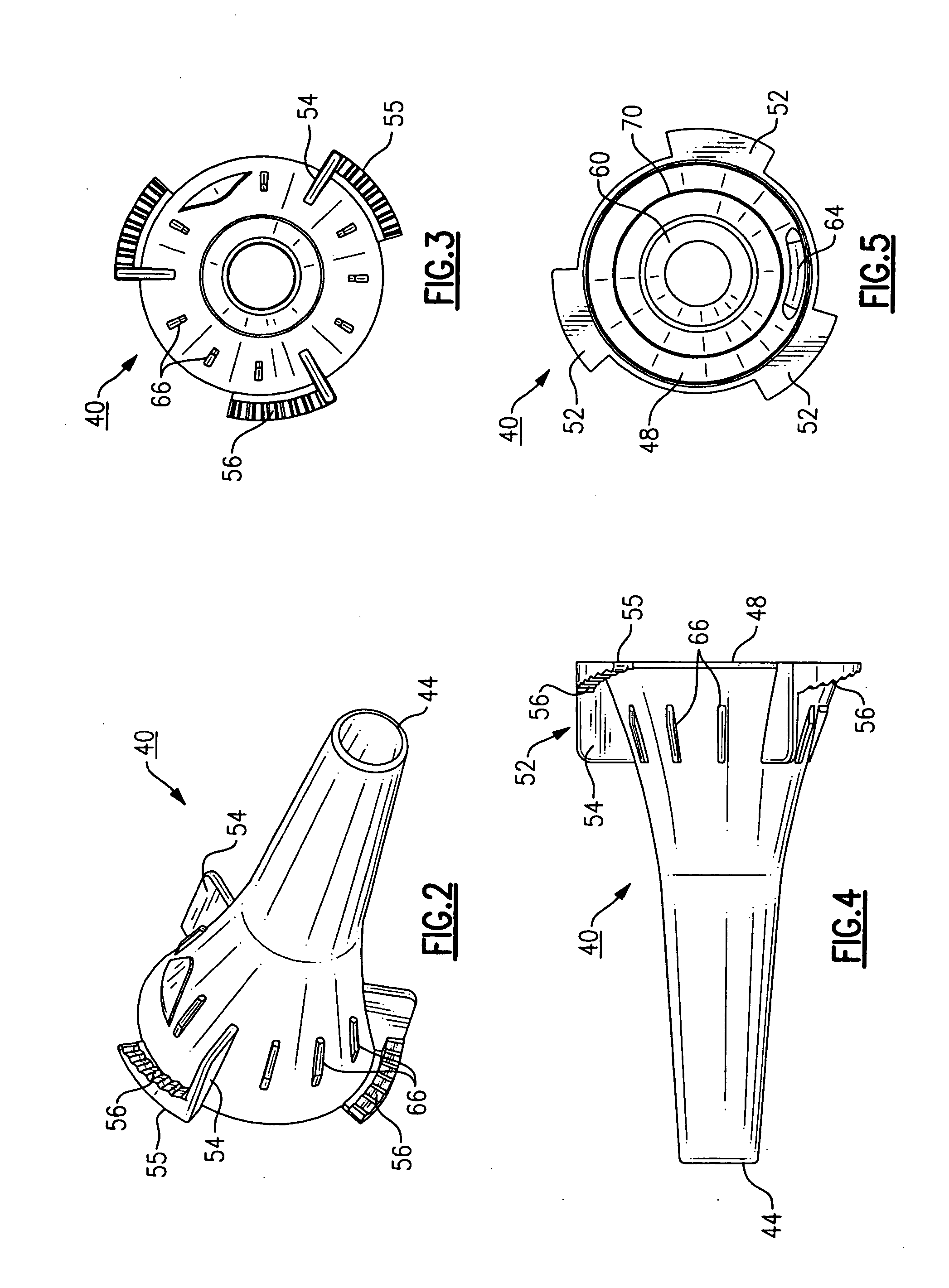
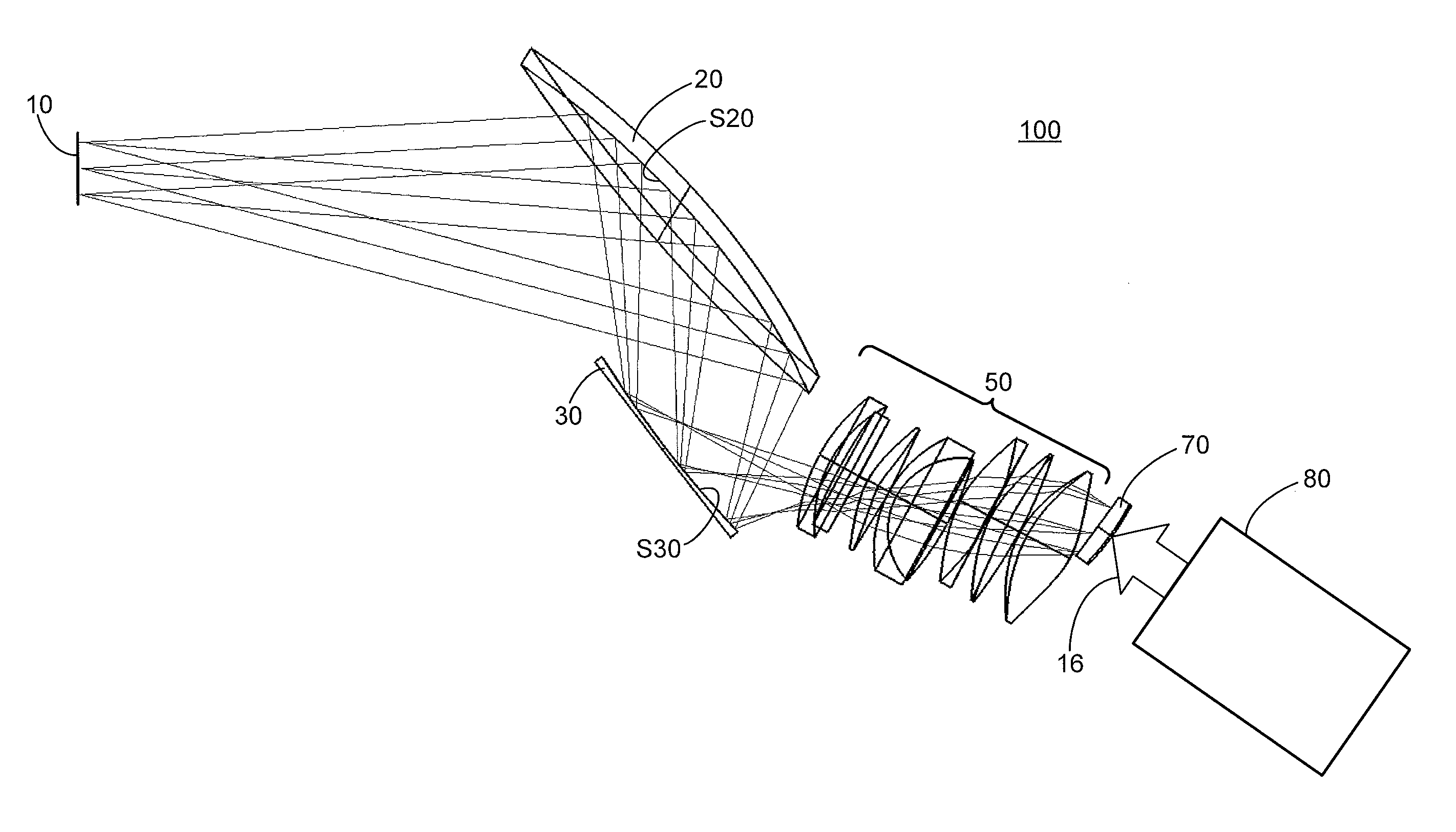
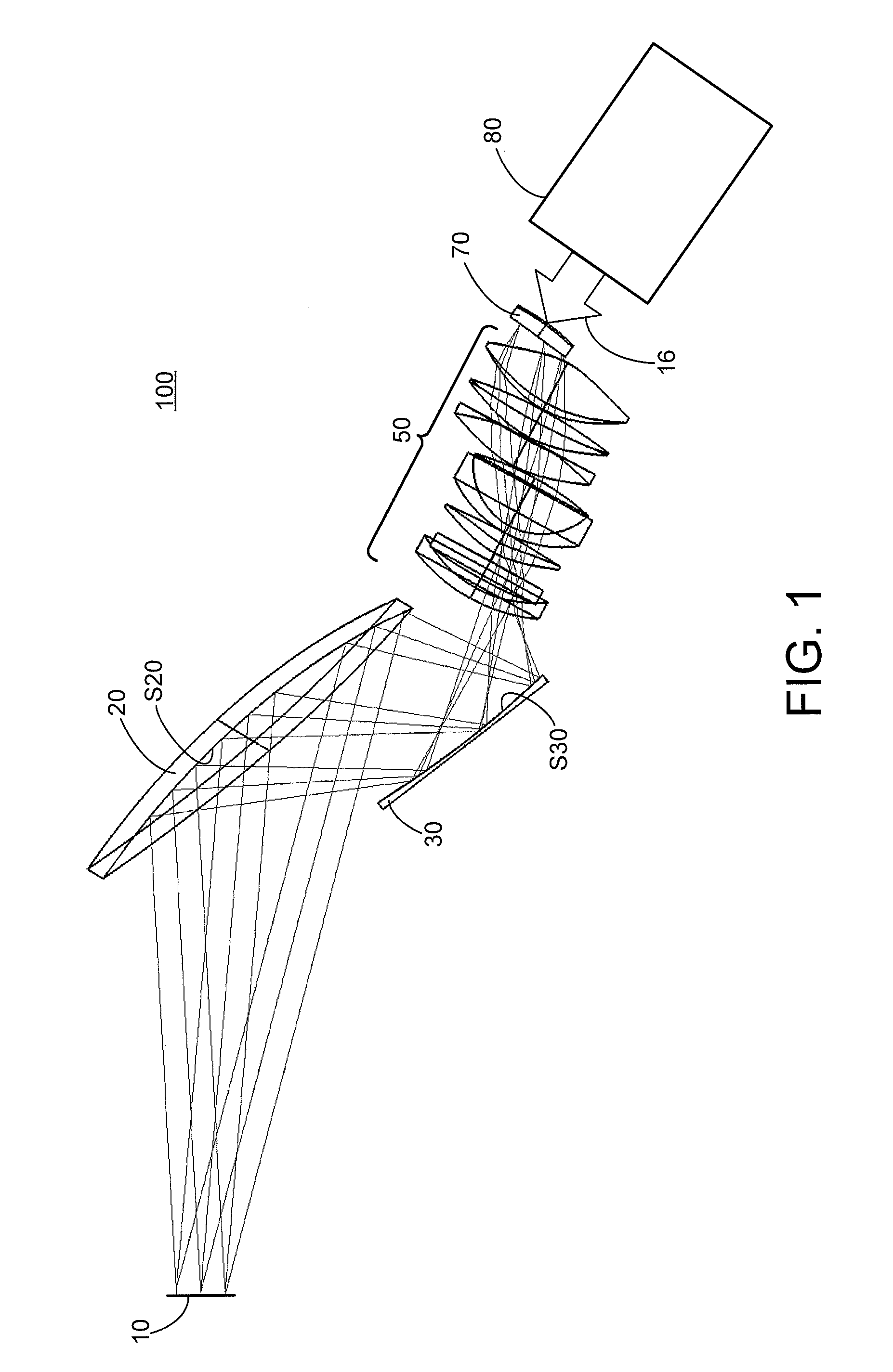
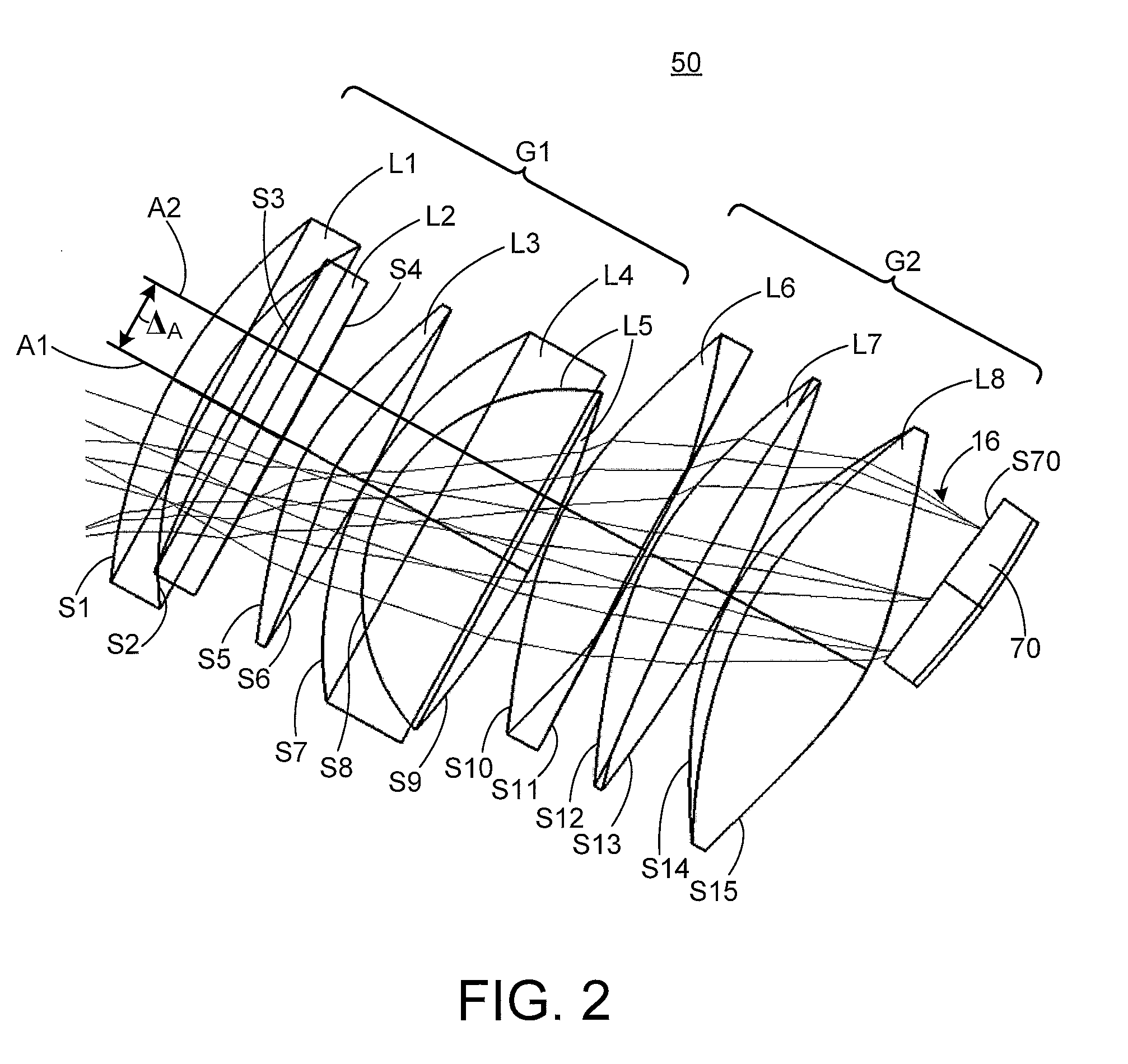
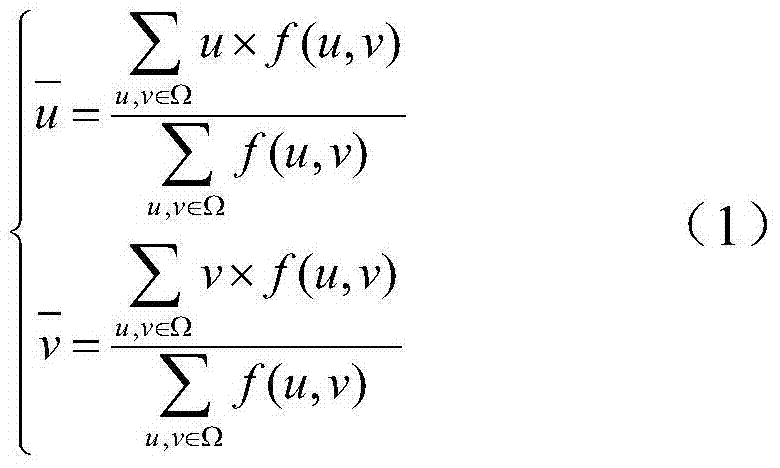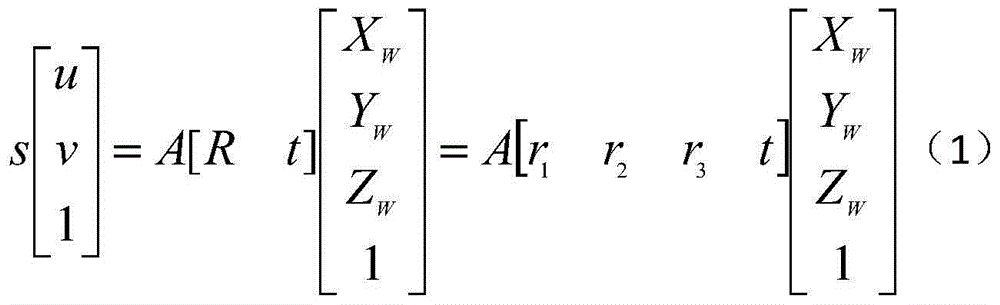Patents
Literature
1370 results about "Large field of view" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
As others have suggested, "wide field of view" is the commonest collocation. "Large field of view" is also possible.
Systems and methods for imaging large field-of-view objects
InactiveUS7108421B2Quantity minimizationAvoiding corrupted and resulting artifacts in image reconstructionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingBeam sourceX-ray
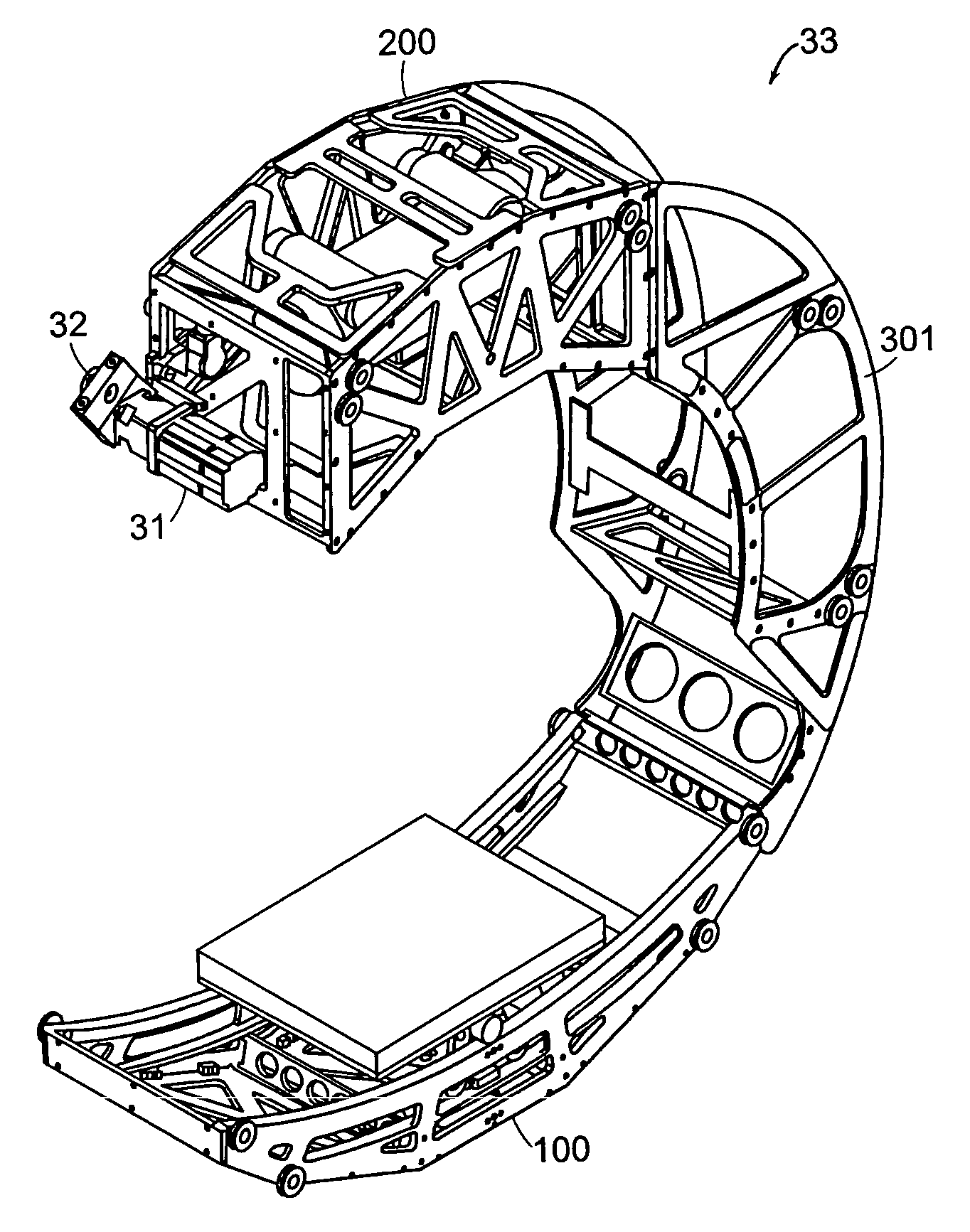
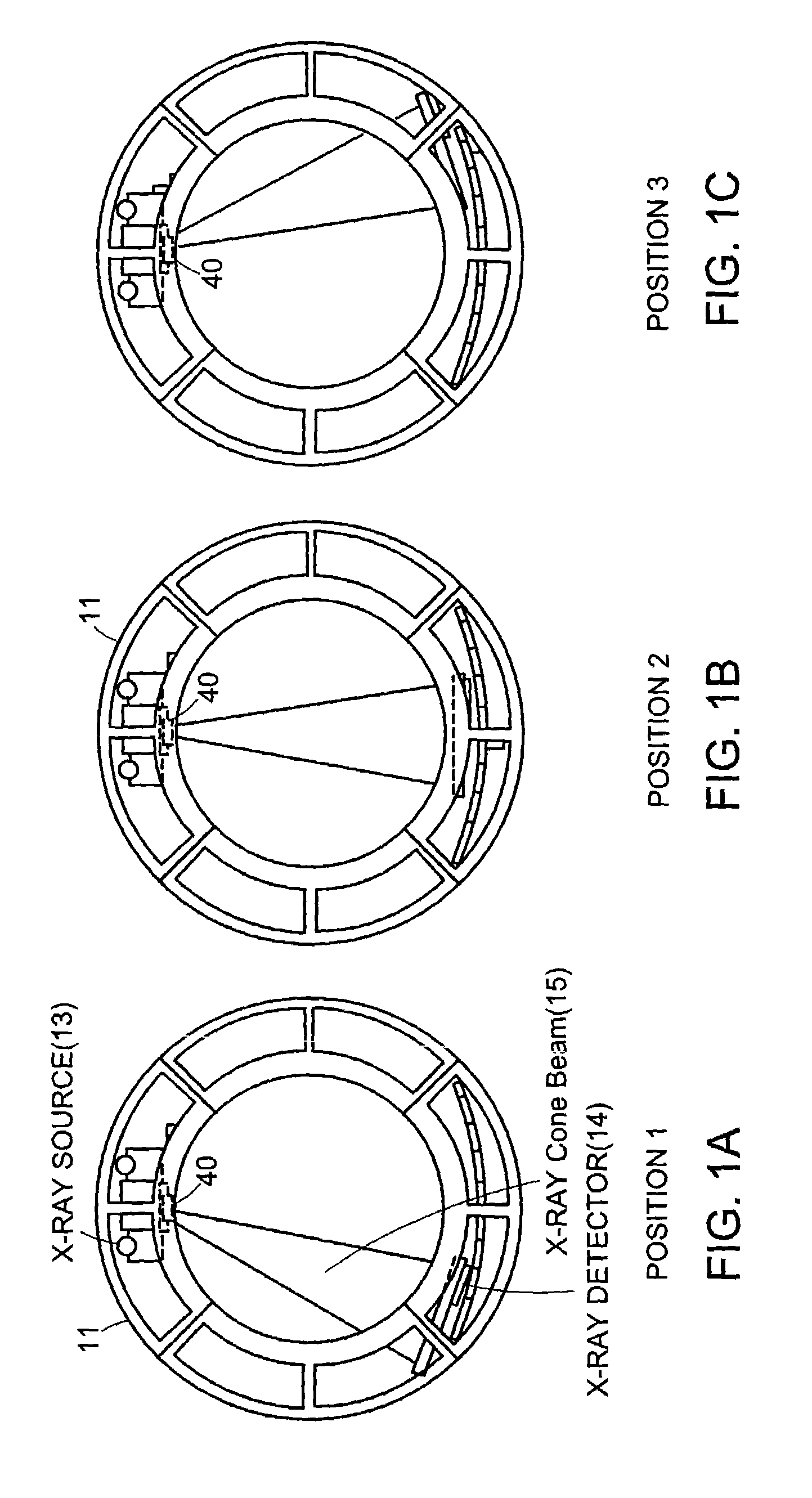
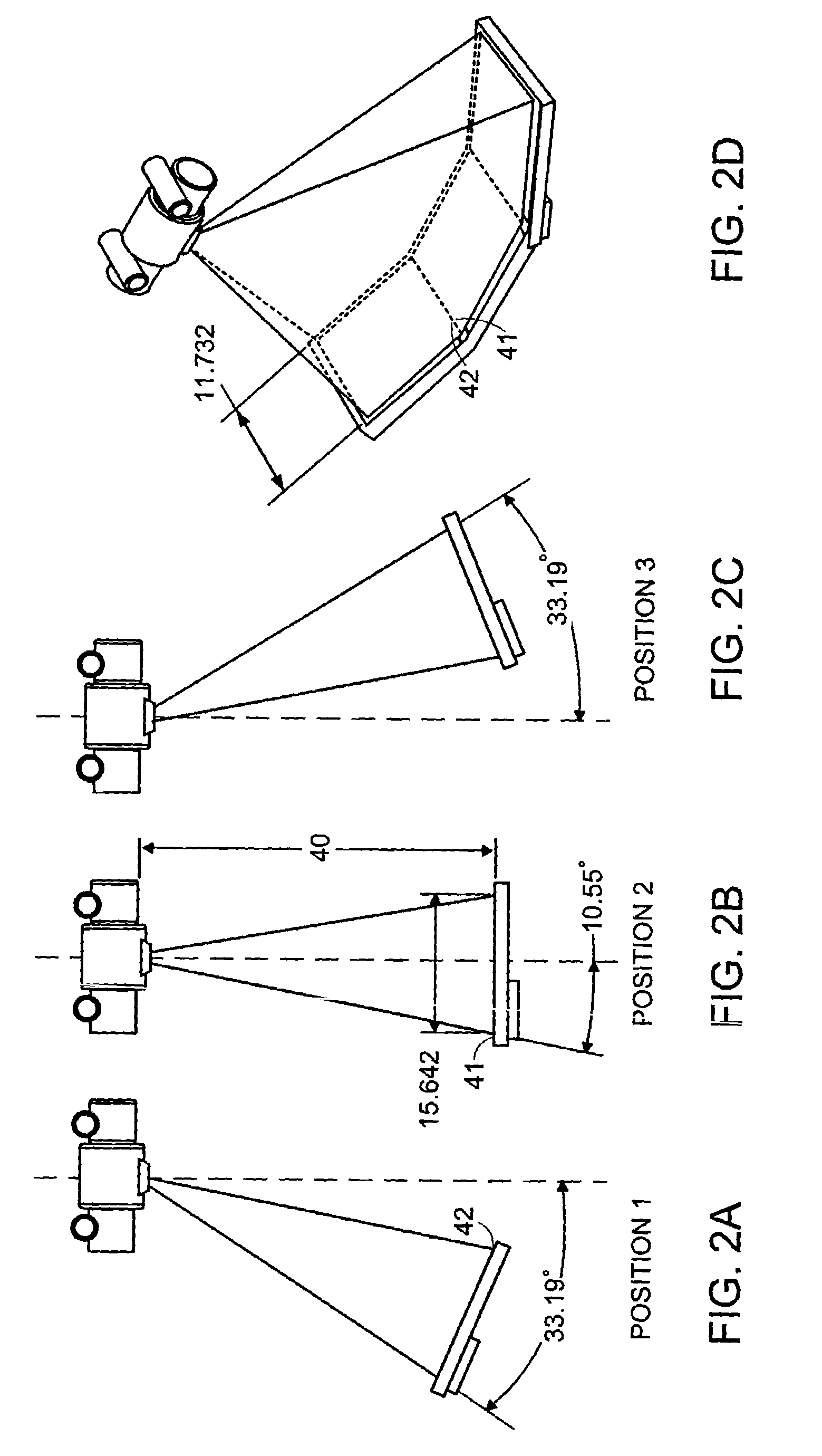
An imaging apparatus and related method comprising a source that projects a beam of radiation in a first trajectory; a detector located a distance from the source and positioned to receive the beam of radiation in the first trajectory; an imaging area between the source and the detector, the radiation beam from the source passing through a portion of the imaging area before it is received at the detector; a detector positioner that translates the detector to a second position in a first direction that is substantially normal to the first trajectory; and a beam positioner that alters the trajectory of the radiation beam to direct the beam onto the detector located at the second position. The radiation source can be an x-ray cone-beam source, and the detector can be a two-dimensional flat-panel detector array. The invention can be used to image objects larger than the field-of-view of the detector by translating the detector array to multiple positions, and obtaining images at each position, resulting in an effectively large field-of-view using only a single detector array having a relatively small size. A beam positioner permits the trajectory of the beam to follow the path of the translating detector, which permits safer and more efficient dose utilization, as generally only the region of the target object that is within the field-of-view of the detector at any given time will be exposed to potentially harmful radiation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
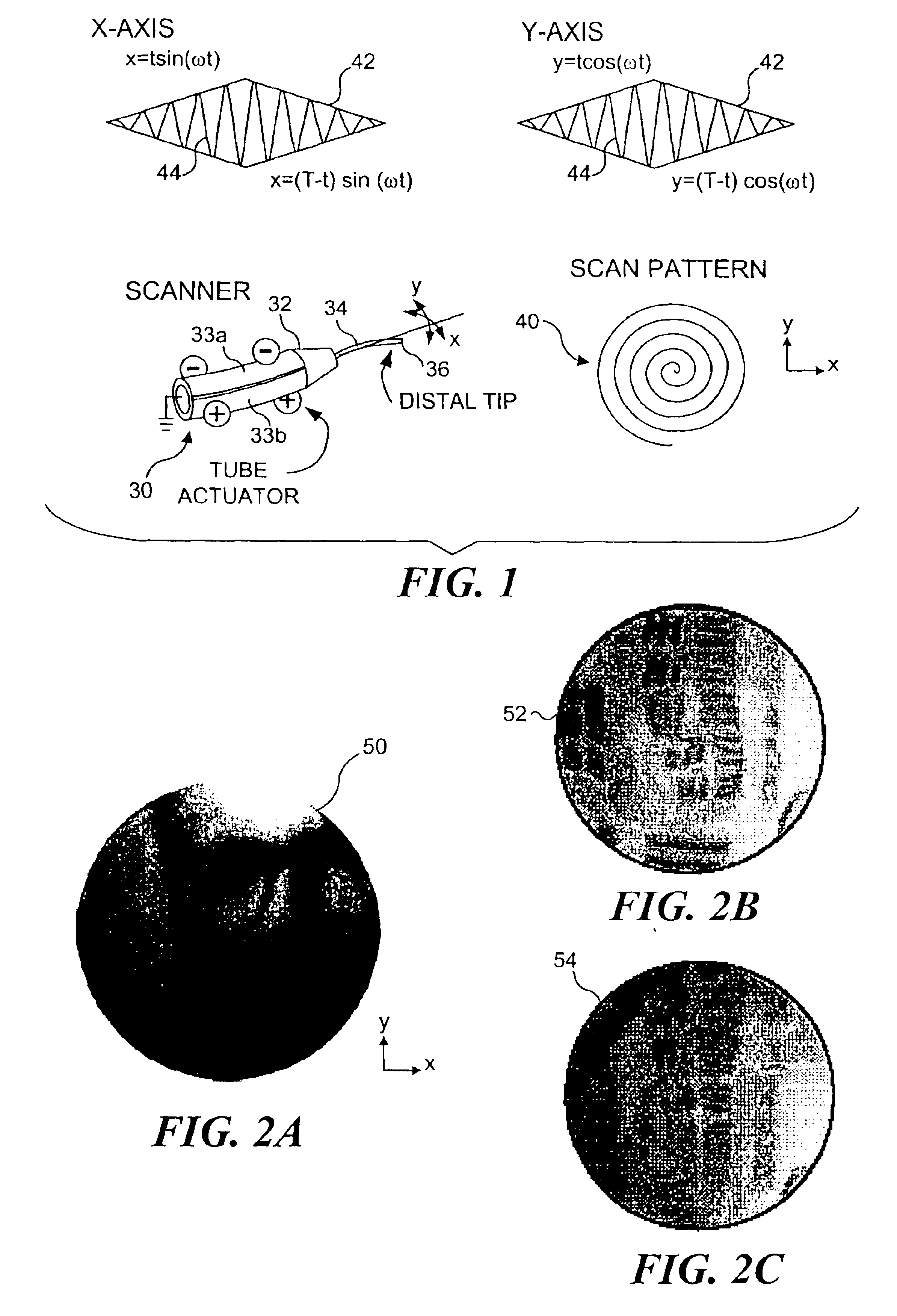
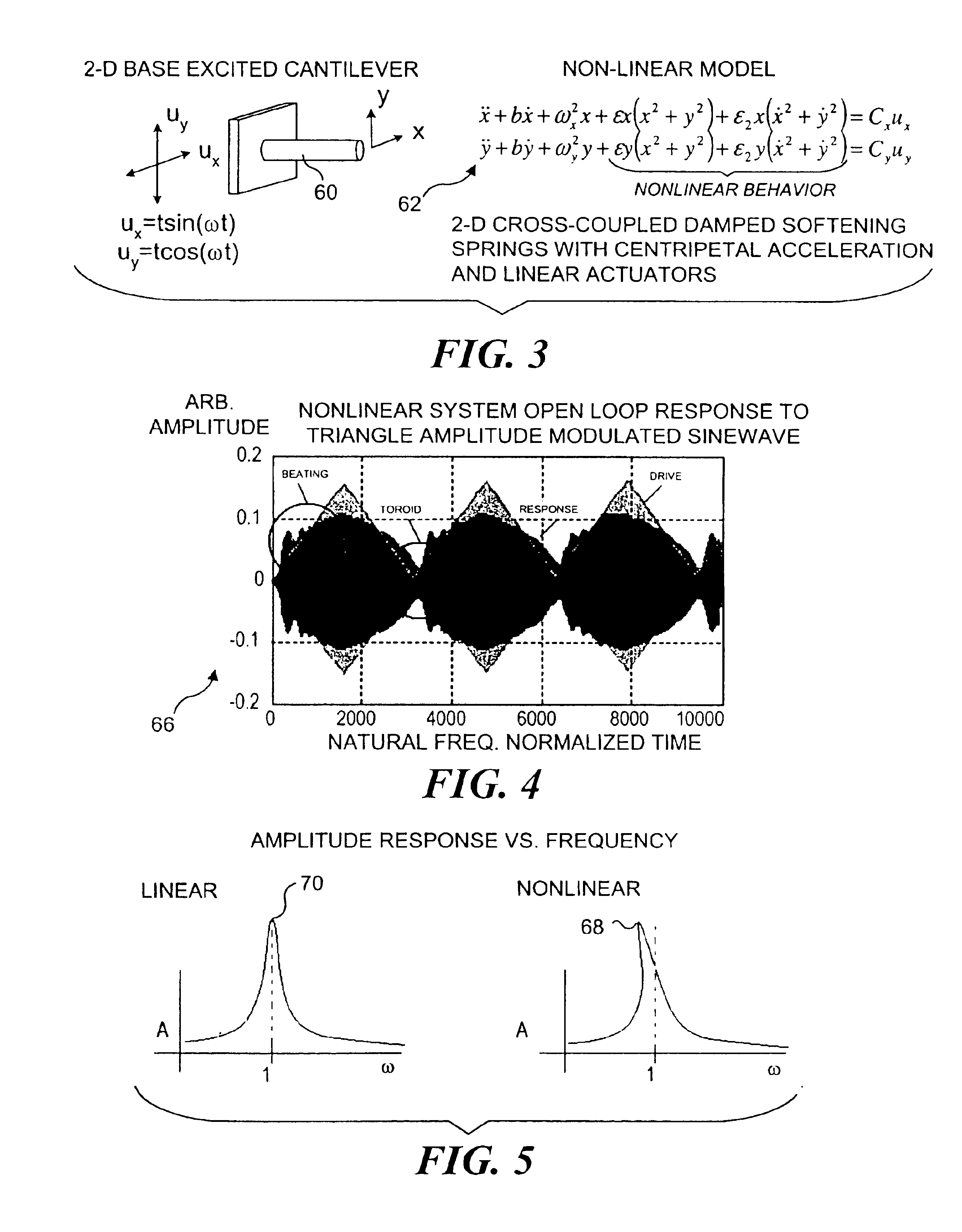
Control of an optical fiber scanner
InactiveUS6845190B1Remove nonlinear behaviorRobust cancellationSurgeryEndoscopesOptical scannersPhotodetector
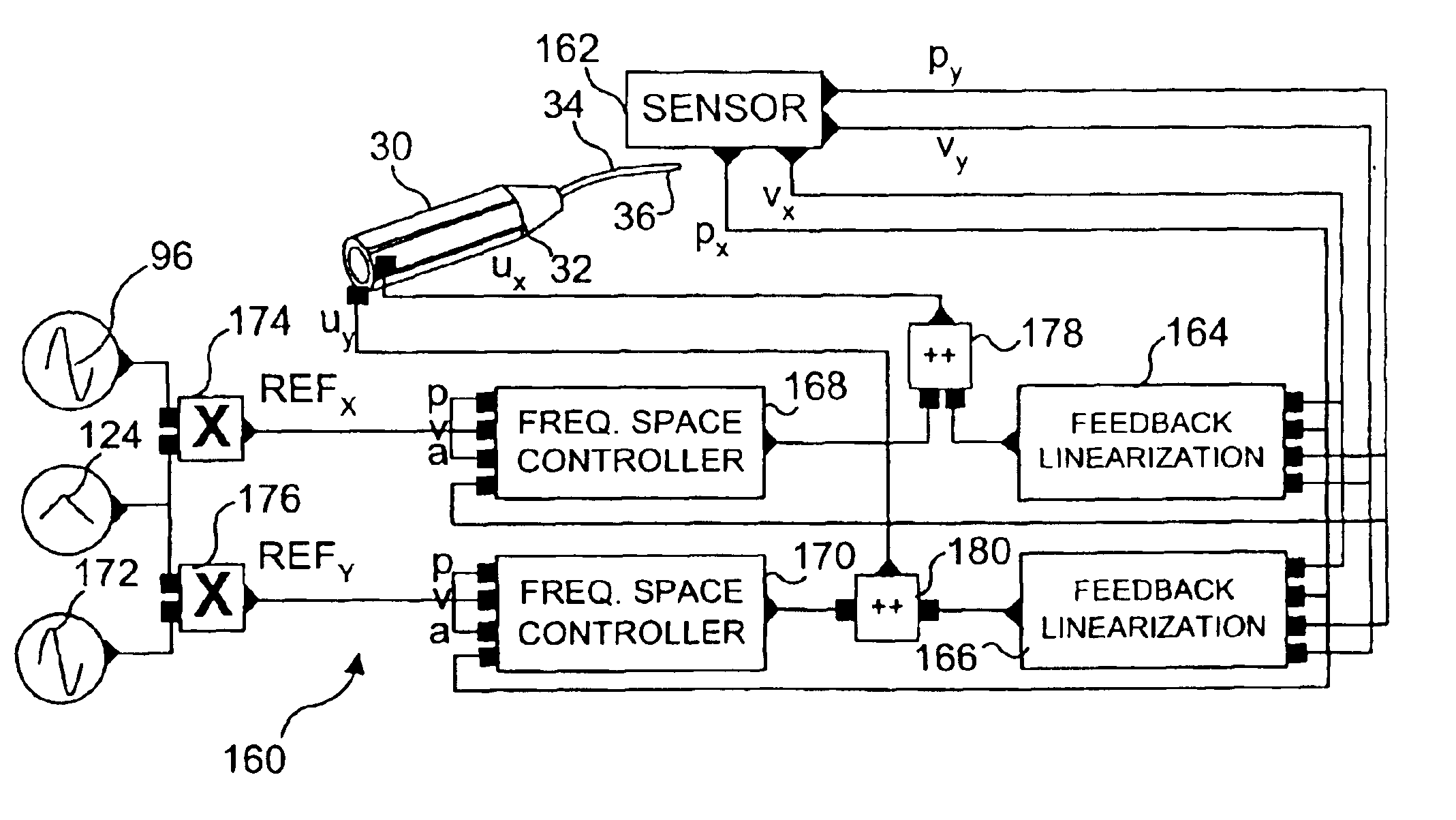
Controls for an optical scanner, such as a single fiber scanning endoscope (SFSE) that includes a resonating optical fiber and a single photodetector to produce large field of view, high-resolution images. A nonlinear control scheme with feedback linearization is employed in one type of control to accurately produce a desired scan. Open loop and closed loops controllers are applied to the nonlinear optical scanner of the SFSE. A closed loop control (no model) uses either phase locked loop and PID controllers, or a dual-phase lock-in amplifier and two PIDs for each axis controlled. Other forms of the control that employ a model use a frequency space tracking control, an error space tracking control, feedback linearizing controls, an adaptive control, and a sliding mode control.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Micro-fabricated optical waveguide for use in scanning fiber displays and scanned fiber image acquisition
