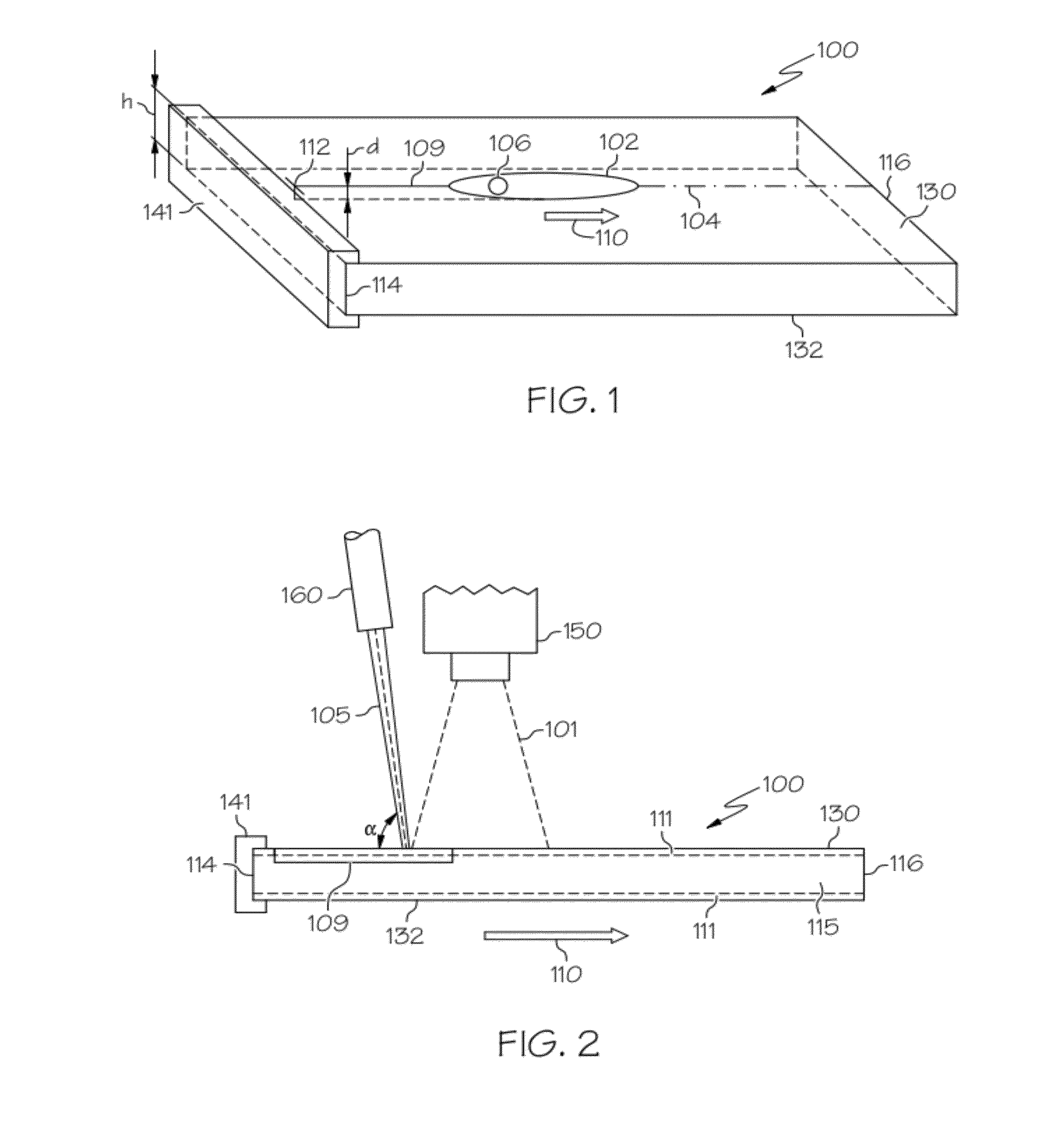
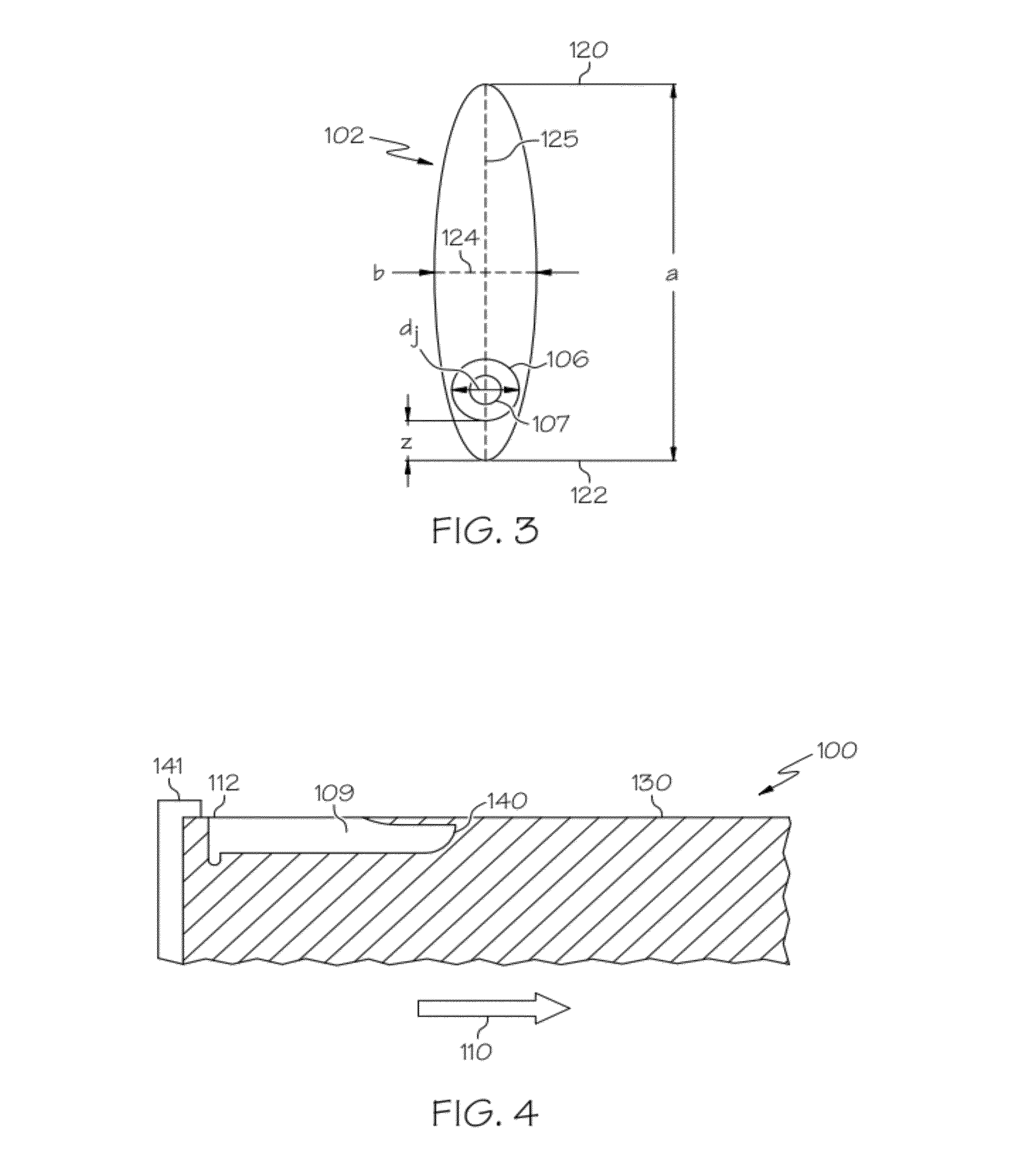
Patents
Literature
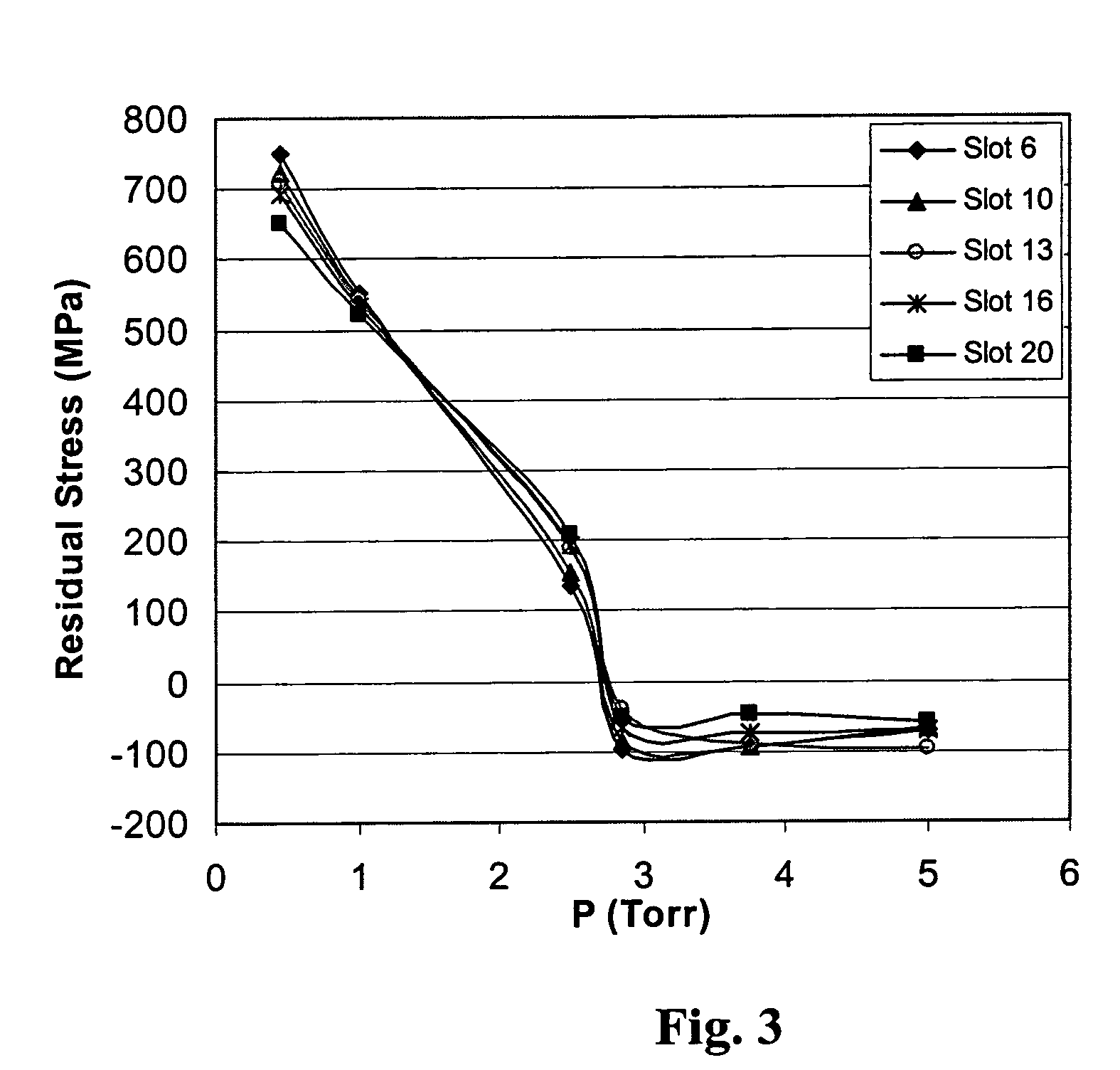
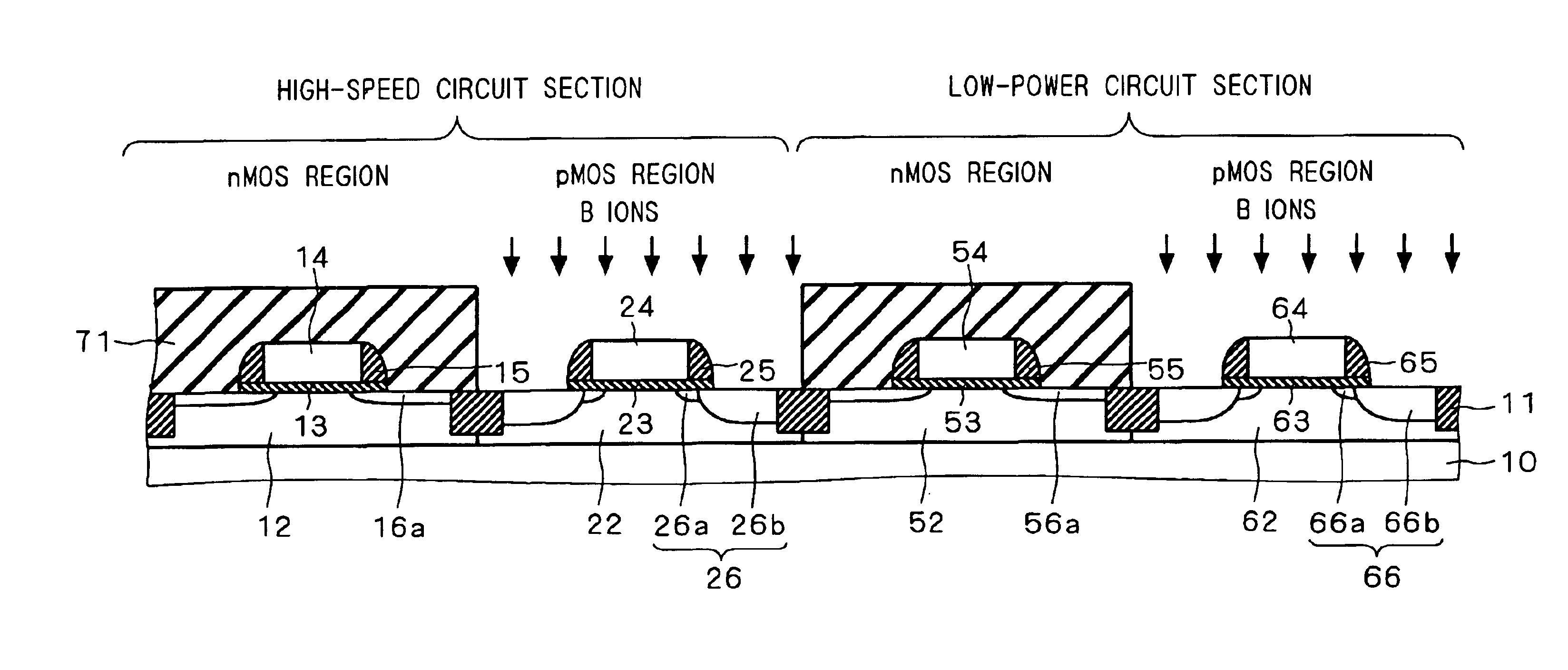
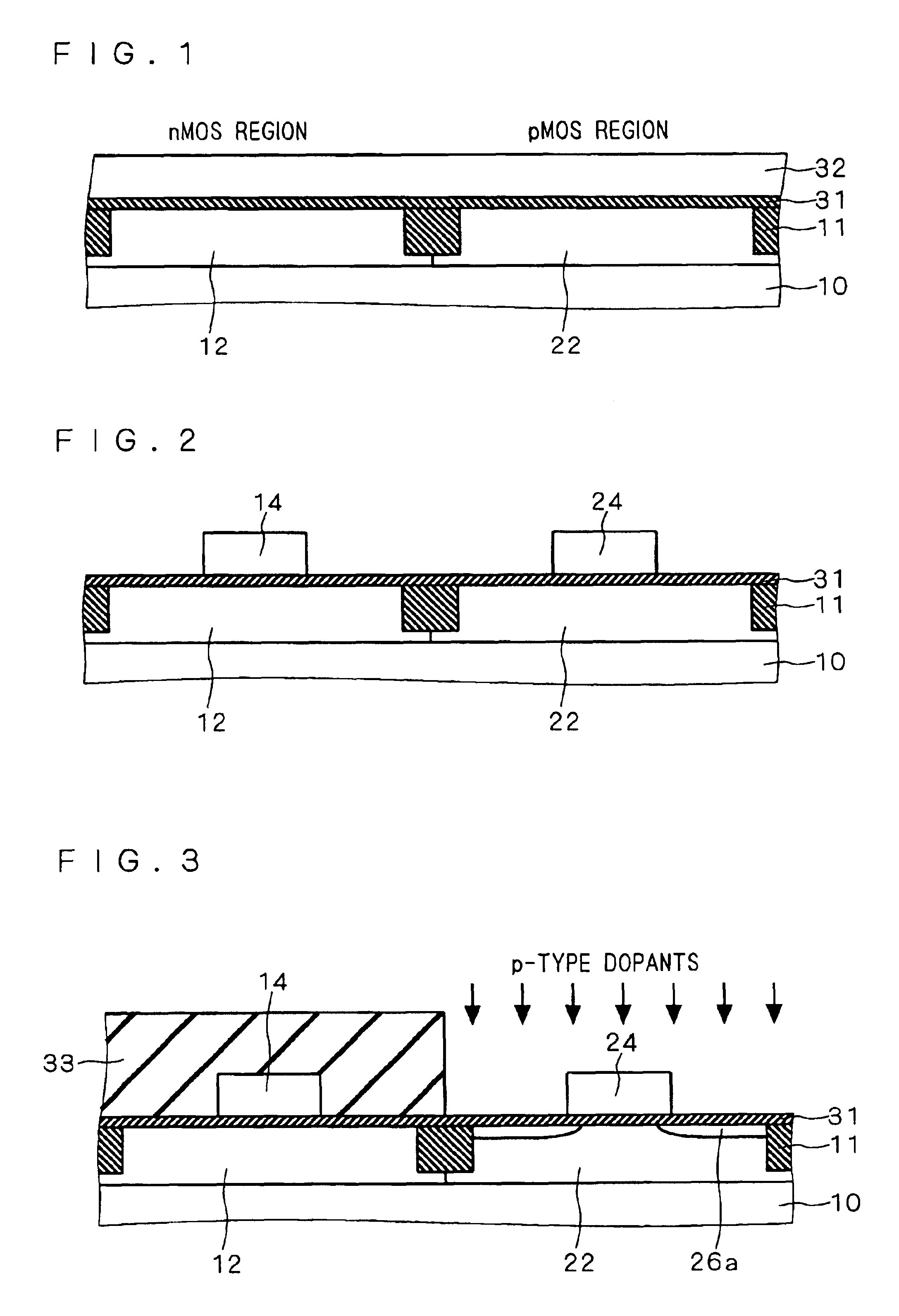
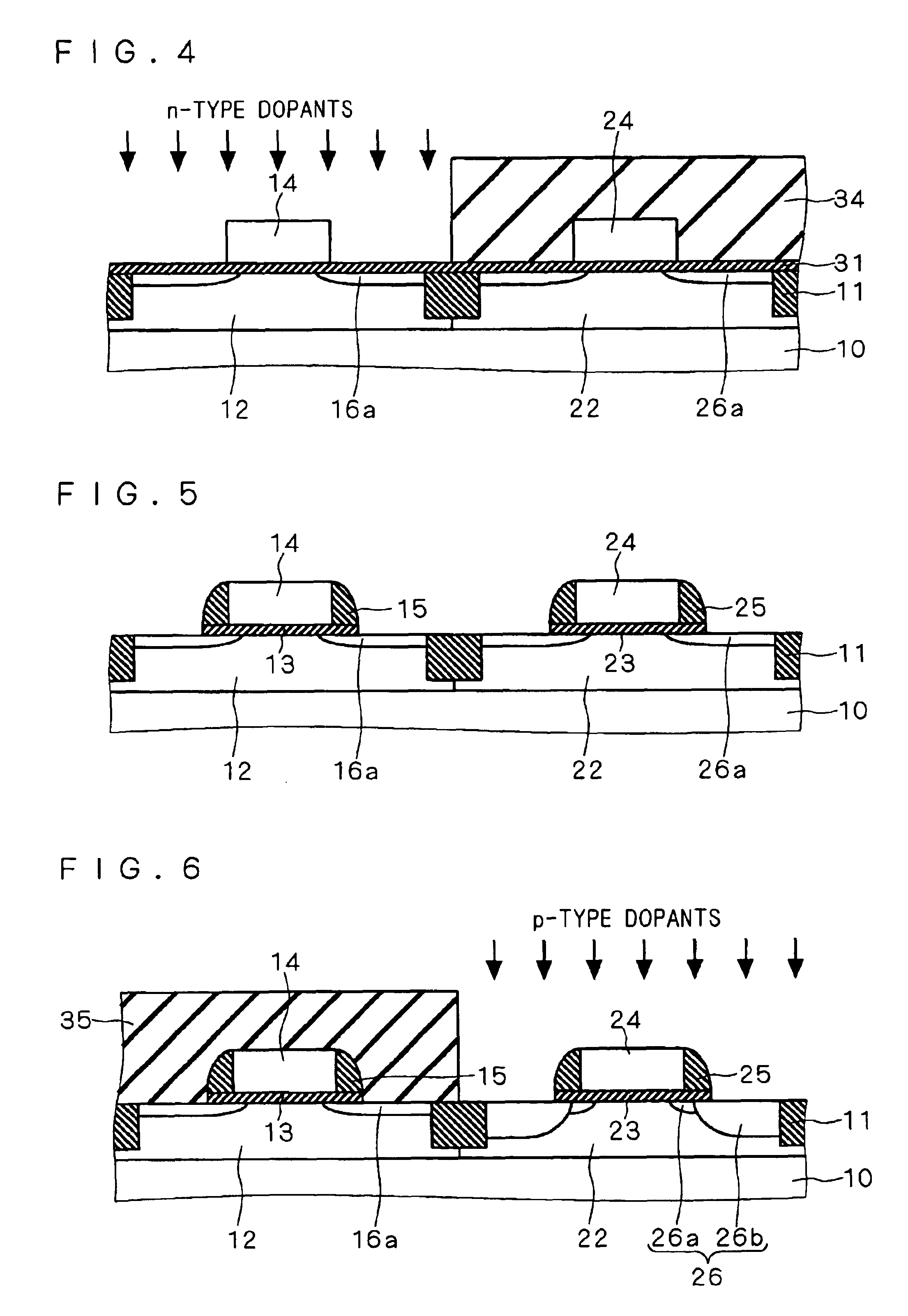
4217 results about "Residual stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Residual stresses are stresses that remain in a solid material after the original cause of the stresses has been removed. Residual stress may be desirable or undesirable. For example, laser peening imparts deep beneficial compressive residual stresses into metal components such as turbine engine fan blades, and it is used in toughened glass to allow for large, thin, crack- and scratch-resistant glass displays on smartphones. However, unintended residual stress in a designed structure may cause it to fail prematurely.
