Patents
Literature
352 results about "Doppler velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
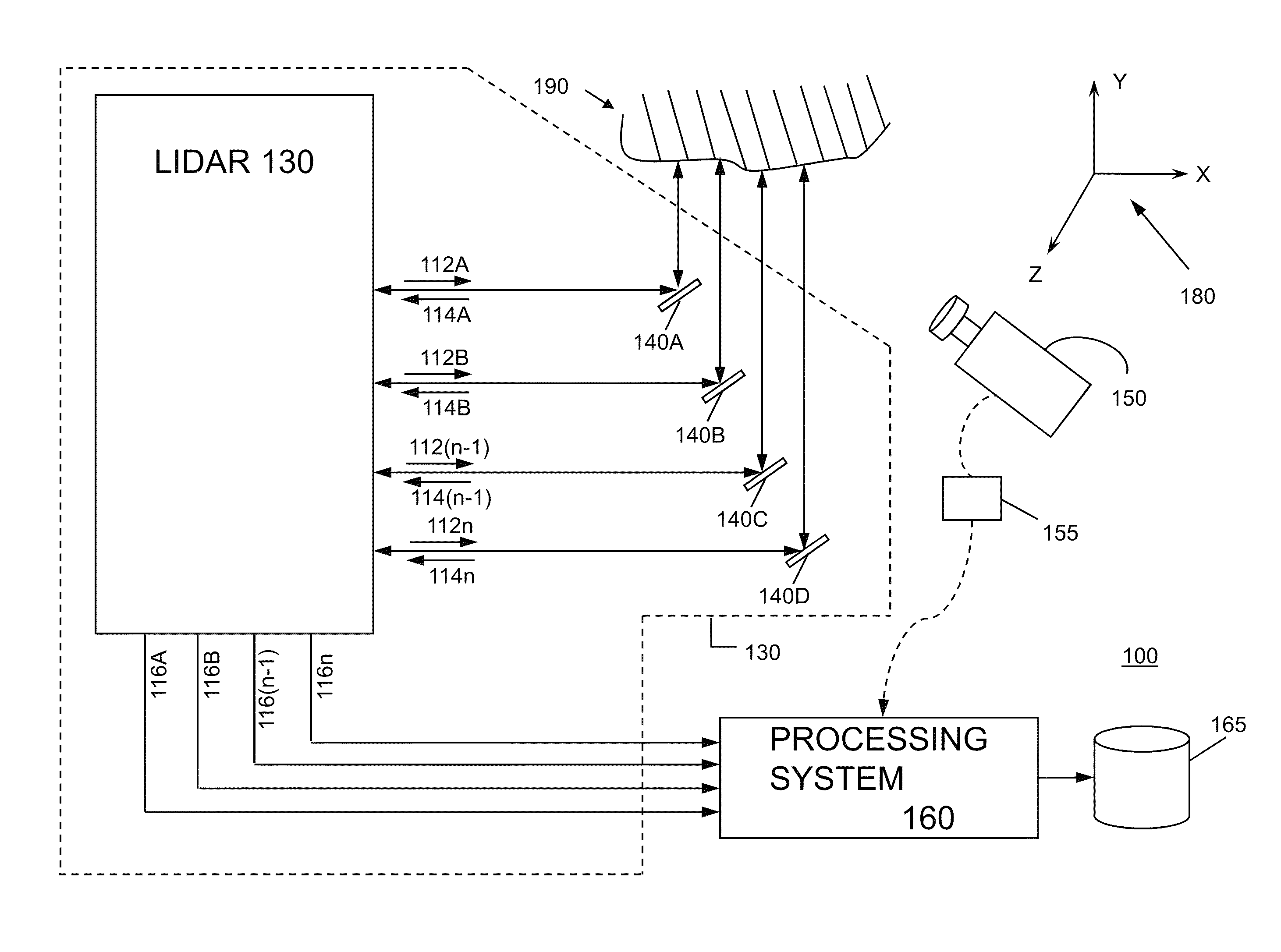
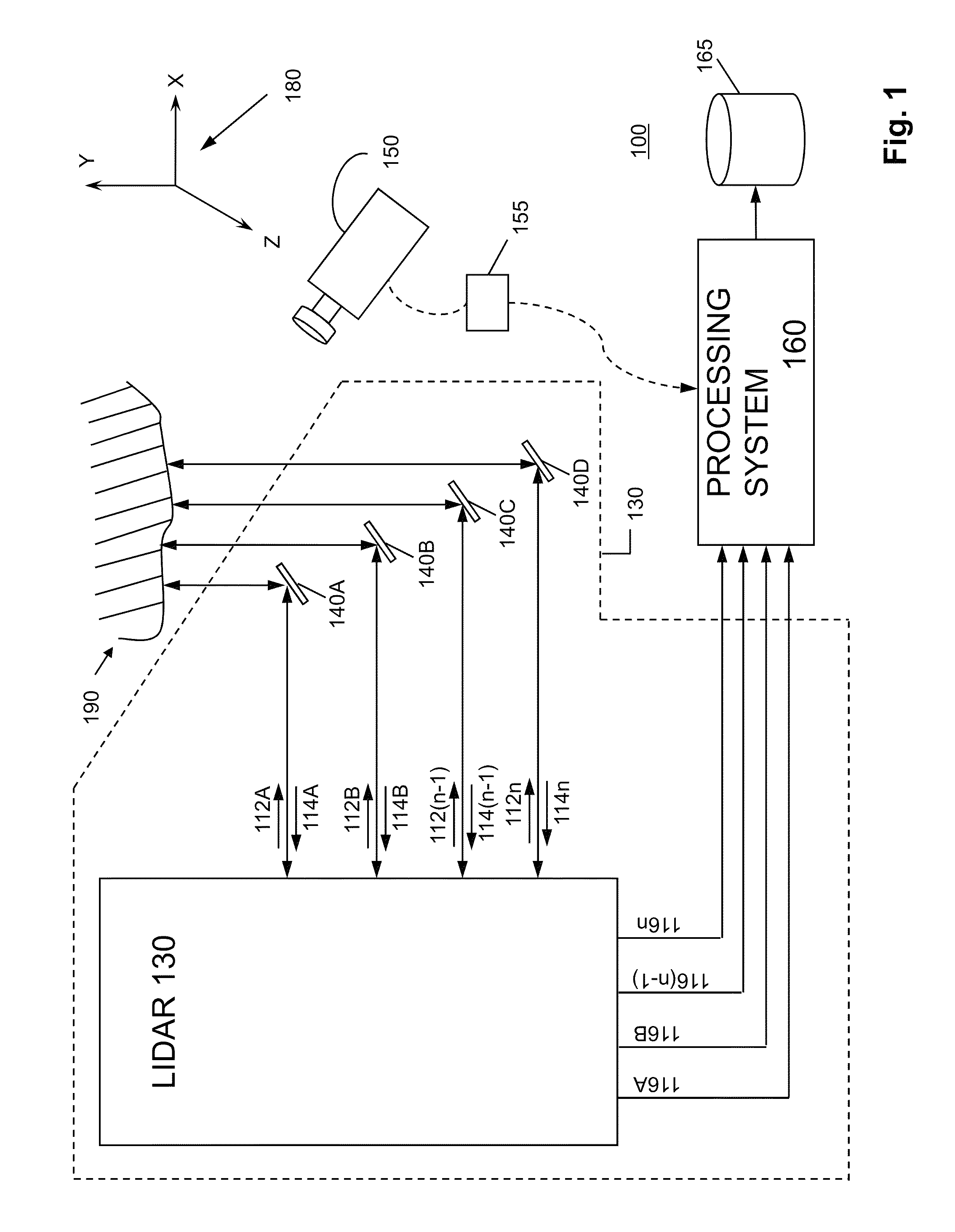
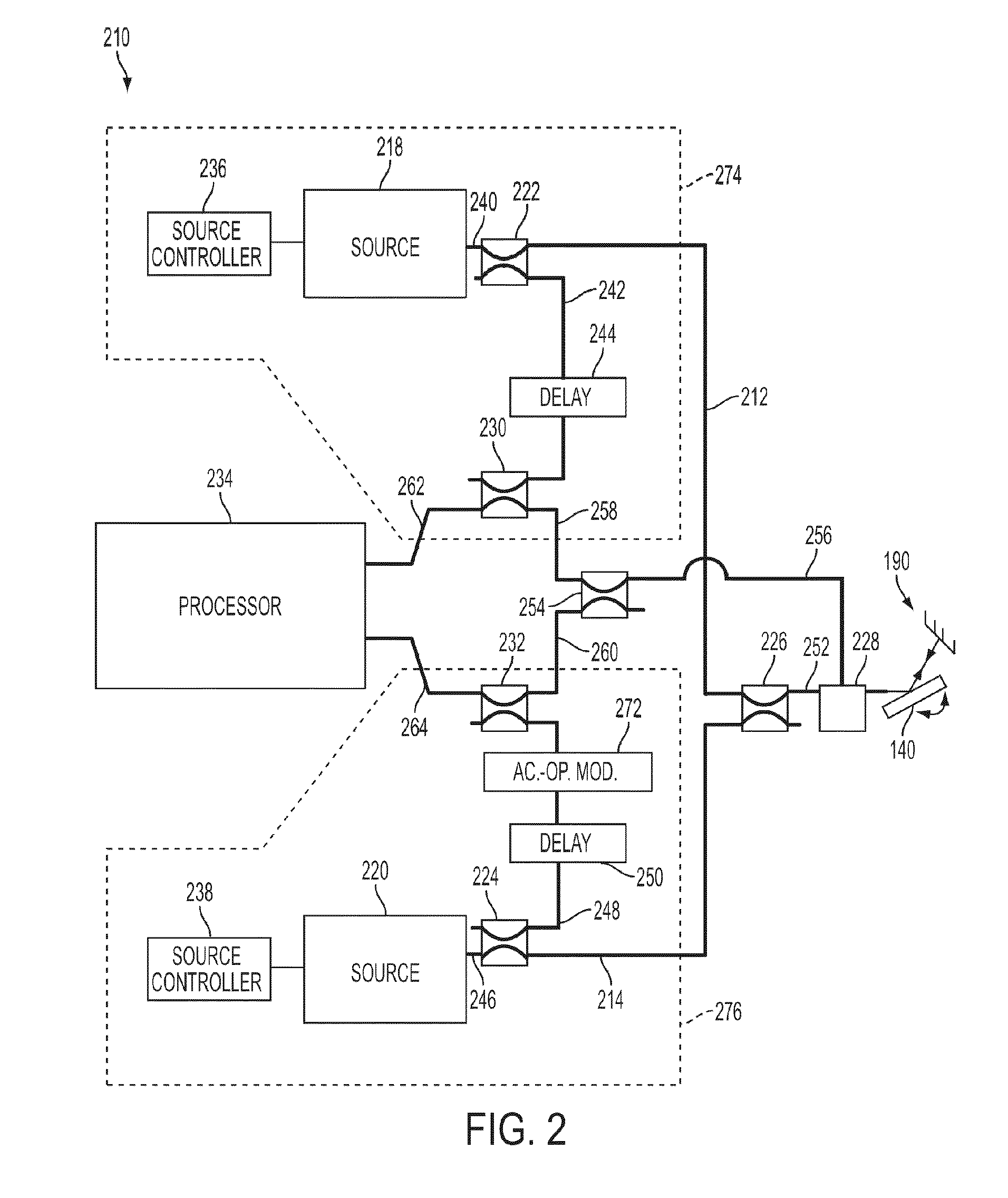
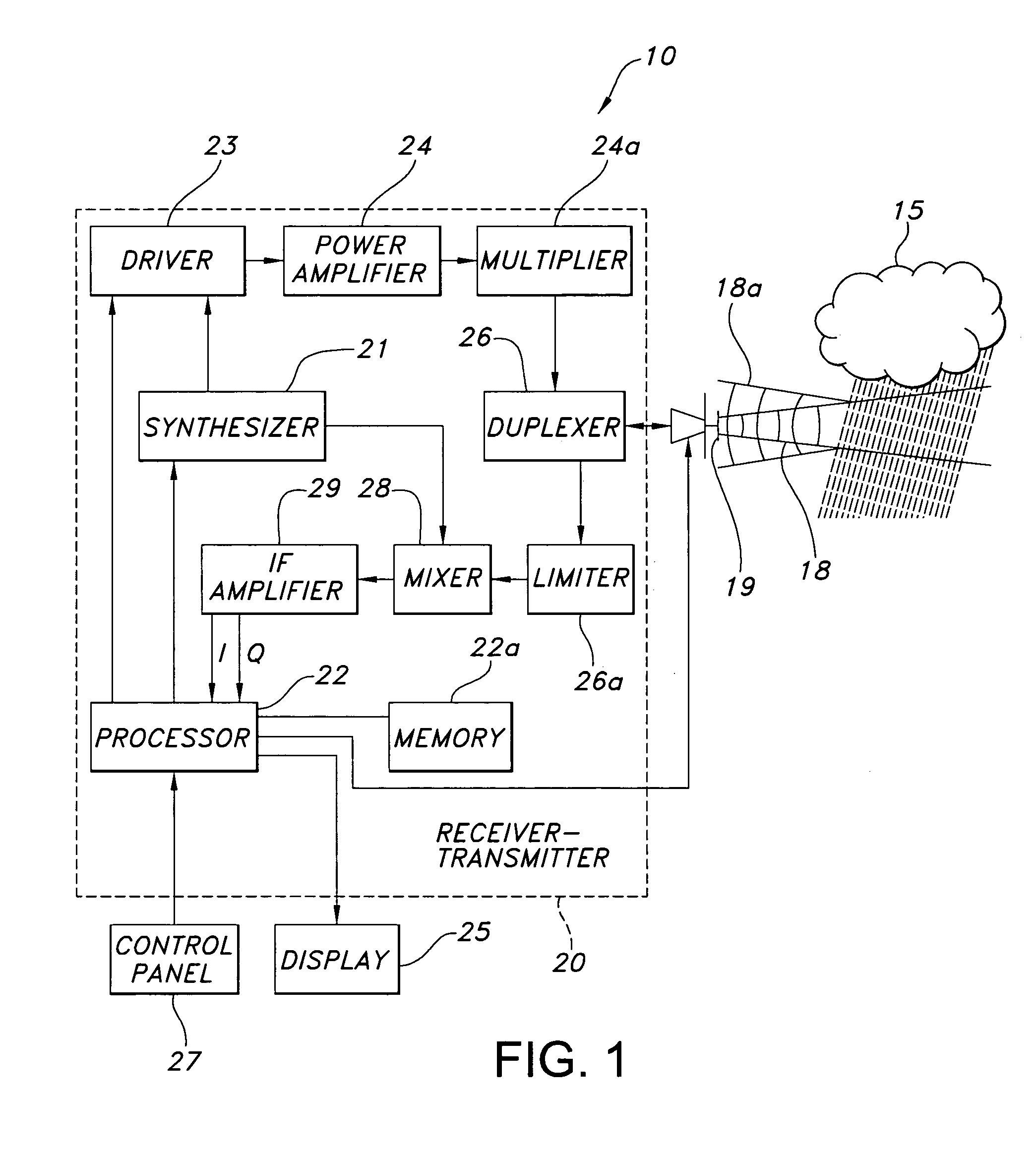
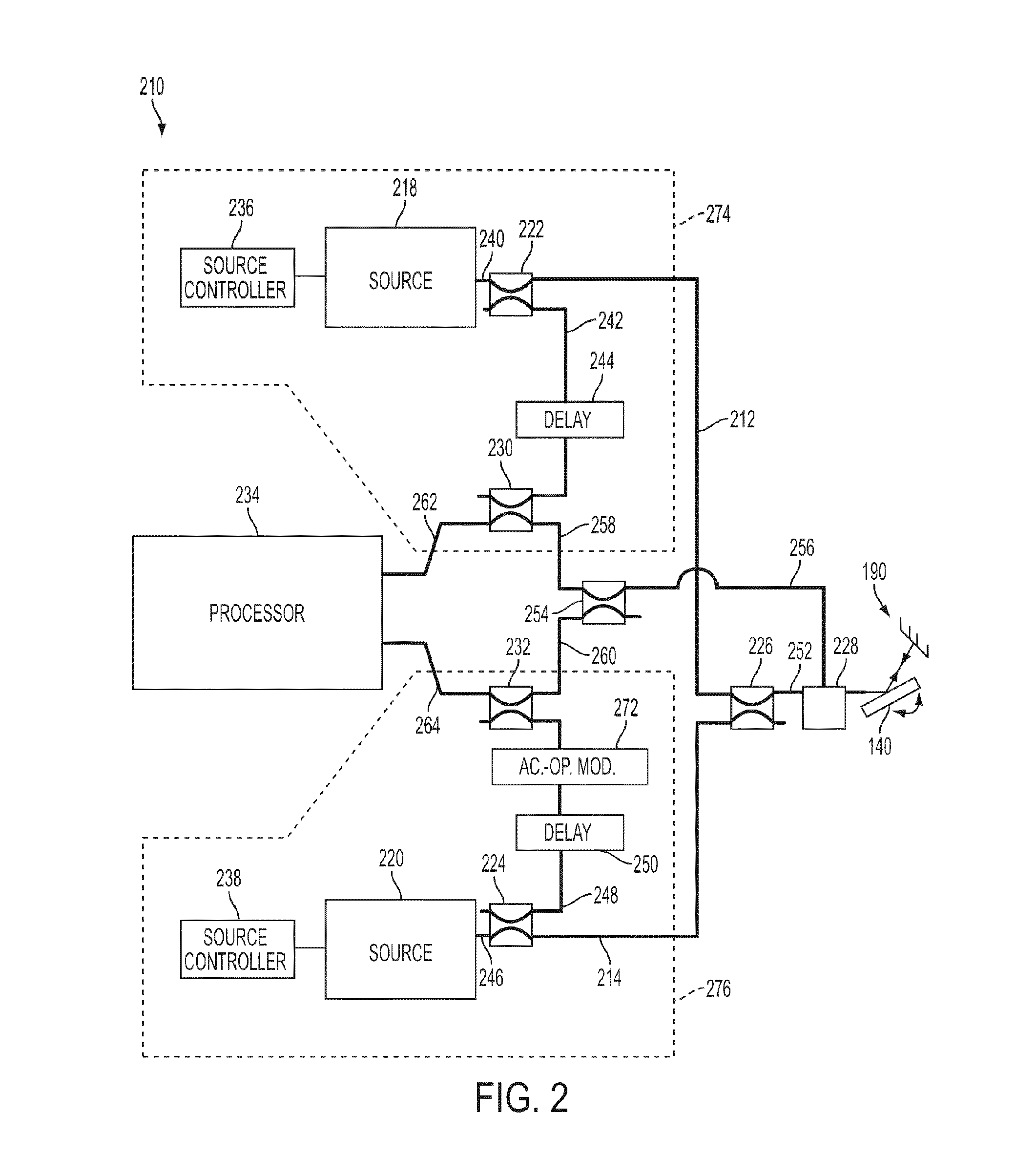
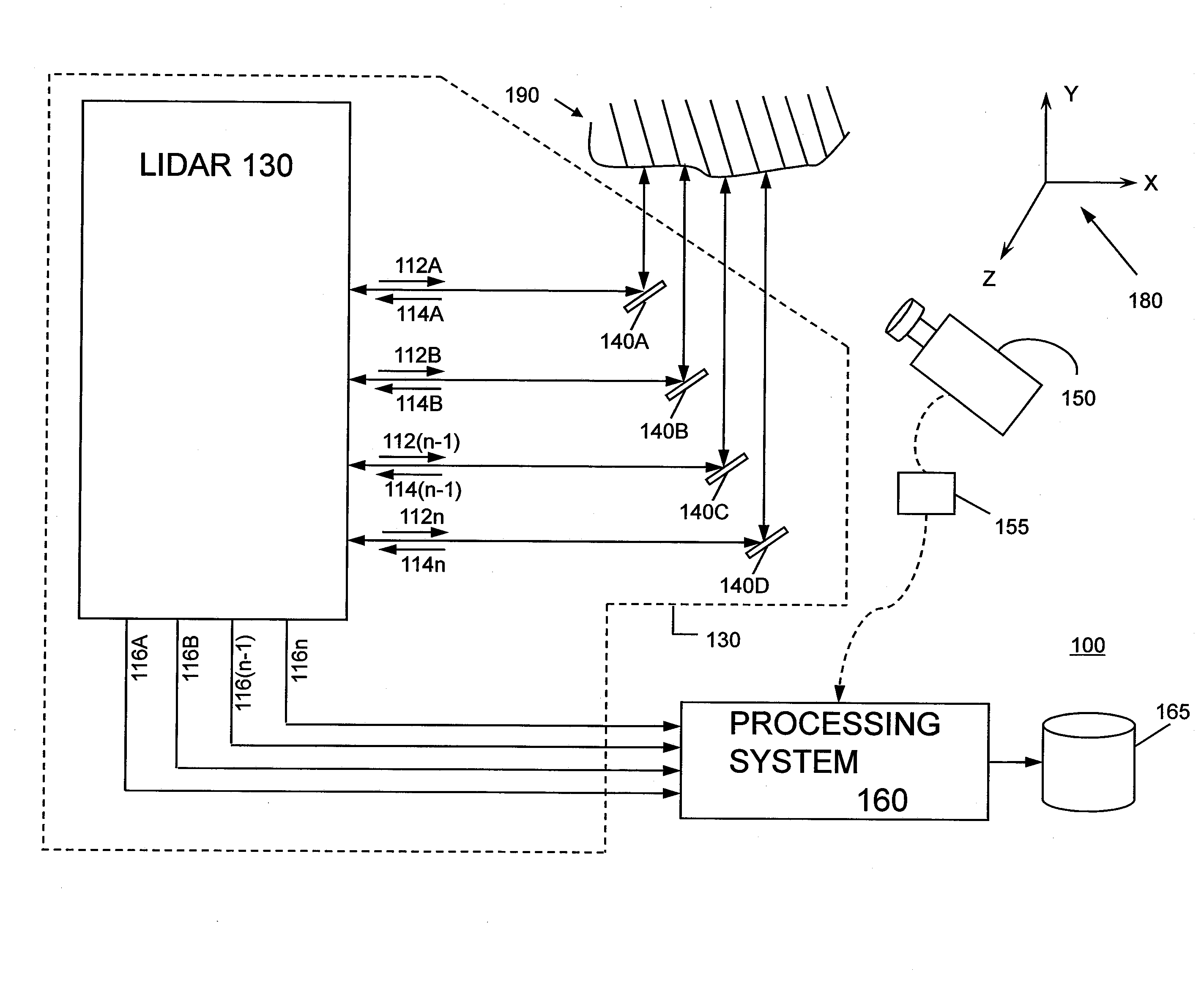
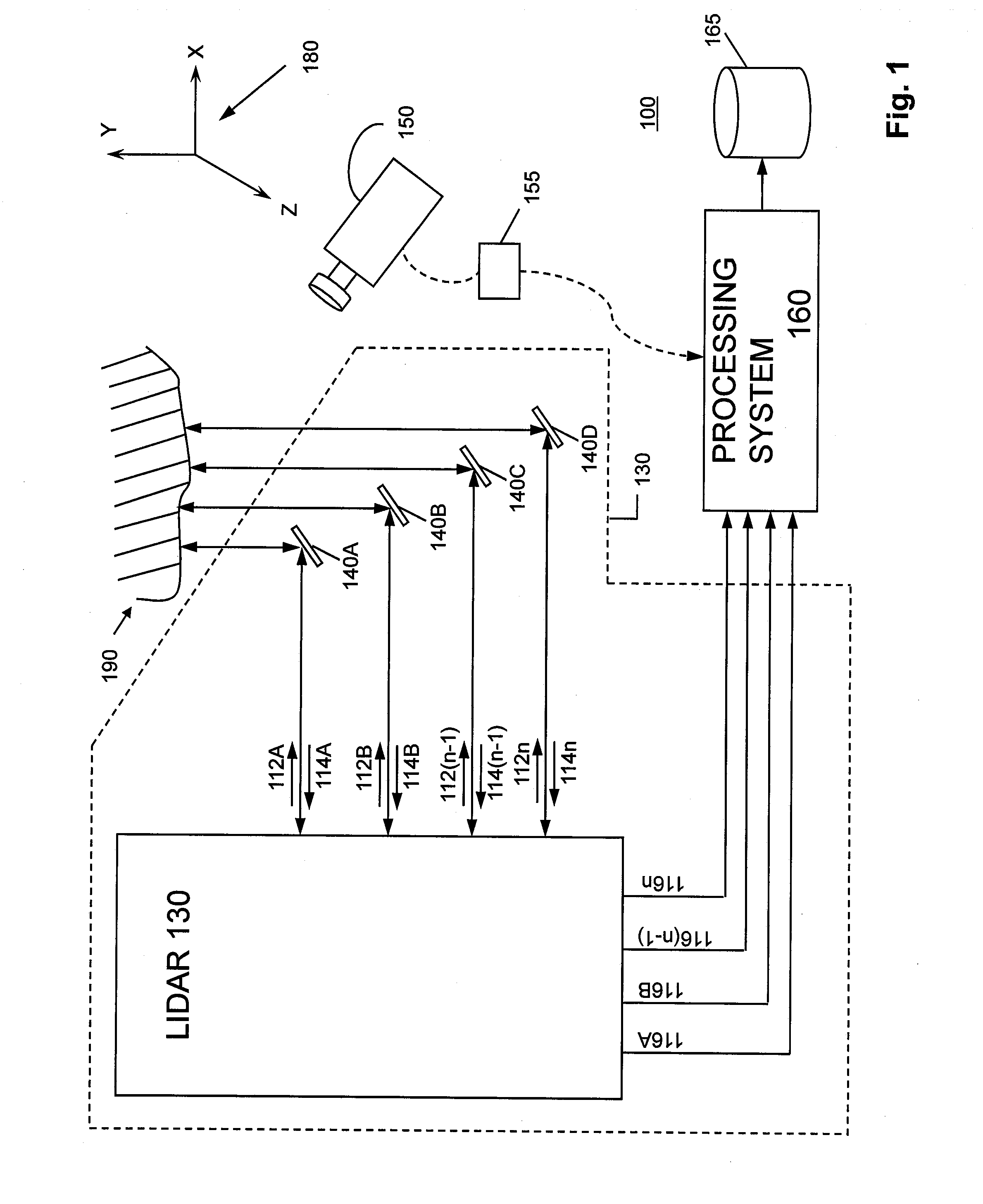
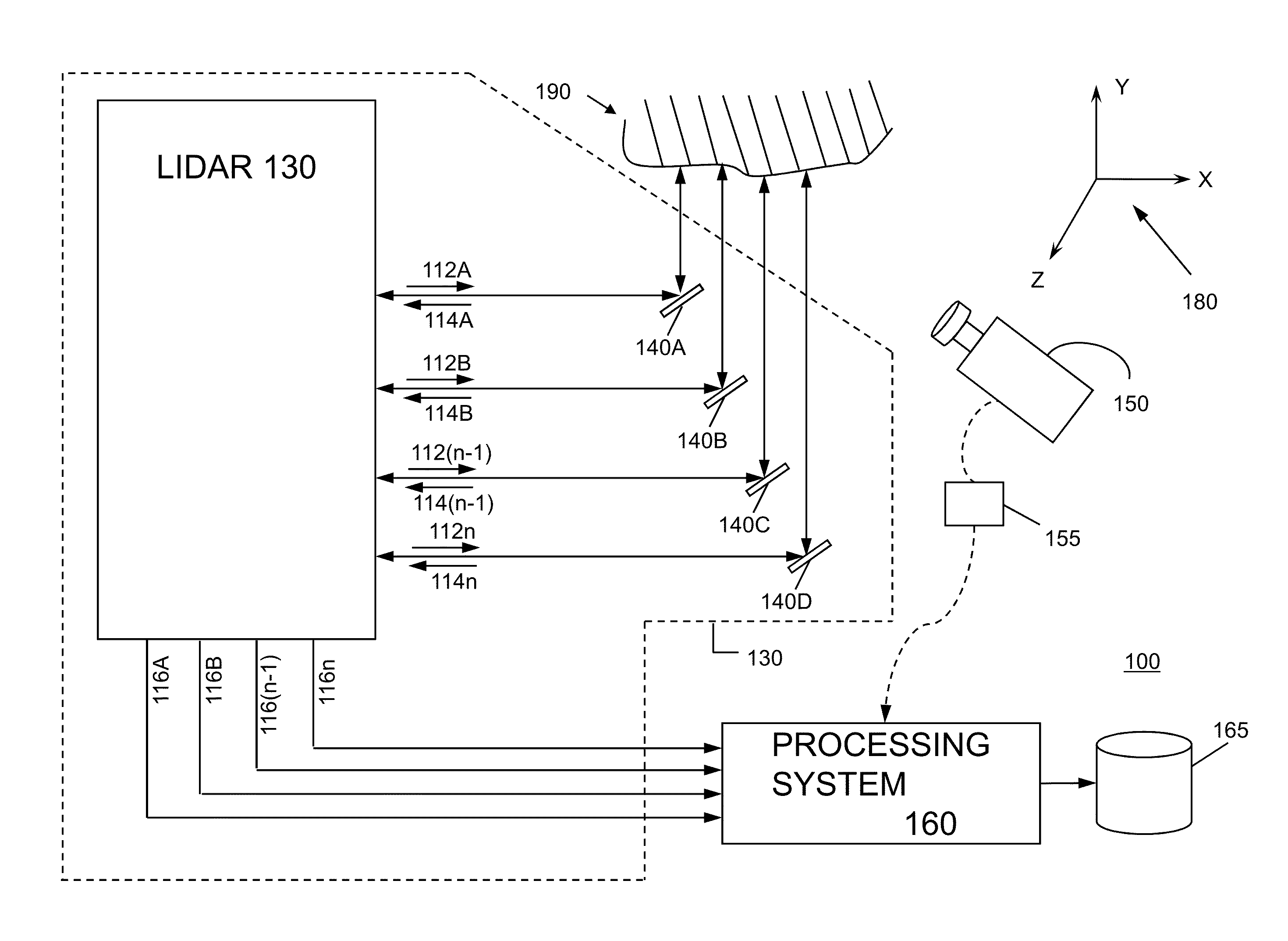
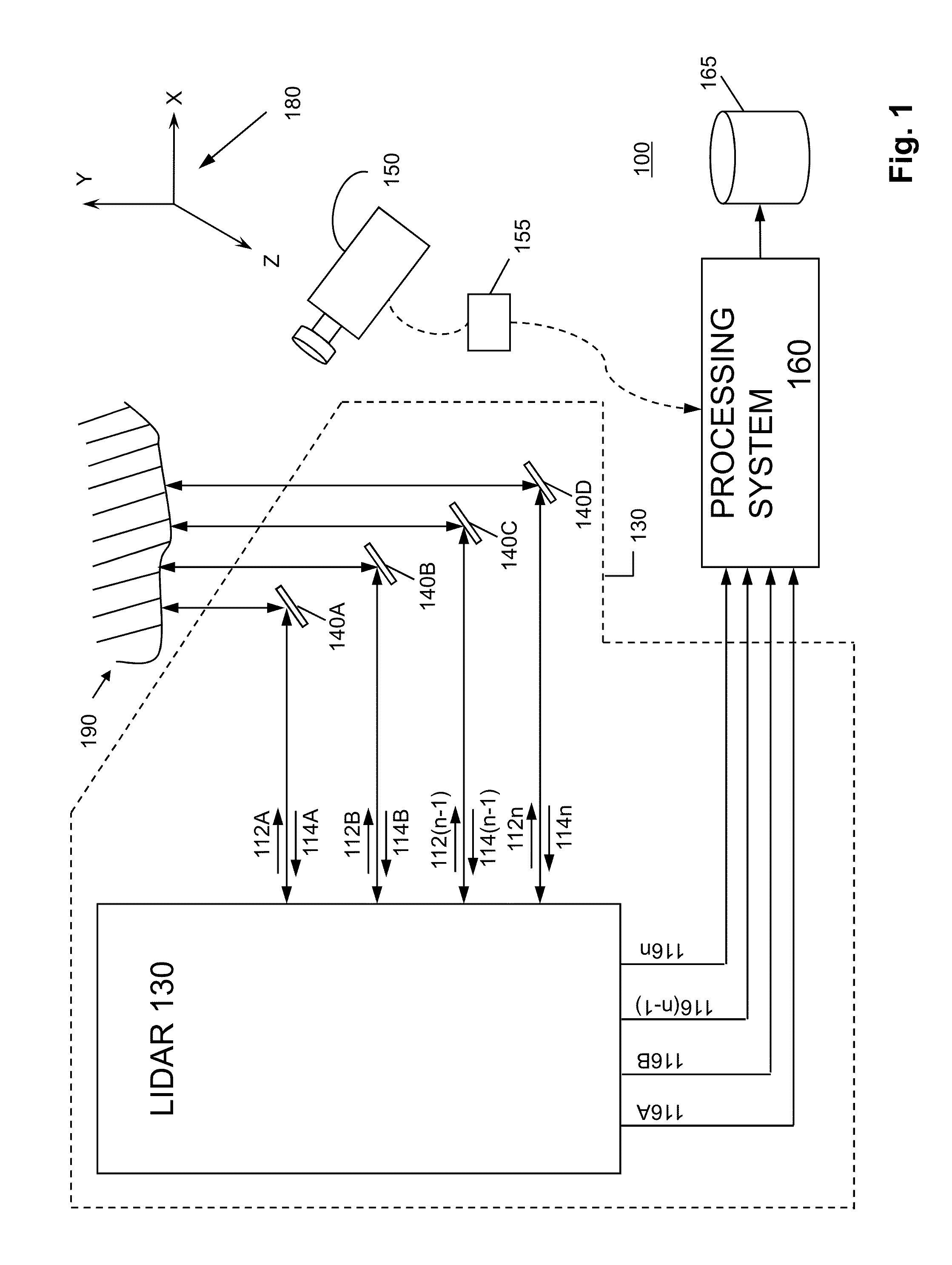
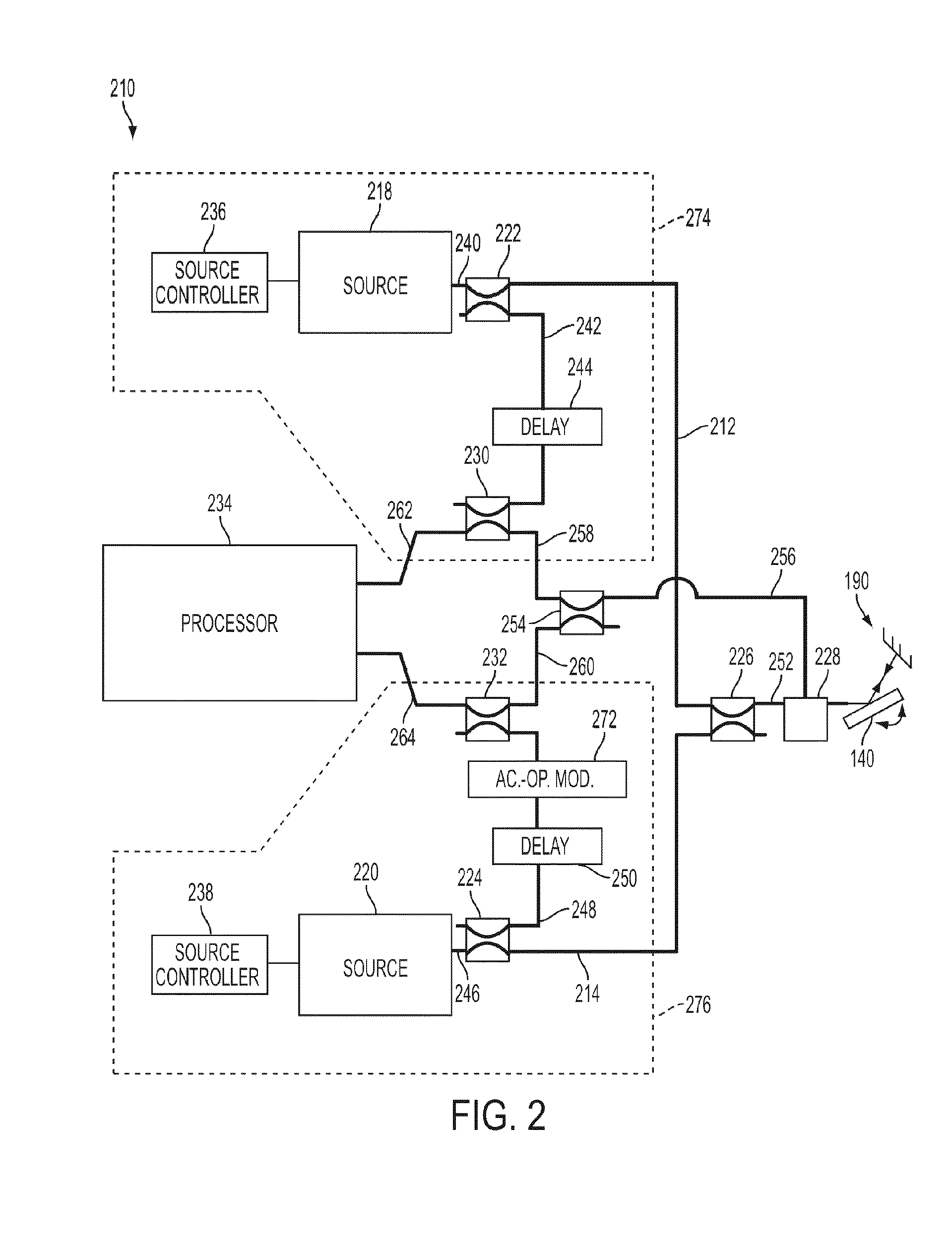
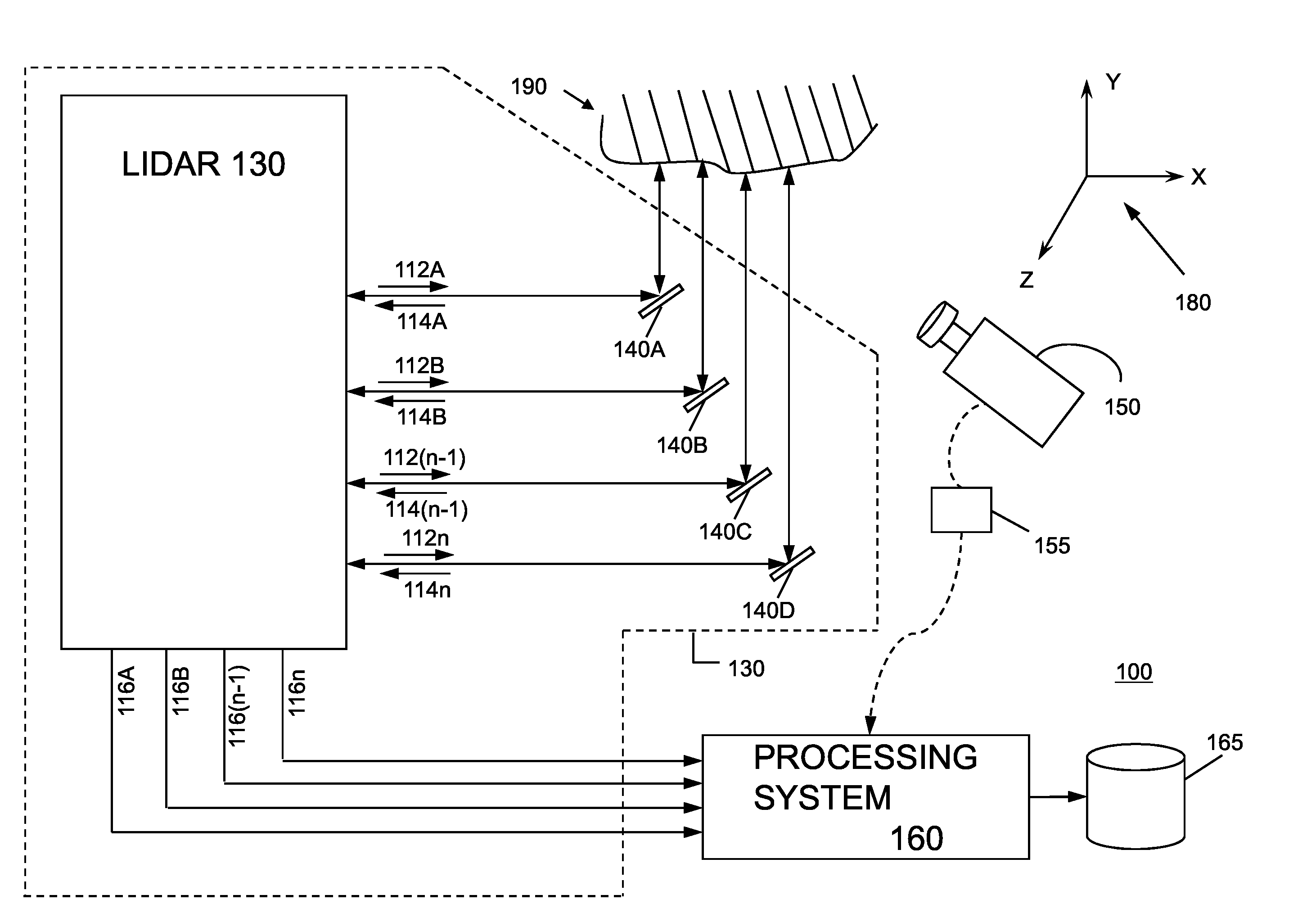
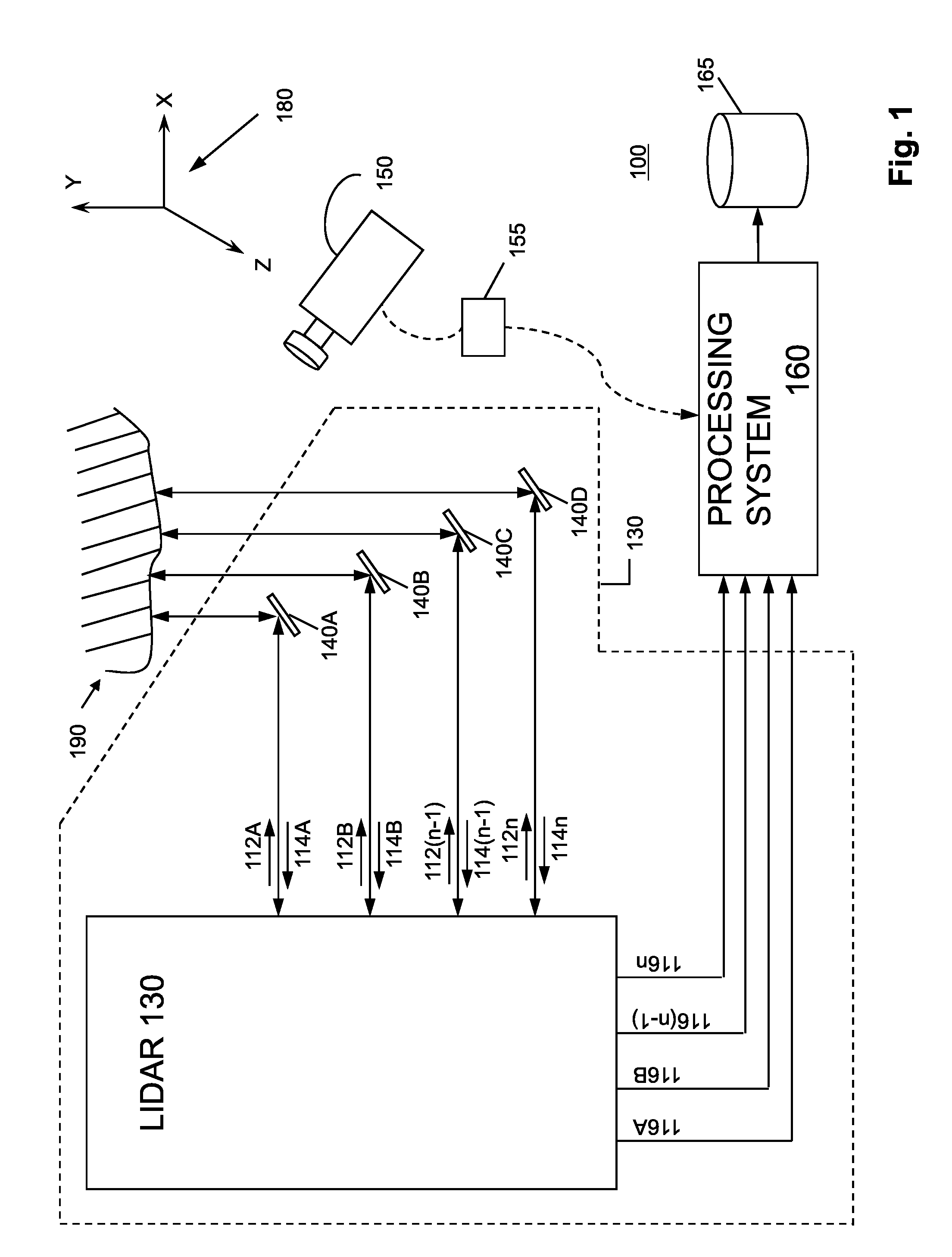
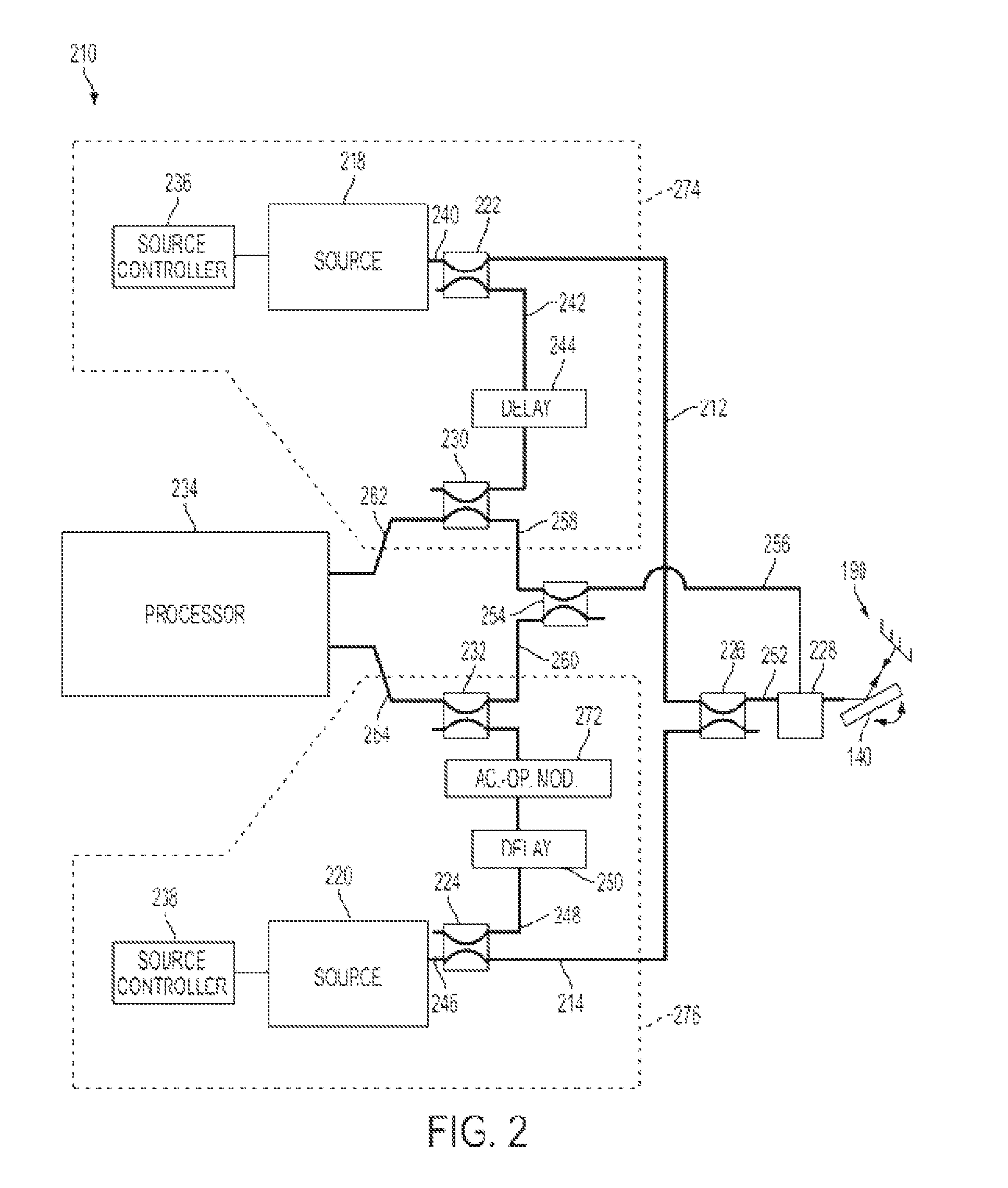
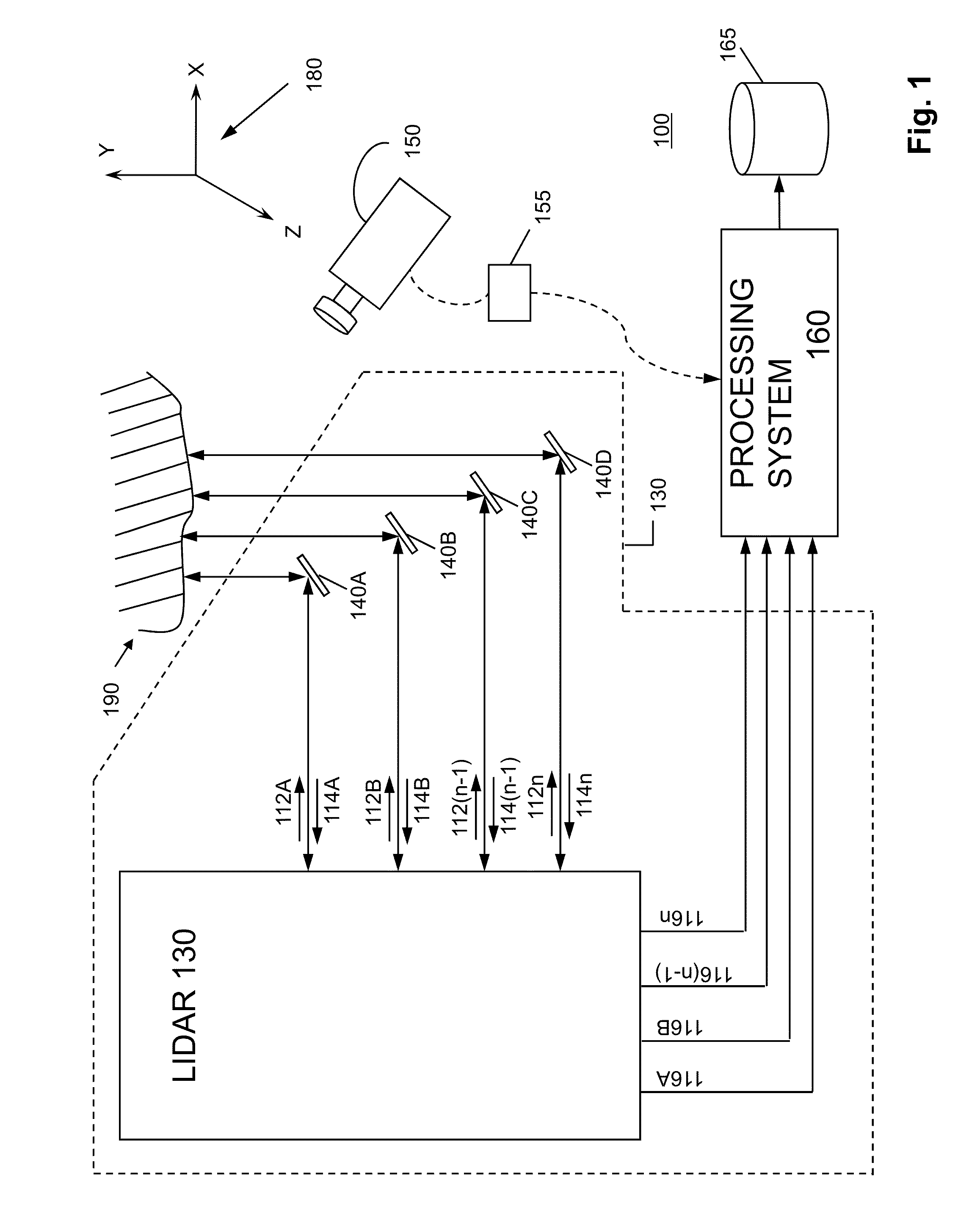