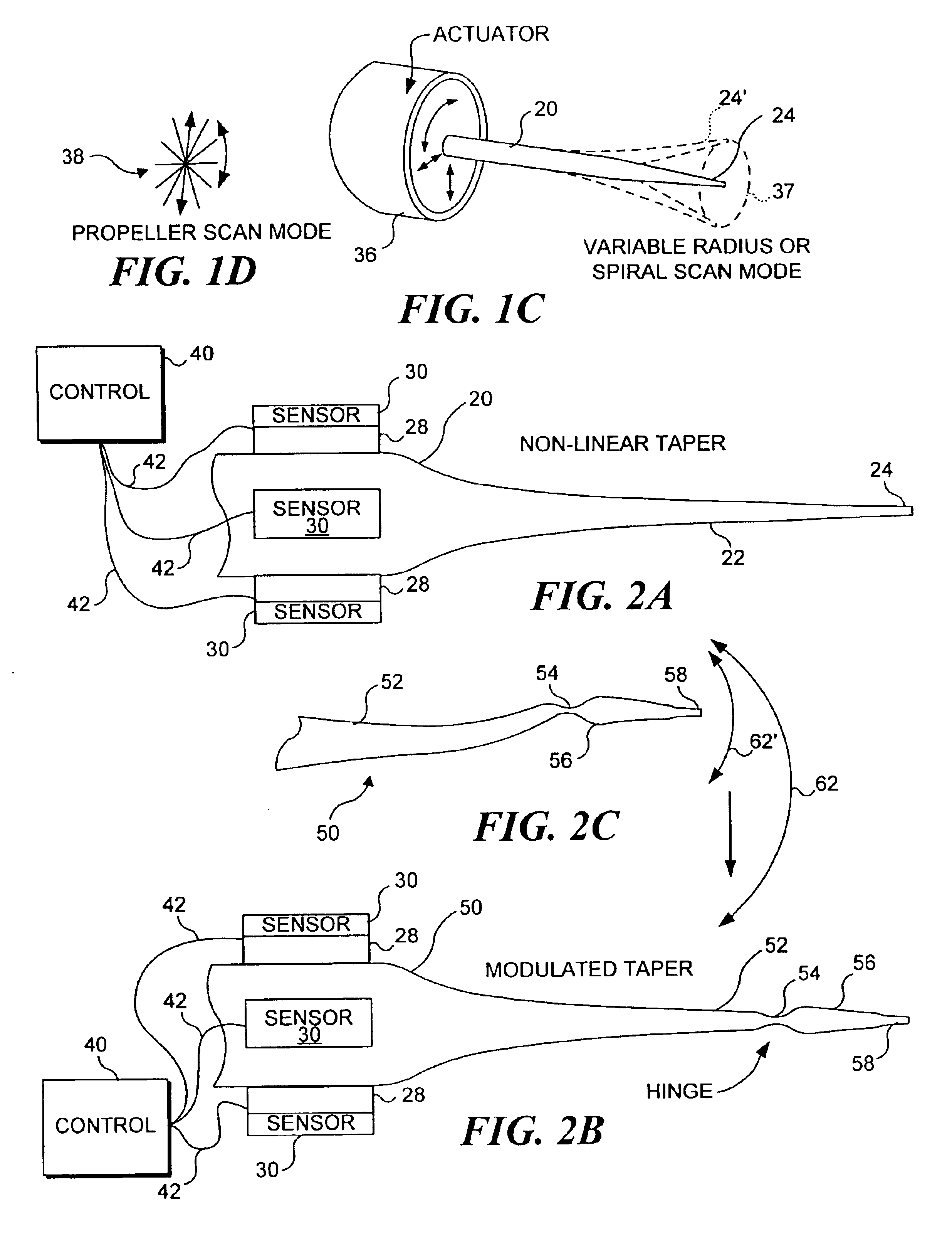
Small, rugged scanners micro-fabricated from commercial optical fibers to form waveguides or other structures. The scanning waveguide has a distal portion on which is formed a non-linear taper with a diameter that decreases toward a distal end. Optionally, a hinge portion having a reduced diameter can be formed in the distal portion, improving the scanning properties of the waveguide. A micro-lens can be integrally formed at the distal tip of the waveguide with either a droplet of an optical adhesive, or by using an energy beam to melt the material of the waveguide to form a droplet. The droplet is shaped with an externally applied force. When mechanically driven in vibratory resonance, the tip of the optical waveguides moves in linear or two-dimensional scan patterns of relatively high amplitude and frequency, and large field of view. The scanner can be used either for image acquisition or image display.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Methods and apparatuses for image guided medical procedures
ActiveUS8303505B2Uncertainty errorLocation uncertaintyMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTime informationImaging data
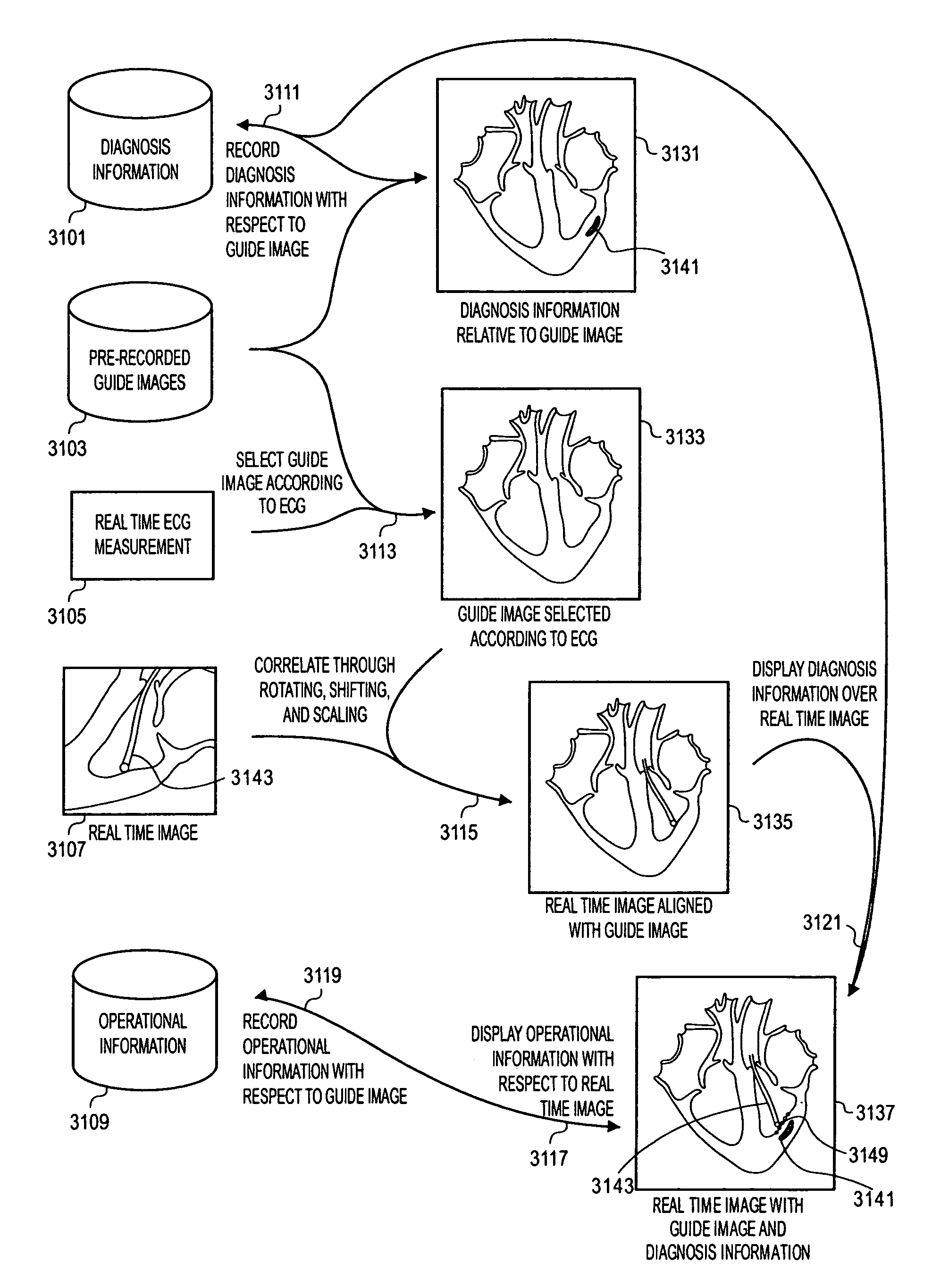
Methods and apparatuses for the image guidance and documentation of medical procedures. One embodiment includes combining small field of view images into a recorded image of with a large field of view and aligning the small field of view real time image with the recorded image through correlation of imaging data. A location and orientation determination system may be used to track the imaging system and provide a starting set of image alignment parameters and / or provide change updates to a set of image alignment parameters, which is then further improved through correlating imaging data. The recorded image may be selected according to real time measurement of a cardiac parameter during an image guided cardiac procedure. Image manipulations planned based on the recorded image can be stored and applied to the real time information. The position of the medical device may be determined and recorded through manipulating a cursor in a 3-D image space shown in two non-parallel views.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Computed tomography with increased field of view
ActiveUS7062006B1Expand field of viewLarge array sizeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingIn planeOffset distance
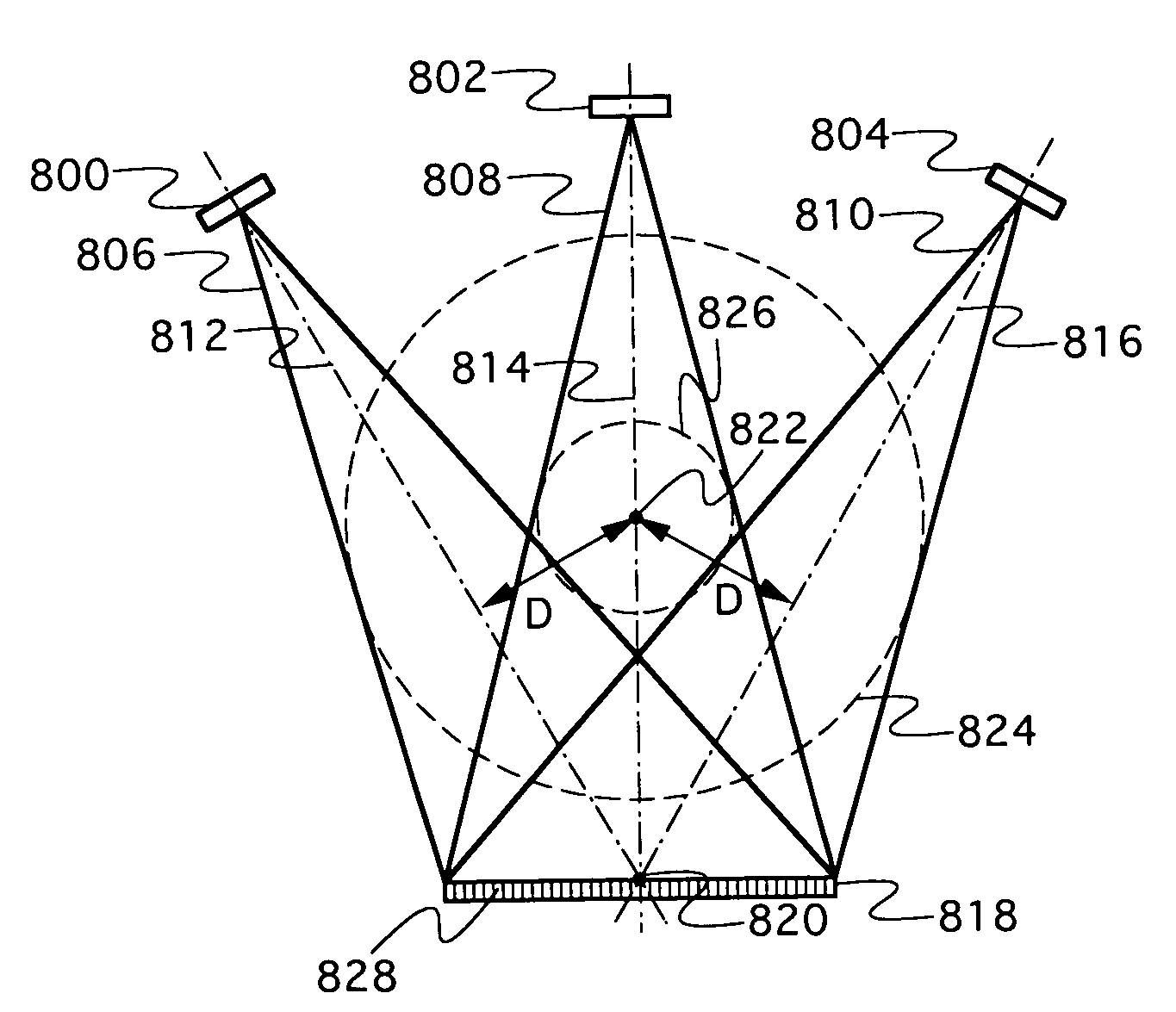
A volumetric computed tomography system with a large field of view has, in a forward geometry implementation, multiple x-ray point sources emitting corresponding fan beams at a single detector array. The central ray of at least one of the fan beams is radially offset from the axis of rotation of the system by an offset distance D. Consequently, the diameter of the in-plane field of view provided by the fan beams may be larger than in a conventional CT scanner. Any number of point sources may be used. Analogous systems may be implemented with an inverse geometry so that a single source array emits multiple fan beams that converge upon corresponding detectors.
