Patents
Literature
28741 results about "Waveguide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
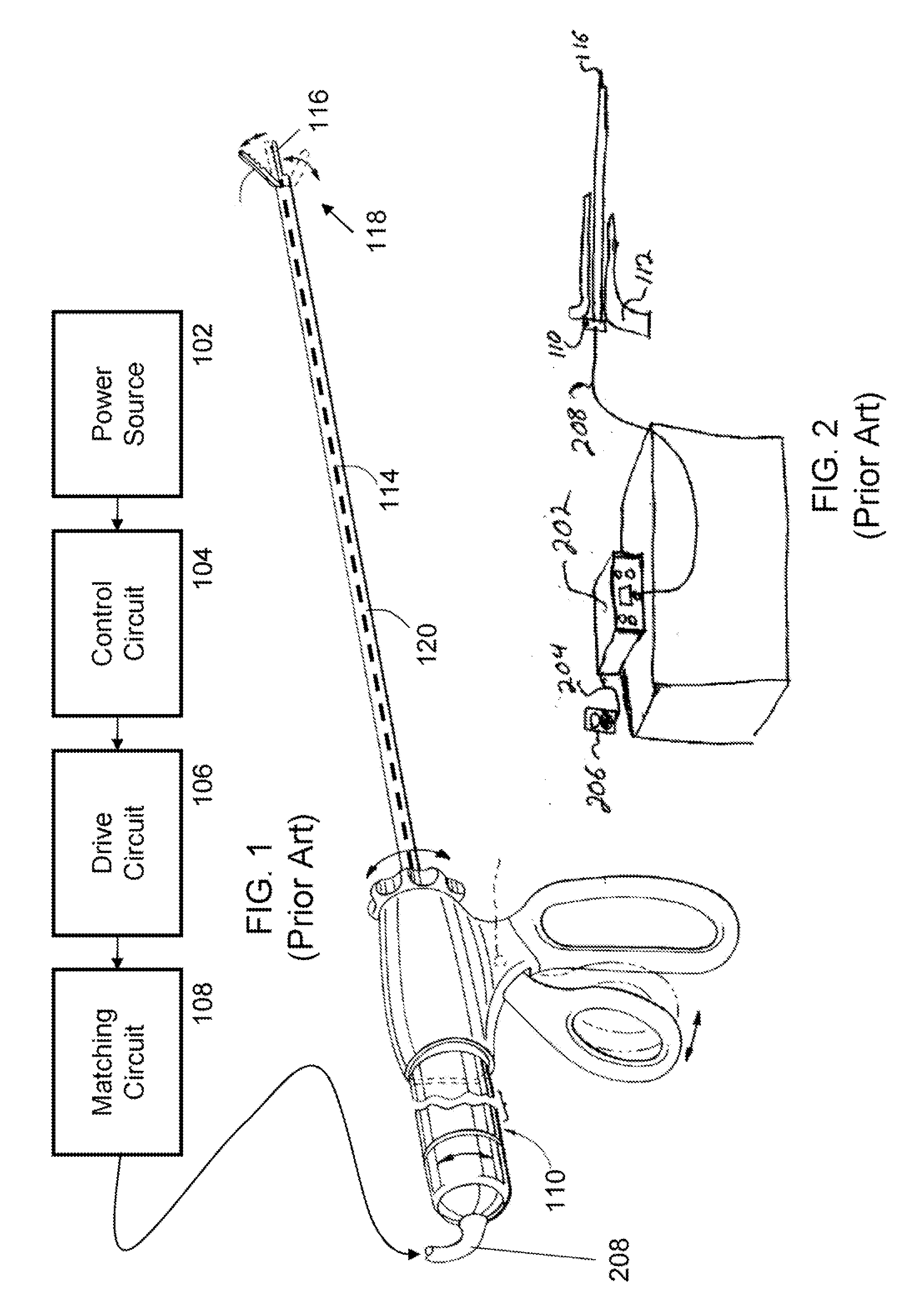
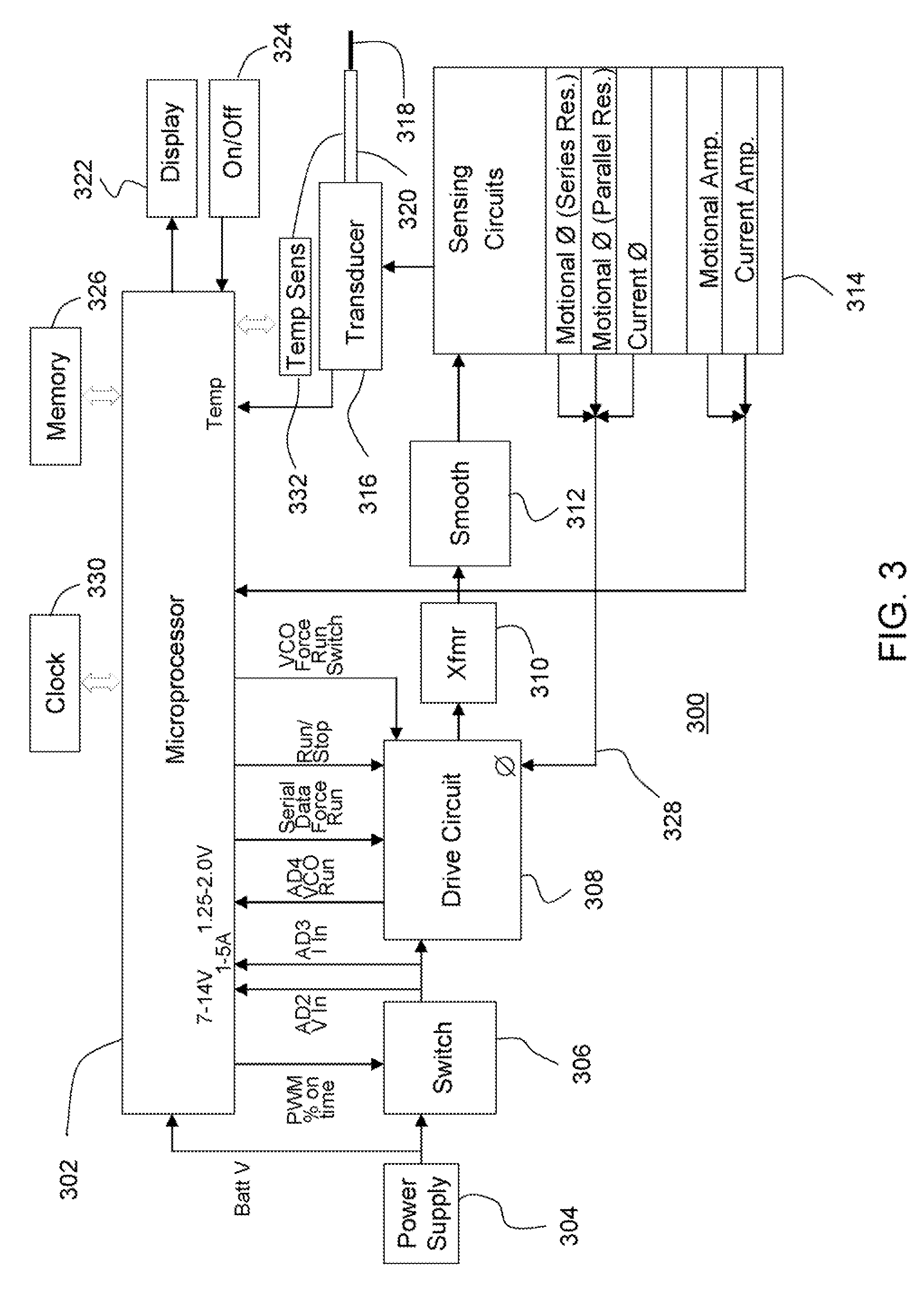
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound, with minimal loss of energy by restricting expansion to one dimension or two. There is a similar effect in water waves constrained within a canal, or guns that have barrels which restrict hot gas expansion to maximize energy transfer to their bullets. Without the physical constraint of a waveguide, wave amplitudes decrease according to the inverse square law as they expand into three dimensional space.
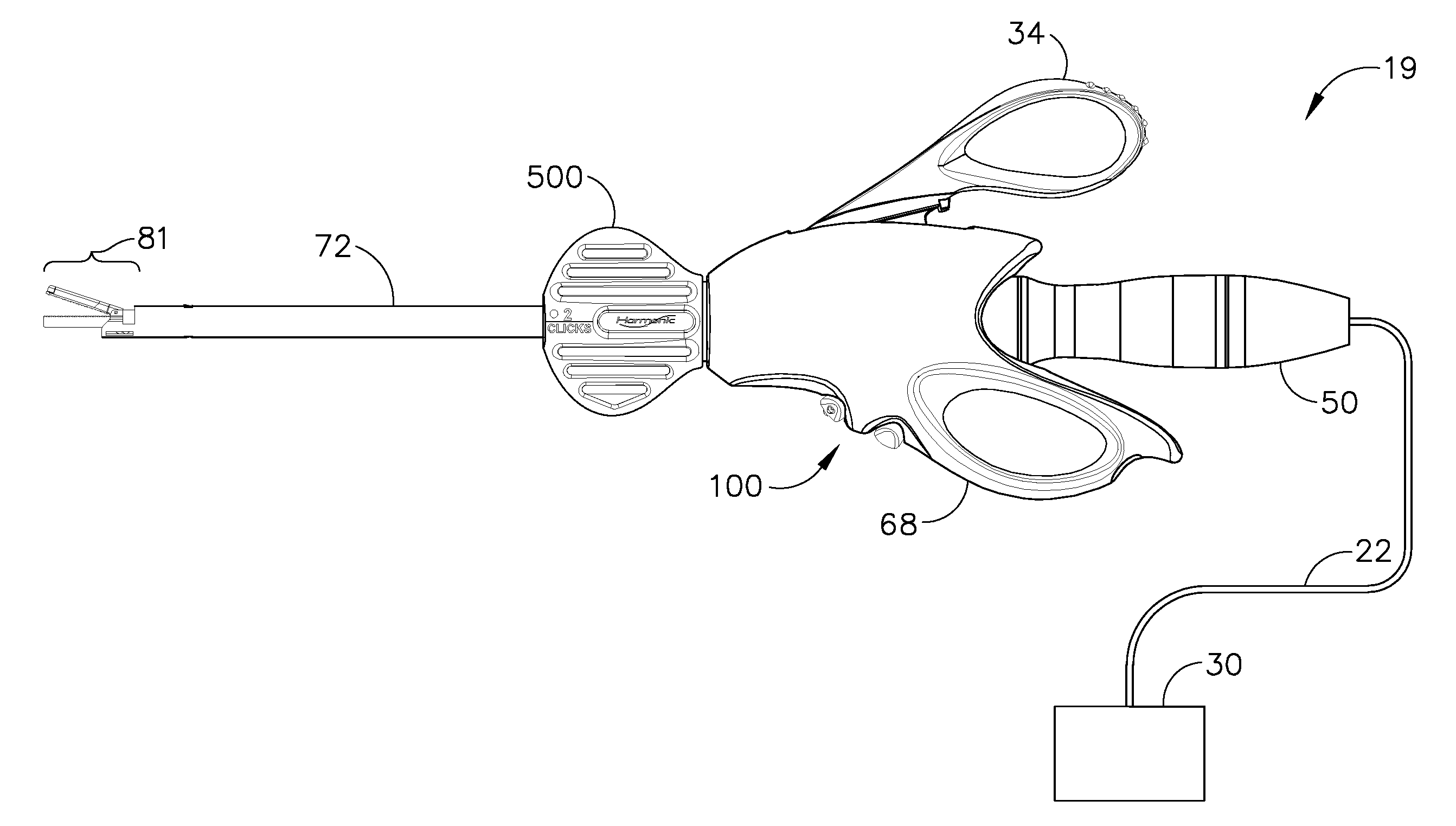
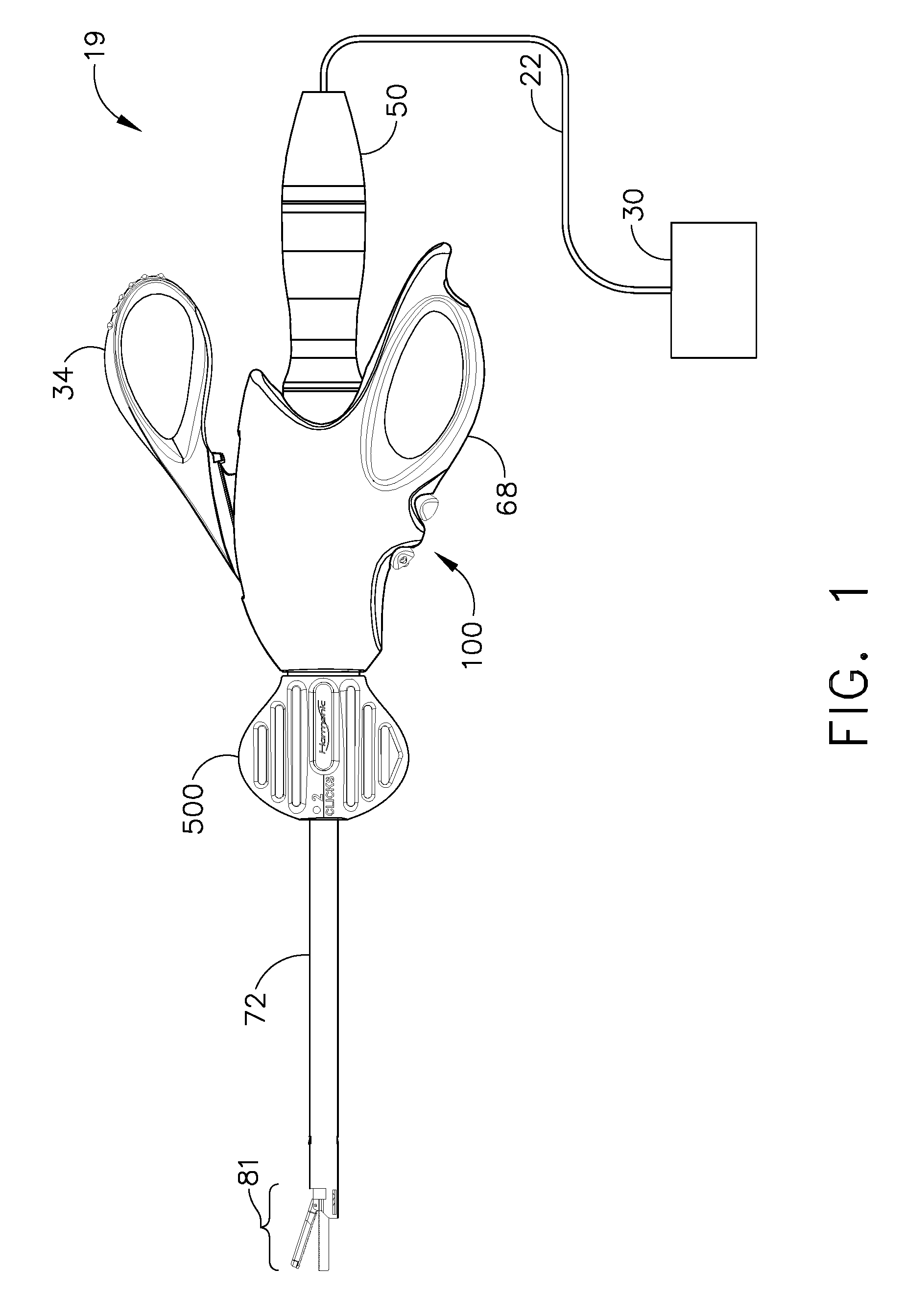
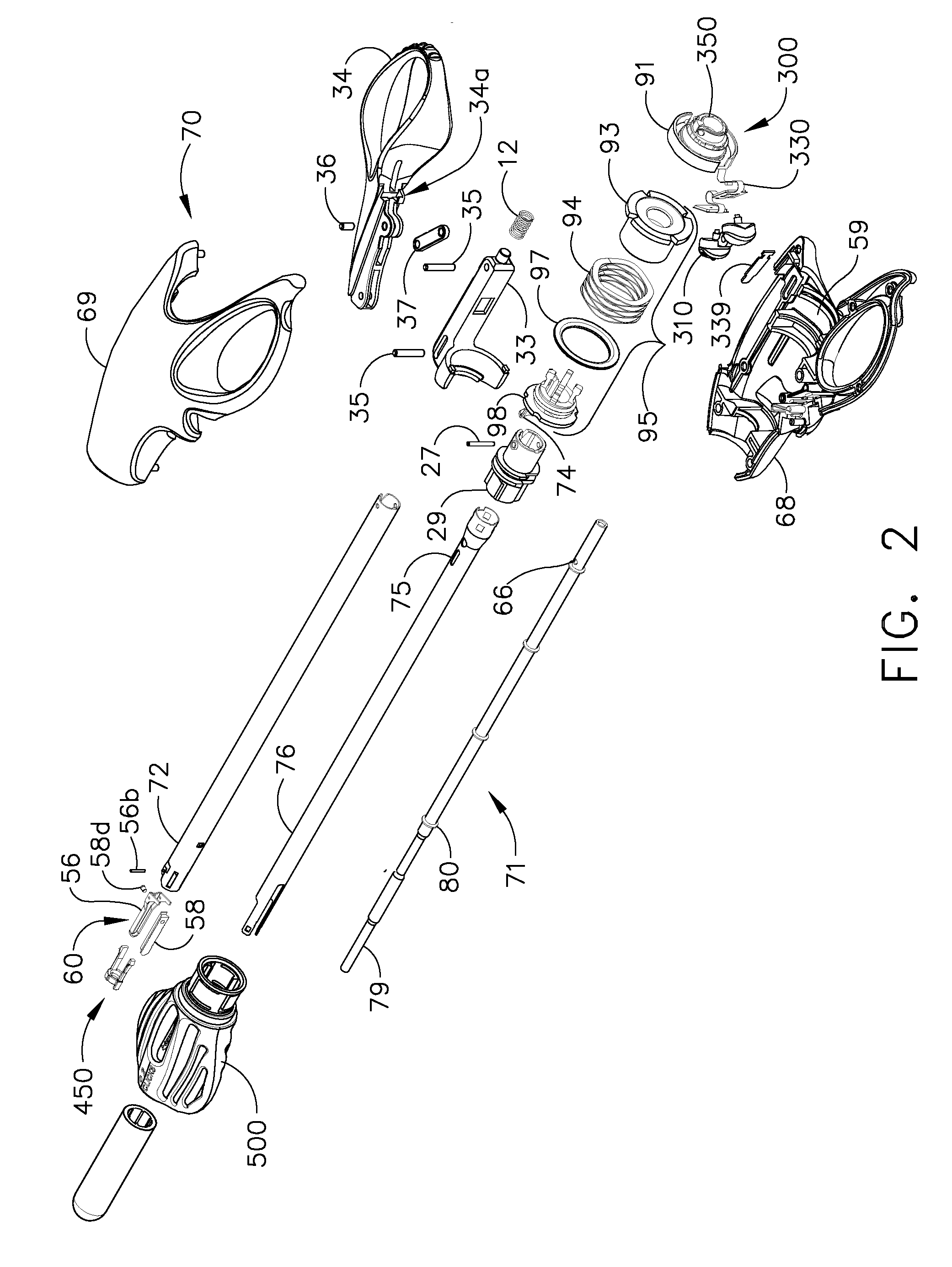
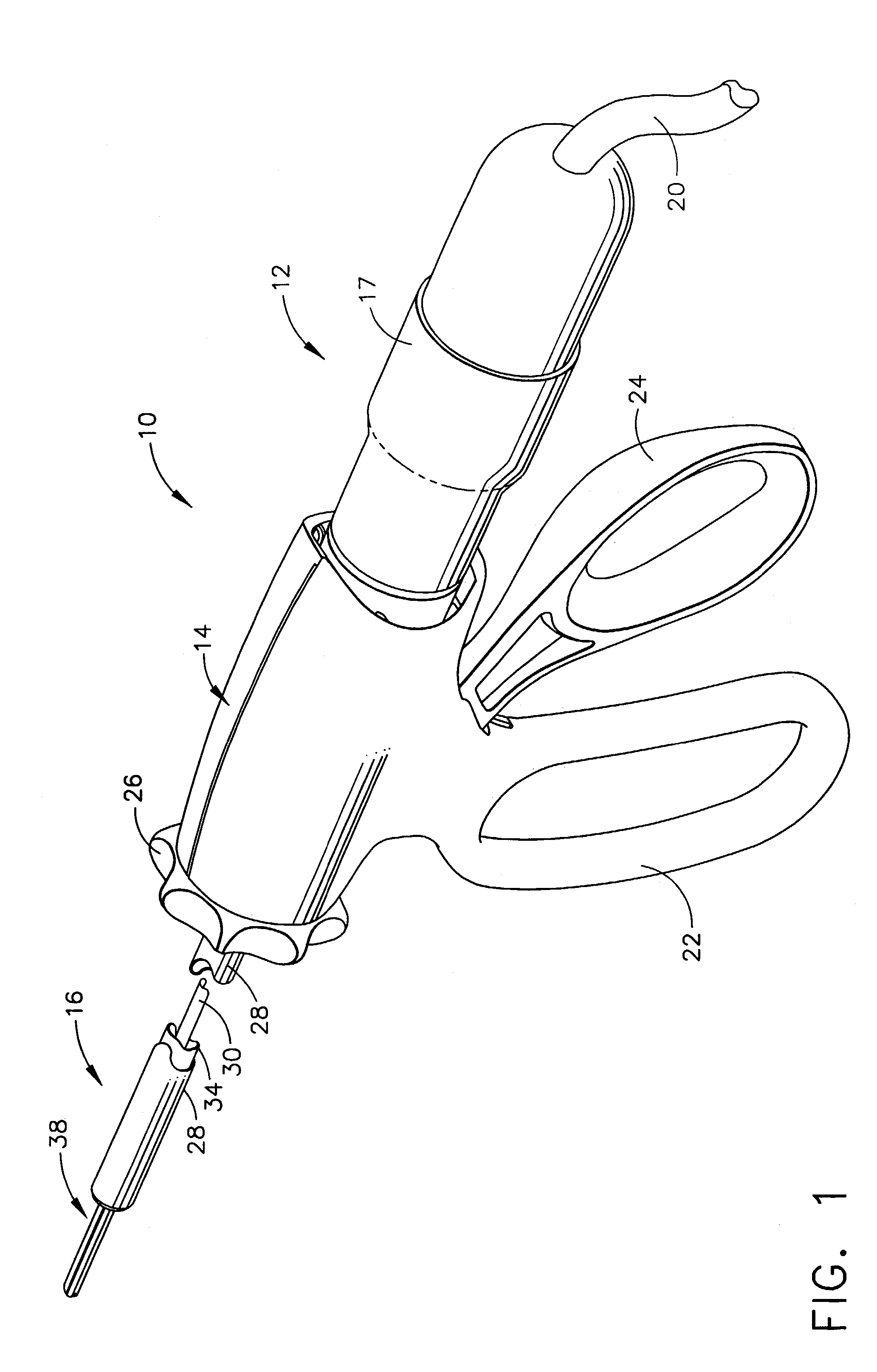
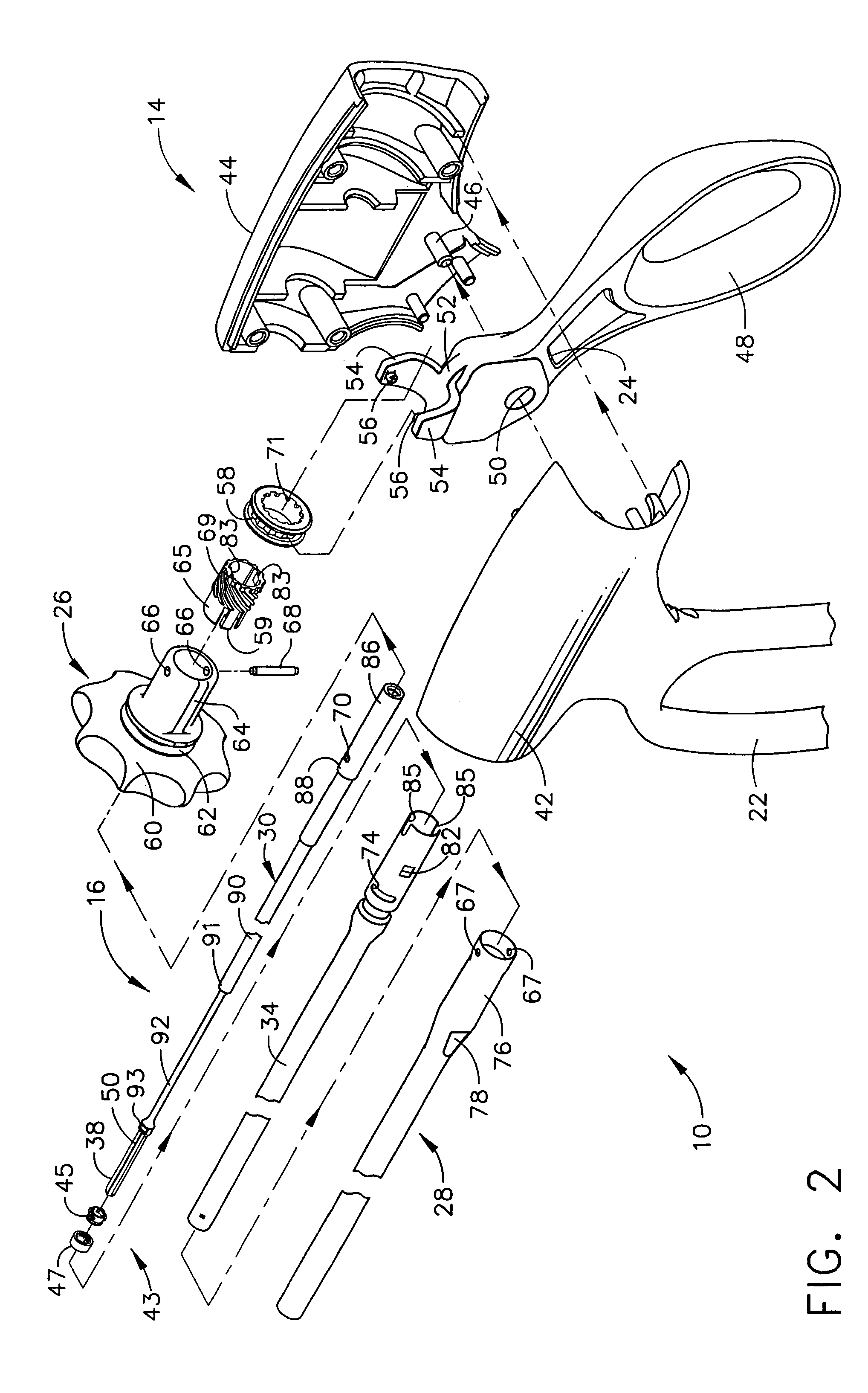
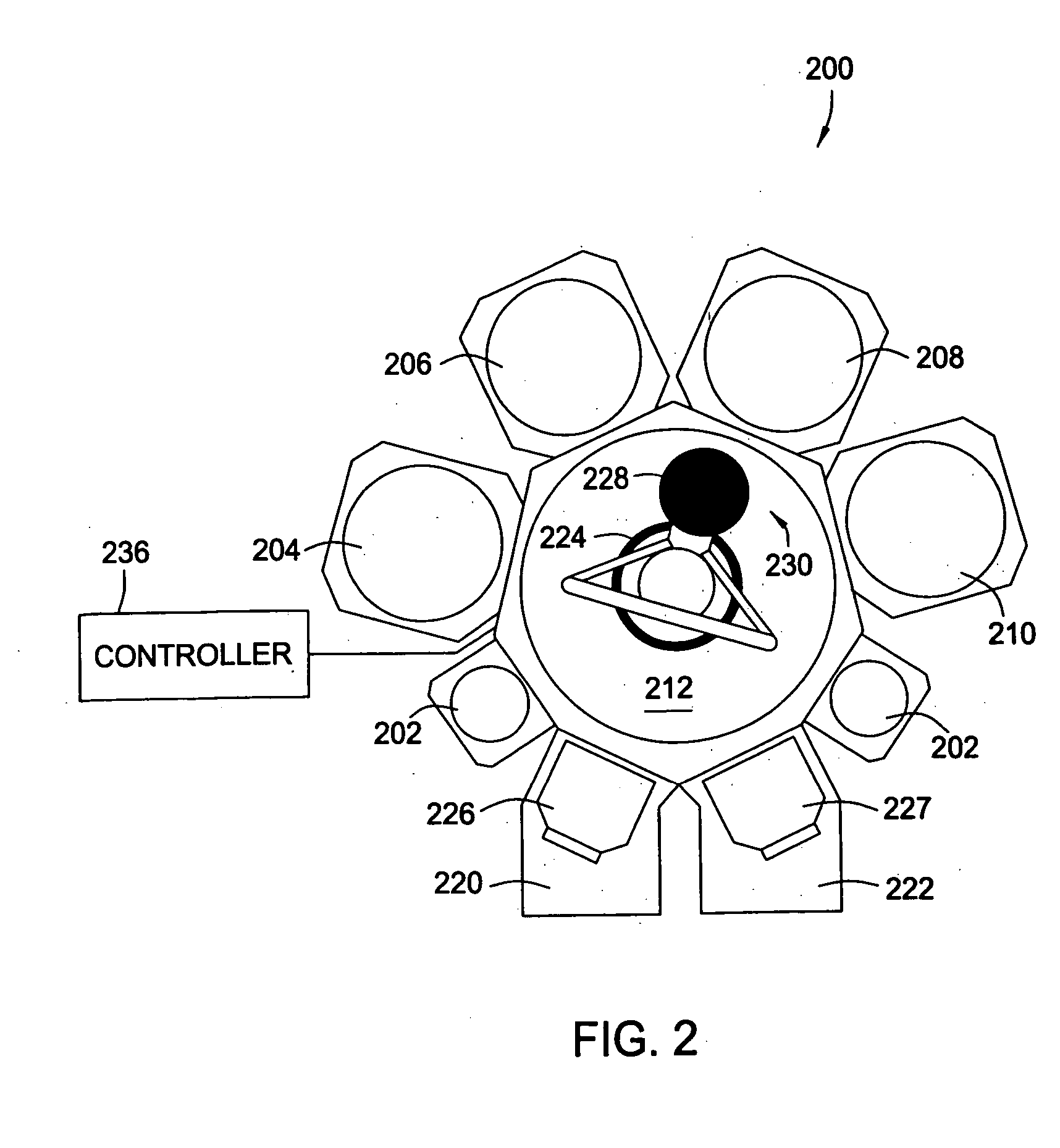
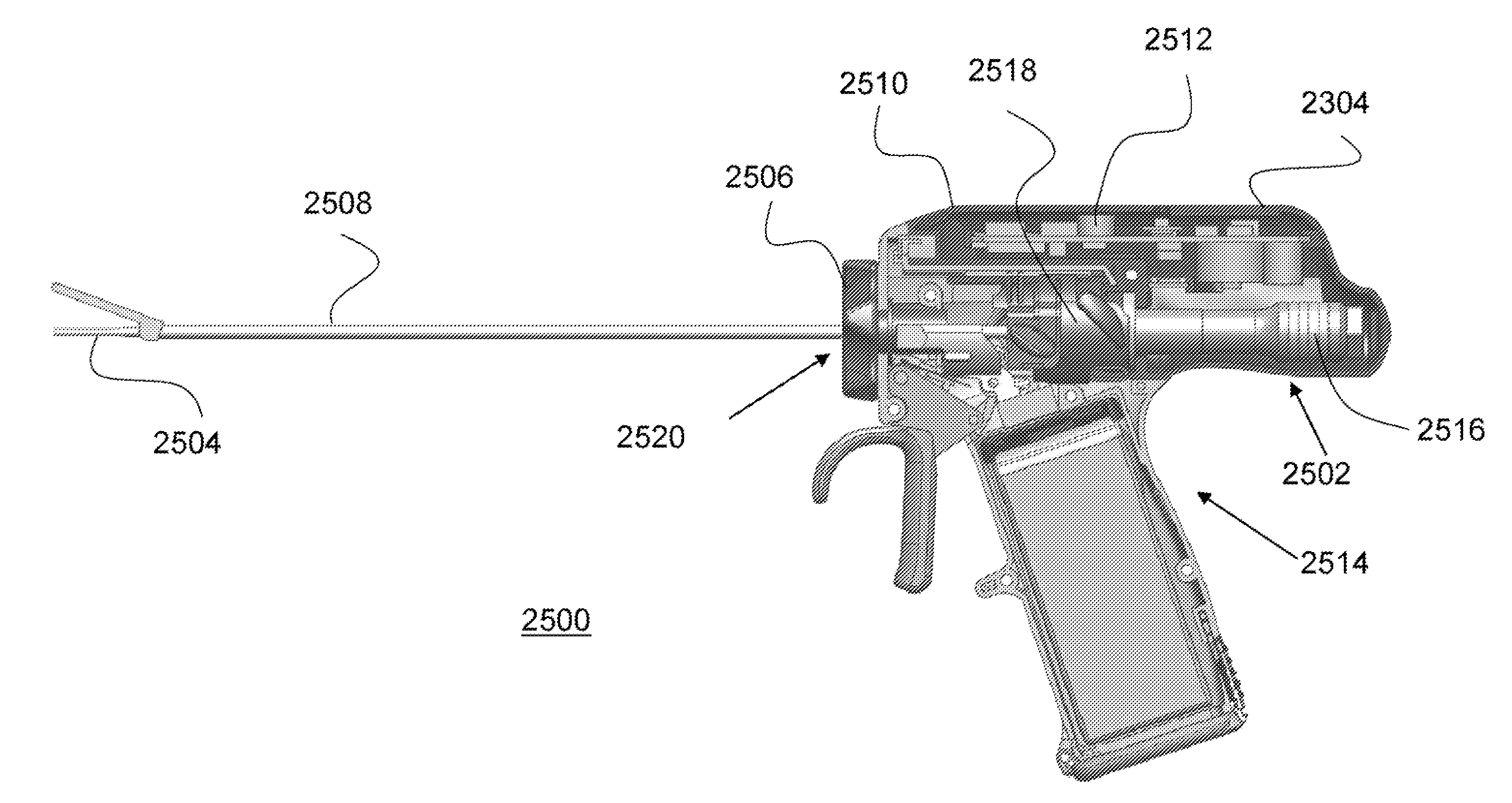
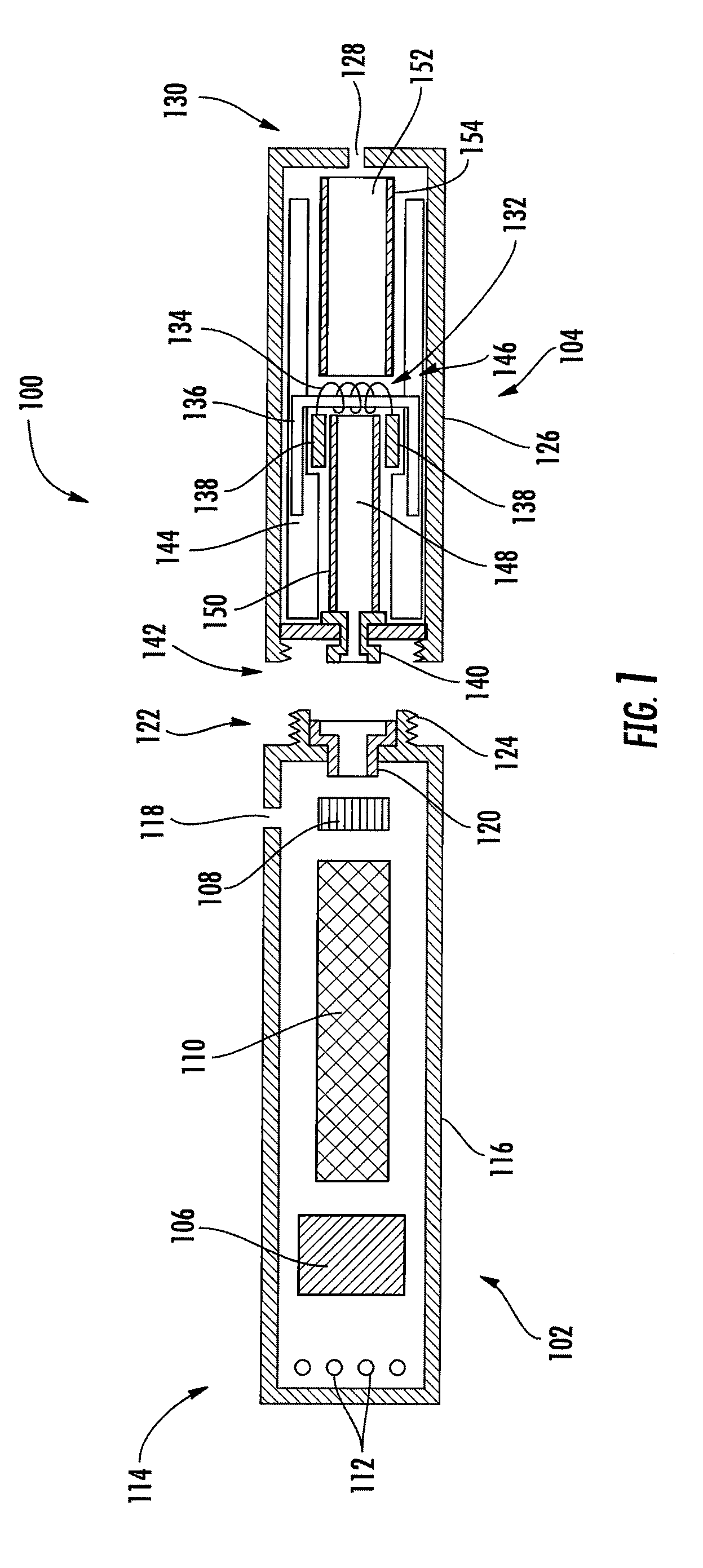
Ultrasonic waveguide and blade
InactiveUS20070282333A1Improve wear resistanceDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsDistal portionEngineering
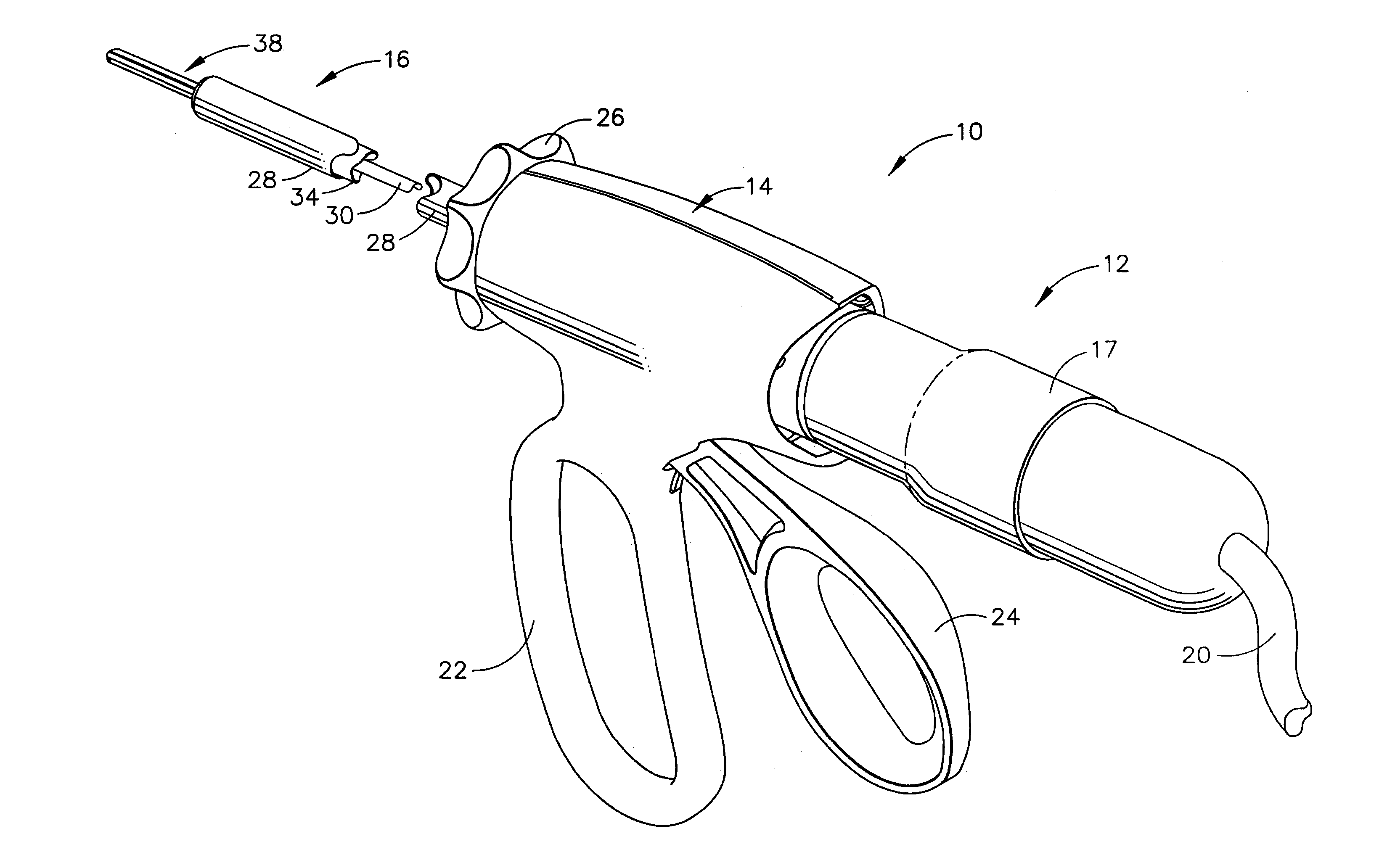
An ultrasonic clamp coagulator assembly that is configured to permit selective cutting, coagulation and clamping of tissue during surgical procedures. An elongated portion of the instrument can be configured for endoscopic applications and has an outside diameter of less than 6 mm. The construction includes a waveguide and blade that enable larger wave amplitude and a longer active blade length and still provide sufficient frequency margin or window. The waveguide is provided with a series of gain steps located at the distal portion of the waveguide preferably at the two most distal nodes in relation to the handpiece, or the two most proximal nodes in relation to the blade tip.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT +1
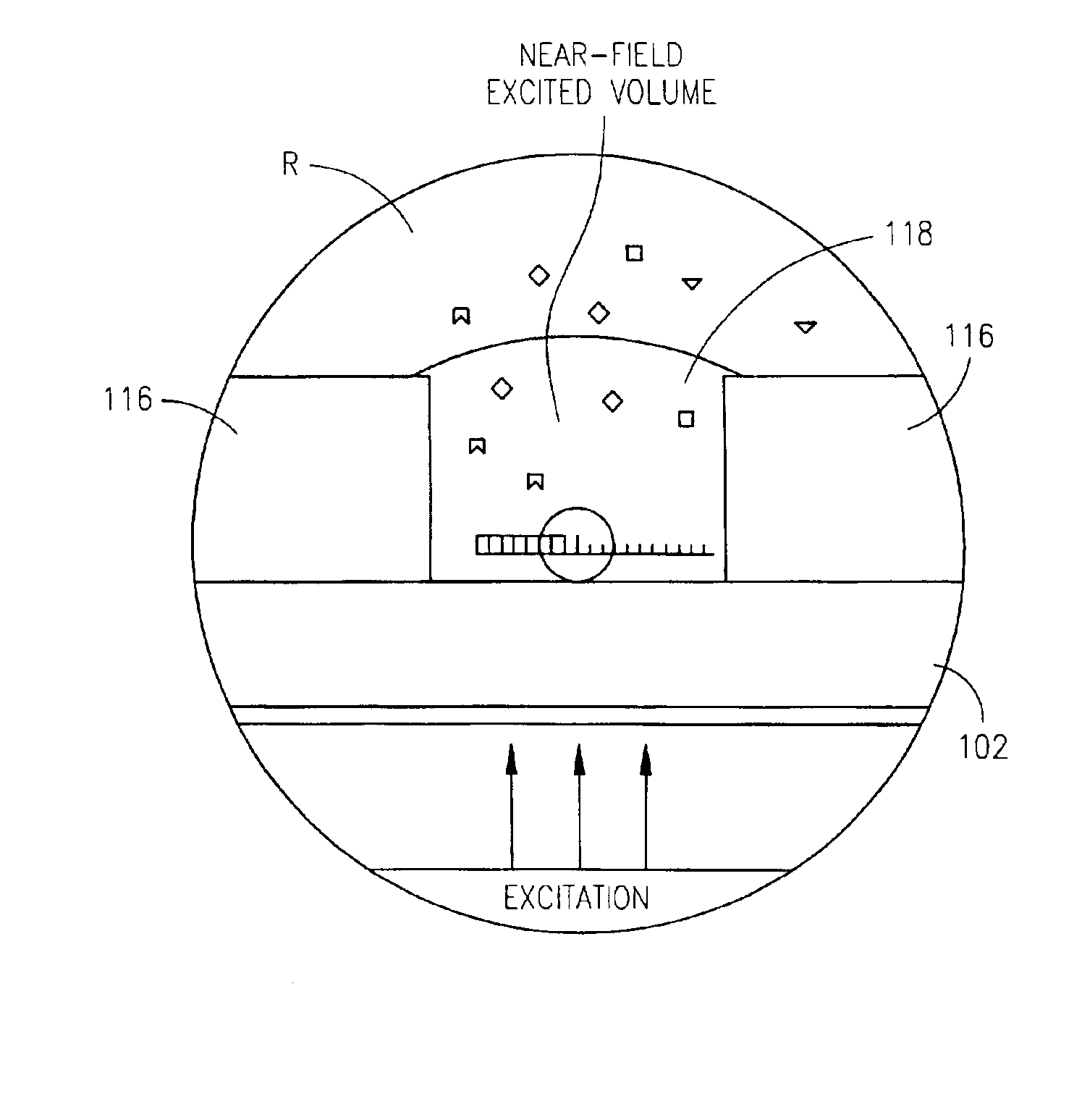
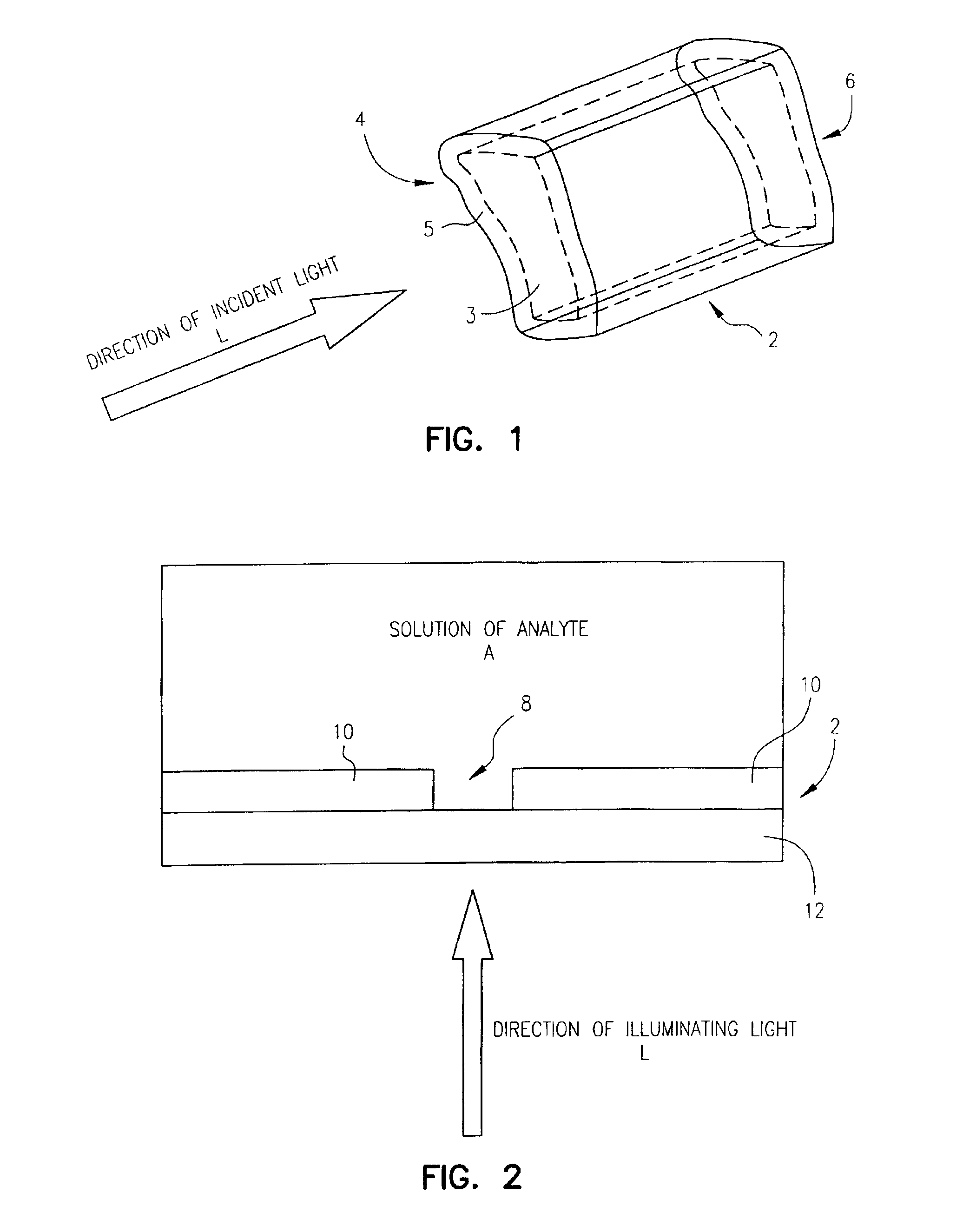
Zero-mode clad waveguides for performing spectroscopy with confined effective observation volumes
InactiveUS6917726B2Effective volumeEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAnalyteSpectroscopy
The present invention is directed to a method and an apparatus for analysis of an analyte. The method involves providing a zero-mode waveguide which includes a cladding surrounding a core where the cladding is configured to preclude propagation of electromagnetic energy of a frequency less than a cutoff frequency longitudinally through the core of the zero-mode waveguide. The analyte is positioned in the core of the zero-mode waveguide and is then subjected, in the core of the zero-mode waveguide, to activating electromagnetic radiation of a frequency less than the cut-off frequency under conditions effective to permit analysis of the analyte in an effective observation volume which is more compact than if the analysis were carried out in the absence of the zero-mode waveguide.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
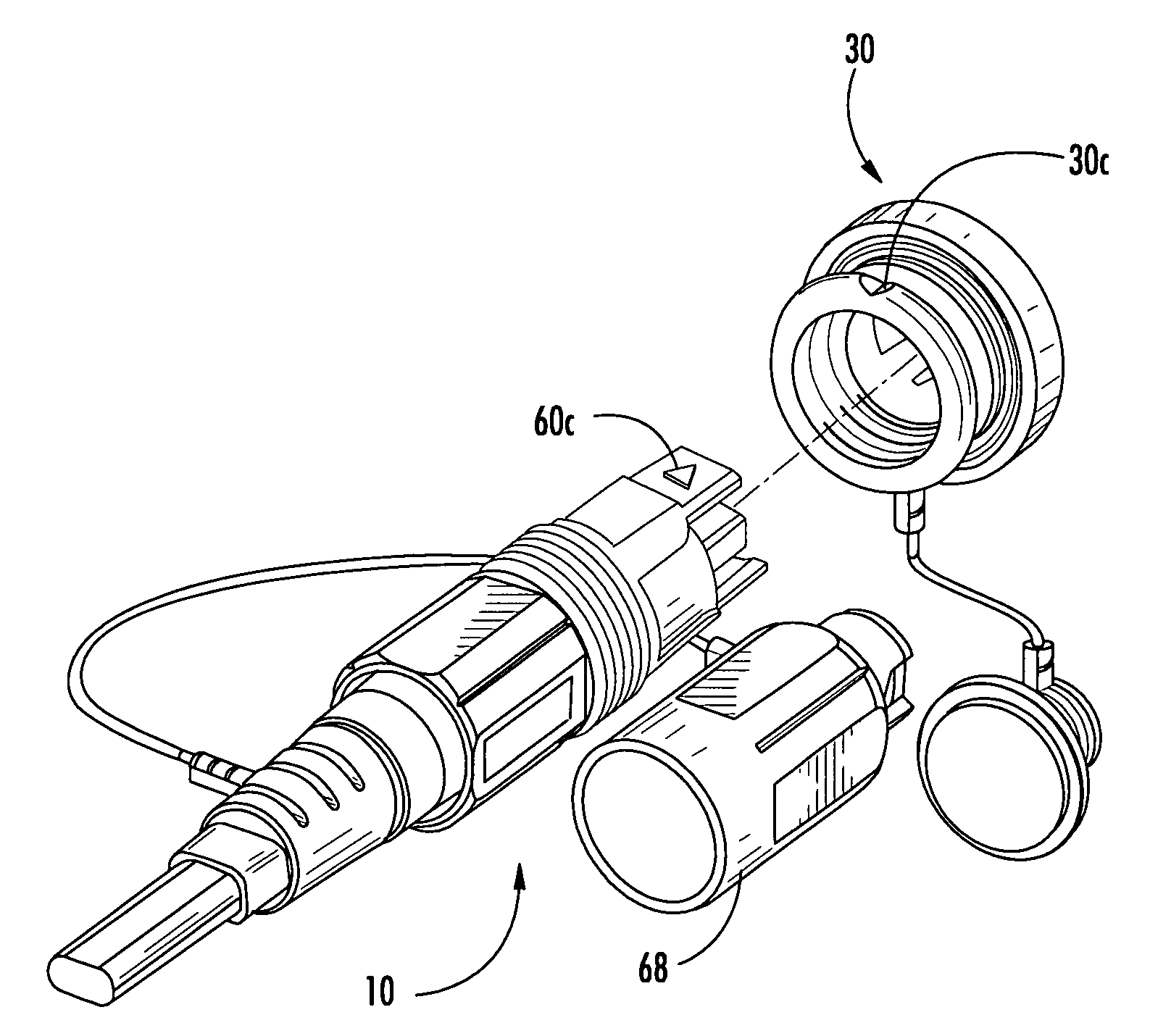
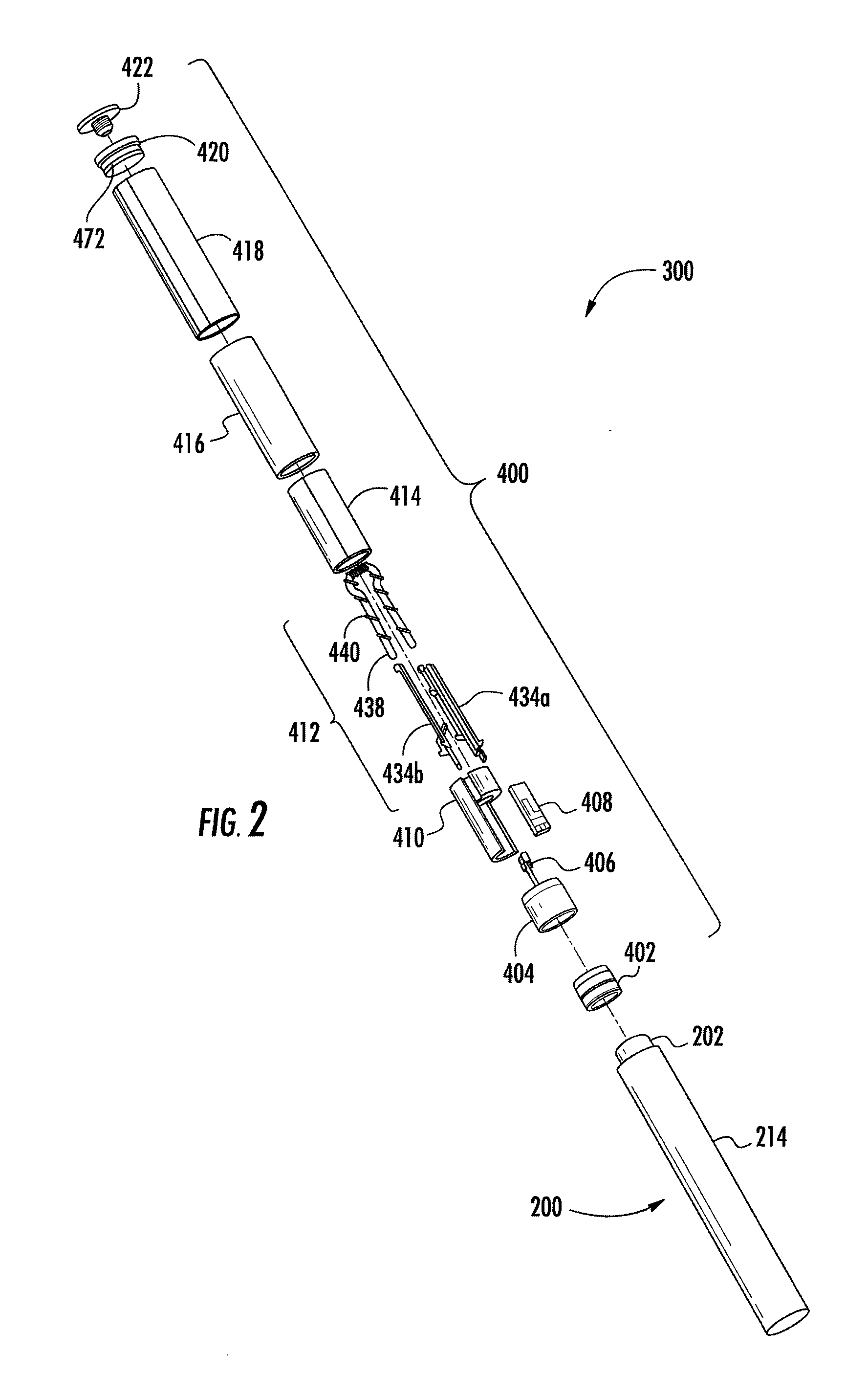
Cordless Hand-Held Ultrasonic Cautery Cutting Device
ActiveUS20090143805A1Alter functionAlter performanceUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingHand heldWaveguide
