Patents
Literature
1617 results about "Air bearing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Air bearings (also known as aerostatic or aerodynamic bearings) are bearings that use a thin film of pressurized gas to provide a low friction load-bearing interface between surfaces. The two surfaces do not touch, thus avoiding the traditional bearing-related problems of friction, wear, particulates, and lubricant handling, and offer distinct advantages in precision positioning, such as lacking backlash and static friction, as well as in high-speed applications.
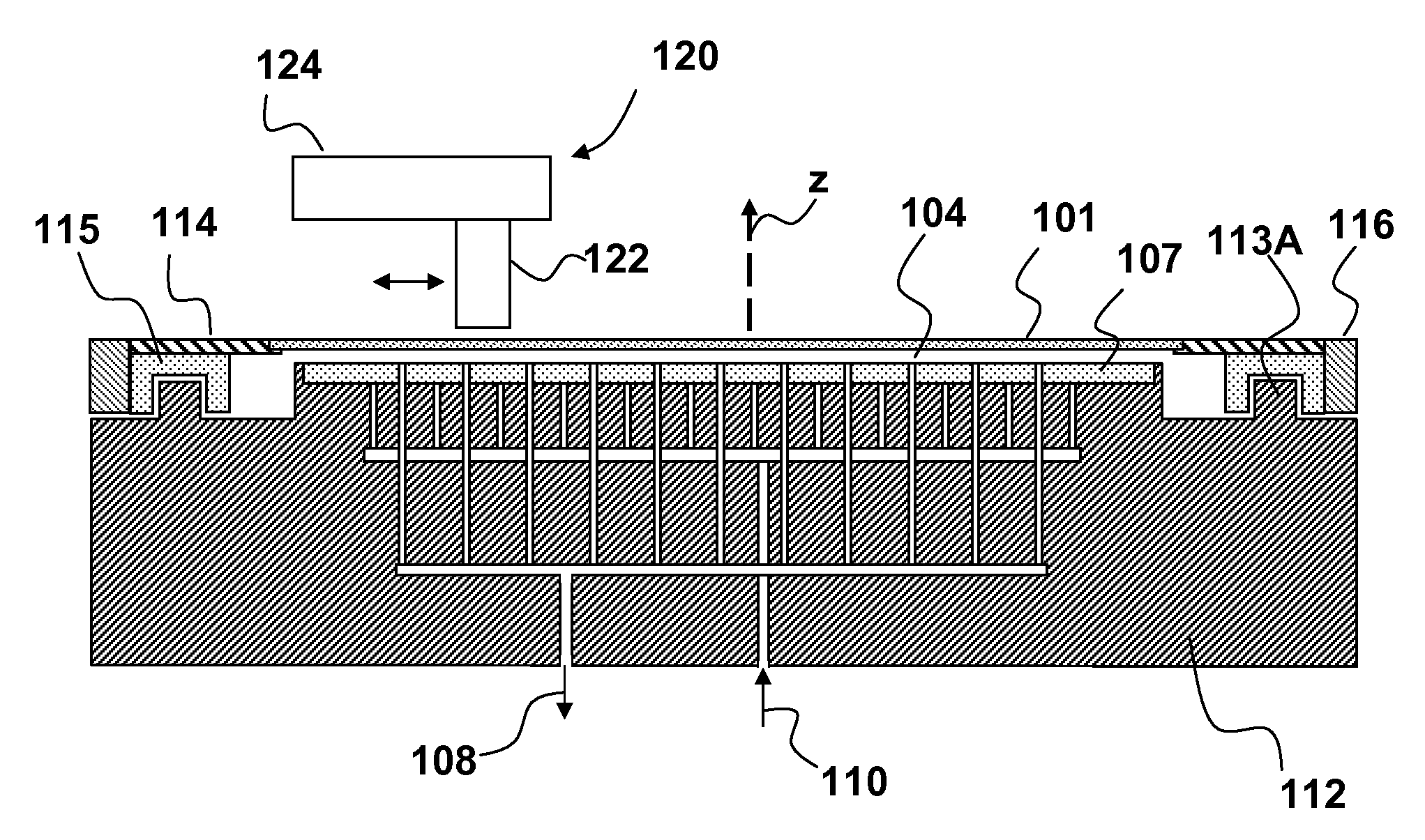
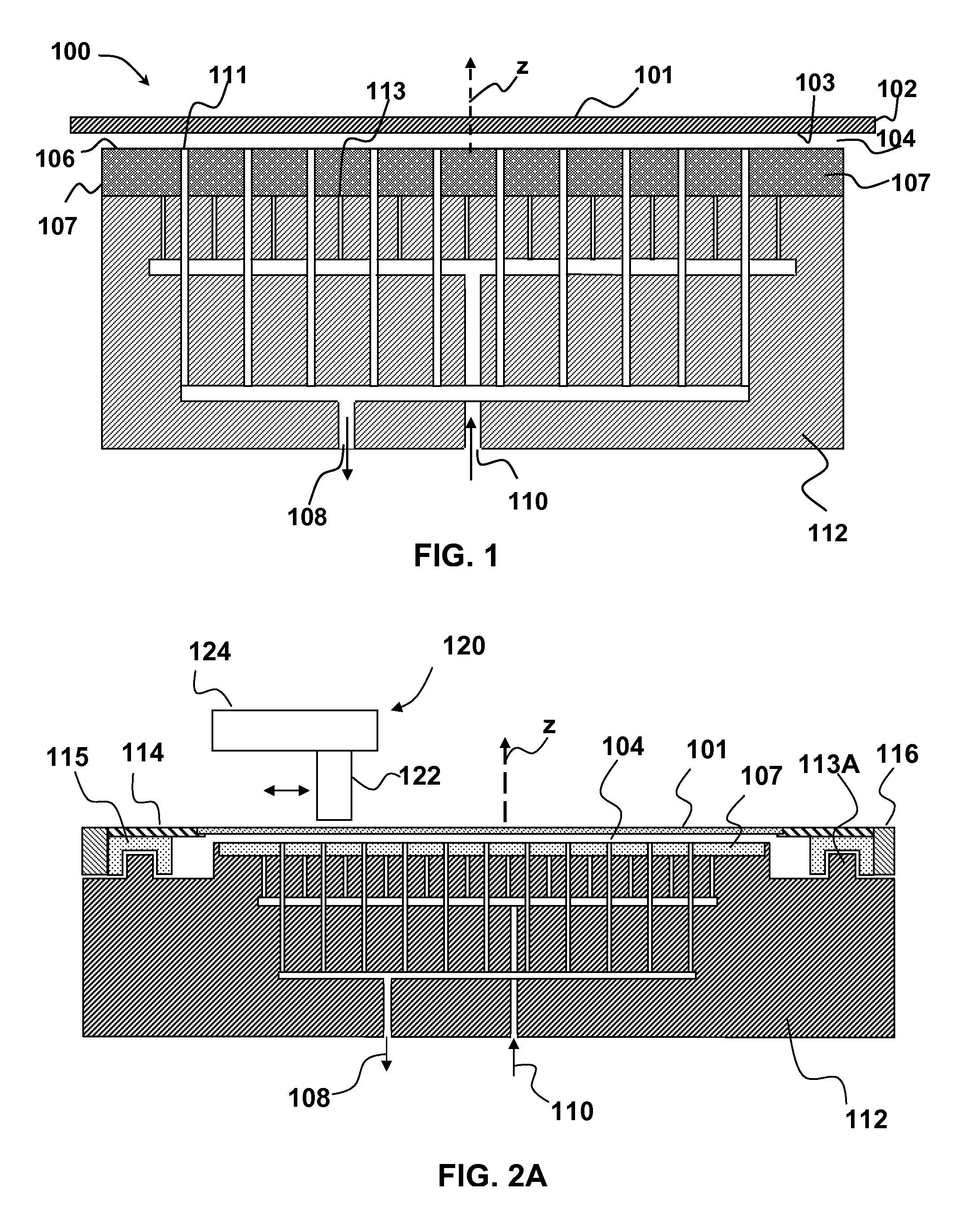
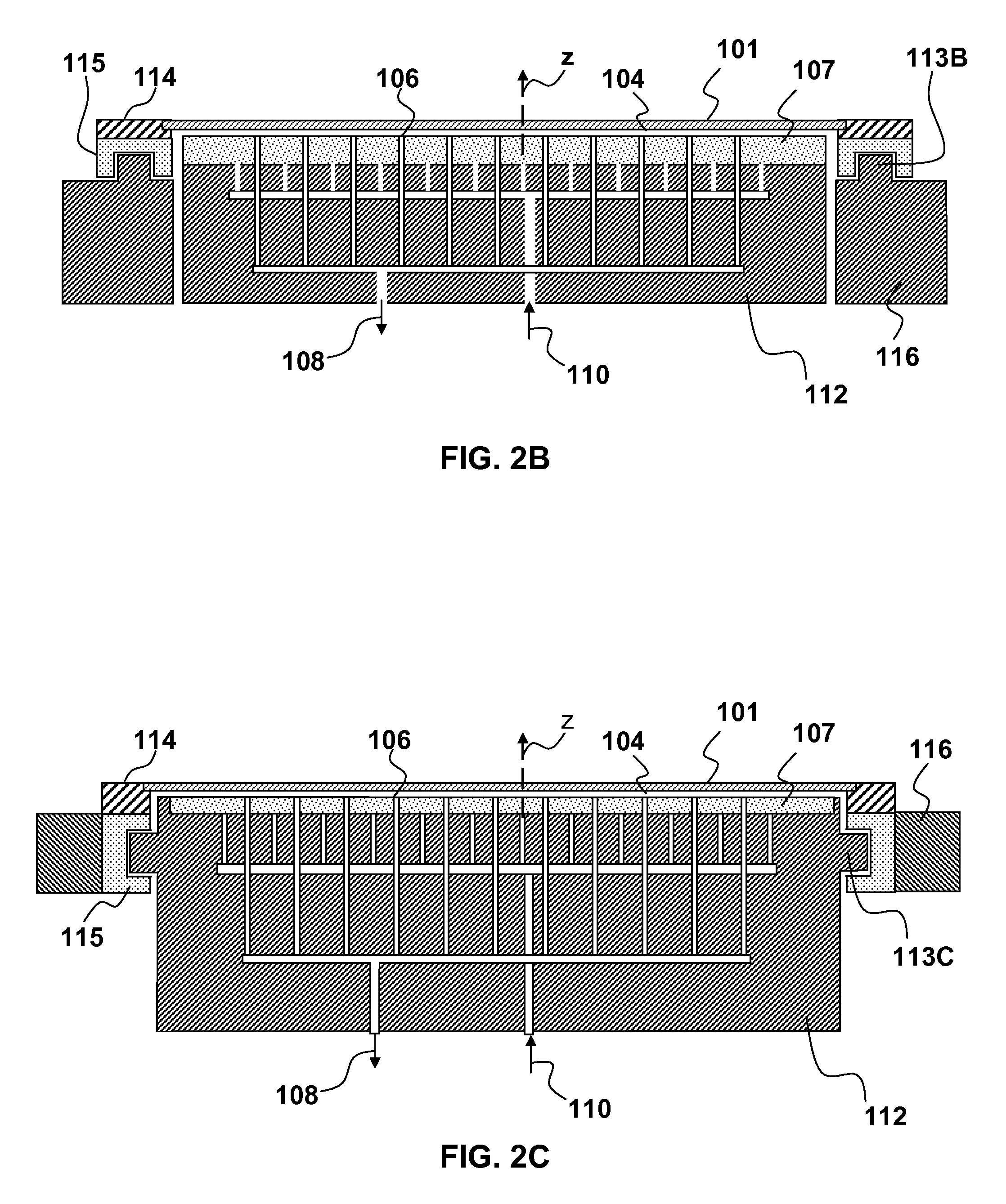
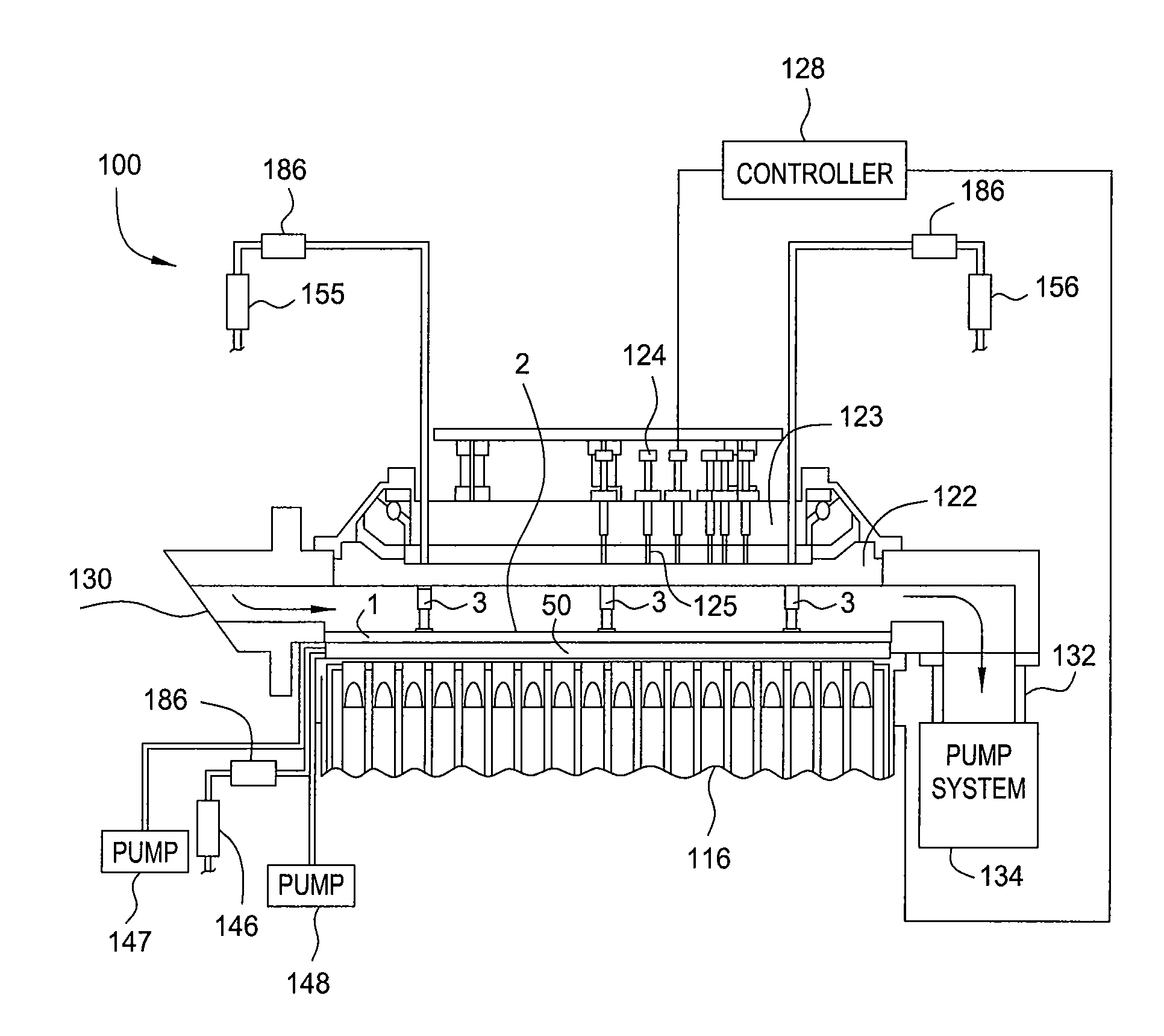
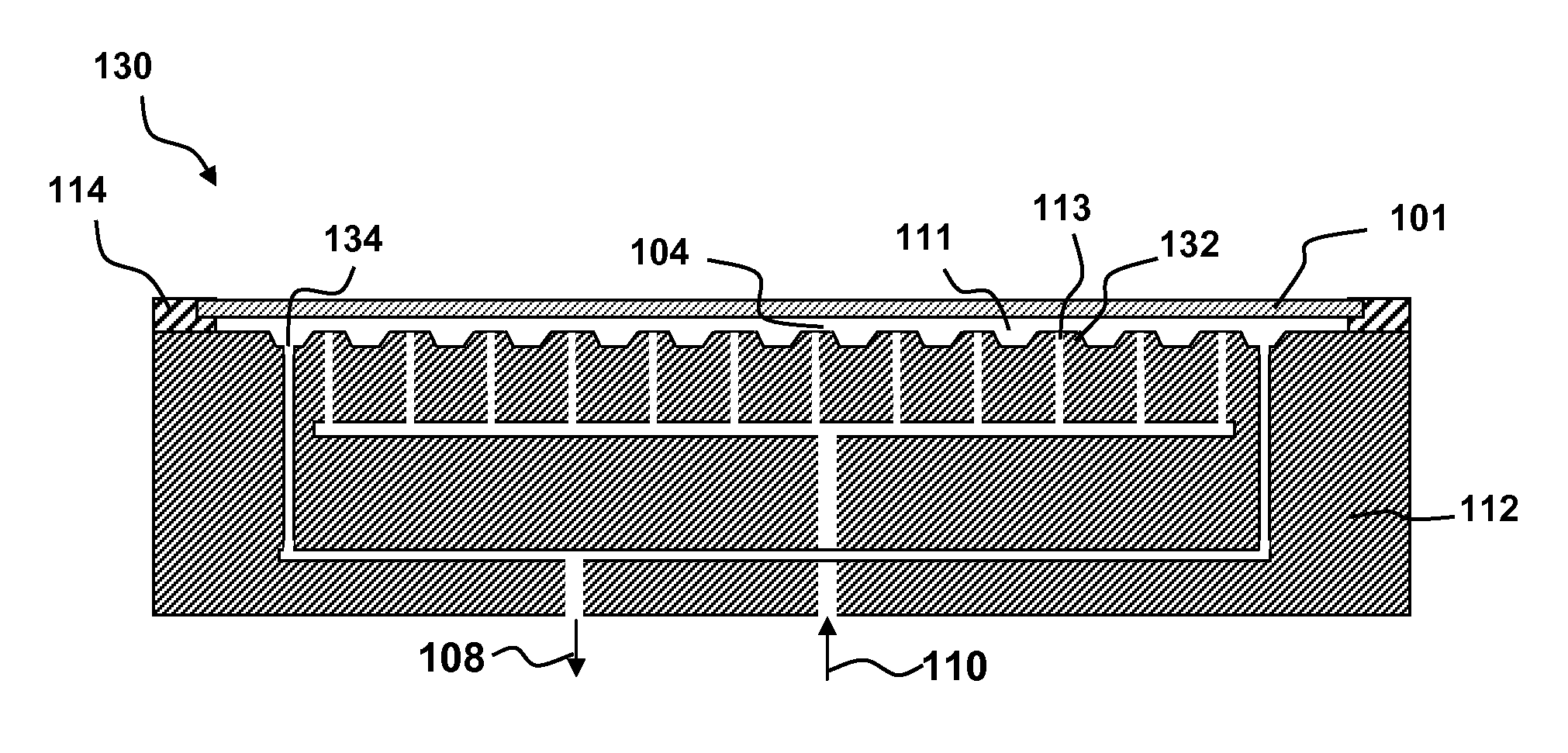
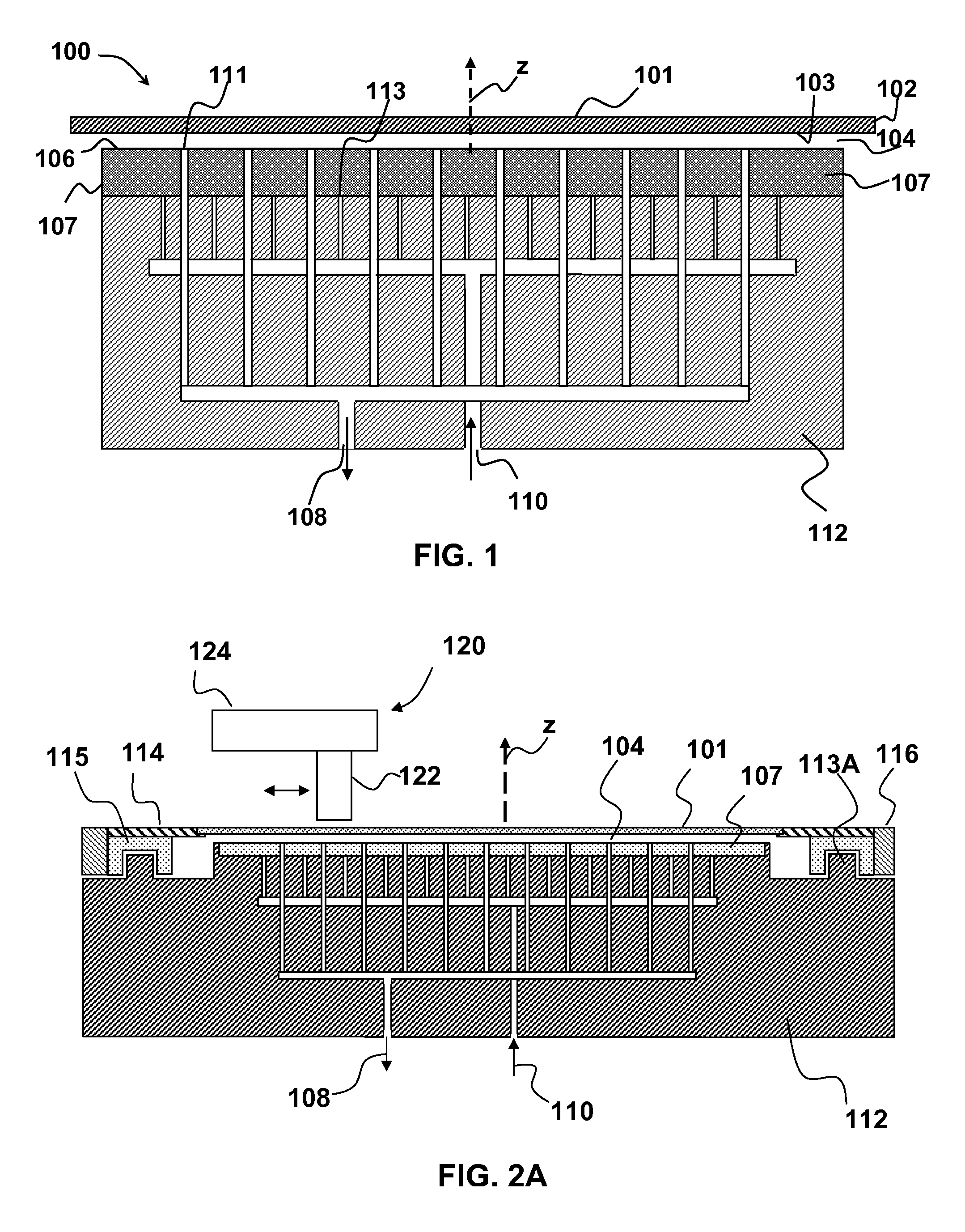
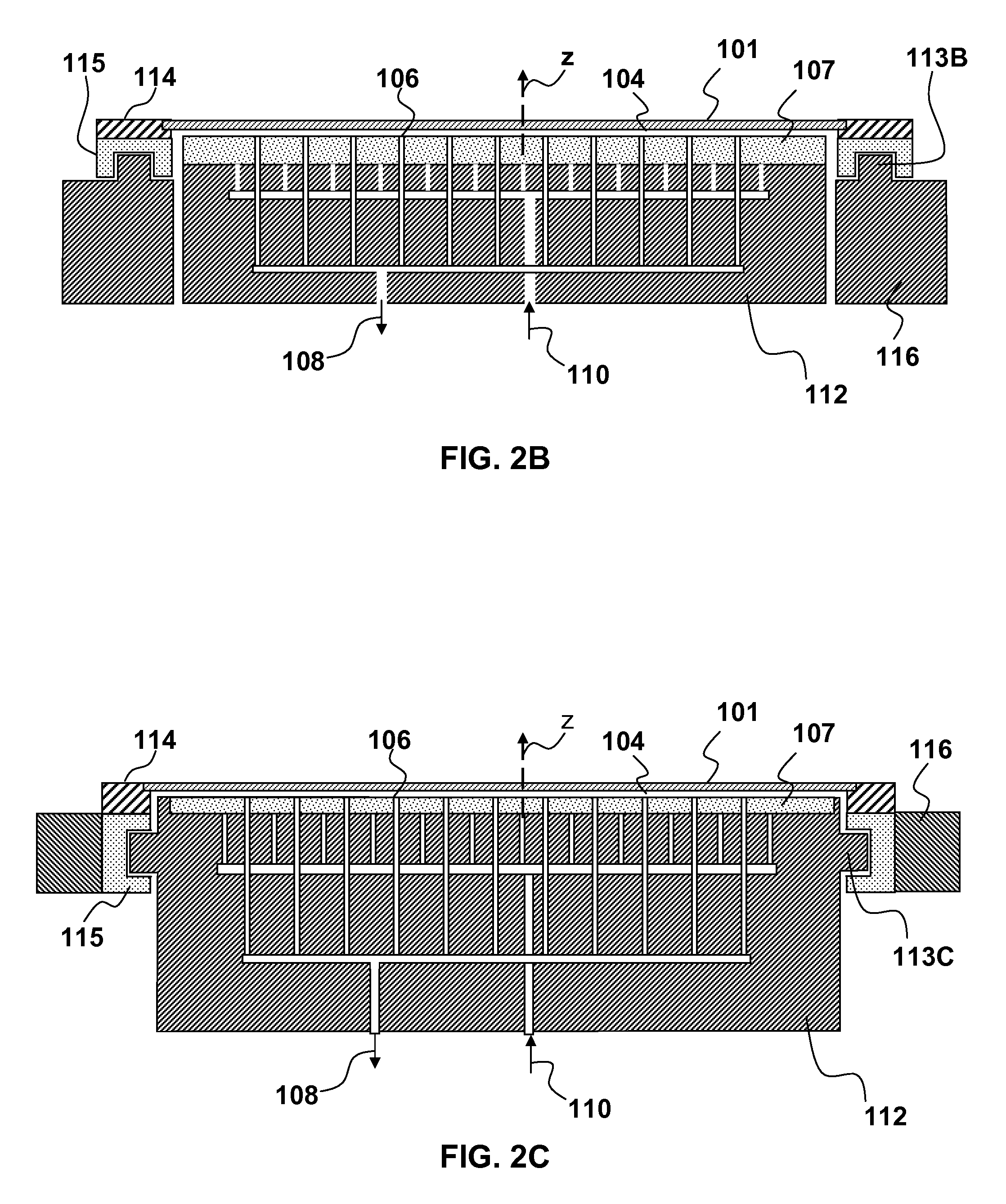
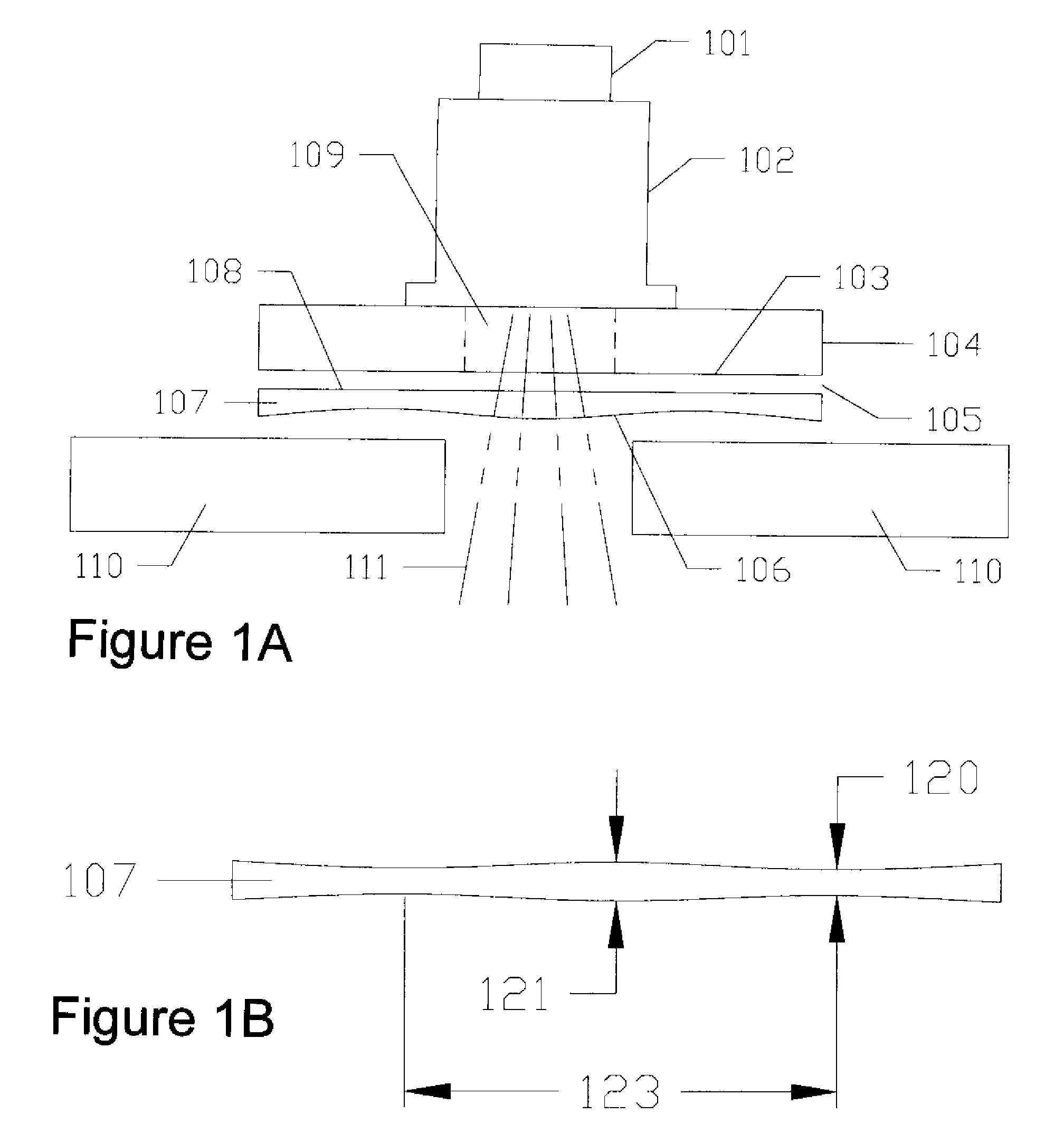
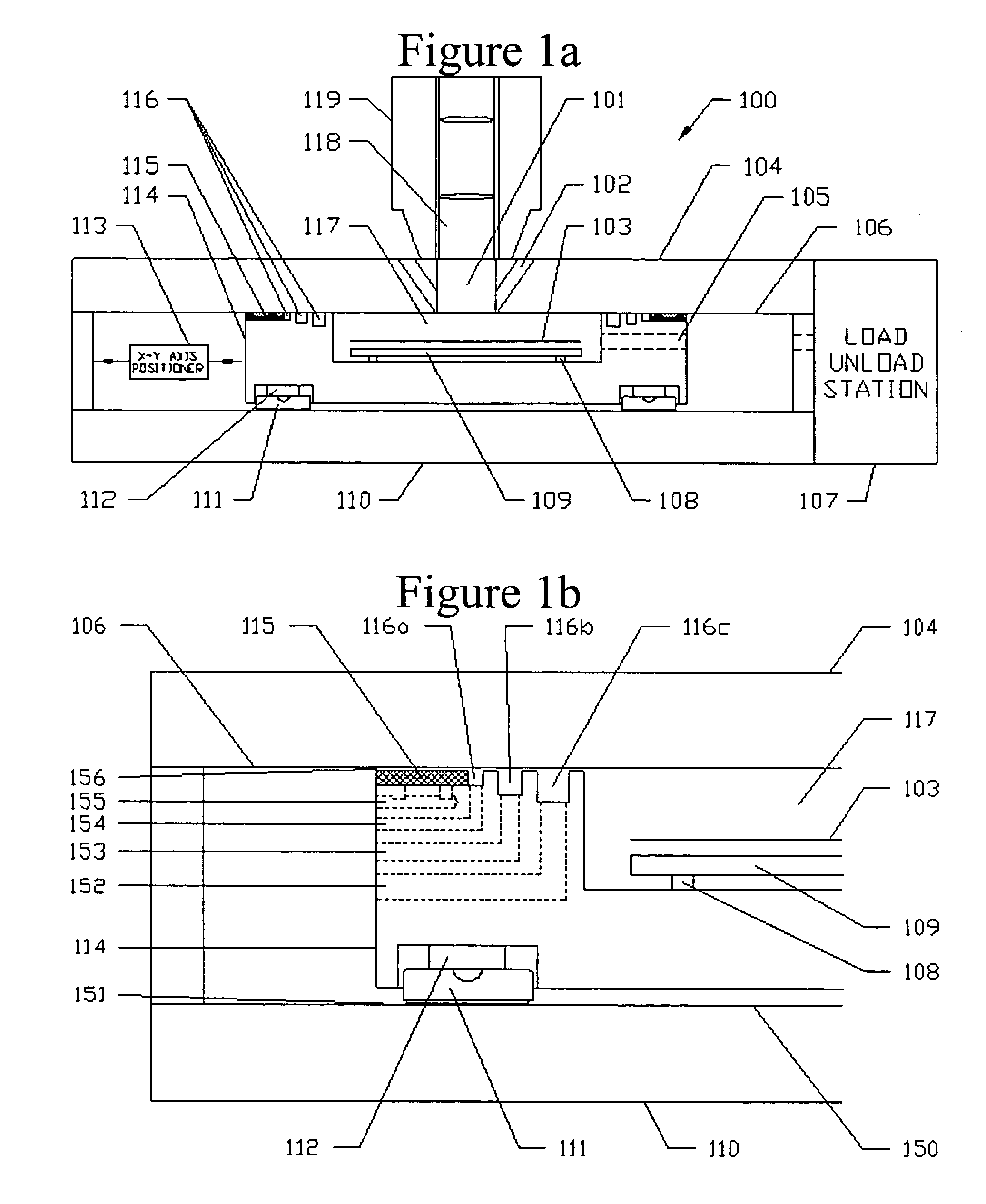
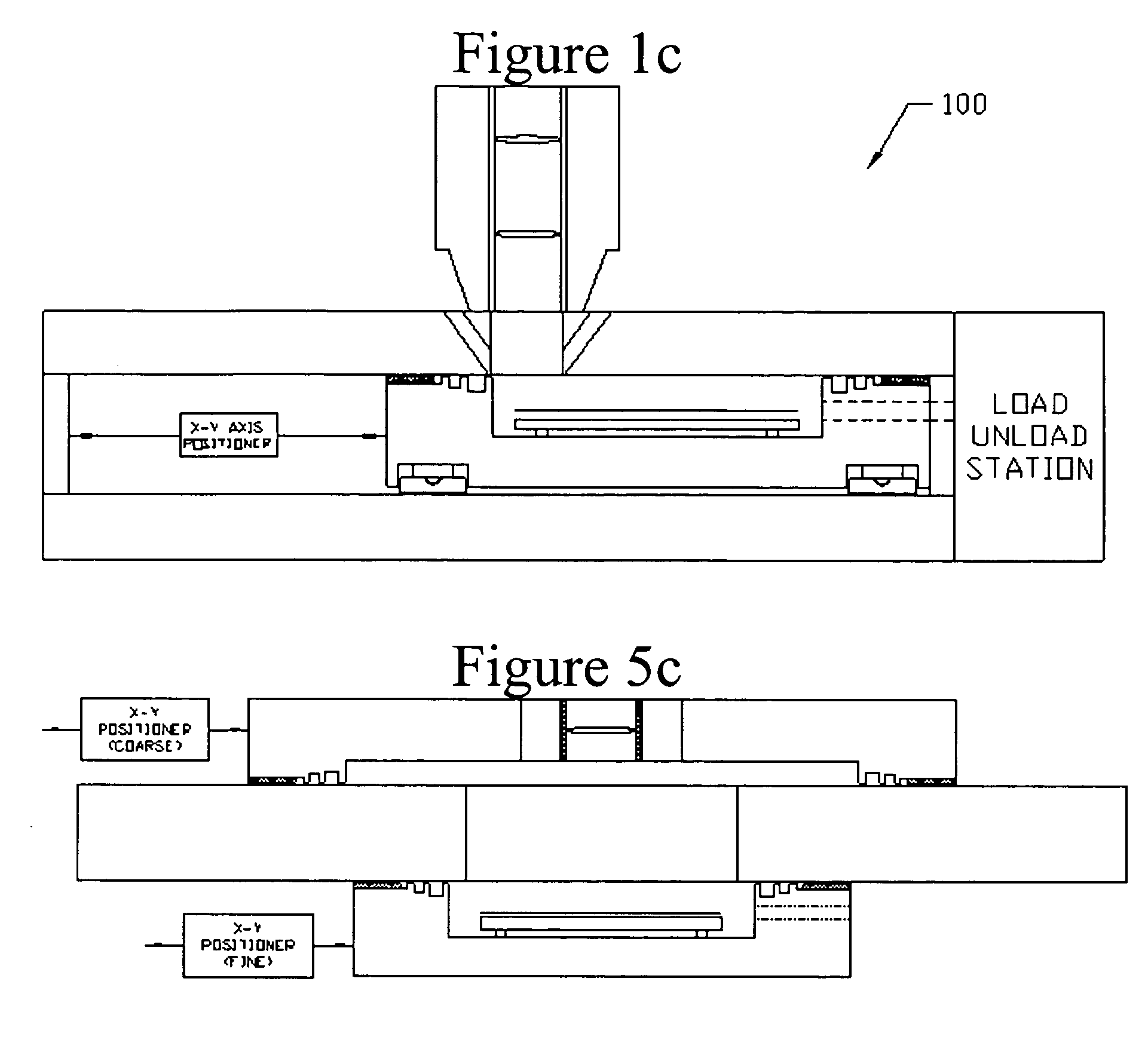
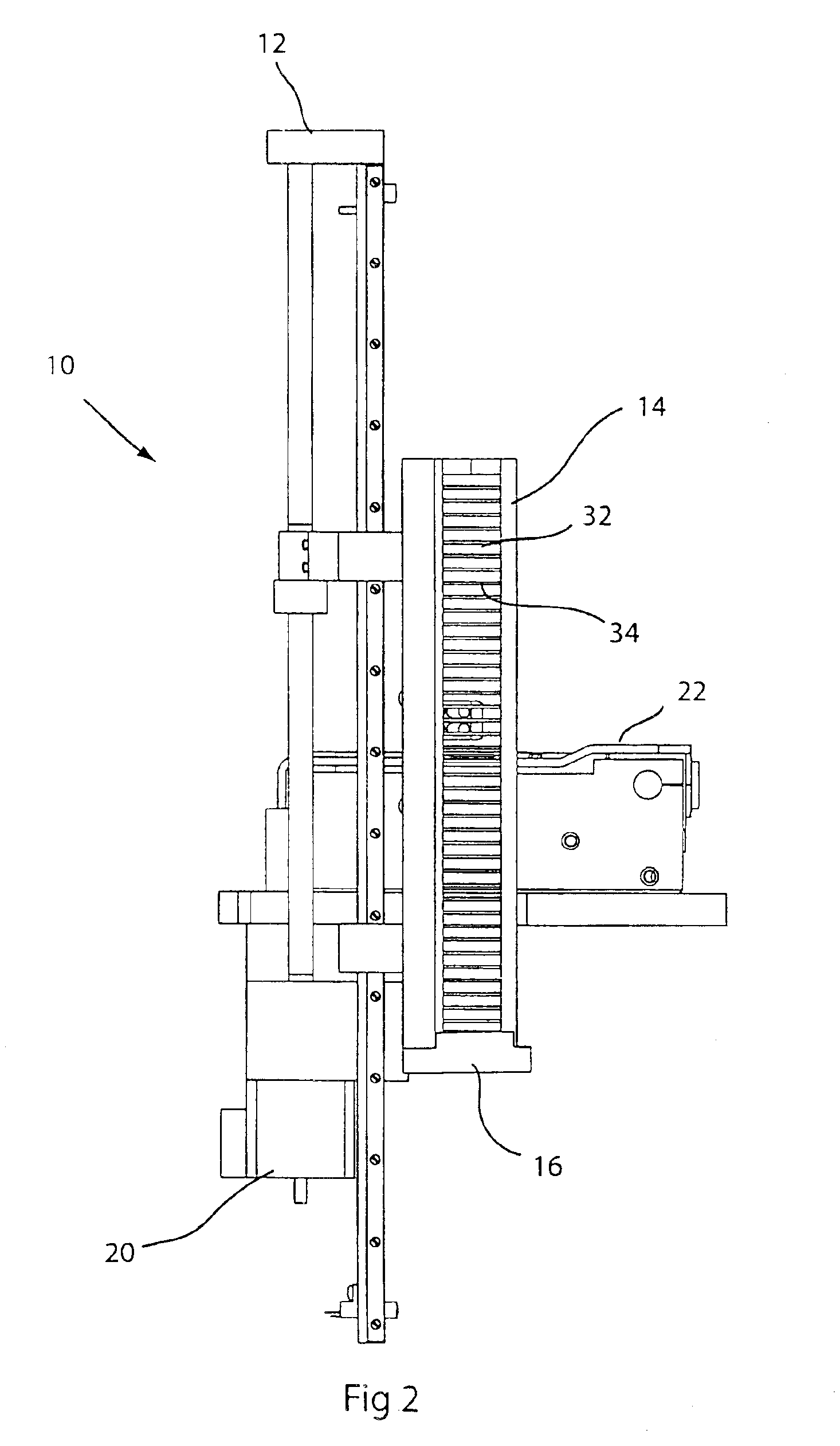
Stabilizing a substrate using a vacuum preload air bearing chuck
ActiveUS20080229811A1Improve rigidityAvoid deformationLinear bearingsGas cushion bearingsAir bearingEngineering
Substrate processing method and apparatus are disclosed. The substrate processing apparatus includes a non-contact air bearing chuck with a vacuum preload.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Apparatus and method for supporting, positioning and rotating a substrate in a processing chamber
ActiveUS20080276864A1Increase pressureReduce stressLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAir bearingThin layer
An apparatus and method for supporting, positioning and rotating a substrate are provided. In one embodiment, a support assembly for supporting a substrate includes an upper base plate and a lower base plate. The substrate is floated on a thin layer of air over the upper base plate. A positioning assembly includes a plurality of air bearing edge rollers or air flow pockets used to position the substrate in a desired orientation inside above the upper base plate. A plurality of slanted apertures or air flow pockets are configured in the upper base plate for flowing gas therethrough to rotate the substrate to ensure uniform heating during processing.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
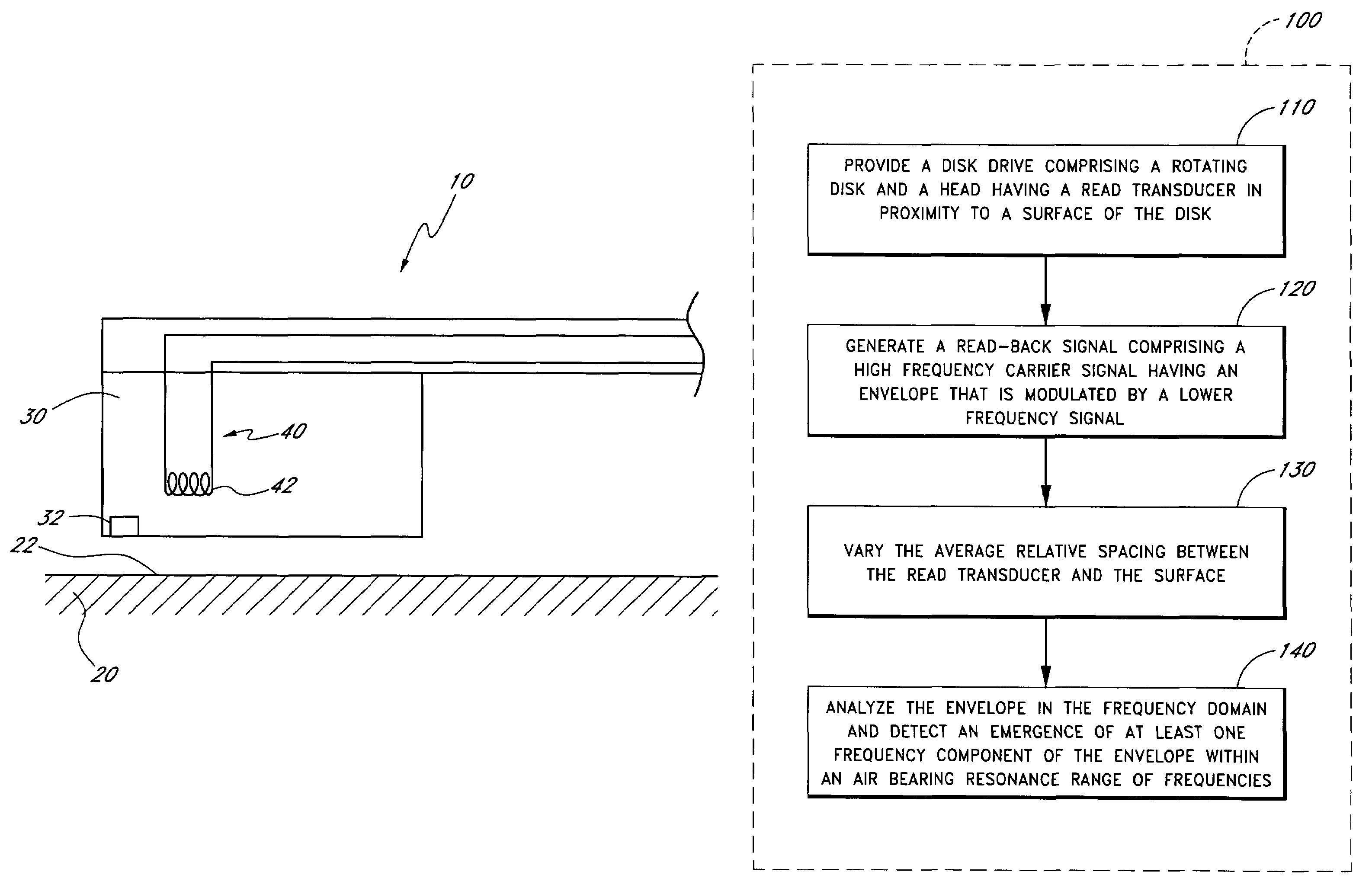
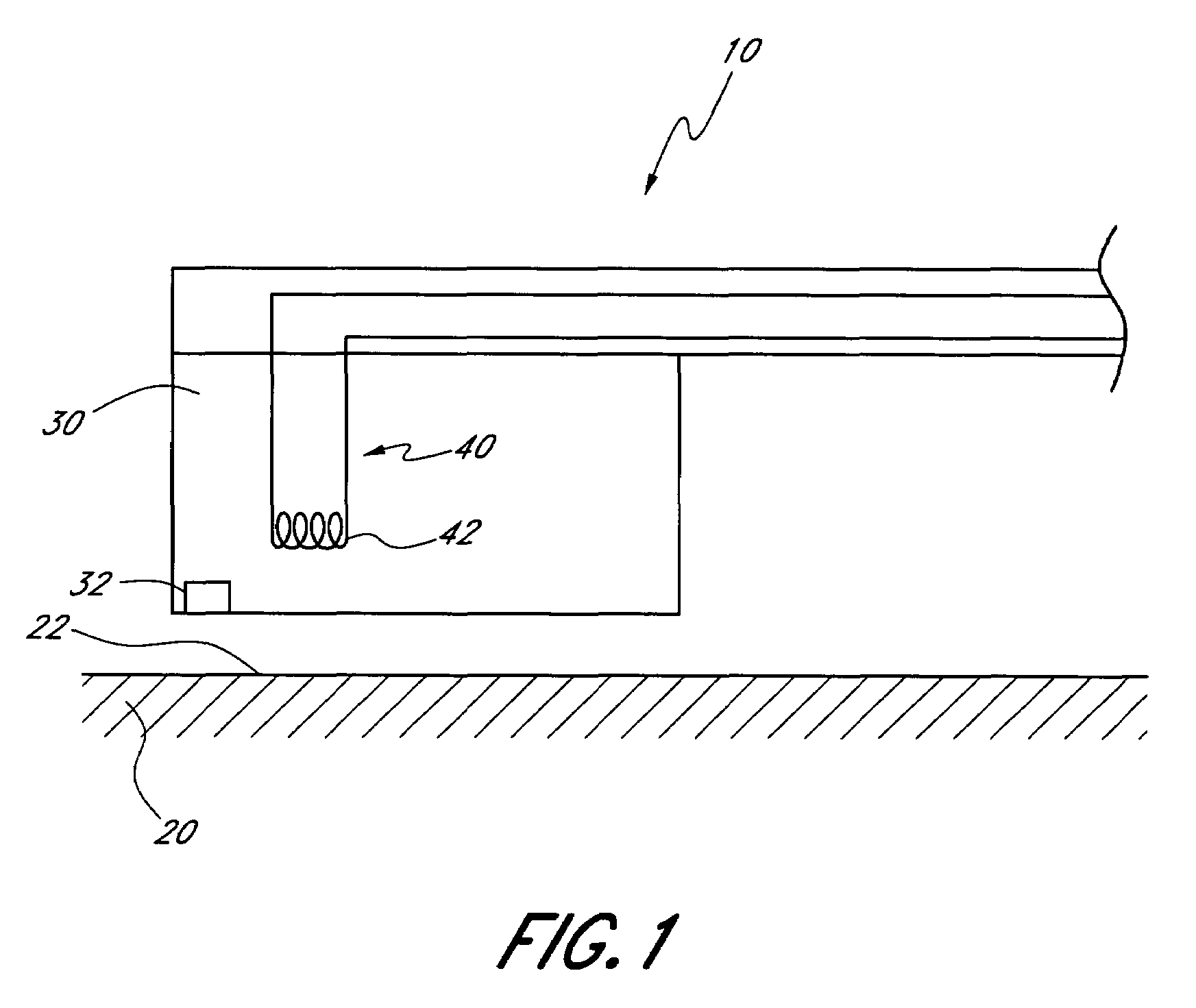
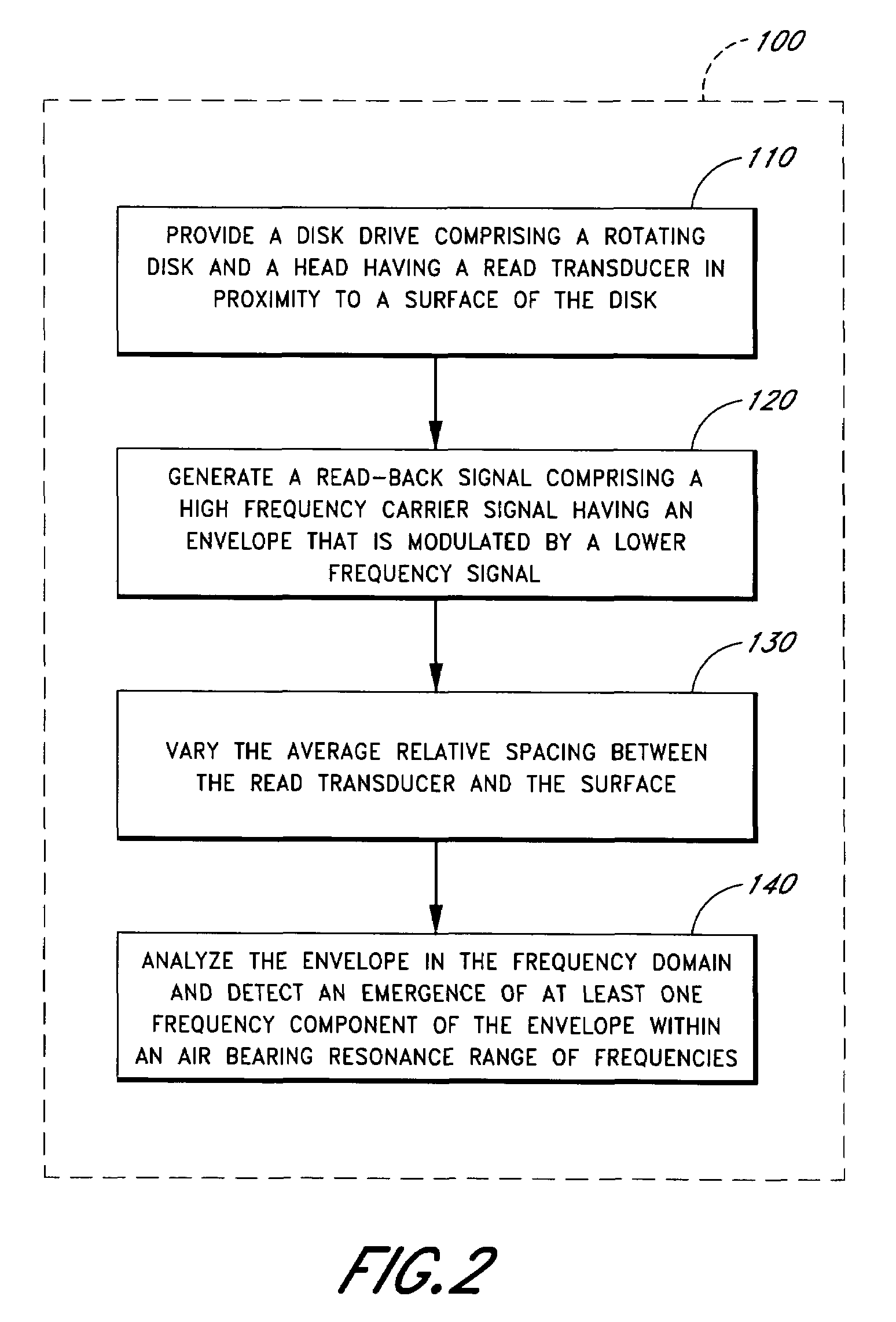
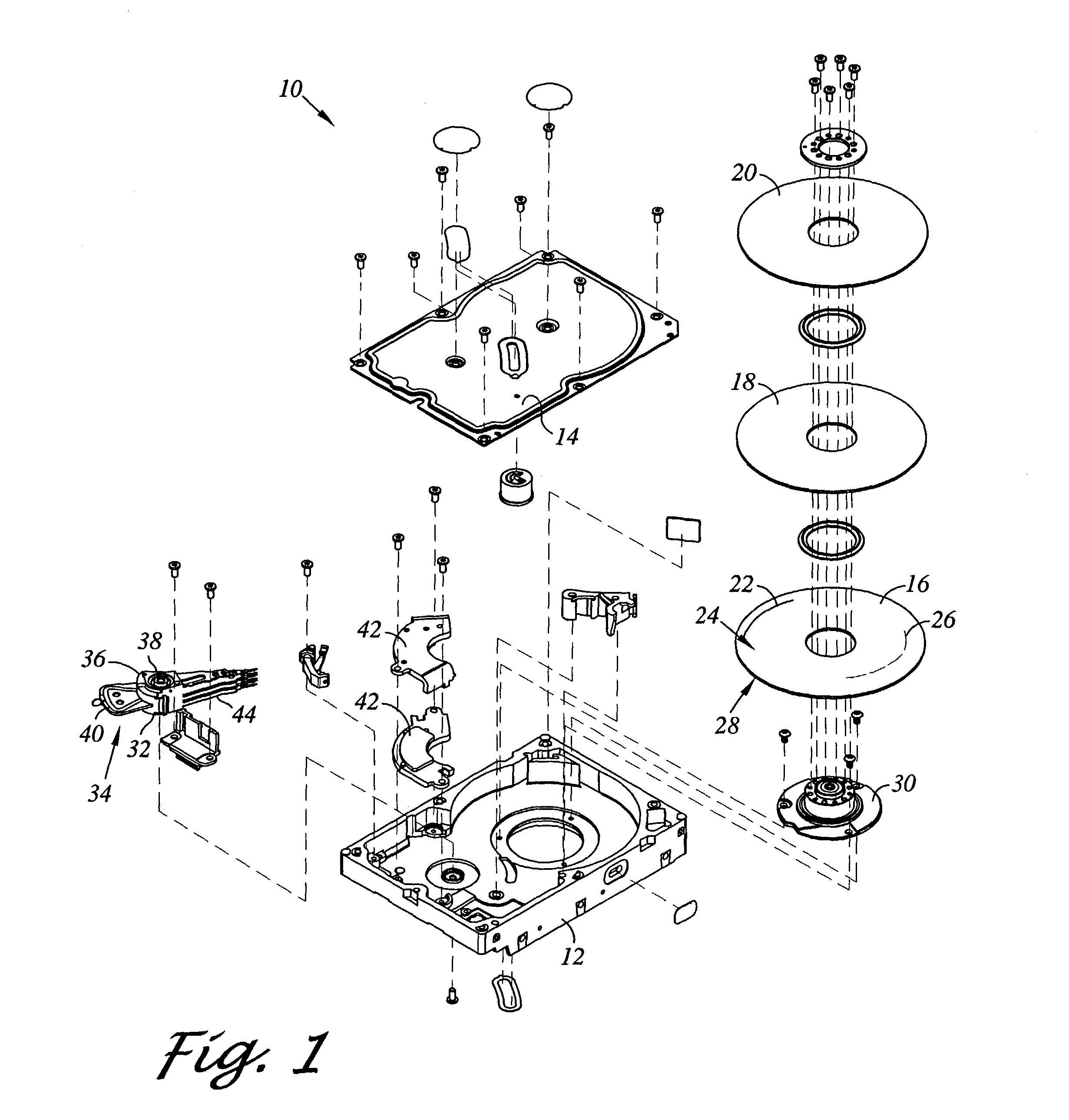
Method of monitoring operation of a disk drive by analyzing the envelope of a read-back signal in the frequency domain