Owner:AIRDRIE PARTNERS I LP +1
Endoscopic vision system
The present invention relates to a novel endoscope or an optical large view endoscopic system with improved depth perception. In particular, a multiple viewpoint endoscope system comprising a multiple viewpoint camera setup and / or an intelligent or cognitive image control system and display device particularly adapted for localising internal structures within a cavity or an enclosing structure, such as an animal body, for instance the abdomen of an animal or human, or for localising a real or synthetic image of such internal structures within an overview image or on an overview 3D model.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Adaptable eye movement measurement device
InactiveUS6113237AOptimization rangeAccurate measurementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using lightEye Movement MeasurementsNose
The presently disclosed invention is a device for measuring horizontal and vertical eye movement. The device is adaptable to utilize multiple measurement technologies (e.g., direct infrared, electro-oculography, ultrasound, or video), and is capable of measuring each eye individually or both eyes jointly. The present invention overcomes the shortcomings of the prior art by requiring minimal adjustment for accurate measurement, only minimally obstructing the user's visual range (i.e., slightly more than the user's own nose), being made of low cost and readily available material, and by being comprised of a comfortable and efficient design of an adjustable nose and forehead piece with an adjustable head strap. An additional advancement over the prior art is that the presently disclosed device does not require an aperture or frame, as did the prior art, or any additional optics such as, lenses, mirrors, or prisms. The device rests on the user's nose with the sensors located near the nasal area of the eye(s) utilizing a nose bridge component to house the measuring technology. The forehead piece and head strap provide for ease of alignment, added stability, and a wide range of test applications. The greater field of vision provided by this device allows for a wide range of test applications.
Owner:BERTEC +1
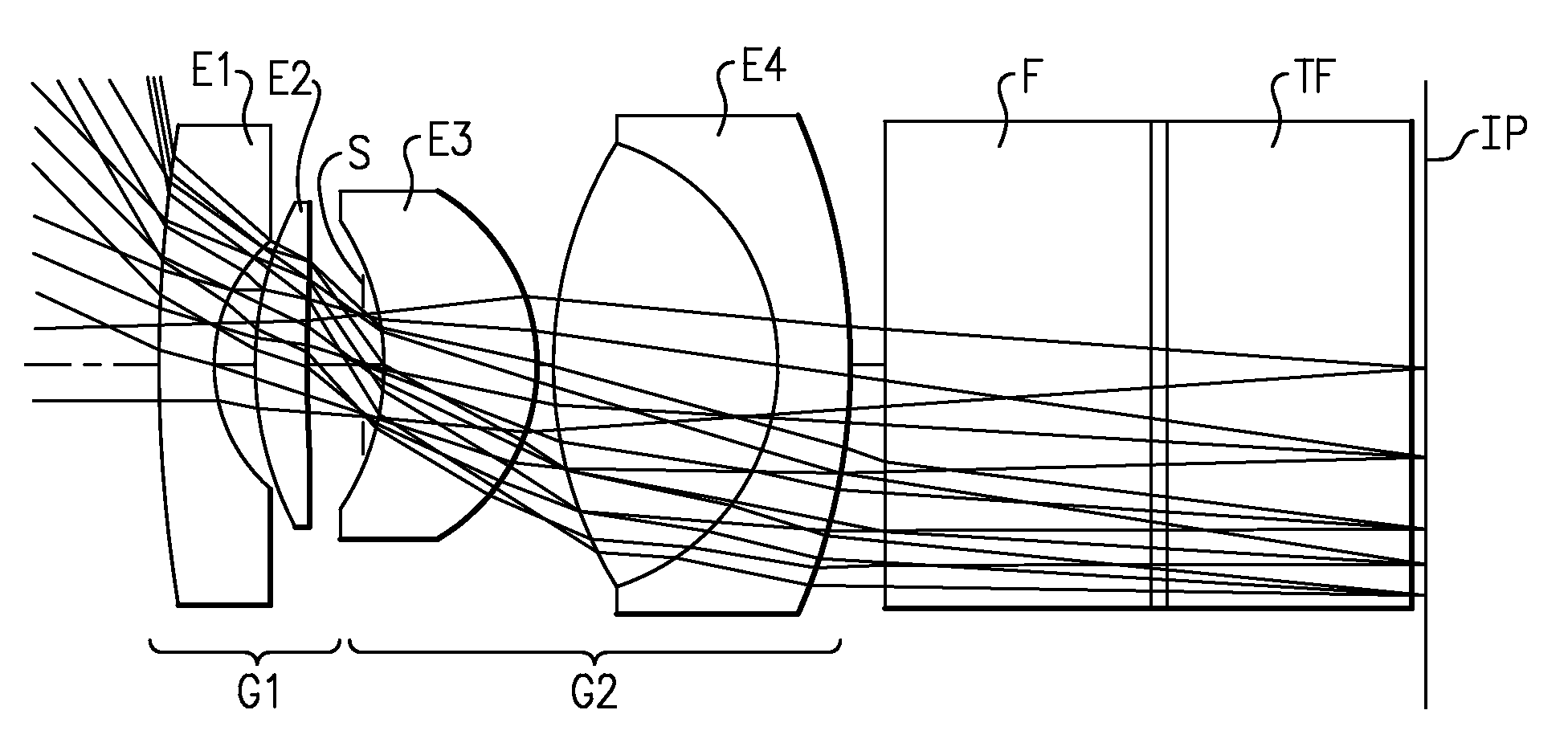
Folded, telecentric projection lenses for use with pixelized panels
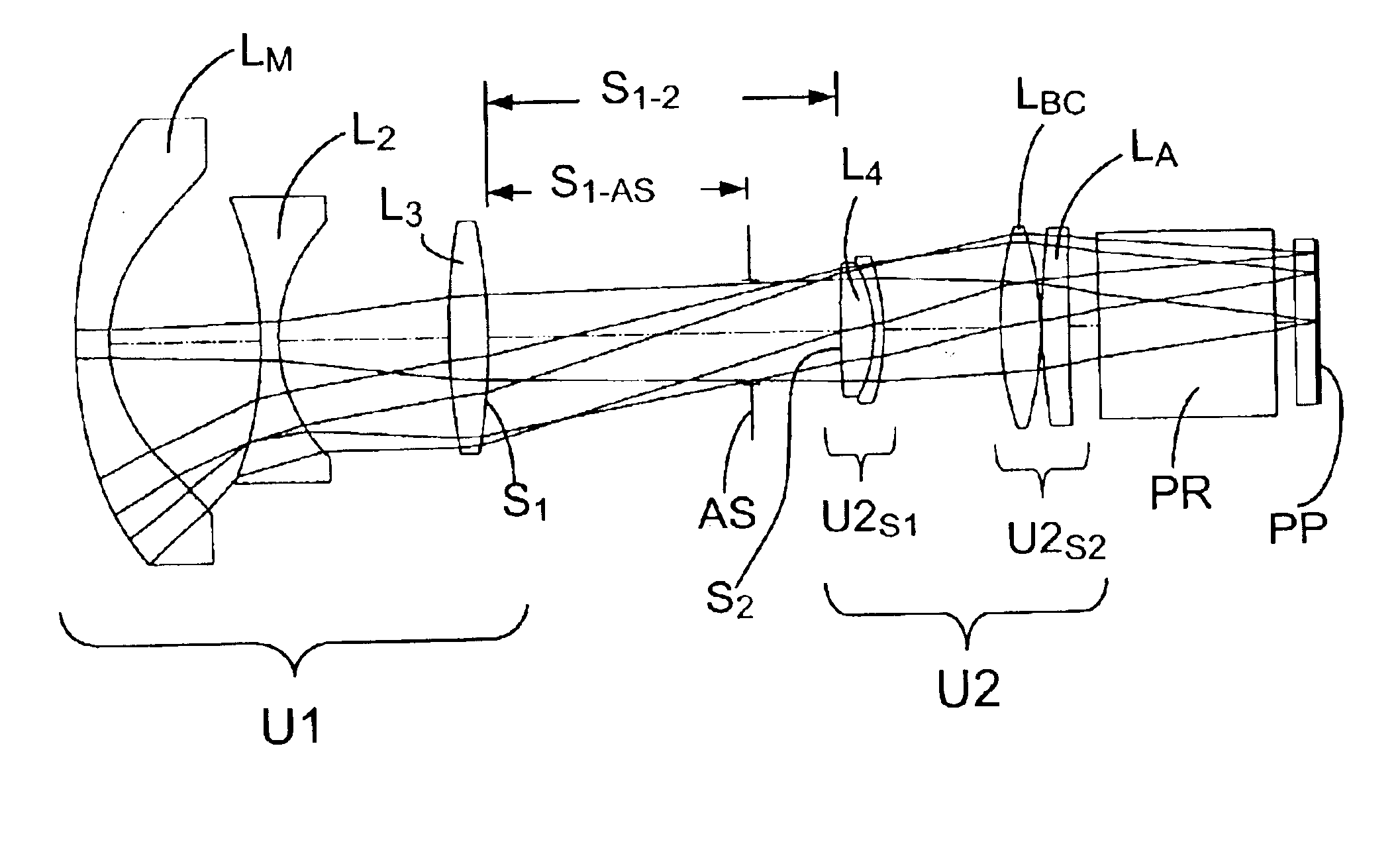
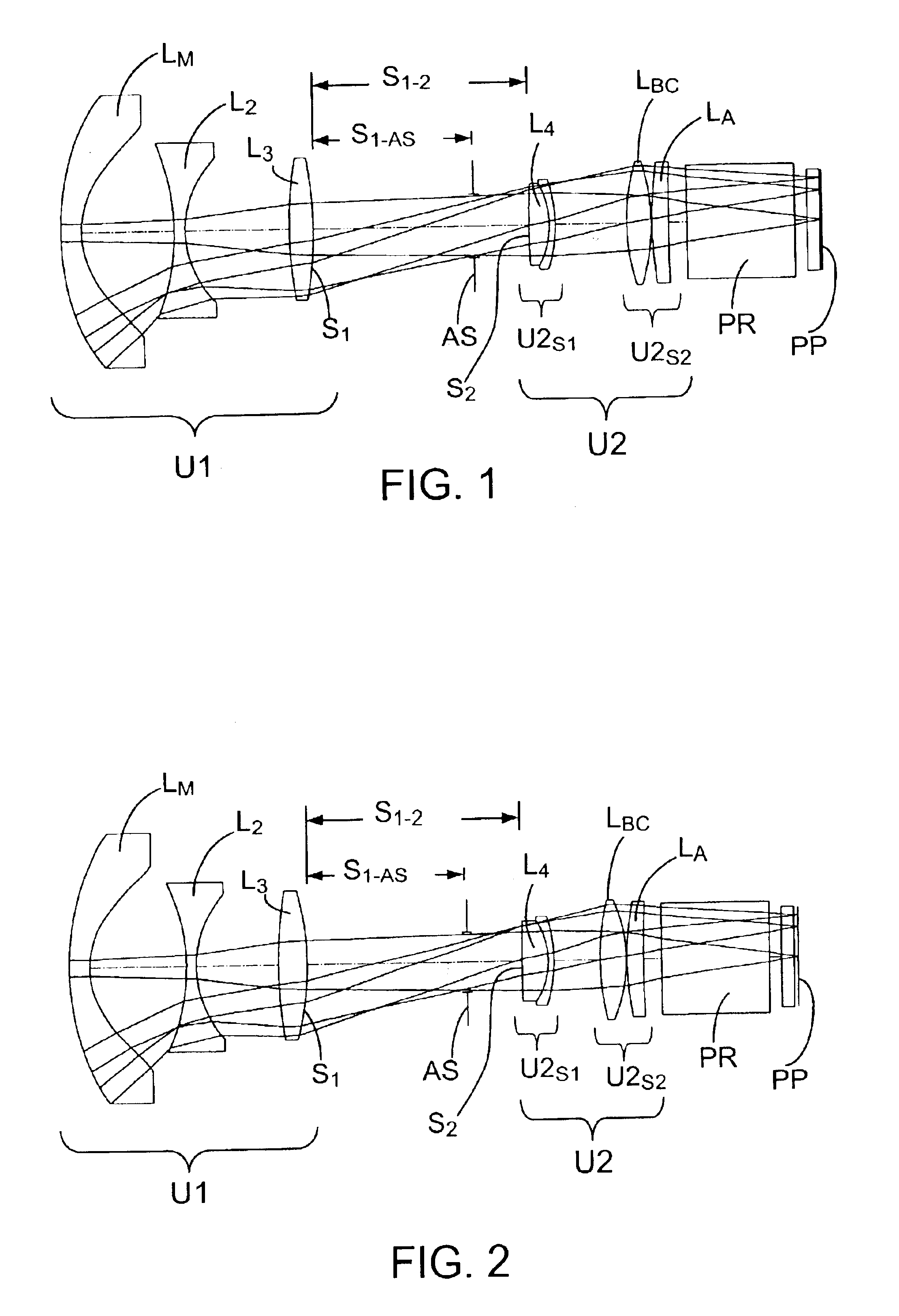
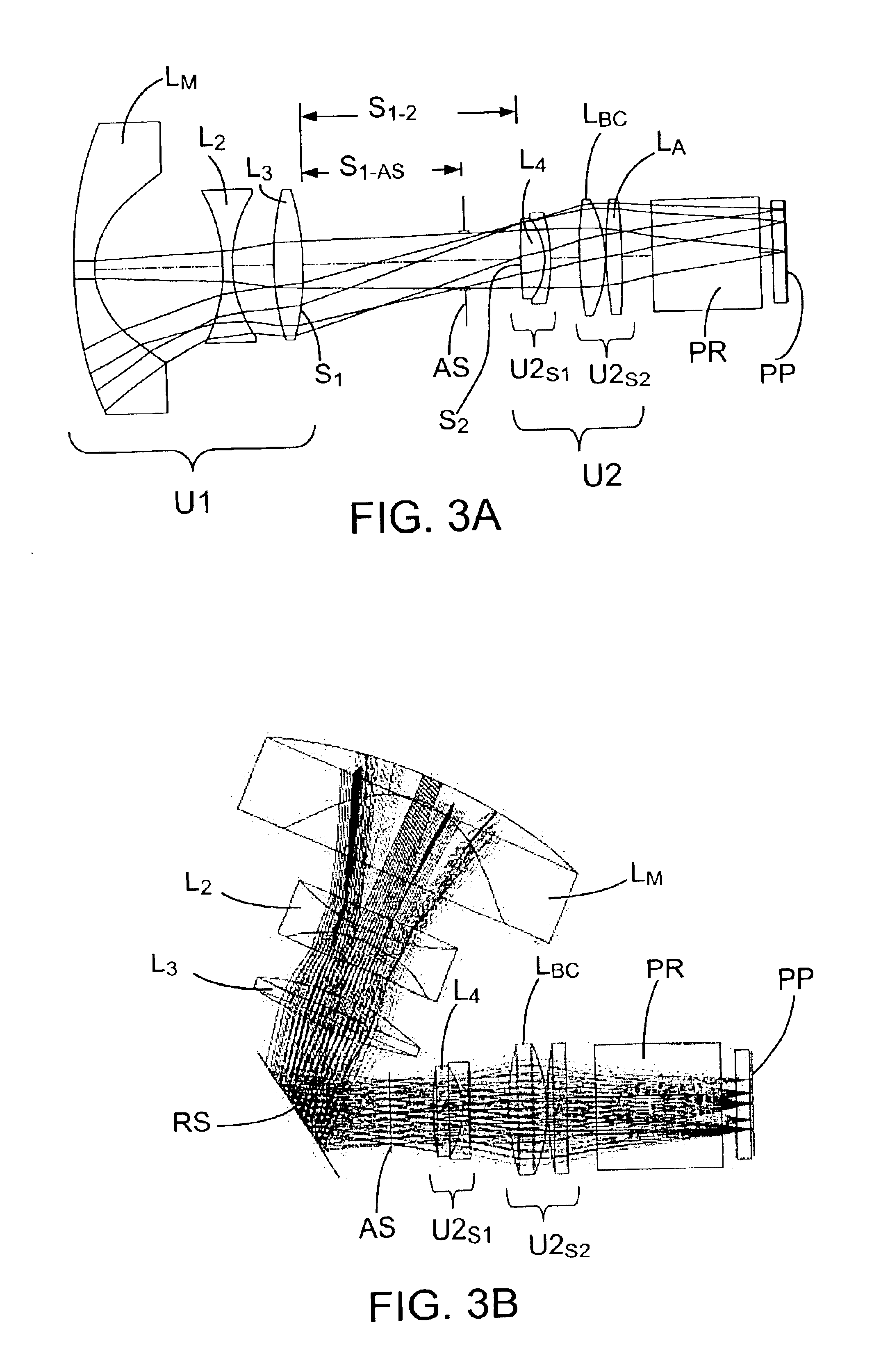
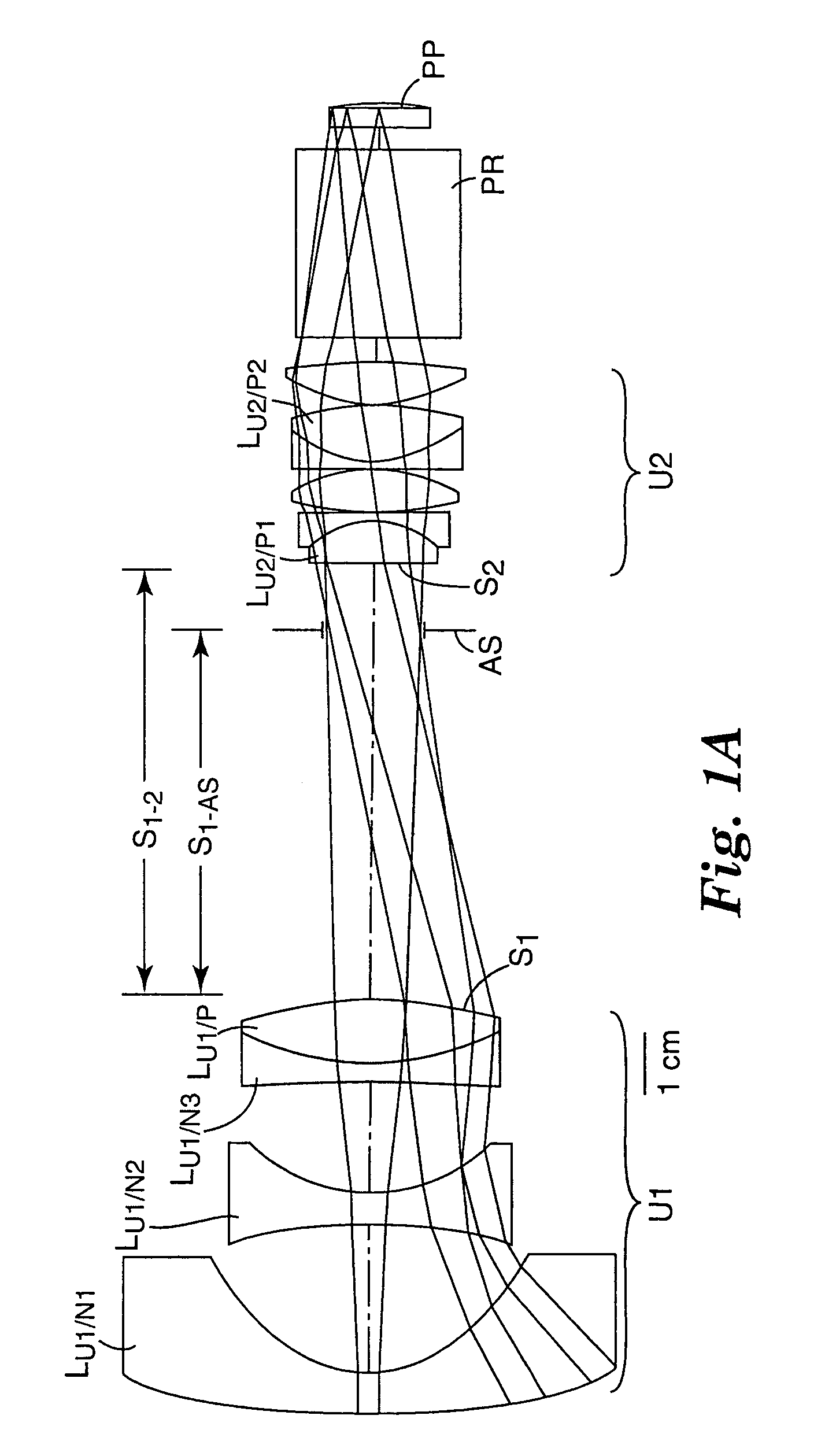
