Patents
Literature
651results about "Burnishing machines" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
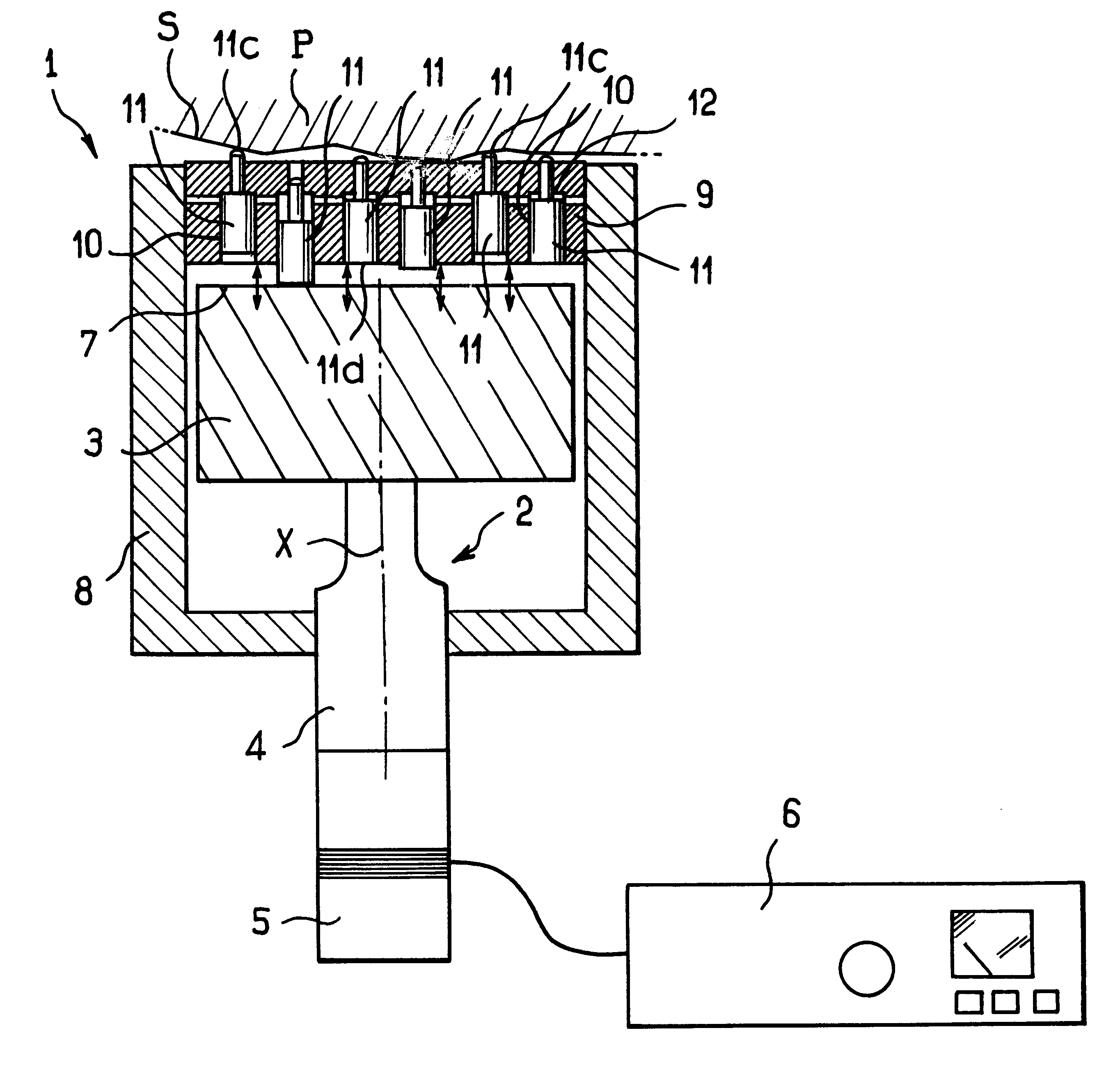
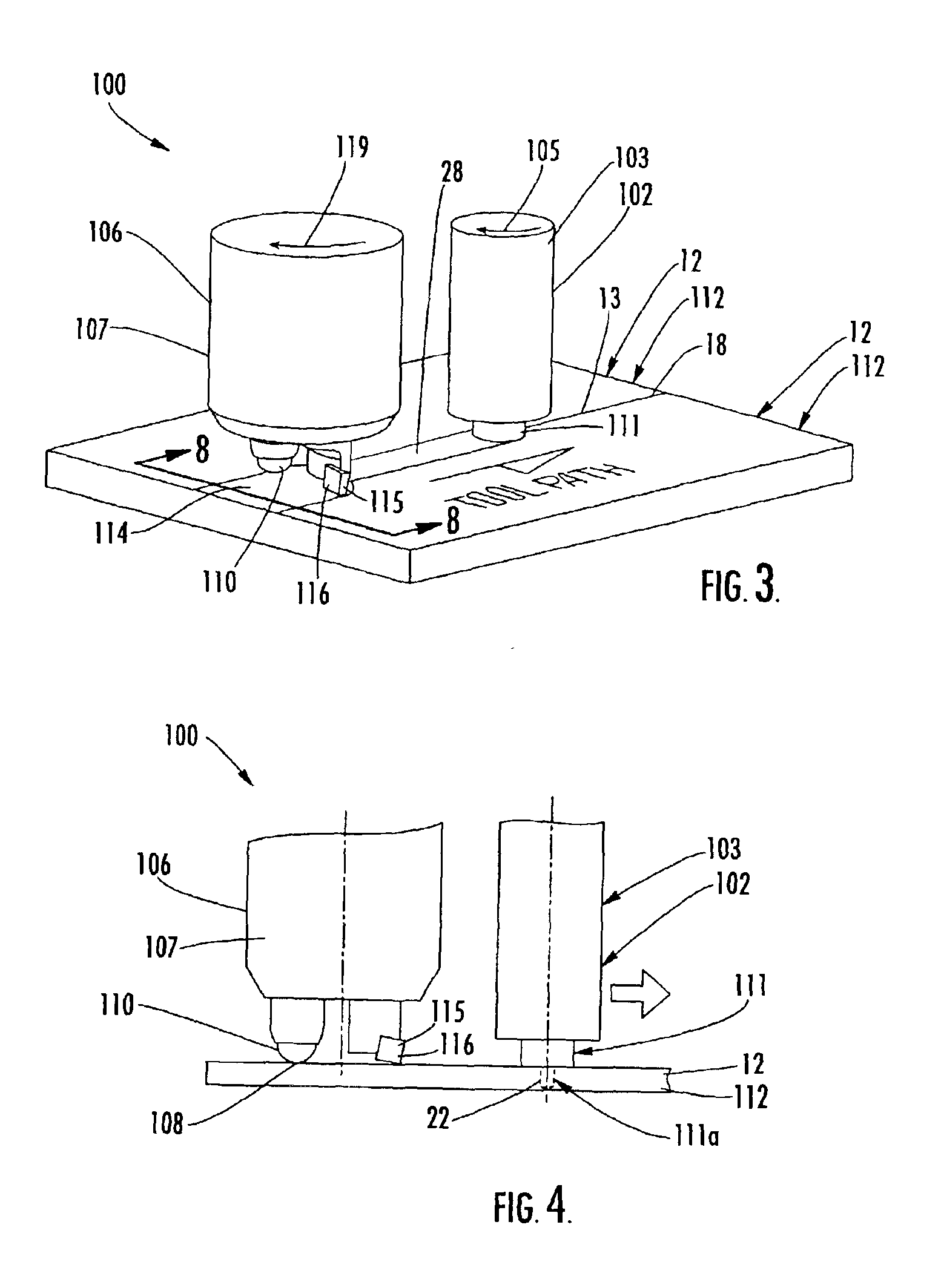
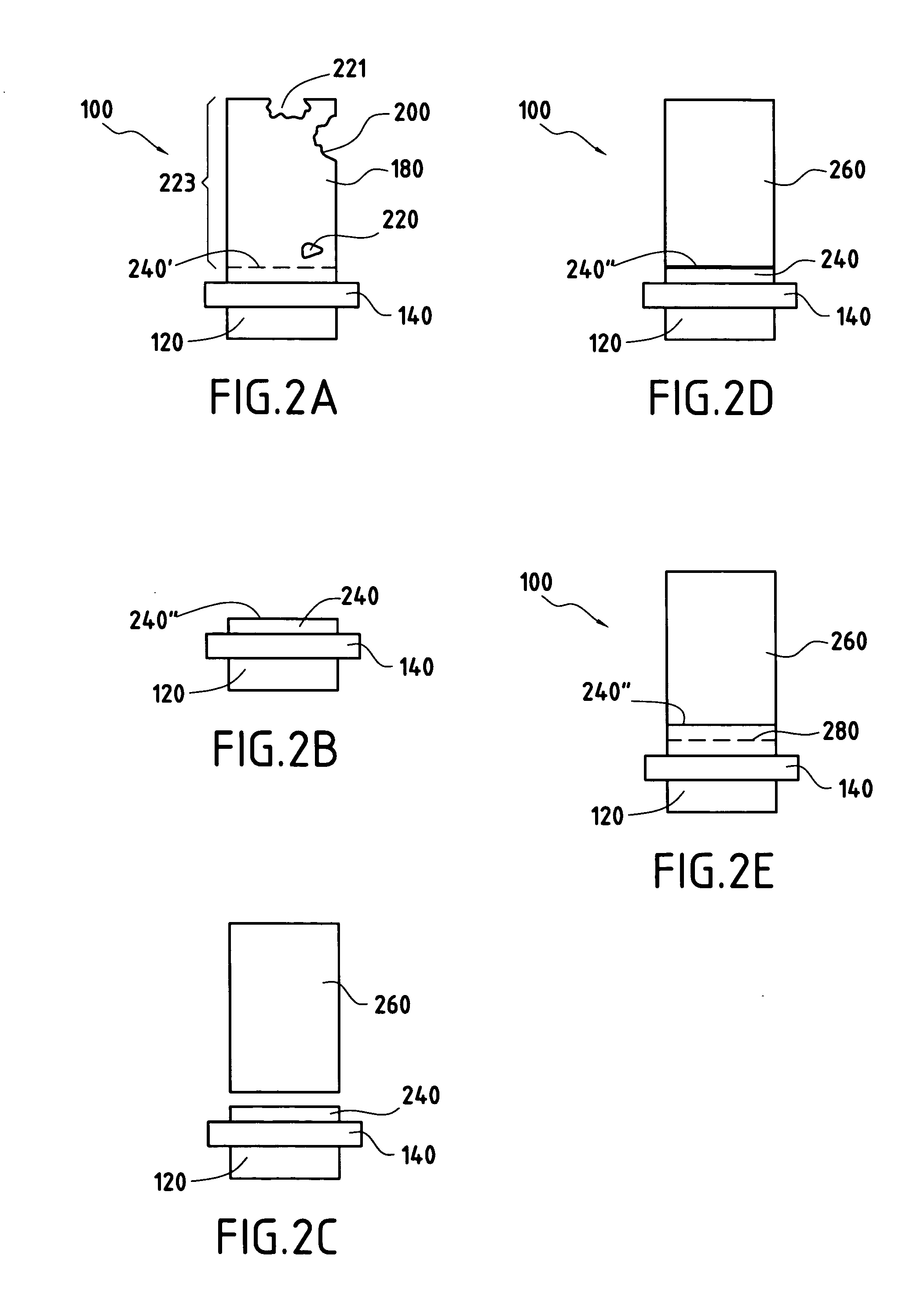
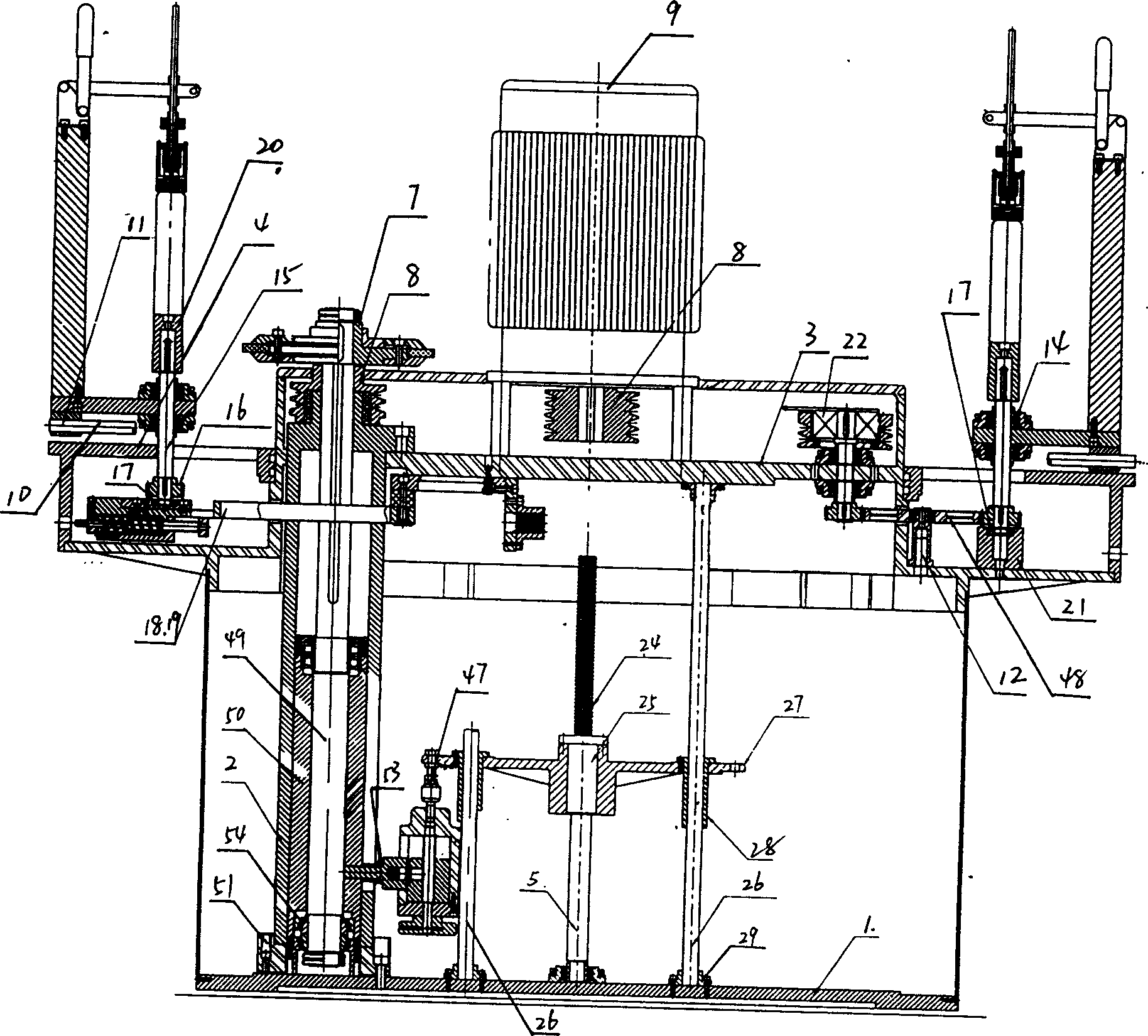
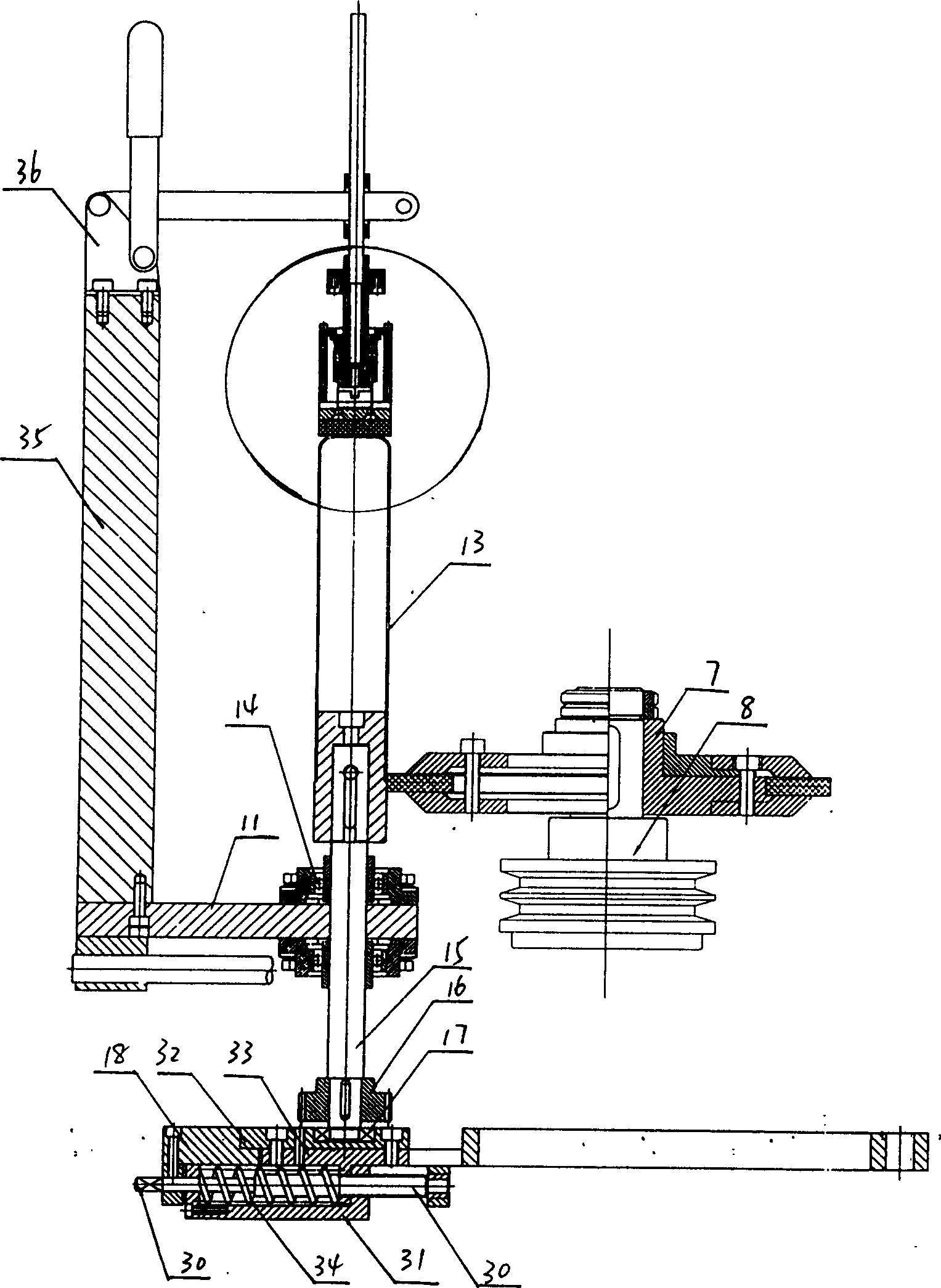
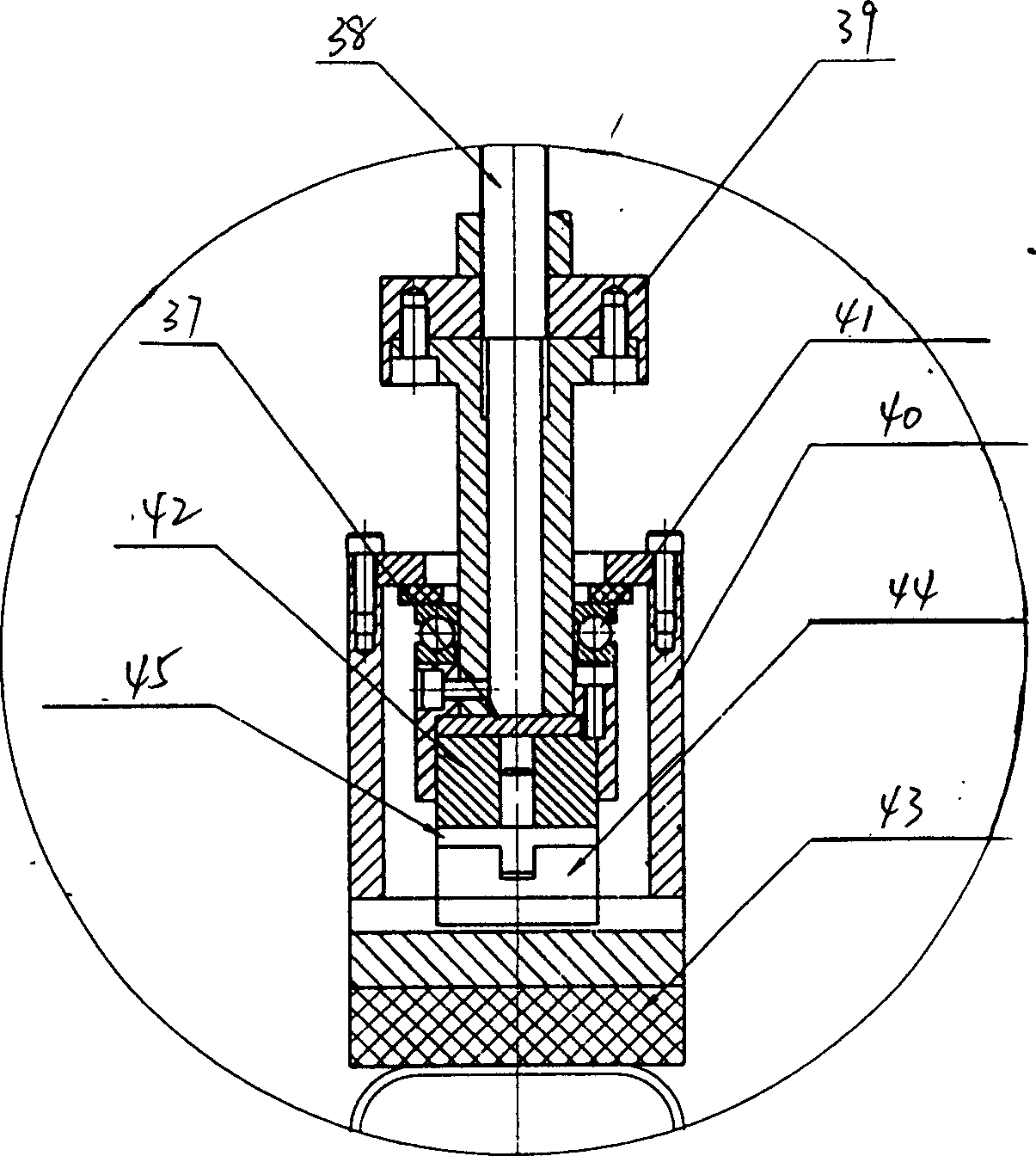
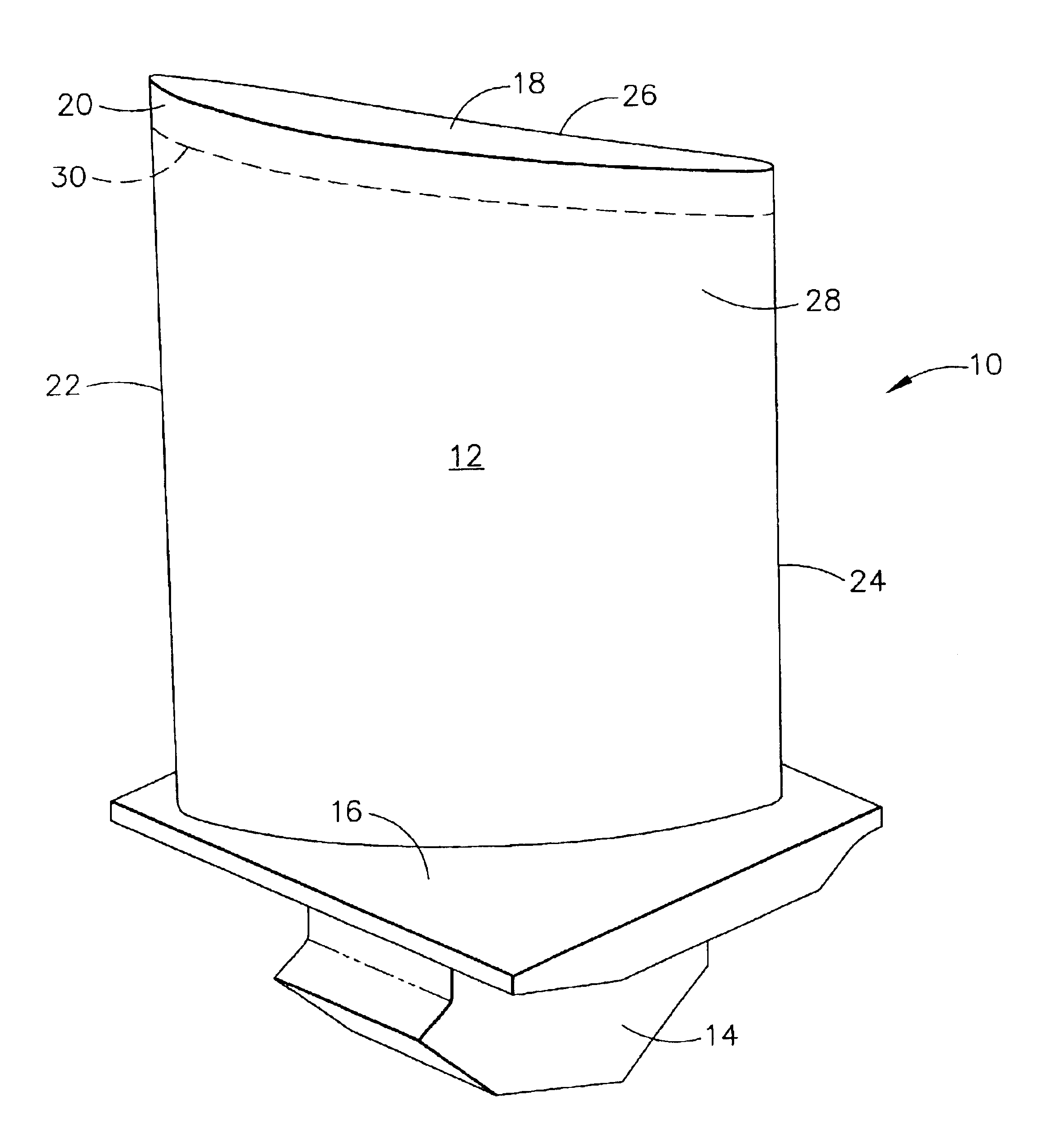
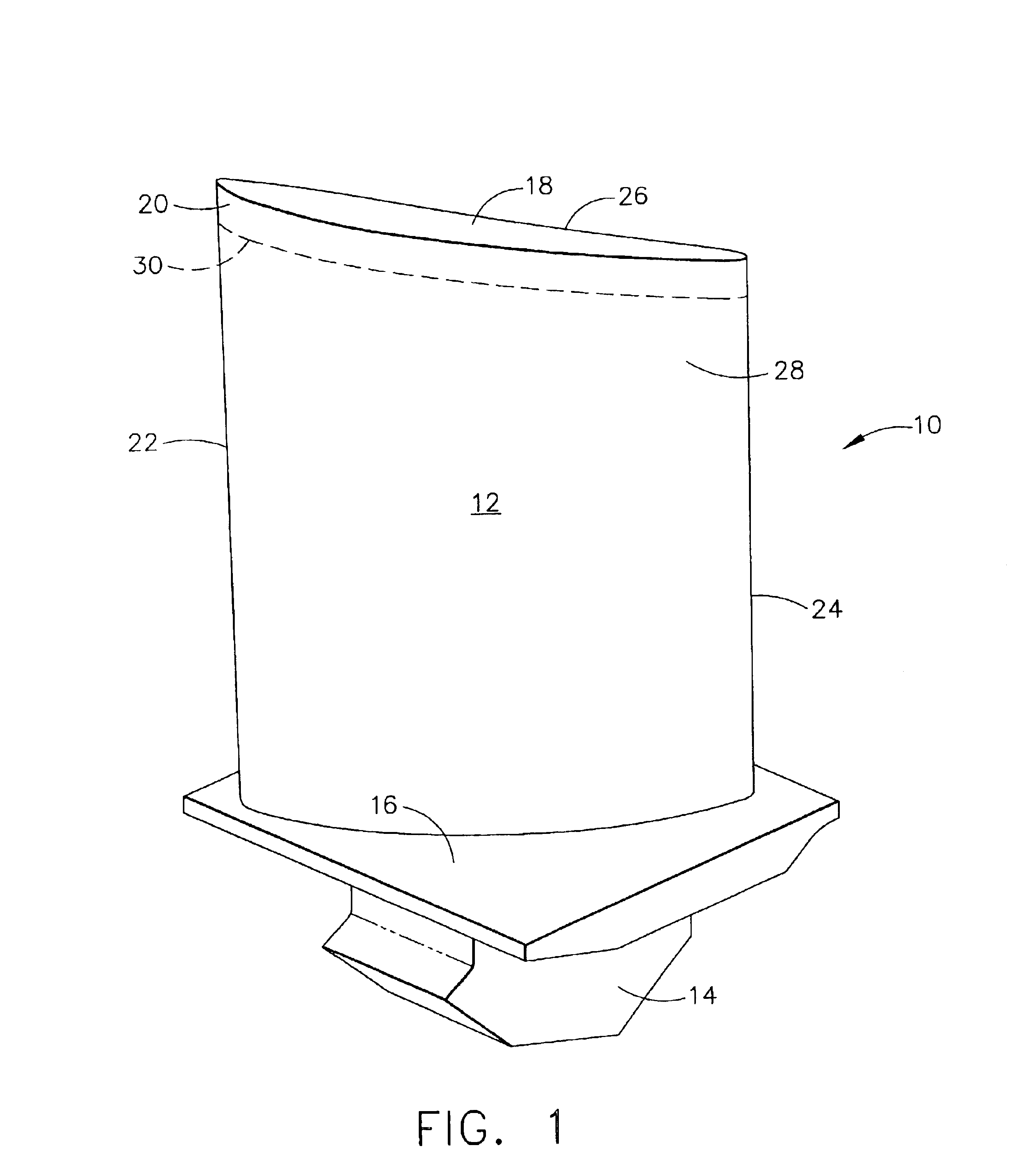
Apparatus for surface treatment by impact
InactiveUS6343495B1Quality improvementSimple treatmentNon-mechanical blast generatorsBurnishing machinesBiomedical engineeringProjectile
The invention relates to apparatus for surface treatment by impact, the apparatus comprising a vibrating surface and at least one projectile suitable for being projected towards the surface to be treated by said vibrating surface. The apparatus includes retaining means for keeping each projectile captive in the apparatus.