A method monitors operation of a disk drive. The method includes providing a disk drive which includes a rotating disk and a head having a read transducer in proximity to a surface of the disk and an adjustment mechanism which controllably adjusts an average relative spacing between the read transducer and the surface. The method further includes generating a read-back signal by reading from the surface using the read transducer. The read-back signal includes a high frequency carrier signal having an envelope that is modulated by a lower frequency signal. The method further includes varying the average relative spacing between the read transducer and the surface using the adjustment mechanism. The method further includes analyzing the envelope in the frequency domain and detecting an emergence of at least one frequency component of the envelope within an air bearing resonance range of frequencies.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
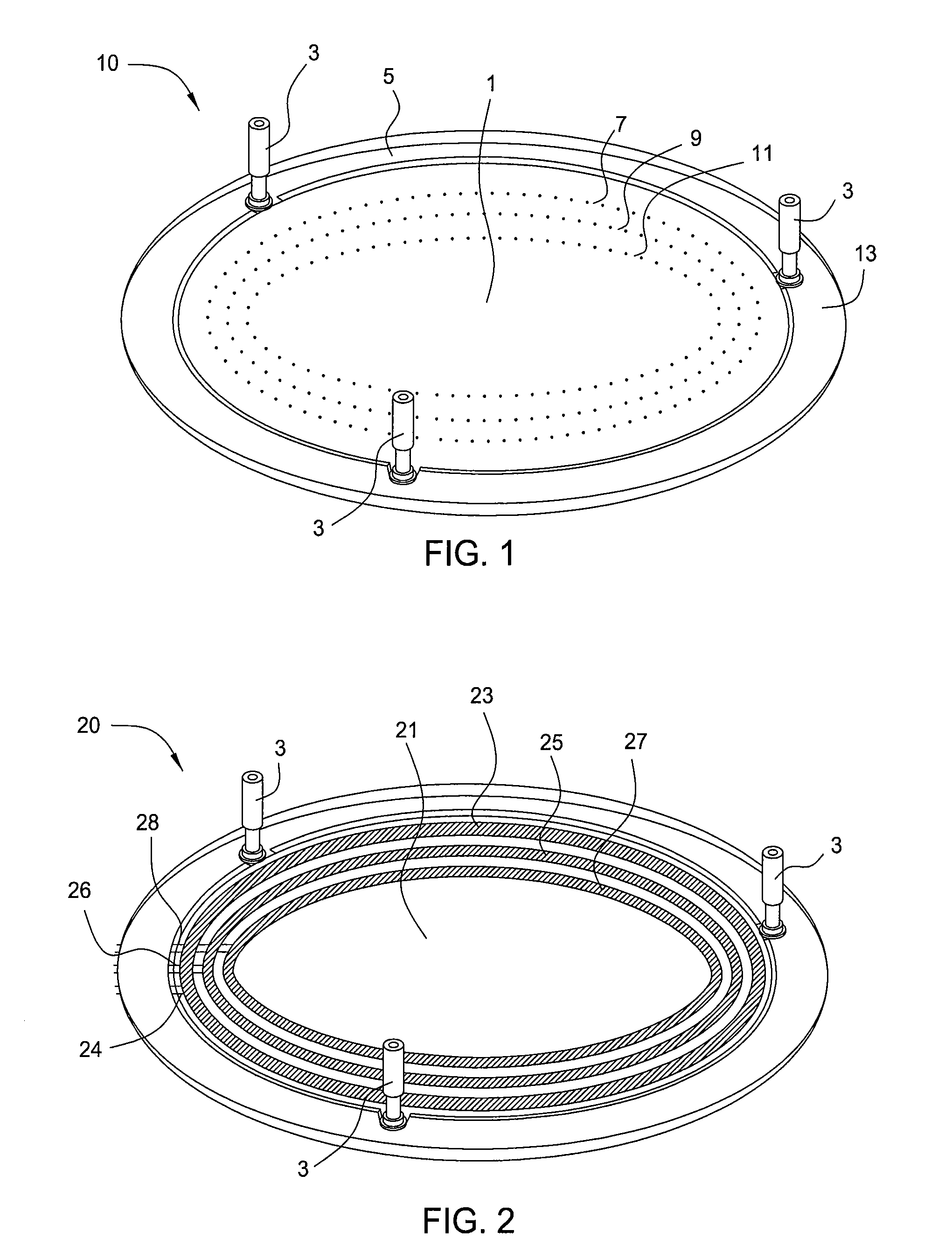
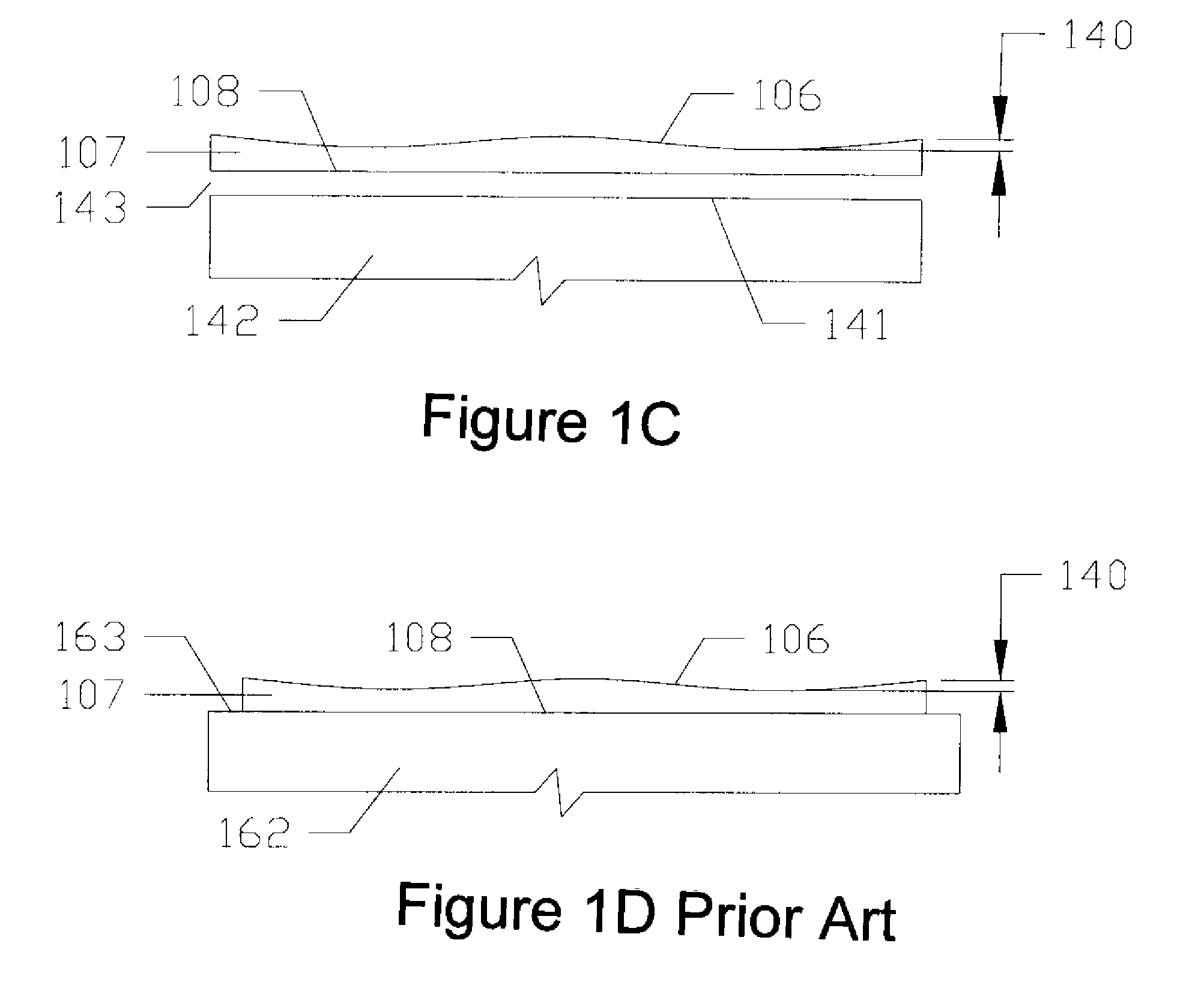
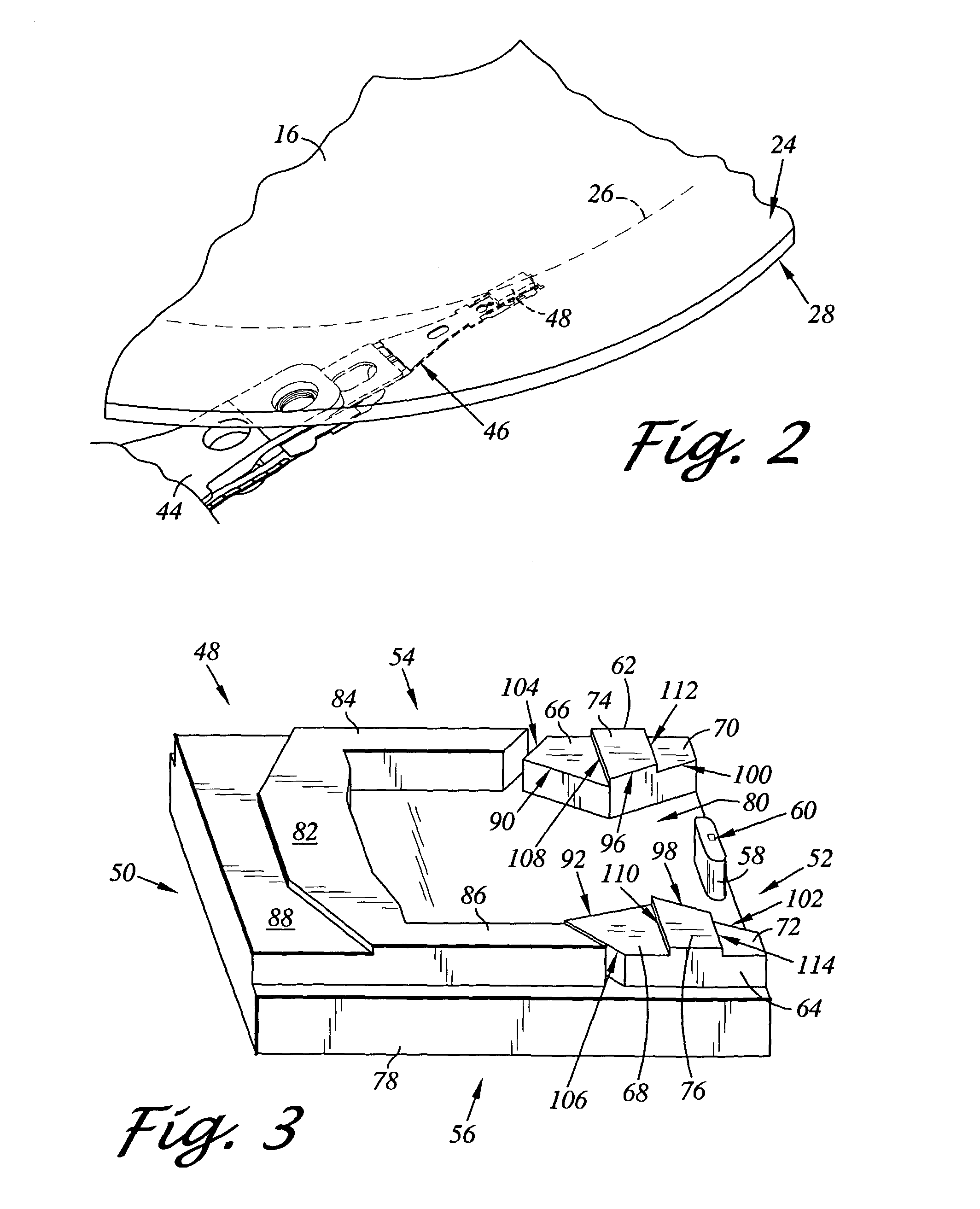
Air bearing having a cavity patch surface coplanar with a leading edge pad surface
InactiveUS6879464B2Improved air bearing surface designIncrease insensitivityFluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageLeading edgeAir bearing
An air bearing surface for read / write head of a magnetic disk drive is disclosed. The air bearing surface includes a trailing edge pad and a leading edge pad with trailing portions. A cavity is defined between the trailing edge pad and the trailing portions of the leading edge pad. A cavity patch is disposed within the cavity. The cavity patch can be disposed within the cavity towards one side of the read / write head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
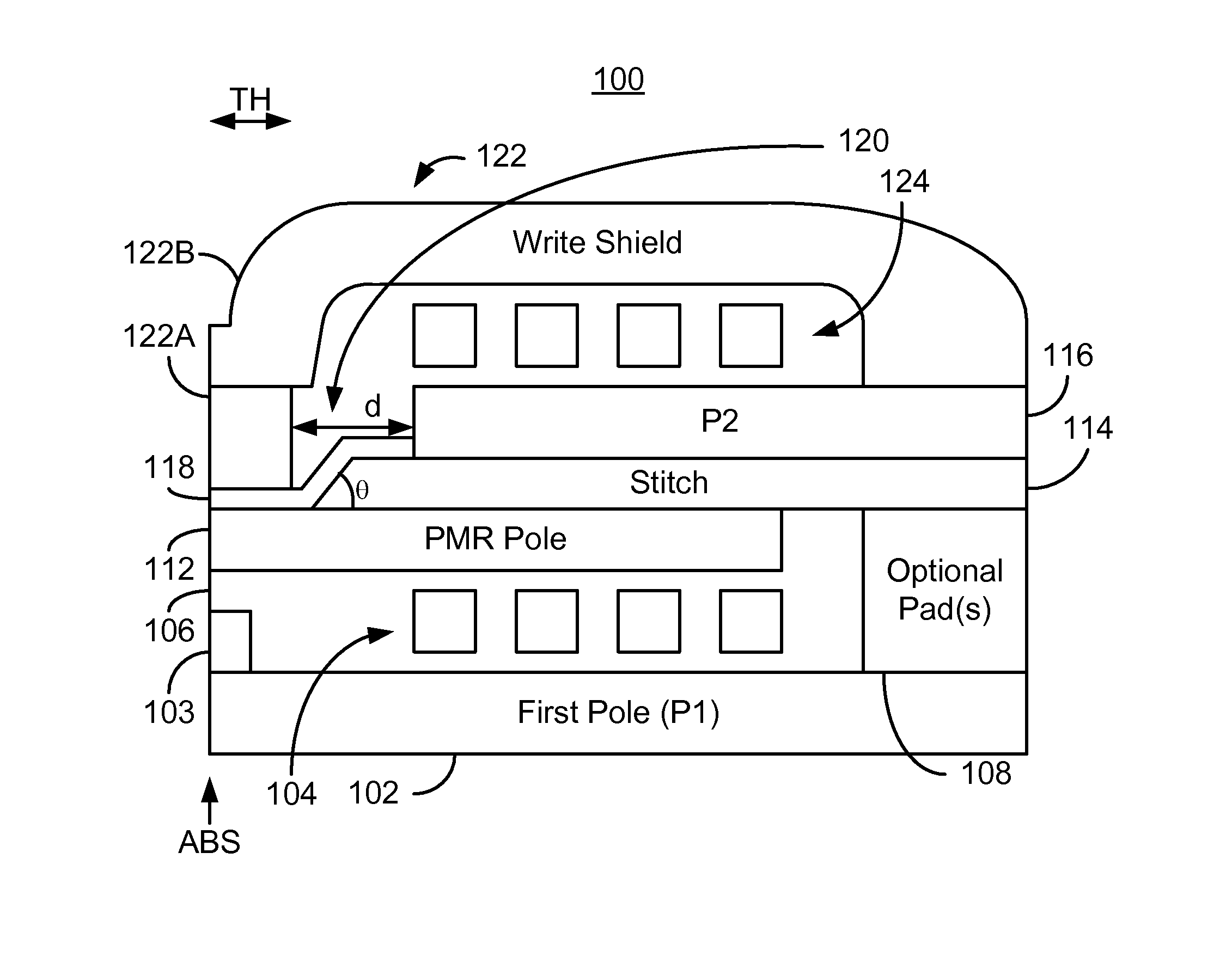
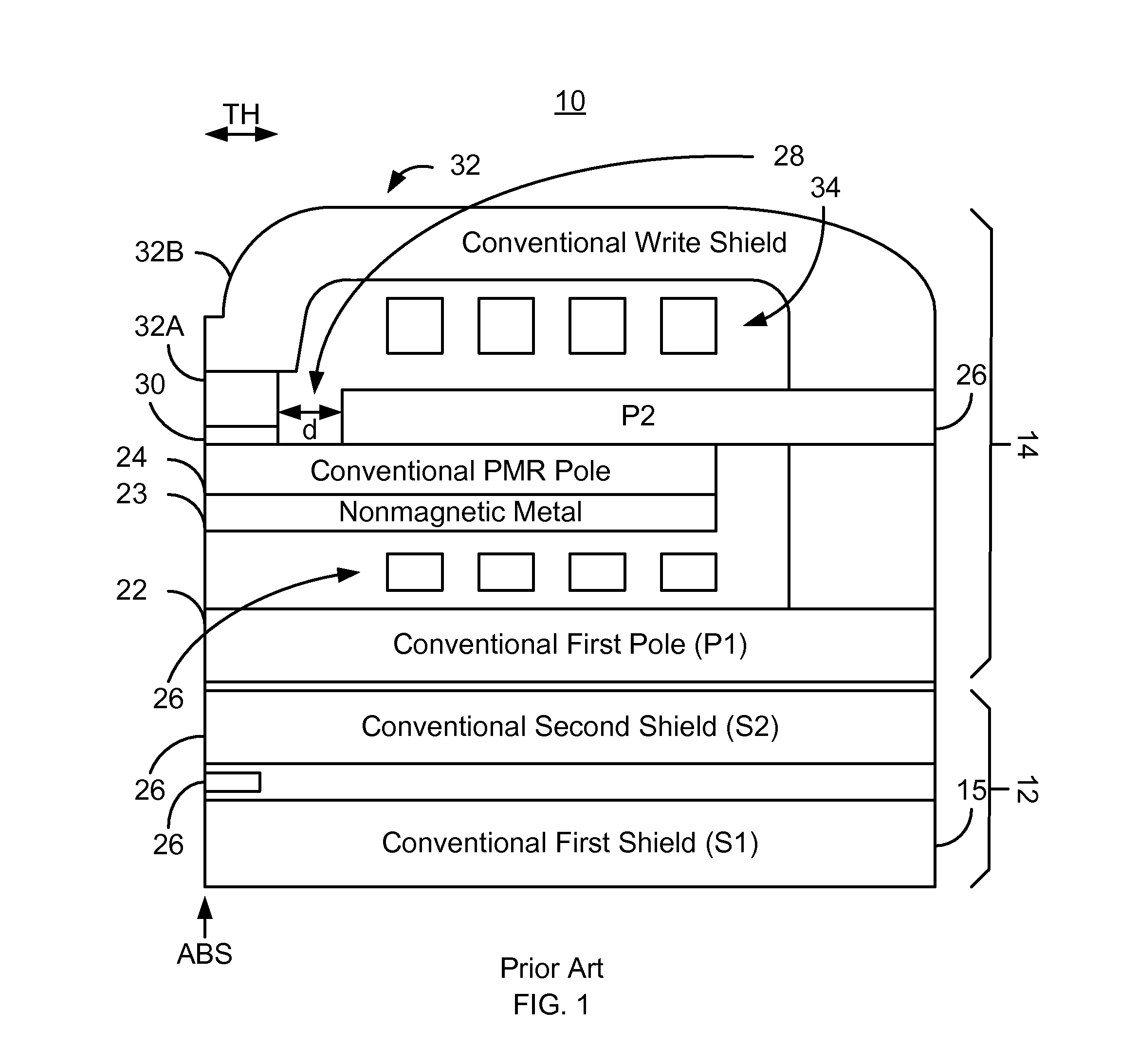
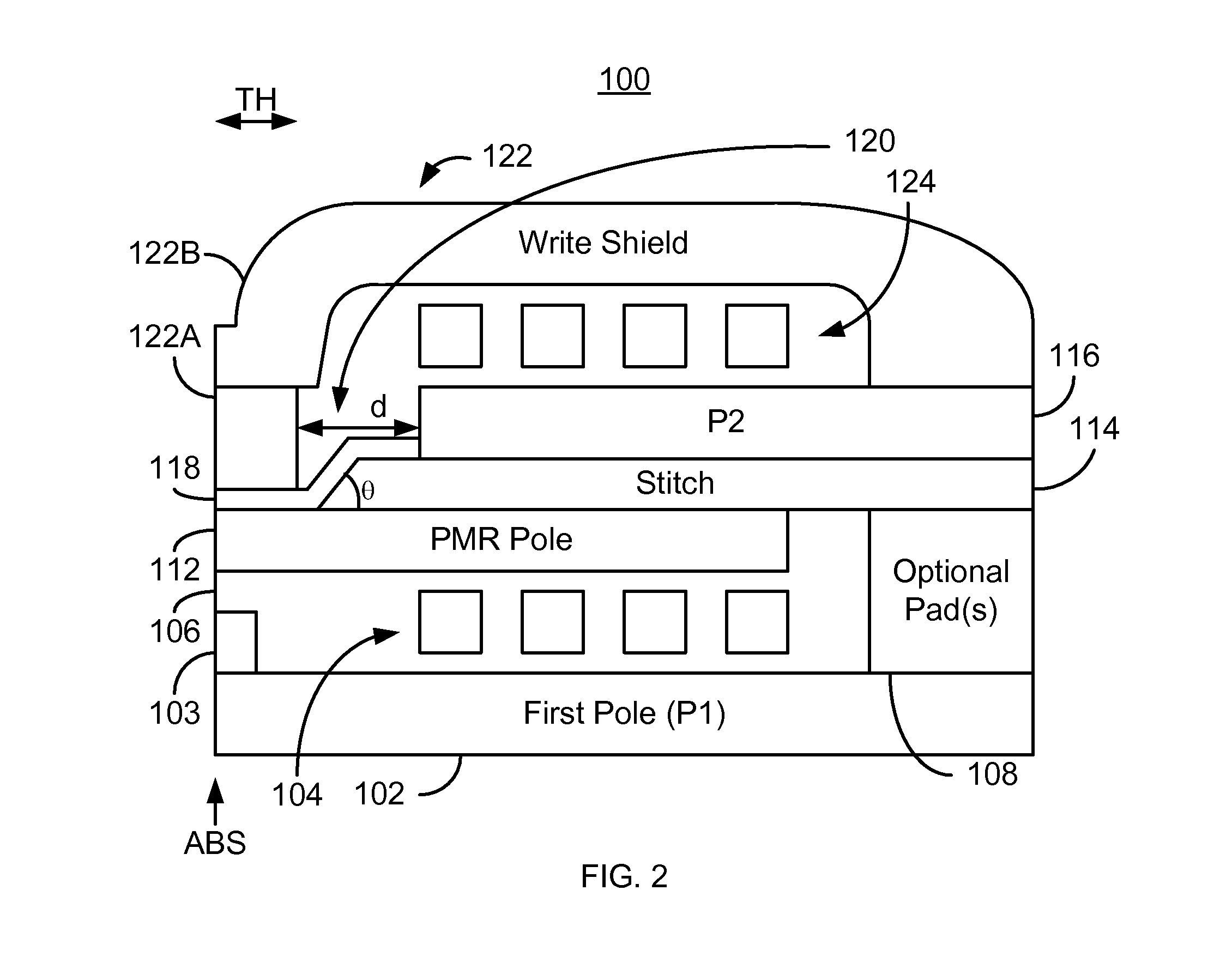
PMR head with an angled stitch layer
ActiveUS8537494B1Record information storageHeads for perpendicular magnetisationsMagnetic transducersAir bearing
A method and system for providing a magnetic transducer having an air-bearing surface (ABS) are described. The magnetic transducer includes a perpendicular magnetic recording (PMR) pole, an additional pole, a stitch, a shield, a write gap between the PMR pole and a portion of the shield, and at least one coil that energizes at least the additional pole. The PMR pole has a first front portion proximate to the ABS, while the additional pole is recessed from the ABS. The stitch resides between the PMR pole and the additional pole and has a stitch front portion between the front portion of the PMR pole and the additional pole. At least a portion of the write gap resides on the front portion of the PMR pole. At least a portion of the additional pole resides between the PMR pole and the shield.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
