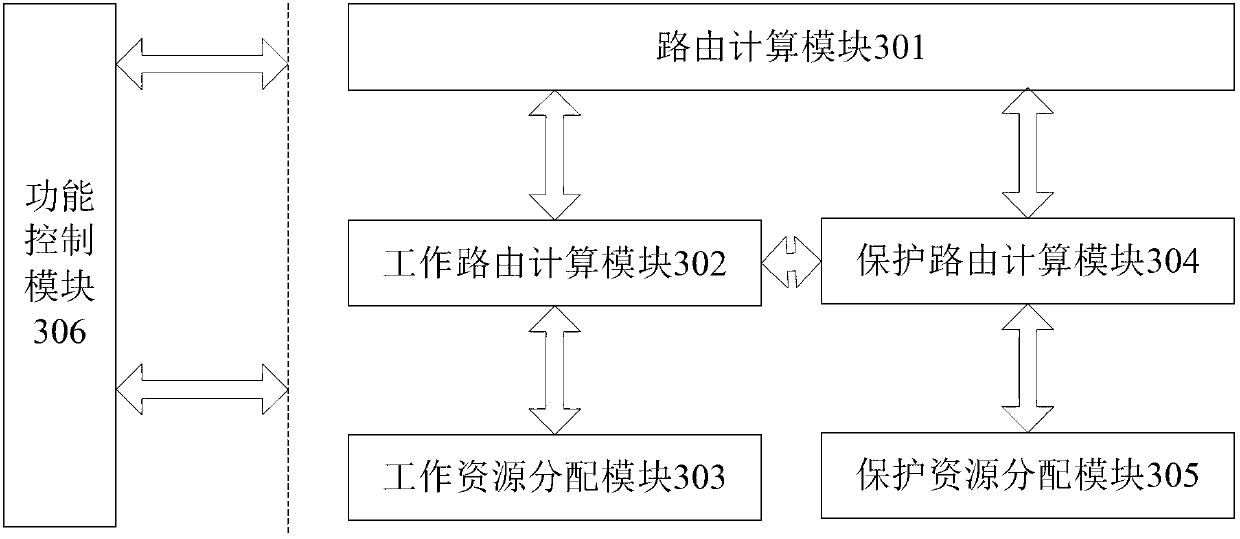
ActiveCN102594688ALow costImprove securityMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksShort path algorithmComputer module
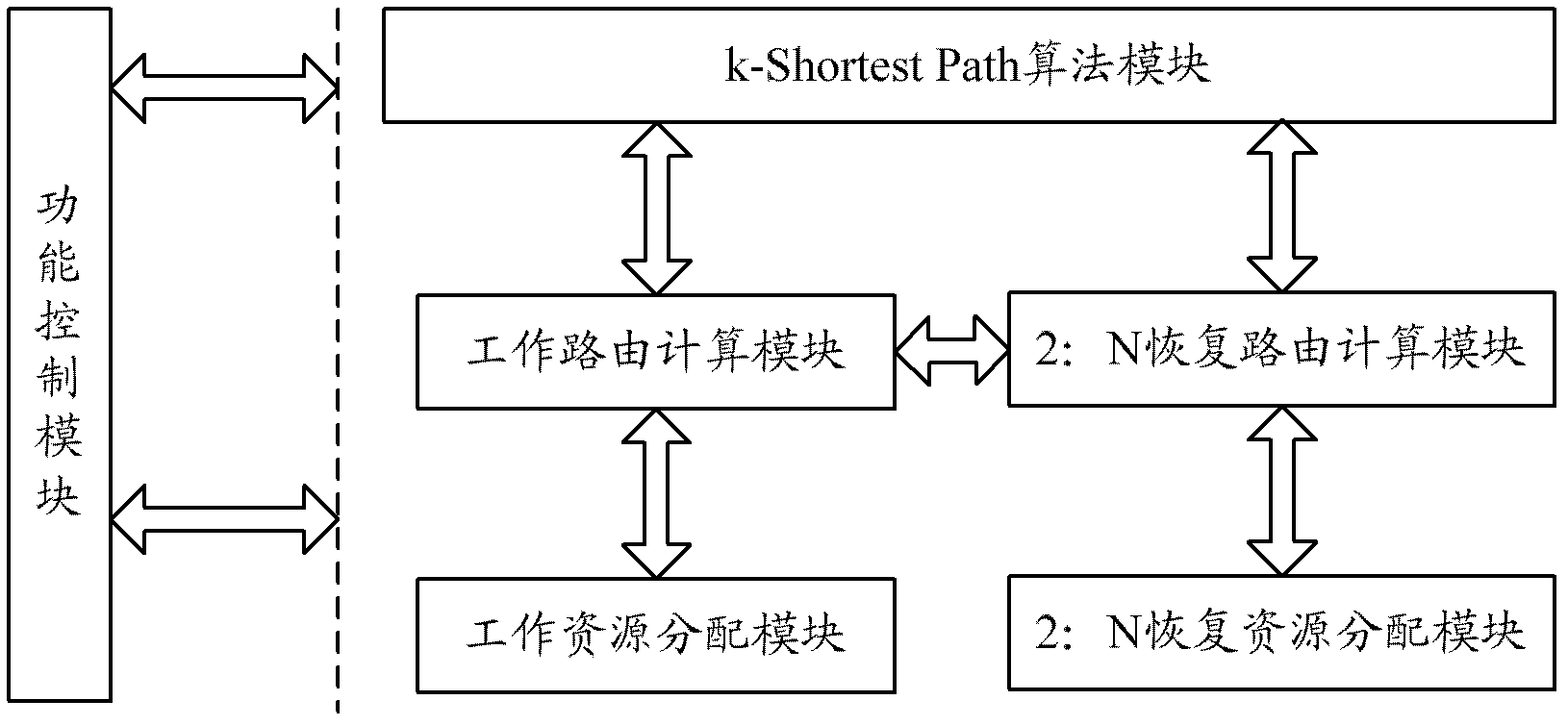
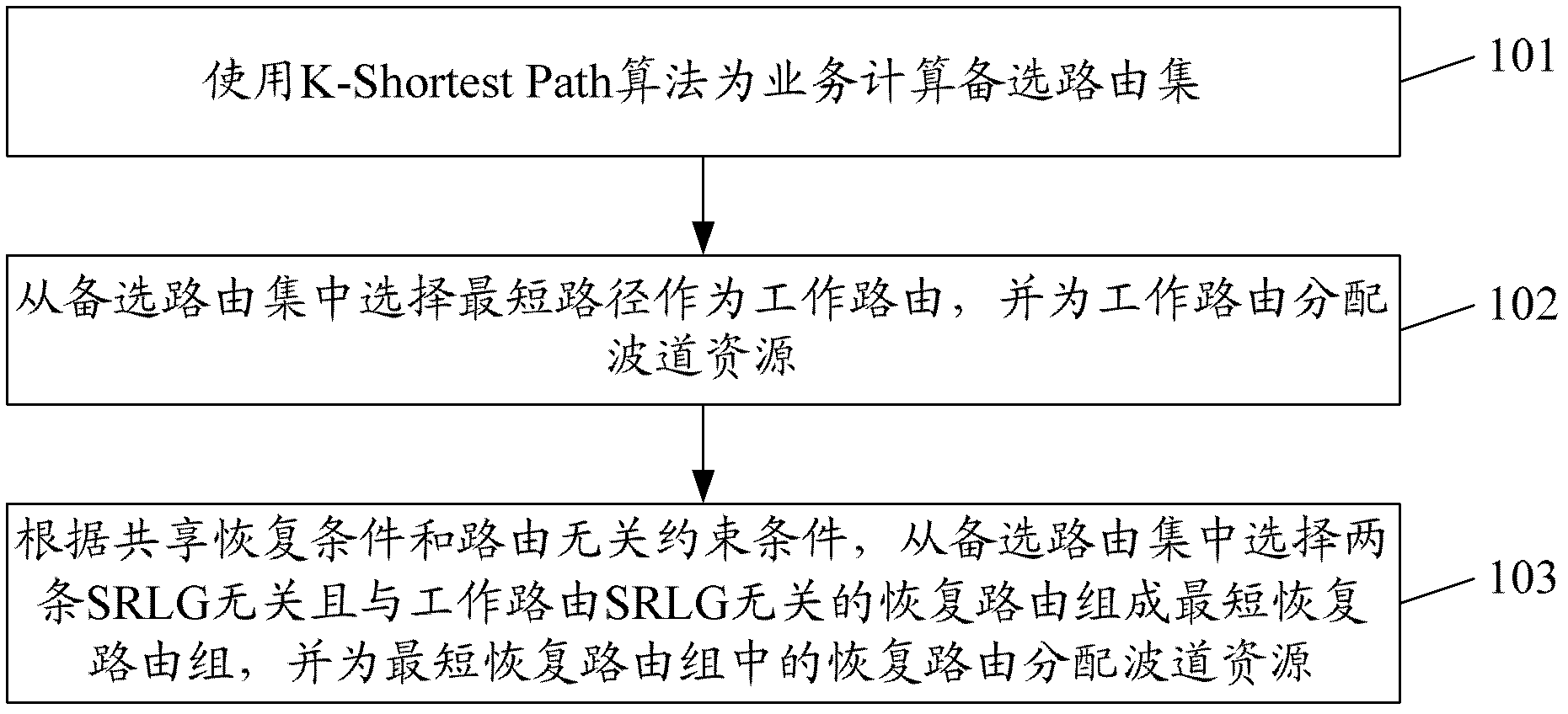
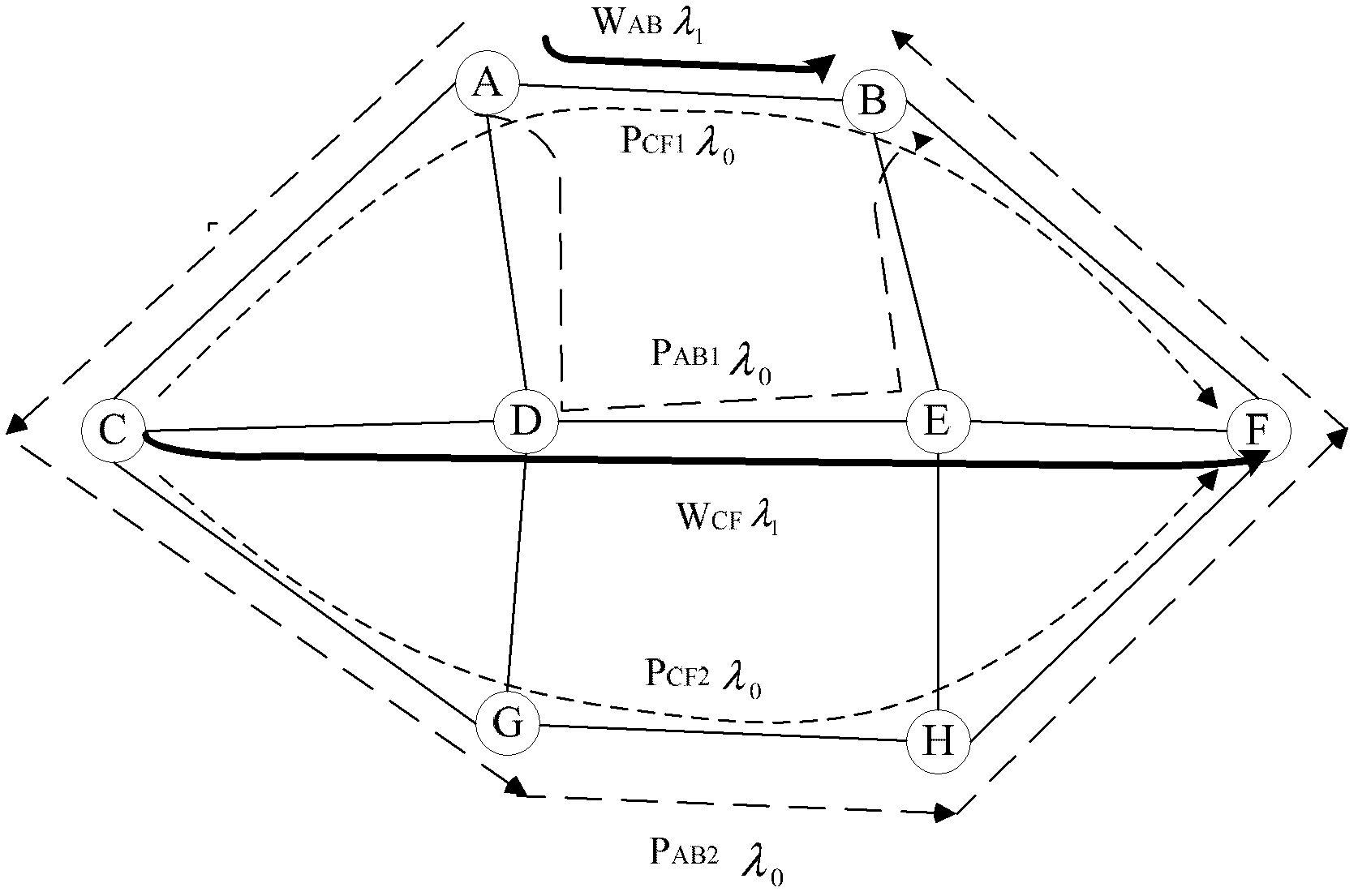
The invention discloses a method and a system for network routing selection. The system comprises the following modules of a k-Shortest Path algorithm module, a work routing calculation module, a 2:N recovery routing calculation module, a 2:N recovery routing calculation module and a function control module, wherein the k-Shortest Path algorithm module is used for calculating an alternative routing set for services; the work routing calculation module is used for selecting a shortest path from the alternative routing set as a working routing, and providing a sharing recovery condition and a routing-independent constraint condition for the 2:N recovery routing calculation module; the work resource allocation module is used for allocating a channel resource for the work routing; the 2:N recovery routing calculation module is used for selecting two SRLG (Shared Risk Link Group)-independent and work routing SRLG-independent recovery routings from the alternative routing set to form a shortest recovery routing group according to the sharing recovery condition and the routing-independent constraint condition; the 2: N recovery resource allocation module is used for allocating the channel resource for the recovery routings in the shortest recovery routing group; and the function control module is used for controlling the works of other modules and coordinating the logical relation among the modules. With the method and the system, the channel resource is saved, and the network security is improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and system for configuring protective resources in dense light wave multiplexing networks