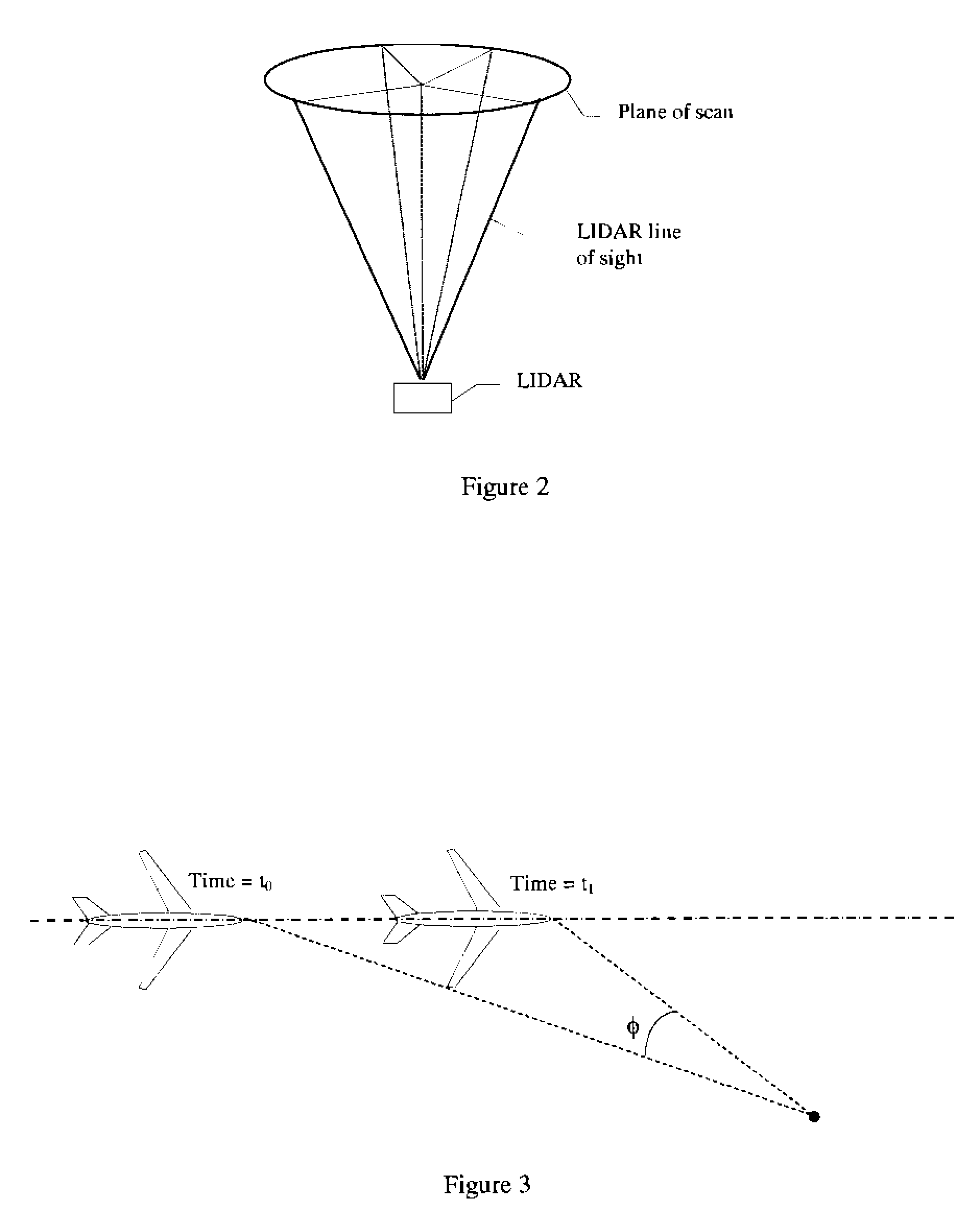
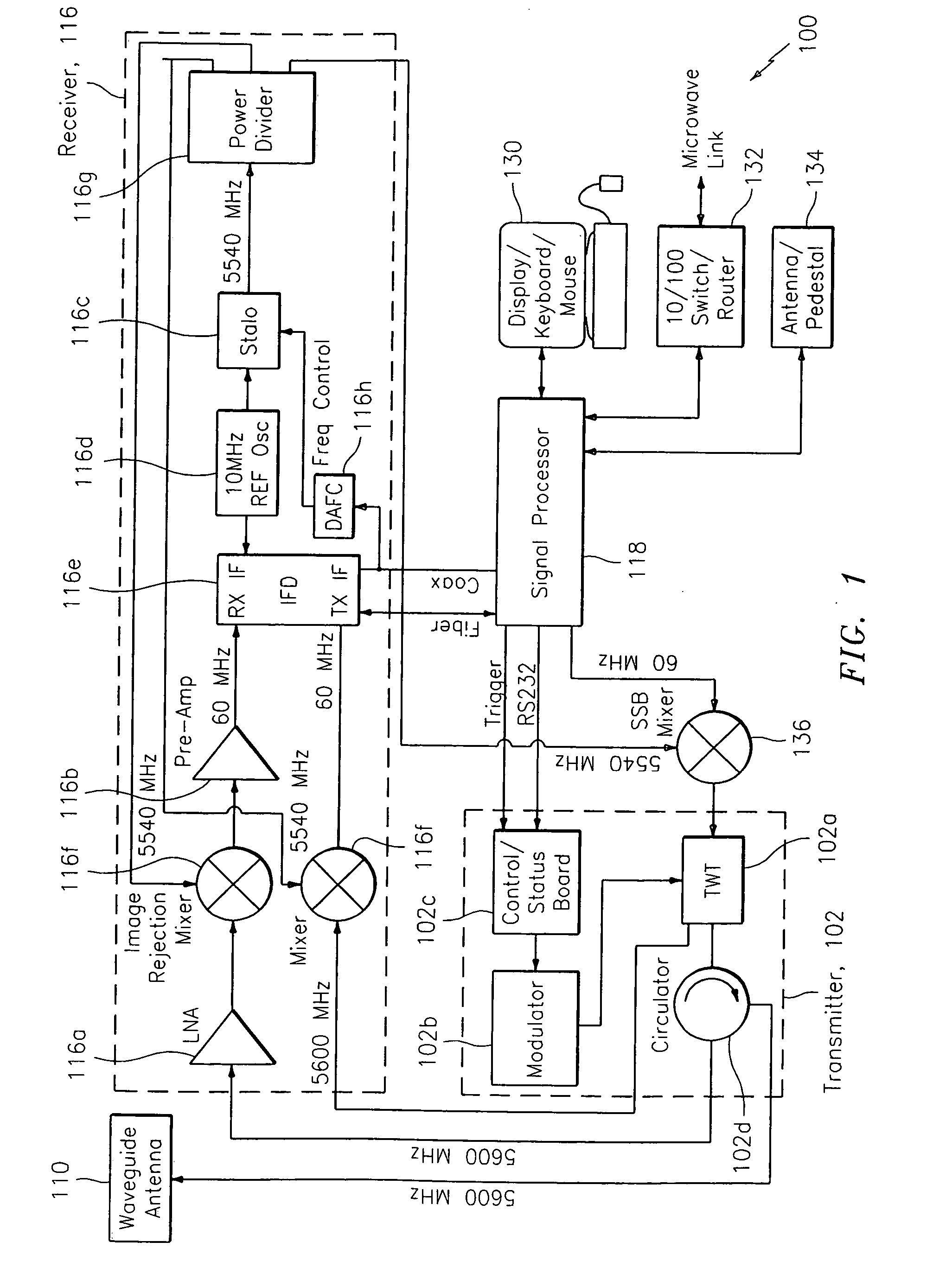
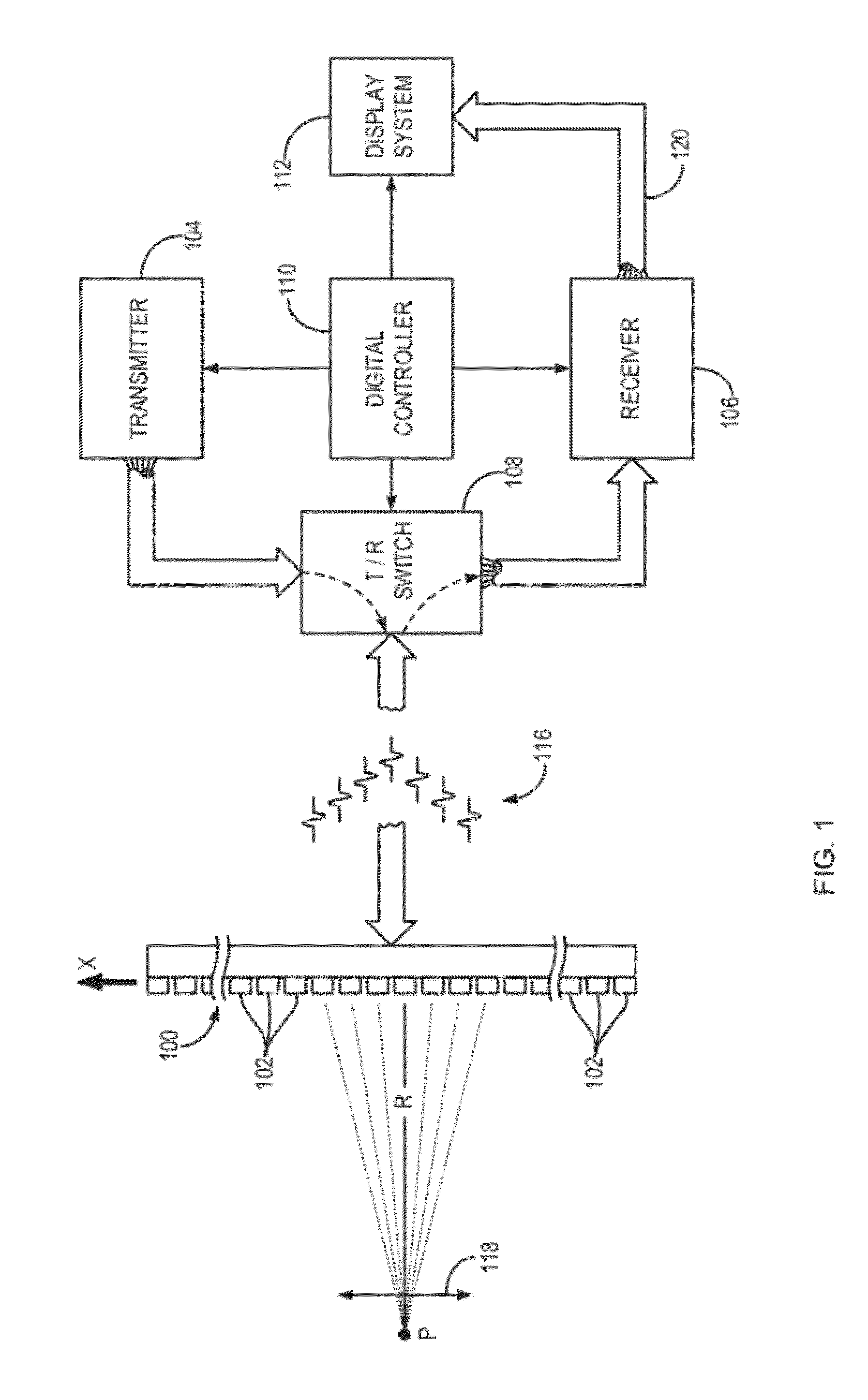
System and method for calibrating video and lidar subsystems
A system uses range and Doppler velocity measurements from a lidar system and images from a video system to estimate a six degree-of-freedom trajectory of a target. The system calibrates the lidar subsystem with the video subsystem in two stages. In a first stage, the system calibrates the lidar subsystem so that lidar measurements provide 3D lidar coordinates. In a second stage, the system relates the 3D lidar coordinates with a video image obtained from the video subsystem.
