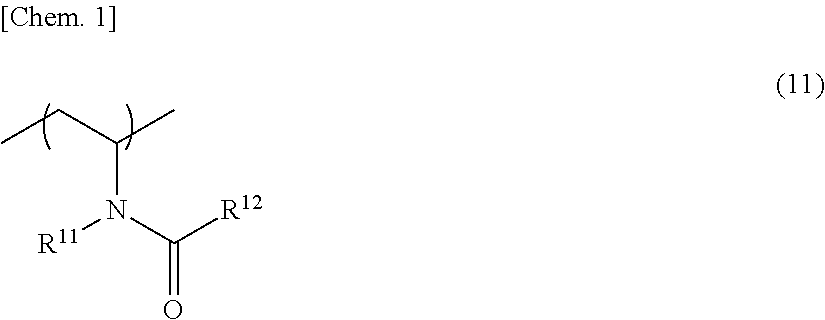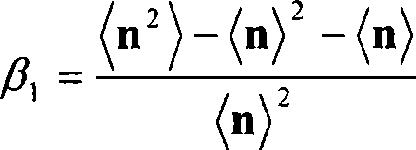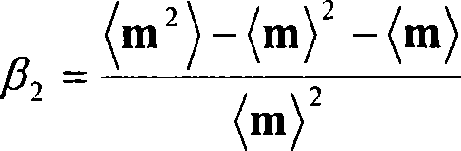Patents
Literature
383 results about "Dynamic light scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
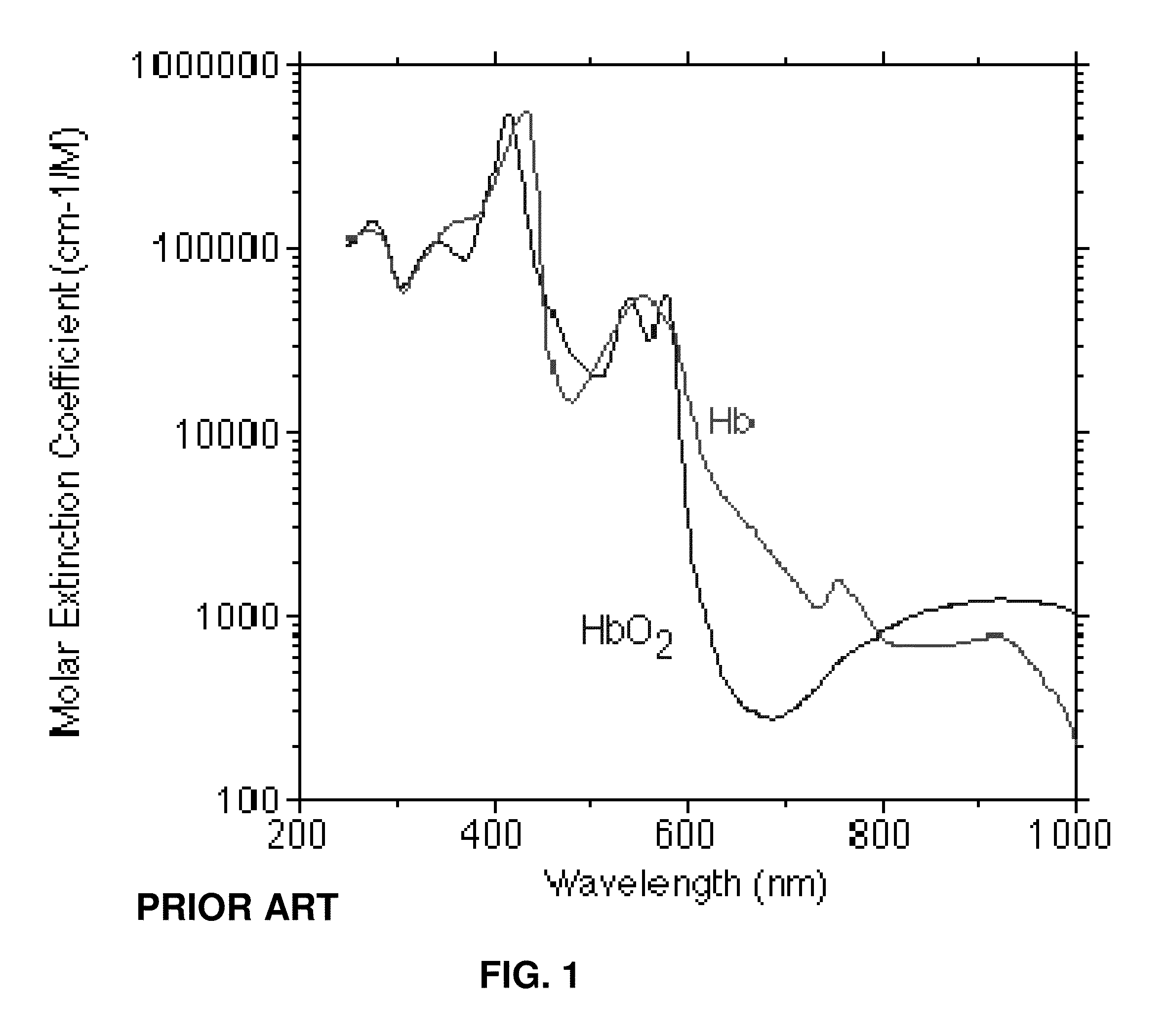
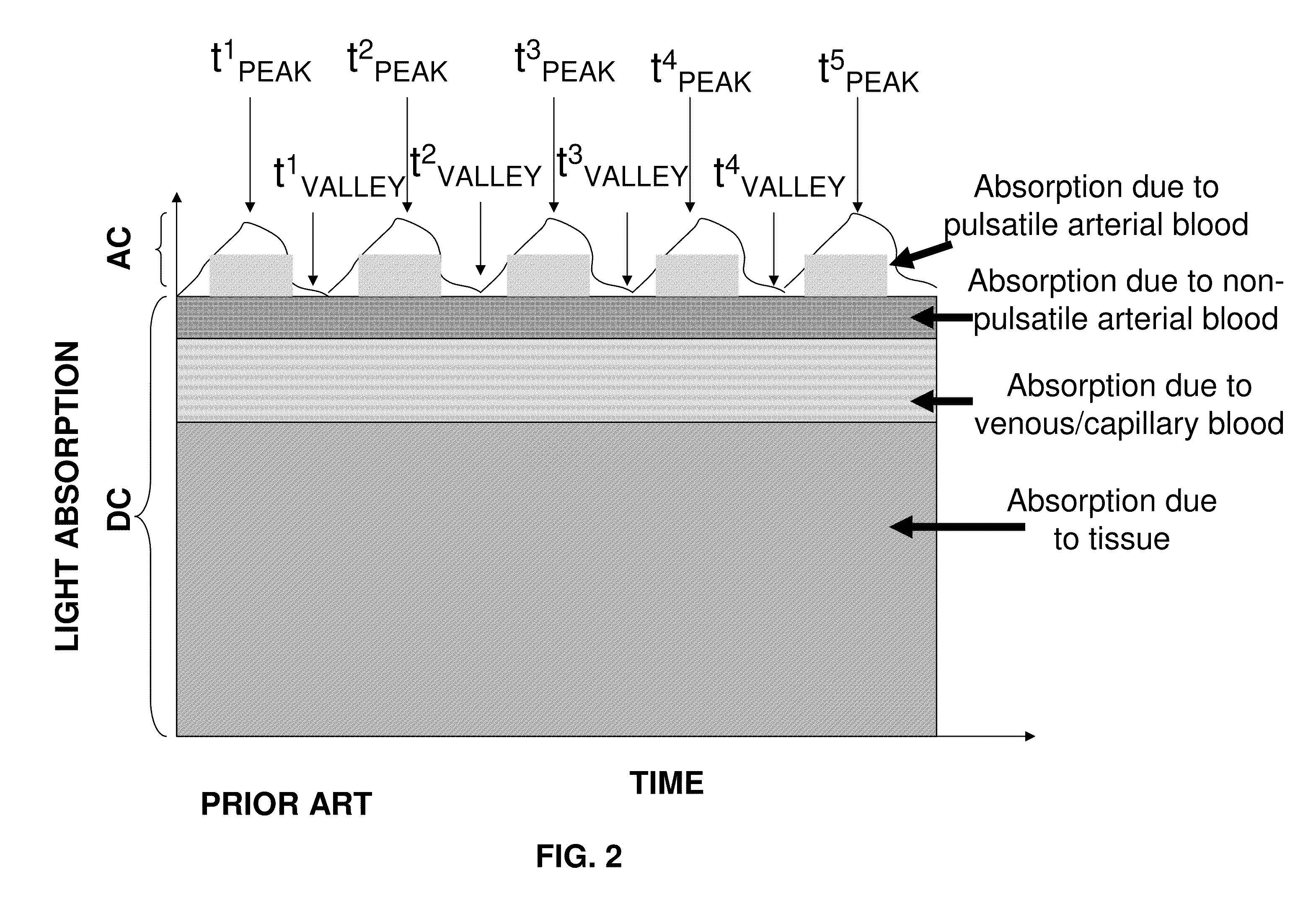
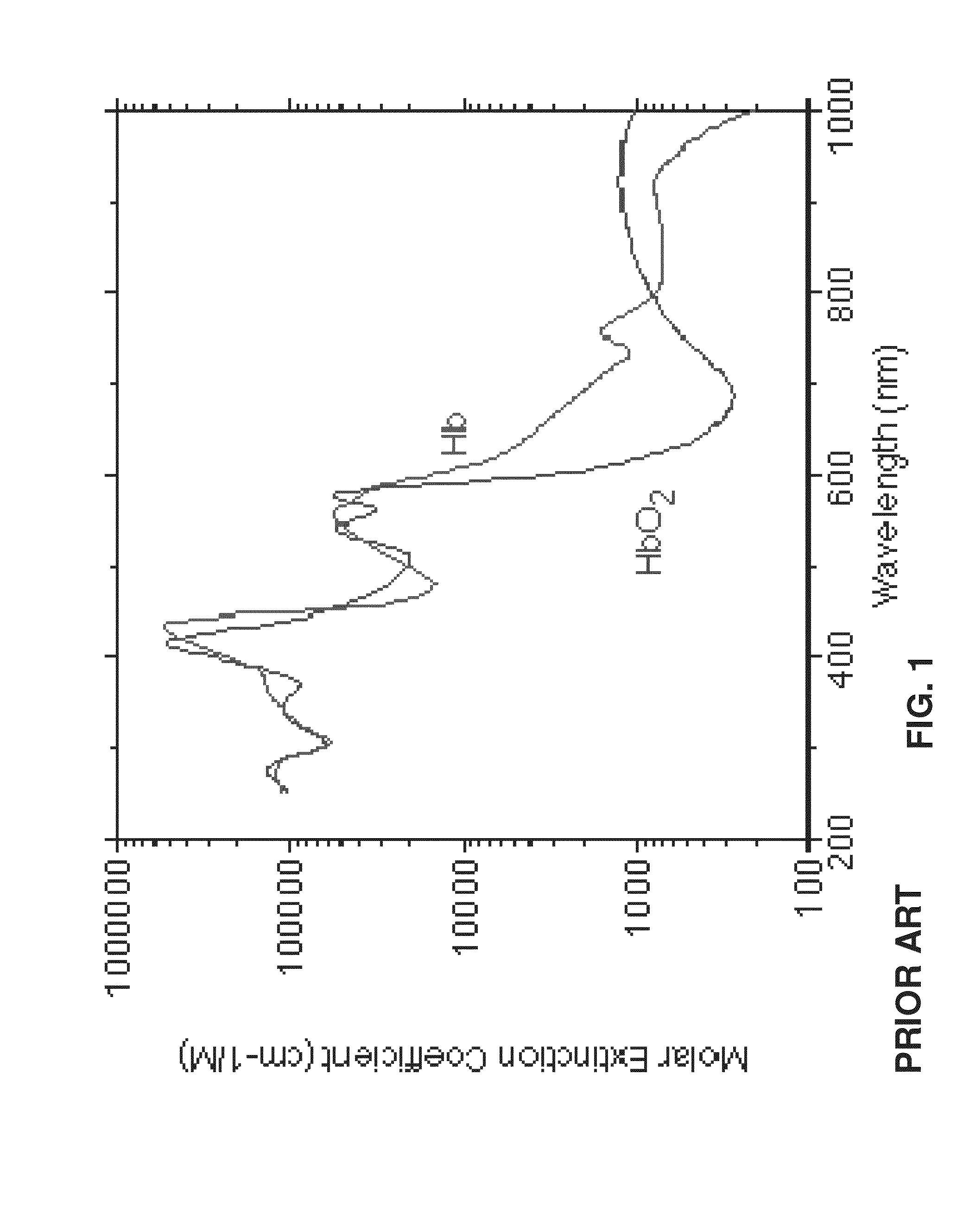
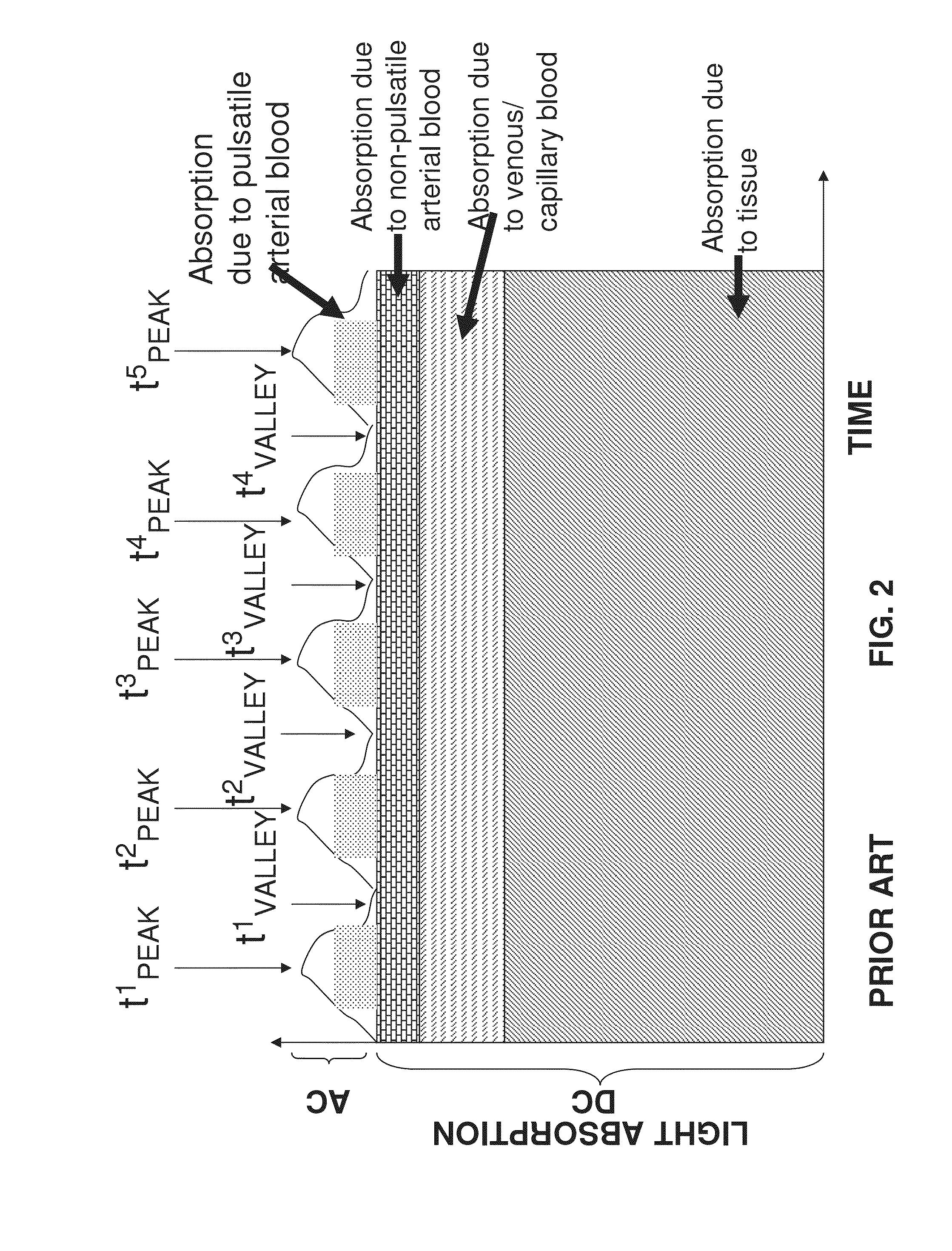
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) is a technique in physics that can be used to determine the size distribution profile of small particles in suspension or polymers in solution. In the scope of DLS, temporal fluctuations are usually analyzed by means of the intensity or photon auto-correlation function (also known as photon correlation spectroscopy or quasi-elastic light scattering). In the time domain analysis, the autocorrelation function (ACF) usually decays starting from zero delay time, and faster dynamics due to smaller particles lead to faster decorrelation of scattered intensity trace. It has been shown that the intensity ACF is the Fourier transformation of the power spectrum, and therefore the DLS measurements can be equally well performed in the spectral domain. DLS can also be used to probe the behavior of complex fluids such as concentrated polymer solutions.
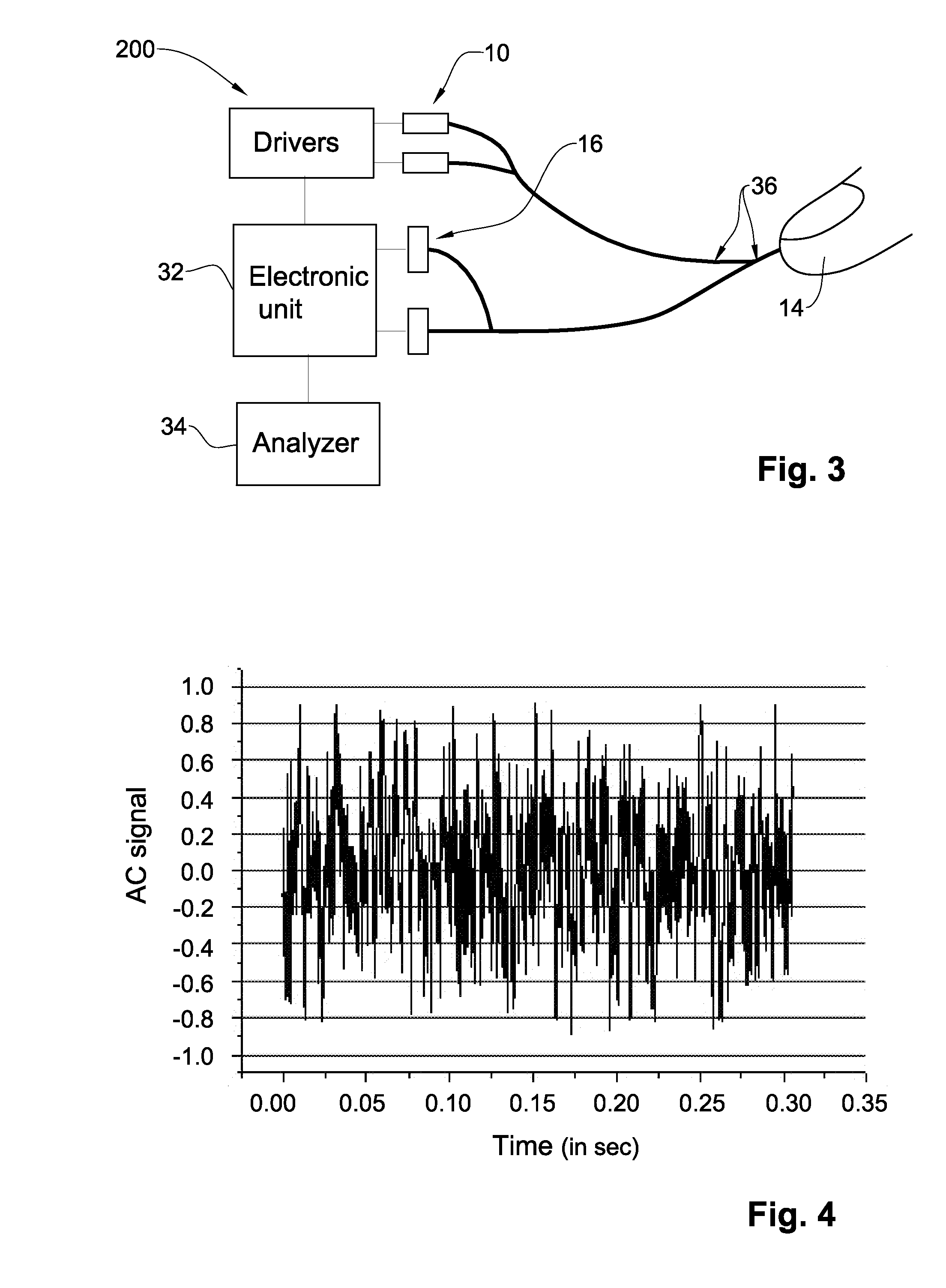
Enhanced LCD backlight
ActiveUS20060056166A1Improved backlight assemblyAvoid less flexibilityElectric discharge tubesDiffusing elementsCompression moldingEllipsoidal particle
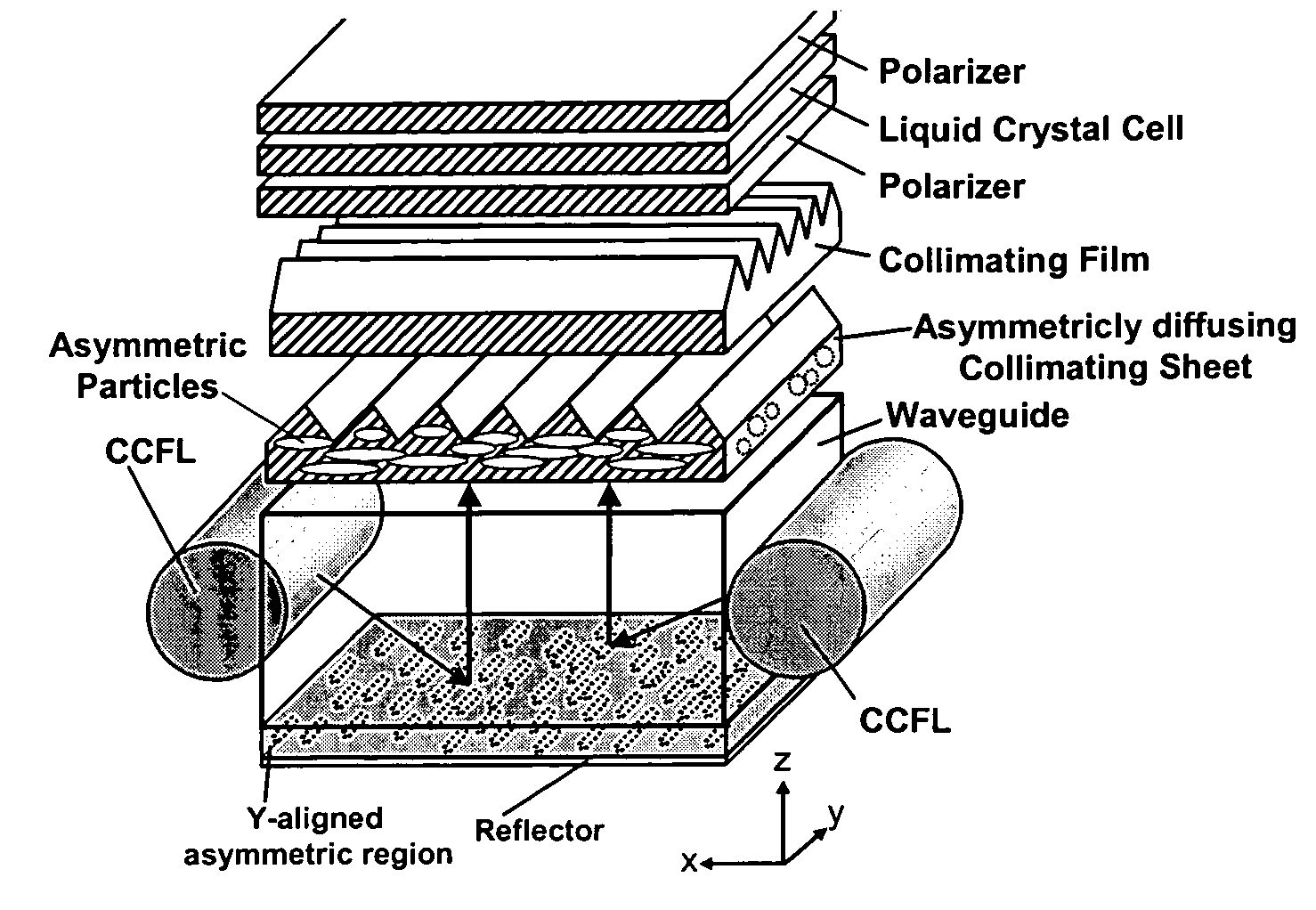
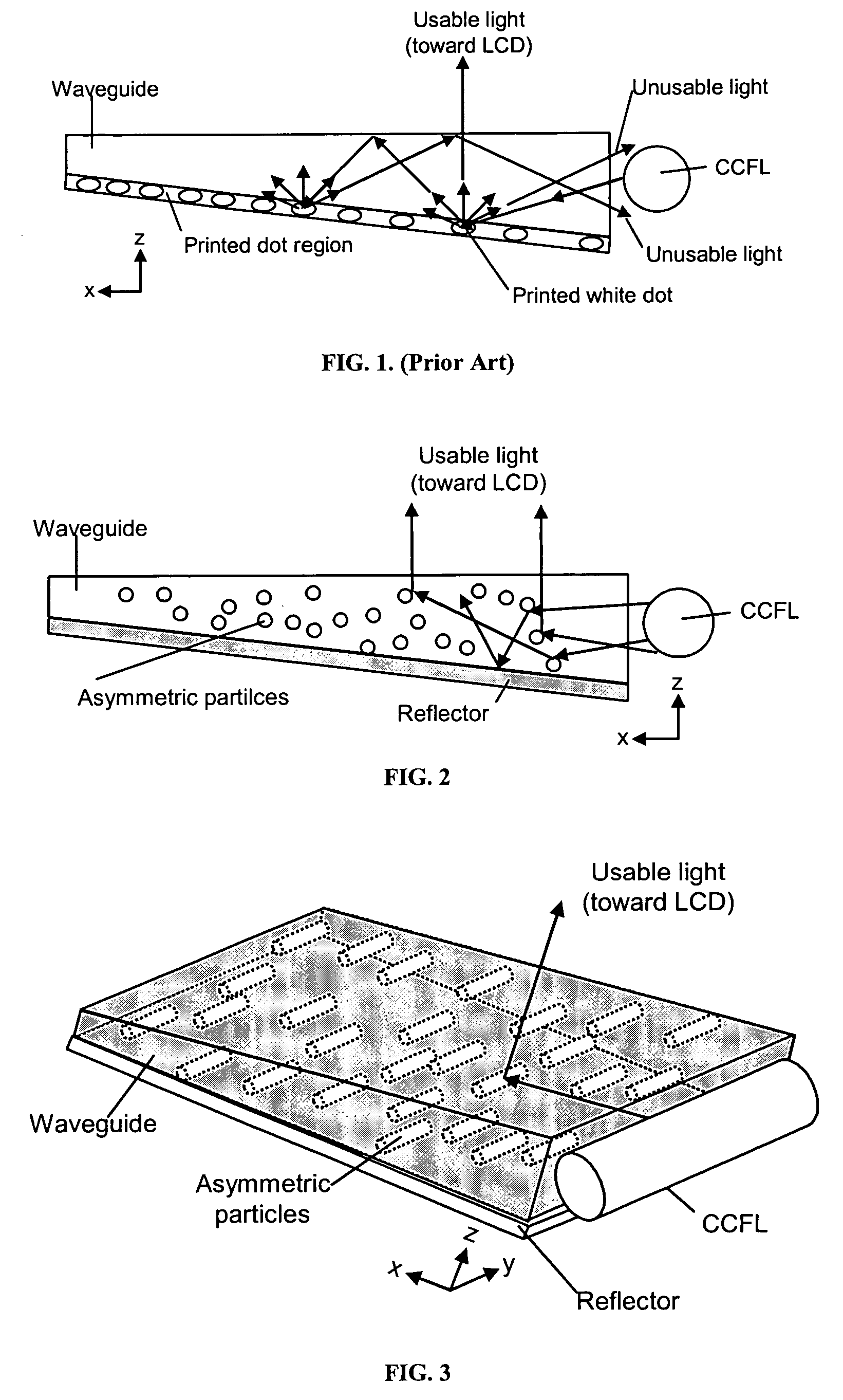
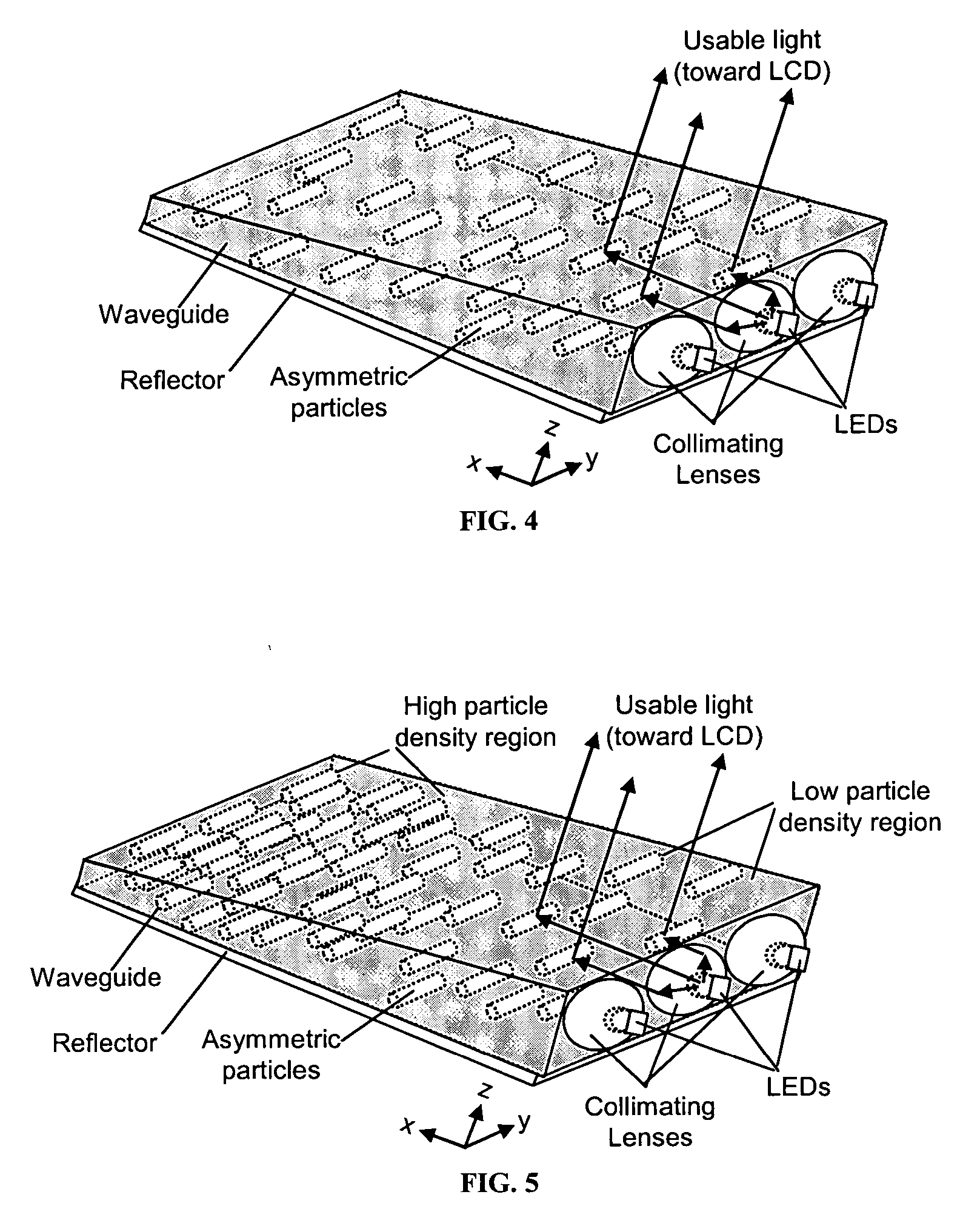
The present invention provides an improved light guide with inherently more flexibility for display system designers and higher optical efficiency. By using a light guide containing substantially aligned non-spherical particles, more efficient control of the light scattering can be achieved. One or more regions containing ellipsoidal particles may be used and the particle sizes may vary between 2 and 100 microns in the smaller dimension. The light scattering regions may be substantially orthogonal in their axis of alignment. Alternatively, one or more asymmetrically scattering films can be used in combination with a backlight light guide and a reflector to produce an efficient backlight system. The light guides may be manufactured by embossing, stamping, or compression molding a light guide in a suitable light guide material containing asymmetric particles substantially aligned in one direction. The light scattering light guide or non-scattering light guide may be used with one or more light sources, collimating films or symmetric or asymmetric scattering films to produce an efficient backlight that can be combined with a liquid crystal display or other transmissive display. By maintaining more control over the scattering, the efficiency of the recycling of light by using reflective polarizers can also be increased.