InactiveCN103327421AImprove resource utilizationImprove reliabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingShort path algorithm
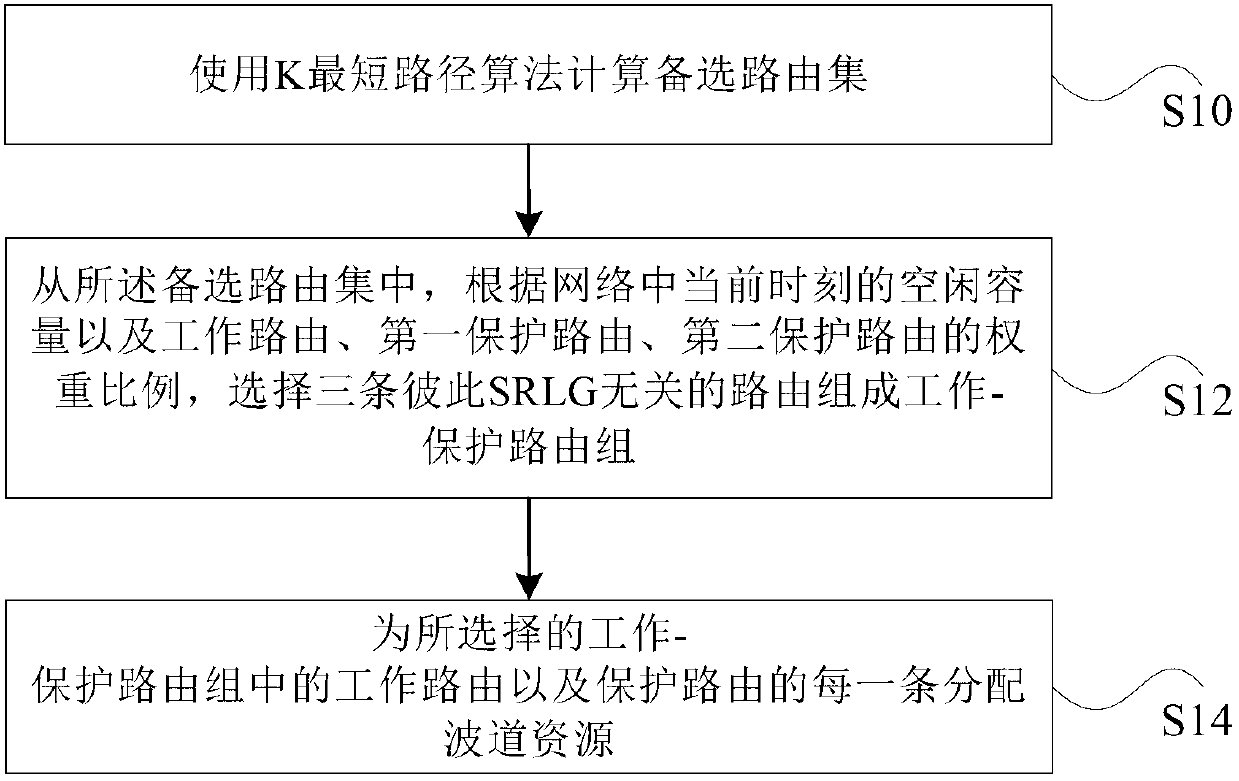
The invention discloses a method and system for configuring protective resources in dense light wave multiplexing networks according to 2:N protection. The method comprises the steps that alternative route sets are calculated by using the shortest path algorithm K; according to idle capacity in the networks at current time and the weight ratio of a work route, a first protective route and a second protection route, three routes, having irrelevant shared risk link groups, of the alternative route sets are selected to constitute a work-protection route set; wave duct resources are distributed for the work routes and the protective routes in the work-protection route set. According to the method and system, the use rate of the resources in the high-dense light wave multiplexing networks can be improved, fault recovery time is shortened, and reliability of the networks is improved.
Owner:北京赛伟网络技术有限责任公司
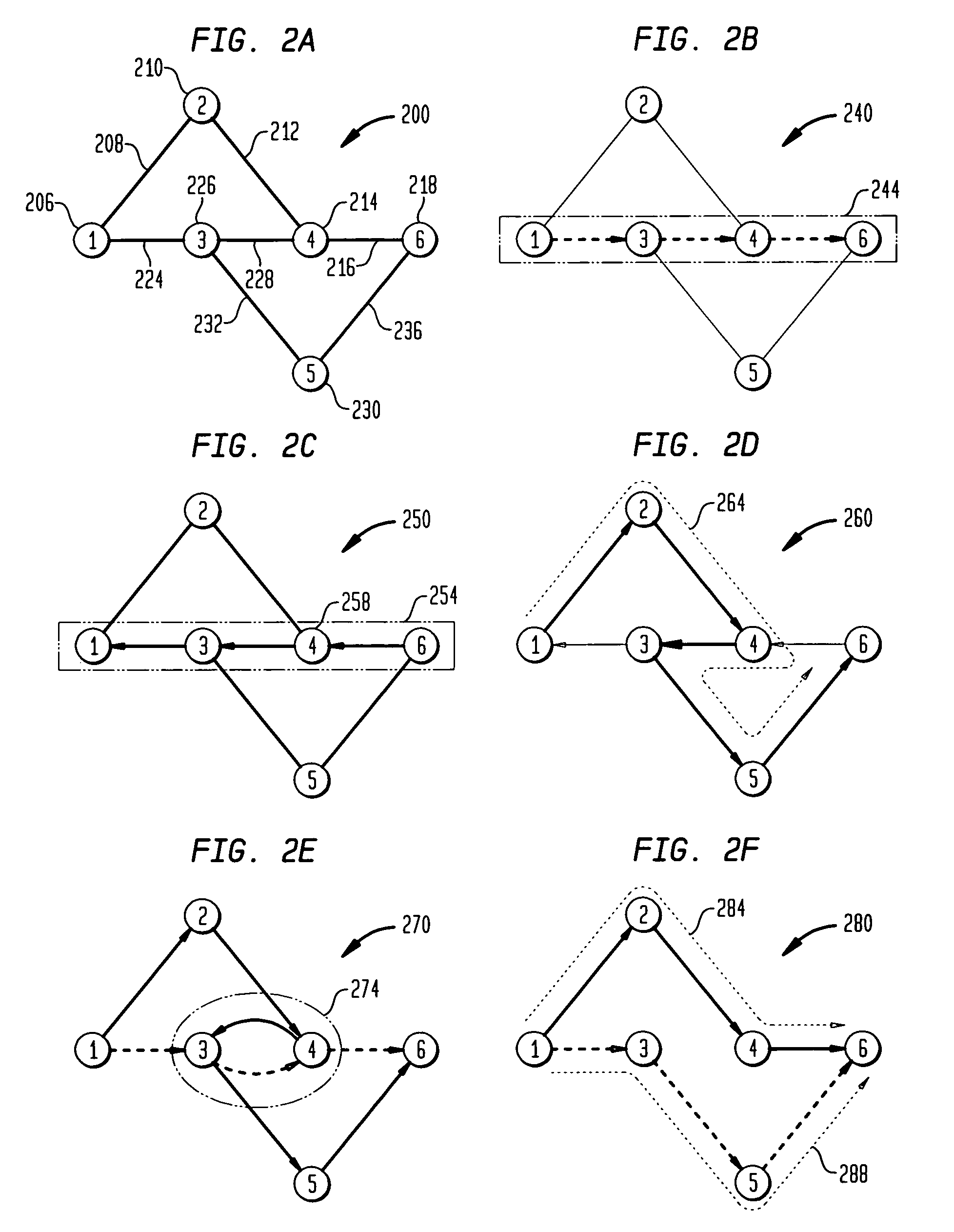
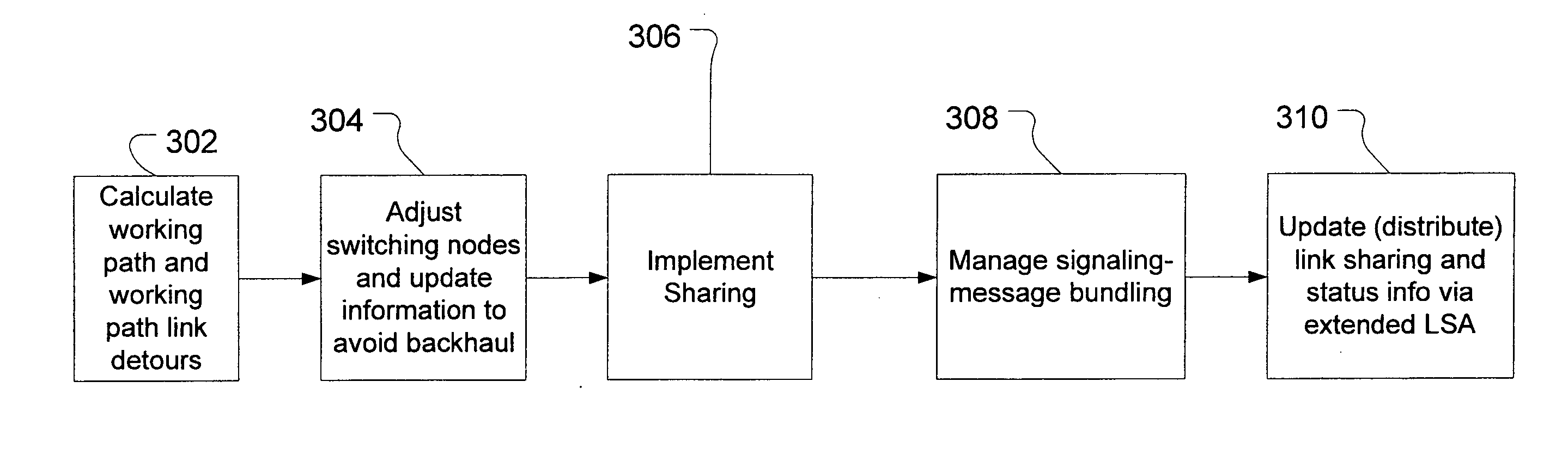
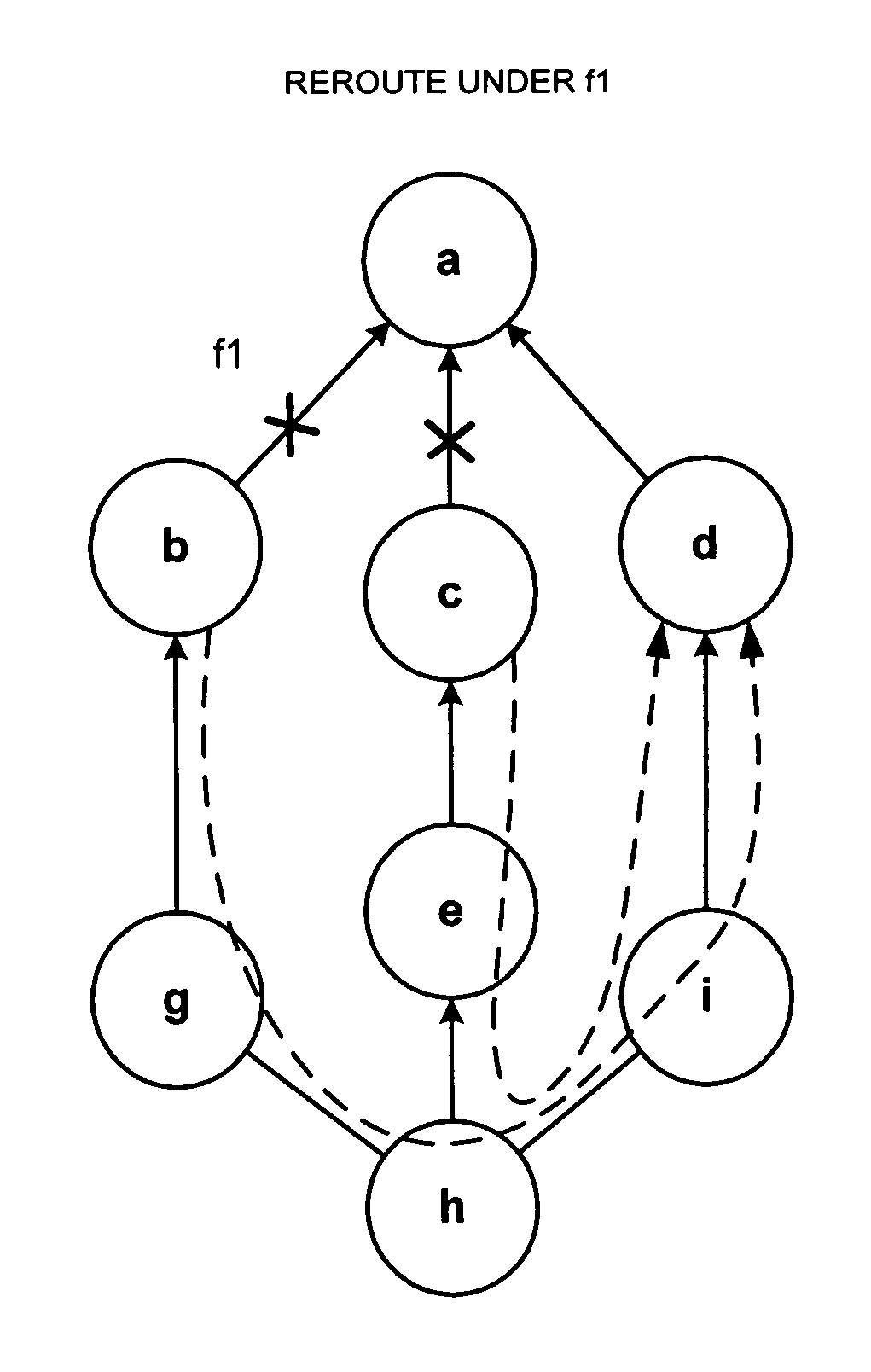
Loop avoidance for recovery paths in mesh networks
A protected communication network utilizes a link-based recovery strategy that incorporates loop-avoidance mechanisms to eliminate redundant traversal of links in recovery paths, thereby improving network efficiency. The loop-avoidance mechanisms can include calculation of recovery paths taking into account protected segments that include shared risk link groups. In