Owner:AEVA INC
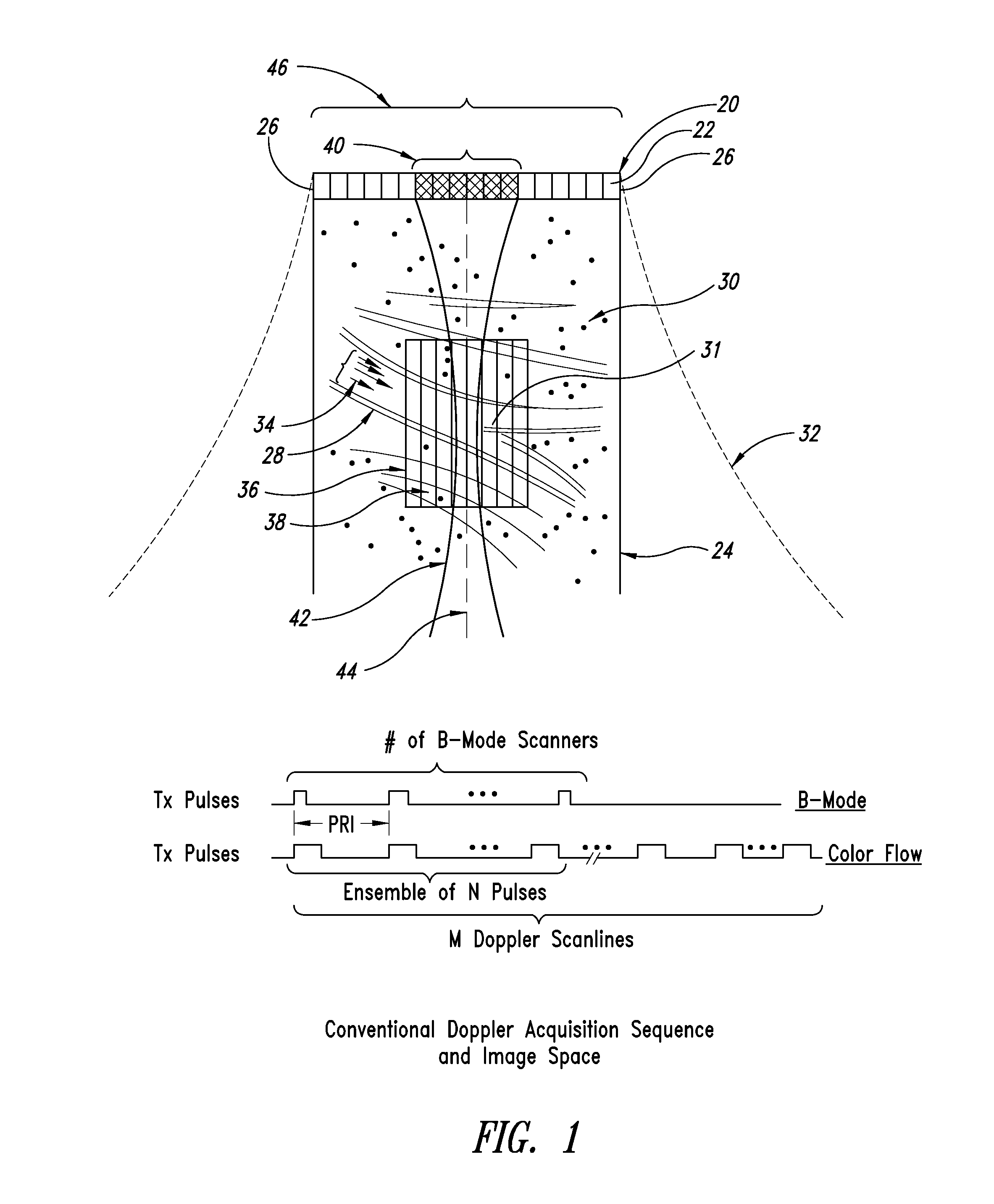
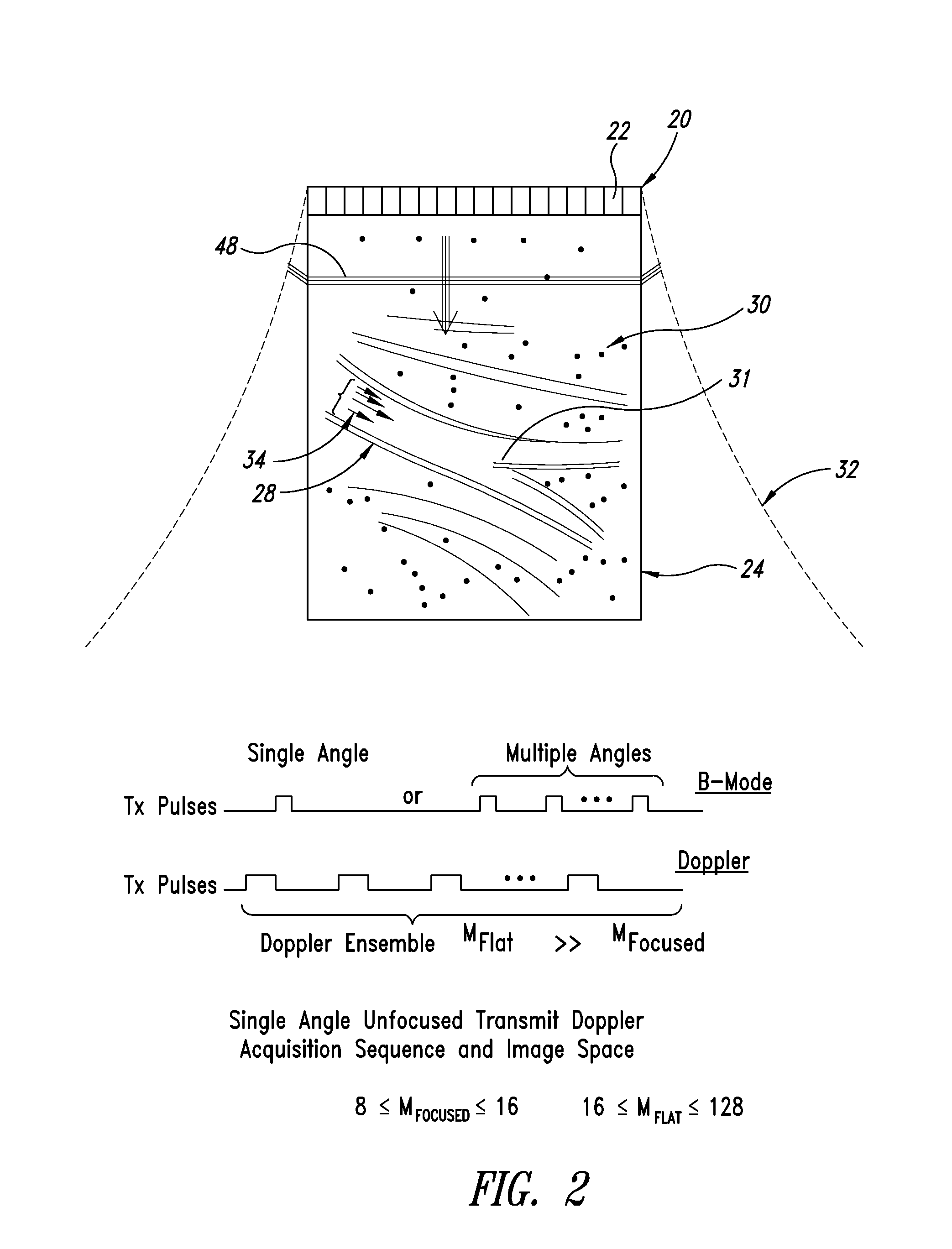
High frame rate quantitative doppler flow imaging using unfocused transmit beams
ActiveUS20090326379A1Enhanced acoustic informationImprovement of contrast resolutionBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingHigh frame rate
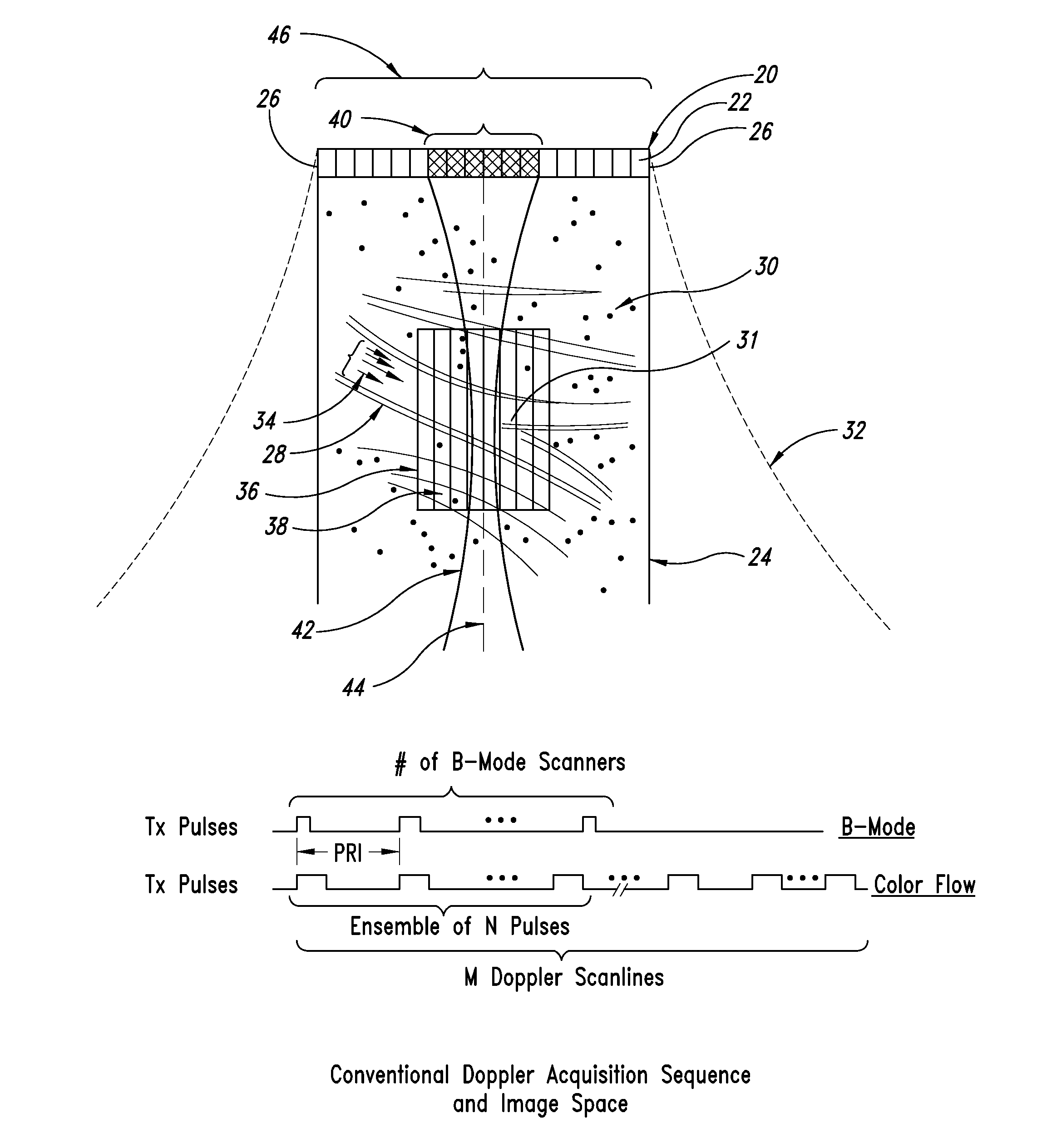
An ultrasound imaging system with pixel oriented processing is provided in which a method of producing a Doppler velocity image is accomplished by emitting unfocused acoustic signals into a medium over substantially an entire field; receiving scattered and reflected ultrasonic signals on a transducer array in response to the emission; processing the received ultrasonic signals to extract information to construct a Doppler velocity signal corresponding to at least one point in the medium; and generating on a display device the Doppler velocity image from the processed Doppler velocity signal. Acquisition sequences and signal processing algorithms are described that provide improved quantification of fluid flow parameters, including improved discrimination between regions of blood flow and tissue. Very high frame rate Spectral Doppler and Vector Doppler acquisition modes for real-time and post-acquisition visualization over a large field of view are described.
Owner:VERASONICS
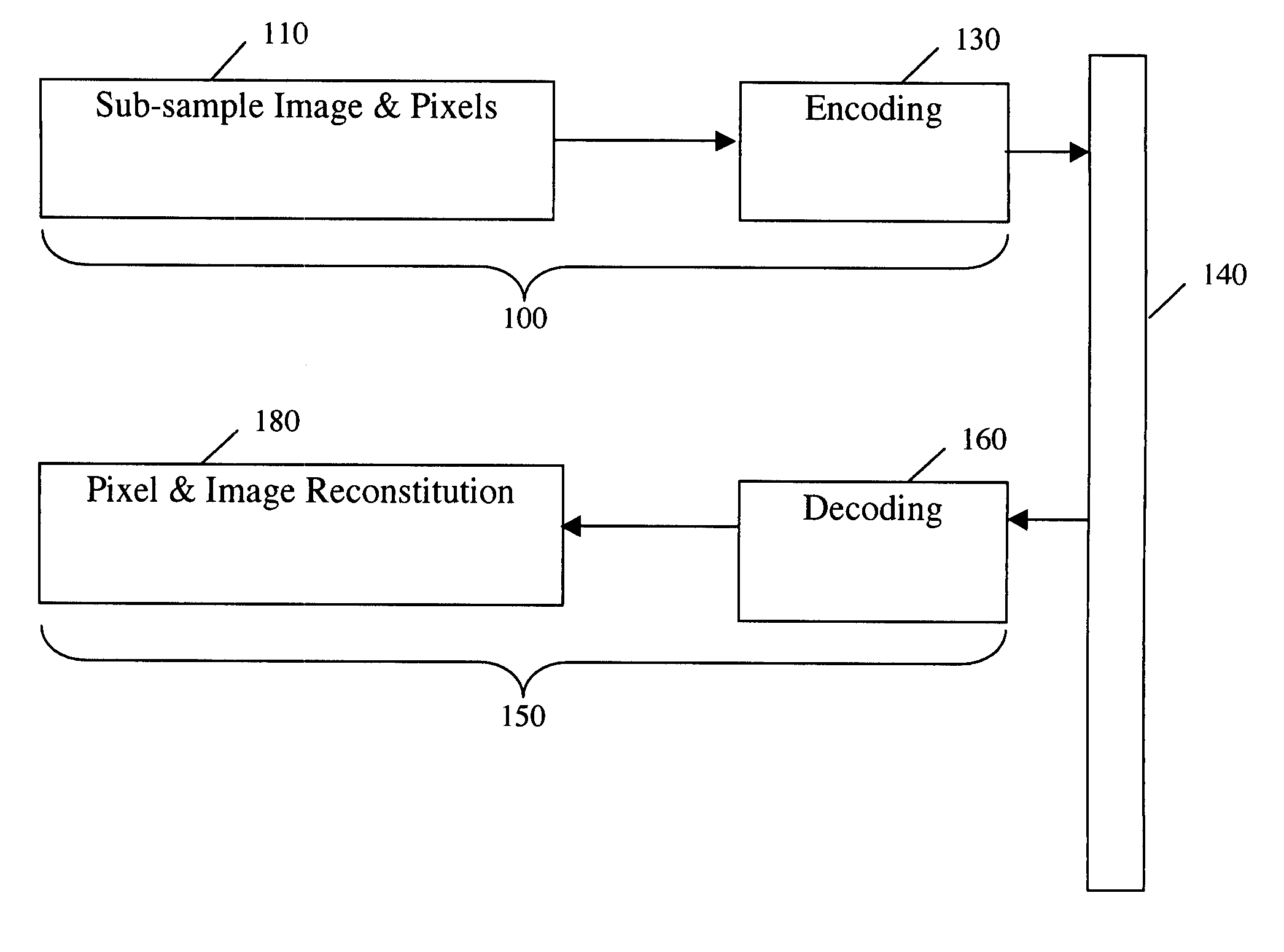
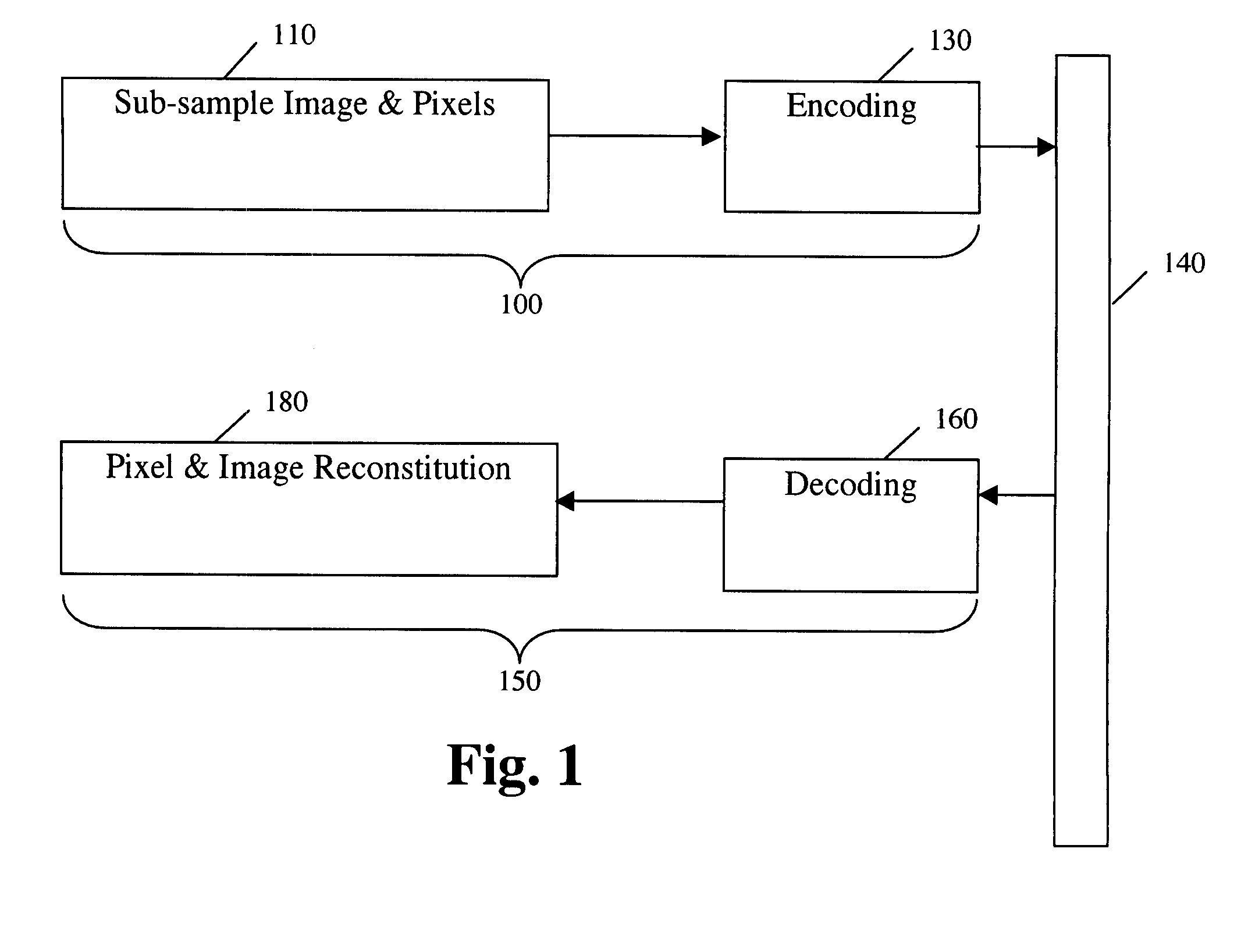
Separate plane compression using plurality of compression methods including ZLN and ZLD methods
InactiveUS8416847B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoDoppler velocity
Methods, medium, and machines which compress, enhance, encode, transmit, decode, decompress and display digital video images. Real time compression is achieved by sub-sampling each frame of a video signal, filtering the pixel values, and encoding. Real time transmission is achieved due to high levels of effective compression. Real time decompression is achieved by decoding and decompressing the encoded data to display high quality images. A receiver can alter various setting including, but not limited to, the format for the compression, image size, frame rate, brightness and contrast. In a Doppler improvement aspect of the invention, Doppler velocity scales are incorporated into grayscale compression methods using two bits. Variable formats may be selected and Doppler encoding can be turned on and off based on the image content. A separate plane compression aspect of the invention provides for distinguishing between regions of an image, separating and masking the original image into multiple image planes, and compressing each separated image plane with a compression method that is optimal for its characteristics. From a video stream, separate image streams can be compressed with different methods, and the separate image streams can be stored or transmitted at different rates. Alternatively, frame differencing can be applied to the separated streams. Regions may be distinguished by user input or by automated analysis of the characteristics of various regions of an image, such as the presence of Doppler enhanced pixels.
Owner:MUSICQUBED INNOVATIONS LLC
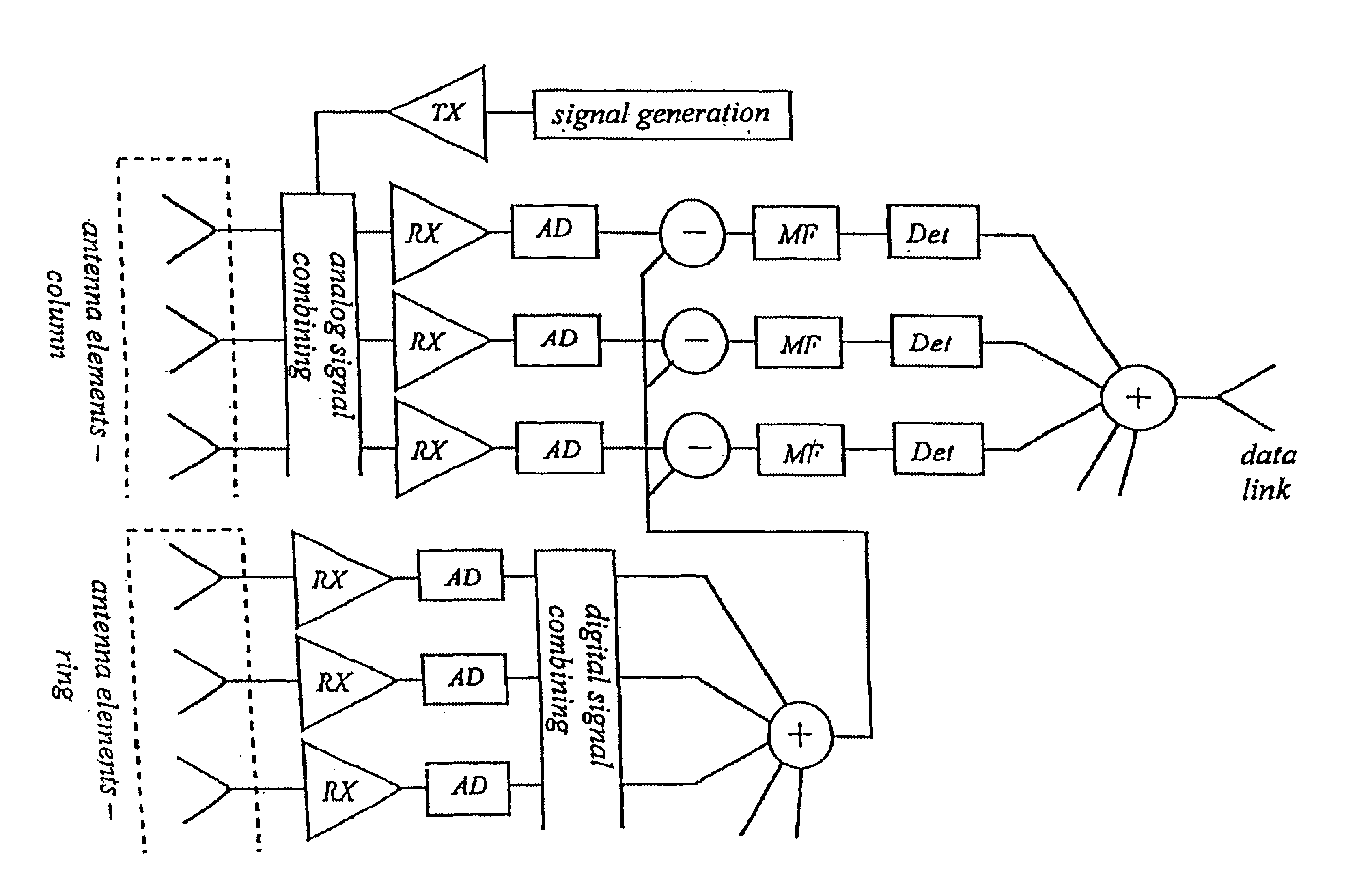
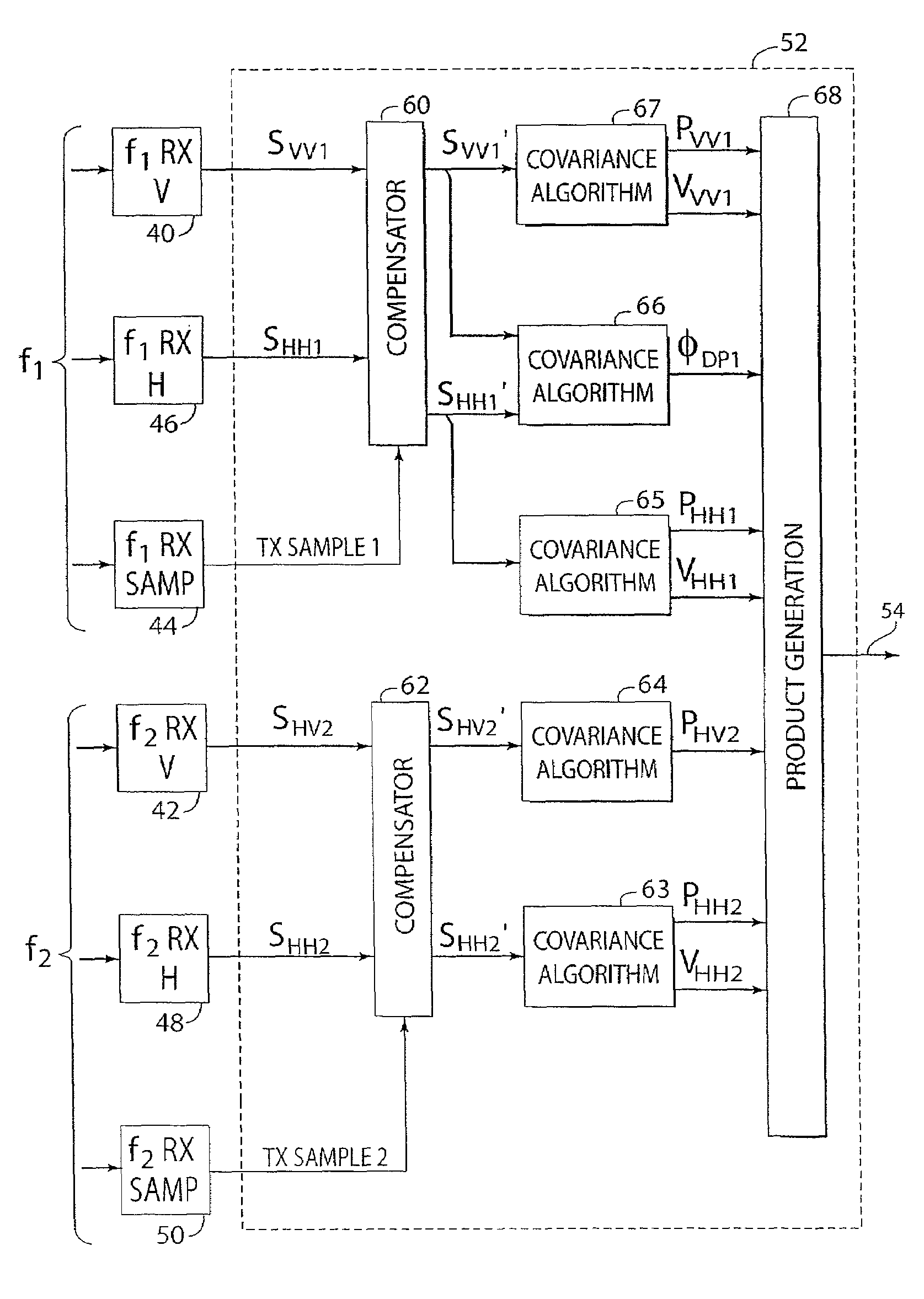
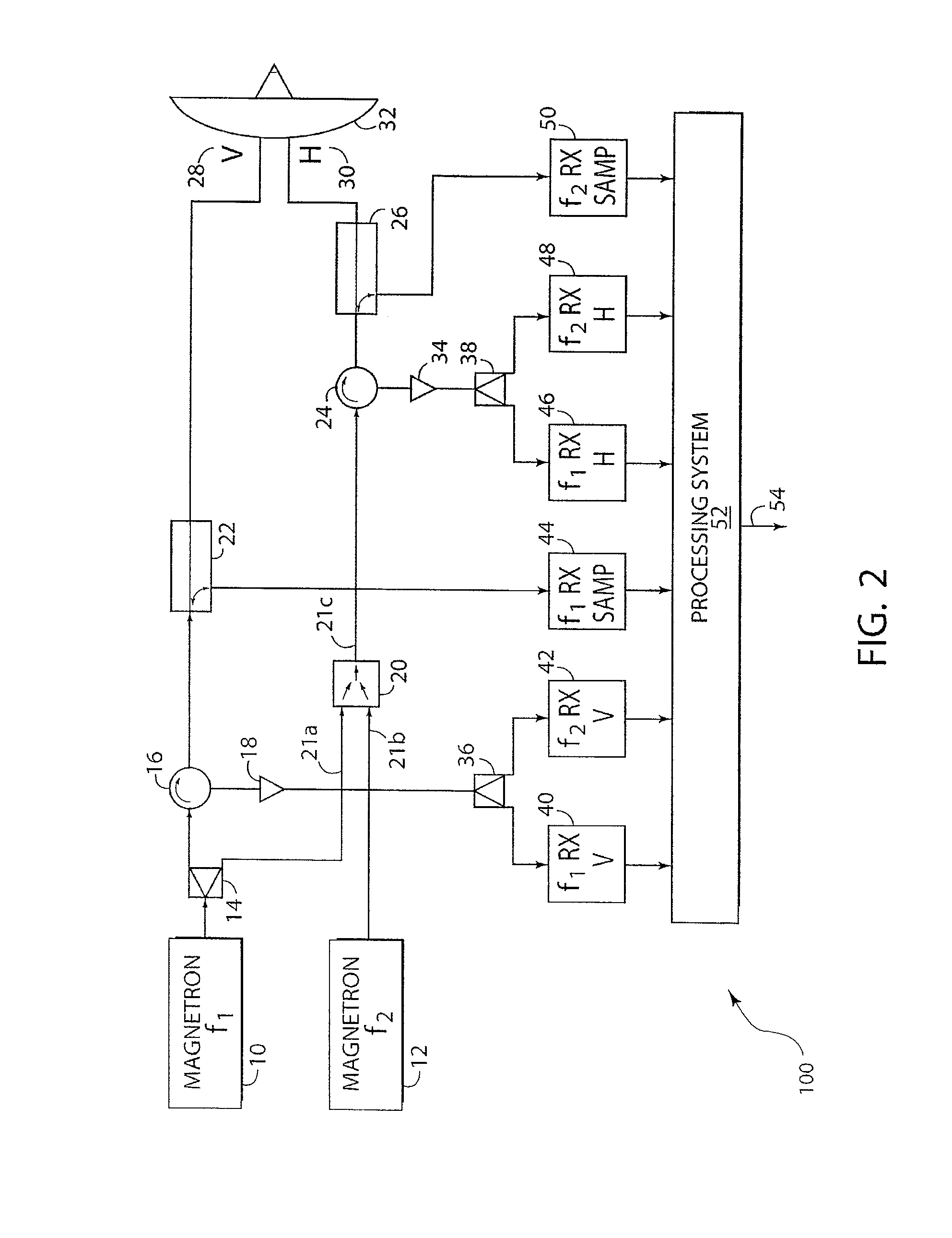
Polarization and frequency diverse radar system for complete polarimetric characterization of scatterers with increased scanning speed
InactiveUS20070152867A1Maximize isolationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationDoppler velocityRadar systems
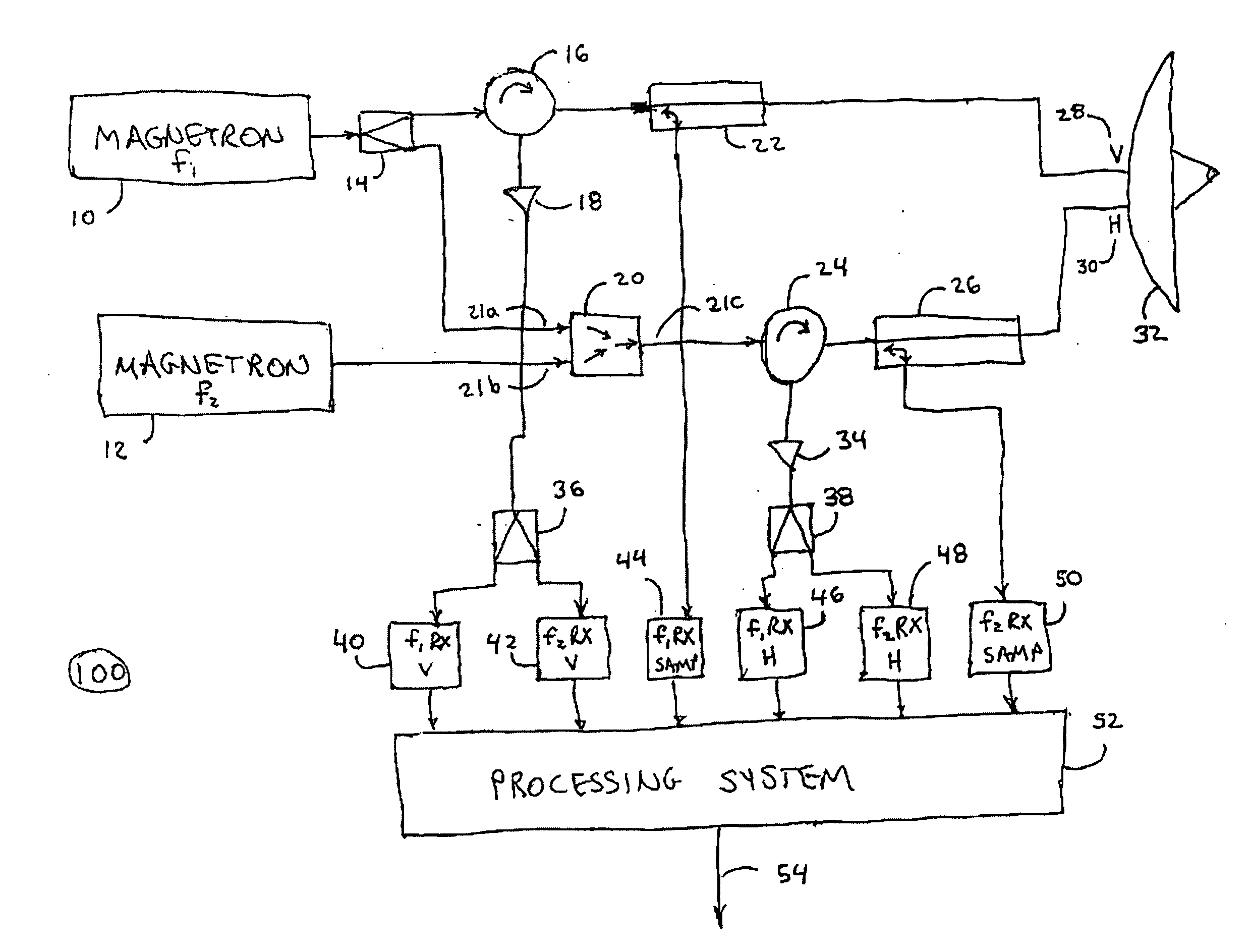
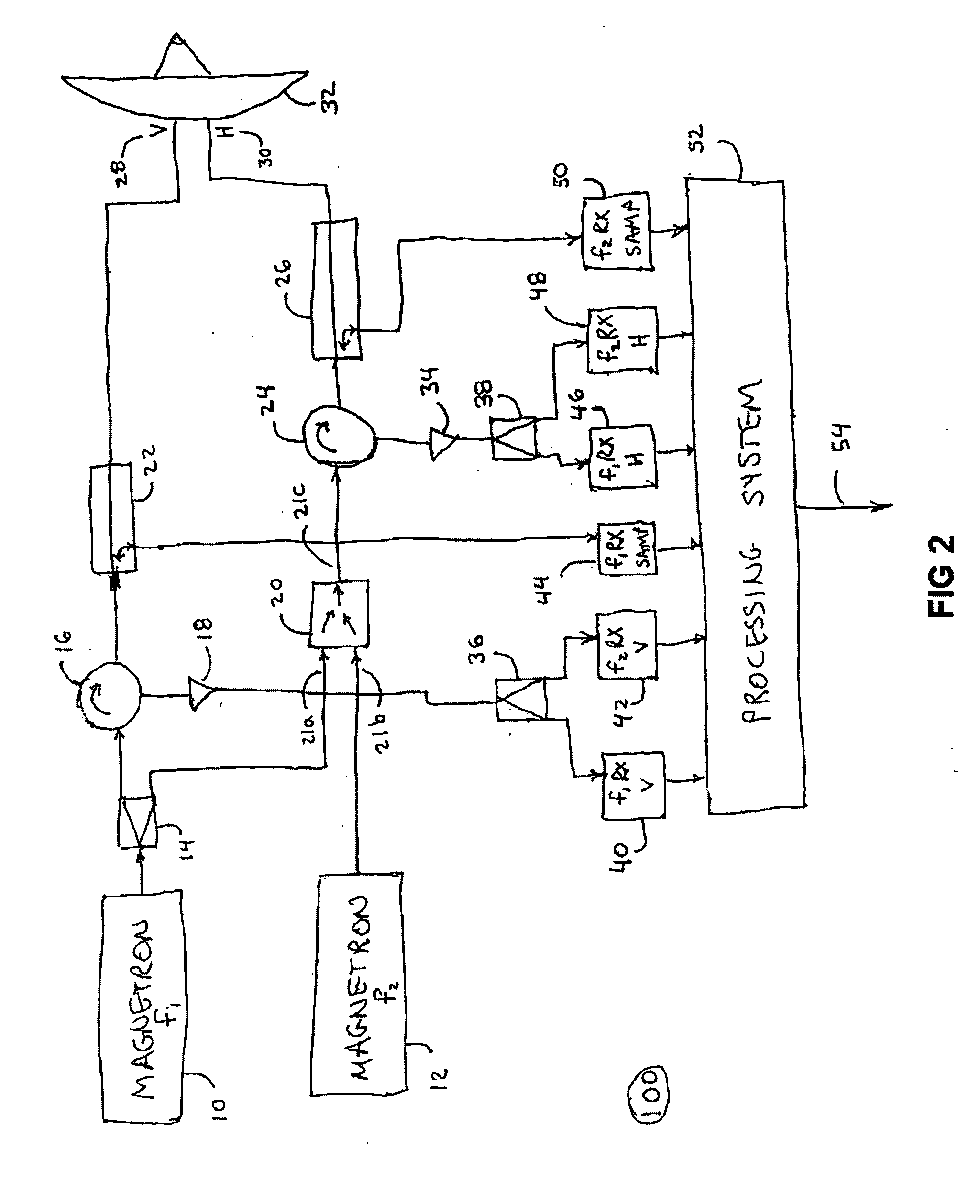
A method and apparatus is provided, whereby a scanning, polarization and frequency diverse radar system measures the complete polarimetric characterization of weather targets without loss of scanning speed and without an additional ambiguity in the Doppler velocity beyond that given by Nyquist's sampling theorem. In one embodiment, a linear combination of a horizontally and a vertically polarized signal are transmitted at a predetermined first frequency. Cotemporaneously or nearly cotemporaneously with the transmitted signal of the first frequency, a horizontally polarized signal is transmitted at a predetermined second frequency. Horizontal and vertical receive channels receive echoes at the predetermined first frequency to determine, but not limited to determine, the co-polar elements of the scattering matrix. Horizontal and vertical receive channels receive echoes at the predetermined second frequency to determine, but not limited to determine, the cross-polar elements of the polarization matrix. The predetermined first and second frequencies are selected to maximize isolation yet allow practical implementation.
