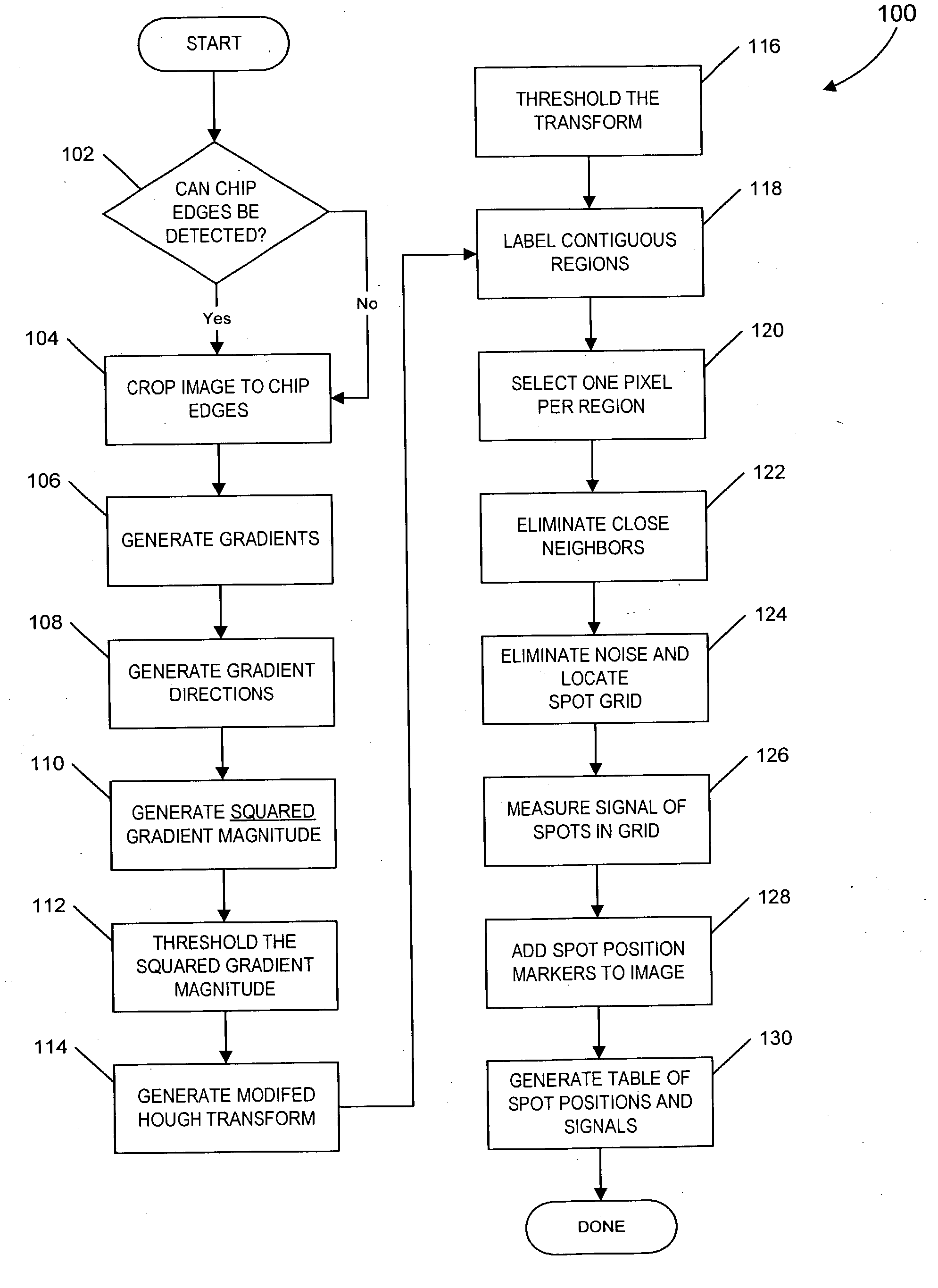
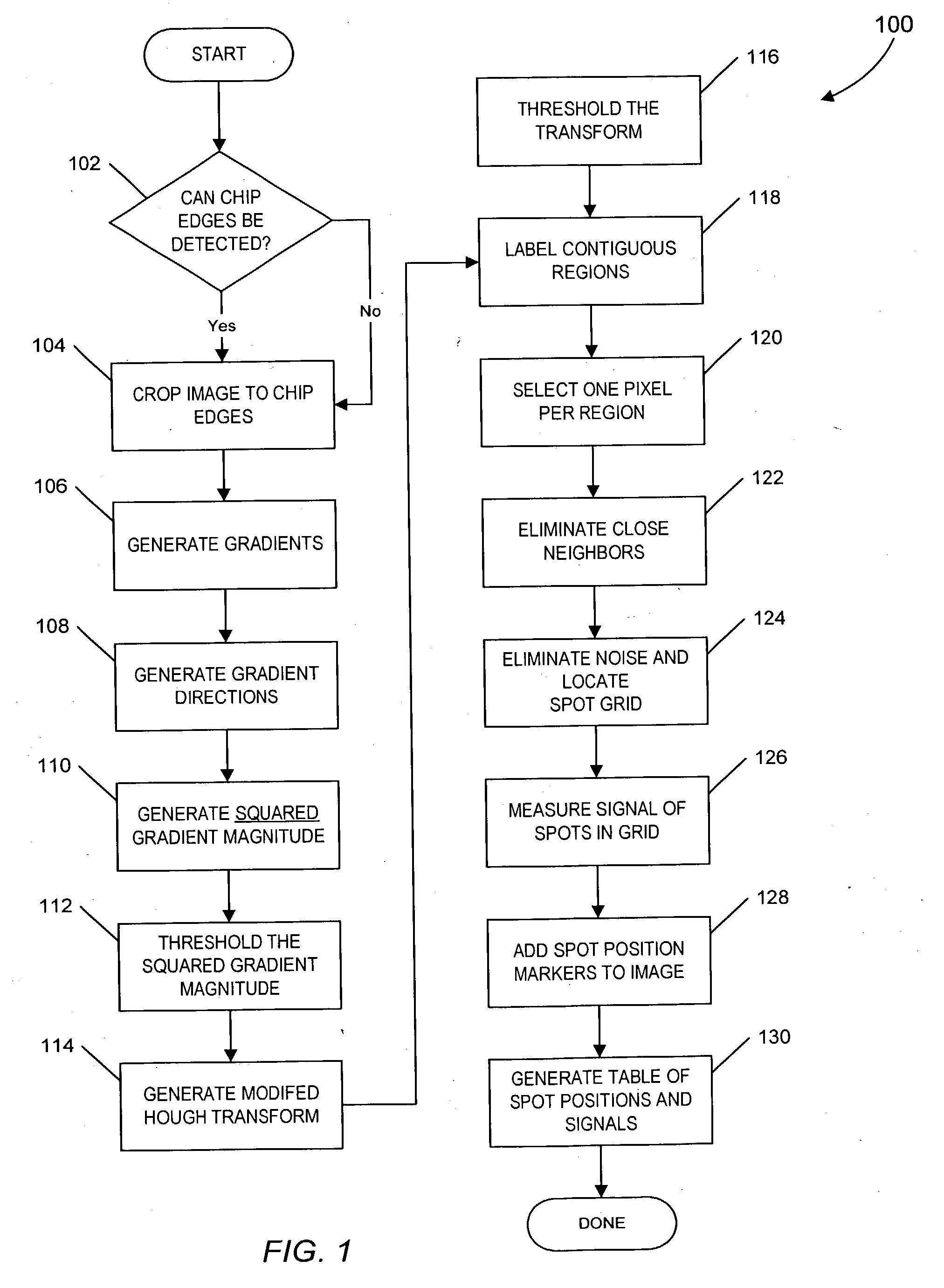
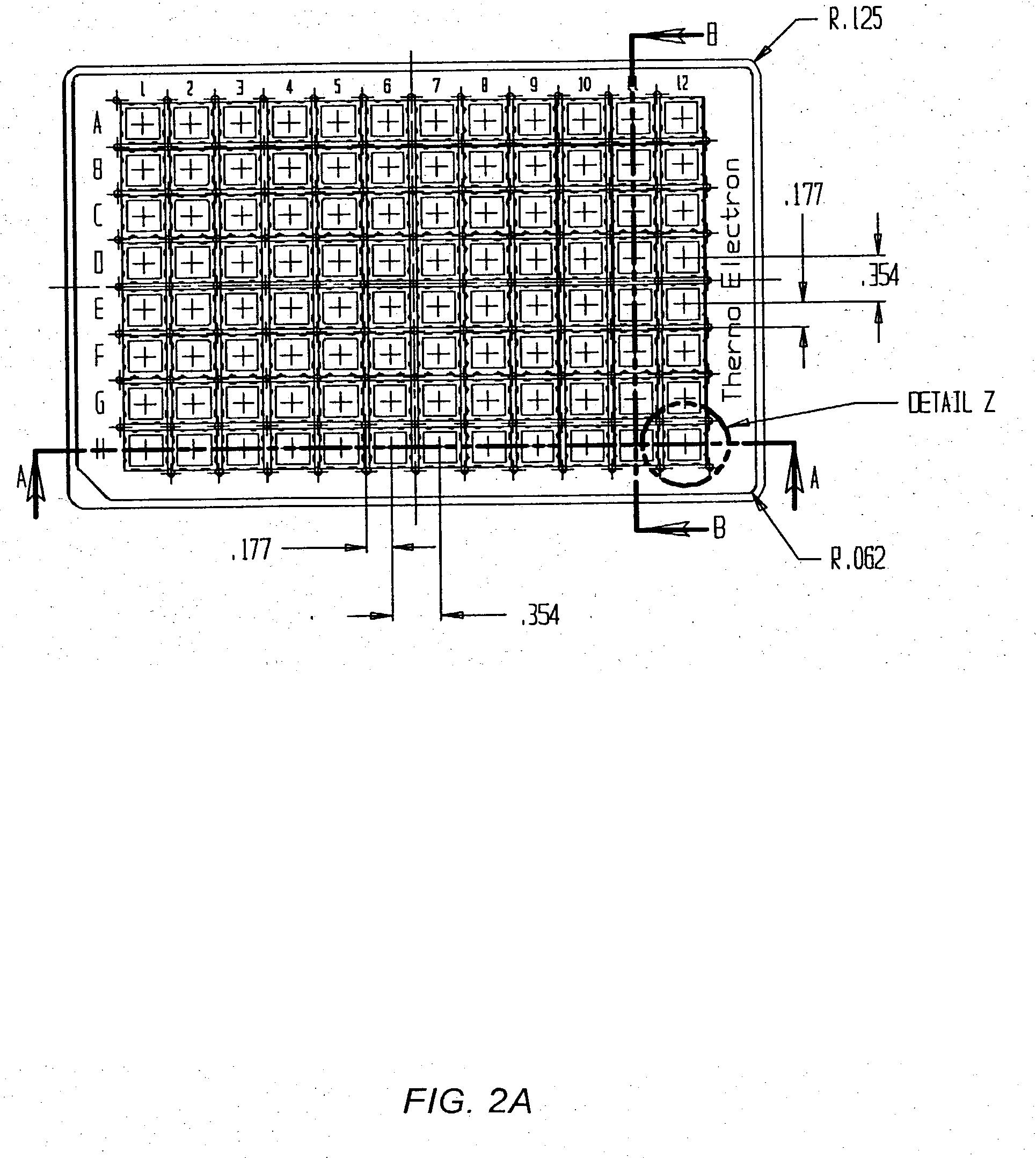
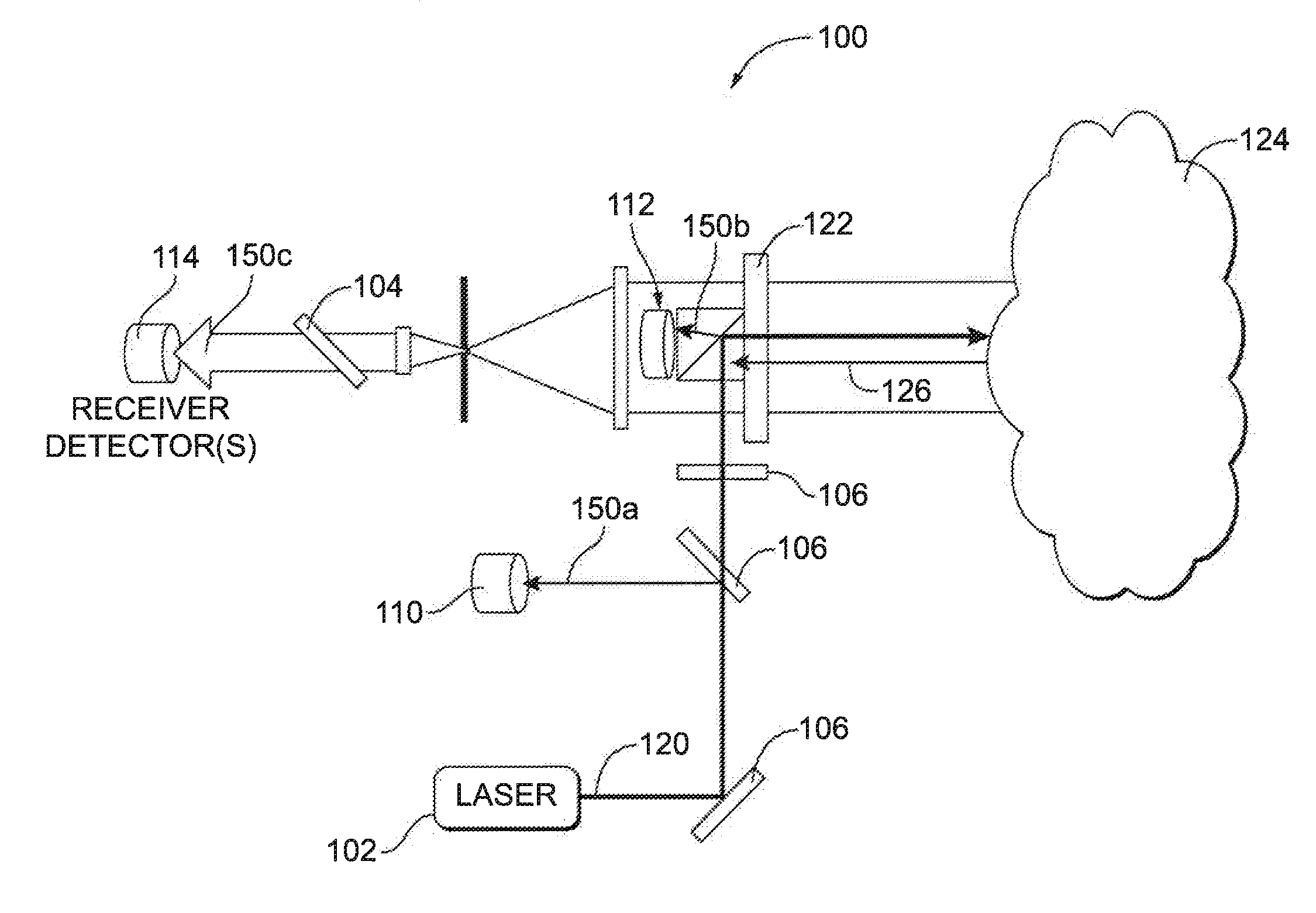
Patents
Literature
4670results about "Optical apparatus testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
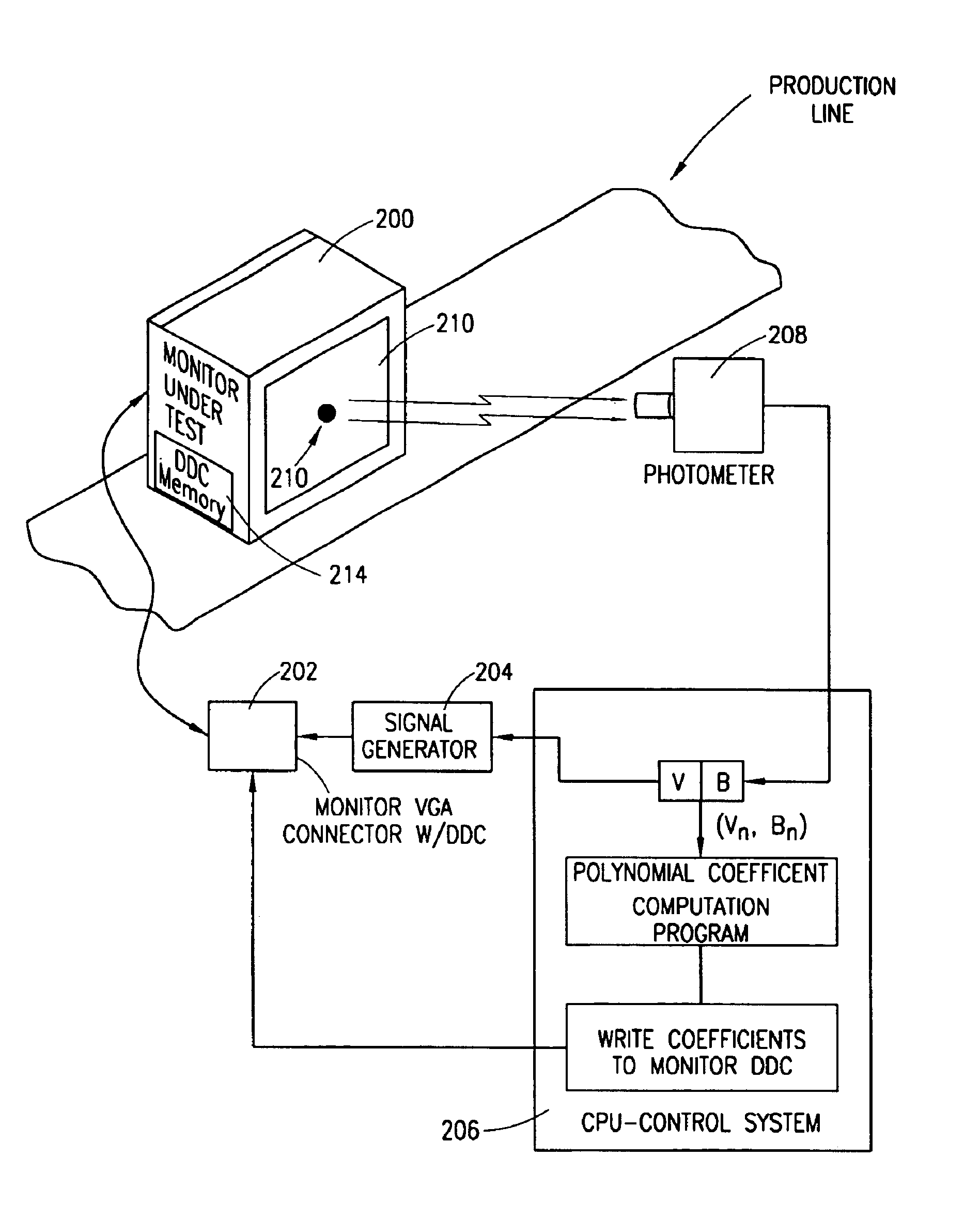
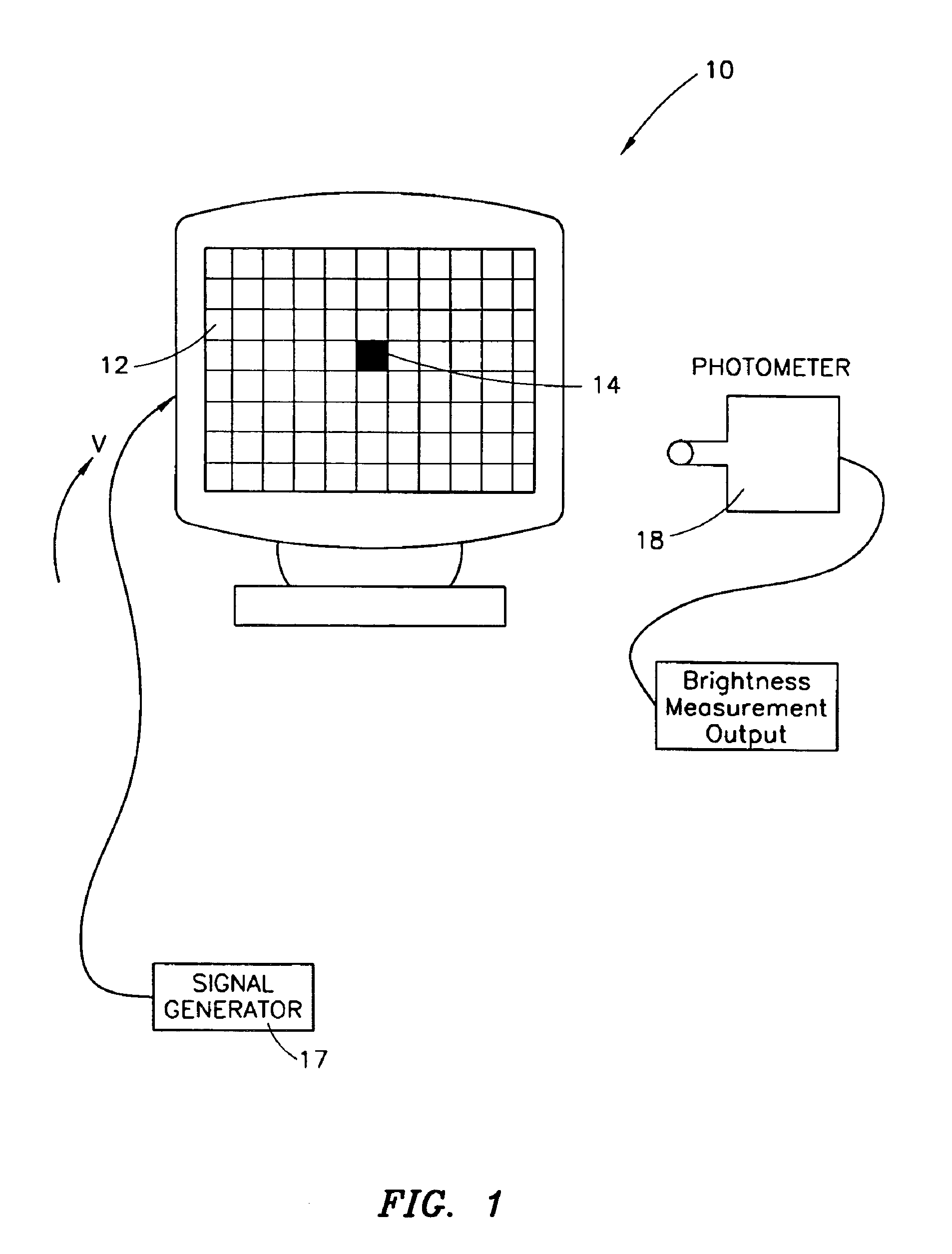
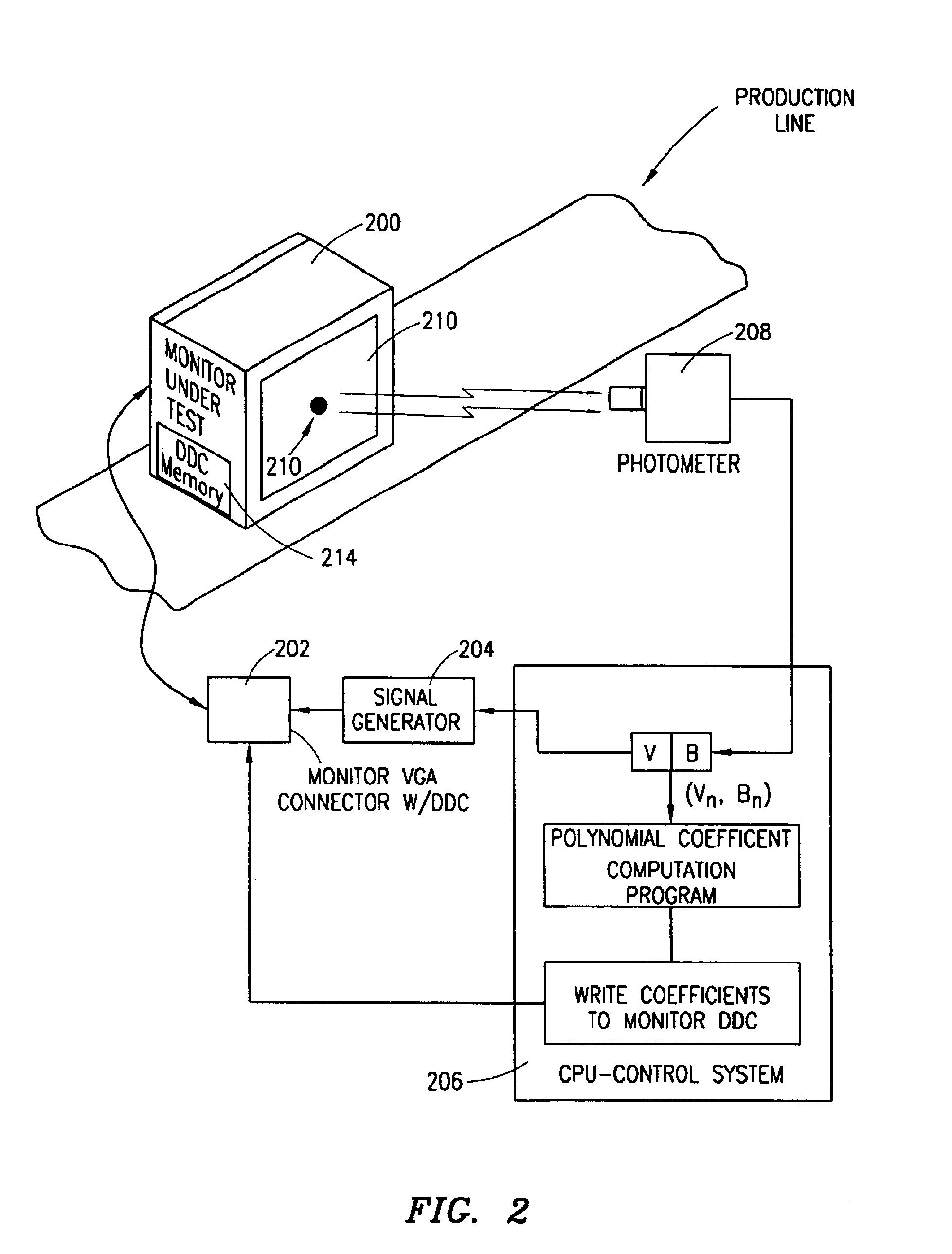
Color display system
InactiveUS6862029B1High color fidelityColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsPattern recognitionDisplay device
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for controlling color displayed on a color monitor. The method includes, in one embodiment, the steps of: activating a first color scheme on the monitor; responsive to the activating of the first color scheme, measuring a first color point of the monitor; storing the first color point within a memory associated with the monitor; activating a second color scheme on the monitor; responsive to the activating of the second color scheme, measuring a second color point of the monitor; storing the second color point within the memory associated with the monitor; activating a third color scheme on the monitor; responsive to the activating of the third color scheme, measuring a third color point of the monitor; and storing the third color point within the memory associated with the monitor.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
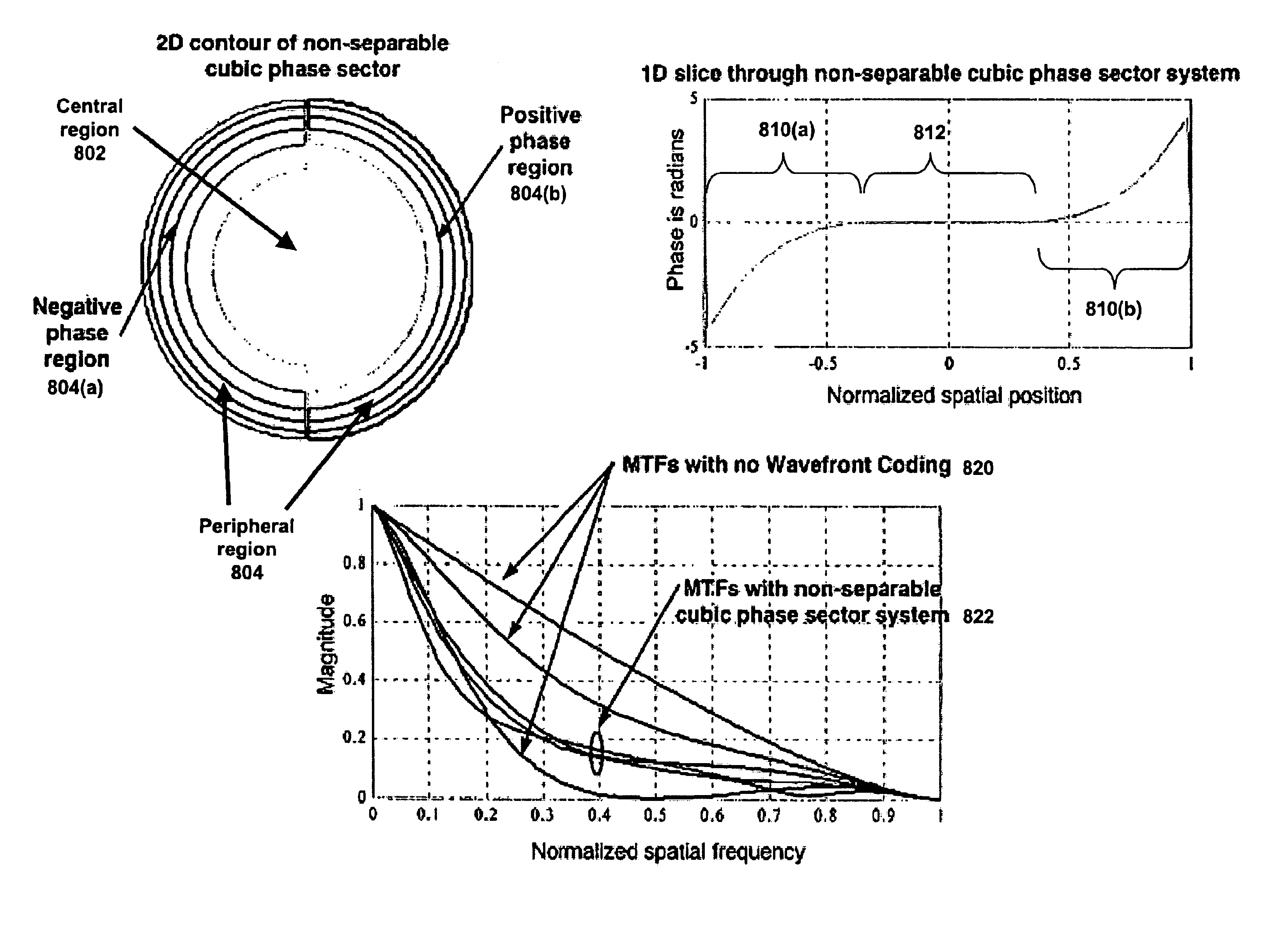
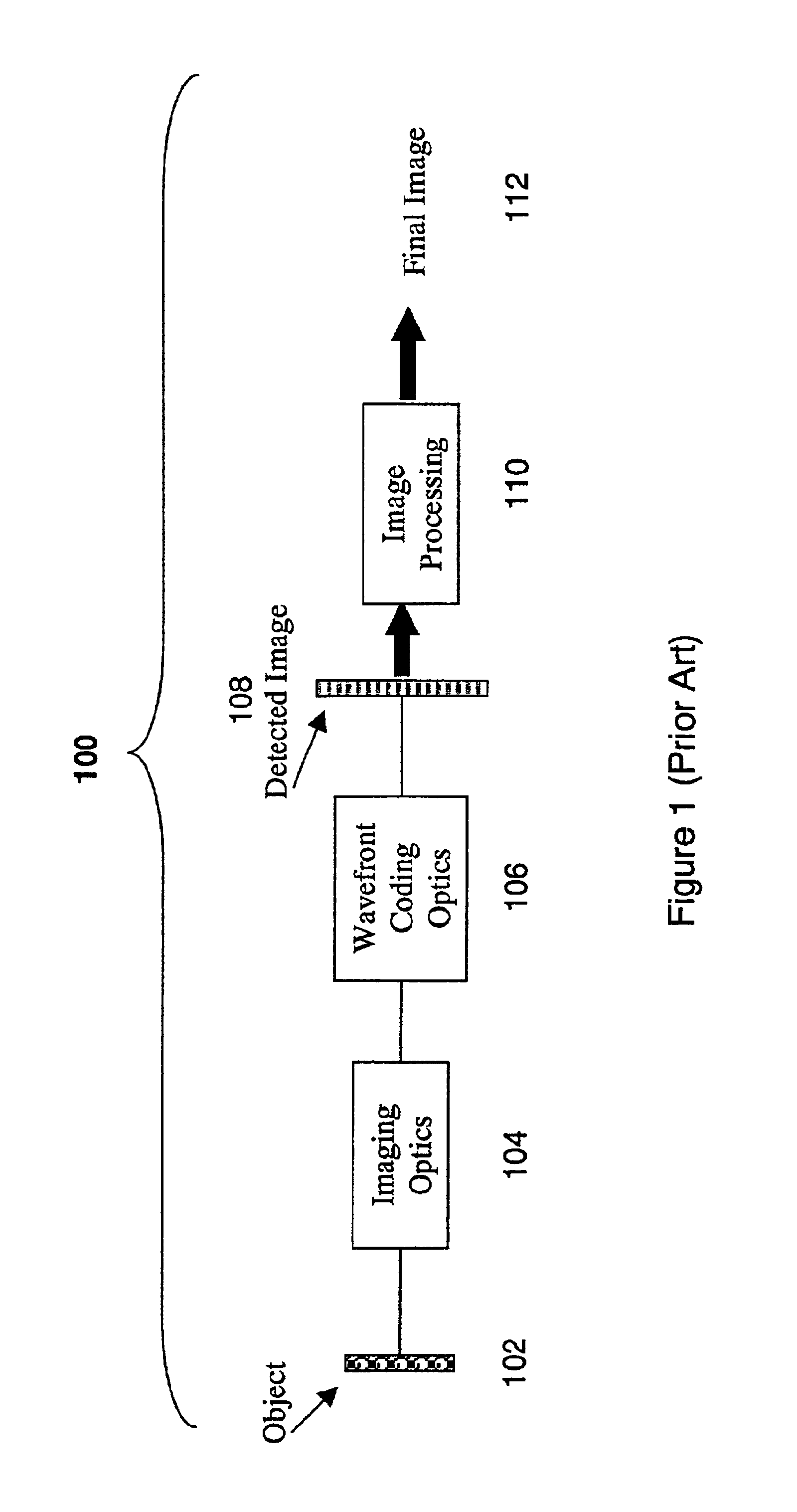
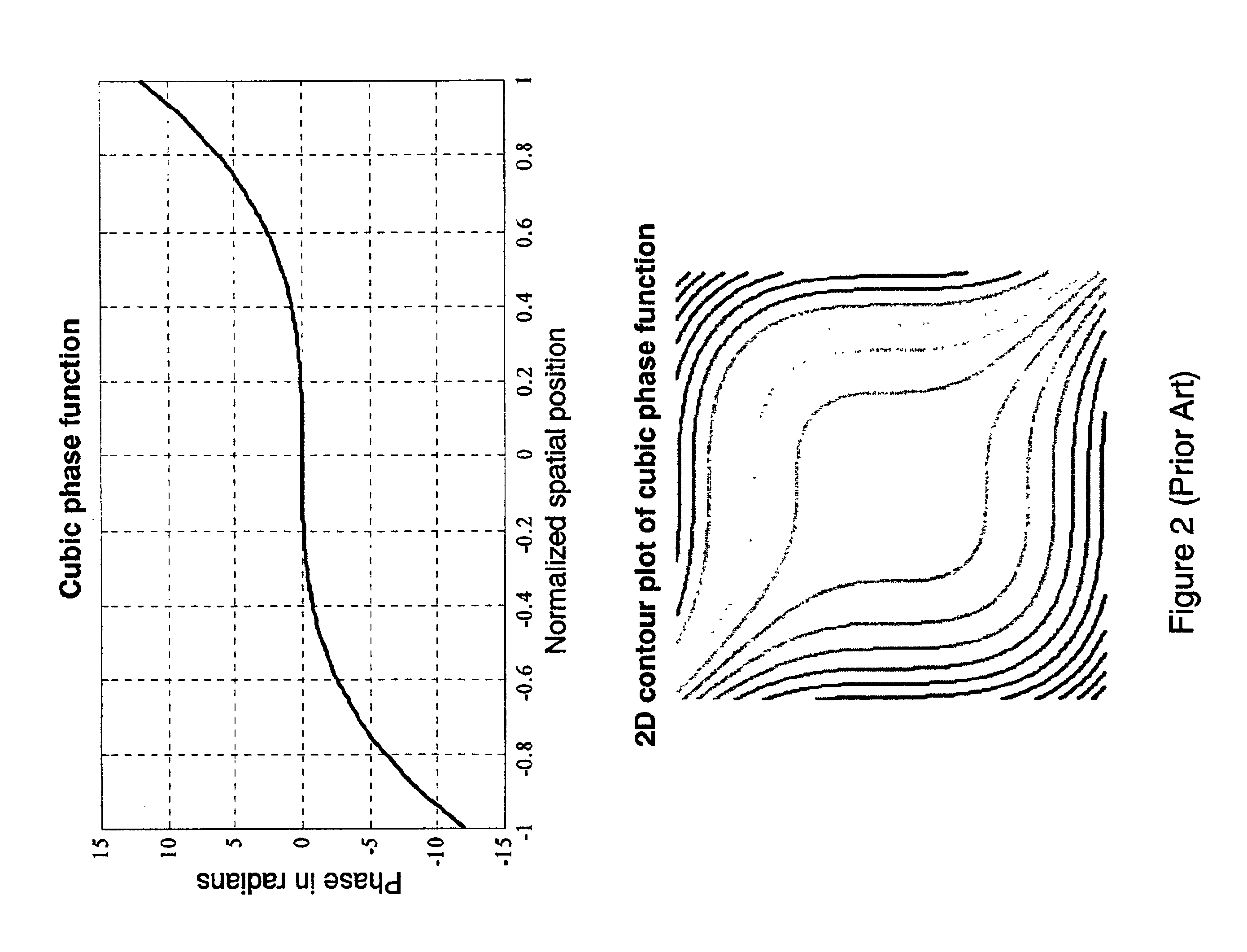
Wavefront coding optics
InactiveUS6842297B2Reduce aberrationIncrease valueBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansNegative phaseWavefront coding
Improved Wavefront Coding Optics, which apply a phase profile to the wavefront of light from an object to be imaged, retain their insensitivity to focus related aberration, while increasing the heights of the resulting MTFs and reducing the noise in the final images. Such improved Wavefront Coding Optics have the characteristic that the central portion of the applied phase profile is essentially flat (or constant), while a peripheral region of the phase profile around the central region alternately has positive and negative phase regions relative to the central region.