one two-phase loop-avoidance mechanism, a full link-detour path is calculated for a primary-path link by generating a minimum cost path between the upstream and downstream terminating nodes for the link. Next, the full link-detour path is shortened by removing redundant links that are shared by the full link-detour path and the original primary path. Calculation of link-detours and elimination of loops is supported in some embodiments by the distribution of link-state parameters via extensions to the link-state-advertisement (LSA) protocol.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Protection path calculation method, related device and system
ActiveCN103688490AAvoid situations that should not be excludedQuality improvementError preventionData switching networksSurvivabilityShared risk link group
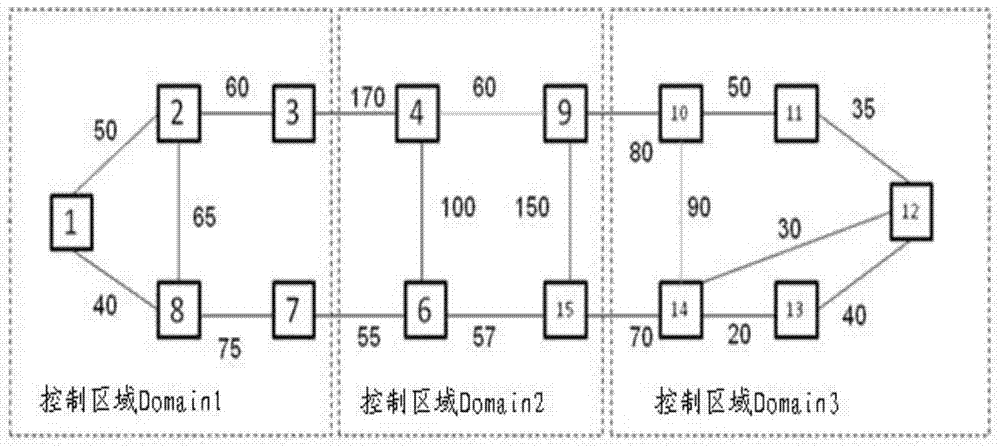
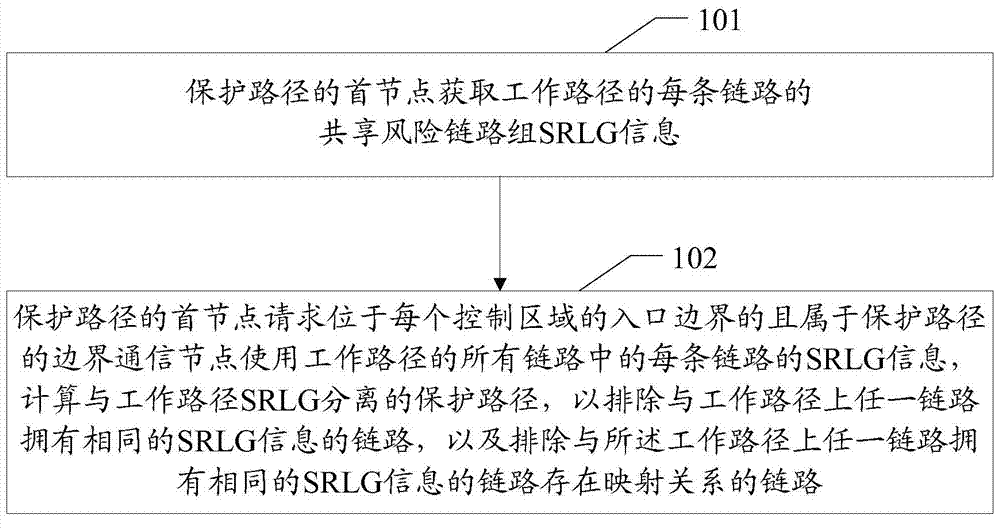
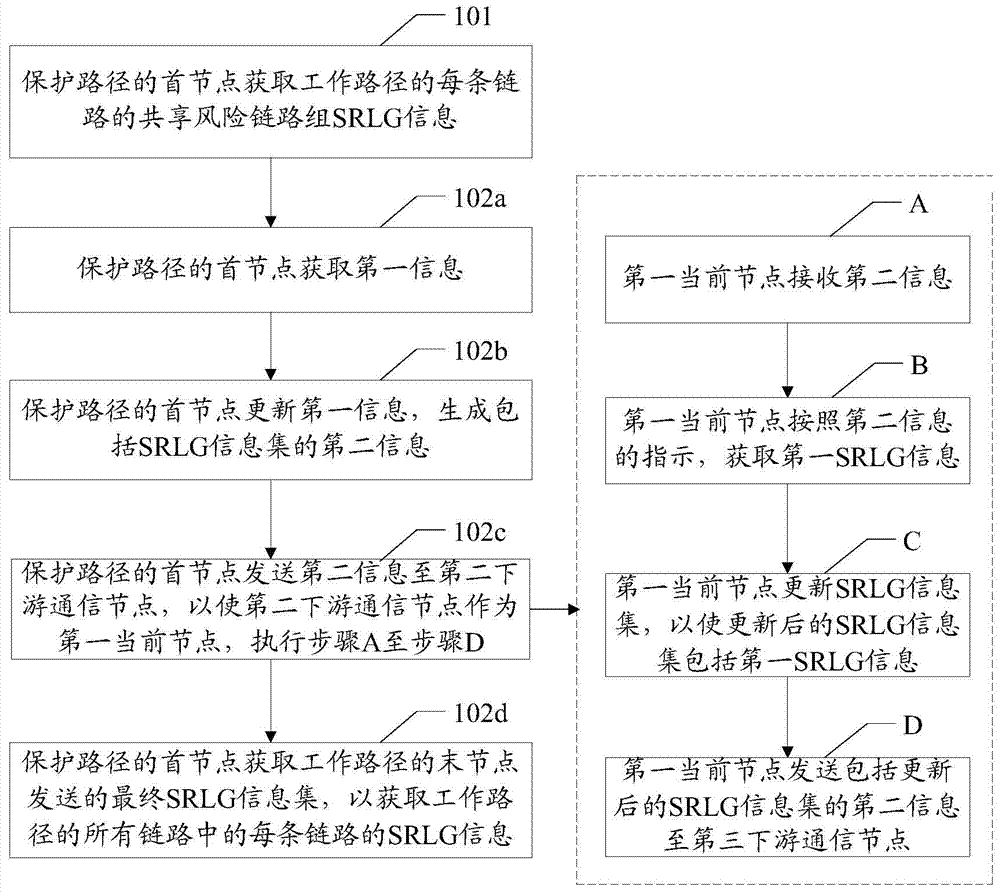
The invention provides a protection path calculation method, a related device and a system. Share risk link group SPLG information of each link of a working path is acquired through first nodes of a protection path. The SPLG information of each link of the working path is sole in a multi-domain scope, and correct expression of the SPLG information of of each link of the working path during cross-domain is achieved, namely, whether a certain link shares risk with another link can be distinguished correctly.By utilization of the SRLG information of each link of all the links of the working path, the protection path separated from the working path SRLG is calculated to exclude a link having the same SRLG information as any link of the working path and exclude a link having a mapping relation with a link having the same SRLG information with any link of the working path. Exclusion of a link, which should not be exluded, of a non-working path is avoided, and survivability of cross-domain business in communication network is raised effectively.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