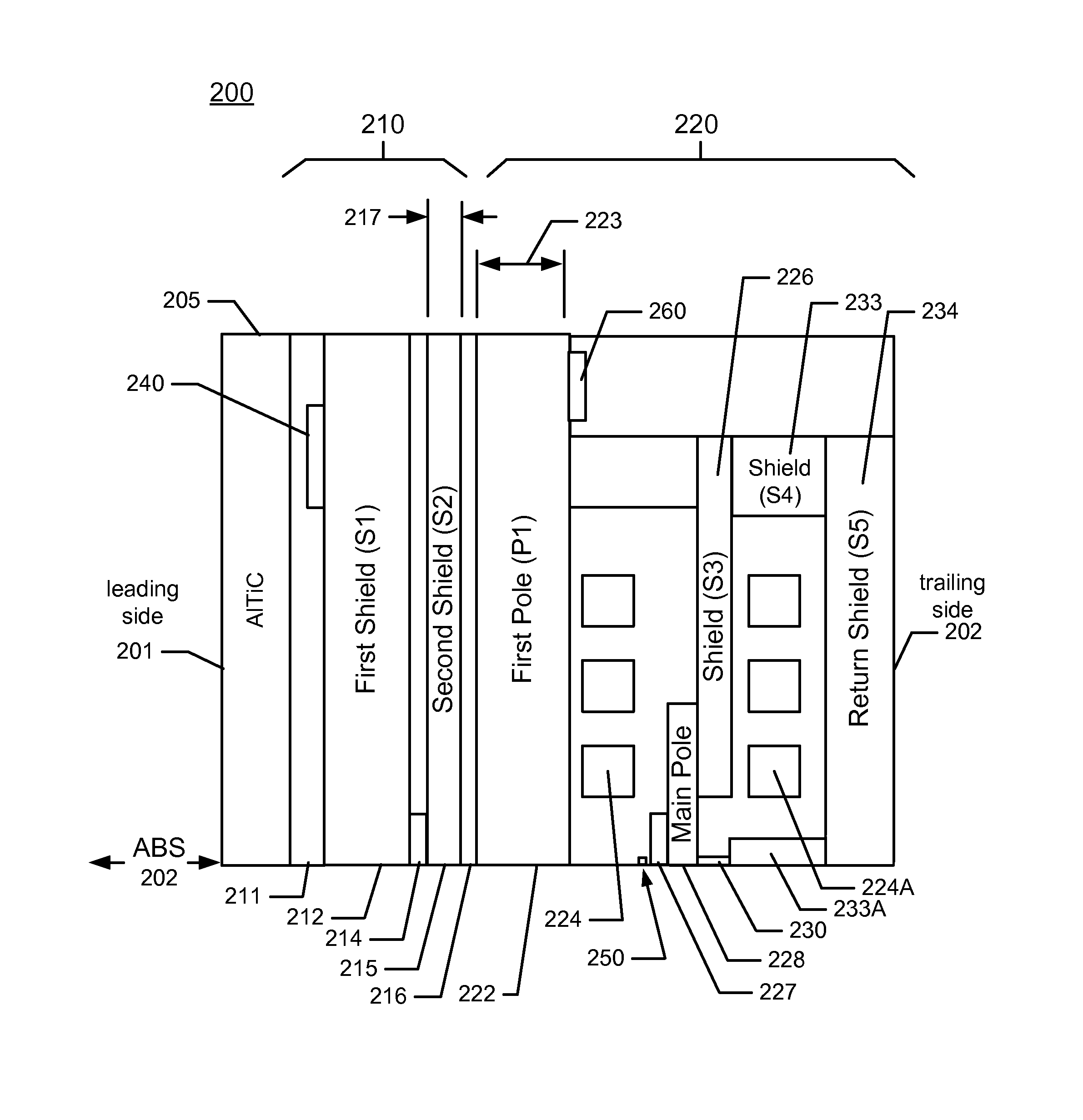
Magnetic recording head with dynamic fly height heating and having thermally controlled pole tip protrusion to control and protect reader element
ActiveUS8749920B1Record information storageHeads for perpendicular magnetisationsHard disc driveMagnetic transducers
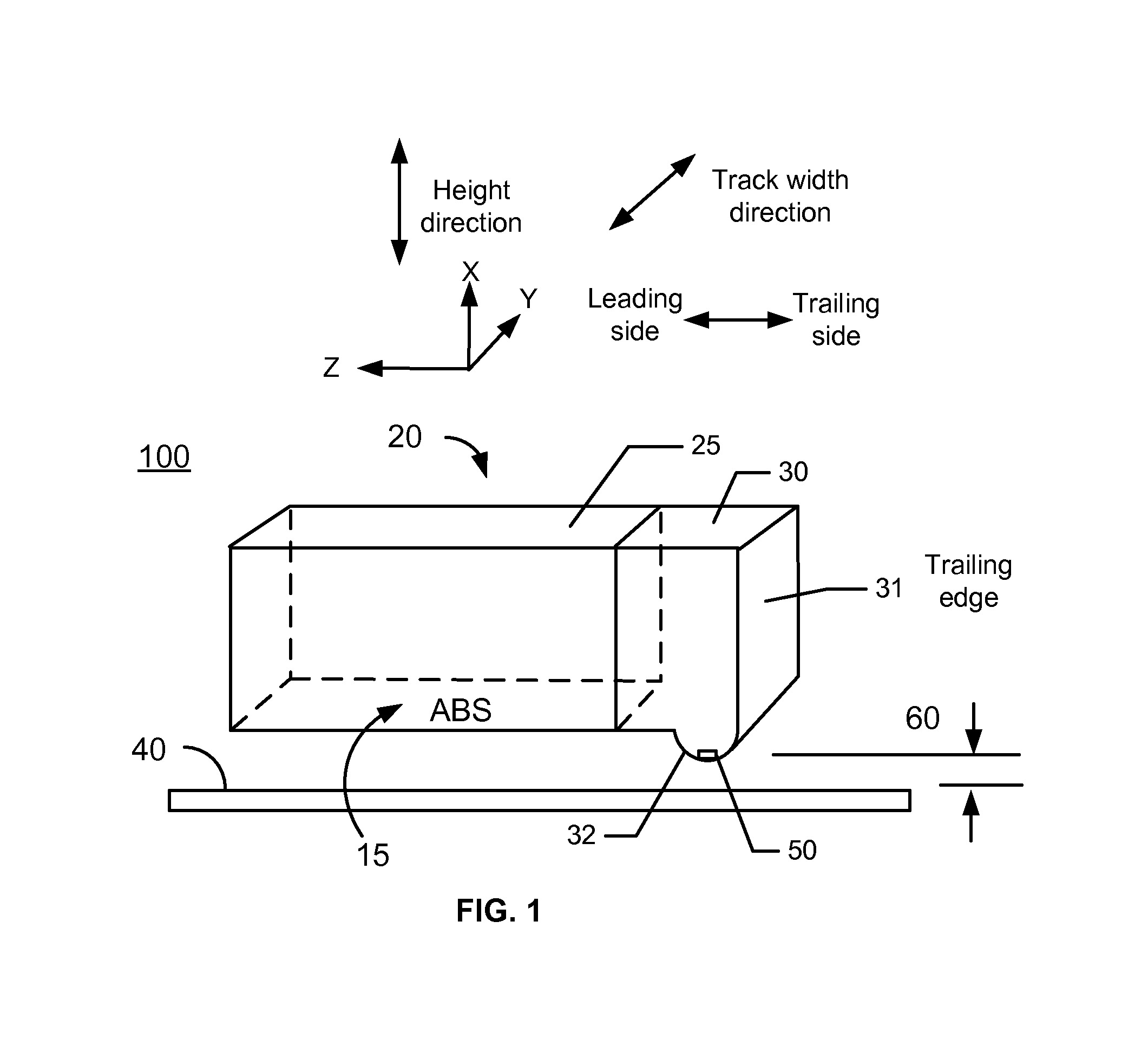
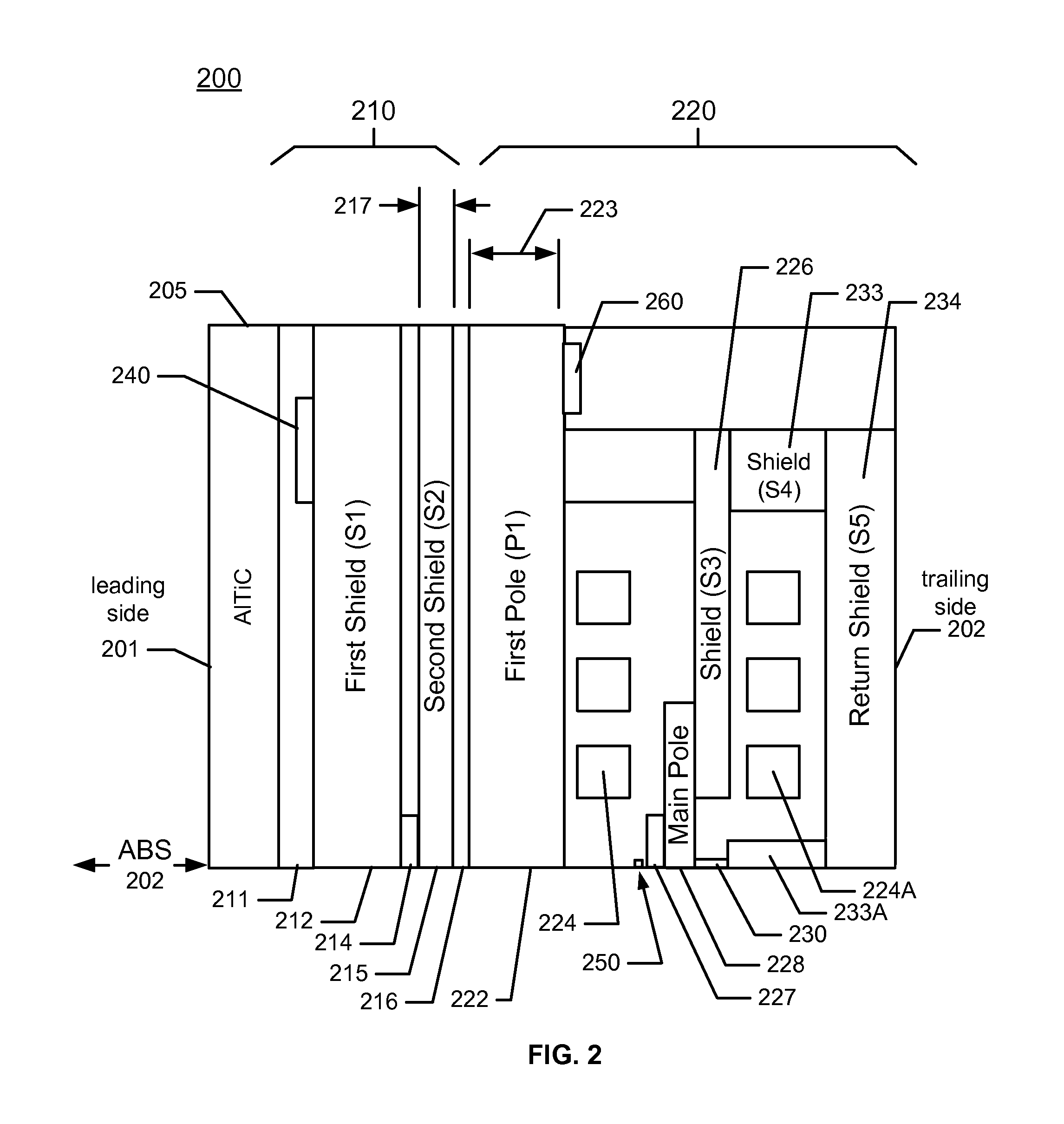
A magnetic recording device includes a slider having an air bearing surface (ABS), a leading side, and a trailing side and a head residing on the slider. The head has a first magnetic transducer and a first heater for heating an area proximal to the first magnetic transducer. A first shield (S1) comprising a first material is on the leading side of the first magnetic transducer and a second shield (S2) comprising the first material is on the trailing side of the first magnetic transducer. A first pole (P1) comprising the first material is on the trailing side of the second shield (S2), and the first pole (P1) is between 0.6 micron and 2.0 micron thick; and the second shield (S2) is less than 0.6 micron thick. A hard disk drive includes the magnetic recording device.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
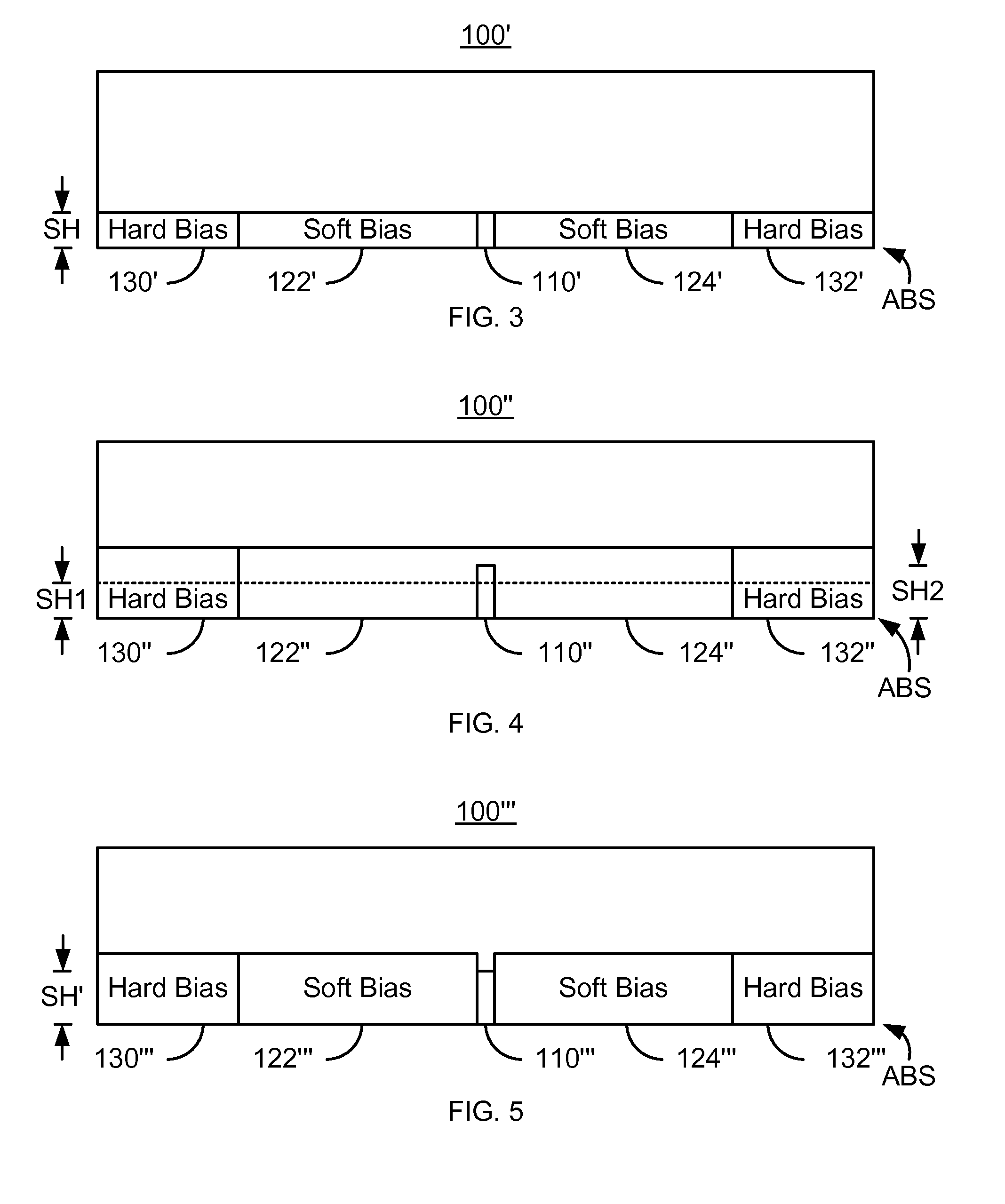
Method and system for providing a read transducer having soft and hard magnetic bias structures
ActiveUS8760823B1Record information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsAir bearingMagnetic transducers
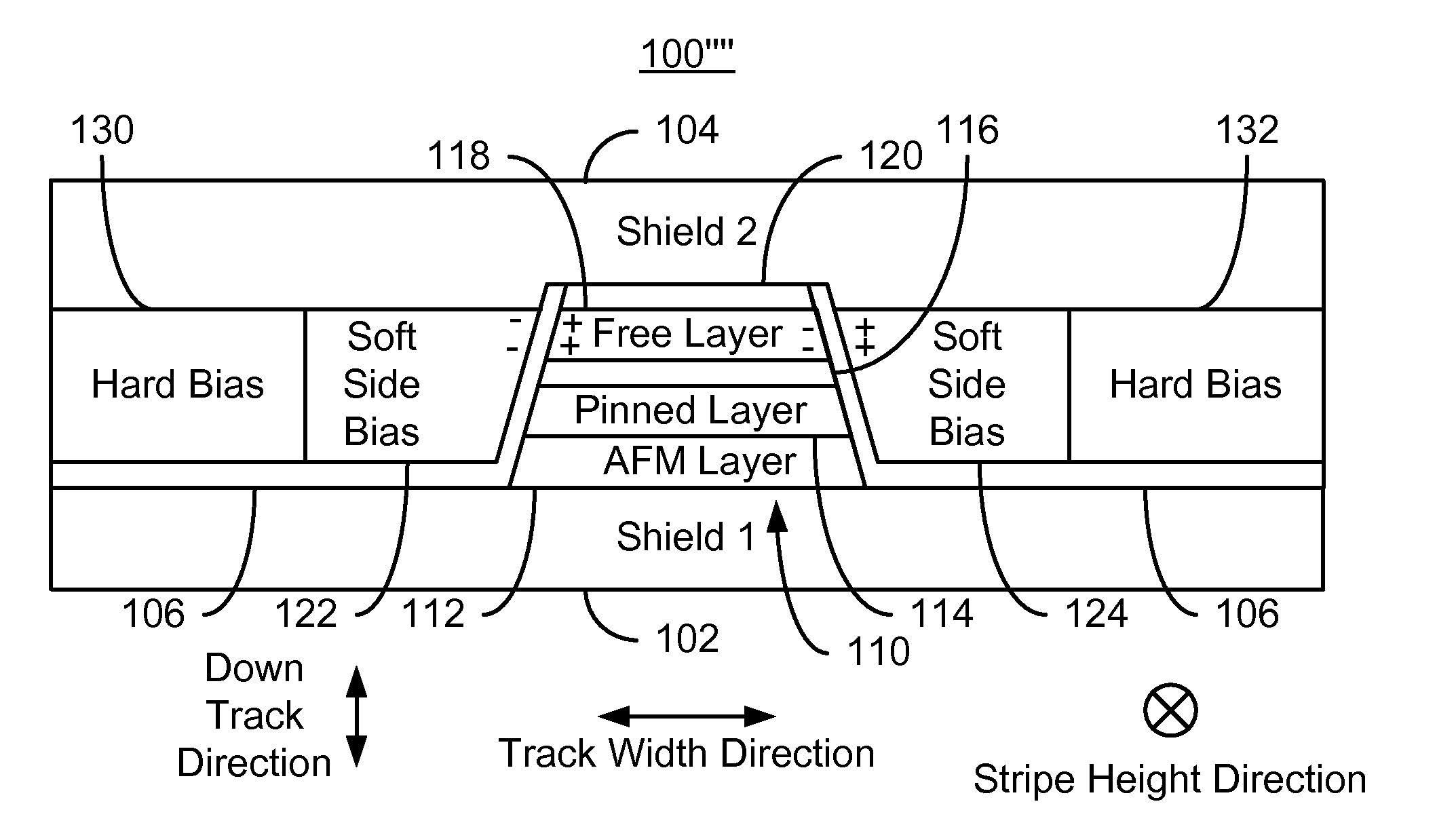
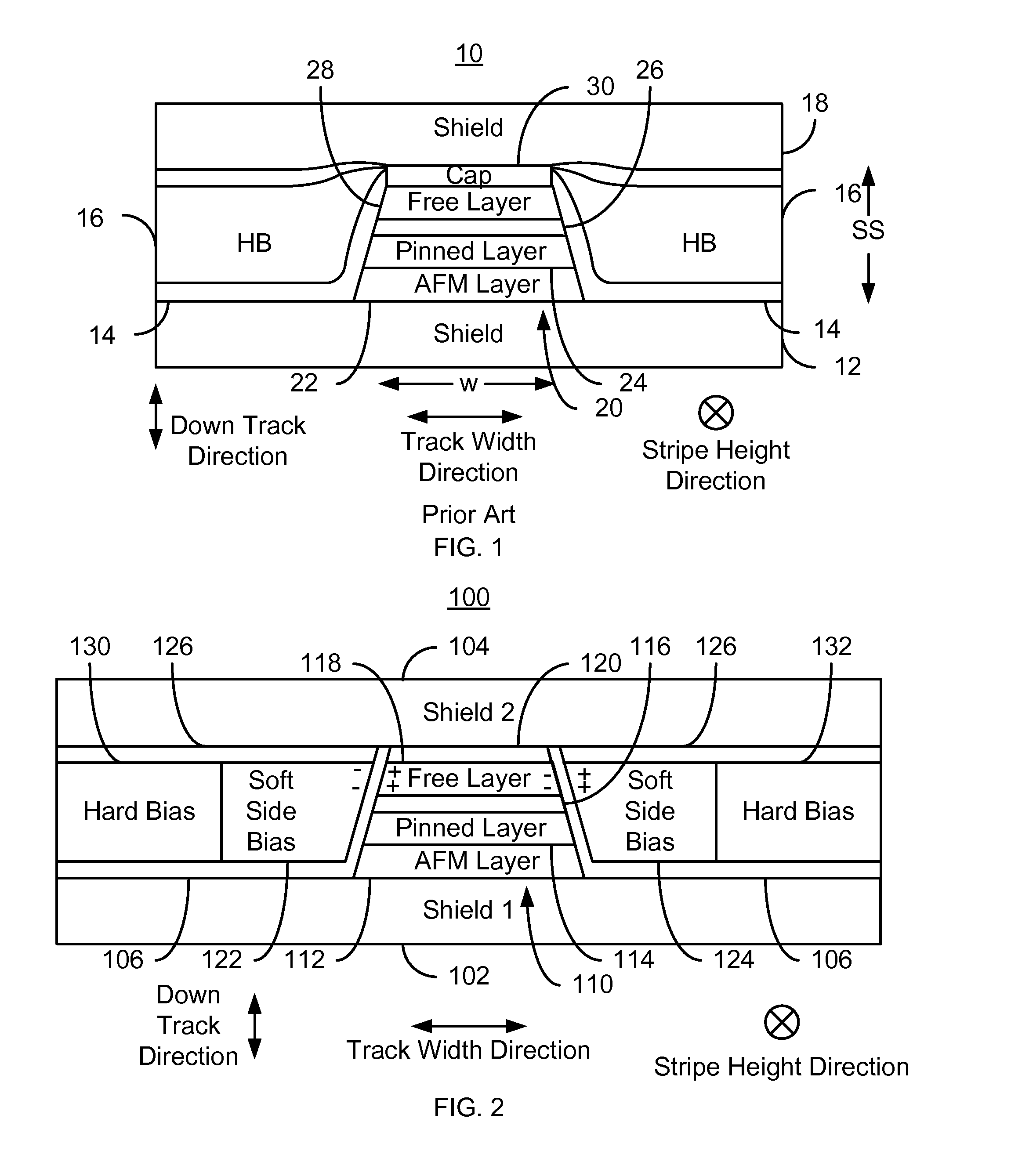
A method and system provide a magnetic transducer having an air-bearing surface (ABS). The magnetic transducer includes a first shield, a read sensor, at least one soft magnetic bias structure and at least one hard bias structure. The read sensor includes a sensor layer that has at least one edge in the track width direction along the ABS. The soft magnetic bias structure(s) are adjacent to the edge(s) of the sensor layer. The soft magnetic bias structure has a first permeability. The soft bias structure(s) are between the read sensor and the hard bias structure(s). The hard bias structure(s) are adjacent to a portion of the soft bias structure(s) and have a second permeability. The first permeability is at least ten multiplied by the second permeability.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Stabilizing a substrate using a vacuum preload air bearing chuck