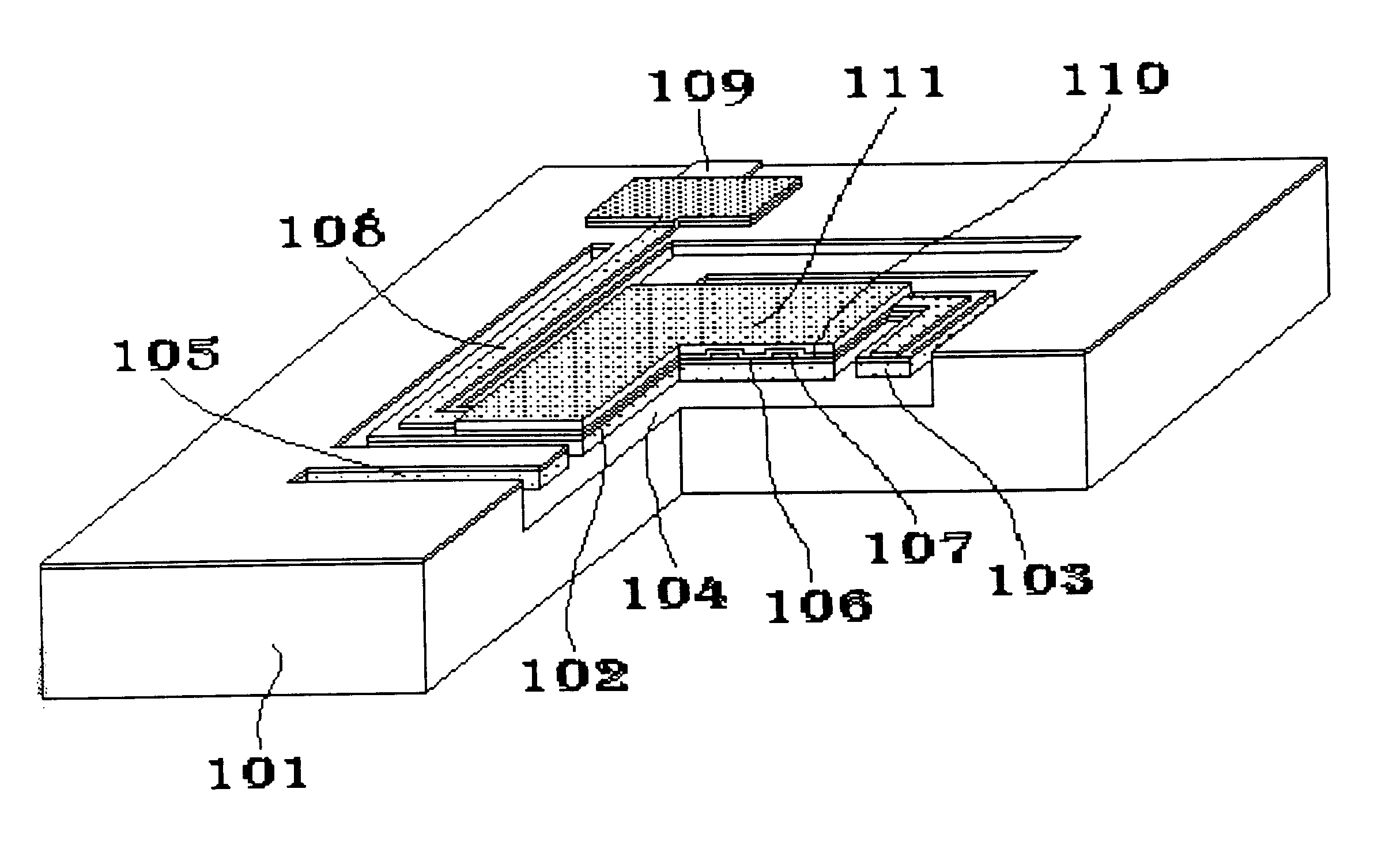
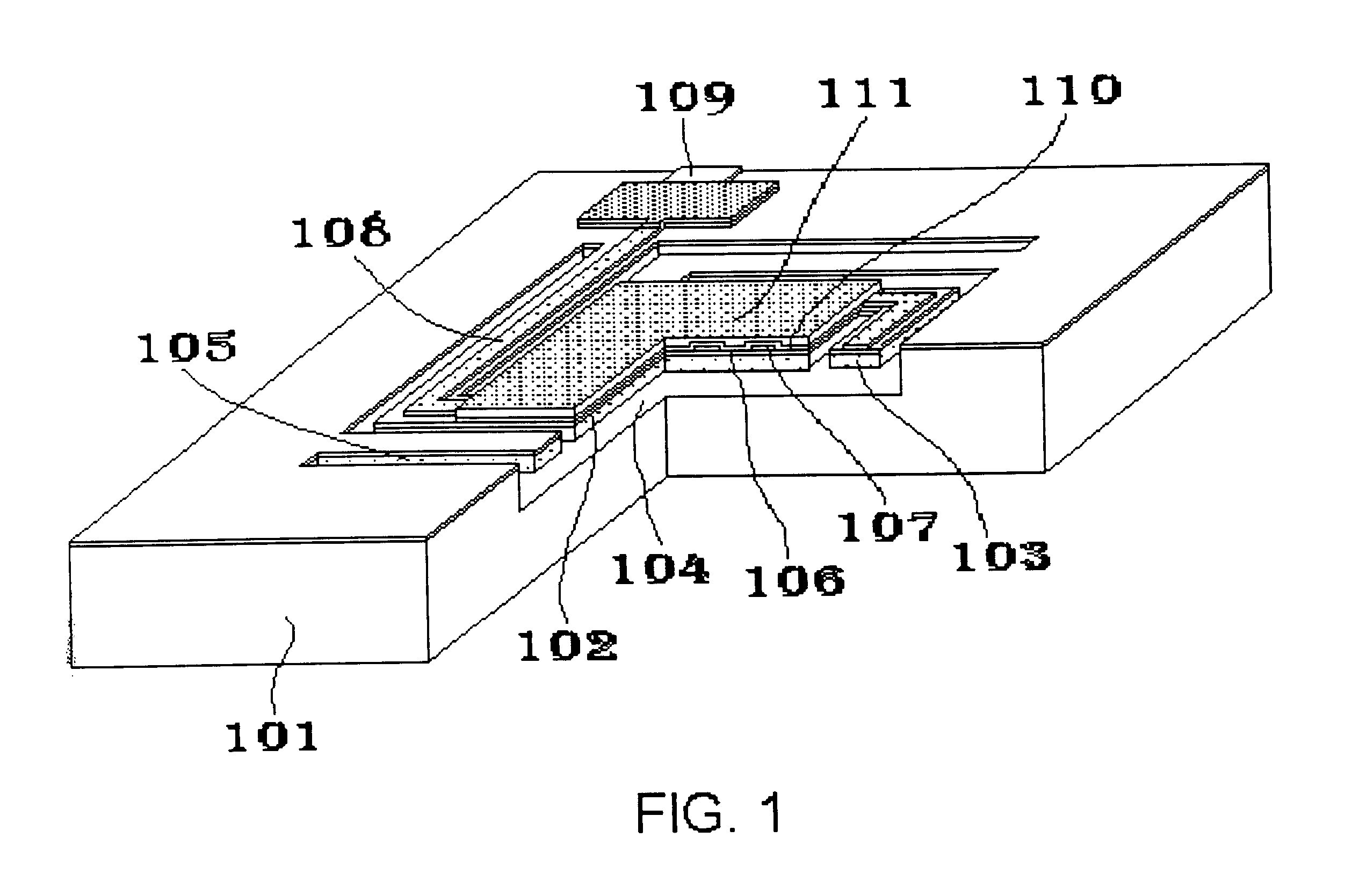
MEMS device and manufacturing process thereof
InactiveUS20070190680A1Relaxation stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingForming microstructural systemsEngineeringWafer bonding
MEMS devices require special cavity formation and sealing steps such as wafer bonding which reduce the yield and increase the cost. In addition, it is difficult to form a cavity of a large area by the LSI process owing to a residual stress of a sealing film which will be a lid. This leads to a difficulty of realizing an integrated MEMS having a MEMS and a high-performance LSI mounted on one substrate. The lid (or diaphragm) covering therewith a cavity is equipped with slits or beams. During the formation of the cavity, the slits are deformed to absorb and relax the internal stress of the thin sealing film. Then, the cavity is sealed by filling the open portions of the film overlying the cavity between the inside and outside of the cavity. The cavity is formed by removing a portion of the interlayer film of LSI multilevel interconnects and the lid is made of a LSI-process thin film.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Condenser microphone
InactiveUS20070201710A1High sensitivityReduce tensile stressMicrophonesLoudspeakersCapacitanceEngineering
A condenser microphone includes a support, a plate having a fixed electrode bridged across the supports, a diaphragm, which has a moving electrode at a center portion thereof and which vibrates due to sound waves applied thereto, and a spacer, in which a first end is fixed to the plate, and a second end is fixed to the near-end portion of the diaphragm so as to surround the center portion of the diaphragm, wherein an air gap is formed between the plate and the diaphragm. This reduces the tensile stress of the diaphragm so as to increase the amplitude of vibration of the diaphragm. Hence, it is possible to increase the sensitivity of the condenser microphone. A structure constituted of the plate, the diaphragm, and the spacer is bridged across the support by means of the bridges, which absorb the residual stress of the diaphragm due to the deformation thereof.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Composite structures, such as coated wiring assemblies, having integral fiber optic-based condition detectors and systems which employ the same
InactiveUS7154081B1Weakening rangeReducing compressive strainControlRadiation pyrometryElectrical conductorGrating
Integral fiber optic-based condition sensors detect conditions of a composite structure, e.g., a coated wire assembly so as to detect damage or conditions that may damage the same. Preferably, at least one optical fiber sensor having a plurality of Bragg gratings written into the fiber at spaced-apart locations along its axial length is integrated into the electrical insulator coating of a wire, wire bundle or wiring harness. The fiber optic sensor may thus be employed to measure the environmental loads on the electrical wiring including stresses from bending, axial loading, pinch points, high temperature excursions and chemical damage. The system is capable of detecting and locating transient conditions that might cause damage to a wiring system or permanent changes in state associated with damage events. The residual stress in the electrical insulator coating of a wire, wire bundle, or wiring harness are used to monitor the evolution of damage by wear or chaffing processes. Detected stress relief on one or more Bragg gratings will thus be indicative of damage to the insulator coating on the conductor. As such, the magnitude of such stress relief may be detected and used as an alert that the wire insulation is damaged to an unsafe extent.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Wire-stranded hollow coil body, a medical equipment made therefrom and a method of making the same
InactiveUS7117703B2Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove straightnessStentsGuide wiresEngineeringMedical device
A wire-stranded hollow coil body (1) has a multitude of coil line elements (2) stranded along a predetermined circular line to form a flexible wire tube having a central axial hollow portion (3), the flexible wire tube is stranded under a strand-turn resistant load and heat treated to remove a residual stress upon formation so as to provide a high rotation-following capability and a high straightness. Further, a method provides a way to strand the coil line elements (2) under a strand-turn resistant load while heat treating the coil line elements (2).
Owner:ASAHI INTECC CO LTD
Microbolometer infrared sensors
InactiveUS6359276B1High mechanical strengthReduce residual stressSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansThermal isolationMicrobolometer
A microbolometer infrared sensor utilizes a porous silicon bridge as its thermal isolating and mechanical supporting structure. Porous silicon formed from single crystal silicon on lightly doped p-type silicon has a thermal conductivity lower than silicon dioxide and silicon nitride, and, therefore, when used as a mechanical supporting structure, can offer better thermal isolation performance. The porous silicon layer can be fabricated much thicker than silicon dioxide and silicon nitride membranes since there is almost no residual stress therein. A thicker porous silicon bridge has higher mechanical support strength. The porous silicon process is a low temperature process. It facilitates a fabrication strategy of microelectronics first and micromechanics last.
