Patents
Literature
797results about How to "Suppression amount" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
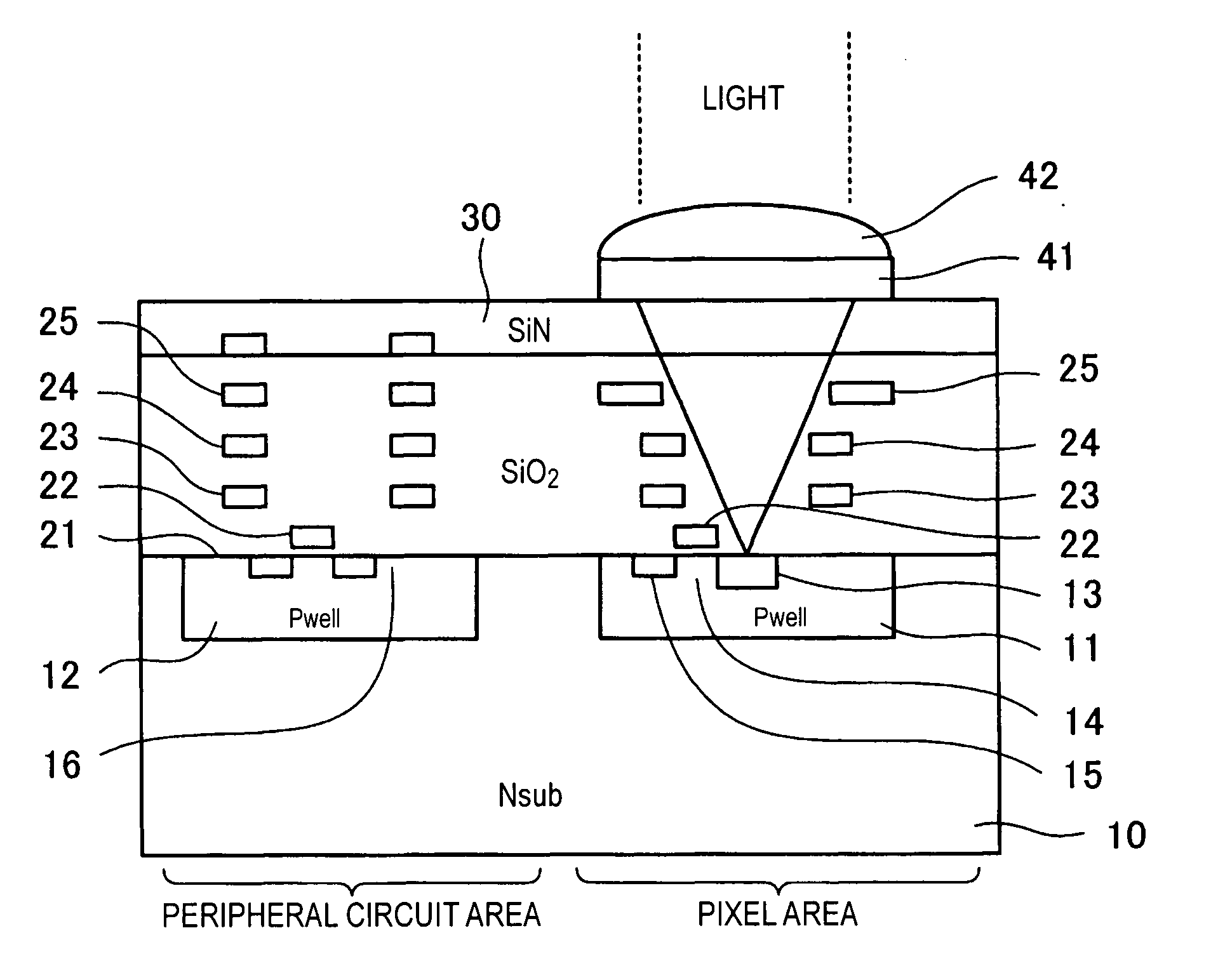
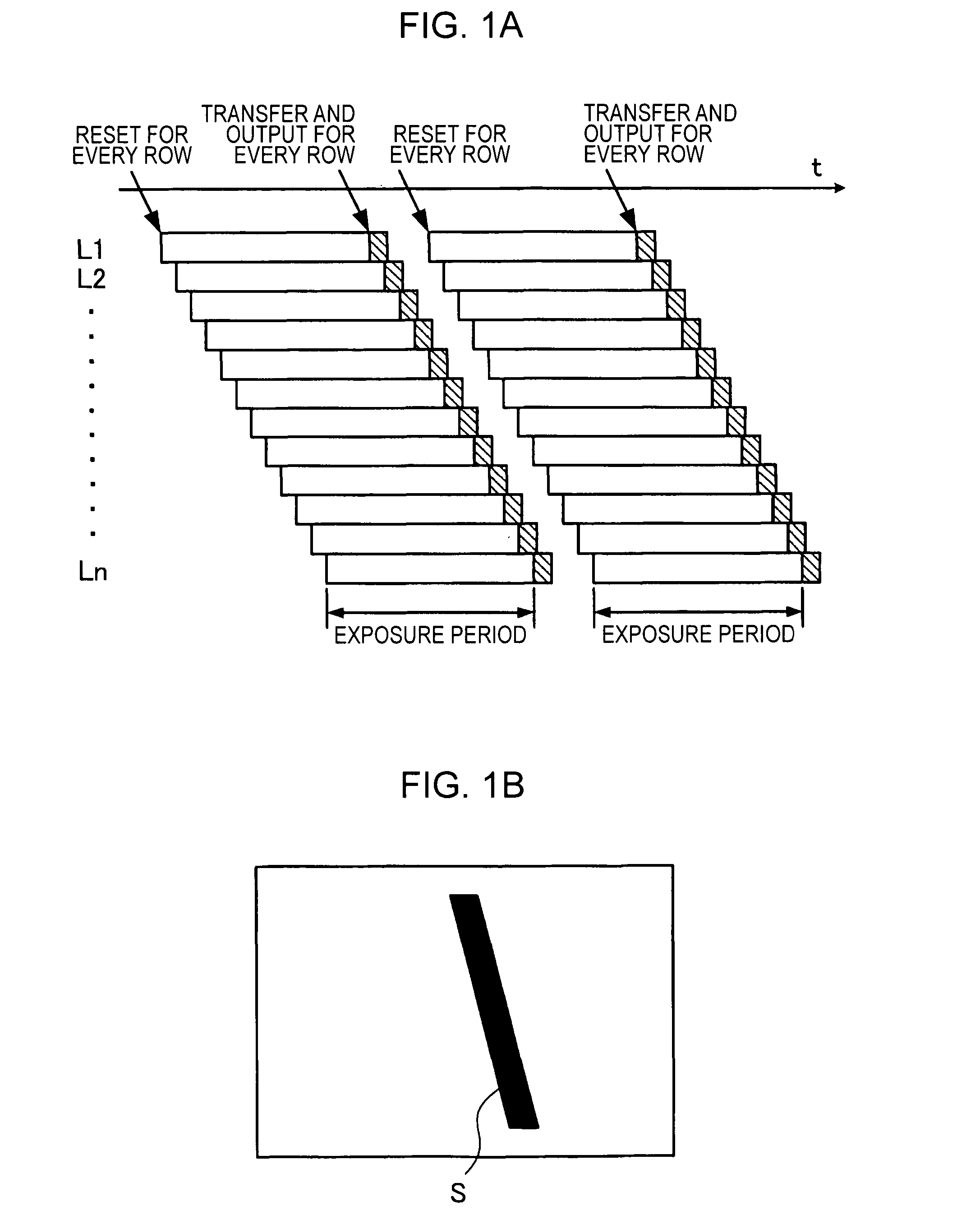
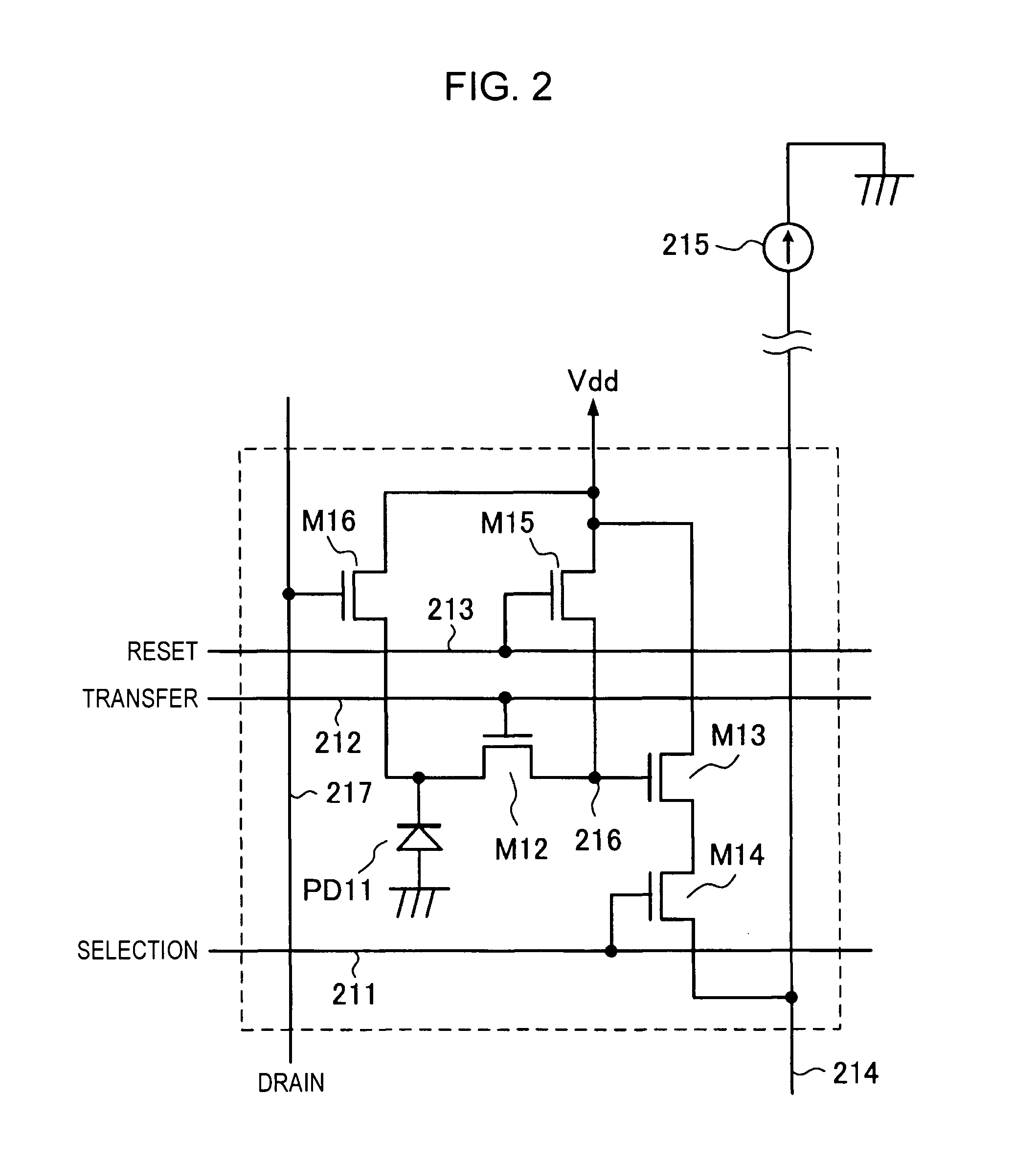
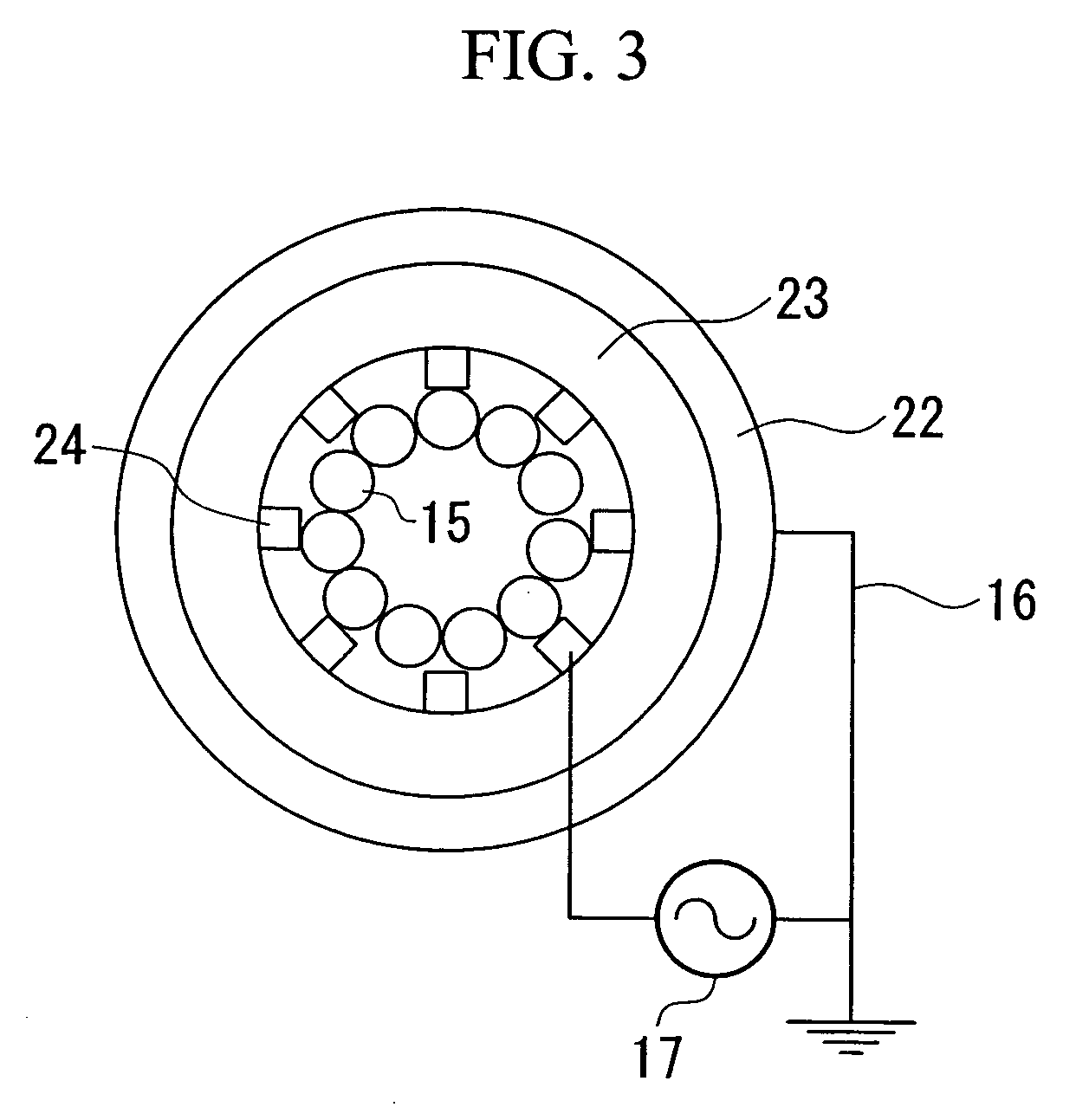
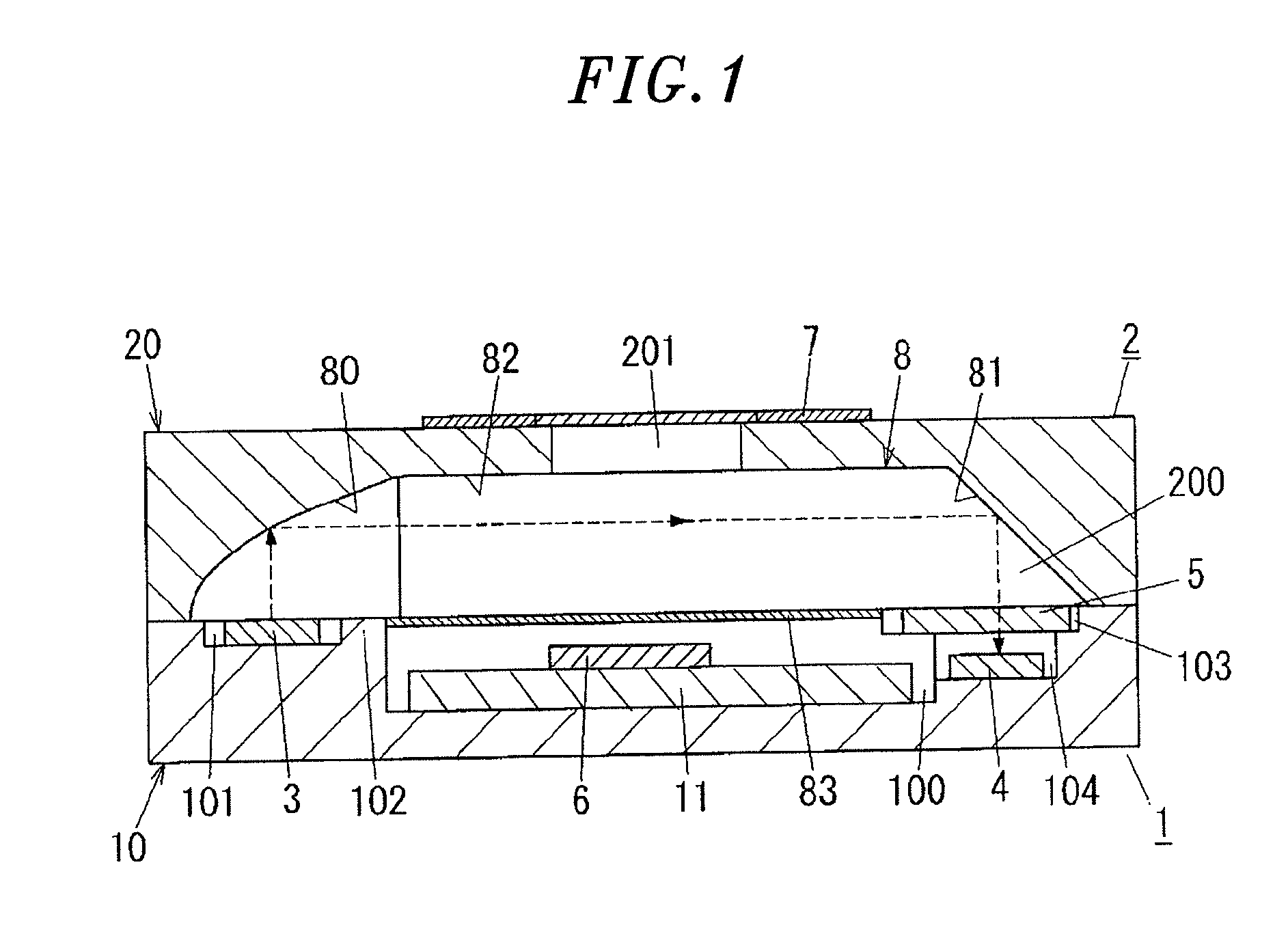
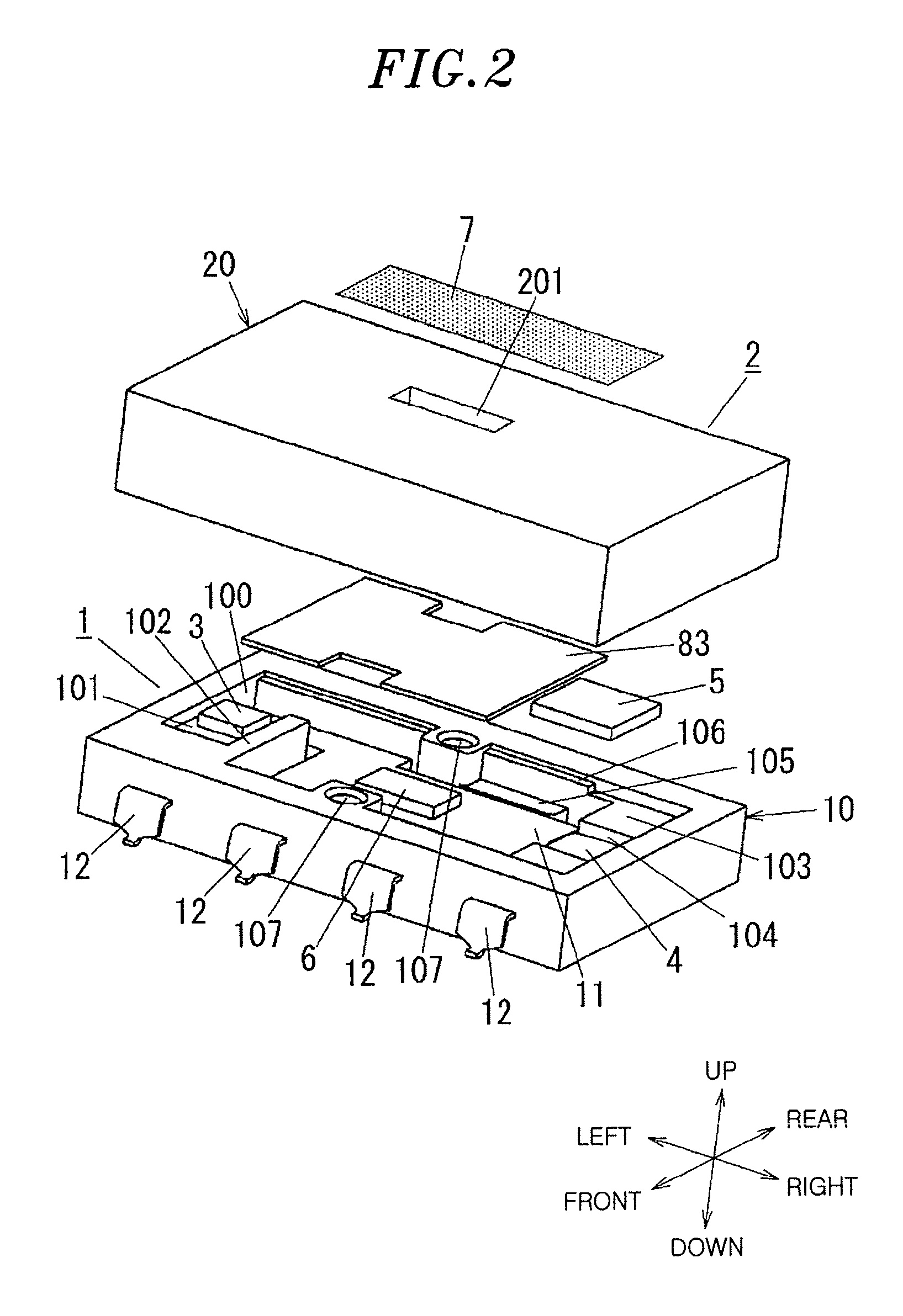
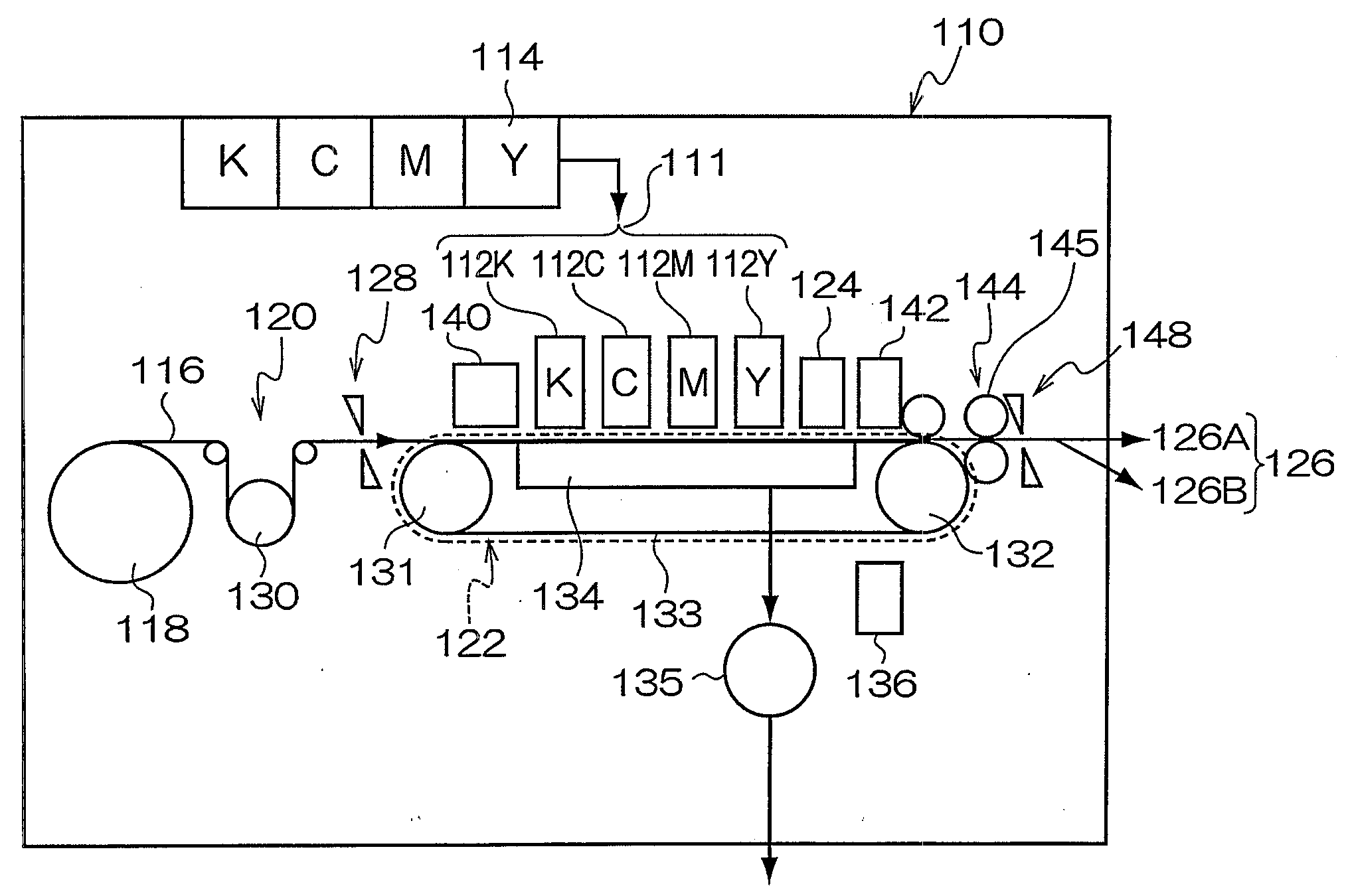
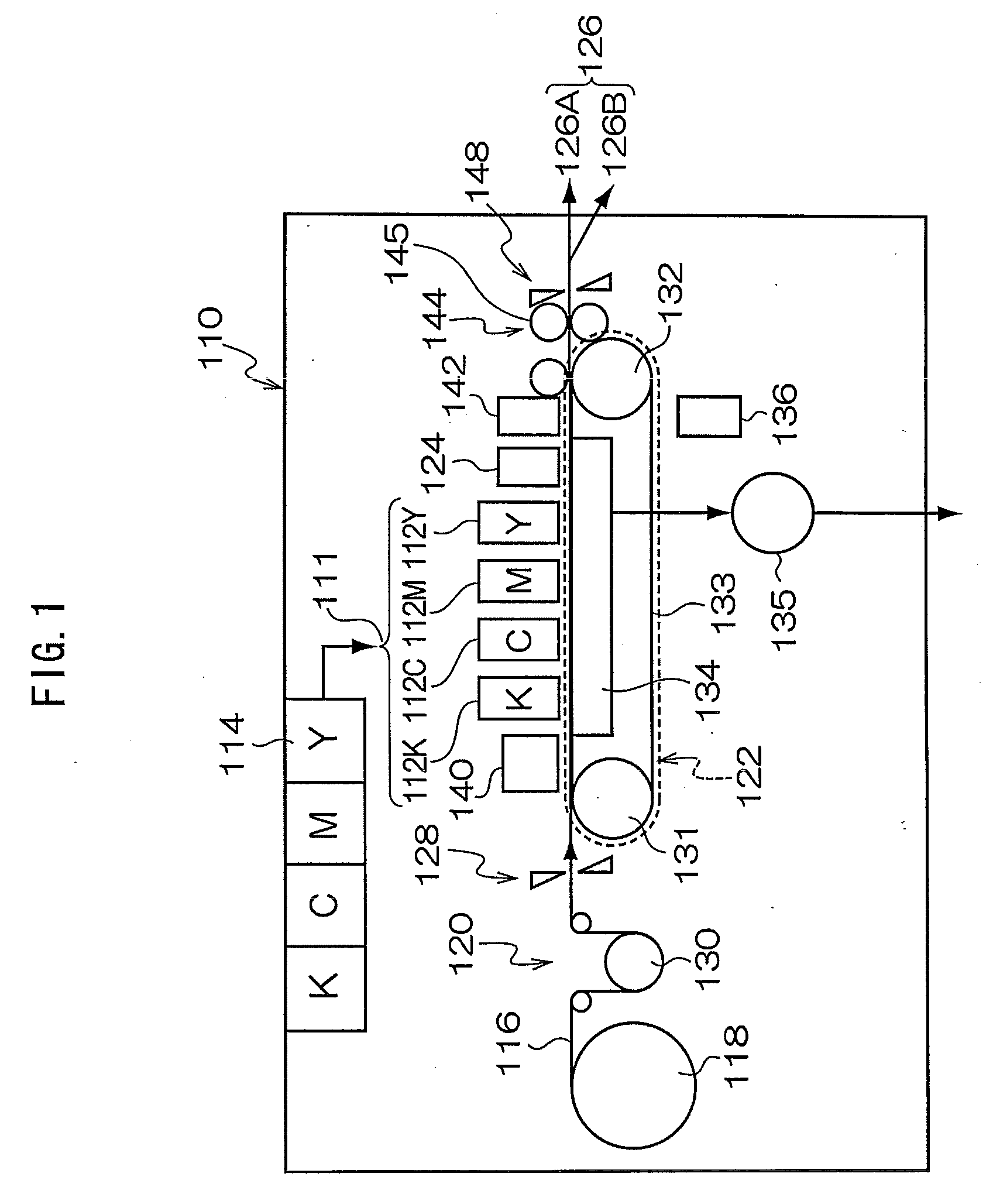
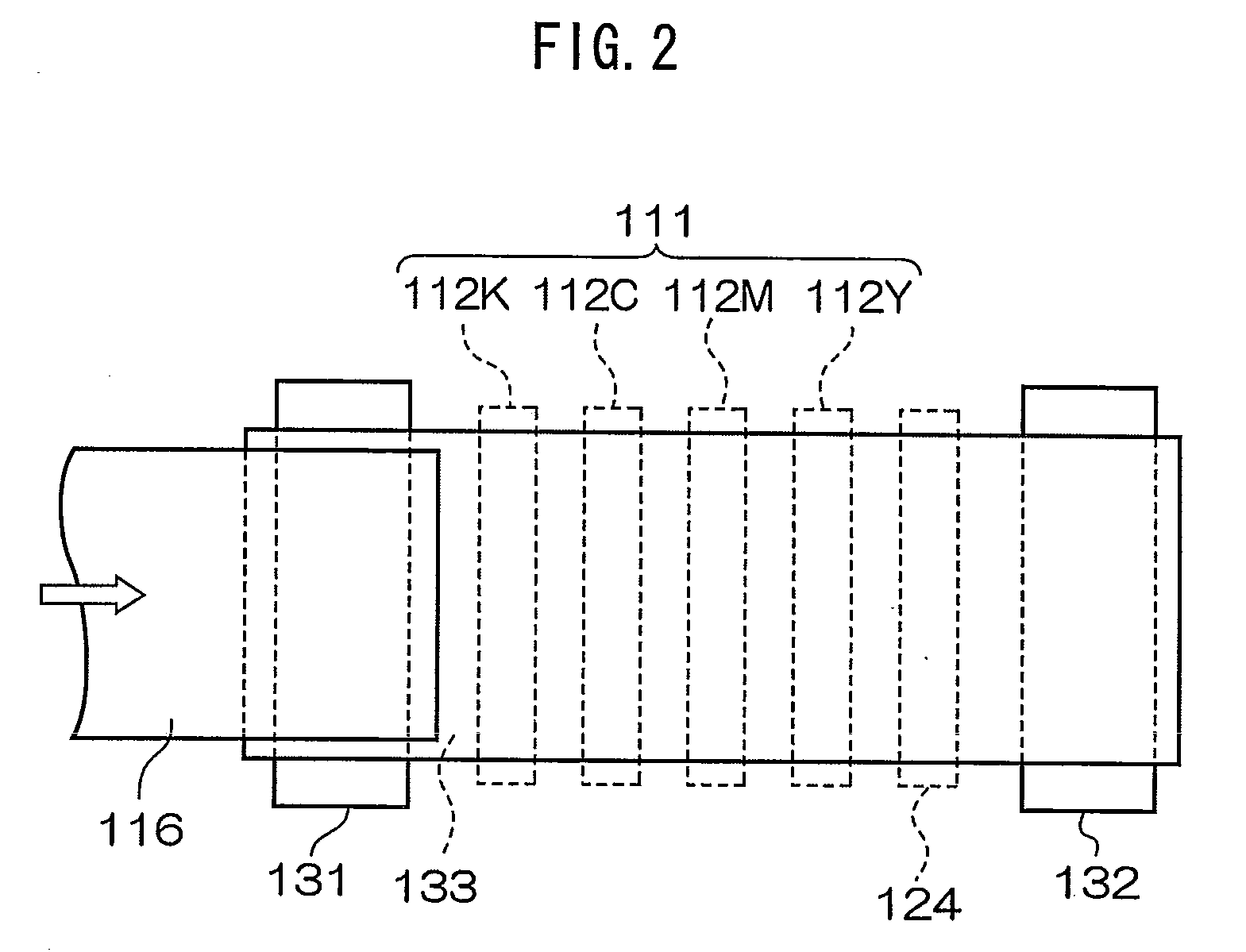
Imaging apparatus and imaging method
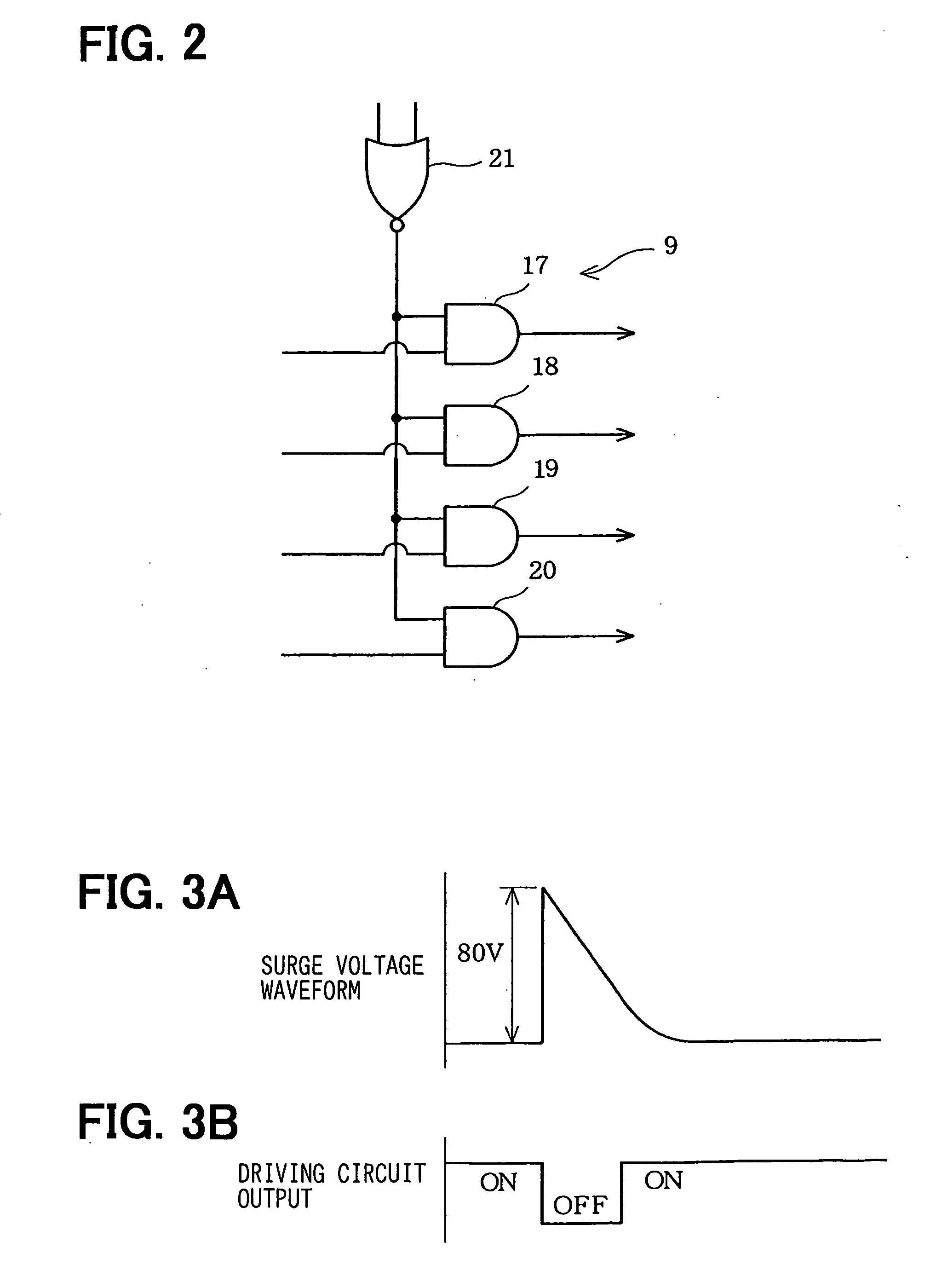
InactiveUS20060157760A1Blocking phenomenonQuality improvementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringExposure period
An imaging apparatus using a solid-state image sensor that reads out a signal of each pixel by an XY address method to capture an image includes a mechanical shutter configured to block light incident on a light receiving surface of the solid-state image sensor; and control means for simultaneously resetting the pixel signals for all rows in the solid-state image sensor to start exposure to the solid-state image sensor, closing the mechanical shutter after a predetermined exposure period is elapsed, and sequentially reading out the pixel signals for every row of the solid-state image sensor with the mechanical shutter being closed.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
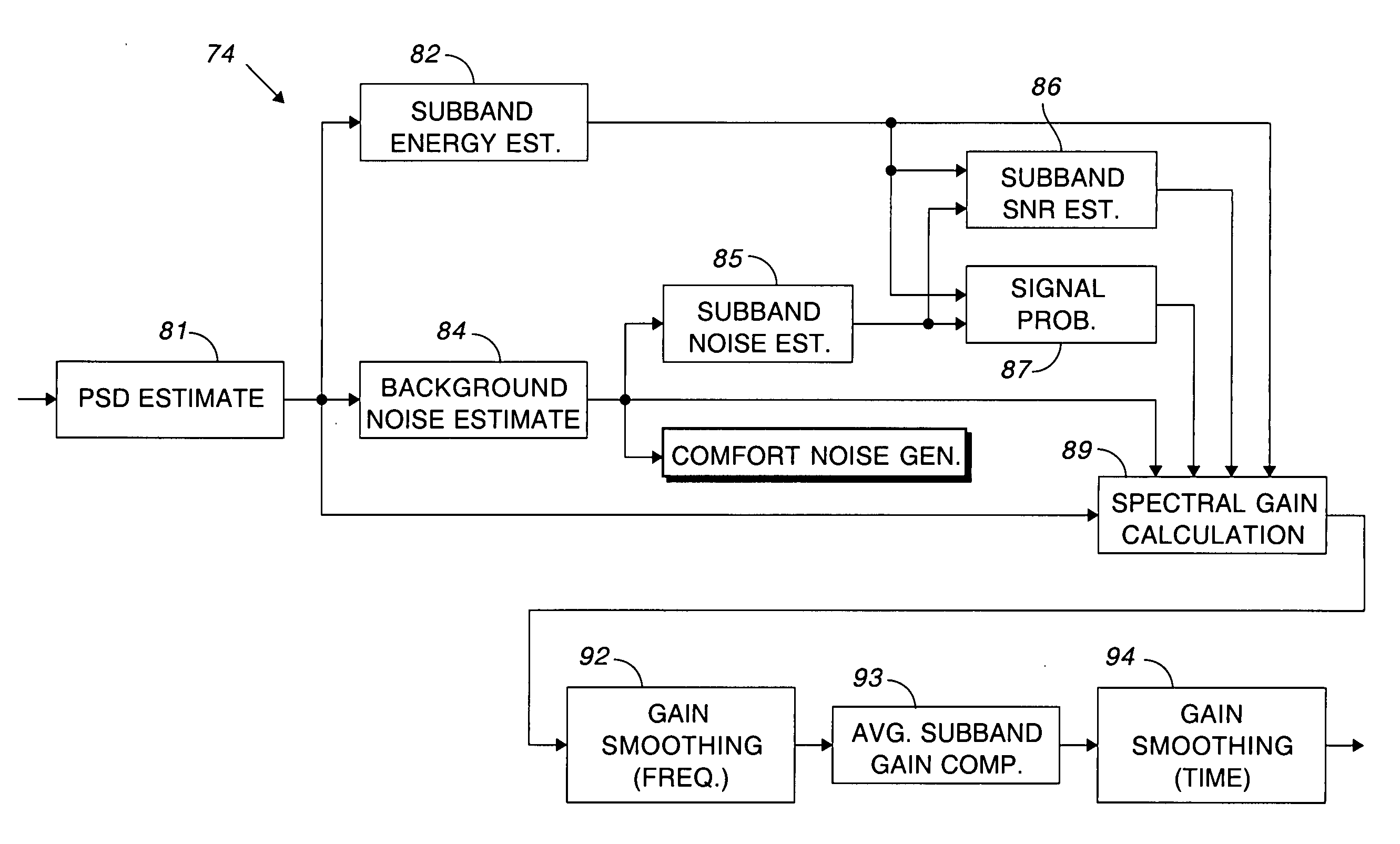
Comfort noise generator using modified doblinger noise estimate
ActiveUS20050278171A1Generate efficientlyEliminates noise pumpingSpeech analysisTime domainComfort noise
A background noise estimate based upon a modified Doblinger noise estimate is used for modulating the output of a pseudo-random phase spectrum generator to produce the comfort noise. The circuit for estimating noise includes a smoothing filter having a slower time constant for updating the noise estimate during noise than during speech. Comfort noise is smoothly inserted by basing the amount of comfort noise on the amount of noise suppression. A discrete inverse Fourier transform converts the comfort noise back to the time domain and overlapping windows eliminate artifacts that may have been produced during processing.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
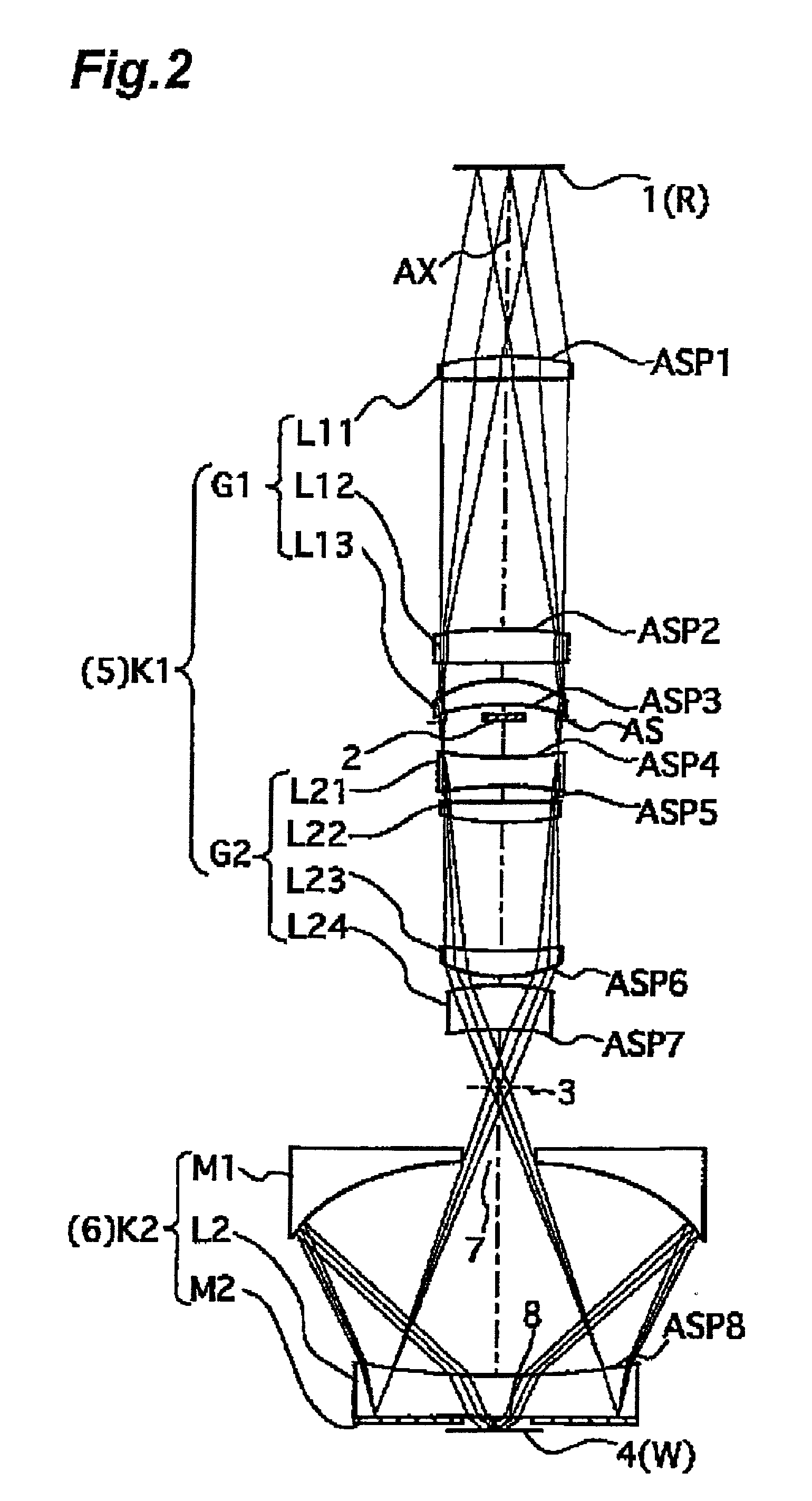
Projection optical system, manufacturing method thereof, and projection exposure apparatus
InactiveUS20020044260A1Suppression amountGood optical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotographic printingImage formationEngineering
A projection optical system forming an image of an object in a first plane onto a second plane, comprising, an optical element group including at least one refractive member and a plurality of reflective members, and a plurality of lens-barrel units holding the optical element group divided into a plurality of groupings, wherein the plurality of reflective members is all held by one lens-barrel unit of the plurality of lens-barrels units.
Owner:NIKON CORP
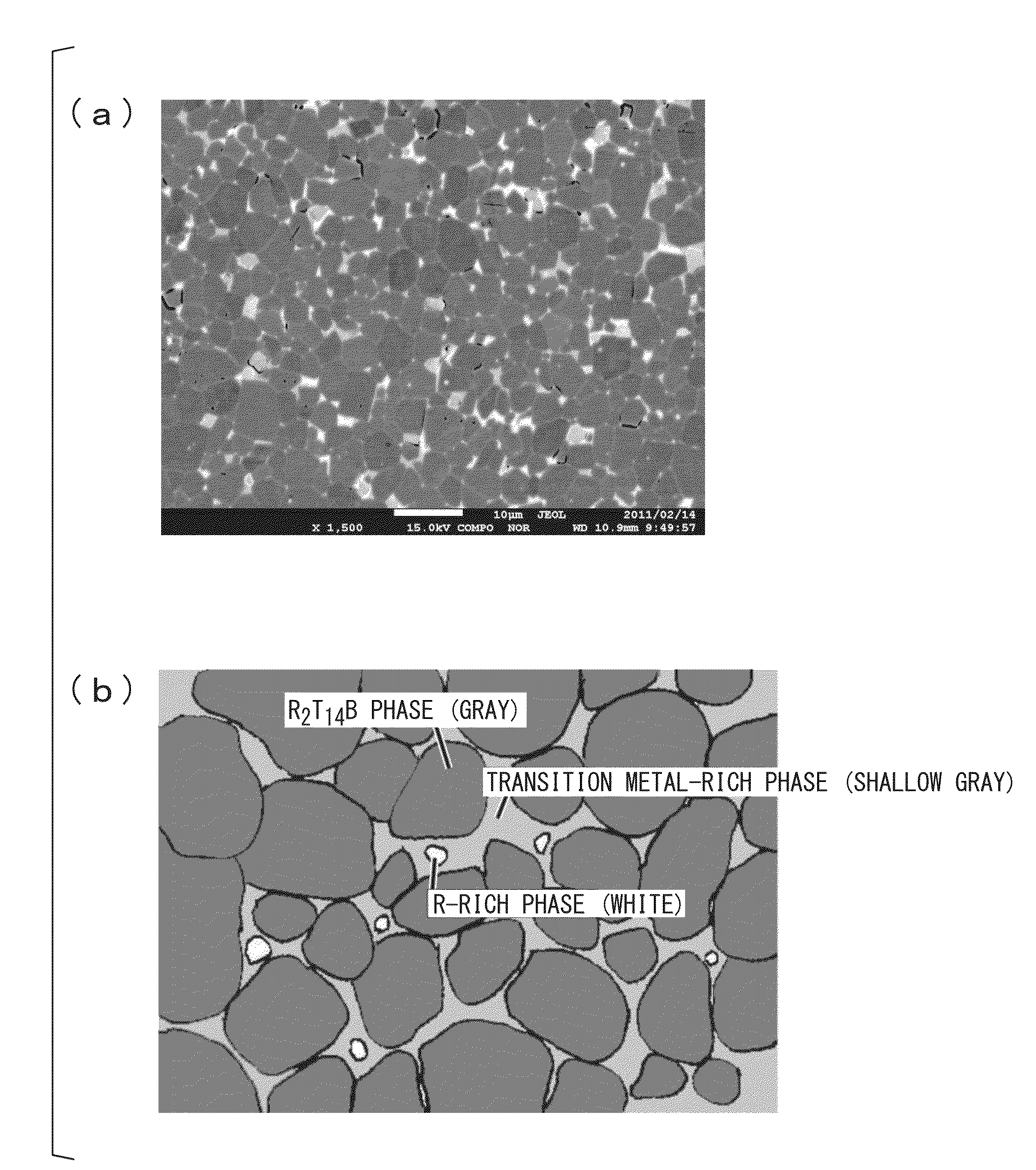
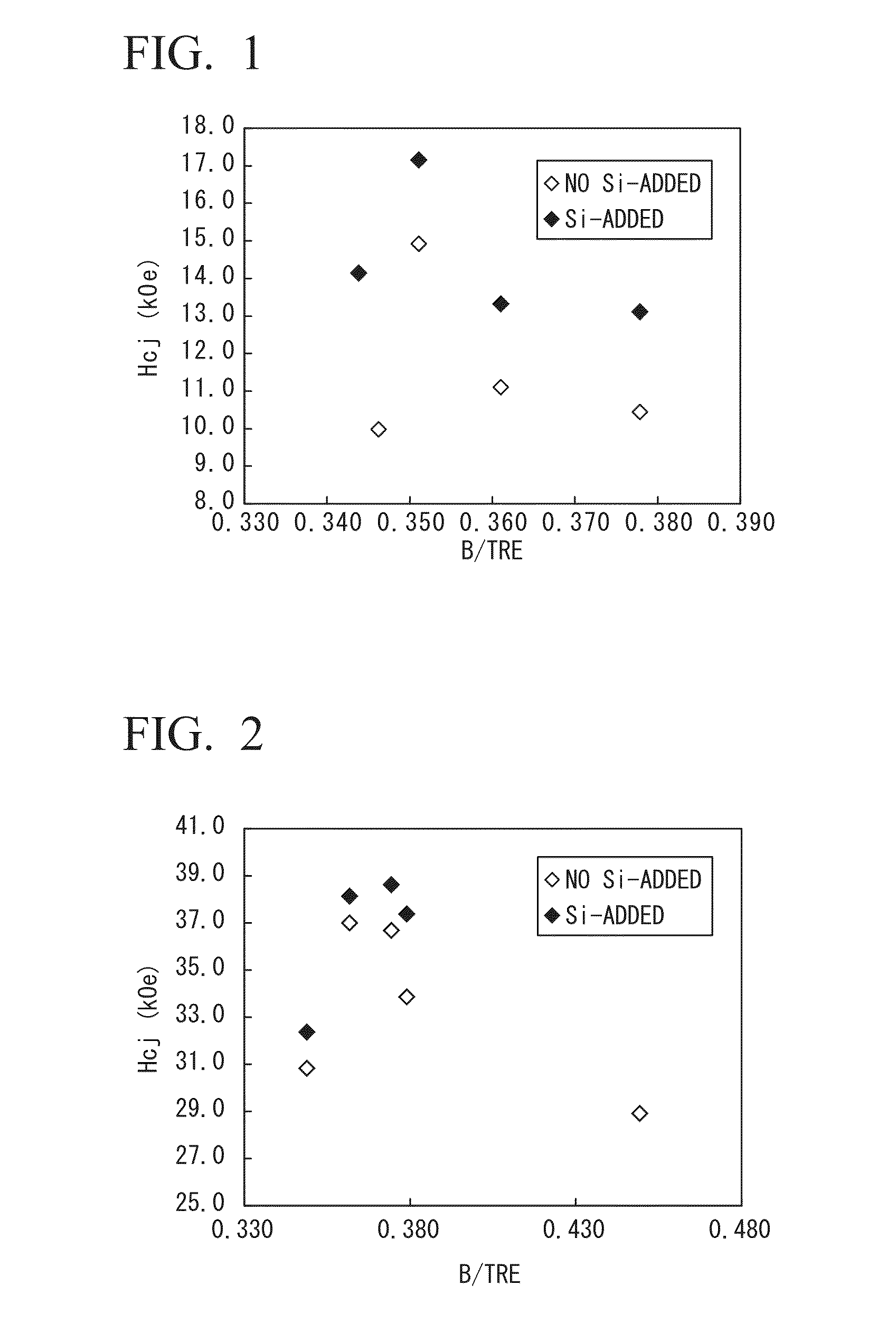