A disposable ultrasonic surgical handle connectable to an ultrasonic waveguide, a battery, and an ultrasonic-movement-generator assembly includes a first handle body portion defining therein an aseptically sealable battery-holding compartment shaped to receive the battery therein, a second handle body portion connected to the first handle body portion, and an electrical couple. The second handle body portion has a waveguide attachment dock exposed to the environment and an ultrasonic-movement-generator assembly dock exposed to the environment and shaped to connect the ultrasonic waveguide in the waveguide attachment dock to the ultrasonic-movement-generator assembly through the second handle body portion. The electrical couple is operable to connect a battery within the battery-holding compartment to the ultrasonic-movement-generator-assembly when the ultrasonic-movement-generator assembly is docked at the ultrasonic-movement-generator assembly dock.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
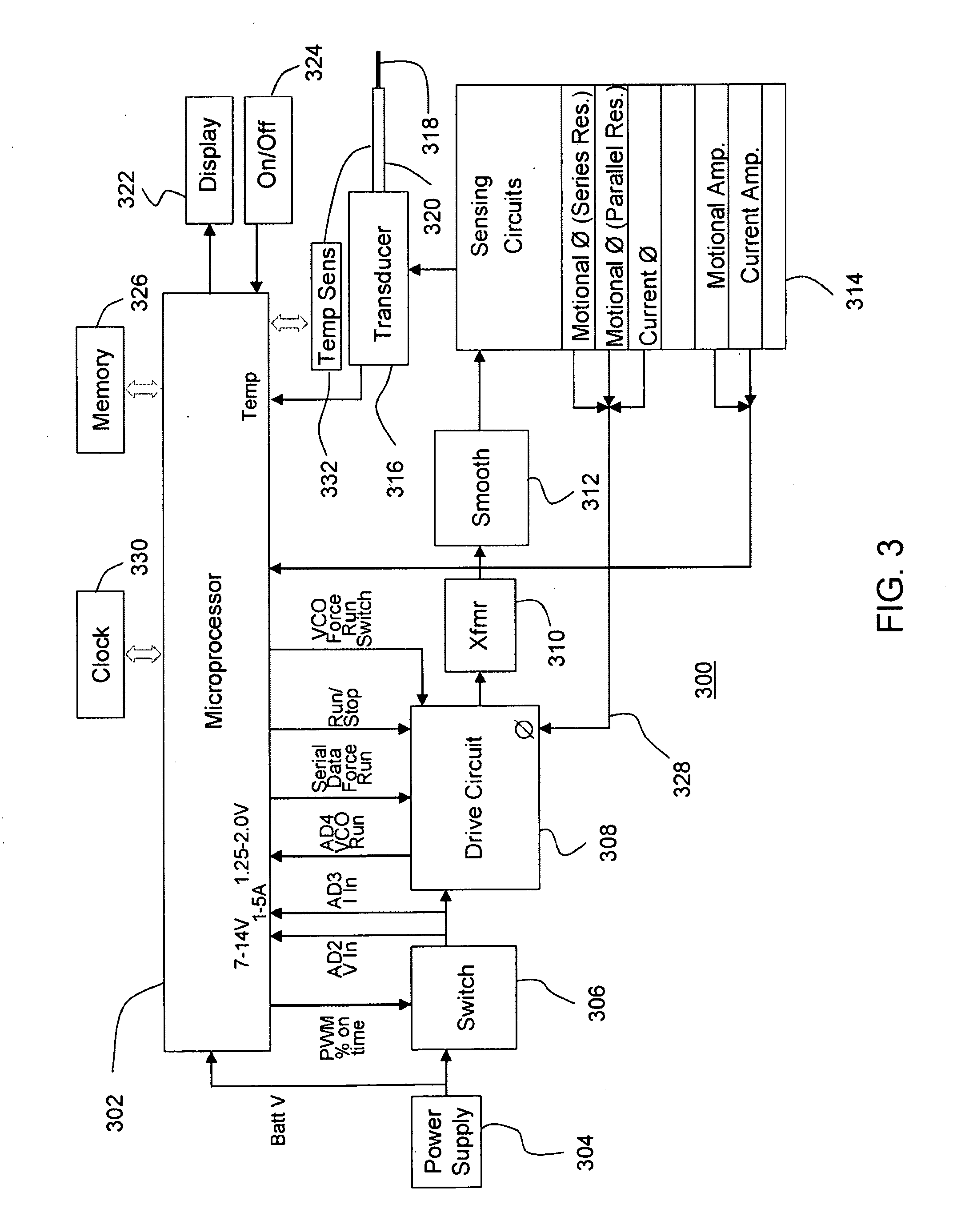
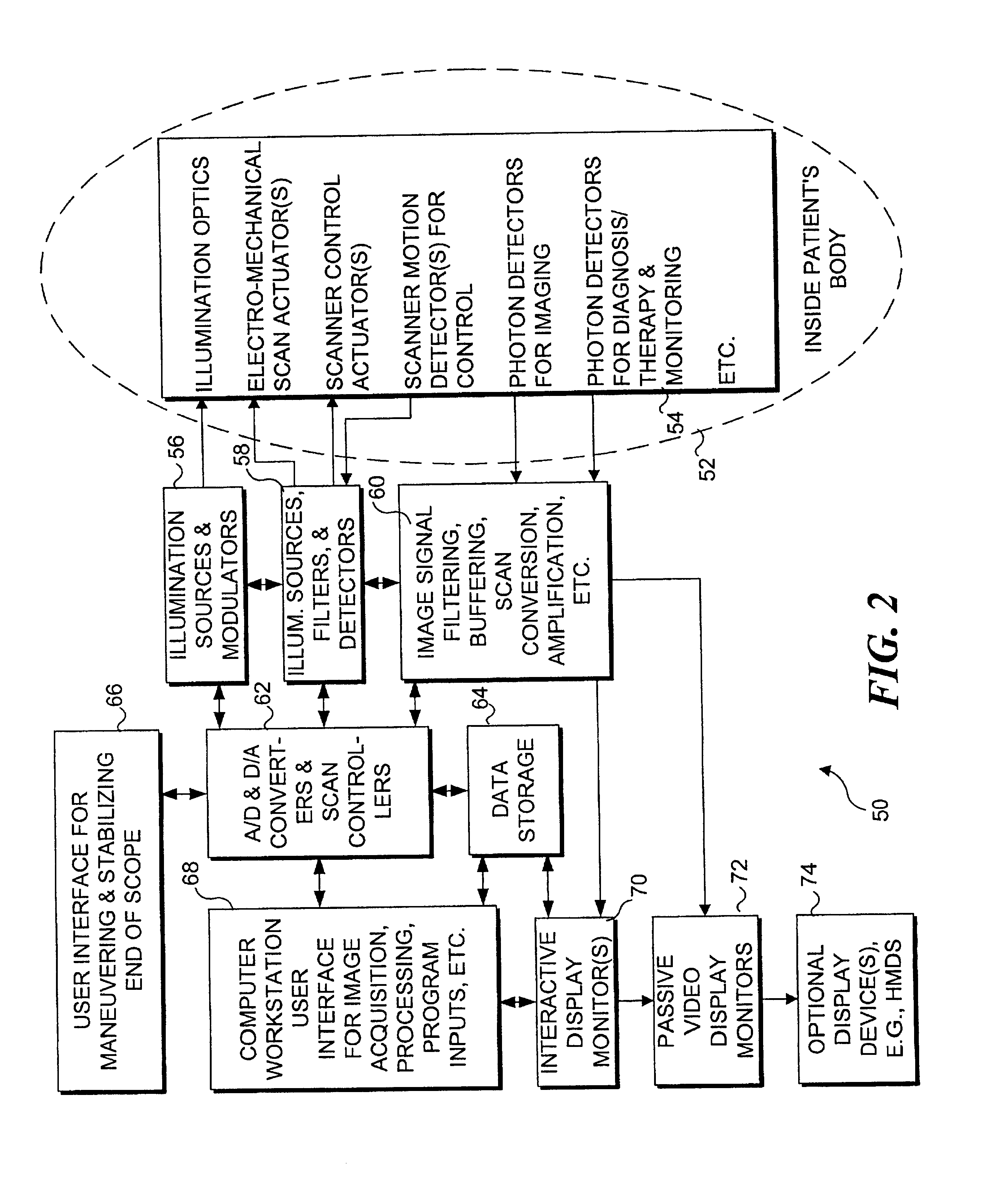
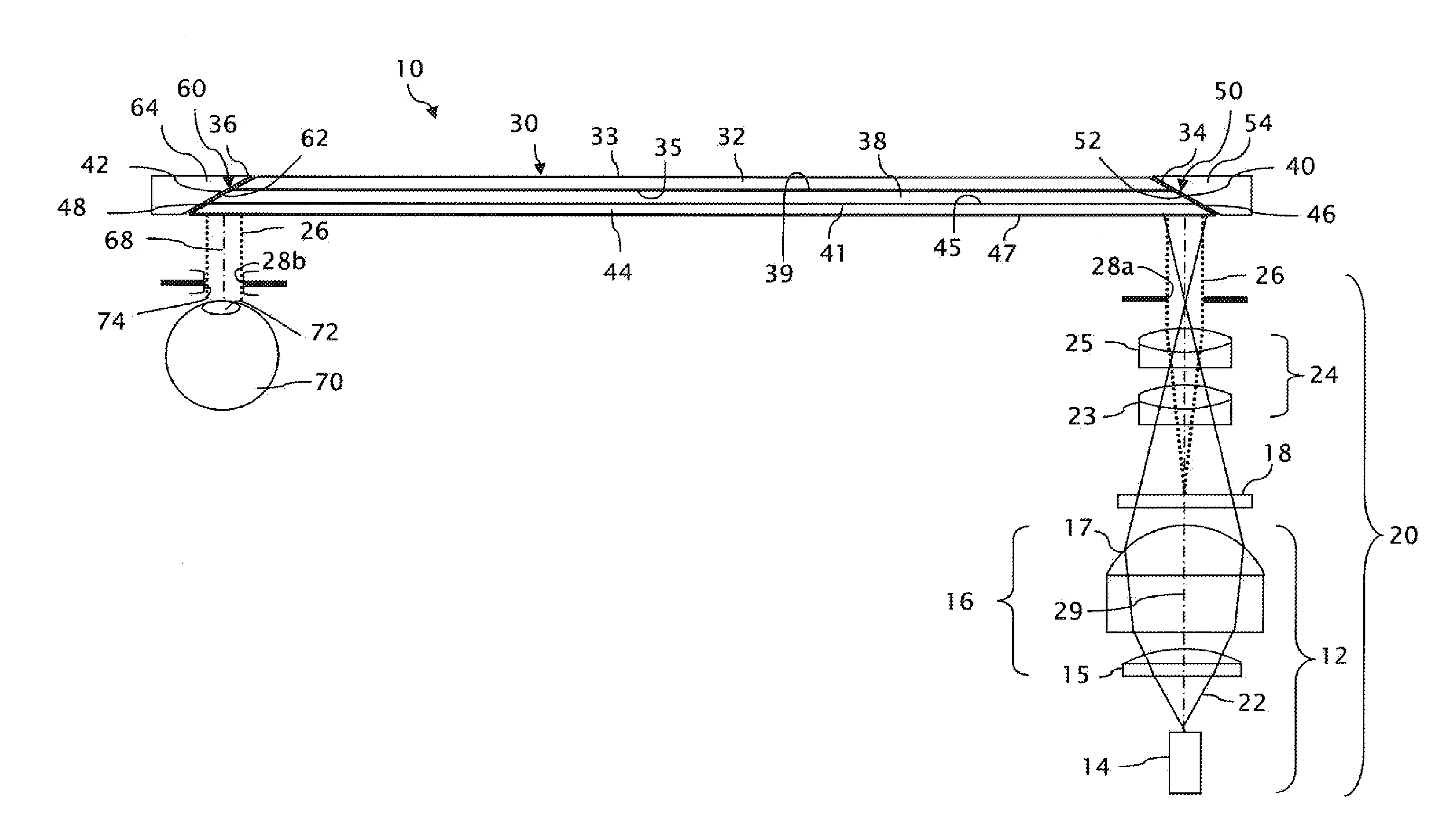
Medical imaging, diagnosis, and therapy using a scanning single optical fiber system
InactiveUS6975898B2High resolutionEasy to viewEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsFlexible endoscopyHigh resolution imaging
An integrated endoscopic image acquisition and therapeutic delivery system for use in minimally invasive medical procedures (MIMPs). The system uses directed and scanned optical illumination provided by a scanning optical fiber or light waveguide that is driven by a piezoelectric or other electromechanical actuator included at a distal end of an integrated imaging and diagnostic / therapeutic instrument. The directed illumination provides high resolution imaging, at a wide field of view (FOV), and in full color that matches or excels the images produced by conventional flexible endoscopes. When using scanned optical illumination, the size and number of the photon detectors do not limit the resolution and number of pixels of the resulting image. Additional features include enhancement of topographical features, stereoscopic viewing, and accurate measurement of feature sizes of a region of interest in a patient's body that facilitate providing diagnosis, monitoring, and / or therapy with the instrument.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
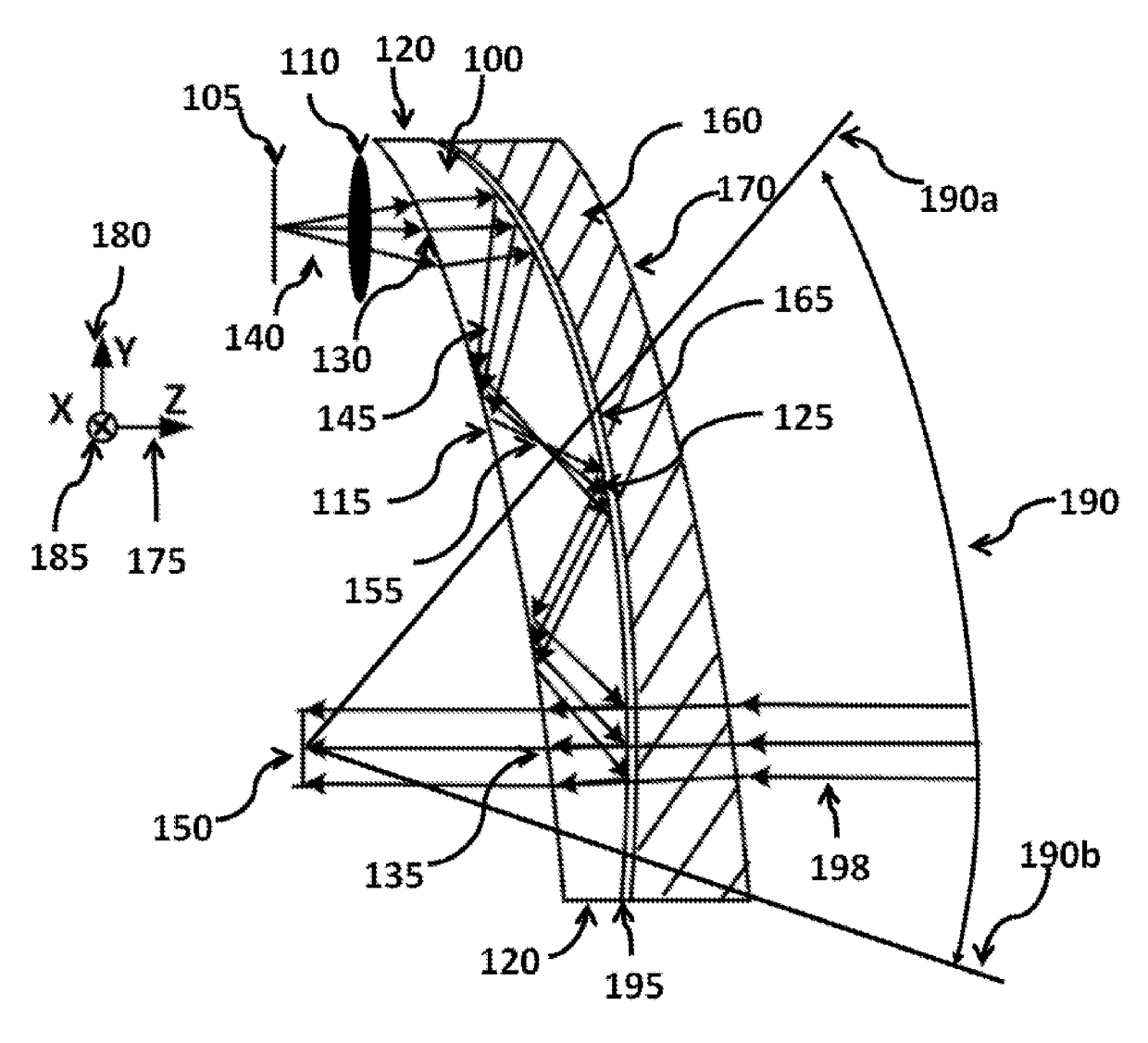
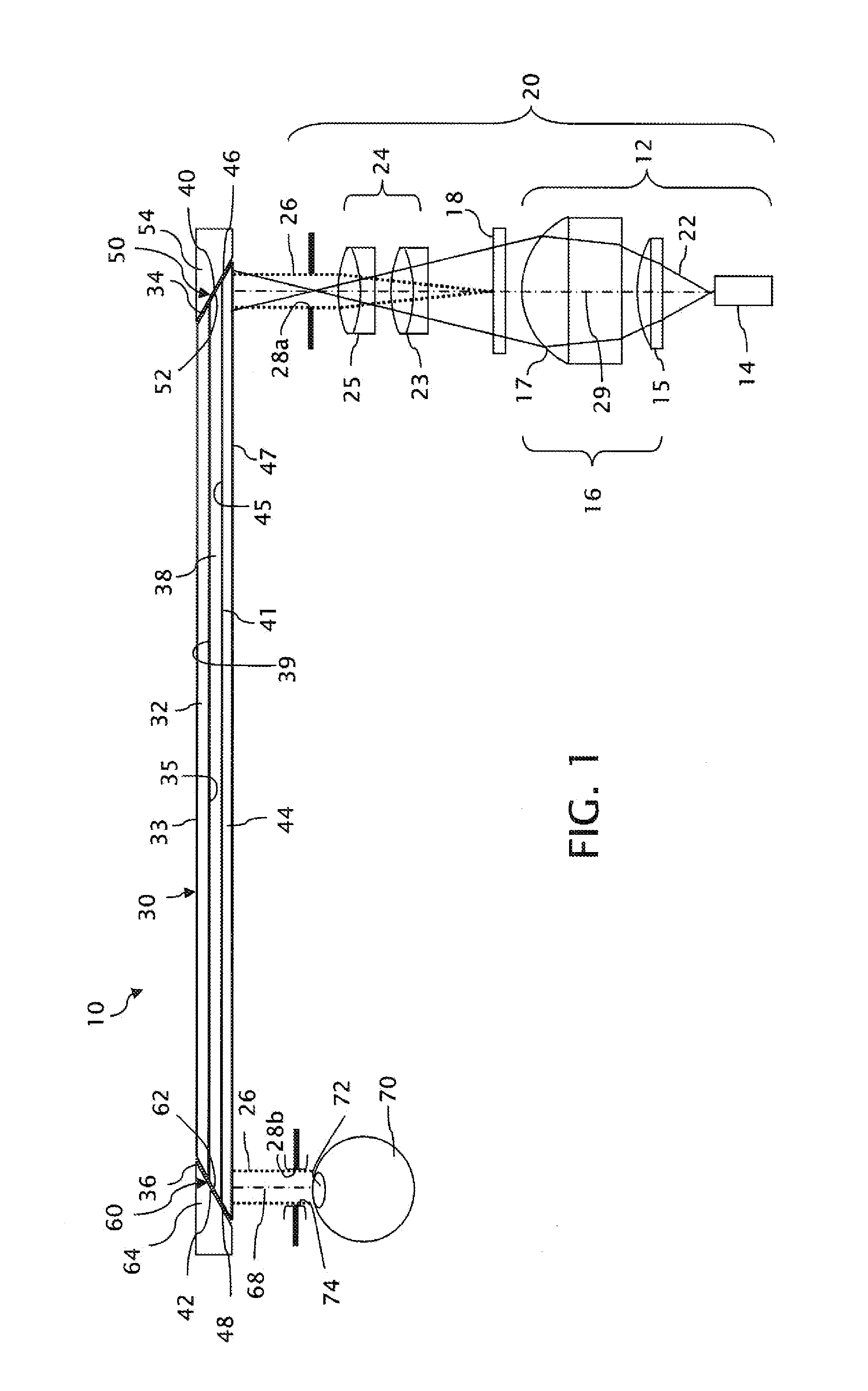
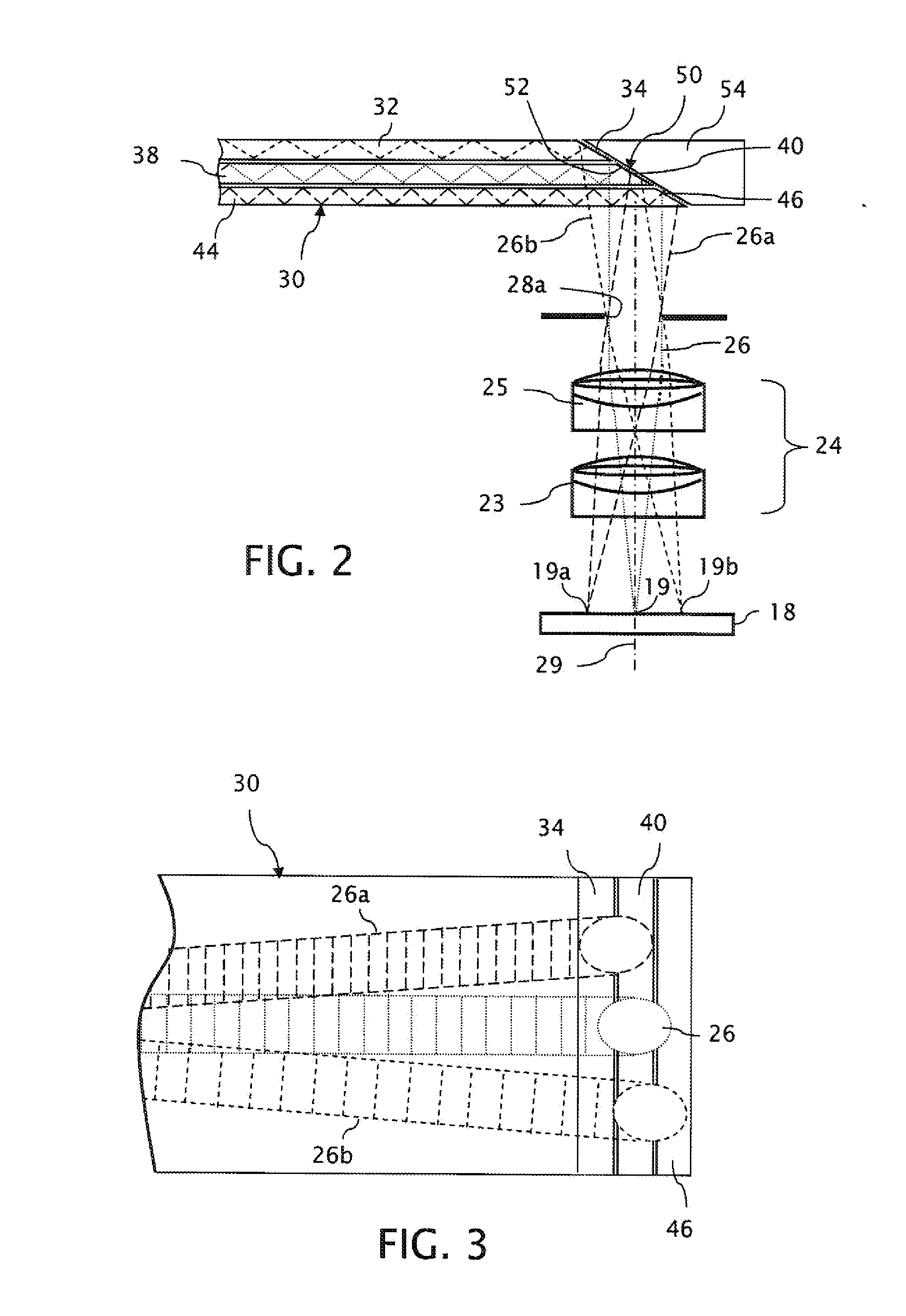
Ergonomic Head Mounted Display Device And Optical System
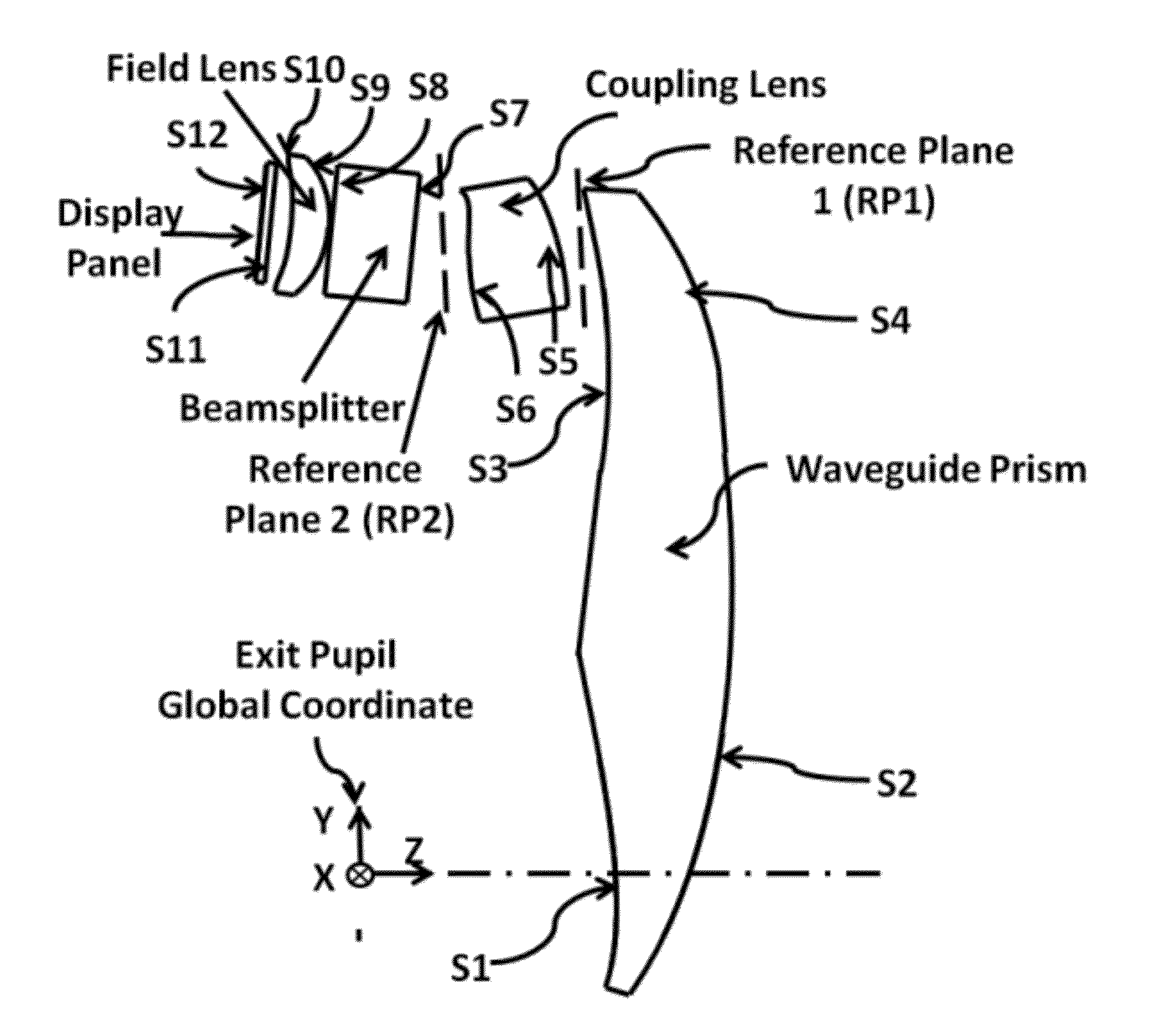
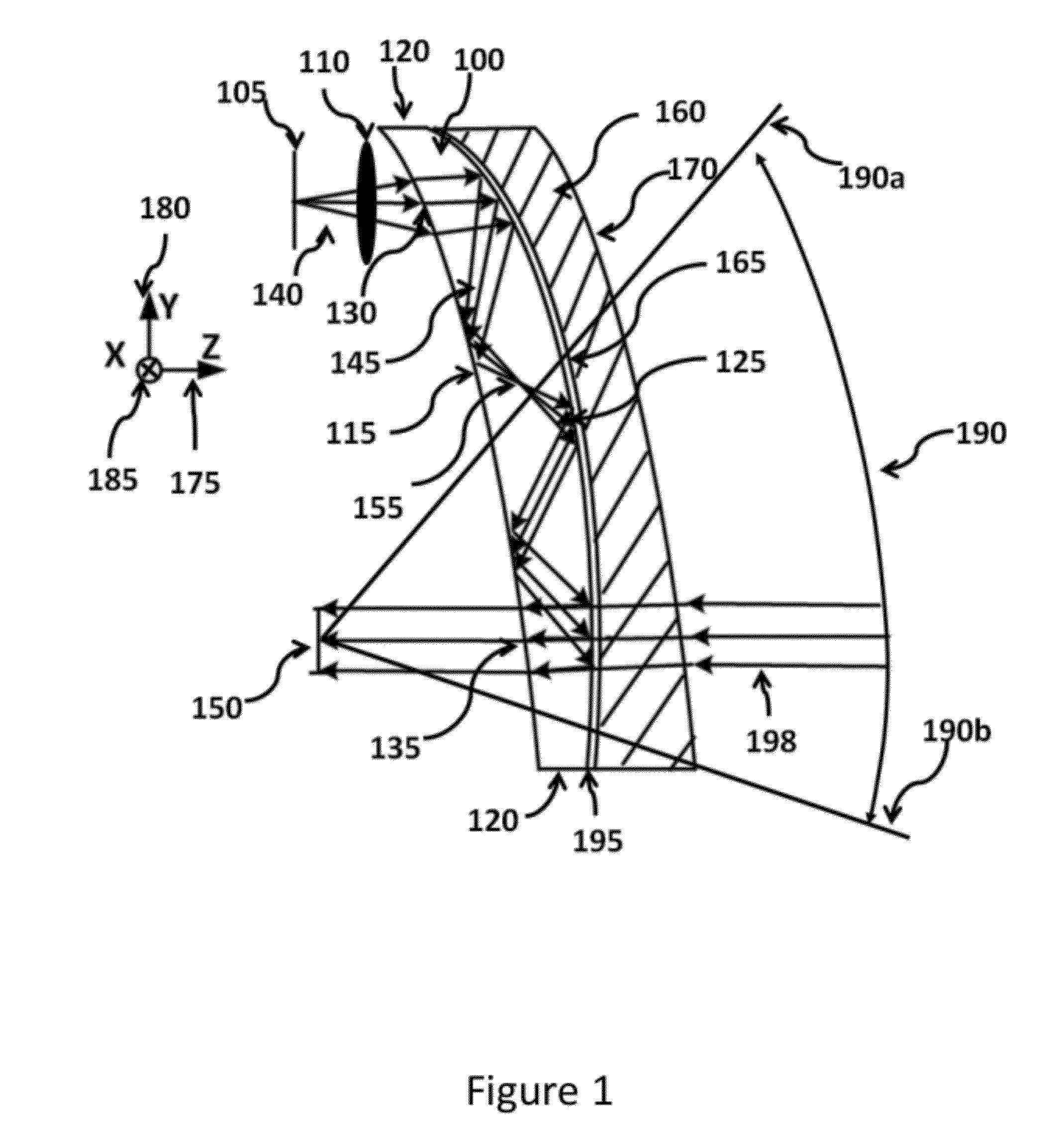
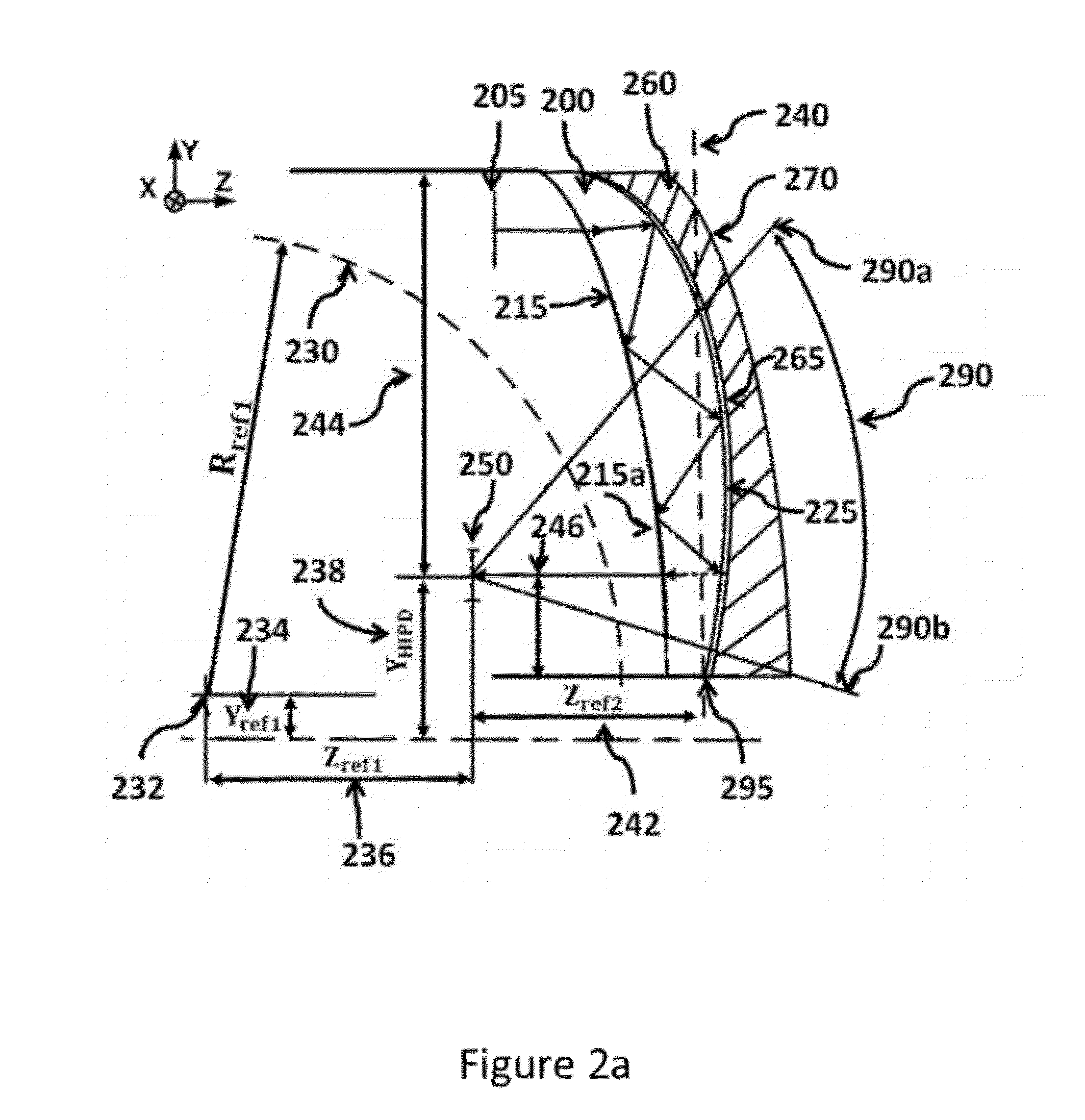
ActiveUS20120162549A1Good optical performanceWide field of viewPolarising elementsPlanar/plate-like light guidesDisplay deviceSee-through display
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
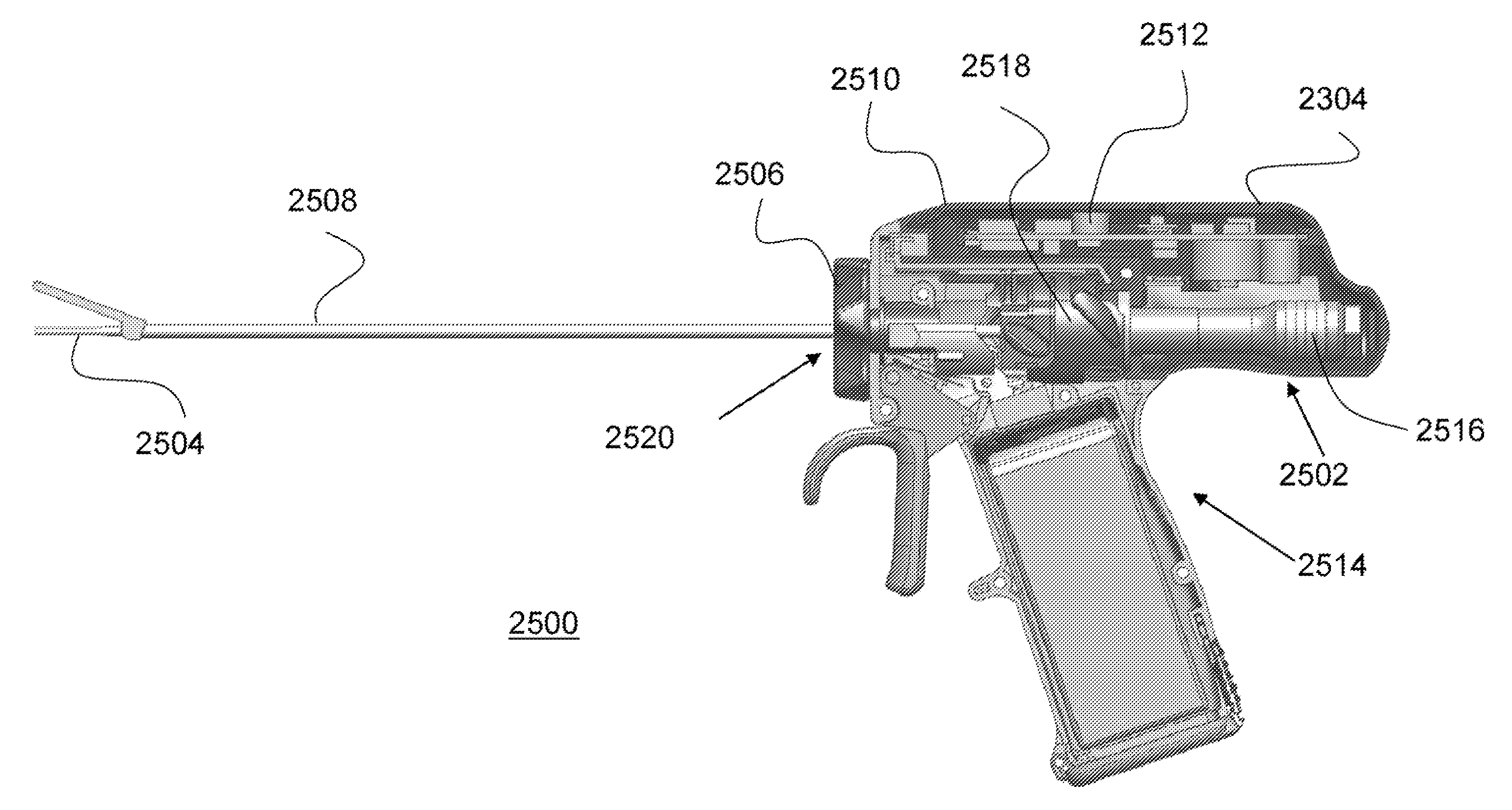
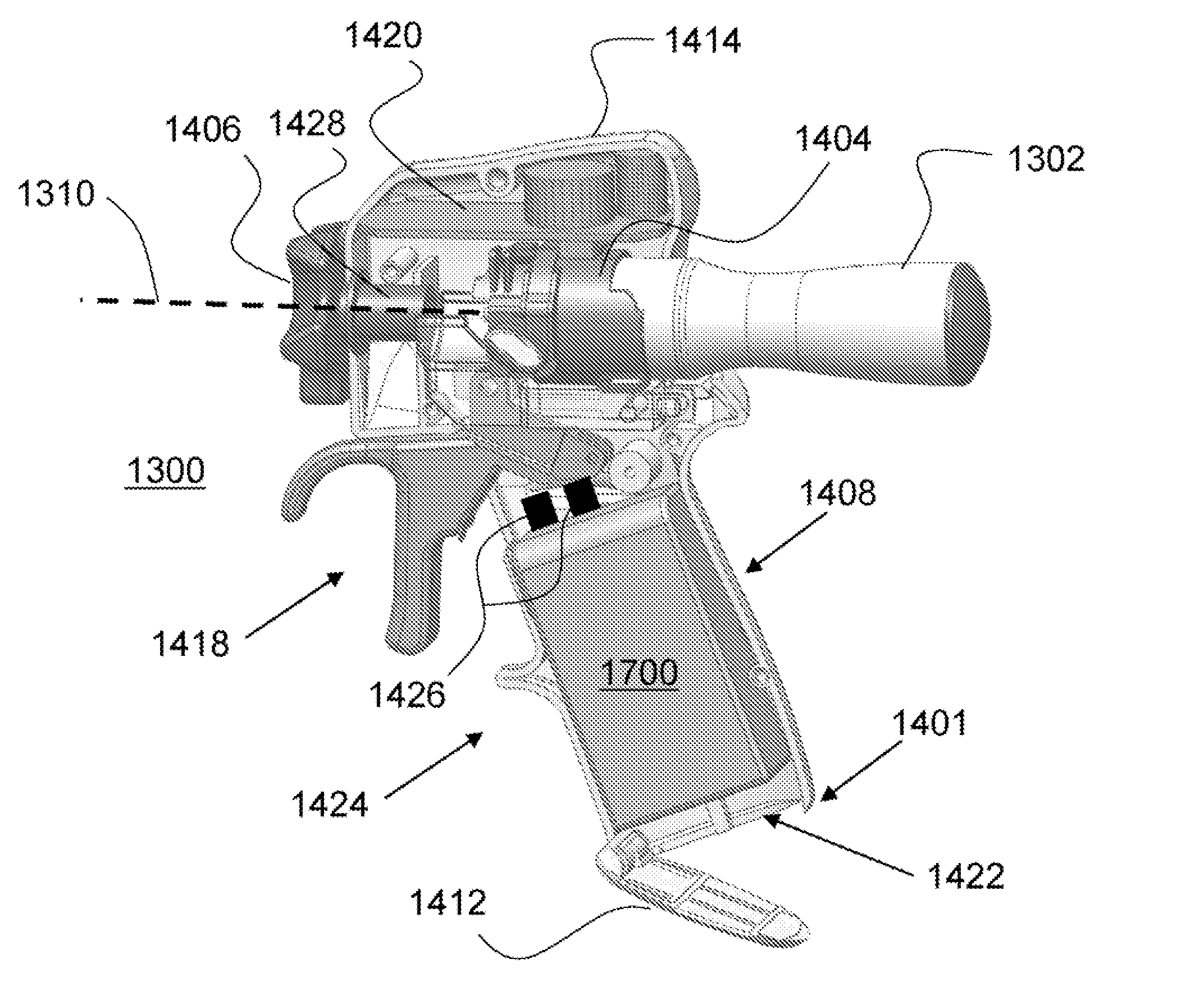
Articulating ultrasonic surgical shears