Owner:TU XIANG ZHENG
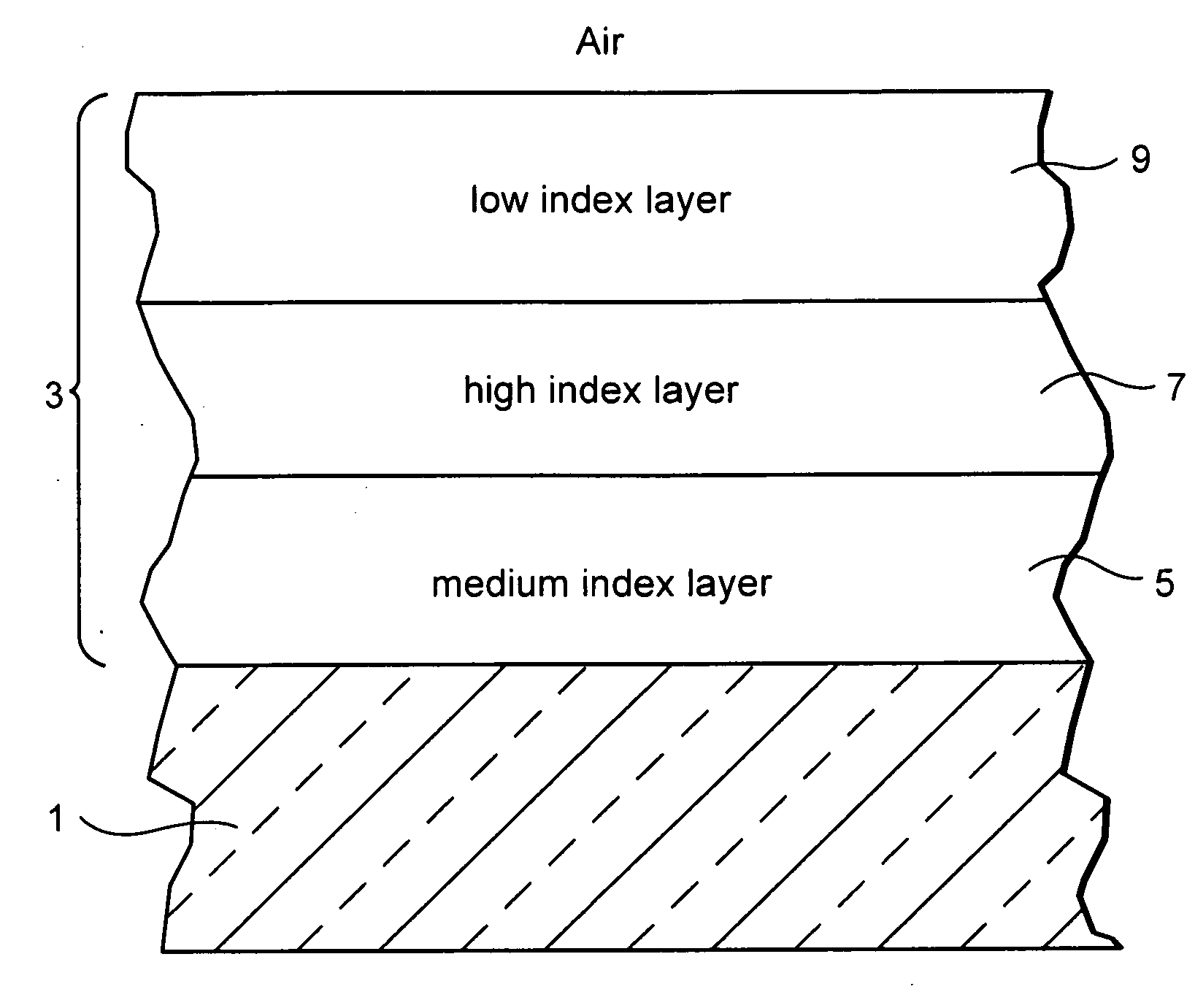
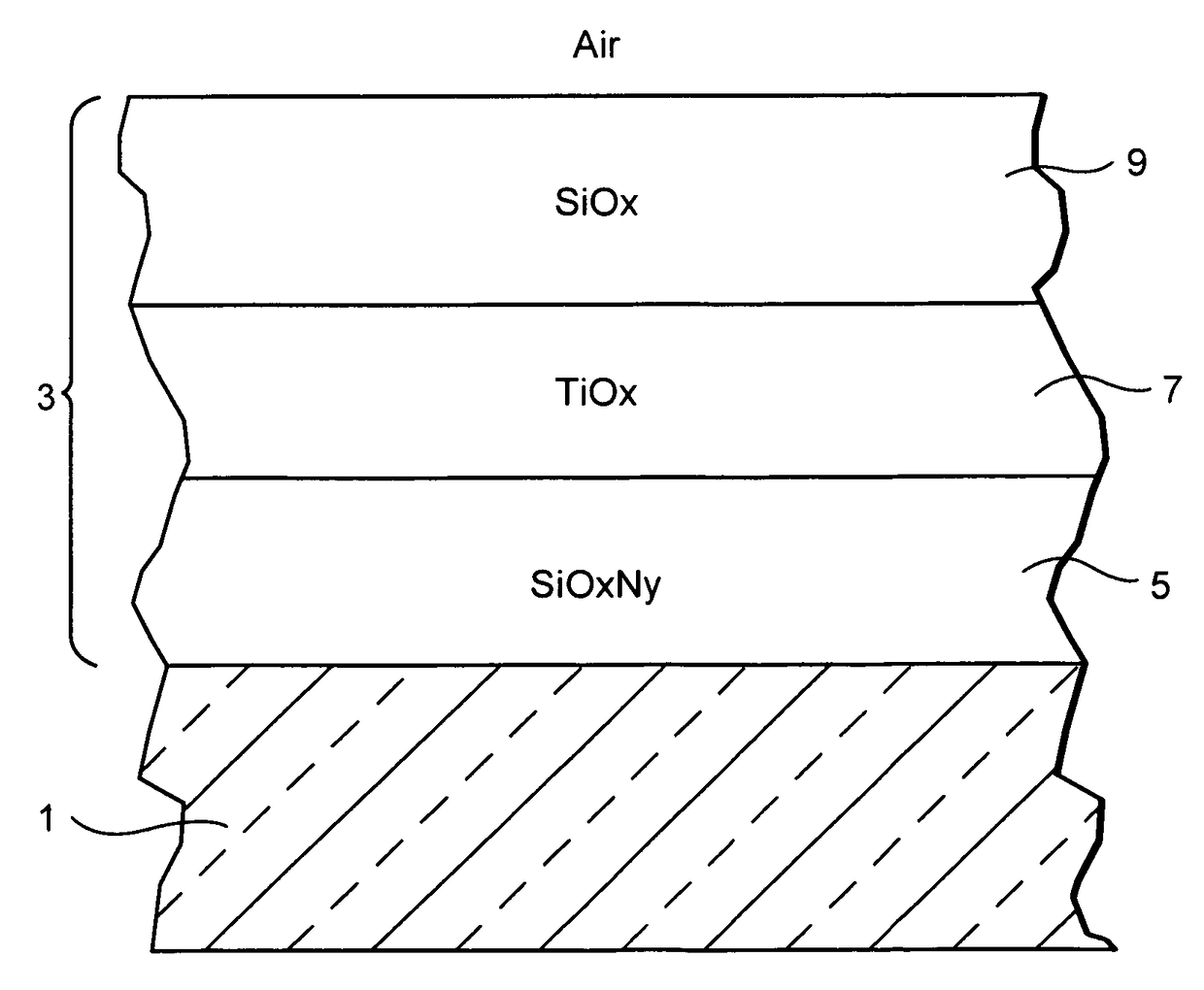
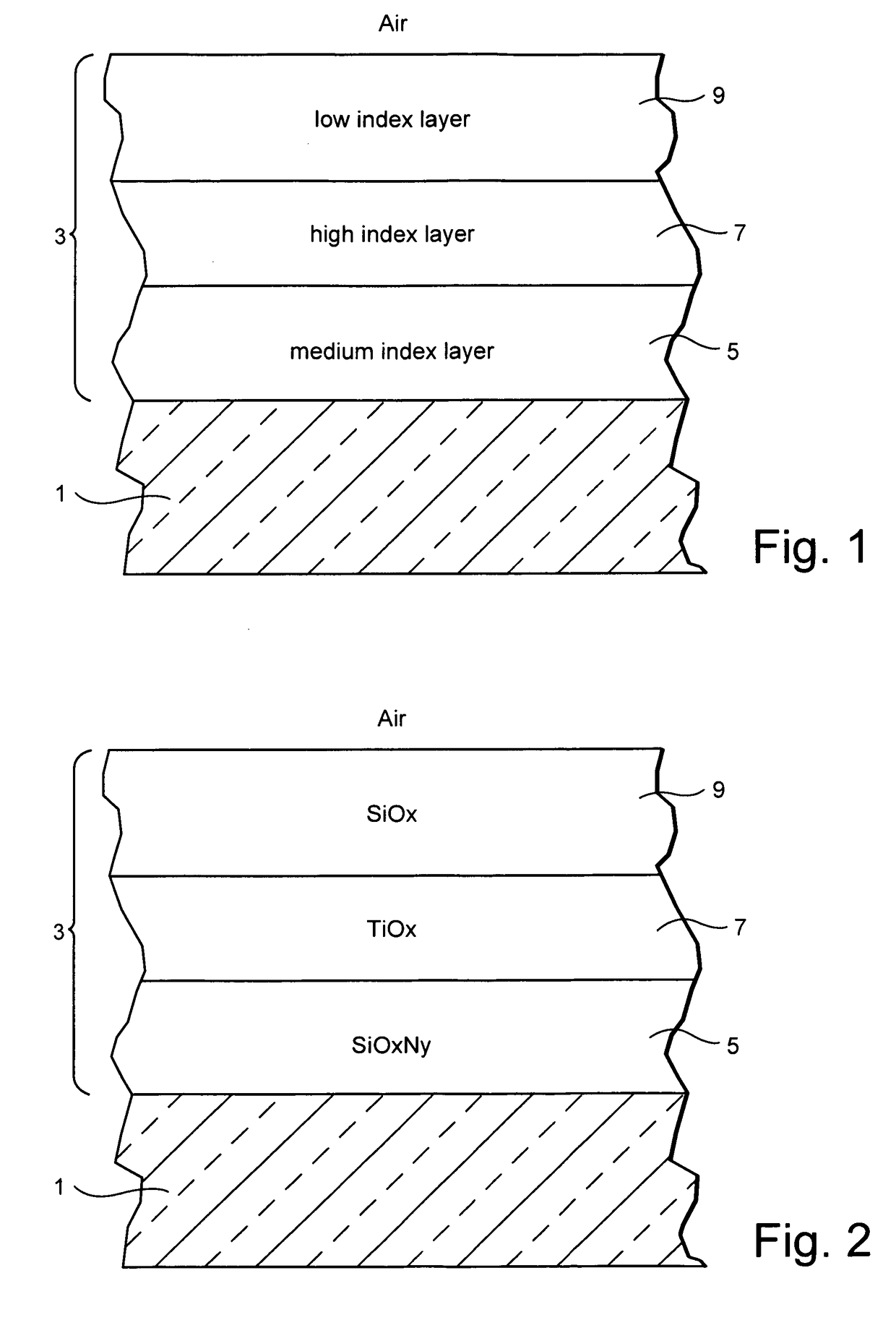
Temperable three layer antireflective coating, coated article including temperable three layer antireflective coating, and/or method of making the same
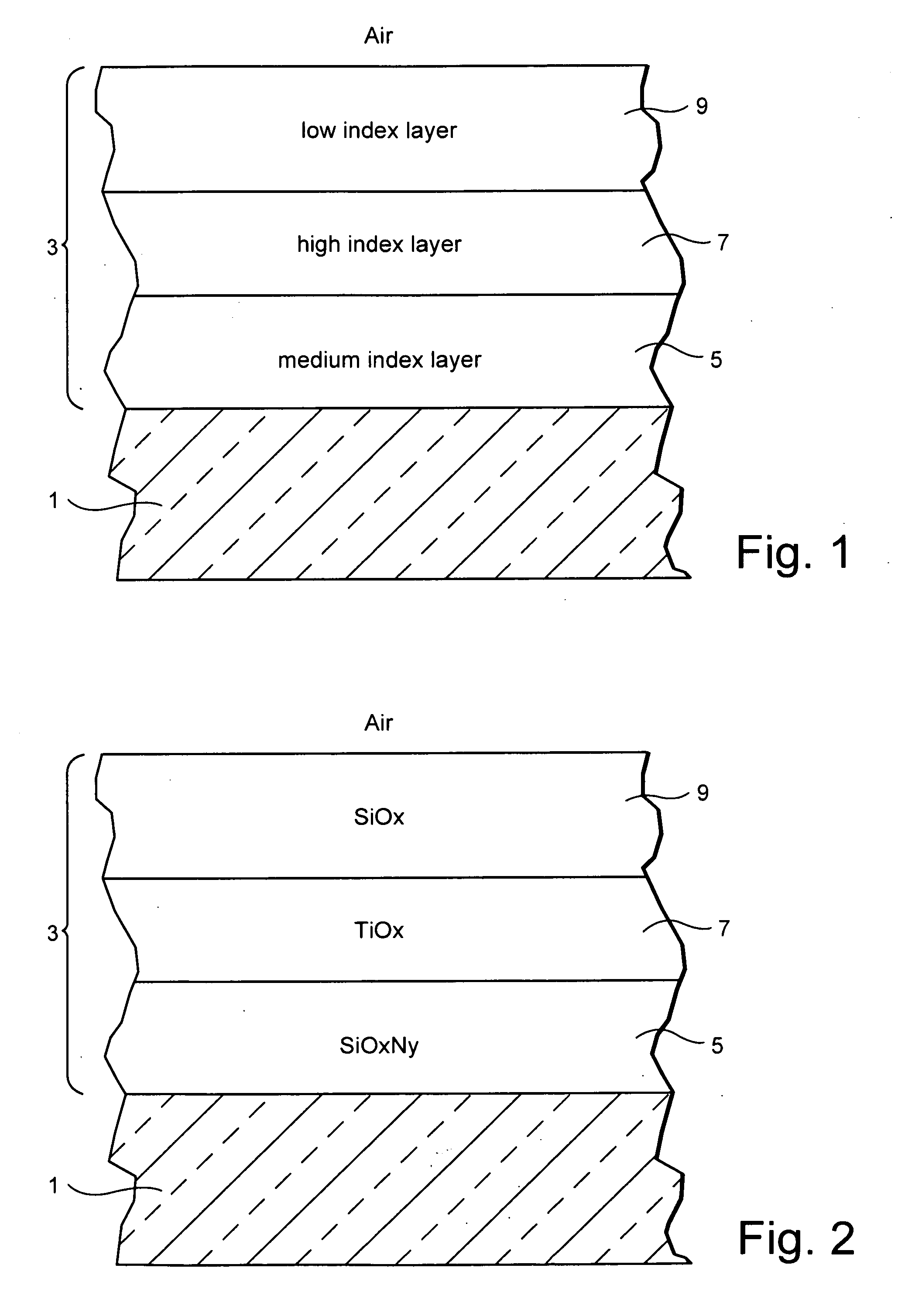
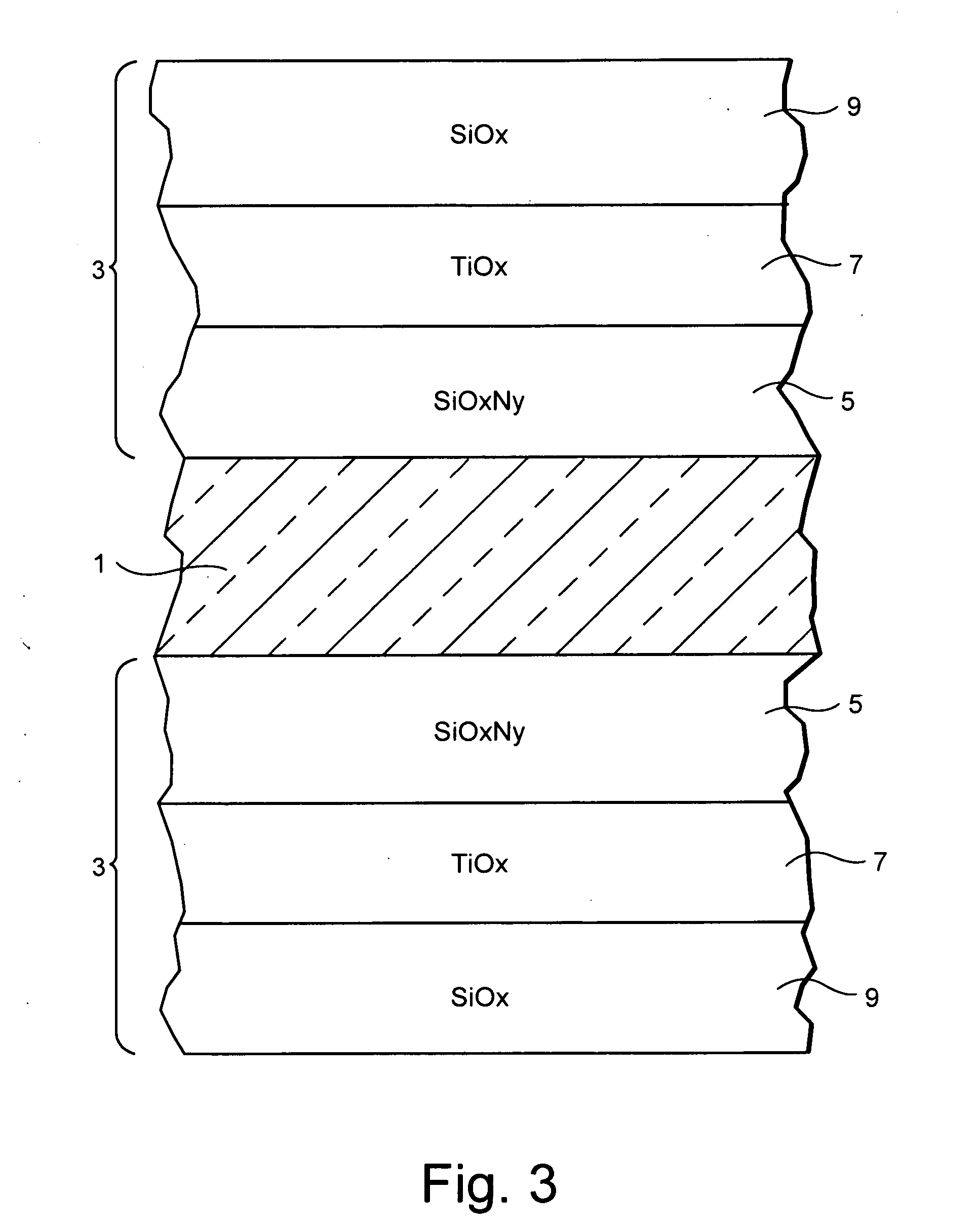
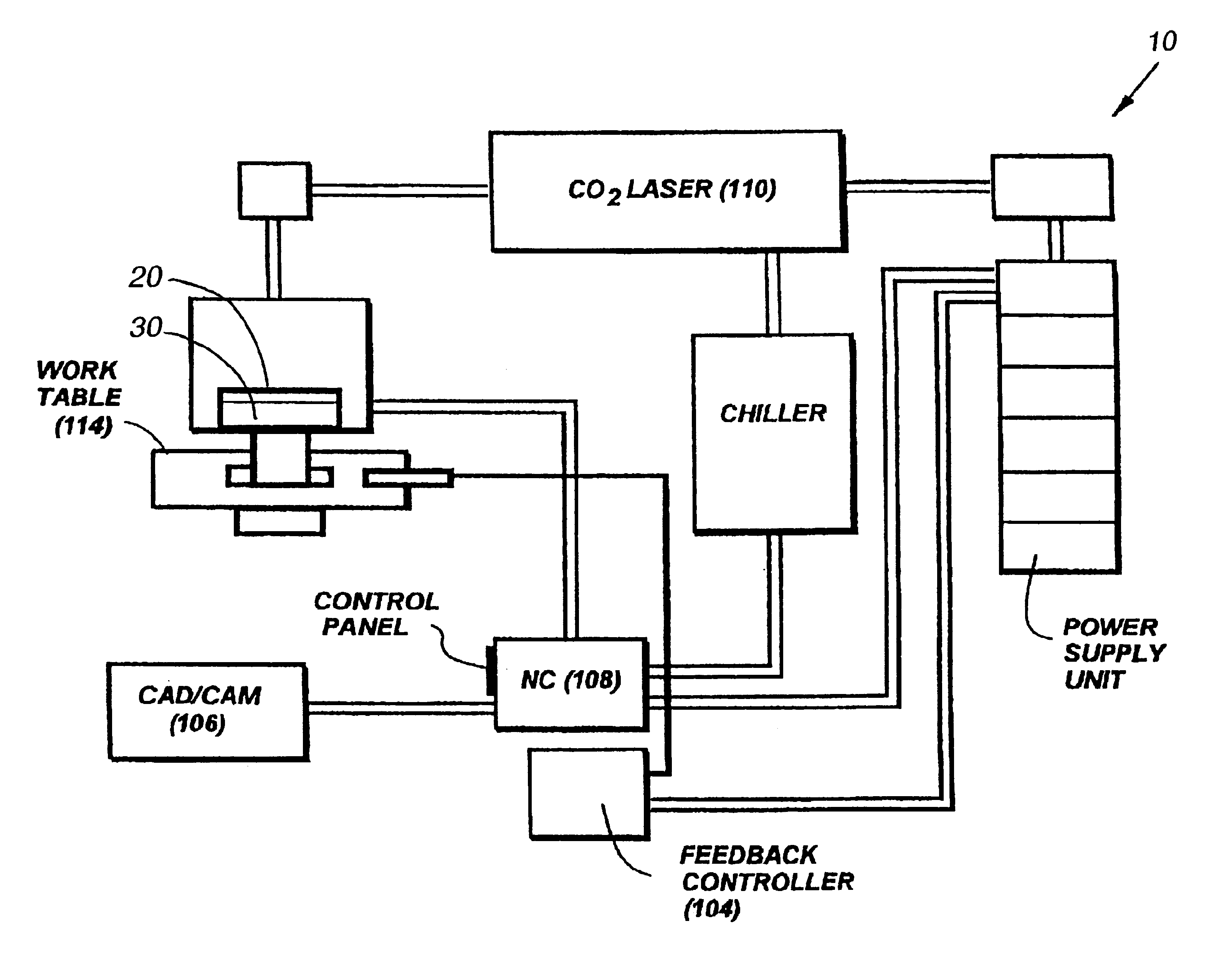
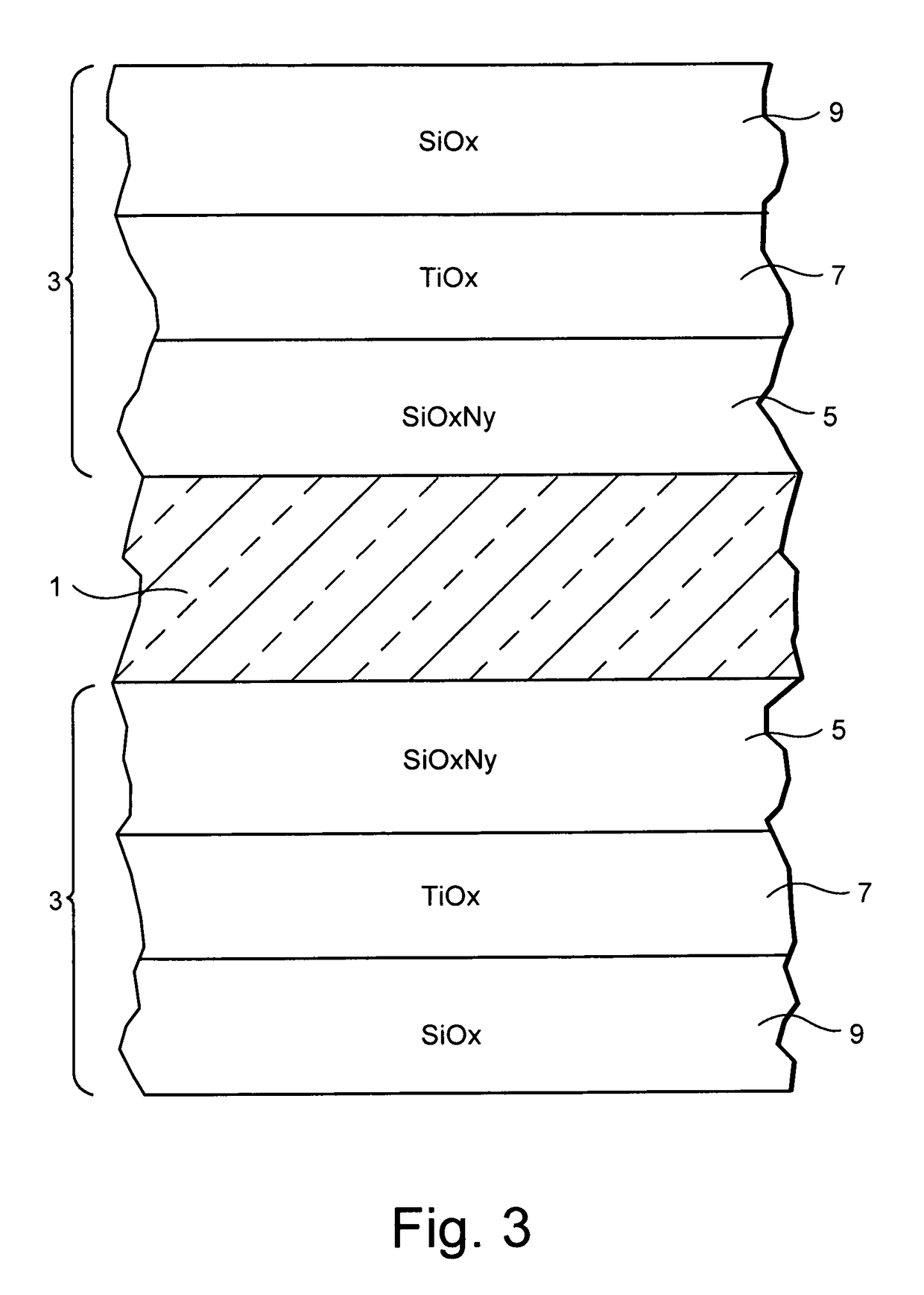
ActiveUS20110157703A1Electrostatic spraying apparatusSpecial surfacesOptical propertyRefractive index
A coated article includes a temperable antireflection (AR) coating that utilizes medium and low index (index of refraction “n”) layers having compressive residual stress in the AR coating. In certain example embodiments, the coating may include the following layers from the glass substrate outwardly: silicon oxynitride (SiOxNy) medium index layer / high index layer / low index layer. In certain example embodiments, depending on the chemical and optical properties of the high index layer and the substrate, the medium and low index layers of the AR coating are selected to cause a net compressive residual stress and thus optimize the overall performance of the antireflection coating when the coated article is tempered and / or heat-treated.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Method for increasing compression stress or reducing internal tension stress of a CVD, PCVD or PVD layer and cutting insert for machining
InactiveUS6884496B2Prolong lifeIncrease resistance to crack formation and corrosion resistance and wear resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMaximum diameterTension stress
A method of increasing the compressive stress or of reducing the tensile residual stress of a CVD layer, a PCVD layer or PVD layer and a cutting insert for machining.The invention relates to a method of increasing the compressive residual stress or of reducing the tensile residual stress of a hard material outer layer or a hard material outermost layer in which the coated substrate after coating is subjected to a dry blast treatment using a granular blast agent that, according to the invention, has a maximum diameter of 150 μm.
