Patents
Literature
7685results about How to "Good optical performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
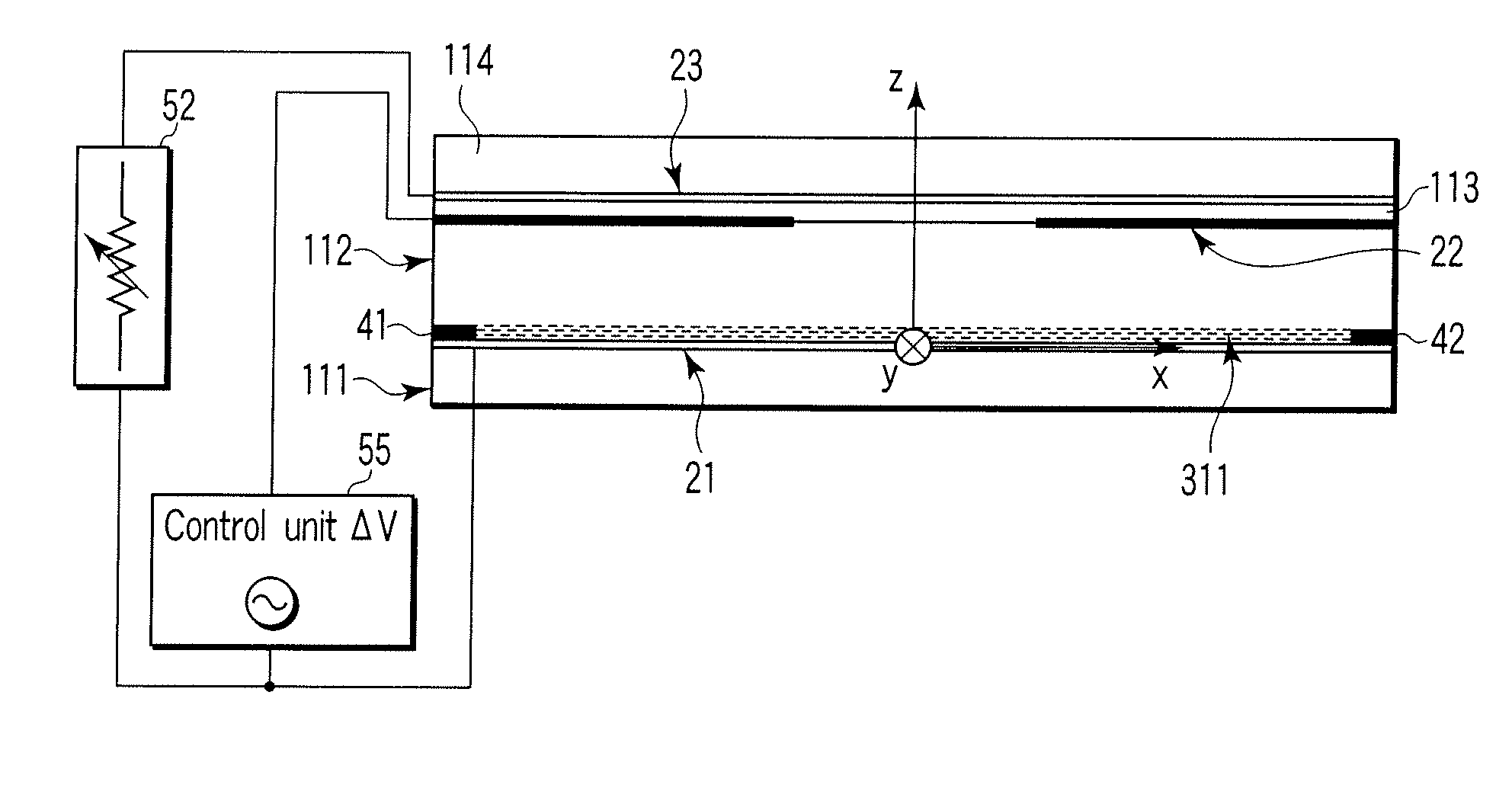
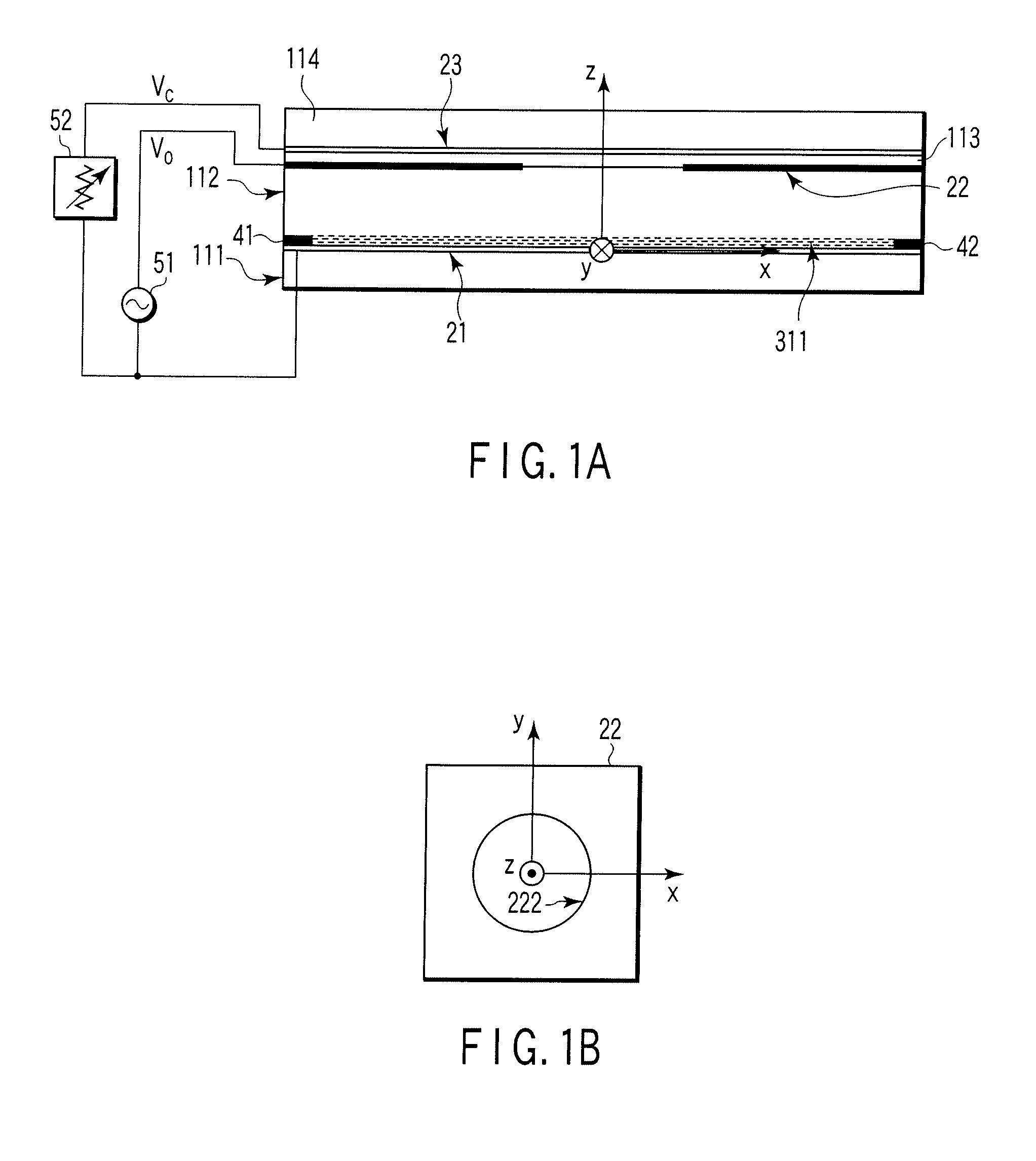
Ergonomic head mounted display device and optical system
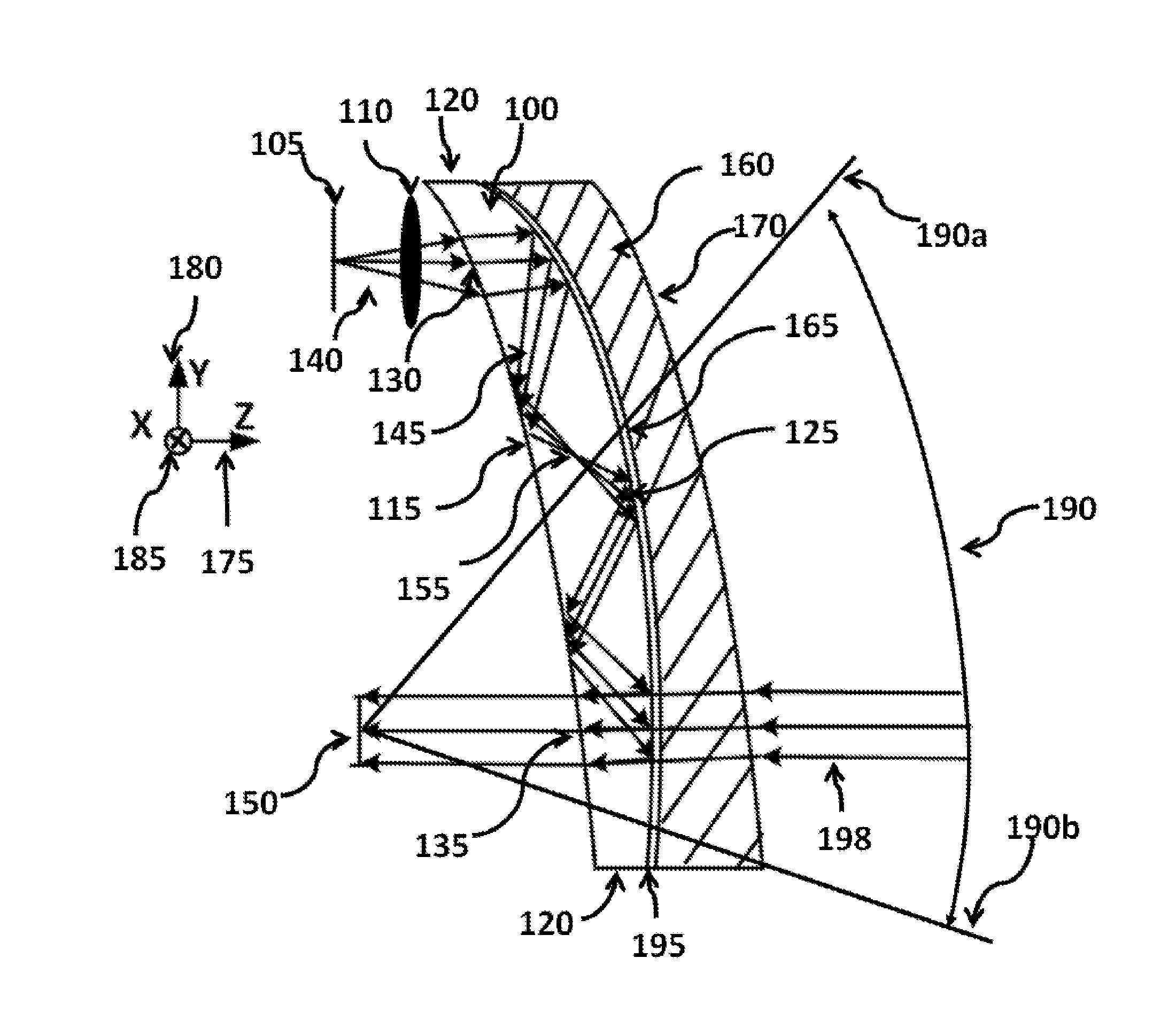
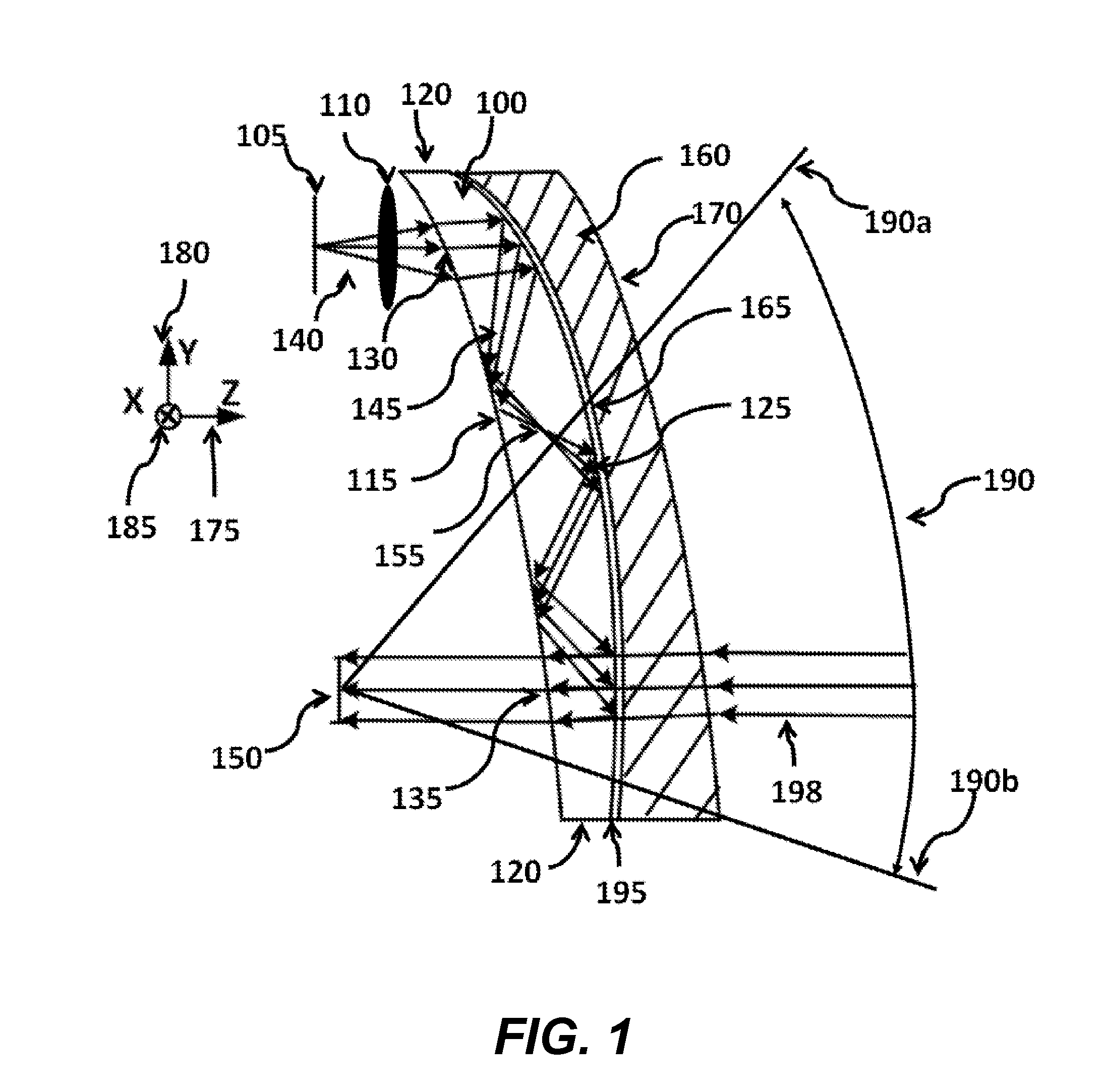
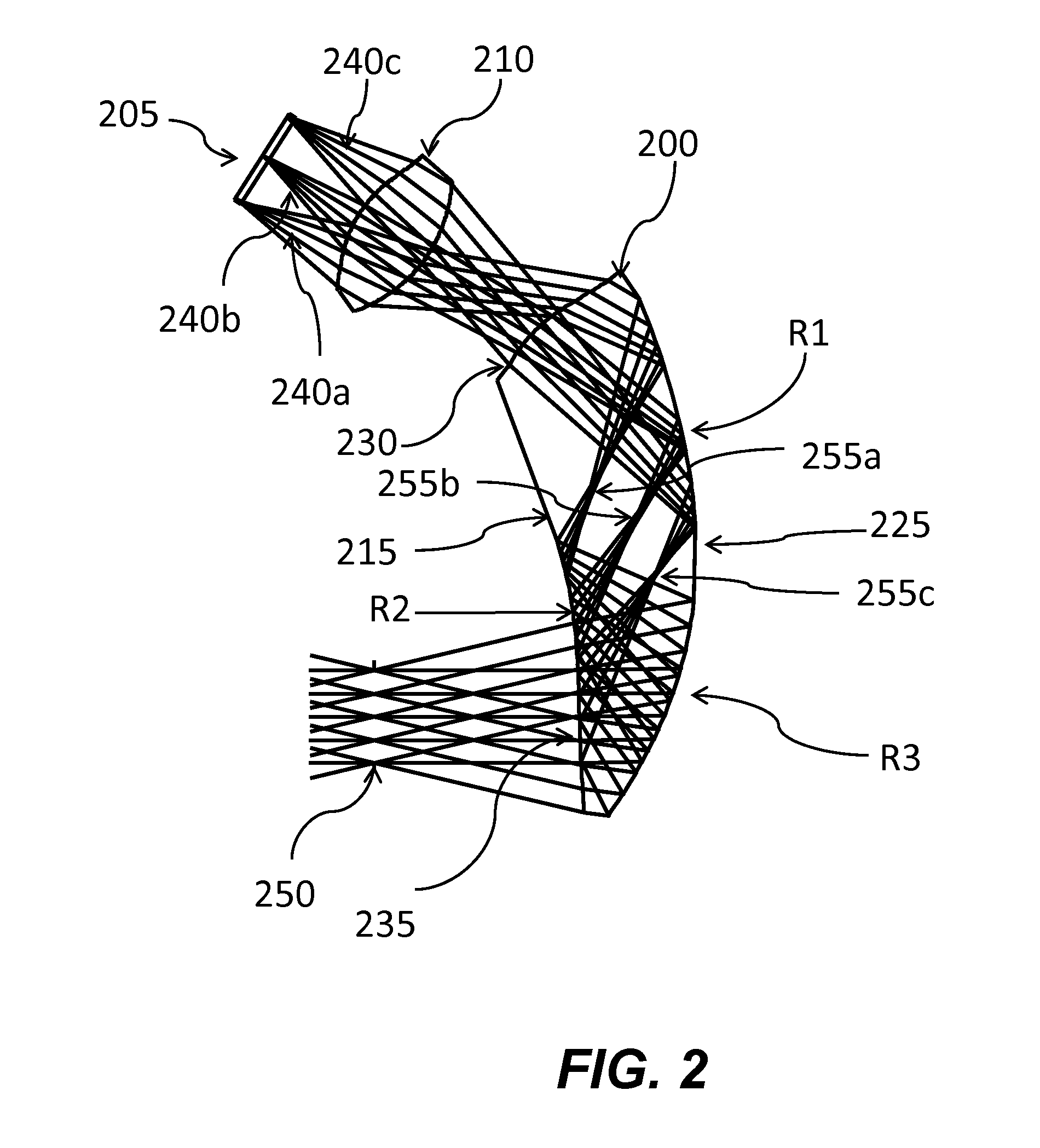
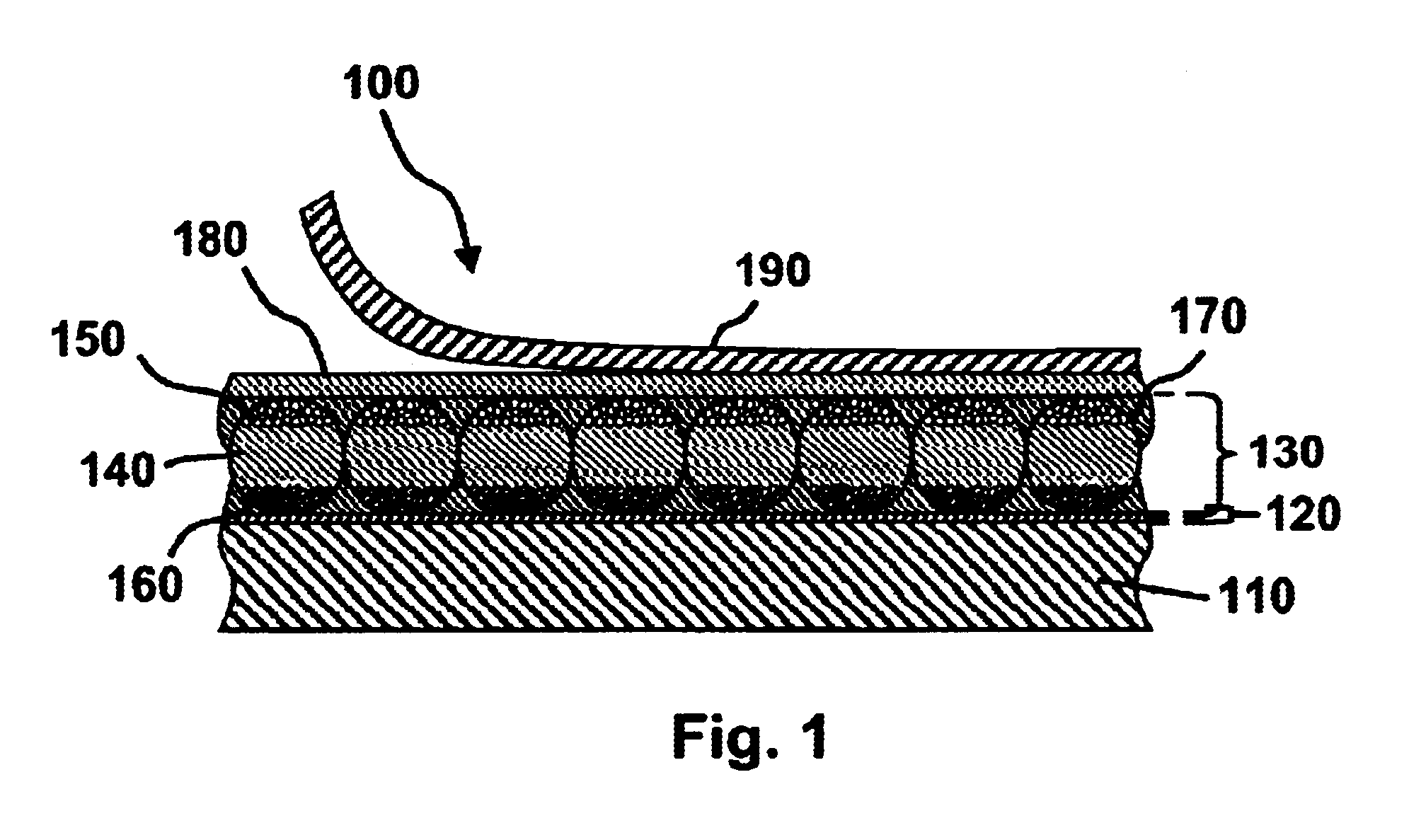
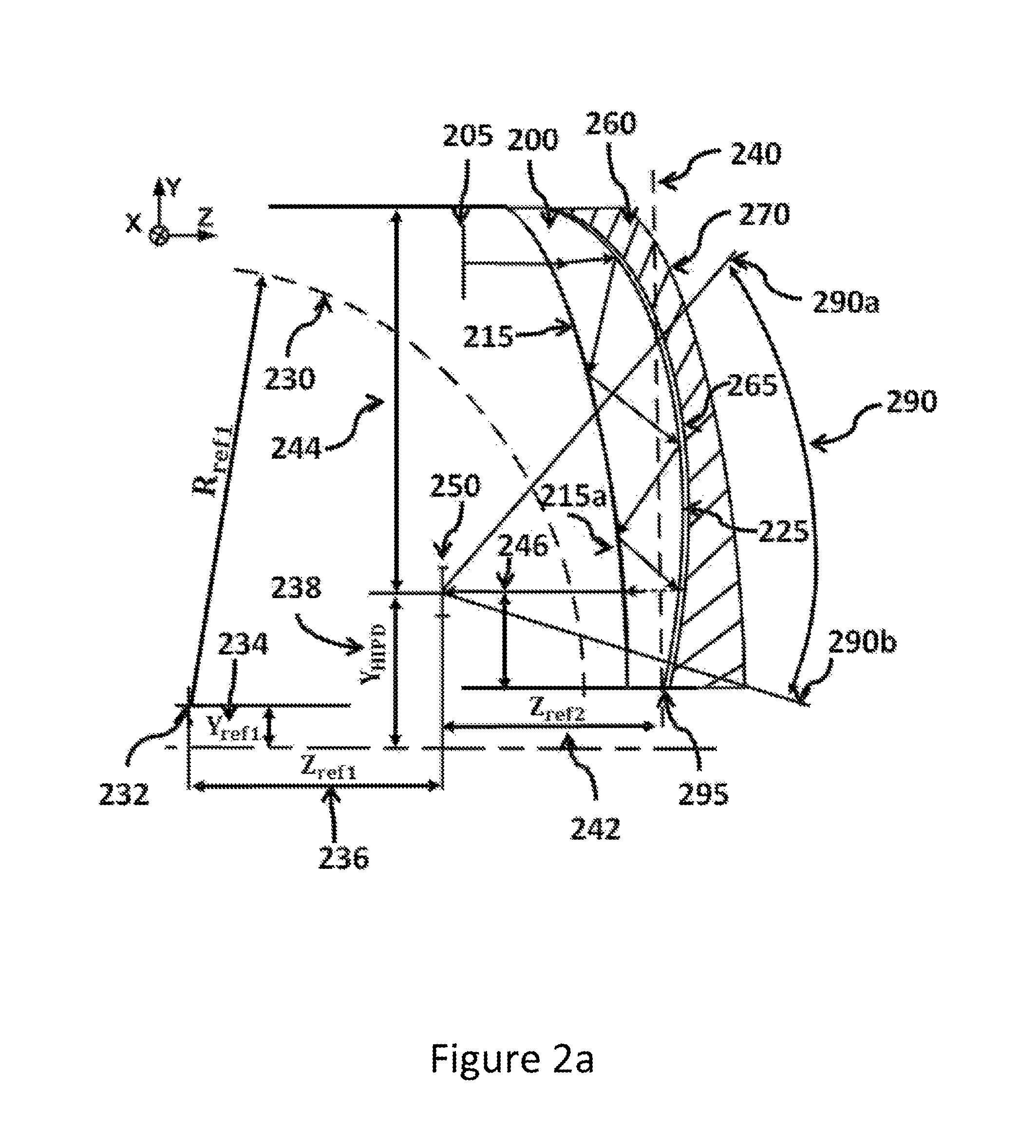
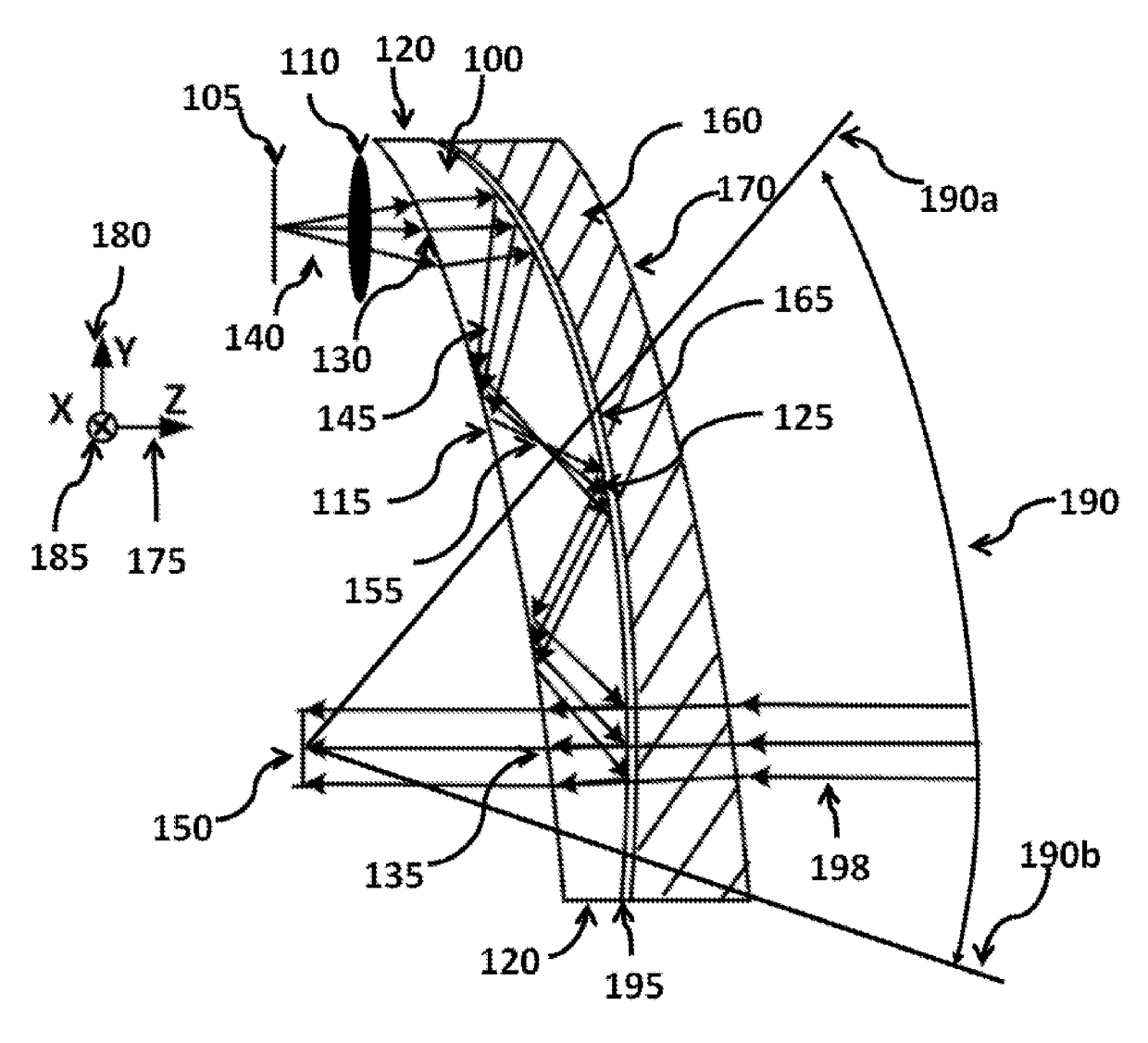
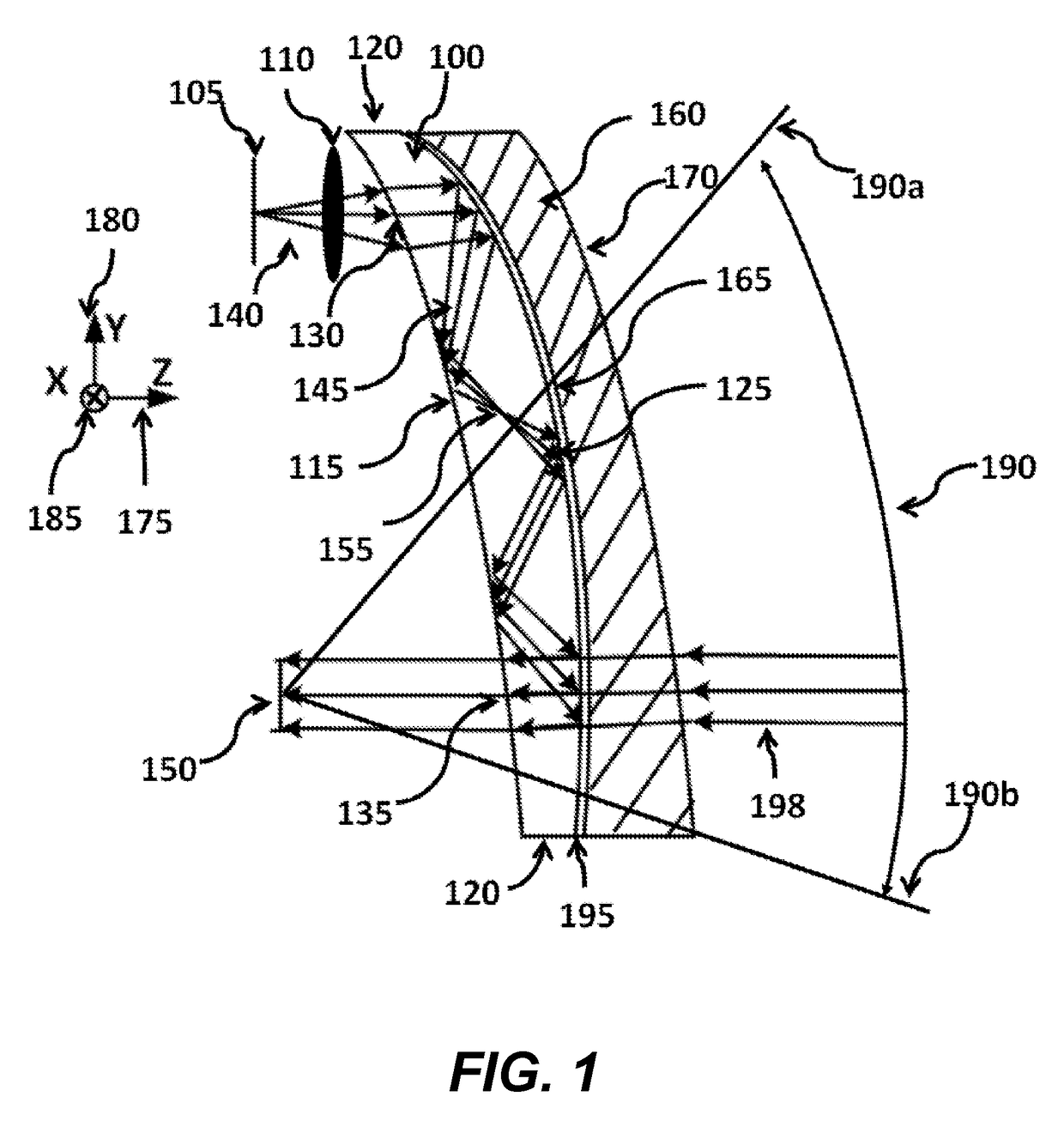
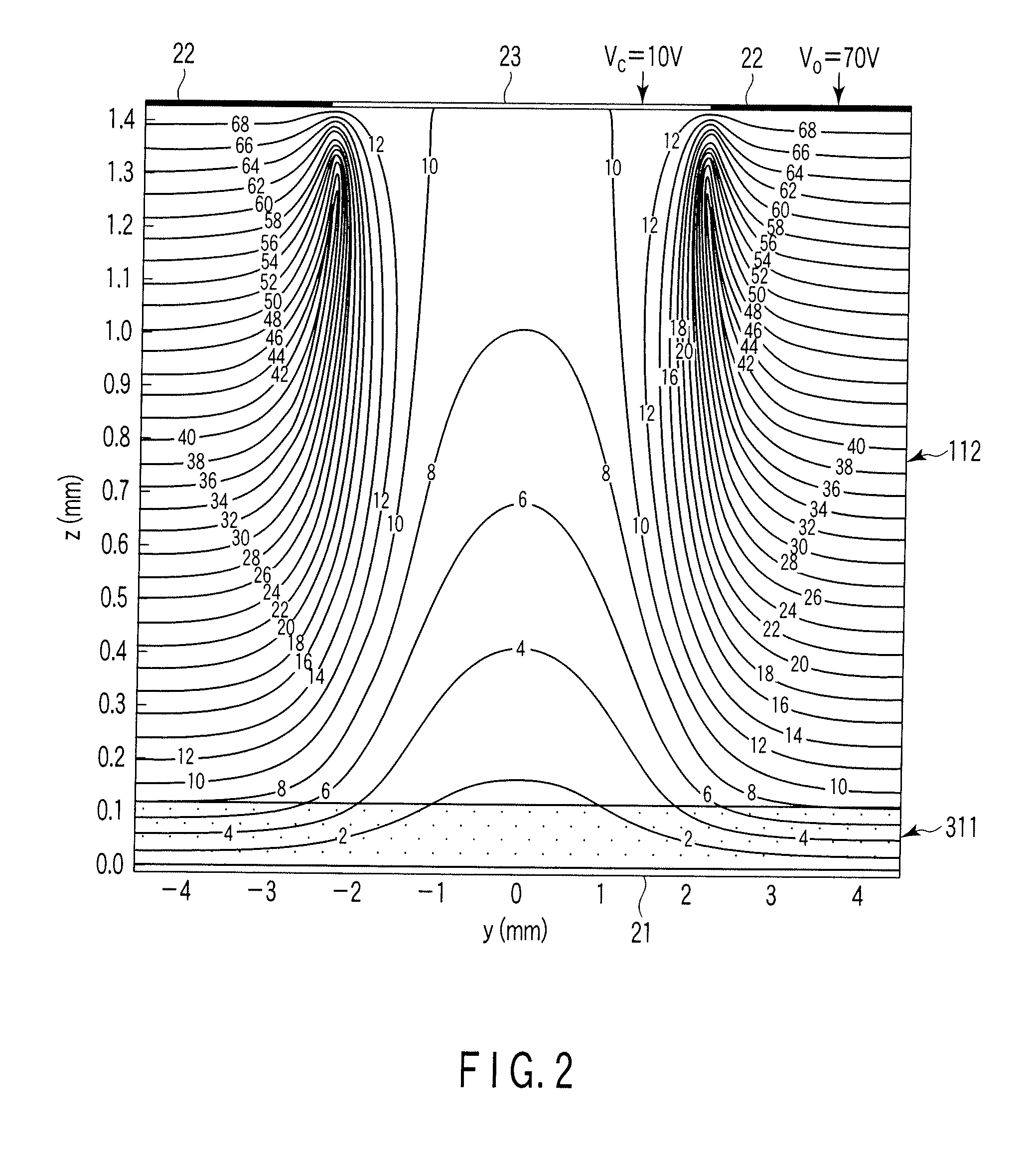
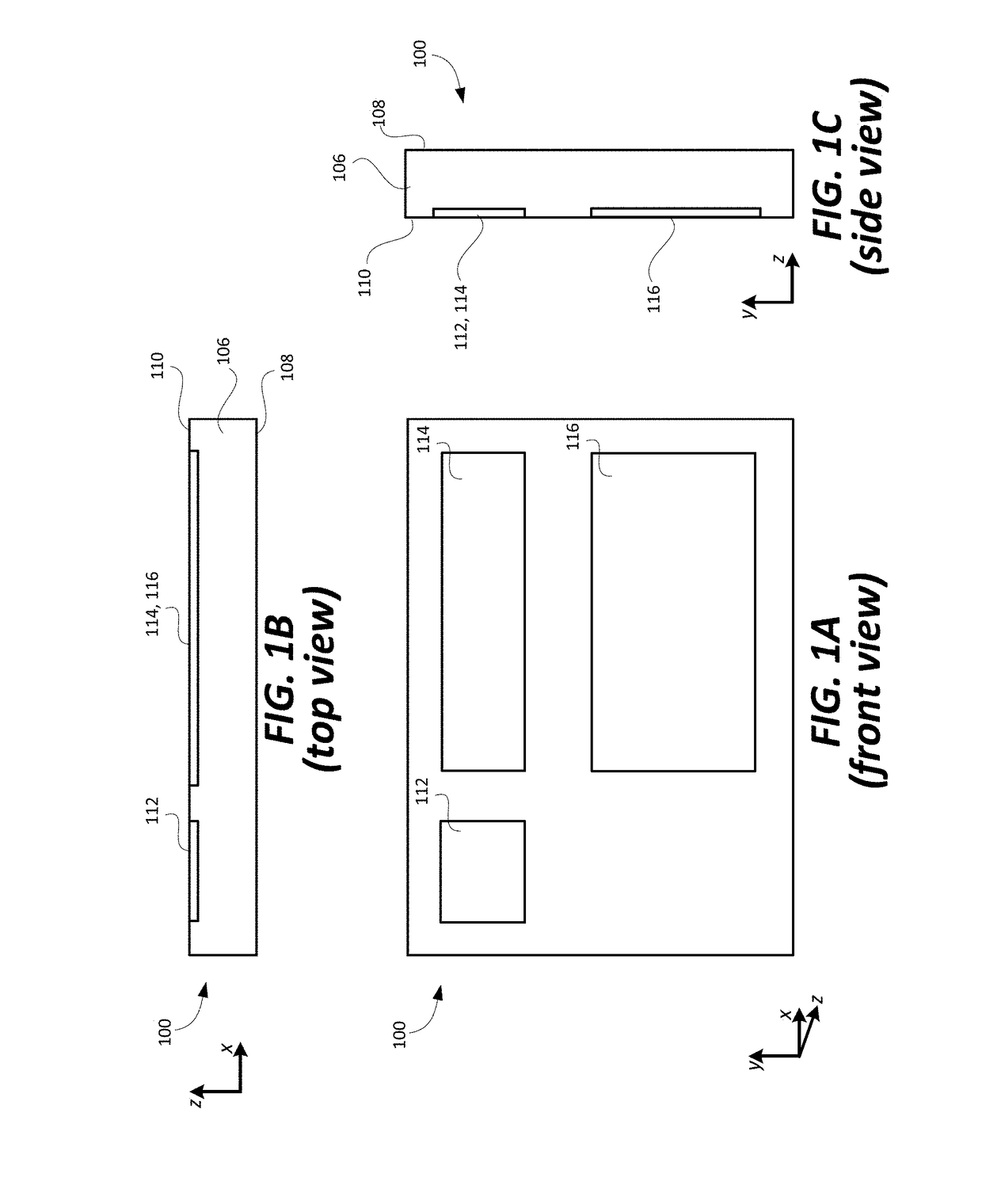
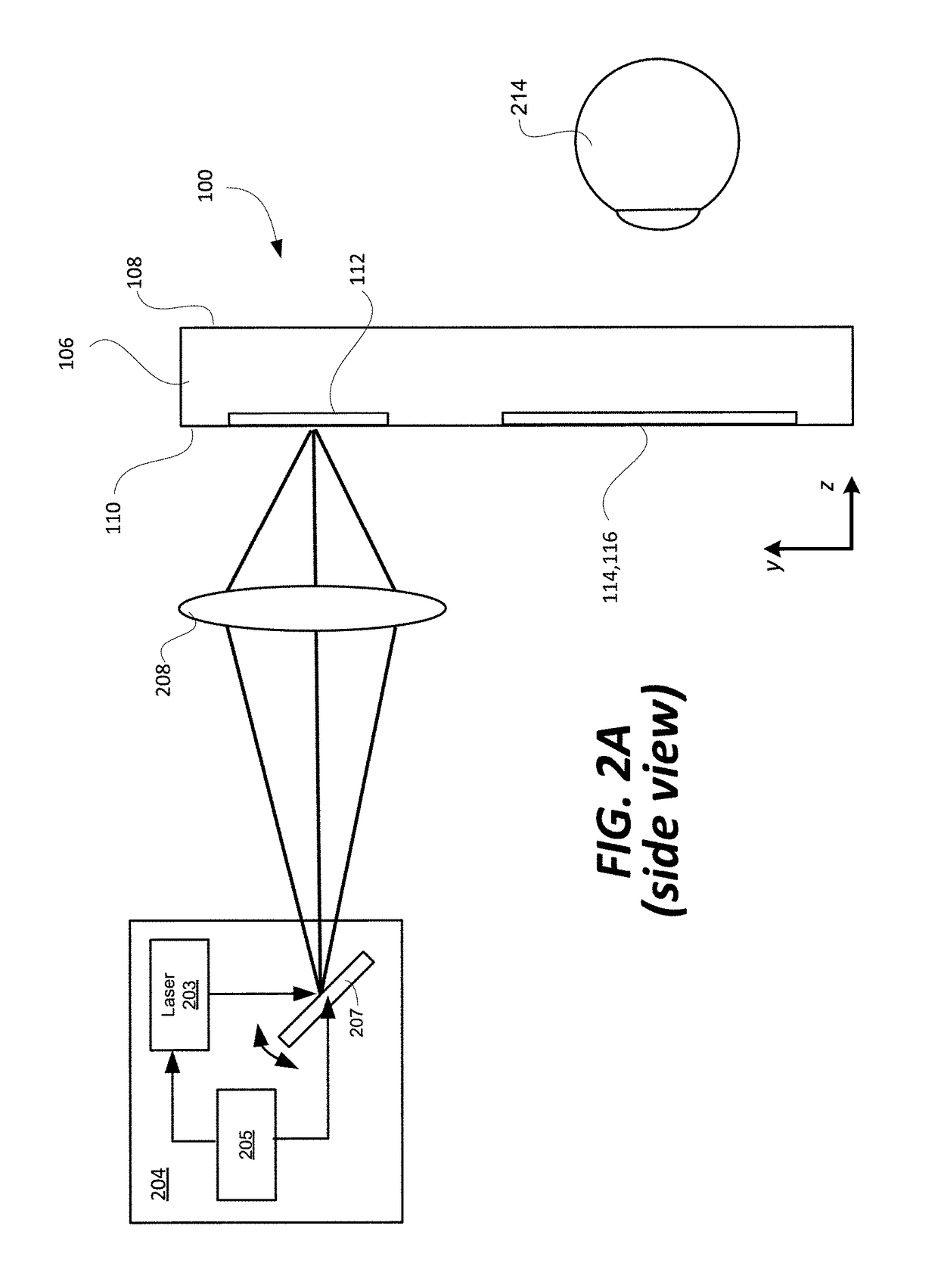
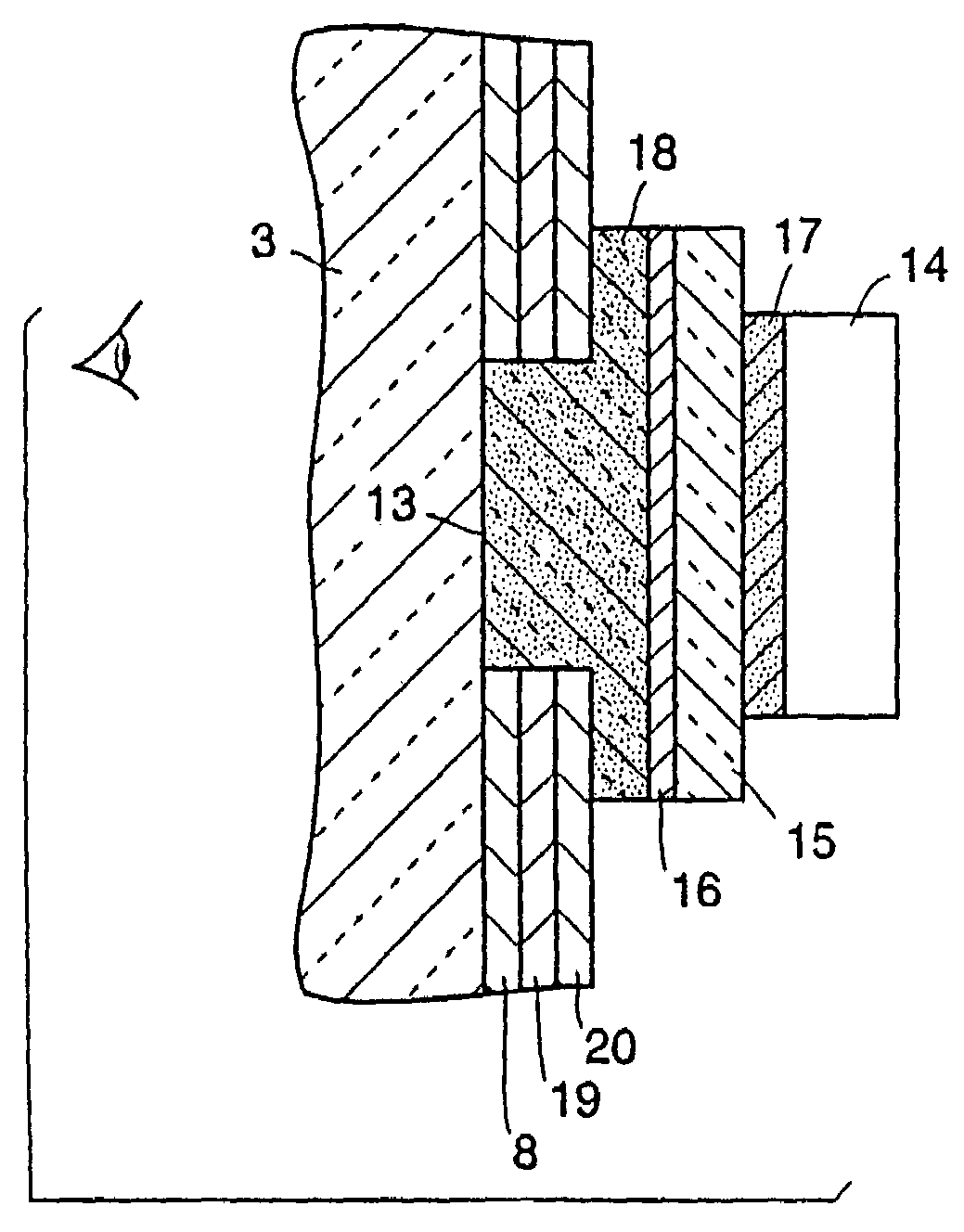
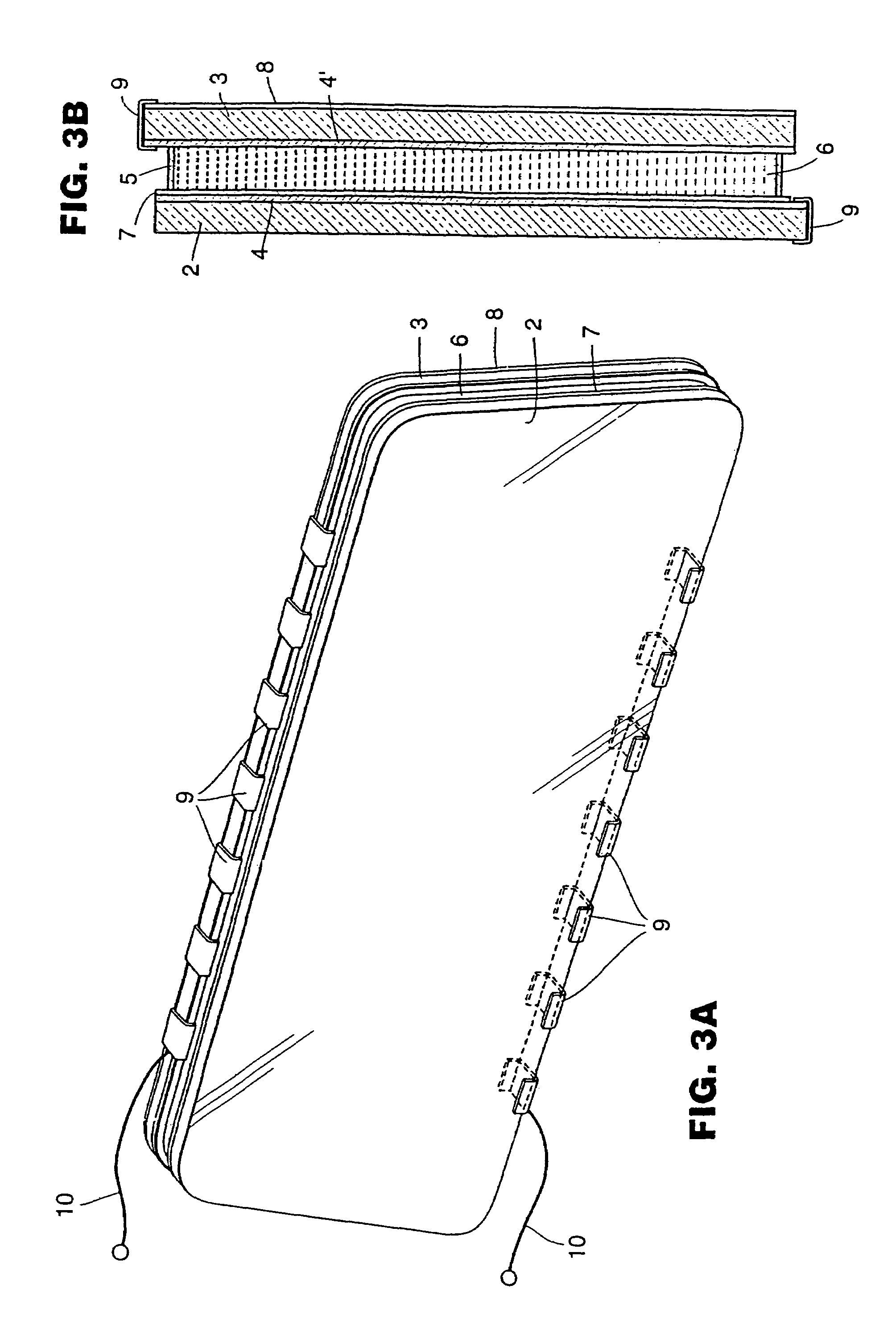
Optical systems such as image display systems include a freeform optical waveguide prism and a freeform compensation lens spaced therefrom by a gap of air or index cement. The compensation lens corrects for aberrations which the optical waveguide prism will introduce in light or images from an ambient real-world environment. The optical waveguide prism receives actively projected images at an entry location, and emits the projected images at an exit location after internally reflecting the images along an optical path therein. The image display system may include an image source and coupling optics. The approach permits design of an optical viewing device, for example in optical see-through HMDs, achieving an eyeglass-form appearance and a wide see-through field of view (FOV).
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
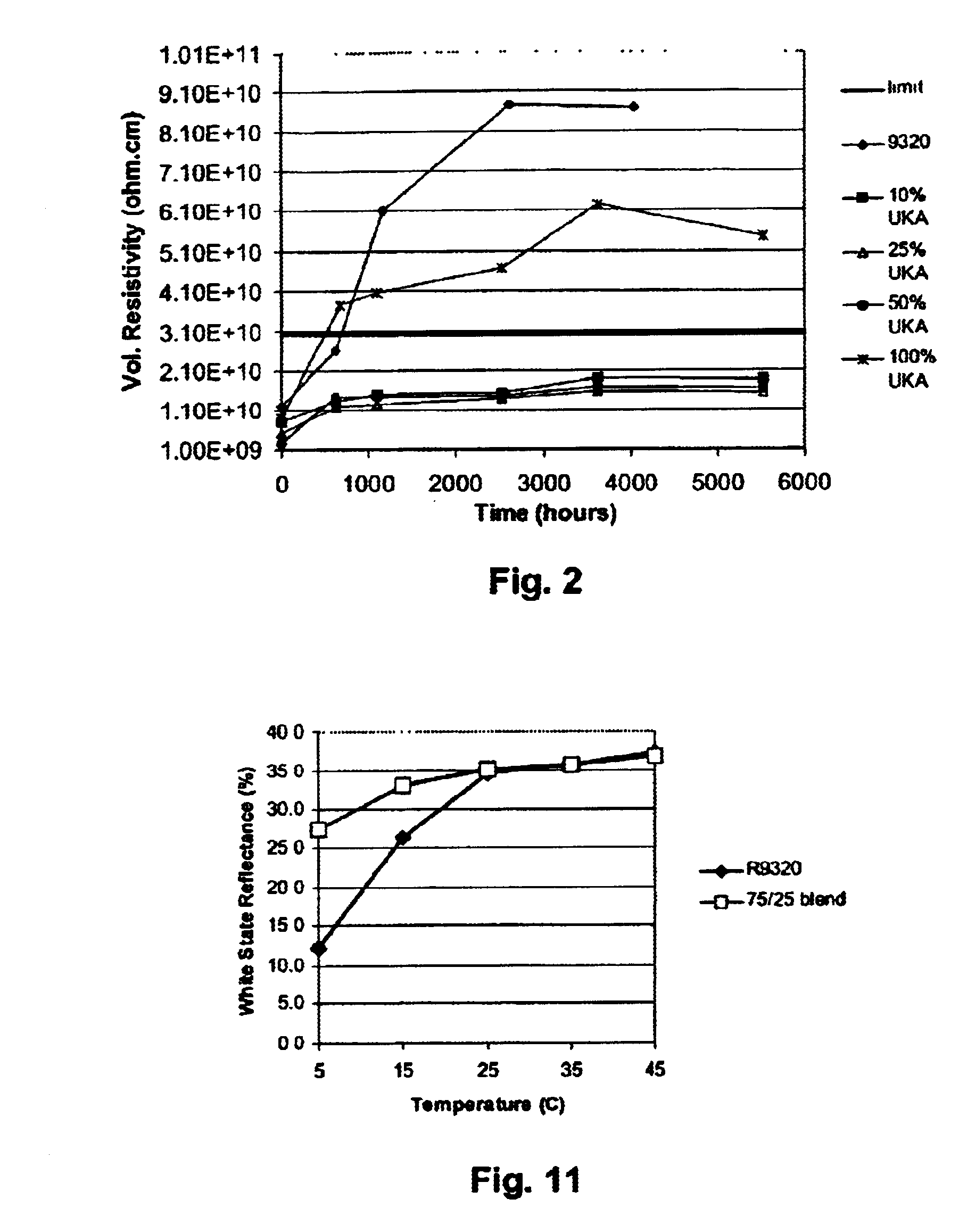
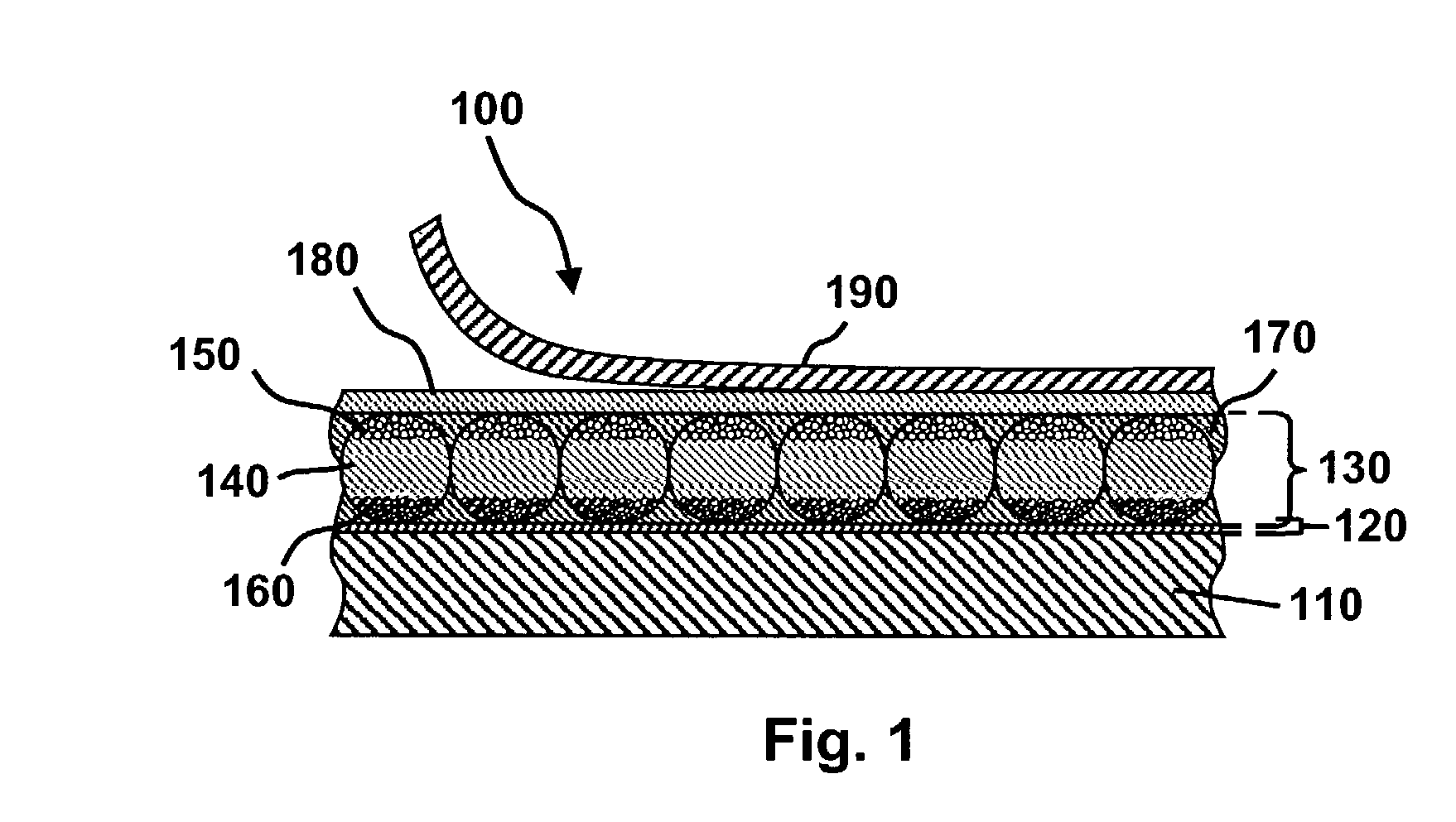
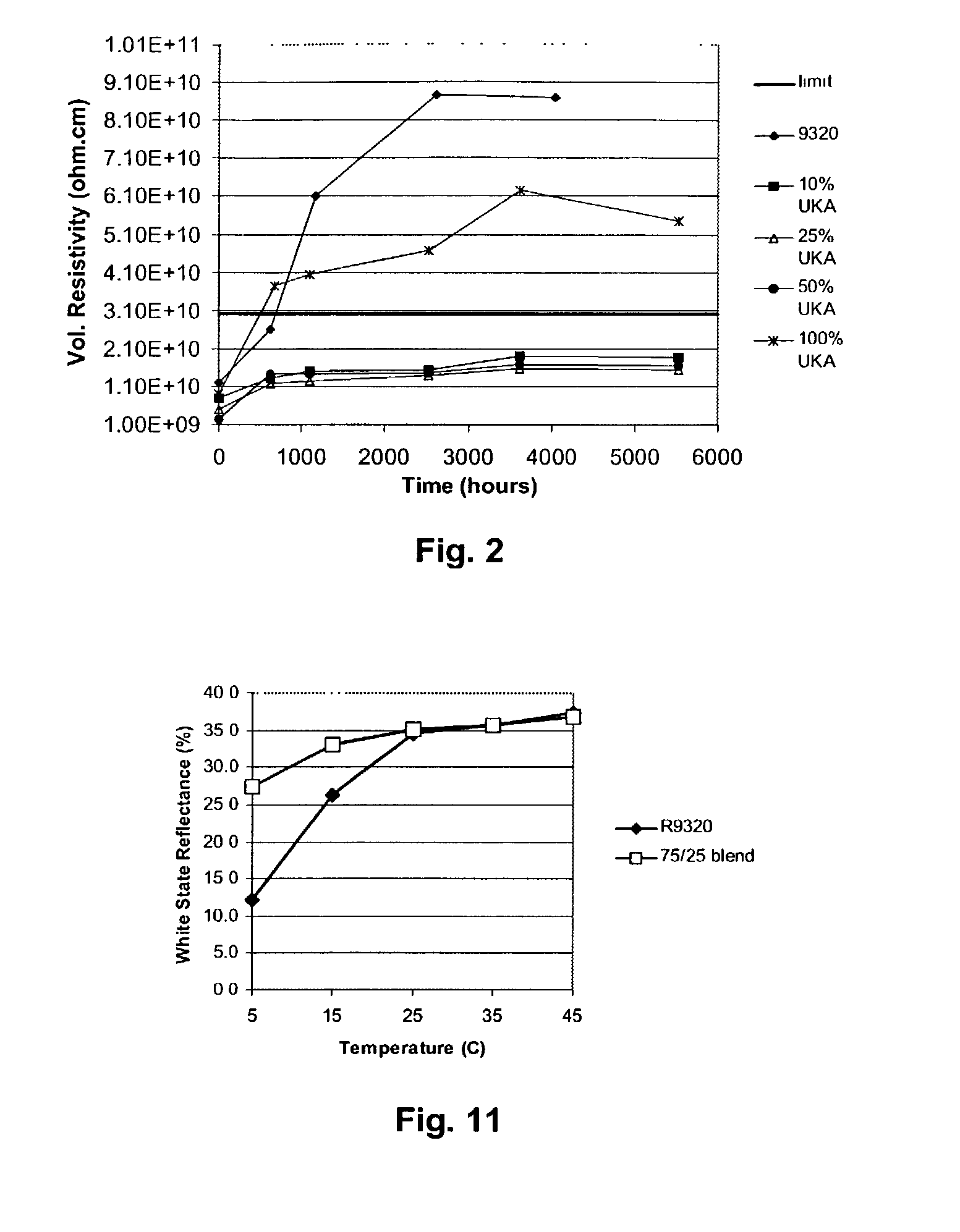
Electro-optic display and lamination adhesive
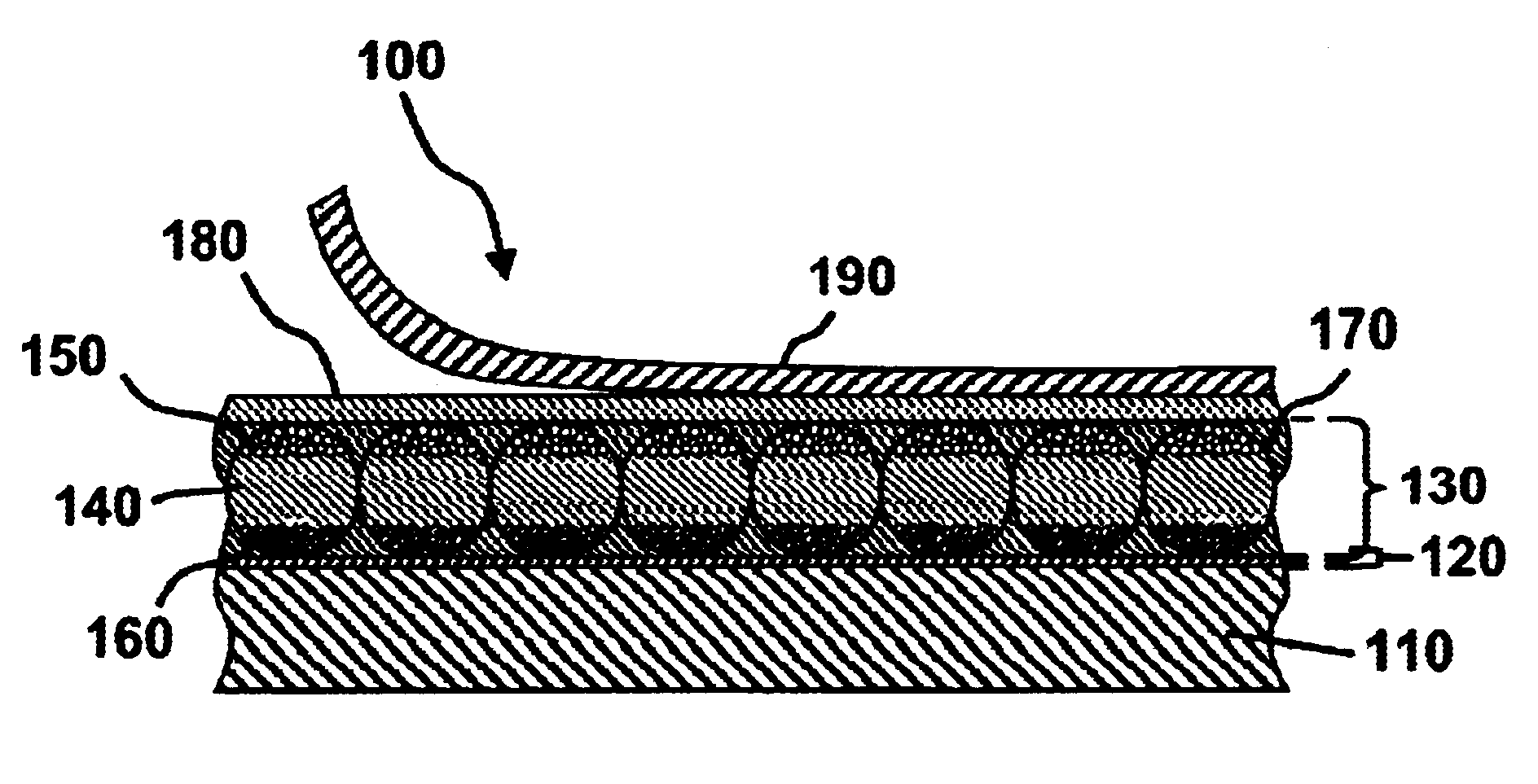
