Patents
Literature
7452 results about "Trailing edge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
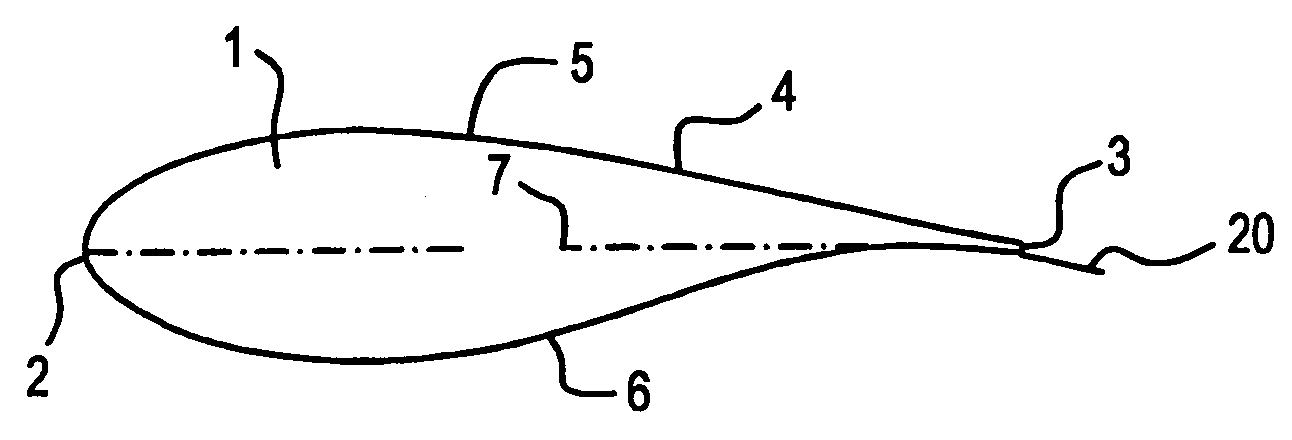
The trailing edge of an aerodynamic surface such as a wing is its rear edge, where the airflow separated by the leading edge rejoins. Essential flight control surfaces are attached here to control the direction of the departing air flow, and exert a controlling force on the aircraft. Such control surfaces include ailerons on the wings for roll control, elevators on the tailplane controlling pitch, and the rudder on the fin controlling yaw. Elevators and ailerons may be combined as elevons on tailless aircraft.
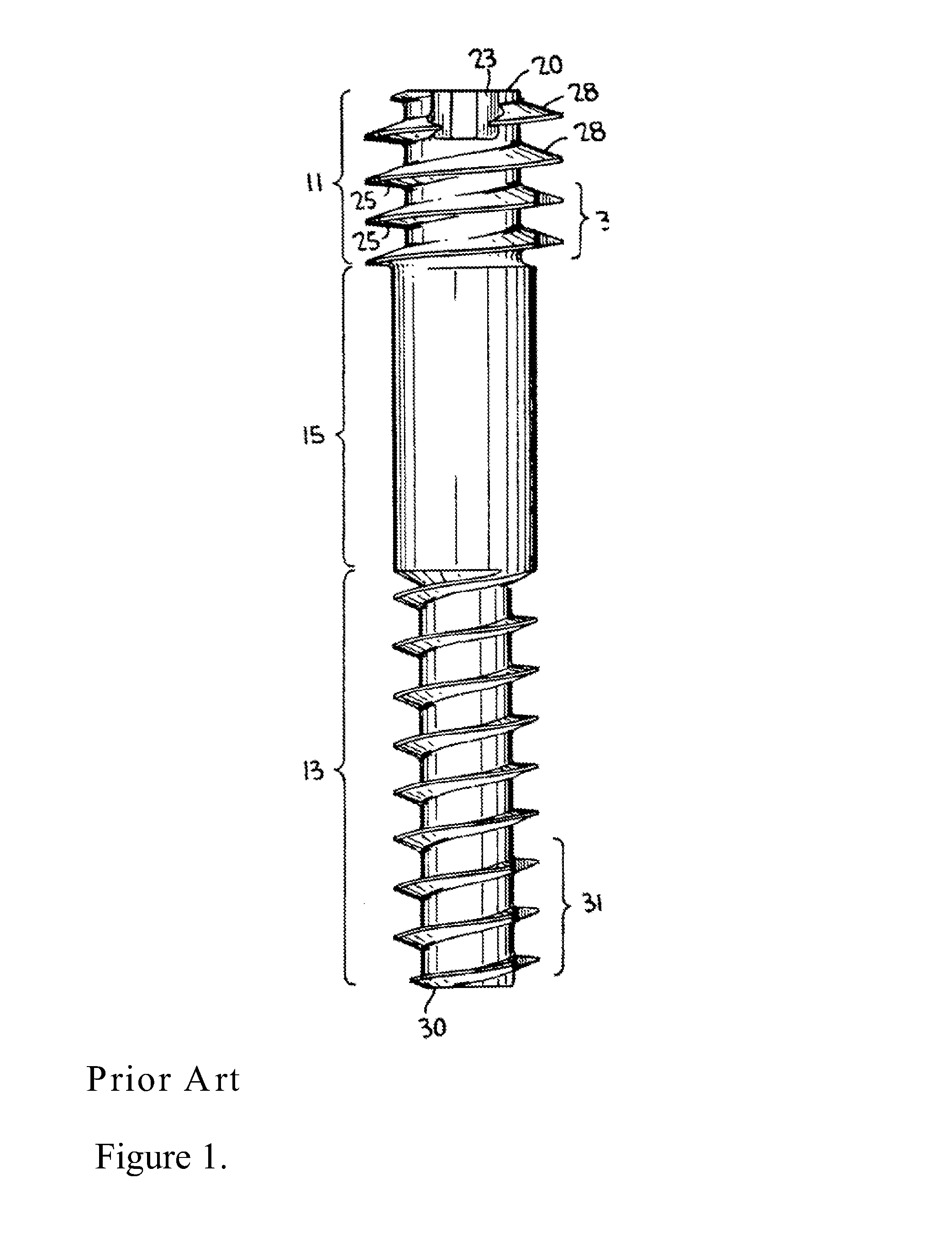
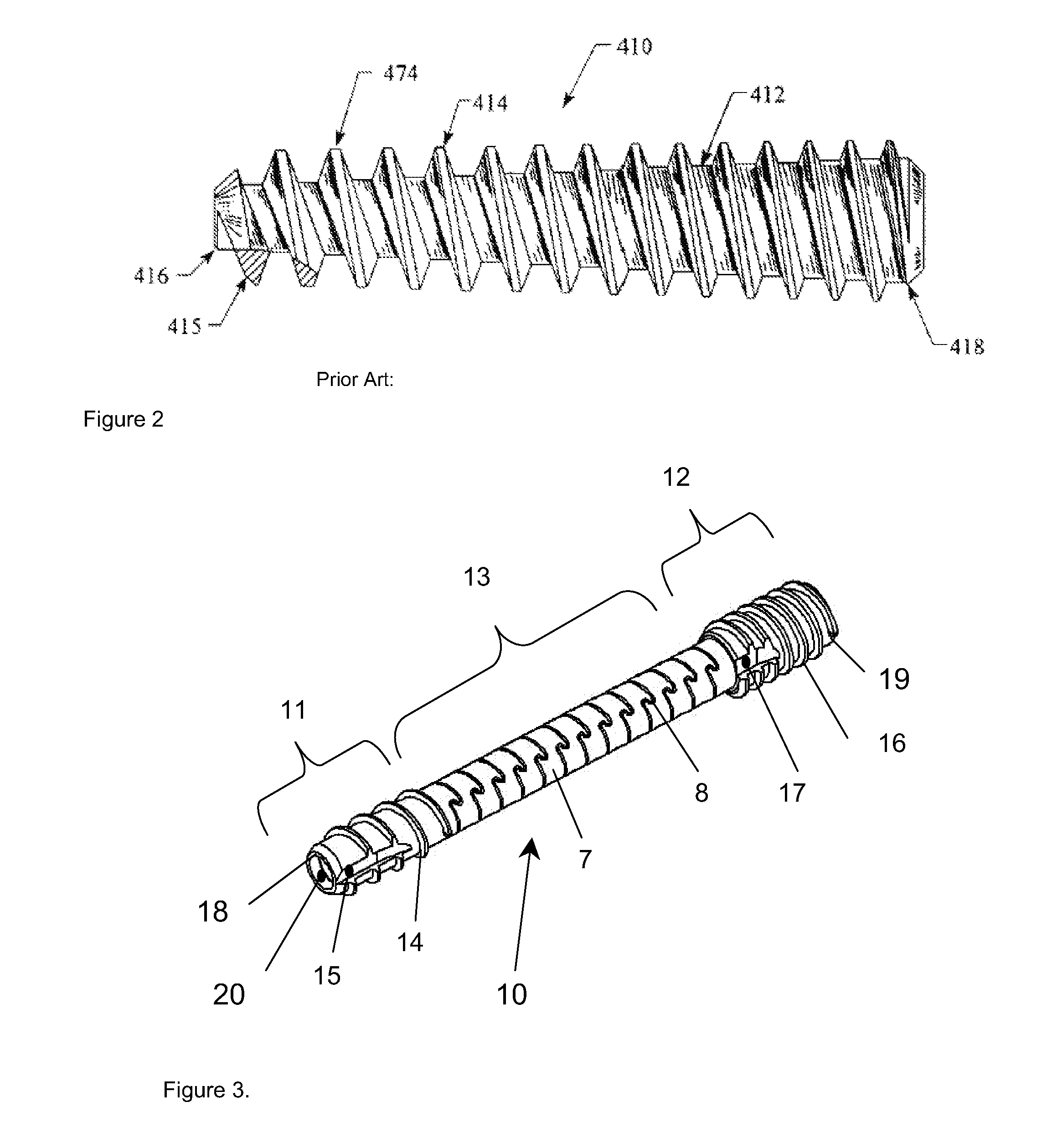
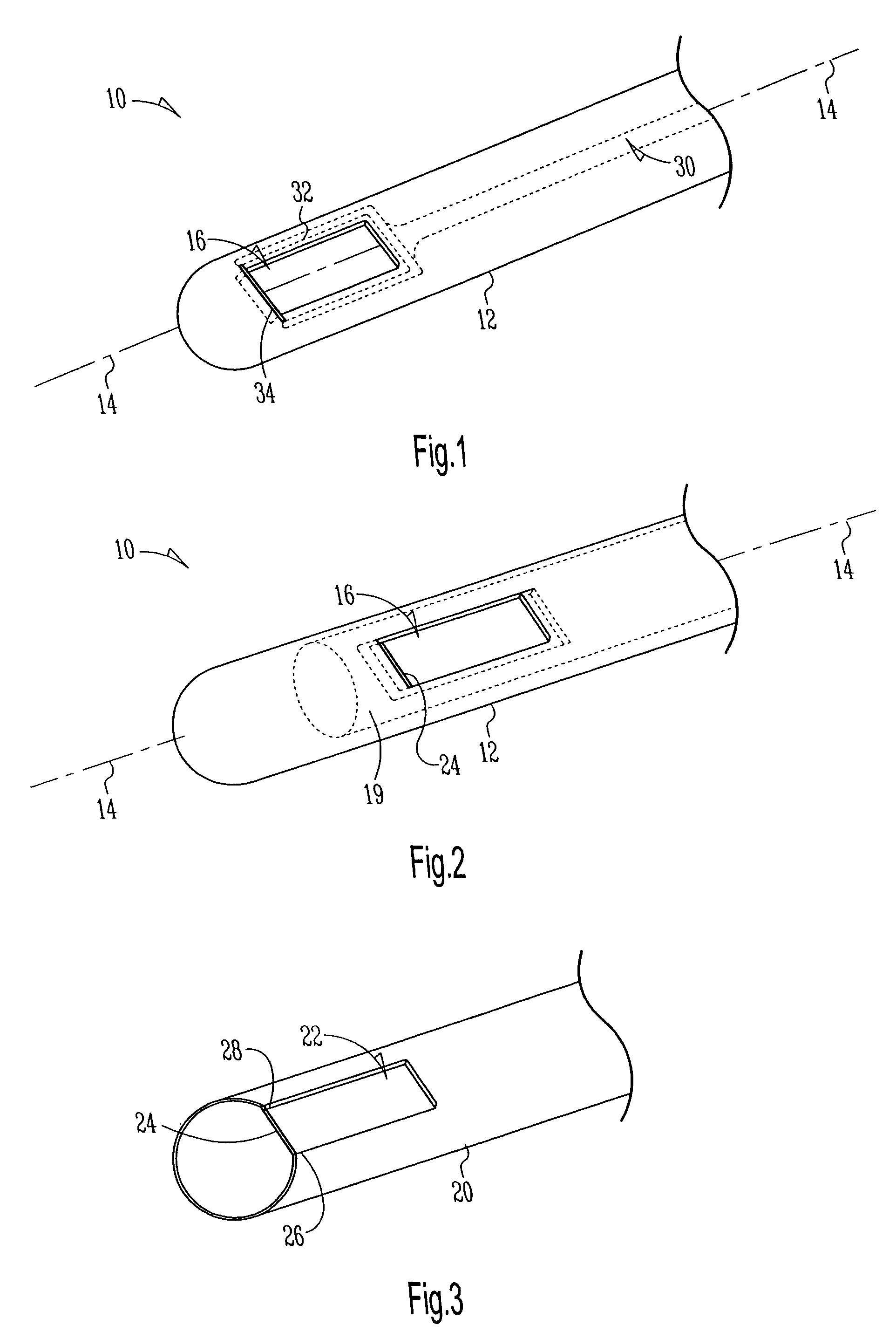
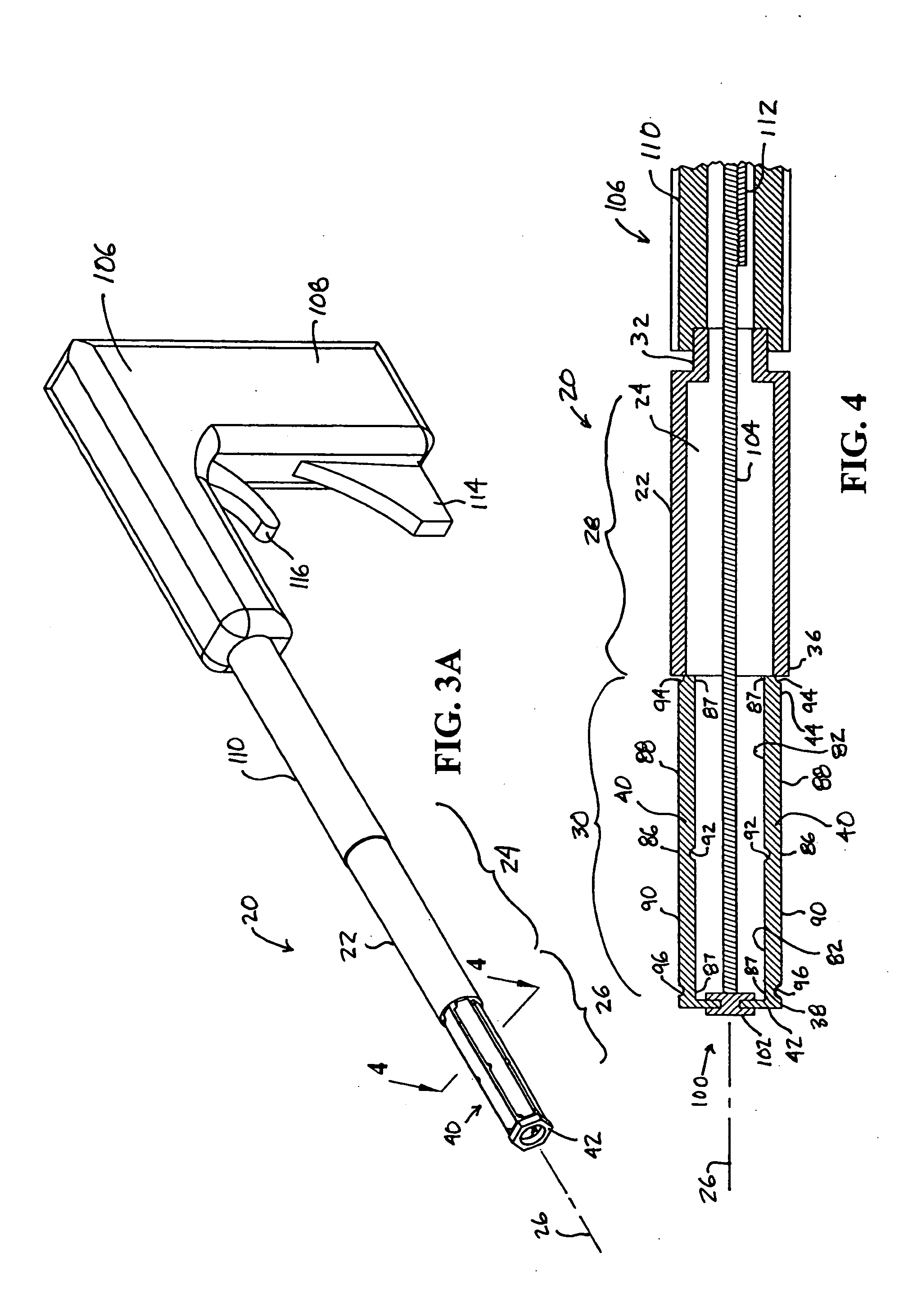
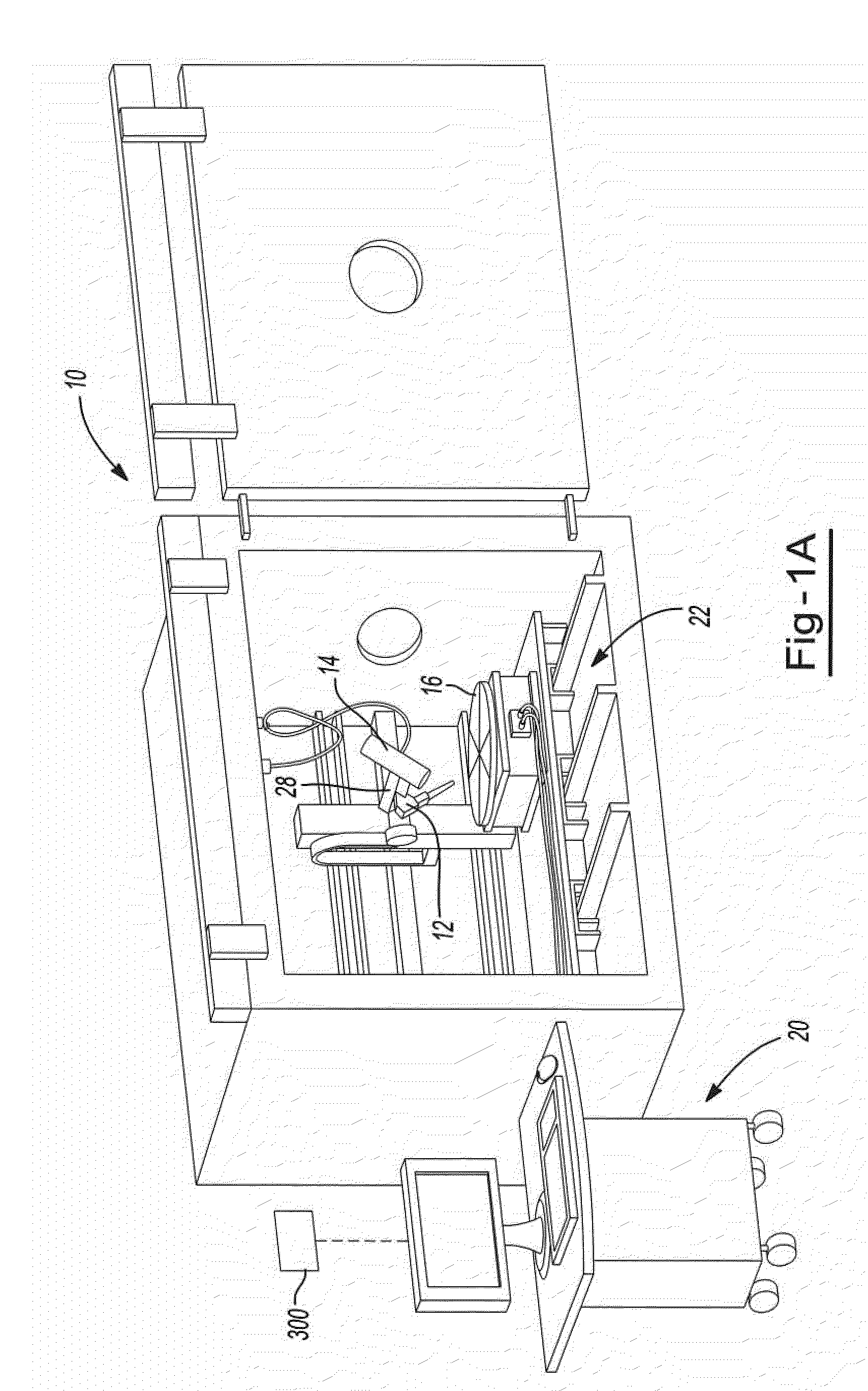
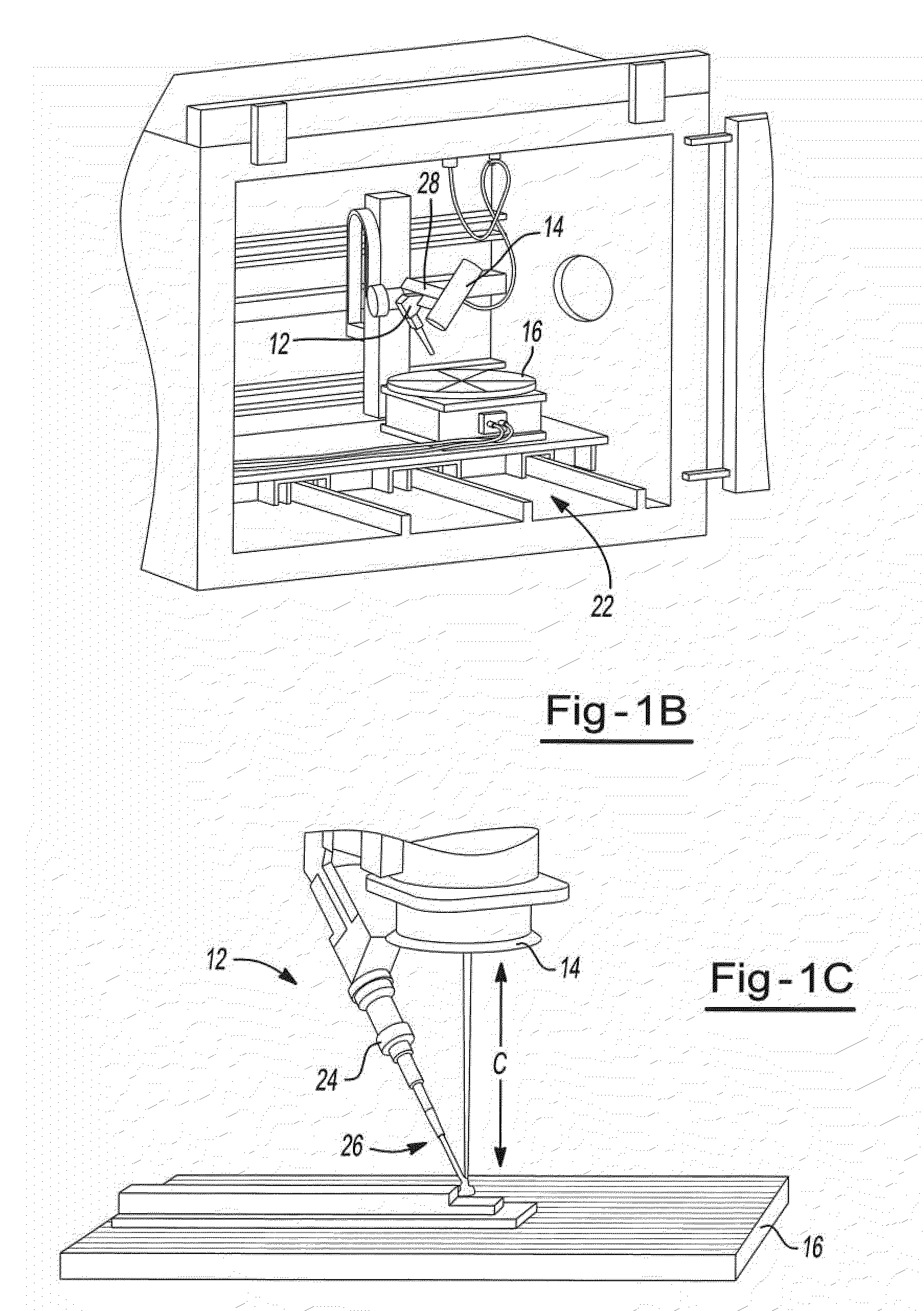
Closure member for a medical implant device
InactiveUS7214227B2Prevent openingIncrease clamping forceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsLeading edgeSet screw
A closure member, such as a set screw, and complementary receiving member are included in a medical implant device. The receiving member has a plurality of noncontiguous, threaded walls substantially defining a bore for receiving the threaded closure member. When the closure member is inserted into the receiving member, their respective threads interlock to join the noncontiguous walls of the receiving member. The closure member has an outer thread configured to interlock with the inner walls of the receiving member in a manner that aids in preventing the noncontiguous walls of the receiving member from moving away from the closure member. In certain embodiments, the closure member's outer thread includes a trailing edge having a point that is rearward of the trailing edge's root, and the outer thread includes a leading edge having a point that is forward of the leading edge's root.