An ultrasonic surgical instrument is described which incorporates an articulating shearing end-effector. The instrument comprises an ultrasonic transducer, an ultrasonically activated end-effector, and a substantially solid ultrasonic waveguide that connects the ultrasonic transducer to the end-effector. The waveguide comprises a transmission section extending from the transducer to a fixed node, and an articulation section extending from the fixed node to a pivoting node. The end-effector includes a bifurcated waveguide segment. A handle is adapted to hold the transducer. An outer sheath extends from the handle to the end-effector and surrounds the waveguide. An actuation trigger is rotatably positioned on the handle, and an actuation arm extends from a distal end of the actuation trigger to the pivoting node.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
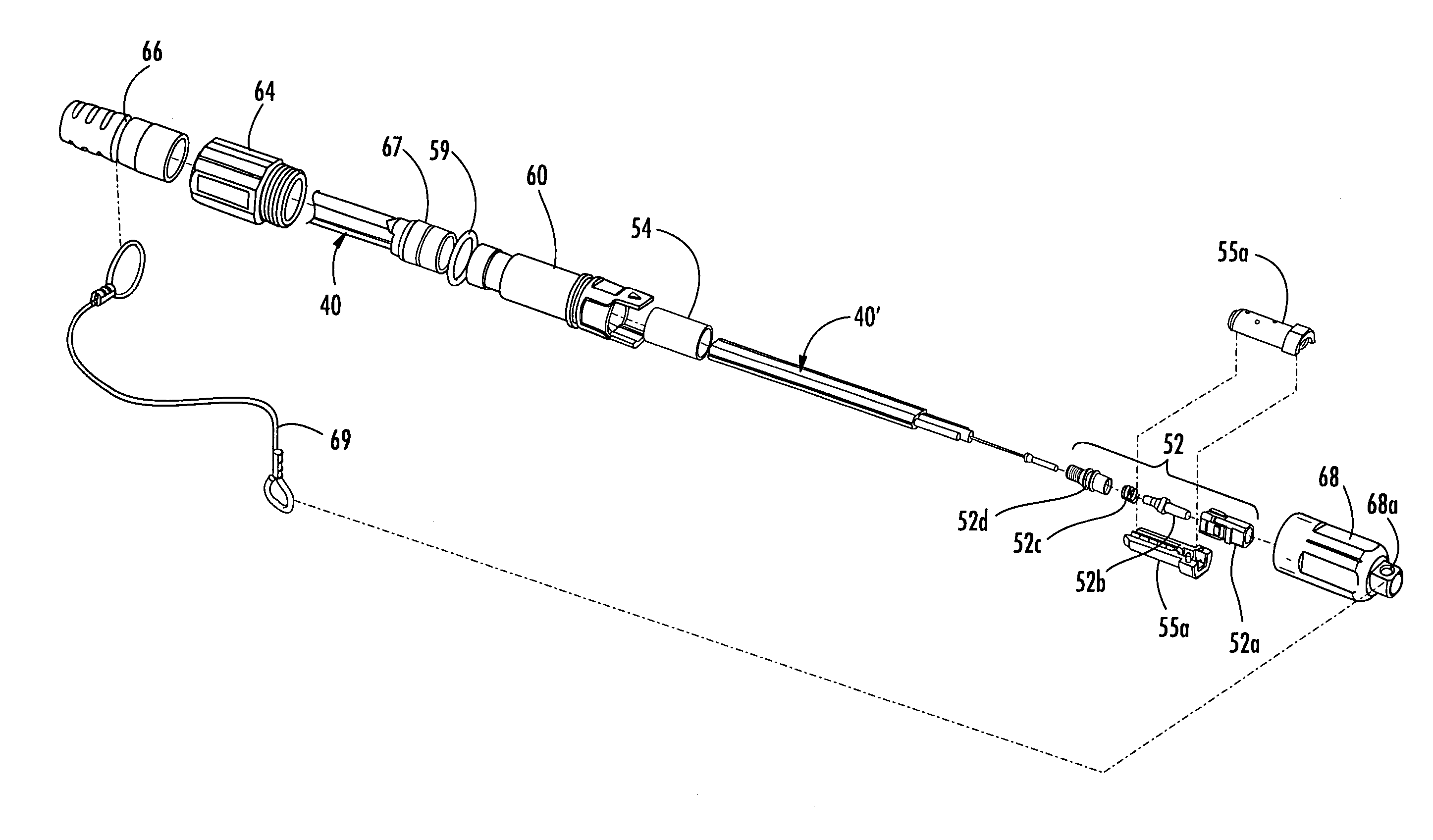
Preconnectorized fiber optic drop cables and assemblies
A preconnectorized outdoor cable streamlines the deployment of optical waveguides into the last mile of a optical network. The preconnectorized outdoor cable includes a cable and at least one plug connector. The plug connector is attached to a first end of the cable, thereby connectorizing at least one optical waveguide. The cable has at least one optical waveguide, at least one tensile element, and a cable jacket. Various cable designs such as figure-eight or flat cables may be used with the plug connector. In preferred embodiments, the plug connector includes a crimp assembly having a crimp housing and a crimp band. The crimp housing has two half-shells being held together by the crimp band for securing the at least one tensile element. When fully assembled, the crimp housing fits into a shroud of the preconnectorized cable. The shroud aides in mating the preconnectorized cable with a complimentary receptacle.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Ergonomic head mounted display device and optical system
ActiveUS9348143B2Wide field of viewGood optical performancePolarising elementsPlanar/plate-like light guidesEyewearDisplay device
This invention concerns an ergonomic optical see-through head mounted display device with an eyeglass appearance. The see-through head-mounted display device consists of a transparent, freeform waveguide prism for viewing a displayed virtual image, a see-through compensation lens for enabling proper viewing of a real-world scene when combined together with the prism, and a miniature image display unit for supplying display content. The freeform waveguide prism, containing multiple freeform refractive and reflective surfaces, guides light originated from the miniature display unit toward a user's pupil and enables a user to view a magnified image of the displayed content. A see-through compensation lens, containing multiple freeform refractive surfaces, enables proper viewing of the surrounding environment, through the combined waveguide and lens. The waveguide prism and the see-through compensation lens are properly designed to ergonomically fit human heads enabling a wraparound design of a lightweight, compact, and see-through display system.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Fiber optic drop cables and preconnectorized assemblies having toning portions