InactiveUS6831769B2Reduce adverse effectsGood optical performanceLamination ancillary operationsPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesAdhesiveElectrophoresis
An electro-optic display comprises first and second substrates and a lamination adhesive layer and a layer of a solid electro-optic material disposed between the first and second substrates, the lamination adhesive layer having a volume resistivity, measured at 10° C., which does not change by a factor of more than about 3 after being held at 25° C. and 45 percent relative humidity for 1000 hours. The electro-optic material is preferably an encapsulated electrophoretic material. Other desirable characteristics of lamination adhesives for use in electro-optic displays are also described.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Ergonomic head mounted display device and optical system
ActiveUS9348143B2Wide field of viewGood optical performancePolarising elementsPlanar/plate-like light guidesEyewearDisplay device
This invention concerns an ergonomic optical see-through head mounted display device with an eyeglass appearance. The see-through head-mounted display device consists of a transparent, freeform waveguide prism for viewing a displayed virtual image, a see-through compensation lens for enabling proper viewing of a real-world scene when combined together with the prism, and a miniature image display unit for supplying display content. The freeform waveguide prism, containing multiple freeform refractive and reflective surfaces, guides light originated from the miniature display unit toward a user's pupil and enables a user to view a magnified image of the displayed content. A see-through compensation lens, containing multiple freeform refractive surfaces, enables proper viewing of the surrounding environment, through the combined waveguide and lens. The waveguide prism and the see-through compensation lens are properly designed to ergonomically fit human heads enabling a wraparound design of a lightweight, compact, and see-through display system.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Method and apparatus for coupling a channeled sample probe to tissue
ActiveUS8504128B2Good optical performanceError minimizationMedical devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansAnalyteThin layer
Sampling is controlled in order to enhance analyte concentration estimation derived from noninvasive sampling. More particularly, sampling is controlled using controlled fluid delivery to a region between a tip of a sample probe and a tissue measurement site. The controlled fluid delivery enhances coverage of a skin sample site with the thin layer of fluid. Delivery of contact fluid is controlled in terms of spatial delivery, volume, thickness, distribution, temperature, and / or pressure.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
Ergonomic head mounted display device and optical system
ActiveUS9740006B2Good optical performancePrecision injectionCathode-ray tube indicatorsTelevision systemsFree formDisplay device
Optical systems such as image display systems include a freeform optical waveguide prism and a freeform compensation lens spaced therefrom by a gap of air or index cement. The compensation lens corrects for aberrations which the optical waveguide prism will introduce in light or images from an ambient real-world environment. The optical waveguide prism receives actively projected images at an entry location, and emits the projected images at an exit location after internally reflecting the images along an optical path therein. The image display system may include an image source and coupling optics. The approach permits design of an optical viewing device, for example in optical see-through HMDs, achieving an eyeglass-form appearance and a wide see-through field of view (FOV).