Owner:THEKEN SURGICAL LLC
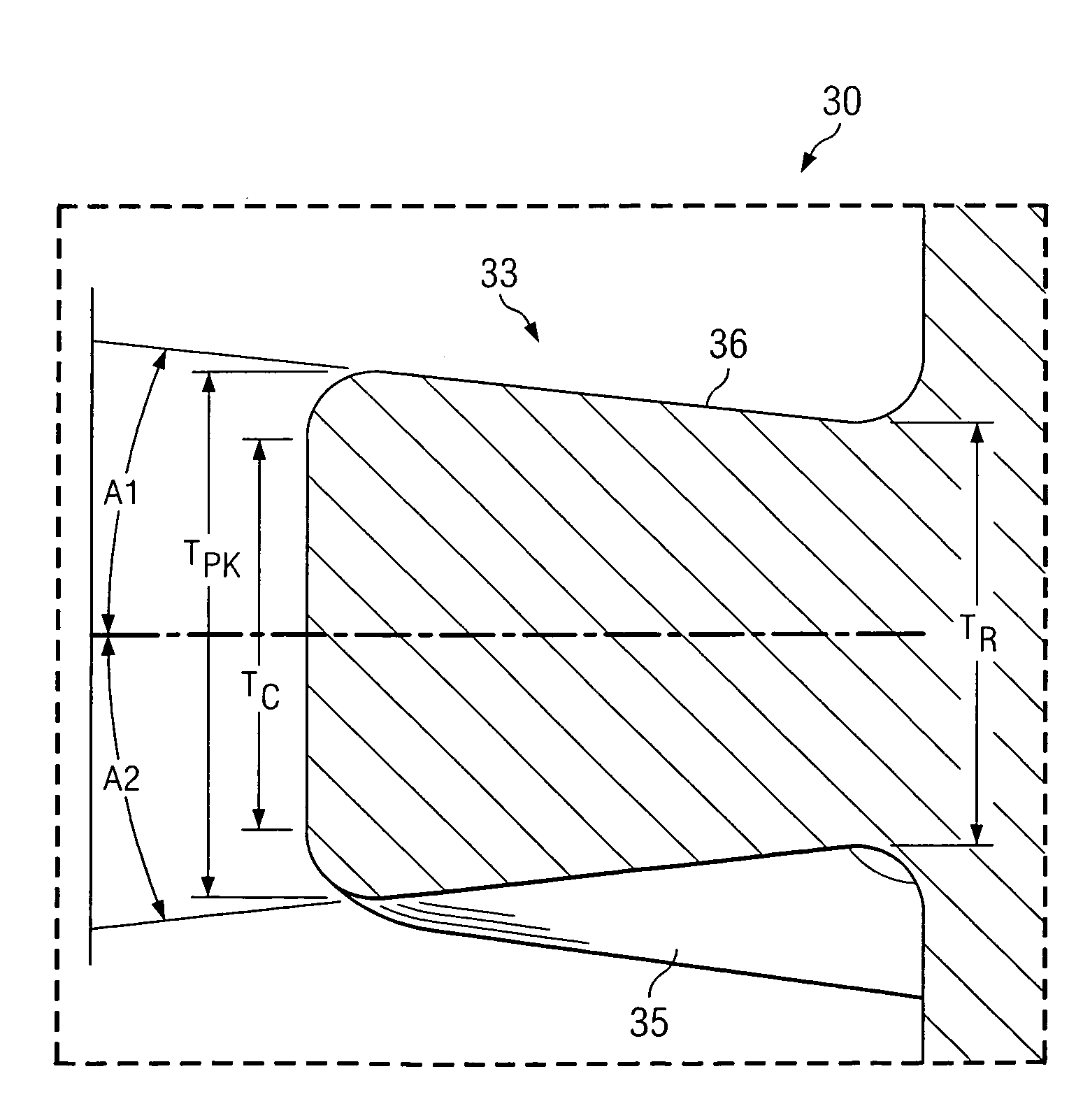
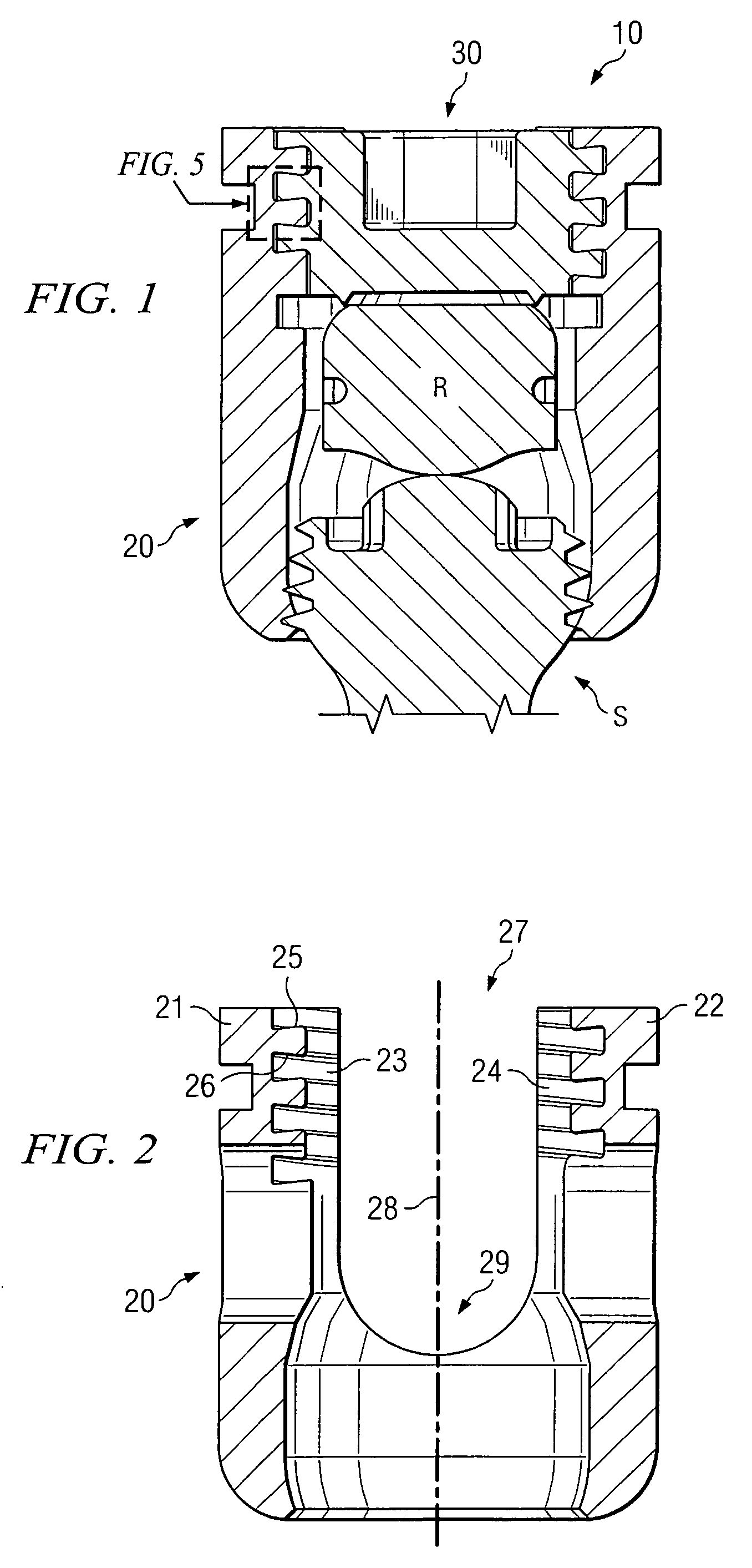
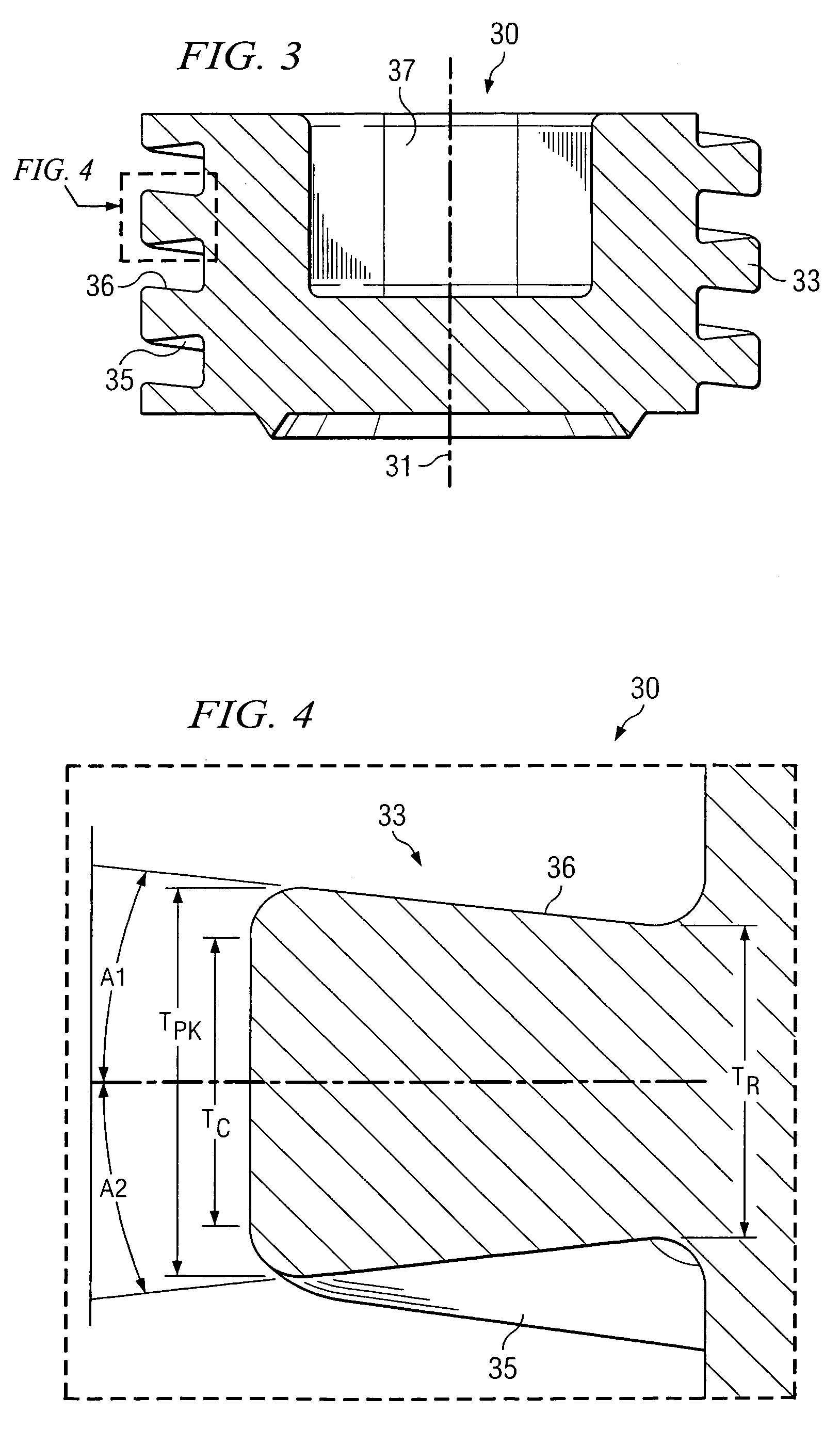
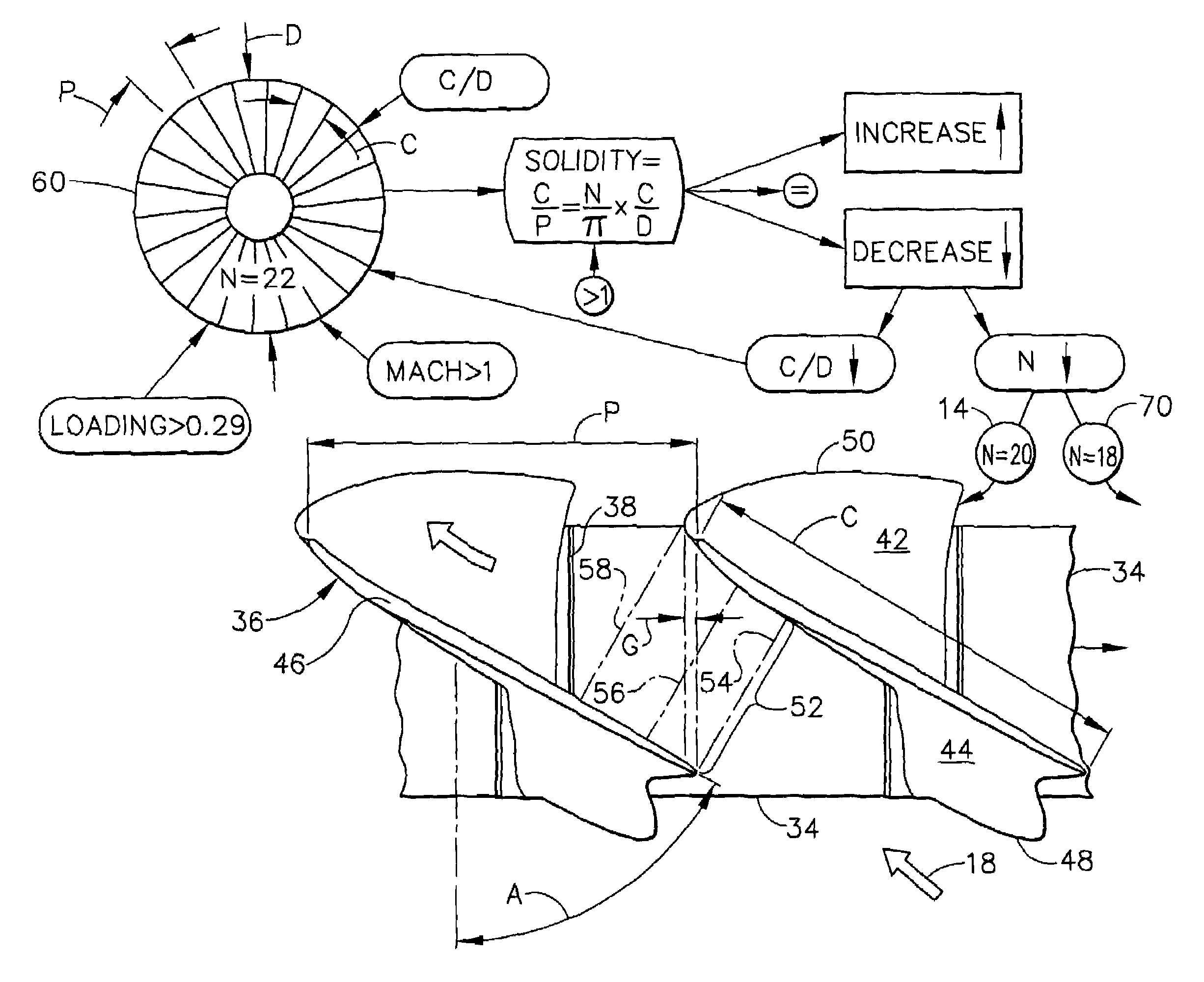
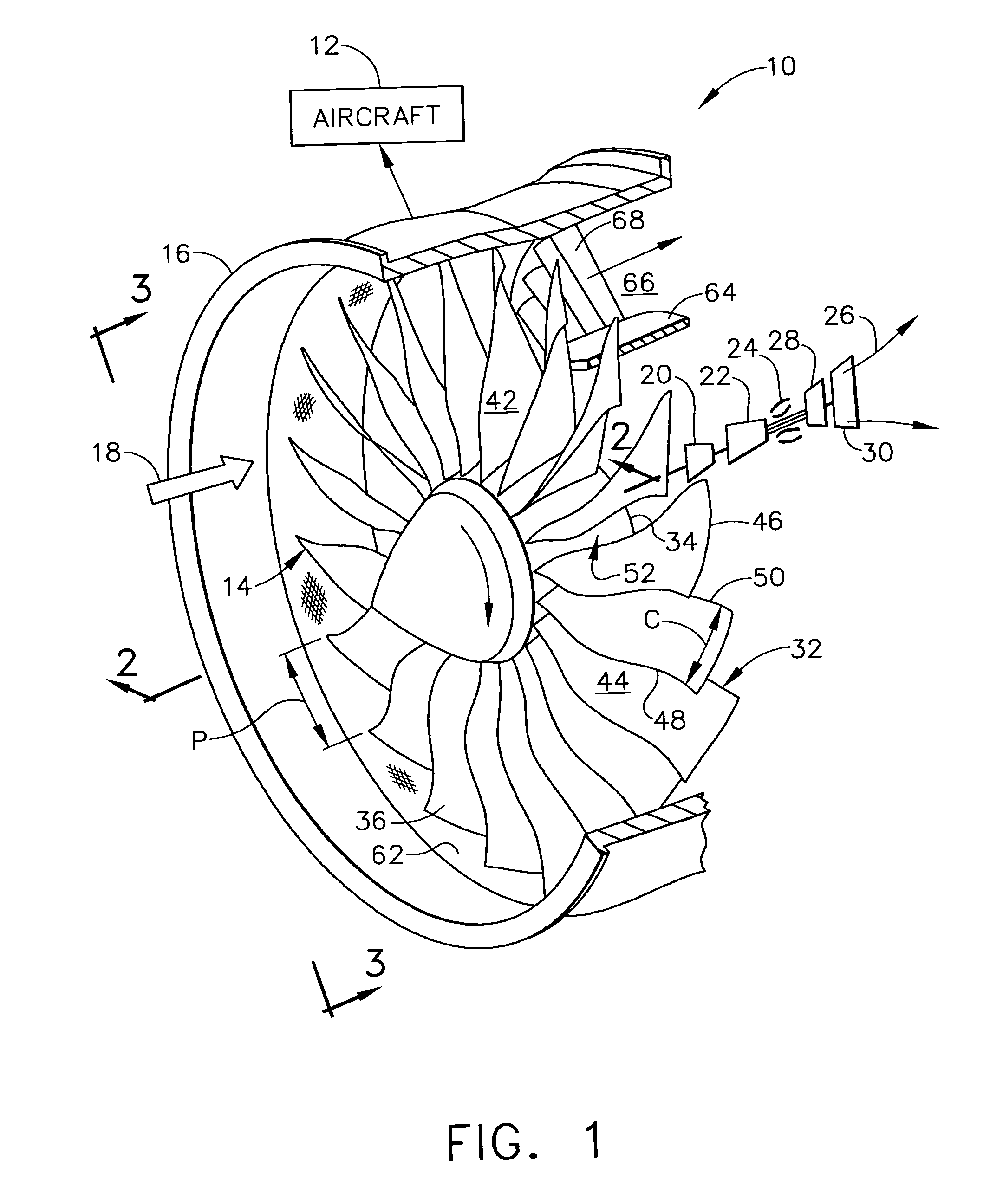
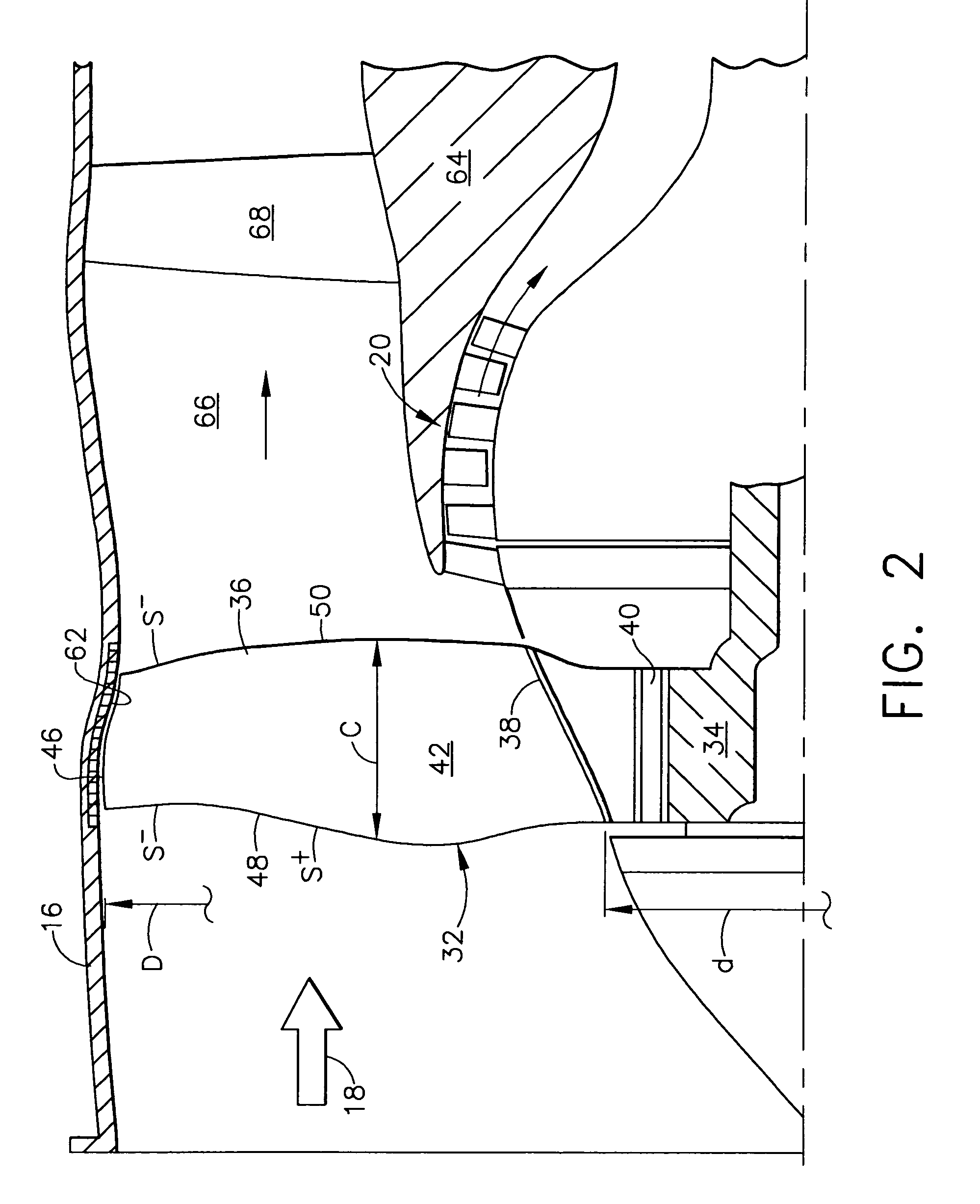
Low solidity turbofan
A turbofan includes a row of fan blades extending from a supporting disk inside an annular casing. Each blade includes an airfoil having opposite pressure and suction sides extending radially in span between a root and tip and axially in chord between leading and trailing edges. Adjacent airfoils define corresponding flow passages therebetween for pressurizing air. Each airfoil includes stagger increasing between the root and tip, and the flow passage has a mouth between the airfoil leading edge and the suction side of an adjacent airfoil and converges to a throat aft from the mouth. The row includes no more than twenty fan blades having low tip solidity for increasing the width of the passage throat.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
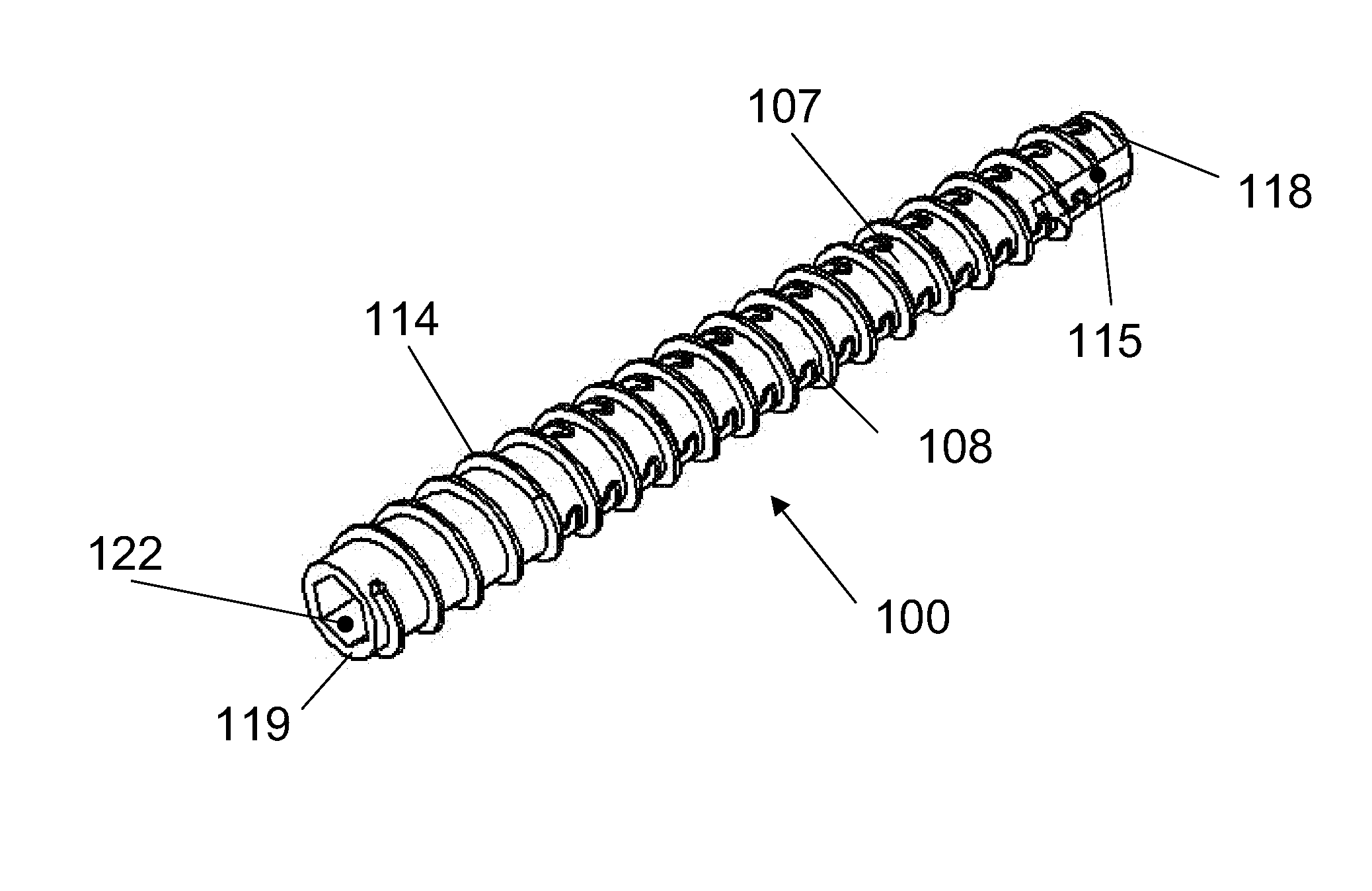
Flexible Screw
InactiveUS20110144703A1Increase flexibilityIncrease widthSuture equipmentsLigamentsLeading edgeEngineering
A flexible compression screw having multiple segments, one or more of which are flexible and one or more segments that also include threads. The flexibility is created through the use of at least one helical slot formed generally in the center segment of the element. Additional flexible segments also have at least one helical slot in either the same helical rotation and pattern or in an opposite rotation and / or different pattern. An elastomeric material can fill the hollow body, extend into the slots and / or encompass the exterior. The flexible screw can have a hollow body, including leading and trailing edge, or can have a partially hollow body.