A preconnectorized outdoor cable streamlines the deployment of optical waveguides into the last mile of an optical network. The preconnectorized outdoor cable includes a cable and at least one plug connector. The plug connector is attached to a first end of the cable, thereby connectorizing at least one optical waveguide. The cable has at least one optical waveguide, at least one tensile element, and a cable jacket. Various cable designs such as figure-eight or flat cables may be used with the plug connector. In preferred embodiments, the plug connector includes a crimp assembly having a crimp housing and a crimp band. The crimp housing has two half-shells being held together by the crimp band for securing the at least one tensile element. When fully assembled, the crimp housing fits into a shroud of the preconnectorized cable. The shroud aides in mating the preconnectorized cable with a complimentary receptacle.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
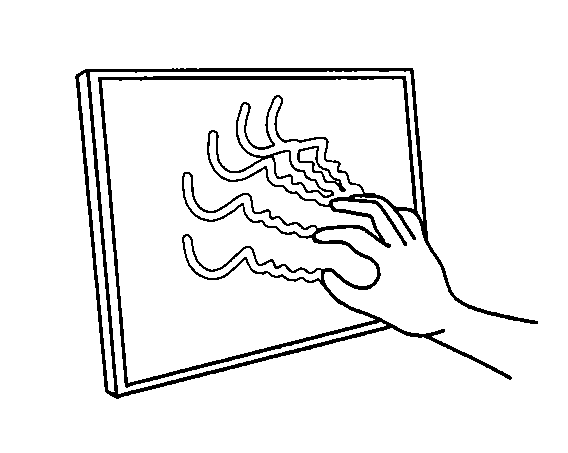
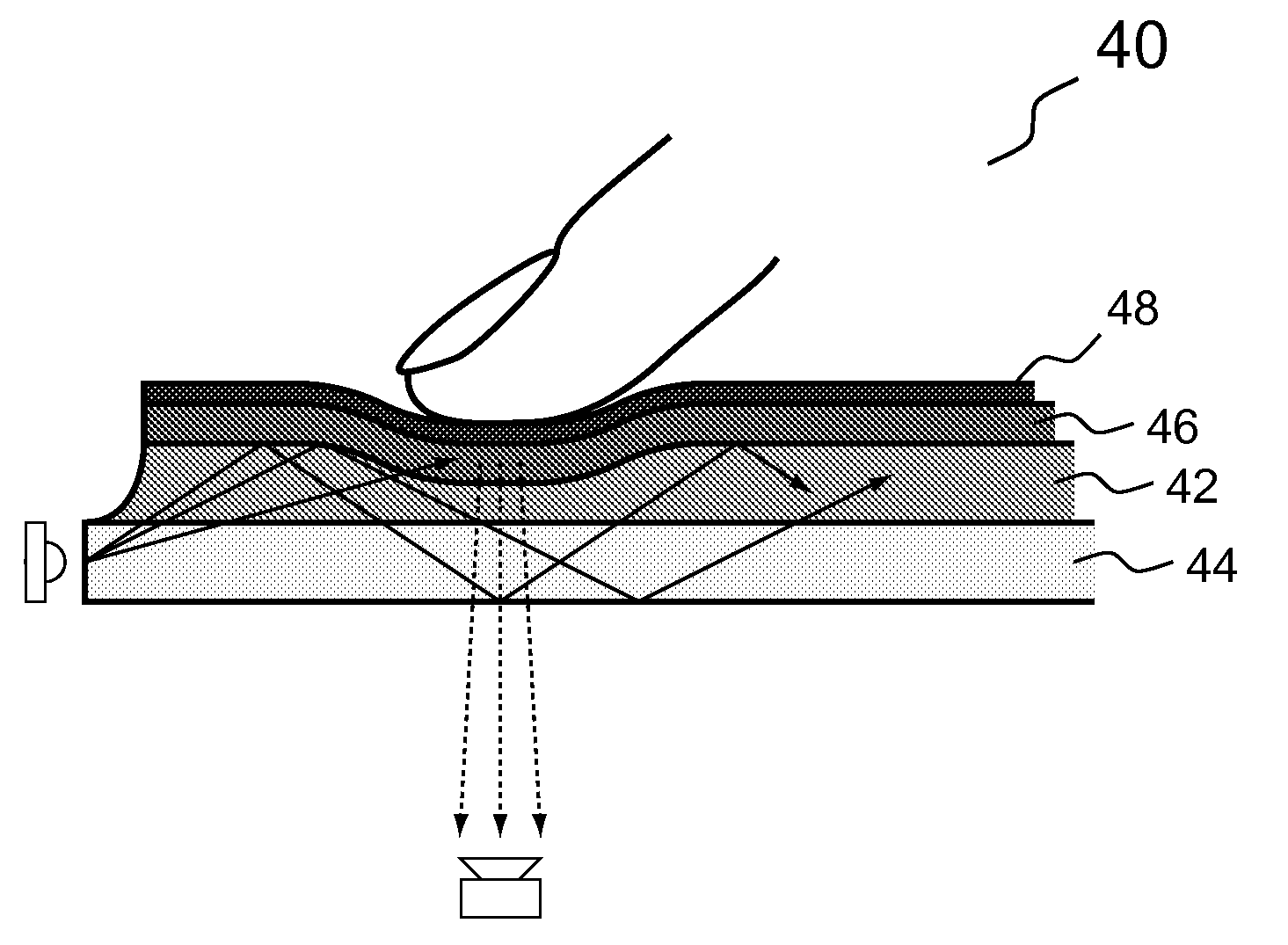
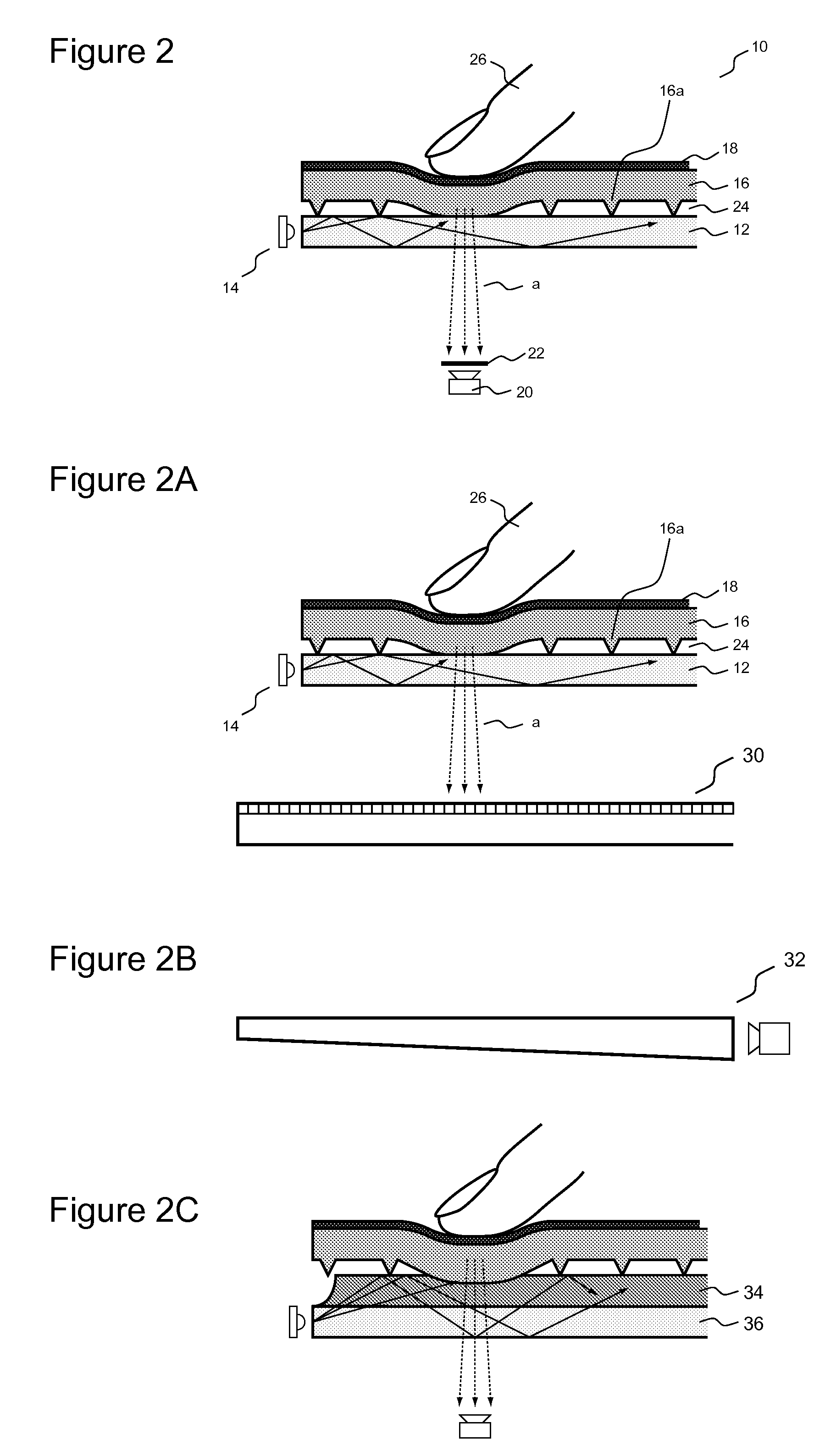
Multi-touch sensing display through frustrated total internal reflection
InactiveUS20080029691A1Cut surfaceReduce glareBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansMulti inputTotal internal reflection
High-resolution, scalable multi-touch sensing display systems and processes based on frustrated total internal reflection employ an optical waveguide that receives light, such as infrared light, that undergoes total internal reflection and an imaging sensor that detects light that escapes the optical waveguide caused by frustration of the total internal reflection due to contact by a user. The optical waveguide may be fitted with a compliant surface overlay to greatly improve sensing performance, minimize the affect of contaminants on and damage to the contact surface, to generally extend system life and to provide other benefits. The systems and processes provide true multi-touch (multi-input) and high-spatial and temporal resolution capability due to the continuous imaging of the frustrated total internal reflection that escapes the entire optical waveguide. Among other features and benefits, the systems and processes are scalable to large installations and are well suited for use with rear-projection and other display devices.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
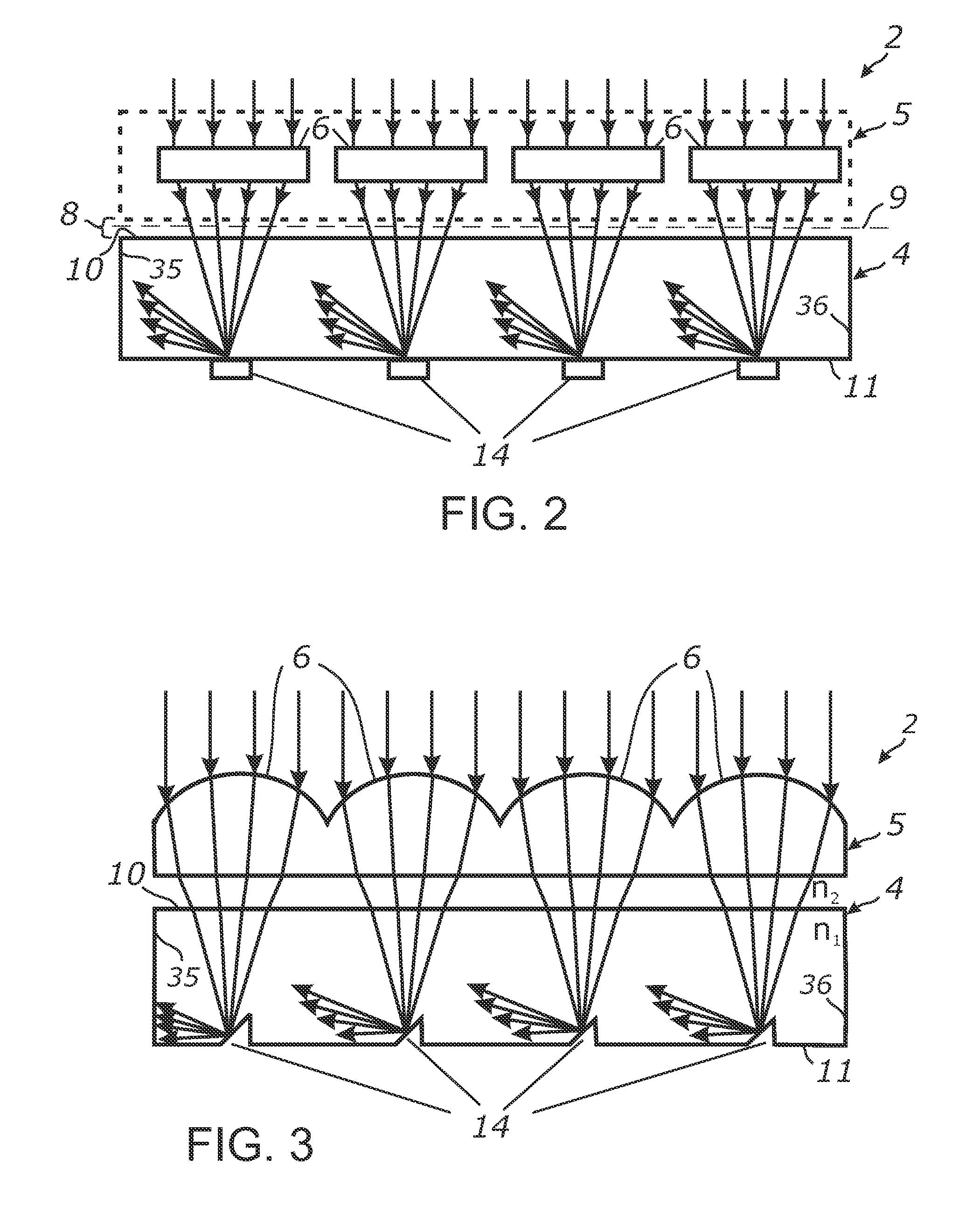
Light collection and illumination systems employing planar waveguide
ActiveUS20100278480A1Easy to transportEasy to harvestProjectorsCoupling light guidesTotal internal reflectionLighting system
An apparatus for distributing light from a waveguide through a collimating array, or collecting light over a given area into a waveguide. Light received within a waveguide is propagated transmissively and retained by total internal reflection, except in response to impinging upon deflector elements which sufficiently redirect the light to escape the waveguide into a collimator array that aligns and distributes the light. In a light collector, a collection array collects and collimates the received light and directs it at the surface of a waveguide, within which deflectors properly positioned in relation to each collector of the collector array, deflect the angle of the light so that it propagates through the waveguide in response to total internal reflection. The apparatus can be fabricated into an efficient and compact form.
Owner:S V V TECH INNOVATIONS
Ultrasonic shear with asymmetrical motion
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Ergonomic head mounted display device and optical system