Projection lenses for use with pixelized panels (PP) are provided. The projection lenses have a negative first unit (U1) separated from a positive second unit (U2) by a reflective surface (RS) which folds the lens' optical axis. The lenses are telecentric on the short conjugate side, have a large field of view in the direction of the long conjugate, and have low aberration levels, including, in particular, low levels of lateral color.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
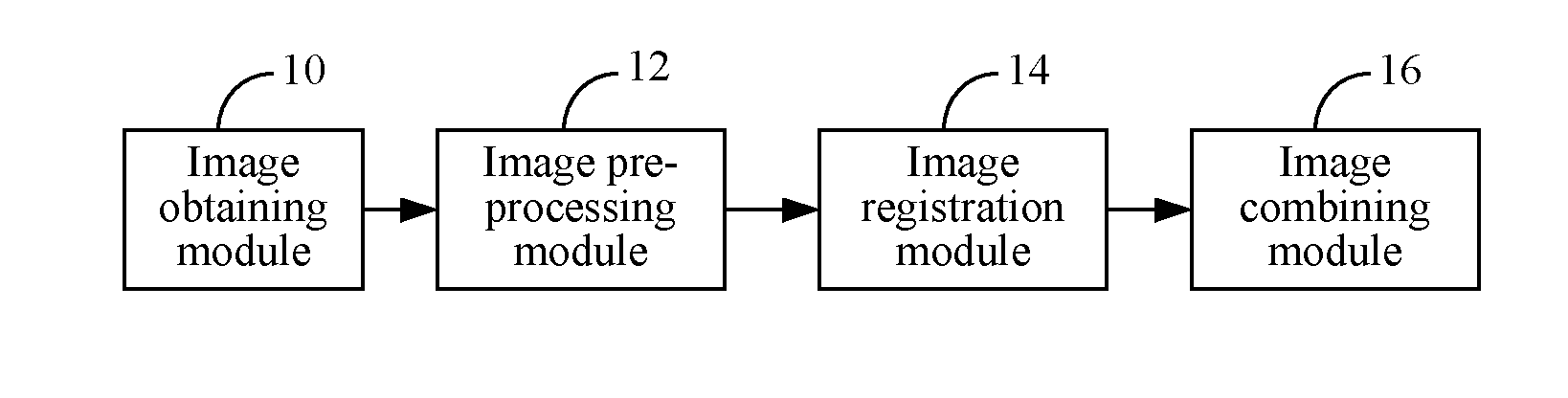
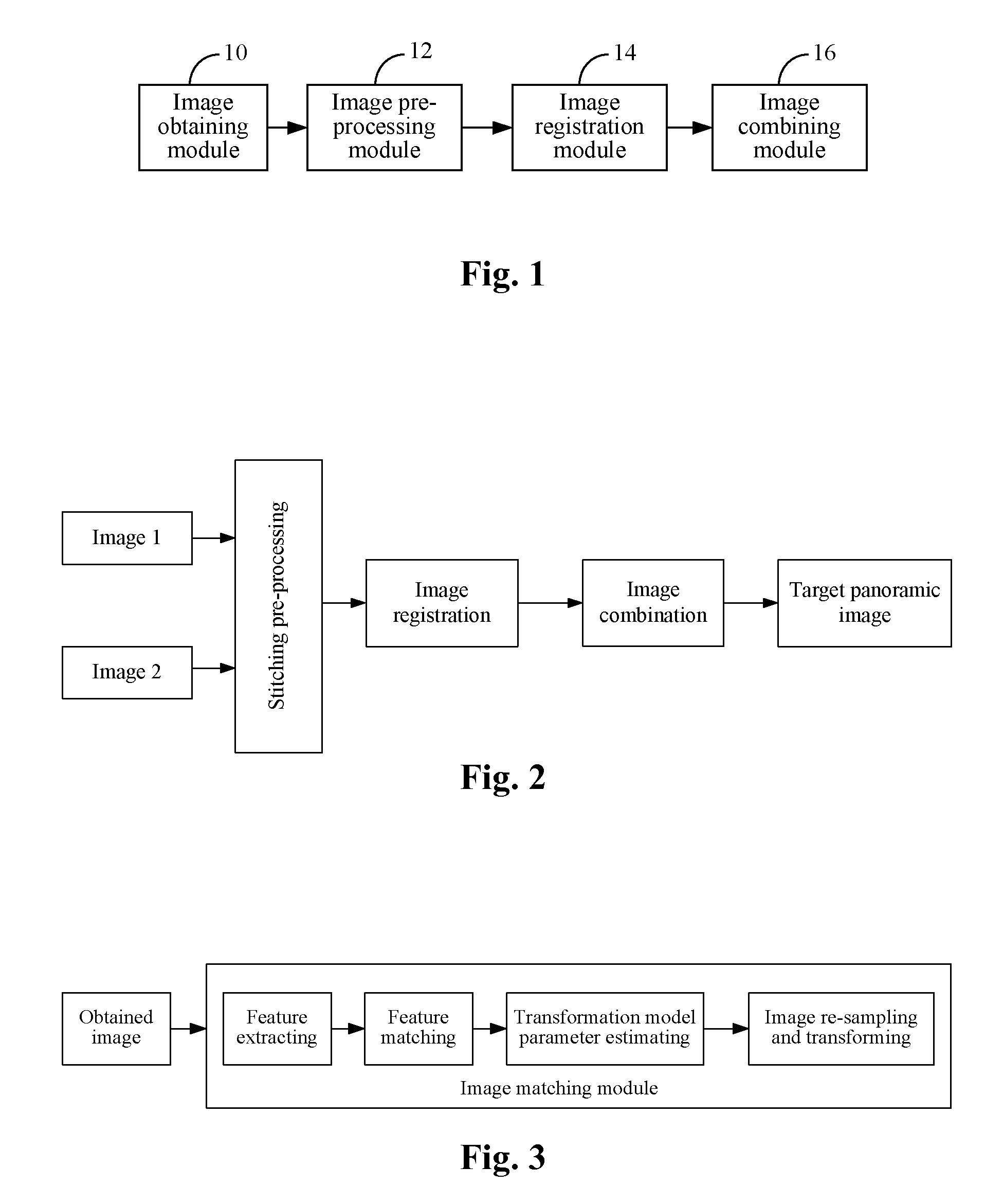
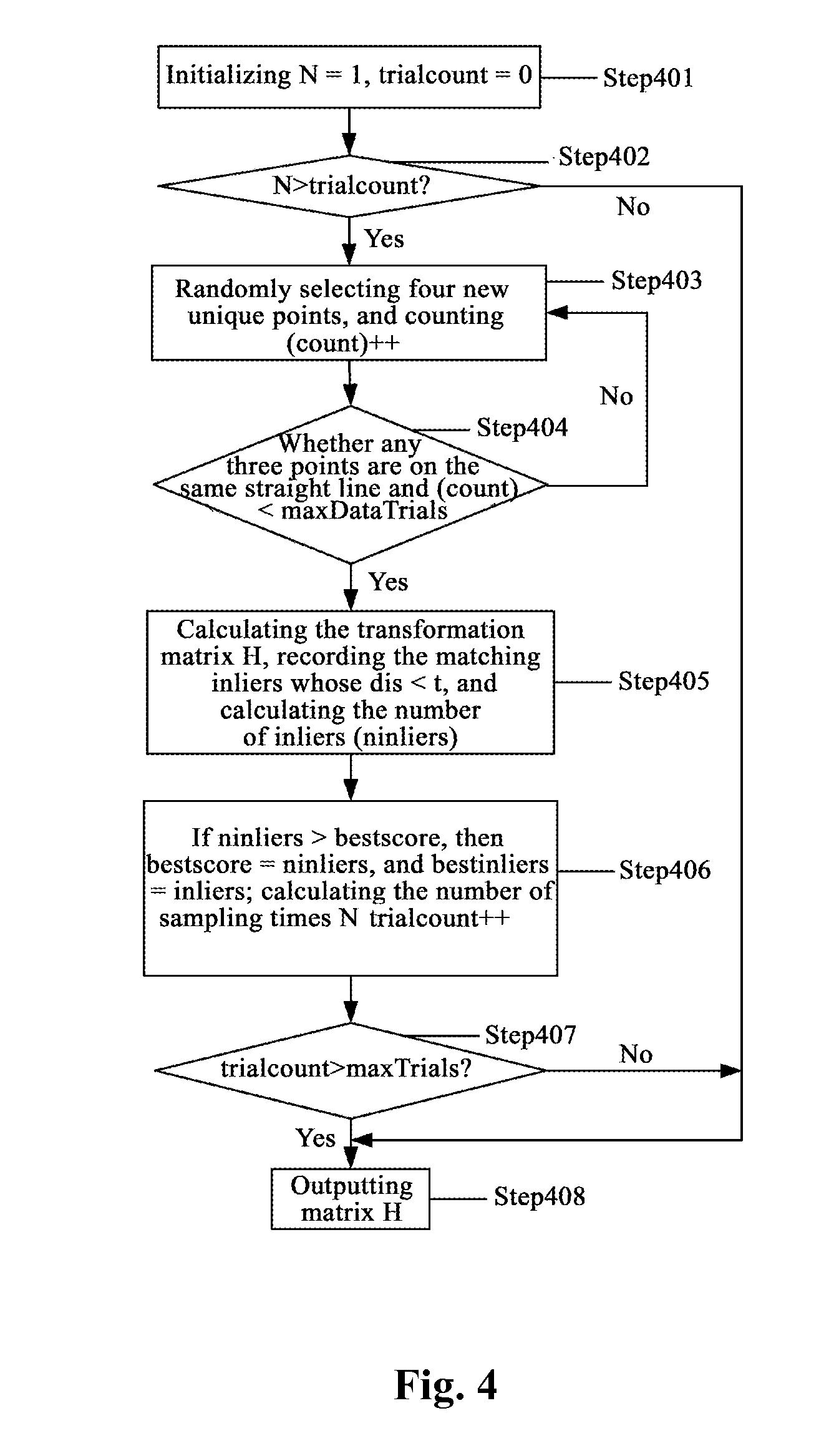
Method and Apparatus for Combining Panoramic Image
ActiveUS20130208997A1High resolutionSmall sizeImage analysisGeometric image transformationFold changePanorama
The disclosure discloses a method and an apparatus for combining panoramic image. The method includes: obtaining multiple original images of the same scene, performing folding change and coordinates transformation to the multiple original images, and determining an overlapping area of the multiple original images; establishing a mathematical model of the multiple original images, aligning the overlapping area of the multiple original images, and transforming the multiple original images to a coordinate system of a reference image; obtaining the space transformation relationship among / between the multiple original images according to the coordinate system of the reference image, selecting an appropriate image combining strategy, and completing the combining of the images. The solution can realize obtaining scene picture with large field of view without reducing image resolution.
Owner:ZTE CORP
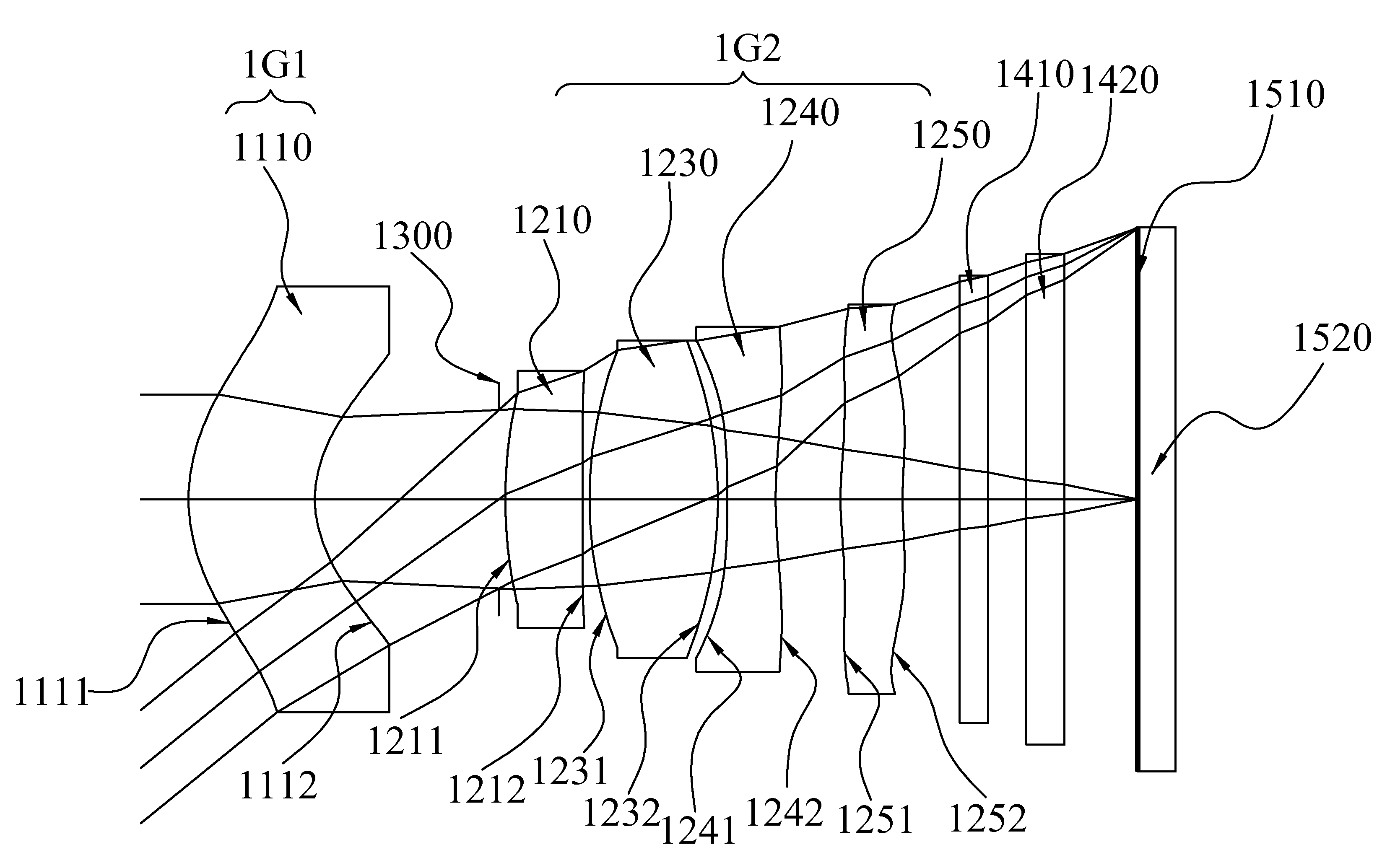
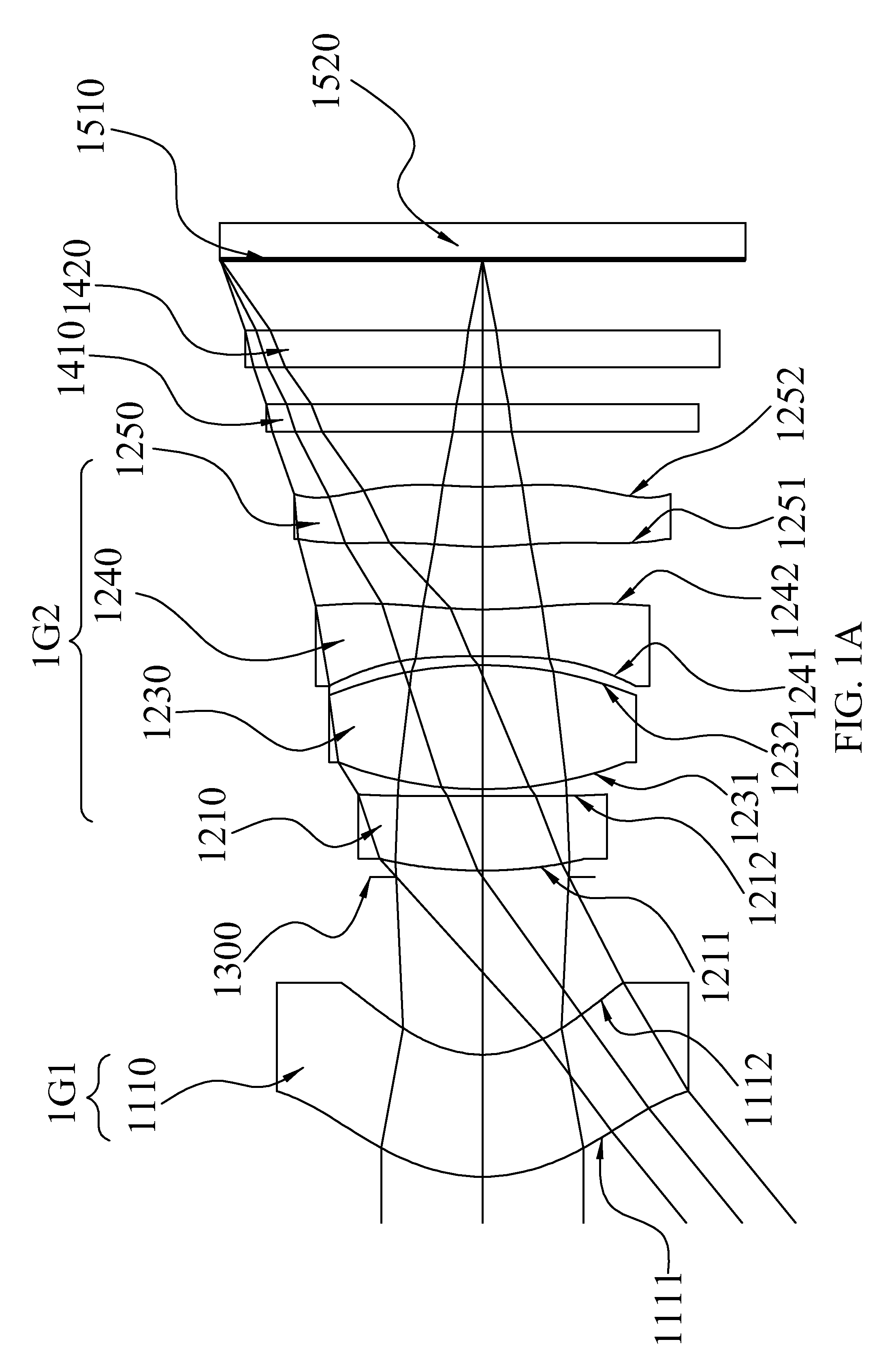
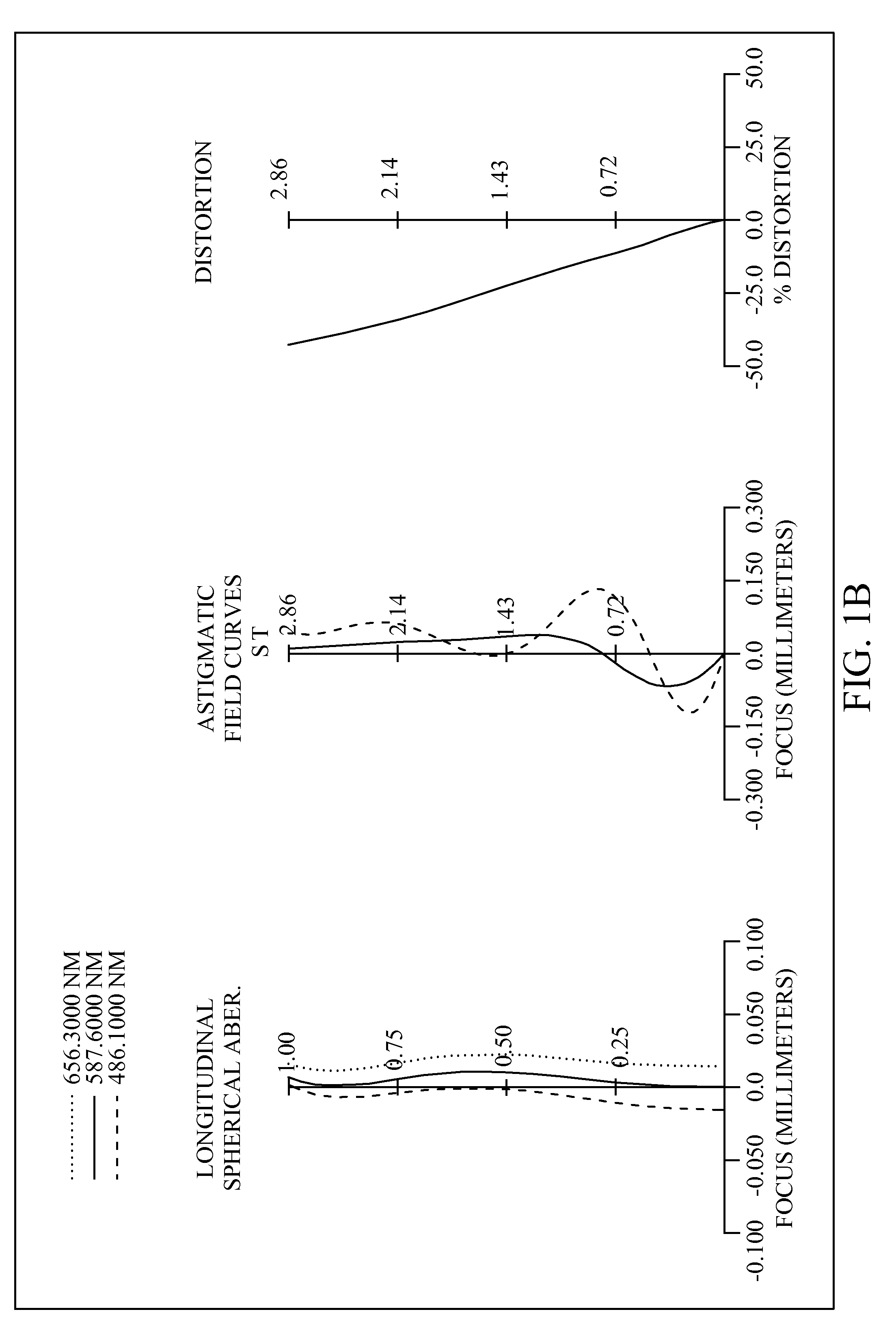
Image taking optical system
An image taking optical system, sequentially arranged from an object side to an image side along an optical axis comprising: a front lens group, a stop and a rear lens group. The front lens group comprises at least a meniscus front-group first lens element with a convex object-side surface. The rear lens group comprises at least three lens elements. Through the means of field adjustments that result in desirable distorted images, the image taking optical system may shorten the total length while enhancing the ability to create a larger field of view for panorama usages in compact cameras and mobile phones.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
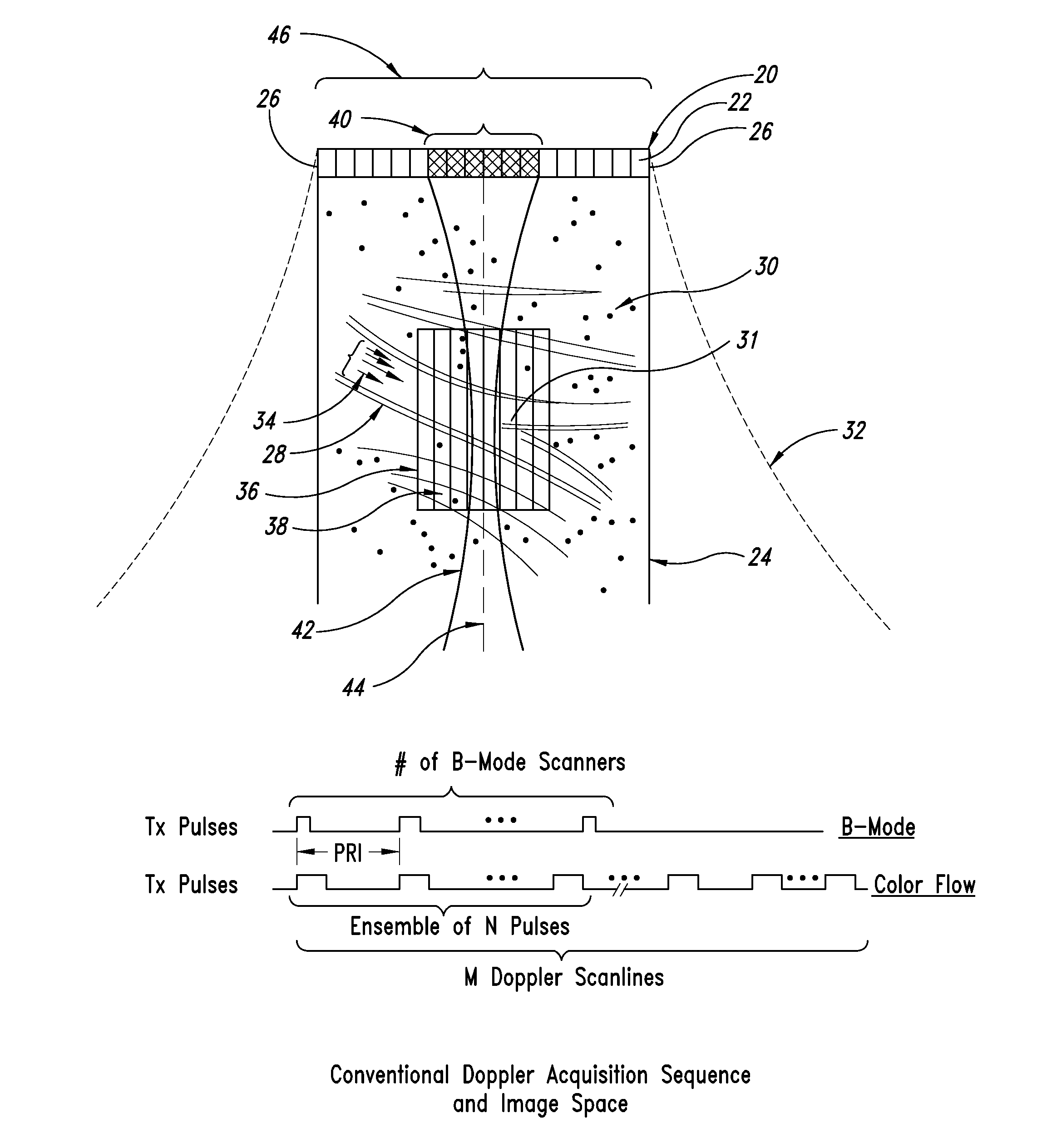
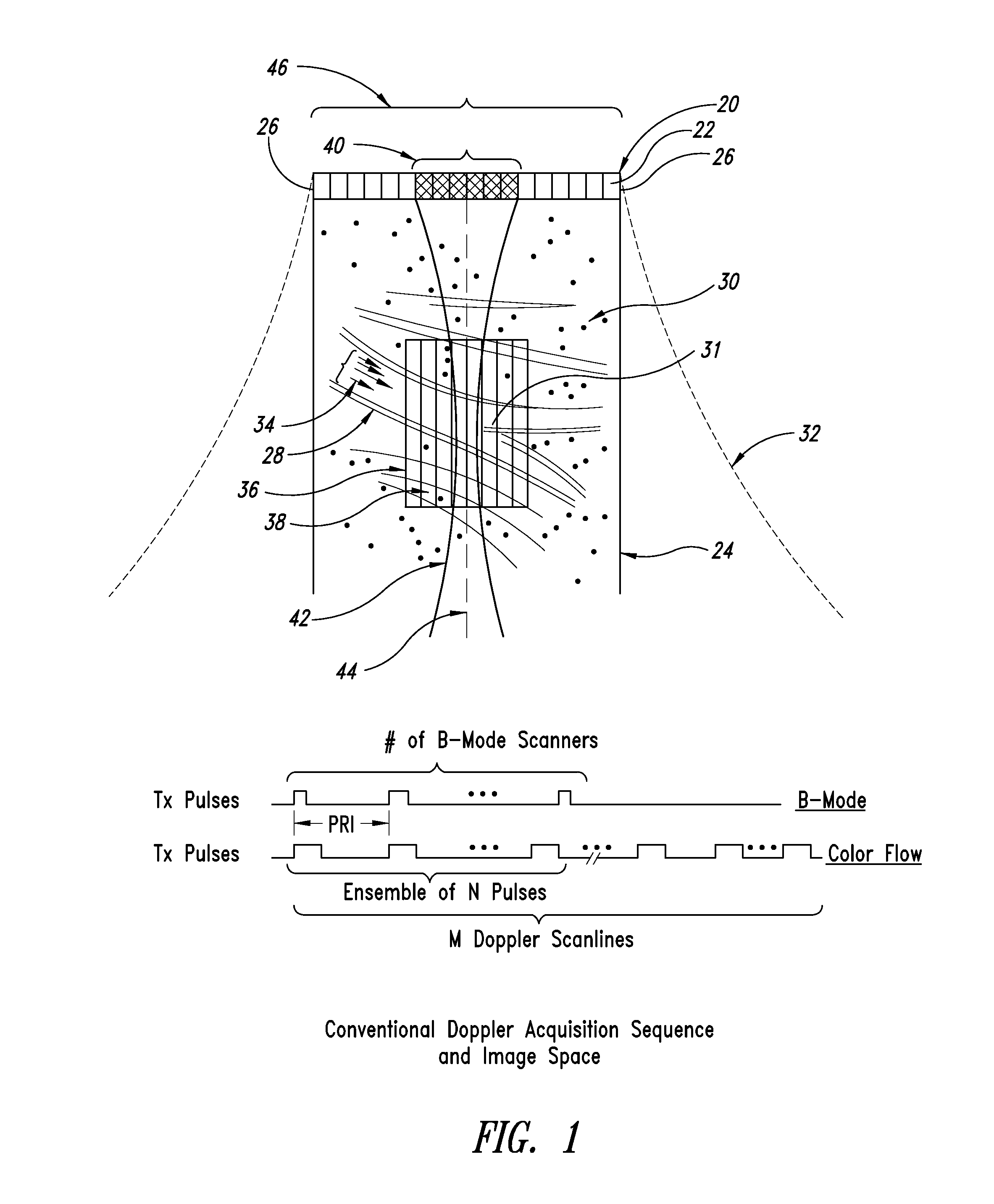
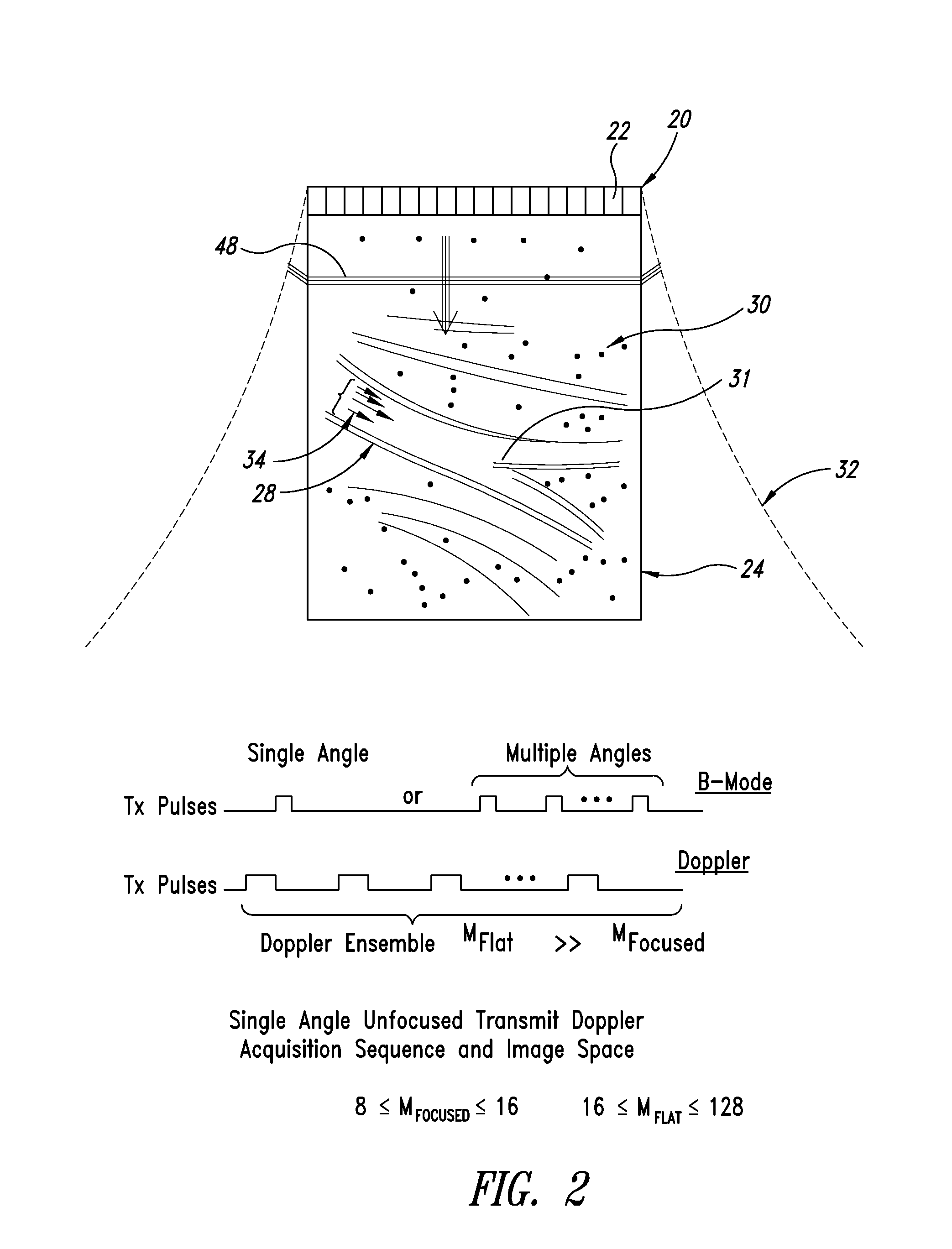
High frame rate quantitative doppler flow imaging using unfocused transmit beams