Owner:ADVANCED RADAR CORP
Multi-radar plot fusion method
InactiveCN106680806AImprove detection distanceImprove tracking performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDoppler velocityRadar network
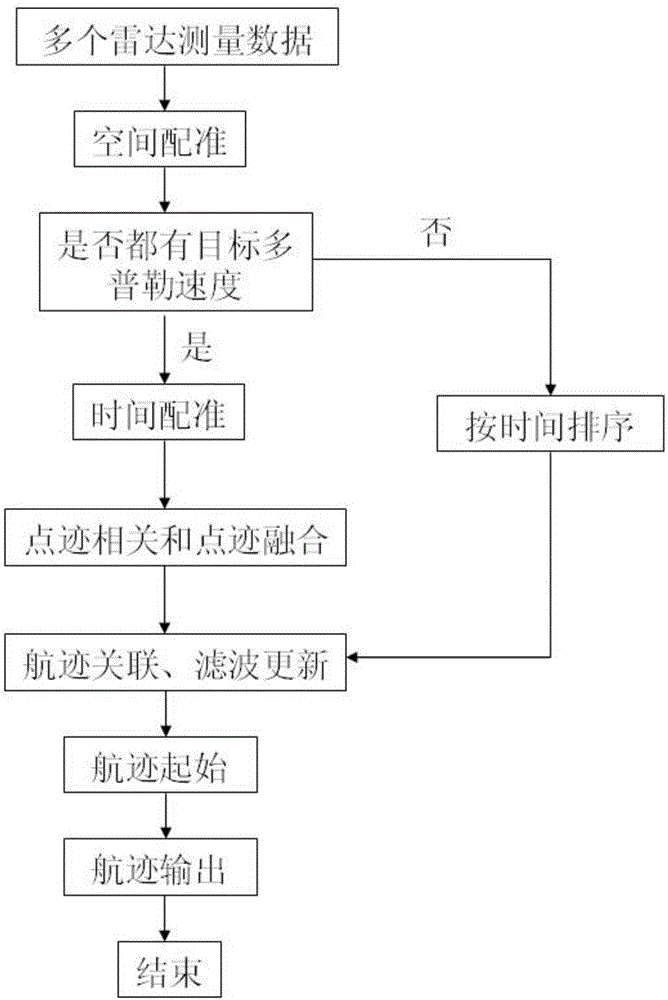
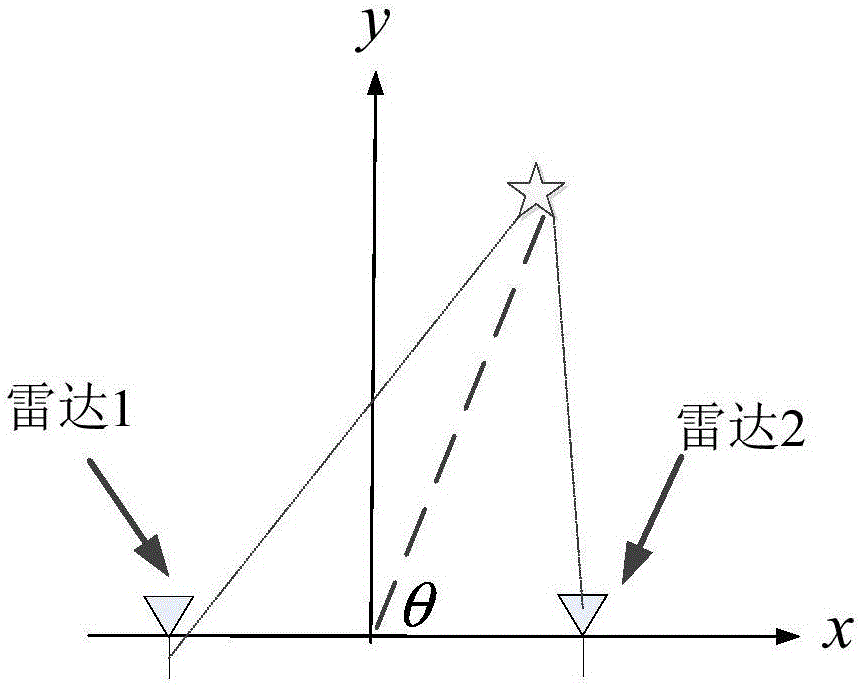
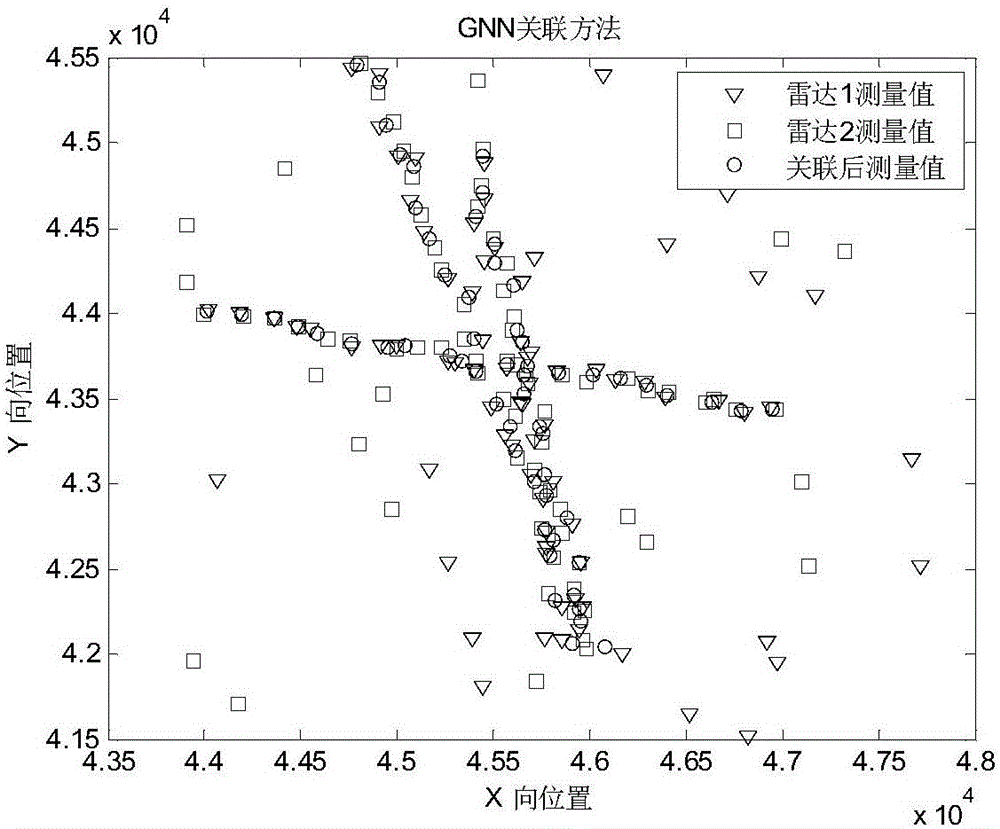
The invention belongs to the technical field of multi-radar networking plot fusion, and particularly relates to a multi-radar plot fusion method. The method comprises the following steps of 1, receiving multiple pieces of radar measurement data, conducting space alignment and setting a uniform measurement coordinate system; 2, judging whether the radar measurement data all contains target Doppler velocity information or not, if yes, executing the step 3, and otherwise, executing the step 6; 3, conducting time alignment; 4, conducting plot association and plot fusion to obtain fused plot information; 5, conducting track association with a formed track and filtering updating by utilizing the fused plot information, and executing the step 7; 6, sorting the data by time, and conducting track association with the formed track and filtering updating in sequence by utilizing the sorted data; 7, conducting track initiation by utilizing the radar data which does not participate in track association; 8, outputting a track result. The multi-radar plot fusion method is beneficial to prolonging the target detection distance and improving the tracking precision and the maneuvering target tracking performance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Removal of spurious aircraft detections on weather radar
ActiveUS7417578B1Improve performanceAvoid confusionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationDoppler velocitySpectral width
A weather radar detects and removes spurious aircraft from a weather radar display by using one of the methods of differentiating radar return length, estimating a vertical gradient of reflectivity, tracking radar returns into regions that are eliminated from the weather display to provide differentiation, tracking areas of radar returns that allow detection and removal of the spurious aircraft in relative geometries, differentiating Doppler velocity, and differentiating spectral width. The methods may be used individually or in combination to improve performance.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
System and Method for Calibrating Video and Lidar Subsystems
ActiveUS20150160332A1Accurate imagingOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationDoppler velocityRadar systems
A system uses range and Doppler velocity measurements from a lidar system and images from a video system to estimate a six degree-of-freedom trajectory of a target. The system calibrates the lidar subsystem with the video subsystem in two stages. In a first stage, the system calibrates the lidar subsystem so that lidar measurements provide 3D lidar coordinates. In a second stage, the system relates the 3D lidar coordinates with a video image obtained from the video subsystem.
Owner:AEVA INC
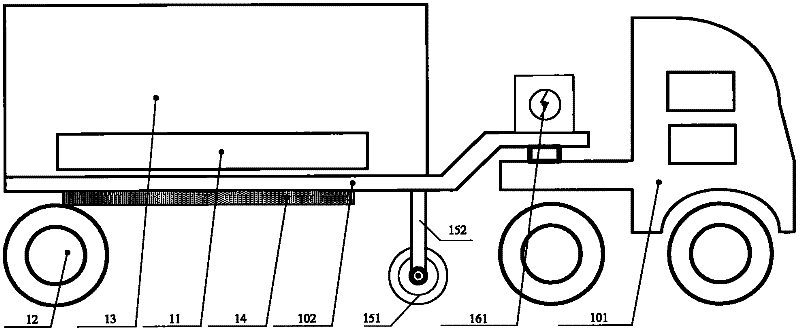
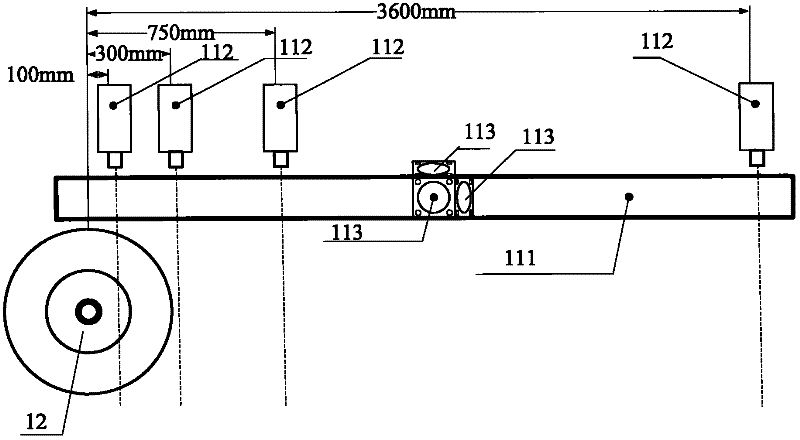
Laser dynamic deflection survey vehicle
ActiveCN102162217AFast measurementWide range of measurement speed variationUsing optical meansRoads maintainenceAccelerometerDoppler velocity
The invention provides a laser dynamic deflection survey vehicle. The survey vehicle comprises a mobile measuring table, a measuring cross beam, a running wheel, a velocity measuring wheel, an accelerometer and a data acquiring and processing device. The laser dynamic deflection survey vehicle provided by the invention has the following advantages: according to the laser Doppler velocity measurement principle and the inertia measurement principle, during the driving process of the vehicle at a normal traffic velocity (15-80km / h), a plurality of laser Doppler vibration meters arranged in the front of loading wheels of the vehicle synchronously measure the relative movement velocity of various measuring points on a road surface; the instantaneous deflection deformation velocity of the road surface is obtained through inertia compensation calculation; and a dynamic deflection value of the road surface is obtained through inversion by utilizing a road layered elastic mechanical model and used for general investigation and assessment of the bearing capacity of a road network.
Owner:WUHAN WUDA ZOYON SCI & TECH
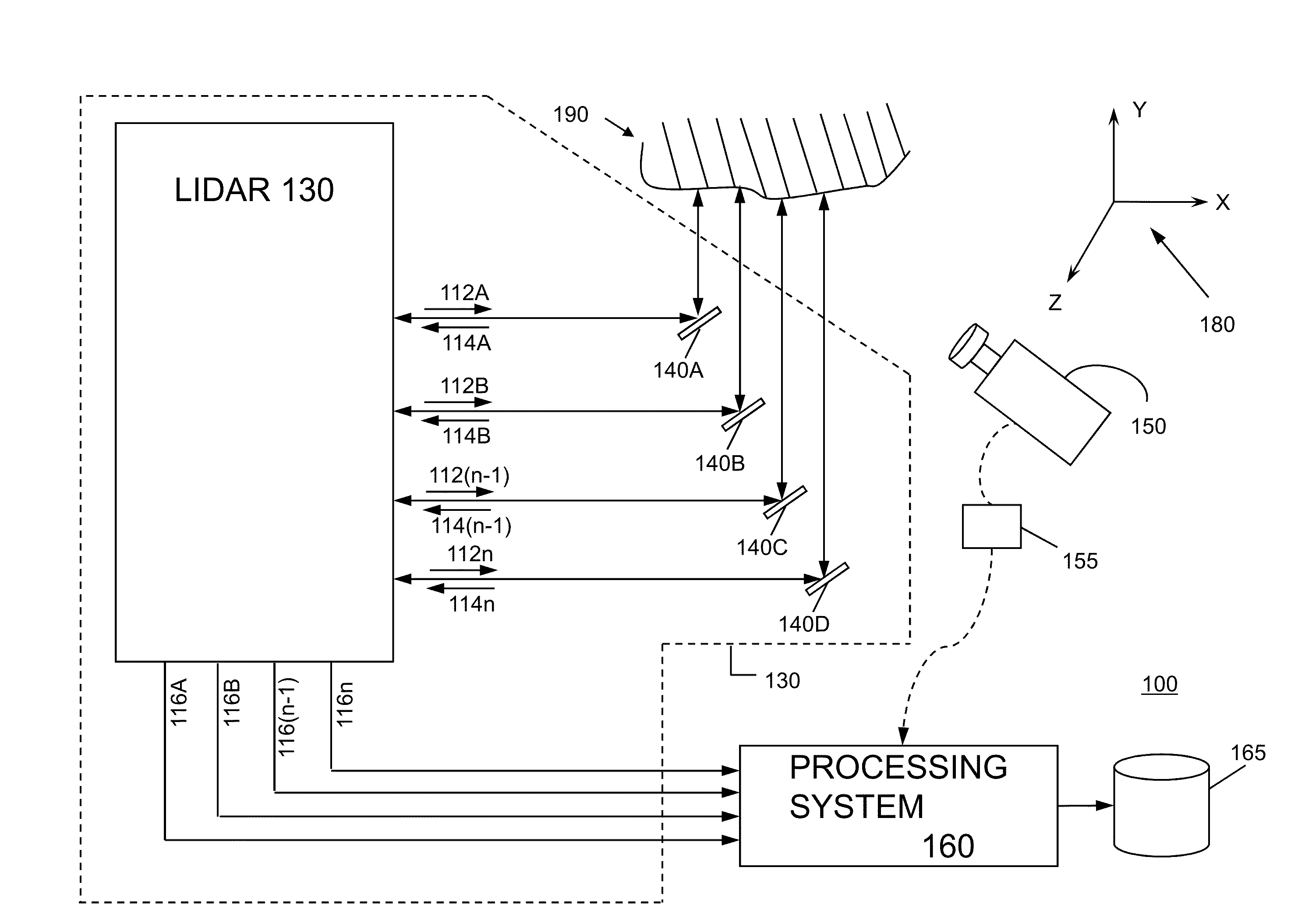
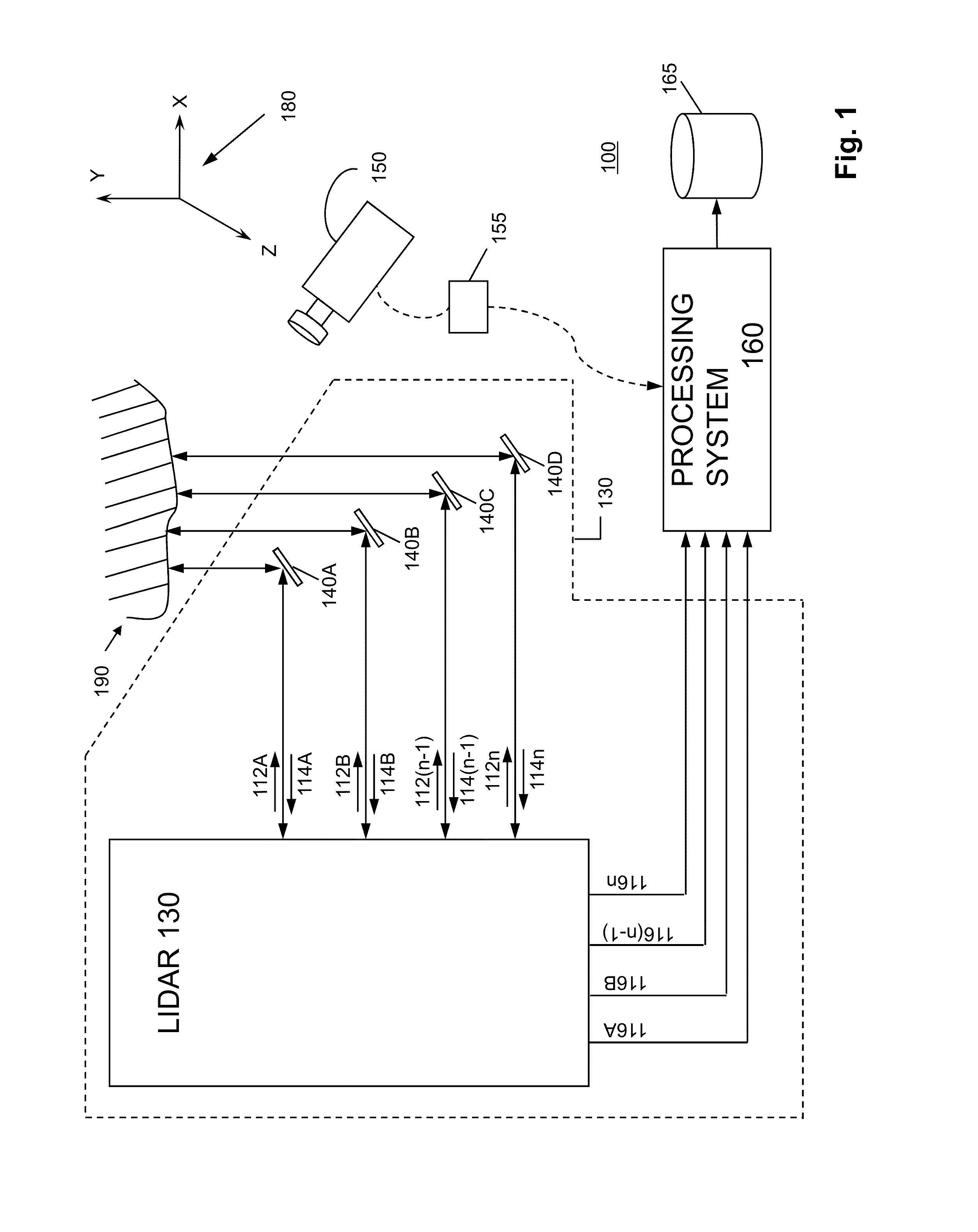
System and method for generating three dimensional images using lidar and video measurements
A system uses range and Doppler velocity measurements from a lidar system and images from a video system to estimate a six degree-of-freedom trajectory of a target. The system estimates this trajectory in two stages: a first stage in which the range and Doppler measurements from the lidar system along with various feature measurements obtained from the images from the video system are used to estimate first stage motion aspects of the target (i.e., the trajectory of the target); and a second stage in which the images from the video system and the first stage motion aspects of the target are used to estimate second stage motion aspects of the target. Once the second stage motion aspects of the target are estimated, a three-dimensional image of the target may be generated.
Owner:AEVA INC
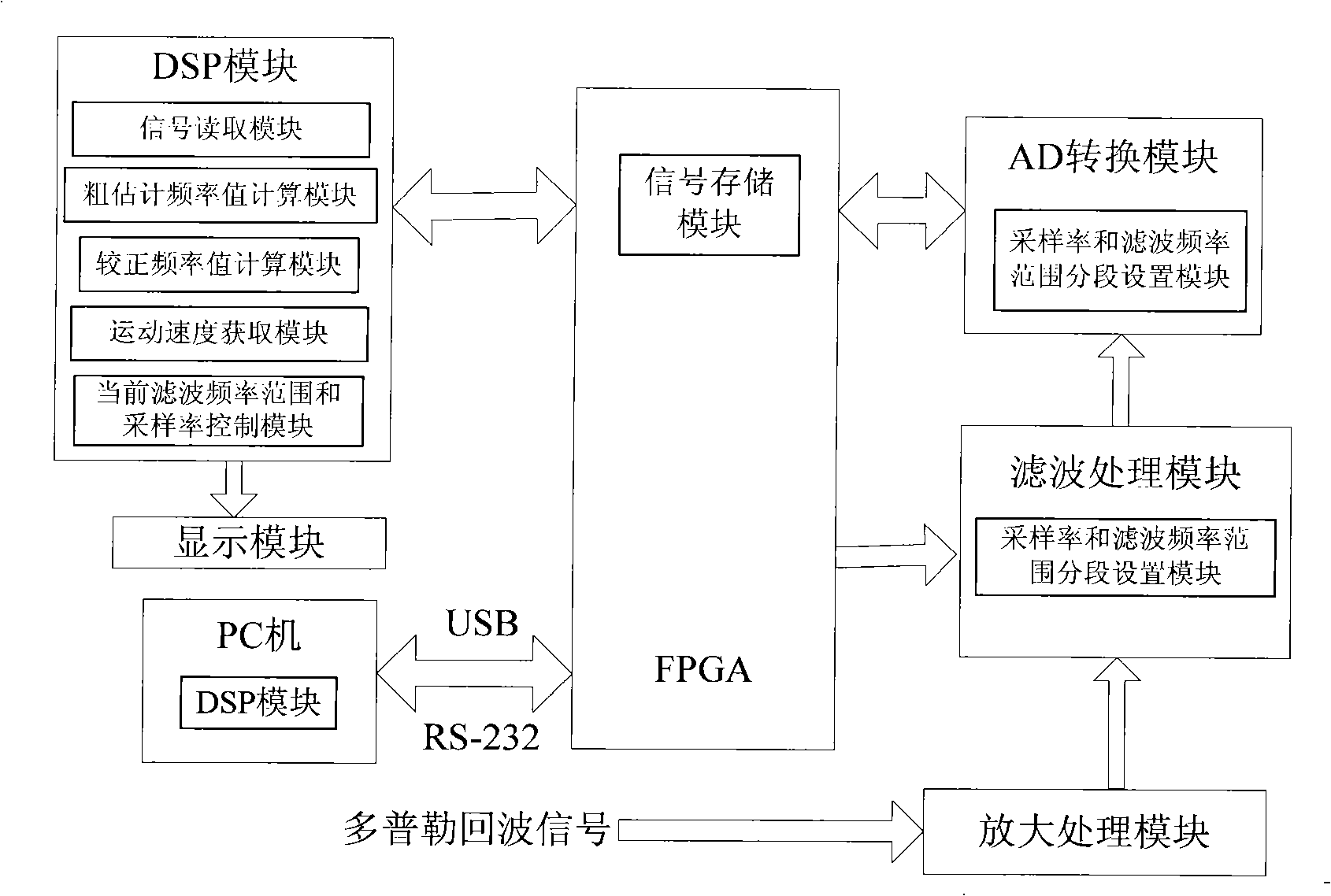
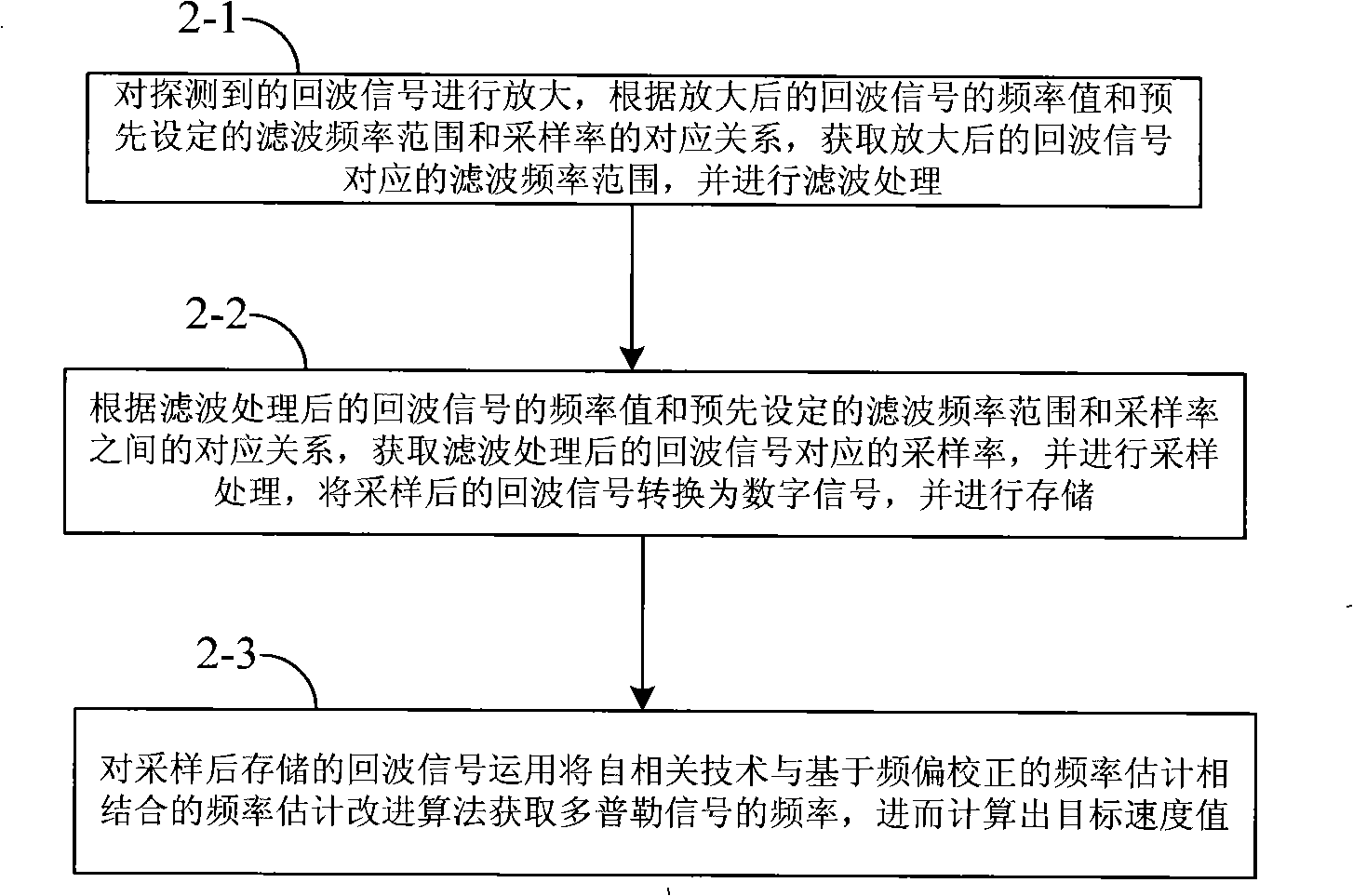
Echo signal processing equipment and method of Doppler speed measuring laser radar
InactiveCN101320086ASmall amount of calculationGuaranteed accuracyElectromagnetic wave reradiationDoppler velocityRadar
The invention provides a Doppler velocity metering laser radar echoed signal processing unit and a method. The processing unit mainly comprises a signal storage module and a DSP module; wherein, the signal storage module is used for storing the echoed signals of a tested object; the echoed signals are digital signals which are converted by A / D; the DSP module is used for reading the echoed signals in the signal storage module and carrying out the FFT to obtain the power spectrum of the signals, and then the rough estimated frequency value is obtained according to the power spectrum; the power spectrum is carried out the inverse FFT and then the self correlation functions of the echoed signals are obtained, the correction frequency value is obtained according to the self correlation functions, the rough estimated frequency value and the correction frequency value are added to obtain the Doppler frequency of the echoed signals, and the movement velocity of the tested object is calculated according to the Doppler frequency. The device and the method combine the self correlation technology with the frequency deviation estimation improvement algorithm which is based on the frequency deviation correction, and the velocity of the test object can be effectively worked out.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
System and Method for Field Calibrating Video and Lidar Subsystems Using Facial Features
ActiveUS20140049765A1Accurate imagingOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationDoppler velocityRadar
A system uses range and Doppler velocity measurements from a lidar subsystem and images from a video subsystem to estimate a six degree-of-freedom trajectory of a target. The video subsystem and the lidar subsystem may be aligned with one another by mapping the measurements of various facial features obtained by each of the subsystems to one another.