Owner:CDM OPTICS +1
System for diagnosing and monitoring structural health conditions
InactiveUS20090157358A1Digital computer detailsNuclear monitoringStructural health monitoringA d converter
Systems for diagnosing / monitoring structural health conditions of objects. The system, which monitors structural health conditions by use of a plurality of patch sensors attached to an object, includes at least one bridge box and at least one relay switch array module having a plurality of switches. Each of the patch sensors is adapted to perform at least one of generating a wave upon receipt of an actuator signal and developing a sensor signal. The bridge box includes an analogue-to-digital converter (ADC) for converting the sensor signal to a digital signal. The switches are adapted to establish a channel between a selected one of the patch sensors and the ADC.
Owner:KIM HYEUNG YUN
Multimode Optical Fibers
ActiveUS20100028020A1Cladded optical fibreWavelength-division multiplex systemsModal dispersionPhysics
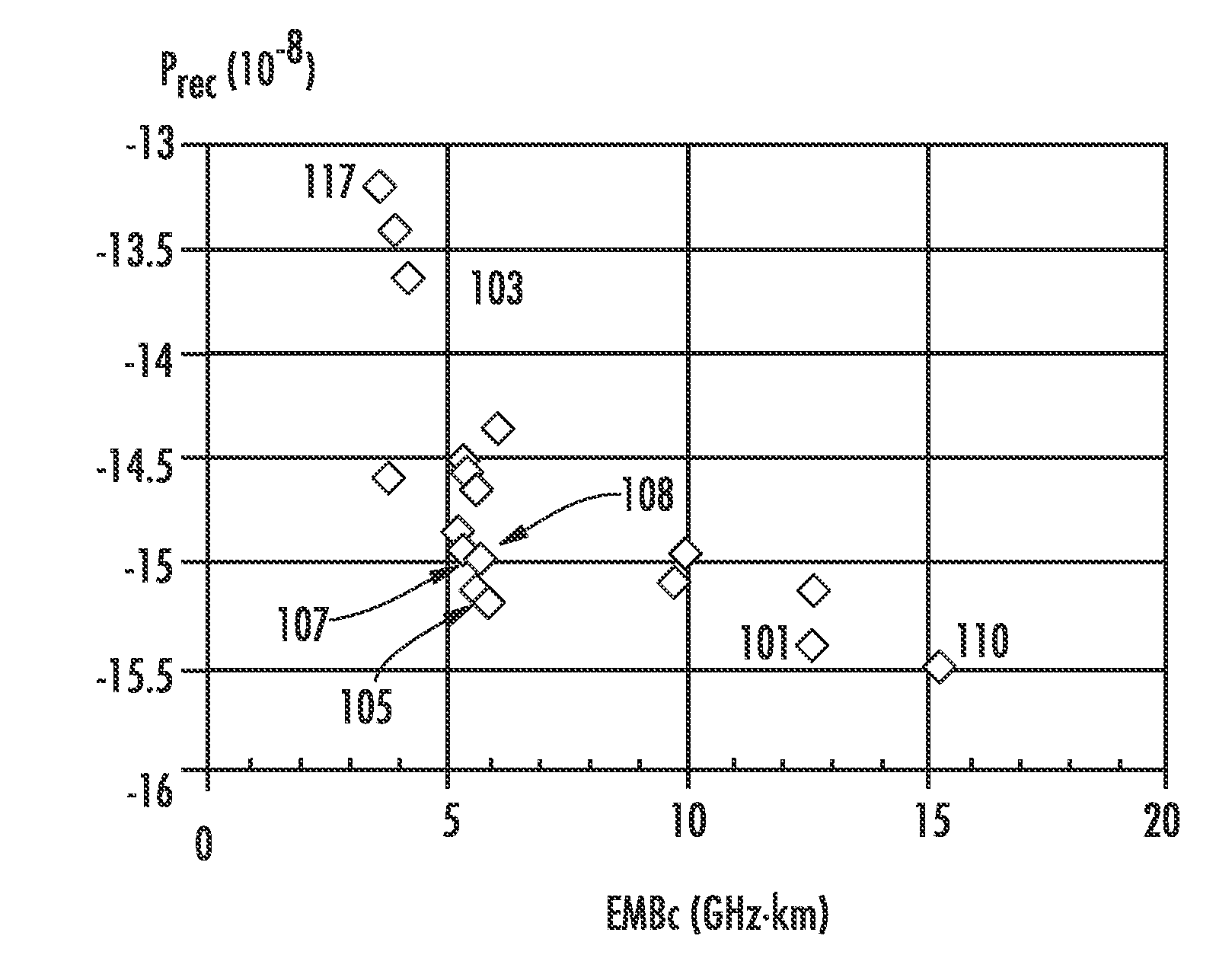
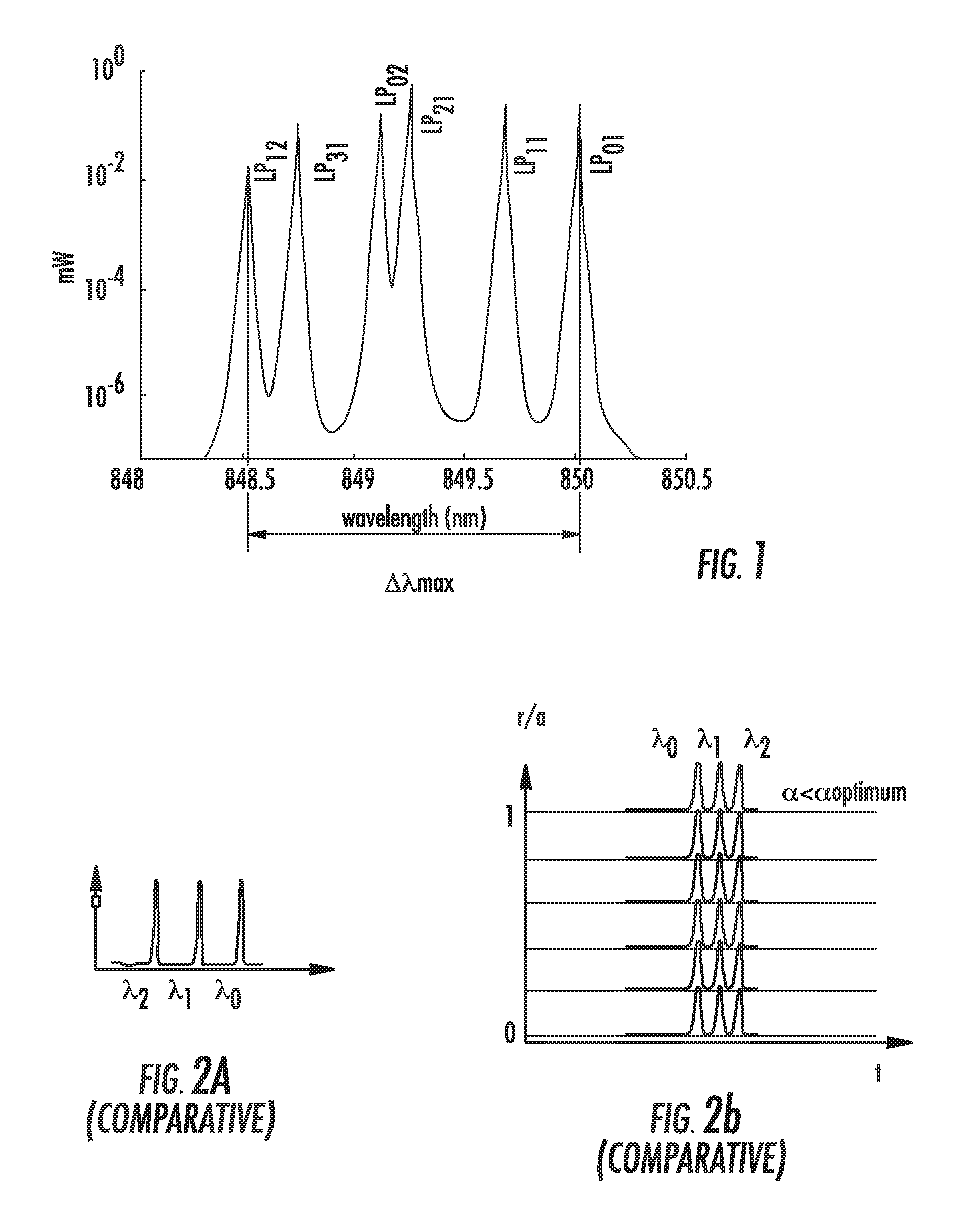
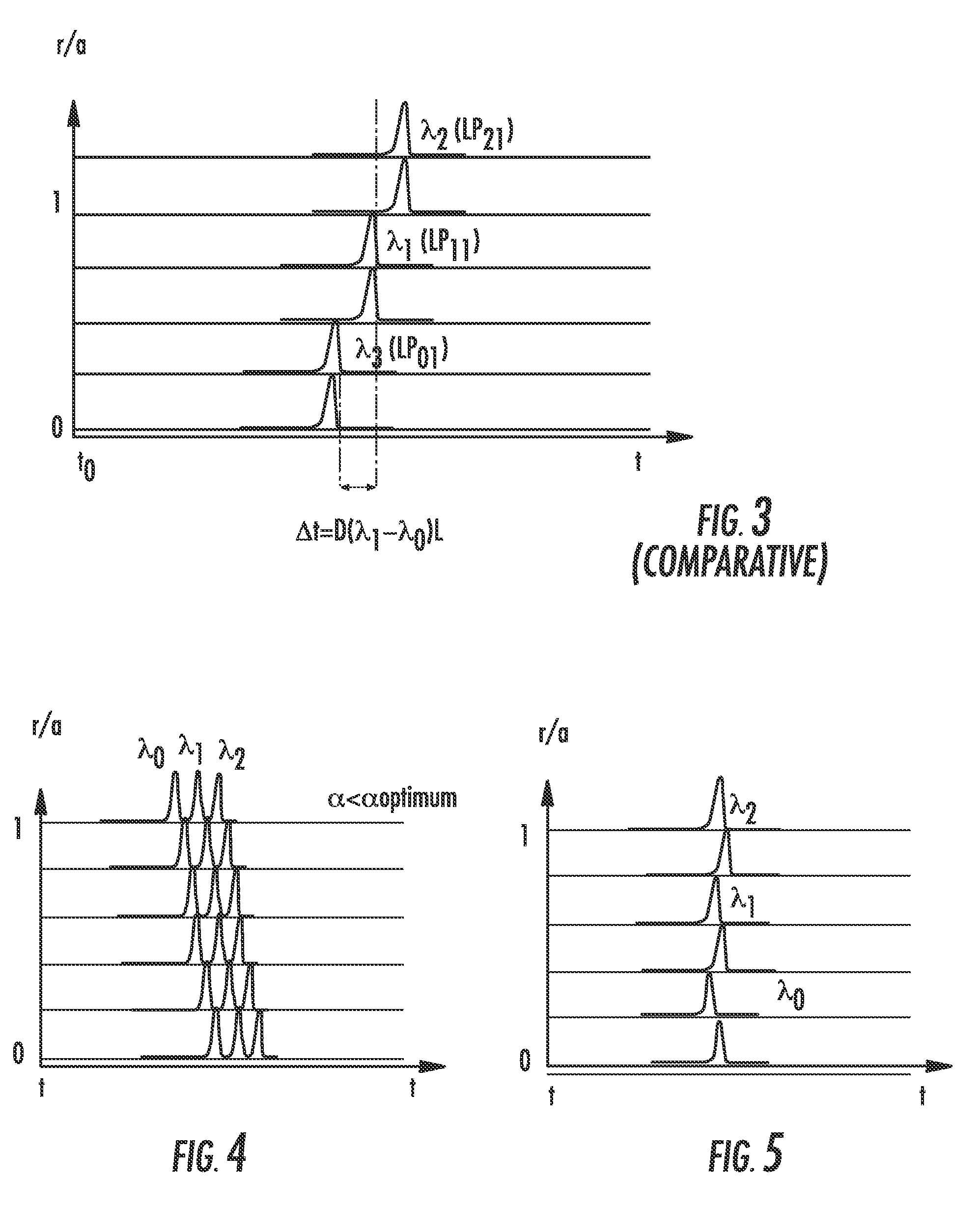
A multimode optical fiber has an equivalent modal dispersion value (DMDinner&outer) of less than 0.11 ps / m for (Δλmax×D)>0.07 ps / m as measured on a modified DMD graph. The modified DMD graph accounts for chromatic dispersion to ensure that the multimode optical fiber has a calculated effective bandwidth EBc greater than 6000 MHz-km when used with multimode transverse sources.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Systems and Methods for Measuring the Shape and Location of an object
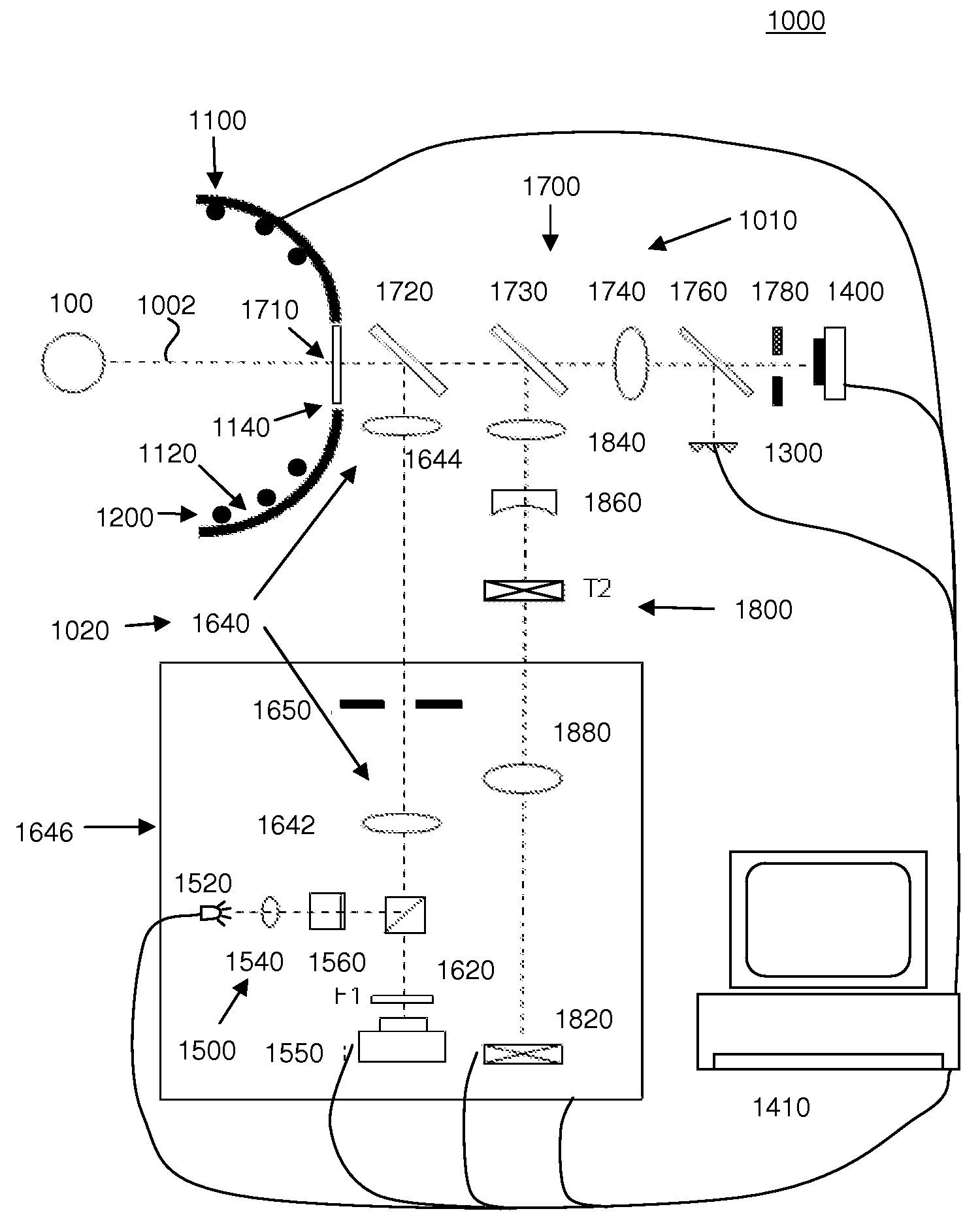
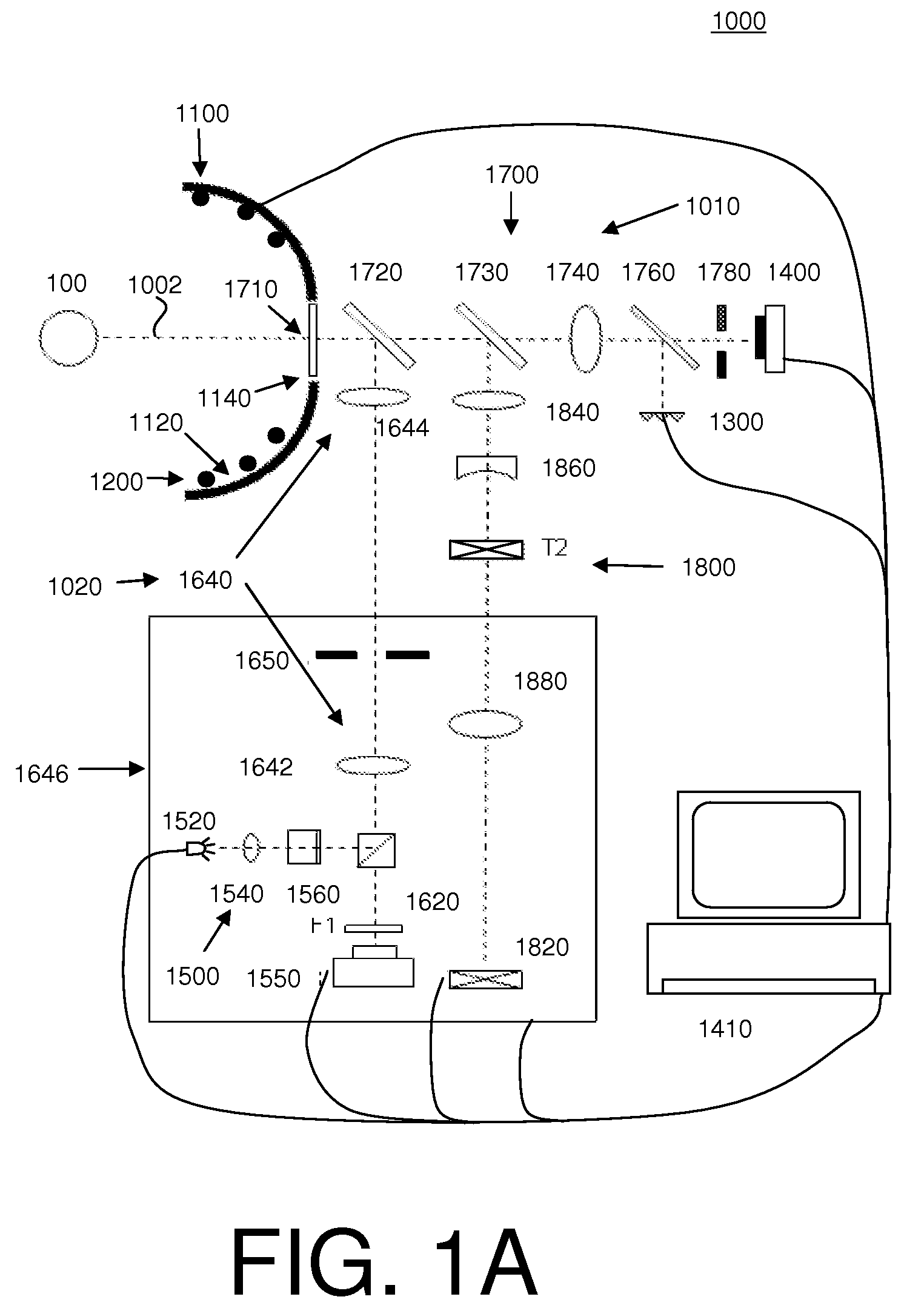
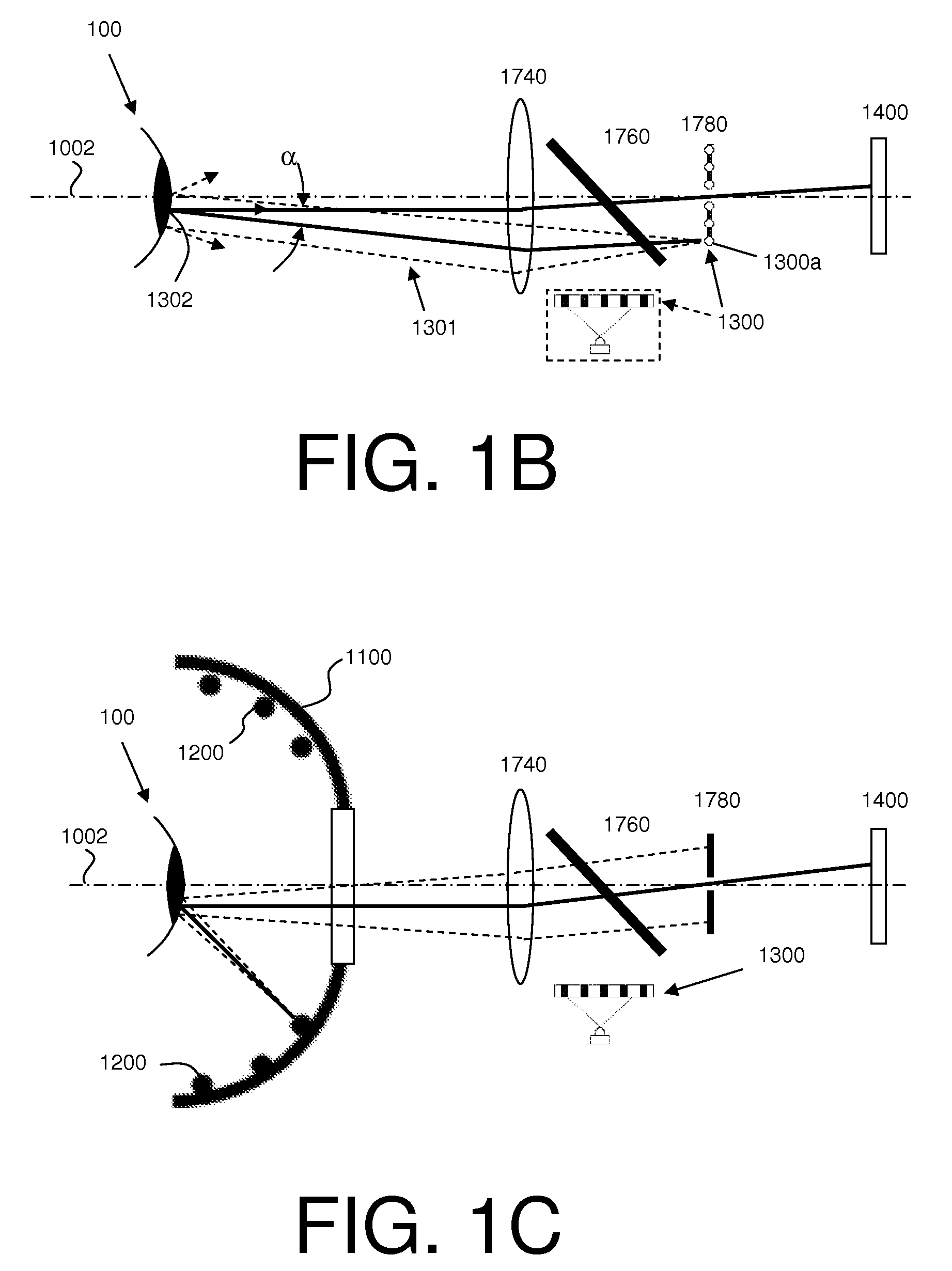
A system for determining the shape of an object and / or a distance of the object from the system includes a first plurality of light source, a second plurality of light sources, and a detector or detector array. The first plurality of light sources are disposed about a central axis and are separated from the central axis by radial distances defining an aperture in the first plurality of light sources. The system also includes an optical system adapted to provide light from the second plurality of light sources through the aperture to the object. The system may further include a computer configured to determine the shape of the object and / or the distance of the object from the system using light from the first and second plurality of light sources that is reflected from the object and received by the detector.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
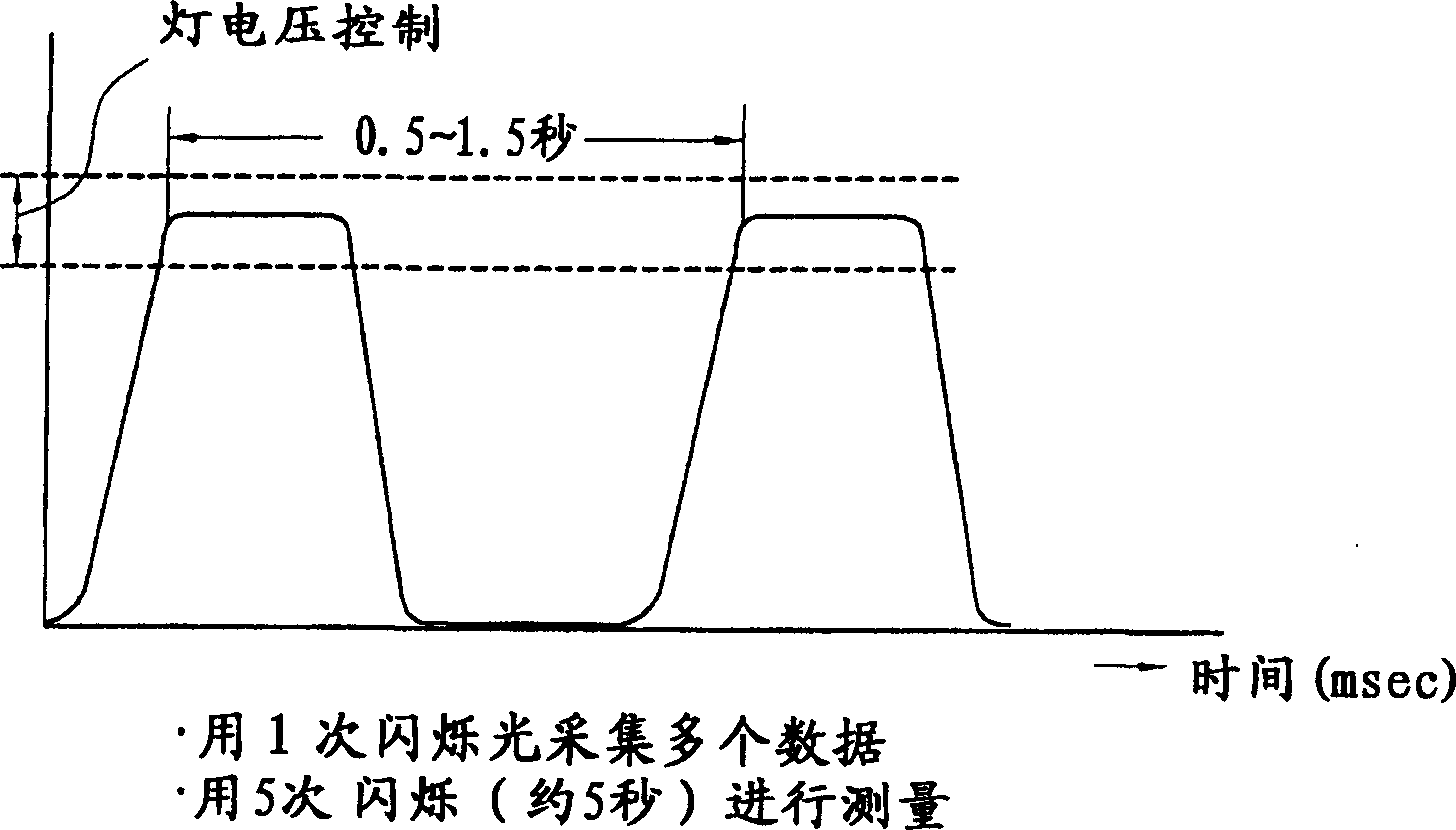
Measurement method using solar simulator
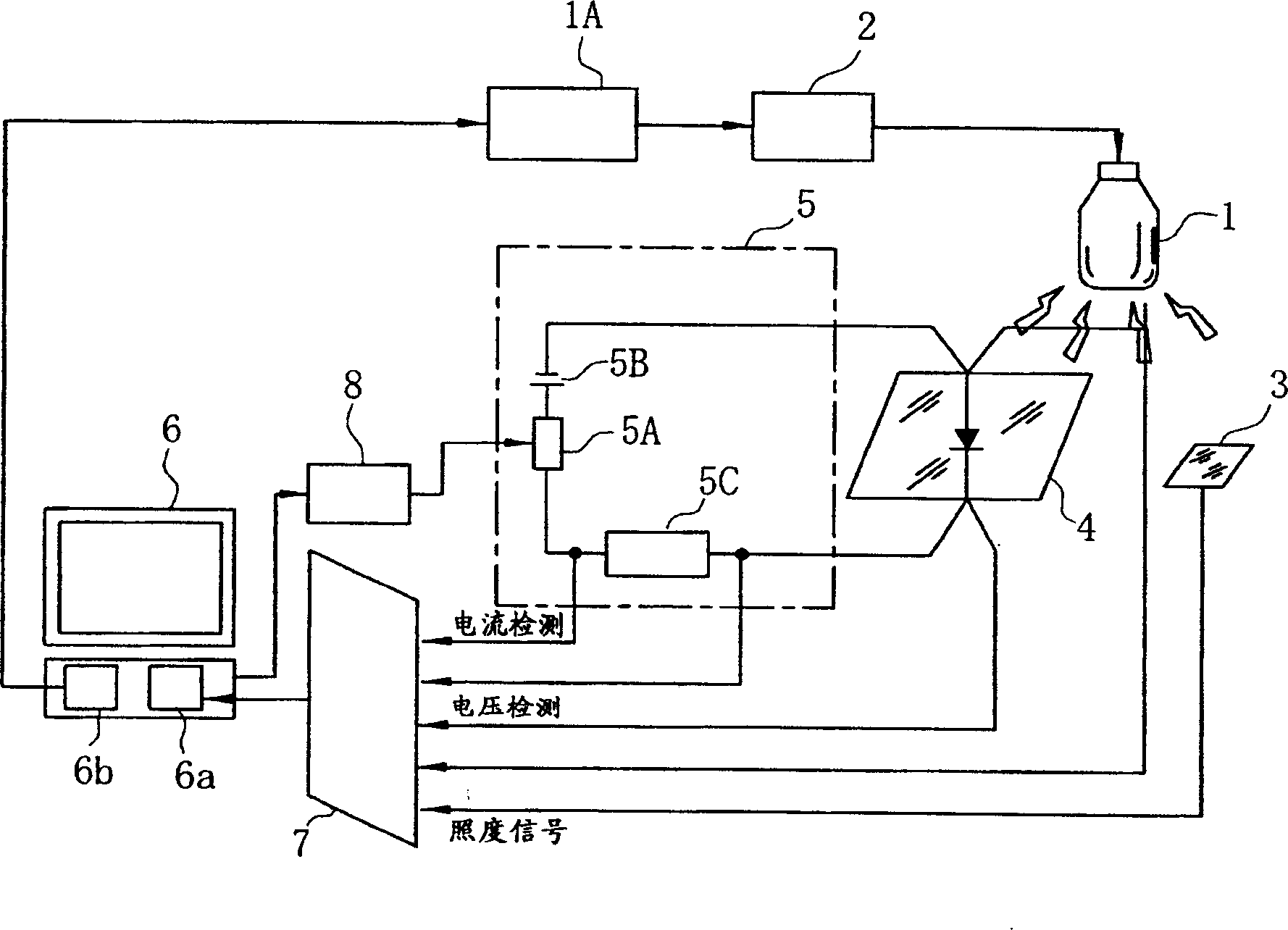
This invention provides a solar simulator measurement method capable of high-accuracy measurements with fast-response photovoltaic devices as well as with slow-response photovoltaic devices, and a solar simulator for implementing the method. A flash having a pulse wave form with a flattened peak is generated from a xenon lamp 1. The flash is sensed by an irradiance detector 3, its irradiance measured, and the irradiance of the light source is adjusted to fall within a prescribed narrow range based on the detected irradiance value. Then, the flash with irradiance within the prescribed range irradiates photovoltaic devices 4 under measurement, and the current and the voltage output by the photovoltaic devices 4 are measured at multiple points while a load of the photovoltaic devices 4 is controlled. This process is repeated with multiple flashes to obtain an I-V curve for the photovoltaic devices.
Owner:NISSHINBO IND INC
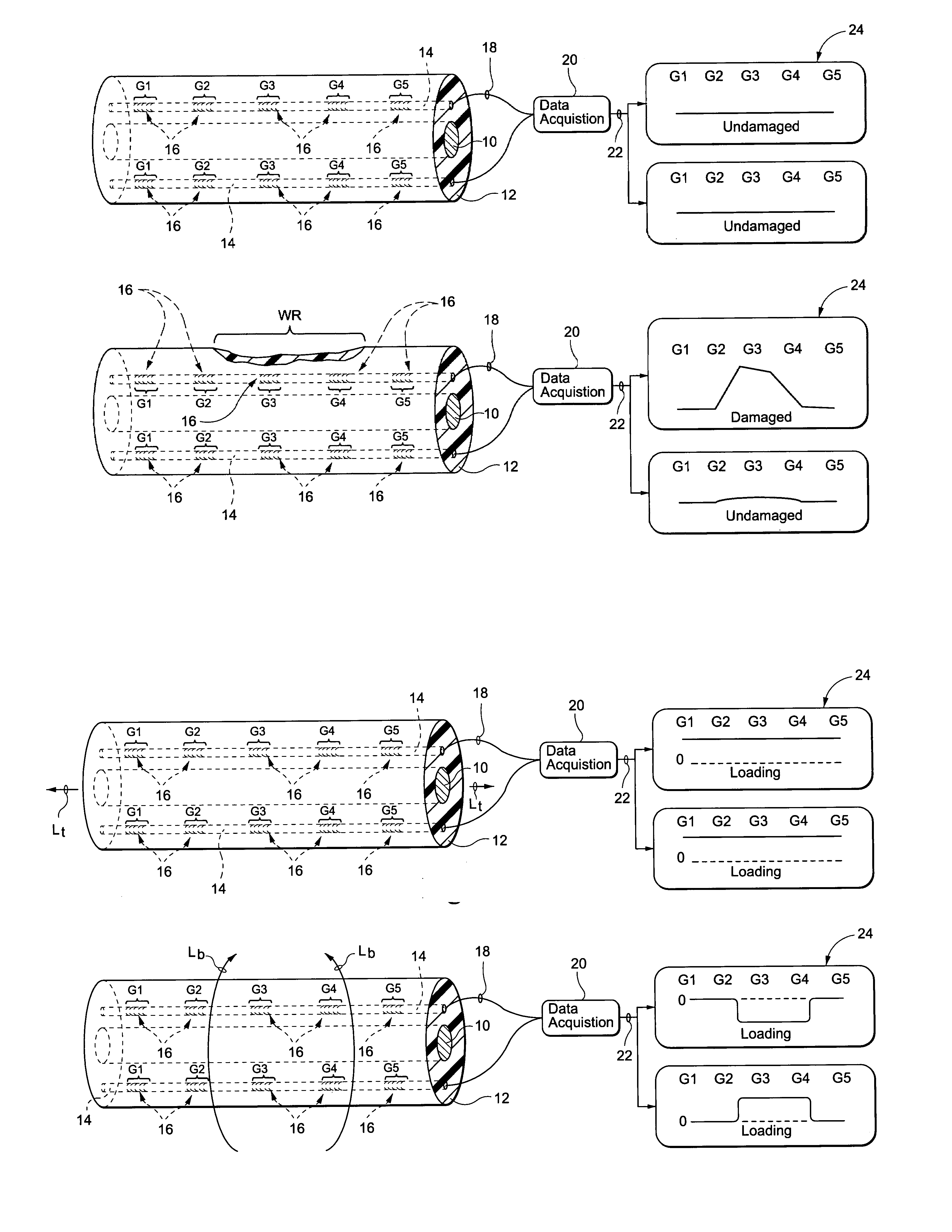
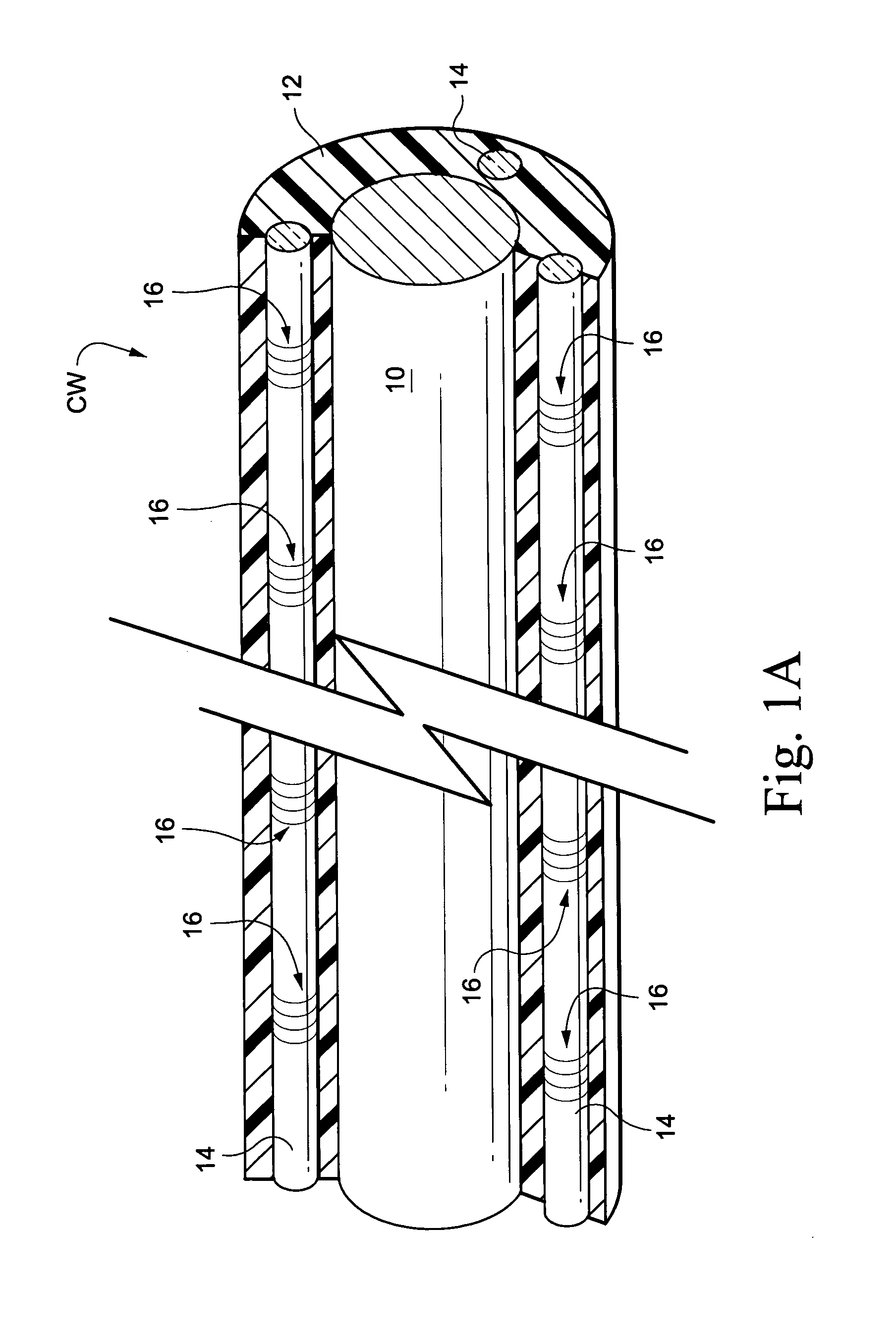
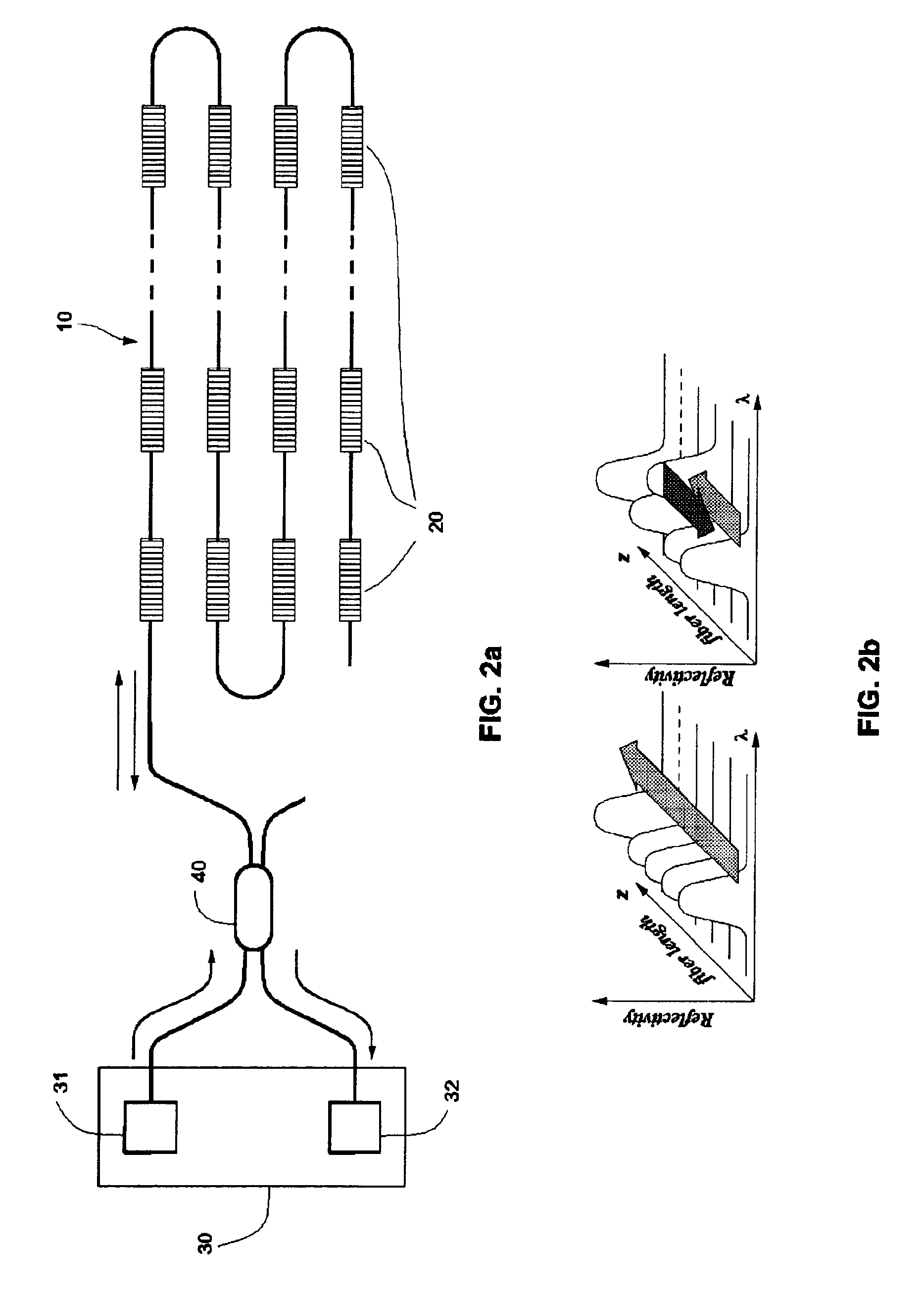
Composite structures, such as coated wiring assemblies, having integral fiber optic-based condition detectors and systems which employ the same
InactiveUS7154081B1Weakening rangeReducing compressive strainControlRadiation pyrometryElectrical conductorGrating