ActiveUS20090326379A1Enhanced acoustic informationImprovement of contrast resolutionBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingHigh frame rate
An ultrasound imaging system with pixel oriented processing is provided in which a method of producing a Doppler velocity image is accomplished by emitting unfocused acoustic signals into a medium over substantially an entire field; receiving scattered and reflected ultrasonic signals on a transducer array in response to the emission; processing the received ultrasonic signals to extract information to construct a Doppler velocity signal corresponding to at least one point in the medium; and generating on a display device the Doppler velocity image from the processed Doppler velocity signal. Acquisition sequences and signal processing algorithms are described that provide improved quantification of fluid flow parameters, including improved discrimination between regions of blood flow and tissue. Very high frame rate Spectral Doppler and Vector Doppler acquisition modes for real-time and post-acquisition visualization over a large field of view are described.
Owner:VERASONICS
Multi-path, multi-magnification, non-confocal fluorescence emission endoscopy apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20100261958A1Efficient collectionGuaranteed normal transmissionSurgeryEndoscopesFluorescenceImage resolution
Embodiments of the invention include an optical system and an optical system module, coupled to a distal end of a fluorescence emission endoscope apparatus, an optical waveguide-based fluorescence emission endoscopy system, and a method for remotely-controlled, multi-magnification imaging of a target or fluorescence emission collection from a target with a fluorescence emission endoscope apparatus. An exemplary system includes an objective lens disposed in a distal end of an endoscope apparatus. The lens is adapted to transmit both a visible target illumination and a fluorescence-emission-inducing target illumination as well as fluorescence-emission and visible light from the target. The system can thus simultaneously provide low magnification, large field of view imaging and high magnification, high-resolution multiphoton imaging with a single lens system.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
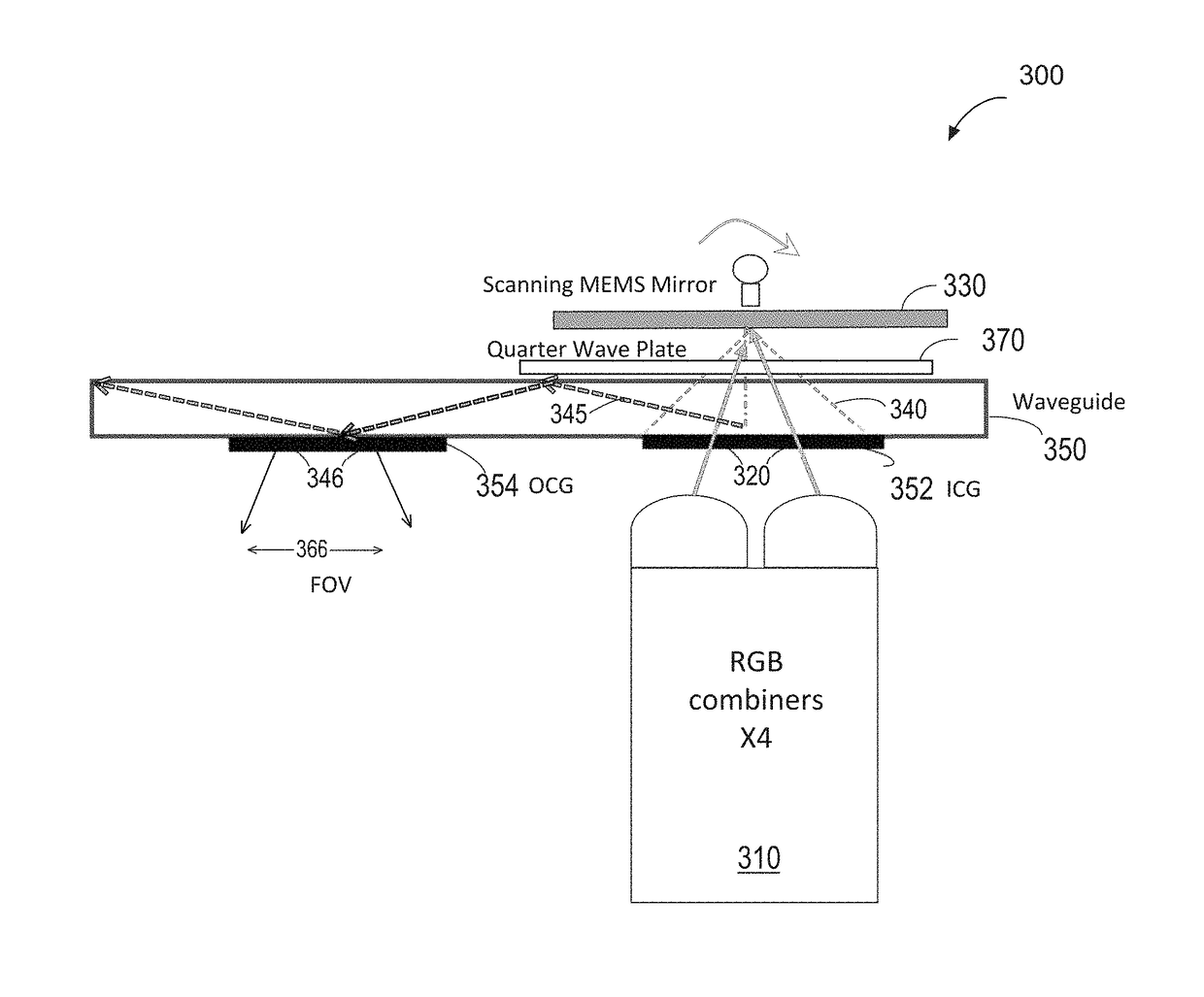
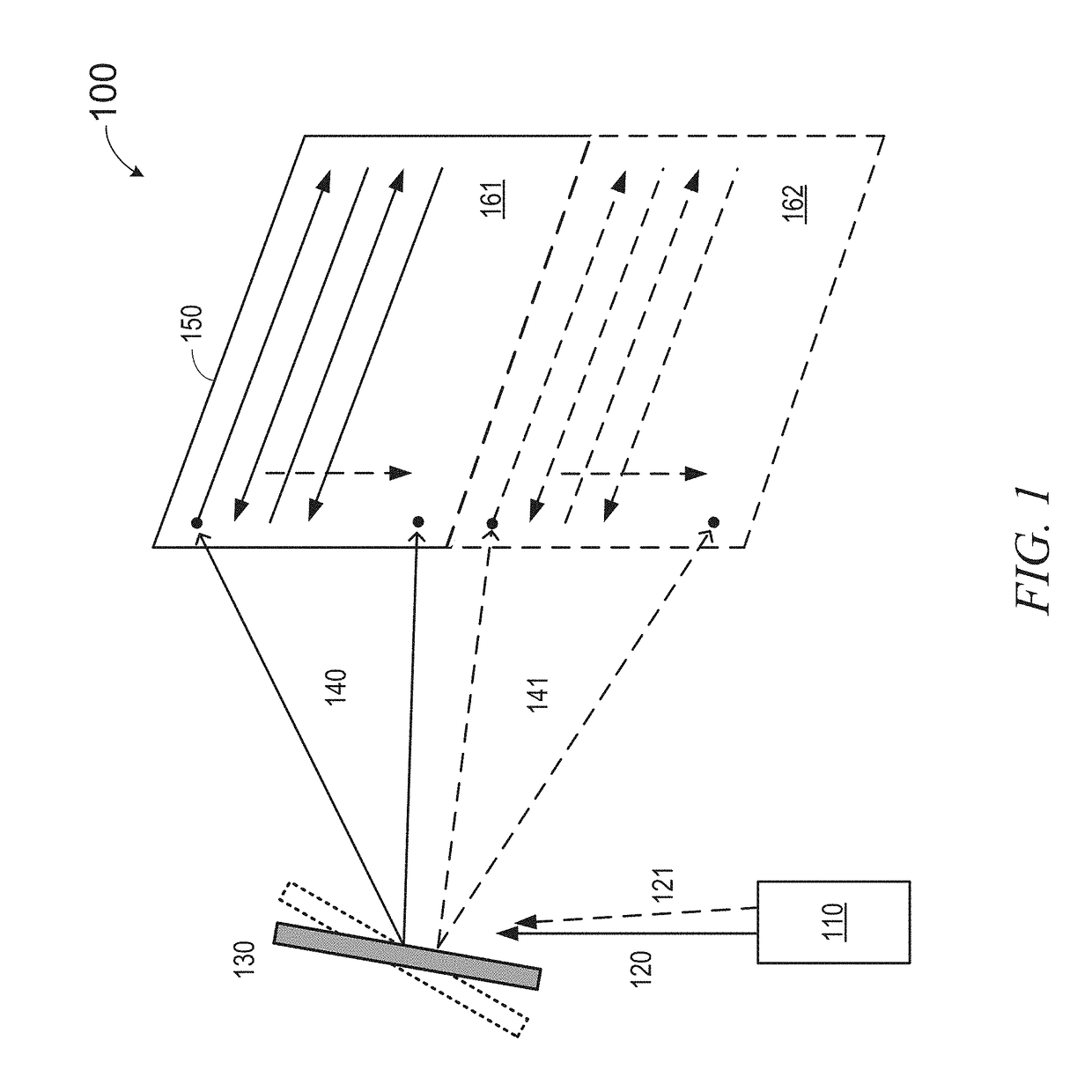
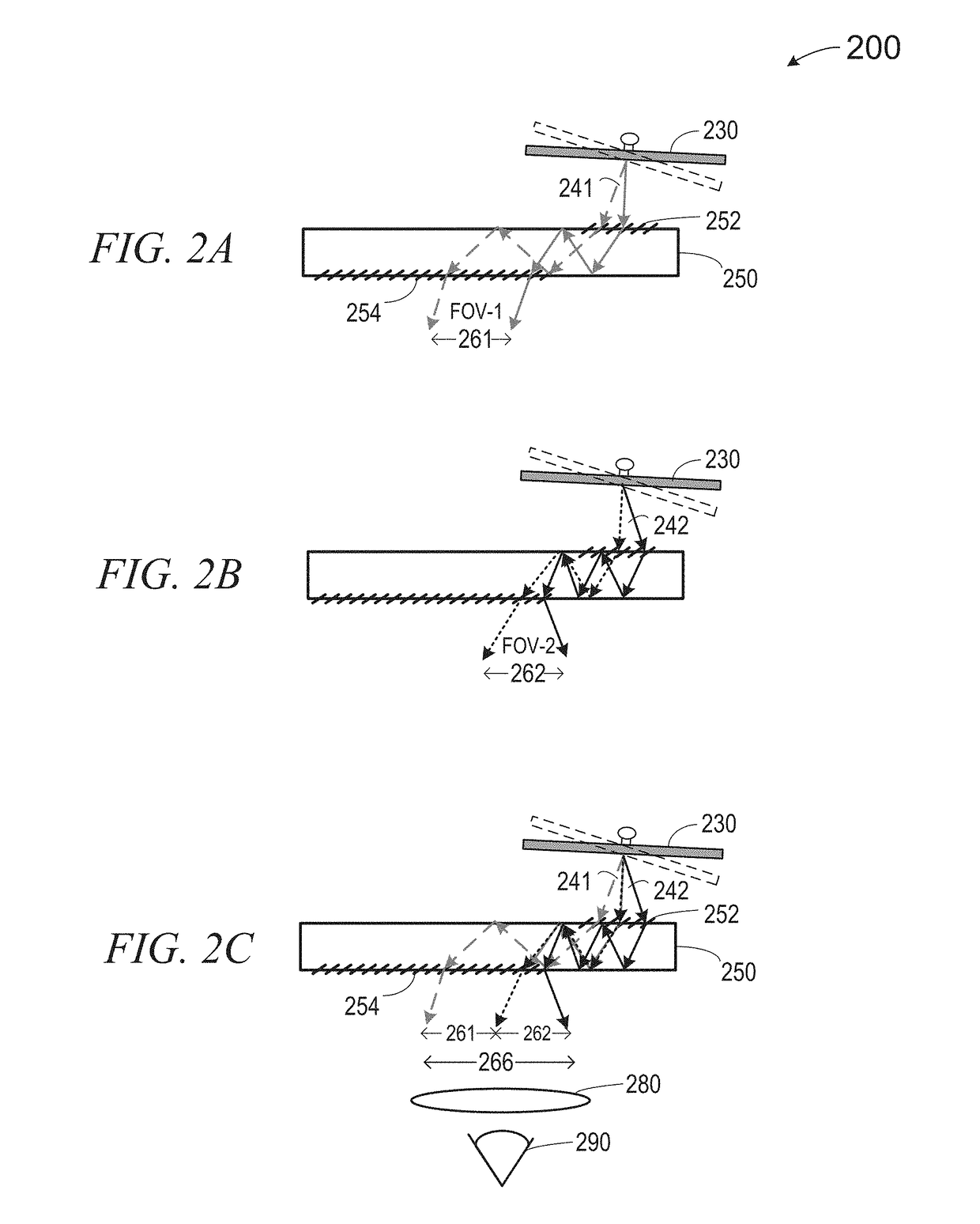
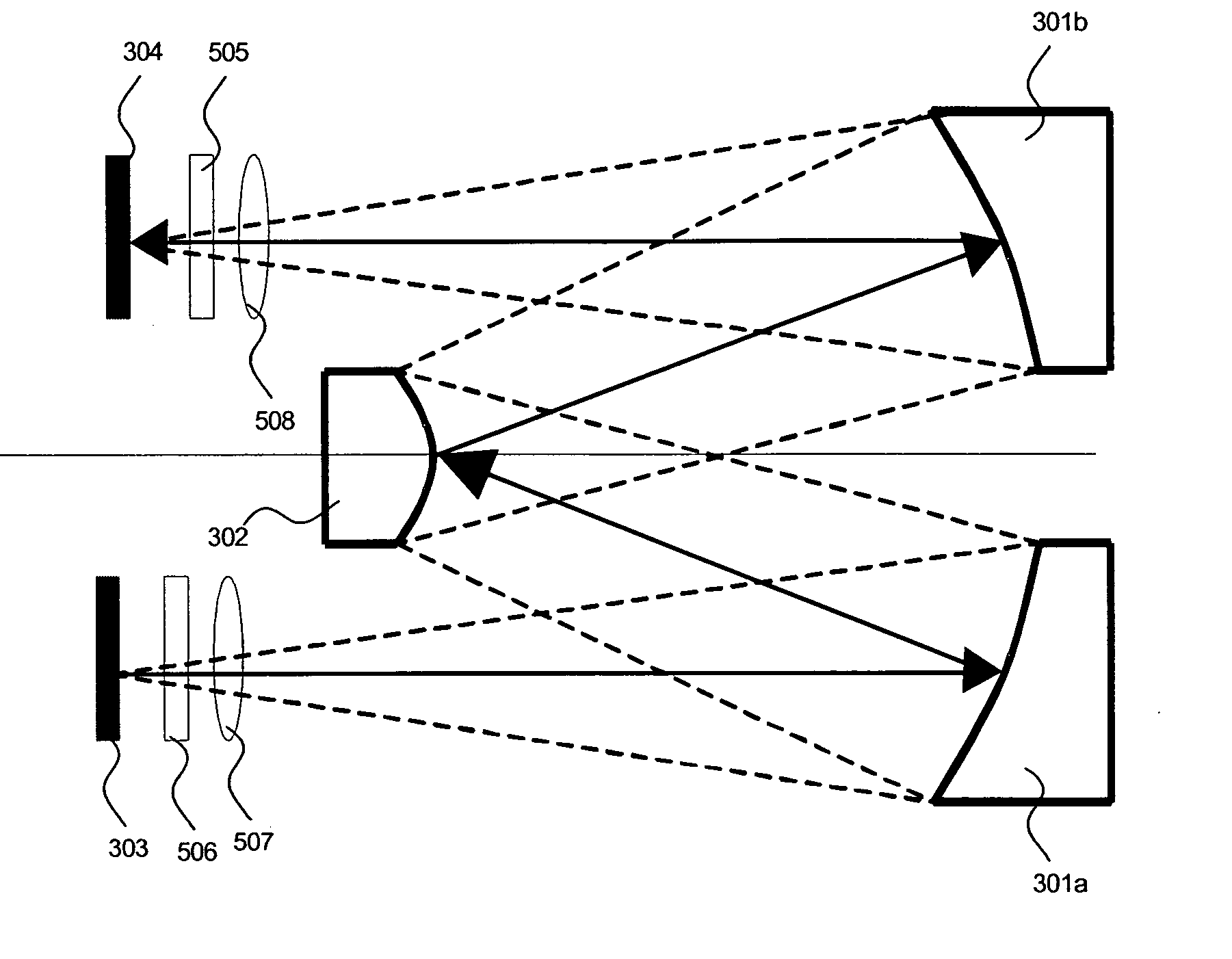
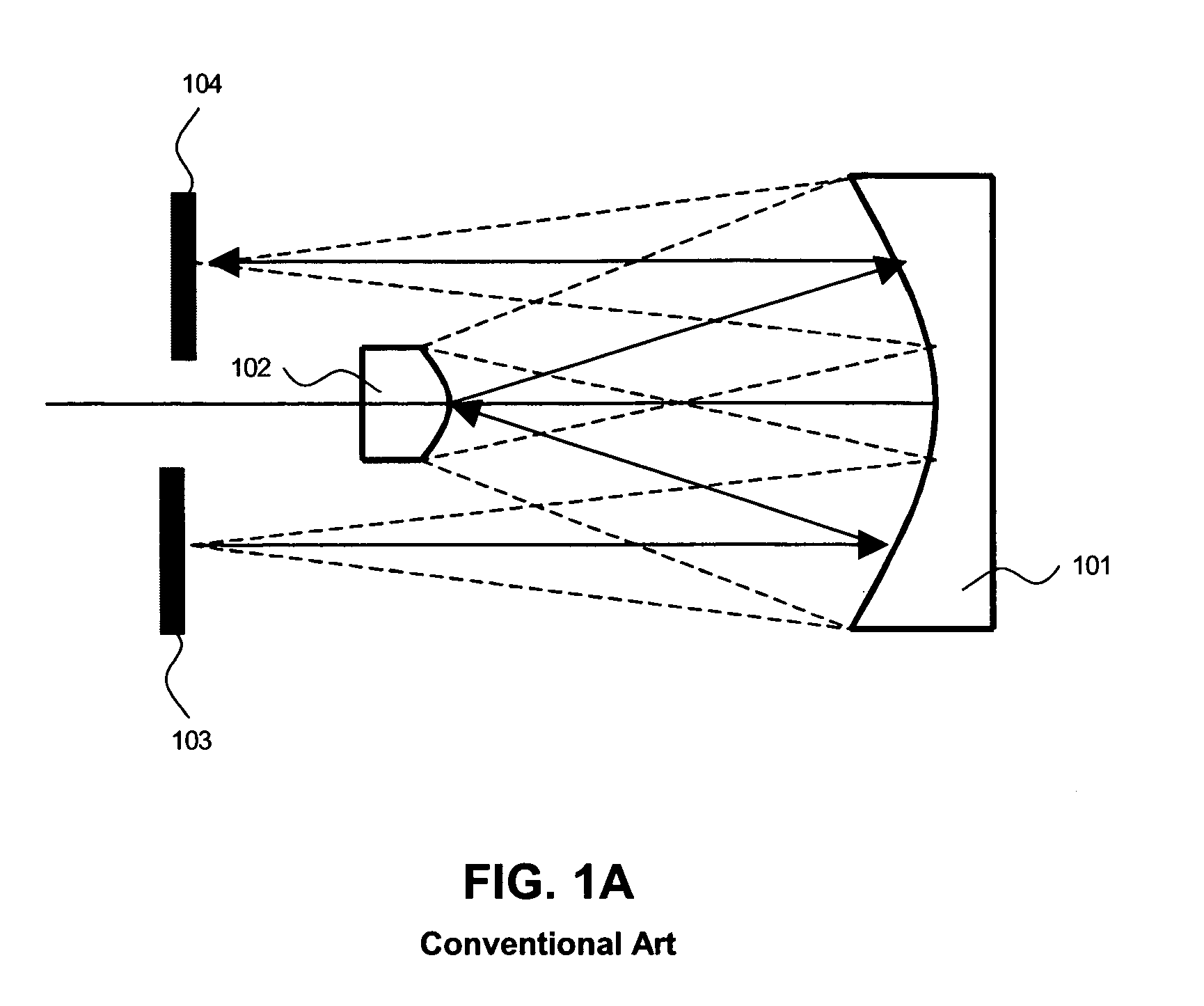
Method and system for large field of view display with scanning reflector