Owner:FLEX TECH
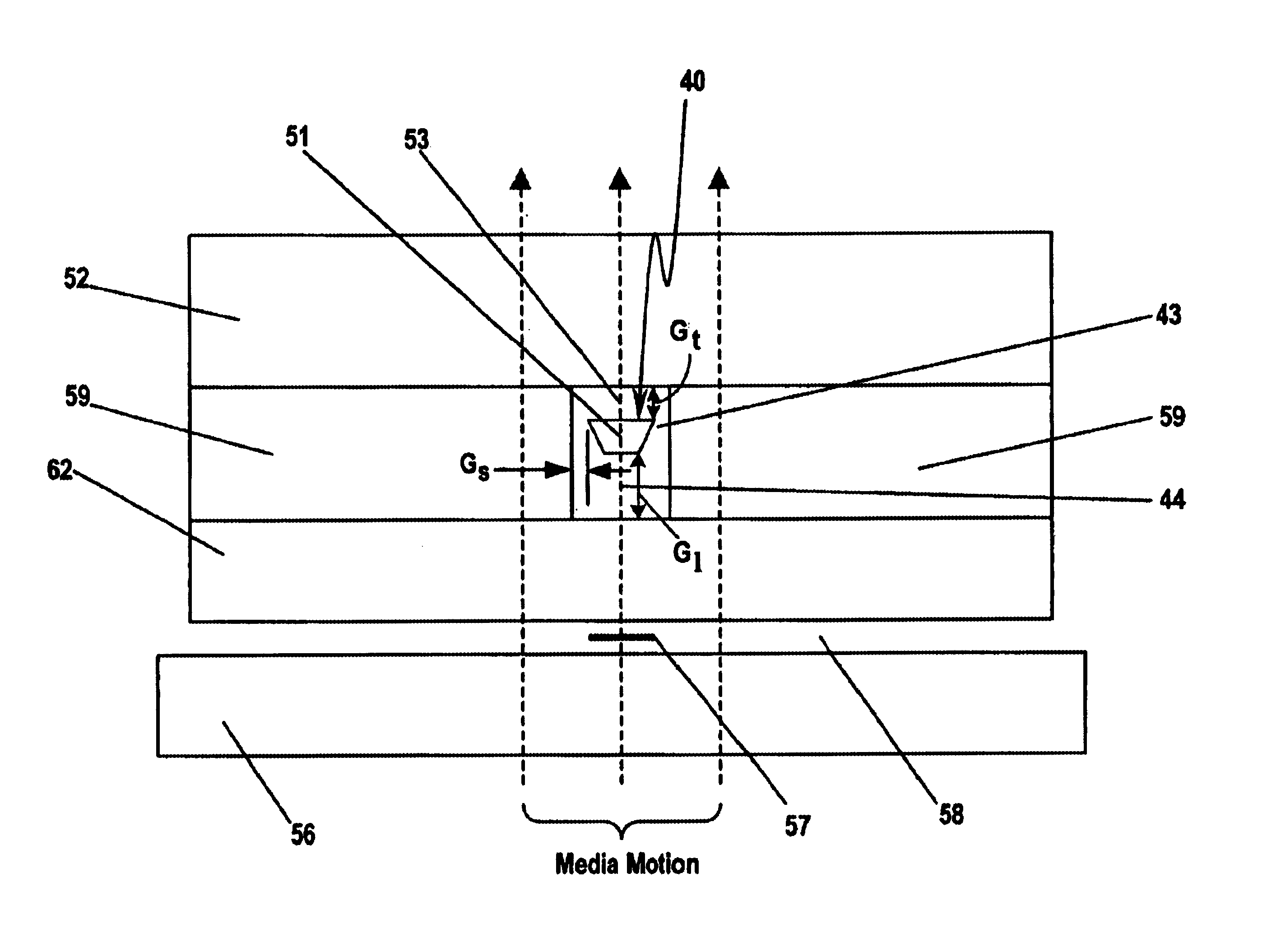
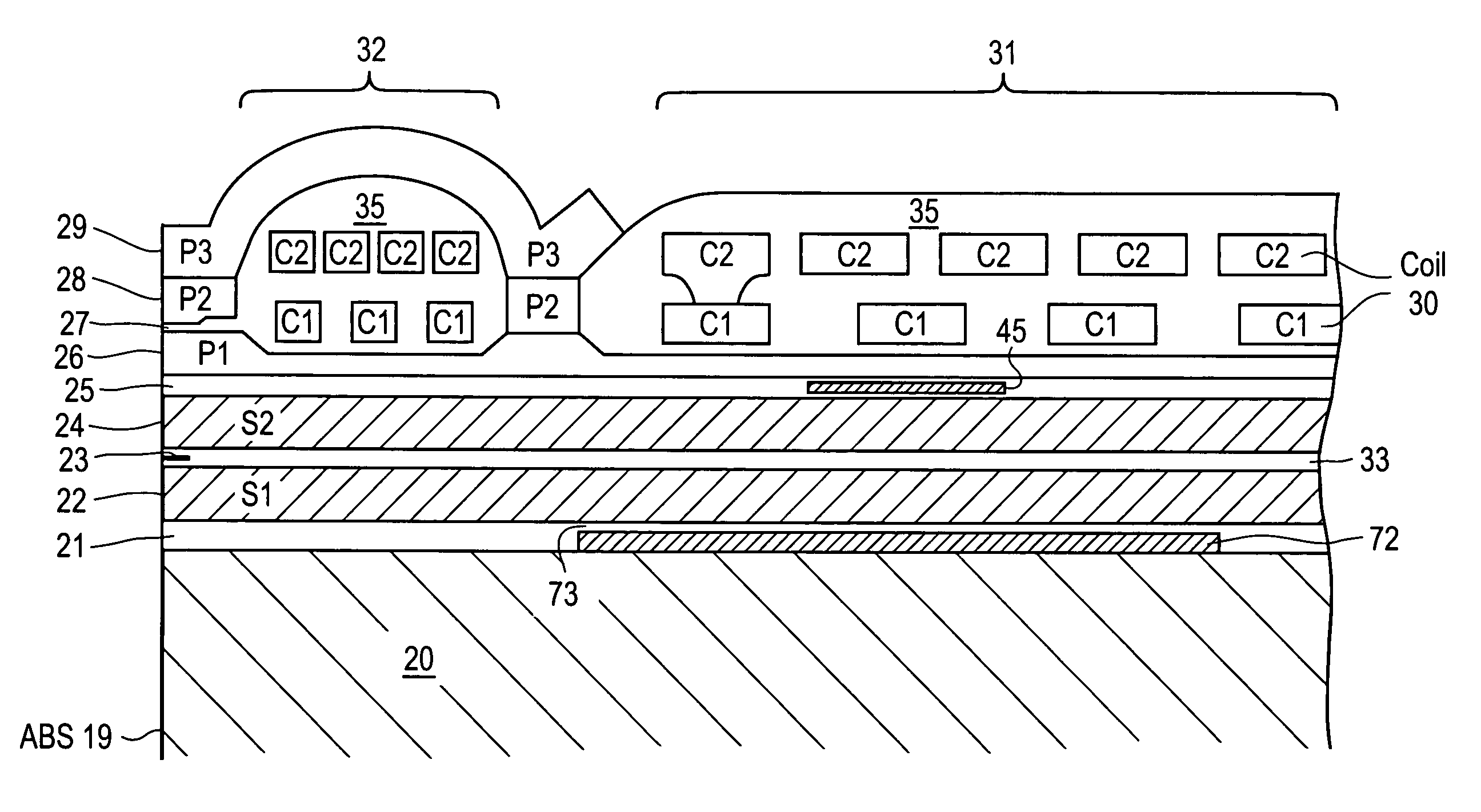
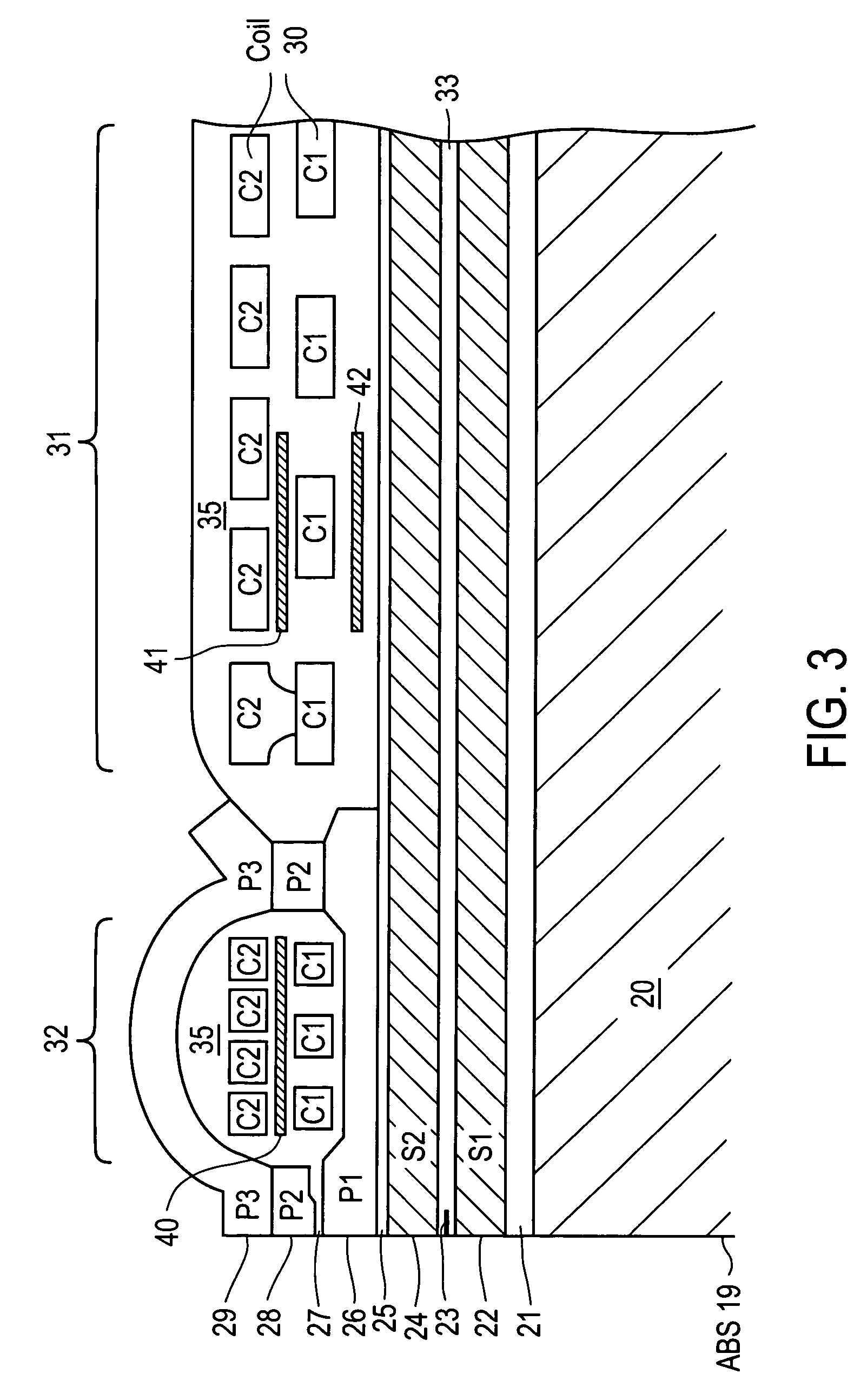
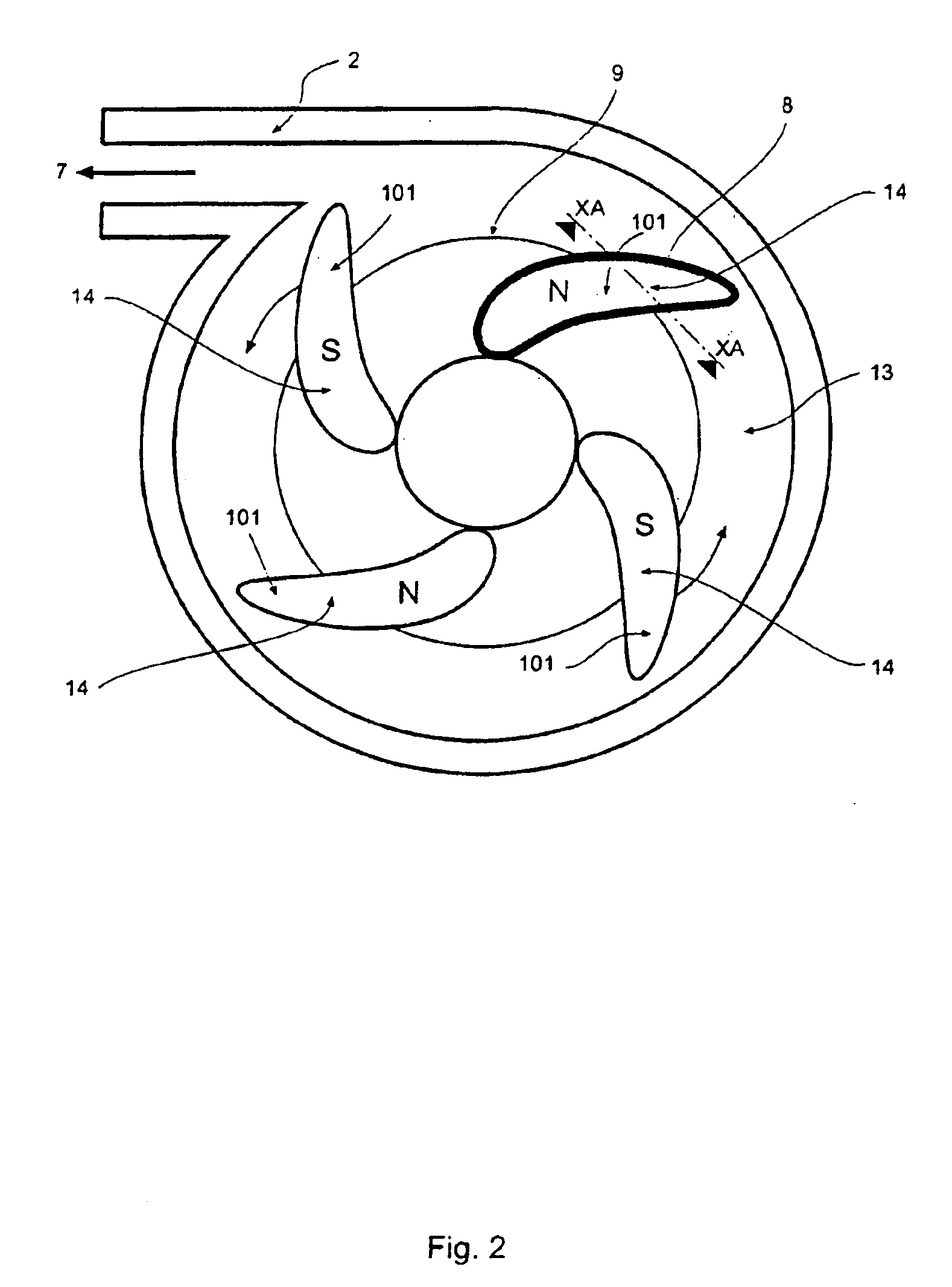
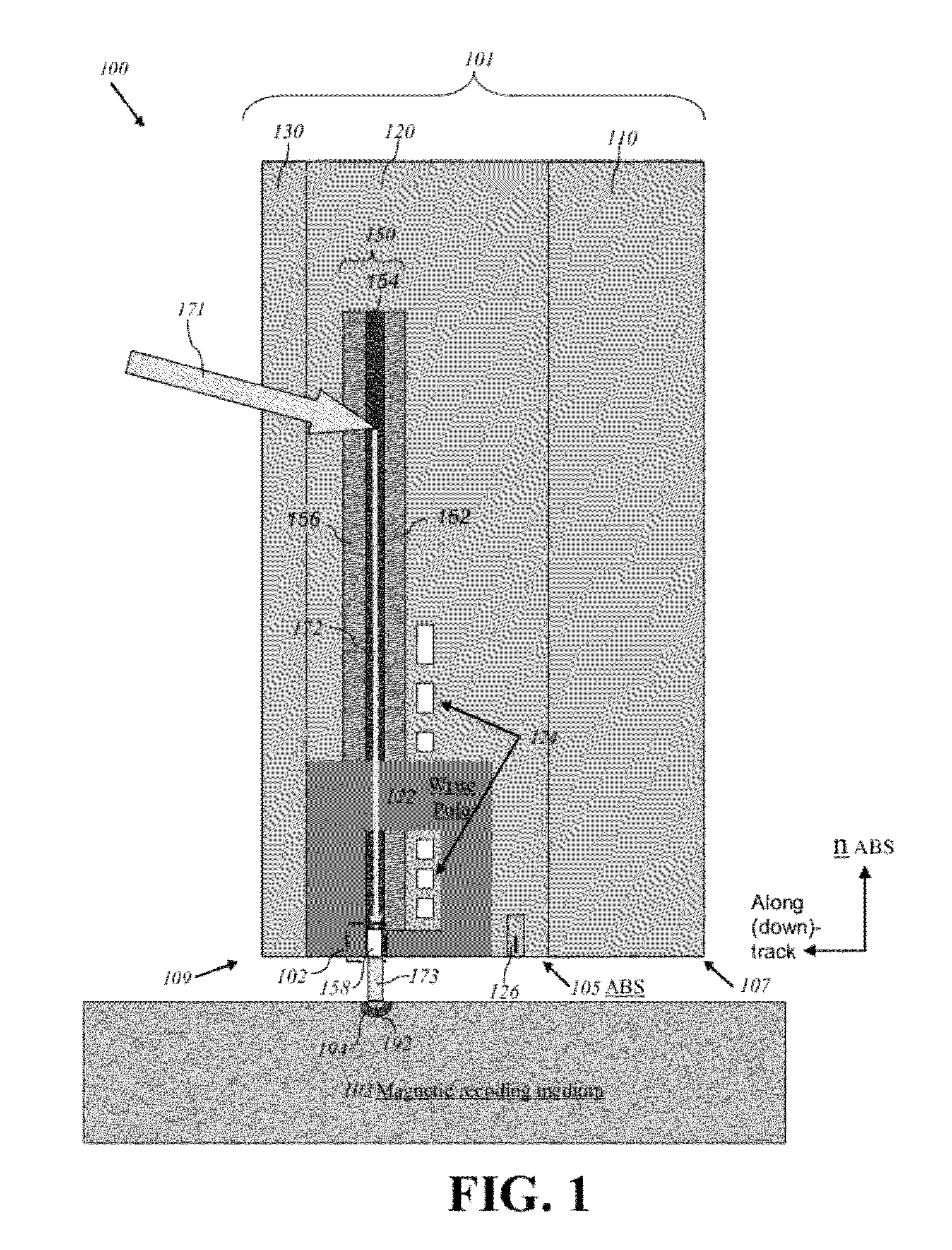
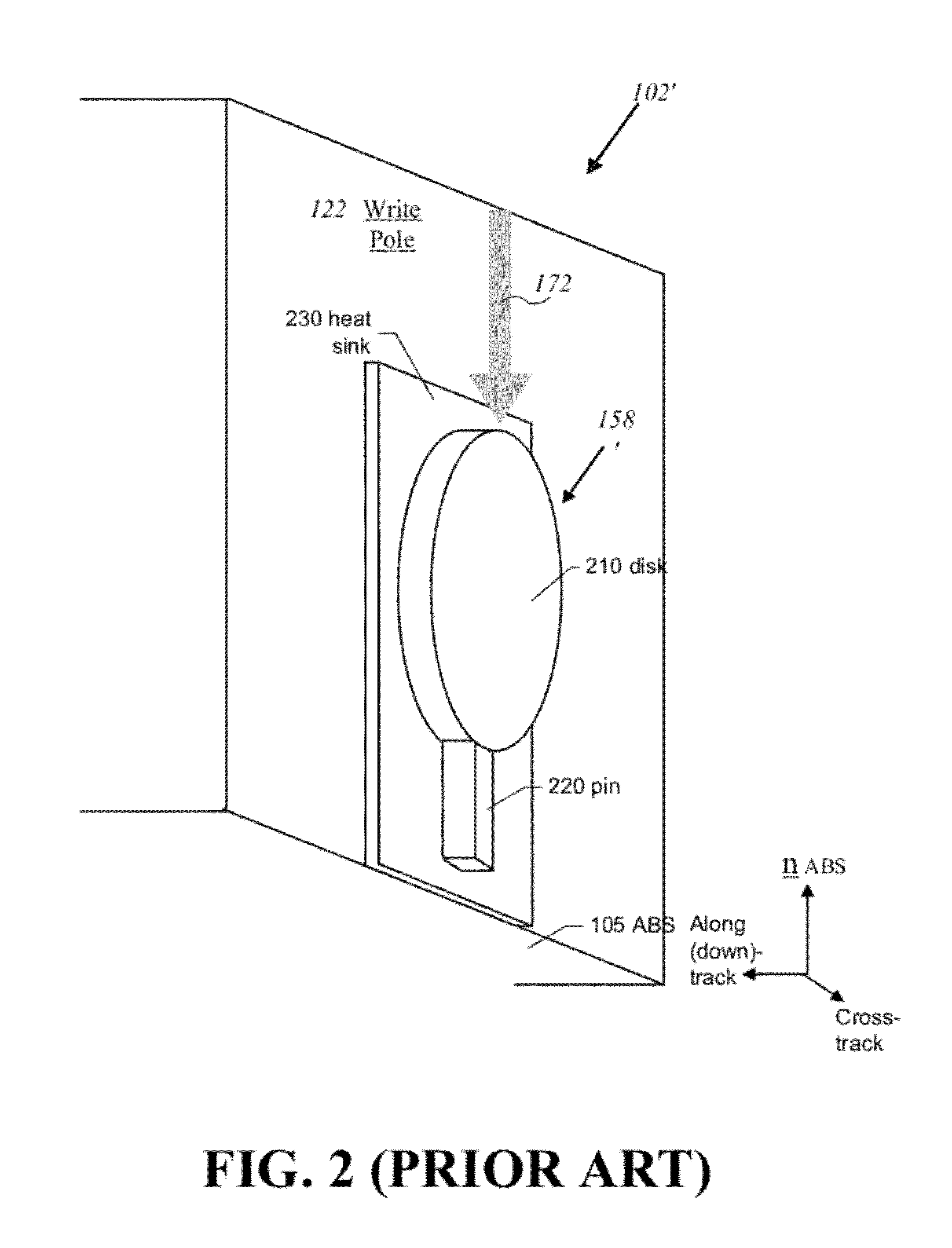
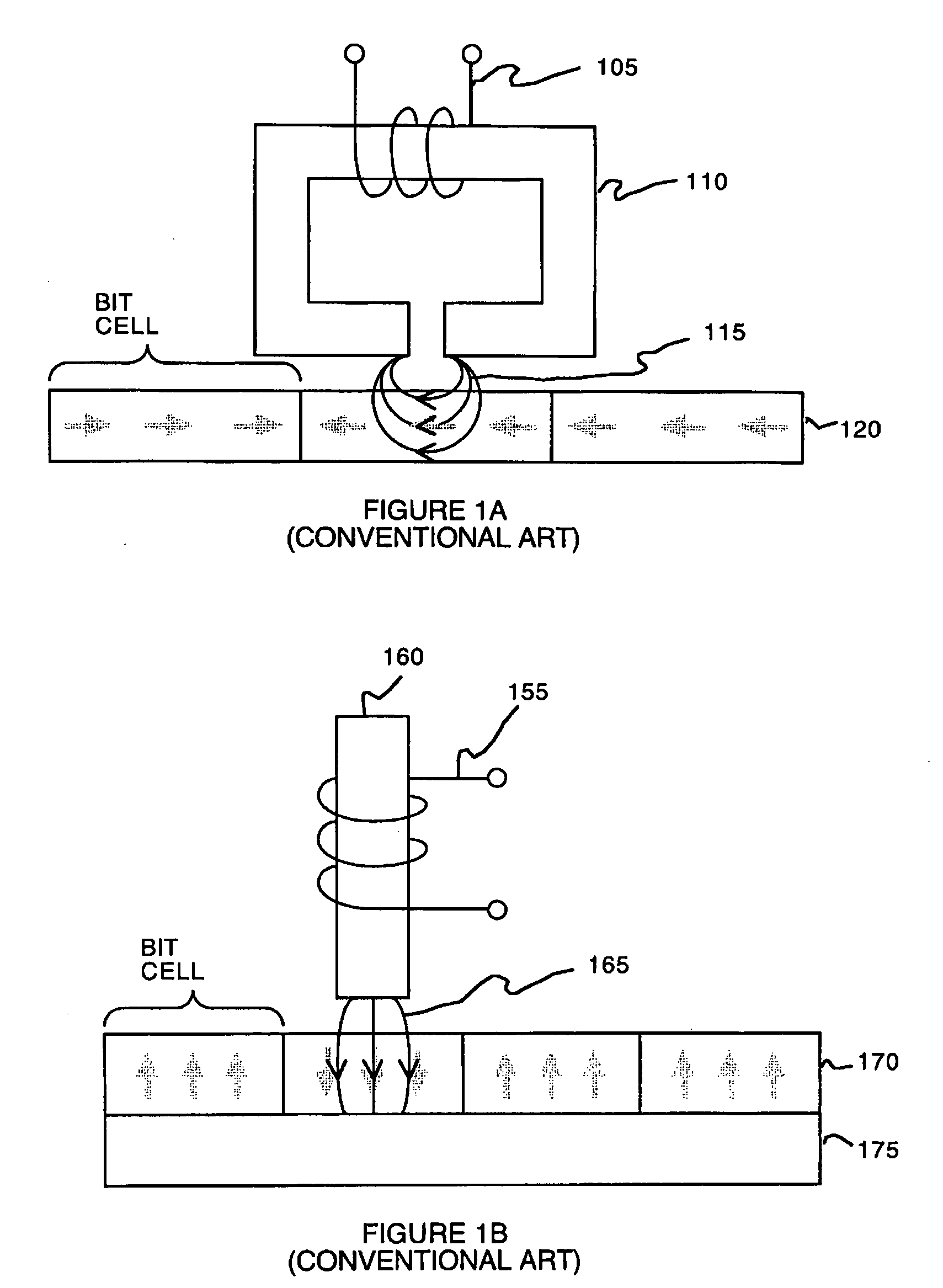
Perpendicular magnetic recording head with nonmagnetic write gap greater than twice side shield gap distance
InactiveUS6954340B2Improve writer efficiencyHigh gradientConstruction of head windingsManufacture head surfaceLeading edgeEngineering
A magnetic head for perpendicular recording on double layer media with suppressed side writing and controlled write width is disclosed. The present invention reduces the problem of side writing and controls the write width of the writing element by providing a writing element with a trailing edge sized dimensionally larger than the leading edge, side shields, and specifically spaced writing gaps placed at various distances between the write element and the side shields, return poles, and the main pole.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Monolithic composite wing manufacturing process
InactiveUS6190484B1Aircraft stabilisationPaper/cardboard wound articlesLeading edgeIncreased torsion
A method of manufacturing a monolithic composite wing without using mechanical fasteners is described. The process begins with the formation of a center wing box in combination with a pair of spars, riblets and a pair of skin-molds including the wrapping and binding of the box by means of resin impregnated composite tapes. Next, additional cells are adjoined contiguously on either side of the current framework and an overlap wrapping and bonding process is continued around the current framework. The overlap wrapping and binding procedure provides increased torsion stiffness and reduced structural weight. All cells up to the leading and trailing edges will be included in the assembly process. Conduits to convey fuel, hydraulic fluid and electrical wiring will also be installed in designated cells. Finally, the completed wing will be cured in an autoclave under uniform pressure and temperature.