Owner:SONATS SOC DES NOUV APPL DES TECHN DE SURFACES
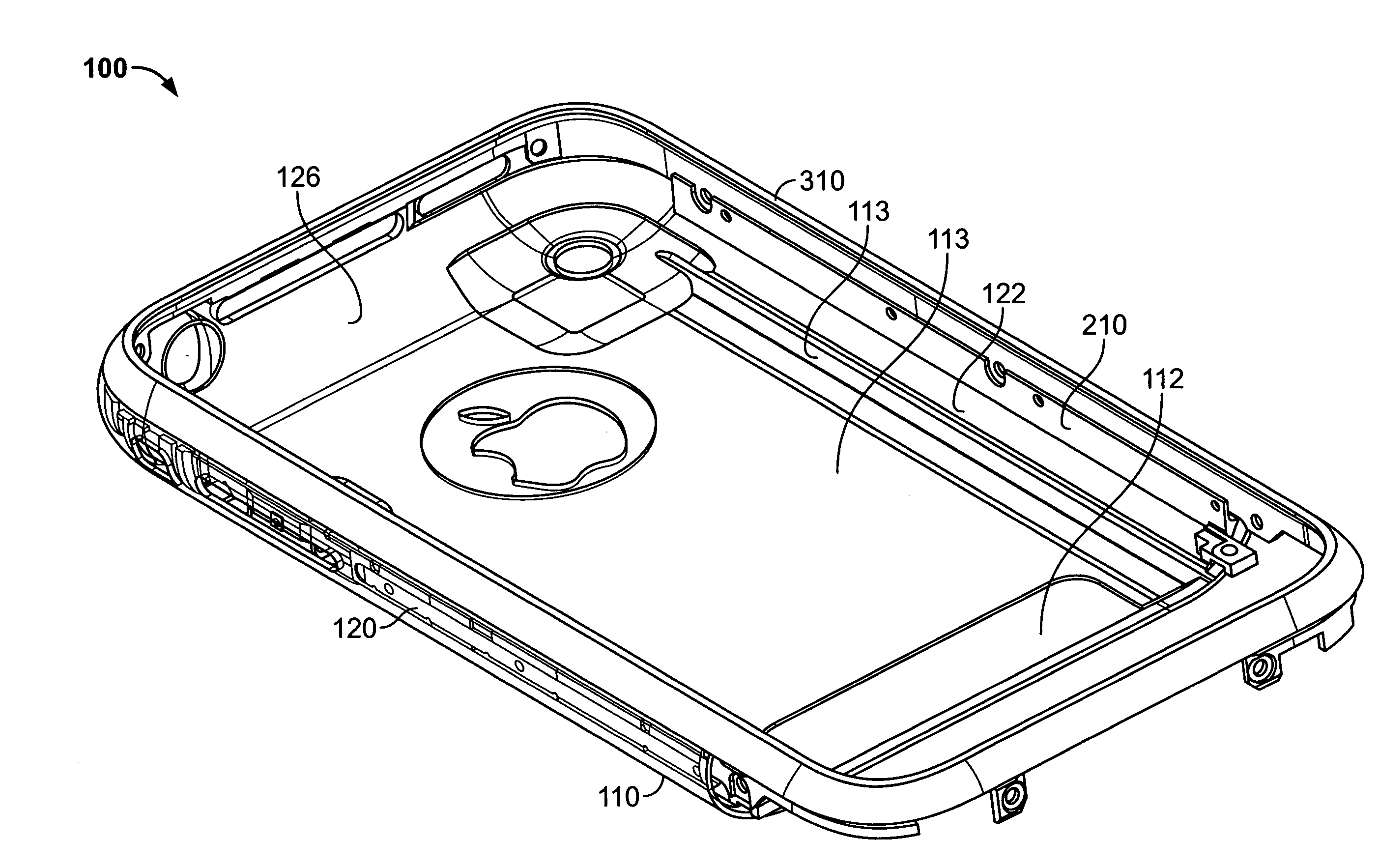
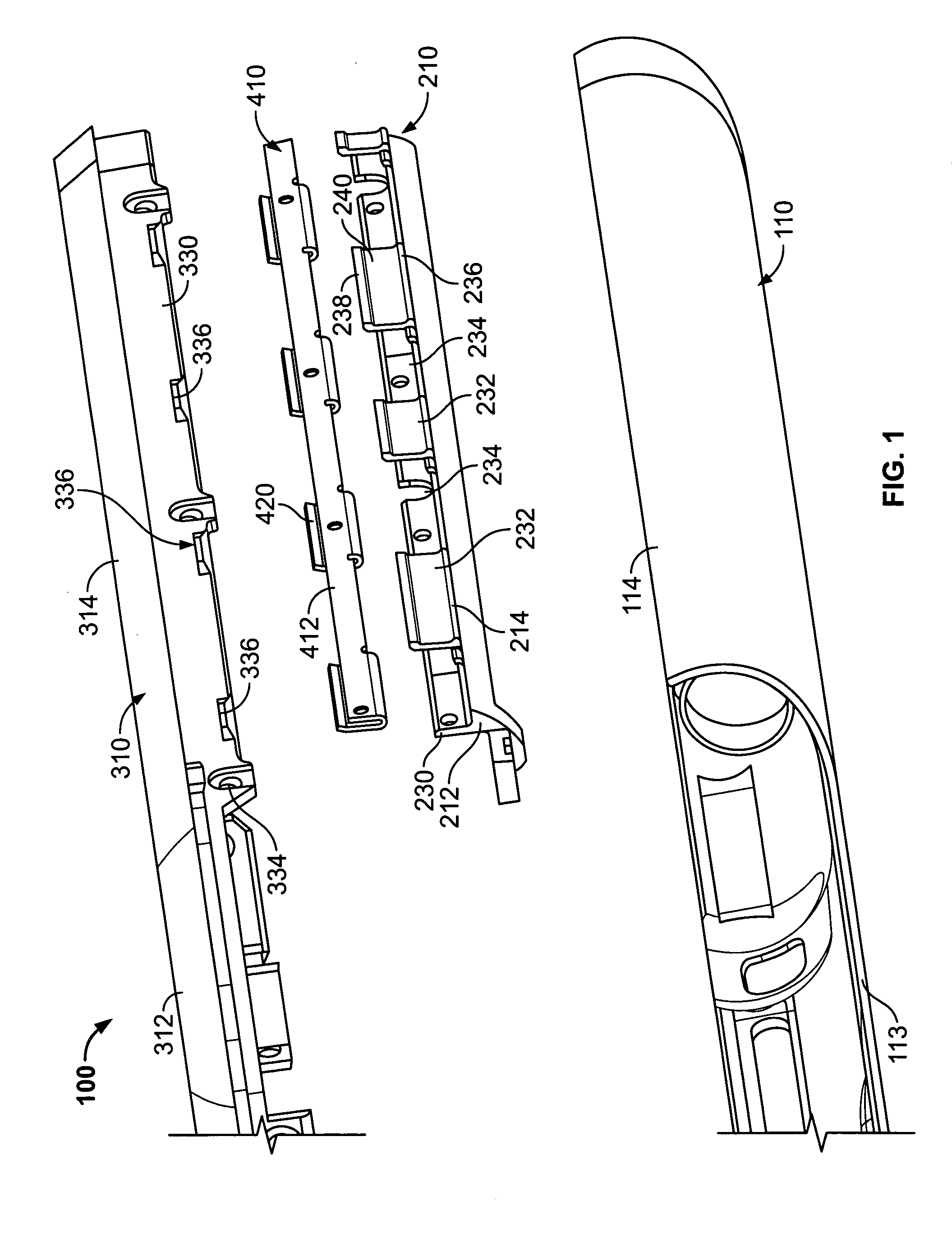
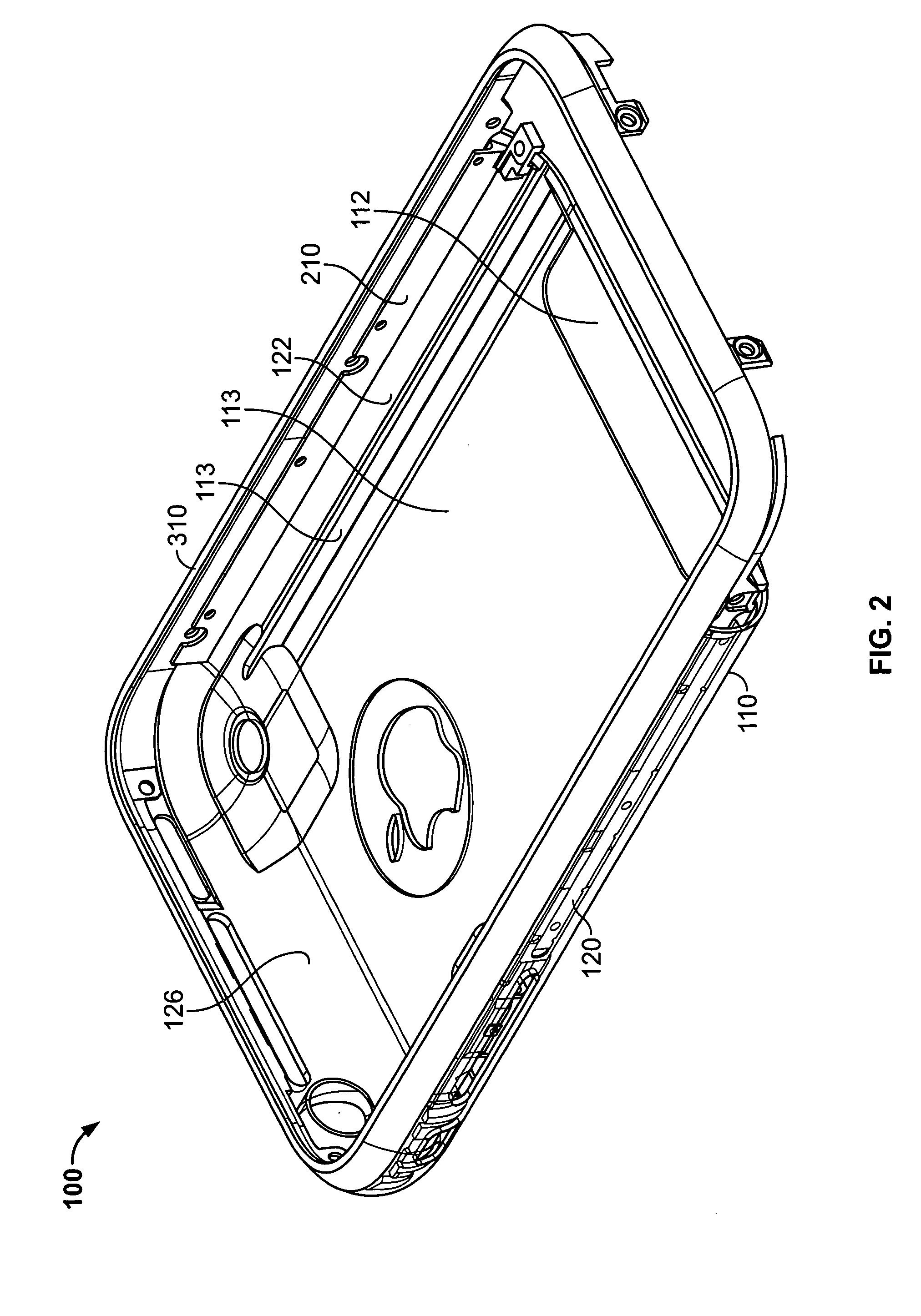
Cold worked metal housing for a portable electronic device
ActiveUS20080165485A1High hardnessDesired impactClosed casingsDigital data processing detailsMachiningElectron
A cold worked stainless steel bezel for a portable electronic device is provided. The bezel is secured flush to a housing to form part of the case of the portable electronic device. A brace that includes a slot for receiving a wall extending from the bezel is fixed to the housing. When the bezel engages the housing, the wall of the bezel is inserted in the slot of the brace and releasably held by a spring that engages both the brace and the wall. The bezel can be released by disengaging the spring, (e.g., using a special tool or a magnetic field). Because the bezel is manufactured from cold worked stainless steel, it is hard and resistant to impacts. Cold worked steel also facilitates manufacturing within design constraints and tolerances, and requires very little machining after manufacturing to comply with those constraints. The portable electronic device may include a personal media device, a mobile telephone, or any other suitable device or combination thereof.
Owner:APPLE INC
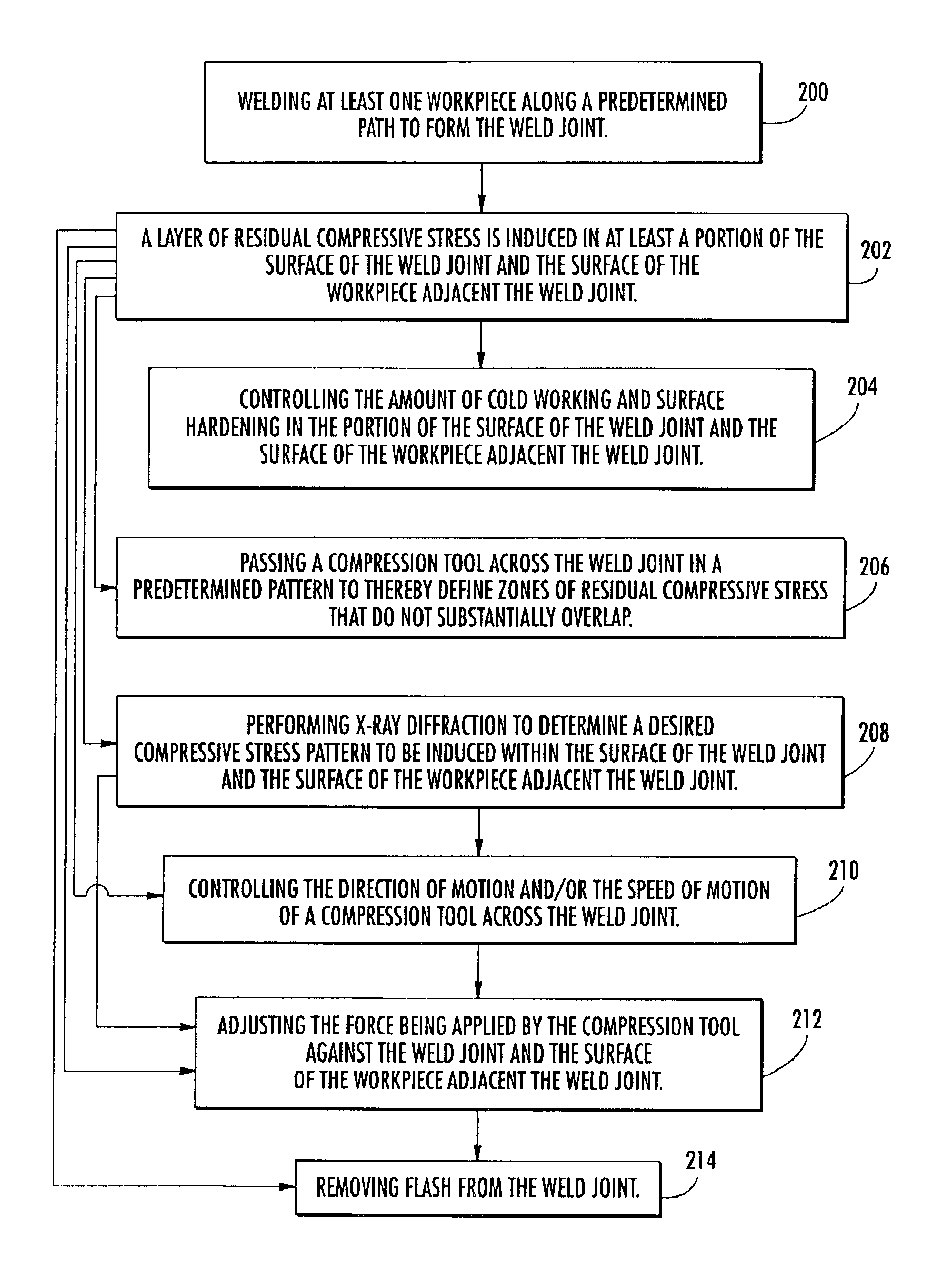
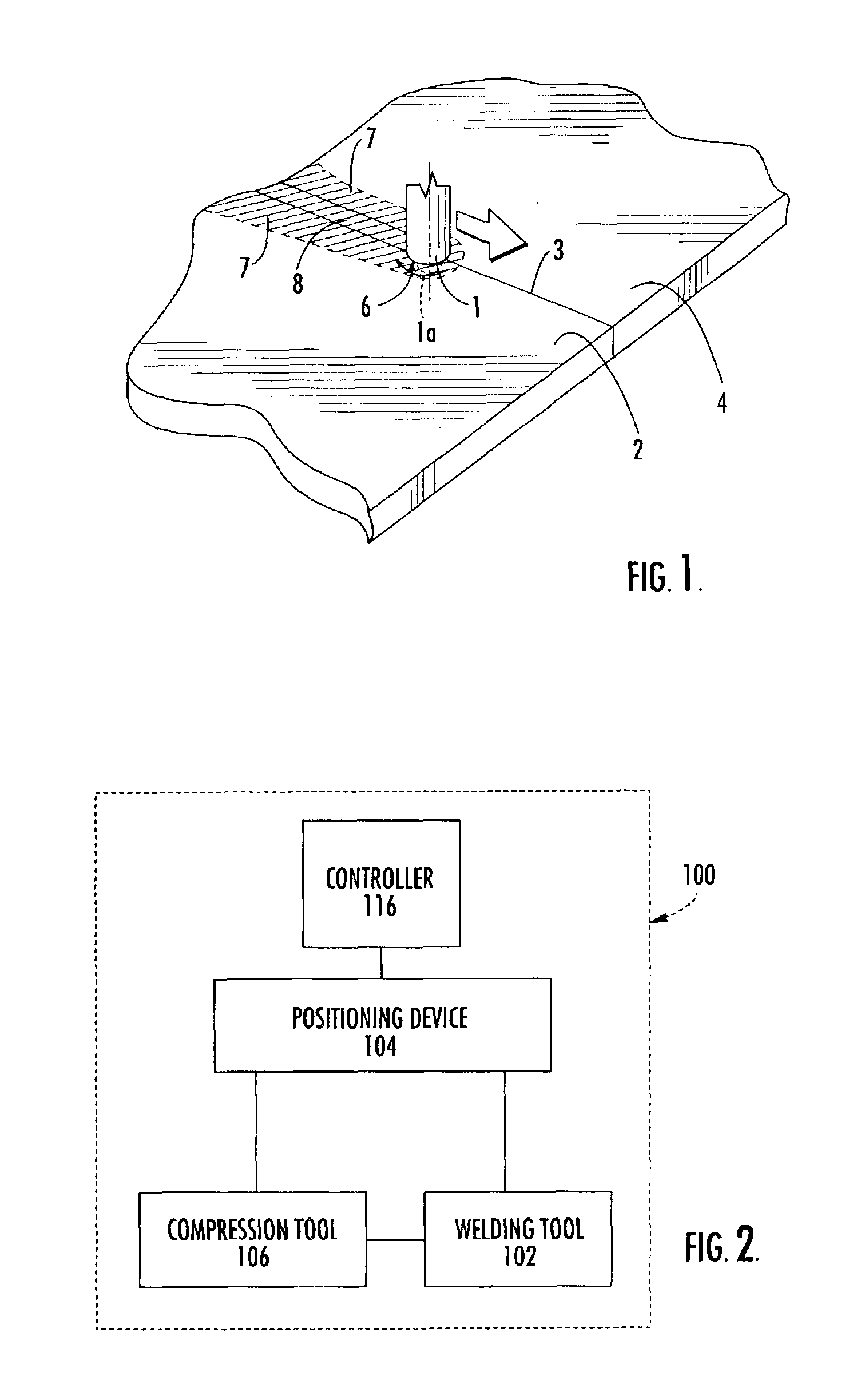
Apparatus and method for forming weld joints having compressive residual stress patterns
InactiveUS6926970B2Improve material propertiesHigh surface finishWelding/cutting auxillary devicesBurnishing machinesUltimate tensile strengthMechanical engineering
The welding apparatus and associated method are provided. The welding apparatus includes a welding tool for forming a weld joint along the surface of at least one workpiece. The welding apparatus also includes a compression tool for selectively inducing a layer of residual compressive stress in at least a portion of the surface of the weld joint and the surface of the at least one workpiece to thereby improve the material properties of the workpiece, including corrosion resistance and fatigue strength.
Owner:SURFACE TECH HLDG +1
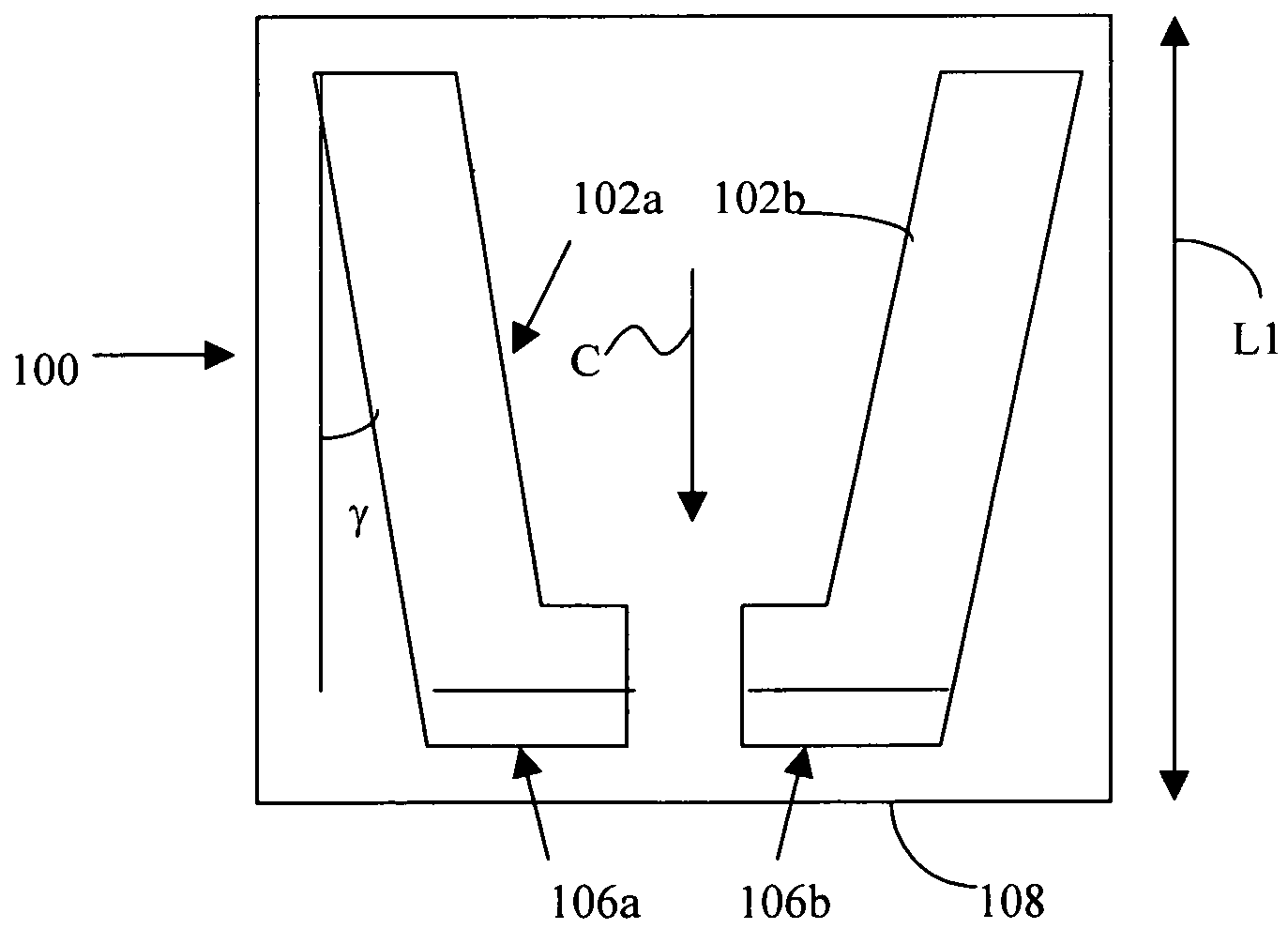
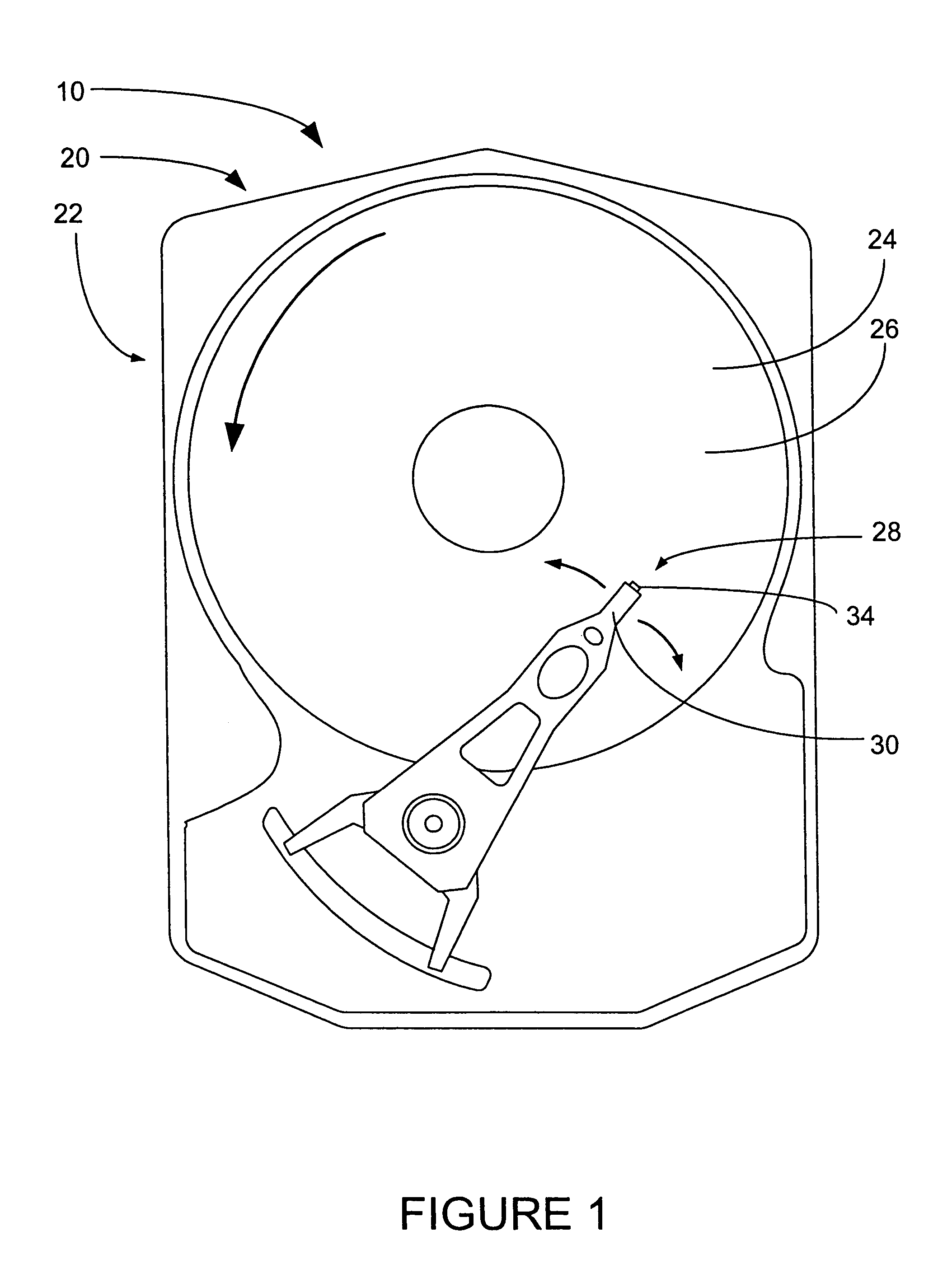
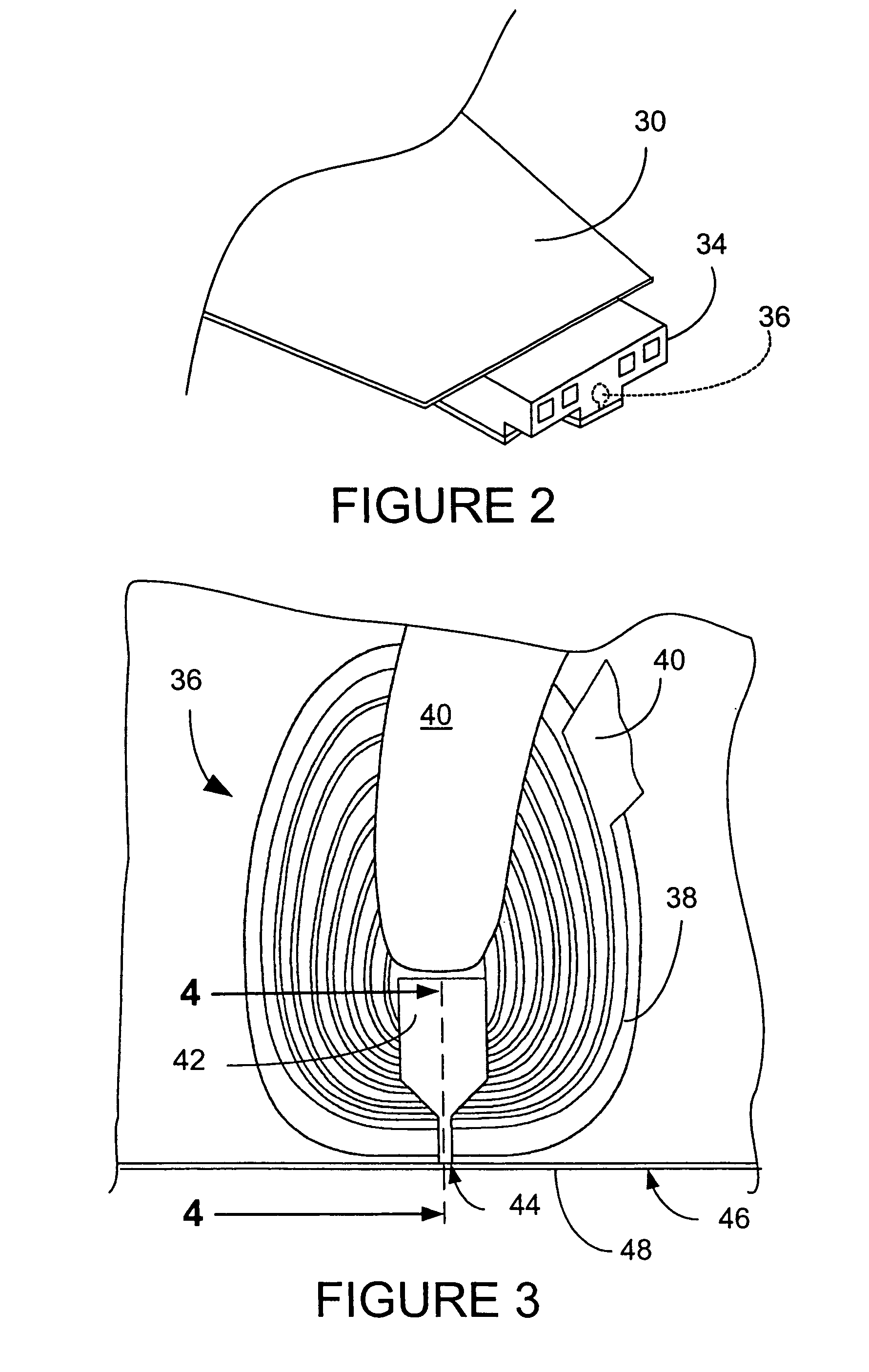
Burnishing head
InactiveUS7314404B2Less time for to recoverIncrease heightRevolution surface grinding machinesFluid-dynamic spacing of headsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A burnishing head comprises at least two rails, each rail having an inner wall and an outer wall. The outer walls are at an angle relative to one another and relative to a central axis of the burnishing head. This angle permits the burnishing head to exhibit improved recovery time if it contacts a disk being burnished. The rail walls are vertical, and the corner between the rail walls and the top surface of the rails is sharp.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC +1