ActiveUS7607647B2Improve rigidityAvoid deformationLinear bearingsGas cushion bearingsAir bearingEngineering
Substrate processing method and apparatus are disclosed. The substrate processing apparatus includes a non-contact air bearing chuck with a vacuum preload.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Non-contact porous air bearing and glass flattening device
Thin substrates, such as flat glass panels, are levitated on a porous media air bearing creating a pressurized film of air and preloaded against the air film by negative pressure areas. The pressure can be distributed most uniformly across the pressure areas by defusing the pressure through a porous medium. Such a bearing can be used for glass flattening by holding the glass such that the unevenness is migrated to the side opposite the side to be worked on.
Owner:NEW WAY MACHINE COMPONENTS
Method and system for continuous large-area scanning implantation process
InactiveUS20080038908A1Reduce channeling effectElectric discharge tubesFinal product manufactureAir bearingBiomedical engineering
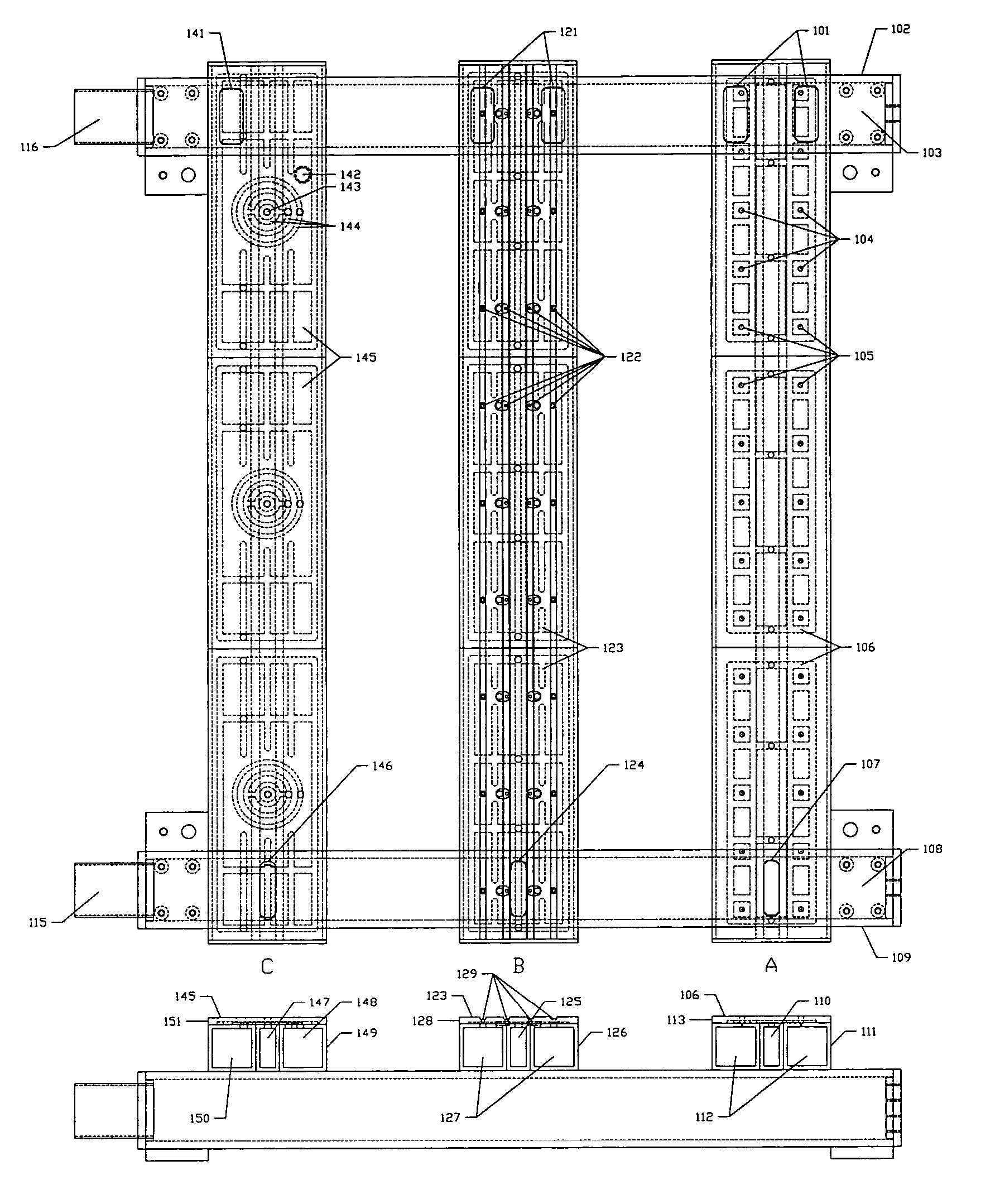
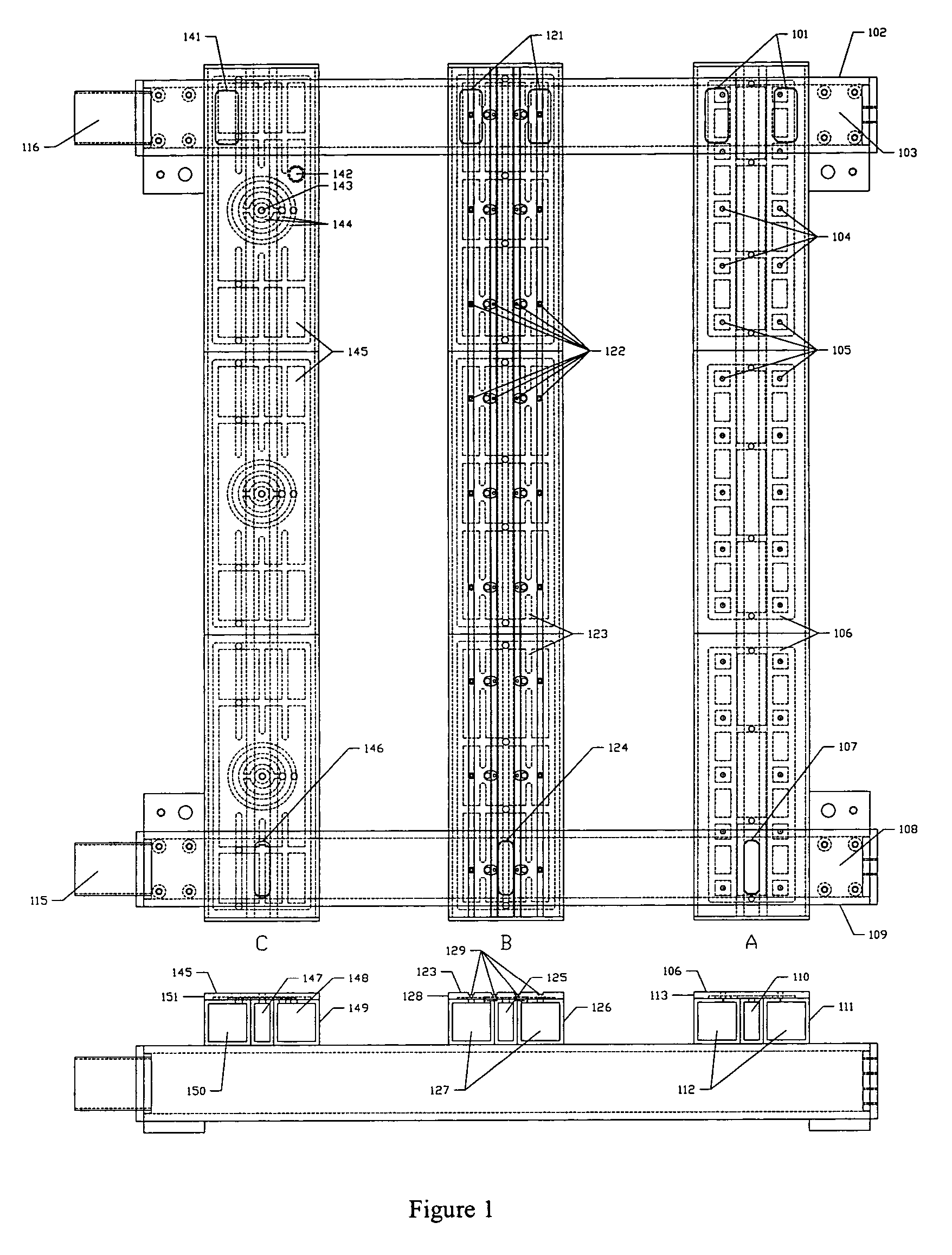
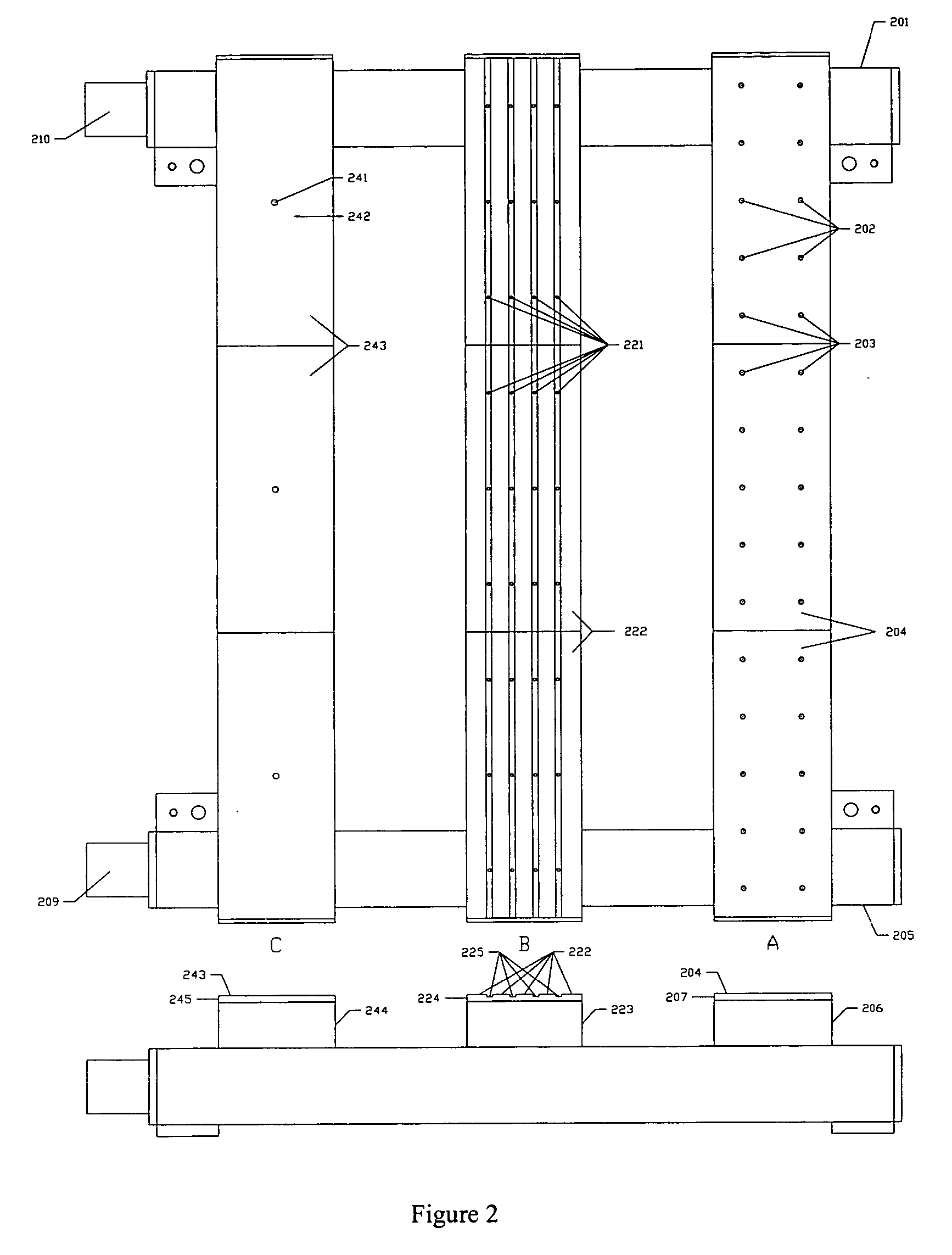
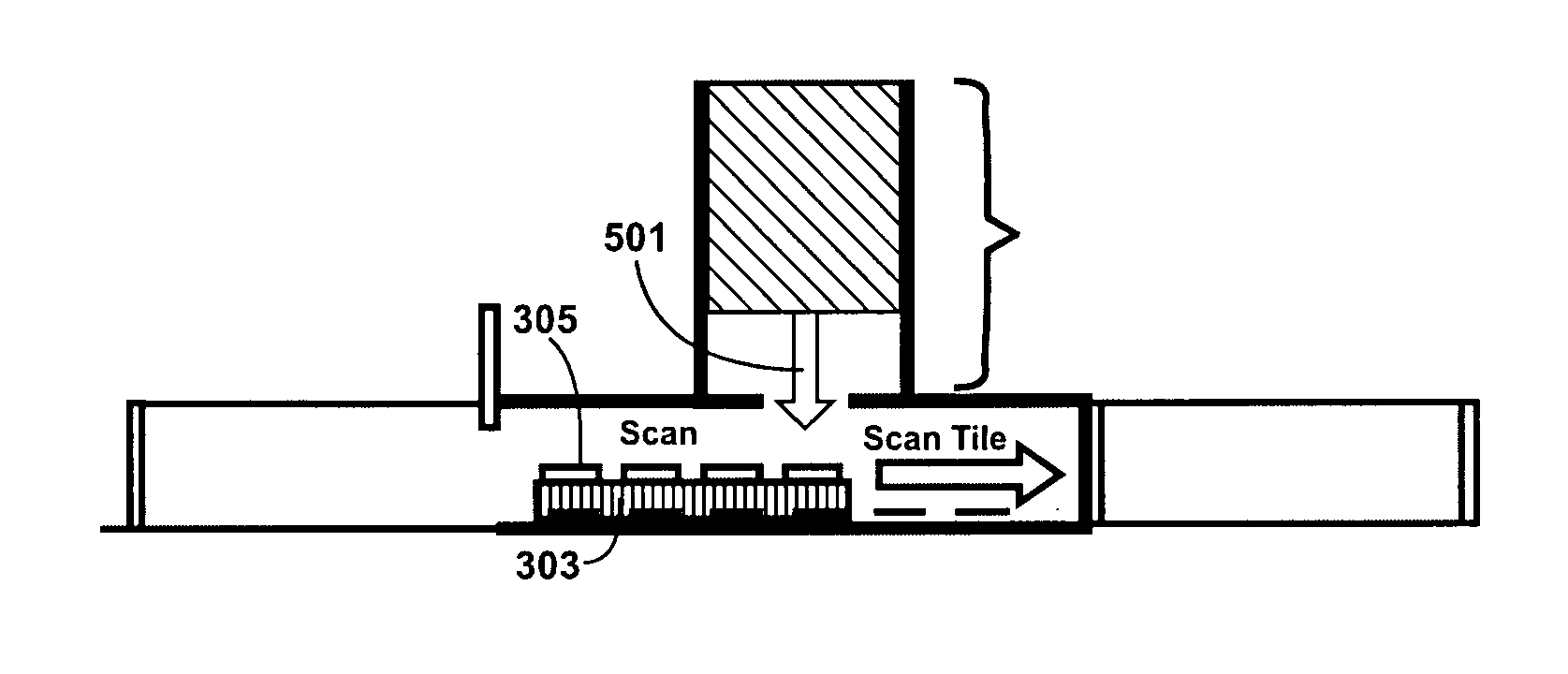
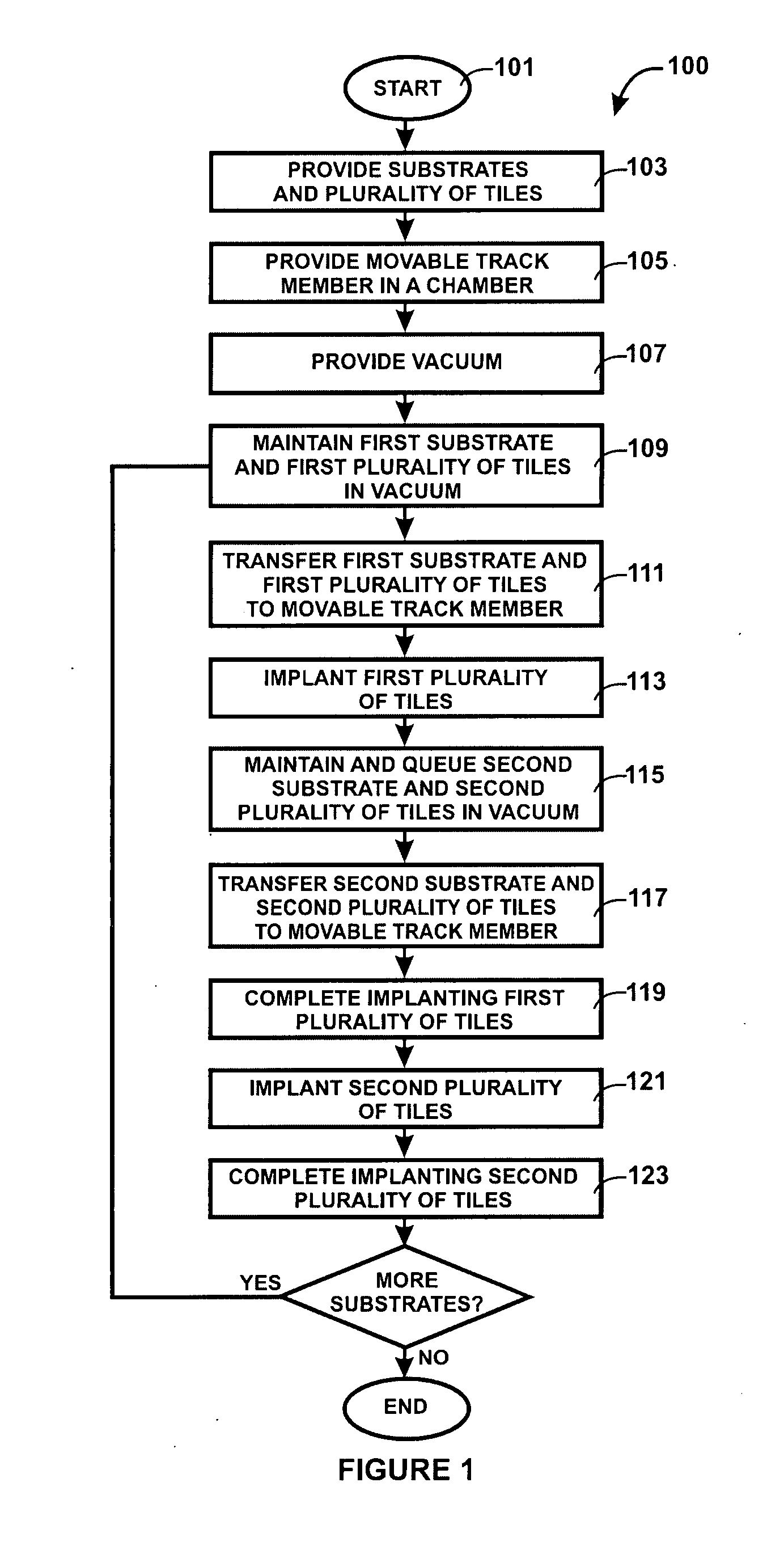
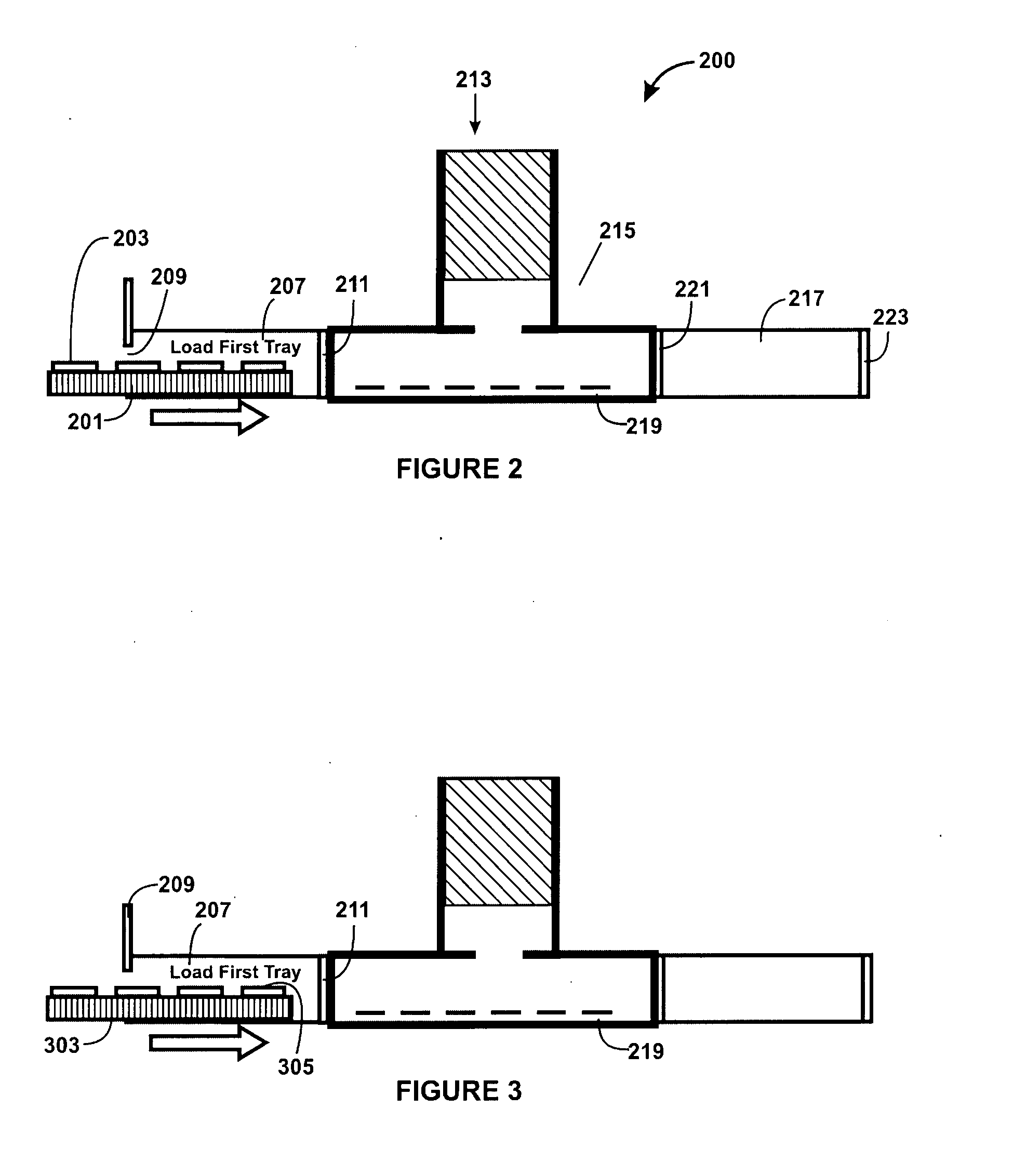
A method for manufacturing doped substrates using a continuous large area scanning implantation process is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method includes providing a movable track member. The movable track member is provided in a chamber. The chamber includes an inlet and an outlet. In a specific embodiment, the movable track member can include one or more rollers, air bearings, belt member, and / or movable beam member to provide one or more substrates for a scanning process. The method may also include providing a first substrate. The first substrate includes a first plurality of tiles. The method maintains the first substrate including the first plurality of tiles in a vacuum. The method includes transferring the first substrate including the first plurality of tiles from the inlet port onto the movable track member. The first plurality of tiles are subjected to a scanning implant process. The method also includes maintaining a second substrate including a second plurality of tiles in the vacuum. The method includes transferring the second substrate including a second plurality of tiles from the inlet port onto the movable track member. The method includes subjecting the second plurality of tiles to an implant process using the scanning implant process.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