Integral fiber optic-based condition sensors detect conditions of a composite structure, e.g., a coated wire assembly so as to detect damage or conditions that may damage the same. Preferably, at least one optical fiber sensor having a plurality of Bragg gratings written into the fiber at spaced-apart locations along its axial length is integrated into the electrical insulator coating of a wire, wire bundle or wiring harness. The fiber optic sensor may thus be employed to measure the environmental loads on the electrical wiring including stresses from bending, axial loading, pinch points, high temperature excursions and chemical damage. The system is capable of detecting and locating transient conditions that might cause damage to a wiring system or permanent changes in state associated with damage events. The residual stress in the electrical insulator coating of a wire, wire bundle, or wiring harness are used to monitor the evolution of damage by wear or chaffing processes. Detected stress relief on one or more Bragg gratings will thus be indicative of damage to the insulator coating on the conductor. As such, the magnitude of such stress relief may be detected and used as an alert that the wire insulation is damaged to an unsafe extent.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Method and apparatus for tensile testing and rethreading optical fiber during fiber draw
InactiveUS7832675B2Processing speedGlass fibre drawing apparatusFilament handlingFiber drawingTensile testing
A method and apparatus for automatic threading and winding of optical fiber onto various components in a fiber draw system, as well as methods and apparatus for conducting online tensile screening of optical fiber at high speeds. In a preferred embodiment, the fiber is tensile tested during fiber draw and wound directly onto a shipping spool to be shipped to a customer. The tensile stress can be imparted to the fiber during the draw process by feeding the fiber through a screener capstan, which works in conjunction with another capstan to impart the desired tensile stress to the fiber during the draw process. Another aspect is a method and apparatus for threading or rethreading of a moving length of fiber through a fiber draw or fiber testing process, in which fiber is wound onto a spool, comprising activating an aspirator to obtain the fiber at a first location and moving said aspirator in at least two dimensions to thereby move the fiber to a second location and thread the fiber through or onto at least one component in the fiber draw or testing process.
Owner:CORNING INC
System and method for calibrating a spatial light modulator
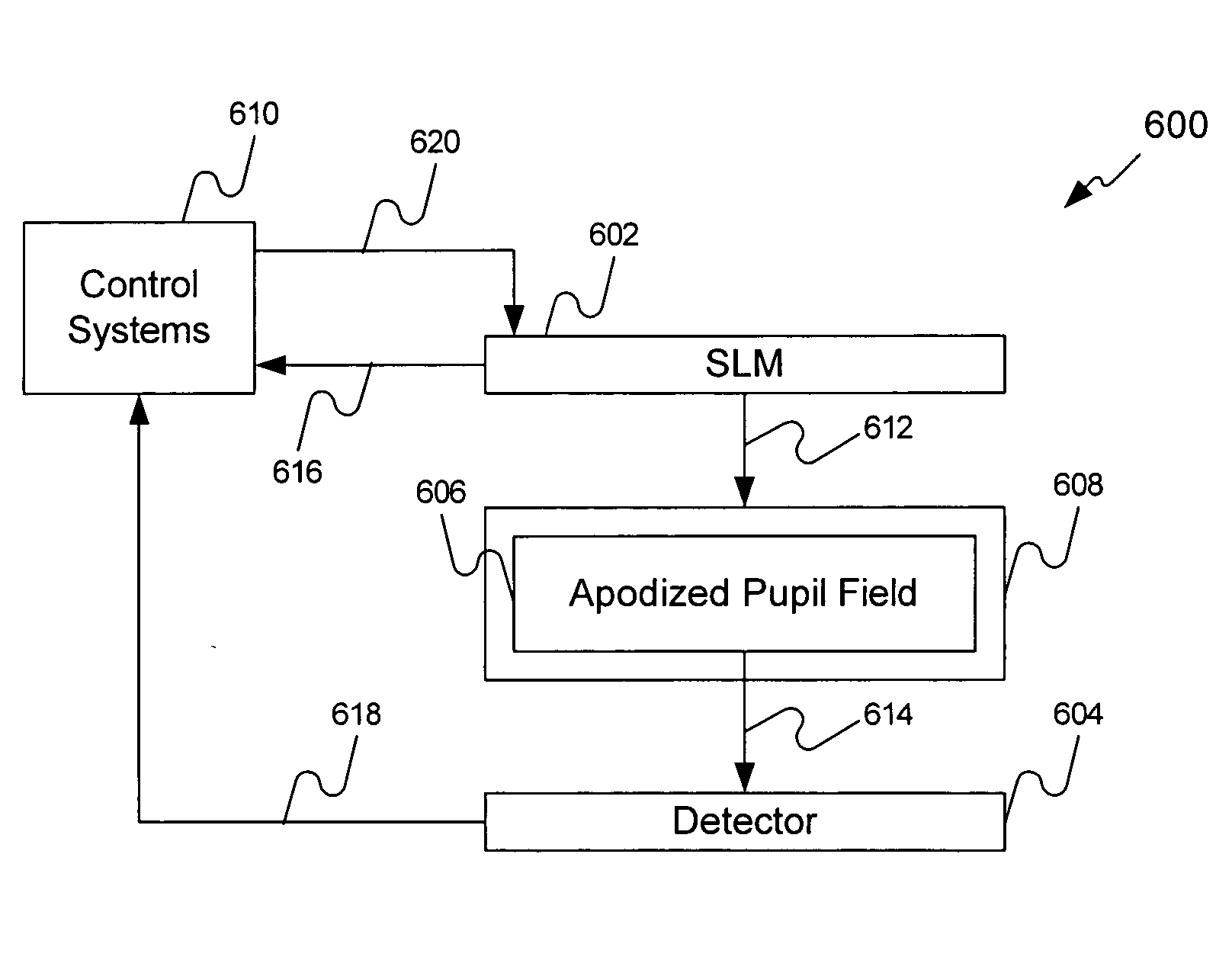
InactiveUS20050168790A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatial light modulatorImage resolution
A method and system as used to calibrate a reflective SLM. The system can include a reflective SLM having an array of pixels (e.g., moving, tilting, rotating, pivoting, etc. pixels) and a projection optical system resolving individual pixels and having an apodized pupil. During a calibration operation, the pixels of the SLM receive varying voltage values to either continuously or incrementally move them through various angles. Light reflecting from each of the pixels during these movements forms individual images for each pixel at each angle. The light passes through the apodized pupil and is received on one or more sections (e.g., pixels) of a detector (e.g., a CCD array). The pupil apodization pattern is selected so that individual pixels remain well resolved and their resolved images have strong sensitivity to the pixel mirror tilt. The light intensity received for each pixel at each angle is correlated to the voltage value received at the pixel to tilt the pixel to that angle. The correlation produces a result signal. The result signal is used by a control device before and during normal operation of the SLM to calibrate the SLM one or more times.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
System and method of measuring and mapping three dimensional structures
InactiveUS7455407B2Improve dynamic rangeOptical measurementsUsing optical meansWavefront sensorLight scattering
A system for mapping a three-dimensional structure includes a projecting optical system adapted to project light onto an object, a correction system adapted to compensate the light for at least one aberration in the object, an imaging system adapted to collect light scattered by the object and a wavefront sensor adapted to receive the light collected by the imaging system and to sense a wavefront of the received light. For highly aberrated structures, a number of wavefront measurements are made which are valid over different portions of the structure, and the valid wavefront data is stitched together to yield a characterization of the total structure.