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS DEV FINANCE AGENCY
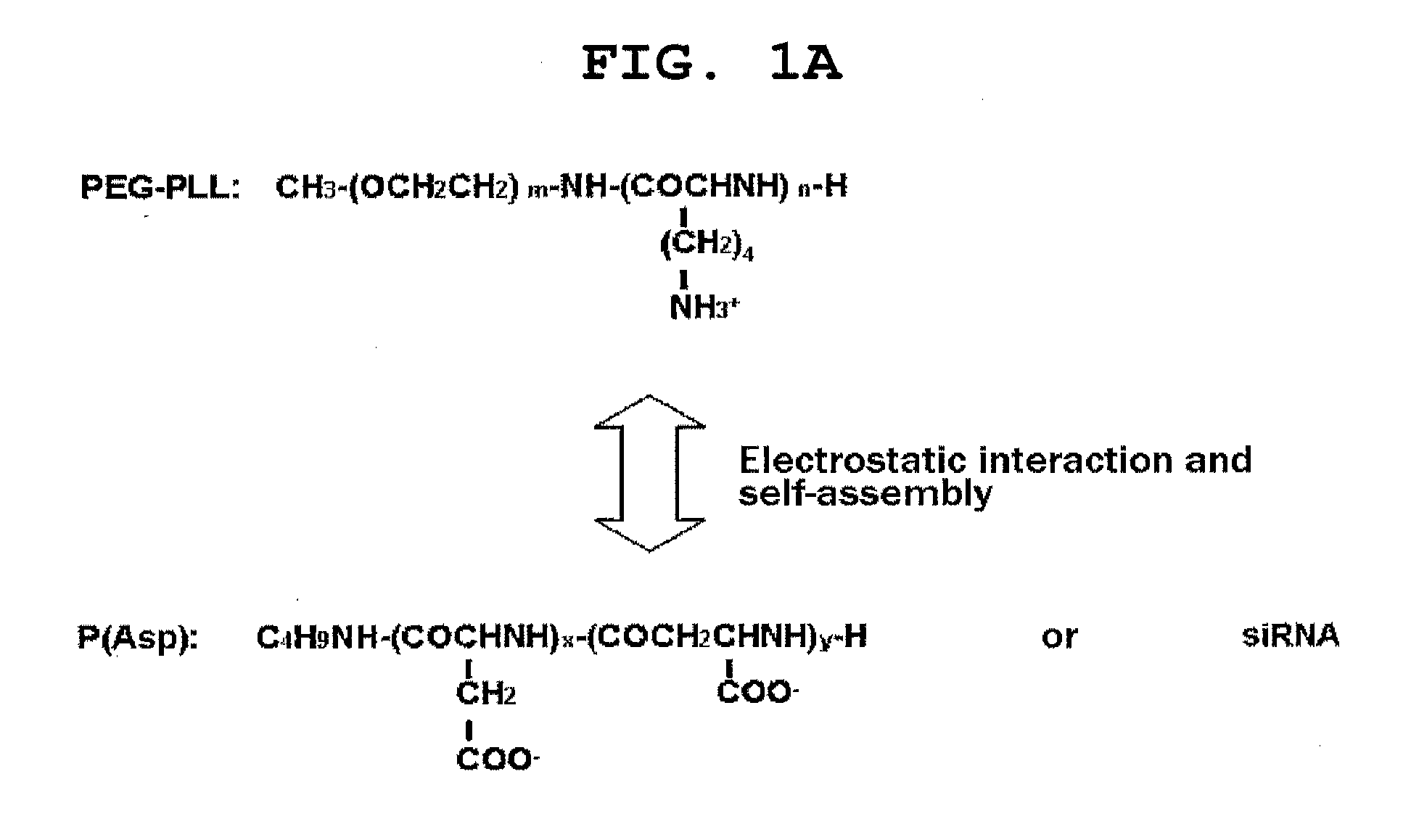
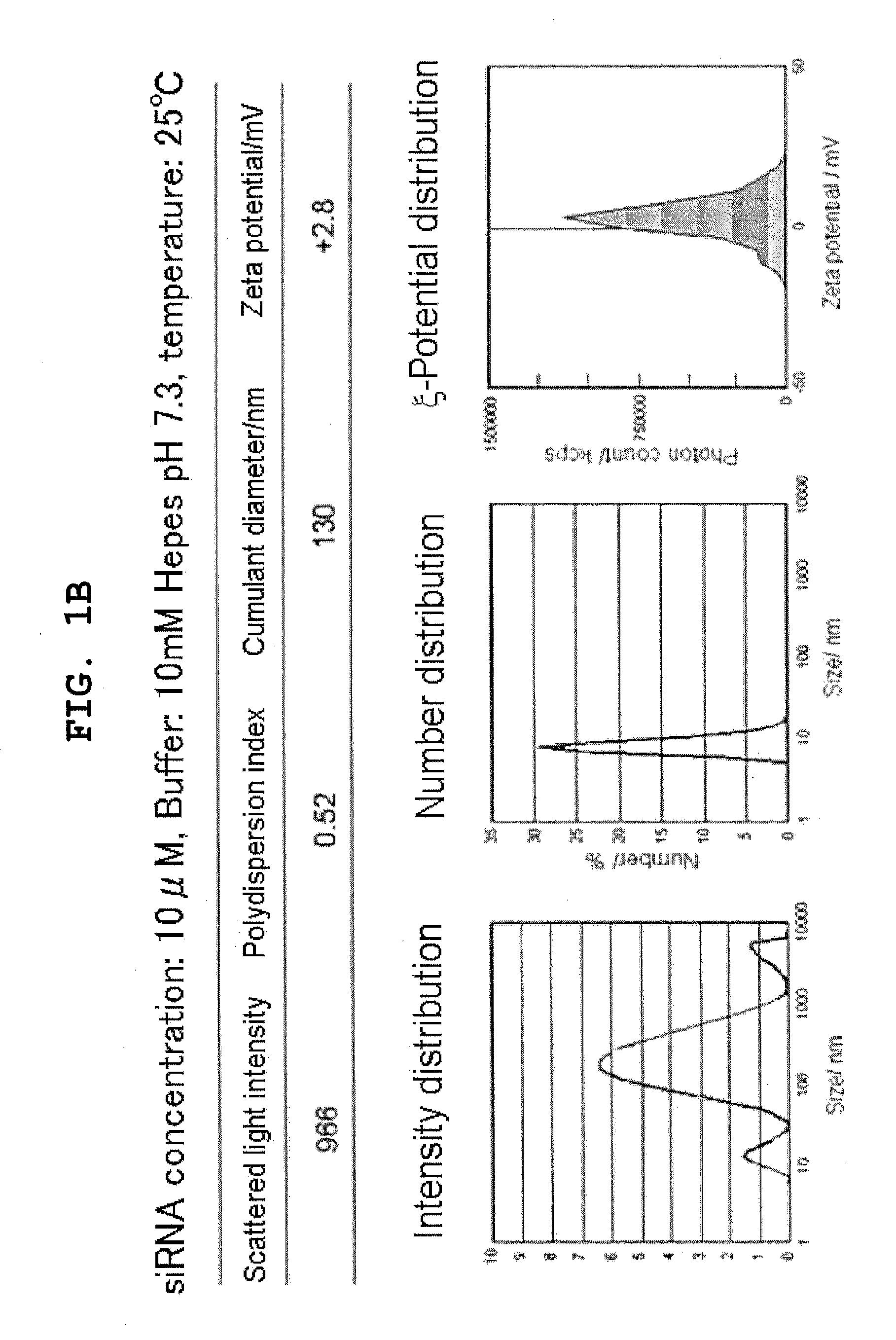
Polyion complex of double-stranded ribonucleic acid
InactiveUS20120076836A1Easy and efficient deliverySmall particle sizePowder deliverySpecial deliveryDynamic light scatteringDouble strand
Provided are a delivery system that is useful in delivering a double-stranded ribonucleic acid that functions in gene silencing in glomeruli, particularly in mesangial cells and the like, to the tissue or cells, and the like. A polyion complex in the form of a non-polymeric micelle consisting of a double-stranded ribonucleic acid and a block copolymer represented by the formula (I) or (II) below, which are electrostatically bound together, wherein the polyion complex has an average particle diameter of less than 100 nm as measured by a dynamic light scattering measuring method:wherein each symbol is as defined in the specification.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
System and Method for In Vivo Measurement of Biological Parameters
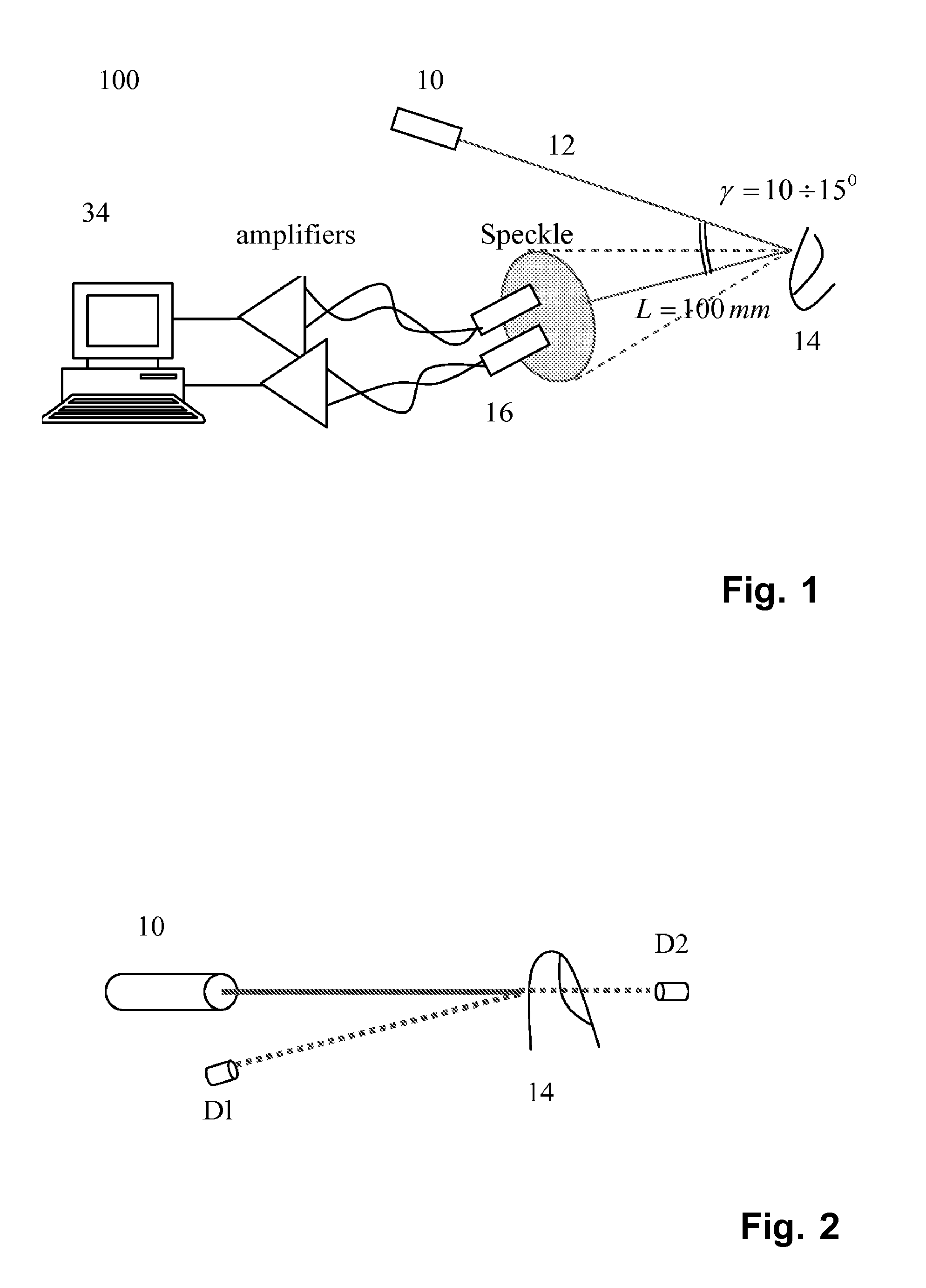
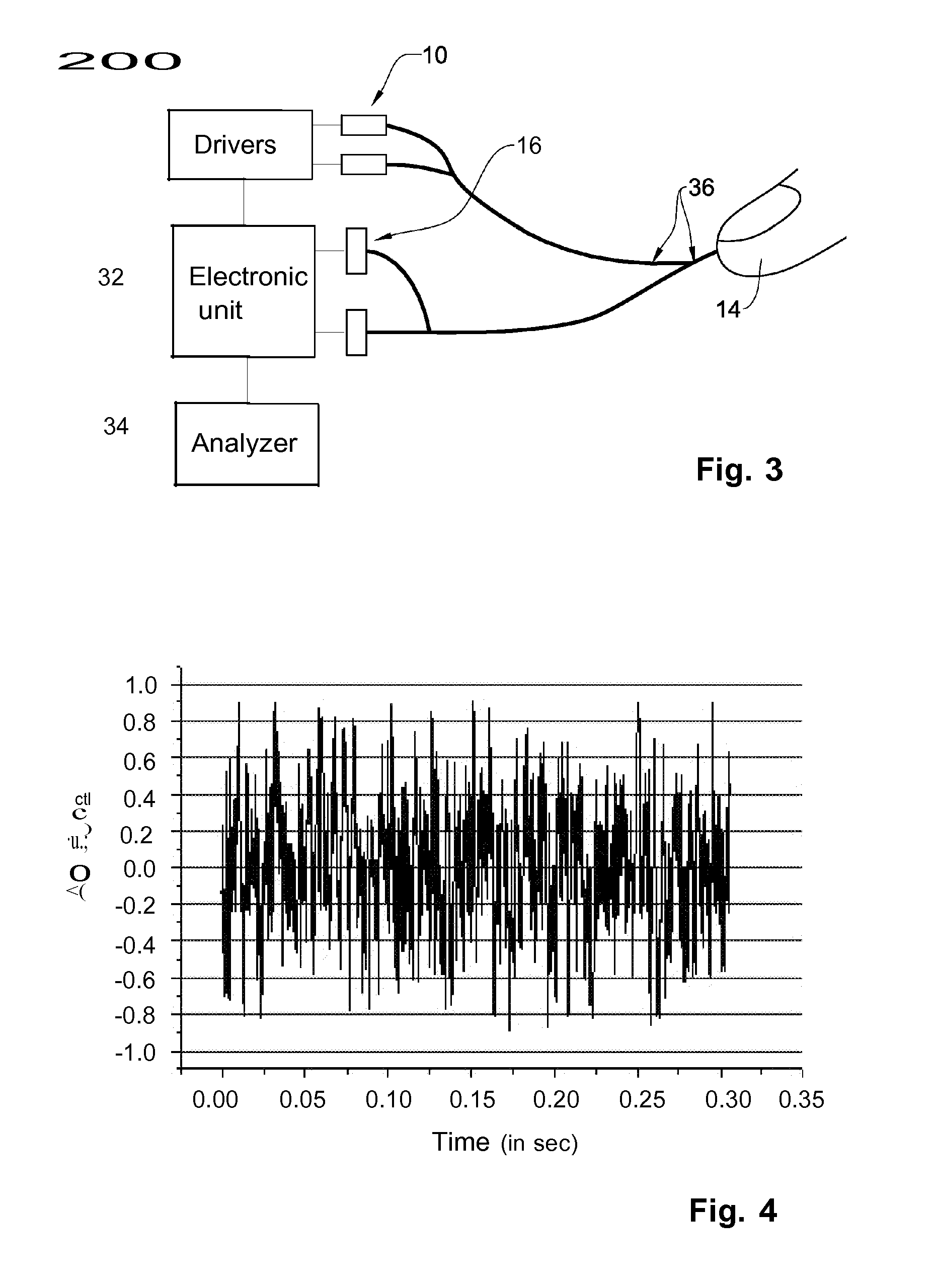
ActiveUS20090209834A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce decreaseCatheterSensorsControl systemDynamic light scattering
A system, method and medical tool are presented for use in non-invasive in vivo determination of at least one desired parameter or condition of a subject having a scattering medium in a target region. The measurement system comprises an illuminating system, a detection system, and a control system. The illumination system comprises at least one light source configured for generating partially or entirely coherent light to be applied to the target region to cause a light response signal from the illuminated region. The detection system comprises at least one light detection unit configured for detecting time-dependent fluctuations of the intensity of the light response and generating data indicative of a dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurement. The control system is configured and operable to receive and analyze the data indicative of the DLS measurement to determine the at least one desired parameter or condition, and generate output data indicative thereof.