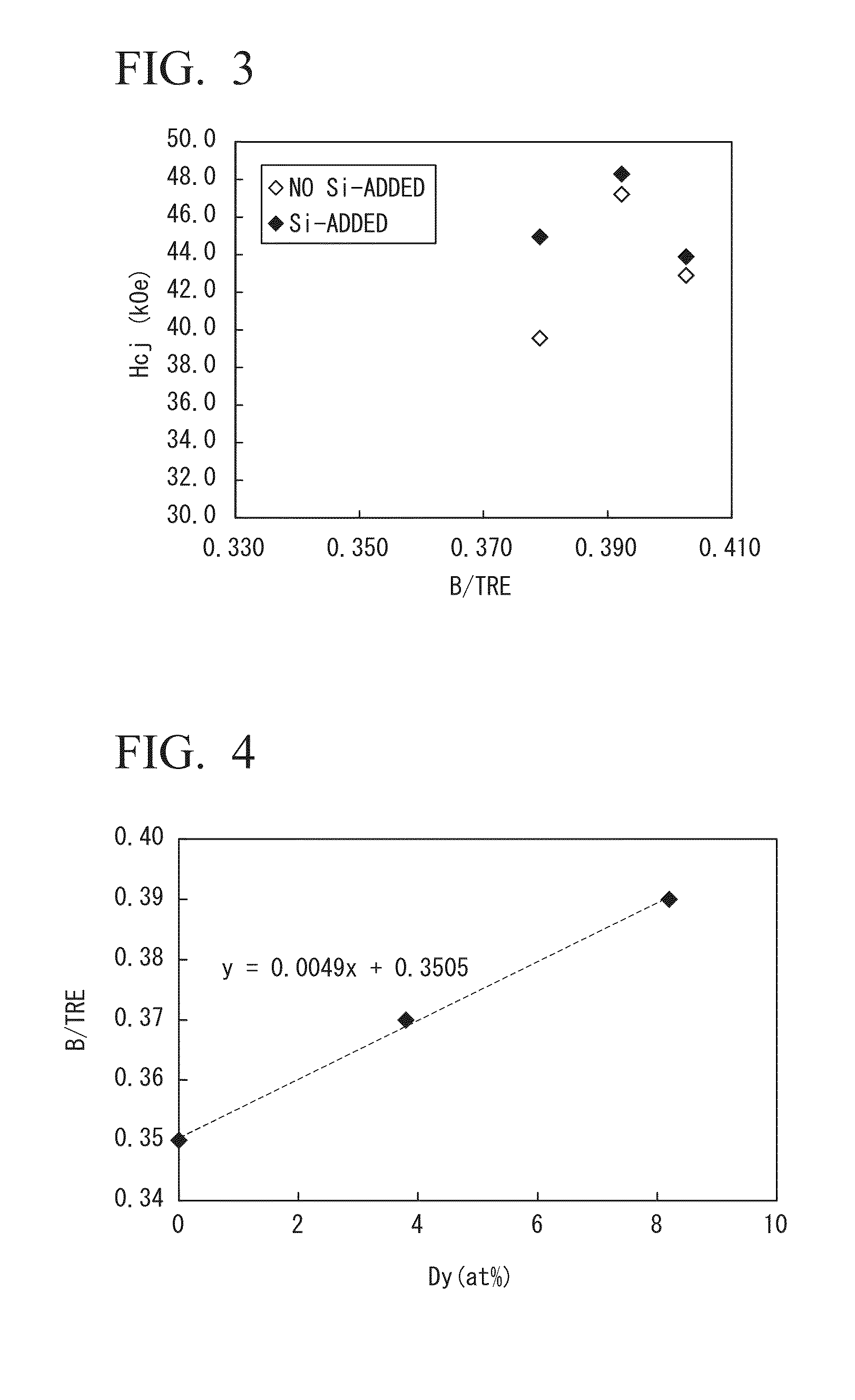
Alloy for r-t-b-based rare earth sintered magnet, process of producing alloy for r-t-b-based rare earth sintered magnet, alloy material for r-t-b-based rare earth sintered magnet, r-t-b-based rare earth sintered magnet, process of producing r-t-b-based rare earth sintered magnet, and motor
InactiveUS20140132377A1Improve coercive forceSuppression amountPermanent magnetsInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementSintered magnets
An alloy for R-T-B-based rare earth sintered magnets which contains R which is a rare earth element; T which is a transition metal essentially containing Fe; a metallic element M containing one or more metals selected from Al, Ga and Cu; B and inevitable impurities, in which R accounts for 13 at % to 15 at %, B accounts for 4.5 at % to 6.2 at %, M accounts for 0.1 at % to 2.4 at %, T accounts for balance, a proportion of Dy in all rare earth elements is in a range of 0 at % to 65 at %, and the following Formula 1 is satisfied,0.0049Dy+0.34≦B / TRE≦0.0049Dy+0.36 Formula 1wherein Dy represents a concentration (at %) of a Dy element, B represents a concentration (at %) of a boron element, and TRE represents a concentration (at %) of all the rare earth elements.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Recording medium, playback device, and integrated circuit
ActiveUS20100245548A1Reducing amount of bufferingSuppression amountTelevision system detailsRecording carrier detailsStreaming dataDepth map
Provided is a recording medium that enables seamless connection between preceding playitems which are stream data arranged prior to a position where a long jump occurs, such as a layer boundary, and succeeding playitems which are stream data arranged subsequent to the position where the long jump occurs. A block exclusively for 2D playback Ln2D is arranged succeeding a 3D extent block in which a depth map data block, a right-view data block, and a left-view data block are arranged in an interleaved manner. A 3D extent block including a block exclusively for 3D playback L3SS is arranged between the block exclusively for 2D playback and a long jump point LB. The block exclusively for 2D playback and the block exclusively for 3D playback are identical in content.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Sound absorbing-insulating structure for vehicles
InactiveUS6524691B2Improve sound absorptionLow costFibreboardWallsCellulose fiberVolumetric Mass Density
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Method and apparatus for gas treatment using non-equilibrium plasma
InactiveUS20050118079A1Low costImprove decomposition efficiencyGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesDecompositionCompound (substance)