Owner:AMO WAVEFRONT SCI
Method and apparatus for determining reflective optical quality using gray-scale patterns
InactiveUS6100990AAccurate and repeatable resultOvercomes shortcomingScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansProduct baseComputer science
A method of determining reflective optical quality of a reflective product includes reflecting a first gray-scale pattern off the product; obtaining a first image of the first pattern with an image pickup device after the first pattern has reflected off of the product; and determining optical quality of the product based on data obtained from the first image. An apparatus for determining reflective optical quality of such a product is also disclosed.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC +1
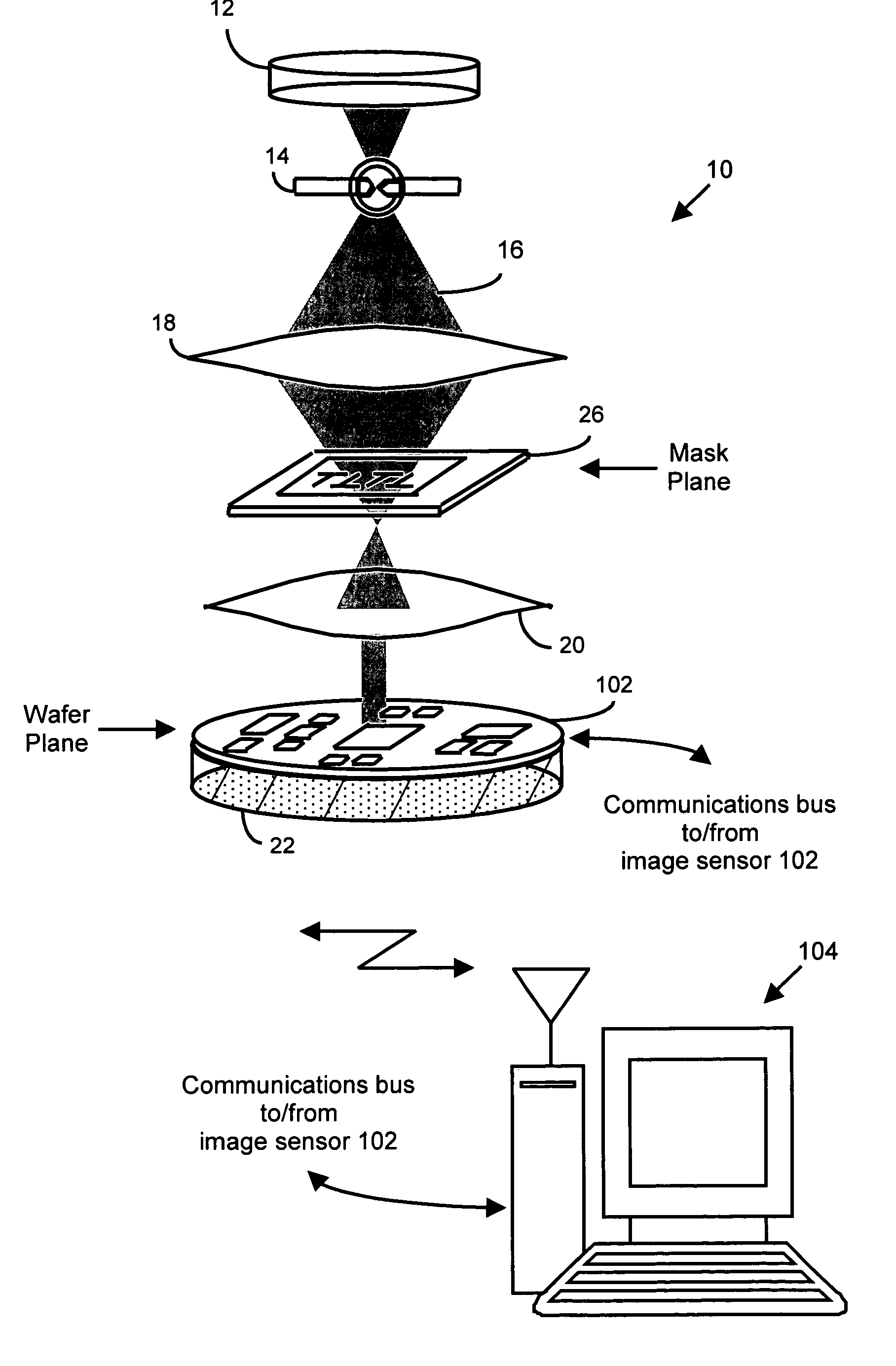
System and method for lithography process monitoring and control
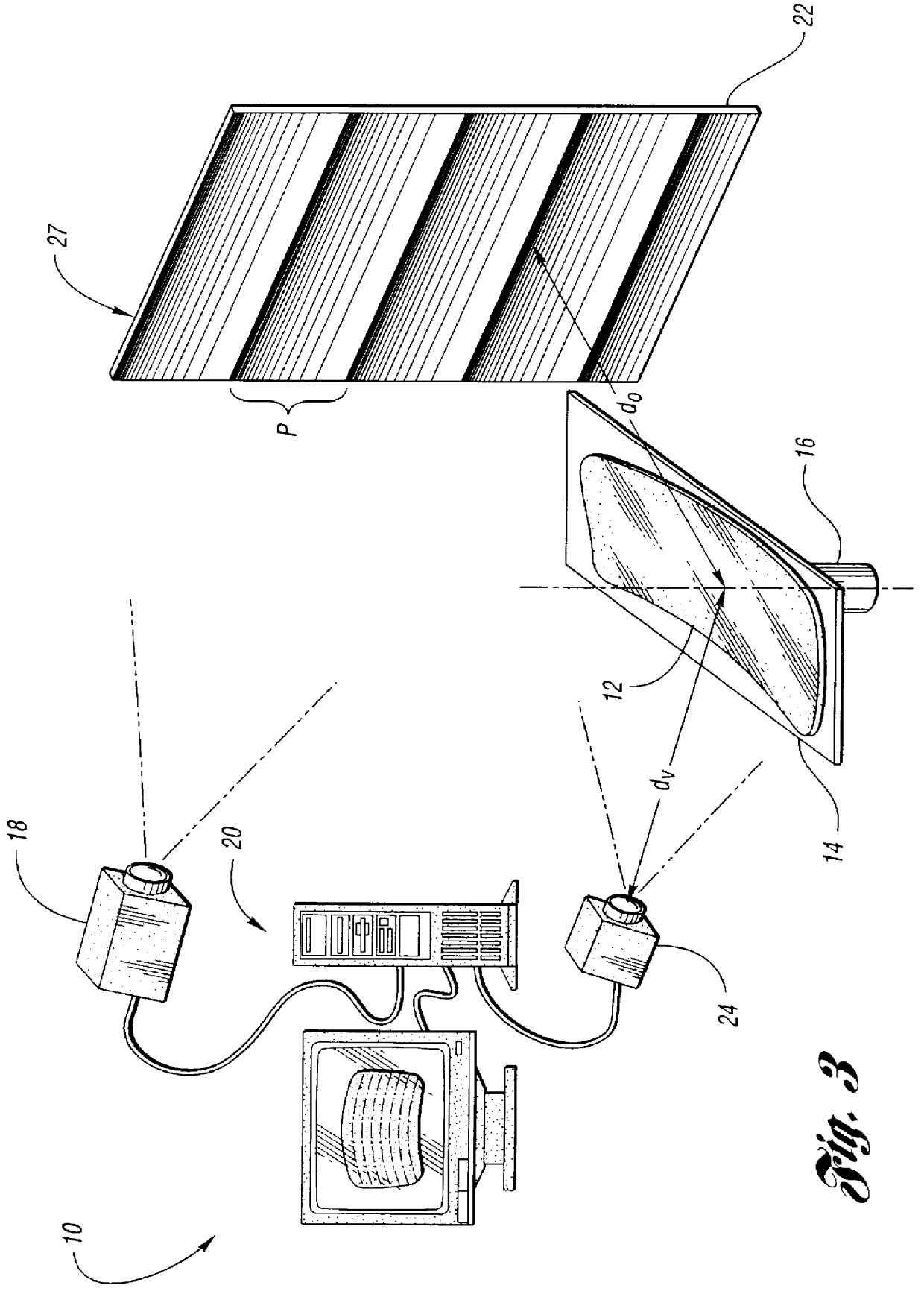
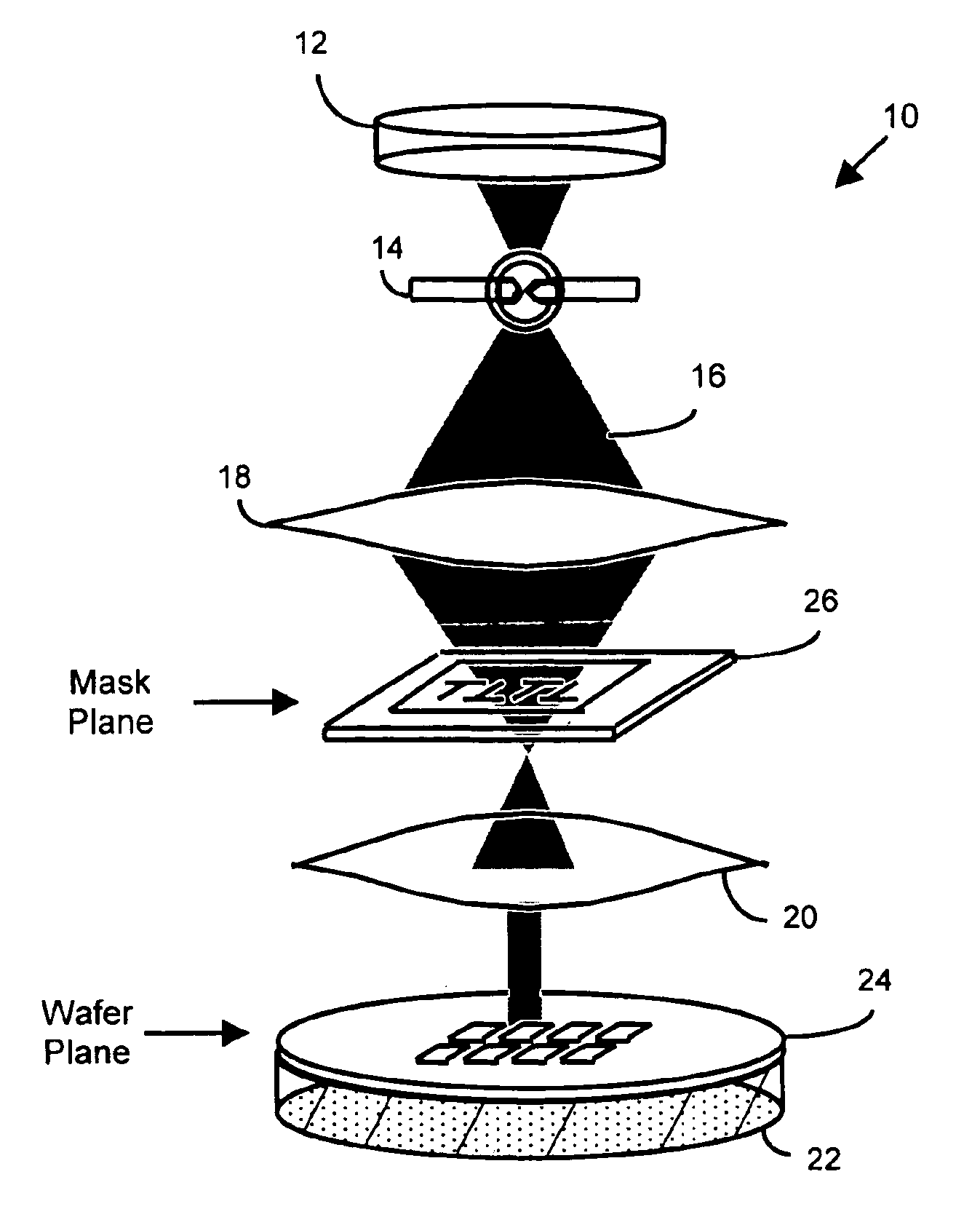
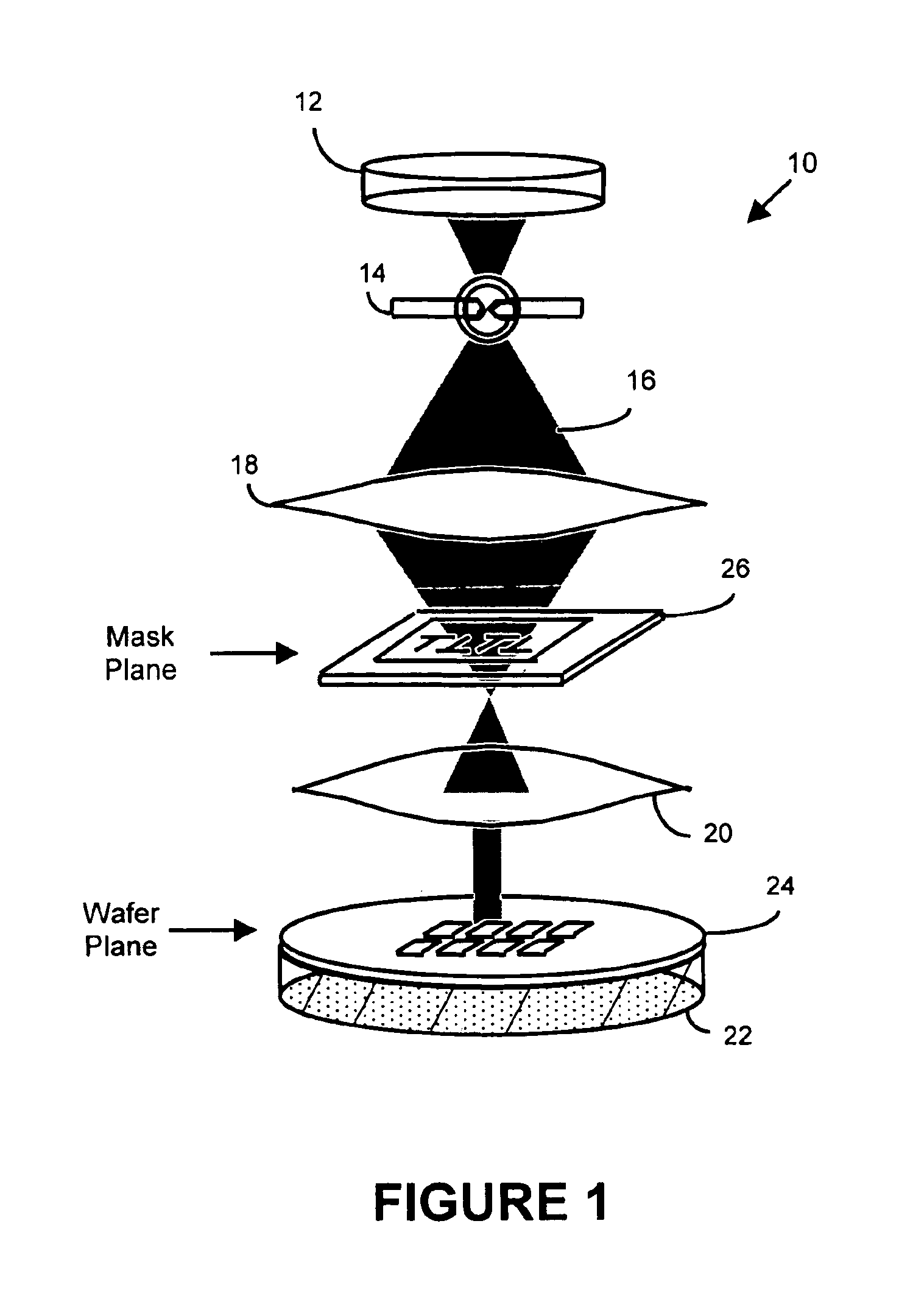
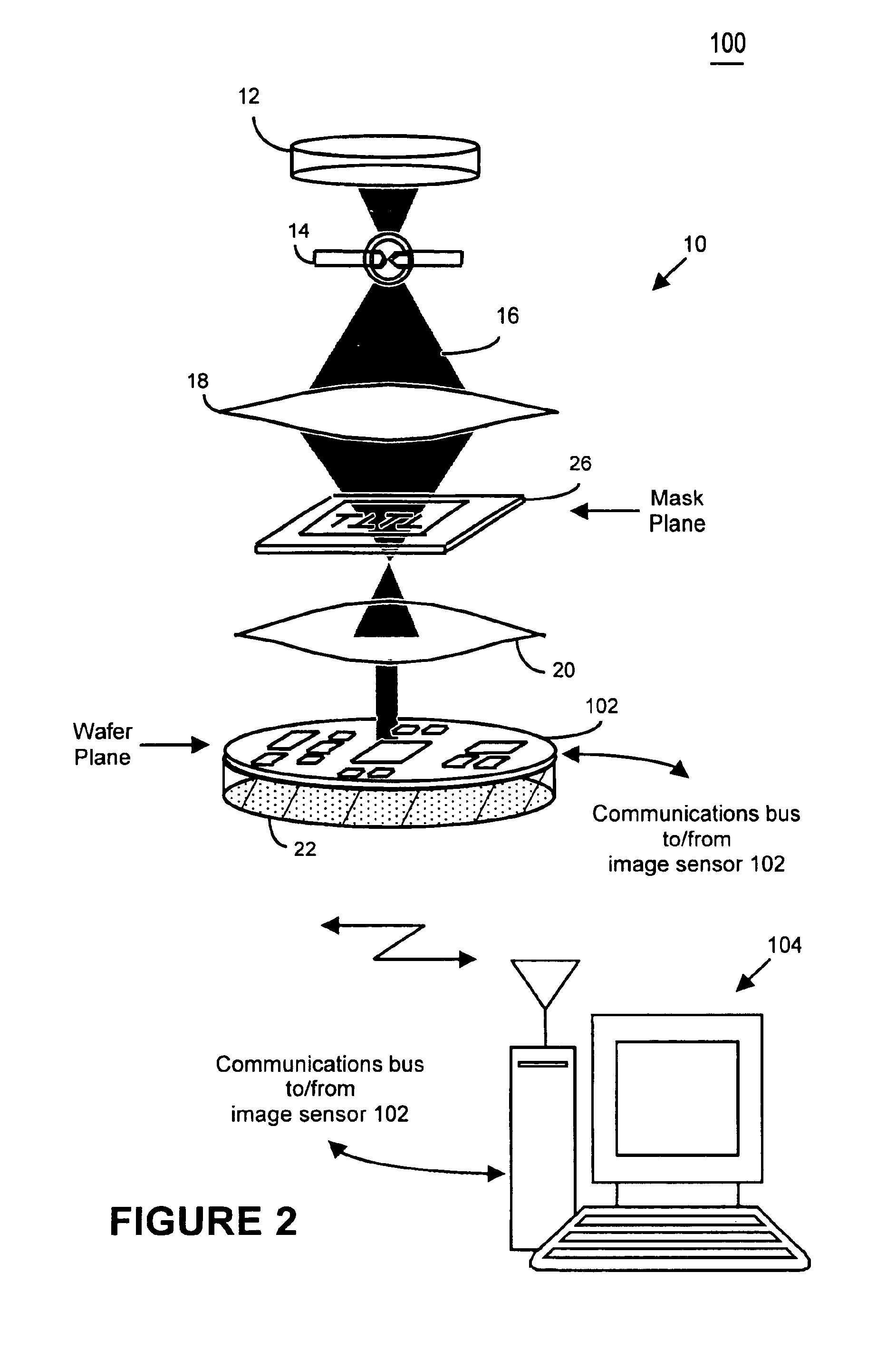
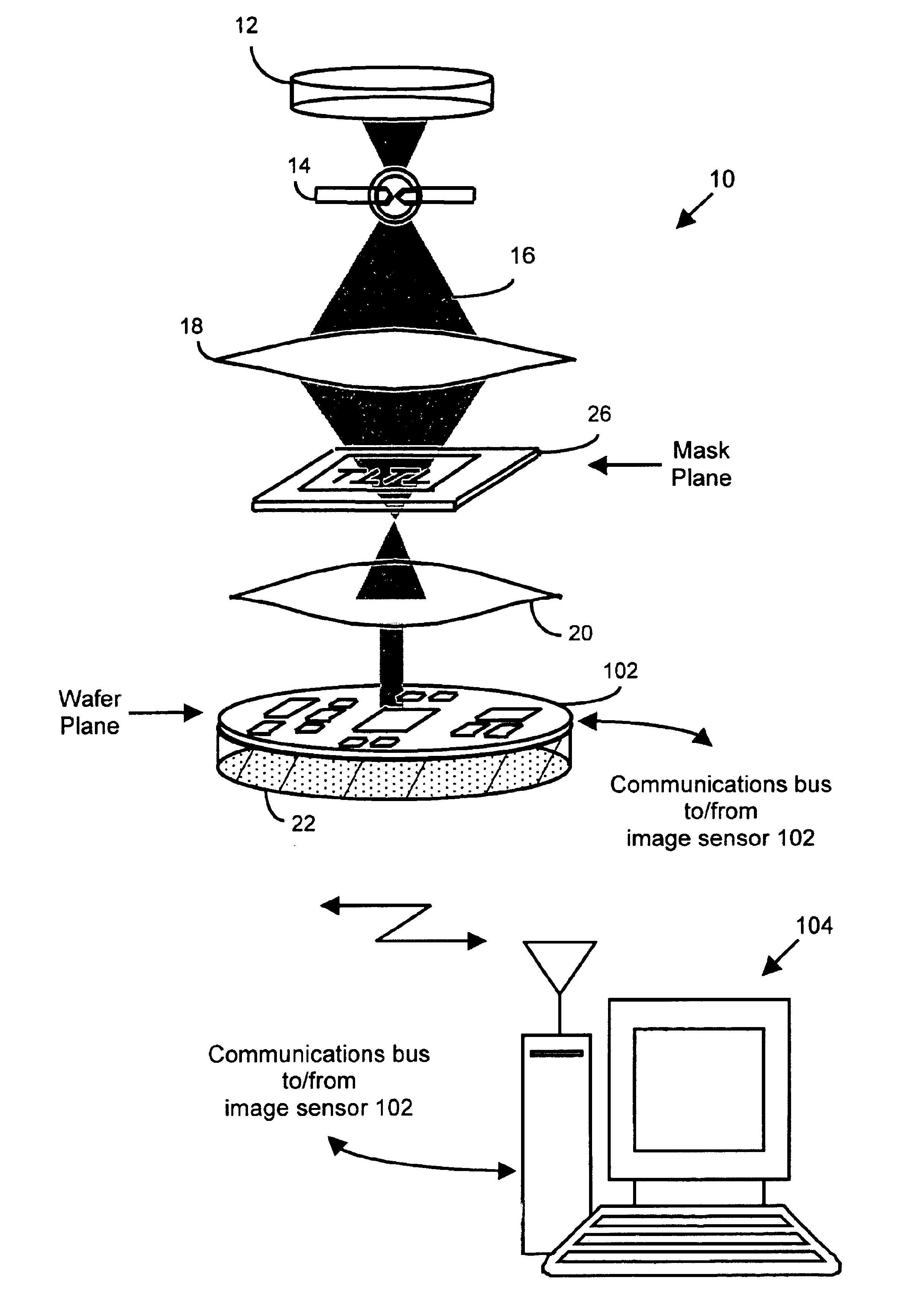
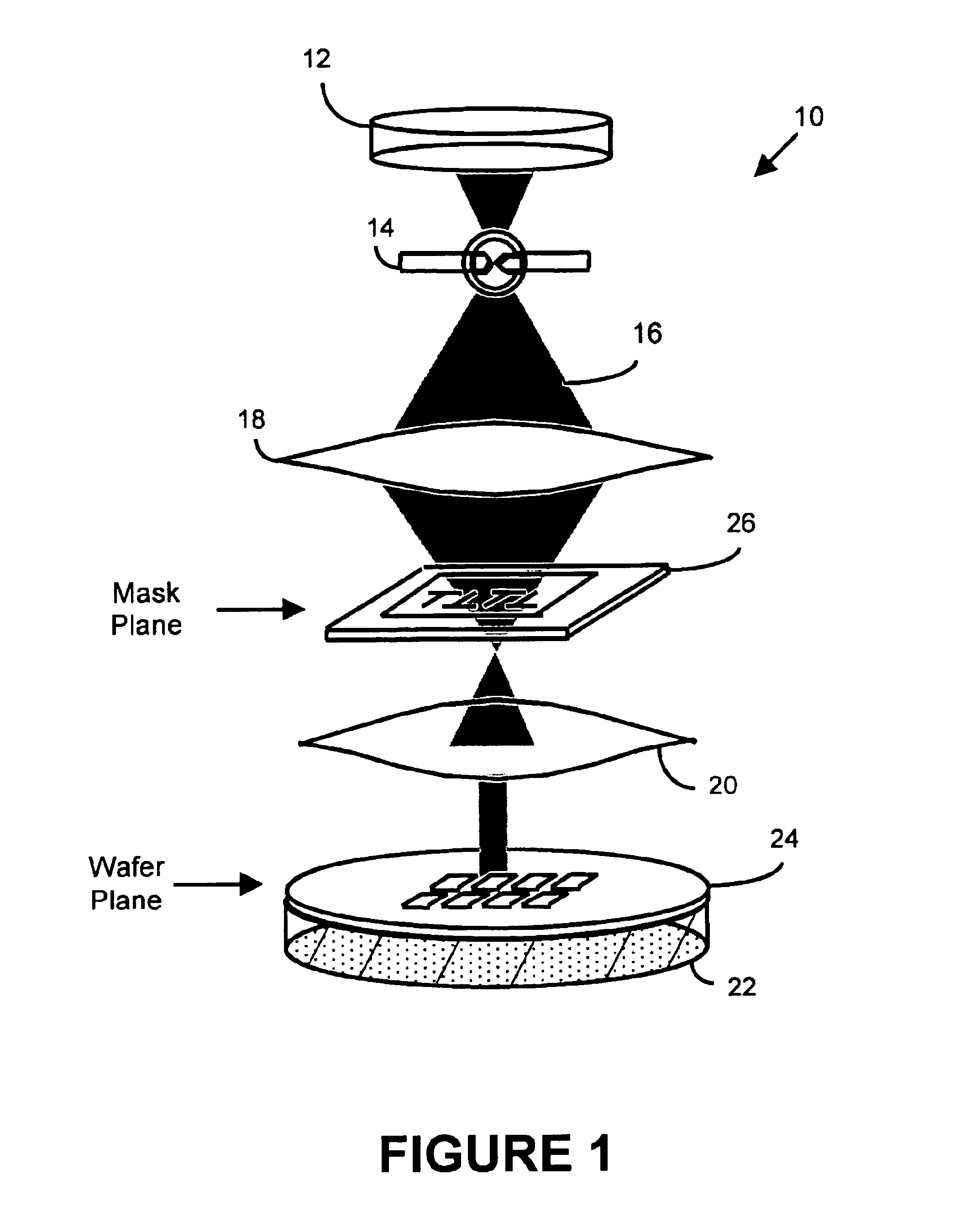
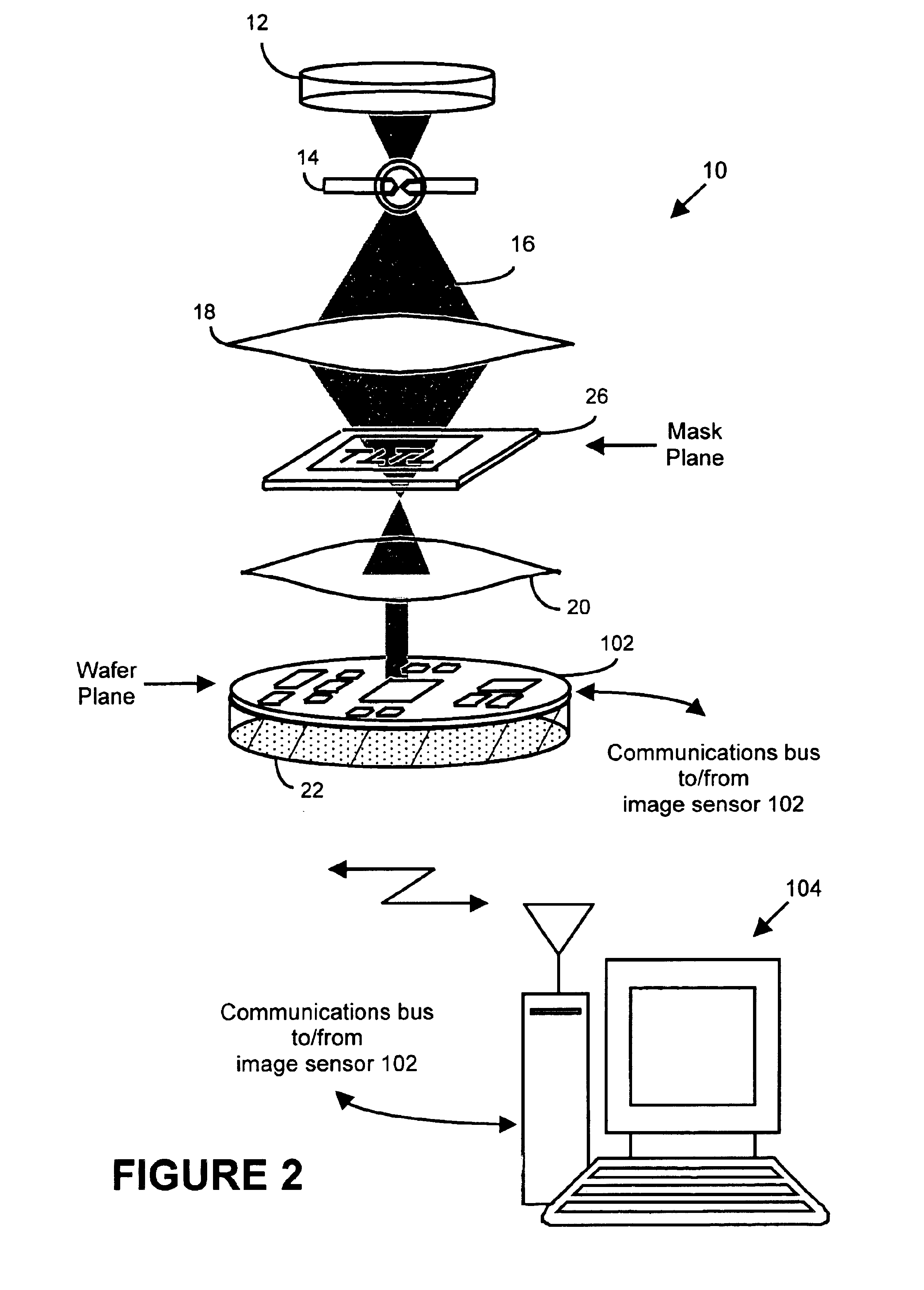
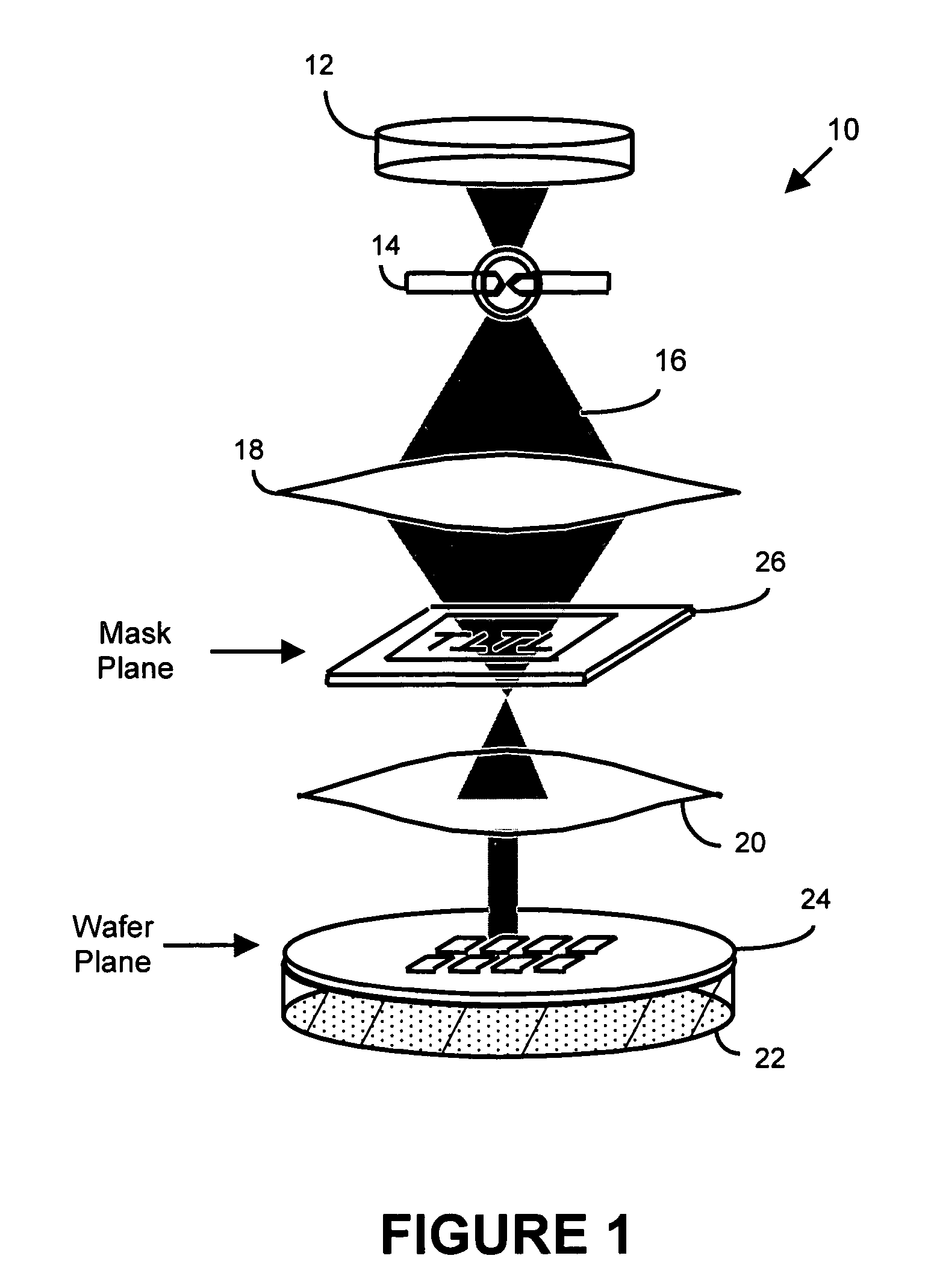
InactiveUS6884984B2Highly precise moveable platformPhotometrySolid-state devicesLithography processEngineering
In one aspect, the present invention is a technique of, and a system and sensor for measuring, inspecting, characterizing and / or evaluating optical lithographic equipment, methods, and / or materials used therewith, for example, photomasks. In one embodiment, the system, sensor and technique measures, collects and / or detects an aerial image (or portion thereof) produced or generated by the interaction between the photomask and lithographic equipment. An image sensor unit may measure, collect, sense and / or detect the aerial image in situ—that is, the aerial image at the wafer plane produced, in part, by a production-type photomask (i.e., a wafer having integrated circuits formed during the integrated circuit fabrication process) and / or by associated lithographic equipment used, or to be used, to manufacture of integrated circuits. A processing unit, coupled to the image sensor unit, may measure the critical dimensions of features of the photomask, using data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the image sensor unit, to control at least one operating parameter of the lithographic equipment.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
System For Distributed Measurement of the Curves of a Structure
InactiveUS20080204706A1Cladded optical fibreForce measurement by measuring optical property variationProcess measurementEngineering
The invention relates to a system for distributed or dispersed measurement of axial and bending deformations of a structure including at least one threadlike device (10) equipped for the distributed or dispersed measurement of these axial and bending deformations, and means for processing measurement signals generated by said device, in which each device includes a cylindrical reinforcement (11) supporting, at its periphery, at least three optical fibres (12) locally parallel to the axis of the reinforcement, and in which the processing means implement means for spectral or time division multiplexing of signals coming from optical fibres.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
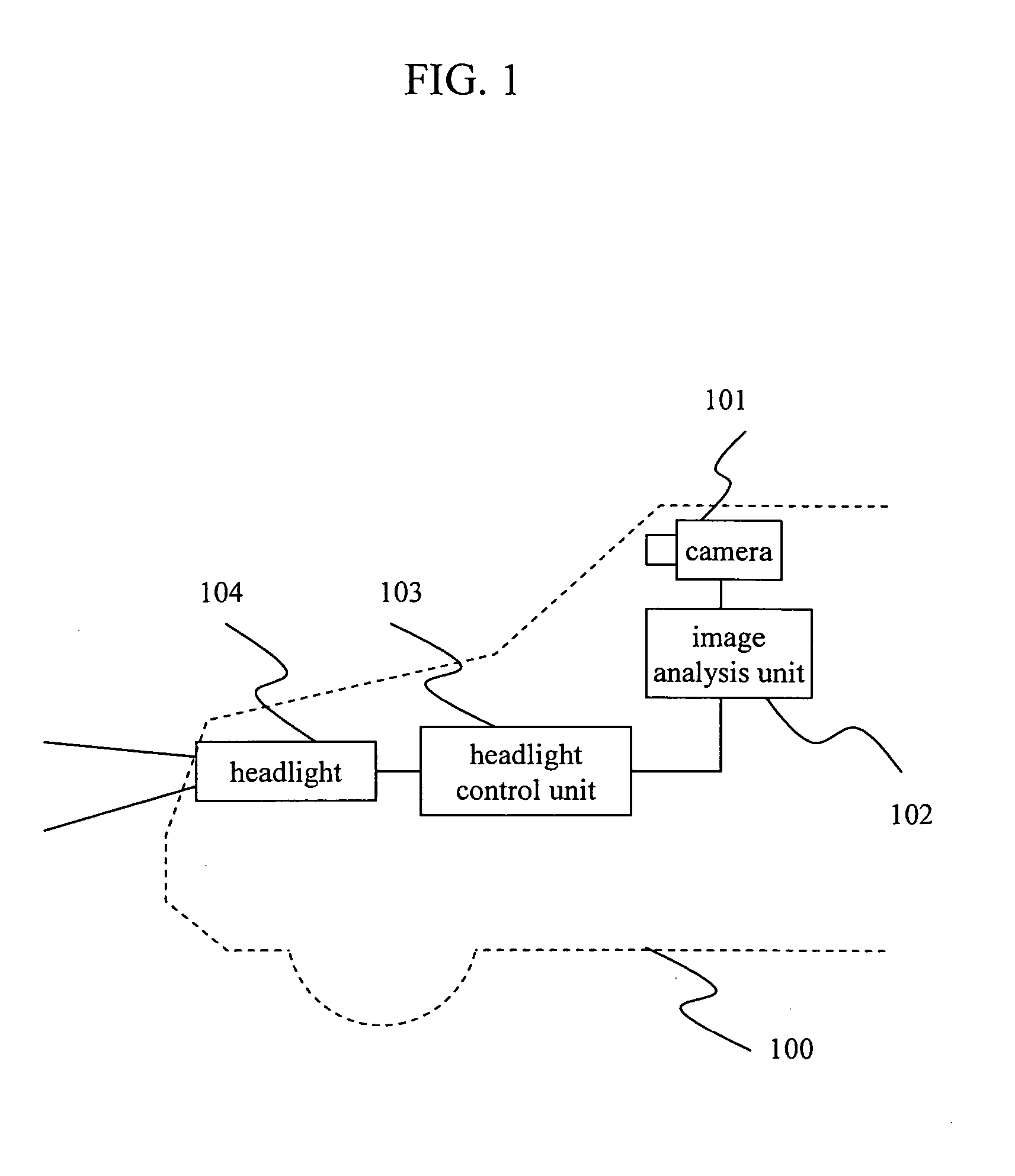
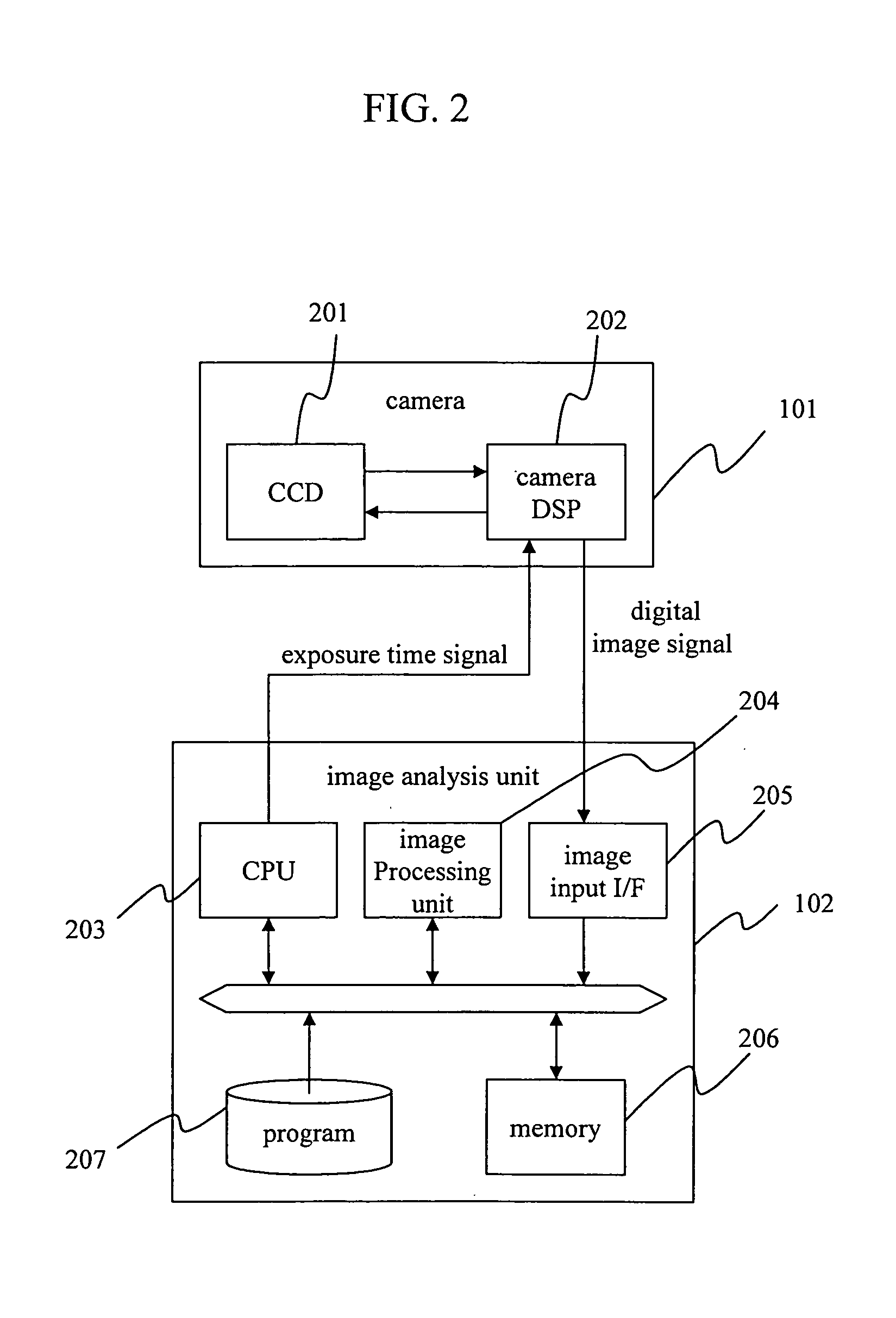
Image processing system and vehicle control system
ActiveUS20050036660A1Easy to detectImprove accuracyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingControl system
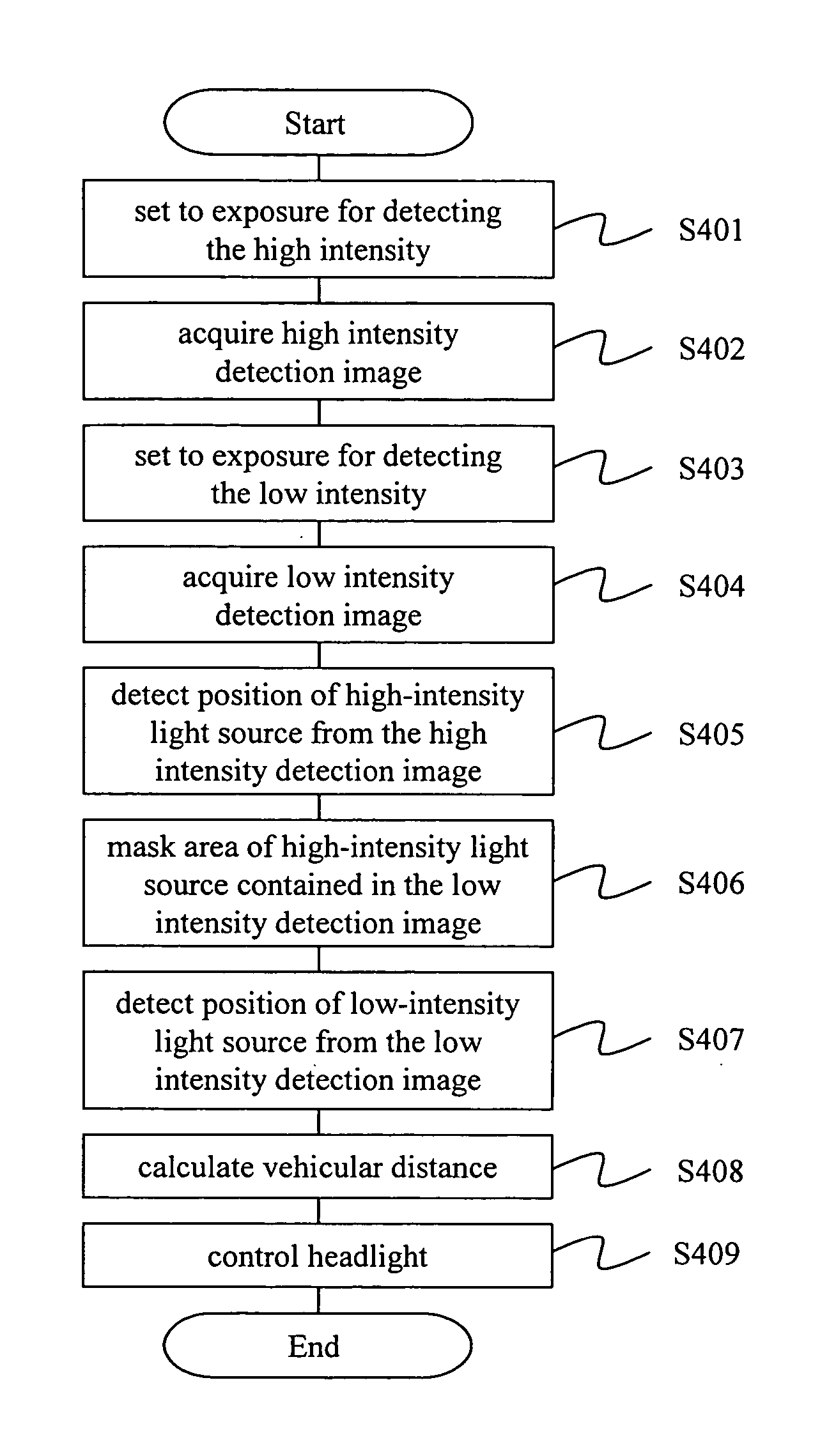