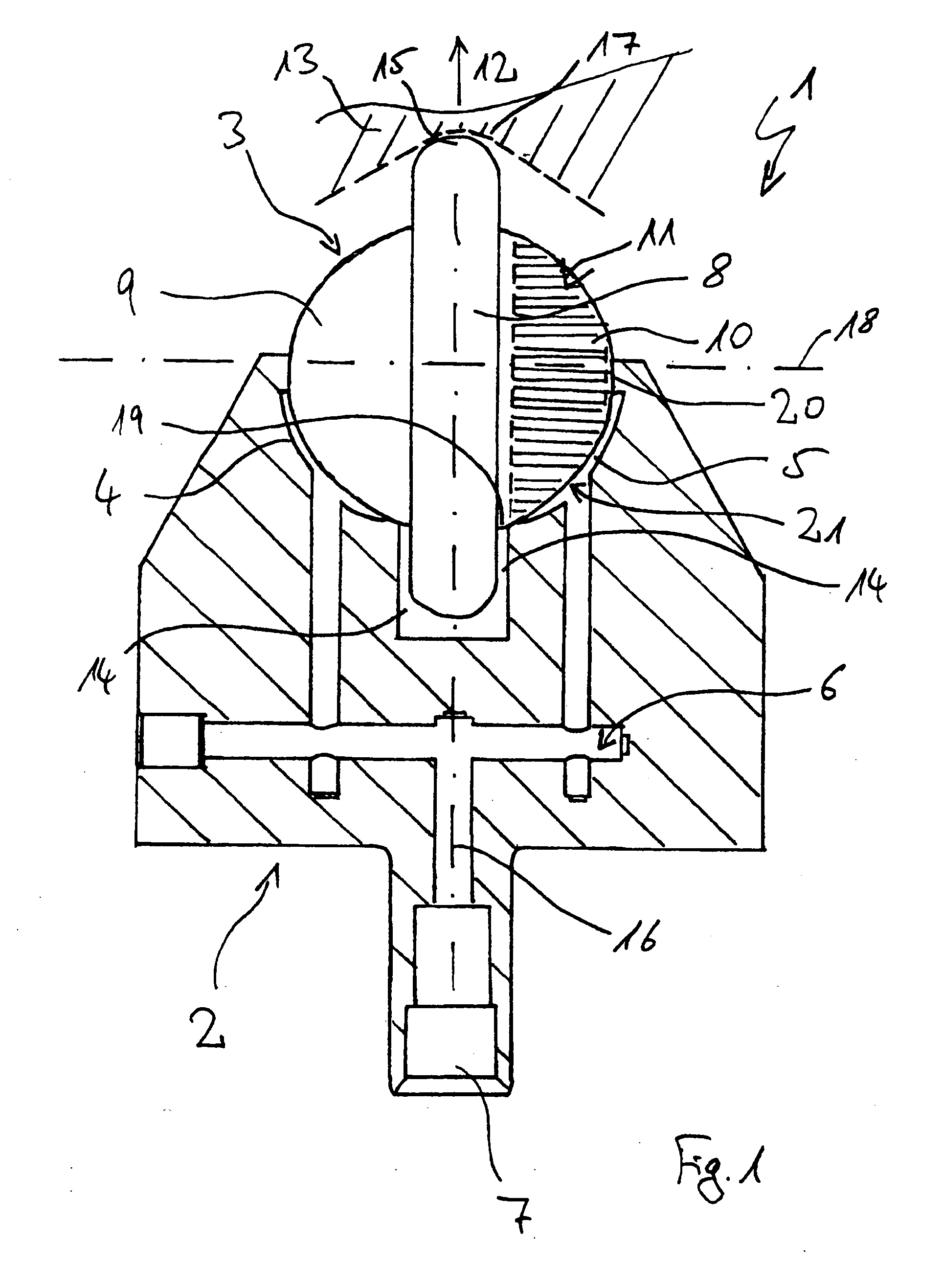
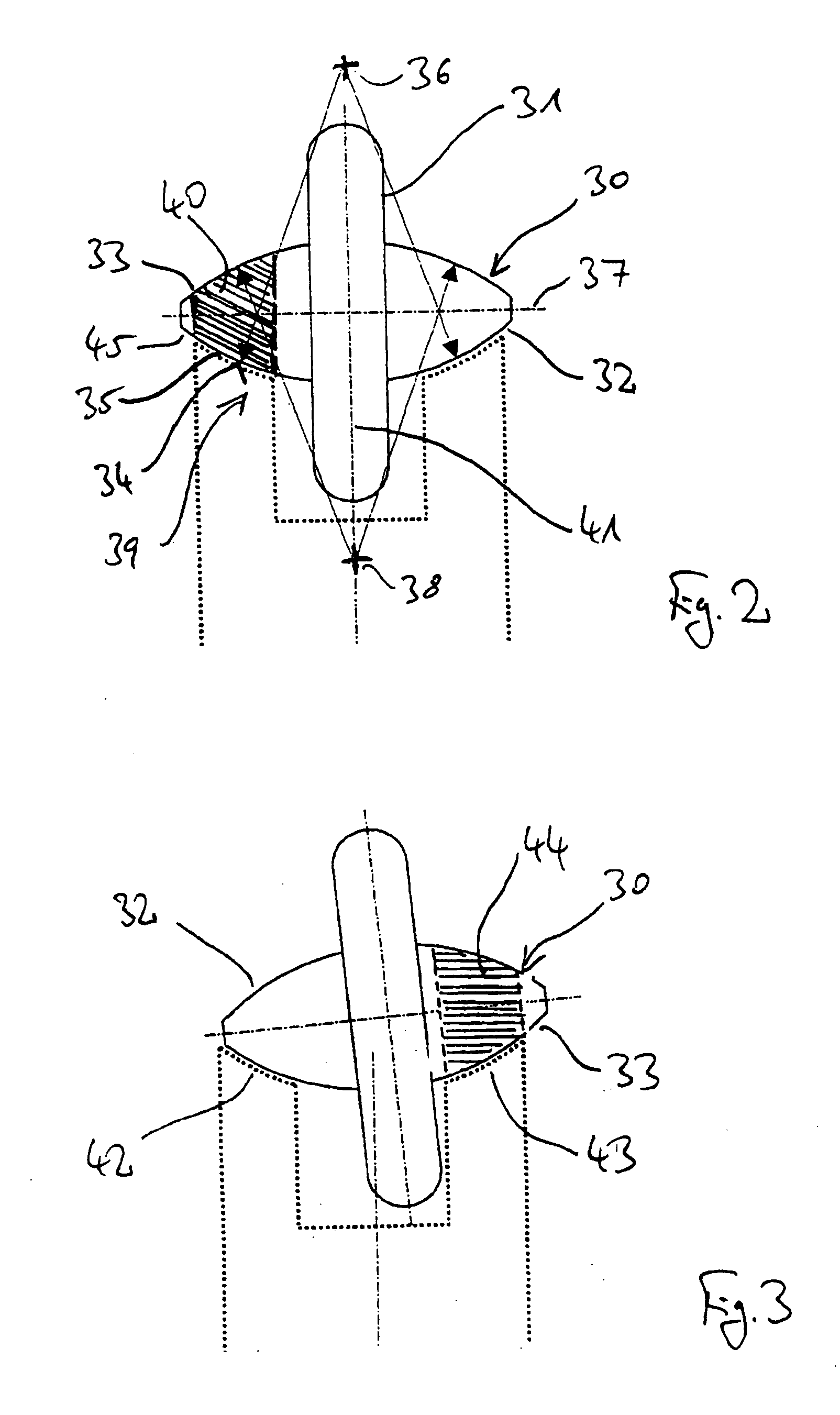
Method and apparatus for improving the magnitude of compressive stress developed in the surface of a part
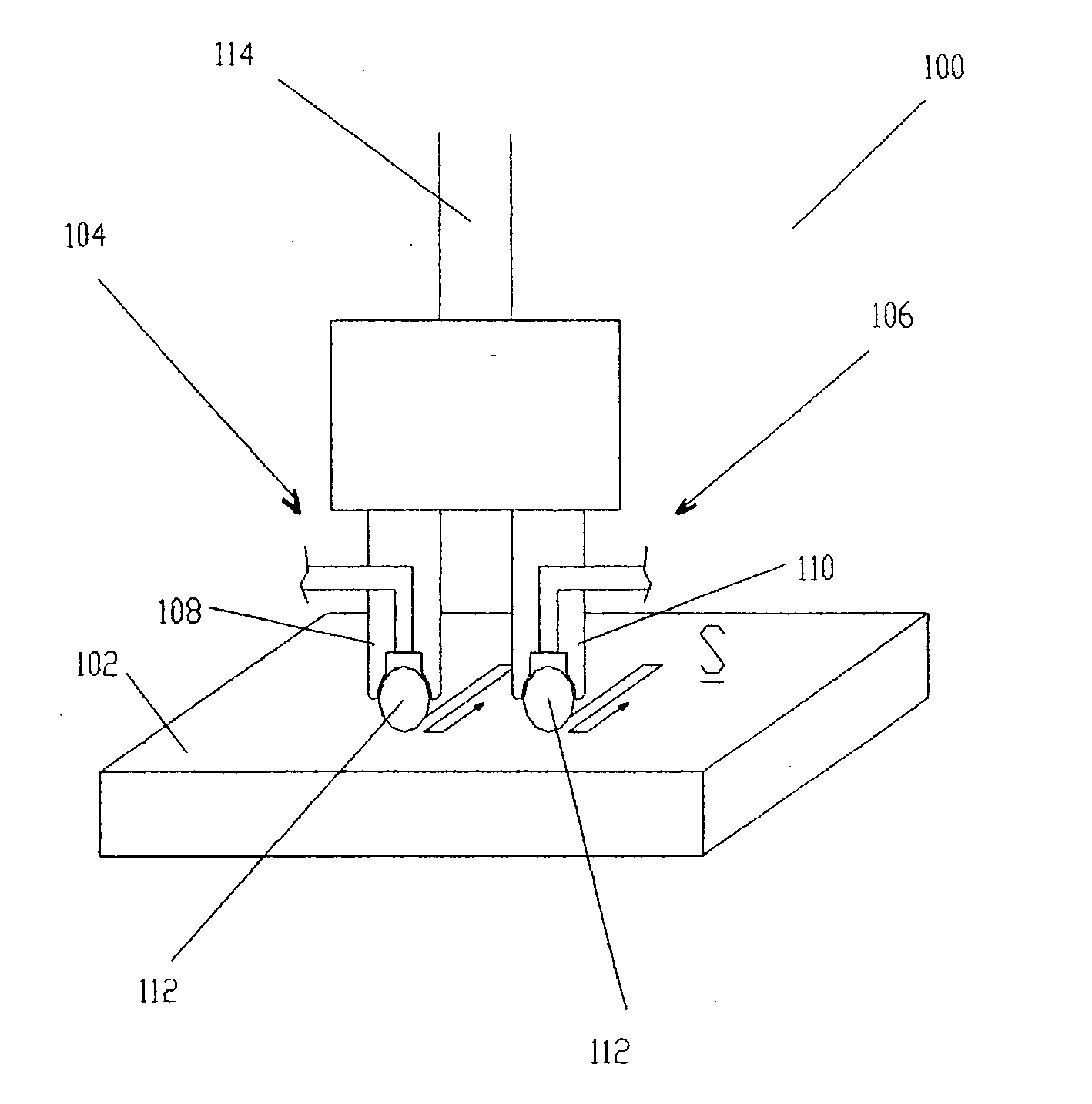
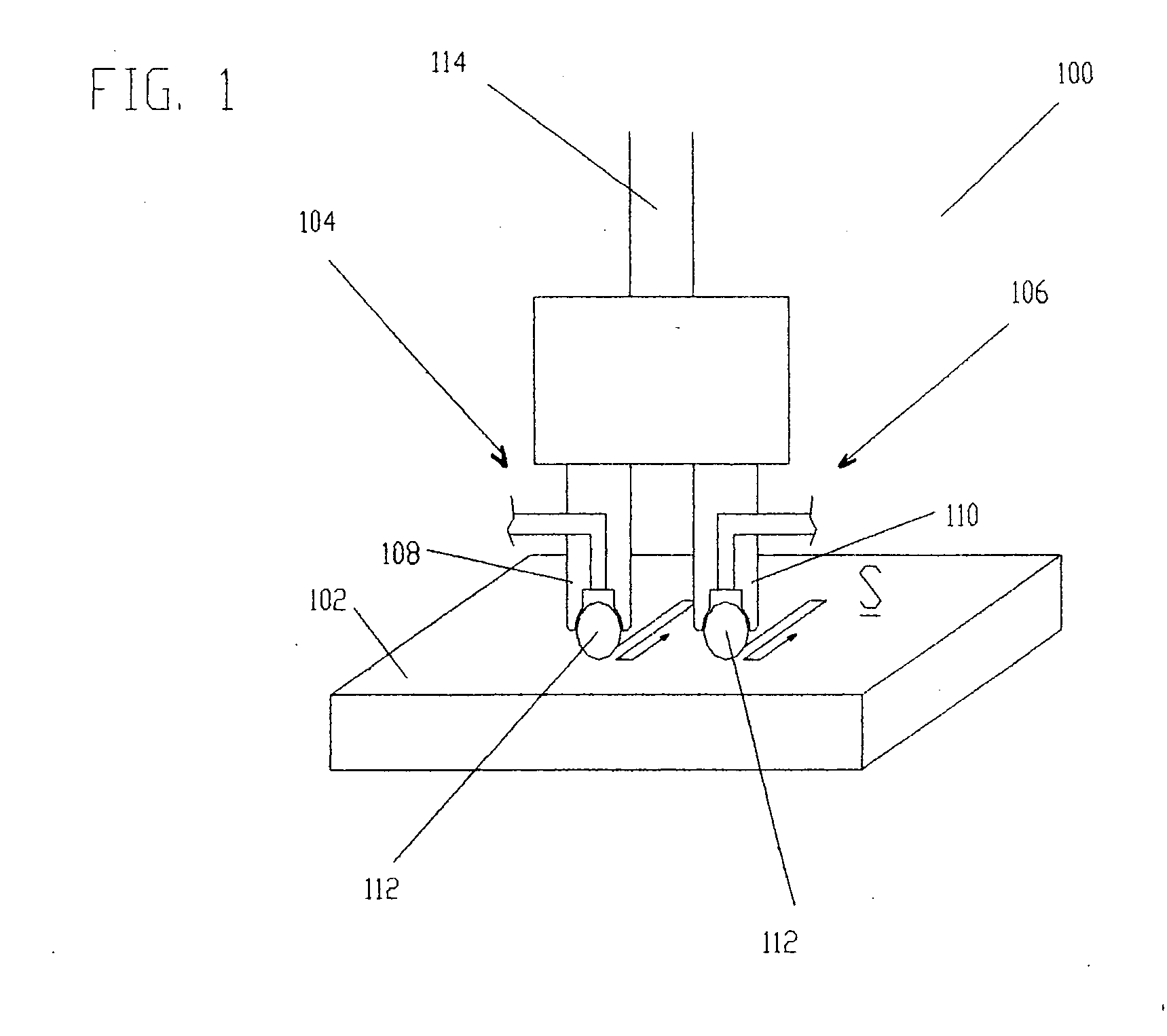
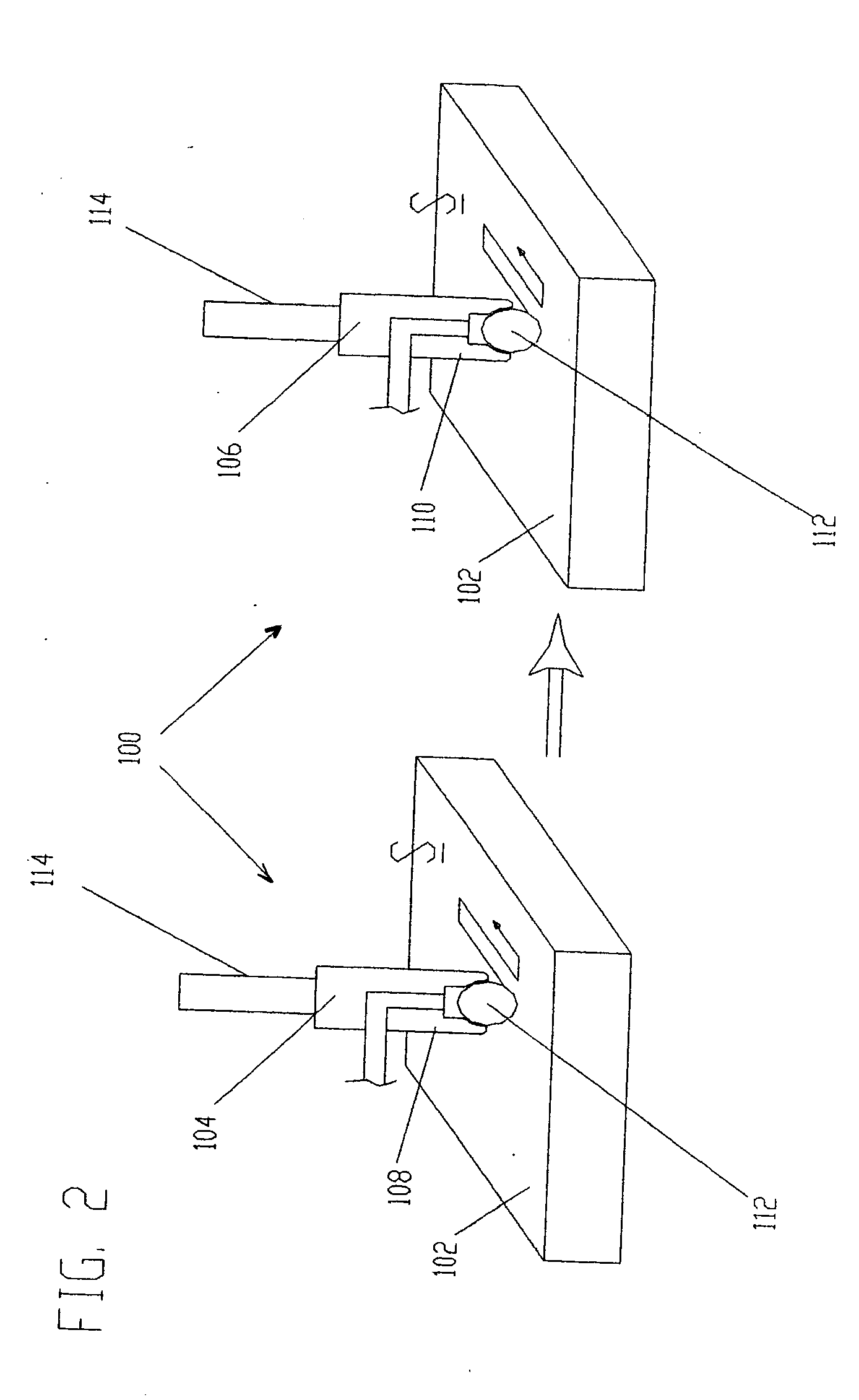
ActiveUS20050155203A1Induce residual stressSmall diameterBurnishing machinesEngineeringCompressive strength
This invention relates to a method and an apparatus for performing the method of inducing compressive residual stress along the surface of a part. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the method includes burnishing or deep rolling a surface using a first and a second roller or ball burnishing members, whereby the first and second burnishing members may have a different diameter and / or modulus of elasticity. In another preferred embodiment of the invention, the burnishing operations may be performed while the surface of the part is at different temperatures.
Owner:SURFACE TECH HLDG
Apparatus and methods for repairing compressor airfoils in situ
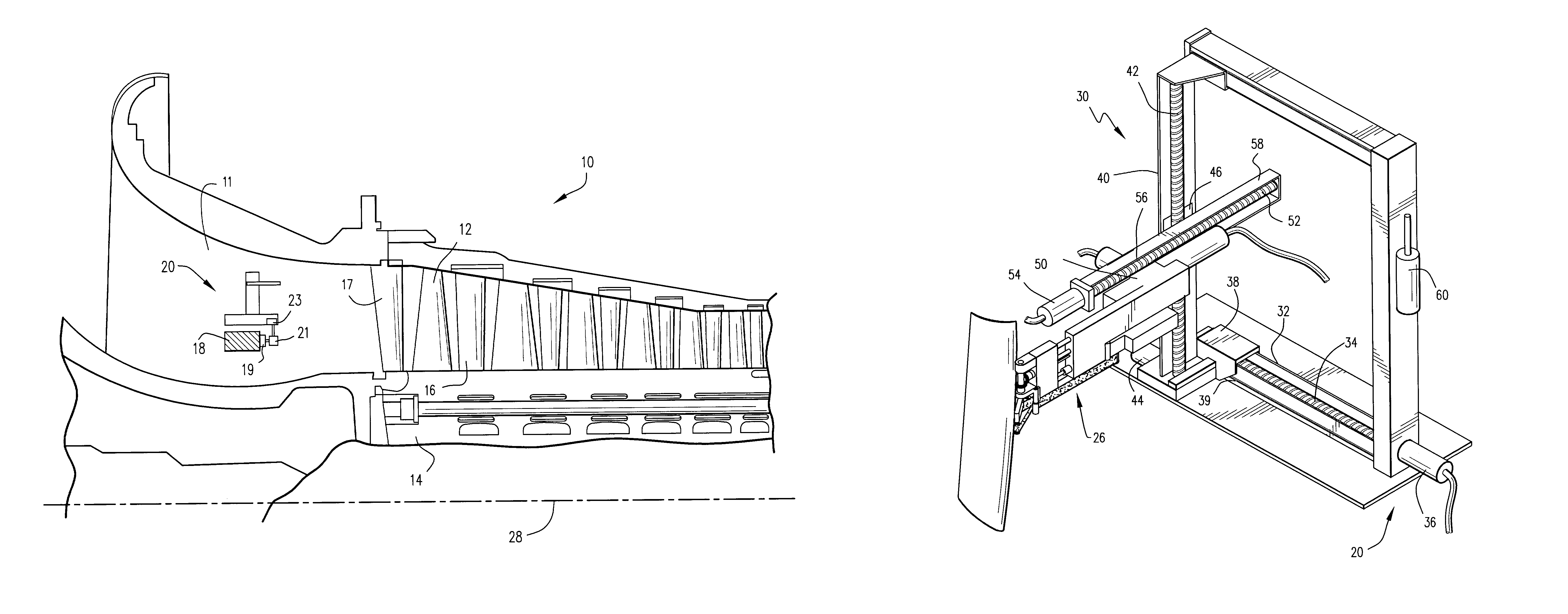
InactiveUS7032279B2Maximize impactFine surfacePump componentsAssembly machinesEngineeringManipulator
The apparatus includes a track mounted in the inlet of a compressor. A manipulator is mounted for movement about the track and carries three modules, the last of which mounts a tool head for movement in a Cartesian coordinate system and about the track. A measuring head measures the location of the airfoil surface. An abrading tool mounted on the third module removes surface material from the airfoil. Subsequently, a shot-peening device, either a flapper with embedded shot or free shot is impacted against the abraded surface to strengthen the surface. Final inspection is performed by a light and camera head mounted on the third module.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of repairing a blade member
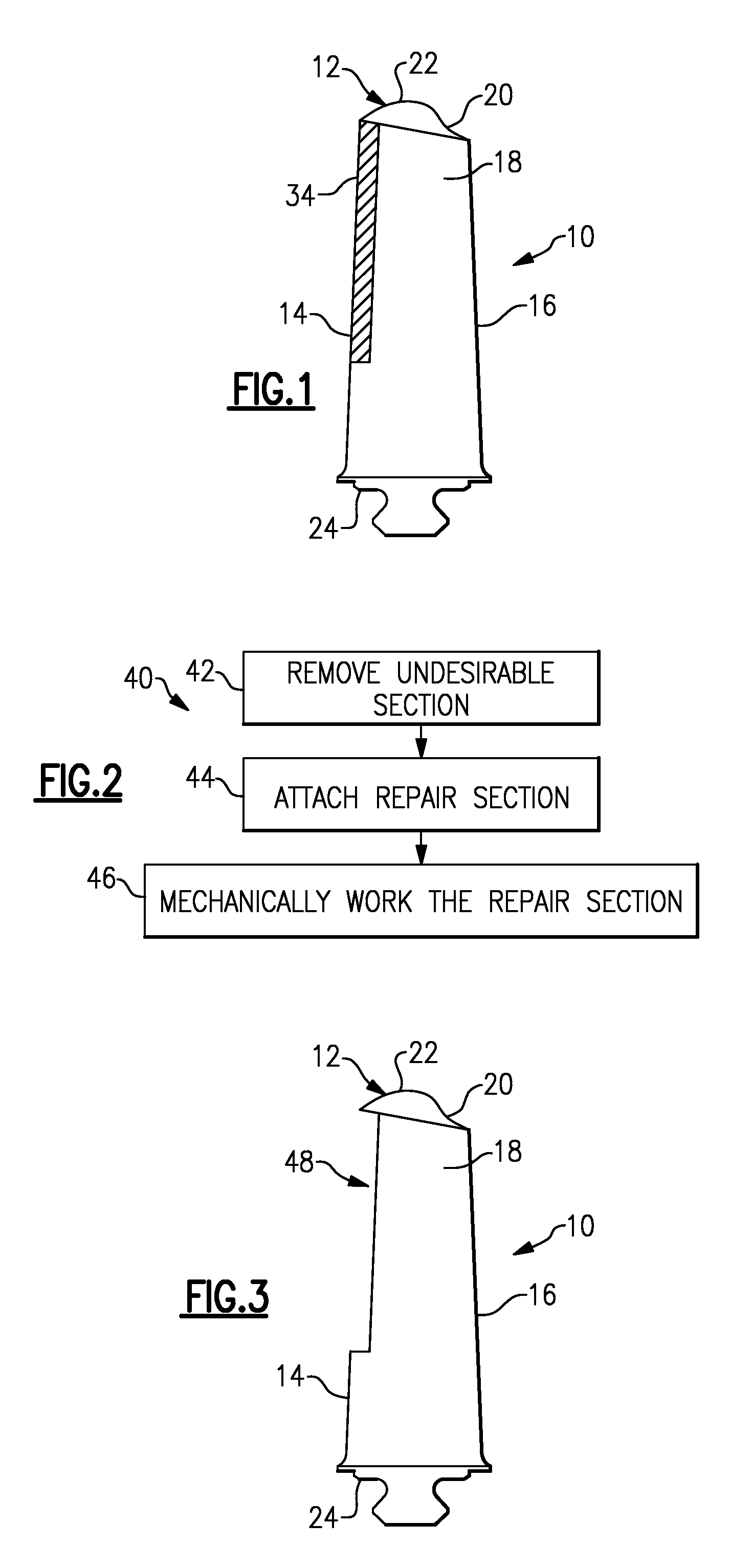
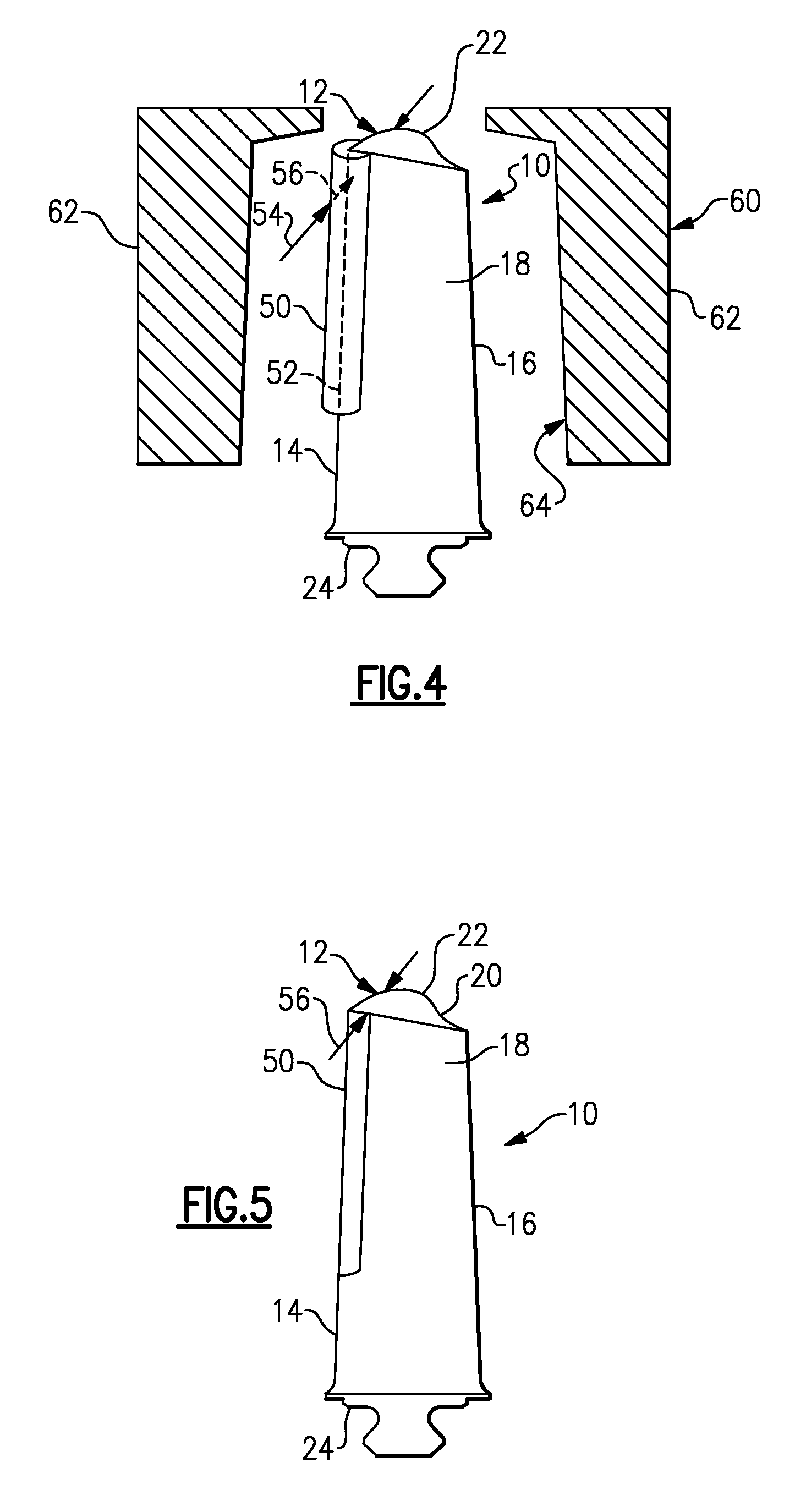
InactiveUS20060277753A1Induce compression stressBlade accessoriesEfficient propulsion technologiesWeld seamResidual stress
A method of repairing blade members, especially blade members in a turbomachine is provided. In one example, a damaged portion of a blade member is cut away from the blade member, by milling for example. The extent of the cut away portion generally corresponds in size and / or shape to the damaged area. A replacement portion is then welded into place in the resultant void in the blade member. The resulting weld seam is then burnished or deep rolled in order to cold work the blade member material at the weld seam. This induces compressive residual stresses in the blade member that counteract tensile residual stresses in and around the weld seam caused by the welding, and therefore strengthens the resulting repaired structure. The disclosed process particularly useful for repairing bladed disks (bladed monoblock disks) where individual blades cannot be removed for replacement or repair.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