An image display system includes an optical subsystem configured to emit a first light beam and a second light beam, wherein the first light beam illuminates a first portion of a composite field of view and the second beam illuminates a second portion of the composite field of view. A scanning mirror is positioned to intercept and reflect the first light beam and the second light beam. The system also has a waveguide with at least one input coupling optical element for receiving the first light beam and the second light beam into the waveguide. The waveguide also has an output coupling optical element for projecting a plurality of output light beams derived from the first light beam and the second light beam from the waveguide to illuminate the composite field of view.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
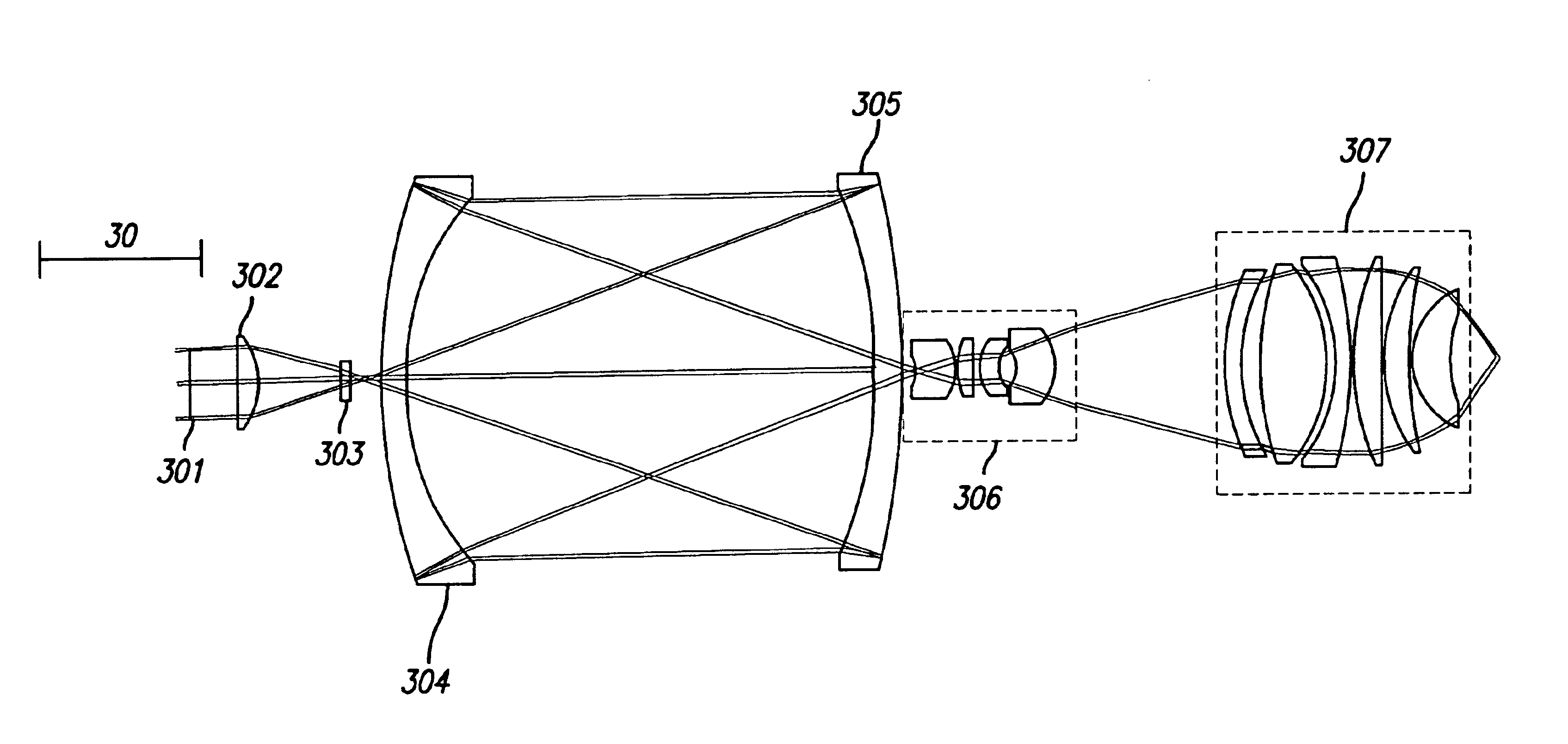
Broad band DUV, VUV long-working distance catadioptric imaging system
InactiveUS6842298B1Long free working distanceMinimize central obscurationMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusPupilLength wave
A high performance objective having very small central obscuration, an external pupil for apertureing and Fourier filtering, loose manufacturing tolerances, large numerical aperture, long working distance, and a large field of view is presented. The objective is preferably telecentric. The design is ideally suited for both broad-band bright-field and laser dark field imaging and inspection at wavelengths in the UV to VUV spectral range.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
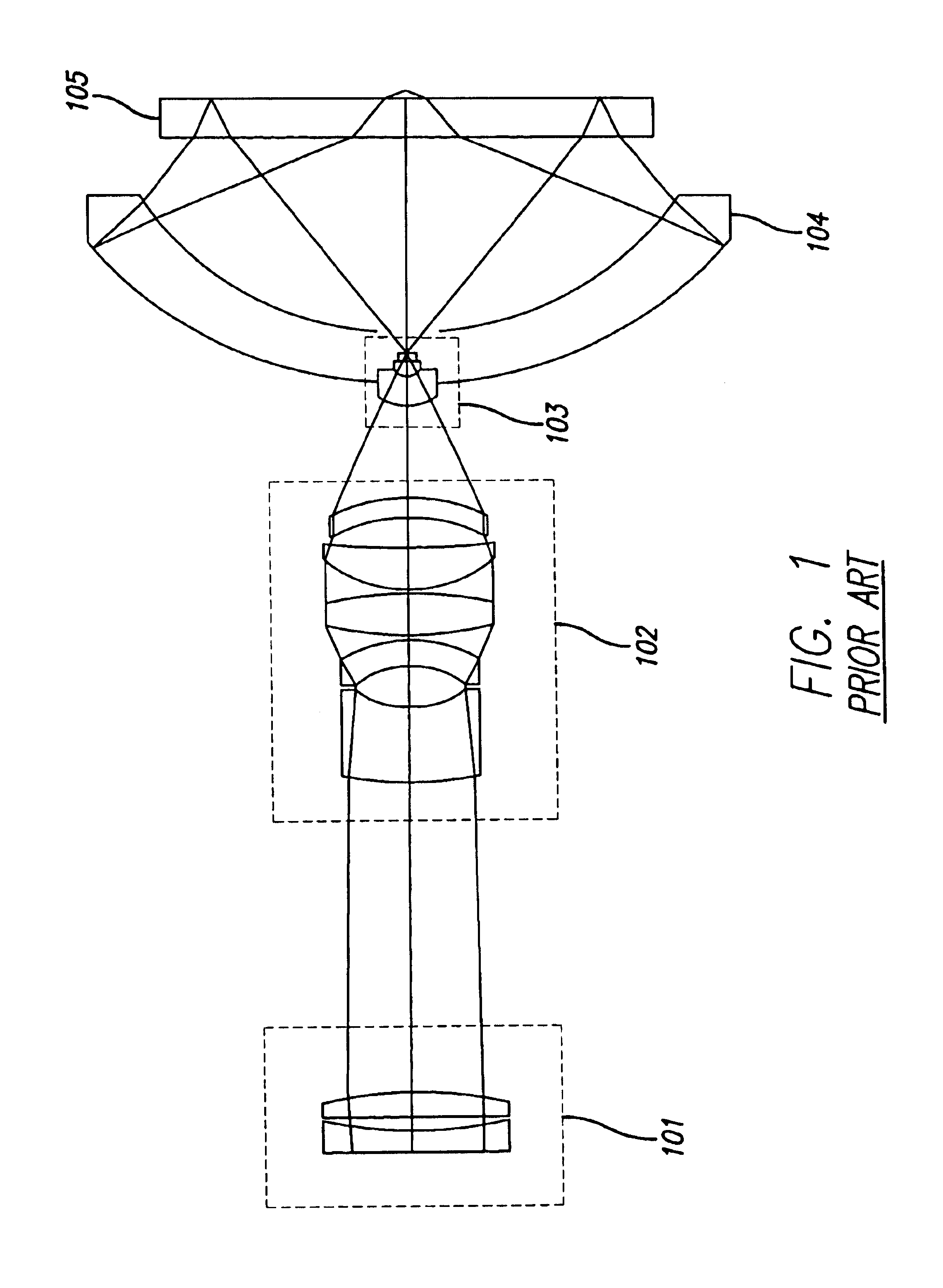
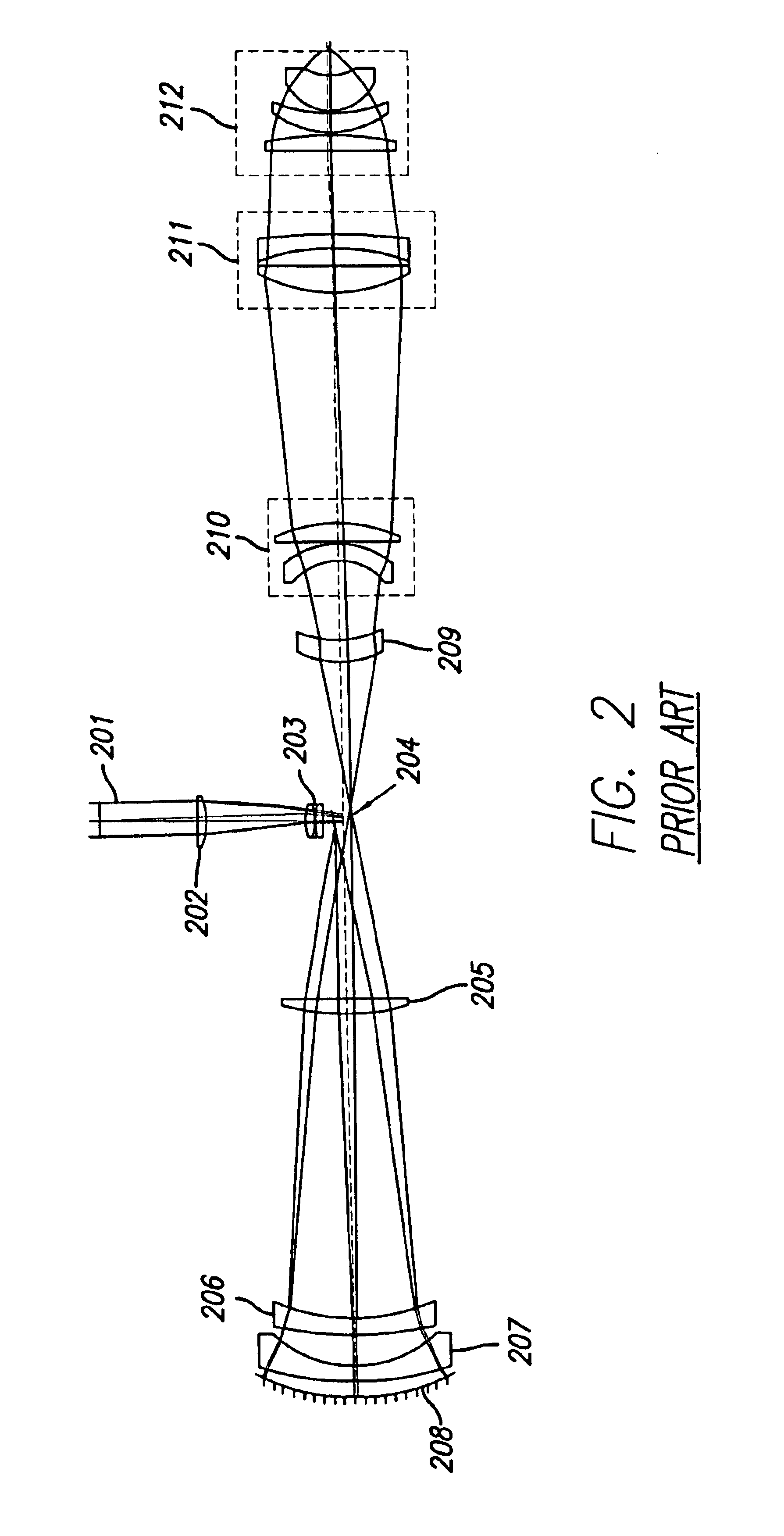
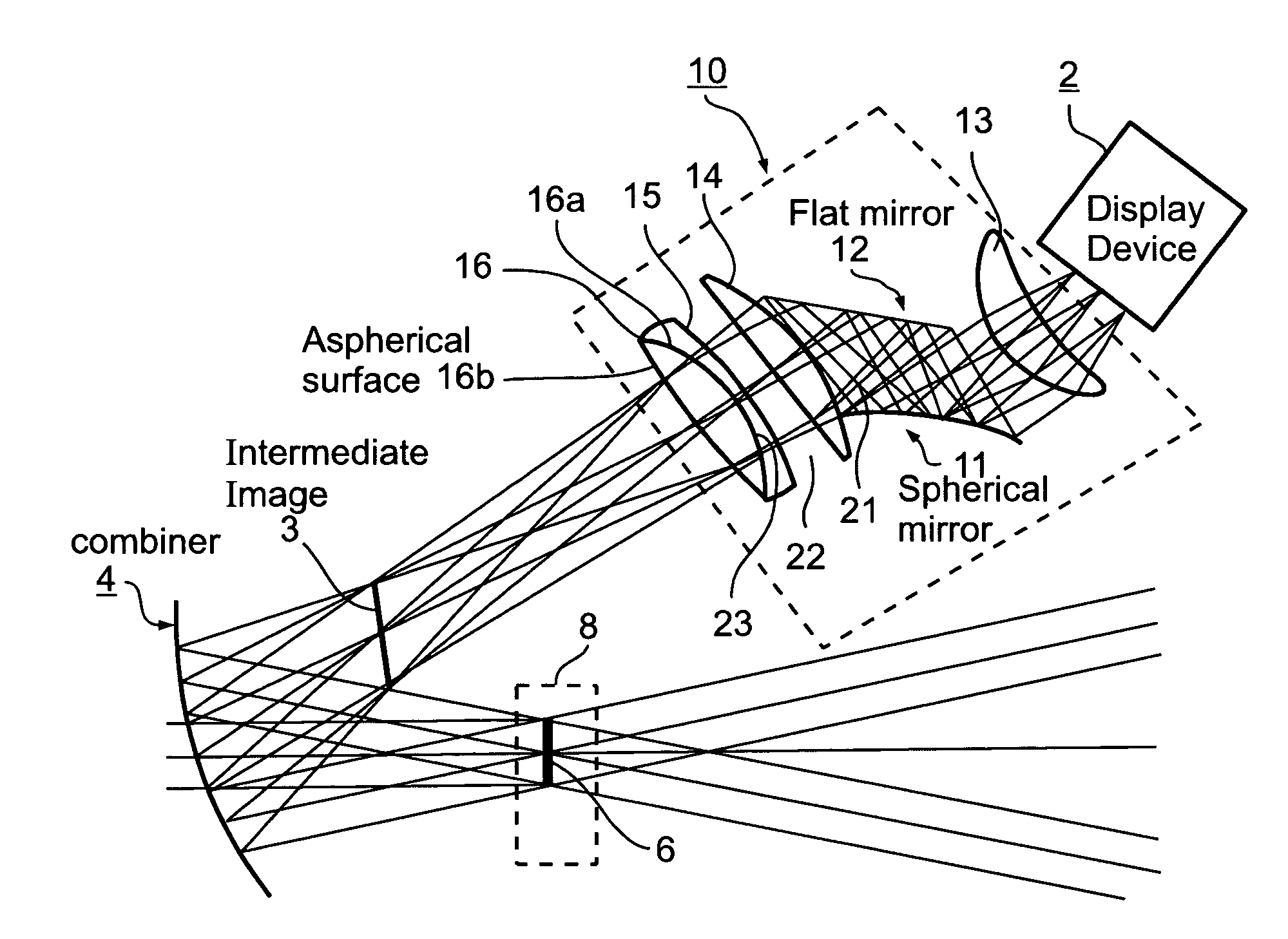
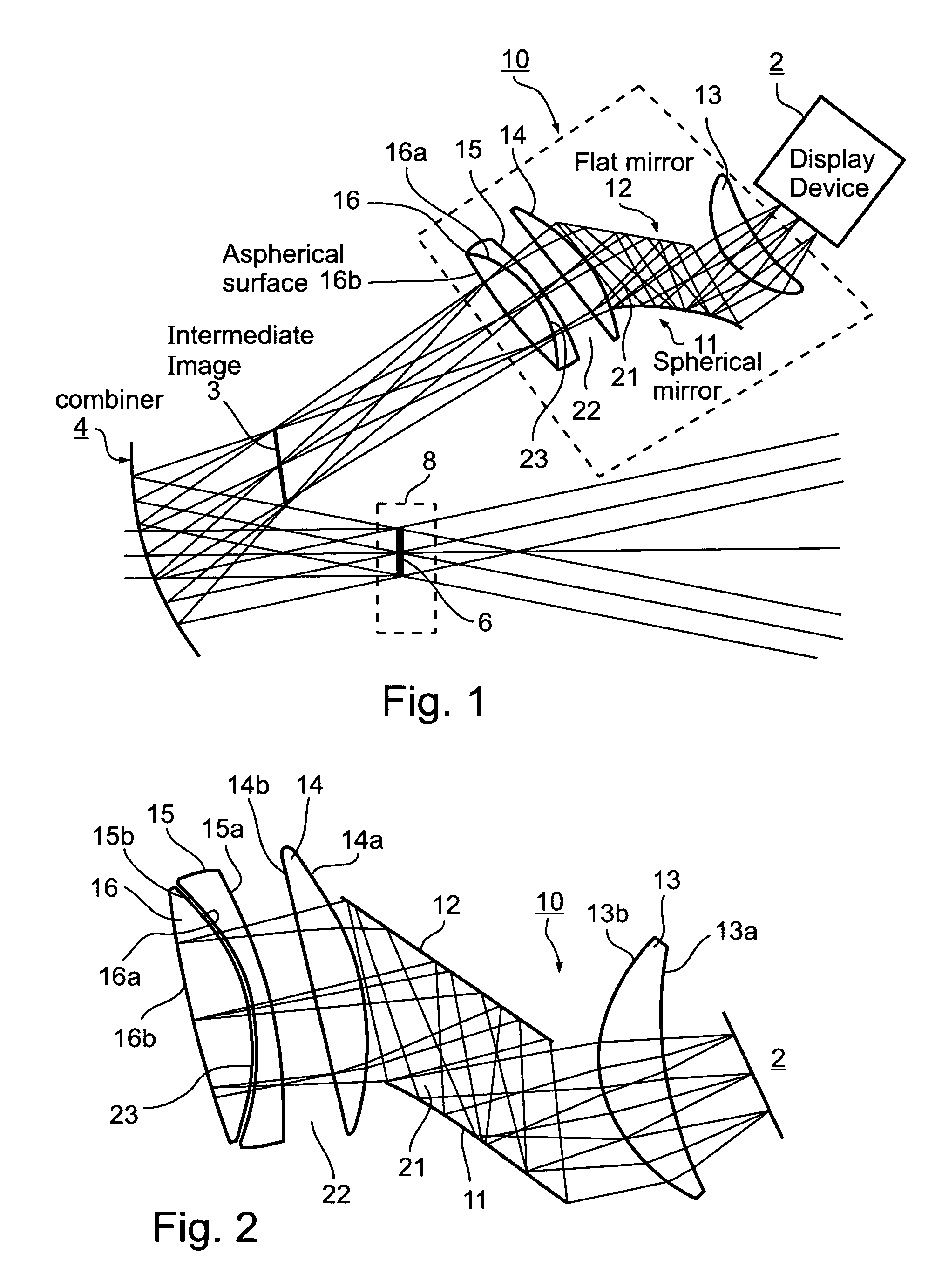
Head-up display system
ActiveUS7602552B1Minimum of development costMinimum of non-recurring expenseOptical elementsHead-up displayPower combiner
A head-up display system includes a display device for generating and displaying information to an eye of an observer; a tilted power combiner for superimposing the information displayed by the display device onto the forward view of the outside by the eye of the observer; and a relay optic assembly between the display device and the tilted power combiner for forming an intermediate image of the displayed information forwardly of the combiner that reflects the image towards the eye of the observer within an eye motion box to produce a large field of view for the observer. The relay optic assembly is void of holographic elements and includes a spherical mirror generating aberrations in the intermediate image tending to compensate for aberrations produced by the tilted power combiner.