The invention provides an image processing system capable of precisely locating the positions of the light spots covering near headlights through far tail lamps by using one camera. The invention, discriminating the headlights and tail lamps from noise lights such as a traffic light, streetlight, and vending machine, enhances the vehicle detection performance at night. The system includes an image input means that inputs images in front of a vehicle, an image analysis means that analyzes the images inputted by the image input means. The image input means has a means of photographing more than two images with different exposures. The image analysis means analyzes the images photographed by the image input means to transform them into the position information of the vehicles traveling in front.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
System and method for monitoring structures
InactiveUS20090132183A1Thermometer detailsSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A technique facilitates the monitoring of elongate structures. An elongate structure is combined with an optical fiber deployed along the structure. An interrogation system is operatively joined with the optical fiber to input and monitor optical signals to determine any changes in parameters related to the structure.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Methods for monitoring structural health conditions
InactiveUS20050075846A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalProcess moduleEngineering
Owner:ADVANCED STRUCTURE MONITORING
Detection, resolution, and identification of arrayed elements
An image analysis workstation for analyzing optical thin film arrays is disclosed. One disclosed embodiment relates to individual arrays that comprise a single optical thin film test surface that provides a plurality of discretely addressable locations, each comprising an immobilized capture reagent for an analyte of interest. These are referred to herein as "arrayed optical thin film test surfaces." Preferably, an individual arrayed optical thin film test surface comprises at least 4, more preferably at least 16, even more preferably at least 32, still more preferably at least 64, and most preferably 128 or more discretely addressable locations. One or more of the discretely addressable locations may provide control signals (e.g., for normalizing signals and / or that act as positive and / or negative controls) or fiducial signals (i.e., information that is used to determine the relative alignment of the arrayed optical thin film test surface within the device.
Owner:INVERNESS MEDICAL - BIOSTAR
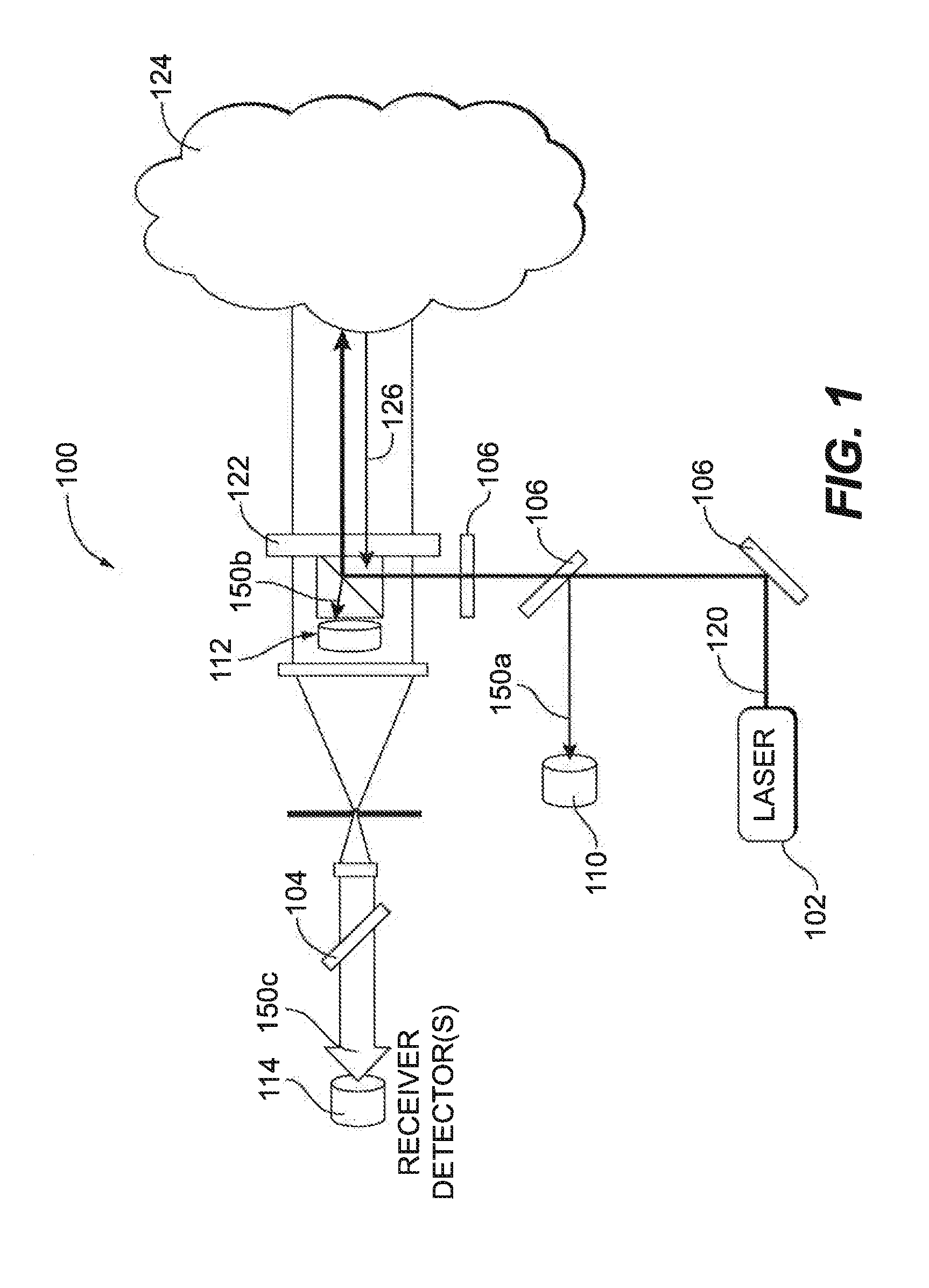
System and method for monitoring optical subsystem performance in cloud lidar systems
ActiveUS20160025842A1Optical apparatus testingElectromagnetic wave reradiationCloud systemsRadar systems
A method of detecting optical subsystem failures includes emitting a pulsed light beam from a laser through a window. A reflection signal indicative of a portion of the beam reflected by the window is compared to an expected signal to monitor for degradation of an optical component.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
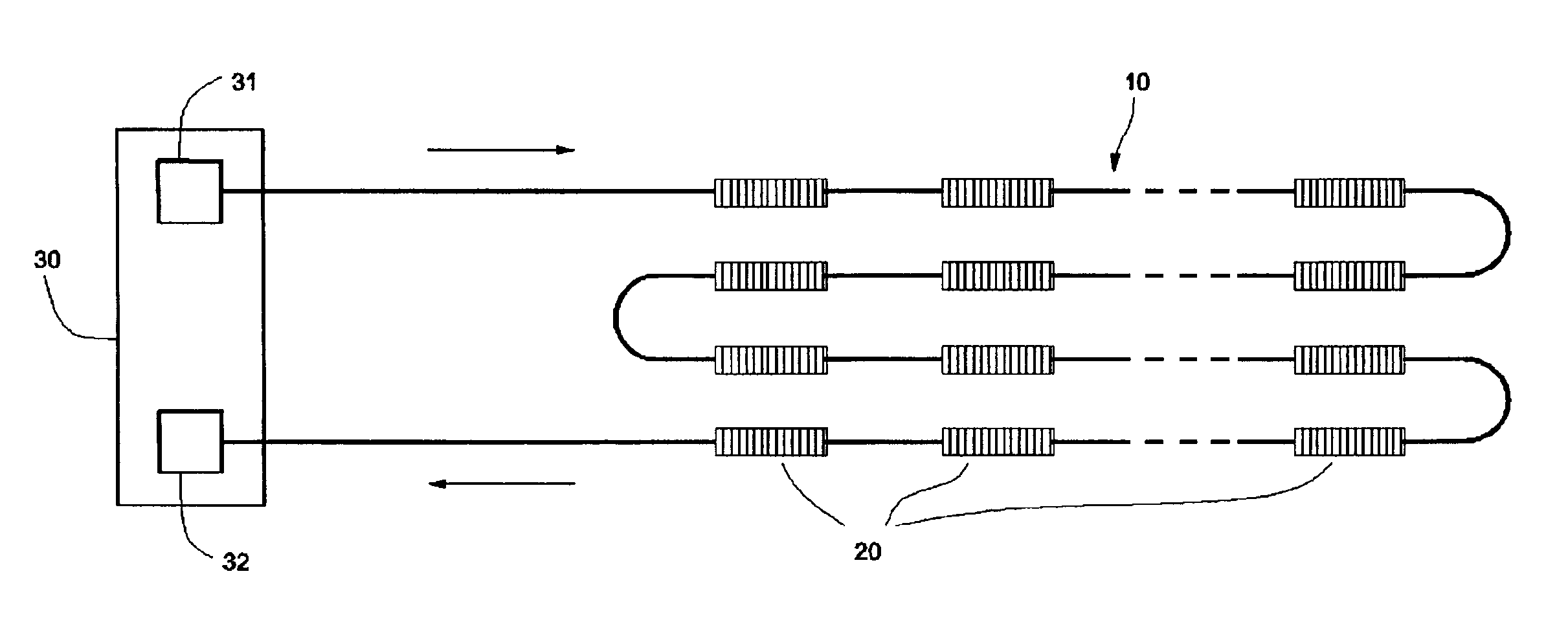
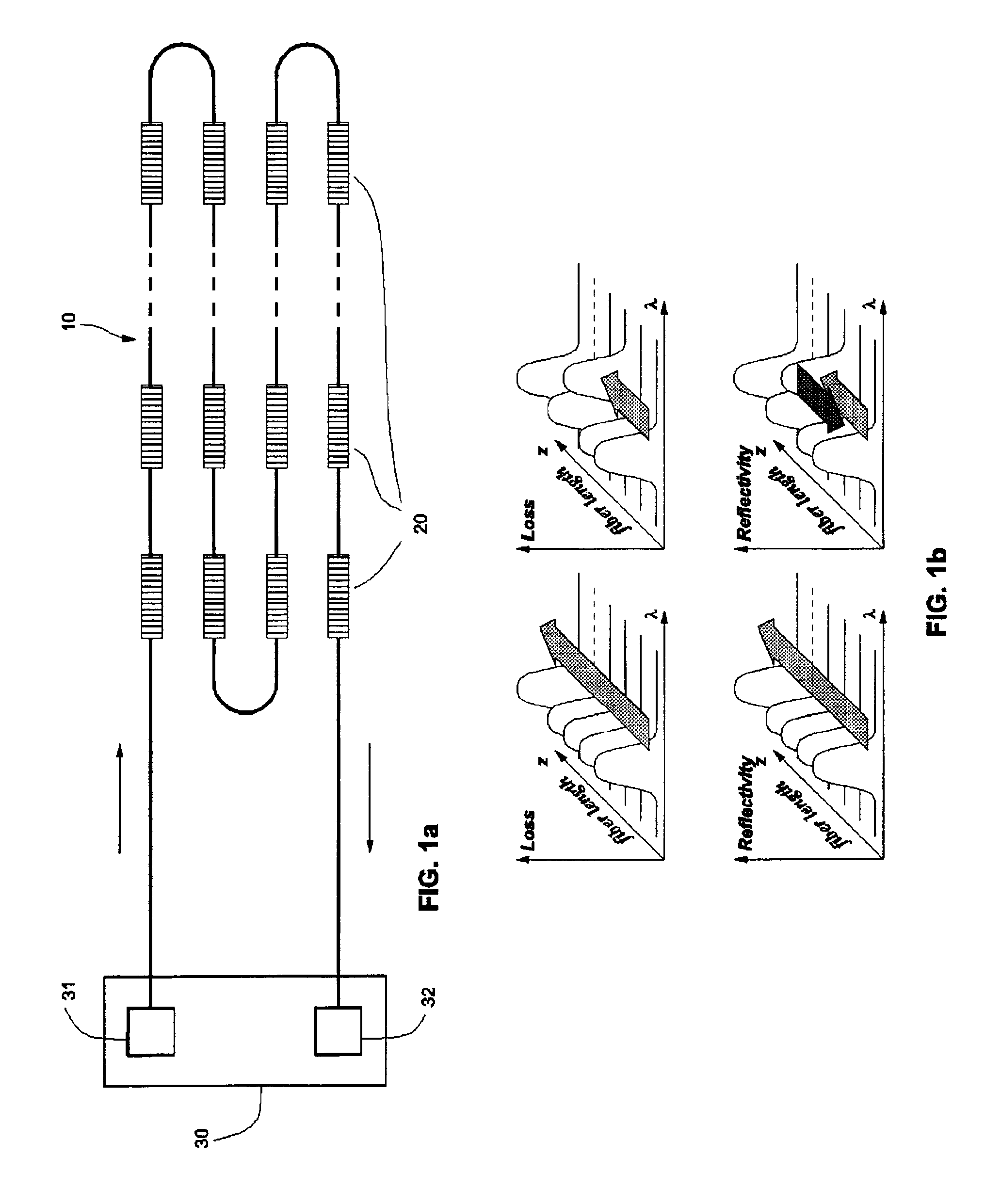
Fiber-optic sensing system for distributed detection and localization of alarm conditions
InactiveUS6876786B2Simple and inexpensiveIncrease the number ofDetection of fluid at leakage pointRadiation pyrometrySpectral bandsLength wave
An optical fiber sensor system comprising of an optical fiber including plurality of sensitive elements, each sensitive element has characteristic spectral band which in normal undisturbed condition lies in a first wavelength range and, under an influence of some specified condition to be detected, shifts to a second wavelength range; first and second wavelength ranges do not overlap. Means for probing an optical transmission or reflection of the fiber operate within second wavelength range to monitor the changes of the transparency or reflectivity of the fiber caused by the shift of characteristic spectral band into the second wavelength range.The invention provides means for distributed monitoring of equipment or construction structures and detection of specified conditions and can provide alarm signal when the specified conditions become effective.