ActiveUS9740006B2Good optical performancePrecision injectionCathode-ray tube indicatorsTelevision systemsFree formDisplay device
Optical systems such as image display systems include a freeform optical waveguide prism and a freeform compensation lens spaced therefrom by a gap of air or index cement. The compensation lens corrects for aberrations which the optical waveguide prism will introduce in light or images from an ambient real-world environment. The optical waveguide prism receives actively projected images at an entry location, and emits the projected images at an exit location after internally reflecting the images along an optical path therein. The image display system may include an image source and coupling optics. The approach permits design of an optical viewing device, for example in optical see-through HMDs, achieving an eyeglass-form appearance and a wide see-through field of view (FOV).
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
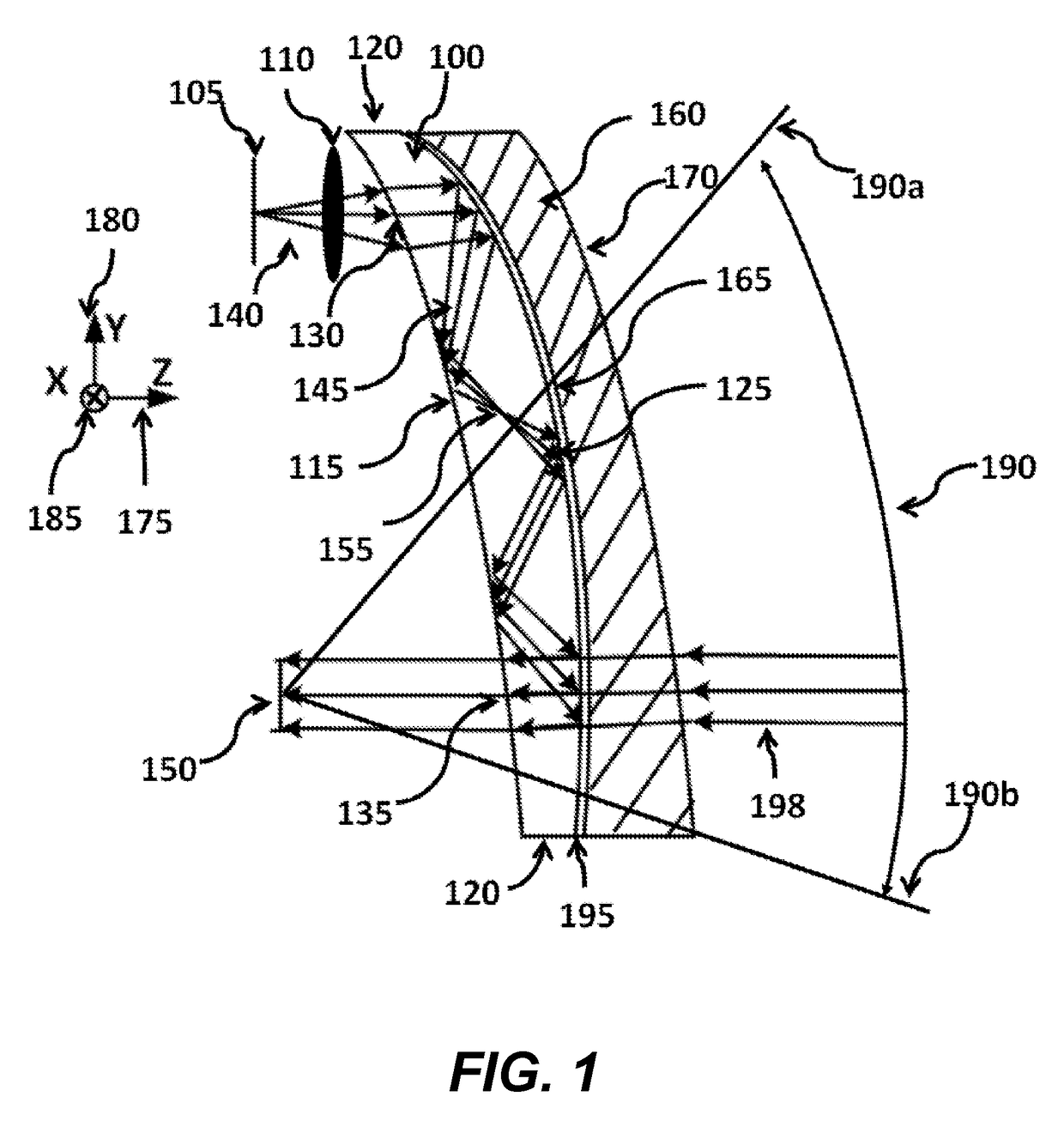
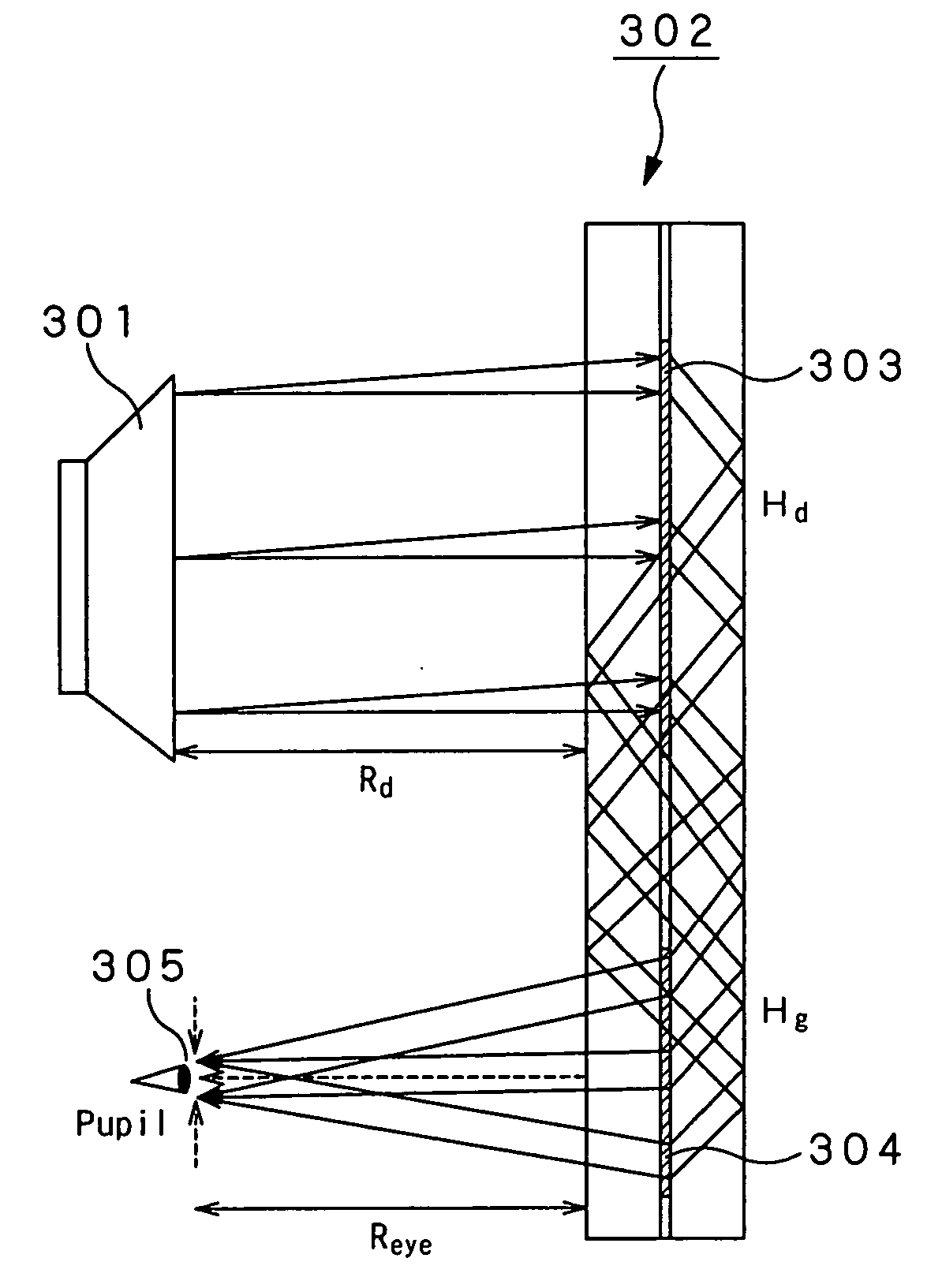
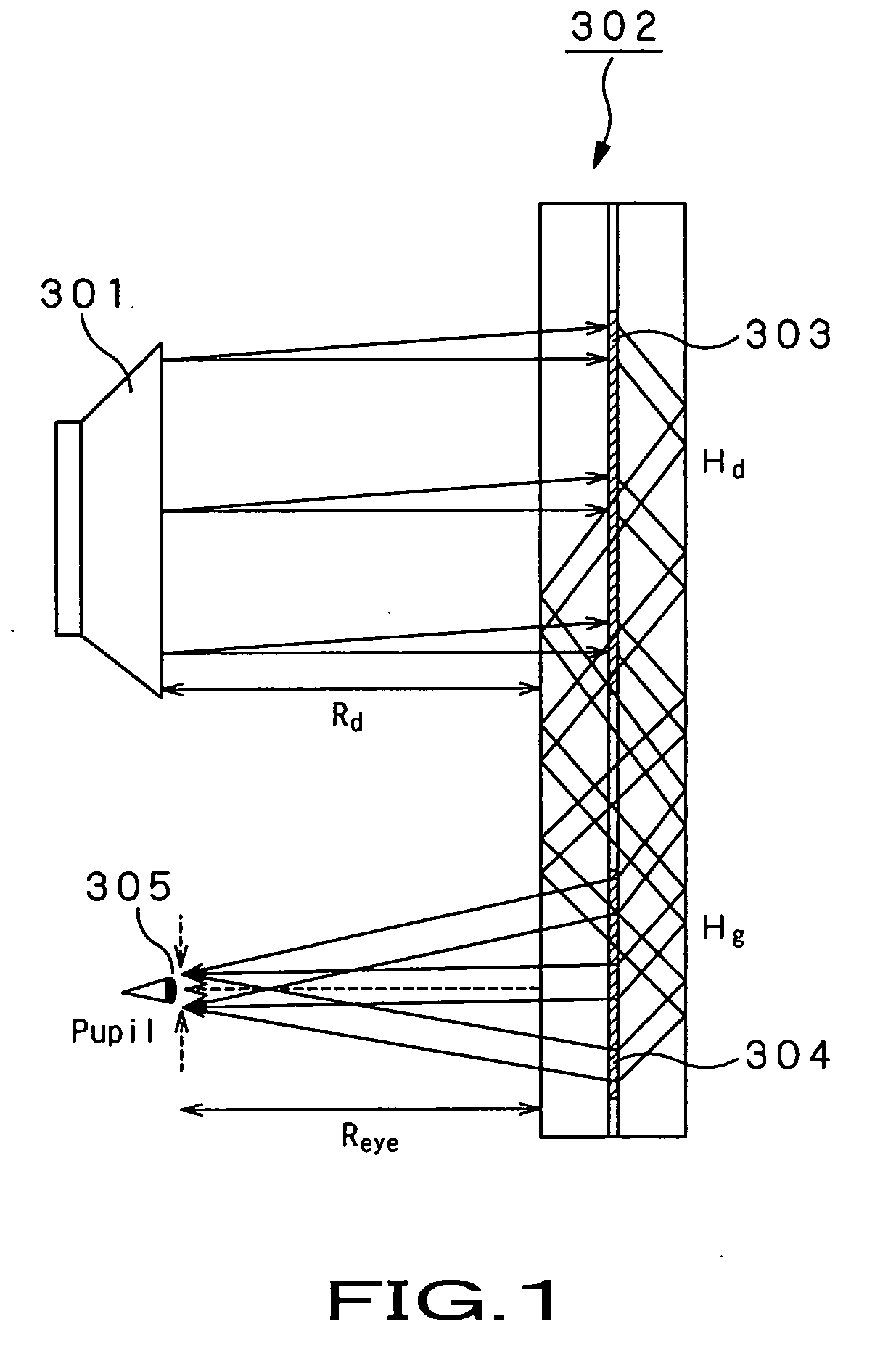
Prismatic multiple waveguide for near-eye display
ActiveUS20120062998A1Compensation effectConvenient and accurateOptical articlesLaminationDisplay devicePupil
A near-eye display includes a compound waveguide for presenting viewers with virtual images visible within an eyebox at a limited relief distance from the compound waveguide. The compound waveguide is assembled from a plurality of waveguides that are at least partially optically isolated for conveying different portions of the virtual image. An input couple injects the different portions of the virtual image into predetermined combinations of the waveguides, and an output coupling ejects the different portions of the virtual image from the waveguides toward the eyebox in a form that at least partially constructs a pupil within the eyebox.
Owner:VUZIX
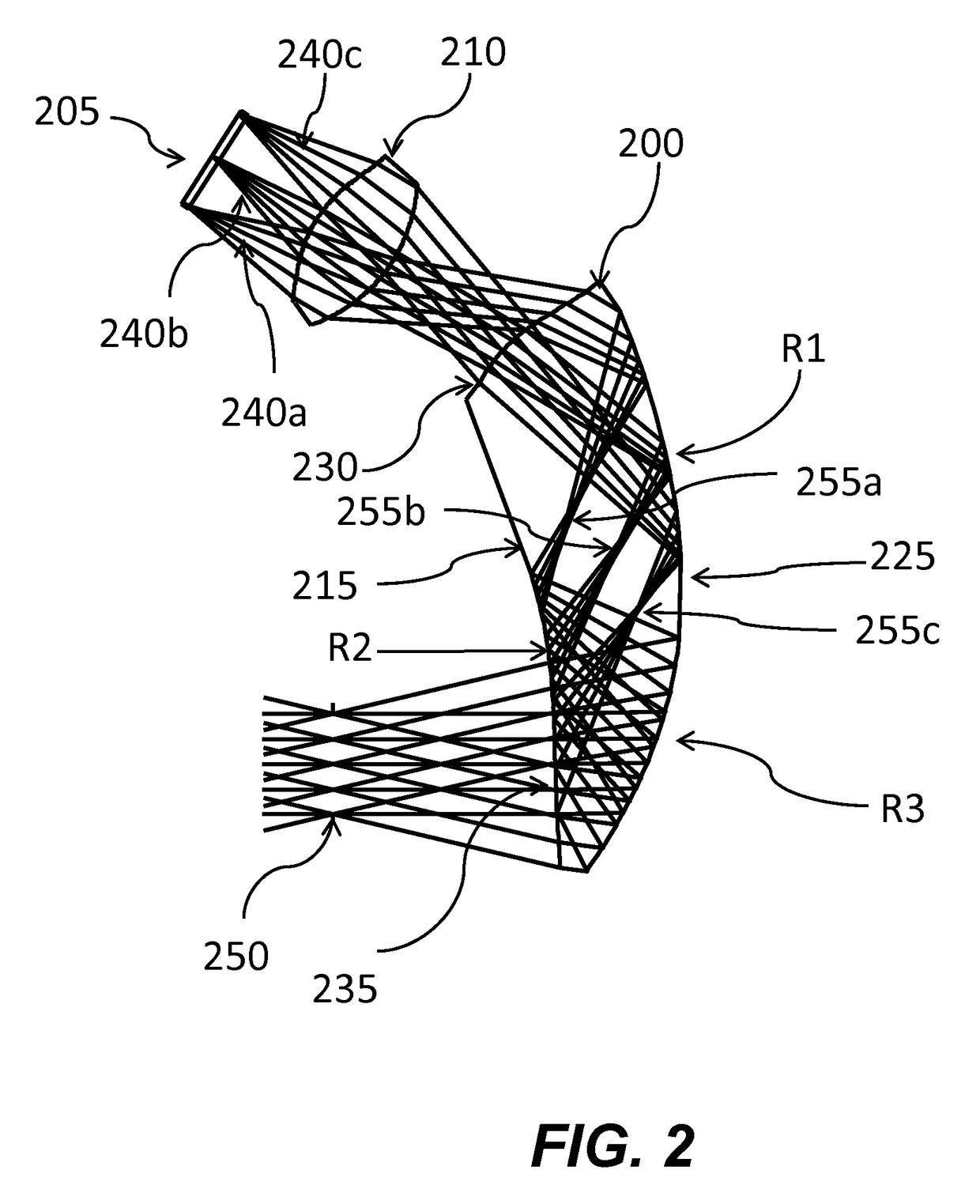
Optical device and virtual image display device
ActiveUS20060228073A1Improve imaging resolutionReduce aberrationDiffraction gratingsPlanar/plate-like light guidesGratingDisplay device
A virtual image display device is provided which displays a two-dimensional image for viewing a virtual image in a magnified form by a virtual optical system. The virtual image display device includes an optical waveguide (13) to guide, by internal total reflection, parallel pencil groups meeting a condition of internal total reflection, a first reflection volume hologram grating (14) to diffract and reflect the parallel pencil groups incident upon the optical waveguide from outside and traveling in different directions as they are so as to meet the condition of internal total reflection inside the optical waveguide and a second reflection volume hologram grating (15) to project the parallel pencil groups guided by internal total reflection inside the optical waveguide as they are from the optical waveguide by diffraction and reflection thereof so as to depart from the condition of internal total reflection inside the optical waveguide. Some of the parallel pencil groups guided through the optical waveguide being totally reflected different numbers of times for a period from external incidence upon the optical waveguide until outgoing from the optical waveguide.