Owner:ELBIT SYST ELECTRO OPTICS ELOP
System and methods for generating spherical mosaic images
InactiveUS7176960B1Efficient scanningSmall sizeTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationSpherical formImage system
Systems and methods for generating an omnidirectional mosaic image are presented in which a number of images are acquired about an axis of rotational. The images have a large field of view along the axis of rotation and a small field of view or image width in a second direction. The images can be image strips, formed from non-parallel rays directed onto an image sensor (1008), which are formed from a narrow width of parallel rays directed onto imaging sensor (1008). The images are combined to form a spherical mosaic. In the case of overlapping image strips, image combination can be performed by identifying common features in the overlapping regions and aligning consecutive image strips accordingly. A blending algorithm can then be used to improve image fidelity in the overlapping regions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Endoscope objective lens with large entrance pupil diameter and high numerical aperture
An endoscope objective lens for collecting combined bright field (white light) and fluorescence images includes a negative lens group, a stop, and a positive lens group. The lens has a combination of large entrance pupil diameter (≧0.4 mm) for efficiently collecting weak fluorescence light, large ratio between the entrance pupil diameter and the maximum outside diameter (Dentrance / Dmax larger than 0.2), large field of view (FFOV≧120°) and favorably corrected spherical, lateral chromatic and Petzval field curvature for both visible and near infrared wavelengths.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
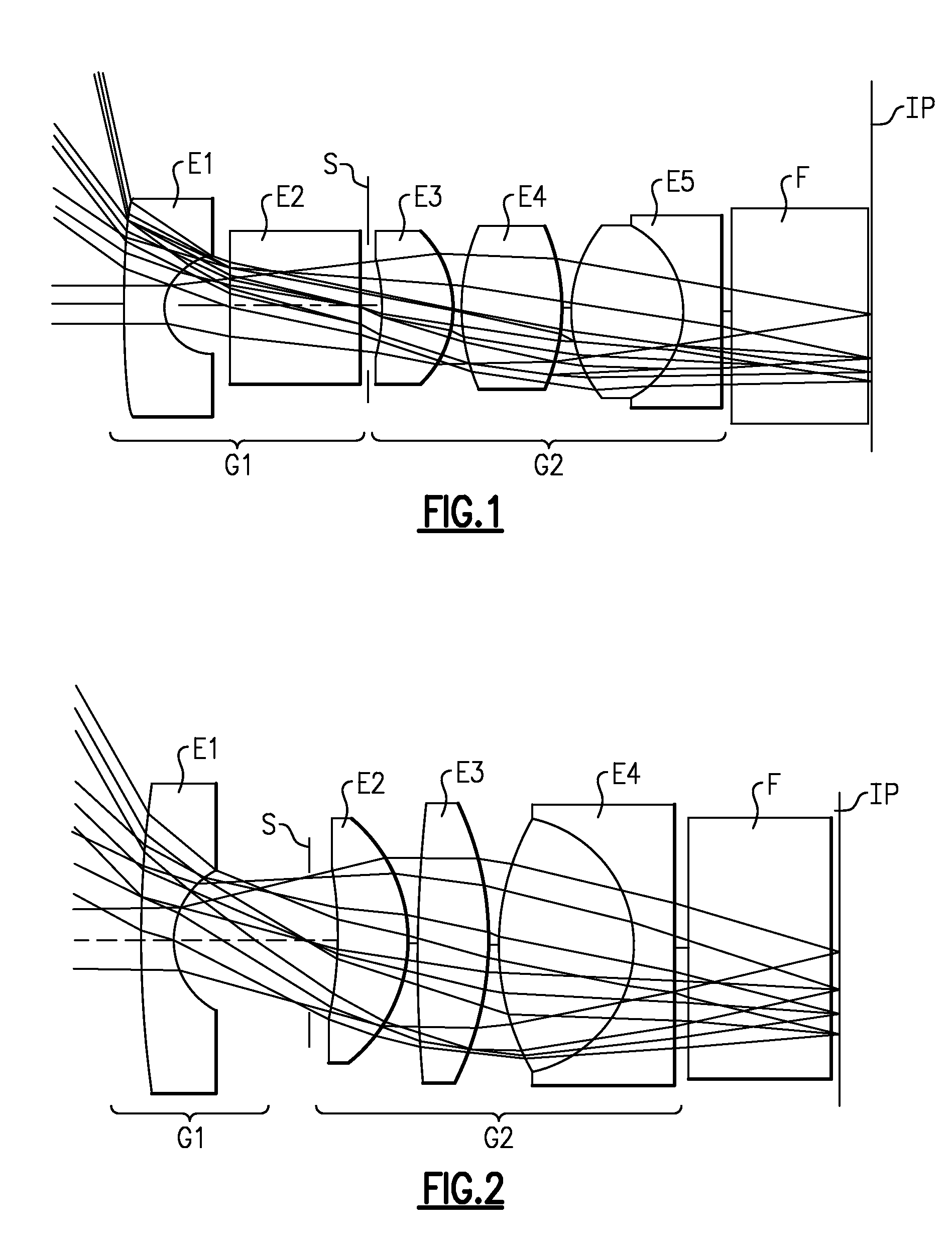
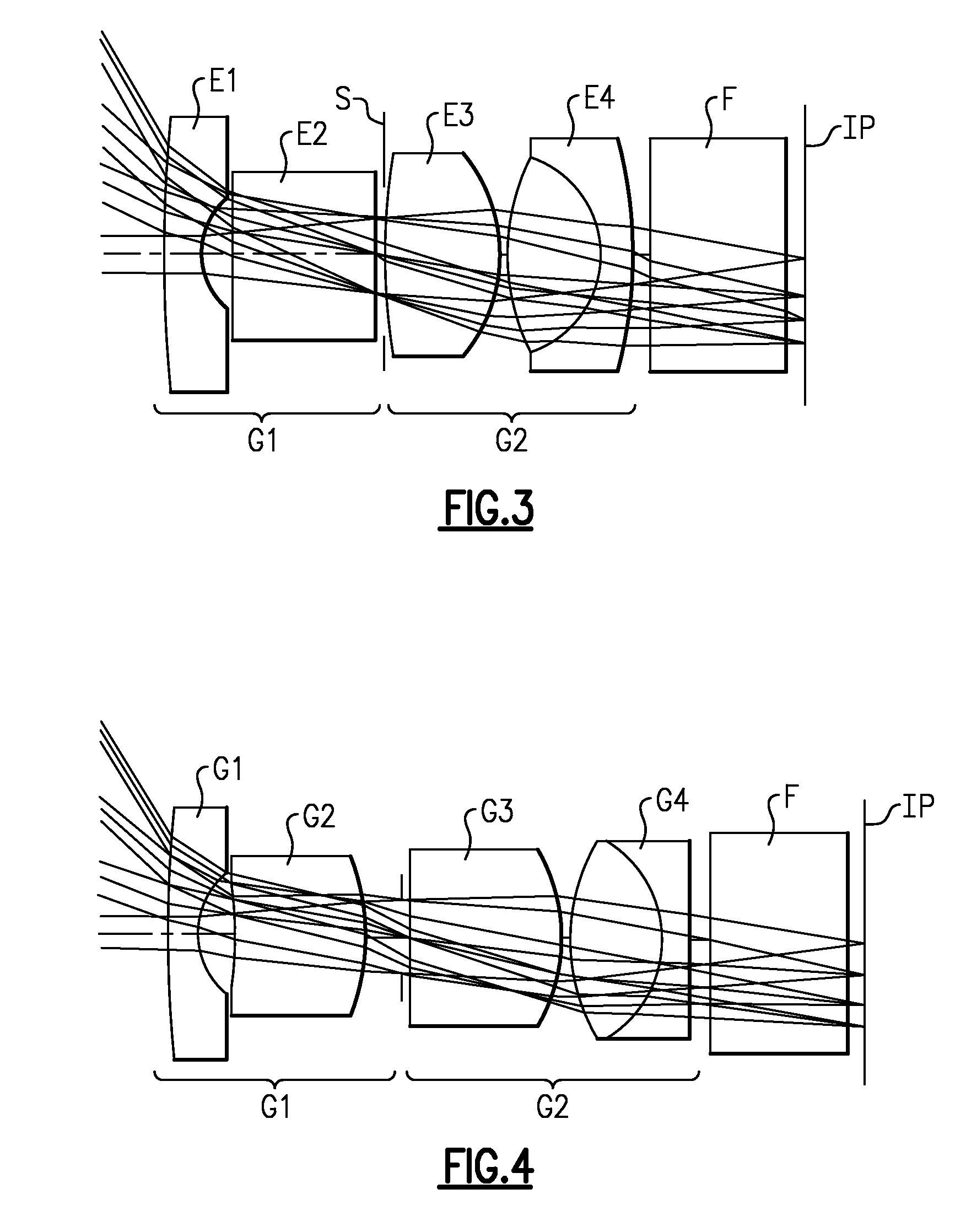
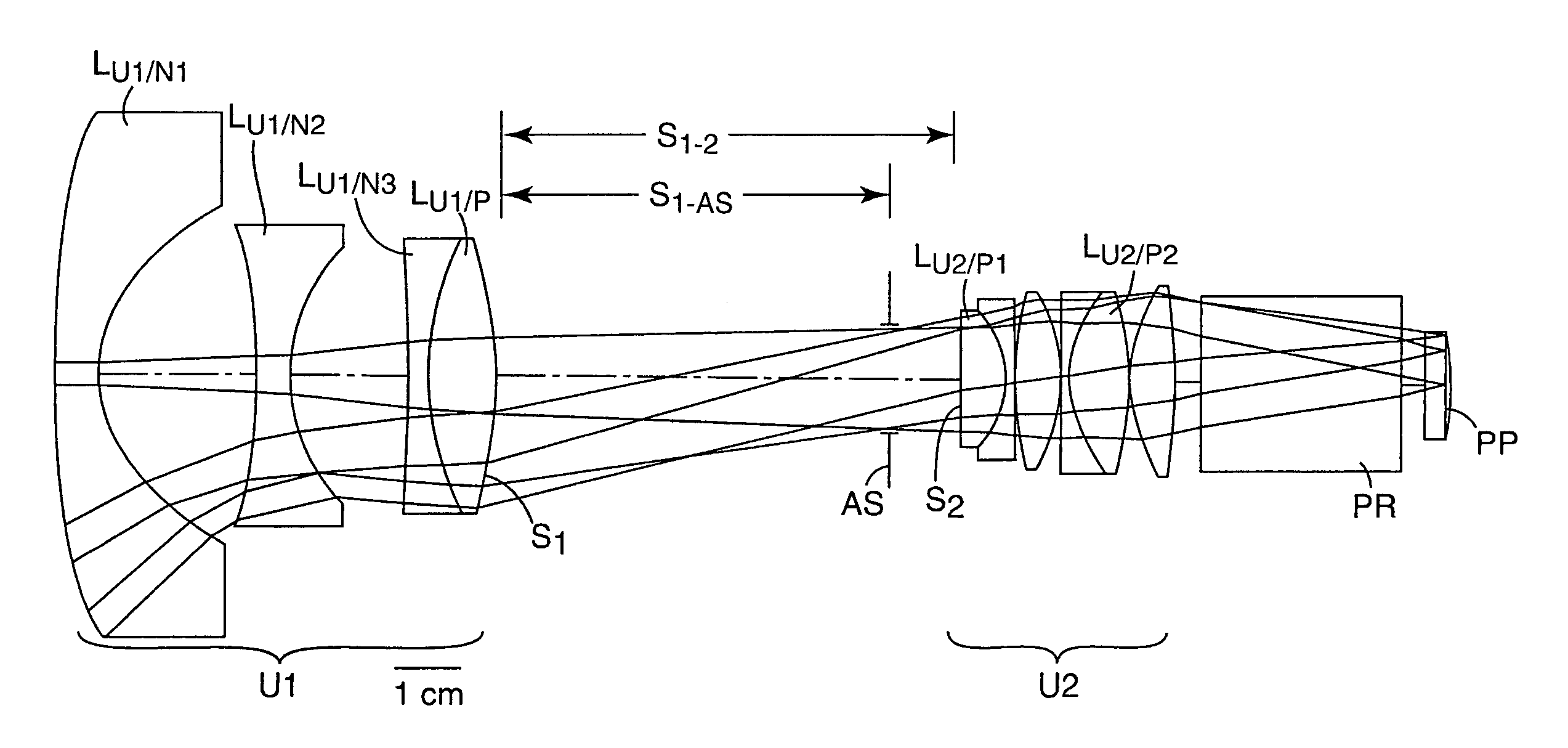
Foldable projection lenses
Projection lenses for use with pixelized panels (PP) are provided. The projection lenses have a first unit (U1) separated from a positive second unit (U2) by a distance sufficient to accept a reflective surface (RS) for folding the lens' optical axis. The lenses are telecentric on the short conjugate side, have a large field of view in the direction of the long conjugate, and have low aberration levels. By using negative lens elements (LU1 / N1 and LU1 / N2) composed of plastic materials having large positive Q-values at the long conjugate side of the first lens unit (U1), the lenses can achieve low levels of lateral color, including low levels of secondary lateral color, with reduced cost compared to lenses which employ anomalous dispersion glasses in the first lens unit.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
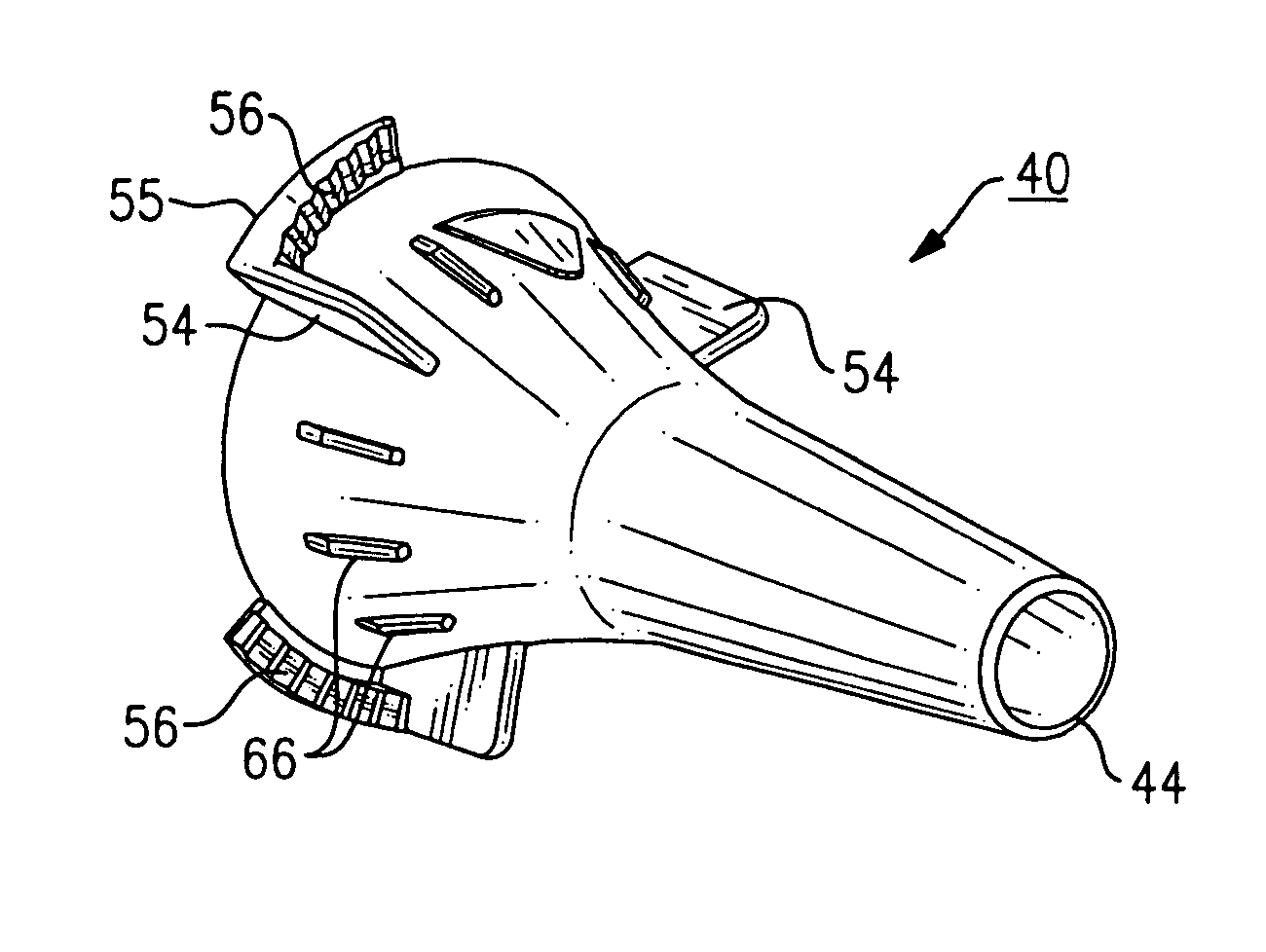
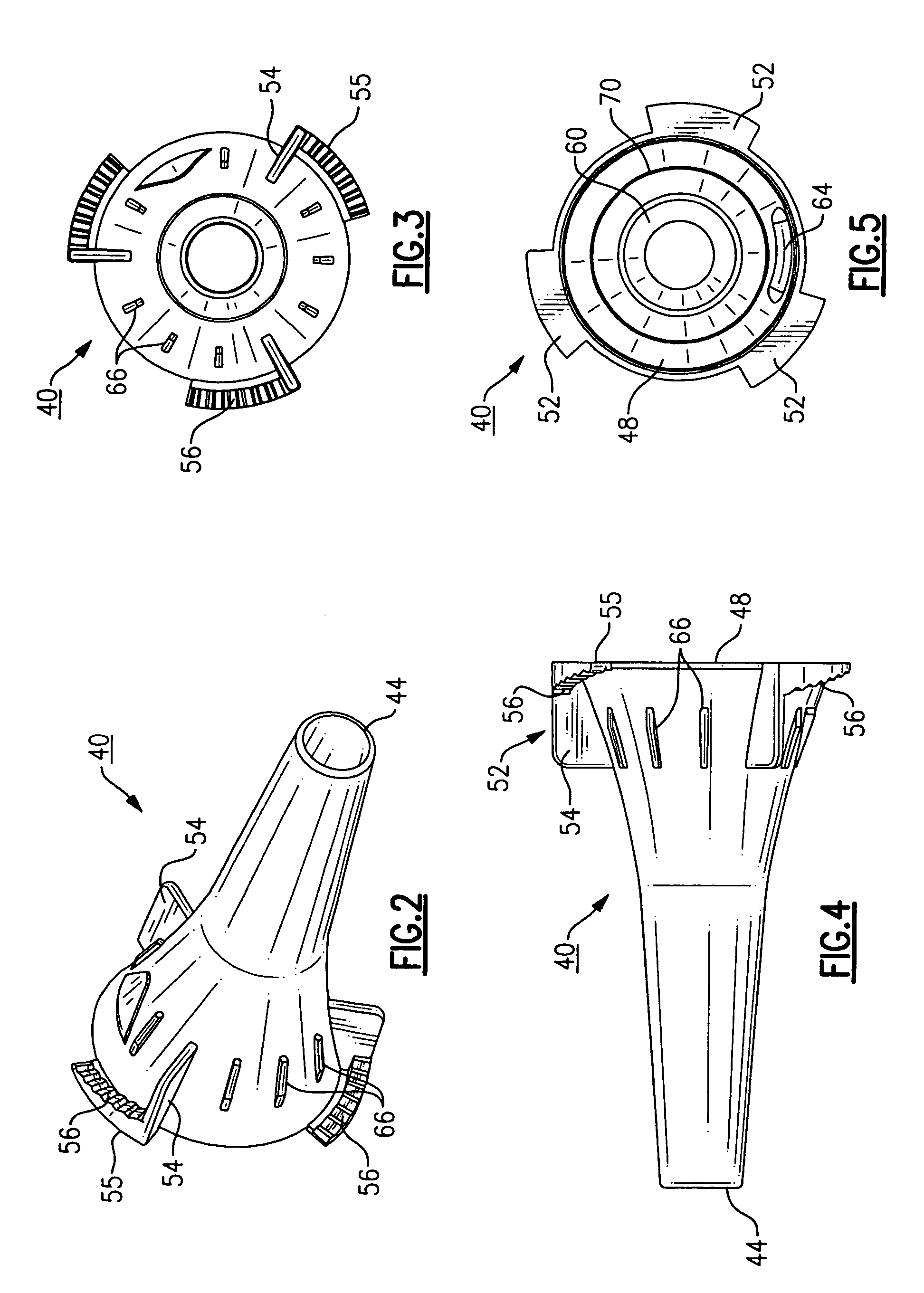
Otoscopic tip element and related method of use
ActiveUS20050027168A1Enhanced otological examinationSimple designBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesOtoscopeEntire tympanic membrane
A tip element for an otoscopic apparatus includes engagement features that permit selective attachment to two different tip attachment mechanisms. The tip element includes both interior and exterior engagement features that provide interchangeability with otoscopes having different tip attachment schemes. The tip element includes an increased distal aperture formed from a decreased slope that enables a larger field of view, permitting the entire tympanic membrane to be viewed at once. External engagement features permit ejection of the tip from the otoscope, as well as stackability of a plurality of tip elements.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
Microdisplay-based head-up display system
A head-up display (HUD) system is provided. The HUD system comprises a microdisplay-based projection system, a diffuser, a relay optical system, and a combiner. The microdisplay-based HUD system includes aberration correction capabilities and may easily and effectively replace a CRT-based HUD system in aircrafts while providing light-weight, multi-color, superior imaging capabilities with a large field-of-view.
Owner:EPIC OPTIX
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery
ActiveUS20130076863A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapies2D-image generationCollocationImage resolution
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery are described that enable hand-eye collocation, high resolution, and a large field of view. A digital stereo microscope apparatus, an operating system with a digital stereo microscope, and a method are described using a display unit located over an area of interest such that a human operator places hands, tools, or a combination thereof in the area of interest and views a magnified and augmented live stereo view of the area interest with eyes of the human operator substantially collocated with the hands of the human operator.