Owner:CICESE CENT DE INVESTIGACION CIETIFICA Y DE EDUCACION SUPERIOR DE ENSENADA B C
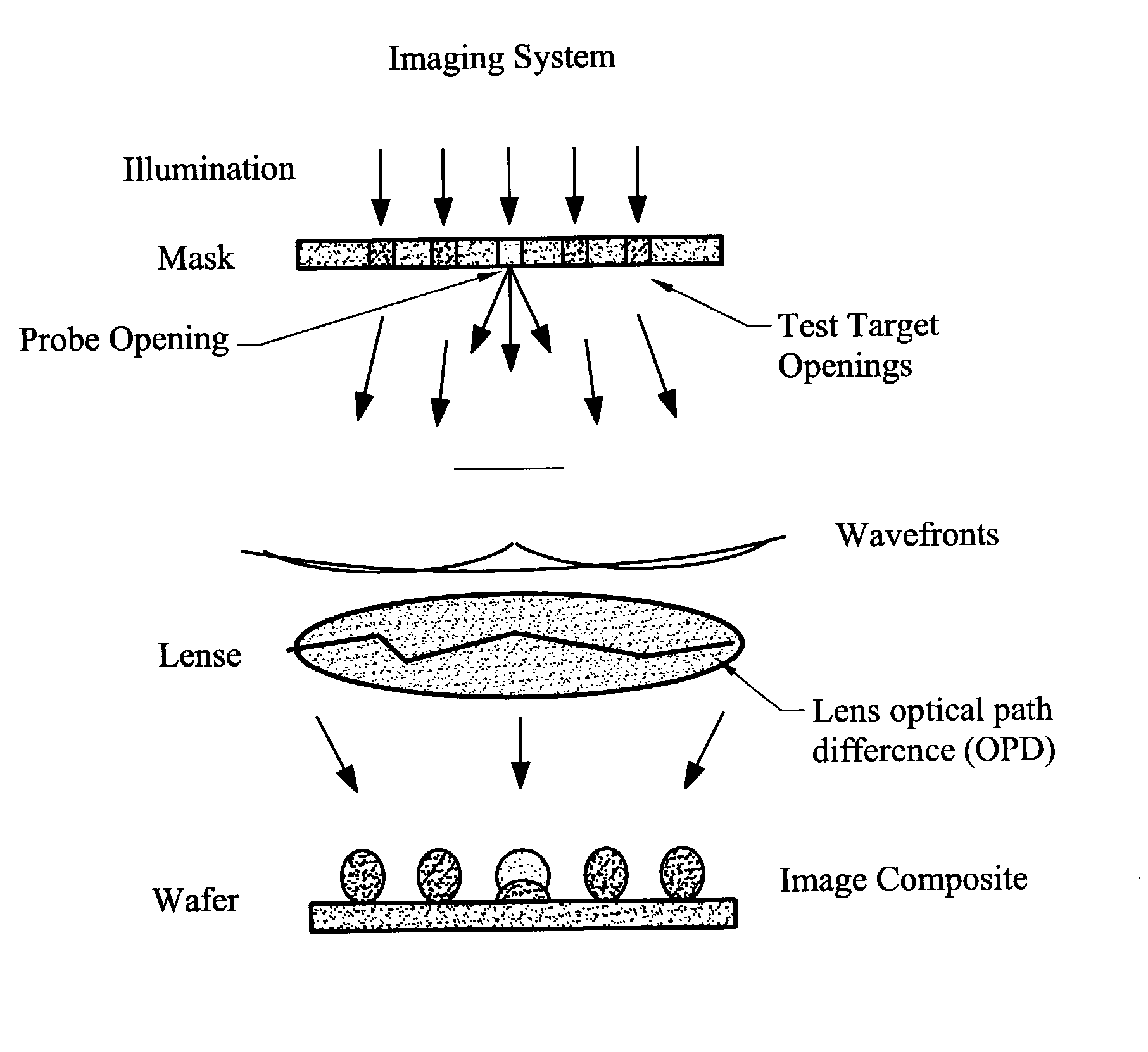
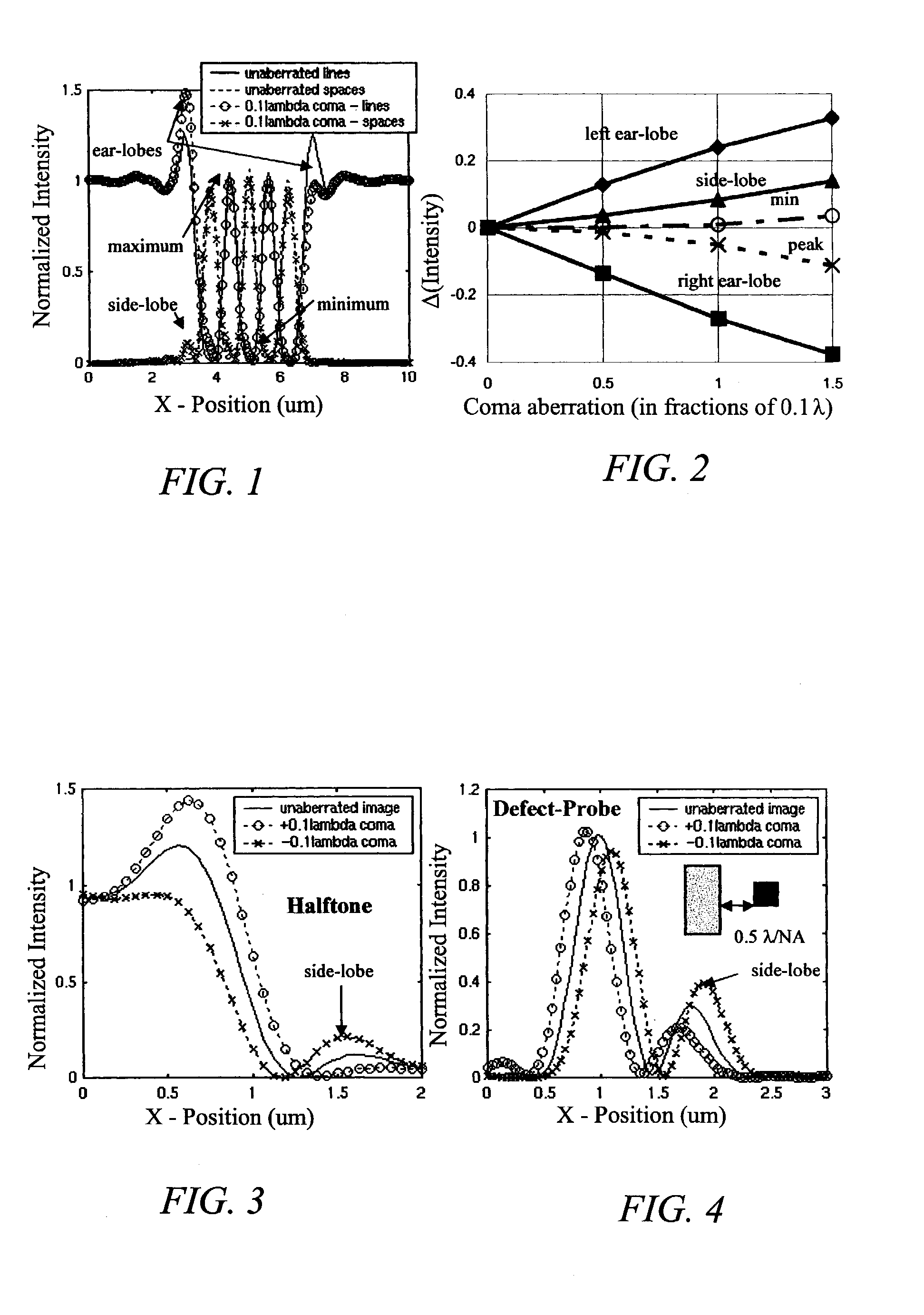
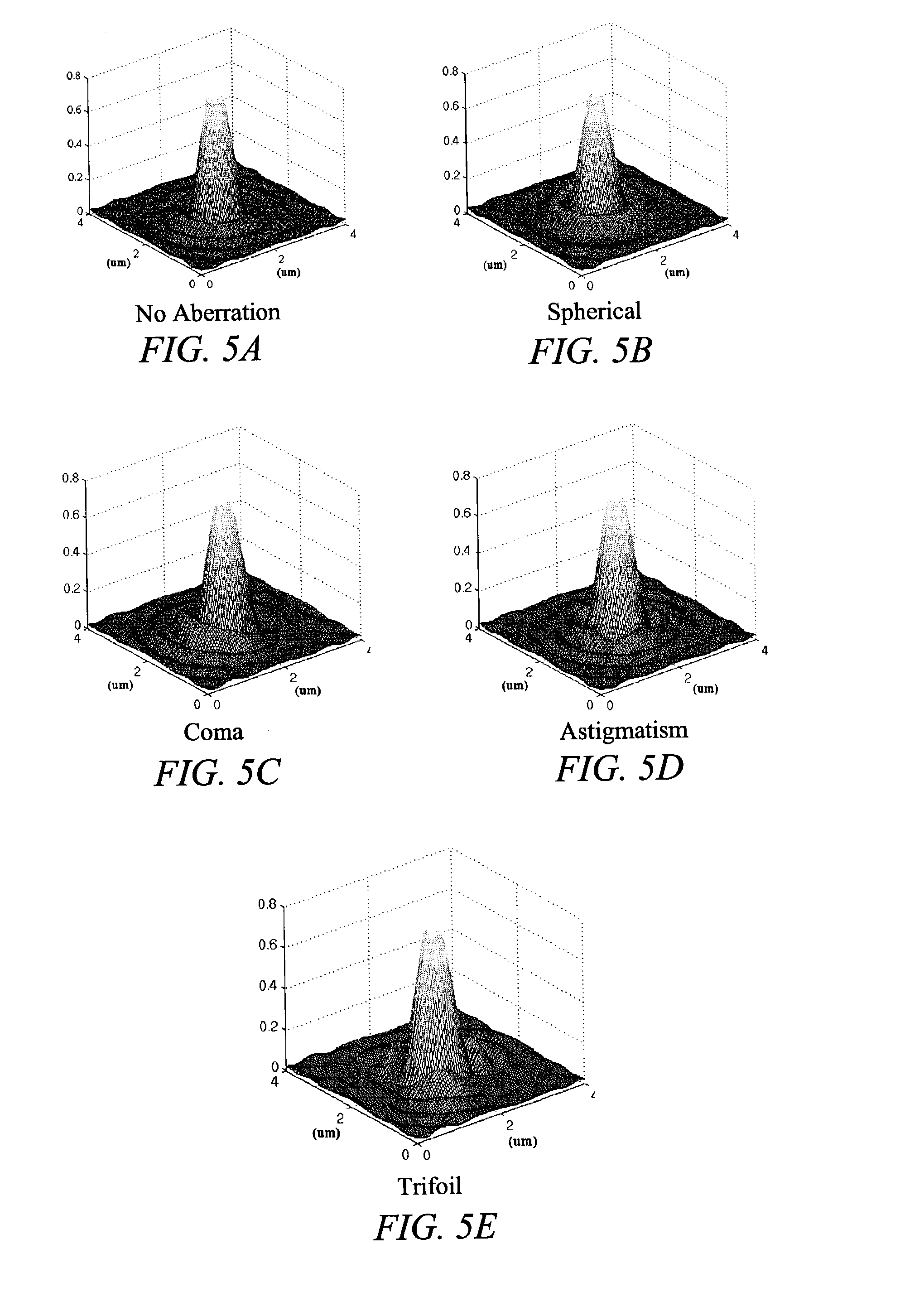
Characterizing aberrations in an imaging lens and applications to visual testing and integrated circuit mask analysis
InactiveUS7030997B2Quick fixAccurate modelingEye diagnosticsUsing optical meansCamera lensVisual test
Aberrations in a lens and lens system are identified by projecting an optical beam through a mask having an opening (probe) and a surrounding open geometry (pattern) and through the lens to an image plane. Lens aberrations are identified from the combined intensity of the beam in the image plane. In one embodiment the pattern is a plurality of rings concentric with the probe. Spillover between the probe and the geometry becomes intermixed in passing through the lens and alters the light intensity in the image plane. Vision of a patient can be tested by providing a plurality of probe openings and surrounding geometries that are illuminated. The patient then compares the images for brighter and darker probes as a measure of pupil aberrations. Areas in an integrated circuit mask layout impacted by aberrations in projection printing can be identified by sequentially comparing an aberration function to a mask layout, which can then be used to modify the mask layout.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
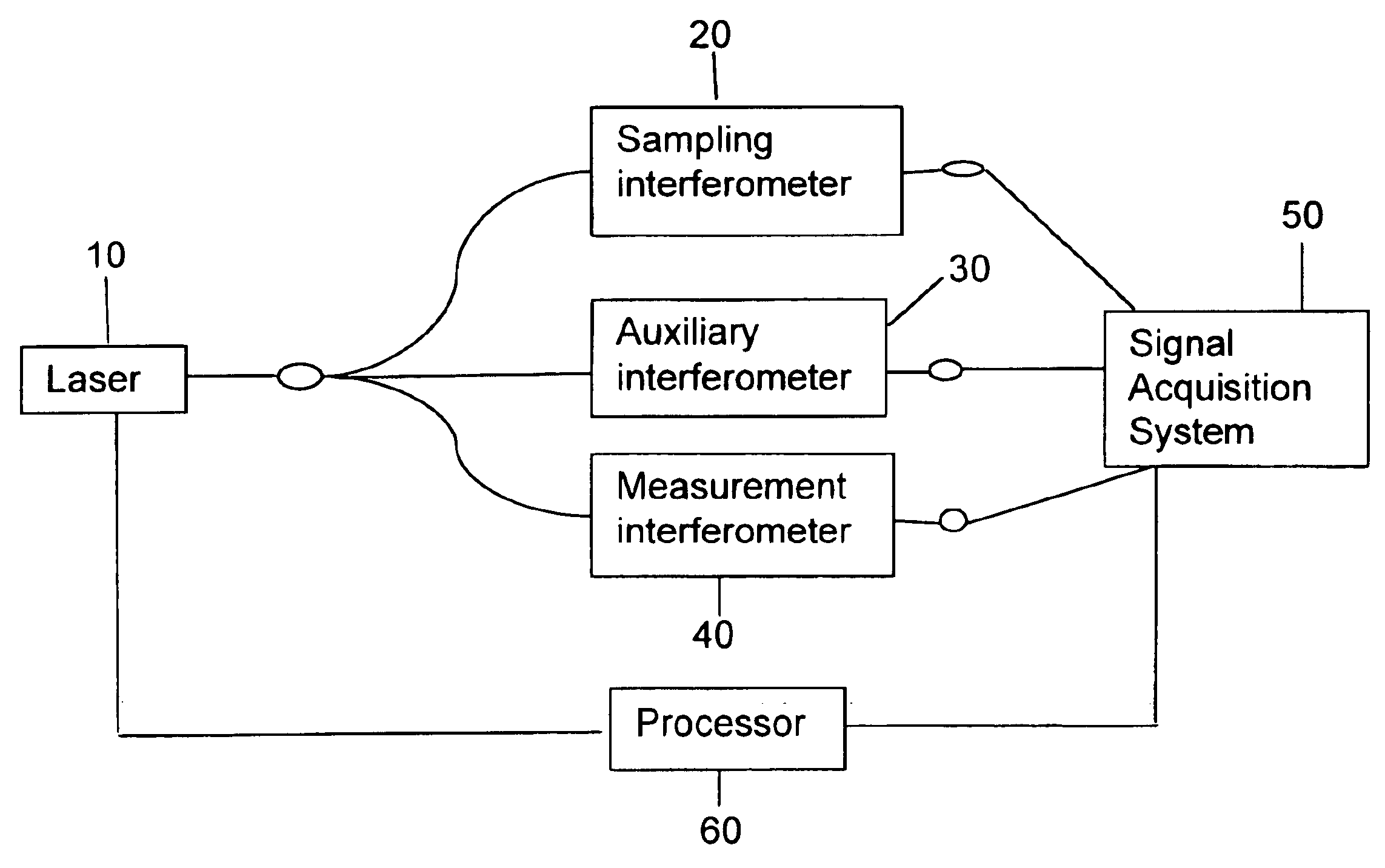
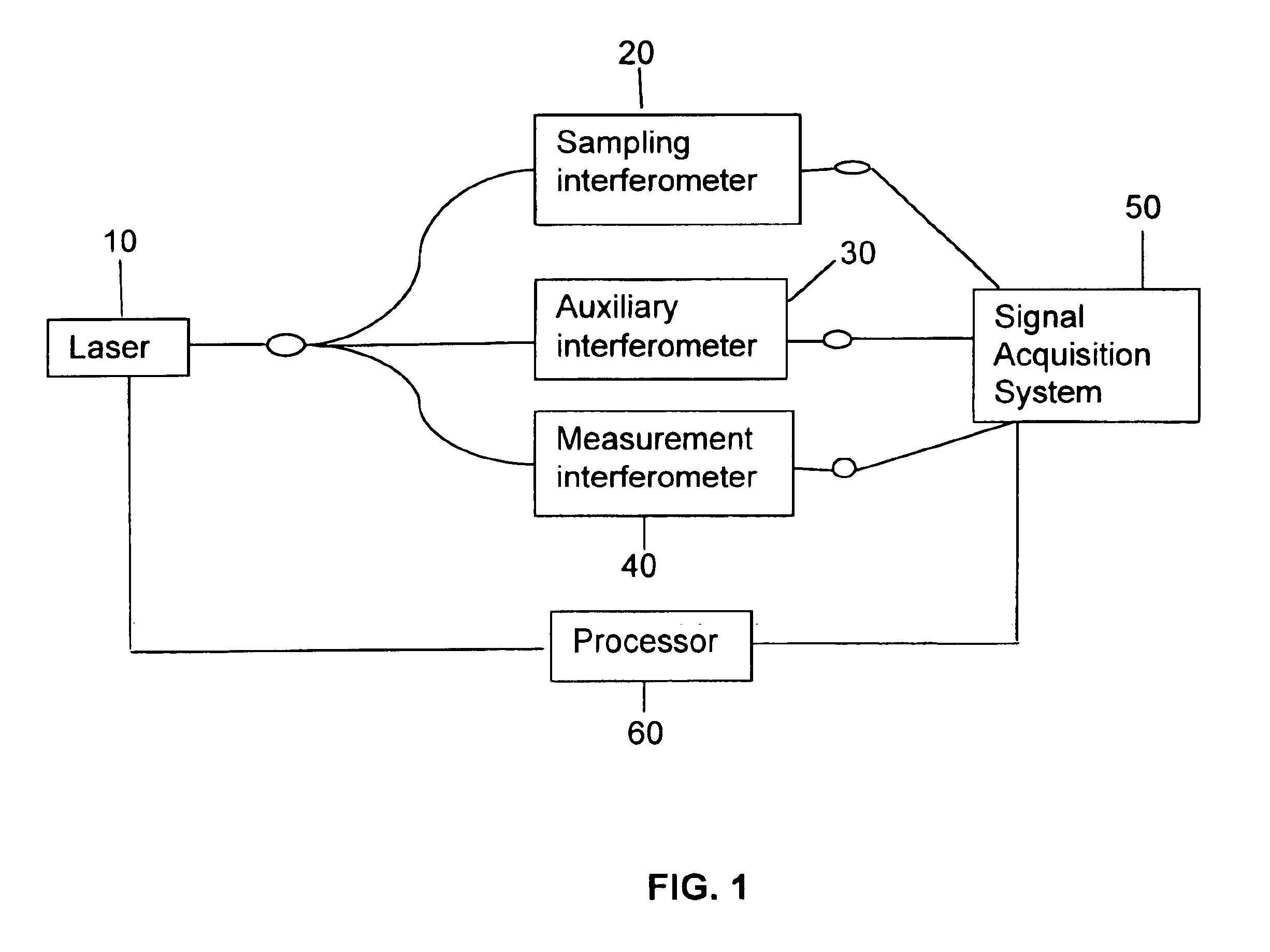
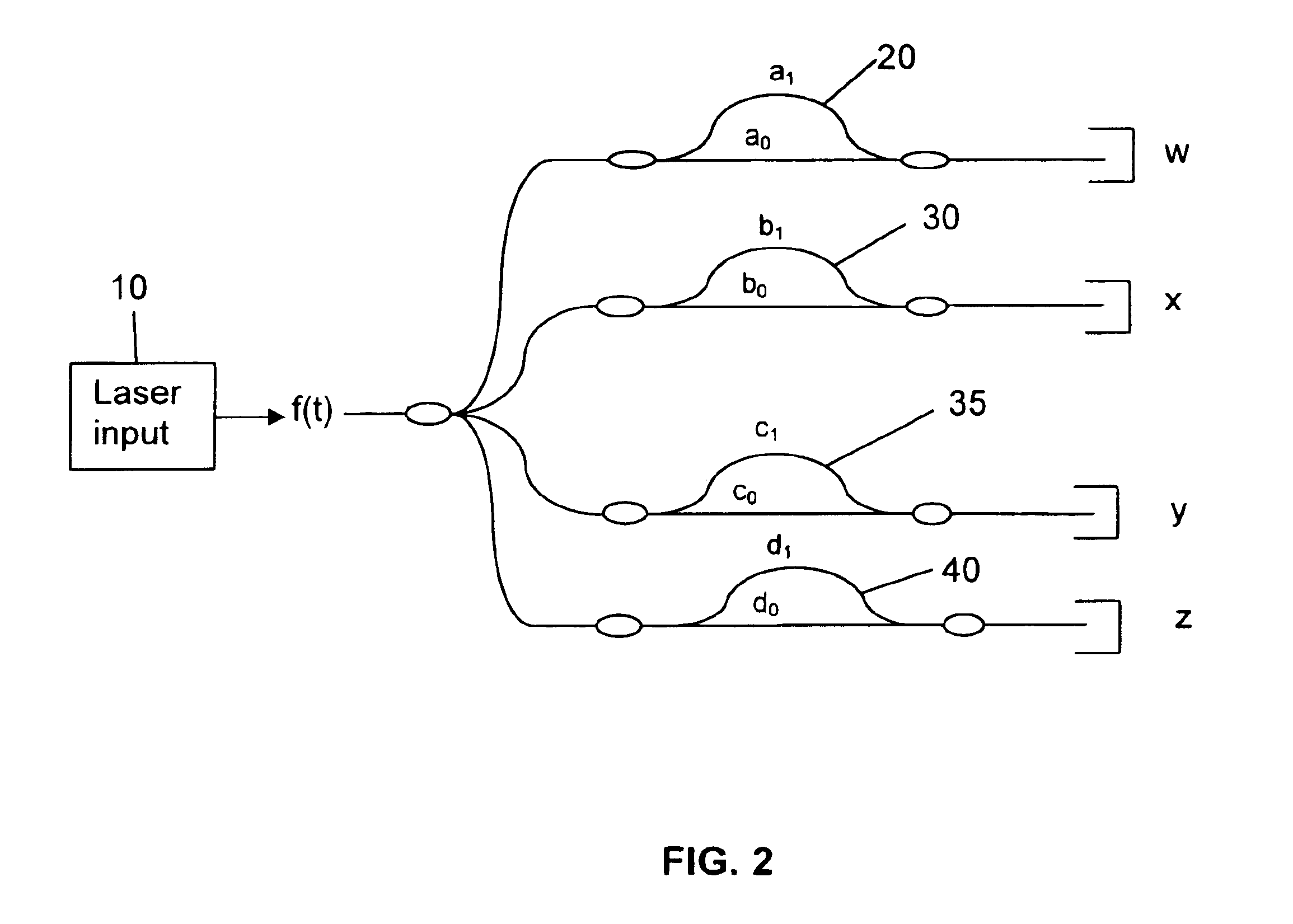
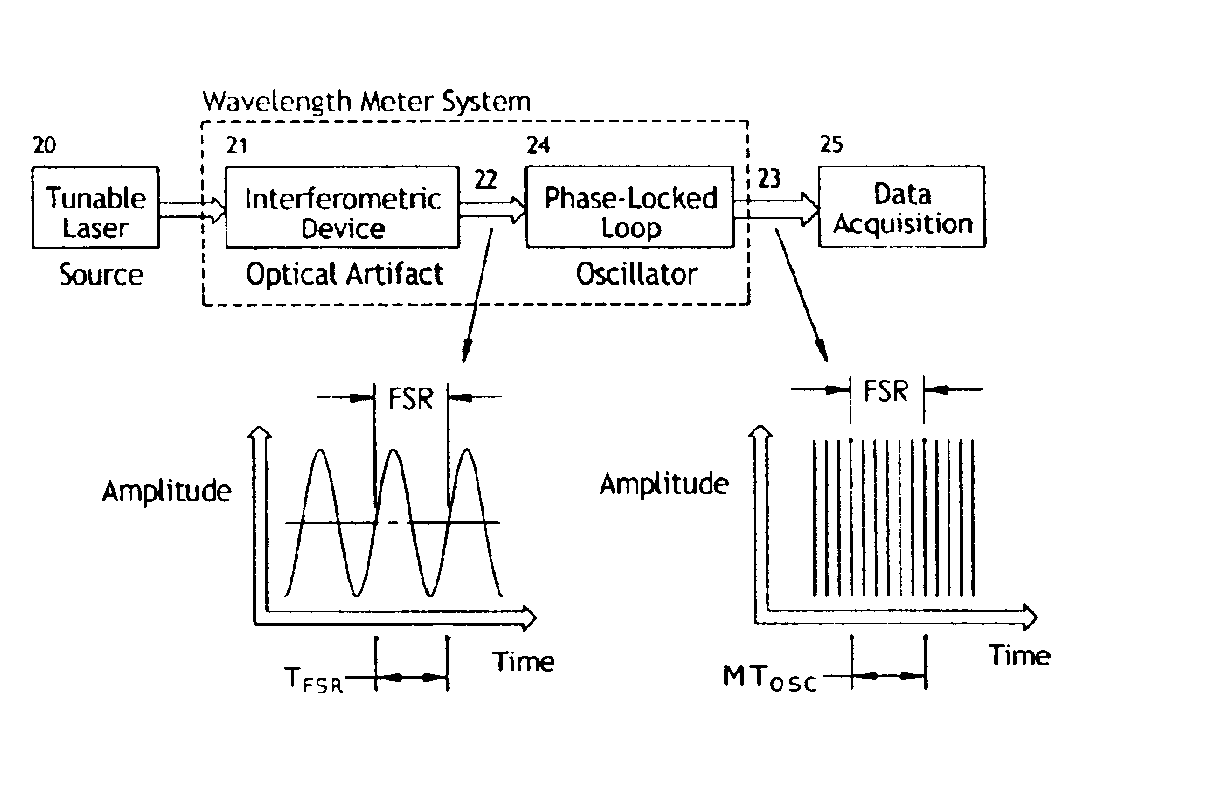
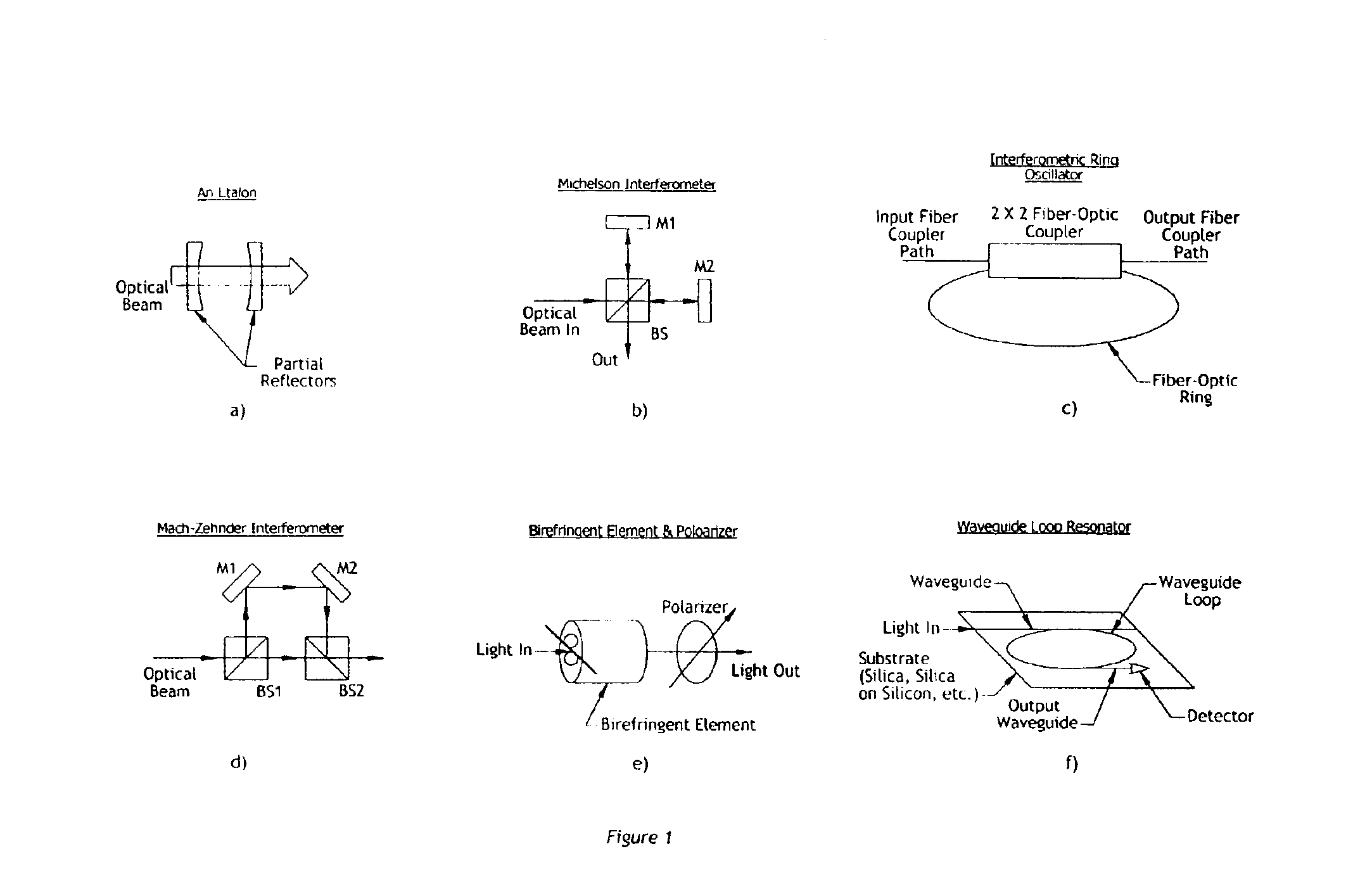
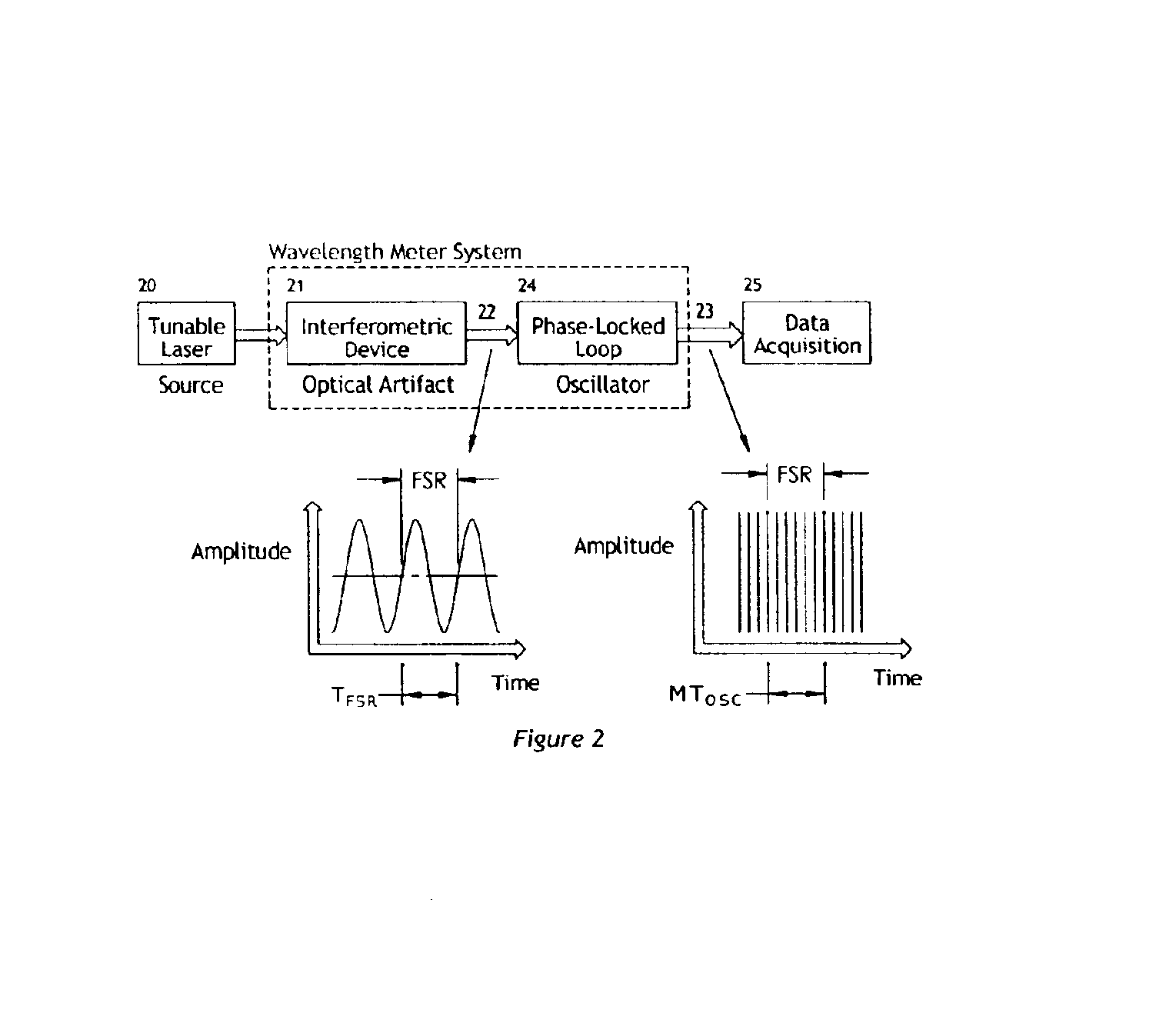
Apparatus and method for correcting errors generated by a laser with non-ideal tuning characteristics
The present invention is an apparatus and method for correcting errors generated by a laser with non-ideal tuning characteristics, the apparatus comprises a laser having non-ideal tuning characteristics. At least three interferometers are positioned in an operable relationship to the laser, wherein a sampling interferometer and at least one auxiliary interferometer correct for residual errors resulting from the laser; and wherein a measurement interferometer makes a measurement. A signal acquisition system is positioned in an operable relationship to each interferometer and a processor is positioned in an operable relationship to the signal acquisition system.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Distributed optical fiber sensor