Owner:WIDIA
Closed-loop, rapid manufacturing of three-dimensional components using direct metal deposition
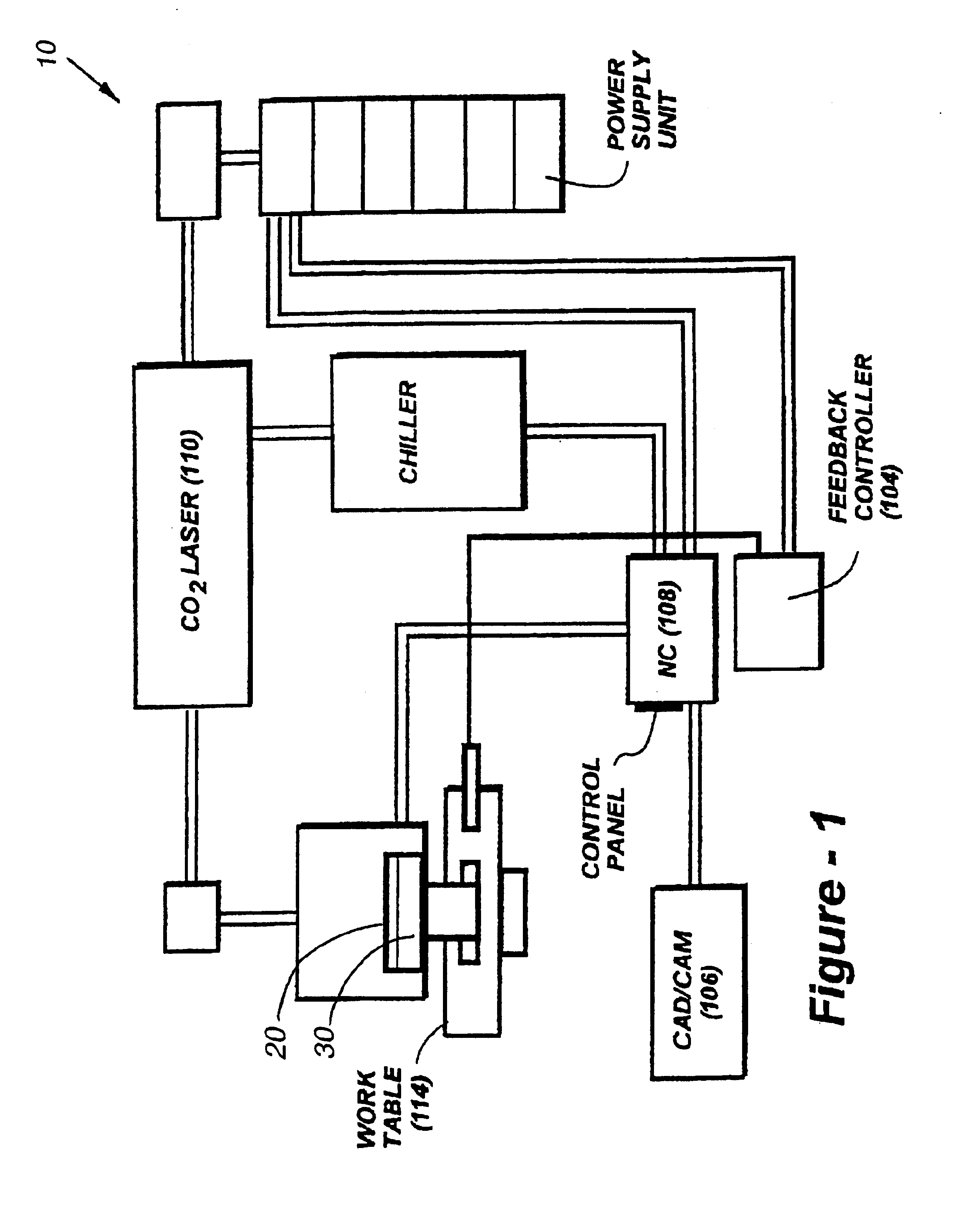
InactiveUS6925346B1Improve throughputImprove lead-timeAdditive manufacturing apparatusMolten spray coatingClosed loopHarmonic vibration
Multiple criteria are monitored and controlled to enhance the success of direct-metal deposition, including greater control over factors such as deposit layer height / thickness, sub-harmonic vibration, contour path shape, powder mass flow, and deposition speed, and stress accumulation. Sensors are used to monitor some or all of the following parameters during the deposition process: deposit height, width, temperature, and residual stress. A predetermined limit with respect to the yield strength of the material is preferably set. If the stress exceeds that limit sensors will automatically introduce one or more remedial measures, the priority of which is established using a look-up table generated in accordance with prior experimental knowledge. To control temperature induced distortion and stress, an infrared temperature detector may be used in conjunction with a controller to reduce temperature, increase speed and decreased power for purpose of stress management.
Owner:DM3D TECH
Joining structure
InactiveUS6857808B1Reduce stiffnessReduce stress concentrationMachine supportsFoundation engineeringStress concentrationPrincipal stress
The present invention provides a joining structure capable of greatly improving the proof stress and the fatigue property by alleviating the stress concentration and residual stress caused by welding heat at one or both ends of a tabular member.In the present invention, one or both ends 4 of a tabular member 3 such as a reinforcing rib, fixed to the surface of a structural member 1 in the direction of the principal stress of the structural member 1 so as to protrude in the shape of T, is / are bent in a direction deviating from the direction of the principal stress and, by this, the rigidity at the end(s) 4 of the tabular member 3 decreases and the stress concentration is alleviated. It is preferable to bend one or both ends of a tabular member 3 in the shape of an gradual curve and to the extent that each bent end is formed at a right angle to the direction of the principal stress. The tabular member may have the shape of a flat plate, or it may be bent so that it has the shape of U or V as a whole. Further, the tabular member may be welded to a structural member or formed as an integral part of a structural member.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +2
Method and apparatus for improving the magnitude of compressive stress developed in the surface of a part
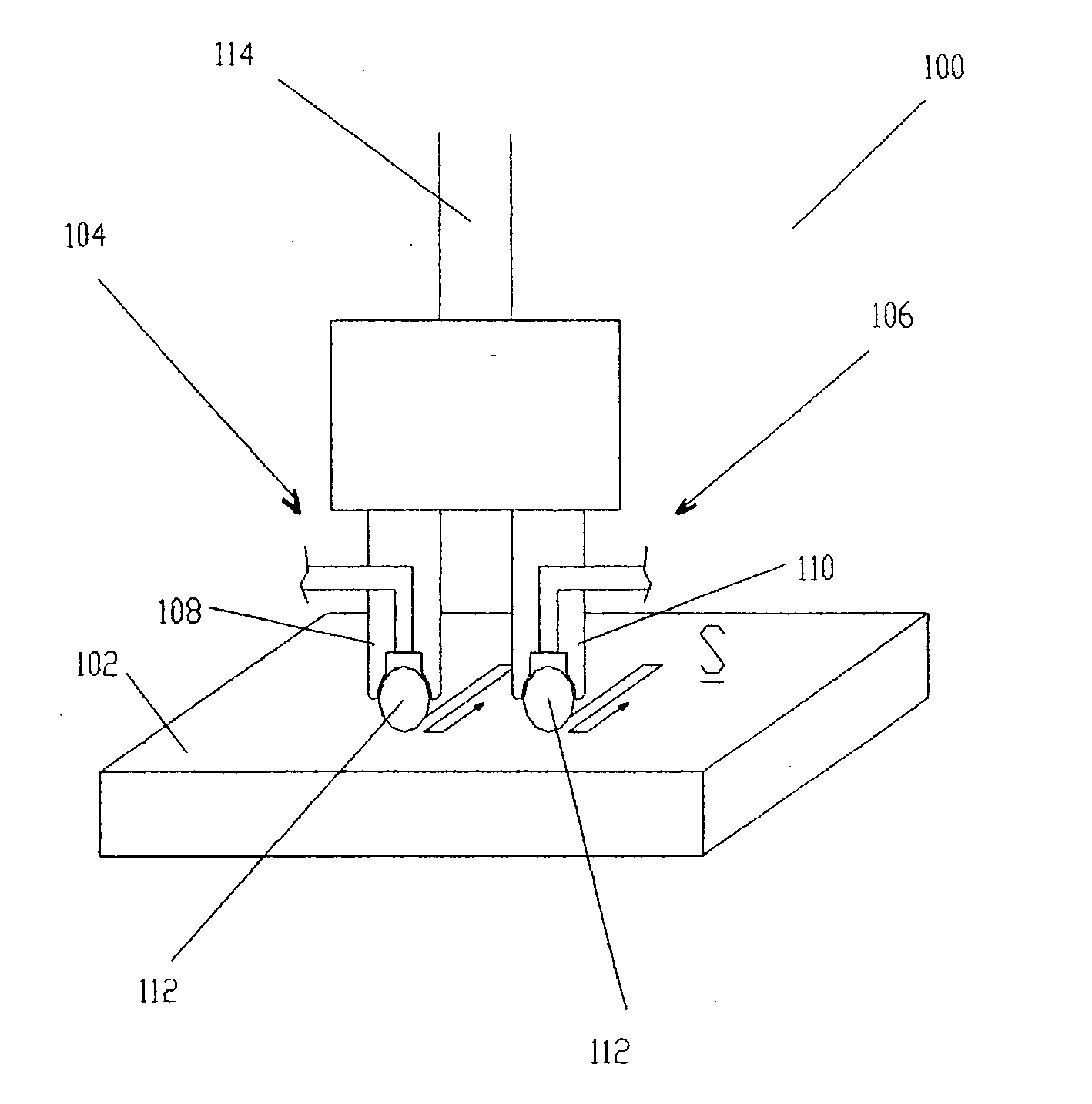
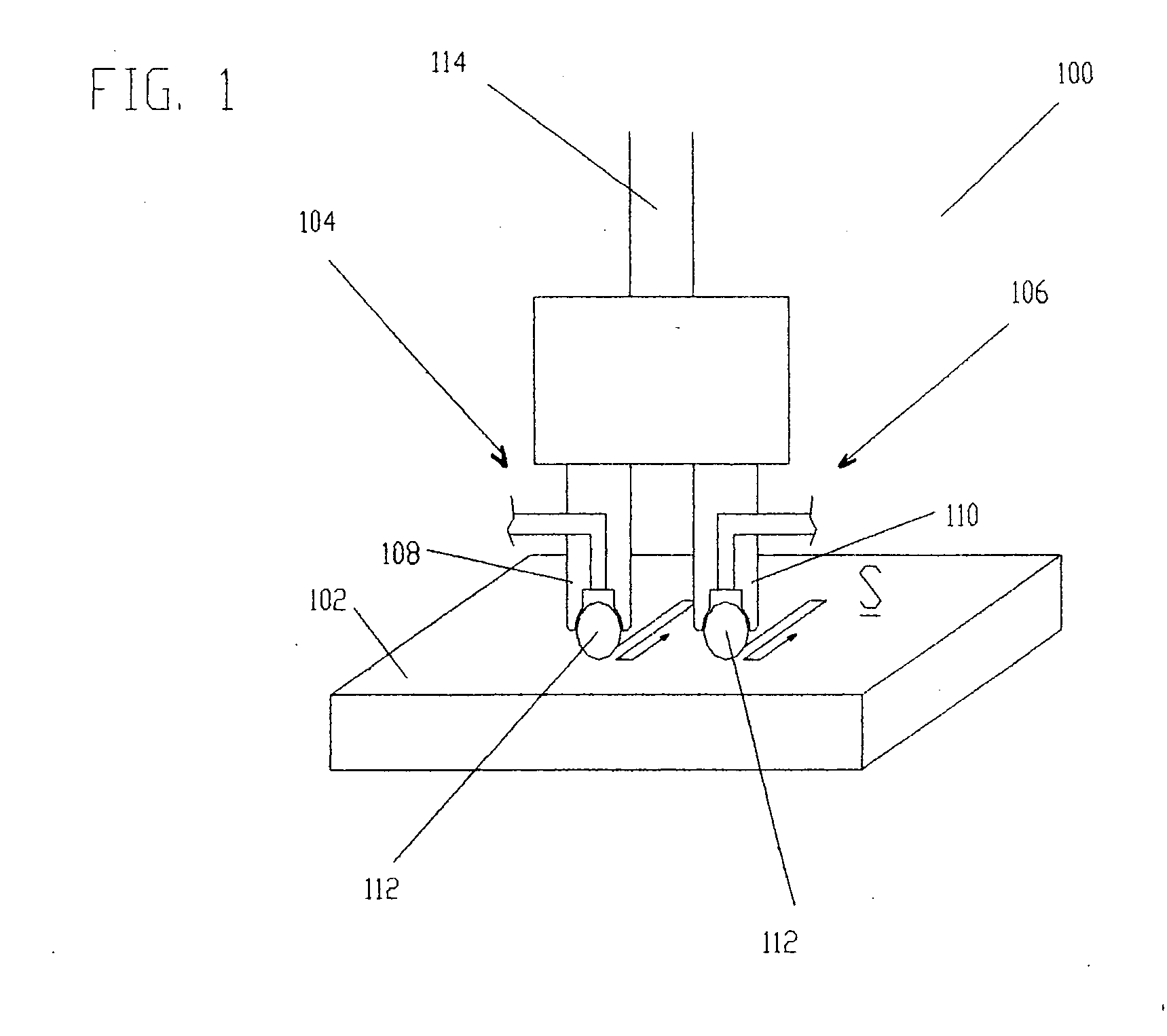
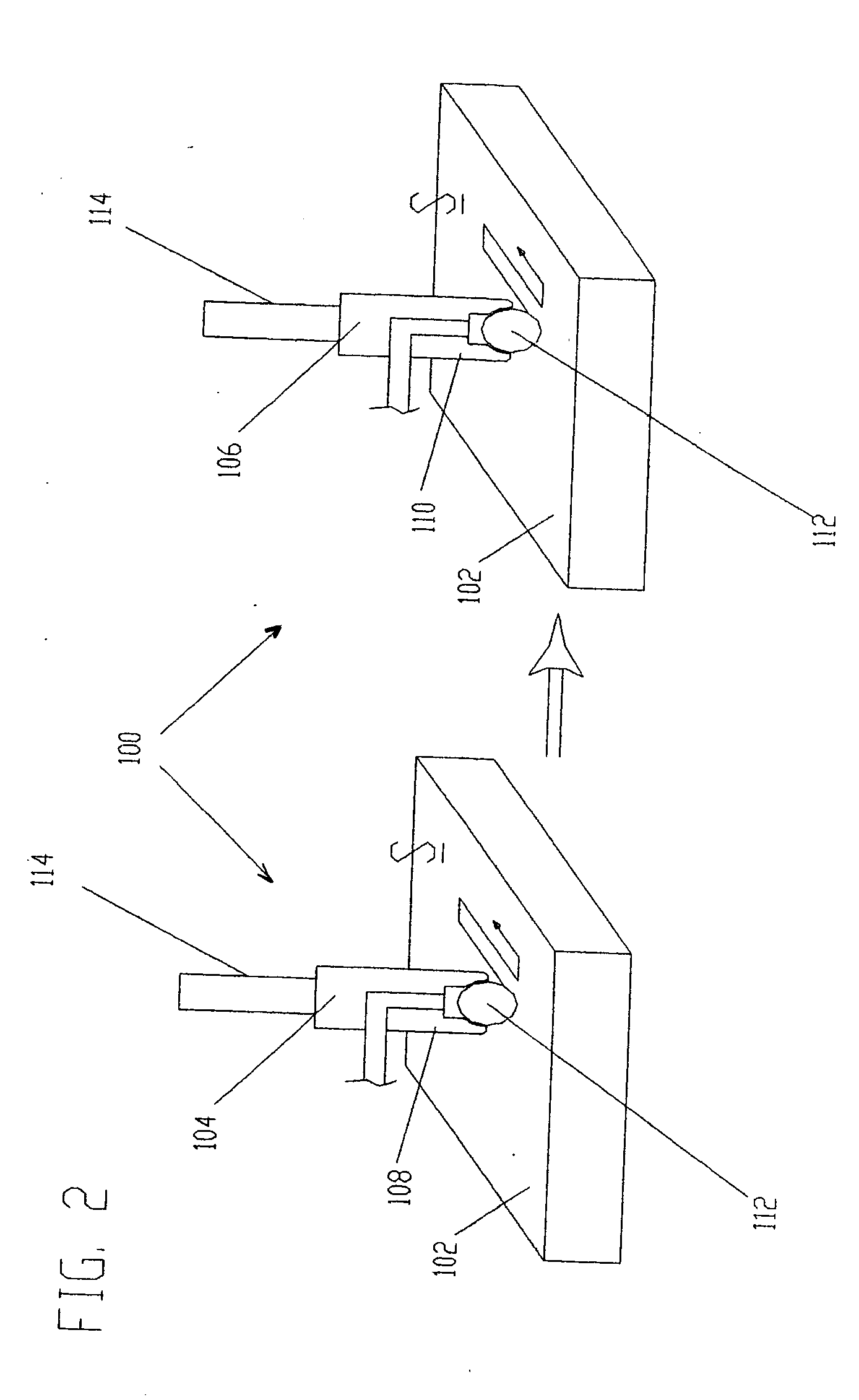
ActiveUS20050155203A1Induce residual stressSmall diameterBurnishing machinesEngineeringCompressive strength
This invention relates to a method and an apparatus for performing the method of inducing compressive residual stress along the surface of a part. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the method includes burnishing or deep rolling a surface using a first and a second roller or ball burnishing members, whereby the first and second burnishing members may have a different diameter and / or modulus of elasticity. In another preferred embodiment of the invention, the burnishing operations may be performed while the surface of the part is at different temperatures.