Owner:ELFI TECH
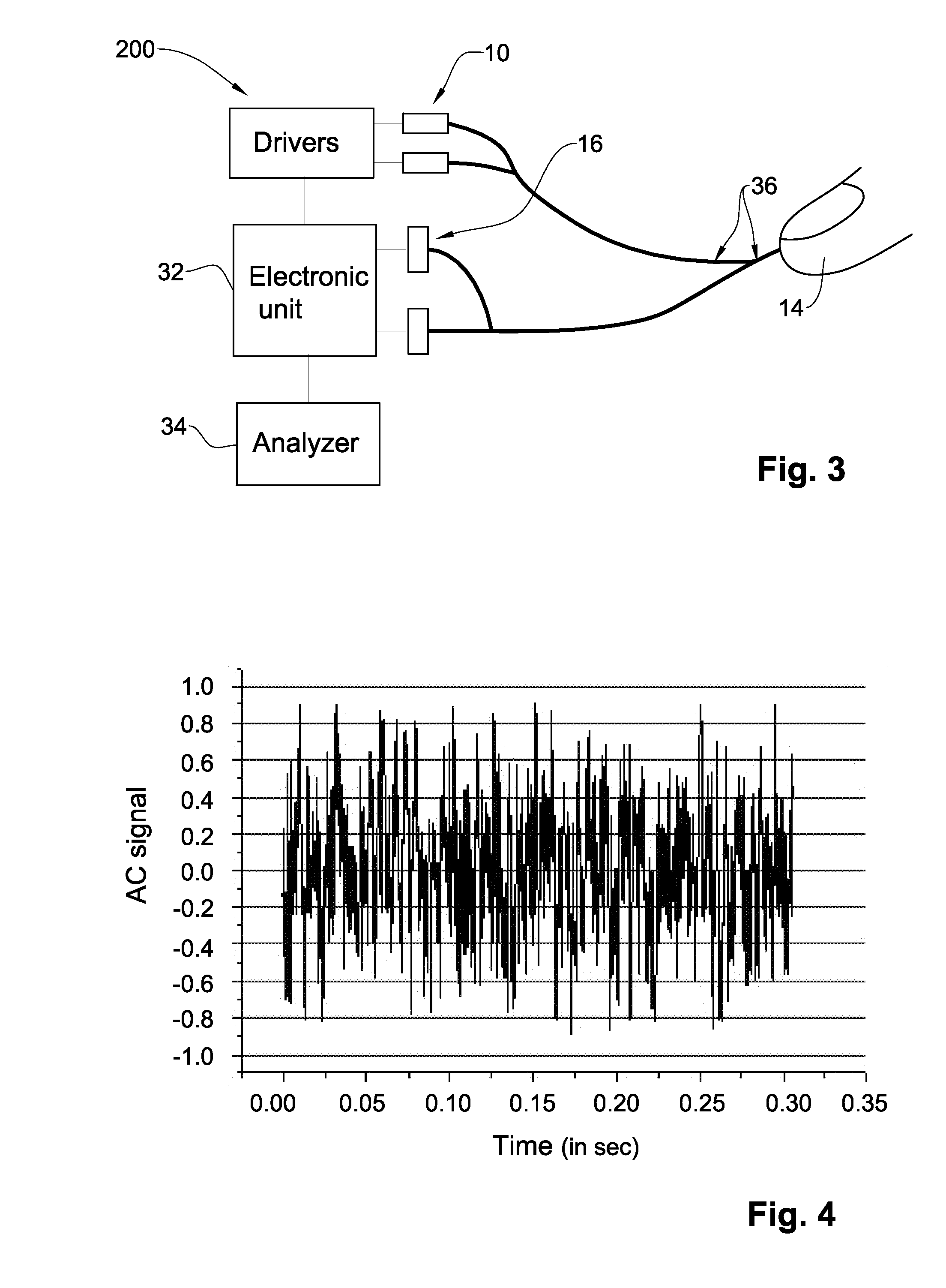
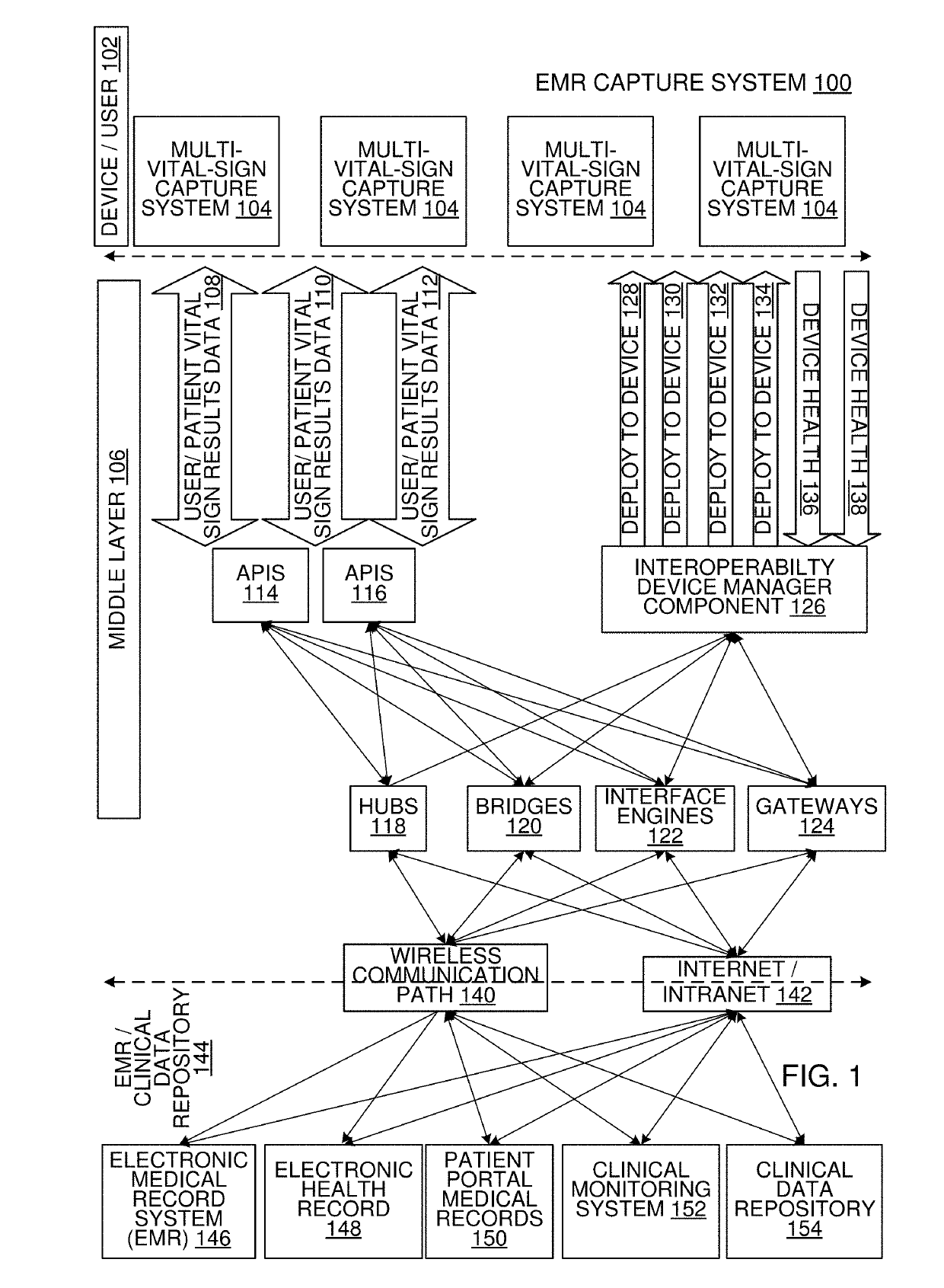
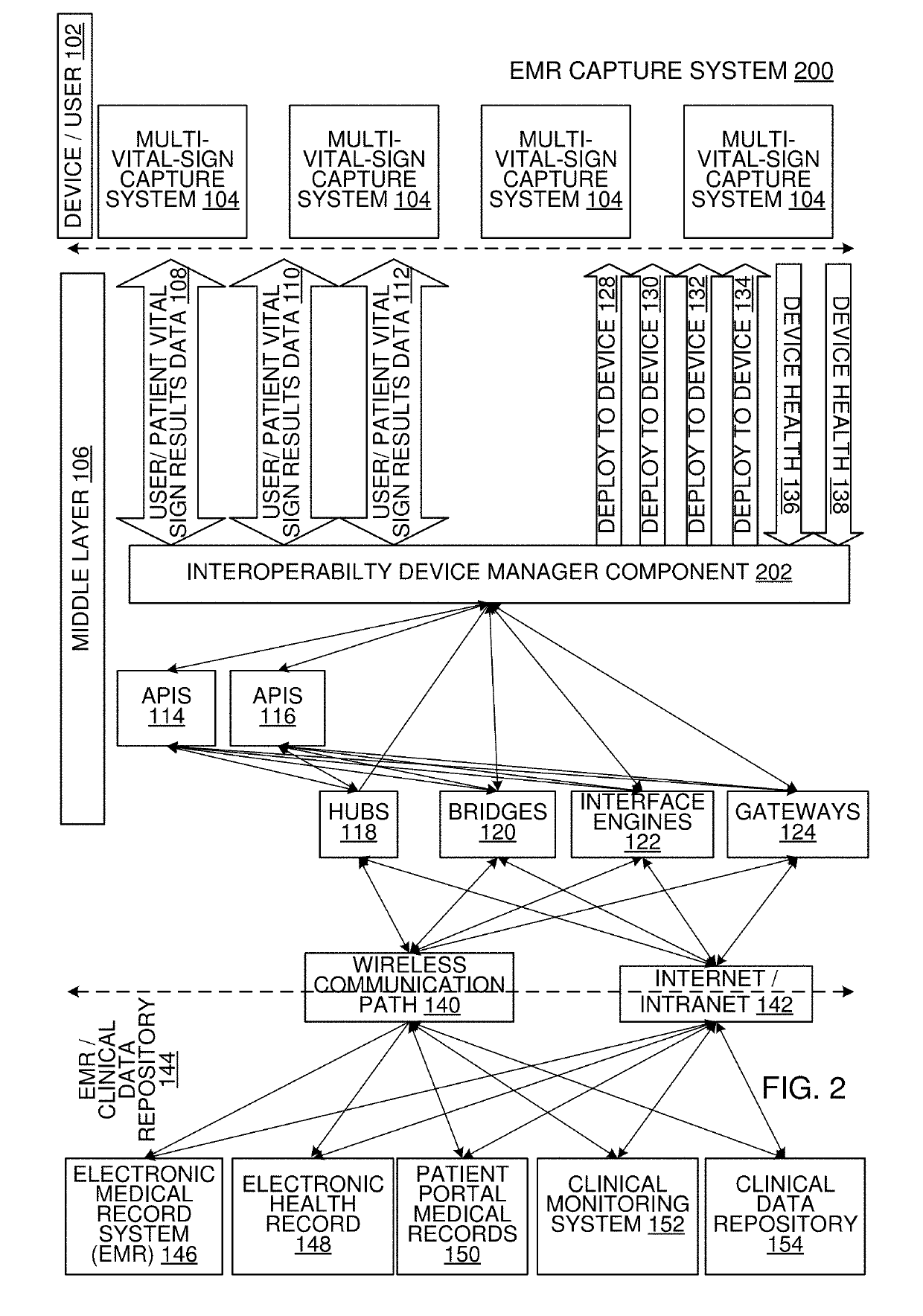
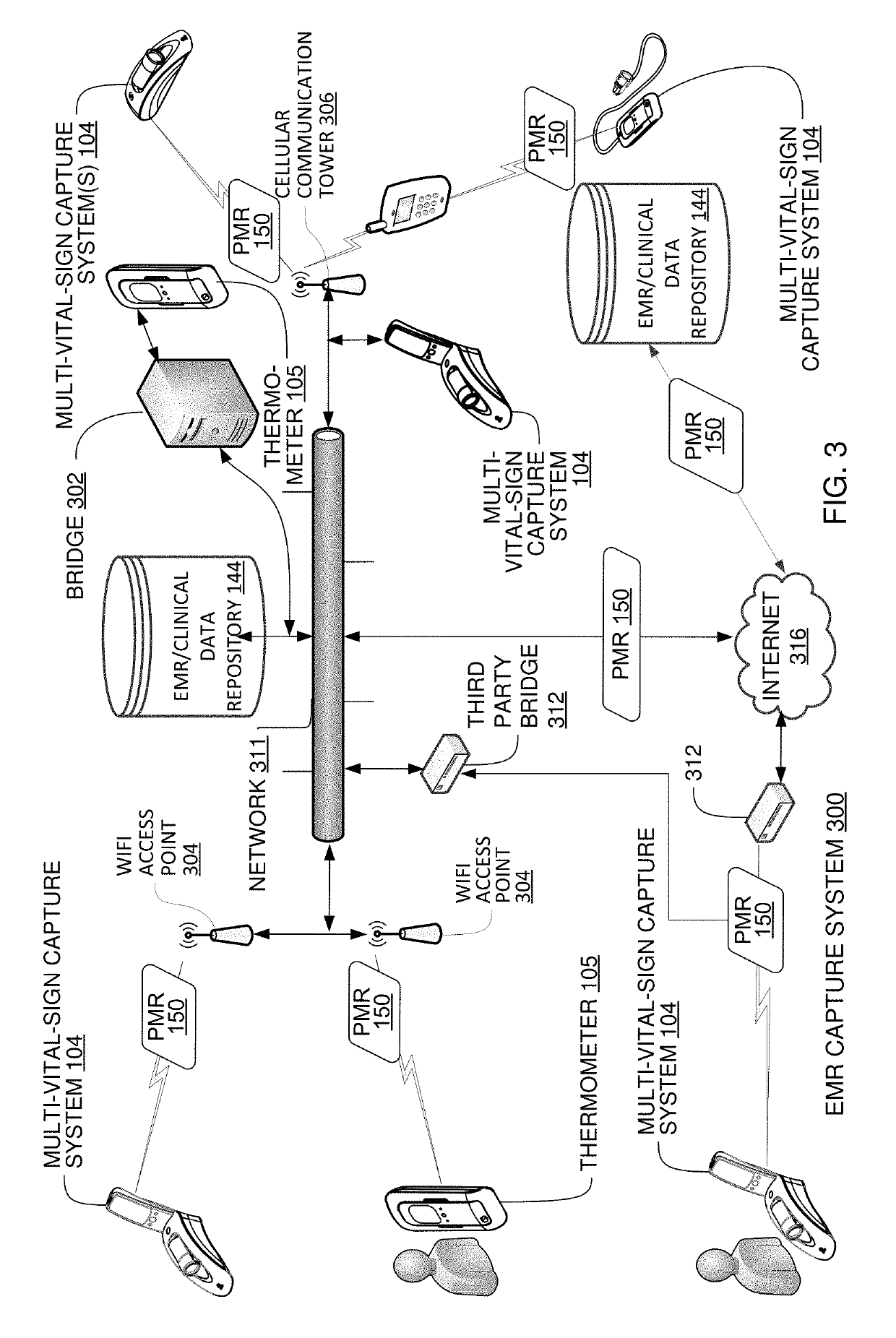
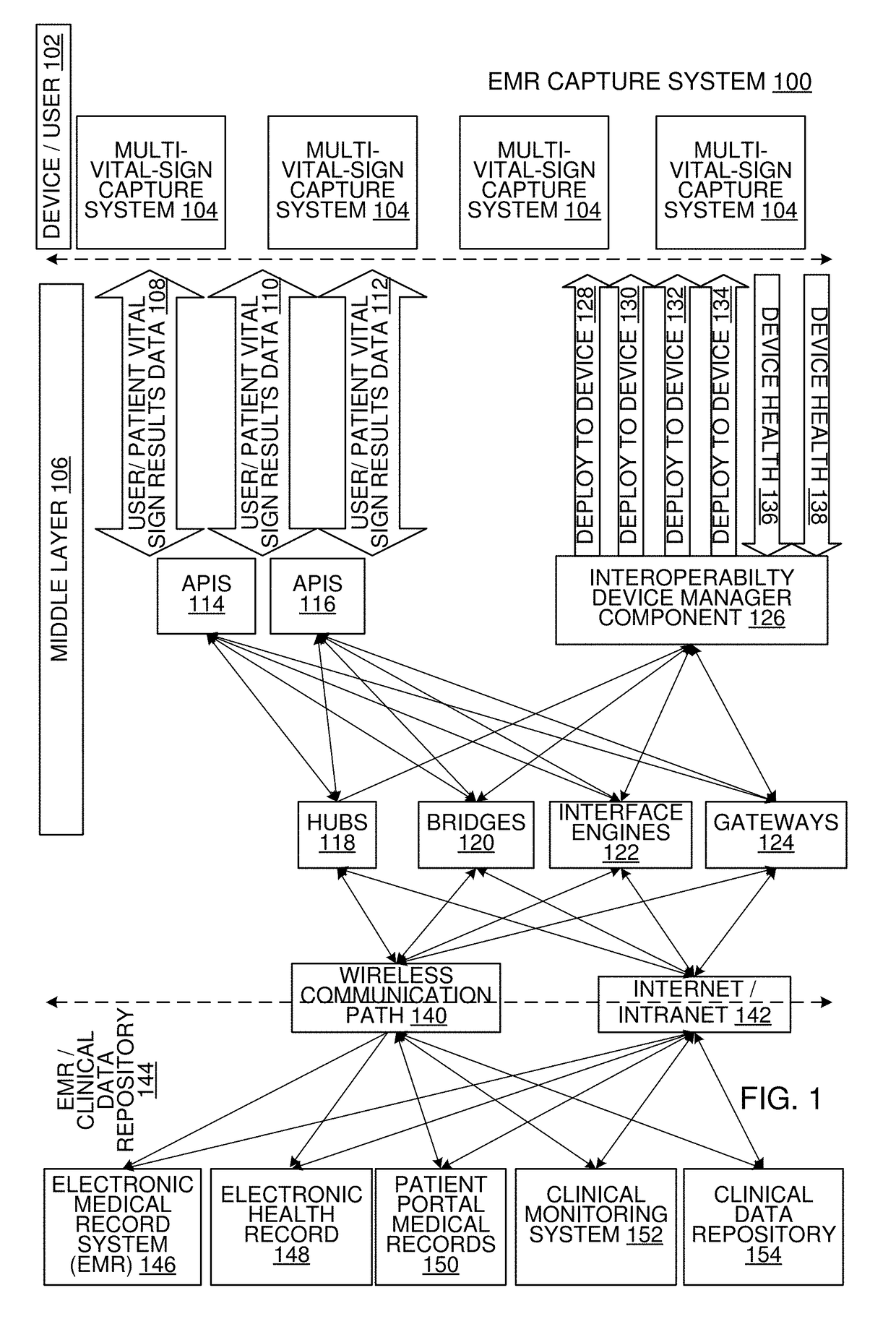
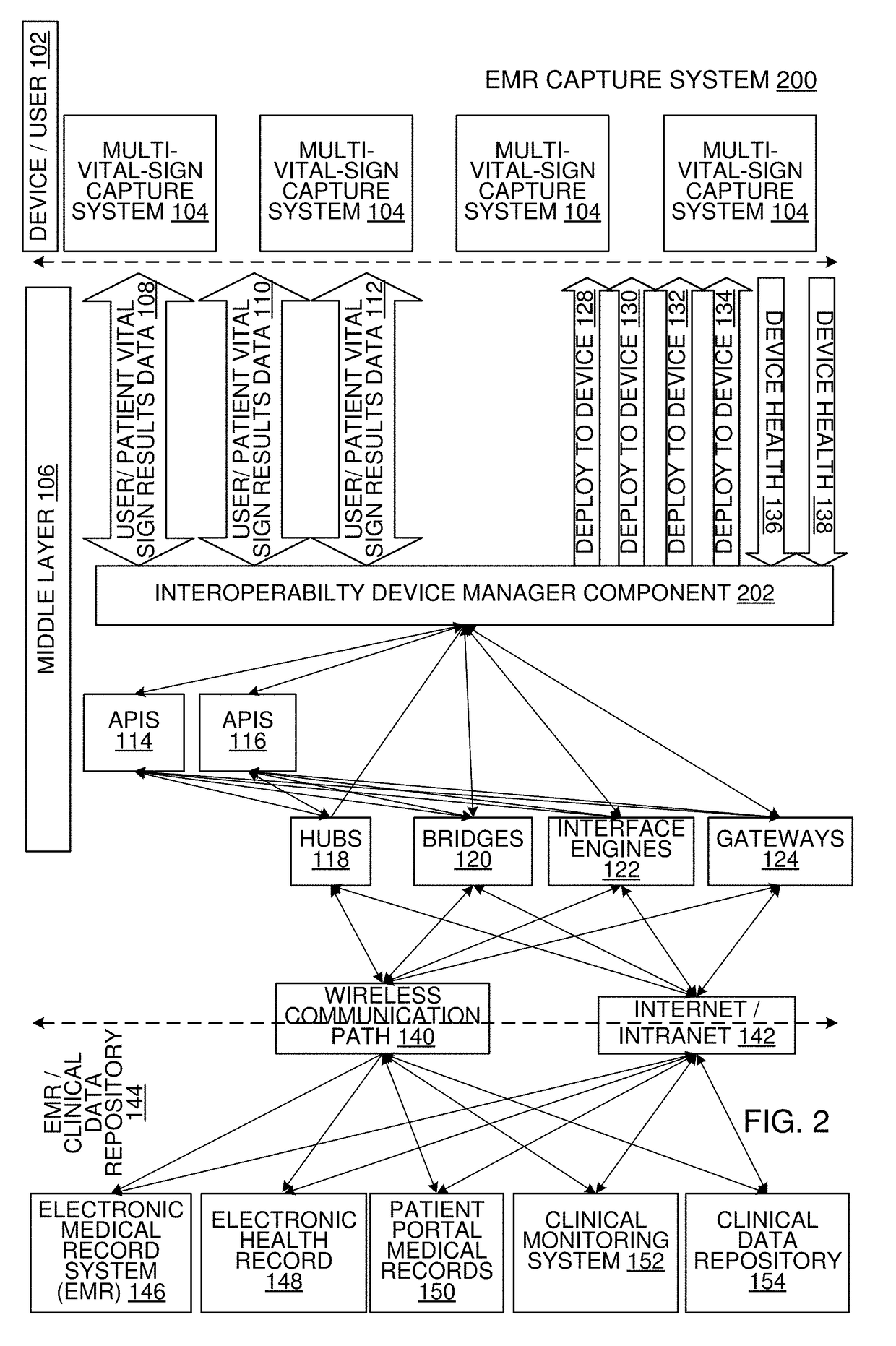
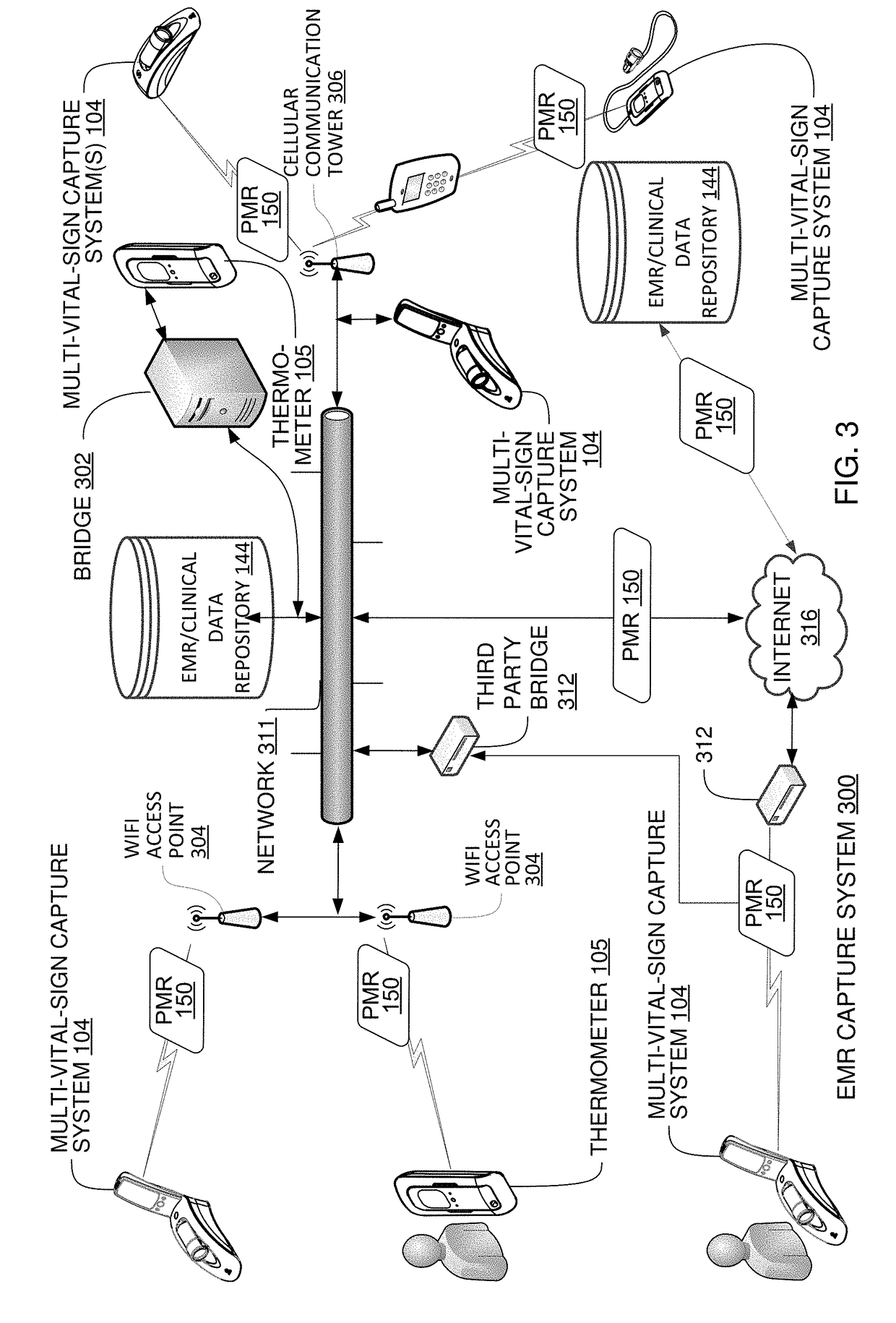
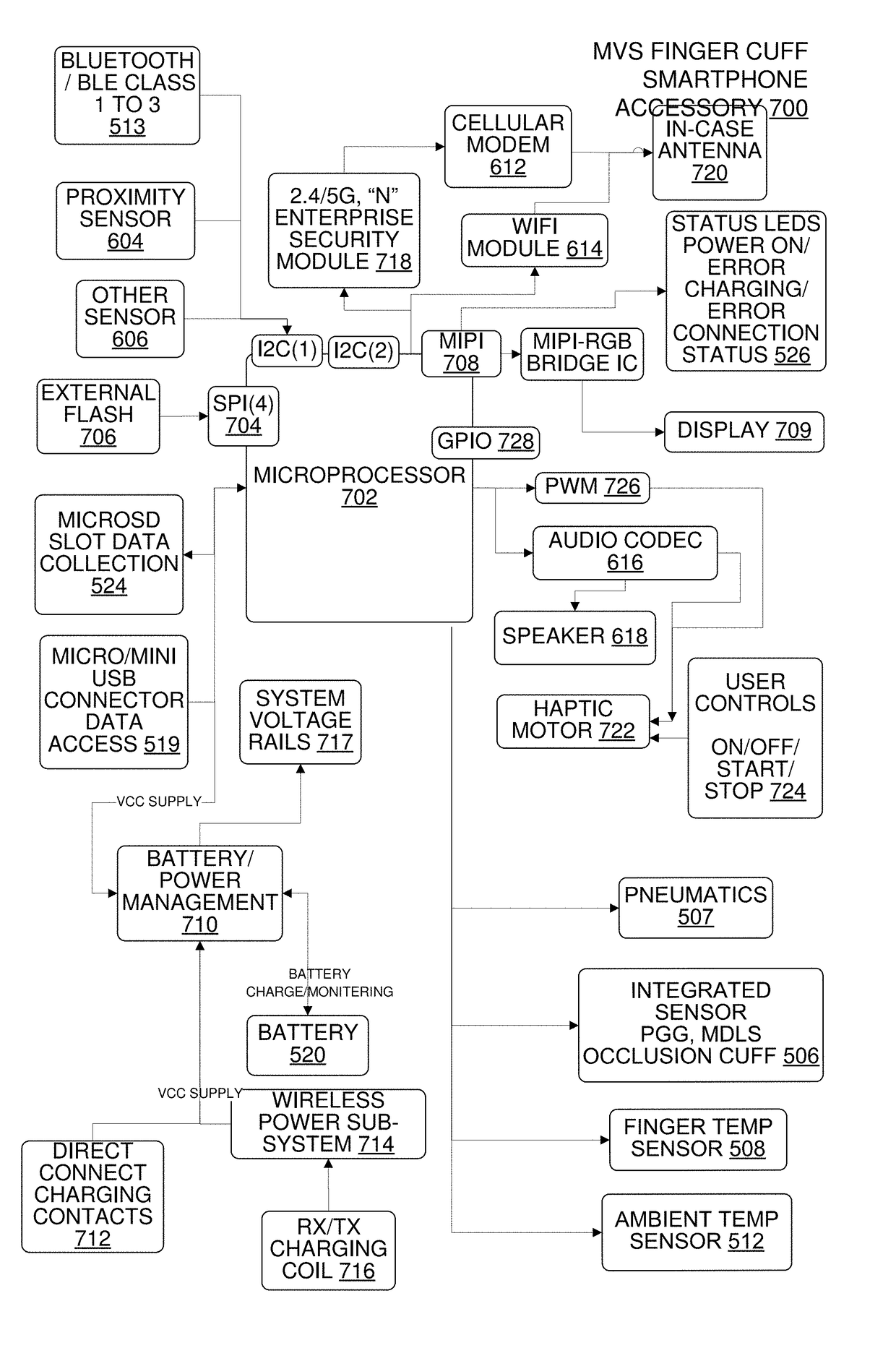
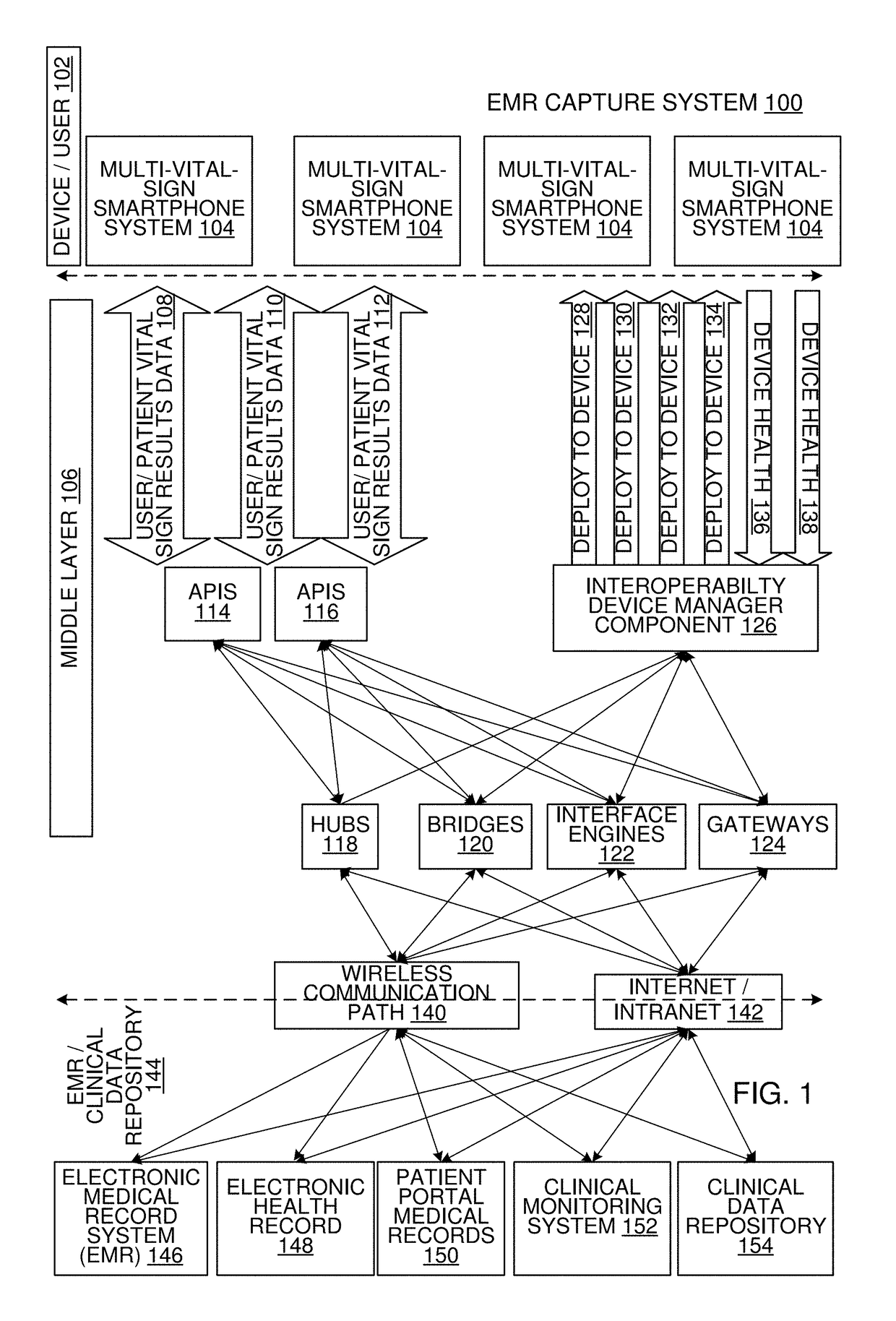
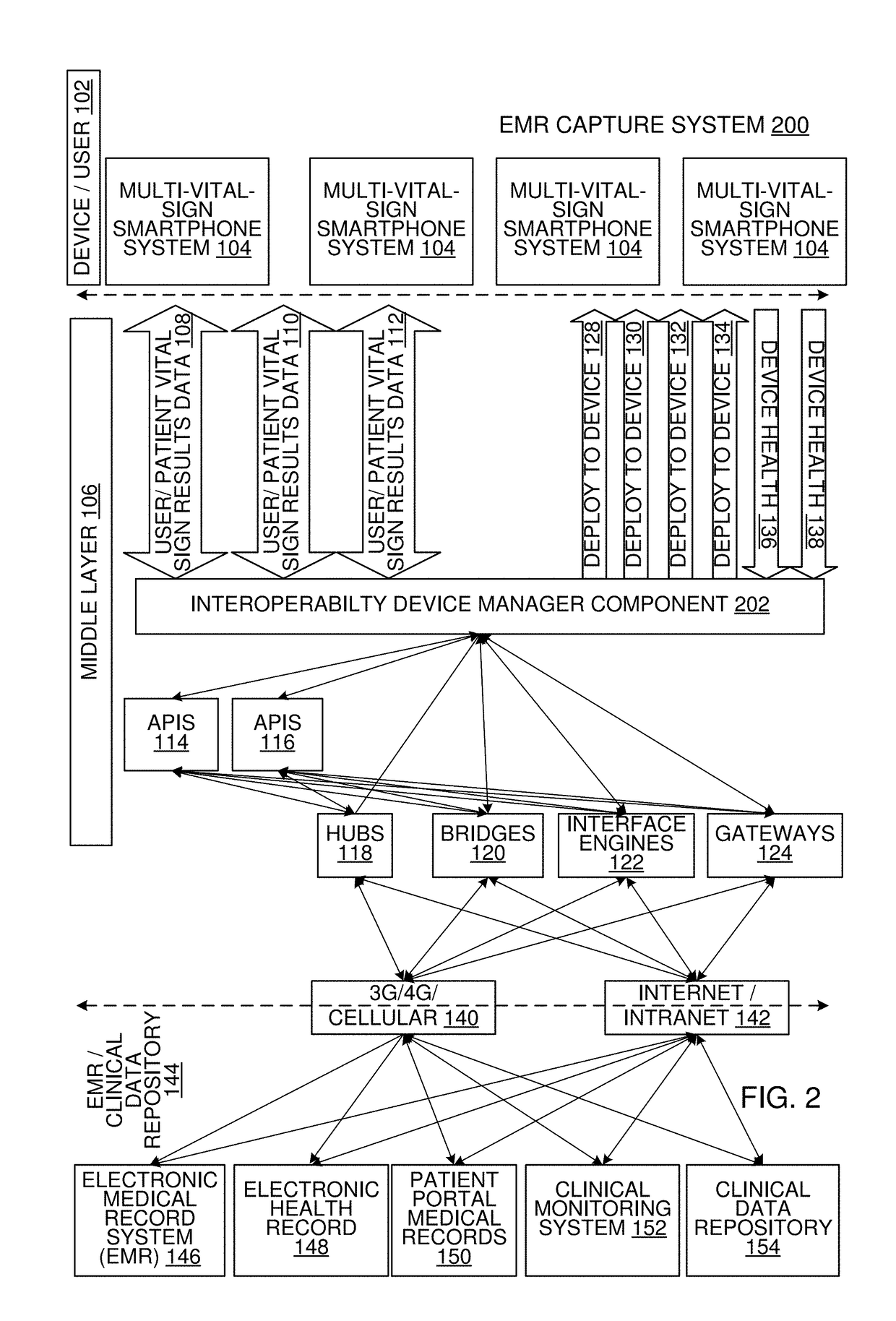
Multi-Vital Sign Detector in an Electronic Medical Records System
ActiveUS20190313907A1Evaluation of blood vesselsMedical automated diagnosisMedical recordDynamic light scattering
In one implementation, a device detects multiple vital signs from sensors such as a digital infrared sensor, a photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor and at least one micro dynamic light scattering (mDLS) sensor, and thereafter in some implementations the vital signs are transmitted to, and stored by, an electronic medical record system.