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Electro-optic display and lamination adhesive
InactiveUS20030025855A1Reduce manufacturing costConveniently preparedPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesNon-linear opticsAdhesiveElectrophoresis
An electro-optic display comprises first and second substrates and a lamination adhesive layer and a layer of a solid electro-optic material disposed between the first and second substrates, the lamination adhesive layer having a volume resistivity, measured at 10° C., which does not change by a factor of more than about 3 after being held at 25° C. and 45 percent relative humidity for 1000 hours. The electro-optic material is preferably an encapsulated electrophoretic material. Other desirable characteristics of lamination adhesives for use in electro-optic displays are also described.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Optical element
InactiveUS20070139333A1Good optical performanceEasy to changeStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptical propertyElectrical control
The focal distance can be greatly changed by performing an electrical control in an optical element. The optical element comprises a first substrate having a first electrode, a second substrate, a second electrode arranged outside the second substrate, and a liquid crystal layer provided between the first substrate and the second substrate and constituted by liquid crystal molecules oriented. A first voltage is applied between the first electrode and the second electrode, thereby controlling the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, whereby the optical element operates. A third electrode is provided on an insulating layer and outside the second electrode. A second voltage independent of the first voltage is applied to the third electrode, thereby changing the optical properties.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Manufacture method for polarization maintaining fiber and polarization maintaining fiber
InactiveCN102351415AImprove the finishImprove processing efficiencyGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with polarisationSurface finishPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
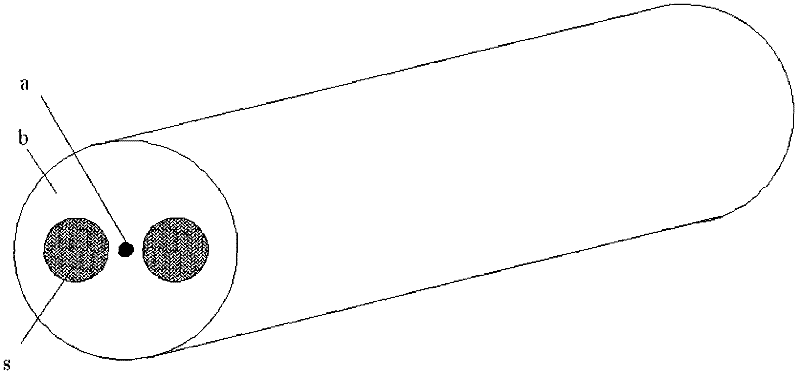
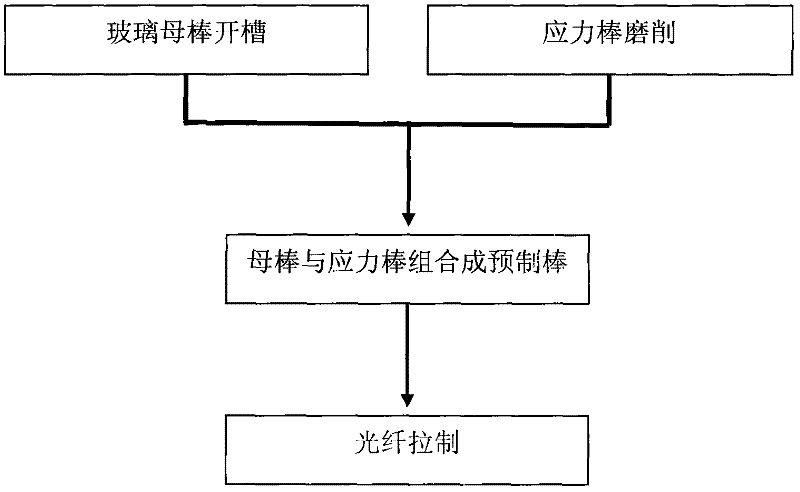
The invention provides a manufacture method for polarization maintaining fiber and a polarization maintaining fiber, and relates to optical waveguide fibers in the field of fiber-optical communication and fiber optical sensors. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) two oppositely arranged open slots with a same shape are inwardly provided at a side surface of a glass mother rod, stress rods are machined to obtain a shape matching the open slots, and the centers of the cross sections of the two open slots and the center of circle in the cross section of the glass mother rod are in a same line; (2) the stress rods are respectively inserted into each open slot on the glass mother rod, and the assembled glass mother rod and stress rods are put in a cannula to form a preformed rod of the polarization maintaining fiber; (3) the preformed rod of the polarization maintaining fiber is drew to form the polarization maintaining fiber. According to the invention, the glass mother rod is provided with the open slots, and the stress rods are embedded in the open slots, thereby obtaining high process repeatability; inner surfaces of the open slots have high fineness, and the open slots have good symmetry, thereby improving processing efficiency; therefore, the optical performance and reliability of the polarization maintaining fiber are substantially improved.
Owner:RUIGUANG TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
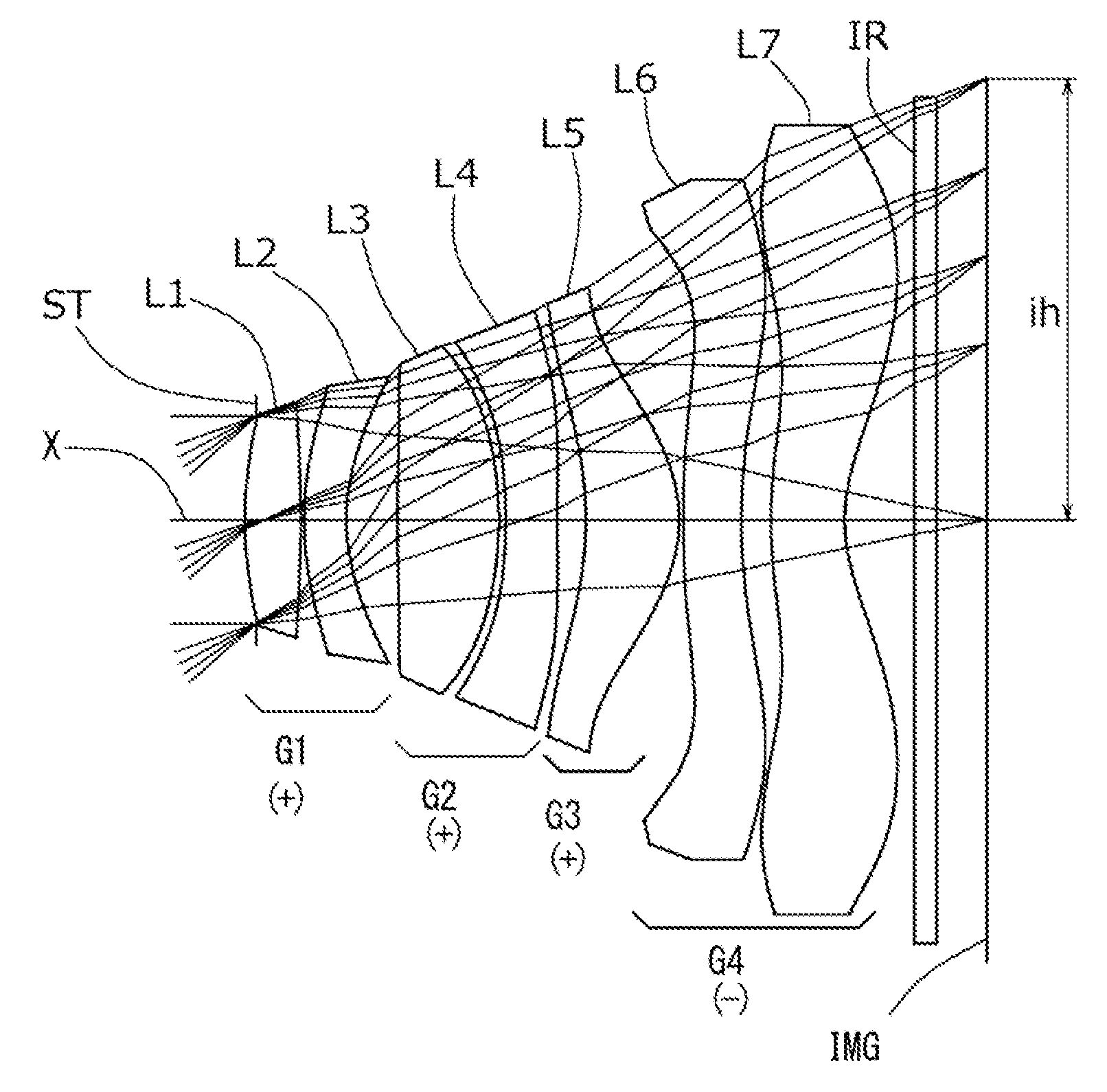
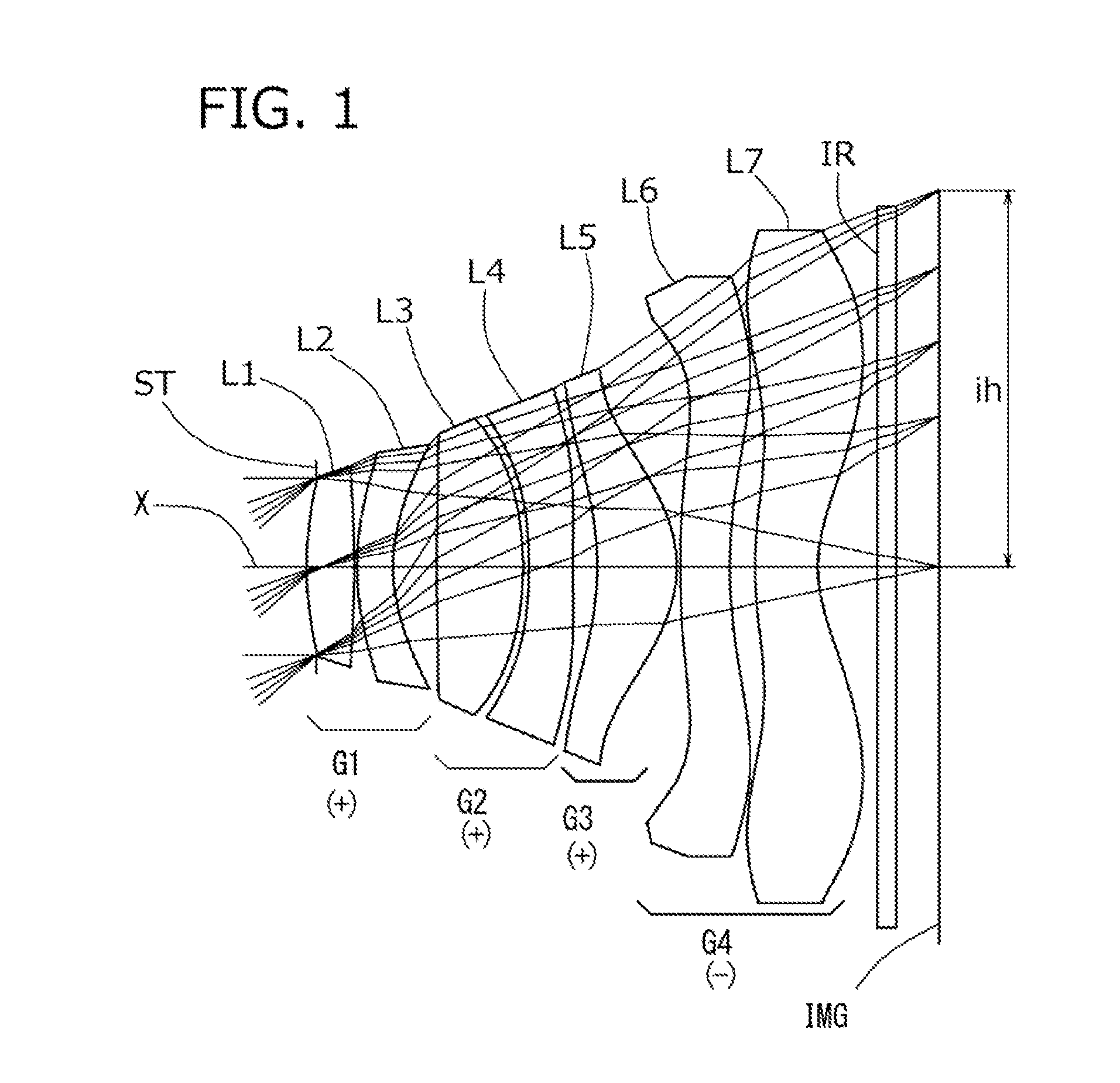
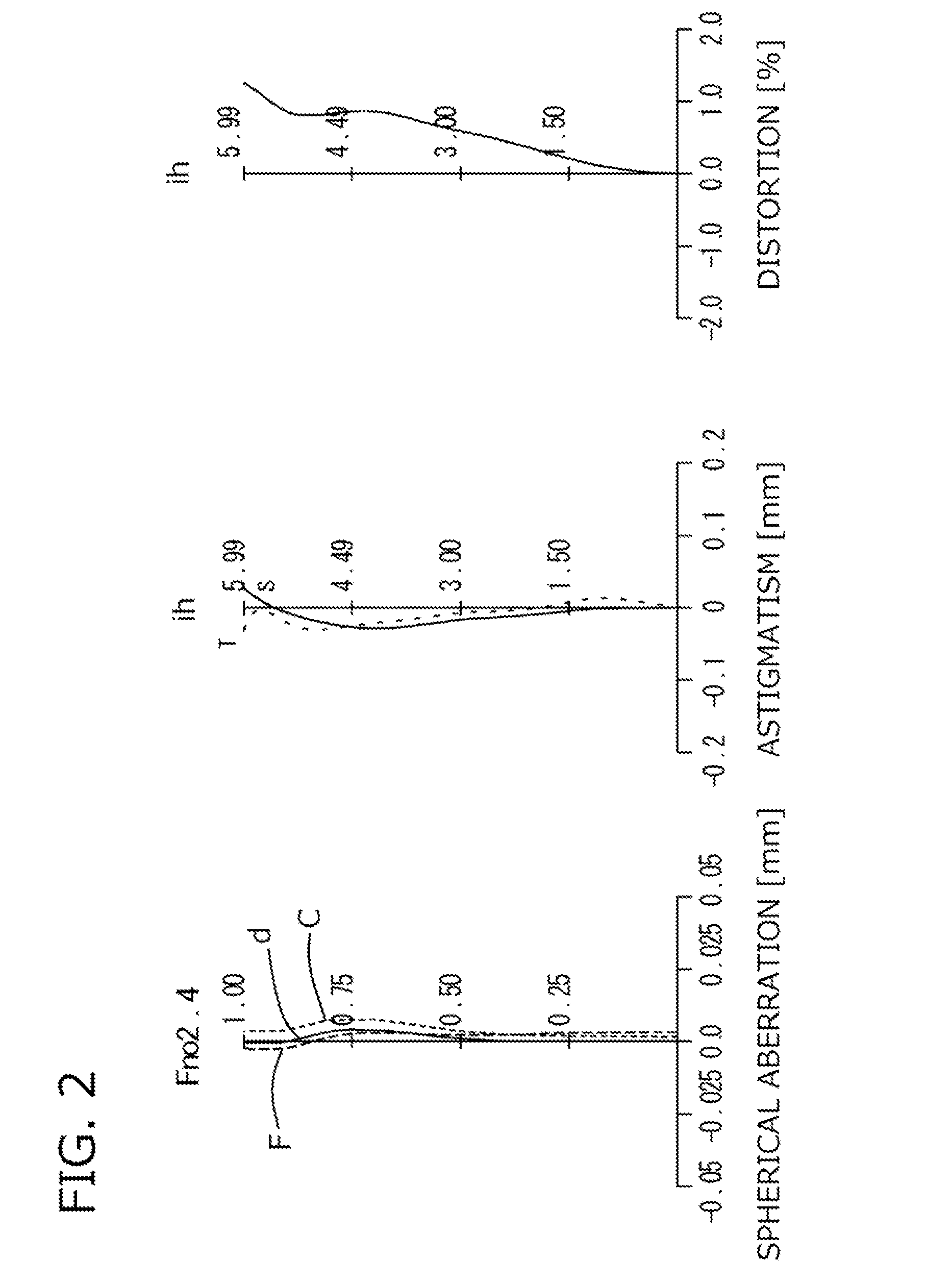
Imaging lens and imaging apparatus
Owner:JIANGXI OFILM OPTICAL CO LTD
Sub-wavelength grating integrated VCSEL
InactiveUS20070153860A1Good optical performanceEasy to manufactureLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserGrating
A vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is described using a sub-wavelength grating (SWG) structure that has a very broad reflection spectrum and very high reflectivity. The grating comprises segments of high and low refractive index materials with an index differential between the high and low index materials. By way of example, a SWG reflective structure is disposed over a low index cavity region and above another reflective layer (either SWG or DBR). In one embodiment, the SWG structure is movable, such as according to MEMS techniques, in relation to the opposing reflector to provide wavelength selective tuning. The SWG-VCSEL design is scalable to form the optical cavities for a range of SWG-VCSELs at different wavelengths, and wavelength ranges.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Light emitting diode
InactiveUS6850001B2Simple structureNo fluctuation in emission colorDischarge tube luminescnet screensSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOptical propertyLength wave