Owner:SURFACE TECH HLDG
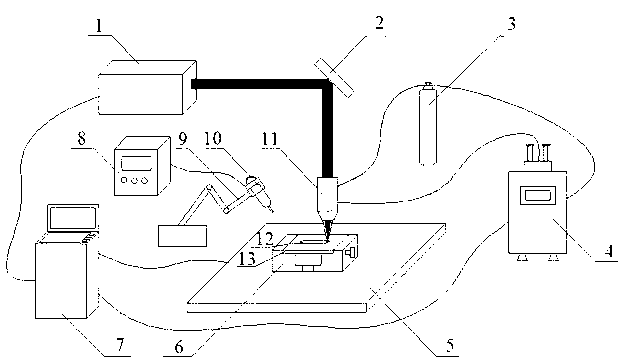
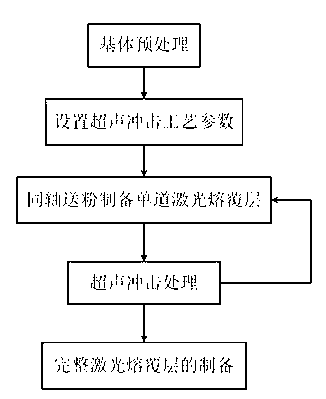
Device for strengthening laser cladding layer by ultrasonic impact and method thereof
ActiveCN103305828ARefining solidified tissueReduce residual stressLaser beam welding apparatusPressure inorganic powder coatingHigh densityOptoelectronics
The invention relates to a device for strengthening a laser cladding layer by ultrasonic impact and a method thereof. A conventional powder feeding type laser cladding method is used for preparing the laser cladding layer on the surface of a cladding base material; after one path of laser cladding is finished, the ultrasonic impact is used for playing effects on the laser cladding layer; when a plurality of paths and layers of laser cladding are carried out, the laser cladding and the ultrasonic impact are alternatively carried out. According to the device and the method disclosed by the invention, the laser cladding layer is obviously strengthened to refine tissues of the laser cladding layer and eliminate residual stress in the laser cladding layer; when the ultrasonic impact is used for playing the effect on the laser cladding layer, a plastic deformation layer with a certain depth is formed in the laser cladding layer; grains and crystal lattices in the plastic deformation layer are distorted to form high-density dislocation so that dendritic crystals in condensation tissues of the laser cladding layer are crushed and are dispersed into the laser cladding layer to form small crystal nucleuses which are uniformly distributed and refine the grains; meanwhile, the ultrasonic impact is used for planting pressing stress into the laser cladding layer to counteract pulling stress in the laser cladding layer and eliminate the residual stress in the laser cladding layer.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
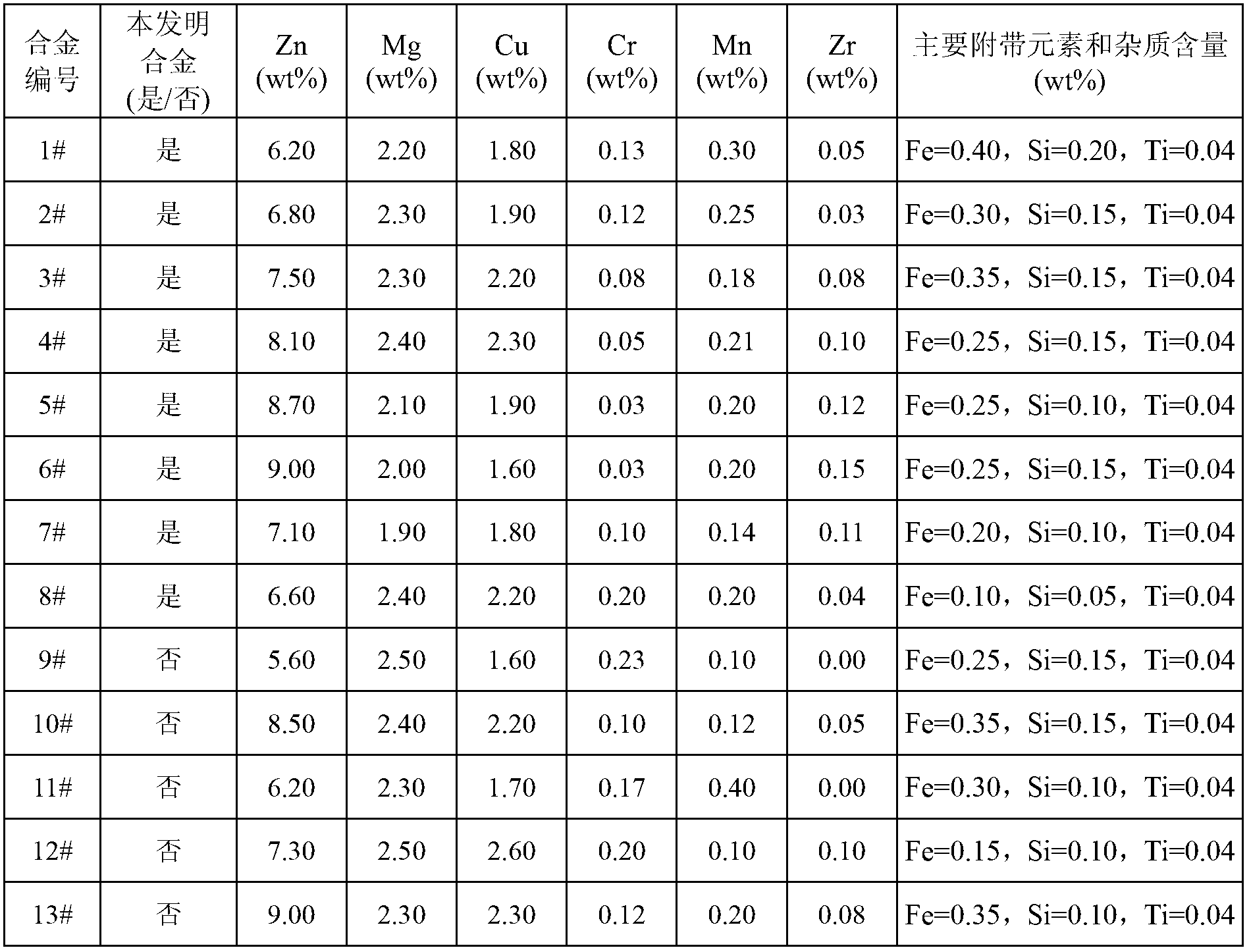
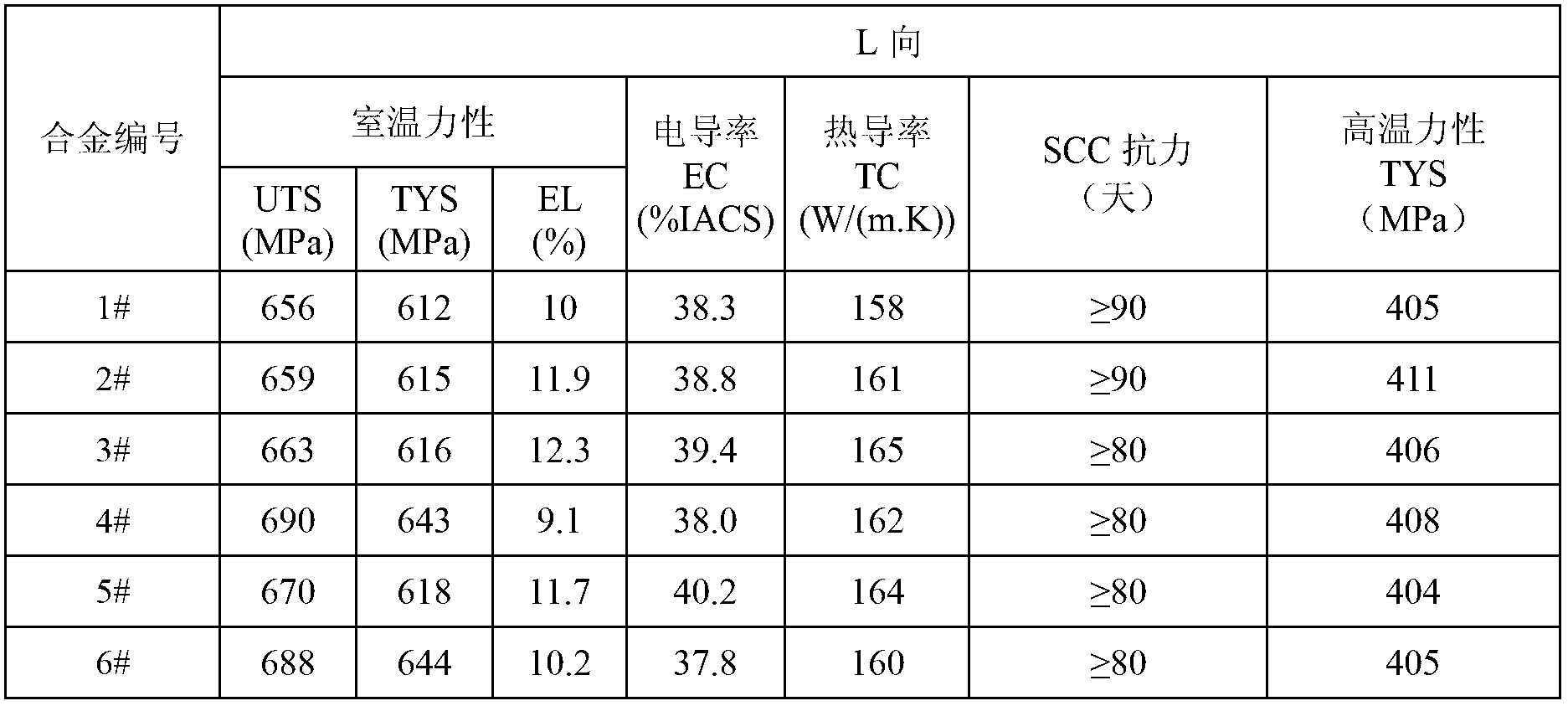
Aluminum alloy product suitable for structure and function integration, and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an aluminum alloy product suitable for structure and function integration, and a preparation method thereof. The aluminum alloy product comprises the components of, by weight, 5.5-10.0% of Zn, 1.5-2.8% of Mg, 1.5-2.5% of Cu, 0.01-0.50% of Cr, 0.05-0.50% of Mn, 0.01-0.20% of Zr, and balance of of Al and incidental elements and impurities. In the aluminum alloy product: (a) Zn+Mg+Cu is no lower than 10.0% and no higher than 14.0%; (b) (Zn / Mg)+Cu is no lower than 4.4 and no higher than 6.5; (c) Cr+Mn+Zr is no lower than 0.10 and no higher than 0.60; and (d) the content of Cr is no higher than that of Mn, and content of Mn is no higher than that of Cr+0.20. The aluminum alloy product has high strength, high electric conductivity, and good thermal conductivity. Also, the aluminum alloy product has low residual stress, good surface quality, and good dimensional precision. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the aluminum alloy product.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
Methods of separating strengthened glass substrates
ActiveUS8720228B2Avoid it happening againGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusSurface layerWhole body
Methods of separating a strengthened glass substrate having a compressive surface layer and an inner tension layer include translating a laser beam on a surface of the strengthened glass substrate along a line of desired separation from a first edge of the strengthened glass substrate toward a second edge of the strengthened glass substrate. Methods further include backward-propagating a controlled full-body crack within the strengthened glass substrate from the second edge toward the first edge substantially along the line of desired separation. A scribe line may be formed on a surface of the strengthened glass substrate such that the strengthened glass substrate self-separates along the scribe line. A residual stress field may be created within the strengthened glass substrate such that a full-body crack backward-propagates from an exit defect located at the second edge toward the first edge along a line of desired separation, thereby separating the strengthened glass substrate.
Owner:CORNING INC
Flexible composite middle layer brazing alloy and method of utilizing brazing ceramic and metal
InactiveCN102699558AEnables direct brazingIncreased shear strengthWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaHeating furnaceUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses flexible composite middle layer brazing alloy and a method of utilizing brazing ceramic and metal, and relates to the composite brazing alloy and the method of utilizing the brazing ceramic and metal. The flexible composite middle layer brazing alloy and the method aim at solving the problems that the conventional method is high in cost and the forming of brittle compound of a joint can not be restrained. The flexible composite middle layer brazing alloy is prepared from upper layer brazing alloy, a flexible middle layer and lower layer brazing alloy. The brazing method comprises the steps of: cleaning greasy dirt and impurity on a pre-welding surface; processing the upper-layer brazing alloy, the flexible middle layer and the lower-layer brazing alloy into small sheets; and ultrasonically cleaning and airing ceramic to be welded, metal to be welded, the upper layer brazing alloy, the flexible middle layer and the lower layer brazing alloy by acetone, assembling a workpiece to be welded, and putting the workpiece to be welded into a vacuum heating furnace to braze. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the operation is simple; the residual stress of the joint is released by adding the flexible middle layer; and the forming of the brittle compound of the joint is restrained, and the shearing strength of the joint is improved by 30-109%. The method disclosed by the invention is used for brazing the ceramic and the metal.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Abrasive tool inserts with diminished residual tensile stresses and their production
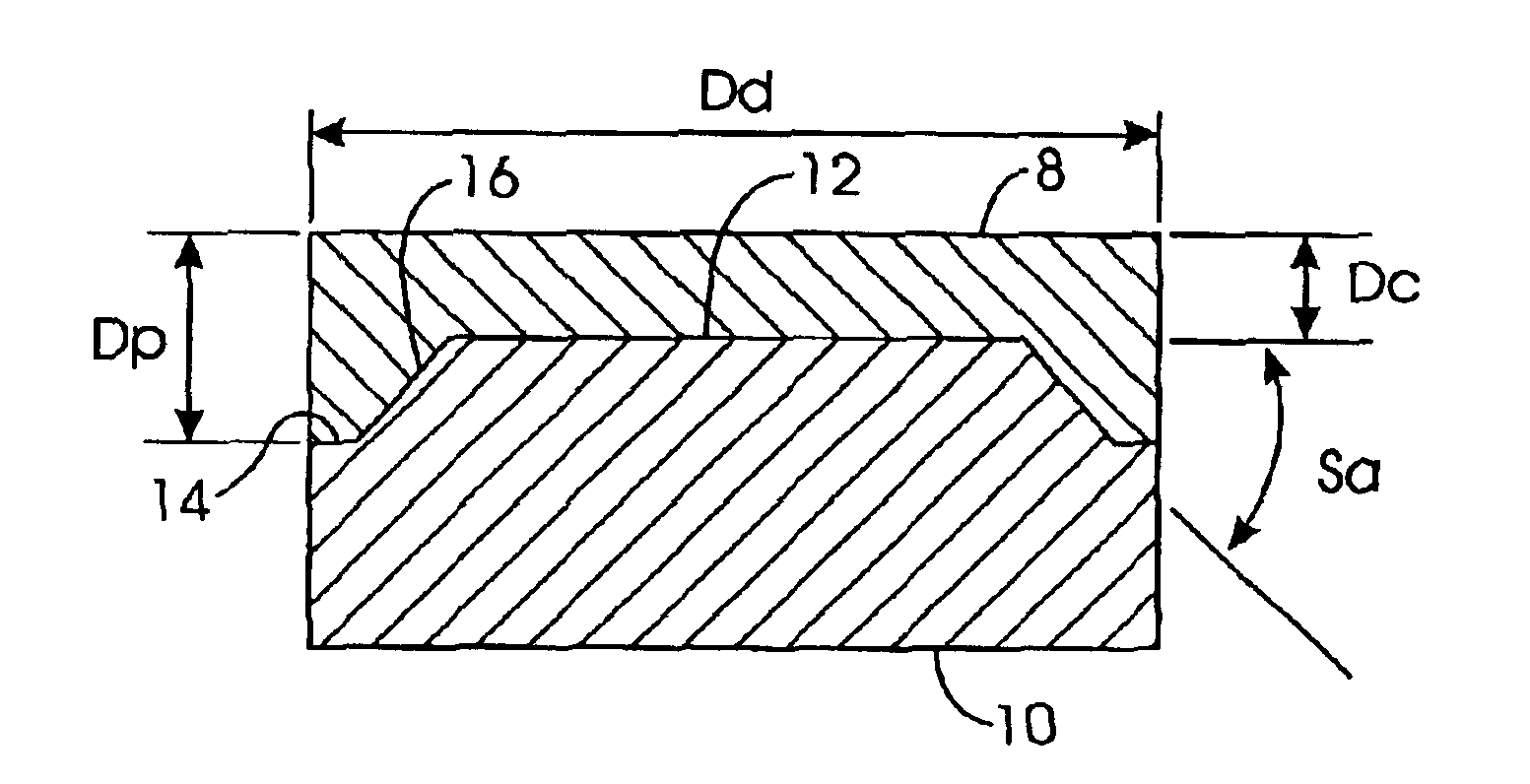
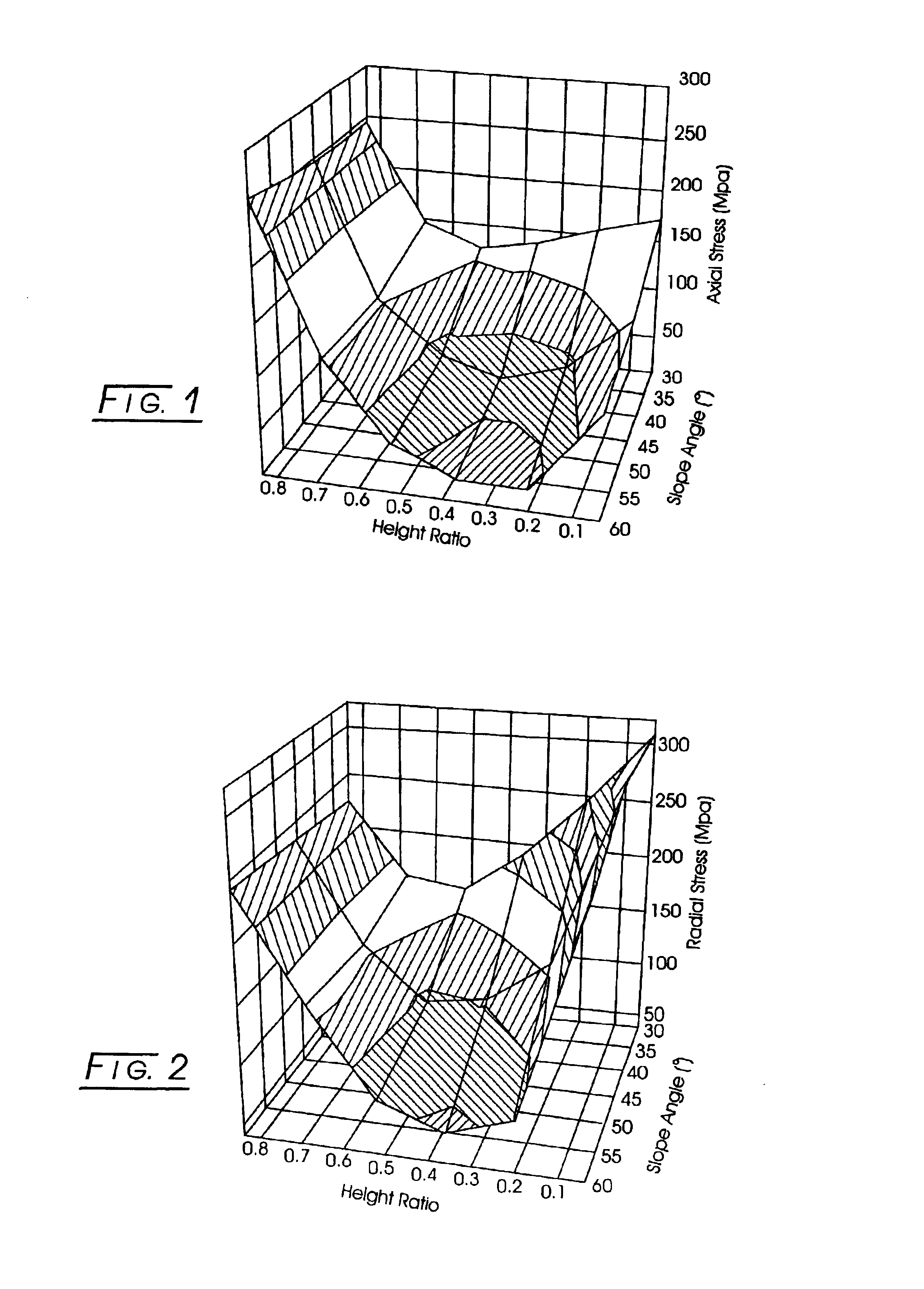
InactiveUS6933049B2Reduce residual stressPigmenting treatmentDrill bitsSlope angleMechanical engineering
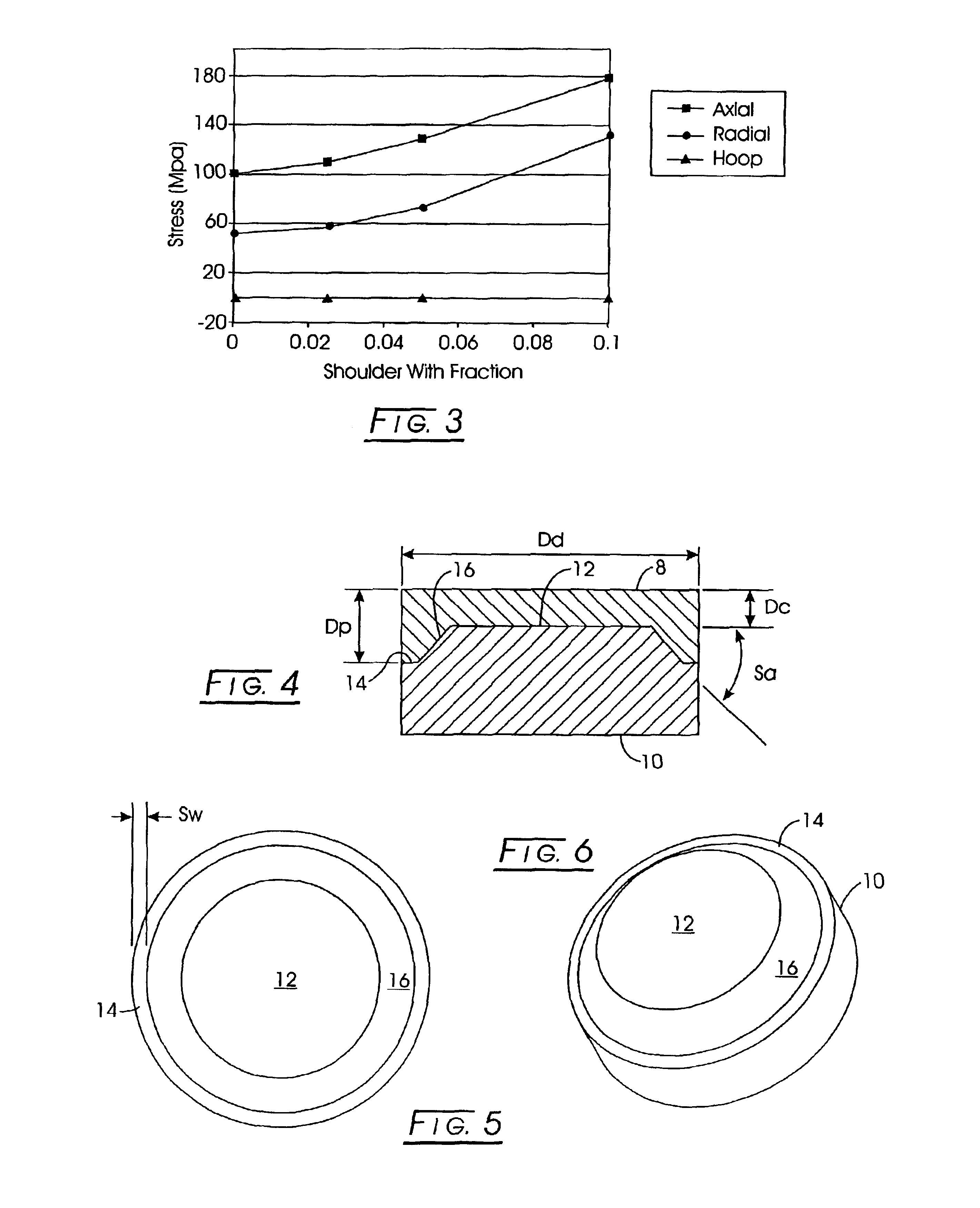
An abrasive tool insert includes (a) a substrate having a support face that includes (1) an inner support table, (2) an outer shoulder having a width, Sw, and (3) a downwardly sloping interface from the support table to the shoulder, which interface has a slope angle, Sa. A continuous abrasive layer, integrally formed on the substrate support face, includes (1) a center having a height, Dc, (2) a diameter, Dd, (3) a periphery having a height, Dp, in contact with the shoulder and which periphery forms a cutting edge. Sw:Dd ranges from between 0 and about 0.5. For each Sa and Sw:Dd, Dc:Dp is selected so as to diminish residual stress in the abrasive layer.