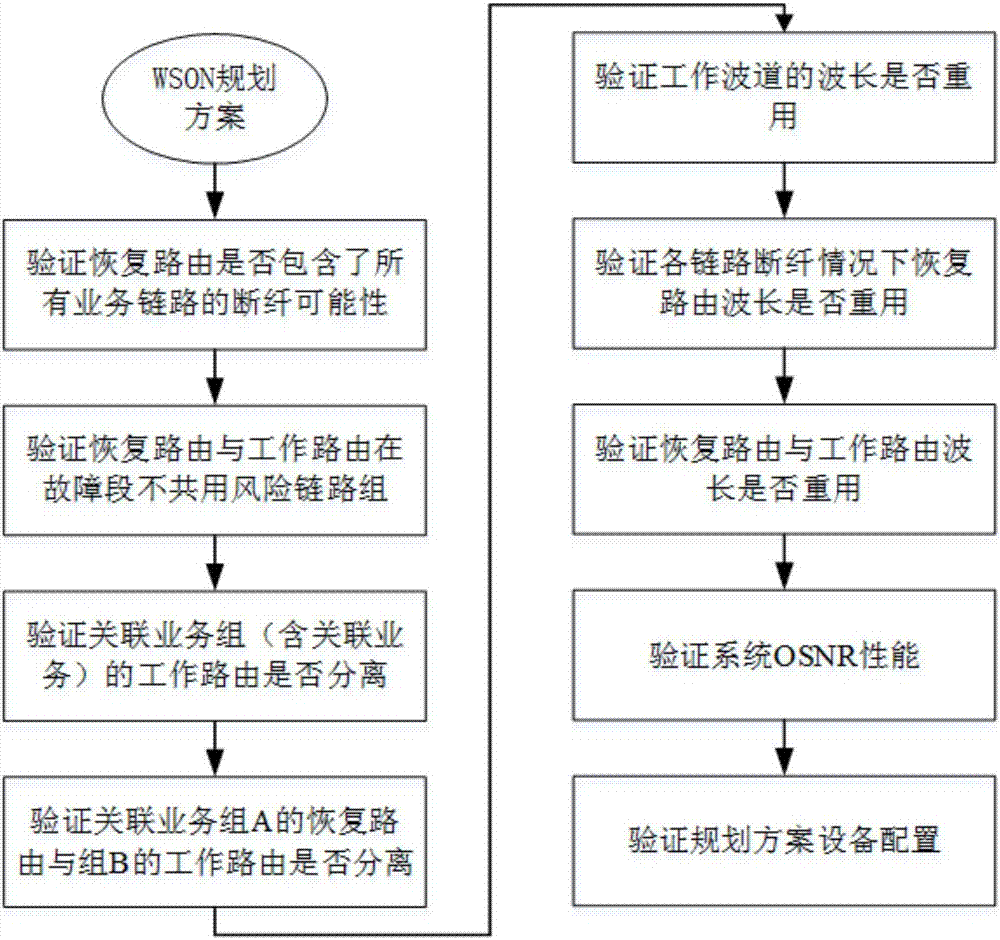
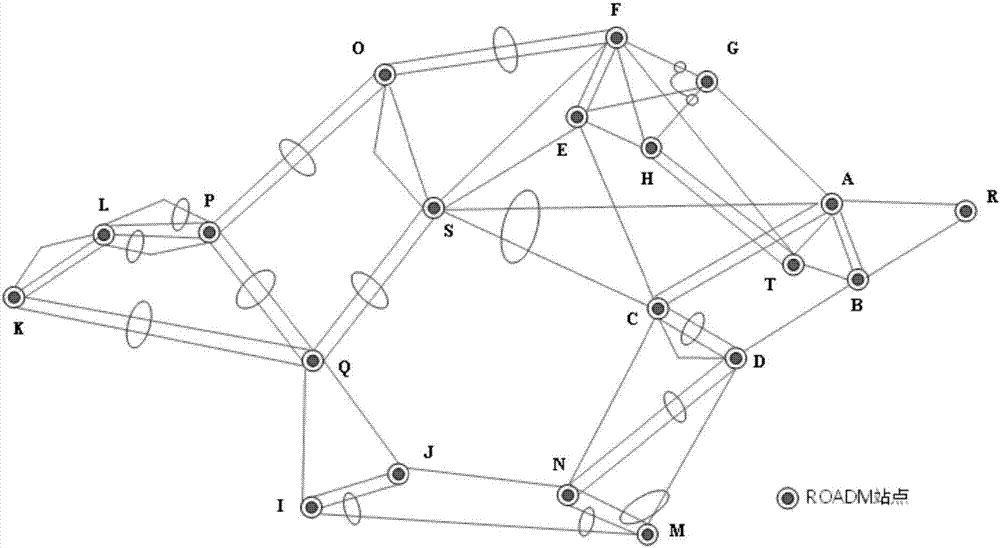
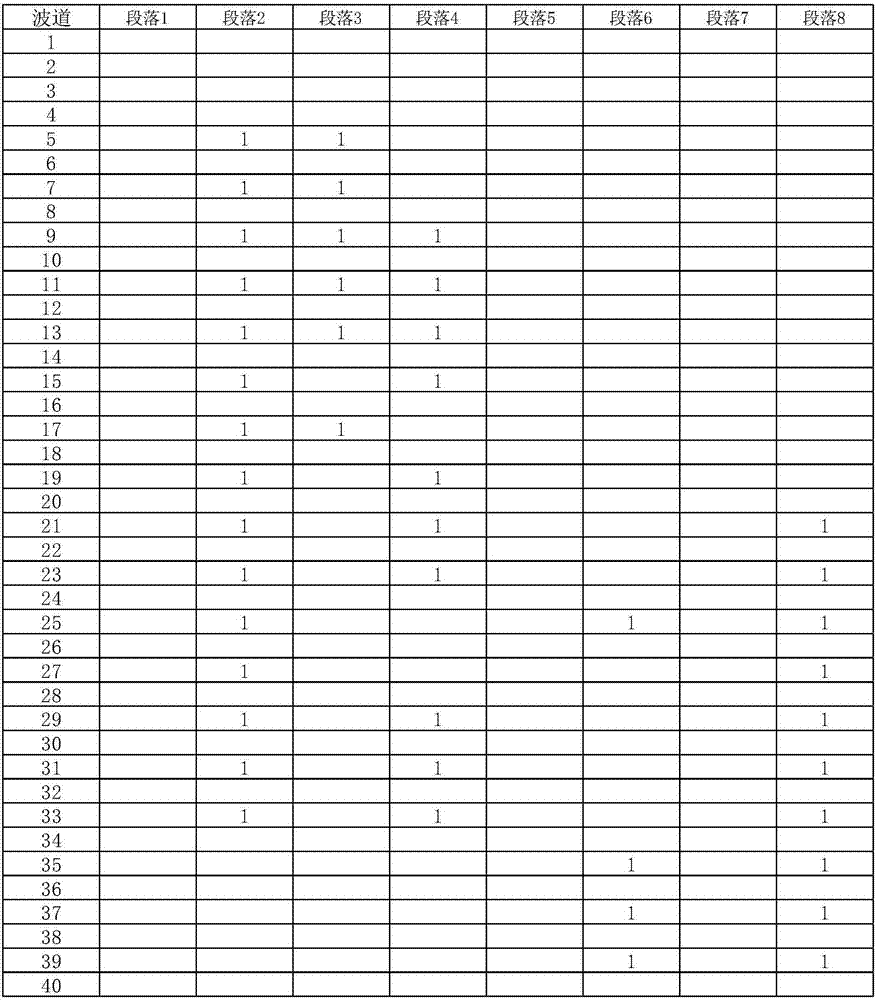
Verification method for WSON network planning scheme
ActiveCN107257256ASolve the problem that cannot be verified manuallyPracticalMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionFiberShared risk link group
The invention discloses a verification method for a WSON network planning scheme, and the method comprises the steps: 1, verifying whether a restoration route provided by a planning scheme has the fiber breaking possibility in all business links or not; 2, verifying whether the restoration route of the business and an original working route of the business share a shared risk link group at a fault segment or not; 3, verifying whether the working routes of the correlated business groups are separated or not; 4, verifying whether the restoration route of the correlated business group A and the restoration route of the correlated business group B are separated or not; 5, verifying whether the wavelengths of working wave channels of all business links are reused or not; 6, verifying whether the wavelength of the restoration route is reused under the fiber breaking condition of each link or not; 7, verifying whether the wavelength of the restoration route and the wavelength of the working route are reused or not; 8, verifying the OSNR performance of a system; 9, verifying whether the number of downlink modules at an ROADM node configured in the planning scheme meets the demands or not.