A light-emitting diode with no fluctuations in optical properties and good sealing properties, and a simple production method for producing this light-emitting diode. The light-emitting diode has a base comprising a cup part on which the light-emitting diode is placed, a resin material introduced into cup part, and a lens member placed on top of a cup for focusing light emitted by a light-emitting diode chip. A layer of fluorescent material, which converts the wavelength of at least some of the light from the light-emitting diode chip, is applied to the inner convex face of the lens member. When the lens member is attached to the base, the inner convex face deforms the resin material and air and excess resin material can be pushed to the outside.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
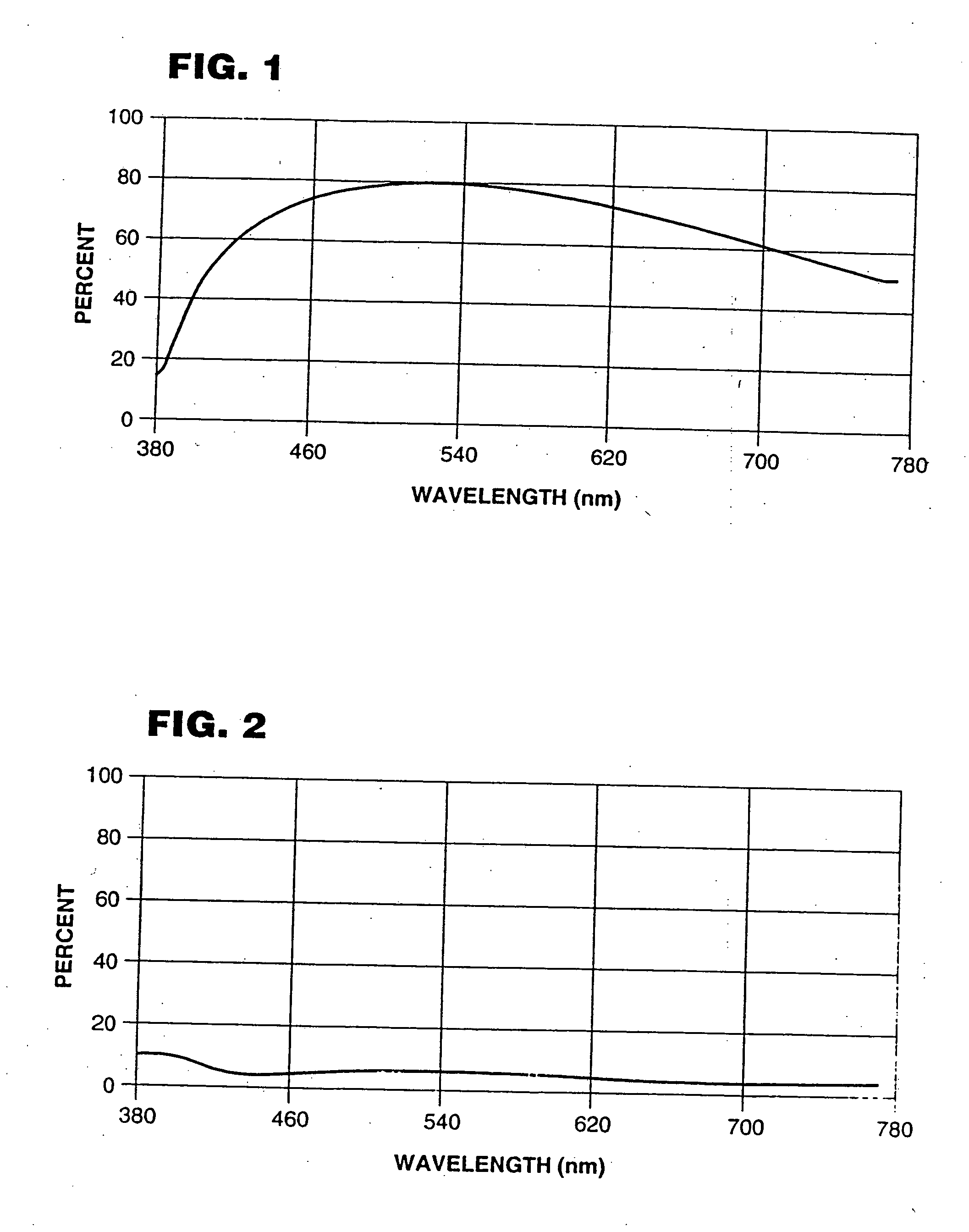
Transparent conductive laminated body and touch panel
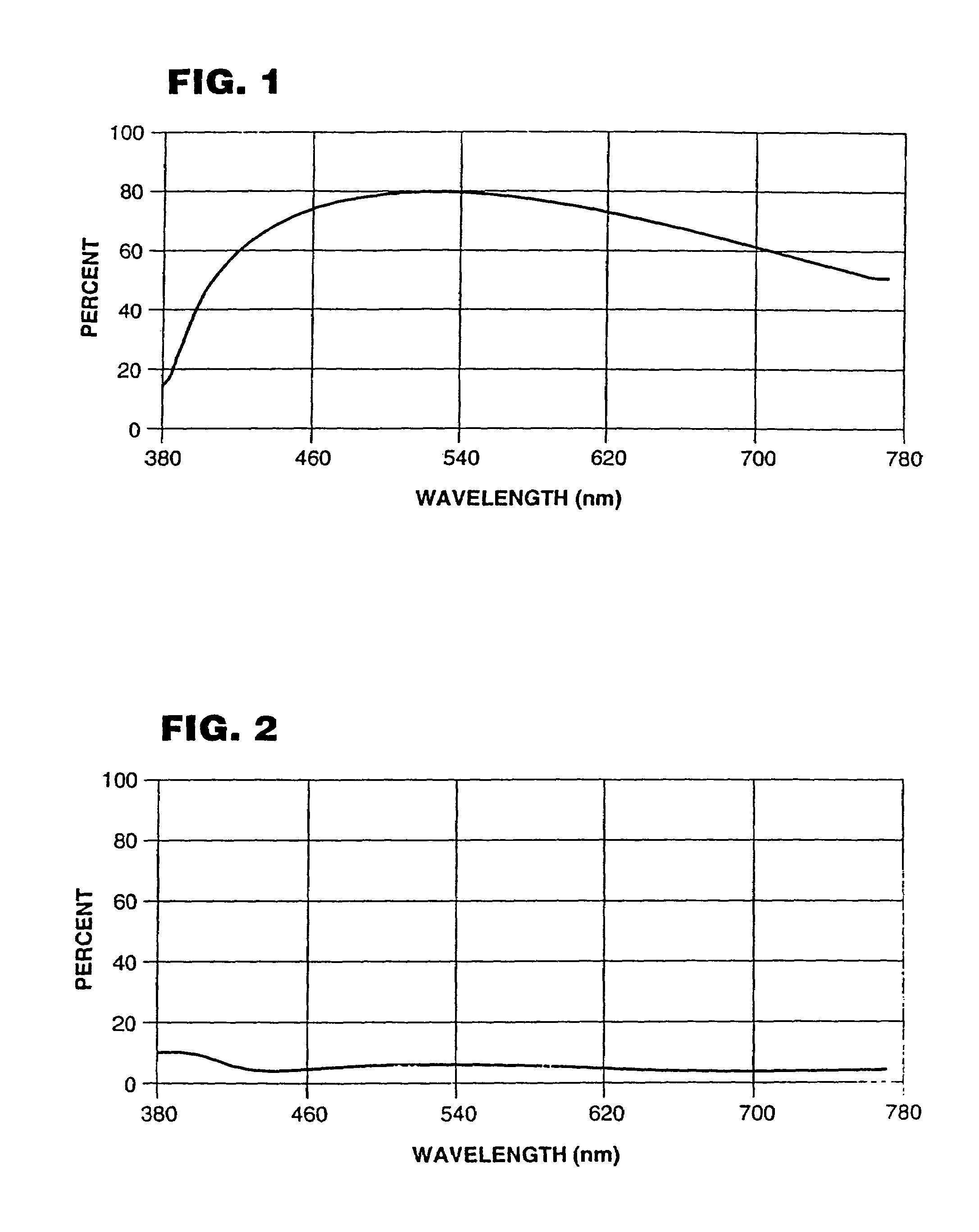
InactiveUS20020158853A1High transparencyGood optical performanceConductive layers on insulating-supportsLayered productsRefractive indexTouch panel
A transparent conductive laminated body comprising a transparent dielectric substance thin film having two layers and furthermore a transparent conductive thin film being formed on one face of a transparent film substrate with thickness of 2 to 120 mum, and a transparent substrate being adhered on another face of the film substrate through a transparent pressure sensitive adhesive layer, wherein a relationship of n3<n1<=n2 <n4 is satisfied where a light index of refraction of the film substrate is defined as n1, a light indexes of refraction of the two layers of the dielectric substance thin films are defined as n2 and n3 from the film substrate side respectively, and a light index of refraction of the conductive thin film is defined as n4 is excellent in transparency and scratch-proof property of the conductive thin film, and, moreover, excellent also in flexibility. A touch panel using the transparent conductive laminated body concerned has an improved dotting property.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Waveguide-Based Displays With Exit Pupil Expander
ActiveUS20170299860A1Good optical performanceMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesHead-up displayExit pupil
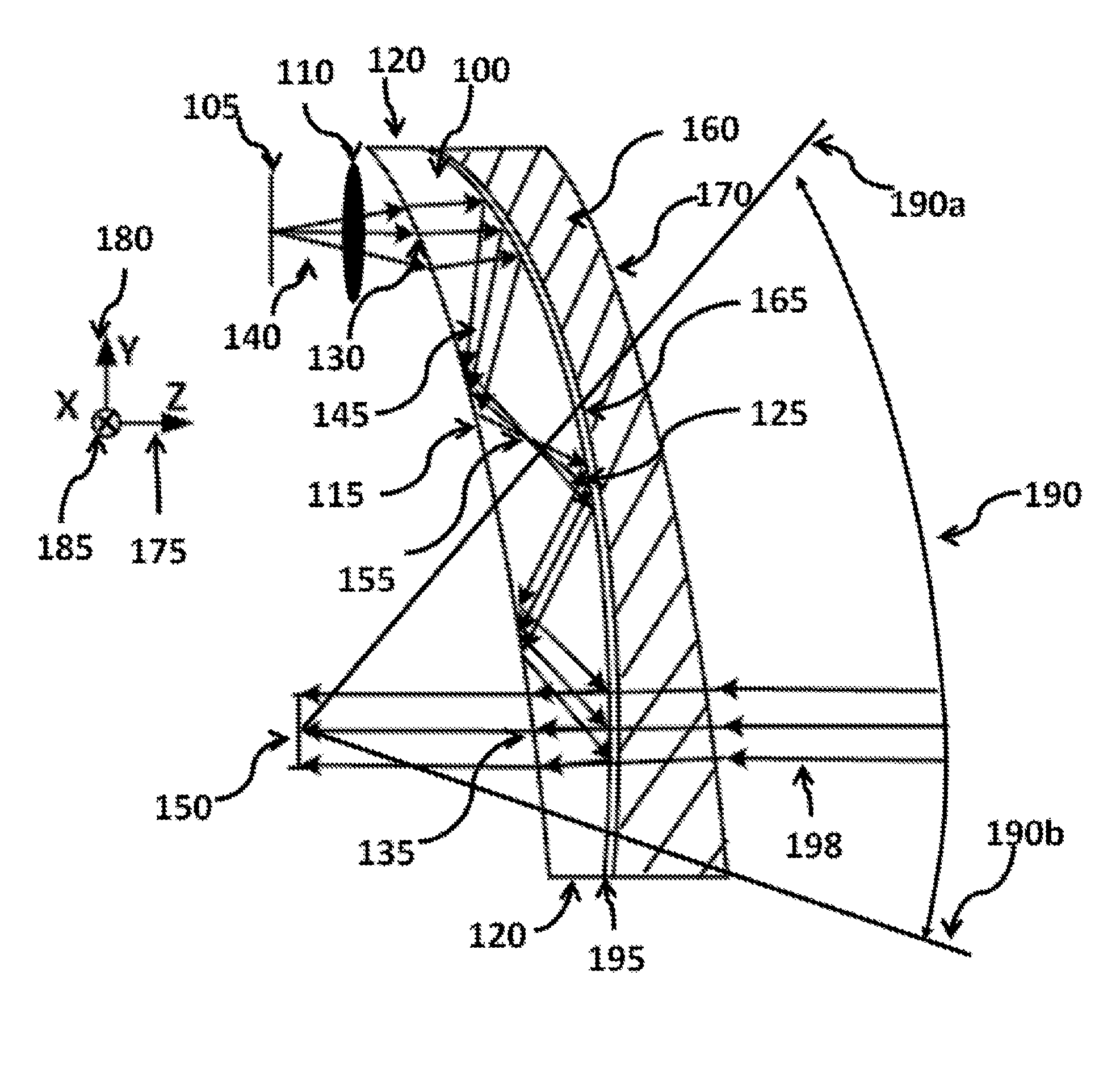
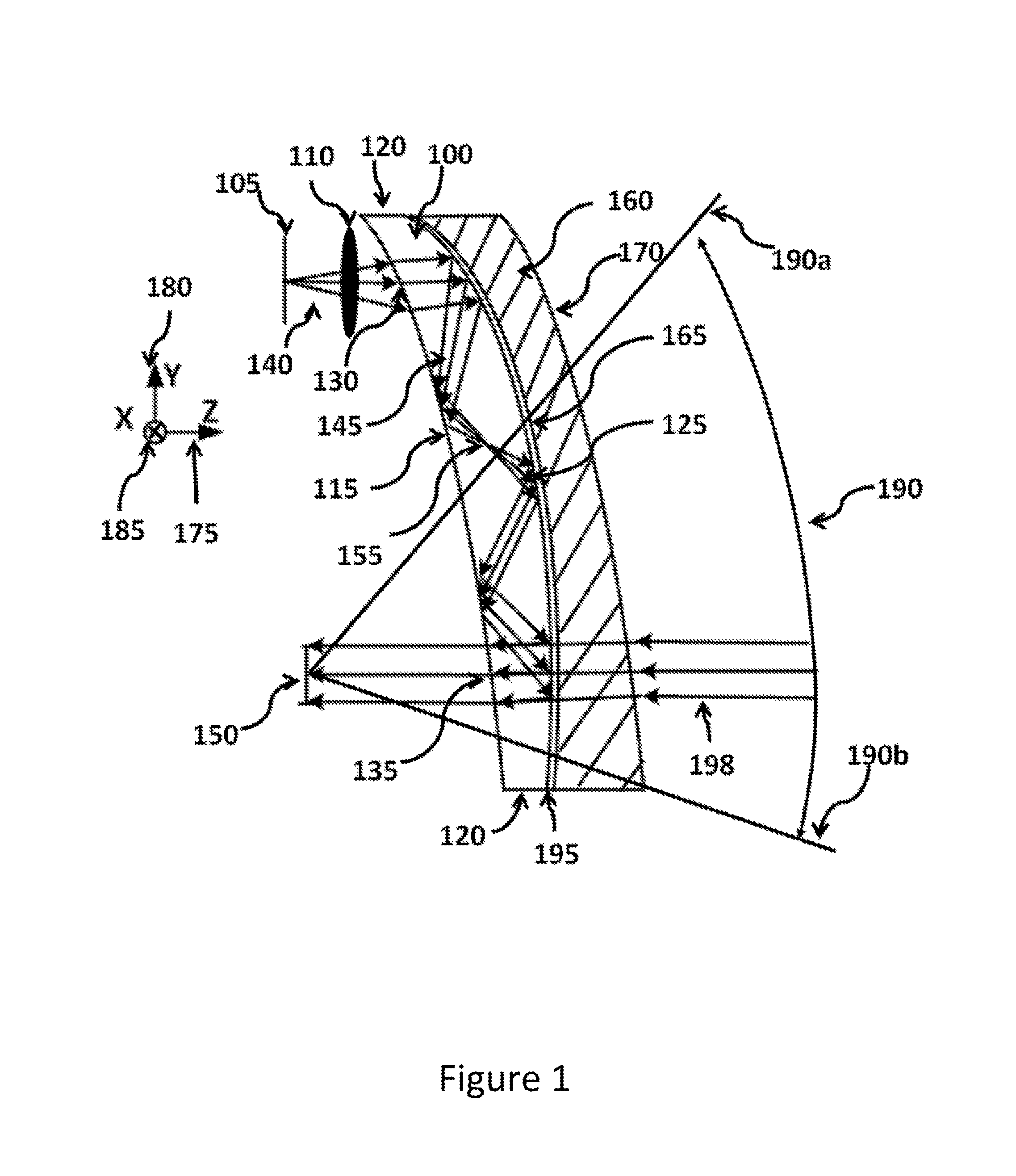
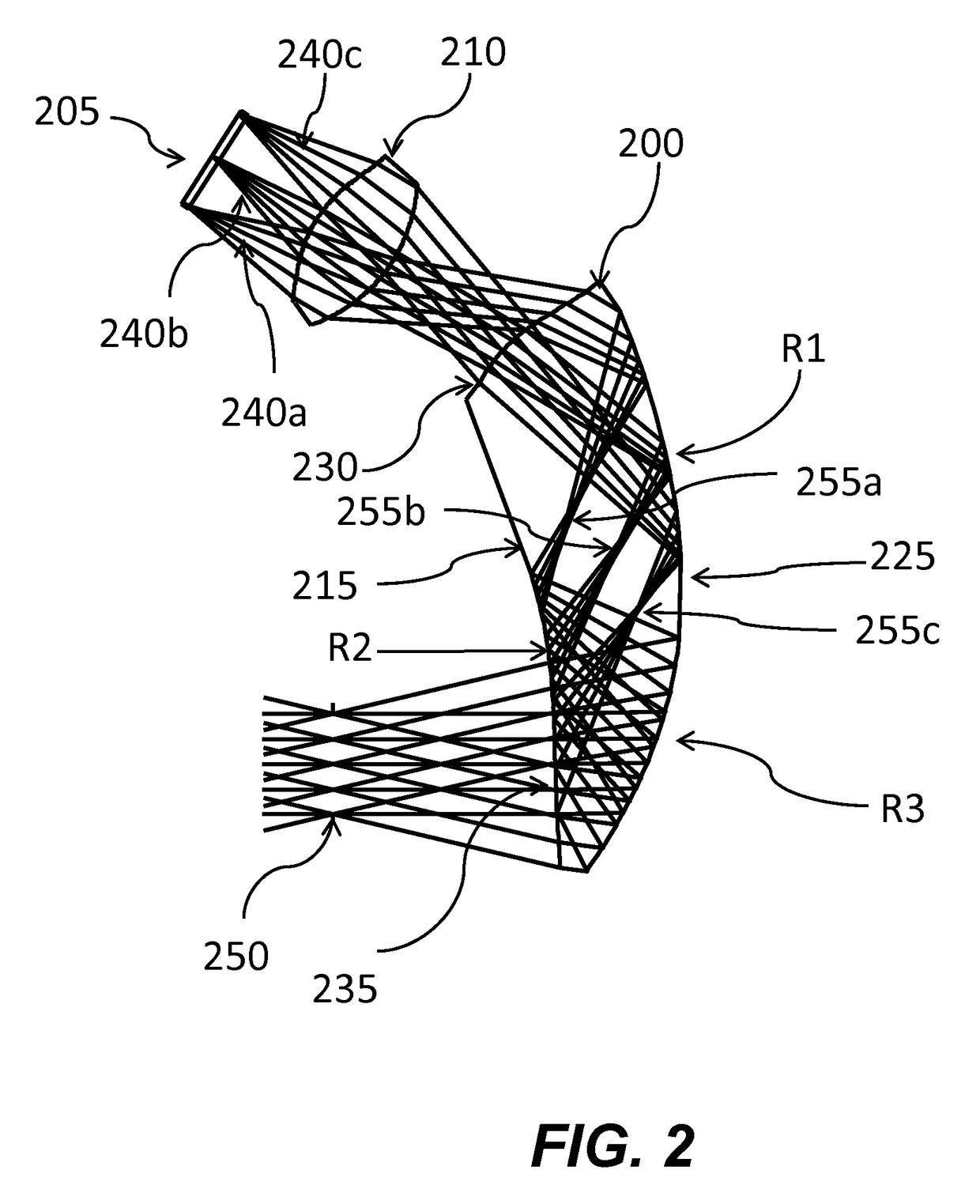
A near eye or heads up display system includes a scan beam projector engine, an optical waveguide, and an exit pupil expander (EPE) optically coupled between the scan beam projector engine and the optical waveguide. The EPE improves the optical performance of the display system. The EPE could include a diffusive optical element, diffractive optical element, micro-lens array (MLA), or relay of aspherical lenses. A dual MLA EPE may have cells that prevent cross-talk between adjacent pixels. A dual MLA EPE may have a non-periodic lens array. The optical power of one MLA may be different from the other MLA.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for manufacturing substrate for semiconductor light emitting element and semiconductor light emitting element using the same
ActiveUS20080303042A1Improve batch productivityReduce the number of processesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorPhysics
A light emitting element having a recess-protrusion structure on a substrate is provided. A semiconductor light emitting element 100 has a light emitting structure of a semiconductor 20 on a first main surface of a substrate 10. The first main surface of the substrate 10 has substrate protrusion portion 11, the bottom surface 14 of each protrusion is wider than the top surface 13 thereof in a cross-section, or the top surface 13 is included in the bottom surface 14 in a top view of the substrate. The bottom surface 14 has an approximately polygonal shape, and the top surface 13 has an approximately circular or polygonal shape with more sides than that of the bottom surface 14.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
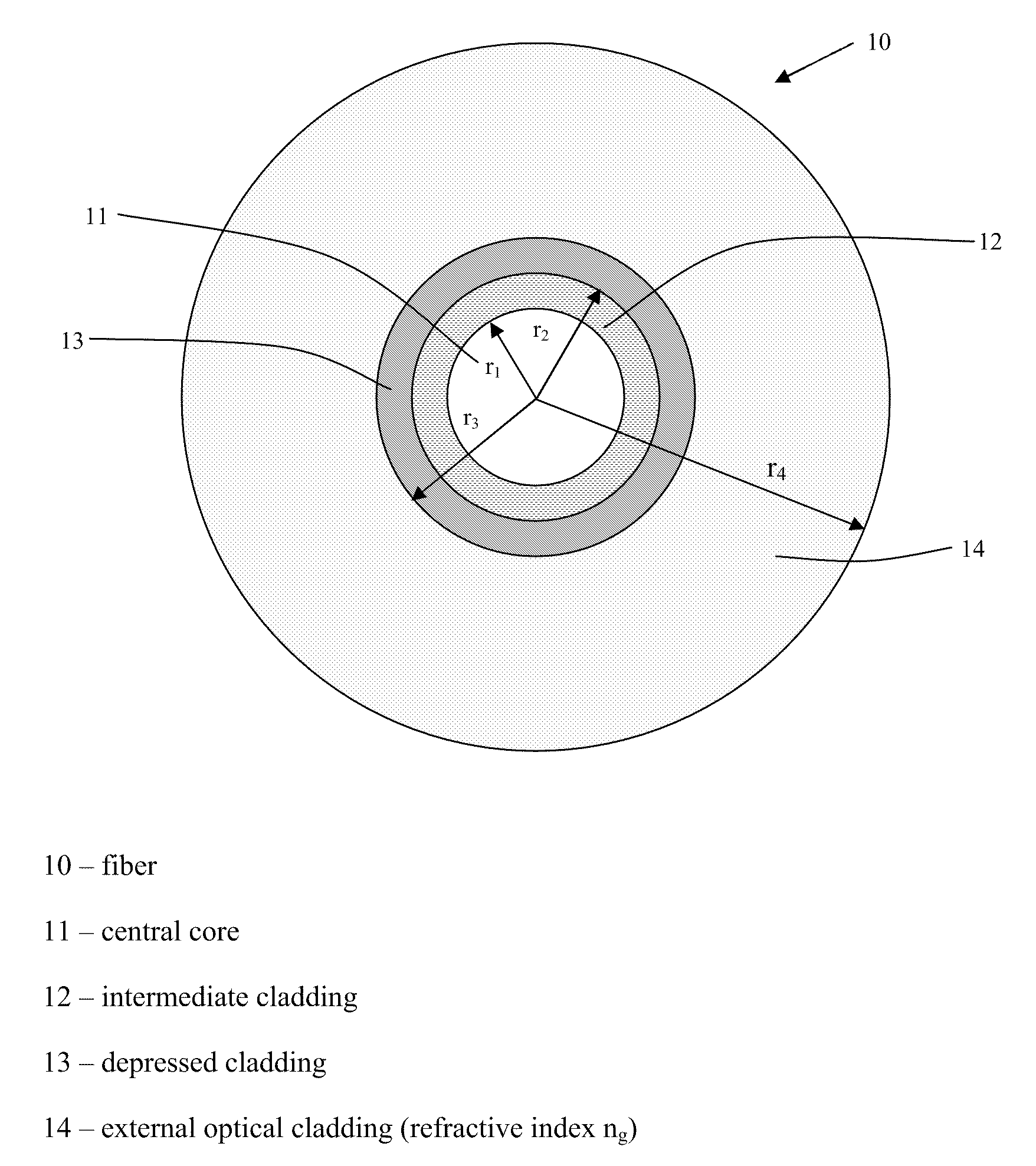
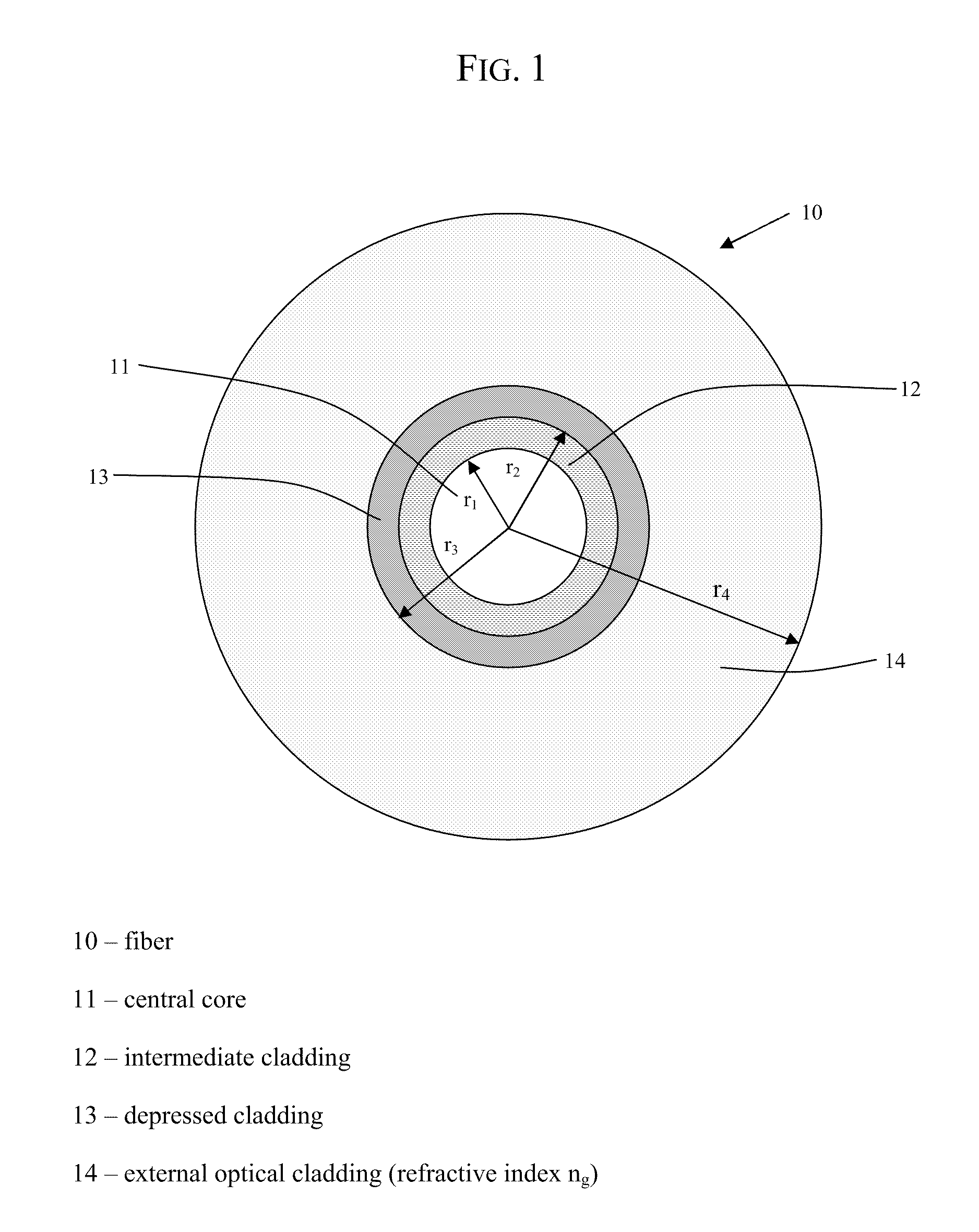
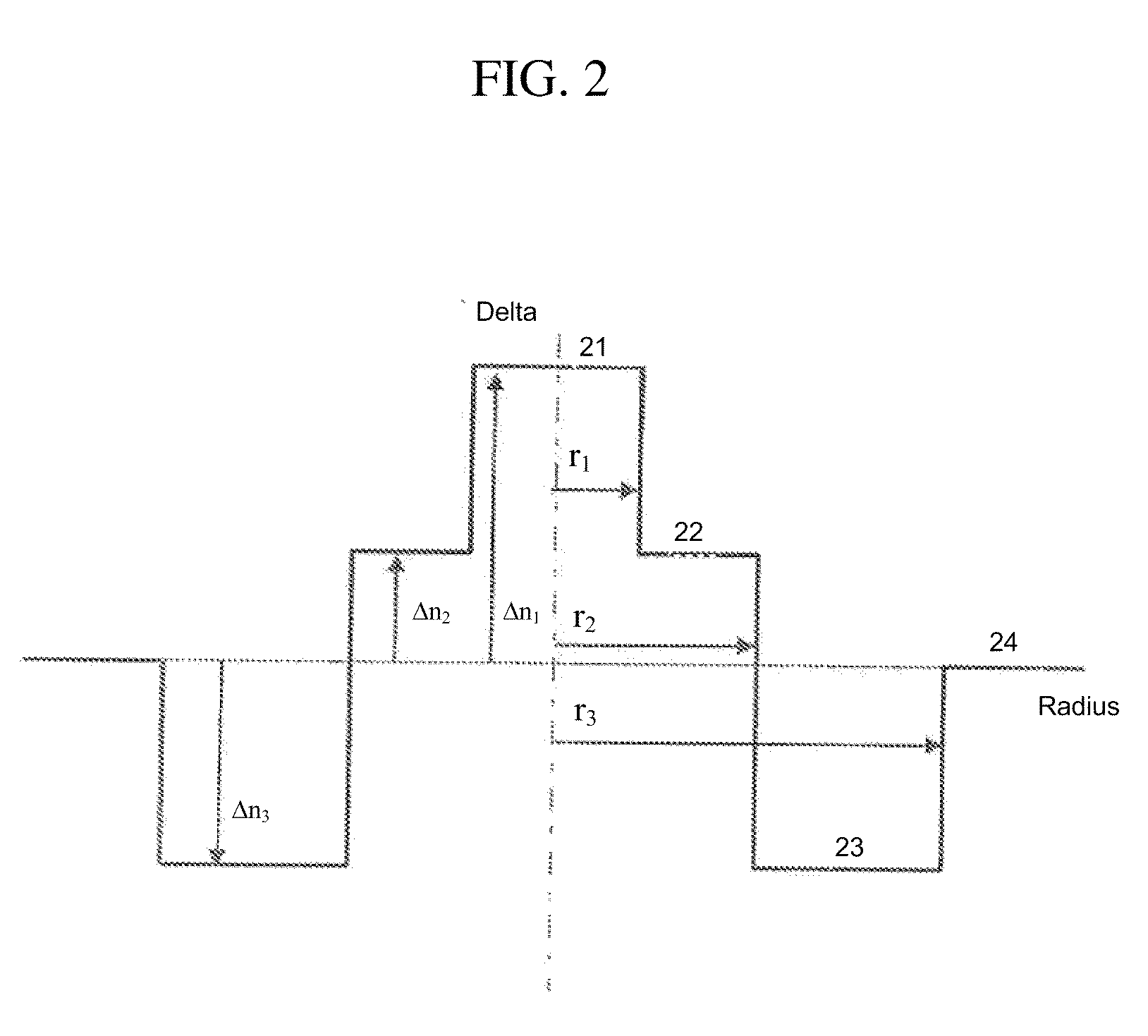
Bend-Insensitive Single-Mode Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20090279836A1Sufficient attenuationImproves the bending lossesGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingWavelengthLength wave
A single-mode optical fiber includes a central core, an intermediate cladding, a depressed trench, and an external optical cladding. The central core has a radius r1 and a positive refractive index difference Δn1 with the optical cladding. The intermediate cladding has a radius r2 and a refractive index difference Δn2 with the optical cladding, wherein Δn2 is less than the central core's refractive index difference Δn1. The depressed trench has a radius r3 and a negative index difference Δn3 with the optical cladding. The optical fiber has a nominal mode field diameter (MFD) between 8.6 microns and 9.5 microns at a wavelength of nanometers, and at a wavelength of 1550 nanometers, the optical fiber has bending losses less than 0.15 dB / turn for a radius of curvature of 5 millimeters and cable cut-off wavelengths of less than or equal to nanometers.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Multi-layer sheet comprising a protective polyurethane layer