Micro-structured drying for inkjet printers
InactiveUS20090031579A1Improve rigidityImprove protectionCombination devicesDrying solid materials with heatAir bearingDiffuse flow
A dryer operable in close proximity to and in series with an inkjet printhead comprises a heat source and an air bearing structure on one side of the predetermined path and having a pressurized air inlet and an air outlet adjacent to the drying position of the receiver medium. Air flow from the air bearing structure outlet forms an air bearing for the receiver medium. A microporous filter positioned at the outlet and being adapted to convert the air flow from the outlet to a diffuse flow, the microporous filter being formed of an inner layer of very fine screen for optimum air diffusion and an outer layer of courser woven screen to add rigidity and protection from scuffing.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Disk alignment apparatus and method for patterned media production
An apparatus and method for aligning a disk with an imprinting surface are described. In one embodiment, the apparatus has a die which includes an air-bearing mandrel having a tapered nose to engage an ID of the disk, a circular imprinting surface having a centerline concentric with the air-bearing mandrel, and an air-bearing cavity to position the disk. The axial movement of the top die towards the bottom die guides the ID of the disk into coincident alignment with the centerline of the top die.
Owner:WD MEDIA
Motor driven centrifugal compressor/blower
This invention provides a small, high efficiency, oil free motor driven compressor / blower suitable for providing pressurized, contamination-free gas and or air to transportation, industrial and aerospace fuel cell systems or other contaminant-intolerant applications. The motor driven compressor / blower rotor assembly is supported by foil air bearings and rotates at high speed by using a high frequency drive. The impeller is a centrifugal type design. The MDC can be easily integrated into the air management system of a fuel cell.
Owner:R & D DYNAMICS
Laser machining and scribing systems and methods
InactiveUS20110132885A1Welding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusAir bearingLight beam