Owner:CHINA INFOMRAITON CONSULTING & DESIGNING INST CO LTD
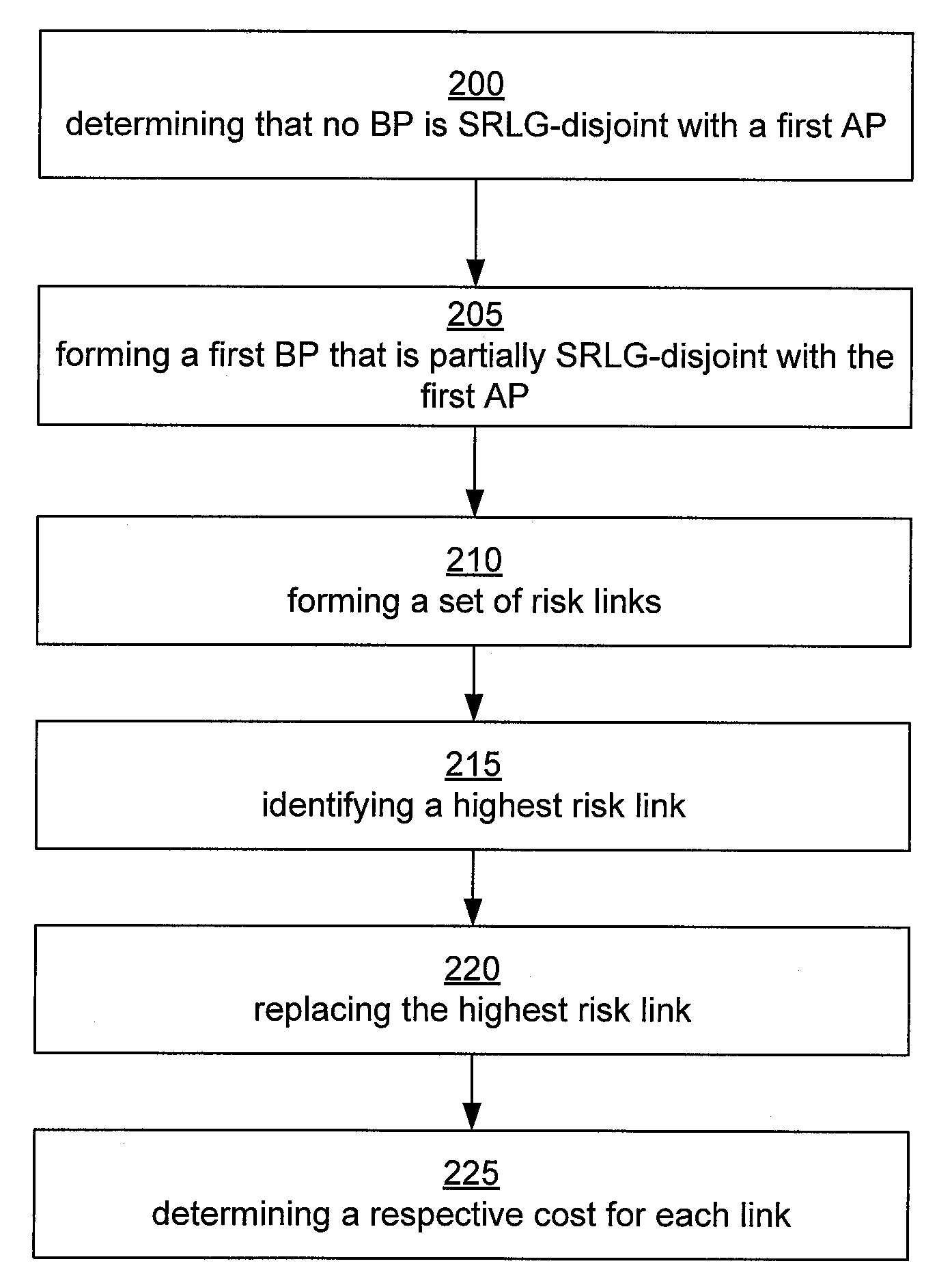
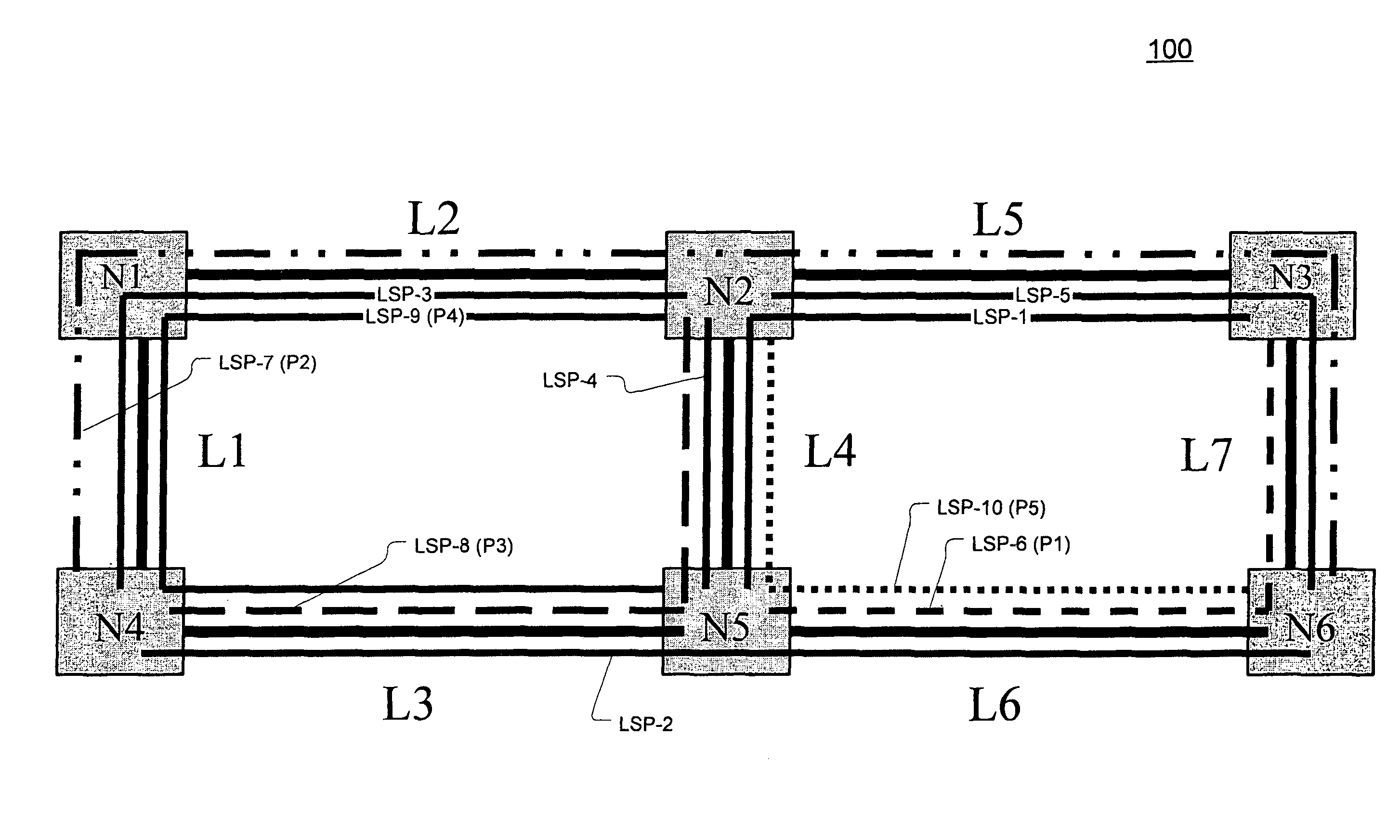
Restoration path calculation considering shared-risk link groups in mesh networks
InactiveUS8867333B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsShared risk link groupPath cost
A method for determining a restoration path for a new service in a mesh network involves selecting between candidate restoration paths corresponding to a primary path for the new service based on the shared-risk link groups (SRLGs) associated with links in the primary path. The method includes, for each of a plurality of candidate restoration paths associated with the primary path, (1) determining whether the primary path requires any additional restoration bandwidth to be reserved on any link of the restoration path based on whether, for each link of the restoration path, the primary path is SRLG-disjoint from each other primary path that is protected by that link, (2) generating a path cost for the restoration path, where the path cost is a function of whether any additional restoration bandwidth is required; and (3) selecting the restoration path for the new service based on the path cost.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Internet protocol fast reroute for shared risk link group failure recovery
InactiveUS8264955B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsInternet protocol suiteShared risk link group
A scheme to achieve fast recovery from SRLG failures in the IP layer is described. An exemplary scheme, called multi-section shortest path first (“MSSPF”), builds on the idea of IP Fast Reroute (“IPFRR”), guarantees 100% recovery of SRLG failures and causes no dead loops. Given a source node, a destination node, and a shared risk group failure on a next hop from the source node to the destination node, failure recovery information may be determined by (1) accepting a graph representing network topology information including the source node and the destination node, (2) determining a node which is able to reach the destination node using a route which does not include the source node, wherein a path from the source node to the determined node is not affected by the shared risk group failure, and (3) storing, in association with the shared risk group failure, both (i) a network address associated with the determined node and (ii) an alternative output port of the source node using the shortest path from the source node to the determined node.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Demand Advertisement Method for Shared Mesh Protection Path Computation
A method includes the steps of: (1) generating, by circuitry of a first node, an advertising message including (a) a working path bandwidth demand; (b) an identification of at least two communication links in a shared risk link group of the working path; and (c) at least one protecting path and a bitmap indicative of failure of at least one first communication link in the shared risk link group that causes the at least one protecting path to be used; and (2) transmitting the advertising message from the first node to second nodes within a mesh network.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Method and device for dynamically adjusting SRLG
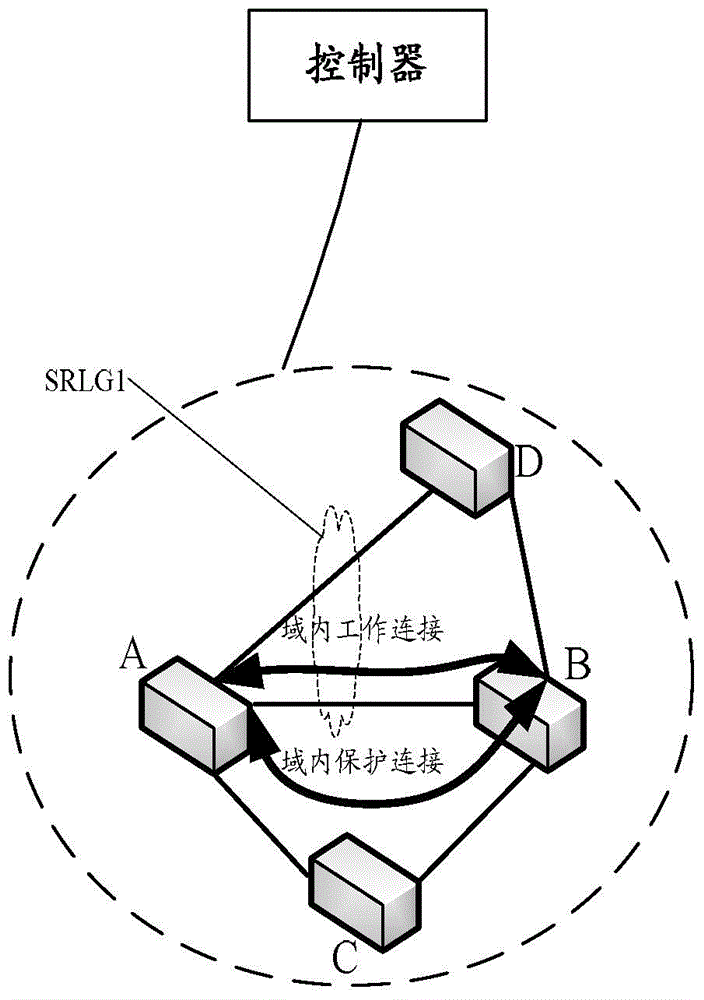
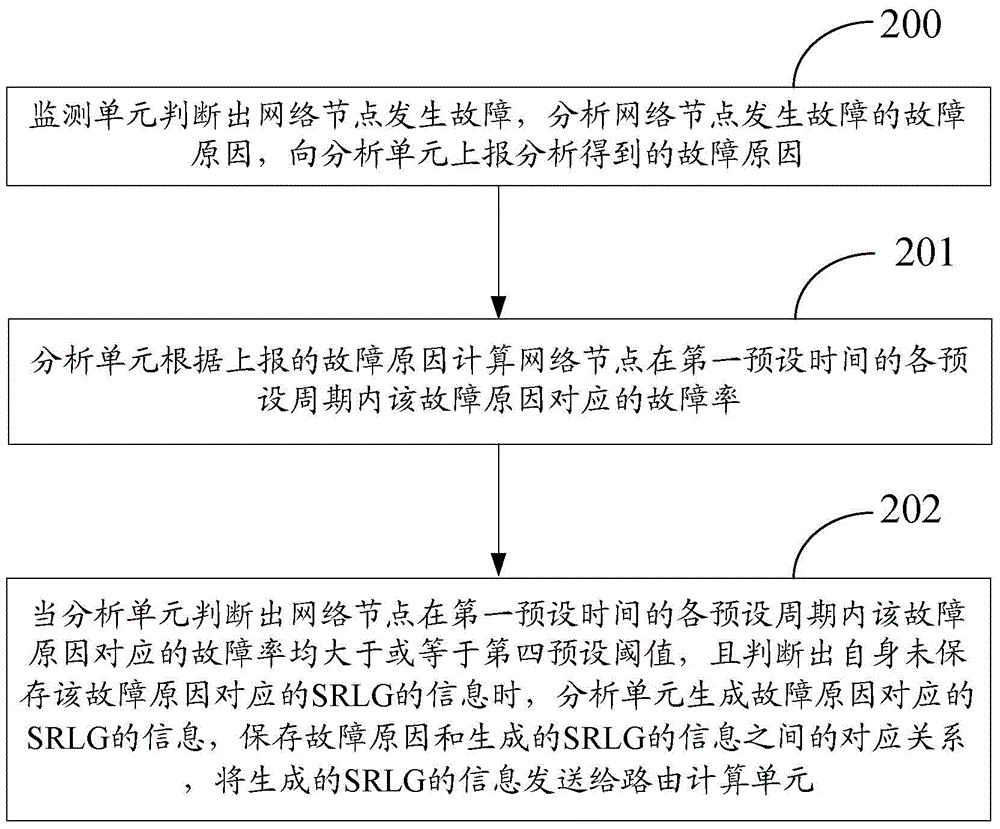
InactiveCN105763344AReduced chance of shared failure riskData switching networksFailure rateShared risk link group