InactiveUS6383644B2Good abrasion and scratch resistanceReadily convertFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsAcid groupPolycarbonate
The present invention provides a multilayer sheet comprising a polymeric film having on a first major side a cross-linked polyurethane layer, the major part of said cross-linked polyurethane layer comprising a polycarbonate based polyurethane containing acid groups and cross-linked with a cross-linker, the polycarbonate-based polyurethane comprising the reaction product of a polycarbonate polyol or a polycarbonate polyamine and an aliphatic polyisocyanate and the uncross-linked polycarbonate-based polyurethane having a Koenig hardness of at least 150 seconds.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Nanocomposite microresonators
InactiveUS6876796B2High refractive indexGood optical performanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanomedicineIsolatorNanoparticle
A microresonator is provided that incorporates a composite material comprising a polymer matrix and nanoparticles dispersed therein. The microresonator includes the composite material having a shape that is bounded at least in part by a reflecting surface. The shape of the microresonator allows a discrete electromagnetic frequency to set up a standing wave mode. Advantageously, the polymer matrix comprises at least one halogenated polymer and the dispersed nanoparticles comprise an outer coating layer, which may also comprise a halogenated polymer. Methods for making composite materials and microresonators are also provided. Applications include, for example, active and passive switches, add / drop filters, modulators, isolators, and integrated optical switch array circuits.
Owner:PHOTON
Photosensitive composition for volume hologram recording and photosensitive medium for volume hologram recording
InactiveUS7323275B2Increase resistanceHigh strengthPhotosensitive materialsPhotomechanical apparatusMetal chelateHydroxy group
A photosensitive composition and A photosensitive medium for volume hologram recording comprises a photopolymerization reactive compound (a monomer) and any one of the following binder: (a) an organic-inorganic hybrid polymer obtainable by copolymerizing an organometallic compound of the formula 1 “R1m M1 (OR2)” and an ethylenic monomer and / or its hydrolyzed polycondensate; (b) an organic-inorganic hybrid polymer obtainable by copolymerizing an organometallic compound of the formula 3 “R4m Si (OR5)n” and an ethylenic monomer and / or its hydrolyzed polycondensate; and (c) a binder resin bonded to a metal or a combination use of a binder resin containing a hydroxyl group and / or carboxyl group and a metal chelate compound.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Vehicular rearview mirror element having a display-on-demand display
InactiveUS7543947B2Reduce material costsGood optical performanceMirrorsAntiglare equipmentDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
A rearview mirror element for a motor vehicle includes a light transmitting substrate having a visible light reflecting and visible light transmitting mirror reflector disposed on a surface thereof. A display-on-demand display device is disposed behind the substrate such that light emitted by the display device when powered passes through both the light transmitting substrate and the mirror reflector. The display device exhibits, when powered during day time driving conditions, a display luminance of at least about 60 foot lamberts. When not emitting light, the disposition of the display device to the rear of the light transmitting substrate is not substantially distinguishable to the driver of the equipped vehicle when viewing the mirror element. To the rear of the light transmitting substrate is rendered substantially opaque by a light absorbing element that is disposed at least adjacent to where, and except at where, the display device is disposed therebehind.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Process for producing propylene based polymer compositions
A process for the production of a propylene based polymer, the process comprising the following steps: (a) a first polymerization stage comprising homopolymerizing propylene or copolymerizing propylene and at least one alpha-olefin in the presence of an alpha-olefin polymerization catalyst whereby to produce a polypropylene component; (b) a second polymerization stage comprising copolymerizing ethylene and at least one alpha-olefin in the presence of an alpha-olefin polymerization catalyst whereby to produce an ethylene / alpha-olefin copolymer component; and (c) blending the polymer components produced in steps (a) and (b) whereby to produce a polymer blend, wherein the first and second polymerization stages are effected in separate polymerization reactors connected in parallel. Also provided are polymer compositions comprising: (i) 30 to 97% by weight, based on the total weight of the polymer composition, of a propylene based polymer; and (ii) 3 to 70% by weight, preferably 5 to 20% by weight, based on the total weight of the polymer composition, of an ethylene copolymer plastomer (e.g., an ethylene-propylene plastomer) containing at least 60% by weight ethylene.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH OY
Light base structure of high-power LED street lamp