A laser machining system may include an opposite side camera to provide workpiece alignment from an opposite side of the system (i.e., the side opposite the laser machining process). The opposite side camera may be used with an air bearing positioning stage, and a portion of the stage and / or the opposite side camera may be moved to allow the opposite side camera to image a feature on the workpiece to be aligned. The opposite side alignment may be used with back side scribing and / or dual side scribing of a workpiece with alignment from one or both sides of the workpiece. Laser machining systems and methods may also be used to provide quasi-stealth scribing and multi-beam scribing.
Owner:IPG PHOTONICS CORP
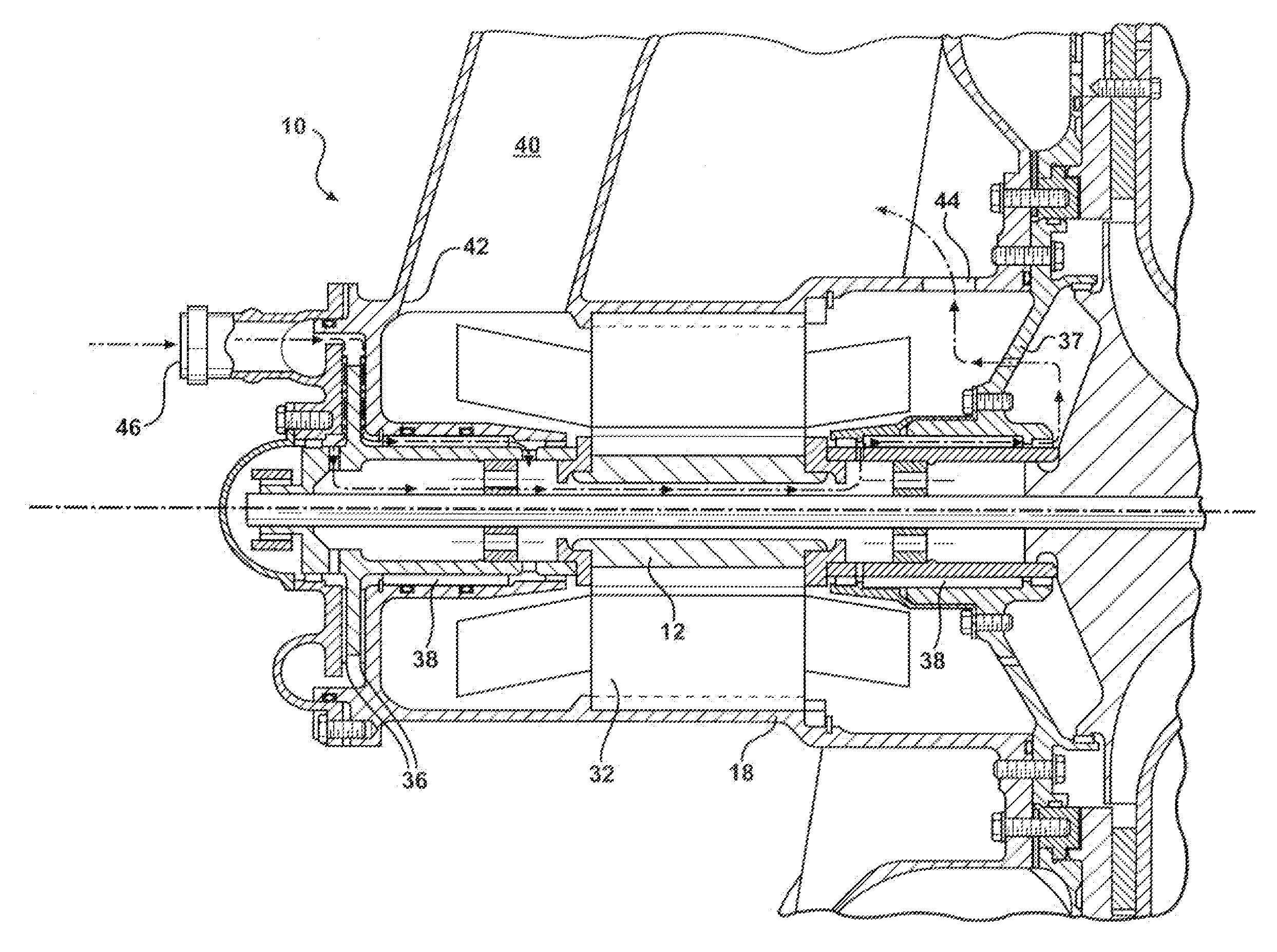
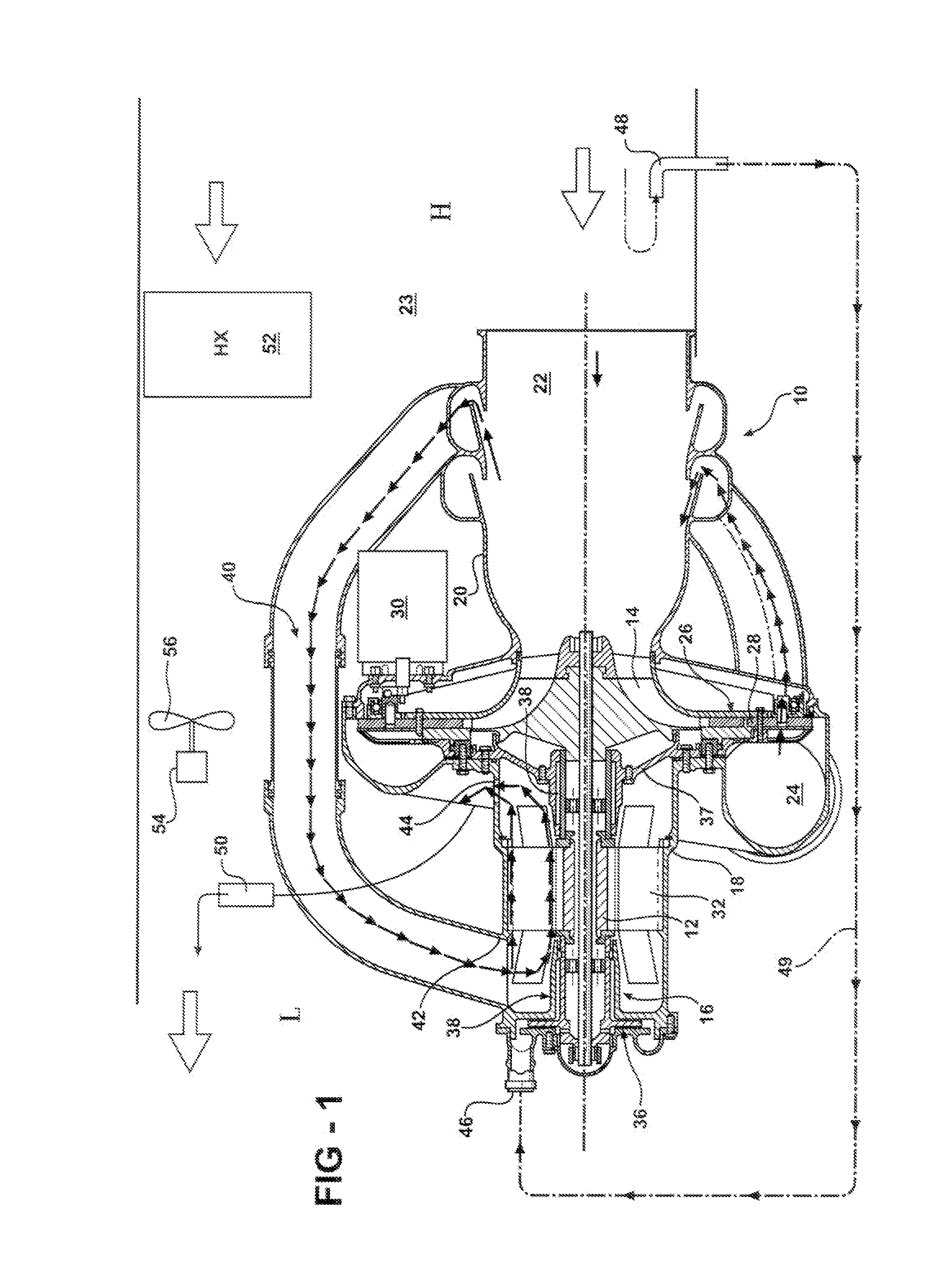
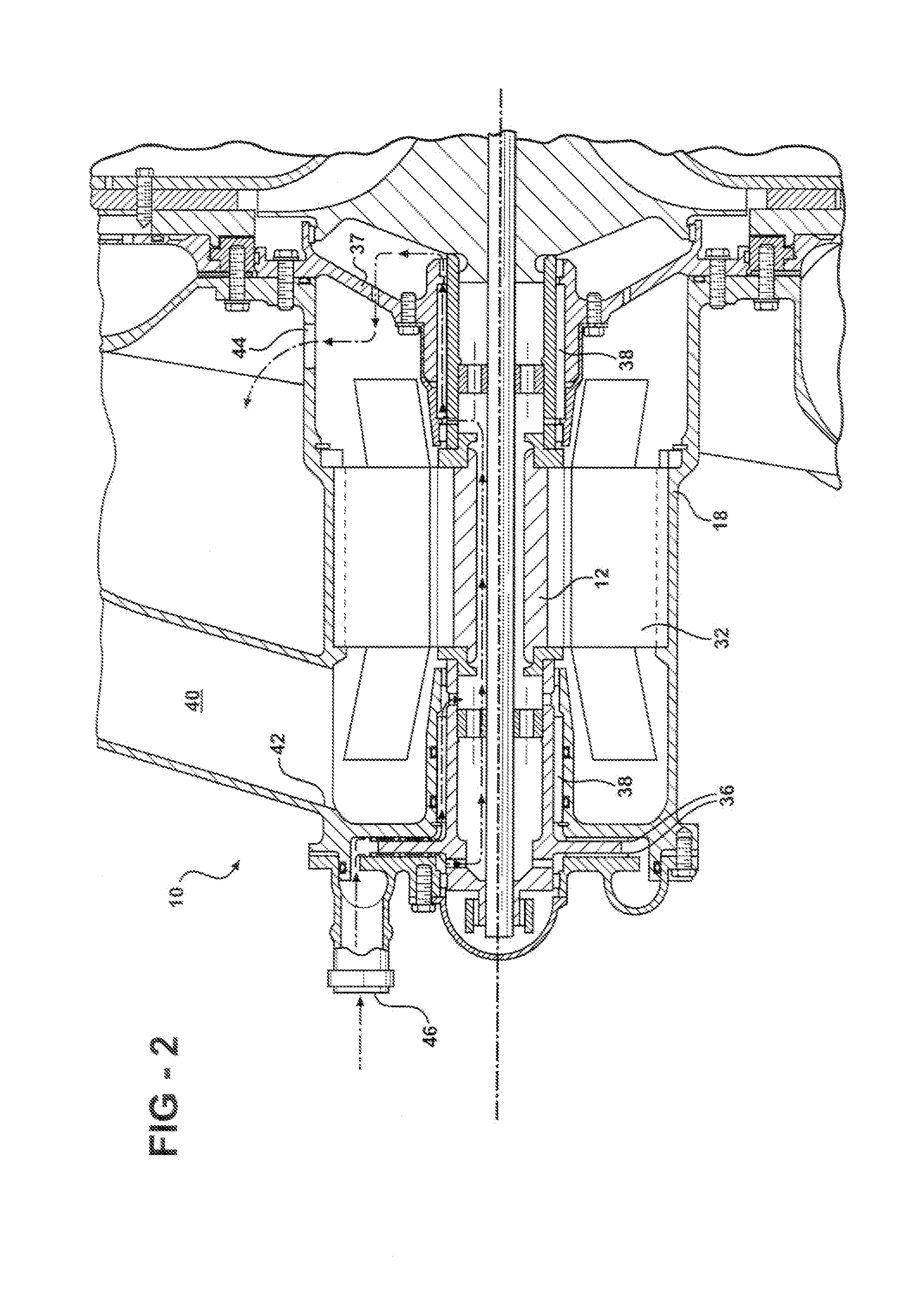
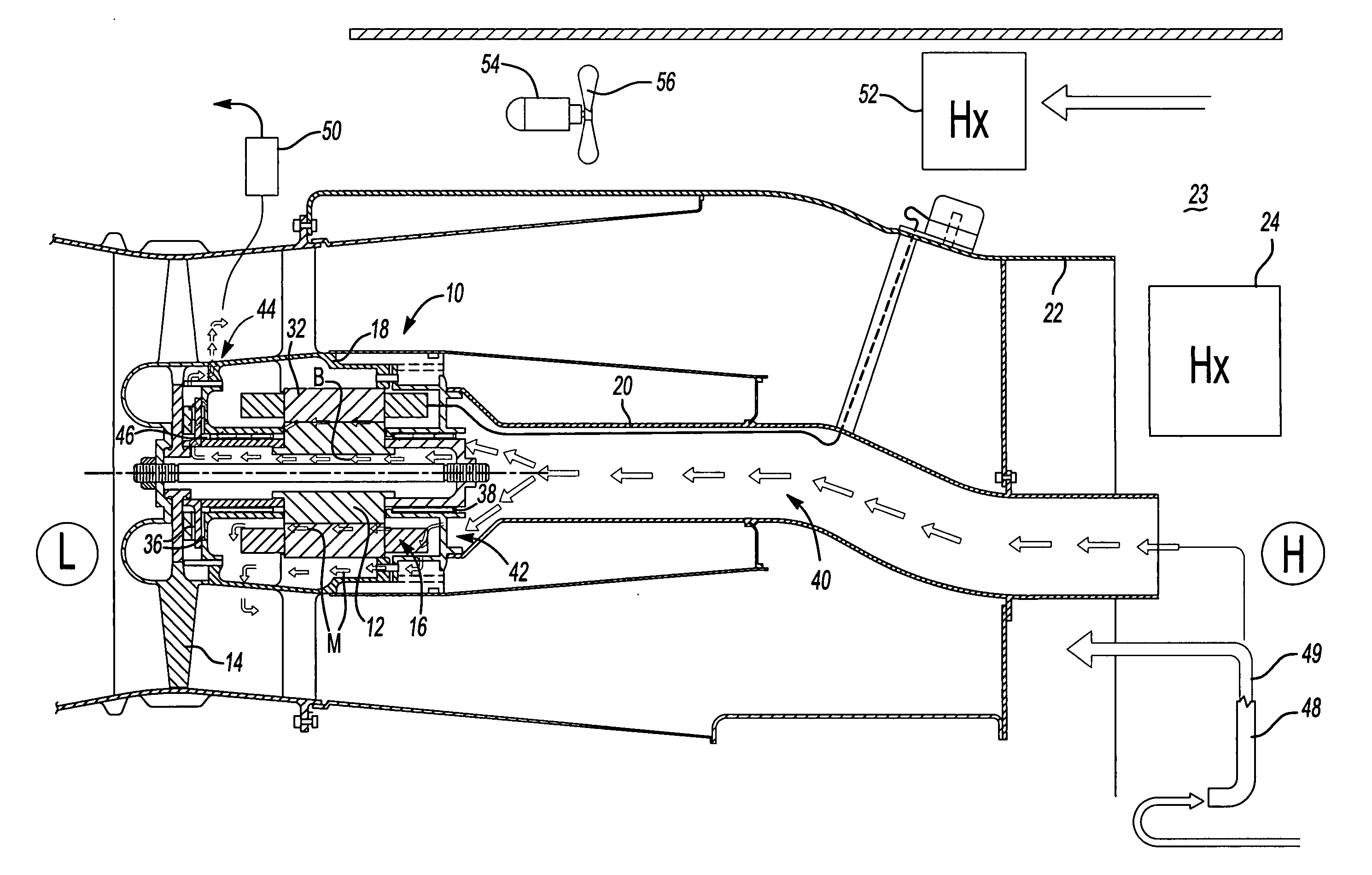
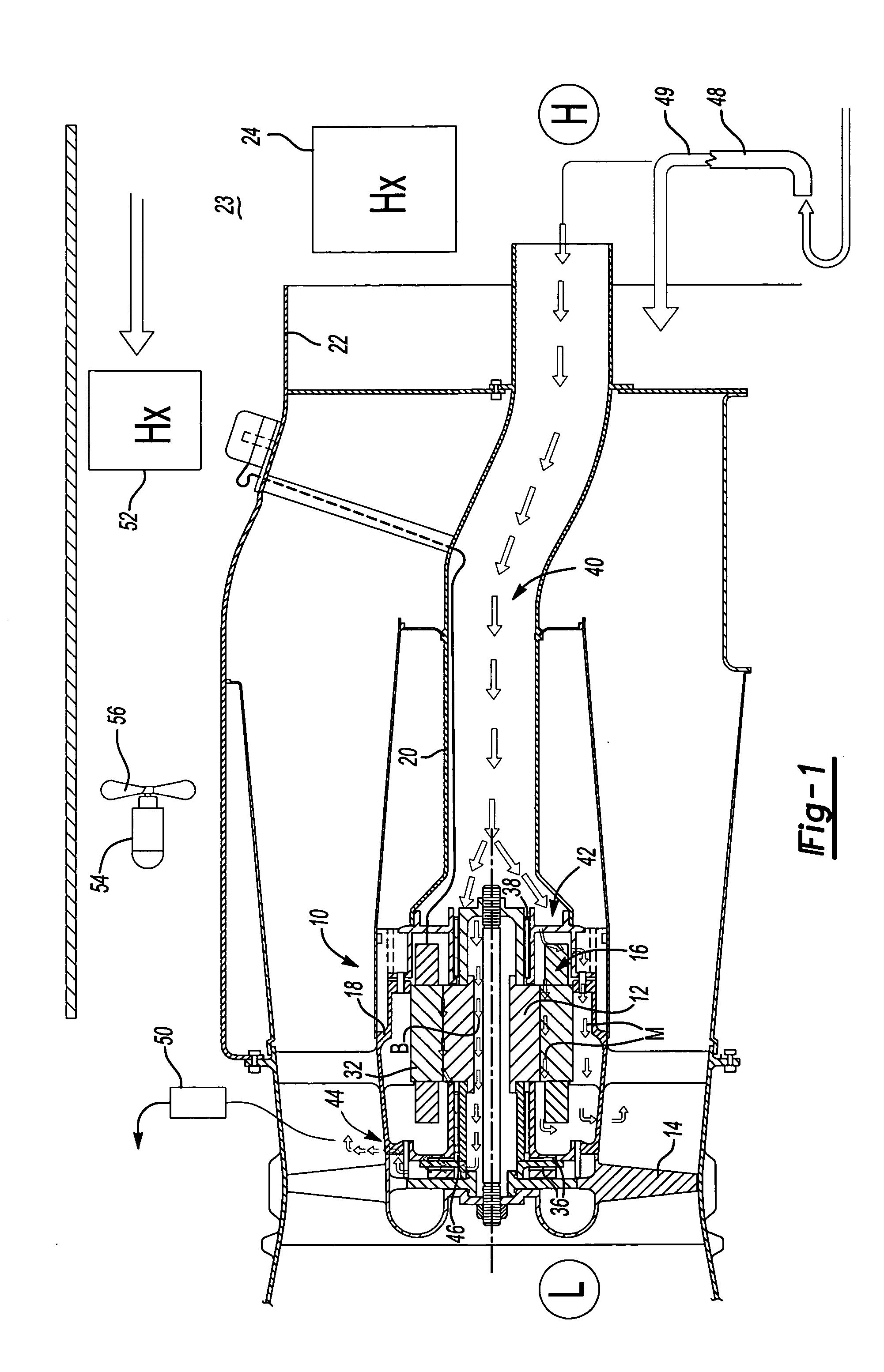
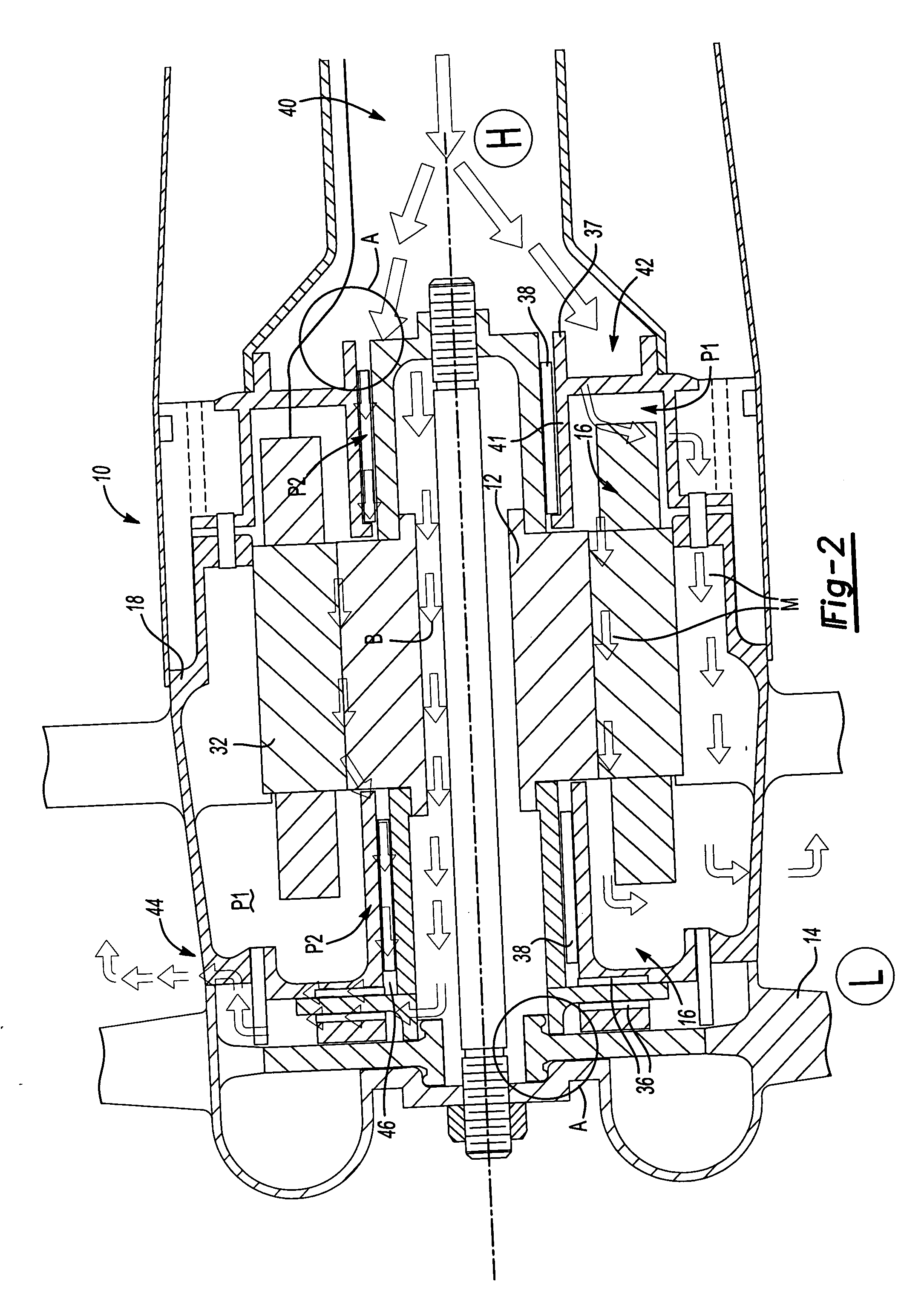
Integral motor and air bearing cooling path
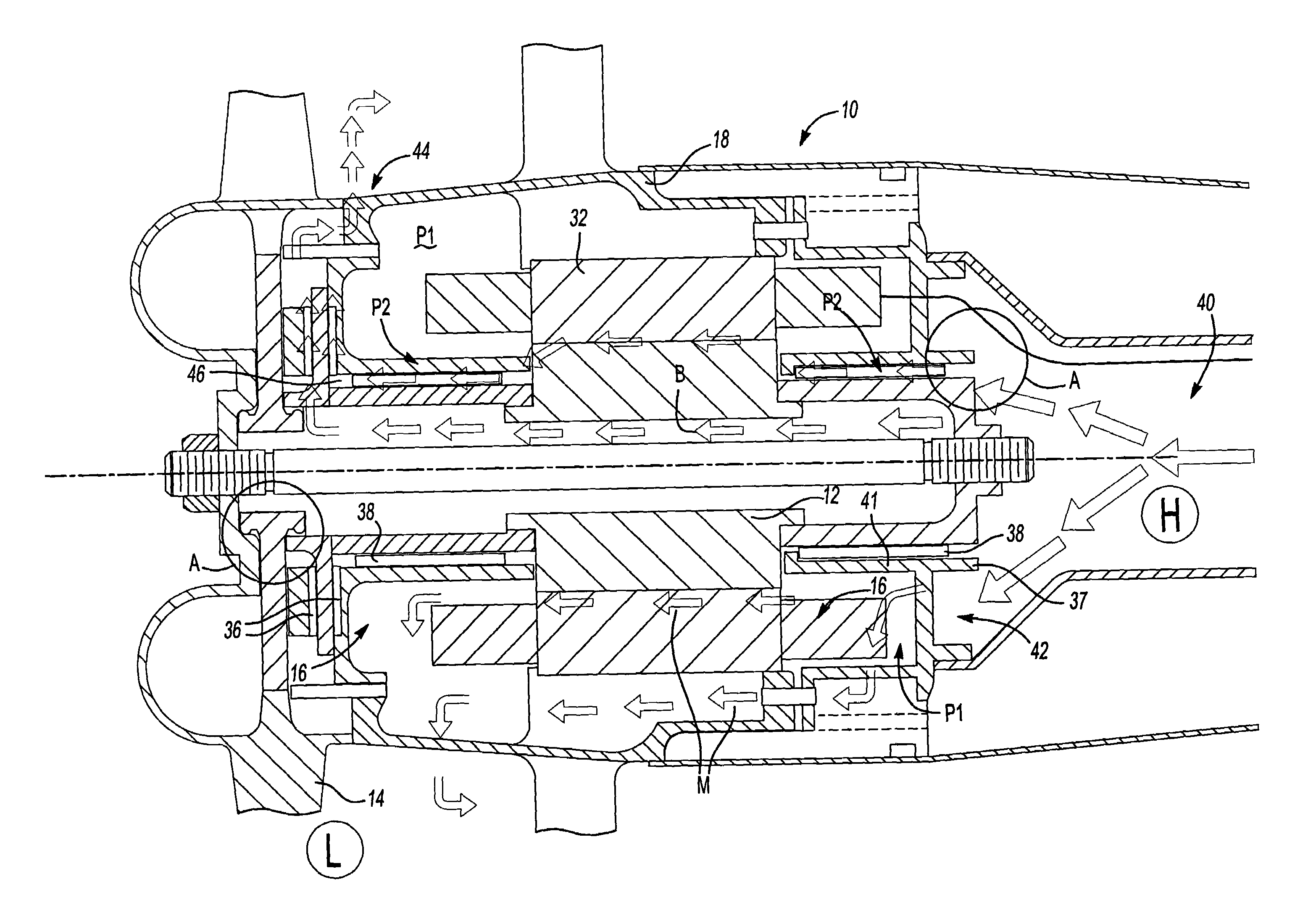
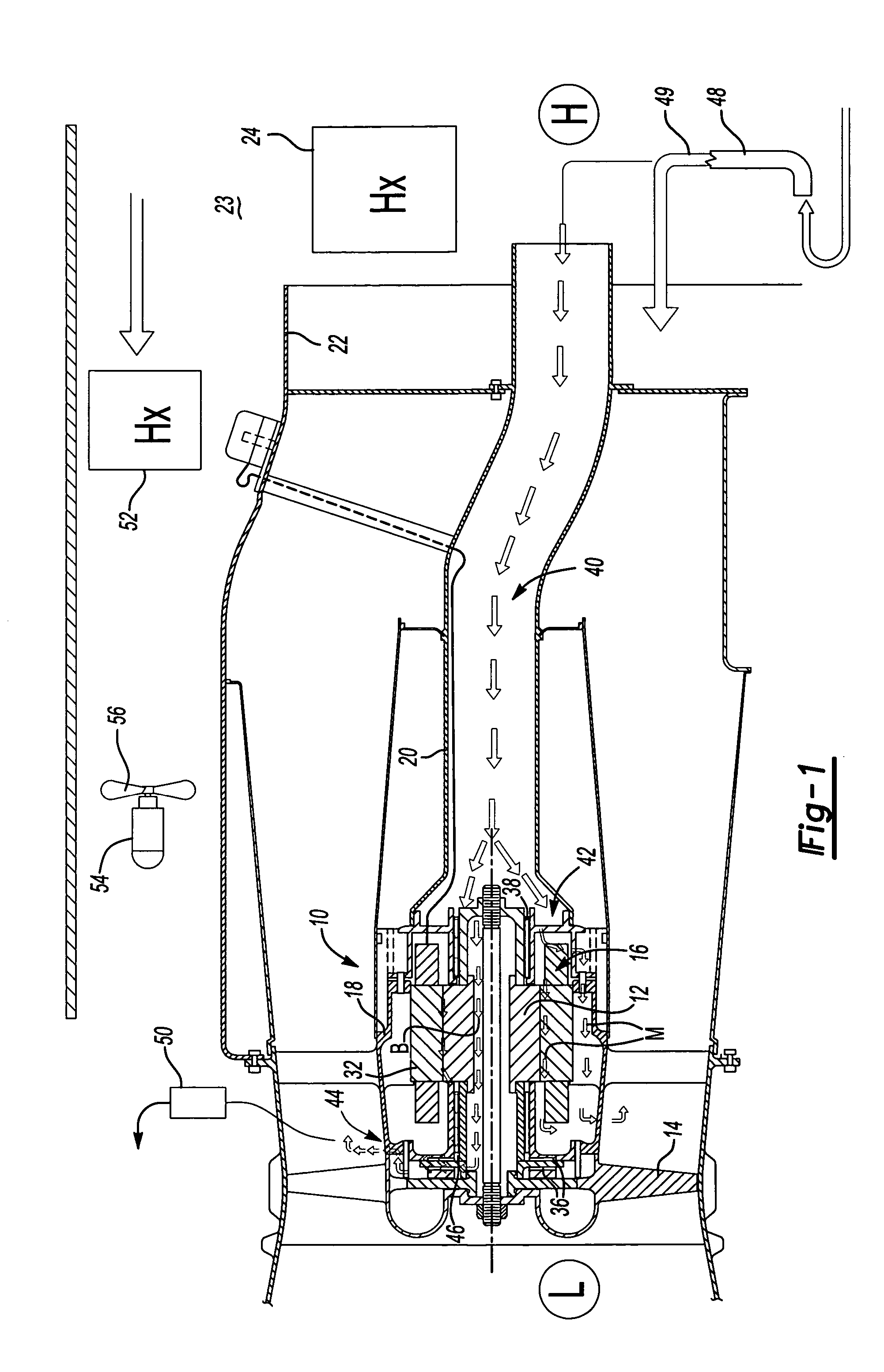
ActiveUS7394175B2Reduce complexityLow costPump componentsMechanical energy handlingPressure generationAir bearing
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Stabilization system for sensors on moving platforms
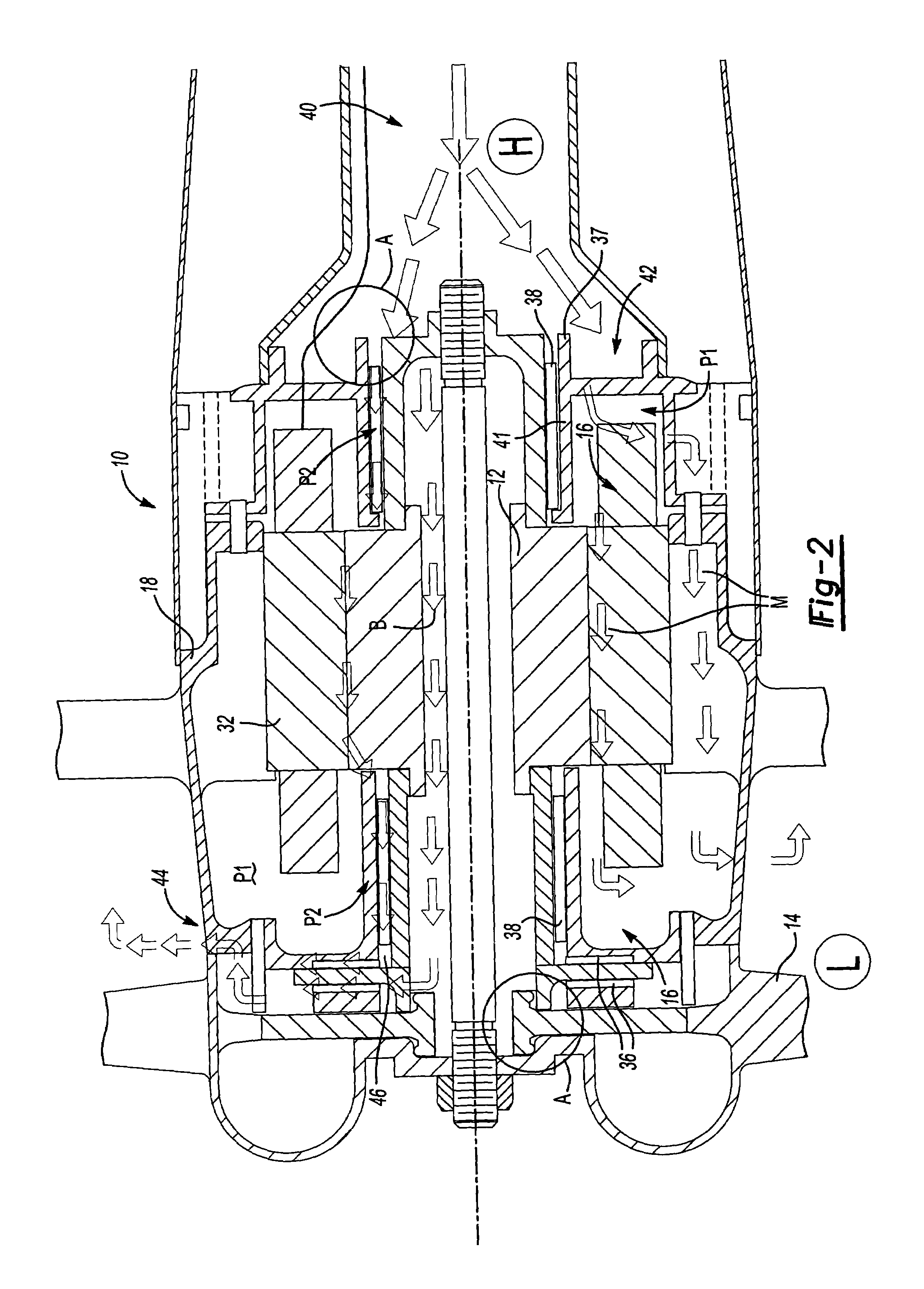
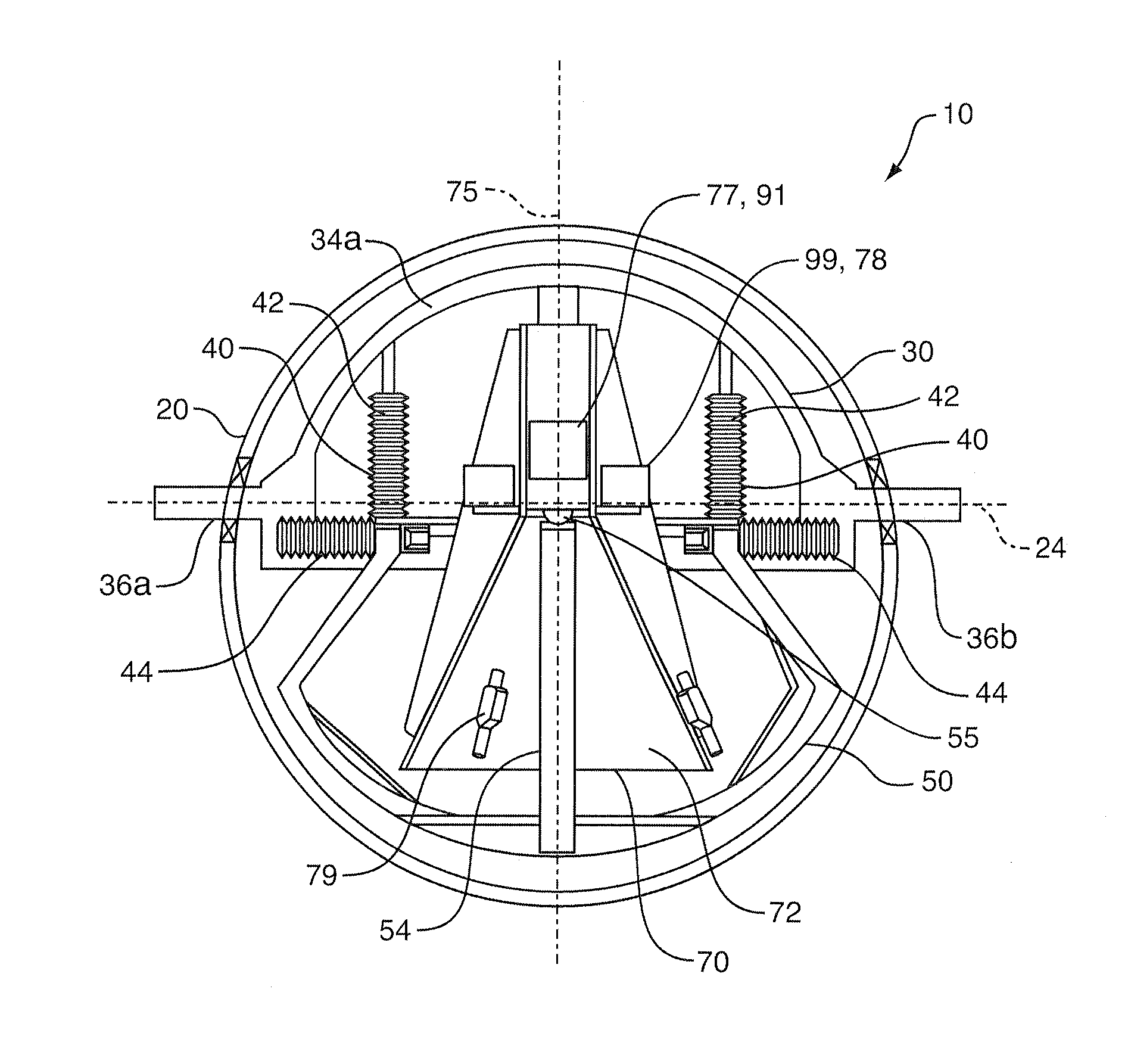
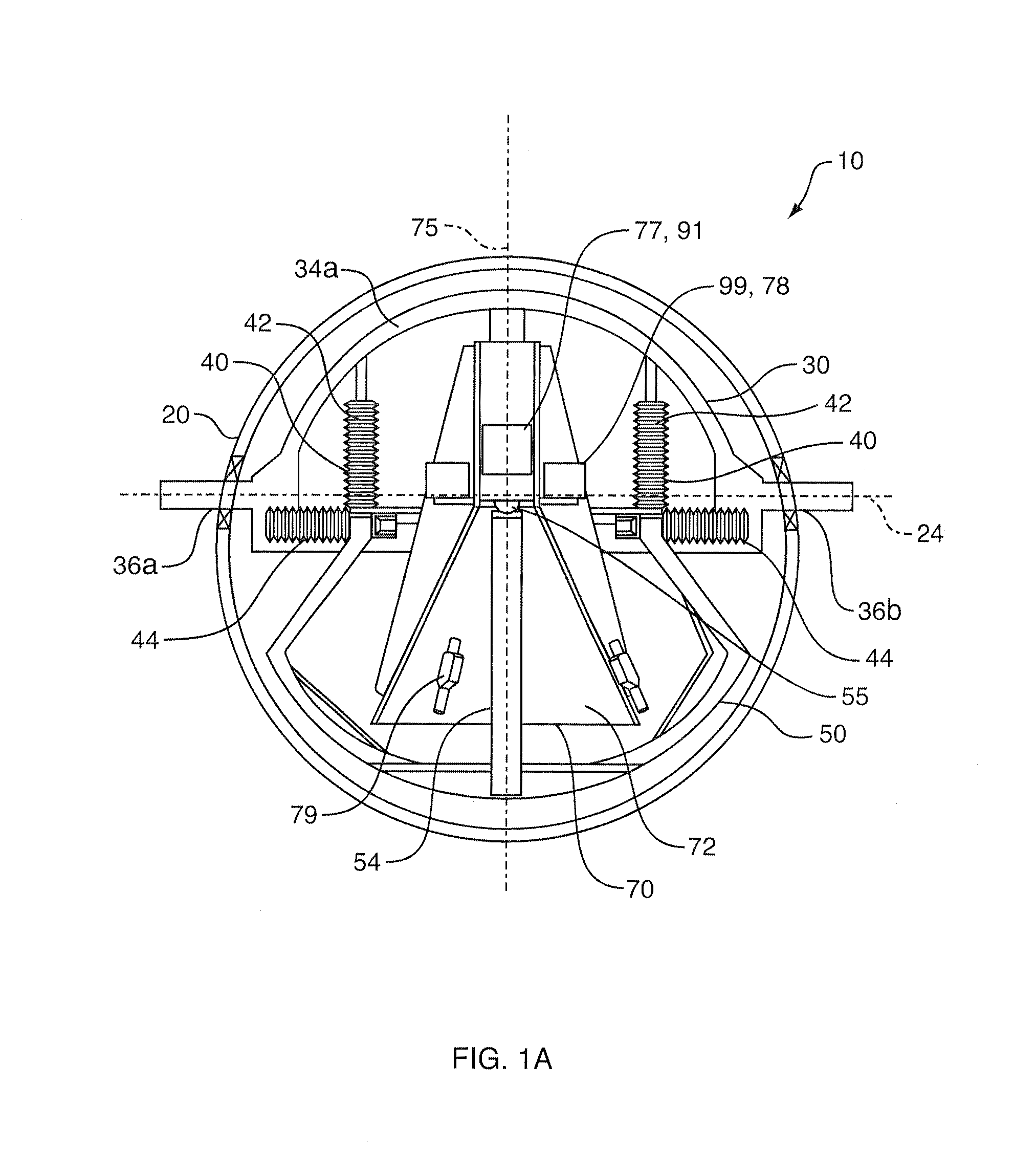
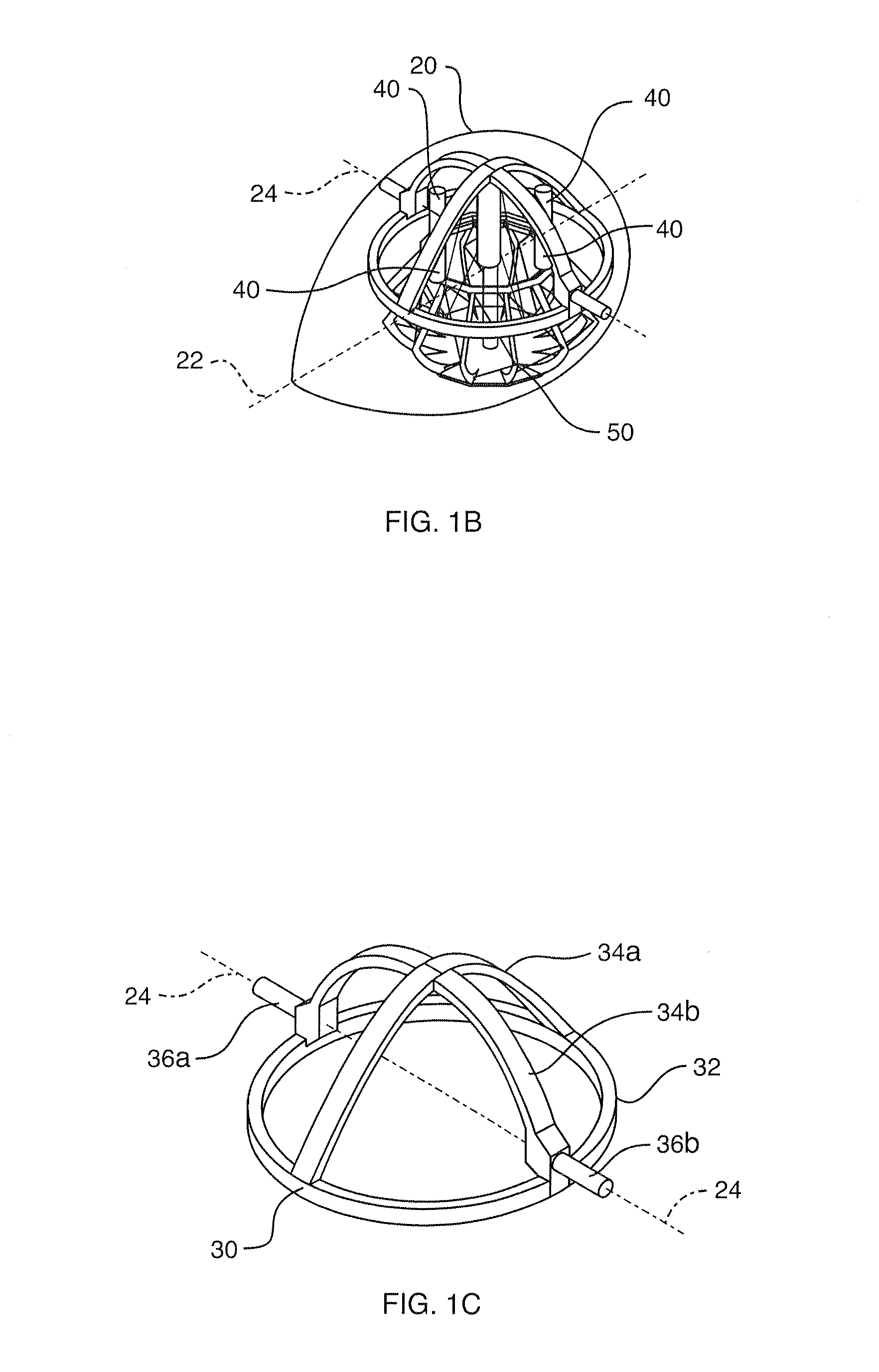
ActiveUS20110175604A1Improve mass balanceSmall biasAcceleration measurementFrequency analysisRotational stabilityAir bearing
A stabilized field sensor apparatus collects field data, in particular magnetic field data, with reduced motion noise. The apparatus includes a tear drop shaped housing, a tow frame in the housing, a plurality of vibration isolating dampers spaced around the frame, a base assembly mounted to the dampers, a support pedestal having a bottom end fixed to the base assembly and an upper free end, a single spherical air bearing connected to the upper free end of the pedestal, an instrument platform with a lower hollow funnel having an upper inside apex supported on the air bearing for a one point support, principal and secondary gyro stabilizers for maintaining pivotal and rotational stability, and at least one field sensor mounted to the instrument platform for collecting the field data while being stabilized against motion noise including vibration, pivoting and rotation from the base assembly, from the tow frame and from the housing. Stabilization of the instrument platform is enhanced by preserving accurate balance through a dynamic balancing system whereby small masses are moved under computer control to maintain the center of mass of the instrument platform at the center of rotation of the spherical air bearing. The dynamic stabilization process is made more precise by actively vibrating the instrument platform by a set of linear vibrators.