The present invention discloses a method and device for dynamically adjusting a shared risk link group (SRLG). The method comprises the steps that a monitoring unit judges that a network node is failed, analyzes the failure reason of the network node, and reports the analyzed failure reason to an analysis unit; the analysis unit calculates the failure rate corresponding to the failure reason of the network node in each preset period of a first preset time according to the reported failure reason; and when the analysis unit judges that the obtained failure rate is larger than or equal to a fourth preset threshold and judges that the analysis does not store the information of the SRLG corresponding to the failure reason, the analysis generates the information of the SRLG corresponding to the failure reason, stores the failure reason and the generated corresponding relation between the generated information of the SRLG, and sends the generated information of the SRLG to a calculation unit. According to the method and the device, the probability of sharing a failure risk by a working path and a protection path is reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Path protection method for optimizing node sleep under delay and shared risk link group restraint
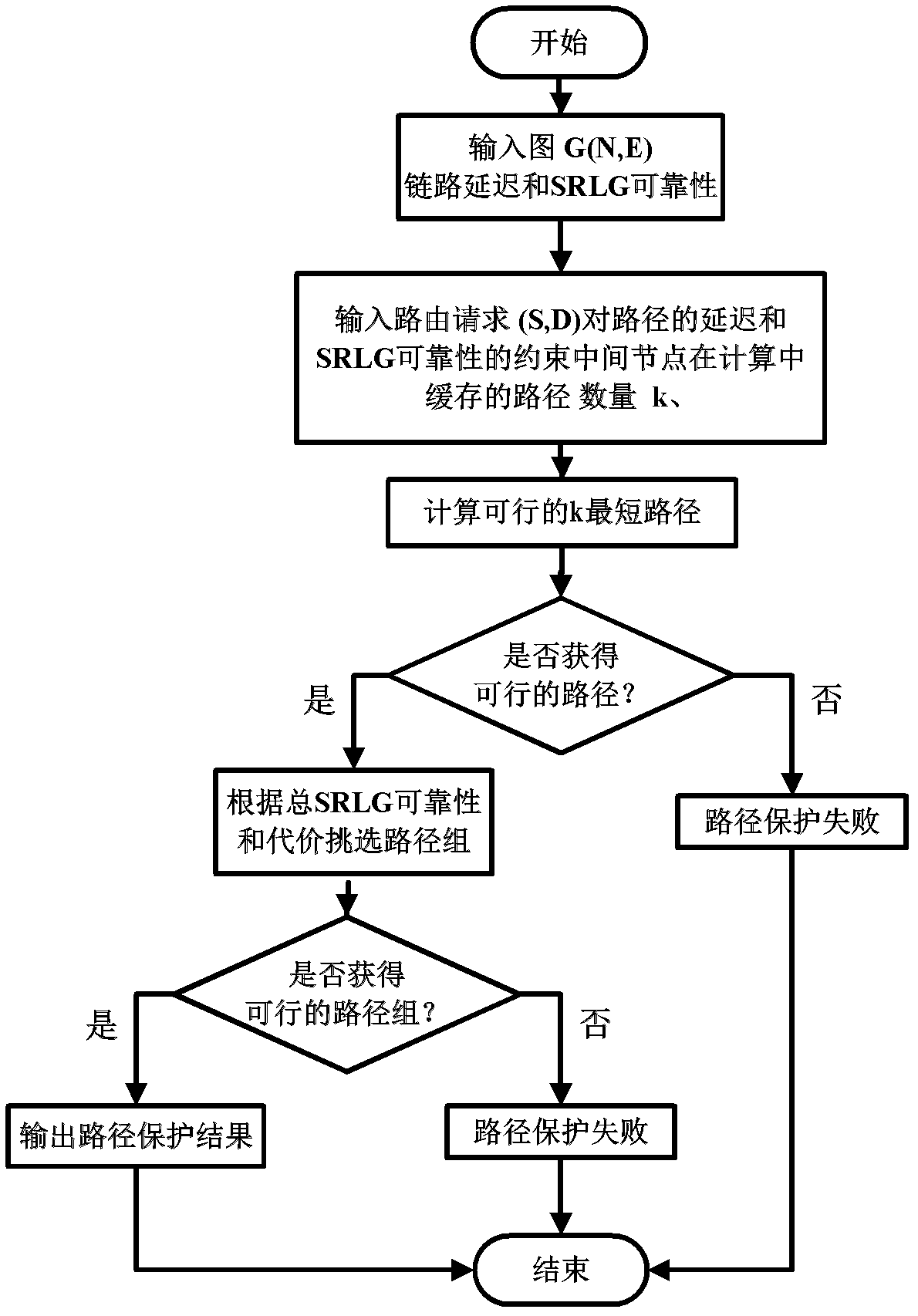
InactiveCN102325088AConvenient route calculationImprove protectionData switching networksRound complexityNetwork link
The invention discloses a path protection method for optimizing node sleep in a green network under delay and shared risk link group restraint. By using the method, in path calculation, the influence of sleep or awakening delay on a node due to path delay before a sleep node is taken into consideration and the path end-to-end delay calculating precision is improved. A cost function used when the obtained path is selected not only ensures that the reliability of a combined path meets restraint, but also encourages link and sleep node resource share between the protecting paths through calculation of path occupied network link and node resources, therefore, the proportion of the sleep node in the network is increased and the awakening frequency on the sleep node is reduced. The complexity of the method approaches that of the traditional k shortest path calculation-based path protection method; and the invention has strong adaptability on the change of the data flow of the network and expresses excellent and stable performance.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Cross layer mapping management method of share risk link group
ActiveCN102868563ASolve difficultySolve the speed problemData switching networksShared risk link groupLength wave
The invention relates to a cross layer mapping management method of a share risk link group. The cross layer mapping management method includes counting bottom layer physical topology sections, counting optical cable topology links and counting wavelength division multiplex / optical transport network (WDM / OTN) topology optical cable sections, then is carried out in six steps, and finally a share risk link group (SRLG) table of a WDM / OTN layer and an SRLG table of an optical cable layer are obtained. According to the cross layer mapping management method of the share risk link group, the bearing relation between an upper layer topology and a bottom layer topology is adopted as the basis, the SRLG of an upper layer network is divided in an automatic mapping method, the problems of large arrangement and management difficulty of the share risk link group, slow human analysis response speed, not high accuracy and the like are effectively solved, main and standby routers of services are ensured to be independent by aid of clear risk link correlation, and service safety is improved.