Owner:APPA KARI
Method and apparatus for taking a biopsy
There is described method and apparatus for taking a biopsy wherein the apparatus is formed of a biocompatible cylindrical member with an outer wall and a hollow core, the cylindrical member having a longitudinal axis. An opening in the outer wall of the member is provided and a cutting device cuts tissue entering the opening as it travels along the opening. Cut tissue is treated with a coagulating agent or member so that the coagulation occurs concurrently or just after the tissue is cut wherein the coagulation occurs at a trailing edge of the opening as it travels.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Expandable reamer
An expandable reamer includes, in one exemplary embodiment thereof, a cannulated shaft and a plurality of straight cutting blades having deformable points. The blades are hingably outwardly rotatable at the deformation points between a contracted position and an expanded position. In the contracted position, the blades are substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis of the cannulated shaft and, in the expanded position, the blades have at least a portion oriented radially outward from the longitudinal axis, thereby forming a larger diameter cutting surface in the expanded position and in the contracted position. The blades are formed from a portion of the cannulated shaft by, e.g. milling longitudinally extending slots through the wall of the cannulated shaft, the slots serving as flutes dividing the cutting edge and trailing edge of each adjacent blade. Each blade may also include more than one segment arranged along its length, the segments coupled by deformation points. The expandable reamer may be used for cutting a cavity in a bone or other structure that is larger than the diameter of the entry point into the bone and greater than the diameter of the contracted reamer.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
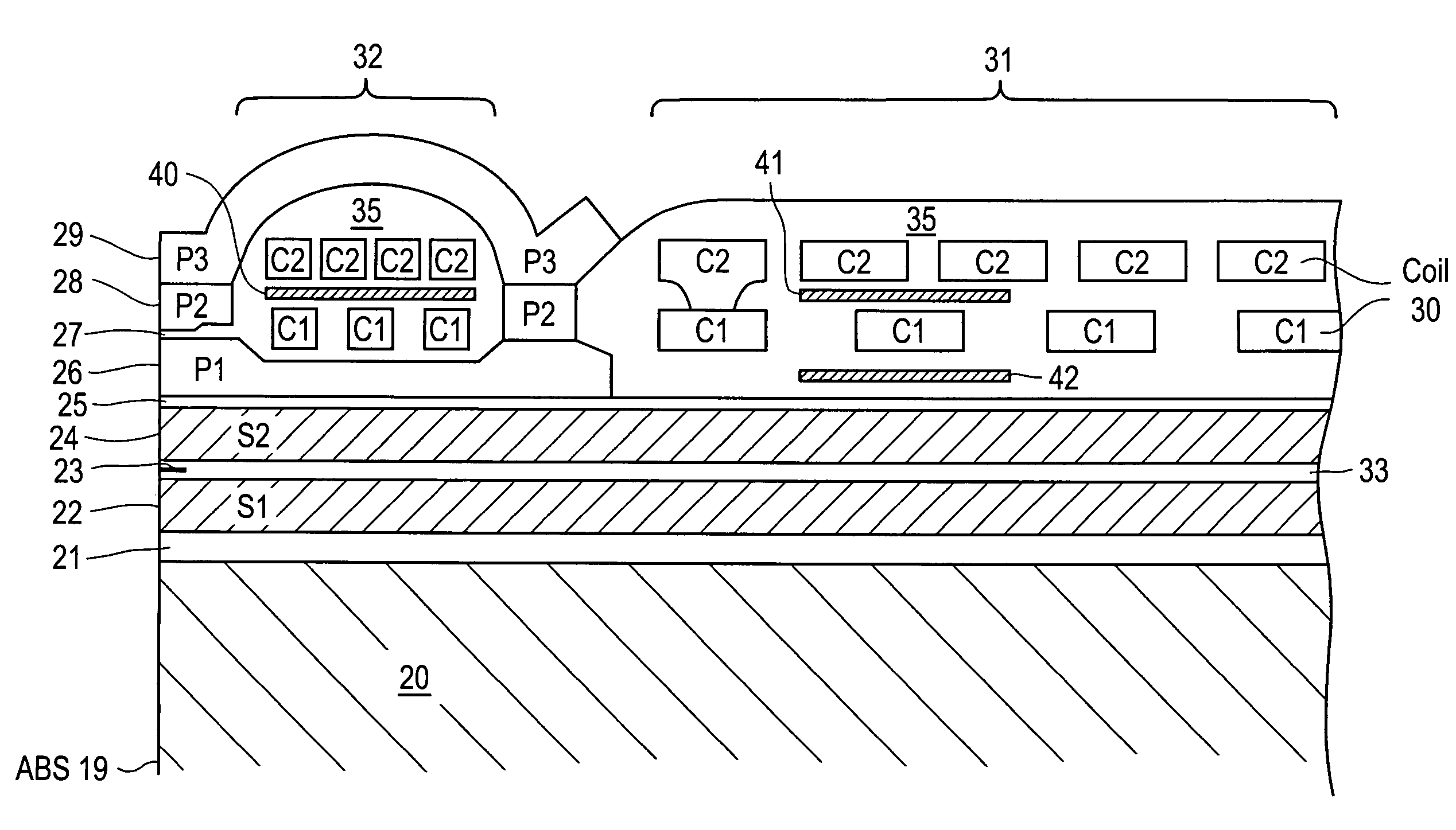
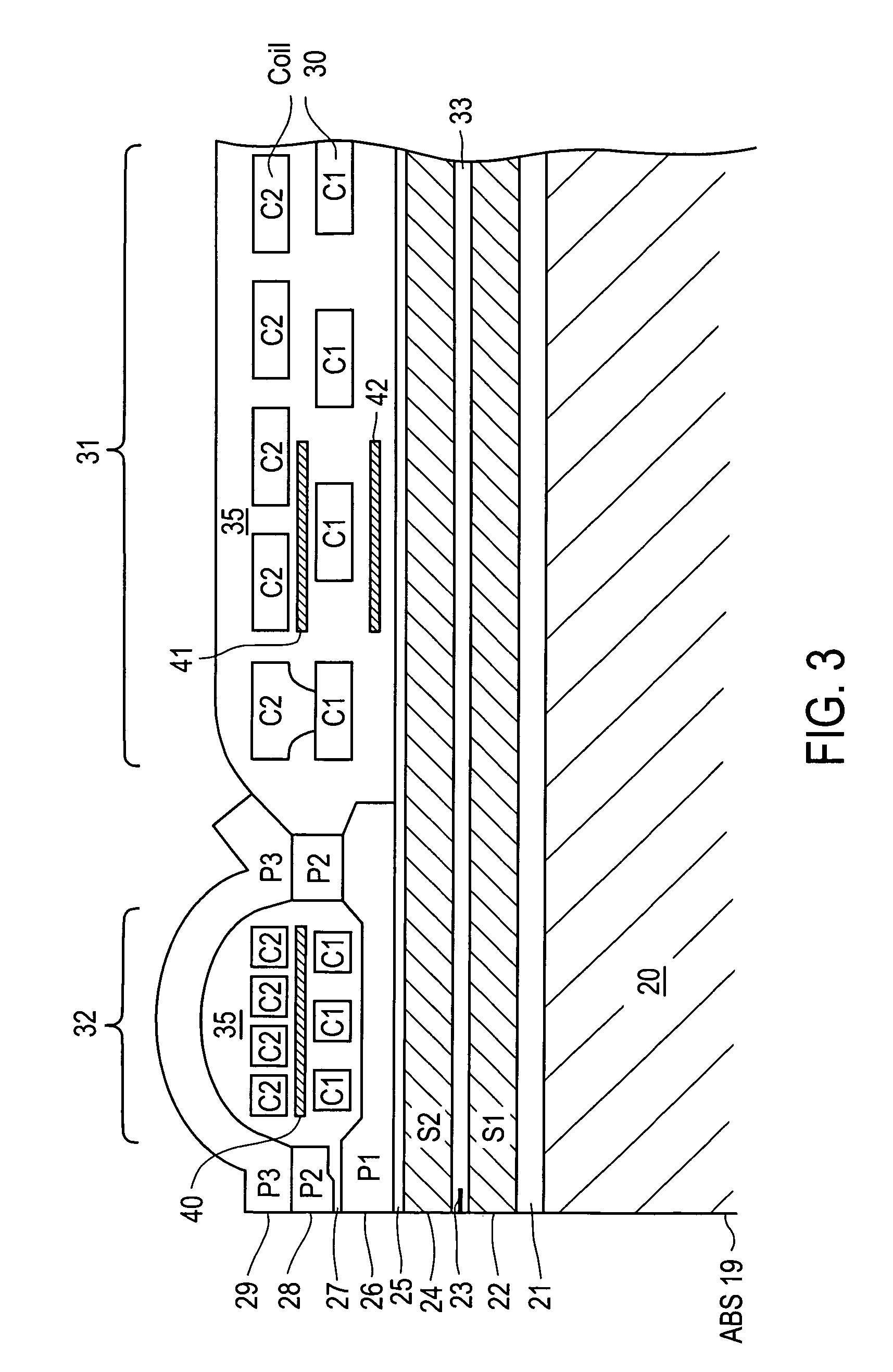
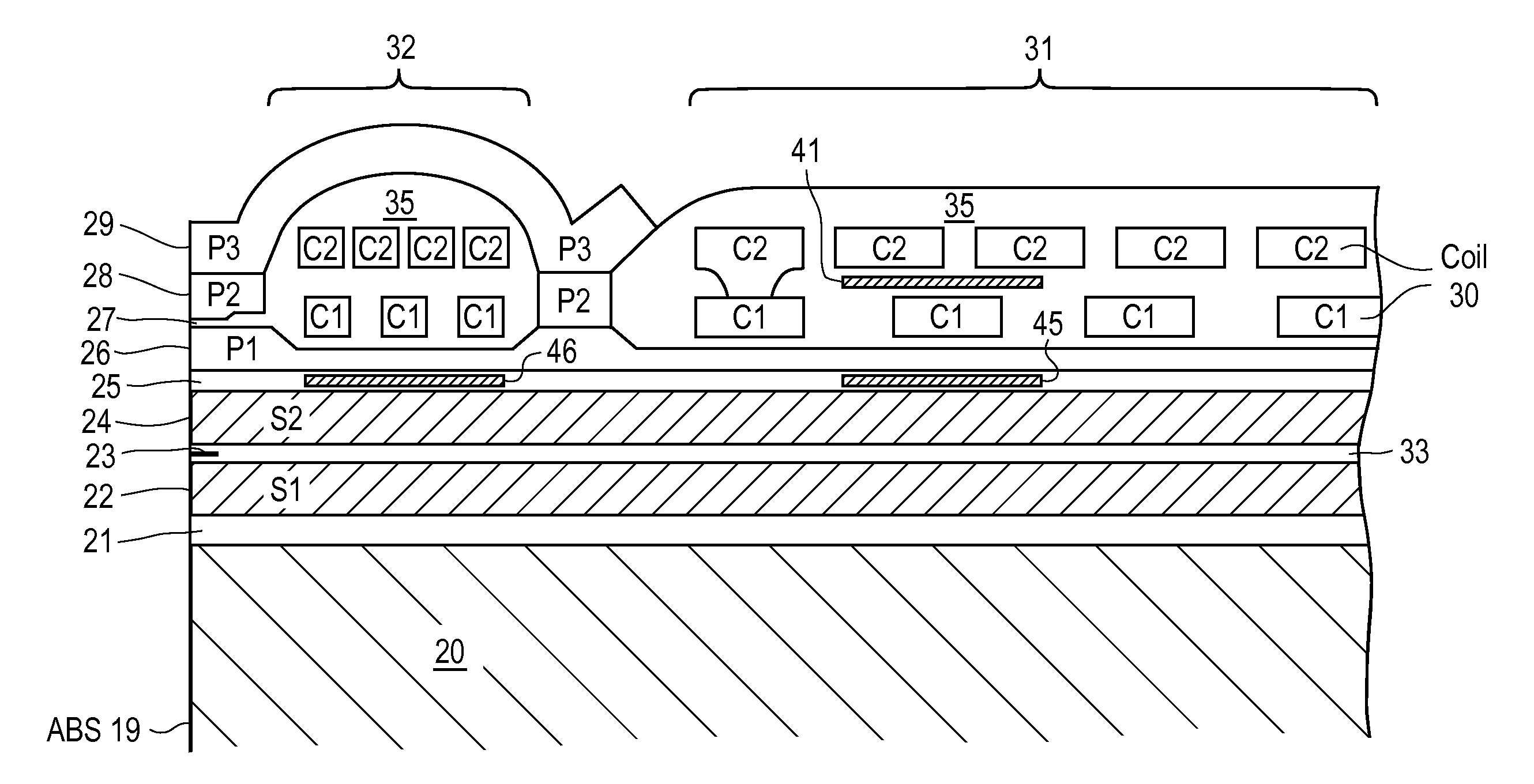
Magnetic recording head with resistive heating element located near the write coil
InactiveUS7372665B1Disposition/mounting of recording headsRecord information storageTransducerTrailing edge
A magnetic head includes a slider body having a trailing surface meeting an air-bearing surface at a trailing edge, with a thin-film transducer disposed on the trailing surface of the slider body near the trailing edge. The thin-film transducer includes a coil embedded between first and second poles. A resistive heating element is disposed adjacent and electrically insulated from, the coil. Application of power to the resistive heating element causes expansion of at least the first and second poles.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic recording head with resistive heating element and thermal barrier layer
ActiveUS7428124B1Record information storageProtective measures for recording headsEngineeringTrailing edge
A thin film magnetic head includes a slider body having a trailing surface meeting an air-bearing surface at a trailing edge. A magnetic read and write elements are disposed along the trailing surface near the trailing edge. The magnetic write element includes write poles and a coil. A portion of a heating element is disposed in a first general plane beneath the coil and above the magnetic read element. At least one thermally-insulating layer of material having a thermal conductivity of less than about 2.0 W / m-K extends in a second general plane substantially beneath the heating element.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Rotary blood pump and control system therefor
Owner:TC1 LLC +1
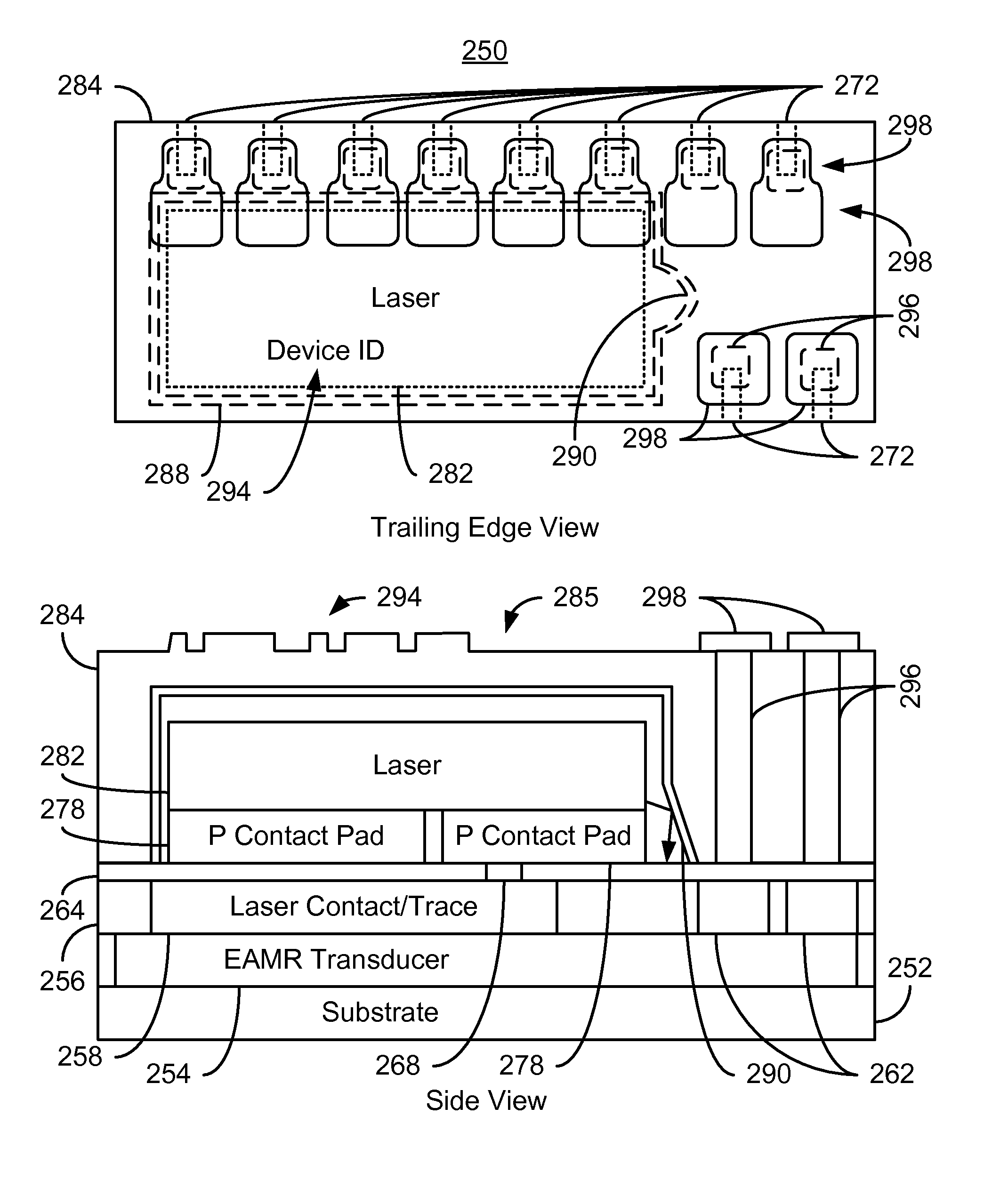
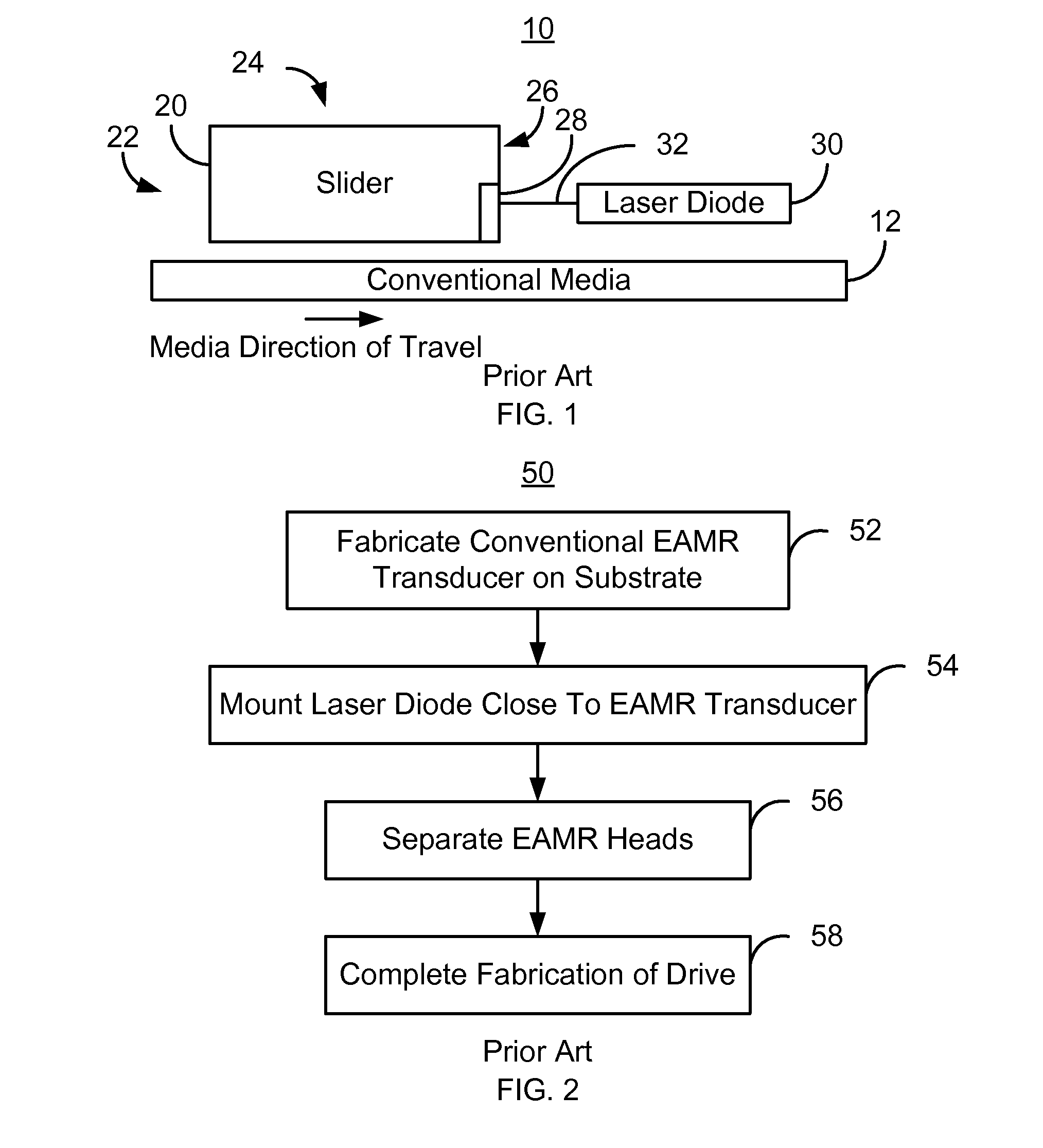
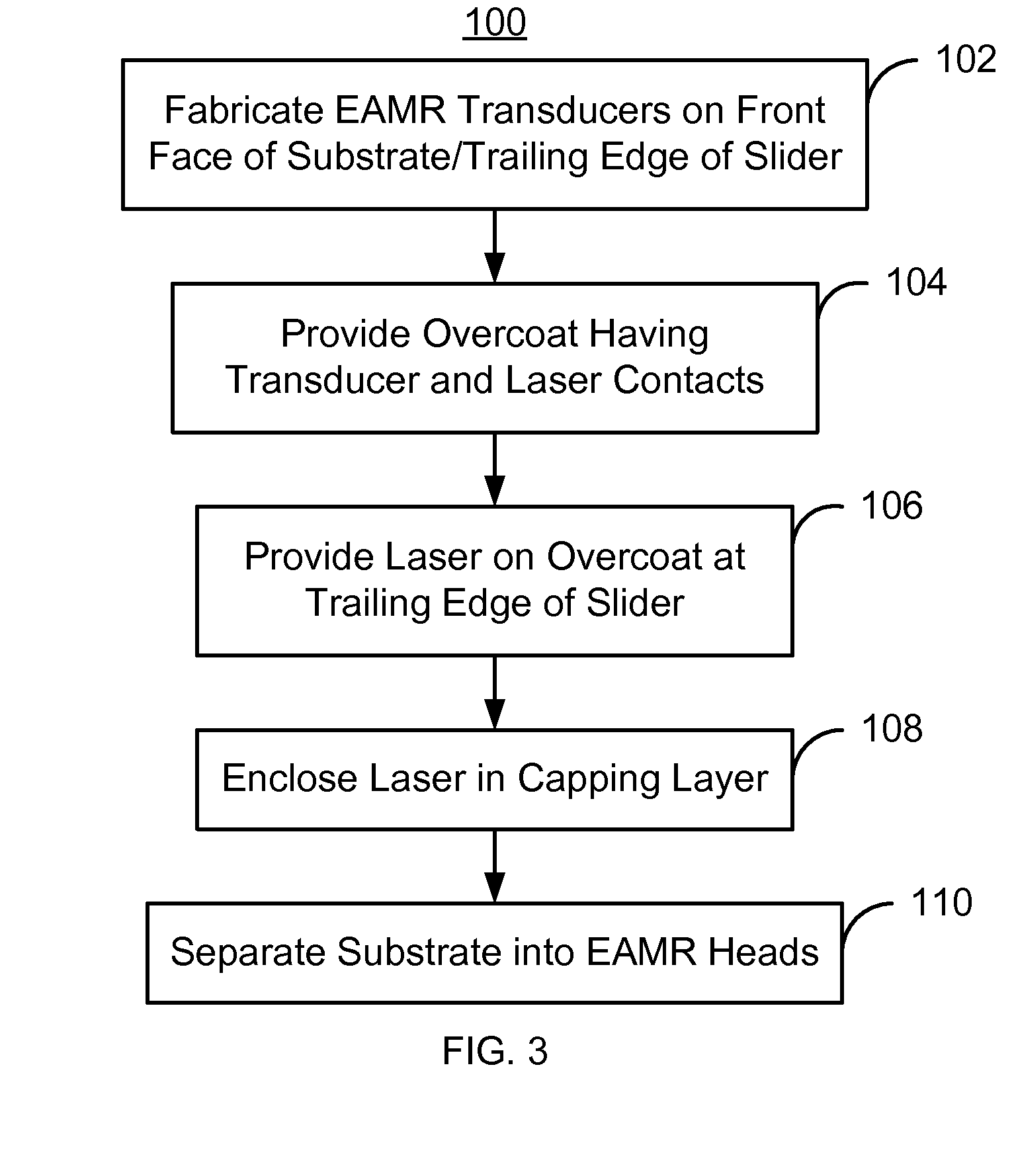
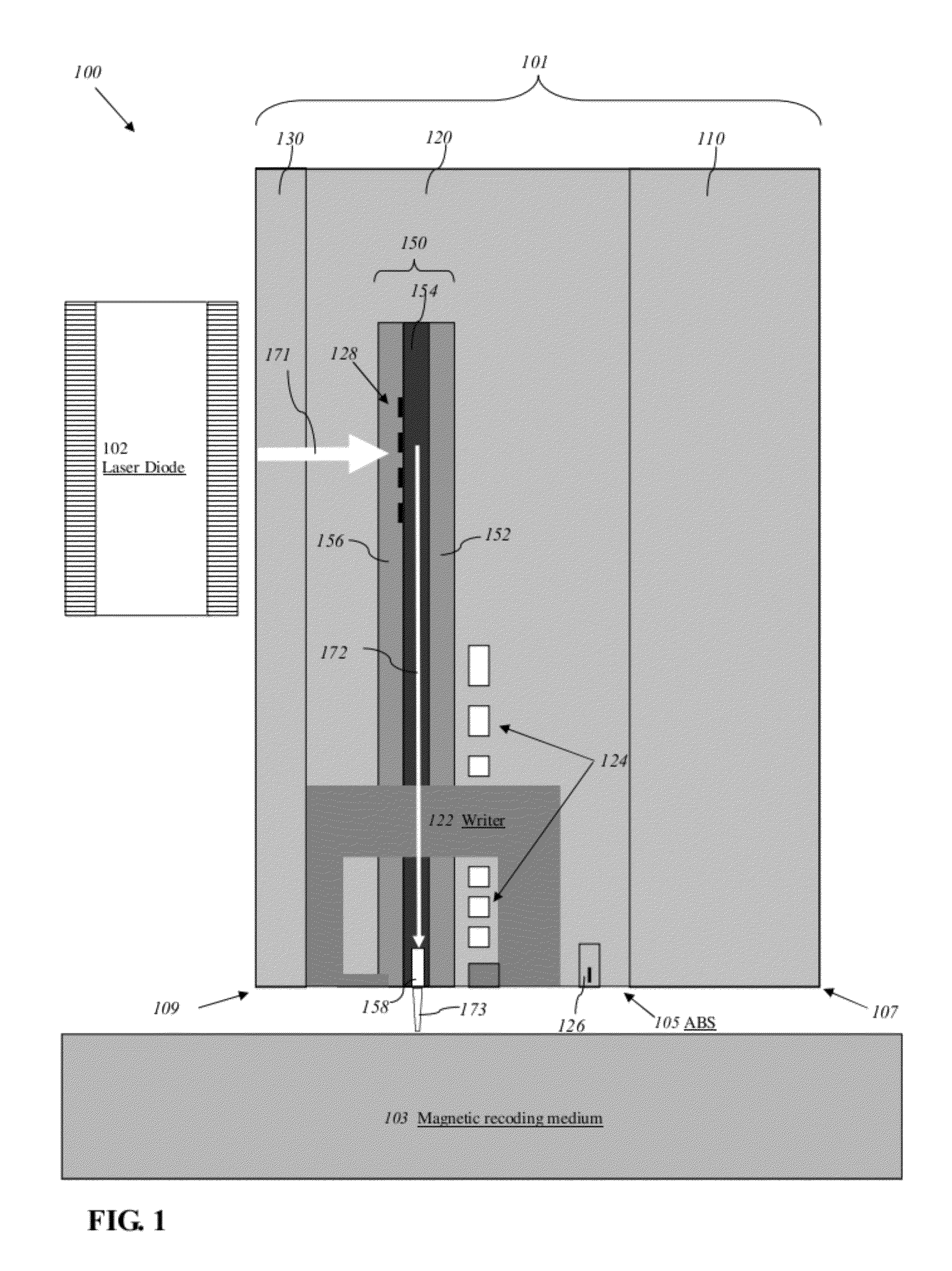
Method and system for providing an energy assisted magnetic recording head in a wafer packaging configuration