Owner:GE SUPERABRASIVES
Low stress thin film microshells
InactiveUS7595209B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterial PerforationMetal
Multi-layered, planar microshells having low stress for encapsulation of devices such as MEMS and microelectronics. The microshells may include a perforated pre-sealing layer, below which a sacrificial layer is accessed, and a sealing layer to close the perforation in the pre-sealing layer after the sacrificial material is removed. The sealing layer may further include a nonhermetic layer to physically occlude the perforation and a hermetic layer over the nonhermetic occluding layer to seal the perforation. The various layers may be formed employing processes having opposing stresses to tune the residual stress of the multi-layered microshell. In an embodiment, the hermetic layer is a metal which is deposited with a process tuned to impart a tensile stress to lower the residual stress in the microshell below the magnitude of cumulative stress present in sealing layer and pre-sealing layer.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
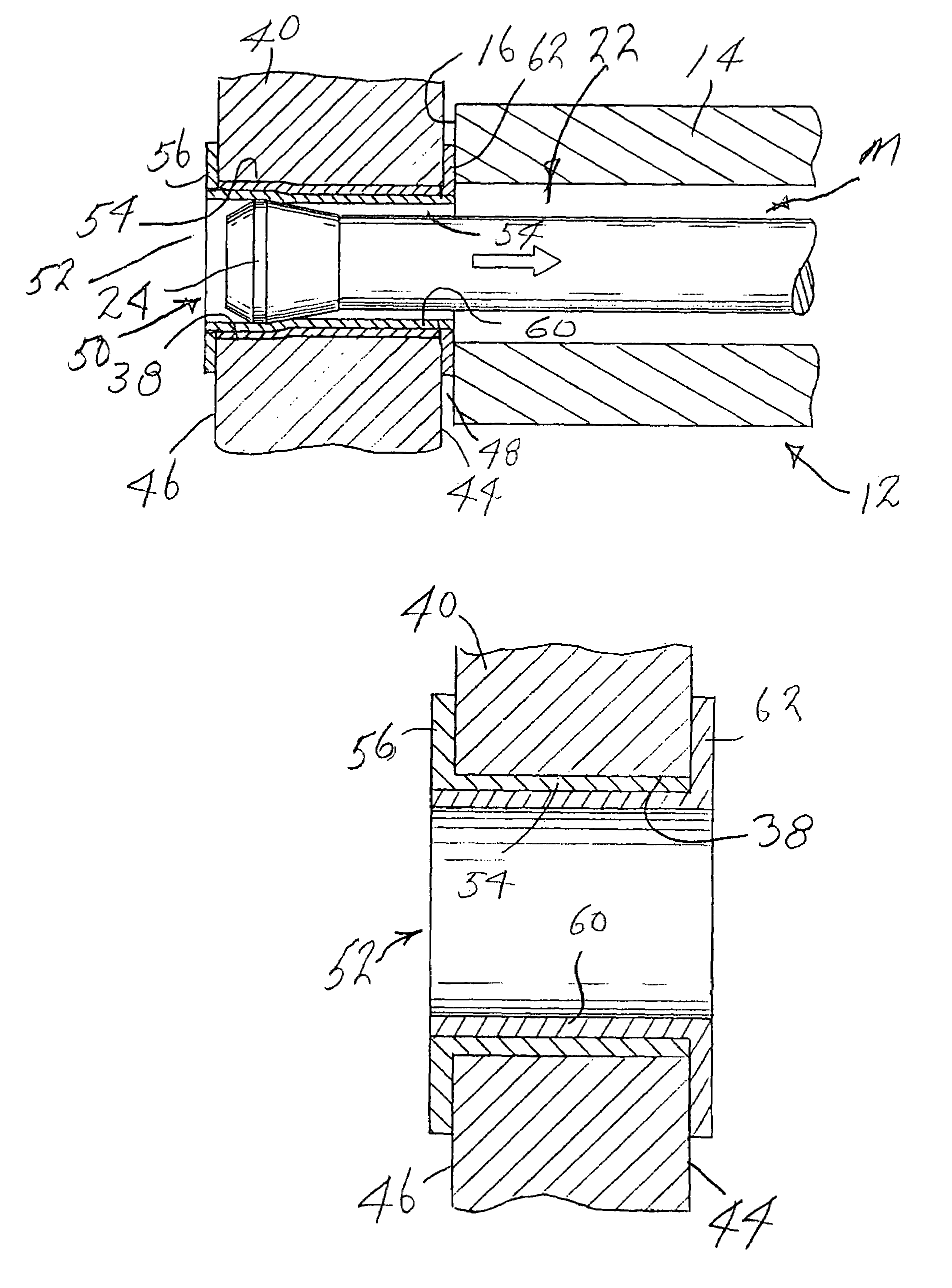
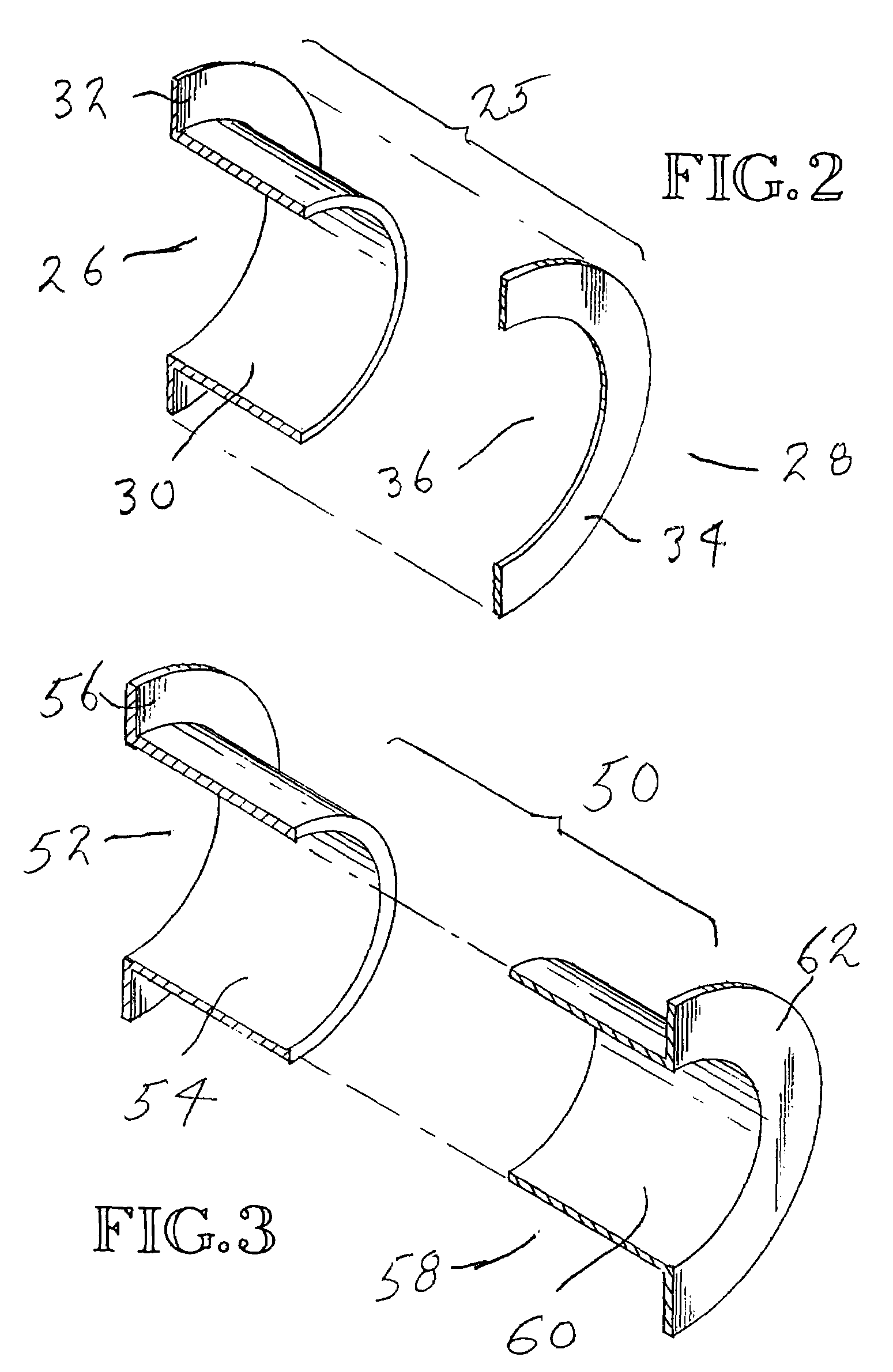
Method of installing double flanged bushings
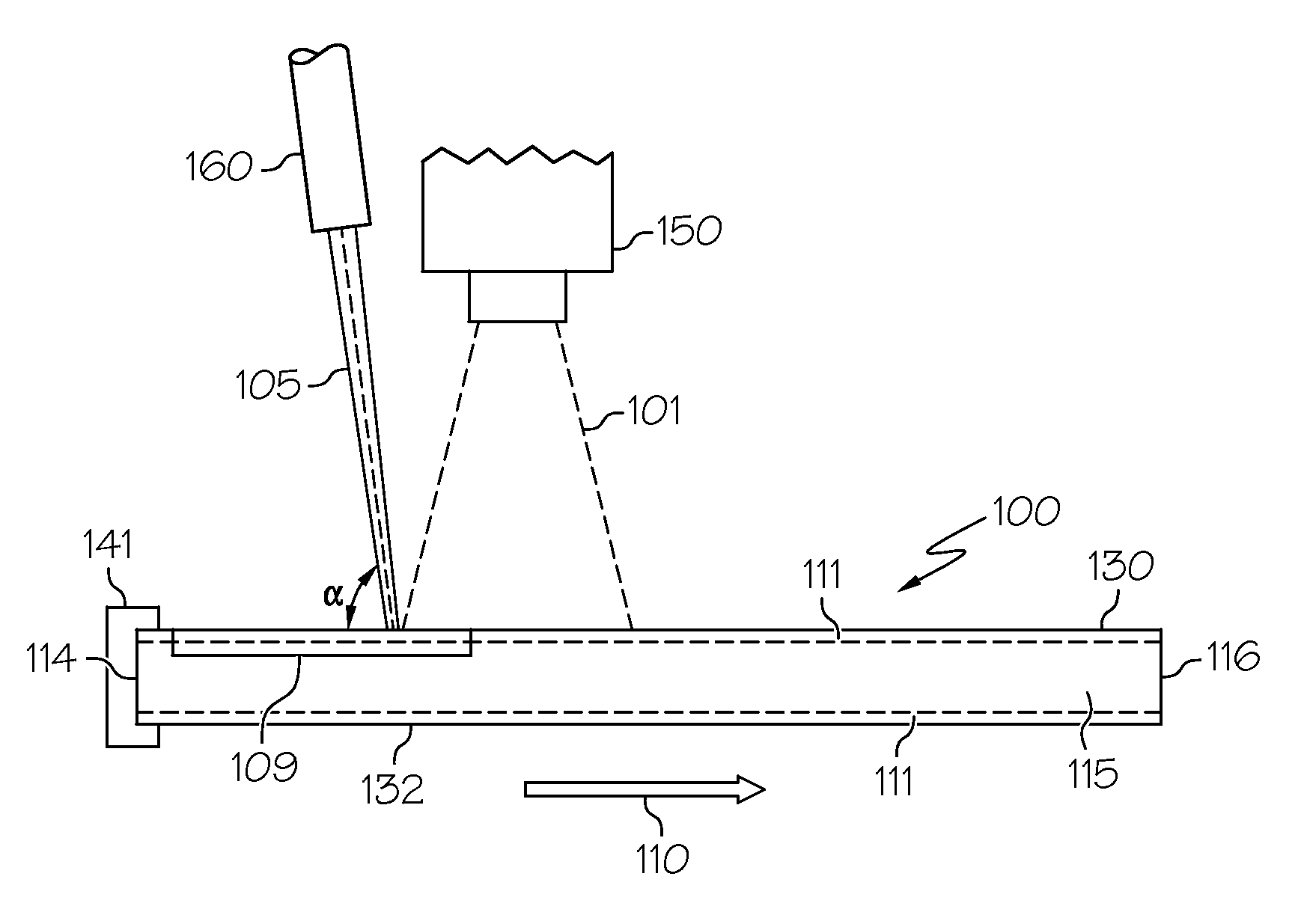
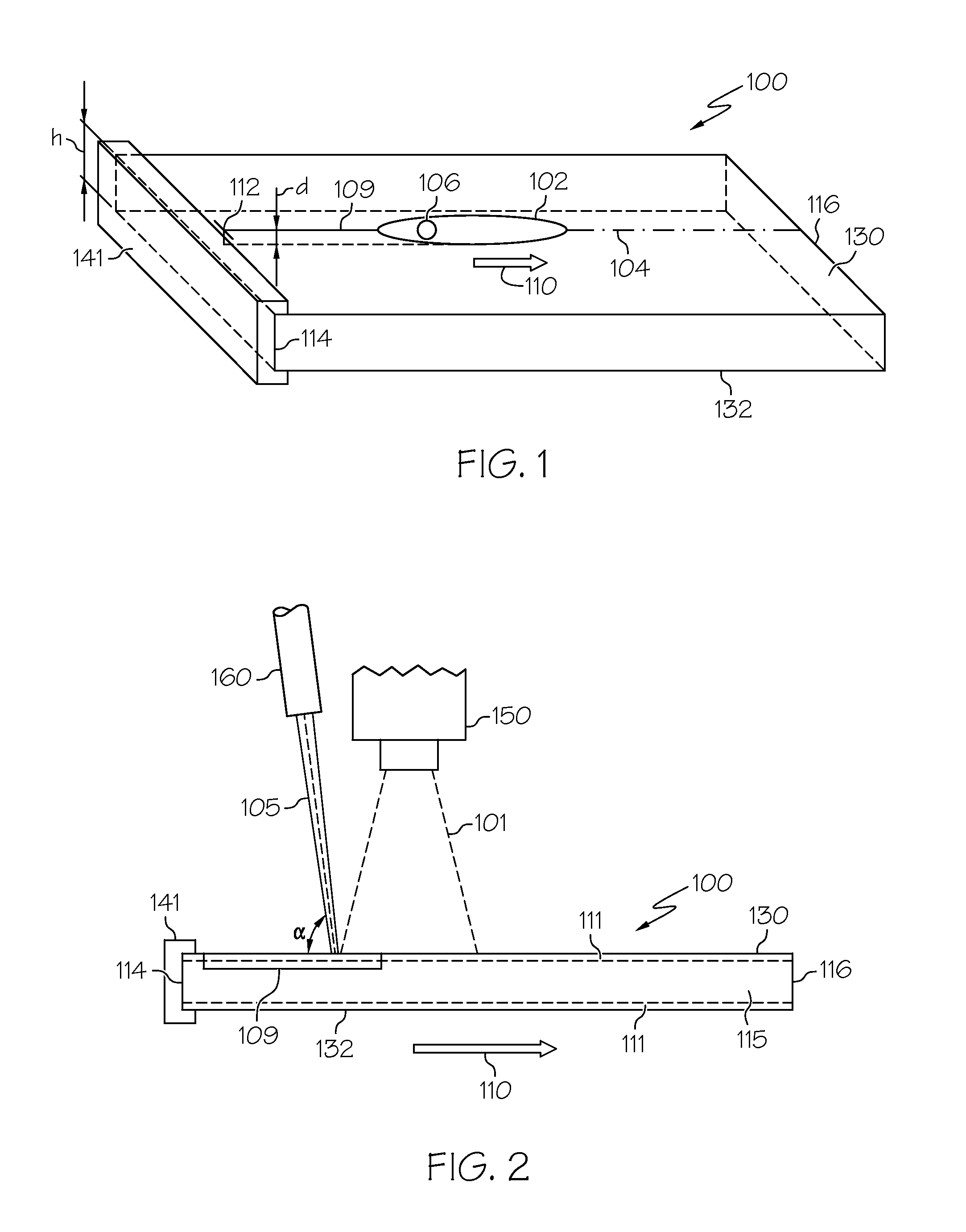
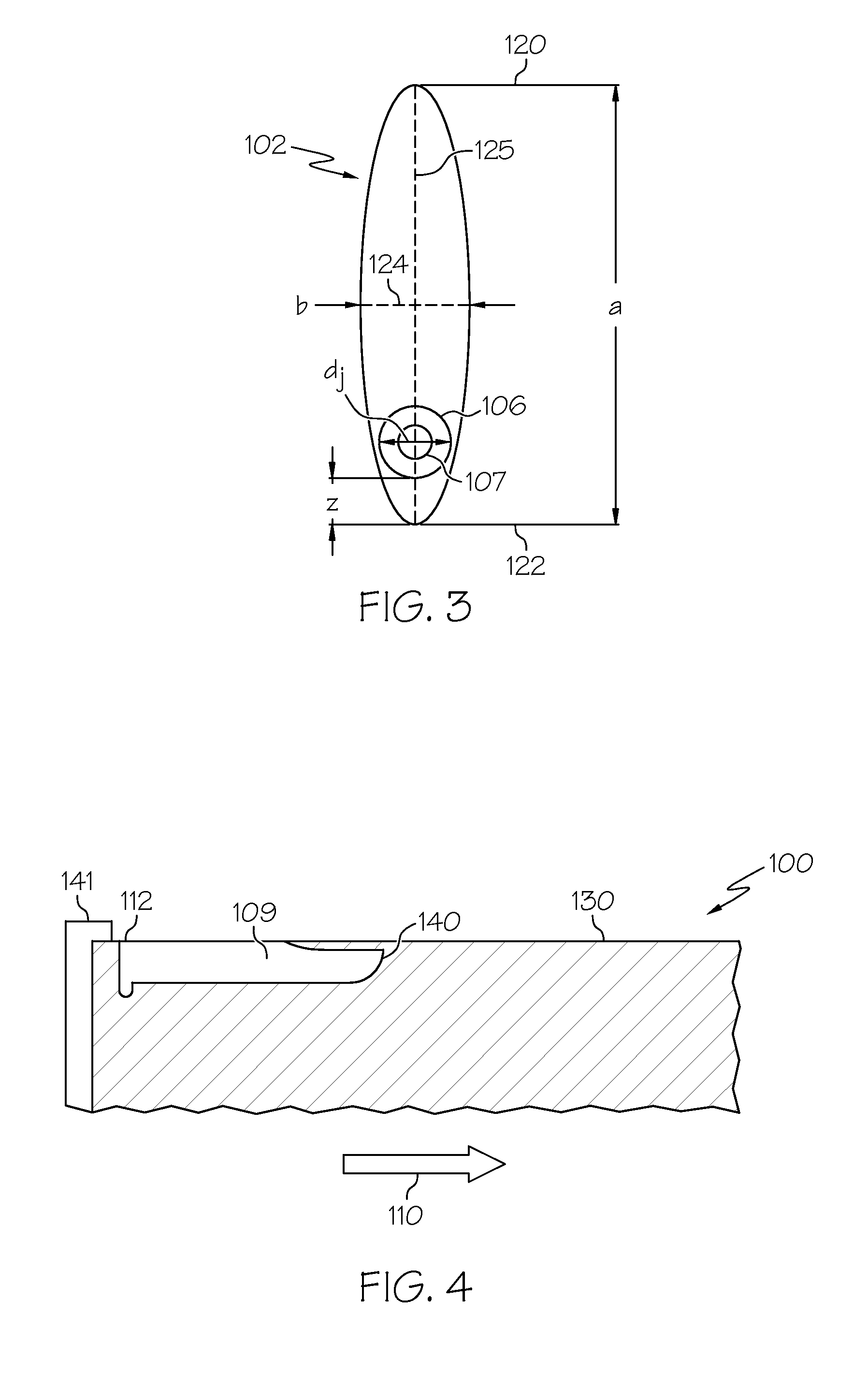
A bushing (52) has two bushing parts (52, 58), each of which includes a tubular section (54, 60) and a radial flange section (56, 62) Tubular section (54) is inserted into an opening (38) in a work member (40), from one side of the work member (40). Tubular section (60) is inserted into tubular section (54) from the opposite side (44) of the work member (40). A mandrel (M) is moved through the interior of the tubular portion of the bushing to radially and circumferentially expand the tubular portion of the bushing and move the flange sections against the opposite sidewalls of the work member (40). The tubular portions (54, 60) of the bushing (52) is radially and circumferentially expanded an amount sufficient to introduce fatigue life enhancing compressive residual stresses in the work member (40) immediately around the opening (38) in the work member (40).