A gas treatment method is actualized by arranging a plurality of photocatalyst members each including photocatalyst, solid substance, and catalyst in a region of non-equilibrium plasma, which is produced using a surface discharge electrode and into which a treated gas such as an exhaust gas and a harmful gas including harmful chemical substances is introduced and is then subjected to decomposition. The surface discharge electrode comprises a ground electrode, an insulator encompassing the ground electrode, and a plurality of surface electrodes that are arranged relative to the ground electrode via the insulator, by which the non-equilibrium plasma is produced upon electrification. A gas treatment apparatus is constituted by arranging a plurality of surface discharge electrodes, each having a plurality of through holes penetrating in a thickness direction, between which a plurality of photocatalyst members are arranged.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
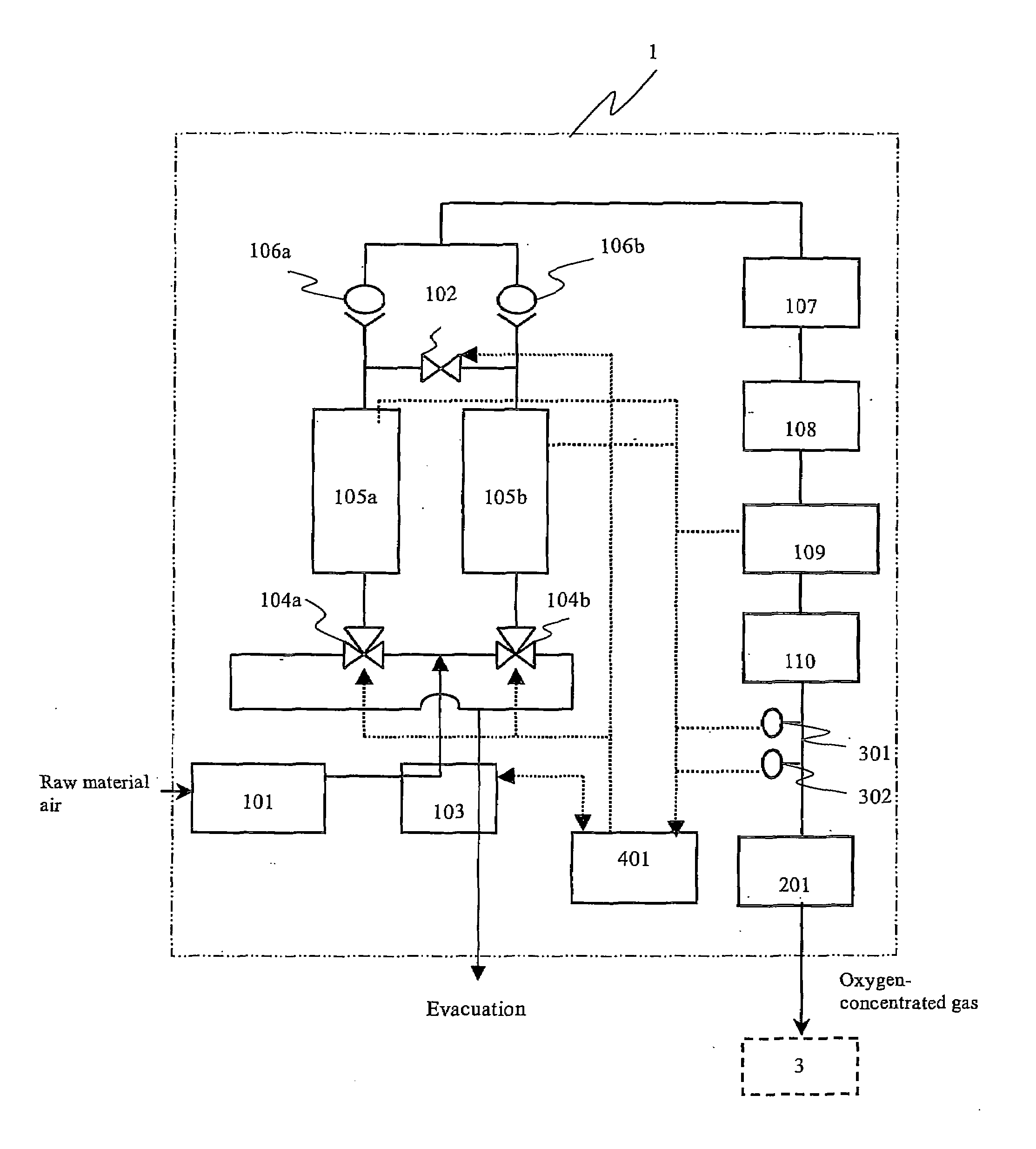
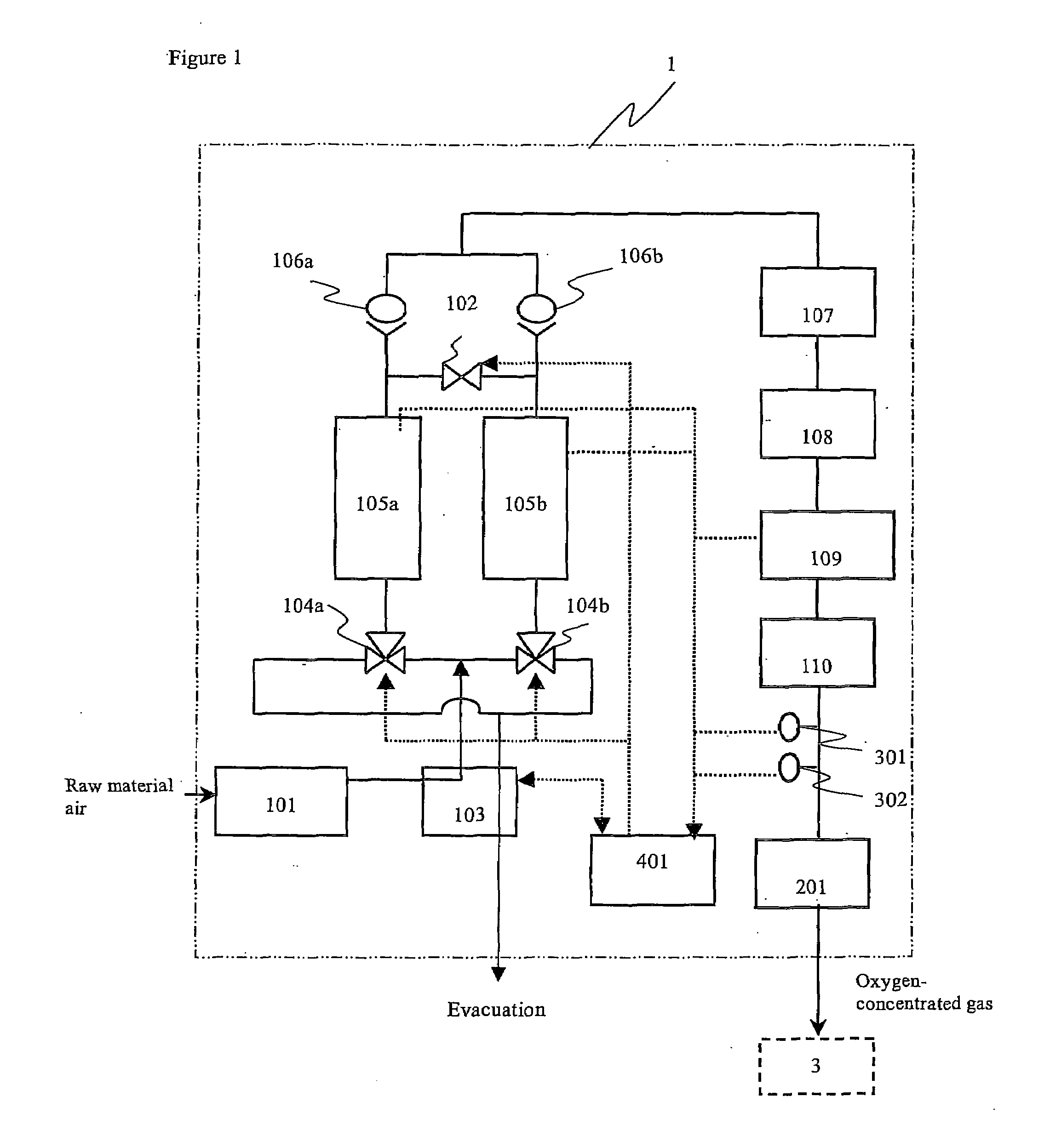
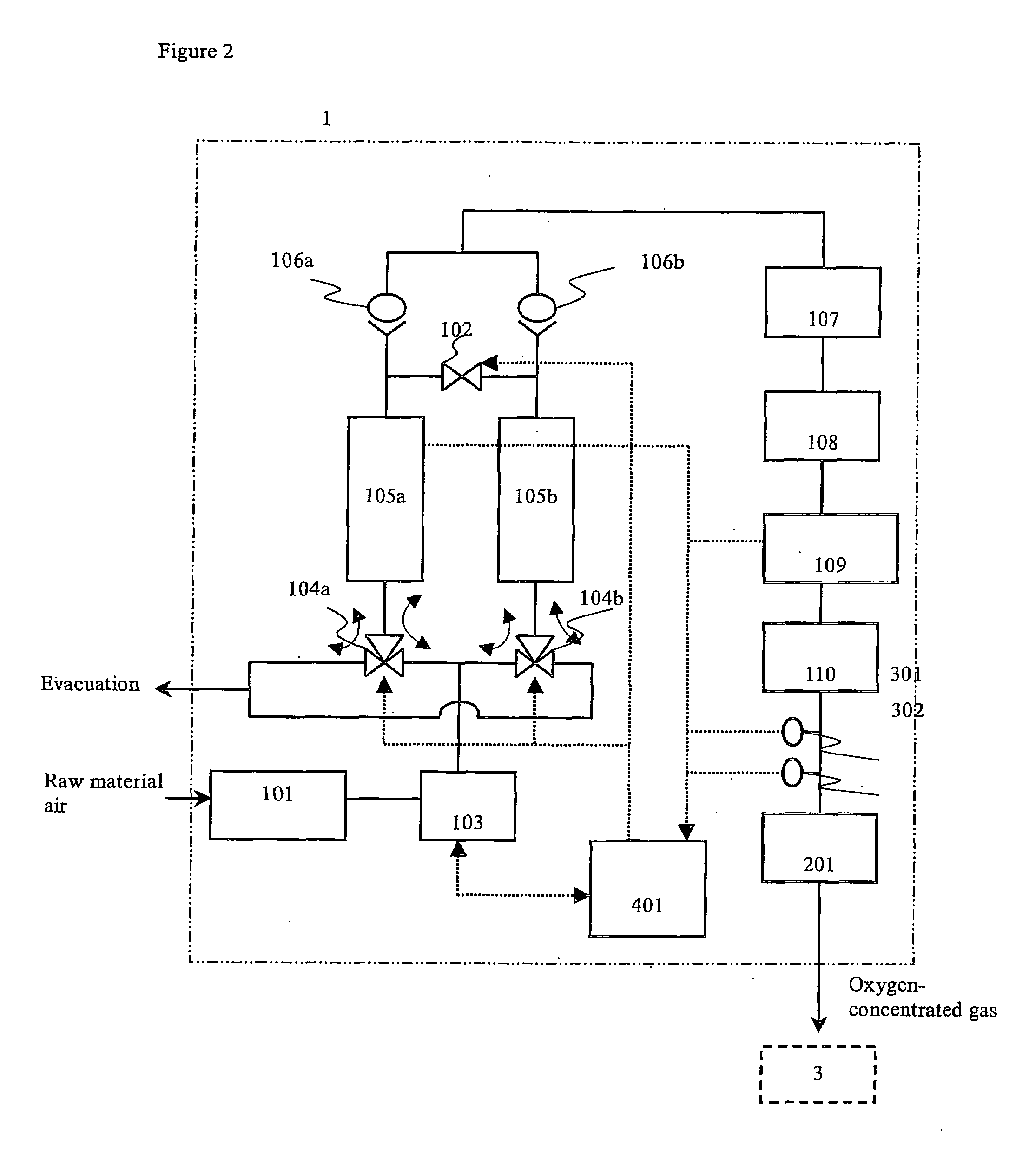
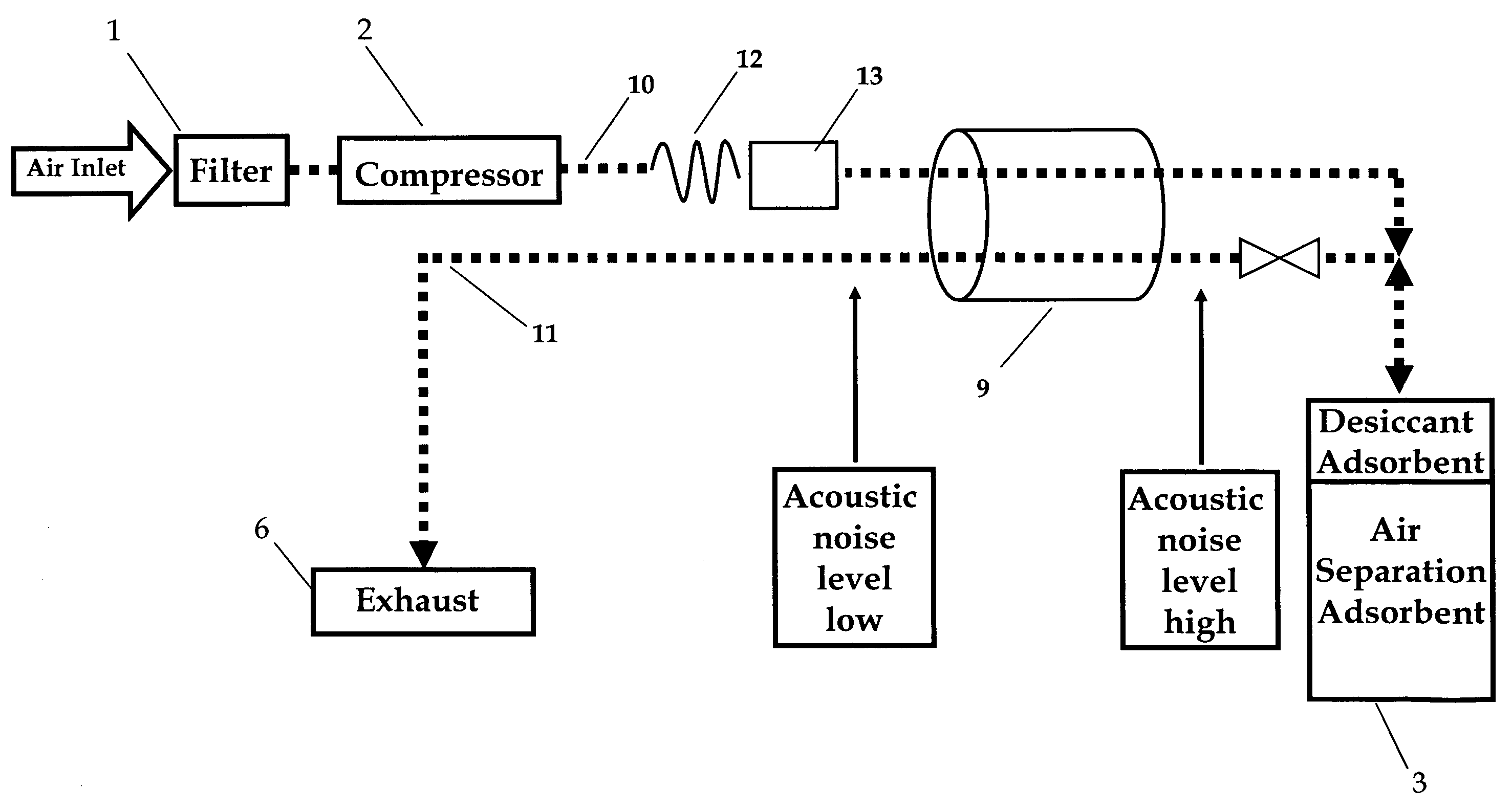
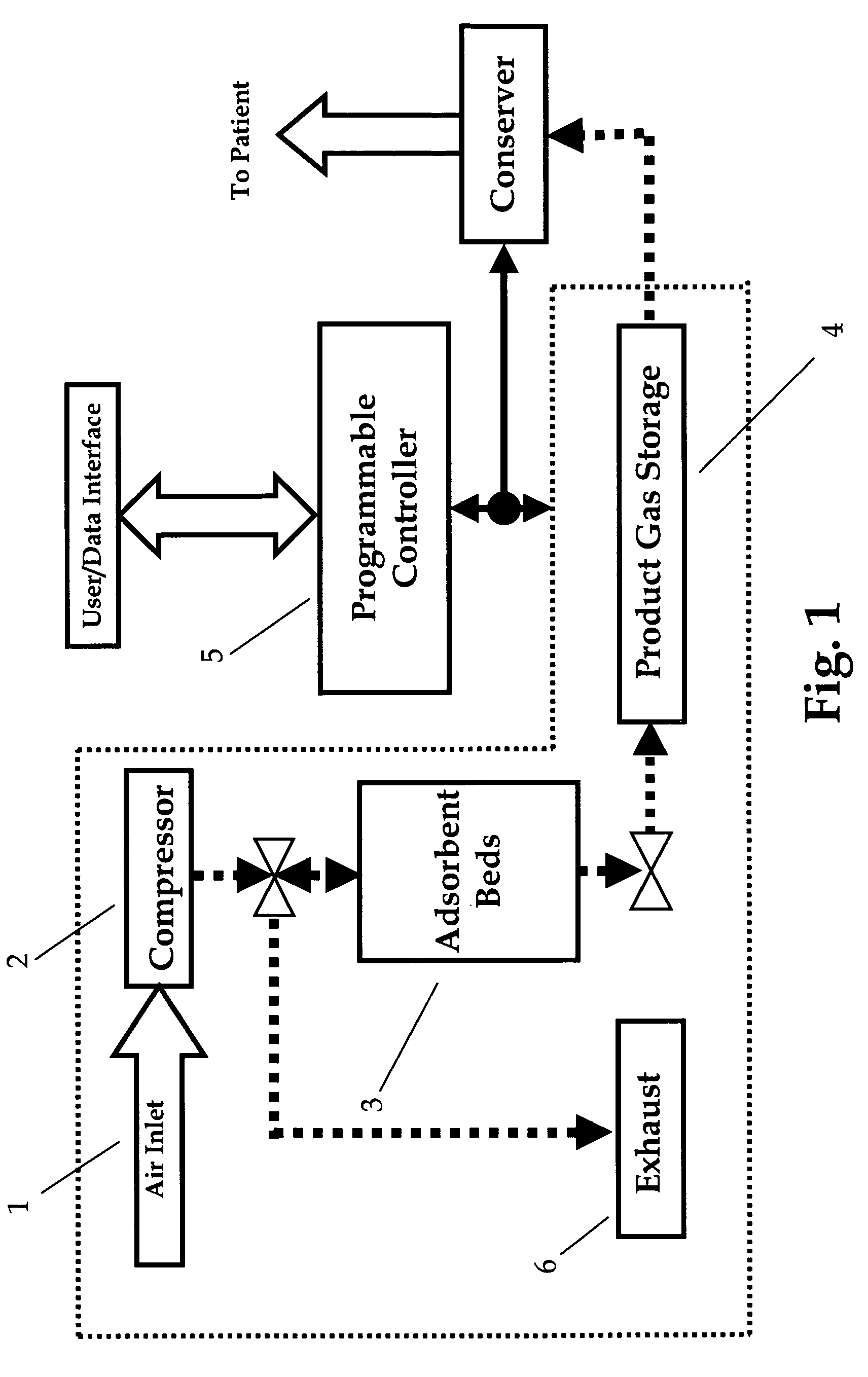
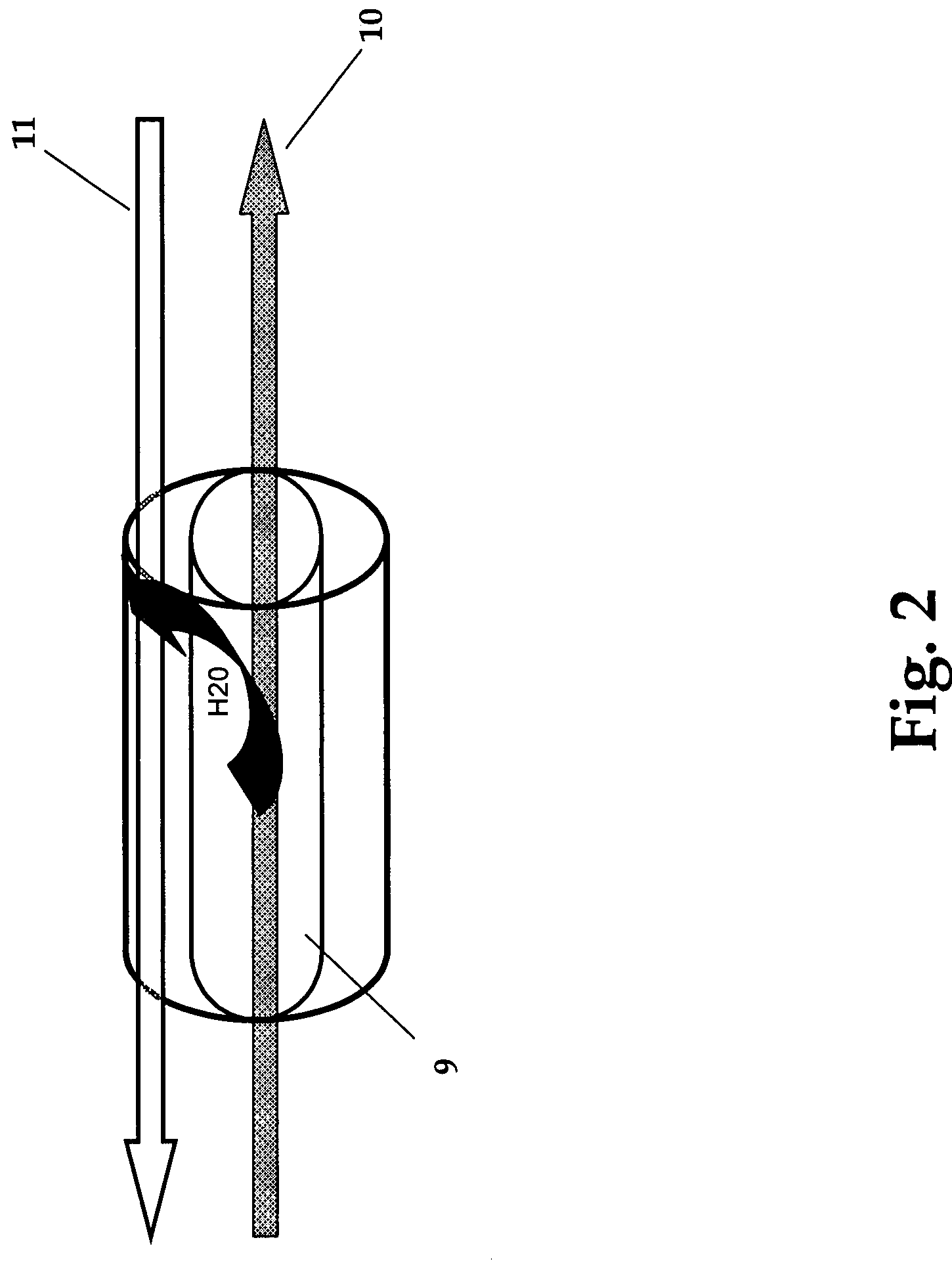
Oxygen concentrator
ActiveUS20100071698A1Increase oxygenIncreased number of spinsRespiratorsGas treatmentDesorptionSorbent
The present invention relates to an oxygen concentrator in which a pulsation detection device for detecting pulsation of oxygen supplied and a control device for controlling an amount of air supplied from a compressor based on the detection results in a pressure swing adsorption-type oxygen concentrator, which is equipped with an adsorption bed filled with an adsorbent capable of selectively adsorbing nitrogen relative to oxygen, the compressor for supplying air to the adsorption bed, a channel switching valve to repeat in a constant timing an adsorption step, in which air is supplied from the compressor to the adsorption bed to isolate concentrated oxygen and a desorption step, in which the adsorption bed is evacuated to regenerate the adsorbent and a flow rate measuring device for determining a supply flow rate of concentrated oxygen produced and an amount of oxygen produced is controlled by a feedback with a flow rate sensor by itself after paying attention to variation of a product flow rate caused by suppressing an amount of oxygen produced, thereby realizing an apparatus to satisfy secondary performance such as miniaturization, low power consumption and silencing.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
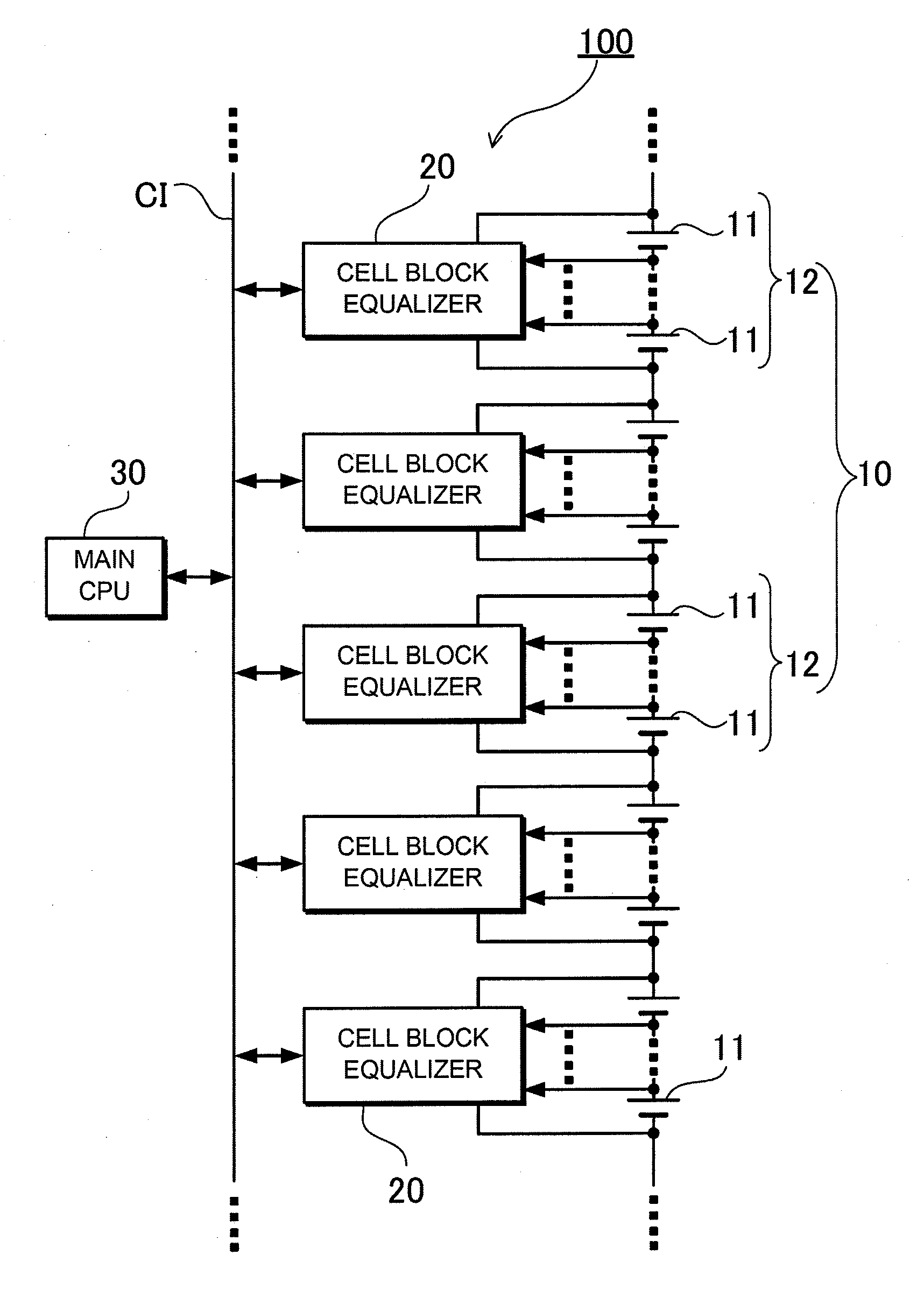
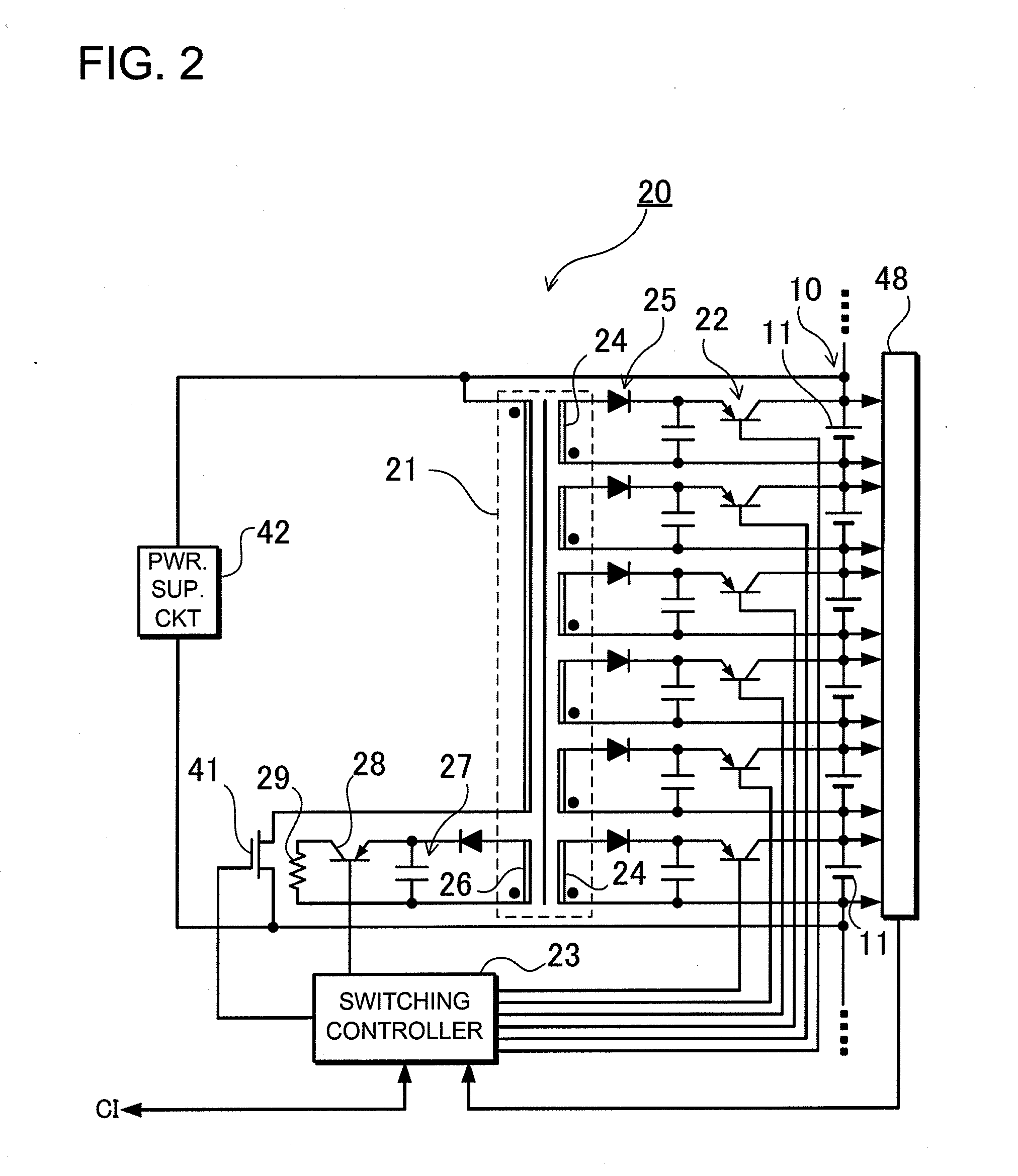
Power supply device capable of equalizing electrical properties of batteries
ActiveUS20110234164A1Maintain balanceReduce the amount requiredCharge equalisation circuitSecondary cellsEngineeringControl switch
A transformer 21 includes charging secondary winding lines 24 that can charge batteries 11 composing a corresponding cell block, and a discharging secondary winding line 26 that can discharge the corresponding cell block. Each of the charging secondary winding lines 24 is connected to corresponding one of the batteries 11 through corresponding one of secondary-side rectification output circuits 25 and corresponding one of output control switches 22. The discharging secondary winding line 26 is connected to a block discharging circuit through a block discharging switch 28. A switching control circuit 23 controls the block discharging switch 28. The switching control circuit 23 controls the output control switches 22 so that the electrical properties of the batteries 11 in the cell block are equalized. In addition, the switching control circuits 23 control the block discharging switches 28 so that the electrical properties of the batteries among the cell blocks are equalized.