Method for defining shared risk link group in optical transmission system
A technology for sharing risk links and optical links, applied in the field of limiting shared risk link groups in optical transmission systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
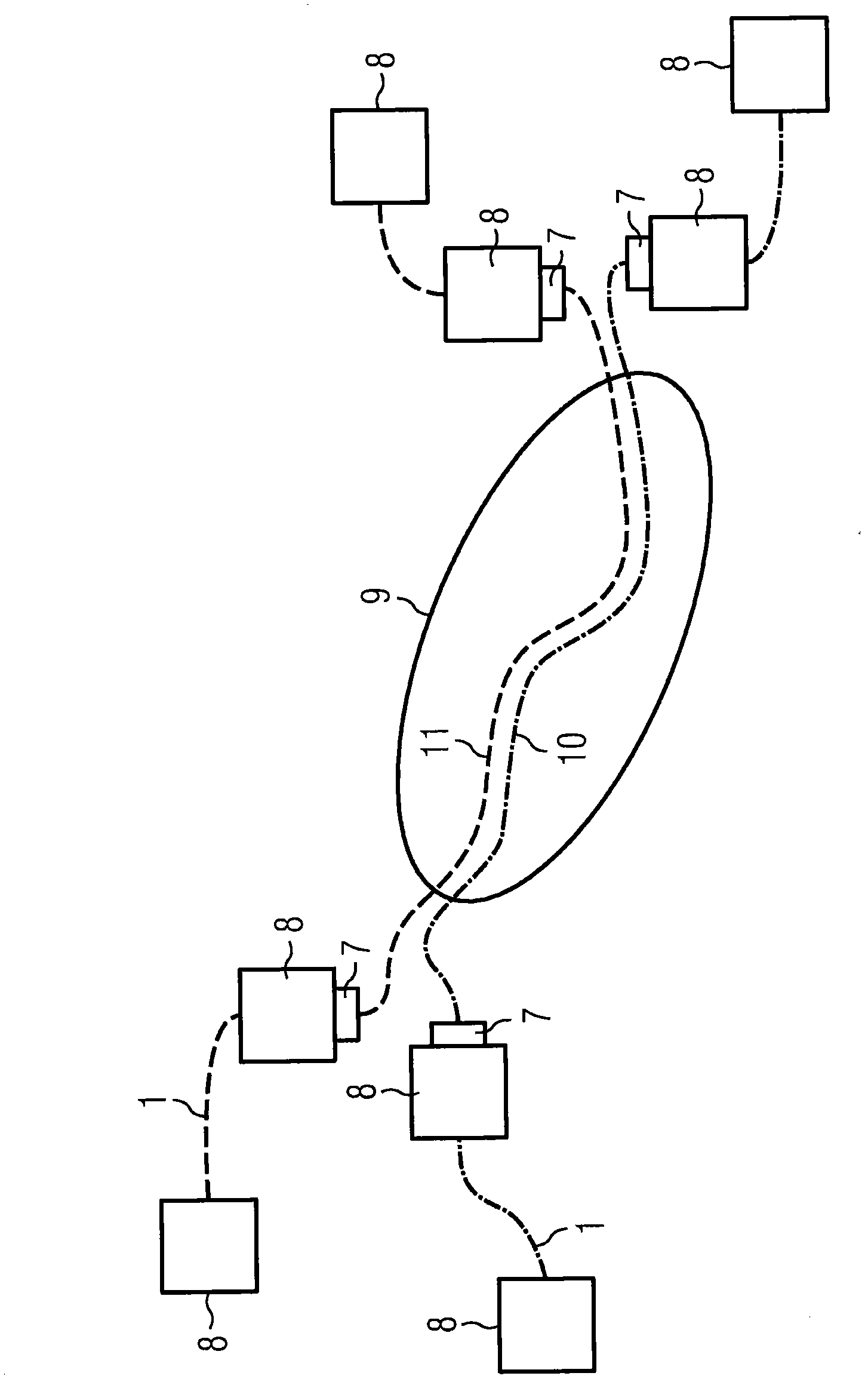
[0019] figure 1 A part of an optical transmission system with two optical links 1 is shown in , where parts 10 and 11 of the two links are wired in parallel, so they are part of a shared risk group 9 . Some network elements 8 are equipped with OTDR measurement devices 7 . If the OTDR measurements of links 10 and 11 show the same SOP characteristics, they are judged to be non-disjoint, and thus they are in the same shared risk link group.