A method and system for providing energy assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) heads are described. The heads include sliders having leading and trailing edges. An EAMR transducer for each head is fabricated on a front face of a substrate that corresponds to the trailing edge of the slider. An overcoat layer that includes transducer and laser contact(s) is provided on the transducer. A laser for providing light to the transducer is provided on each slider. The laser is electrically coupled to the laser contact(s) and electrically insulated from at least part of the transducer contacts. The laser is enclosed in a capping layer, which has a laser-facing surface including a laser cavity, via(s), a trailing surface, and pads on the trailing surface. The laser cavity encloses the laser between the overcoat and capping layers. The via(s) provide electrical connection to the transducer contacts. The substrate is separated into the heads.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
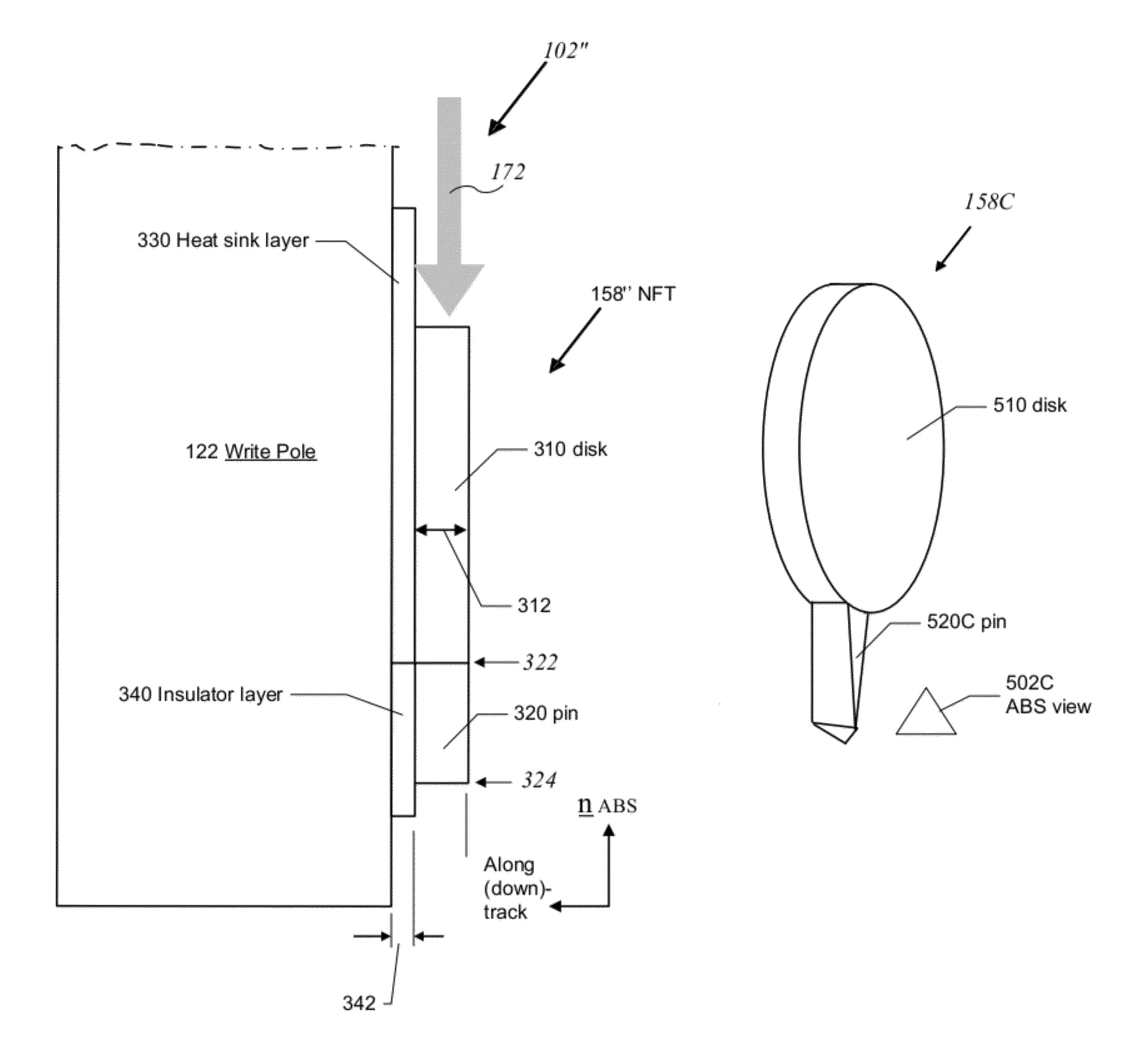
Trailing edge optimized near field transducer having non-rectangular pin cross section
A near field transducer (NFT) for use in an energy assisted magnetic recording (EAMR) head and configured to direct energy to a recording media is disclosed. The NFT comprises a disk section; and a pin section extending towards an air bearing surface (ABS) from the disk section. The pin section has a proximal end adjoining the disk section and a distal end opposite to the proximal end and facing the ABS, wherein at least the distal end of the pin section has a non- rectangular cross section in a plane parallel to the ABS.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Self aligned wrap around shield for perpendicular magnetic recording
InactiveUS20060044682A1Lower switching fieldAvoid Flux LeakageManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageTrailing edgeWrap around
A write element for use in perpendicular magnetic recording. The write element including a write pole and a self aligned wrap around shield that can have a trailing shield gap thickness that is different from its side shield gap thickness. The materials making up the trailing shield gap and the side shield gaps can be different materials or can be the same material deposited in two different steps. The side or wrap around portions of the trailing shield can extend down to the level of the leading edge of the write pole or can terminate at some point between the levels of the leading and trailing edge to form a partial wrap around trailing shield.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Magnetic recording head with resistive heating element located near the write coil
A magnetic head includes a slider body having a trailing surface meeting an air-bearing surface at a trailing edge and a thin-film transducer that includes a magnetic reproducing element with a magnetoresistive (MR) element disposed near the trailing edge within a gap material bounded by upper and lower shield layers. The thin-film transducer also includes a lower pole layer of a magnetic recording element disposed in a first general plane. The magnetic recording element further includes a coil having first and second turn layers disposed in second and third general planes, respectively. The magnetic head also includes resistive heating element with at least a portion of the heating element being disposed in a fourth general plane beneath both the lower pole layer and the coil but above the upper shield layer. Current flow through the heating element causes expansion of the magnetic reproducing and recording elements at the ABS.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
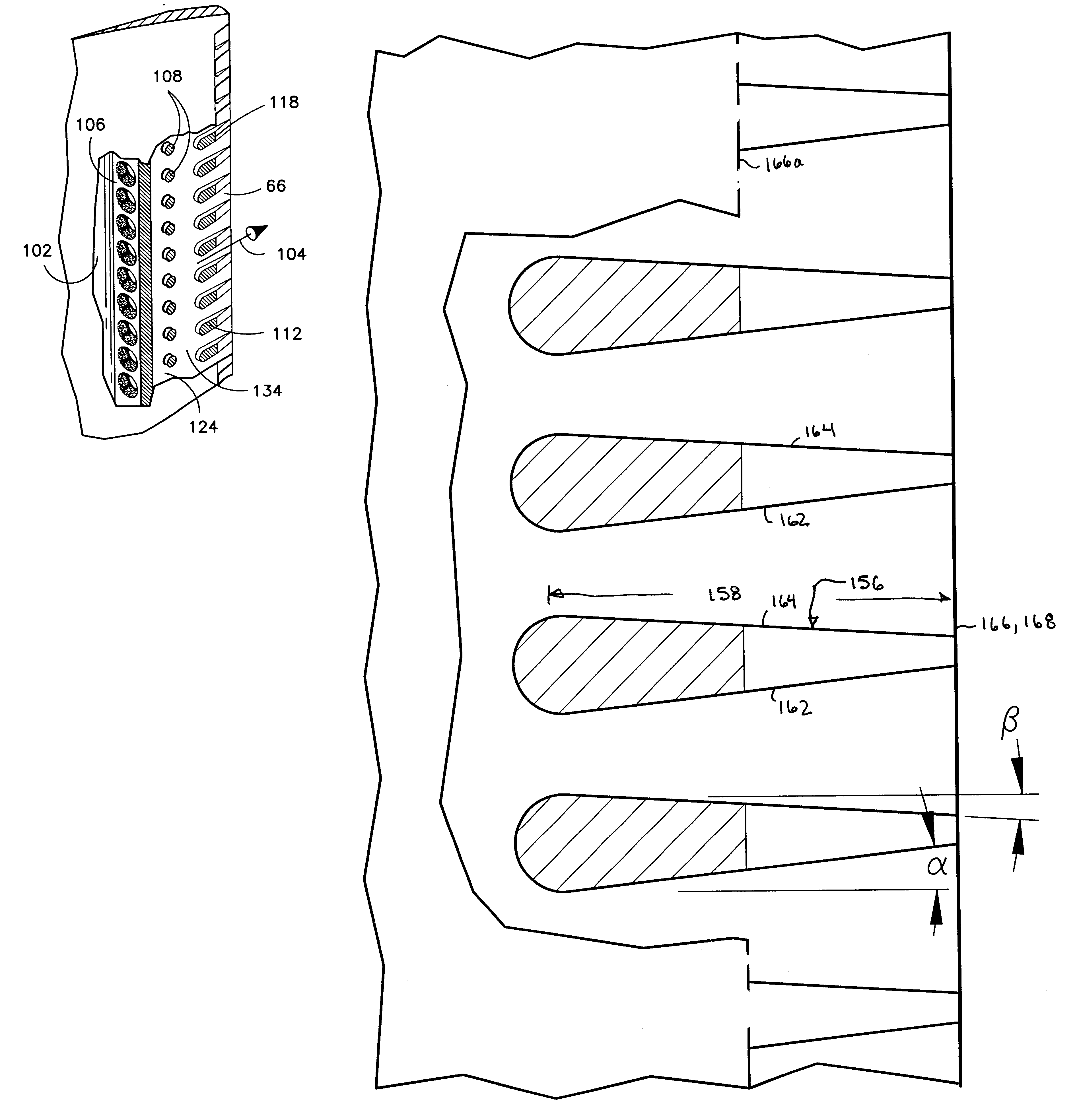
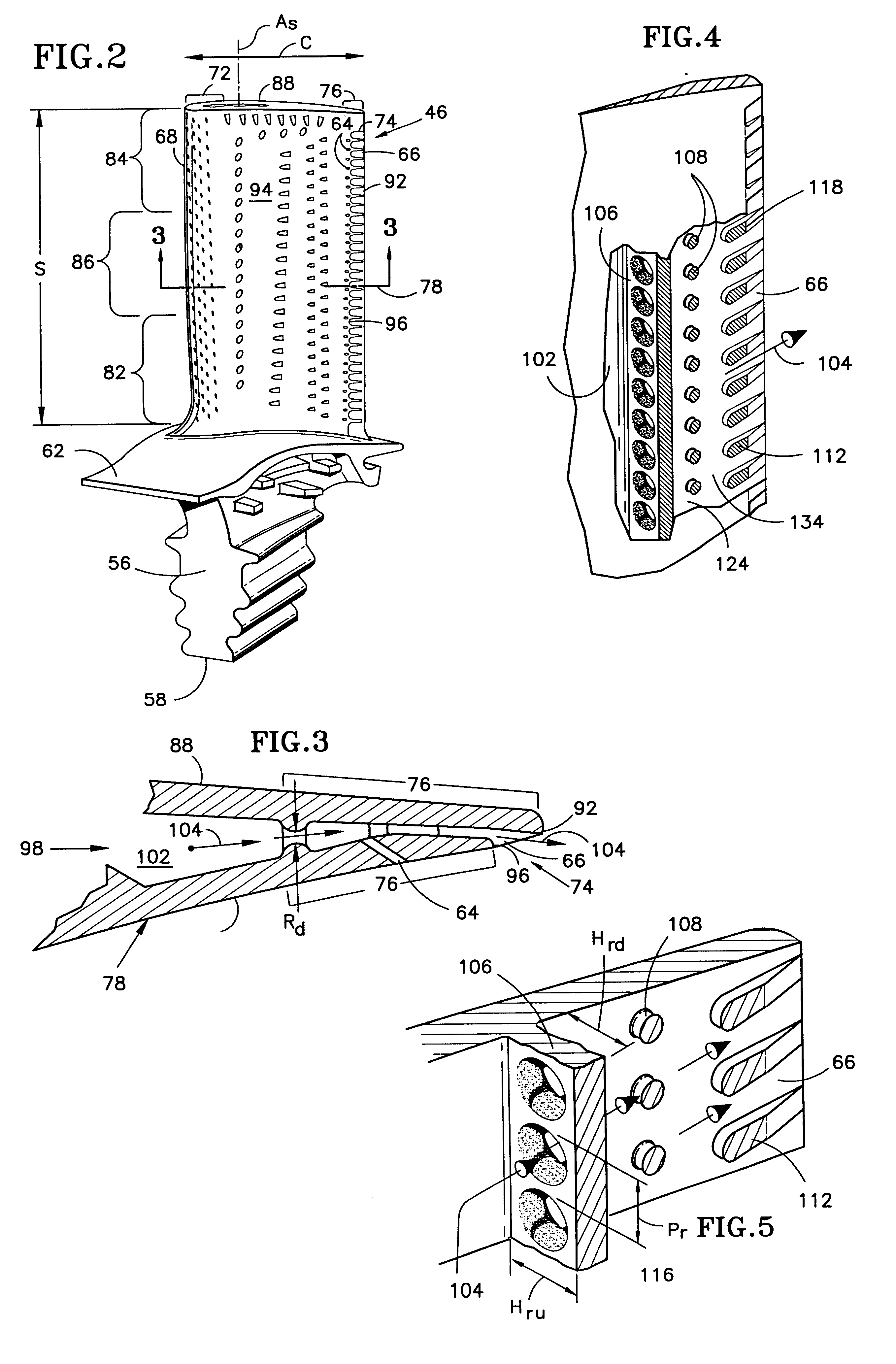
Write head with variable side shield gaps
ActiveUS8400731B1Improved cross-track field gradientHigh gradientManufacture head surfaceRecord information storageLeading edgeEngineering
A magnetic recording head comprises a write pole including a throat region with a leading edge, a trailing edge opposite the leading edge, and first and second side edges opposite one another. The magnetic recording head further comprises a first side wall gap layer disposed alongside the first side edge of the throat region, and a second side wall gap layer disposed alongside the second side edge of the throat region. Each of the first and second side wall gap layers has a first width at the leading edge of the throat region smaller than a second width at the trailing edge of the throat region.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