Owner:SONY CORP
Aperture matched polyrod antenna
InactiveUS20080252541A1Minimizes and reduces end reflection and phase variationMinimizing and reducing diameterAdditive manufacturing apparatusWaveguide type devicesGaussian beamLight beam
A dielectric polyrod having at least one tapered section, where a section exposed outside of the waveguide is tapered a long a curve that depends on the dielectric constant of the material used. The invention also relates to an aperture matched polyrod antenna which includes the same and an inductive tuning element used to achieve wideband impedance match and to create a Gaussian beam in the radiating near field of the antenna, suitable to mimic a small region plane wave.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Semiconductor components, in particular photodetectors, light emitting diodes, optical modulators and waveguides with multilayer structures grown on silicon substrates
InactiveUS6403975B1Cost advantagePromote absorptionNanoopticsNon-linear opticsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
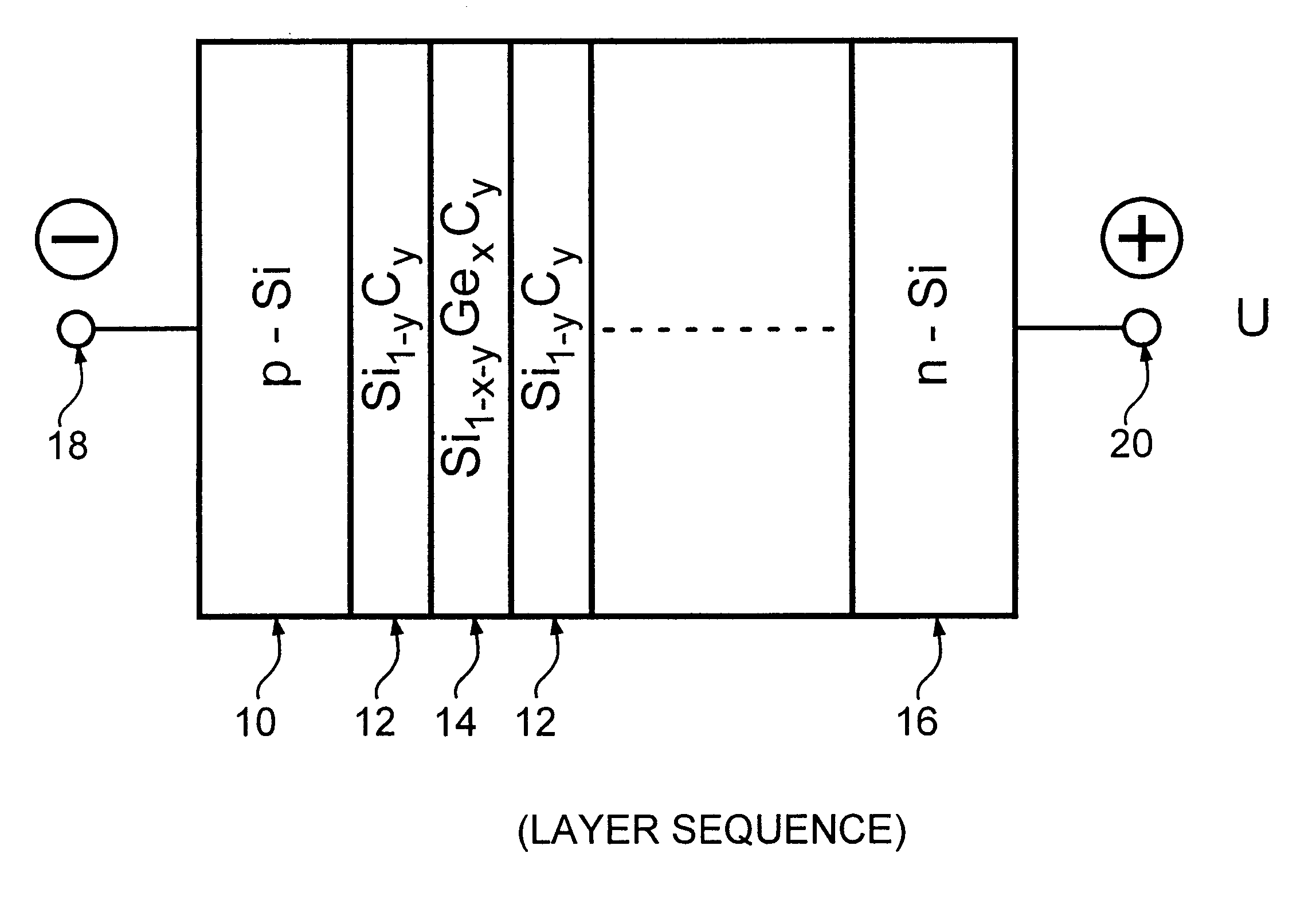
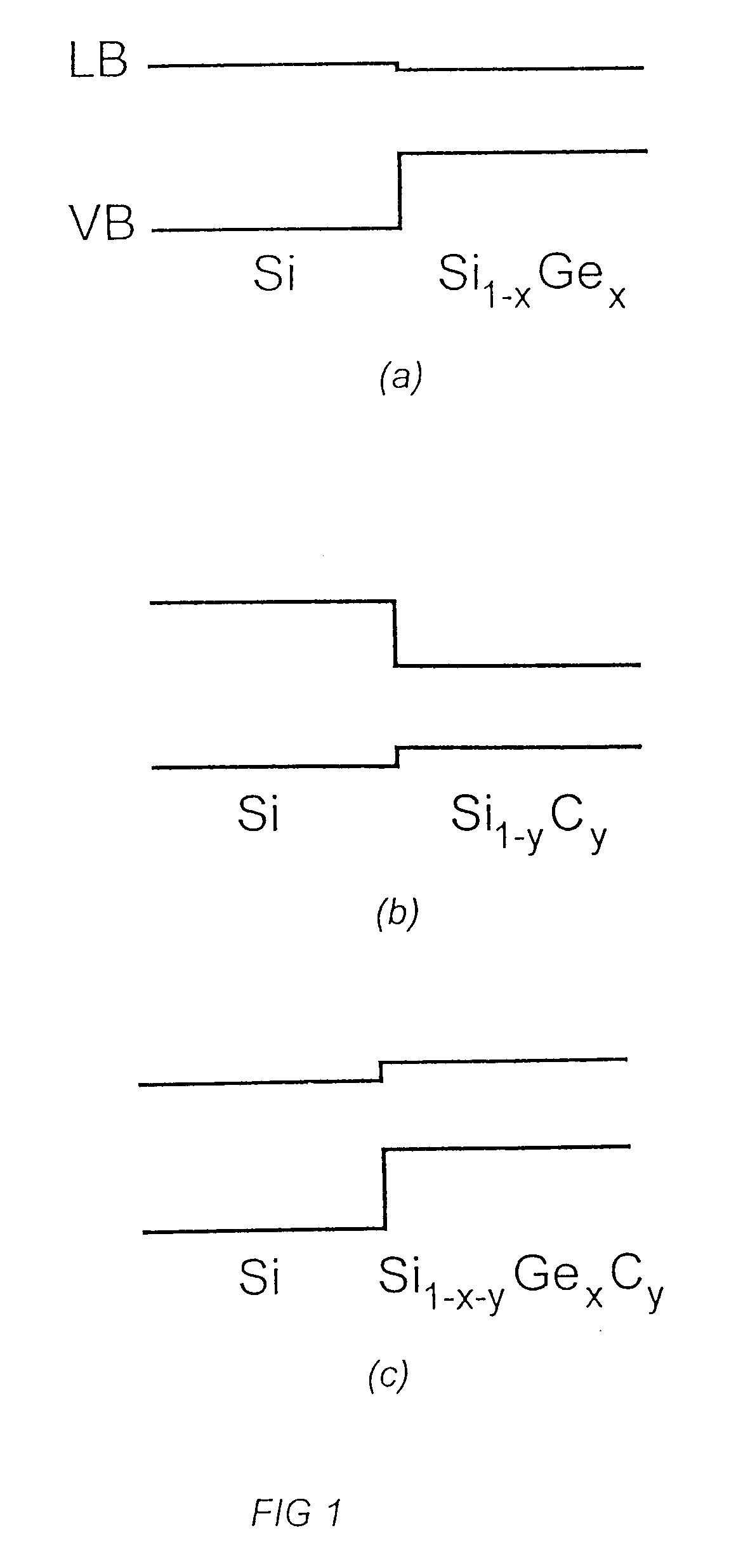
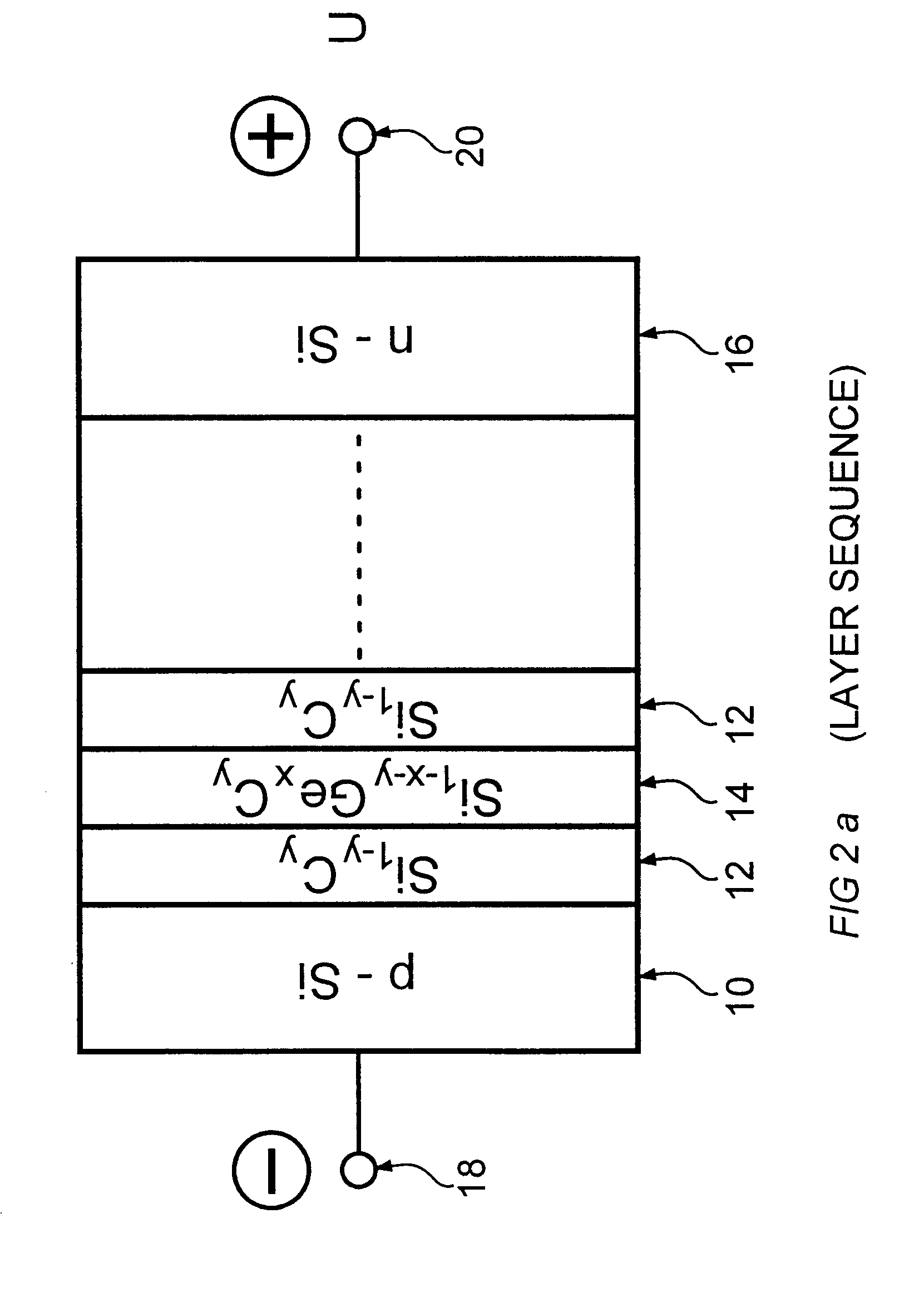
A semiconductor component, selected from the group comprising a photodetector, a light emitting diode, an optical modulator and a waveguide. The semiconductor component comprises an Si substrate, an active region formed on said substrate, and an Si capping layer on said active region. In one embodiment the active region is a superlattice comprising alternating layers of Si1-yCy and Si1-x-yGexCy, with the atomic fraction y of the Si1-x-yGexCy layers being equal to or different from the atomic fraction y of the Si1-yCy layers. In another embodiment it is a superlattice comprising a plurality of periods of a three-layer structure comprising Si, Si1-yCy and Si1-xGex layers. In a third embodiment it is a superlattice comprising a plurality of periods of a three-layer structure comprising Si, Si1-yCy and Si1-x-yGexCy layers, with the atomic fraction y of the Si1-x-yGexCy layers being equal to or different from the atomic fraction y of the Si1-yCy layers. The components have faborable optical and electrical properties and are suitable for integration on a Si substrate.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
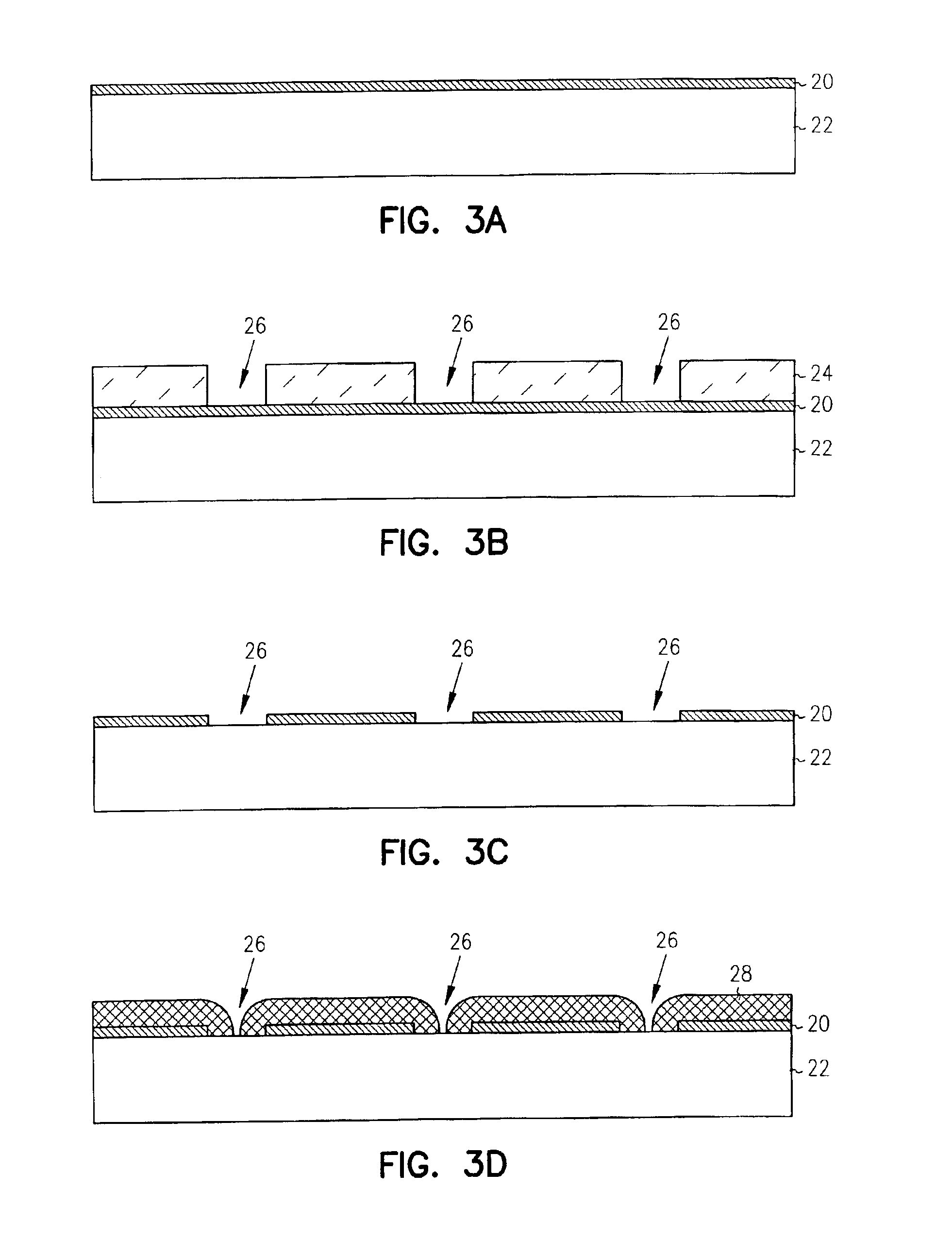
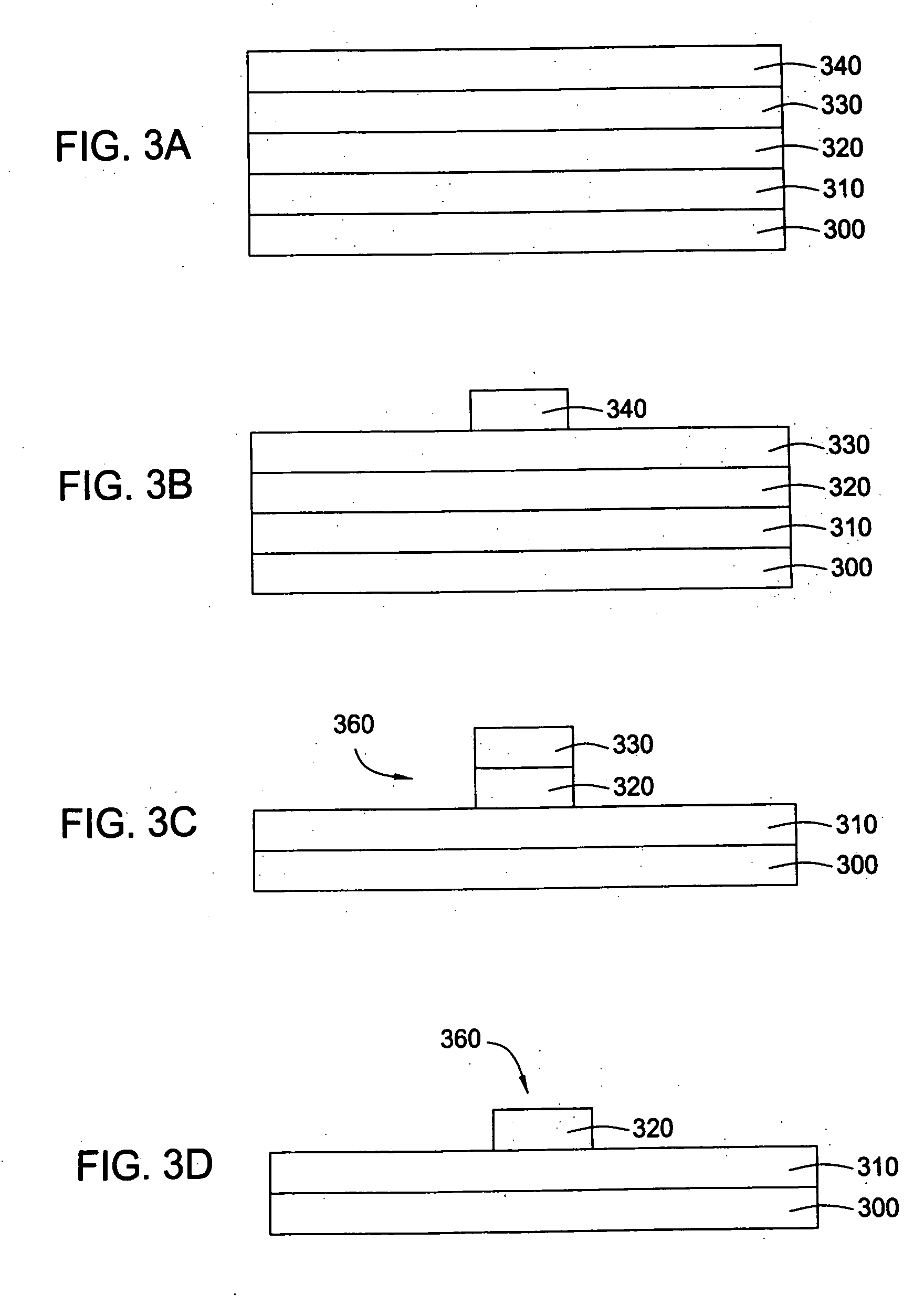
Use of amorphous carbon film as a hardmask in the fabrication of optical waveguides
Methods are provided for forming optical devices, such as waveguides, with minimal defect formation. In one aspect, the invention provides a method for forming a waveguide structure on a substrate surface including forming a cladding layer on the substrate surface, forming a core layer on the cladding layer, depositing an amorphous carbon hardmask on the core layer, forming a patterned photoresist layer on the amorphous carbon hardmask, etching the amorphous carbon hardmask, and etching the core material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Cordless Hand-Held Ultrasonic Cautery Cutting Device
ActiveUS20090143797A1Alter functionAlter performanceUltrasound therapySurgical instrument detailsUltrasonic sensorTransducer
An ultrasonic surgical assembly includes a reusable cordless ultrasonic transducer and a disposable handle body that defines a battery-holding compartment therewithin, having an ultrasonic surgical waveguide, and operable to removably couple the transducer to the waveguide, the transducer being removably couplable to the handle body.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Electooptical Communications and Power Cable
InactiveUS20080247716A1Increase forceImprove protectionCommunication cablesFibre mechanical structuresVoltage converterPower cable
An electrooptical communications and power cable has at least one light waveguide, which is arranged in a central multifibre bundle consisting of a smooth flexible metal tube and provided with a primary jacket. Two layers of stranded metal wires are extended coaxially to the multifibre bundle. The metal wires are also used for relieving a traction and / or transversal load. The internal metal wire layer consists of metal wires exhibiting a good electric conductivity. The external metal wire layer has metal wires which are arranged alternately individually and / or group groupwisely and exhibit a good electrical conductivity and metal wires exhibiting a high traction strength. The two wire layers are held at a distance (a) from each other by an insulating layer. The communications and power cable is used first of all for an electrooptical power connection between two voltage converters in an intelligent system.