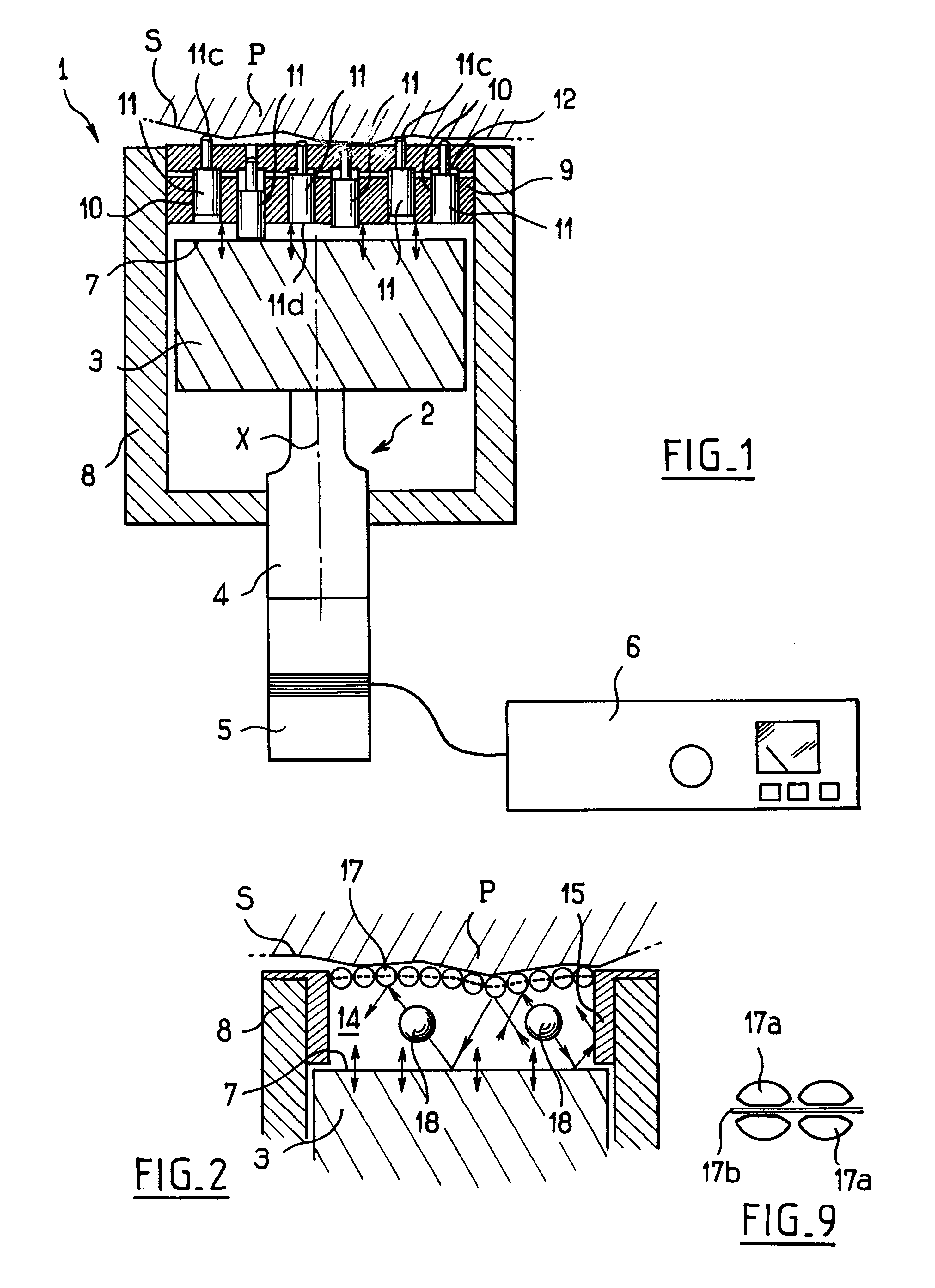
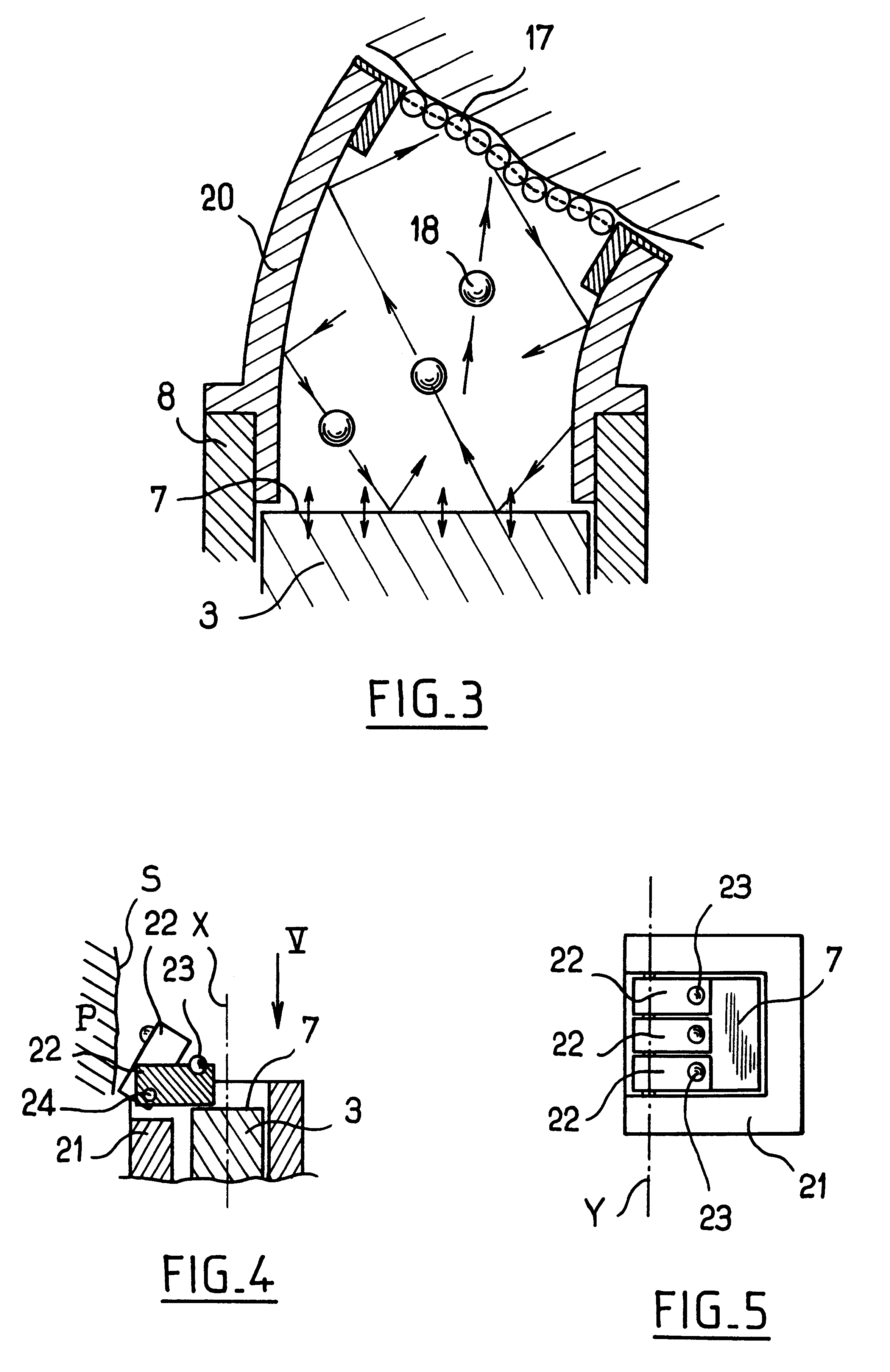
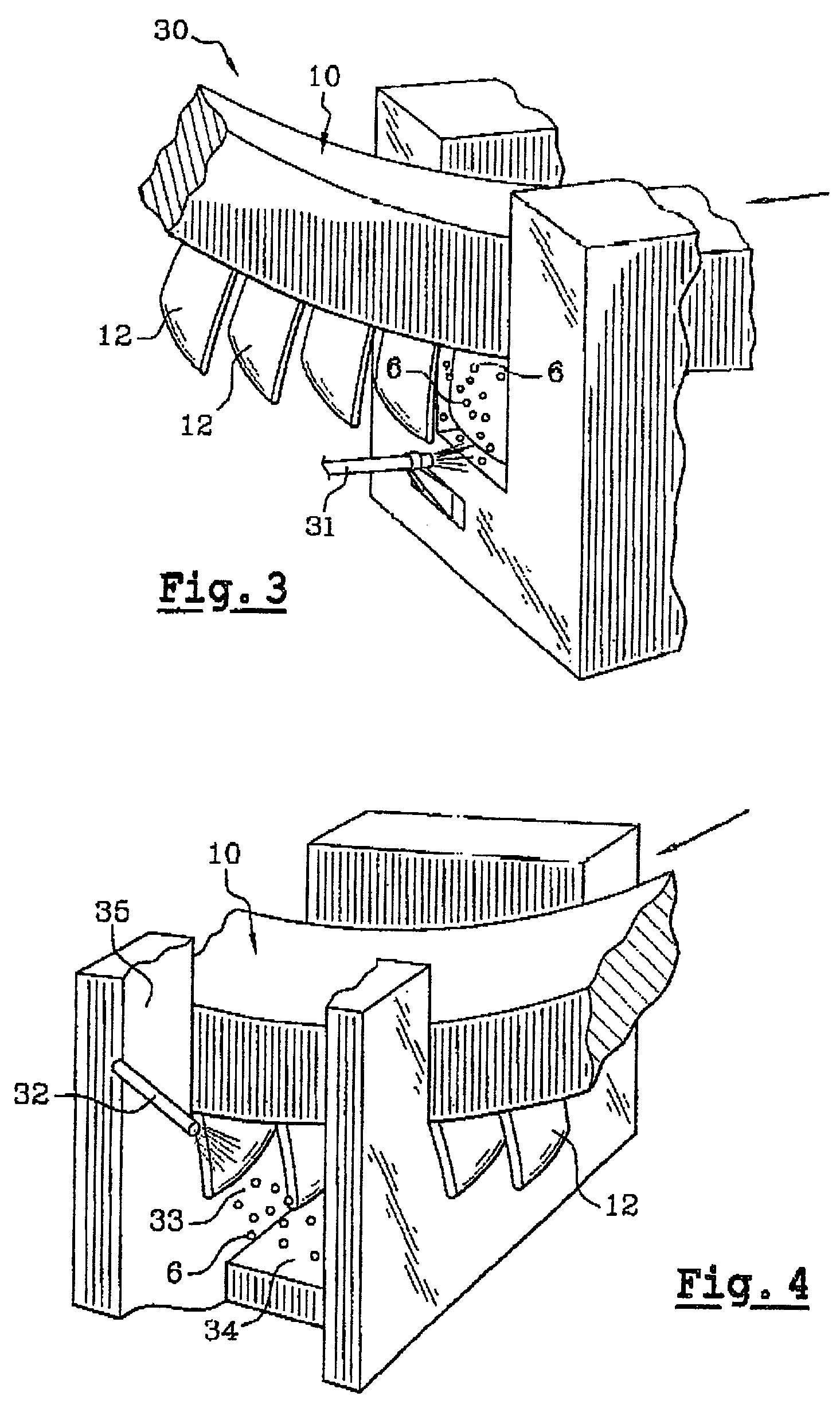
Method for the ultrasonic peening of large sized annular surfaces of thin parts
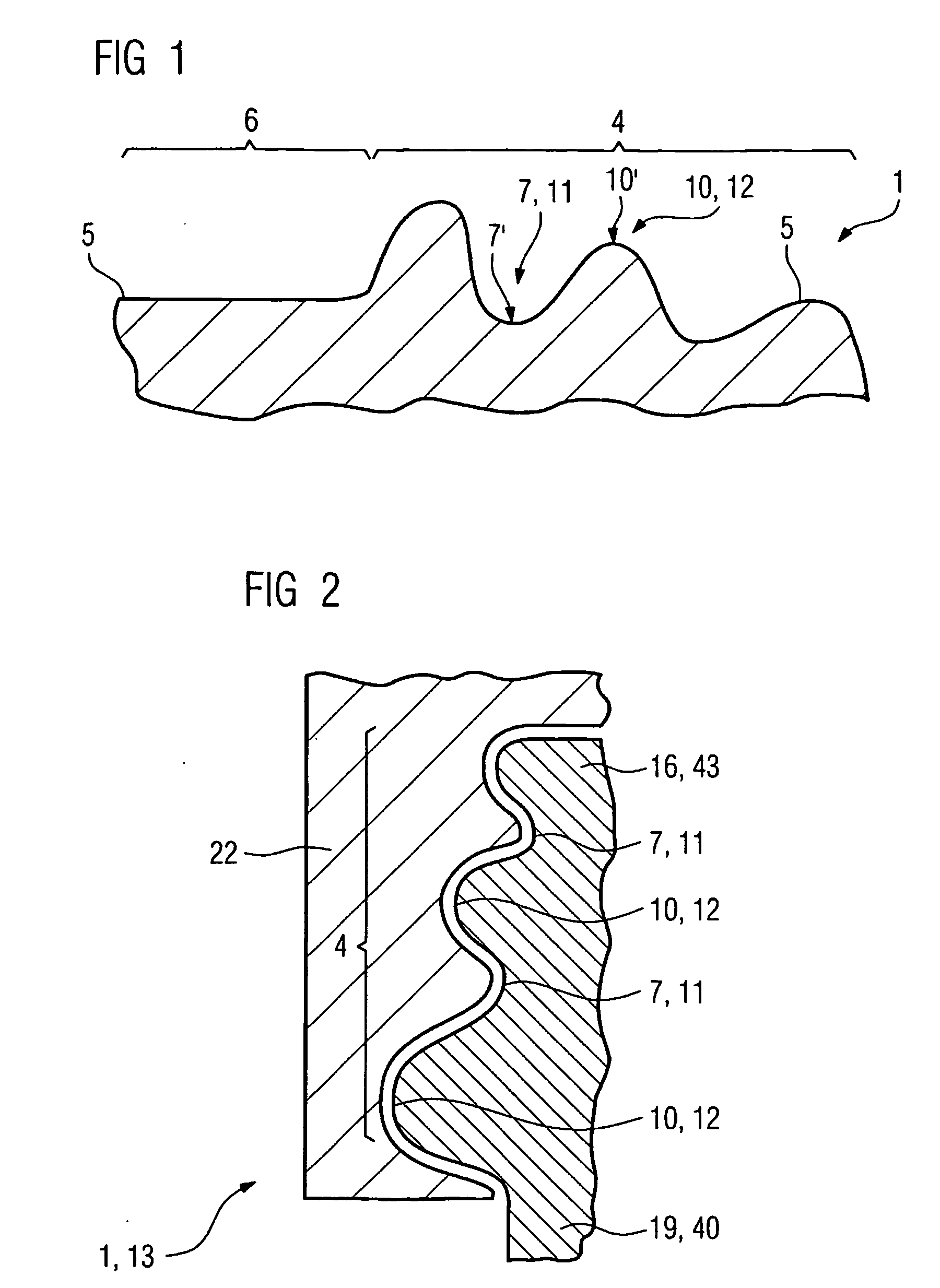
InactiveUS6289705B1Inhibits initiation and propagationImprove fatigue strengthBurnishing machinesVibratory devicesPeeningMaterials science
A method of so-called "ultrasonic" peening is described for peening large sized annular surfaces on thin parts. The method uses a microbead mist vibrated in a chamber with an opening so that the surface that is to be peened makes at least five movements past the opening of the peening chamber during peening so as to reduce deformation of the part.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
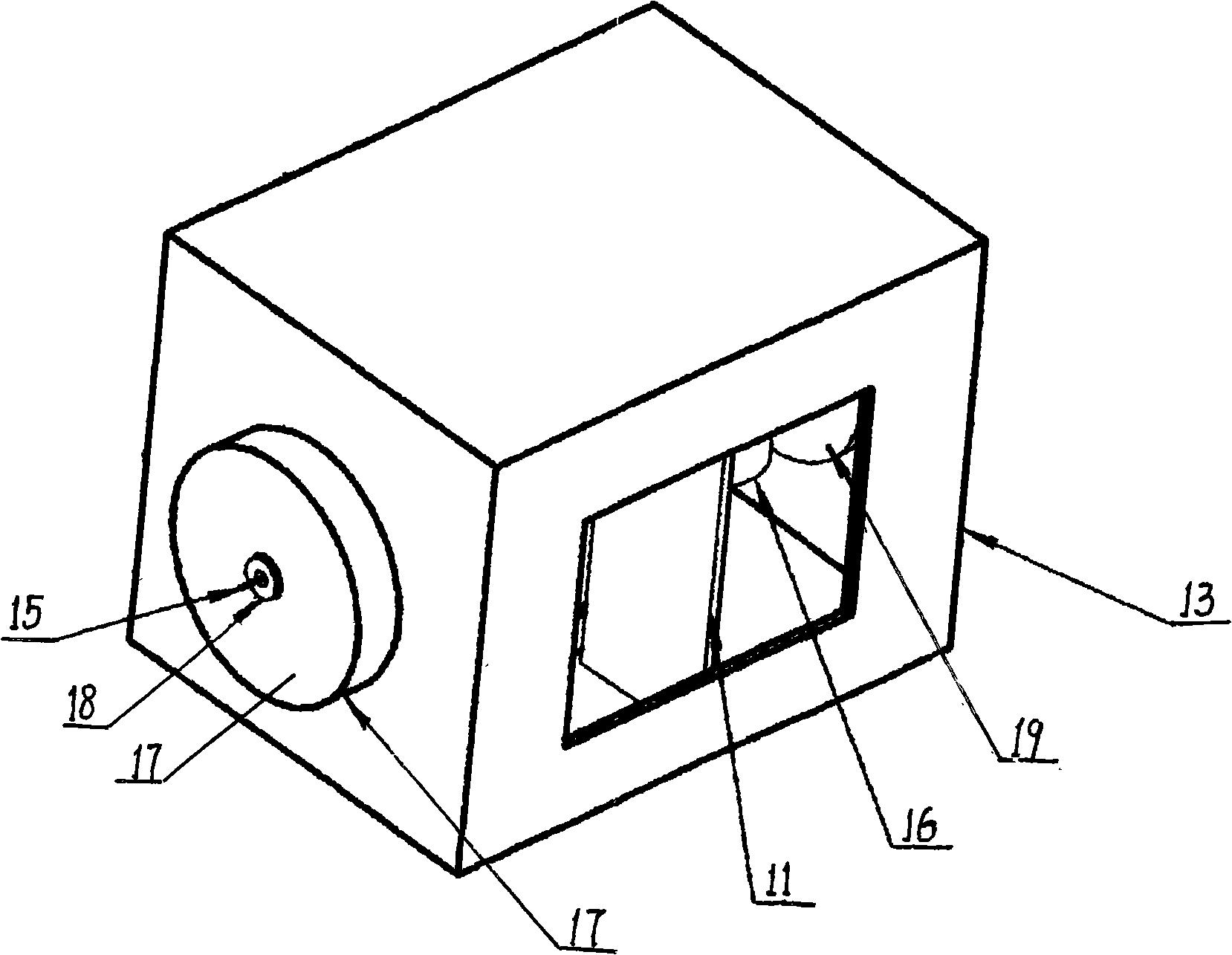
Shot-blasting installation for blasting work pieces made from light metal alloys
InactiveUS7421872B2Promote accumulationValve arrangementsFluid-tightness measurementAbrasive blastingEngineering
A shot-blasting installation (1) for blasting work pieces (30) made from light metal alloys, comprising at least one blasting chamber (3) for receiving the work pieces that are to be blasted, at least two blasting wheels (6) arranged in walls of the blasting chamber for introducing a blasting agent into the blasting chamber, and a separator (8) for separating the mixture of blasting agent and material that has been removed by blasting, wherein the separator (8) is arranged directly beneath the blasting chamber (3), and wherein a manipulator (10) for handling the cast work piece (30) during blasting is arranged in the blasting chamber (3).
Owner:DISA IND
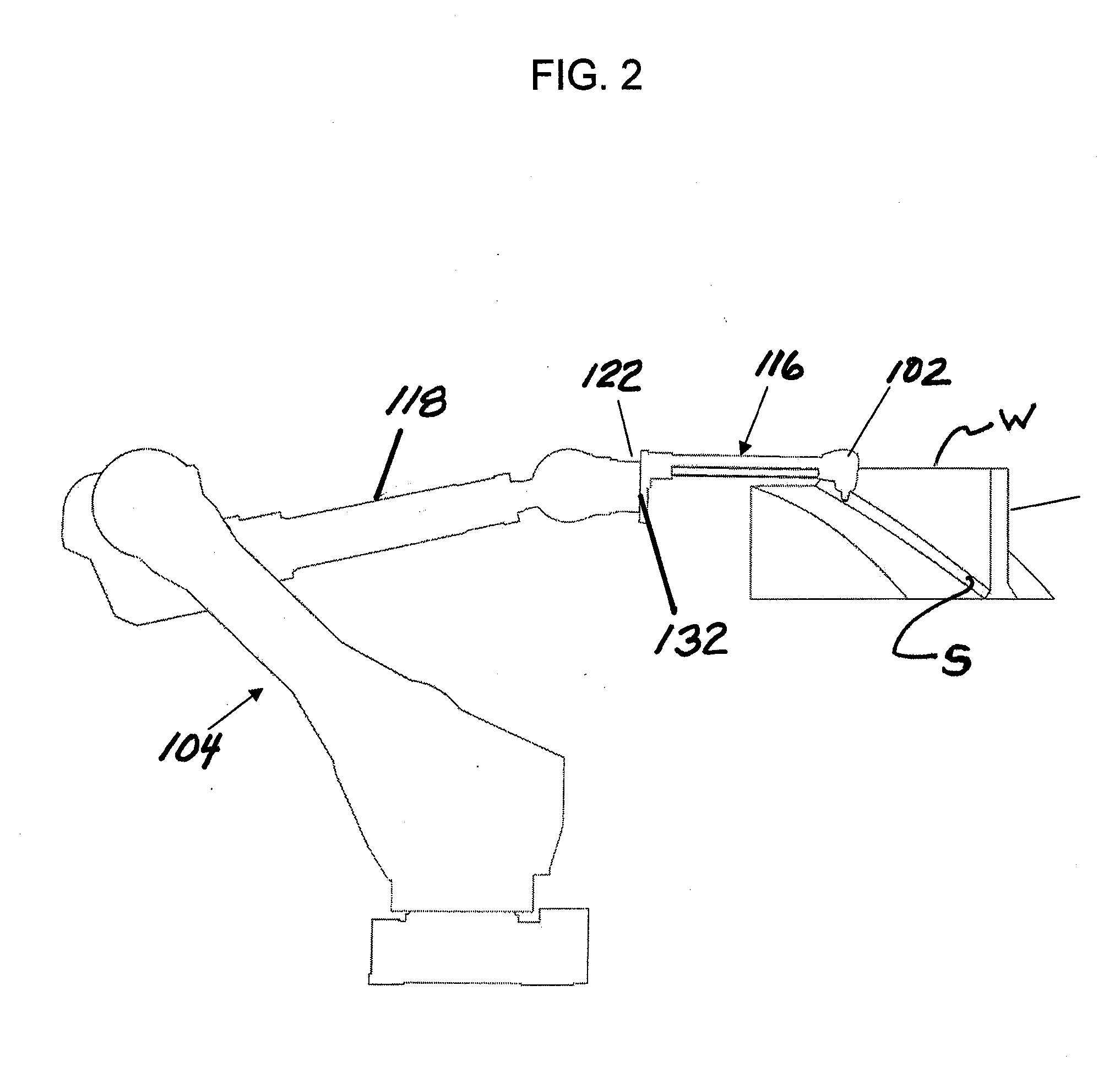
Method and compression apparatus for introducing residual compression into a component having a regular or an irregular shaped surface
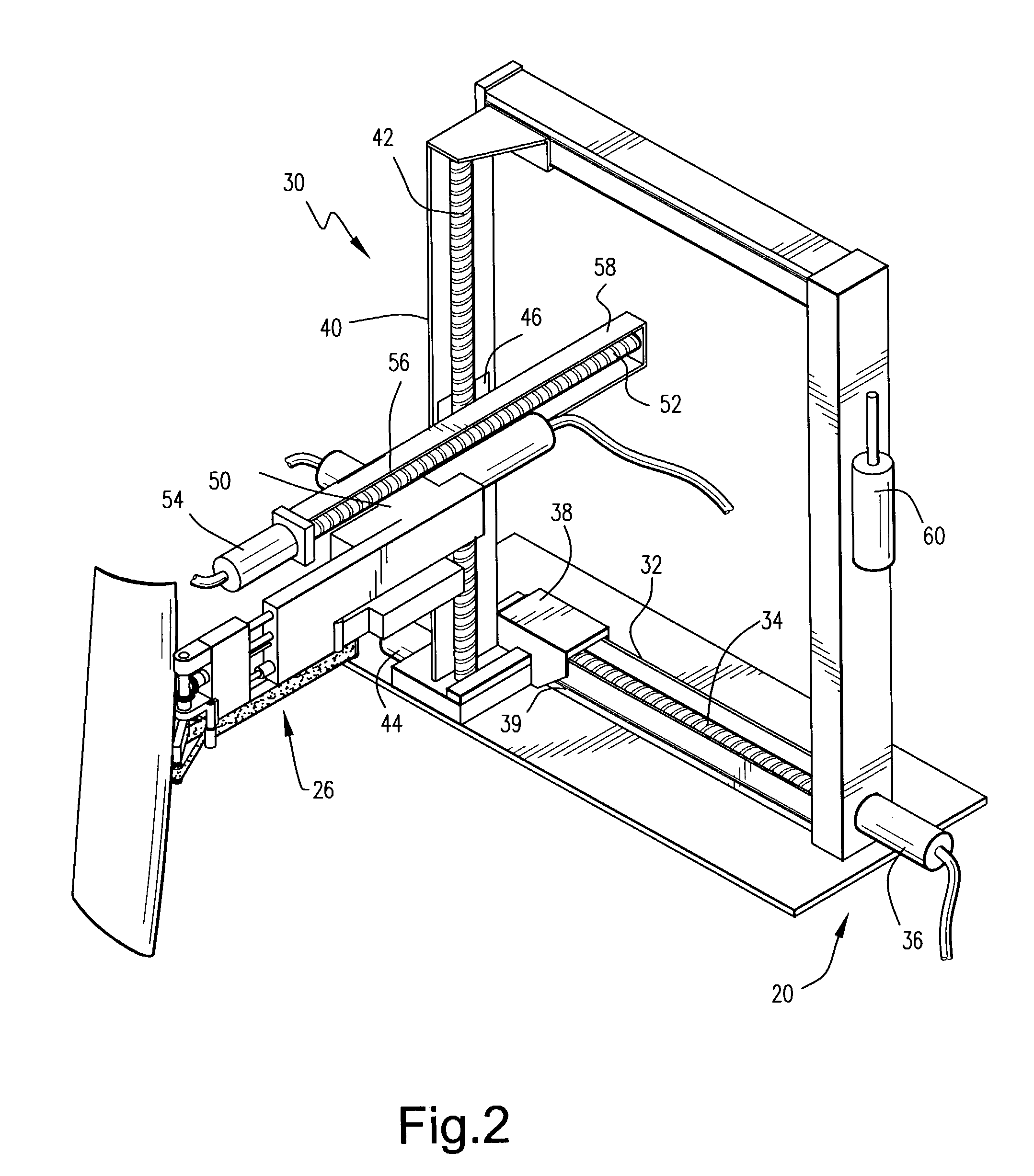
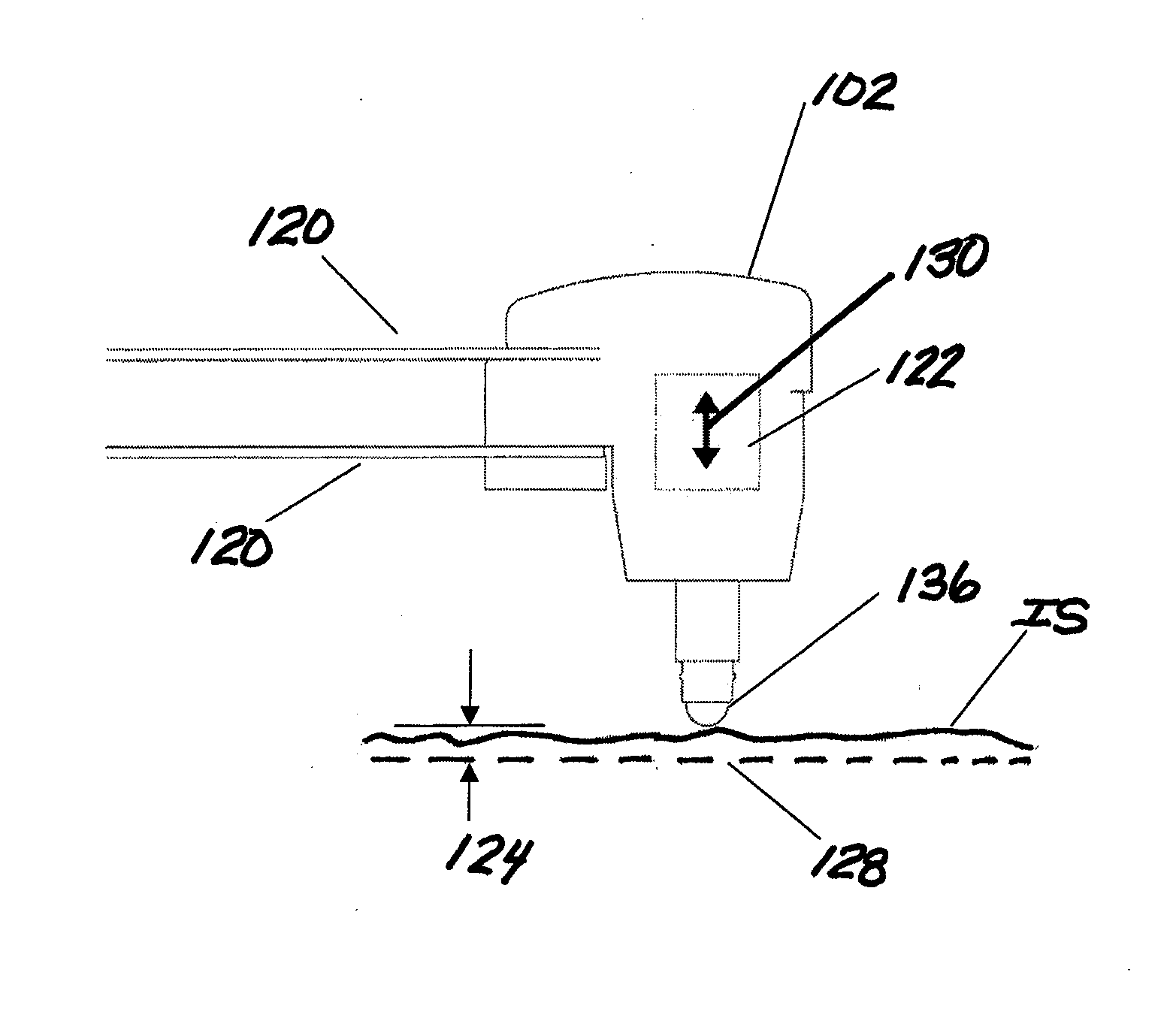
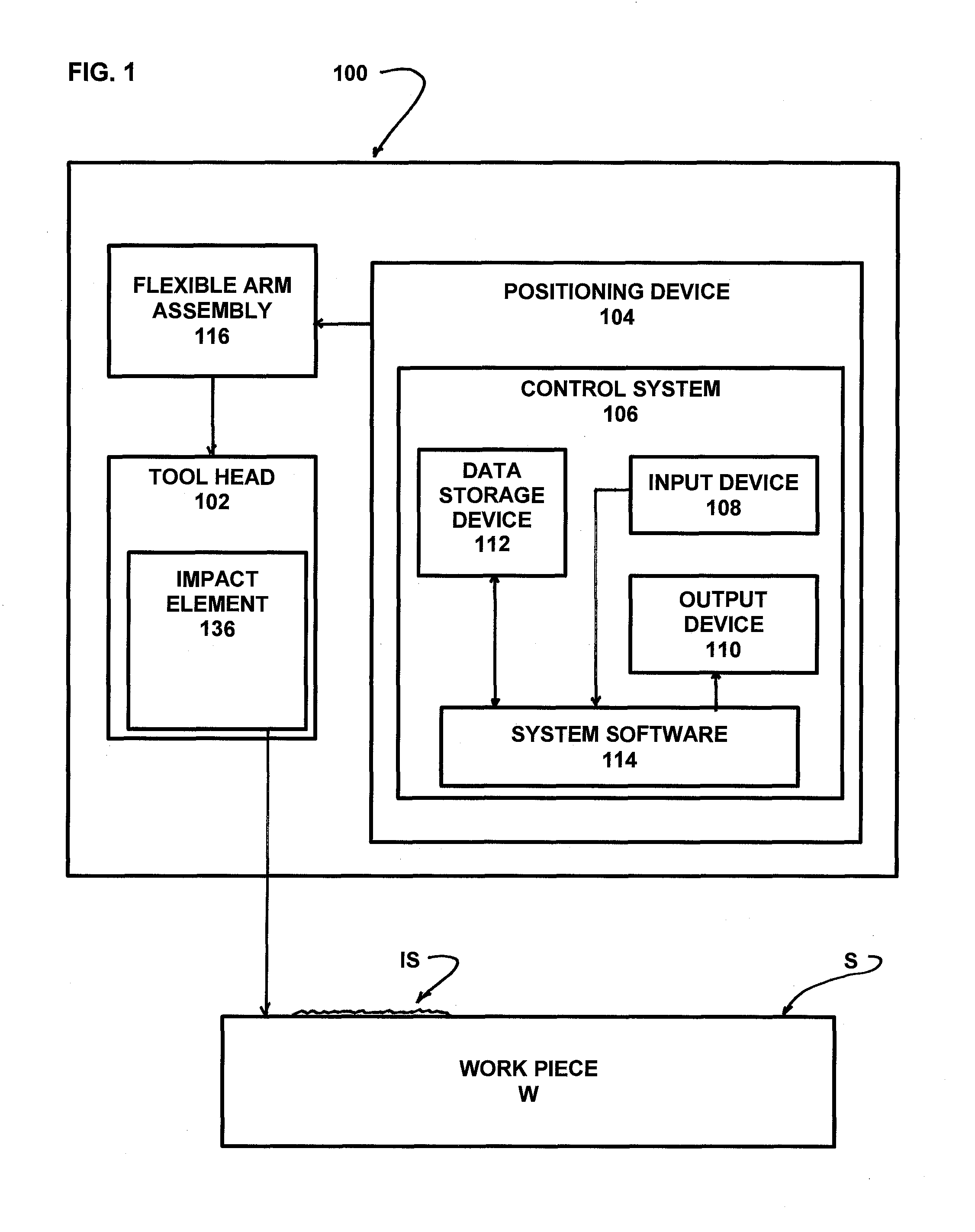
ActiveUS20140007394A1Freedom of movementDeformation MinimizationBurnishing machinesGrinding machinesCompression deviceClosed loop
A method and apparatus for improving the fatigue and stress corrosion cracking performance of irregular surfaces, such as welds assemblies of components, using a positioning system, such as a robotic or CNC machine, to position a tool head for inducing compression along and into the surface of a workpiece to automatically follow the surface irregularities. The method and apparatus operates to follow a virtual control surface located below the actual surface of the workpiece thereby allowing the irregular topography surface to be uniformly processed with closed loop process control.