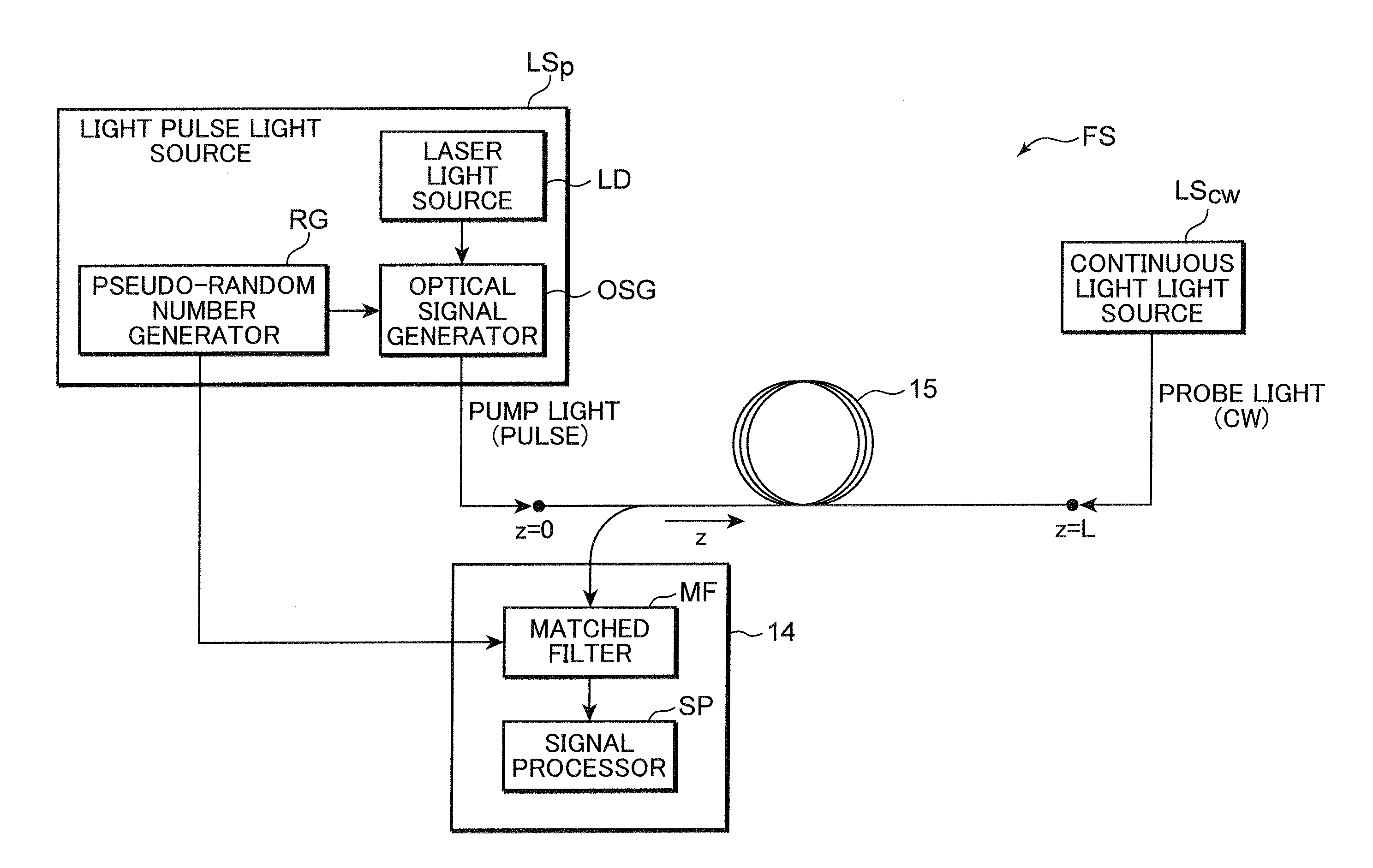
ActiveUS20110228255A1Improve spatial resolutionPolarisation-affecting propertiesForce measurementRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
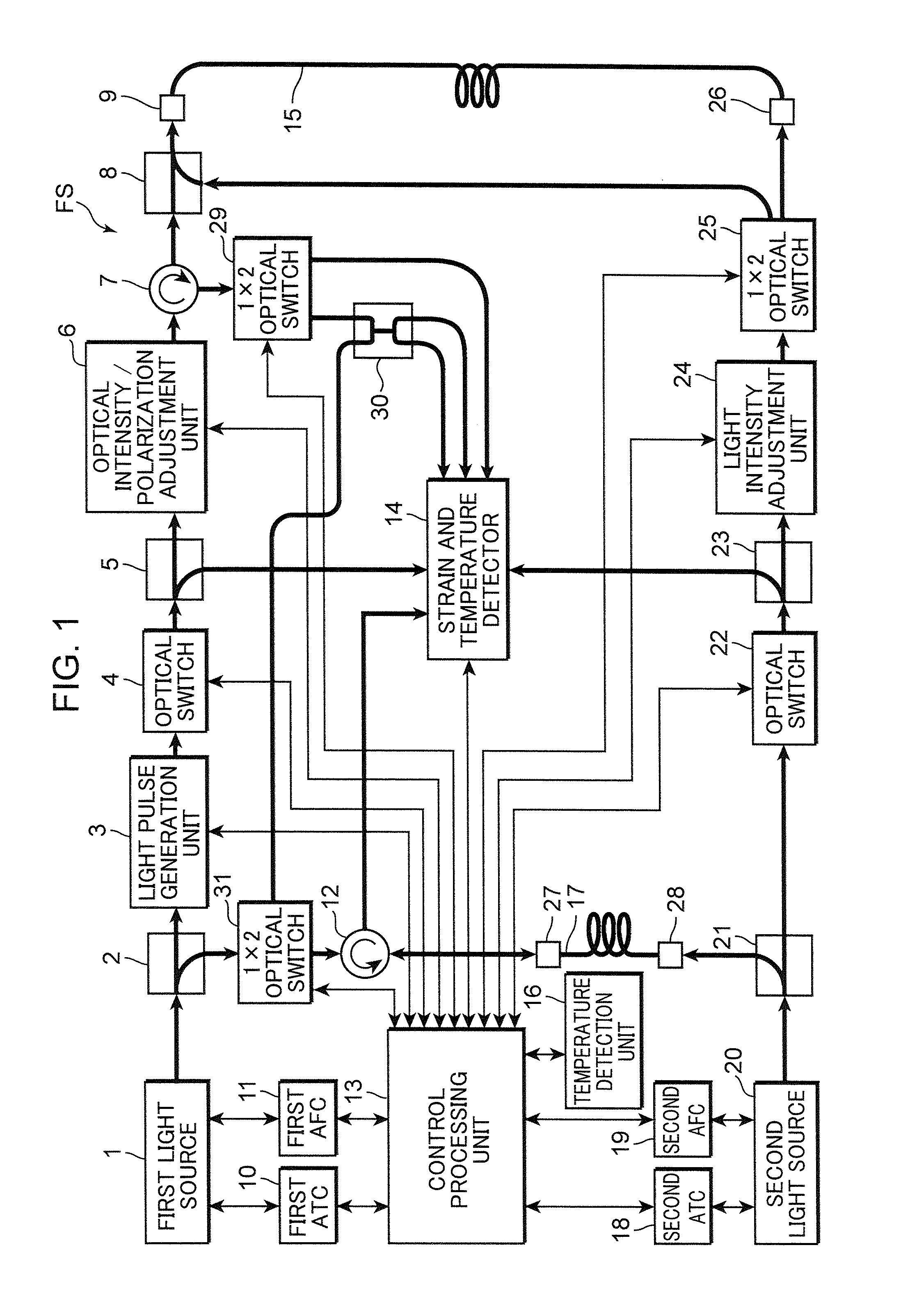
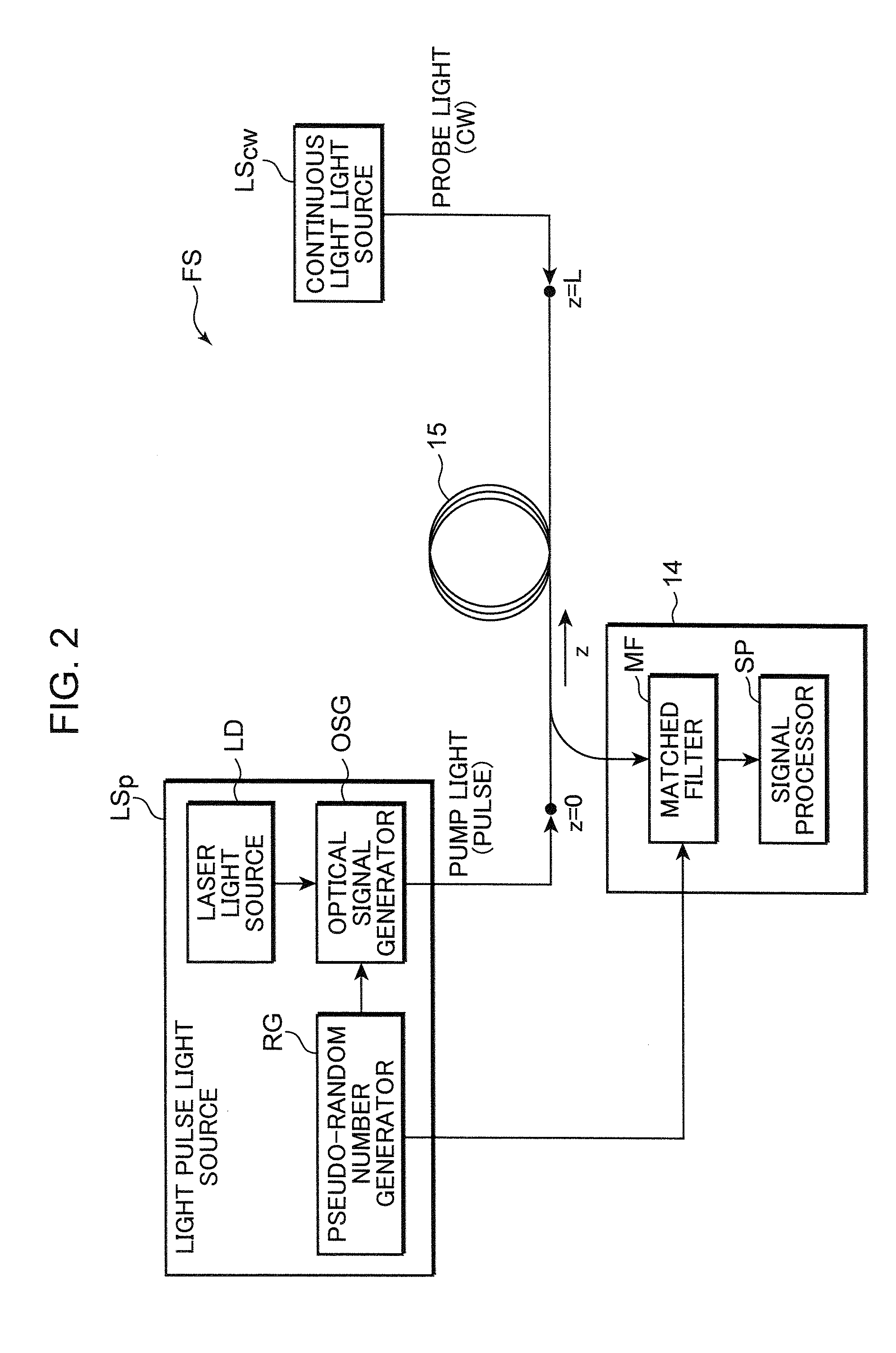
The present invention provides a distributed optical fiber sensor capable of measuring the strain and temperature of an object to be measured simultaneously and independently with high spatial resolution. A distributed optical fiber sensor FS is a distributed optical fiber sensor which uses an optical fiber 15 as a sensor, and a strain and temperature detector 14 measures a Brillouin frequency shift amount caused by a strain and a temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 by using a Brillouin scattering phenomenon, measures a Rayleigh frequency shift amount caused by the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 by using a Rayleigh scattering phenomenon, and calculates the strain and temperature generated in the optical fiber 15 from the measured Brillouin frequency shift amount and Rayleigh frequency shift amount.
Owner:NEUBREX
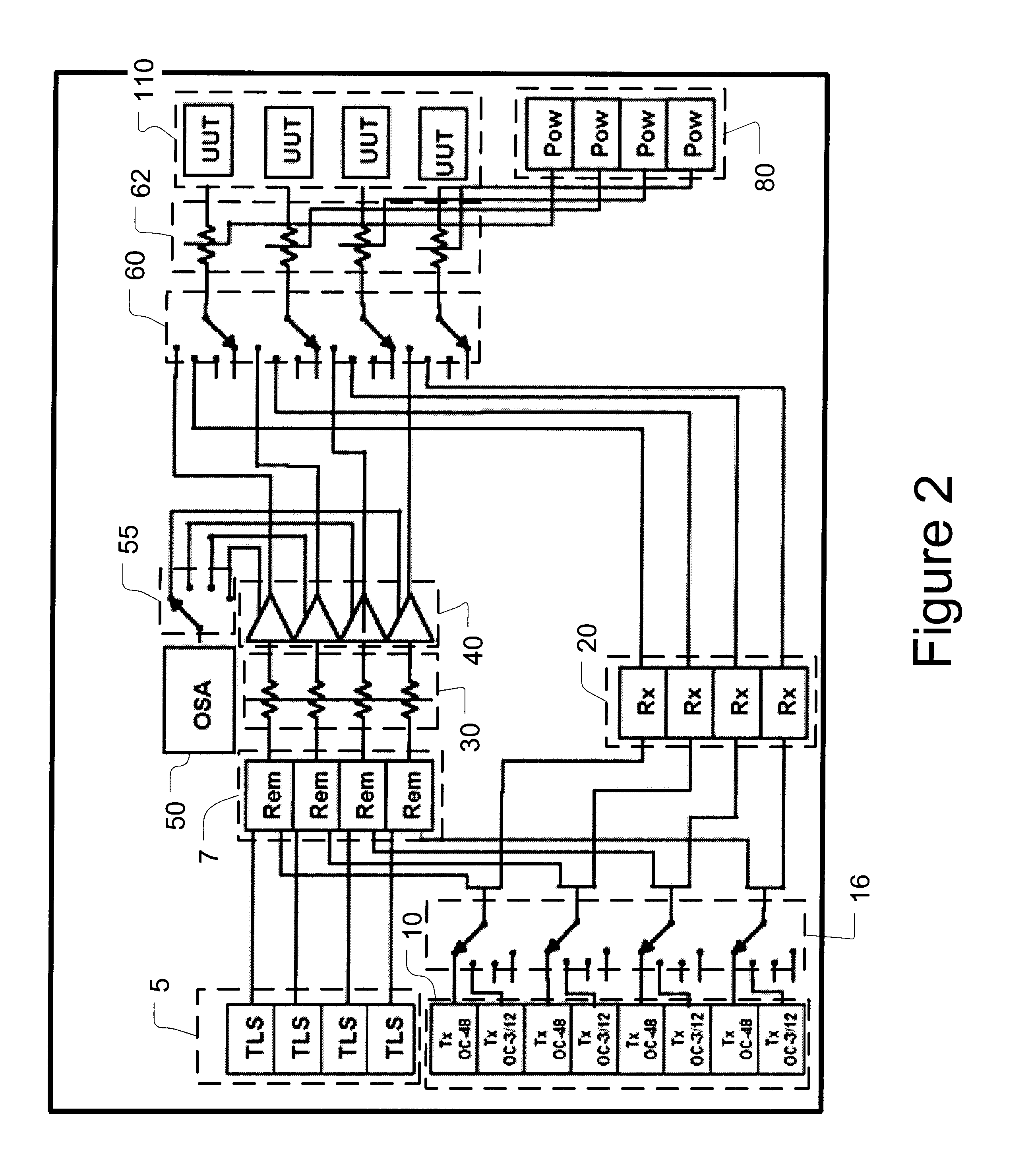
Optical module calibration system
InactiveUS6590644B1Fluid pressure measurement using elastically-deformable gaugesMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical power meterEngineering
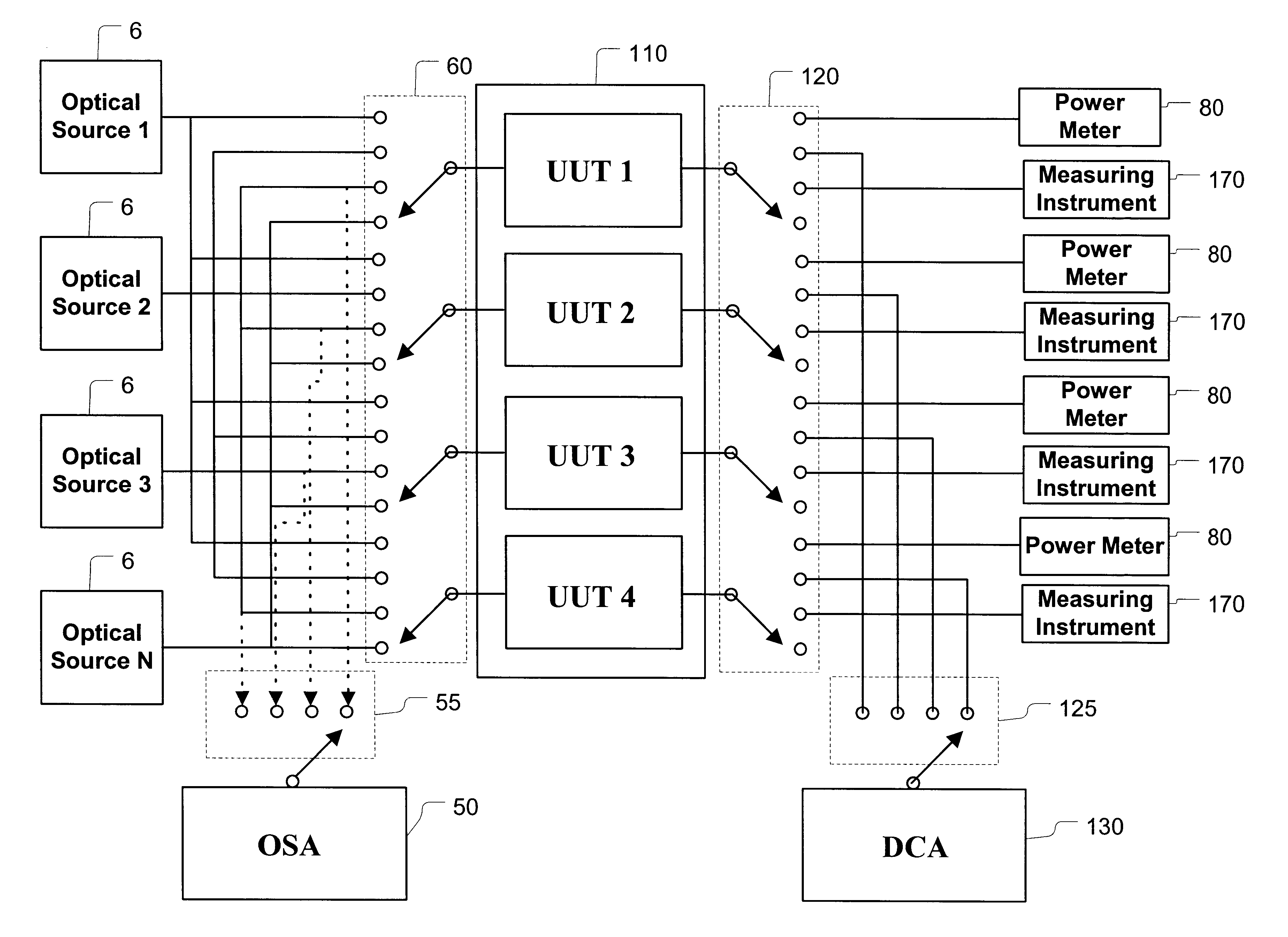
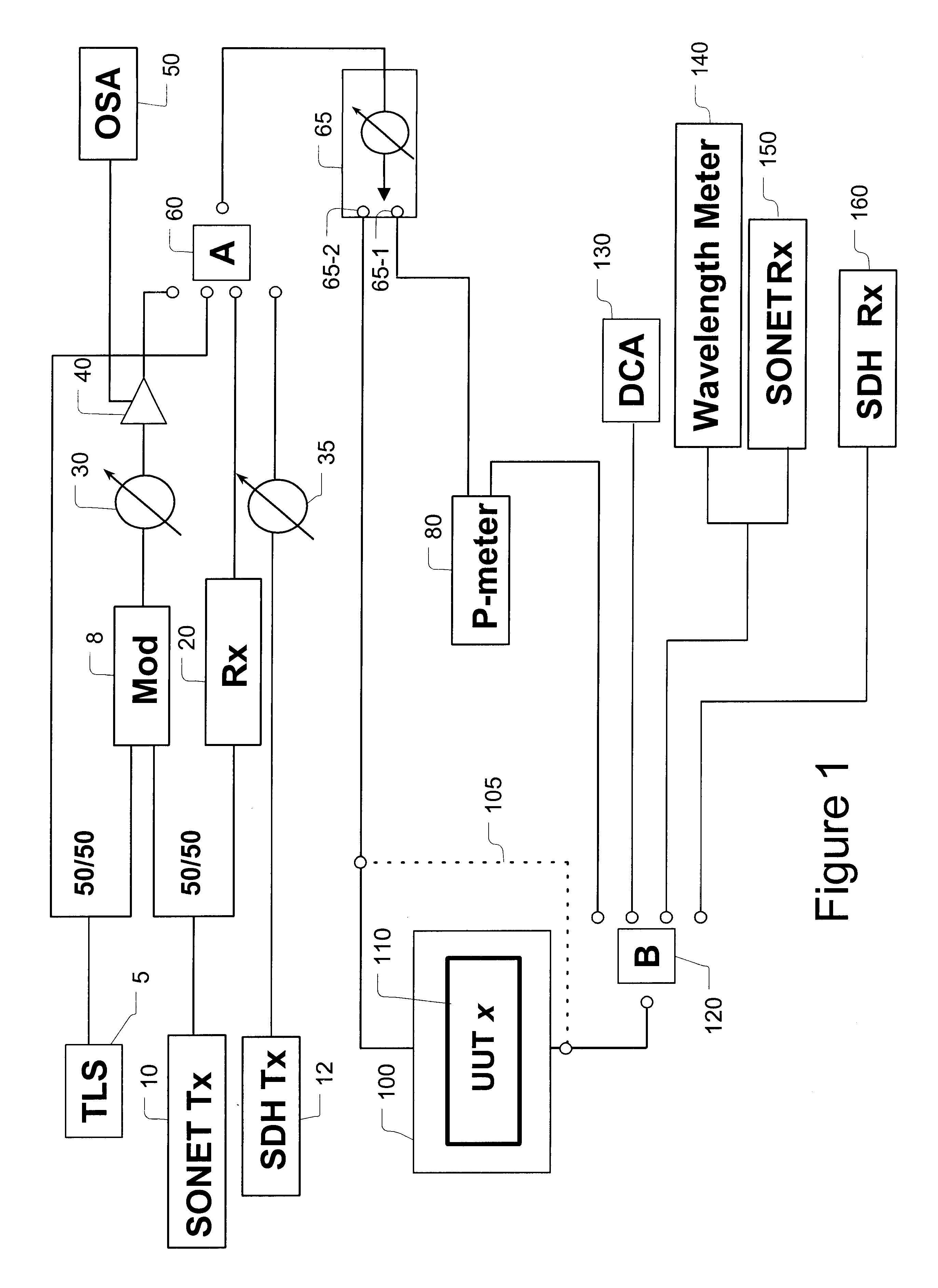
A system for calibrating a plurality of optical modules includes a plurality of optical signal sources and optical signal degradation elements optically communicating with input switches. The input switches supply optical test signals to optical modules (units under test) plugged into a common shelf. Calibration switches including variable optical attenuators may be used to adjust the input signal levels and alternately supply adjusted signals to an optical power meter and the units under test. A controller is used to control the adjustment and thereby provide defined, measured signal levels to the units under test. By reading data from the units under test and using these defined signal levels, the optical modules may be calibrated or diagnosed. Output optical switches are used in a similar fashion to calibrate or diagnose the outputs of the units under test. In addition to input / output power calibration, the invention may also perform wavelength calibrations.