Owner:HUAXIN CONSULTATING CO LTD
Method for defining shared risk link group in optical transmission system
A method defines shared risk link groups in optical transport systems, in which two optical links sharing at least one single point of failure are considered to be non-disjoint. For each optical link there is measured and recorded a polarization state characteristic and two links having the same characteristic are judged to be non-disjoint and to be in the same shared risk link group.
Owner:XIEON NETWORKS SARL
Method and device for detecting sharing risk link group
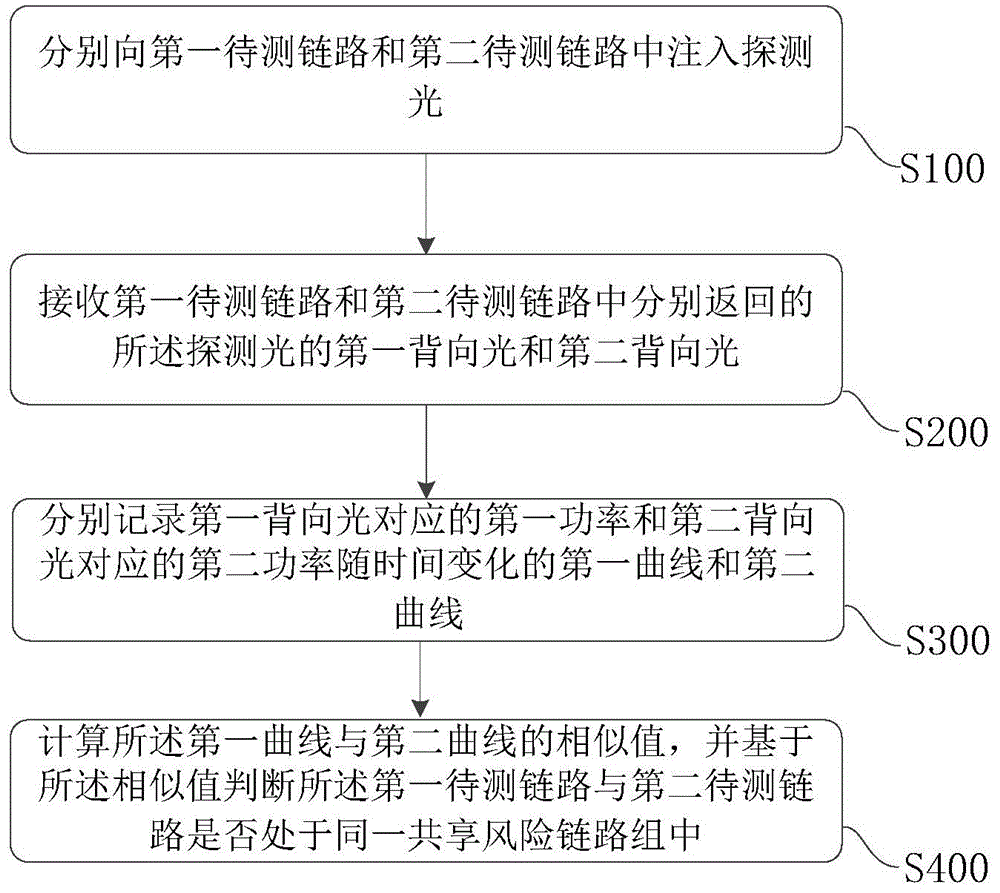
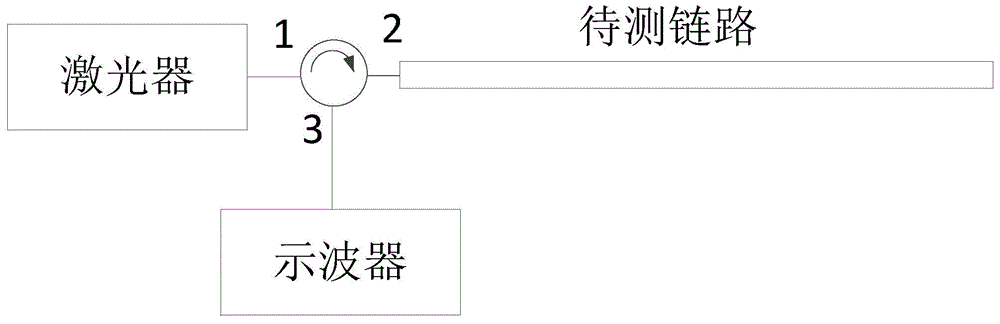
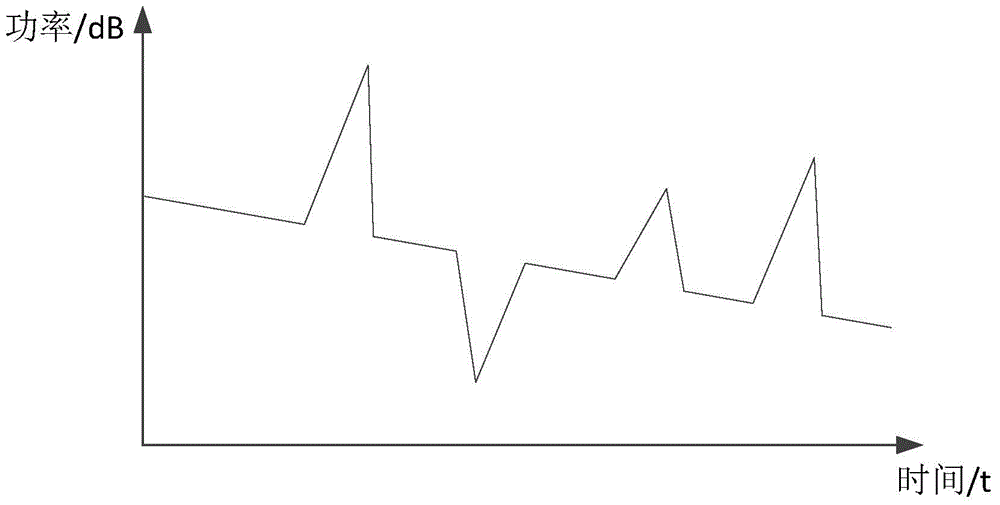
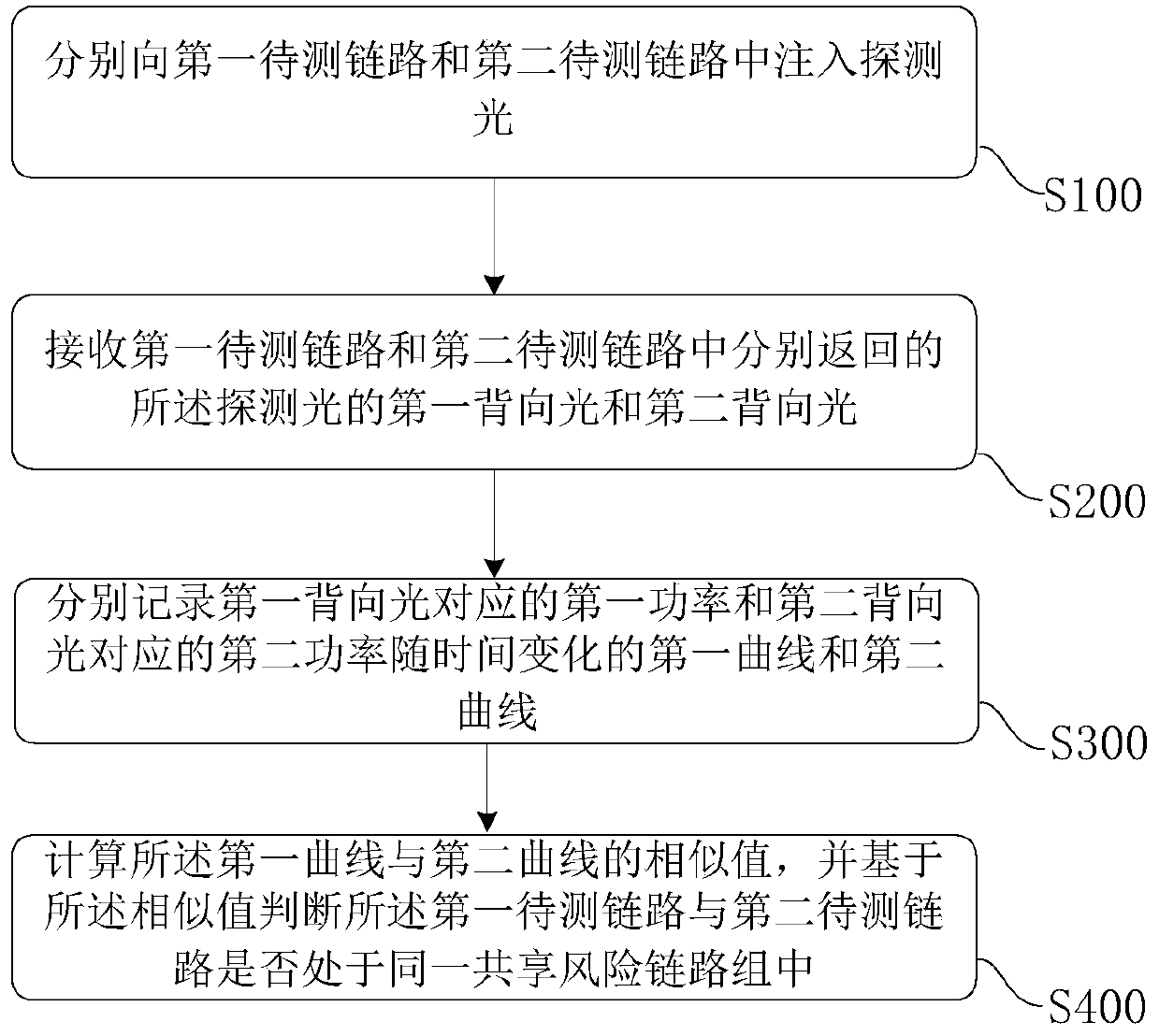
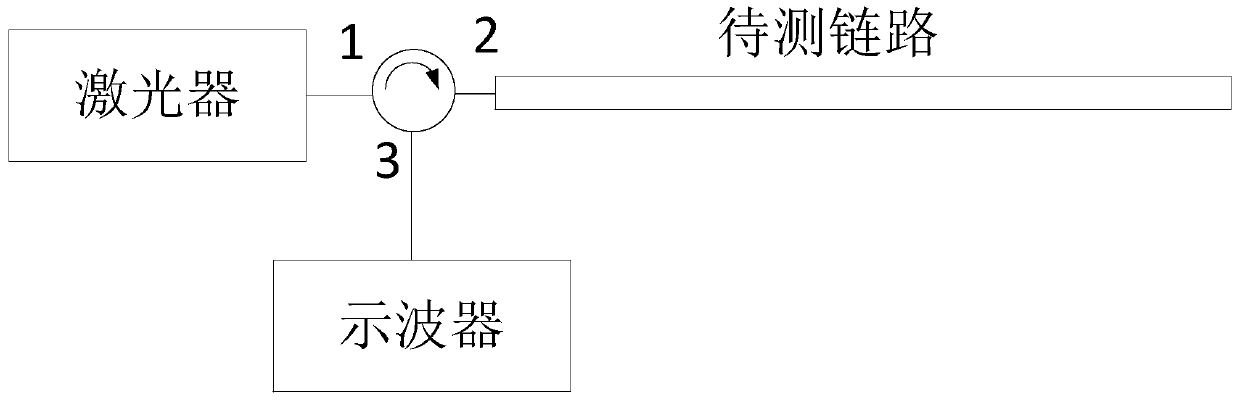
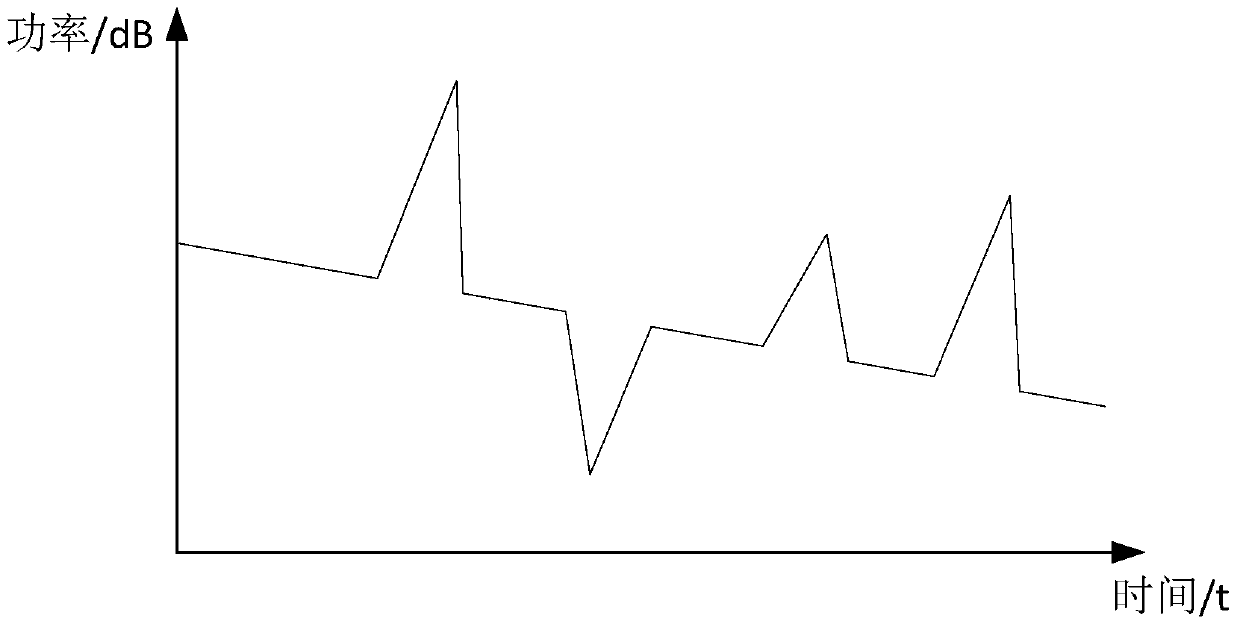
ActiveCN105991188AEasy to testEasy analysisElectromagnetic transmissionOptical apparatus testingTemporal changeShared risk link group
The invention provides a method and device for detecting a sharing risk link group. The method includes the following steps that: a first curve about the change of power corresponding to backward light in a first link to be detected with time and a second curve about the change of power corresponding to backward light in a second link to be detected with time are recorded respectively; and the similarity value of the first curve and the second curve is calculated, whether the first link to be detected and the second link to be detected are located in the same sharing risk link group is judged based on the similarity value. According to the method and device for detecting the sharing risk link group provided by the embodiments of the invention, the power characteristics of the backward light of detection light in the links to be detected are tested, and whether the links to be detected are located in the same sharing risk link group is judged based on the one-dimensional power characteristics. The method and device are relatively simple in practical application.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Drop port based shared risk link group systems and methods
ActiveUS9197355B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsData switching networksShared risk link groupSingle point of failure
Drop port based shared risk link group (SRLG) systems and methods assign SRLG information to drop ports in another level or layer of a network. Thus, drop side SRLG information can be shared between different networks or layers enabling a combination with line side SRLG information within a network to identify and prevent single points of failure across the networks. Typically, SRLG details are assigned to line ports (NNI ports) within a network and this information is not shared with external networks or network layers for routing a connection through the network and the external networks. By assigning SRLG details to a drop port, this information can be relayed between the network and the external networks and considered when planning a route through all of the networks.