Owner:VALE LIMITED
Air bearing and motor cooling
ActiveUS7342332B2Extend the flow pathEfficiently providePositive displacement pump componentsPiston pumpsAir bearingDifferential pressure
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Non-contact porous air bearing and glass flattening device
Owner:NEW WAY MACHINE COMPONENTS
Closed-loop planar linear motor with integral monolithic three-degree-of-freedom AC-magnetic position/orientation sensor
InactiveUS6175169B1High quality positionEasy to manufactureDC motor speed/torque controlMagnetic circuitAir bearingLoop control
Owner:RALPH L HOLLIS JR
Motor-driven centrifugal compressor
InactiveUS20110243762A1Simple and compact structureEffective coolingPump componentsCombustion enginesMotor driveAir bearing
A motor-driven centrifugal compressor includes a journal air bearing having a bump foil and a top foil for restraining a bearing shaft in a resting state and forming an air layer between the top foil and the bearing shaft in a rotating state. The top foil and the bump foil are fixed to an inner circumferential surface of a ring member, which is fixed to an inner circumferential surface of a first stationary holding member of the ring member. The first stationary holding member has a coolant water channel defined therein. The bearing shaft, the air layer, the top foil, the bump foil, and the coolant water channel are arranged in the order named along a normal direction.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Integral motor and air bearing cooling path
ActiveUS20060061221A1Low costReduce complexityPump componentsMechanical energy handlingPressure generationAir bearing
A motor is provided including a housing having single and integral motor and bearing cooling inlets. The motor is arranged within the housing and includes a stator and a rotor assembly supported on air bearings. The cooling inlet is in fluid communication with the motor stator and with the air bearings. The motor cooling inlet provides and the bearing cooling inlet provides a uniform pressure on the rotor assembly. The uniform pressures exerted on the rotor assembly produce bearing loads that generally cancel one another. The source of the cooling flow is uncompressed air at low pressure. This may be achieved by providing a vent in the housing that is common to both the motor cooling inlet and the bearing cooling inlet. As a result, journal bearings and seals of substantially the same size may be used.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Moving vacuum chamber stage with air bearing and differentially pumped grooves
InactiveUS20060060259A1Structural loopSimple structureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPretreated surfacesAir bearingMechanical engineering
A stage for processing a substrate, especially useful for vacuum applications, has a recess just large enough to hold a substantially flat substrate and a chuck or holder but not much more. The perimeter of the recessed side has an air bearing surface separated from the recess by differentially pumped groves and seal lands. The air bearing lands are urged against a reference plate guide surface and the seal lands being substantially coplanar create a resistance to flow between the groves and recess, on the other side of the base reference plate mounts the radiation source. The VCS may operate in a vacuum environment itself, or in another preferred embodiment, it provides the possibility for multiple stages moving between process or inspection steps within the same tool or process sequence.
Owner:NEW WAY MACHINE COMPONENTS
Slide feeder with air bearing conveyor
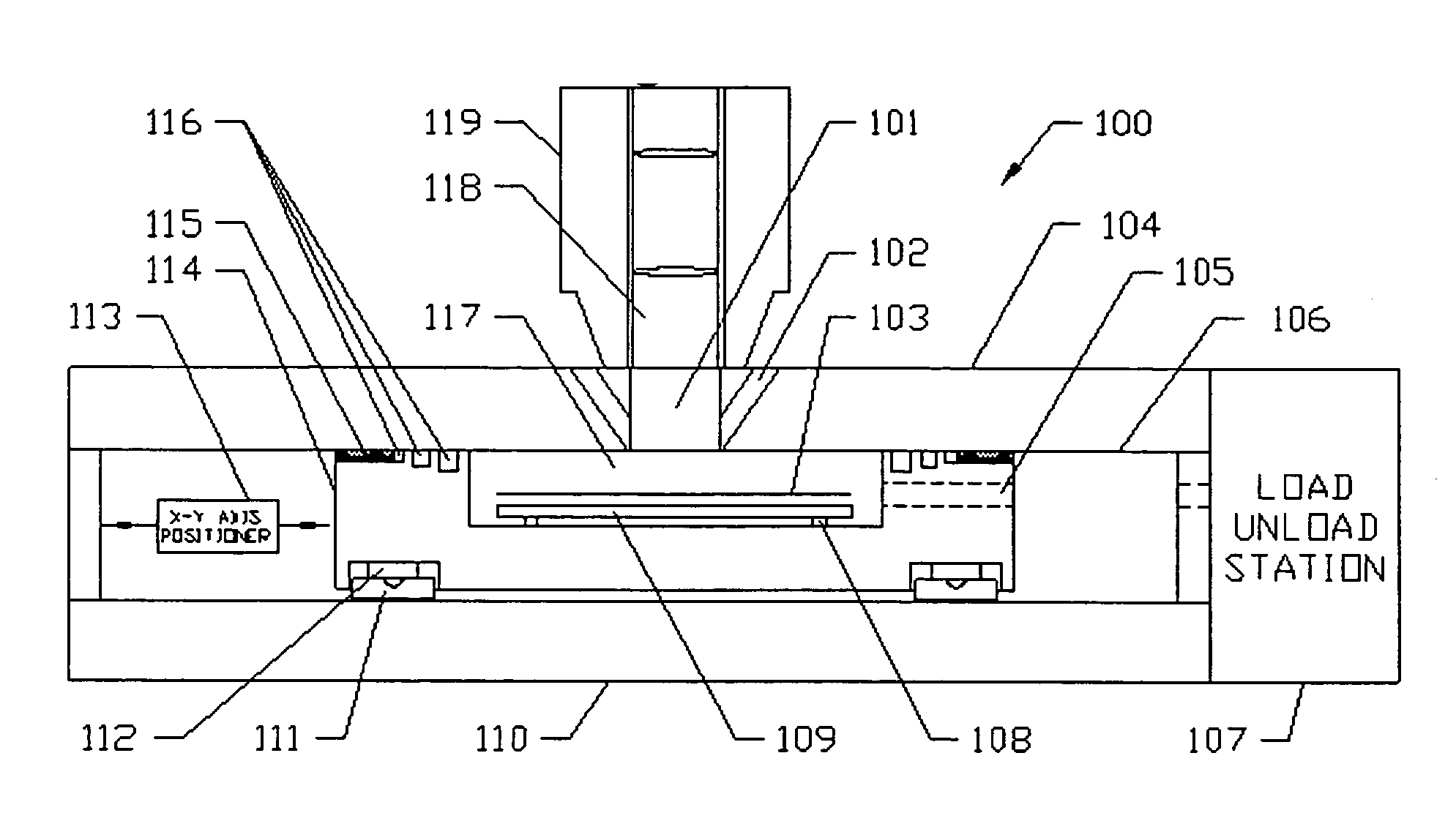
A slide loading mechanism utilizes compressed air as the transport medium to move the slides from a magazine to the stage of a microscope. The stage is provided with a carriage moving horizontally along a direct path between the stage and the magazine. A conveyor coupled to the carriage includes a tongue suitable for positioning under the slide of interest in the magazine when the carriage is at one end of its travel path, so that the slide may be picked up for translation to the stage of the microscope. When the carriage is moved to the opposite end of its travel path, the tongue is completely removed from the magazine, which may be freely moved vertically by an elevator to align another slide for processing. Directional air flow is used to suspend and transport the slide back and forth between the two ends of the conveyor
Owner:DMETRIX INC
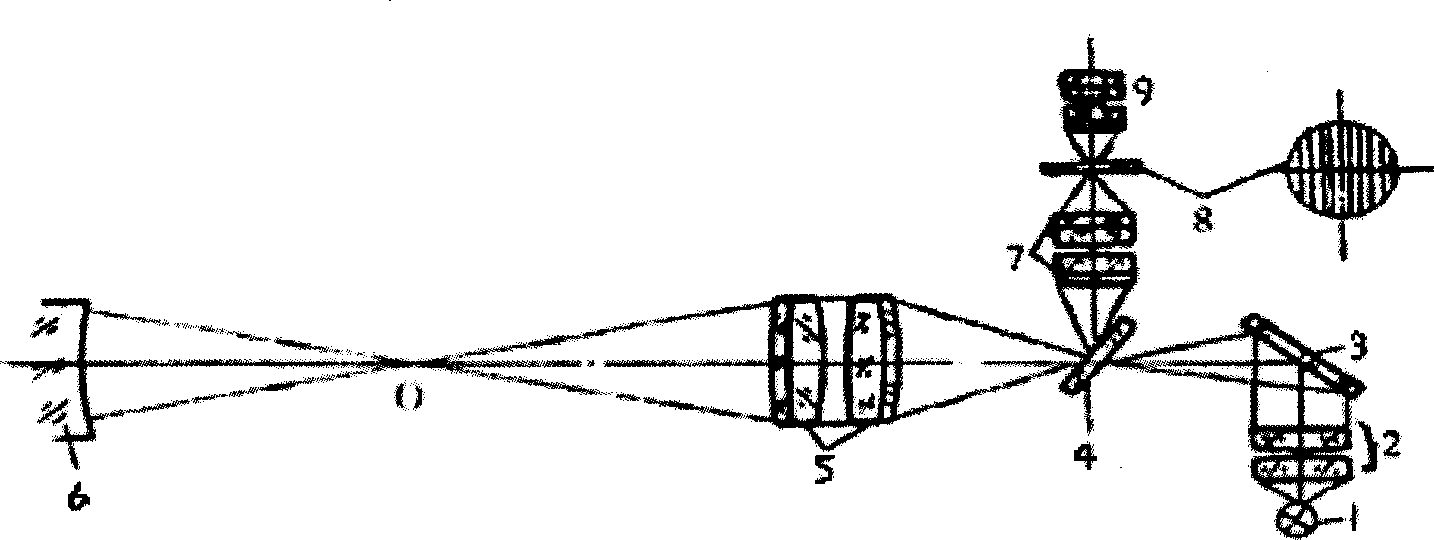
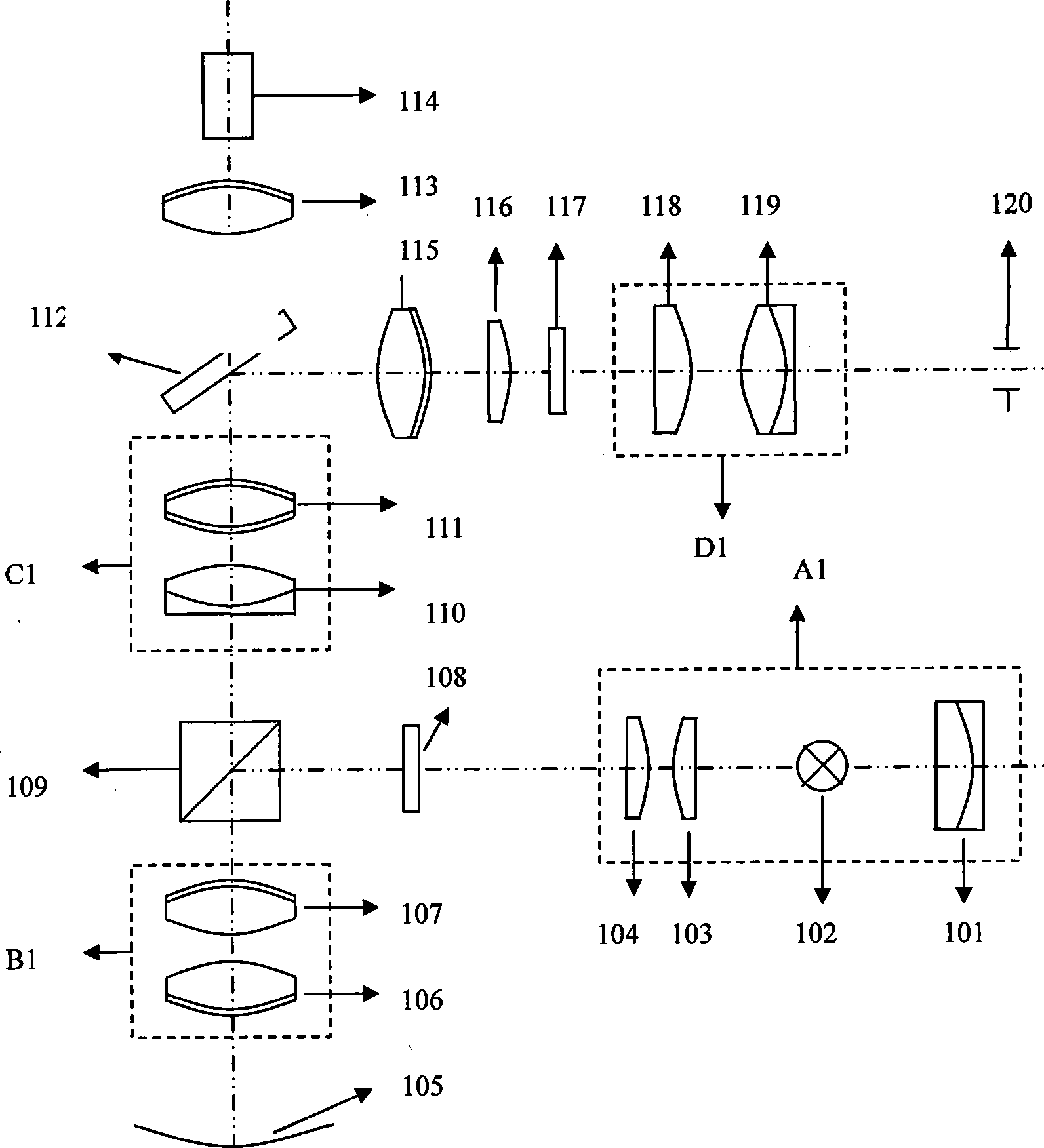
Center aligning assembling and regulating apparatus and method for optical system
ActiveCN101387761AMeet the school requirementsHigh precisionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusBeam splitterAir bearing
The invention provides a device for aligning, assembling and adjusting optical systems and a method thereof. The device comprises an auto-collimate microscope and a turntable with an air bearing, wherein the optical axis of the auto-collimate microscope is accurately aligned with a rotation shaft of the air bearing, the auto-collimate microscope comprises a lighting module, a mask board with carved lines, a beam splitter prism, a focusing objective lens group, a microscope objective lens group, a spectroscope, a measurement reticule, a CCD and a microscope eyeglass group, to confirm the eccentricity measurement accuracy and lens assembly and adjustment accuracy of the device. The device can be applied in high accuracy centering machines to fit the high accuracy air bearings, thereby effectively improving the centering accuracy of the centering machines and satisfying the lens assembly and adjustment demands of high accuracy optical systems.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
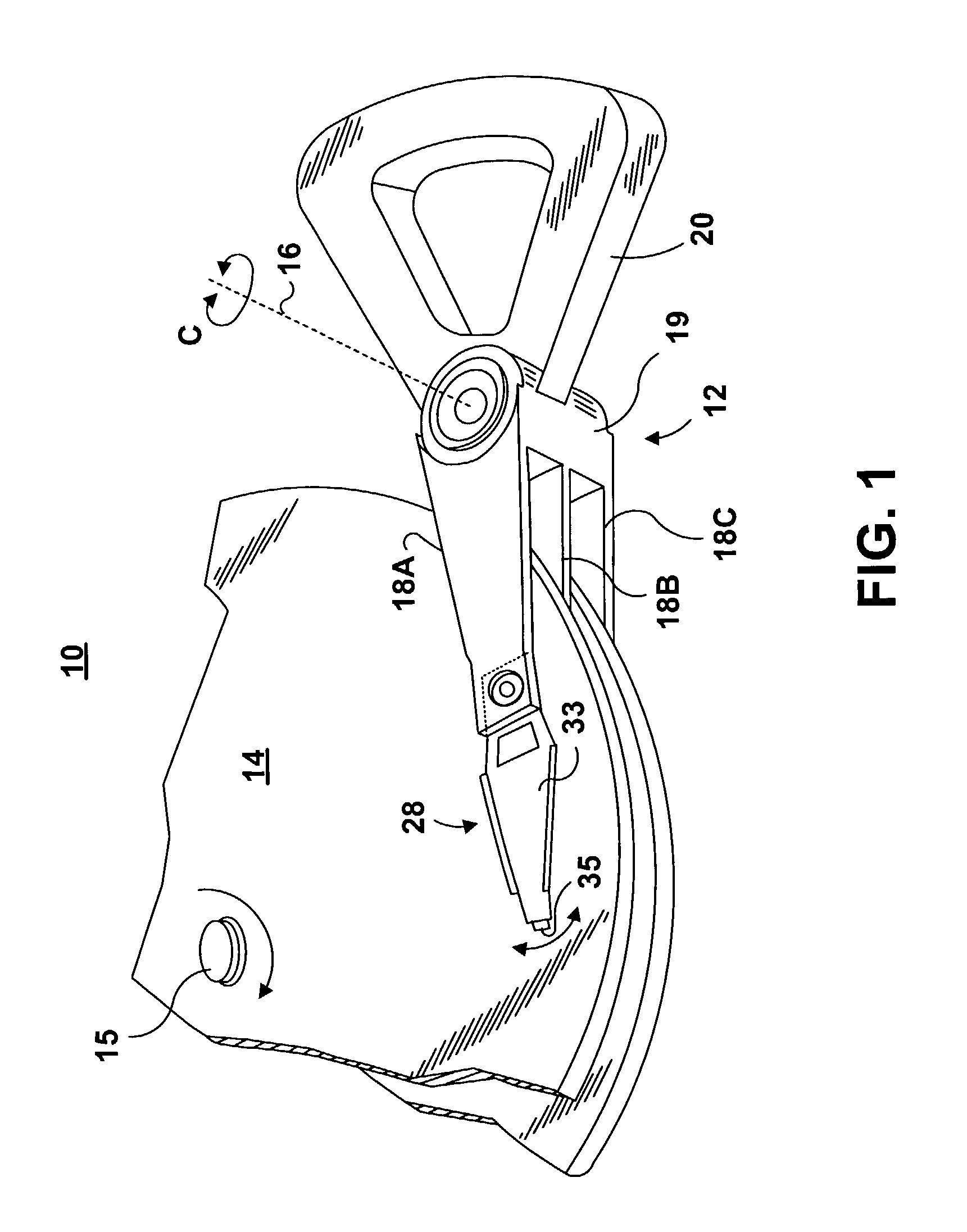
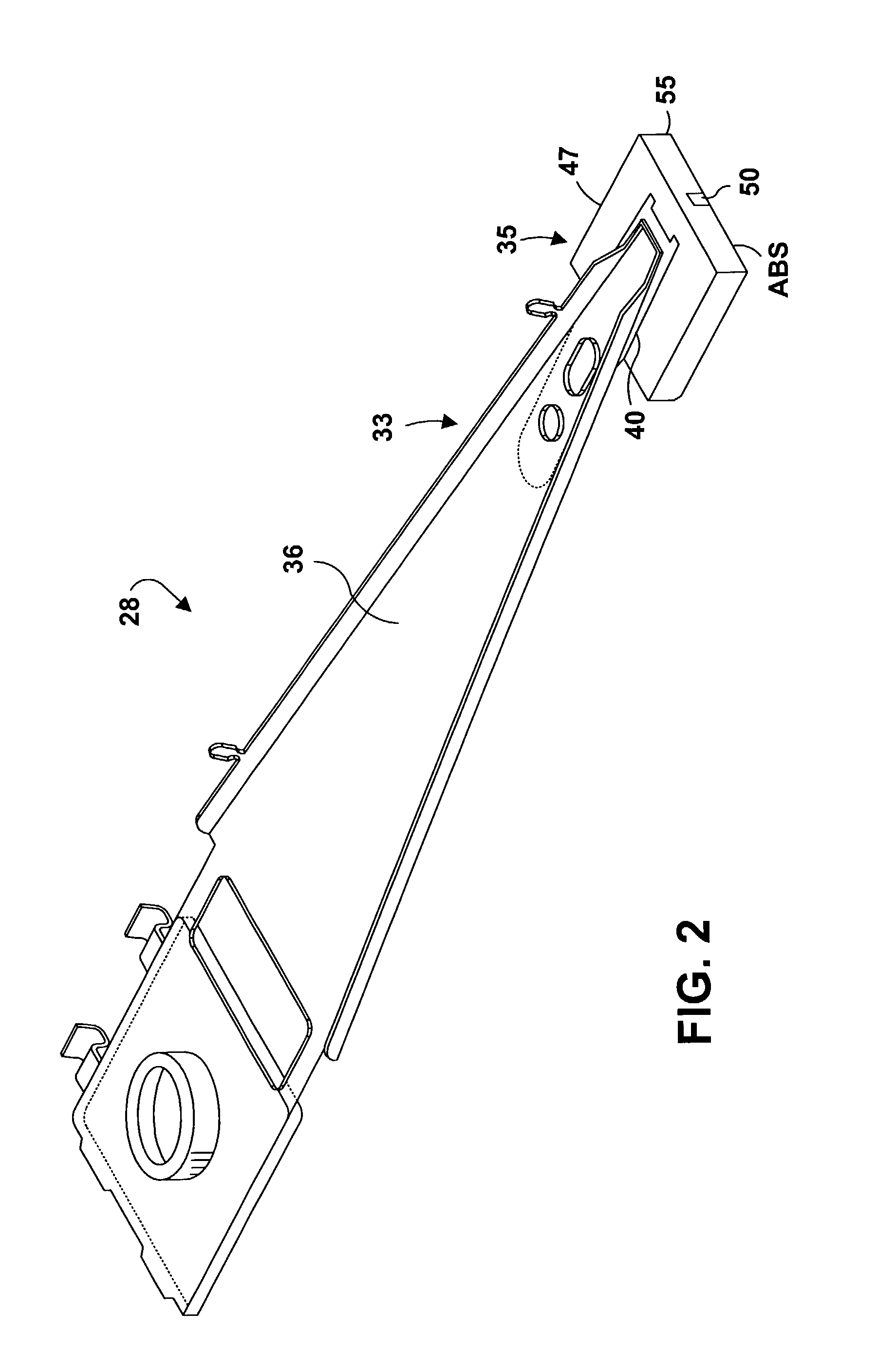
Magnetic head suspension assembly fabricated with integral load beam and flexure