Owner:AEVA INC
System and Method for Increasing Resolution of Images Obtained from a Three-Dimensional Measurement System
ActiveUS20140064555A1Improve imaging resolutionAccurate imagingImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionDoppler velocityFrame time
A system uses range and Doppler velocity measurements from a lidar system and images from a video system to estimate a six degree-of-freedom trajectory (6DOF) of a target. The 6DOF transformation parameters are used to transform multiple images to the frame time of a selected image, thus obtaining multiple images at the same frame time. These multiple images may be used to increase a resolution of the image at each frame time, obtaining the collection of the superresolution images.
Owner:AEVA INC
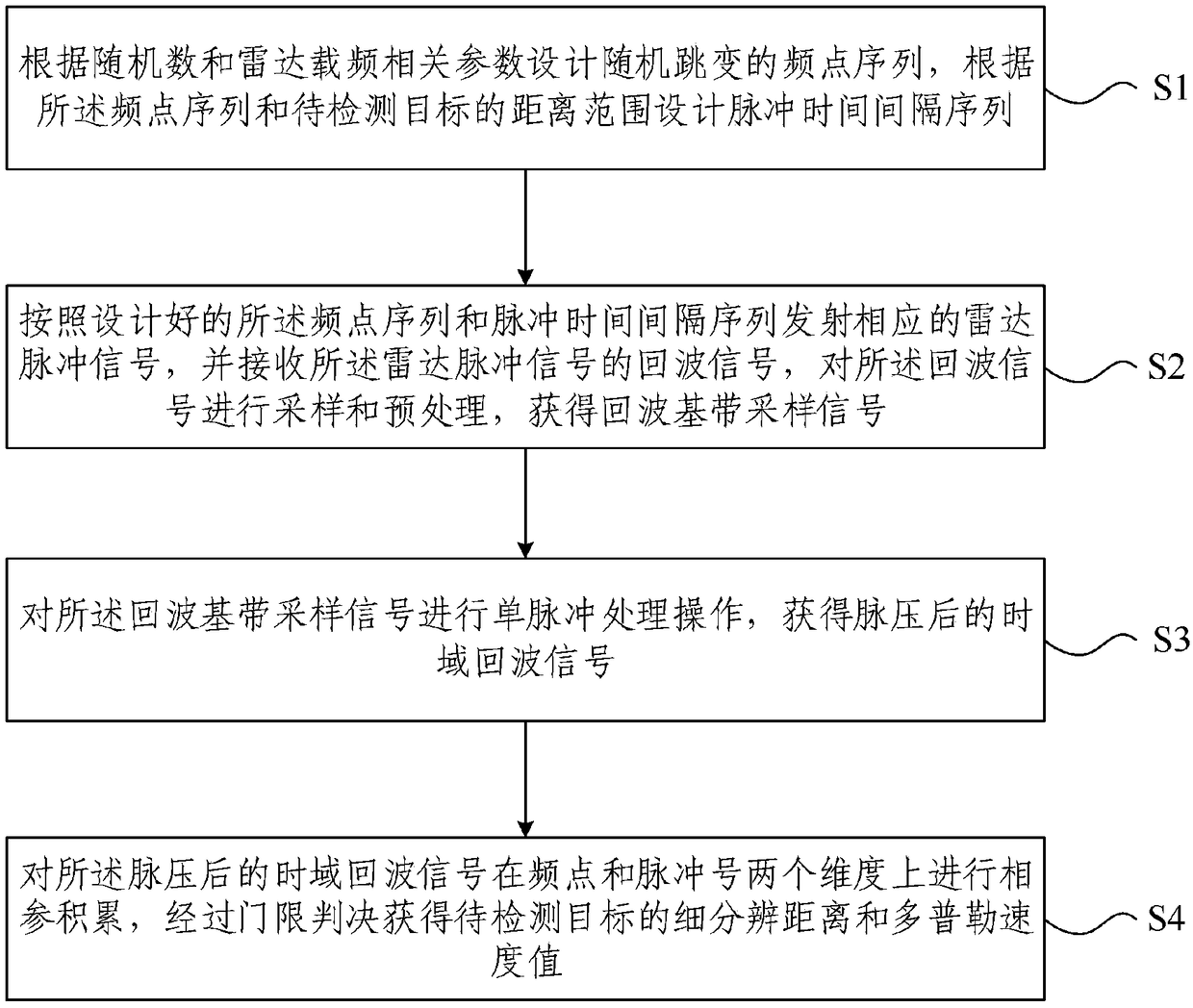
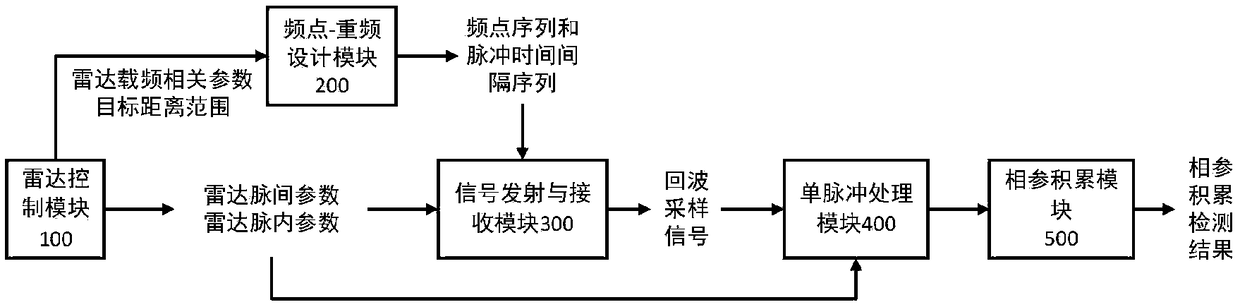
Signal processing method and device for frequency-agile radar based on variable repetition frequency technology
ActiveCN109143179AReal-time processingReduce processingWave based measurement systemsBasebandEcho signal
The invention provides a signal processing method and device for frequency-agile radar based on a variable repetition frequency technology. The method includes the following steps: designing a frequency point sequence of random hopping according to a random number and the carrier frequency related parameters of radar, and designing a pulse time interval sequence according to the frequency point sequence and the distance range of a target to be detected; emitting a radar pulse signal according to the designed frequency point sequence and the designed pulse time interval sequence, receiving an echo signal of the radar pulse signal, and sampling and preprocessing the echo signal to obtain a baseband echo sampling signal; processing the baseband echo sampling signal by a single pulse to obtaina time-domain echo signal after pulse compression; and coherently accumulating the time-domain echo signal after pulse compression in the two dimensions of frequency point and pulse number, and obtaining the fine resolution distance and Doppler velocity values of the target to be detected through threshold decision. Accurate detection of the distance and velocity of a moving target by coherent frequency-agile radar is realized, and the amount of computation for the processing of coherent frequency-agile signals can be reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
System and Method for Off Angle Three-Dimensional Face Standardization for Robust Performance
InactiveUS20140071121A1Electromagnetic wave reradiation3D-image renderingDoppler velocityFacial region
A system uses range and Doppler velocity measurements from a lidar system and images from a video system to estimate a six degree-of-freedom trajectory of a target. The system utilizes a two-stage solution to obtain 3D standardized face representations from non-frontal face views for a statistical learning algorithm. The first stage standardizes the pose (non-frontal 3D face representation) to a frontal view and the second stage uses facial symmetry to fill in missing facial regions due to yaw face pose variations (i.e. rotation about the y-axis).
Owner:AEVA INC
System for determining position and velocity of targets from signals scattered by the targets
InactiveUS6850186B2Good conditionEasy to transportBeacon systems using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDoppler velocityImage resolution
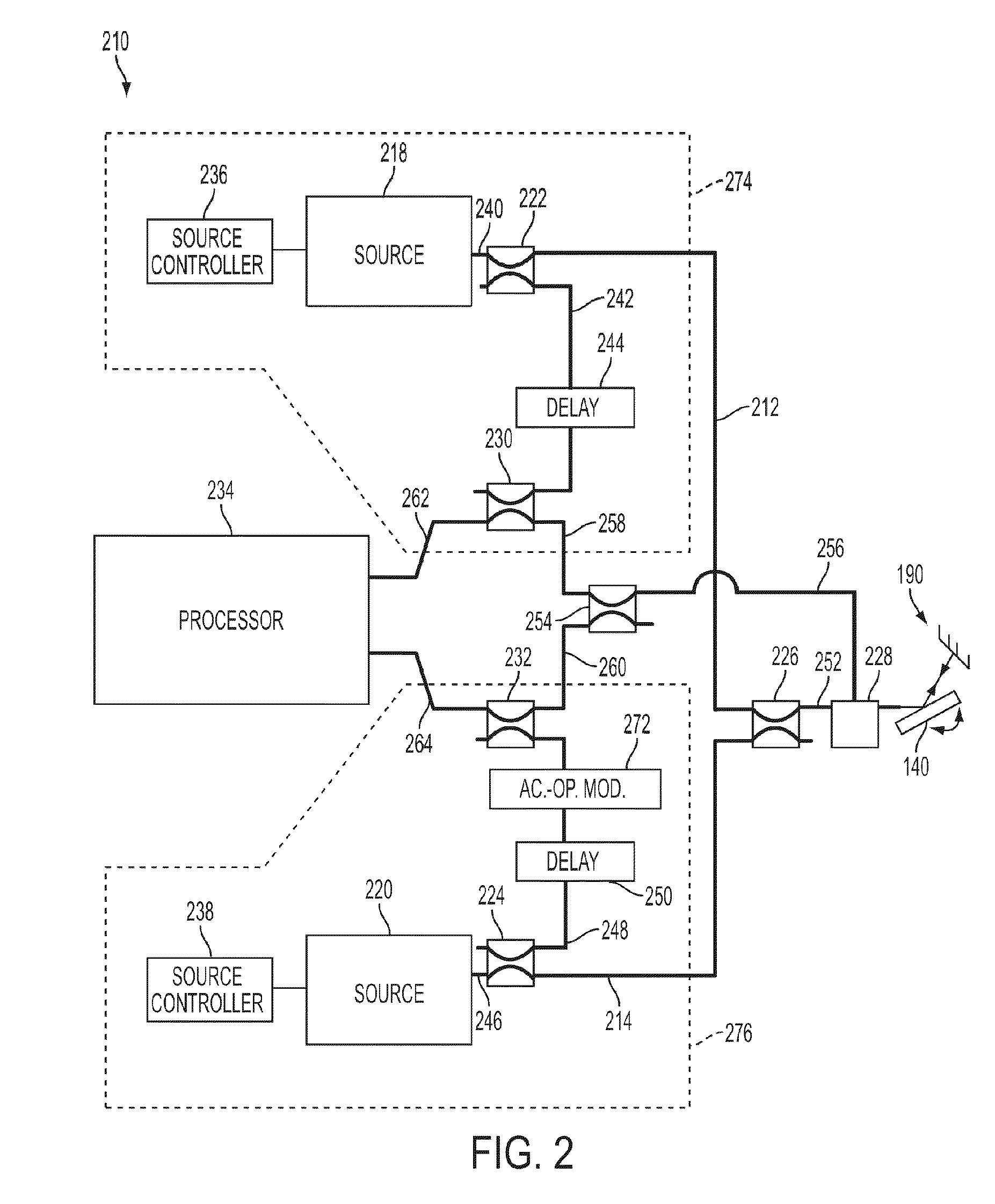
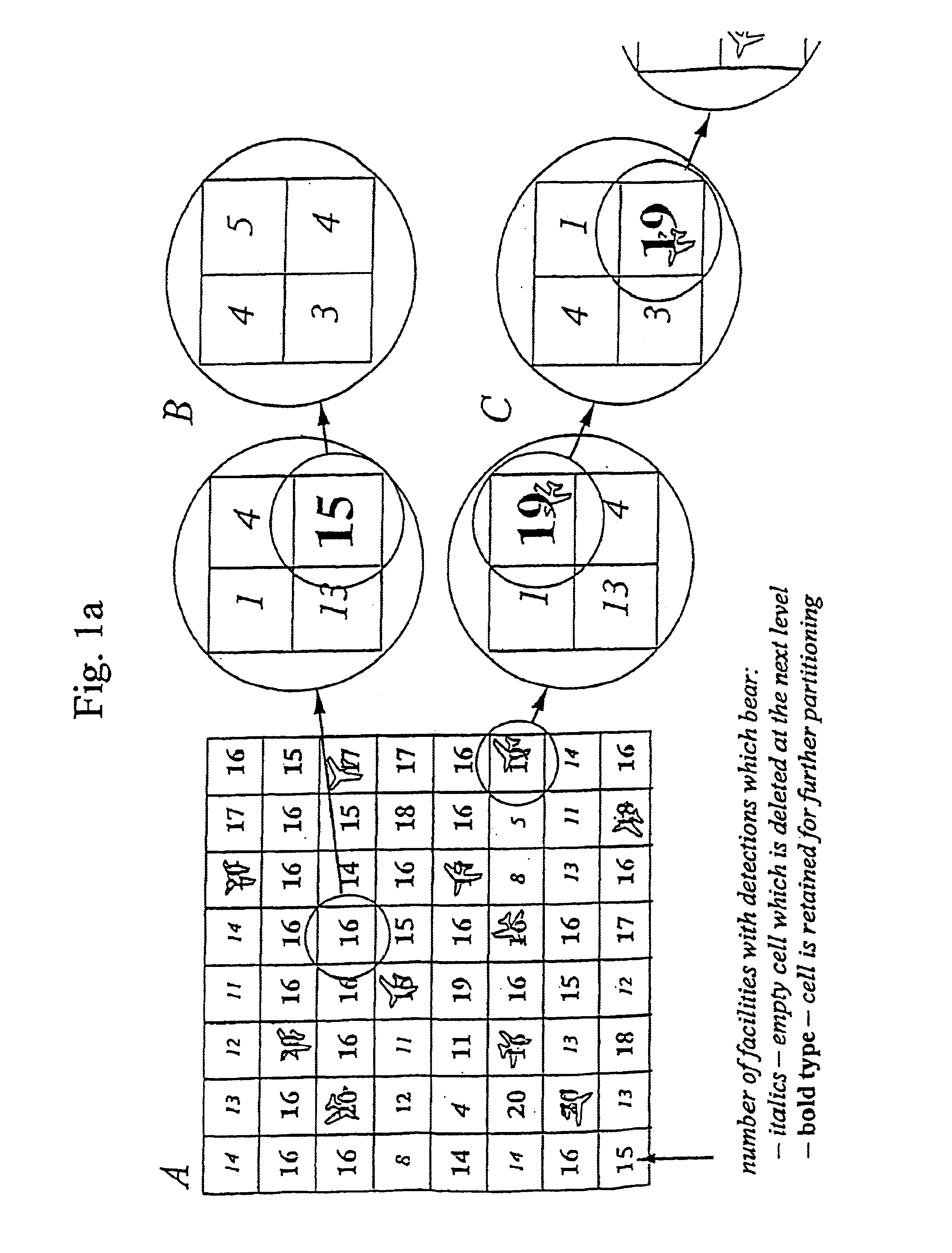
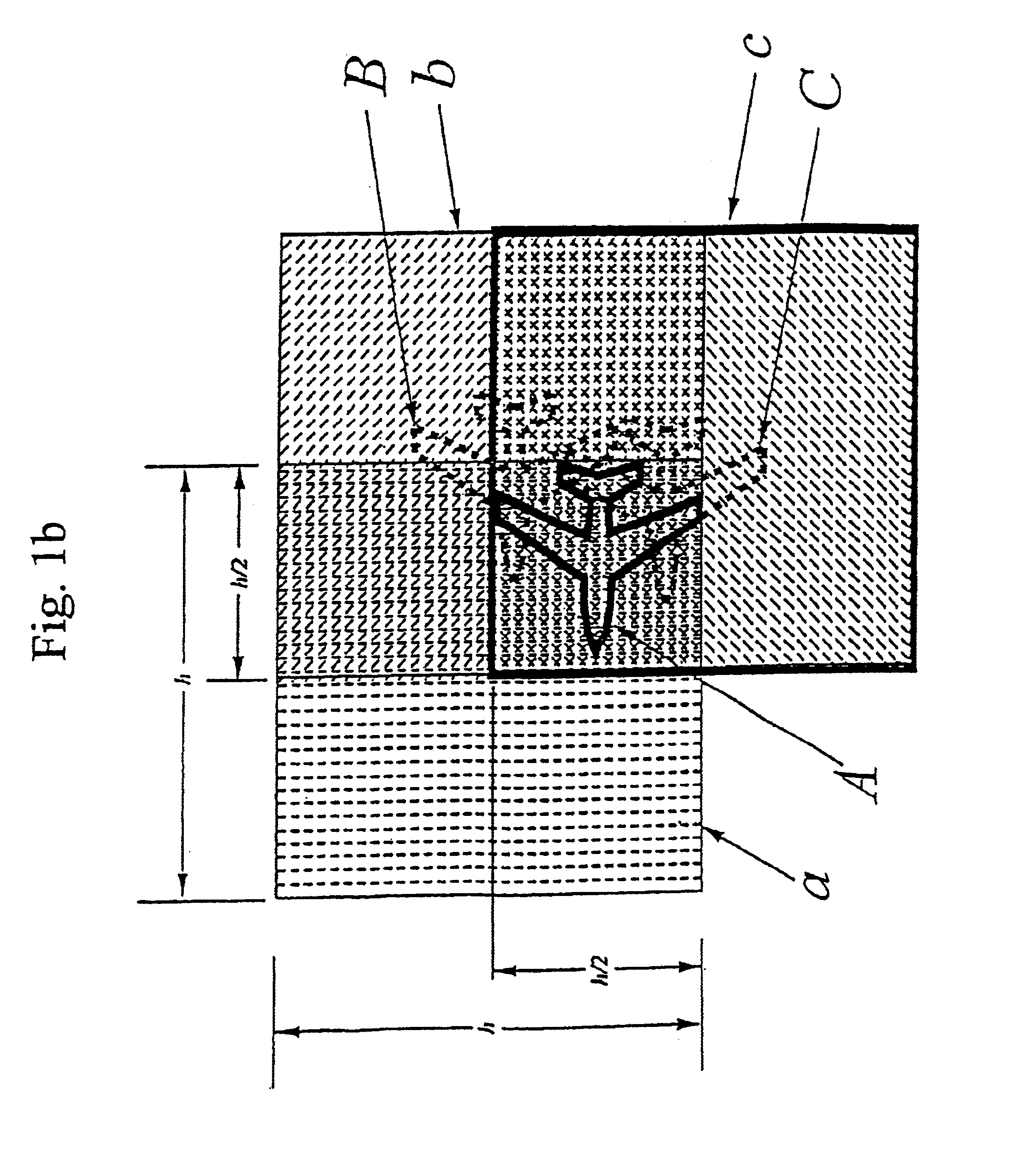
The present invention relates to a system for using signals scattered by targets to determine position and velocity for each of the targets and comprises a set of transmitters and receivers of electromagnetic or acoustic signals, said transmitters and receivers dispersed to known points. Each pair of transmitter and receiver, monostatic or bistatic, is named a measuring facility. The ranges of the transmitters are chosen so that a target at an arbitrary point within the position space can be measured via scattering in the target by at least four measuring facilities. For each measuring facility, target detection occurs with constant false alarm rate in the form of probabilities over resolution cells with regards to range and Doppler velocity and conceivable targets are placed in a 2-dimensional linear space belonging to the measuring facility. The 3-dimensional positions and 3-dimensional Doppler velocities are represented as a 6-dimensional linear position and velocity space subdivided into resolution cells with the same resolution of range and Doppler velocity that is found at the measuring facilities. For each intersection representing detections at at least four measuring facilities the probability is calculated that the intersection is a false alarm emanating intersections between subsets from different targets and when the probability falls below a predefined value, it is given that the intersection contains at least one target. The target positions and target velocities are extracted in this way.”
Owner:TOTALFORSVARETAB FORSKNINGSINSTITUT FOI
Dual-polarization Doppler weather radar ground clutter inhibition method based on fuzzy logic
InactiveCN105548984AAchieve inhibitionSolve the problem that the precipitation echo is over suppressedWave based measurement systemsCorrelation coefficientDoppler velocity
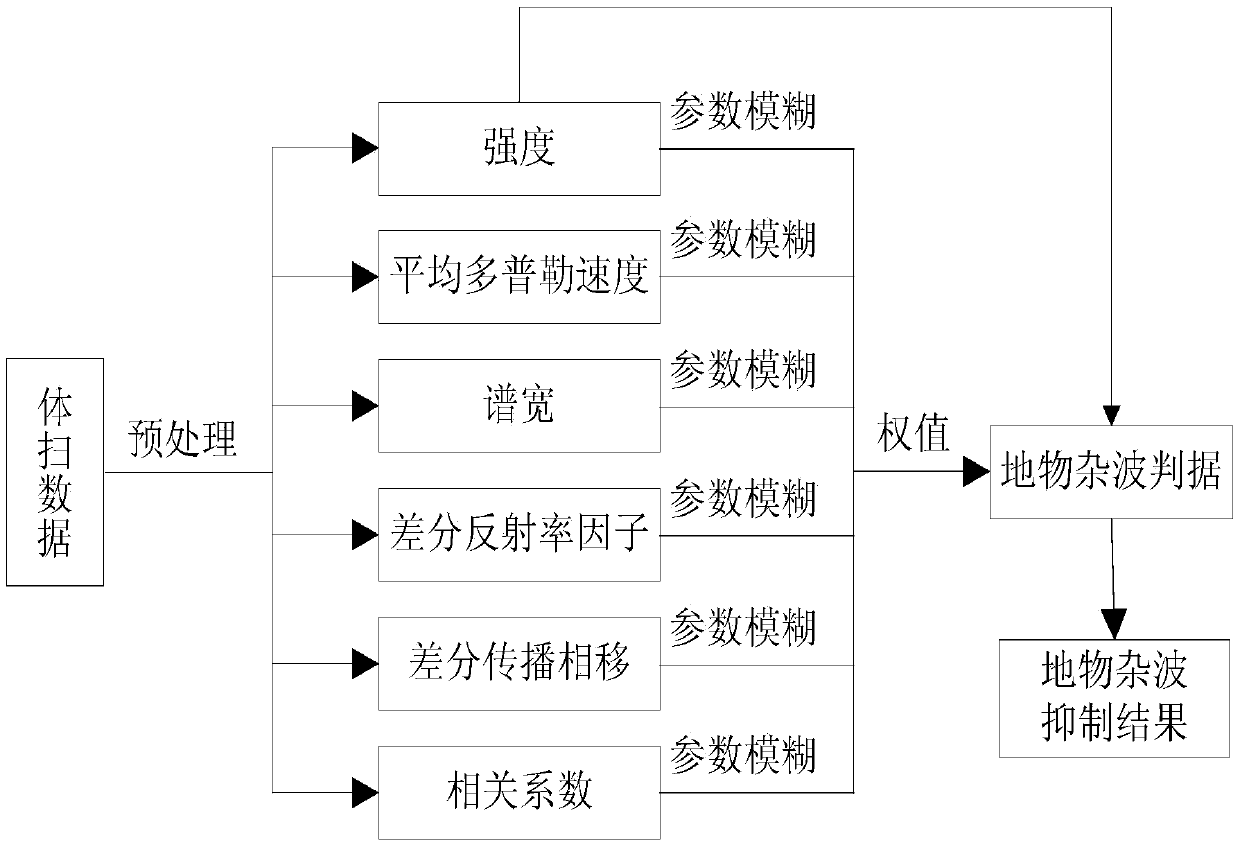
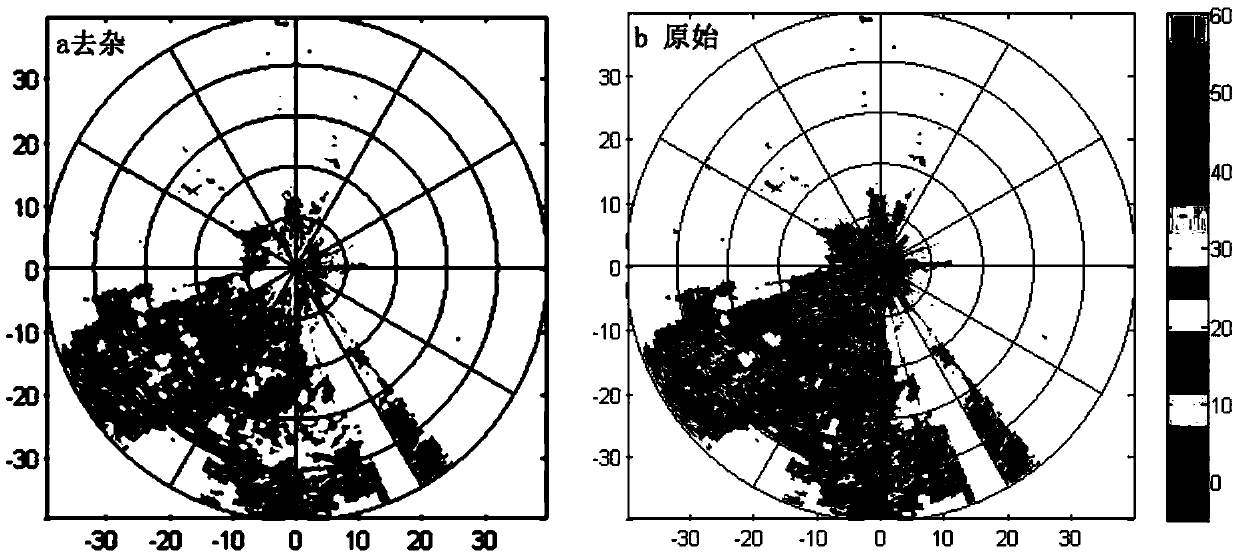
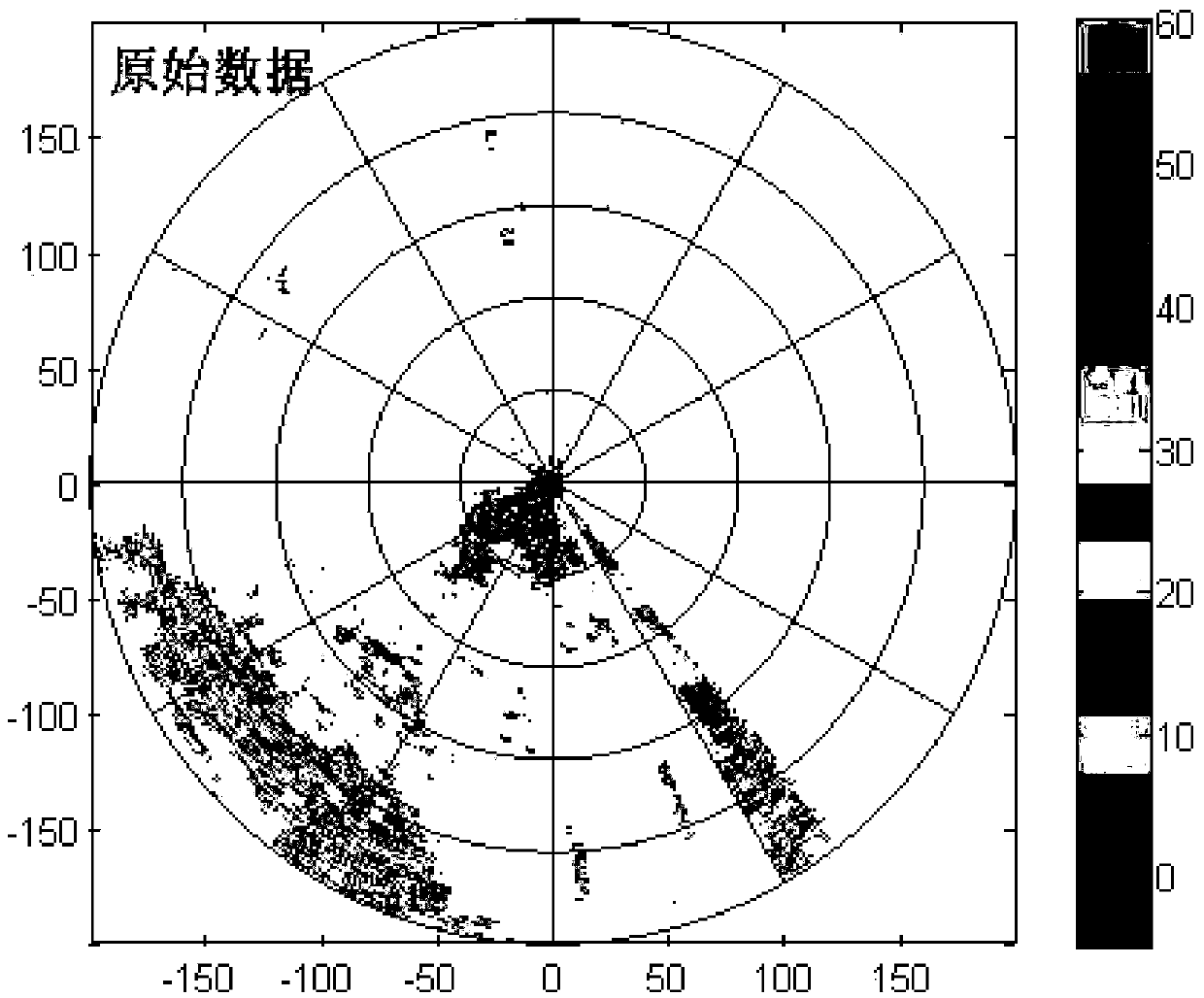