Owner:DIGITAL SURGICALS
Auto calibration and personalization of eye tracking system using larger field of view imager with higher resolution
InactiveUS6873714B2Person identificationAcquiring/recognising eyesPersonalizationCamera auto-calibration
In preferred embodiments, apparatus for and method of eye tracking, including, in sequence, the steps of: viewing an entire face of a person to obtain predetermined facial features of the person to identify or not the said person; if the person is identified, retrieving a previously stored ocular profile of the person based on said predetermined facial features; using said ocular profile to track movement of an eye of said person. If the person is not identified, an ocular profile is created.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Microscope with extended field of vision
ActiveUS7253946B2High resolutionFree of and aberrationCharacter and pattern recognitionMicroscopesExtended field of viewImaging lens
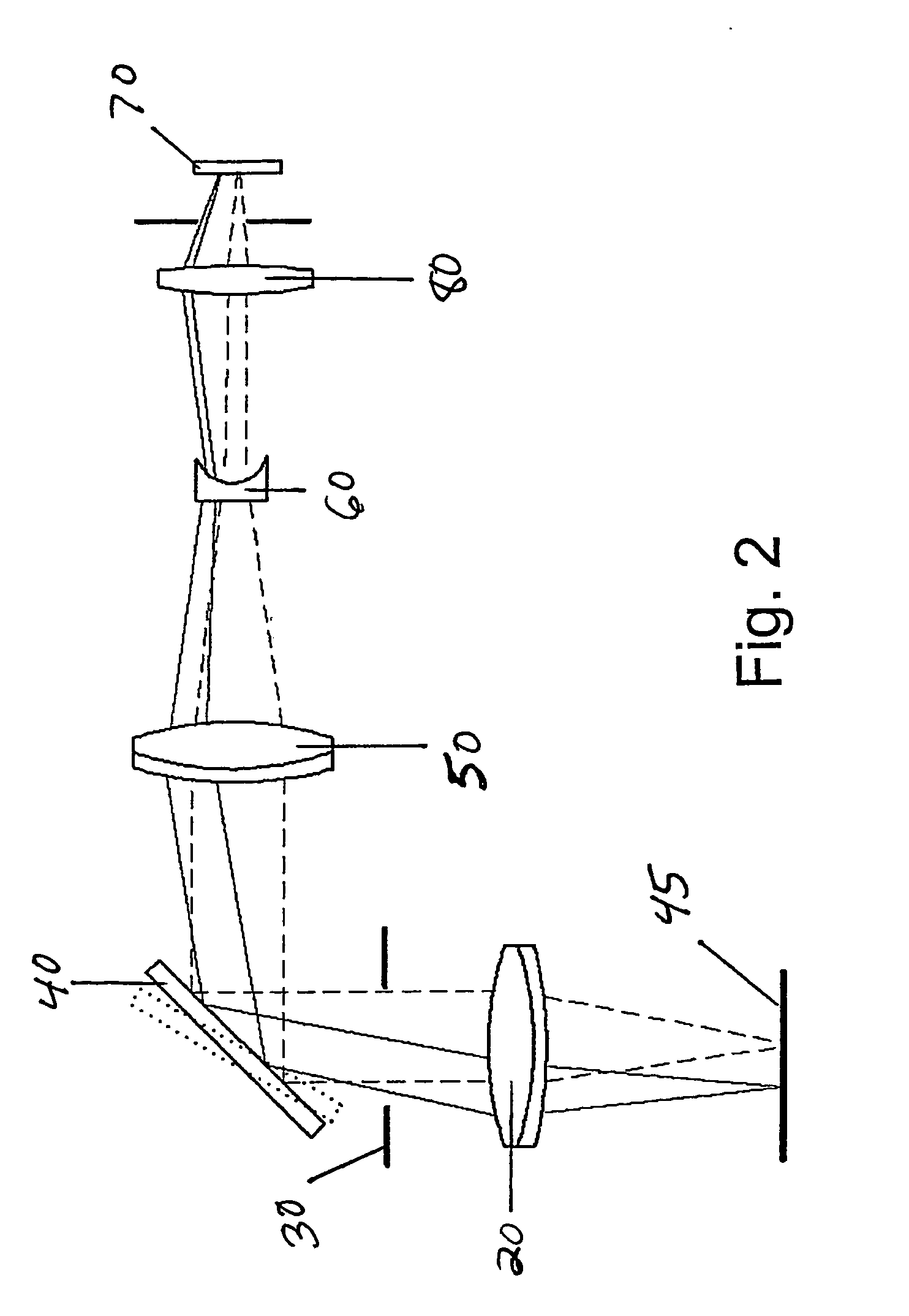
An optical system is provided for creating a mosaic image of a large field of view through a microscope at fast refresh rates of about 25 Hz with a high resolution that is free of blurring or aberrations. The optical system includes an objective lens assembly (20), an iris (30), one or more scanning mirrors (40) for high-speed scanning, one or more imaging lenses and irises (50, 60, 80), and a high-speed imaging device (70) arranged in that order from an object. The optical system also includes a mechanism for processing and constructing scanned and captured images into a mosaic image.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Otoscopic tip element and related method of use
A tip element for an otoscopic apparatus includes engagement features that permit selective attachment to two different tip attachment mechanisms. The tip element includes both interior and exterior engagement features that provide interchangeability with otoscopes having different tip attachment schemes. The tip element includes an increased distal aperture formed from a decreased slope that enables a larger field of view, permitting the entire tympanic membrane to be viewed at once. External engagement features permit ejection of the tip element from the otoscope, as well as stackability of a plurality of tip elements.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
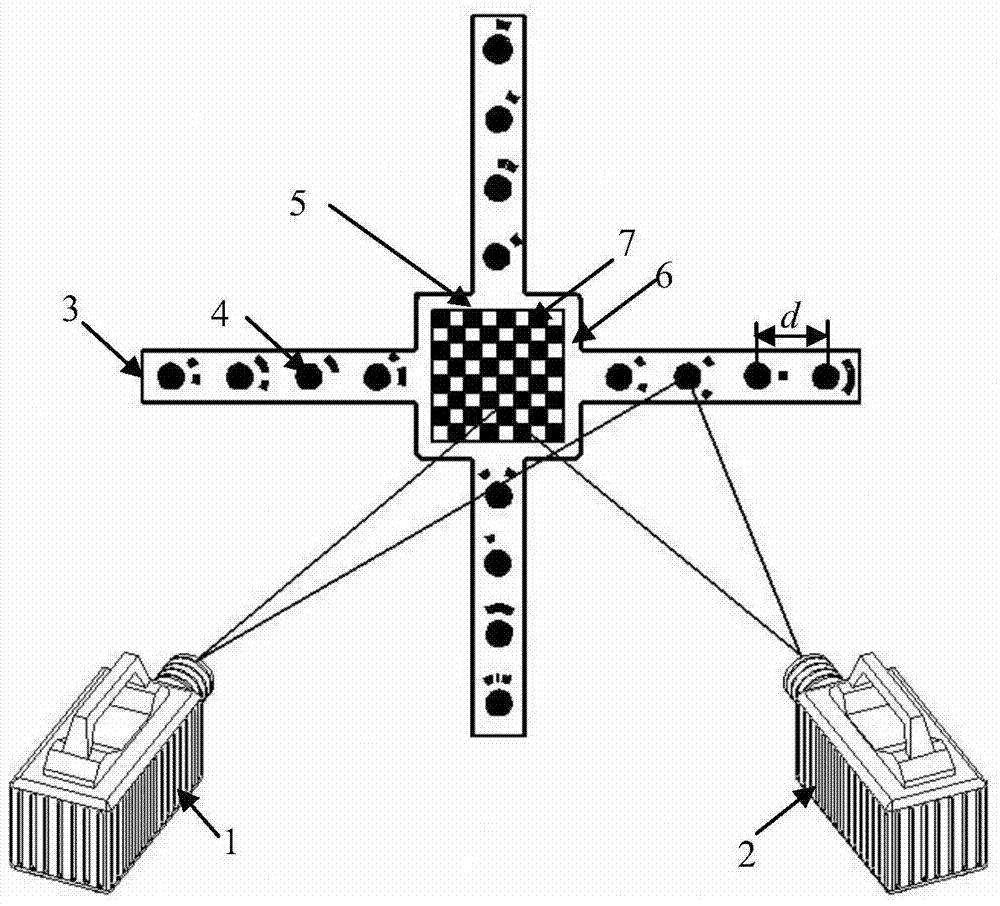
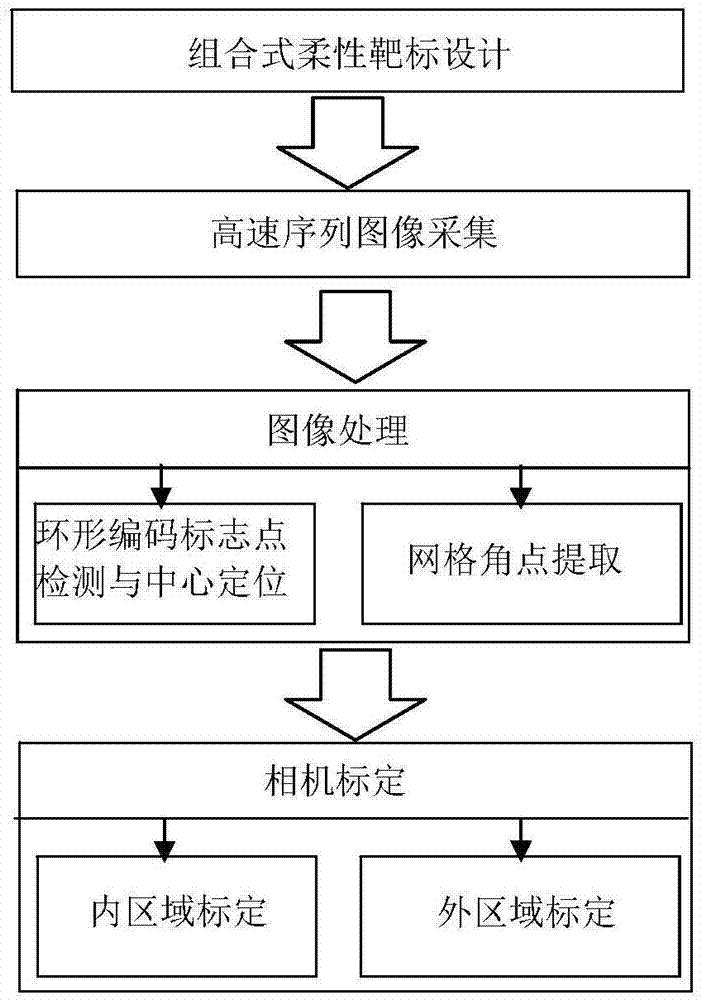
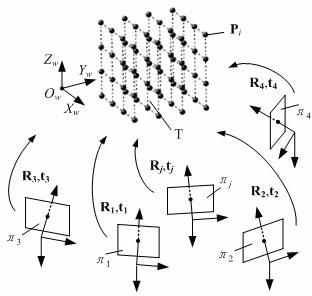
Flexible-target-based close-range large-field-of-view calibrate method of high-speed camera
The invention, which belongs to the computer vision field, provides a flexible-target-based close-range large-field-of-view calibrate method of a high-speed camera and relates to a close-range large-field-of-view binocular-visual-sense camera calibration method in a wind tunnel. According to the method, a flexible target is used for fill an overall calibration view field for calibration; the internal region of the target is formed by a planar chessboard mesh and distances between angular points of the chessboard mesh are known; the external region of the target is formed by cross target rods perpendicular to each other and a plurality of coding marking points with known distances are distributed on the target rods uniformly. During calibration, regional and constraint calibration is carried out on a high-speed camera by using different constraint information provided by different regions of the target. When the internal region of the target is calibrated, calibration is carried out by using a homography matrix; and the external region is calibrated by using distance constraints of the coding marking points. According to the invention, the cost is lowered and the operation portability is realized. During calibration, distortion of different regions is considered by using the regional and constraint camera calibration method, so that the calibration precision is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
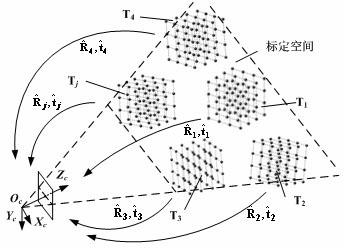
Camera calibration method for large field-of-view high-accuracy vision measurement
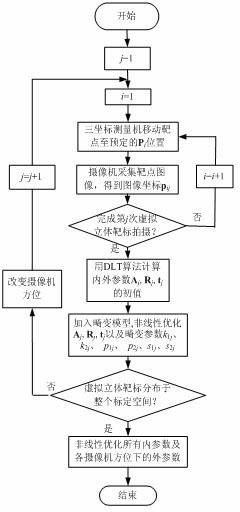
ActiveCN102663763AImprove consistencyGuaranteed measurement accuracyImage analysisNumerical controlThree-dimensional space
The invention provides a camera calibration method for large field-of-view high-accuracy vision measurement and belongs to the fields of measuring and testing. According to the camera calibration method for the large field-of-view high-accuracy vision measurement, a single infrared light-emitting diode (LED) with self-adapting brightness is used as a target spot, and the target spot is fixed on a three-dimensional numerical control mechanical device and is controlled to move to a preset space position. A virtual stereo target is constructed in three-dimensional space. When the target spot reaches the preset space position, a camera subjects the target spot to image acquisition. The virtual stereo target is shot in a plurality of directions by means of freely moving the camera, so that a plurality of virtual stereo targets are distributed in calibration space of the whole camera, when the shooting of the virtual stereo target in each direction is achieved, a set of inner parameters and a set of outer parameters are calculated to serve as trailing optimized initial values. Finally, the calibration parameters of the virtual stereo target shot in multiple directions are subjected to whole optimization. The camera calibration method for the large field-of-view high-accuracy vision measurement can effectively improve the accuracy of the large field-of-view camera.
Owner:NANJING VICCAM TECH CO LTD
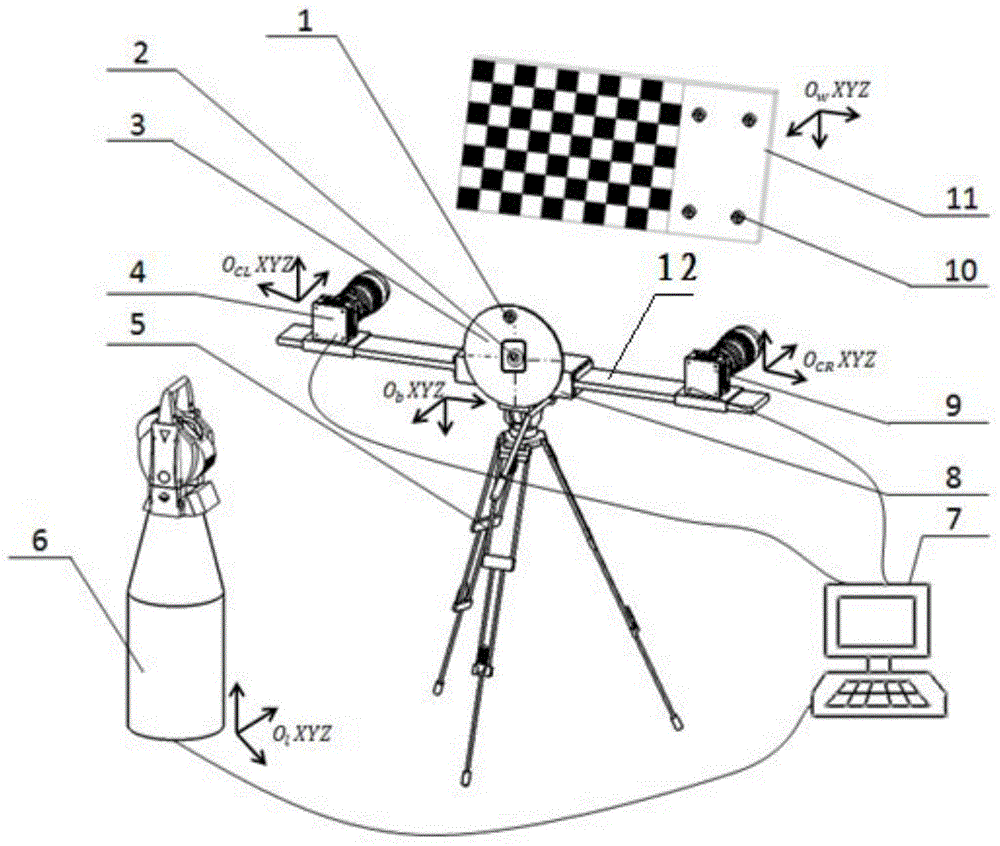
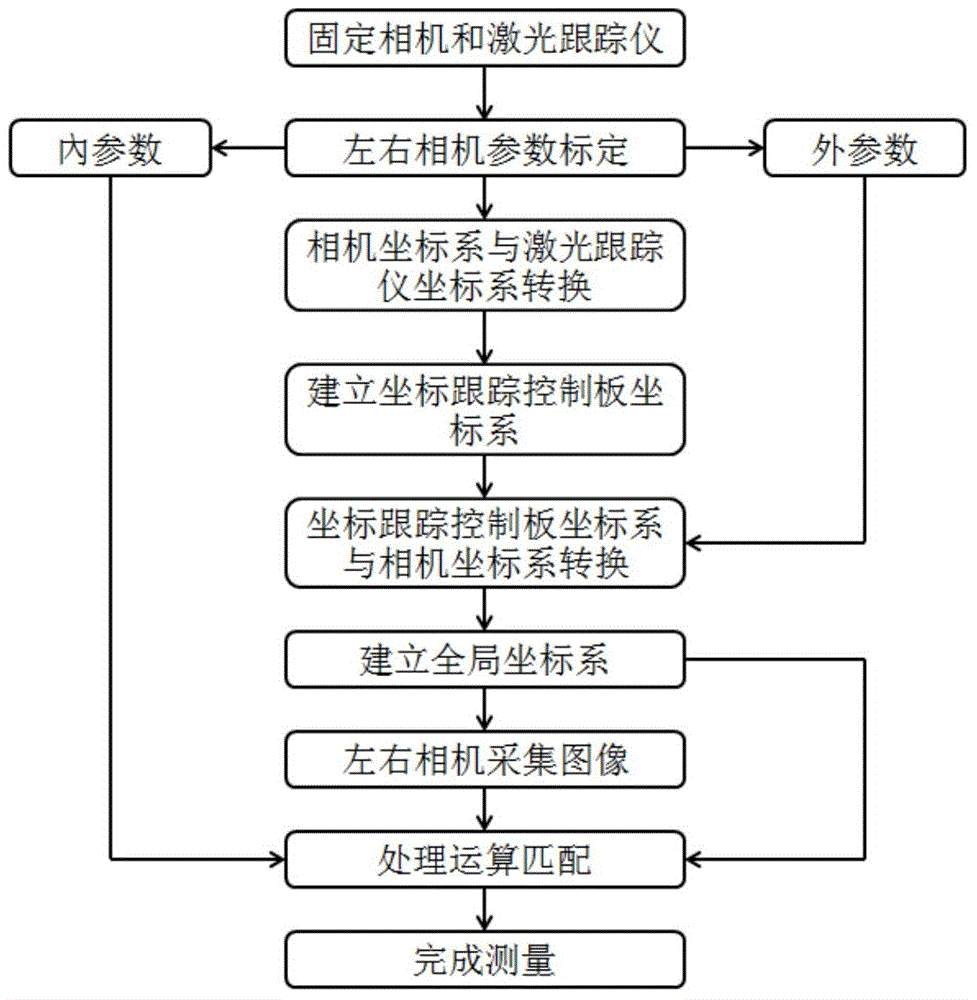
Large large field of view global measurement method using coordinates tracking control board
ActiveCN104897060AFast Global Survey JobsQuickly complete the global measurement workUsing optical meansLaser trackerVisual perception
This invention provides a large field of view global measurement method using a coordinates tracking control board, belonging to the visual measurement field. The method employs a coordinates tracking control board installed on an adapter bracket, effectively integrates a visual measuring device and a laser tracker under the condition of not sharing a same field of view, and separates and calibrates internal and external parameters of left and right cameras to build an overall coordination system of a measurement scene so as to complete overall measurement based on a large field of view. The method can realize rapid and highly accurate measurement of large parts under a complex operating condition in a large field of view scope, is a measurement mode combining a plurality of types of optical components. The measurement method has the characteristics of large field of view and high efficiency, and can conveniently measure covered parts of target components, and rapidly complete large field of view global measurement in the industrial field.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery
ActiveUS9330477B2Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapies2D-image generationCollocationImage resolution
Surgical stereo vision systems and methods for microsurgery are described that enable hand-eye collocation, high resolution, and a large field of view. A digital stereo microscope apparatus, an operating system with a digital stereo microscope, and a method are described using a display unit located over an area of interest such that a human operator places hands, tools, or a combination thereof in the area of interest and views a magnified and augmented live stereo view of the area interest with eyes of the human operator substantially collocated with the hands of the human operator.
Owner:DIGITAL SURGICALS
Large field of view protection optical system with aberration correctability for flat panel displays
InactiveUS7158215B2Improve performanceReadingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCatoptricsDisplay device
An exposure system for manufacturing flat panel displays (FPDs) includes a reticle stage adapted to support a reticle. A substrate stage is adapted to support a substrate. A reflective optical system is adapted adapted to image the reticle onto the substrate. The reflective optical system includes a primary mirror including a first mirror and a second mirror, and a secondary mirror. The reflective optical system has sufficient degrees of freedom for both alignment and correction of third order aberrations when projecting an image of the reticle onto the substrate by reflections off the first mirror, the secondary mirror, and the second mirror.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
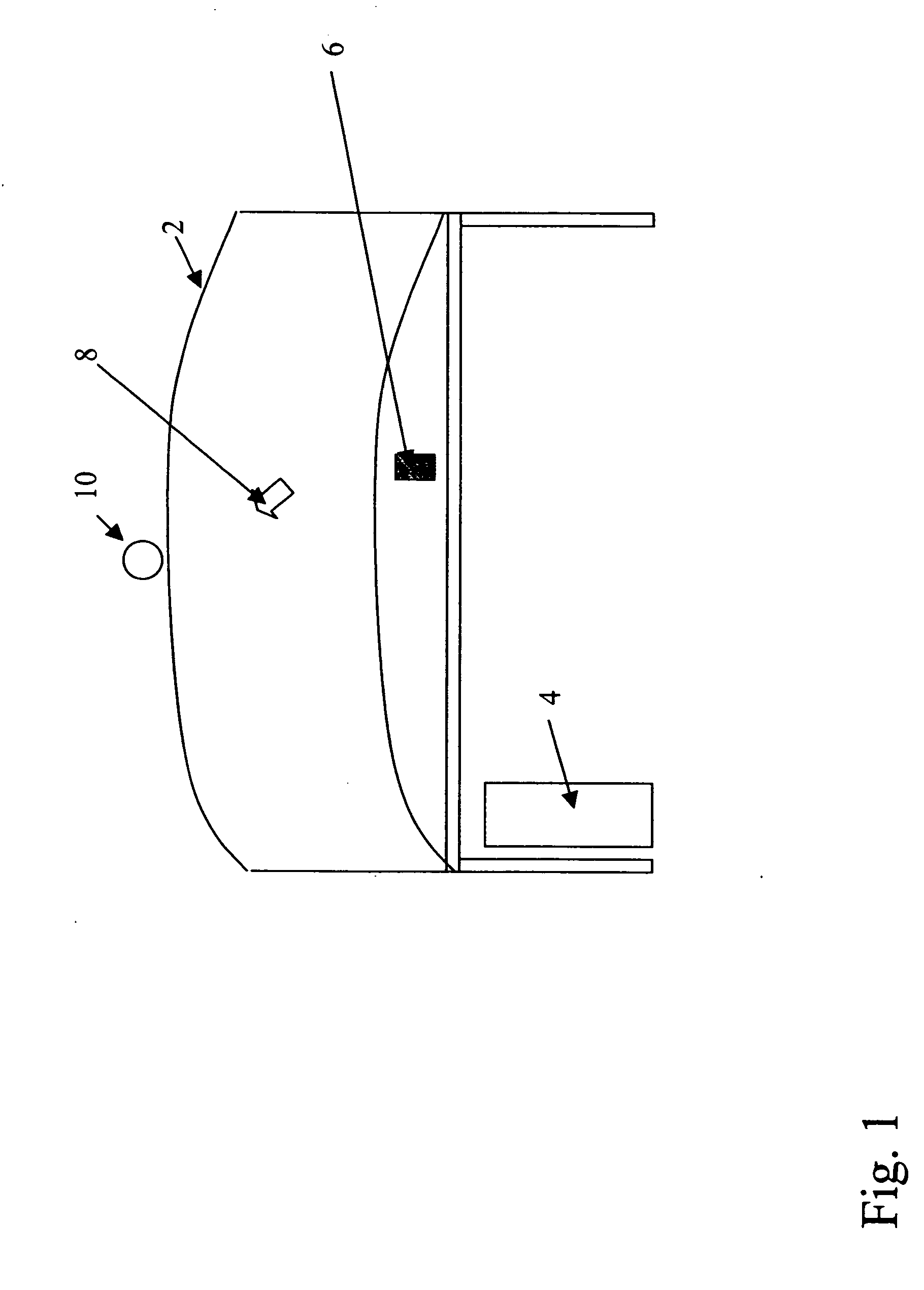
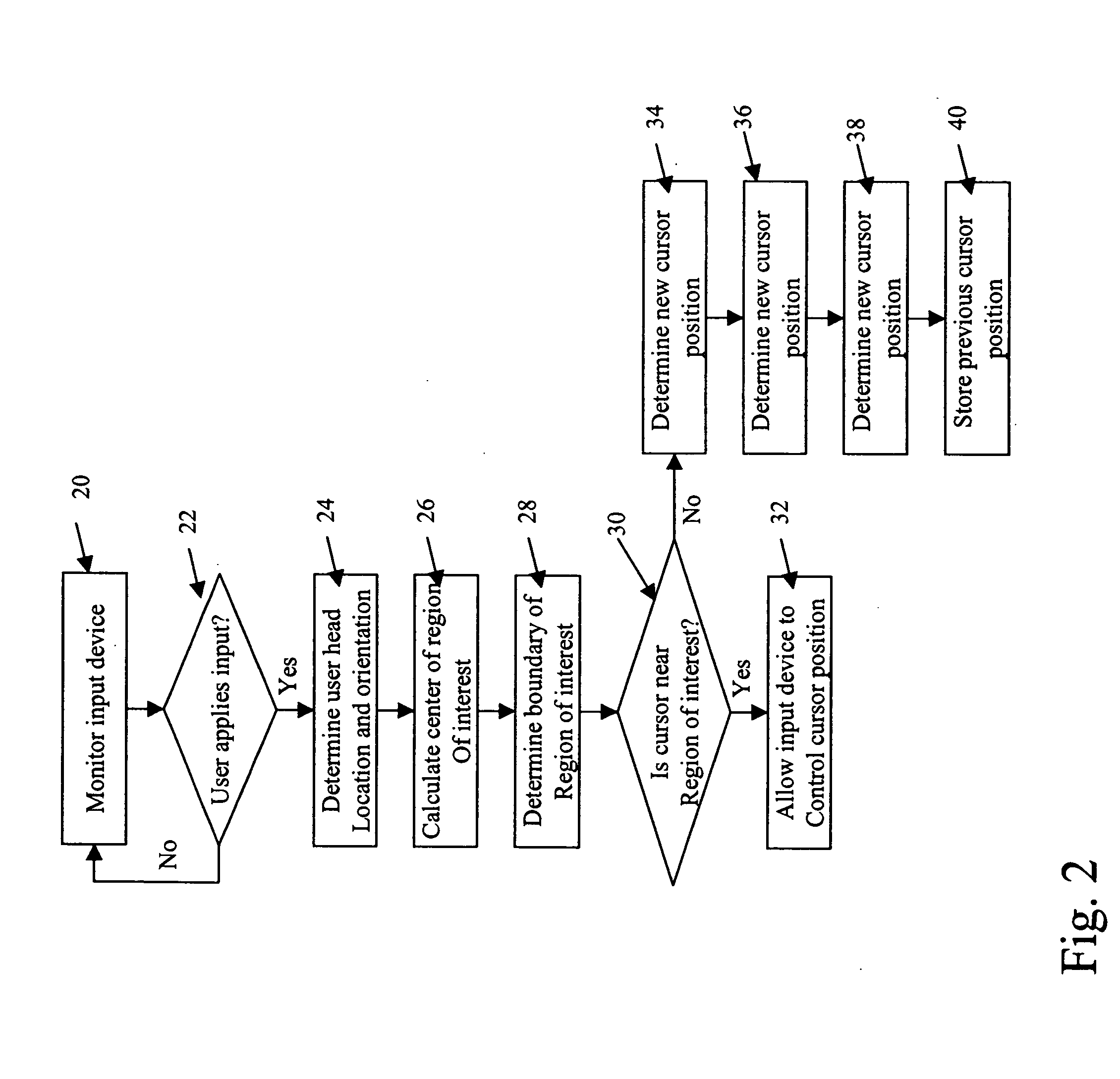
Pointing device for large field of view displays
InactiveUS20060214911A1Improving cursor positioningCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay devicePointing device
An interactive system for improving cursor positioning on a display comprising a screen or series of screens having a field of view of greater than 30 degrees with respect to a user, wherein the system includes: a user controlled input device for positioning a cursor on the display; a means for determining the relative location and orientation of the user's head with respect to the display; and a cursor repositioning means for determining an implied region of interest on the display based on the relative location and orientation of the user's head and moving the cursor to a selected position within the implied region of interest.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com