Owner:SURFACE TECH HLDG
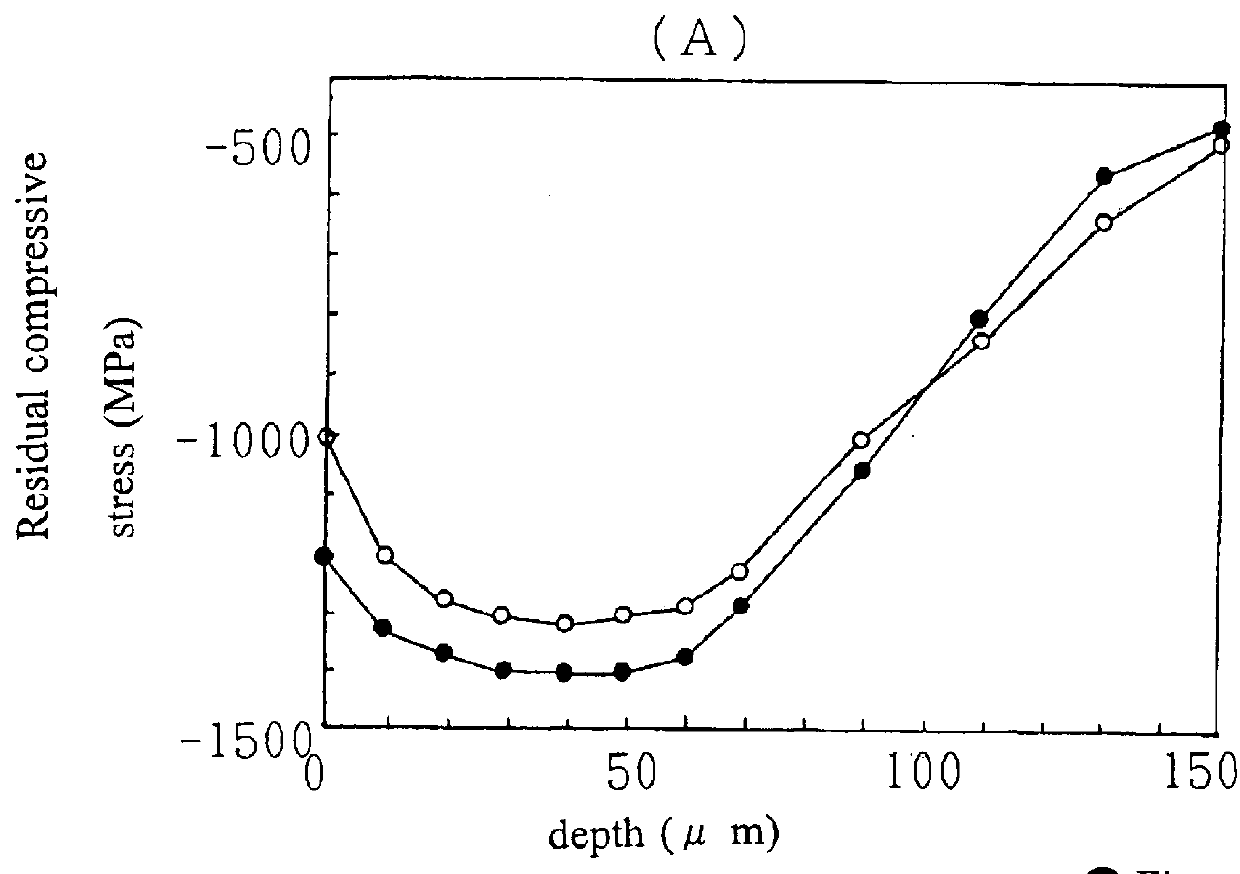
Method for a surface treatment of metallic product
The present invention relates to a method for a surface treatment of a metallic product. In this method, by conducting one step of injecting mixture shots including at least two types of shots comprised of different or same materials consisting of high hardness metal or metallic component and having different shot diameters between 0.6 and 0.03 mm onto the surface of a metallic product at an injection pressure of not less than 0.29 MPa or not less than 50 m / sec, the residual compressive stress of the surface of the metallic product and that of a lower surface layer are made at least -1200 MPa and that of a portion having a depth of about 50 mu m below the surface of the metallic product is made -1300 MPa or higher.
Owner:FUJI KIHAN CO LTD
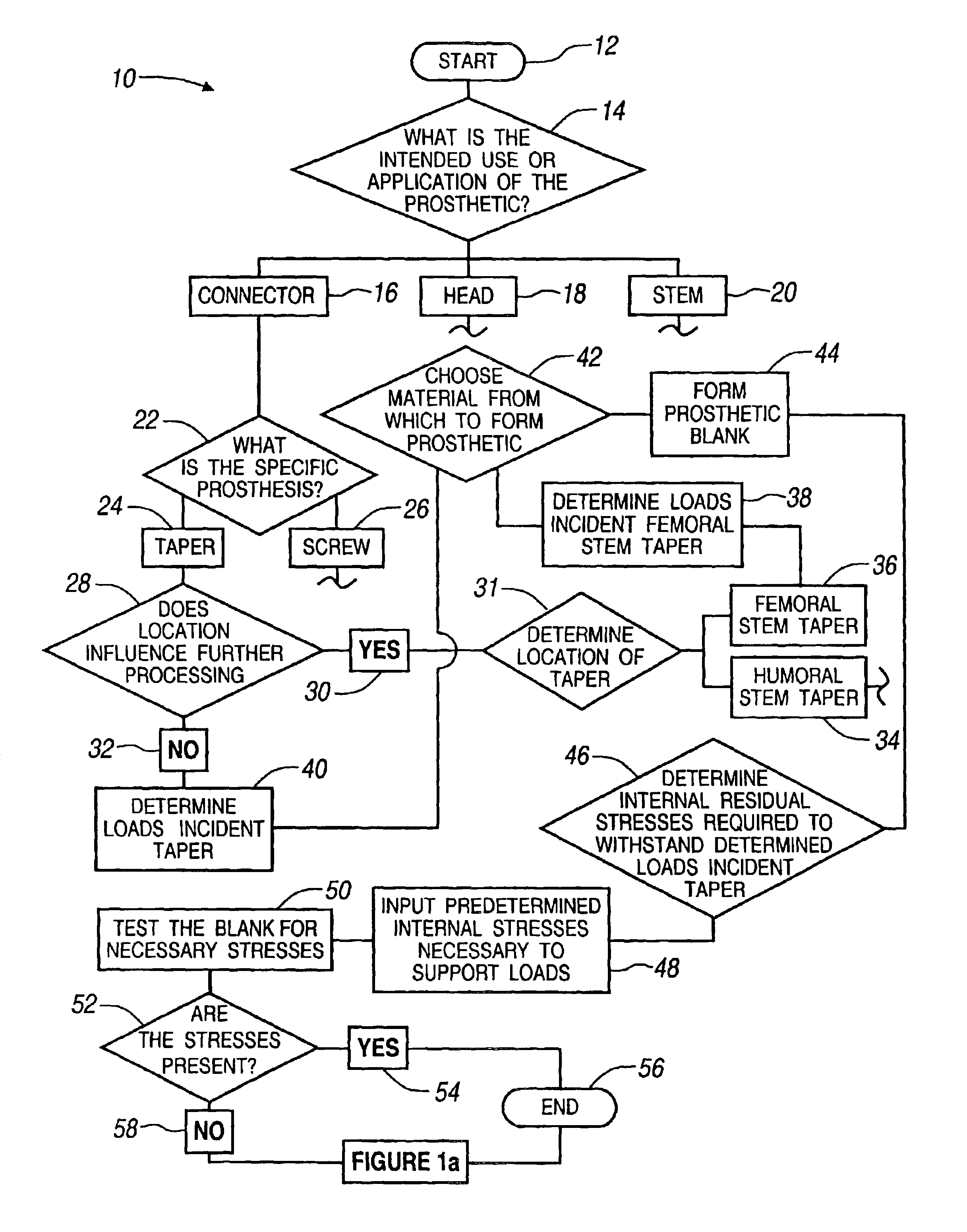
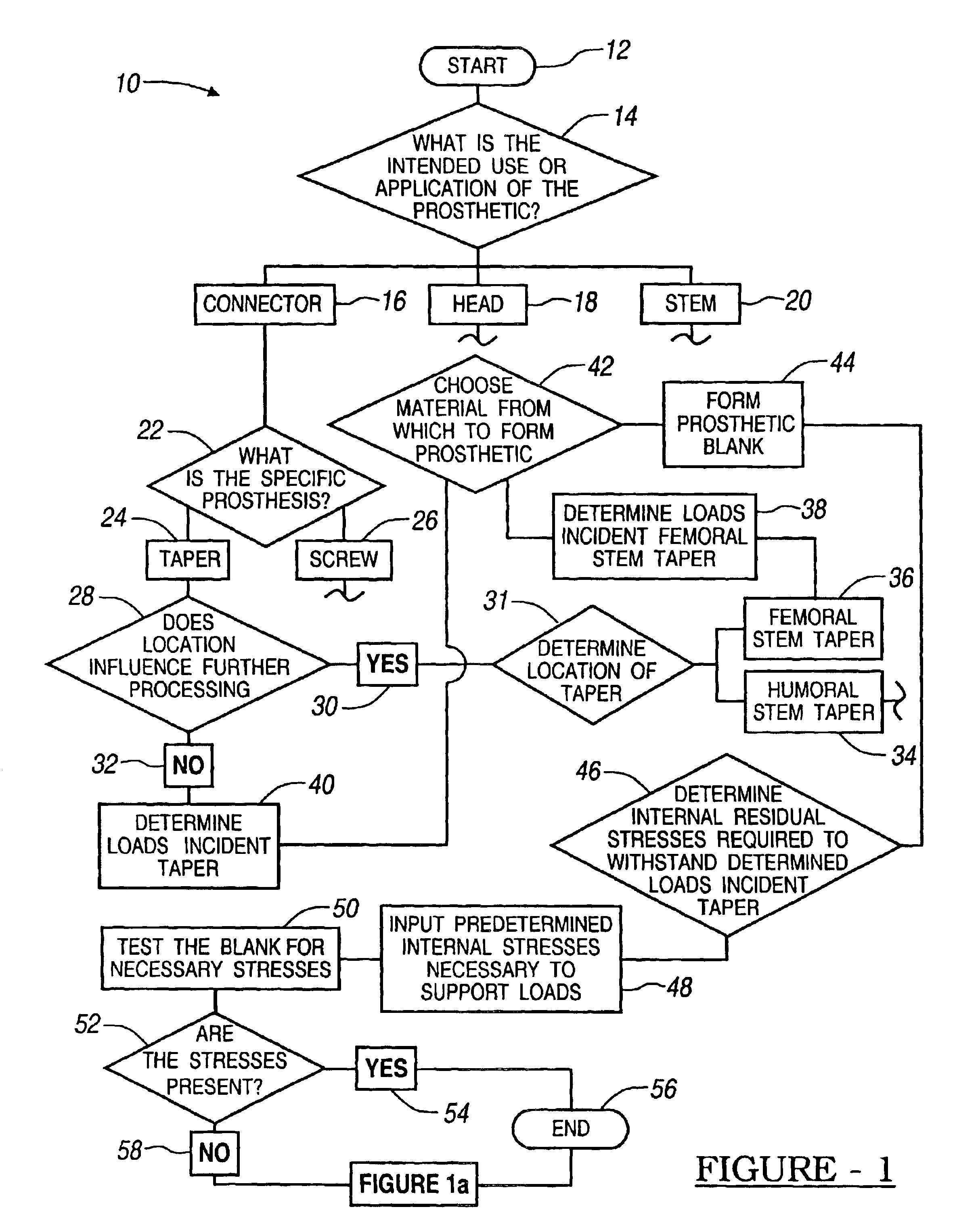
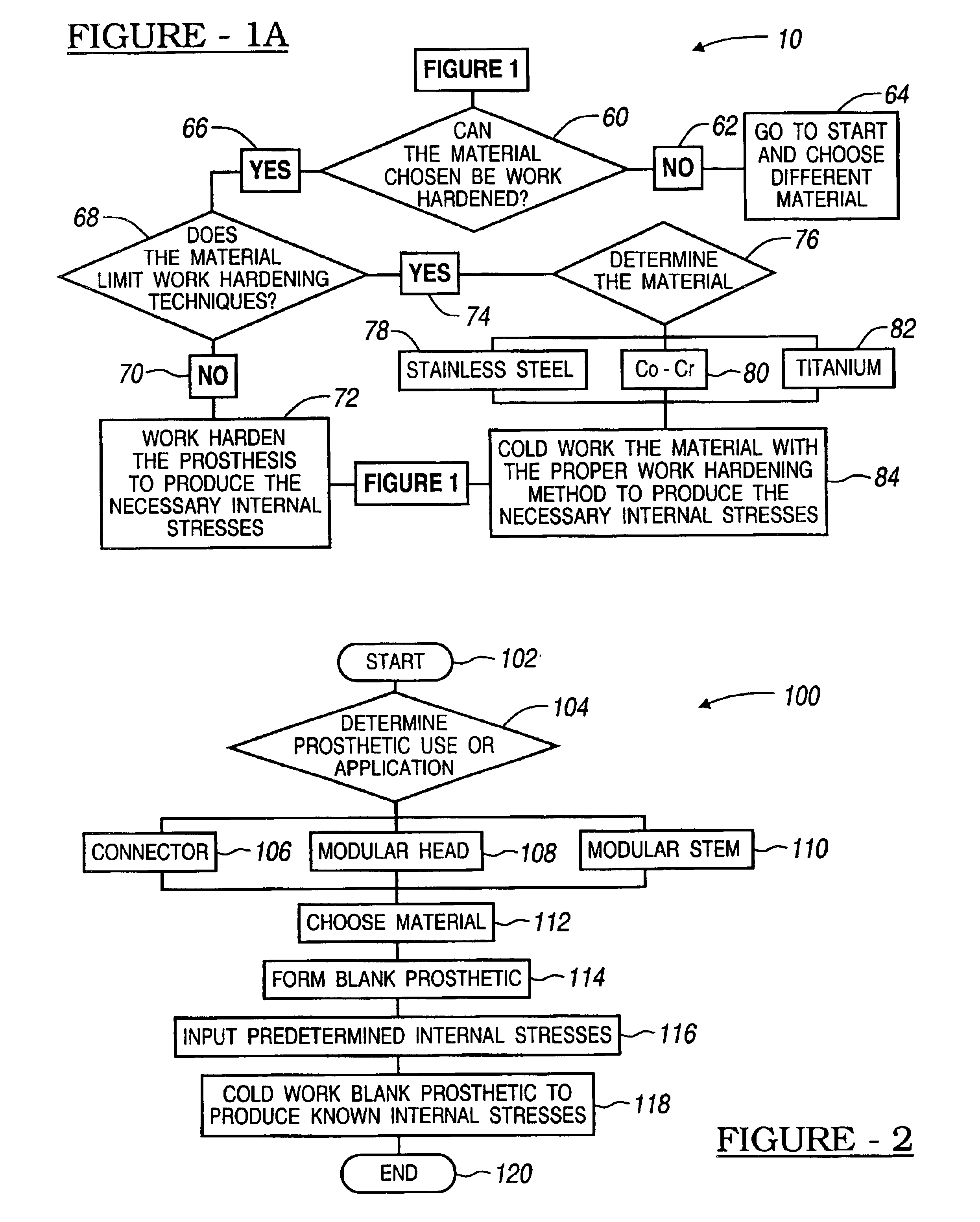
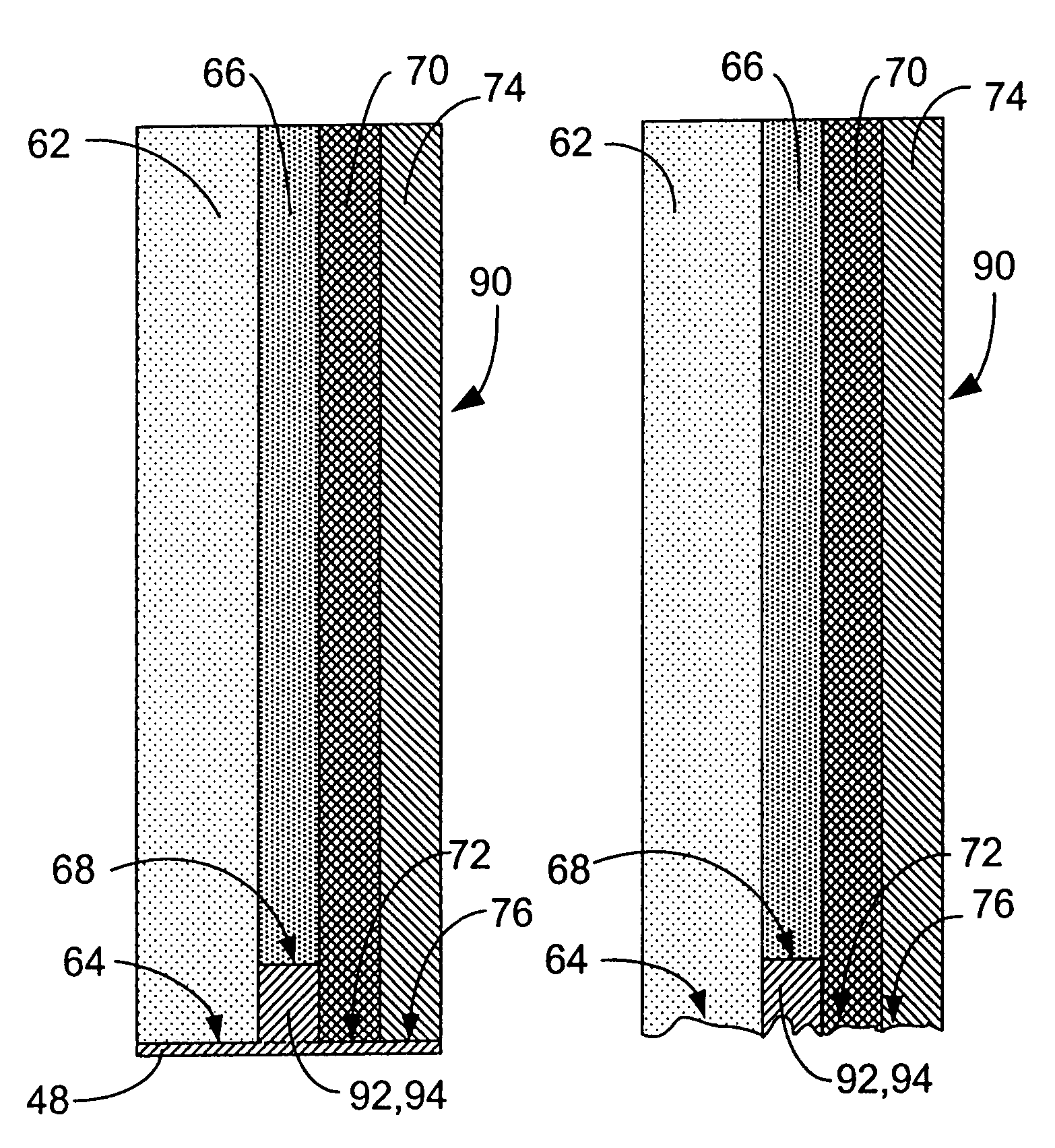
Method for controlling residual stress in prosthetics
InactiveUS6911100B1High strengthParticular longevityMeasurement/indication equipmentsJoint implantsProsthesisUltimate tensile strength
A method for producing predetermined internal stresses in a prosthetic device for implantation. The method includes first determining internal stresses which are preferred in prosthetics to instill a particular strength and longevity to the prosthetic. In particular, internal stresses may be used to increase the strength of smaller prosthetic devices. Additionally, once the preferred internal stresses are determined, the internal stresses can be cold worked into subsequent prosthetic devices to instill the same characteristics. Once parts are manufactured, internal stresses can be measured to validate manufacturing process and serve as verification for quality control purposes. Producing prosthetic devices, including predetermined internal stresses through work hardening the prosthetic devices, is described.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Process of making a non-corrosive GMR slider for proximity recording
InactiveUS7174622B2Fly height can be minimizedMinimise currentElectrical transducersNanomagnetismEngineeringNon magnetic
A method of fabrication of a slider includes forming a first ferromagnetic layer, a second ferromagnetic layer, and an antiferromagnetic layer and applying a layer of protective material to proximal ends of those layers that are proximal to the disk surface. The method further includes recessing a proximal end of a non-magnetic metal layer formed on the first ferromagnetic layer from the disk surface to form at least one recessed area. The method also includes filling the recessed area with protective material to a depth such that when the layer of protective material is worn from the ends of the first ferromagnetic layer, the second ferromagnetic layer, and the antiferromagnetic layer by burnishing of the ends by the disk surface, protective material still remains in the recessed area of the non-magnetic metal layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
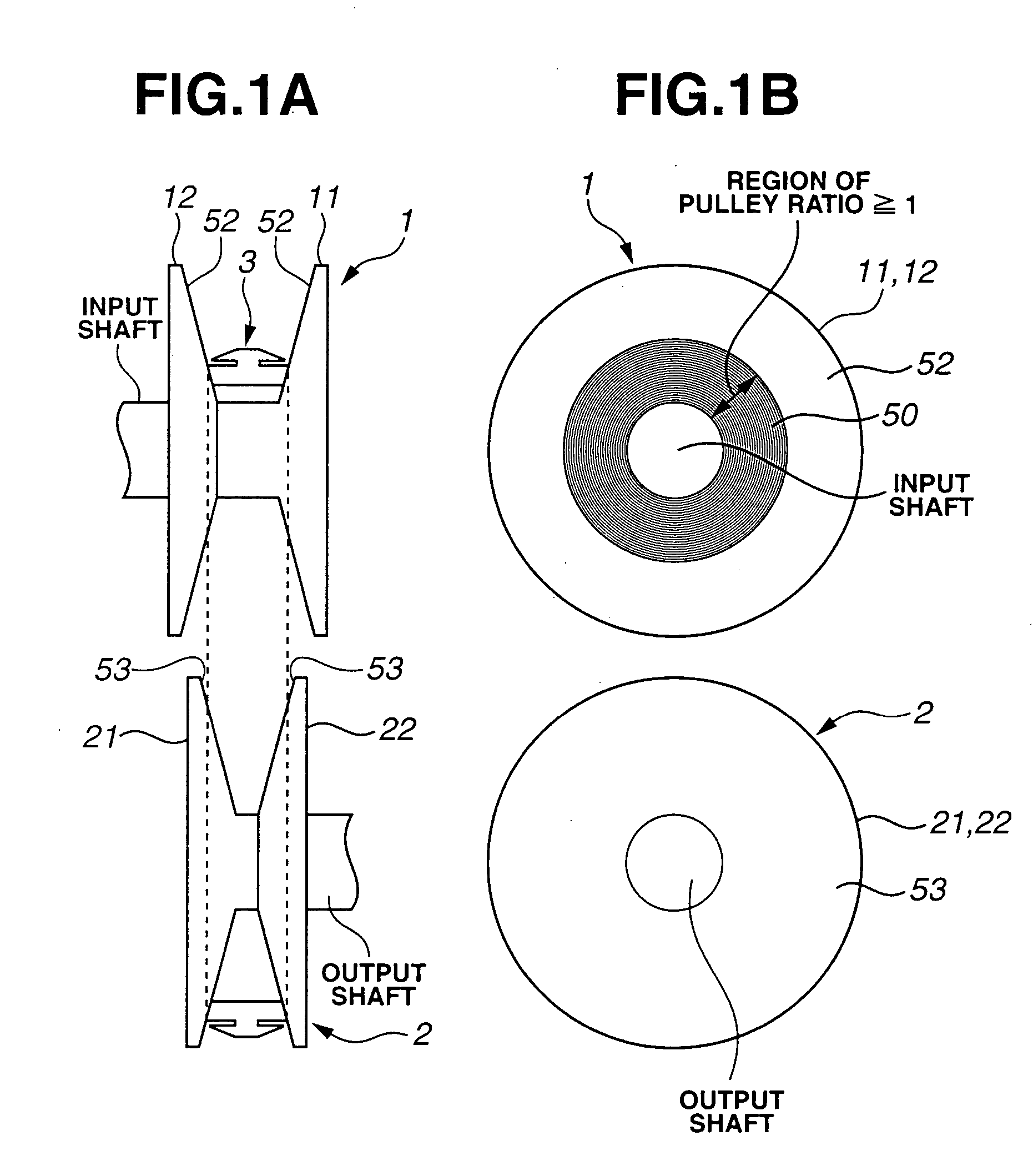
Process for producing a pulley for a continuously variable belt drive transmission
InactiveUS20050217111A1Increase frictionHigh dimensional accuracyGearingPortable liftingPeeningPulley
A process for producing a pulley for a belt drive CVT, including subjecting tapered surfaces of a preform of at least one of input and output pulleys to surface hardening, subjecting the surface-hardened tapered surfaces of the preform to hard turning to form microgrooves radially spaced from one another thereon, between which microprojections are formed, and reducing a height of the microprojections. Alternatively, a process for producing a pulley for a belt drive CVT, including subjecting tapered surfaces of a preform of at least one of input and output pulleys to surface hardening, subjecting the surface-hardened tapered surfaces of the preform to shot peening, and subjecting the shot-peened tapered surfaces of the preform to finishing to form microgrooves having a substantially equal pitch thereon.
Owner:JATCO LTD
High Durability Structures of Amorphous Alloy and a Method of Forming
Articles of bulk-solidifying amorphous alloys with improved durability and fatigue resistance, and more specifically articles of bulk-solidifying amorphous alloys subjected to a surface treatment, such as shot-peening, which creates deformations in the exterior surface, and methods of improving the durability and fatigue resistance of bulk-solidifying amorphous alloys using a surface treatment, such as shot-peening.