Owner:FATIGUE TECH
Methods of separating strengthened glass substrates
ActiveUS20120047956A1Avoid it happening againGlass reforming apparatusGlass severing apparatusSurface layerWhole body
Methods of separating a strengthened glass substrate having a compressive surface layer and an inner tension layer include translating a laser beam on a surface of the strengthened glass substrate along a line of desired separation from a first edge of the strengthened glass substrate toward a second edge of the strengthened glass substrate. Methods further include backward-propagating a controlled full-body crack within the strengthened glass substrate from the second edge toward the first edge substantially along the line of desired separation. A scribe line may be formed on a surface of the strengthened glass substrate such that the strengthened glass substrate self-separates along the scribe line. A residual stress field may be created within the strengthened glass substrate such that a full-body crack backward-propagates from an exit defect located at the second edge toward the first edge along a line of desired separation, thereby separating the strengthened glass substrate.
Owner:CORNING INC
Rare-earth-containing ultrahigh strength collapse-resistant petroleum casing and production method thereof
InactiveCN102251180ALow elemental contentReduce residual stressDrilling rodsProcess efficiency improvementRare earthFlame cutting
A rare-earth-containing ultrahigh strength collapse-resistant petroleum casing and a production method thereof belong to the technical fields of ferrous metal smelting and metal press working. The petroleum casing comprises the following raw materials by weight percent: 90% of blast furnace molten iron and 10% of high quality steel scrap. The casing blank comprises the following chemical components by weight percent: 0.18-0.35% of C, 0.10-0.35% of Si, 0.55-1.10% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.025% of P, less than or equal to 0.020% of S, 0.60-1.10% of Cr, 0.15-0.50% of Mo, 0.01-0.03% of Al, 0.0005-0.0100% of RE ( RE is the mixed rare earth metals of Ce and La and the weight percents of Ce and La are 67% and 33% respectively), less than 0.10% of Cu, less than 0.10% of Ni and the balance of Fe and trace elements. The process flow of the production method is as follows: pretreating molten iron, smelting in a top-bottom blowing converter, refining in a ladle furnace (LF), performing VD vacuum treatment, performing continuous casting of round billets, performing flame cutting, heating the casing blanks, boring, performing continuous rolling, performing sizing and diameter reducing, cooling, performing saw cutting, performing heat treatment, straightening, performing flaw inspection and lathing screw threads. The mechanical properties of the petroleum casing are as follows: the strength is no less than 140000PSI, the residual stress is no more than 80MPa, the impact power is no less than 80J and the grain size is no less than the grade 8. The product is characterized in that the residual stress is low, the content of harmful elements is low, the impact toughness is high, the grains are small, and the product resists extrusion and is difficult to damage.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
Temperable three layer antirefrlective coating, coated article including temperable three layer antirefrlective coating, and/or method of making the same
A coated article includes a temperable antireflection (AR) coating that utilizes medium and low index (index of refraction “n”) layers having compressive residual stress in the AR coating. In certain example embodiments, the coating may include the following layers from the glass substrate outwardly: silicon oxynitride (SiOxNy) medium index layer / high index layer / low index layer. In certain example embodiments, depending on the chemical and optical properties of the high index layer and the substrate, the medium and low index layers of the AR coating are selected to cause a net compressive residual stress.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Wafer level package structure, and sensor device obtained from the same package structure
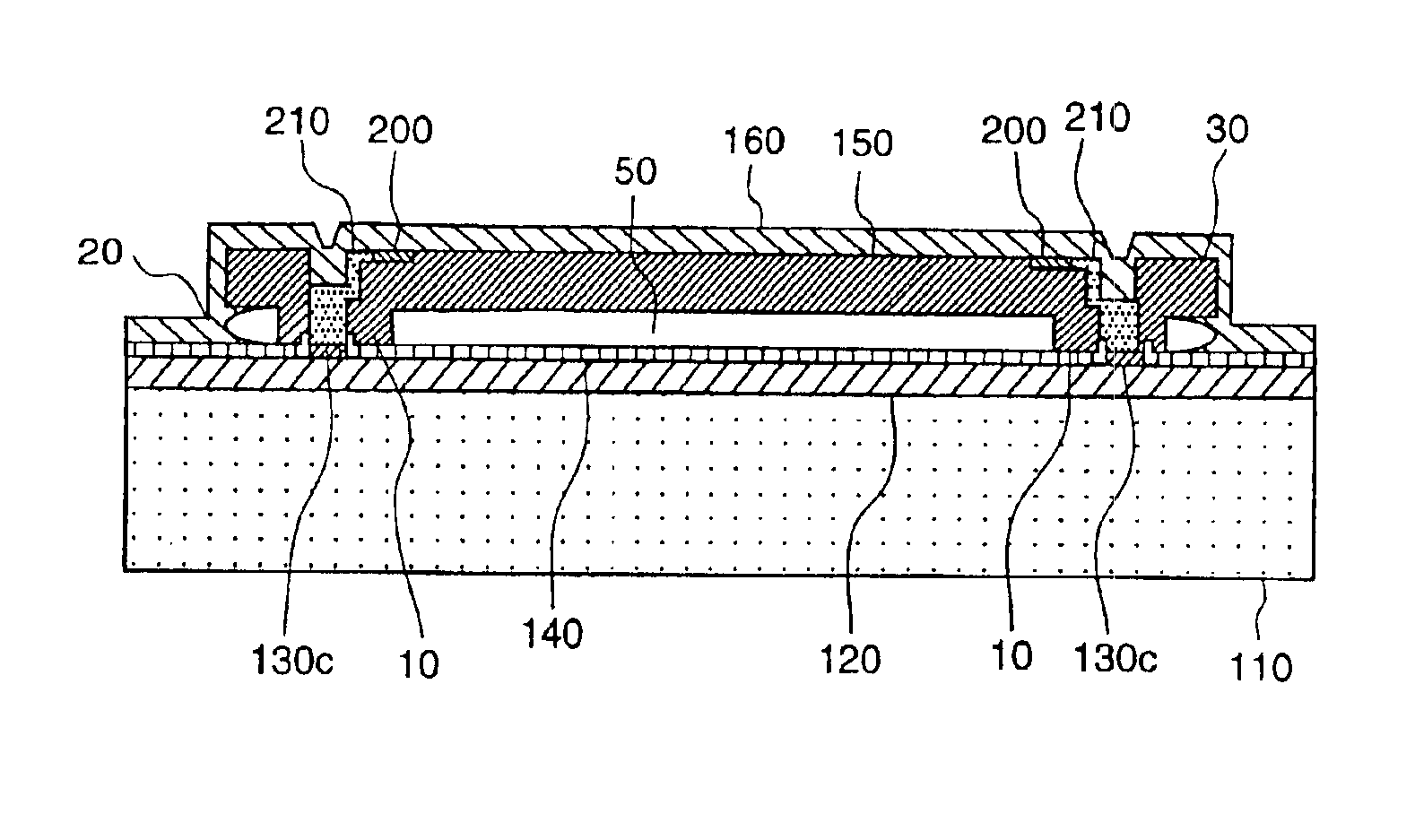
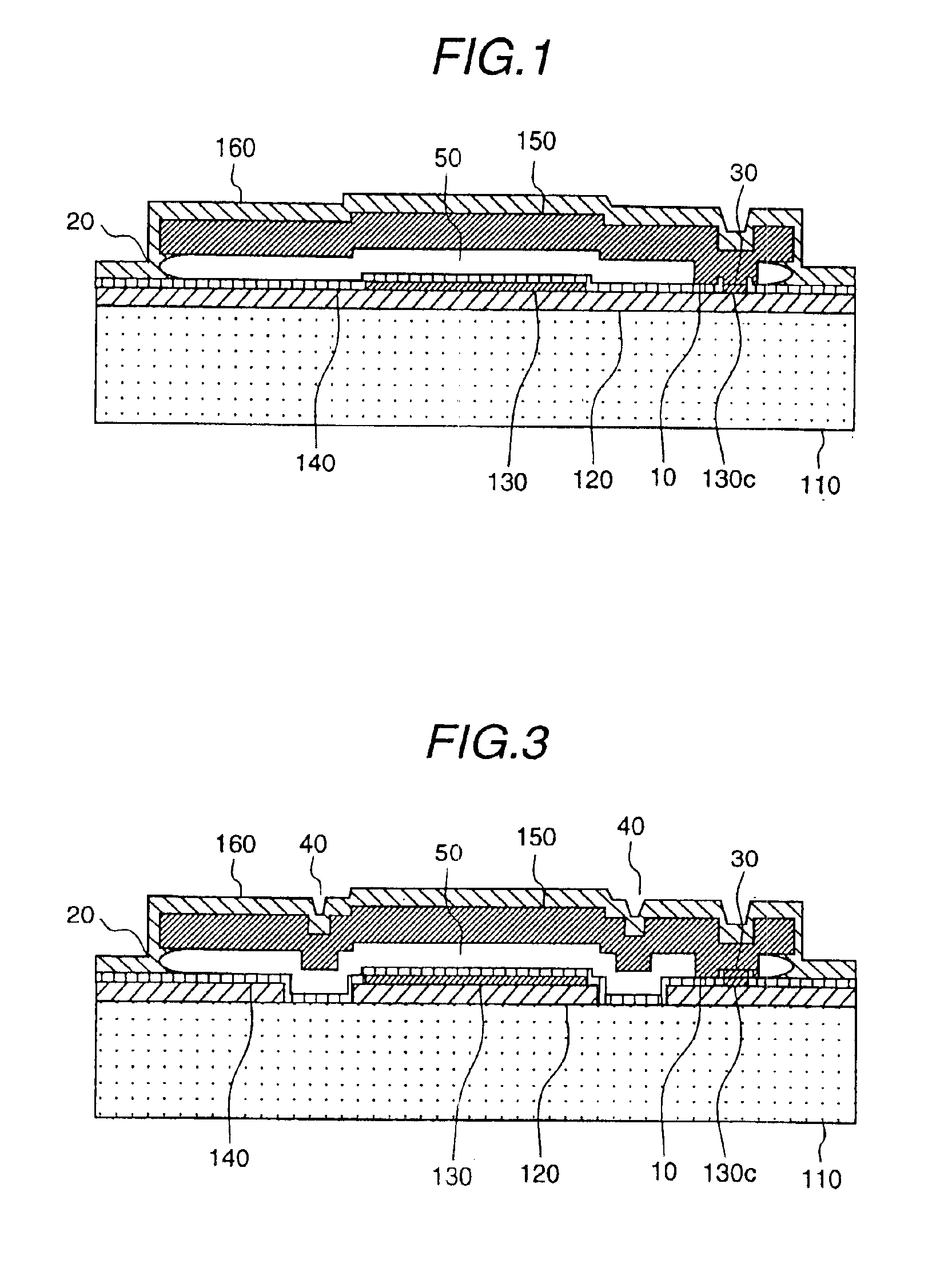
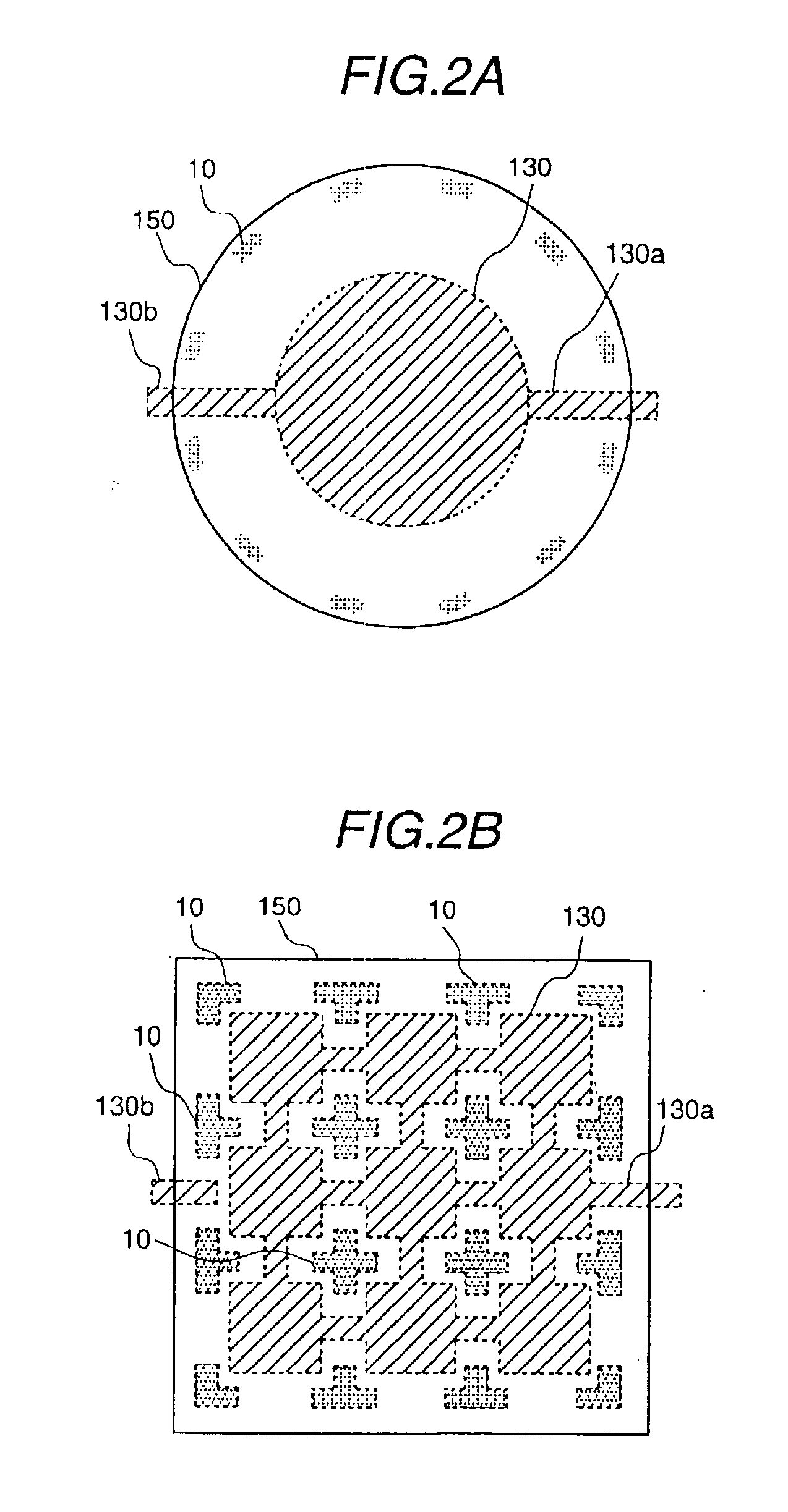
InactiveUS20090267165A1Little changeReducing atmosphereAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDiffusionGyroscope
A wafer level package structure with a plurality of compact sensors such as acceleration sensors and gyro sensors is provided. This package structure is composed of a semiconductor wafer with plural sensor units, and a pair of package wafers bonded to both surfaces of the semiconductor wafer. Each of the sensor units has a frame having an opening, a movable portion held in the opening to be movable relative to the frame, and a detecting portion for outputting an electric signal according to a positional displacement of the movable portion. Since the semiconductor wafer is bonded to each of the package wafers by a solid-phase direct bonding without diffusion between a surface-activated region formed on the frame and a surface-activated region formed on the package wafer, it is possible to prevent that variations in sensor characteristics occur due to residual stress at the bonding interface.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
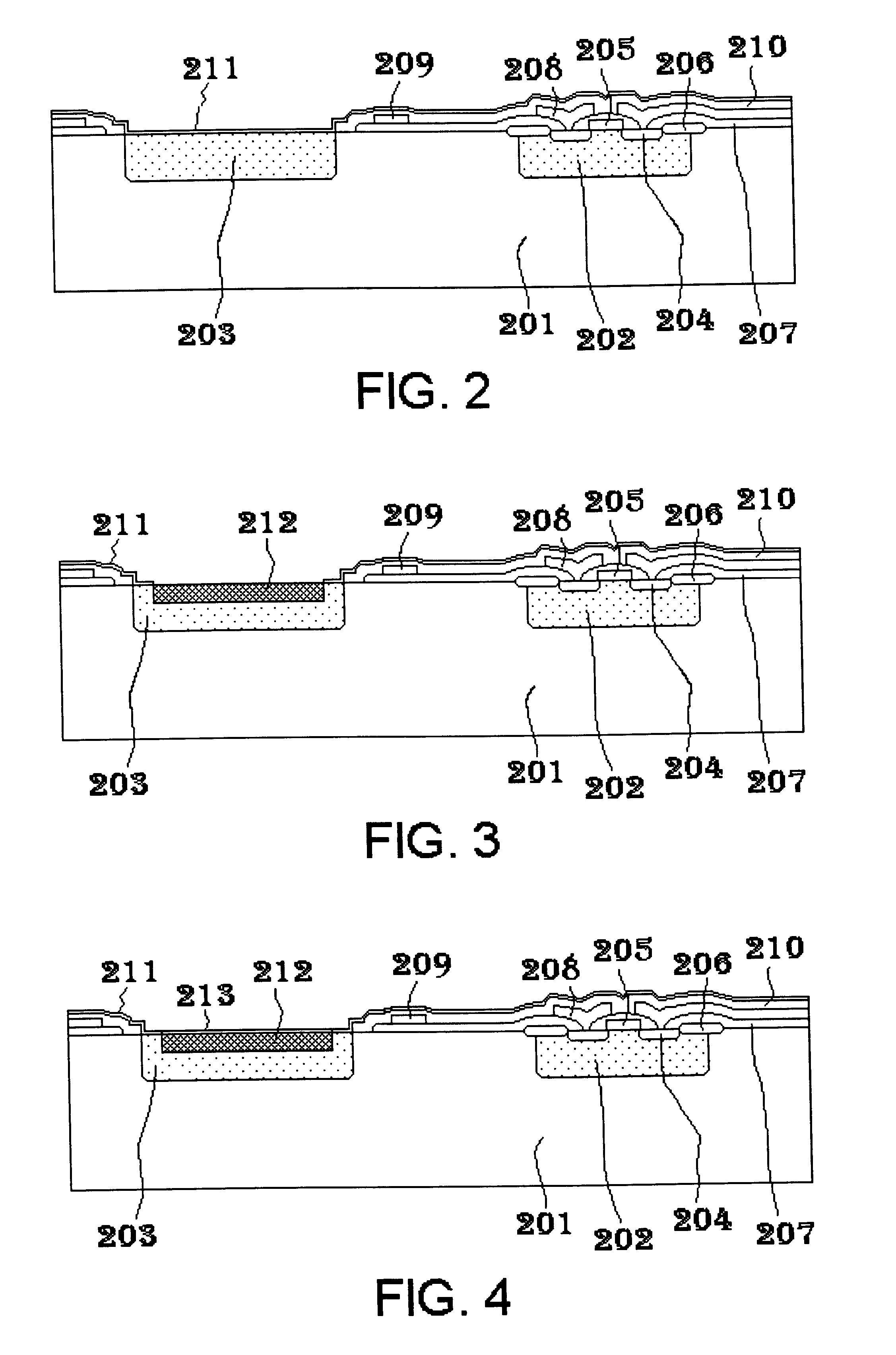
Capacitive type pressure sensor
InactiveUS6877383B2Avoid problemsHigh sensitivityFluid pressure measurement using capacitance variationCapacitive pressure sensorEngineering
By sealing a diaphragm with less processes and lower cost and reducing deformation due to remaining stress, a stable and highly reliable pressure sensor construction is proposed. The pressure sensor is low in measurement error and small in floating capacitance and leakage current and good in characteristic. As a means to attain the above object, a polycrystalline silicon diaphragm is sealed with a silicon oxide film deposited through a LPCVD method and then completely covered. The diaphragm is placed on a surface of a semiconductor substrate with a nearly constant gap of 0.15 to 1.3 μm, and has difference-in-grade constructions of a deformation reducing means due to remaining stress.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Method of repairing a blade member
InactiveUS20060277753A1Induce compression stressBlade accessoriesEfficient propulsion technologiesWeld seamResidual stress
A method of repairing blade members, especially blade members in a turbomachine is provided. In one example, a damaged portion of a blade member is cut away from the blade member, by milling for example. The extent of the cut away portion generally corresponds in size and / or shape to the damaged area. A replacement portion is then welded into place in the resultant void in the blade member. The resulting weld seam is then burnished or deep rolled in order to cold work the blade member material at the weld seam. This induces compressive residual stresses in the blade member that counteract tensile residual stresses in and around the weld seam caused by the welding, and therefore strengthens the resulting repaired structure. The disclosed process particularly useful for repairing bladed disks (bladed monoblock disks) where individual blades cannot be removed for replacement or repair.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Method for removing cracks of Rene104 nickel-based superalloy during laser additive manufacturing