Owner:BRUGG KABEL
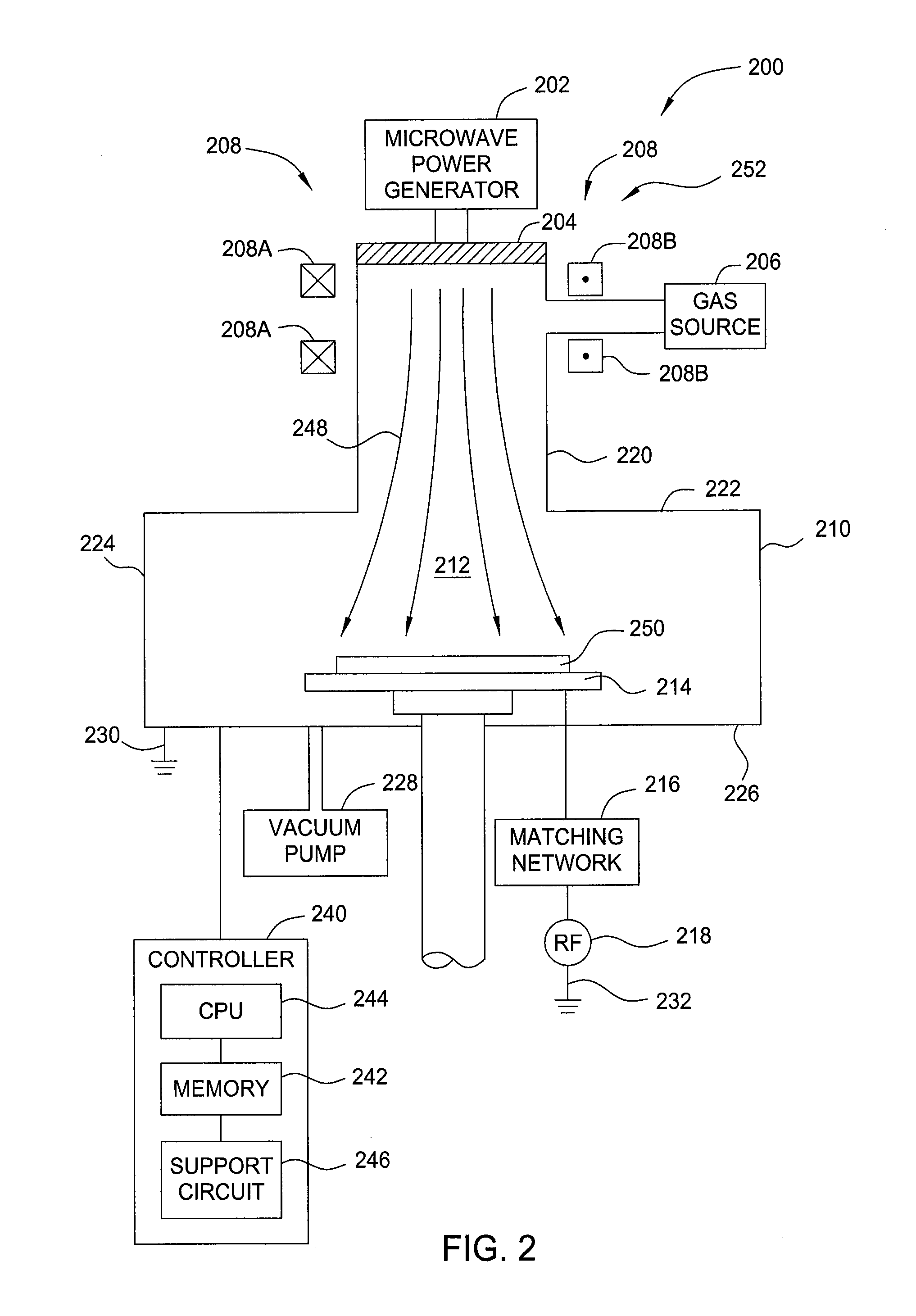
Methods and apparatus for controlling photoresist line width roughness
The present invention provides methods and an apparatus for controlling and modifying line width roughness (LWR) of a photoresist layer. In one embodiment, an apparatus for controlling a line width roughness of a photoresist layer disposed on a substrate includes a chamber body having a top wall, side wall and a bottom wall defining an interior processing region, a microwave power generator coupled to the to the chamber body through a waveguild, and one or more coils or magnets disposed around an outer circumference of the chamber body adjacent to the waveguide, and a gas source coupled to the waveguide through a gas delivery passageway.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Preconnectorized fiber optic drop cables and assemblies for efficient deployment
A preconnectorized outdoor cable streamlines the deployment of optical waveguides into the last mile of a optical network. The preconnectorized outdoor cable includes a cable and at least one plug connector. The plug connector is attached to a first end of the cable, thereby connectorizing at least one optical waveguide. The cable has at least one optical waveguide, at least one tensile element, and a cable jacket. Various cable designs such as figure-eight or flat cables may be used with the plug connector. In preferred embodiments, the plug connector includes a crimp assembly having a crimp housing and a crimp band. The crimp housing has two half-shells being held together by the crimp band for securing the at least one tensile element. When fully assembled, the crimp housing fits into a shroud of the preconnectorized cable. The shroud aides in mating the preconnectorized cable with a complimentary receptacle.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Multi-touch sensing through frustrated total internal reflection
InactiveUS20080284925A1Simple and inexpensive and scalableDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesMulti inputTotal internal reflection
High-resolution, scalable multi-touch sensing display systems and processes based on frustrated total internal reflection employ an optical waveguide that receives light, such as infrared light, that undergoes total internal reflection and an imaging sensor that detects light that escapes the optical waveguide caused by frustration of the total internal reflection due to contact by a user. The optical waveguide when fitted with a compliant surface overlay provides superior sensing performance, as well as other benefits and features. The systems and processes described provide true multi-touch (multi-input) and high-spatial and temporal resolution capability due to the continuous imaging of the frustrated total internal reflection that escapes the entire optical waveguide. Among other features and benefits, the systems and processes are scalable to large installations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for manufacturing photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20090029503A1Quality improvementReduce deterioration rateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateMicrowave
To form a microcrystalline semiconductor with high quality which can be directly formed at equal to or less than 500° C. over a large substrate with high productivity without decreasing a deposition rate. In addition, to provide a photoelectric conversion device which employs the microcrystalline semiconductor as a photoelectric conversion layer. A reactive gas containing helium is supplied to a treatment chamber which is surrounded by a plurality of juxtaposed waveguides and a wall, the pressure in the treatment chamber is maintained at an atmospheric pressure or a subatmospheric pressure, microwave is supplied to a space sandwiched between the juxtaposed waveguides to generate plasma, and a photoelectric conversion layer of a microcrystalline semiconductor is deposited over a substrate which is placed in the treatment chamber.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
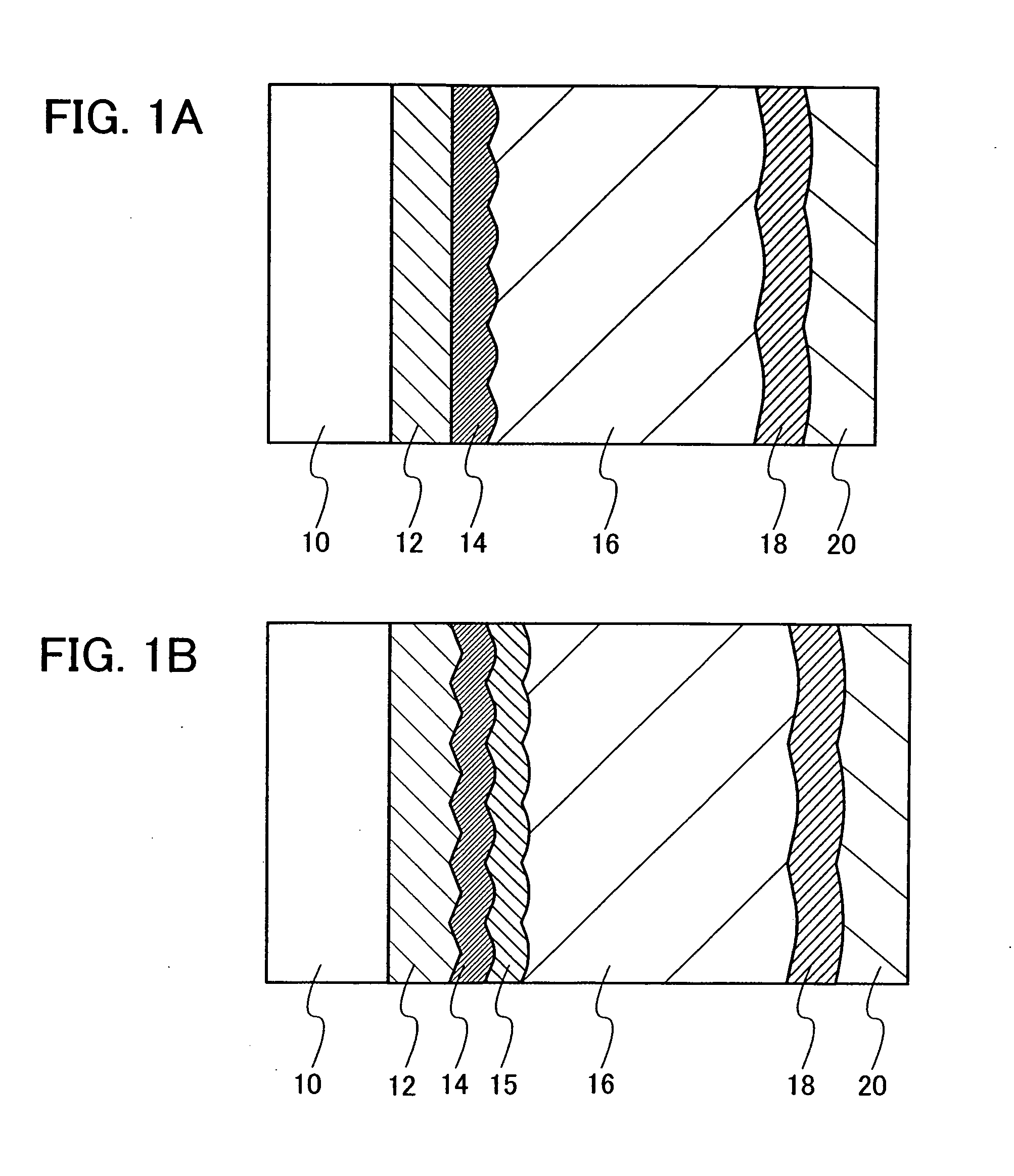
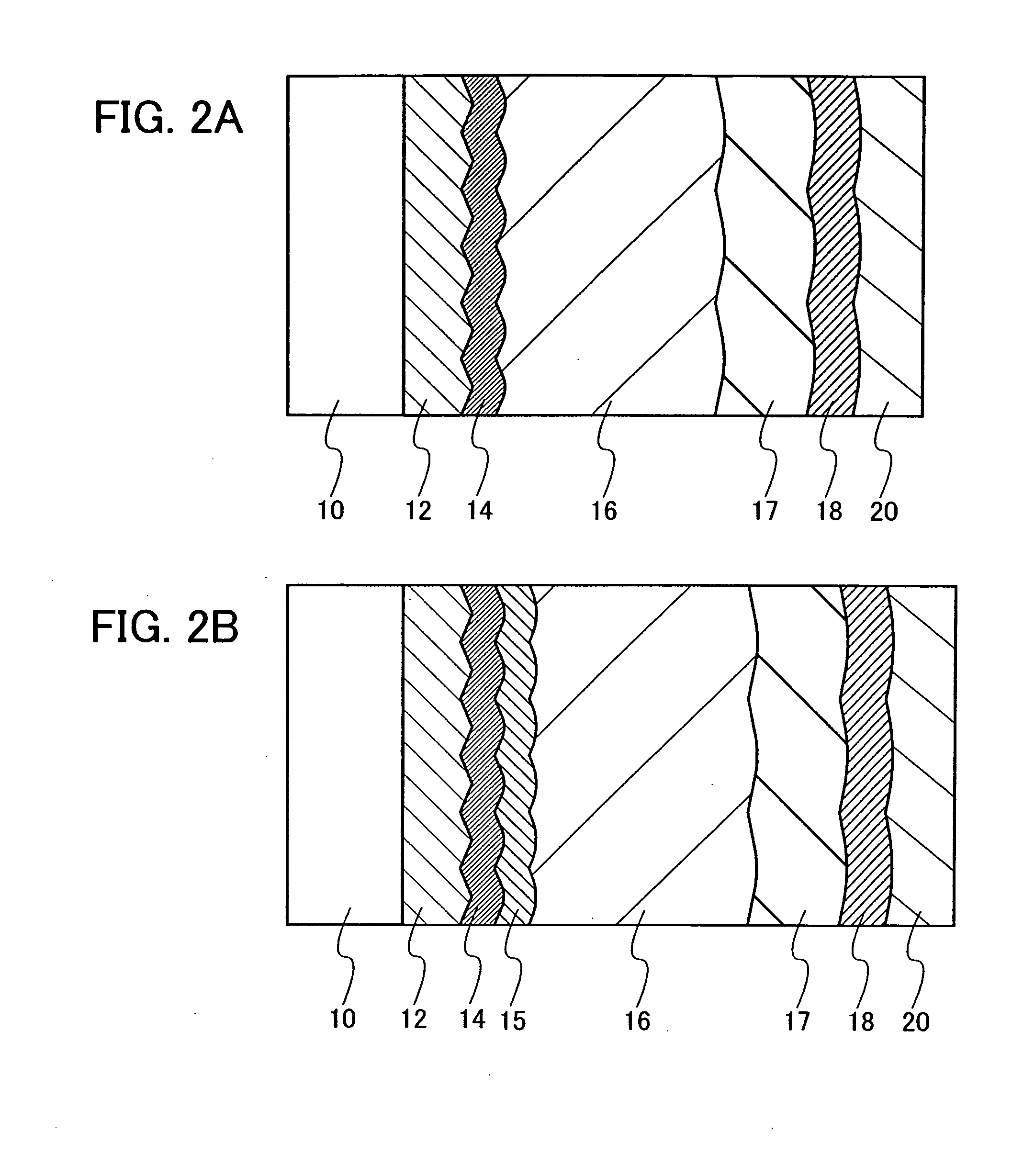
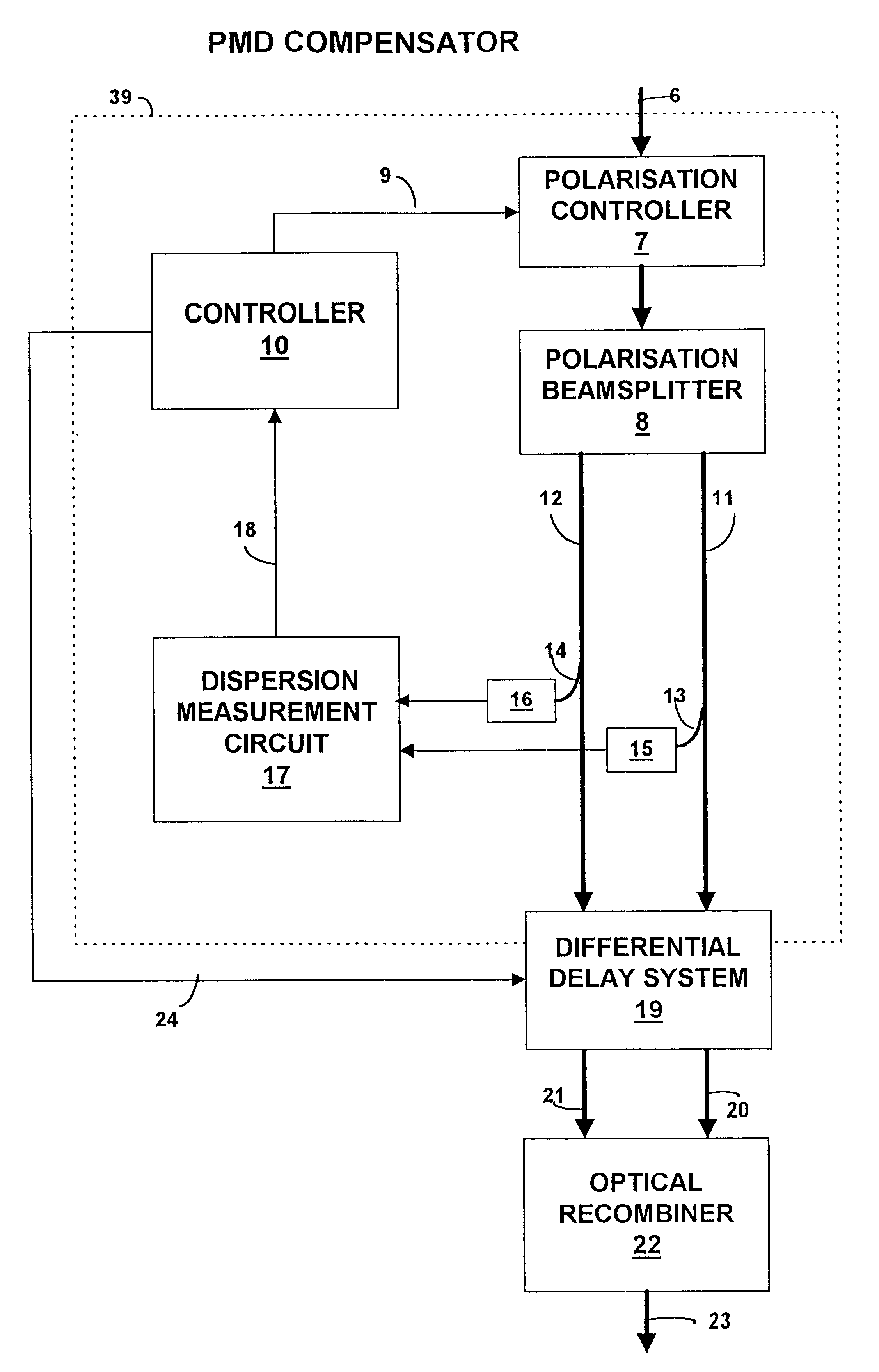
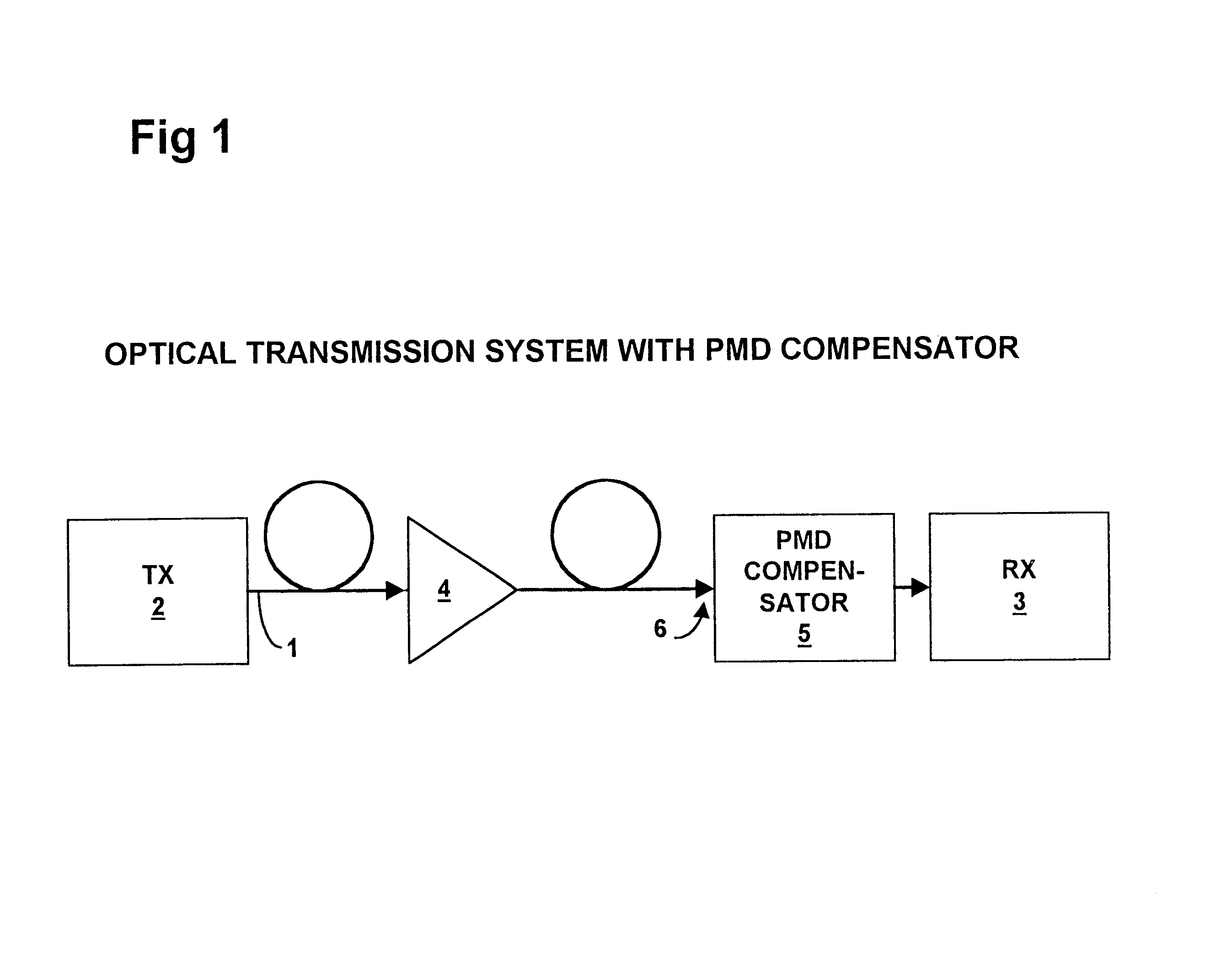
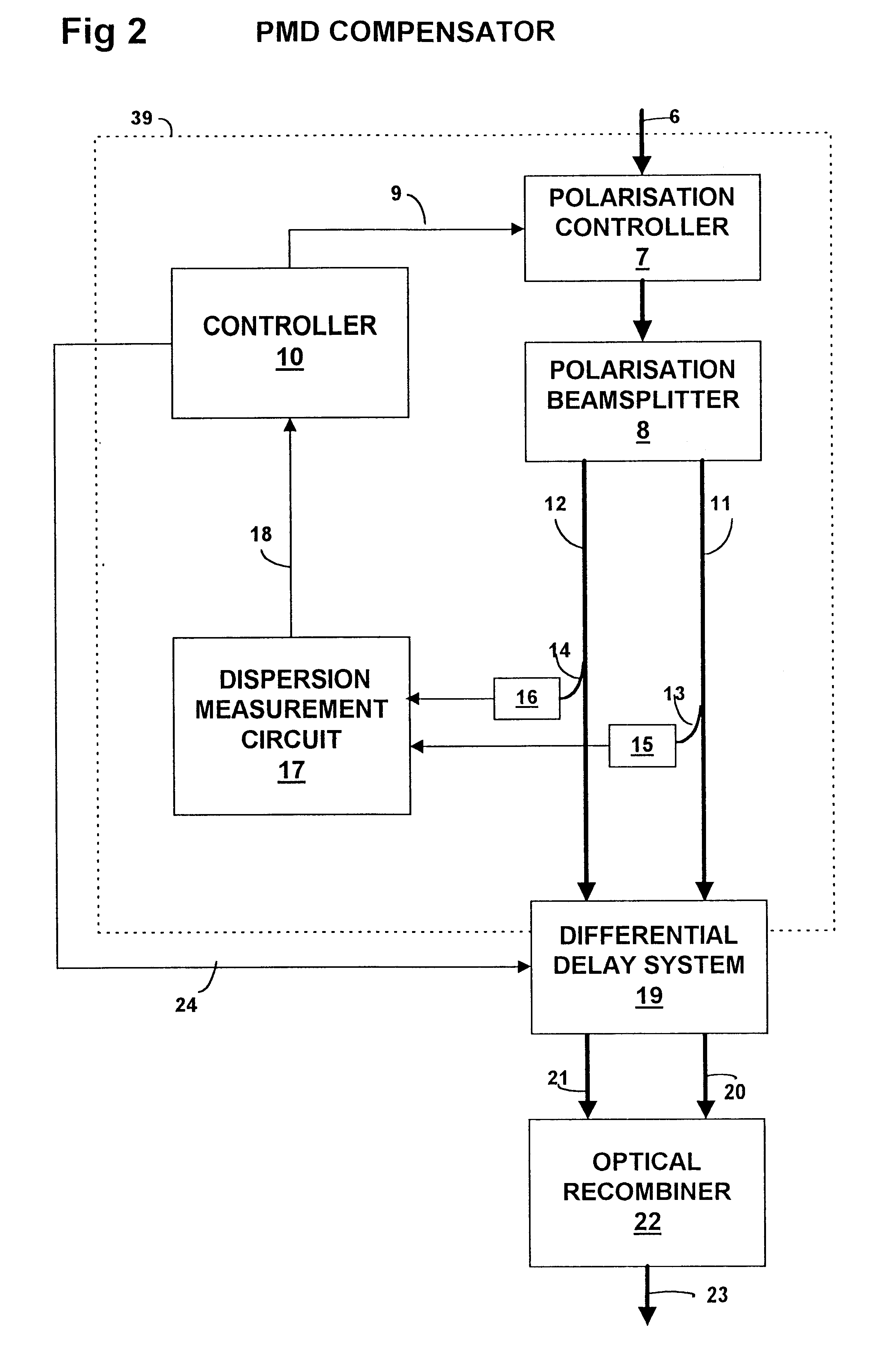
Polarization mode dispersion compensation
InactiveUS6271952B1Producing strainTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsGratingCommunications system
Polarization mode dispersion in an optical signal transmitted through a waveguide of a communications system is compensated by separating the dispersed signal into components corresponding to principal polarization states. The components are delayed by respective delays differing by a delay increment which is controlled to correspond to the dispersion delay and the delayed components are recombined to provide a dispersion compensated optical output signal. Each of the delays is provided by an chirped Bragg reflector forming part of a delay line, the Bragg reflectors comprising optical fibres with chirped intracore index gratings. Transducers or temperature controllers acting on one of the fibres allows dimensional control of the grating periodicity such that the position of Bragg reflection is variable. Wavelength division multiplexed optical signals are compensated using sampled gratings which allow a common Bragg reflection position for each wavelength.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