Owner:CRUCIBLE INTPROP LLC
Turbocharger compressor wheel having a counterbore treated for enhanced endurance to stress-induced fatigue and configurable to provide a compact axial length
InactiveUS6994526B2Avoiding and reducing overhangProlong lifePropellersPump componentsImpellerStress induced
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Selective and oriented assembly of platelet materials and functional additives
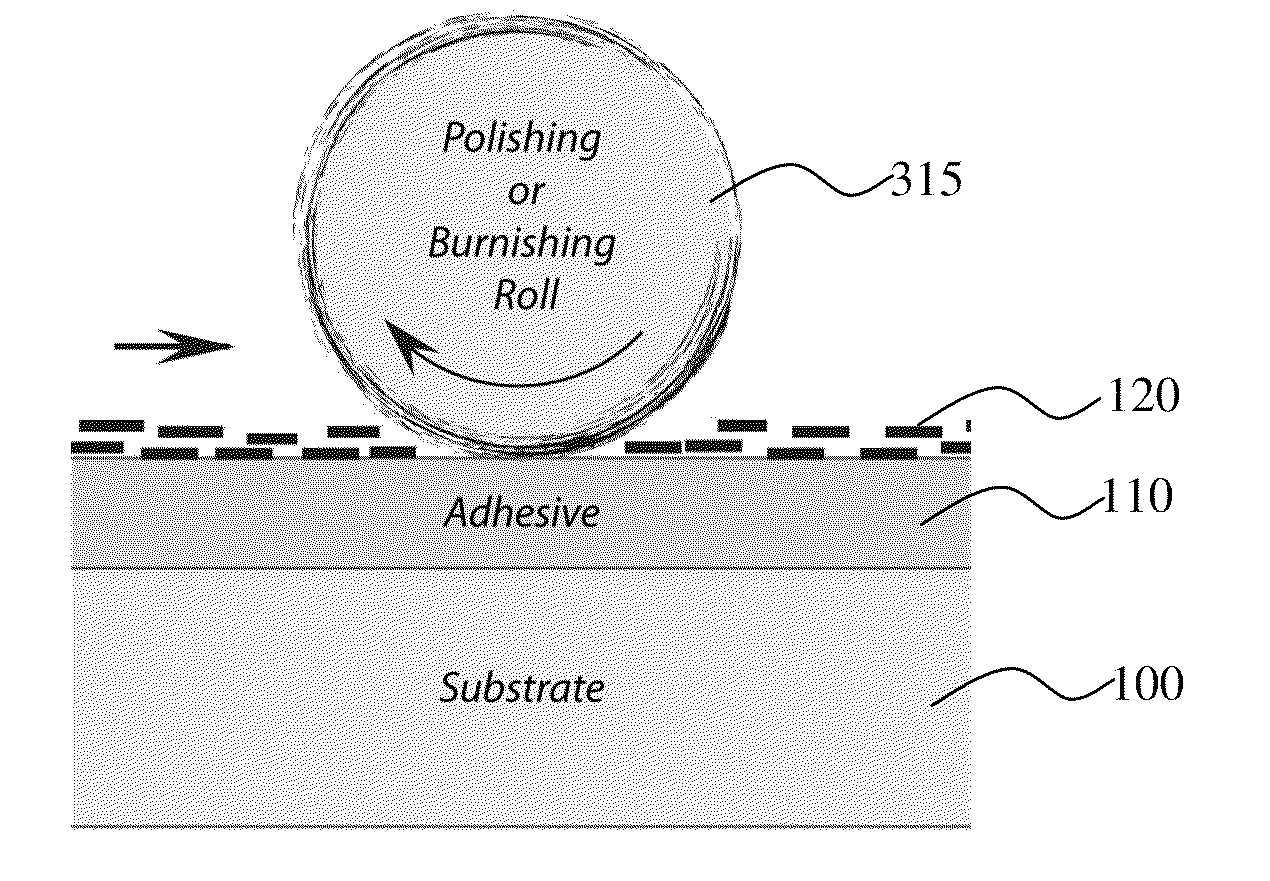
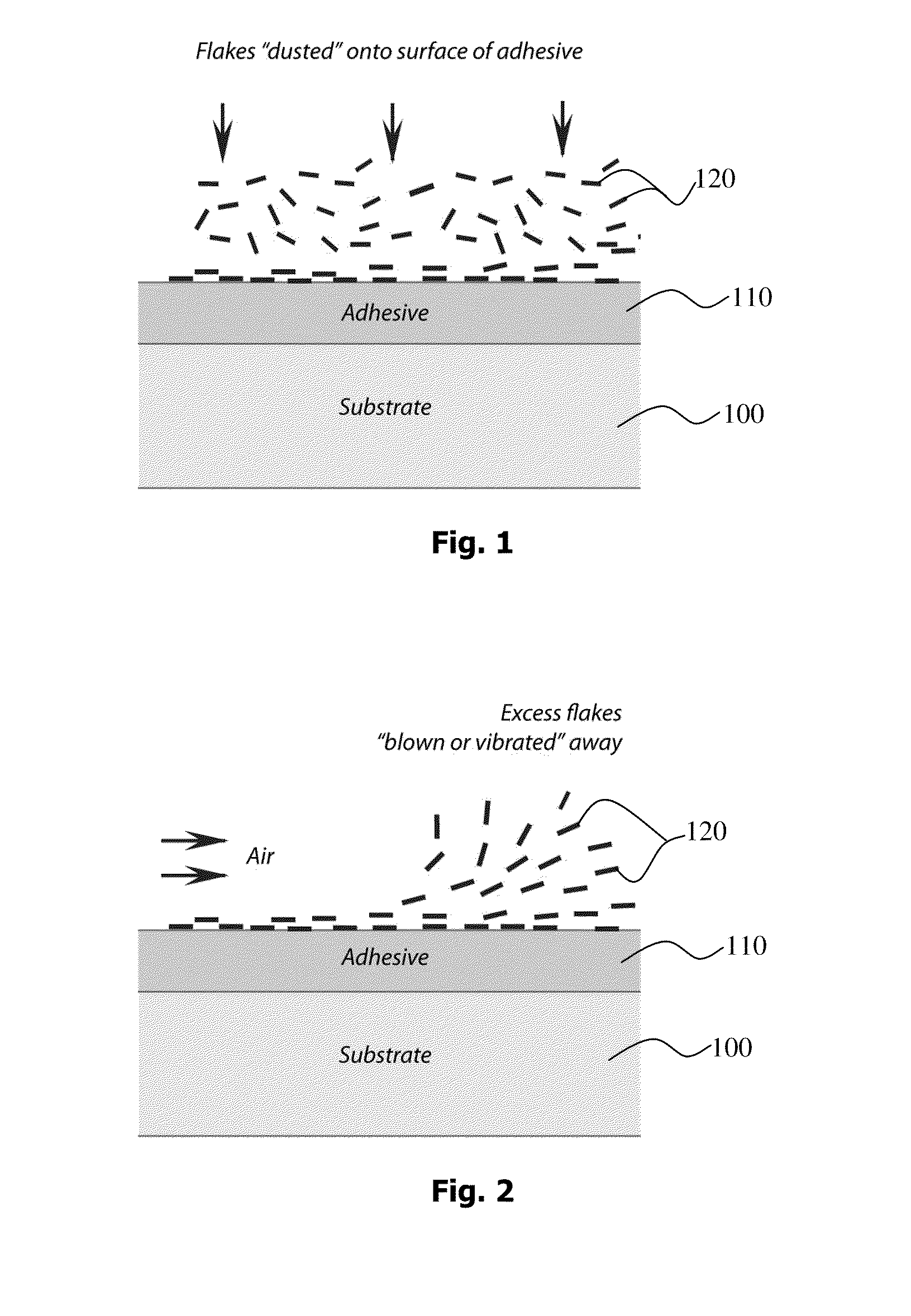
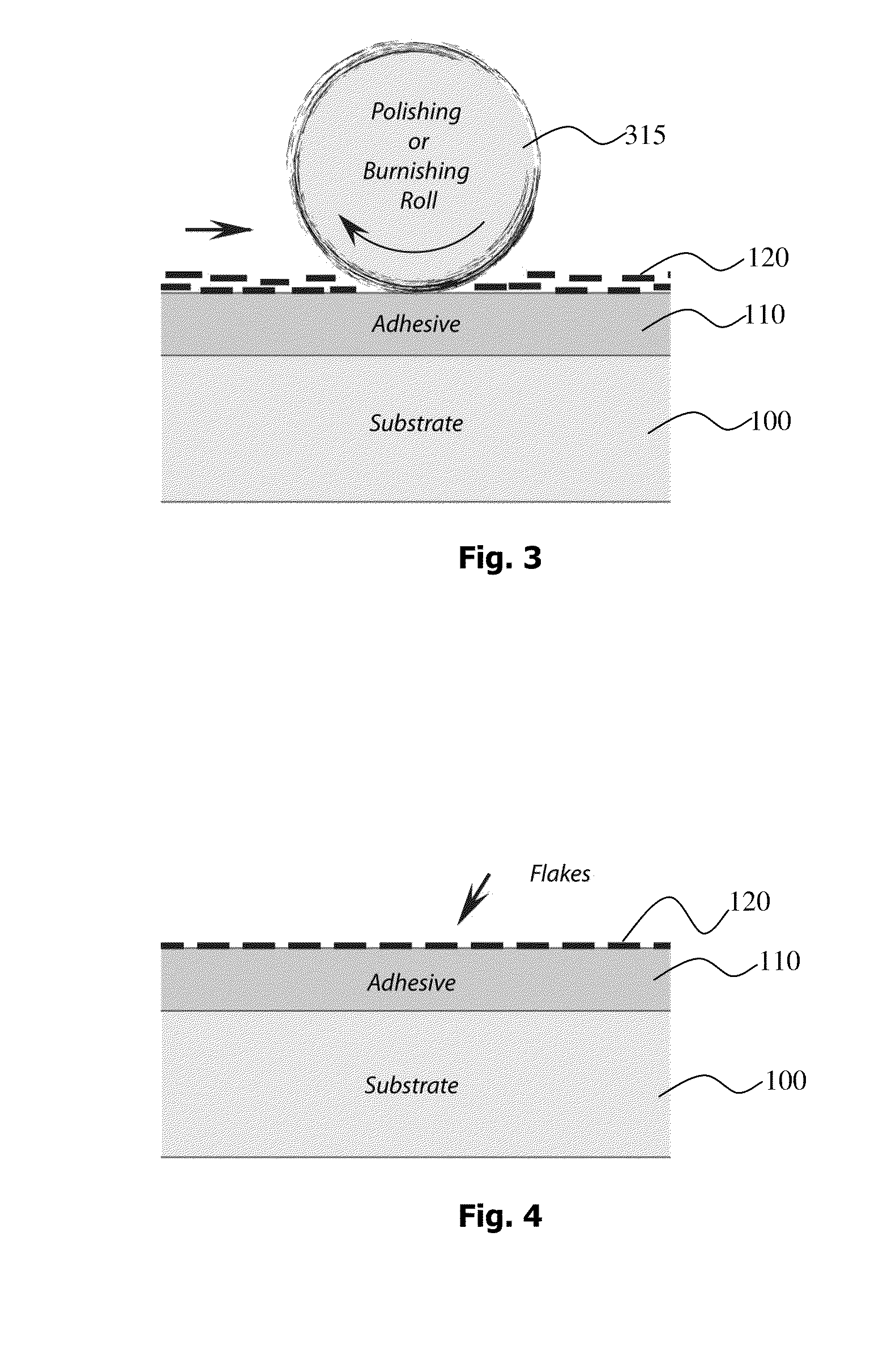
InactiveUS20100208351A1Good optical performanceLamination ancillary operationsMirrorsAdhesiveActive layer
A method of conforming non-ductile flakes to a surface is provided wherein a surface is coated with the non-ductile flakes. A first step of coating at least a portion of the surface with a coating of adhesive or a paint is required and subsequently before the coating cures a plurality of thin film flakes having a non-ductile insulating or semiconductor layer are sprinkled upon the adhesive or paint while it is still tacky. Typically the thin-film flakes have a thickness of between 50 nm and 2,000 nm, and have a length of between 2 microns and 200 microns. The flakes having a non-ductile layer are then burnished upon the surface so as to provide an active layer, which conforms to the surface.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
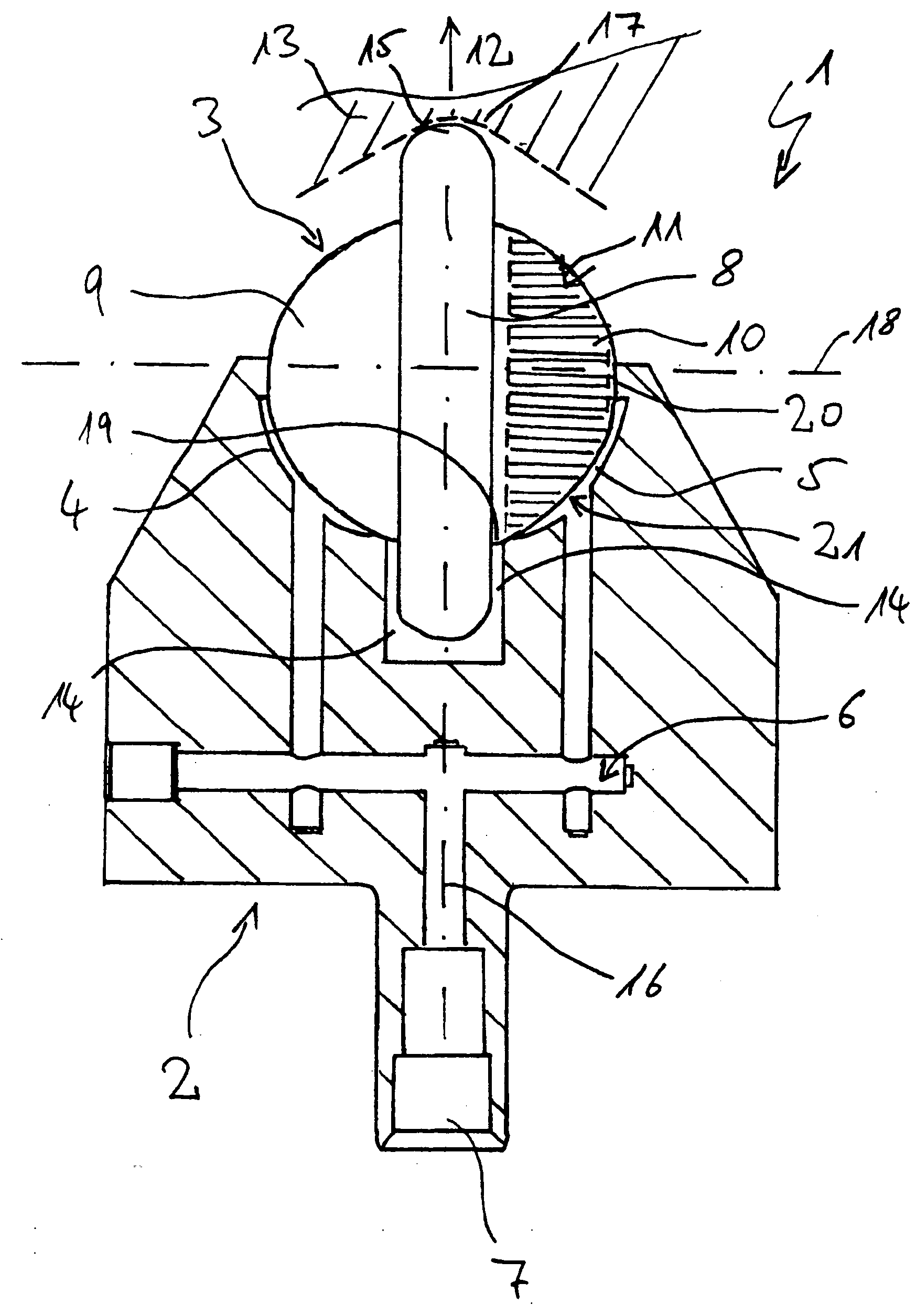
Rolling tool and roller for rolling, particularly deep rolling, a work piece
InactiveUS20050107230A1High quality and reproducibilityRolling force can be constantRolling equipment maintainenceBurnishing machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ECOROLL WERKZEUGTECHN
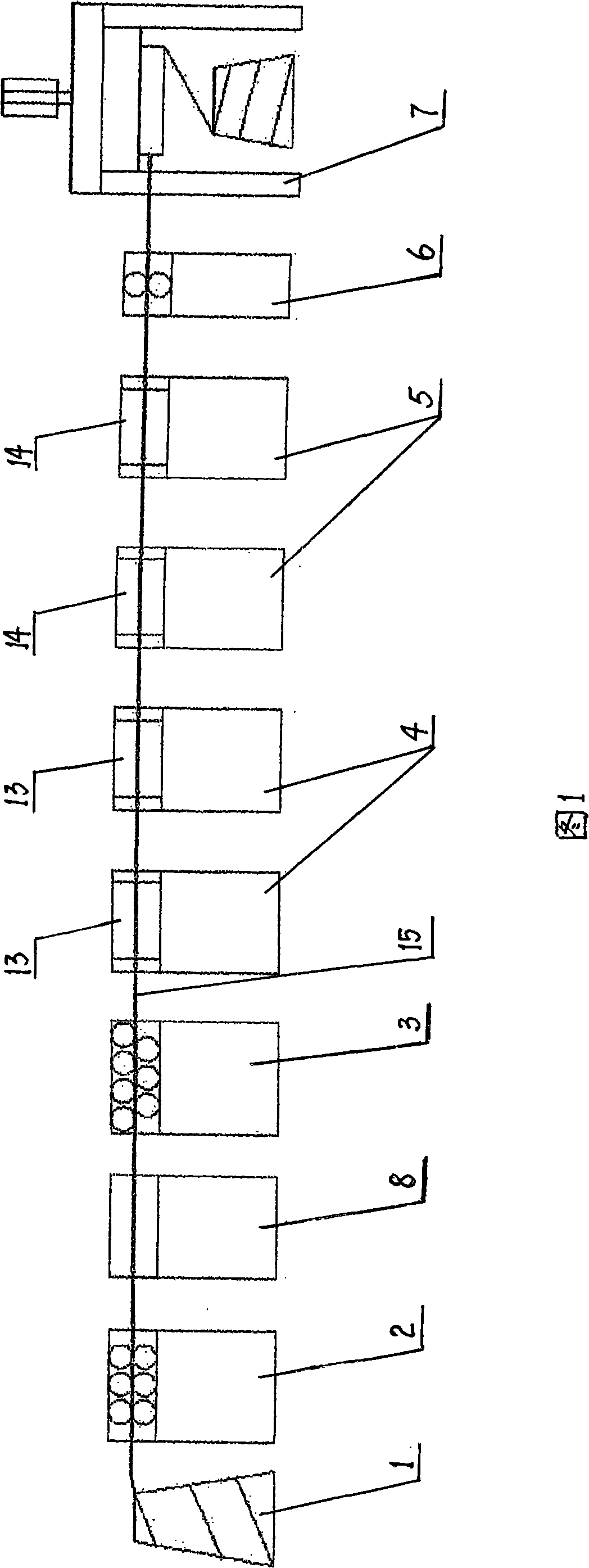
Method and equipment for removing oxidizing layer of titanium and titanium alloy wire material
ActiveCN101269397AEnsure consistencyGuaranteed uniformityWire articlesBurnishing machinesProduction lineTitanium
The invention relates to a method for removing an oxidation layer on titanium and titanium alloy wires and a device thereof. The method includes the following steps: 1. straightening: a straightening machine is used for straightening the titanium and titanium alloy wires; 2. phosphorus removal: a steel wheel phosphorus removal machine is used for removing the oxidation layer on the surface of the titanium and titanium alloy wires; 3. polishing: a sand belt wheel polisher is used for polishing the surface of the titanium and titanium alloy wires. The device is sequentially provided from left to right with a pay-off stand (1), a clamping device (2), a heating device (8), a straightening device (3), two steel wheel phosphorus removal machines (13), sand belt wheel polishers (14), a guide and guard (6) and a vertical down drawing machine (7). On the basis of the present steel wheel phosphorus removal machine, the method is additionally provided with a heating device, a phosphorus removing and polishing machine, a cooling device, a dust removing device and a tension device, thereby forming a production line for removing the oxidation layer on a large and heavy titanium alloy wire, so as to reach the purpose of removing the oxidation layer and polishing.
Owner:BAOJI TITANIUM IND
Methods for altering residual stresses using mechanically induced liquid cavitation
InactiveUS6993948B2Altering residual tensile stressEffectively water-hammeringBurnishing machinesForging press detailsCavitationTransducer
A mechanical transducer induces liquid cavitation, causing pressure waves in a liquid which are applied against a metal surface to afford localized elastic and plastic tensile microstrain. The pressure waves alter the surface tensile stresses in the treated metal by reducing the tensile stresses or forming surface compressive stresses. A boot is provided about the operating face of the transducer for confining a liquid through which compression waves are generated and applied to the metal surface, the boot sealing about the transducer and the surface undergoing treatment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
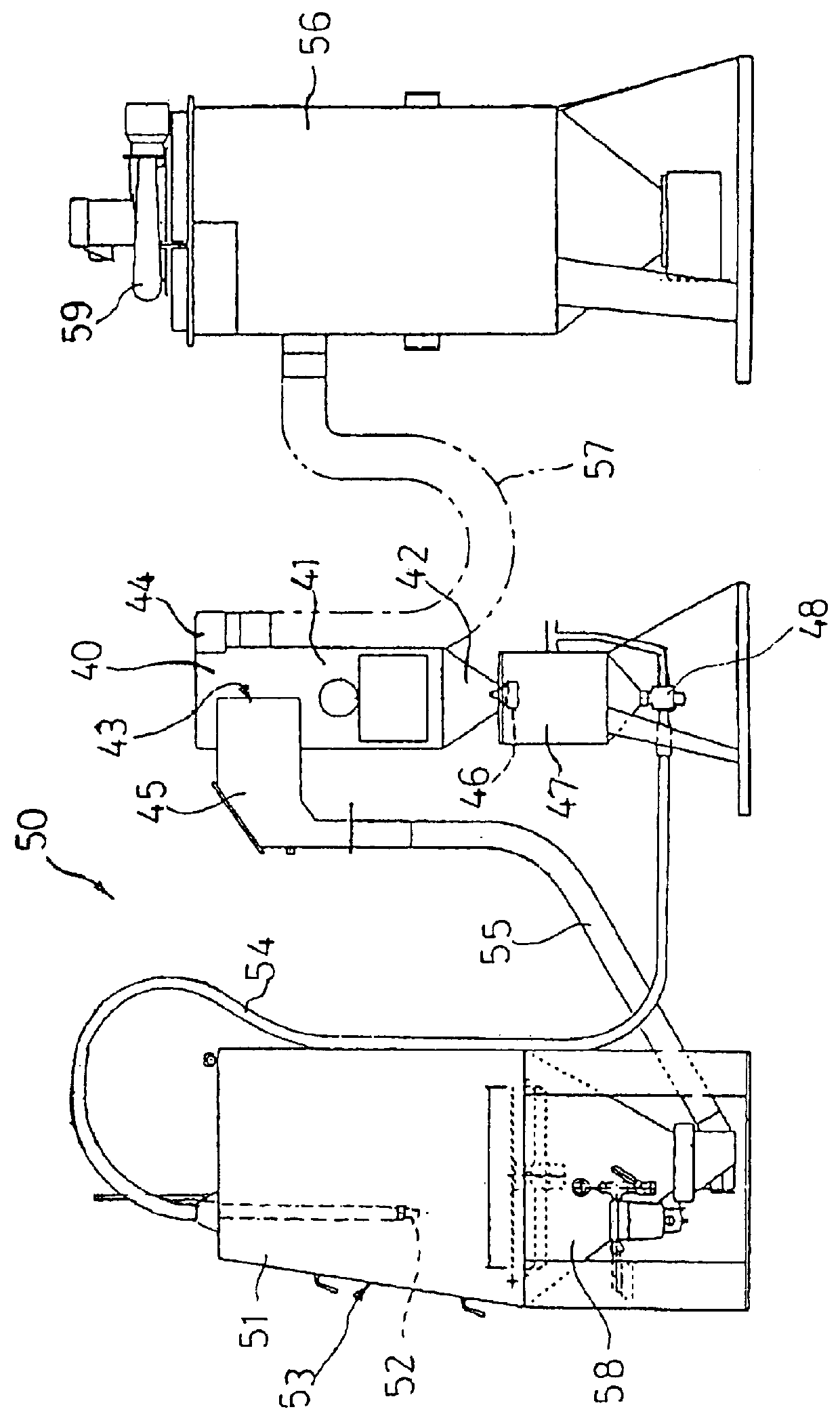
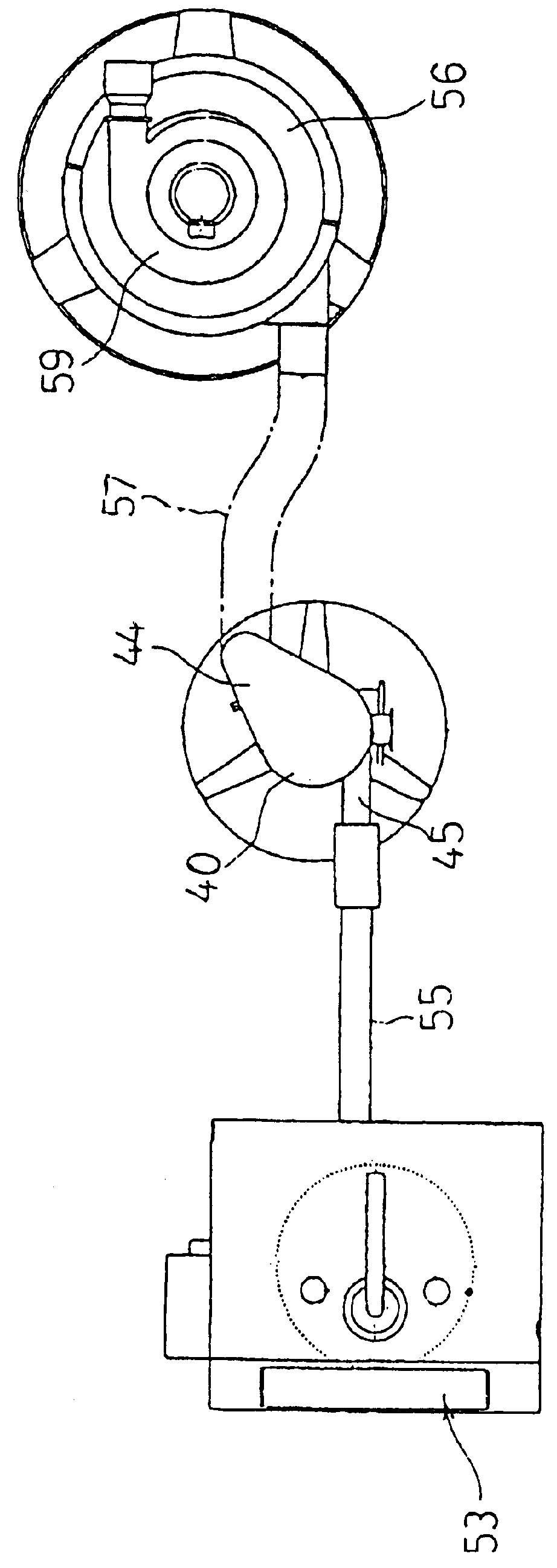
Method and apparatus for providing a layer of compressive residual stress in the surface of a part
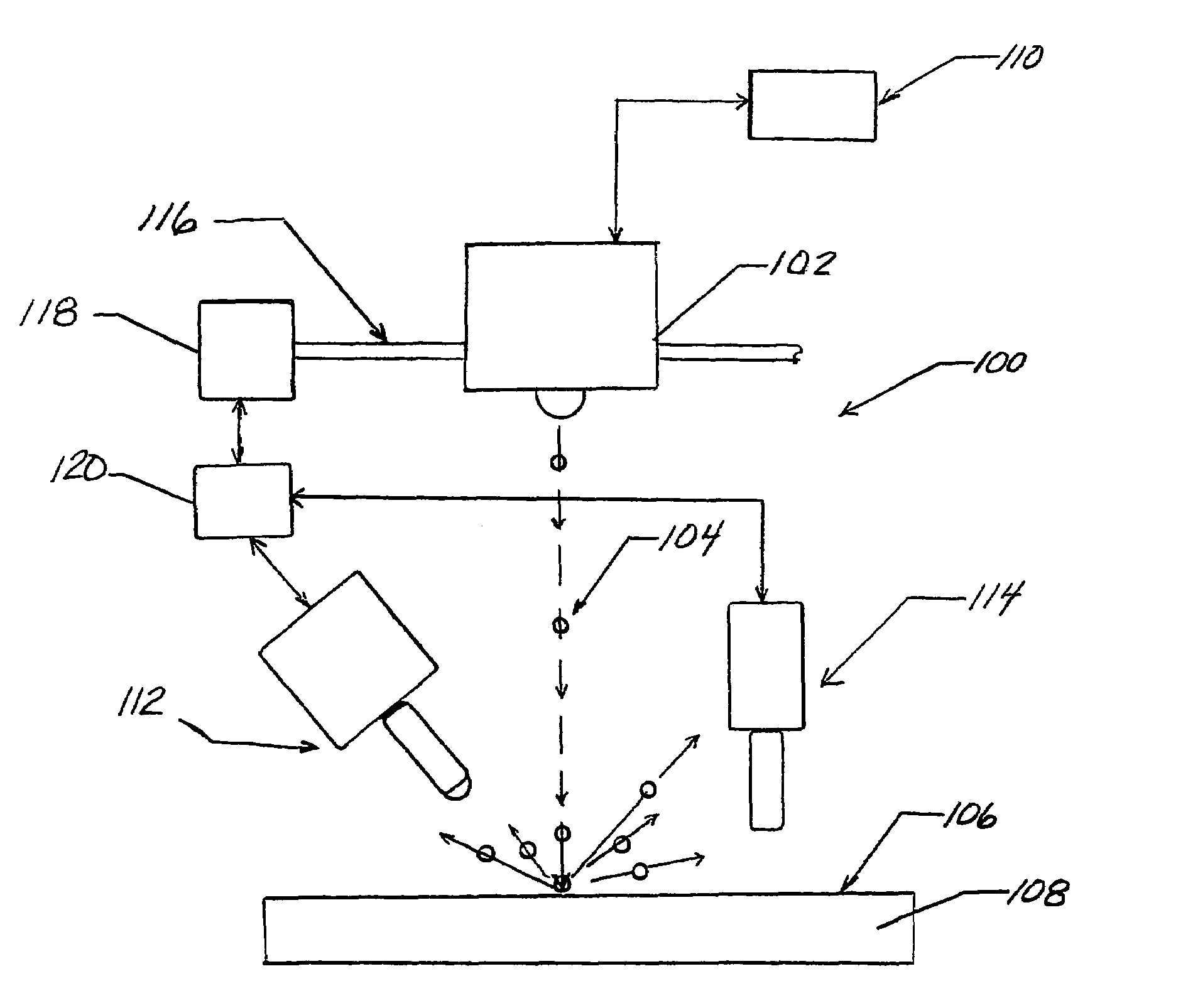
ActiveUS7159425B2Reduce processing timeWork lessBurnishing machinesHeat treatment process controlX-rayHigh surface
The shot peening method and apparatus (FIG. 13) of the present invention utilizes control of the shot peening coverage to provide higher surface compression and comparable depth of compression to conventional 100% coverage peening but with reduced cold working providing improved thermal stability and reduction in shot peening time and cost. A preferred embodiment of this invention employs x-ray diffraction (FIG. 13) residual stress and percent cold work determinated by line broadening to establish the optimal degree of coverage for a given material and shot peening intensity.