Owner:ARC DEVICES +1
Multi-Vital Sign Detector in an Electronic Medical Records System
In one implementation, a device detects multiple vital signs from sensors such as a digital infrared sensor, a photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor and at least one micro dynamic light scattering (mDLS) sensor, and thereafter in some implementations the vital signs are transmitted to, and stored by, an electronic medical record system.
Owner:VVV HLDG LTD +1
Photoplethysmography device and method
InactiveUS20110082355A1Accurate descriptionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAnalytePulse parameter
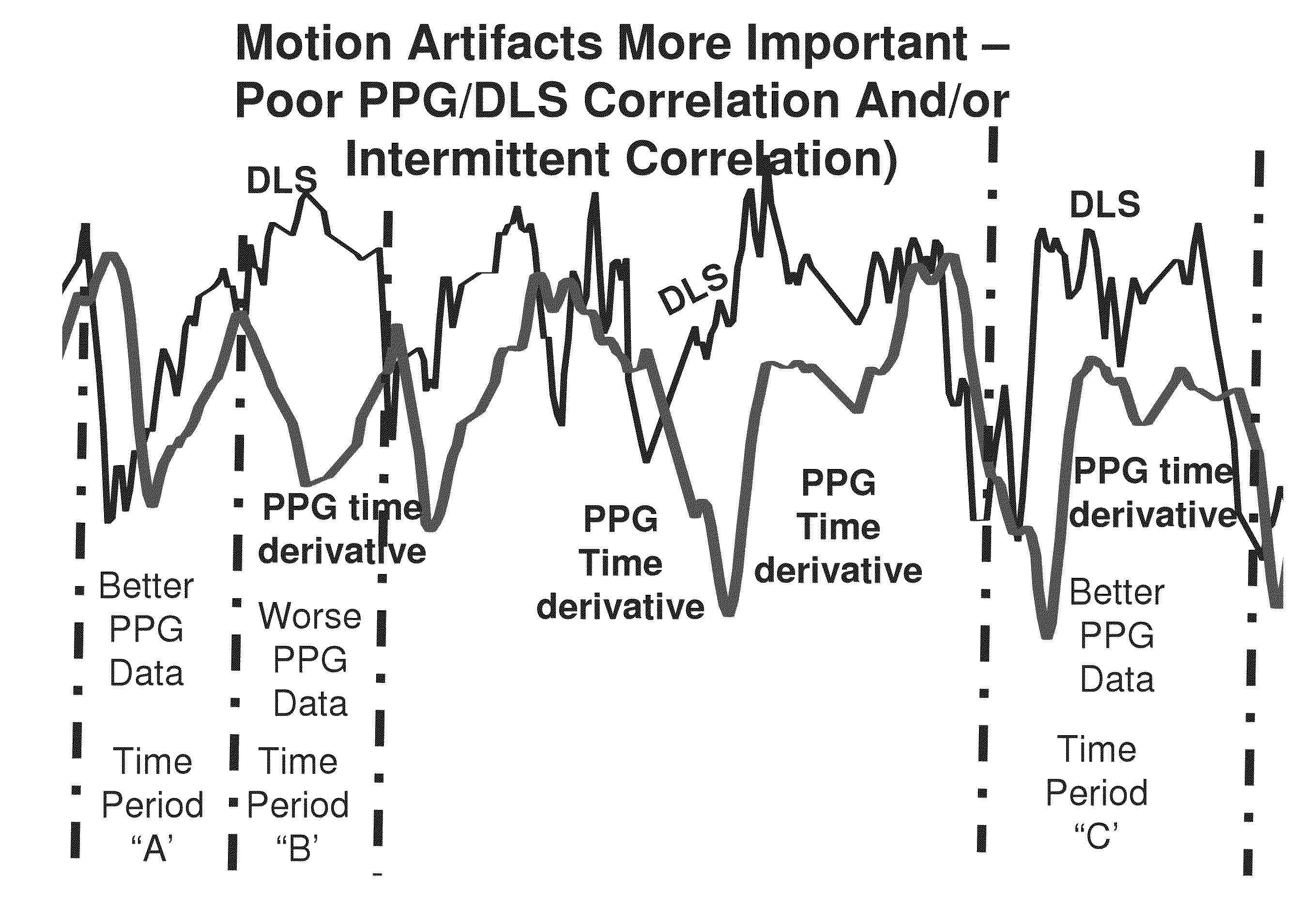
A system and method for measuring one or more light-absorption related blood analyte concentration parameters of a mammalian subject, is disclosed. In some embodiments, the system comprises: a) a photoplethysmography (PPG) device configured to effect a PPG measurement by illuminating skin of the subject with at least two distinct wavelengths of light and determining relative absorbance at each of the wavelengths; b) a dynamic light scattering measurement (DLS) device configured to effect a DLS measurement of the subject to rheologically measure a pulse parameter of the subject; and c) electronic circuitry configured to: i) temporally correlating the results of the PPG and DLS measurements; and ii) accordance with the temporal correlation between the PPG and DLS measurements, assessing value(s) of the one or more light-absorption related blood analyte concentration parameter(s).
Owner:OXITONE MEDICAL
Inorganic porous fine particles
InactiveUS20050020699A1Material nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentDynamic light scatteringPore diameter
An object of the present invention is to provide a sol of an inorganic porous substance having a small particle diameter and a uniform pore diameter, and a synthetic method thereof, and uses using the same, in particular, an ink-jet recording medium excellent in ink absorbing property, transparency, water resistance and light resistance, and a coating liquid for an ink-jet recording medium. The invention relates to a sol containing an inorganic porous substance, the inorganic porous substance having an average particle diameter, measured by the dynamic light scattering method, of 10 nm to 400 nm, an average aspect ratio of its primary particles of 2 or more and meso-pores extending in the longitudinal direction, and suffering from substantially no secondary aggregation.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
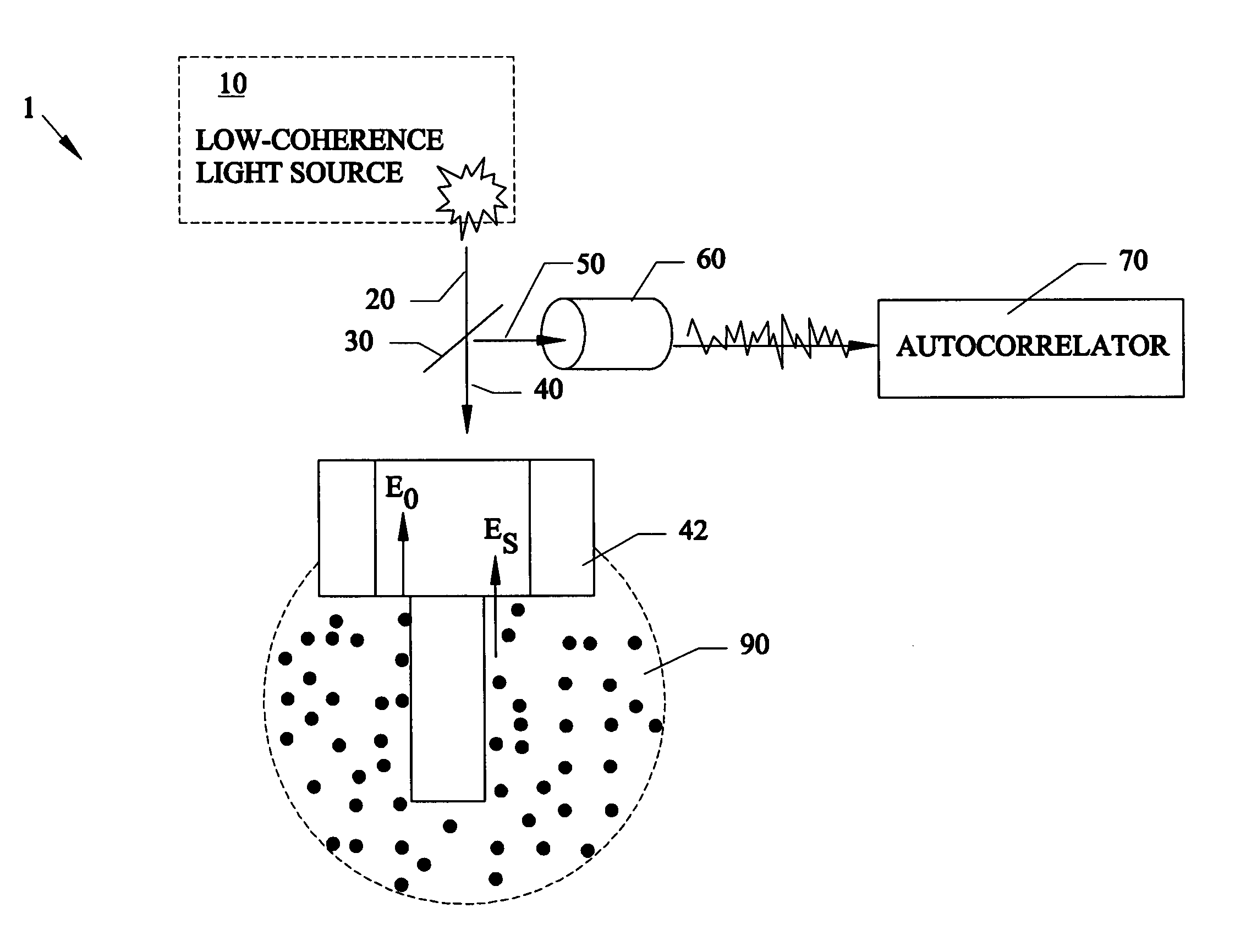
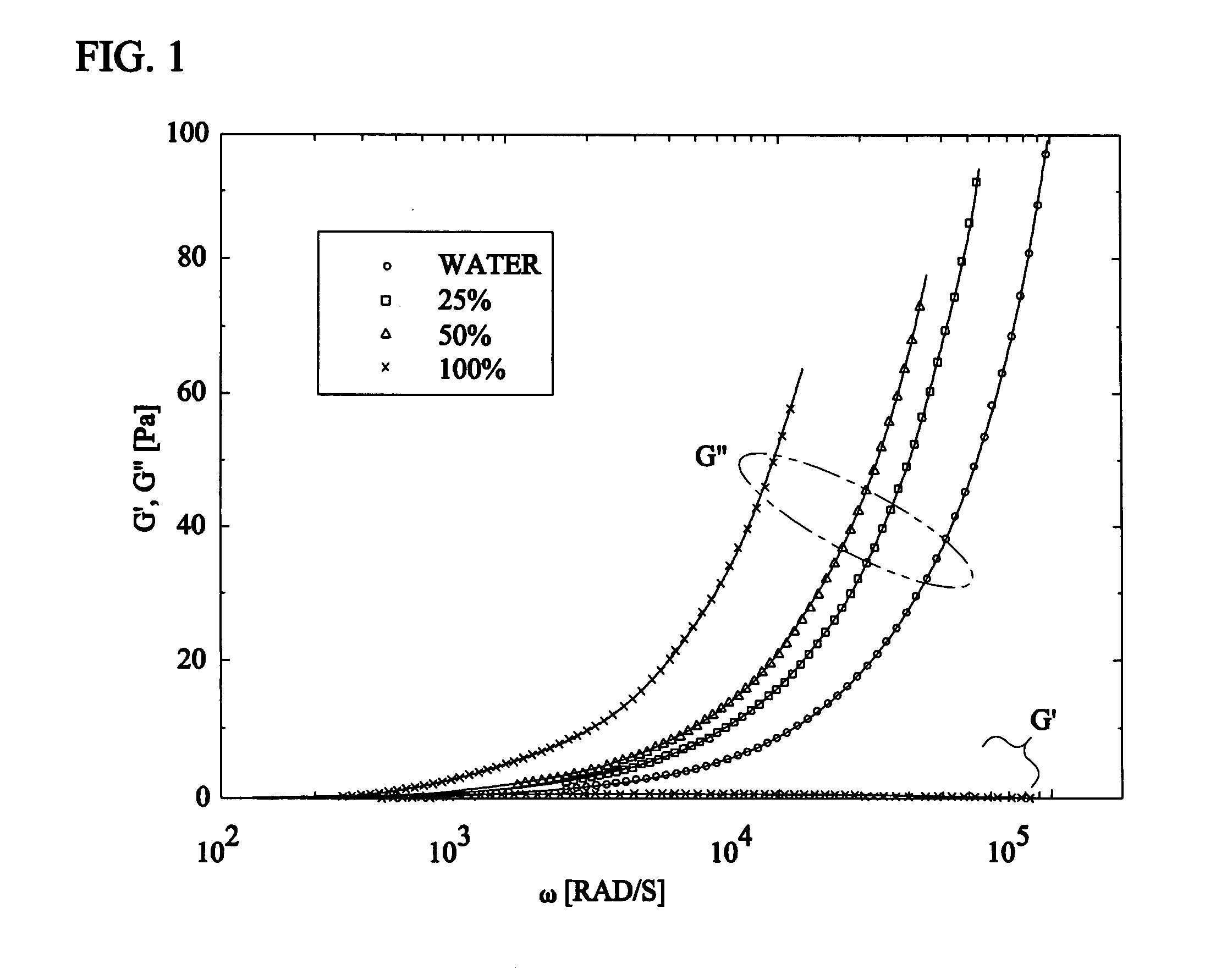
Microrheology methods and systems using low-coherence dynamic light scattering
ActiveUS6958816B1High degree of experimental flexibilityHigh degree of applicabilityScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansFiberDynamic light scattering
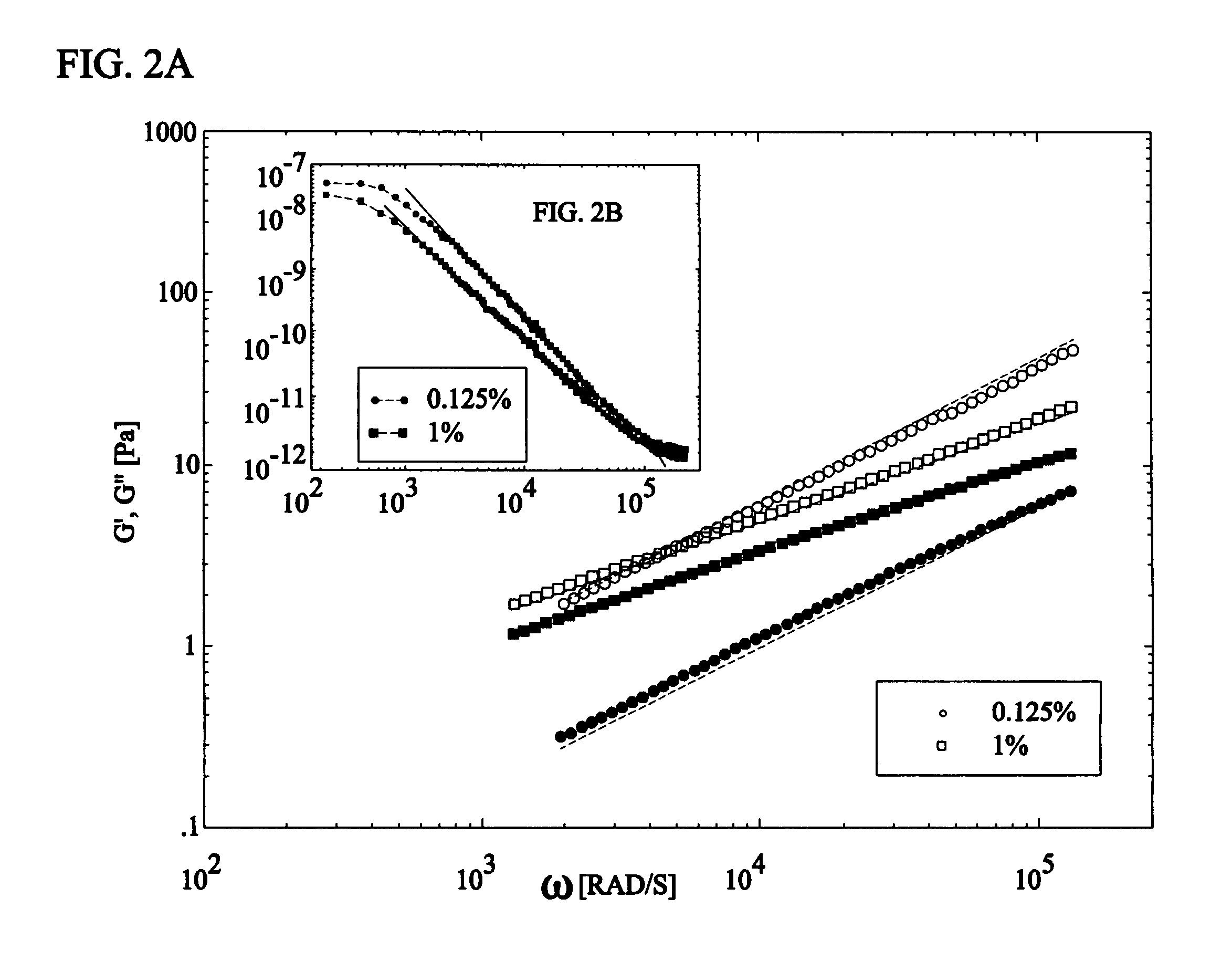
Methods and systems for using dynamic light scattering, for investigating local rheological responses of complex fluids over a frequency range larger than that provided by standard instrumentation. A low-coherence radiation source is used with fiber optics to allow measurements of small volume spacing of up to approximately 1 / 10 of a picoliter. The methods and systems are based on dynamic light scattering, for investigating the local rheological response of a complex fluid over a frequency range larger than that provided by standard mechanical instrumentation. The low-coherence radiation used in a fiber optics configuration allows the measurements to be confined to a small volume around a tenth of a picoliter. The ability of the method to accurately measure both loss and storage moduli has been tested using both simple Newtonian liquids and viscoelastic, complex fluids. Monitoring liquid-gel transitions in polymer solutions has also been demonstrated. The unique capability of the technique to localize the measurement volume can be used for three-dimensional mapping of rheological properties in heterogeneous systems. Other embodiments can use open-air setups instead of optical fibers to transmit and receive the low coherence light.