The invention discloses a dual-polarization Doppler weather radar ground clutter inhibition method based on fuzzy logic, and the method comprises the steps: processing volume scanning data of a dual-polarization Doppler weather radar into 360 radial lines, wherein the interval between each two adjacent radial lines is one degree, and the data of each radial line comprises seven echo characteristic physical quantities: intensity, a mean Doppler speed, a spectrum width, a difference reflectivity factor, a difference propagation phase shift, and a correlation coefficient; setting the seven physical quantities which respectively comprise the intensity, the mean Doppler speed, the spectrum width, the difference reflectivity factor, the difference propagation phase shift, and the correlation coefficient; enabling seven fuzzy results to be assigned with corresponding weight values, carrying out accumulating and obtaining a ground clutter criterion of one echo point; Determining that the intensity echo of the point is the ground clutter when the ground clutter criterion of one echo point is greater than a threshold value; inhibiting the ground clutter of the dual-polarization Doppler weather radar through the ground clutter criterion of each echo point, and compensating a hole of a current layer after clutter inhibiting through employing the echo intensity value of a corresponding point in an upper layer in the volume scanning data.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mutual butt joint device for double intelligent underwater robots and butt joint method
ActiveCN103057679AReduce sailing resistanceServe as a docking guideUnderwater equipmentSonarDoppler velocity
The invention provides a mutual butt joint device for double intelligent underwater robots and a butt joint method. The mutual butt joint device comprises a positioning system and a butt joint system, wherein the positioning system comprises a Doppler velocity sonar, an ultra-short base line energy converter, an ultra-short base line processor, a camera, a light vision guide processing computer and a control navigation computer; and the butt joint system comprises a sliding sleeve, a butt joint supporting rod, a butt joint vision positioning light emitter, a butt joint supporting rod positioning mechanism, a sliding barrel sliding channel, a sliding barrel sliding channel motor and a transmission gear. According to different mutual distances between the two butt joint double-intelligent underwater robots, the control navigation computer can be used for positioning according to different sensor information. When the butt-joint robots are about 10 meters away from a target position, a control system sends out an instruction to slide out of the sliding sleeve; and the butt joint supporting rod is unfolded to be navigated to the target position, and is positioned and suspended by power to wait for accurate butt joint of the butt-joint robots. The intelligent underwater robot mutual butt joint device can be far away from a manual operation platform.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
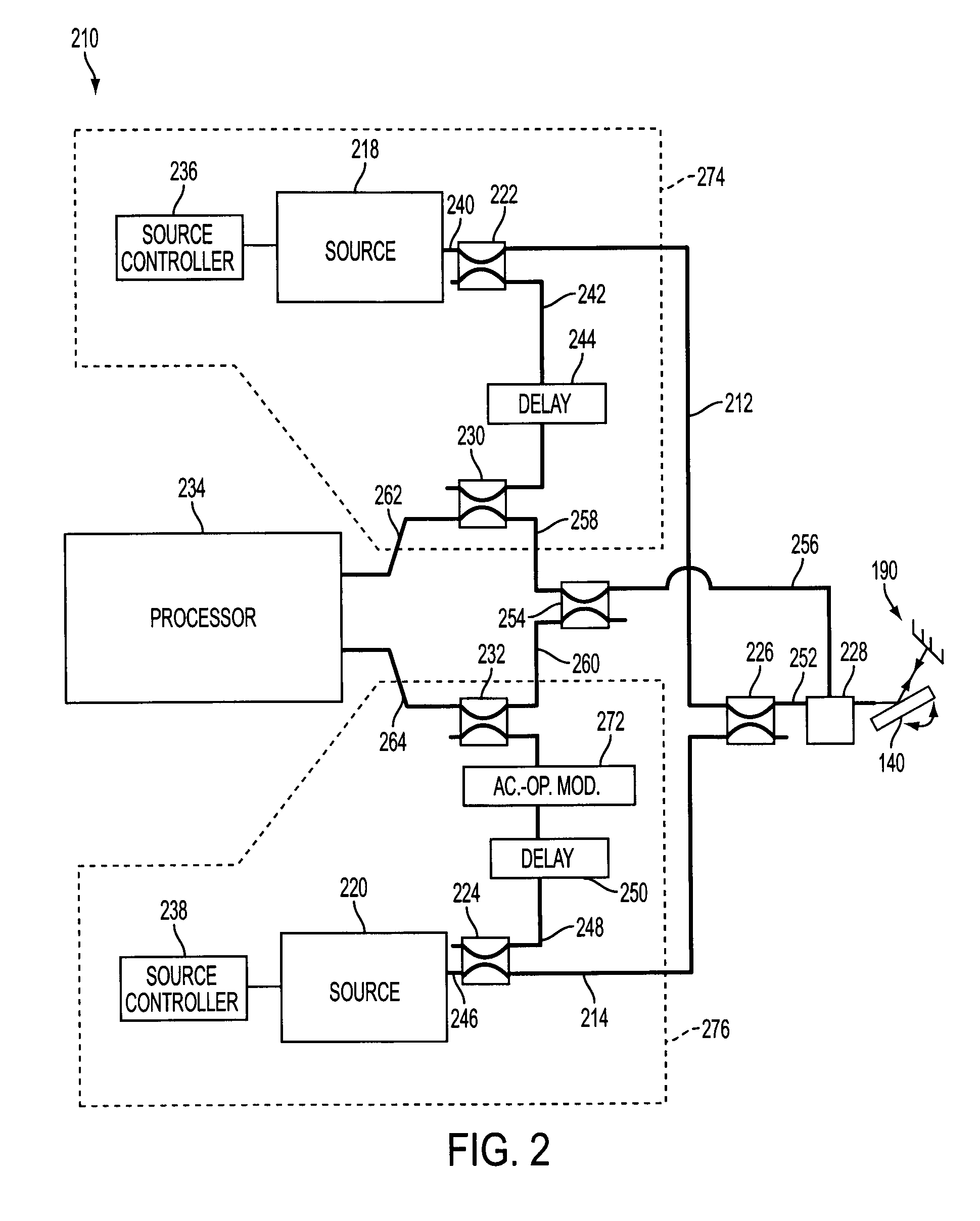
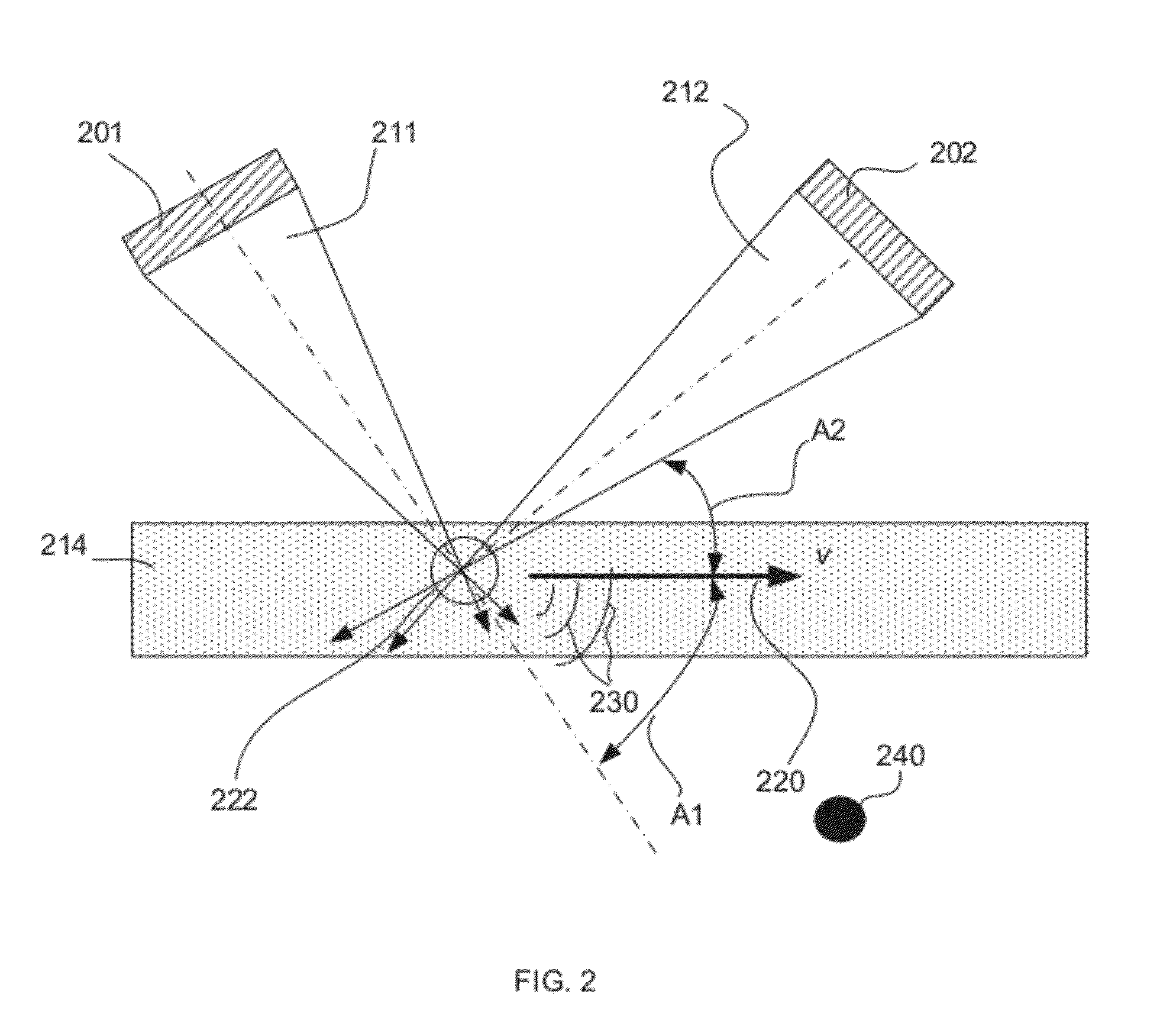
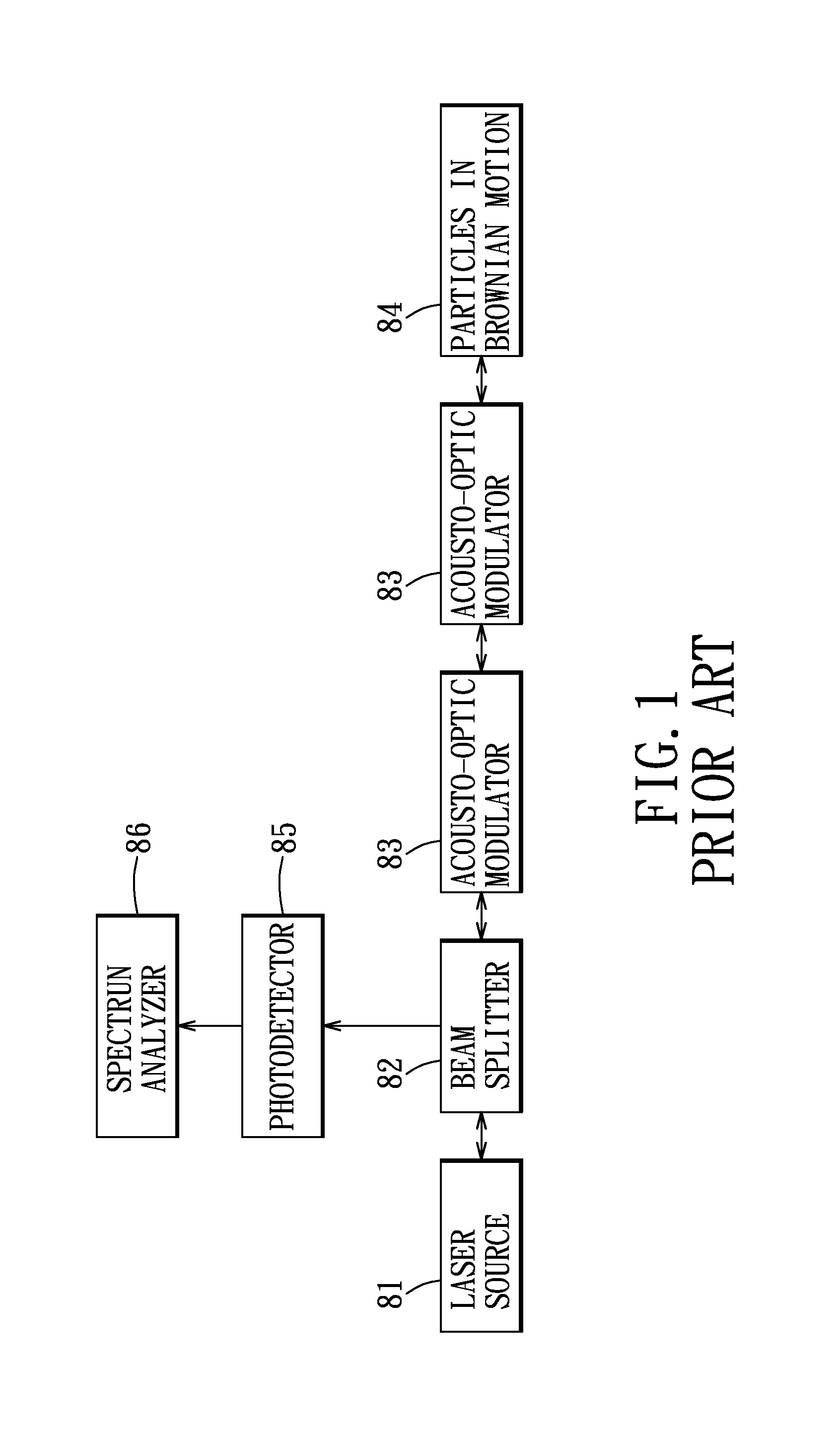
Fixed difference, dual beam laser Doppler velocimetry
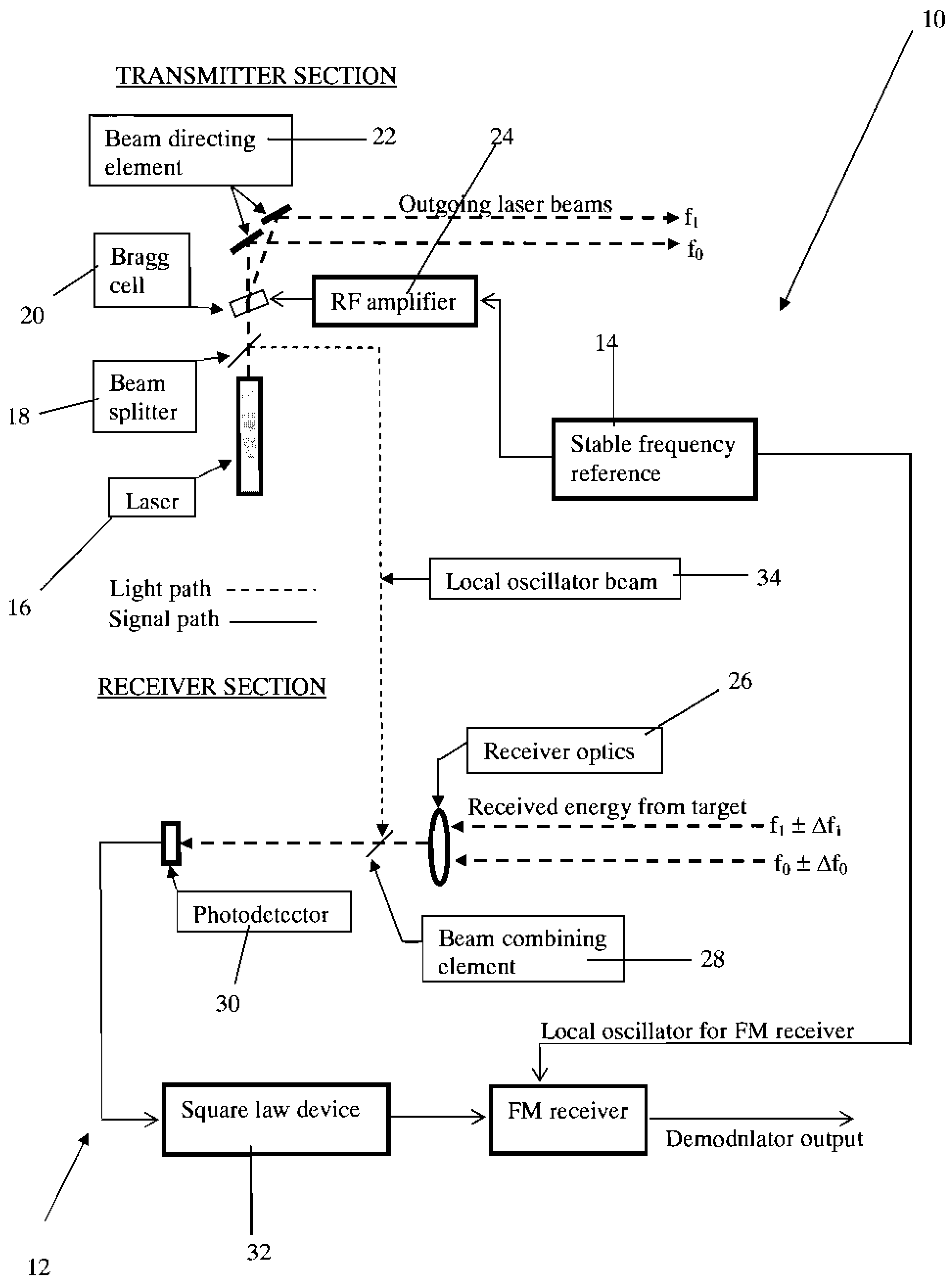
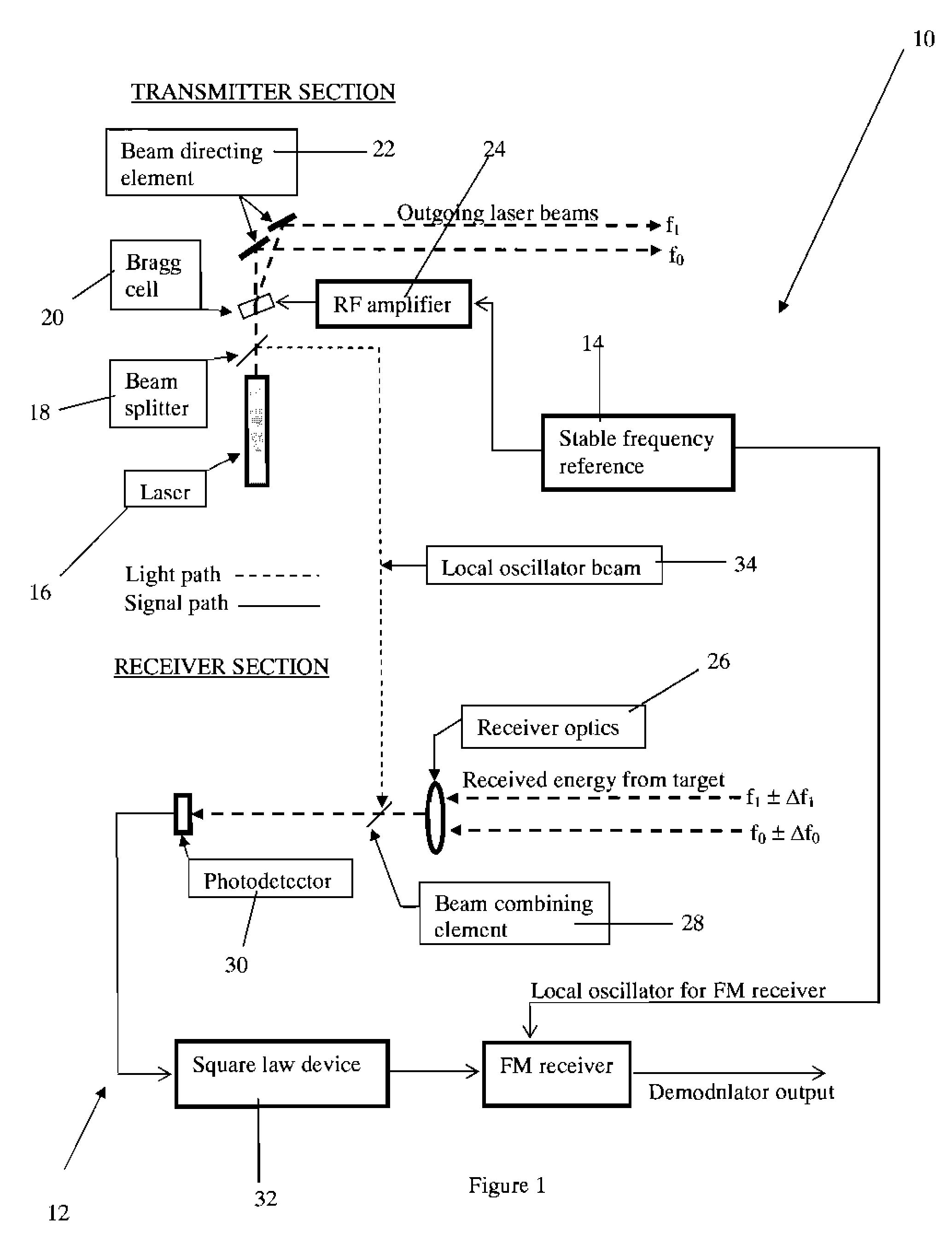
A method and apparatus for laser Doppler velocity measurements with a fixed difference, dual beam receiver and using a non-laser, stable frequency reference.
Owner:KYRAZIS DEMOS T
Redundant controlled microminiature underwater robot, and method for failure diagnosis and fault tolerant control
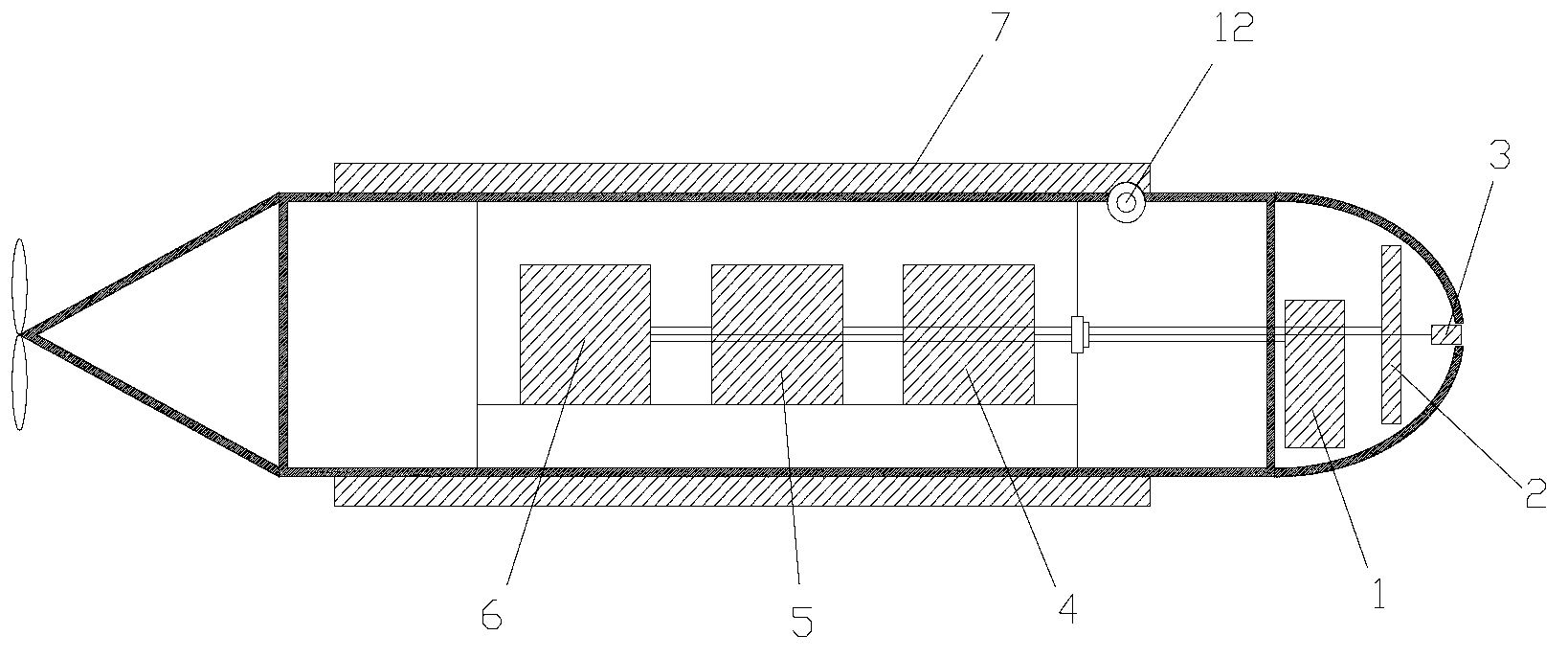
InactiveCN101462587AWith fault diagnosisWith fault-tolerant control capabilityUnderwater vesselsUnderwater equipmentImpellerDoppler velocity
The invention provides a redundant controlled micro underwater robot and a fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control method. A shell has a streamline shape spliced by a lower shell, an upper front shell and an upper back shell; an inclination compass cabin, a depth gauge, a battery tank, a Doppler speed meter, an electronic cabin, horizontal propeller impellers and a turning rise-sink control actuator are arranged inside the shell from the front to the back; and the depth gauge, the battery tank and the Doppler speed meter are arranged in parallel and positioned at the back of the inclination compass cabin together, the turning rise-sink control actuator is positioned in the middle of two horizontal propeller impellers, and the two horizontal propeller impellers and the turning rise-sink control actuator are arranged transversely in parallel and positioned at the tail of the underwater robot together. The robot and the method have the characteristics of high intellectualization degree, strong fault-tolerant capability, good safety, flexile motion, and convenient structural adjustment.
Owner:如皋市生产力促进中心
S face control method of flotation under water robot motion
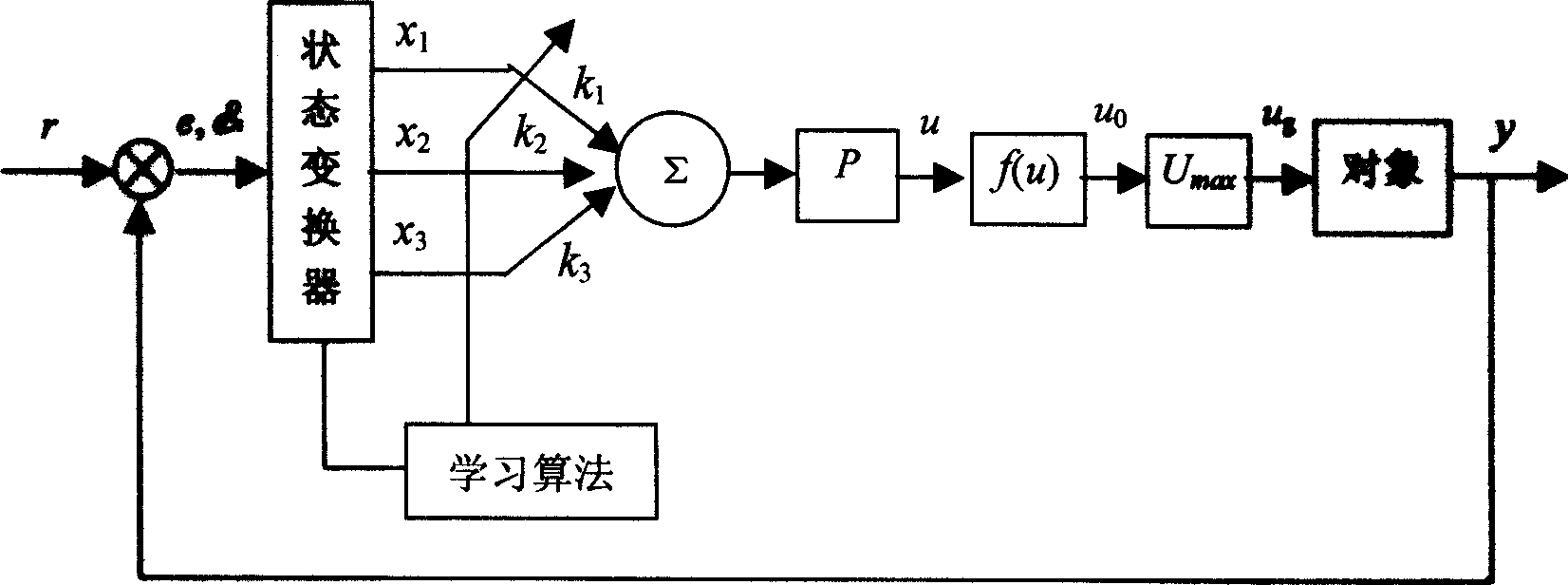
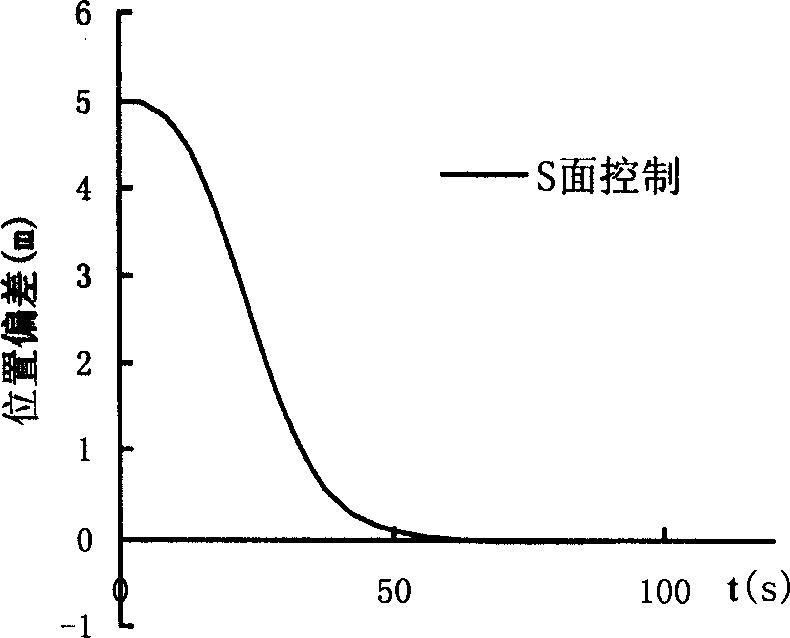
An S-surface control method for the movement of the pelagic underwater robot includes such steps as using short base line and depth meter to obtain position information, using compass to obtain attitude angle, using Doppler speedmeter to obtain speed, calculating by controller, executing movement via propeller, wings and helm, using 6-freedom position offset and variation rate as input for position control and location, using 6-freedom speed offset and variation rate as input for controlling speed, and using the indexing of PD control for non-linear control.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
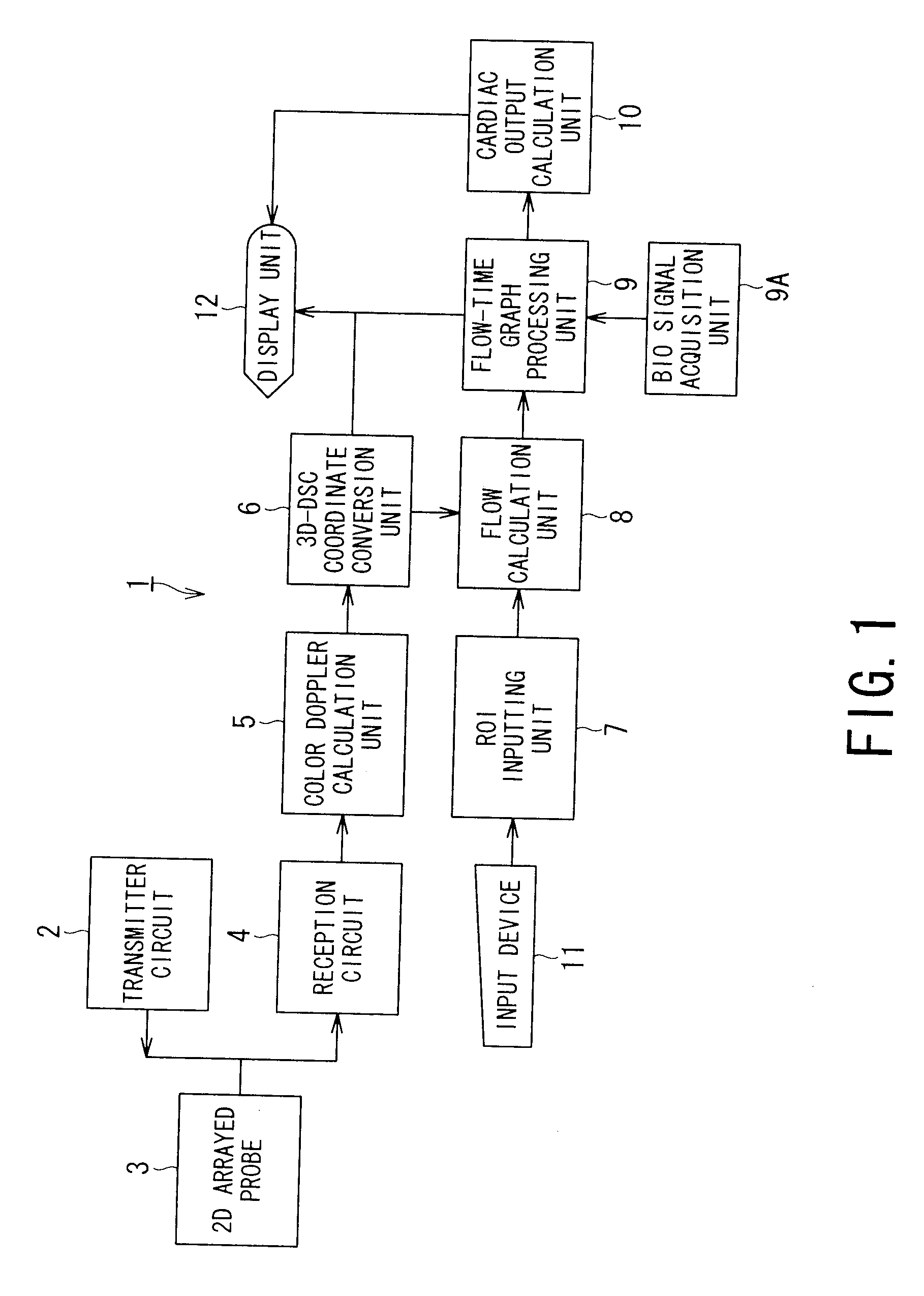
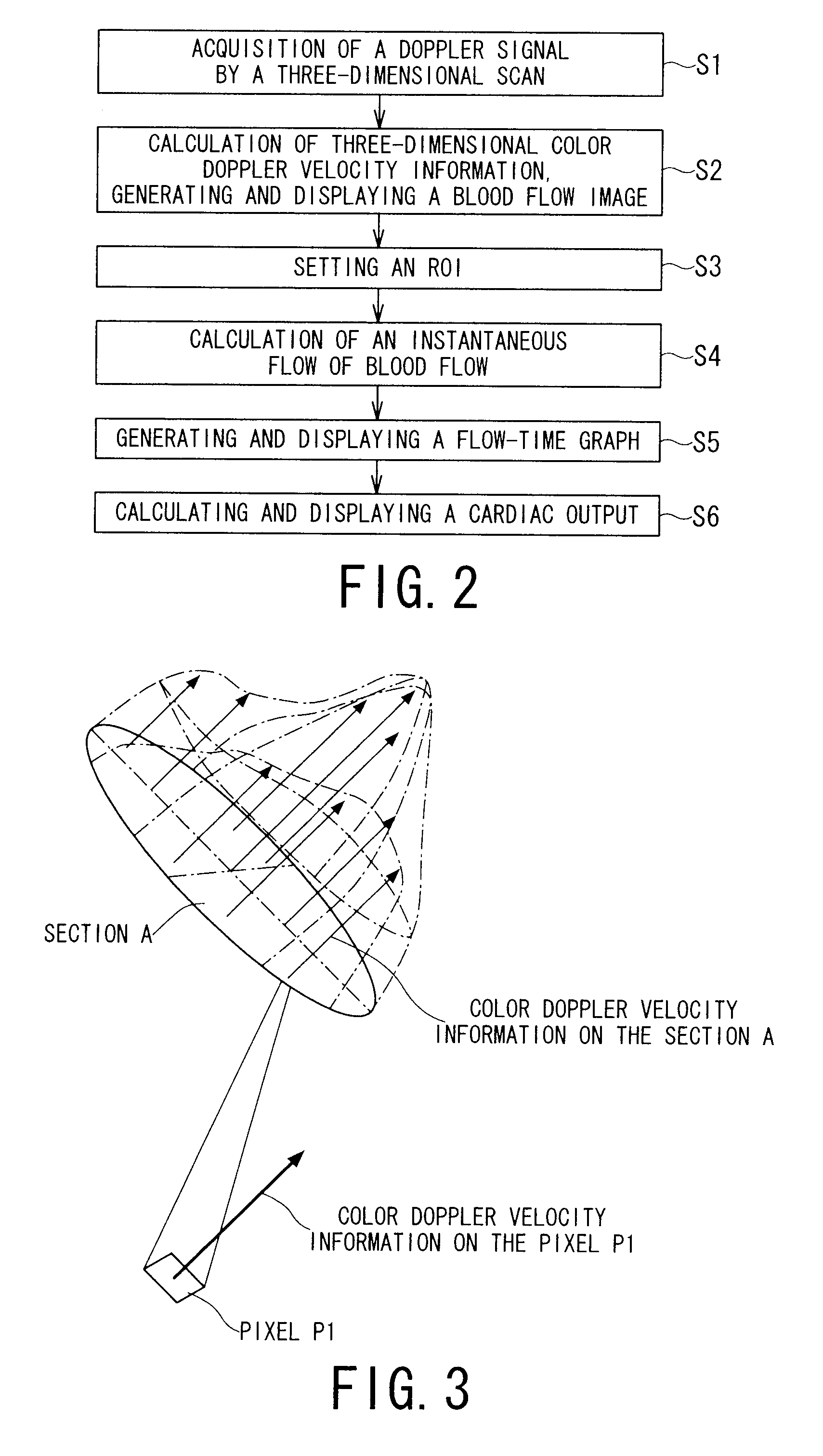