Owner:SURFACE TECH HLDG
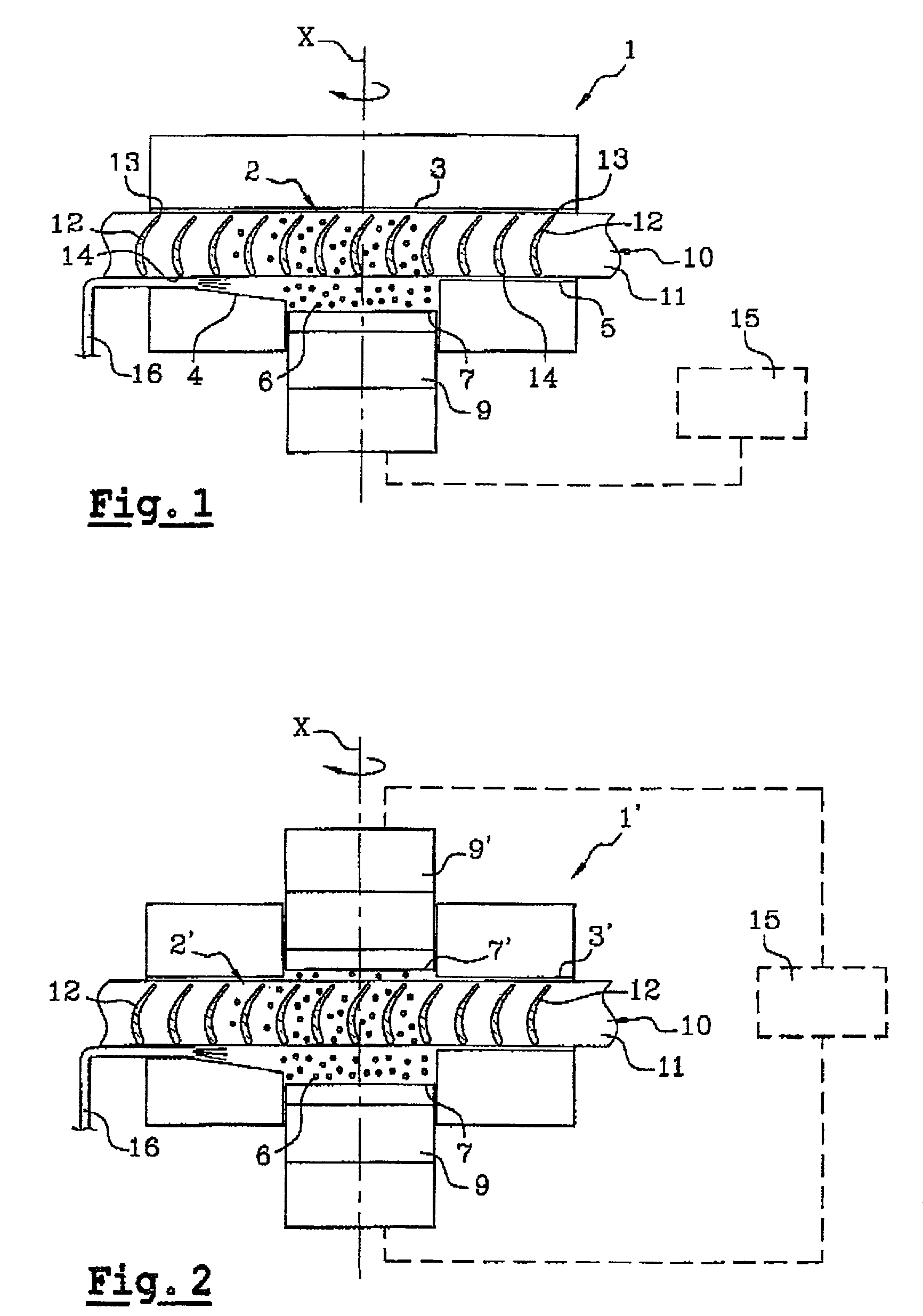
Component With Compressive Residual Stresses, Process For Producing And Apparatus For Generating Compressive Residual Stresses
The inventive method discloses the local, adapted and controlled introduction of internal compressive stress in convex and concave regions, such as the root region of turbine blades, by means of at least two pressure generators.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
Method of shot blasting and a machine for implementing such a method
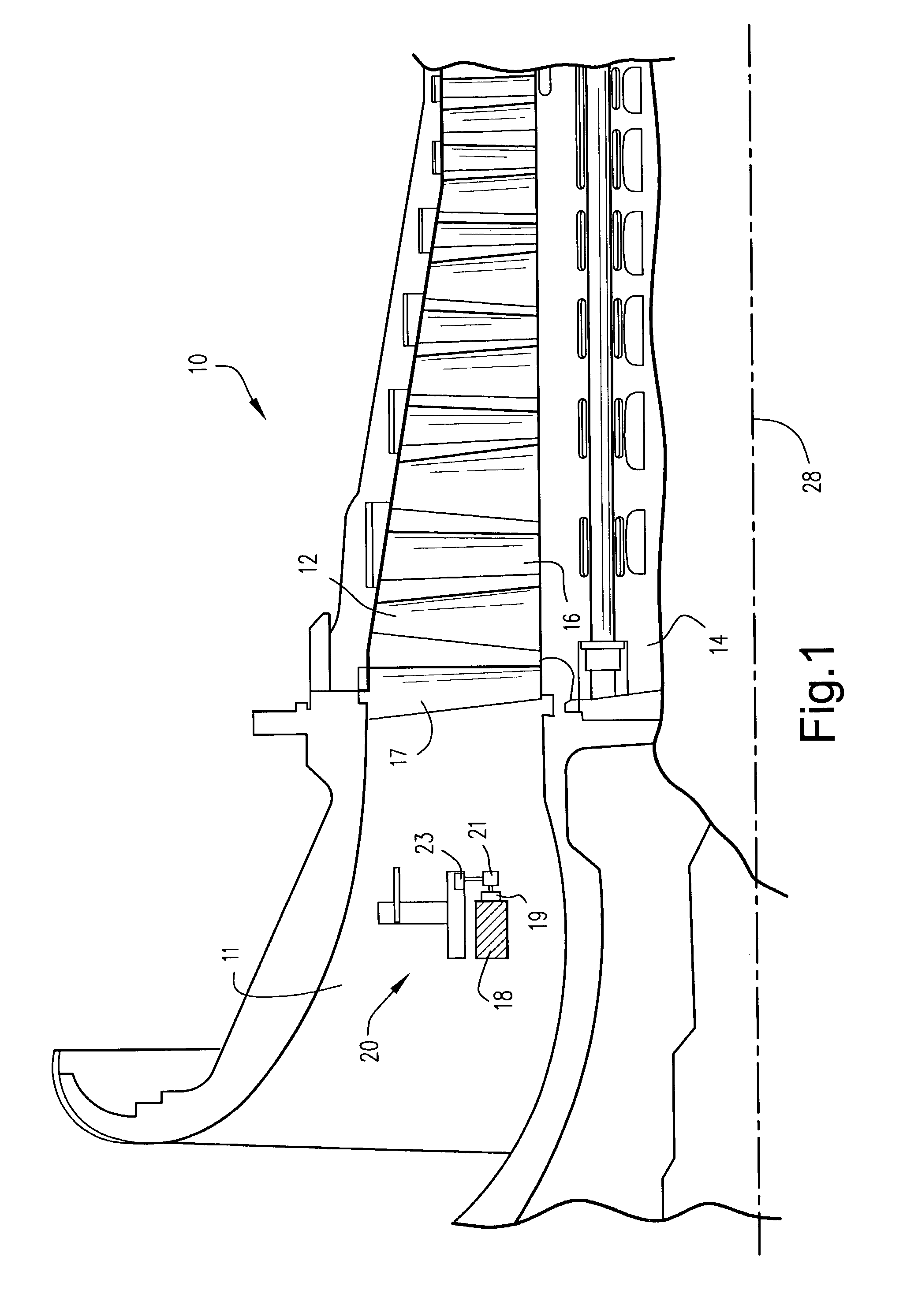
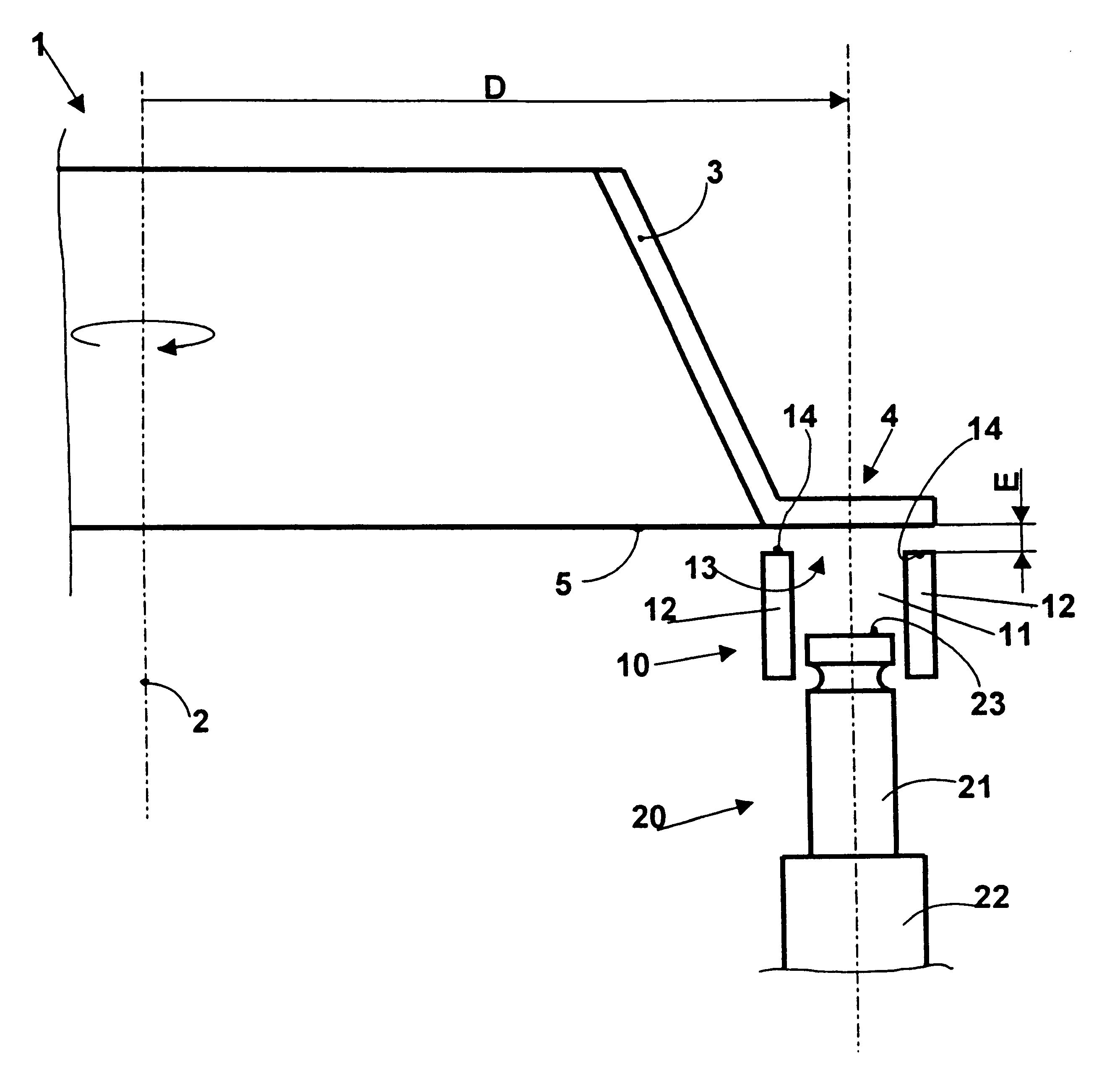
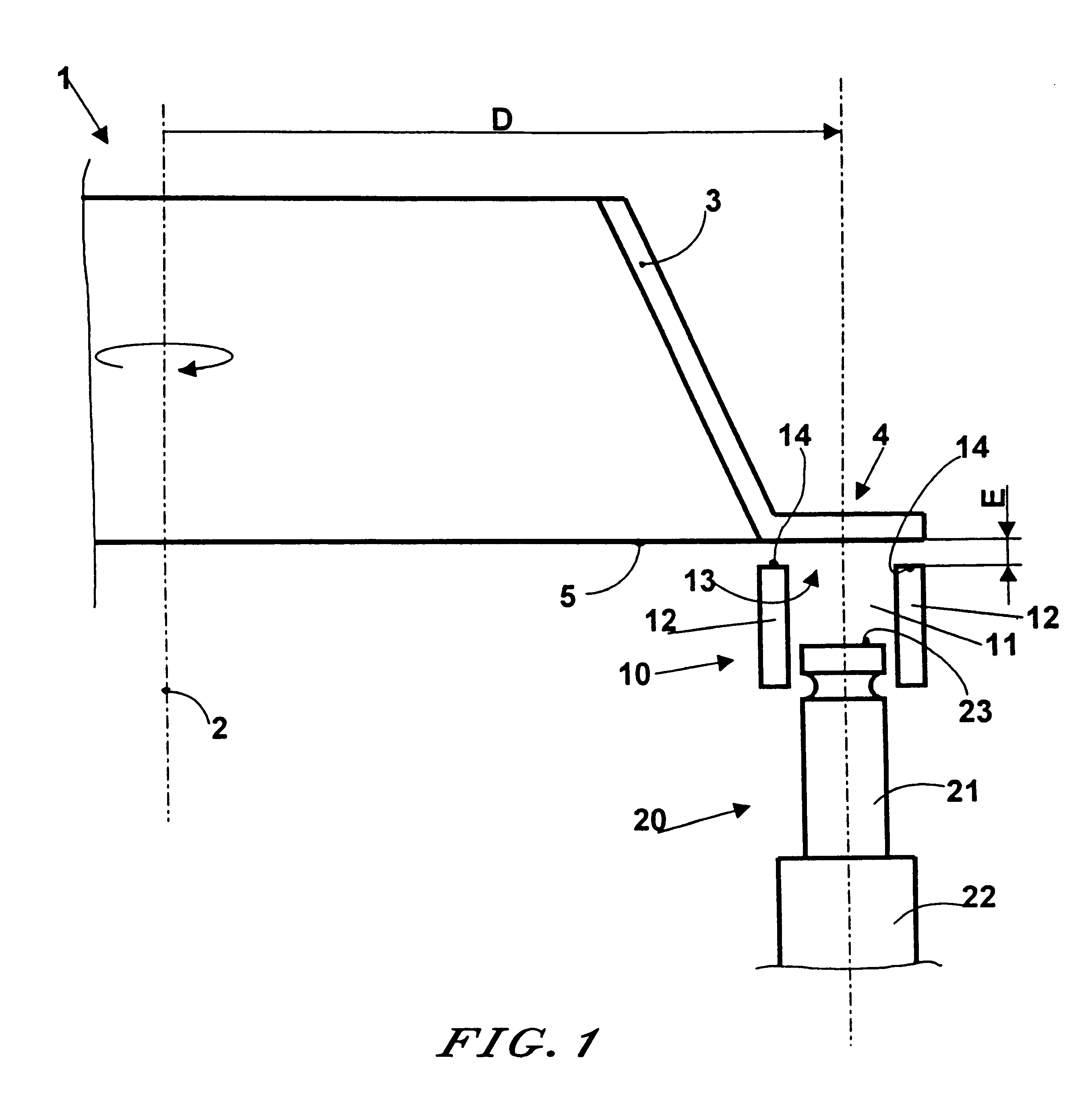
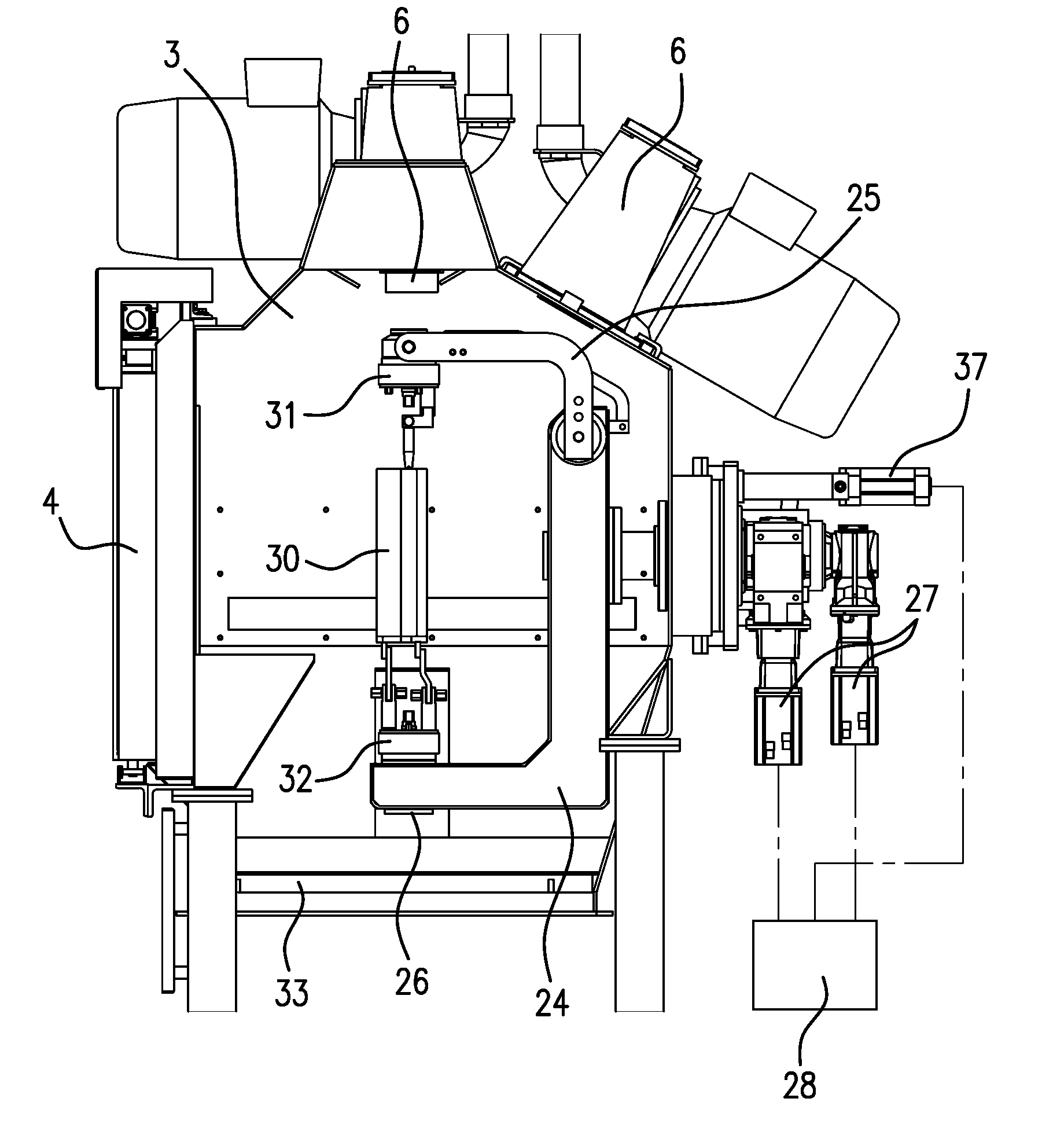
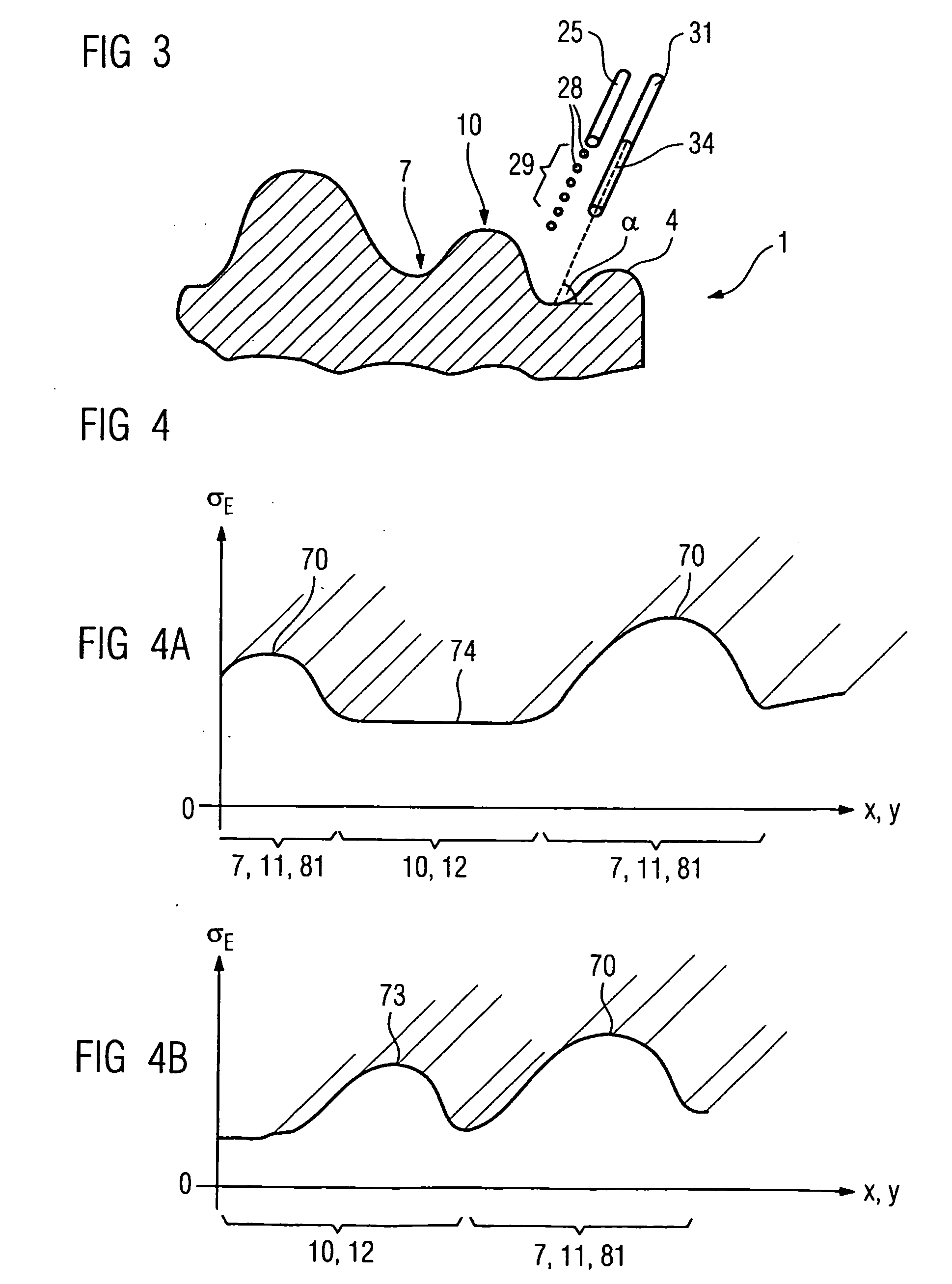
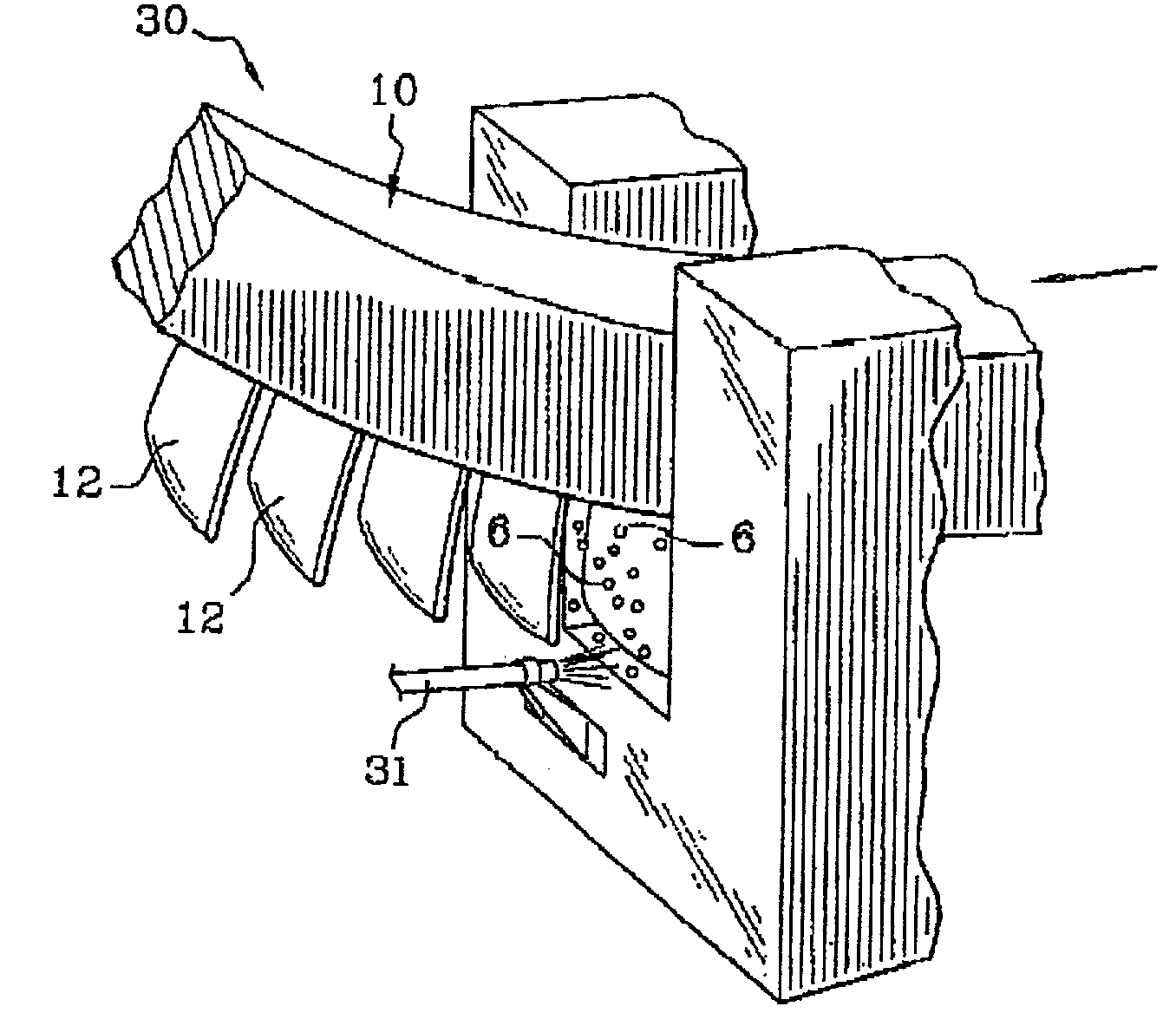
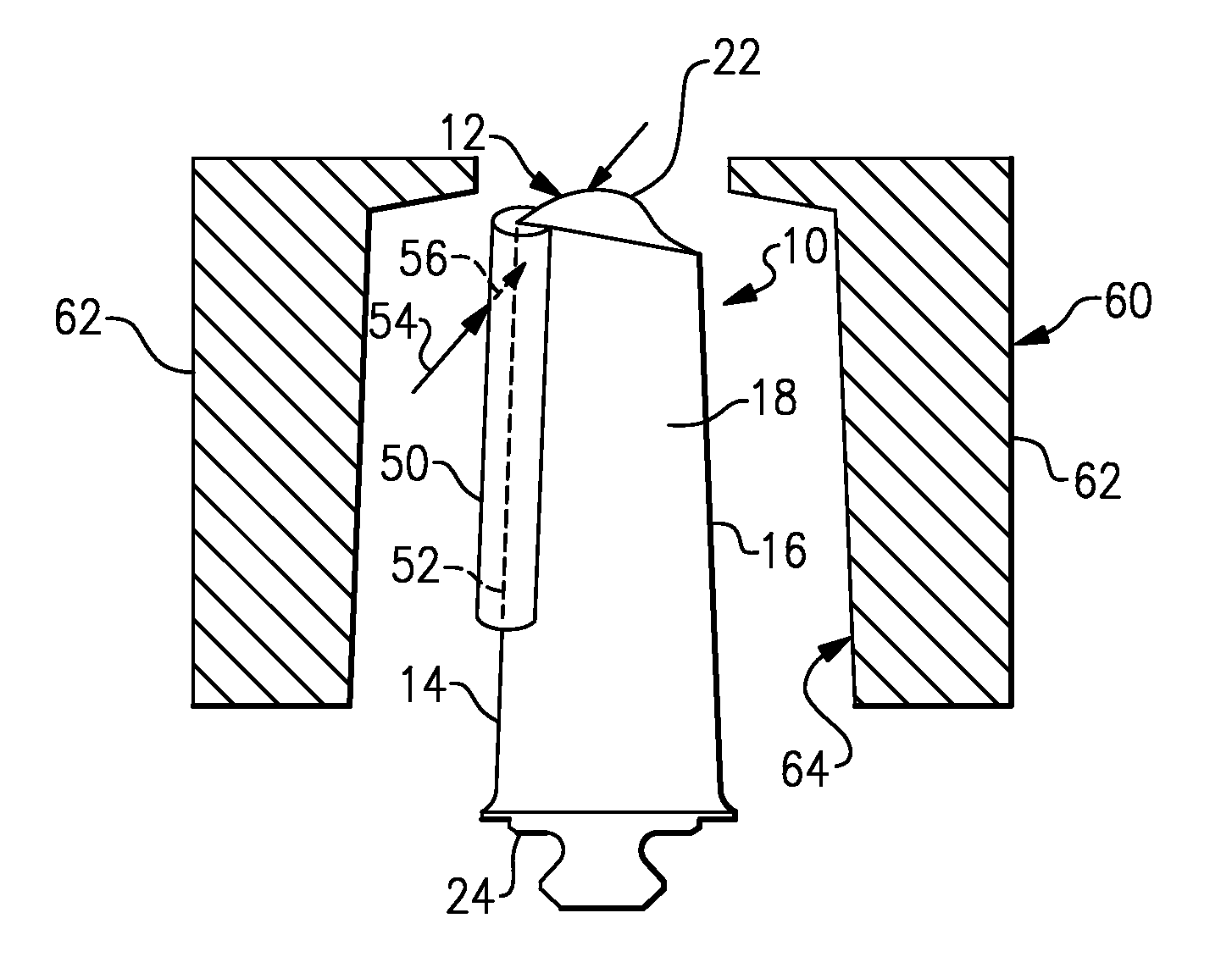
InactiveUS7028378B2Reduce usageHigh energyNon-mechanical blast generatorsBlade accessoriesEngineeringPeening
A part to be shot peened includes at least one thin wall (12″) defining two opposite main faces, the square root of the area of each face being greater than the mean distance between the two faces by a factor of at least five, and preferably by a factor of at least ten. According to the method, the part is caused to rotate at least intermittently relative to one or more vibrating surfaces, with at least one of the main faces being exposed to projectiles (6) set into motion by one or more of the vibrating surfaces, treatment taking place progressively on the face(s) so as to impart compression stresses thereto, with a portion only of the part being treated at any one time and with regions of the part preferably being exposed on several occasions to the projectiles, with relative rotation taking place between the exposures.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
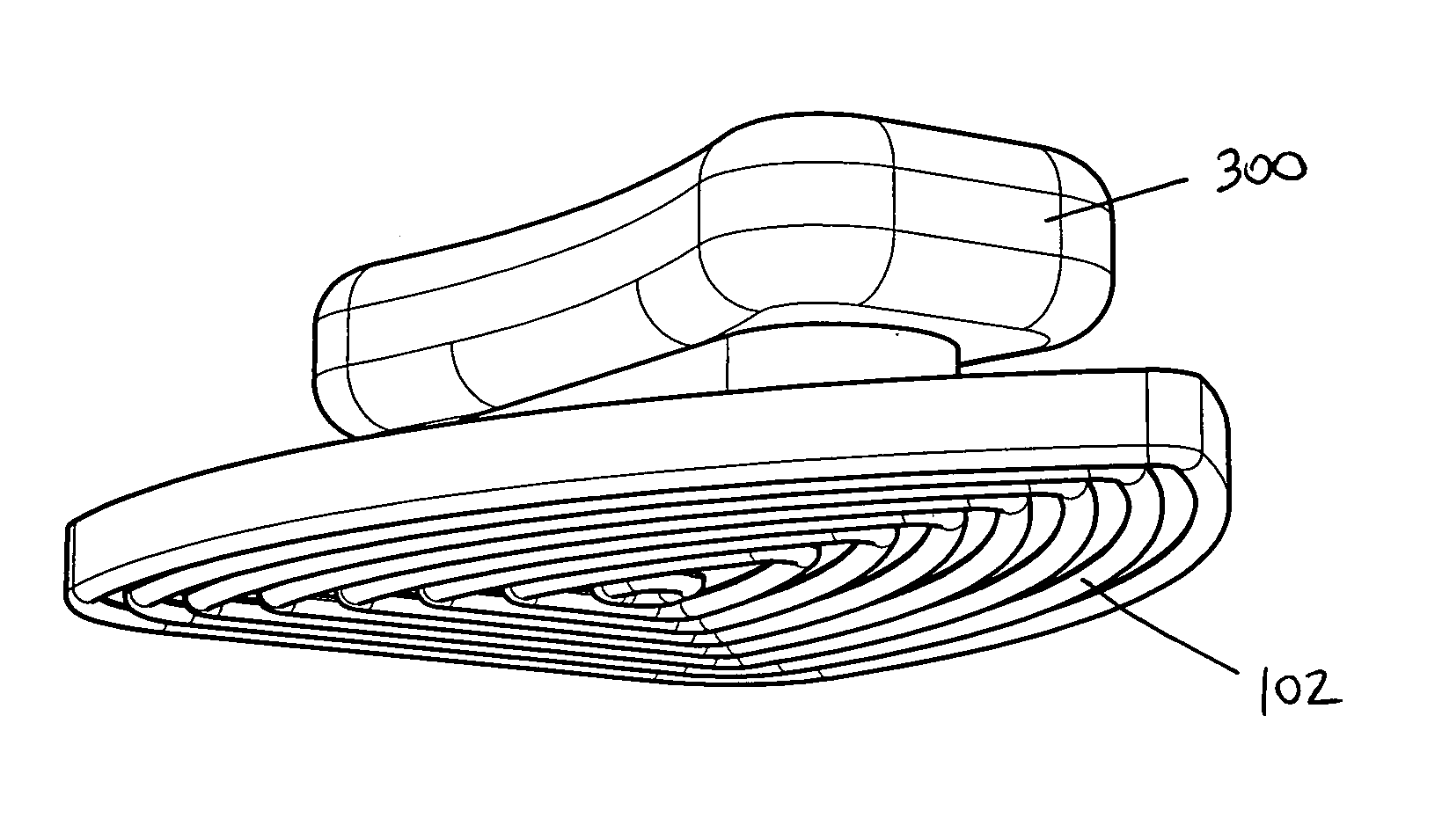
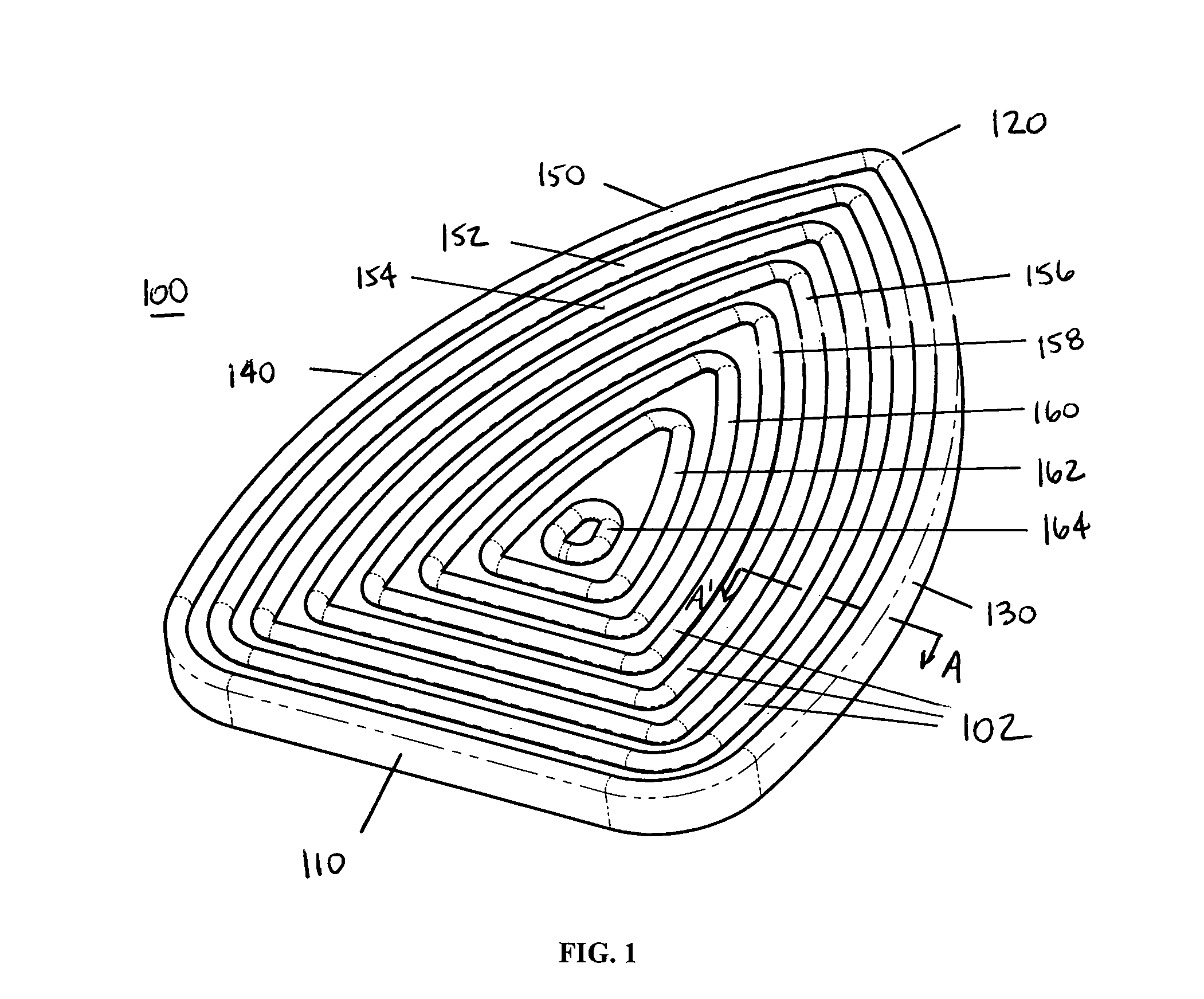
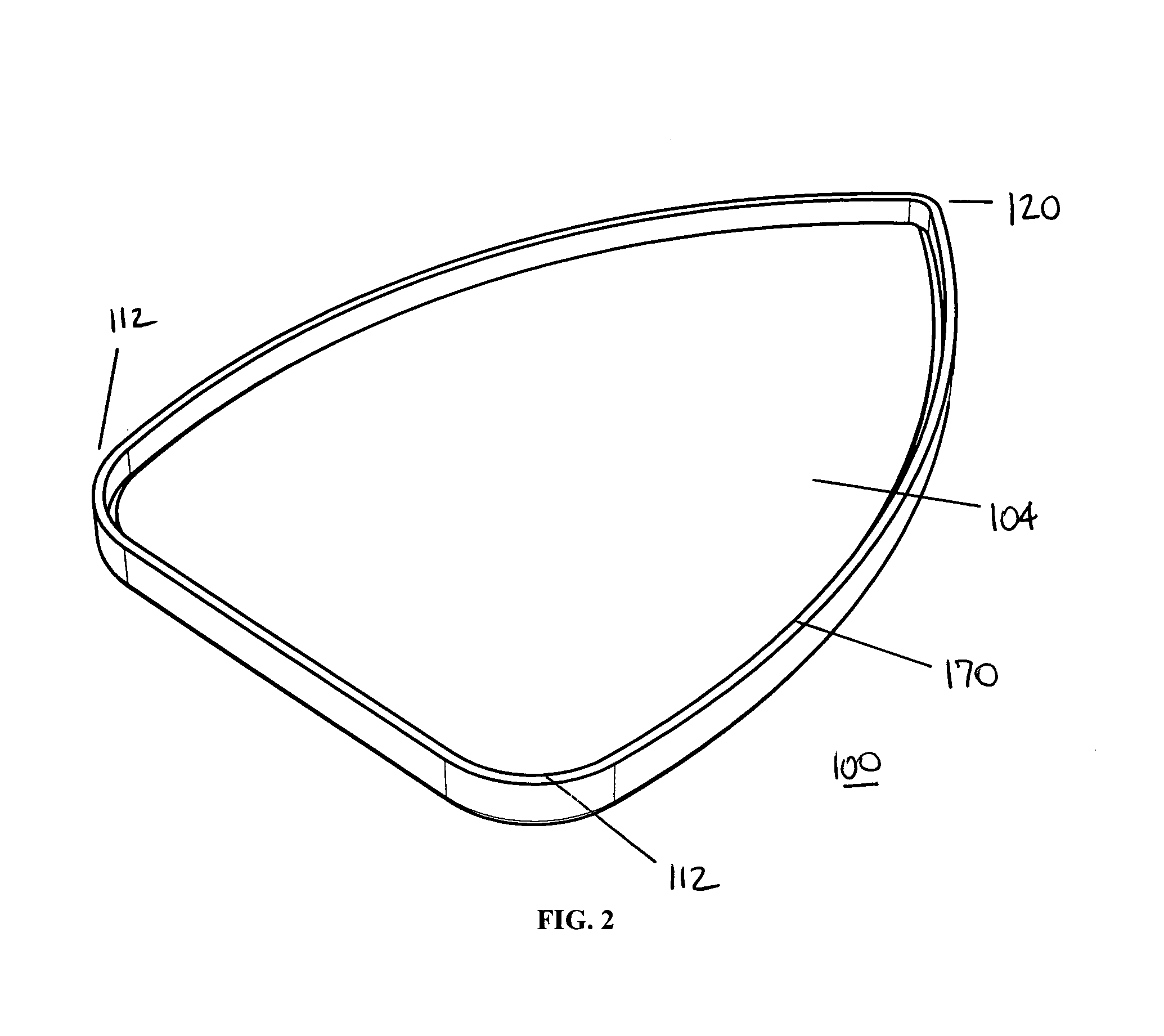
Method and apparatus for plaster burnishing tool
ActiveUS7115172B1High glossTedious and expensive processLiquid surface applicatorsCeramic shaping apparatusSanderEngineering
An Advanced Burnishing Tool for burnishing Venetian plaster surfaces comprises a base with a working surface with a plurality of concentric ribs. The tool may be used manually or may be mounted on a power tool such as an oscillating sander. Each rib has a rounded upper portion for contacting the surface, so that each rib acts in a manner similar to the rounded edge of conventional burnishing tools. The plurality of ribs provide a simultaneous working of multiple points in the plaster surface. Efficiency is further improved when a power tool is used to reduce the manual effort required for burnishing.