Owner:CENT FLORIDA UNIV OF +2
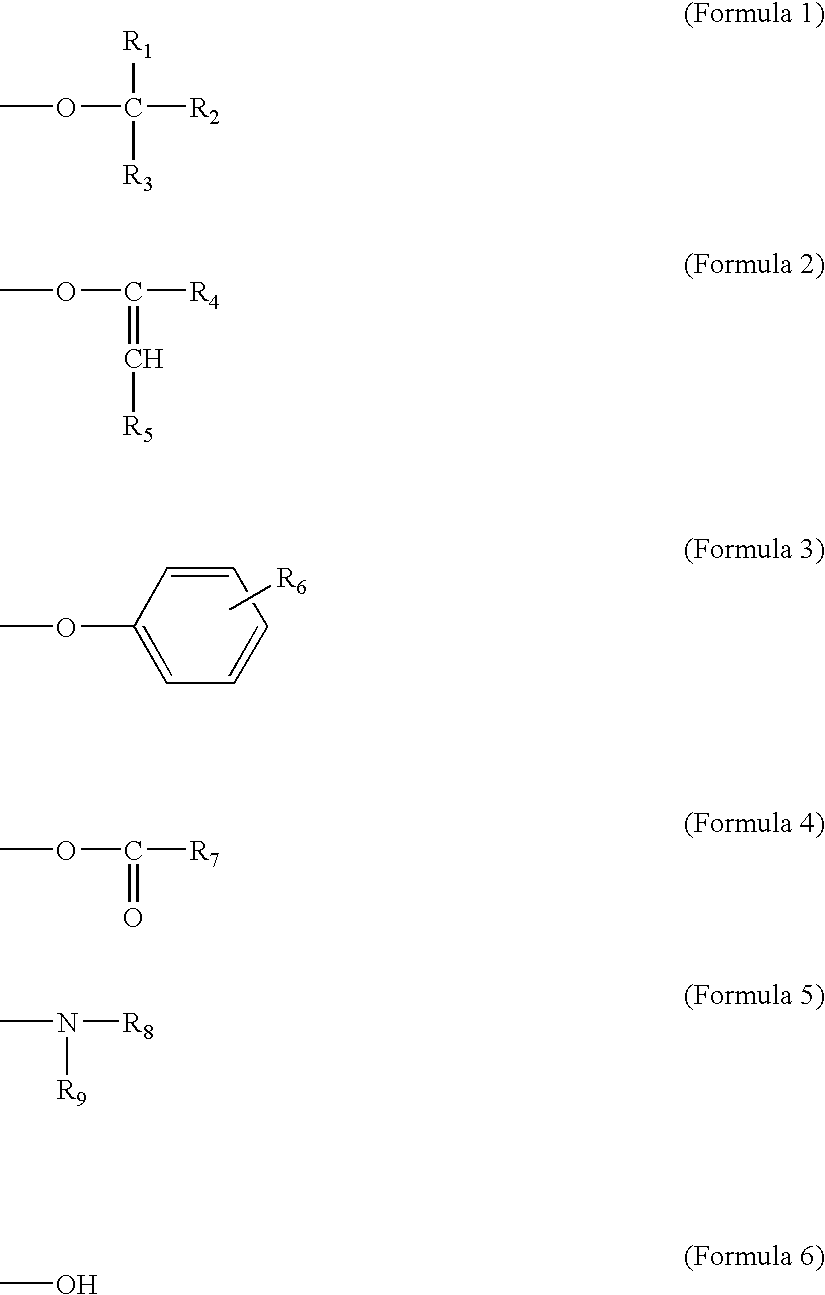
Binder Resin for Nonaqueous Secondary Battery Electrode, Binder Resin Composition for Nonaqueous Secondary Battery Electrode Slurry Composition for Nonaqueous Secondary Battery Electrode, Electrode for Nonaqueous Secondary Battery, and Nonaqueous Secondary Battery
InactiveUS20140287308A1Good flexibilityImprove bindingNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsElectrode collector coatingPolymer scienceDynamic light scattering
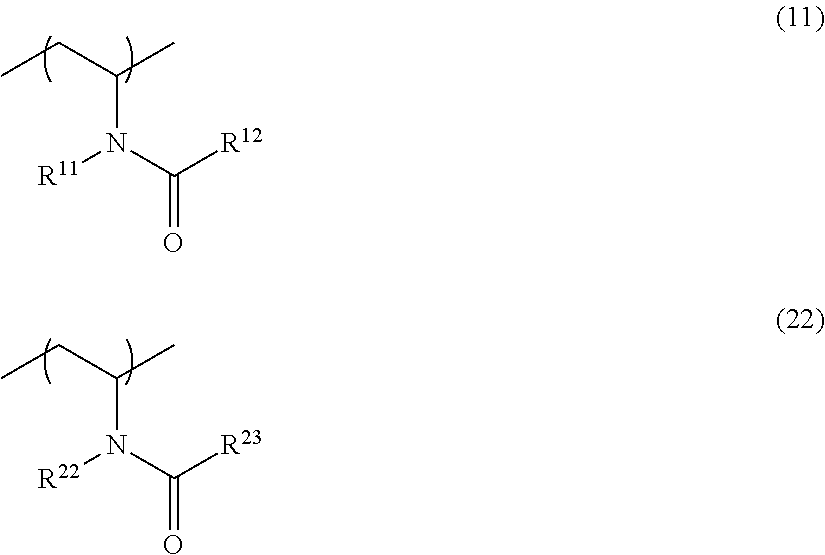
A binder resin for a nonaqueous secondary battery electrode of the invention satisfies Is≧30 (Is indicates a sum of scattering intensities observed in a particle size range of from 1 to 100 nm) when a solution is formed by dissolving the binder resin in water at a concentration of 5% by mass and particle size distribution is measured by a dynamic light scattering method at 25° C. The binder resin contains a polymer (B) having a structural unit represented by the following Formula (11) and a specific structural unit. The binder resin also contains a polymer (α) having a specific structural unit and a structural unit represented by the following Formula (22), and / or a mixture of a polymer (β1) having a specific structural unit and a polymer (β2) having a structural unit represented by the following Formula (22).
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Silicon inks for thin film solar cell formation, corresponding methods and solar cell structures
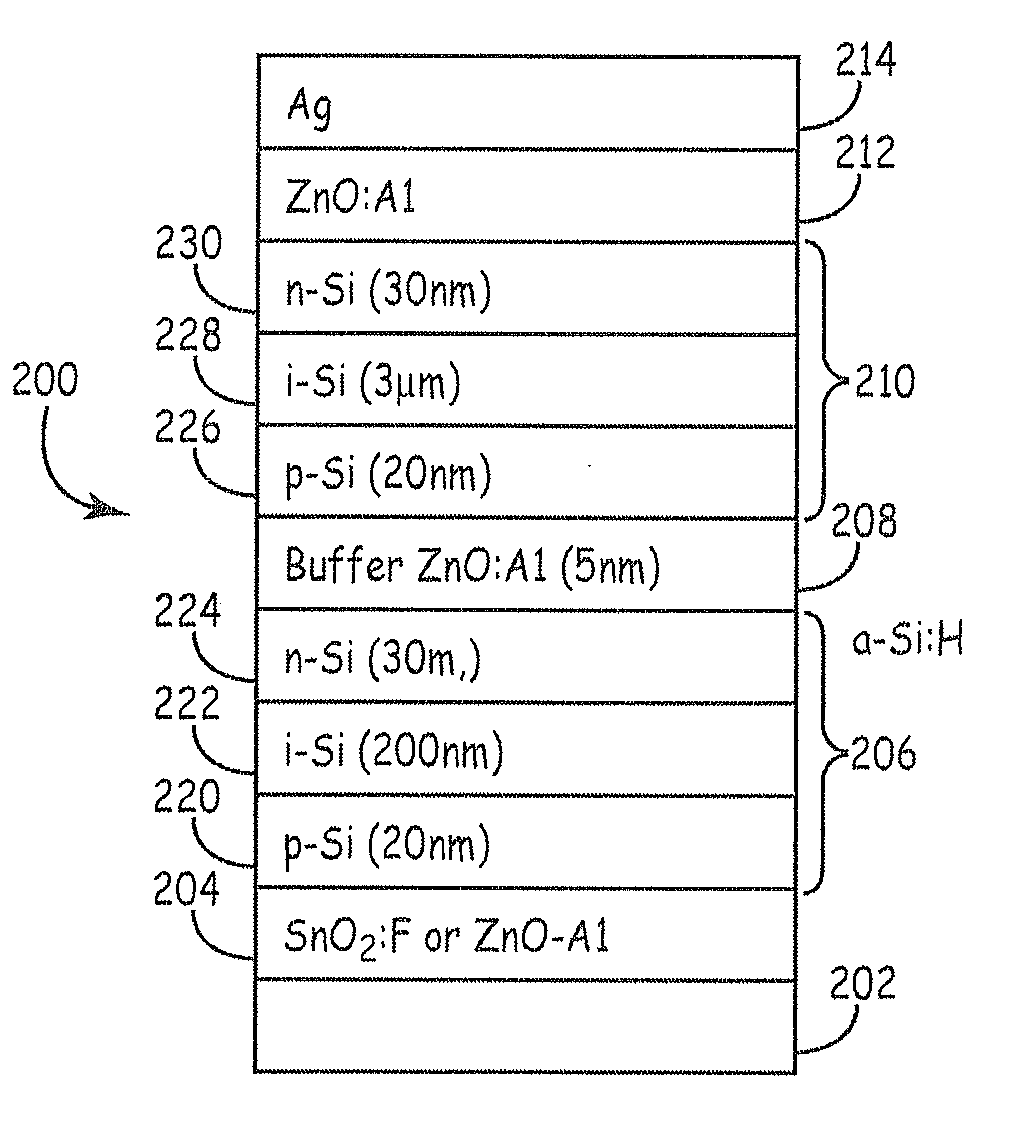
High quality silicon inks are used to form polycrystalline layers within thin film solar cells having a p-n junction. The particles deposited with the inks can be sintered to form the silicon film, which can be intrinsic films or doped films. The silicon inks can have a z-average secondary particle size of no more than about 250 nm as determined by dynamic light scattering on an ink sample diluted to 0.4 weight percent if initially having a greater concentration. In some embodiments, an intrinsic layer can be a composite of an amorphous silicon portion and a crystalline silicon portion.
Owner:NANOGRAM
Simultaneous detection apparatus of raman and light scattering
ActiveUS20100020312A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDynamic light scatteringProtein antigen
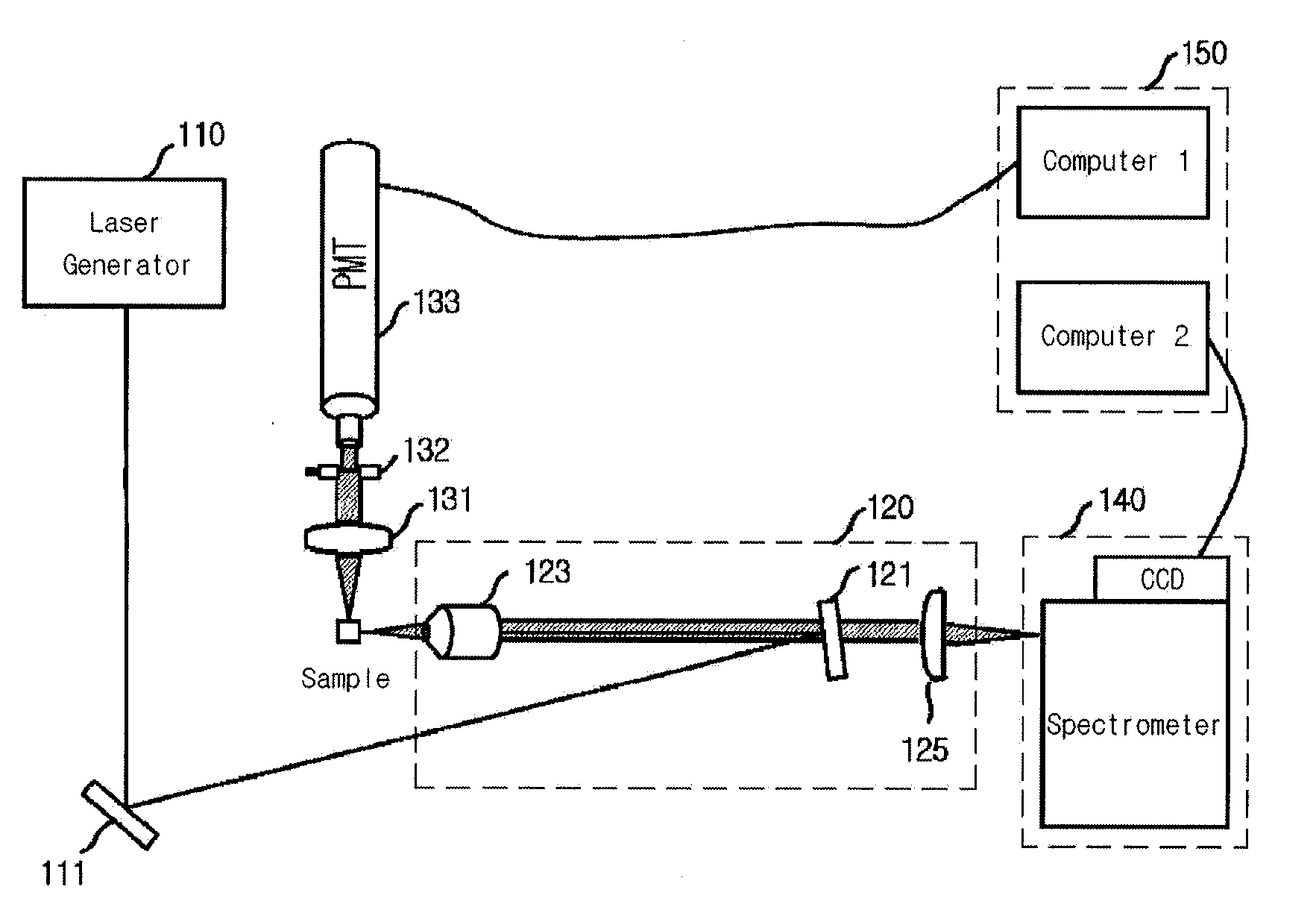
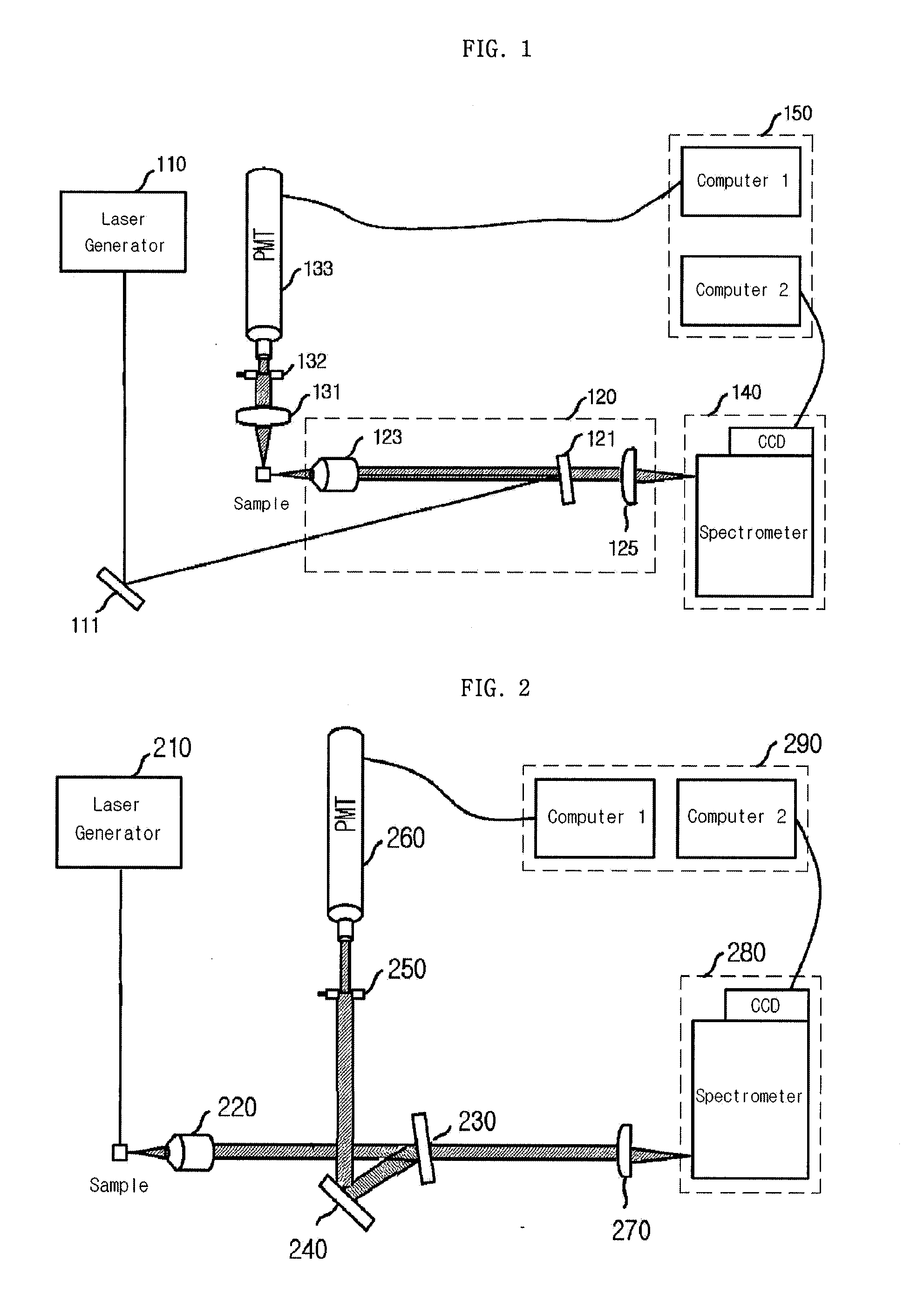
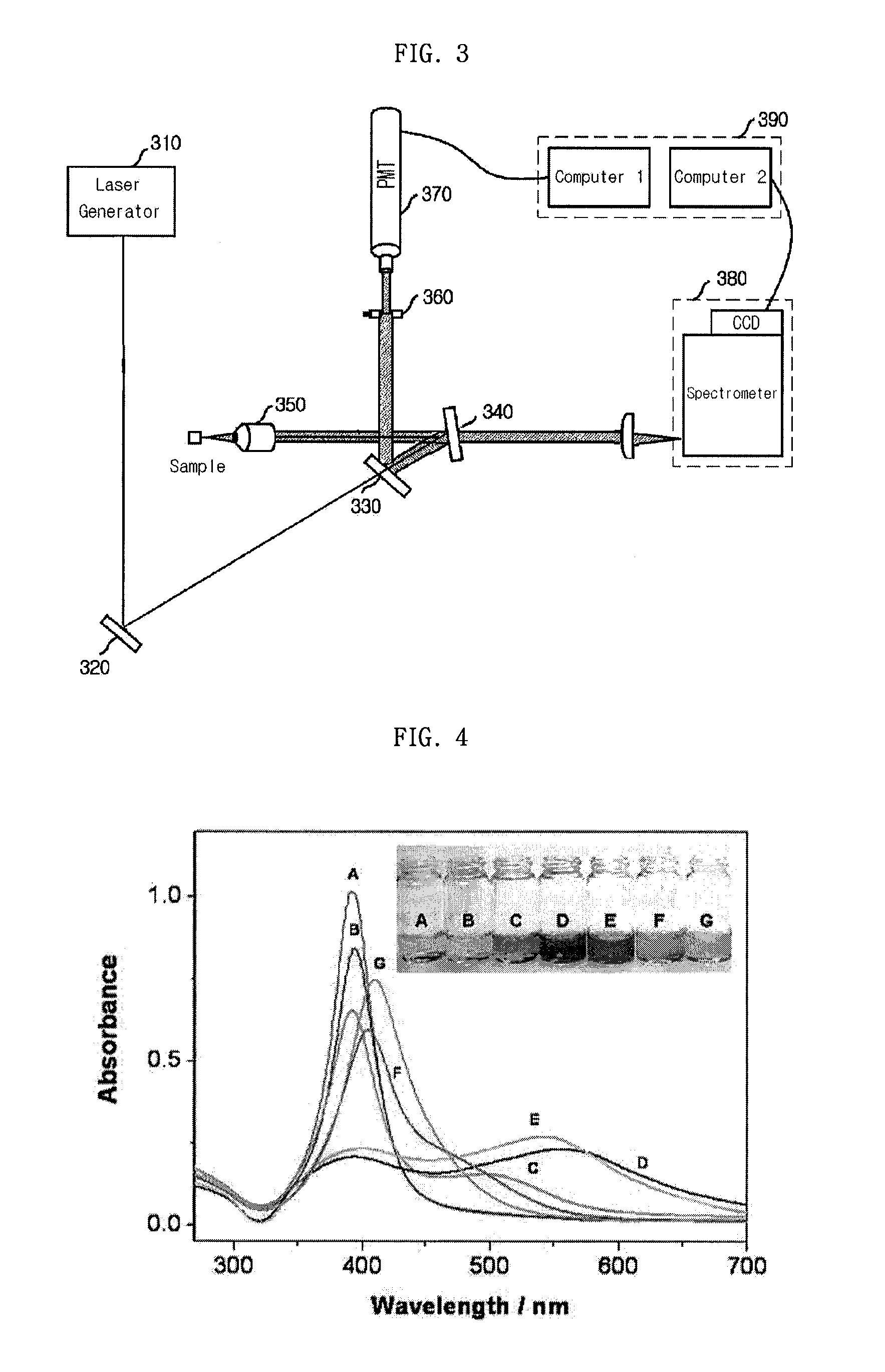
Provided is a detection apparatus of Raman scattering and light scattering, and more particularly, a simultaneous detection apparatus of Raman scattering and dynamic light scattering and a detection method using the same. The simultaneous detection apparatus of Raman scattering and light scattering includes: a detection unit for applying incident light to a sample, and detecting Raman scattering in 90° or 180° geometry and light scattering in 90° or 180° geometry in order to simultaneously collect Raman scattering and light scattering; and a computer connected to the detection unit to obtain at least one of the size and distribution of particles from the detected light scattering, and to obtain information of the molecular structure from the detected Raman scattering. This apparatus may simultaneously observe the size of nano-sized or larger material and molecular information thereof, and phenomena accompanying changes in molecular environment according to material variation and changes of the material in size and distribution, and thus is very useful for studying nano materials and protein antigens and antibodies.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Dynamic and depolarized dynamic light scattering colloid analyzer
ActiveUS20120044493A1Improve accuracyIncrease rangeScattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisDynamic light scatteringLight beam
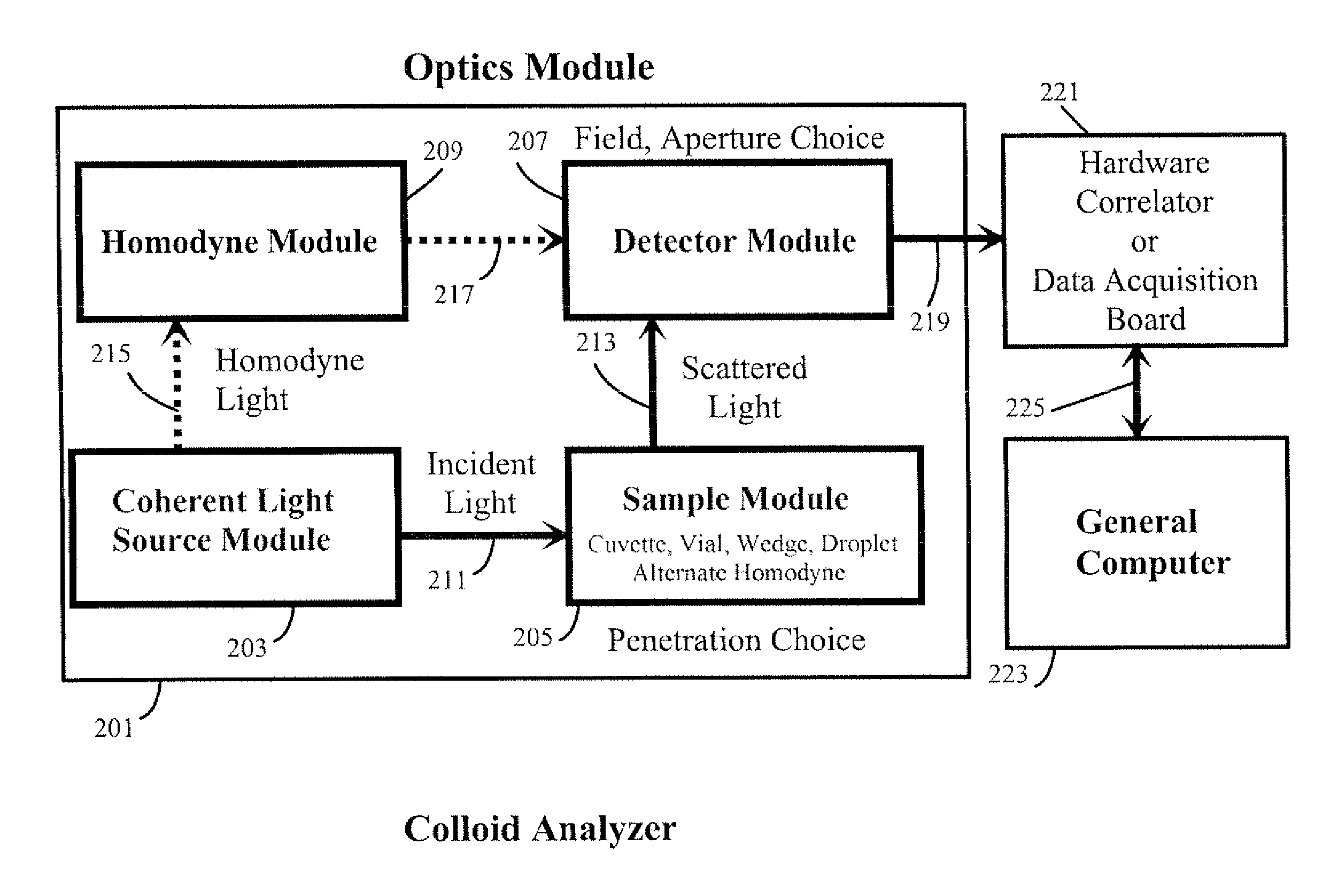
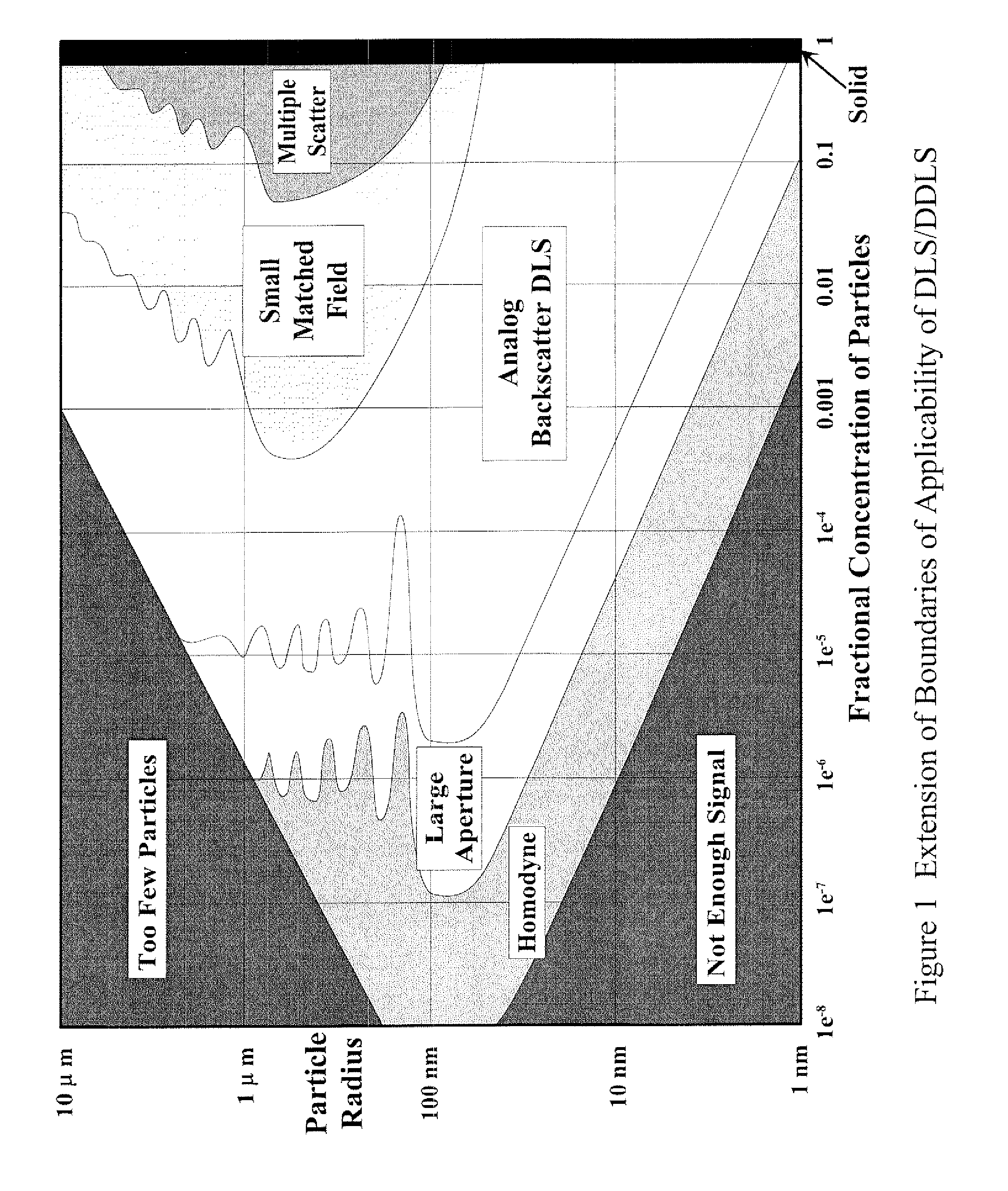
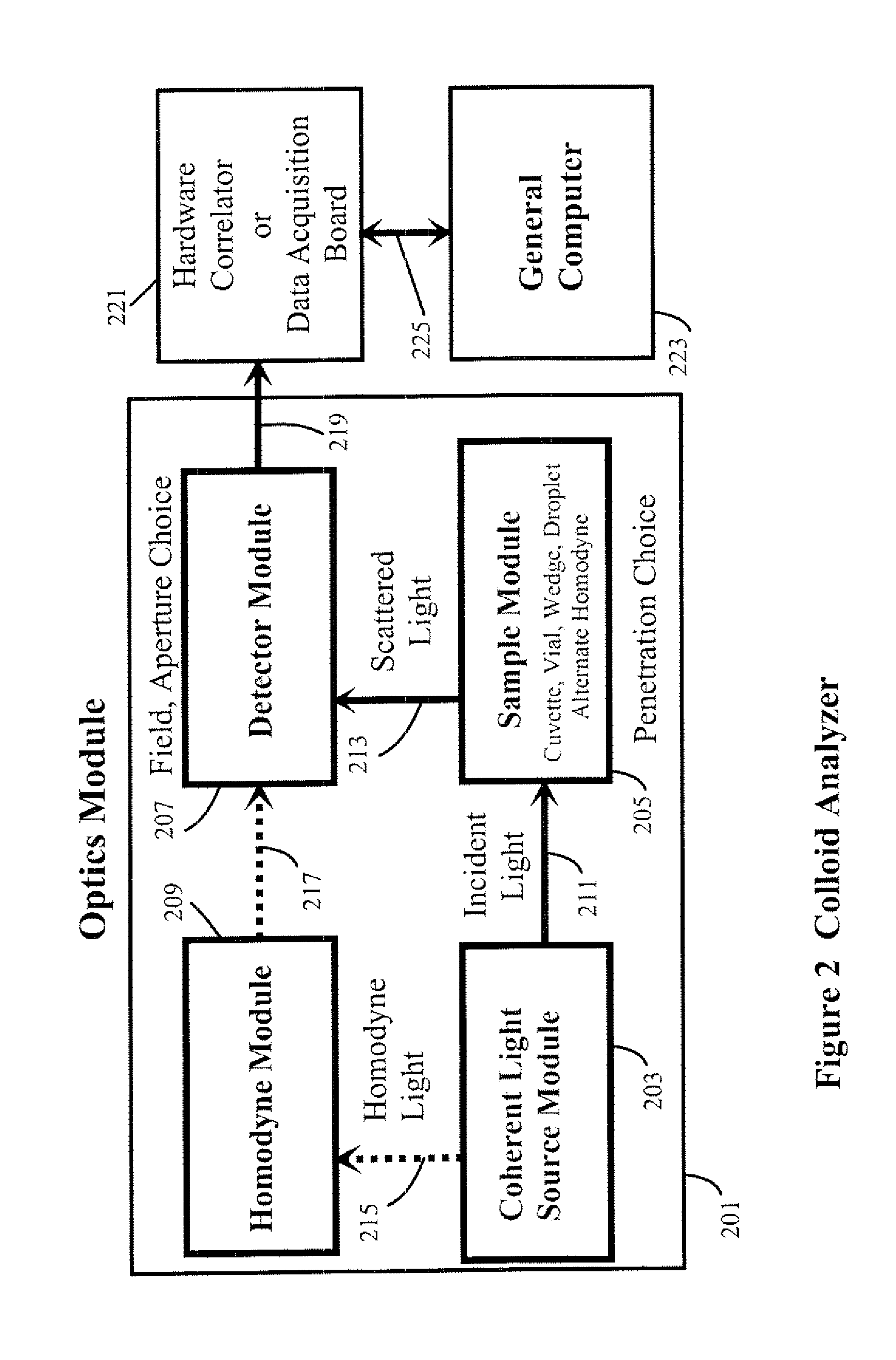
Apparatus are described for measuring the characteristics of colloidal particles suspended in transparent media by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Depolarized Dynamic Light Scattering (DDLS) into regions where conventional measurements are difficult or impractical. Matching the diameter of an illuminating beam and an intersecting diameter of a field stop image extends measurements into regions that include concentrated turbid suspensions that frequently appear so visually opaque that multiple scattering typically gives a falsely low estimate of particle size. At the opposite extreme, where insufficient signal is available to determine either or both of the translational and / or rotational relaxation times of the particles, typically where they are too small, too few, or of insufficient refractive index difference from the medium to scatter enough light, measurements can be improved by: a) using a sufficiently large aperture such that many coherence areas fall upon the detector; and b) optical homodyne amplification of the scattered signal.