Owner:CIENA
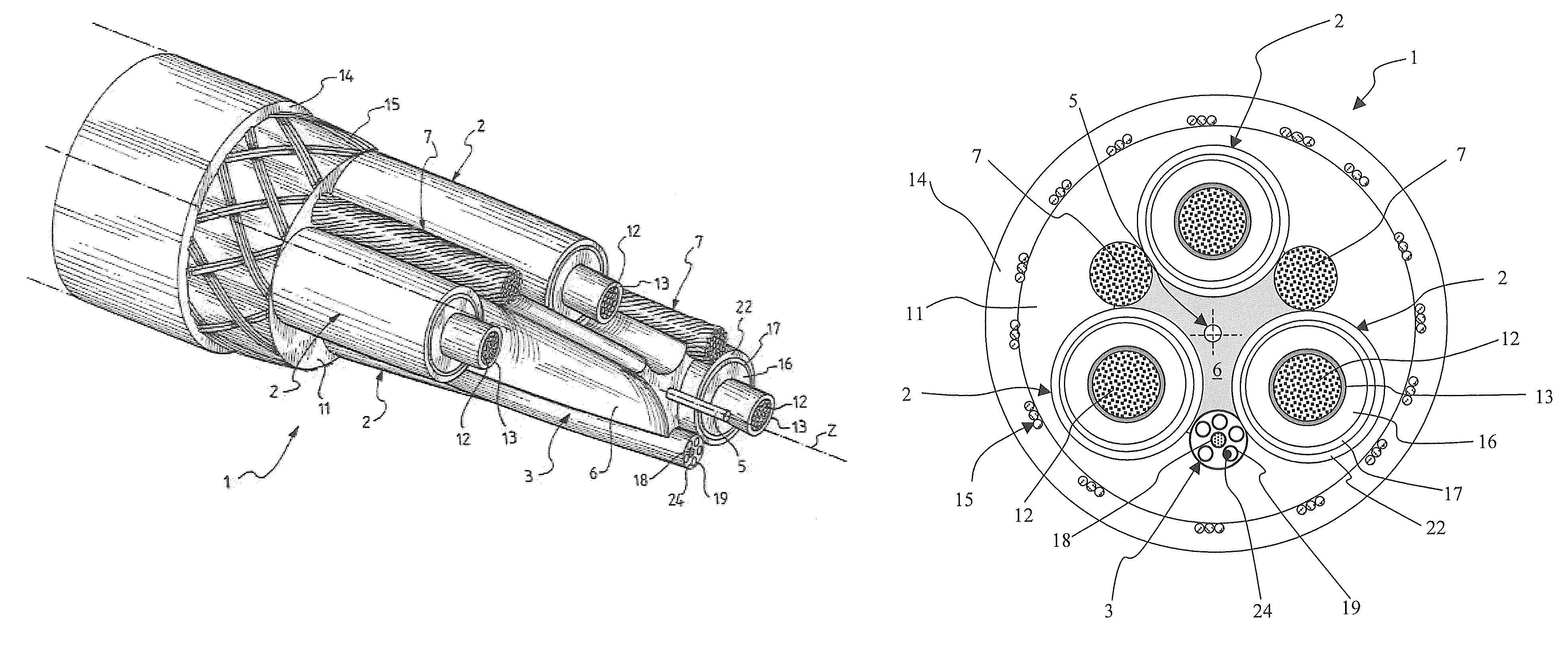
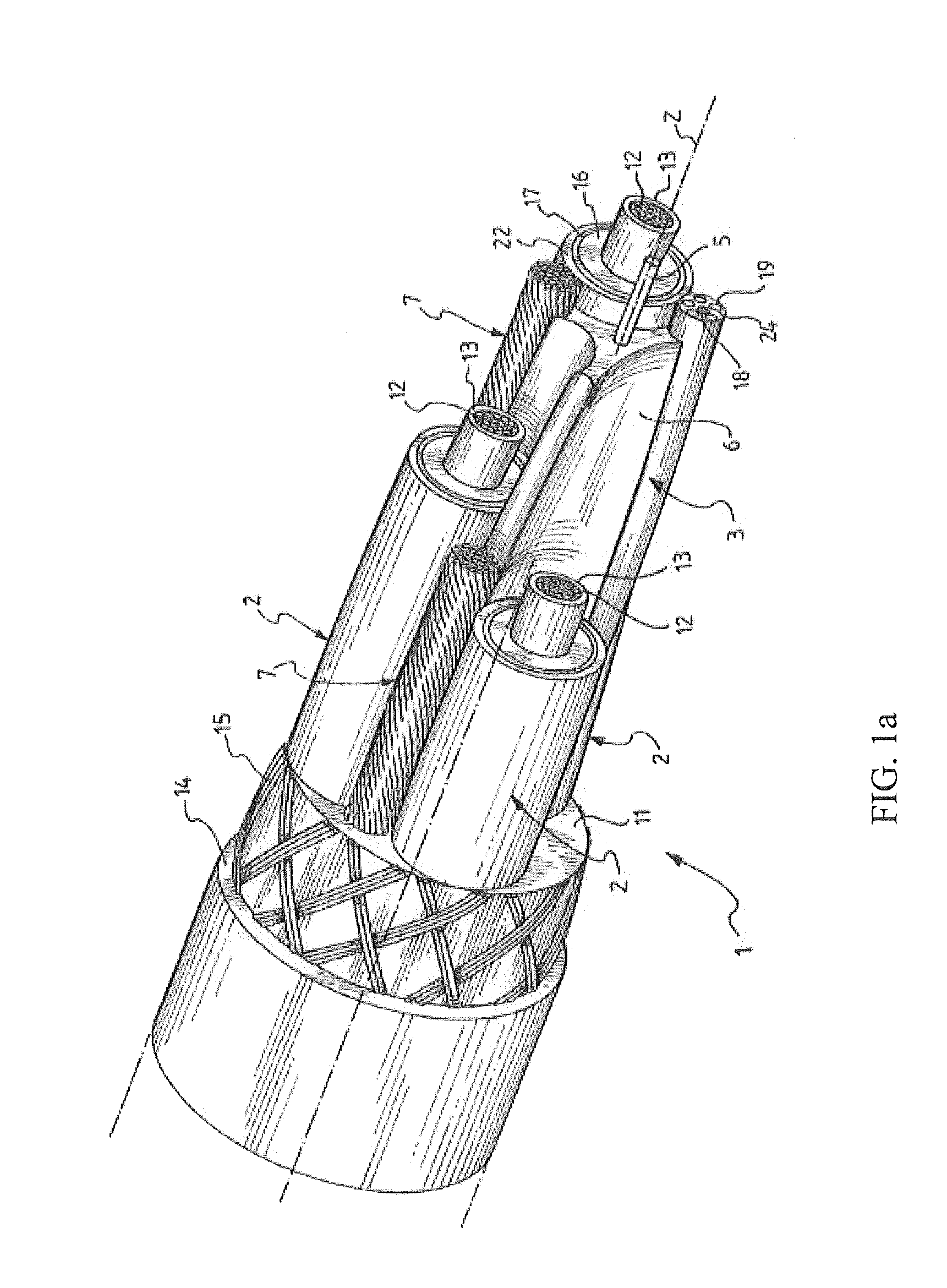
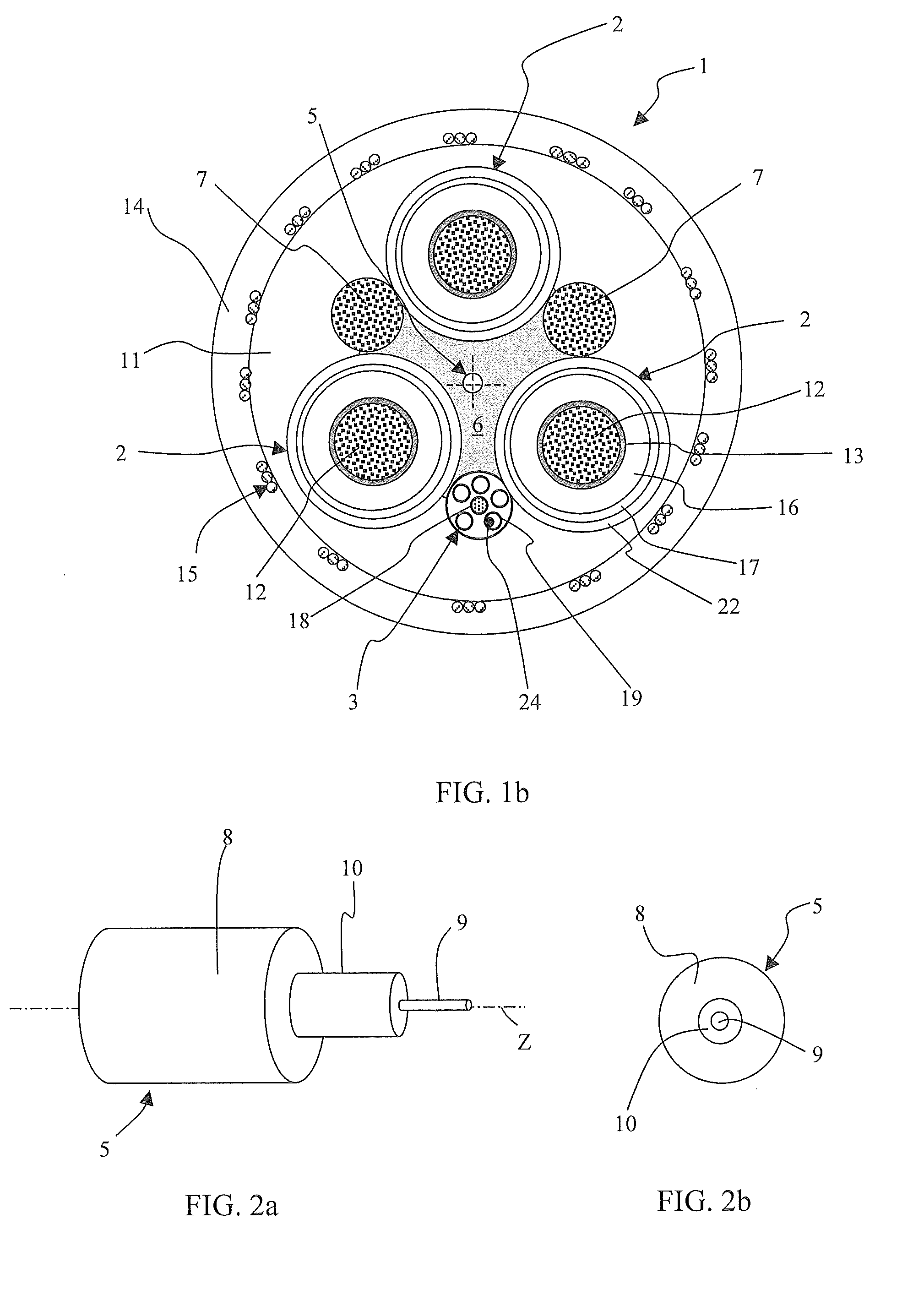
Electric cable with strain sensor and monitoring system and method for detecting strain in at least one electric cable
ActiveUS20120082422A1Effective periodic maintenanceHigh mechanical stressControlForce measurement by measuring optical property variationElectrical conductorMonitoring system
An electric cable includes a strain sensor longitudinally extending along the cable and including a strain optical fibre arranged within a bending neutral region surrounding and including a bending neutral longitudinal axis of the electric cable, and at least two longitudinal structural elements, at least one of the at least two longitudinal structural elements being a core including an electrical conductor, wherein the strain sensor is embedded in a strain-transferring filler mechanically coupling at least one of the at least two longitudinal structural elements with the strain sensor. With the disclosed cable construction, the strain experienced by the at least one of the at least two longitudinal structural elements is transferred to the strain sensor at least in a strained condition. In the preferred embodiments, the electric cable is a heavy-duty cable.
Owner:PRYSMIAN SPA
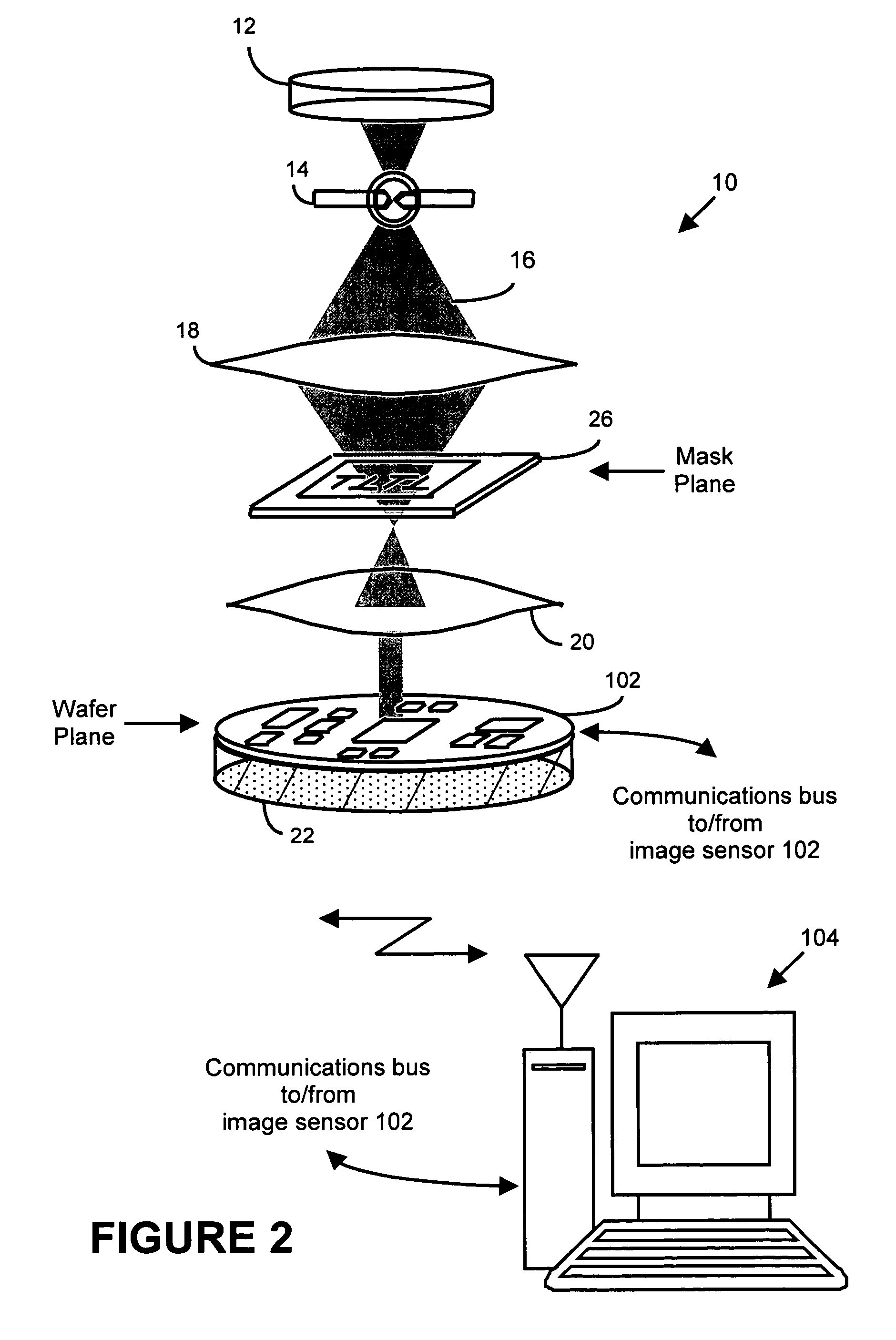
System and method for lithography process monitoring and control
InactiveUS6969837B2Highly precise moveable platformPhotometrySolid-state devicesLithography processEngineering
A system and sensor for measuring, inspecting, characterizing, evaluating and / or controlling optical lithographic equipment and / or materials used therewith, for example, photomasks. In one embodiment, the system and sensor measures, collects and / or detects an aerial image (or portion thereof) produced or generated by the interaction between the photomask and lithographic equipment. An image sensor unit may measure, collect, sense and / or detect the aerial image in situ—that is, the aerial image at the wafer plane produced, in part, by a production-type photomask (i.e., a wafer having integrated circuits formed therein / thereon) and / or by associated lithographic equipment used, or to be used, to manufacture of integrated circuits. A processing unit, coupled to the image sensor unit, may generate image data which is representative of the aerial image by interleaving the intensity of light sampled by each sensor cell at the plurality of location of the platform.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
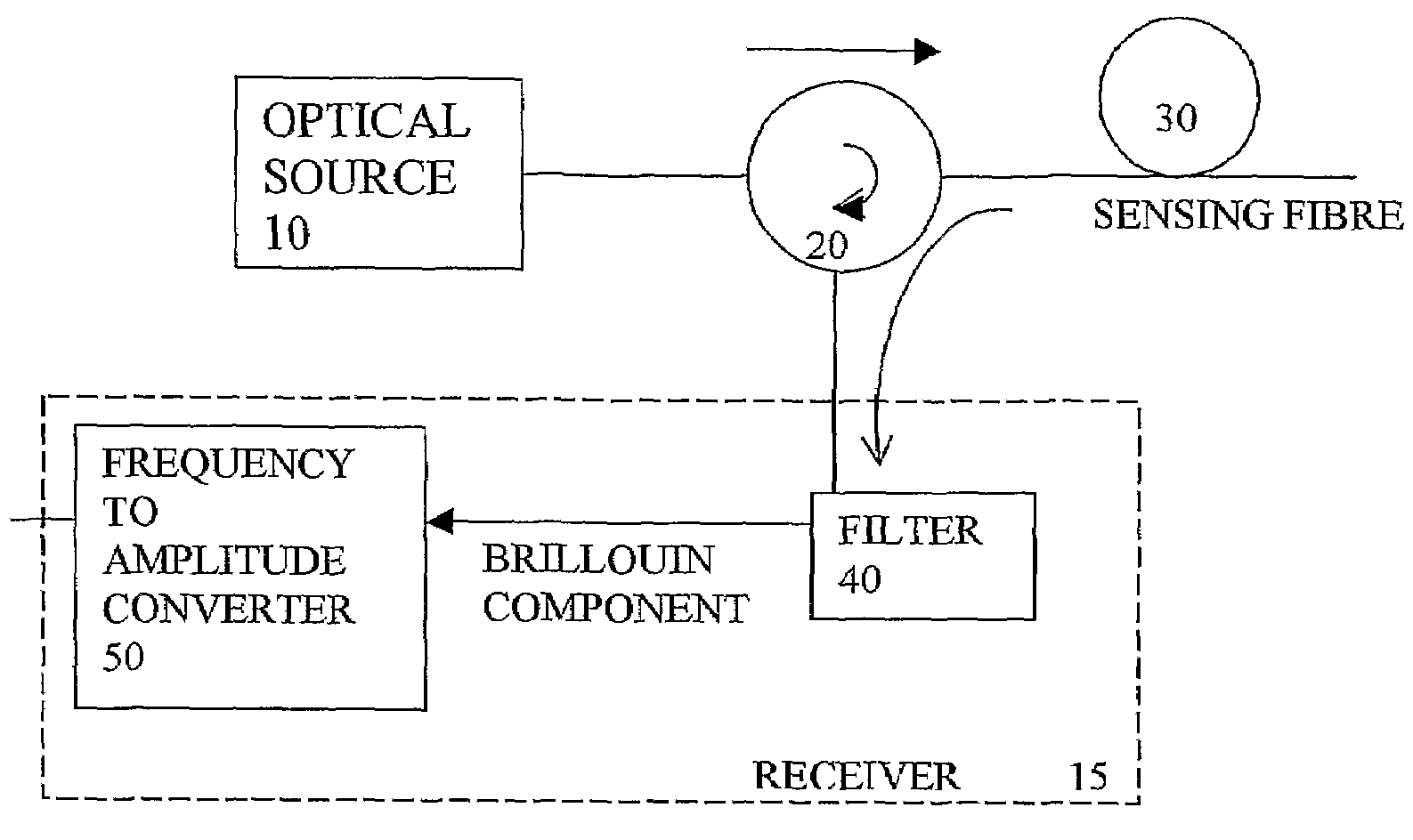
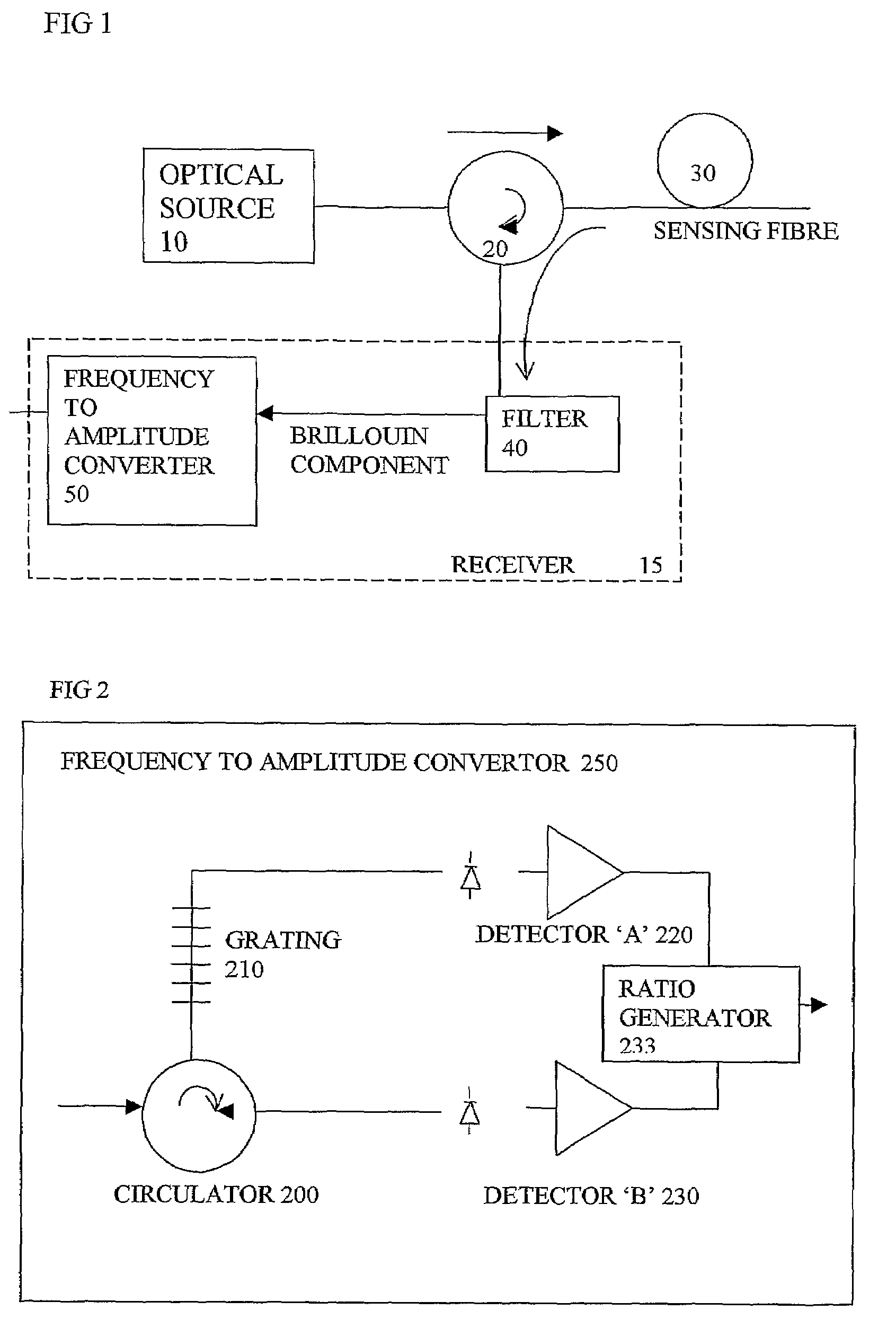
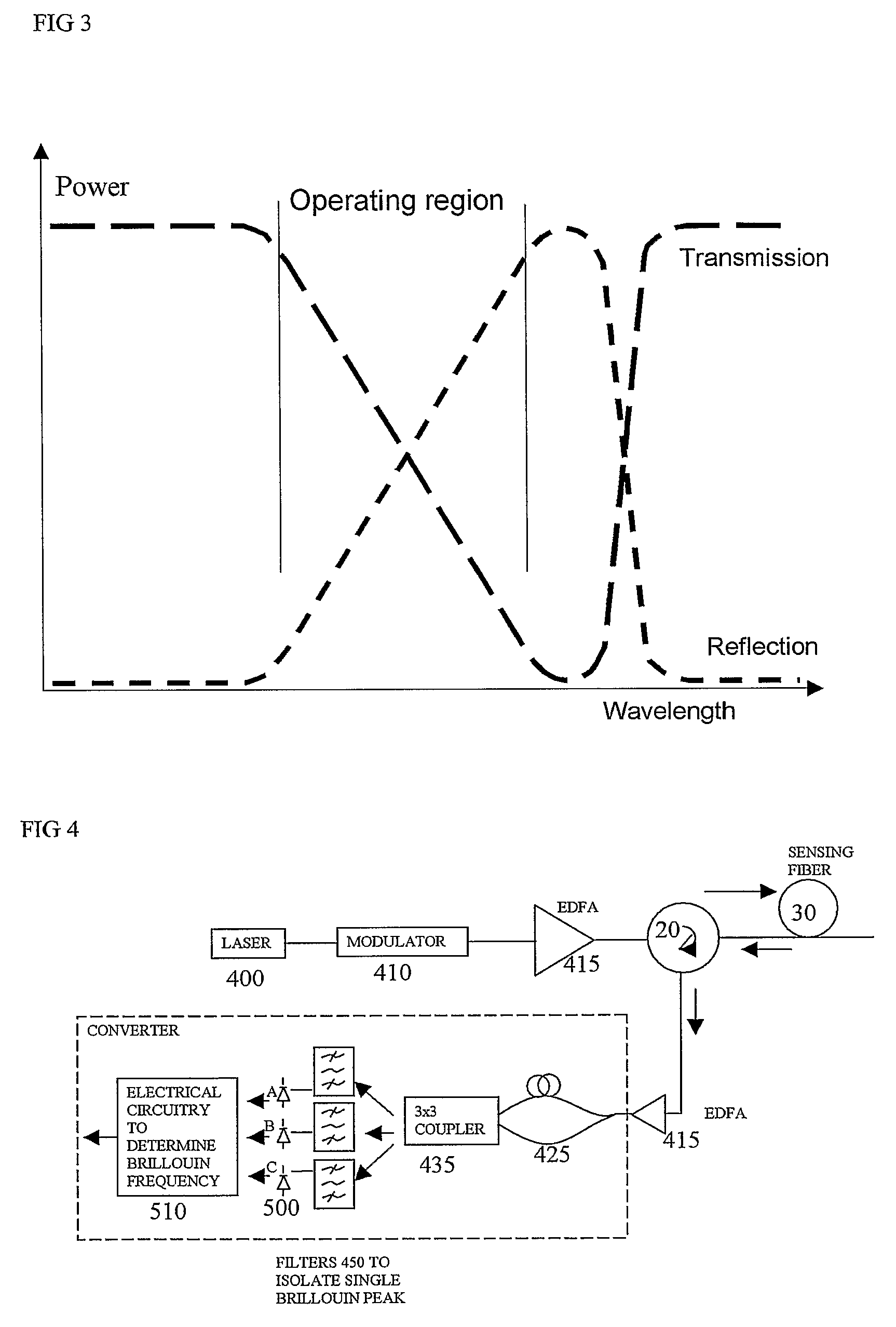
Direct measurement of Brillouin frequency in distributed optical sensing systems
InactiveUS7355163B2Avoid frequencyIncrease flexibilitySurveyRadiation pyrometryElectron interferometerGrating
An optical sensing system uses light scattered from a sensing fibre to sense conditions along the fibre, and has a receiver with a frequency to amplitude converter to obtain a frequency of a Brillouin component of the received scattered light, to deduce the conditions. This converter can avoid time consuming scanning of frequencies to obtain the Brillouin frequency spectrum, and avoids the heavy processing load of deducing a peak or average frequency from the spectrum. The converter can be implemented in the optical domain using a grating or interferometer, or in the electrical domain using a diplexer or electrical interferometer. It can generate complementary signals, having opposite signs, a ratio of these signals representing the frequency. This can avoid sensitivity to amplitude changes in the received scattered signals and provide common mode rejection of noise.
Owner:SENSORNET
Optical frequency sweep control and readout by using a phase lock
InactiveUS6870629B1Reduce frequencyFrequency errorOptical measurementsLaser detailsOptical frequenciesControl signal
The invention allows for the accurate, real-time readout of the optical frequency of a swept-wavelength laser device by counting the number of fringes of a calibrated etalon that occur as the laser is swept. The distinguishing feature of the present invention is that the etalon fringe signal is phase-locked to a slave signal of a higher multiple frequency. The higher frequency of the slave signal divides the frequency interval of the etalon fringe spacing by the additional frequency multiple. The slave signal therefore generates a scale for optical frequency that is of higher resolution than possible with the etalon alone. The phase-lock also insures that the slave signal tracks monotonic scans of the optical frequency regardless of scan profile.The invention also allows for the precise, real-time control of the optical frequency of a laser during the sweep of the laser. By comparing a signal proportional to the transmission of light through a calibrated Fabry-Perot etalon to a reference control signal, the phase difference between etalon transmission signal and the reference signal may be fed back to the laser to drive the phase difference to zero (phase-lock). The phase-lock ensures that the optical frequency profile of the sweep follows exactly the frequency profile of the reference signal. Tailoring the input reference signal controls the velocity of the optical-frequency sweep.
Owner:PRECISION PHOTONICS CORP
Sensors and systems for structural health monitoring
InactiveUS20050061076A1Improve reliabilityImprove maintainabilityVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectric forceElectricity
Sensors and systems for monitoring structural health conditions. The present invention provides a device for monitoring structural health conditions including a dielectric substrate, a piezoelectric device for actuating and / or sensing Lamb waves, a molding layer deposited over the piezoelectric device, a cover layer deposited over the molding layer and a hoop layer surrounding the piezoelectric device and being attached to the substrate. The device further includes an optical fiber coil sensor attached to the dielectric substrate, where the coil sensor has a rolled optical fiber cable and a coating layer applied to the rolled optical fiber cable. The present invention also provides a diagnostic patch network that includes a plurality of patch sensors attached to a host structure and a bridge box connected to the patch sensors. The bridge box sends information of structural health conditions to and receive power from a ground control system using a wireless communication technique.
Owner:ADVANCED STRUCTURE MONITORING
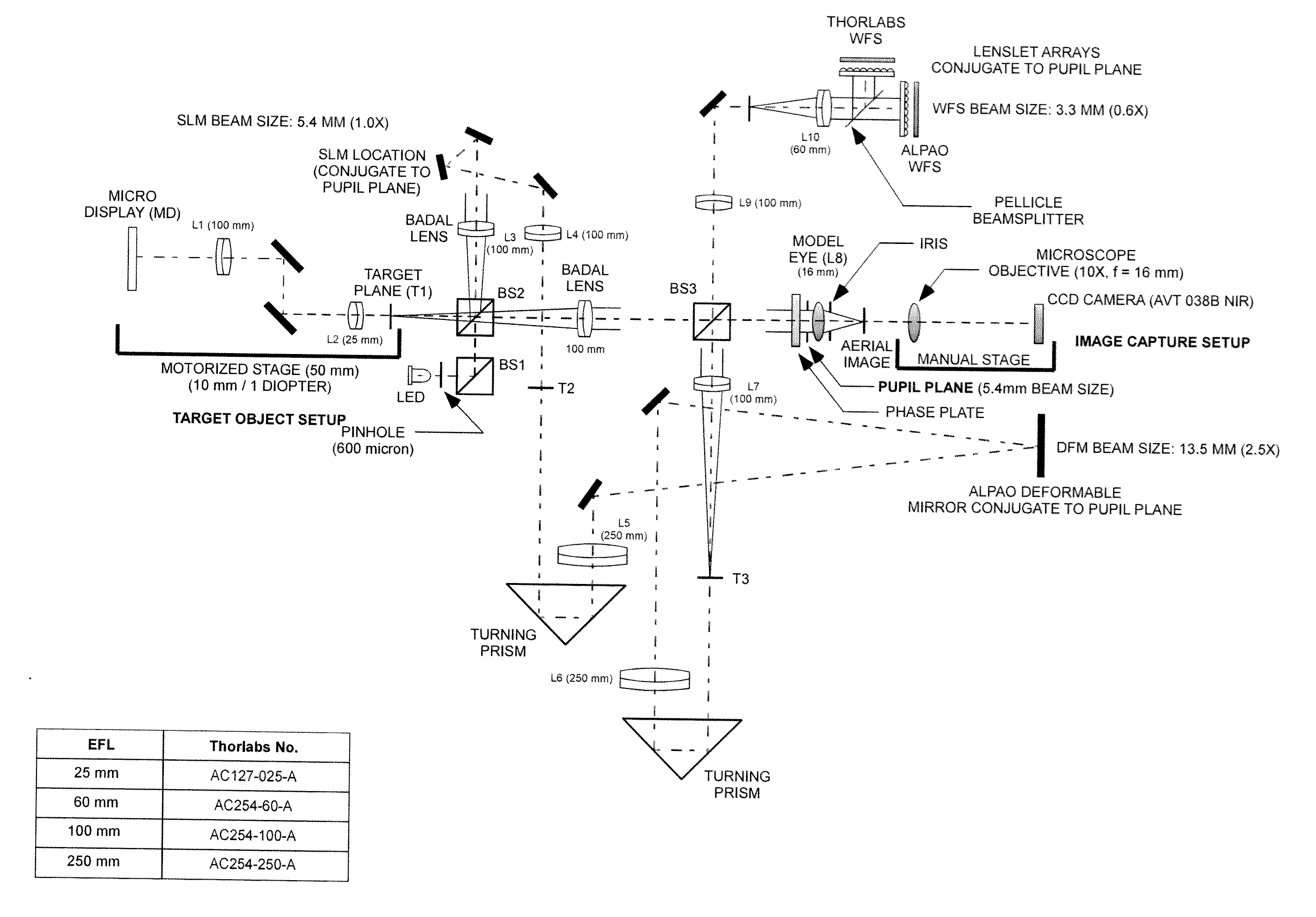
Use of an optical system simulating behavior of human eye to generate retinal images and an image quality metric to evaluate same
A method of predicting clinical performance of an ophthalmic optical correction using simulation by imaging a series of objects of different sizes by each of a plurality of eye optical systems, each of the eye optical systems including the ophthalmic optical correction, the method providing an output value representing the resolution and contrast performance of the optical design at that vergence for the eye optical systems.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
System and method for lithography process monitoring and control
InactiveUS6969864B2Highly precise moveable platformPhotometrySolid-state devicesLithography processEngineering
A system and sensor for measuring, inspecting, characterizing, evaluating and / or controlling optical lithographic equipment and / or materials used therewith, for example, photomasks. In one embodiment, the system and sensor measures, collects and / or detects an aerial image (or portion thereof) produced or generated by the interaction between the photomask and lithographic equipment. An image sensor unit may measure, collect, sense and / or detect the aerial image in situ—that is, the aerial image at the wafer plane produced, in part, by a production-type photomask (i.e., a wafer having integrated circuits formed therein / thereon) and / or by associated lithographic equipment used, or to be used, to manufacture of integrated circuits. A processing unit, coupled to the image sensor unit, may generate image data which is representative of the aerial image by, in one embodiment, interleaving the intensity of light sampled by each sensor cell at the plurality of location of the platform. Notably, many inventions / embodiments are disclosed herein.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com