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
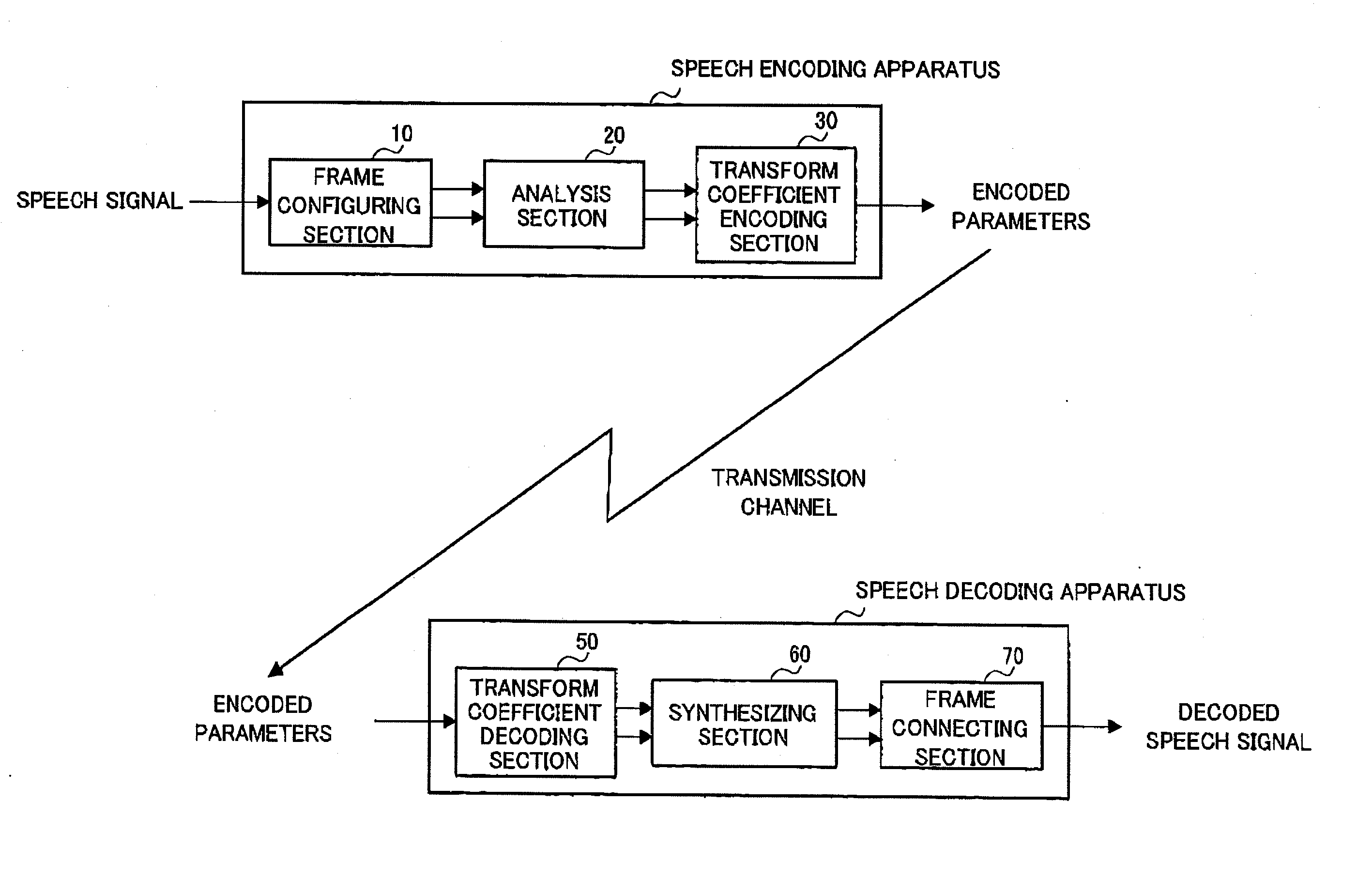
Sound Encoding Device And Sound Encoding Method
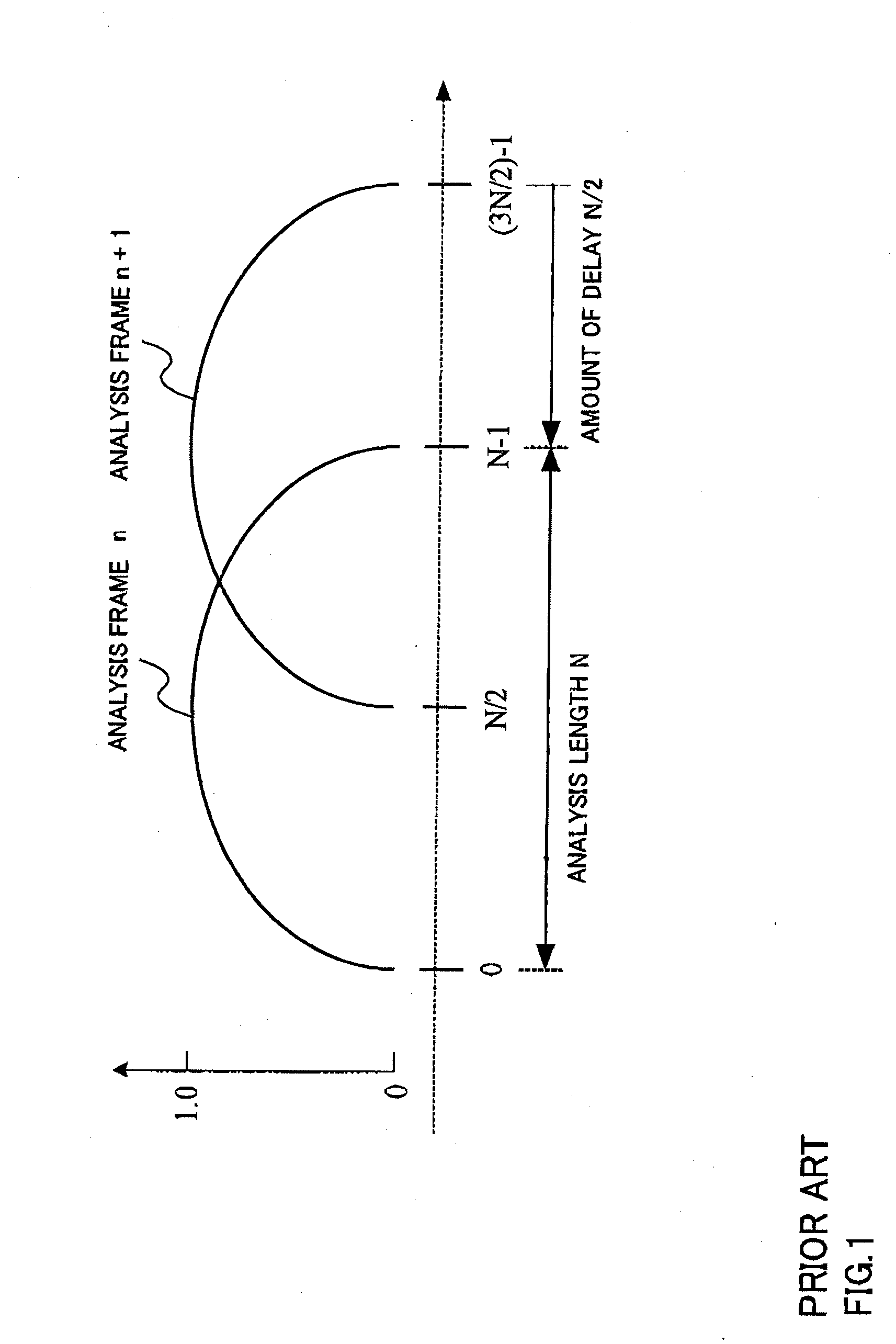
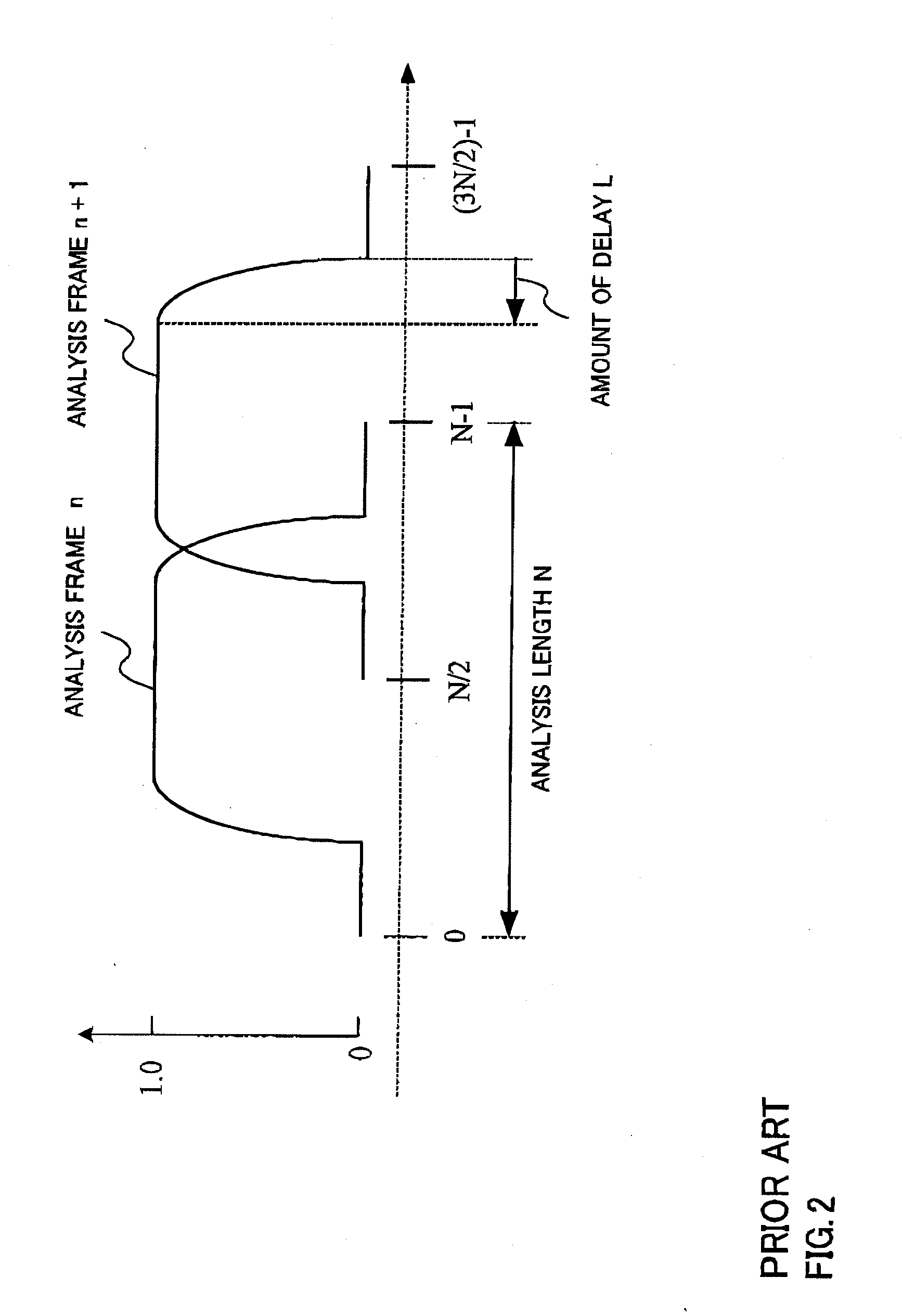
ActiveUS20080065373A1Reduce distortion problemsSuppress amount of delaySpeech analysisCode conversionComputer scienceDistortion
A sound encoding device enabling the amount of delay to be kept small and the distortion between frames to be mitigated. In the sound encoding device, a window multiplication part (211) of a long analysis section (21) multiplies a long analysis frame signal of analysis length M1 by an analysis window, the resultant signal multiplied by the analysis window is outputted to an MDCT section (212), and the MDCT section (212) performs MDCT of the input signal to obtain the transform coefficients of the long analysis frame and outputs it to a transform coefficient encoding section (30). The window multiplication part (221) of a short analysis section (22) multiplies a short analysis frame signal of analysis length M2 (M2<M1) by an analysis window and the resultant signal multiplied by the analysis window is outputted to the MDCT section (222). The MDCT section (222) performs MDCT of the input signal to obtain the transform coefficients of the short analysis frame and outputs it to the transform coefficient encoding section (30). A transform coefficient encoding section (30) encodes these transform coefficients and outputs them.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
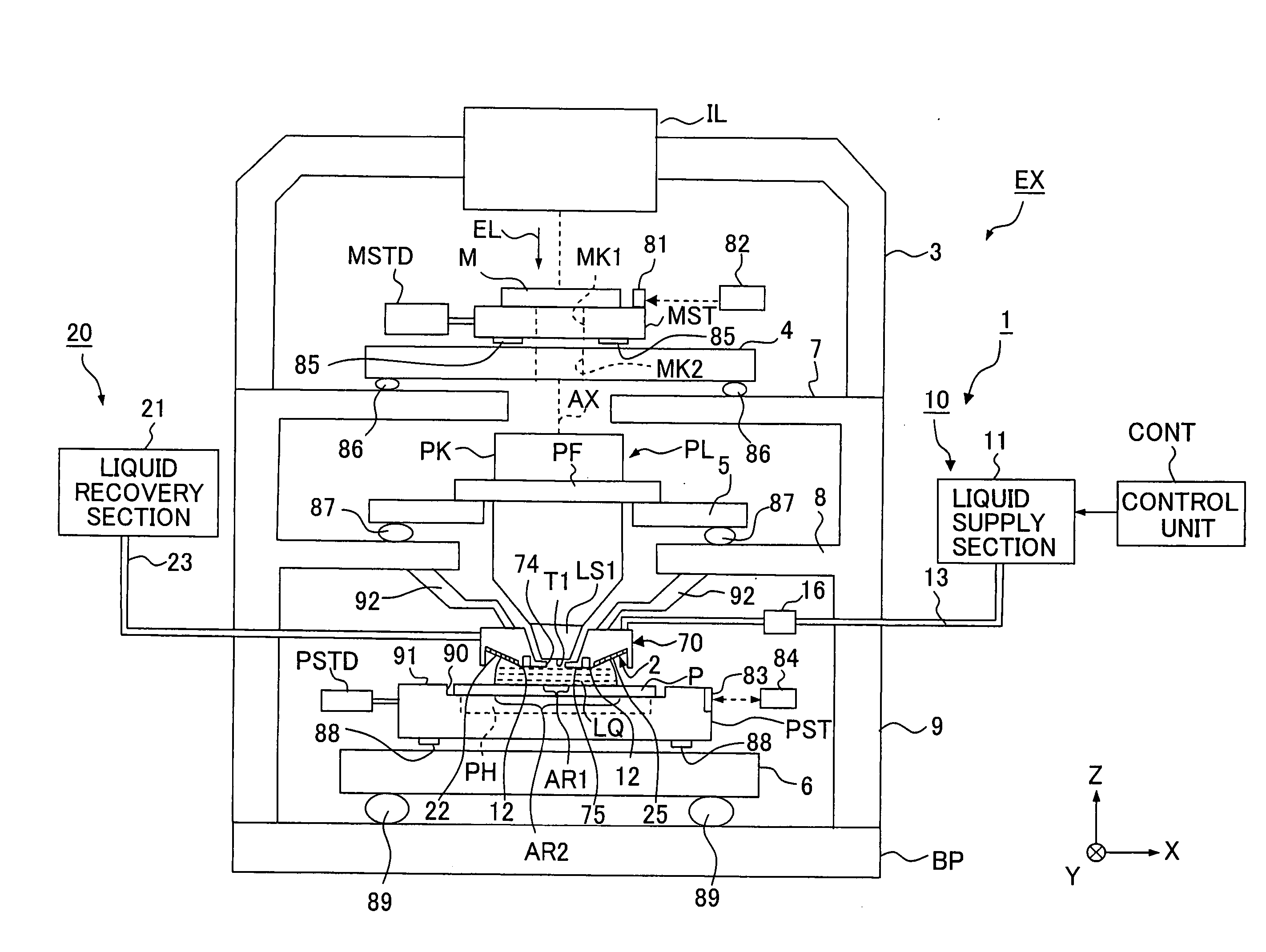
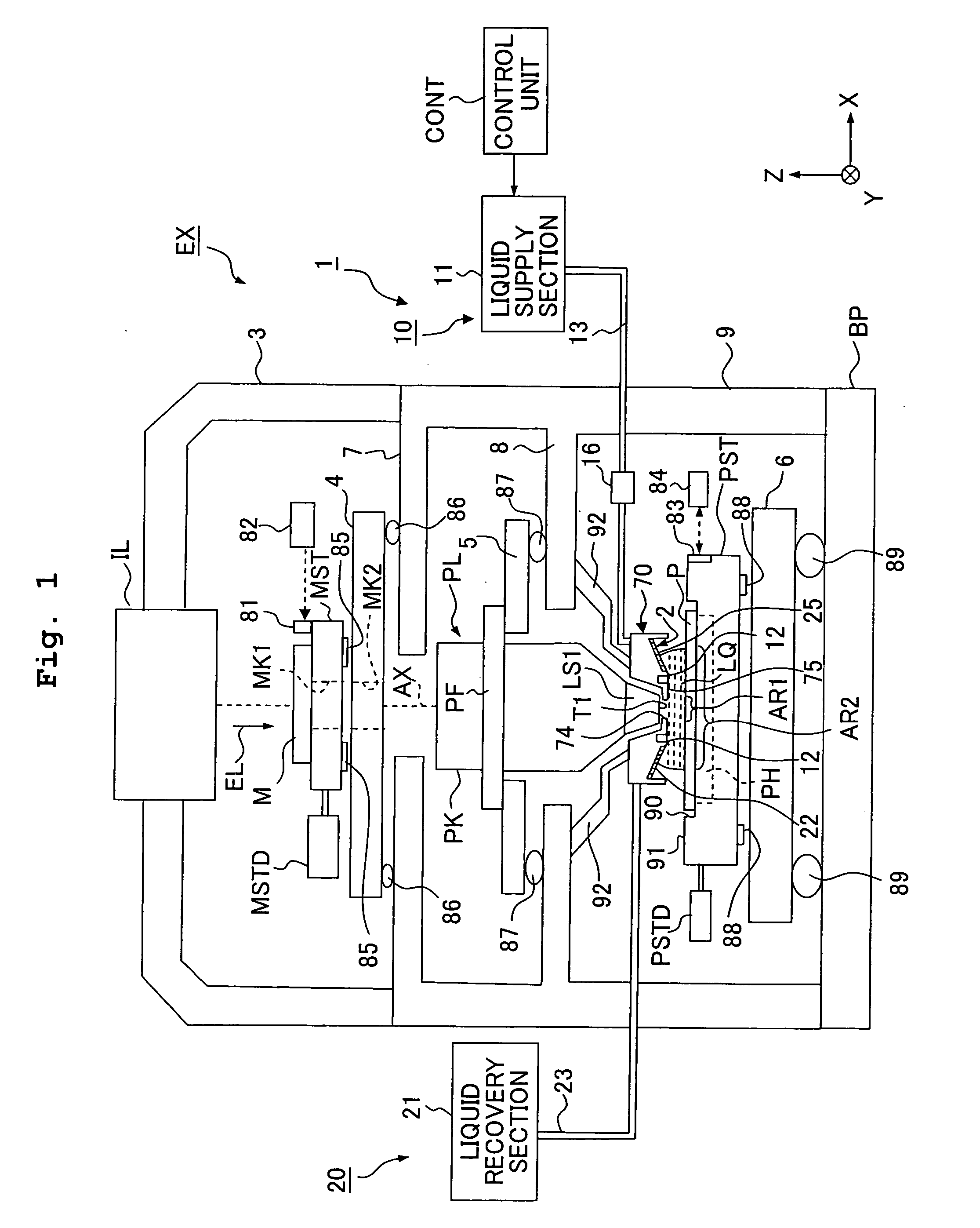
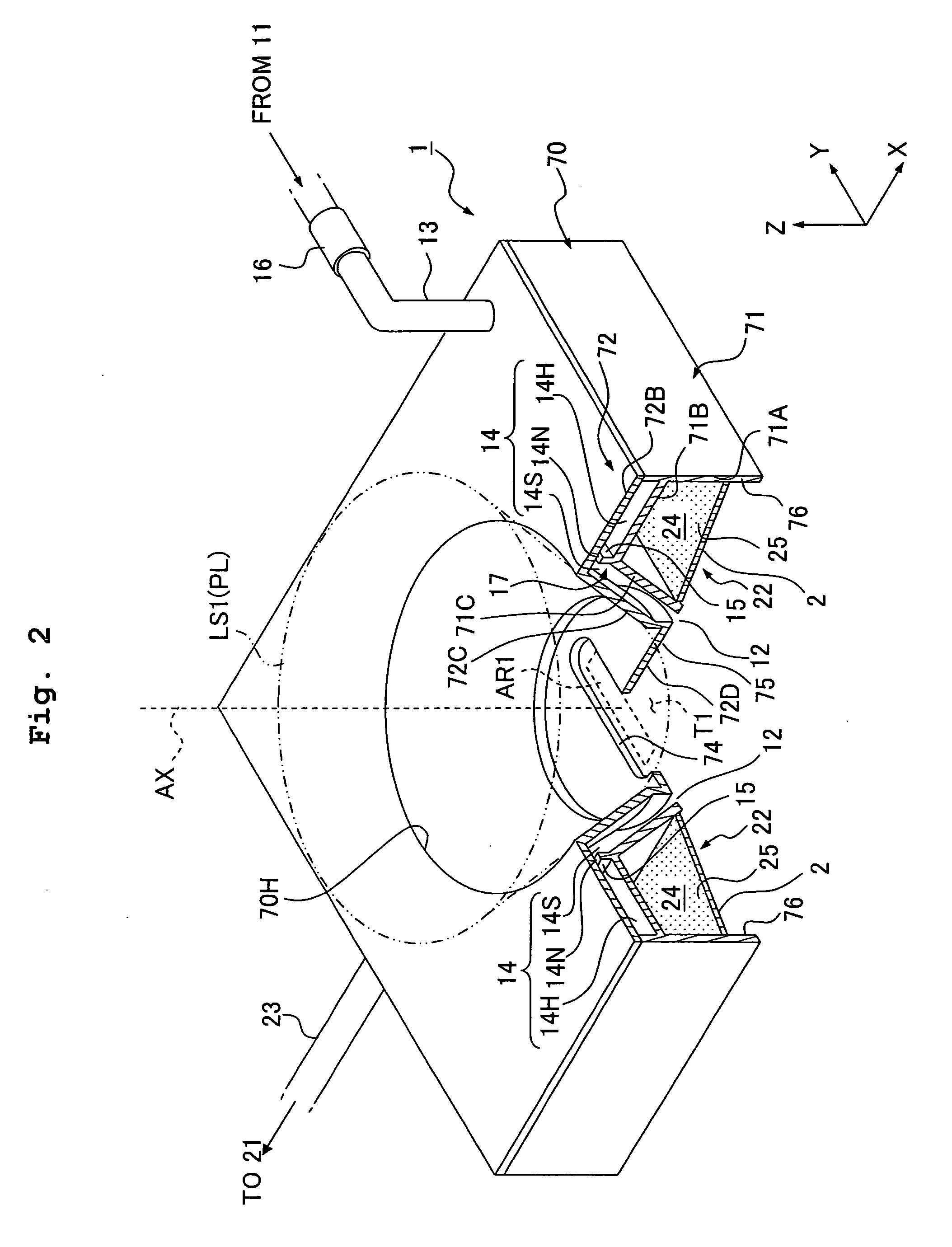
Exposure Apparatus, Exposure Method, and Method for Producing Device
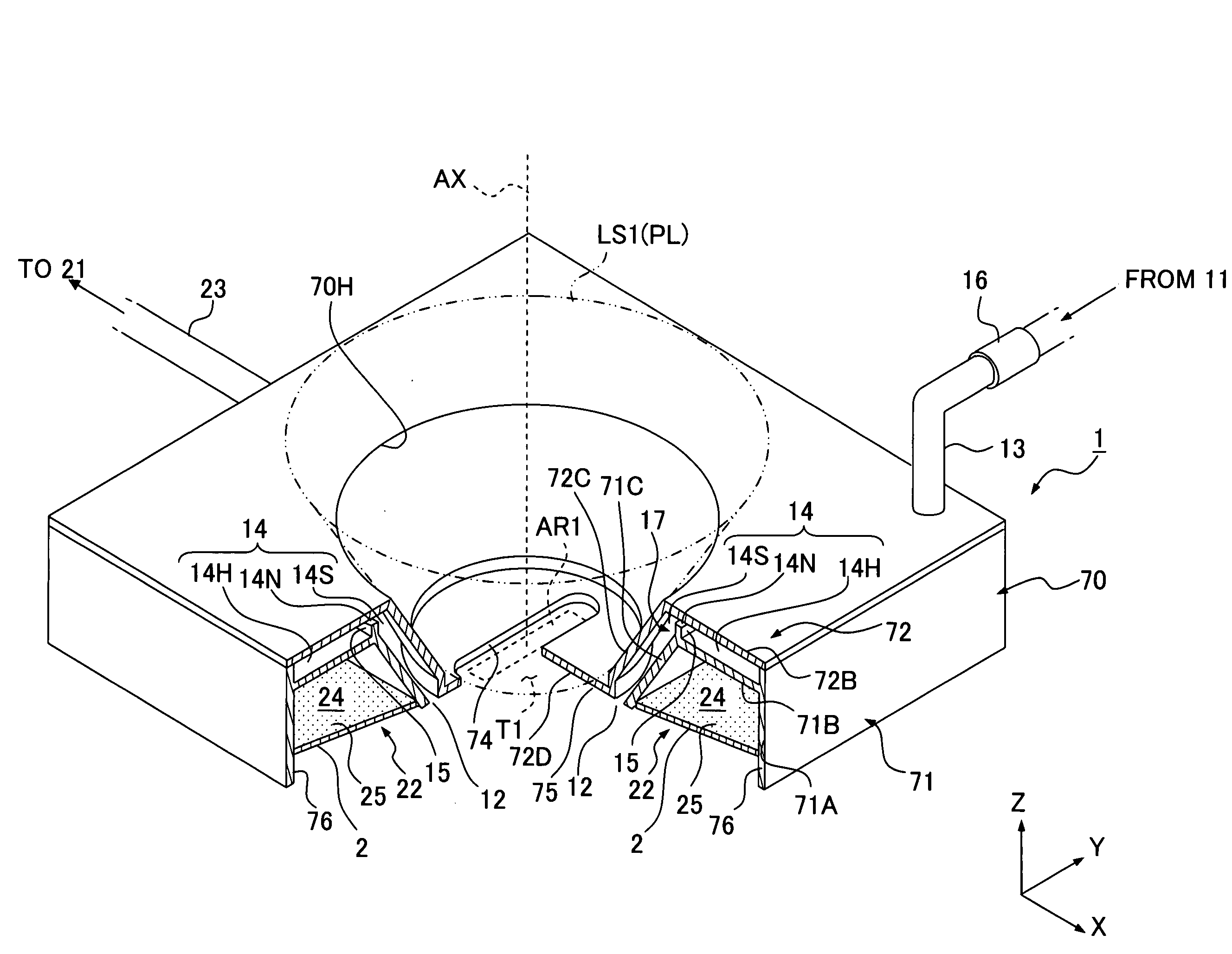
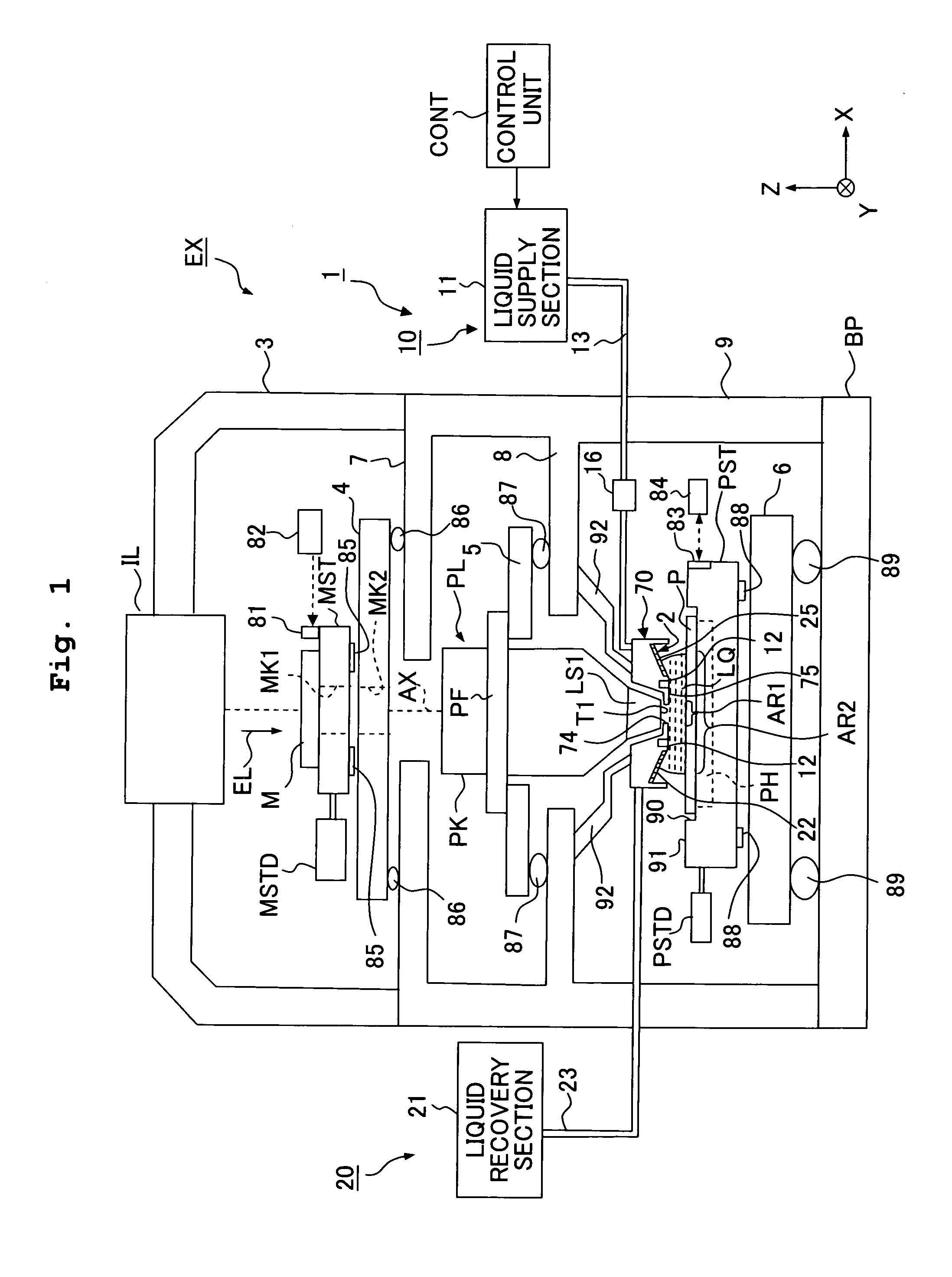
InactiveUS20080266533A1Suppressing amount of movementSuppress large change of shapeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageBiomedical engineering
Exposure apparatus exposes a substrate by irradiating the substrate with exposure light via a projection optical system and a liquid. The exposure apparatus is provided with a liquid immersion mechanism for supplying the liquid and recovering the liquid. The liquid immersion mechanism has an inclined surface, which is opposite to a surface of the substrate and is inclined with respect to the surface of the substrate, and a liquid recovering port of the liquid immersion mechanism is formed in the inclined surface. A flat portion is provided between the substrate and the projection optical system. A liquid immersion area can be maintained to be small.