InactiveUSRE39478E1Lower Z heightLow pitchDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageAir bearingEngineering
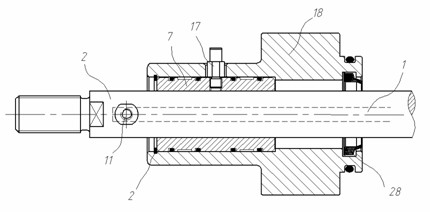
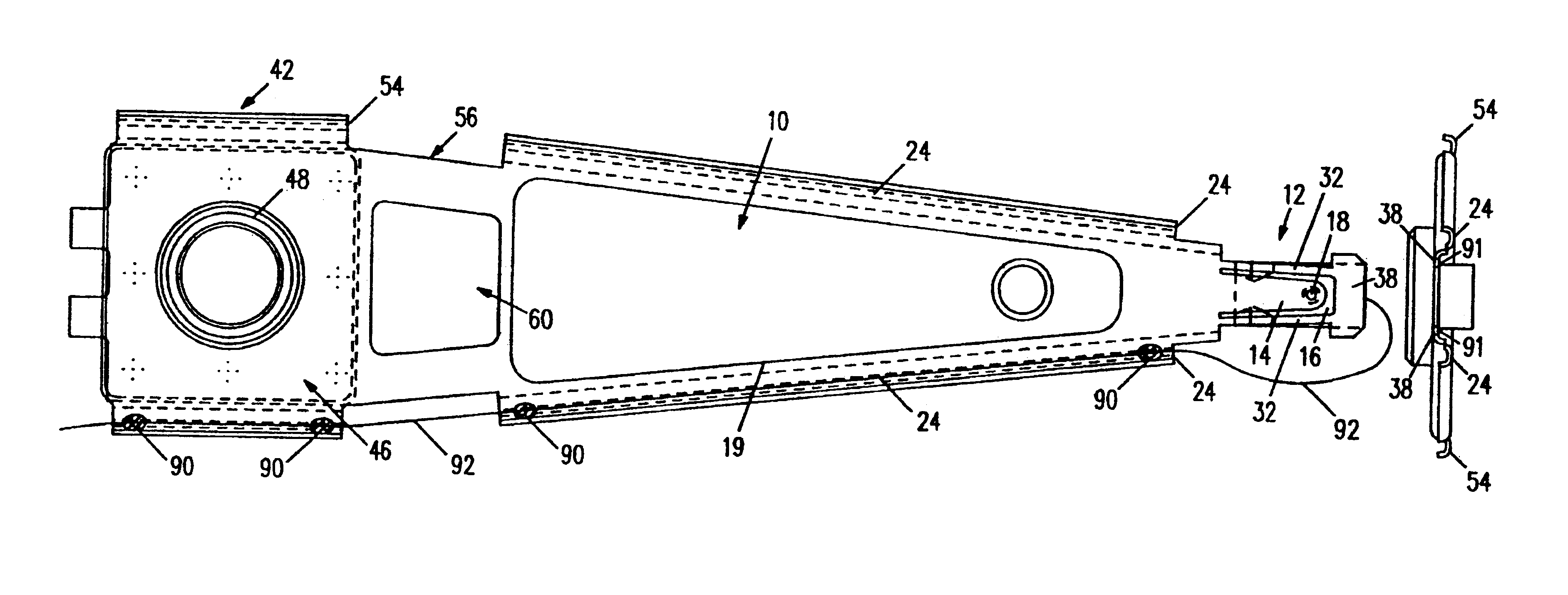
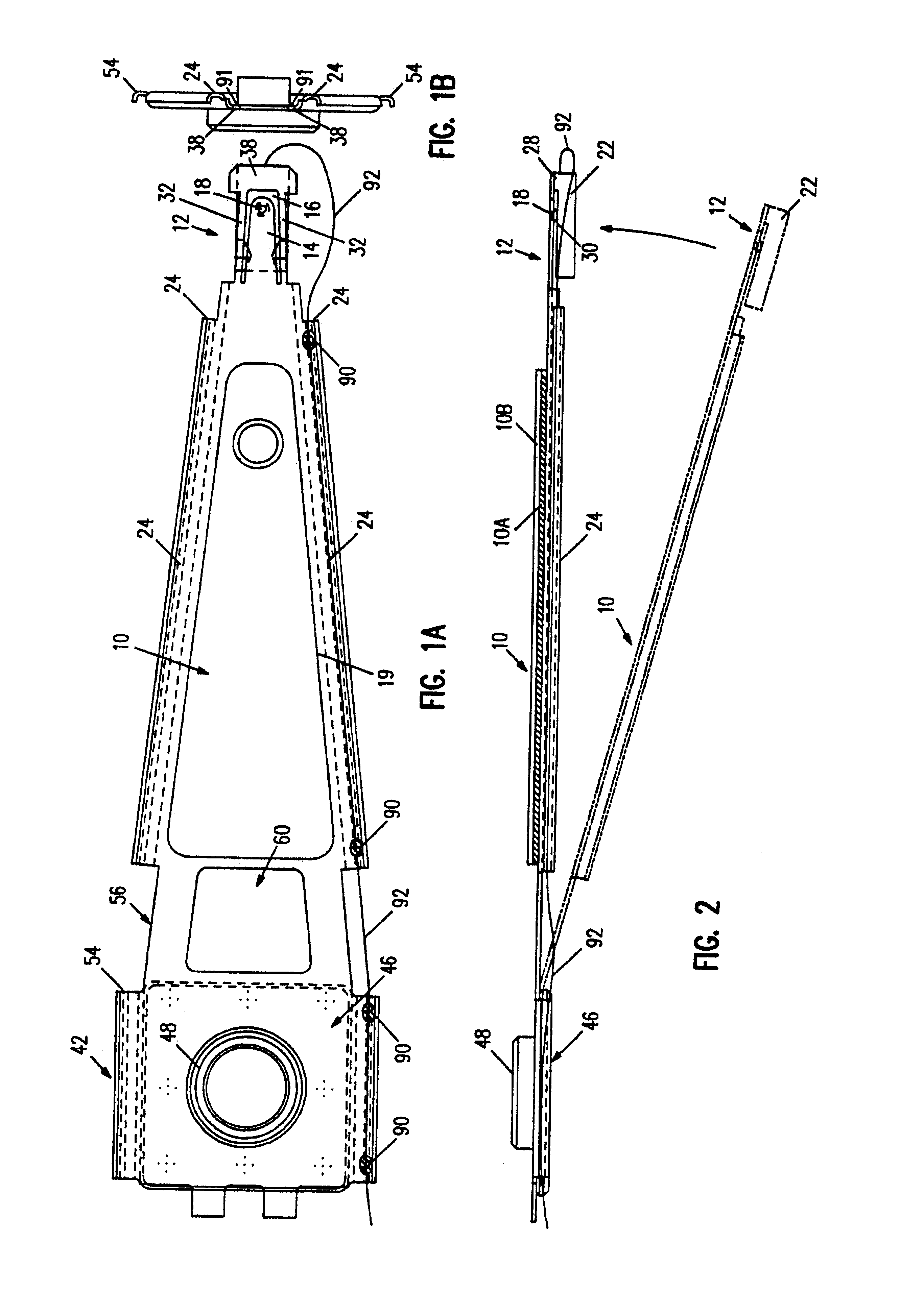
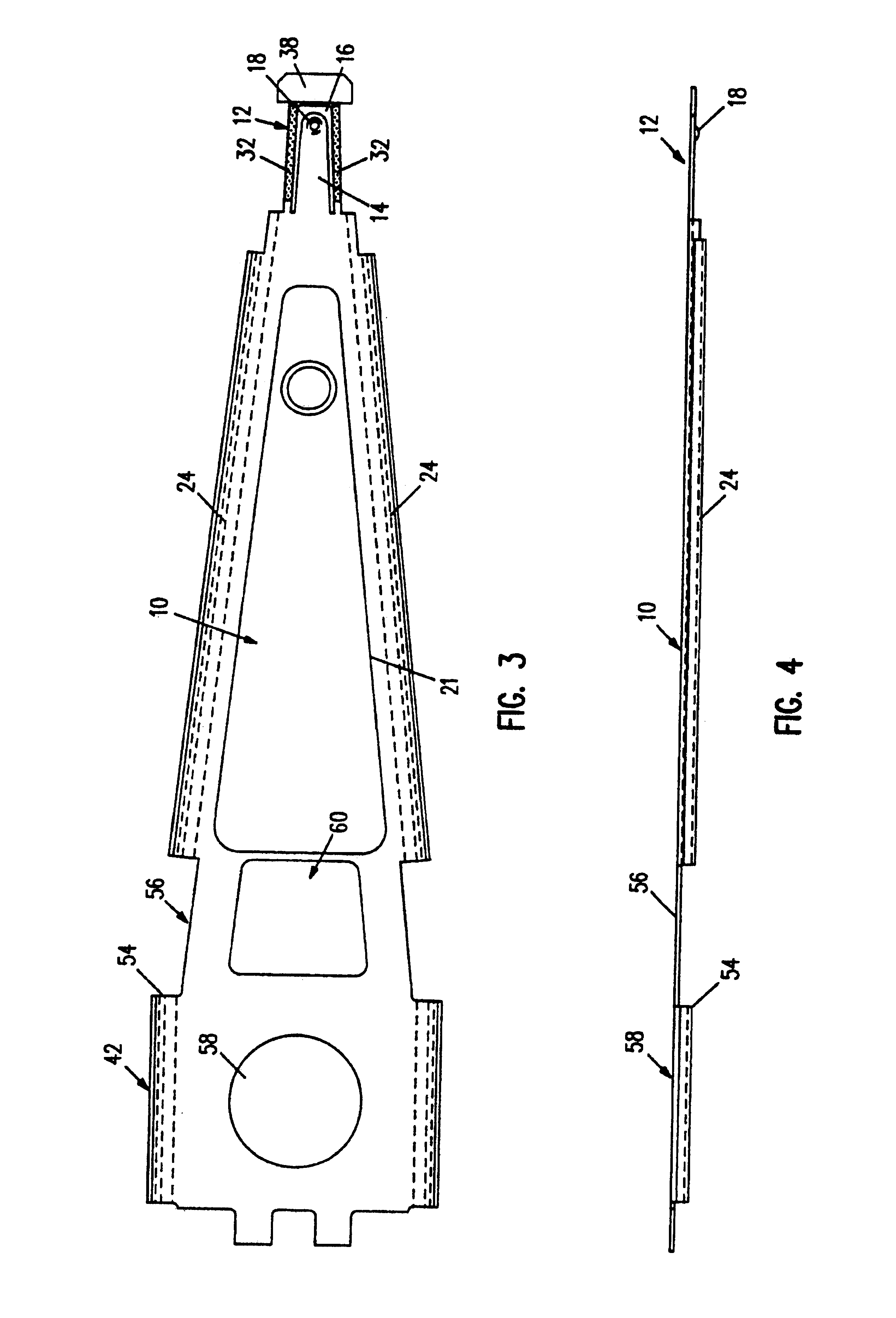
A magnetic head suspension assembly is fabricated with an integral piece which includes a load beam section, a flexure section, a rest mount section and a leaf spring section between the load beam and rear mount. A tongue extends from the load beam to the flexure and has a down-facing load dimple which contacts the non-air bearing surface of an attached air bearing slider. The flexure includes narrow thin legs adjacent to a cutout that delineates the load beam tongue. The head suspension is characterised by a high first bending mode frequency and low pitch and roll stiffness.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
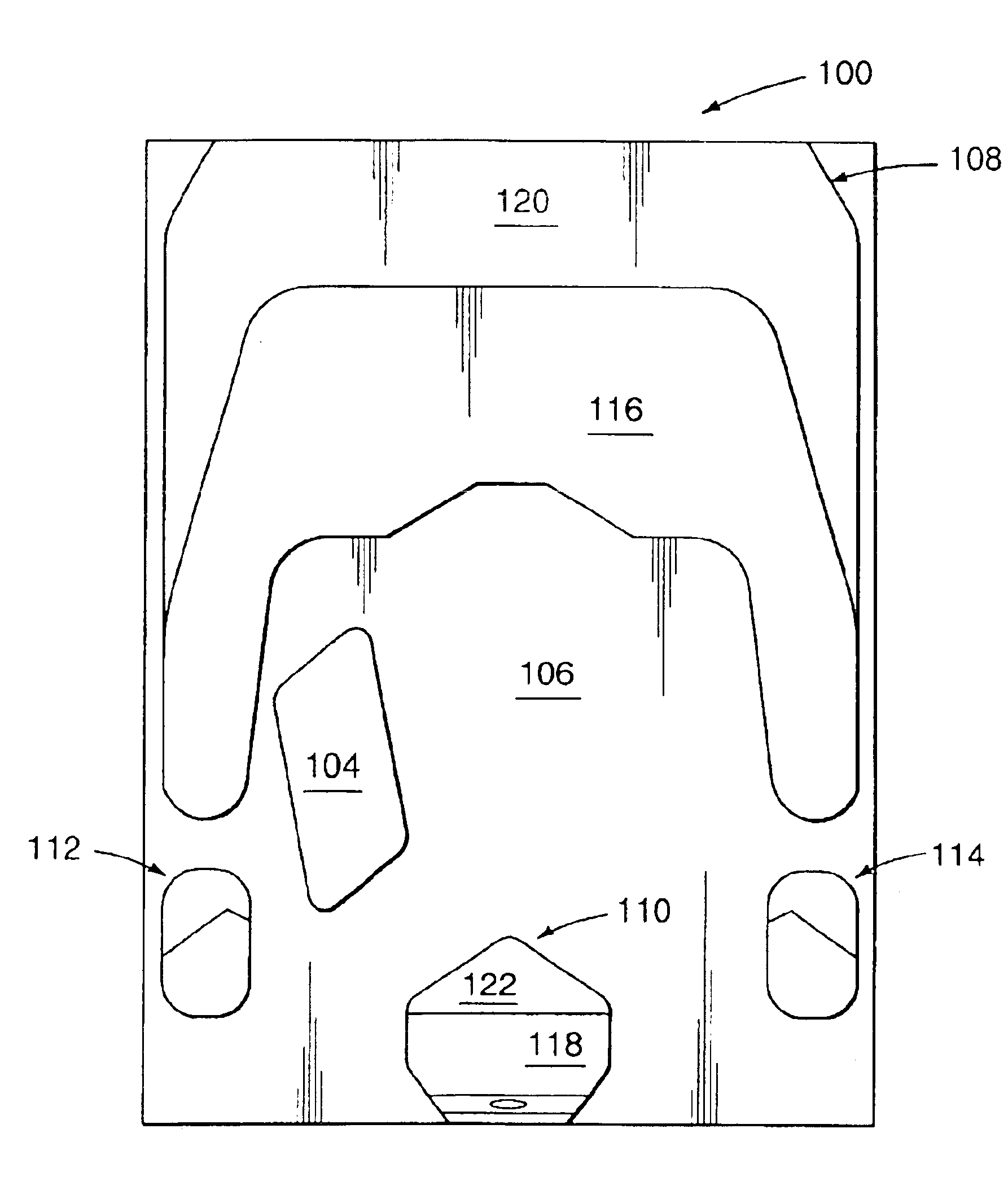
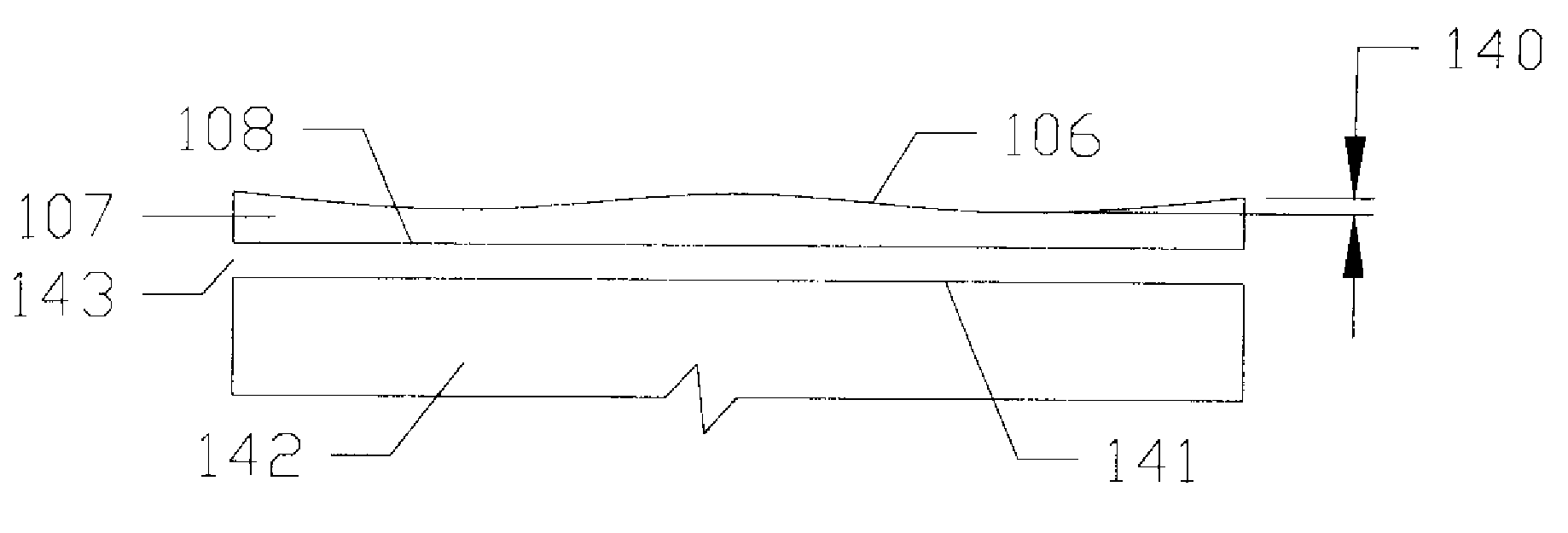
Air bearing slider including pressurized side pads with forward and trailing shallow etched surfaces
An aspect of the invention can be regarded an air bearing slider for use in a disk drive including a rotatable magnetic disk. The slider includes a leading side and a trailing side. The slider further includes opposing lateral sides extending between the leading and trailing sides. The slider further includes a transducer pad disposed adjacent the trailing side. The transducer pad includes a transducer for reading and writing data from and to the magnetic disk. The slider further includes a pair of pressurized side pads each respectively disposed laterally between the transducer pad and a respective one of the lateral sides. Each side pad includes a forward shallow etched surface, a trailing shallow etched surface extending from adjacent the trailing side toward the leading side, and a side pad air bearing surface disposed between and above the forward and trailing shallow etched surfaces.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
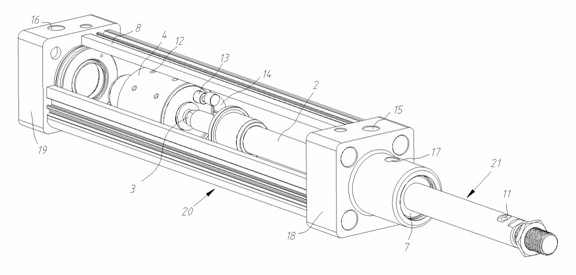
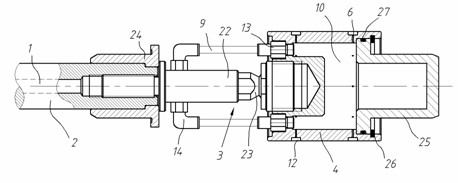
Zero-friction air cylinder with air bearing
InactiveCN102155465AReduce frictionIncrease the itineraryFluid-pressure actuatorsAir bearingEngineering
The invention discloses a zero-friction air cylinder with an air bearing. The zero-friction air cylinder comprises the air bearing and a piston, wherein the air bearing is matched with the piston rod; the piston is designed according to an air-float principle; and the zero-friction support of a moving part and a fixed part of the air cylinder can be realized by the air-float bearing and the piston, namely a high-pressure air film is formed at a contact surface to isolate two surfaces which are supported mutually. Air is provided for the piston in the inner part of the air cylinder by the zero-friction air cylinder through the hollow piston rod and a soft pipe, and spherical hinge connection is applied, thus the zero-friction air cylinder can bear certain radial loading, and the piston is not stuck in the air cylinder; by the zero-friction air cylinder provided by the invention, the friction of the air cylinder is reduced greatly, greater stroke can be realized without lubrication and sealing, the radial force in a certain range can be borne, and the structure is simple and is convenient to maintain.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Magnetic head suspension assembly fabricated with integral load beam and flexure
InactiveUSRE40203E1Lower Z heightLow pitchDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageAir bearingEngineering
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
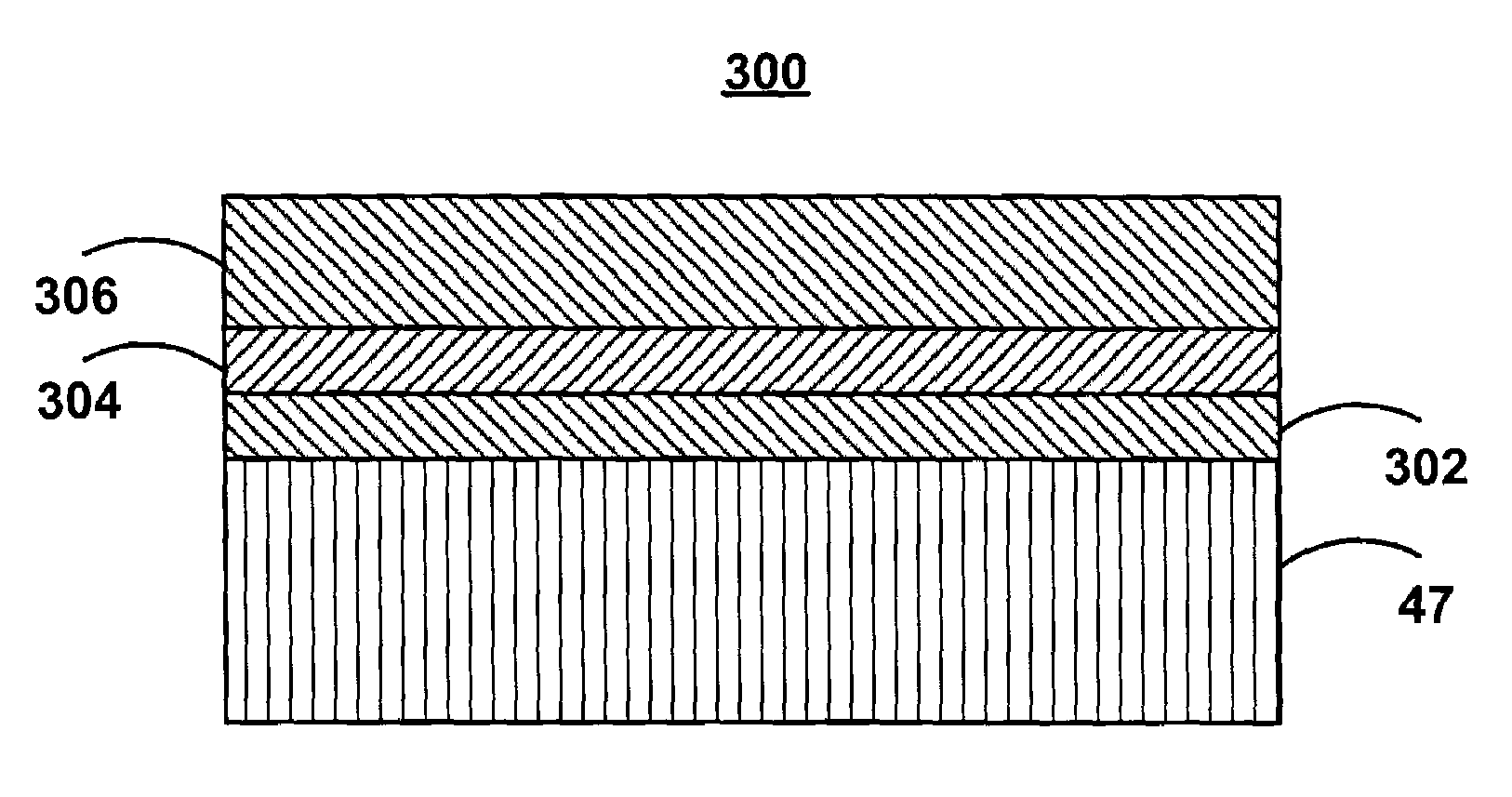
Sandwich diamond-like carbon overcoat for use in slider designs of proximity recording heads
InactiveUS6956718B1Record information storageFluid-dynamic spacing of headsDiamond-like carbonAir bearing
A slider is formed of an air bearing surface coated with a wear limiting coating that substantially limits surface wear of the air bearing surface encountered in proximity recording. The wear limiting coating is comprised of a wear inhibiting layer formed on the air bearing surface and a sacrificial layer formed on the wear inhibiting layer. The two coatings of the wear limiting coating have different mechanical properties so that the sacrificial layer is burnished, exposing the wear inhibiting layer. This design substantially limits the surface wear of the air bearing surface typically encountered in proximity recording, resulting in less debris accumulation, which could otherwise adversely affect the performance of the proximity recording head. This self-limiting burnishing action overcomes the flying height variation due to manufacturing tolerances and provides extremely small and uniform magnetic spacing, which greatly enhances the proximity recording. Moreover, the burnishing action also achieves an improved flying stability and a reduction in the altitude sensitivity.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
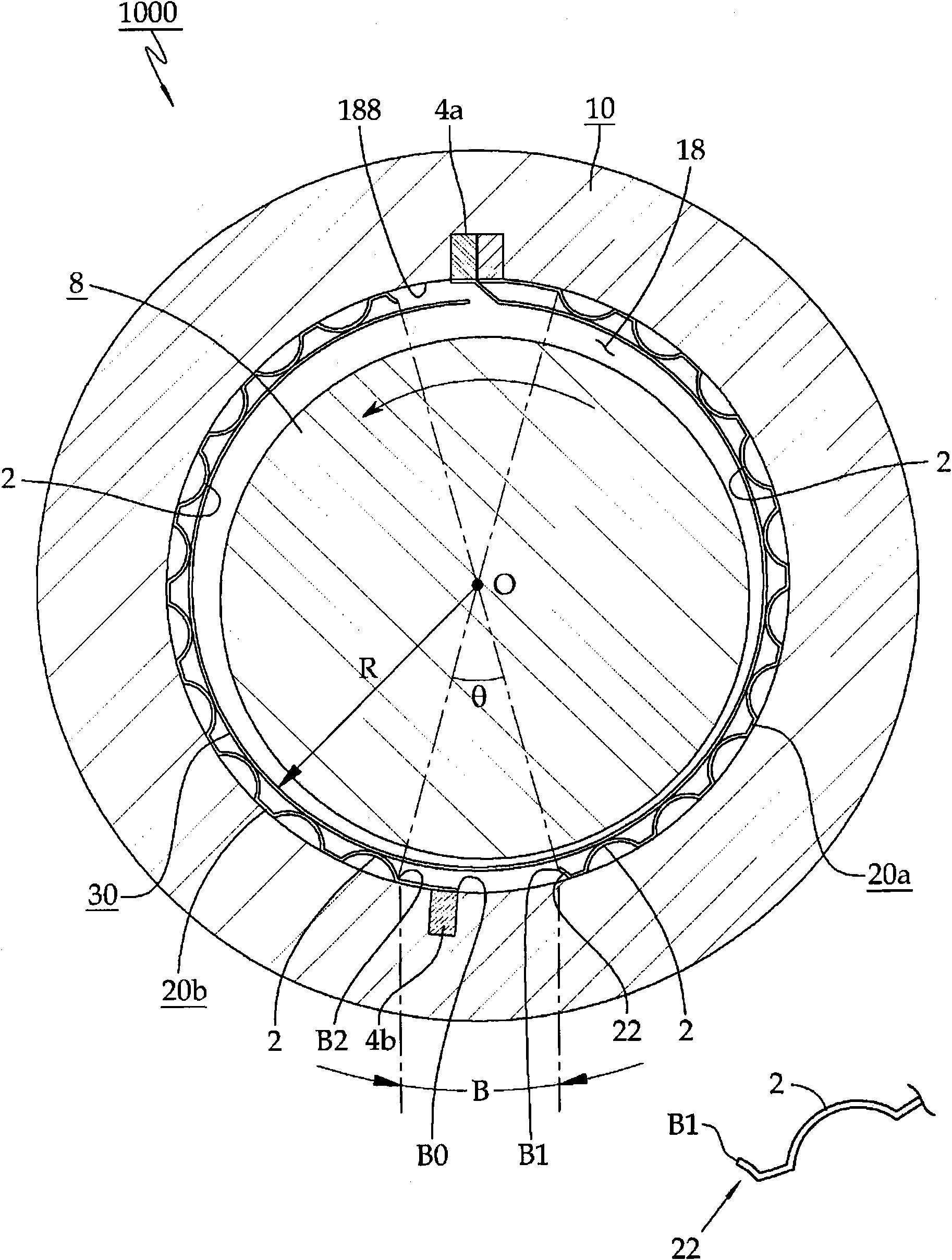
Journal-foil air bearing
ActiveCN102003463AAvoid damageReduce in quantityBearing componentsSliding contact bearingsAir bearingEngineering
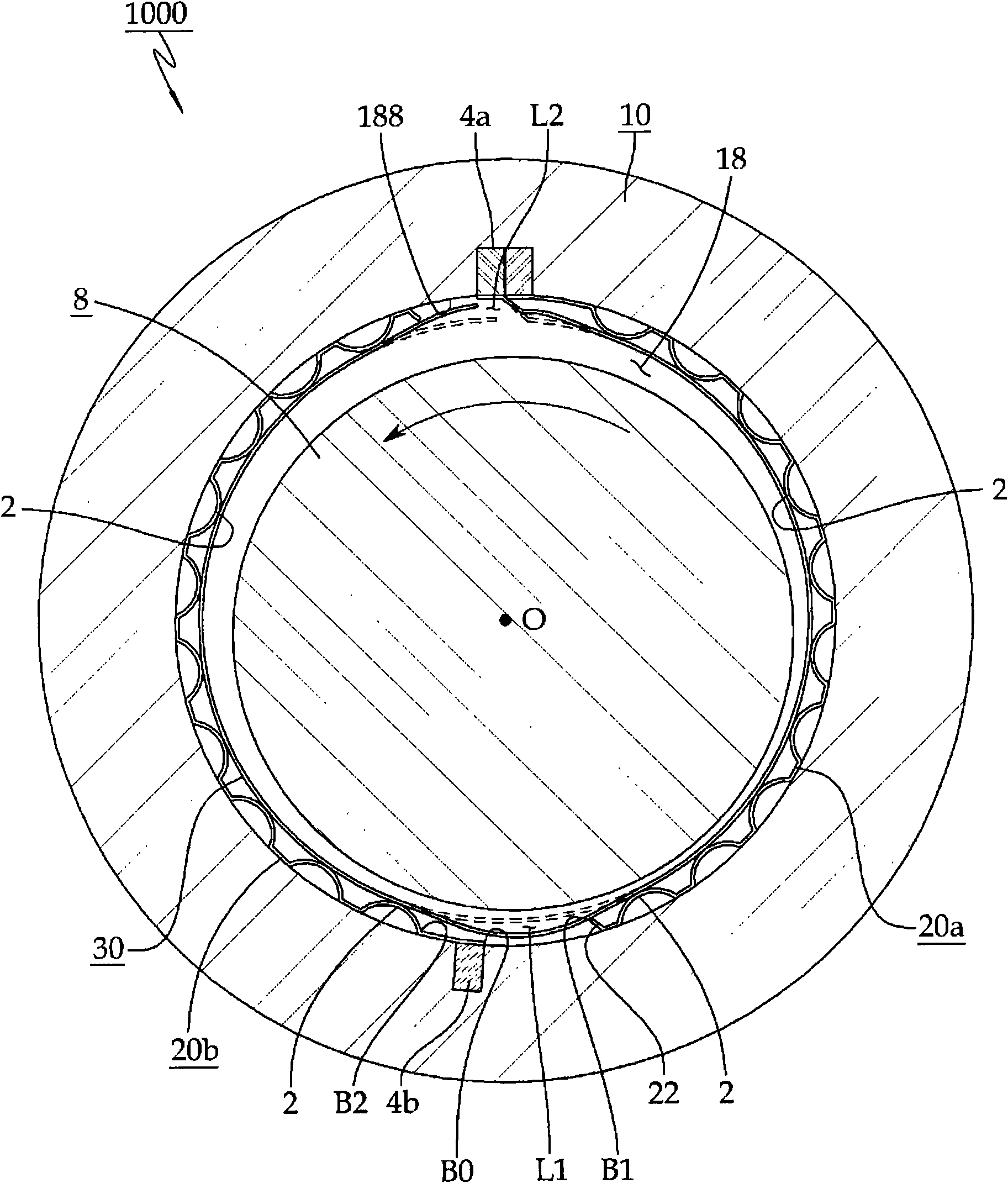
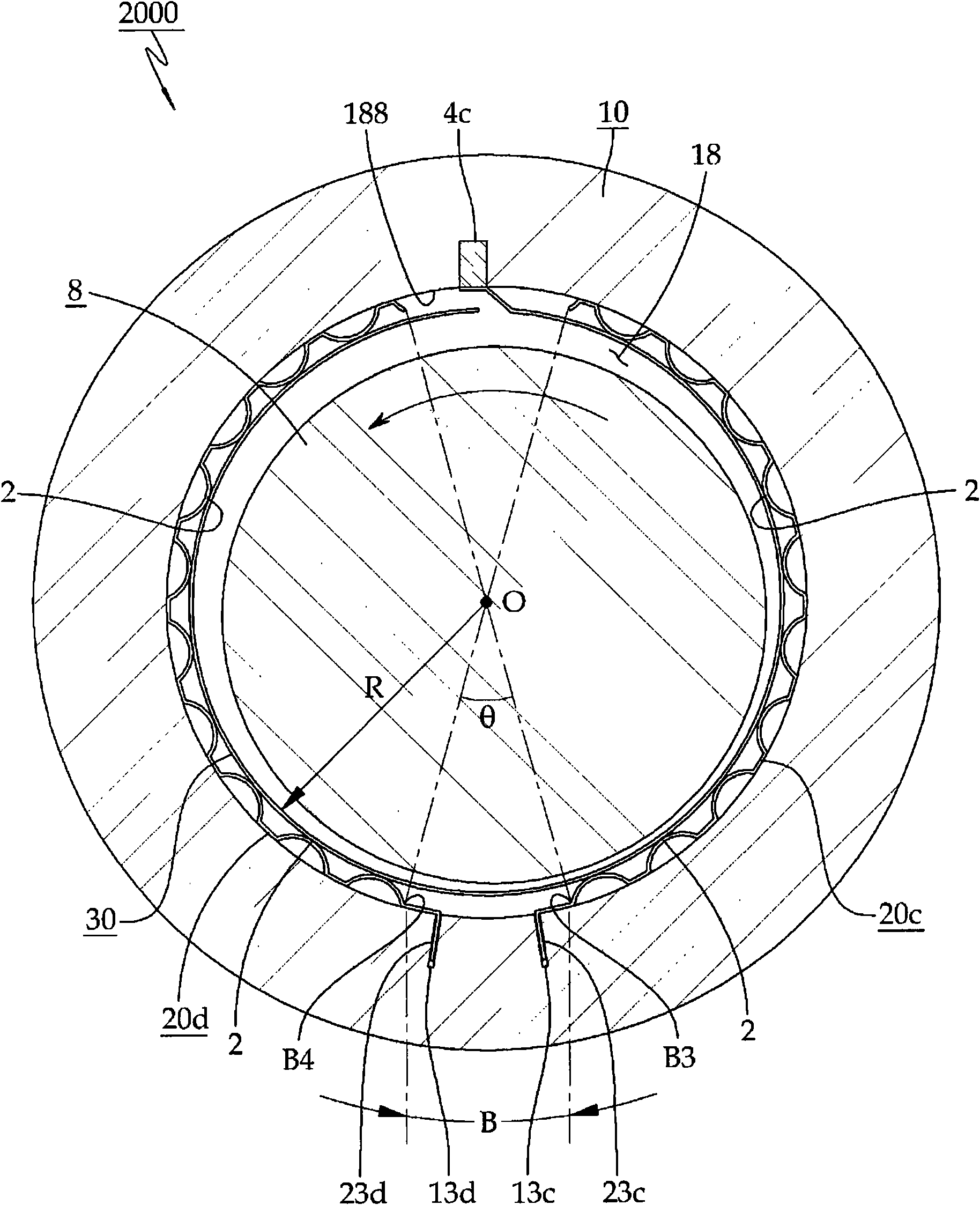
A journal foil air bearing 5000 according to the present invention is provided with one top foil 300 along an inner periphery of a hole 18 of a bearing housing 10. Bump foils 20c and 20d are installed at the inner periphery of the hole 18 of the bearing housing 10 where they are distanced from each other. Both ends of the top foil 300 form bent portions 308a and 308b and the bent portions 308a and 308b are mounted in a slot 414 of a slot body 40 mounted in a slot 140 provided in the inner periphery of the hole 18 in the bearing housing 10 and the top foil 300 is elastically movable therein.
Owner:NEUROS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com