Owner:SCATTERING SOLUTIONS
Nanogels and their production using liposomes as reactors
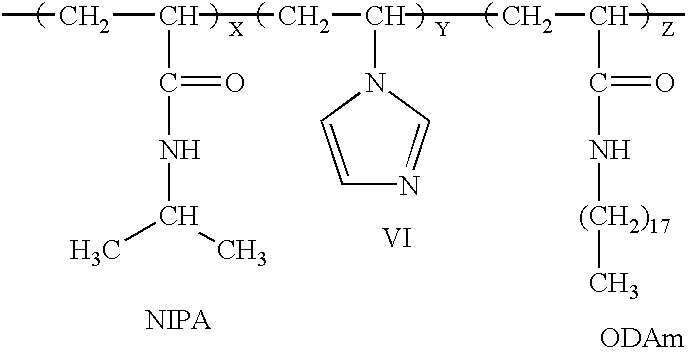
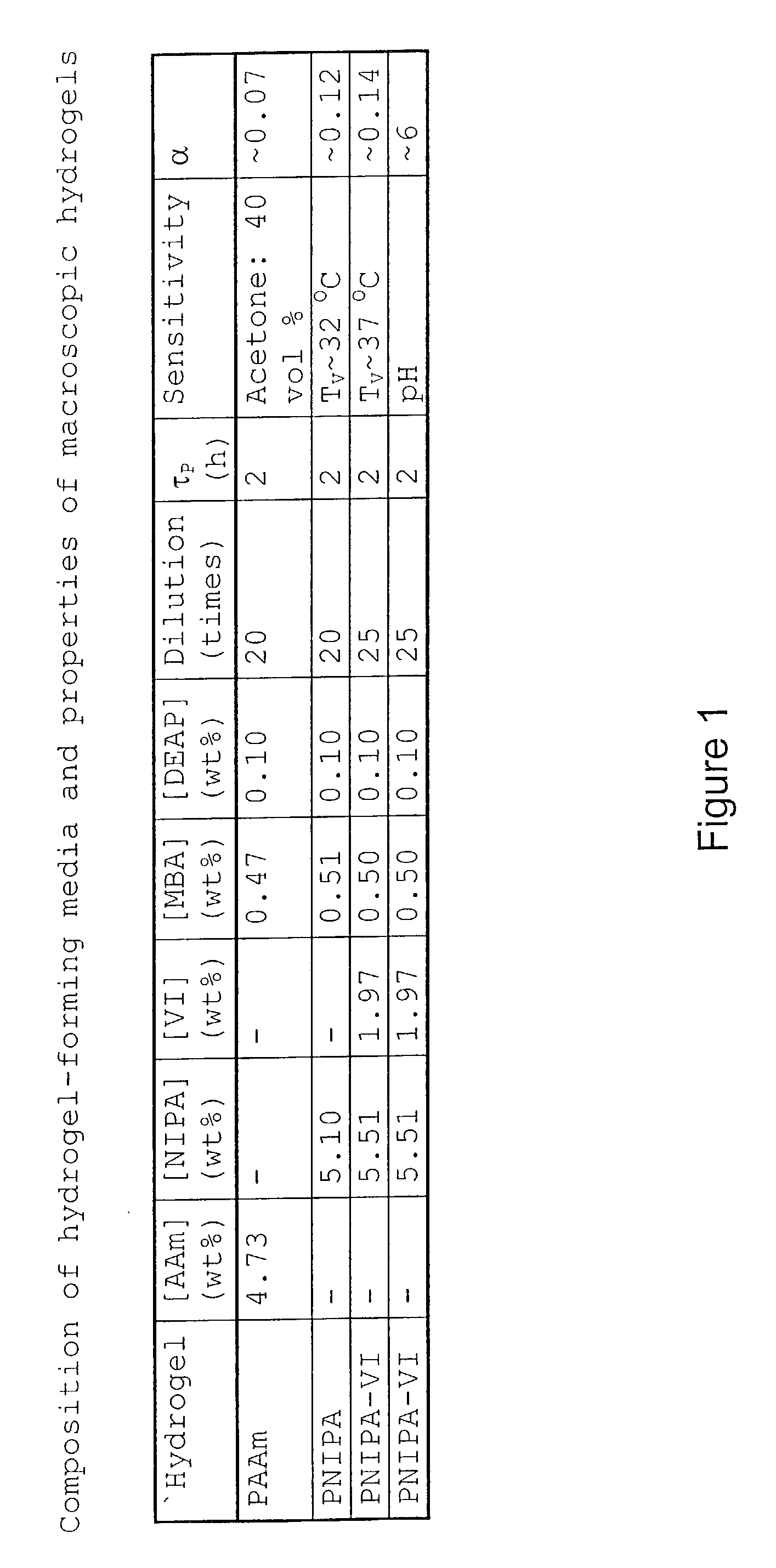
The present invention includes a method for preparing polymer hydrogel spherical particles on a nanometer scale (nanogels). The method includes encapsulating hydrogel-forming components into liposomes, diluting the large unilamellar liposomes suspension to prevent polymerization outside the liposomes, and polymerizing the encapsulated hydrogel-forming components. The lipid bilayer may be solubilized with detergent. The phospholipid and detergent molecules and their micelles may then be removed by dialysis. The resulting nanogels may then be dried by evaporation in a temperature gradient. Poly(acrylamide), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide), and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-1-vinylimidazole) hydrogel particles with a diameter from 30 to 300 nm were detected and characterized by dynamic light scattering technique. The solvent, temperature, pH, and ionic sensitivities of the nanogels were studied.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Hologram recording medium
InactiveUS20080160421A1High mechanical strengthGood holographic memory recording propertyPhotomechanical apparatusHolographic storageRefractive index
The present invention provides a hologram recording medium which is suitable for volume hologram record and can attain high refractive index change, flexibility, high sensitivity, low scattering, environment resistance, durability, low dimensional change (low shrinkage) and high multiplicity in holographic memory record using not only a green laser but also a blue laser. A hologram recording medium (11) comprising at least a hologram recording layer (21), wherein the hologram recording layer contains a metal oxide matrix comprising metal oxide fine particles, and a photopolymerizable compound; the metal oxide fine particles comprise metal oxide fine particles containing Ti as a metallic element; and at the time of subjecting the hologram recording layer before exposure to light to an extraction operation in n-butyl alcohol having a mass 100 times the mass (W) of said recording layer, thereby yielding a sol solution; filtrating the sol solution to obtain a filtrated sol solution; and measuring particle diameter distribution of sol particles in the filtrated sol solution by a dynamic light scattering method; and obtaining an average particle diameter thereof, the average particle diameter of the sol particles is in the range of 5 nm or more and 50 nm or less.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Synthesis of polymer coated ceria nanoparticles for biomedical applications
ActiveUS8333993B1Eliminate needImprove solubilityPowder deliveryInorganic active ingredientsSynthesis methodsPhosphate
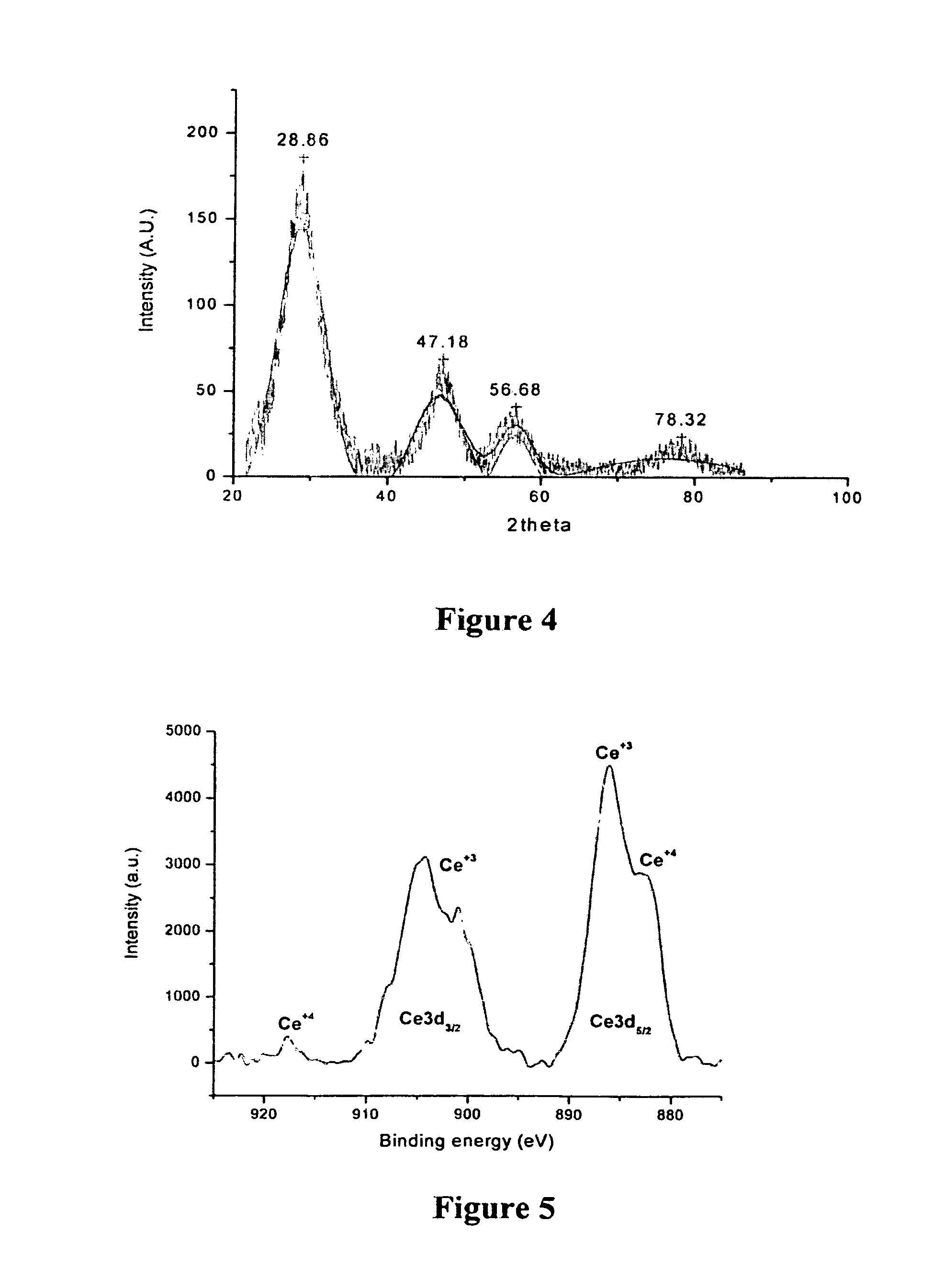
Procedures and methods for synthesizing biodegradable polymer coated nanoceria result in stable nanoparticle preparations in aqueous systems and physiological relevant colloidal solutions, such as phosphate buffer saline. The coated nanoceria preparations increase the nanoparticle concentration in aqueous or colloidal solutions as most needed for antioxidant, free-radical scavenger, and autocatalytic biomedical applications, including, biological, pharmacological and potential clinical use. To meet this need, a facile synthetic procedure for preparation of a biodegradable polymer-coated nanoceria is disclosed; the preferred biodegradable polymer is dextran. The synthesis method occurs under ambient conditions in an aqueous phase without the use of surfactants and results in a monodispersed preparation that is dextran-coated as determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS). Preliminary characterization of polymer coated nanoceria by XPS, TEM, XRD, and the like shows that these nanoparticles have the necessary physical properties for the desired biological potency, such as Ce+4 / Ce+3 mixed valence state.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Photoplethysmography device and method
ActiveUS20130131475A1Robust and accurateAccurate descriptionSensorsBlood characterising devicesAnalytePulse parameter
A system and method for measuring one or more light-absorption related blood analyte concentration parameters of a mammalian subject, is disclosed. In some embodiments, the system comprises: a) a photoplethysmography (PPG) device configured to effect a PPG measurement by illuminating skin of the subject with at least two distinct wavelengths of light and determining relative absorbance at each of the wavelengths; b) a dynamic light scattering measurement (DLS) device configured to effect a DLS measurement of the subject to rheologically measure a pulse parameter of the subject; and c) electronic circuitry configured to: i) temporally correlating the results of the PPG and DLS measurements; and ii) accordance with the temporal correlation between the PPG and DLS measurements, assessing value(s) of the one or more light-absorption related blood analyte concentration parameter(s).
Owner:OXITONE MEDICAL
Device for synchronously measuring granularity of dynamic light scattering nanometer particles of multi-particles and method thereof
InactiveCN102109454AReduced measurement timeThe result is accurateParticle size analysisGranularityMicrometer
The invention discloses a device for synchronously measuring granularity of dynamic light scattering nanometer particles of multi-particles and method thereof. The device is characterized by comprising a laser source, a sample pond, a lens and a face array photosensitive element which are coaxially arranged with each other; the method of the invention comprises the following steps: a laser beam radiates on the particles in the sample pond; the particles doing Brownian movement in the sample pond generate dynamic light scattering; dynamic light scattering signals of the particles are collectedafter passing through the lens, and are continuously recorded by the face array photosensitive element to generate continuous movement images of the particles in M amplitude time sequences; and lightspots generated through scattering the particle light on the continuous images form the Brownian movement tracks of the measured particles. The invention can synchronously measure the dynamic light scattering signals of many particles by a face array digital camera and process the dynamic light scattering signals of the particles so as to obtain the particle distribution of the particles and greatly reduce the measuring time; furthermore, the invention can synchronously measure the particles with large distribution range from nanometer to micrometer.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
System and method for in vivo measurement of biological parameters
InactiveUS20140094666A1Reduce decreaseClear distinctionSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateControl systemDynamic light scattering