Owner:NIKON CORP +1
Control apparatus of internal combustion engine
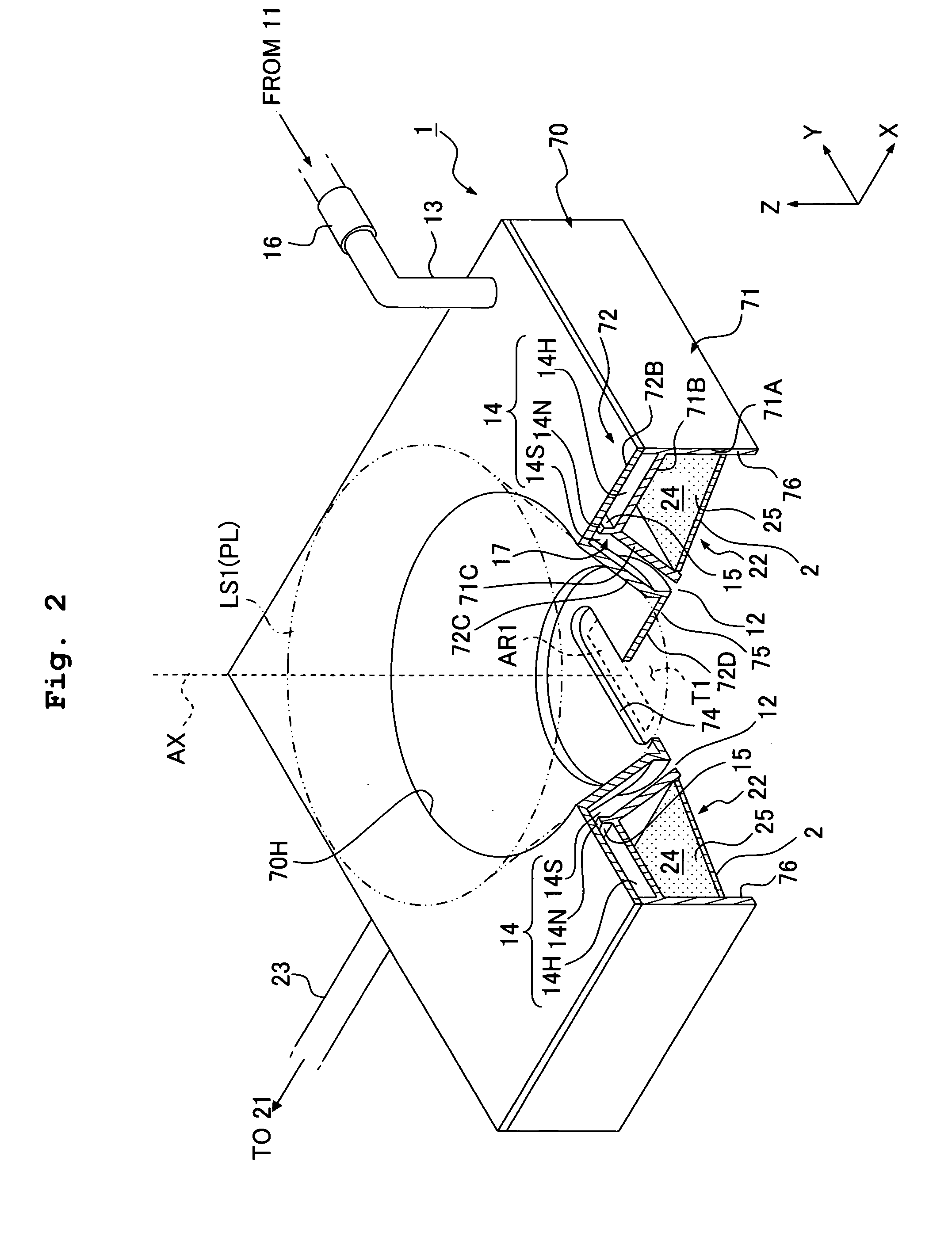
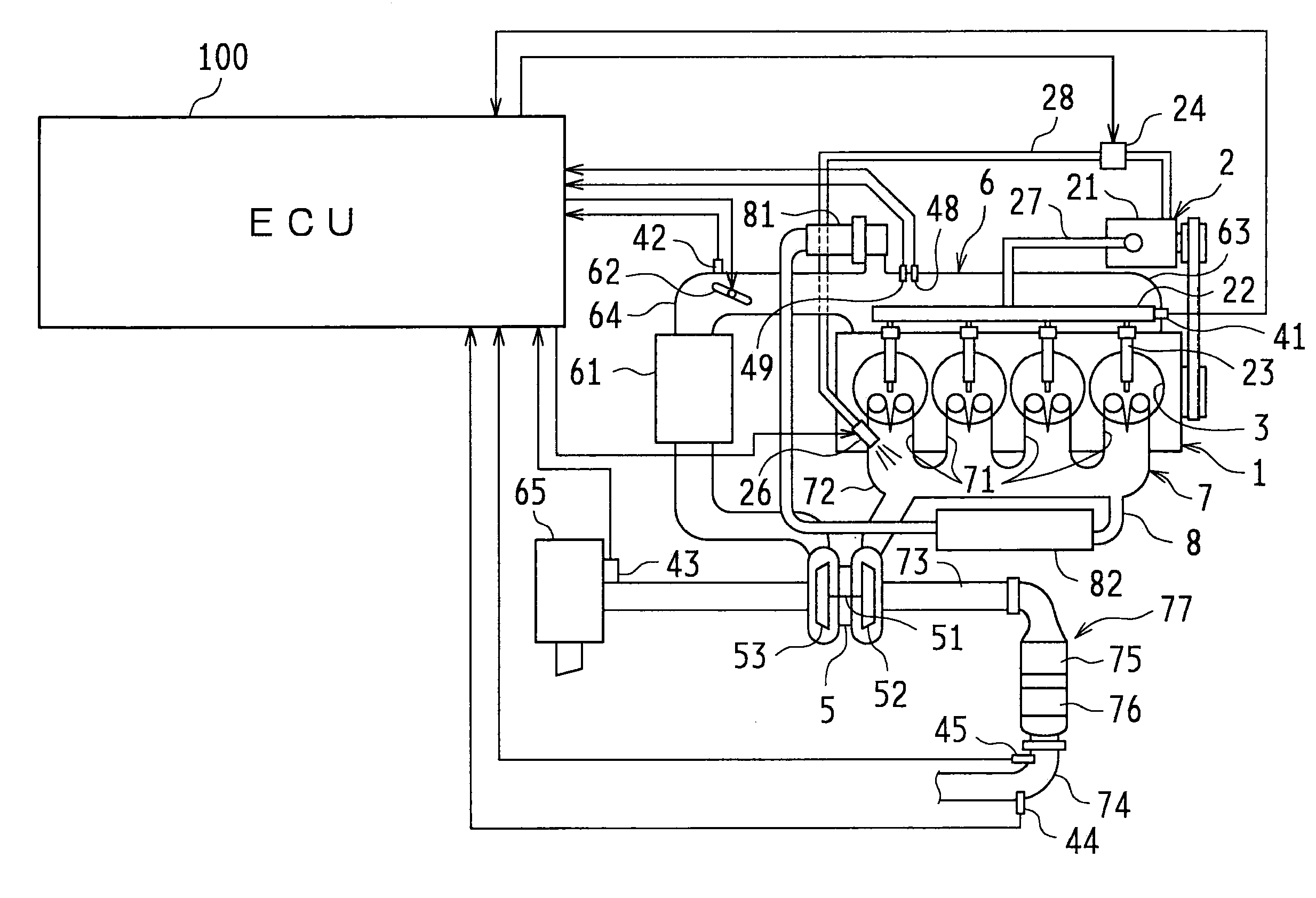
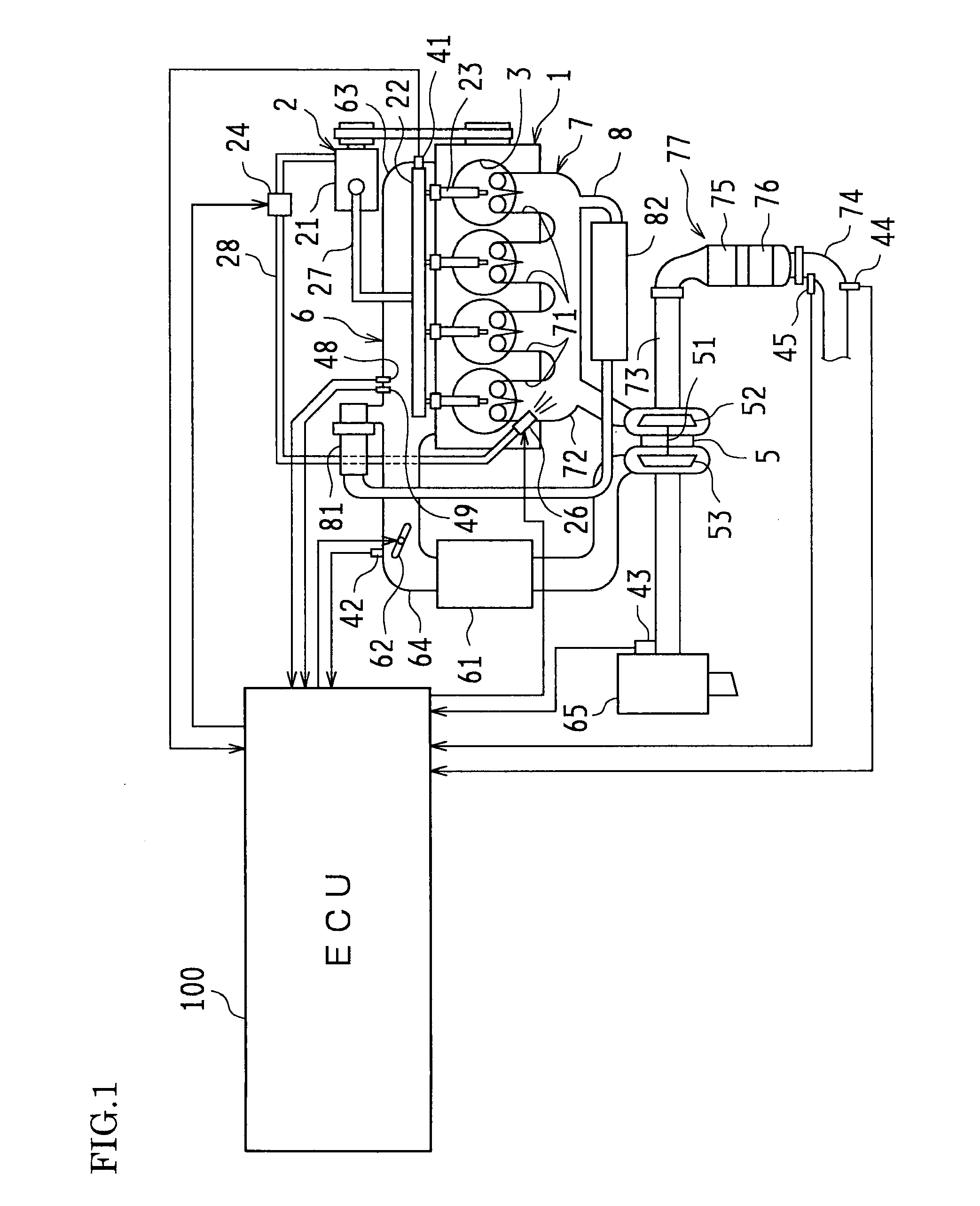
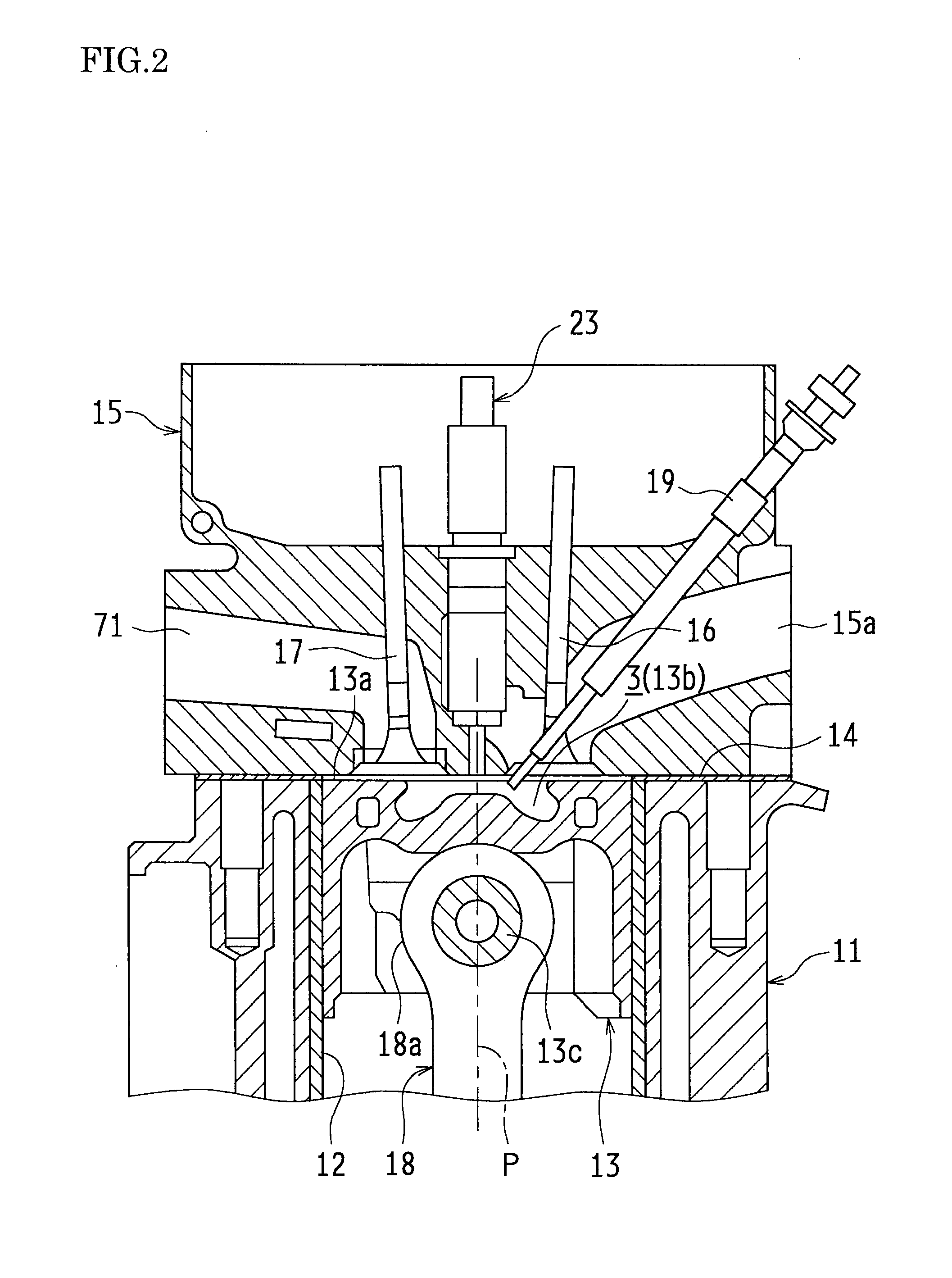
InactiveUS20120016571A1Suppress amount of NOx generatedSuppress amount of smokeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesLow loadEngineering
A series of combustion forms including initial low-temperature combustion, premixed combustion, and diffusive combustion are performed when an engine operates under a low load and a medium load. The initial low-temperature combustion is carried out by performing a small-amount injection while performing an operation for lowering the encounter rate between oxygen and a fuel spray in a cylinder, and thereby the heat generation rate is kept low and the amount of NOx generated is suppressed. The premixed combustion is carried out as fuel receives heat in the initial low-temperature combustion, and the amount of smoke generated is suppressed. The diffusive combustion is accomplished as fuel travels through the combustion field of the premixed combustion, and by controlling the fuel injection timing thereof, it is possible to suitably control the timing at which the heat generation rate reaches its maximum in the aforementioned series of combustion. Thereby, it is possible to concurrently suppress the amount of NOx generated, suppress the amount of smoke generated, and secure the required torque.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Gas concentrator with improved water rejection capability
Owner:INOGEN SA
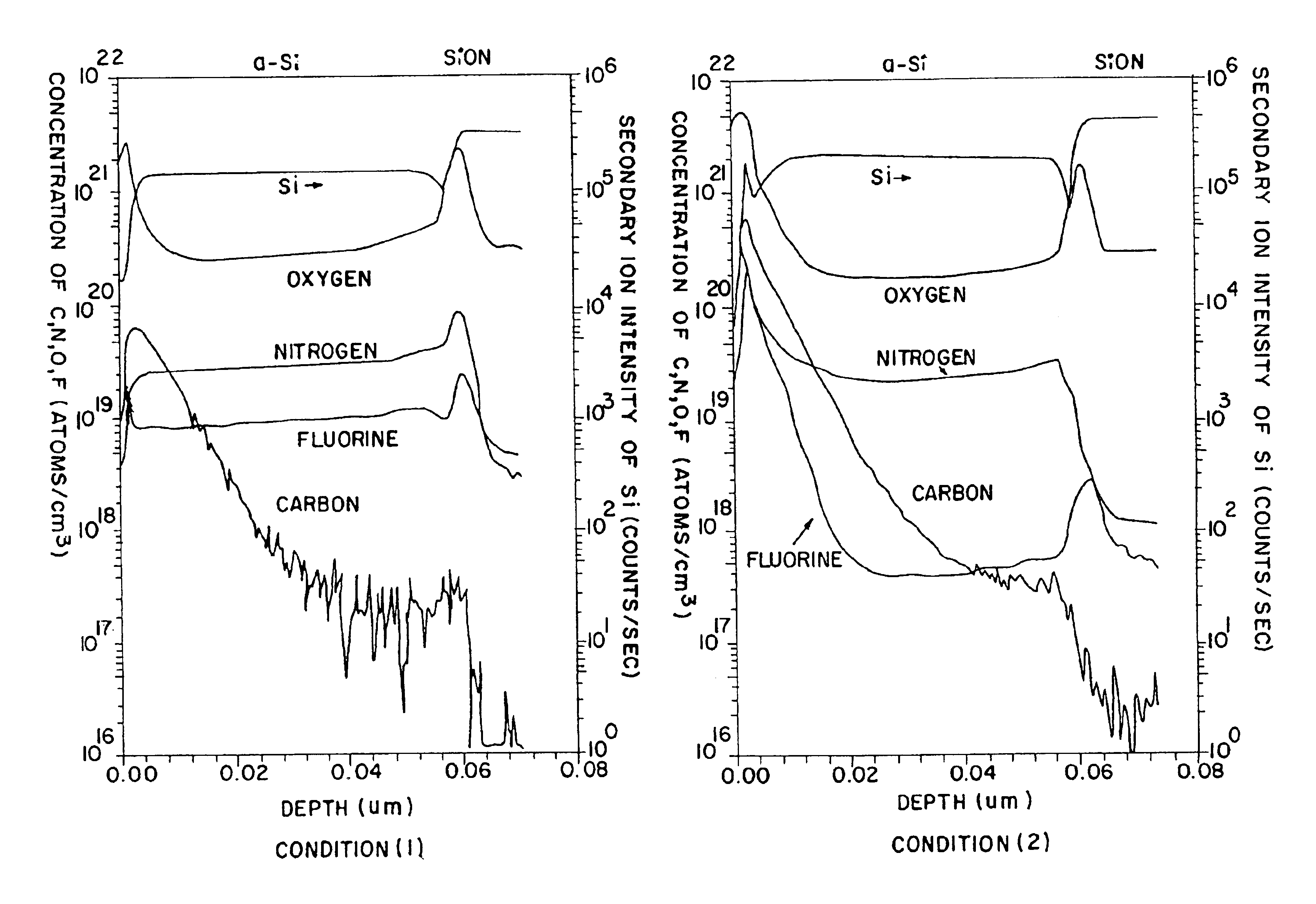
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device with fluorine concentration
InactiveUS6875674B2Reduce processing timeSuppression amountTransistorSolid-state devicesHydrogenSilanes
At present, a forming process of a base film through an amorphous silicon film is conducted in respective film forming chambers in order to obtain satisfactory films. When continuous formation of the base film through the amorphous silicon film is performed in a single film forming chamber with the above film formation condition, crystallization is not sufficiently attained in a crystallization process. By forming the amorphous silicon film using silane gas diluted with hydrogen, crystallization is sufficiently attained in the crystallization process even with the continuous formation of the base film through the amorphous silicon film in the single film forming chamber.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
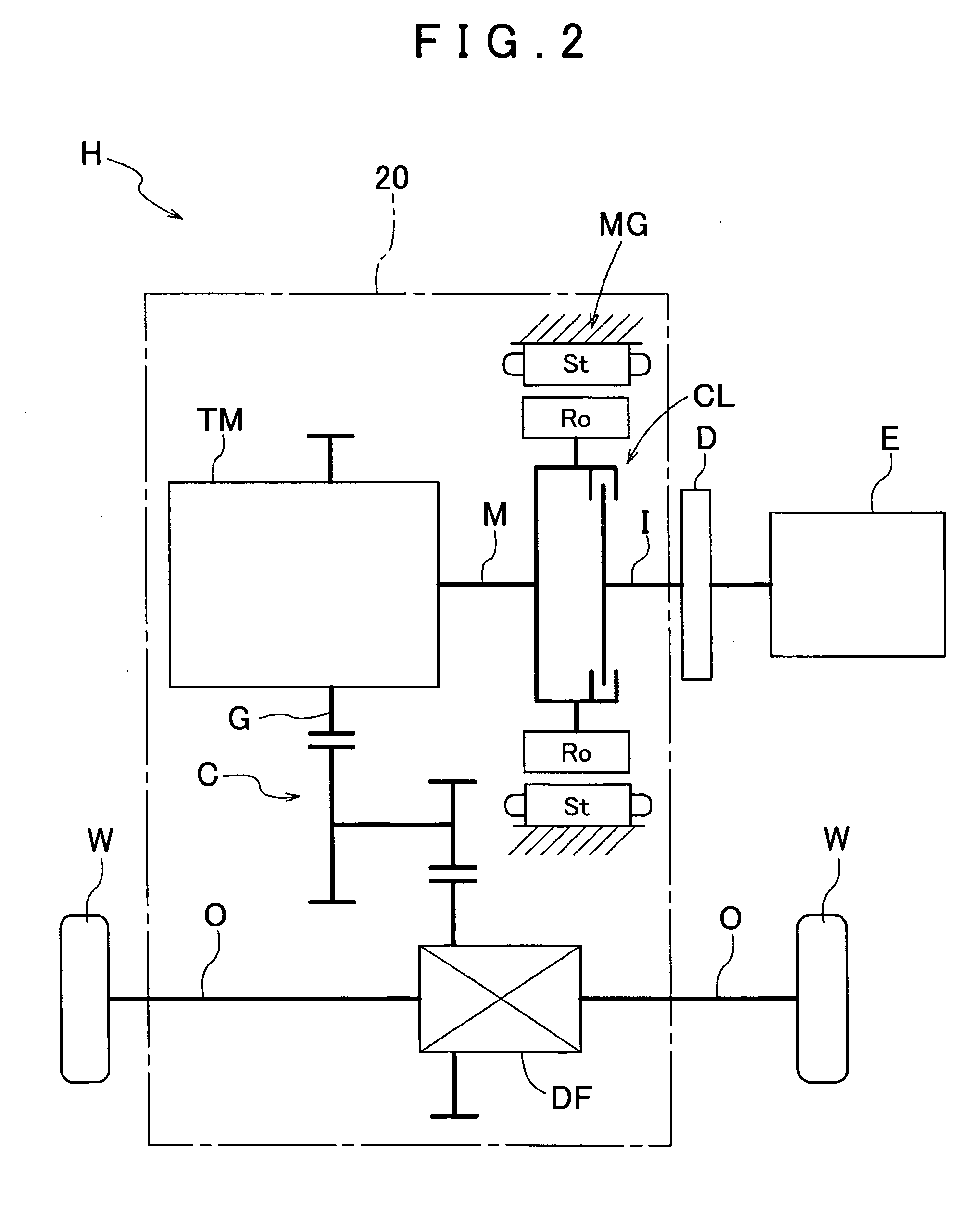
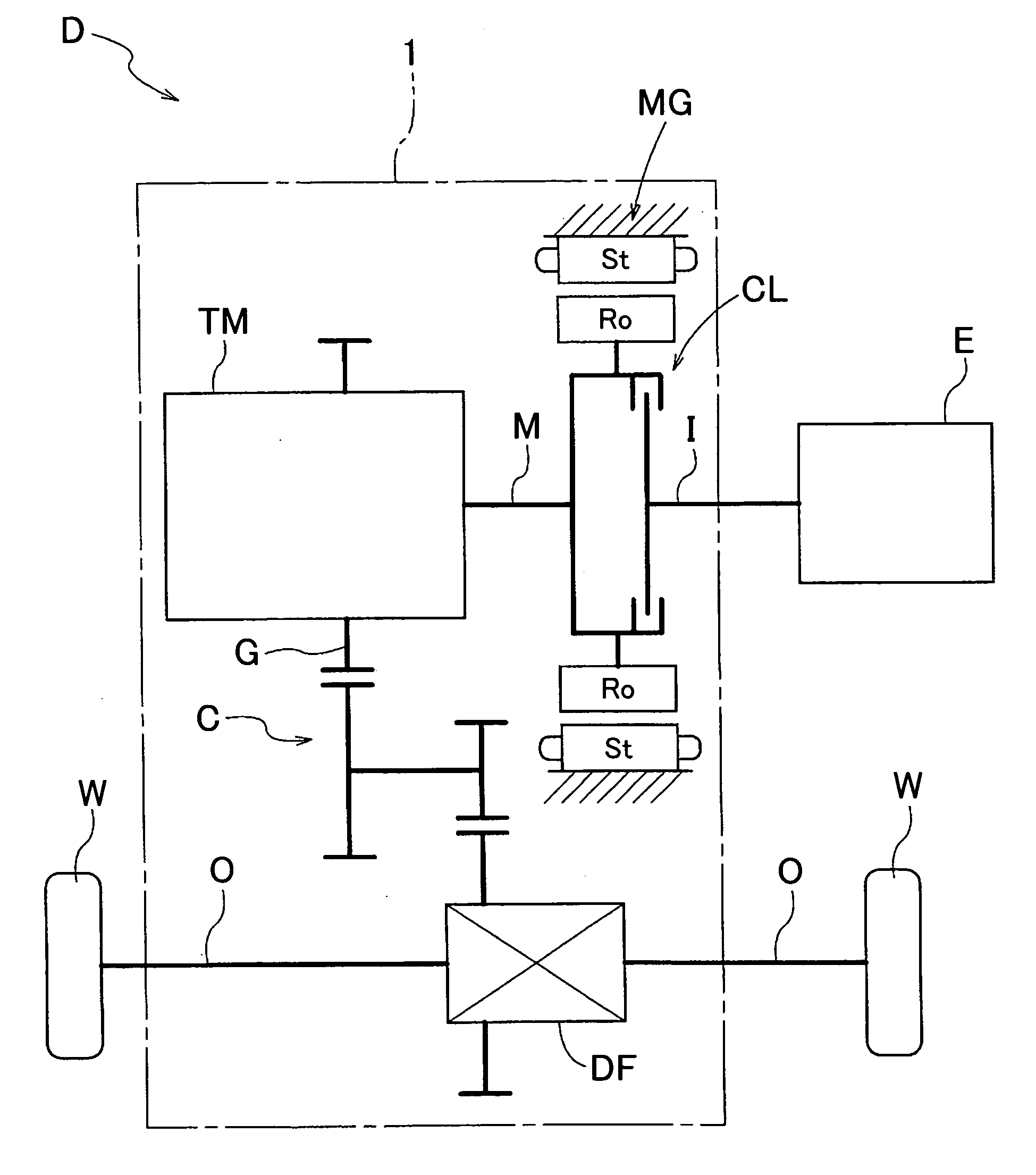
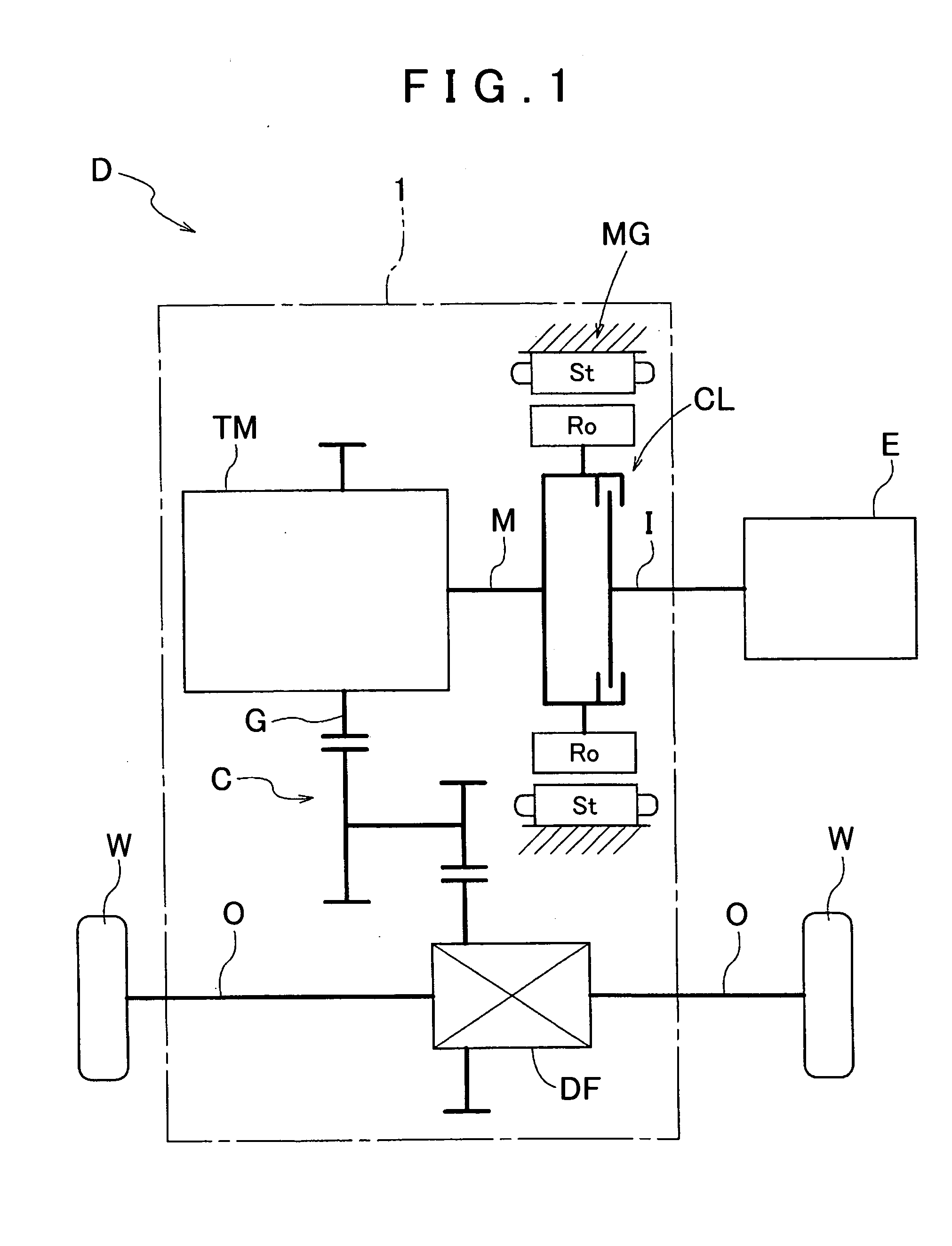
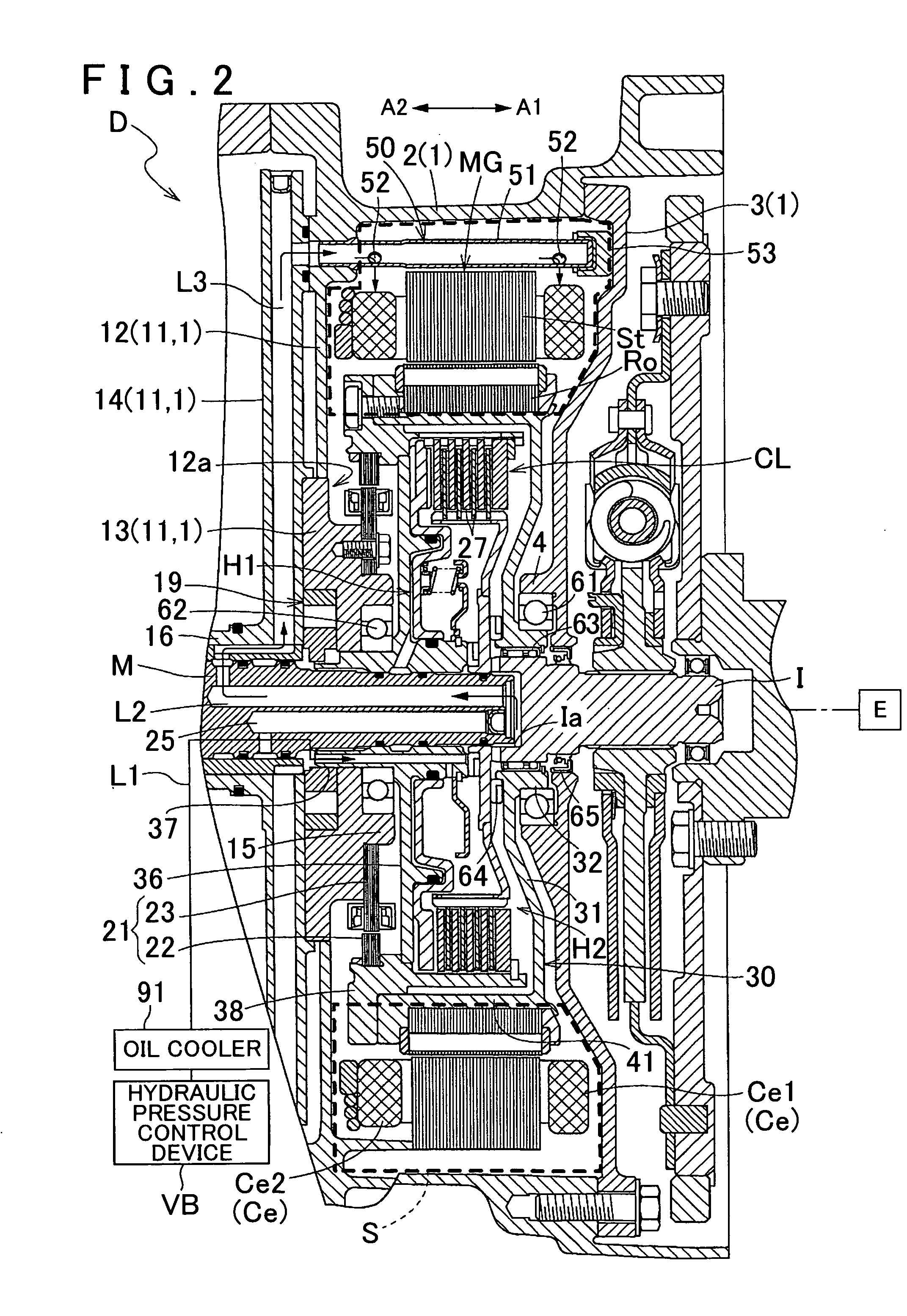
Vehicle drive device
InactiveUS20120080248A1Improve cooling effectSmall amountGas pressure propulsion mountingPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsElectric machineInternal combustion engine
A vehicle drive device configured with an input member drivably coupled to an internal combustion engine. The drive device is also configured with an output member drivably coupled to wheels, a friction engagement device that selectively drivably couples the input member and the output member to each other, and a rotary electric machine provided on a power transfer path connecting between the input member and the output member. On the vehicle drive device, a housing oil chamber houses at least friction members of the friction engagement device and is filled with oil, a housing space houses the rotary electric machine, and there exists a first oil passage through which oil is supplied to the housing oil chamber. There is also a second oil passage through which oil is discharged from the housing oil chamber and a third oil passage through which oil is supplied to the housing space.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Exposure apparatus, exposure method, and method for producing device
InactiveUS20070139628A1Suppressing amount of movementSuppress large change of shapePhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingBiomedical engineeringEngineering
Exposure apparatus exposes a substrate by irradiating the substrate with exposure light via a projection optical system and a liquid. The exposure apparatus is provided with a liquid immersion mechanism for supplying the liquid and recovering the liquid. The liquid immersion mechanism has an inclined surface, which is opposite to a surface of the substrate and is inclined with respect to the surface of the substrate, and a liquid recovering port of the liquid immersion mechanism is formed in the inclined surface. A flat portion is provided between the substrate and the projection optical system. A liquid immersion area can be maintained to be small.
Owner:NIKON CORP +1
Prepreg and printed wiring board using thin quartz glass cloth
ActiveUS20090266591A1Low dielectric constantLoss tangentSynthetic resin layered productsPrinted circuit aspectsGlass fiberDielectric loss
It is an object of the present invention to provide a high frequency-capable printed wiring board material reduced in the dielectric loss tangent, weight, thickness and cost without compromising the workability, and provide electronic components using the same. The present invention provides a prepreg obtained by using a quartz glass cloth composed of low-density quartz glass fibers as a base material and impregnating the cloth with a thermosetting resin composition having a low dielectric loss tangent, and provides electronic components using a cured product of the prepreg as an insulating layer.
Owner:RESONAC CORP
Vehicle Drive Device
InactiveUS20120080286A1Accurate detectionLow costFluid actuated clutchesPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsElectric machineInternal combustion engine