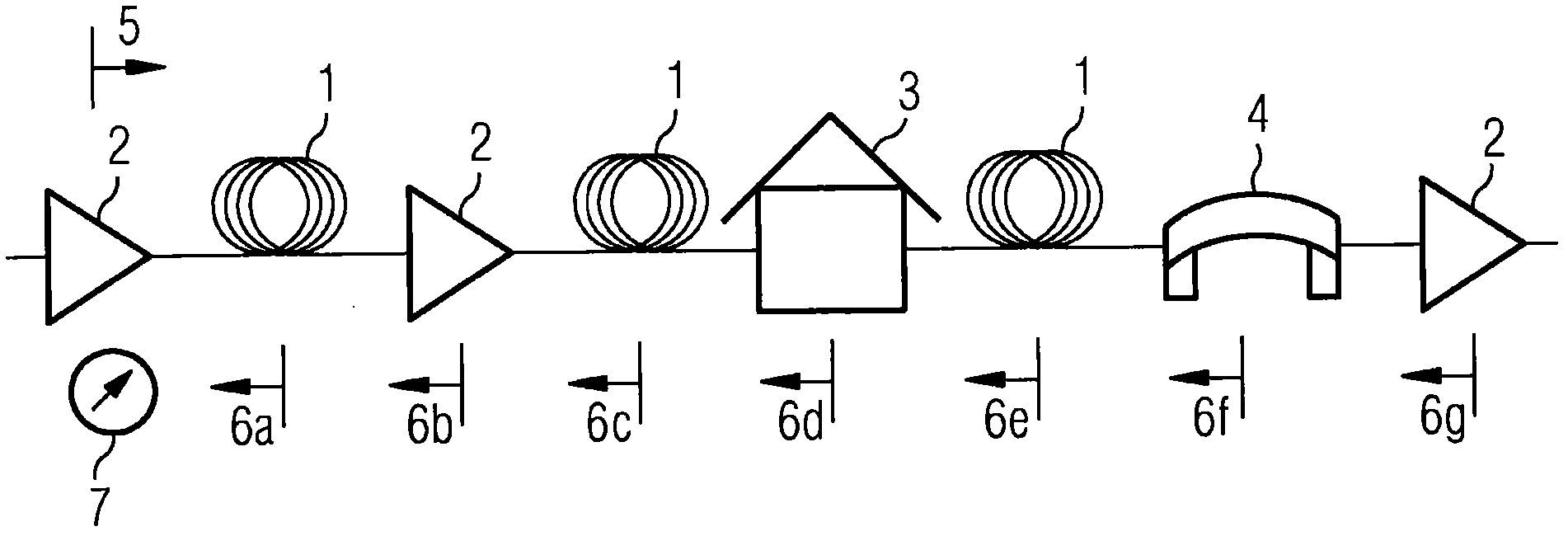
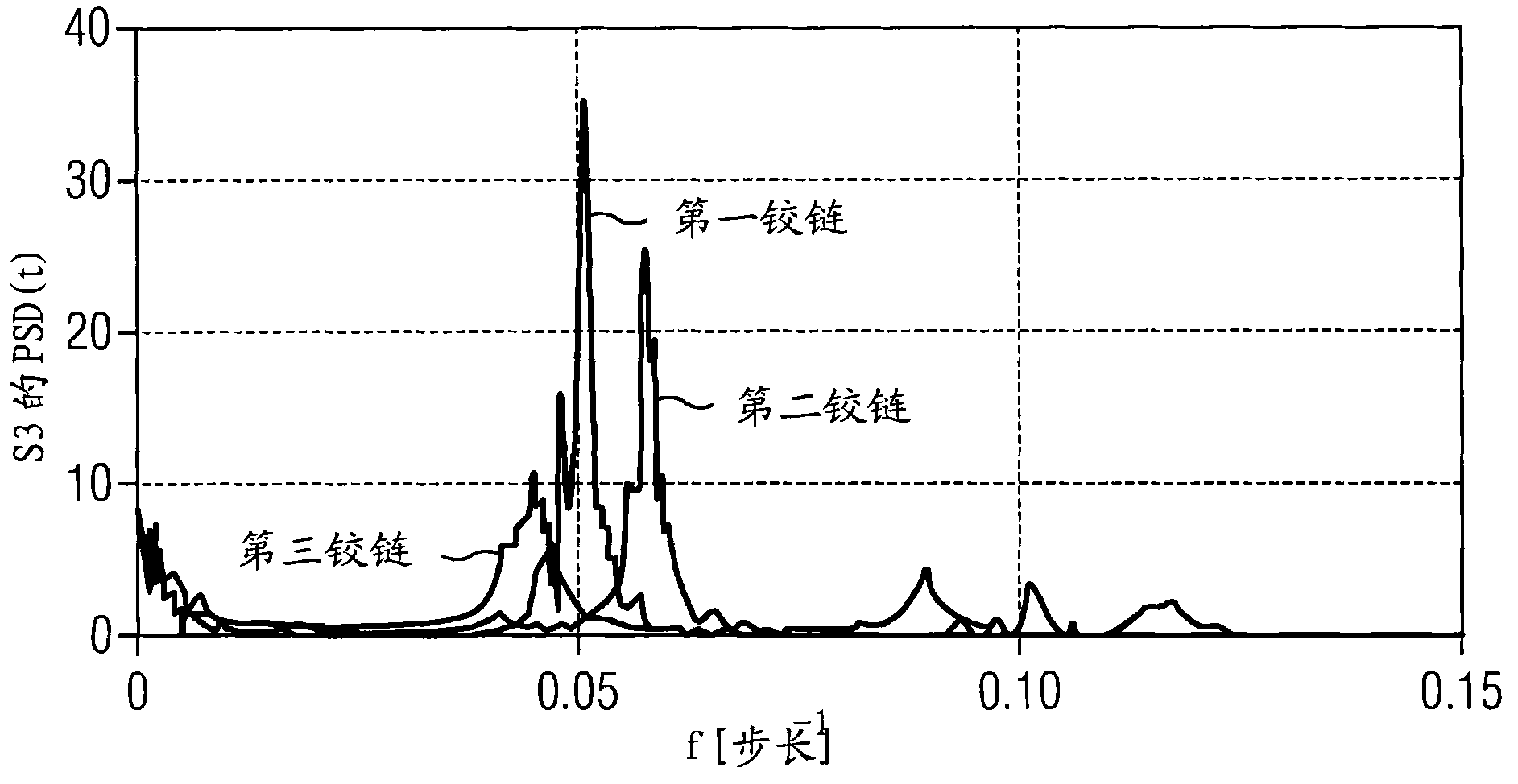
[0020] figure 2 The hinge model for sample optical link 1 is shown in . This link is routed between optical amplifiers 2 . There may be additional amplifiers 2, service huts (huts) 3 and bridges 4 on this link. On the optical link, the light rays of the test signal 5 are scattered back from all these network elements or "hinges", these being indicated by arrows 6a to 6e. The backscattered light is analyzed in OTDR measurement 7. The measurements are used to establish a fingerprint of the optical link. This measurement is even more im...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com