A system, method and medical tool are presented for use in non-invasive in vivo determination of at least one desired parameter or condition of a subject having a scattering medium in a target region. The measurement system comprises an illuminating system, a detection system, and a control system. The illumination system comprises at least one light source configured for generating partially or entirely coherent light to be applied to the target region to cause a light response signal from the illuminated region. The detection system comprises at least one light detection unit configured for detecting time-dependent fluctuations of the intensity of the light response and generating data indicative of a dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurement. The control system is configured and operable to receive and analyze the data indicative of the DLS measurement to determine the at least one desired parameter or condition, and generate output data indicative thereof.
Owner:ELFI TECH
Polyester resin compositions, catalyst for polyester production, polyester film, and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20050239929A1Satisfactory hueBase layers for recording layersSynthetic resin layered productsNumber densityDynamic light scattering
The present invention aims to provide a practical polyester that can be produced substantially without using an antimony compound as a polycondensation catalyst. (I) The present invention provides a polyester resin composition containing, on a weight basis, 30 ppm or less of antimony, 0.5 to 50 ppm of titanium, and 0.1 to 100 ppm of phosphorus, in which the number density of titanium-containing particles, the equivalent circular diameter of which is 1 μm or more, is less than 100 / 0.02 mg; and (II) The present invention provides a polyester resin composition containing, on a weight basis, 30 ppm or less of antimony, 0.5 to 50 ppm of titanium, and 0.1 to 100 ppm of phosphorus, in which organic polymer particles are contained in amount of 0.1 to 5 wt %, the organic polymer particles having an average particle diameter determined by dynamic light scattering of 0.05 to 3 μm and containing 0.01% or less of coarse particles relative to the total number of the particles, the coarse particles having a diameter at least twice the average particle diameter.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
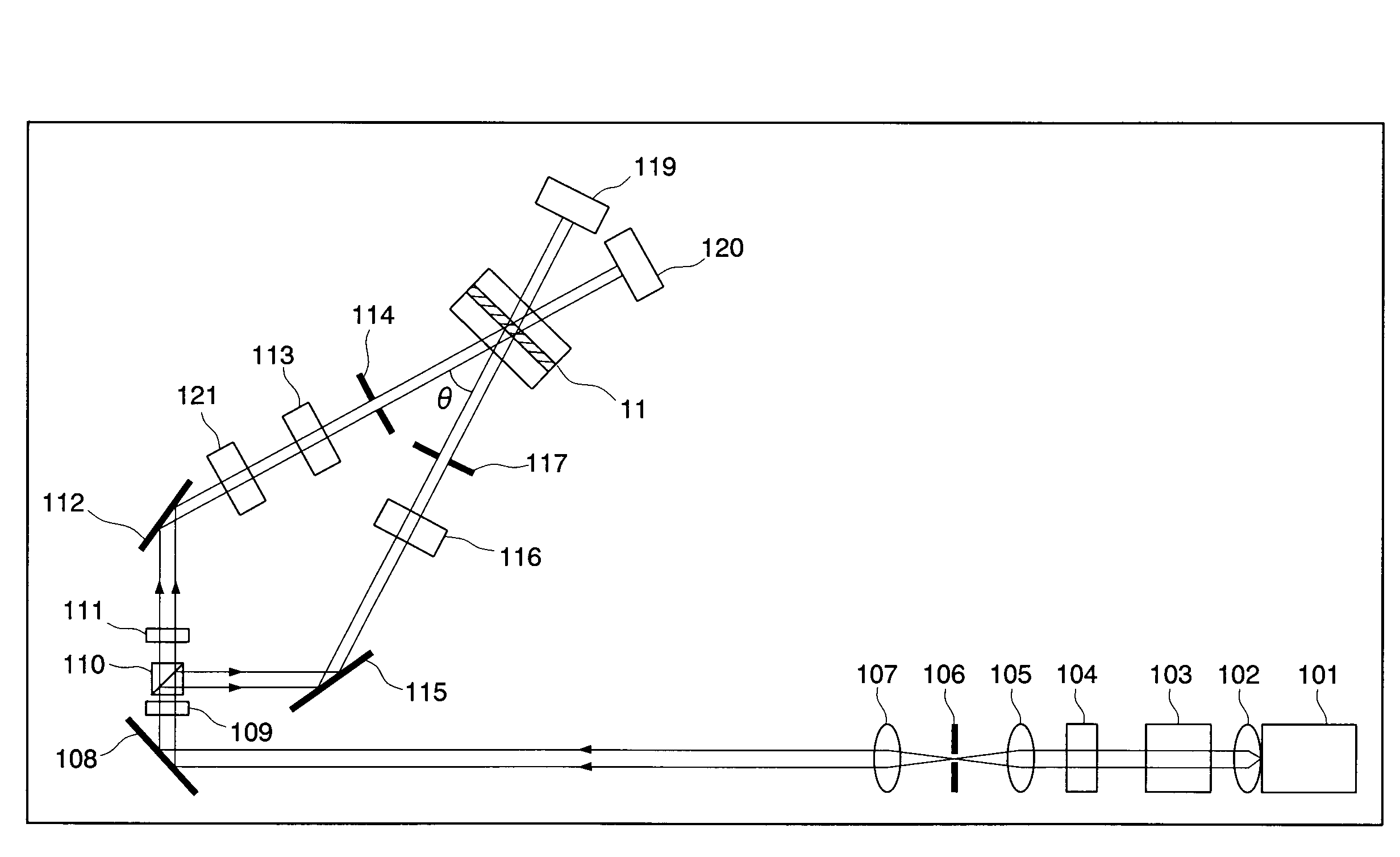
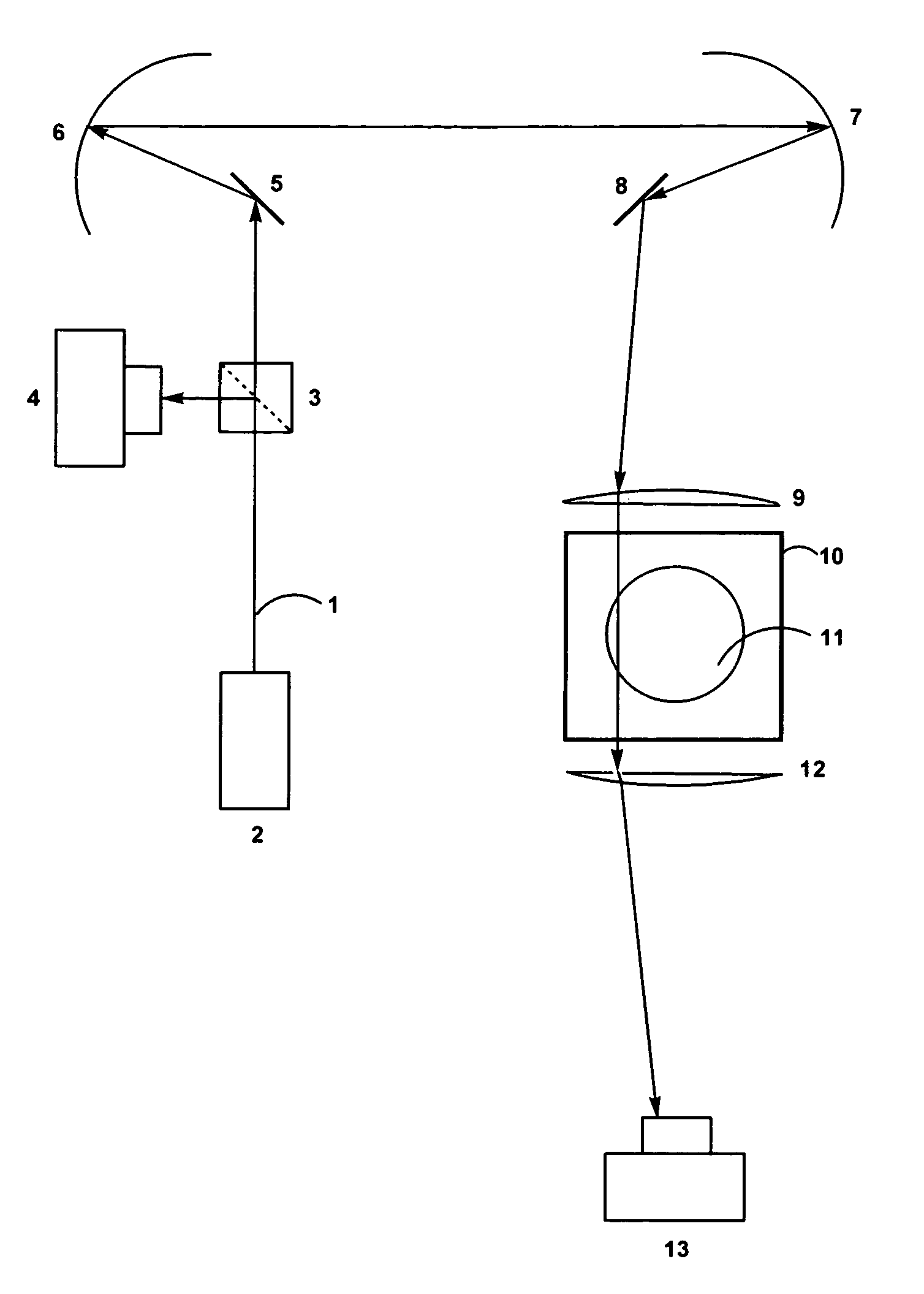
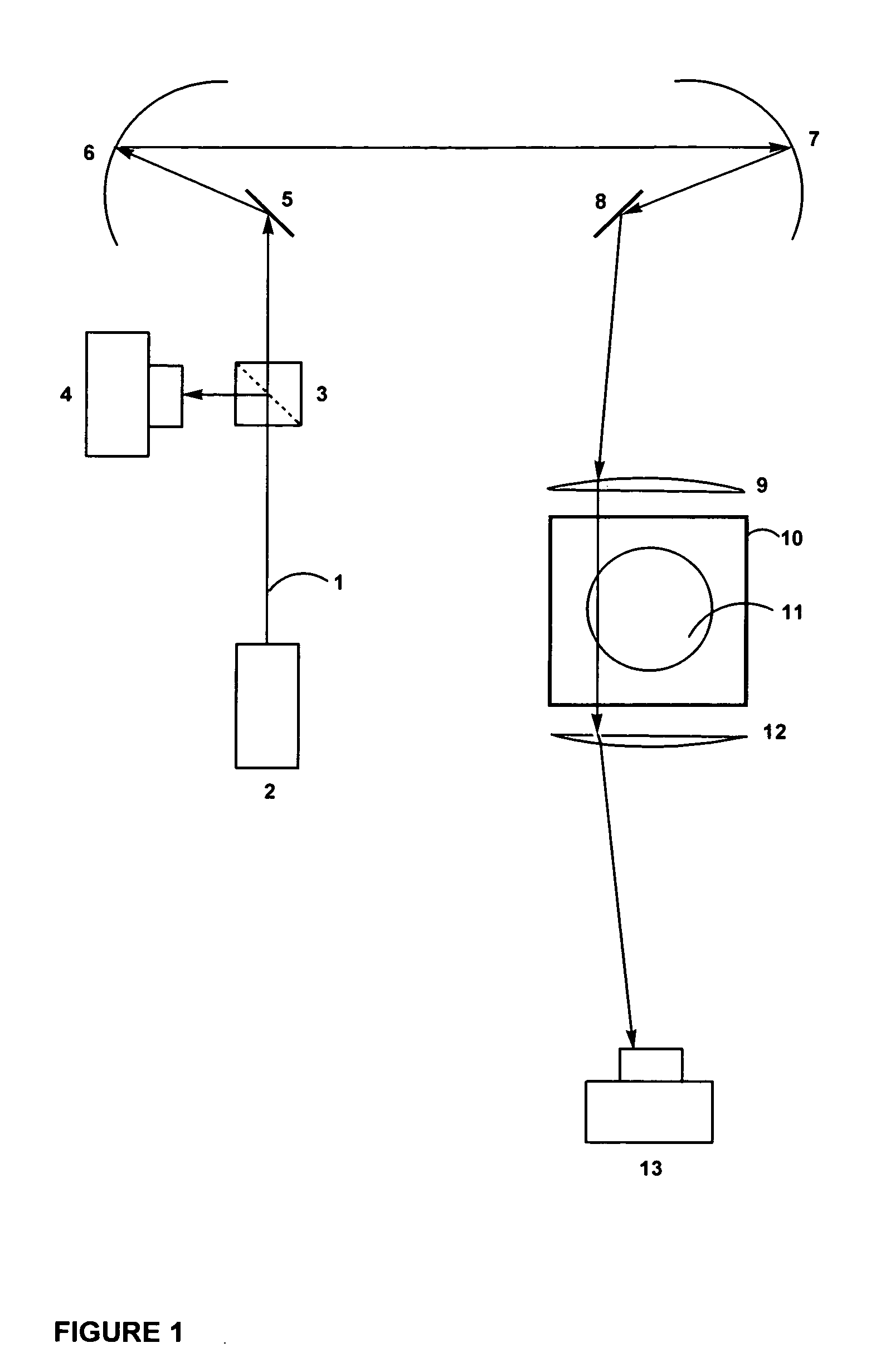
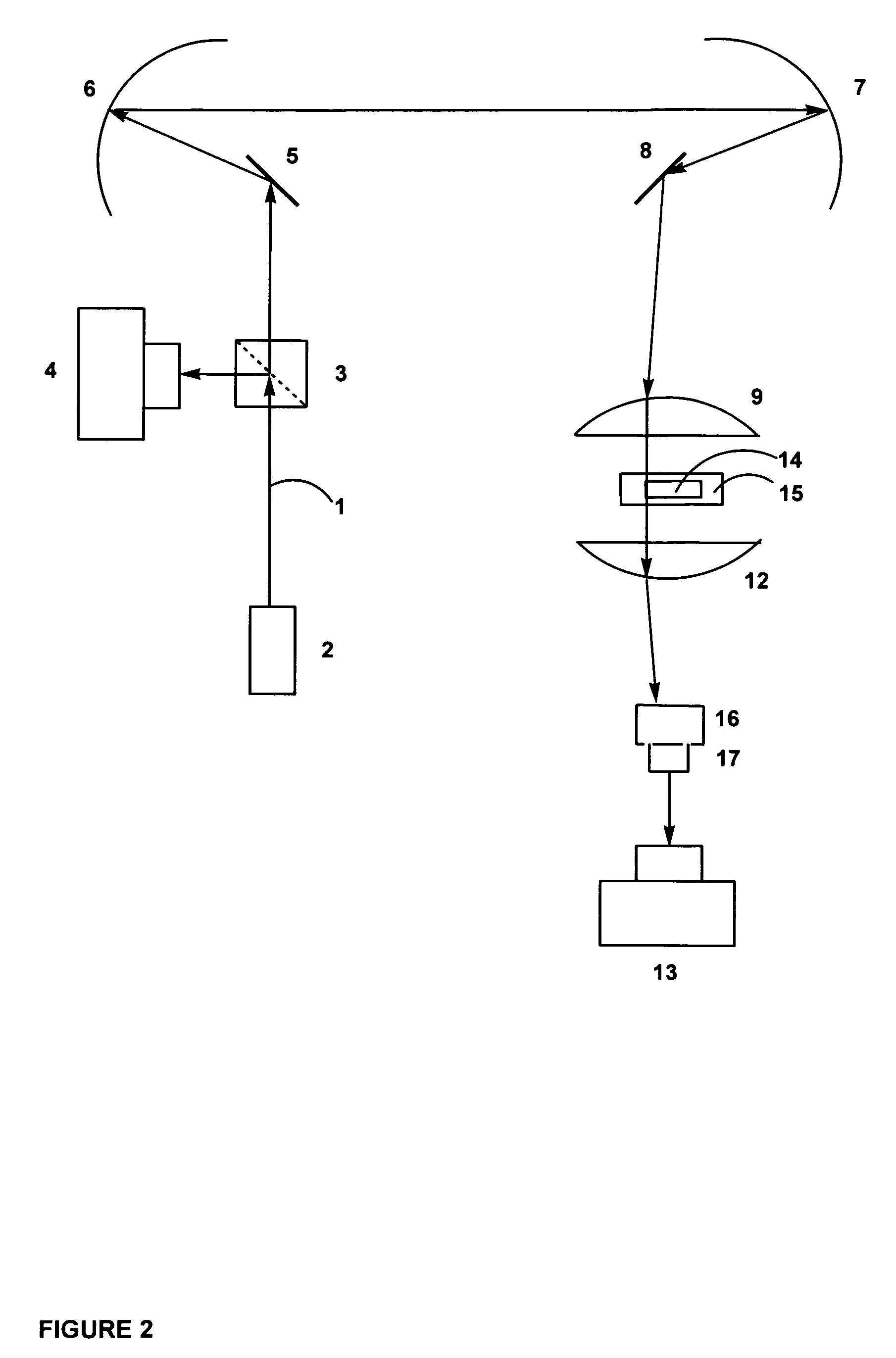
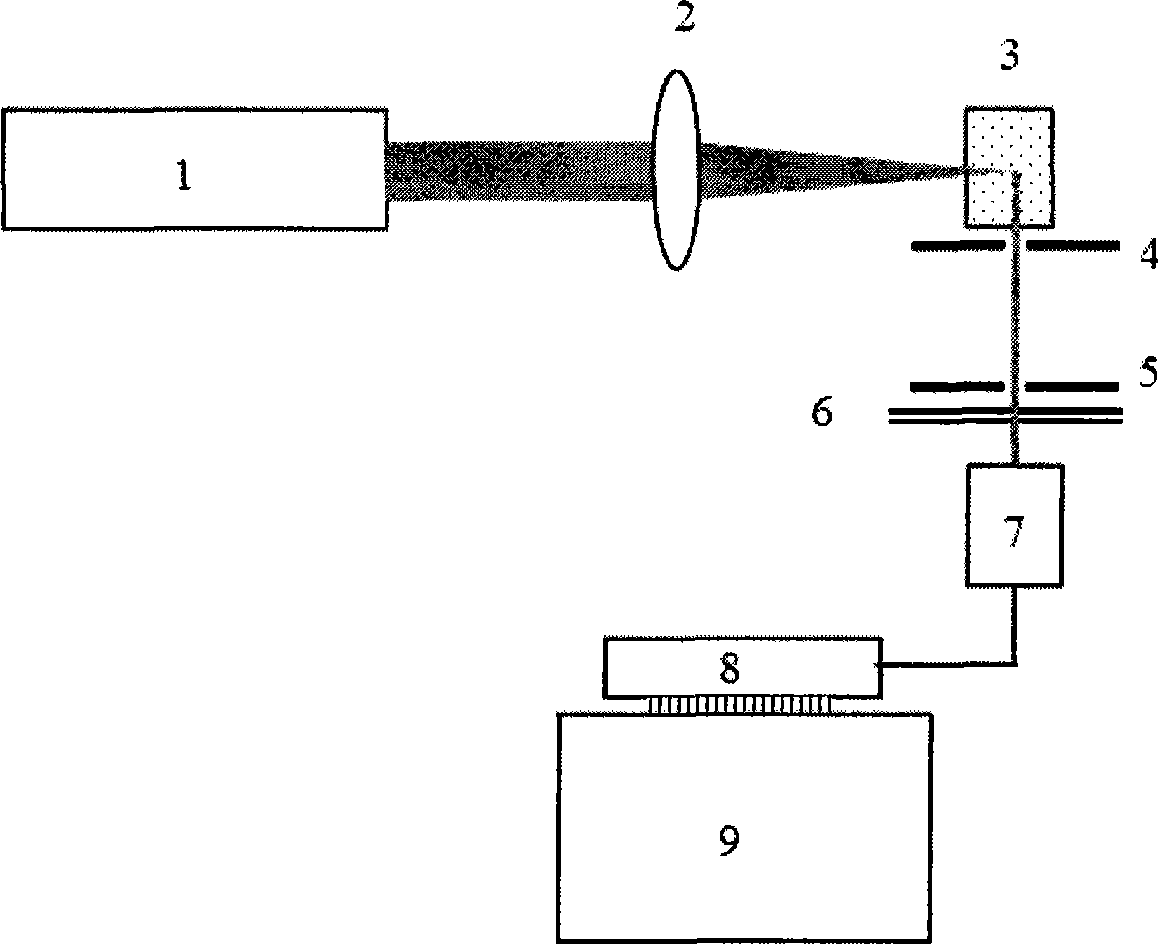
Fast laser scanning optical CT apparatus
InactiveUS20080277567A1Fast optical CT scanningInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsPlane mirrorRefractive index
Disclosed are scanning devices which measure and quantify optical properties within an object such as the absorption of light, refractive index, light scattering, fluorescence, and phosphorescence. Through the use of two rotating plane mirrors and two paraboloid mirrors, a laser light beam is made to traverse the object to be scanned wherein the beam is always parallel to the optical axis. The invention provides an improvement over previously reported scanning devices by virtue of increased speed and resolution. Two-dimensional projections gleaned by each scan of the object are reconstructed into a three-dimensional image through the use of various computer techniques.
Owner:DORAN SIMON JOHN +1
Copper Microparticle and Process for Producing the Same
Copper microparticles that are fine and contain substantially none of agglomerated particles. For example, there are provided copper microparticles of 0.005 to 2.0 μm average particle diameter (D) as measured by an electron microscope, 0.005 to 2.0 μm average particle diameter (d) as measured by a dynamic light scattering particle size distribution measuring apparatus and 0.7 to 2 d / D ratio. There is provided a process comprising mixing a divalent copper oxide with a reducing agent in the presence of a complexing agent and a protective colloid in a liquid medium to thereby produce copper microparticles without formation of a univalent copper oxide from the divalent copper oxide. Further, there is provided a process comprising reducing a divalent copper oxide in the presence of a complexing agent and a protective colloid, such as a protein, to thereby form metallic copper microparticles, adding a protective colloid scavenger, such as a protease, to thereby remove the protective colloid and effect agglomeration of metallic copper microparticles, and filtering the mixture by means of a pressure filter, a vacuum filter, a suction filter, etc.
Owner:ISHIHARA SANGYO KAISHA LTD +1
Photoplethysmography device and method
ActiveUS8868149B2Accurate descriptionSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateAnalytePulse parameter
Owner:OXITONE MEDICAL
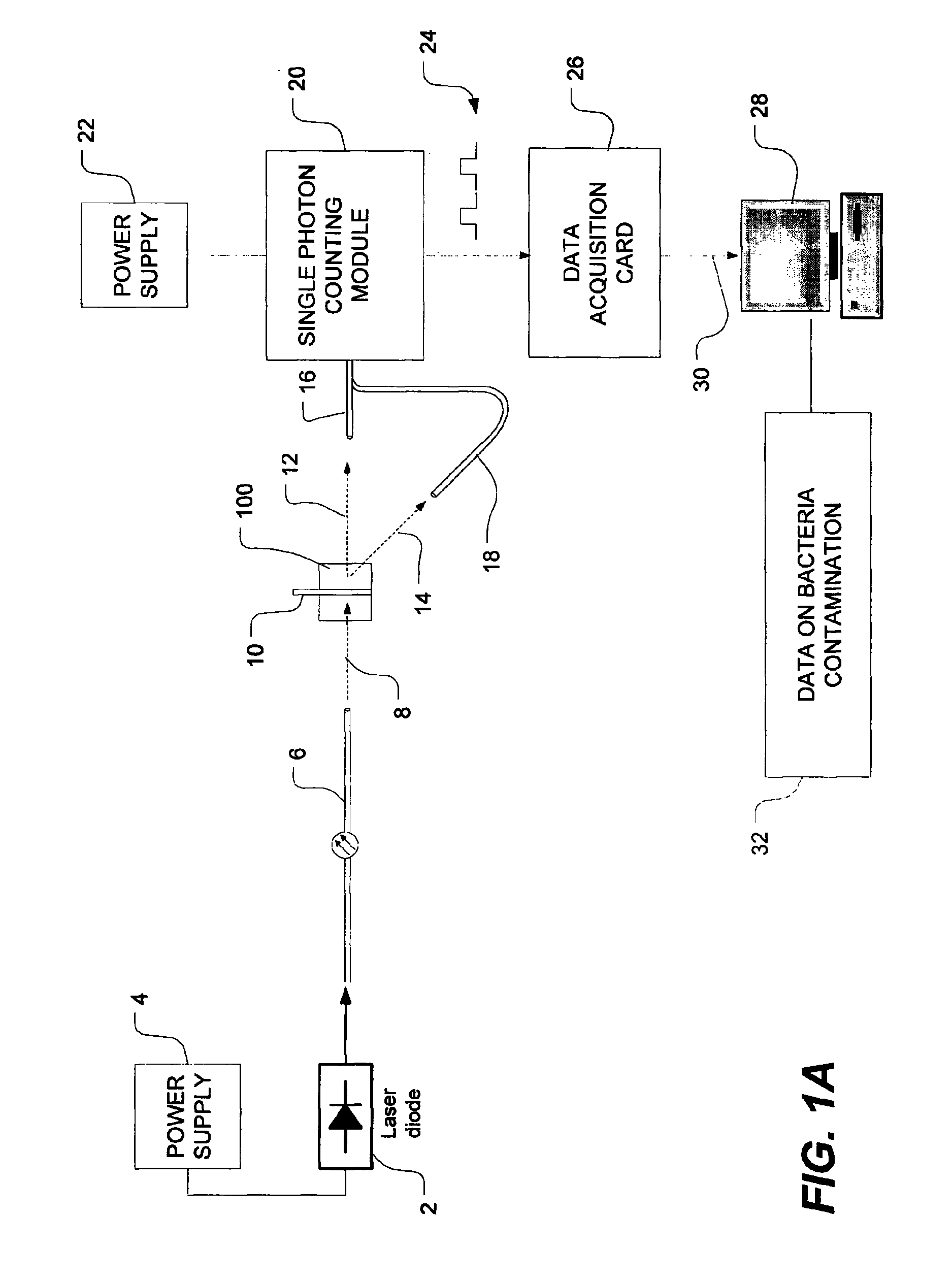
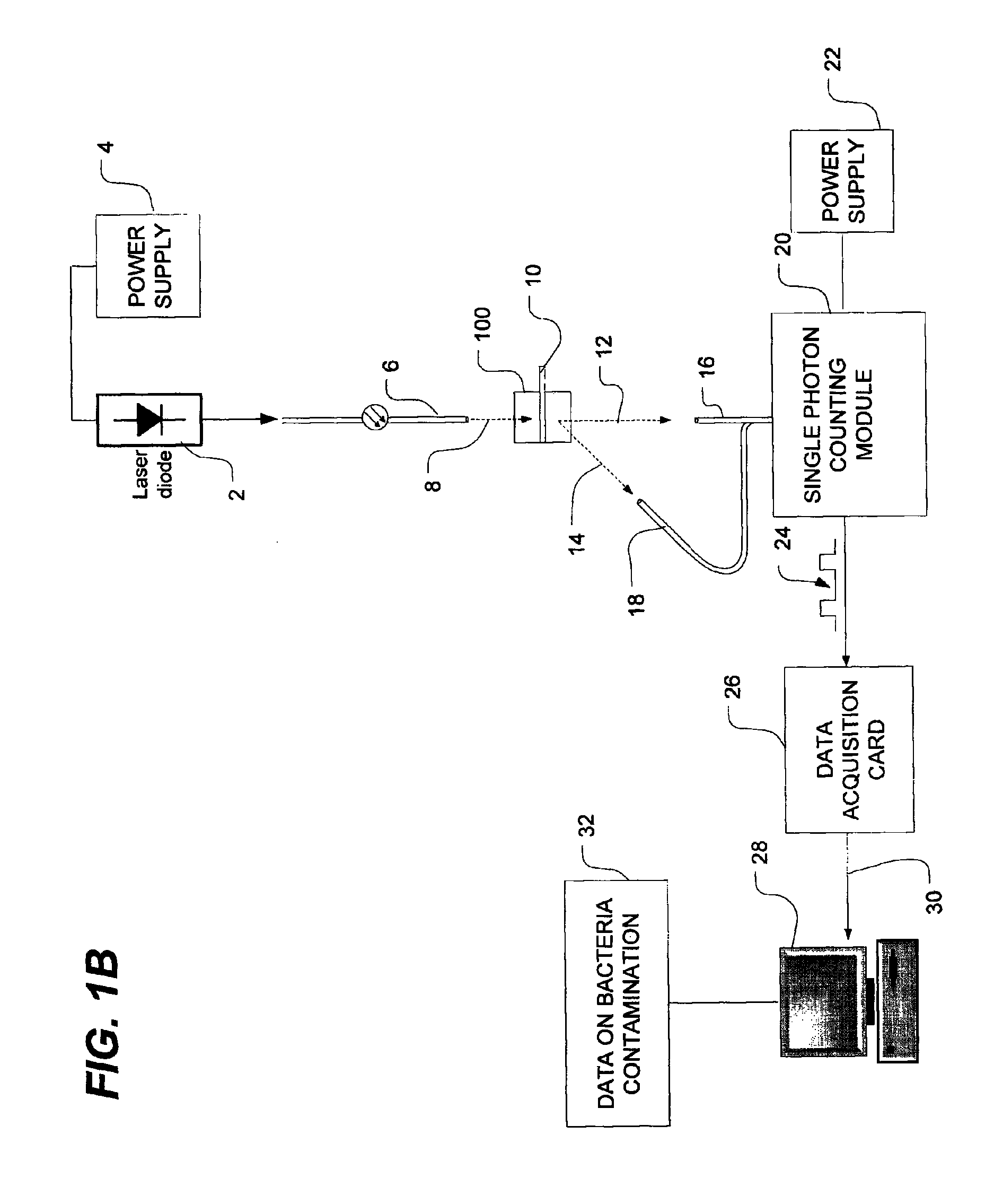
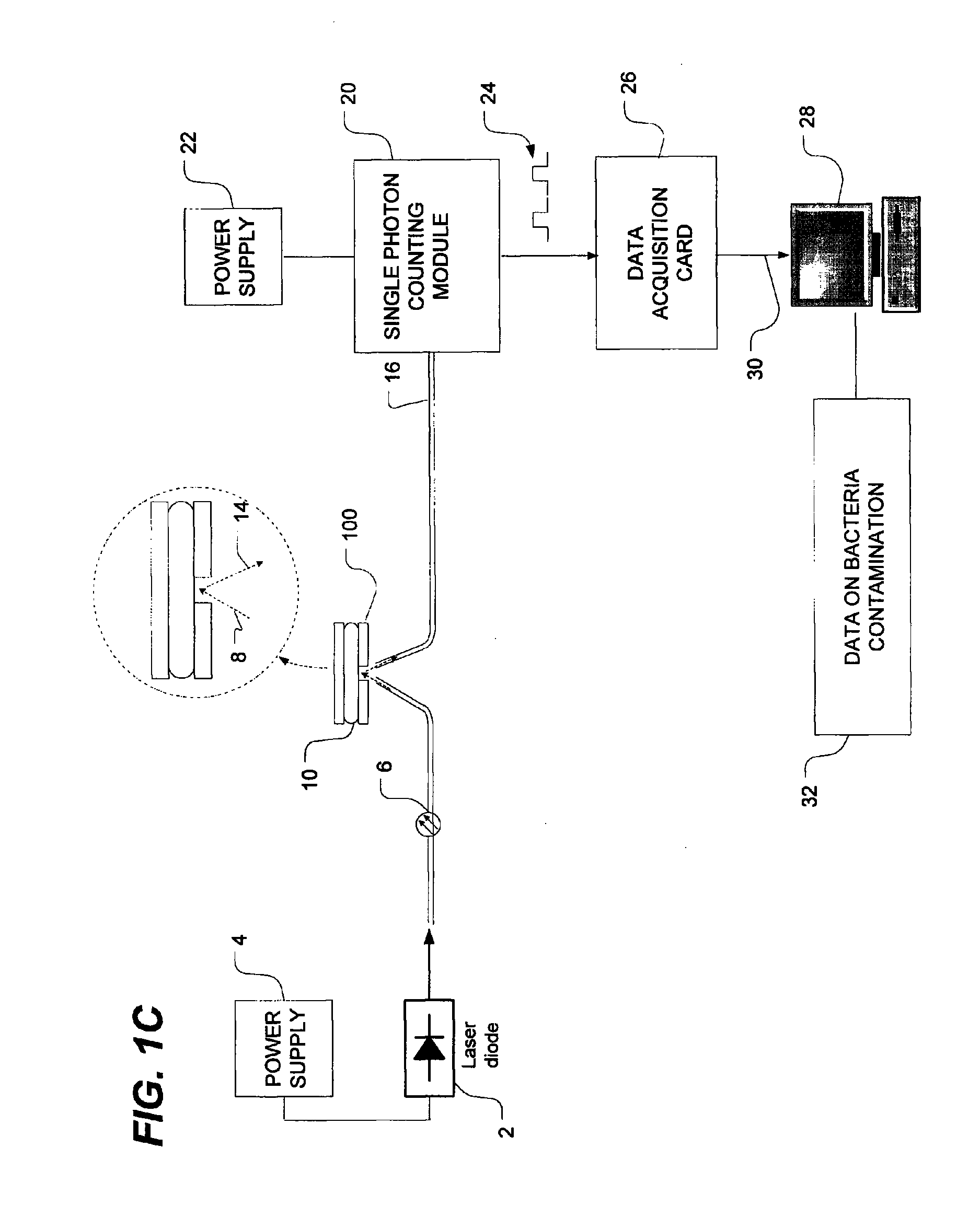
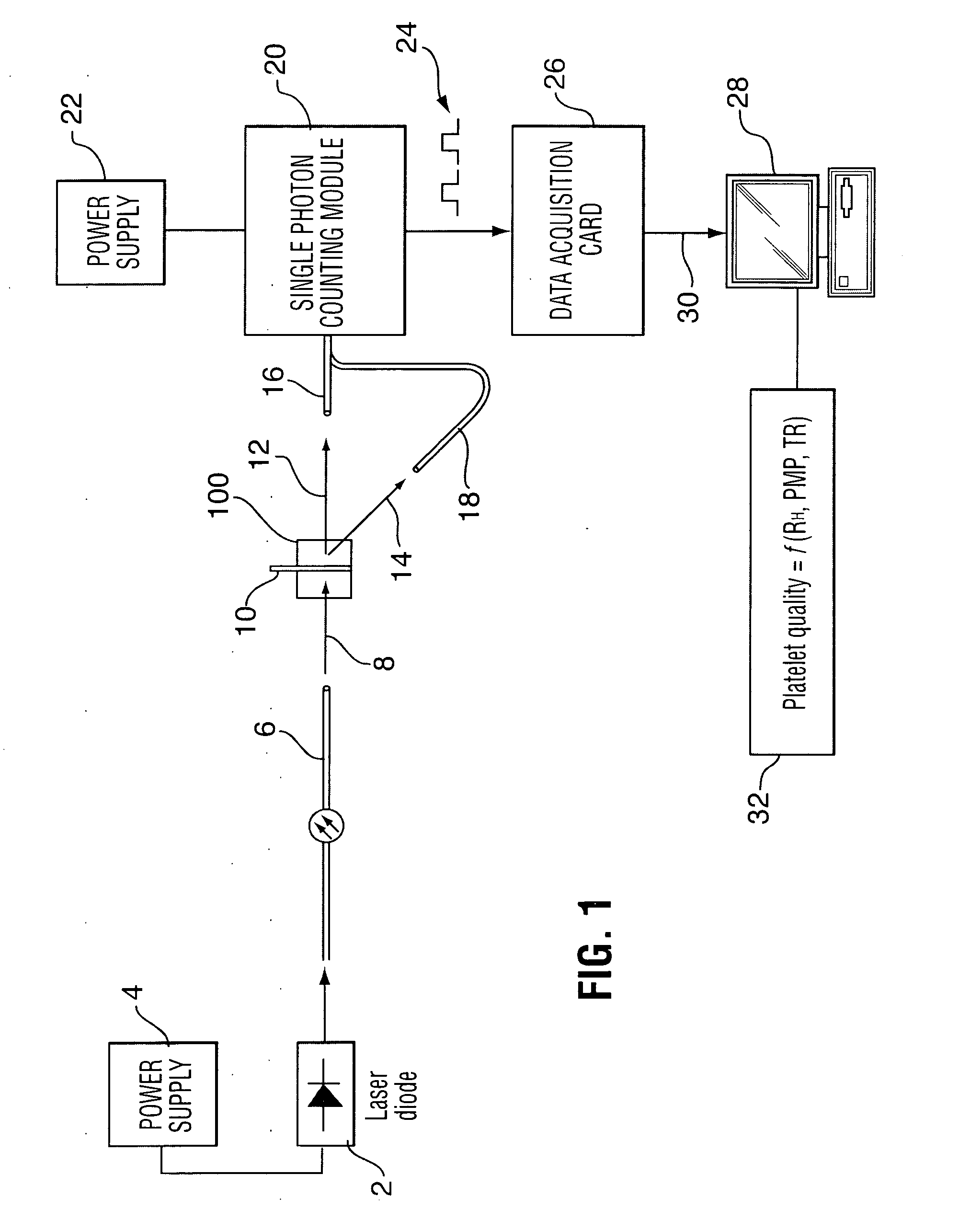
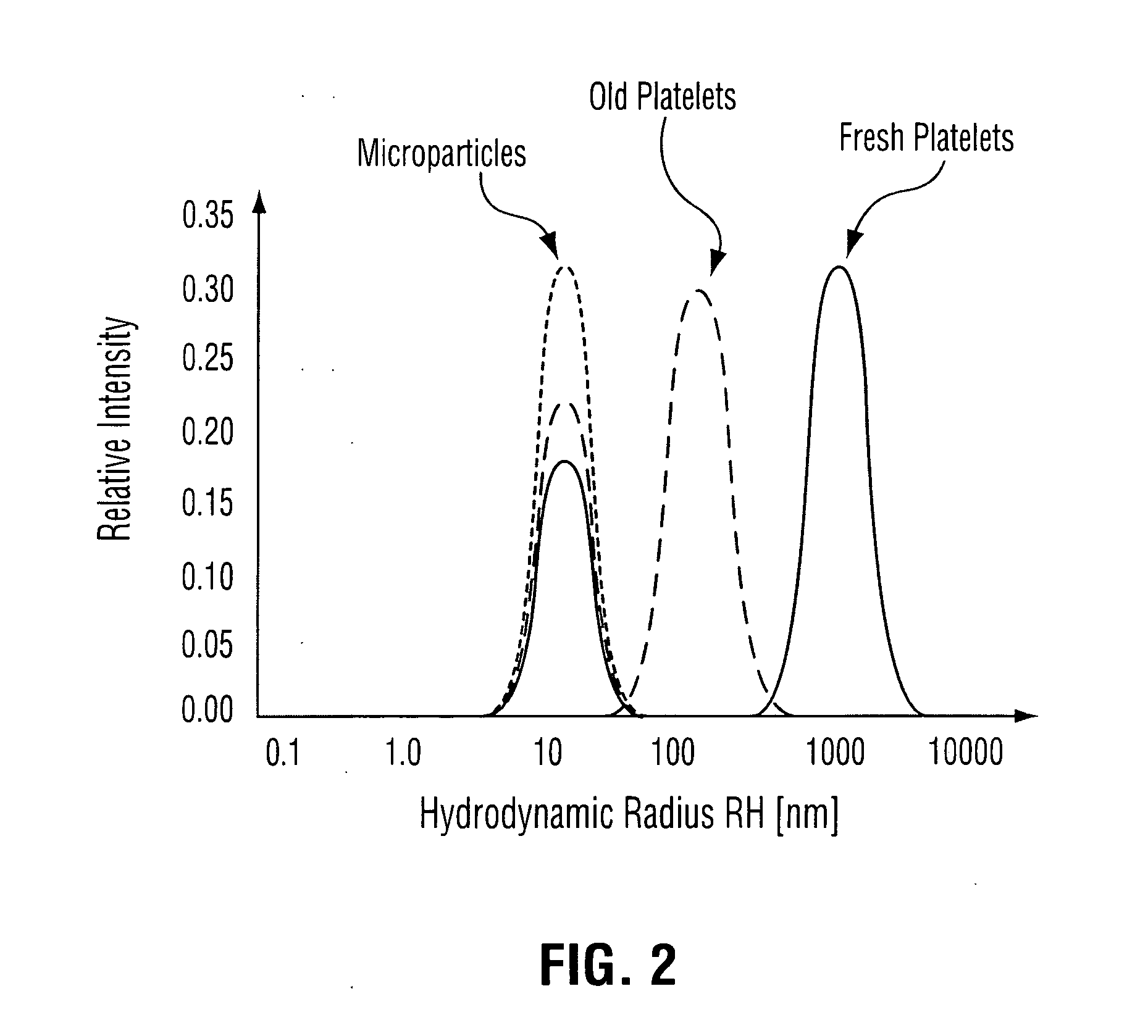
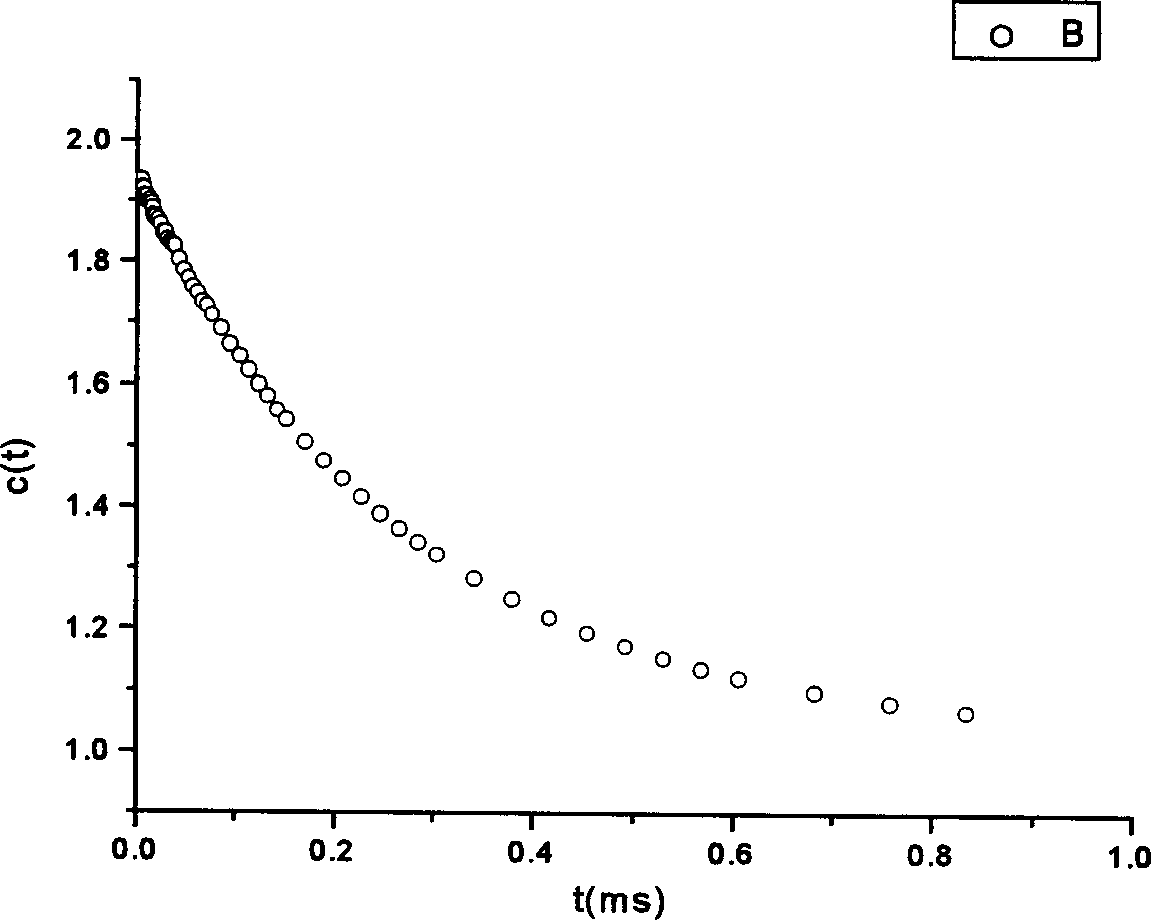
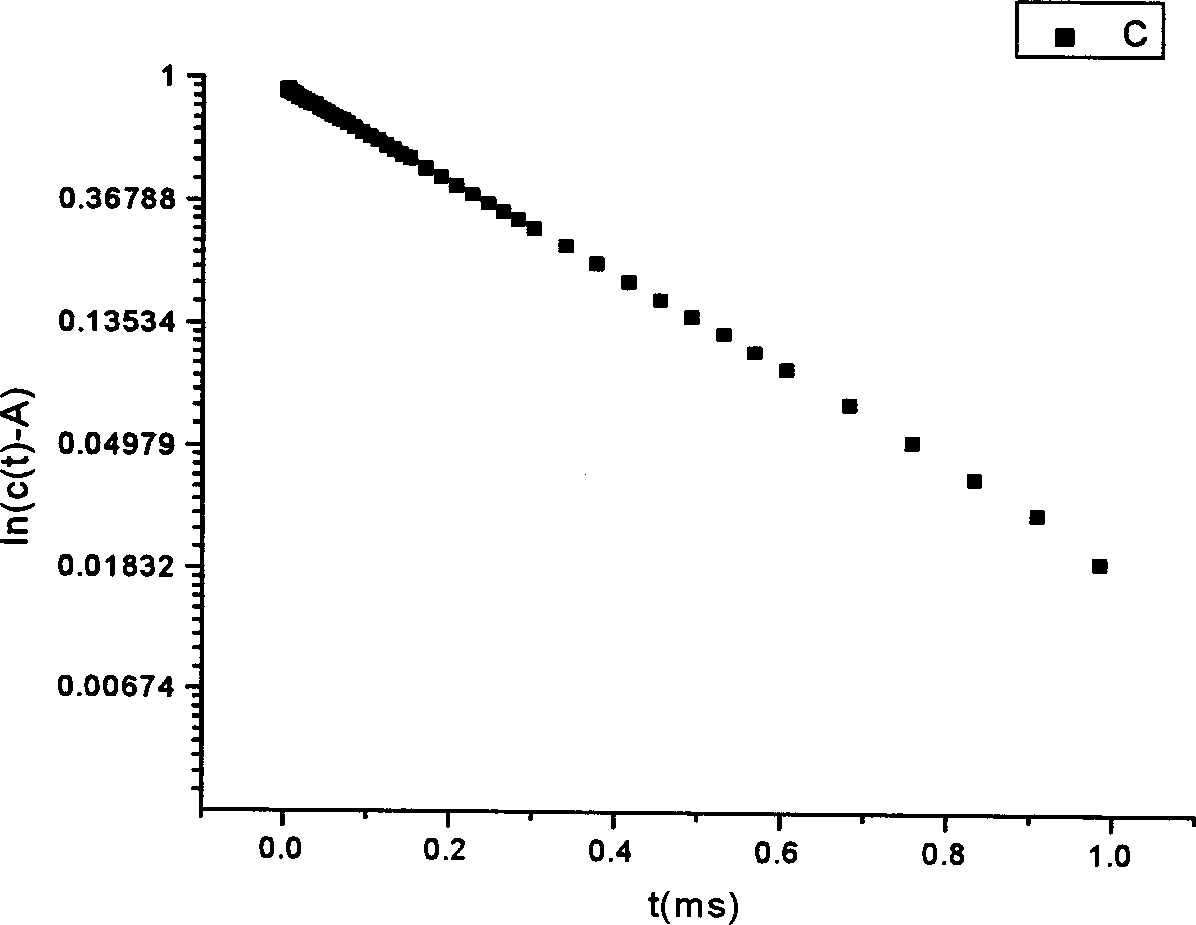
Method of detecting bacterial contamination using dynamic light scattering
InactiveUS8877458B2High strengthReduce intensityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDynamic light scatteringMicroparticle
Methods of detecting bacterial contamination in a platelet concentrate are performed using a dynamic light scattering (DLS) instrument and a sample holder. A sample of platelet concentrate can be held vertically or horizontally in a capillary in the sample holder. Alternatively, novel platelet storage bags modified to include an optically translucent window can be held within another variant of the sample holder. Still alternatively, platelet storage bags having one or more tubes detachably appended to the bag can be used. A sample is drawn off into an appended tube for placement directly into the sample holder. This method provides a number of related, non-invasive techniques for detecting whether bacteria has contaminated a platelet concentrate. Contamination indicators include a population of particles different from platelets, microparticles or proteins, bad-quality platelets, i.e. low DLS score, and very high or very low scattering intensity.
Owner:CANADIAN BLOOD SERVICES
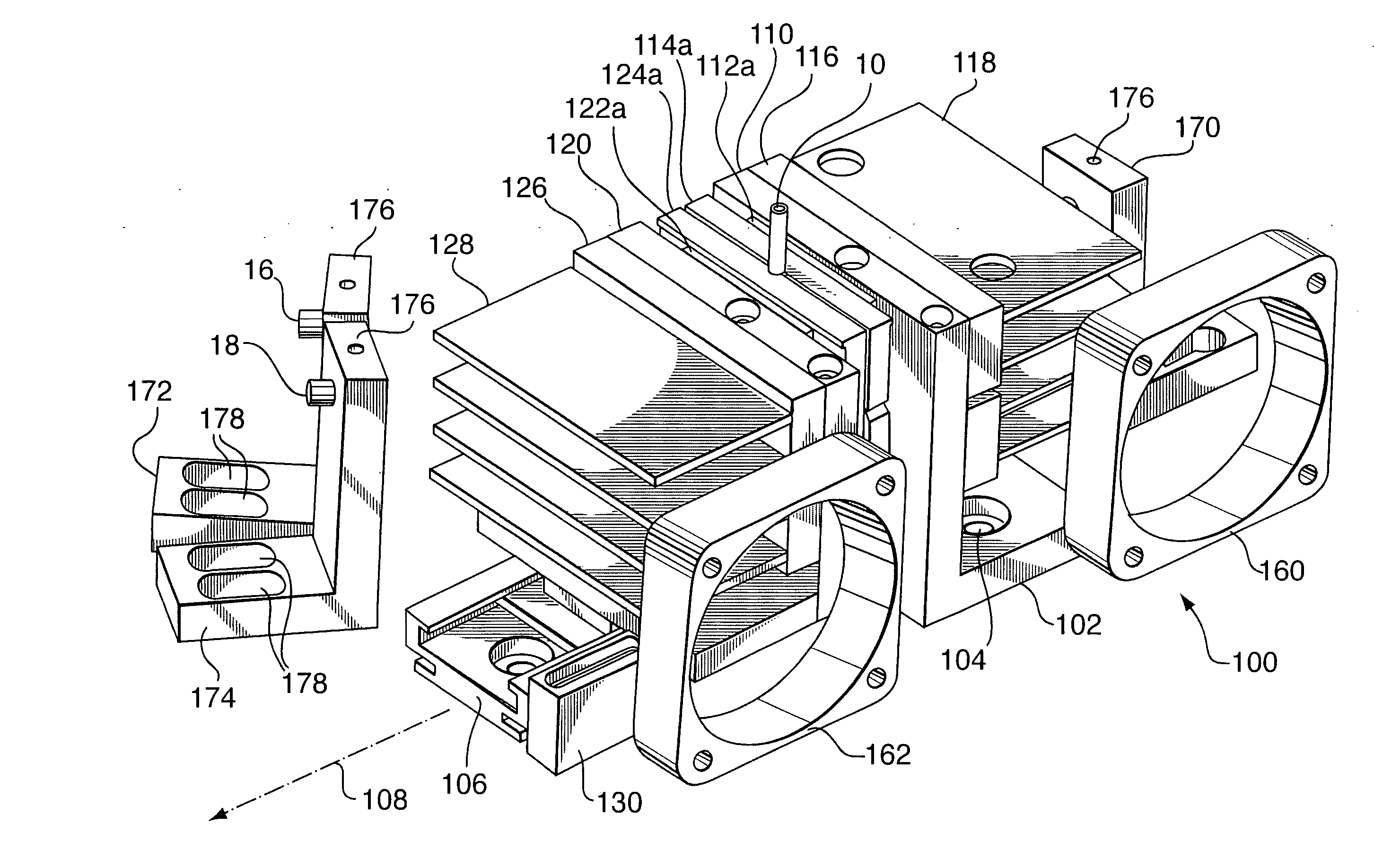
Sample holder for dynamic light scattering
InactiveUS20070041877A1Improve cooling effectEasy accessBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuvetteDynamic light scattering
A sample holder holds various sizes of capillaries or cuvettes for use in dynamic light scattering (DLS) or quasi-elastic light scattering (QELS), such as in DLS of fluid samples such as platelet solutions, whole blood, colloids or the like. The sample holder has a base with a stationary backing member and a sliding, rail-mounted clamping member that is magnetically biased toward the backing member. The sample holder has Peltier-type thermoelectric heating / cooling elements that extend the full height of the clamping and backing members to optimize heat transfer efficiency. The sample holder further includes horizontal slots that enable collection of scattered light from various angles around the device. Finned heat sinks are mounted above and below the horizontal slots on the outwardly facing surfaces of the backing and clamping members to stabilize the temperature of the fluid sample in the sample holder without interfering with incident or scattered light.
Owner:CANADIAN BLOOD SERVICES
Particle size analyzer
InactiveCN104089858AMeet the measurement requirementsEasy to carryParticle size analysisBrownian excursionDynamic light scattering