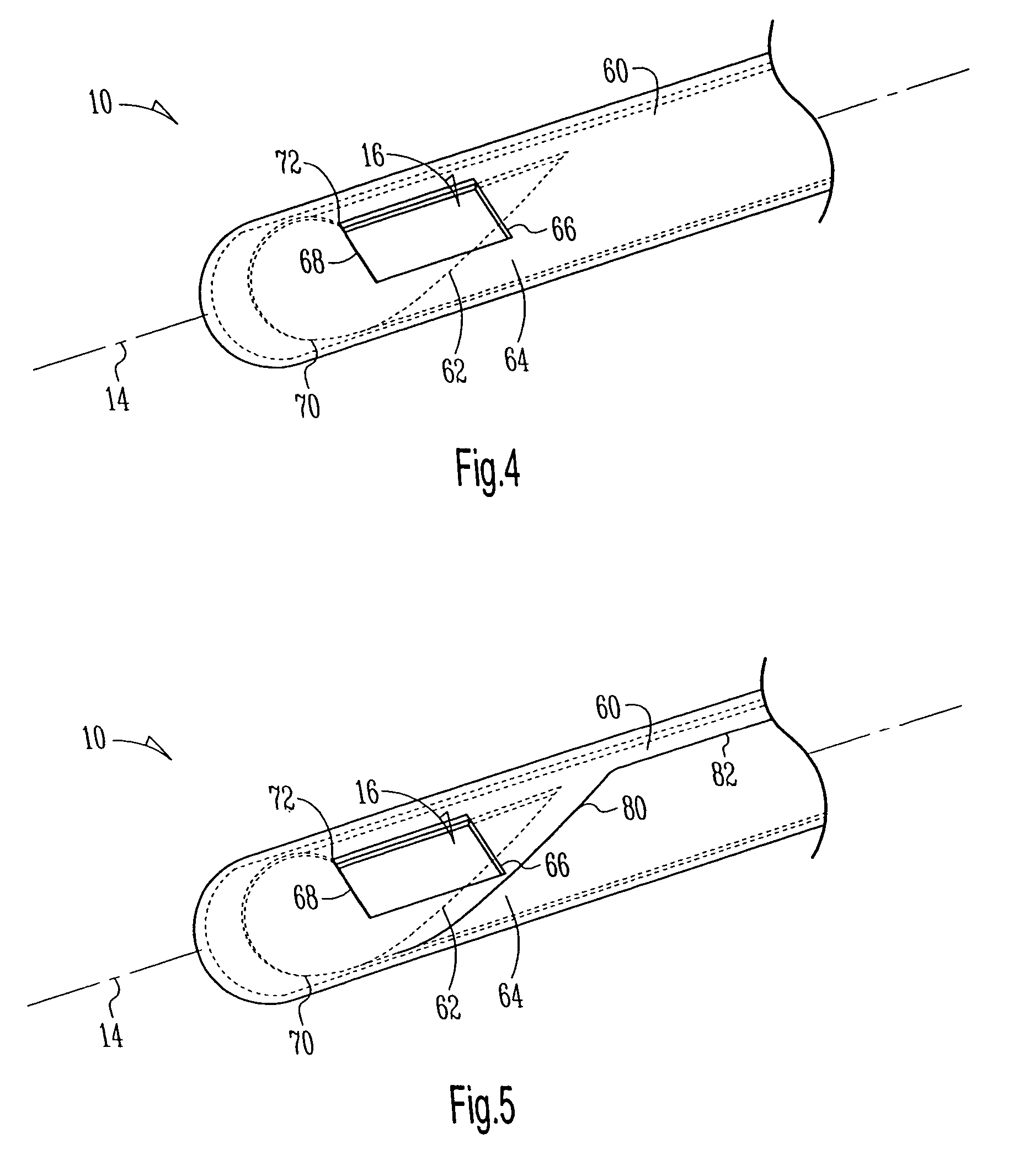
Air bearing having a cavity patch surface coplanar with a leading edge pad surface
InactiveUS6879464B2Improved air bearing surface designIncrease insensitivityFluid-dynamic spacing of headsRecord information storageLeading edgeAir bearing
An air bearing surface for read / write head of a magnetic disk drive is disclosed. The air bearing surface includes a trailing edge pad and a leading edge pad with trailing portions. A cavity is defined between the trailing edge pad and the trailing portions of the leading edge pad. A cavity patch is disposed within the cavity. The cavity patch can be disposed within the cavity towards one side of the read / write head.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
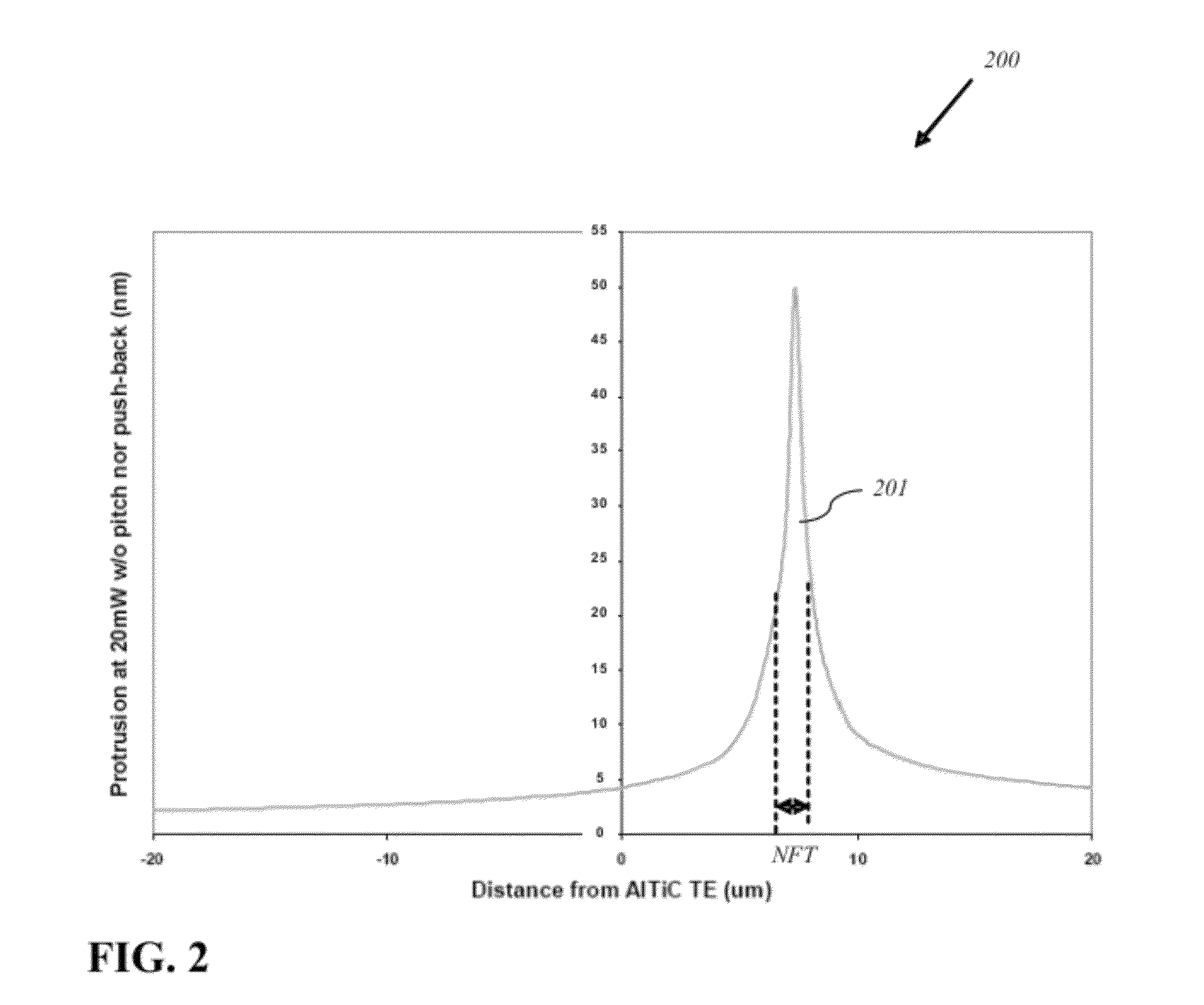
Energy assisted magnetic recording head having a near field transducer with reduced thermal protrusion
ActiveUS8208350B1Preventing protrusion-related damageImprove reliabilityCombination recordingElectrical transducersLeading edgeTransducer
An energy assisted magnetic recording head comprises a slider having a leading edge, a trailing edge, and an air bearing surface (ABS), and a near field transducer (NFT) disposed in the slider and having a distal end proximate the ABS. The distal end is recessed from the ABS when no optical power is applied to the NFT, and is co-planar with the ABS when a predetermined amount of optical power is applied to the NFT. A portion of the slider surrounding the distal end forms a concave surface having a continuously varying slope when no optical power is applied to the NFT, and a flat surface coplanar with the ABS and the distal end when the predetermined amount of optical power is applied to the NFT. Applying optical power comprises coupling light into a waveguide formed in the head and directing the coupled light to the NFT via the waveguide.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
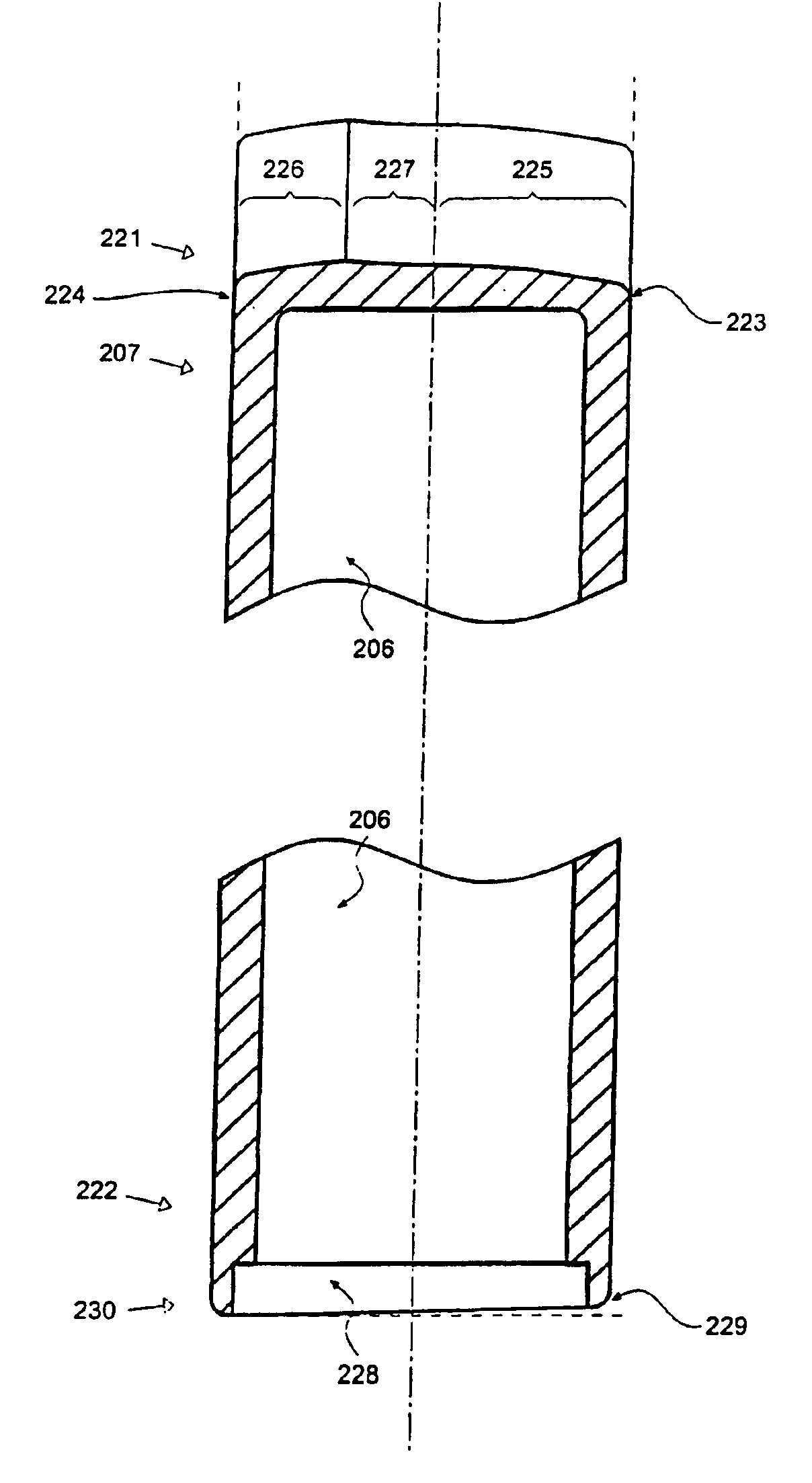
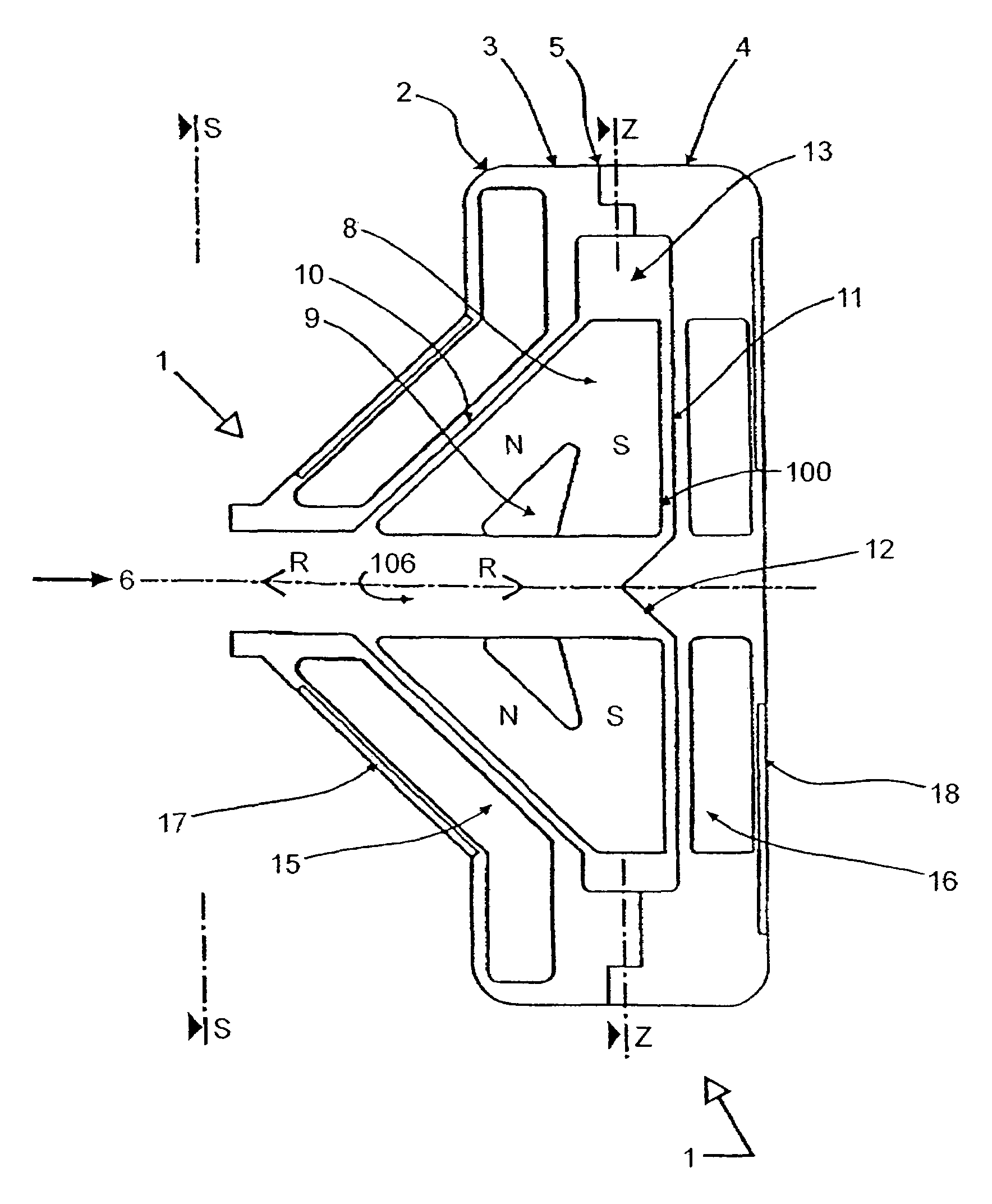
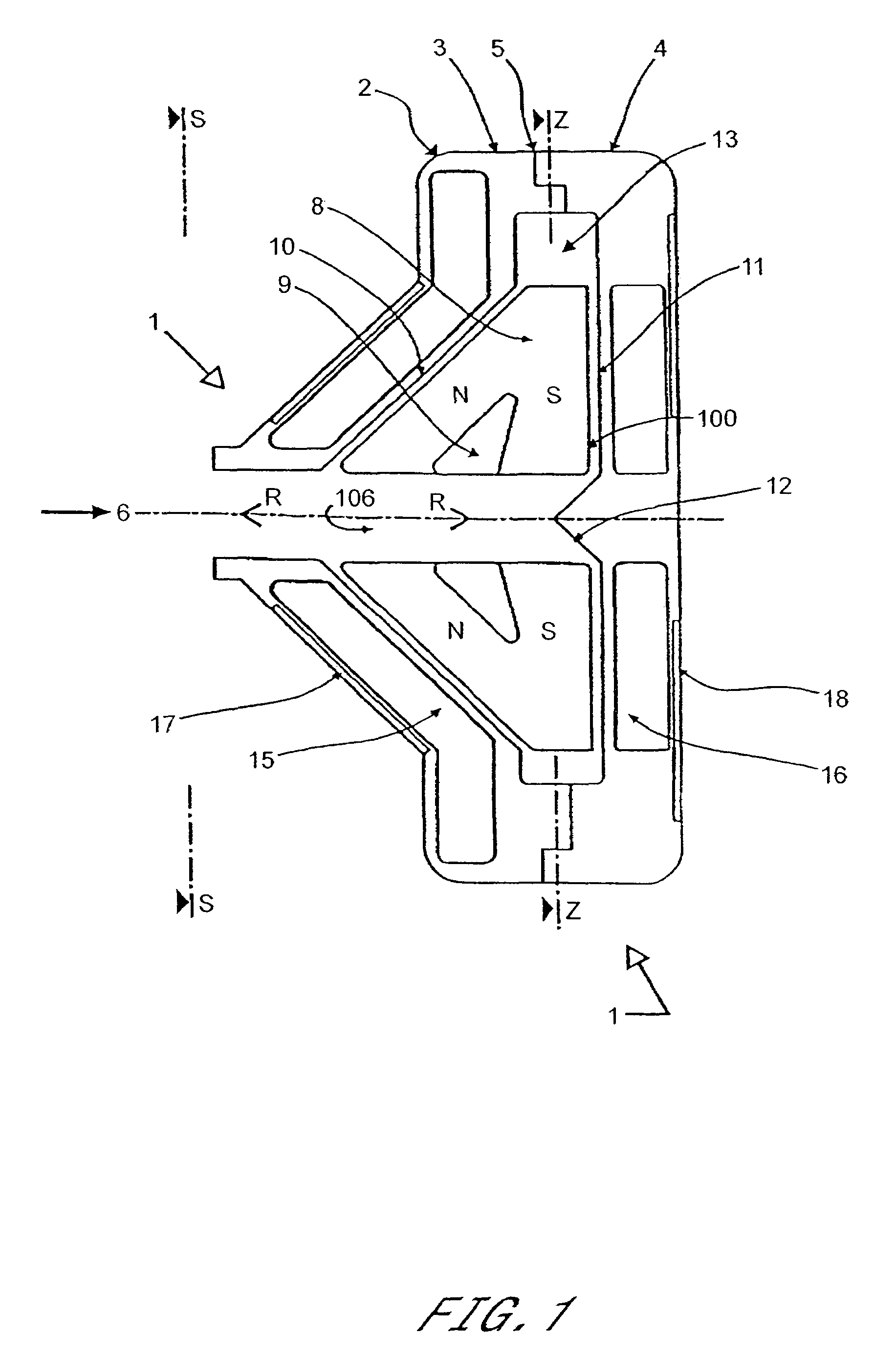
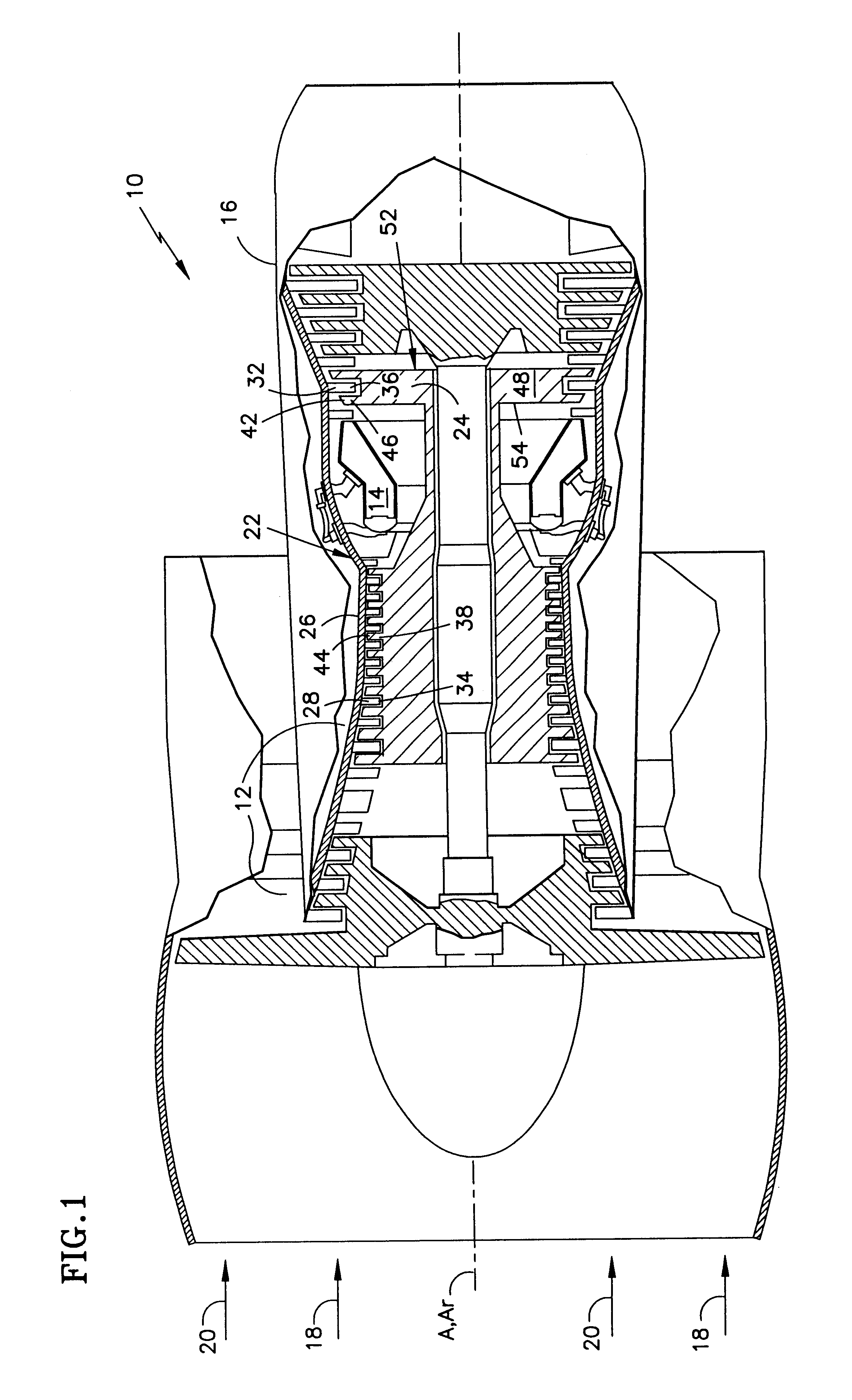
Rotary pump with exclusively hydrodynamically suspended impeller
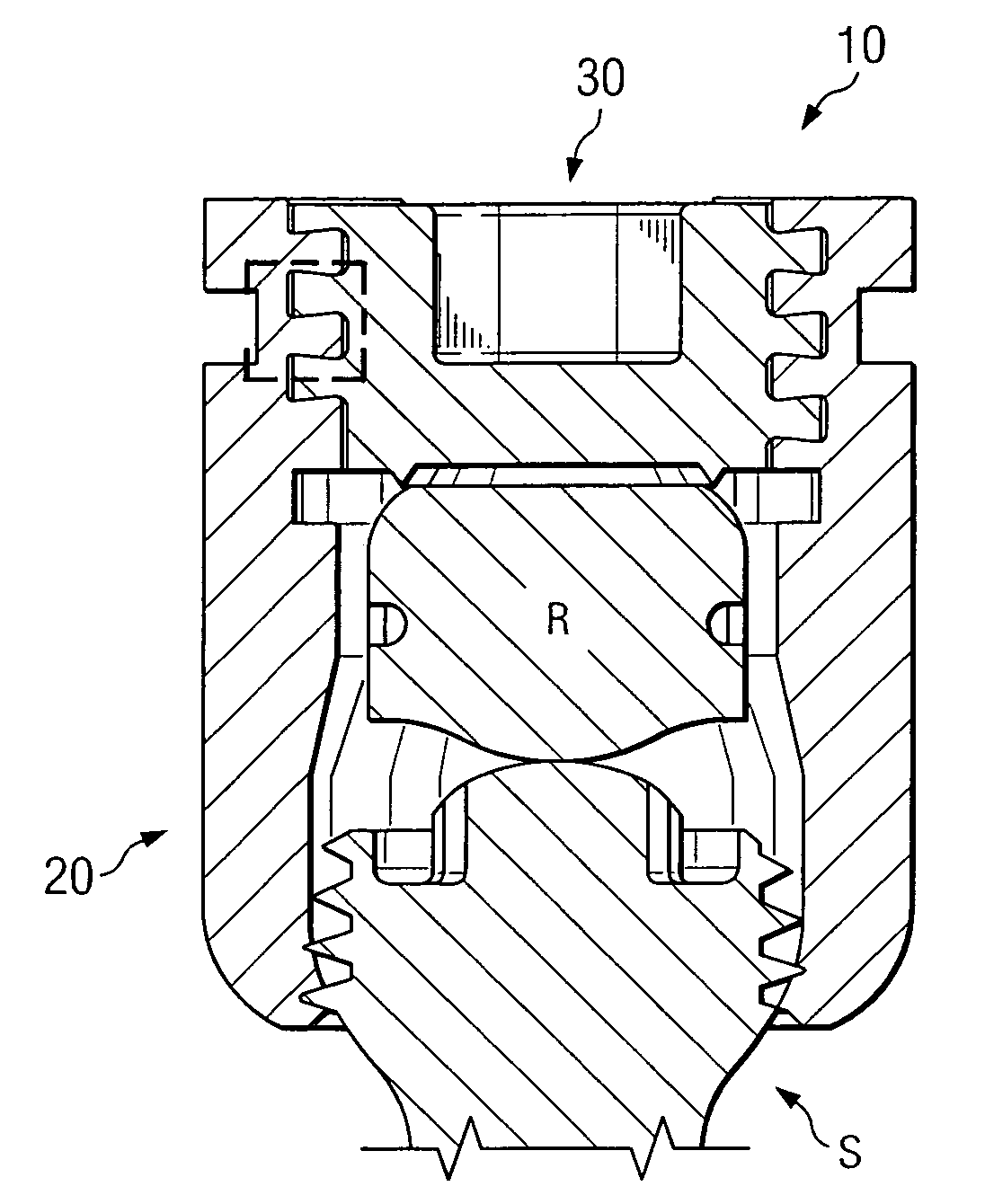
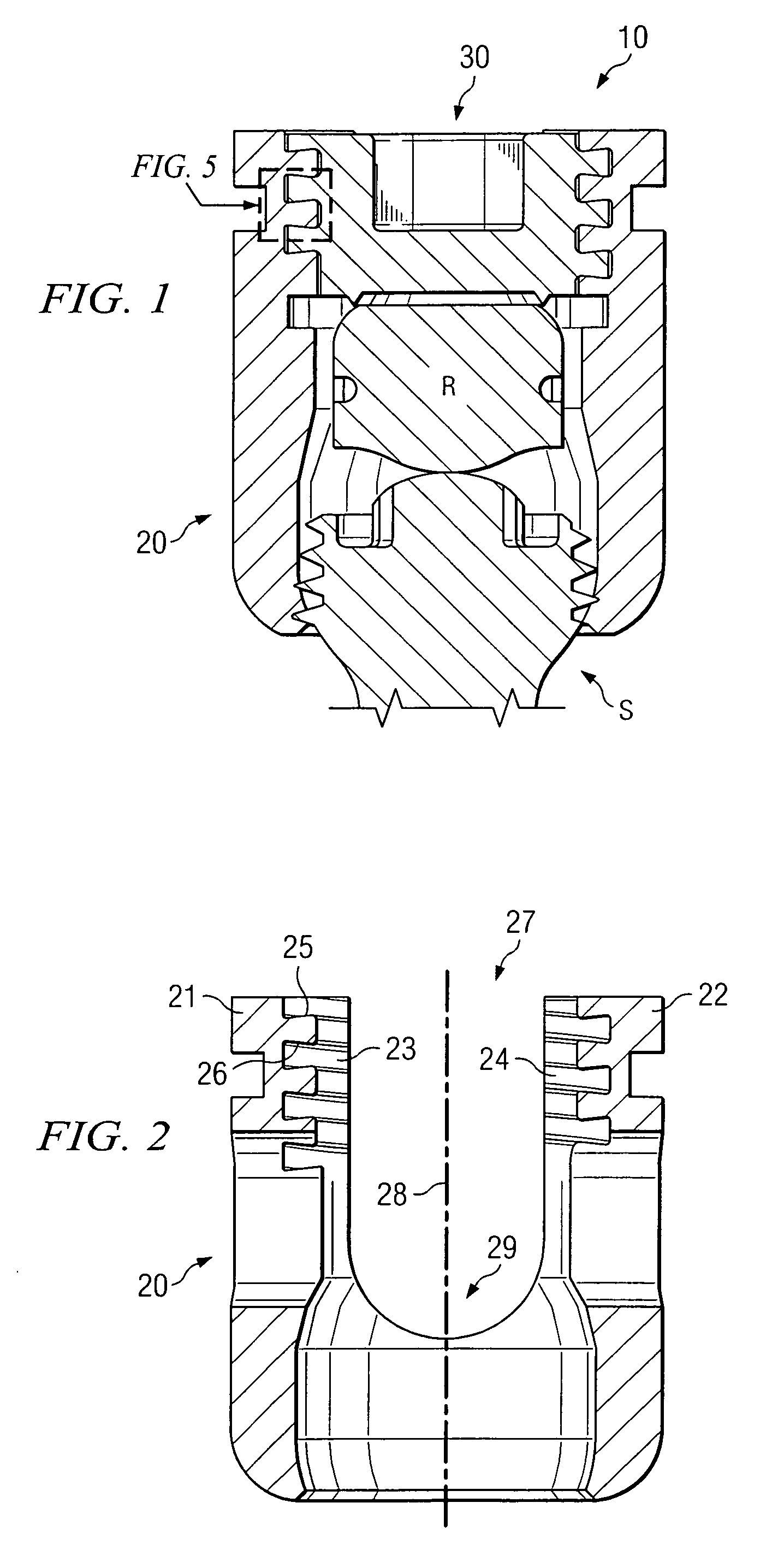
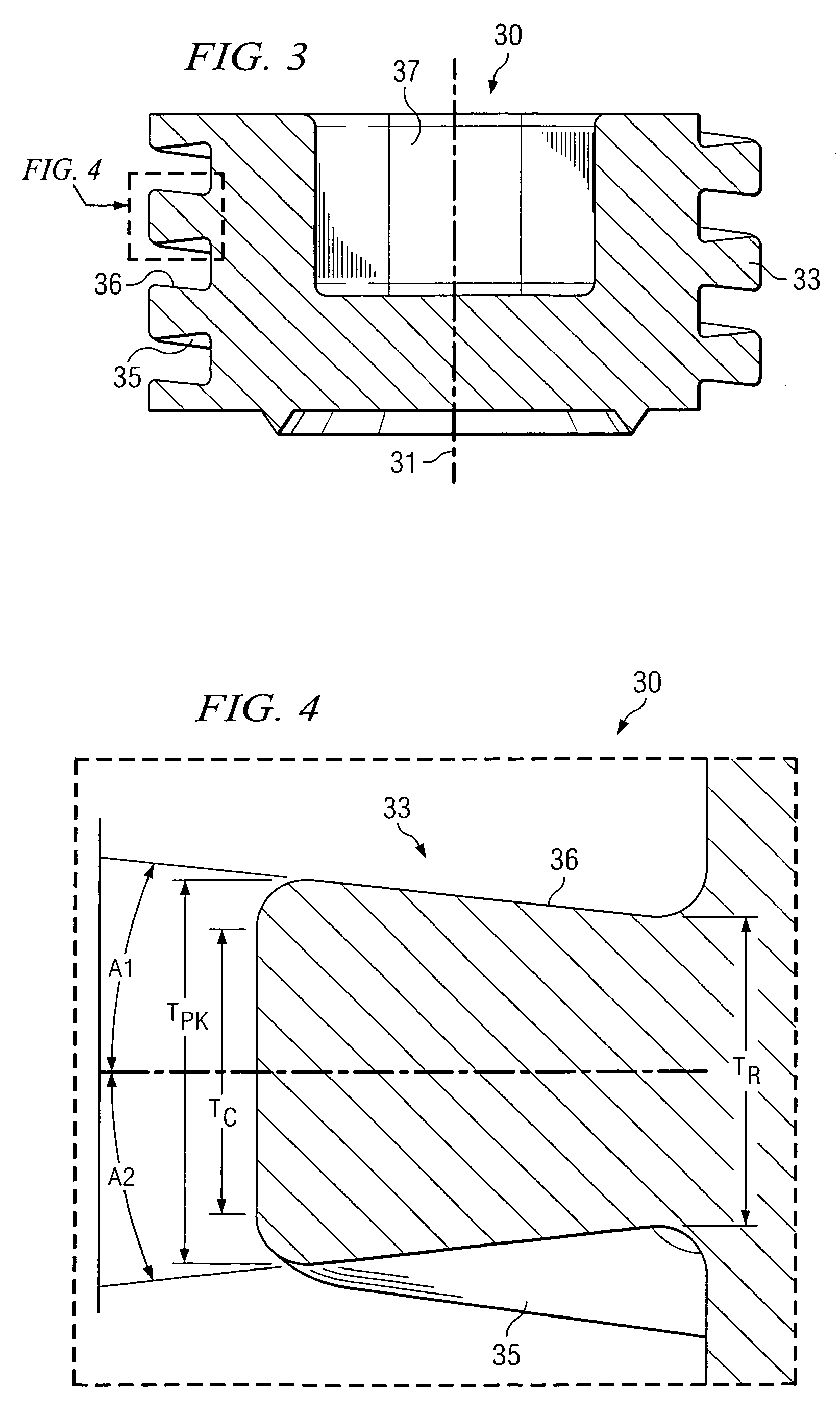
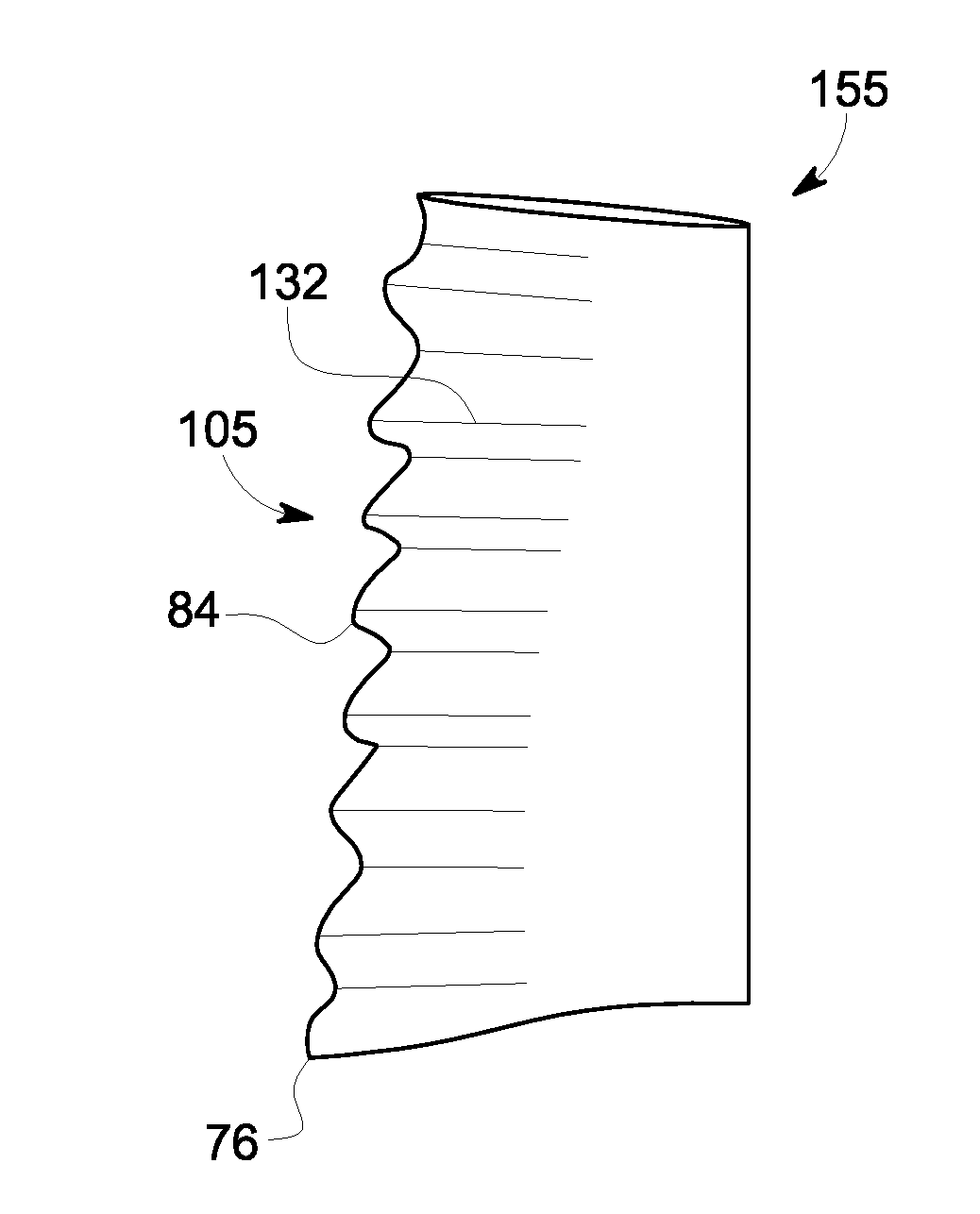
A pump assembly 1, 33, 200 adapted for continuous flow pumping of blood. In a particular form the pump 1, 200 is a centrifugal pump wherein the impeller 100, 204 is entirely sealed within the pump housing 2, 201 and is exclusively hydrodynamically suspended therein as the impeller rotates within the fluid 105 urged by electromagnetic means external to the pump cavity 106, 203. Hydrodynamic suspension is assisted by the impeller 100, 204 having deformities therein such as blades 8 with surfaces tapered from the leading edges 102, 223 to the trailing edges 103, 224 of bottom and top edges 221, 222 thereof.
Owner:TC1 LLC +2
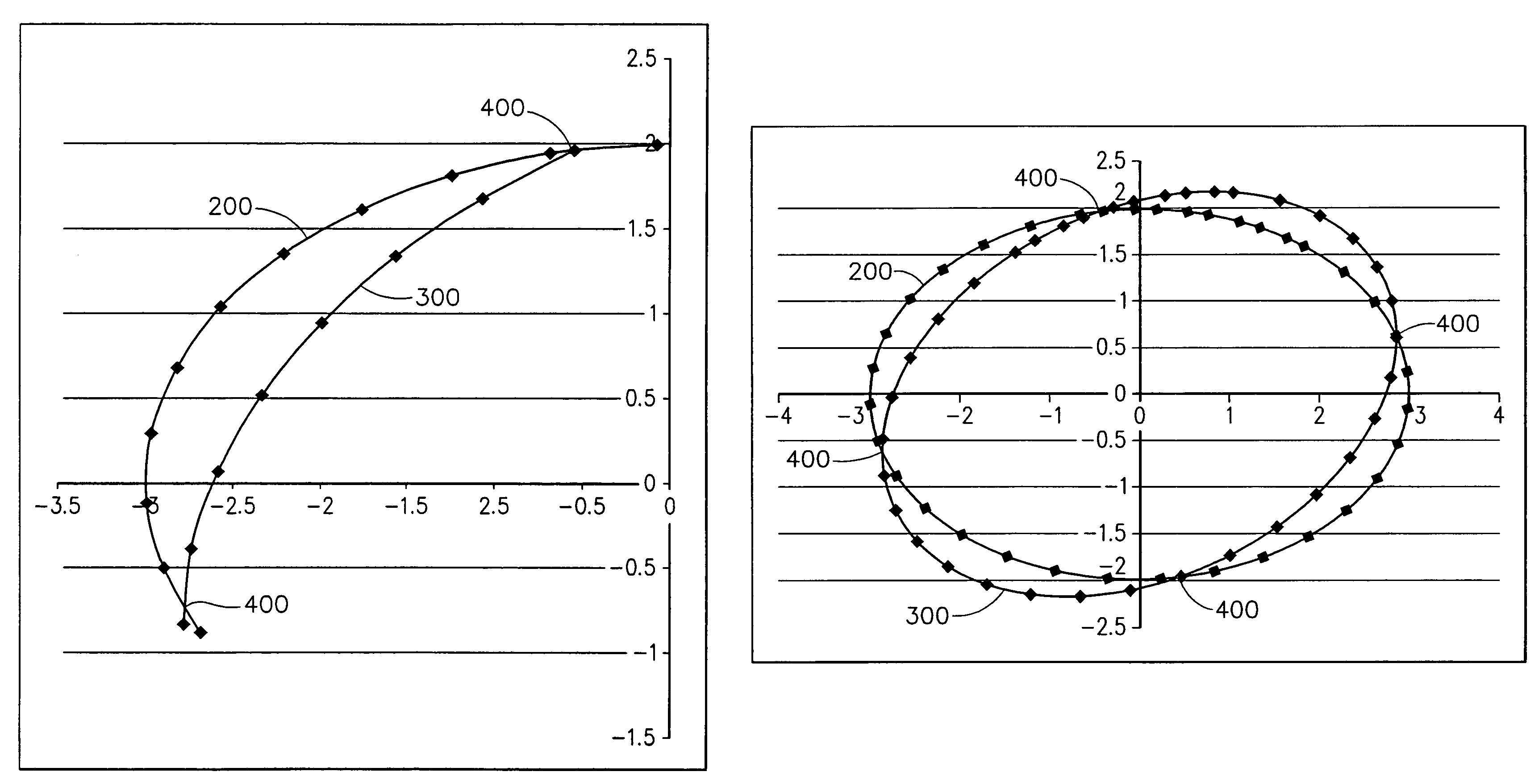
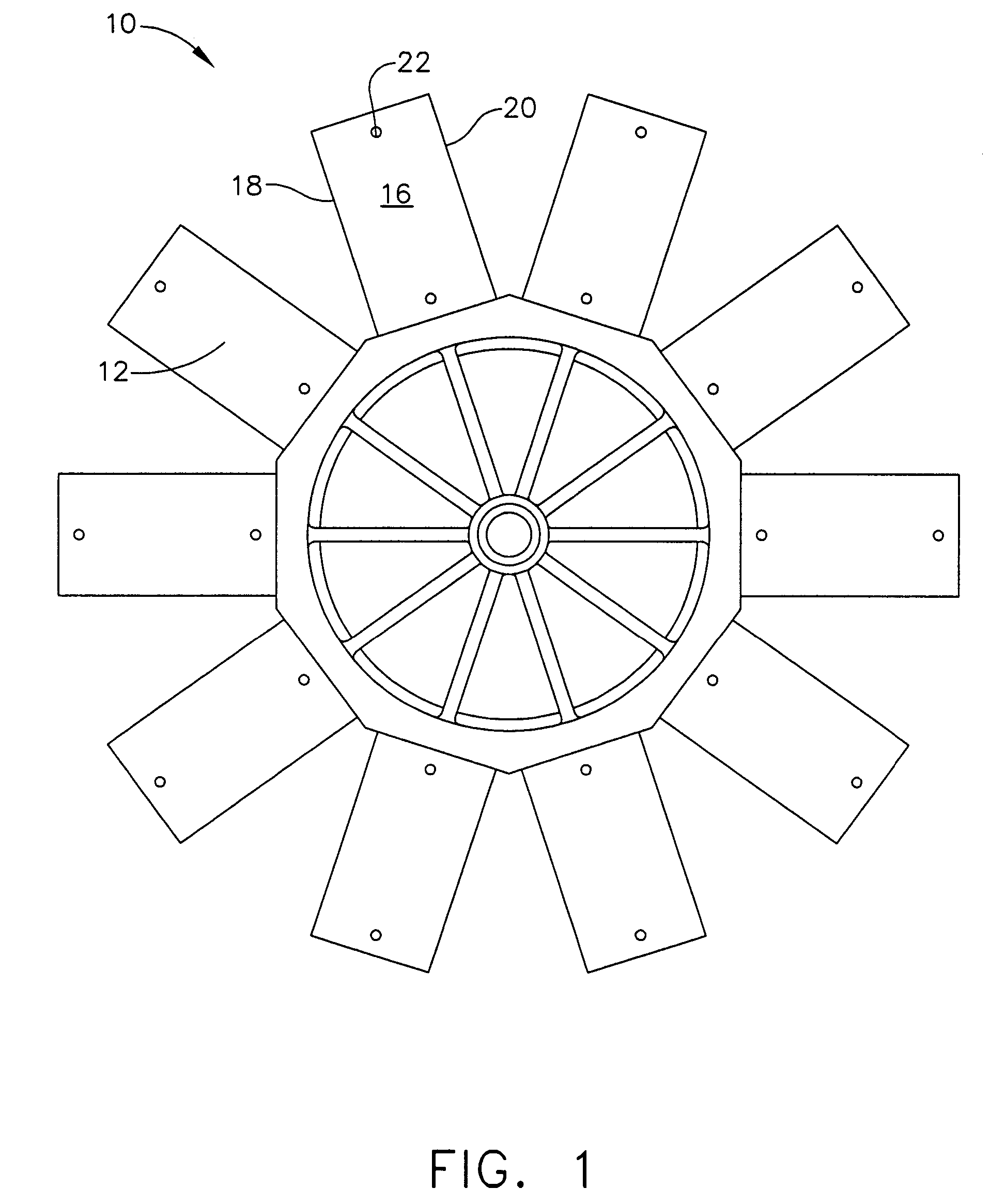
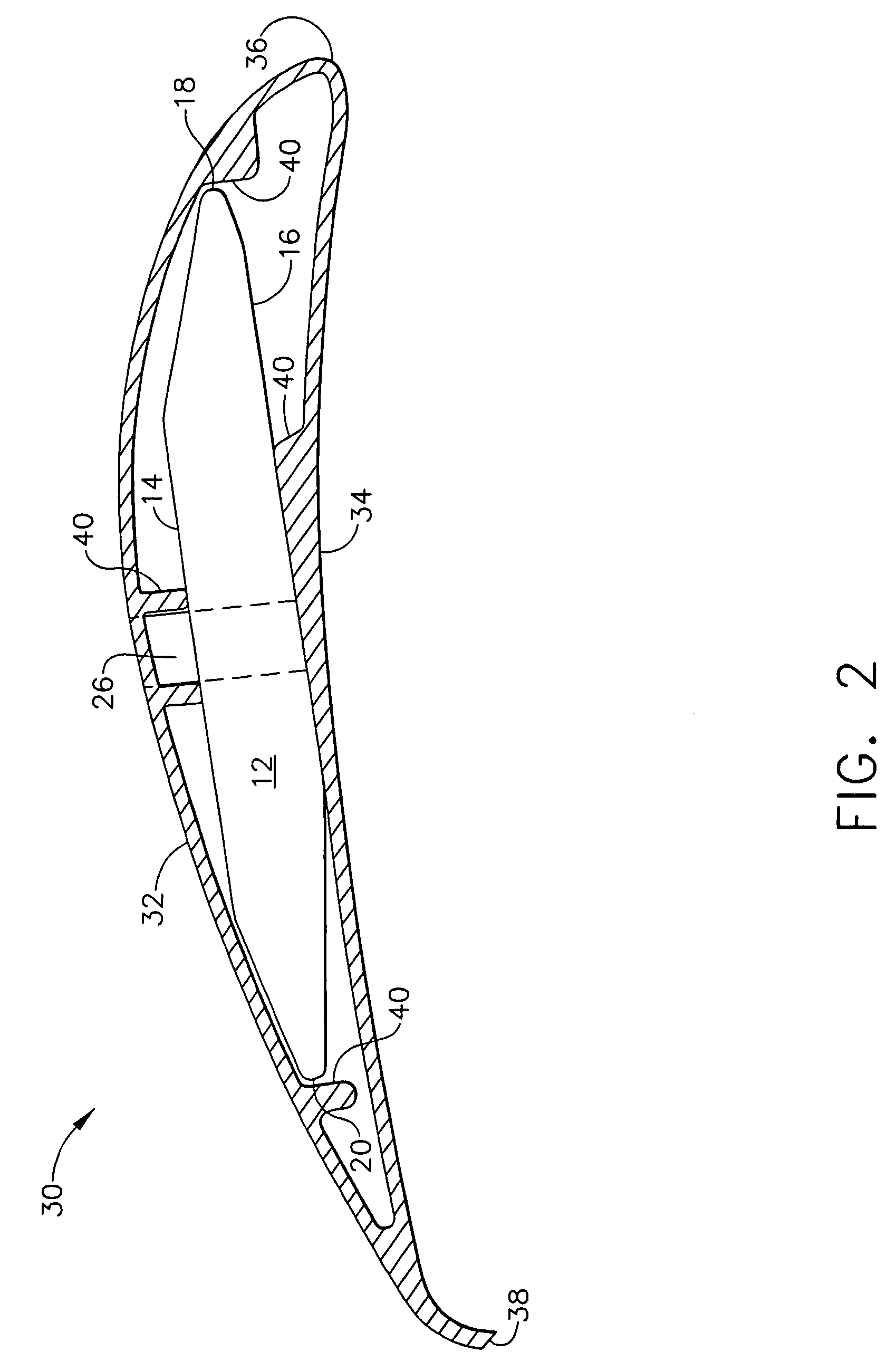
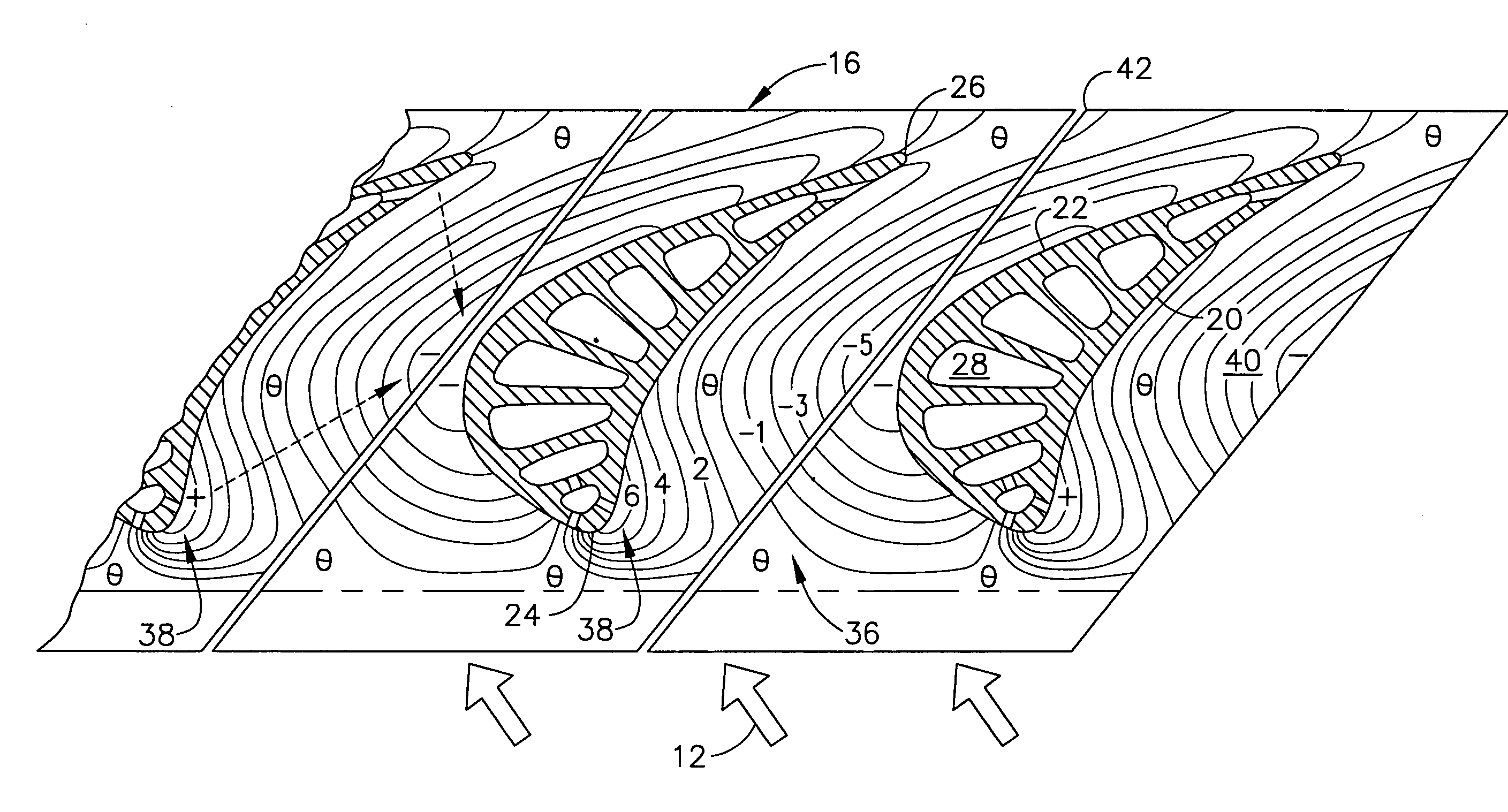
Fan blades
Owner:DELTA T
Scalloped surface turbine stage
A turbine stage includes a row of airfoils joined to corresponding platforms to define flow passages therebetween. Each airfoil includes opposite pressure and suction sides and extends in chord between opposite leading and trailing edges. Each platform has a scalloped flow surface including a bulge adjoining the pressure side adjacent the leading edge, and a bowl adjoining the suction side aft of the leading edge.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Earth boring apparatus and method offering improved gage trimmer protection
InactiveUS6883623B2Less wear resistantWear down quicklyDrill bitsDrilling rodsLeading edgeEngineering
A rotary drill bit for drilling subterranean formations configured with at least one protective structure proximate to the rotationally leading and trailing edges of a gage trimmer, wherein the at least one protective structure is positioned at substantially the same exposure as its associated gage trimmer. Particularly, the apparatus of the present invention may provide protection for gage trimmers during drilling, tripping, and / or rotation within a casing; i.e., when changing a drilling fluid. Protective structures may be configured and located according to anticipated drilling conditions including helix angles. In addition, a protective structure may be proximate to more than one gage trimmer while having a substantially equal exposure to each associated gage trimmer. Methods of use and a method of rotary bit design are also disclosed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