A vehicle drive device configured with an input member drivably coupled to an internal combustion engine, an output member drivably coupled to wheels, and a friction engagement device that selectively drivably couples the input member and the output member to each other. A rotary electric machine is connected between the input member and the output member. A housing oil chamber houses at least friction members of the friction engagement device and is filled with oil. A housing space houses the rotary electric machine, a first oil passage through which oil is supplied to the housing oil chamber, a second oil passage through which oil is discharged from the housing oil chamber; and a third oil passage through which oil discharged from the second oil passage is supplied to the housing space.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
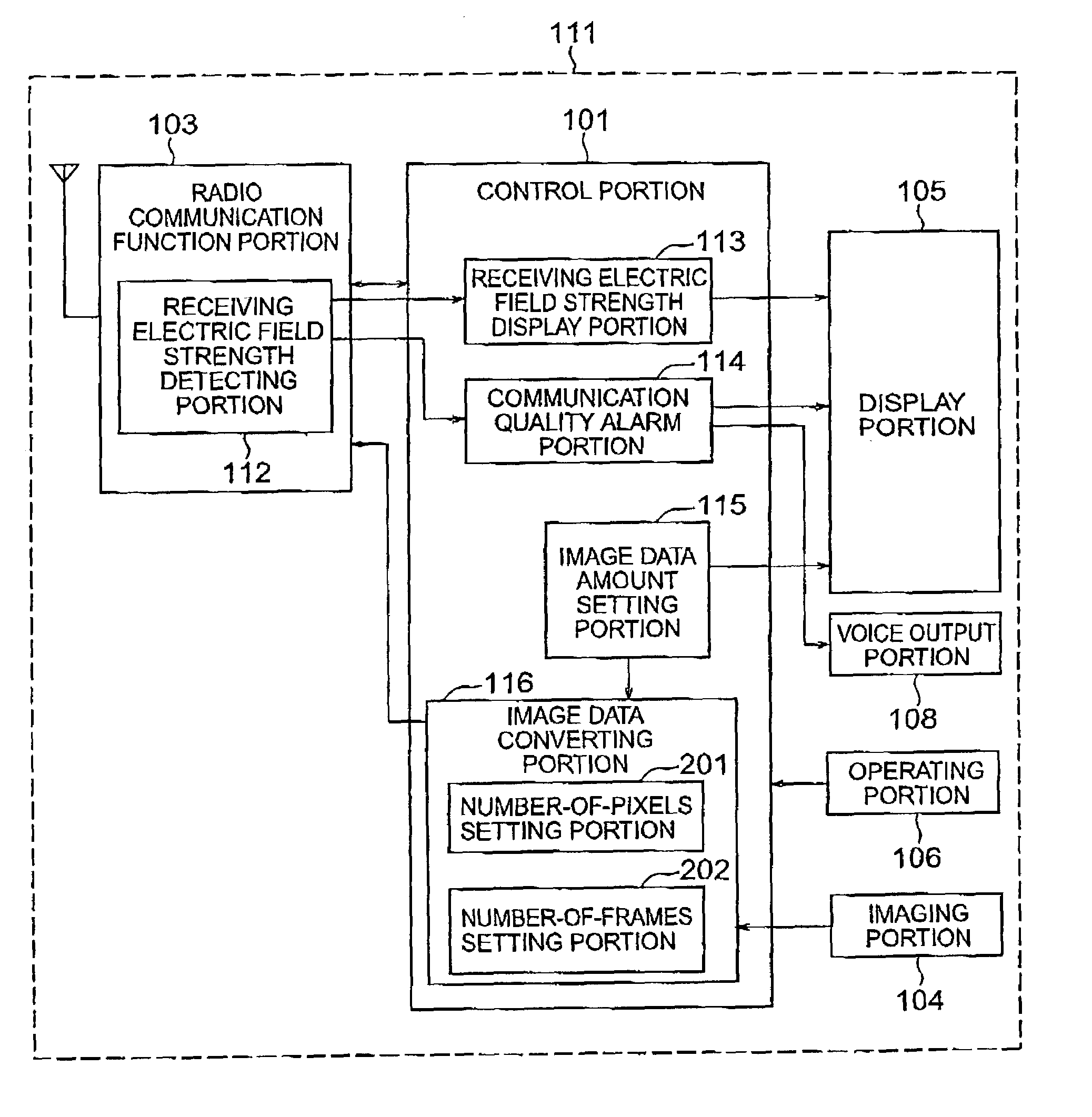
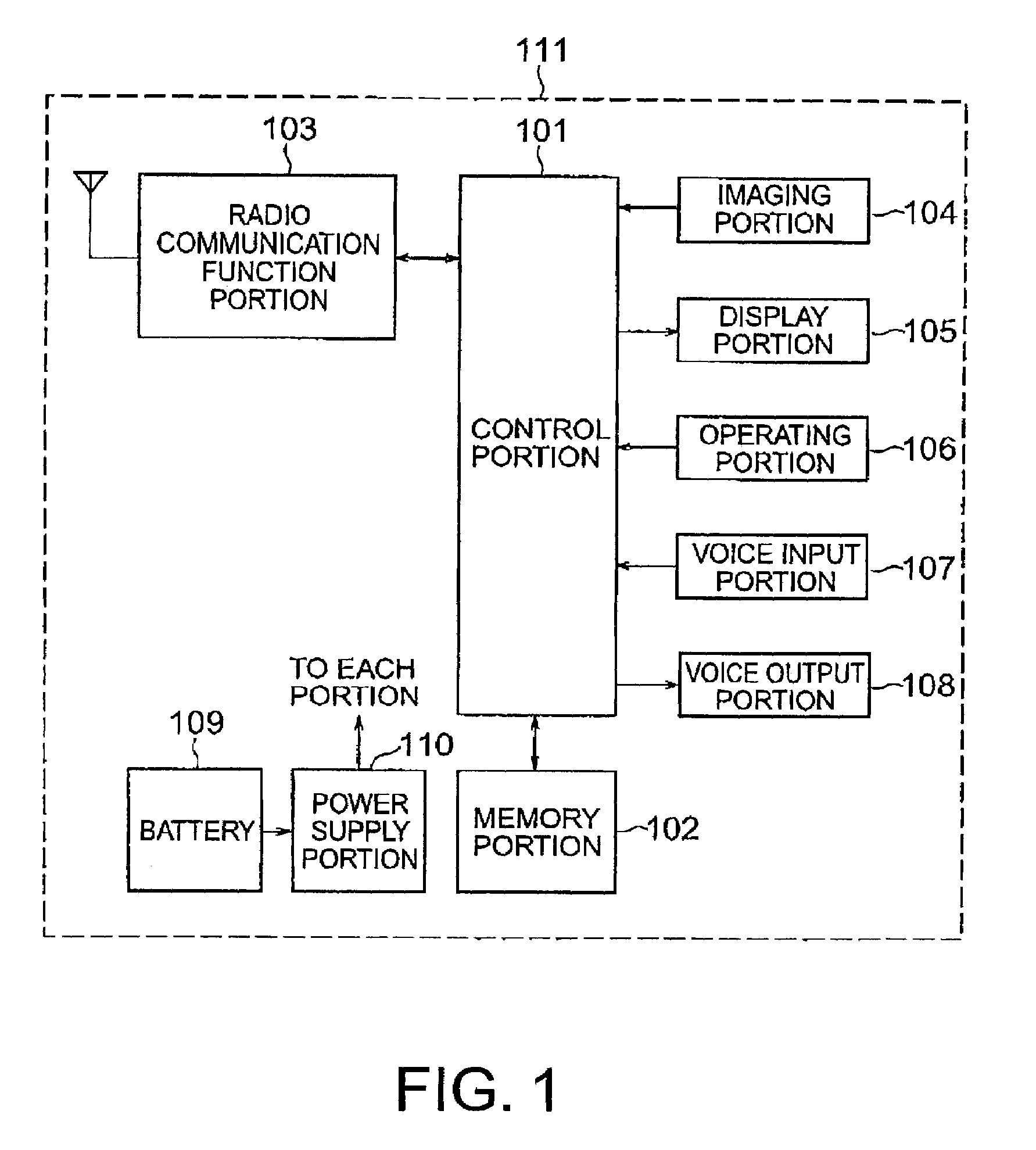
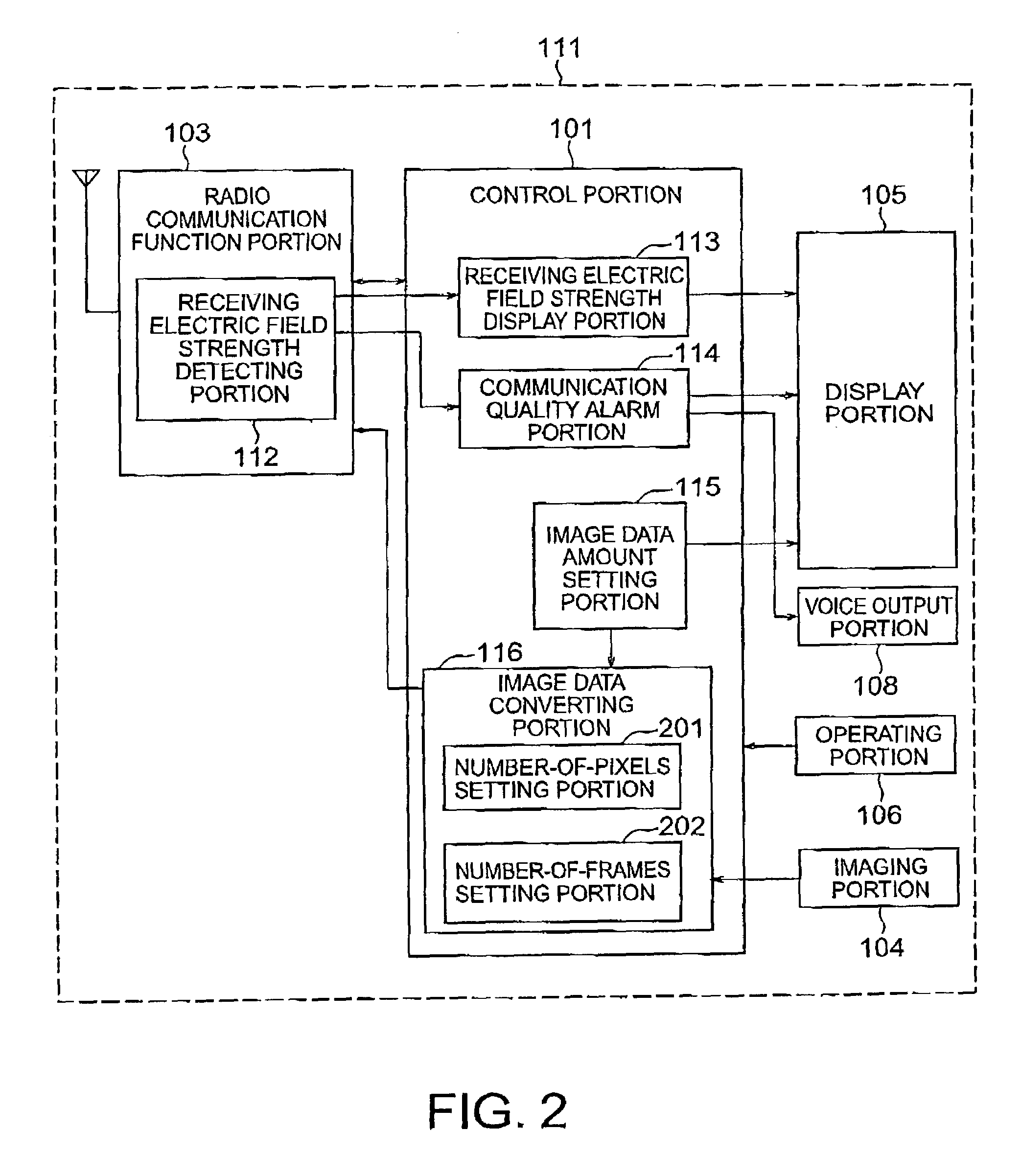
Mobile telephone terminal apparatus having television telephone function
InactiveUS7202885B2Maintaining communicationKeep in touchSubstation equipmentTwo-way working systemsTelephone terminalMobile phone
A mobile telephone terminal apparatus for exchanging images. Predetermined physical amounts of an internal portion and a peripheral portion of the mobile telephone terminal apparatus are measured, and a data amount of an imaged image is changed based on the result. After that, the image data is sent to the other communicating party.
Owner:NEC CORP
Magnetic heads for perpendicular recording and magnetic recording disk apparatus using the same
InactiveUS6891697B2Suppression amountHigh track densityManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsLeading edgeTrailing edge
A magnetic head having at least a main pole having a profile on a magnetic head air bearing surface composed of a first portion having a length in a cross-track direction which continuously increases from a leading edge to a trailing edge, and a second portion located on the side of the trailing edge of the first portion. A length of the second portion in the cross-track direction at the trailing edge is substantially equal to a length in the cross-track direction at the point of contact between the first and second portions. A rate of change in the length of the second portion in the cross-track direction from the leading edge to the trailing edge is different from a rate of increase in the length of the first portion in the cross-track direction.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH JAPAN LTD
Method and apparatus for purification of argon
InactiveUS6123909ASimple stepsReduce energy consumptionCombination devicesSolidificationHydrogenDistillation
PCT No. PCT / JP98 / 03977 Sec. 371 Date May 4, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date May 4, 1999 PCT Filed Sep. 4, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO99 / 11437 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 11, 1999A process for purifying argon to obtain a high-purity argon from argon gas containing at least nitrogen, carbon monoxide, oxygen, and methane, including a first step of adding air or oxygen to the argon gas in an amount sufficient to oxidize the contained carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide in the presence of a catalyst while maintaining a temperature sufficient to oxidize the contained carbon monoxide without substantially oxidizing the methane, a second step of adding hydrogen into the argon gas obtained in the first step and reacting the contained oxygen with the hydrogen into water in the presence of a catalyst, a third step of removing the carbon dioxide and the water from the argon gas obtained in the second step by use of an adsorbent, and a fourth step of cooling the argon gas obtained in the third step, introducing the argon thus cooled into a distillation column and performing distillation by use of a reflux containing argon as a main component to remove nitrogen, hydrogen, and methane, thereby recovering a high purity argon gas.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE JAPAN LTD
Gas component detection device
ActiveUS20140070101A1Suppressing decrease amountSuppression amountSolid-state devicesColor/spectral properties measurementsInfraredAngle dependence
An optical path of infrared rays (see the broken lines in FIG. 1) is modified to a substantially U-like shape by a first reflecting mirror and a second reflecting mirror. An incidence angle of the infrared rays incident on the wavelength filter (an angle between the infrared rays incident on the surface of the wavelength filter and the line perpendicular to the surface of the wavelength filter) is nearly zero. For this reason, as compared with a conventional example, the influence of the incidence angle dependence of the wavelength filter can be reduced. As a result, the amount of the infrared rays reaching the light receiving unit through the wavelength filter is increased, thereby suppressing a decline in the detection accuracy of the gas component.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
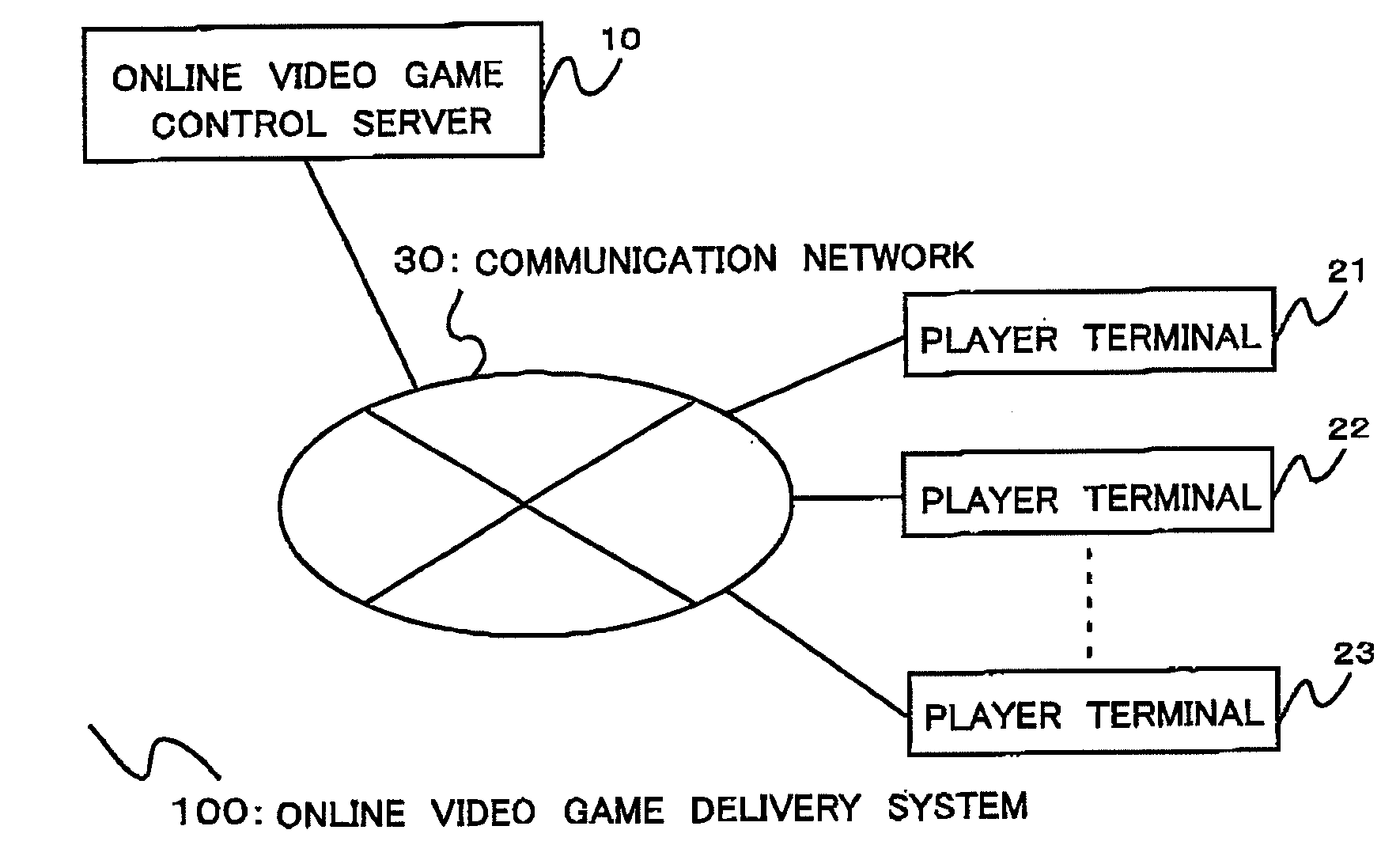
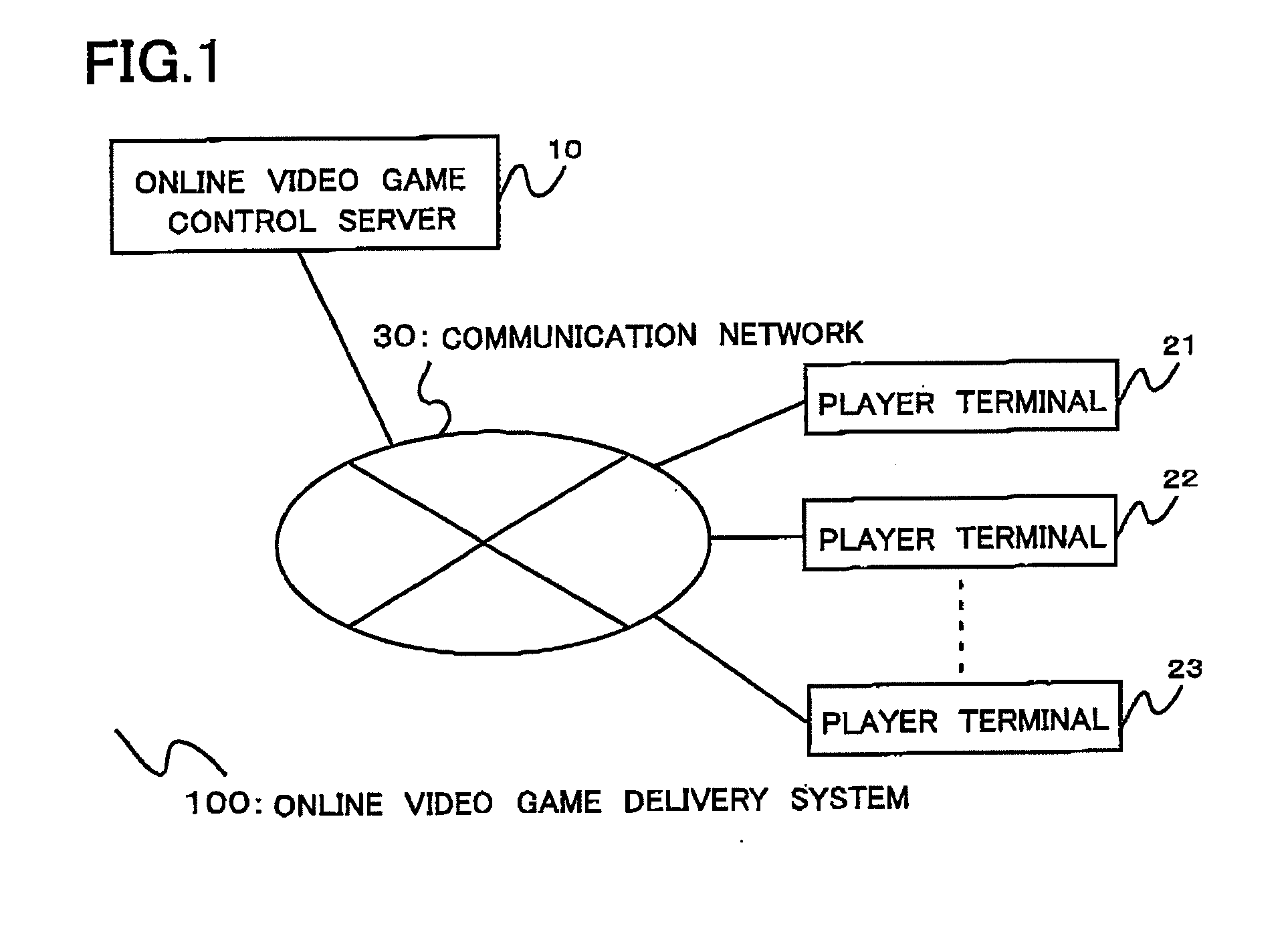
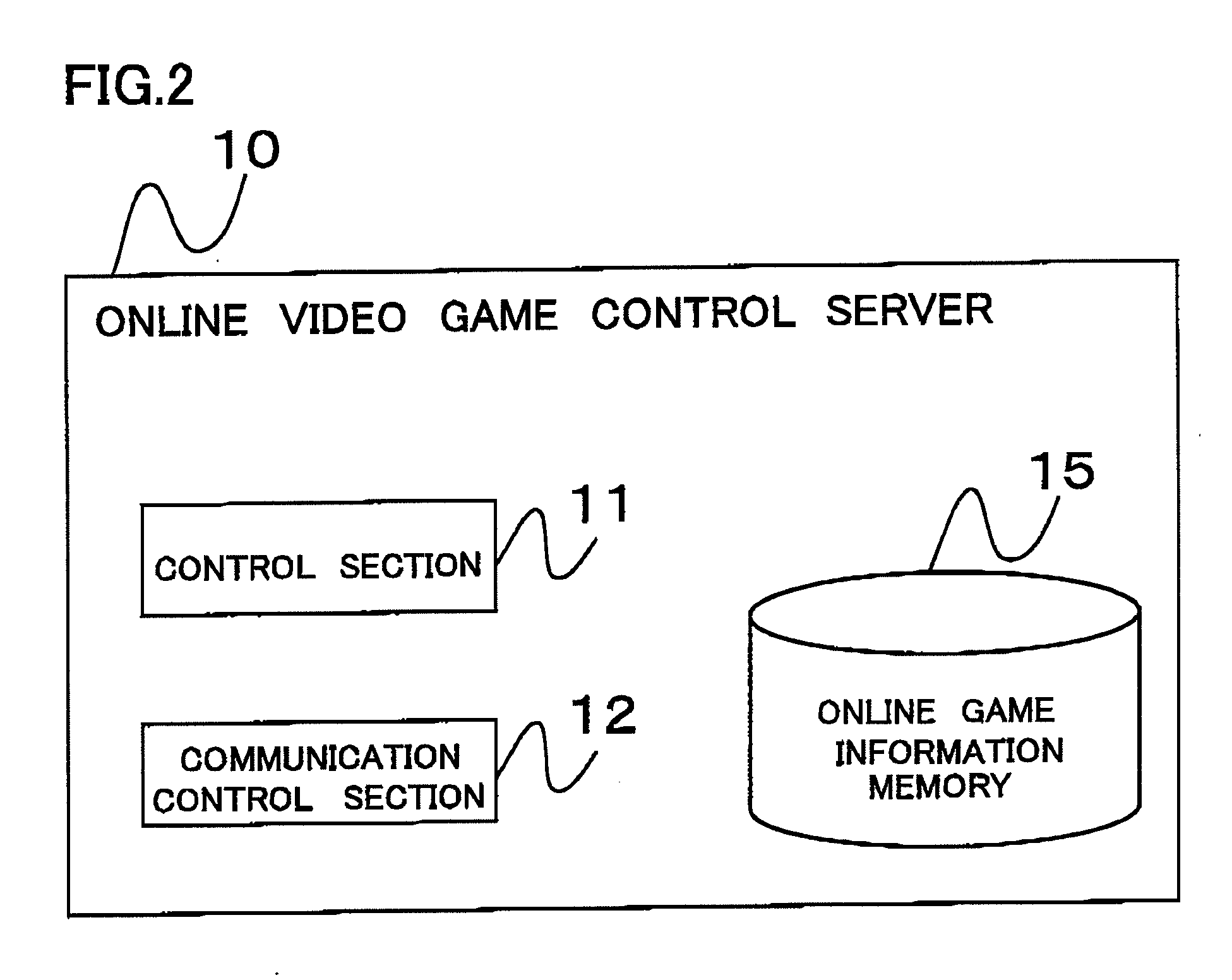
Online video game control server and a method of controlling an online video game
ActiveUS20080009352A1Reduce processing loadReduce loadVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsGame basedInformation storage
An online video game controlling server includes an online game information storage database for storing game information on an online video game that includes player information on player characters and area information on a game area of the online video game, and a control section for controlling the progress of the video game on the basis of the game information. A shared area and an unshared area are provided in the game area of the online video game. When one player character moves to the unshared area, the control section creates instance information including area specifying information, character identification information and instance creating necessary object information. In addition, the control section server breaks communication between the one player character and the other belonging player character to update the instance information whenever the progress state of the instance creating necessary object changes due to the action of the one player character.