Owner:TEODOROVICH MISHKO
Rotating disk style multi-position automative polisher
InactiveCN1424179ALow technical requirementsConvenient for manual processingBurnishing machinesDrive motorControl theory
Owner:陈晓峰
Method of repairing an article
Owner:RTX CORP
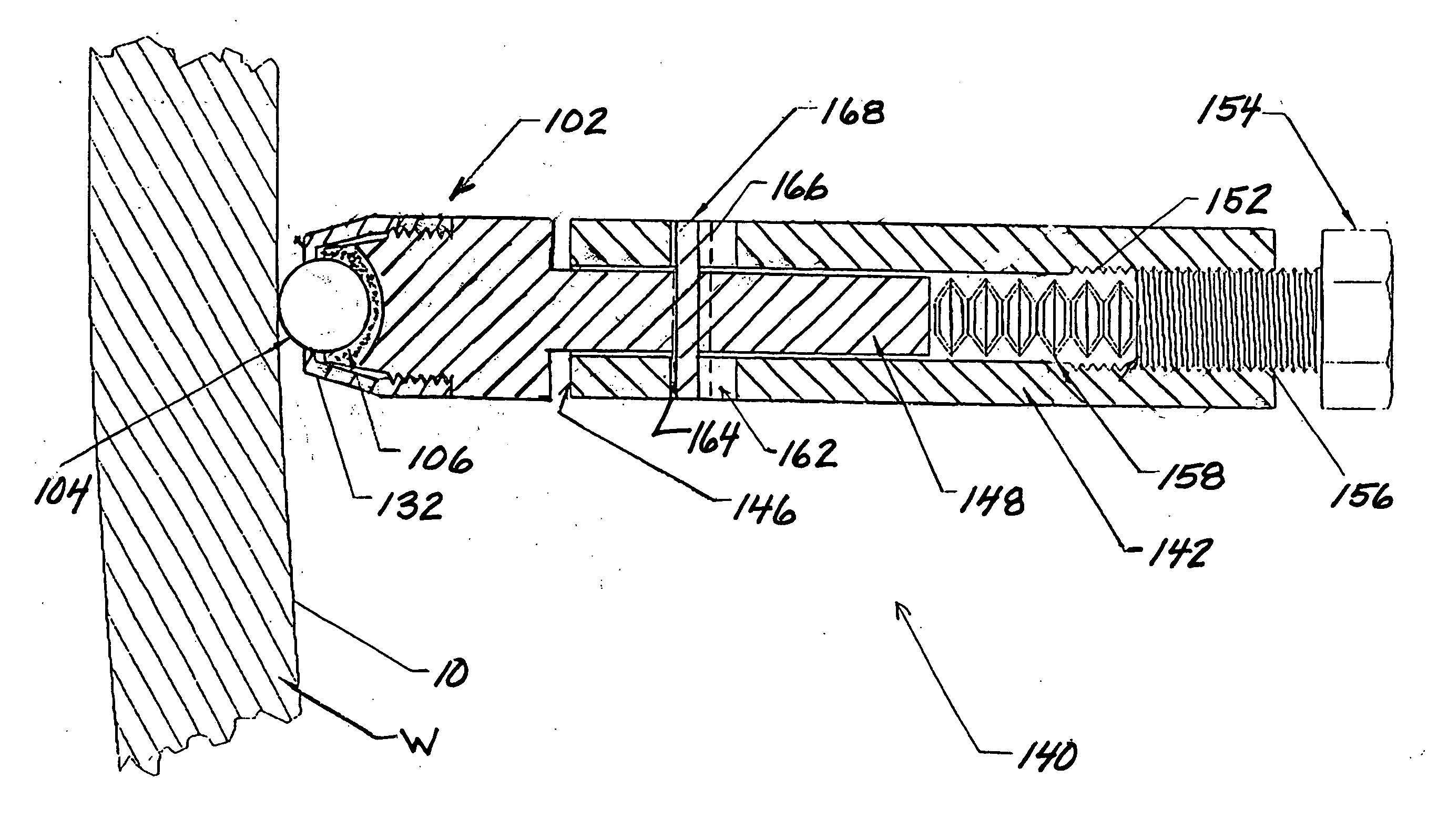
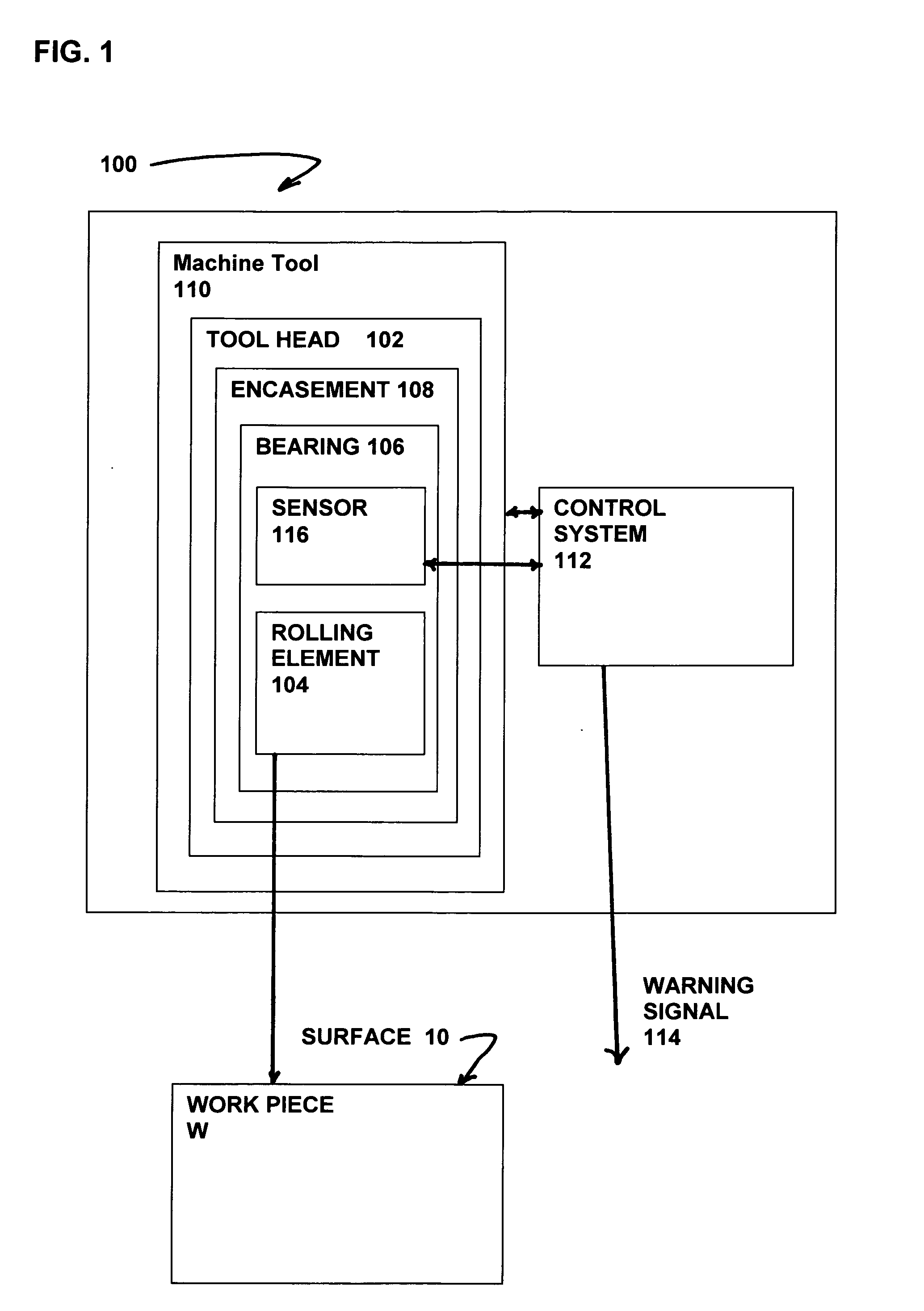
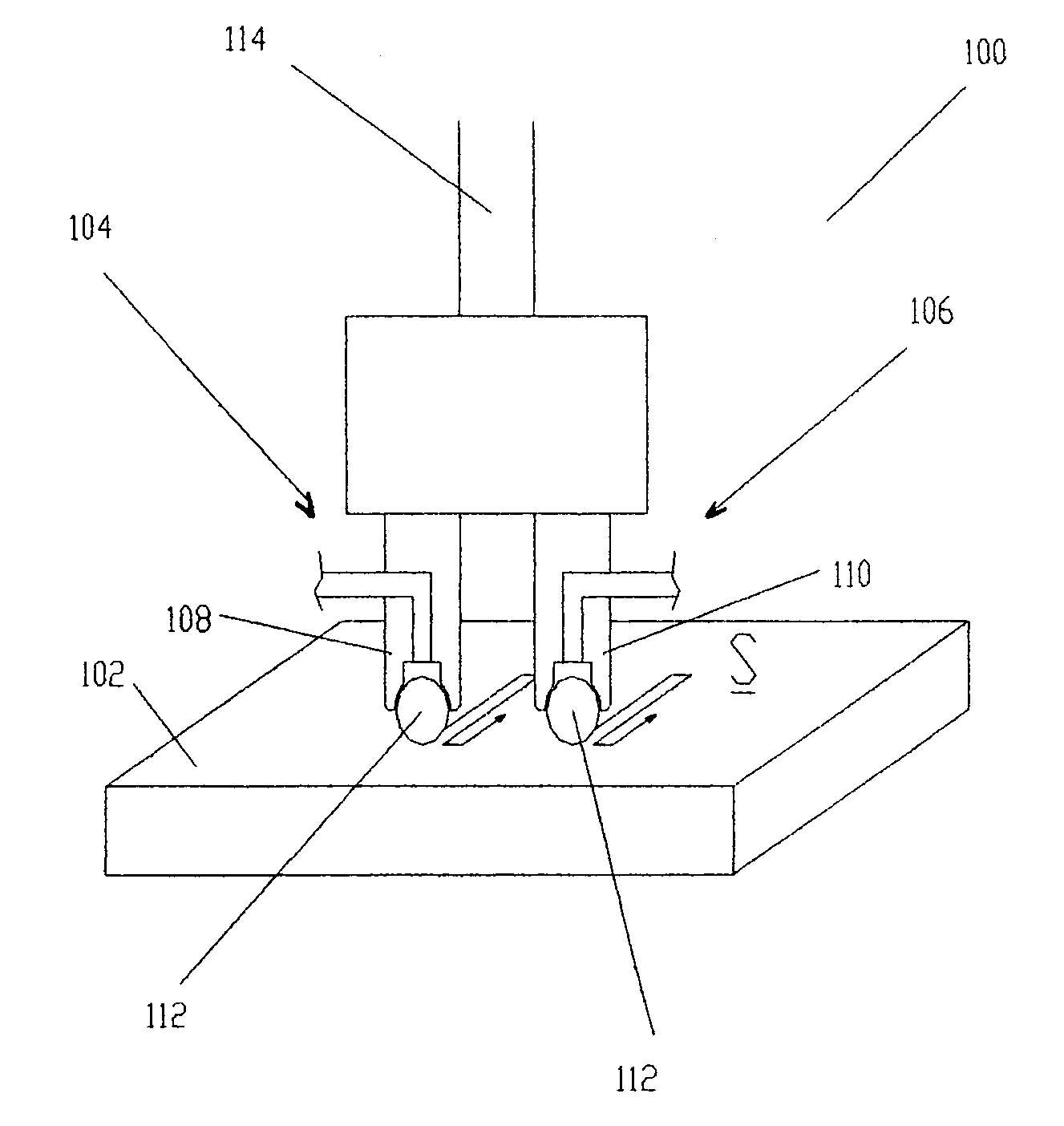
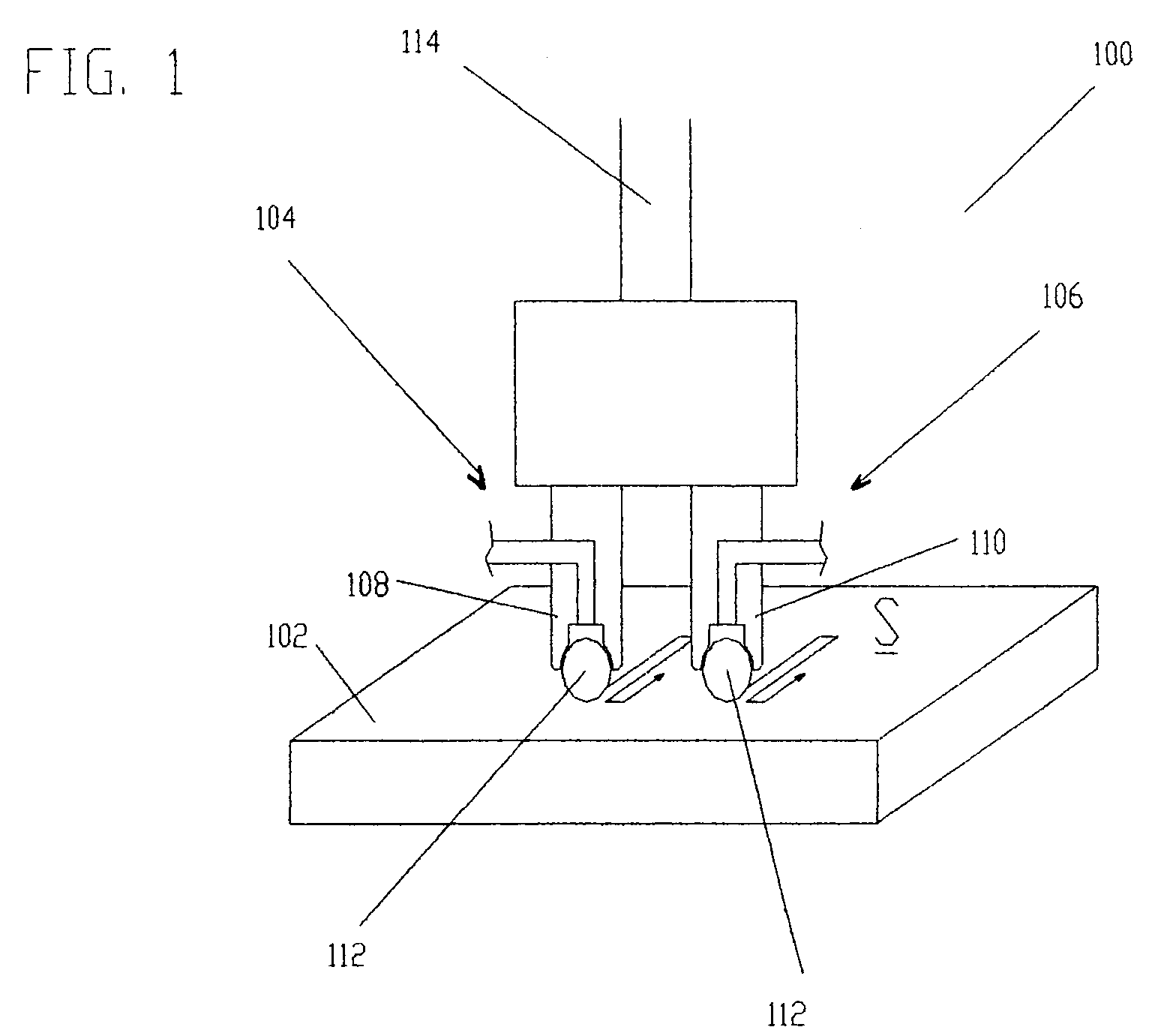
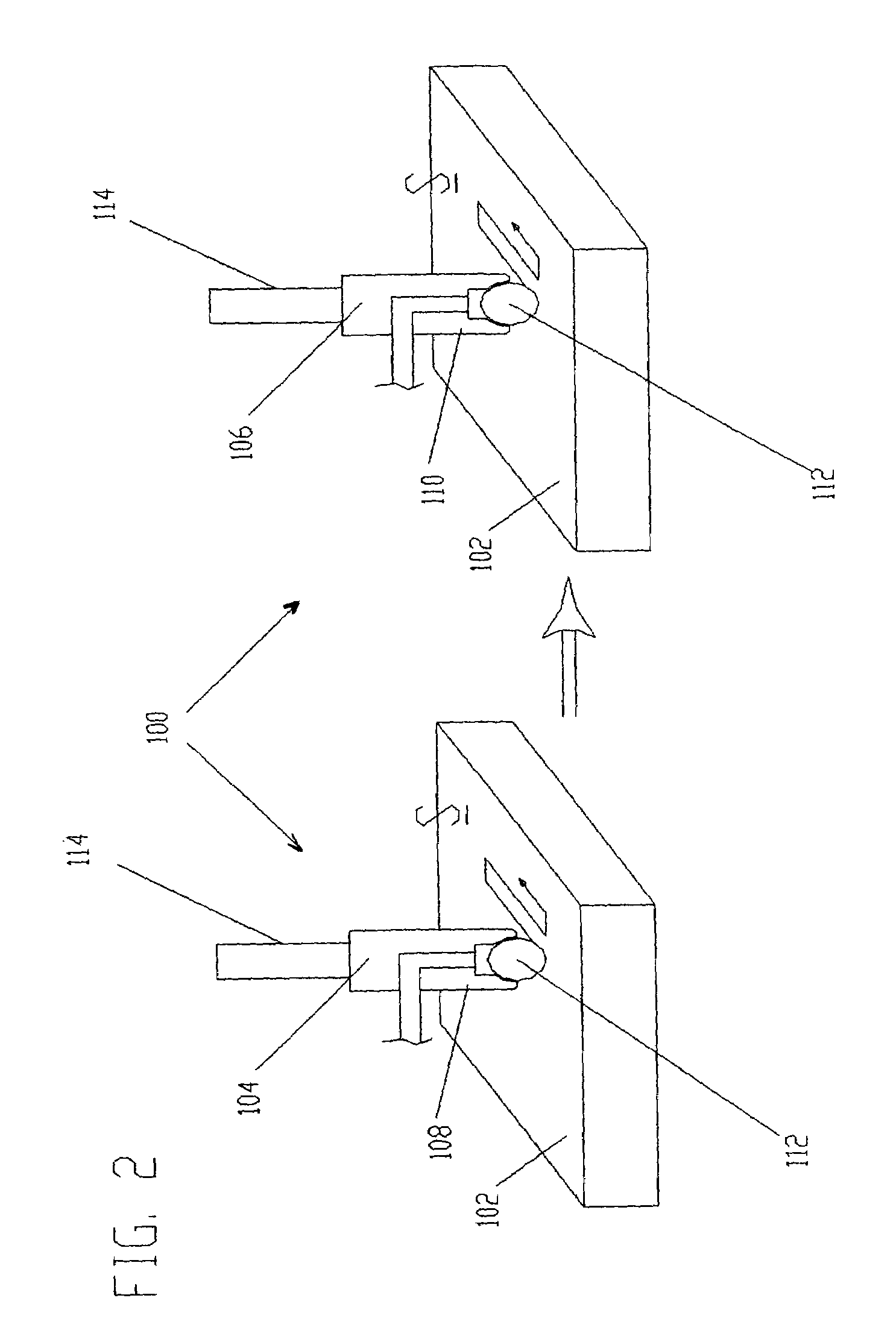
Burnishing tool and method for burnishing
A burnishing tool and method for providing a surface treatment along the surface of a work piece, the burnishing tool having a tool head comprising a bearing for supporting a rolling element and an encasement for supporting the bearing. The bearing is formed from a self-lubricating polymer such as, but not limited to, polytetrafluoroethylene based resin, ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene based resin.
Owner:SURFACE TECH HLDG
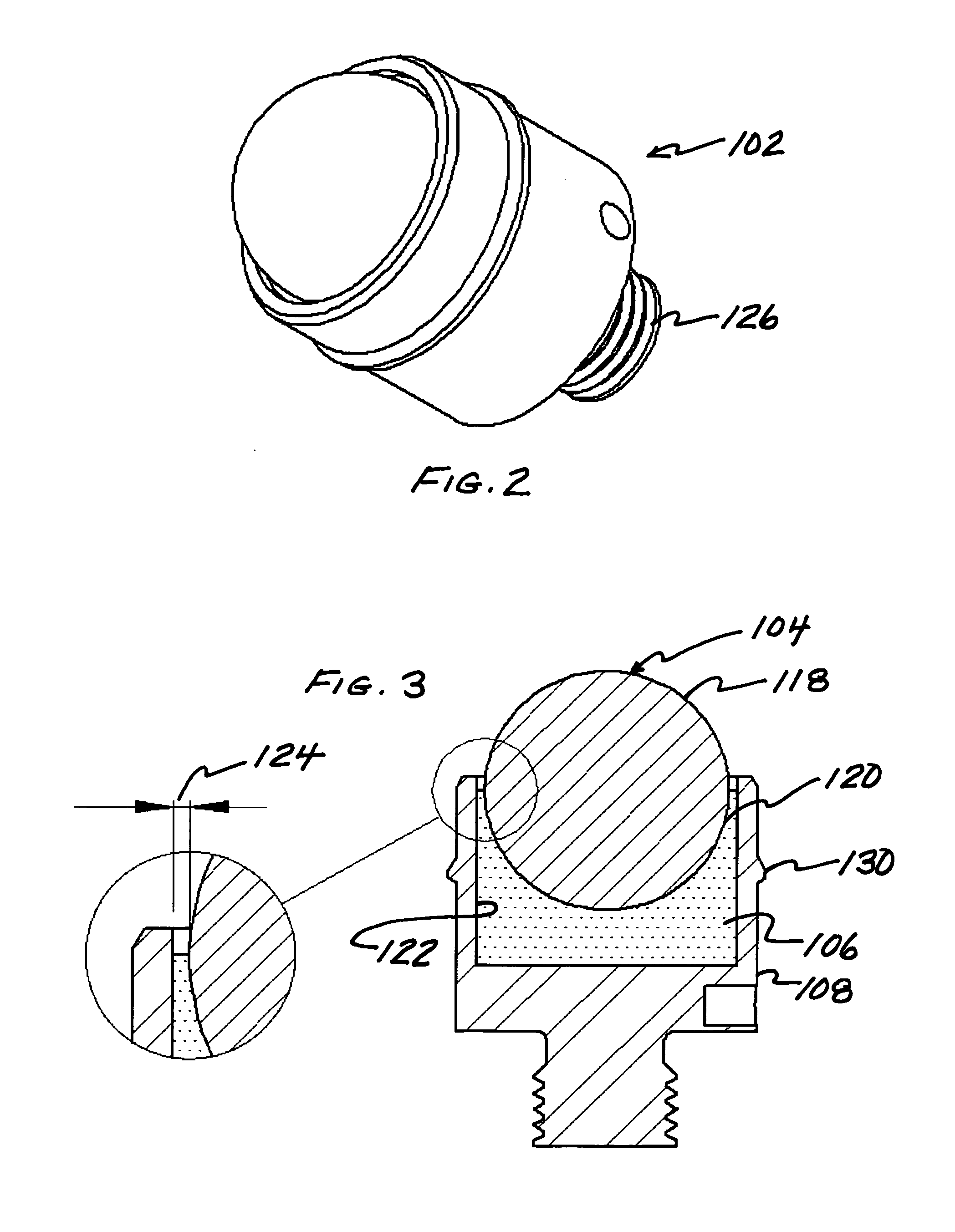
Deburring device, and deburring method for punch press, and punch press
ActiveUS20060042341A1Continuously and smoothly removeEliminate burrsBurnishing machinesPunch pressEngineering
The present invention provides a deburring device for a punch press which can remove burrs produced along a slot or a cut portion formed in a plate material by punching or cutting using a punch press so that the removal is carried out as a process with the same punch press. A deburring device 6 for a punch press has an upper tool 7 and a lower tool 8 arranged opposite each other. The upper and lower tools 7, 8 each have a ball holding member 22, 32, respectively, and a ball 23, 33, respectively, rotatably supported by the ball holding member and projecting from a surface of the ball holding member 22, 32 toward an opposite surface of the opposite ball holding member 32, 22. Each of the upper and lower balls 23, 33 has a diameter larger than the width of the slot A, in its portion projecting from the ball holding member 22, 32, respectively, the slot A being formed in the plate material W so as to extend across the plane. The plate material W moves with the vertical pair of balls 23, 33 partly fitted into the slot A and with the plate material W sandwiched between the upper and lower balls 23, 33 to continuously remove burrs (a) produced along a longitudinal direction of the slot A. The deburring device 6 continuously removes not only the burrs produced along the slot A but also those produced along a cut portion in the plate material W as described above.
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD
Metallic article with integral end band under compression
An article made of a metallic material and comprising a body and a body end portion integral with the body, includes a band of the metallic material at the end portion substantially through the entire end portion, the band being under a compressive stress greater than the body. An example of the article is a turbine engine balding member in which the body is the airfoil of the member and the band is disposed at the radially outer tip portion of the airfoil. One method for providing the band includes performing roller deformation on the end portion until a desired amount of compressive stress is developed in the band substantially through the entire end portion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for improving the magnitude of compressive stress developed in the surface of a part
This invention relates to a method and an apparatus for performing the method of inducing compressive residual stress along the surface of a part. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, the method includes burnishing or deep rolling a surface using a first and a second roller or ball burnishing members, whereby the first and second burnishing members may have a different diameter and / or modulus of elasticity. In another preferred embodiment of the invention, the burnishing operations may be performed while the surface of the part is at different temperatures.
Owner:SURFACE TECH HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com