InactiveUS20090262543A1Optimal effectLight uniformly and efficientlyMechanical apparatusLight source combinationsEngineeringBrightness perception
Owner:GENIUS ELECTRONICS OPTICAL CO LTD
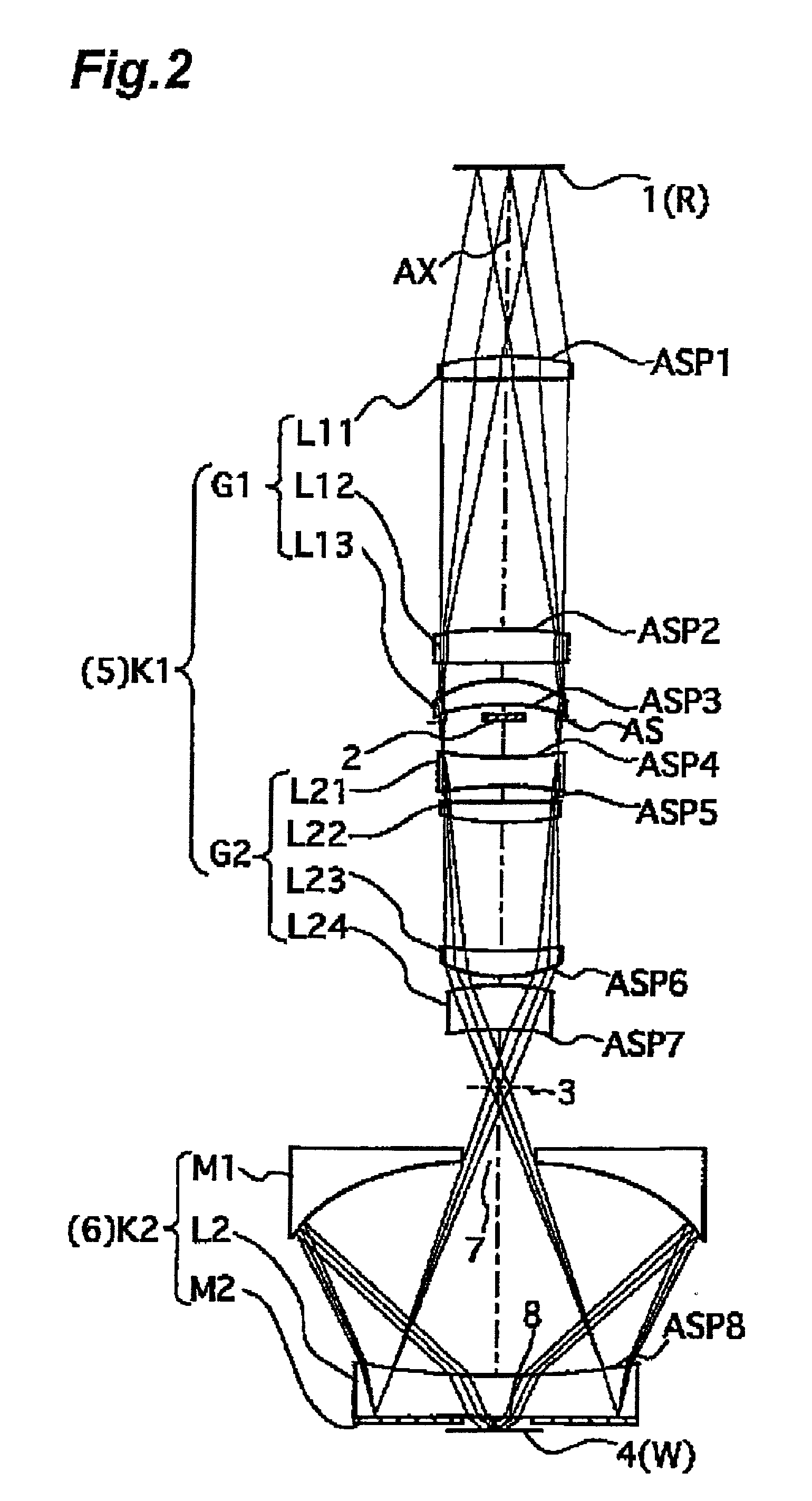
Image pickup optical systems, image pickup apparatuses and digital apparatuses
InactiveUS20070024739A1Low costImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsPrismsImaging qualityLight beam
The present invention provides image pickup optical systems capable of suppressing the degradation of the image quality due to unnecessary light beams while attaining compaction by optimizing the shapes of the emission surfaces of reflection prisms. The image pickup optical system includes an incidence-side prism for reflecting incident light while folding it by about 90 degree and an image-surface side prism. An image pickup device is placed near the emission surface of the image-surface side prism. The incidence-side prism is formed to have a convex emission surface. This can reduce the amount of the unnecessary light beams (stray light) reflected by the aforementioned reflection surface and also causes the unnecessary light beams reflected by the emission surface and the reflection surface to be diffused, thereby significantly reducing the amount of unnecessary light beams directed to the light receiving surface of the image pickup device. This can suppress the occurrence of ghosts and the like due to unnecessary light beams as aforementioned.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
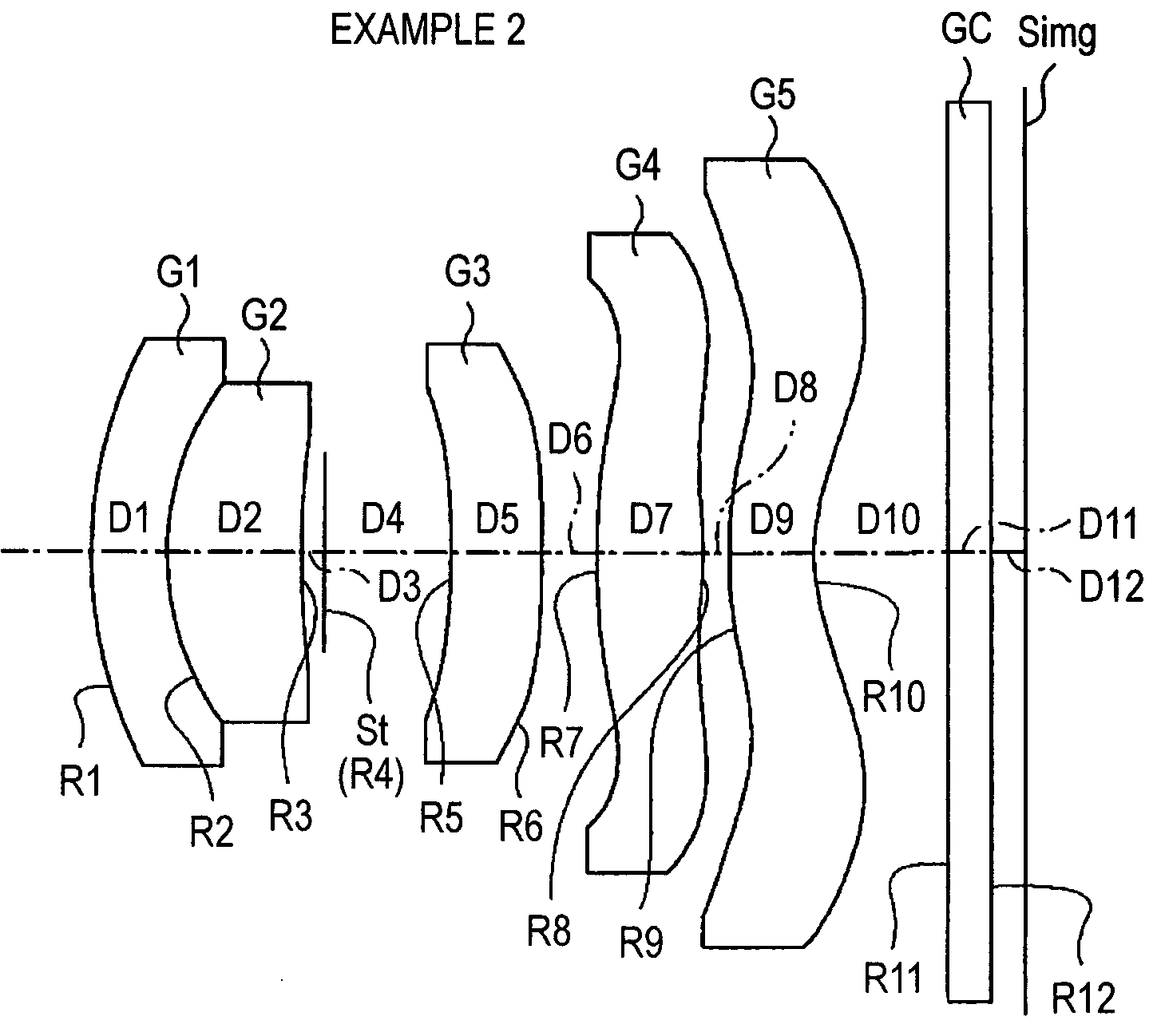
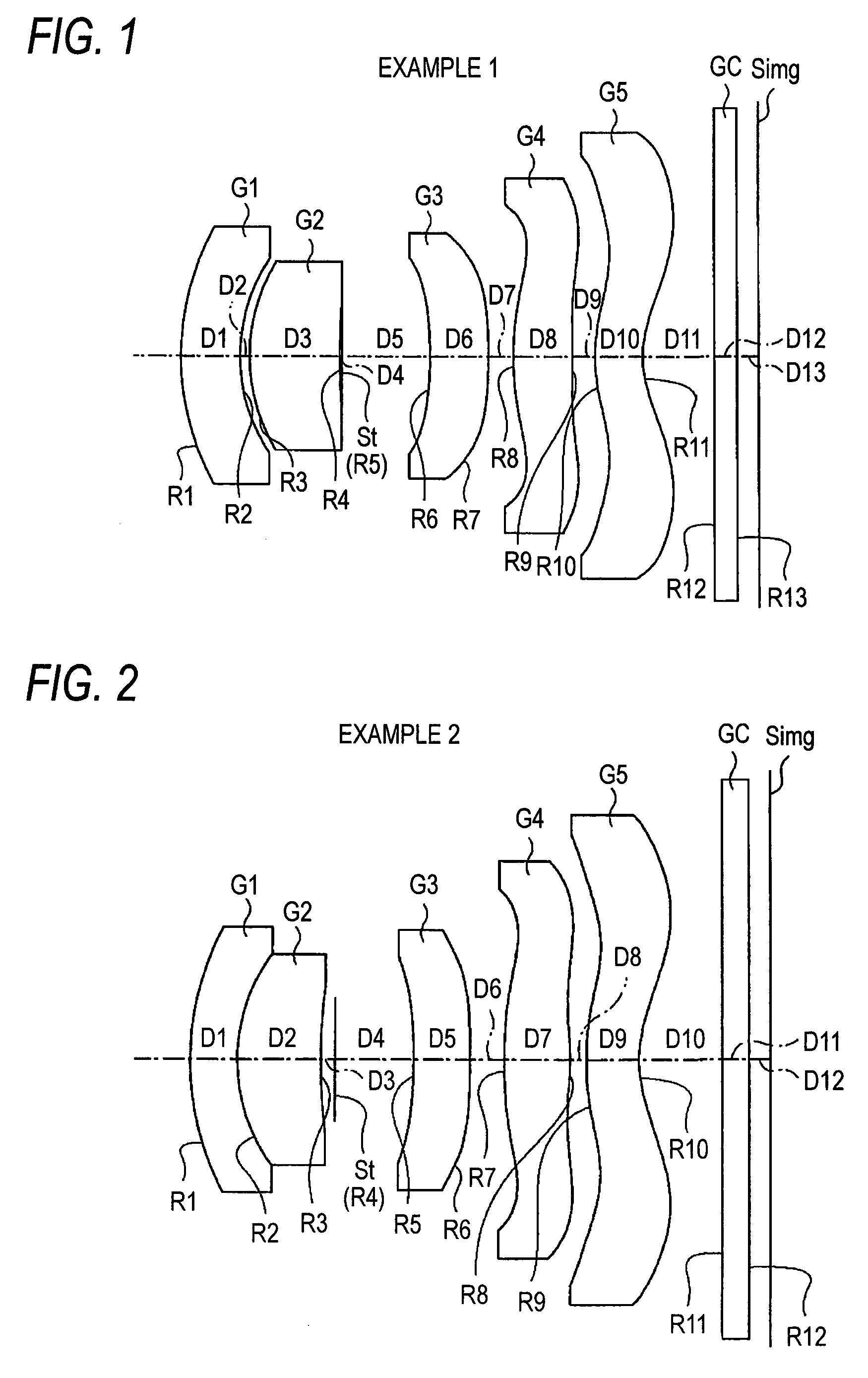
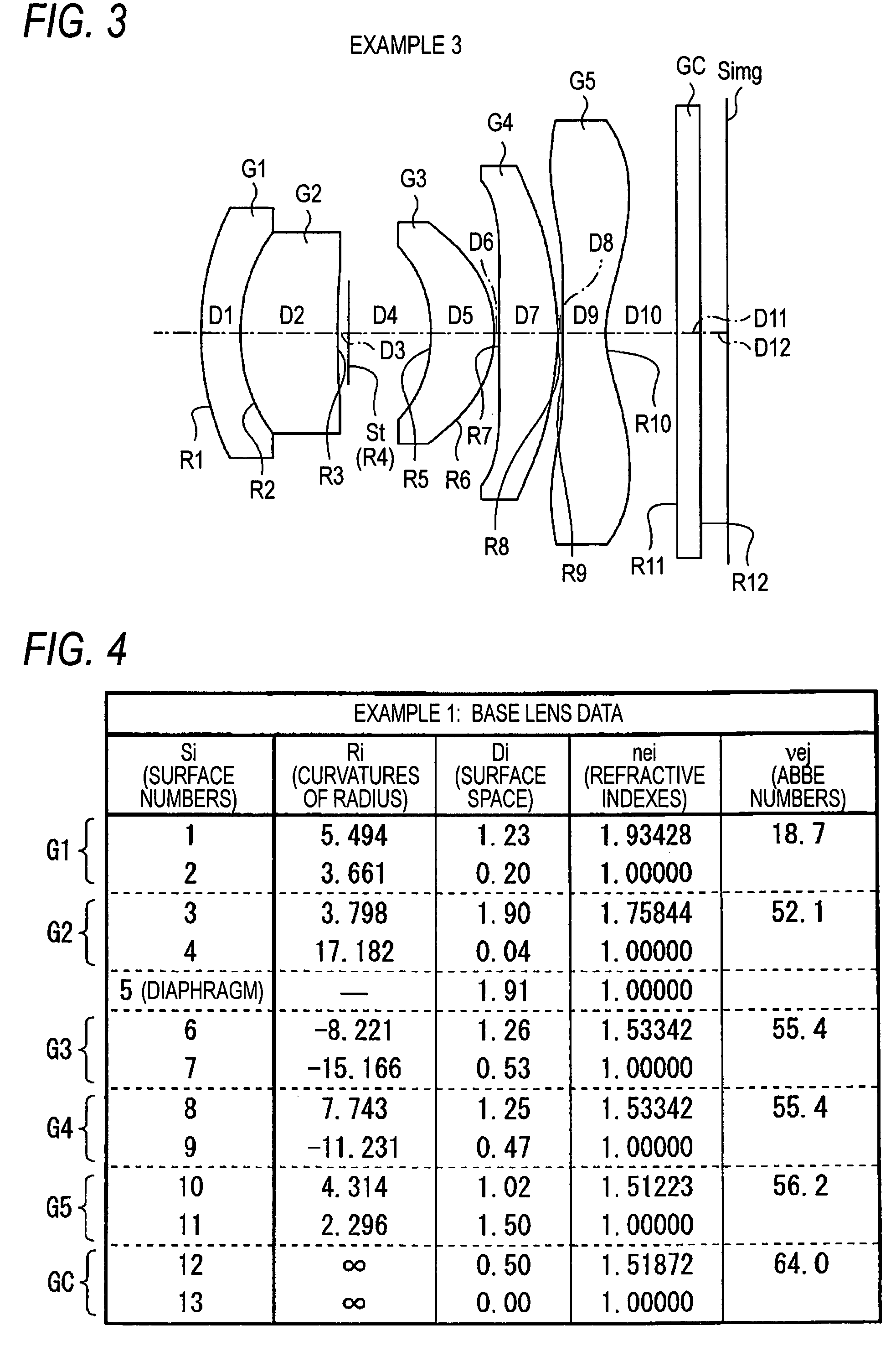
Imaging lens
An imaging lens which uses a larger number of constituent lenses for higher performance and features a low F-value, low-profile design and a wide field of view. Designed for a solid-state image sensor, the imaging lens includes constituent lenses arranged in order from an object side to an image side: a first positive refractive power lens having a convex object-side surface; a second negative refractive power lens having a concave image-side surface; a third positive refractive power lens having a convex image-side surface; a fourth negative refractive power lens having a concave image-side surface; a fifth positive refractive power lens as a meniscus lens having a convex image-side surface; a sixth lens as a meniscus double-sided aspheric lens having a concave image-side surface near an optical axis; and a seventh negative refractive power lens as a double-sided aspheric lens having a concave image-side surface near the optical axis.
Owner:TOKYO VISIONARY OPTICS CO LTD
Imaging optical system and imaging lens device
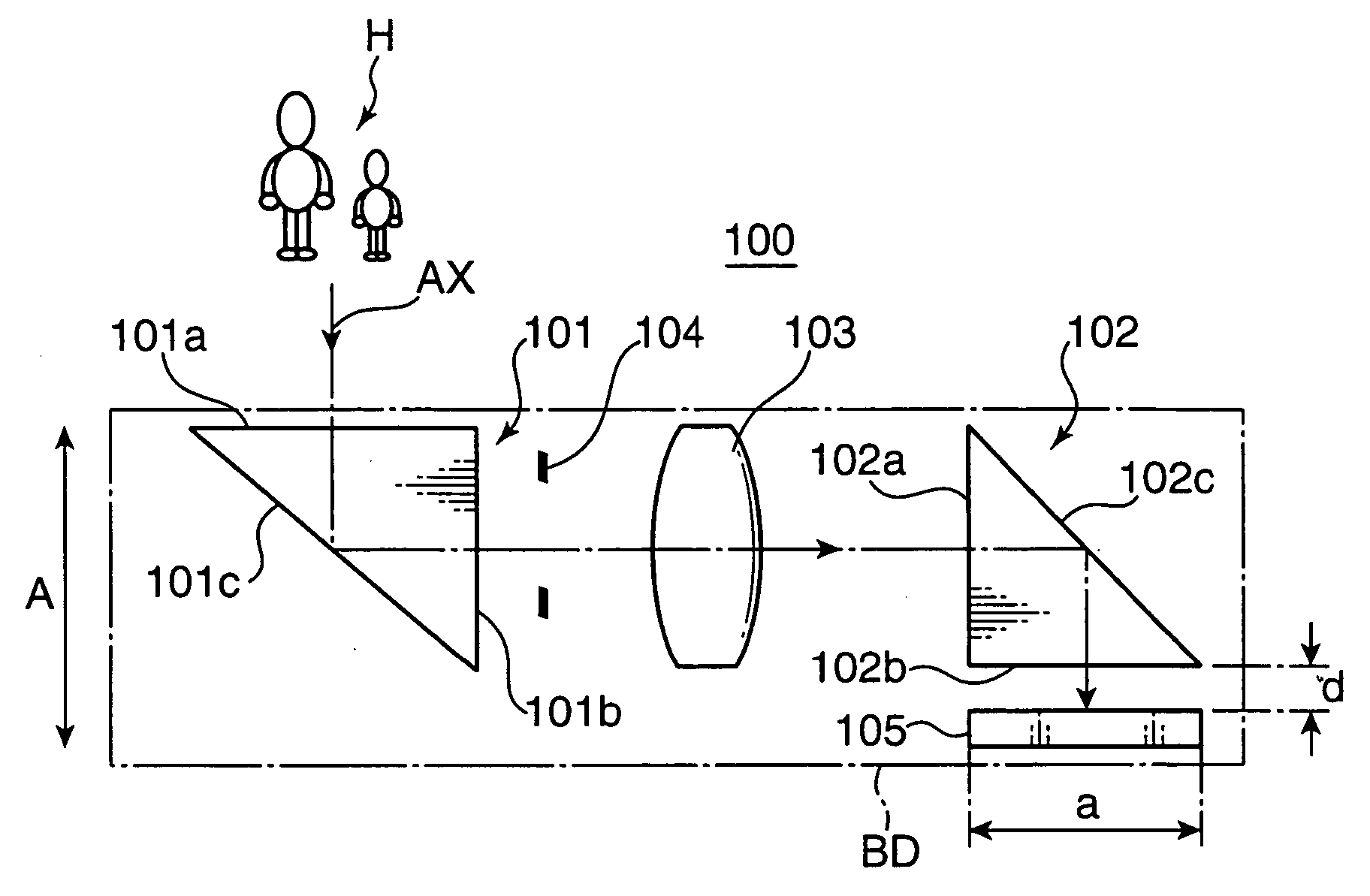
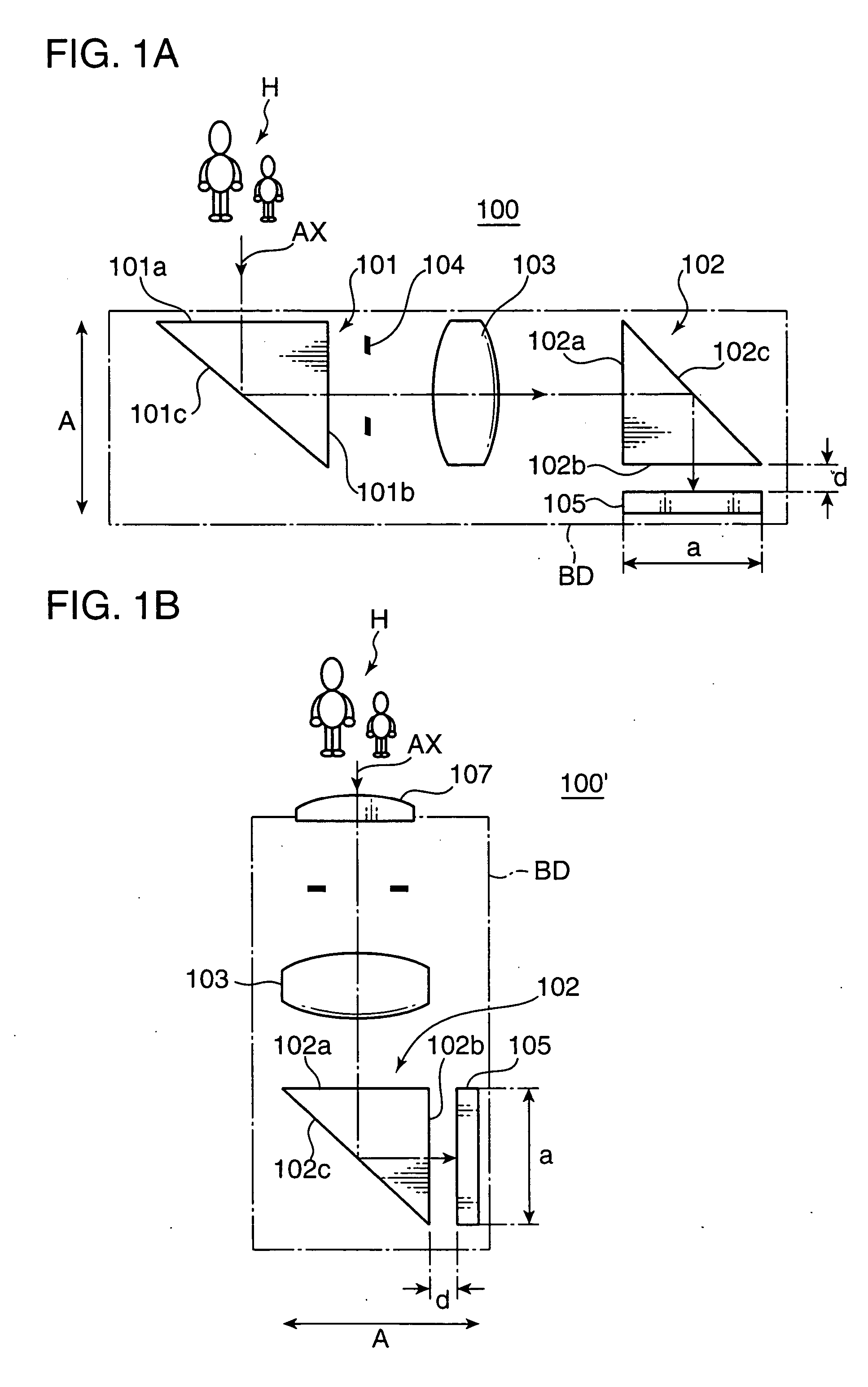
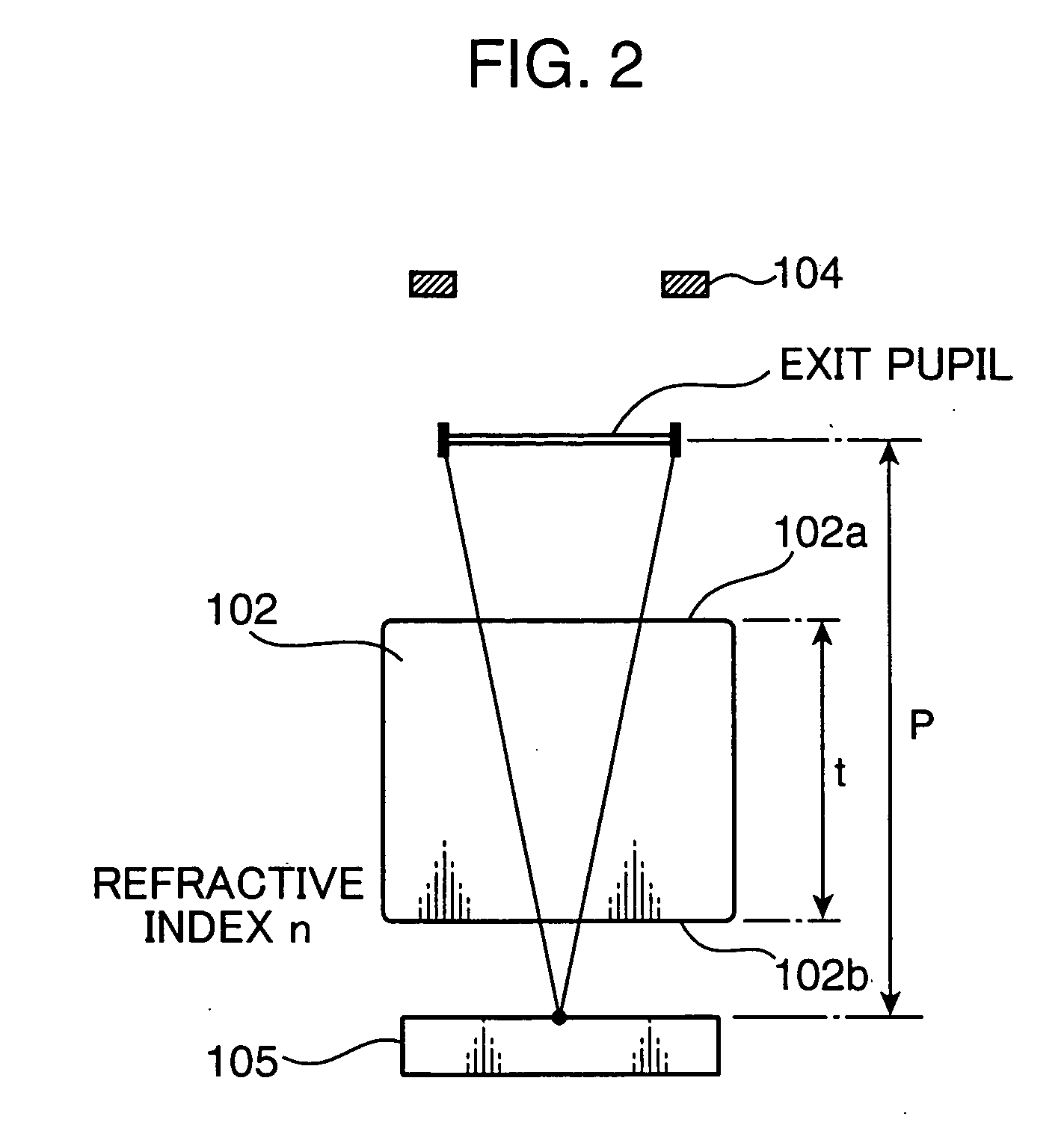
InactiveUS20060017834A1Inexpensive and compactGood optical performanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical powerImaging lens
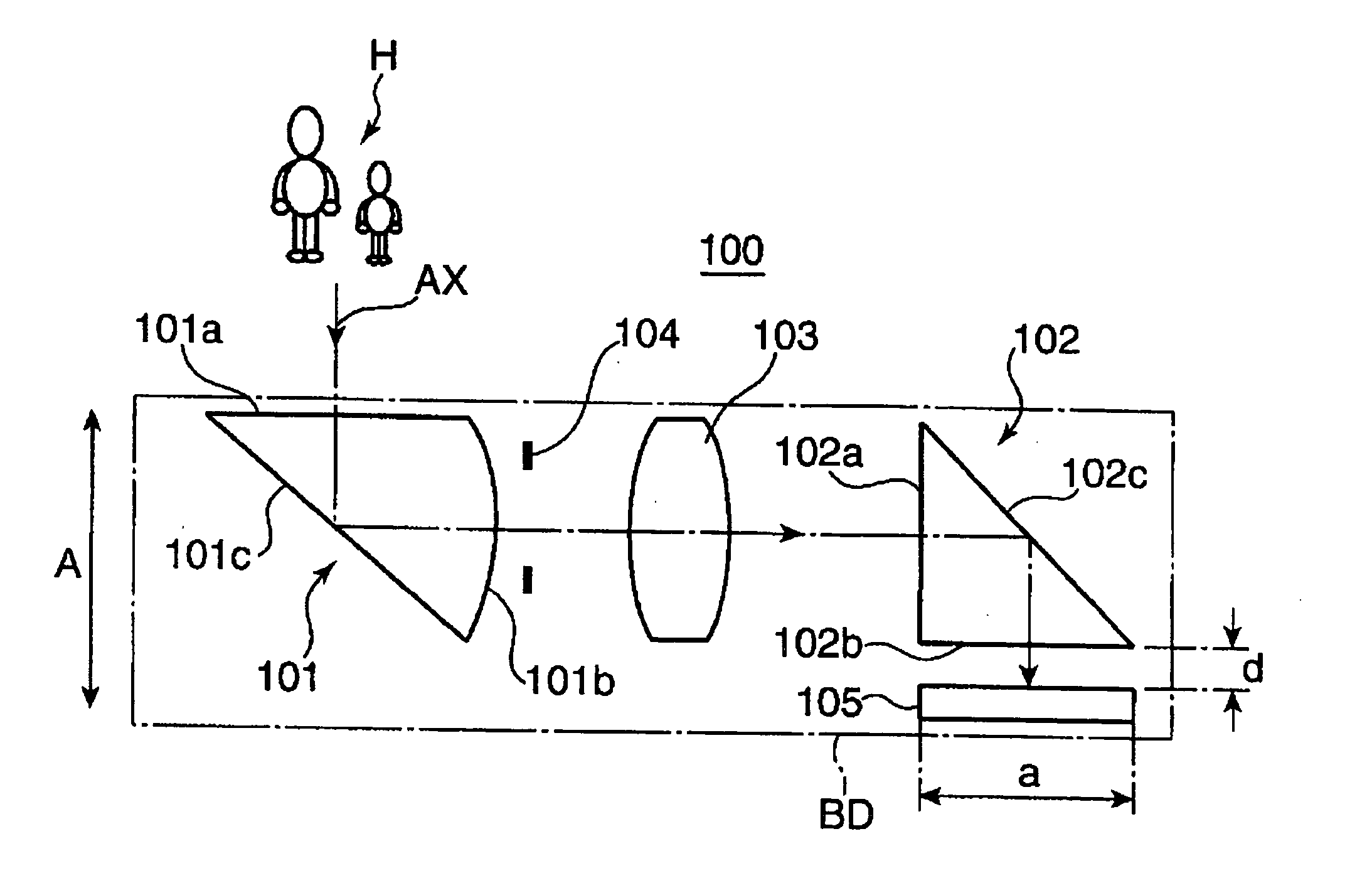
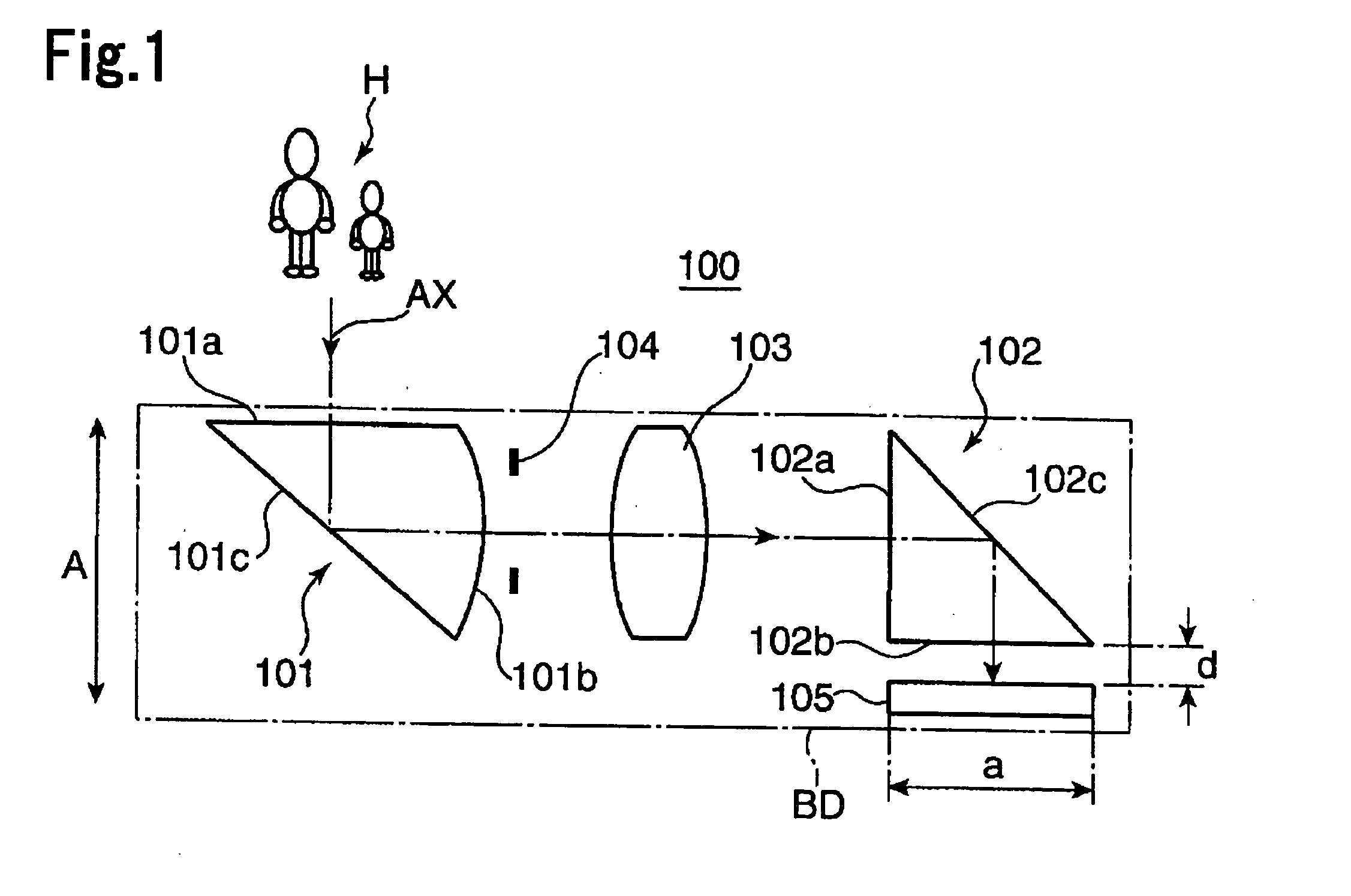
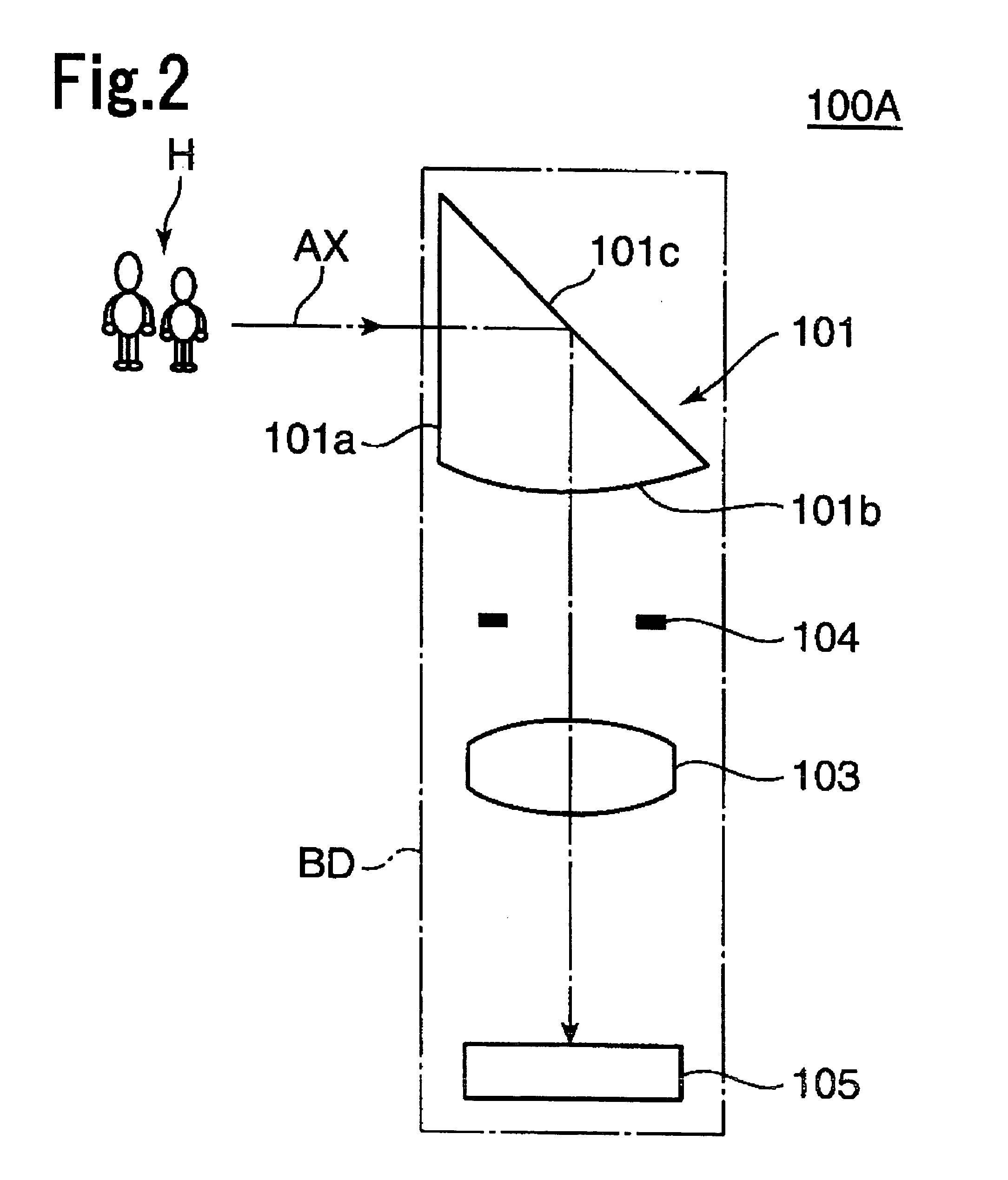
An imaging optical system 100 has an imaging side prism 102 for bending incident light at about 90 degrees for reflection, and an image sensor 105 having a light receiving surface opposing to an exit surface 102b of the imaging side prism 102. At least one of an incident surface 101a of an incident side prism 101 and an incident surface 101a of the imaging side prism 102, or at least one of an exit surface 101b of the incident side prism 101 and the exit surface 102b of the imaging side prism 102 has an optical power. An arrangement relation between the exit surface 102b of the imaging side prism 102 and the image sensor 105 is established to satisfy the conditional formula (1): 0.0≦d / a<0.8 (1) where d represents a distance between the exit surface 102b and the light receiving surface of the image sensor 105, and a represents a height of the light receiving surface of the image sensor 105 on a plane where an optical path of the imaging optical system 100 is folded, e.g., the size of the image sensor 105 in the shorter side direction thereof. This arrangement enables to reduce the thickness of an apparatus housing BD for incorporating the imaging optical system 100.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Lighting apparatus and display device including the same
ActiveUS20120274882A1Increase resistanceGood optical performanceNanoopticsIlluminated signsOptical propertyLight equipment
A lighting apparatus and a display device including the same are disclosed. The present invention relates to a lighting apparatus, which can enhance resistance against gas or humidity and which can present a stable optical property and which can enhance light-emitting efficiency, and a display device including the lighting apparatus.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Signal mirror system for a vehicle
InactiveUS20070183066A1Reduce material costsGood optical performanceMirrorsAntiglare equipmentDisplay deviceLight reflectance