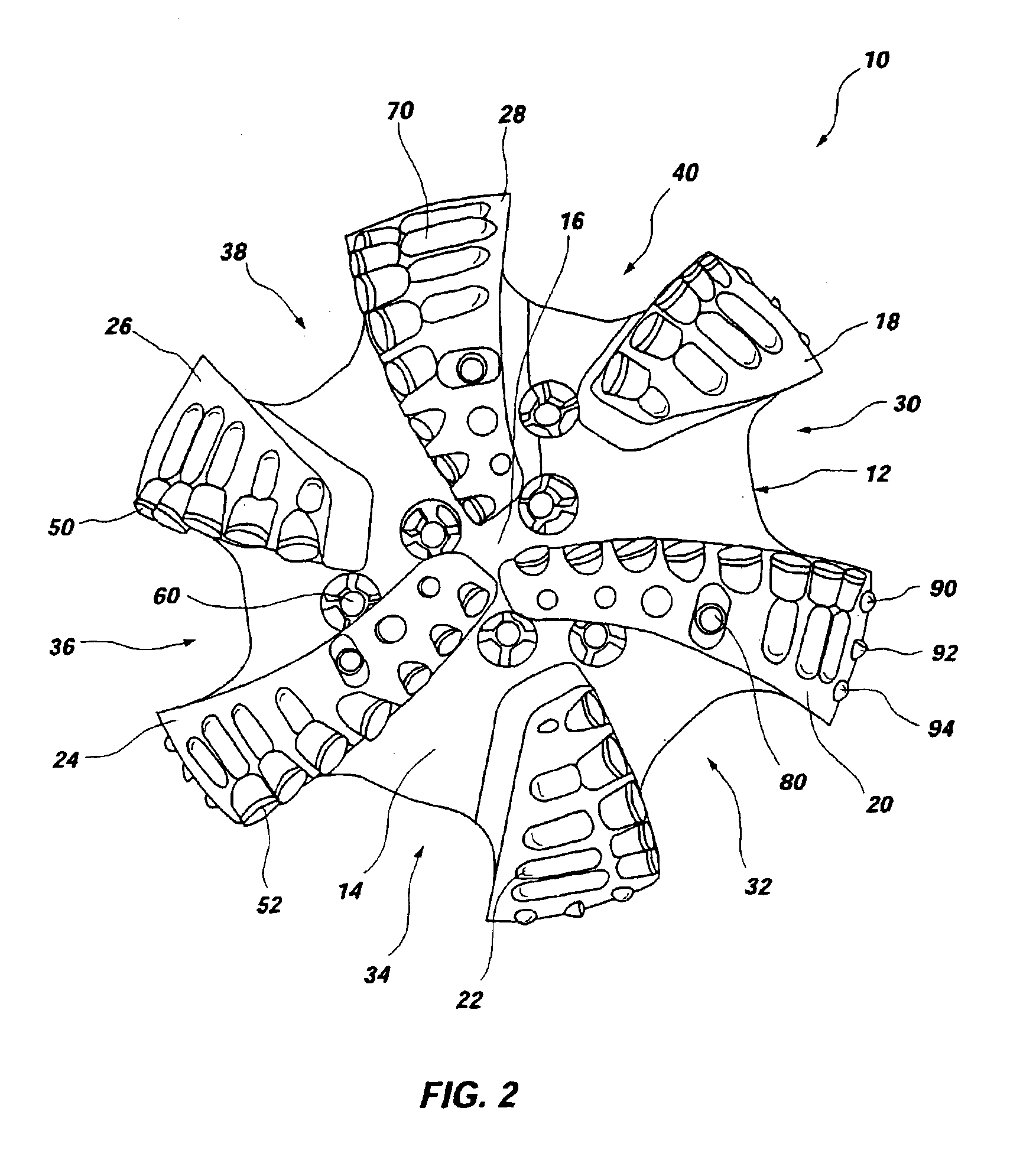
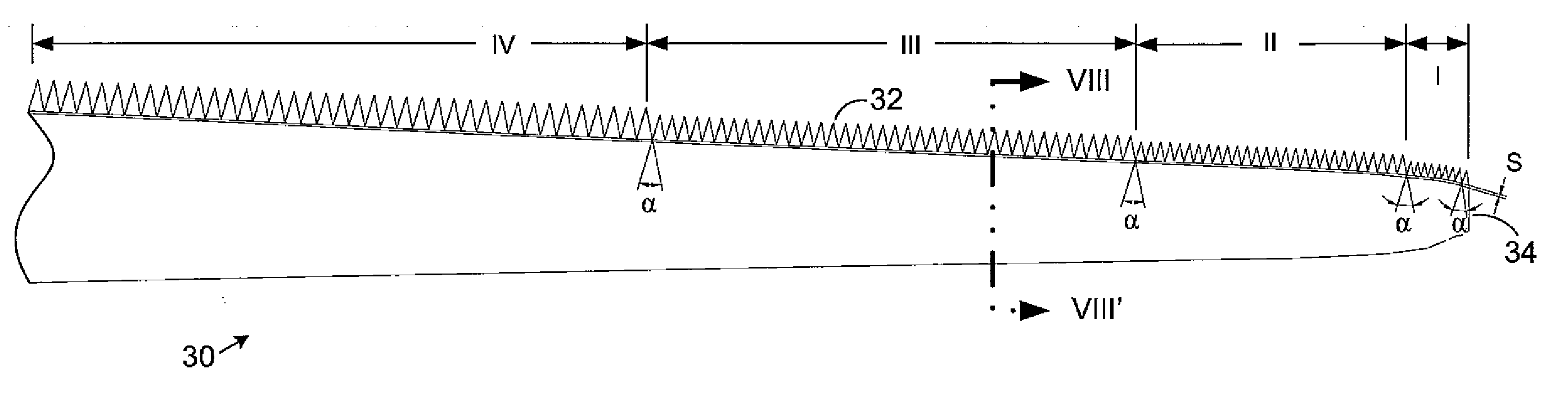
Wind turbine blades with trailing edge serrations
A wind generator and turbine blade includes a trailing edge having several serrations, a length of the serrations in each of a plurality of sections of the trailing edge is between approximately 10% and 40% of a mean chord for the corresponding section; and a length to width ratio of each of the serrations is between approximately 1:1 to 4:1.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Closure member for a medical implant device
InactiveUS20050216000A1Prevent openingIncrease clamping forceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisLeading edgeSet screw
A closure member, such as a set screw, and complementary receiving member are included in a medical implant device. The receiving member has a plurality of noncontiguous, threaded walls substantially defining a bore for receiving the threaded closure member. When the closure member is inserted into the receiving member, their respective threads interlock to join the noncontiguous walls of the receiving member. The closure member has an outer thread configured to interlock with the inner walls of the receiving member in a manner that aids in preventing the noncontiguous walls of the receiving member from moving away from the closure member. In certain embodiments, the closure member's outer thread includes a trailing edge having a point that is rearward of the trailing edge's root, and the outer thread includes a leading edge having a point that is forward of the leading edge's root.
Owner:THEKEN SPINE
Airfoils for wake desensitization and method for fabricating same
ActiveUS20130164488A1Reducing desensitizationEngine manufacturePump componentsLeading edgeTrailing edge
An airfoil and method of fabricating an airfoil including a first and a second side coupled together at a leading and a trailing edge and extending there between. The airfoil includes a plurality of first chord sections having a first chord length and extending outward from one of the first side or second side of the airfoil at the leading edge and a plurality of second chord sections having a second chord length and extending outward from the one of the first side or the second side of the airfoil at the leading edge. The leading edge including spaced-apart wave-shaped projections defining a waveform. The configuration defining a three-dimensional crenulated airfoil configured to facilitate desensitization of an airfoil unsteady pressure response to at least one impinging upstream generated wake or vortex by decorrelating spatially and temporally and reducing in amplitude an unsteady pressure caused by interaction of the airfoil with the upstream generated wake or vortex.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
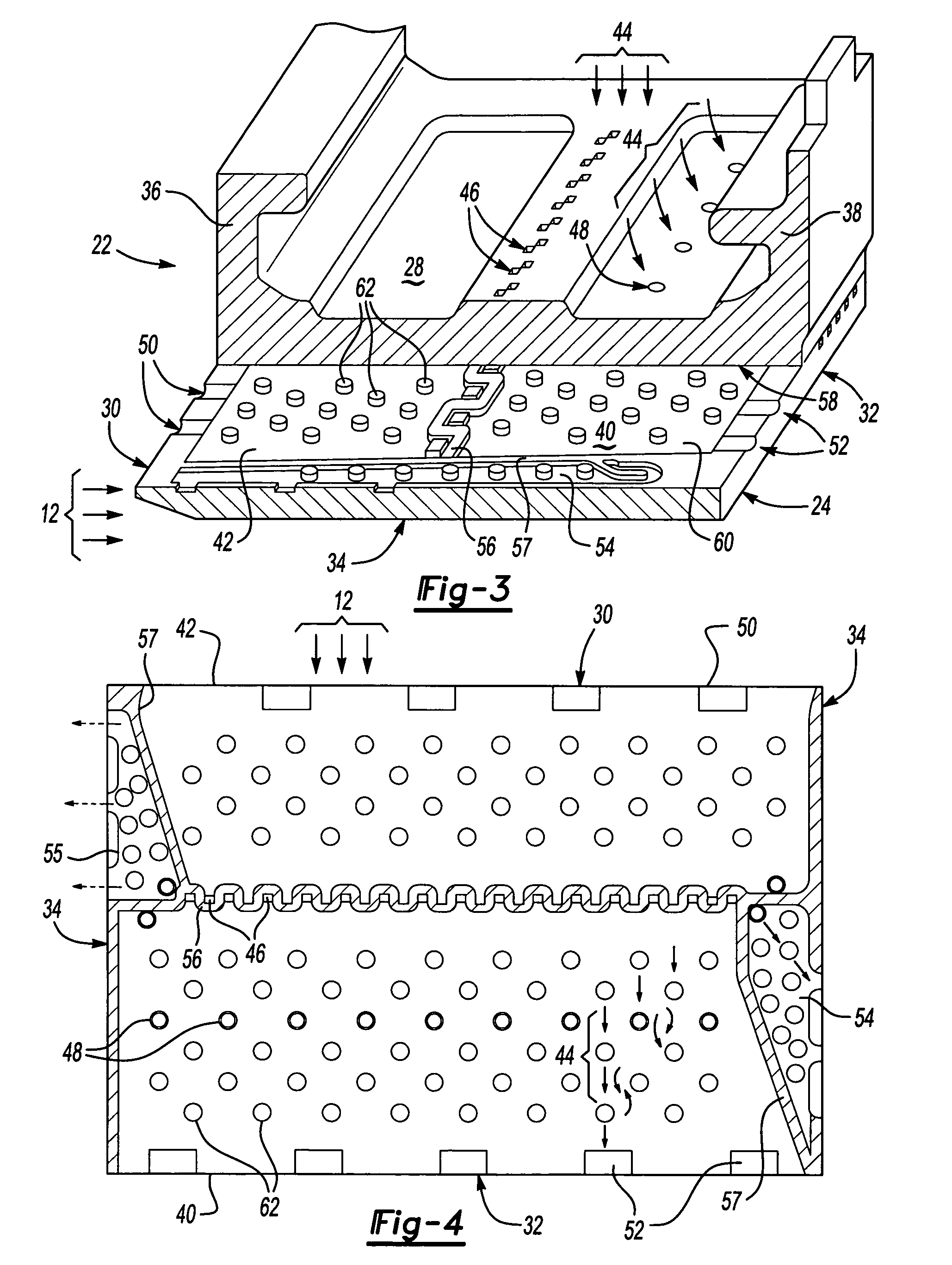
Blade outer seal with micro axial flow cooling system
ActiveUS7306424B2Increase surface areaImprove cooling effectPump componentsEngine fuctionsLeading edgeCombustion
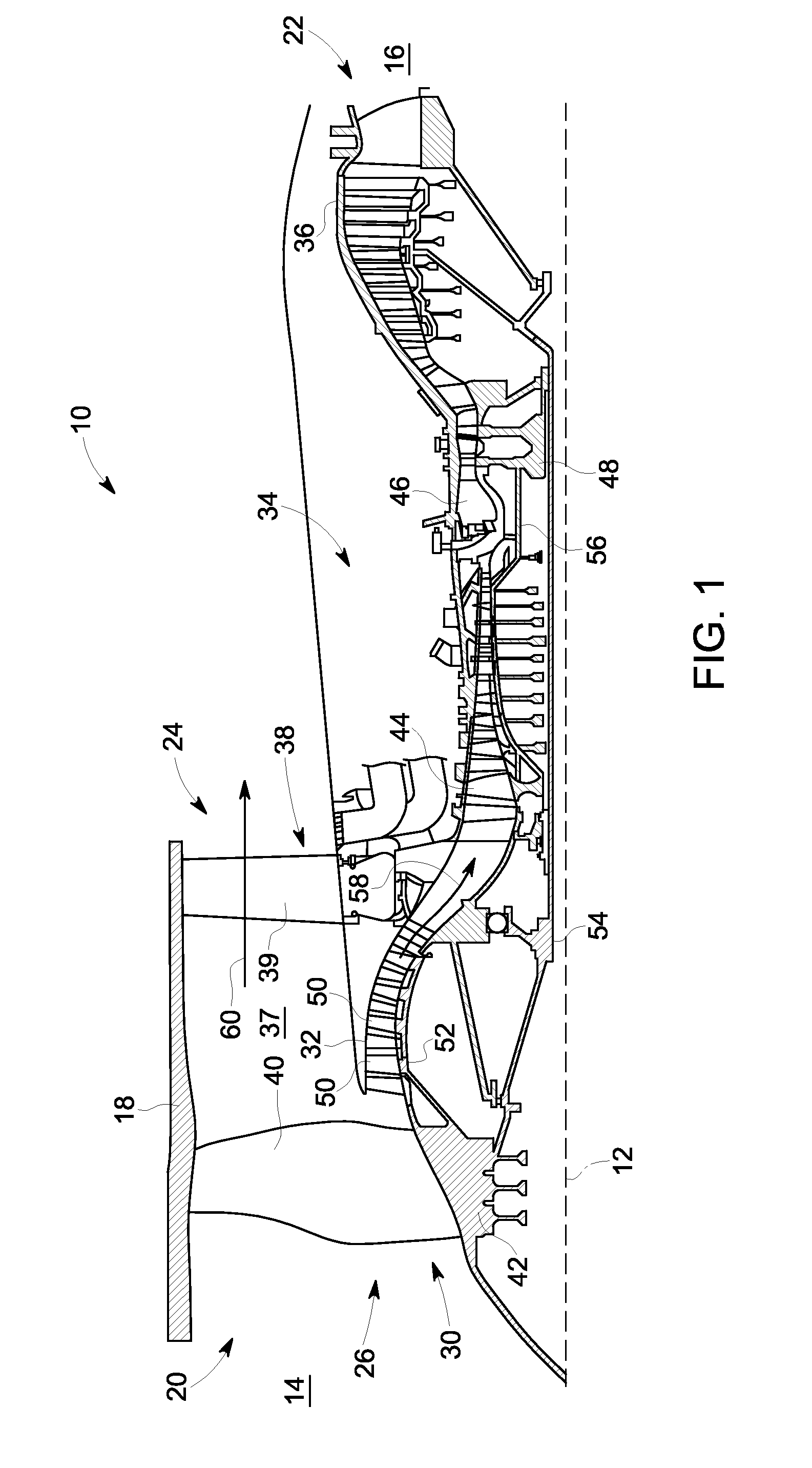
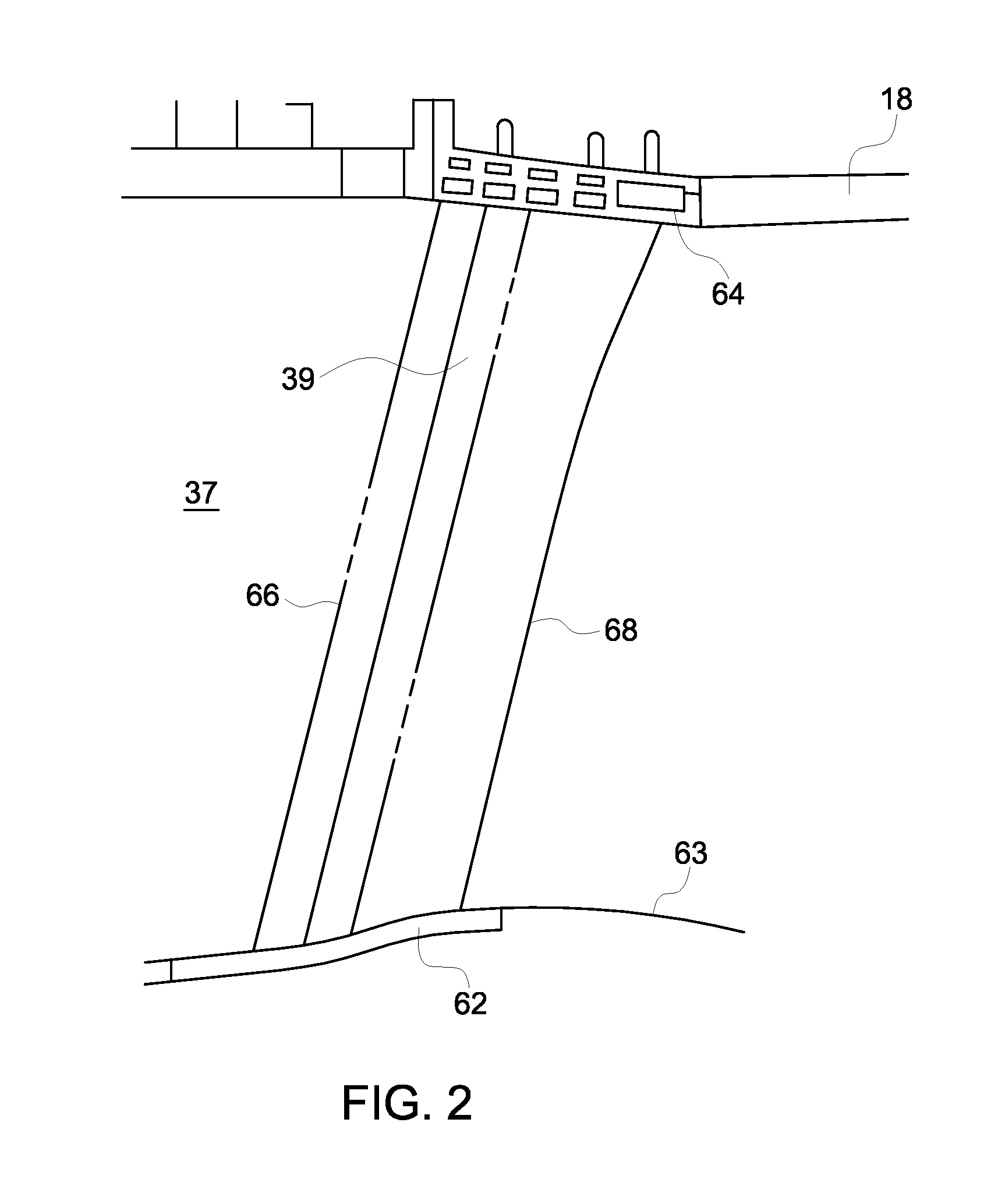
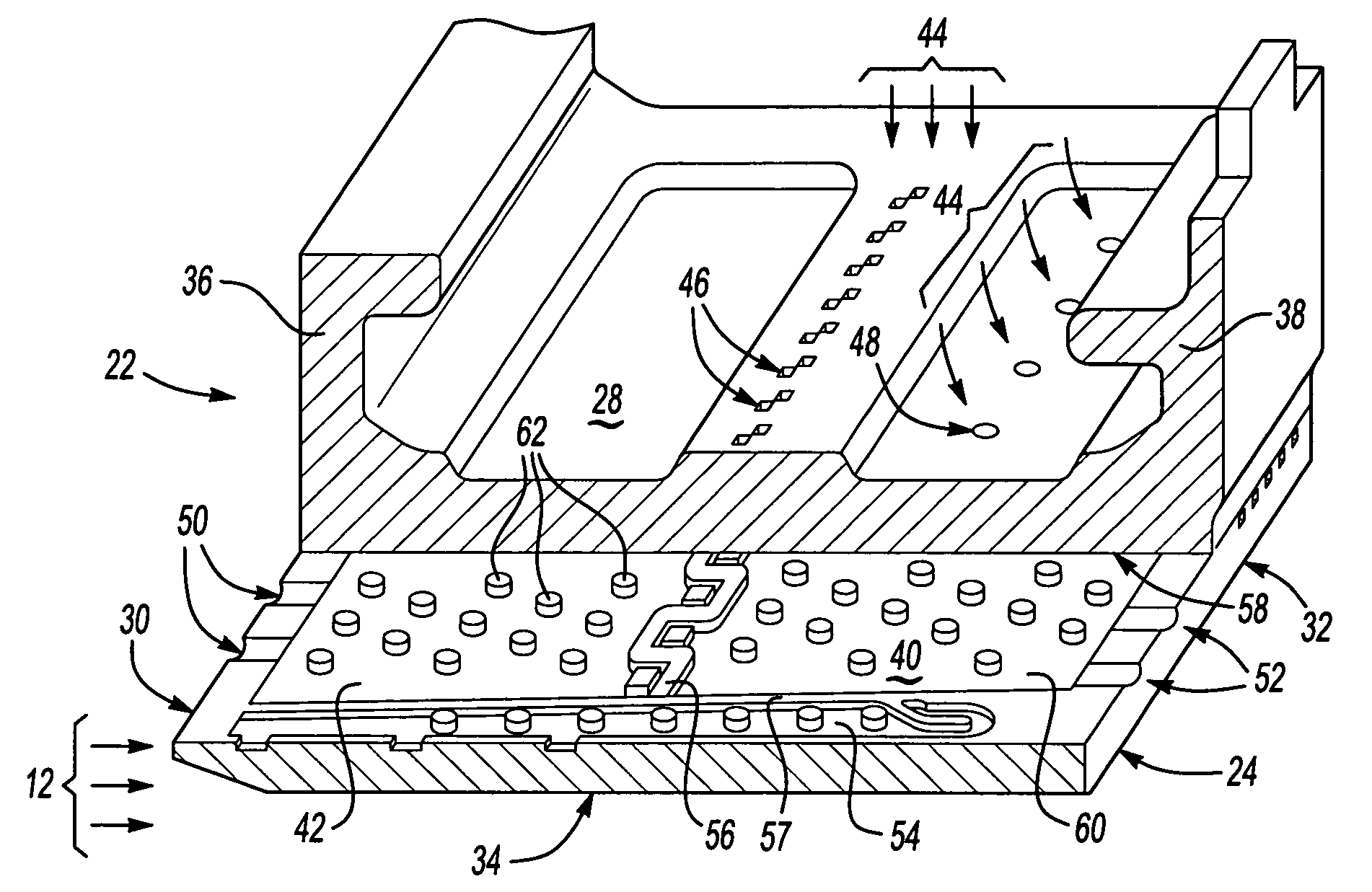
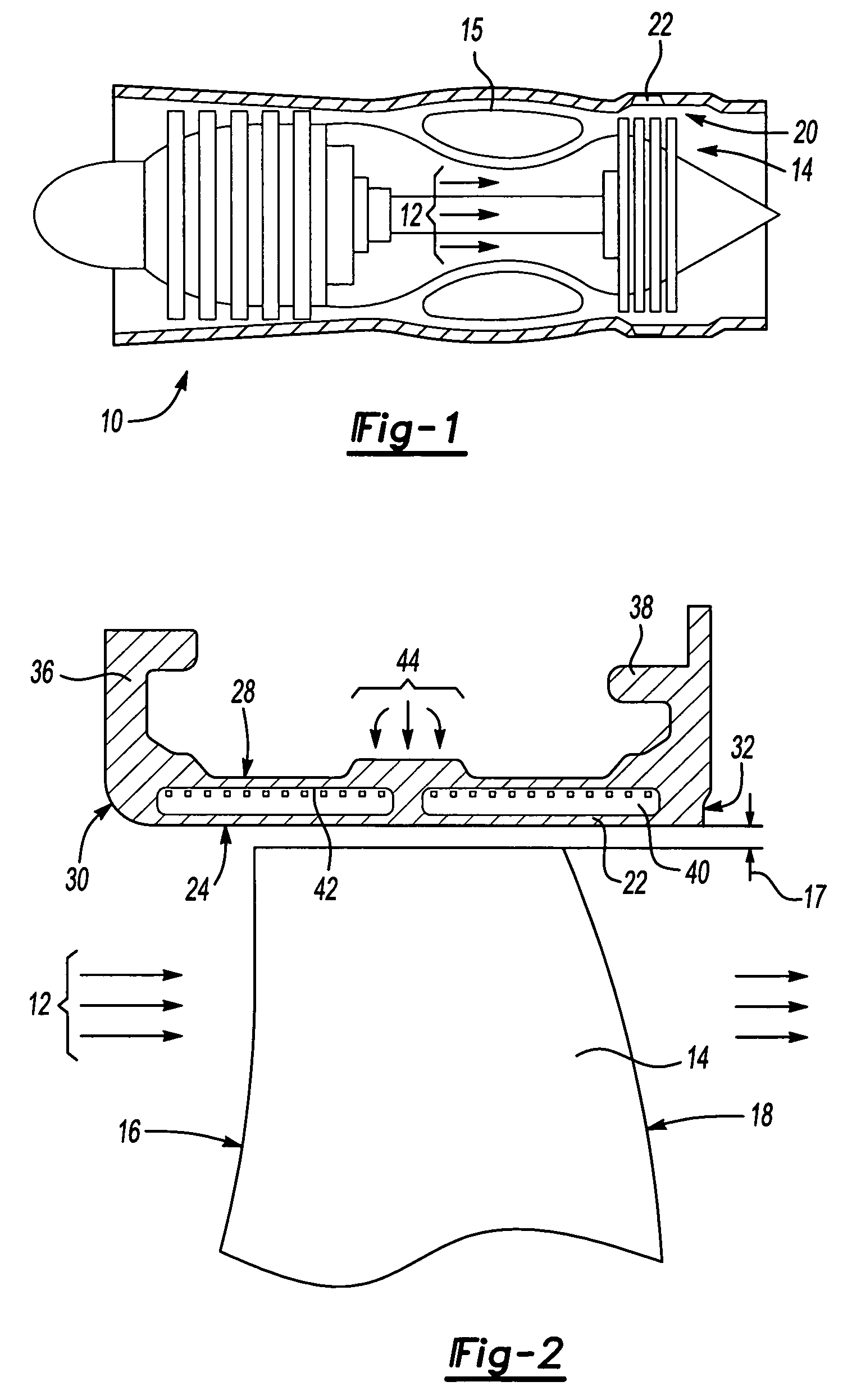
A turbine blade outer air seal assembly includes a hot side exposed to a combustion hot gas flow, and a back side that is exposed to a supply of cooling air. The outer air seal segment includes a trailing edge cavity and a leading edge cavity separated by a divider. The cavities are feed cooling air through a plurality of inlet openings disposed transverse to the gas flow. The cooling air enters the cavities and flows toward a plurality of outlets at the leading edge and a plurality of outlets along the trailing edge. A plurality of pedestals within each of the cavities disrupts cooling air flow to increase heat absorption capacity and to increase the surface area capable of transferring heat from the hot side.