Owner:SQUARE ENIX HLDG CO LTD
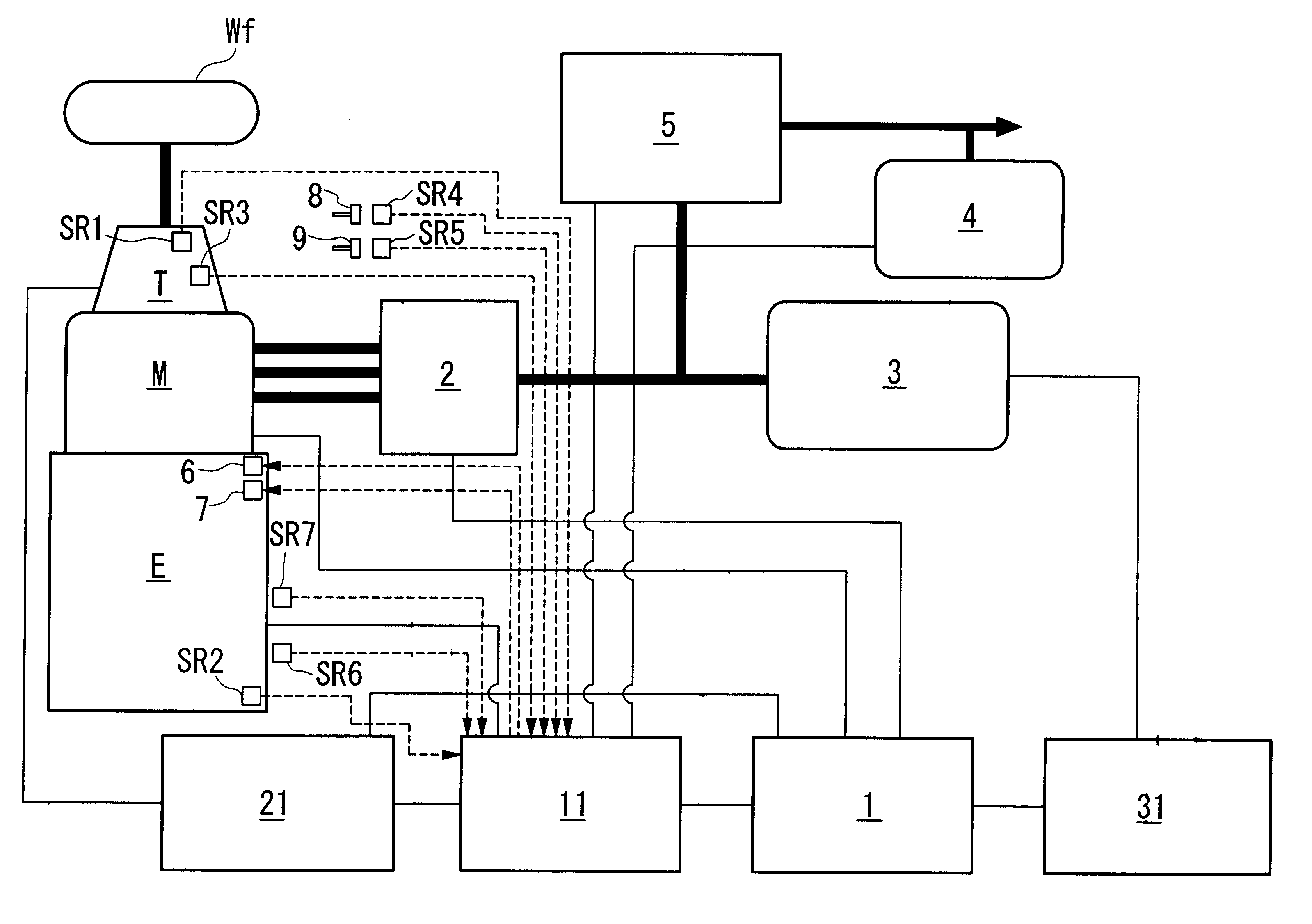
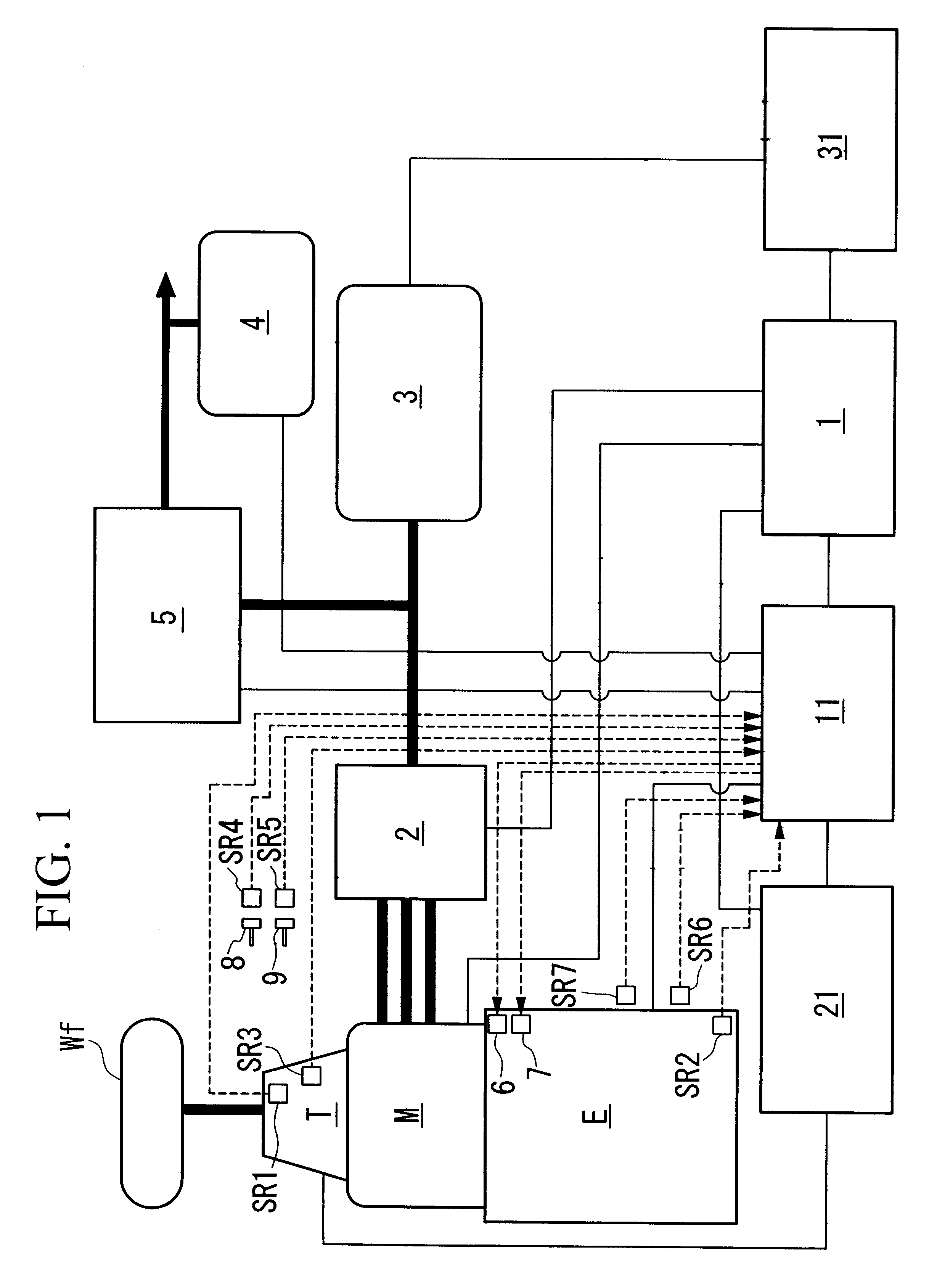
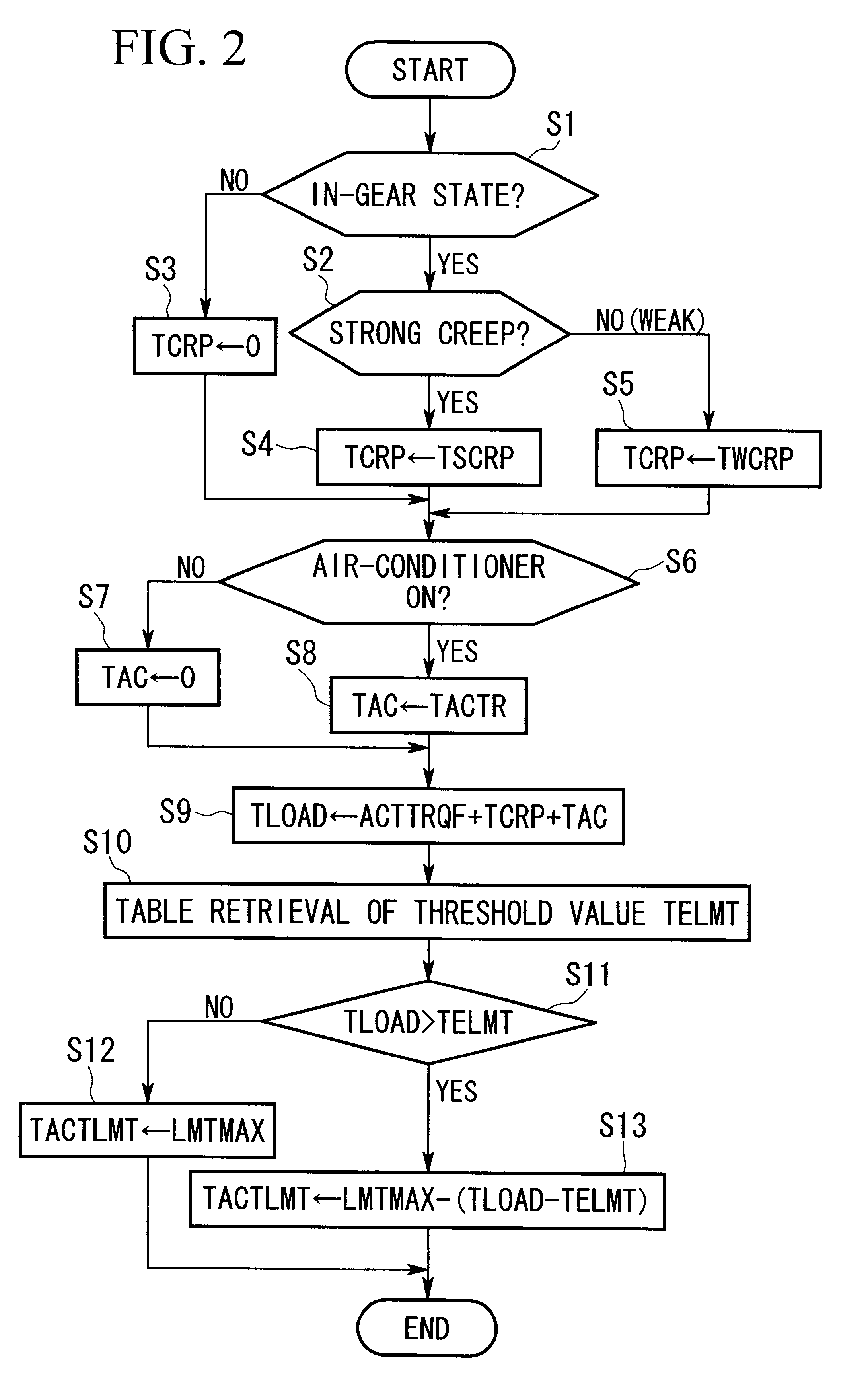
Apparatus and method for controlling power generation for hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS6362536B1Smooth startReduce generationGas pressure propulsion mountingPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsControl powerLoad torque
The present invention relates to a power generation control apparatus for a hybrid vehicle. The hybrid vehicle comprises an engine which outputs a driving force for the hybrid vehicle; a motor which outputs an assistant driving force so as to assist the driving force of the engine; a power storage unit; and a power generation control apparatus which controls the power generation by the motor. The power generation control apparatus comprises a load torque calculation device which calculates the load torque to be applied to an engine of the hybrid vehicle for generating electrical power used in the hybrid vehicle when the engine is idling; a generable torque calculation device which calculates torque generable by the engine when the engine is idling; and a power generation load torque determination device which determines a limiting value of a power generation load torque to be applied to the engine in accordance with the load torque calculated by the load torque calculation device and the generable torque calculated by the generable torque calculation device.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Control apparatus and control method for vehicle
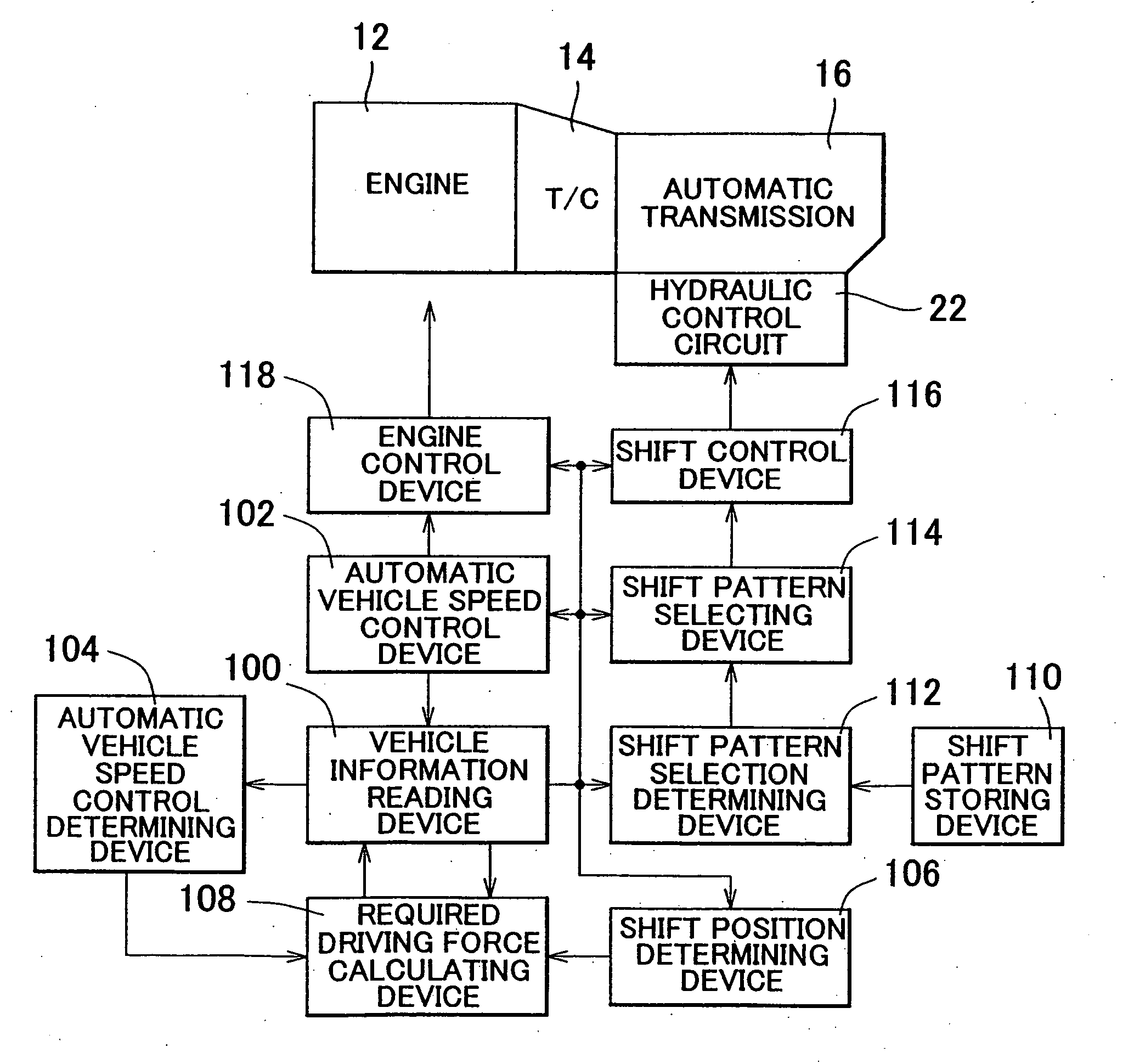
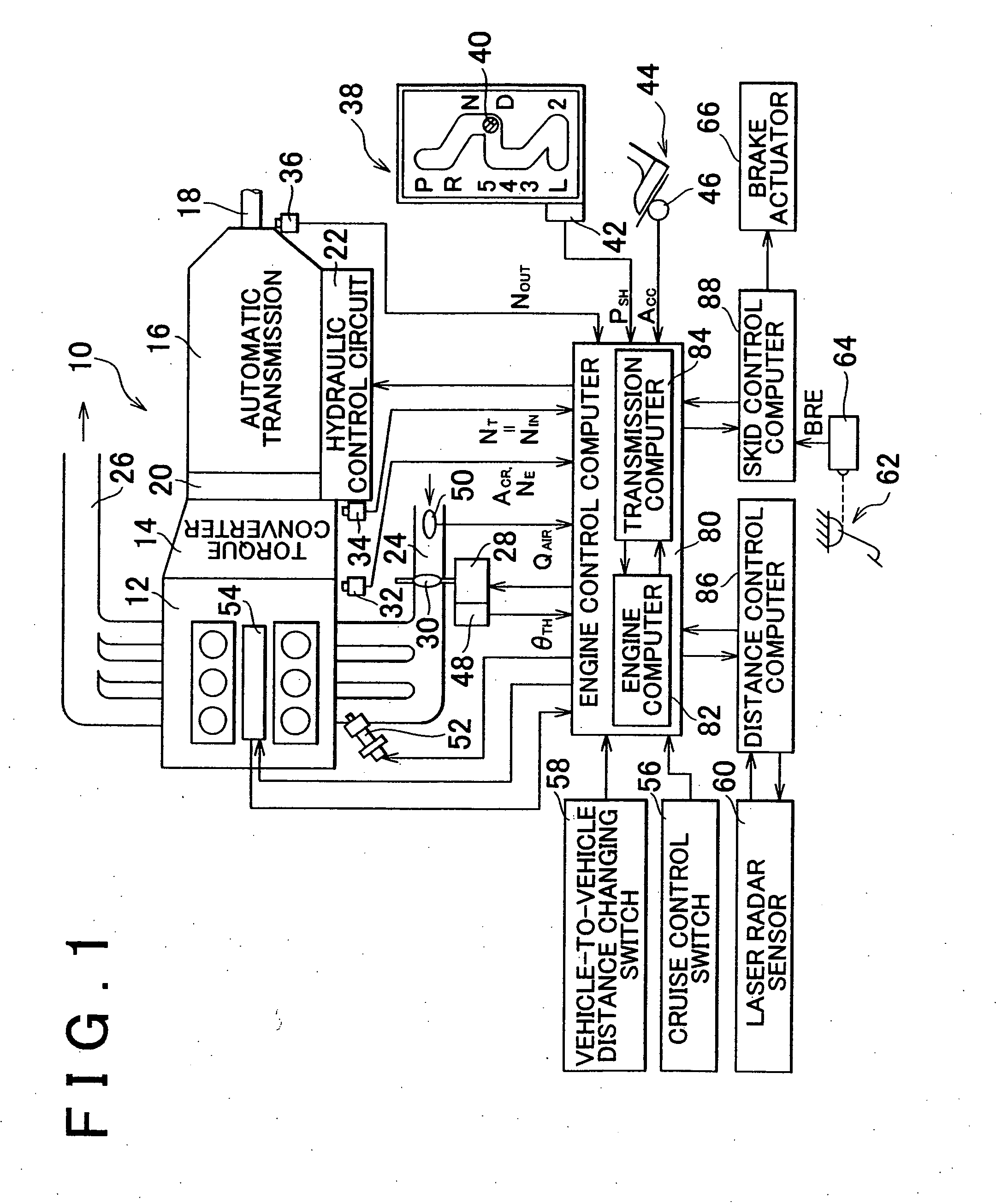
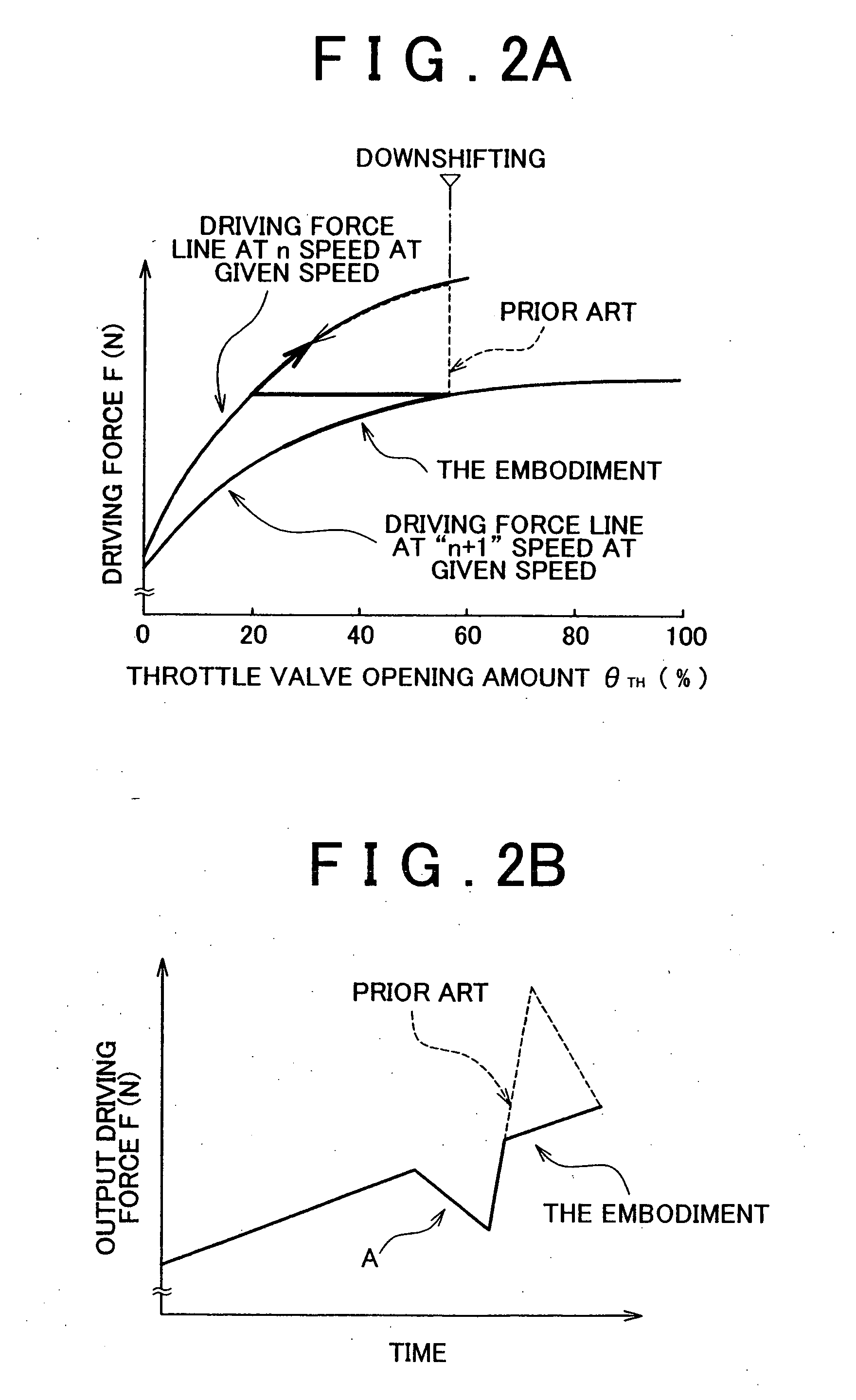
InactiveUS20050143221A1Improve drivabilityImprove efficiencyDigital data processing detailsGearing controlAutomatic transmissionControl equipment
A control apparatus and method for a vehicle including a stepped automatic transmission and a shift control device which controls an operation of the automatic transmission based on a vehicle state such as a value corresponding to a driving force required for the vehicle, according to a pre-stored shift pattern having a shift line for determining whether shifting is performed from one shift speed to an adjacent shift speed. In the control apparatus and control method, one shift pattern is automatically selected, based on the vehicle state, from among multiple shift patterns including at least a first shift pattern in which the shift line is set such that the driving force for the vehicle, that is decided by a gear ratio of the shift speed and engine output characteristics, continuously and smoothly changes when shifting is performed from one shift speed to an adjacent shift speed, and a second shift pattern in which the shift line is set such that the use of a region, where an engine rotational speed for obtaining the driving force for the vehicle becomes a predetermined high rotational speed, is avoided.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
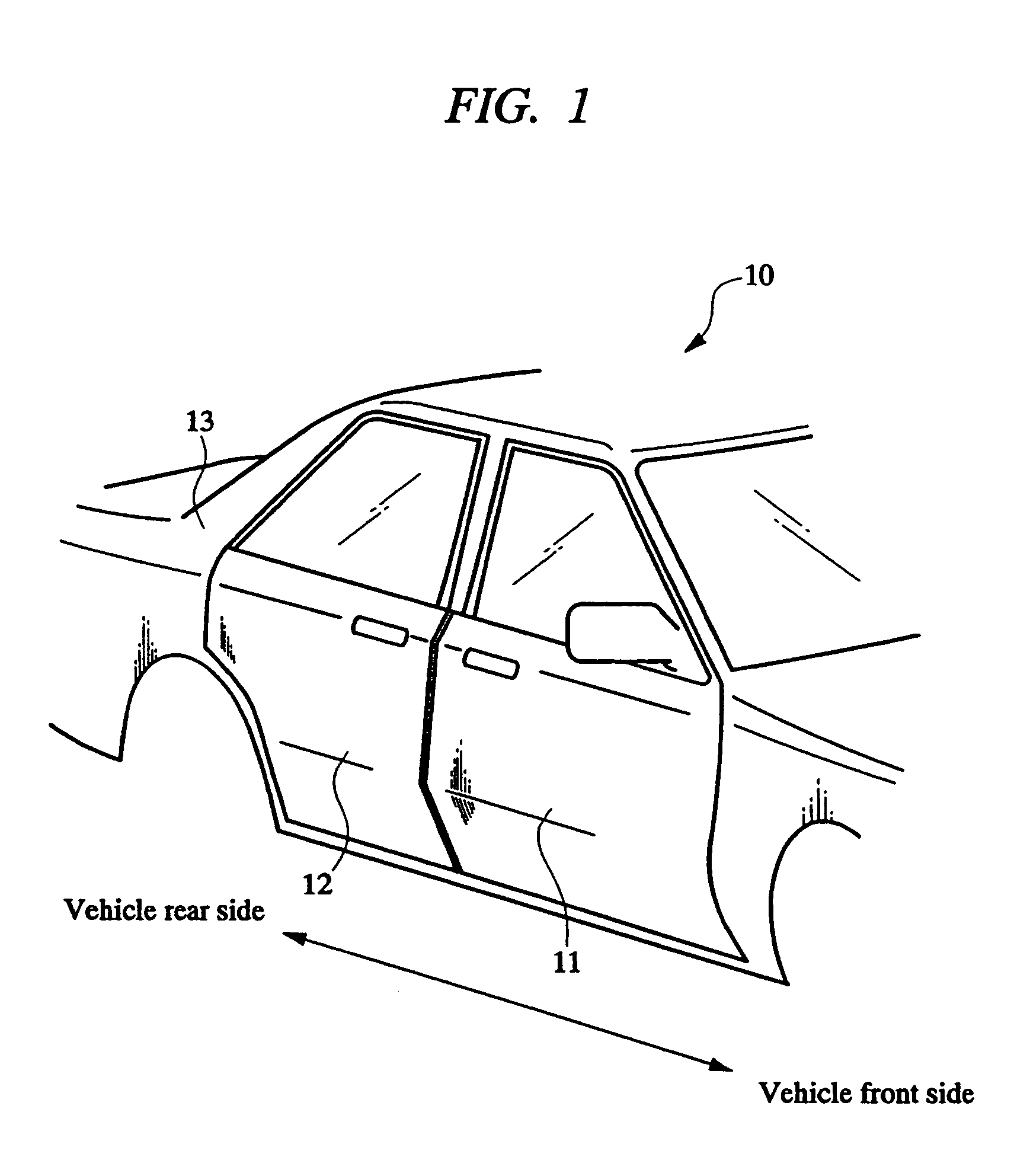
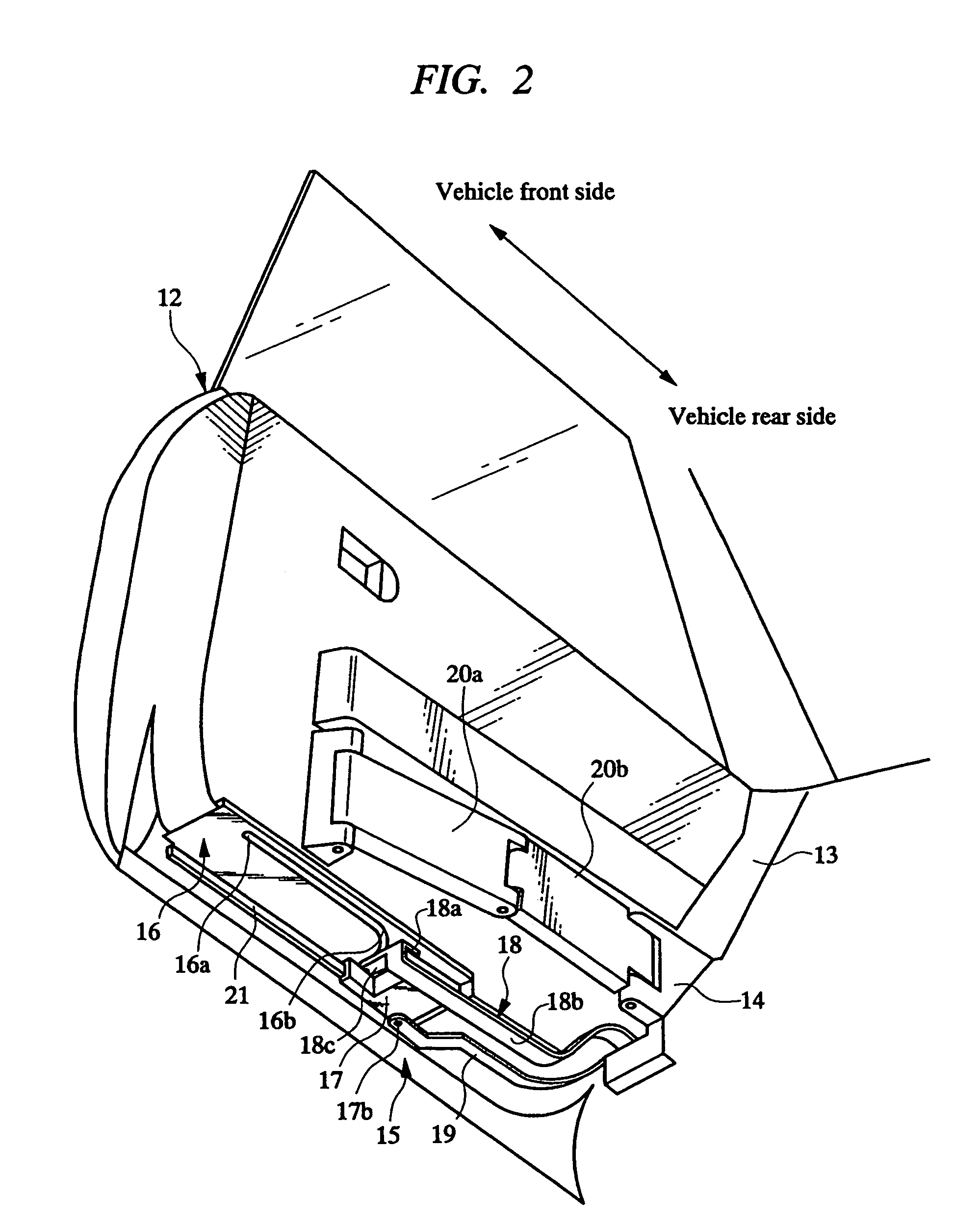
Vehicle door opening and closing structure
InactiveUS7393044B2Improve operativityQuality improvementMan-operated mechanismPower-operated mechanismReciprocating motionControl arm
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
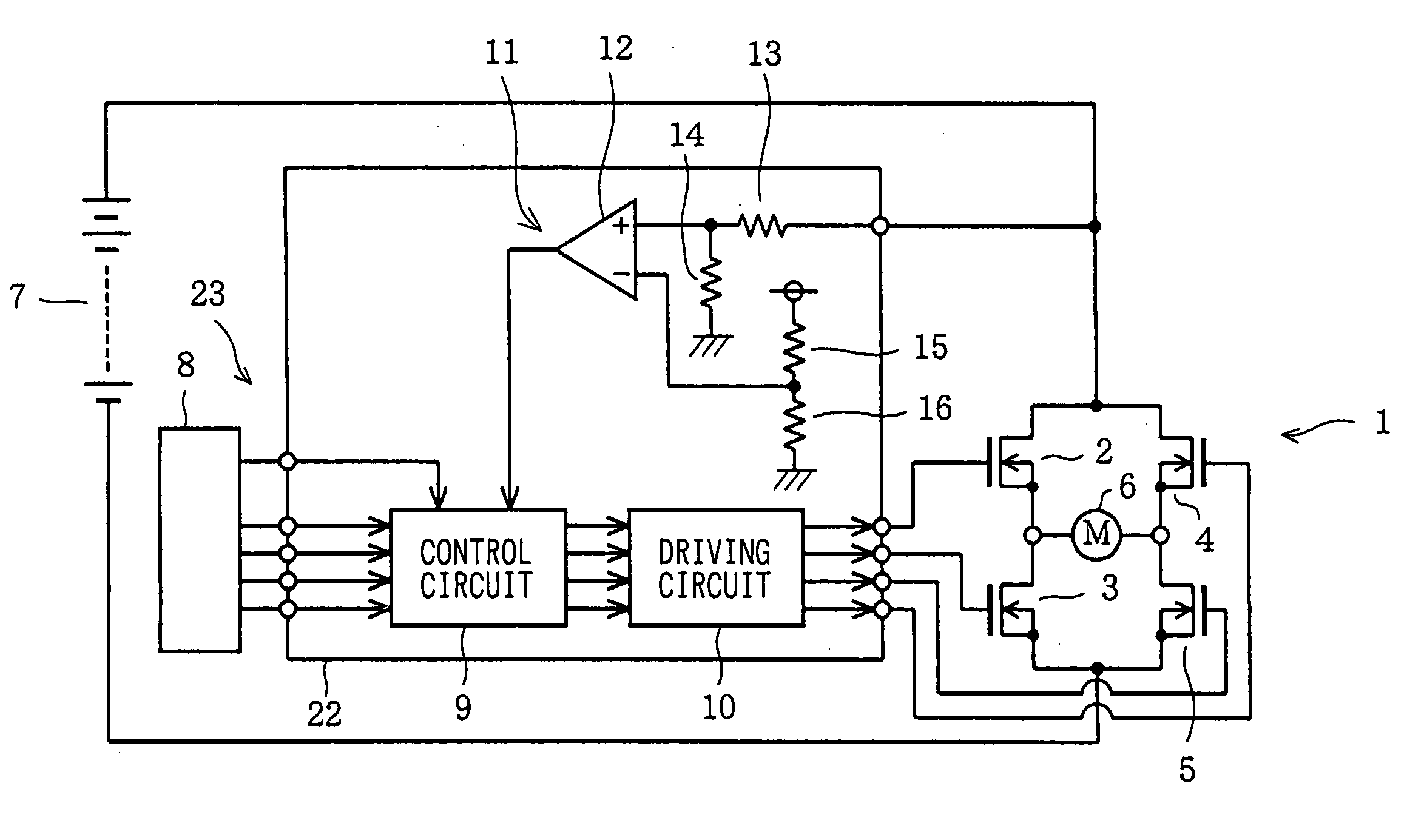
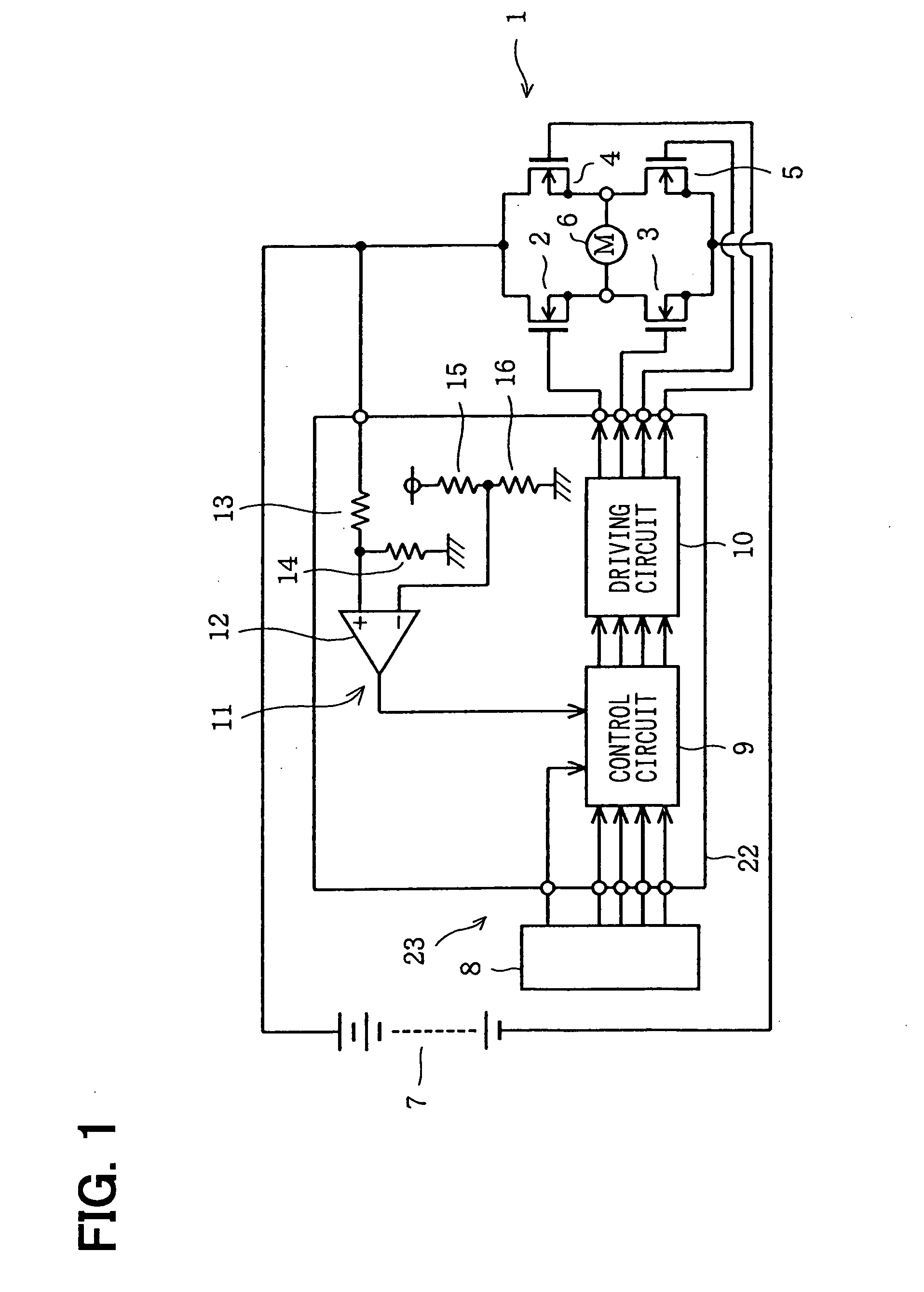
Driving apparatus of H bridge circuit and protection method of the same