ActiveCN108941560AEliminate cracksInhibition of large size cracksAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingRoom temperatureStress relief
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
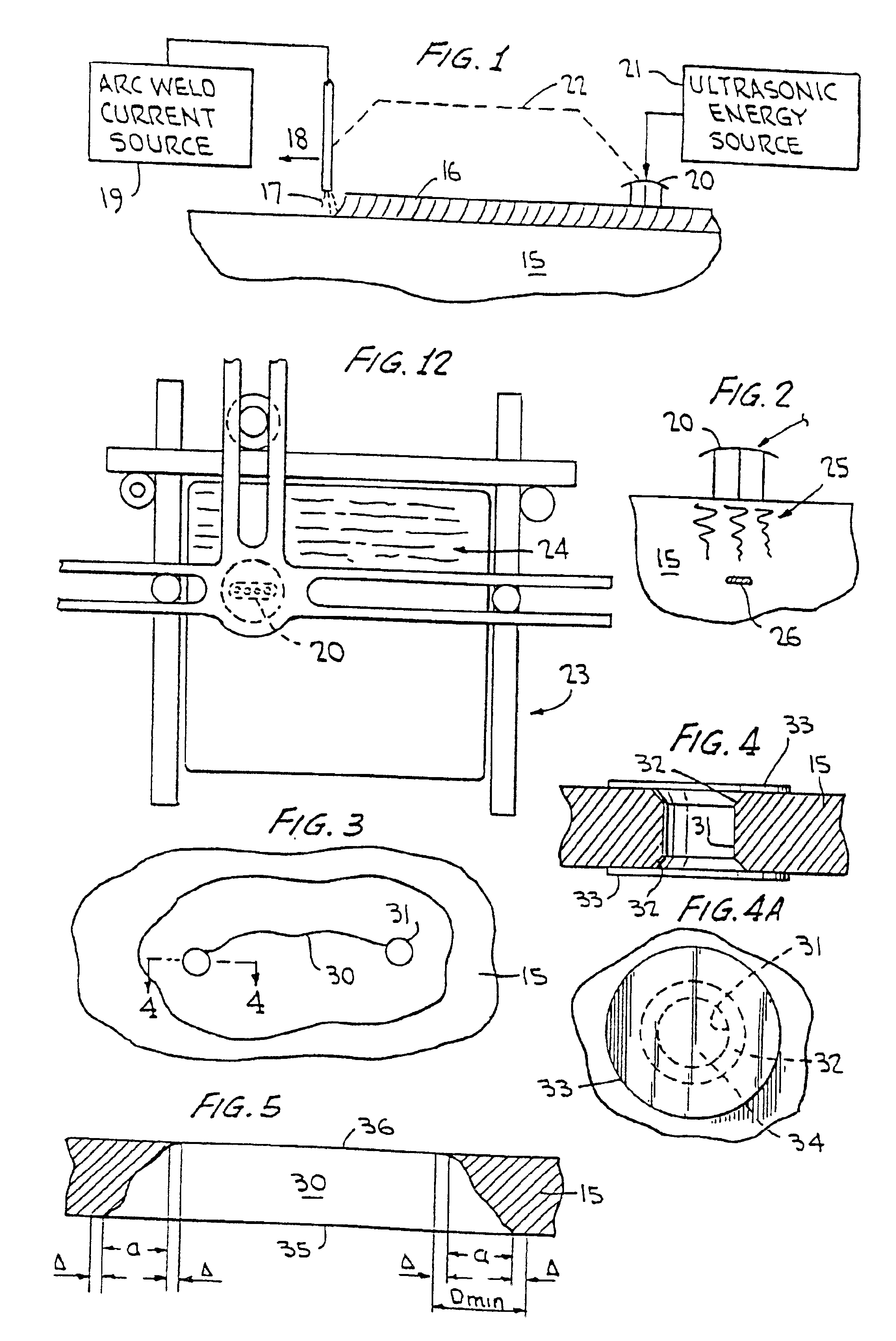
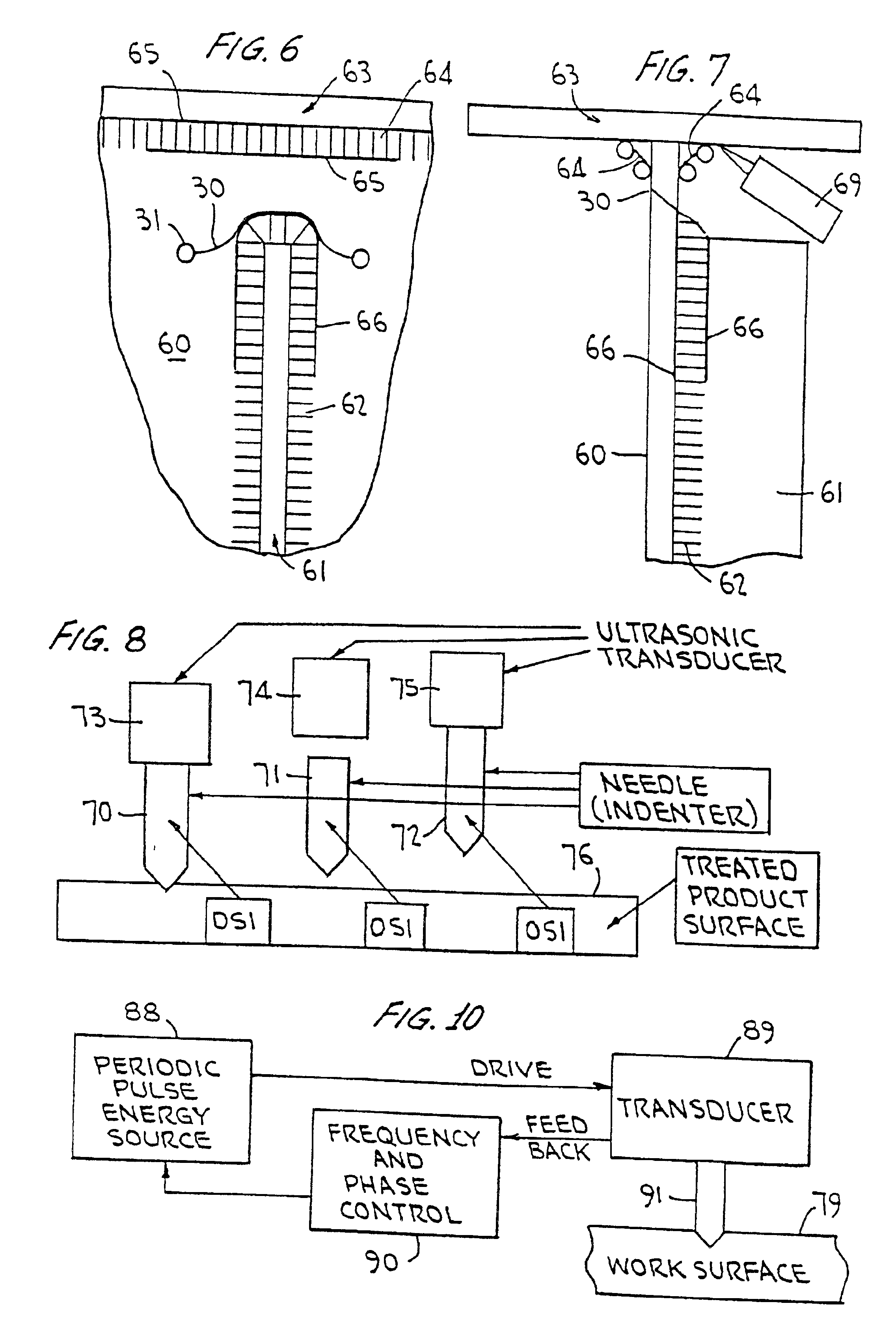
Ultrasonic impact methods for treatment of welded structures
InactiveUS6843957B2Improve corrosion fatigue strengthIncreased durabilityBlast furnace detailsHigh frequency current welding apparatusUltrasonic sensorEngineering
This invention provides methods of treatment for work products of materials such as steel, bronze, plastic, etc. and particularly welded steel bodies by pulse impact energy, preferably ultrasonic, to relax fatigue and aging and extend expectant life. The treatment may occur (a) at original production, (b) during the active life period for maintenance or (c) after failure in a repair stage. The ultrasonic treatment improves the work product strength. In welded products residual stress patterns near the weld sites are relaxed and micro-stress defects such as voids and unusual grain boundaries are reduced. The basic method steps are non-destructive in nature, inducing interior pulse compression waves with ultrasonic transducers and accessory tools impacting an external product surface with enough impulse energy to heat and temporarily plasticize the metal interior and relax stresses. The nature of the work product interior structure being treated is determined by sensing the mechanical movement at the impact surface of the work body to produce feedback frequency and phase signals responsive to input impact signals. These signals automatically conform driving pulse energy frequency and phase to the input transducers to match the mechanical resonance frequency of the working transducers and increase efficiency of energy transfer. Such feedback signals also are available for automated procedures which can improve product quality and consistency.
Owner:PROGRESS RAIL SERVICES
Silicon carbide and other films and method of deposition
ActiveUS7261919B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanotechnologyResidual stressSilicon carbide
A method of depositing a ceramic film, particularly a silicon carbide film, on a substrate is disclosed in which the residual stress, residual stress gradient, and resistivity are controlled. Also disclosed are substrates having a deposited film with these controlled properties and devices, particularly MEMS and NEMS devices, having substrates with films having these properties.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Semiconductor device including gate electrode for applying tensile stress to silicon substrate, and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6906393B2High carrier mobilitySimplify manufacturing stepsTransistorSolid-state devicesMass numberCharge carrier mobility
A gate insulating film (13) and a gate electrode (14) of non-single crystalline silicon for forming an nMOS transistor are provided on a silicon substrate (10). Using the gate electrode (14) as a mask, n-type dopants having a relatively large mass number (70 or more) such as As ions or Sb ions are implanted, to form a source / drain region of the nMOS transistor, whereby the gate electrode (14) is amorphized. Subsequently, a silicon oxide film (40) is provided to cover the gate electrode (14), at a temperature which is less than the one at which recrystallization of the gate electrode (14) occurs. Thereafter, thermal processing is performed at a temperature of about 1000° C., whereby high compressive residual stress is exerted on the gate electrode (14), and high tensile stress is applied to a channel region under the gate electrode (14). As a result, carrier mobility of the nMOS transistor is enhanced.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Polycrystalline diamond construction with controlled gradient metal content
ActiveUS20090152017A1Hardness resistanceResistance to stabilityDrill bitsConstructionsDiamond crystalPolycrystalline diamond
Polycrystalline diamond constructions comprises a diamond body attached to a metallic substrate, and having an engineered metal content. The body comprises bonded together diamond crystals with a metal material disposed interstitially between the crystals. A body working surface has metal content of 2 to 8 percent that increases moving away therefrom. A transition region between the body and substrate includes metal rich and metal depleted regions having controlled metal content that provides improved thermal expansion matching / reduced residual stress. A point in the body adjacent the metal rich zone has a metal content that is at least about 3 percent by weight greater than that at a body / substrate interface. The metal depleted zone metal content increases gradually moving from the body, and has a thickness greater than 1.25 mm. Metal depleted zone metal content changes less about 4 percent per millimeter moving along the substrate.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Methods and apparatus for detecting and quantifying surface characteristics and material conditions using light scattering
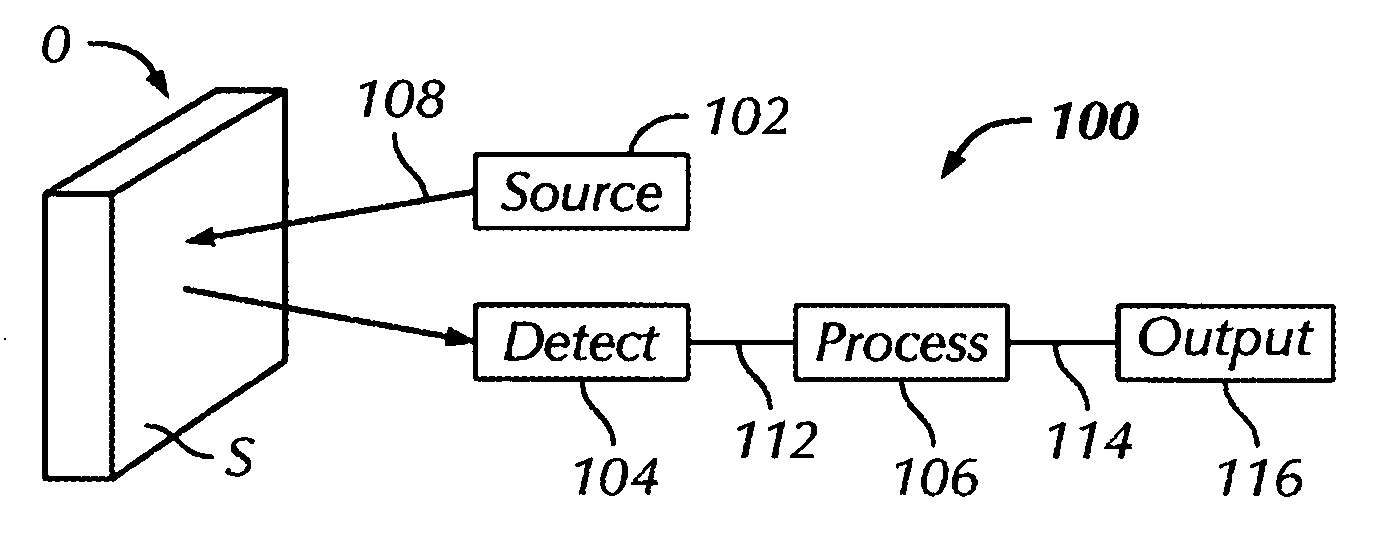
ActiveUS20050036135A1Scattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationSurface roughnessSignal detector
A system for quantifying surface characteristics detects and quantifies characteristics of a surface of an object. For example, the system may quantify changes in surface roughness without contacting the specimen and without requiring precise temporal or spatial stability. The system may also quantify the evolution or progression of a particular characteristic of a surface, such as a defect, a slipband, a crack, a microcrack, a pit, a damage feature, corrosion, a contour change, an impact crater, a change in residual stress, and so on. The system may include an energy source, a detector section, and a process section. The energy source transmits a source signal to the surface of the object. The source signal is specularly reflected and / or scattered by the surface to yield one or more received signals. The detector section receives the received signal and, in turn, provides a detector signal indicative of the received signal. The processor applies an algorithm to the detector signal to quantify an evolution in one or more characteristics of the surface.
Owner:METROLASER
Bonded Assembly Having Low Residual Stress
InactiveUS20100326740A1Heating fastImprove impact performanceDrill bitsLamination ancillary operationsPolycrystalline diamondCobalt
In one aspect of the present invention, a method for forming a bonded assembly comprises providing a first and second portion of the assembly; preparing a mating surface on each portion that conforms substantially to the mating surface of the other portion; rapidly heating a bonding material while substantially heating no more than a thin surface zone adjacent each mating surface, and rapidly assembling the two portions in such a manner as to confine a fraction of the bonding material between the mating surfaces. The first portion may comprise polycrystalline diamond or thermally stable polycrystalline diamond; the second portion may comprise cobalt-cemented tungsten carbide. The assembly may comprise a tool for high-impact applications.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com