The invention discloses a particle size analyzer which is characterized in that a microscope objective is arranged below an area array sensor; a sample tank is arranged on the focusing plane of the microscope objective; two light sources, namely a transmission light source and a scattering light source are arranged below the sample tank; when micron-grade particles are measured, the transmission light source emits illumination light to illuminate particle samples to be detected, particle images are amplified by the microscope objective to be imaged on an image plane, and image signals obtained after receiving of the images by the area array sensor are transmitted to a computer to be processed to obtain particle size distribution; when nano particles are measured, the transmission light source is turned off while the scattering light source is turned on, laser emitted by the transmission light source is irradiated to nano particle samples, dynamic light scattering signals generated by Brownian movement of the nano particles are received by the area array sensor through the microscope objective, and the obtained signals are transmitted to the computer to be processed to obtain the particle size distribution. According to the particle size analyzer, the particles with the size range from nanometers to hundreds of microns can be measured by only one image sensor, so as to meet the requirements of wide-range particle measurement.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
System and method for in vivo measurement of biological parameters
ActiveUS8277384B2Reduce decreaseClear distinctionCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringControl systemDynamic light scattering
A system, method and medical tool are presented for use in non-invasive in vivo determination of at least one desired parameter or condition of a subject having a scattering medium in a target region. The measurement system comprises an illuminating system, a detection system, and a control system. The illumination system comprises at least one light source configured for generating partially or entirely coherent light to be applied to the target region to cause a light response signal from the illuminated region. The detection system comprises at least one light detection unit configured for detecting time-dependent fluctuations of the intensity of the light response and generating data indicative of a dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurement. The control system is configured and operable to receive and analyze the data indicative of the DLS measurement to determine the at least one desired parameter or condition, and generate output data indicative thereof.
Owner:ELFI TECH
Ultrafine grain measuring apparatus and method based on dynamic light scattering signal time coherence
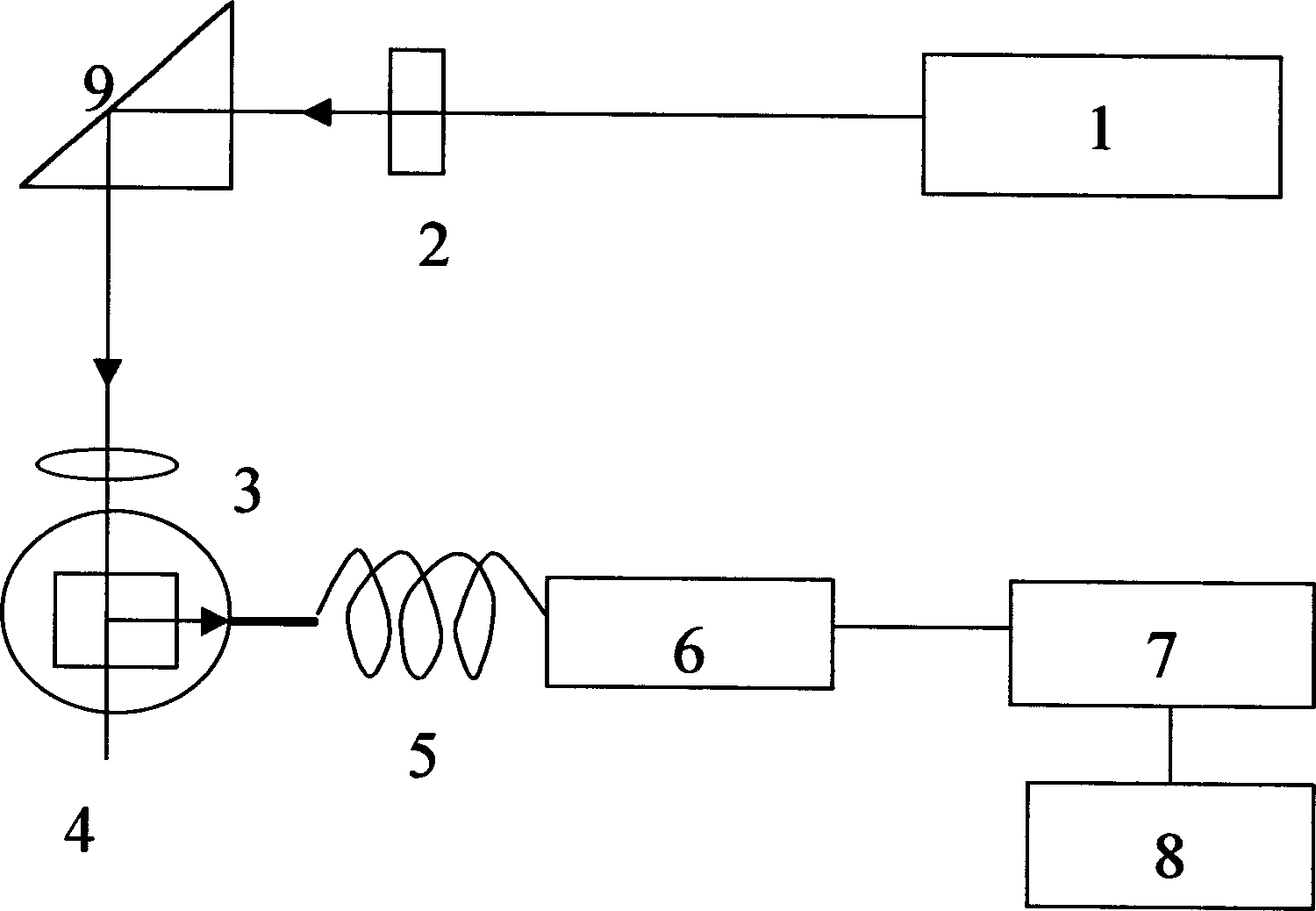
InactiveCN101477023AThe principle is simpleReduce hardware costsScattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisContinuous measurementDegree of coherence
The invention relates to a device and a method for measuring ultrafine grains based on dynamic light scattering signal time coherence degree. An incidence light path consists of a laser, a convex lens and a sample cell; a receiving light path consists of a sample cell, a pinhole diaphragm and an optical filter; and an acquisition and processing unit for scattering signals consists of a photoelectric detector, a photon counting plate and a computer. The measuring method comprises the following steps: 1, using the laser as a light source to irradiate the sample cell filled with the grains; 2, using a photoelectric multiplier tube as the photoelectric detector to continuously measure scattered light signals generated by the grains at a scattering angle of 90 degrees; 3, using the photon counting plate to count impulse signals output by the photoelectric multiplier tube, wherein the time coherence degree of the signals is gradually reduced along with the improvement of a sampling cycle; and 4, calculating the grain sizes of the grains by the computer according to the change of the calculated signal time coherence degree. The device and the method have the advantages of low cost, simple steps, quick measuring speed, and simple device.
Owner:杨晖 +2
Nano scale particle size measuring method and device with scattered dynamic low-strength laser
InactiveCN1403797AWide measurement rangeKeep naturalScattering properties measurementsParticle size analysisFiberRefractive index
The present invention provides nano particle size measuring method and device with scattered dynamic low-strength laser. The method includes: radiating liquid sample with monochromic laser beam of proper length to produce scattered light signal; collecting and transmitting to light signal with single-modular fiber with gradient refractive index; recording with single-photon counter module the scattered photons and converting into output electric pulse signal; and processing the signal in an autocorrelator. The device includes: light source, polarizer, focusing lens, two-layered refractive index sample matching pool, fiber, single-photon counter module, autocorrelator and computer. The present invention can measure nano particle size fast and accurately.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Multi-Vital-Sign Smartphone System in an Electronic Medical Records System
ActiveUS20180235468A1Digital data processing detailsDiagnostics using spectroscopyMedical recordDynamic light scattering
In one implementation, a multi-vital-sign smartphone system detects multiple vital signs from sensors such as a digital infrared sensor, a photoplethysmogram (PPG) sensor and at least one micro dynamic light scattering (mDLS) sensor, and thereafter in some implementations the vital signs are transmitted to, and stored by, an electronic medical record system.
Owner:ARC DEVICES
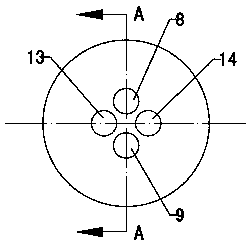
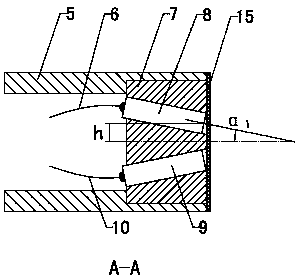
Integrated optical fiber probe for measuring dynamic light scattering particles and detection method
InactiveCN104266945AMiniaturizationOvercome the disadvantage of large sizeParticle size analysisHigh concentrationDynamic light scattering
The invention discloses an integrated optical fiber probe for measuring dynamic light scattering particles and a detection method and belongs to the technical field of measuring devices for dynamic light scattering nano particles. The integrated optical fiber probe is characterized by comprising transmitting optical fibers and receiving optical fibers, wherein one end of an outer casing (5) of the optical fiber probe is a closed end and the other end of the outer casing (5) is an open end; a fixed disk (7) is tightly mounted at the open end; self-focusing lenses are fixedly mounted through built-in through holes of the fixed disk (7) and comprise a transmitting lens and a receiving lens; inner end parts of the transmitting lens and the receiving lens are respectively and correspondingly connected with the transmitting optical fibers and the receiving optical fibers. According to the integrated optical fiber probe and the detection method, the optical path of the traditional light scattering device is changed; the optical fibers are introduced into a dynamic light scattering technology; a transmitting optical path and a receiving optical path are integrated together trough the optical fibers, so that a high-concentration sample can be measured and online detection of industrial production can be realized.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com