InactiveUS20050179463A1Improve reliabilityLow costTransistorEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDriver circuitControl signal
In order to protect semiconductor switching-devices employed in an H bridge circuit against an over-voltage without using a special protection circuit, a control circuit outputs a control signal to a driving circuit for driving the H bridge circuit in order to turn off FETs serving as the semiconductor switching-devices when an over-voltage detection circuit detects the over-voltage applied to the H bridge circuit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Liquid ejecting device
InactiveUS20090244226A1Excellent ability to remove air bubbleGood removal effectOther printing apparatusLiquid jetBuffer tank
Ink is supplied to a supply tank from a second buffer tank, and ink is pressure-fed from the supply tank to a head. Further, ink is supplied from the second buffer tank to a recovery tank, and ink is pressure-fed from the recovery tank to the head. In both pressure-feedings, ink containing air bubbles within the head is recovered at a first buffer tank. The ink, that contains the air bubbles and is recovered at the first buffer tank, is sent to the second buffer tank via an ink flow path. A degassing section is provided on the ink flow path, and a degassing process is carried out while ink is being fed.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Electronic apparatus
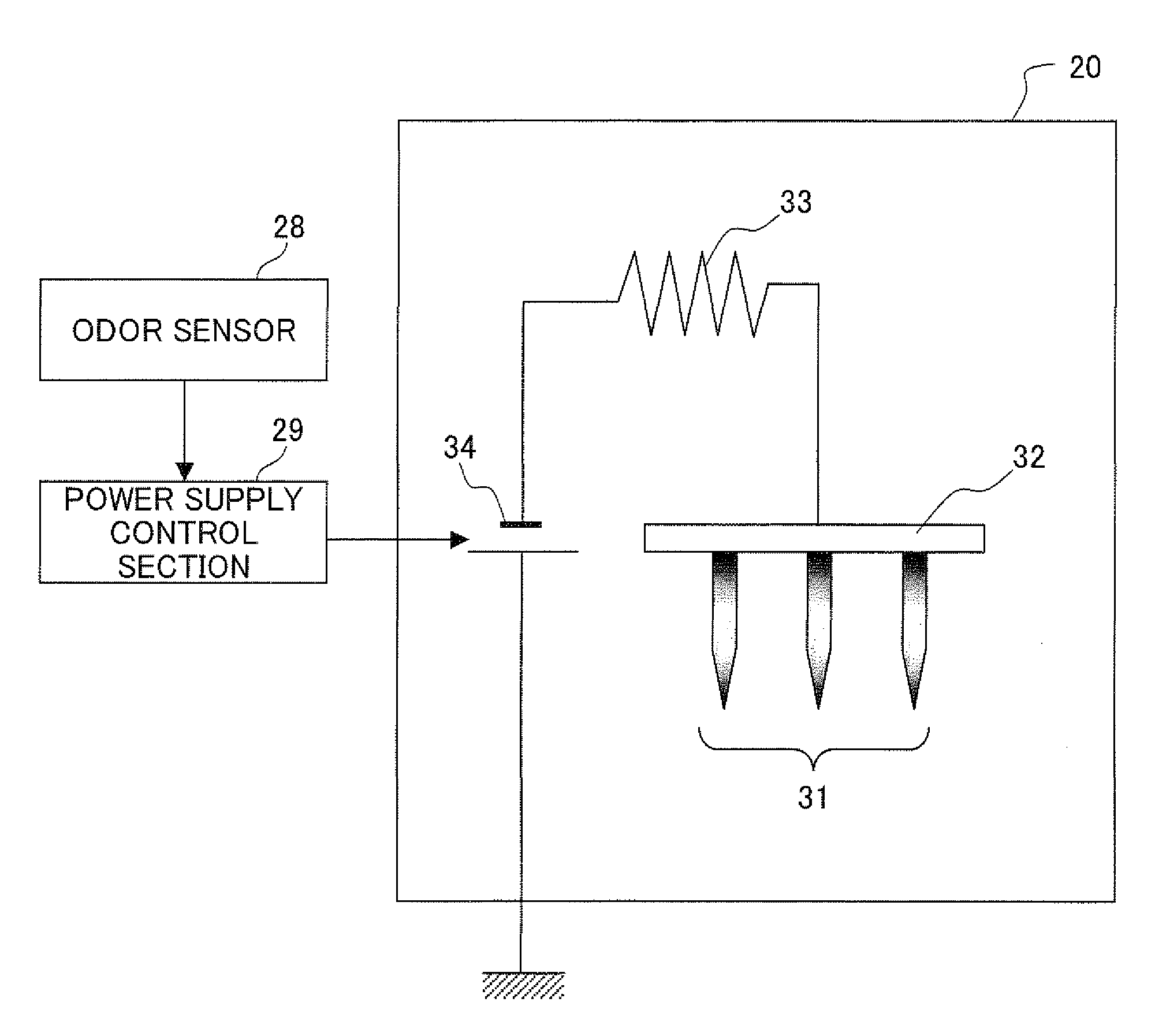
ActiveUS20080217556A1Suppresses diffusionSuppress DiffuseParticle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysicsIon
An electronic apparatus of the present invention includes an ion generator which generates ions in an atmosphere to remove chemical emission such as VOC and odor. The ion generator is arranged inside the duct which leads the chemical emission generated from the fixing unit to the discharge opening, and also generates positive ions and negative ions in the atmosphere, thereby can efficiently remove the chemical emission. With this arrangement, an electronic apparatus is realized which sufficiently suppresses the chemical emission such as VOC and odor, and is less likely to dirty the surroundings of the electronic apparatus such as the outer surface thereof and the walls surrounding the electronic apparatus.
Owner:SHARP KK
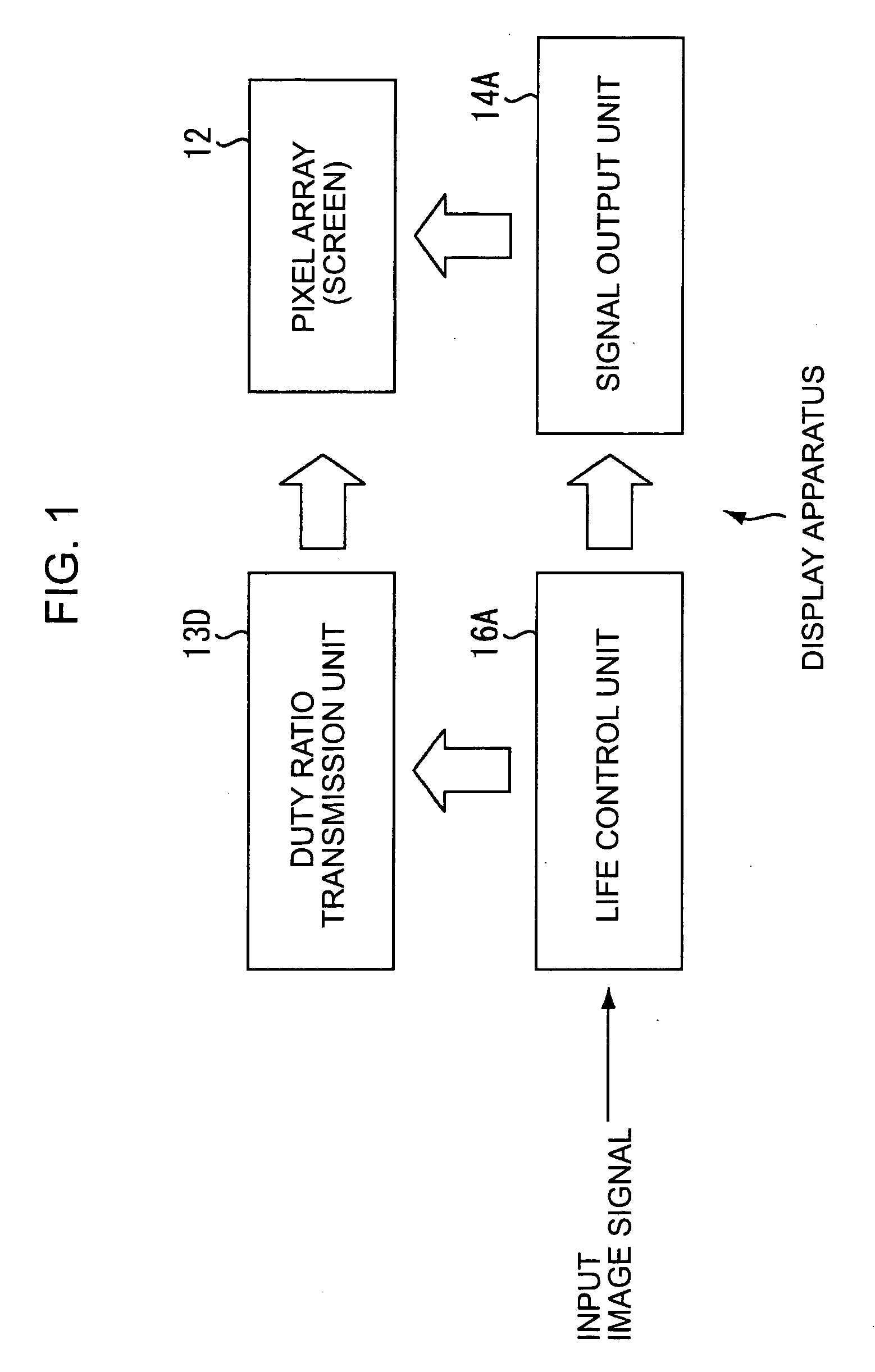
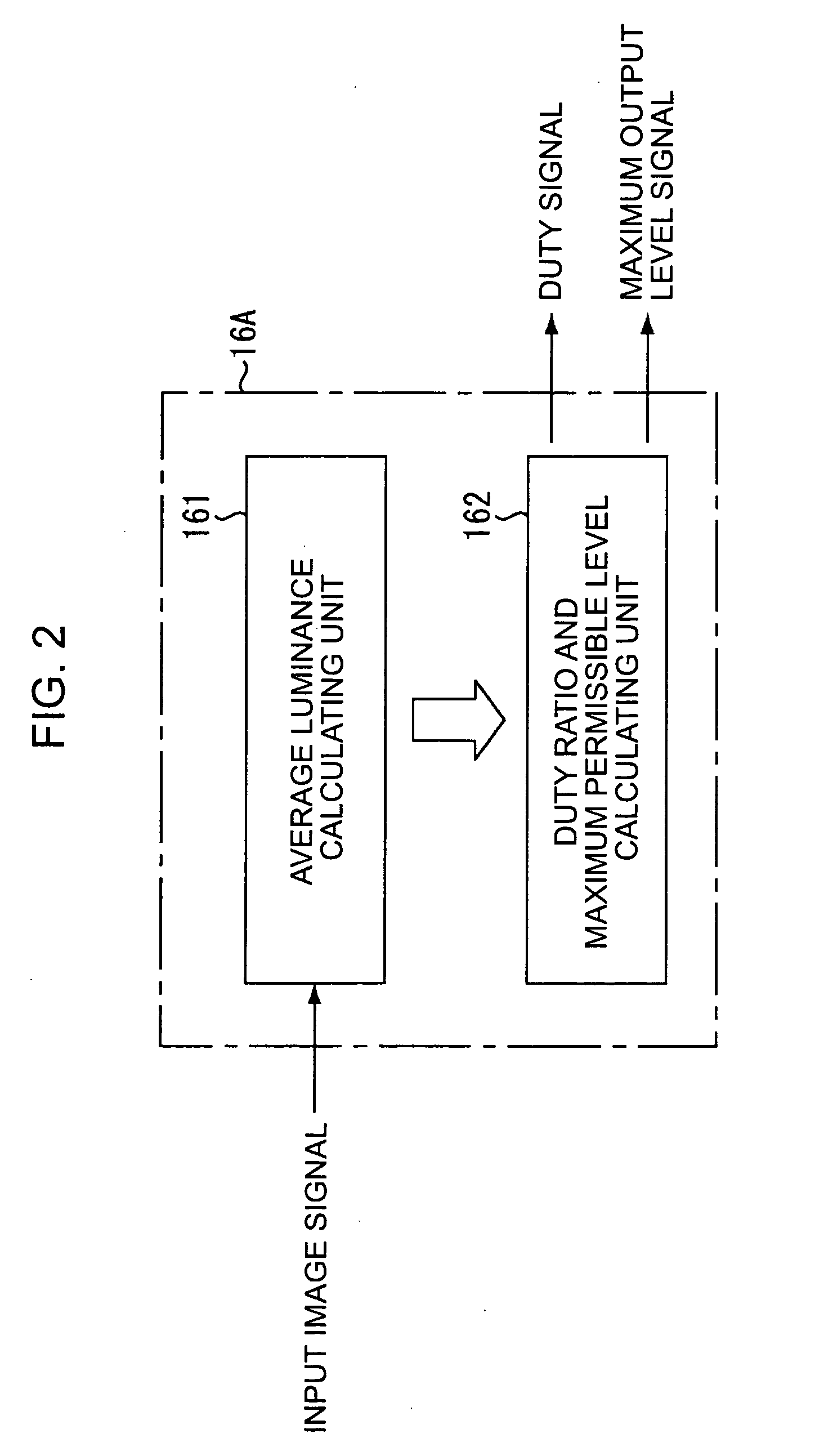
Display apparatus and driving method for the same
ActiveUS20060017394A1Prolong lifeSuppress amount of lightCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringImage signal
A display apparatus includes a pixel array, a life control unit, a signal output unit, and a duty ratio transmission unit. The pixel array, including light-emitting elements constituting a screen, displays each frame of an image on the screen by emitting light having a luminance in accordance with a level of an image signal and continuously emits light from the screen within each frame for an amount of time specified by a duty ratio. The life control unit extends the life of the light-emitting elements by simultaneously adjusting the maximum permissible level of the image signal and the duty ratio. The signal output unit drives the screen to display an image by outputting an image signal adjusted within the maximum permissible level to the pixel array. The duty ratio transmission unit for enabling the screen to emit light for an amount of time specified transmitting an adjusted duty ratio to the pixel array.
Owner:JOLED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com