A signal mirror system for a vehicle includes a reflective mirror element comprising a semitransparent nondichroic mirror reflector coated onto a light-transmitting substrate. The visible light transmission through the reflective mirror element is in the range of from about 1% visible light transmission to about 30% visible light transmission and the visible light reflectance is in the range from 40% visible light reflectance to 80% visible light reflectance for visible light incident upon the front side of the reflective mirror element. The reflective mirror element exhibits substantial non-spectral selectivity in its reflectance. The semitransparent nondichroic reflector comprises a metal thin film layer. A turn signal display, preferably having at least one light emitting diode, is disposed to the rear of the reflective mirror element and configured so it emits light emitted that passes through the semitransparent mirror reflector to be viewed by a viewer viewing from the front of said reflective mirror element with a display luminance of at least about 30 foot lamberts.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Fisheye lens and imaging device using it
A fisheye lens with a field angle of at least one hundred sixty degrees is formed of two lens groups, arranged in order from the object side, as follows: a first lens group having negative refractive power and a second lens group having positive refractive power. The first lens group includes, arranged in order from the object side, two lens elements, each having negative refractive power and a meniscus shape with the convex surface on the object side, a lens element having negative refractive power with a concave surface on the image side, and two lens elements of opposite refractive powers. The second lens group includes, arranged in order from the object side, two lens elements of opposite refractive powers, a stop, and two lens elements of opposite refractive powers. The fisheye lens preferably satisfies specified conditions related to spacings of lens surfaces and to distortion characteristics of the fisheye lens.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Single piece top surface display layer and integrated front cover for an electronic device
InactiveUS20070229475A1Reduce the possibility of damageReduces parallax effectNon-enclosed substationsInput/output for user-computer interactionSurface displayDisplay device
A single-piece top surface display and integrated front cover for an electronic device. In one embodiment, the cover comprises a thin, flexible, transparent layer coupled with a supporting structure. The flexible layer is supported above a display screen which is coupled with pressure activated sensors located under the display screen. The cover is dust-free, waterproof, and has a flat outer surface that is free of any steps or indentations. Users input data by applying pressure on the cover which causes the display screen to deflect and activate the sensors. The pressure exerted on the sensors is triangulated to register the position of the user input. In another embodiment, the cover is transparent, rigid, and directly contacts the pressure activated sensors which are located in front of the display screen or in the housing behind it. When pressure is applied to the cover, the cover deflects and activates the sensors. In both embodiments, an accelerometer identifies valid input events.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Projection optical system, manufacturing method thereof, and projection exposure apparatus
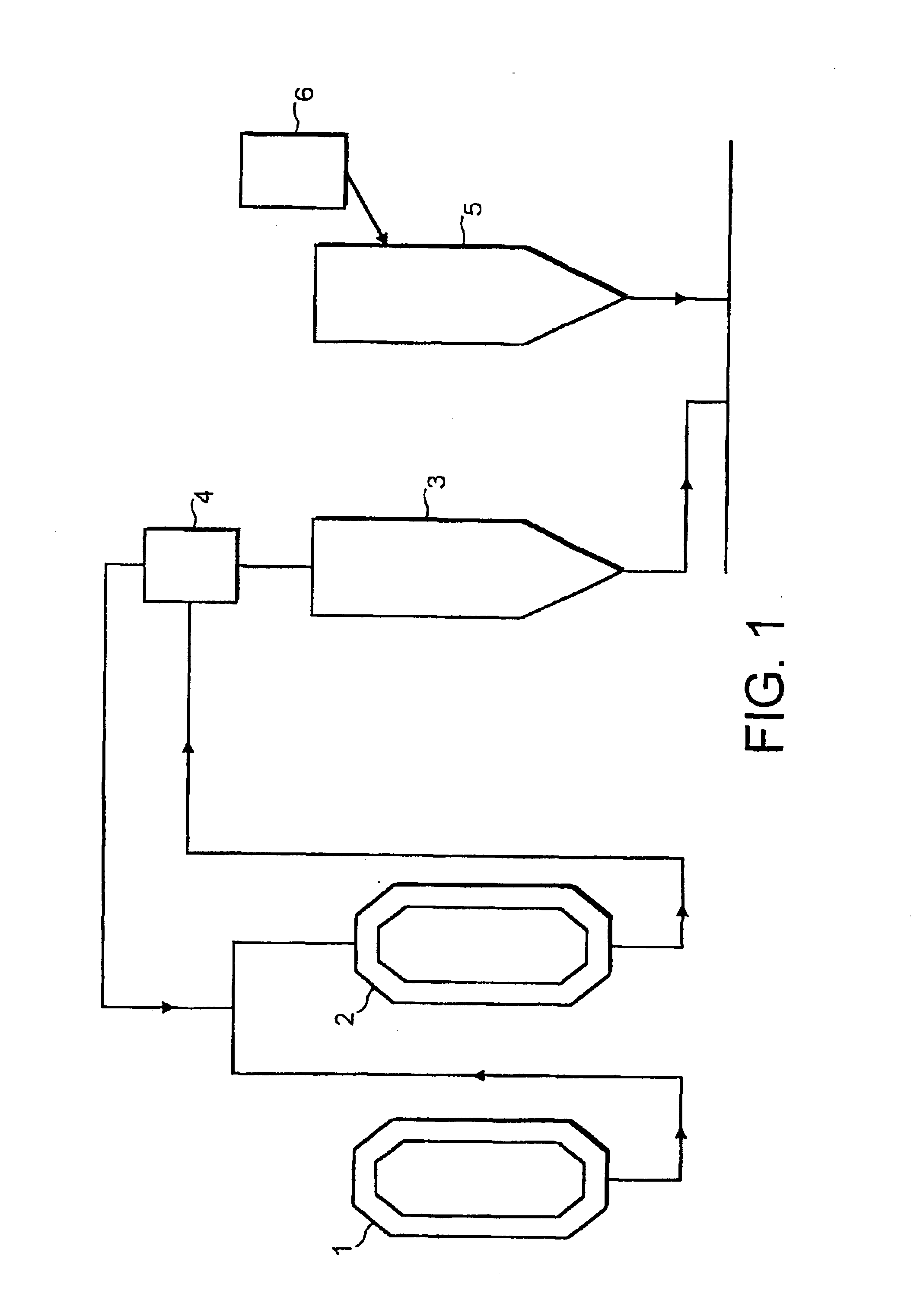
InactiveUS20020044260A1Suppression amountGood optical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotographic printingImage formationEngineering
A projection optical system forming an image of an object in a first plane onto a second plane, comprising, an optical element group including at least one refractive member and a plurality of reflective members, and a plurality of lens-barrel units holding the optical element group divided into a plurality of groupings, wherein the plurality of reflective members is all held by one lens-barrel unit of the plurality of lens-barrels units.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Electrochromic mirrors and devices
InactiveUS20060028730A1Reduce material costsGood optical performanceMirrorsAntiglare equipmentDisplay deviceEngineering
An electrochromic rearview mirror element for a motor vehicle comprises a first substantially transparent front substrate having a first and a second surface (and with a substantially transparent conductive electrode on its second surface) and a rear substrate having a third and a fourth surface. The rear substrate is positioned in spaced-apart relationship with the front substrate and with its third surface opposing the second surface of the front substrate. A mirror reflector is disposed on the third surface and a seal is positioned toward a peripheral edge of the substrates forming a cavity therebetween. An electrochromic medium is disposed in the cavity. The mirror reflector preferably comprises a metal layer that reflects at least about 70% of visible light. A display device can be disposed behind the rear substrate. The display device preferably exhibits, when electrically powered, a display luminance of at least about 30 foot lamberts as measured with the display device placed behind, and emitting light through, the electrochromic medium and with the electrochromic medium in its bleached state.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com