Owner:CIENA
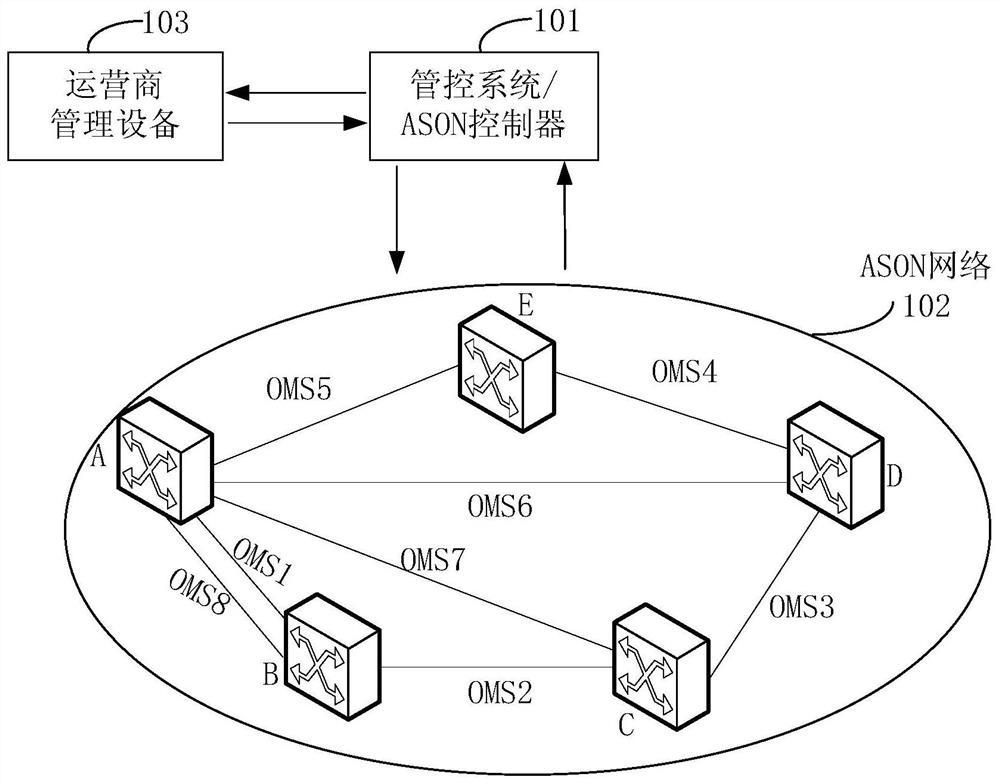
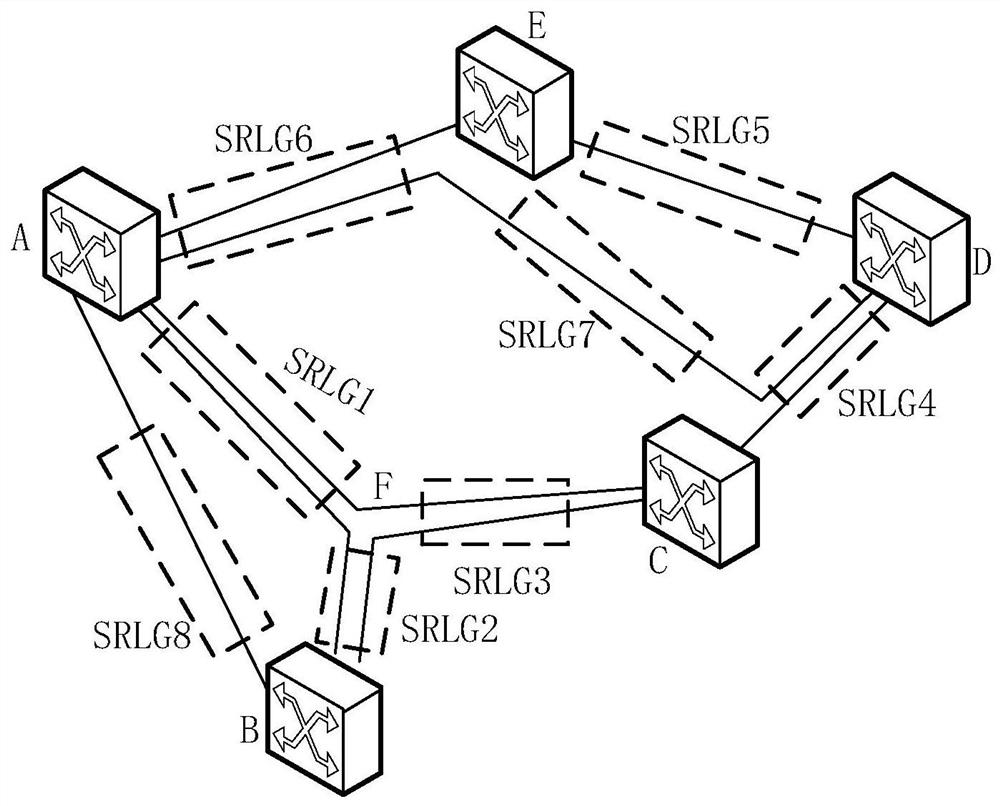
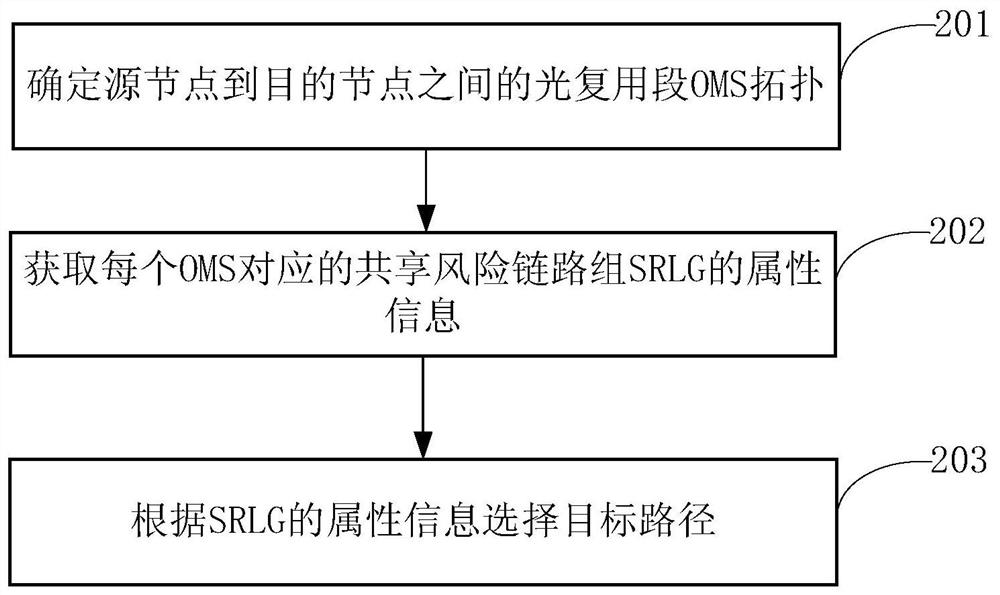
Path selection method and path selection device
ActiveCN114520935AImprove reliabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsHigh level techniquesMultiplexingPathPing
The embodiment of the invention discloses a path selection method and a path selection device, which are used for selecting a target path for transmitting service data based on attribute information of an SRLG bearing an OMS. Specifically, the path selection device determines an optical multiplexing segment (OMS) topology between a source node and a destination node, and obtains attribute information of a shared risk link group (SRLG) corresponding to each OMS. Then, a target path is selected according to the attribute information of the SRLG, the target path being used for transmitting traffic data from the source node to the destination node through at least one OMS of the plurality of OMSs. As the attribute information of the SRLG can reflect the actual attribute of the physical optical fiber section / optical cable section, the target path with lower fault risk is selected according to the attribute of the SRLG, which is beneficial to improving the reliability of service transmission.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and device for configuring OTU (optical transform unit)
InactiveCN102638303BReduce configurationIncrease the frequency of reuseTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsSurvivabilityShared risk link group
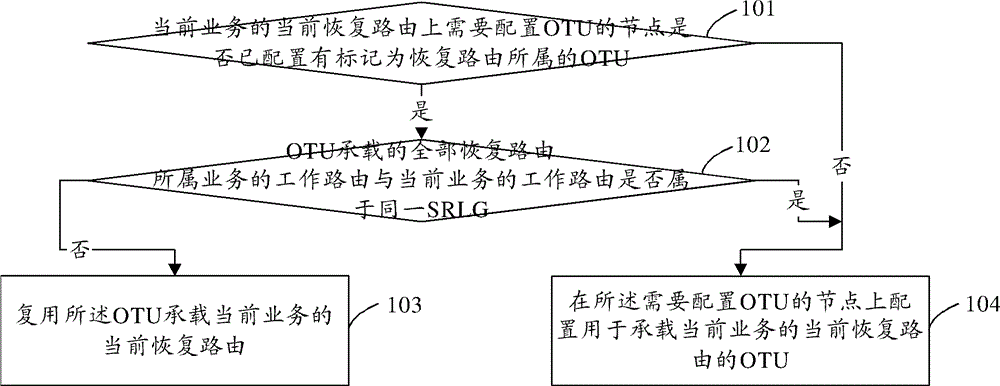
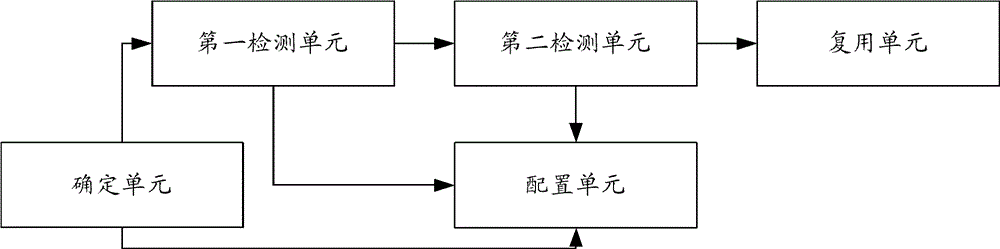
The invention discloses a method for configuring an OTU (optical transform unit). The method comprises the following steps of detecting whether a node on a current recovery route of a current service and needing to configure the OTU, is configured with the OTU marked to be of the recovery route or not; if the node is configured with the OTU marked to be of the recovery route, detecting whether a working route of a service to which all recovery routes loaded by the OTU belong, and a working route of a current service belong to a same SRLG (shared risk link group) or not; if so, configuring the OTU for bearing the current recovery route of the current service for the node needing of configuring the OUT; otherwise, multiplexing the OTU to bear the current recovery route of the current service; and if the node is not configured with the OTU marked to be of the recovery route, configuring the OTU for bearing the current recovery route of the current service for the node needing of configuring the OUT. Correspondingly, the invention further discloses a device for configuring the OTU, thereby reducing the use cost of the OTU and further improving the survivability of network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
A method and device for detecting a shared risk link group
ActiveCN105991188BEfficient use ofElectromagnetic transmissionOptical apparatus testingTemporal changeShared risk link group
The present application provides a method and device for detecting a shared risk link group. The method includes: respectively recording a first curve and a second curve of the power corresponding to the backlight in the first link to be tested and the second link to be tested as a function of time; calculating the first curve and the second curve The similarity value of the curve, and based on the similarity value, it is judged whether the first link under test and the second link under test are in the same shared risk link group. A method and device for detecting a shared risk link group provided in an embodiment of the present application, by testing the power characteristics of the backlight of the detection light in the link to be tested, and judging the link group to be tested based on the one-dimensional power characteristic Whether they are in the same shared risk link group is relatively simple in practical applications.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com