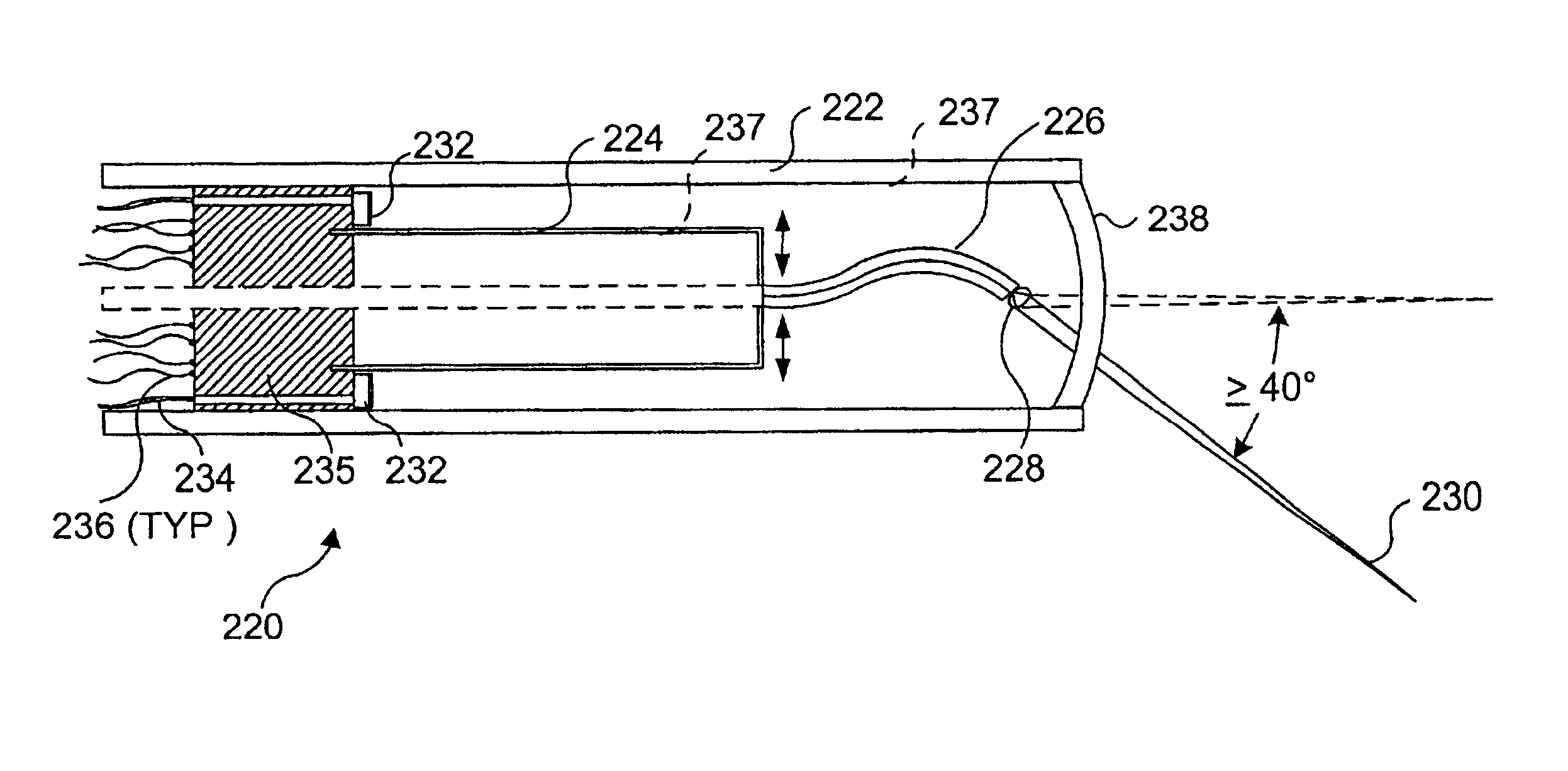
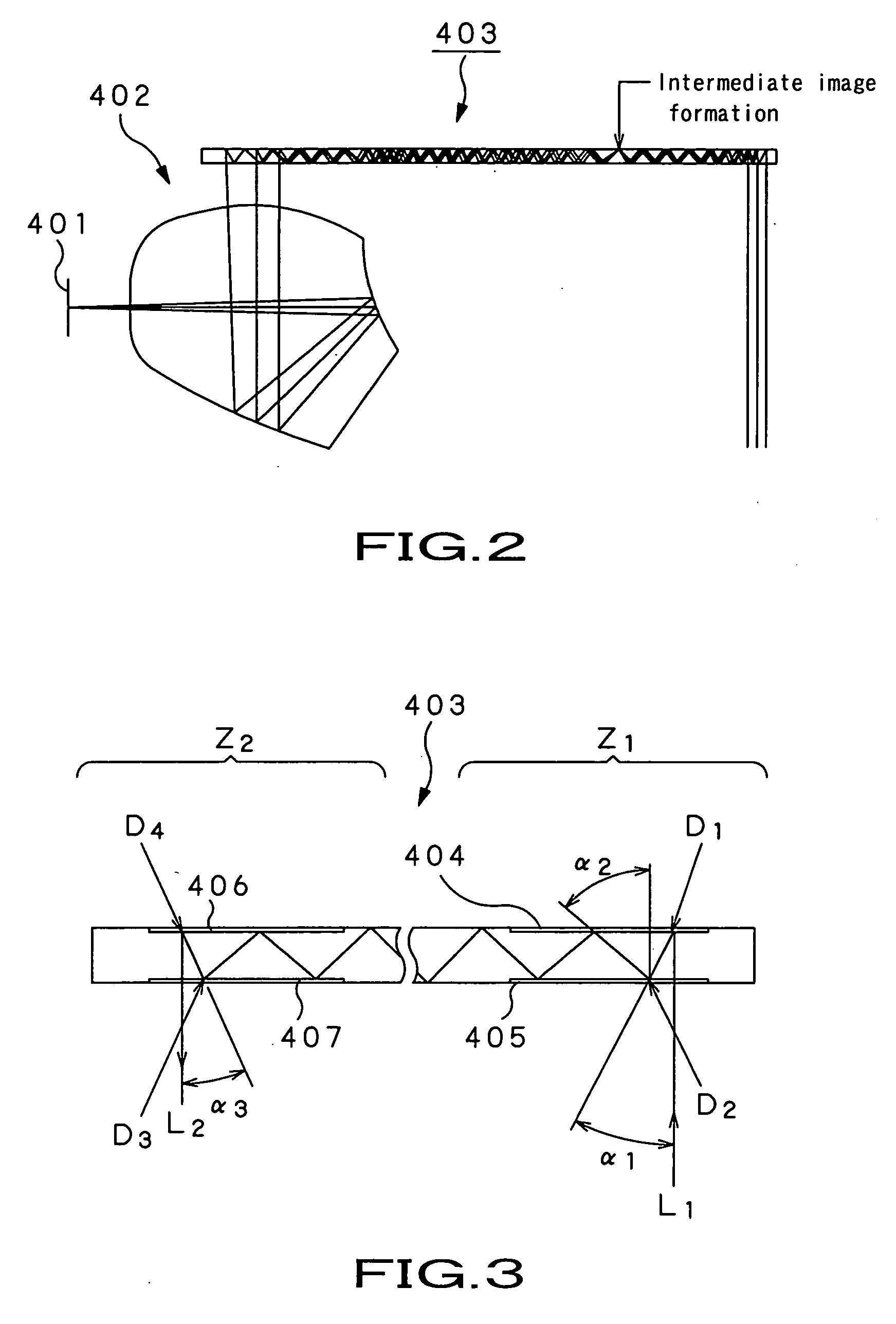
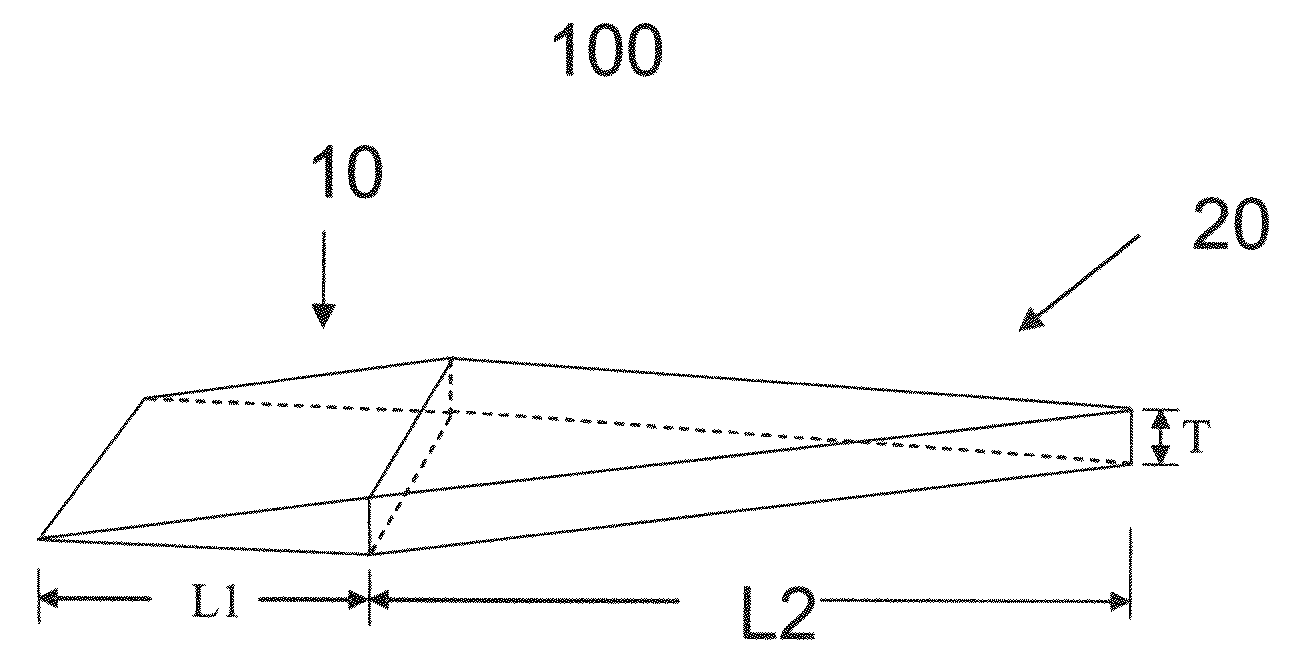
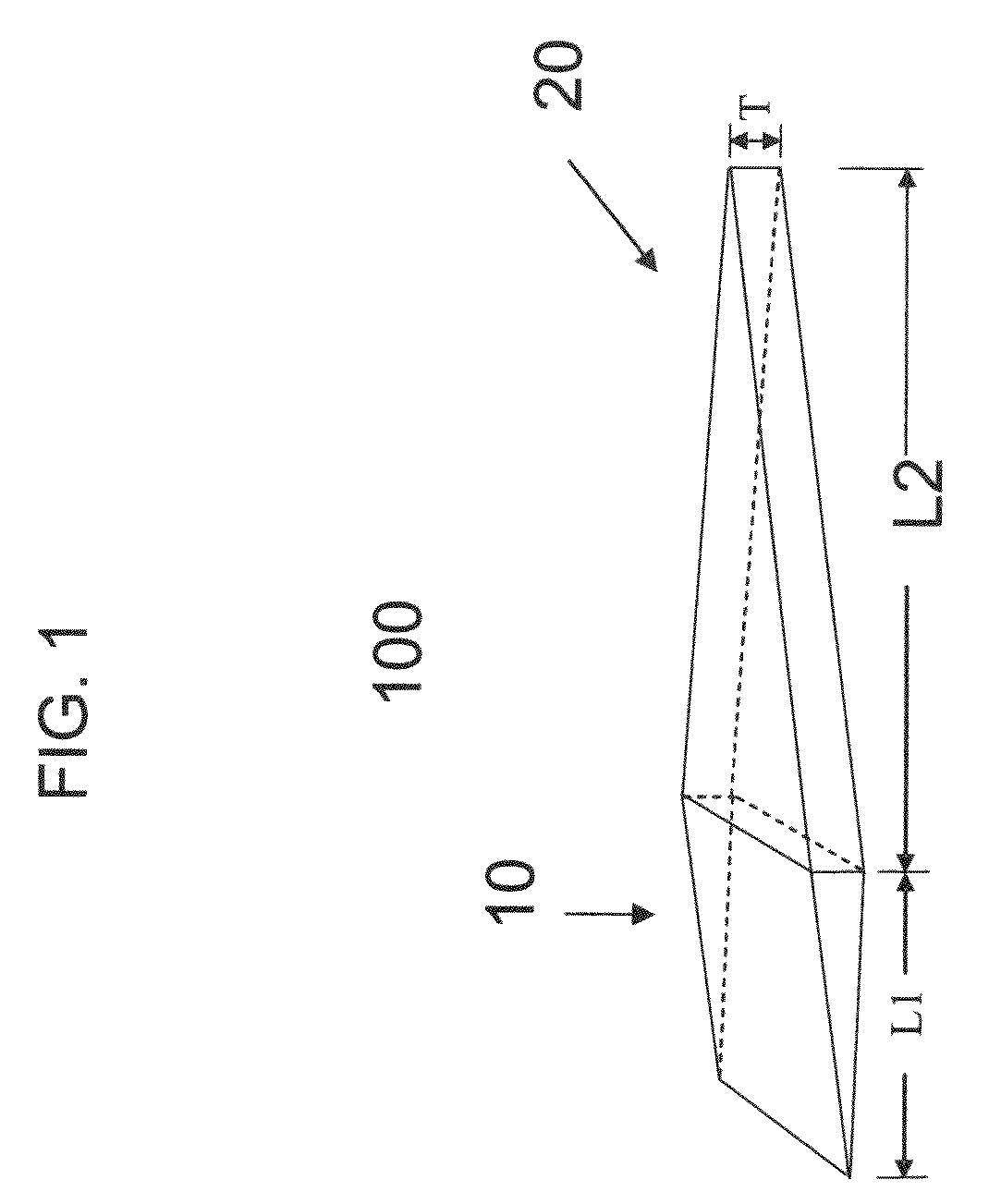
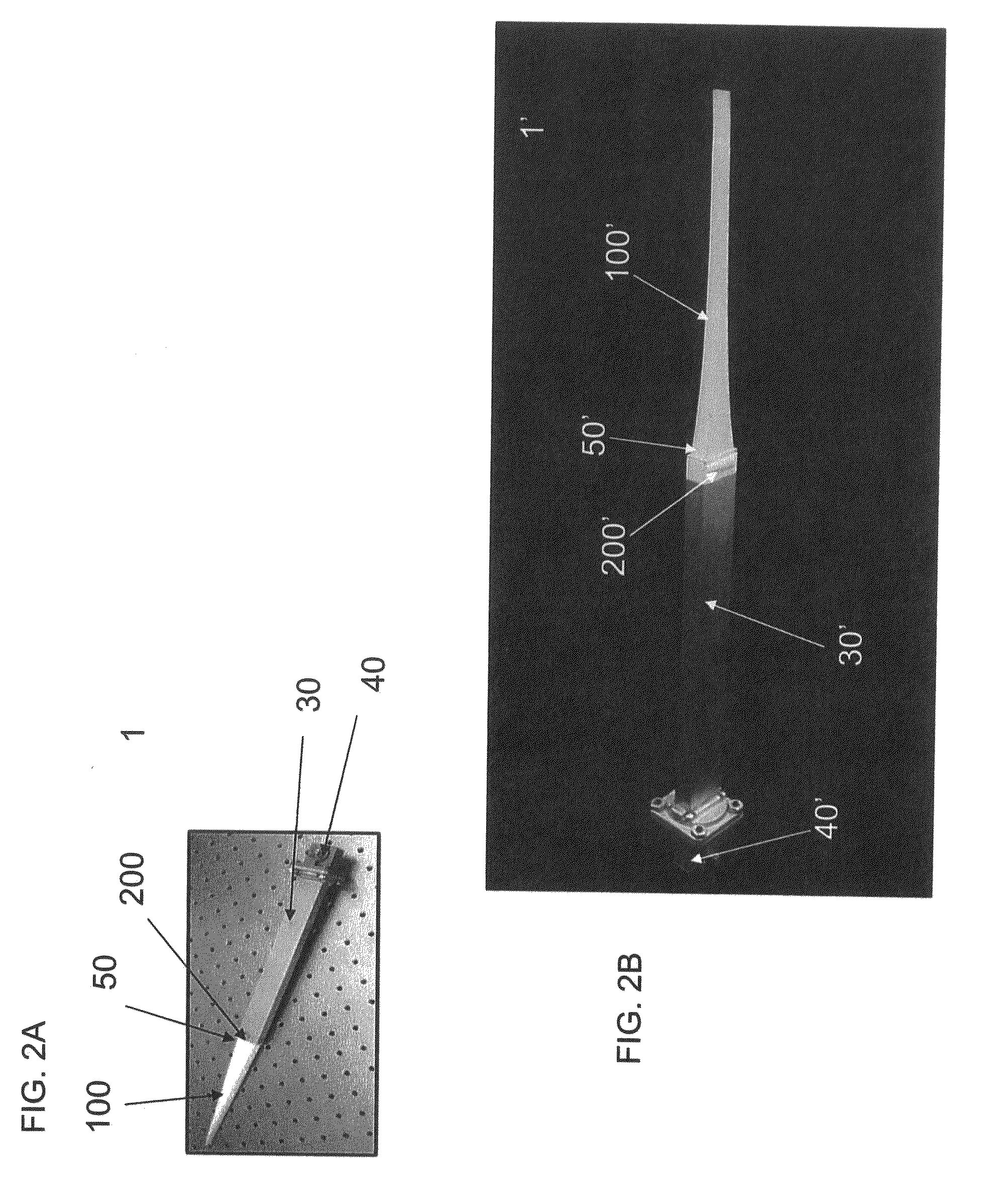
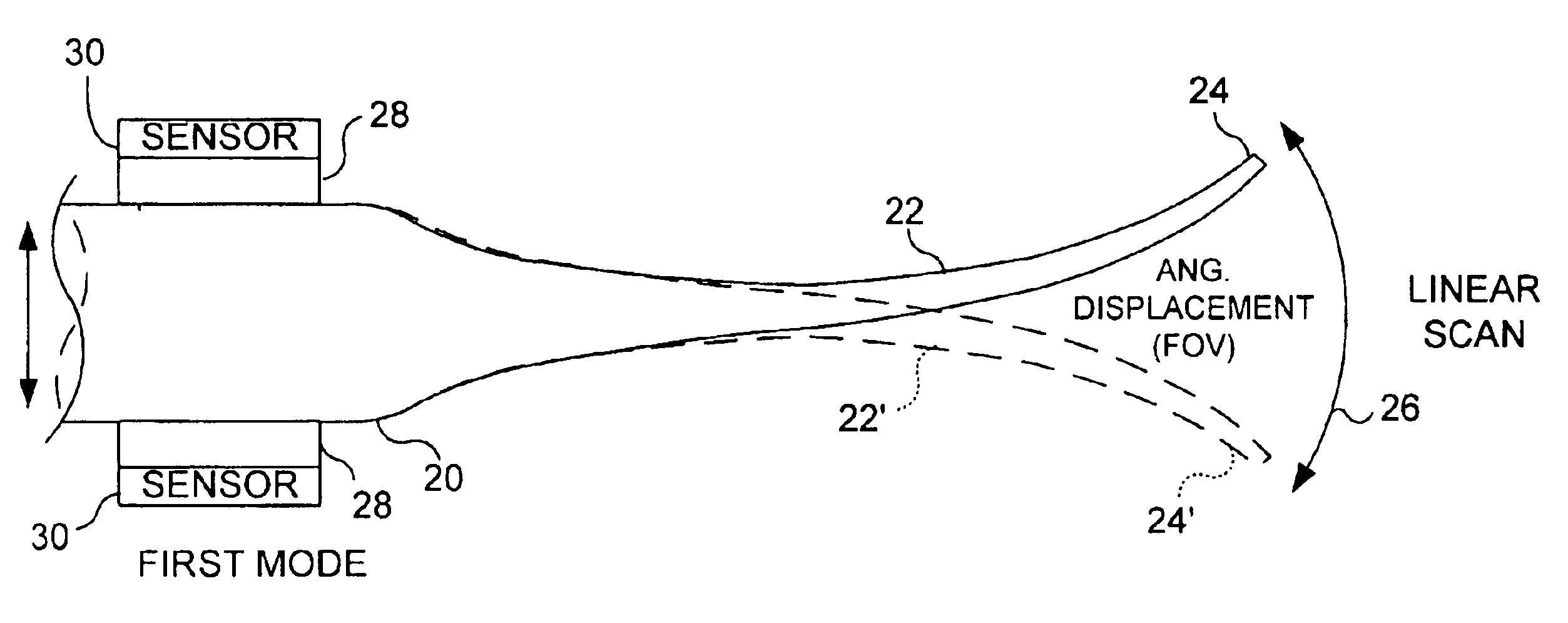
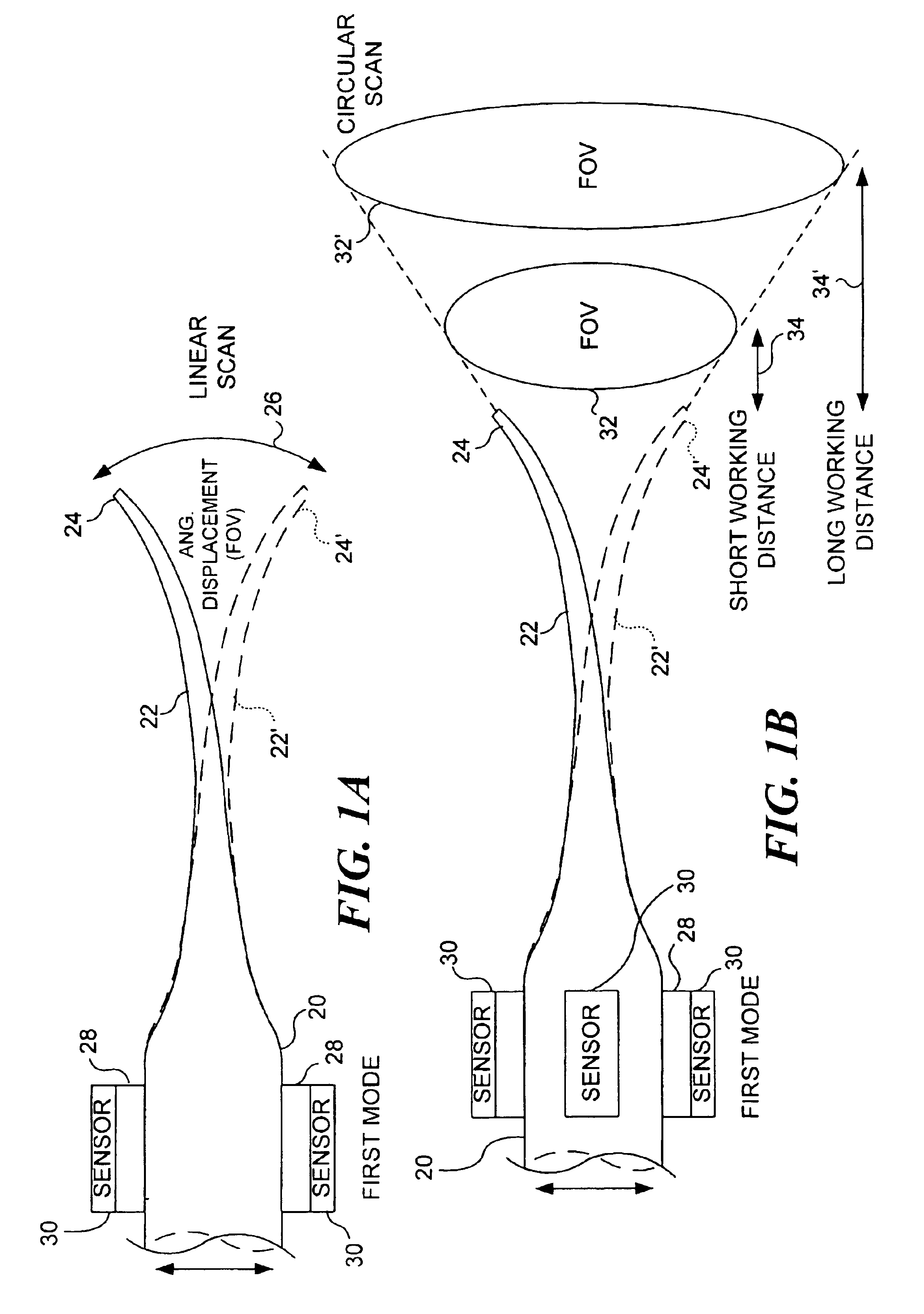
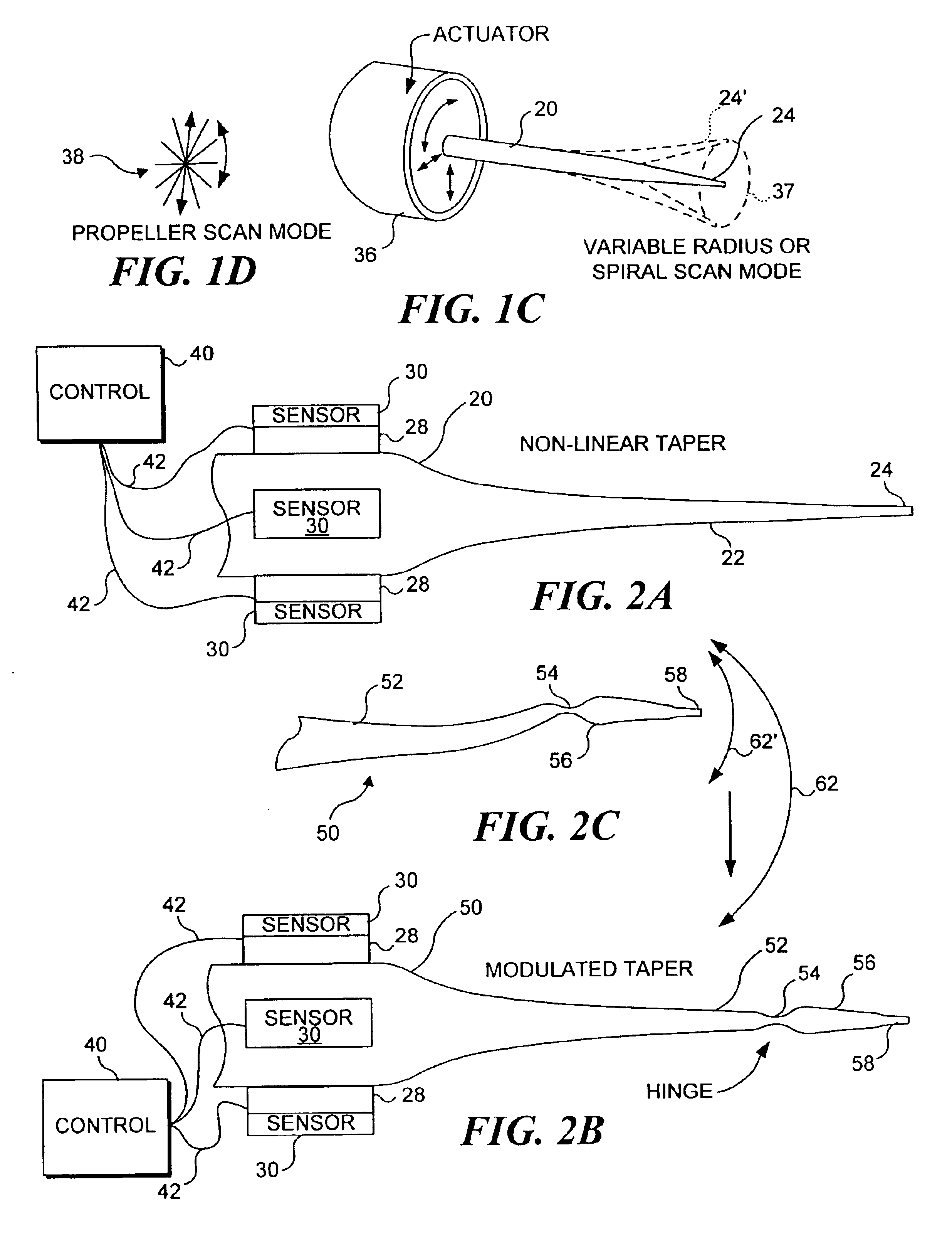
Micro-fabricated optical waveguide for use in scanning fiber displays and scanned fiber image acquisition
Small, rugged scanners micro-fabricated from commercial optical fibers to form waveguides or other structures. The scanning waveguide has a distal portion on which is formed a non-linear taper with a diameter that decreases toward a distal end. Optionally, a hinge portion having a reduced diameter can be formed in the distal portion, improving the scanning properties of the waveguide. A micro-lens can be integrally formed at the distal tip of the waveguide with either a droplet of an optical adhesive, or by using an energy beam to melt the material of the waveguide to form a droplet. The droplet is shaped with an externally applied force. When mechanically driven in vibratory resonance, the tip of the optical waveguides moves in linear or two-dimensional scan patterns of relatively high amplitude and frequency, and large field of view. The scanner can be used either for image acquisition or image display.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Cordless Hand-Held Ultrasonic Cautery Cutting Device
InactiveUS20090143799A1Alter functionAlter performanceUltrasound therapySurgical instrument detailsUltrasonic sensorWave shape
A disposable ultrasonic surgical handle includes a disposable handle body defining a battery-holding compartment shaped to receive a battery therein and operable to couple a proximal end of an ultrasonic waveguide to an ultrasonic transducer therethrough. The body has a transducer dock exposed to the environment and interchangeably housing the transducer and a waveguide attachment dock shaped to align and attach the proximal end of the waveguide to the transducer and hold them at the body when the respectively docked at the transducer and attachment docks. A disposable driving-wave generation circuit in the handle body electrically contacts the battery and the transducer when the battery and the transducer are disposed respectively in the battery-holding compartment and the transducer dock. The circuit generates an output waveform sufficient to cause ultrasonic movement along the waveguide by exciting the transducer when the transducer is coupled to the waveguide.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
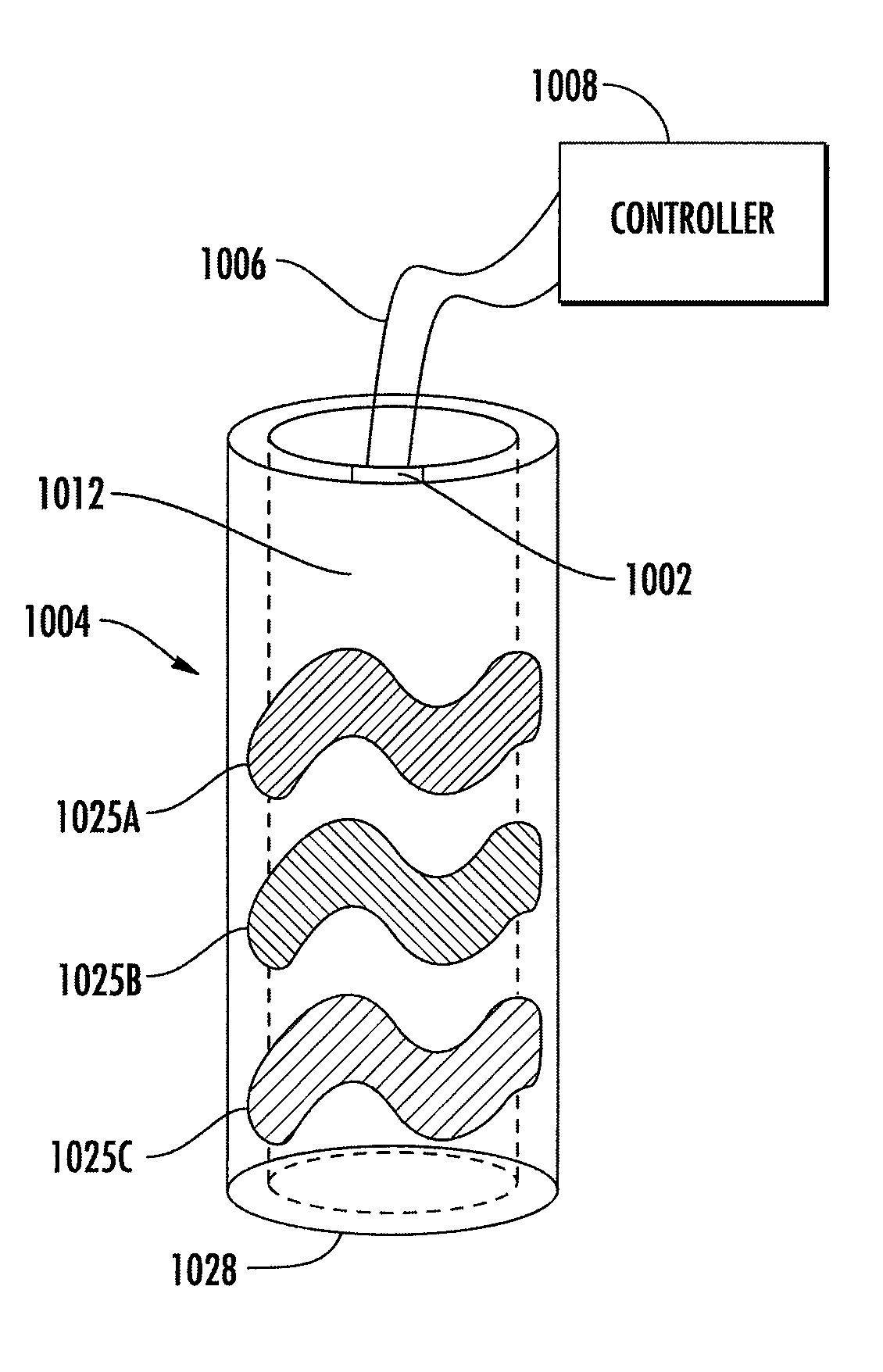
Aerosol Delivery Device With an Illuminated Outer Surface and Related Method
ActiveUS20150216233A1Lighting applicationsPoint-like light sourceAerosol deliveryElectromagnetic radiation
The present disclosure relates to aerosol delivery devices that may include components configured to convert electrical energy to heat and atomize an aerosol precursor composition. An outer body may at least partially enclose the components. An illumination source may be configured to output electromagnetic radiation. For example, a light emitting diode may output light. A waveguide may be configured to receive the electromagnetic radiation from the illumination source and provide illumination at an outer surface of the outer body. The waveguide may include an energy conversion material configured to alter a wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation outputted by the illumination source to change a color of, or otherwise affect, the illumination. The illumination may also be dynamically adjusted. The waveguide may define the outer body, or the waveguide may be received with a separate outer body. Related methods are also provided.
Owner:RAI STRATEGIC HLDG INC +1
Cordless Hand-Held Ultrasonic Cautery Cutting Device
InactiveUS20090143800A1Alter functionAlter performanceUltrasound therapySurgical instrument detailsRechargeable cellHand held
An ultrasonic surgical assembly for connection to an ultrasonic surgical handle includes a reusable exterior body defining an internal compartment and having a connection operable to removably secure the body in a body-holding compartment within the ultrasonic surgical handle, a reusable cordless ultrasonic-movement-generation assembly disposed in the compartment and having an output couple removably attachable to an ultrasonic waveguide and operable to impart ultrasonic movement to the ultrasonic waveguide, and a reusable and rechargeable battery disposed in the compartment and electrically connected to and powering the assembly.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com