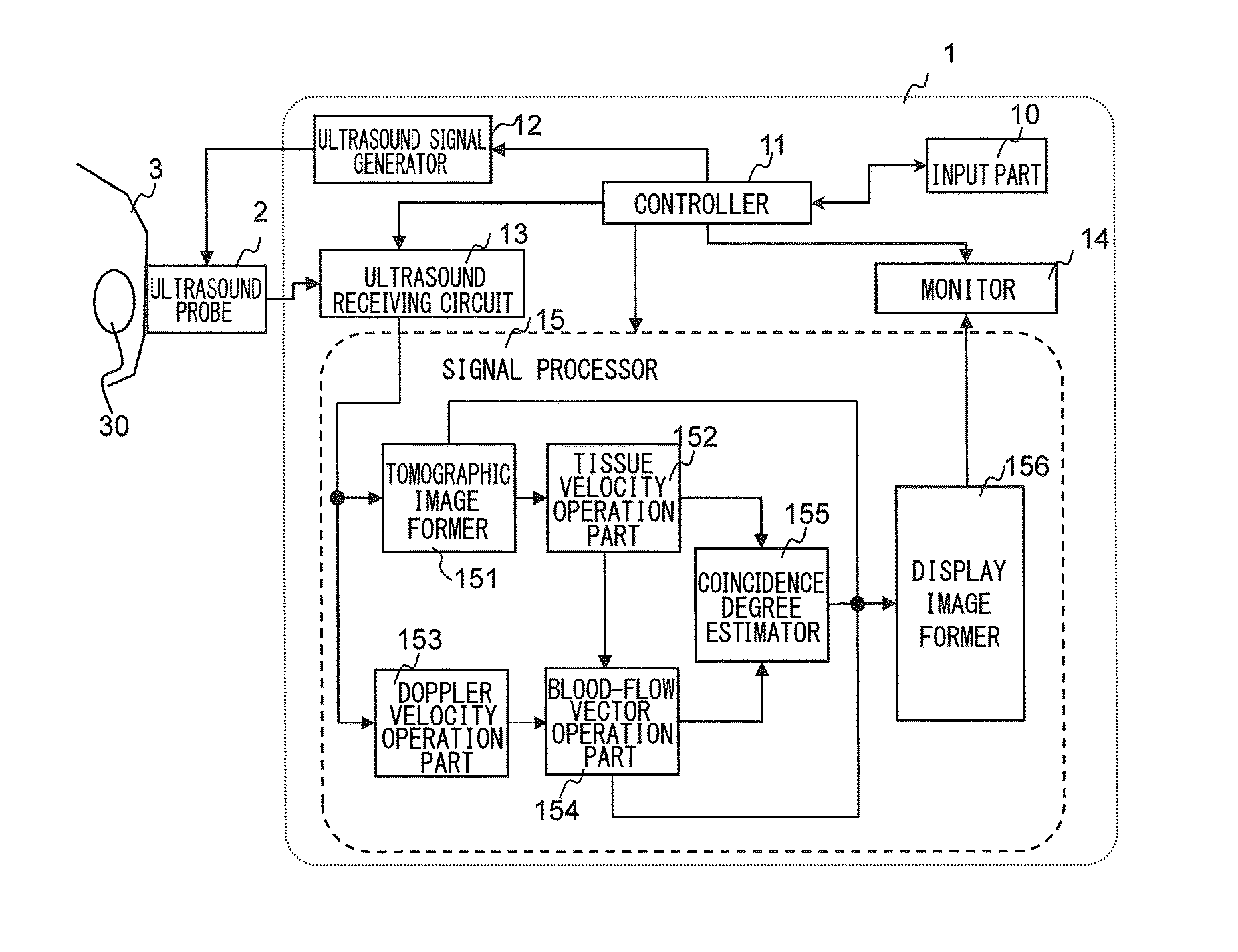
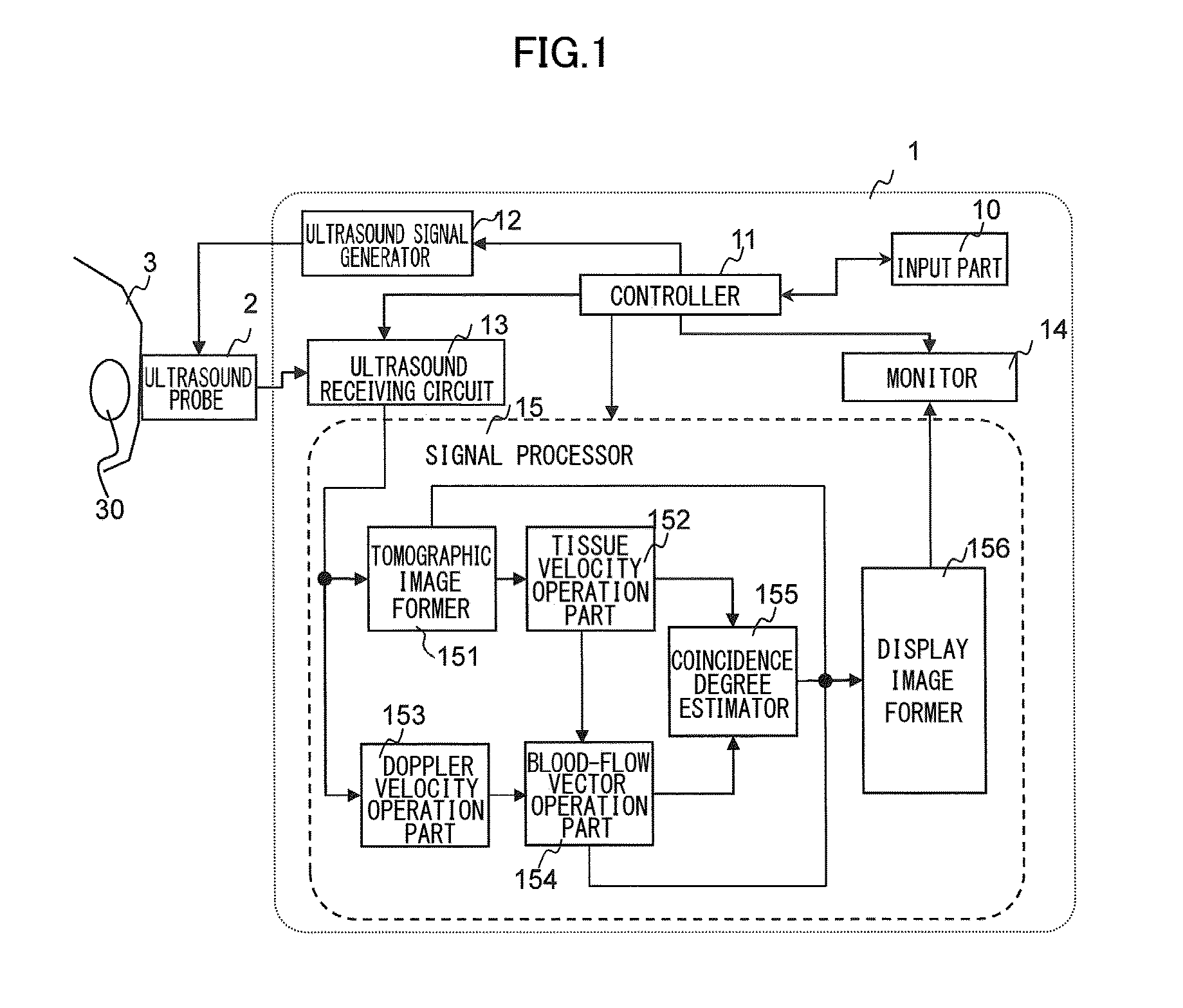
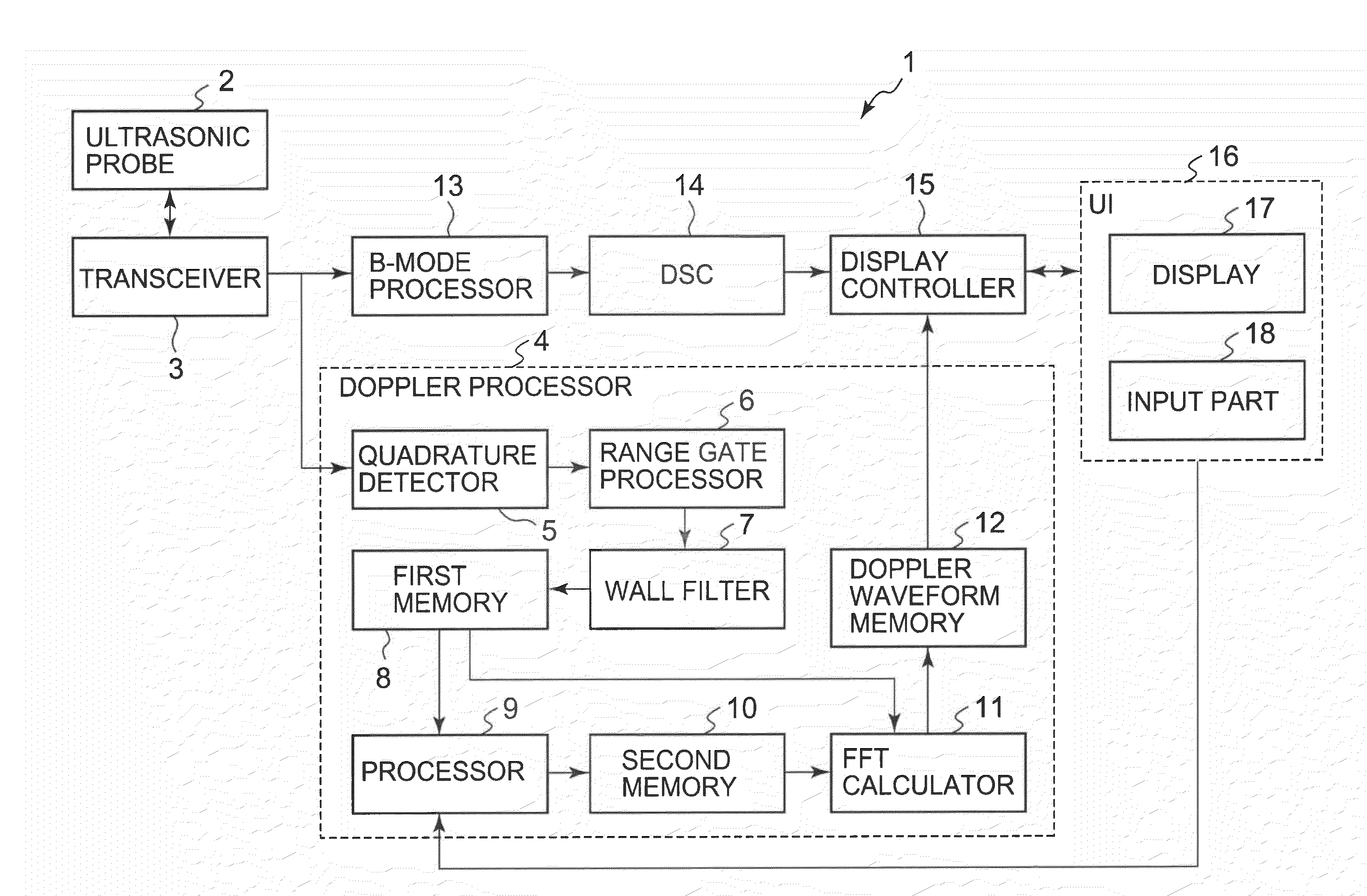
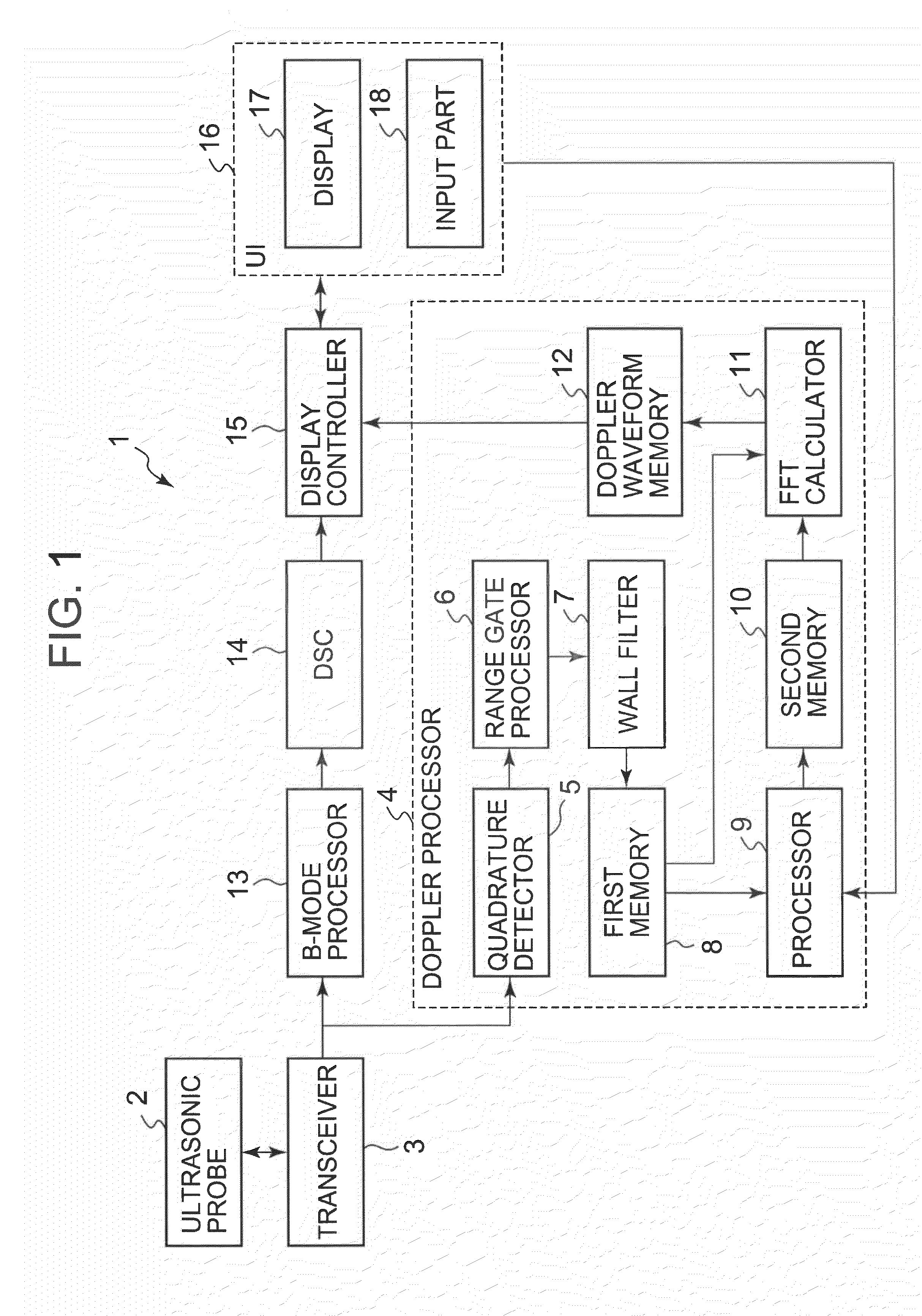
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus and ultrasonic diagnostic method
InactiveUS20080051661A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyDoppler velocity3d scanning
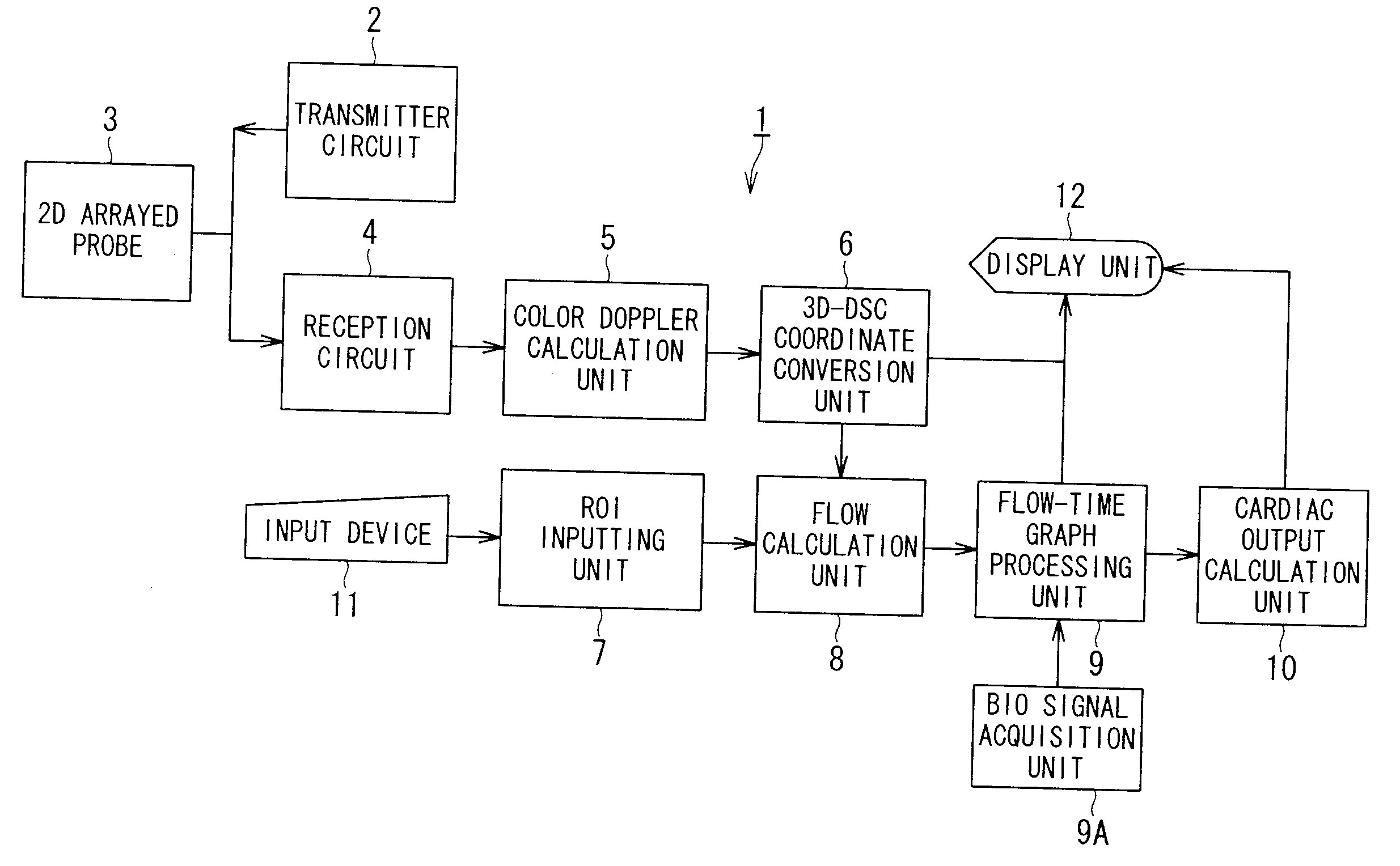
An ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus includes a Doppler velocity information acquiring unit, a region-of-interest-setting unit and an instantaneous flow calculating unit. The Doppler velocity information acquiring unit is configured to acquire three-dimensional Doppler velocity information from an object by a three-dimensional scan with transmission and reception of an ultrasonic wave. The region-of-interest-setting unit is configured to set a region of interest spatially. The instantaneous flow calculating unit is configured to calculate an instantaneous blood flow in the region of interest with using the three-dimensional Doppler velocity information.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Polarization and frequency diverse radar system for complete polarimetric characterization of scatterers with increased scanning speed
InactiveUS7355546B2Maximize isolationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationDoppler velocityRadar systems
Owner:ADVANCED RADAR CORP
Travelable area acquisition method, computer readable storage medium and terminal device
ActiveCN110045376ASolve detection inaccuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDoppler velocityPoint cloud
The invention provides a travelable area acquisition method, a computer readable storage medium and a terminal device. The method comprises the following steps: collecting point cloud data frame by frame through a millimeter wave radar installed on a vehicle; obtaining CFAR points that are relatively stationary with respect to the ground from the point cloud data according to a traveling speed ofthe vehicle and the Doppler speed of each CFAR point in the point cloud data detected by the millimeter wave radar; obtaining an operation state of the vehicle according to the traveling speed of thevehicle and the heading angle information of the vehicle, and translating a grid probability map; projecting all CFAR points that are relatively stationary with respect to the ground in each frame into the grid probability map, and calculating a probability value of each CFAR point in the grid probability map; and taking the CFAR point with the probability value higher than a first preset value asthe point of an obstacle, and taking other areas other than the point of the obstacle as a travelable area. By processing the point cloud data, the obstacle information that is relatively stationarywith respect to the ground is accurately obtained, and the obstacle is displayed on a display screen to obtain the travelable area.
Owner:WHST CO LTD
Method for using pulse compression in weather radar
ActiveUS20070046526A1High sensitivityHigh quality meteorological radar imageryRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationWeather radarRadar systems
A system and method for processing data related to weather phenomena in a meteorological radar system. The method includes receiving an echo signal generated by transmitting a long pulse and employing a mismatched windowed filter on the echo signal such that the echo signal is compressed in time to achieve fine range resolution without substantially degrading sensitivity and while achieving low range time side lobes for Doppler velocities expected to be measured by the meteorological radar system.
Owner:VAISALA
Ultrasound image capture device and ultrasound image capture method
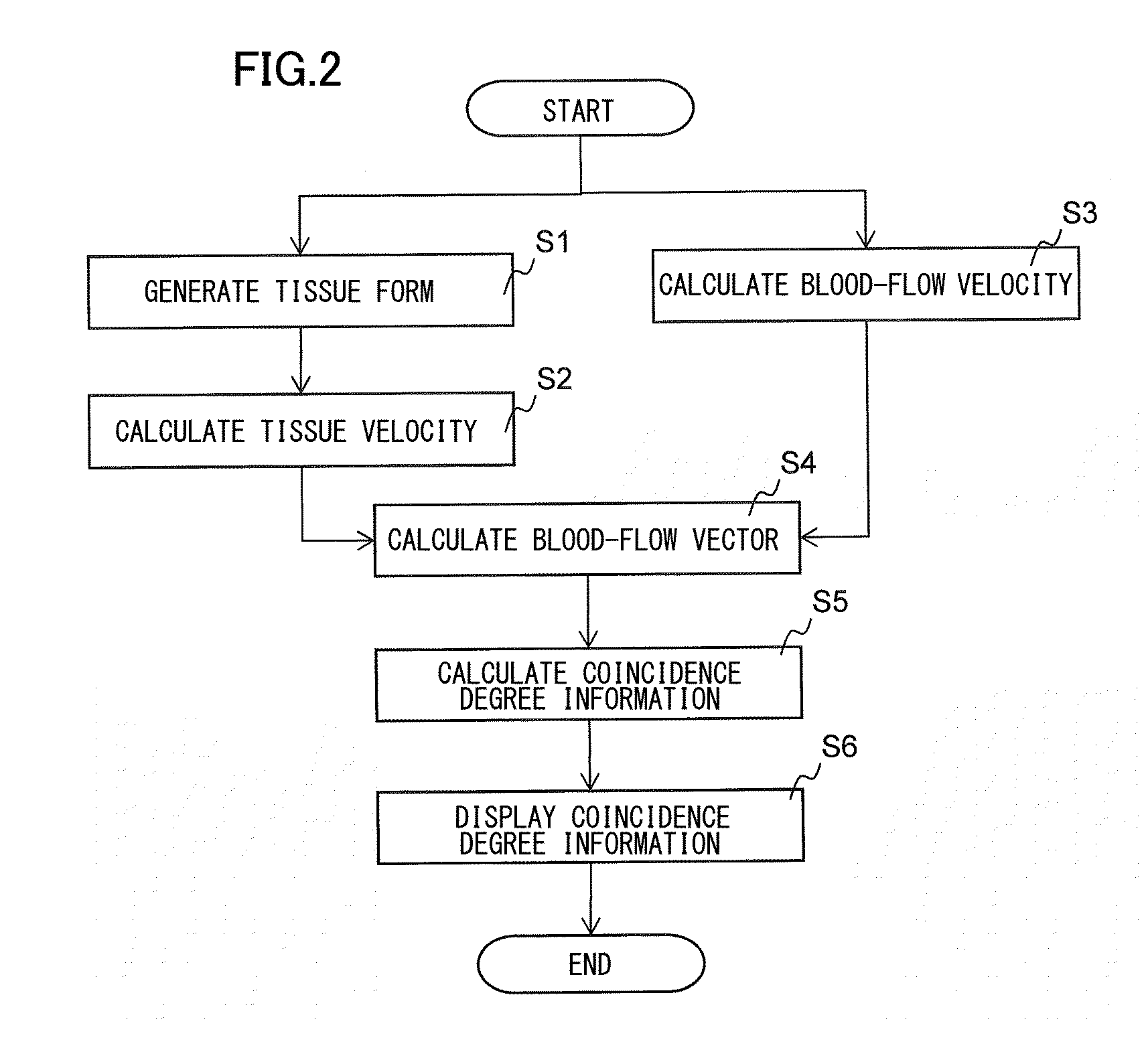
ActiveUS20150094582A1Reduce inherent uncertaintyEfficient inspectionAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesBlood flow measurement devicesUltrasound imagingDoppler velocity
The present invention obtains certainty of the blood-flow velocity information that is estimated in the blood-flow mapping display. The signal processor in the ultrasound imager is provided with a Doppler velocity operation part configured to calculate a Doppler velocity from echo signals by using the Doppler effect, and a first blood-flow velocity operation part configured to generate a tissue tomographic image from the echo signals and calculate a blood-flow velocity of a predetermined portion from a motion of the tissue, on the basis of the tissue tomographic image. It is further provided with a second blood-flow velocity operation part configured to calculate the blood-flow velocity of the predetermined portion by using the Doppler velocity calculated by the Doppler velocity operation part. Then, a coincidence degree is calculated between the blood-flow velocity calculated by the first velocity operation part and the blood-flow velocity calculated by the second velocity operation part, as to the predetermined portion, and according to the coincidence degree, certainty / reliability of the blood-flow velocity information is obtained and displayed.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
Vehicular radar device
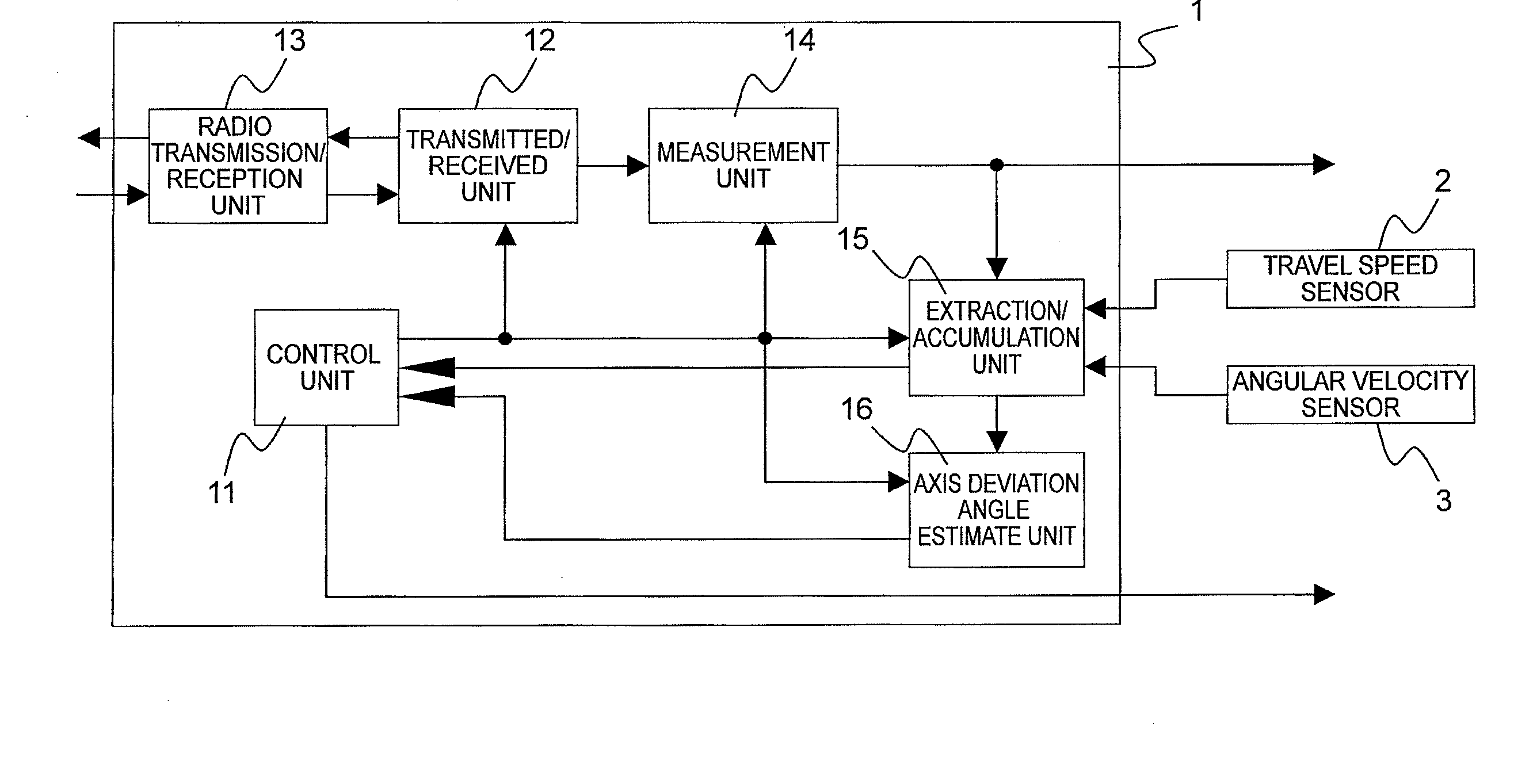
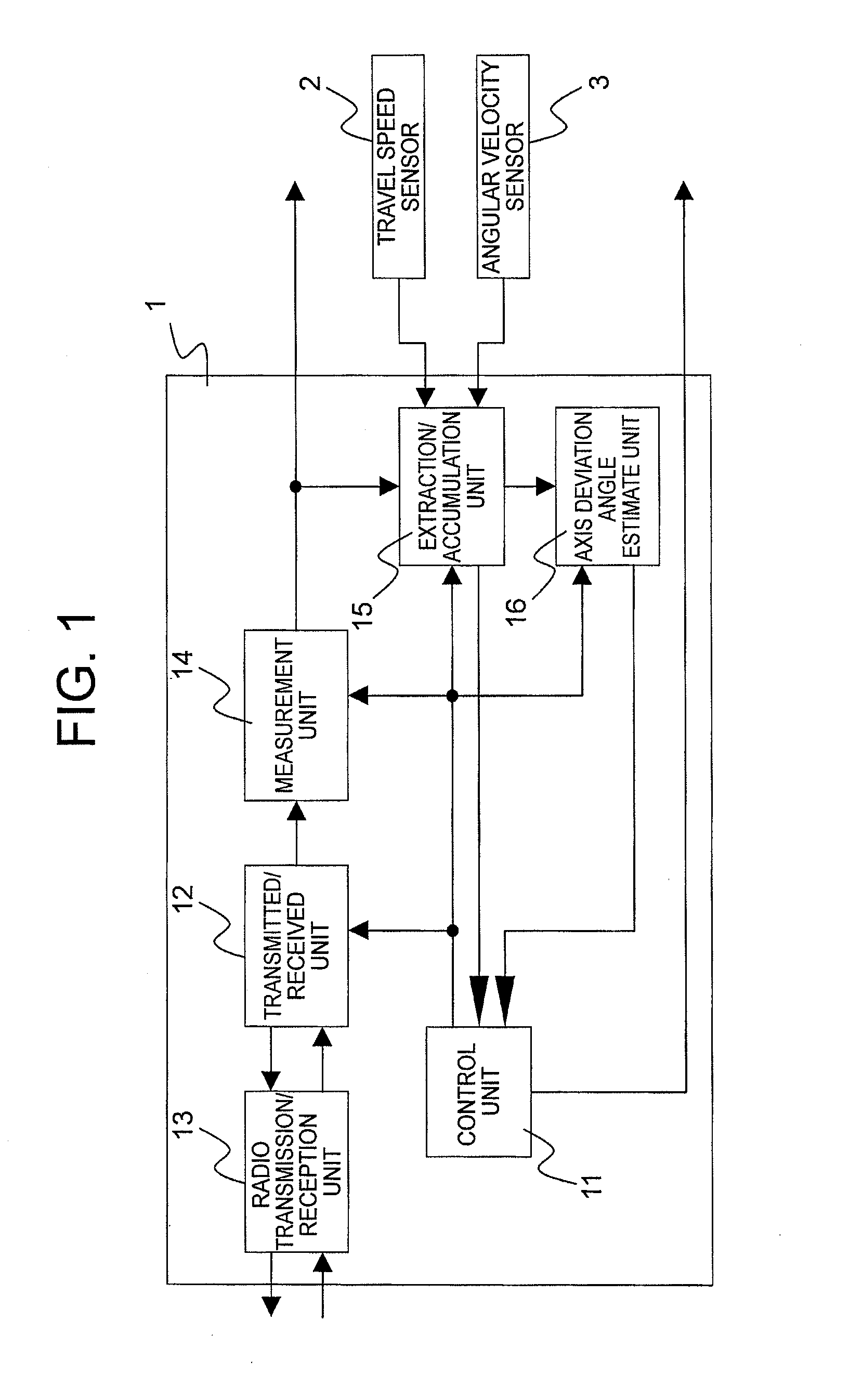
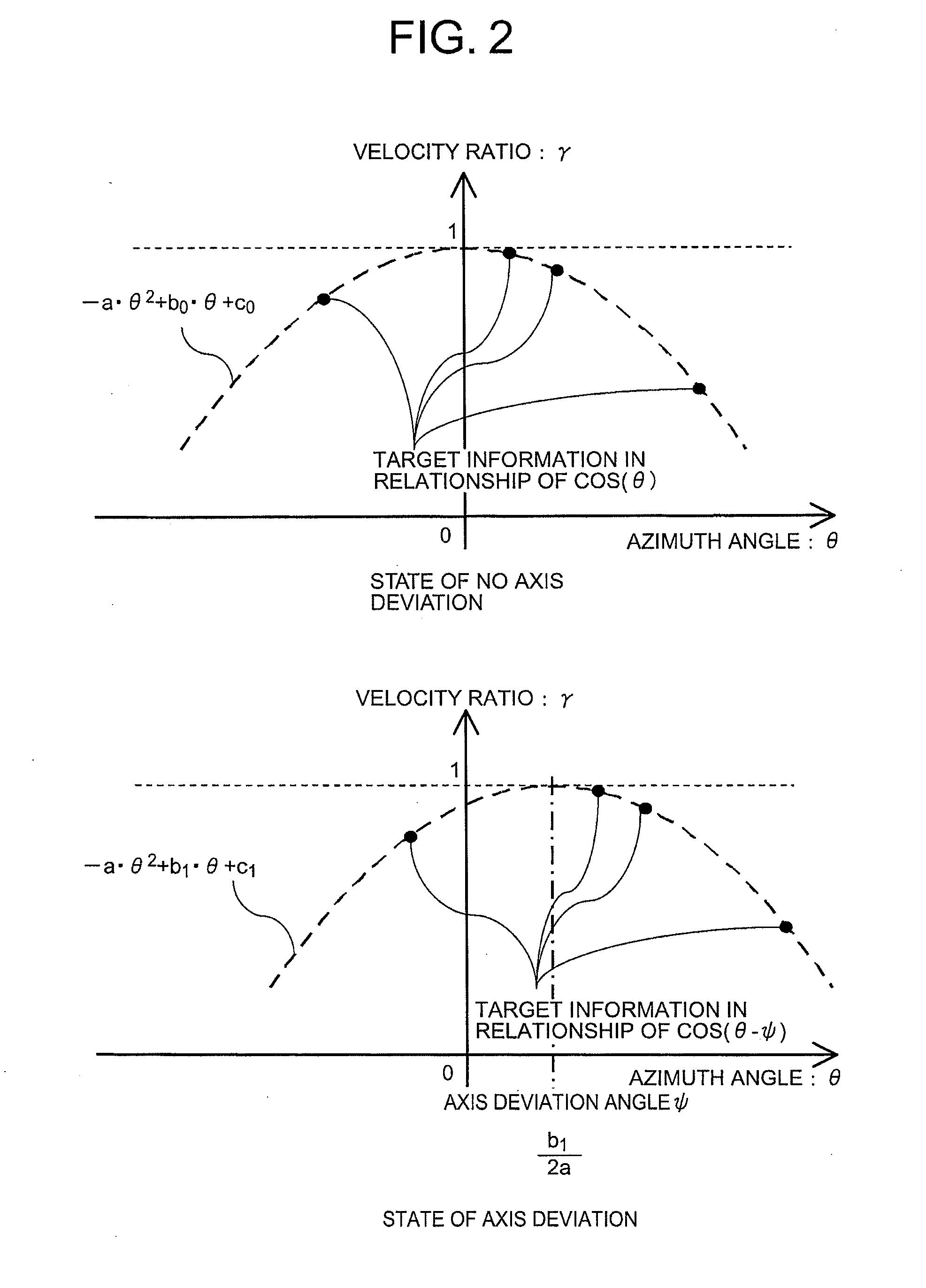
ActiveUS20110068970A1Reduce in quantitySmall sizeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDoppler velocityVelocity ratio