Owner:RTX CORP
Coolable airfoil structure
InactiveUS6234754B1Durability and thermomechanical performanceIncreased durabilityPump componentsEngine fuctionsCastabilityInternal heat transfer
A coolable airfoil structure having internal heat transfer features through which cooling air is flowed under operative conditions is disclosed. Various construction details and features are developed which affect the castability and core strength during manufacture and strength and cooling effectiveness of the airfoil after manufacture. In one particular embodiment, the airfoil has a plurality of heat transfer members disposed in the rearmost section of the trailing edge region which comprises a single impingement rib, a single row of pedestals and a single row of chordwisely extending flow dividers.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
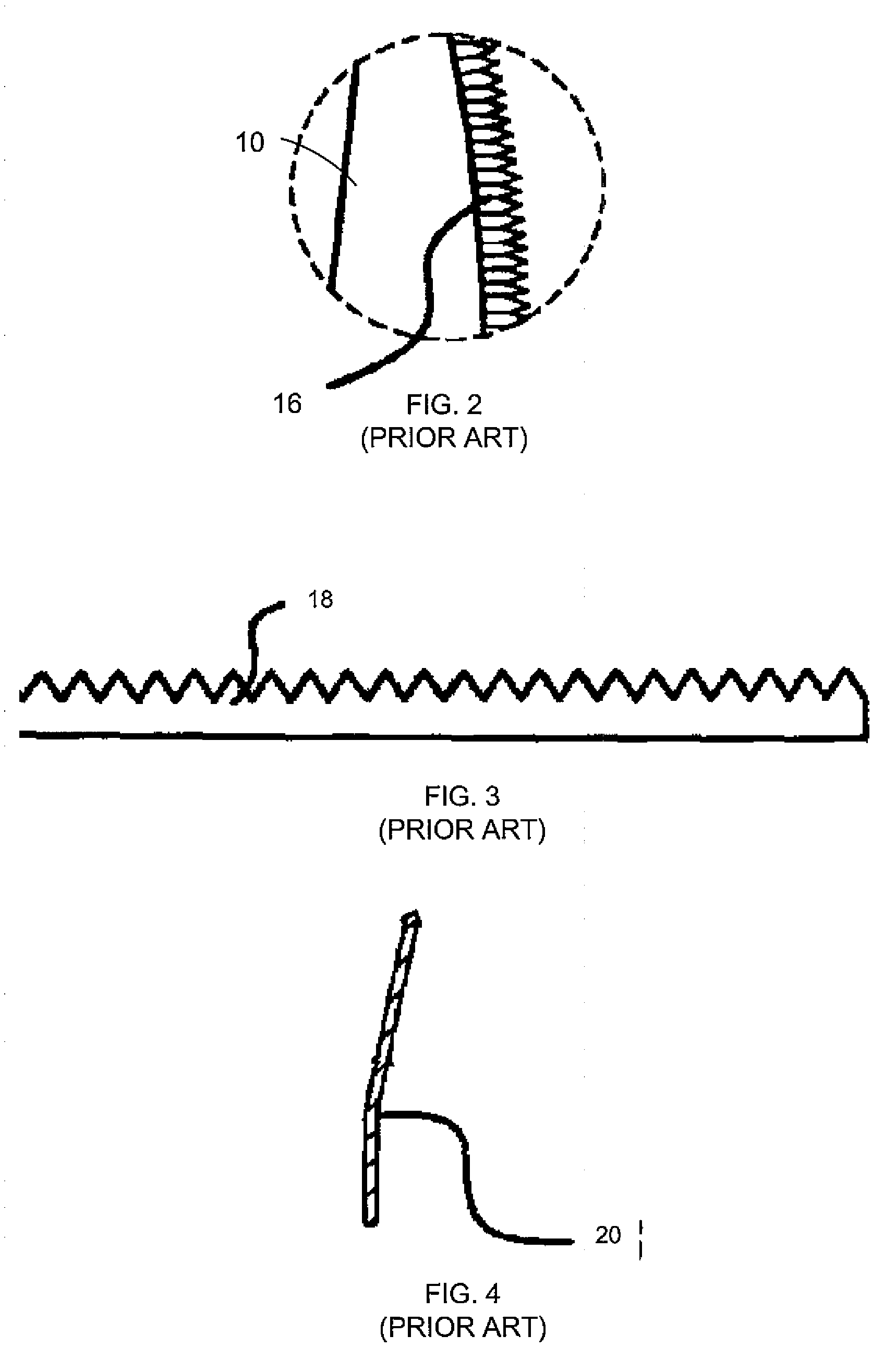
Method for improvement of the efficiency of a wind turbine rotor
InactiveUS7059833B2Improvement of wind turbine rotor efficiencyImprove efficiencyPropellersWind motor controlTurbine bladeTrailing edge
A method for the improvement of wind turbine rotor efficiency blades of a wind turbine rotor with serrated trailing edges each having a plurality of span-wise, periodic indentations, in the form of saw teeth having approximately 60 degrees included angles between adjacent vertices. The efficiency of an existing wind turbine rotor is improved by the attachment of an apparatus to at least part of the trailing edge of the wind turbine blades, the apparatus being in the form of a serrated panel that is fixed to the surface of the blade and has the serrations extending into the airflow behind the trailing edge of the existing blade. The efficiency of a new wind turbine blade is improved by manufacturing the blade with serrations of at least part of the trailing edge of the wind turbine blade.
Owner:BONUS ENERGY +1
Electron beam layer manufacturing using scanning electron monitored closed loop control
ActiveUS20110114839A1Speed up the processQuick buildAdditive manufacturing apparatusMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationClosed loopTrailing edge
A process (and apparatus for performing the process) for layer manufacturing a three-dimensional work piece comprising the steps of; feeding raw material in a solid state to a first predetermined location; exposing the raw material to an electron beam to liquefy the raw material; depositing the raw material onto a substrate as a molten pool deposit, the deposit having a forward edge region in an x-y plane with a forward edge region width and a trailing edge region in the x-y plane with a trailing edge region width, under at least one first processing condition; monitoring the molten pool deposit for at least one preselected condition using detecting of scatter from a scanning electron beam contemporaneously with the depositing step; solidifying the molten pool deposit; automatically altering the first processing condition to a different processing condition based upon information obtained from the comparing step; and repeating steps at one or more second locations for building up layer by layer, generally along a z-axis that is orthogonal to the x-y plane, a three-dimensional work piece.
Owner:SCIAKY SA
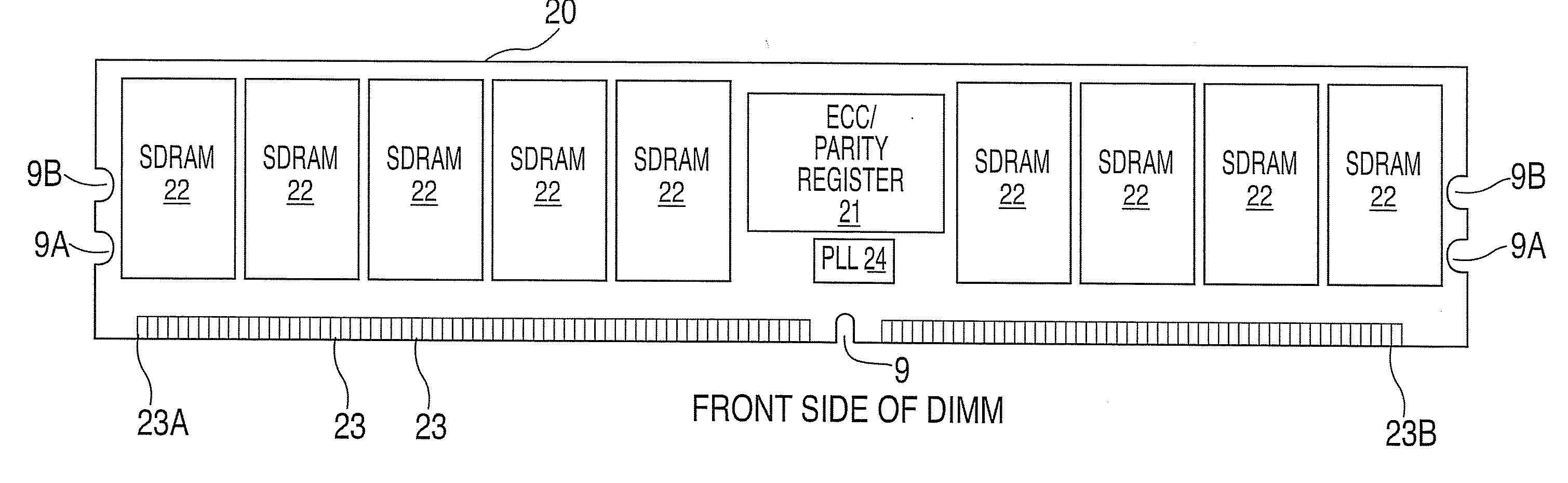
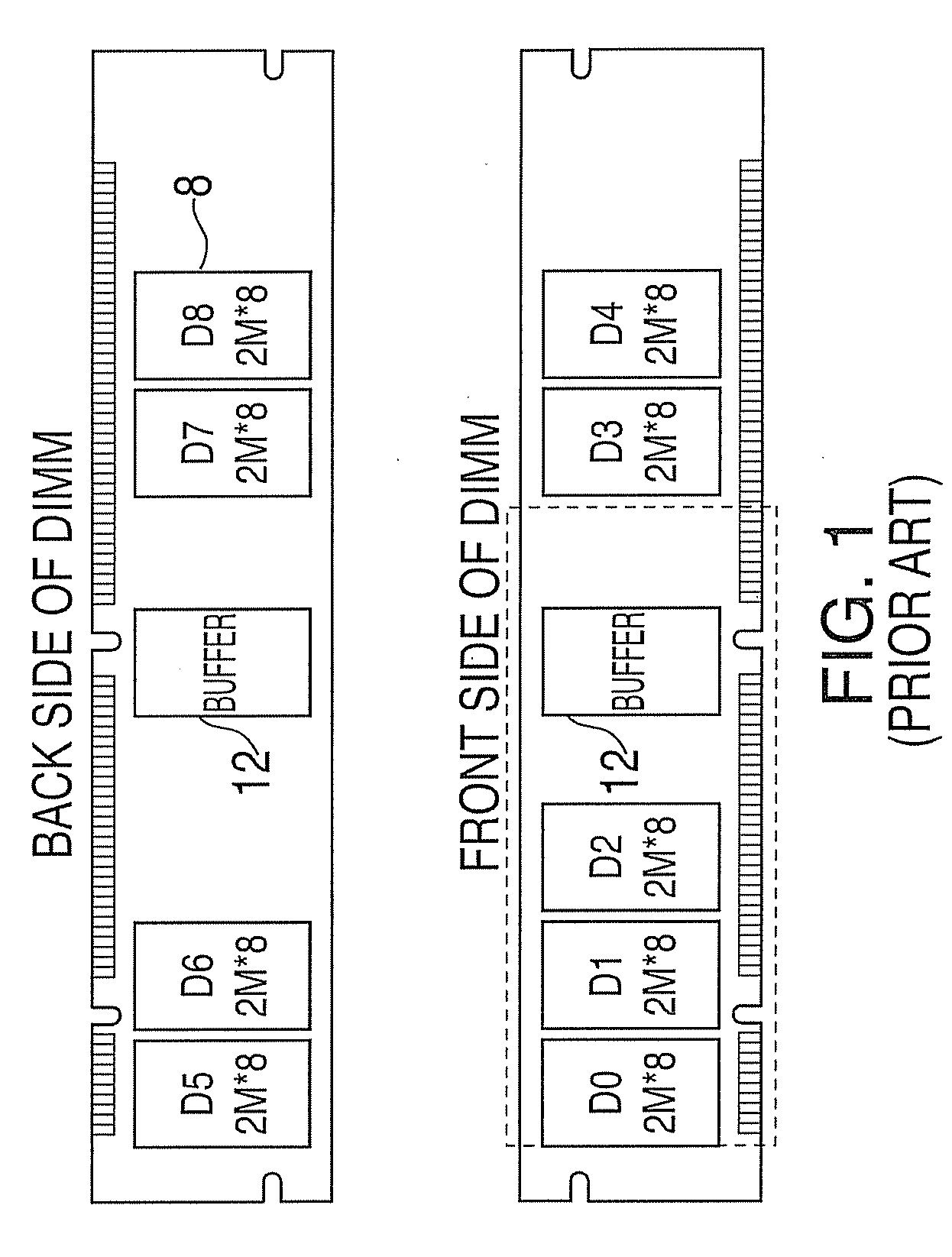
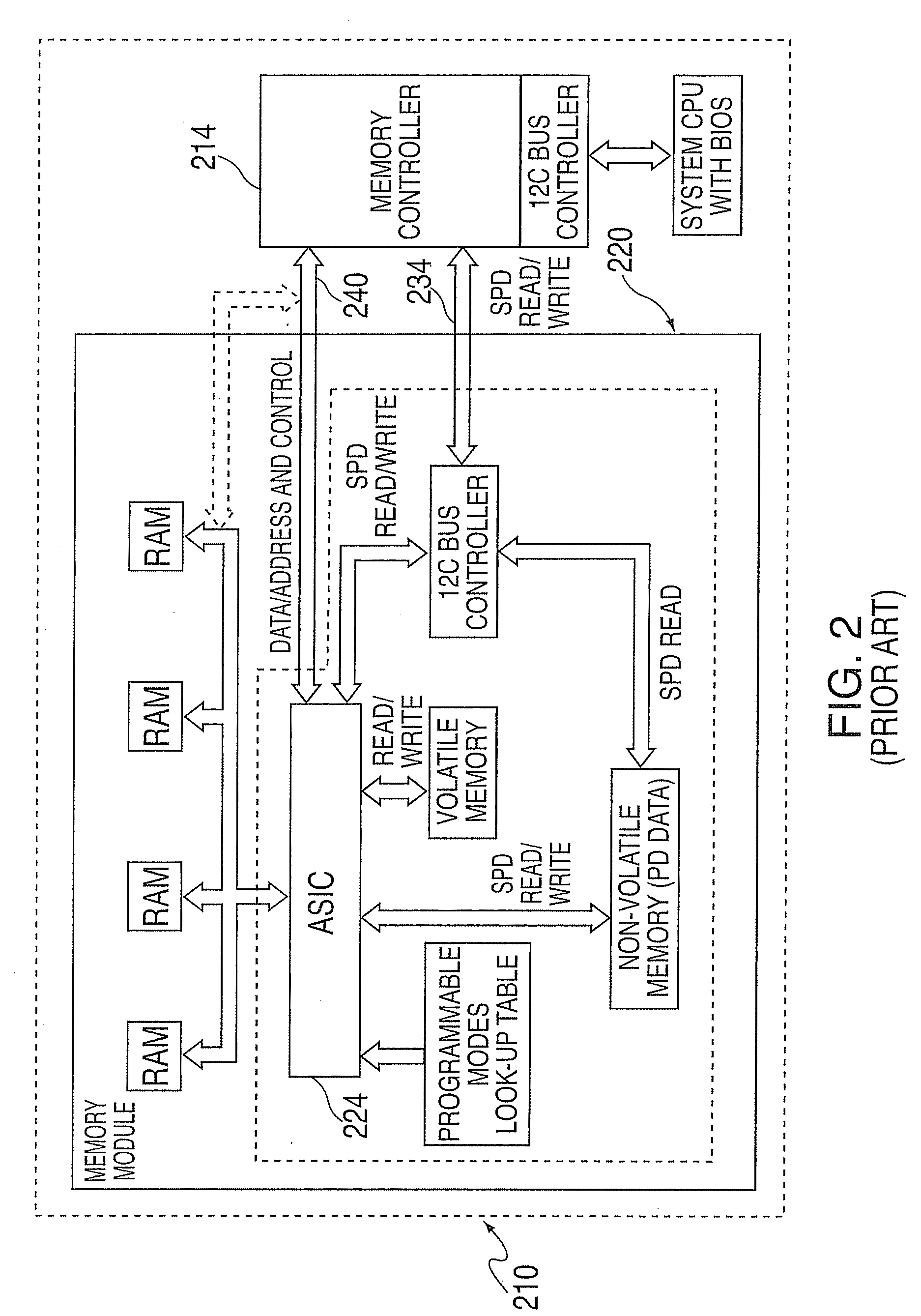
System and method for providing an adapter for re-use of legacy dimms in a fully buffered memory environment
A system and method for providing an adapter for re-use of legacy DIMMS in a fully buffered memory environment. The system includes a memory adapter card having two rows of contacts along a leading edge of a length of the card. The rows of contacts are adapted to be inserted into a socket that is connected to a daisy chain high-speed memory bus via a packetized multi-transfer interface. The memory adapter card also includes a socket installed on the trailing edge of the card. In addition, the memory adapter card includes a hub device for converting the packetized multi-transfer interface into a parallel interface having timings and interface levels that are operable with a memory module having a parallel interface that is inserted into the socket. In addition, the hub device converts the packetized multi-transfer interface into a parallel interface having timings and interface levels that are operable with a memory module having a parallel interface that is inserted into the socket. The hub device also converts the parallel interface into the packetized multi-transfer interface.
Owner:IBM CORP
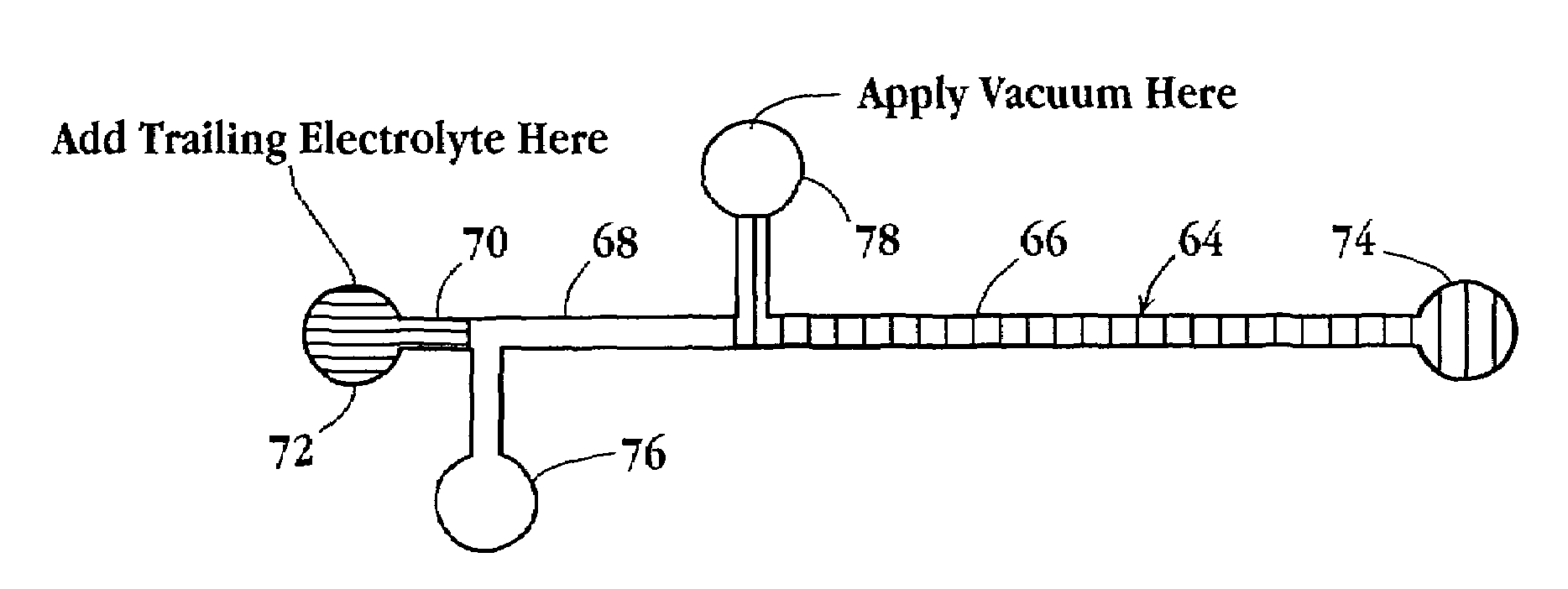
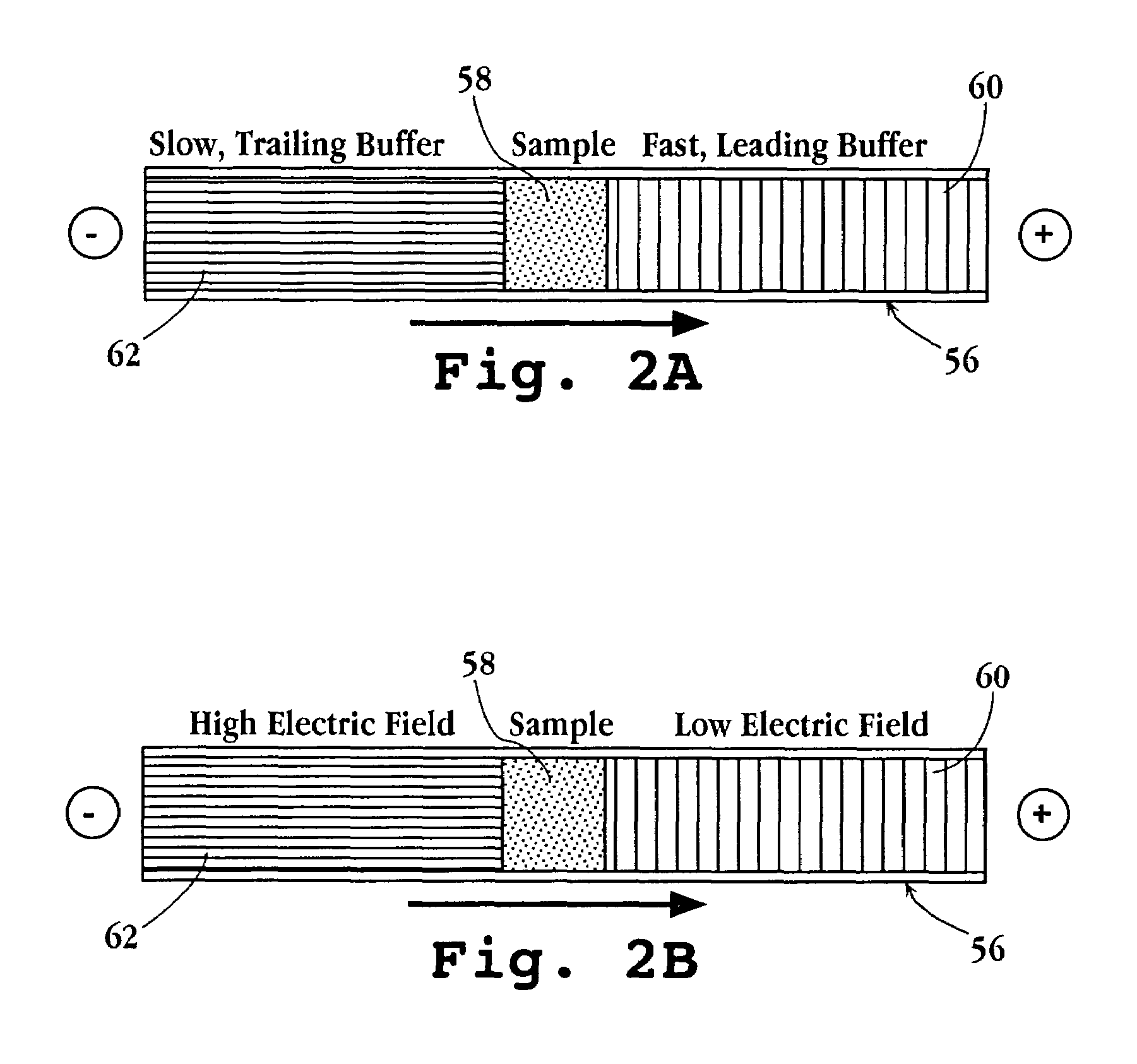
Tandem isotachophoresis/zone electrophoresis method and system
A method of separating components having a given negative or positive charge and contained in a sample is disclosed. The method involves, in one embodiment, loading a microchannel with a sample, placed between a trailing-edge electrolyte having a selected concentration of a titratable species, and a leading-edge electrolyte. With the application of a voltage potential across the microchannel, charged components in the sample stack by isotachophoresis, and electrolytic hydroxyl or hydrogen ions formed by electrolysis at the upstream-end electrode migrate into the trailing-edge ion buffer, titrating the titratable species therein, where the concentration of the titratable species in the trailing-edge electrolyte is selected , in relation to the lengths of the upstream channel region and sample-loading volume, to permit the sample to stack into a relatively small sample volume before electrolytic-ion migration from the upstream electrode into and through the sample-volume region is effective to overtake the charge sample components. With continued application of an electric potential across the channel ends, charged sample components in the stacked sample volume separated by zone electrophoresis.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com