Provided is a vehicular radar device which is capable of reducing an operation resource quantity necessary for a process of estimating an axis deviation angle in a radar measurement coordinate system, to thereby reduce a device size. The vehicular radar device includes: a measurement unit that measures an azimuth angle and a relative Doppler velocity; an extraction / accumulation unit that extracts target information satisfying conditions related to the relative Doppler velocity, a travel speed and a turning velocity, and accumulates the azimuth angle and a velocity ratio obtained by dividing the relative Doppler velocity by the travel speed of the subject vehicle among the extracted target information; and an axis deviation angle estimate unit that reads the target information accumulated in the extraction / accumulation unit, and estimates an axis deviation angle of the measurement coordinate system of a radar based on a second-order polynomial expression of the azimuth angle of the target.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Ultrasonic imaging apparatus and a method for generating an ultrasonic image
ActiveUS20090088641A1Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsDoppler velocityUltrasonic imaging
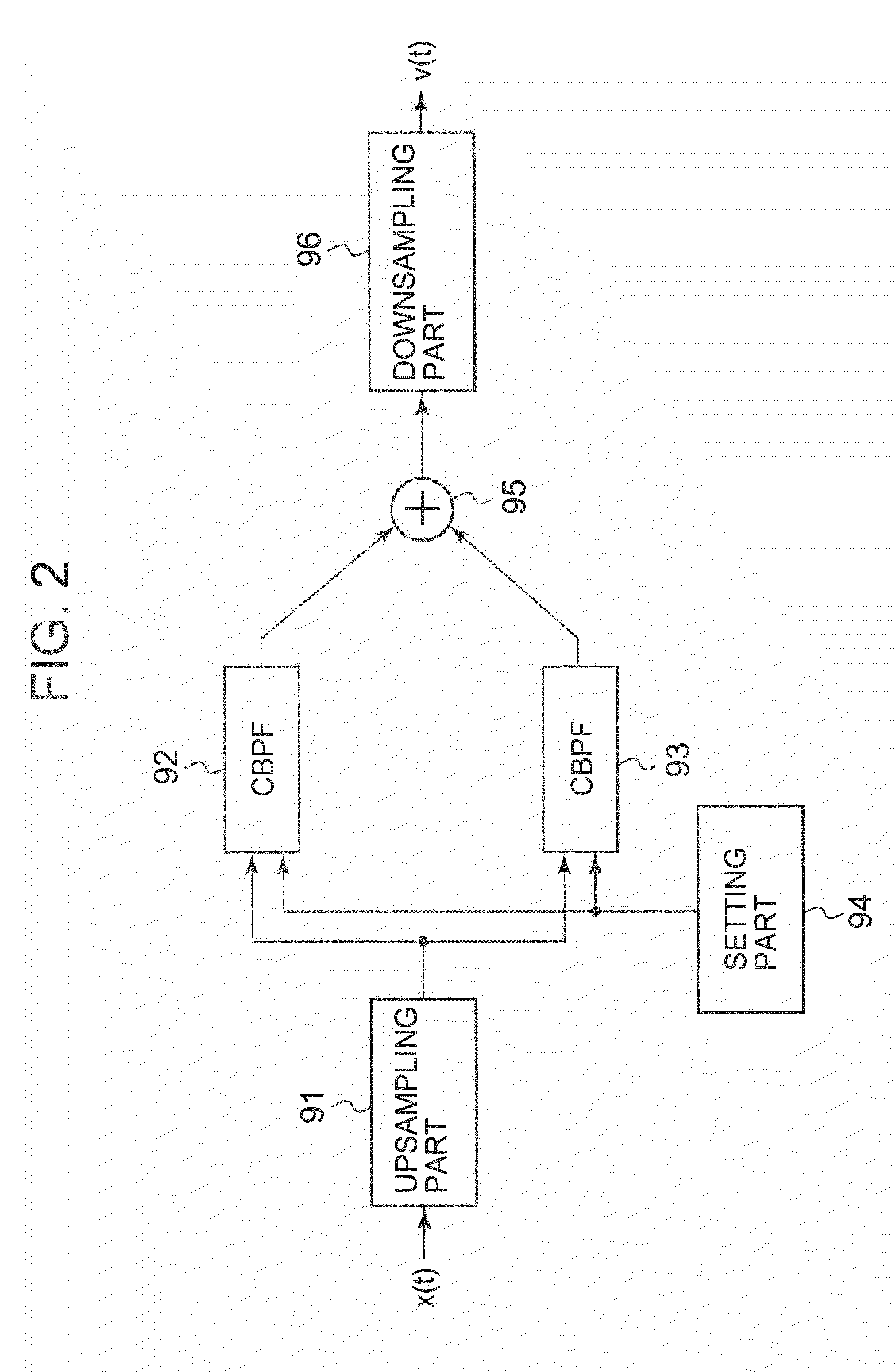
A scanner transmits and receives ultrasonic waves at a specified pulse repetition frequency (PRF). A storage stores received signals acquired through the transmission and reception. A calculator generates a Doppler spectrum image by executing frequency analysis on the received signals. A display displays the Doppler spectrum image. When a desired Doppler velocity range for the displayed Doppler spectrum image is inputted, a processor reads out the received signals from the storage, and executes a resampling process on the read-out received signals at a sampling frequency corresponding to the desired Doppler velocity range. The calculator generates a new Doppler spectrum image by executing frequency analysis corresponding to the desired Doppler velocity range on the received signals having been subjected to the resampling process by the processor. The display displays the new Doppler spectrum image.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method and apparatus for multiple-wave doppler velocity meter
ActiveUS20120130248A1Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsDoppler velocityClassical mechanics
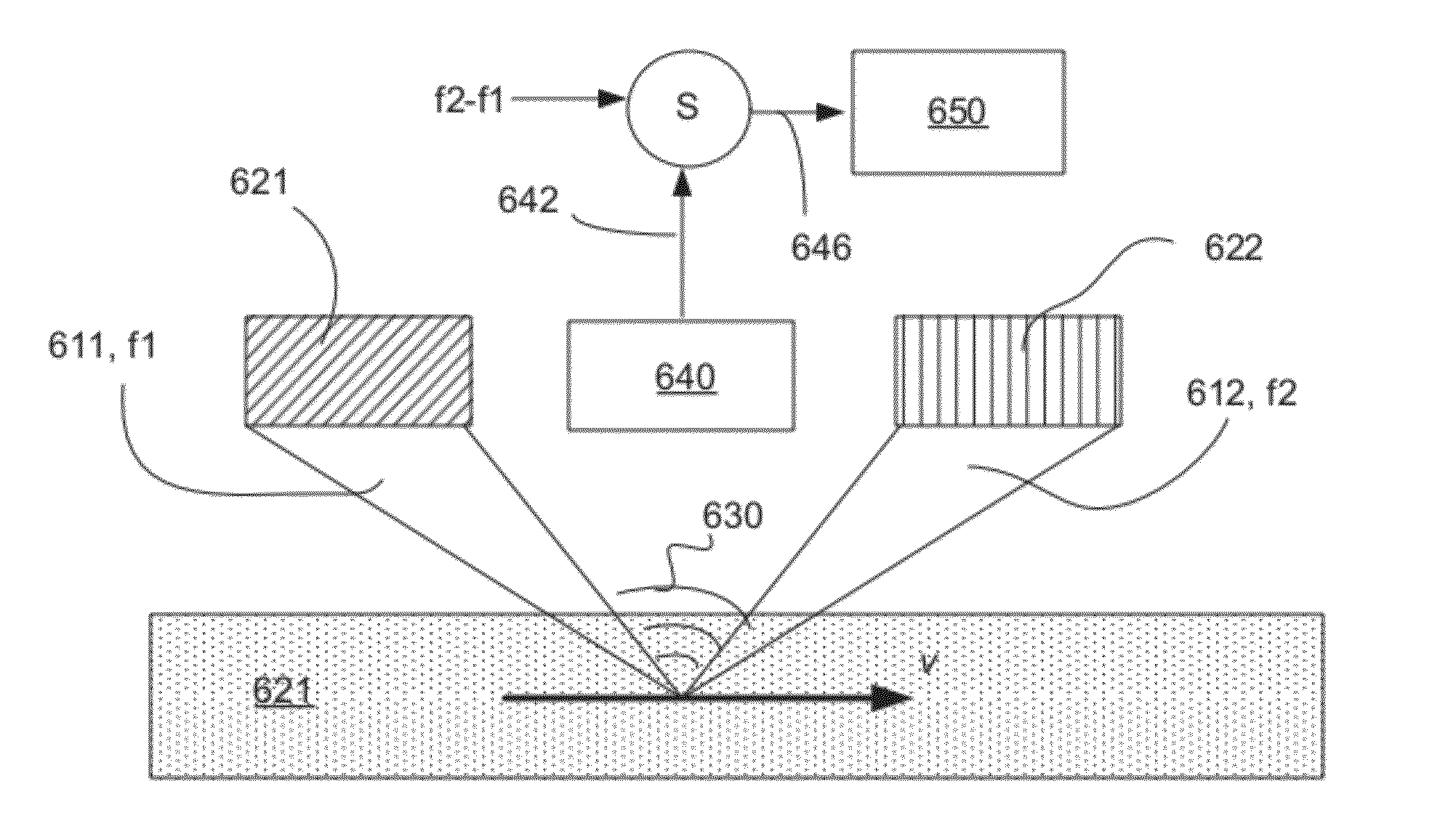
A method and system for determining a velocity of a moving object such as a body or a stream. The object is irradiated in a non-collinear configuration with multiple ultrasound waves overlapping in a region-of-interest (ROI) of the object. An response wave, resulting from the non-linear interaction among the incident waves and the object, is detected and the frequency variations of the response wave are determined. Data representing a Doppler-shift of this frequency is further determined and processed to calculate the velocity of the moving object.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
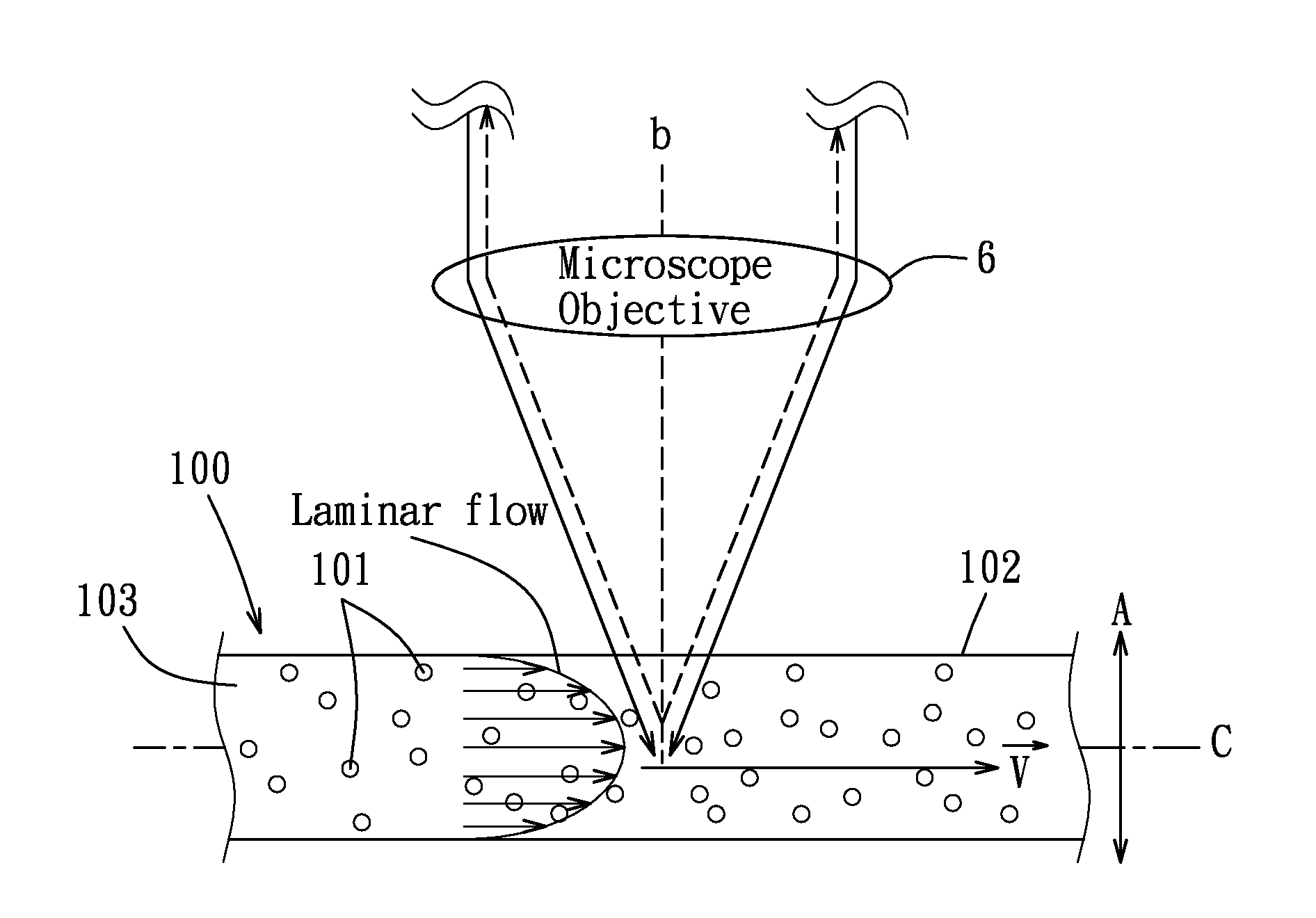
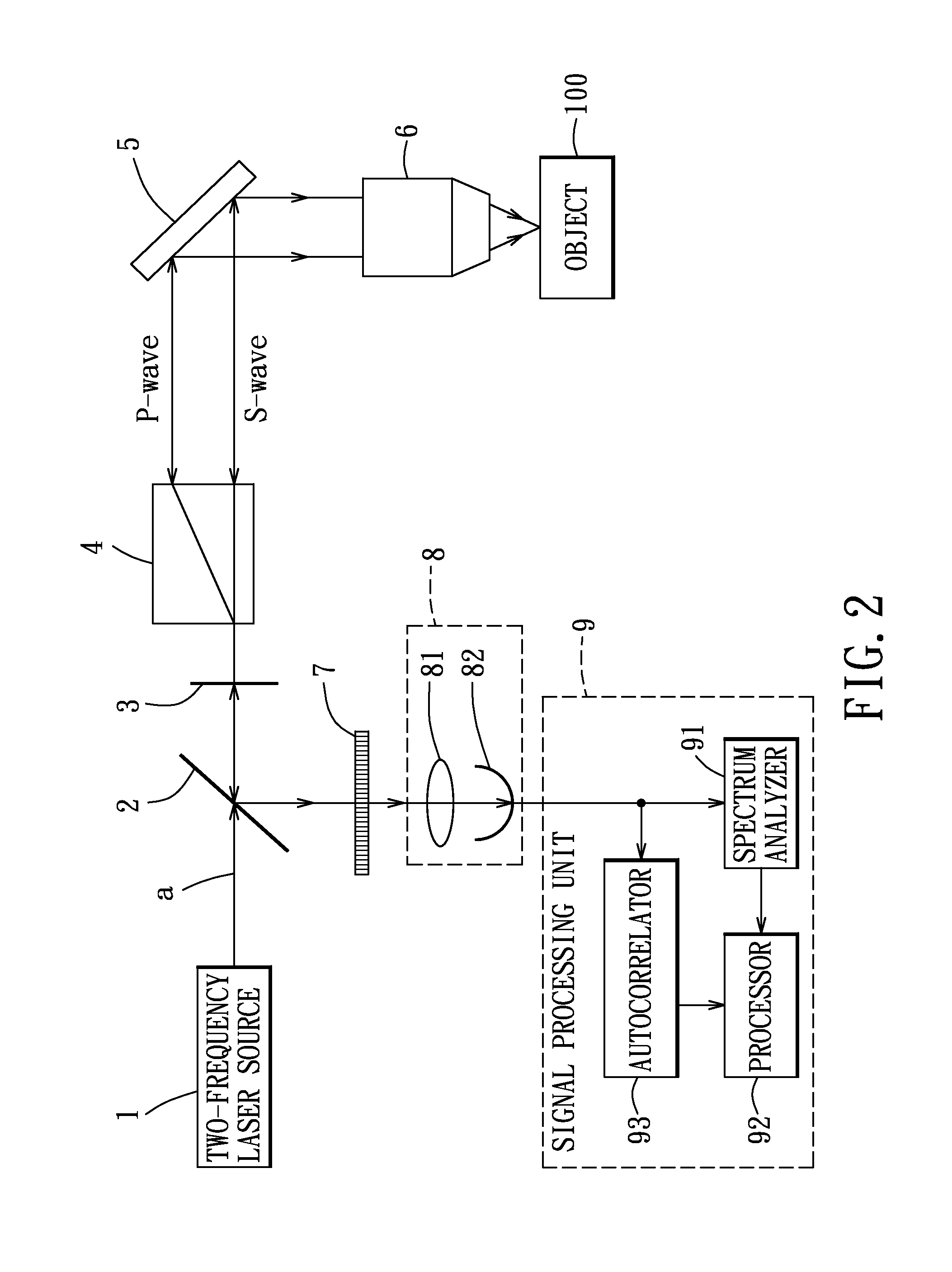
Localized dynamic light scattering system with doppler velocity measuring capability
ActiveUS20140132943A1High sensitivityNanoparticle analysisScattering properties measurementsObject basedPolarizer
A localized dynamic light scattering measurement system includes a beam displacer for splitting an incident beam having two orthogonal linearly polarized beam components with slightly different frequencies into two orthogonal linearly polarized output beams focused onto an object to be measured. The beam displacer cooperates with an iris to collect and recombine scattering beams each reversely backscattered at 180 degrees from the object so as to form a signal beam, which is polarized by a polarizer to produce two polarization components, thereby generating a heterodyne interference signal associated with the polarization components. A signal processing unit obtains measurement data on the object based on power spectrum or autocorrelation data corresponding to the heterodyne interference signal.
Owner:CHOU LIDEK
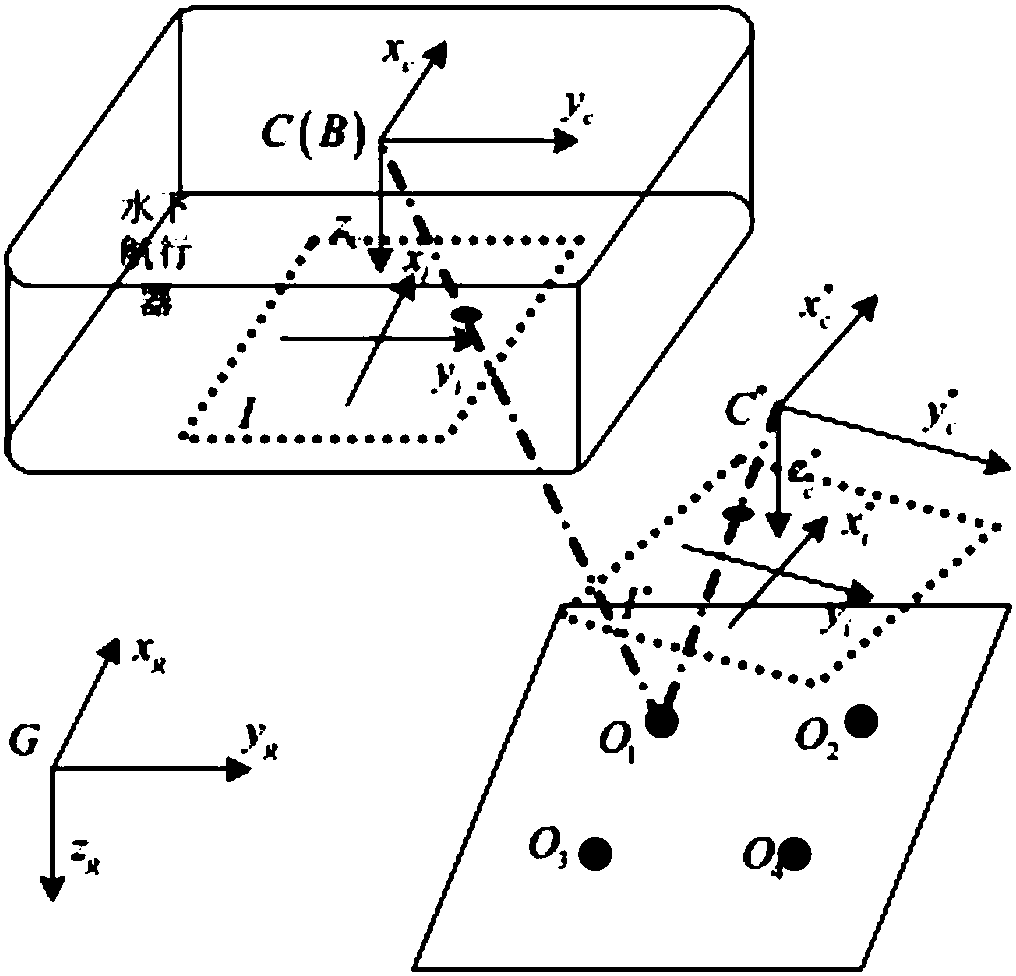
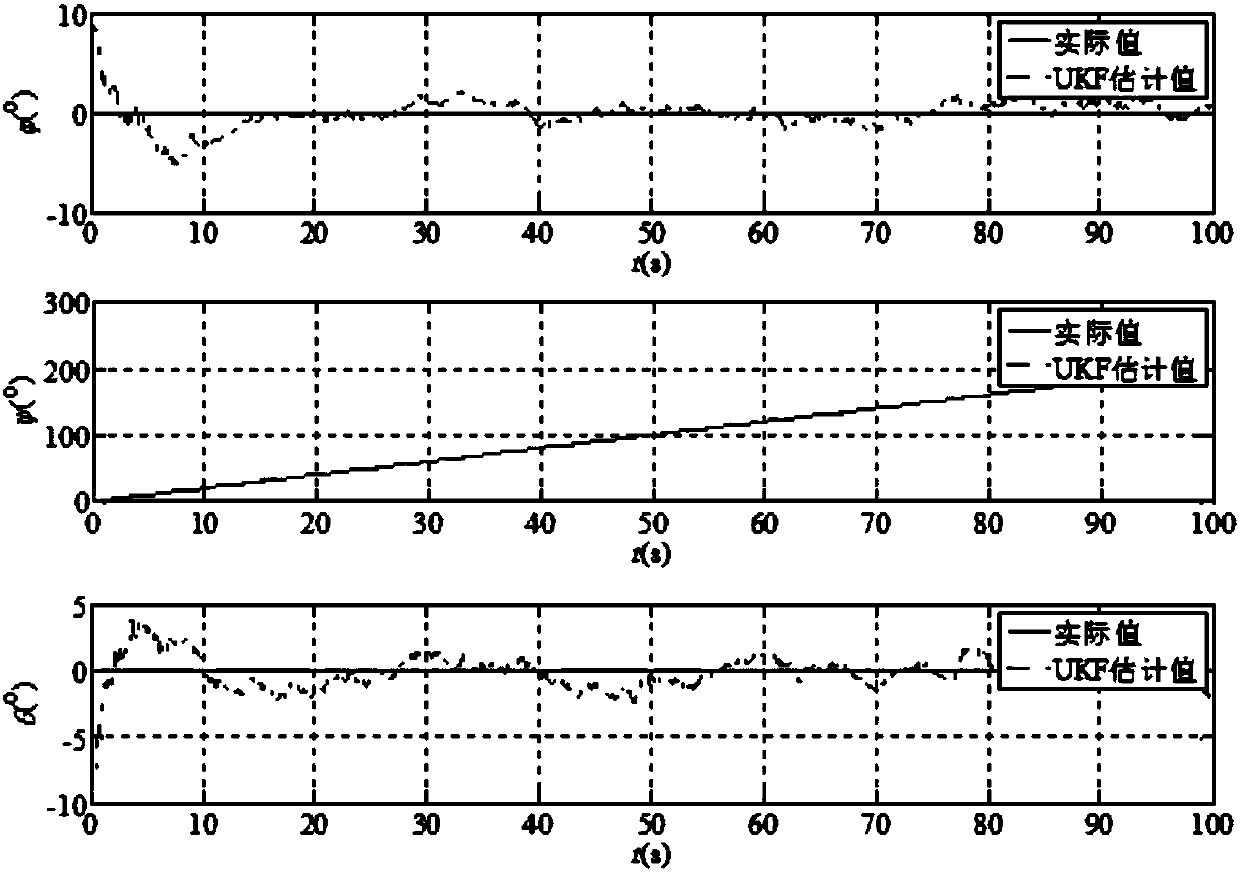
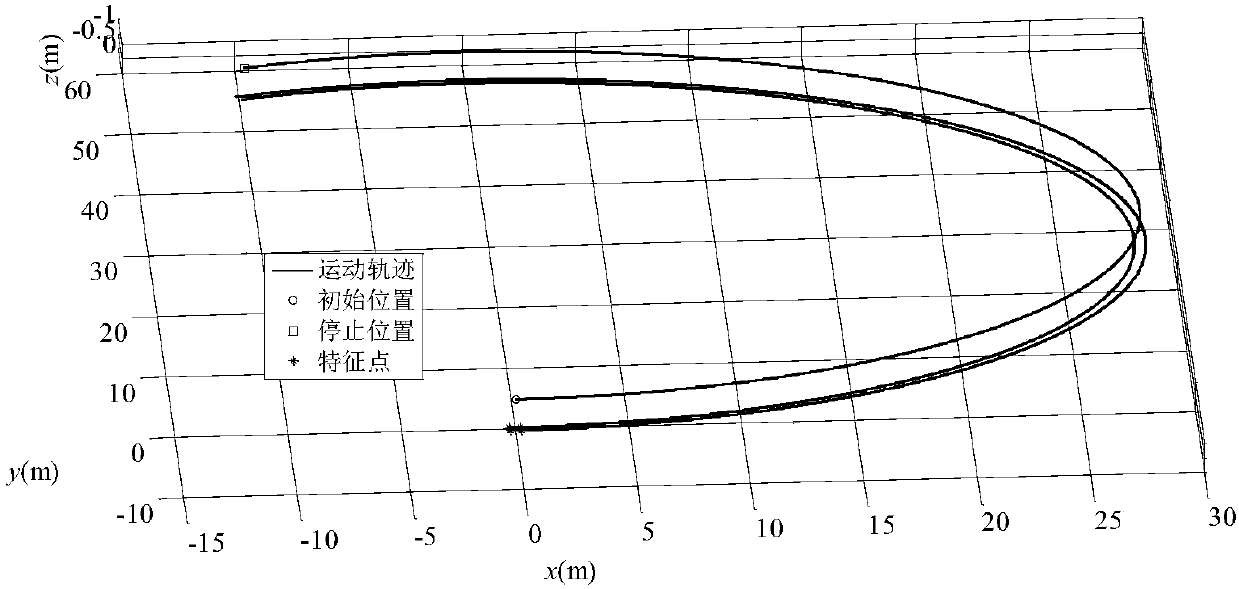
Method for estimating visual gestureattitudes of moving target for underwater vehicle
ActiveCN108444478AAccurate estimateNavigational calculation instrumentsDoppler velocityCarrier system
The invention provides a method for estimating visual gestureattitudes of a moving target for an underwater vehicle. The method comprises the following steps of according to a mathematics model of theunderwater vehicle, enabling sensors (such as a Doppler velocimeter and a bearing and gestureattitude measuring system) to measure the linear speed, angular speed and angle of the underwater vehicleunder a carrier system, so as to obtain state information; obtaining a plurality of known feature points on the moving target, and transforming coordinate systems on the basis of a kinematics model ofthe underwater vehicle, so as to obtain the positions of the feature points of the global system under the image system, thereby obtaining the measuring information; estimating the relative positiondifference distance and moving gestureattitude of the underwater vehicle and the center of the target object by an unscented Kalman filter algorithm. Compared with the geometric method, the method hasthe advantages that the limitation of the layout of feature points requiring to meet the special conditions in the geometric method is overcome; the relative position difference distance and moving gestureattitude of the underwater vehicle and the center of the target object can be accurately estimated.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com